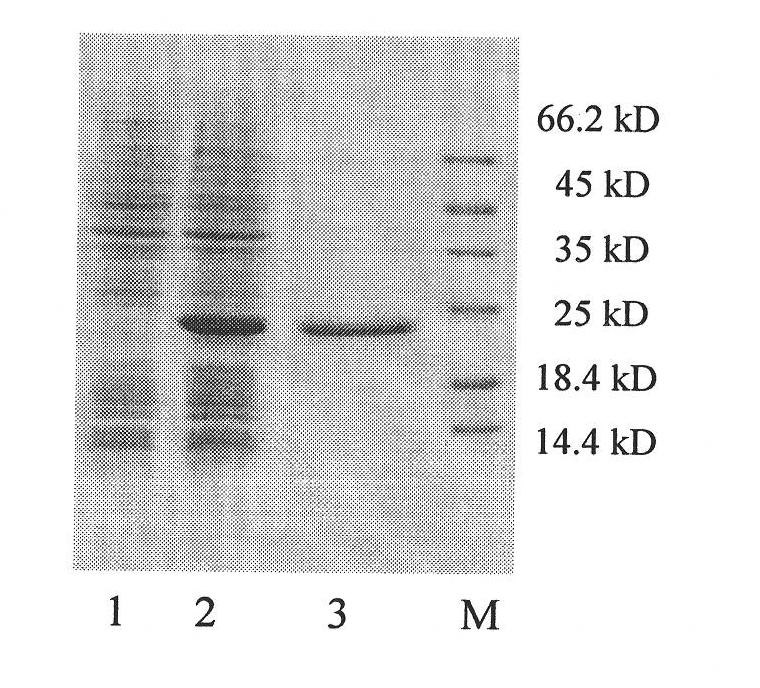
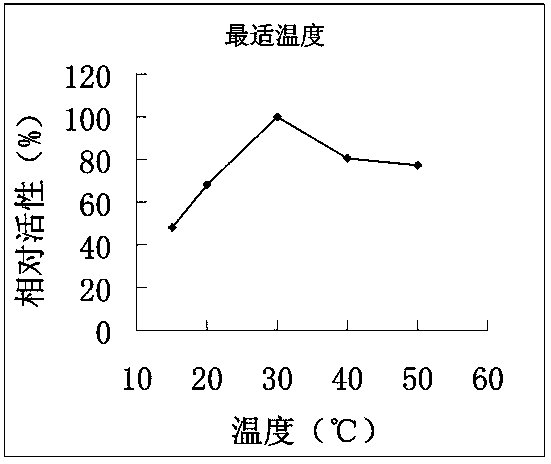
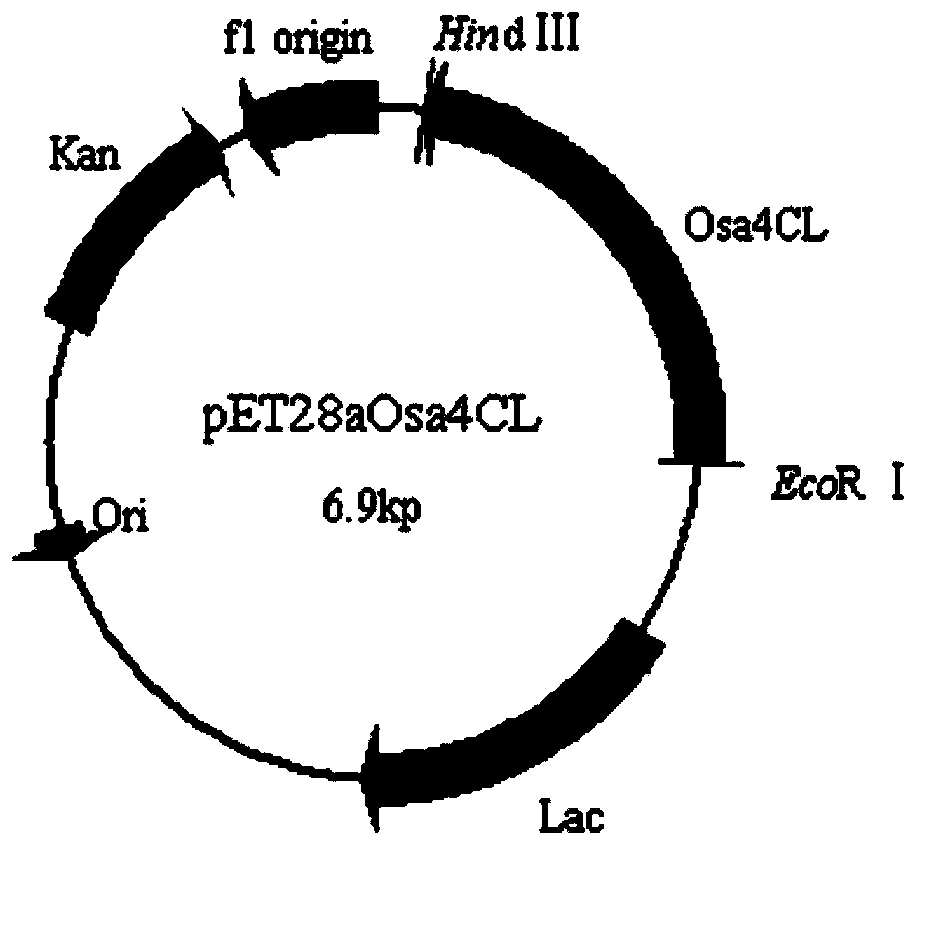
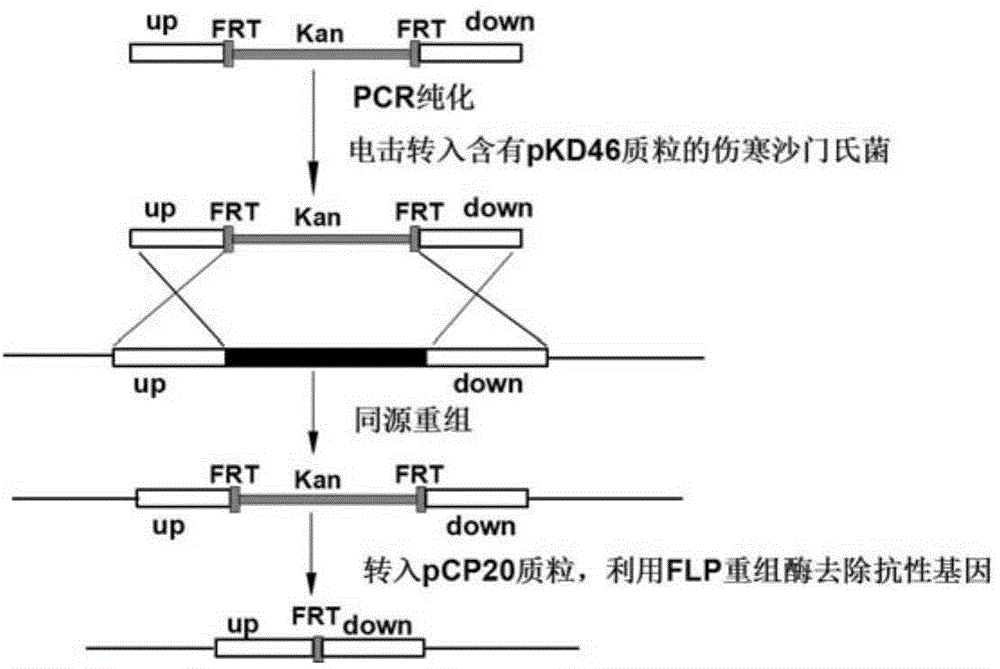
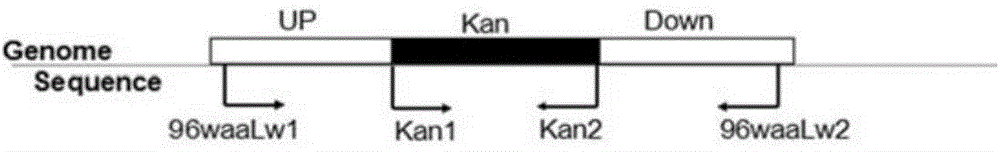
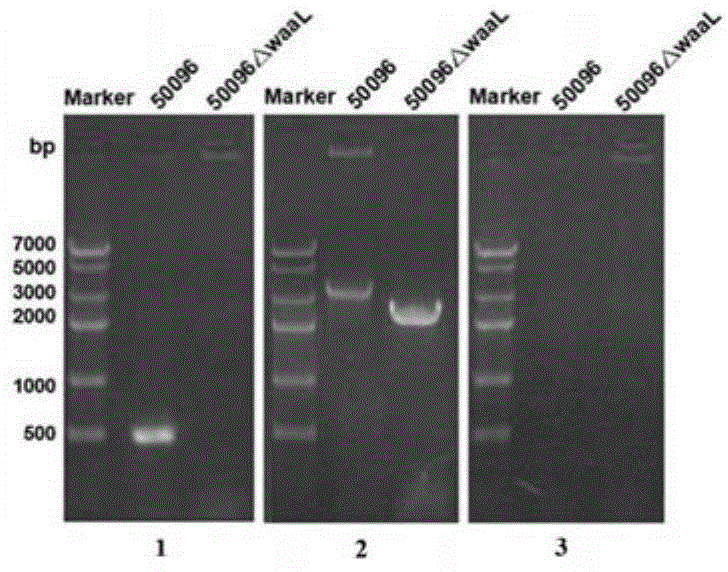
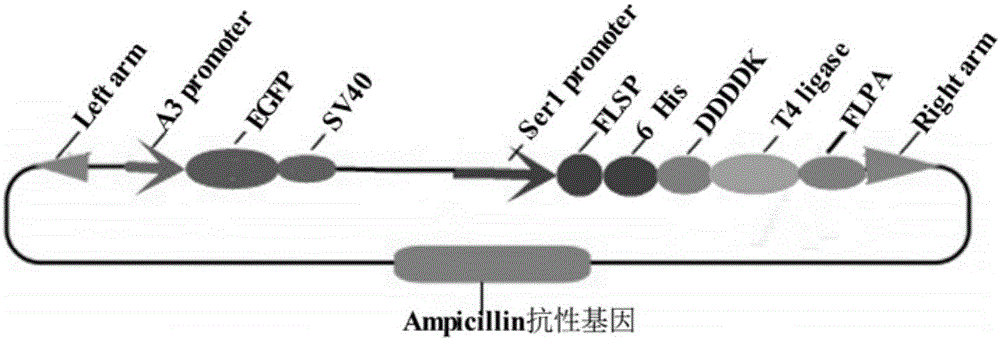
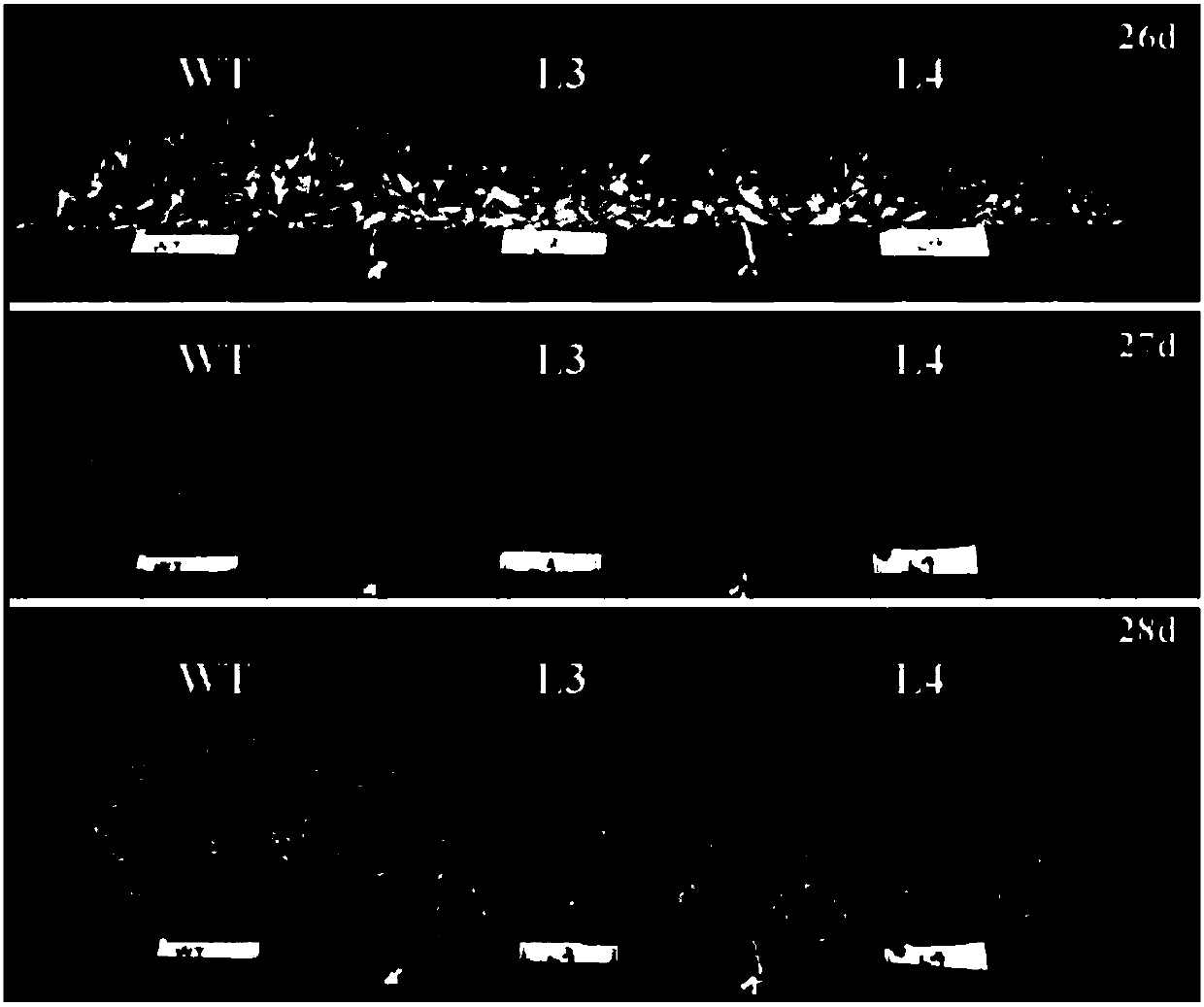
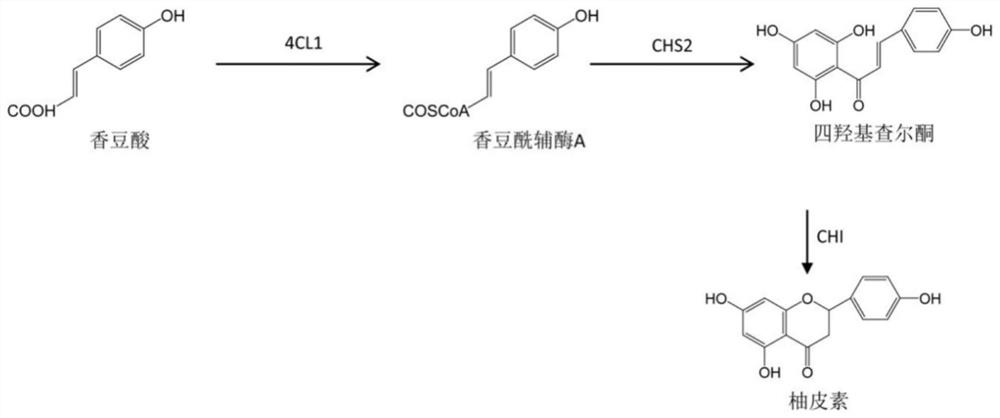
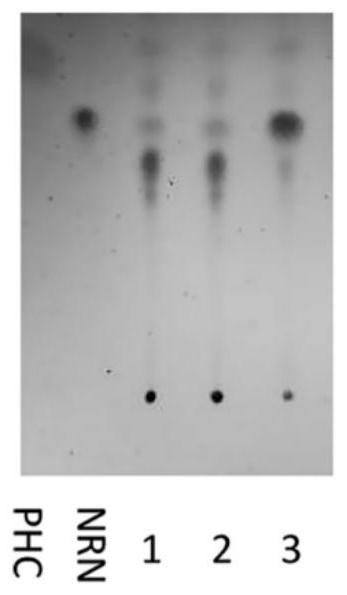
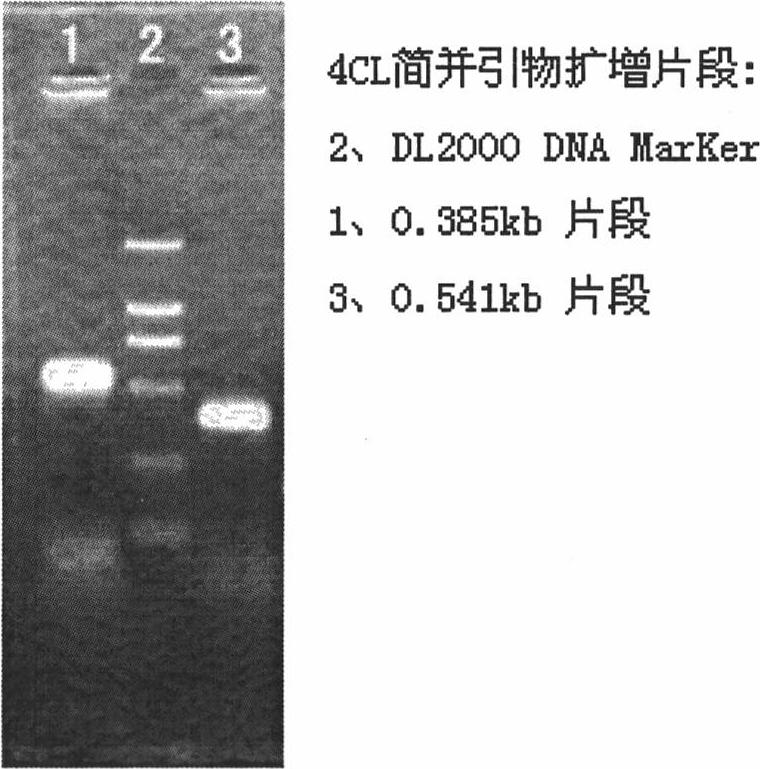
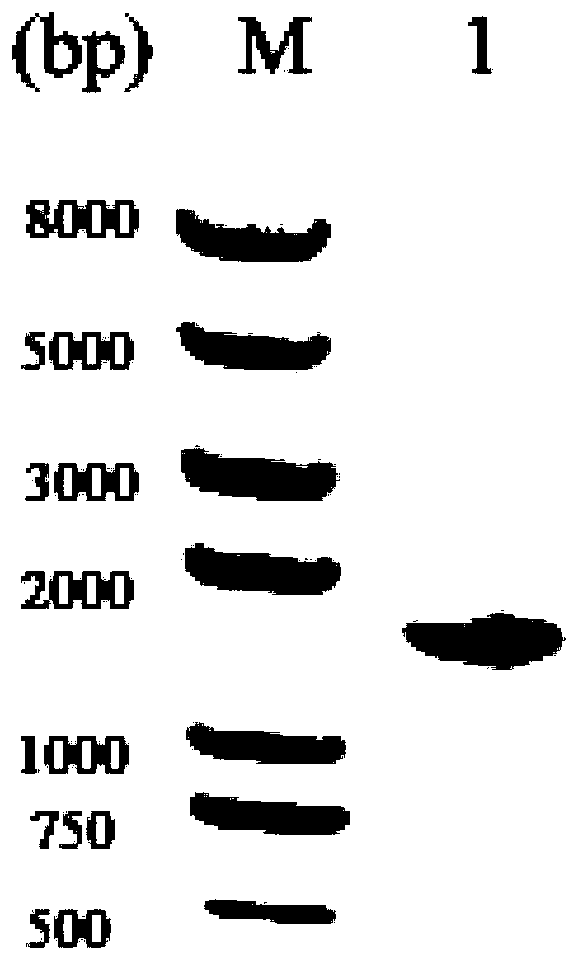Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Ligase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ligase Genes encode Ligases, a large major class of enzymes that catalyze the formation of a linking covalent bond between two substrate molecules, coupled with the hydrolysis of a pyrophosphate bond in ATP or a similar energy donor. (NCI)
A preparing method of a recombinant fusion protein modified with bacterial polysaccharides and applications thereof
ActiveCN105695497AUniform polysaccharide binding siteQuality controllableAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsConjugate vaccineBacteroides
A preparing method of a recombinant fusion protein modified with bacterial polysaccharides and applications thereof are disclosed. The method includes co-expressing a recombinant fusion protein and neisseria meningitide O-oligosaccharyltransferase PglL in a bacterium with O-antigen ligase gene defect, and allowing polysaccharides of the bacterium or exogenous polysaccharides to be connected to the recombinant fusion protein through the neisseria meningitide O-oligosaccharyltransferase PglL to obtain the recombinant fusion protein modified with the bacterial polysaccharides. A specific antibody resisting bacterial polysaccharides can be prepared through immunizing mice with the prepared recombinant fusion protein modified with the bacterial polysaccharides. Through applying the recombinant fusion protein modified with the bacterial polysaccharides to preparation of bacterial polysaccharide protein conjugate vaccines, a plurality of problems of culturing of pathogenic bacteria can be avoided, homogeneity and a production efficiency of the vaccines can be increased and a vaccine preparing cost can be reduced.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
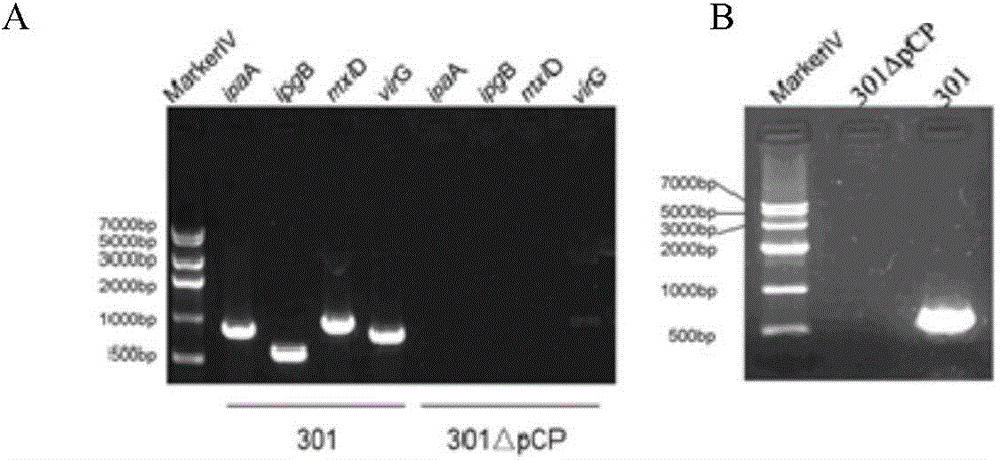
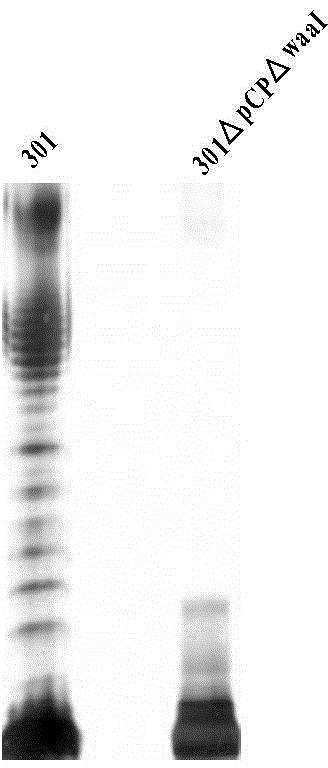
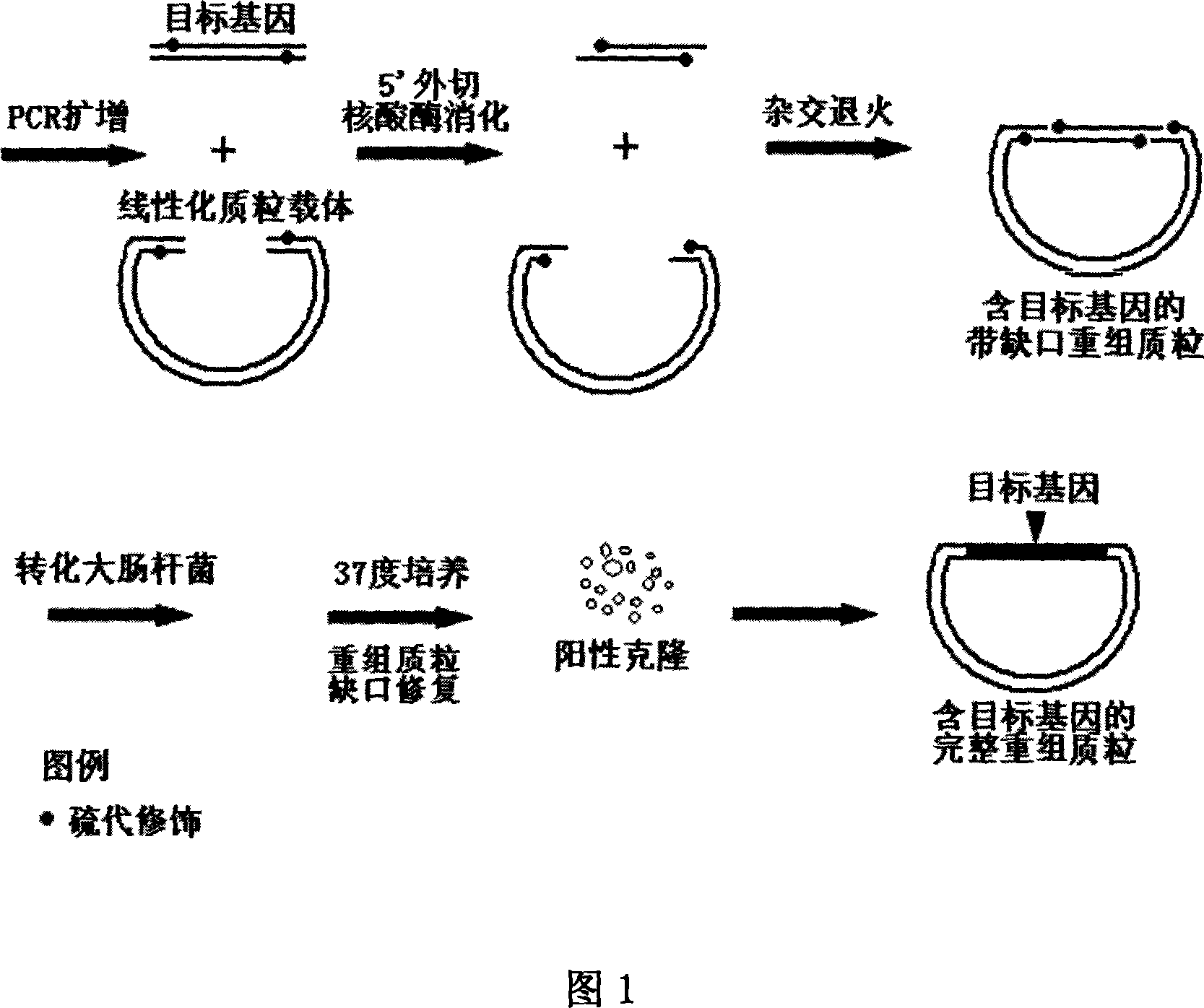
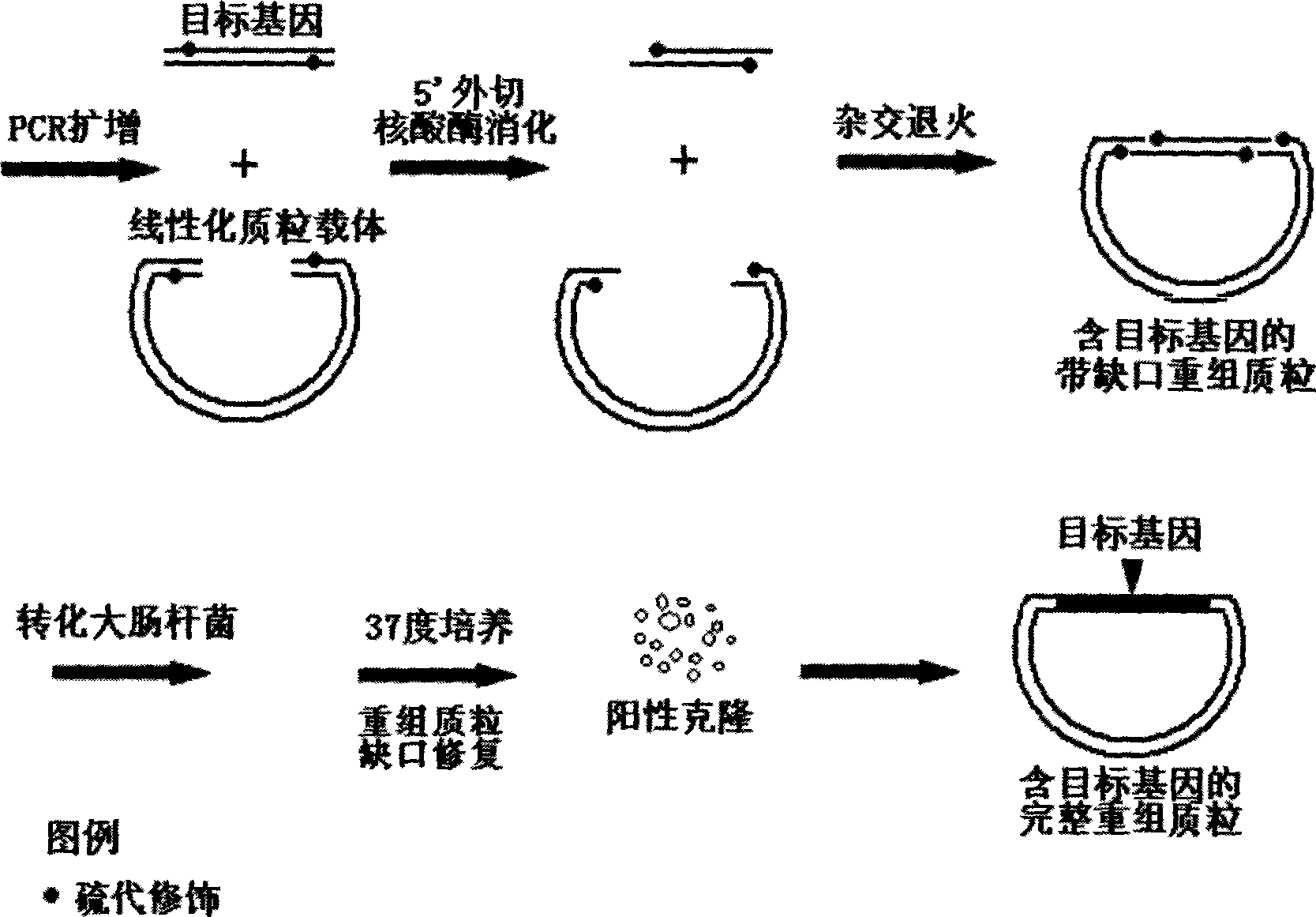
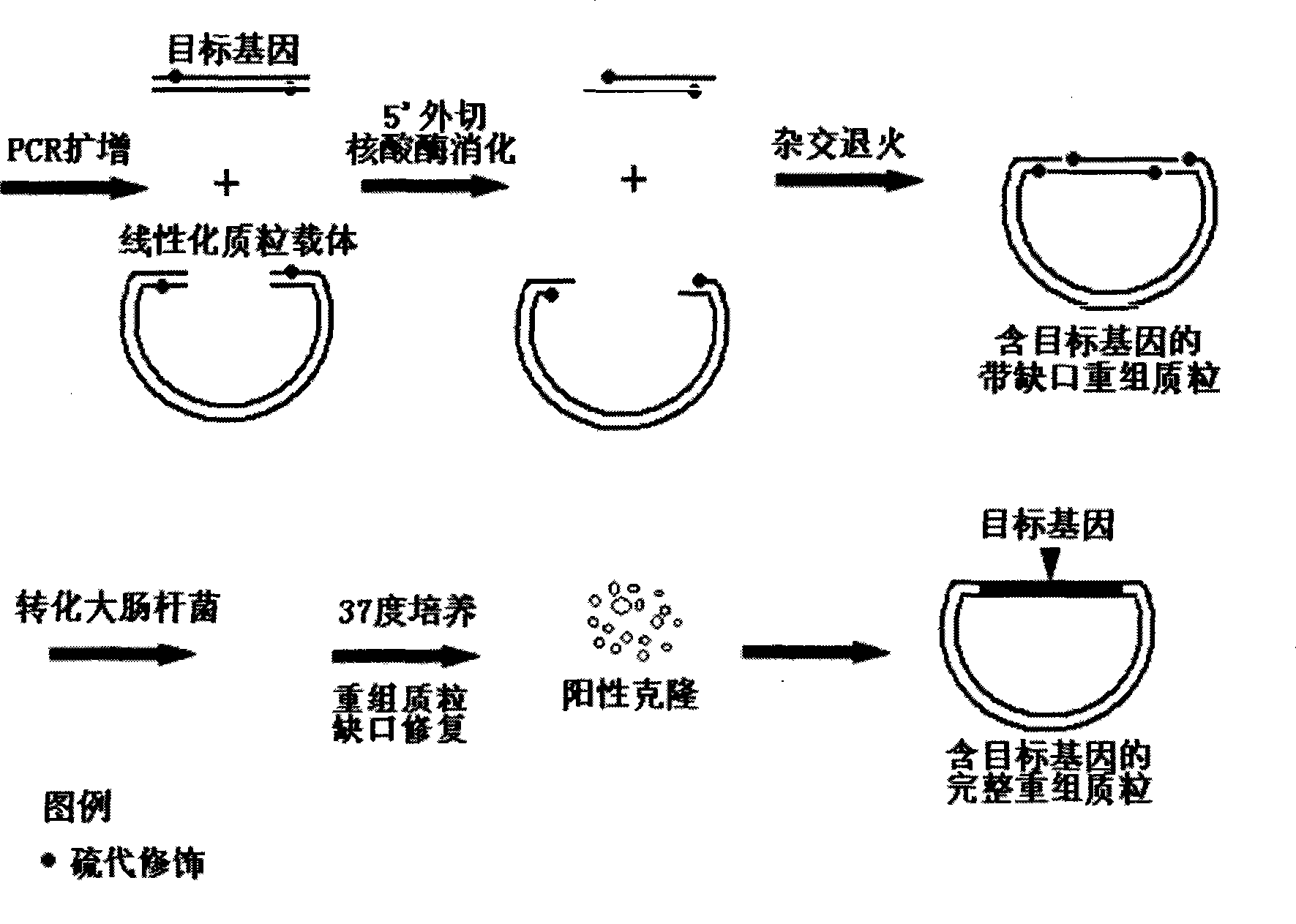
Non-dependent ligase gene cloning process based on thio-modification
The present invention relates to non-dependent ligase gene cloning process based on thio-modification. Each of the amplified target gene and the primer of the plamid vector has The 5' end thio-modified. The cloning process includes: PCR amplification of target gene and plamid vector and purification of PCR products; degrading DNA chain from the 5' end with 5' exonuclease and thio-modification to create 10-20 of 3' single chain raised ends of nucleoside; and direct transformation to colibacillus. The target gene cloning of the present invention has no dependence on restrictive endonuclease and DNA ligase and great operation flux, and may be used in large scale gene cloning.
Owner:苏州博睐恒生物科技有限公司
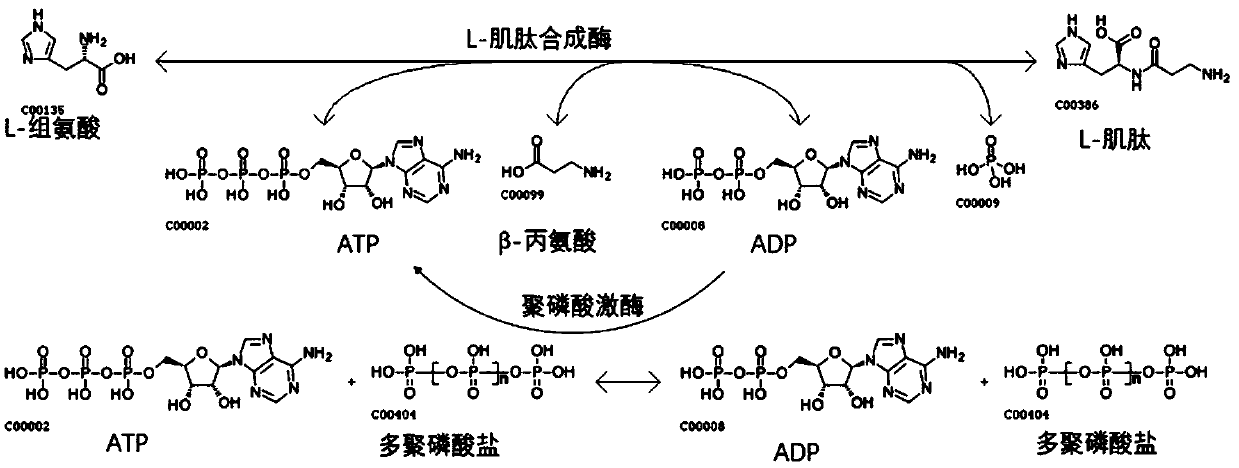
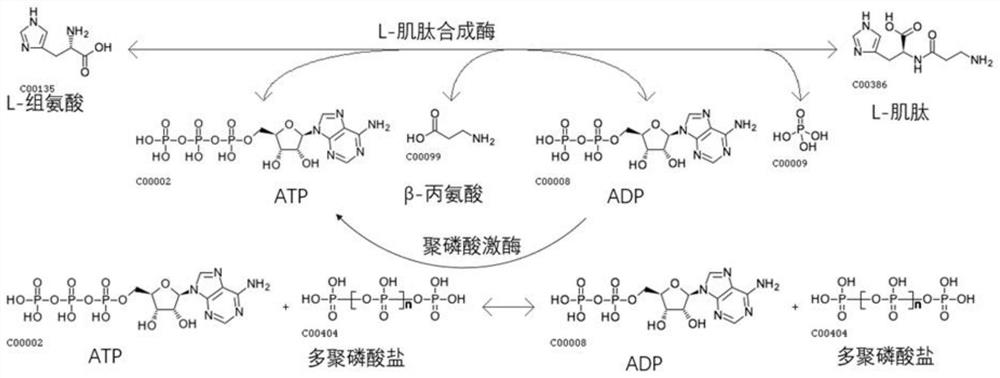
Method of synthesizing L-carnosine using L-amino acid ligase by one-step method
ActiveCN109593805AAchieve recyclingWide variety of sourcesTransferasesNucleic acid vectorPhosphorylationL-Carnosine
The invention discloses a method of synthesizing L-carnosine using L-amino acid ligase by a one-step method. The method comprises the steps of taking beta-alanine, L-histidine, ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and polyphosphate as raw materials, and MgCl2 as an activator, adding L-amino acid ligase and polyphosphate kinase, and synthesizing L-carnosine through an enzymatic reaction and coupled coupleunder conditions of a pH of 6.5-8.5 and a temperature of 30-45 DEG C. According to the method, a sequence optimized L-amino acid ligase gene is successfully expressed in escherichia coli, and beta alanine and L-histidine can be catalyzed to synthesize L-carnosine at one step. A substrate is not required to be methylated or subjected to group protection; ATP required by a catalytic reaction is continuously regenerated by allowing polyphosphate kinase to catalyze phosphorylation of ADP (adenosine diphosphate); cyclic regeneration of ATP can be achieved only by consuming a small amount of ADP; and a renewable raw material, sodium hexametaphosphate, is wide in source, low in cost, simple to operate and easy in large-scale production.
Owner:苏州百因诺生物科技有限公司
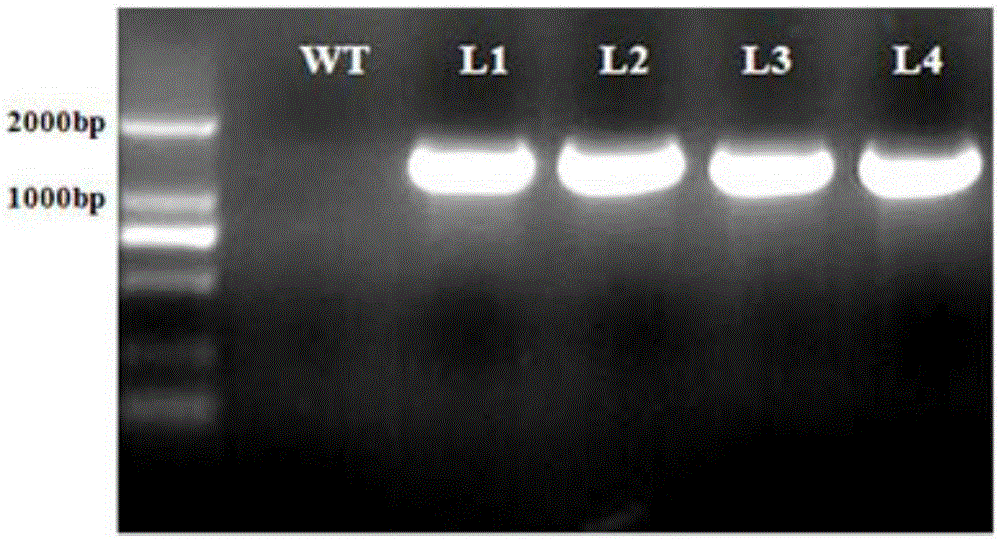
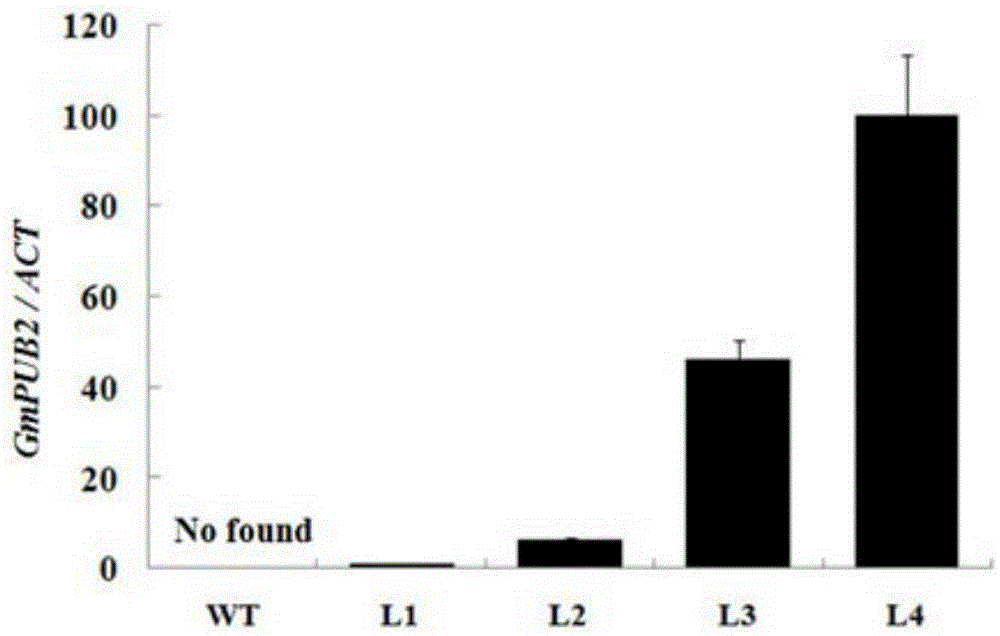
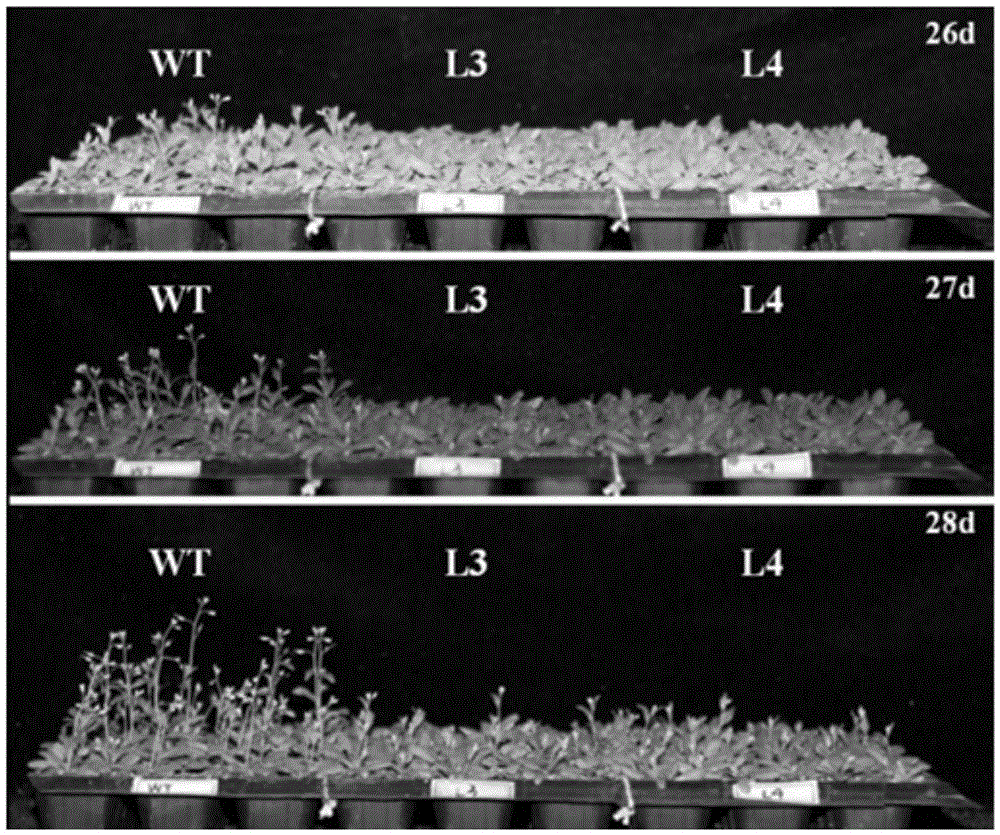
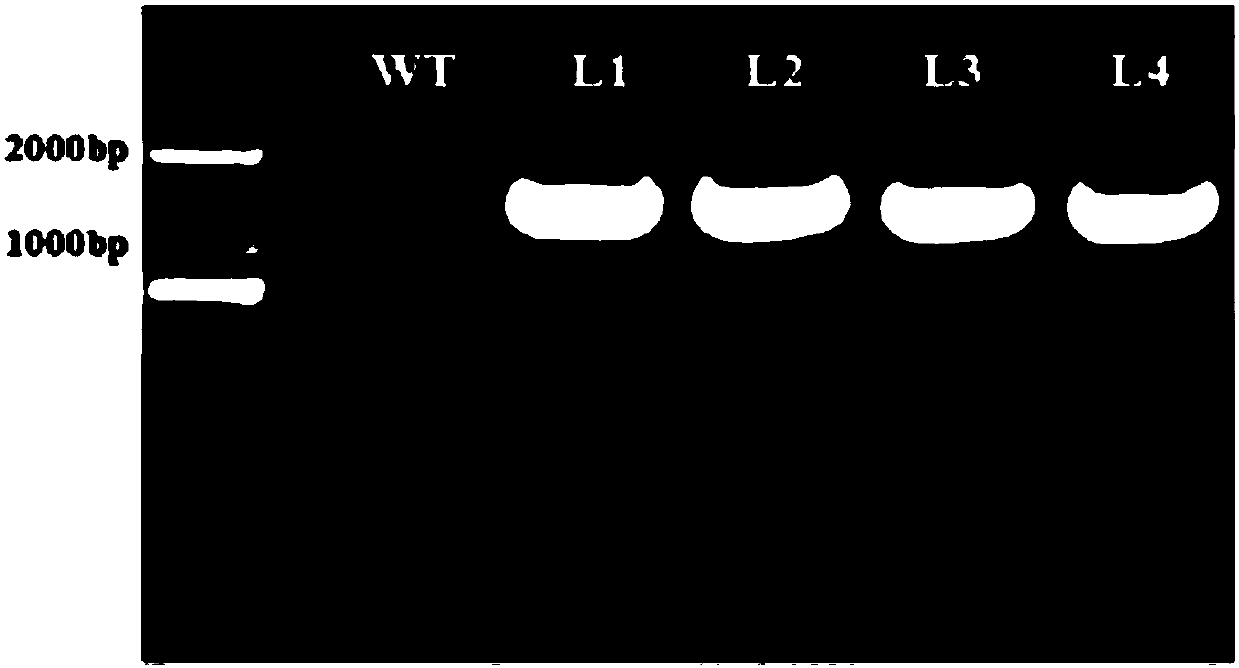
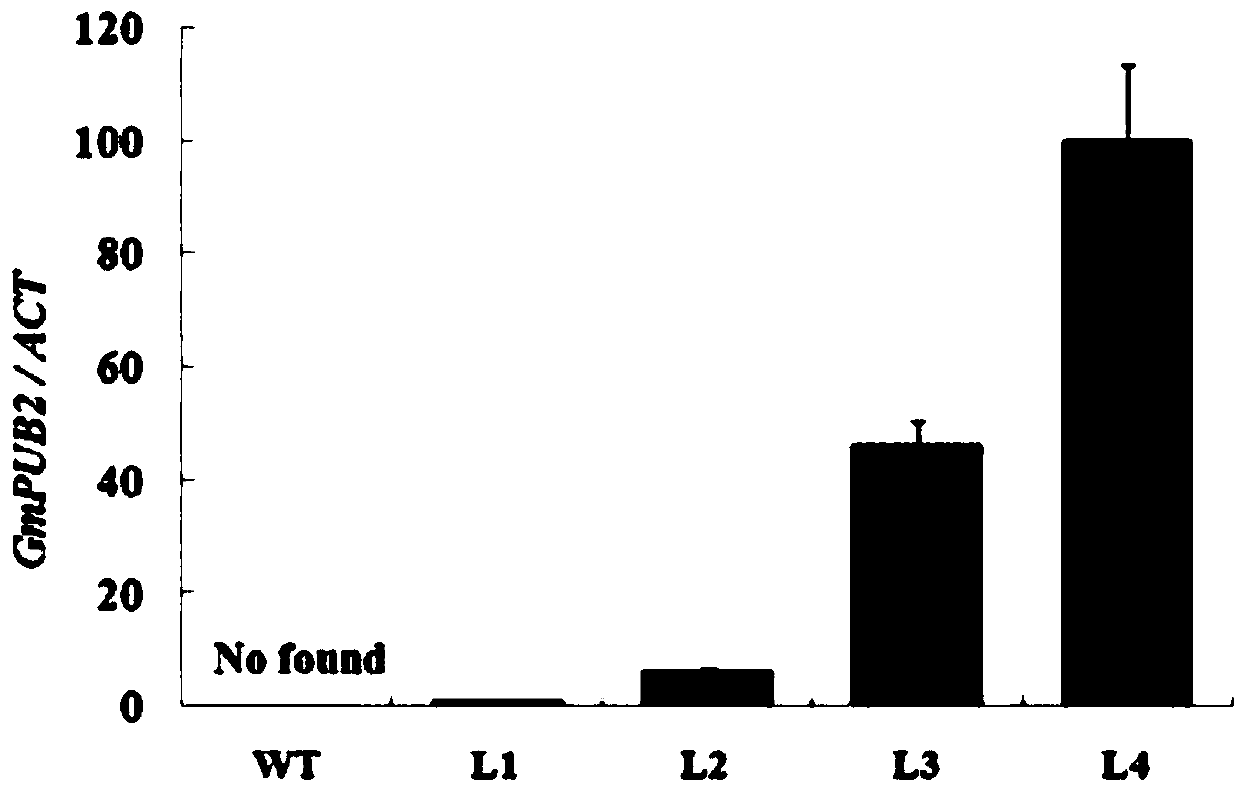
Application of soybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 capable of regulating flowering of plants
ActiveCN105400800ADelayed floweringLate floweringEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionUbiquitin ligaseWild type
The invention discloses an application of soybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 capable of regulating flowering of plants, namely, the application of the oybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 in regulating flowering of plants. A late-flowering plant is obtained after the GmPUB2 gene is transplanted into a target plant through a plant expression vector; an early-flowering plant is obtained after the GmPUB2 gene is transplanted into a target plant through a gene silencing carrier; after the target gene GmPUB2 is transplanted into arabidopsis thaliana, compared with the wild arabidopsis thaliana, the results show that the bolting time and the flowering time of the transgenic plant are obviously later than those of the wild plant, namely, the GmPUB2 gene has the function of delaying the flowering of the plants. With the established GmPUB2 gene silencing carrier to silence the transgenic arabidopsis thaliana with over-expressed target gene GmPUB2, the results show that the flowering time of the plant after silencing is obviously earlier than that of a control plant.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
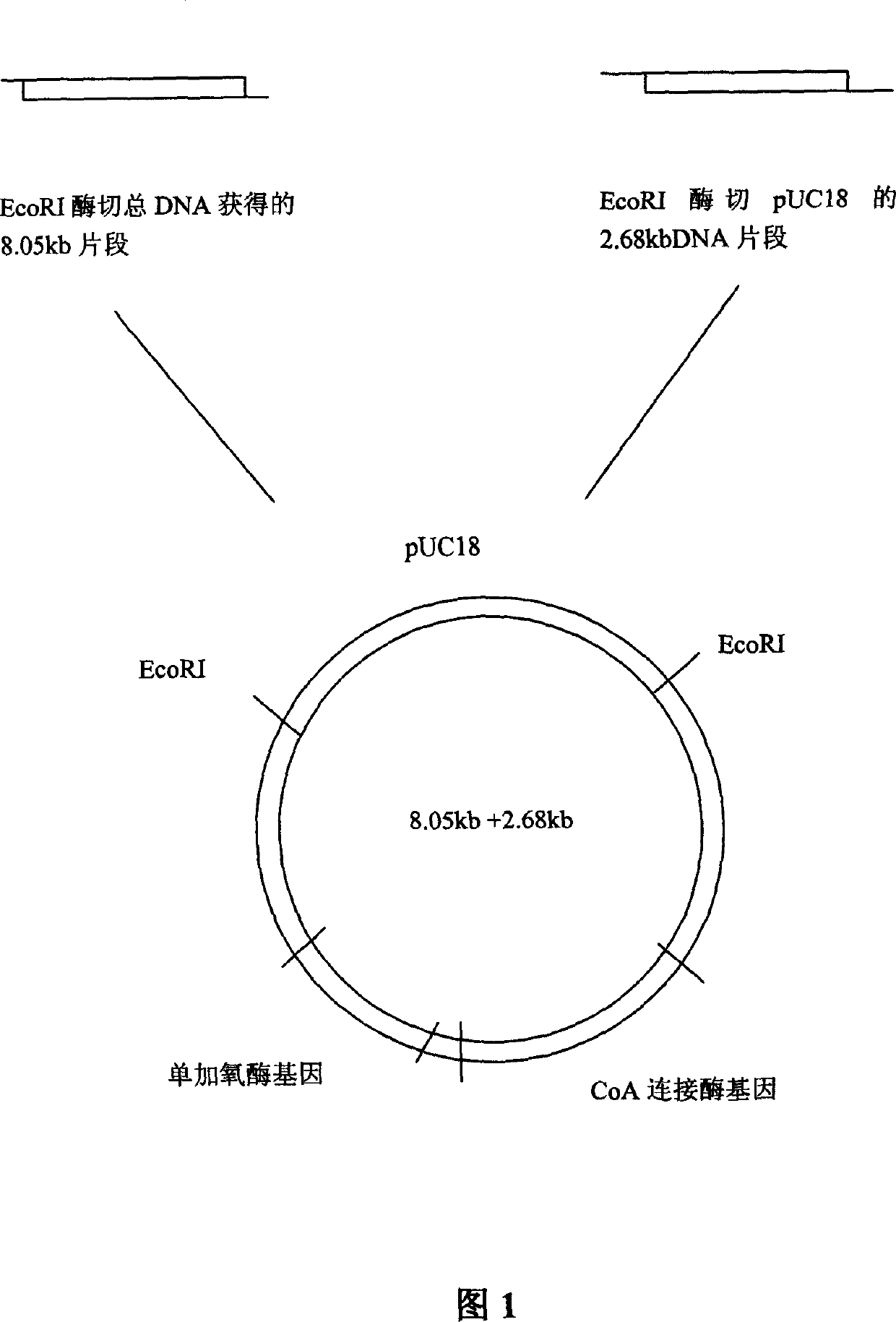
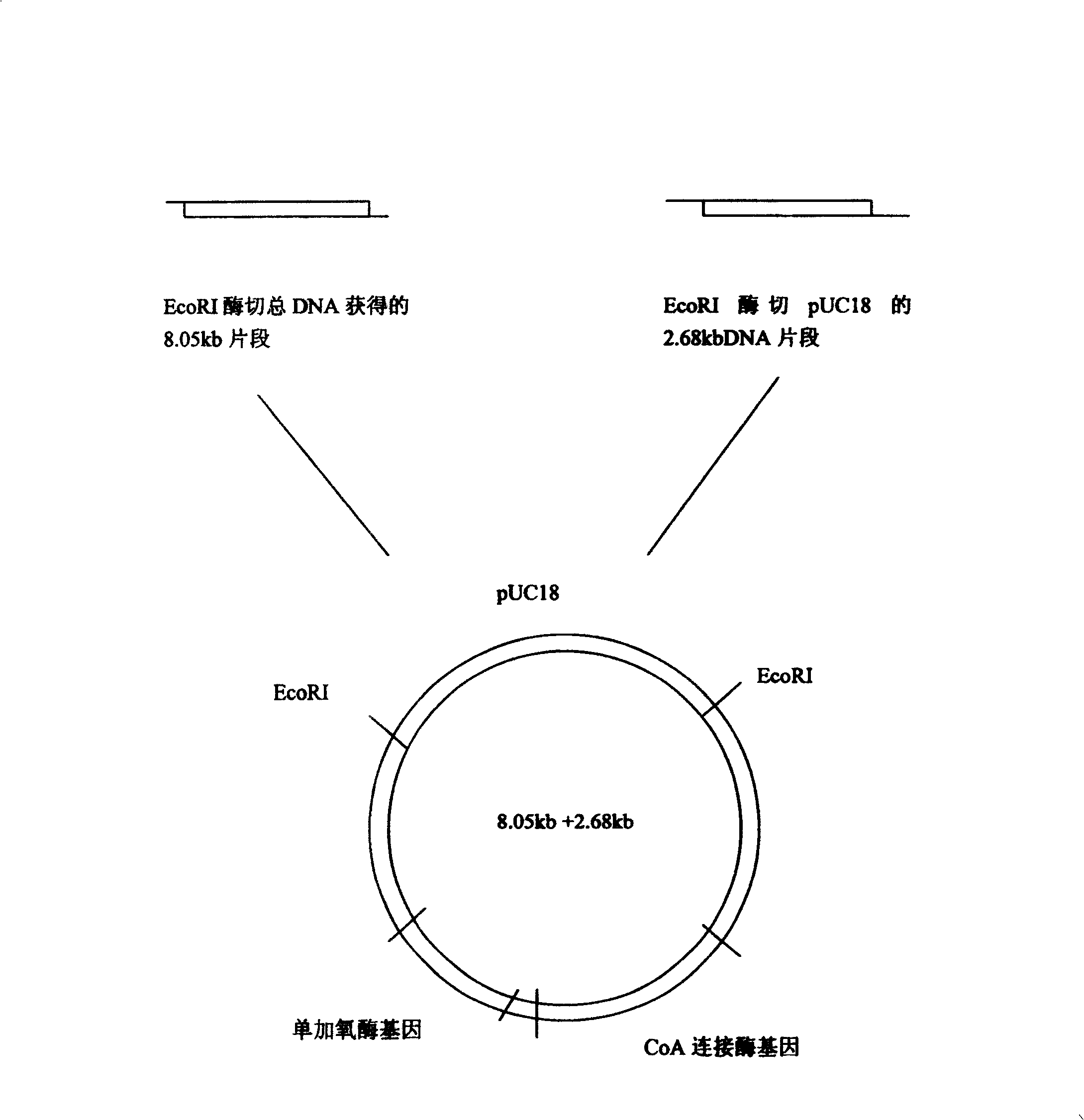
Ribotide sequence of 2-naphthanic acid degradation bacteria DNA segment and its preparation method and application
A DNA fragment (8050 bp) for the 2-naphthalene acid degradating bacterium (Burkholderia sp. JT1500) and its preparing process are disclosed. Its prokaryotic expression plasmid is configured. Its recombinant bacterium strain containing said DNA fragment is obtained by transferring to cobacillus, which can effectively degradating 2-naphthalene acid and sodium benzoate, so degradating the environmental pollutants.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Construction and fermentation method of artificial strain with high yield of fengycin
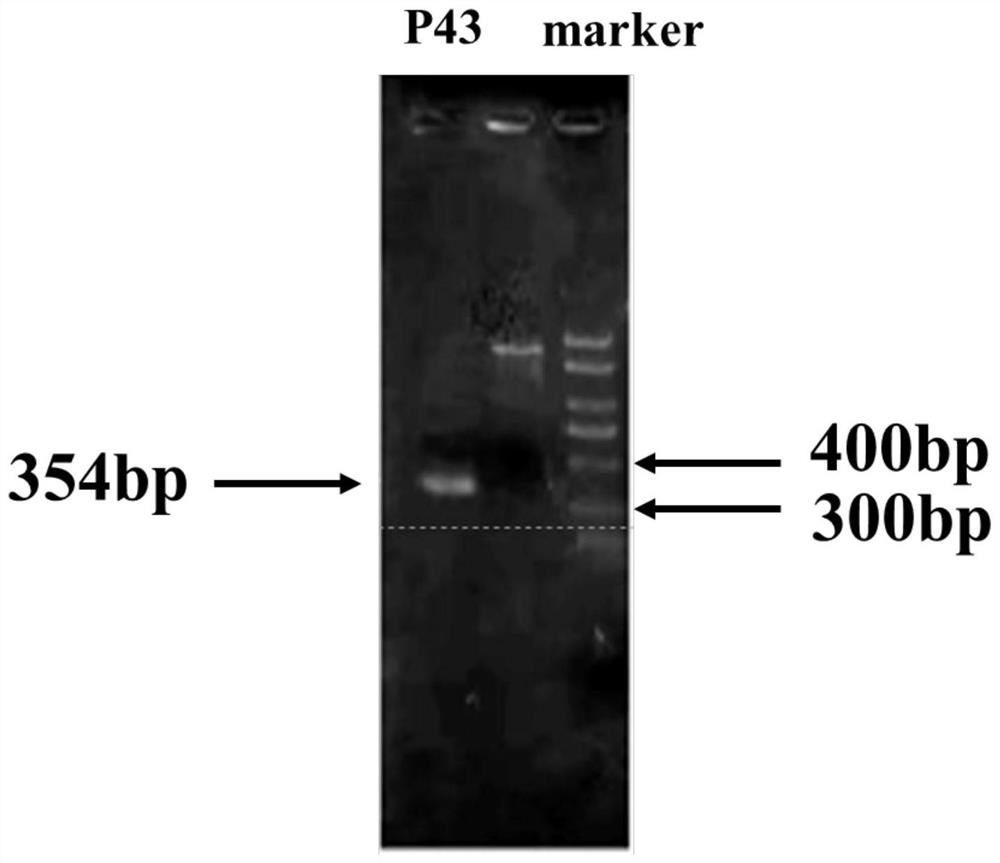
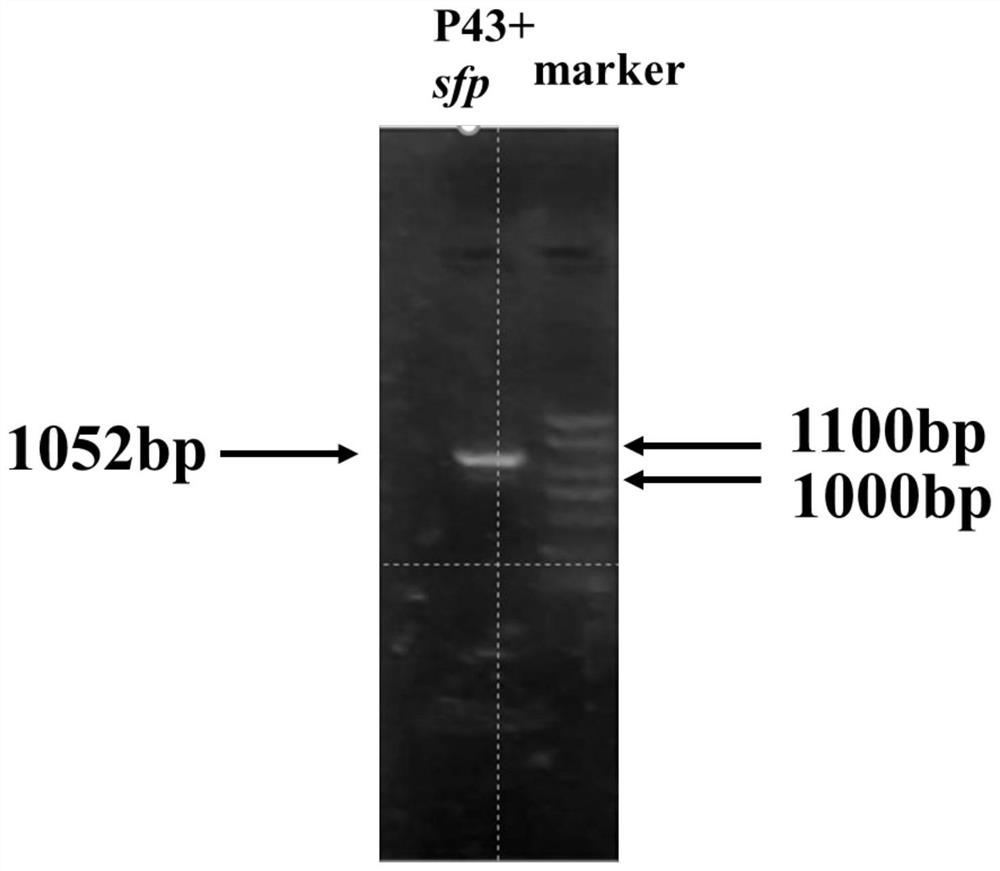
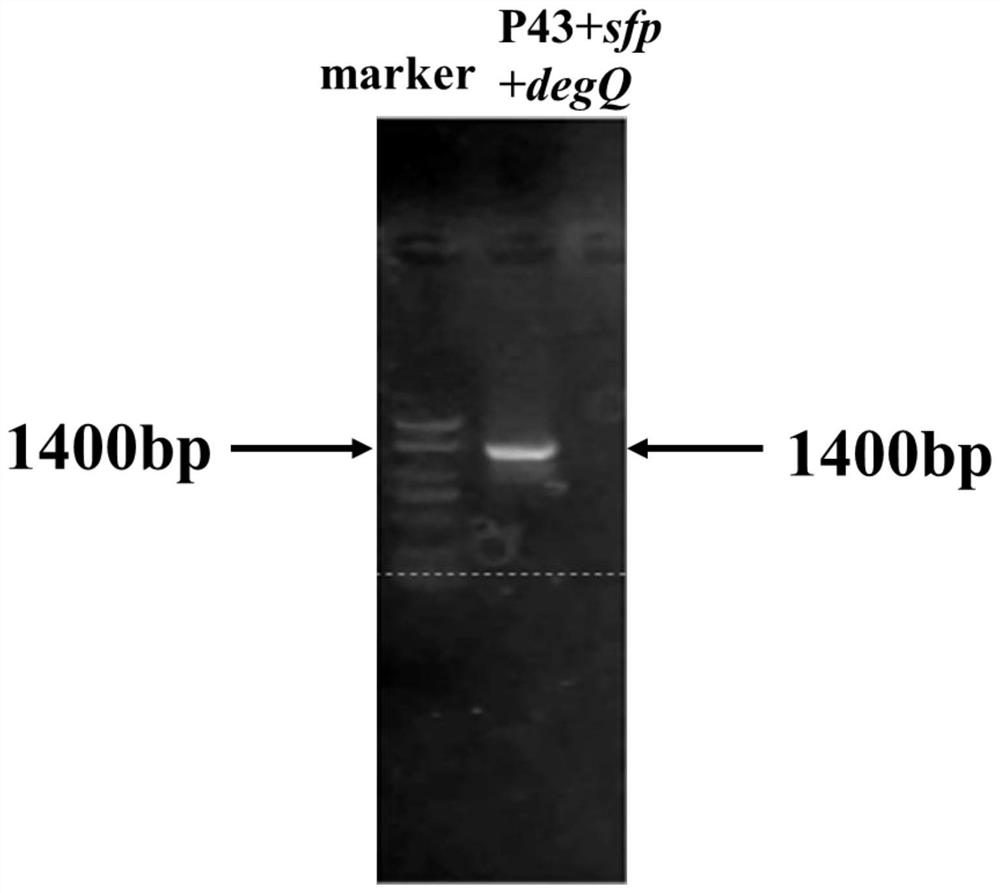
The invention provides a construction and fermentation method of an artificial strain with high yield of fengycin. The 4'-phosphoric acid pantetheinyl transferase gene sfp from bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42, a multi-effect factor gene degQ from bacillus subtilis 168 and a strong promoter P43 are integrated in series onto a genome of the bacillus subtilis 168 by utilizing CRISPR gene editing to construct a strain B.subtilis ds; an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs of Escherichia coli BL21, an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene accACD of Salmonella enterica and a biotin ligase gene bisA of Corynebacterium glutamicum are connected in series to an expression vector pHT43, and the expression vector pHT43 is introduced into a fengycin synthesis strain B.subtilis ds, so that a fengycin high-yield strain B.subtilis dspabacd is constructed; the constructed engineering strain is fermented and cultured in a shake flask to produce the fengycin.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
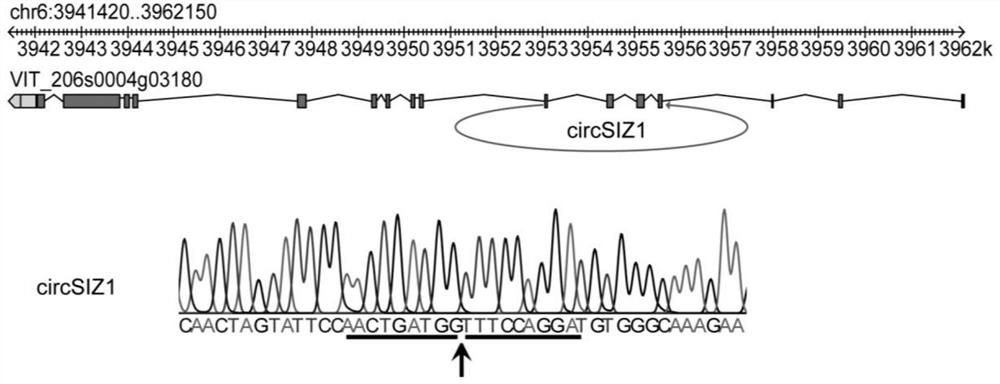
Application of grape circSIZ1 in regulation and control of plant growth and development and salt stress resistance
ActiveCN111718935AIncrease awarenessVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsBiotechnologyGrowth plant
The invention discloses application of grape circSIZ1 to regulation and control of plant growth and development and salt stress resistance, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The circSIZ1provided by the invention is circRNA derived from a SUMO E3 ligase gene, the full length of the circSIZ1 is 433bp, and the nucleotide sequence of the circSIZ1 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. And the expression quantity of circSIZ1 after salt stress treatment is in a rising trend. The circSIZ1 is overexpressed in tobacco, so that the growth and development of a root system are promoted, and in addition,the salt resistance of a transgenic plant is remarkably improved. The invention provides a theoretical basis for improving the stress resistance of plants by utilizing a gene engineering technology inthe future, and has a great application value.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Nitrogen limitation adaptability gene and protein and modulation thereof
InactiveUS20090328255A1Improve expression levelImprove nitrogen utilizationSugar derivativesClimate change adaptationUbiquitin ligaseAdaptive response
The present invention relates to a nitrogen-regulated RING-like ubiquitin E3 ligase gene required for sugar sensing and the modulation of the expression of this gene to modulate a characteristic in a plant. The RING-like ubiquitin E3 ligase of the present invention is involved in mediating nitrogen limitation adaptive responses in plants and its expression is influenced by nitrogen status. Increased expression of this or substantially similar genes can produce plants with improved nitrogen utilization and increased yield.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Nitrogen limitation adaptibility gene and protein and modulation thereof
InactiveCN101501195AMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationNitrogenAdaptive response
The present invention relates to a nitrogen-regulated RING-like ubiquitin E3 ligase gene required for sugar sensing and the modulation of the expression of this gene to modulate a characteristic in a plant. The RING-like ubiquitin E3 ligase of the present invention is involved in mediating nitrogen limitation adaptive responses in plants and its expression is influenced by nitrogen status. Increased expression of this or substantially similar genes can produce plants with improved nitrogen utilization and increased yield.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
Construction and fermentation optimization method of amino-bis-demethoxycurcumin high-yield strain
The invention relates to construction and fermentation optimization methods of an amino-bis-demethoxycurcumin high-yield strain. The invention discloses an escherichia coli engineering strain for synthesizing aminodidemethoxycurcumin by taking p-aminocinnamic acid as a substrate, and belongs to the field of synthetic biology or metabolic engineering. A synthetic route composed of a 4-coumaroyl coenzyme A ligase gene 4cl, a dimer ketone synthase gene dcs, a curcumin synthase gene curs3 and acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase genes accBC and dtsR1 is transferred into Escherichia coli MG1655 (DE3), andthe synthetic route is subjected to modular division and optimization to obtain an engineering bacterium with optimal yield. Through optimization of fermentation conditions, the yield of amino didemethoxycurcumin reaches 33mg / L after the strain is fermented for 48h by taking p-aminocinnamic acid as a substrate. The invention lays a foundation for industrial production and application of the high-activity amino didemethoxycurcumin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Fenneropenaeus chinensis ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene and ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme coded by same and application
The invention discloses a fenneropenaeus chinensis ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene with a nucleotide sequence expressed as SEQ ID No. 1, and provides a recombinant expression and purification method thereof. The invention also provides ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme coded by the fenneropenaeus chinensis ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene, wherein the amino acid sequence of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme is expressed as SEQ ID No. 2; and the invention provides application of the gene sequence and application of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, namely the fenneropenaeus chinensis ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme gene can be used for preparing a prokaryotic expression vector, transforming escherichia coli and expressing recombinant protein with antiviral activity. The recombinant ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme protein obtained by using the invention can be used for antiviral feed additive, animal and plant gene transformation and medicament development.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
4-coumarate coenzyme a ligase originated from ornithogalum caudatum, nucleotide sequence, and applications thereof
The invention provides a 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase originated from ornithogalum caudatum, and the amino acid sequence of the ligase is represented by the SEQ ID No.1. The invention further provides a nucleotide sequence, which encodes the gene of the 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase and is represented by the SEQ ID No.2, a carrier containing the nucleotide sequence and a host cell. The invention also provides an application of 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase or cells containing 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase on catalyzing substrates such as p-coumaric acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid, cinnamic acid, and the like into corresponding thioester compounds.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Biological preparation method of typhoid glycoprotein and application thereof
The invention discloses a biological preparation method of typhoid glycoprotein and an application thereof. The invention discloses a method for preparing bacteria polysaccharide-modified protein, a substrate protein of neisseria meningitidis O-oligosaccharyltransferase PglL and the neisseria meningitidis O-oligosaccharyltransferase PgIL are co-expressed in a bacteria defective in O-antigen ligase genes, and the bacteria polysaccharide-modified protein is obtained. The biological preparation method has wide application prospect for increasing uniformity of vaccine, increasing the production efficiency of the vaccine, and reducing cost; and the vaccine can be used for preventing the diseases caused by typhoid pathogen.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
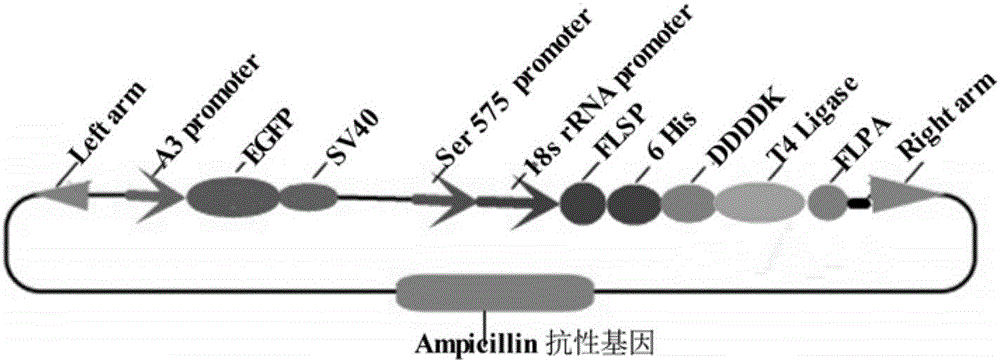
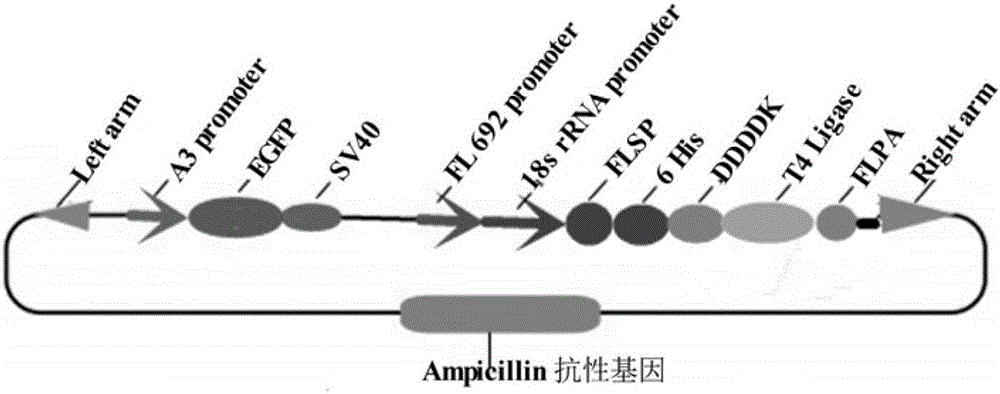
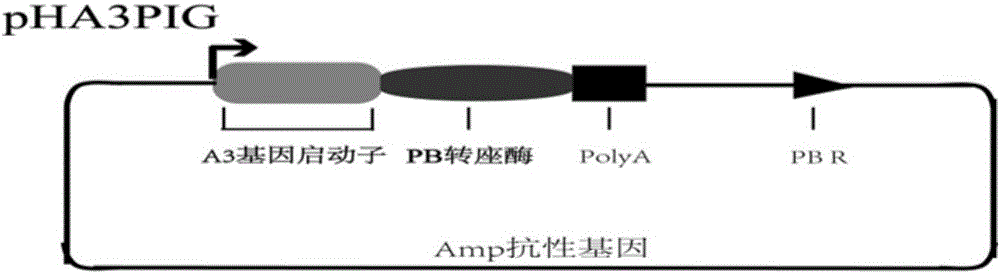
Bombyx mori middle silkgland bioreactor universal plasmid for expressing T4 ligase as well as application and method of universal plasmid
The invention discloses a bombyx mori middle silkgland bioreactor universal plasmid for expressing T4 ligase as well as an application and a method of the universal plasmid. The plasmid takes a piggyBac transposon as a base and contains an Amp resistance gene, and the plasmid comprises functional expression cassettes of the T4 ligase which serves as an exogenous gene and a green fluorescent EGFP gene which is used as a marker gene; the plasmid is constructed by virtue of a molecular biological method, and two specific restriction enzyme cutting sites, namely ApaI and NheI, exist between DDDDK and a light-chain fibroin gene polyA; the double-enzyme-digestion universal plasmid of the ApaI and NheI, after linked to the T4 ligase gene, is injected into fertilized eggs of bombyx mori together with an auxiliary plasmid; on the basis of the property of the transposon, the green fluorescent protein gene and the T4 ligase gene are delivered into a bombyx mori genome and are stably inherited and expressed, so that transgenic bombyx mori is obtained. According to the universal plasmid disclosed by the invention, the transgenic bombyx mori is screened by virtue of the fluorescent marker gene, and T4 ligase protein is specifically synthesized and secreted by virtue of bombyx mori gland cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing bacterial polysaccharide-modified recombinant fusion protein and use of the protein
ActiveUS10844098B2Improve efficiencyImprove homogeneityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenEnzyme Gene
The invention provided a method for preparing a bacterial polysaccharide-modified recombinant fusion protein and use of the bacterial polysaccharide-modified recombinant fusion protein. The method comprises: co-expressing a recombinant fusion protein and the Neisseria meningitidis O-oligosaccharyltransferase PglL in an O-antigen ligase gene-defective bacterium, and linking a polysaccharides endogenous or exogenous for the bacterium to the recombinant fusion protein by the O-oligosaccharyltransferase PglL, to obtain the bacterial polysaccharide-modified recombinant fusion protein. The protein can be used for preparing antibodies against bacterial polysaccharides and vaccines.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Tomato ubiquitination E3 ligase gene SlCHIP1, application and gene SlCHIP2
ActiveCN111254149AImprove high temperature resistanceLigasesVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a tomato ubiquitination E3 ligase gene SlCHIP1, application and a gene SlCHIP2. The nucleotide sequences of the tomato ubiquitination E3 ligase genes SlCHIP1 and SlCHIP2 are cloned, the homology of the two genes, the evolutionary relationship with homologous genes of other species, and the effect and mechanism in high-temperature resistance of tomatoes are studied and discussed, and a new gene resource and a possible molecular marker are provided for high-temperature-resistant breeding and seed selection of the tomatoesand other species.
Owner:LISHUI UNIV
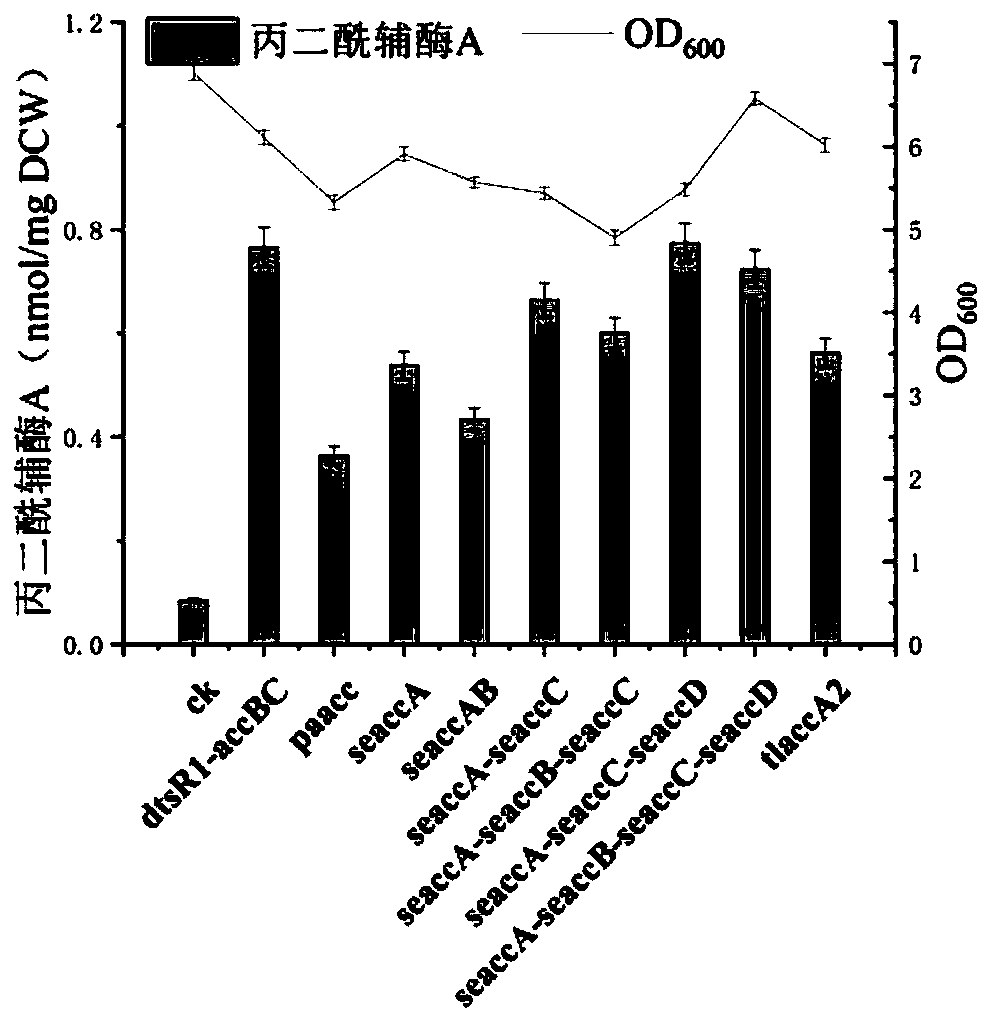
Gene engineering bacteria with high-yield malonyl coenzyme A and construction method and application thereof
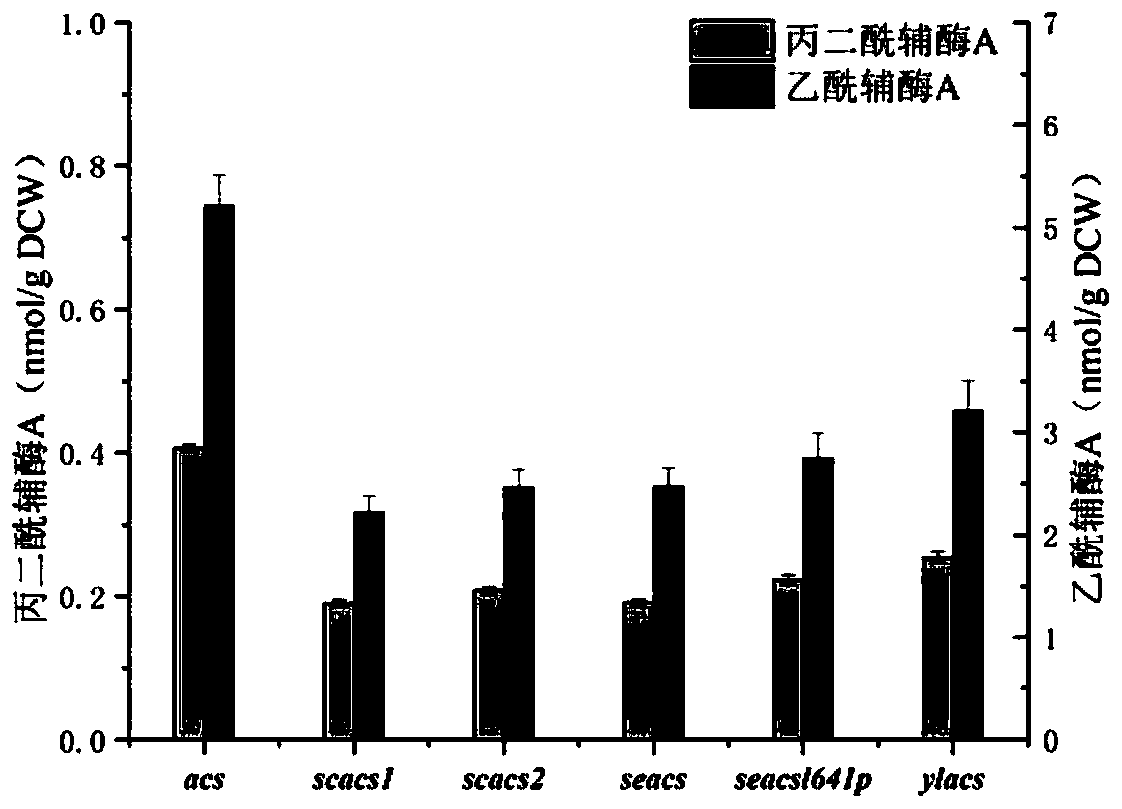
ActiveCN110713962AIncrease contentIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliAcetyl Coenzyme A Synthetase
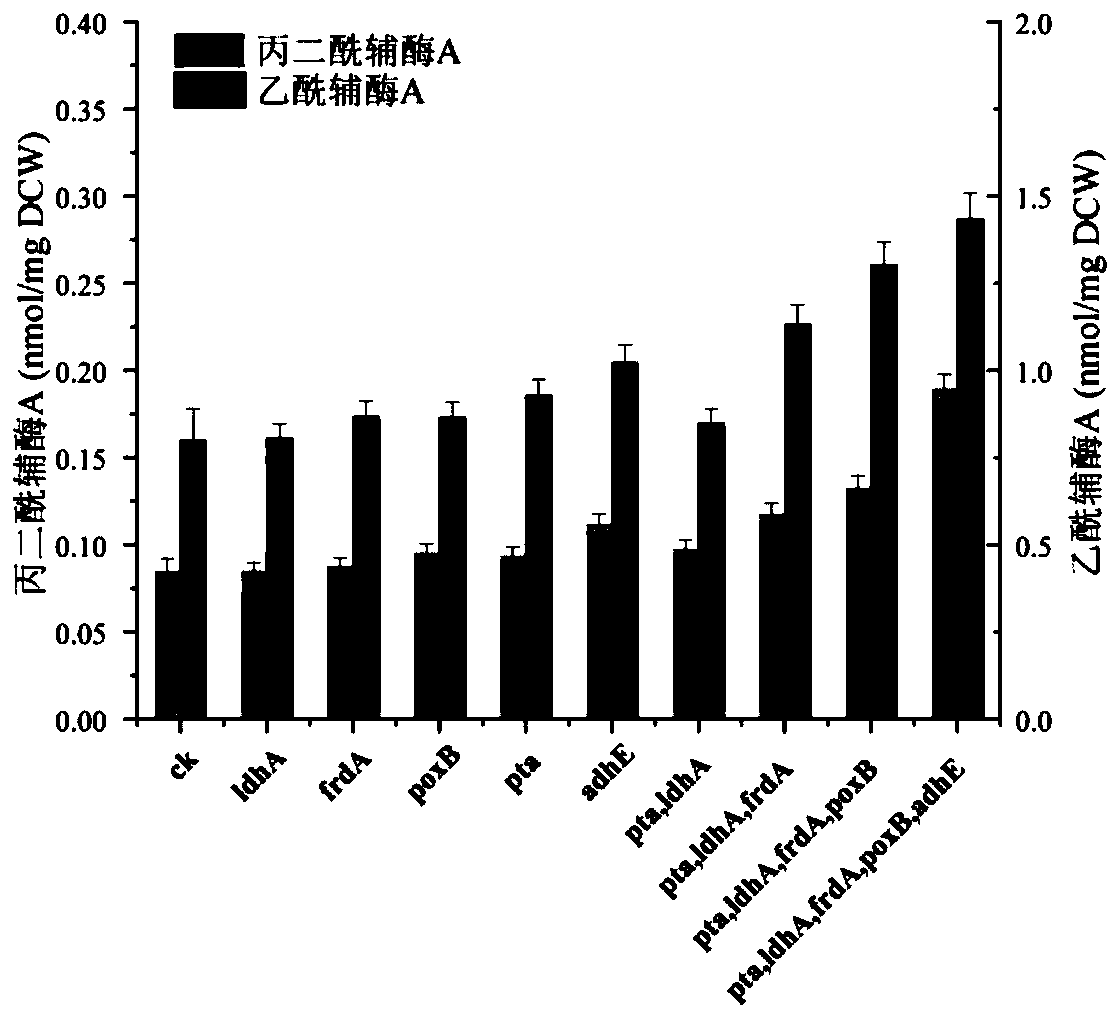
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacteria with high-yield malonyl coenzyme A and a construction method and application thereof. The gene engineering bacteria is constructed by: knocking outfive genes (ldhA, pta, frdA, poxB and adhE) in the Escherichia coli genome, and then introducing malonyl coenzyme A synthesis pathway genes including acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene of the Escherichia coli, acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene of Salmonella enteritidis and biotin ligase gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum. According to the gene engineering bacteria of the invention, a highly-efficient accumulation of the malonyl coenzyme A can be realized by inhibiting internal acetyl coenzyme A outflow pathways of the engineering bacteria and constructing malonyl coenzyme A synthesis pathwaysinto different expression vectors to be transferred into the engineering bacteria; the engineering bacteria can efficiently synthesize a precursor, malonyl coenzyme A, of flavonoid compounds by takingacetic acid, a metabolite by-product of the Escherichia coli, as a substrate; and the engineering bacteria can be used to increase the yield of naringenin, a skeleton precursor of the flavonoid compounds, synthesized by a microbiological method.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of β-picric acid
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Dual-promoter universal plasmid for expressing T4 ligase of domestic silkworm middle silk gland bioreactor as well as application and method of dual-promoter universal plasmid
The invention discloses a dual-promoter universal plasmid for expressing T4 ligase of a domestic silkworm middle silk gland bioreactor as well as application and a method of the dual-promoter universal plasmid. The plasmid takes piggy Bac transposons as a foundation and carries an Amp resistance gene; the plasmid comprises function expression frames of a T4 ligase gene used as an exogenous gene and a green fluorescence EGFP (Enhanced Green Fluorescent Protein) gene used as a marker gene; the plasmid is constructed by utilizing a molecular biology method and two special restriction enzyme cutting sites containing ApaI and NheI are formed between DDDDK and a fibroin light-chain gene polyA; the universal plasmid is subjected to dual-enzyme digestion by adopting the ApaI and the NheI; after the universal plasmid is connected with the T4 ligase gene, the universal plasmid and an auxiliary plasmid are commonly injected into a domestic silkworm fertilized ovum; the green fluorescence protein gene and the T4 ligase gene are transferred into a domestic silkworm genome through utilizing properties of the transposons and are stably inherited and expressed to obtain transgenic domestic silkworms. The transgenic domestic silkworms are screened with the help of a fluorescence marker gene and domestic silkworm silk gland cells are used for specifically synthesizing and secreting T4 ligase protein.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Tomato ubiquitin ligase gene and application thereof
ActiveCN108034663ALigasesVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotideUbiquitin ligase activity
The invention discloses a tomato ubiquitin ligase gene and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the tomato gene S1SINAL is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the amino acid sequence of the gene coding protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The tomato gene S1SINAL has ubiquitin ligase activity, has an inhibition effect on plant resistant protein mediated hypersensitivity reaction, and can inhibithypersensitivity reaction caused by pathogen effect protein. The tomato gene exerts negative regulation and control effects in plant immune reaction and can be used for adjusting the disease resistance of plants.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Ligase independent gene cloning process based on thio-modification
The present invention relates to non-dependent ligase gene cloning process based on thio-modification. Each of the amplified target gene and the primer of the plamid vector has The 5' end thio-modified. The cloning process includes: PCR amplification of target gene and plamid vector and purification of PCR products; degrading DNA chain from the 5' end with 5' exonuclease and thio-modification to create 10-20 of 3' single chain raised ends of nucleoside; and direct transformation to colibacillus. The target gene cloning of the present invention has no dependence on restrictive endonuclease andDNA ligase and great operation flux, and may be used in large scale gene cloning.
Owner:苏州博睐恒生物科技有限公司
Animal model of angelman syndrome
The present invention concerns non-human animals with cells having a genome that is lacking the entire E3 ubiquitin ligase (Ube3a) gene (including all isoforms and alternative promoters). These animals are useful for modeling Angelman Syndrome. The invention also includes methods for assessing the effect of an agent, such as potential therapeutics, on an animal model by exposing the animal or cells, tissues, or organs isolated therefrom, to an agent of interest.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +2
Bombyx mori posterior silk gland bioreactor dual-promoter universal plasmid for expressing T4 ligase and application and method thereof
The invention discloses a Bombyx mori posterior silk gland bioreactor dual-promoter universal plasmid for expressing T4 ligase and application and a method thereof. The plasmid takes a piggyBac transposon as a basis, carries an Amp resistant gene and contains a T4 ligase gene serving as an exogenous gene and a function expression box of a green fluorescent EGFP gene serving as a marker gene. The plasmid is constructed by using a molecular biology method, and two restriction enzyme cutting sites unique to ApaL and NheI are contained between DDDDK and a fibroin light chain gene poly. After the ApaL and NheI double restriction enzyme cutting universal plasmid is connected with the T4 ligase gene, the plasmid and an auxiliary plasmid are jointly injected into Bombyx mori zygote, and characteristics of the transposon are utilized to guide the green fluorescent protein gene and the T4 ligase gene into a Bombyx mori genome and to be stably inherited and expressed to obtain transgenic Bombyx mori. The transgenic Bombyx mori is screened with the help of the fluorescent marker gene, and a Bombyx mori silk gland cell is utilized to specifically synthesize T4 ligase protein.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
4-coumarate-CoA ligase gene Th4CL and application thereof
The invention discloses a 4-coumarate-CoA ligase gene Th4CL derived from tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg and an application of the 4-coumarate-CoA ligase gene Th4CL. The nucleotide sequence of the 4-coumarate-CoA ligase gene Th4CL is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg is used as a biological source design primer to amplify the cDNA sequence of the tetrastigma hemsleyanum Diels et Gilg to obtain the 4-coumarate-CoA ligase gene Th4CL, and the gene is used as one of key enzymes in a phenylpropane metabolic pathway and can be used for producing resveratrol.
Owner:HANGZHOU SANYEQING AGRI TECH
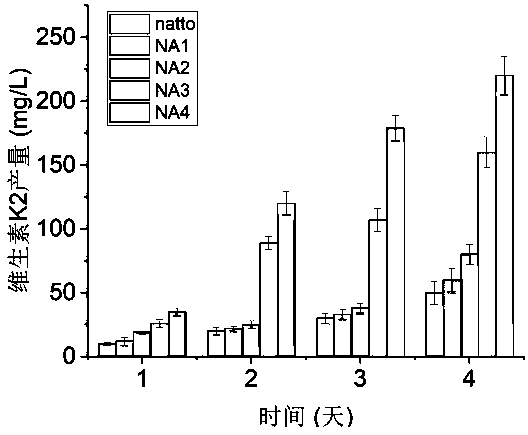
Method for increasing yield of vitamin K2 by utilizing recombinant bacillus natto
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of vitamin K2 by utilizing recombinant bacillus natto. The method comprises the following steps: overexpressing a flutalosin synthetase gene mqnA on a bacillus natto chromosome through a constitutive promoter P43; on the basis of the obtained strain NA1, the strain NA1 is obtained; the method comprises the following steps: overexpressing agene of deoxyxanthine flutalosin synthetase on a bacillus natto chromosome by using a P43 promoter; on the basis of the obtained bacterial strain NA2; a Phbs promoter is used for replacing a natural promoter of an O-succinylbenzoic acid-CoA ligase gene in bacillus natto; on the basis of the obtained strain NA3, isobranching acid genes on bacillus natto chromosomes are replaced with 1, 4-dihydroxy-6-naphthoic acid synthase genes which contain Phbs promoters and are derived from streptomyces coelicolor, and a seed solution of the recombinant bacteria is inoculated into a fermentation culture medium according to the inoculation amount of 3%-6%. According to the invention, four recombinant bacteria NA1-NA4 are constructed, wherein the NA3-NA4 significantly improves the yield of vitamin K2.
Owner:西宝生物科技(上海)股份有限公司
Ribotide sequence of 2-naphthanic acid degradation bacteria DNA segment and its preparation method and application
A DNA fragment (8050 bp) for the 2-naphthalene acid degradating bacterium (Burkholderia sp. JT1500) and its preparing process are disclosed. Its prokaryotic expression plasmid is configured. Its recombinant bacterium strain containing said DNA fragment is obtained by transferring to cobacillus, which can effectively degradating 2-naphthalene acid and sodium benzoate, so degradating the environmental pollutants.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Application of a soybean e3 ubiquitin ligase gene gmpub2 that regulates plant flowering
ActiveCN105400800BDelayed floweringLate floweringEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyUbiquitin ligase
The invention discloses the application of soybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 for regulating plant flowering. Application of soybean E3 ubiquitin ligase gene GmPUB2 regulating plant flowering in regulating plant flowering. The GmPUB2 gene is transferred into the target plant through the plant expression vector to obtain the late flowering plant. The GmPUB2 gene is transferred into the target plant through the gene silencing vector to obtain the early flowering plant. The target gene GmPUB2 was transformed into Arabidopsis. Compared with wild-type Arabidopsis, it was proved that the bolting and flowering time of the transgenic plants were significantly later than those of the wild-type, indicating that the GmPUB2 gene has the effect of delaying plant flowering. Using the constructed GmPUB2 gene silencing vector, the transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing the target gene GmPUB2 was silenced, and it was proved that the flowering time of the silenced plants was significantly earlier than that of the control plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Trifunctional enzyme for de novo synthesis of flavanone as well as synthesis method and application of trifunctional enzyme
ActiveCN113528471ASimple and fast operationEasy to separateAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorEscherichia coliEnzymatic synthesis
The invention discloses a trifunctional enzyme for de novo synthesis of flavanone, wherein 4-coumaroyl-coenzyme A ligase genes, chalcone isomerase genes and chalcone synthase genes are cloned to a prokaryotic expression vector to construct recombinant plasmids, then escherichia coli is converted to induce expression of recombinase; and then purified recombinase is utilized to establish a cell-free synthesis system, and in-vitro enzymatic synthesis of flavanone is realized. According to the invention, the problems of low yield and low substrate conversion rate in an in-vitro multi-enzyme synthesis system of flavanone are solved, and an in-vitro enzymatic synthesis system with simple components is established at the same time. The system does not have a complex regulation effect in engineering bacteria cells, the reaction process is easy to accurately control, byproducts are few, product separation is relatively simple, the production period is obviously shortened, and the production cost is obviously reduced.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Paulownia 4-coumaric acid: coenzyme A ligase gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101434937BChange compositionChange physical and chemical propertiesFungiBacteriaCoumaric acidGenetics
The invention discloses a paulownia 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase, encoding genes and application thereof. Amino acid residue sequence of the 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase is shown in SEQ ID No. of 1. The information can be used for constructing genes of the 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase, or antisense genes and RNA disturbing mass of the genes, which can be used for improving plantmaterials and constructing new materials with higher or lower lignin content.
Owner:河南省绿士达林业新技术研究所
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com