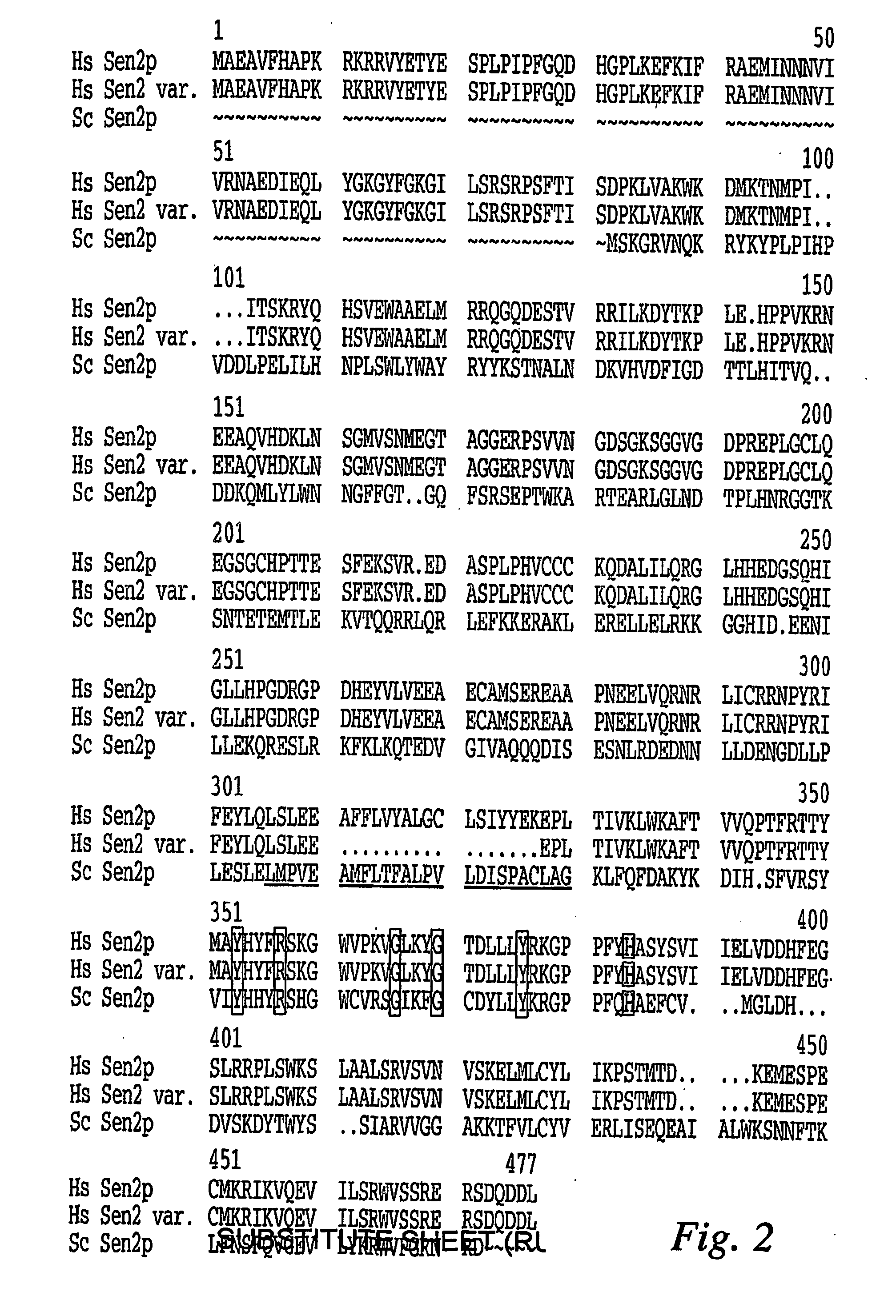
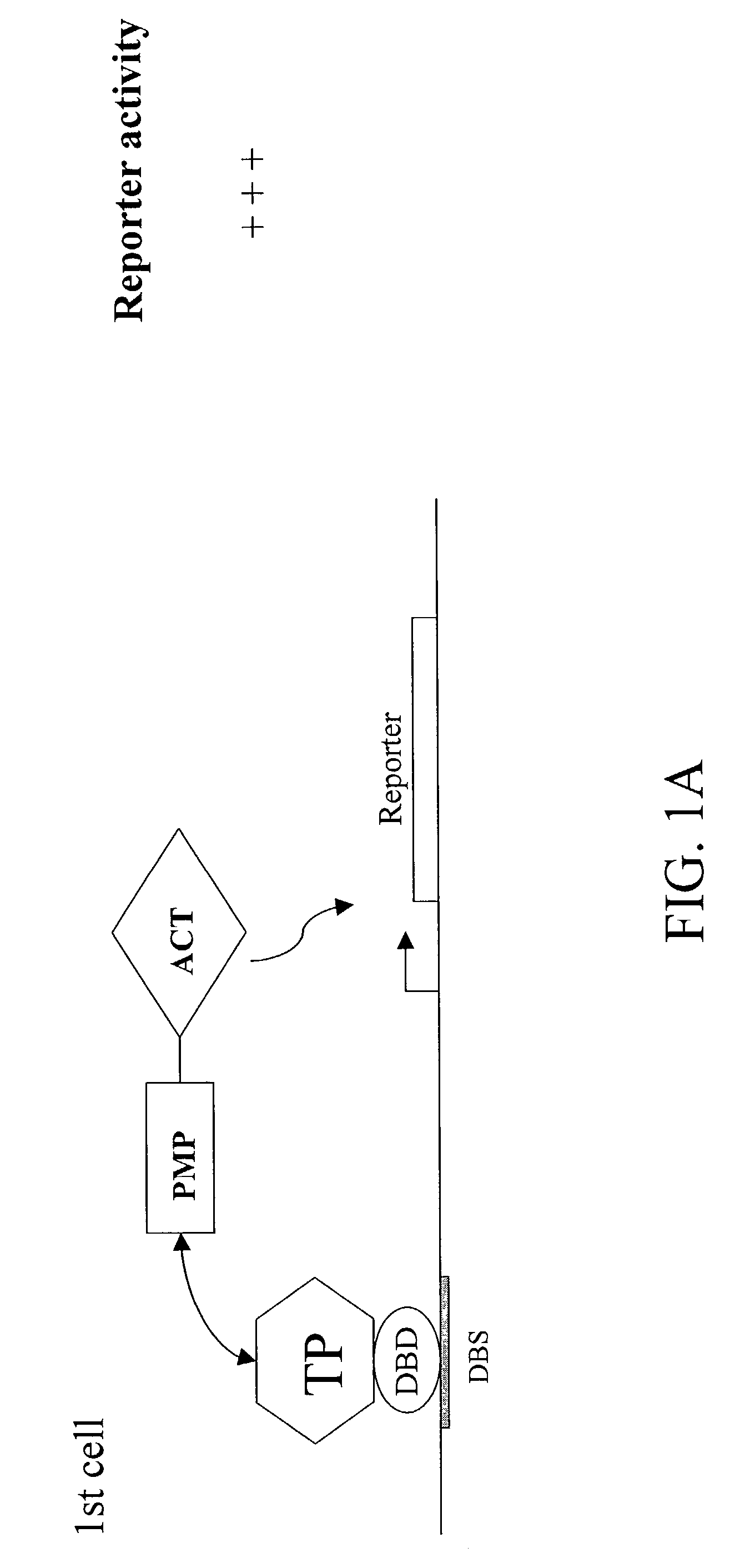
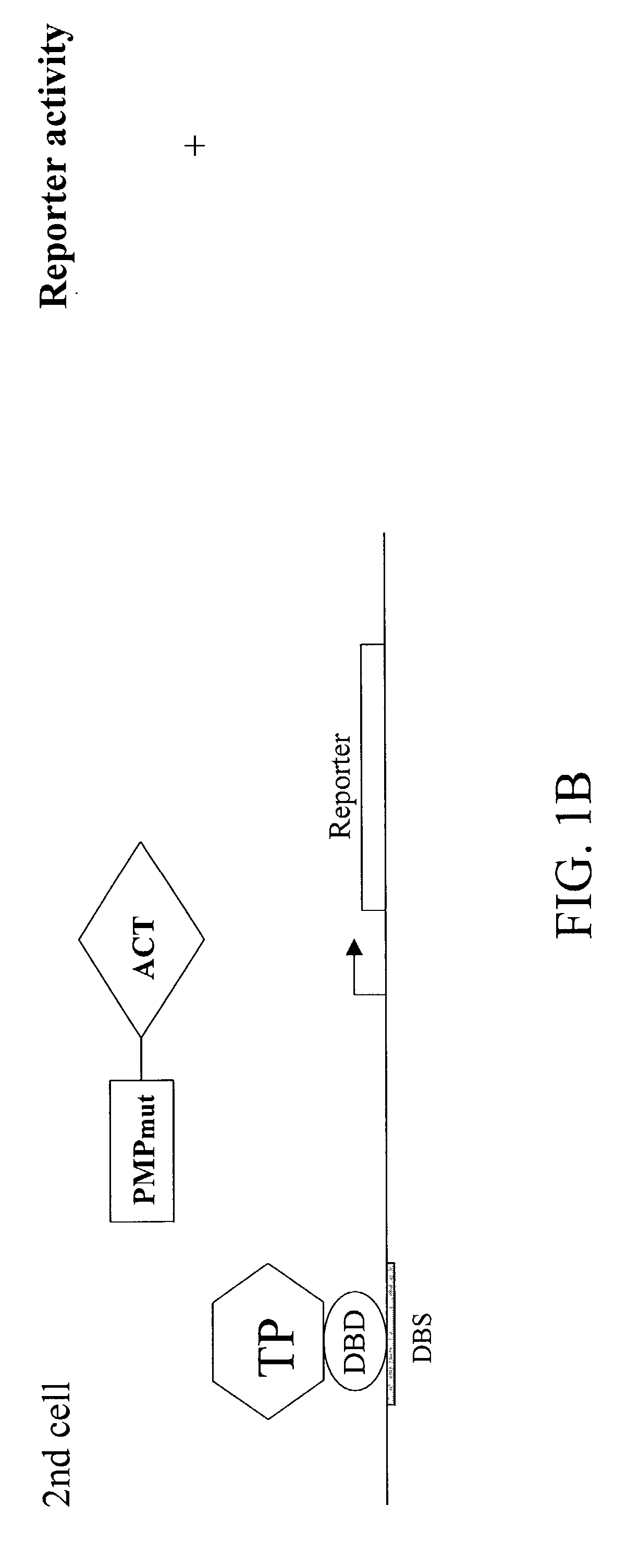
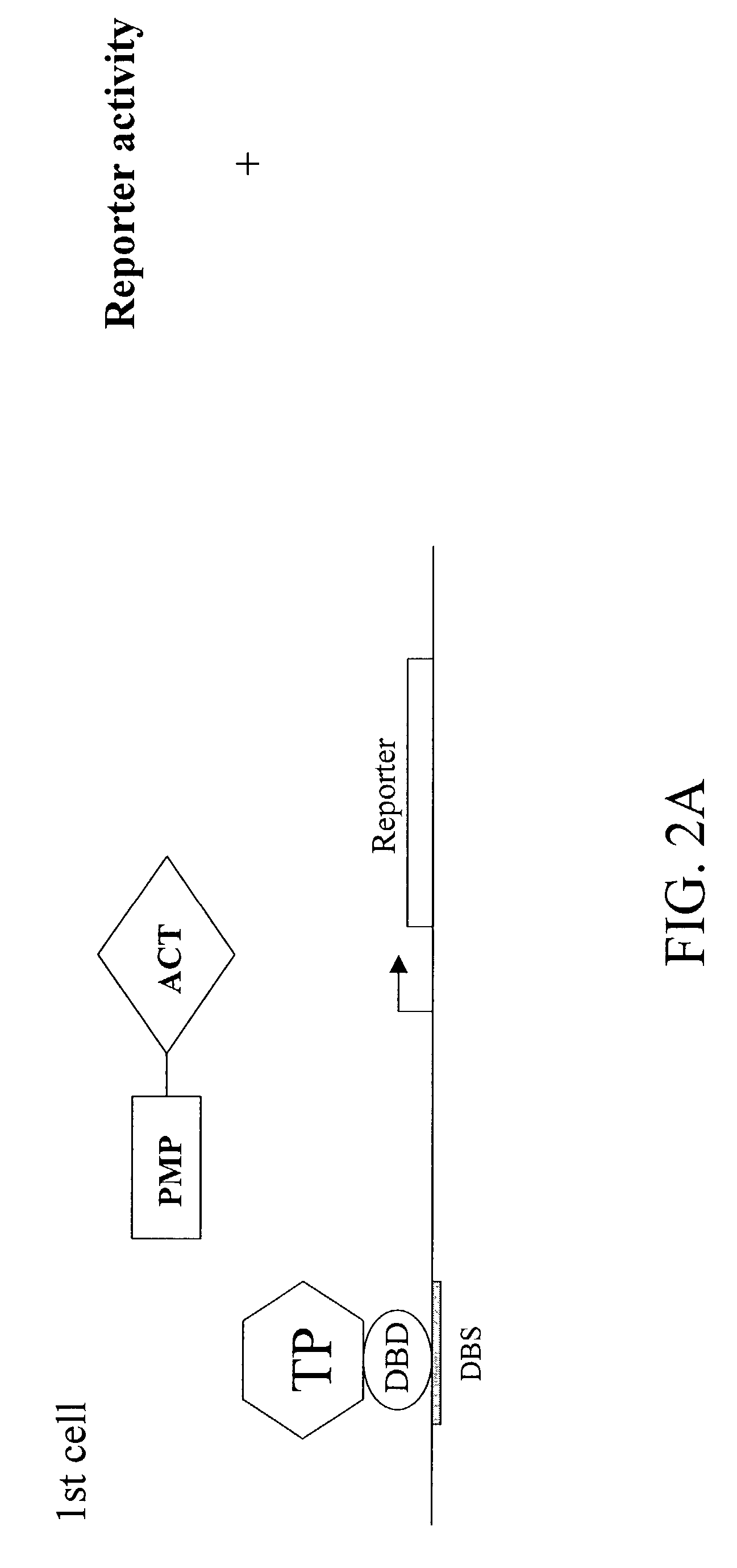
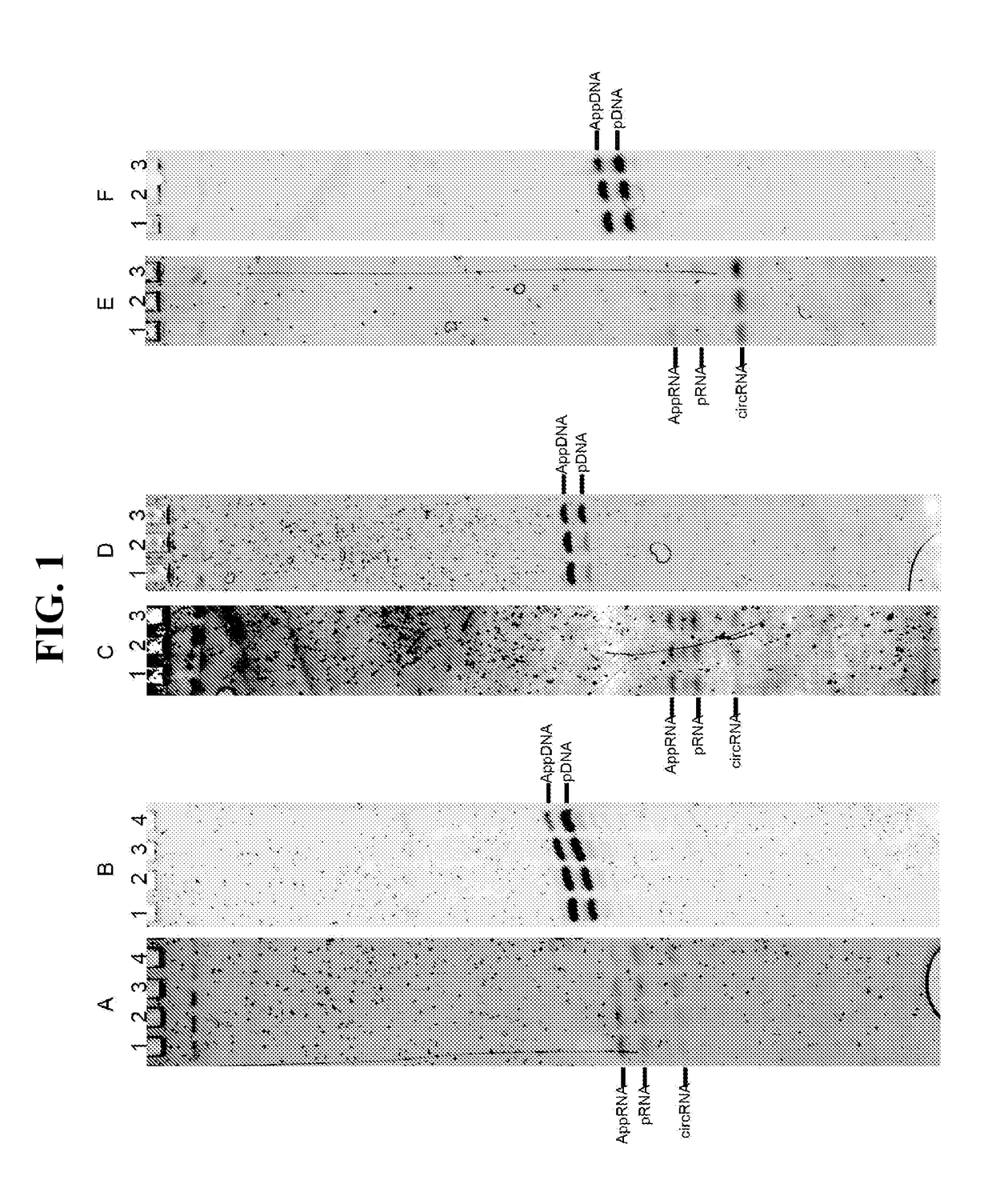
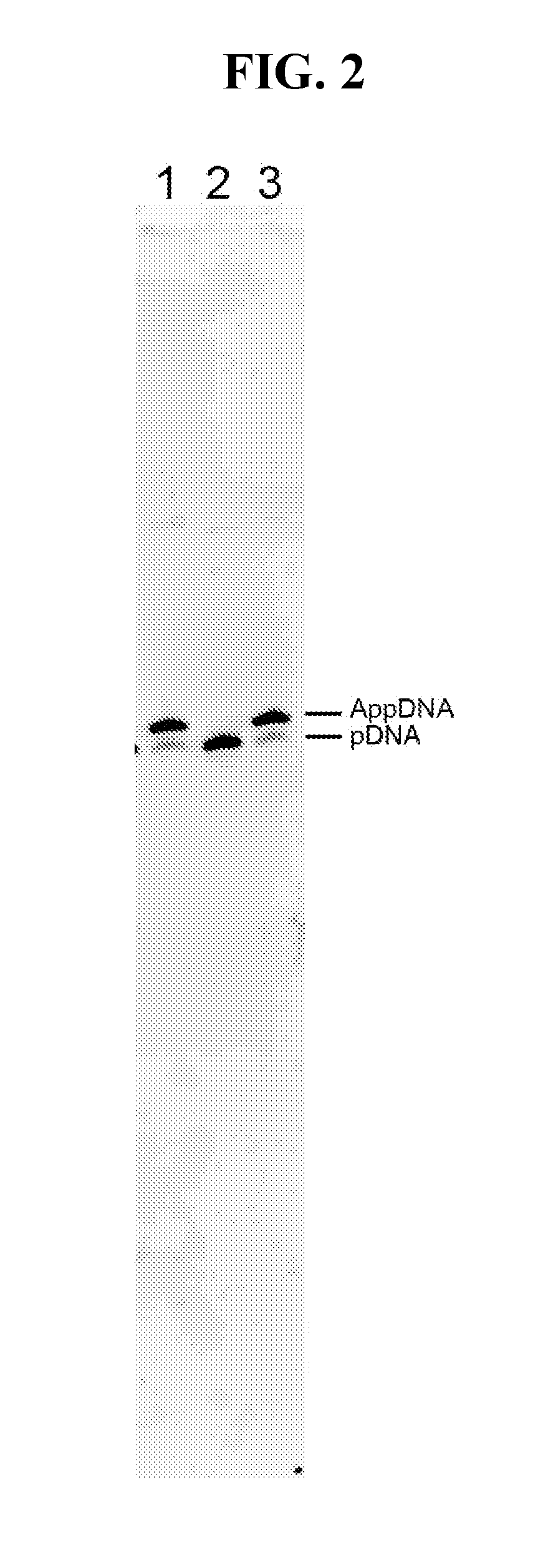
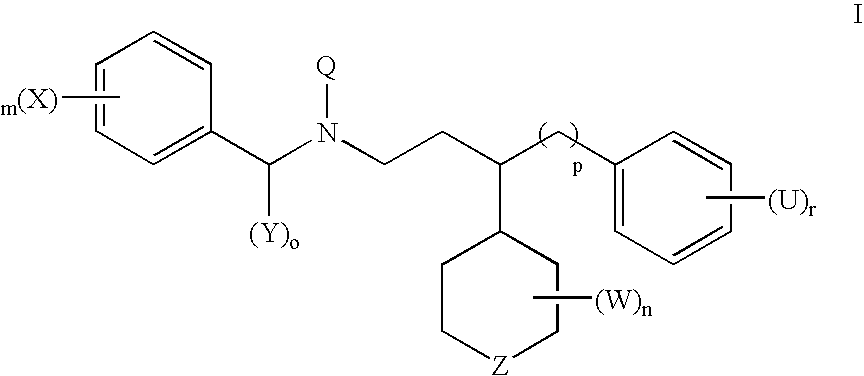
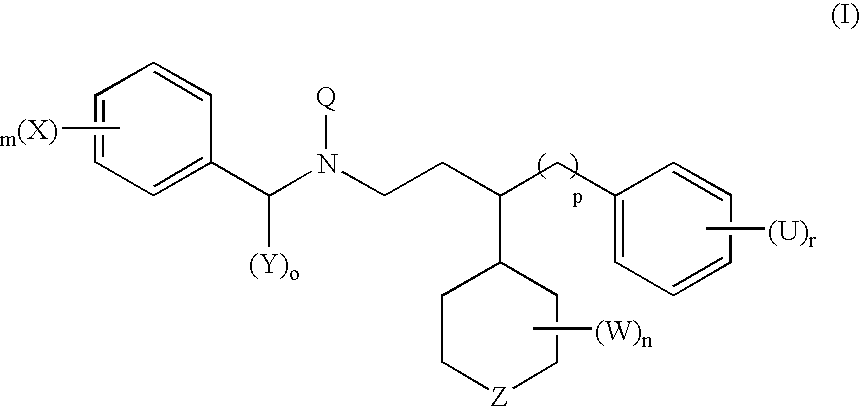
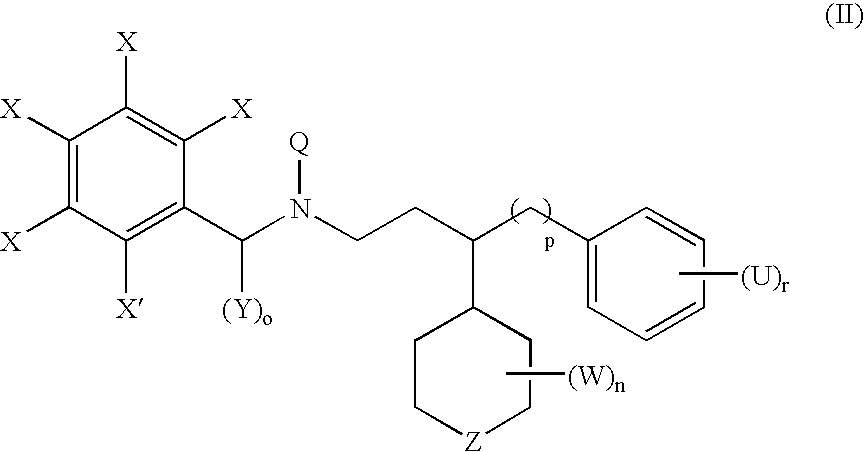
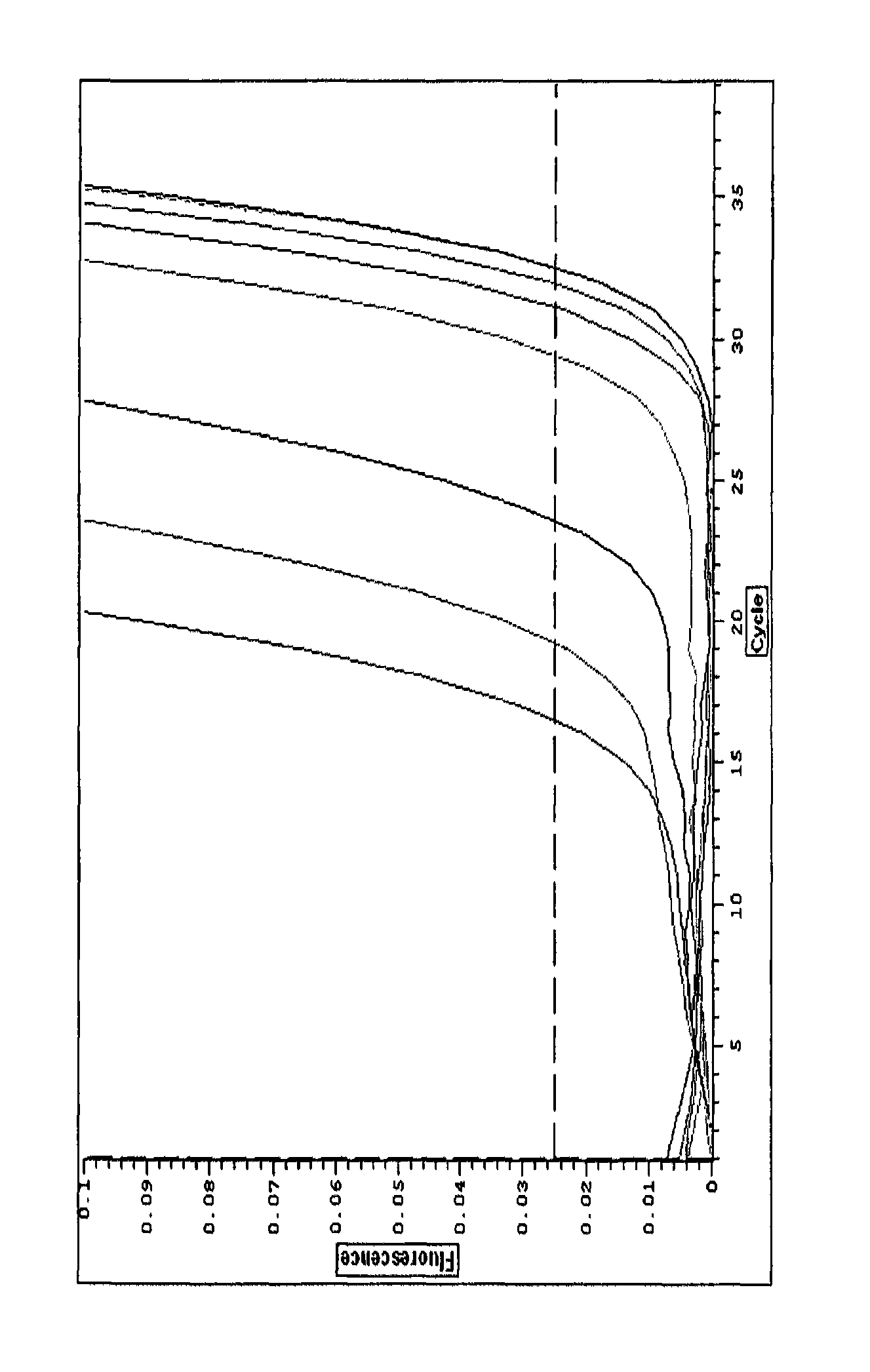
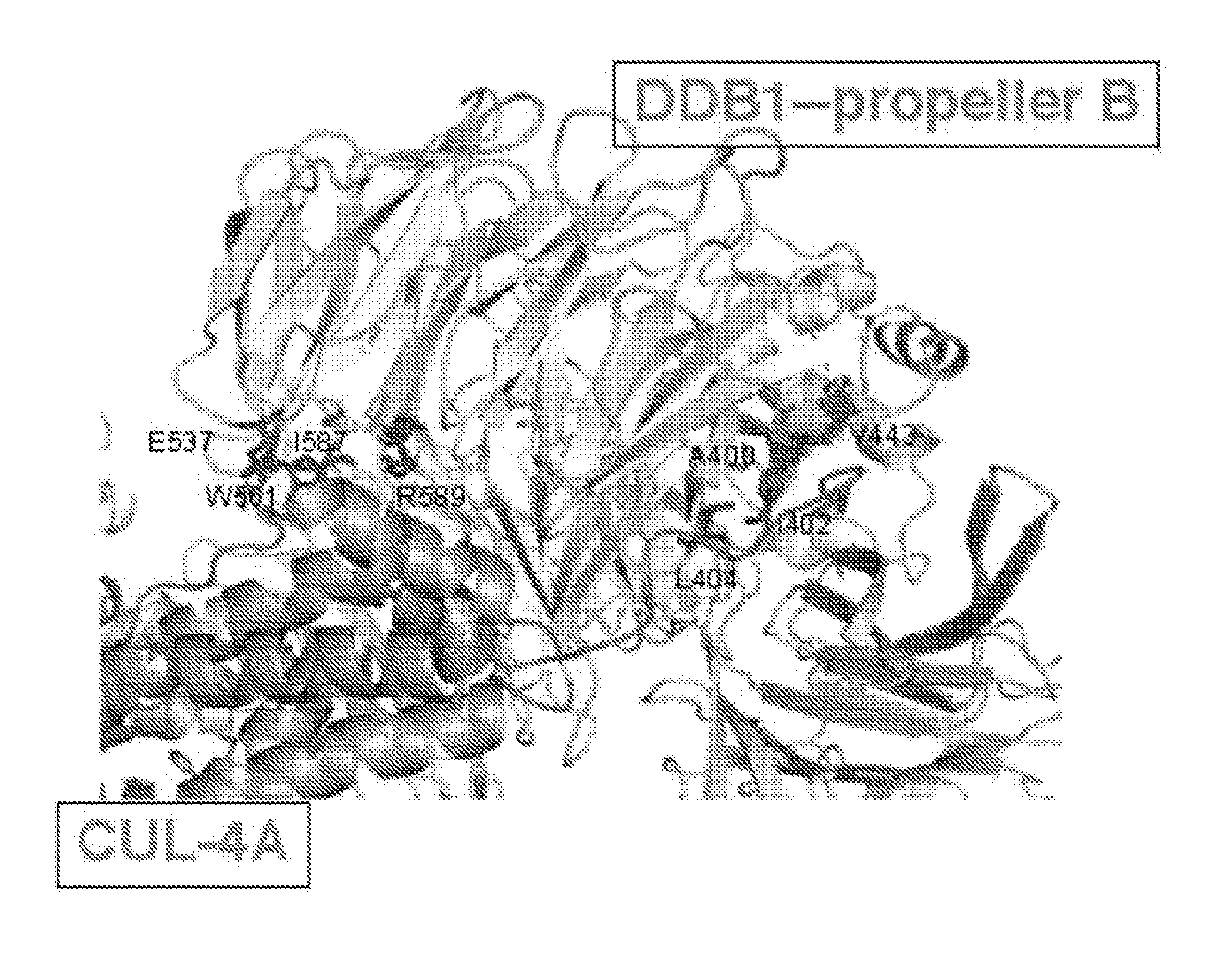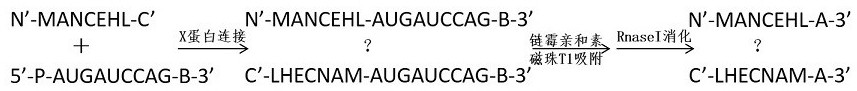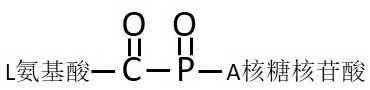Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Ligase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Catalysis of the joining of two substances, or two groups within a single molecule, with the concomitant hydrolysis of the diphosphate bond in ATP or a similar triphosphate. [EC:6, GOC:mah]
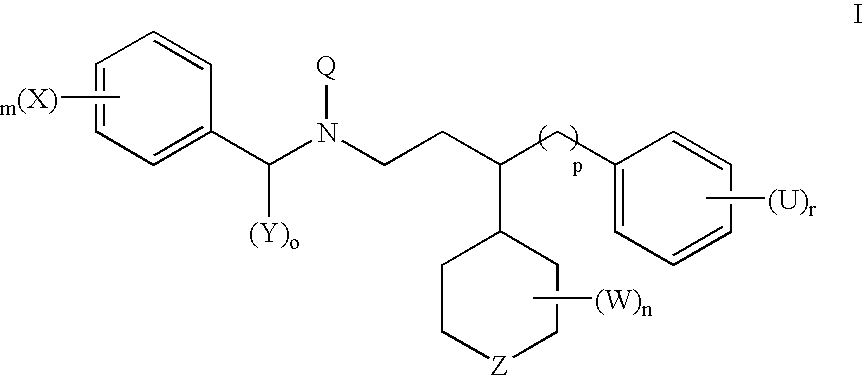
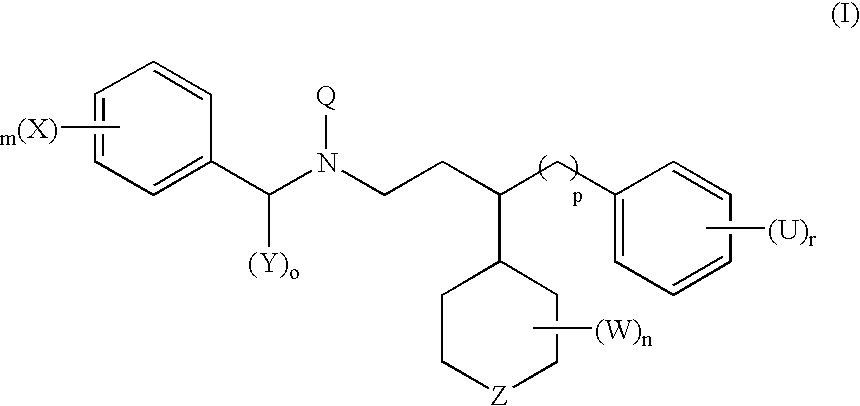
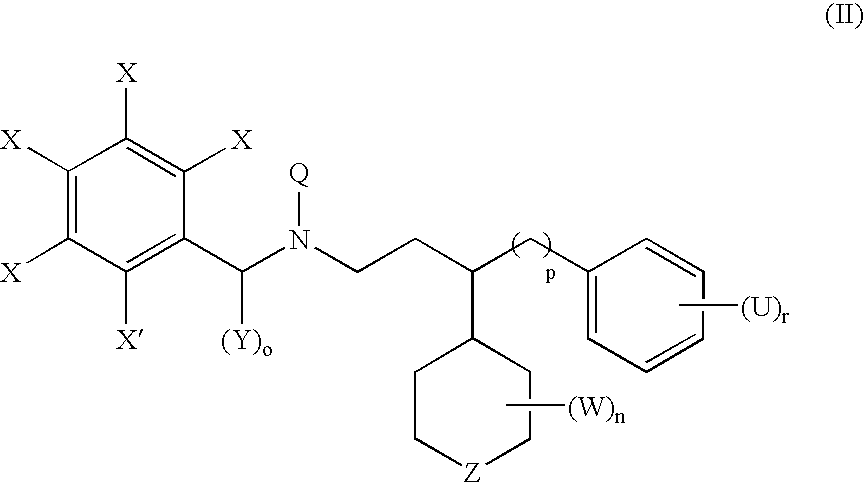
Nucleic acid enzymes and complexes and methods for their use
ActiveUS20110143338A1High catalytic activityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisLigase activityNuclease
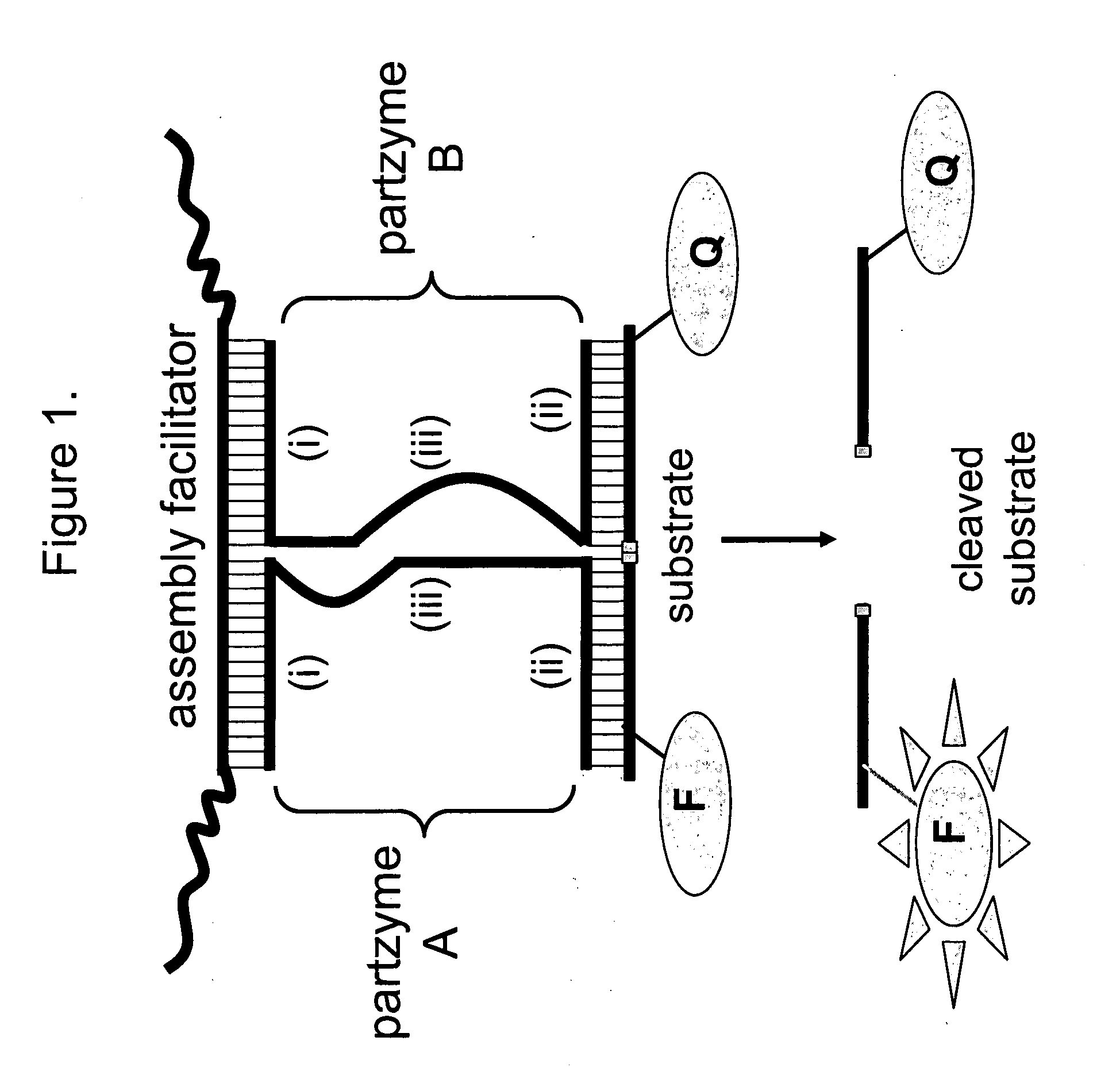
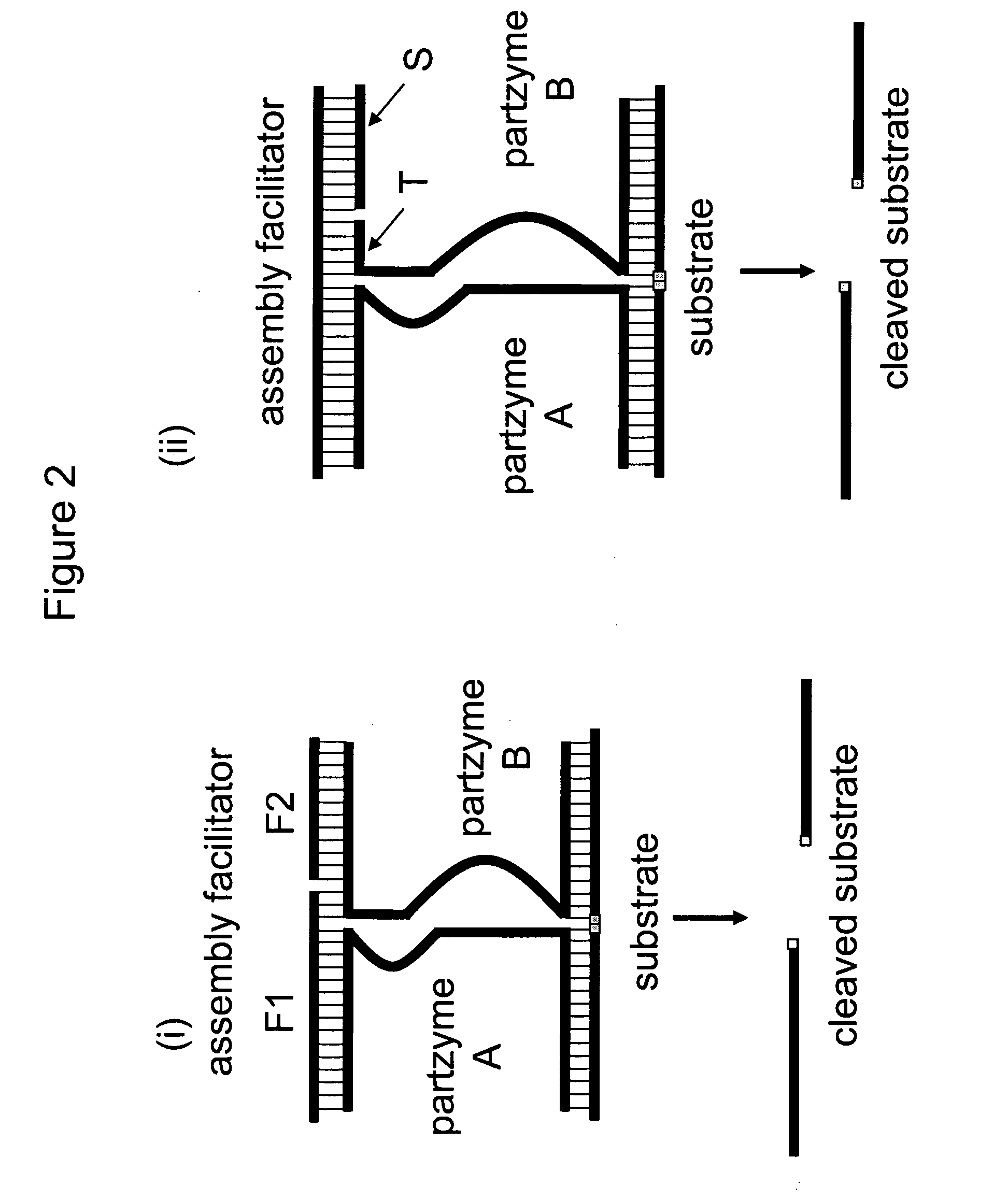
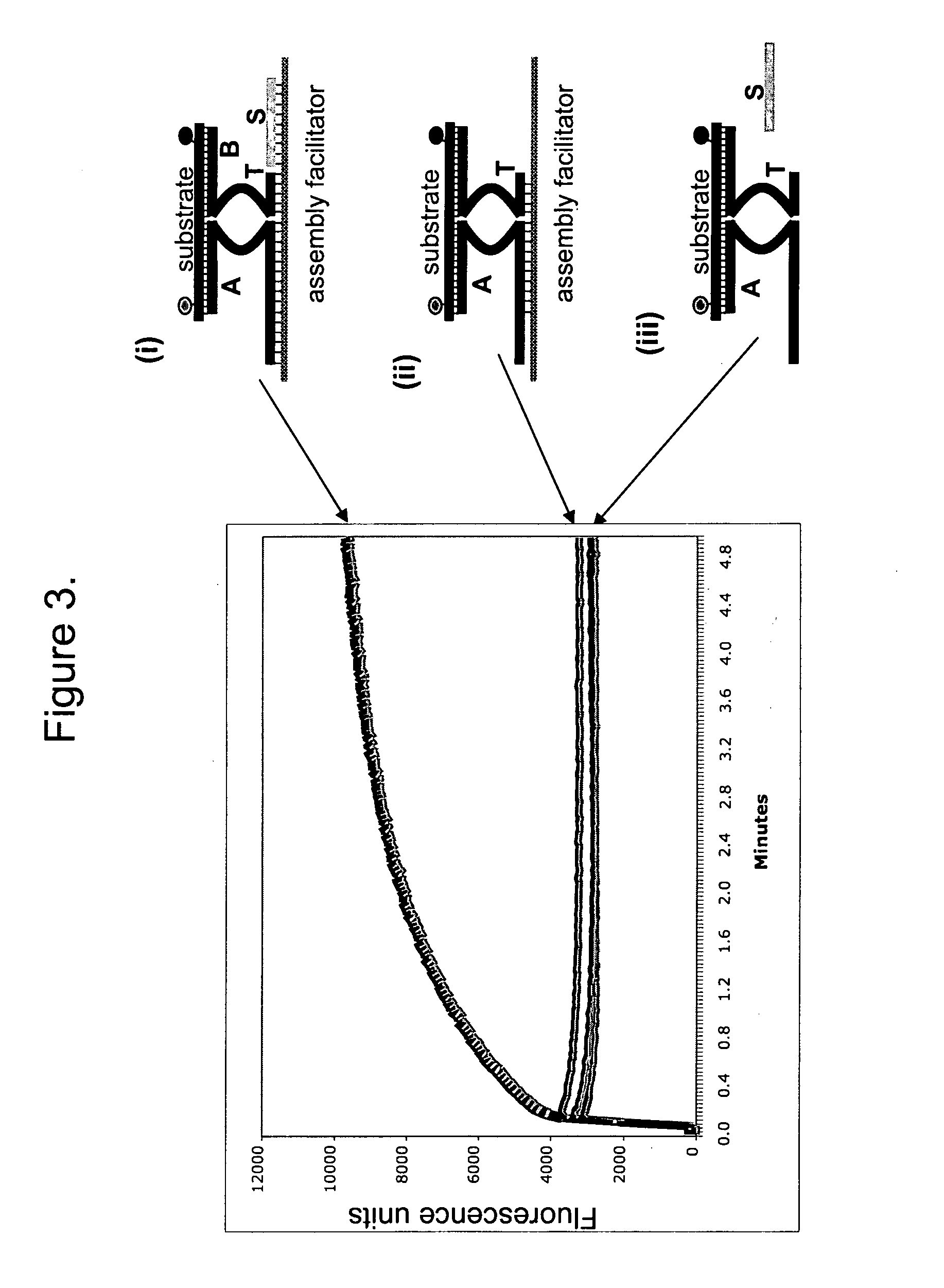
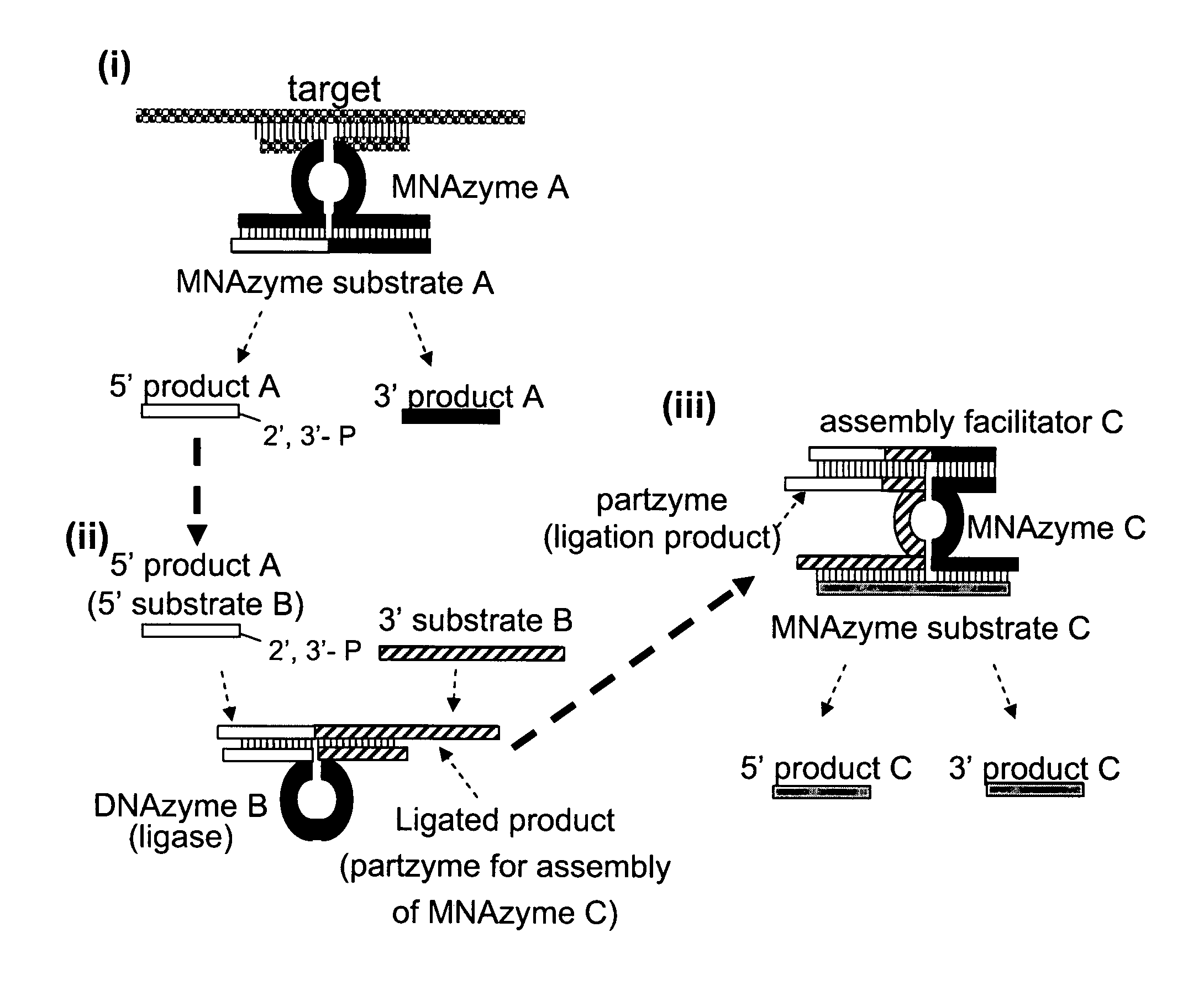
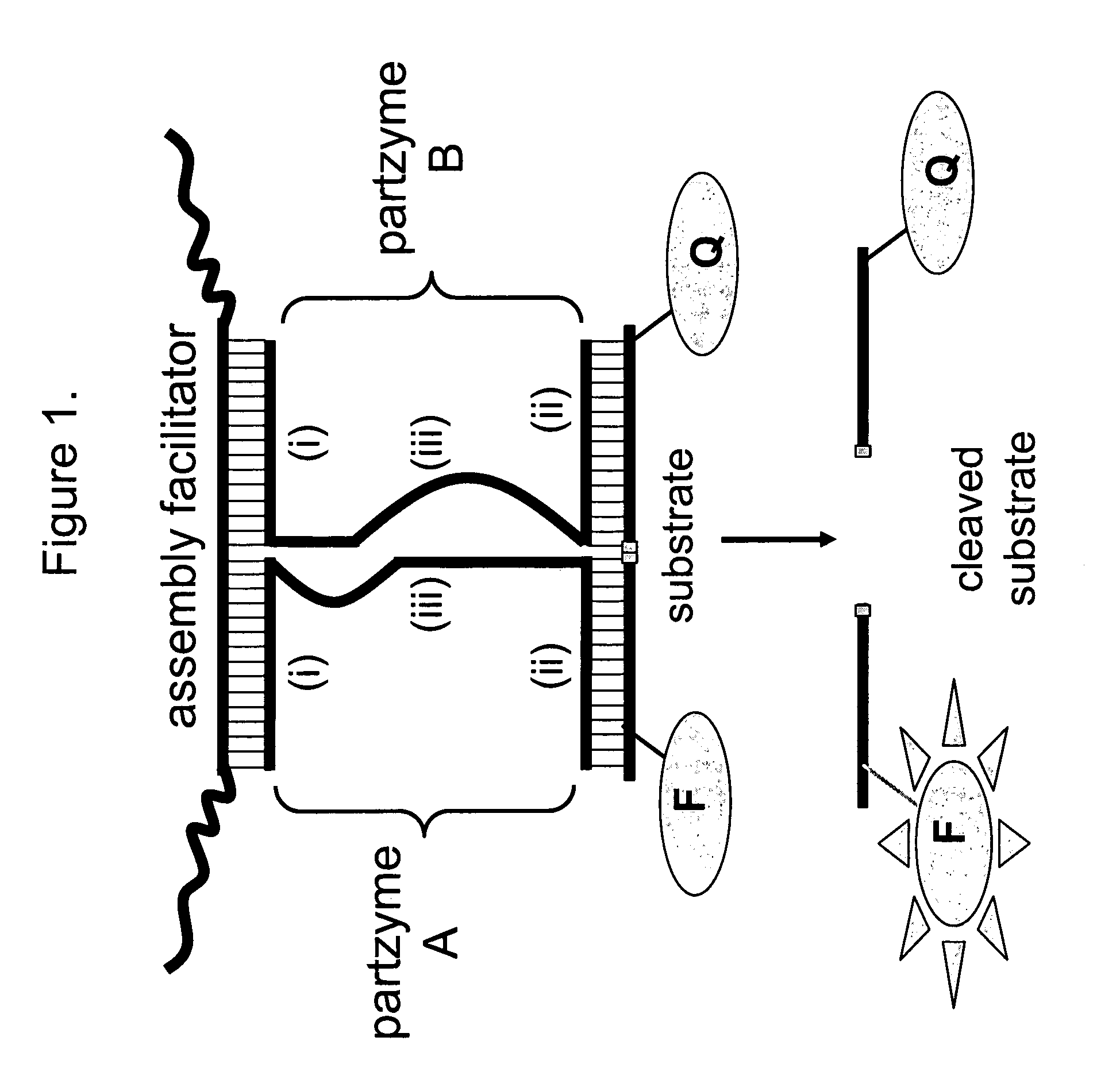
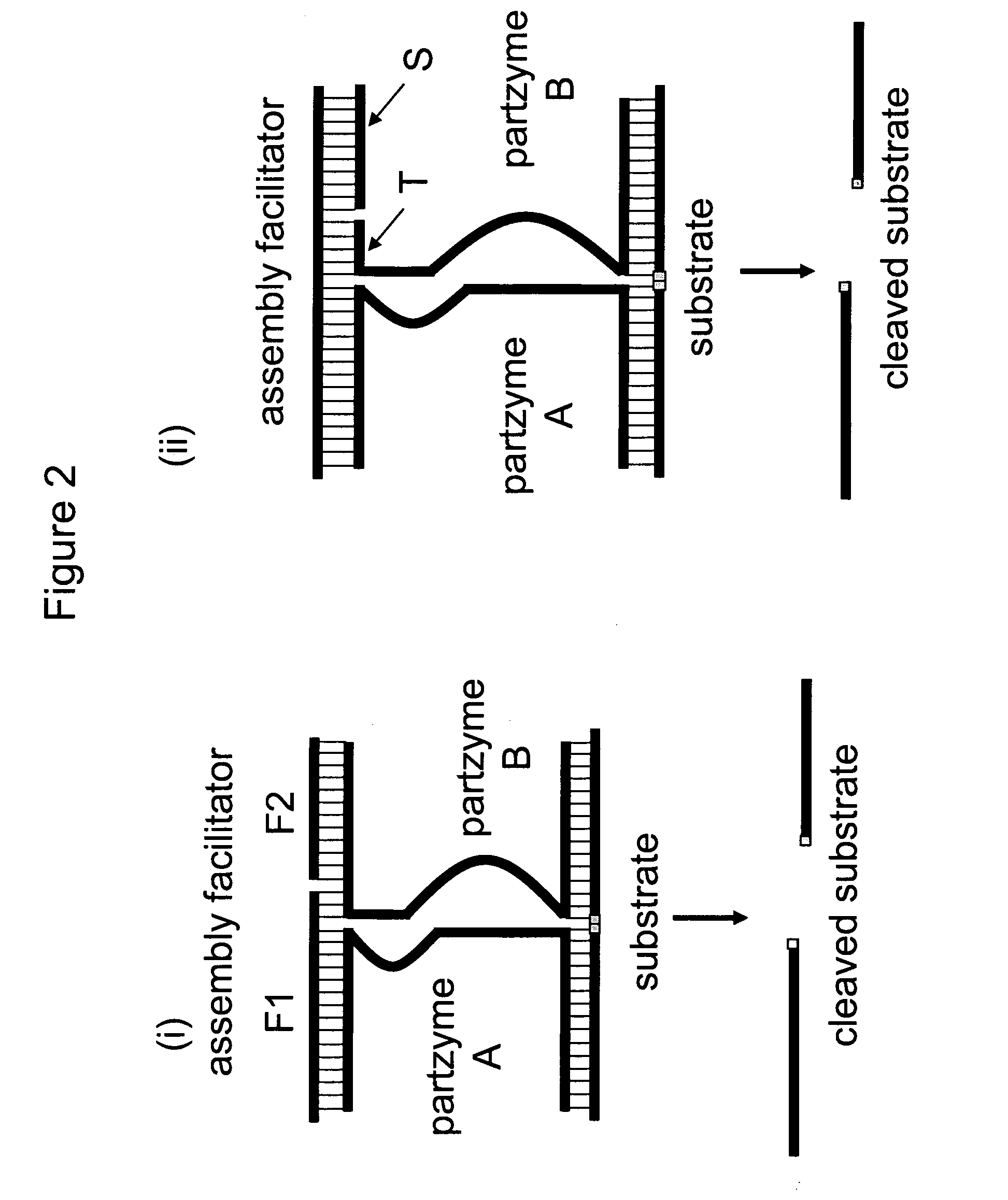
The present invention relates to methods that utilise multi-component nucleic acid complex (MNA complex) cascades. The MNA complexes may have cleavage or ligase activity. Further, the invention provides cascades which may include one or more DNAzymes. The invention also provides methods which use these cascades for the identification, detection and quantification of targets.
Owner:SPEEDX
P53 modulator and cancer target
Methods of screening for modulators of TRIM24 (also known as TIF1-ALPHA) expression and / or biological activity are described. In particular, methods of screening of screening for modulators of TRIM24 E3 ligase activity, and specifically an E3 ligase activity directed at p53 as the target polypeptide are also described. Modulators of TRIM24 expression and activity are provided and their use in treatment of cancer, particularly in breast, colon, prostate, renal cancers and in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Suitable modulators of TRIM24 expression include siRNA and shRNA and can be used in the treatment of cancer and for targeting cancer stem cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
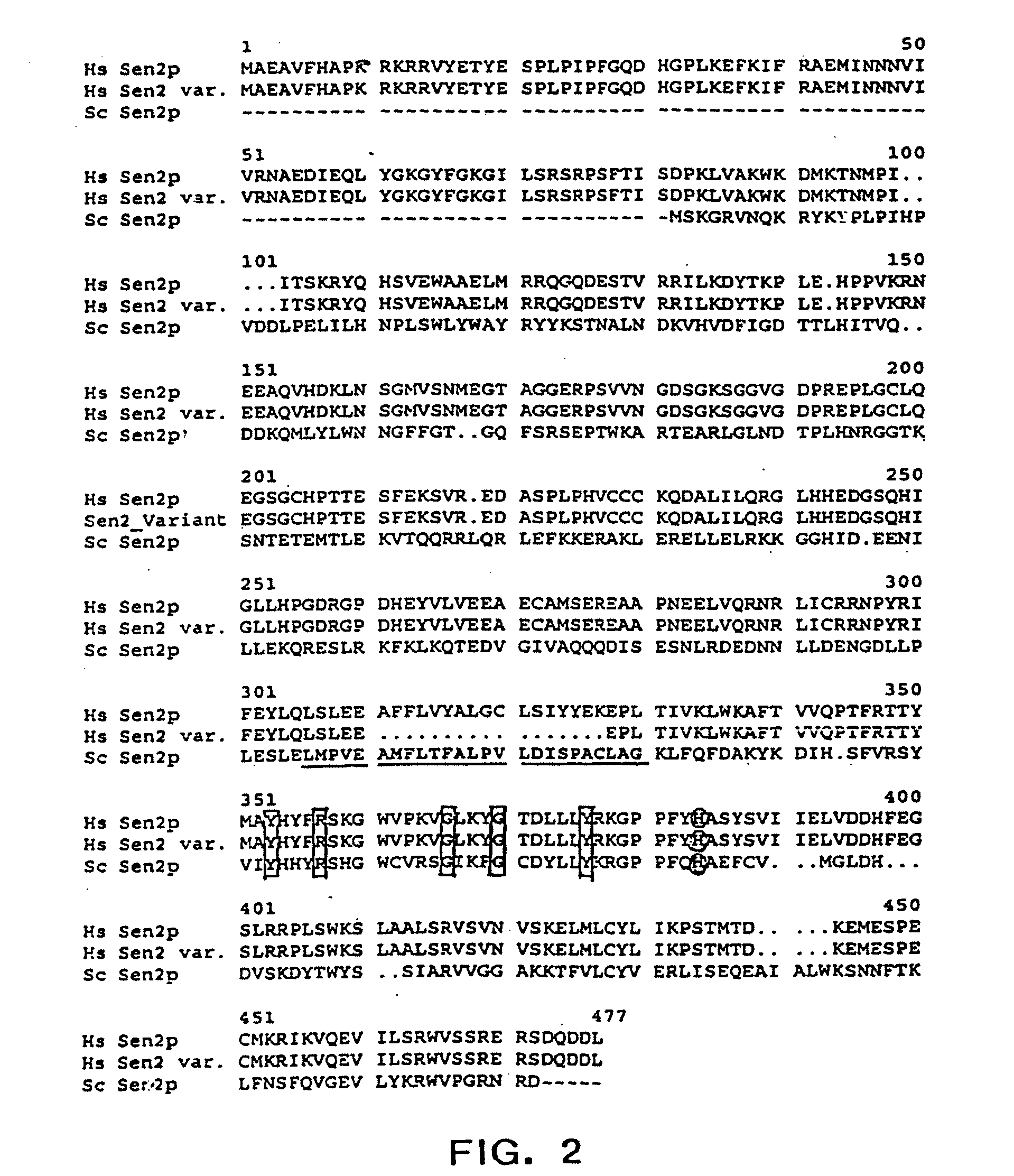
Targeting enzymes of the trna splicing pathway for identification of anti-fungal and/or anti-proliferative molecules
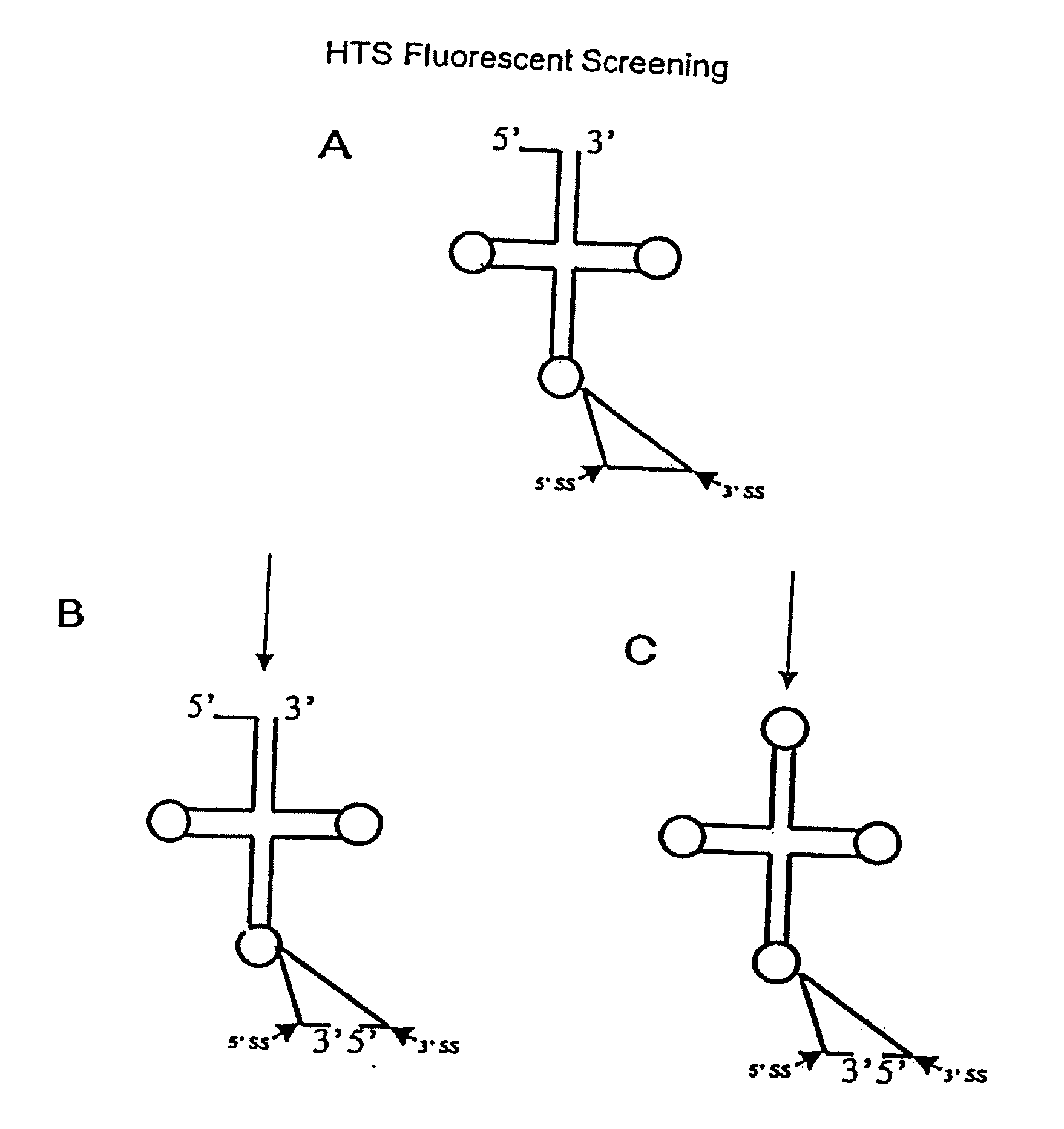
InactiveUS20070178456A1Enhance and improve effectEmission reductionBiocideAntimycoticsCancer preventionHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying compounds that modulate the activity of one or more components in the tRNA splicing pathway. In particular the invention relates to a method for screening and identifying compounds that modulate the activity tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or tRNA splicing ligase. The invention provides assays for the identification of compounds that inhibit animalia tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or animalia tRNA splicing ligase. The invention also provides assays for the identification of compounds that inhibit fungal tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or fungal tRNA splicing ligase. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads useful for treating and / or preventing cancer and / or fungal infections.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Transcription-based assay for identification of post-translational modification and its application in proteomics
InactiveUS7052843B2Simple and rapid assayLess time-consumingAnimal cellsSugar derivativesProtein targetPost translational
The present invention relates to a method for detecting the post-translational modification of a target protein by a post translational modifier polypeptide molecule; a method for screening a candidate protein for E3 ligase activity; a method of screening a test compound for the ability to regulate the post-translational modification of a target protein by a post-translational modifier polypeptide molecule; and a method for the large-scale detection of candidate target proteins of post-translational modification by a modifier polypeptide molecule. The present invention also relates to a kit for determining whether a test protein is post-translationally modified by a modifier polypeptide molecule; a kit for screening a test compound for the ability to regulate the post-translational modification of a target protein by a post-translational modifier peptide molecule, and another kit for determining whether a test protein is post-translationally modified by a modifier polypeptide molecule.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Substances and compositions for enhancing DNA repair and methods of use
ActiveUS8513181B2Enhance nucleotide excision repair activityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsLigase activityNucleotide excision repair
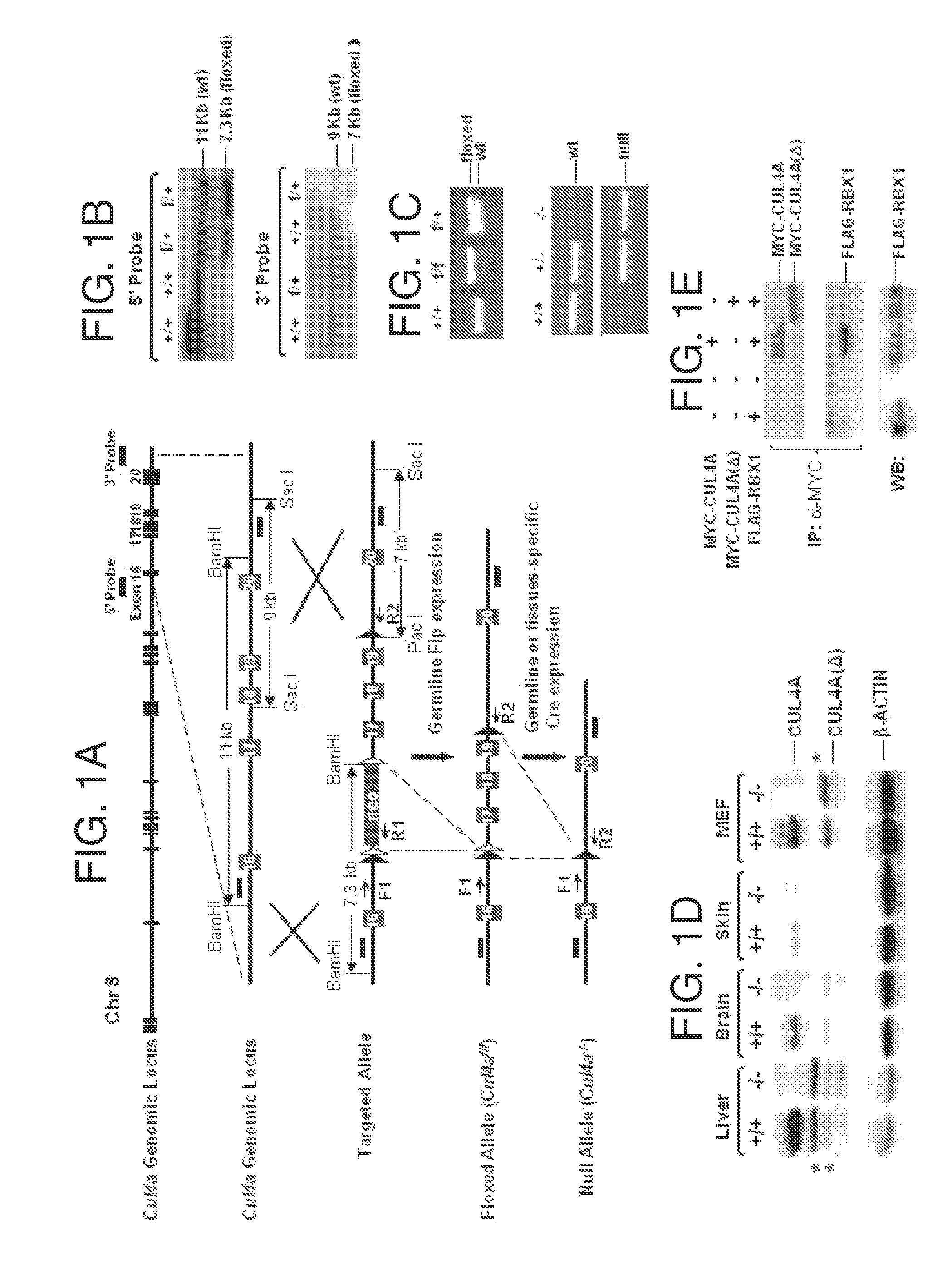
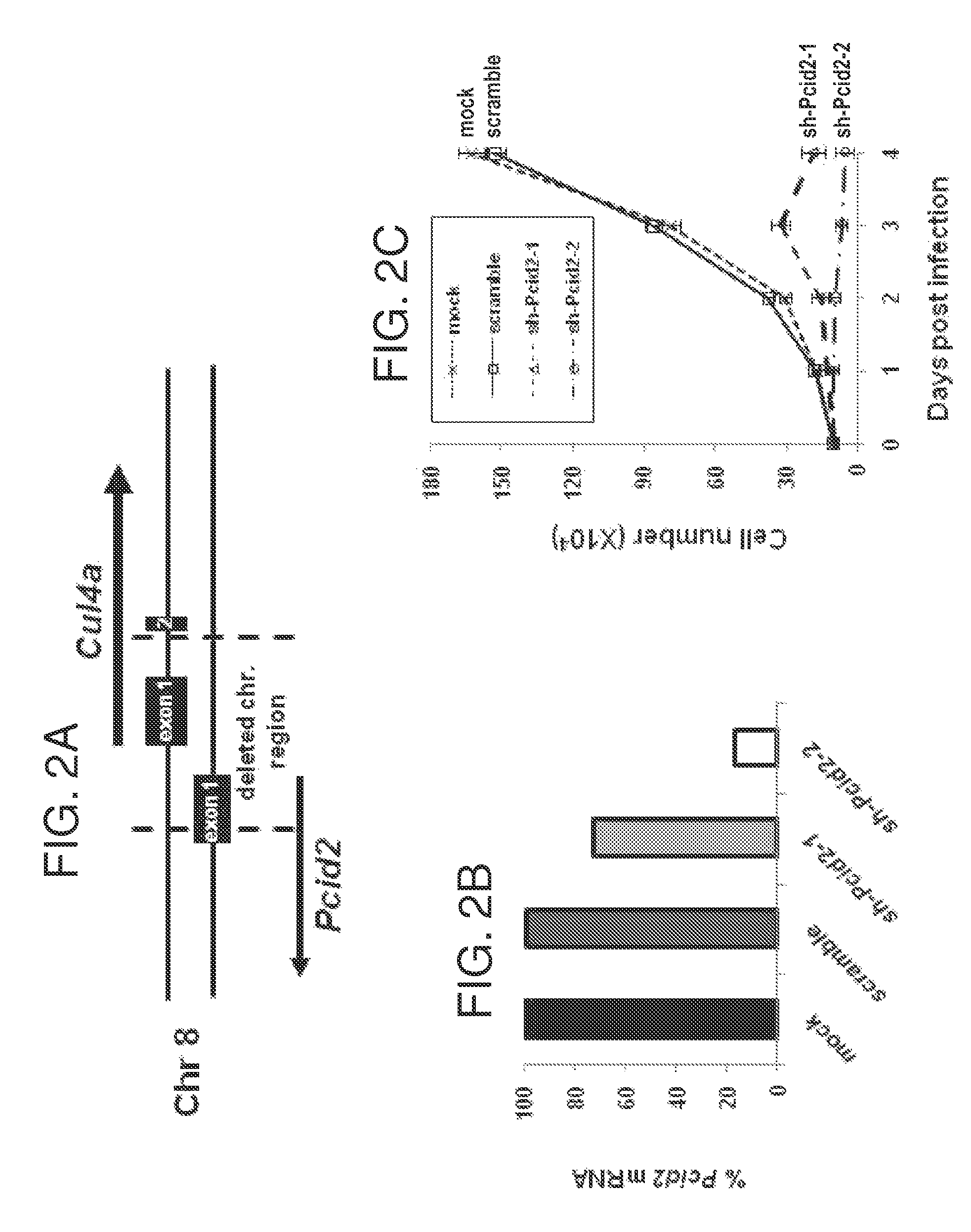
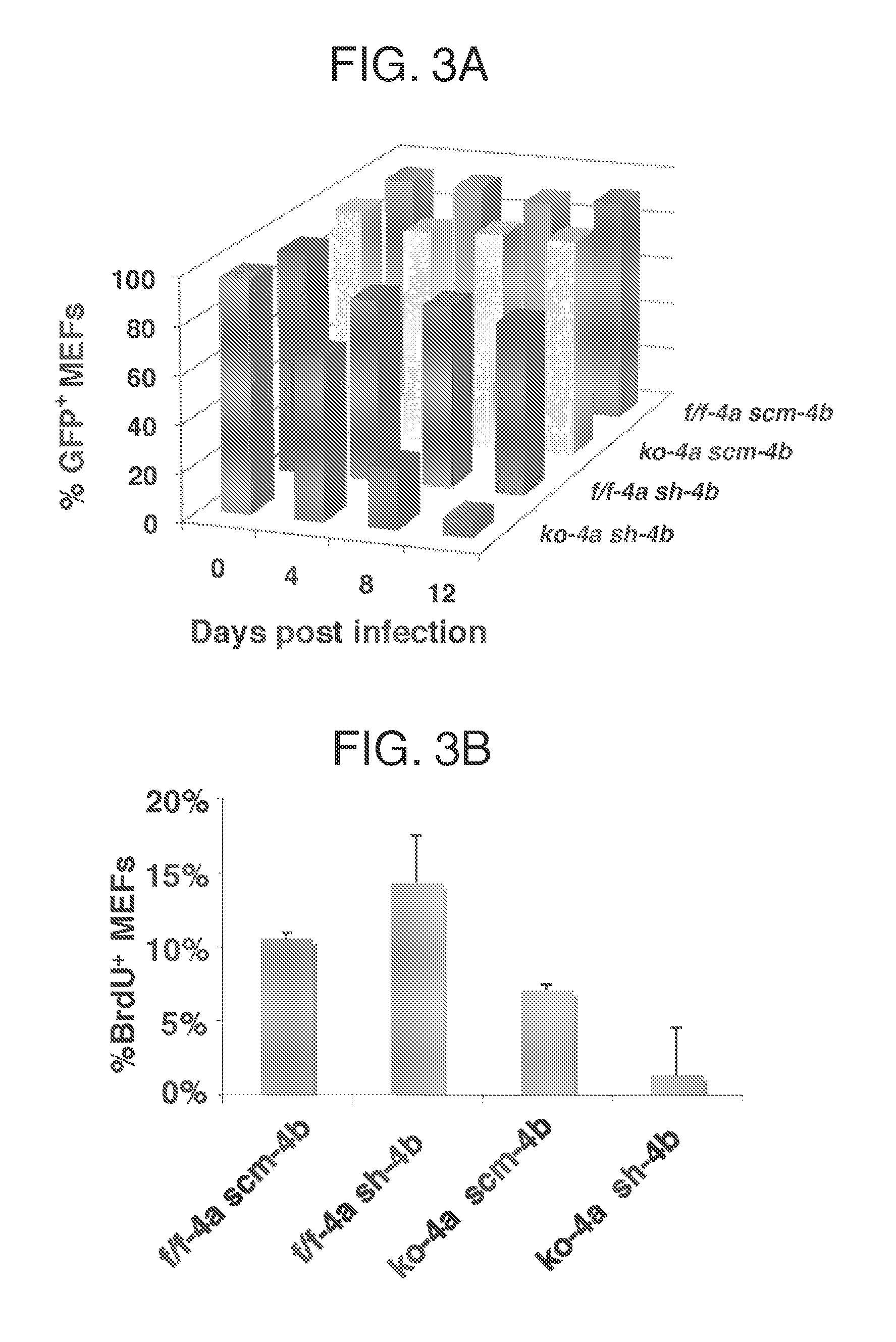
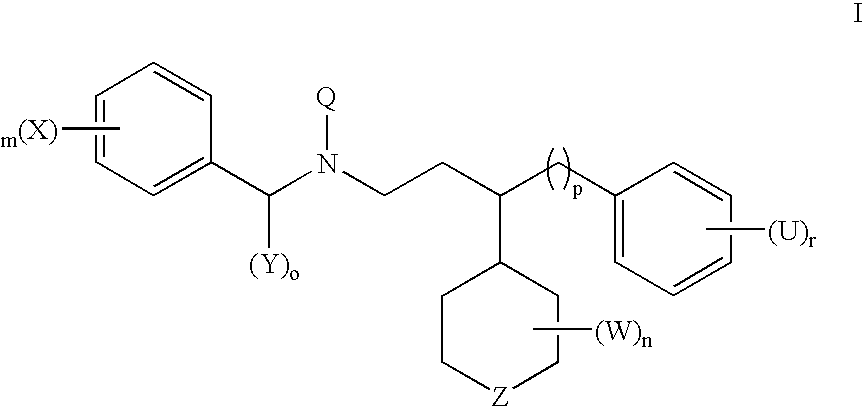
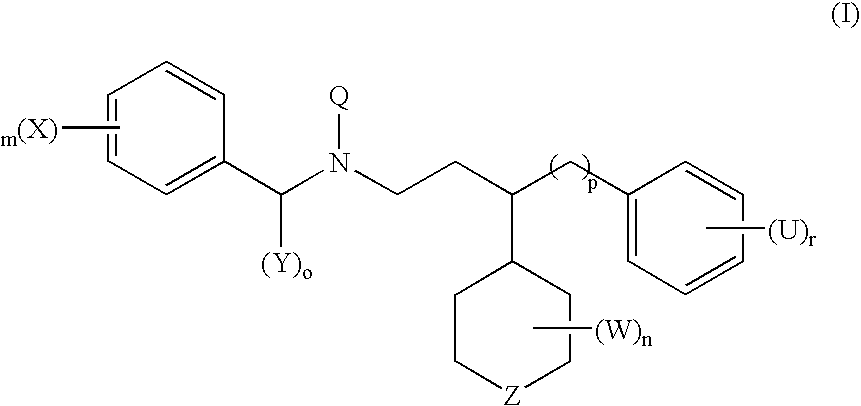
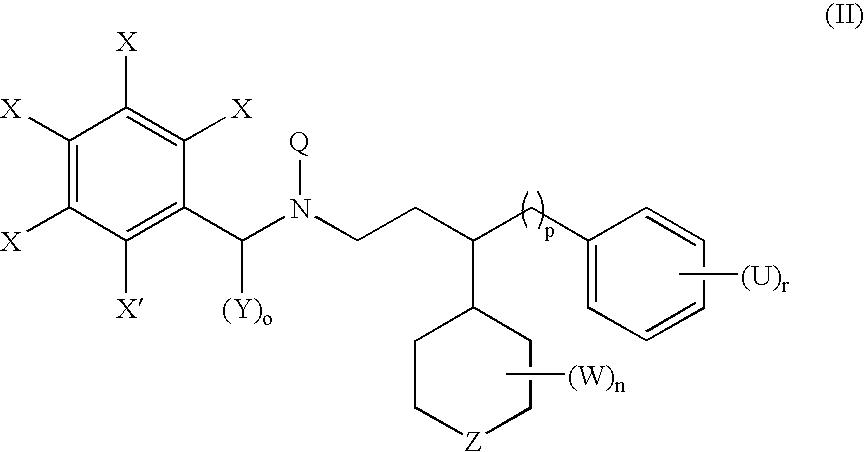
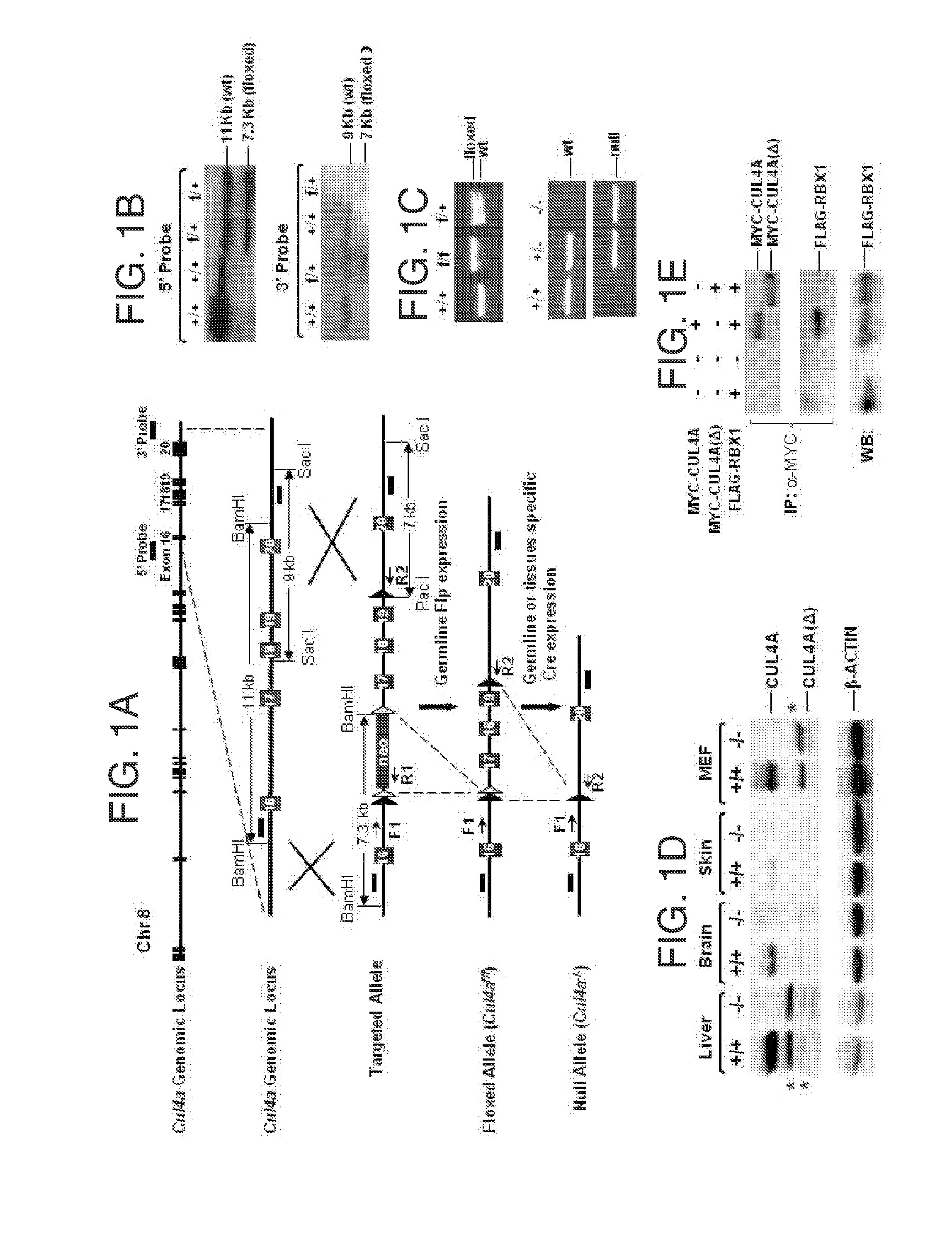
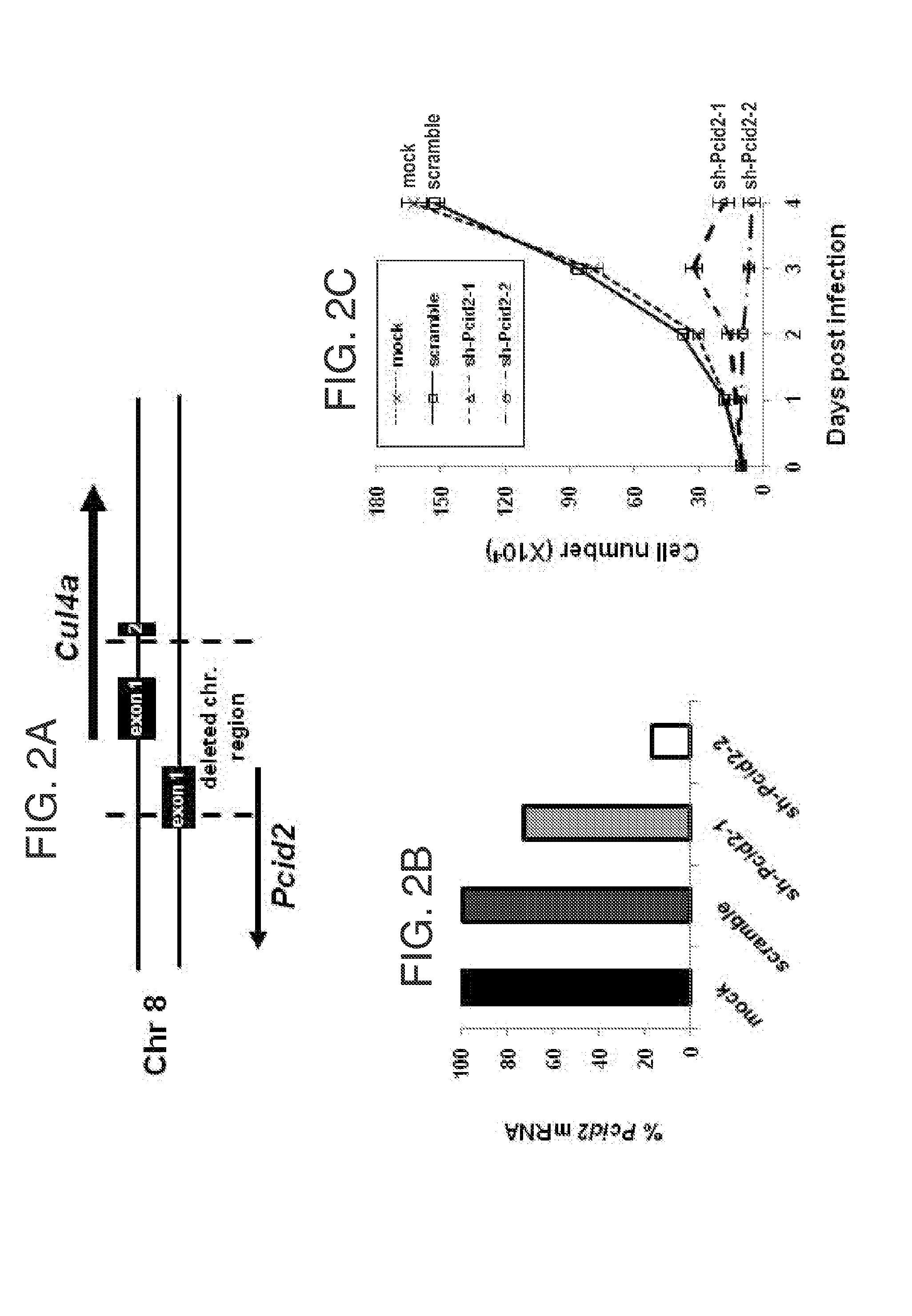
The invention provides methods of preventing or treating a condition associated with DNA damage in an animal comprising the administration of a substance that interferes with the activity of the CUL4A ubiquitin ligase. The invention also provides a substance that interferes with the activity of CUL4A, as well as compositions comprising the interfering substance and a carrier. The substance of the invention preferably enhances nucleotide excision repair activity in an animal. The invention further provides methods of identifying substances that negatively or positively modulate the expression and / or activity of CUL4A.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
HYPER-THERMOSTABLE LYSINE-MUTANT ssDNA/RNA LIGASES
InactiveCN109477127ASimple working processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingLigase activity
Owner:RGENE INC
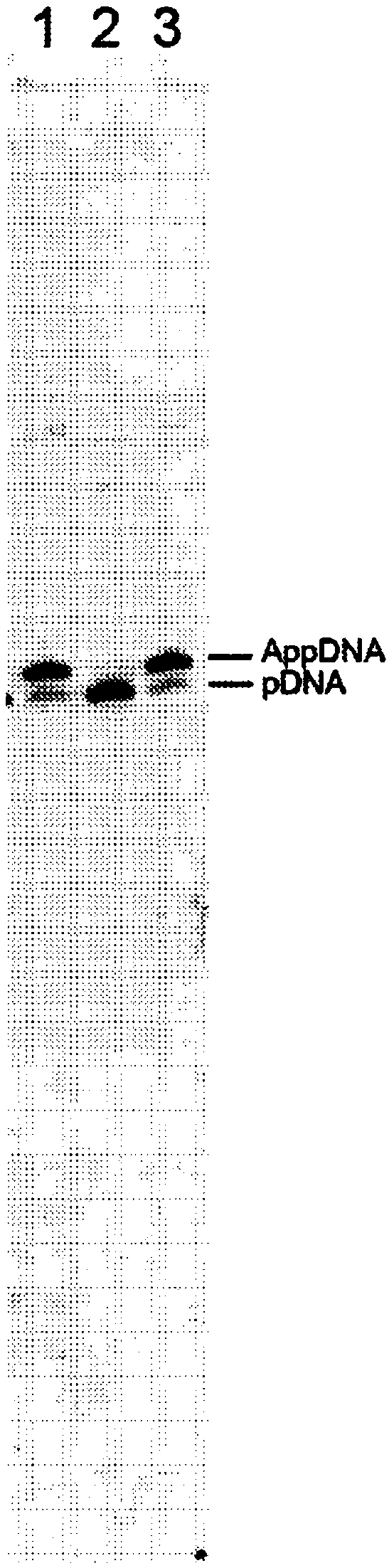
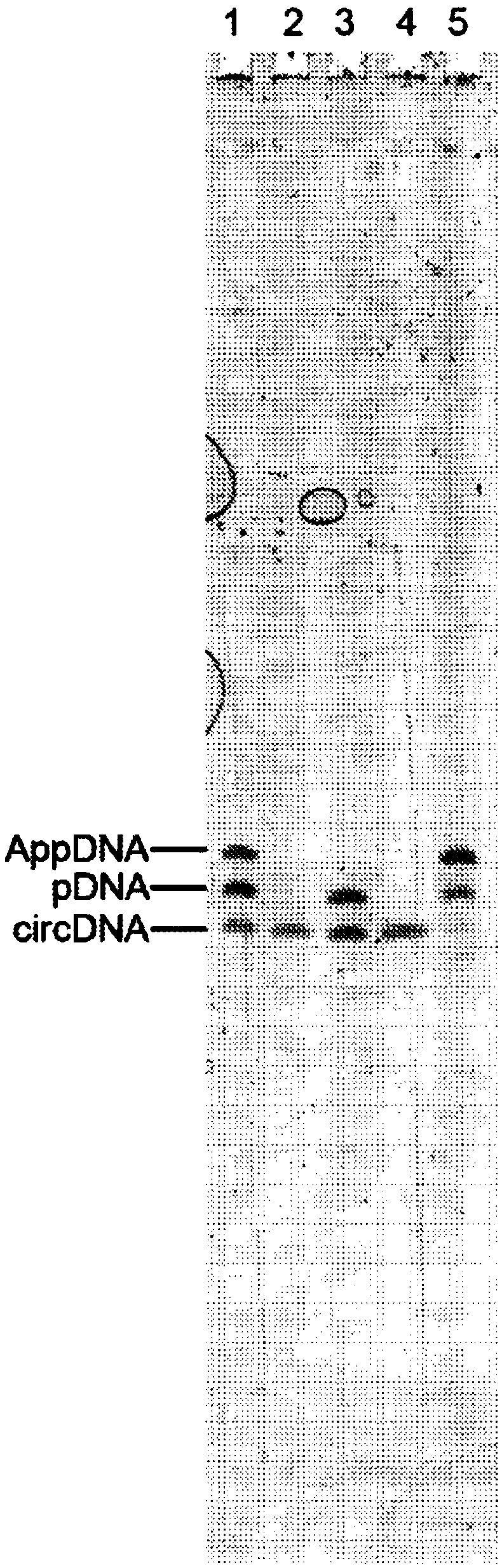
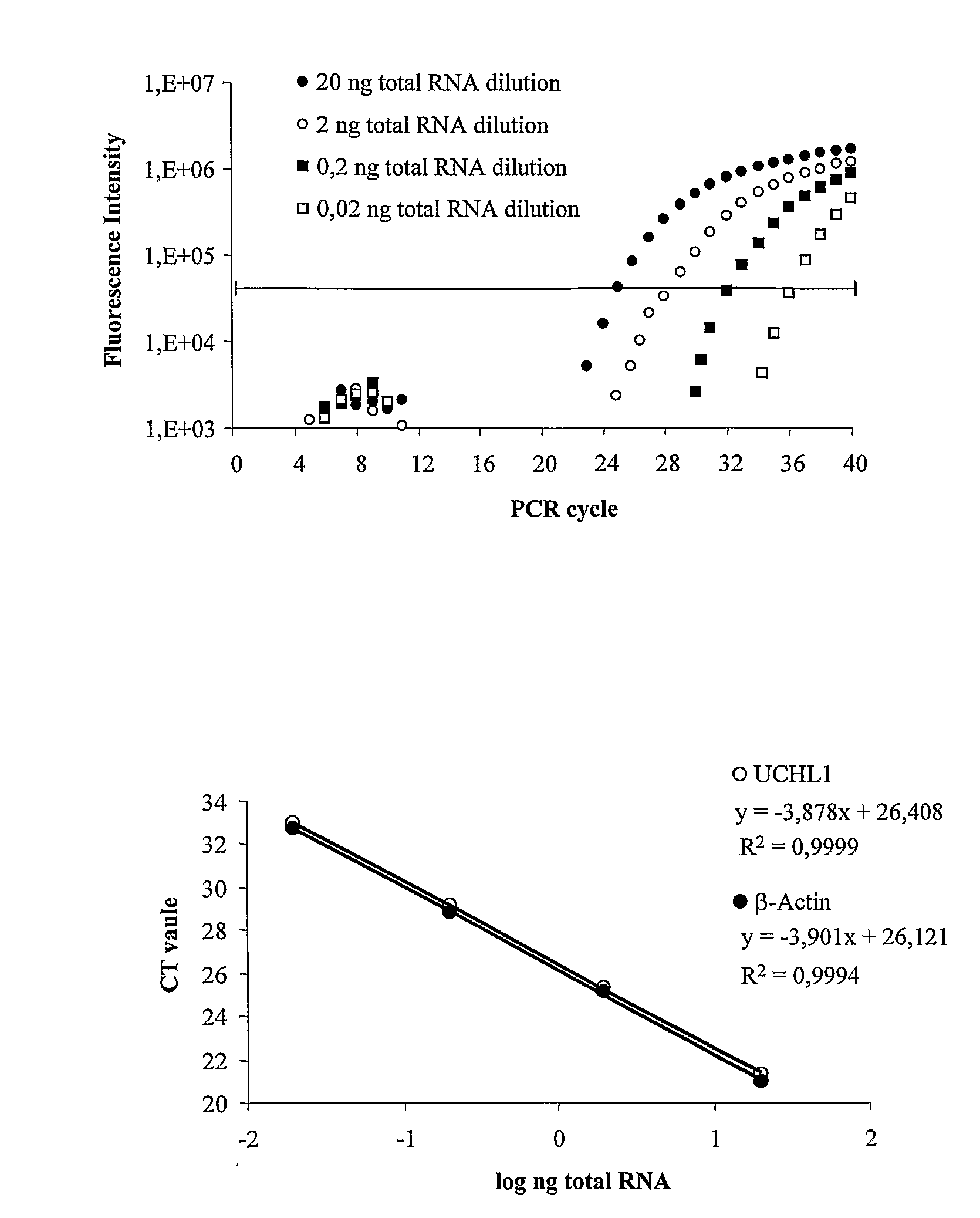
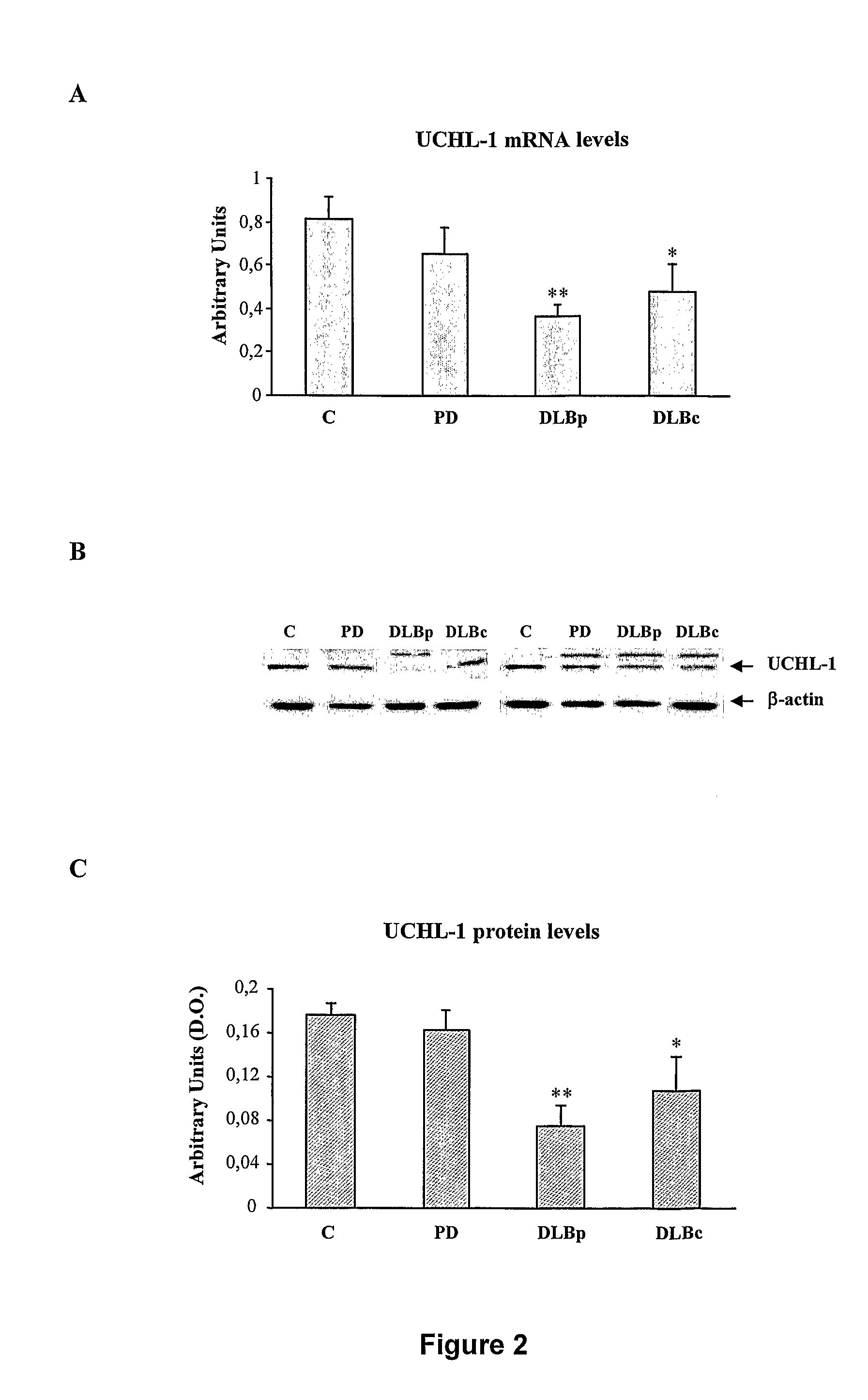
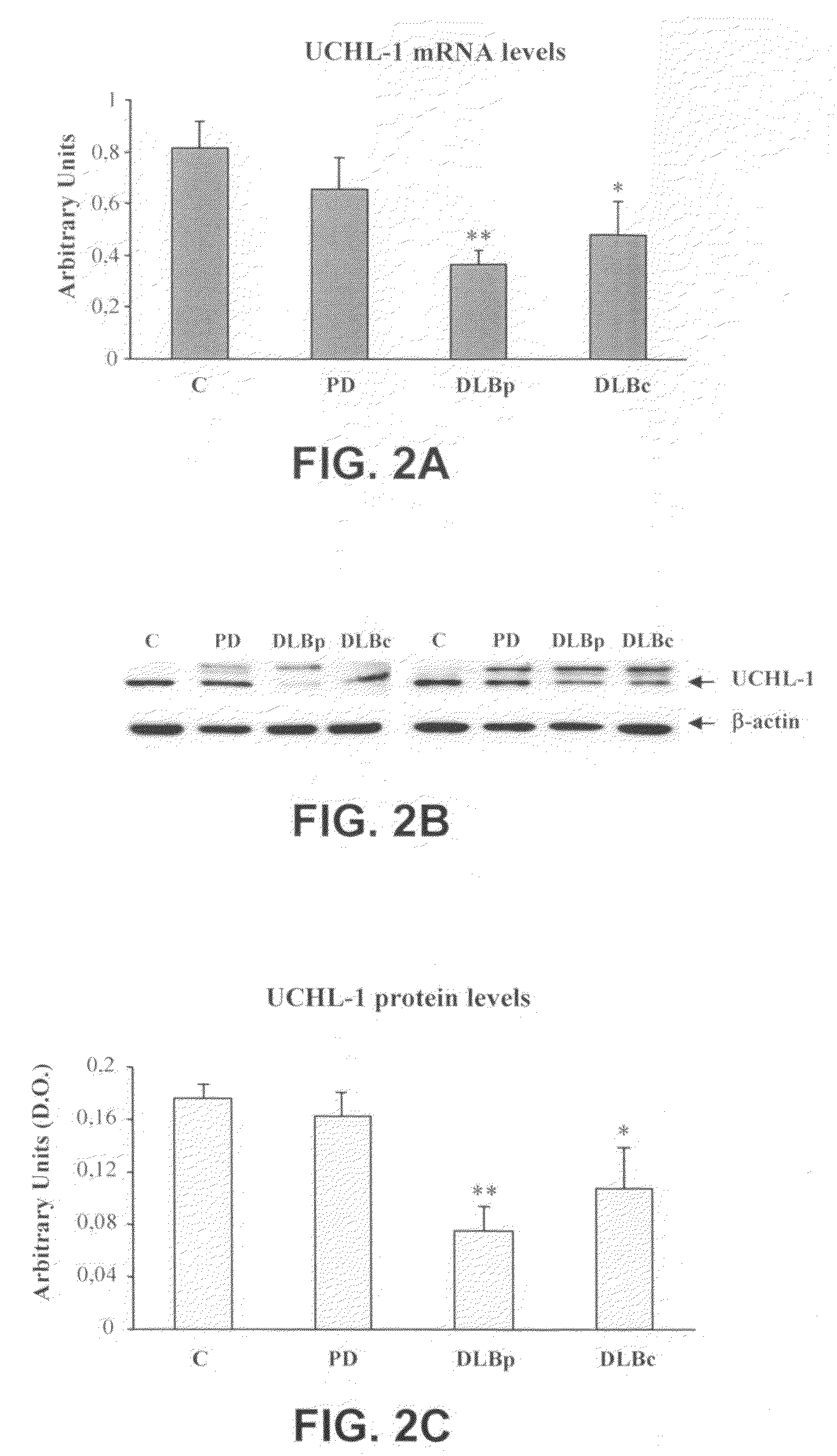
Molecular Diagnostic Method and Treatment in Dementia With Lewy Bodies
InactiveUS20090028845A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderUbiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1Dementia with Lewy bodies
The present invention describes methods of molecular diagnosis of a concrete form of a-synucleinopathy, the dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), associated to the levels of ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-1) or the alteration of its ubiquityl-ligase activity. It also refers to the use of compounds that permit the modification of the UCH-L1 levels or of the enzymatic activity of UCH-L1. This invention has application in the diagnosis and treatment of patients suffering from DLB.
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
Compounds useful for the treatment of cancer, compositions thereof and methods therewith
InactiveUS7037936B2Modulate activityArrest cell growthBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer preventionPreservative
The present invention generally relates to compounds and compositions useful for the modulation of ligase activity. The invention further relates to Compounds of the Invention, compositions thereof, and methods for treating or preventing cancer, a neoplastic disorder, acute or chronic renal failure, an inflammatory disorder, an immune disorder, a cardiovascular disease, an effect of aging or an infectious disease comprising administering an effective amount of a Compound of the Invention. The invention further relates to the use of a Compound of the Invention as a preservative of a cell, blood, tissue or an organ or as an agent to modulate stem cells.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Substances and compositions for enhancing DNA repair and methods of use
ActiveUS20110044921A1Enhance nucleotide excision repair activityCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideTreated animal
The invention provides methods of preventing or treating a condition associated with DNA damage in an animal comprising the administration of a substance that interferes with the activity of the CUL4A ubiquitin ligase. The invention also provides a substance that interferes with the activity of CUL4A, as well as compositions comprising the interfering substance and a carrier. The substance of the invention preferably enhances nucleotide excision repair activity in an animal. The invention further provides methods of identifying substances that negatively or positively modulate the expression and / or activity of CUL4A.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
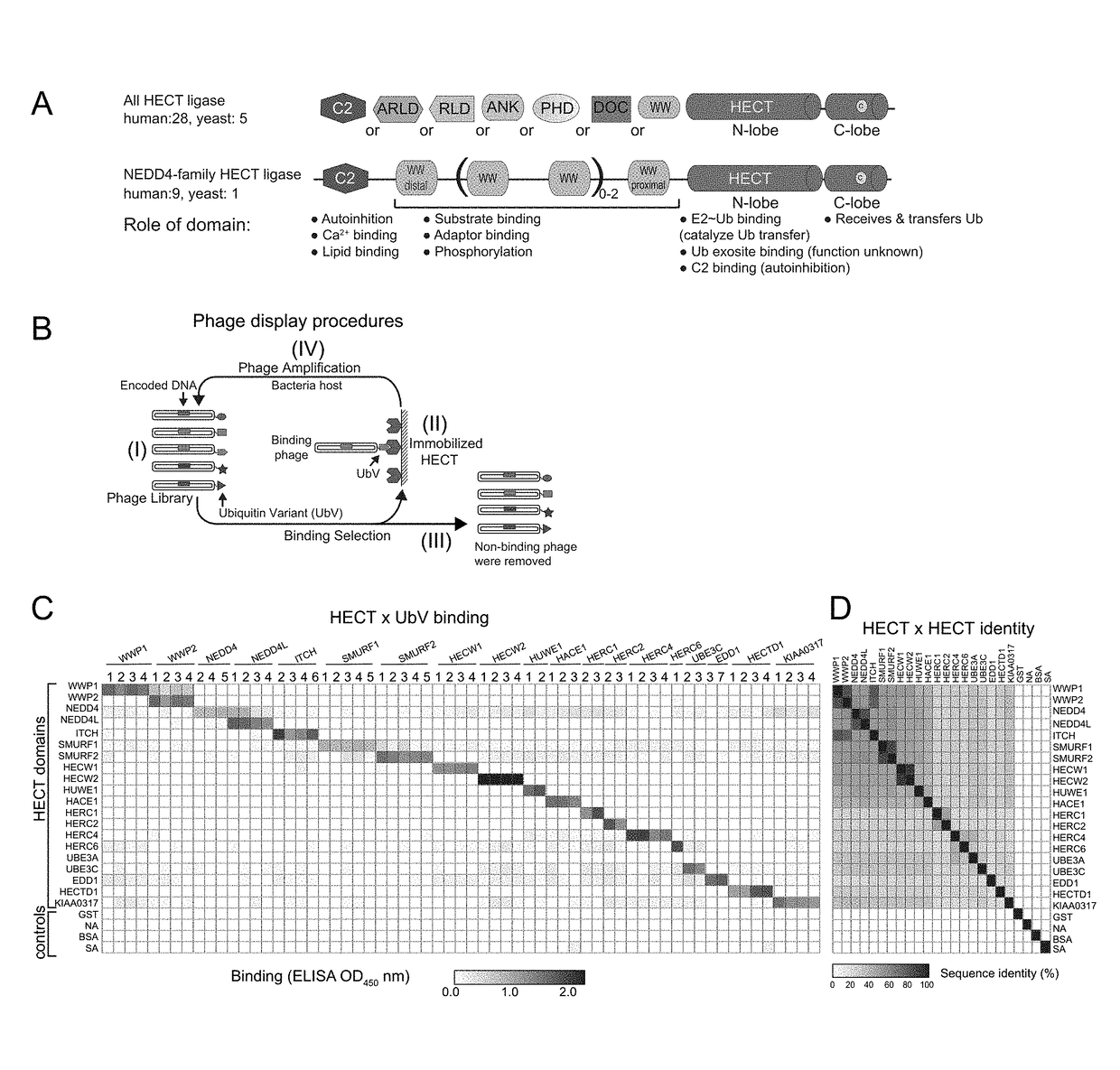
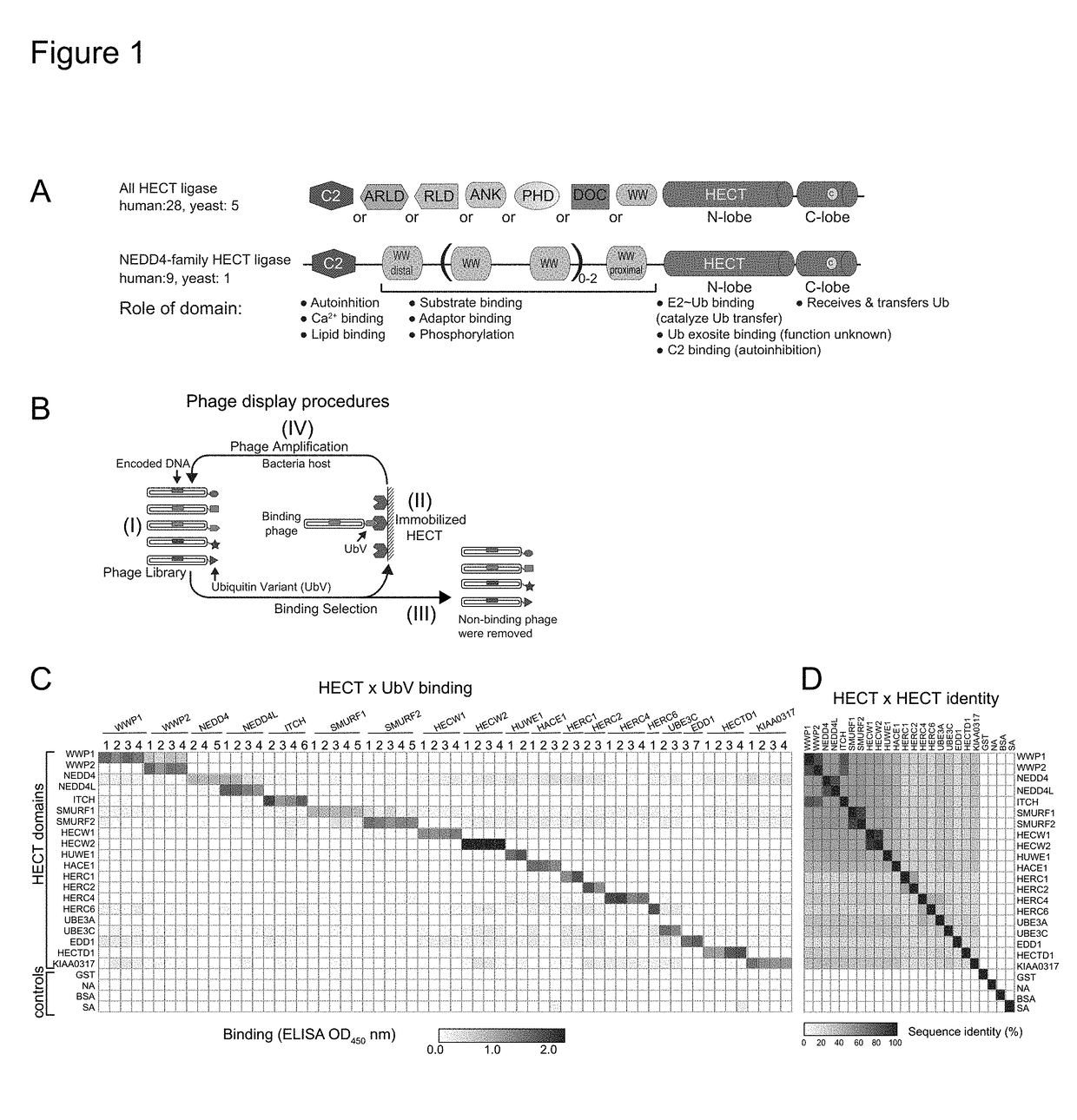
Ubiquitin variant modulators of hect e3 ligases and their uses
The invention provides ubiquitin variants that specifically bind to HECT E3 ligases, and methods of using these variants to modulate the activity of HECT E3 ligases.
Owner:SIDHU SACHDEV +1
Nucleic acid enzymes and complexes and methods for their use
The present invention relates to methods that utilize multi-component nucleic acid complex (MNA complex) cascades. The MNA complexes may have cleavage or ligase activity. Further, the invention provides cascades which may include one or more DNAzymes. The invention also provides methods which use these cascades for the identification, detection and quantification of targets.
Owner:SPEEDX
HYPER-THERMOSTABLE LYSINE-MUTANT ssDNA/RNA LIGASES
InactiveUS20190062827A1Simple sample preparationSimple working processSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSingle strandLigase activity
Provided herein are compositions, systems, and methods employing hyper-thermostable lysine-mutant ssDNA / RNA ligases that possesses both ssRNA ligase and ssDNA ligase activity. In certain embodiments, such hyper-thermostable lysine-mutant ssDNA / RNA ligases are used to ligate an first single stranded nucleic acid sequence with a 5′ adenylated end to a second single stranded nucleic acid sequence (e.g., at a temperature of at least 75° C.) to form a ligated nucleic acid sequence. In further embodiments, the ligated nucleic acid sequence is sequenced.
Owner:RGENE INC
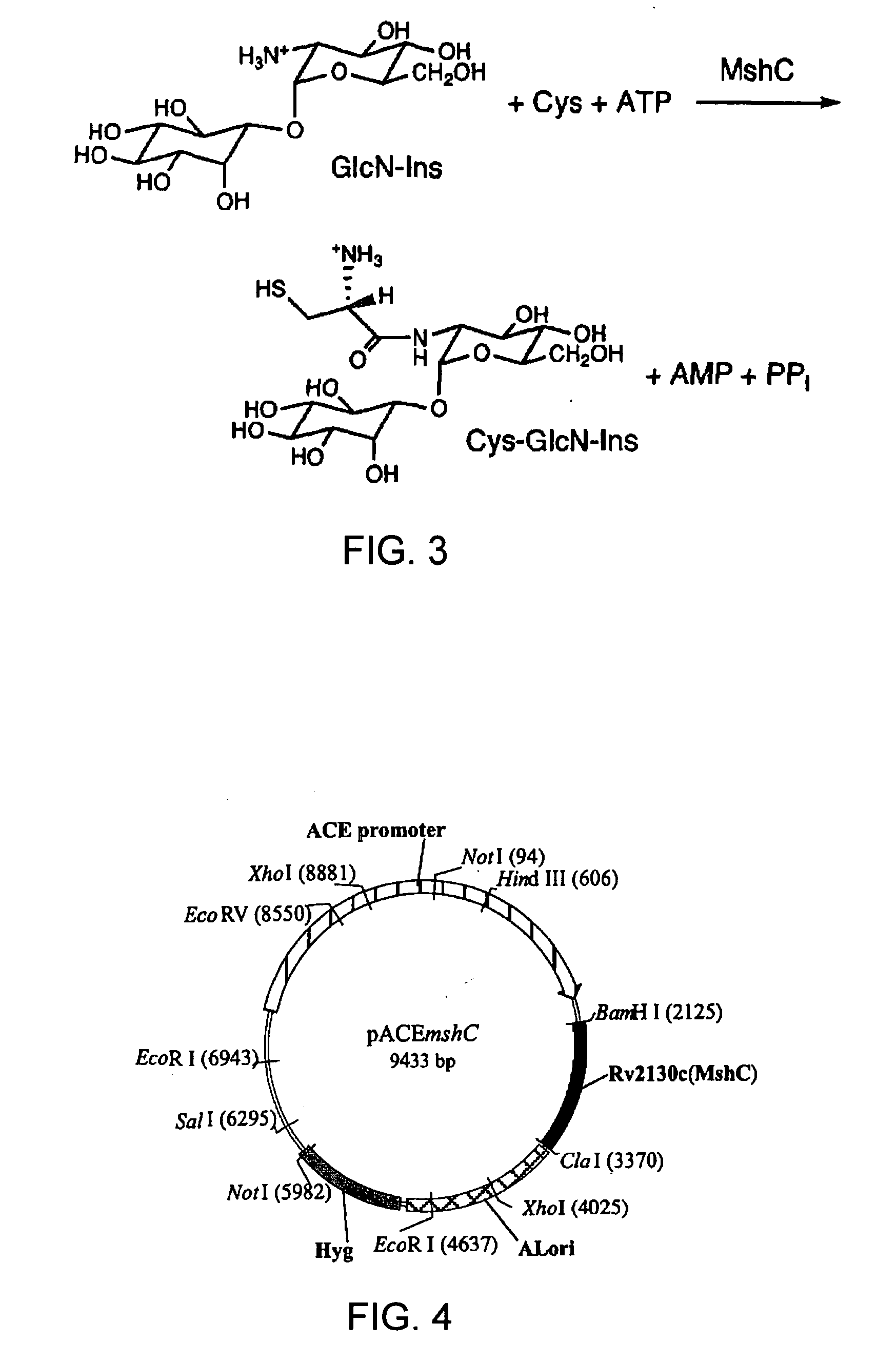
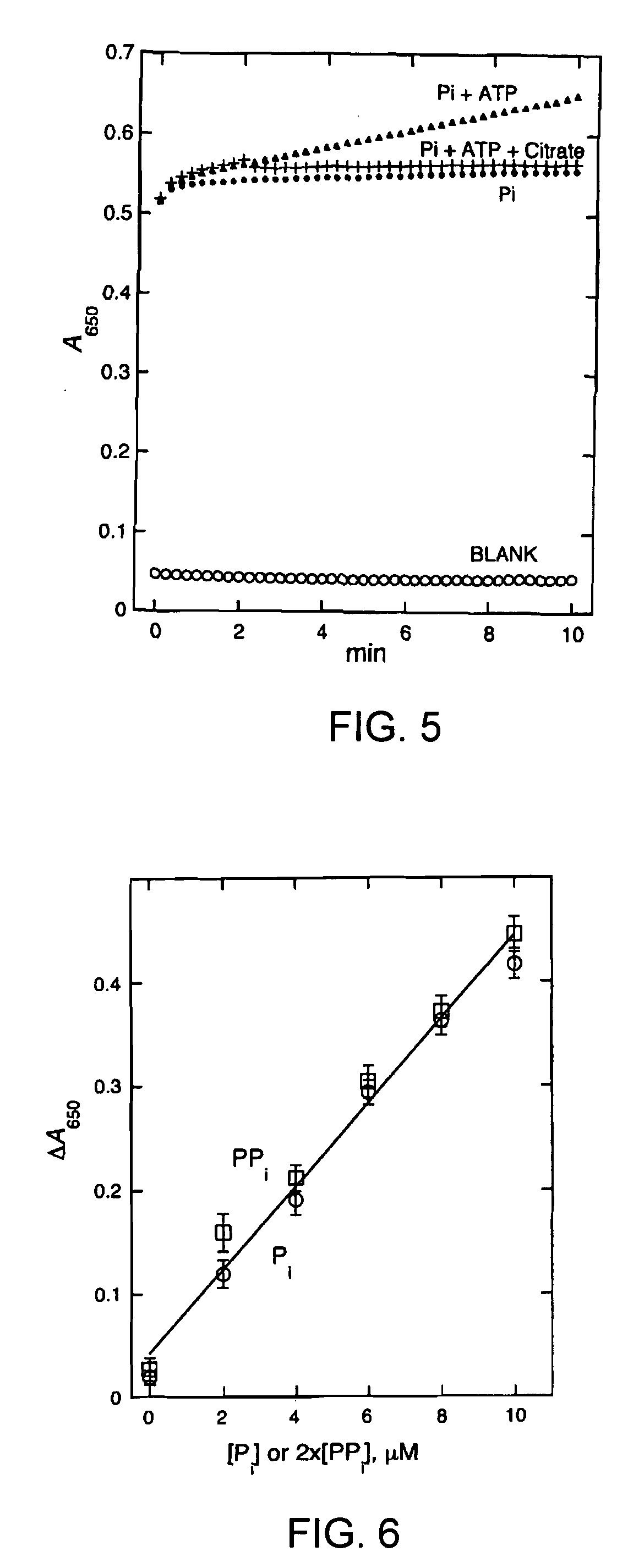
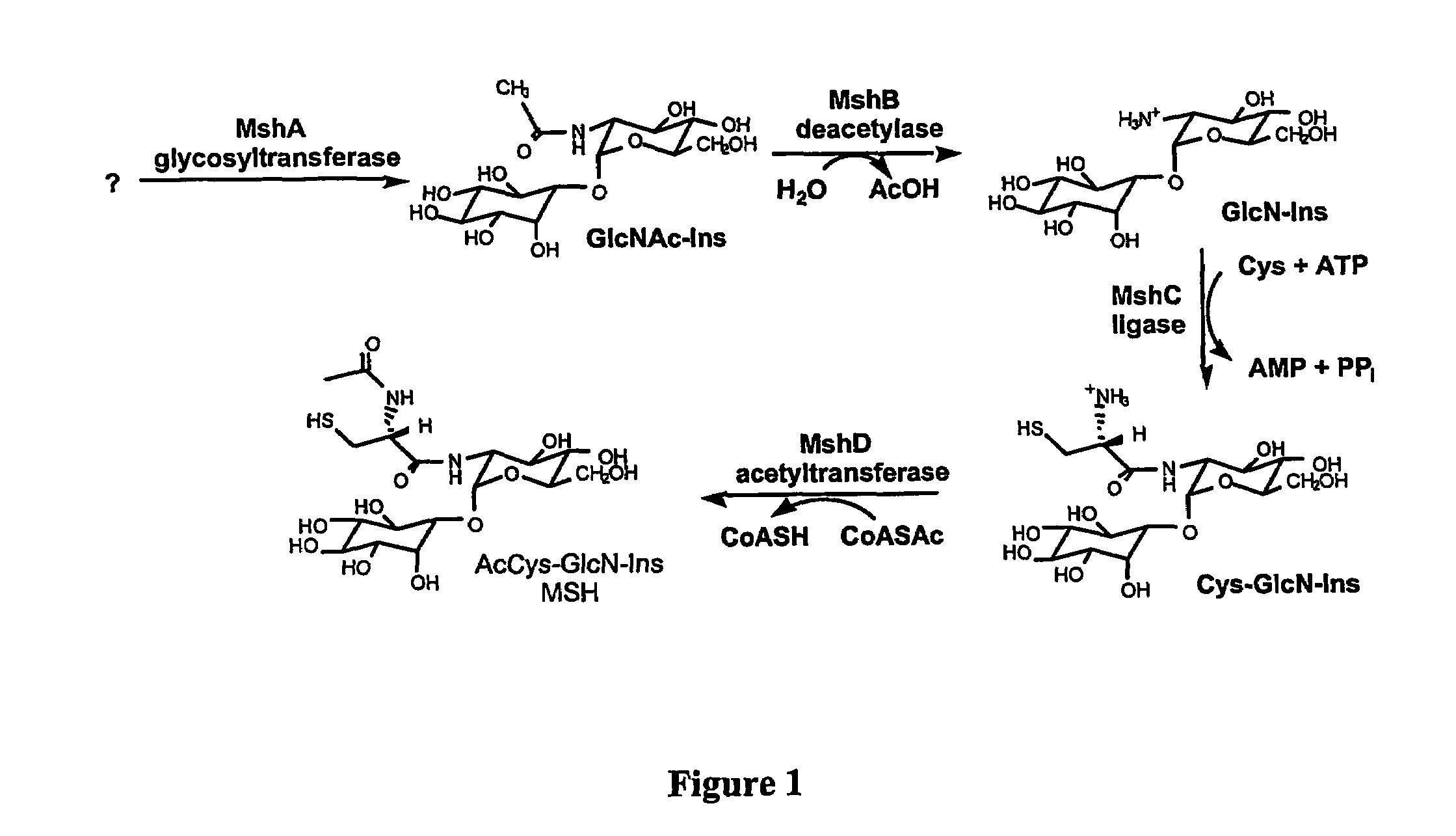
Inhibitors of MshC and Homologs Thereof, and Methods of Identifying Same
InactiveUS20100022509A1Reduced virulenceReduced activityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyBacteroides
The present invention utilizes three families of bacterial enzymes, which play a key role in mycothiol biosynthesis. The three families are bacterial cysteine:glucosaminyl inositol ligases (MshC) with catalytic ligase activity for ligation of glucosaminyl inositol and cysteine, bacterial acetyl-CoA:Cys-GlcN-Ins acetyltransferases (MshD) with catalytic activity for addition of an acetyl group to Cys-GlcN-Ins and bacterial MshA glycosyltransferase with catalytic activity for production of GlcNAc-Ins. The invention provides methods for using the mycothiol biosynthesis ligases, acetyltransferases or glycosyltransferases in drug screening assays to determine compounds that inhibit activity. The invention also provides inhibitors of the production or activity of the enzymes of mycothiol biosynthesis, and use of the inhibitors for treating microbial infection.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Molecular diagnostic method for dementia with lewy bodies
InactiveUS7745127B2Nervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementDementia with Lewy bodiesUbiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1
Owner:ORYZON GENOMICS SA
Compounds useful for the treatment of cancer, compositions thereof and methods therewith
InactiveUS20060142352A1Modulate activityArrest cell growthBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer preventionPreservative
The present invention generally relates to compounds and compositions useful for the modulation of ligase activity. The invention further relates to Compounds of the Invention, compositions thereof, and methods for treating or preventing cancer, a neoplastic disorder, acute or chronic renal failure, an inflammatory disorder, an immune disorder, a cardiovascular disease, an effect of aging or an infectious disease comprising administering an effective amount of a Compound of the Invention. The invention further relates to the use of a Compound of the Invention as a preservative of a cell, blood, tissue or an organ or as an agent to modulate stem cells.
Owner:SIGNAL PHARMA LLC +1
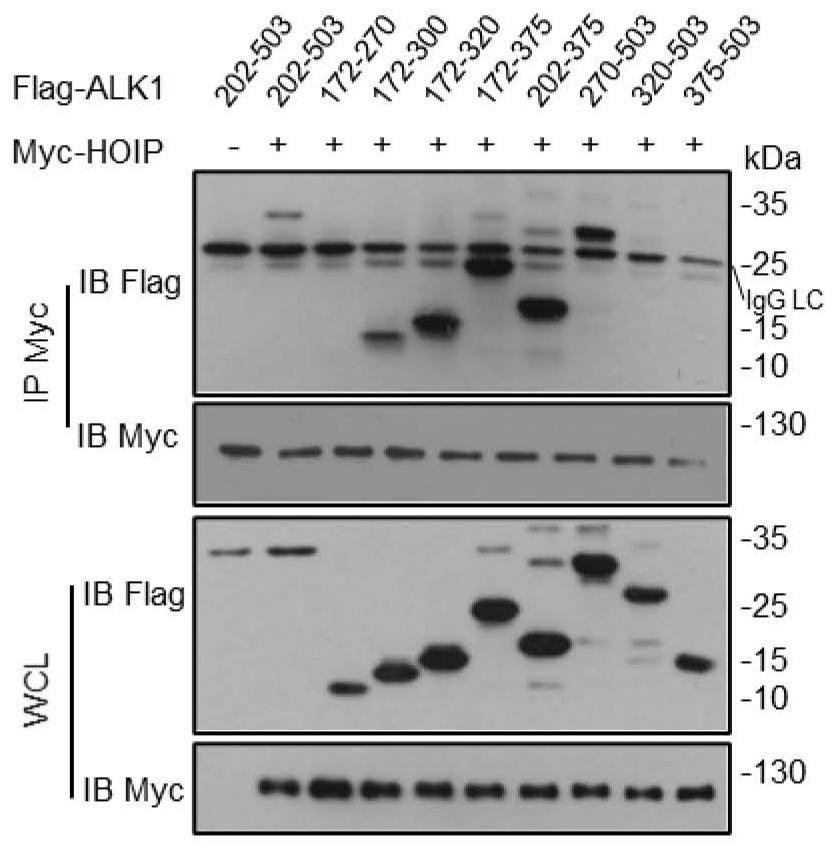
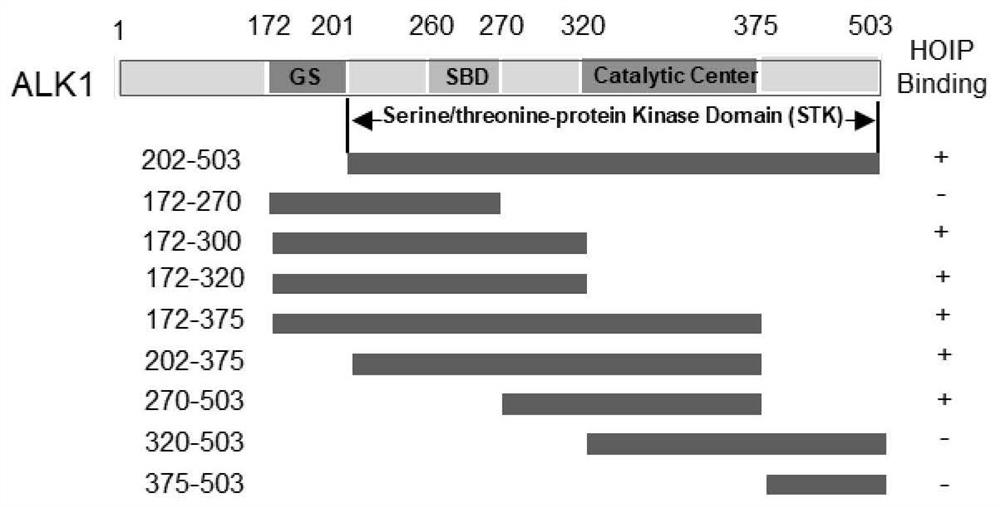
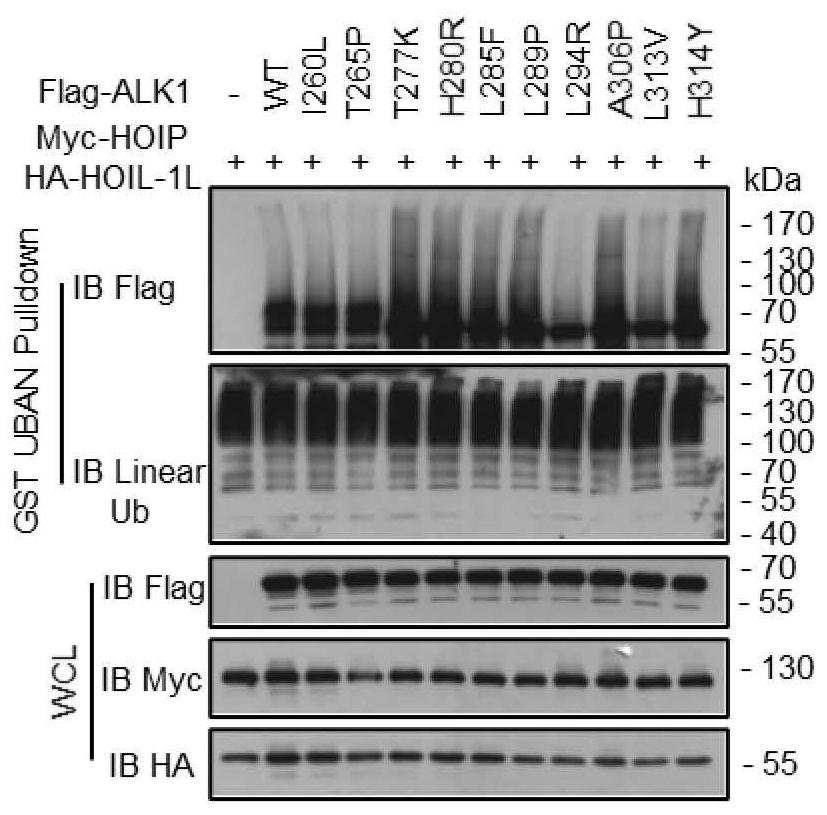
Application of HOIP inhibitor in preparation of medicine for treating type II hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
ActiveCN113368247AProof of combinationEnhanced ubiquitination modificationMicrobiological testing/measurementNitrile/isonitrile active ingredientsSignalling pathwaysPharmaceutical drug
The invention discloses application of an HOIP inhibitor in preparation of a medicine for treating type II hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT2). Firstly, a binding domain and a binding mechanism of ALK1 kinase and HOIP are disclosed, and it is found that binding enhancement of an ALK1 mutant and HOIP promotes obvious enhancement of the ubiquitination levels. By inhibiting the activity of HOIP ubiquitin ligase, the ubiquitination level of the ALK1 mutant is reduced, so that an ALK1-Smad1 / 5 signaling pathway is recovered, and symptoms of HHT2 are relieved. The invention proves that the pathogenesis of the ALK1 mutation-induced HHT2 is the reduction of the enzyme activity of ALK1 kinase, and a specific mutant of ALK1 can be inhibited through the HOIP inhibitor, so that the HOIP inhibitor can be used for treating HHT2, and the HOIP inhibitor becomes a potential medicine for treating the specific ALK1 mutation-induced HHT2.
Owner:ACADEMY OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI
P53 modulator and cancer target
Methods of screening for modulators of TRIM24 (also known as TIF1-ALPHA) expression and / or biological activity are described. In particular, methods of screening of screening for modulators of TRIM24 E3 ligase activity, and specifically an E3 ligase activity directed at p53 as the target polypeptide are also described. Modulators of TRIM24 expression and activity are provided and their use in treatment of cancer, particularly in breast, colon, prostate, renal cancers and in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Suitable modulators of TRIM24 expression include siRNA and shRNA and can be used in the treatment of cancer and for targeting cancer stem cells.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Live-attenuated compositions for bacterial infections
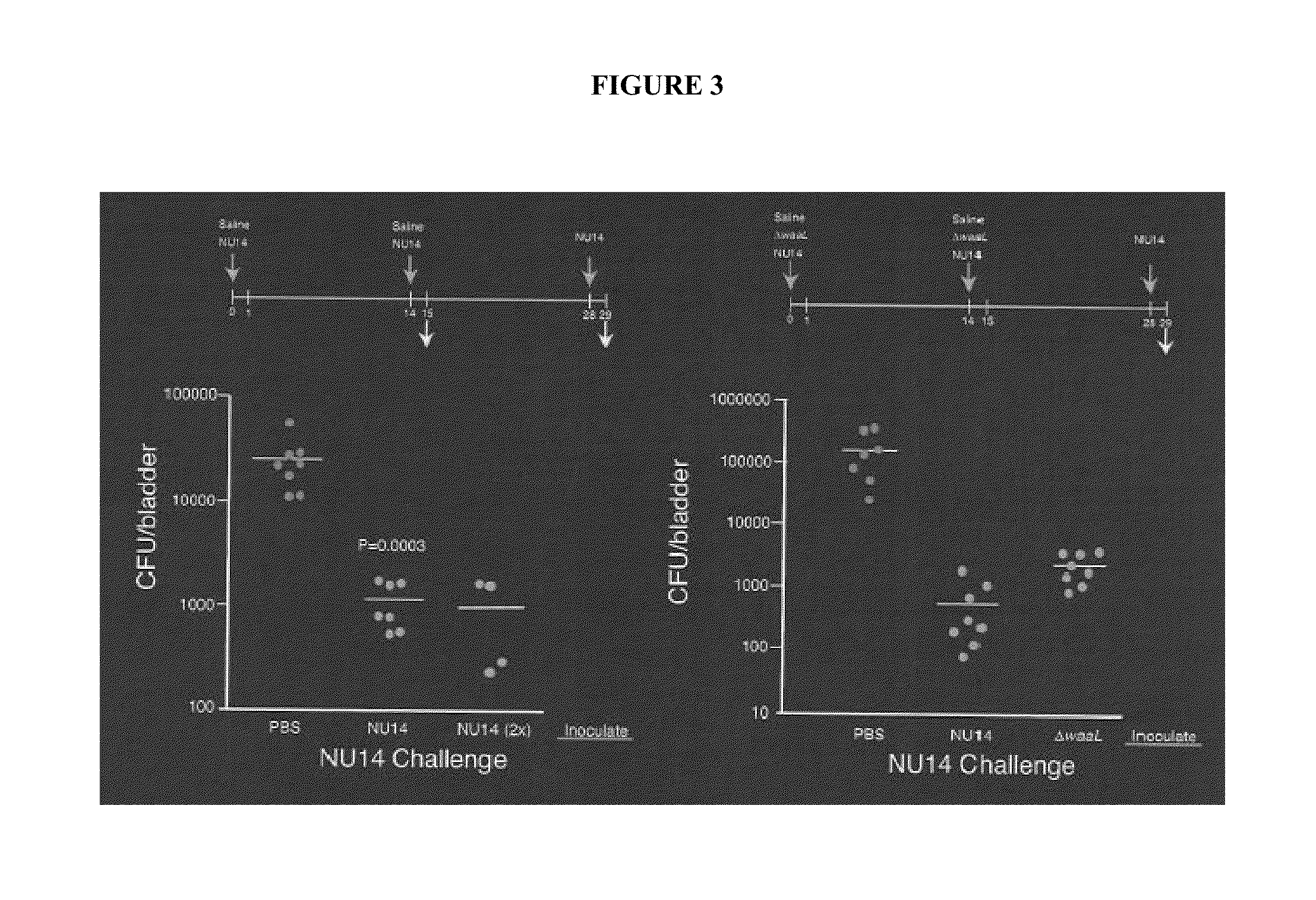
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for disease treatment and prevention through administration of a live attenuated composition. In particular, the present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment and prevention of urinary tract infection by administration of a live attenuated compositions lacking O-antigen ligase activity.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Compounds useful for the treatment of cancer, compositions thereof and methods therewith
InactiveUS20060030617A1Arrest cell growthModulate activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCancer preventionPreservative
The present invention generally relates to compounds and compositions useful for the modulation of ligase activity. The invention further relates to Compounds of the Invention, compositions thereof, and methods for treating or preventing cancer, a neoplastic disorder, acute or chronic renal failure, an inflammatory disorder, an immune disorder, a cardiovascular disease, an effect of aging or an infectious disease comprising administering an effective amount of a Compound of the Invention. The invention further relates to the use of a Compound of the Invention as a preservative of a cell, blood, tissue or an organ or as an agent to modulate stem cells.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Detection of bacteria and fungi
ActiveUS9096884B2Reduce sizeMinimizes sample volumeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBacteroidesMicroorganism
A method of detecting a ligase expressing micro-organism in a sample comprises steps of treating the sample under conditions that inhibit the activity of ATP-dependent ligase from mammalian cells but which do not inhibit the activity of the microbial ligases, contacting the sample or a portion of the sample with a nucleic acid molecule which acts as a substrate for ligase activity in the sample, incubating the thus contacted sample under conditions suitable for ligase activity; and specifically determining the presence and / or the amount of a ligated nucleic acid molecule resulting from the action of the ligase on the substrate nucleic acid molecule to indicate the presence of the ligase expressing micro-organism. The micro-organism may be a fungus or a bacterium or both. High pH conditions may be employed to inactivate mammalian ligases. Related kits are described.
Owner:MOMENTUM BIOSCI
Live-attenuated compositions for bacterial infections
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Method of producing a tripeptide gamma-glu-val-gly using enterobacteriaceae
A method for producing γ-Glu-Val-Gly is described, wherein the method includes the steps of cultivating a γ-Glu-Val-Gly-producing bacterium belonging to the family Enterobacteriaceae in a culture medium so that the γ-Glu-Val-Gly accumulates in the culture medium or the cells of the bacterium, or both, and collecting the γ-Glu-Val-Gly from the culture medium or the cells of the bacterium, or both. The bacterium has been modified to overexpress a gene encoding a protein having L-threonine 3-dehydrogenase activity and a gene encoding a protein having 2-amino-3-oxobutanoate coenzyme A ligase activity.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
A kind of double-stranded dna peptide ligase ddplasei and using method thereof
The present invention provides a novel double-stranded DNA peptide ligase dDPlaseI, which can be used to catalyze the covalent connection of a specific double-stranded DNA and a specific polypeptide, and its enzymatic properties and use methods. The amino acid sequence of the dDPlaseI enzyme is shown in SEQ ID NO: 6, and the corresponding gene coding sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 5; The 5'-terminal deoxyribonucleotide A is a specific DNA double-strand in the phosphorylated state and the C-terminal start is a specific polypeptide chain with 7 peptides of N'‑MANCEHL‑C', and catalyzes the covalent bond between the two Together; double-stranded DNA and polypeptide ligation products have characteristic absorption peaks at 360nm wavelength, which can be used for the determination of dDPlaseI ligase activity. dDPlaseI ligase buffer was composed of 450 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM Mg, pH 7.8 2+ , 80mM NaCl, 20mM ATP and 8mM Triton X-100, the optimal reaction temperature range is 35℃-45℃, and the ligation reaction time is 3min-10min. The novel double-stranded DNA polypeptide ligase provided by the present invention can be used as a tool enzyme for genetic engineering and gene analysis.
Owner:黄种山
Methods of use of the enzymes of mycothiol synthesis
InactiveUS7560229B2Low toxicityReduced activityCompound screeningBiocideBacteroidesVirulent characteristics
The present invention utilizes three families of bacterial enzymes, which play a key role in mycothiol biosynthesis. The three families are bacterial cysteine:glucosaminyl inositol ligases (MshC) with catalytic ligase activity for ligation of glucosaminyl inositol and cysteine, bacterial acetyl-CoA:Cys-GlcN-Ins acetyltransferases (MshD) with catalytic activity for addition of an acetyl group to Cys-GlcN-Ins and bacterial MshA glycosyltransferase with catalytic activity for production of GlcNAc-Ins. The invention provides methods for using the mycothiol biosynthesis ligases, acetyltransferases or glycosyltransferases in drug screening assays to determine compounds that inhibit activity. The invention provides for treatment of actinomycete infections in mammals using antibiotics that inhibit production or activity of the enzymes of mycothiol biosynthesis, in particular MshC, MshD or MshA, and thereby reduce the production of mycothiol and the virulence of the infecting bacteria. Additionally, the invention provides a live mutant with a genome containing a modification in an endogenous enzyme of mycothiol biosynthesis gene. The invention also provides an expression vector comprising polynucleotides of mshA, mshB, mshC and mshD.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
TARGETING ENZYMES OF THE tRNA SPLICING PATHWAY FOR IDENTIFICATION OF ANTI-FUNGAL AND/OR ANTI-PROLIFERATIVE MOLECULES
InactiveUS20110172108A1Enhances the activity of an animaliaInhibit and reduce activityBiocideAntimycoticsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAnti fungal
The present invention relates to a method for screening and identifying compounds that modulate the activity of one or more components in the tRNA splicing pathway. In particular the invention relates to a method for screening and identifying compounds that modulate the activity tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or tRNA splicing ligase. The invention provides assays for the identification of compounds that inhibit animalia tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or animalia tRNA splicing ligase. The invention also provides assays for the identification of compounds that inhibit fungal tRNA splicing endonuclease and / or fungal tRNA splicing ligase. The methods of the present invention provide a simple, sensitive assay for high-throughput screening of libraries of compounds to identify pharmaceutical leads useful for treating and / or preventing cancer and / or fungal infections.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
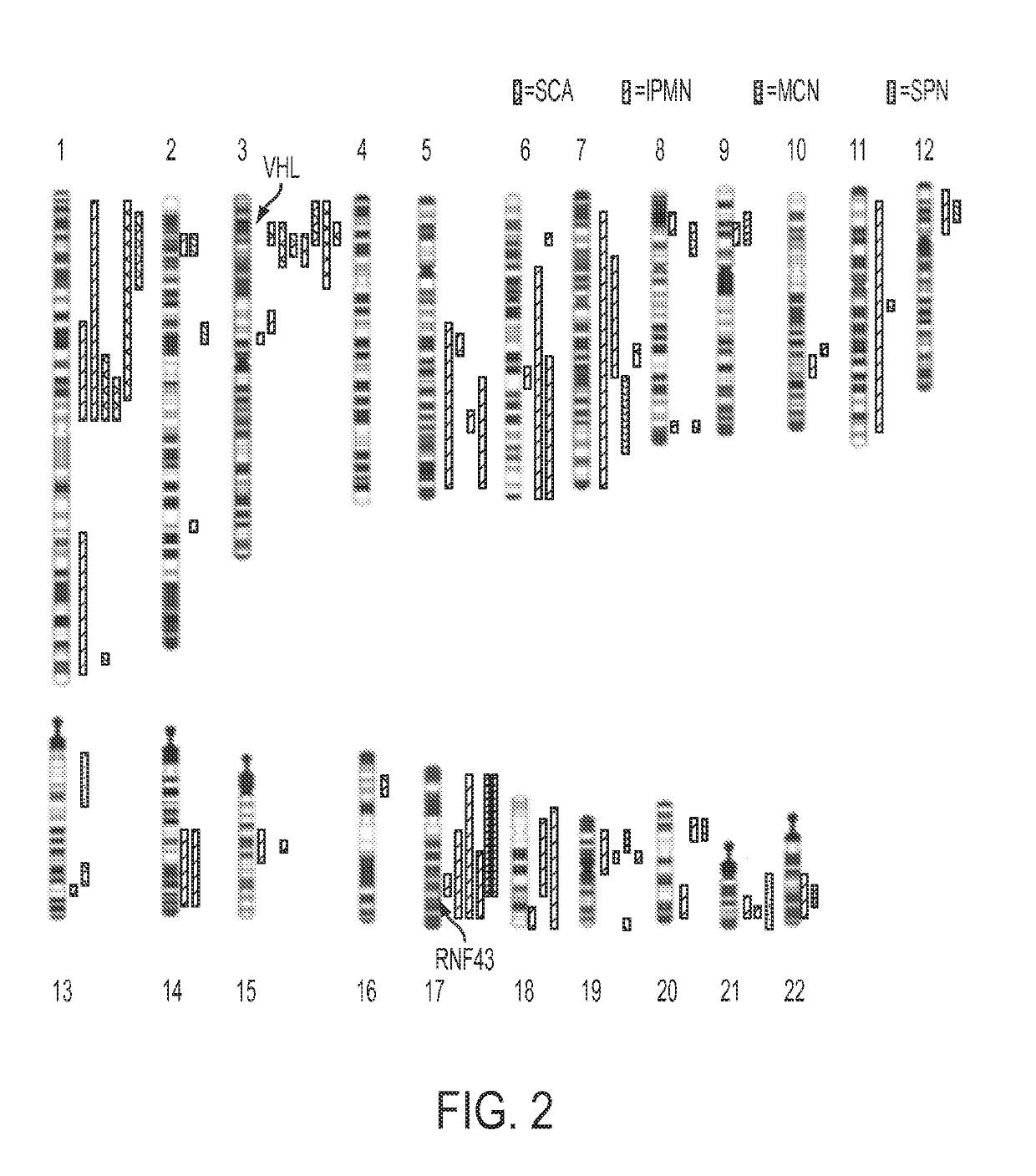
Differential Identification of Pancreatic Cysts
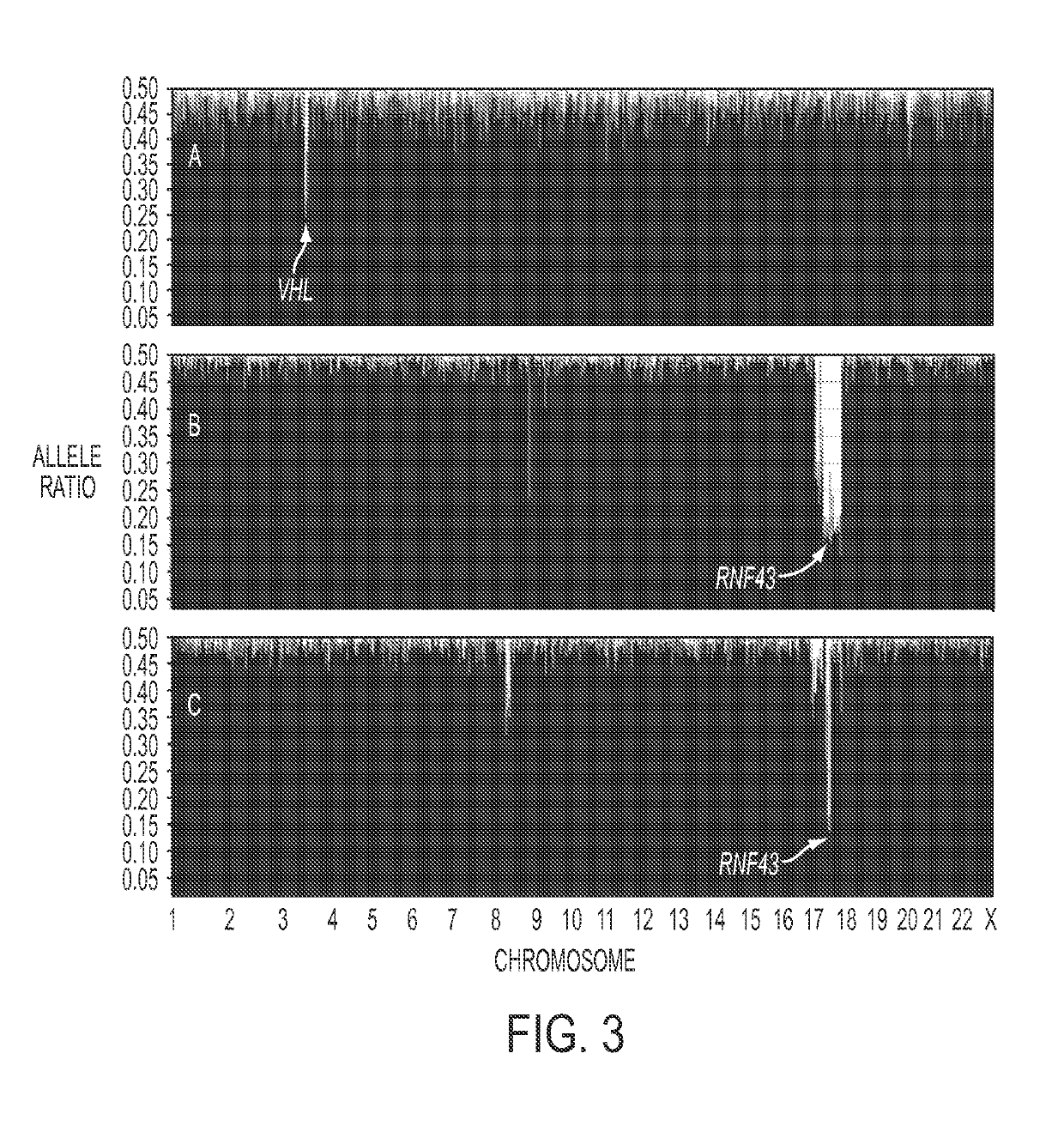
More than 2% of adults harbor a pancreatic cyst, a subset of which progress to invasive lesions with lethal consequences. To assess the genomic landscapes of neoplastic cysts of the pancreas, we determined the exomic sequences of DNA from the neoplastic epithelium of eight surgically resected cysts of each of the major neoplastic cyst types: serous cystadenomas (SCAs), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms (IPMNs), mucinous cystic neoplasms (MCNs) and solid pseudo-papillary neoplasms (SPNs). SPNs are low-grade malignancies, and IPMNs and MCNs, but not SCAs, have the capacity to progress to cancer. We found that SCAs, IPMNs, MCNs, and SPNs contained 10=4.6, 27=12, 16=7.6, and 2.9=2.1 somatic mutations per tumor, respectively. Among the mutations identified, E3 ubiquitin ligase components were of particular note. Four of the eight SCAs contained mutations of VHL, a key component of the VHL ubiquitin ligase complex that has previously been associated both with renal cell carcinomas, SCAs, and other neoplasms. Six of the eight IPMNs and three of the eight MCNs harbored mutations of RNF43, a gene coding for a protein with intrinsic E3 ubiquitin ligase activity that has not previously been found to be genetically altered in any human cancer. The preponderance of inactivating mutations in RNF43 unequivocally establish it as a suppressor of both IPMNs and MCNs. SPNs contained remarkably few genetic alterations, but always contained mutations of CTNNB1, previously demonstrated to inhibit degradation of the encoded protein (β-catenin) by E3 ubiquitin ligases. These results highlight the essential role of ubiquitin ligases in these neoplasms and have important implications for the diagnosis and treatment of patients with cystic tumors.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
A kind of single-chain dna peptide ligase sdplasei and using method thereof
The present invention provides a novel single-stranded DNA peptide ligase sDPlaseI, which can be used to catalyze the covalent connection of a specific single-stranded DNA and a specific polypeptide, and its enzymatic properties and use methods. The amino acid sequence of the sDPlaseI enzyme is shown in SEQ ID NO: 4, and the corresponding gene coding sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 3; A specific DNA single strand with terminal deoxyribonucleotide A in phosphorylated state and a specific polypeptide chain with 7 peptides starting from N'‑MANCEHL‑C' at the C terminus, and catalyzing the covalent bond between the two ; Single-stranded DNA and polypeptide ligation products have characteristic absorption peaks at 358nm wavelength, which can be used for the determination of sDPlaseI ligase activity. sDPlaseI ligase buffer was composed of 500 mM Tris-HCl, 100 mM Mg, pH 7.5 2+ , 10mM ATP and 10mM DTT, the optimum reaction temperature range is 30℃-40℃, and the ligation reaction time is 5min-15min. The novel single-chain DNA polypeptide ligase provided by the present invention can be used as a tool enzyme for genetic engineering and gene analysis.
Owner:黄种山
Interaction factor gene Actin for zinc finger binding protein of corn, and recombinant expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN109912704ARaise the level of expressivenessImprove translation efficiencyPlant peptidesFermentationResponse processNicotiana tabacum
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to an interaction factor gene Actin for zinc finger binding protein of corn, and a recombinant expression vector and application thereof. The full length of the gene is 12712 bp, and the gene is a complete expression frame. The gene comprises 6 exons and is encoded with 123 amino acids. Through expression detection in yeast, it is found that a Zm-Actin gene and a Zm-ZnRing gene can have obviously mutual regulation effect and play a role in chloroplasts through co-localization. The gene Actin has a function of improving the translation efficiency of foreign genes, the zinc finger binding protein has the activity of E3 ubiquitin ligase, the E3 ubiquitin ligase involves in a salt stress response process of plants, and the growth and metabolism of cells are regulated through control of membrane transport and generation of reactive oxygen; the gene can be applied to increase the reactive oxygen in tobacco leaves so as to regulate the growth and metabolism of the cells.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 mutant, coding gene and application
ActiveCN110592032AArrestin activitySuppress cancerPeptide/protein ingredientsLigasesUbiquitin ligaseProtein function
The invention belongs to the field of biomedicines, and relates to discovery and verification of the function of a new locus of carcinogenic related protein Smurf1. Mutation of the new locus causes complete loss of the protein function of the new site. A meaning is that the function of the activity of the Smurf1 as E3 ligase after mutation of the 69 locus of the protein Smurf1 can be reduced and then tumors can be inhibited. Furthermore, tumor study is expanded and perfected, and a new target locus is provided for tumor treatment and target drug development.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for easily and rapidly evaluating efficiency of molecular cloning system
ActiveCN107941887ALow costEasy to testMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRestriction enzyme digestionLarge fragment
The invention discloses a method for easily and rapidly evaluating the efficiency of a molecular cloning system. A DNA fragment is designed, at least two multiple cloning sites are arranged on the DNAfragment, restriction enzyme digestion sites of to-be-assayed restriction endonuclease are provided in the multiple cloning sites, and the restriction enzyme digestion sites only exist in the multiple cloning sites; sticky ends which are produced in the different multiple cloning sites by the same endonuclease can be complementarily connected; for the DNA fragment undergoes restriction enzyme digestion, electrophoresis is carried out after the restriction enzyme digestion product is connected by ligase, and the formed electrophoretic band is analyzed: if the electrophoretic band exists as a large fragment or a single complete vector fragment, then the endonuclease has lower or no activity; and if the electrophoretic band exists as a small fragment, then the ligase has lower or no activity. The provided method for evaluating the efficiency of a molecular cloning system can easily and rapidly test the activity of a main ingredient (endonuclease or ligase) in a restriction enzyme digestion connecting system.
Owner:HUBEI BOYUAN SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com