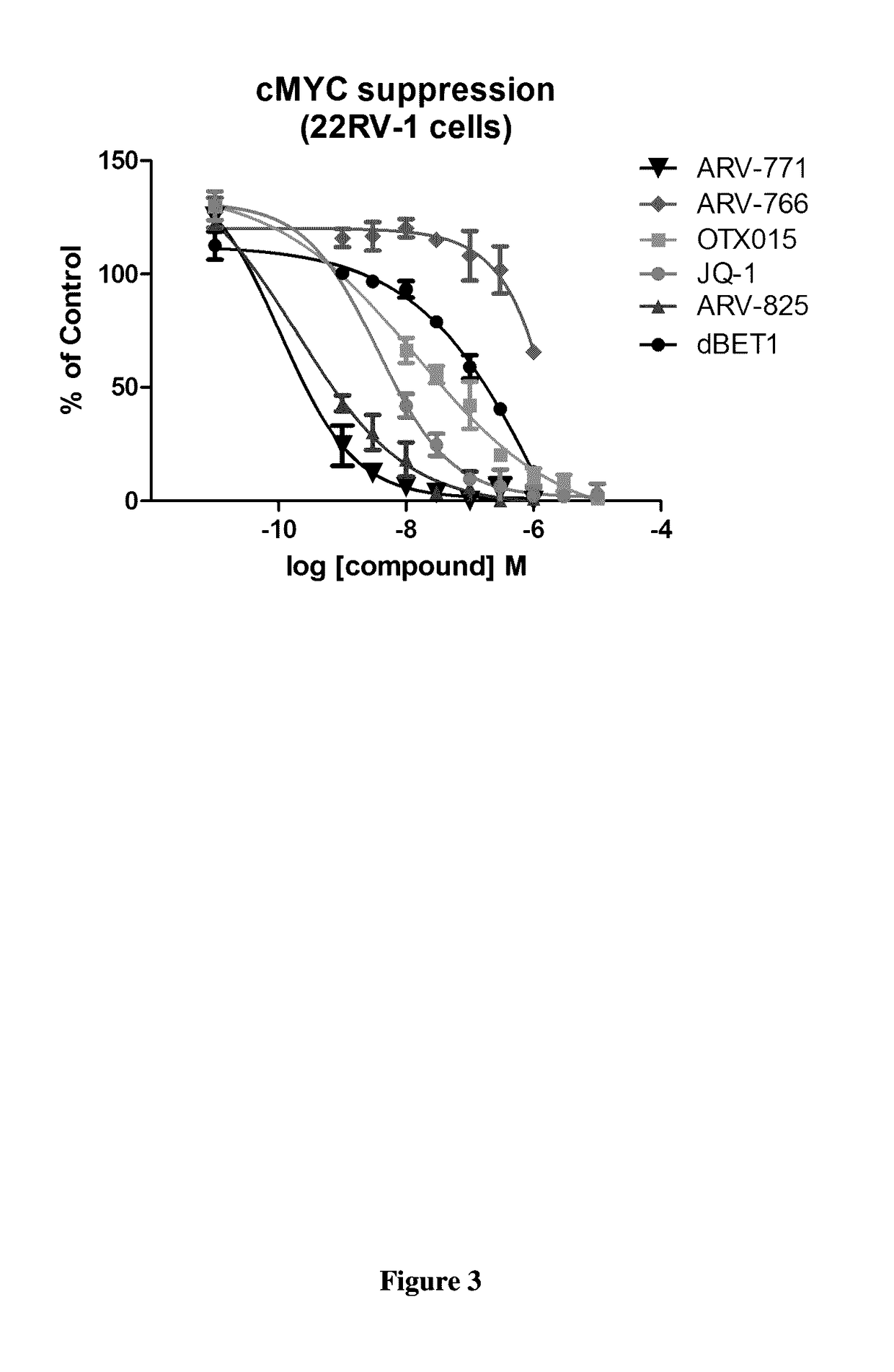
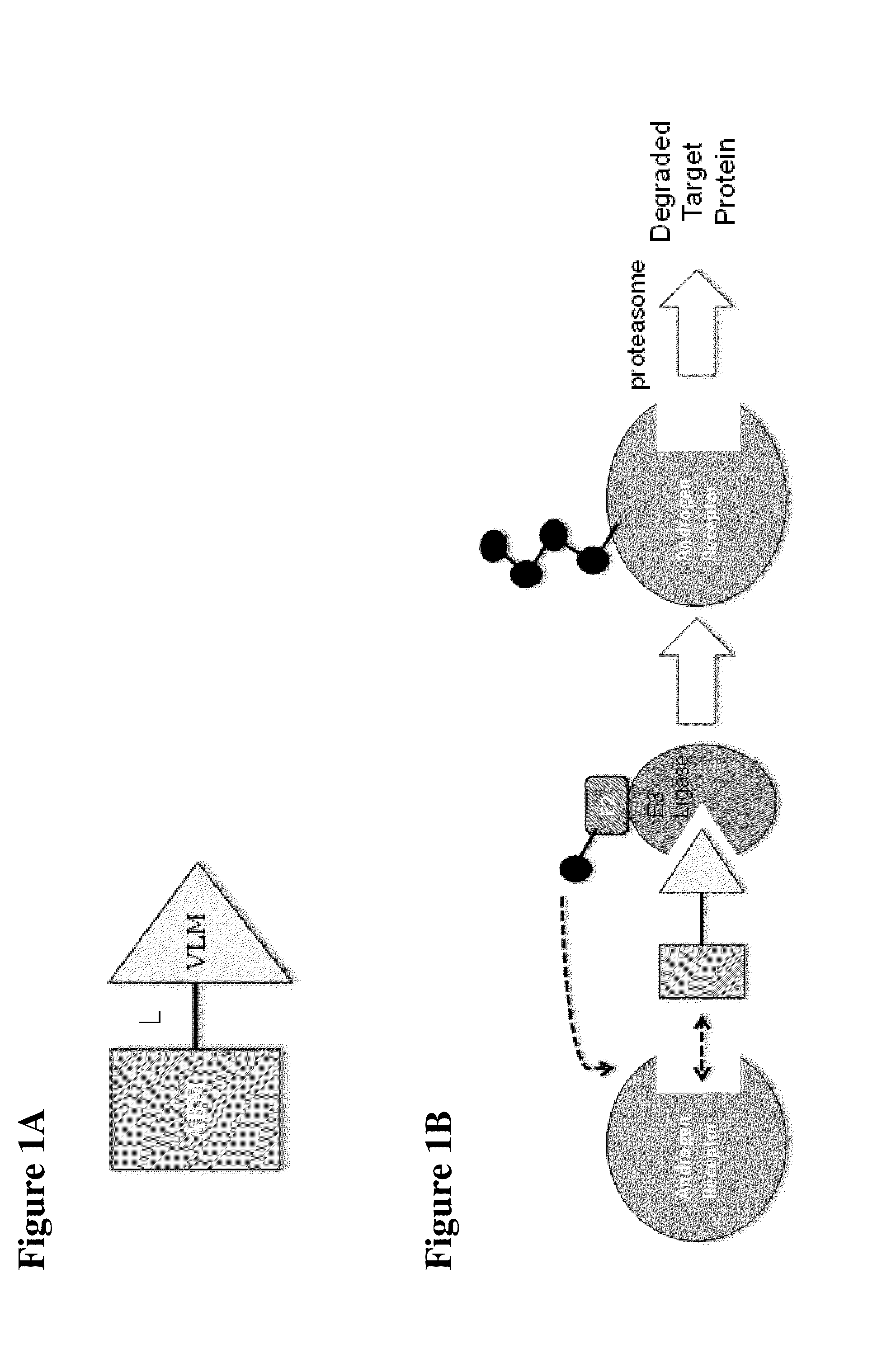
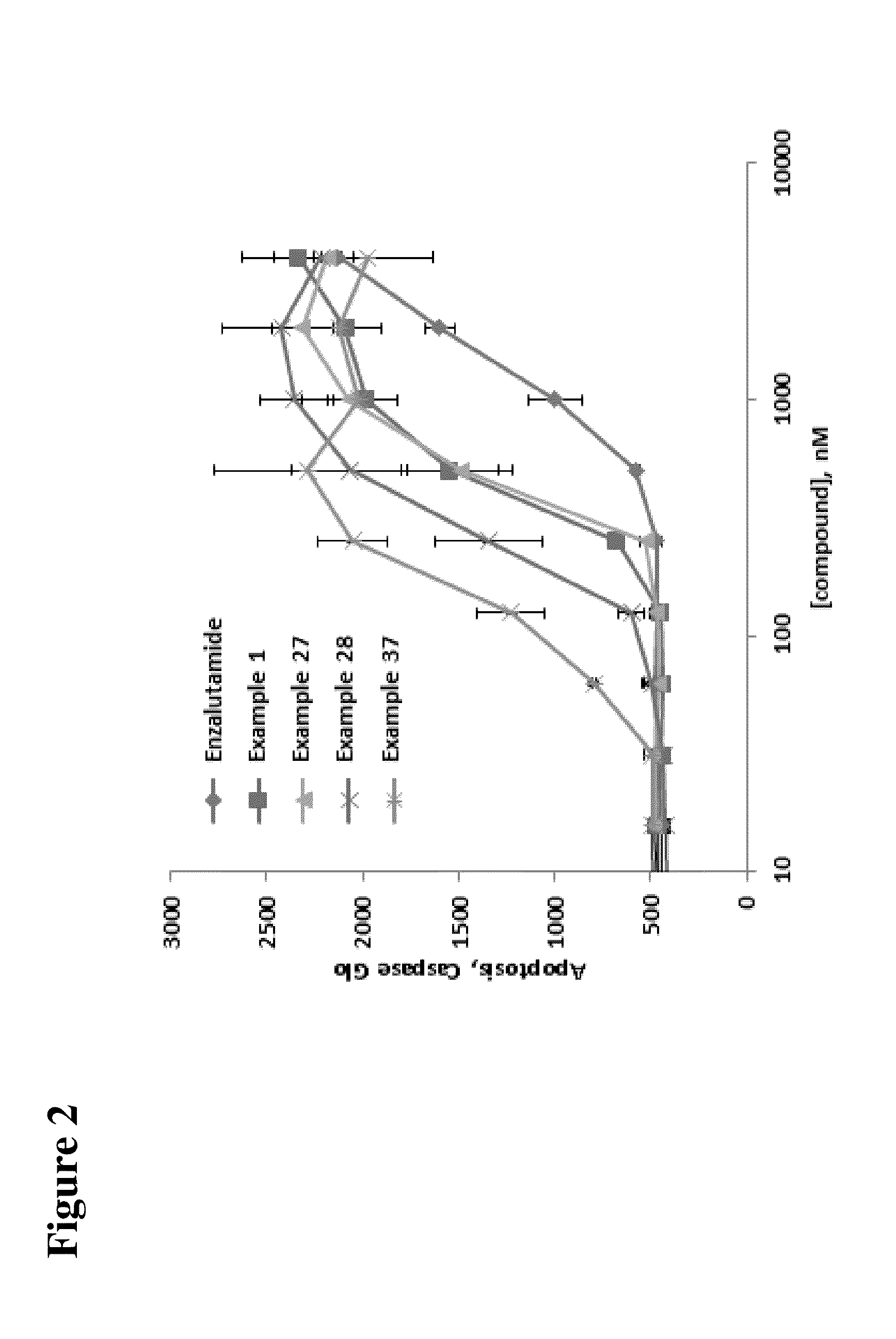
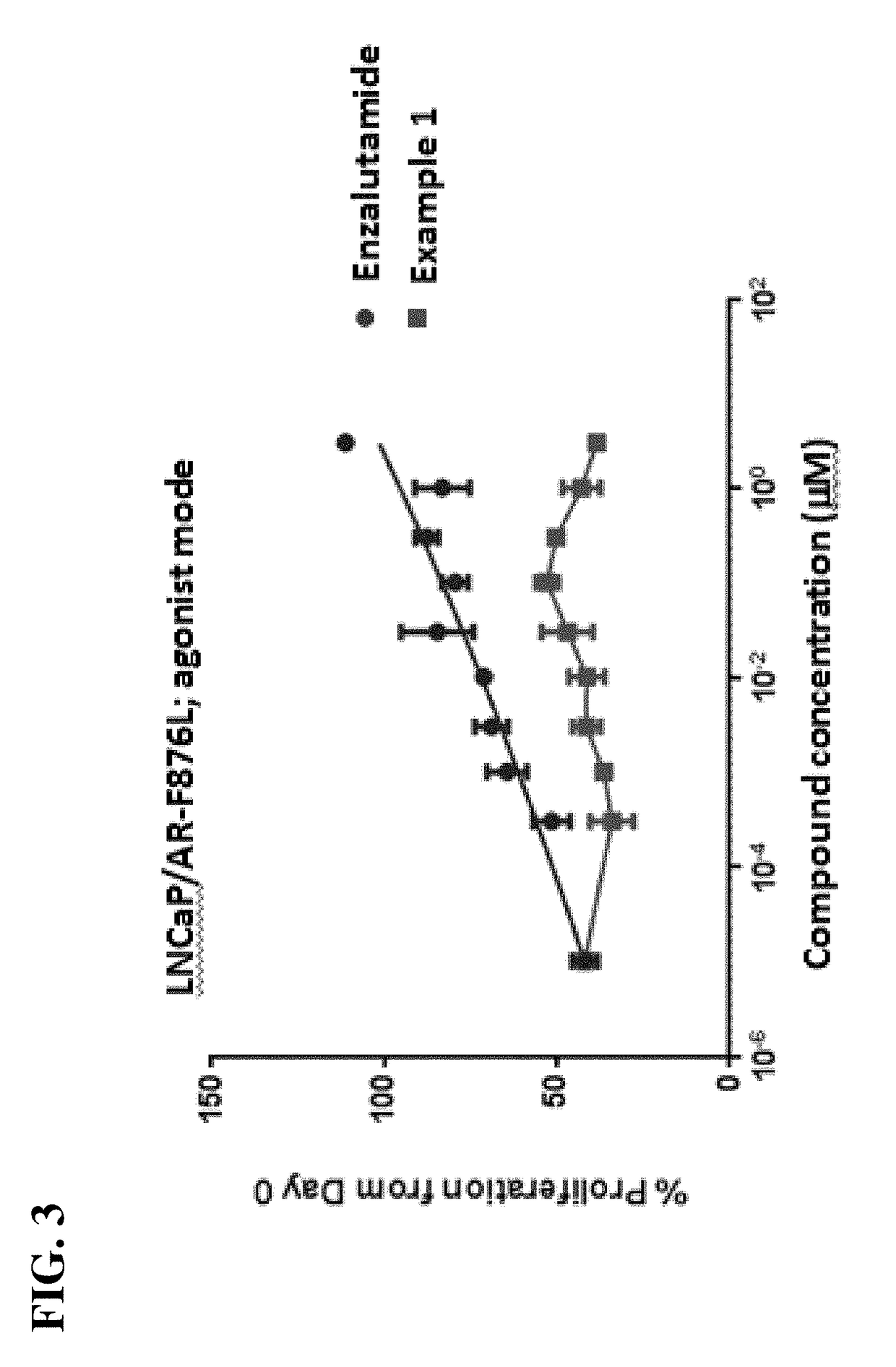
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
217 results about "Ubiquitin ligase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
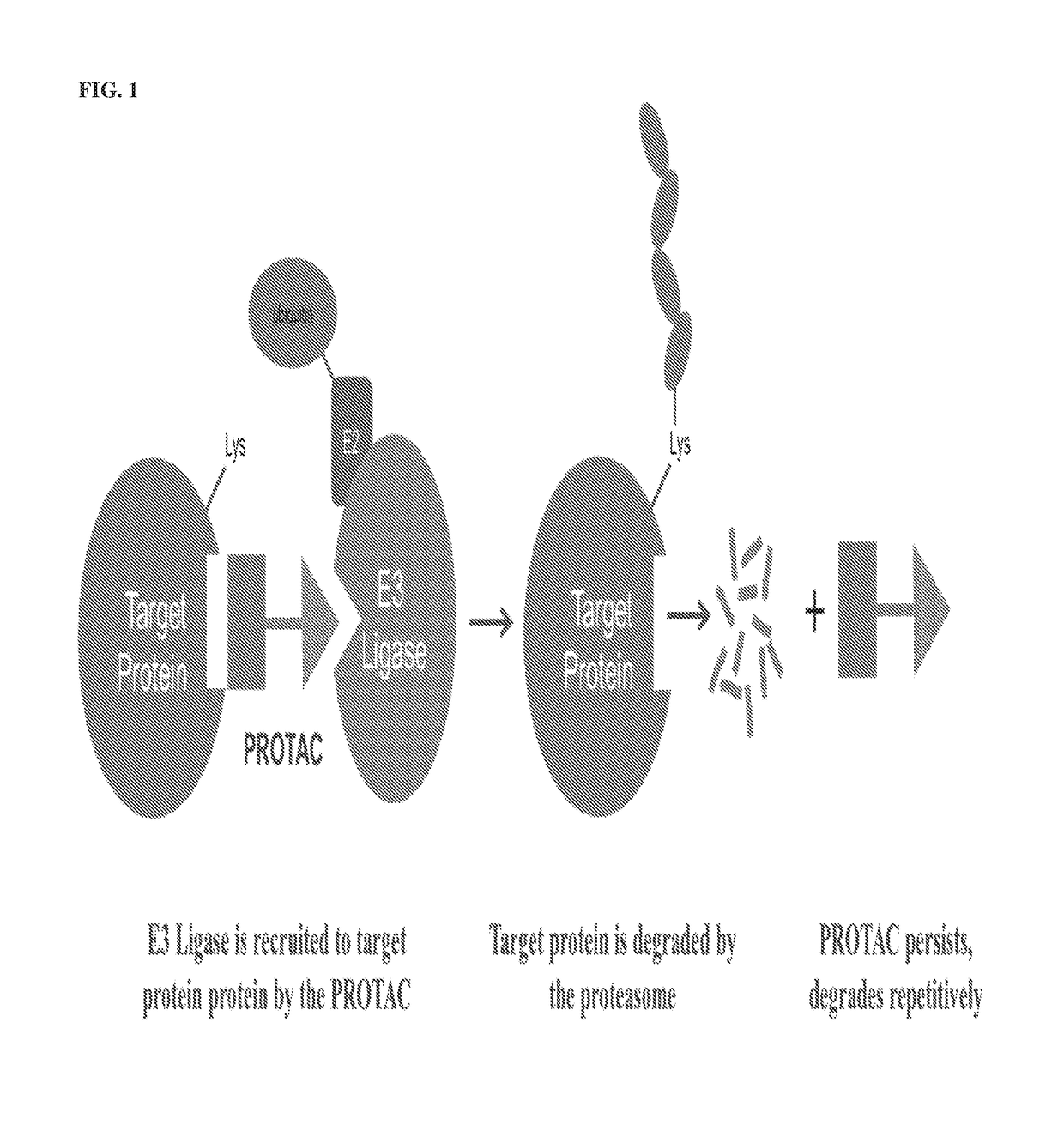
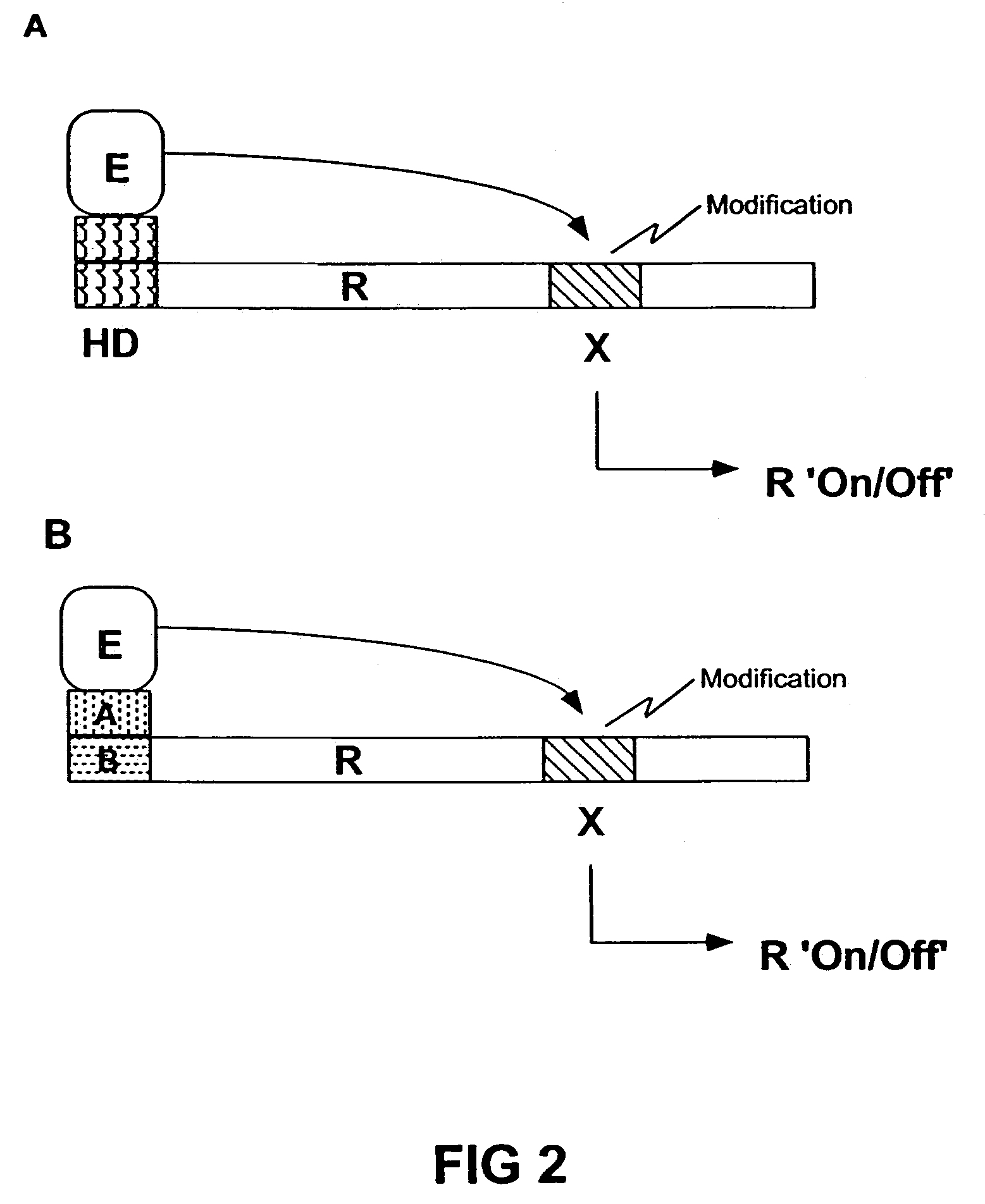
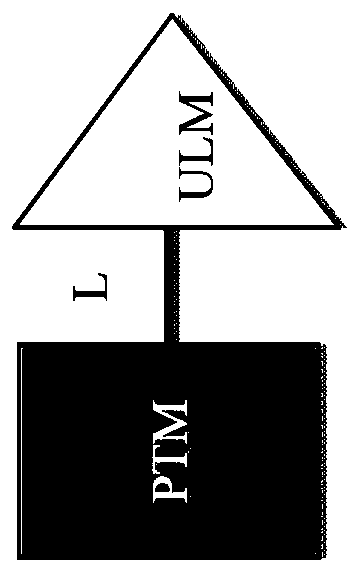
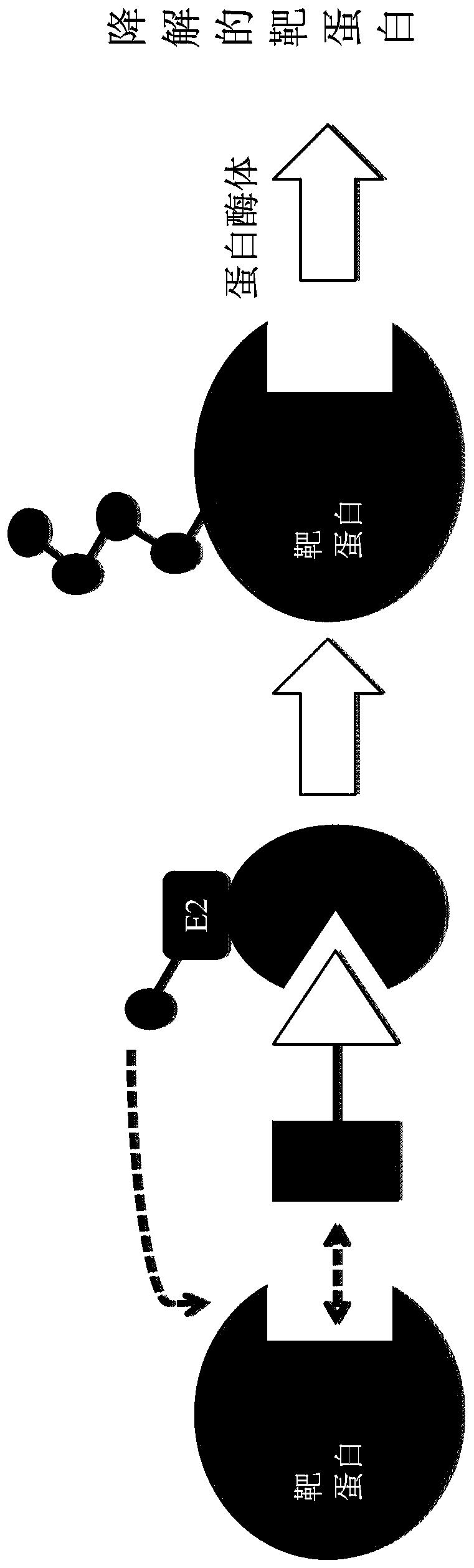
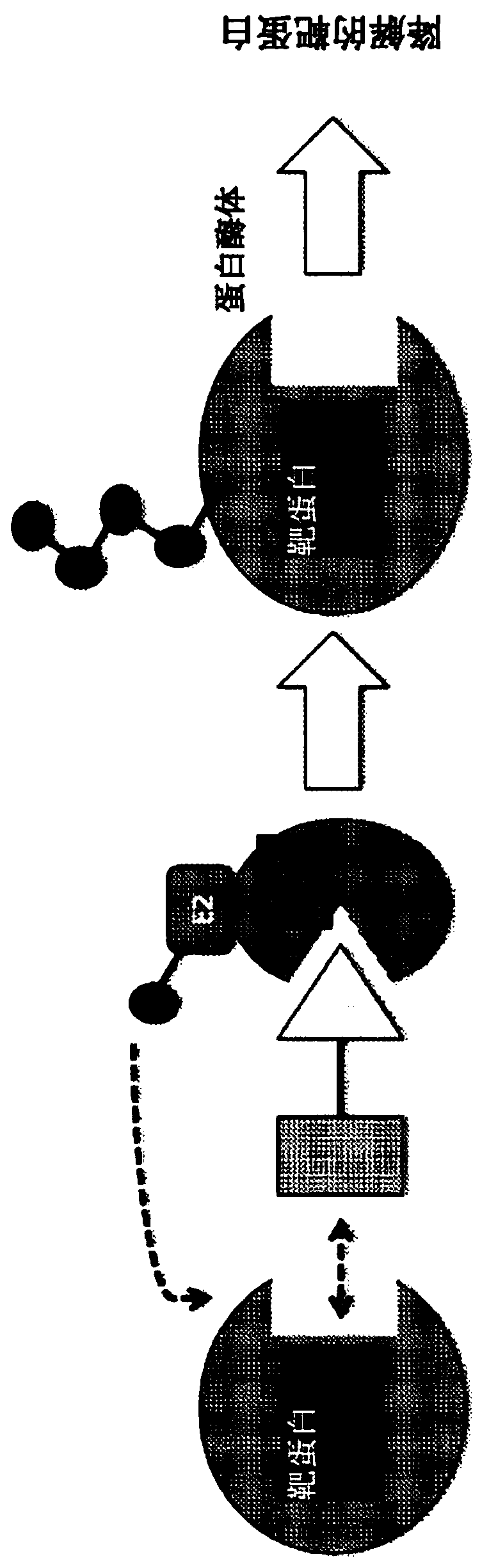
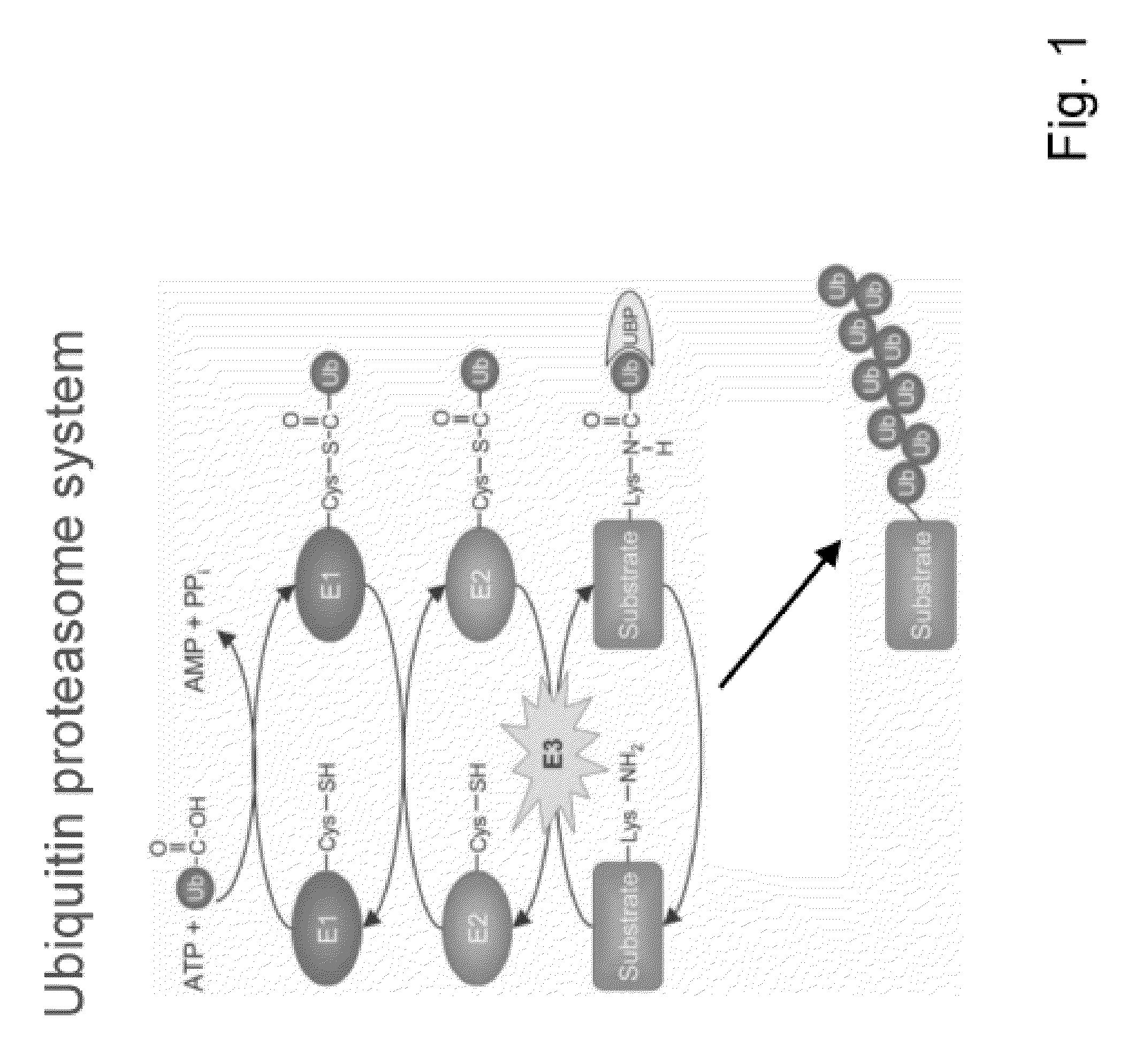
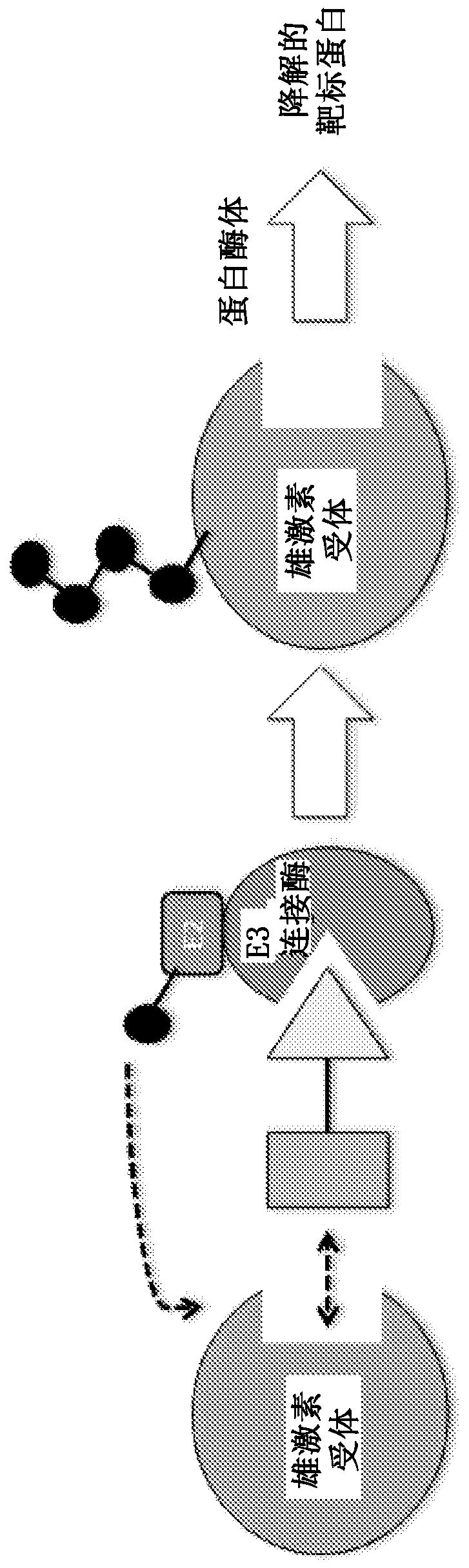
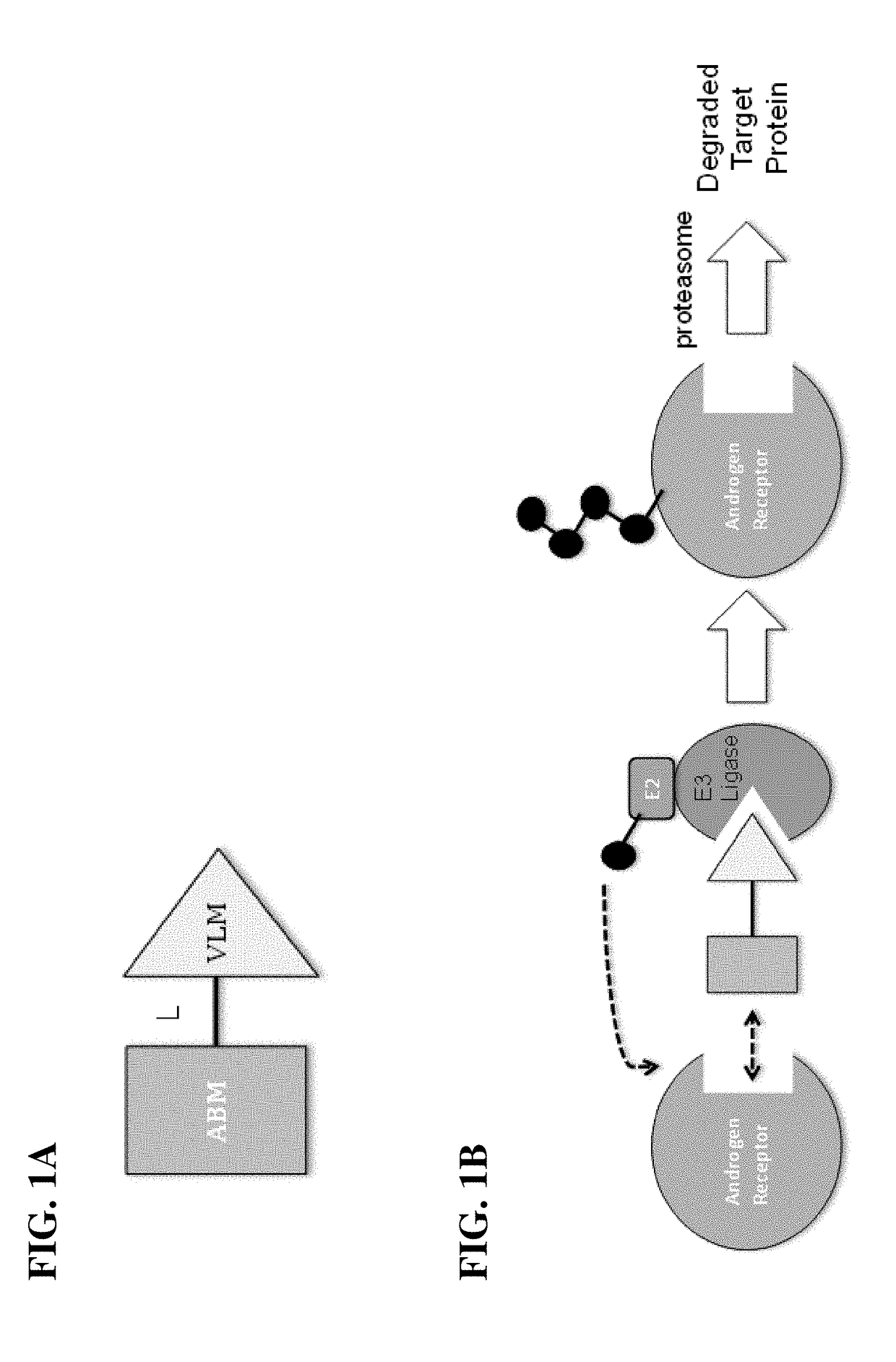
A ubiquitin ligase (also called an E3 ubiquitin ligase) is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. The ubiquitin is attached to a lysine on the target protein by an isopeptide bond. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases regulates diverse areas such as cell trafficking, DNA repair, and signaling and is of profound importance in cell biology. E3 ligases are also key players in cell cycle control, mediating the degradation of cyclins, as well as cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor proteins. The human genome encodes over 600 putative E3 ligases, allowing for tremendous diversity in substrates.
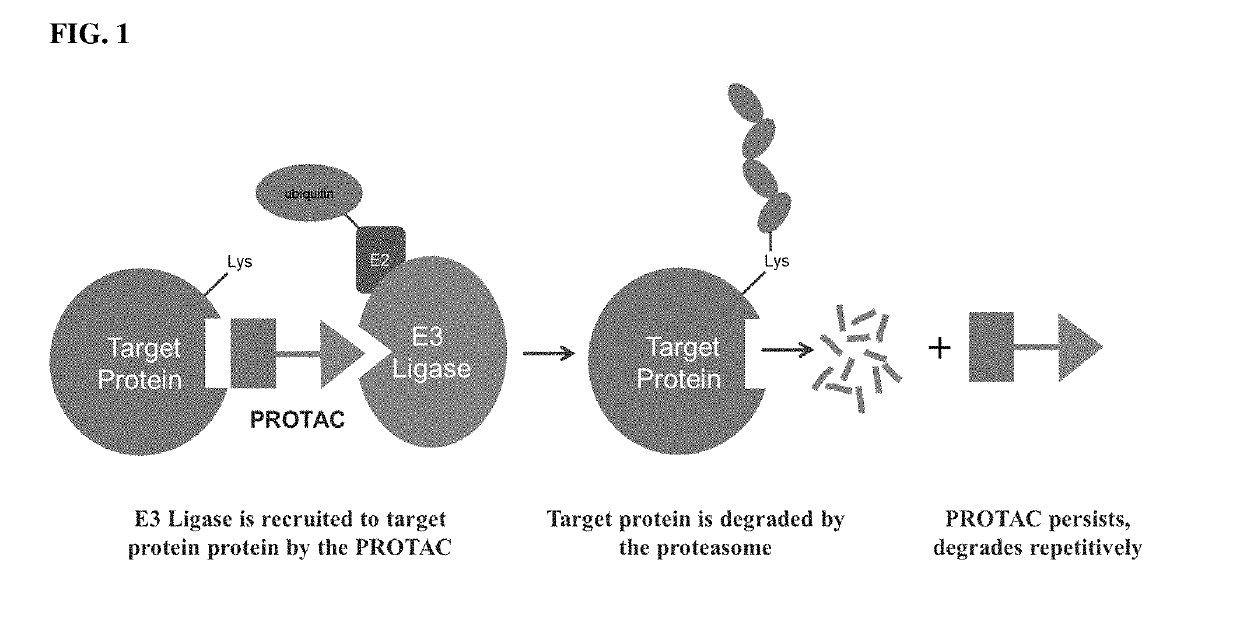
Compounds & Methods for the Enhanced Degradation of Targeted Proteins & Other Polypeptides by an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase
ActiveUS20140356322A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsProtein targetEnhanced degradation
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of targeted ubiquitination, especially inhibitors of a variety of polypeptides and other proteins that are degraded and / or otherwise inhibited by bifunctional compounds of the present invention. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand that binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety that binds a target protein, such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of that protein. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds of the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of targeted polypeptides.
Owner:YALE UNIV +2
Compounds and methods for the enhanced degradation of targeted proteins
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of targeted ubiquitination, especially inhibitors of a variety of polypeptides and other proteins which are degraded and / or otherwise inhibited by bifunctional compounds according to the present invention. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds a target protein such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of that protein. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of targeted polypeptides.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Compounds and methods for the targeted degradation of bromodomain-containing proteins
ActiveUS20170065719A1Symptoms improvedLimit scopeOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryProteinUbiquitin ligase
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of targeted ubiquitination, especially inhibitors of a variety of polypeptides and other proteins which are degraded and / or otherwise inhibited by bifunctional compounds according to the present invention. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds a target protein such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of that protein. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of targeted polypeptides.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC +1
Compounds and methods for the targeted degradation of androgen receptor
ActiveUS20160214972A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderAndrogen Receptor GeneUbiquitin ligase
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility to degrade and (inhibit) Androgen Receptor. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds Androgen Receptor such that Androgen Receptor is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of Androgen Receptor. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of Androgen Receptor.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Compounds and methods for the targeted degradation of androgen receptor
PendingUS20170327469A1Organic chemistryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsAndrogen Receptor GeneUbiquitin ligase
The present disclosure relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility to degrade (and inhibit) Androgen Receptor. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds Androgen Receptor such that Androgen Receptor is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of Androgen Receptor. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of Androgen Receptor.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
TANK-BINDING KINASE-1 PROTACs AND ASSOCIATED METHODS OF USE
InactiveUS20180147202A1Easy to useOrganic active ingredientsPeptidesTANK-binding kinase 1Ubiquitin ligase
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility to degrade and (inhibit) TBK 1. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end an E3 ubiquitin ligase binding moiety which binds to an E3 ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds TBK1 such that TBK1 is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of TBK1. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of TBK1.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Transcriptional repression leading to parkinson's disease
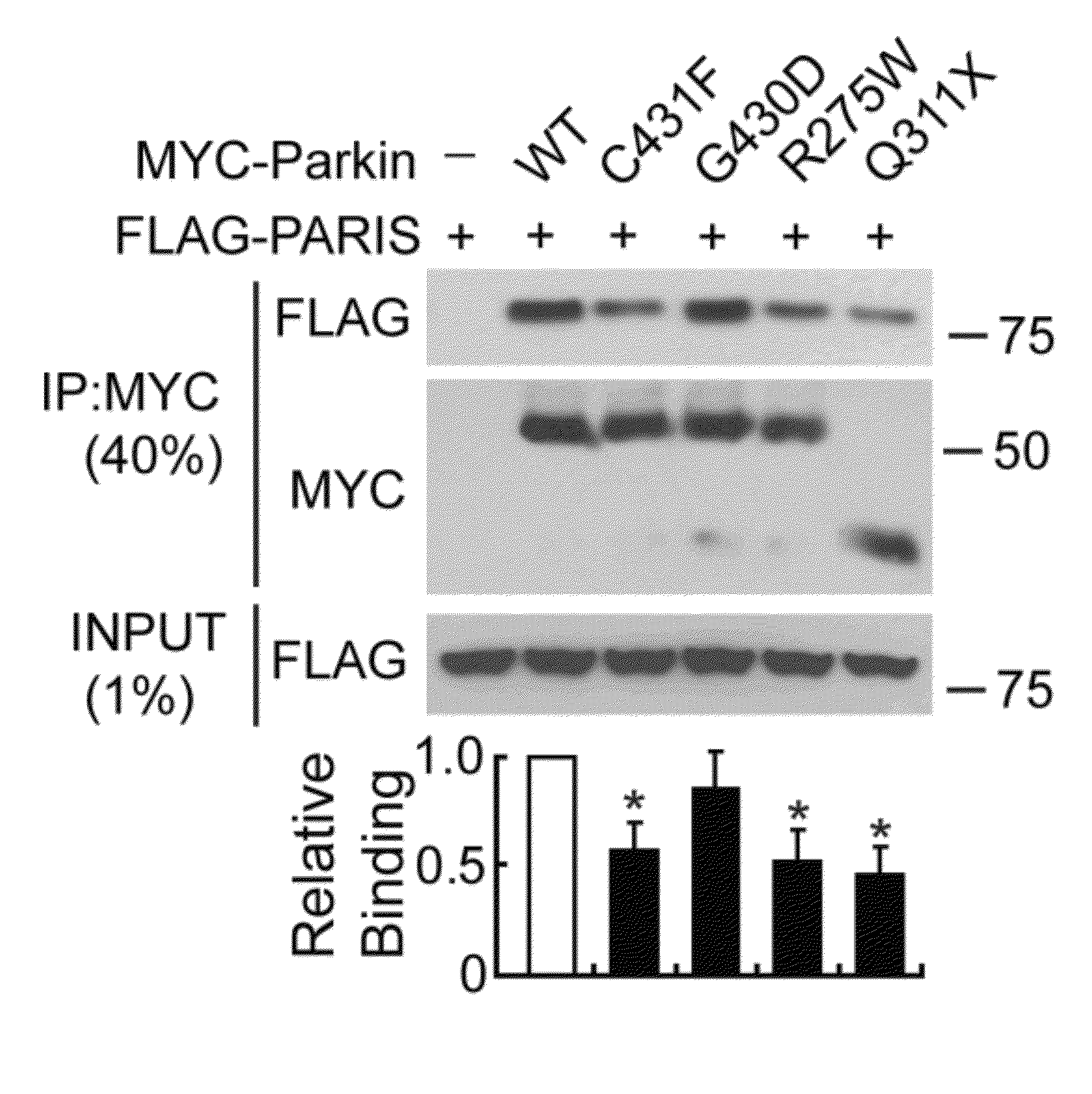
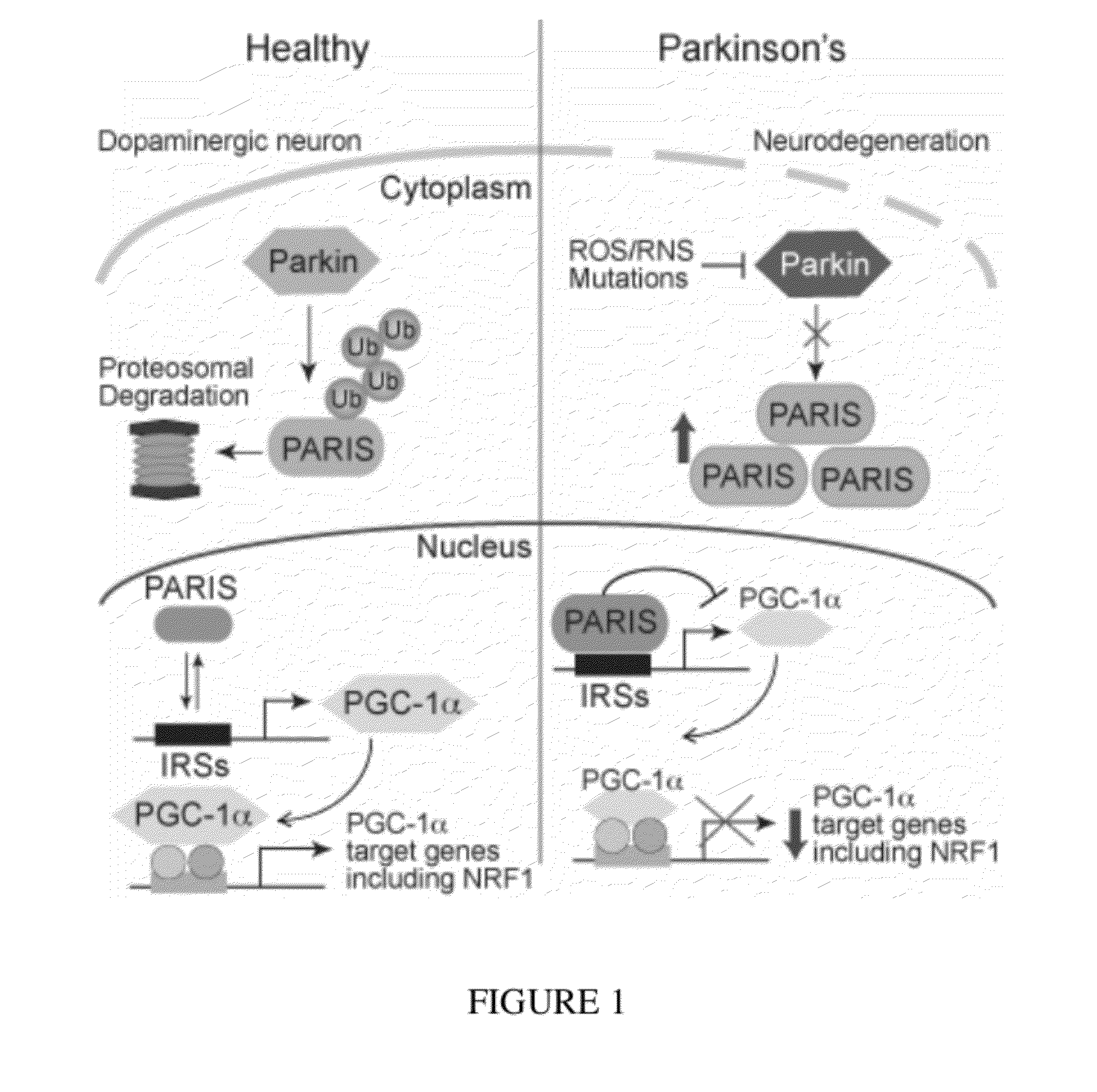
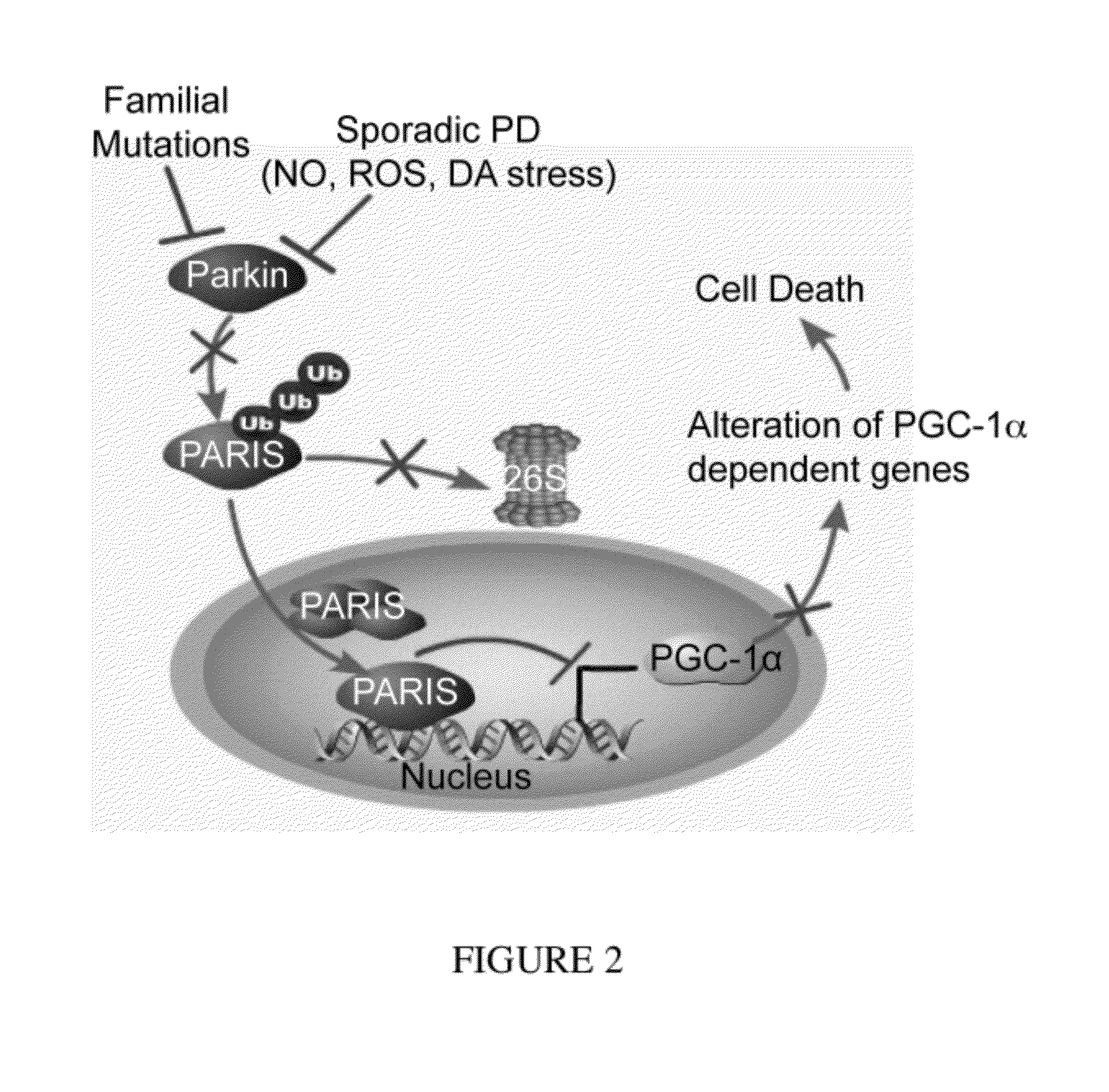
Parkinson's disease is caused by the preferential loss of substantia nigra dopamine neurons. A Parkin Interacting Substrate, PARIS (ZNF746) is identified. The levels of PARIS are regulated by the ubiquitin proteasome system via binding to and ubiquitination by the E3 ubiquitin ligase, parkin. PARIS is a KRAB and zinc finger protein that accumulates in models of parkin inactivation and in human brain Parkinson's disease patients. PARIS represses the expression of the transcriptional co-activator, PGC-1α and the PGC-1α target gene, NRF-1 by binding to insulin response sequences in the PGC-1α promoter. Conditional knockout of parkin in adult animals leads to progressive loss of dopamine (DA) neurons that is PARIS dependent. Overexpression of PARIS causes selective loss of DA neurons in the substantia nigra, which is reversed by either parkin or PGC-1α co-expression. The identification of PARIS provides a molecular mechanism for neurodegeneration due to parkin inactivation.
Owner:VALTED
Transgenic animals expressing light-emitting fusion proteins and diagnostic and therapeutic methods therefor
InactiveUS7176345B2Modify activityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCompound screeningBinding siteUbiquitin ligase
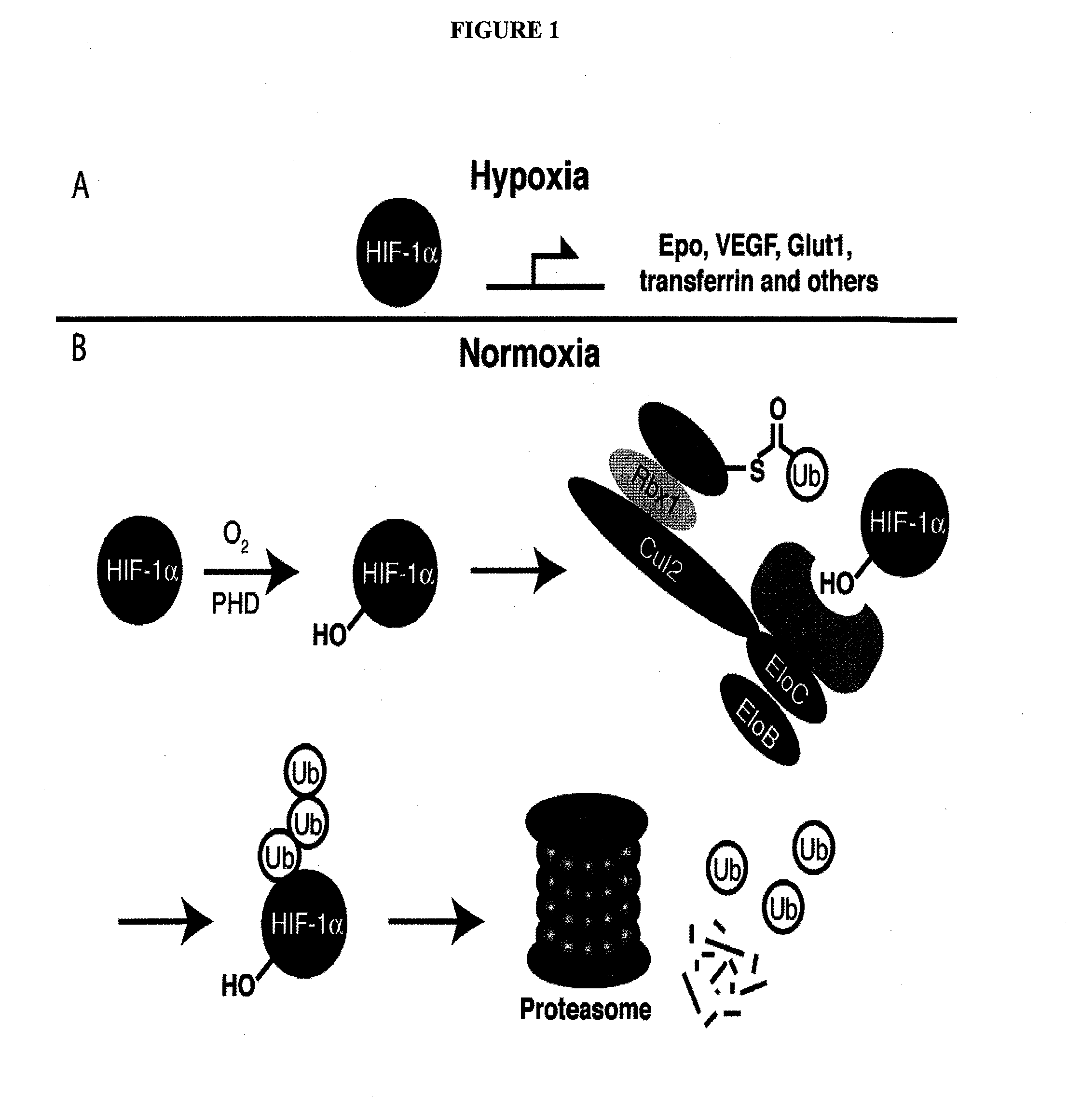
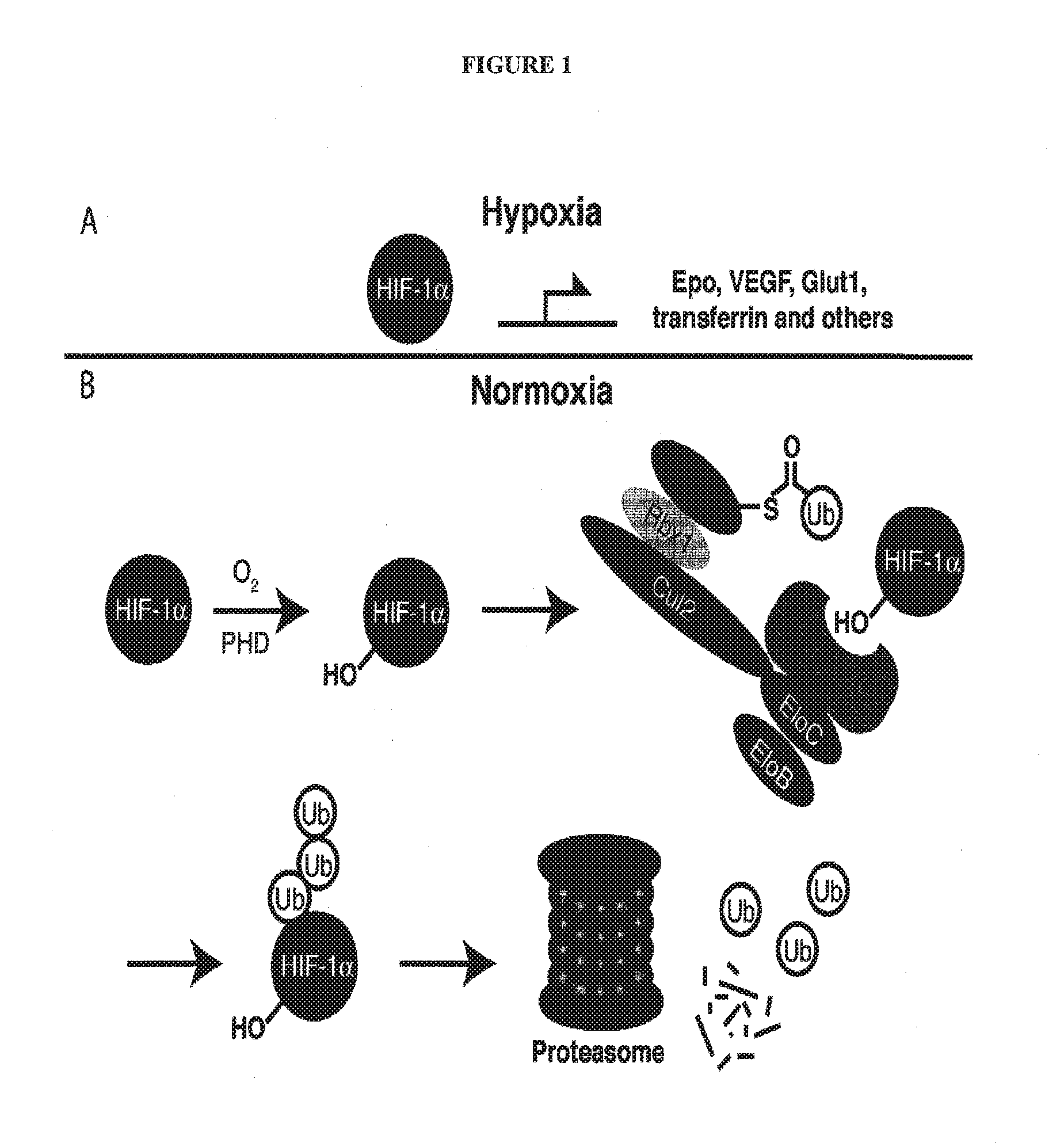
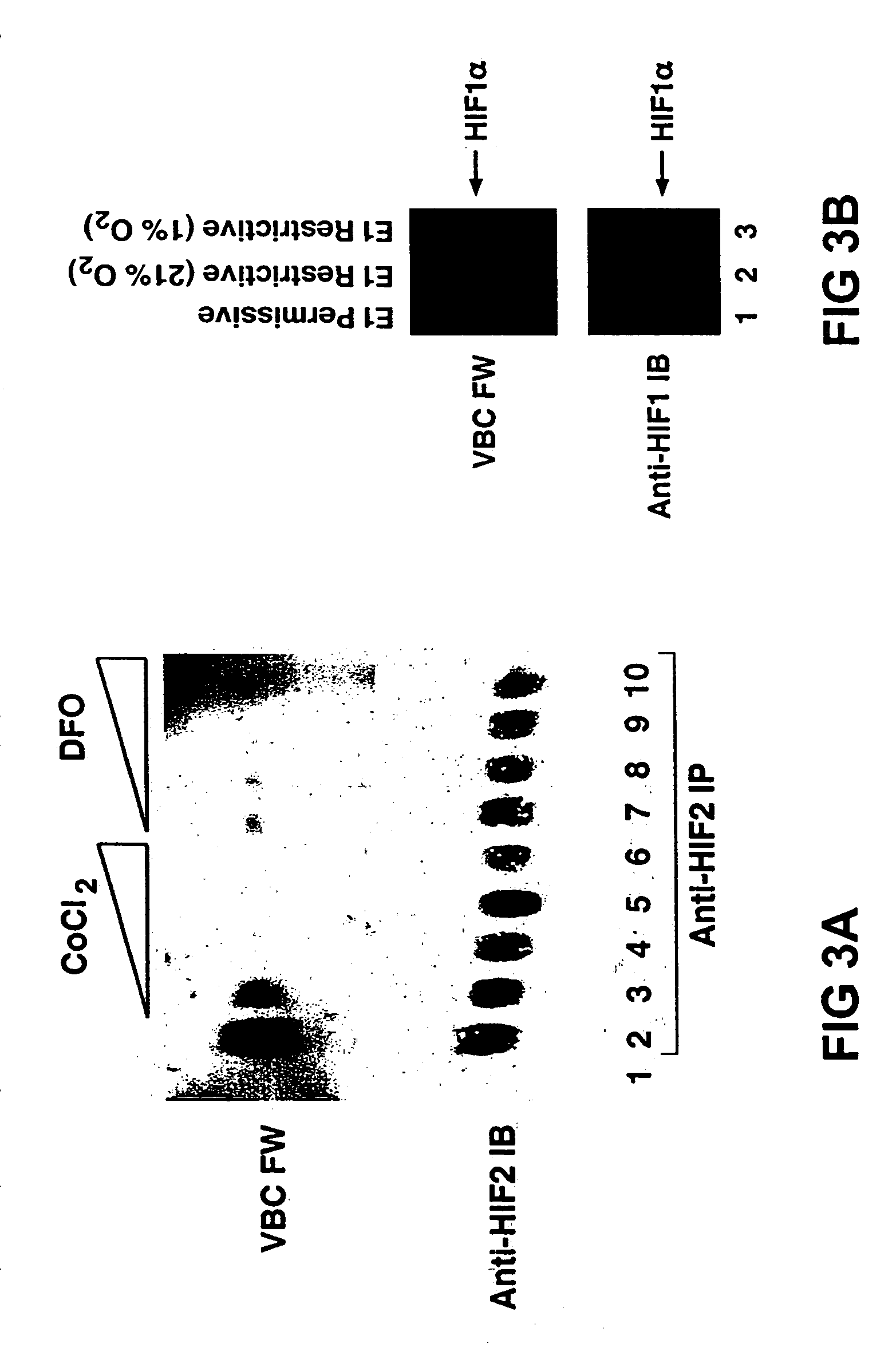
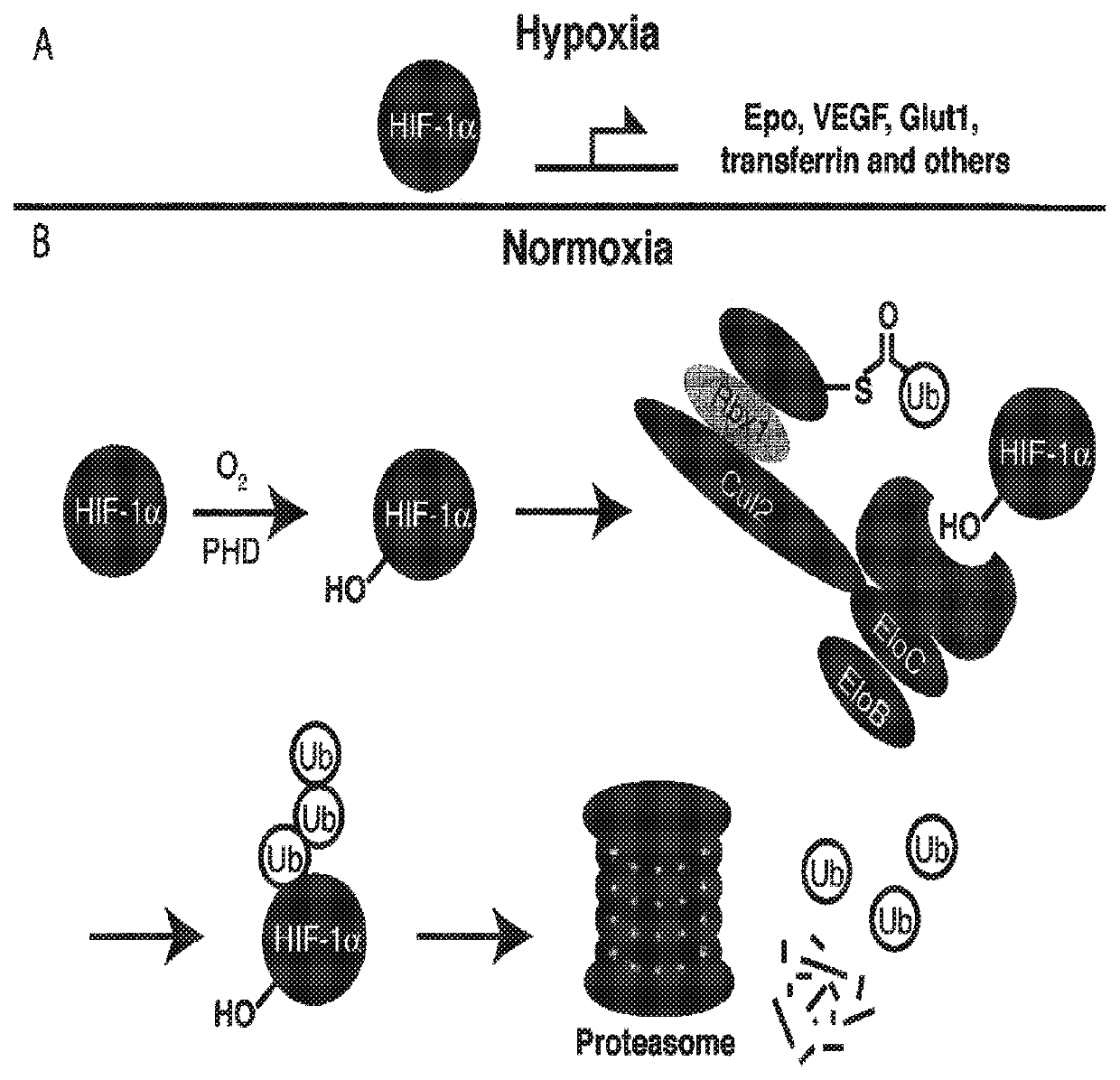
Light-generating fusion proteins having a ligand binding site and a light-generating polypeptide moiety and their use as diagnostics, in drug screening and discovery, and as therapeutics, are disclosed. The light-generating fusion protein has a feature where the bioluminescence of the polypeptide moiety changes upon binding of a ligand at the ligand binding site. The ligand may be, for example, an enzyme present in an environment only under certain conditions, e.g., ubiquitin ligase in a hypoxic state, such that the light-generating fusion protein is “turned on” only under such conditions.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
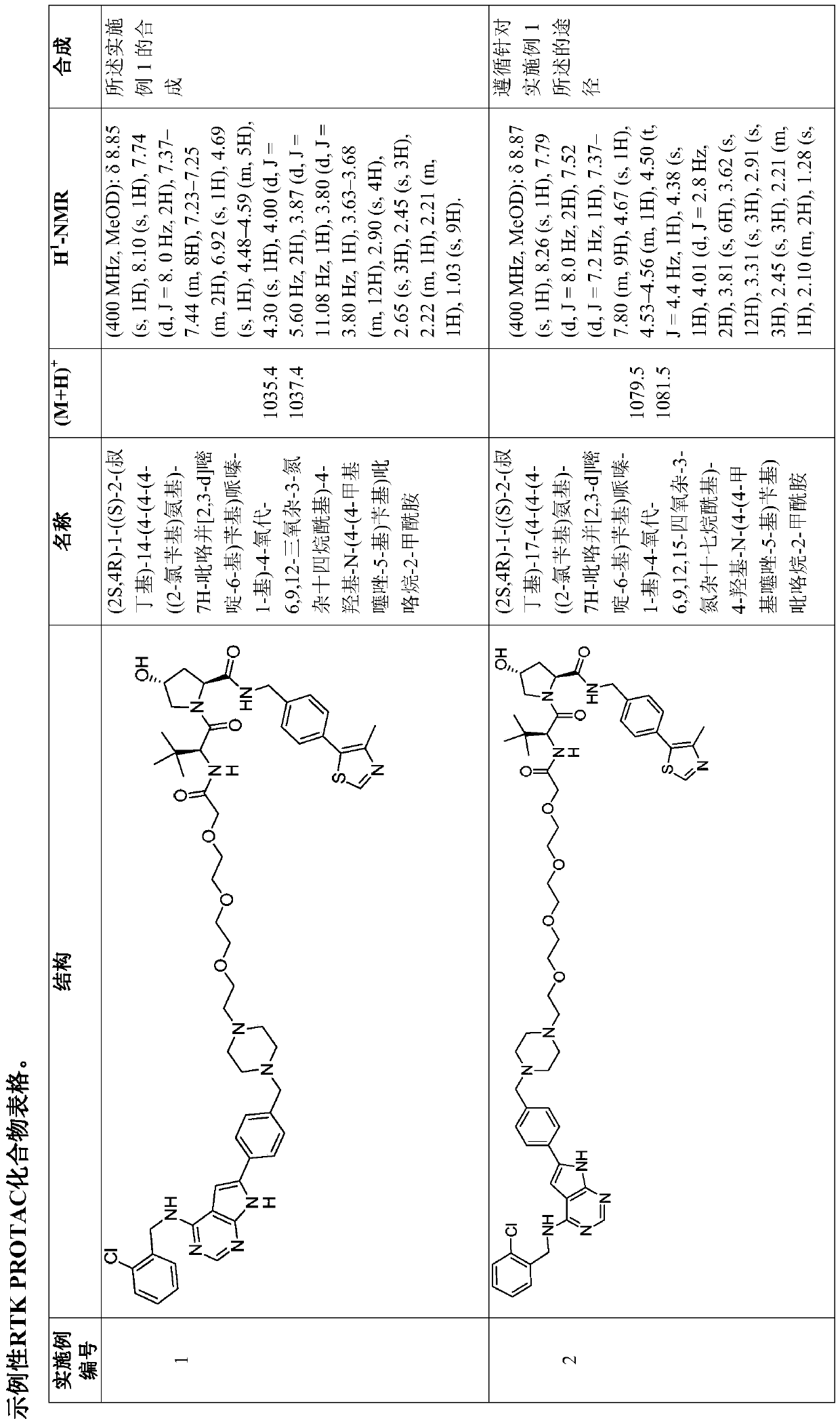
EGFR proteolysis targeting chimeric molecules and associated methods of use
The present disclosure relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) proteins. In particular, the present disclosure is directed to bifunctionalcompounds, which contain on one end a ligand which binds to an E3 ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds a target protein, such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effectuate ubiquitination, and therefore, degradation (and inhibition) of the target protein. The present disclosure exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with degradation / inhibition of target protein. Diseases or disorders that result from aggregation or accumulation of the target protein are treated or prevented with compounds and compositions ofthe present disclosure.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC +1
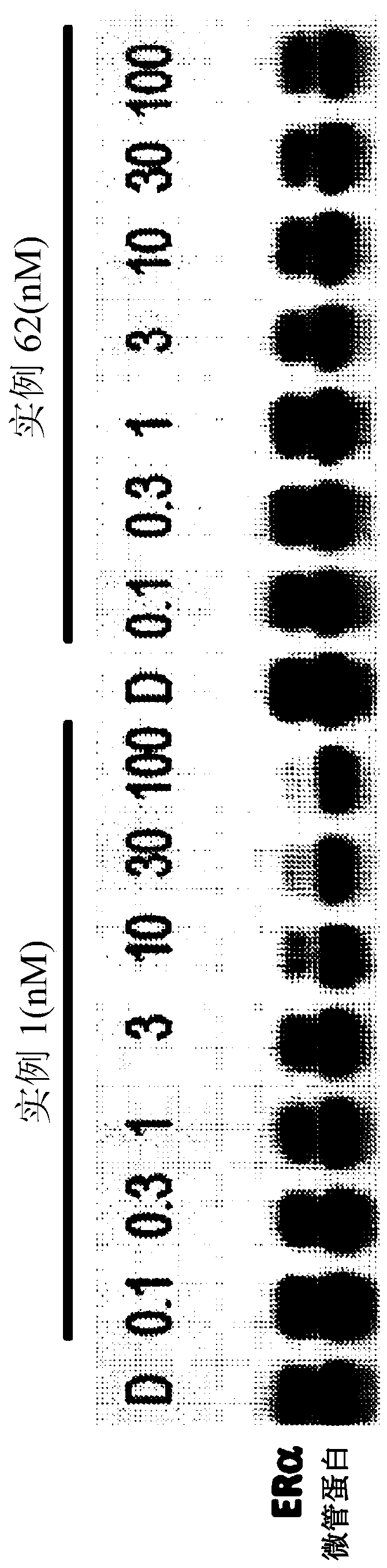
Tetrahydronaphthalene and tetrahydroisoquinoline derivatives as estrogen receptor degraders
The present disclosure relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of estrogen receptor (target protein). In particular, the present disclosure is directed to bifunctional compounds, which contain on one end at least one of a Von Hippel-Lindau ligand, a cereblon ligand, Inhibitors of Apoptosis Proteins ligand, mouse double-minute homolog 2 ligand, or a combination thereof, which binds to the respective E3 ubiquitin ligase, and on the other end a moiety which binds the target protein, such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of target protein. The present disclosure exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with degradation / inhibition of target protein. Diseases or disorders that result from aggregation or accumulation of the target protein are treated or prevented with compounds and compositions of the present disclosure.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Compounds & Methods for the Enhanced Degradation of Targeted Proteins & Other Polypeptides by an E3 Ubiquitin Ligase
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of targeted ubiquitination, especially inhibitors of a variety of polypeptides and other proteins which are degraded and / or otherwise inhibited by bifunctional compounds according to the present invention. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds a target protein such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of that protein. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of targeted polypeptides.
Owner:YALE UNIV +2
Ubiquitin ligases as therapeutic targets
InactiveUS6720181B1Enhance ubiquitin ligase gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsFungiUbiquitin ligaseENCODE
The present invention relates to the discovery, identification and characterization of nucleotides that encode novel substrate-targeting subunits of ubiquitin ligases. The invention encompasses nucleotides encoding novel substrate-targeting subunits of ubiquitin ligases: FBP1, FBP2, FBP3, FBP4, FBP5, FBP6, FBP7, FBP8, FBP9, FBP10, FBP11, FBP12, FBP13, FBP14, FBP15, FBP16, FBP17, FBP18, FBP19, FBP20, FBP21, FBP22, FBP23, FBP24, and FBP25, transgenic mice, knock-out mice, host cell expression systems and proteins encoded by the nucleotides of the present invention. The present invention relates to screening assays that use the novel substrate-targeting subunits to identify potential therapeutic agents such as small molecules, compounds or derivatives and analogues of the novel ubiquitin ligases which modulate activity of the novel ubiquitin ligases for the treatment of proliferative and differentiative disorders, such as cancer, major opportunistic infections, immune disorders, certain cardiovascular diseases, and inflammatory disorders. The invention further encompasses therapeutic protocols and pharmaceutical compositions designed to target ubiquitin ligases and their substrates for the treatment of proliferative disorders.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Compounds and methods for the targeted degradation of androgen receptor
ActiveUS10584101B2Halogenated hydrocarbon active ingredientsNervous disorderAndrogen Receptor GeneUbiquitin ligase
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
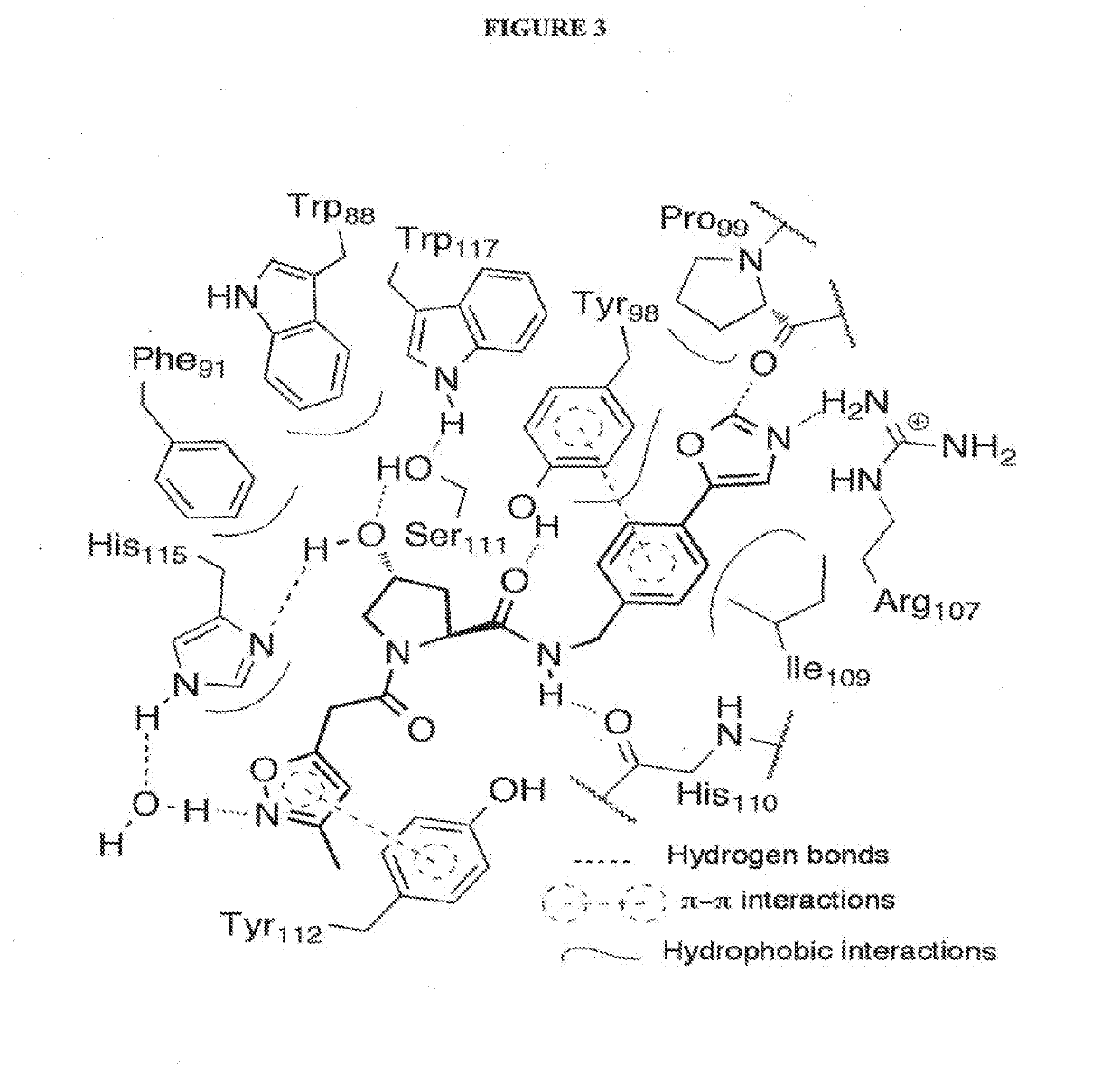
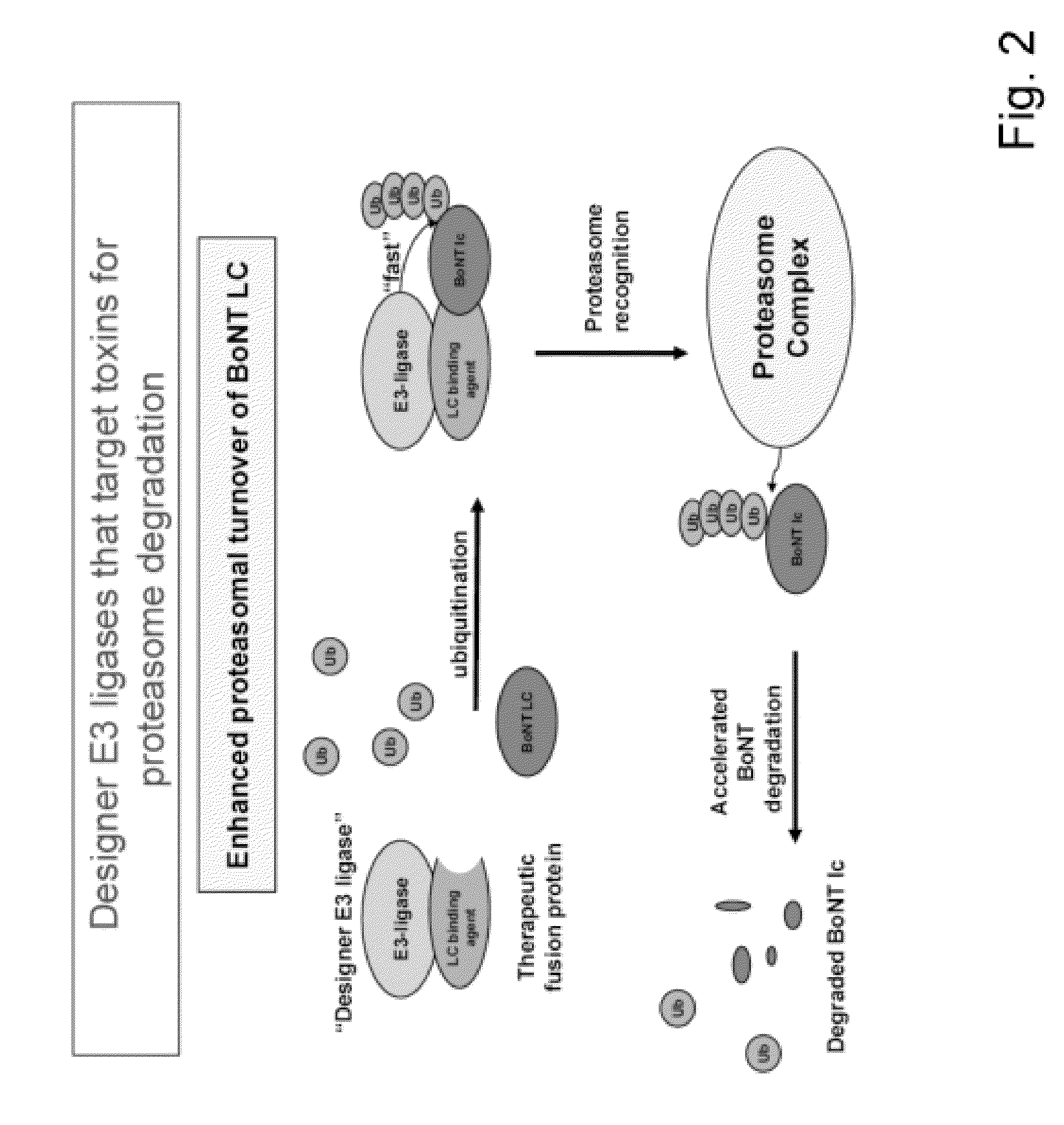
Designer Ubiquitin Ligases For Regulation Of Intracellular Pathogenic Proteins
The present invention relates to a designer or recombinant ubiquitin ligase molecule that includes a toxin binding domain that is specific for a toxin active fragment, wherein the toxin active fragment is an enzymatically active fragment of one or more toxins or toxin serotypes; and an E3-ligase domain that comprises an E3-ligase or polypeptide that facilitates E2-mediated ubiquitination of the toxin active fragment. In an embodiment, the composition further includes a delivery system that allow the designer ubiquitin ligase to enter the cell. The present invention further includes methods for treating an individual intoxicated with a toxin by administering the designer ubiquitin ligase of the present invention.
Owner:SYNAPTIC RES
Pyrrolopyridone bifunctional molecular compound based on VHL ligand-induced BET degradation
The invention relates to a novel kind of pyrrolopyridone bifunctional molecule and its pharmaceutically acceptable salt, hydrate and prodrug and a pharmaceutical composition using the compounds as active ingredients, and application in the preparation of these compounds and their pharmaceutical composition and in the treatment or prevention of tumors, inflammation, diseases related immunity, etc.The bifunctional molecule involved in the invention is a proteolytic targeting chimera (PROTAC). A small molecule inhibitor of BET protein and a Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein ligand in E3 ubiquitinligase complex are linked by a connecting arm to obtain the bifunctional molecule. The obtained compound can selectively induce the degradation of BET protein, and has significant anti-tumor effect.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE +1
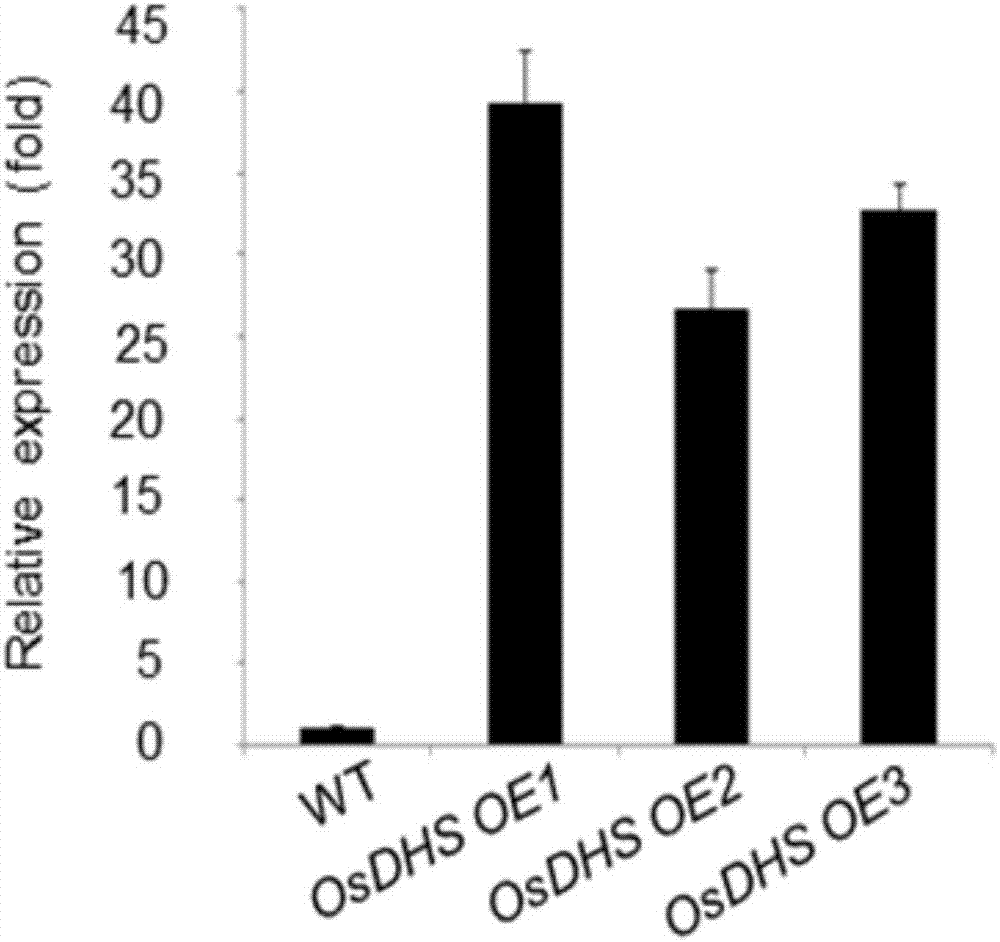
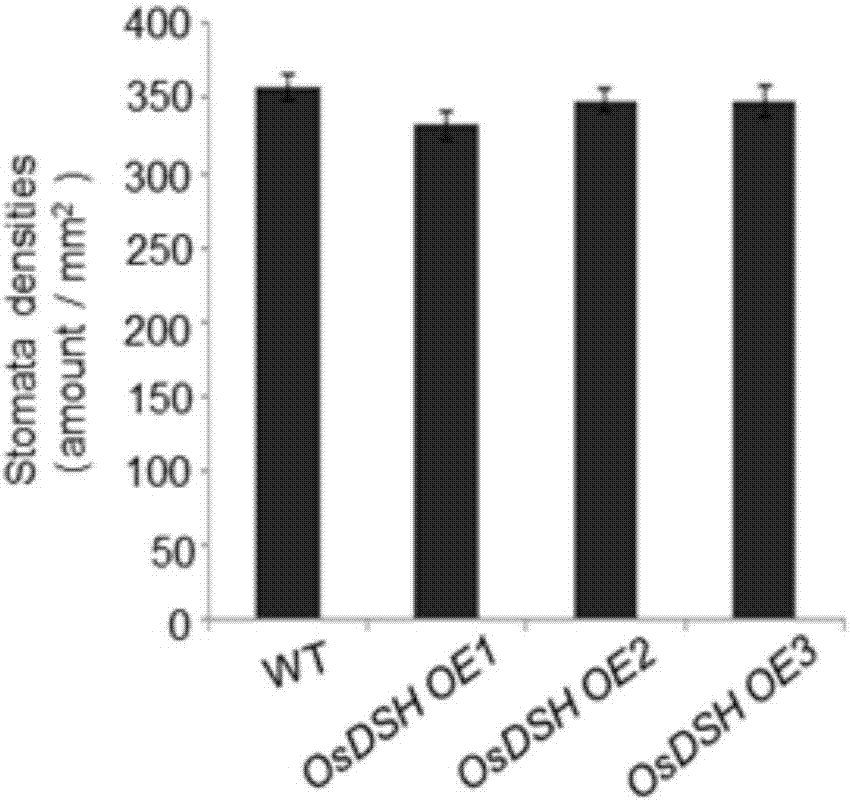
Rice RING finge family E3 ubiquitin ligase OsDHS gene as well as encoding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN107354163ARegulation of synthesisImprove drought toleranceLigasesVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified riceNucleotide
The invention relates to and aims at providing a rice RING finge family E3 ubiquitin ligase OsDHS gene as well as an encoding protein and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the OsDHS gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1 in a sequence table. The amino acid sequence of the encoding protein is represented by SEQ ID NO:2. By carrying out overexpression or knockout on the OsDHS gene in rice, a series of experiments prove that OsDHS gene overexpressed transgenic rice is super-sensitive to drought, and epicuticular wax is seriously lacked; otherwise, a dhs mutant presents that the drought resistance is enhanced. According to the OsDHS gene, by adjusting and controlling the synthesis of the epicuticular wax of the rice, the response of plants to drought stress is adjusted and controlled.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Designer Ubiquitin Ligases For Regulation Of Intracellular Pathogenic Proteins
InactiveUS20100278826A1Improve the degradation problemReduce deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsUbiquitin ligaseSerotype
The present invention relates to a designer or recombinant ubiquitin ligase molecule that includes an antibody fragment that is specific for a toxin active fragment, wherein the toxin active fragment is an enzymatically active fragment of one or more toxins or toxin serotypes; and an E3-ligase domain that comprises an E3-ligase or polypeptide that facilitates E2-mediated ubiquitination of the toxin active fragment. In an embodiment, the composition further includes a delivery system that allow the designer ubiquitin ligase to enter the cell. The present invention further includes methods for treating an individual intoxicated with a toxin by administering the designer ubiquitin ligase of the present invention.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF TUFTS COLLEGE TUFTS UNIV
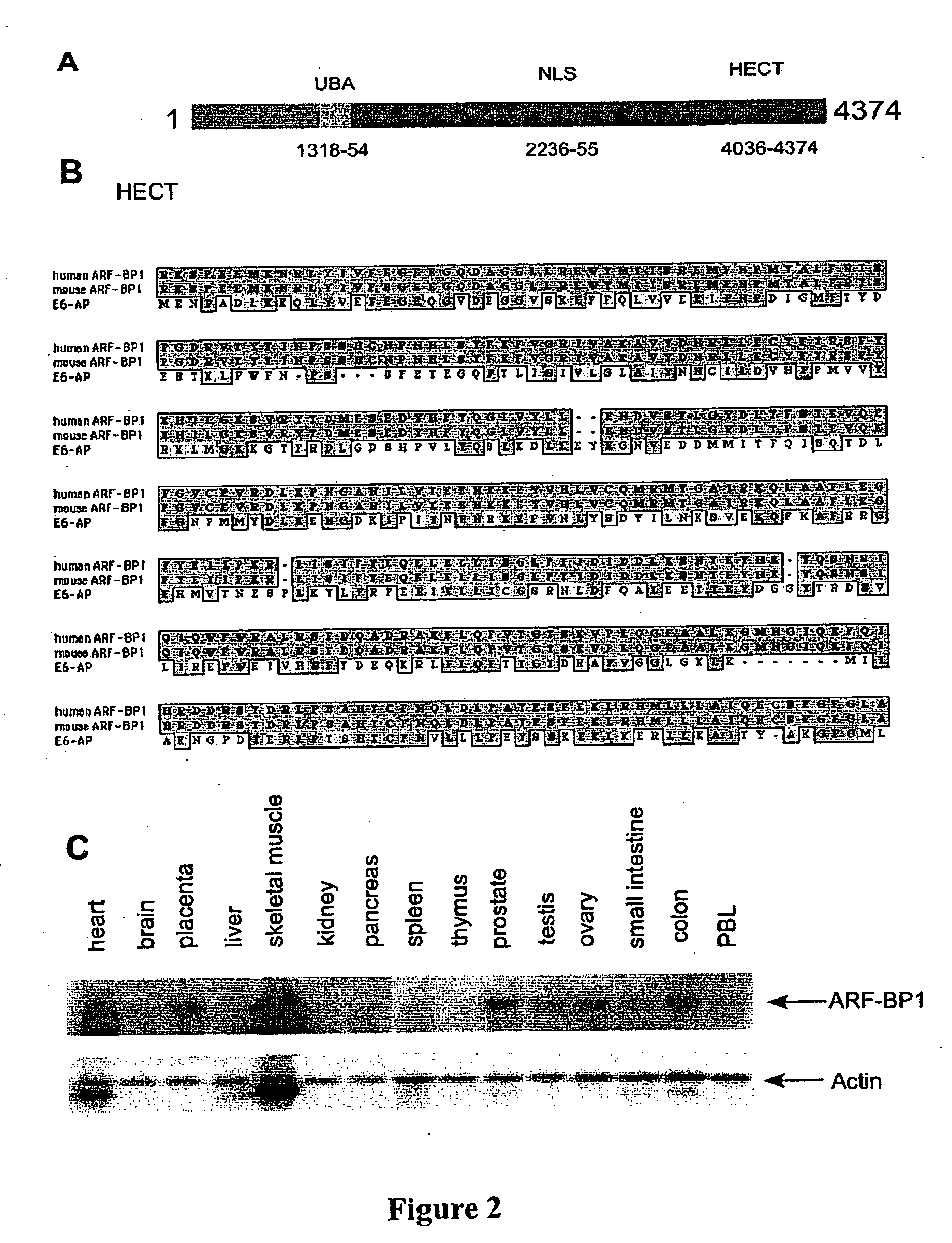
ARF-BP1 as mediator of p53-dependent and independent tumor suppression and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060088847A1Assessing abilityAvoid interactionHydrolasesTissue cultureUbiquitin ligaseSomatic cell
The present invention relates to the mechanism of ARF-mediated cell growth suppression. ARF-BP1 is identified as a novel ubiquitin ligase, and a major component of ARF-containing nuclear complexes in human cells. The present invention discloses a novel mechanism of ARF-mediated p53 activation and that ARF-BP1 is a critical mediator of both p53-independent and p53-dependent tumor suppression functions of ARF. Inactivation of ARF-BP1 in normal cells stabilizes p53 and induces p53-dependent apoptosis. Inactivation of ARF-BP1, but not Mdm2, in p53-wildtype cells promotes cell growth inhibition in a manner reminiscent of ARF induction. ARF-BP1 directly binds and ubiquitinates p53 and inactivation of endogenous ARF-BP1 is crucial for ARF-mediated p53 stabilization in Mdm2-null cells. ARF-BP1 is advantageous over Mdm2 as a target for suppressing tumor cell growth regardless of p53 status.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Methods to identify compounds useful for the treatment of proliferative and differentiative disorders
The present invention relates to the discovery, identification and characterization of nucleotides that encode novel substrate-targeting subunits of ubiquitin ligases. The invention encompasses nucleotides encoding novel substrate-targeting subunits of ubiquitin ligases: FBP1, FBP2, FBP3, FBP4, FBP5, FBP6, FBP7, FBP8, FBP9, FBP1O, FBP11, FBP12, FBP13, FBP14, FBP15, FBP16, FBP17, FBP18, FBP19, FBP20, FBP21, FBP22, FBP23, FBP24, and FBP25, transgenic mice, knock-out mice, host cell expression systems and proteins encoded by the nucleotides of the present invention. The present invention relates to screening assays that use the novel substrate-targeting subunits to identify potential therapeutic agents such as small molecules, compounds or derivatives and analogues of the novel ubiquitin ligases which modulate activity of the novel ubiquitin ligases for the treatment of proliferative and differentiative disorders, such as cancer, major opportunistic infections, immune disorders, certain cardiovascular diseases, and inflammatory disorders. The invention further encompasses therapeutic protocols and pharmaceutical compositions designed to target ubiquitin ligases and their substrates for the treatment of proliferative disorders.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Compounds and methods for the targeted degradation of androgen receptor
The present disclosure relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility to degrade (and inhibit) Androgen Receptor. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain onone end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds Androgen Receptor such that Androgen Receptor is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of Androgen Receptor. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of Androgen Receptor.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Isoindoline compound, and preparation method, pharmaceutical composition and application thereof
ActiveCN110963994AStrong inhibitory activityNovel structureNervous disorderAntipyreticDiseaseUbiquitin ligase
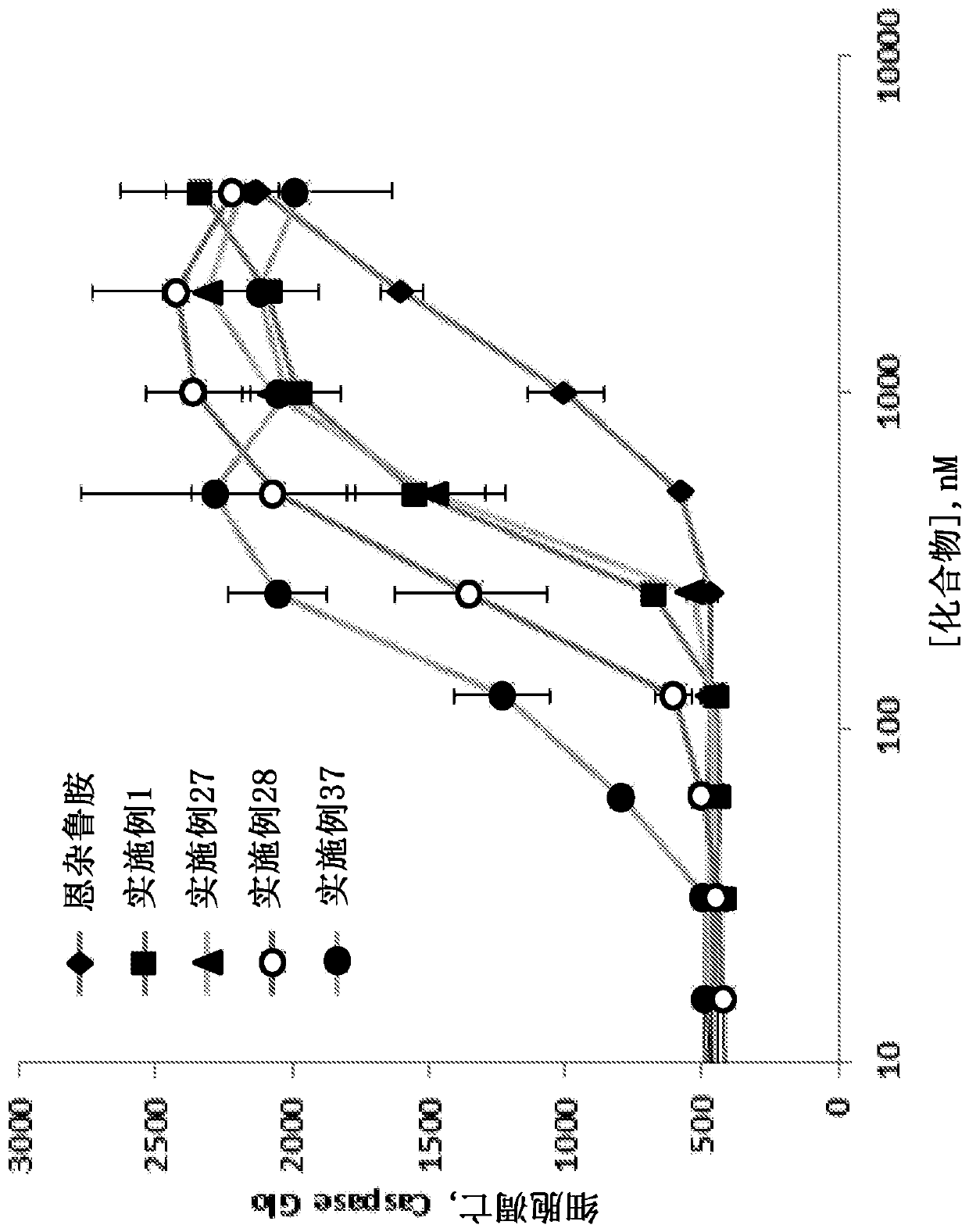
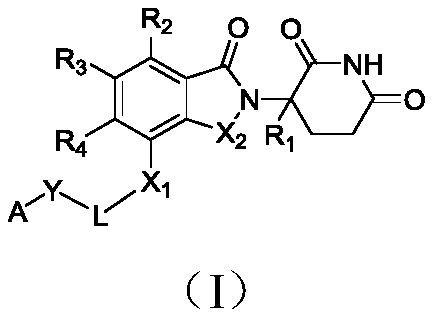
The invention relates to a polysubstituted isoindoline compound represented by a general formula (I), and a preparation method, a pharmaceutical composition and an application thereof. Specifically, as a CRL4CRBNE3 ubiquitin ligase regulator with a novel structure, the polysubstituted isoindoline compound provided by the invention has stronger anti-tumor activity and an anti-tumor spectrum, and can be used for preparing medicines for treating diseases related to CRL4CRBNE3 ubiquitin ligase.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
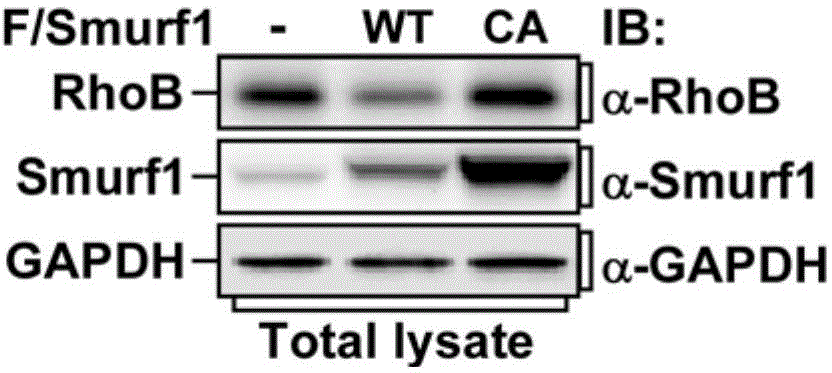
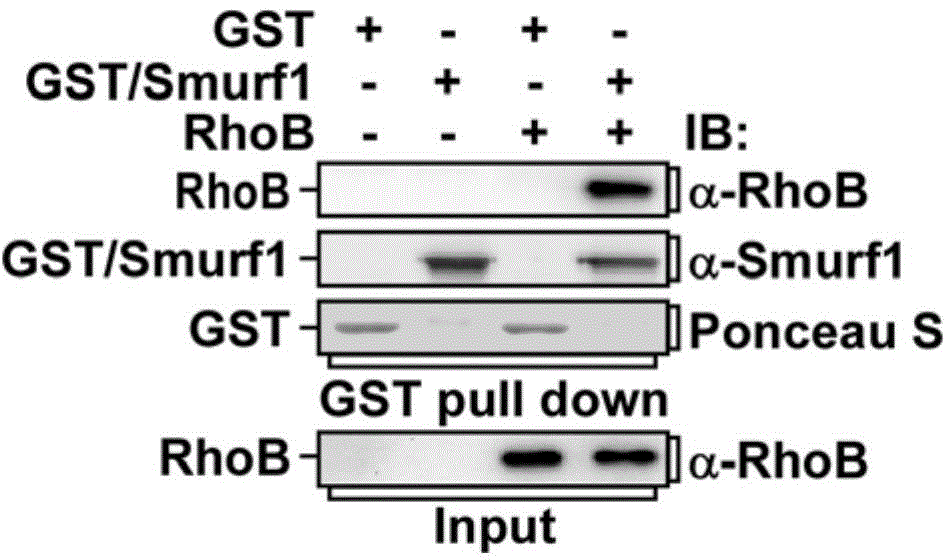
Antitumor drug screening method using RhoB inhibiting ubiquitination degradation of Smurf1 as therapeutic target
ActiveCN104101714AClear target functionIntuitive function and effectCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCancer cellScreening method
The invention provides an antitumor drug screening method using RhoB inhibiting ubiquitination degradation of Smurf1 as a therapeutic target, and relates to the screening of anti-cancer drugs. The screening method comprises the following steps: a candidate compound is in contact with a material substance; the influence of the candidate compound on the detection result of RhoB for inhibiting the E3 ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 ubiquitination degradation substrate is observed, and if the candidate compound enables the detection result in cells to generate negative changes, namely, the ability that the ubiquitination degradation of the Smurf1 for the RhoB is weakened, which indicates that the candidate compound is a potential antitumor drug. After the candidate compound is indicated to be the potential antitumor drug, the compound which can increase the RhoB protein content in cancer cells can be further selected. The specific method comprises the following steps: the candidate compound is in contact with different kinds of tumor cells; the influence of the candidate compound on the RhoB protein content in different kinds of tumor cells is observed. The experiment cycle is short, the detection process is fast, the sensitivity is high, and the application range is wide.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Compounds and methods for the targeted degradation of androgen receptor
InactiveUS20180346461A1Organic active ingredientsNervous disorderAndrogen Receptor GeneUbiquitin ligase
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility to degrade and (inhibit) Androgen Receptor. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds Androgen Receptor such that Androgen Receptor is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of Androgen Receptor. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of Androgen Receptor.
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
Application of RING1 protein for improving RDV (rice dwarf virus) resistance of plants
InactiveCN103194431APromote degradationReduce accumulationEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionAnti virusBiotechnology
The invention discloses application of RING1 protein for improving RDV (rice dwarf virus resistance) of plants, and particularly provides application of protein RING1 or a coding gene of the protein RING1 or a recombinant vector containing the coding gene for regulating RDV resistance of plants. The amino acid sequence of the protein RING1 is the sequence one in the sequence table. The experiment disclosed by the invention proves that the RING1 is E3 protein-ubiquitin ligase and capable of interacting with RDV coat protein P2 to promote the P2 to be degraded by 26S proteosome, and the cumulant of the P2 can be reduced by excessively expressing the RING1 protein in rice, thereby inhibiting the amplification of RDV and improving the anti-virus capability of rice.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
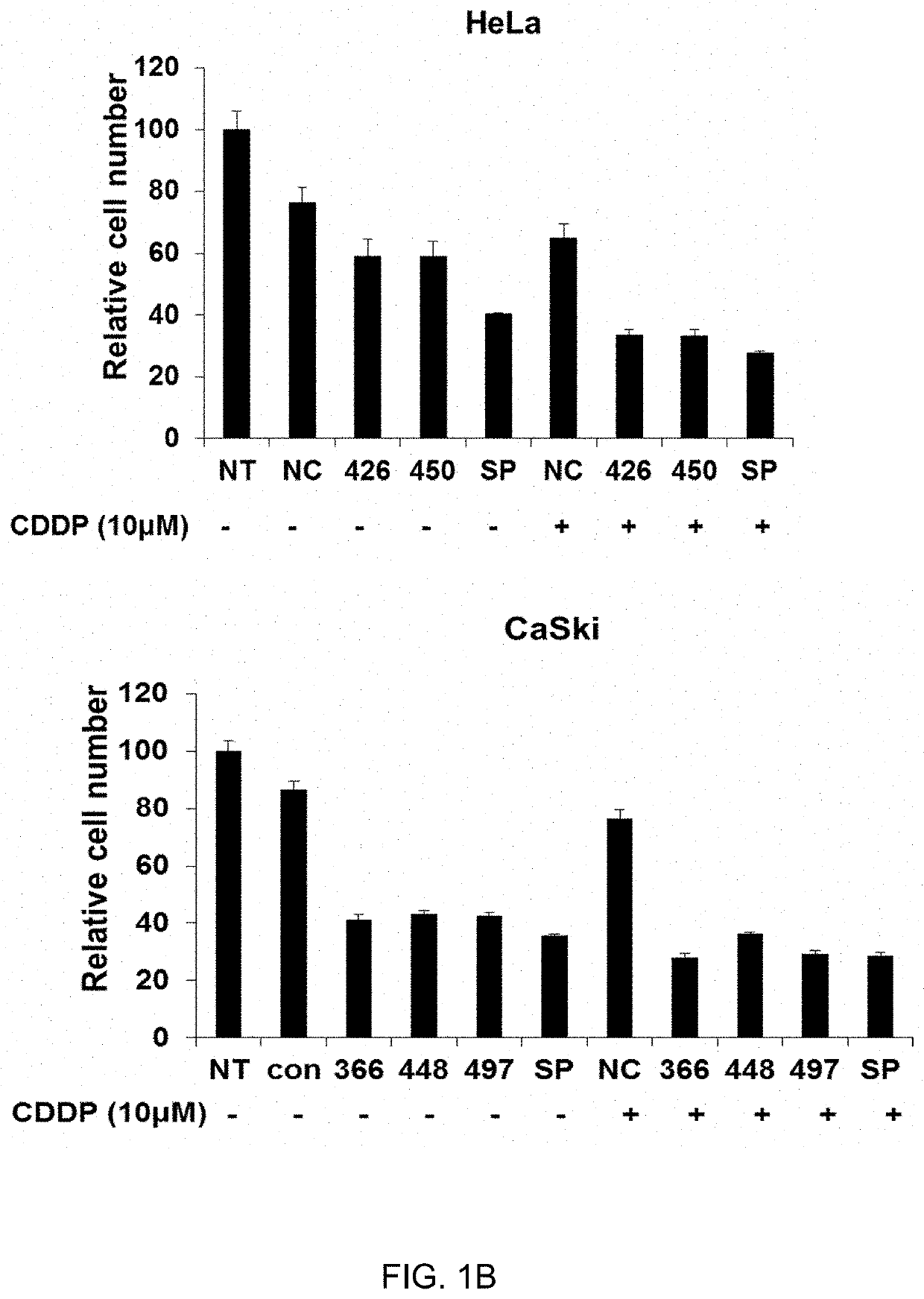
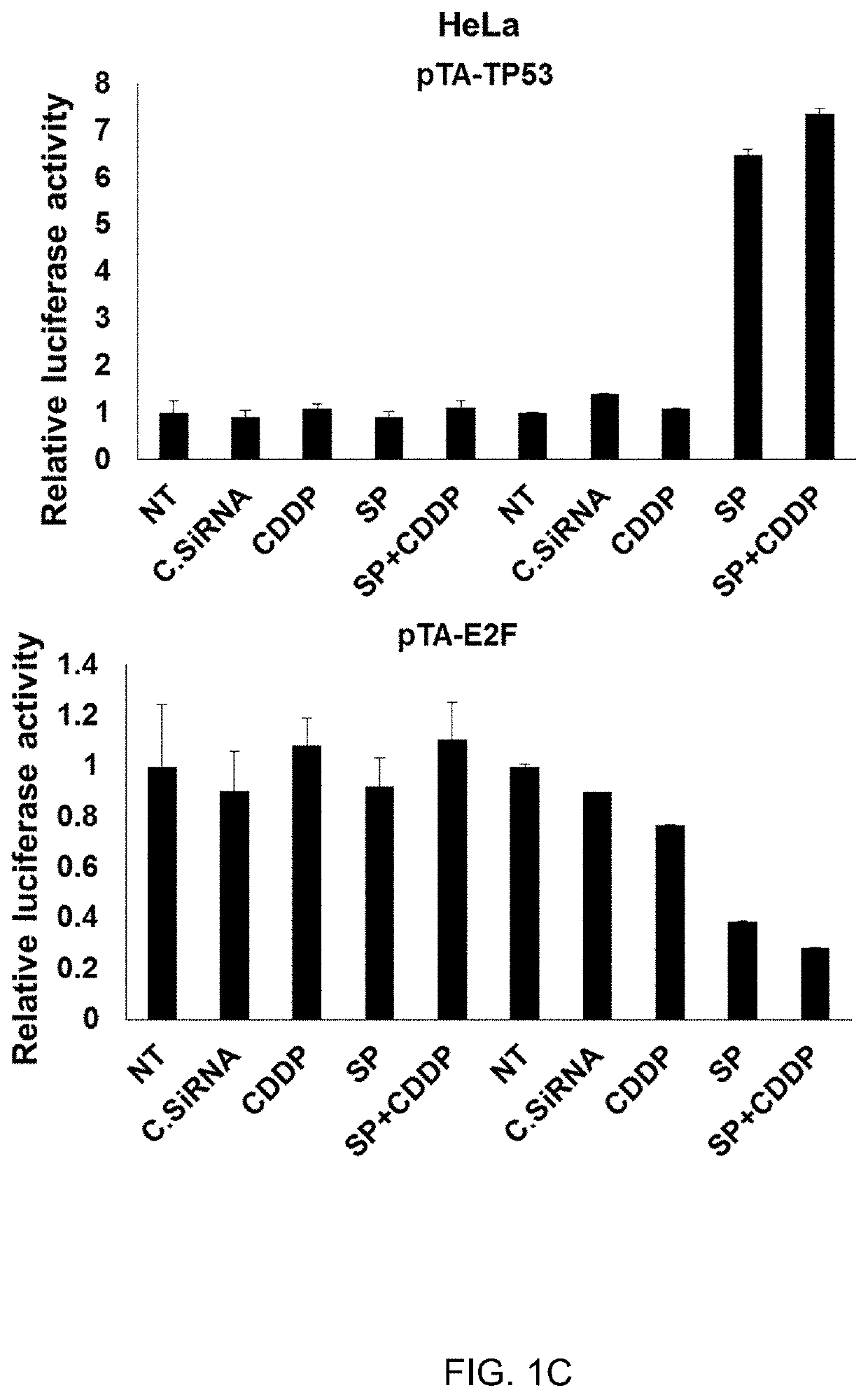
METHOD FOR MAINTAINING INCREASED INTRACELLULAR p53 LEVEL, INDUCED BY PLATINUM-BASED ANTICANCER DRUG, AND APPLICATION THEREOF
InactiveUS20200009185A1Effectively death of cancer cellMinimize side effectsHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsIntracellularUbiquitin ligase
The present invention relates to a method for maintaining the increased intracellular p53 level, induced by a platinum-based anticancer drug, and an application thereof and, more specifically, to a method for maintaining the increased intracellular p53 level in cells by administering a platinum-based anticancer drug and siRNA to ubiquitin ligase for p53 to a subject in need thereof in combination and sequentially, and a composition for promoting cancer cell apoptosis using the same.According to the method of the present invention, the increased intracellular p53 expression level can be maintained for a long period of time in spite of the treatment with a low-concentration platinum-based anticancer drug, thereby effectively inducing the apoptosis of cancer cells and minimizing the drug side effect caused by the administration of the platinum-based anticancer drug, and thus the present invention can be favorably used in the prevention of cancer or the development of cancer medicines.
Owner:ENHANCEDBIO INC
TANK-BINDING KINASE-1 PROTACs AND ASSOCIATED METHODS OF USE
ActiveUS20190192514A1Easy to useOrganic active ingredientsPeptidesTANK-binding kinase 1Ubiquitin ligase
Owner:ARVINAS OPERATIONS INC
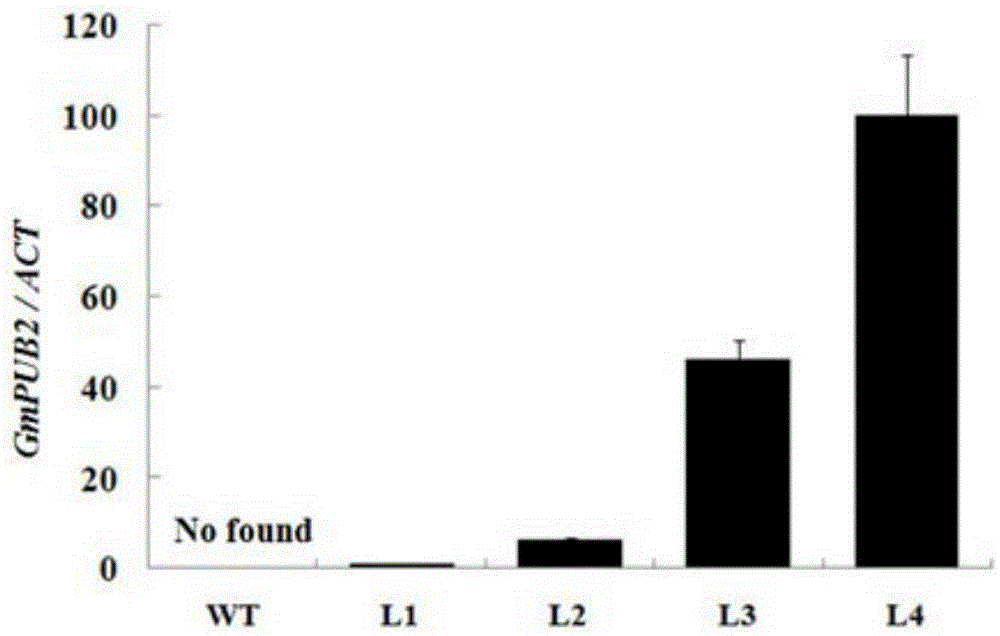
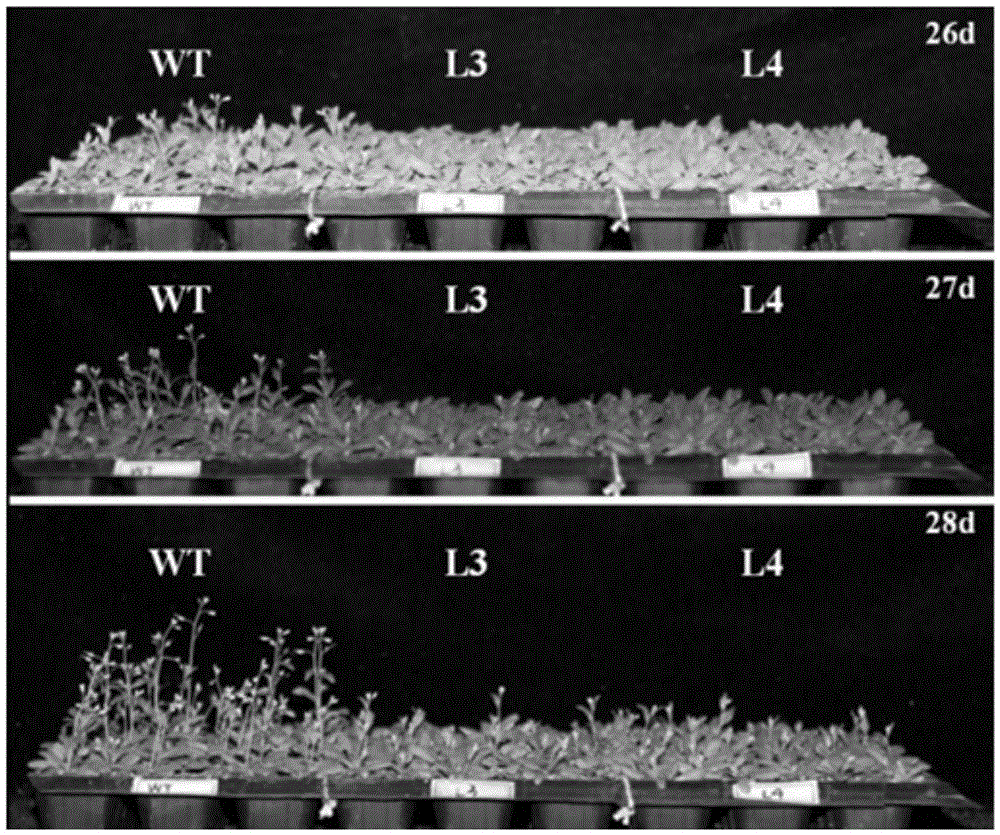
Application of soybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 capable of regulating flowering of plants
ActiveCN105400800ADelayed floweringLate floweringEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin ligaseWild type
The invention discloses an application of soybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 capable of regulating flowering of plants, namely, the application of the oybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 in regulating flowering of plants. A late-flowering plant is obtained after the GmPUB2 gene is transplanted into a target plant through a plant expression vector; an early-flowering plant is obtained after the GmPUB2 gene is transplanted into a target plant through a gene silencing carrier; after the target gene GmPUB2 is transplanted into arabidopsis thaliana, compared with the wild arabidopsis thaliana, the results show that the bolting time and the flowering time of the transgenic plant are obviously later than those of the wild plant, namely, the GmPUB2 gene has the function of delaying the flowering of the plants. With the established GmPUB2 gene silencing carrier to silence the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana with over-expressed target gene GmPUB2, the results show that the flowering time of the plant after silencing is obviously earlier than that of a control plant.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Compounds and methods for the enhanced degradation of targeted proteins
The present invention relates to bifunctional compounds, which find utility as modulators of targeted ubiquitination, especially inhibitors of a variety of polypeptides and other proteins which are degraded and / or otherwise inhibited by bifunctional compounds according to the present invention. In particular, the present invention is directed to compounds, which contain on one end a VHL ligand which binds to the ubiquitin ligase and on the other end a moiety which binds a target protein such that the target protein is placed in proximity to the ubiquitin ligase to effect degradation (and inhibition) of that protein. The present invention exhibits a broad range of pharmacological activities associated with compounds according to the present invention, consistent with the degradation / inhibition of targeted polypeptides.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
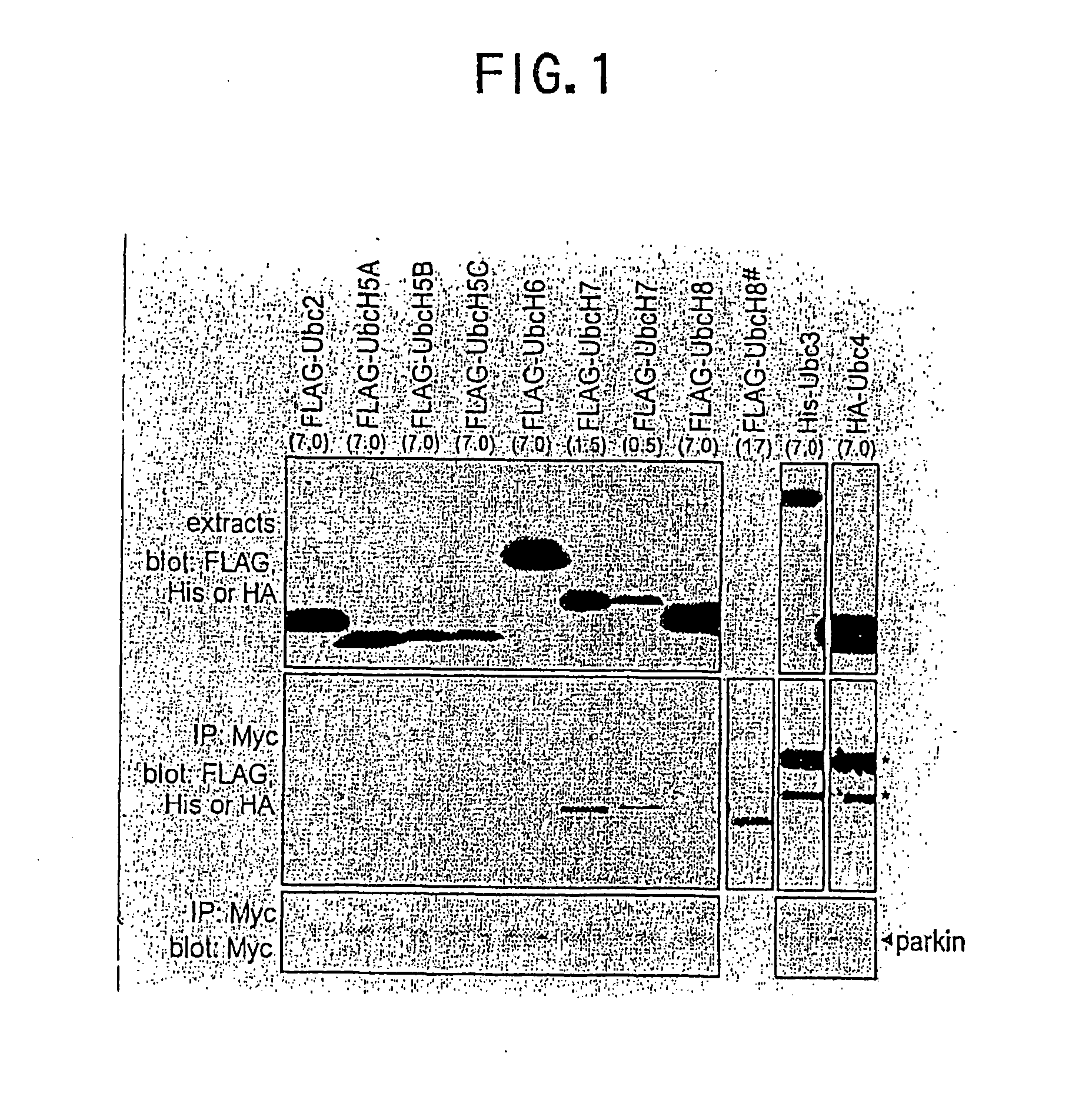
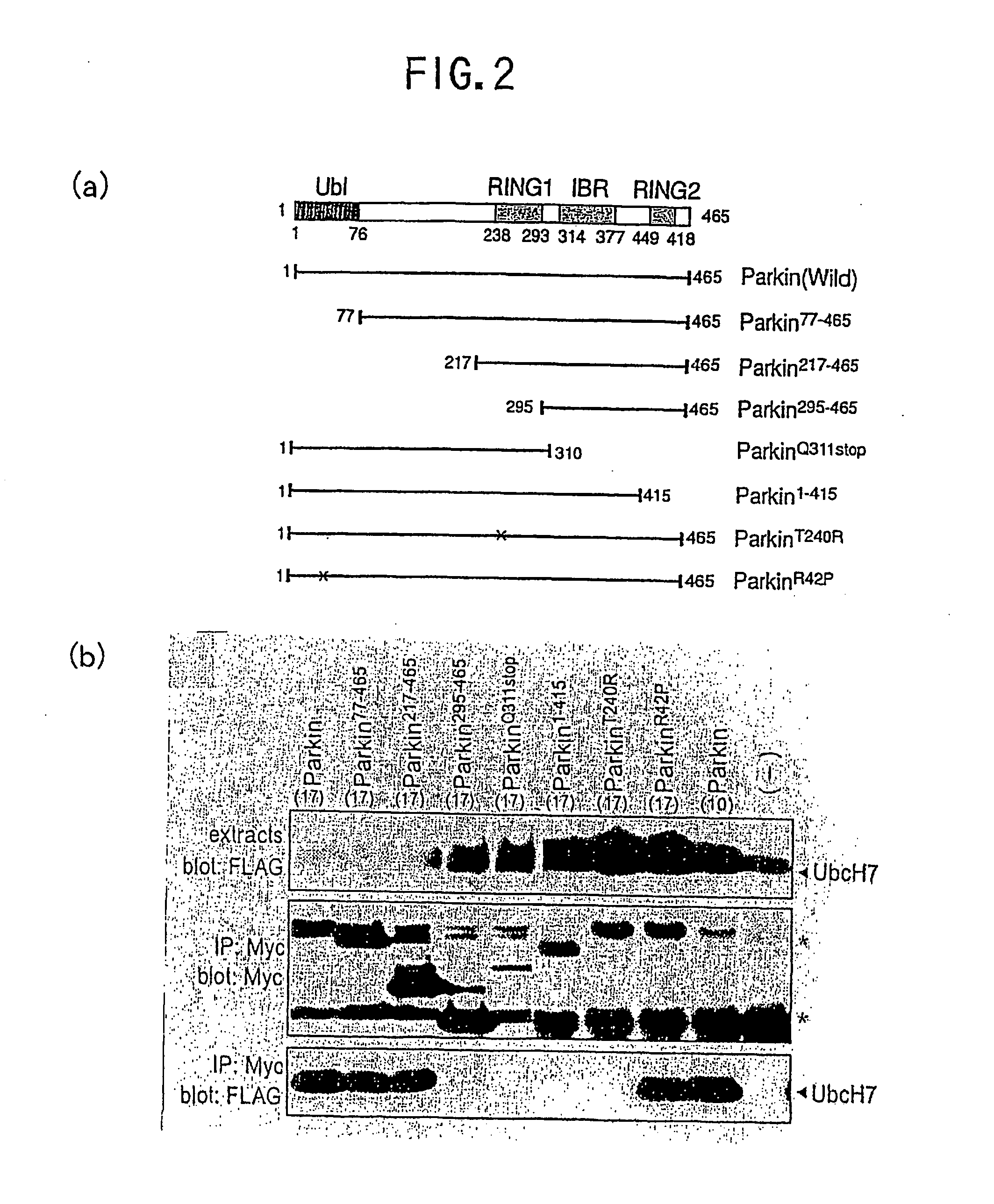
Parkin protein as ubiquitin ligase
The use of Parkin protein (Parkin) as ubiquitin ligase (E3), and a new method of diagnosing juvenile Parkinsonism based on the use thereof.
Owner:MIZUNO YOSHIKUNI +1
Modified UBE3A gene for a gene therapy approach for angelman syndrome
Angelman Syndrome (AS) is a genetic disorder occurring in one in every 15,000 births. It is characterized by severe mental retardation, seizures, difficulty speaking and ataxia. The gene responsible for AS was discovered to be UBE3A and encodes for E6-AP, an ubiquitin ligase. A unique feature of this gene is that it undergoes maternal imprinting in a neuron-specific manner. In the majority of AS cases, there is a mutation or deletion in the maternally inherited UBE3A gene, although other cases are the result of uniparental disomy or mismethylation of the maternal gene. While most human disorders characterized by severe mental retardation involve abnormalities in brain structure, no gross anatomical changes are associated with AS. We have generated a Ube3a protein with additional sequencesthat should allow the secretion from cells and uptake by neighboring neuronal cells. This would confer a functional E6-AP protein into the neurons and rescue disease pathology.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com