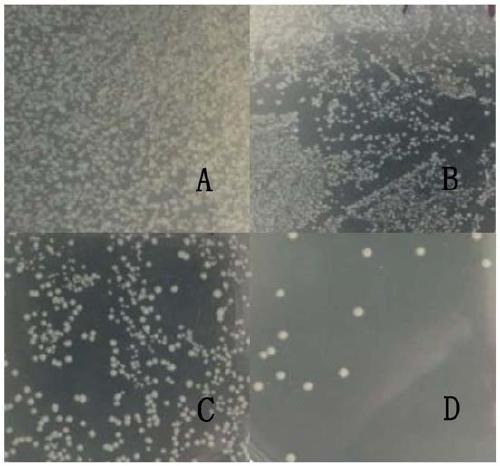
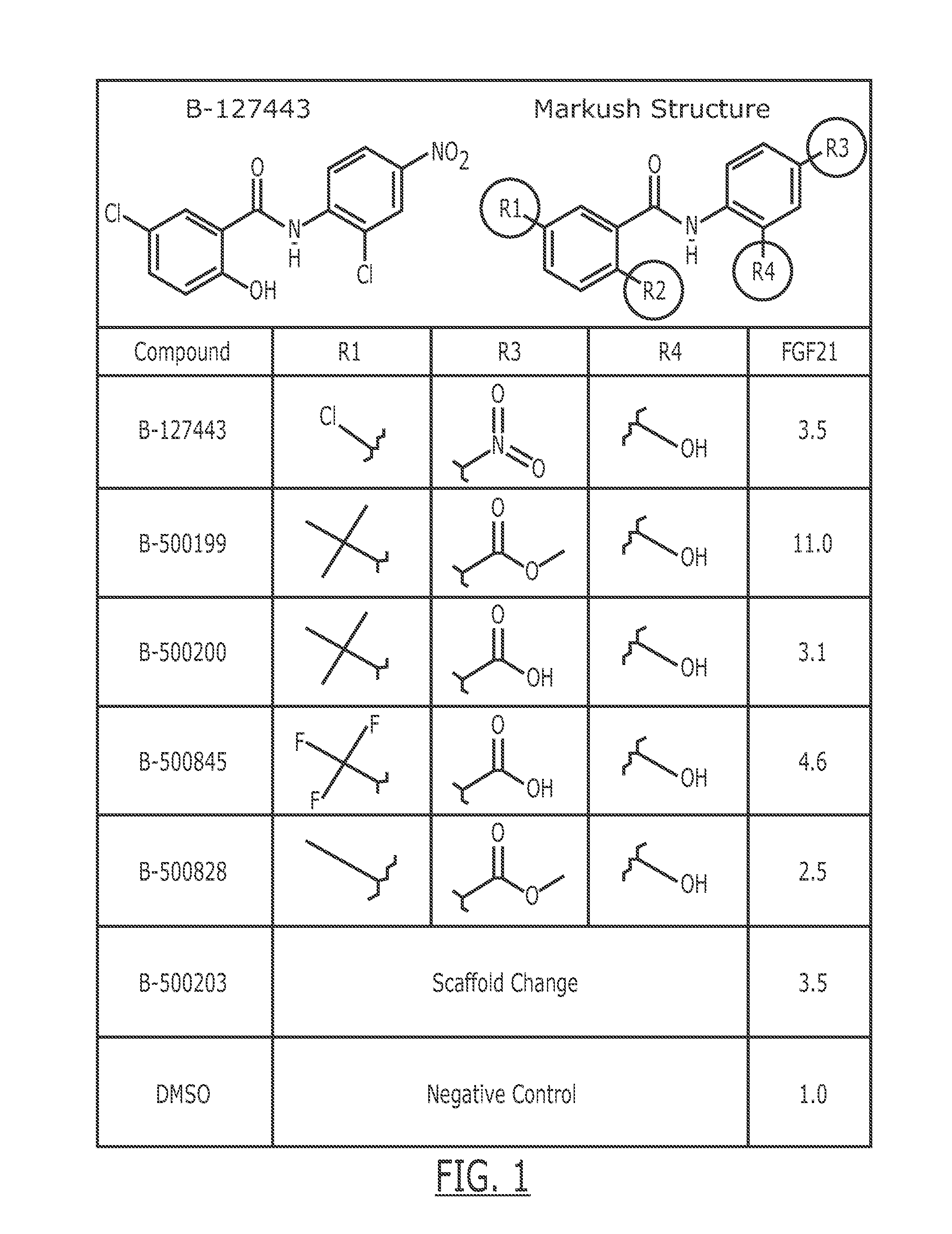
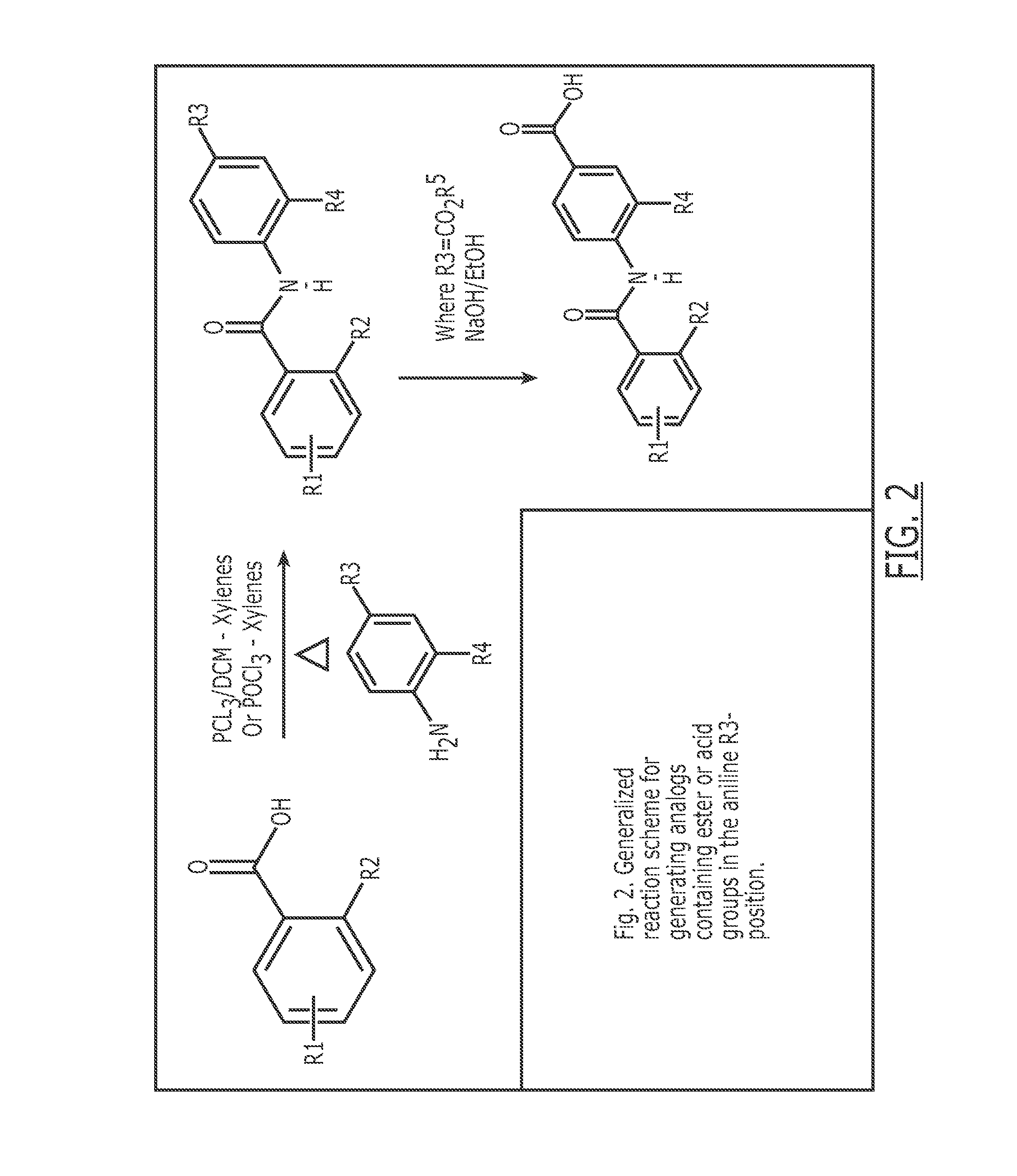
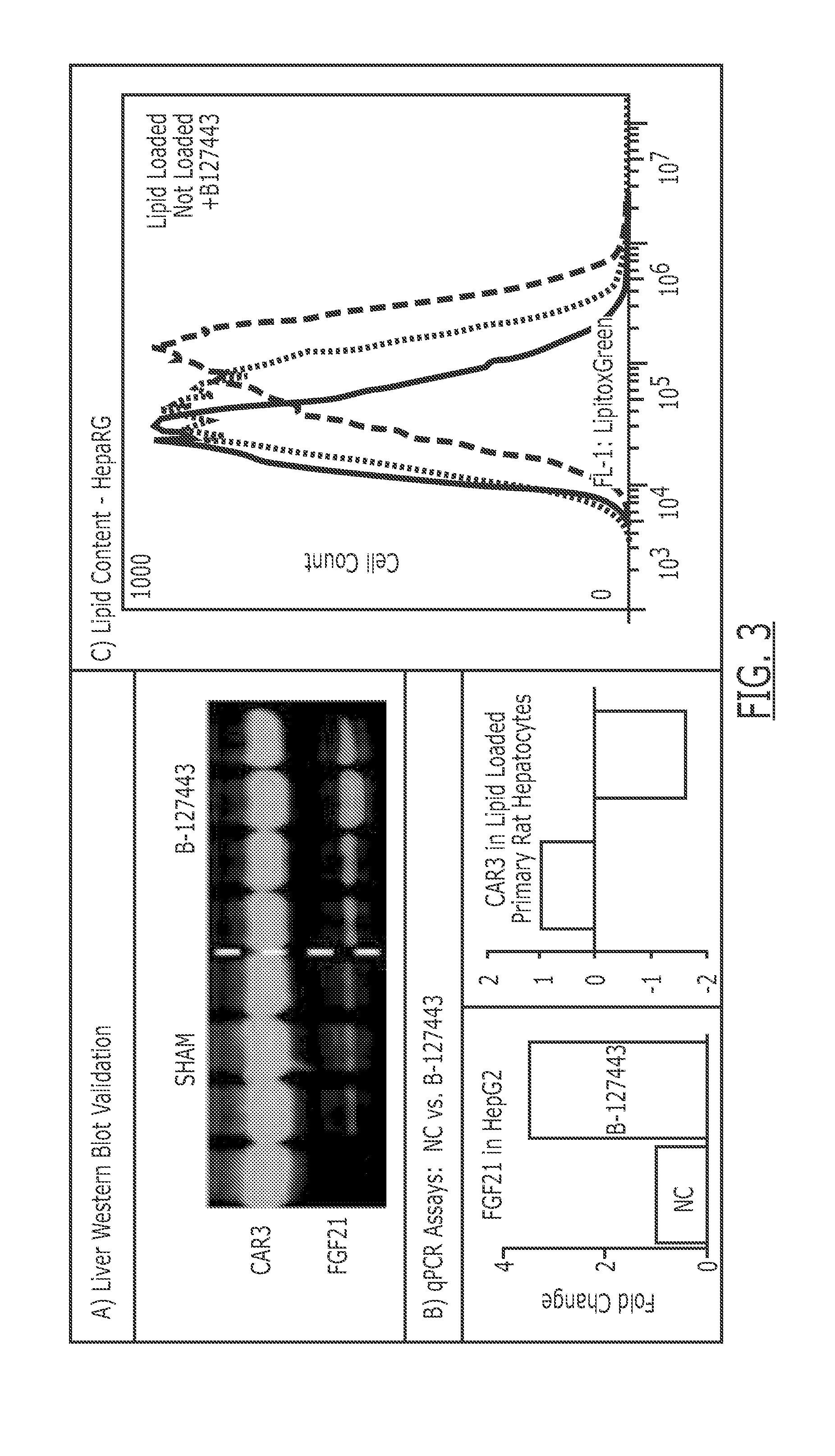
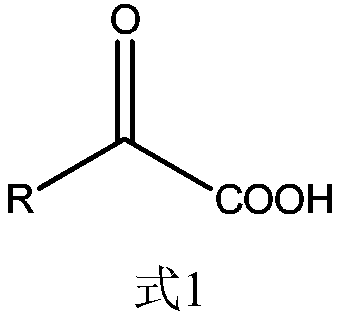
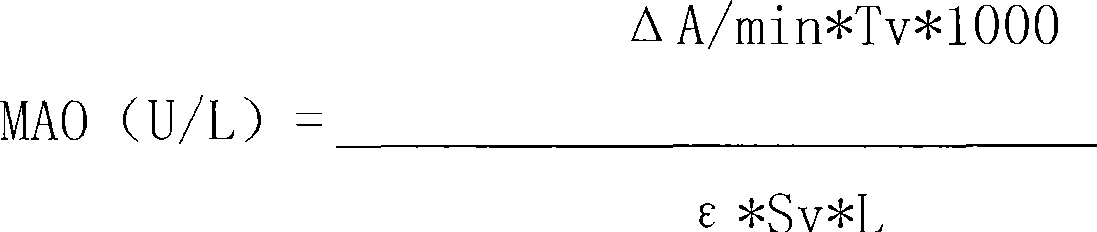Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
200 results about "Glutamate dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
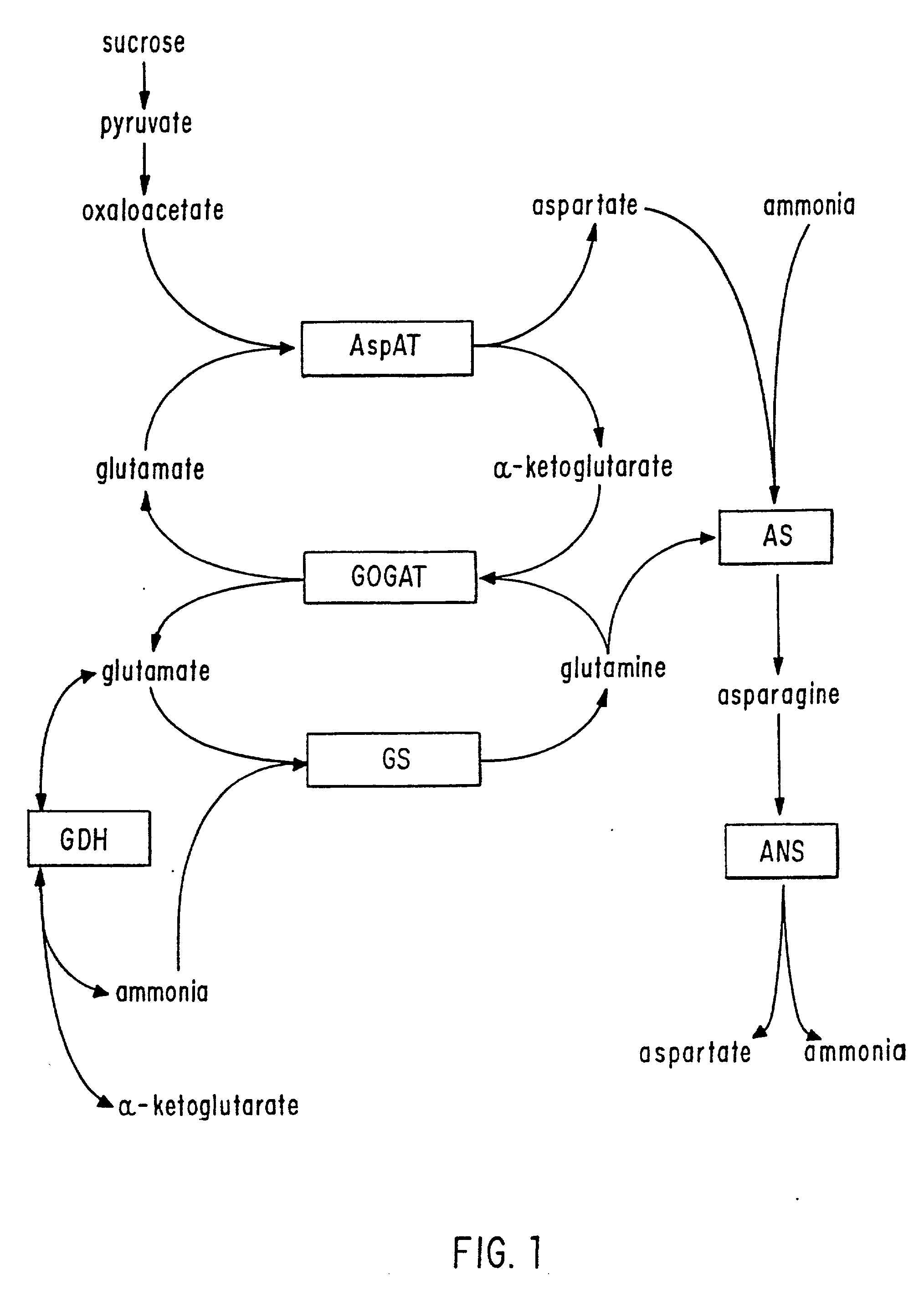
Glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH, GDH) is an enzyme, present in most microbes and the mitochondria of eukaryotes, as are some of the other enzymes required for urea synthesis, that converts glutamate to α-ketoglutarate, and vice versa. In animals, the produced ammonia is usually used as a substrate in the urea cycle. Typically, the α-ketoglutarate to glutamate reaction does not occur in mammals, as glutamate dehydrogenase equilibrium favours the production of ammonia and α-ketoglutarate.
Transgenic plants that exhibit enhanced nitrogen assimilation
InactiveUS20020069430A1Improve growth characteristicsImproved vegetativeClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesPlant cellThreonine
Transgenic plants containing free amino acids, particularly at least one amino acid selected from among glutamic acid, asparagine, aspartic acid, serine, threonine, alanine and histidine accumulated in a large amount, in edible parts thereof, and a method of producing them are provided. In this method, glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) gene is introduced into a plant together with a regulator sequence suitable for over expressing the sequence encoding GDH gene in plant cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
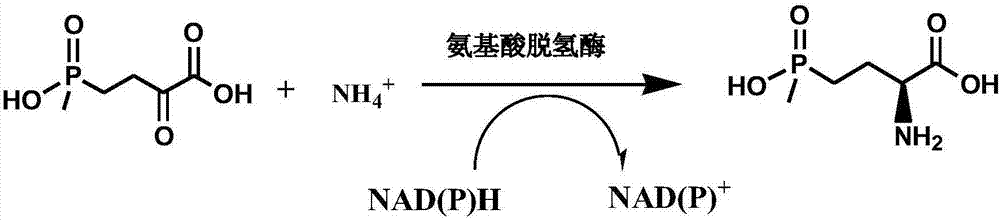
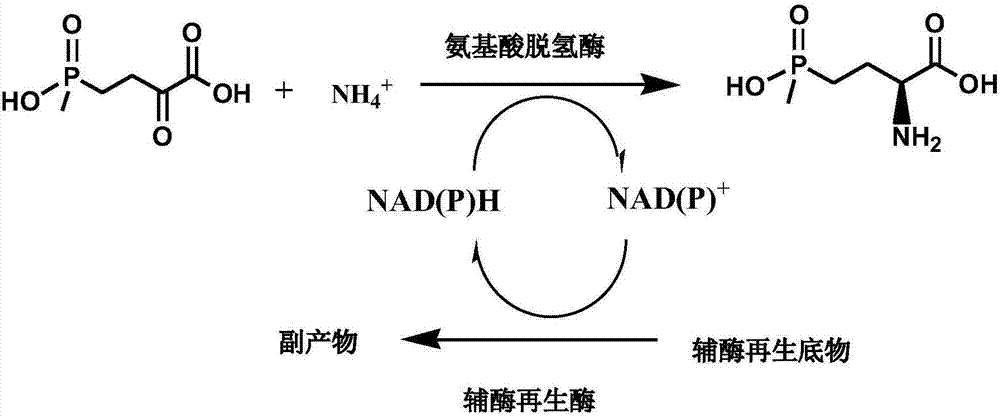
Method for preparing L-glufosinate-ammonium by use of amino acid dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a method for preparing L-glufosinate-ammonium by use of amino acid dehydrogenase. The method comprises the following steps: taking 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethylphosphonyl)butyric acid or a salt thereof as a substrate, taking a cell of the isolated glutamate dehydrogenase or in vitro expression glutamate dehydrogenase as a catalyst to perform reductive amination reaction under the condition of the existence of inorganic amino donor and reduced coenzyme, thereby acquiring the L-glufosinate-ammonium. The method disclosed by the invention is high in raw material conversion rate and high in yield, the product is easy to separate and purify, and the chirality purity is high; compared with the transaminase and like catalysis technology, the process is relatively simple, and the raw material conversion rate reaches up to 100%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
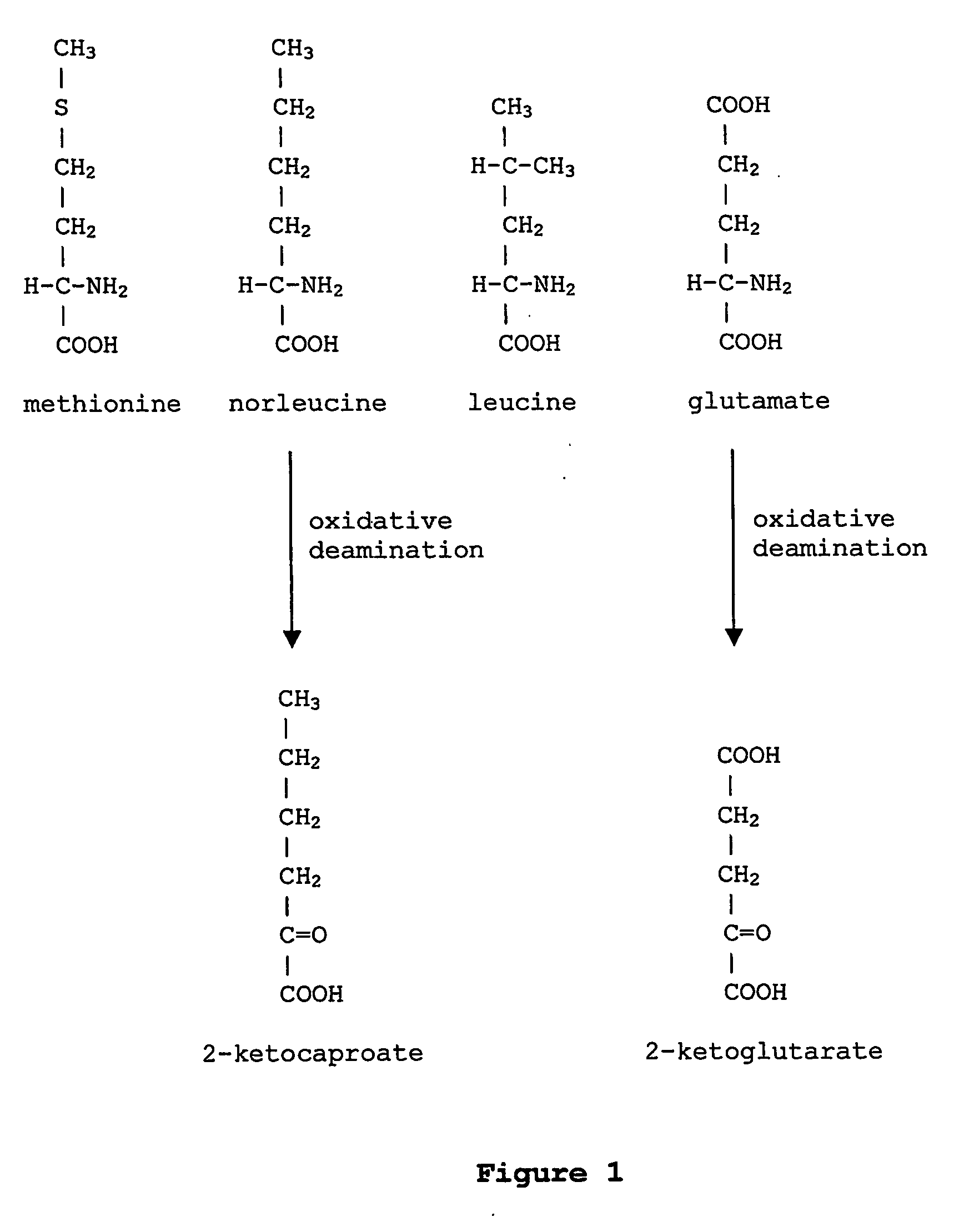
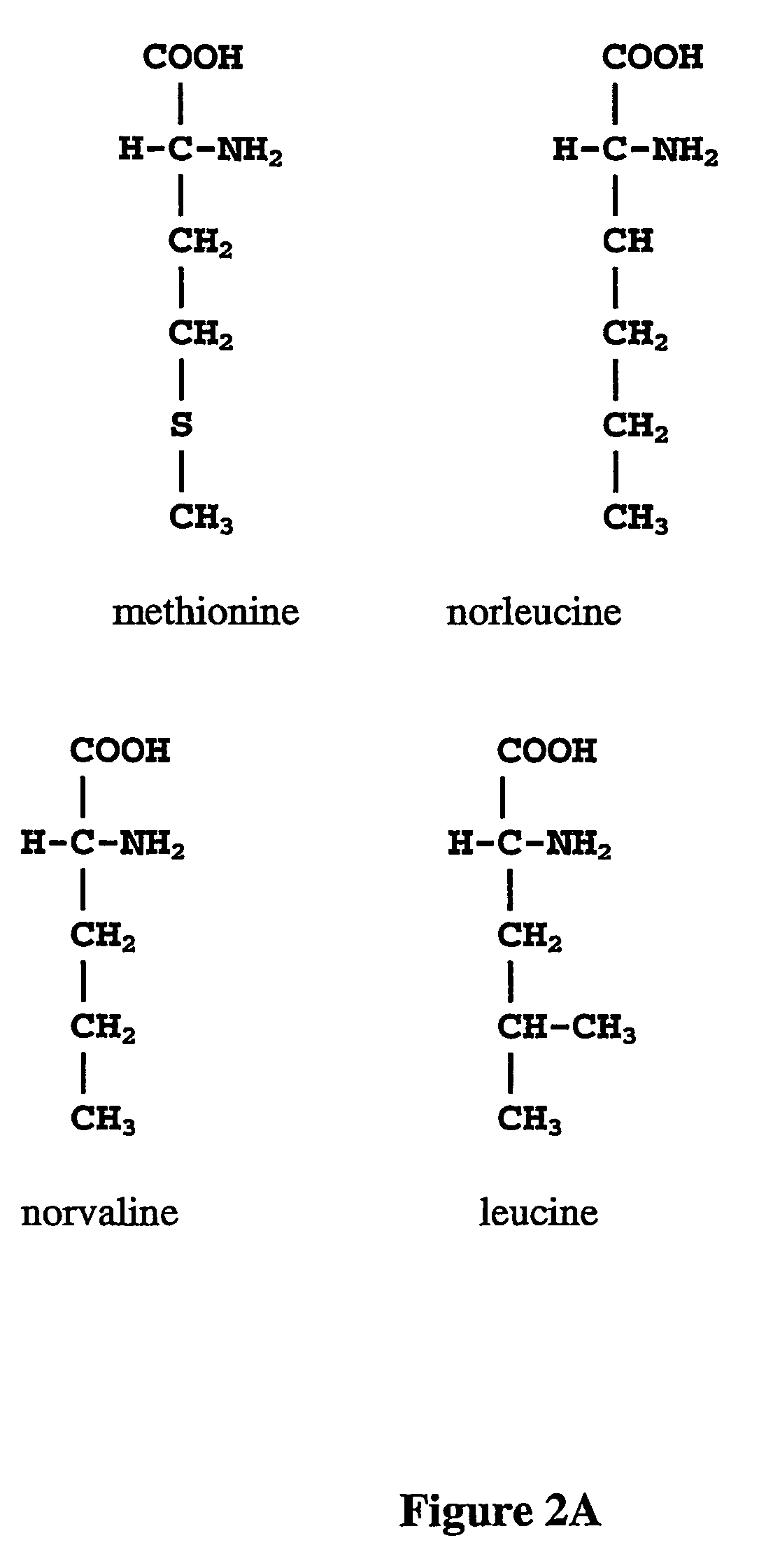
Prevention of incorporation of non-standard amino acids into protein
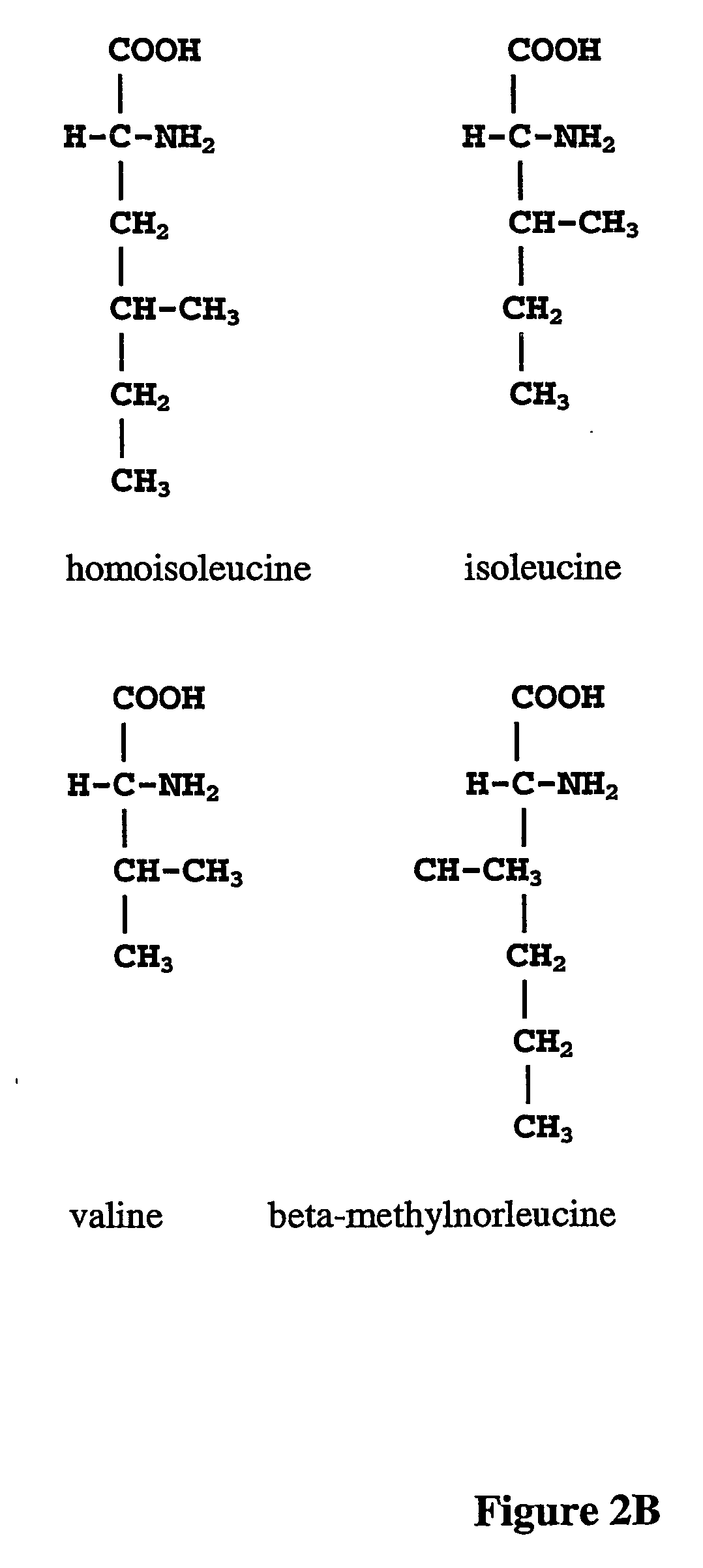
ActiveUS20070009995A1Cellular level is reducedReducing, or substantially eliminating, endogenous cellular levels of norleucineBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsBeta-methylnorleucinePhenylalanine dehydrogenase
The instant invention is drawn to the methods and compositions necessary to provide recombinant proteins with a substantially reduced or eliminated content of norleucine or other non-standard amino acids. Various embodiments of the invention provide for the substantial elimination of the incorporation of non-standard amino acids into recombinant proteins by the co-expression or enhanced expression of a protein (or the enzymatically active portion thereof) capable of degrading norleucine or other non-standard amino acids, including norvaline, beta-methylnorleucine, and homoisoleucine. In certain particular embodiments of the invention, the norleucine is degraded by a glutamate dehydrogenase, a leucine dehydrogenase, a valine dehydrogenase, a phenylalanine dehydrogenase, a glutamate / leucine / phenylalanine / valine dehydrogenase, or an opine dehydrogenase. Also provided are the cells and DNA constructs for carrying out these methods.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of MEK and 2-butanol
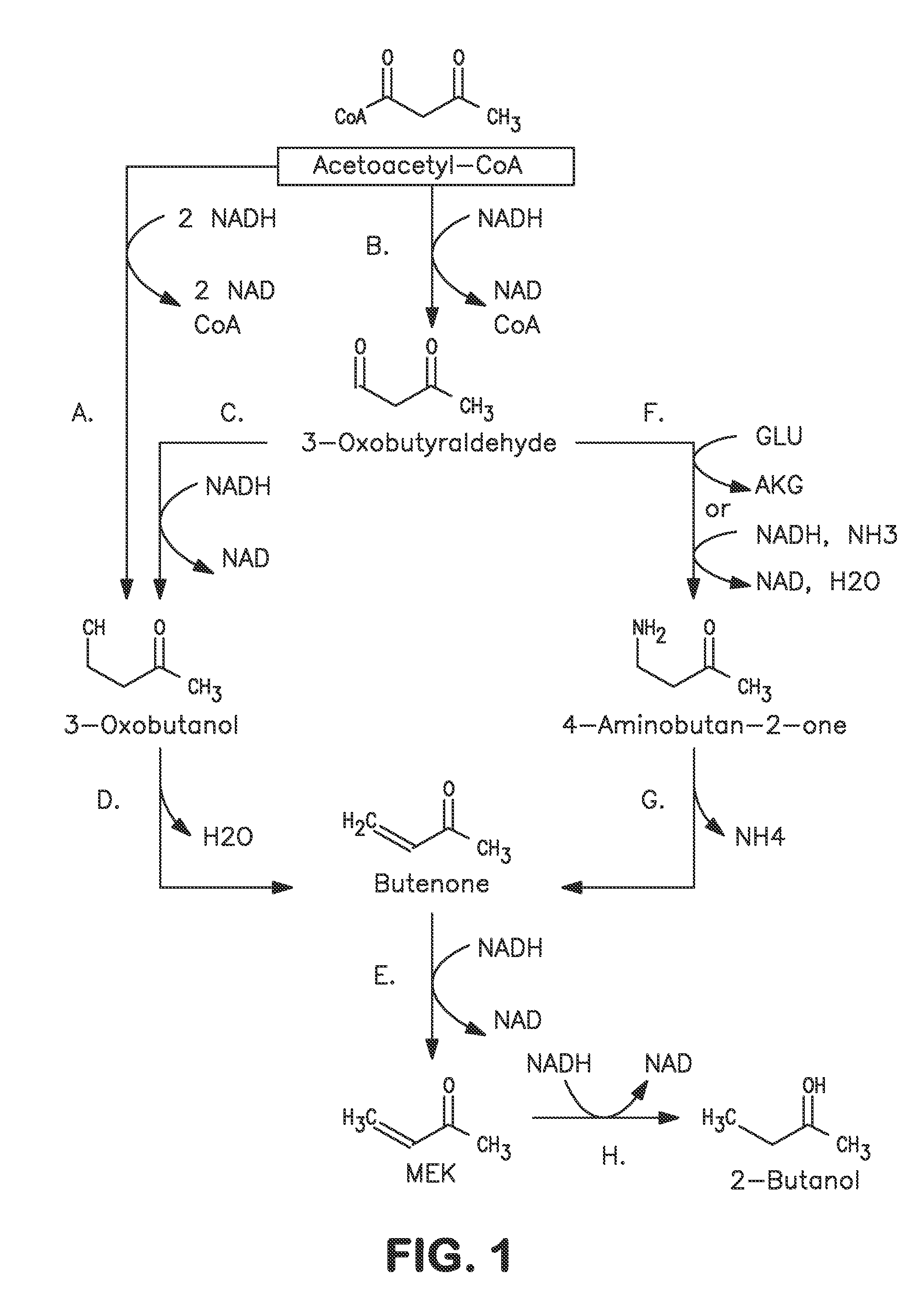
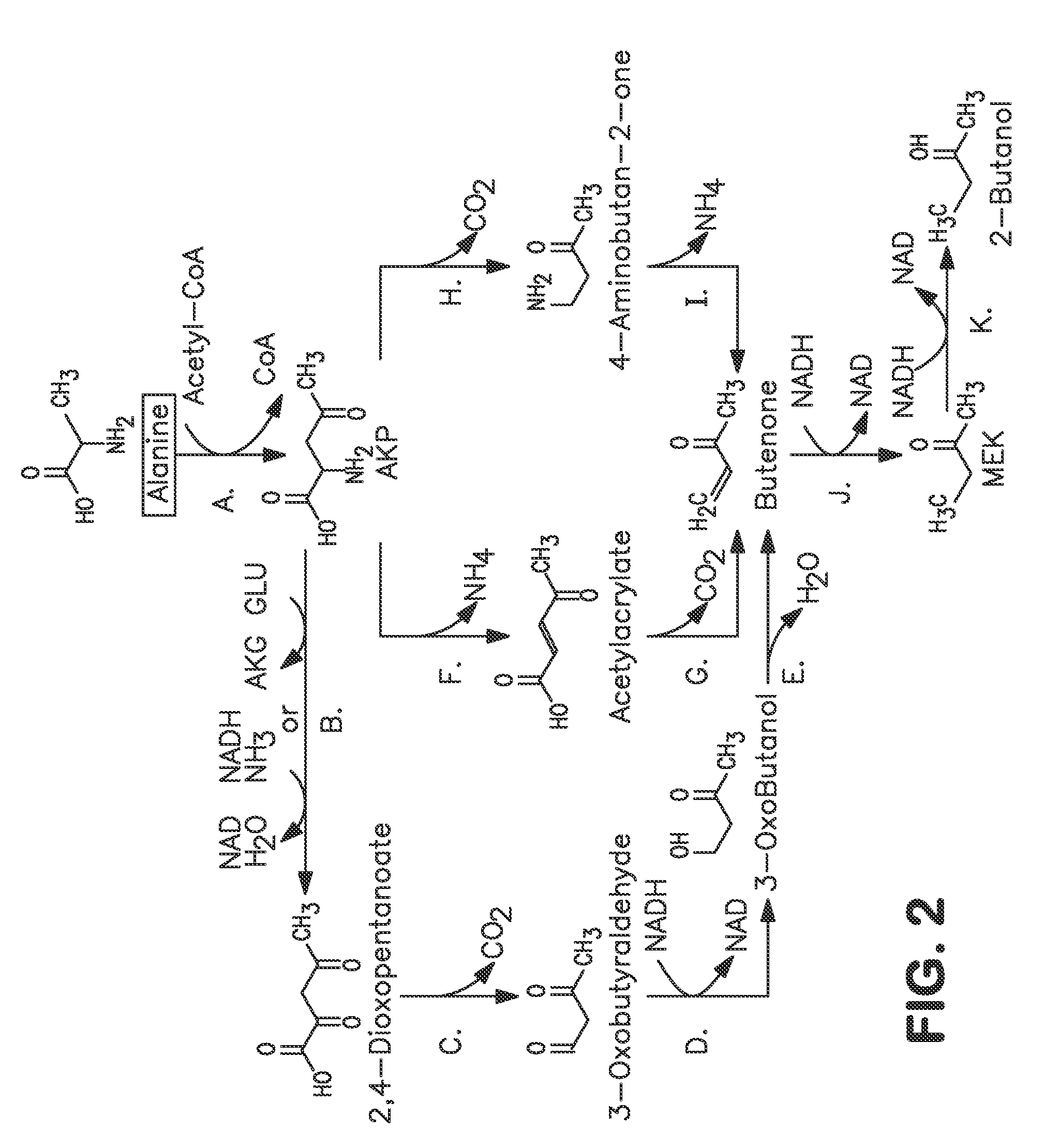
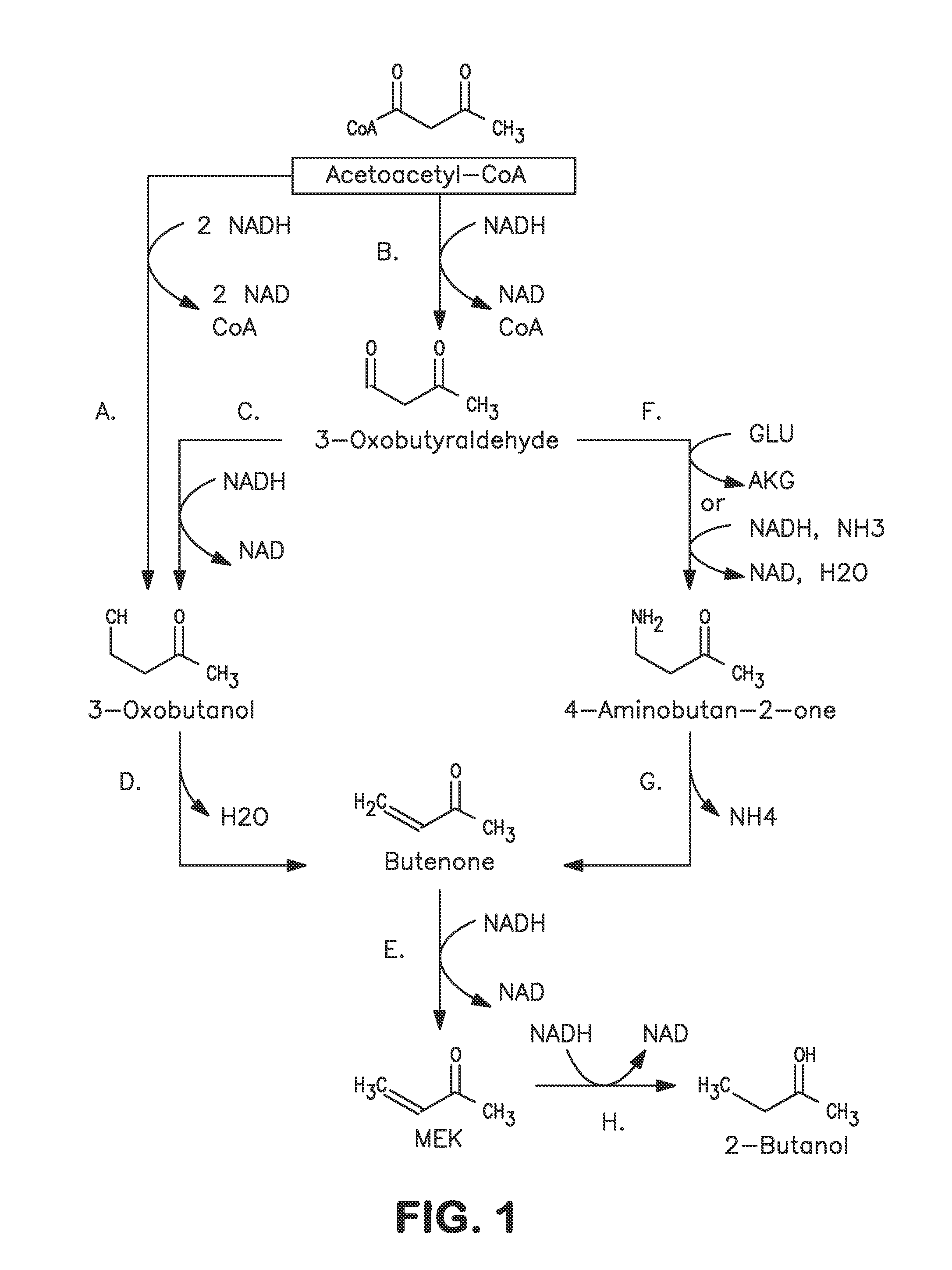
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
A genetically engineered bacterium producing 2-phenylethanol and an applying method thereof
ActiveCN106566794AImprove cycle efficiencyDisinhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhenethyl alcoholPhenylpyruvate decarboxylase
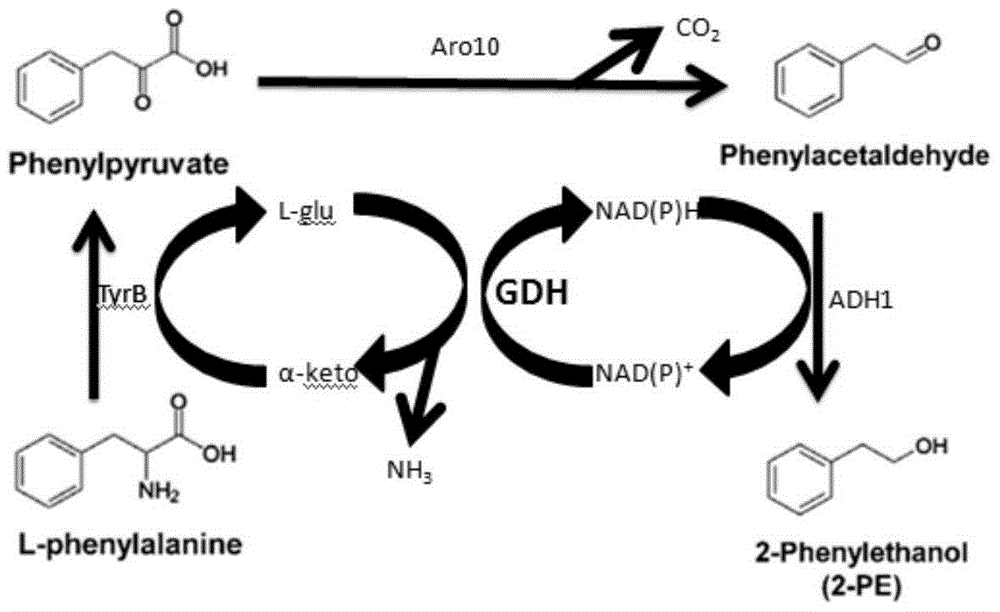
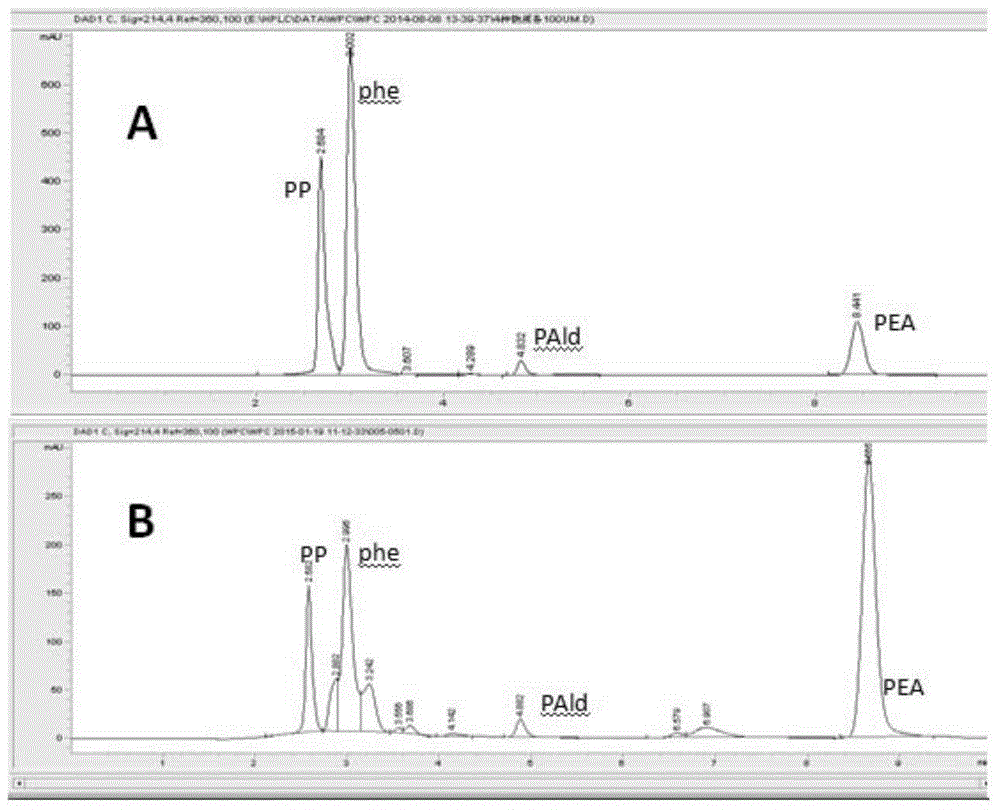
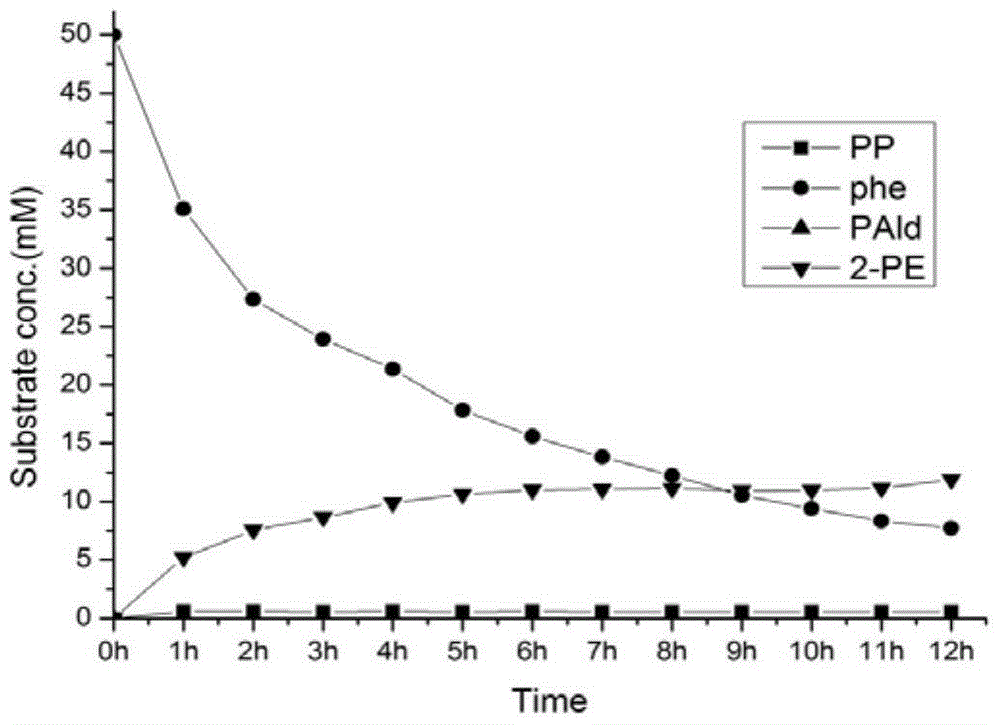
A genetically engineered bacterium producing 2-phenylethanol and an applying method thereof are disclosed. The recombinant bacterium is constructed by coexpressing aromatic amino acid aminotransferase and exogenous phenylpyruvate decarboxylase (Aro10) (or indole-3-pyruvic acid decarboxylase), phenylethanol dehydrogenase or phenylacetaldehyde reductase in escherichia coli to obtain the recombinant bacterium producing the 2-phenylethanol. Glutamate dehydrogenase is coexpressed on this basis to achieve self-balancing cofactor circulation, thus increasing the yield of the 2-phenylethanol. The conversion ratio of the 2-phenylethanol prepared through the recombinant bacterium is high. The bacterium and the method have important application value in production of the 2-phenylethanol in the future.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microorganisms and methods for carbon-efficient biosynthesis of mek and 2-butanol
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism has at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding a MEK pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce MEK. The MEK pathway includes an enzyme selected from an acetoacetyl-CoA dehydrogenase (bifunctional), an acetoacetyl-CoA aldehyde dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde reductase, a 3-oxobutanol dehydratase, an MEK oxidoreductase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde aminotransferase, a 4-aminobutan-2-one deaminase, a 2-amino-4-ketopentanoate (AKP) thiolase, an AKP aminotransferase, a 2,4-dioxopentanoate decarboxylase, an AKP deaminase, an acetylacrylate decarboxylase, an AKP decarboxylase, a glutamate dehydrogenase, a 3-oxobutyraldehyde oxidoreductase (aminating) and an AKP oxidoreductase (aminating). A 2-butanol pathway further includes an MEK reductase. A method for producing MEK or 2-butanol includes culturing these organisms under conditions and for a sufficient period of time to produce MEK or 2-butanol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Glycine diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and glycine concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464279AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsGlycine2-ketoglutaric acid
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring glycine by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of the glycine, and belongs to the technical field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, coenzyme, a 2-ketoglutaric acid, glycine aminotransferase, glutamate dehydrogenase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the increase in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the active concentration of the glycine.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Kit for diagnosing diseases in system of liver and gall
InactiveCN101003831AExtended storage timeUndisturbedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDisease causePolymer
This invention relates to a test kit for diagnosing hepatic and biliary diseases. The test kit has such advantages as high stability, high accuracy and high sensitivity. The test kit comprises two reagents. Reagent 1 comprises oxidized thio coenzyme, buffer solution, preservative, and anti-interference agent. Reagent 2 comprises 3alpha-HSD, reduced coenzyme, buffer solution, preservative, complexing agent, polymer accelerator, stabilizer, and one of formate dehydrogenase-formic acid-NAD, glutamate dehydrogenase-glutamic acid-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase-glucose-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme, glucose dehydrogenase-xylose-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme, lactate dehydrogenase-alpha-ketoglutarate-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme, and glycerol dehydrogenase-ethylene glycol-oxidized nicotinamide coenzyme.
Owner:王贤理
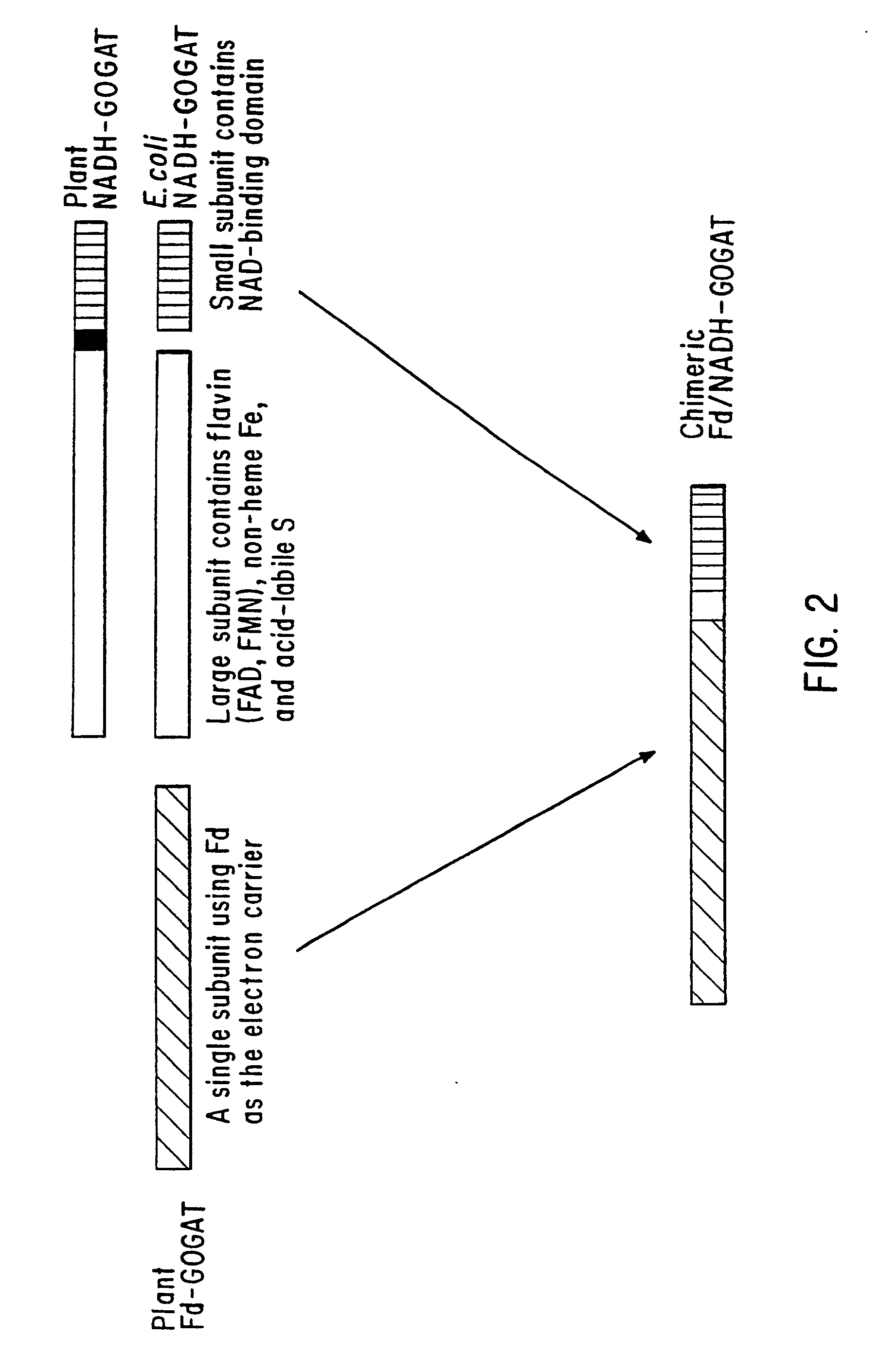
Promoters of the genes glutamate dehydrogenase beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase and gamma-actin and their use in filamentous fungi expression, secretion and antisense systems
InactiveUS6300095B1Less efficiencyUndesirable enzyme activityFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to promoters of the genes glutamate dehydrogenase, beta-acetylhexosaminidase and gamma-actin and their use in systems of expression, secretion and anti-sense of filamentary fungi. The invention also relates to the use of the promoters of the genes which code: (I) glutamate dehydrogenase NADP depending (EC.1.4.1.4) of Penicillium chrysogenum, (II) gamma-N-actylhexosaminidase (EC.3.2.1.52) of Penicillium chrysogenum and (III) gamma-actin of Penicillium chrysogenum and Acrimonium chrysogenum, which can be used for the construction of potent vectors of expression and secretion useful both for P. chrysogenum and for A. chrysogenum and related species. These promoters can also be used for blocking the genic expression through anti-sense construction. Under the control of the above mentioned promoters, it is possible to conduct the expression of other genes in filamentary fungi, thereby increasing the production of antibiotics and / or proteins inherent to the same.
Owner:ANTIBIOTICOS SA
Methylovorus sp. MP688 and application thereof
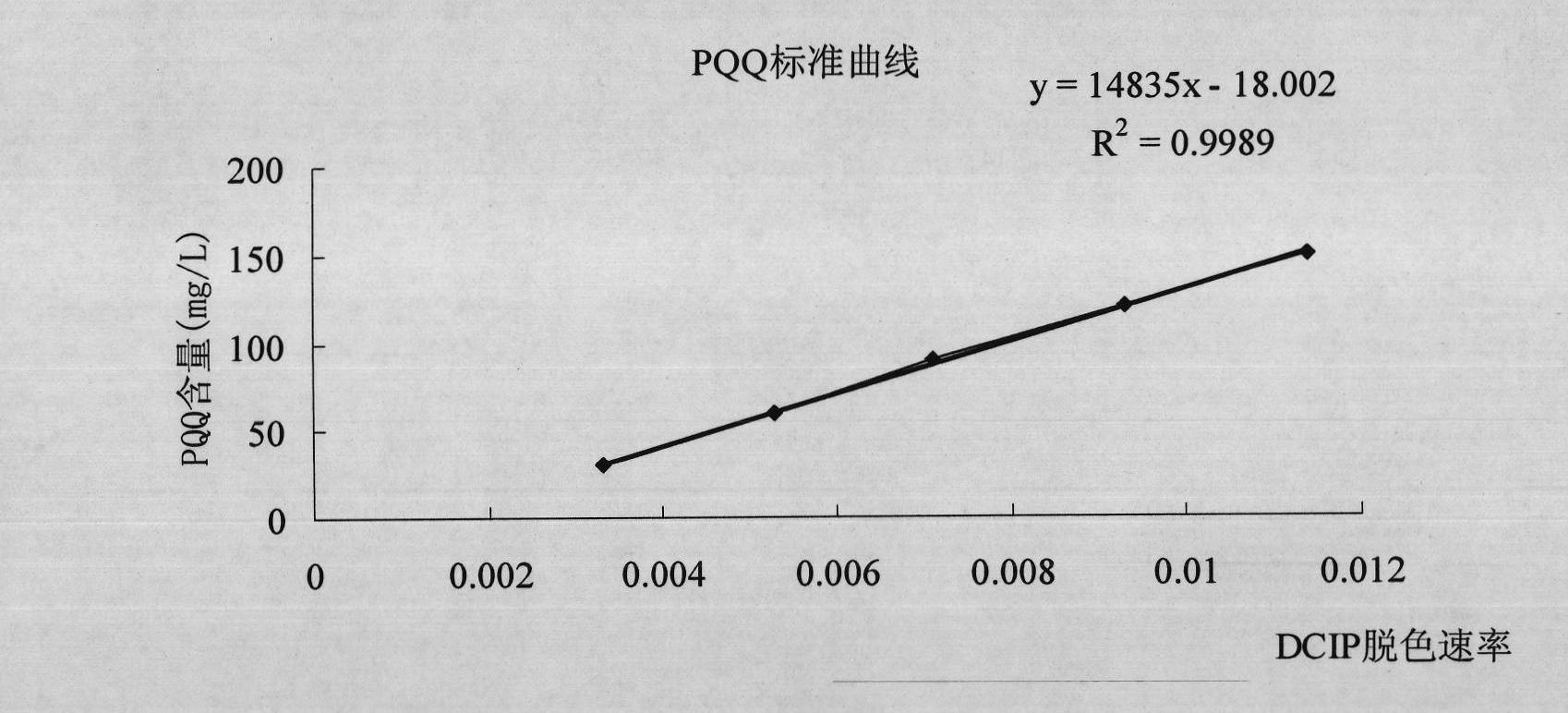
The invention discloses a new strain MP688 of Methylovorus sp., of which the preservation number is CGMCC No.4096, the preservation date is August 20th, 2010, and the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center. The strain MP688 is separated from soil by using a GDH (glutamate dehydrogenase) recombinase method of PQQ (pyrroloquinoline quinone). By using the Methylovorus sp. strain disclosed by the invention, the yield of PQQ can reach 125 mg / L in a conventional culture medium under conventional culture conditions; and the Methylovorus sp. strain can be used for industrial production of PQQ, and has important meaning for promoting the industrialization of PQQ.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Metabolic gene, enzyme, and flux targets for cancer therapy
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Recombinant strain for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN106148259AIncrease productionHigh substrate conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-2-Aminobutyric AcidThreonine
The invention discloses a recombinant strain for producing L-2-aminobutyric acid and a preparing method and application thereof. The recombinant strain is a strain obtained in the mode that threonine dehydratase, transaminase and glutamate dehydrogenase are subjected to overexpression at the same time. Due to the recombinant strain for producing the L-2-aminobutyric acid with threonine serving as a substrate, the yield of the L-2-aminobutyric acid and the substrate conversion ratio are remarkably increased, accumulation of by-products is effectively reduced, and the production technology is simplified.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nano antibody of clostridium difficile glutamate dehydrogenase, and encoding sequence, screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN109336979ASimple and fast operationReduced operating requirementsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionScreening methodCoat protein
The invention provides a nano antibody of clostridium difficile glutamate dehydrogenase, and an encoding sequence, a screening method and the application thereof and belongs to the technical field ofimmunology. The invention provides an amino sequence of the nano antibody of clostridium difficile glutamate dehydrogenase. By using a phage display technology, a sequence with a constant region specific gene is inserted into a vector of a phage encoding coat protein, after recombination expression, an exogenous gene expression product is fused with the phage encoding coat protein and demonstratedon the surface of phage to form a phage demonstration library, phage monocloning of the nano antibody is expressed through screening, and the nano antibody is prepared through sequencing. Phage-ELLSAidentification shows that the phage that the nano antibody is expressed on the surface can be specifically combined with clostridium difficile glutamate dehydrogenase antigen and has a good developing property, the result shows that the nano antibody has a good combination property with glutamate dehydrogenase, therefore, the nano antibody can be adopted to replace a common antibody applied to aclostridium difficile immunodetection kit.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Compounds useful for the treatment of metabolic disorders and synthesis of the same
InactiveUS20160046560A1Prevent and treat diseaseBiocideCarboxylic acid nitrile preparationMetabolic disorderStereochemistry
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I): wherein variables X, Y, Z and R1 are as described herein. Some of the compounds described herein are glutamate dehydrogenase activators. The invention is also directed to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these compounds, uses of these compounds and compositions in the treatment of metabolic disorders as well as synthesis of the compounds.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA CENTRAL UNIVERSITY +1
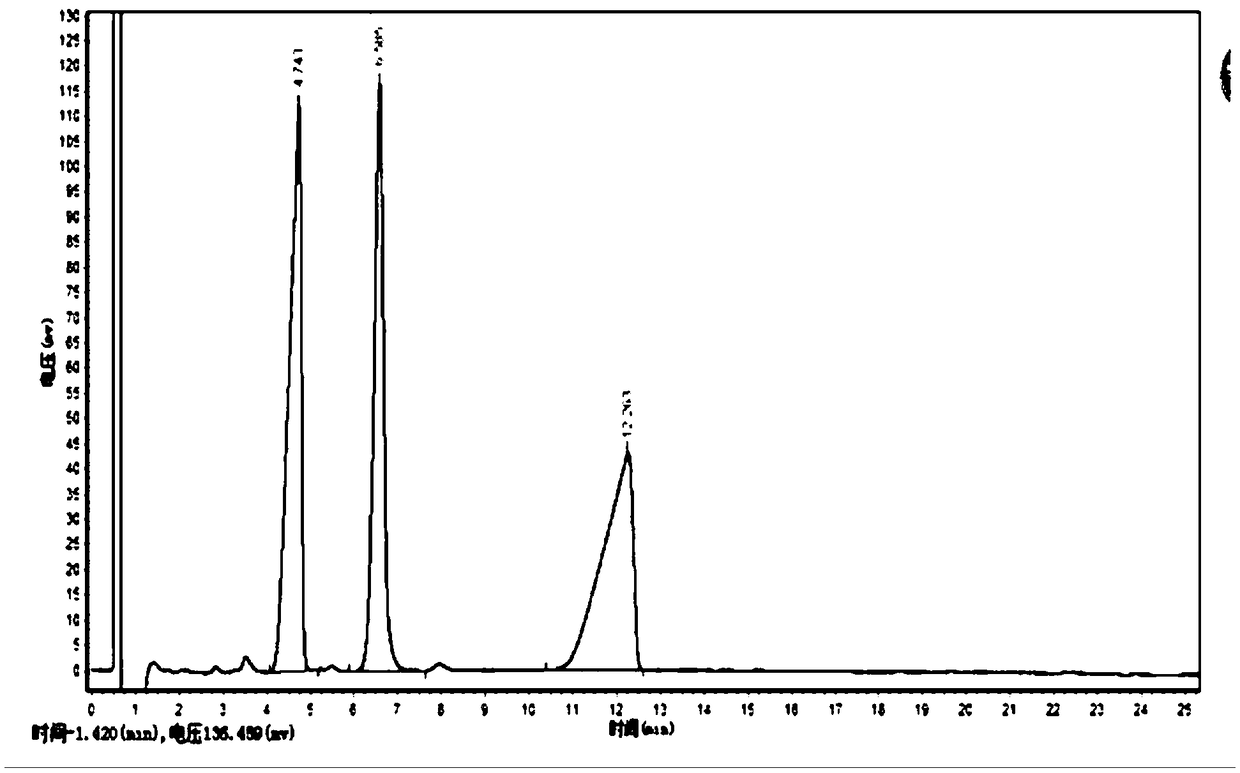
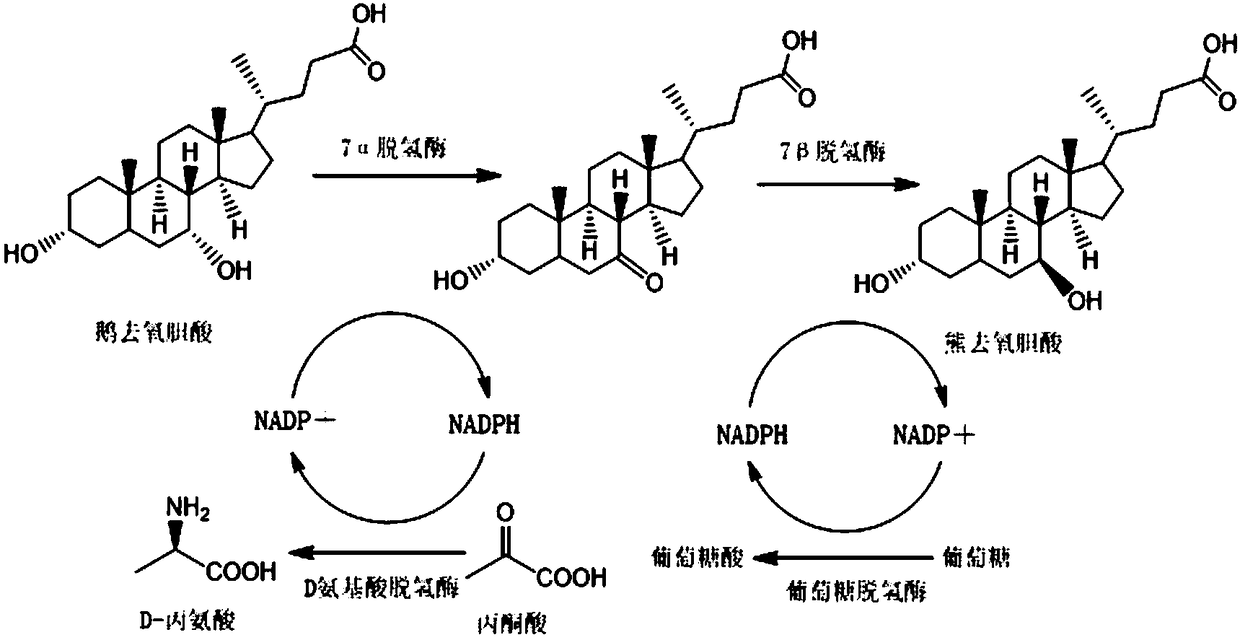
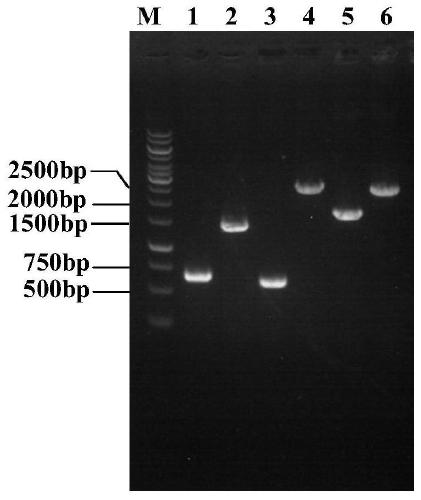
Method for synthesizing ursodeoxycholic acid and high-chiral-purity D-amino acid based on enzyme-method coupling technology
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and high-chiral-purity D-amino acid based on an enzyme-method coupling technology. The method comprises the following steps: putting chenodeoxycholic acid and alpha-ketonic acid into a solution system containing 7alpha-HSDH (Homoserine Dehydrogenase), DAADH and NADP (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate) and carrying out enzyme catalysis reaction; separating a reaction solution by adopting an ultra-filtration membrane to obtain a concentrated mixed enzyme solution; regulating the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) ofa dialysis solution and crystallizing; filtering and separating to obtain 7-KLCA wet powder and filtrate; carrying out chromatographic treatment on the filtrate to obtain the D-amino acid; putting the7-KLCA wet powder into a solution system containing glucose, the NADP, the 7alpha-HSDH and GDH (Glutamate Dehydrogenase) and carrying out enzyme catalysis reaction; separating the reaction solution by adopting the ultra-filtration membrane to obtain the concentrated mixed enzyme solution; crystallizing, filtering and separating the dialysis solution, so as to obtain ursodeoxycholic acid. By adopting the method provided by the invention, UDCA and the high-chiral-purity D-amino acid can be obtained at the same time, the enzyme utilization rate is high, synthesis steps are simple and the cost isreduced; meanwhile, a metal reduction reagent and an organic solvent do not need to be added in a reaction process and conditions are mild; the method is environmentally friendly and is suitable forindustrial production.
Owner:HUNAN BAOLISHI BIOTECH
Genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof
ActiveCN109777763AIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCitrate synthase
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Plants having enhanced yield-related traits and a method for making the same
The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for improving various plant growth characteristics by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a GDH (Glutamate DeHydrogenase) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a GDH polypeptide, which plants have improved growth characteristics relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing various economically important yield-related traits in plants. More specifically, the present invention concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a FLA-like (Fasciclin-like) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a FLA-like polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to control plants. The invention also provides constructs comprising FLA-like- encoding nucleic acids, useful in performing the methods of the invention. The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing yield-related traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a SAUR polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a SAUR polypeptide, which plants have enhanced yield-related traits relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention. Furthermore, the present invention also relates to a SAUR-based protein complex. It further relates to the use of the complex to enhance yield-related traits, and to a method for stimulating the complex formation, by overexpressing at least two members of the complex. The present invention relates generally to the field of molecular biology and concerns a method for enhancing yield traits in plants by modulating expression in a plant of a nucleic acid encoding a dehydroascorbate reductase (DHAR) polypeptide. The present invention also concerns plants having modulated expression of a nucleic acid encoding a DHAR polypeptide, which plants have enhancing yield traits relative to corresponding wild type plants or other control plants. The invention also provides constructs useful in the methods of the invention.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Enzyme combination for producing L-phosphinothricin, and production method of L-phosphinothricin
InactiveCN111139270AReduce manufacturing costTake full advantage of catalytic activityOxidoreductasesFermentationPhosphorous acidPhosphite dehydrogenase
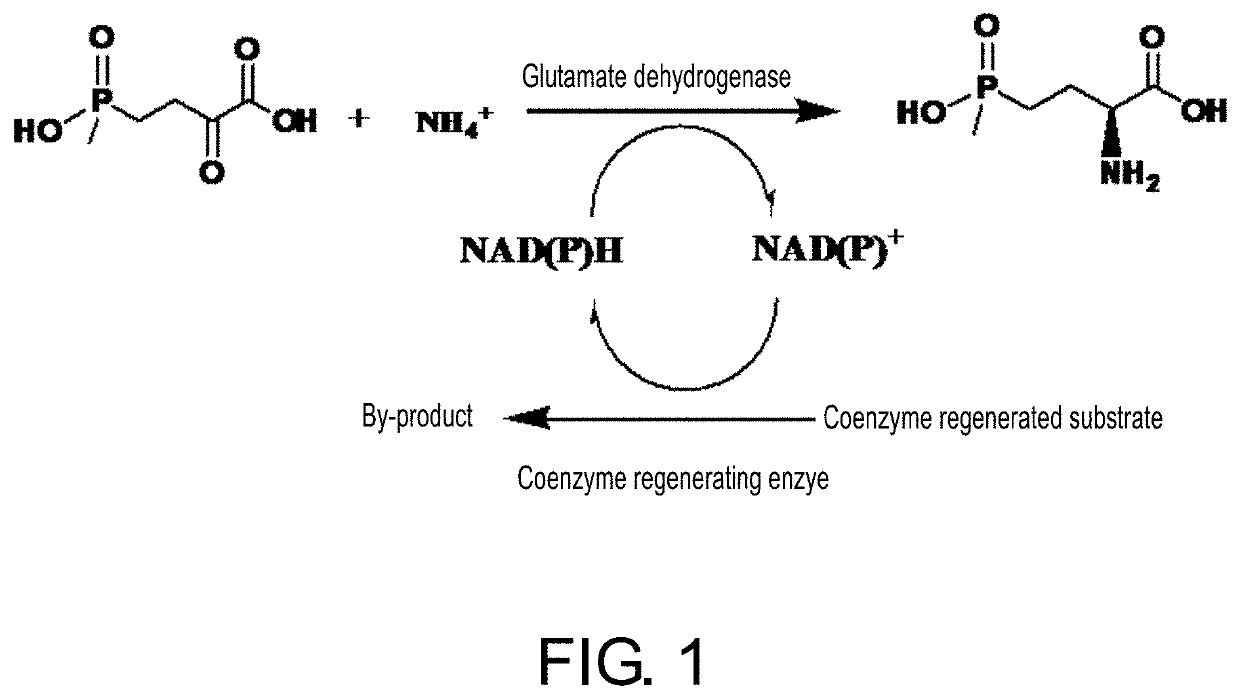
The invention discloses an enzyme combination for producing L-phosphinothricin. The enzyme combination comprises glutamate dehydrogenase and a coenzyme regenerating enzyme, wherein the coenzyme regenerating enzyme is alcohol dehydrogenase, formate dehydrogenase and phosphite dehydrogenase. The invention also discloses a production method of L-phosphinothricin, 4-(methylhydroxyphosphinyl)-2-oxobutyric acid is used as a raw material, NH<4><+>, a coenzyme NADP<+> / NADP, and a coenzyme regeneration substrate are added, and then the enzyme combination is used for catalysis, wherein the glutamate dehydrogenase is used to catalyze a reaction of 4-(methylhydroxyphosphinyl)-2-oxobutyric acid to obtain L-phosphinothricin, and the coenzyme regenerating enzyme is used to reduce NADP<+> to NADP. According to the enzyme combination and the production method of L-phosphinothricin provided by the invention, by-products produced are very easy to remove, a post-treatment process of the product is simplified, the total yield of the product is greater than 95%, and the production cost of L-phosphinothricin is reduced, so that the method is a green, environment-friendly, and low-carbon process route, and is suitable for large-scale industrial production applications.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Glycine diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and glycine concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464280AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurements2-ketoglutaric acidEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring glycine by utilizing the technologies of the enzymatic doubling amplification method, the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of the glycine, and belongs to the technical field of medical / food inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, coenzyme, a 2-ketoglutaric acid, guanosine monophosphate, glycine aminotransferase, glutamate dehydrogenase, guanosine monophosphate reduced enzyme and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the degree / velocity of the increase in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the active concentration of the glycine.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Spectrophotometric method for quickly detecting content of ethyl carbamate
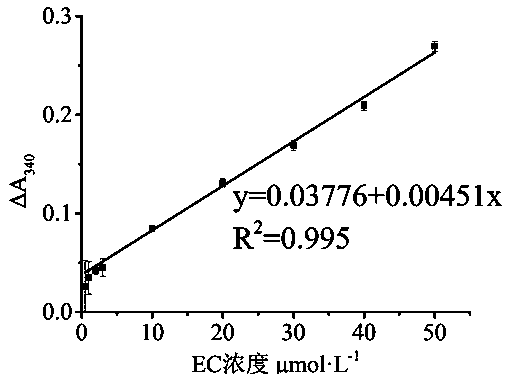
ActiveCN104266984AColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotochemistryNicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
The invention discloses a spectrophotometric method for quickly detecting the content of ethyl carbamate, and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry and food safety inspection. Ethyl carbamate degrading enzyme and glutamate dehydrogenase construct a double-enzyme coupled system; the ethyl carbamate degrading enzyme hydrolyzes the ethyl carbamate to generate ethyl alcohol, water and ammonia, the ammonia reacts with a cosubstrate alpha-ketoglutarate under the catalysis of the glutamate dehydrogenase to generate glutamic acid, and reduced coenzyme namely NADH (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Hydrogen) is oxidized concomitantly, so that the system changes the content of the ethyl carbamate into the content of the NADH, and the content of the ethyl carbamate in a liquid-state system can be detected by using the change of the light absorption value of the NADH at 340nm. By virtue of the method, the ethyl carbamate in a solution can be quickly detected, the ethyl carbamate in a yellow wine system can be simulated, the detection limit is as low as 0.1mu mol. L<-1>, and an effective way is provided for the detection of the ethyl carbamate in fermented food and beverages.
Owner:ANHUI HUATENG AGRI TECH CO LTD
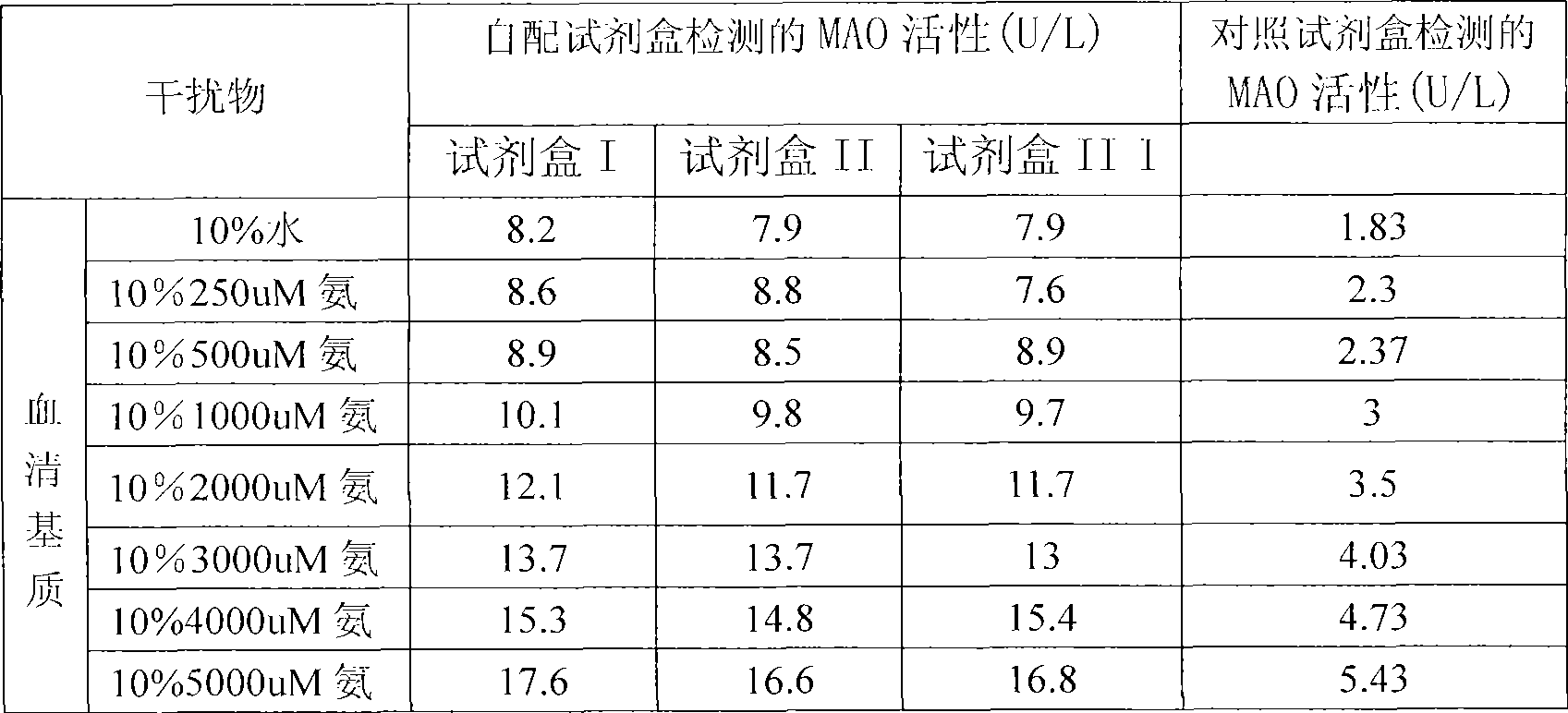
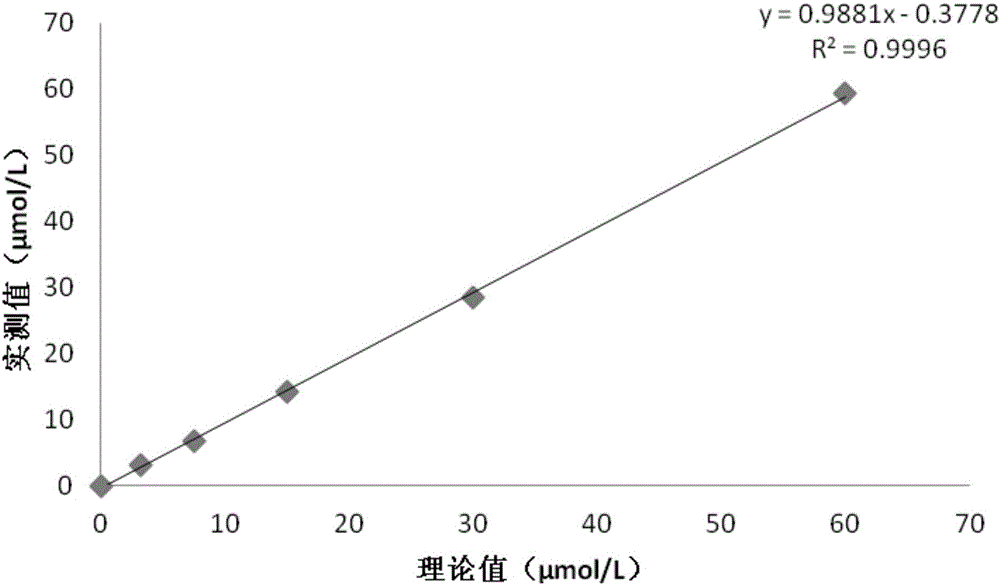
Blood ammonia reagent kit for enzyme detection
The reagent kit for enzyme detection of blood ammonia consists of tromethamine in 50-150 mmol, Tween-20 in 0.1-2 ml, sodium azide om 0.5-2 g, lactose in 5-50 g, glutamate dehydrogenase in 500-1500 u, alpha-ketoglutaric acid in 2-20 mmol, sodium acetonate in 1-10 mmol, and reducing nicotin-amide-adenine dinuclectide phosphate in 0.1-0.5 mmol. After regulating pH to optimal value of 8.0, the components are dissolved, packed and freeze dried and may be cold stored for two years. After being re-dissolved, the components are stabilized at room temperature for 1 week and cold stored to stabilize for 1 month. The reagent kit has powerful interference resistance, medium hemolysis and chylemia, blood sugar below 20 mmol / L, bilirubin below 0.1 mmol / L, enzyme activity loss less than 5 %, MADPH loss less than 10 %, linearity reaching 0.2 mmol / L, CV inside batch of 3.8 % and CV between batches of 5.1 %, and recovering rate of 96.1 %.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of urea determination reagent ball, reagent ball and detection chip
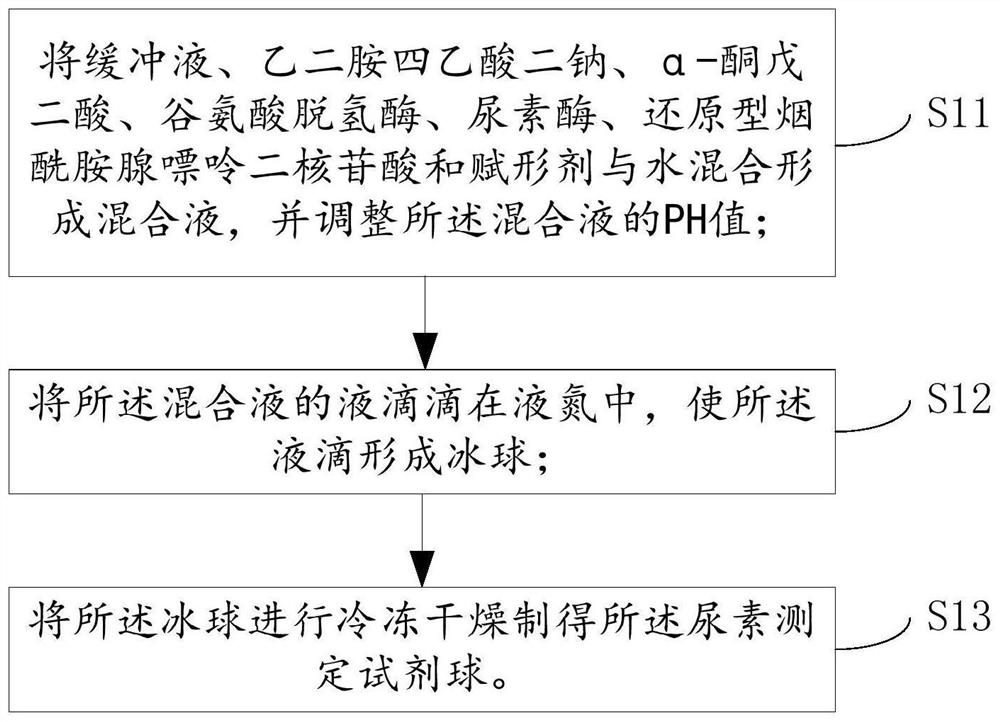
PendingCN111707631AWide effective test rangeHigh maximum concentrationPreparing sample for investigationLaboratory glasswaresGlutaric acidFreeze-drying
The invention relates to the technical field of urea detection, in particular to a preparation method of a urea determination reagent ball, the reagent ball and a detection chip. The embodiment of theinvention provides a preparation method of a urea determination reagent ball. The method comprises the following steps of mixing a certain dosage of buffer solution, disodium ethylene diamine tetraacetate, alpha-ketoglutarate, glutamate dehydrogenase, urease, reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and excipient with water to form a mixed solution, dropwise adding the mixed solution into liquidnitrogen to enable liquid drops of the mixed solution to form ice balls, and freeze-drying the ice balls to obtain spherical urea determination reagent balls. The urea determination reagent ball prepared by the method has good thermal stability, can be stored for 8 days at a high temperature of 37 DEG C, is not easy to deteriorate in the storage process, has a wide effective test range on urea inblood, and can test the highest concentration of blood urea as high as 35mmol / L.
Owner:GENRUI BIOTECH INC
Sirt4 and uses thereof
Provided herein are SIRT4 compositions and methods of use thereof. The invention provides functional information for use in the identification and design of compounds that modulate SIRT4 enzyme activity (e.g., inhibition of fatty acid oxidation, ADP ribosylation, and / or downregulation of glutamate dehydrogenase), and to the compounds identified by such methods and the research, diagnostic and therapeutic uses of such compounds.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and their application in preparation of l-phosphinothricin
ActiveUS20200102546A1High catalytic activityLow glutamateOxidoreductasesFermentationValineAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The present invention relates to glutamate dehydrogenase mutants and their application in preparation of L-phosphinothricin. The amino acid sequences of the glutamate dehydrogenase mutants are as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1˜9, 11, 13, 15, 17˜19 and 22. By means of molecular engineering, mutating the specific alanine in glutamate dehydrogenase substrate-binding pocket into glycine and / or mutating the specific valine in glutamate dehydrogenase substrate-binding pocket into alanine, the present invention has obtained NADPH-specific glutamate dehydrogenase mutants with high enzyme activity in catalyzing the substrate 2-oxo-4-[(hydroxy)(methyl)phosphinoyl]butyric acid or its salt for L-phosphinothricin preparation or NADH-specific glutamate dehydrogenase mutants with catalytic activity toward PPO; this has significantly improved substrate conversion, and increased the product concentration of the L-phosphinothricin preparation process.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
5'-nucleotidase diagnosing reagent kit and 5'-nucleotidase activity concentration measurement method
InactiveCN101097200AMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidaseExtinction
The invention relates to a 5'-nucleotidase diagnosis reagent box of Enzymatic Recycling Method, and the invention also relates to method principle for detecting the solution of 5'-nucleotidase, constitute and component of reagent, which belongs to the technical field of medical checking measurements. The reagent box in the invention can be dry powder state, and used after dissolution; it also can be formulated to be liquid agent for direct usage. The component of reagent box mainly contains: buffering liquid, alpha- ketoglutaric acid, reduction type coenzyme, Adenosine Deiminase EC 3.5.4.4, glutamate dehydrogenase EC 1.4.1.2, EC 1.4.1.3, EC 1.4.1.4, Glutamate oxidase EC 1.4.3.7, EC 1.4.3.11, peroxidase EC 1.11.1.7, reduction type chromogen assembly, stabilizer and anti-interference agent; and the component can be mixed to form single-reagent reagent box, two-reagent reagent box, and three-reagent reagent box; by series of enzymatic reaction, the colorless reduction type chromogen assembly is oxygenated to form color dye, and the content of dye can be measured by visible light analyzer at wavelength of 400-700nm to reflect the concentration of 5'-nucleotidase directly. Comparing with present technique, the invention can be spread easily, and because the produced dye has higher molar extinction coefficient, the sensitivity is high, and the precision is well.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Reagent kit for monoamine oxidase MAO single-reagent measurement
InactiveCN101498662AEasy to operateEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsSemi automaticOxygen
The invention discloses a kit of single reagent used for diagnosing monoamine oxidase (MAO) in serum. MAO hydrolyzed benzylamine, butyl amine, amyl amine, Beta-phenylethyl amine and other amine compounds are utilized to produce oxygen; the oxygen reacts with glutamate dehydrogenase in a coupling way; oxidized coenzyme is formed by the reaction of reduced coenzyme; and the activity of sample MAO formed by quantitative reaction is calculated through measuring the descending speed of the absorbance of light with a wavelength of 340 nm; in addition, enzyme and substrate enzyme which can slowly generate reduced nicotinoyl coenzyme are added in the reaction process, so that an enzyme-substrate enzyme-nicotinoyl coenzyme slow reaction system is formed in single reagent and the nicotinoyl coenzyme can be compensated slowly and circularly and further the single reagent can be stabilized when the concentration of the single reagent achieves a certain balance. The kit is convenient for use and simple is structure, can be used on a common ultraviolet / visible light analyzer or a semi-automatic / full-automatic biochemical analyzer for rapid measurement without using a special or additional apparatus and has low cost.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
Homocysteine diagnosis kit and homocysteine concentration measuring method
InactiveCN106198995AEasy to detectLow priceColor/spectral properties measurementsBiological testingFluorescencePhosphine
The invention relates to a homocysteine concentration measuring method. The method includes: oxidizing homocysteine to generate alpha-butanone acid, ammonia and hydrogen sulfide; using ammonia to convert NADH into NAD+ under action of glutamate dehydrogenase; quantifying by measuring light absorbance of NADH at a position of 340nm. The homocysteine diagnosis kit comprises a reagent I and a reagent II, the reagent I contains reduced coenzyme I, glutamate dehydrogenase, tri(2-carboxyethyl) phosphine hydrochloride, alpha-ketoglutaric acid, surfactant, buffer solution and stabilizer, and the reagent II contains HCYase, phosphopyridoxal, buffer solution and stabilizer. The homocysteine diagnosis kit and the homocysteine concentration measuring method have the advantages that the kit for detecting homocysteine in human serum through two liquid reagents is built, and an additional fluorescence detector is not needed, so that convenience is brought to detection of plenty of samples; the method is free of interference by pyruvic acid, methionine and cysteine in the samples and lower in cost.
Owner:ENZYMAKER LABCHANGZHOU CO LTD
Method of producing transgenic plants having improved amino acid composition
InactiveUS6969782B2Increase the content of free amino acidsGreat tasteClimate change adaptationStable introduction of DNAThreoninePlant cell
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for simultaneous determination of double items of urea nitrogen and creatinine in serum
The invention discloses a method for simultaneous determination of double items of urea nitrogen and creatinine in serum, and belongs to the method for testing a material through testing color changes of reaction results by using visible light; the technical scheme comprises that a reagent II only comprises effective components of creatinine amidohydrolase and creatine amidinohydrolase; a reagent I contains effective components of urease, glutamate dehydrogenase, alpha-ketoglutarate and NADH. The determination method comprises the steps: firstly, carrying out 37 DEG C warm bath of serum with the reagent I for 3-5 minutes; carrying out a reaction of urea in the serum with the reagent I to generate NAD+; adding the reagent II, carrying out 37 DEG C warm bath for 4-7 minutes, hydrolyzing creatinine with the creatinine amidohydrolase to generate creatine; making the creatine generate urea under the action of the creatine amidinohydrolase, and making the urea and the reagent I generate NAD+ under the action of urease; at the wavelength of 340 nm, comparing the reaction speed with that of a standard treated by the same way, determining the change of the first-step reaction NADH, namely the content of urea nitrogen in the serum, and determining the change of the second-step reaction NADH, namely the content of the creatinine in the serum.
Owner:TIANJIN BAODI HOSPITAL
A genetically engineered bacterium for the production of l-theanine and its construction and application
ActiveCN109777763BIncrease enzyme activityGene expression is stableBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to novel high-efficiency gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthetase and a plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium for L-theanine production and construction and application thereof. The plasmid-free genetic engineering bacterium which performs denovo synthesis on L-theanine efficiently by taking cheap carbon sources such as glucose as a substrate is provided, escherichia coli serves as a host, and gamma-glutamyl methylamine synthase genes gmas-Mu copied three times are integrated on a genome of the escherichia coli; a glutamate dehydrogenase gene Cgl2079 is copied once; a pyruvate carboxylase gene Cgl0689 is copied once; a citrate synthase gene gltA is copied once, and the genetic engineering bacterium is obtained. After metabolic transformation of a system, the engineering bacterium can perform denovo synthesis on the L-theanine by taking the glucose as the raw material, the fermentation yieldand sugar-acid conversion rate are the highest values reported so far, in fermentation of a 5 L fermentor, the maximum production of the L-theanine can reach 60 g / L, and the sugar-acid conversion ratecan reach 40%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com