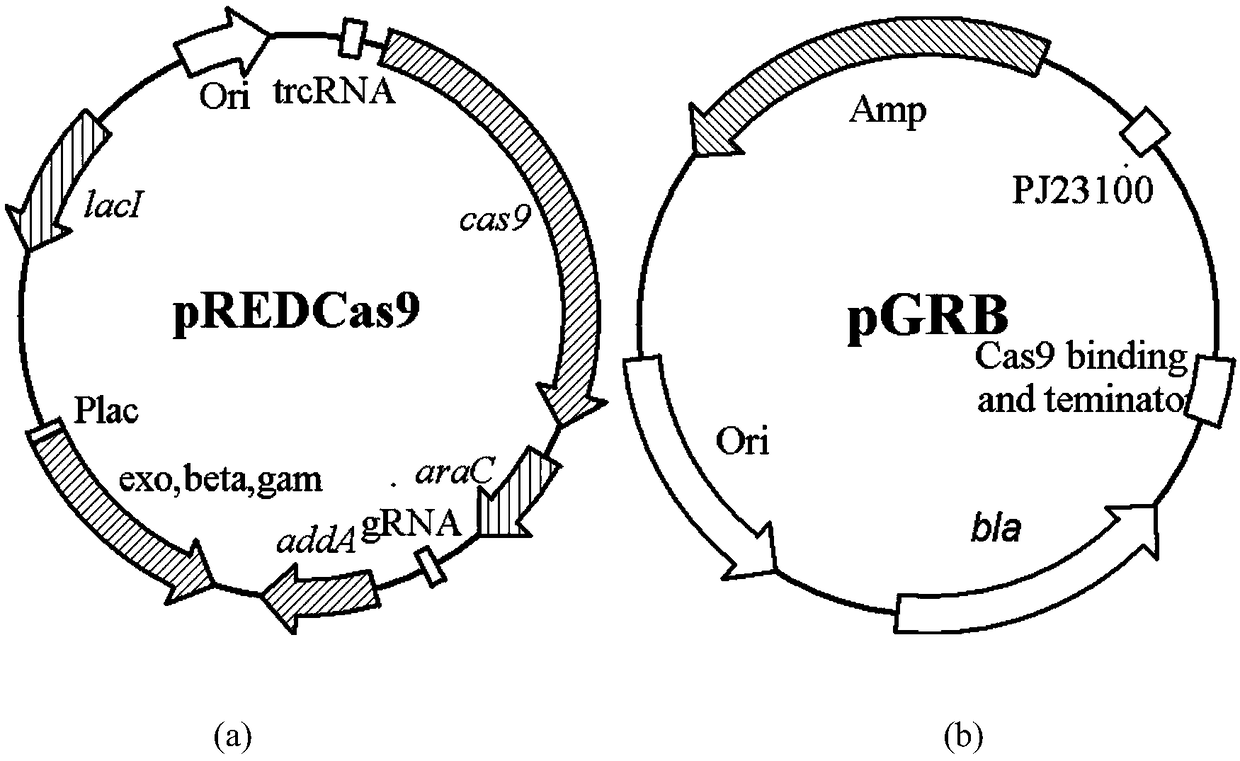
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
148 results about "De novo synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
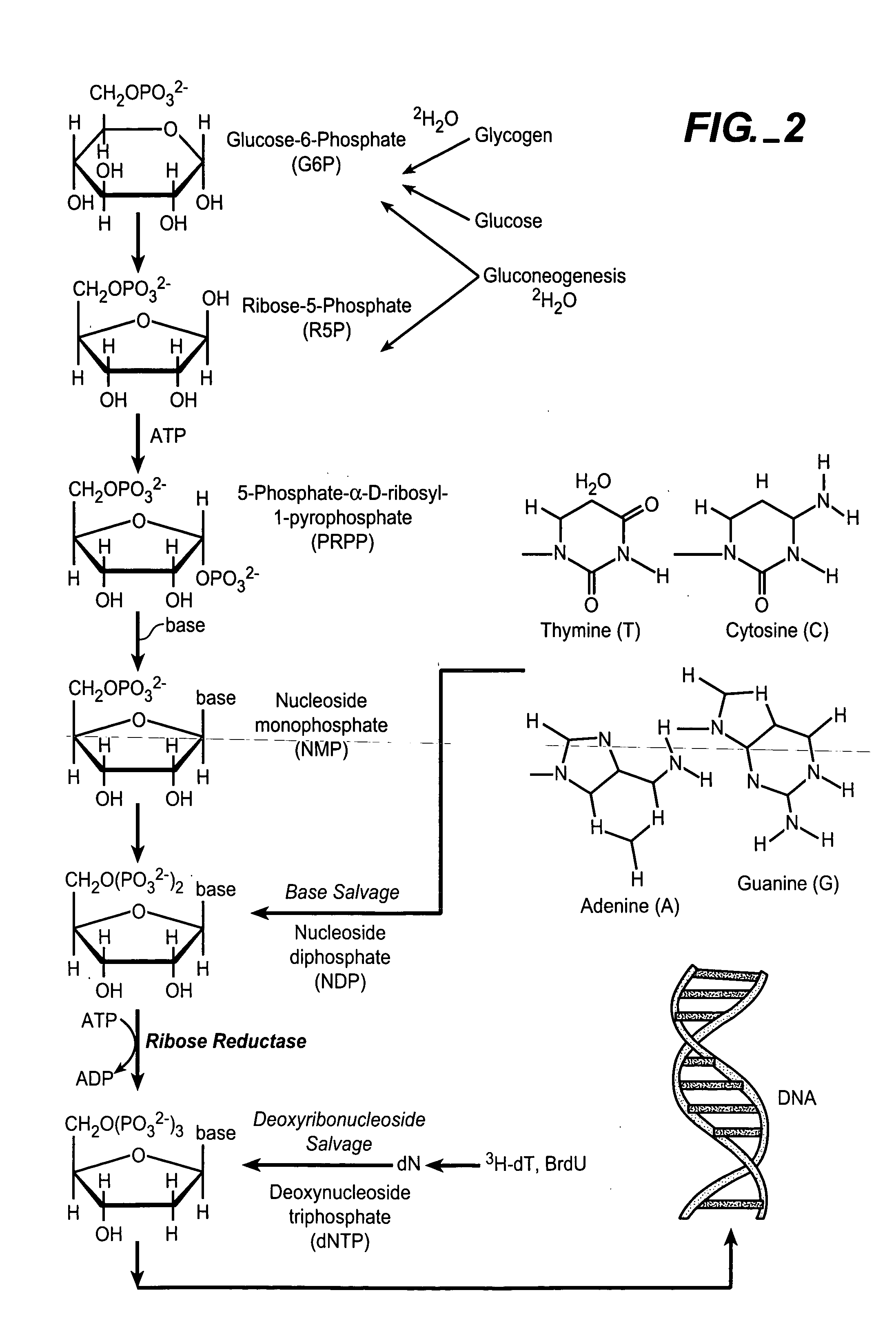
De novo synthesis refers to the synthesis of complex molecules from simple molecules such as sugars or amino acids, as opposed to recycling after partial degradation. For example, nucleotides are not needed in the diet as they can be constructed from small precursor molecules such as formate and aspartate. Methionine, on the other hand, is needed in the diet because while it can be degraded to and then regenerated from homocysteine, it cannot be synthesized de novo.
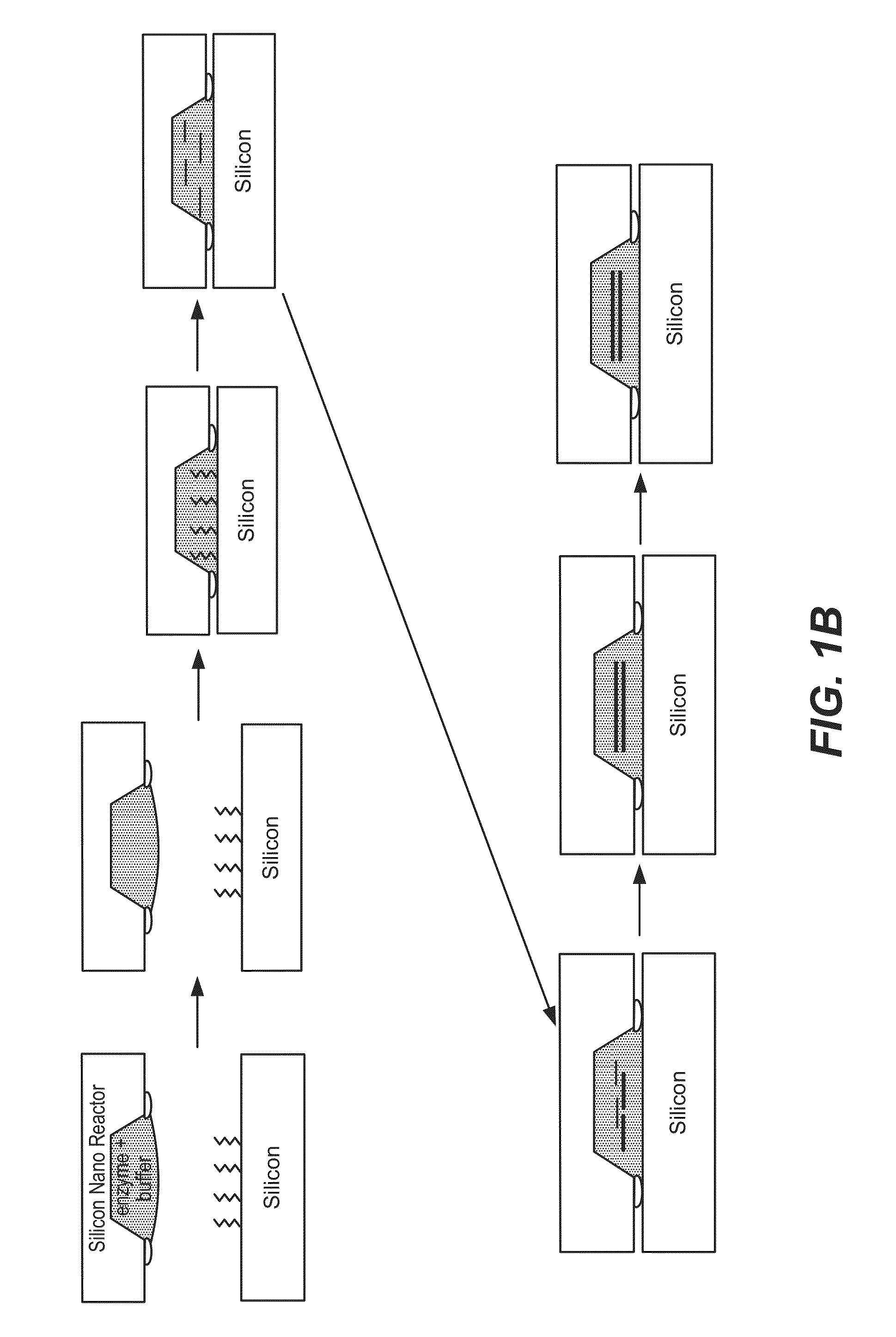
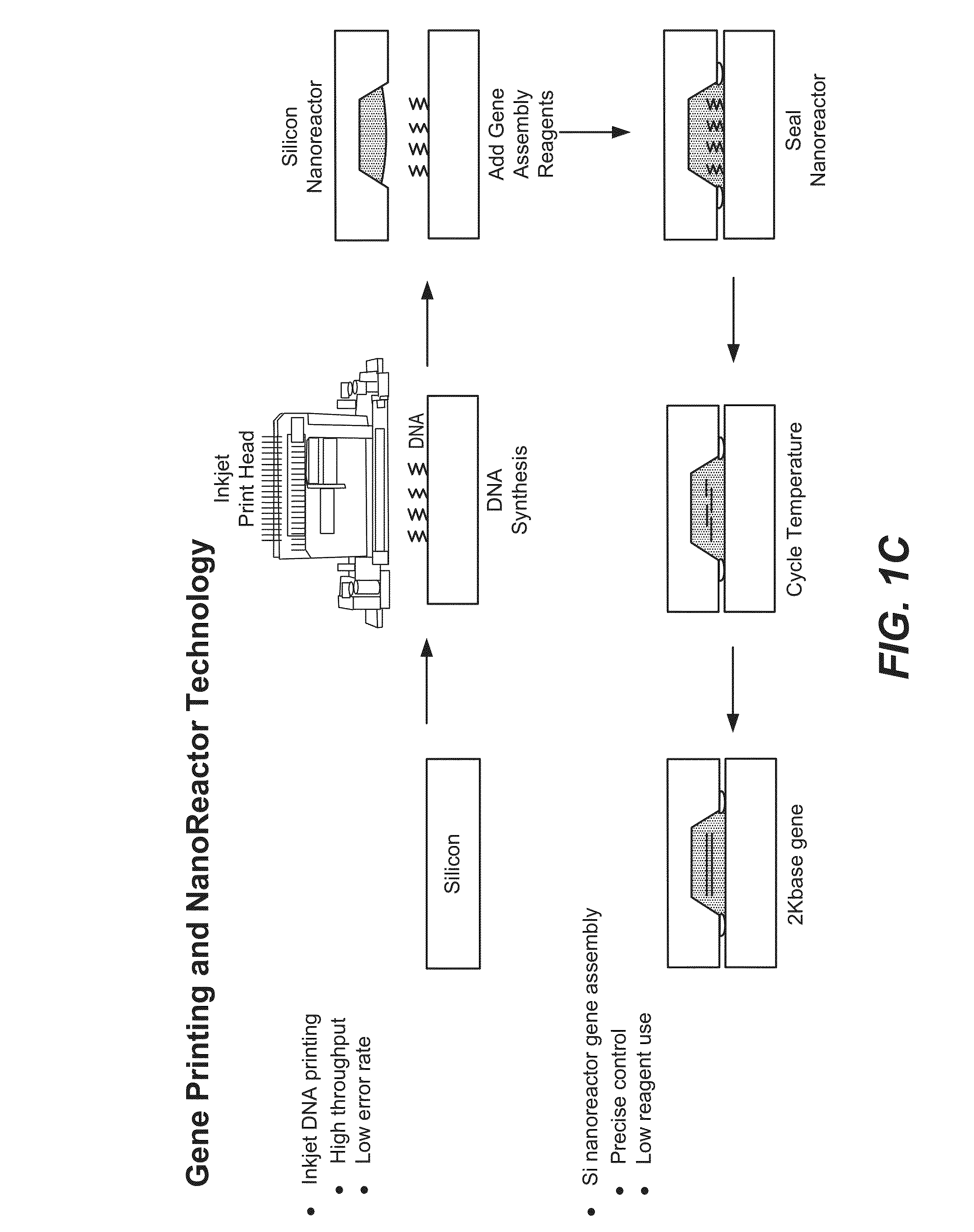
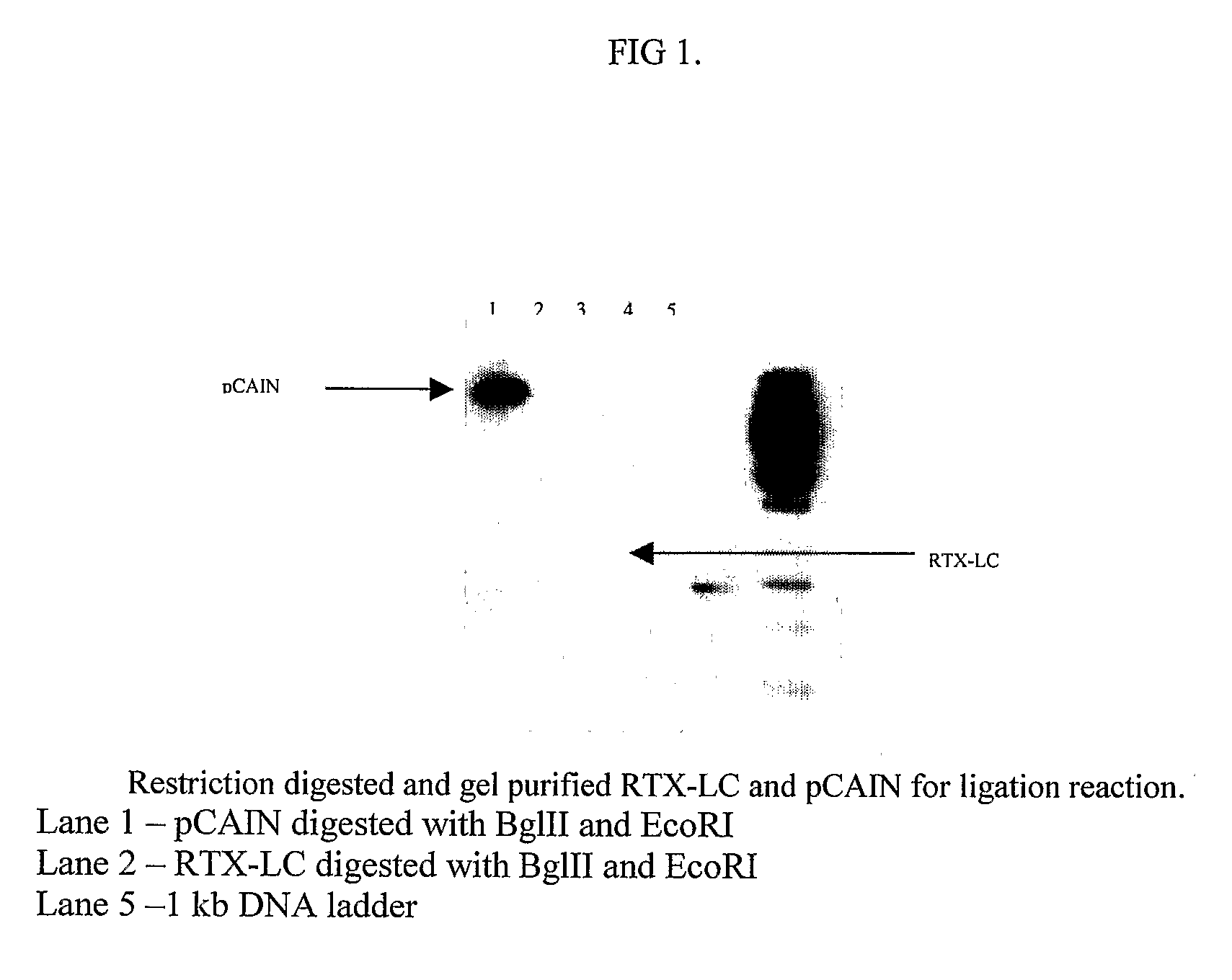
Devices and methods for oligonucleic acid library synthesis
ActiveUS20160310927A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMain channelCombinatorial chemistry
Devices and methods for de novo synthesis of large and highly accurate libraries of oligonucleic acids are provided herein. Devices include structures having a main channel and microchannels, where the microchannels have a high surface area to volume ratio. Devices disclosed herein provide for de novo synthesis of oligonucleic acids having a low error rate.
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
De novo synthesized gene libraries
ActiveUS20160089651A1Less errorHigh surface energySequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic libraryDe novo synthesis
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
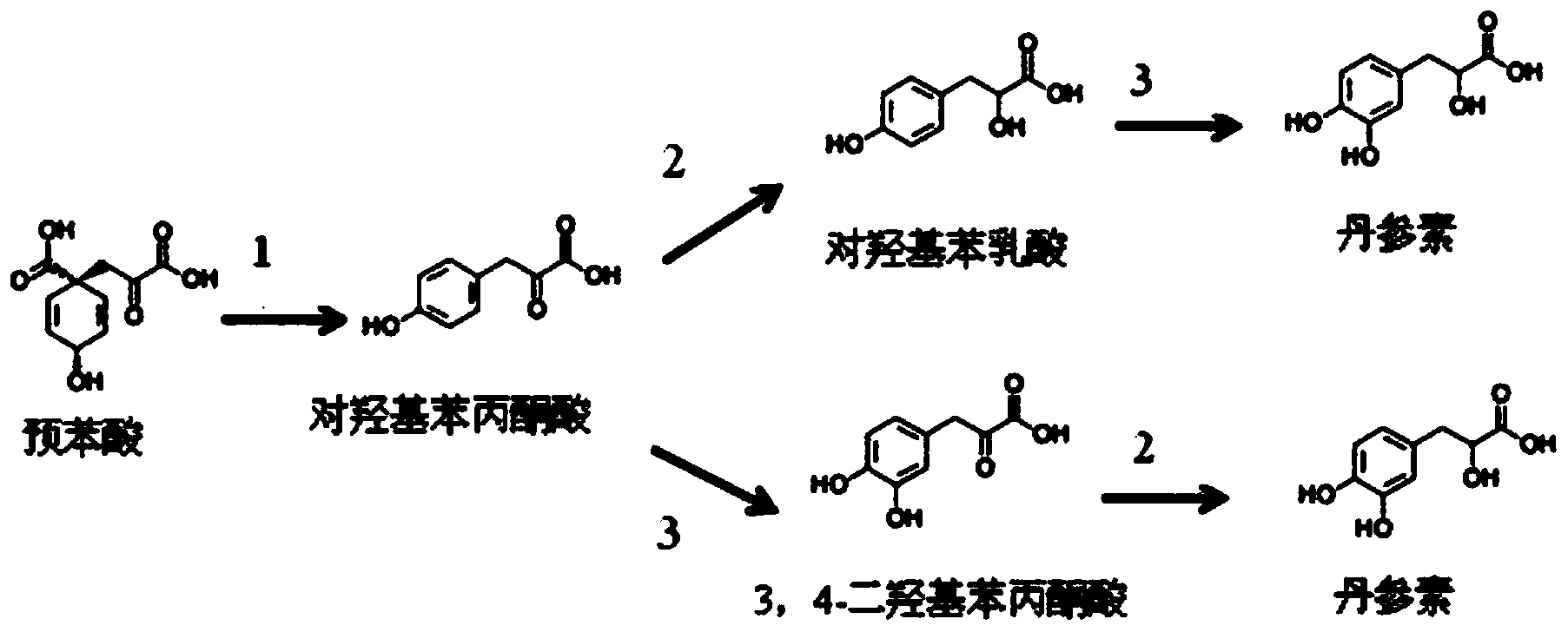
Biological production method of tanshinol
ActiveCN103667371ADe novo synthesisResolve source issuesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSalvia miltiorrhizaEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a biological production method of tanshinol, which comprises the following steps: synthesizing p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid into 3,4-dihydroxyphenylpyruvic acid under the catalytic action of a p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid meta-position hydroxylation enzyme, and then, synthesizing to obtain the tanshinol under the catalytic action of a D-lactate dehydrogenase; or synthesizing p-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid into p-hydroxyphenyllactic acid under the catalytic action of a D-lactate dehydrogenase, and then, synthesizing to obtain the tanshinol under the catalytic action of a p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid meta-position hydroxylation enzyme. According to the invention, gene engineering glutamic acid corynebacteria and Escherichia coli are used to produce the tanshinol through fermentation, and the tanshinol can be synthesized without adding a substrate, thereby realizing de novo synthesis of the tanshinol and solving the problem on the source of the tanshinol; and meanwhile, the production cost is lowered to the greatest extent. Thus, the biological production method is beneficial to industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Devices and methods for oligonucleic acid library synthesis
ActiveUS9981239B2Sequential/parallel process reactionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMain channelCombinatorial chemistry
Devices and methods for de novo synthesis of large and highly accurate libraries of oligonucleic acids are provided herein. Devices include structures having a main channel and microchannels, where the microchannels have a high surface area to volume ratio. Devices disclosed herein provide for de novo synthesis of oligonucleic acids having a low error rate.
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
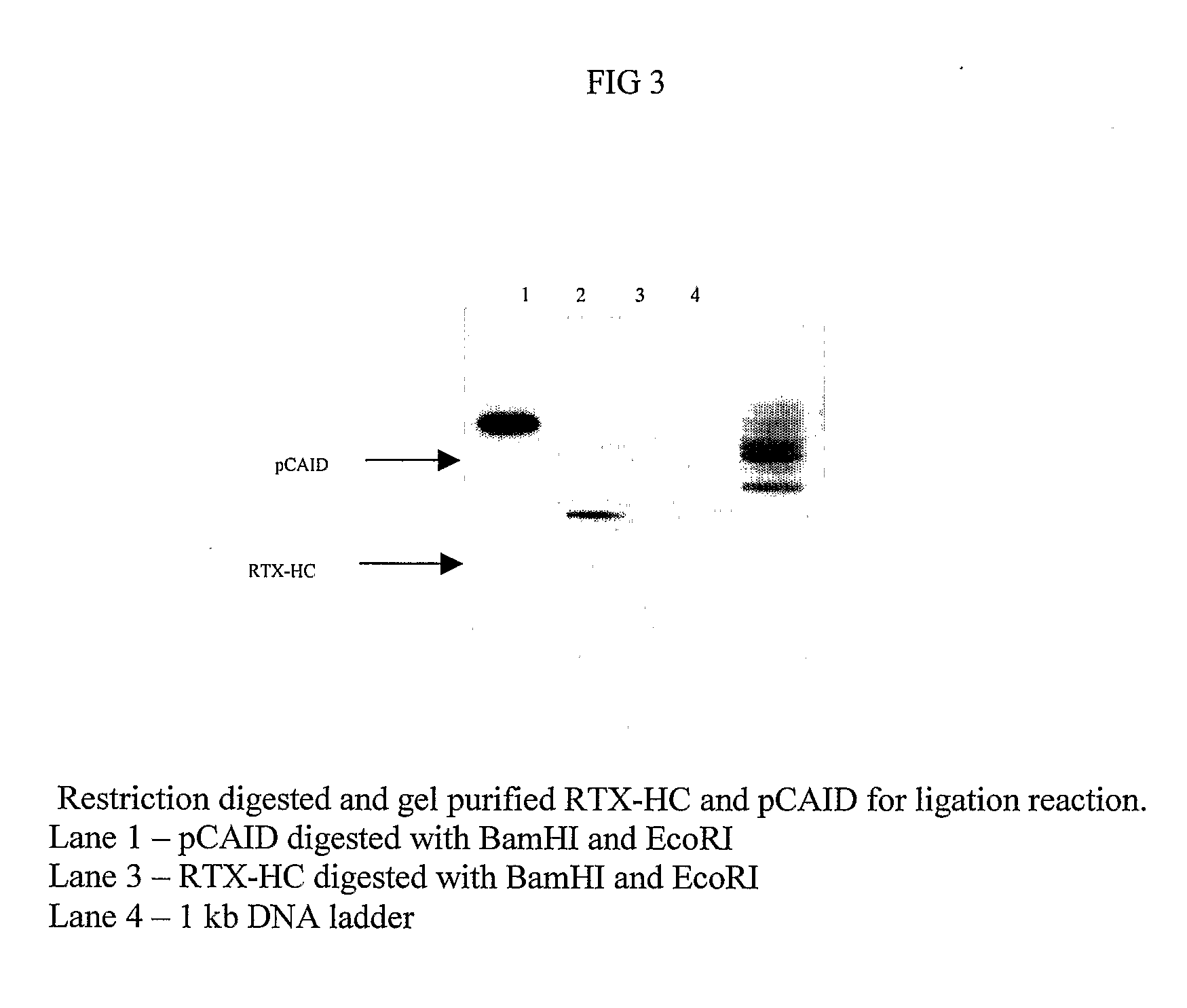
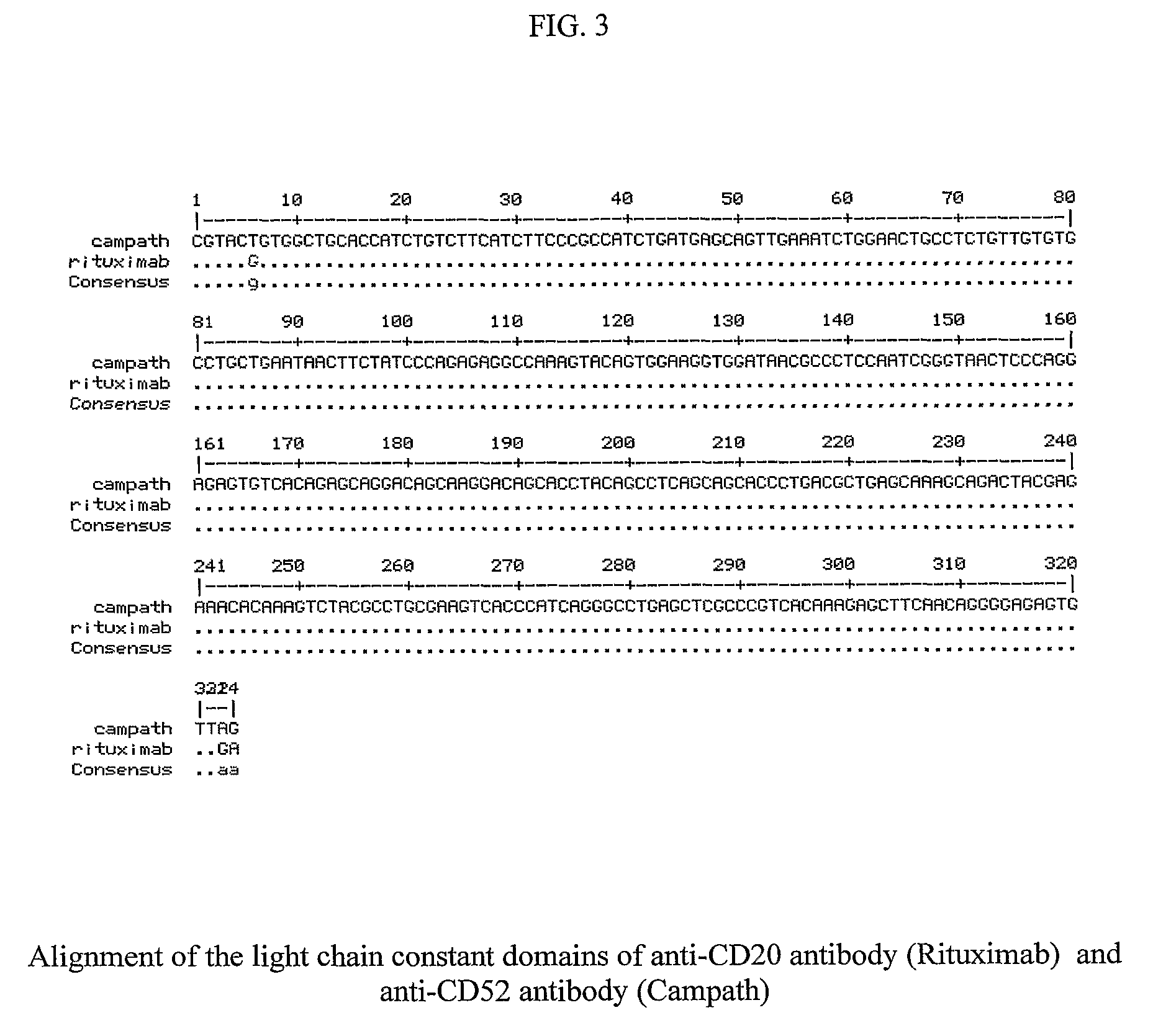
Method for the Production of a Monoclonal Antibody to CD20 for the Treatment of B-Cell Lymphoma
InactiveUS20090285795A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDNA constructMammalian expression
The present invention relates to the recombinant method used for the production of soluble form of an antibody that binds to CD20 for treatment of patients with relapsed or refractory, low-grade or follicular, CD20-positive, B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL). The treatment will comprise the use of immunologically active anti-CD20 antibodies; or radiolabeled anti-CD20 antibodies and or cooperative strategies where both labeled and non-labeled antibodies will be used for treatment of NHL. The procedure describes the de novo synthesis of the nucleic acid sequence encoding anti-CD20, transformation of the constructed nucleic acid sequences into competent bacteria and the sub-cloning of the same into mammalian expression vectors for expression of the desired protein. DNA constructs comprising the control elements associated with the gene of interest has been disclosed. The nucleic acid sequence of interest has been codon optimized to permit expression in the suitable mammalian host cells.
Owner:AVESTHAGEN
De novo synthesized combinatorial nucleic acid libraries
Disclosed herein are methods for the generation of highly accurate nucleic acid libraries encoding for predetermined variants of a nucleic acid sequence. The degree of variation may be complete, resulting in a saturated variant library, or less than complete, resulting in a non-saturating library of variants. The variant nucleic acid libraries described herein may be designed for further processing by transcription or translation. The variant nucleic acid libraries described herein may be designed to generate variant RNA, DNA and / or protein populations. Further provided herein are method for identifying variant species with increased or decreased activities, with applications in regulating biological functions and the design of therapeutics for treatment or reduction of disease.
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
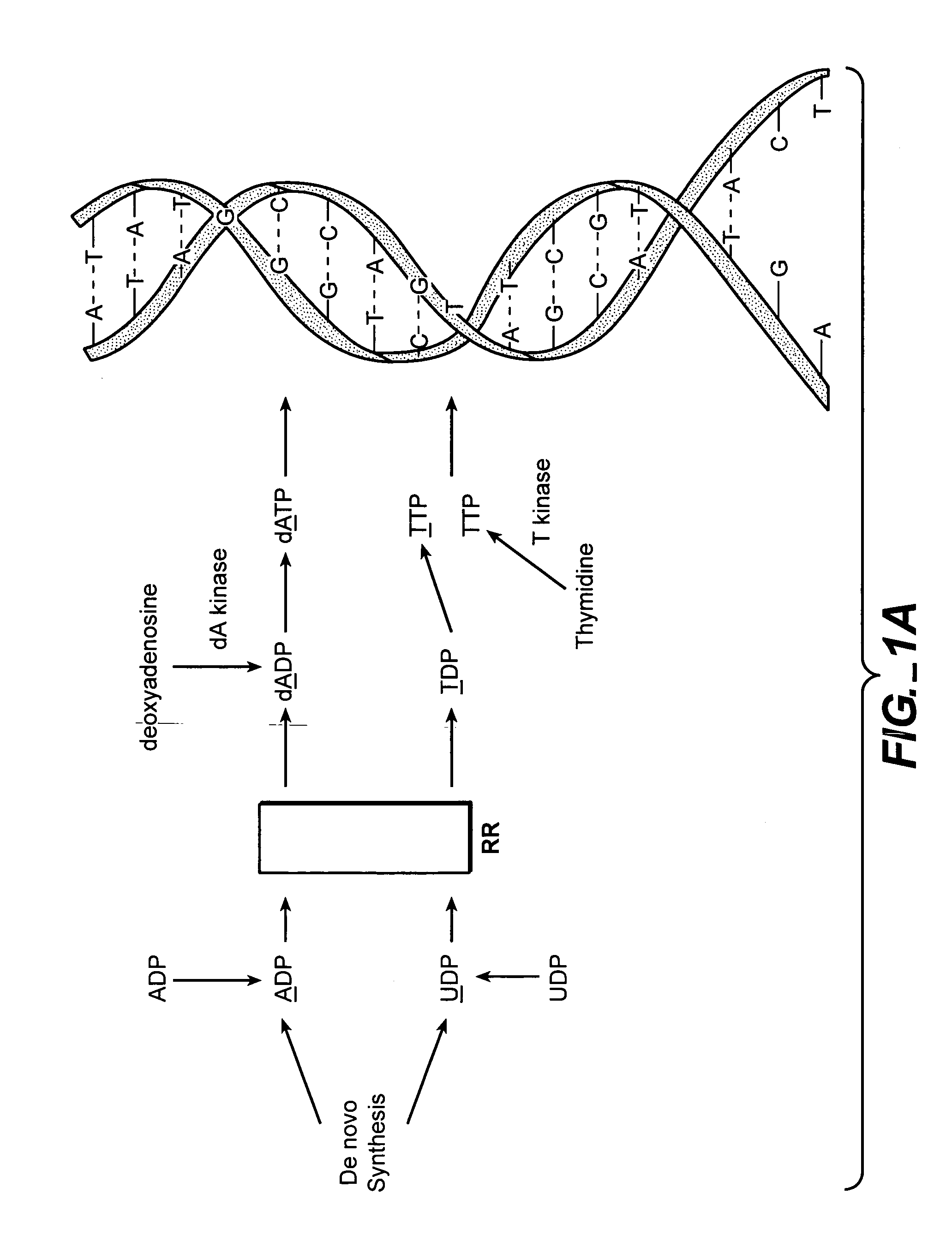
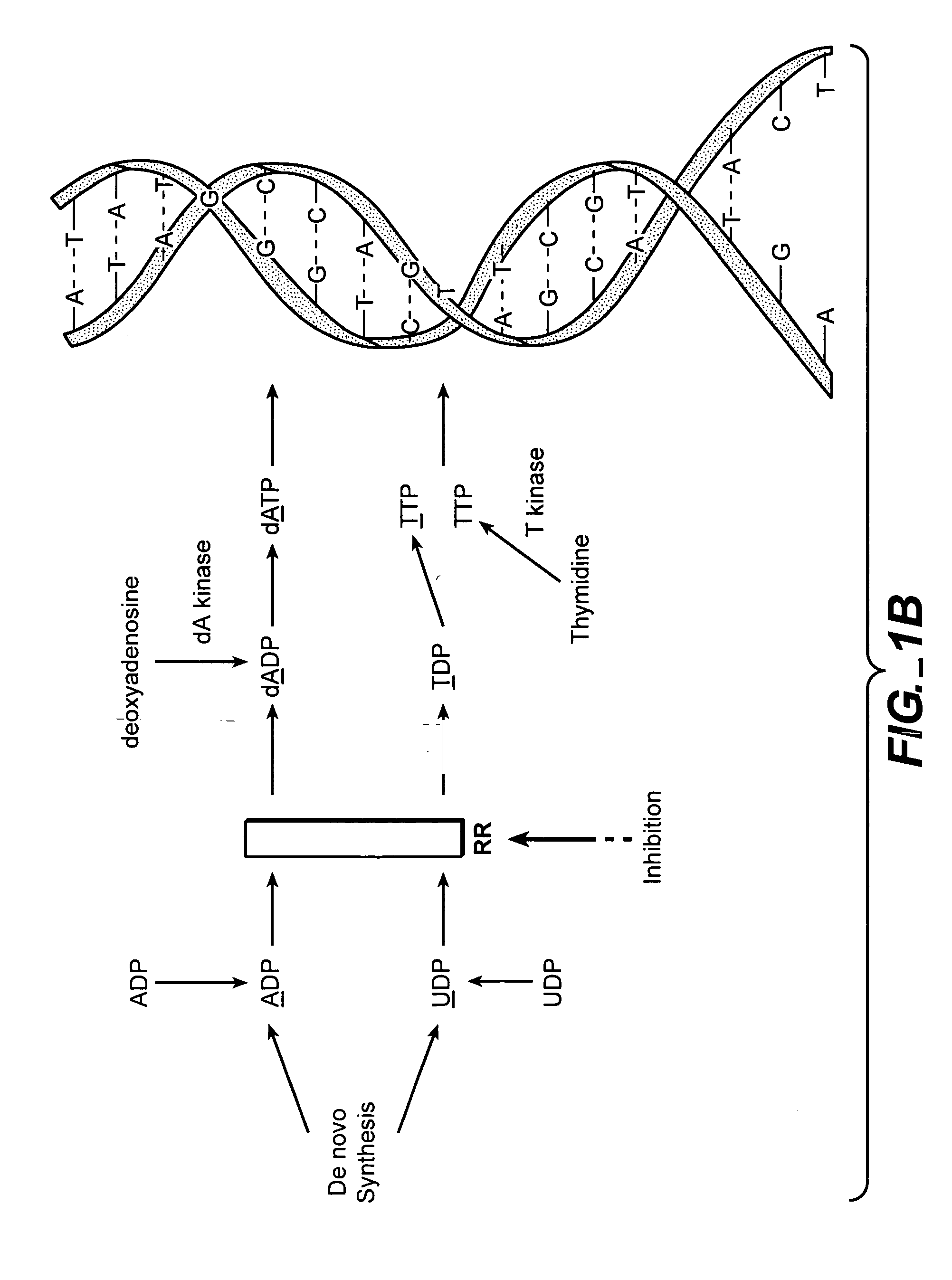
In vivo measurement of the relative fluxes through ribonucleotide reductase vs. deoxyribonucleoside pathways using isotopes
InactiveUS20050255509A1Increase salvageHigh activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionRate-determining stepDeoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis
The methods of the present invention allow for the measurement of ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity, an important enzyme in the de novo DNA synthesis pathway. Ribonucleotide reductase converts all four ribonucleotides to their deoxy form and is a rate-controlling step in this pathway. Biosynthetic pathways of deoxyribonucleotides (dN) have received considerable attention in the context of anti-proliferative chemotherapy. Inhibitors of various steps in dN biosynthesis, including inhibitors of RR are among the most useful chemotherapeutic agents in cancer, viral infections, and other therapeutic uses. DNA synthesis from the dN salvage pathway is also an important component to DNA replication. The relative contributions from RR vs. salvage pathways are critical to the actions and effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents that act on nucleoside metabolic pathways. Until now, however, it has not been possible to study these metabolic processes in vivo. Disclosed within are methods of measuring RR activity in vivo and in vitro which find use, among other things, in drug discovery, development, and approval.
Owner:KINEMED
De novo synthesis of bacteriochlorins
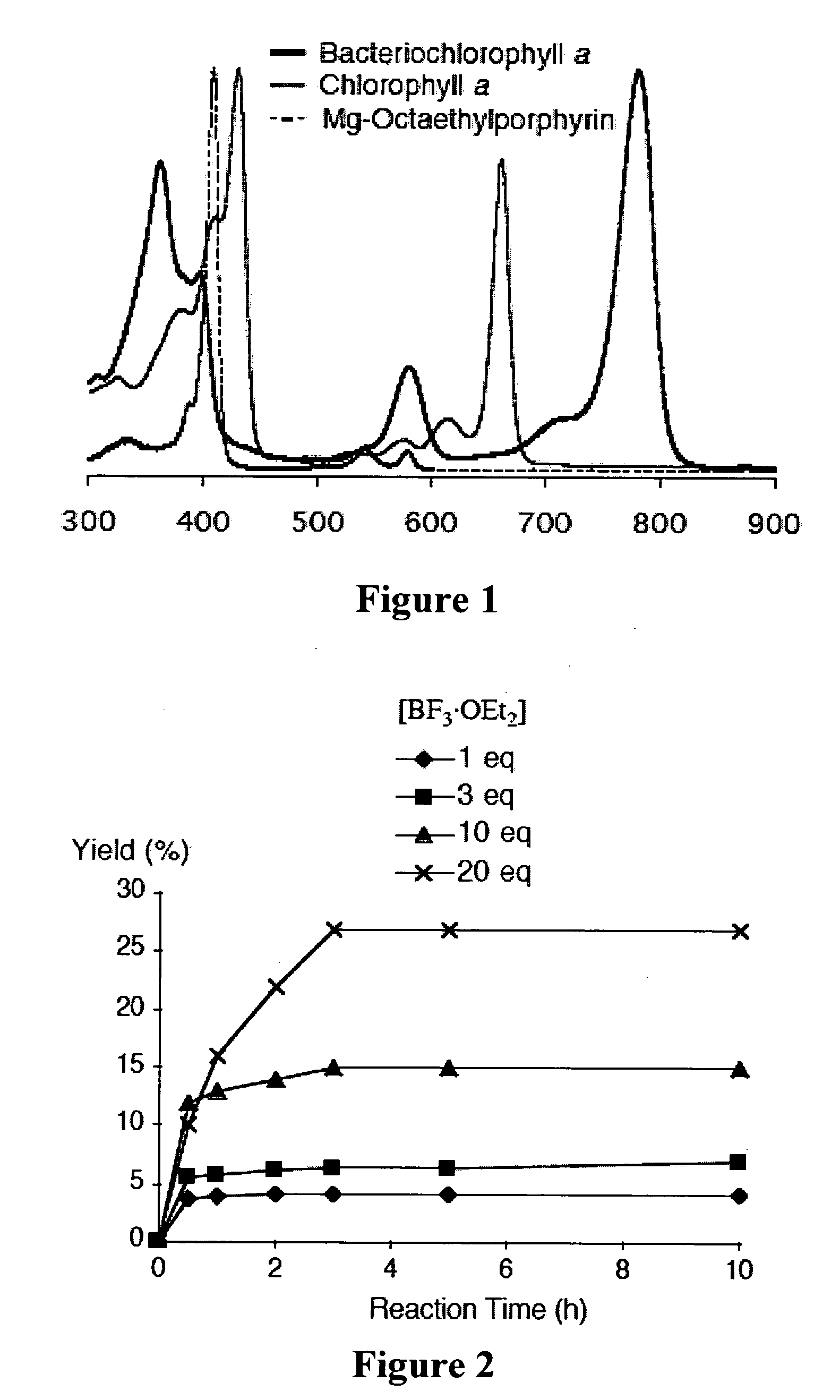
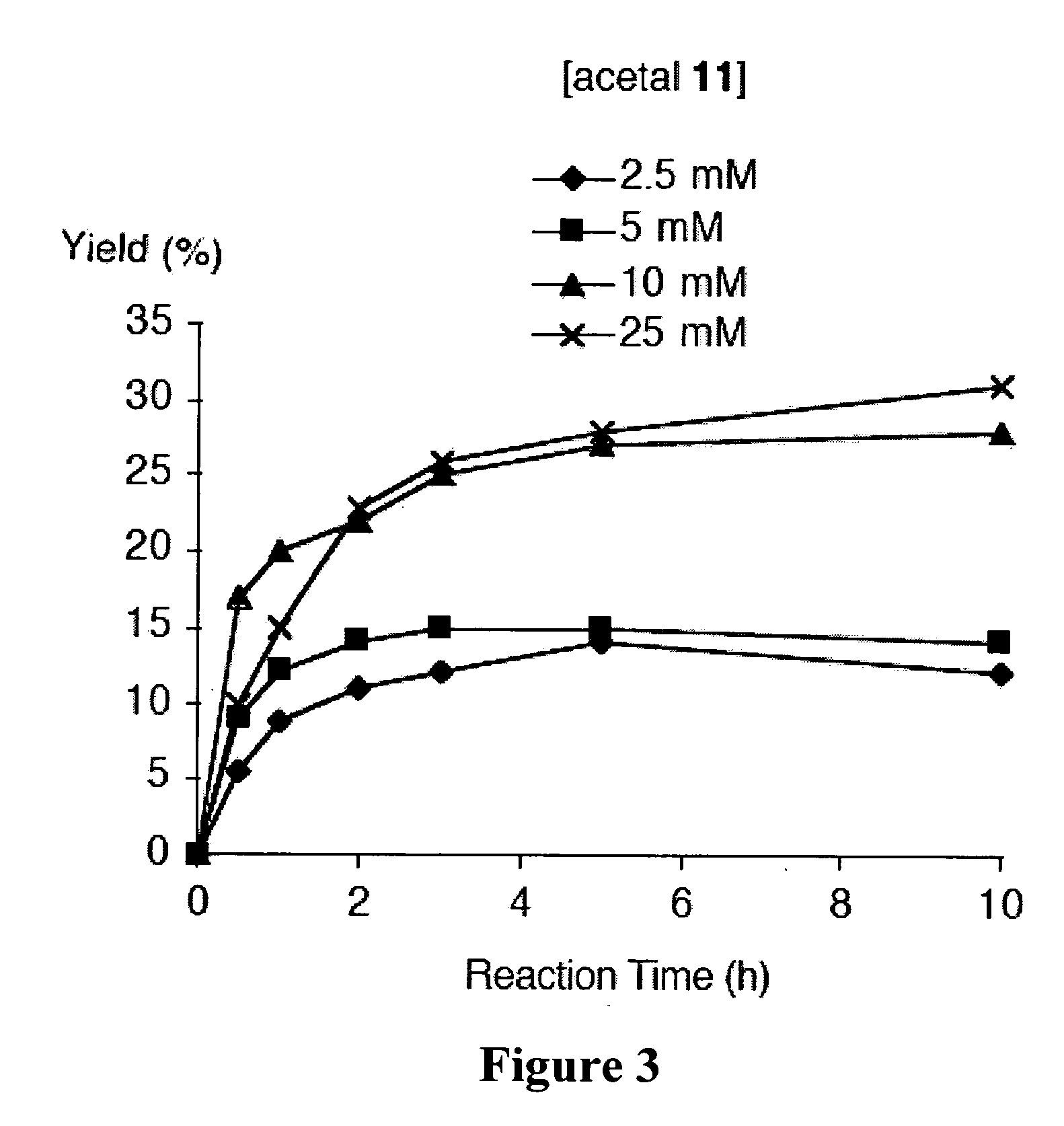
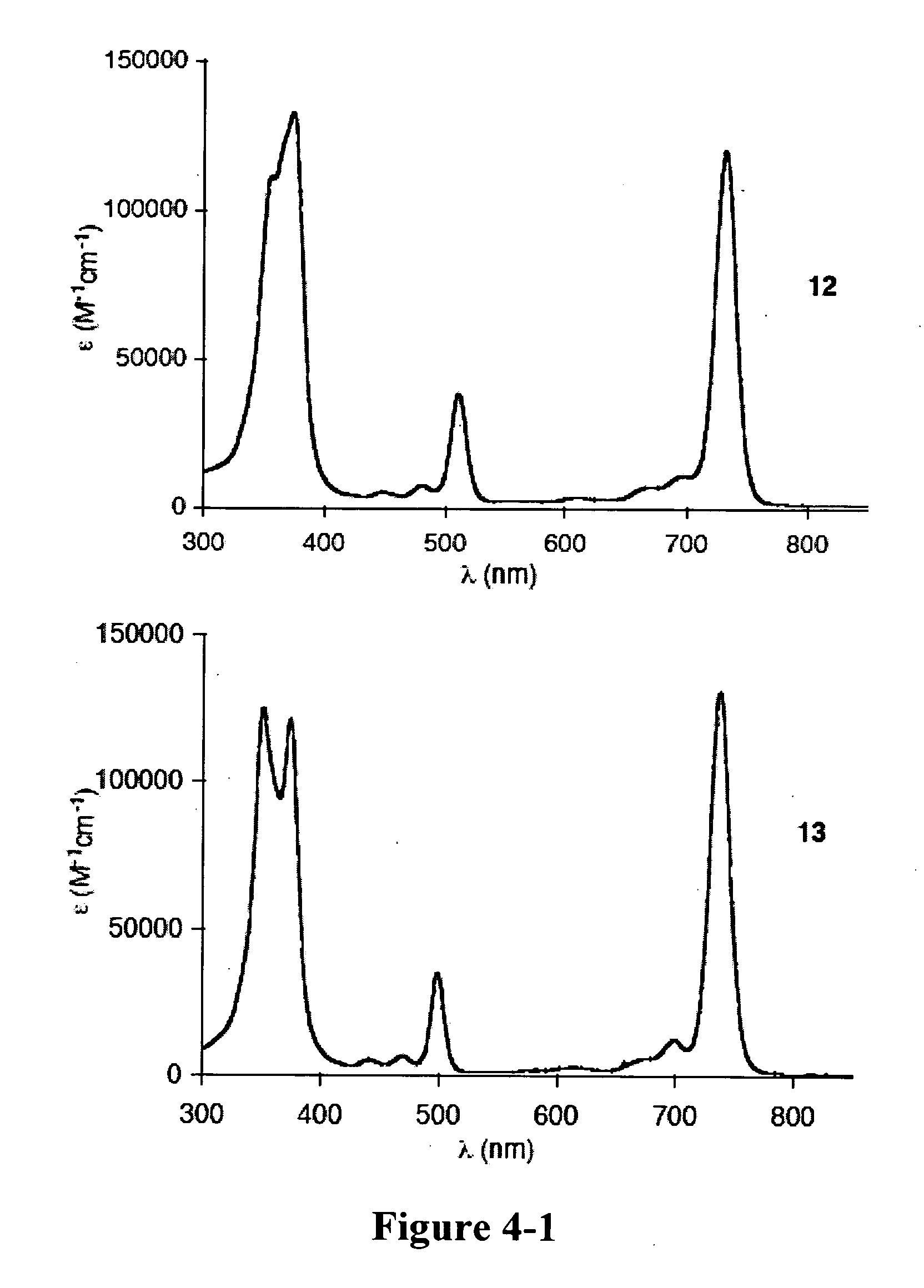
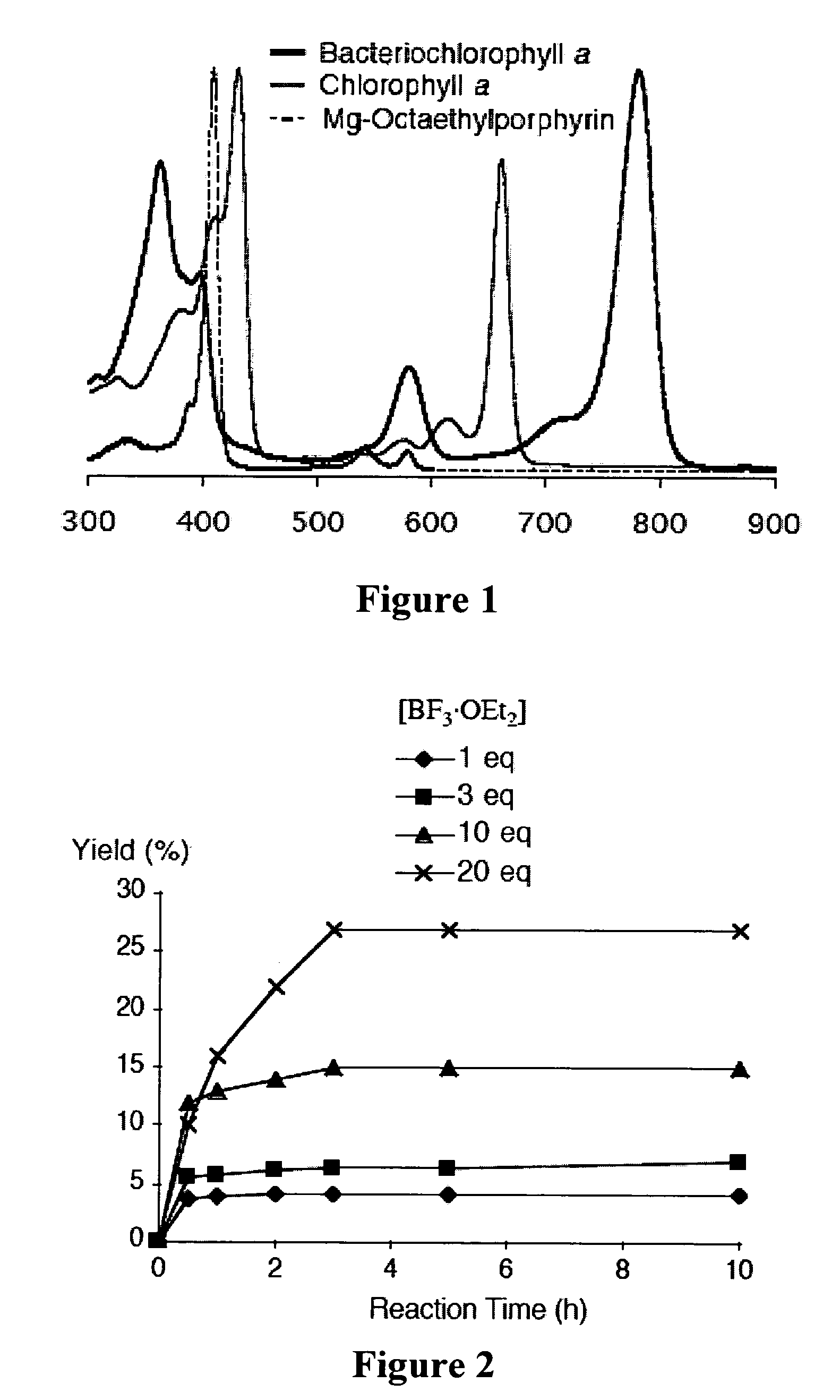
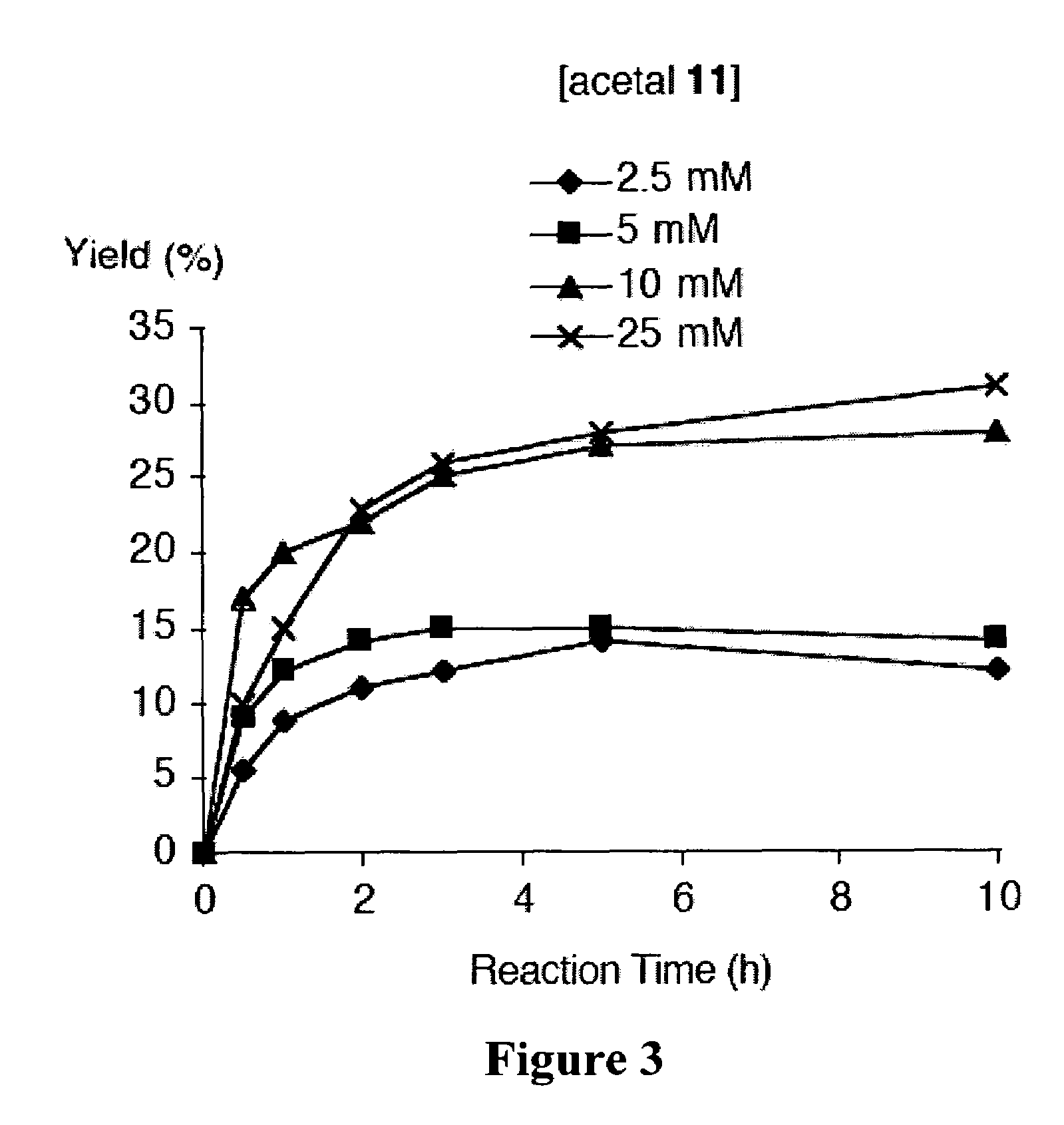
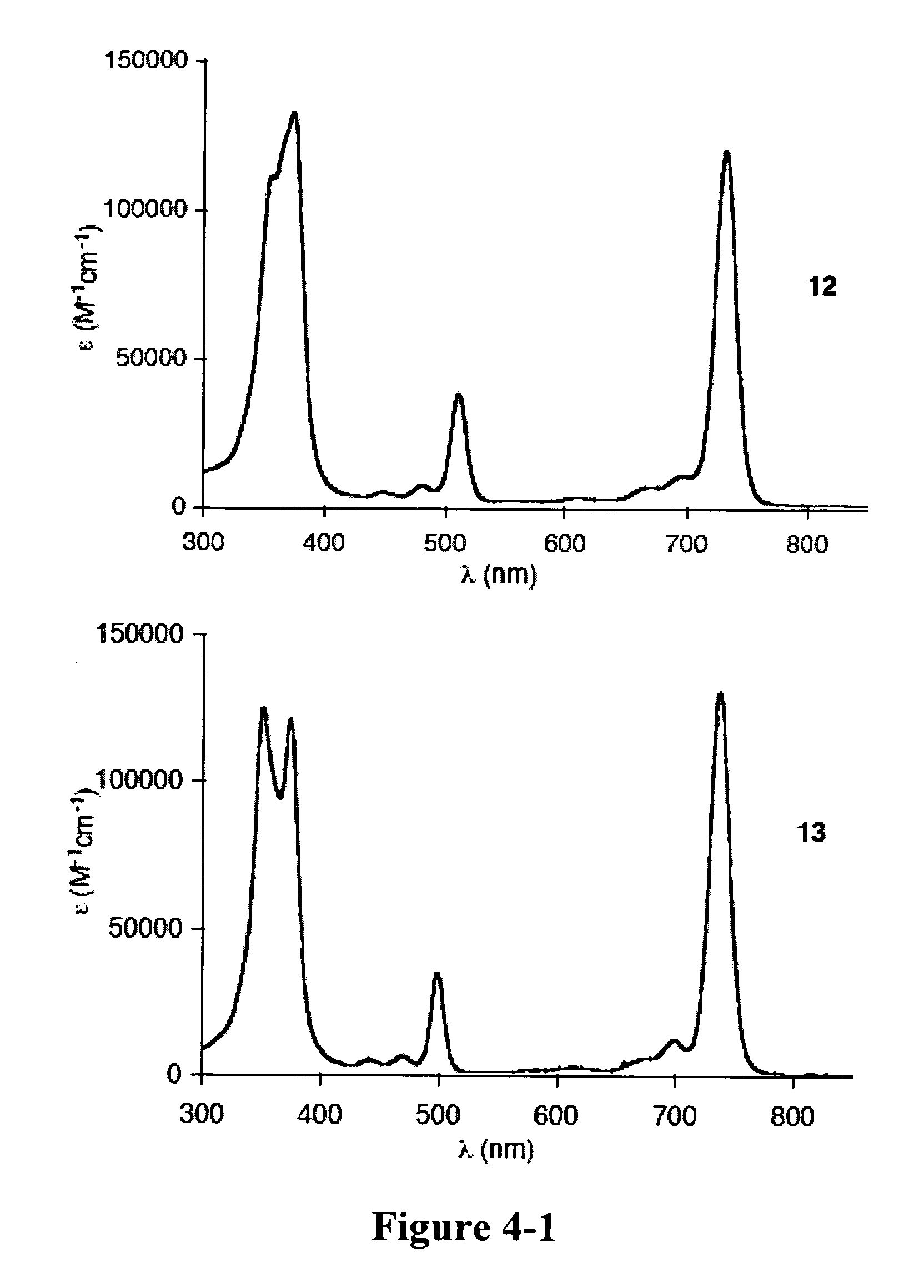
A method of making a bacteriochlorin is carried out by condensing a pair of compounds of Formula II to produce the bacteriochlorin, wherein R is an acetal or aldehyde group. The condensing may be carried out in an organic solvent, preferably in the presence of an acid. The bacteriochlorins are useful for a variety of purposes such as active agents in photodynamic therapy, luminescent compounds in flow cytometry, solar cells, light harvesting arrays, and molecular memory devices.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Screening systems utilizing RTP801
InactiveUS20070281326A1Useful in treatmentCompound screeningApoptosis detectionGene targetsUnique gene
RTP801 represents a unique gene target for hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Down-regulation of the mTOR pathway activity by hypoxia requires de novo mRNA synthesis and correlates with increased expression of RTP801. The present invention relates to screening systems utilizing RTP801 and / or RTP801 interactors and / or RTP801 biological activity, to drug candidates identified by such screening systems, and to the use of such drug candidates in the treatment of various disorders.
Owner:QUARK FARMACUITIKALS INC
Methods and devices for de novo oligonucleic acid assembly
ActiveUS10669304B2Sequential/parallel process reactionsSugar derivativesOrganic chemistryDe novo synthesis
Methods and devices are provided herein for surfaces for de novo nucleic acid synthesis which provide for low error rates. In addition, methods and devices are provided herein for increased nucleic acid mass yield resulting from de novo nucleic acid synthesis.
Owner:TWIST BIOSCI
Epidithiodioxopiprazines and uses thereof in treating cancer
InactiveUS20120219568A1Good effectGood curative effectHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic chemistryNatural resourceCancer cell
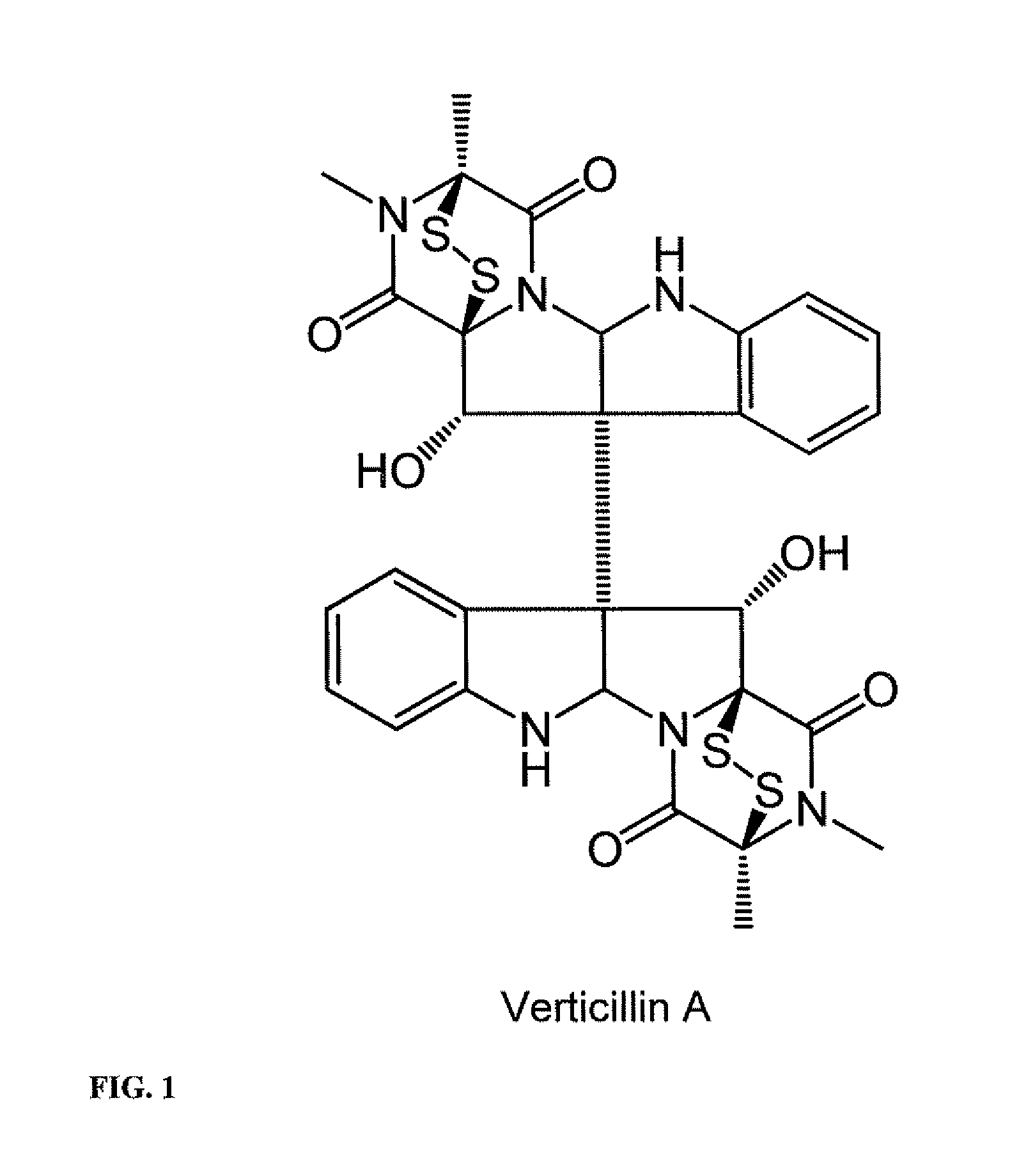
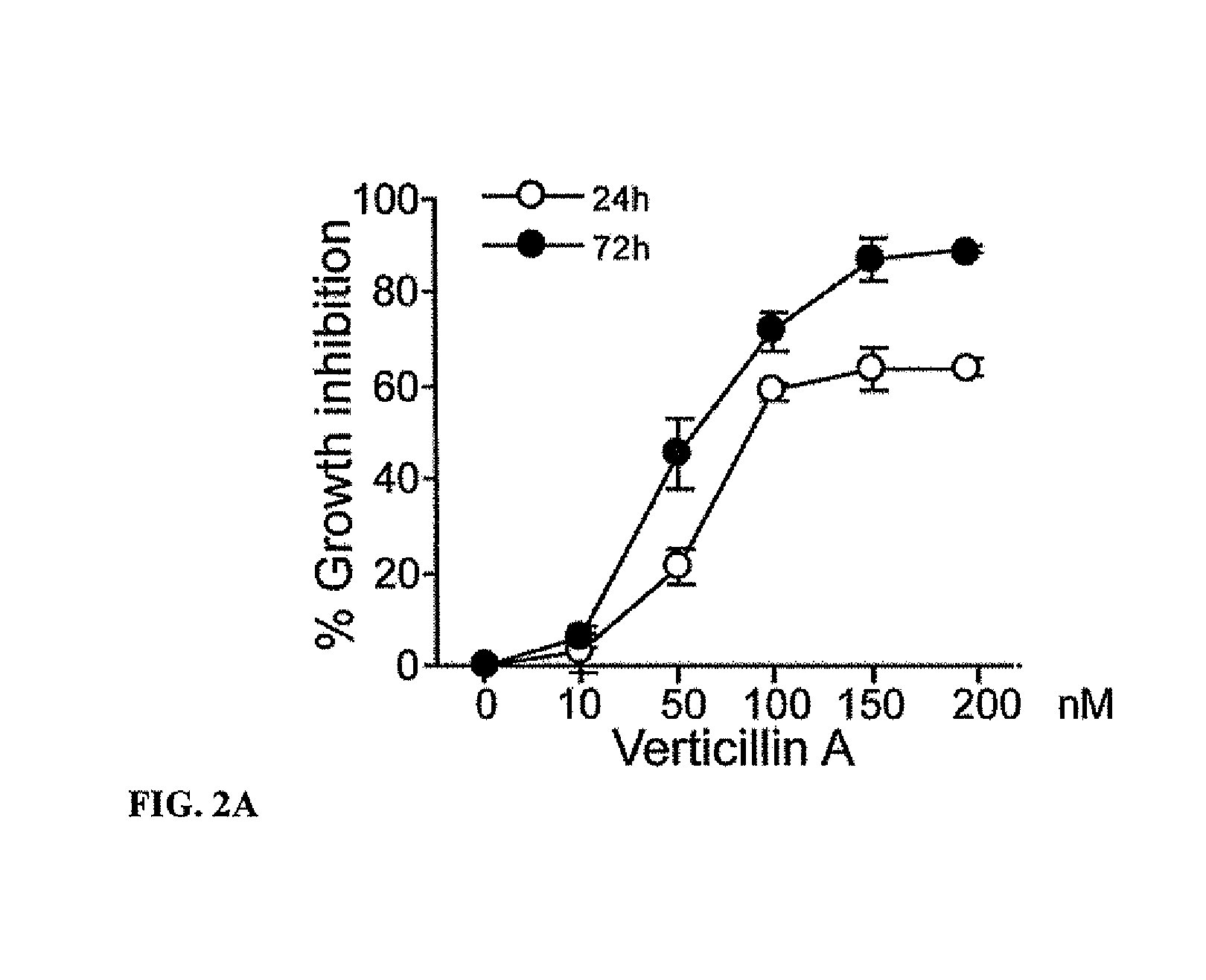
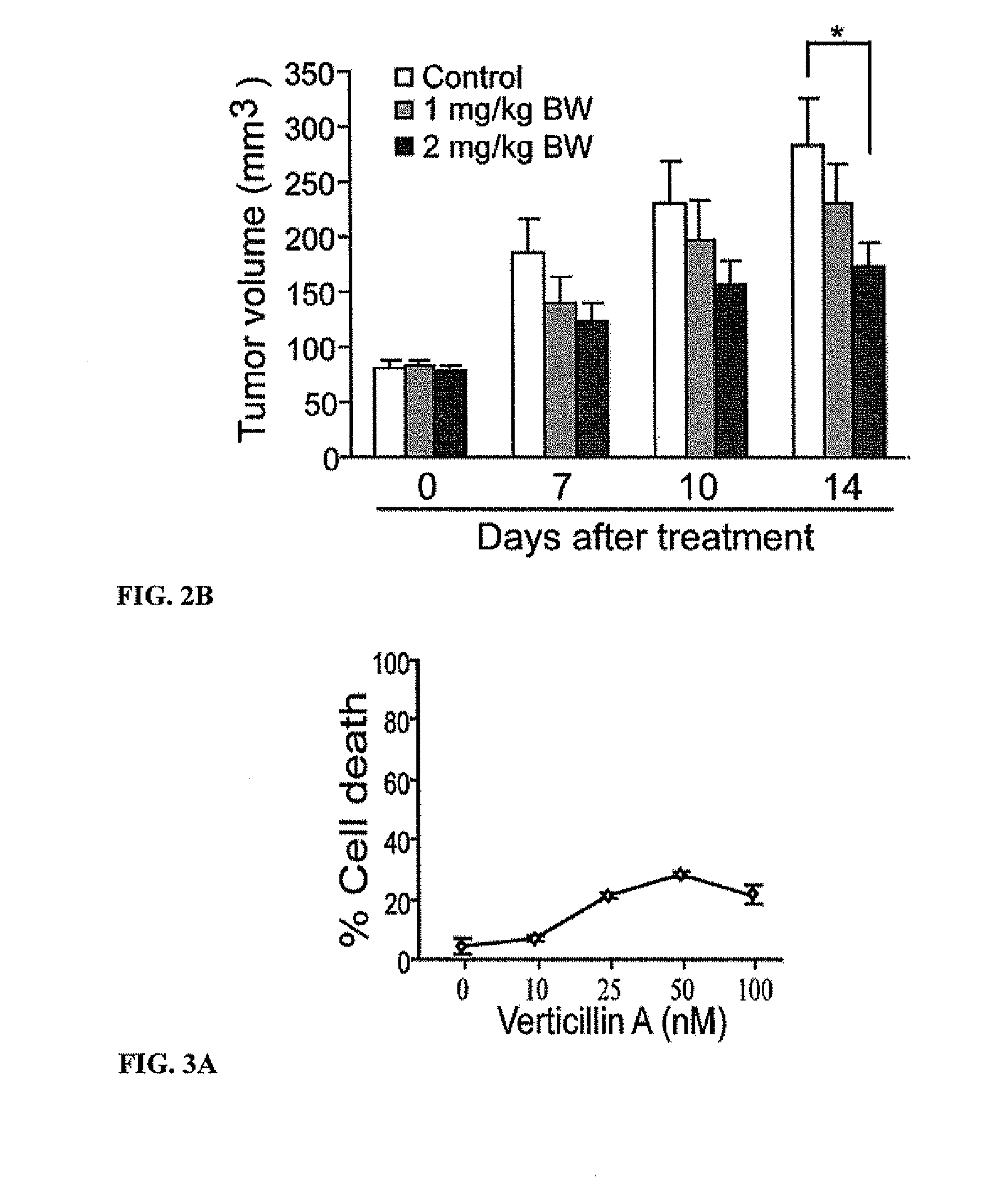
Compositions containing epidithiodioxopiprazines and methods of their use are provided. Epidithiodioxopiprazines can be isolated from natural resources or synthesized de novo. Moreover, epidithiodioxopiprazines, including Verticillin A, are shown to effectively sensitize multiple types of tumor cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. In addition, epidithiodioxopiprazines, including Verticillin A, are shown to effectively overcome cancer cell resistance to existing drugs (i.e. Etoposide, Cisplatin, 5-FU and Doxorubicin). Therefore, compositions and methods are provided for use in sensitizing target cancer cells to death receptor- and other anticancer drugs-induced apoptosis. Methods of treating cancer in a subject in need thereof are also provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Biological method for producing resveratrol
InactiveCN102605006ADe novo synthesisResolve source issuesBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPhenylalanine hydroxylase
The invention discloses a biological method for producing resveratrol, which comprises the following steps: ligating target genes obtained by restriction enzyme digestion to an expression vector, wherein the target genes include the sequences of phenylalanine hydroxylase (PAH), tyrosine ammonia lyase (TAL) 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase (4CL) and resveratrol synthase (RS); transforming the constructed expression vector into a strain to obtain a recombinant engineered strain; and fermenting the recombined engineered strain. Compared with the prior art, the technical scheme provided by the invention uses the genetically engineered strain for fermentation to produce resveratrol, so as to realize denovo synthesis of resveratrol with no need of adding substrates. The method disclosed by the invention solves the source problem of resveratrol, and at the same time, reduces the production cost in a maximum extent, and is beneficial for industrial production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
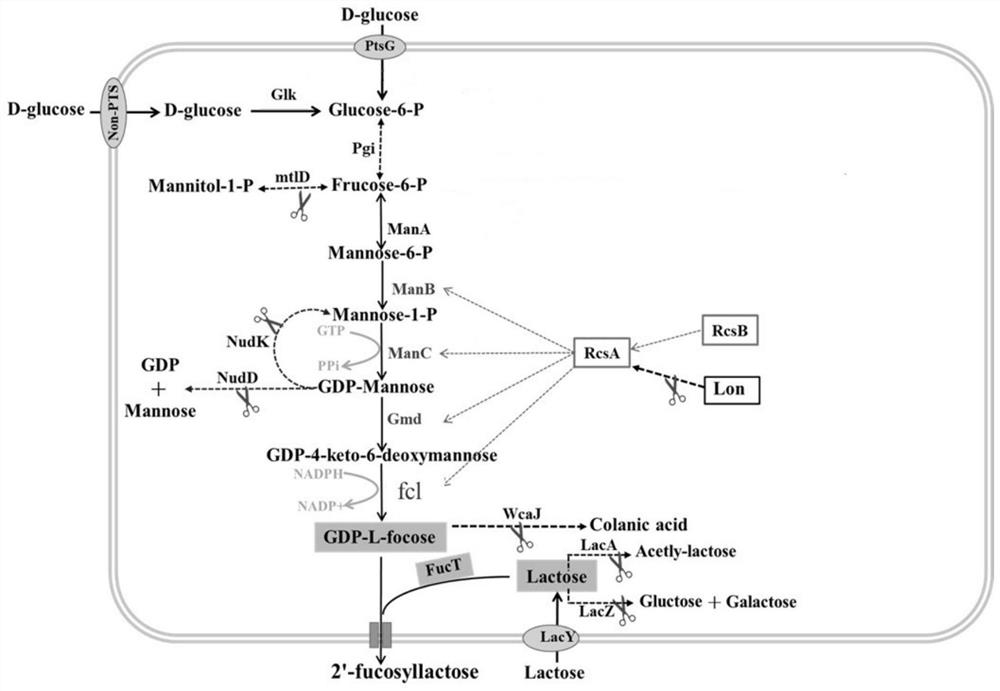
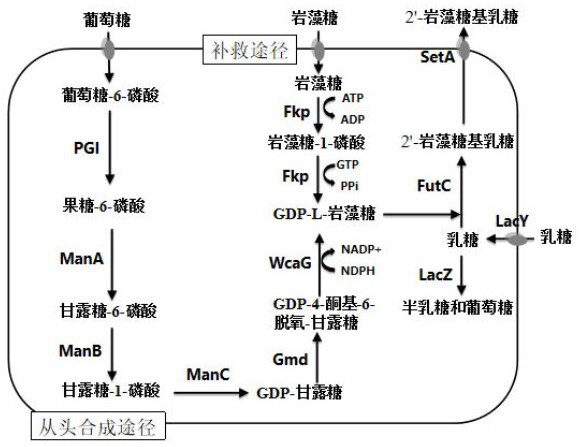
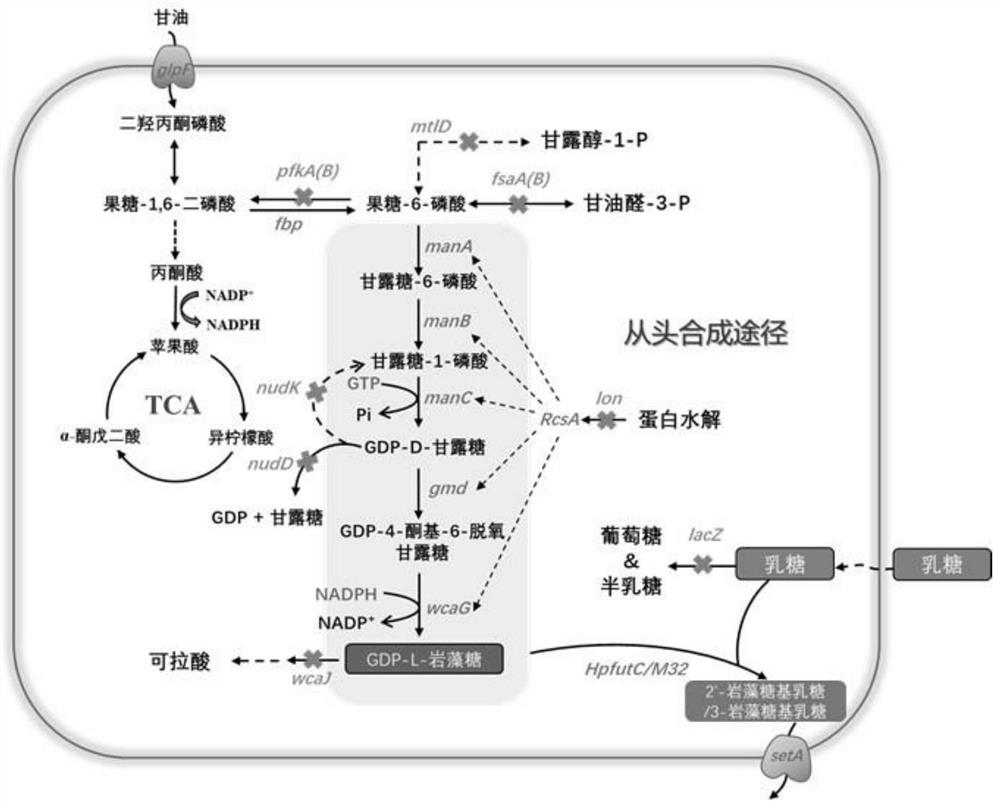
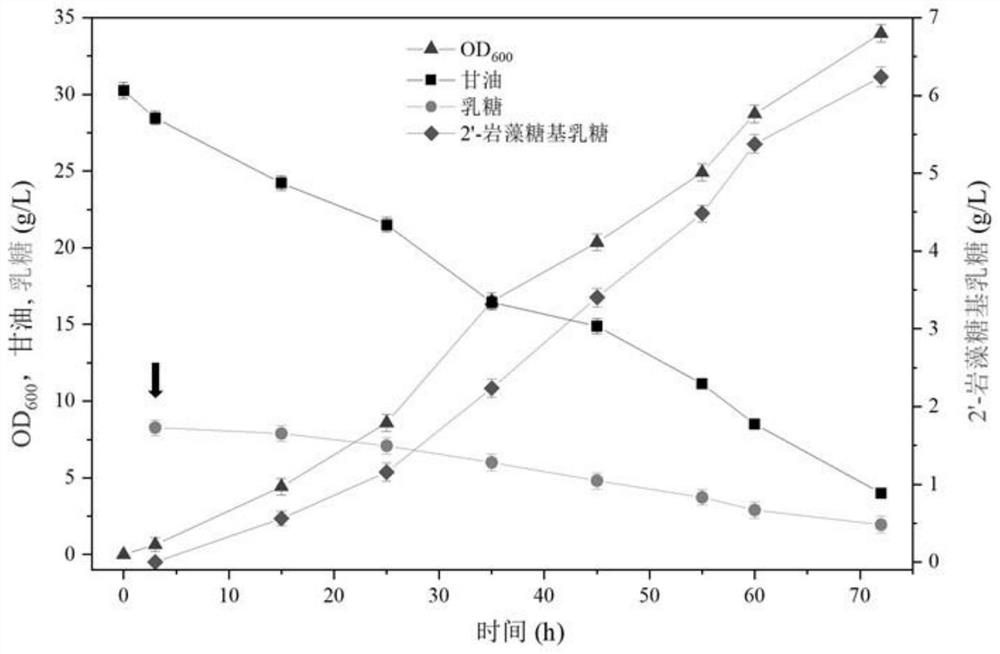
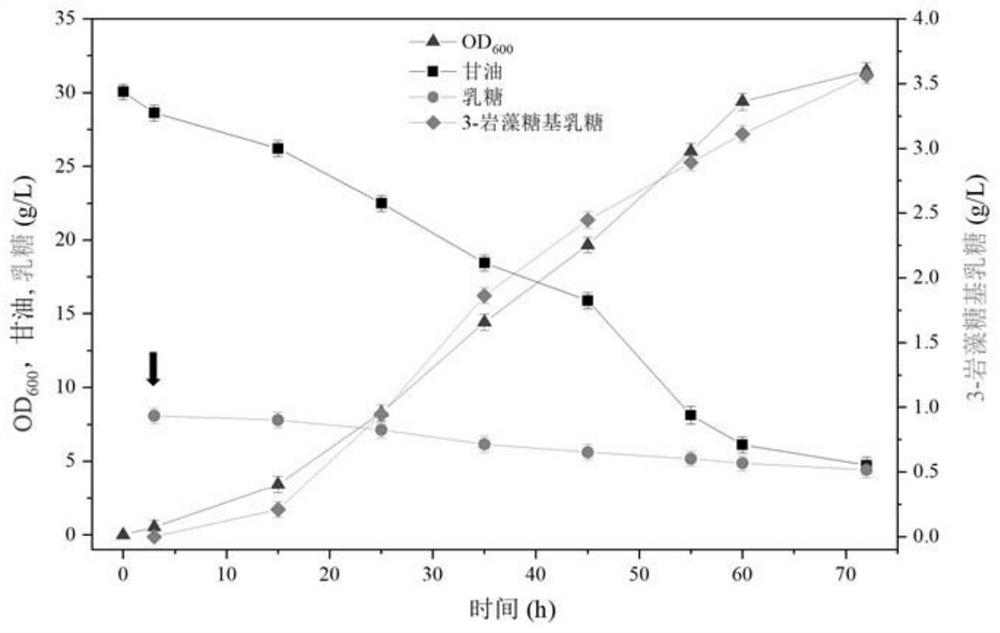
Recombinant expression plasmid vector for producing fucose-based lactose, metabolic engineering bacteria, and production method
The invention relates to a recombinant expression plasmid vector for producing fucose-based lactose, metabolic engineering bacteria, and a production method and belongs to the fields of metabolic engineering, food fermentation and the like. In the invention, genes for encoding GDP-mannose-6-dehydrogenase, GDP-fucose synthetase, lactose permease, and alpha-1,2-fucose transferase or alpha-1,3-fucosetransferase, which are required in a de-novo synthesis route of the fucose-based lactose, are expressed in corynebacterium glutamicum, so that recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum is constructed toachieve synthesis of 2'-fucose-based lactose or 3'-fucose-based lactose. In addition, by over-expression of the genes for encoding phosphomannose isomerase, phosphomannose mutase, and mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase in the corynebacterium glutamicum, high yield of the fucose-based lactose is achieved. According to the method, the engineering bacteria can synthesize the fucose-based lactose by means of glucose or glycerol, has advantages of high growth speed and good safety, and has significant industrial potential.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Escherichia coli and application thereof to synthesis of fucosylated oligosaccharide
ActiveCN111808790AReduce lossesIncreased synthesis throughputBacteriaStable introduction of DNAEscherichia coliFucosylation
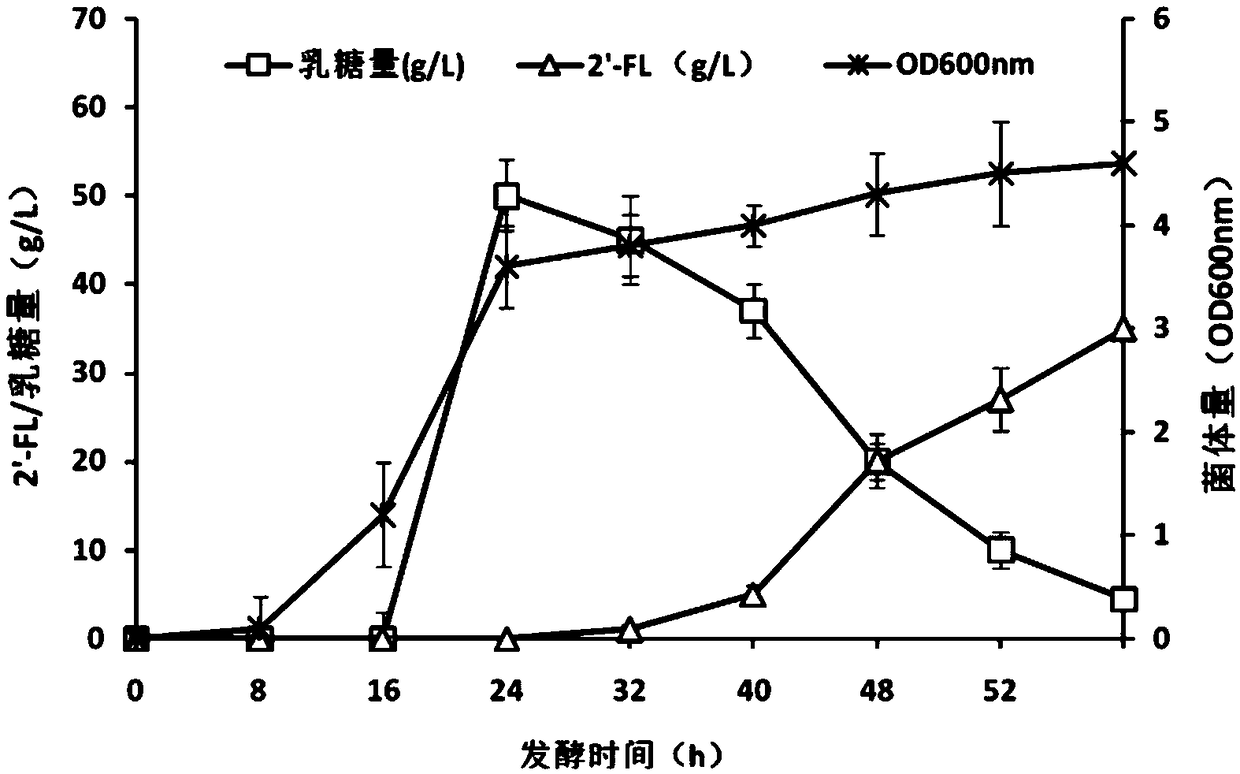
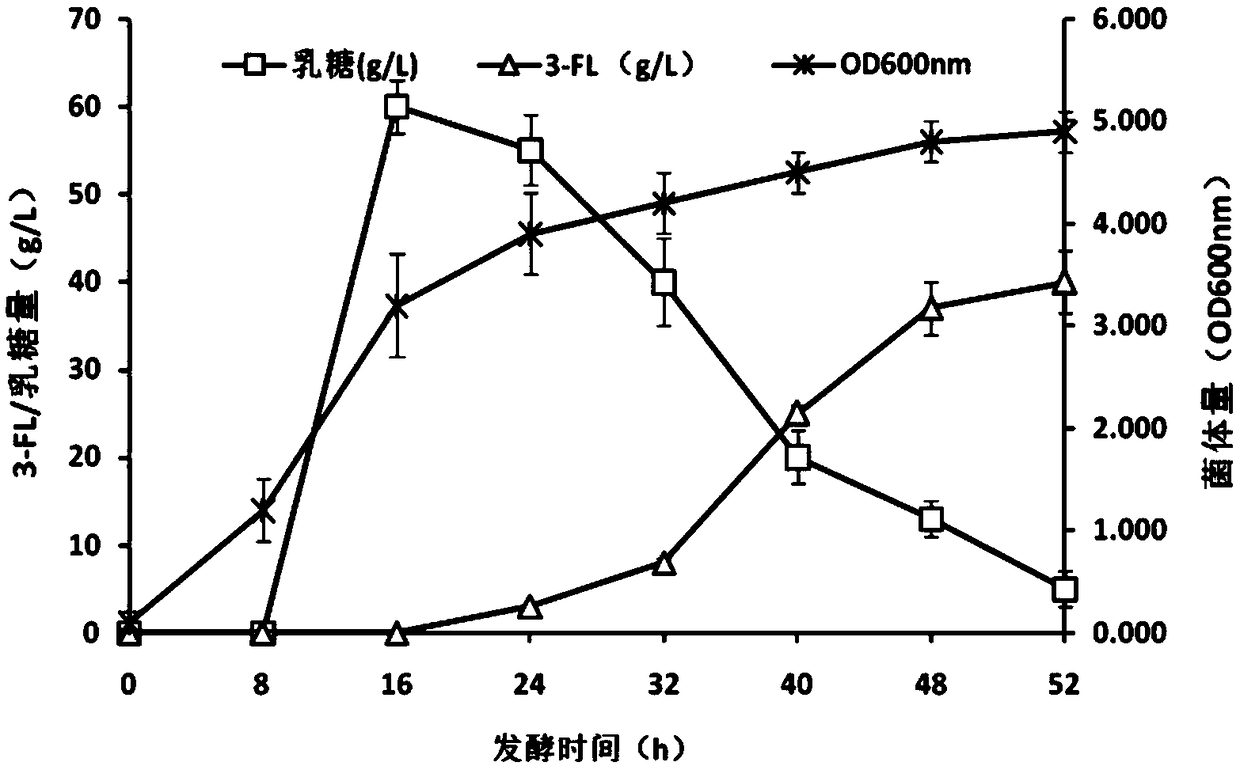
The present invention discloses a construction method of escherichia coli for synthesizing fucosylated oligosaccharide by fermentation. The construction method includes the steps: (1) overexpressing at least one gene for encoding enzymes required for denovo synthesizing GDP-L-fucose in a prokaryotic host cell; (2) expressing an exogenous gene for encoding a fucosyltransferase in the prokaryotic host cell; (3) reducing or eliminating the activity of GDP-mannanohydrolase in the prokaryotic host cell; and (4) reducing or eliminating the activity of beta-galactosidase in the prokaryotic host cell.According to the present invention, the escherichia coli is constructed by using the method, and the escherichia coli may be used for preparing the fucosylated oligosaccharide. Shown by a result generated by performing fermentation production verification on the fucosylated oligosaccharide (with 2'-fucosyllactose as an example) in a 5L tank by adopting an engineering strain constructed by the present invention, the highest production level of the 2'-fucosyllactose (2'-FL) may reach 50 g / L.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司 +1
Escherichia coli for producing 2'-fucosyllactose and application thereof
The invention relates to recombinant escherichia coli for producing 2'-fucosyllactose and application thereof, and belongs to the field of microbial metabolic engineering. According to a regulation and control strategy for the expression level of 2'-fucosyllactose de novo synthesis route key enzyme, different enzymes are subjected to regulation and control of genome overexpression or plasmid overexpression, the efficiency of a metabolic pathway can be greatly improved, compared with the prior art, the efficiency of a genetic engineering strain constructed through related strategies is improvedby 13 times or above, and a foundation is laid for industrial production of the 2'-fucosyllactose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
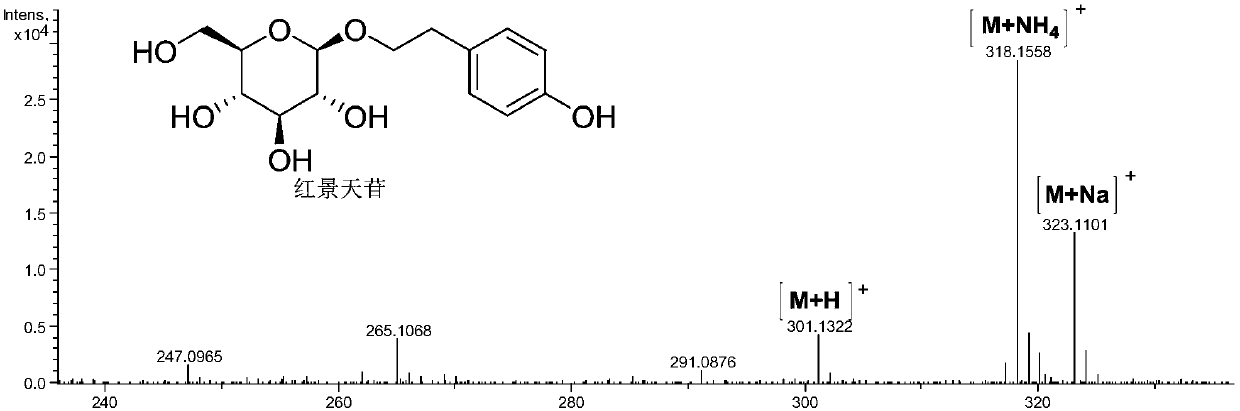
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and application thereof to producing tyrosol and/or salidroside
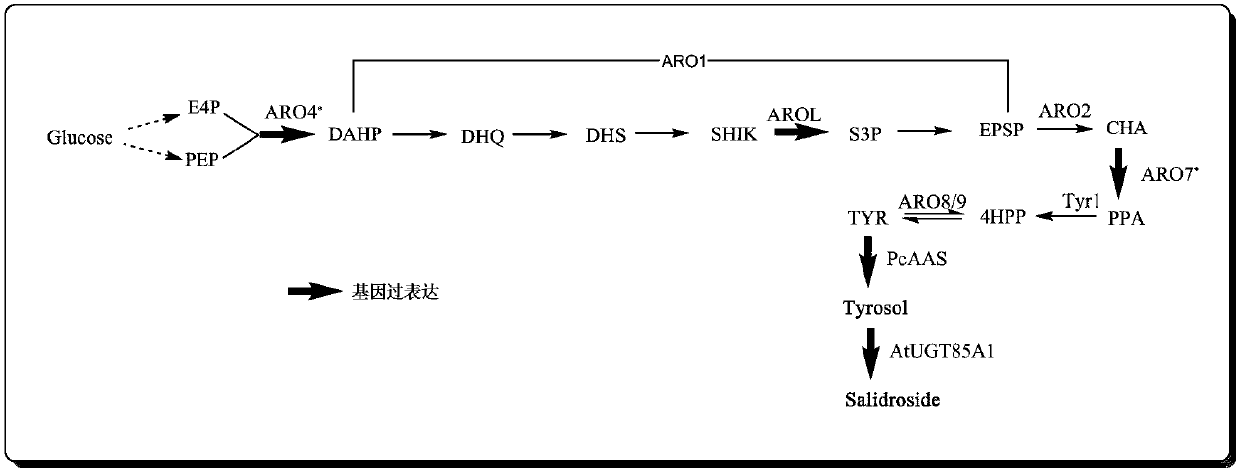
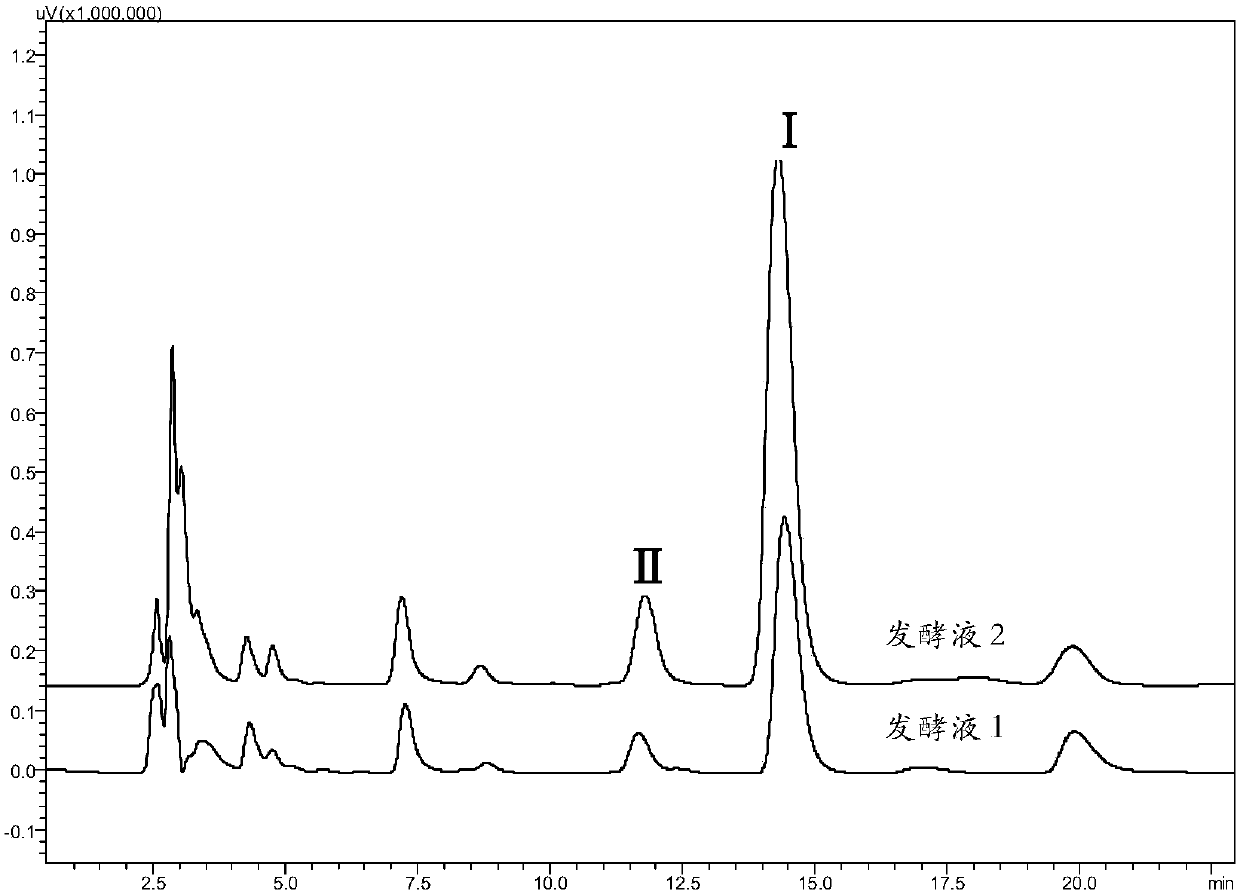
The invention provides a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing tyrosol and / or salidroside and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing the tyrosol and / or salidroside, applied exogenous genes comprises AROL gene, PcAAS gene, AtUgt85A1 gene, ARO4* gene and ARO7* gene,which serve as five key enzyme encoding genes during biosynthesis of the tyrosol and / or salidroside and are introduced and overexpressed in saccharomyces cerevisiae, so that metabolic flux from glucose to tyrosine can be reduced to enhance the biosynthesis of the tyrosol and / or salidroside and further to achieve construction of a route of de novo synthesis from glucose to the tyrosol and / or salidroside for the saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
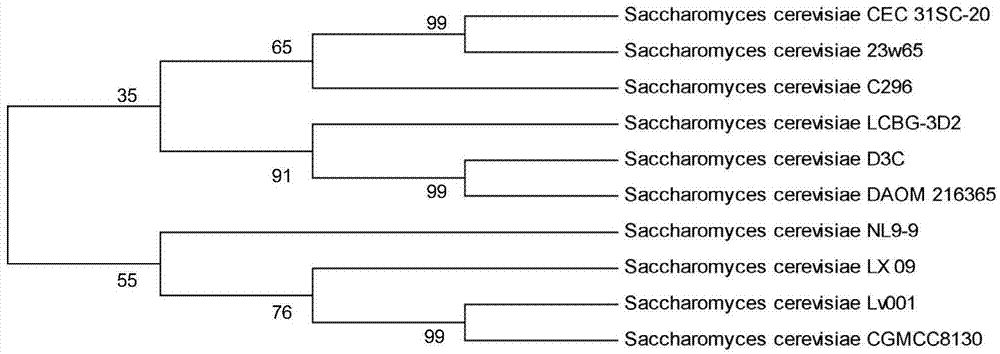
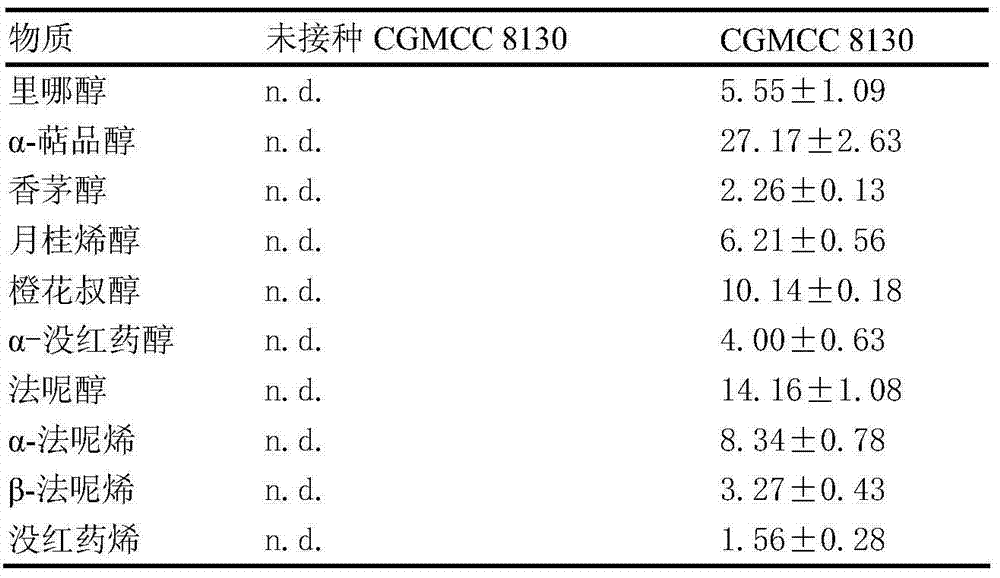
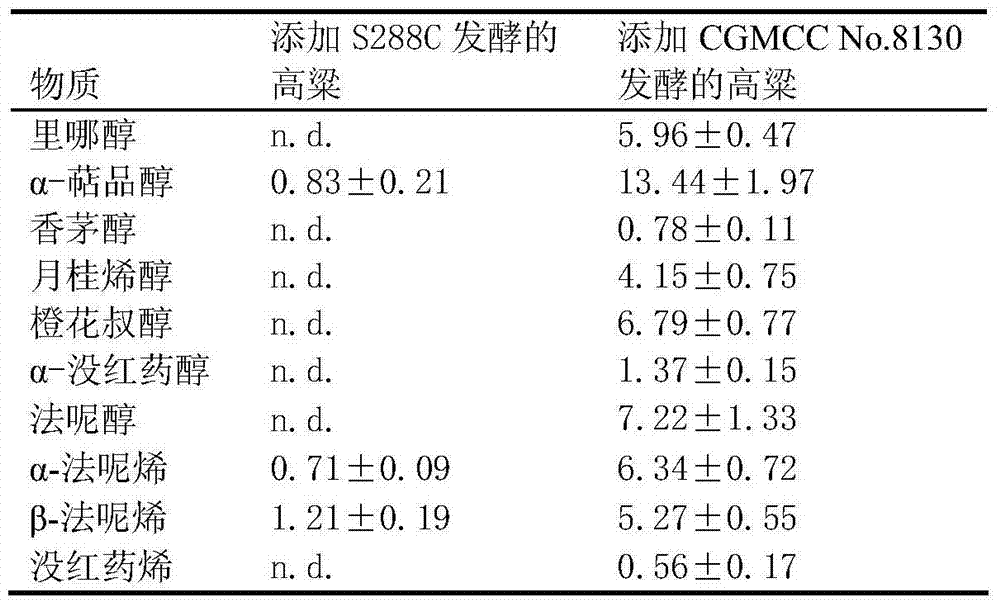
Saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of auto-synthesizing terpenoid substances and applications thereof
ActiveCN103571763AAdd flavorHigh nutritional valueFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationBiotechnologyNutritive values
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of auto-synthesizing terpenoid substances and applications thereof, belonging to the field of fermentation engineering. The saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of auto-synthesizing various terpenoid substances denovo is screened from fermented grains of white wine. The stain is preserved in the general microbiology centre in China on September 4, 2013, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.8130. The strain is subjected to liquid-state or solid-state fermented cultivation so as to generate ten kinds of terpenoid substances including linalool, alpha-terpineol, citronellol, myrcenol, nerolidol, alpha-dragosantol, farnesol, alpha-farnesene, beta-farnesene and bisabolene. The cerevisiae strain is added in the wine making process and can improve the flavor of white wine and increase the nutritive value of white wine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing fucosyllactose and production method
PendingCN114480240AGrow fastImprove expression levelBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCell factory
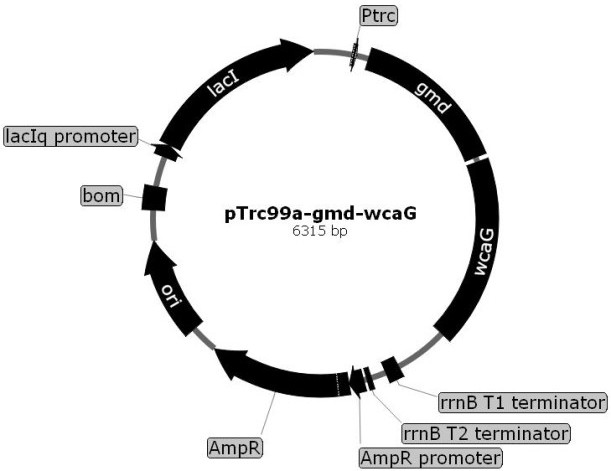
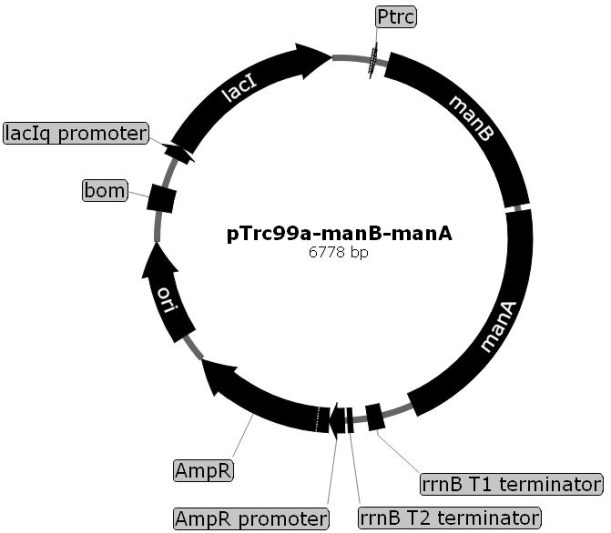
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing fucosyllactose and a production method of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to metabolic engineering and food fermentation technologies. According to the invention, a synthetic biological means is utilized, an escherichia coli cell factory of fucosyllactose is constructed based on a de novo synthetic route, bypass related genes lacZ, wcaJ, nudD, pfkA and lon in host cells are knocked out by adopting a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology, and genes manB, manC, gmd and wcaG are assembled through a multi-plasmid expression system, so that the fucosyllactose is obtained. Constructing expression vectors with different copy numbers to increase the expression level of key genes; fucosyltransferase from different sources is screened, so that the activity of rate-limiting enzyme is improved. The constructed recombinant escherichia coli can be used for synthesizing 2 '-fucosyllactose and 3-fucosyllactose by utilizing glycerol, is stable in heredity and high in expression level, and has obvious industrial production potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
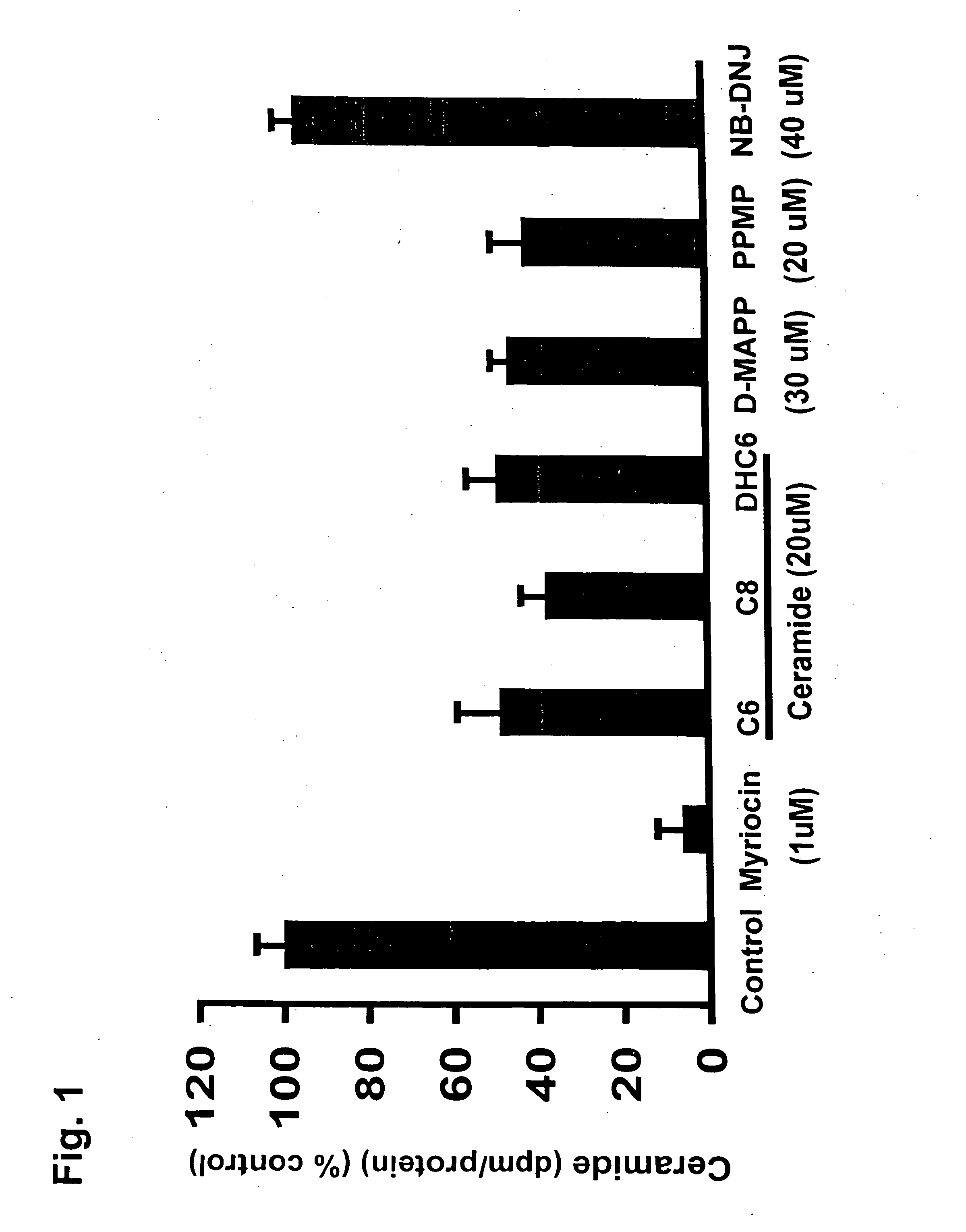
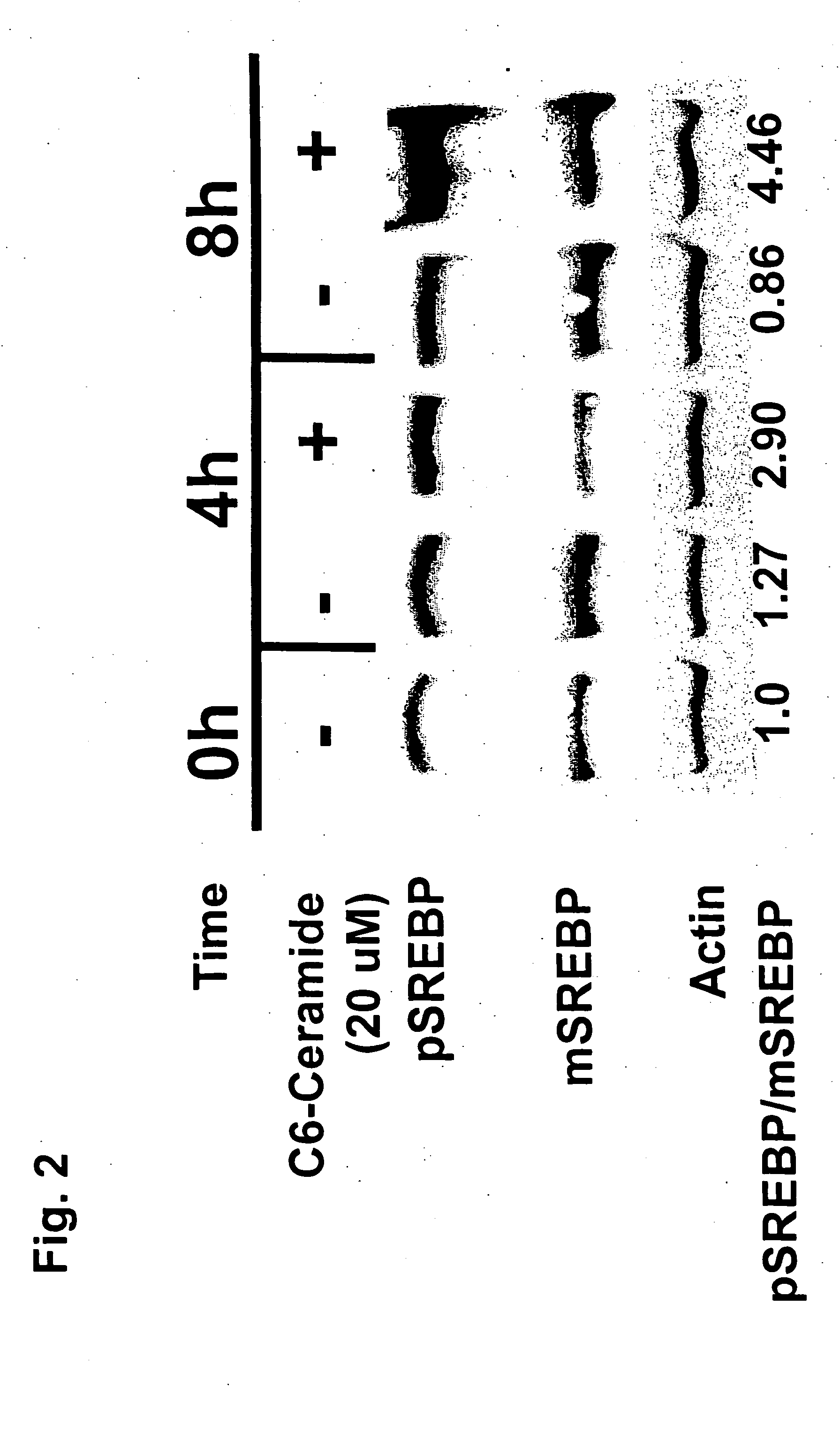
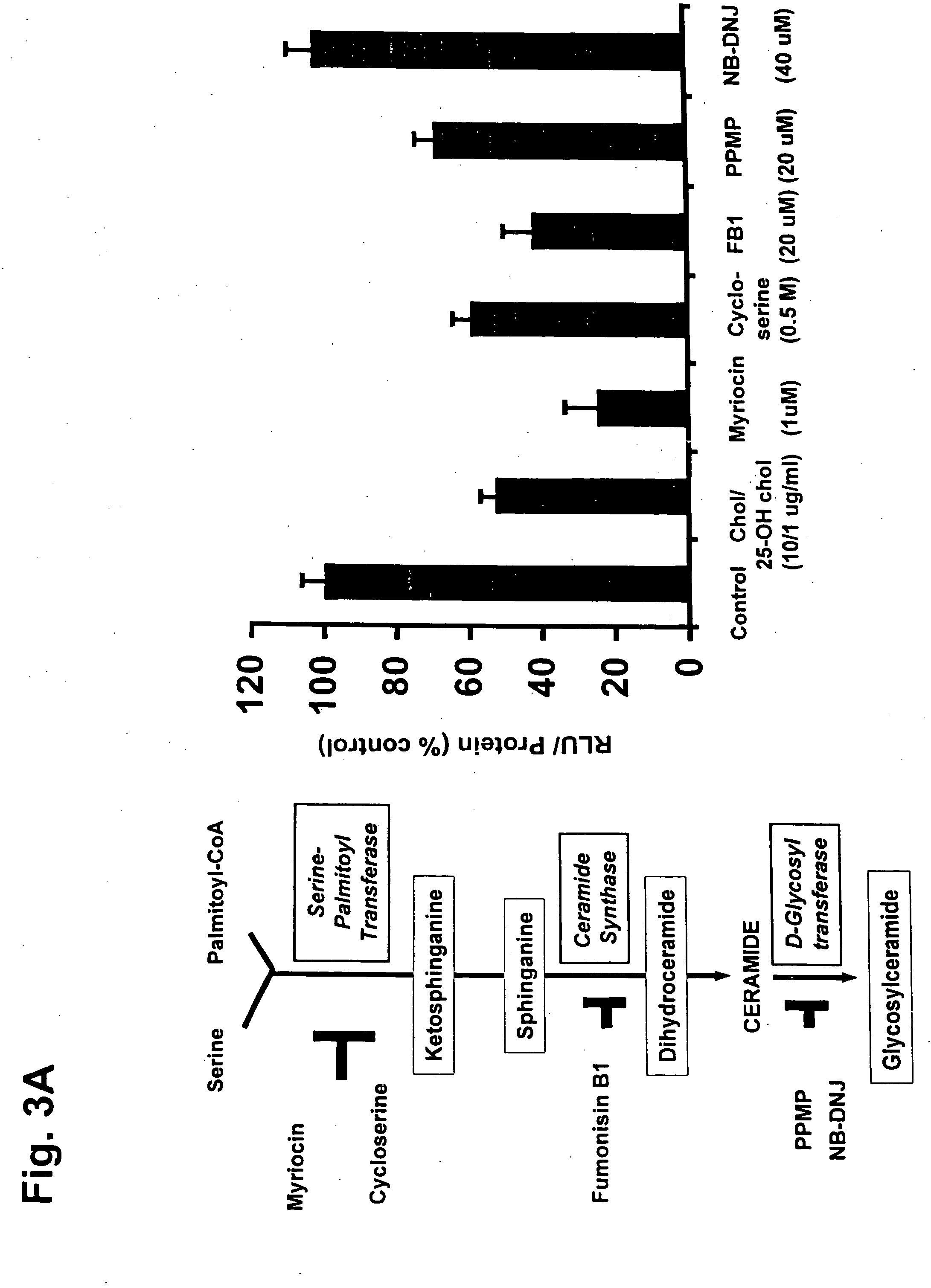
Ceramide de novo synthesis-based therapeutic and prophylactic methods, and related articles of manufacture
InactiveUS20050182020A1Reduce amountImprove the level ofBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsGeneticsDe novo synthesis
Described is a method for decreasing the amount of mSREBP in a cell characterized by an elevated level of mSREBP comprising contacting the cell with an agent that specifically inhibits de novo synthesis of ceramide in the cell, thereby decreasing the amount of mSREBP in the cell. Also described are related methods and articles of manufacture.
Owner:WORGALL TILLA S +1
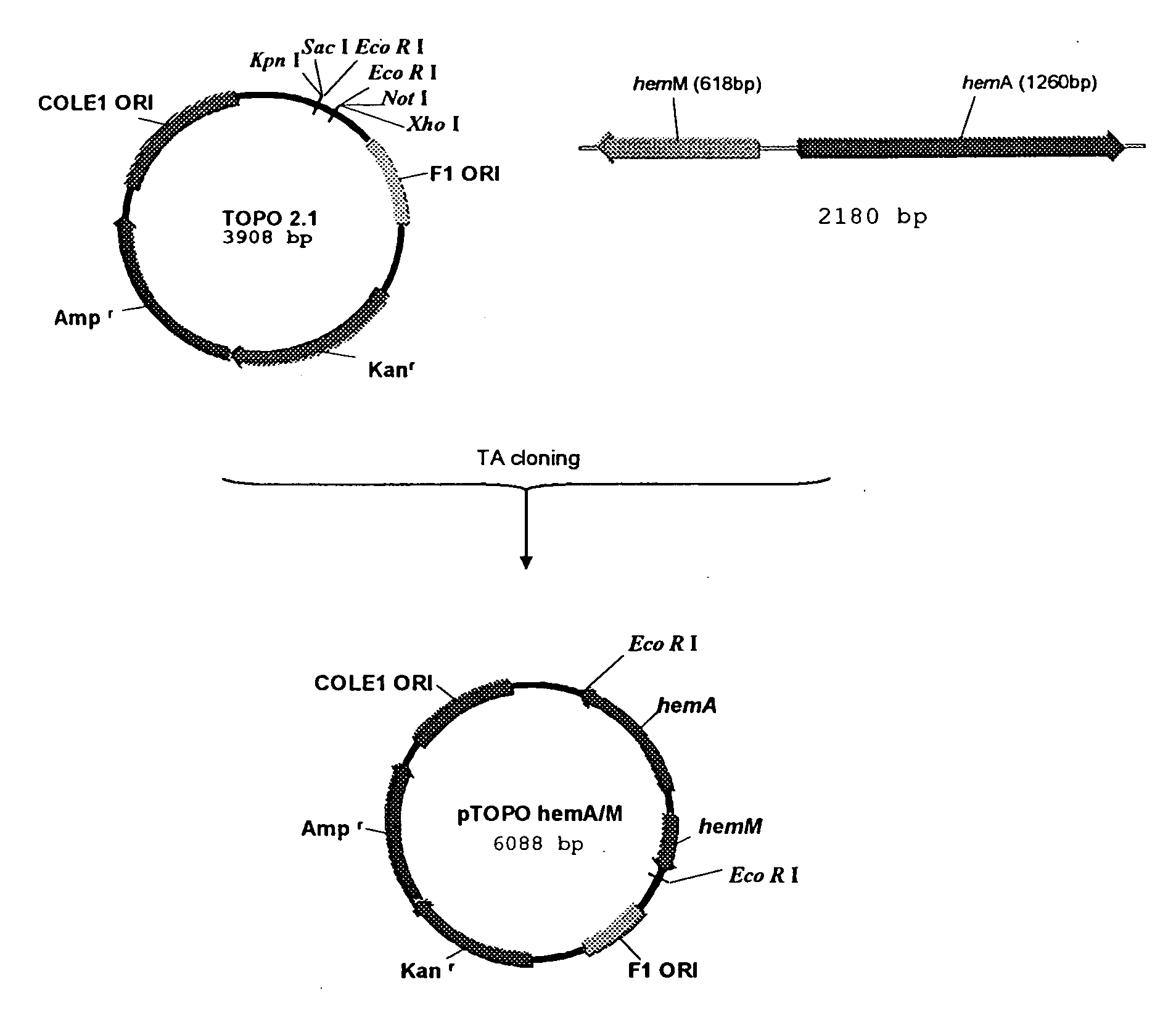
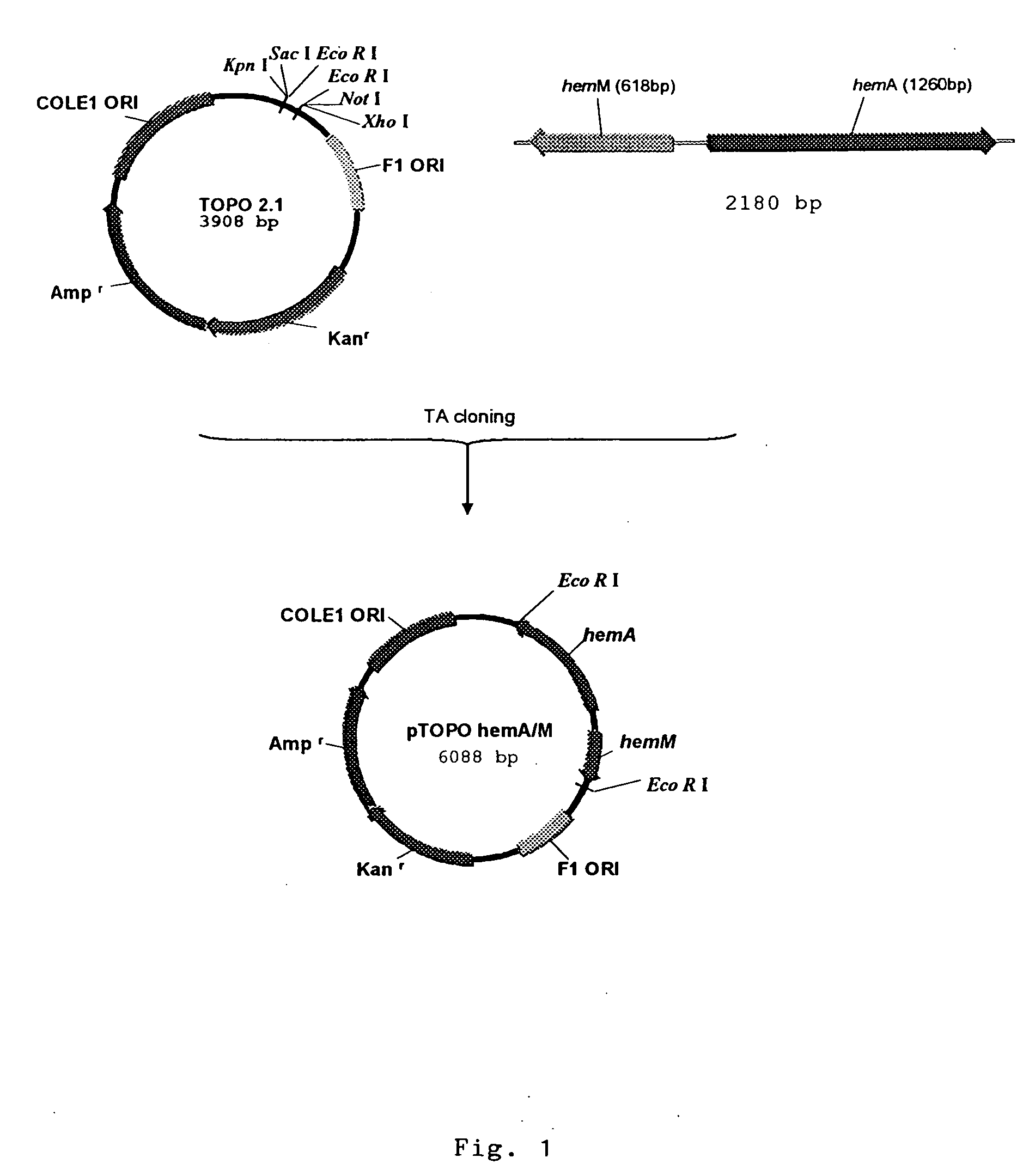
Vibrio cholerae strains VCUSM1 and VCUSM4, method of producing same, and vaccine derivatives thereof
InactiveUS20060099229A1Limited in vitroLimited in in vivo growthAntibacterial agentsBacteriaAmino-Levulinic AcidKanamycin
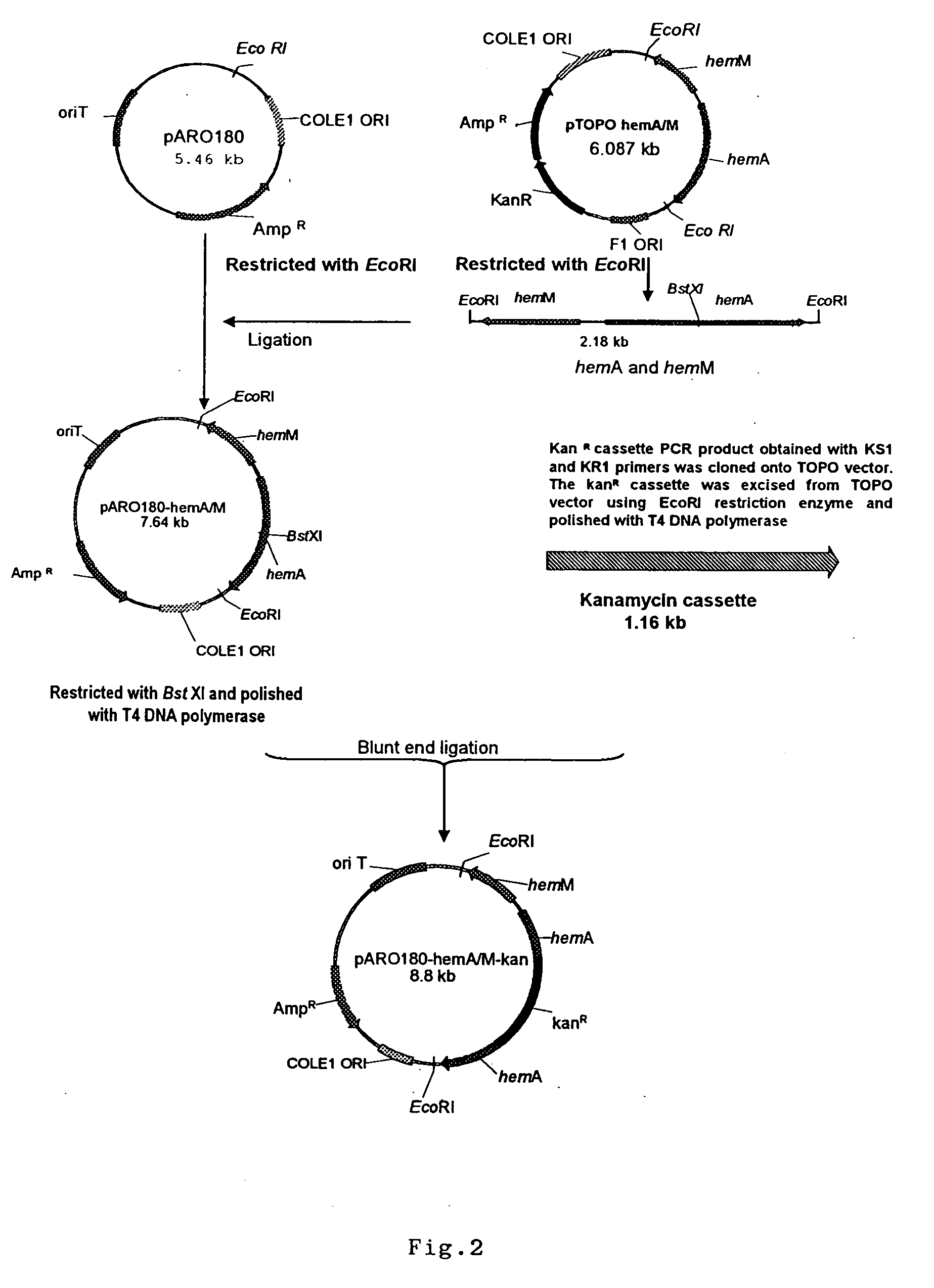
Metabolic auxotroph of Vibrio cholerae 0139 synonym Bengal which has a mutation in its hem A gene and which is not capable of synthesizing aminolevulinic acid (ALA) de novo and which is obtained from a parent strain originally isolated from a patient's coproculture having all the identifying characteristics of Vibrio cholerae 0139 synonym Bengal is described. In this strain the hem A gene is mutated by inserting a kanamycin resistant gene cassette. Another metabolic auxotroph of Vibrio cholerae 01 El Tor where the hem A gene is mutated by a frame shift mutation is disclosed. Methods of producing the strains are disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITI SAINS MALAYSIA
Ophiobolin compound mother nucleus synthetic gene AuOS and application thereof
The invention discloses an ophiobolin compound mother nucleus synthetic gene AuOS and an application thereof and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The ophiobolin compound mother nucleus synthetic gene AuOS is derived from aspergillus ustus 094102, wherein the gene sequence, the cDNA sequence and the amino acid sequence of coded AuOS protein are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO.1-3. The AuOS protein has the functions of catalyzing the substrate chain length extension and the structure cyclization, and the protein can be reacted with the IPP to generate the ophiobolin compound mother nucleus by taking the DMAPP, GPP, FPP and GGPP as substrates. The invention first discovers the AuOS gene of the aspergillus ustus 094102, wherein the coded gene has the functions of catalyzing the substrate chain length extension and the structure cyclization, the ophiobolin compound mother nucleus can be synthesized by taking the DMAPP as a substrate, and the ophiobolin compound mother nucleus can be used for preparing the ophiobolin compound and researching the biosynthetic pathway.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Electricity-producing genetically engineered bacteria used in microbial fuel cell, and construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103215301AIncrease production capacityBacteriaCell electrodesDe novo synthesisBio engineering
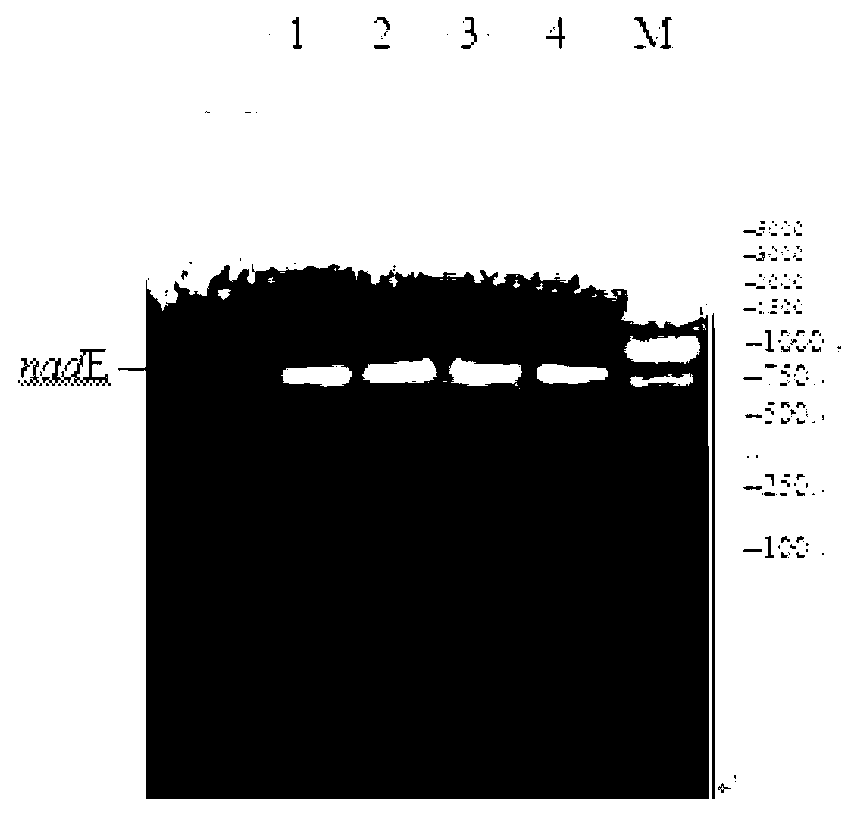
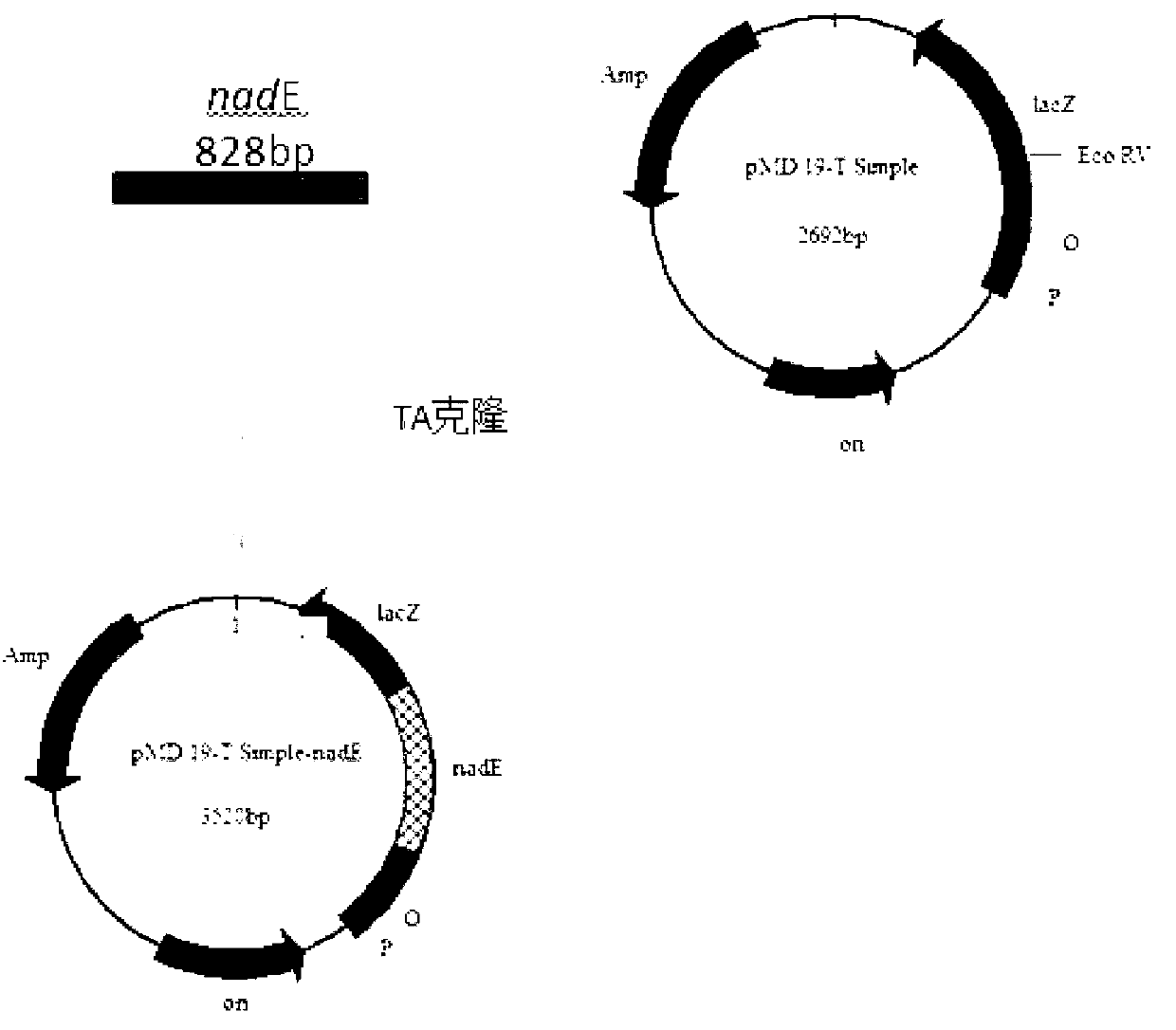
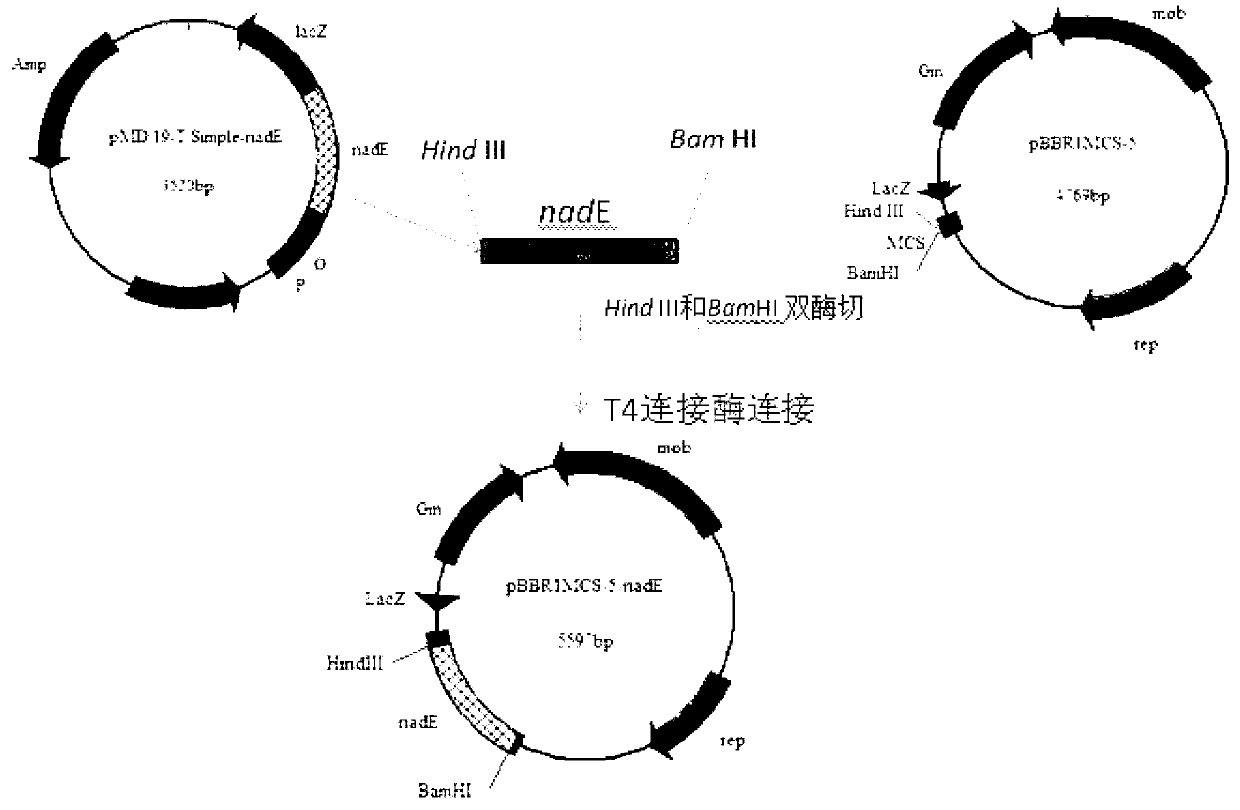
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, and relates to the construction, strain, and application of a microbial fuel cell electricity-producing genetically engineered bacteria. With a molecular biology method, a common key gene nadE in Escherichia coli NAD<+> de-novo synthesis pathway and anaplerotic pathway is heterologously expressed in pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1, such that the high-electricity-production genetically engineered strain pseudomonas aeruginosa PA-nadE is obtained, and can be applied in the development of the field of microbial fuel cell. Also, good basis is provided for the genetic engineering researches of electricity-producing pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing 2'-fucosyllactose and construction method thereof
ActiveCN112625990AEfficient Genome Editing SolutionFermentation does not affectBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneColanic acid
The invention provides a recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing 2'-fucosyllactose and construction method thereof, and the recombinant Escherichia coli is obtained by knocking out a beta-galactosidase gene in the genome of Escherichia coli, synthesizing a key enzyme gene of colanic acid from guanosine diphosphate fucose, enhancing expression key enzyme genes of lactose permease genes and a guanylate diphosphate fucose denovo synthesis route and expressing exogenous fucosyltransferase genes. According to the scheme, lactose hydrolysis can be reduced, and the rate of transferring exogenous lactose into cells is increased, so that the concentration of lactose in the cells is effectively increased; meanwhile, the consumption of the guanosine diphosphate fucose is reduced, and the concentration of the guanosine diphosphate fucose in cells is effectively improved; through codon optimization, the expression of an exogenous fucosyltransferase gene is improved, and synthesizing of the 2'-fucosyllactose is effectively promoted.
Owner:量子高科(广东)生物有限公司
L-proline-4-hydroxylase and genetic engineering bacterium thereof, construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN108949706AGood genetic stabilityStrong fermentative acid production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicromonospora sp.Biotechnology
The invention provides novel L-proline-4-hydroxylase, amino acid sequence of which is as shown in the SEQ ID No.2. The L-proline-4-hydroxylase is derived from Micromonospora sp. CNB394. The inventionalso provides genetic engineering bacterium E. coli HYP for high-efficiency expression of the above L-proline-4-hydroxylase and denovo synthesis of high-yield trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline. The genetic engineering bacterium has advantages of good genetic stability and strong fermentation and acidogenesis capability, and contains no plasmid. By genome expression of the above novel L-proline-4-hydroxylase and using a cheap carbon source such as glucose and the like as a substrate, efficient denovo synthesis of trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline is achieved. After fermentation for 42 h, yield of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline reaches up to 51 g / L. The invention has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
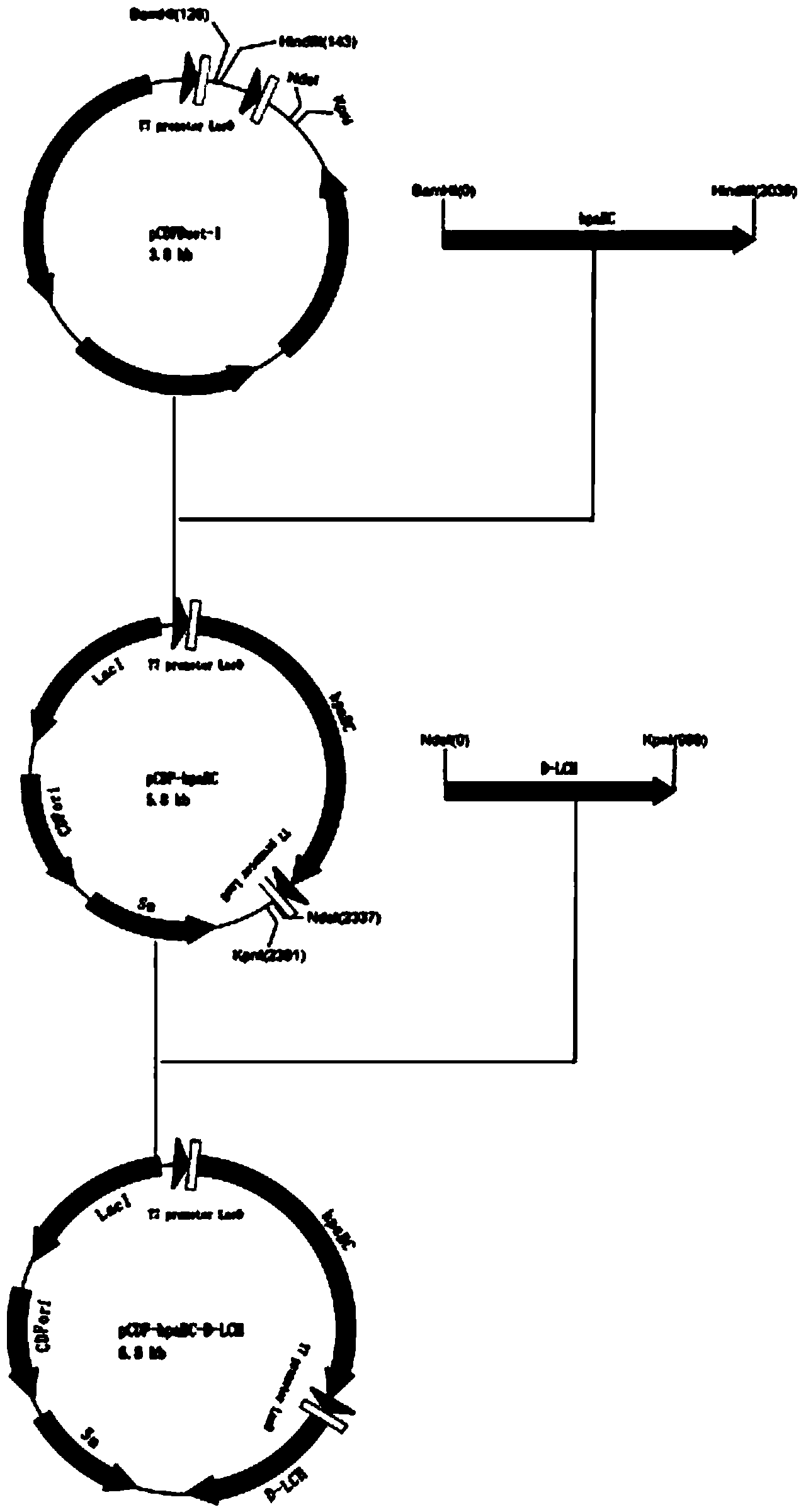
Synthesis of hybrid polynucleotide molecules using single-stranded polynucleotide molecules
A method to make libraries of hybrid polynucleotide molecules of two parental polynucleotide molecules utilizing single-stranded DNA was invented. Example of the method comprises several steps: (i) preparation of two single-stranded polynucleotide molecules comprising sequences containing one or more parts of homology and one or more parts of heterology, (ii) random or non-random fragmentation of said polynucleotides, (iii) hybridization of the fragmented molecules followed by de novo polynucleotide synthesis (i.e. polynucleotide chain elongation) on the hybridized molecules, (iv) separation of the chain elongation products (i.e. double-stranded polynucleotide molecules) into single-stranded polynucleotide molecules (denaturation) (v) hybridization of the resultant single-stranded polynucleotide molecules followed by de novo polynucleotide synthesis on the hybridized molecules, and (vi) repeating at least two further cycles of steps (iv) and (v).
Owner:ALLIGATOR BIOSCI
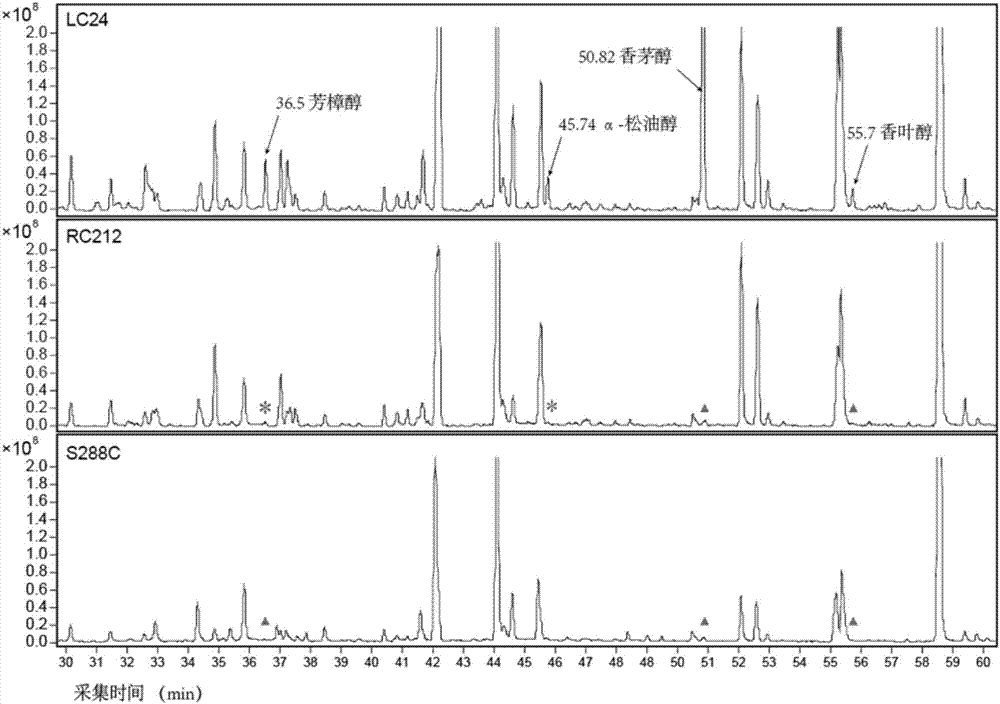
Wine saccharomycopsis vini and application of wine saccharomycopsis to production of monoterpene
The invention discloses a wine saccharomycopsis vini LA24, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13676. The saccharomycopsis vini can be applied to the production of monoterpene organisms and the mixed fermentation with saccharomyces cerevisiae to brew wine. Compared with a model saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, a YPD culture medium is taken as a substrate, the strain is fermented to acquire four monoterpenes of citronellol, geraniol, linalool and alpha-terpilenol, but the saccharomyces cerevisiae rarely produces or completely does not produce monoterpenes. The strain is separated and identified from a grape garden for the first time in the domestic country, and that the strain in the wine saccharomycopsis vini has the capability of de novo synthesis of the monoterpenes is confirmed for the first time. The acquisition of the strain provides important material and technique supports for the development of the high-yield monoterpene engineering bacteria.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Compounds for Treatment or Prevention of Disorders of the Nervous System and Symptoms and Manifestations Thereof, and for Cyto-Protection Against Diseases and Aging of Cells, and Symptoms and Manifestations Thereof
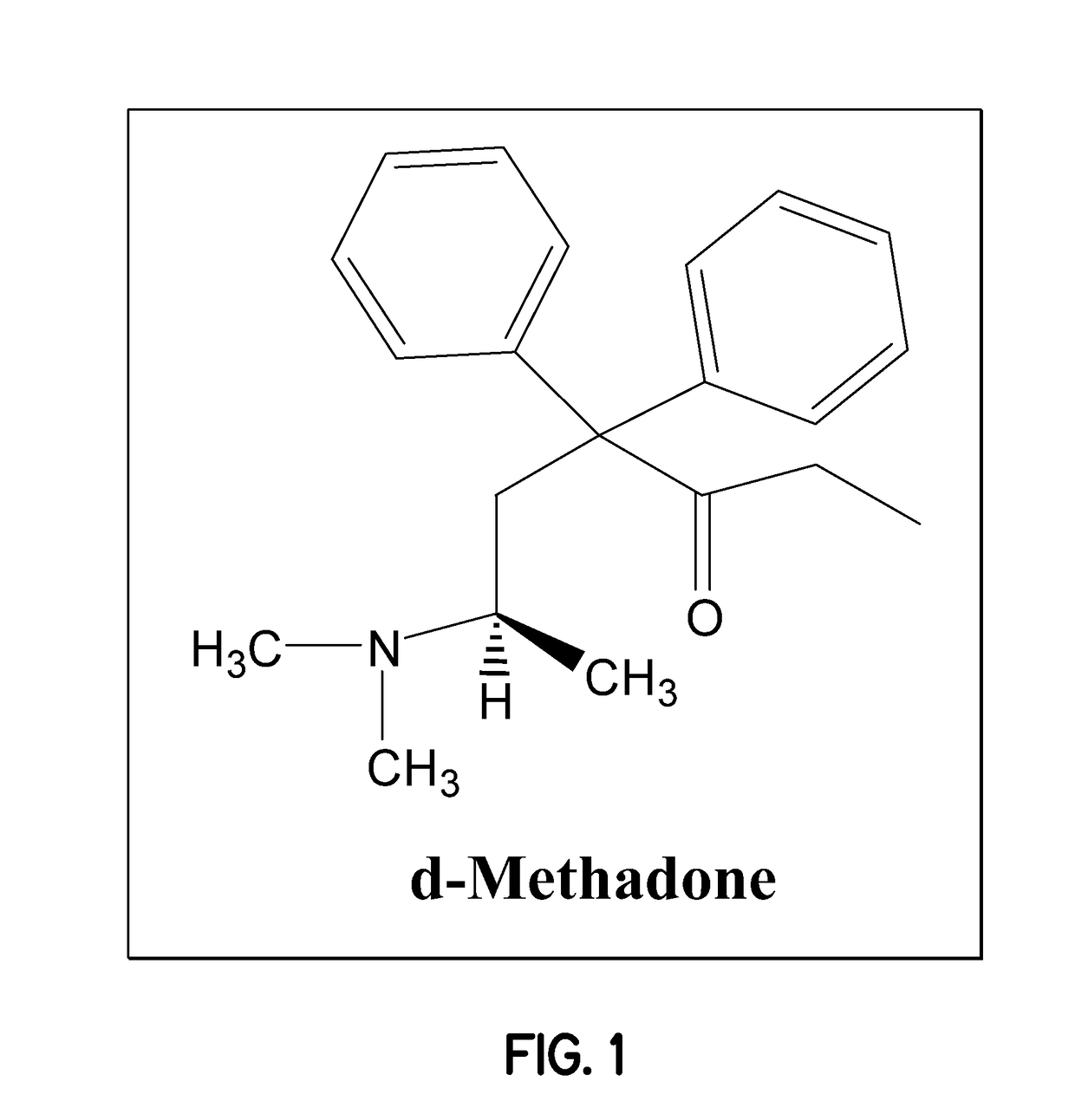
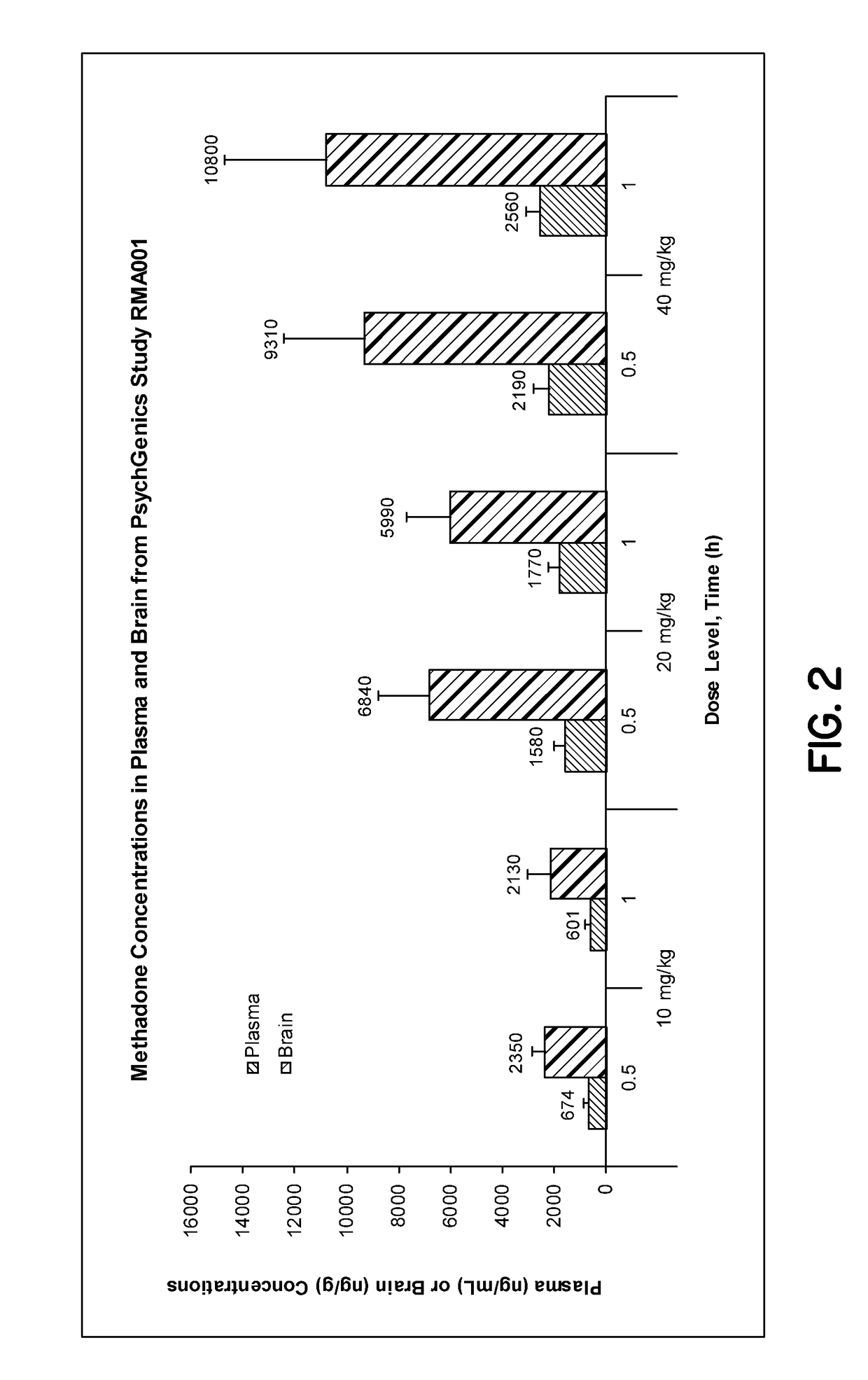
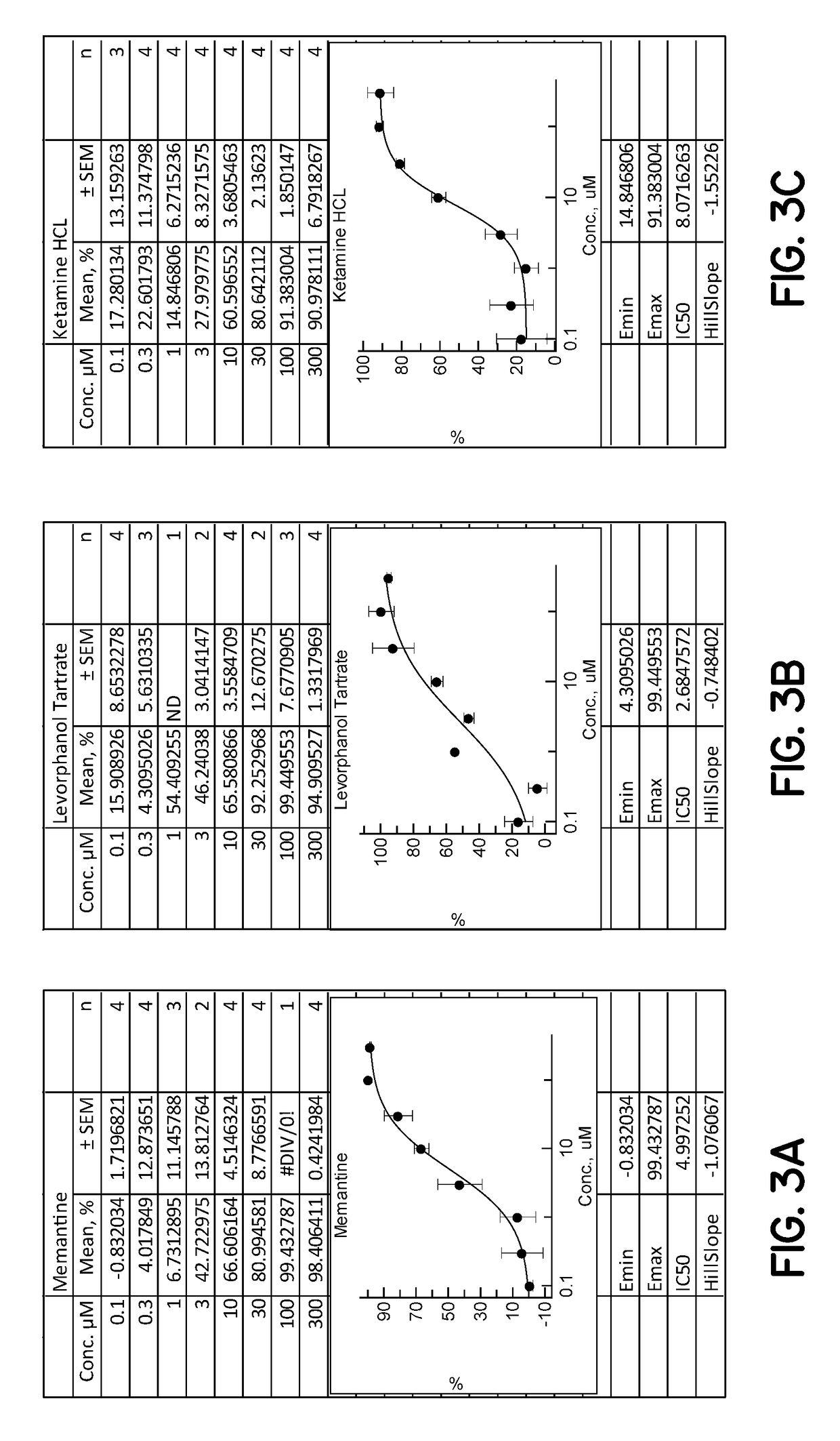
PendingUS20180214395A1Better cognitive functionImprove cognitive abilityNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLevopropoxypheneNervous system
The present invention relates to a method of treating or preventing cellular dysfunction and death caused by genetic, degenerative, toxic, traumatic, ischemic, infectious, neoplastic and inflammatory diseases and aging—and their neurological symptoms and manifestations, which includes administering d-methadone, beta-d-methadol, alpha-l-methadol, beta-l-methadol, alpha-d-methadol, acetylmethadol, d-alpha-acetylmethadol, l-alpha-acetylmethadol, beta-d-acetylmethadol, beta-l-acetylmethadol, d-alpha-normethadol, l-alpha normethadol, noracetylmethadol, dinoracetylmethadol, methadol, normethadol, dinormethadol, EDDP, EMDP, d-isomethadone, normethadone, N-methyl-methadone, N-methyl-d-methadone, N-methyl-l-methadone, l-moramide, levopropoxyphene, pharmaceutically acceptable salts, or mixtures thereof, including deuterated and tritium analogues, whether isolated from its enantiomer or synthesized de novo.
Owner:MANFREDI PAOLO L +1
A genetically engineered bacterium for the production of l-theanine and its construction and application
ActiveCN109777763BIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
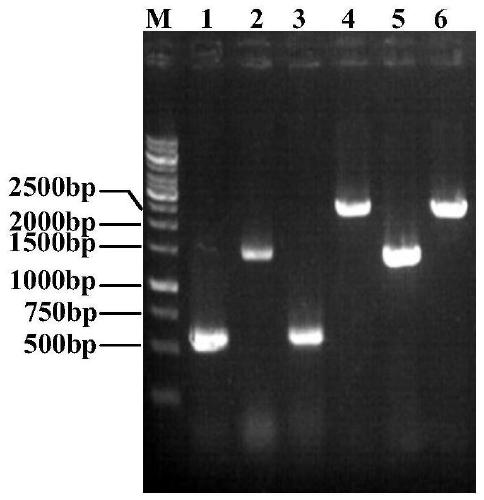
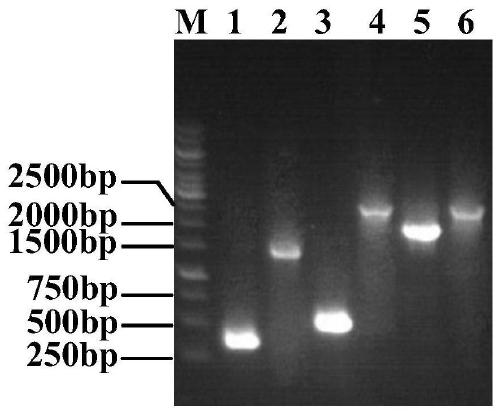
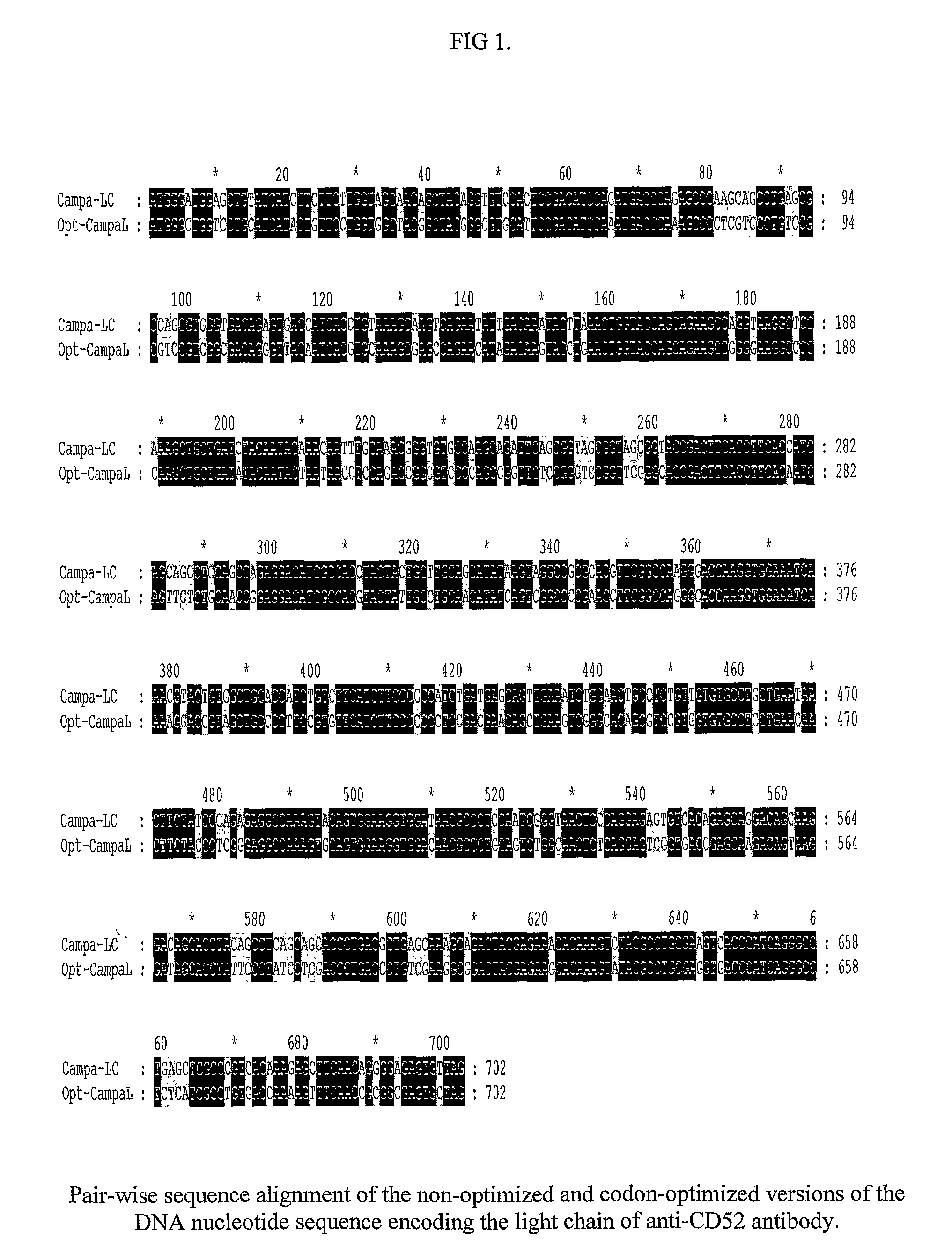
Recombinant method for the production of a monoclonal antibody to CD52 for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
InactiveUS20090220520A1Stable expressionImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsDNA constructChronic lymphocytic leukemia
The present invention relates to the recombinant method used for the production of soluble form monoclonal antibody that binds to CD52. The procedure describes the de novo synthesis of the nucleic acid sequence encoding anti-CD 52, transformation of the constructed nucleic acid sequences into competent bacteria and the sub-cloning of the same into mammalian expression vectors for expression of the desired protein. DNA constructs comprising the control elements associated with the gene of interest has been disclosed. The nucleic acid sequence of interest has been codon optimized to permit expression in the suitable mammalian host cells.
Owner:AVESTHAGEN
De novo synthesis of bacteriochlorins
A method of making a bacteriochlorin is carried out by condensing a pair of compounds of Formula IIto produce the bacteriochlorin, wherein R is an acetal or aldehyde group. The condensing may be carried out in an organic solvent, preferably in the presence of an acid. The bacteriochlorins are useful for a variety of purposes such as active agents in photodynamic therapy, luminescent compounds in flow cytometry, solar cells, light harvesting arrays, and molecular memory devices.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com