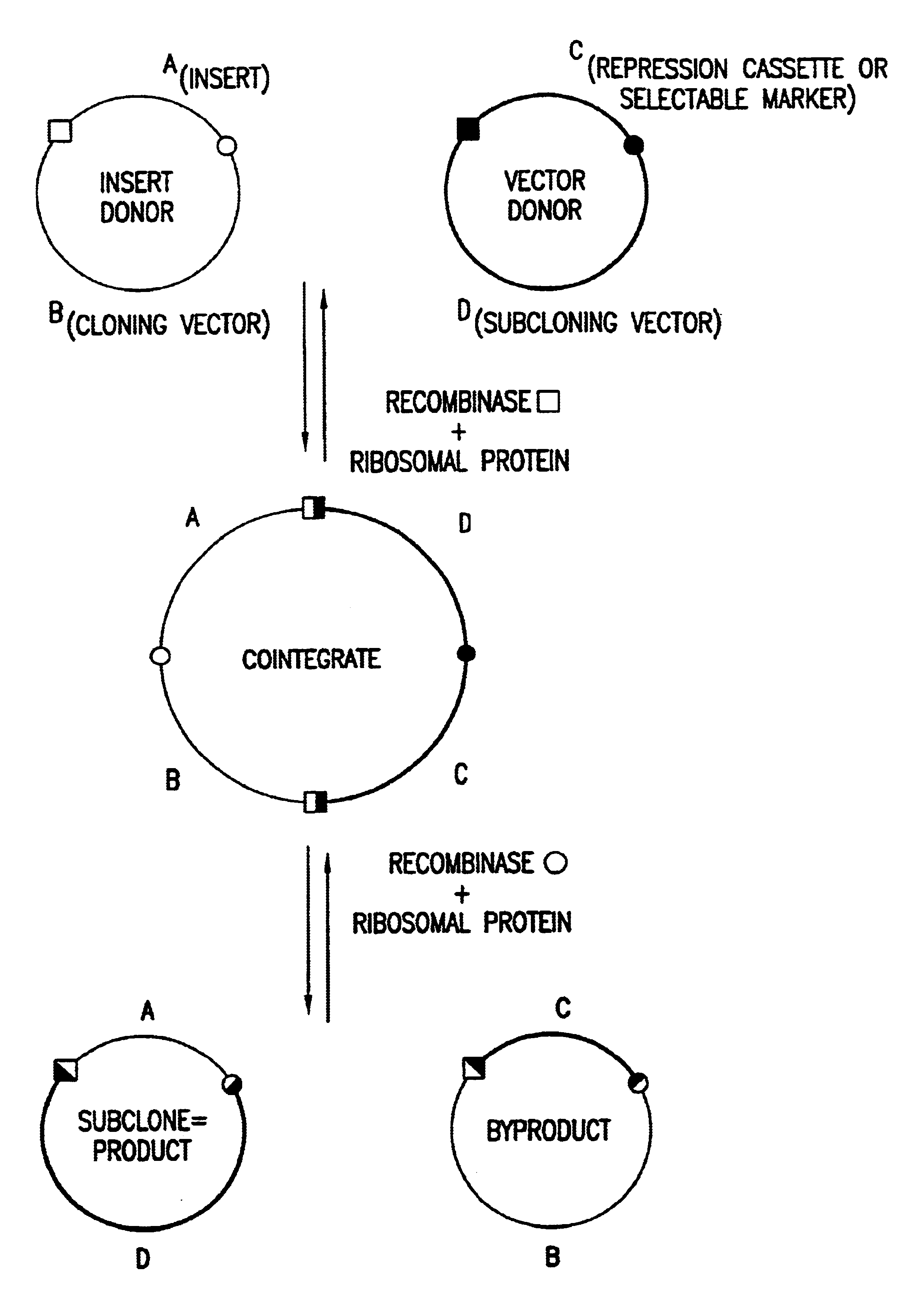
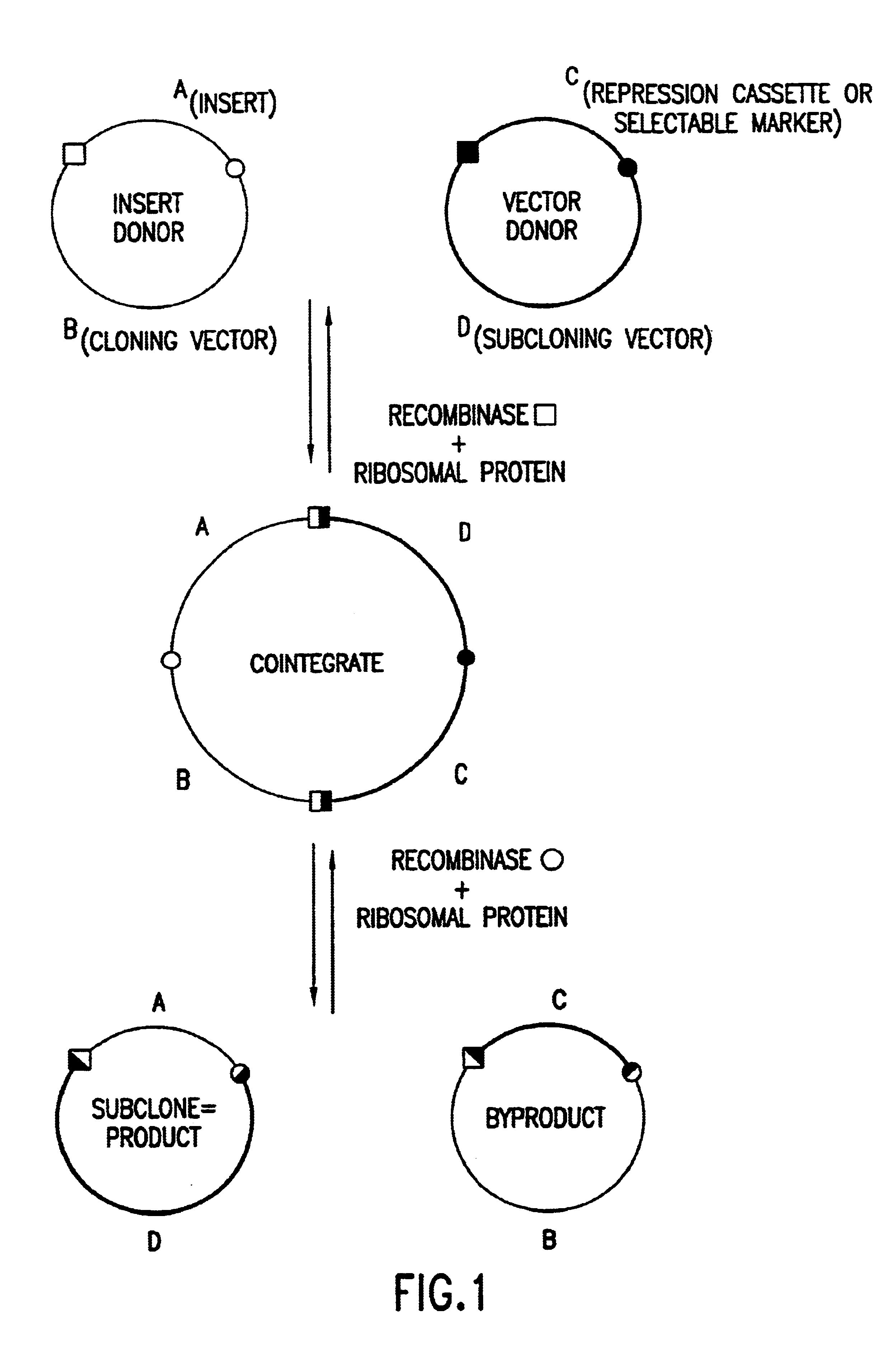
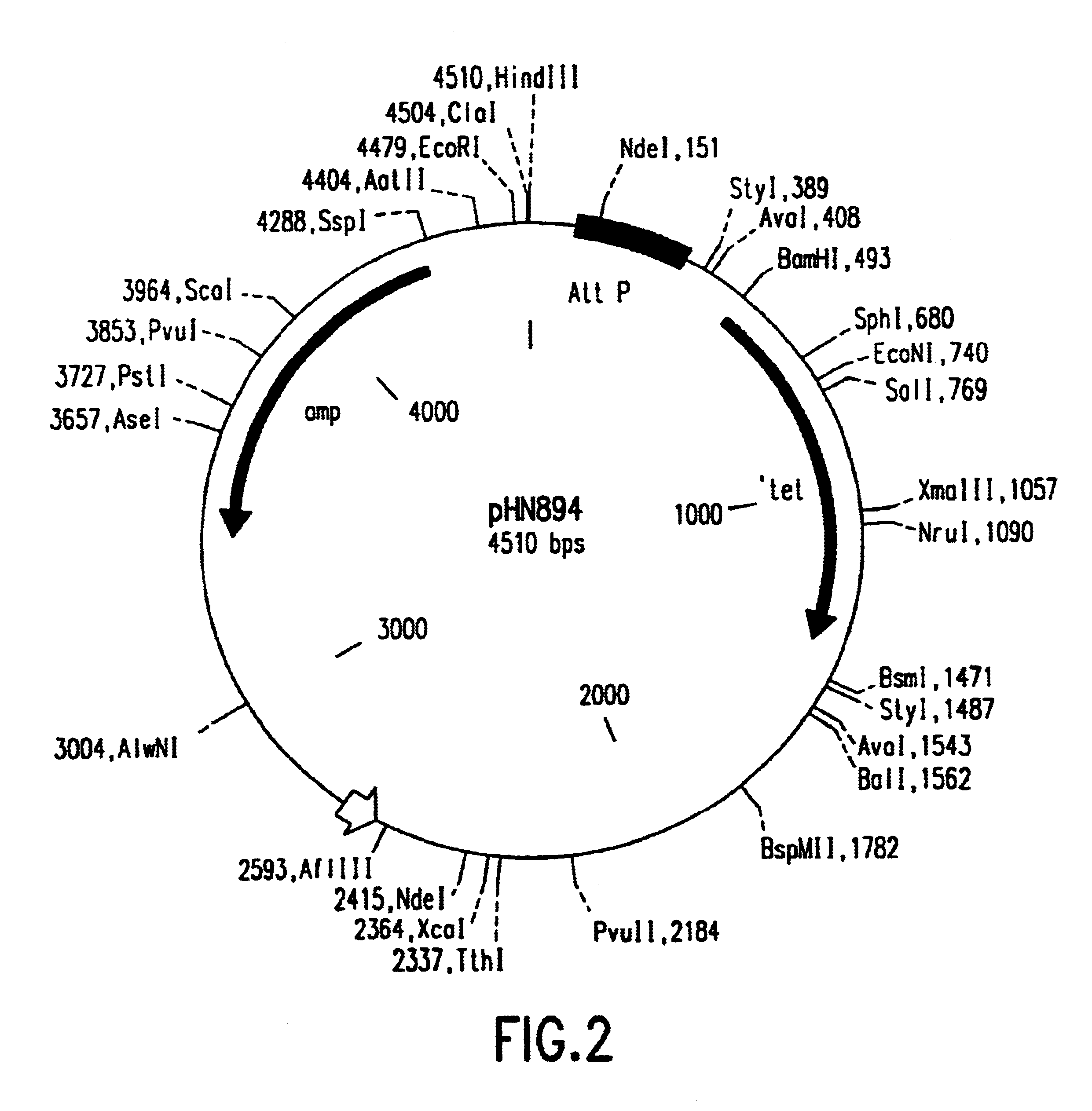
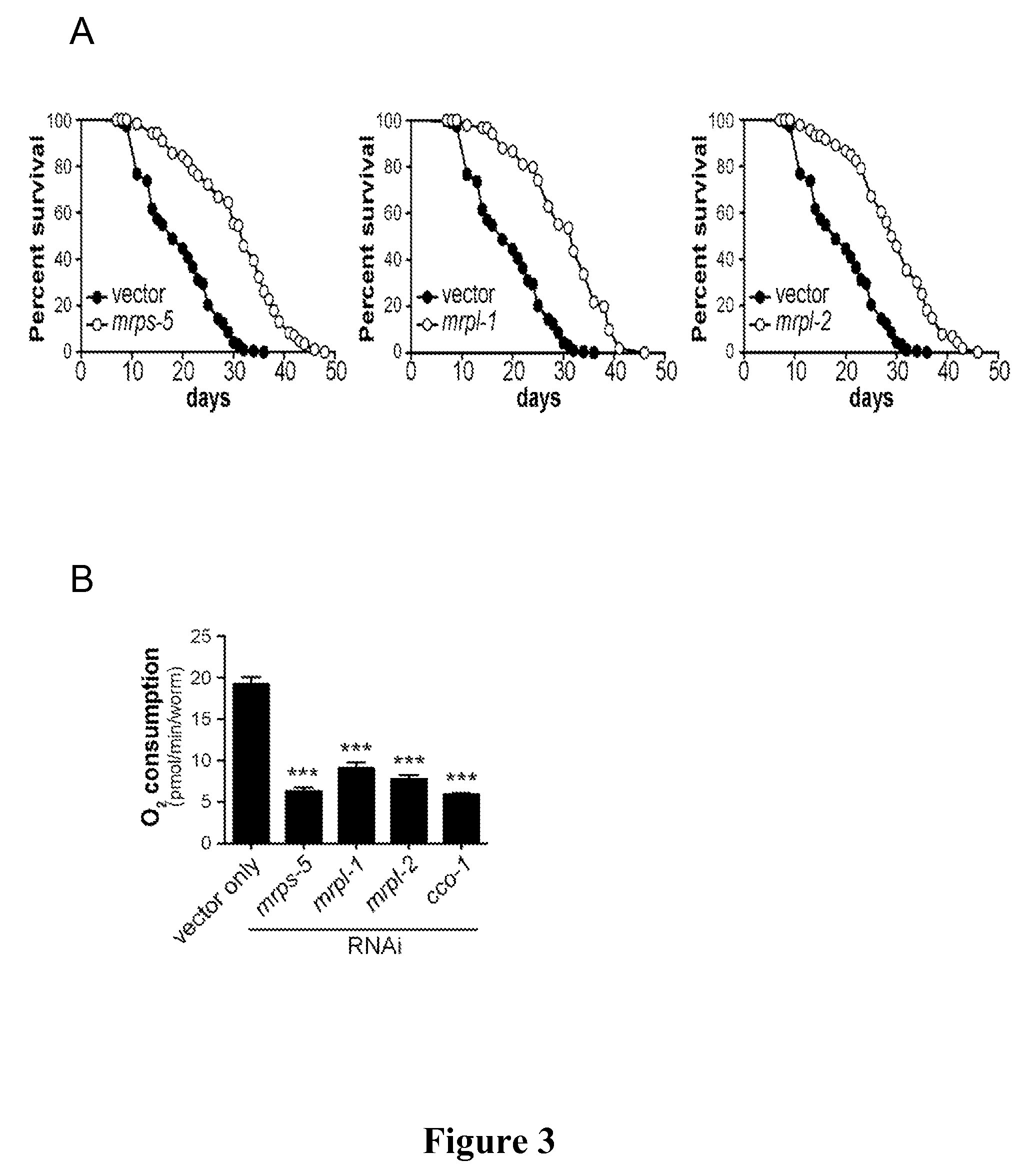Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
172 results about "Ribosomal protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A ribosomal protein (r-protein or rProtein) is any of the proteins that, in conjunction with rRNA, make up the ribosomal subunits involved in the cellular process of translation. A large part of the knowledge about these organic molecules has come from the study of E. coli ribosomes. All ribosomal proteins have been isolated and many specific antibodies have been produced. These, together with electronic microscopy and the use of certain reactives, have allowed for the determination of the topography of the proteins in the ribosome. E. coli, other bacteria and Archaea have a 30S small subunit and a 50S large subunit, whereas humans and yeasts have a 40S small subunit and a 60S large subunit. Equivalent subunits are frequently numbered differently between bacteria, Archaea, yeasts and humans. More recently, a near-complete (near)atomic picture of the ribosomal proteins is emerging from the latest high-resolution cryo-EM data (including PDB ID: 5AFI).
Enhanced in vitro recombinational cloning of using ribosomal proteins
InactiveUS6964861B1Strong specificityIncrease speedBacteriaSugar derivativesRibosomal protein E-L30Escherichia coli
The present invention relates generally to compositions and methods for enhancing recombinational cloning of nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the invention relates to compositions comprising one or more ribosomal proteins and one or more additional protein components required for recombinational cloning. More particularly, the invention relates to such compositions wherein the ribosomal proteins are one or more E. coli ribosomal proteins, still more particularly wherein the ribosomal proteins are selected from the group of E. coli ribosomal proteins consisting of S10, S14, S15, S16, S17, S18, S19, S20, S21, L20, L21, and L23 through L34, and most particularly S20, L27, and S15. The invention also relates to the use of these compositions in methods for recombinational cloning of nucleic acids, in vitro and in vivo, to provide chimeric DNA molecules that have particular characteristics and / or DNA segments. The invention also relates to isolated nucleic acid molecules produced by the methods of the invention, to vectors comprising such nucleic acid molecules, and to host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules and vectors.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Method for isolating cell-type specific mrnas
ActiveUS20050009028A1Maximum protein expressionImprove translation efficiencySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRibosomal protein E-L30Ribosomal protein
The invention provides methods for isolating cell-type specific mRNAs by selectively isolating ribosomes or proteins that bind mRNA in a cell type specific manner, and, thereby, the mRNA bound to the ribosomes or proteins that bind mRNA. Ribosomes, which are riboprotein complexes, bind mRNA that is being actively translated in cells. According to the methods of the invention, cells are engineered to express a molecularly tagged ribosomal protein or protein that binds mRNA by introducing into the cell a nucleic acid comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding a ribosomal protein or protein that binds mRNA fused to a nucleotide sequence encoding a peptide tag. The tagged ribosome or mRNA binding protein can then be isolated, along with the mRNA bound to the tagged ribosome or mRNA binding protein, and the mRNA isolated and further used for gene expression analysis. The methods of the invention facilitate the analysis and quantification of gene expression in the selected cell type present within a heterogeneous cell mixture, without the need to isolate the cells of that cell type as a preliminary step.
Owner:TAKEDA SAN DIEGO
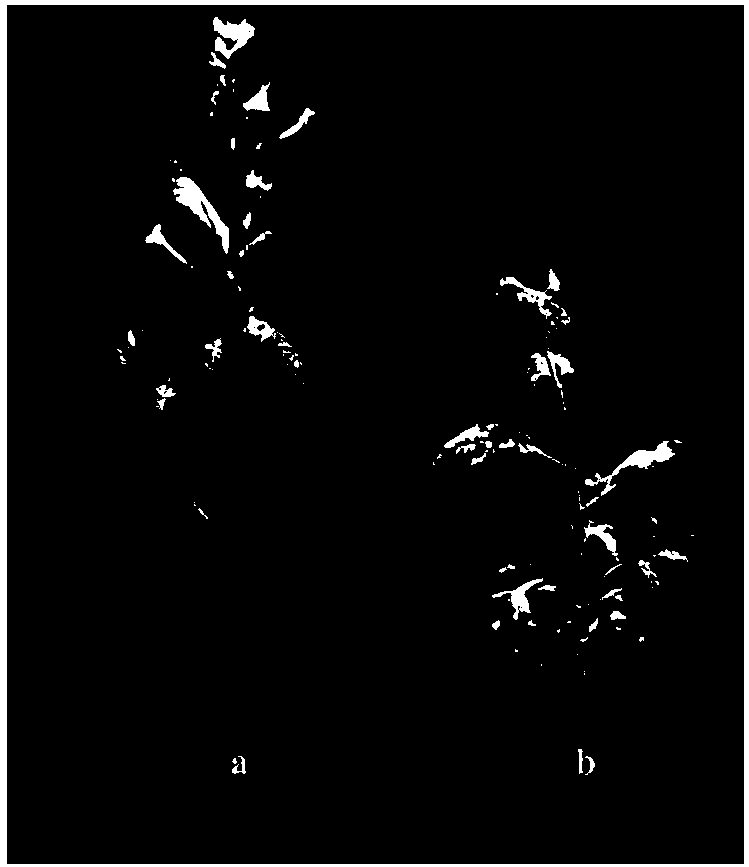
Plants with Increased Yield
InactiveUS20120227134A1MicroorganismsVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin-Protein LigasesSerine hydroxymethyltransferase
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase, 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase, 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphate phosphatase, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-D-erythritol kinase, 5OS chloroplast ribosomal protein L21, 57972199. R01.1-protein, 60952769. R01.1-protein, 60S ribosomal protein, ABC transporter family protein, AP2 domain-containing transcription factor, argonaute protein, AT1 G29250.1-protein, AT1 G53885-protein, AT2G35300-protein, AT3G04620-protein, AT4G01870-protein, AT5G42380-protein, AT5G47440-protein, CDS5394-protein, CDS5401_TRUNCATED-protein, cold response protein, cullin, Cytochrome P450, delta-8 sphingolipid desaturase, galactinol synthase, glutathione-S-transferase, GTPase, haspin-related protein, heat shock protein, heat shock transcription factor, histone H2B, jasmonate-zim-domain protein, mitochondrial asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase, Oligosaccharyltransferase, OS02G44730-protein, Oxygen-evolving enhancer protein, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase, peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase family protein, plastid lipid-associated protein, Polypyrimidine tract binding protein, PRLI-interacting factor, protein kinase, protein kinase family protein, rubisco subunit binding-protein beta subunit, serine acetyltransferase, serine hydroxymethyltransferase, small heat shock protein, S-ribosylhomocysteinase, sugar transporter, Thioredoxin H-type, ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, ubiquitin-protein ligase, universal stress protein family protein, and Vacuolar protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Live attenuated mycoplasma strains
InactiveUS20090068231A1Reduce expressionReduced virulenceAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesVaccination
The present invention provides live, attenuated Mycoplasma bacteria that exhibit reduced expression of one or more proteins selected from the group consisting of pyruvate dehydrogenase, phosphopyruvate hydratase, 2-deoxyribose-5-phosphate aldolase, and ribosomal protein L35, relative to a wild-type Mycoplasma bacterium of the same species. Also provided are vaccines and vaccination methods involving the use of the live, attenuated Mycoplasma bacteria, and methods for making live attenuated Mycoplasma bacteria.
Owner:WYETH LLC
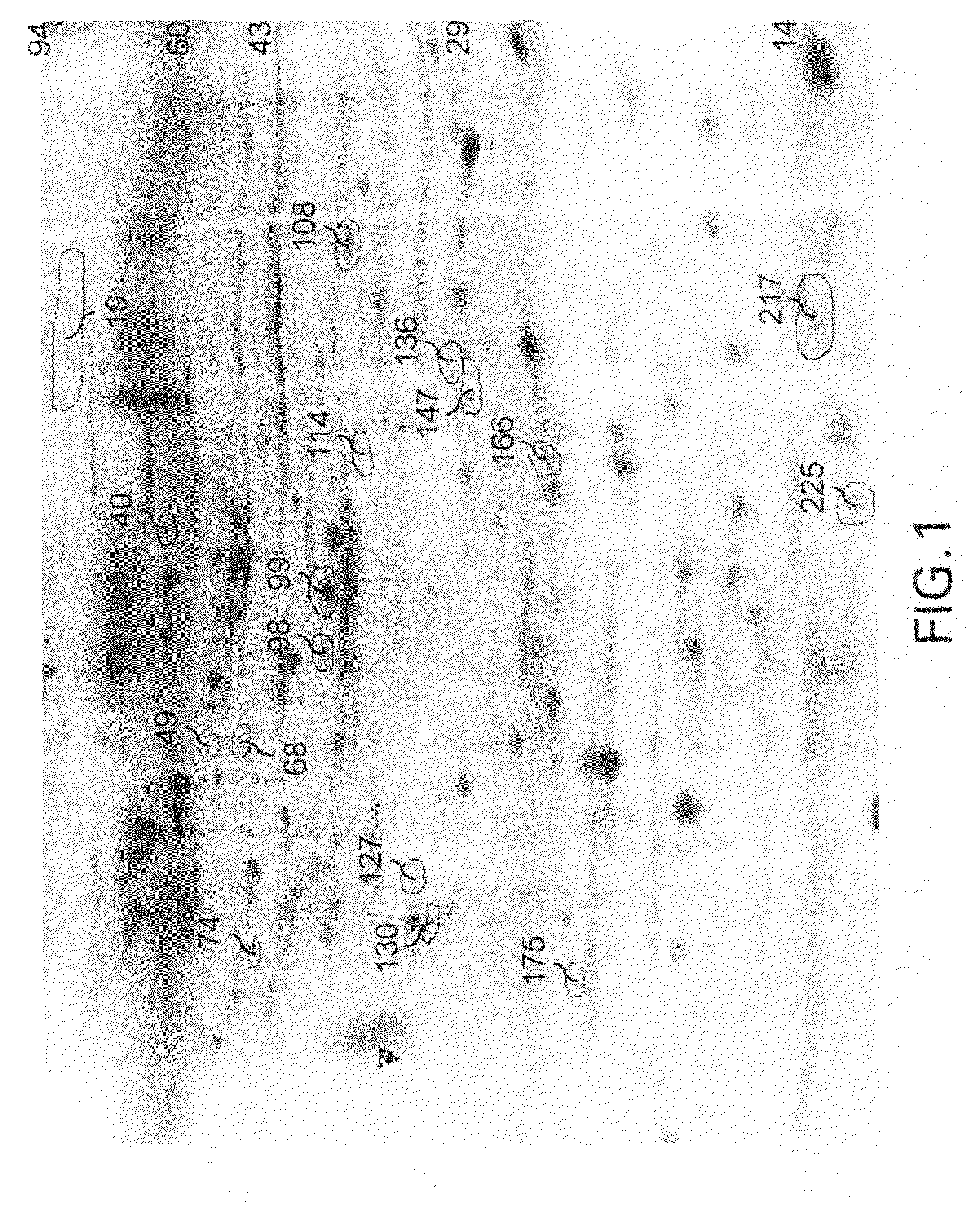
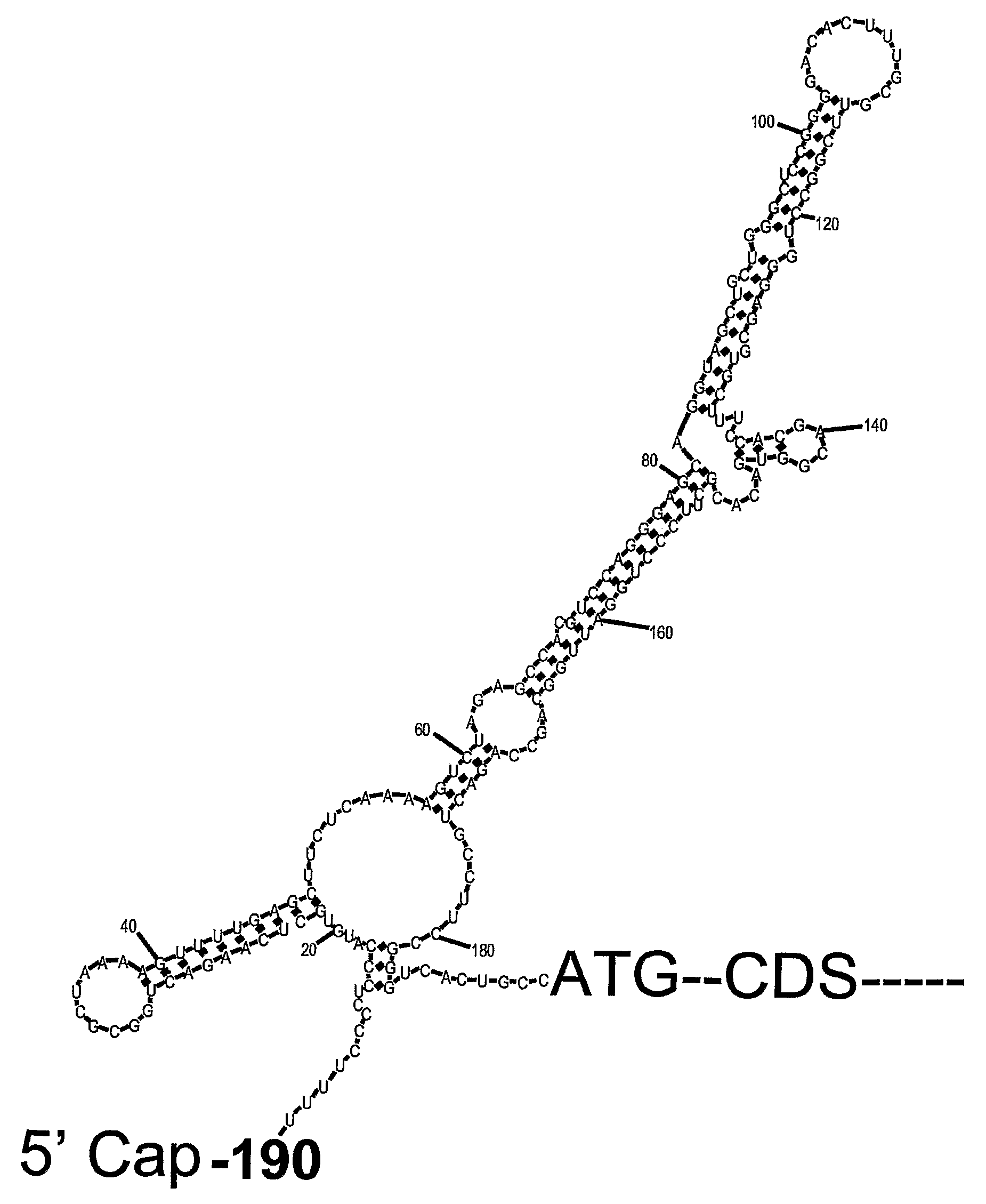
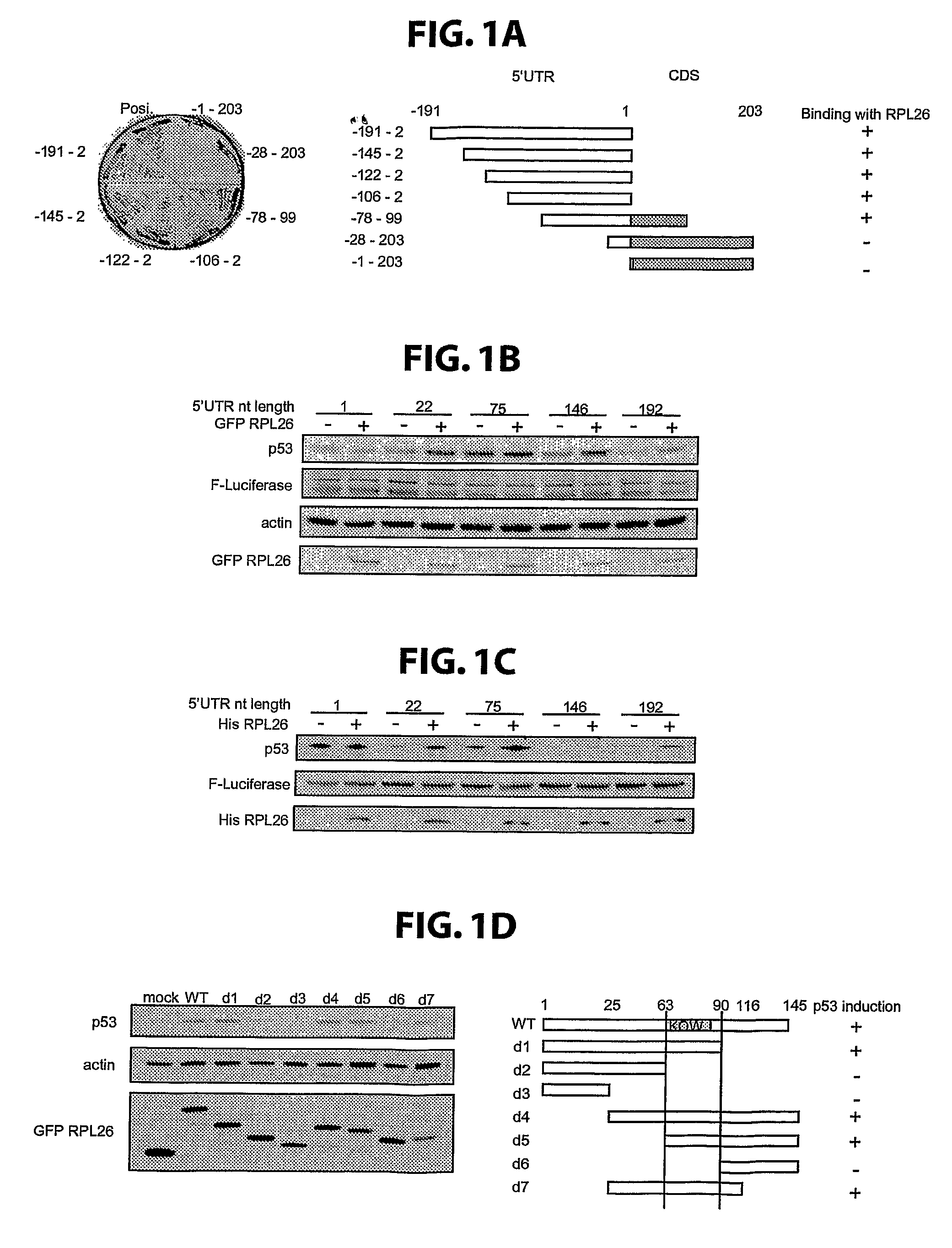
METHODS FOR REGULATION OF p53 TRANSLATION AND FUNCTION
ActiveUS20090149377A1Reducing and eliminating p53-dependent neuronal deathSuppressing tissue agingPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsRibosomal proteinP53 Tumor Suppressor Protein
The present invention relates to novel methods for modulating the activity of p53 tumor suppressor protein by affecting p53 translational regulation. More specifically, the invention relates to novel methods for modulating p53 mRNA translation in a cell by affecting a function of a p53 5′-untranslated region (5′UTR), including its interaction with proteins such as Ribosomal Protein L26 (RPL26), nucleolin, and p53. The invention also relates to the use of these methods for treating cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and minimizing the negative effects of cellular stresses.
Owner:ST JUDE CHILDRENS RES HOSPITAL INC
Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Ribosomal protein L9-B based on gene-silencing technology and dsRNA thereof
InactiveCN102220339AResistance to degradationLower synthesis costFermentationPlant genotype modificationRibosomal proteinPest control
Belonging to the field of agricultural biotechnology, the invention relates to a laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment. By a laboratory improved dsRNA feeding method, the invention, from laodelphax striatellus, screens out the laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment Ribosomal protein L9-B which can lead to laodelphax striatellus death and has sequences as shown in SEQ ID No.1. Feeding laodelphax striatellus with the dsRNA of the gene fragment provided in the invention can have good lethal effect, thus providing sequence and data bases for establishing new strategies of pest control with RNA interference technology.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Recombinant materials for carotenoid production
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the amino acid sequences depicted in any one of SEQIDNOs: 24 to 50. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided, preferably wherein said enzyme has an activity selected from isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase activity, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase activity, phytoene synthase activity, phytoene desaturase activity and lycopene cyclase activity, still more preferably those coding for an enzyme having an amino acid sequence selected from the one represented by SEQIDNO: 13, SEQIDNO: 15, SEQIDNO: 17, SEQIDNO: 19, SEQIDNO: 21 or SEQIDNO: 23. Further embodiments concern vectors, transformed host organisms, methods for making proteins and / or carotenoids, such as astaxanthin, and methods for isolating highly expressed promoters from Phaffa.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Laodelphax striatellus lethal gene fragment
InactiveCN102220339BSignificant lethal effectResistance to degradationFermentationPlant genotype modificationRibosomal proteinPest control
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Polysome-mediated cell type-, tissue type- or condition-enhanced transcript profiling
InactiveUS20100071086A1BryophytesOther foreign material introduction processesRibosomal protein E-L30Rna profiling
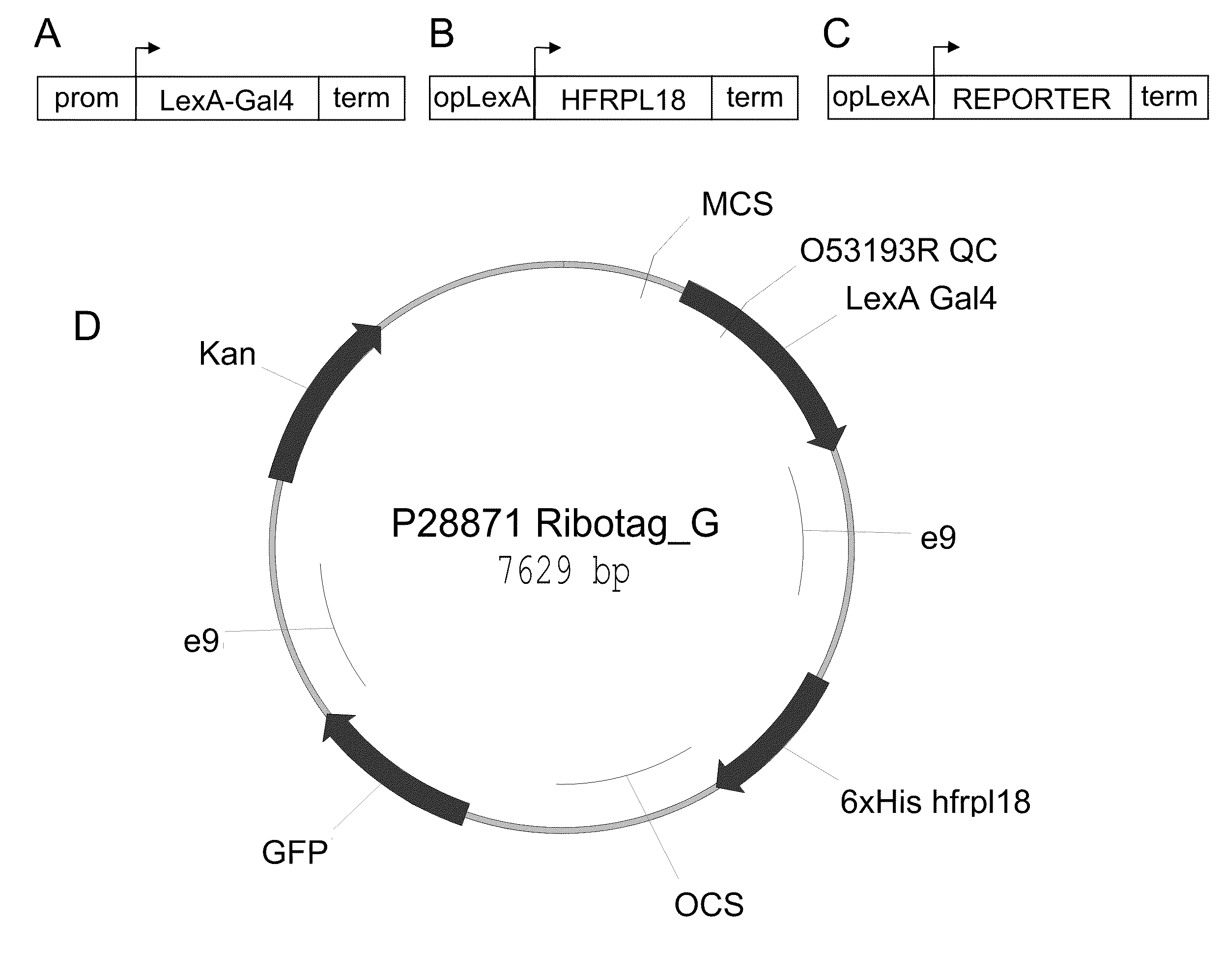
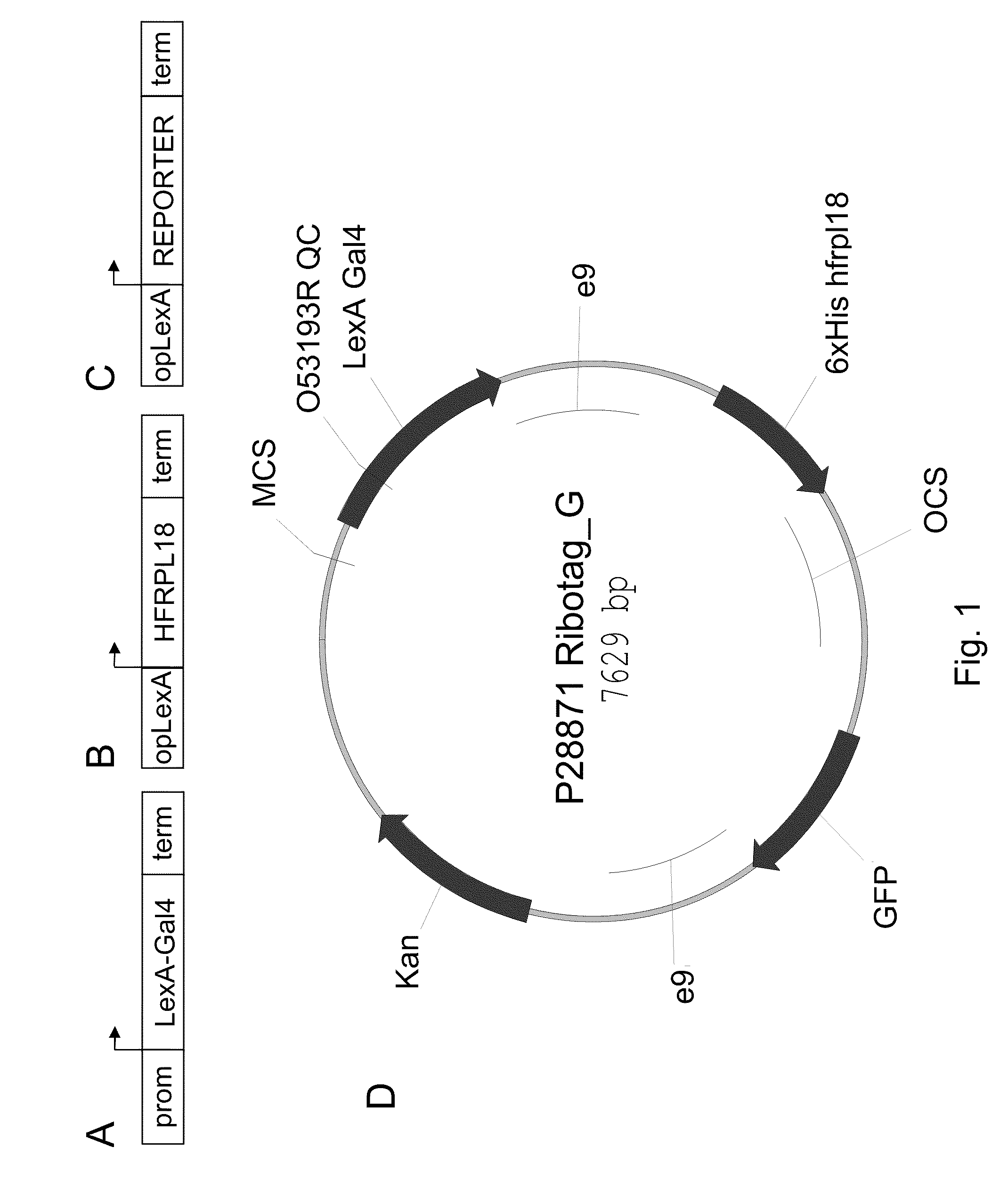
In this invention, a method is described that allows for the efficient creation and identification of validated biological materials that greatly enhance the ability to perform polysome-mediated RNA profiling, such as constitutive, cell type-, tissue type-, or condition-enhanced RNA profiling. The method relies on the use of a tri-partite plant binary expression vector comprised of the following components: a) a DNA promoter element that drives expression of a sequence specific transcription activator protein such as a LexA:Gal4 fusion protein in a unique desired pattern, b) a DNA promoter element comprising a target site for the transcriptional activator protein, such as opLexA, fused to a nucleotide encoding an epitope tagged ribosomal component protein and c) a DNA promoter element comprising a target site for the transcriptional activator protein, such as opLexA, fused to a nucleotide encoding an in vivo reporter protein. By visualization of the co-regulated reporter, this method allows for in planta confirmation that the promoter element is driving expression, such as constitutive, cell type-, tissue type-, or condition-enhanced expression, of the tagged ribosomal protein in the desired cell or tissue types.
Owner:MENDEL BIOTECHNOLOGY INC
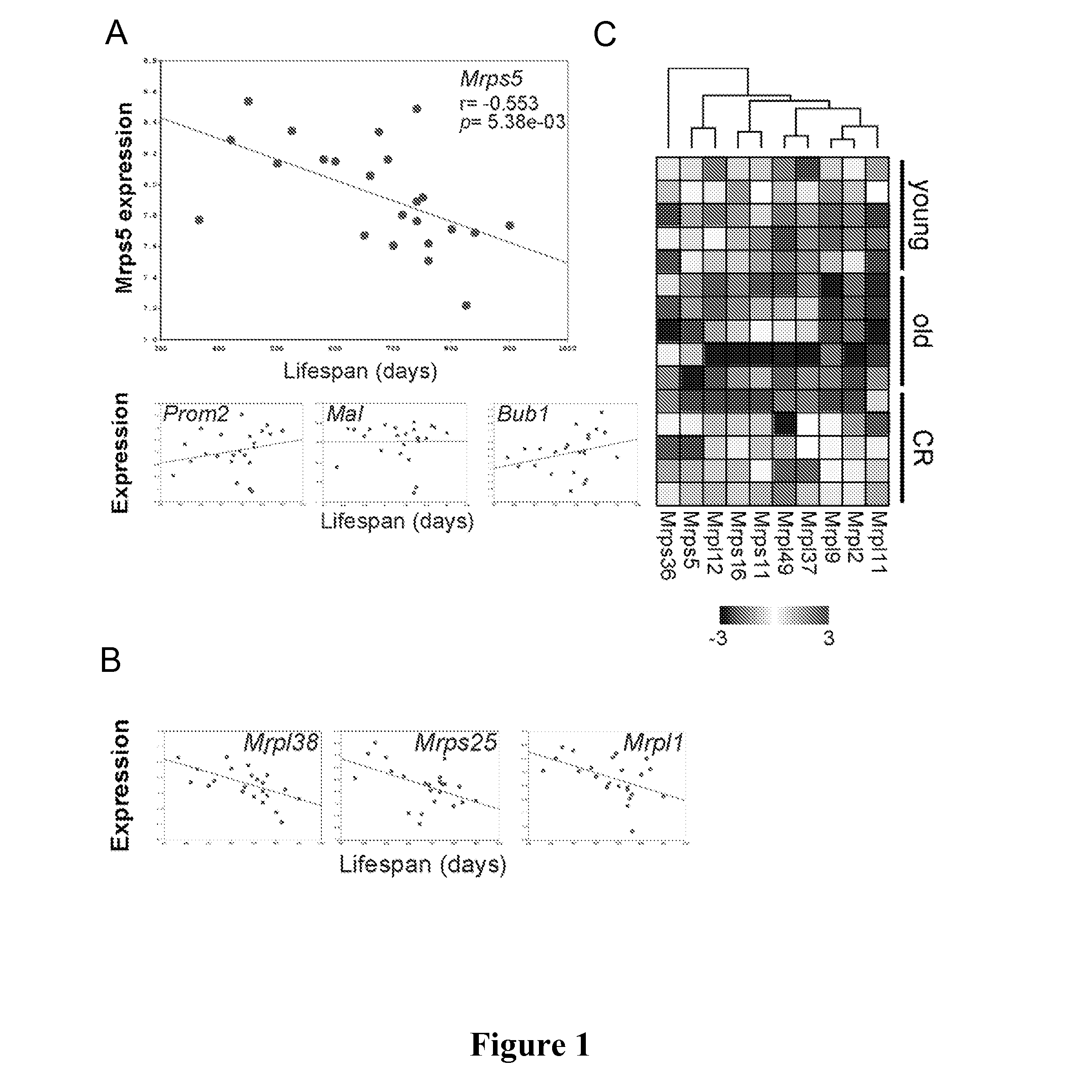
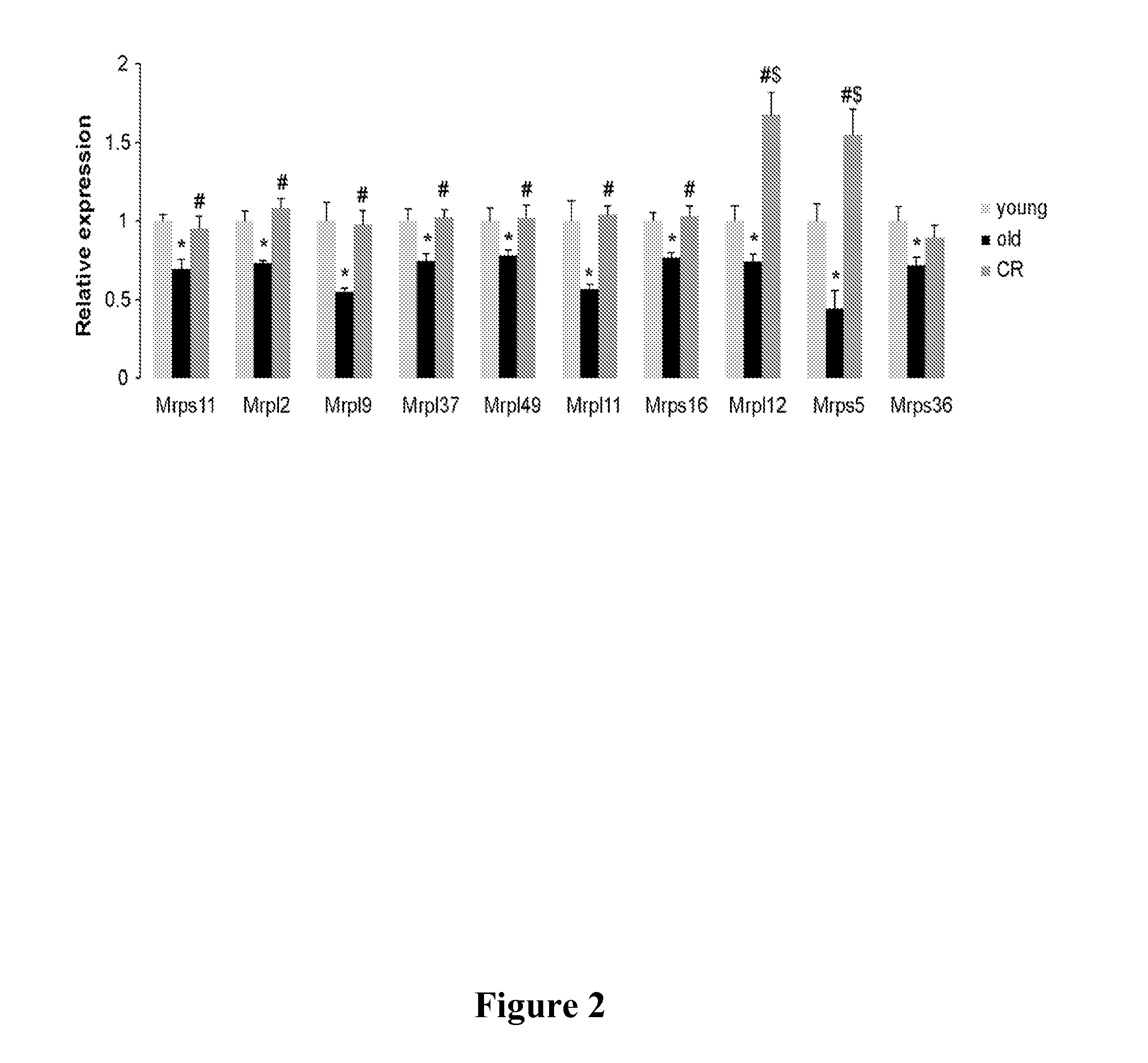
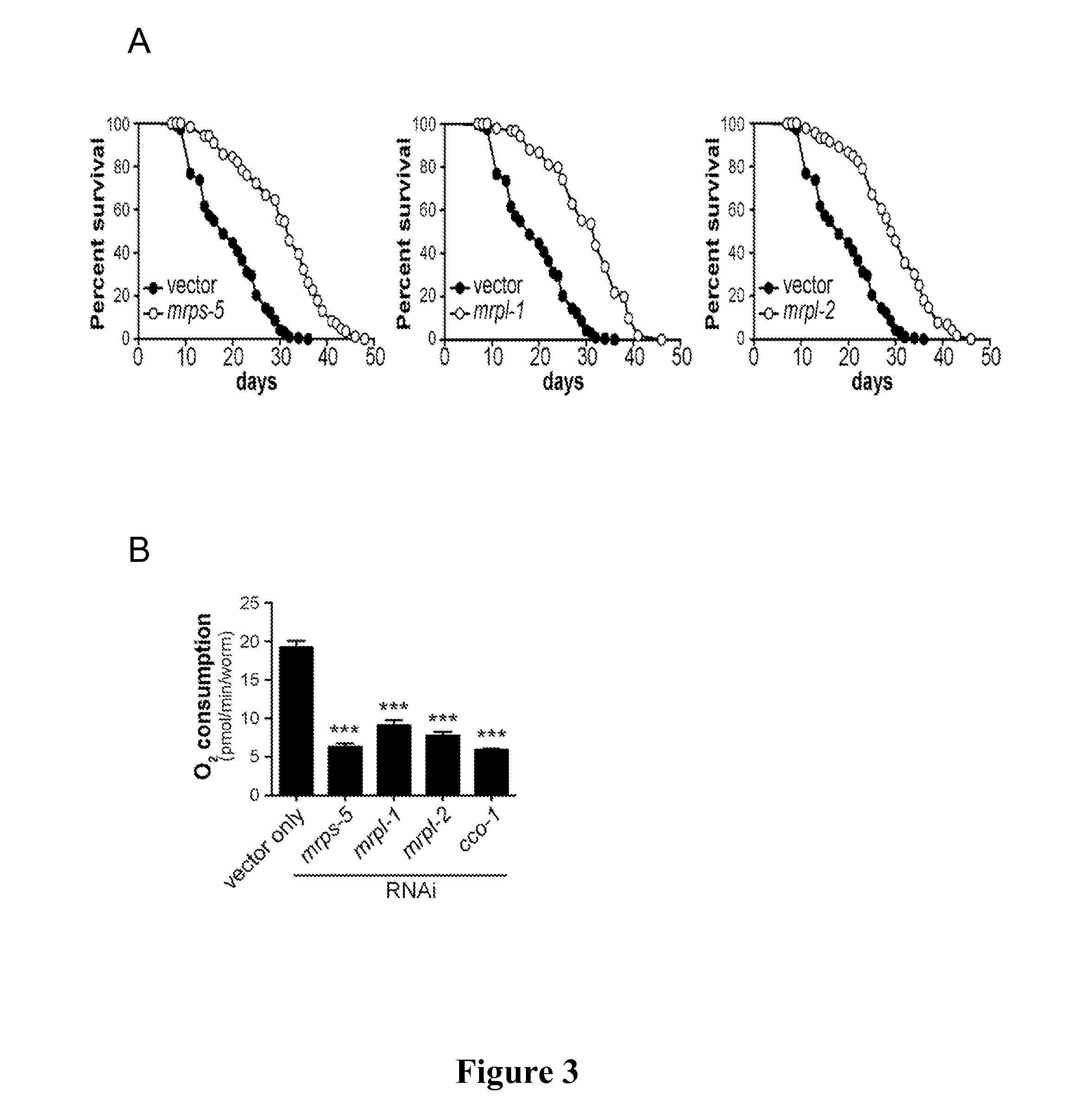
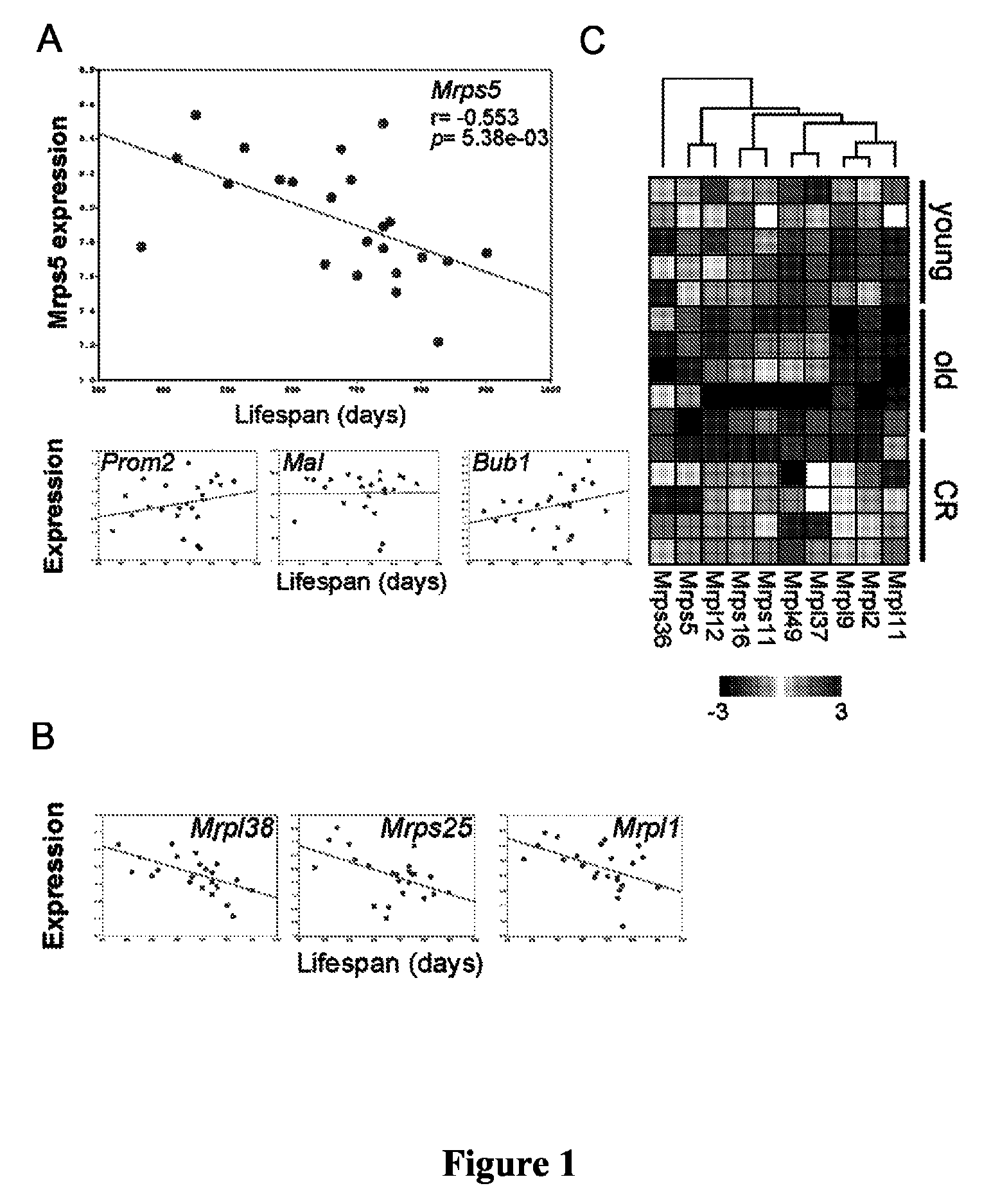
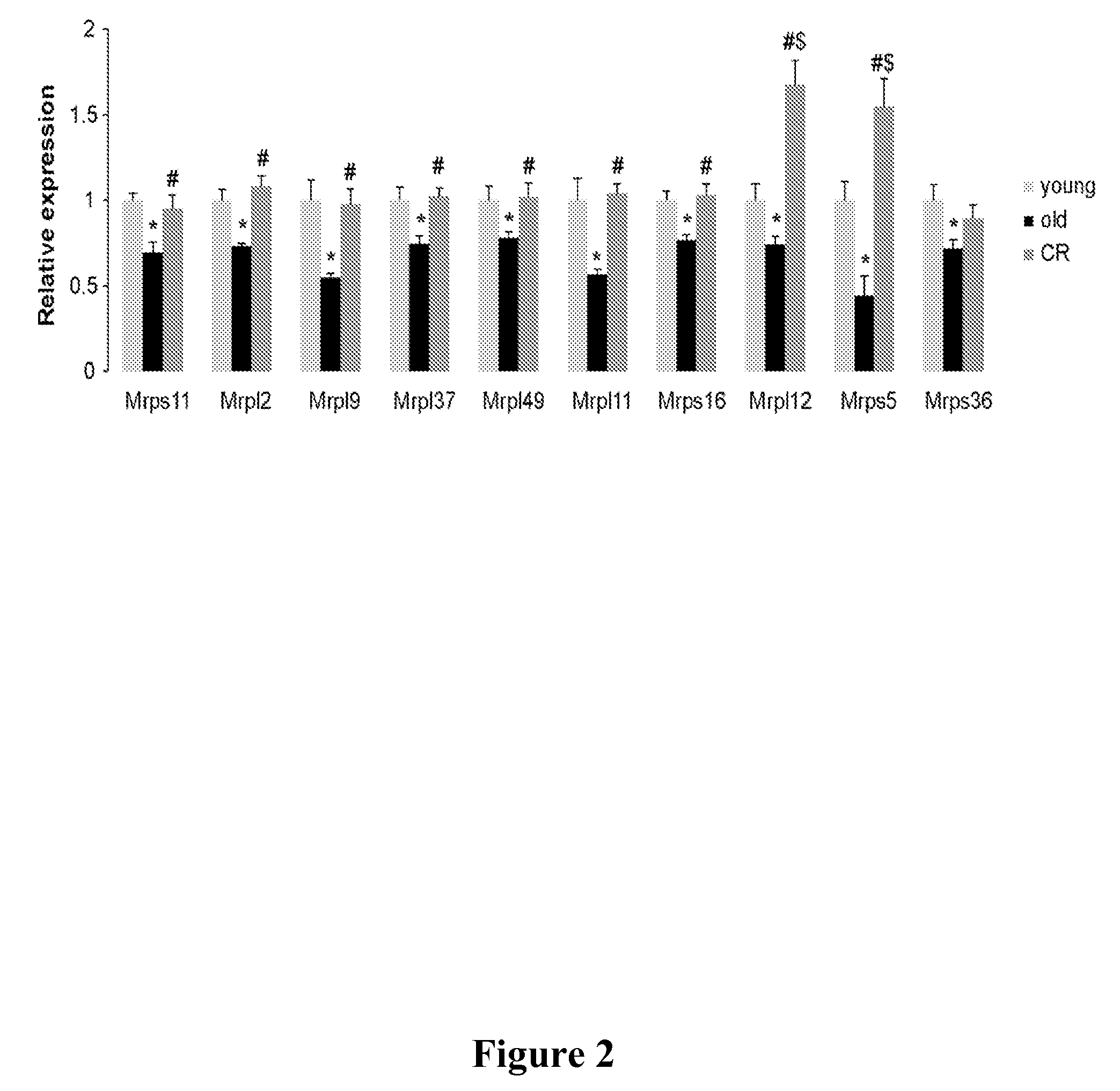
Mitochondrial ribosomal proteins as aging regulators
The present invention relates to methods of increasing lifespan, delaying aging, and / or preventing or treating an age-related disease or a mitochondrial disease in a subject, comprising inducing a nuclear-mitochondrial OXPHOS protein dyssynchrony, including inhibiting the mitochondrial translation machinery function, as well as methods for screening agents that are able to increase lifespan, inhibit or delay aging, and / or prevent or treat an age-related disease or disorder, or a mitochondrial disease or disorder, in a subject.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Special slow sinking type feed for bighead and preparation process of feed
InactiveCN104026413APromote growthGrow fastFood processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyRibosomal protein
The invention belongs to the technical field of the aquaculture feed and discloses a special slow sinking type feed for bighead. The slow sinking type feed comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 25-35% of wheat flour, 0.5-9% of soya bean meal, 0-38% of casein, 8-10% of cottonseed meal, 8-12% of white fish meal, 1-2% of mineral premix, 1-3% of vitamin premix, 3-9% of soybean oil, 0.1-0.5% of choline chloride, 0.1-0.5% of salt, 2-3% of monocalcium phosphate, 0.05-0.2% of VC-lipid and 0.1-27% of cellulose powder. By researching the life habits of the bighead and the requirement amount of nutrient substances such as protein in the growth process, the slow sinking type feed applicable to bighead is researched; the slow sinking type feed is capable of promoting the growth of the bighead, facilitating the deposition of the ribosomal protein and facilitating the secretion of digestive enzymes in the enteric canal; after the slow sinking type feed is popularized, the slow sinking type feed has great social significance and economic significance.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Methods for transforming Phaffia strains, transformed Phaffia strains so obtained and recombinant DNA in said methods
InactiveUS6329141B1High expressionSuitable for productionFungiBacteriaRibosomal protein E-L30Open reading frame
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the disclosed amino acid sequences. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided.
Owner:GIST BROCADES NV +1
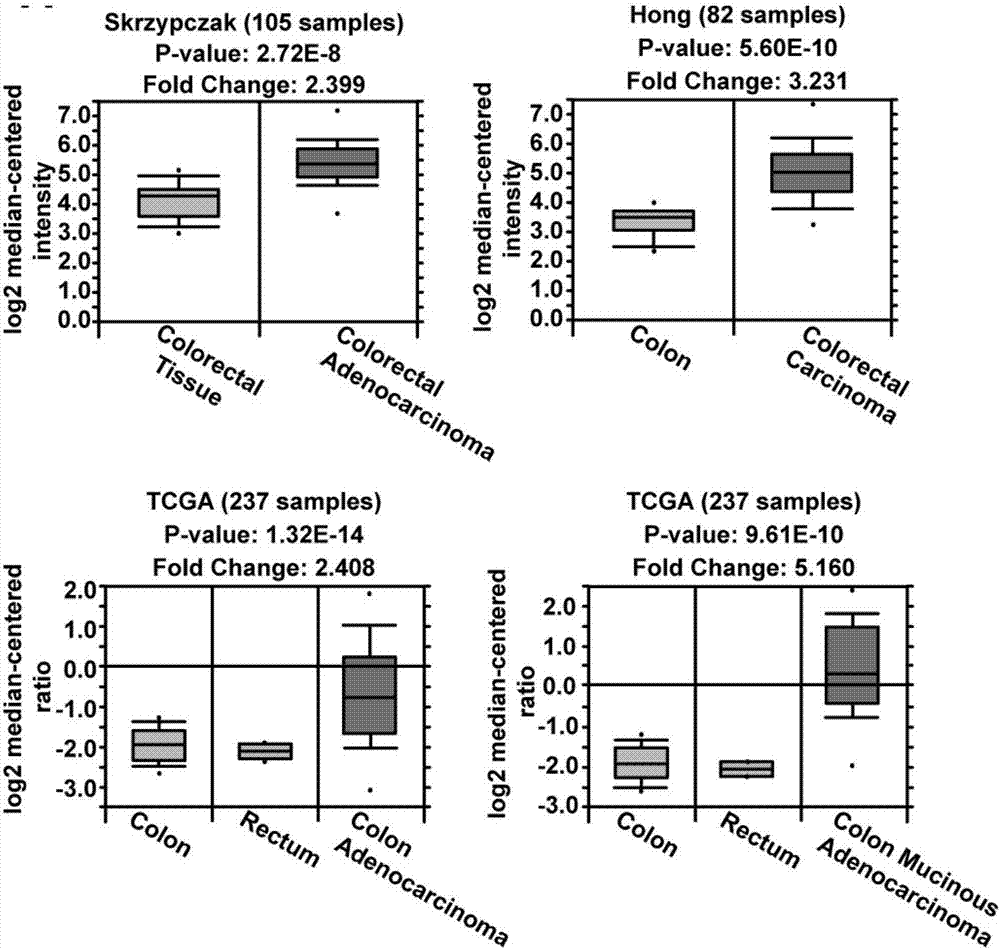
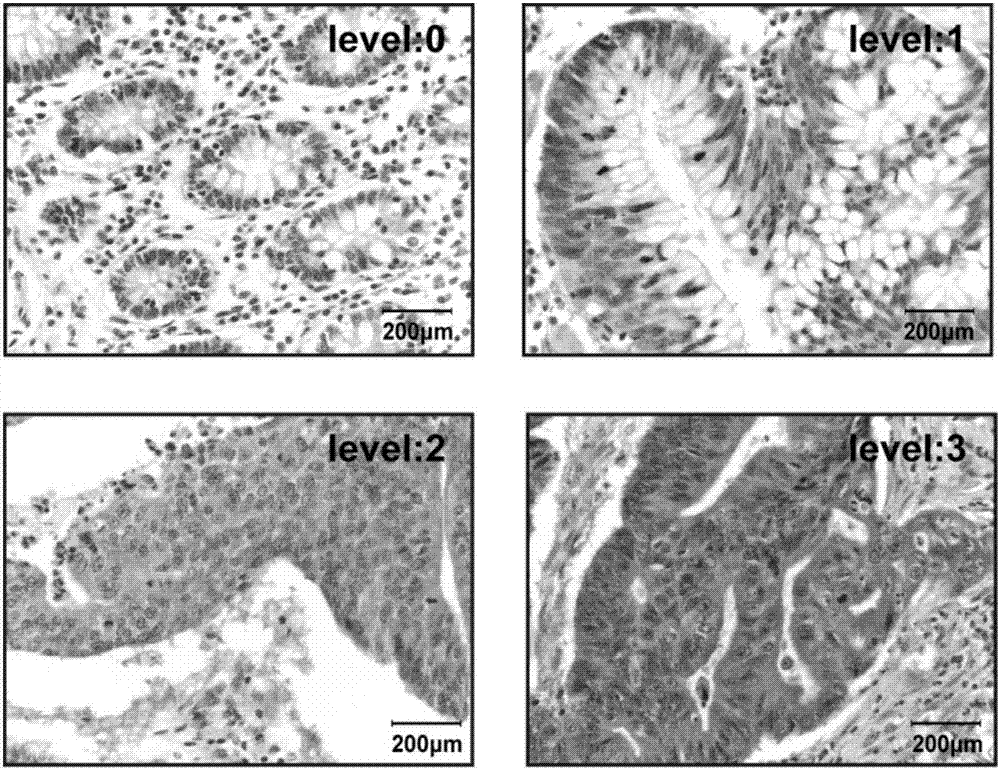
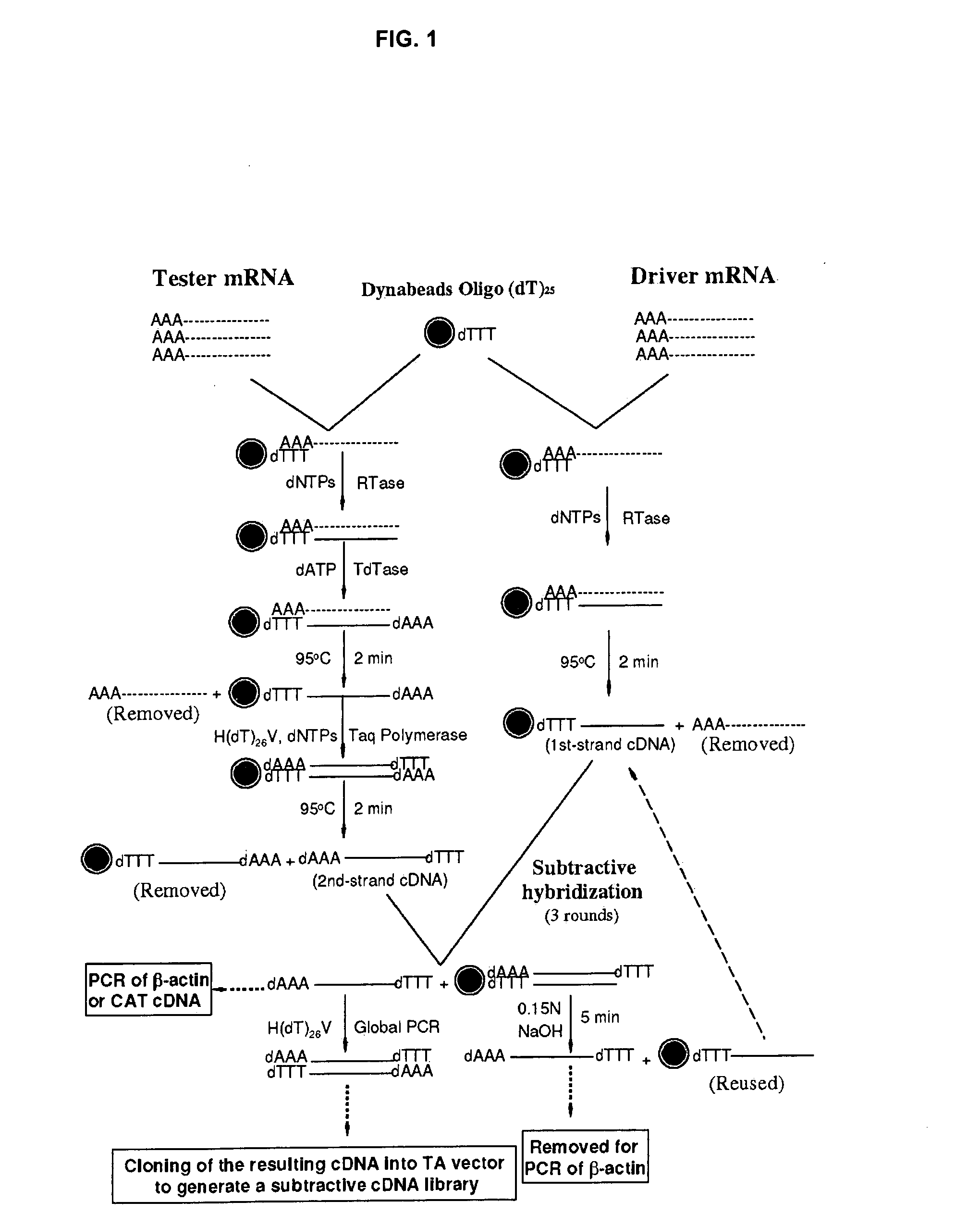
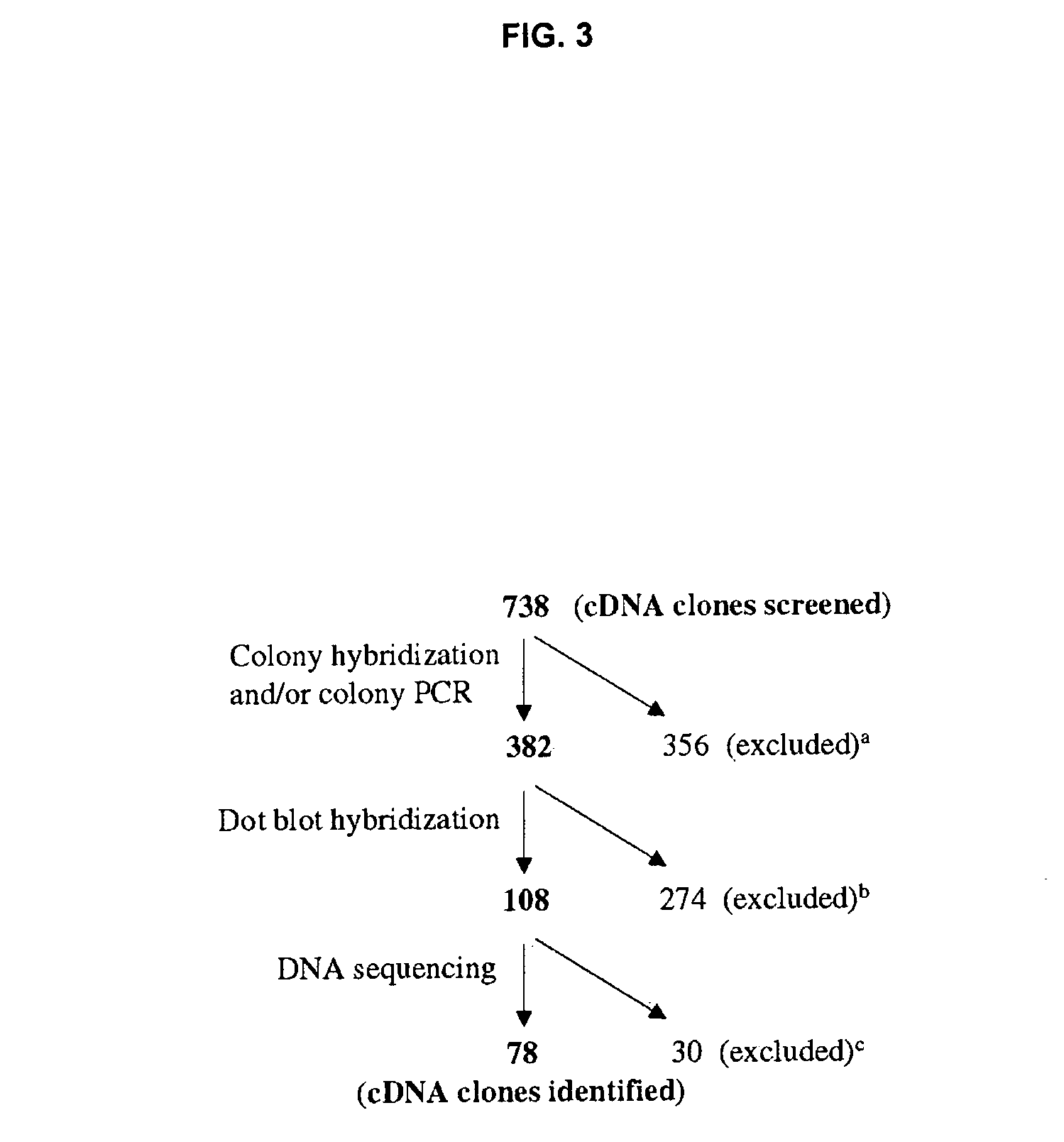
Molecular marker associated with colorectal carcinoma metastasis and prognosis as well as application of molecular marker
InactiveCN107099584AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisRibosomal protein E-L30Lymphatic Spread
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Methods and probes for diagnosing a gynaecological condition
InactiveUS20050142580A1Monitor progressSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseDLX5
DNA sequences are identified that are useful in the diagnosis of gynaecological conditions such as endometriosis. Some of the sequences have a high identity with gene of known function such as Pim-2 oncogenes, IGFBP-5, ribosomal protein L41, propsaponin, fibulin-1, DLX5, 11β hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2, SET, and RhoE. Methods for diagnosing or monitoring the progression of a gynaecological condition such as endometriosis may use primers directed to the DNA sequences identified herein.
Owner:TAY SUN +1
Screening method of non-ribosomal protein-RNA composite near-nature structure
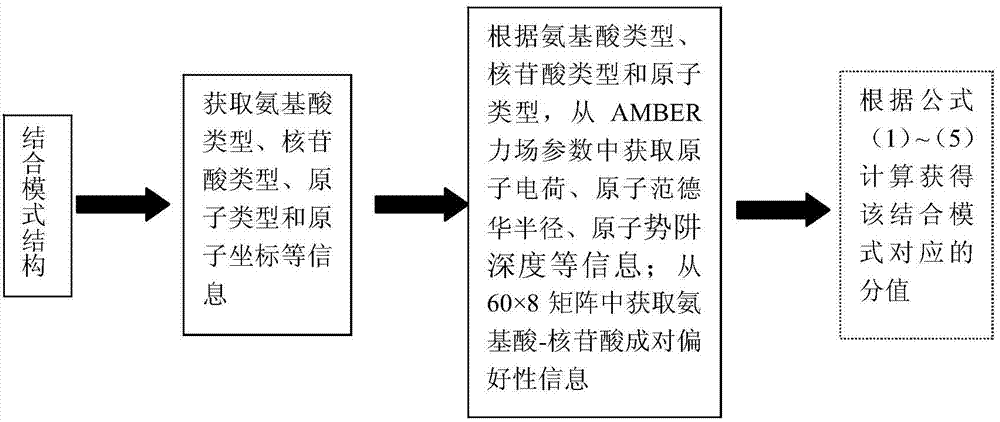
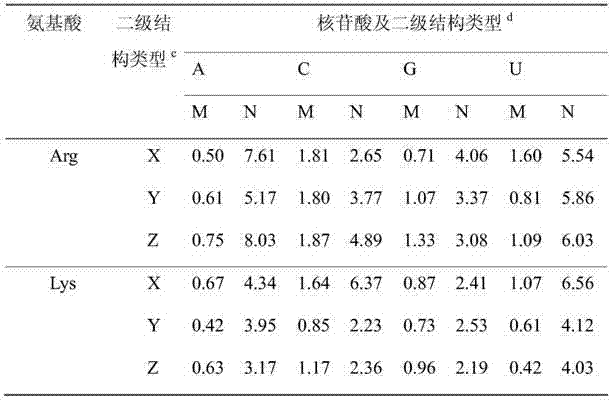
InactiveCN103500293AReduce the scope of investigationReduce workloadSpecial data processing applicationsNucleotideRibosomal protein
The invention provides a screening method of a non-ribosomal protein-RNA composite near-nature structure, and belongs to the field of protein-RNA molecular docking composite structure prediction. Firstly, various possible combination modes of protein-RNA are obtained through conformation searching; then rationality of the combination modes is assessed, static and van and der waals interaction energy among the protein-RNA molecules and amino acid nucleotide pairing preference on composite interfaces are comprehensively taken into consideration, and the weight of each item is obtained in the mode that a linear regression method is adopted and accordingly fitting of a ligand root-mean-square deviation and weighted combination values of energy items of a docking structure is carried out; finally, according to the order that the values are sequenced from smaller ones to larger ones, a near-nature structure is judged. The screening method has a good effect on screening of the non-ribosomal protein-RNA molecular docking near-nature structure, the successful rate is high, and the method can be used for the field of protein-RNA composite structure prediction and provides an important basis for molecule improvement and design.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
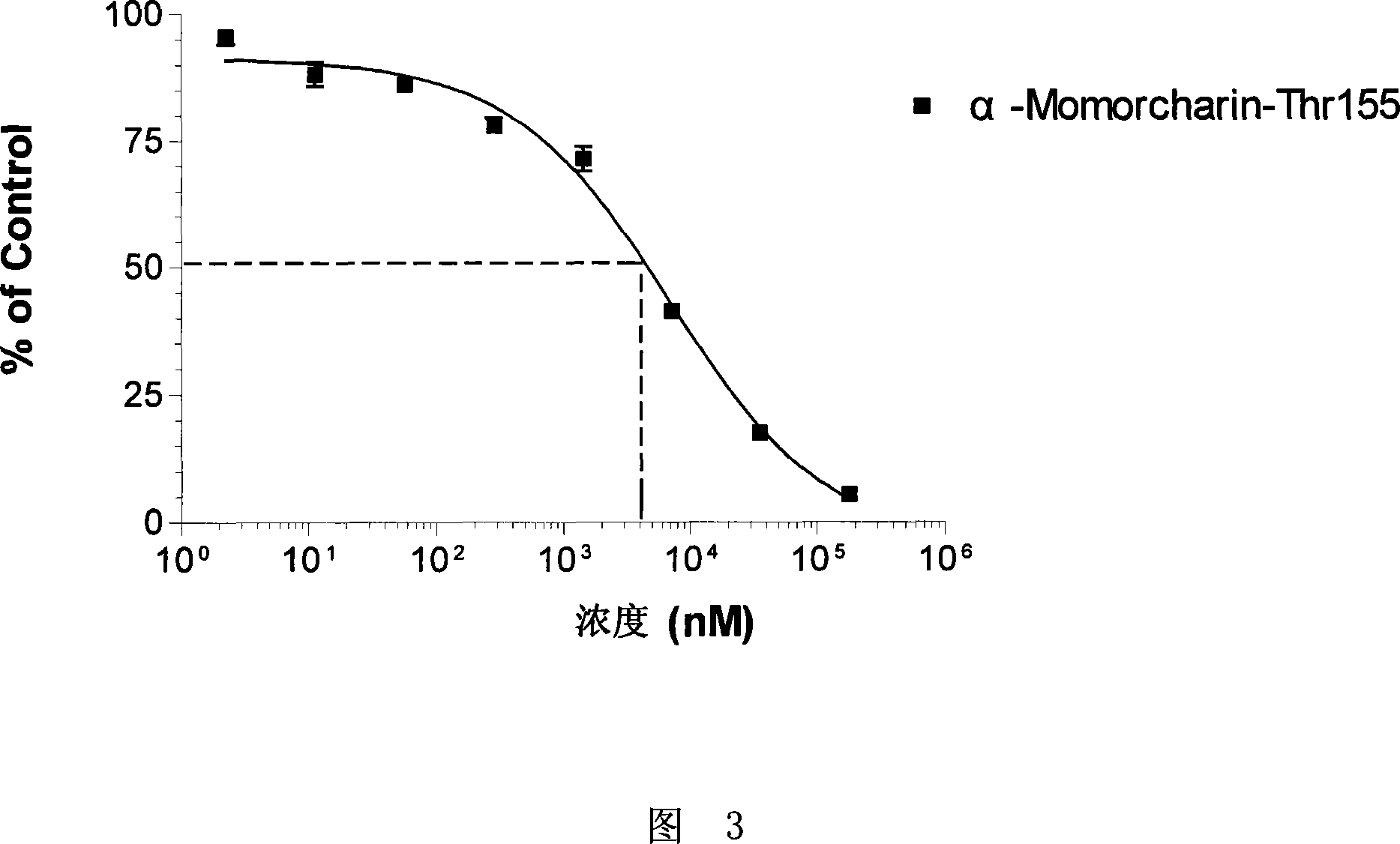
Balsm-pear-seed ribosome inactivated protein and its coding gene and use
InactiveCN101070342AImprove securityExpression conditions are simplePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsRibosomal protein E-L30Ribosomal protein
This invention relates to a balsam pear seed ribosome inactivating protein(RIP) and its encode gene and application. This protein has one of the undermentioned amino acid residue sequence: (1) SEQ ID NO:1 in the sequence table; (2) carry out substitution, deficiency or addition of protein that possess activity of inhibiting ribosomal protein synthesis to one to ten amino acid residue of SEQ ID NO: 1 amino acid residue sequence in sequence table. This protein possess hereinafter point: (1) notable effect of resisting tumour and virus infection; (2) high security; (3) simple protein expression condition, easy purification. low cost.
Owner:SHANXI KANGBAO BIOLOGICAL PROD +2
Plants with Increased Yield
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 26S proteasome-subunit, 50S ribosomal protein L36, Autophagy-related protein, B0050-protein, Branched-chain amino acid permease, Calmodulin, carbon storage regulator, FK506-binding protein, gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate hydrolase, GM02LC38418-protein, Heat stress transcription factor, Mannan polymerase II complex subunit, mitochondrial precursor of Lon protease homolog, MutS protein homolog, phosphate transporter subunit, Protein EFR3, pyruvate kinase, tellurite resistance protein, Xanthine permease, and YAR047C-protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Construction and application of gene silencing vector induced by Chinese wheat yellow mosaic virus
InactiveCN108517332ARich varietyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsRibosomal proteinTriticeae
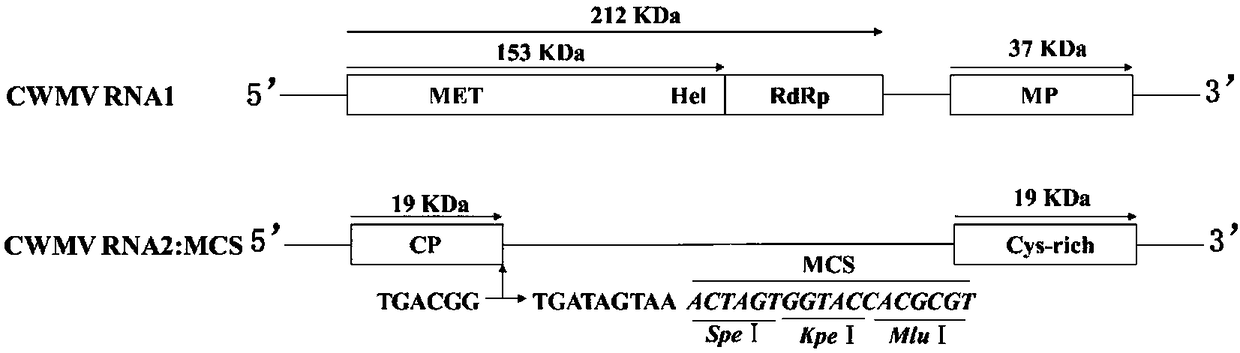
The invention mainly relates to construction of a gene silencing vector induced by Chinese wheat yellow mosaic virus, and application thereof to nicotiana benthamiana. The biological active analysis results show that the constructed CWMV-VIGS can successfully infect the nicotiana benthamiana and can realize the silencing after the effective transcription on relevant genes such as phytoene desaturase and 50S ribosomal protein L12. The types of the VIGS vectors are enriched; in addition, the effective technical measures are provided for the gene function study.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Reference gene combination for gene expression analysis of polycystic ovarian syndrome and application thereof
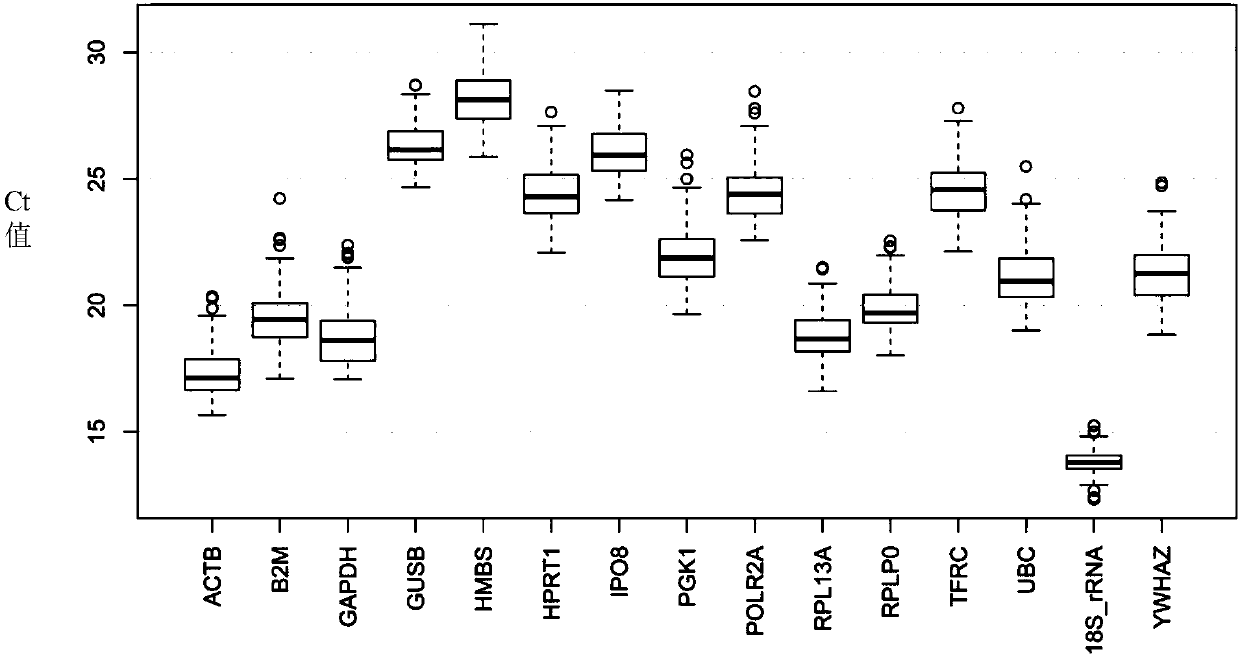
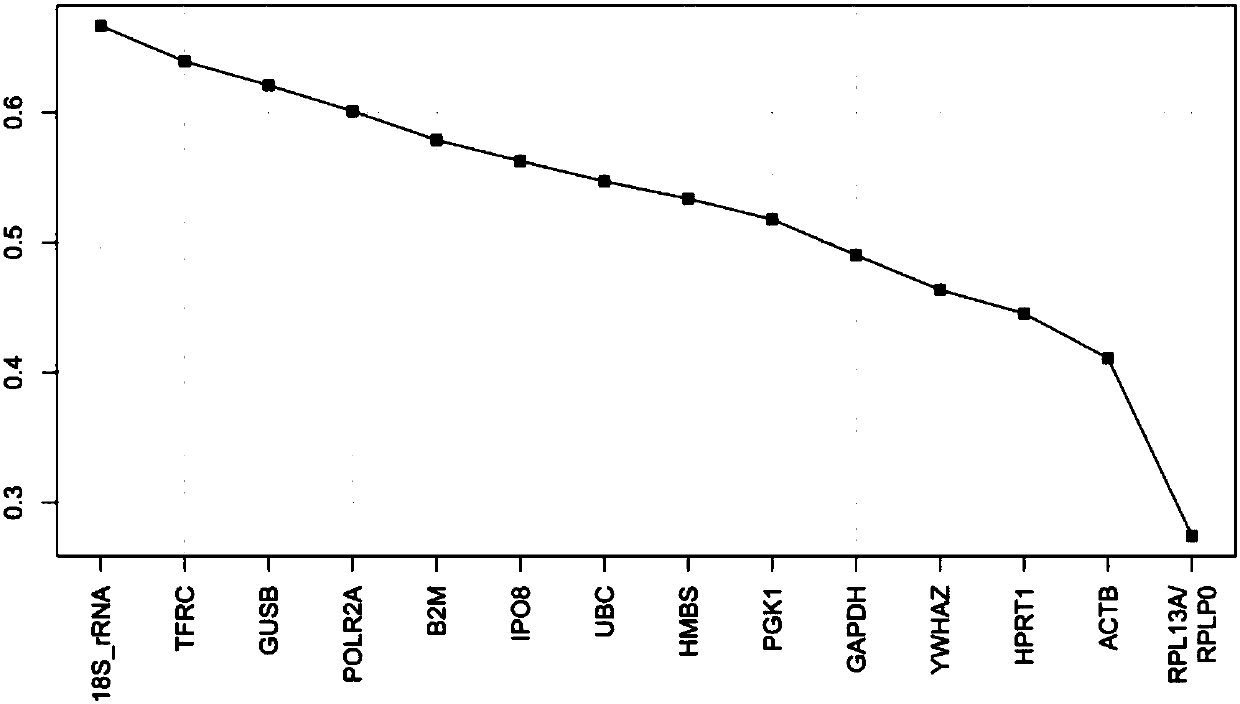
The invention provides application of HPRT1 (hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase 1), RPLP0 (ribosomal protein, large, P0) and HMBS (hydroxymethylbilane synthase) in the preparation as a reference gene in the preparation of kits or devices for studying or detecting polycystic ovarian syndrome. The invention also provides application of the HPRT1, RPLP0 and HMBS combination as kits or devices for studying or detecting hydroxymethylbilane synthase, such as real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR kits or gene chips.
Owner:SDIVF R&D CENT LTD
Chemoenzymatic synthesis of peptide beta-lactones and beta-hydroxy acids
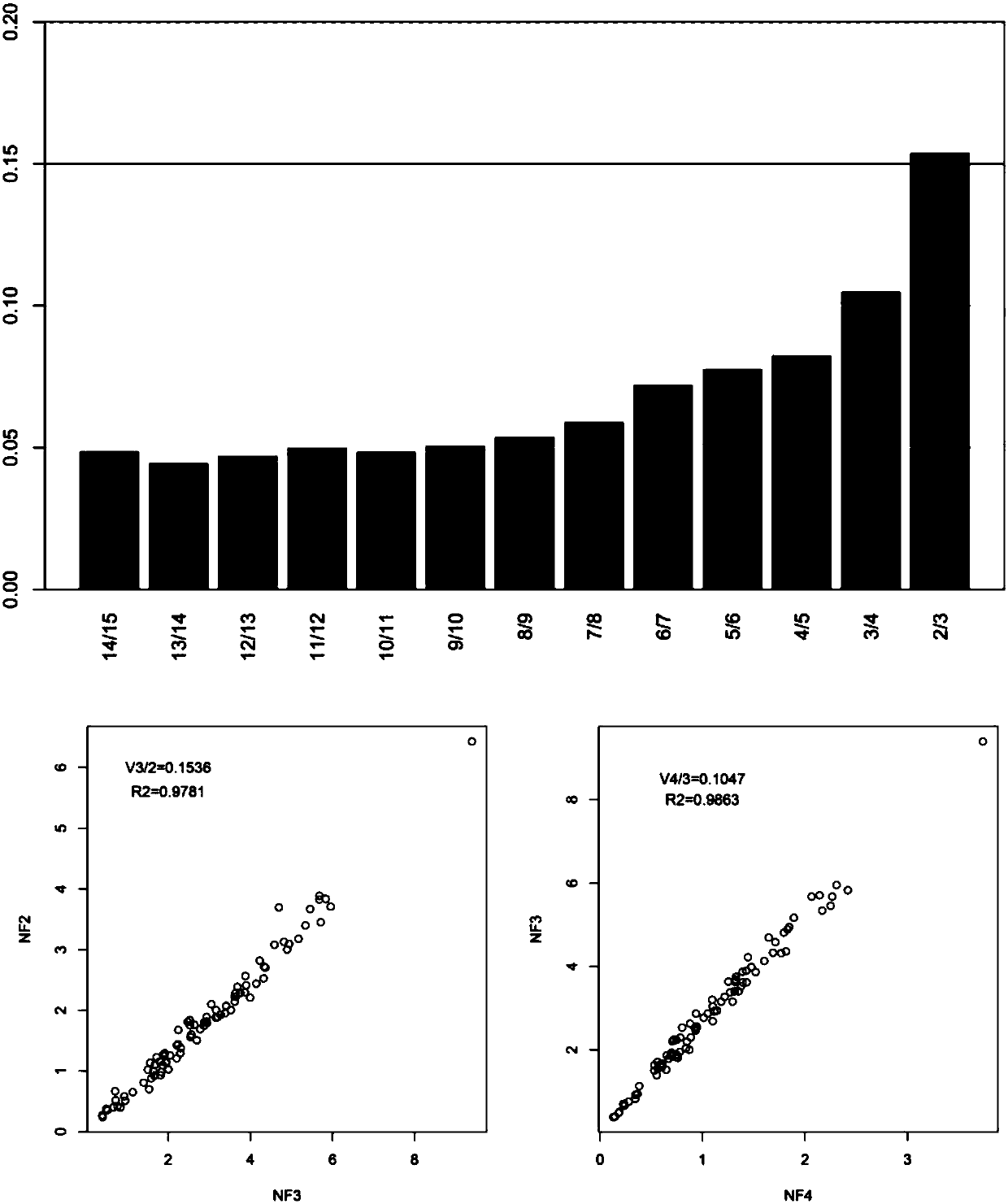
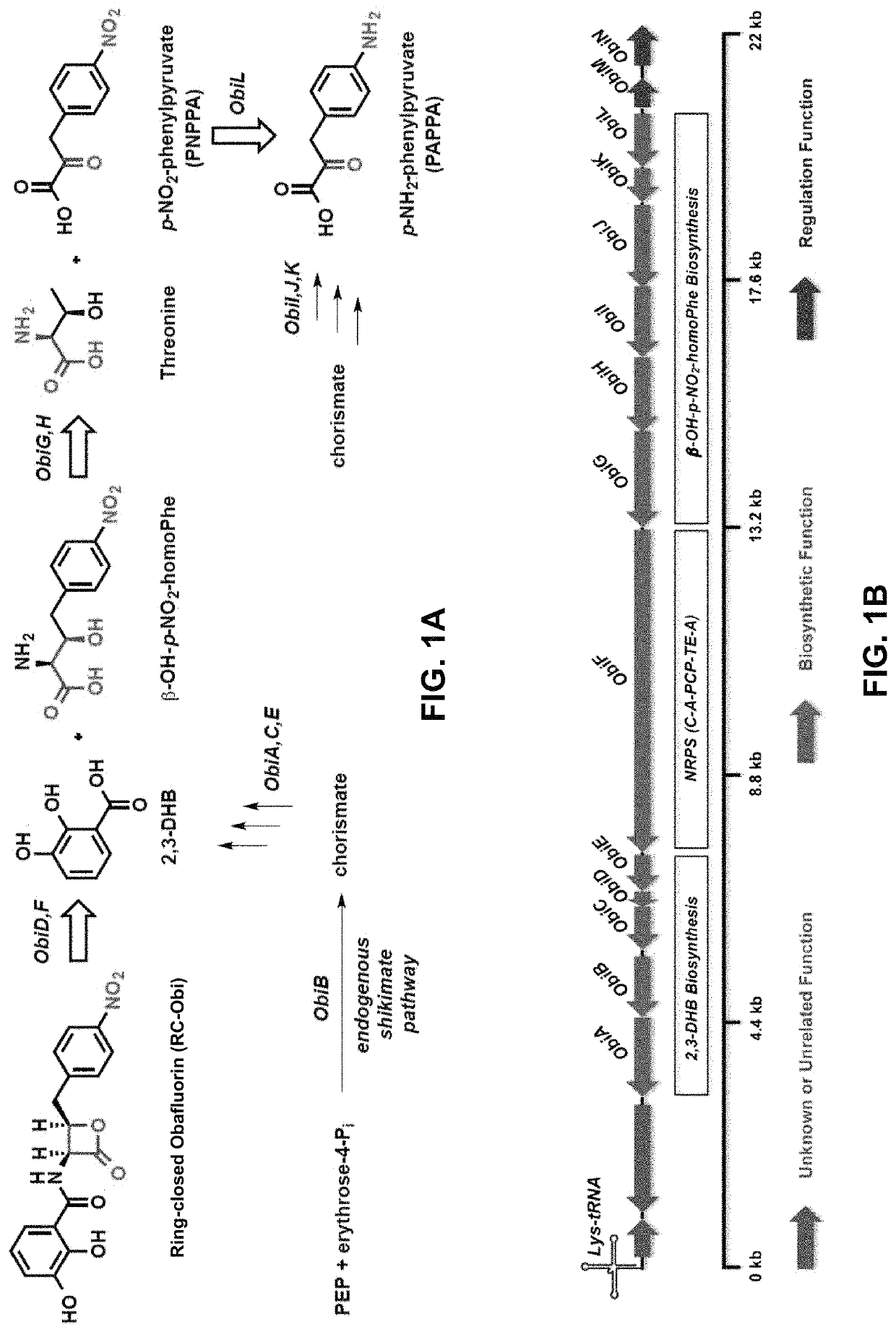
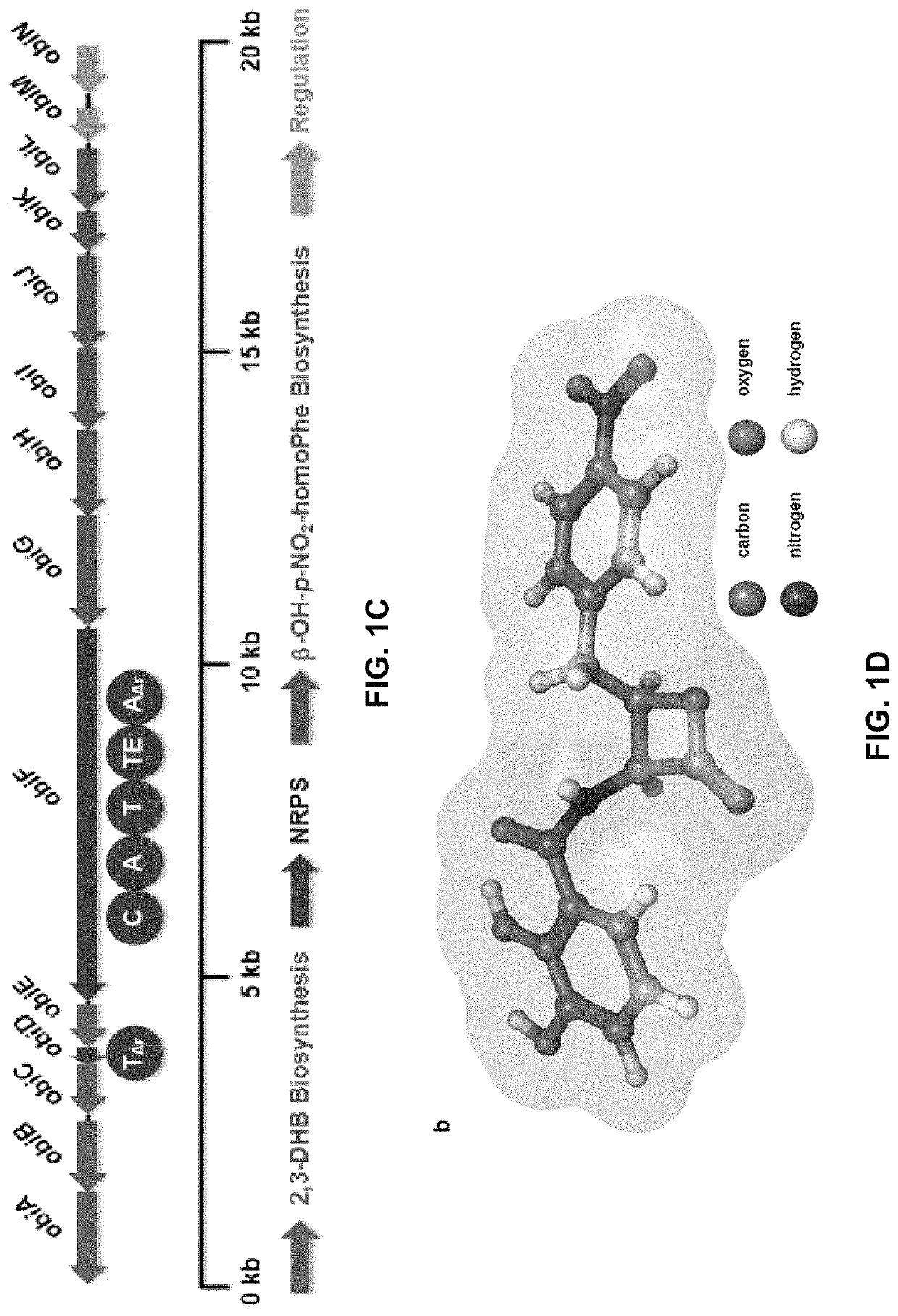
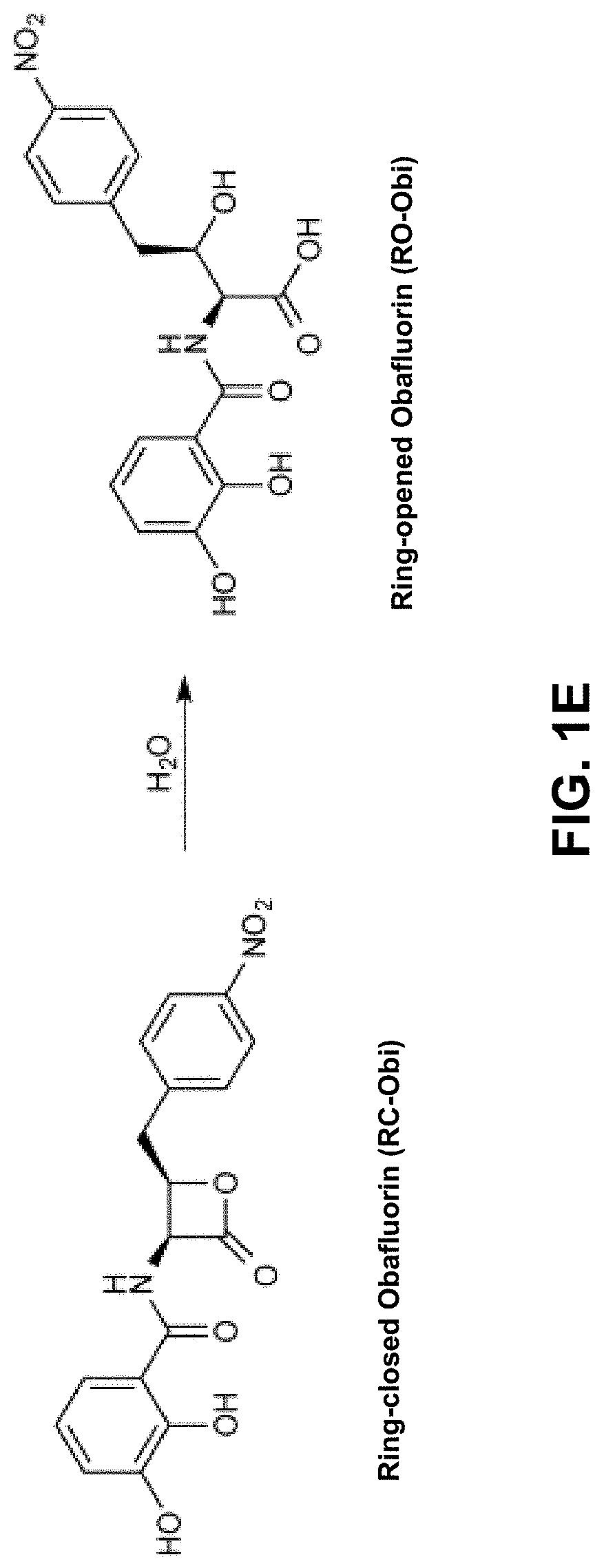
ActiveUS10655153B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRibosomal protein E-L30Ribosomal protein
Methods of producing peptide beta-lactones and beta-hydroxy acids are disclosed that include contacting a beta-hydroxy-alpha-amino acid, an aryl carrier protein (ObiD), and ATP with a non-ribosomal protein synthetase. A continuous flow reactor is disclosed that includes an elongate conduit with at least one region that includes a first region with a non-ribosomal protein synthetase immobilized to a substrate. The non-ribosomal protein synthetase of the continuous flow reactor is configured to contact a flow of a reaction mixture that includes a beta-hydroxy-alpha-amino acid and an aryl carrier protein. The non-ribosomal protein synthetase is further configured to release a peptide beta-lactone into the flow of the reaction mixture.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Organ transplant rejection and associated conditions
The application discloses markers associated with organ transplant rejection and associated conditions, and in particular provides materials and methods for the diagnosis, prognosis or treatment of chronic rejection of transplanted organ such as heart and kidney. Examples of the markers include ribosomal protein L7, β-transducin, 1-TRAF (also known as TANK) or lysyl-tRNA synthetase, or antibodies against these antigens.
Owner:IMPERIAL INNOVATIONS LTD
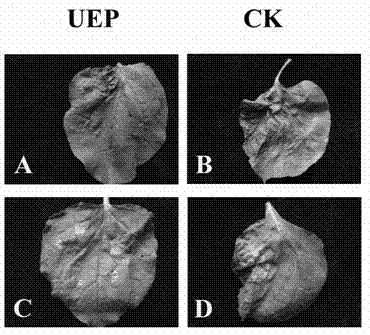
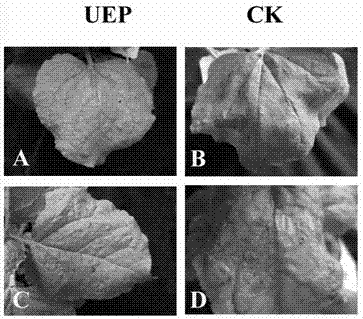
Plant disease-resistant regulation and control gene UEP and application thereof
ActiveCN102191253AStrong resistanceBroad spectrum of disease resistanceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyHigh resistance
The invention provides a plant disease-resistant regulation and control gene. An open reading frame of the gene is 471 bp in length; and the gene encodes a ubiquitin extended protein consisting of 156 amino acids. The N end of the gene coded product is a ubiquitin molecule comprising 76 amino acids and the C end of the gene coded product is 40S ribosomal protein s27a comprising 80 amino acids. The gene is a high-quality disease-resistant gene resource. A disease-resistant material obtained by the gene has high resistance and a wide disease-resistant spectrum and can promote growth of plants. The gene widely joints in the regulation and control on resistance of various diseases caused by various pathogens by translating various kinds of targeted proteins and regulating modification after translation and joints in the regulation and control on growth and development of the plants. Due to overexpression of a tobacco UEP gene, the resistance of tobacco to various diseases such as Leptosphaeria maculans, wildfire, viral disease and the like is obviously improved. The plant disease-resistant regulation and control gene is applicable to creation and breeding of disease-resistant plant materials and varieties which have high resistance and wide disease-resistant objects and can promote growth of the plants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
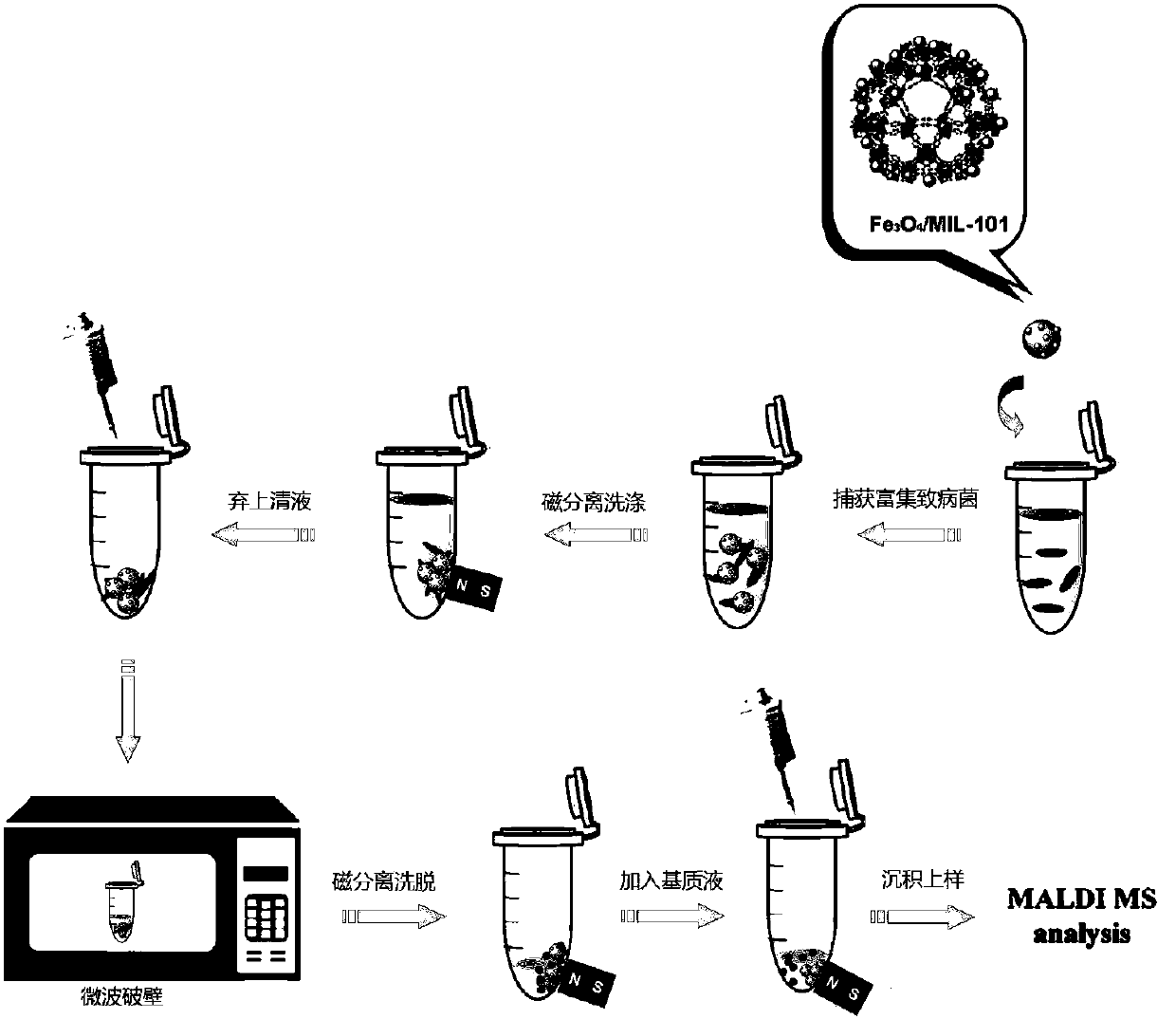
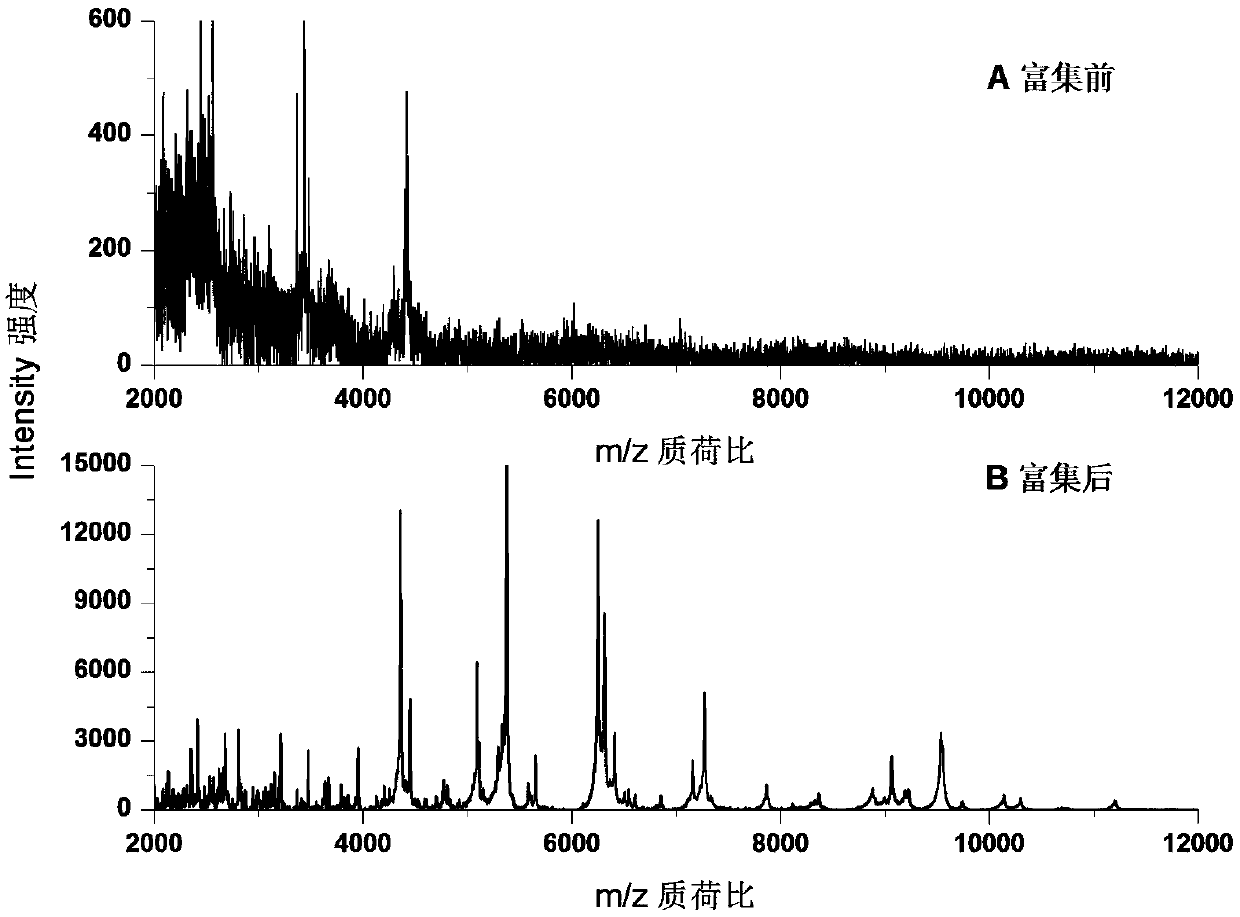
Method for rapidly identifying strain-level pathogenic bacteria in food through double adsorption
InactiveCN108020674AHigh-resolutionStrengthen the effect of microwave wall breakingBiological testingProtein DatabasesRibosomal protein E-L30
The invention discloses a method for rapidly identifying strain-level pathogenic bacteria in food through double adsorption. The method comprises main steps as follows: a) strain-level pathogenic bacteria in liquid food are adsorbed by MIL-101 magnetic particles, and wall breaking is performed under microwave assistance; after wall breaking, to-be-identified pathogenic bacterium protein is rapidlyenriched through the MIL-101 magnetic particles; b) a mass spectrum graph of the pathogenic bacterium protein is collected through MALDI / TOF MS (matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization / time of flight mass spectrometry); c) a Tagident search tool is used for performing protein database searching on mass spectrum peak, and ribosomal protein is selected; d) a rapid microorganism identification database is sought by use of ribosomal protein obtained through searching, and the attributes of the strain-level pathogenic bacteria are determined. The method has the advantages of simplicity and rapidness. Enrichment of pathogenic bacteria, wall breaking and mycoprotein enrichment are integrated, finally, a ribosomal protein database is used for rapidly identifying the pathogenic bacteria, and the strain level of pathogenic bacteria in the liquid food is rapidly identified.
Owner:TIANJIN MODERN VOCATIONAL TECH COLLEGE
Gene of sheep type brucella M5 mycopremna ribosomal protein L7, its encoding protein and application
InactiveCN101153284AEfficient detectionEffective preventionOrganic active ingredientsBacterial antigen ingredientsRibosomal proteinADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides a gene of ribosomal protein L7 / L12 of strain M5 of brucellaovis as well as the encoding protein and the application of the gene. The encoding protein of the gene of the present invention has the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.2. Gene vaccine can be prepared by utilizing the gene of the present invention; siRNA or shRNA or microRNA, which is designed and synthesized according to the sequence of the present invention, can be used for gene silencing. Developing a recombinant protein vaccine or exploring a detection kit can be realized by preparing the expressing protein of the gene of the present invention, thereby providing new effective solving ways to brucellosis.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
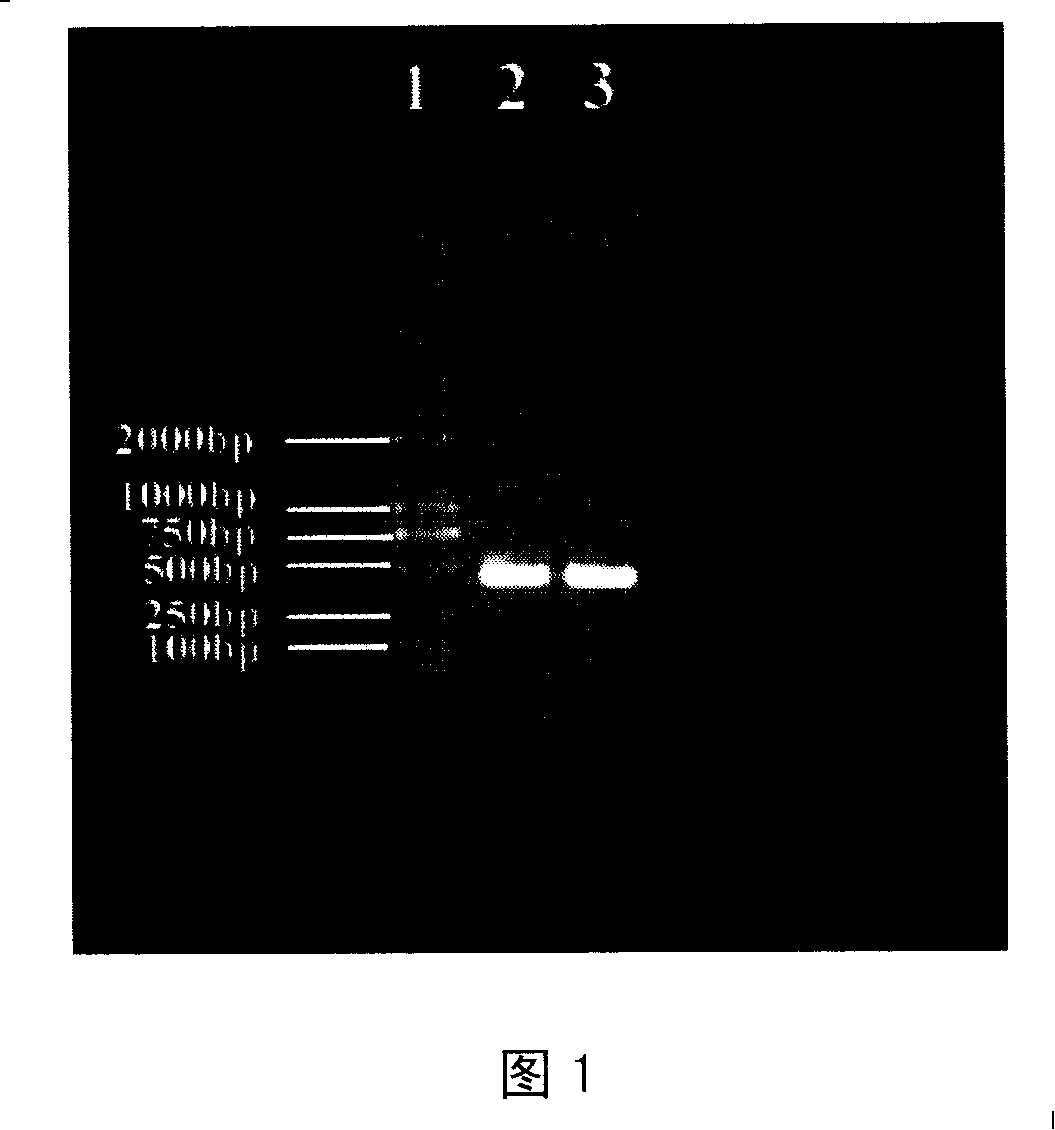
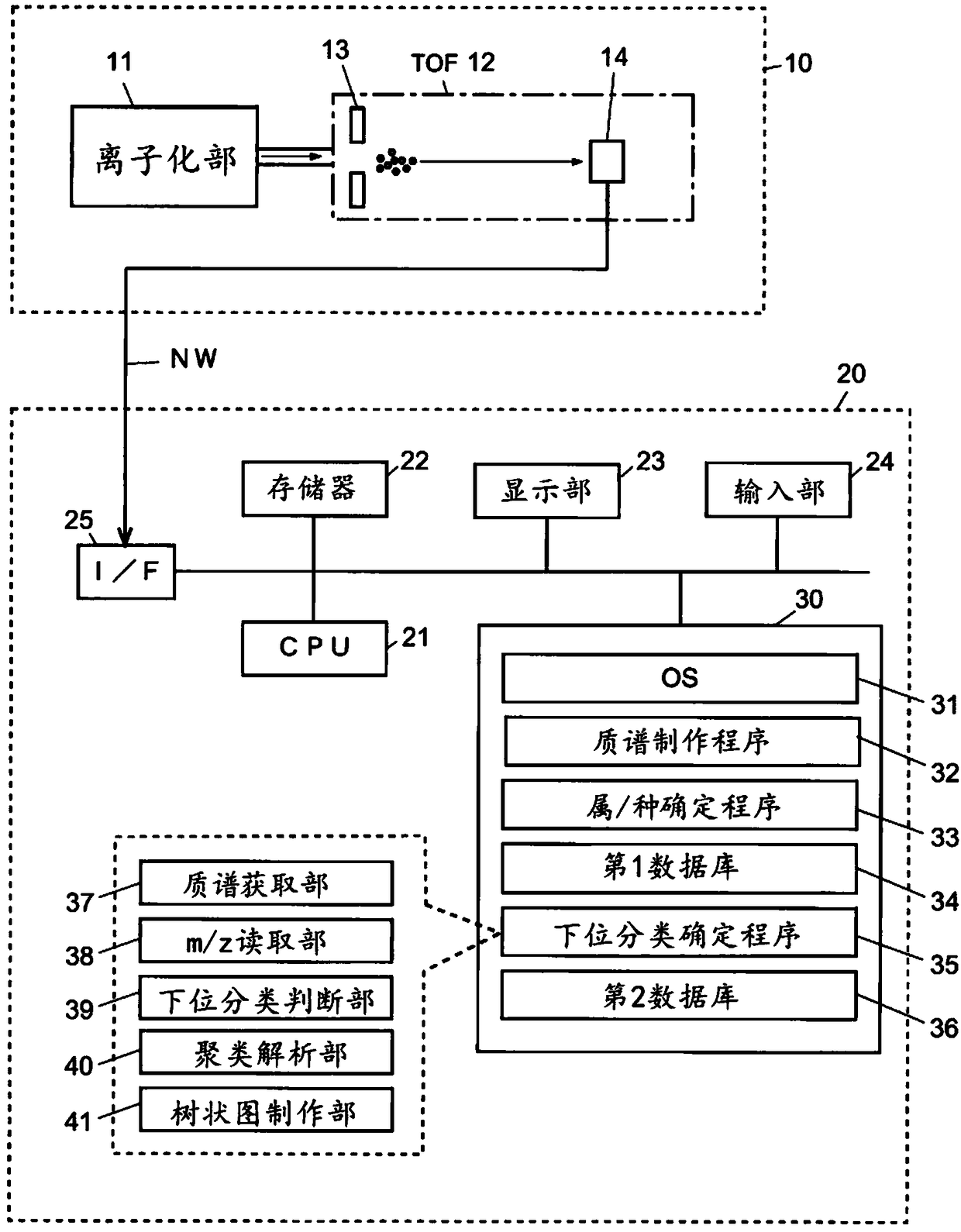
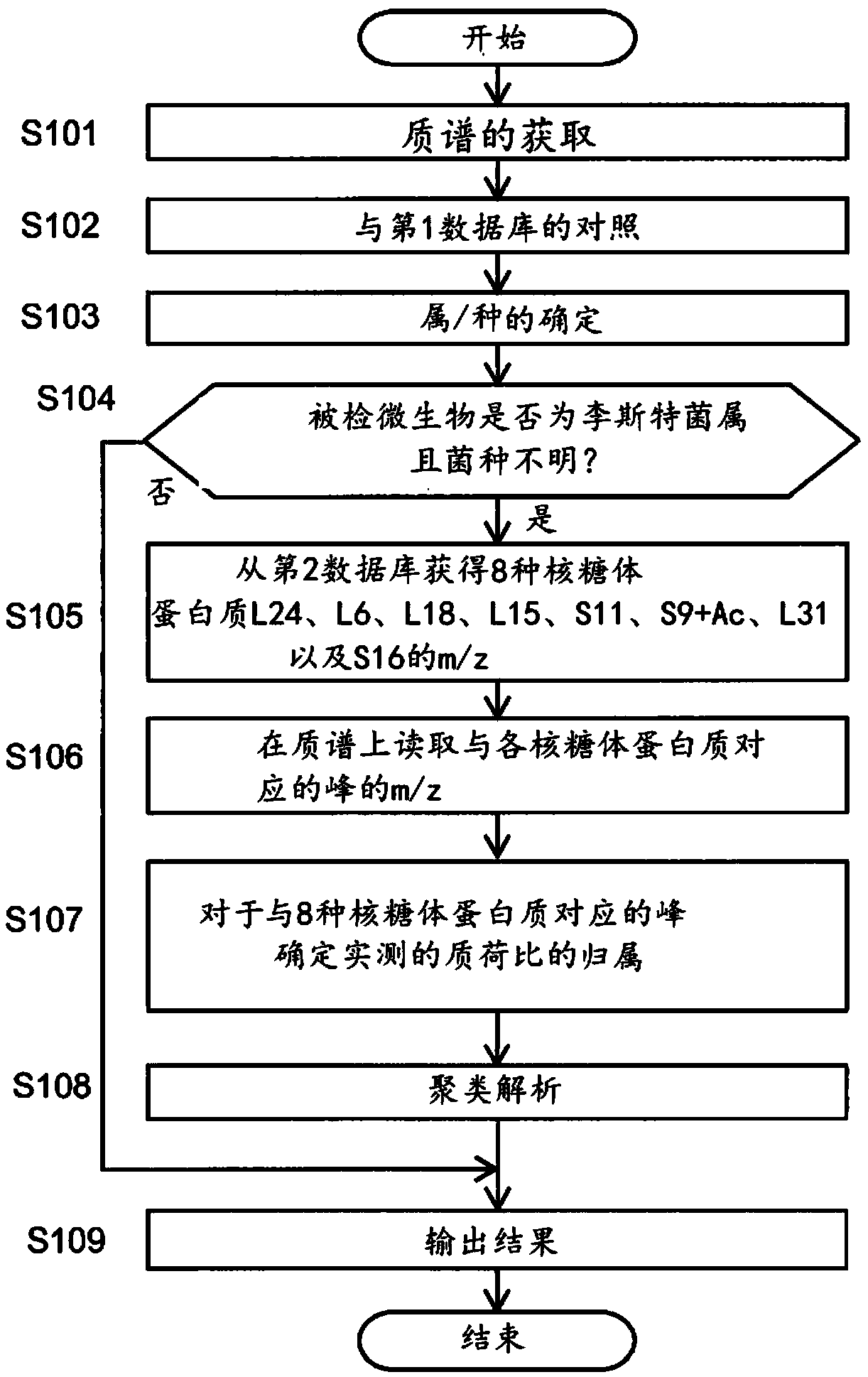
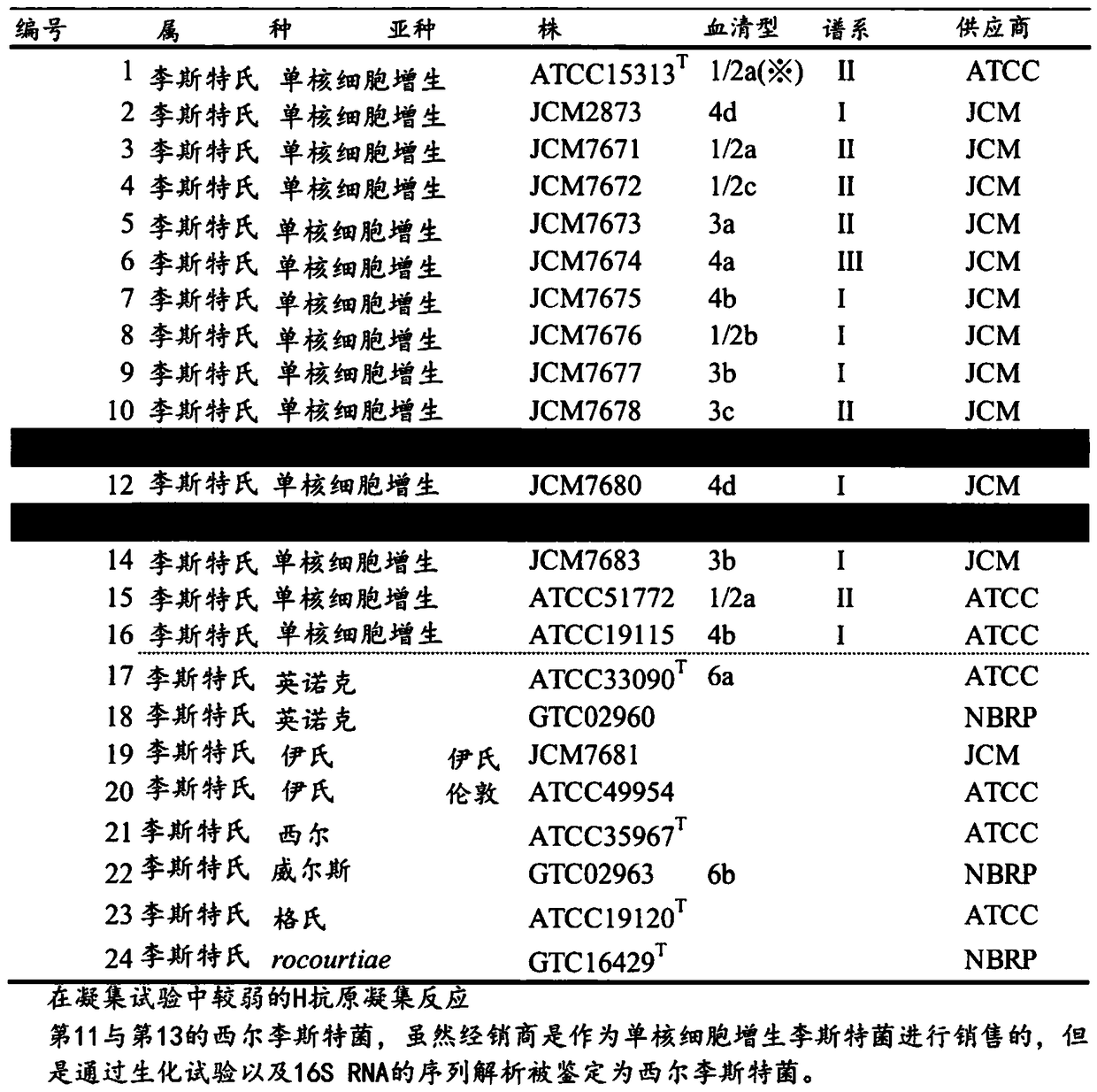
Microorganism identification method
PendingCN109154018AGood reproducibilityEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometric analysisRibosomal protein E-L30Microorganism
Provided is a microorganism identification method involving the selection and use of a marker protein that makes it possible to quickly identify bacterial species of the genus Listeria with good reproducibility. The microorganism identification method comprises: a step in which a sample containing microorganisms is subjected to mass spectrometry and a mass spectrum is obtained; a reading step in which the mass-to-charge ratio m / z of peaks derived from a marker protein is read from the mass spectrum; and an identification step in which the mass-to-charge ratio m / z is used as a basis to identifywhether the microorganisms included in the sample include any bacterial species of the genus Listeria. The microorganism identification method is characterized in that one or more of the following seventeen types of ribosomal proteins is used as the marker protein: L3; L4; L23; L2; L24; L6; L18; S5; L15; S13; S11; L10; L21; L13; S9; L31; and S16. The microorganism identification method is also characterized in that among the seventeen types of ribosomal proteins, particularly one or more of the following eight types of ribosomal proteins is used: L24; L6; L18; L15; S9; L31; and S16.
Owner:SHIMADZU SEISAKUSHO CO LTD +1
Method for discriminating microorganism
ActiveUS20190242903A1Rapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisEscherichia coliMicroorganism
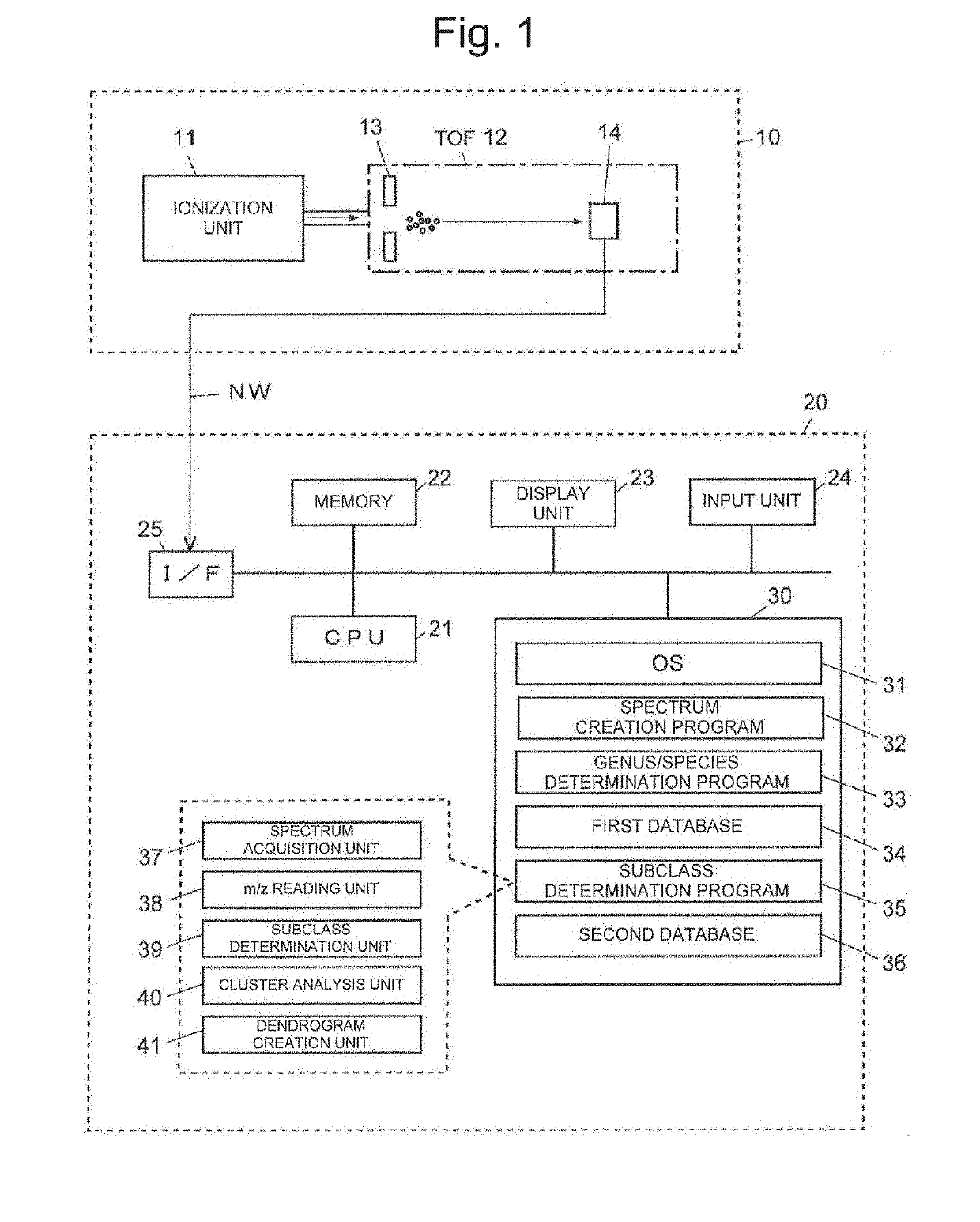
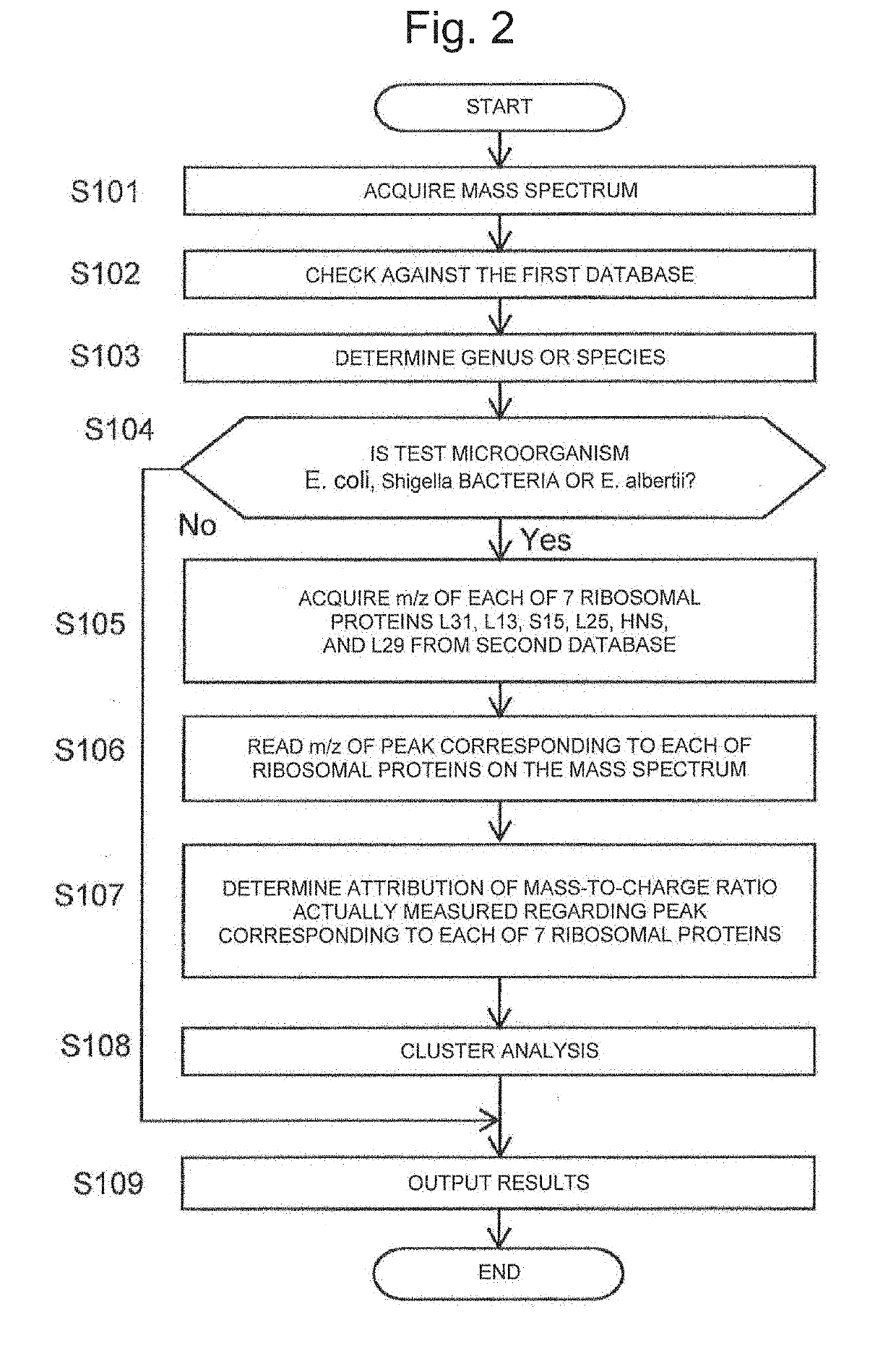
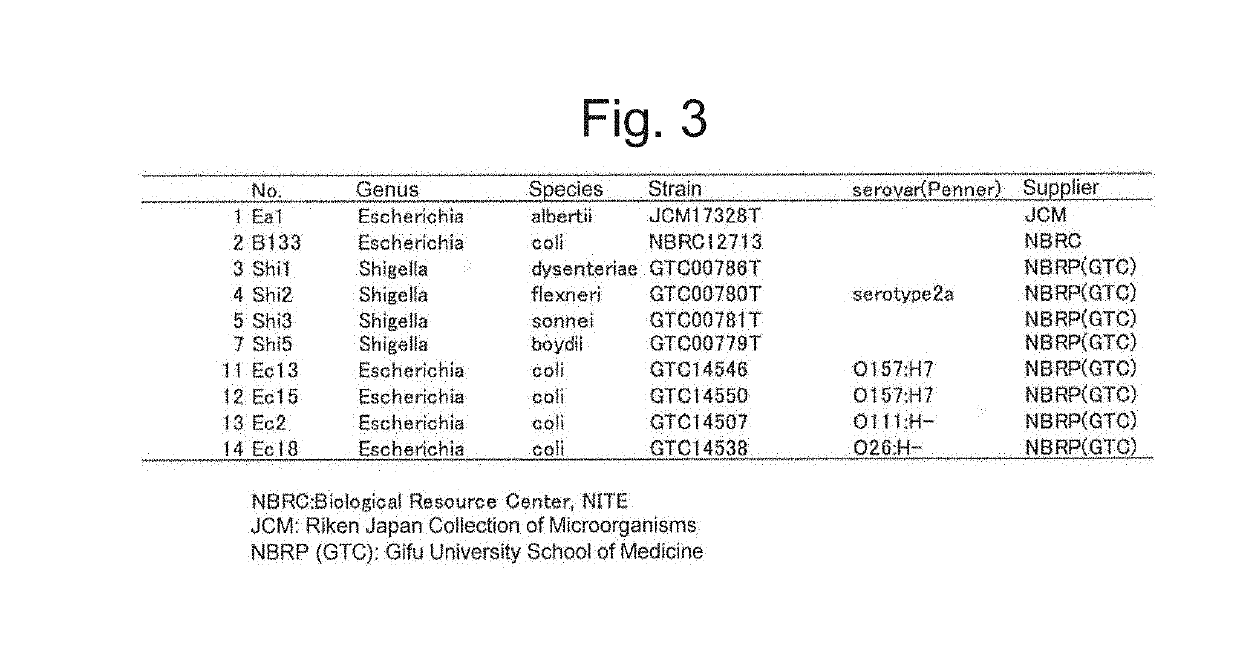
To provide a method for discriminating a microorganism including: a step of subjecting a sample containing a microorganism to mass spectrometry to obtain a mass spectrum; a reading step of reading a mass-to-charge ratio m / z of a peak derived from a marker protein from the mass spectrum; and a discrimination step of discriminating which bacterial species of Escherichia coli, Shigella bacteria, and Escherichia albertii the microorganism contained in the sample contains based on the mass-to-charge ratio m / z, in which at least one of 13 ribosomal proteins S5, L15, S13, L31, L22, L19, L20, L13, S15, L25, HNS, HdeB, and L29 is used as the marker protein.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP +1
Vaccine composition for controlling ectoparasite infestations
ActiveUS20130273095A1Enhance immune responseHarm viabilityProtozoa antigen ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisRibosomal protein
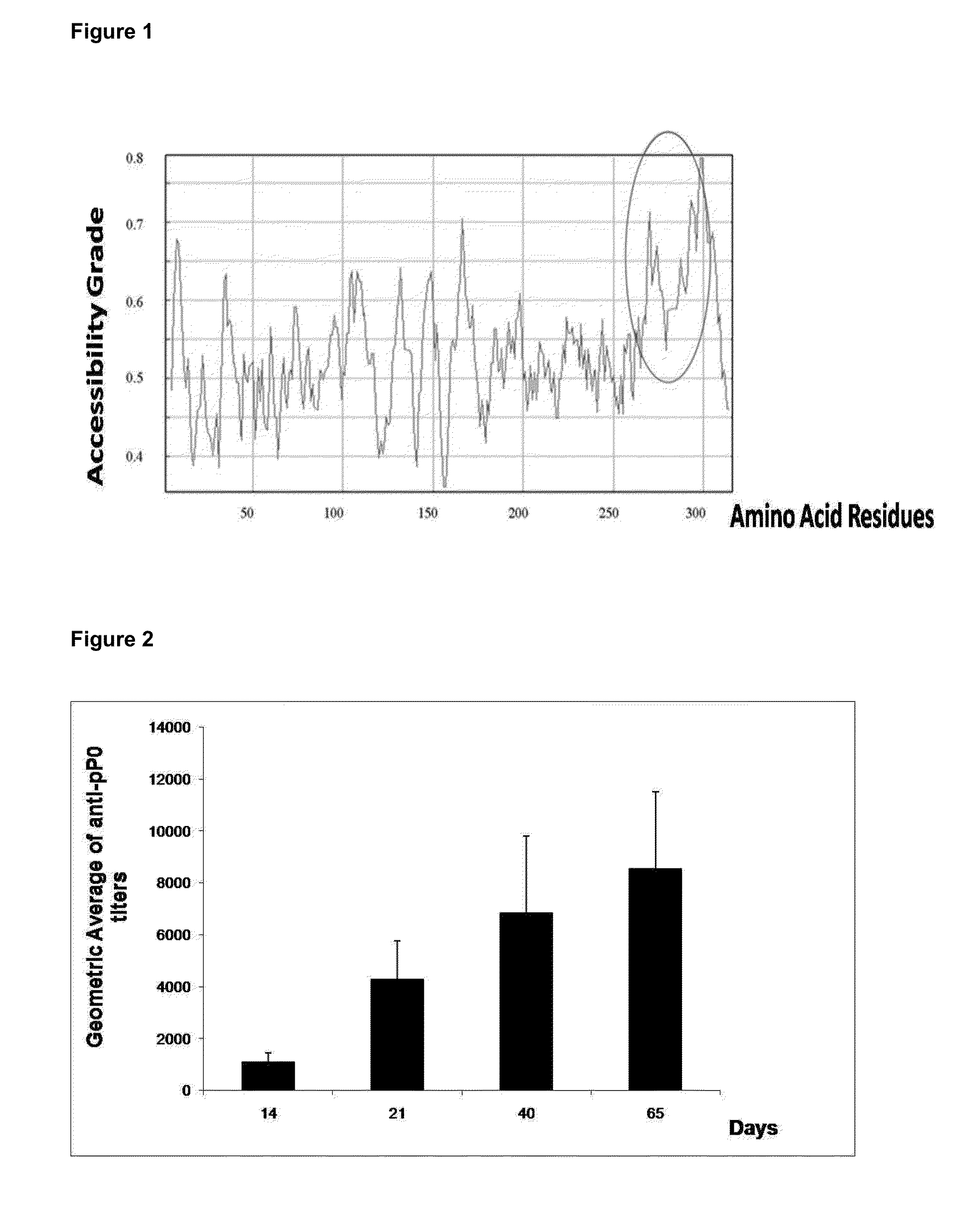
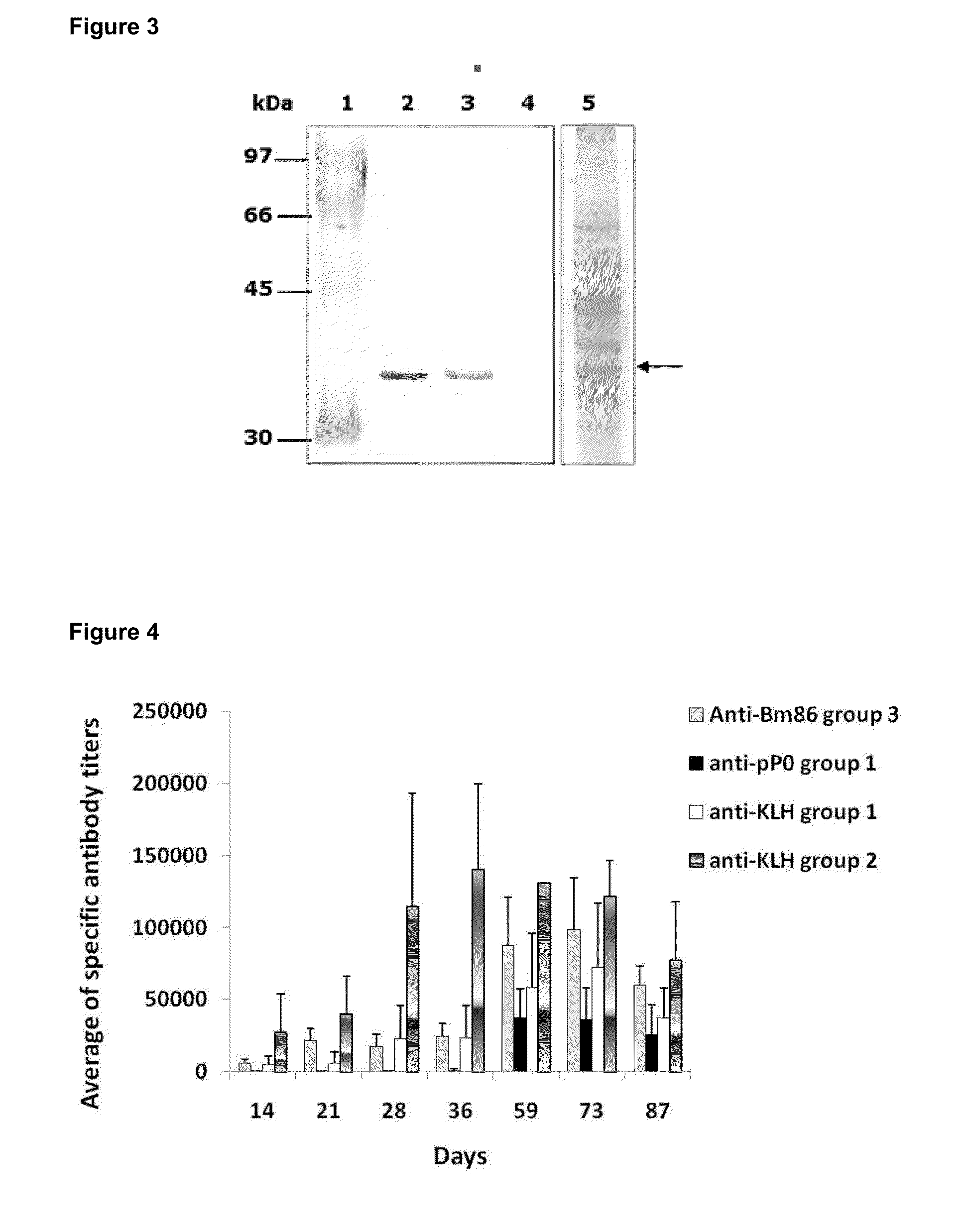
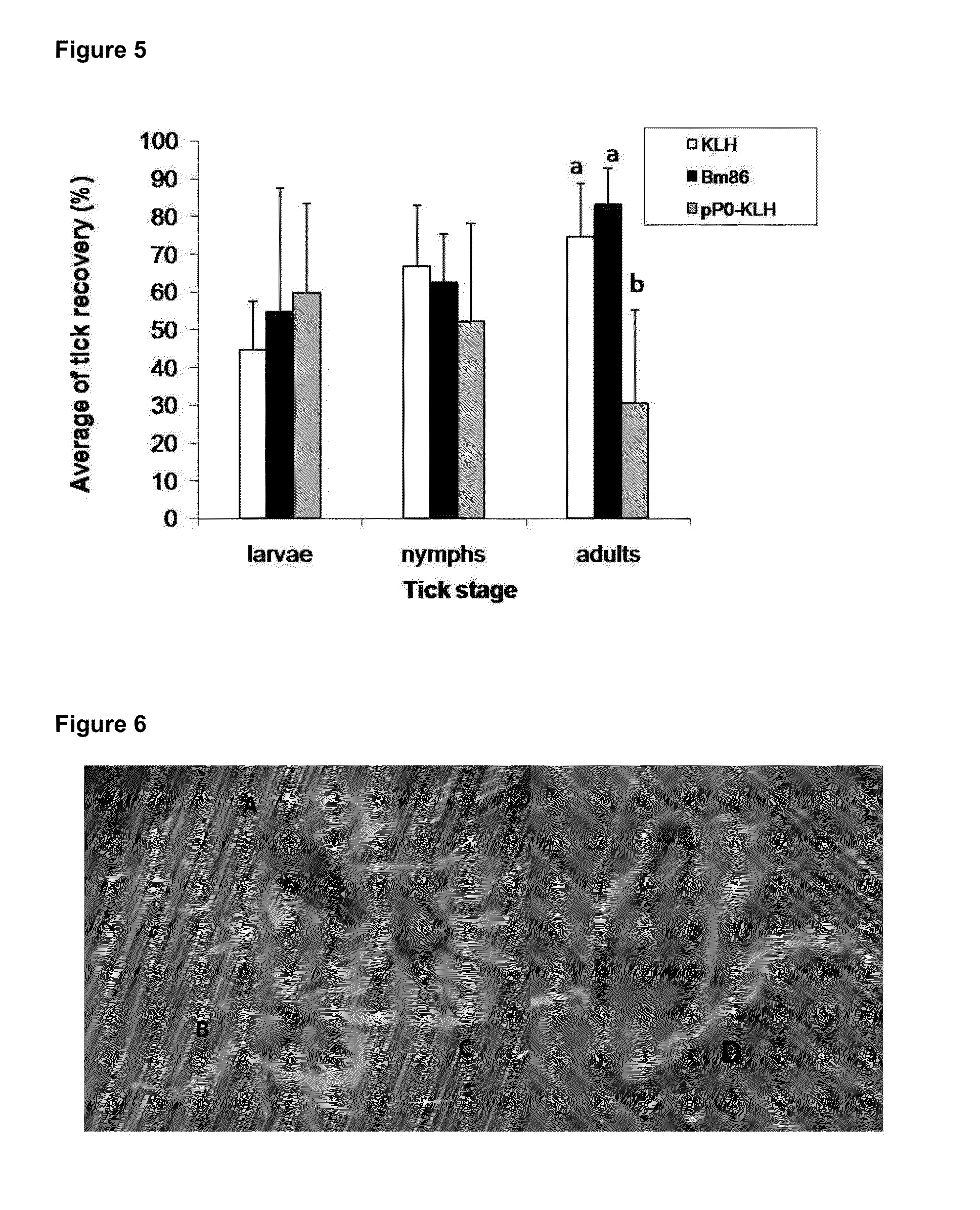
The present invention relates to the use of a peptide of P0 ribosomal protein in the manufacture of a vaccine composition to control of ectoparasite infestations and therefore the transmission of their associated pathogens. This peptide is located between 267 and 301 amino acids of the P0 protein, and can be obtained by recombinant means or by chemical synthesis. This peptide can be fused to a carrier protein or peptide, or an immuno-carrier and be included in an oily formulation. The formulations comprising the peptide vaccine confer protection against ticks and ectoparasites known as “sea lice” without generating autoimmunity in the host organism. Among these ticks may be mentioned species as Rhipicephalus microplus, Rhipicephalus sanguineus and Ixodes scapularis, and between sea lice are those of the Caligus and Lepeophtheirus genera.
Owner:CENT DE ING GENETICA & BIOTECNOLOGIA
Mitochondrial ribosomal proteins as aging regulators
InactiveUS9180134B2Compounds screening/testingTetracycline active ingredientsAge related diseaseMitochondrial ribosome
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Drug target of tumor related diseases and application thereof
The invention discloses an application of a human ribosomal protein L10 as a drug target for preventing and treating tumor related diseases. The amino acid sequence of the human ribosomal protein L10 is represented by the SEQ ID No.1. The human ribosomal protein L10 can be used as a drug target for in-vitro screening to prevent and treat tumor related diseases.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Drug for inhibiting proliferation of tumor cells and application thereof
InactiveCN101775073AReduce ubiquitin ligase activityImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsRibosomal proteinUbiquitin ligase activity
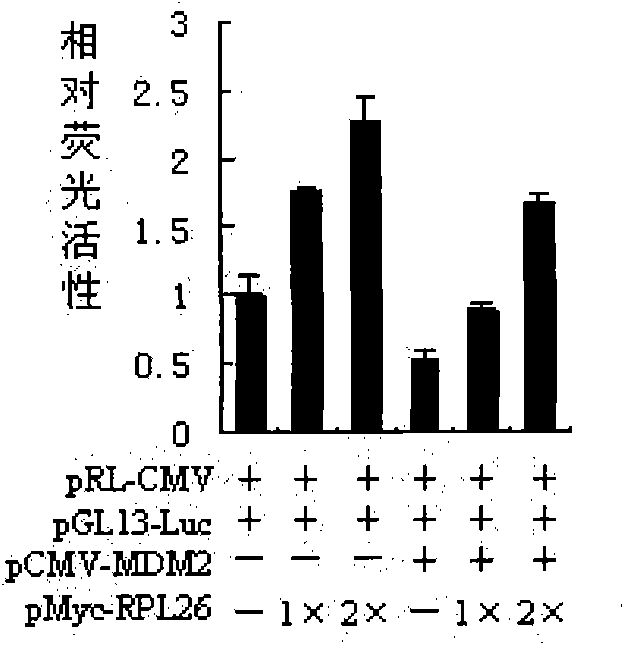
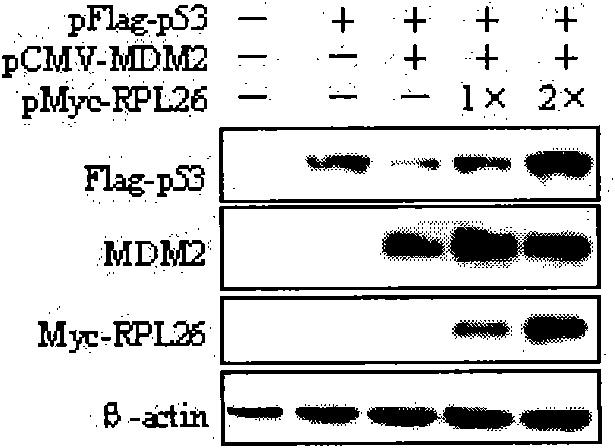
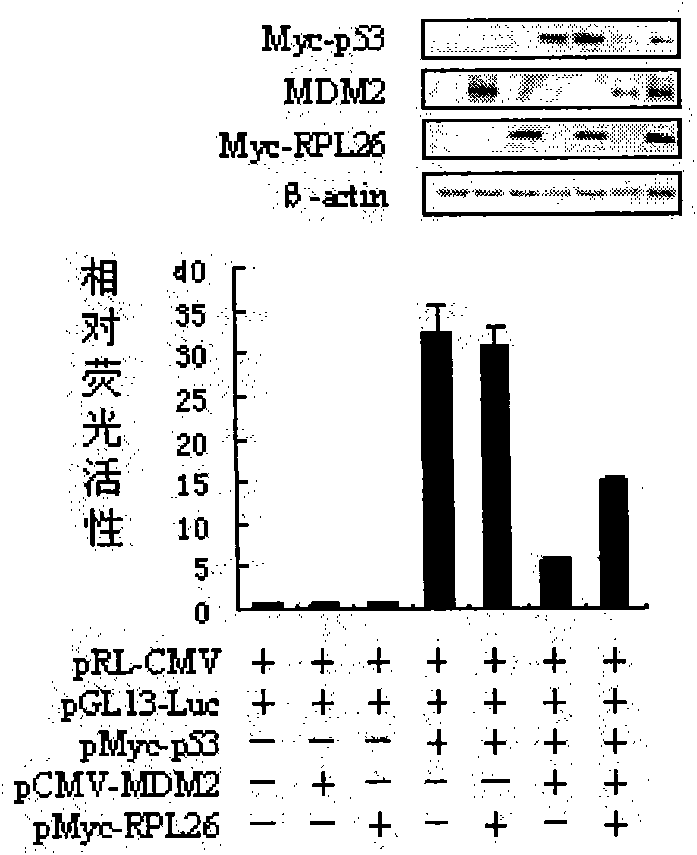
The invention discloses a polypeptide for inhibiting proliferation of tumor cells, which is of a fragment with maximum length of 145 amino acid residues at 46-100 position from N-terminal, comprising ribosomal protein RPL26. The reporter gene experiments, Western blotting, co-immunoprecipitation and cell proliferation detection experiments confirm that RPL26 as well as MDM2 and p53 form a complex, and the combination of RPL26 and MDM2 can obviously reduce the ubiquitin ligase activity of MDM2, thereby improving the stability and transcriptional activation of p53. The overexpression of RPL26 can obviously inhibit the proliferation of the tumor cells, and the function is related to the activity of p53. RPL26 can be assisted for the clinical treatment of cancer and has great significance.
Owner:INST OF RADIATION MEDICINE ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com