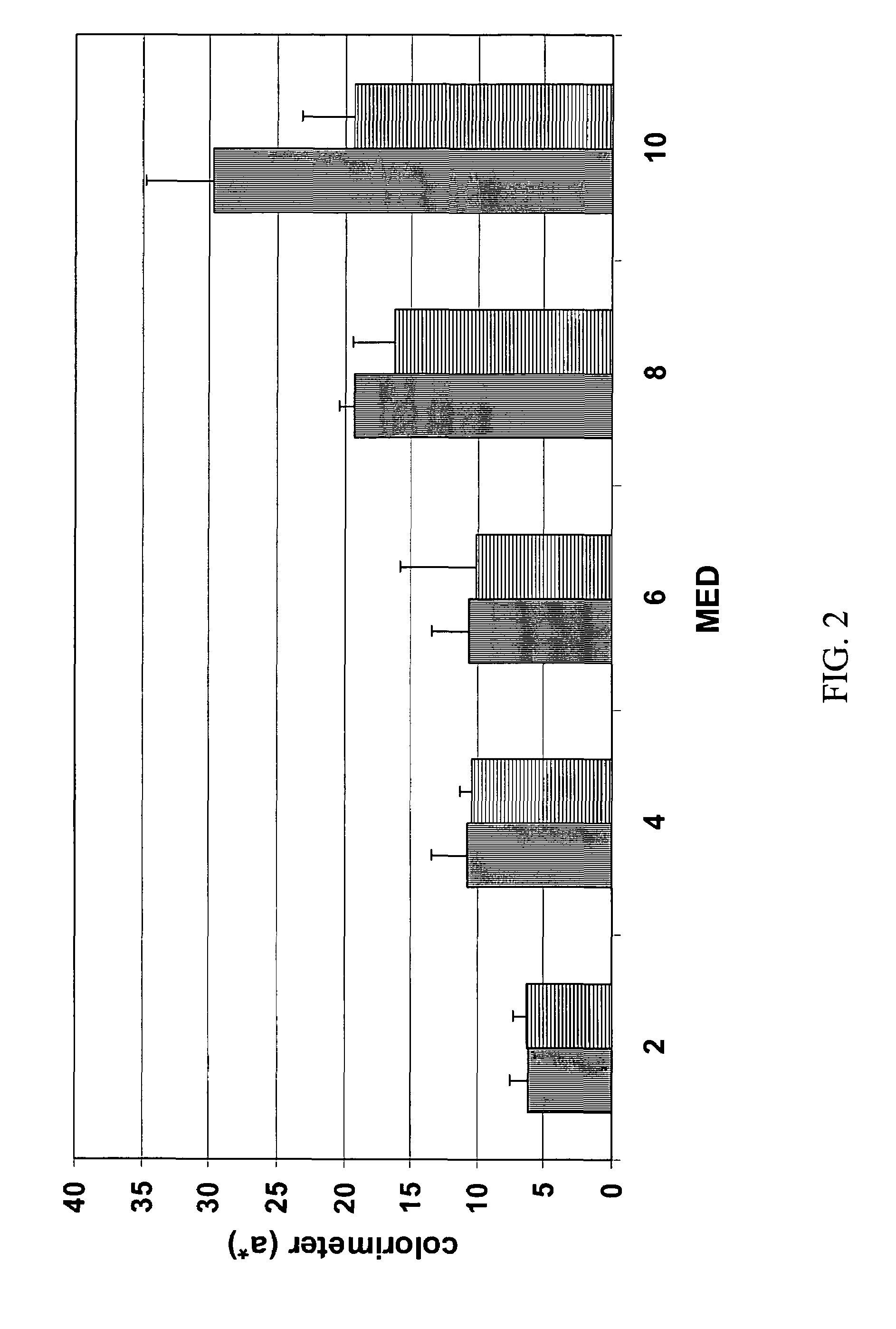
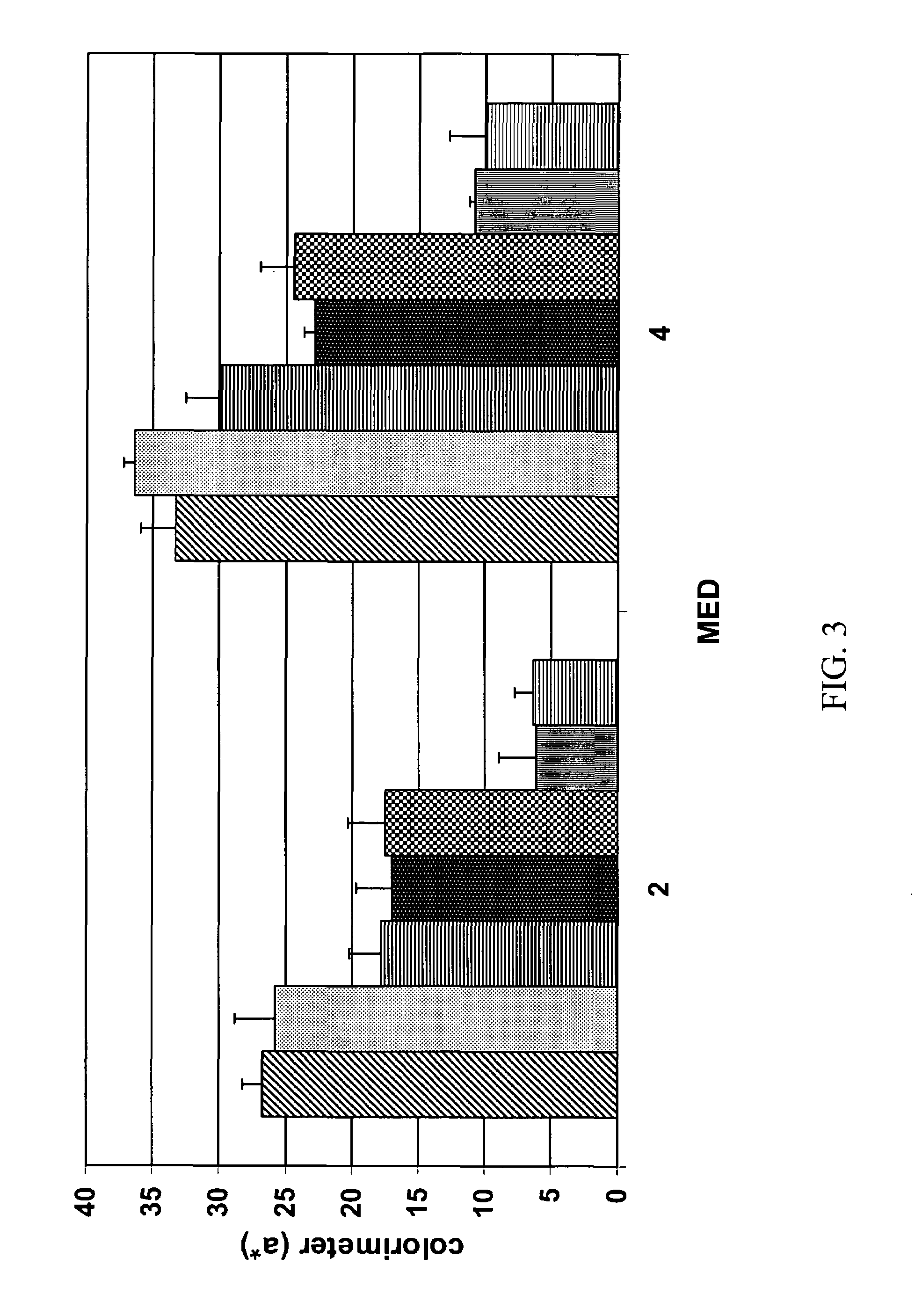
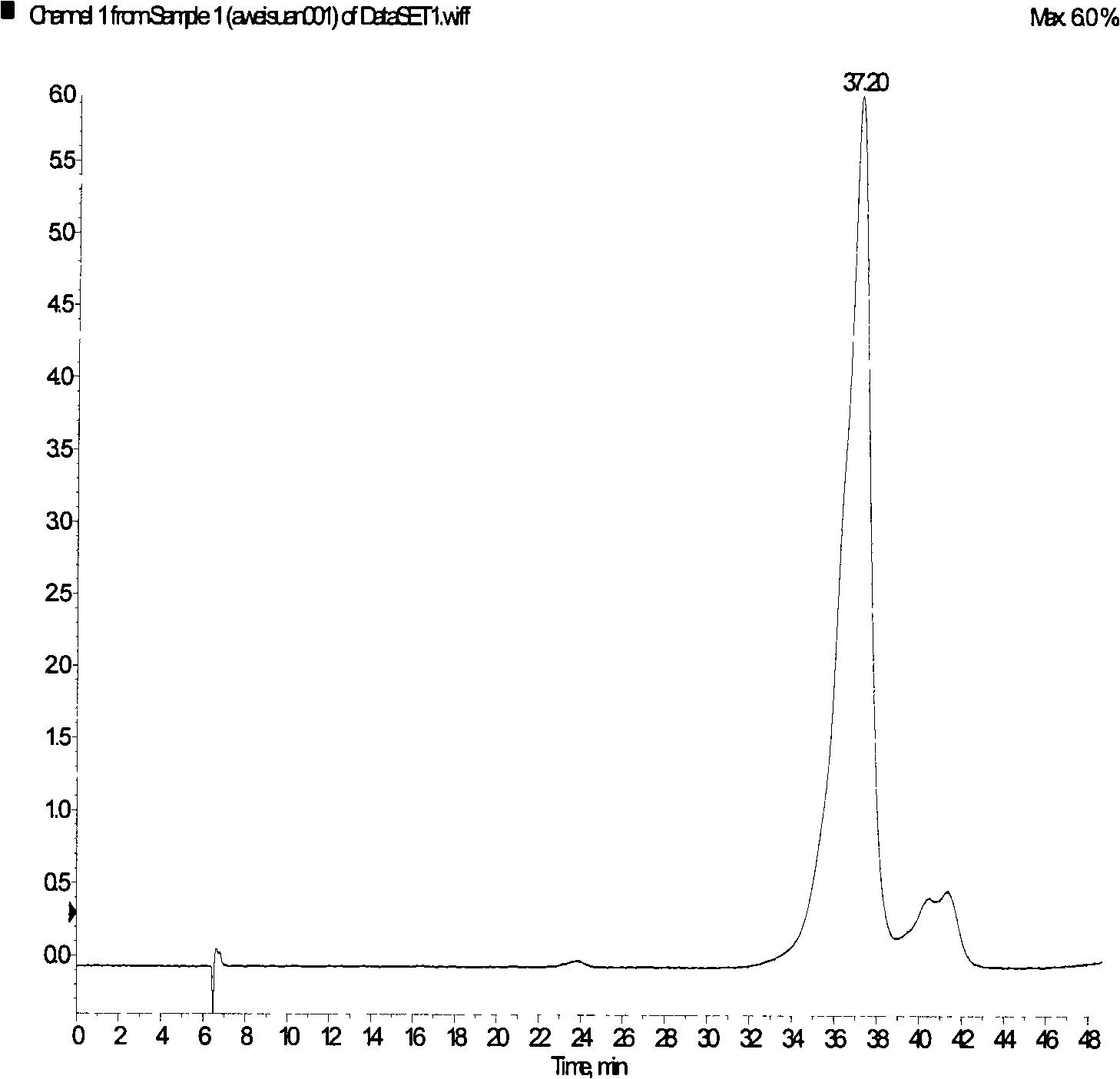
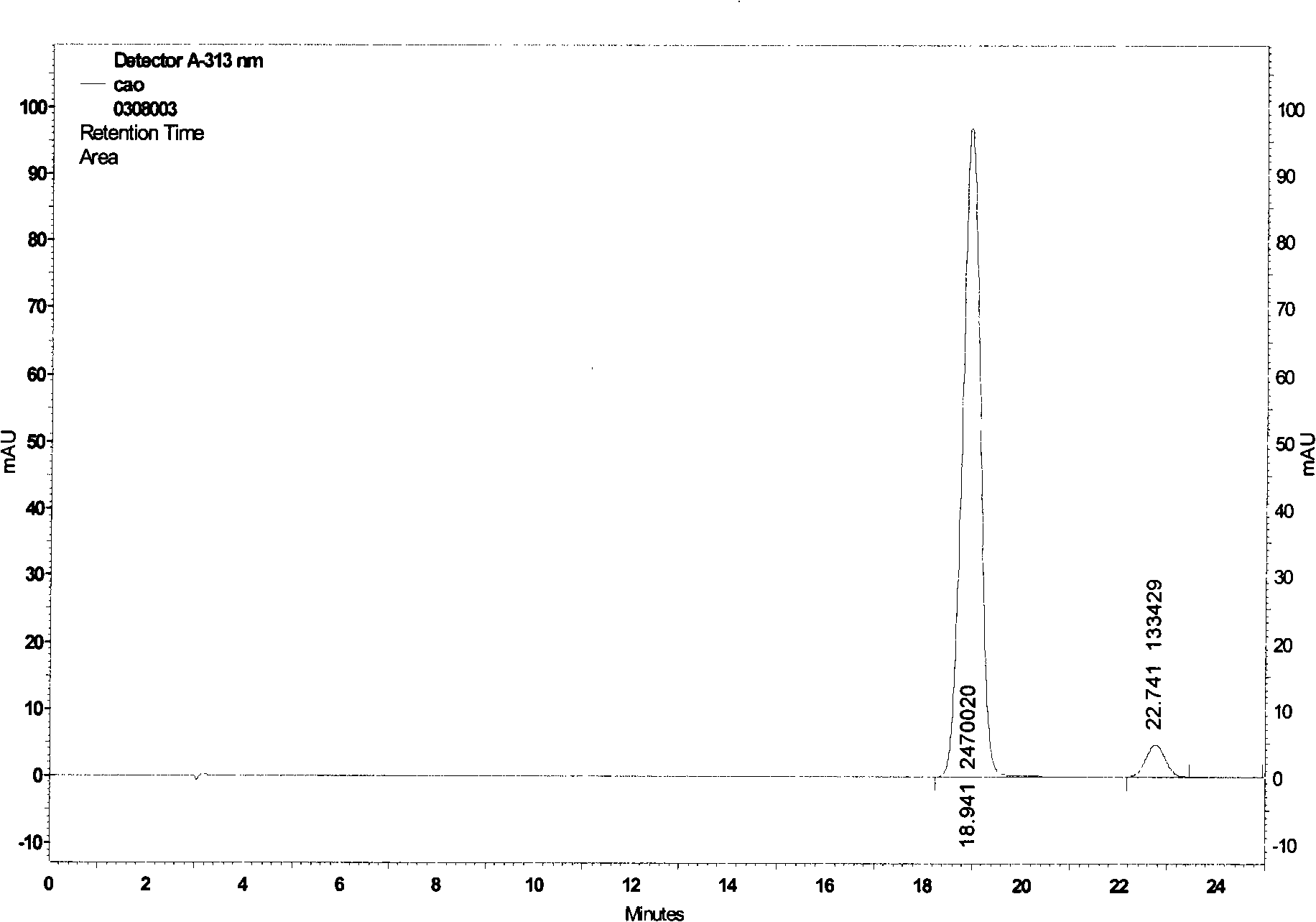
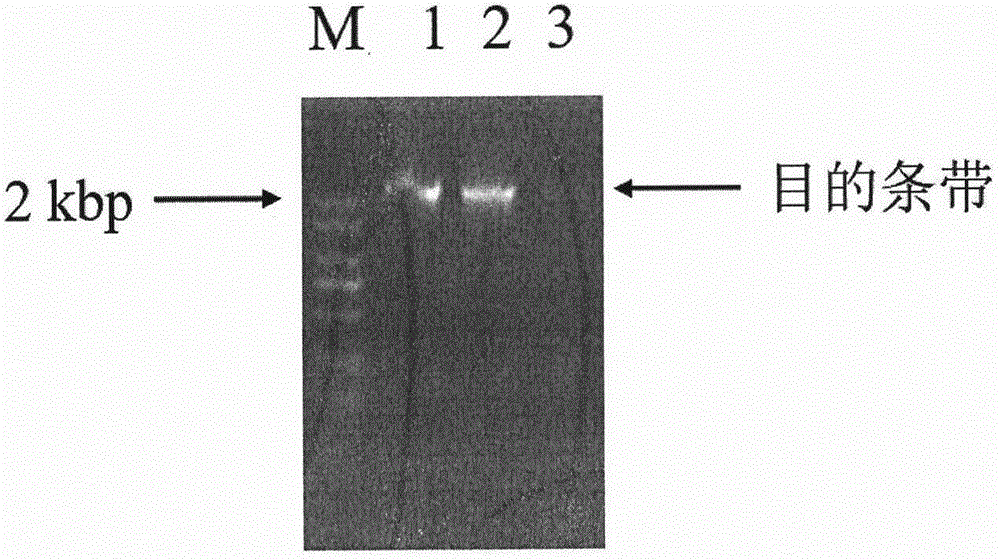
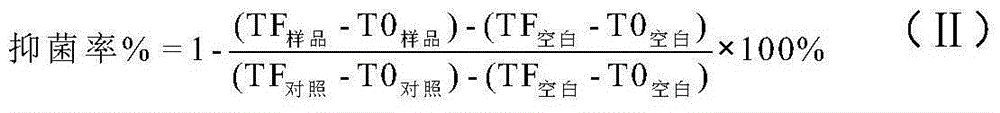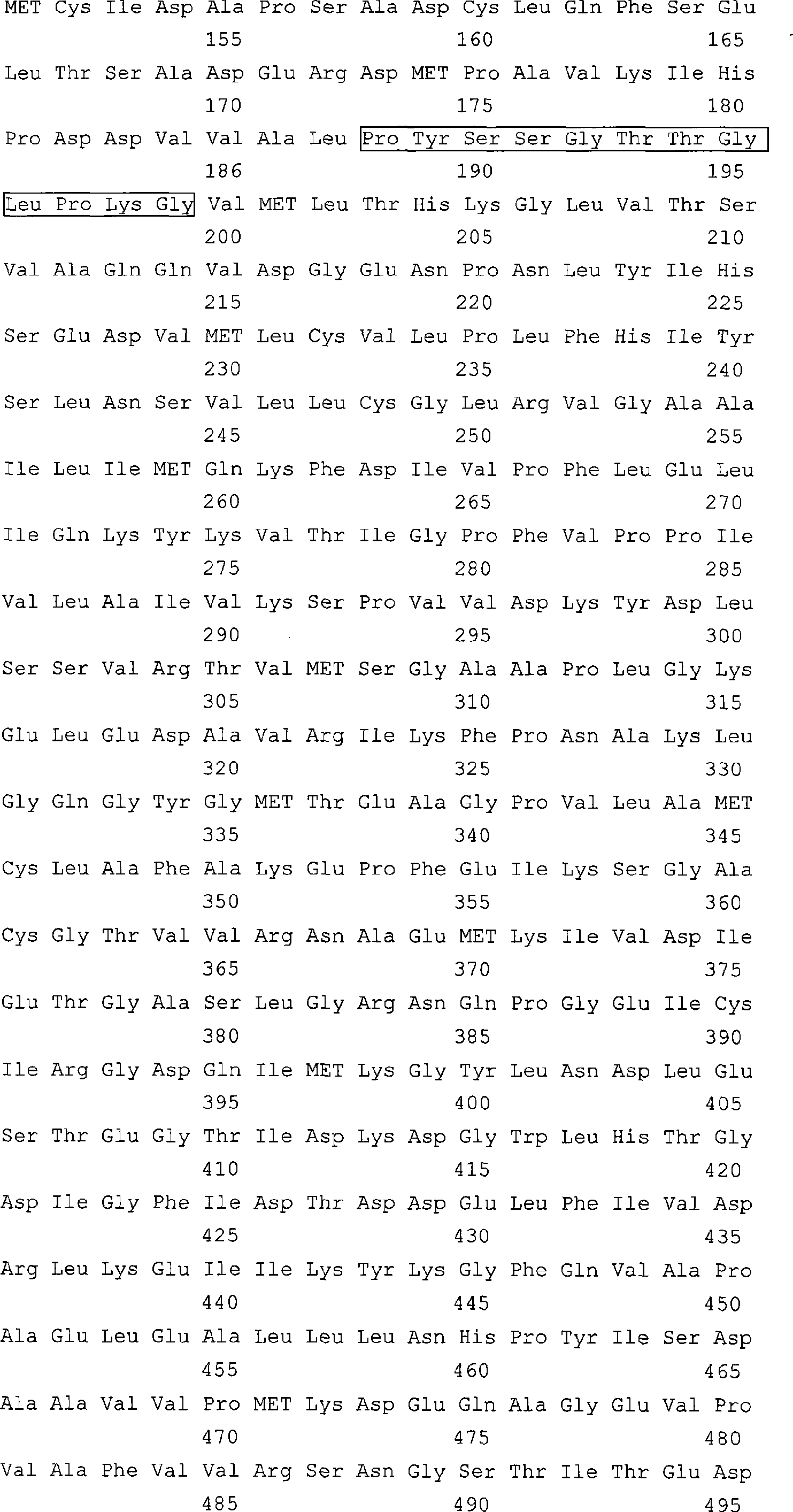Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
169 results about "Coumaric acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
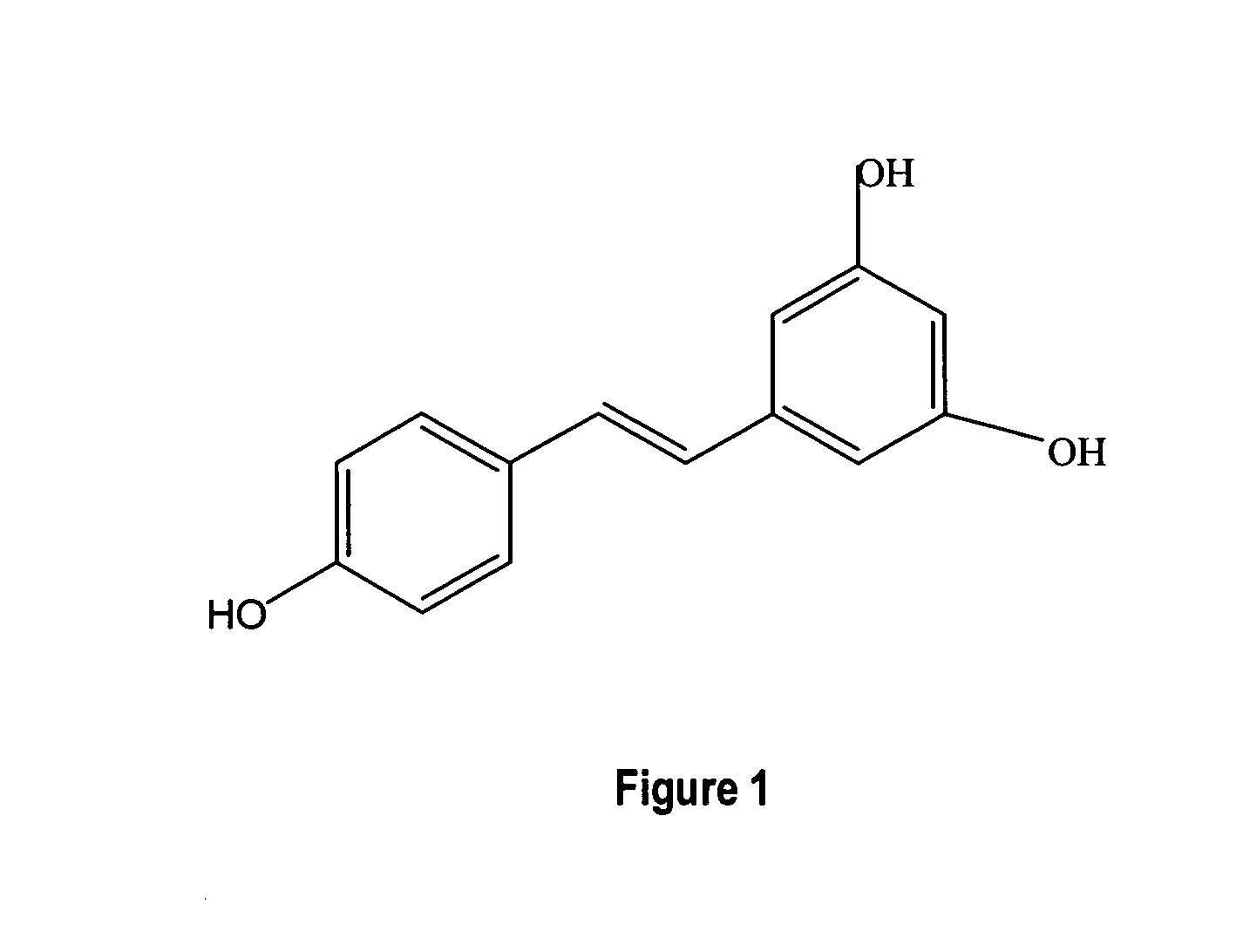
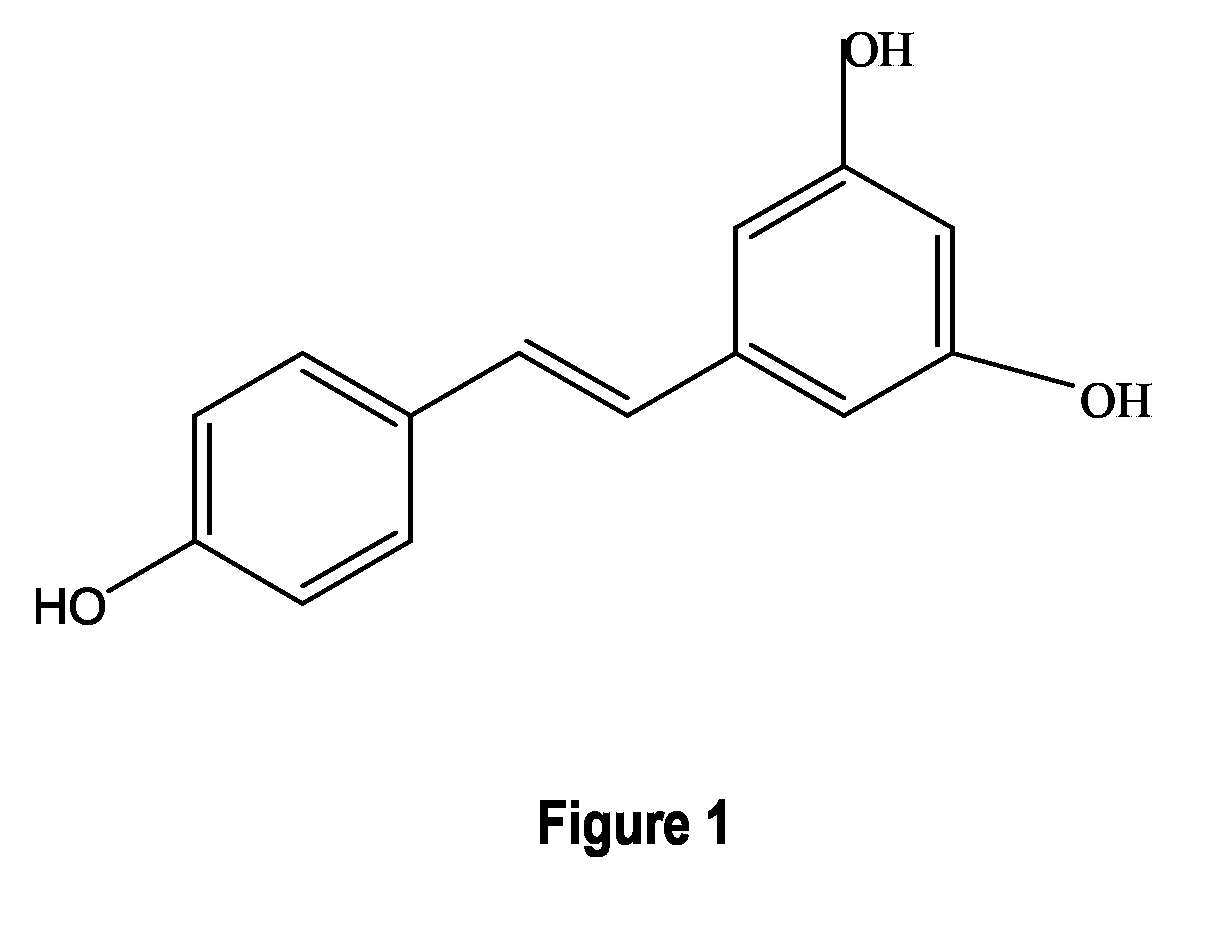
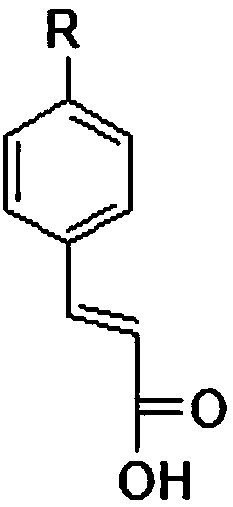
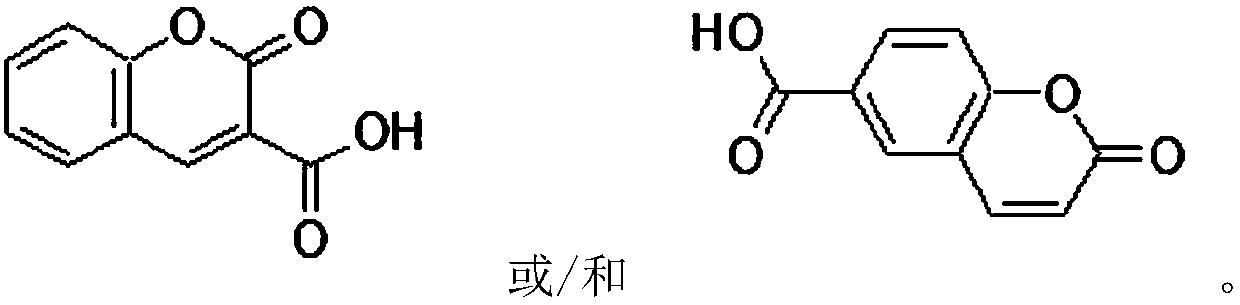
Coumaric acid is a phenolic derivative of cinnamic acid having a hydroxy group as substituent at one of the aromatic positions...
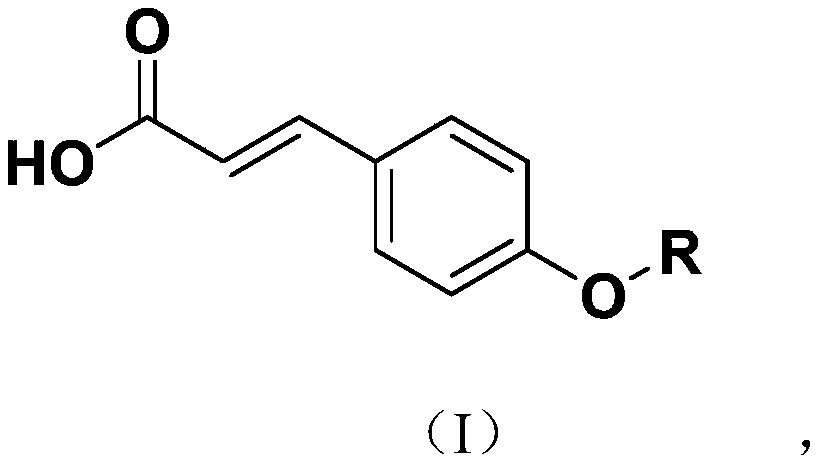
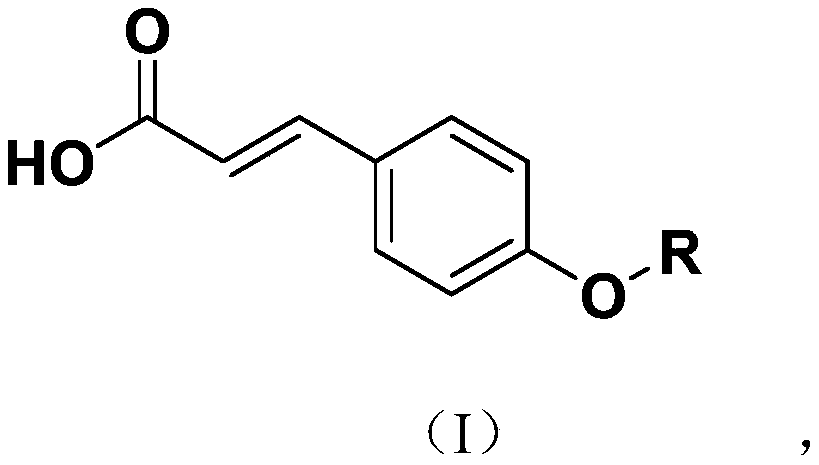
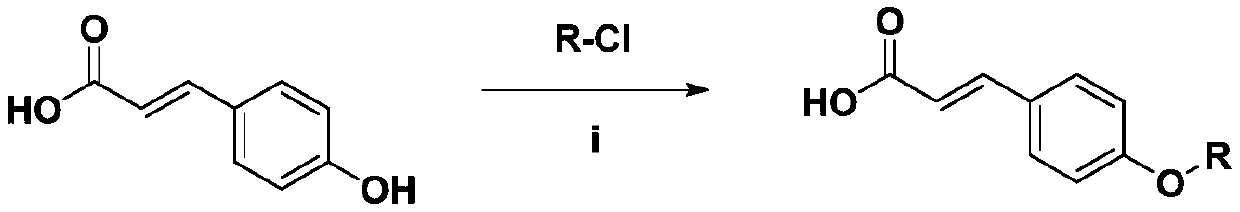
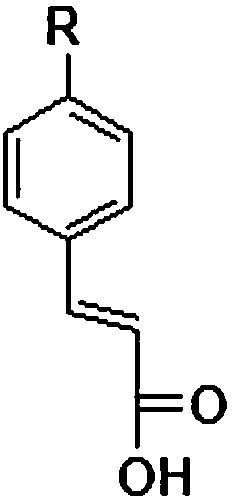
Para-coumaric acid or para-hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives and their use in cosmetic or dermatological compositions
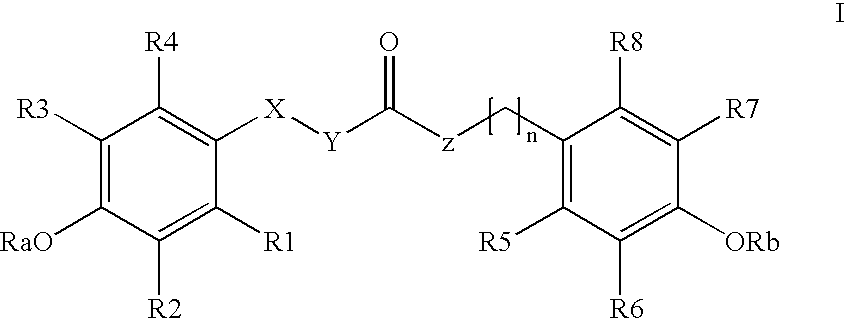
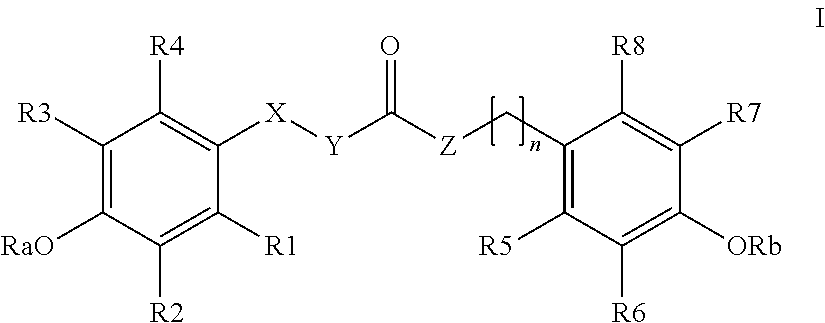
The invention relates to the use of para-coumaric acid or para-hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in cosmetic or dermatological compositions, specifically to the use of at least one compound derived from para-coumaric acid having a general formula (I) below: in which, especially, Z represents an oxygen or an —NH— group; X and Y are identical and each represent a CH or CH2 group, as an active principle with depigmenting, free-radical-scavenging and / or antiinflammatory activity. The invention also relates to the use of the above compounds for cosmetic care or for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition, especially for depigmenting an area of skin, having antiradical and / or antiinflammatory activity.
Owner:BASF BEAUTY CARE SOLUTIONS FRANCE SAS +1
Stabilized ascorbic acid compositions and methods therefor
ActiveUS7179841B2Improve stabilityImprove solubilityCosmetic preparationsBiocideCoumaric acidCaffeic acid
Owner:LOREAL USA CREATIVE INC
Method for preparing trans-ferulaic acid, p-cumaric acid and pentosan
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously preparing trans-ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid and pentosan, which comprises the following steps: processing a cellulose material with a low-concentration alkali to release coumaric acid, and hydrolyzing with a high-concentration alkali to release ferulic acid and pentosan; ultrafiltering the alkaline hydrolytic solution, precipitating the concentrated solution with ethanol to obtain pentosan; and adsorbing coumaric acid and ferulic acid in the filtrate with cation exchange resin, eluting with an ethanol-acid-water mixed eluent, removing ethanol from the eluent, crystallizing, centralizing or filtering the eluent at a low temperature or a normal temperature to obtain ferulic acid or coumaric acid crystals, and recrystallizing to obtain the high-purity product. The alkaline hydrolytic solution can be recovered and used for hydrolyzing the material, thereby obviating the production of a great amount of wastewater due to the alkaline hydrolysis. The method can produce ferulic acid and coumaric acid widely used in the industries of food, medicine and cosmetics, and pentosan used for producing xylooligosaccharide as food gum by utilizing solid wastes produced in agricultural and food processing, thereby achieving significant economic and social meanings.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
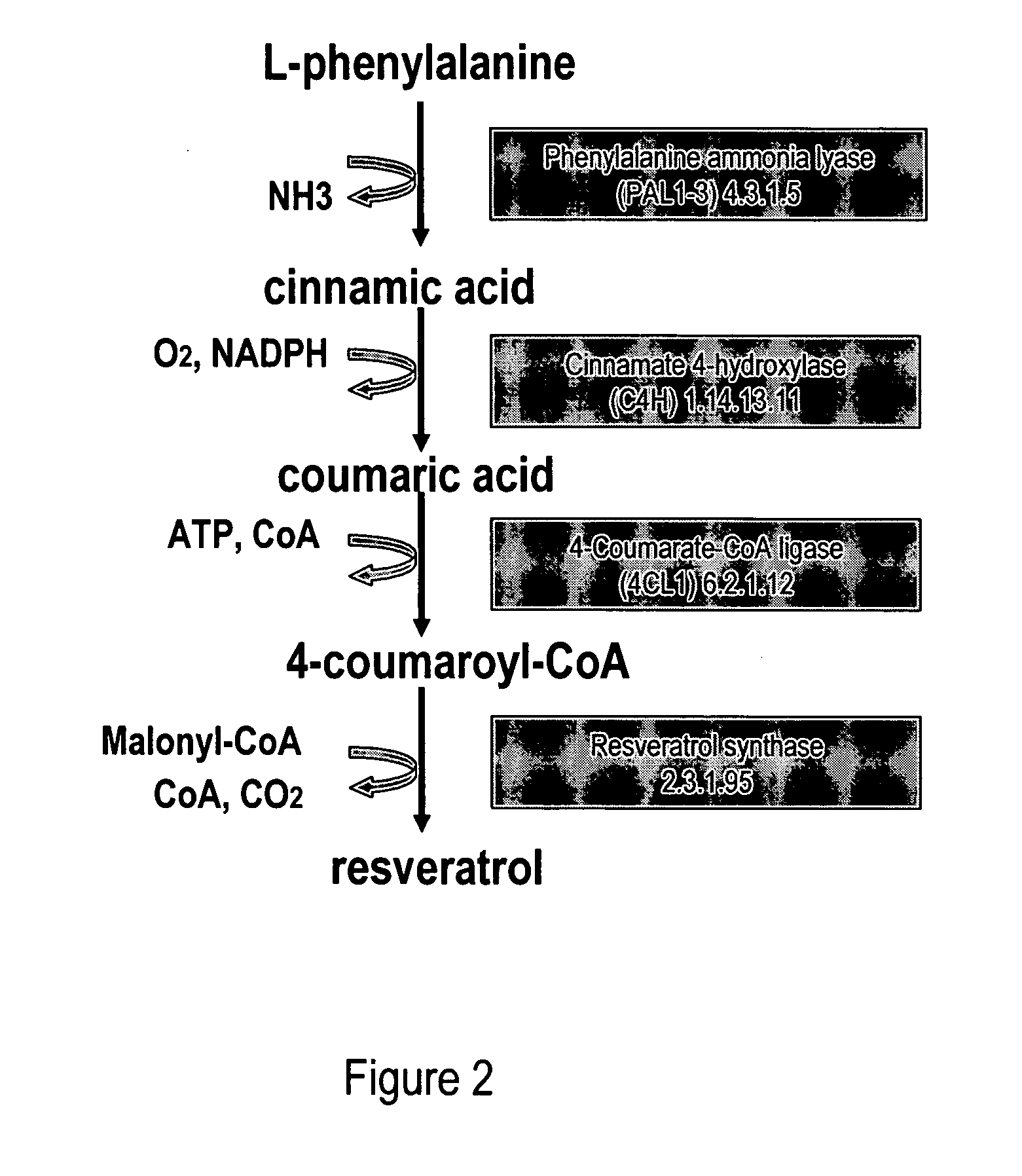
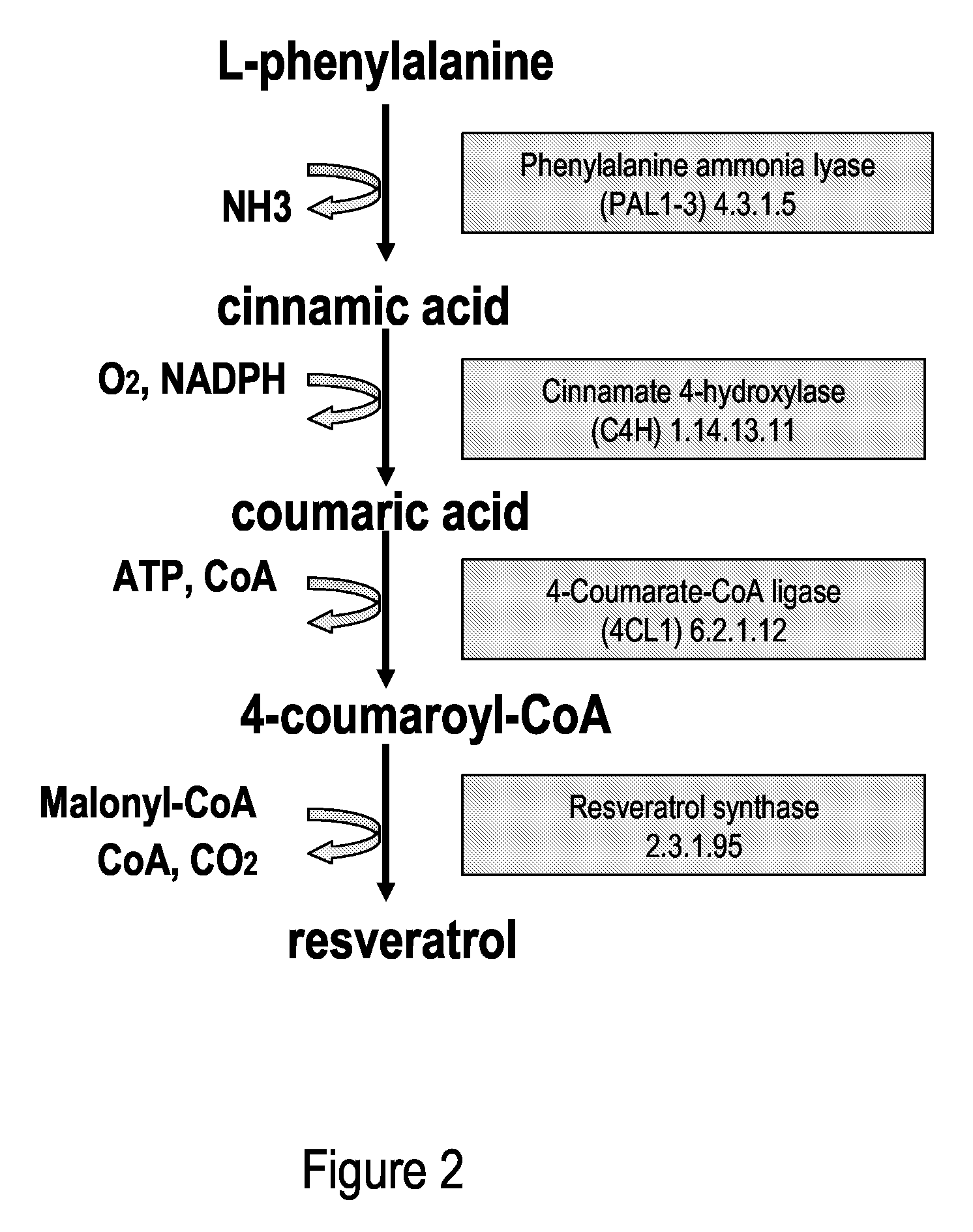
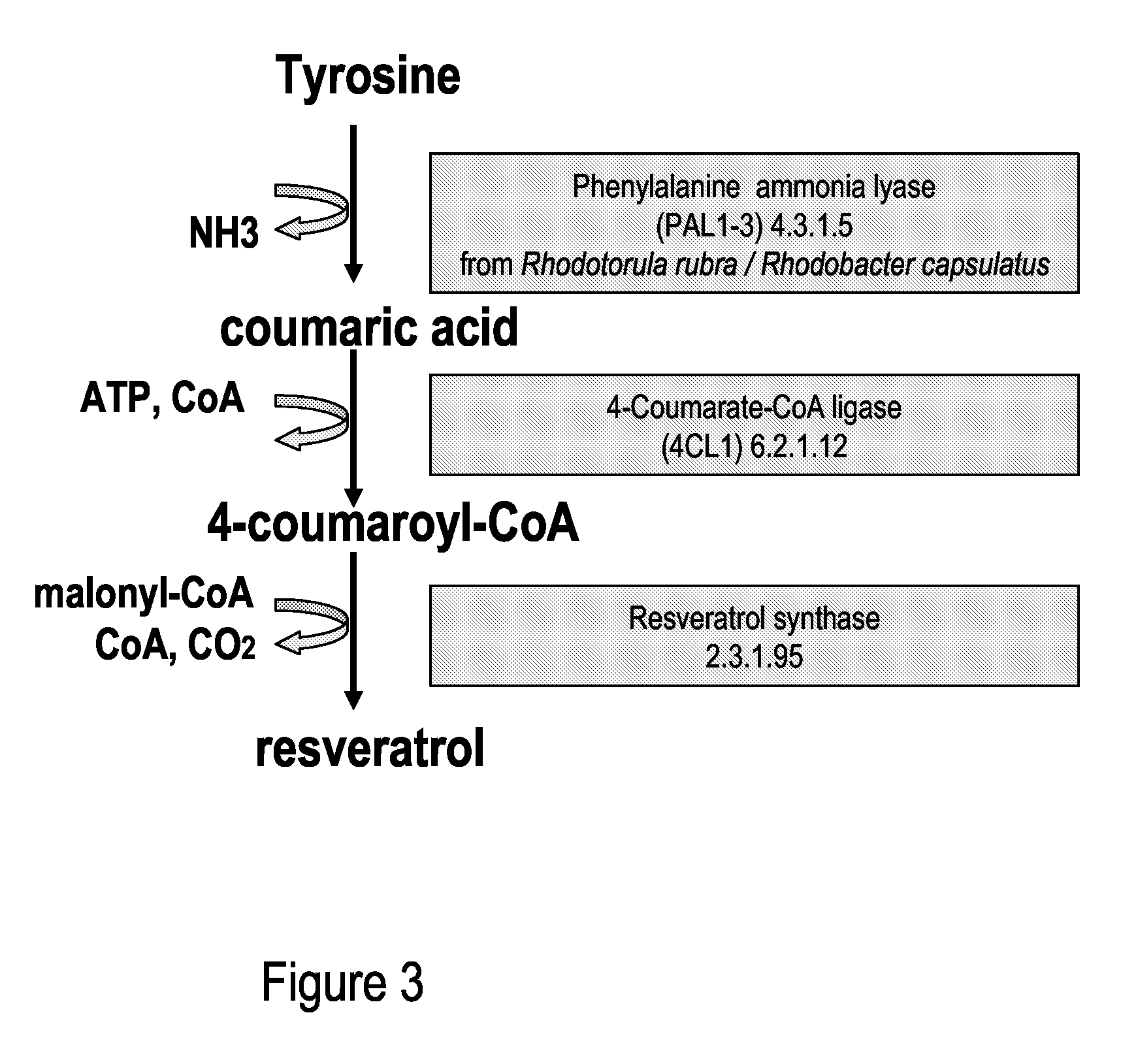
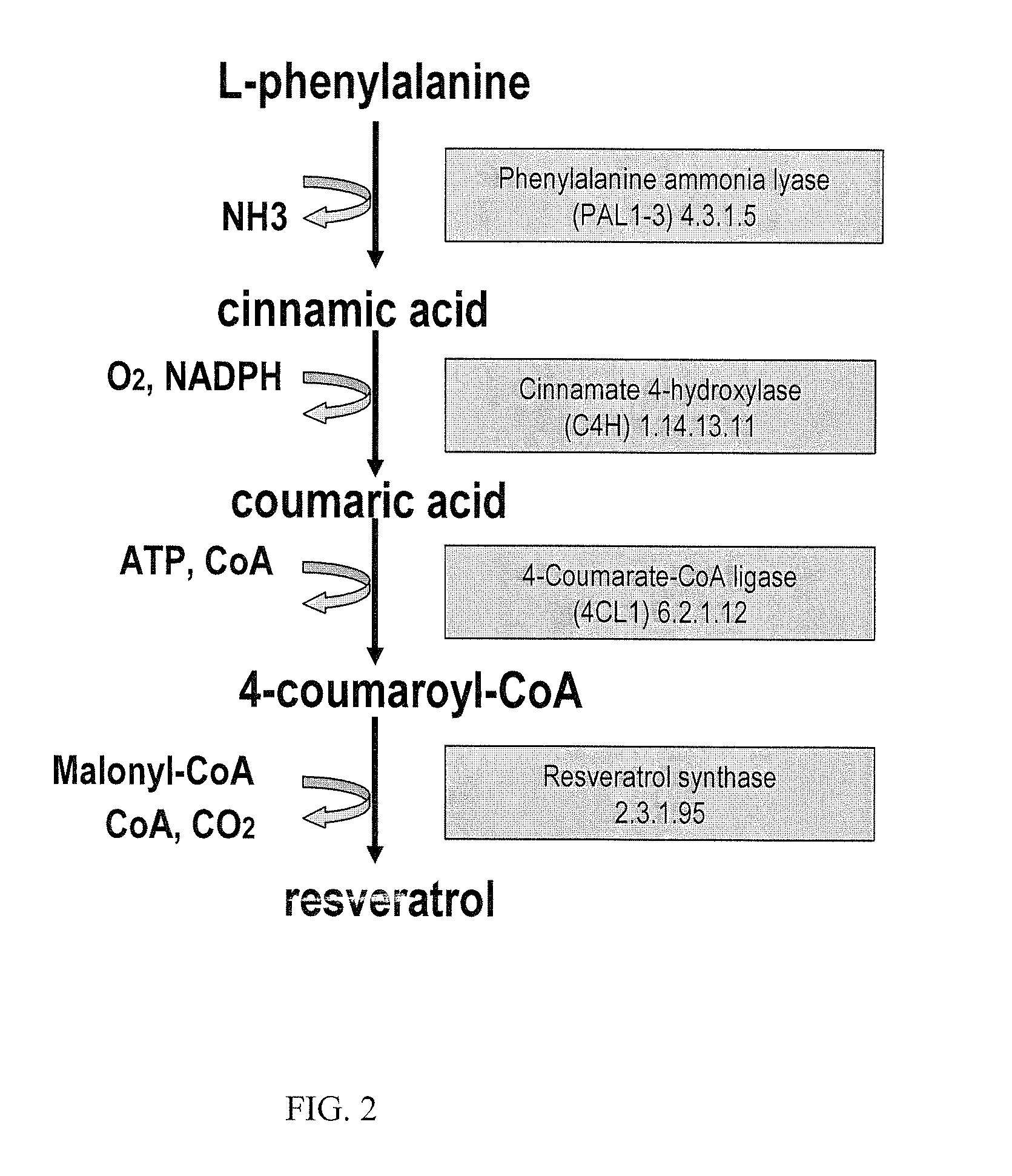
Metabolically engineered cells for the production of resveratrol or an oligomeric or glycosidically-bound derivative thereof
A recombinant micro-organism producing resveratrol by a pathway in which phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) produces trans-cinnamic acid from phenylalanine, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) produces 4-coumaric acid from said trans-cinnamic acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA, or in which L-phenylalanine- or tyrosine-ammonia lyase (PAL / TAL) produces 4-coumaric acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA. The micro-organism may be a yeast, fungus or bacterium including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli, Lactococcus lactis, Aspergillus niger, or Aspergillus oryzae.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
Authenticity evaluating method for populus-type propolis based on multi-index quality control
The invention provides an authenticity evaluating method for a populus-type propolis based on multi-index quality control, and caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, rutin, myricetin, cinnamic acid, galangin, chrysin, pinocembrin and CAPE in the propolis are detected by high performance liquid chromatography. A mixing standard sample of caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid, ferulic acid, rutin, myricetin, cinnamic acid, galangin, chrysin, pinocembrin and CAPE is taken as a reference index in the method; wherein whether the propolis is from a populus-type material is defined by the existence or inexistence of cinnamic acid, galangin, chrysin, pinocembrin and CAPE, a poplar tree's gum and the propolis are distinguished by the existence or inexistence of caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid, adulteration or no adulteration of rutin or myricetin is determined by taking rutin or myricetin as a reference; and thus a detection method for distinguishing between the poplar tree's gum and the populus-type propolis, and adulteration or no adulteration of rutin or myricetin, is constructed, and the method helps to evaluate whether a sample is from populus plants, and helps to achieve discarding of the false and retaining of the true about the populous-type propolis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Metabolically engineered cells for the production of resveratrol or an oligomeric or glycosidically-bound derivative thereof
A recombinant micro-organism producing resveratrol by a pathway in which phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) produces trans-cinnamic acid from phenylalanine, cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H) produces 4-coumaric acid from said trans-cinnamic acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA, or in which L-phenylalanine- or tyrosine-ammonia lyase (PAL / TAL) produces 4-coumaric acid, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase (4CL) produces 4-coumaroyl CoA from said 4-coumaric acid, and resveratrol synthase (VST) produces said resveratrol from said 4-coumaroyl CoA. The micro-organism may be a yeast, fungus or bacterium including Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli, Lactococcus lactis, Aspergillus niger, or Aspergillus oryzae.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
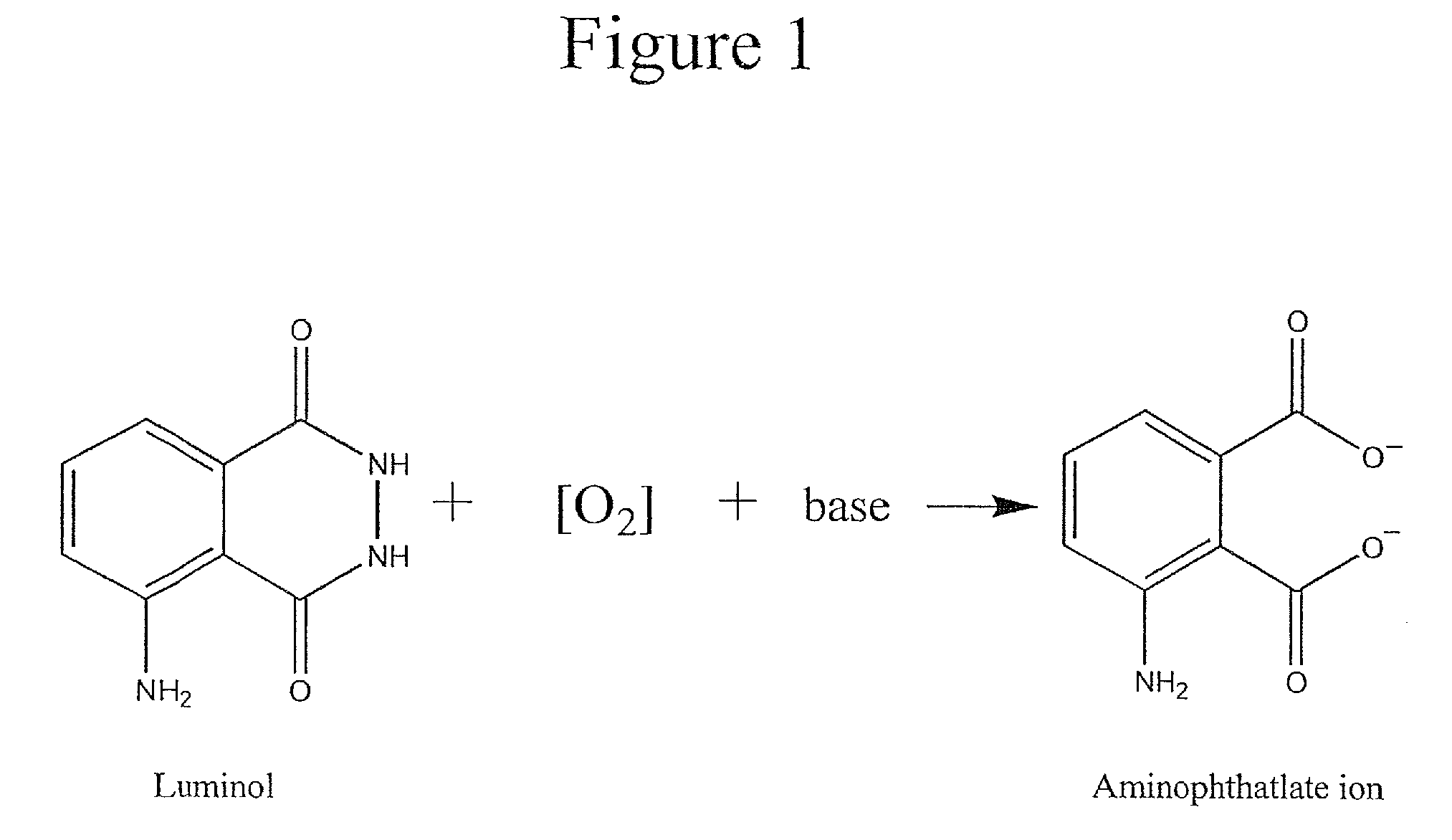
Method for improving chemiluminescent signal
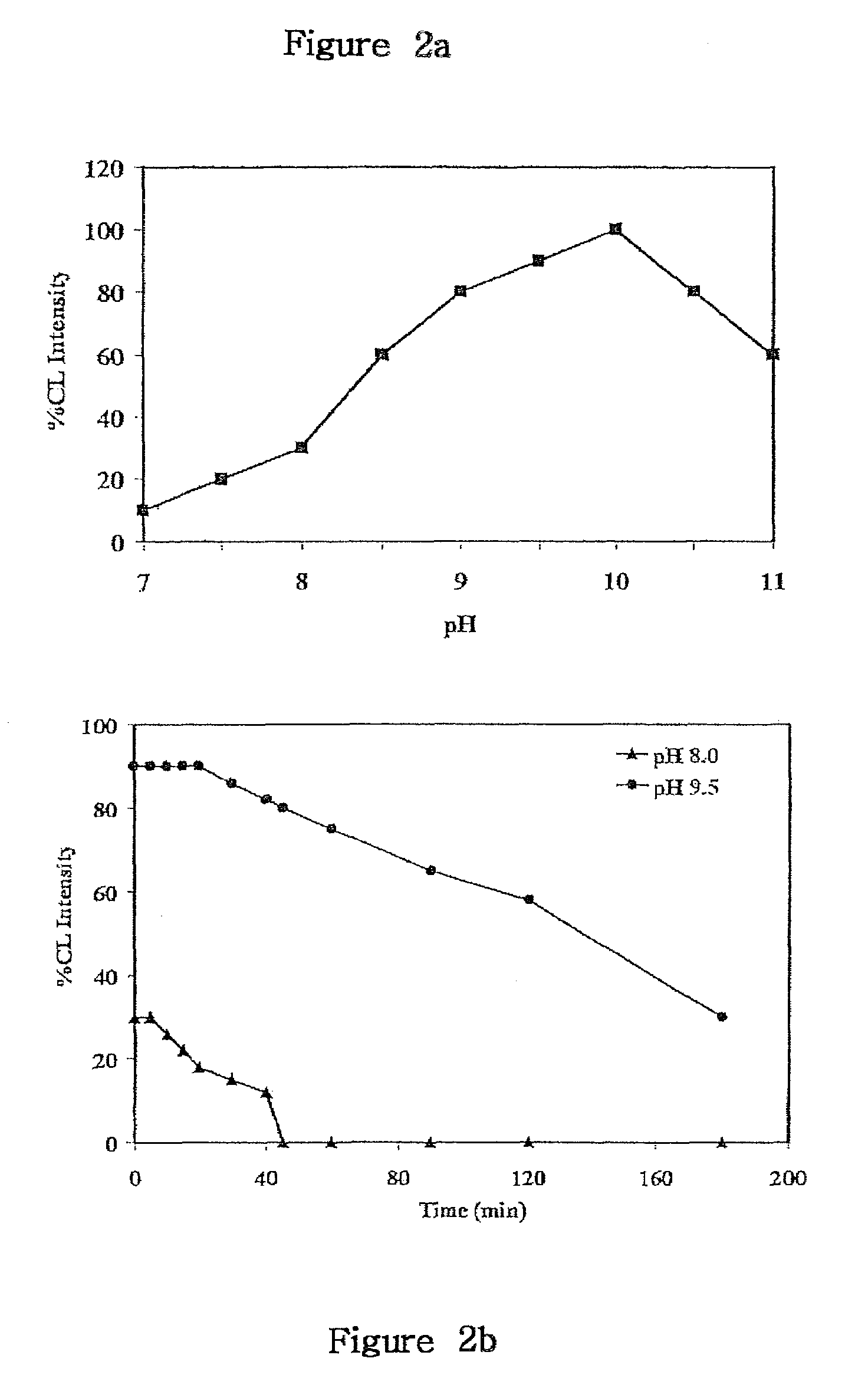
The present invention is directed to compositions and methods for improving a chemiluminescent signal. In particular, a reaction buffer with an alkaline pH range of about 9 to 10 provides a maximal chemiluminescent intensity and longevity of luminol that is catalyzed by superoxide anions. The addition of carbonate to the reaction buffer provides an optimal signal to background ratio and stability of a chemiluminescent signal from luminol catalyzed by superoxide anions. The method includes preparing a buffer with an alkaline pH, combining the buffer with a working reagent to produce and detect a chemiluminescent signal. The working reagent includes luminol, a coumaric acid and a peroxide. The composition includes a buffer having a pH from about 9 to about 10, a stock reagent comprising luminol, a coumaric acid, a peroxide, and a second buffer having a pH of about 8.5.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
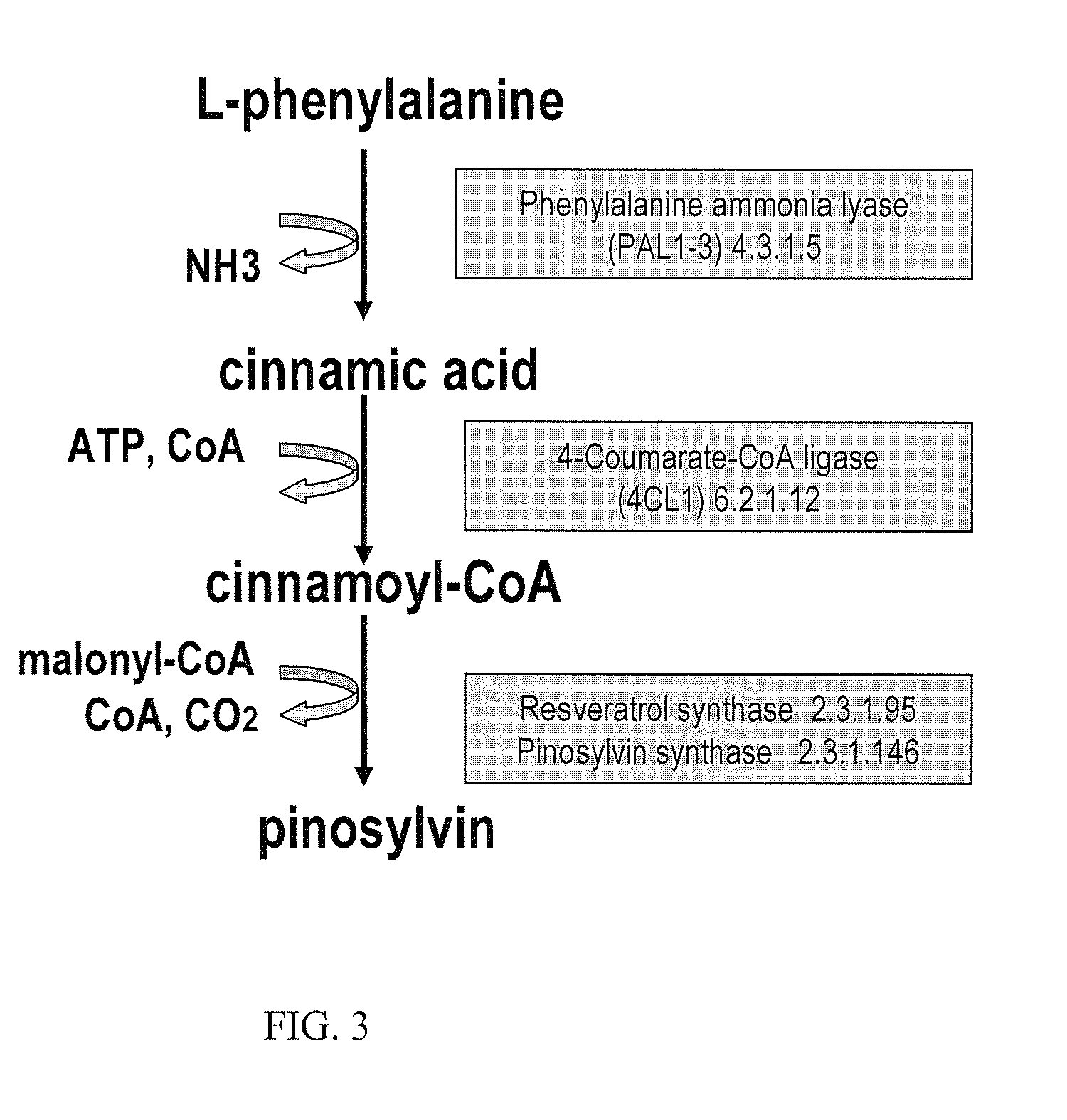
Metabolically engineered cells for the production of pinosylvin
A genetically engineered micro-organism having an operative metabolic pathway producing cinnamoyl-CoA and producing pinosylvin therefrom by the action of a stilbene synthase is used for pinosylvin production. Said cinnamic acid may be formed from L-phenylalanine by a L-phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL) which is one accepting phenylalanine as a substrate and producing cinammic acid therefrom, preferably such that if the PAL also accepts tyrosine as a substrate and forms coumaric acid therefrom, the ratio Km(phenylalanine) / Km(tyrosine) for said PAL is less than 1:1 and if said micro-organism produces a cinammate-4-hydroxylase enzyme (C4H), the ratio Kcat(PAL) / Kcat(C4H) is at least 2:1.
Owner:EVOLVA SA
Para-Coumaric Acid or Para-Hydroxycinnamic Acid Derivatives and Their Use in Cosmetic or Dermatological Compositions
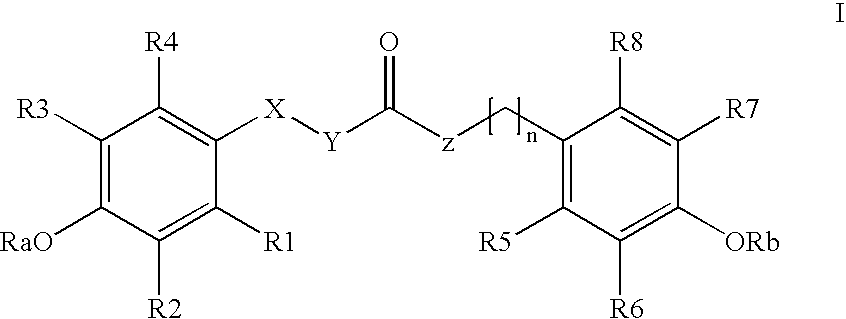
The invention relates to the use of para-coumaric acid or para-hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives in cosmetic or dermatological compositions, specifically to the use of at least one compound derived from para-coumaric acid having a general formula (I) below:in which, especially, Z represents an oxygen or an —NH— group; X and Y are identical and each represent a CH or CH2 group, as an active principle with depigmenting, free-radical-scavenging and / or antiinflammatory is activity.The invention also relates to the use of the above compounds for cosmetic care or for the preparation of a pharmaceutical composition, especially for depigmenting an area of skin, having antiradical and / or antiinflammatory activity.
Owner:BASF BEAUTY CARE SOLUTIONS FRANCE SAS +1
Cloning of mulberry resveratrol synthase gene and construction of plant expression vector
InactiveCN103898130AIncrease contentImprove disease resistanceBacteriaEnzymesNicotiana tabacumCoumaric acid
The invention relates to cloning of a mulberry resveratrol synthase gene and construction of a plant expression vector. The gene has a nucleotide sequence shown by SEQ ID NO.7. Total RNA is extracted from fresh mulberry fruits, and the mulberry resveratrol synthase gene (MaRS) is cloned by using 3'RACE technology to obtain a complete gene sequence of 1496bp. A plant expression vector pCAMBIA2300-MaRS-Kana is constructed. The plant expression vector pCAMBIA2300-MaRS-Kana is transferred into agrobacterium C58 cells by electroporation, the activity of the enzyme coded by the cloned MaRS gene is verified by using a tobacco plant expression system, the MaRS gene can catalyze the combination of trans coumaric acid COA and malonyl-COA in tobacco to form resveratrol, and move the metabolic direction to downstream to synthesize a resveratrol derivative, and the gene is proved to be capable of improving the resveratrol content of a plant, therefore the MaRS gene has a development value of being applied to health food and beauty products. In addition, the MaRS gene can improve the disease resistance of the plant, thereby having a value of being applied to plant stress-tolerance gene engineering.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
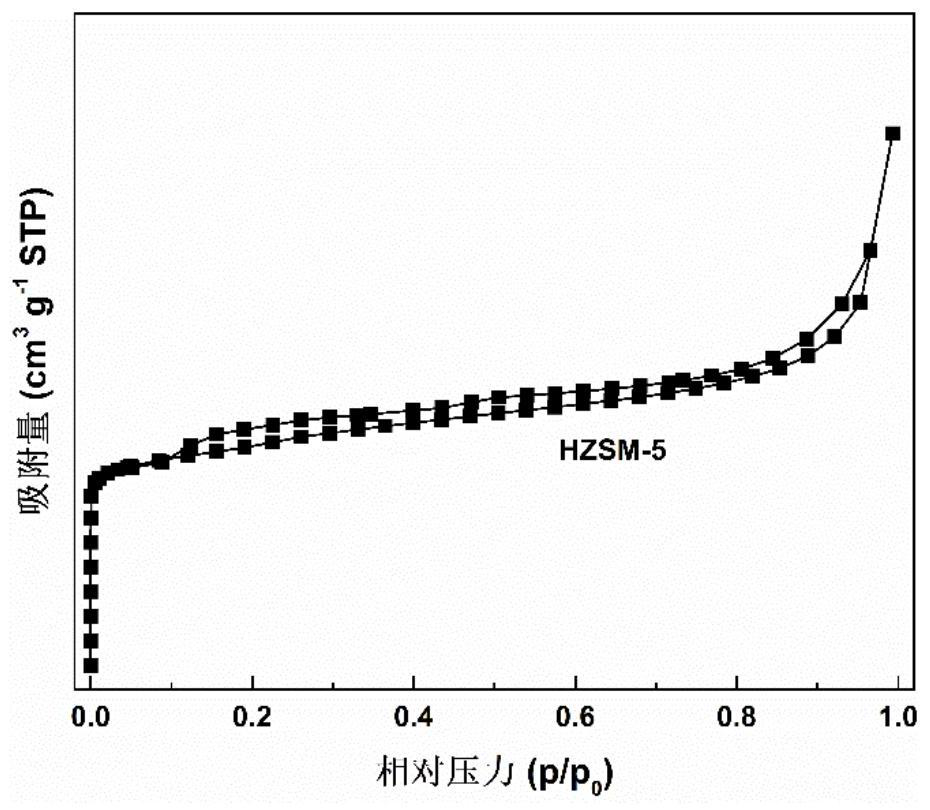
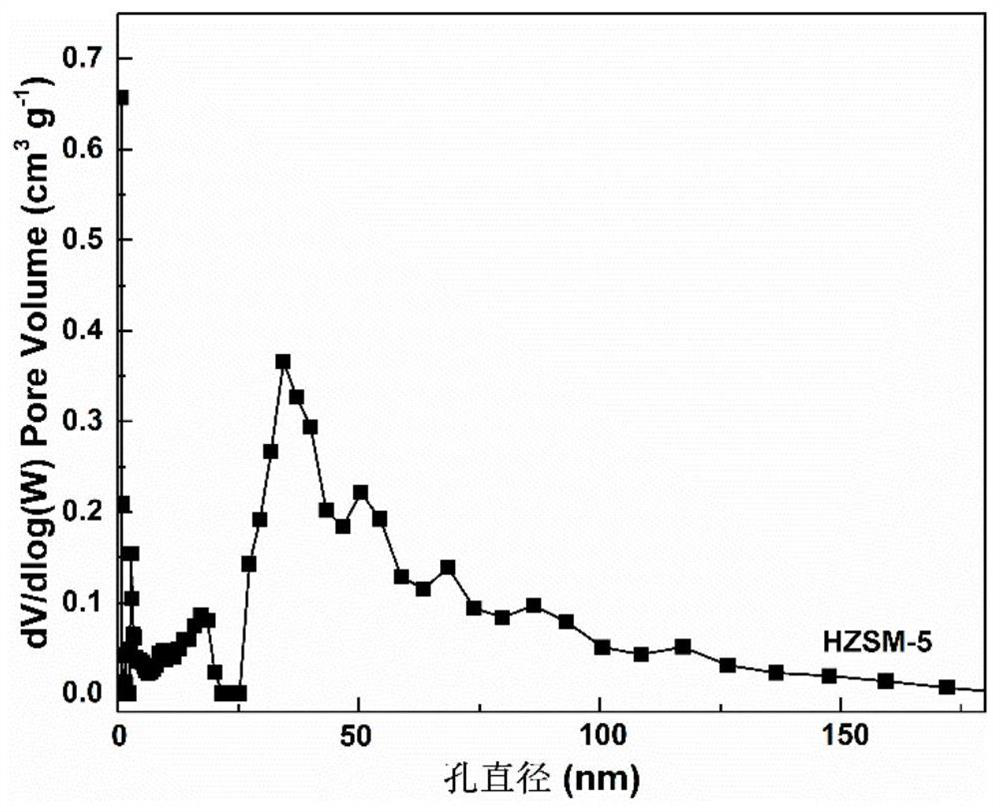
Method for preparing p-coumarate by catalyzing lignin depolymerization through hierarchical pore molecular sieve loaded molybdenum oxide
ActiveCN112495425AHigh selectivityHigh value utilizationMolecular sieve catalystsOrganic compound preparationMolecular sievePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing p-coumarate by catalyzing lignin depolymerization through hierarchical pore molecular sieve loaded molybdenum oxide. The method comprises the following steps: by taking lignin as a raw material, adding a reaction medium and a hierarchical pore molecular sieve loaded molybdenum oxide catalyst, replacing with nitrogen, pressurizing to 0.1-1MPa, heatingto 120-160 DEG C, reacting for 2-10 hours while stirring, removing the catalyst after the reaction, and catalytically degrading the lignin into p-coumarate. By regulating and controlling the catalyststructure, the reaction medium and the reaction condition factors, high-yield and high-selectivity depolymerization of lignin is achieved, p-coumarate serving as a high-added-value chemical is obtained, and the purpose of high-valued utilization of lignin is achieved. The heterogeneous catalyst is used, the process is simple, reaction conditions are mild, lignin can be selectively converted to obtain the target product p-coumarate, and the yield and selectivity of p-coumarate can reach up to 11.78 wt.% and 85.24 wt.% respectively.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Novel p-coumaric acid sulfonate derivative, preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN110627690APharmaceutically activeRealize resource utilizationAntibacterial agentsBiocideSulfonateResource utilization
The invention discloses a novel p-coumaric acid sulfonate derivative, a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the novel p-coumaric acid sulfonate derivative is shown asformula (I) in the specification, wherein R is selected from the following groups shown as the specification. The compound provided by the invention has potential pharmaceutical activity, and the preparation raw material p-coumaric acid can be obtained by natural extraction method, thus having a positive effect on resource utilization of spartina alterniflora.
Owner:南京施倍泰生物科技有限公司
Separation method of effective components of sharpleaf galangal fruit aqueous extract
ActiveCN104557505AClear structureCarbonyl compound separation/purificationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationCoumaric acidEthyl acetate
The invention discloses a separation method of effective components of a sharpleaf galangal fruit aqueous extract, belonging to the field of pharmaceutical analysis. The separation method comprises the following steps: (A) fetching dried sharpleaf galangal fruit, grinding, carrying out reflux extraction with water, combining filtrate, carrying out reduced pressure distillation to obtain extractum, dissolving the extractum into distilled water, respectively extracting by virtue of petroleum ether, ethyl acetate and normal butanol, and recycling solvents, so as to obtain ethyl acetate extract dry powder; (B) dissolving the dry powder obtain in the step (A), filtering, and processing by virtue of a sephadex LH20 gel column, so as to obtain six components from F1 to F6; and (C) carrying out HPLC separation and purification on the components from F2 to F6, so as to obtain compounds including protocatechualdehyde, protocatechuic acid, p-coumaric acid, (-)-epicatechin and (+)-catechinic acid. According to the separation method, the effective active components are separated and extracted from the sharpleaf galangal fruit, the structures of the effective components are further defined, the basis is provided for later medication, and required components can be extracted according to different requirements.
Owner:HEBEI YILING MEDICINE INST
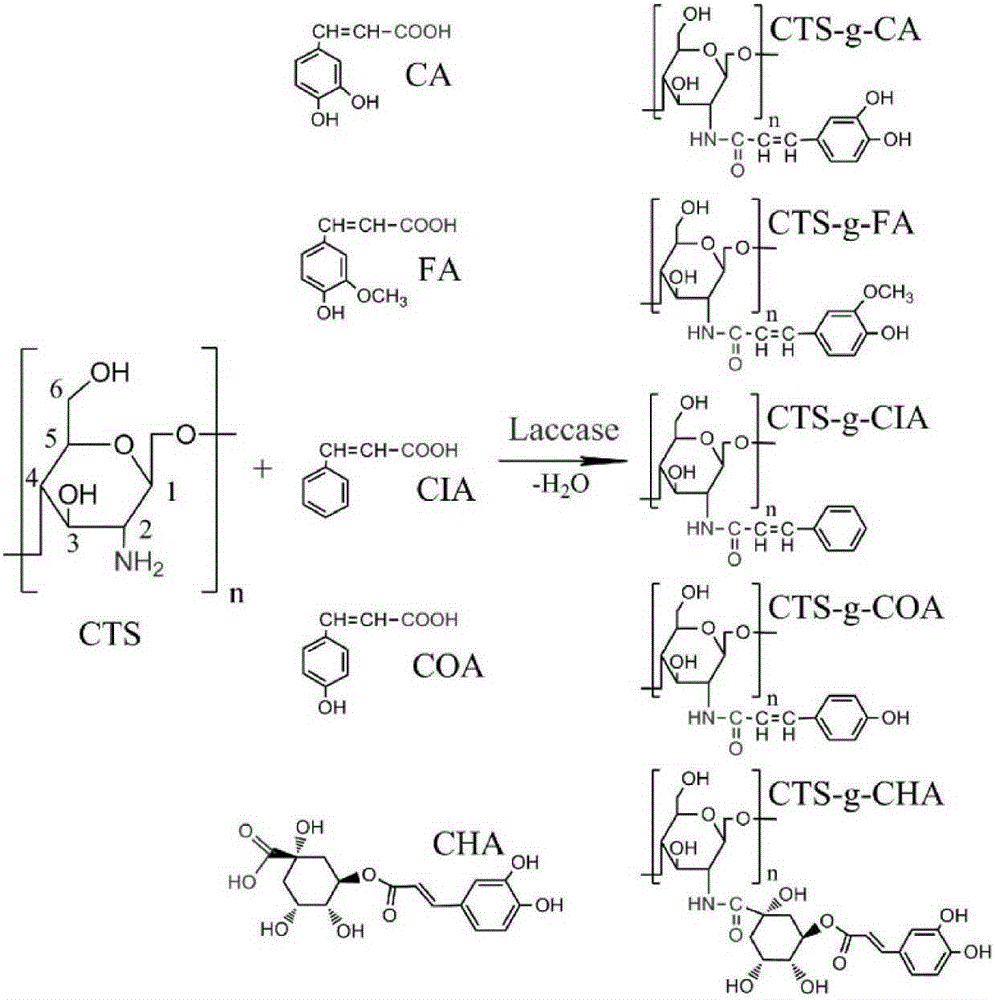
Application of chitosan derivative in bacterial wilt prevention and treatment
InactiveCN105191940AInhibition is effectiveEffective controlBiocideDisinfectantsChlorogenic acidCaffeic acid
The invention relates to application of a chitosan derivative in bacterial wilt prevention and treatment. The structure of the chitosan derivative is shown in the formula (I), wherein R represents H or caffeic acid, or ferulic acid, or cinnamic acid, or p-coumaric acid or chlorogenic acid with a decarboxylated hydroxyl group. The medial lethal concentration of the chitosan derivative used for restraining bacterial wilt pathogenic bacteria is provided, the low-concentration chitosan derivative can be used for effectively restraining bacterial wilt bacteria, an effective method for preventing and treating bacterial wilt is provided, and the environment is not polluted.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Medicinal composition for treating turtle cavity disease and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103463387AEasy to solveGood treatment effectAntibacterial agentsAnthropod material medical ingredientsBiotechnologyCoumaric acid
The invention discloses a medicinal composition for treating a turtle cavity disease. The medicinal composition for treating the turtle cavity disease comprises the following Chinese herbs in parts by weight: 15-30 parts of hedyotis diffusa, 20-30 parts of groundsel, 5-15 parts of gallnut, 10-25 parts of golden cypress, 2-10 parts of wild chrysanthemum flower and 5-15 parts of onion. The invention further discloses a preparation of the medicinal composition. The hedyotis diffusa and the groundsel have a very strong anti-virus effect, so that the hedyotis diffusa and the groundsel as effective components can prevent and treat the turtle cavity disease better, with the cure rate as high as 99%. In the preparation method, the hedyotis diffusa is extracted with a supercritical carbon dioxide extraction method, so that effective components of the hedyotis diffusa, namely hentriacontane, stigmasterol, ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, beta-sitosterol, beta-sitosterol-D-glucoside and p-coumaric acid, have relatively high contents. The preparation method is simple and feasible and is applicable to large-scale production.
Owner:XINGHUA HENGWEI BIOTECH
Method for extracting plant extract for preventing and treating diabetes as well as extract product and uses thereof
InactiveCN101406519AImprove preparation safetyQuality improvementMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaSide effect
The invention relates to a method for extracting plant extract for preventing and treating diabetes, wherein linseed hulls are subjected to crushing and sieving, extracted by ethanol, subjected to alkaline hydrolysis, neutralization, concentration and spray drying to obtain the extract. The plant extract comprises the following effective constituents for treating or preventing diabetes: flax lignan, ferulic acid, coumaric acid and dietary fiber. The contents of various constituents are as follows respectively: 15 to 45 weight percent of the flax lignan, 1.2 to 6.0 weight percent of the ferulic acid, 1.0 to 4.0 weight percent of the coumaric acid and 40 to 70 weight percent of the dietary fiber. The method for extracting the plant extract for preventing and treating diabetes takes the naturally grown linseed hulls or naturally grown linseed cakes as a raw material of the extract, has simple manufacturing technique, low production cost, low investment and no harmful solvent residue, and is suitable for industrialized production. Simultaneously the variety of the effective constituents of the plant extract is numerous; the content is high; the preparation safety is high; the quality is stable; the plant extract can be orally taken for a long time and has no side effect; and medicines for preventing and treating symptoms such as hyperglycemia and so on caused by diabetes have good hypoglycemic effect and no adverse reaction as proved by clinic trails.
Owner:INST OF COMPREHENSIVE AGRI PROD UTILIZATION SHANXI PROV ACAD OF AGRI
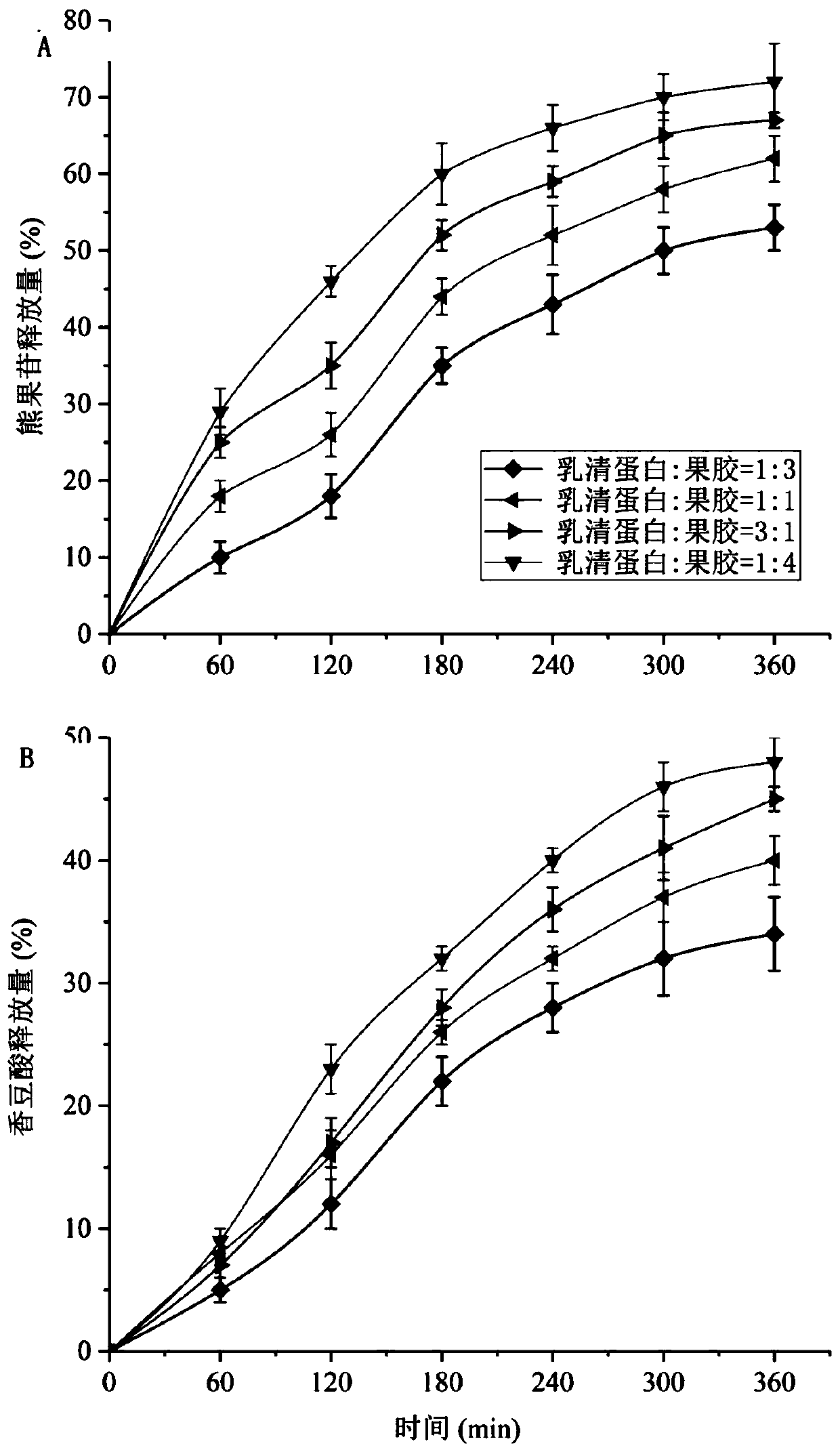
Preparation method of whey protein and pectin composite double-emulsion simultaneously embedding arbutin and coumaric acid and product thereof
InactiveCN110368322AMethod environmentally friendlyEasy to operateCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsArbutinCoumaric acid
The invention discloses a whey protein and pectin composite double-emulsion simultaneously embedding arbutin and coumaric acid and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that (1) the hydrophilic arbutin, gelatin and sodium chloride are dissolved in water, the hydrophobic coumaric acid and a W / O type emulsifier are dissolved in oil, an aqueous solution is dropwiseadded into the oil solution, and ultrasonic treatment is carried out to obtain an emulsion; (2) whey protein and pectin are dissolved in water, the pH value is adjusted, and an evenly mixed whey protein and pectin compound solution is obtained; (3) the emulsion is dropwise added into the whey protein and pectin compound solution, ultrasonic treatment is conducted, and the double-emulsion is obtained. The process is simple, the obtained double-emulsion can simultaneously embed the arbutin and the coumaric acid, the sustained-release performance is good, the double-emulsion is stable in storageand is applied to food and cosmetics as an additive, the biological activity function of products is enhanced, and therefore, the double-emulsion has wide application prospects in the fields of food and cosmetics.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
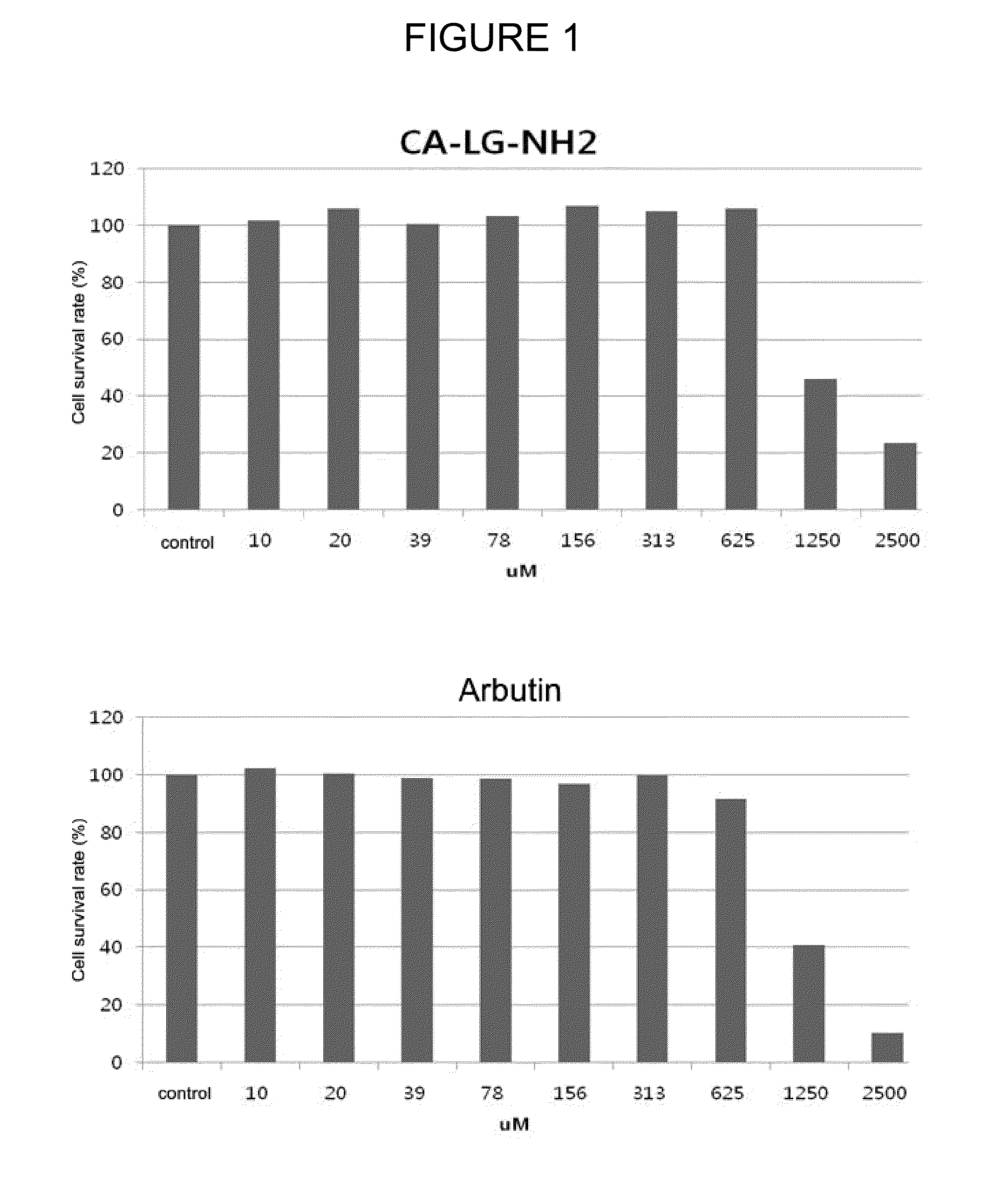
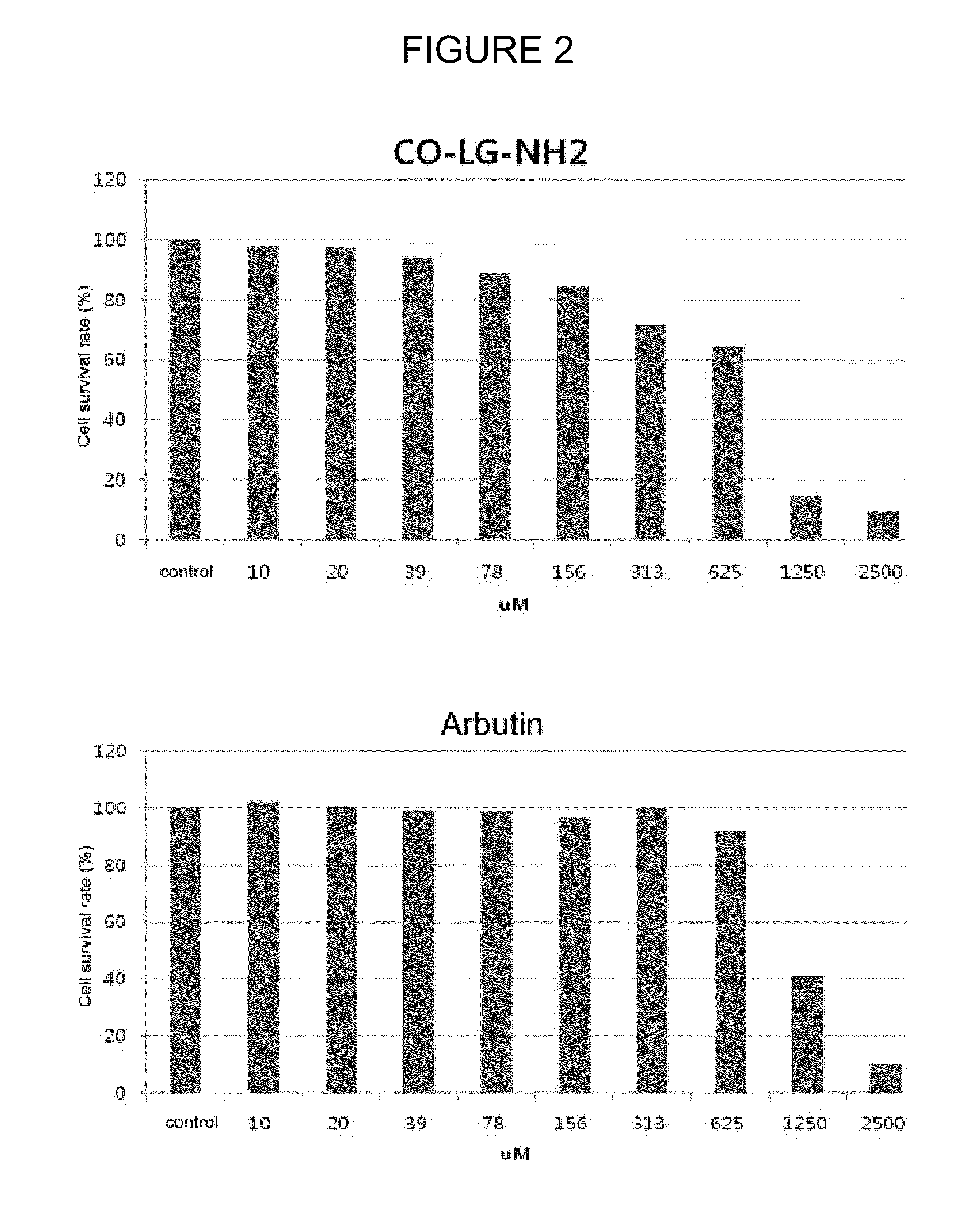
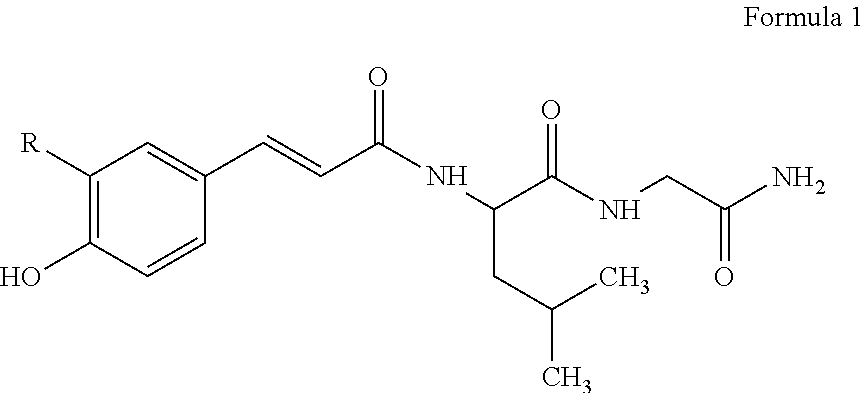
Cosmetic composition for skin whitening comprising small molecule-peptide conjugate
InactiveUS20140056835A1Effective in skin whiteningMinimal skin irritationCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsMedicineCoumaric acid
The present invention relates to a cosmetic composition for skin whitening comprising a small molecule-peptide conjugate. More specifically, it concerns the cosmetic composition for skin whitening comprising Caffeic acid-LG-NH2 or Coumaric acid-LG-NH2 as an active ingredient, which inhibits tyrosinase activity and melanin production, thereby showing an excellent skin whitening effect, and having no side effects to the skin by using a peptide component.
Owner:AE KYUNG IND CO LTD
Effective parts of schisandra bee pollen and application thereof in liver injury prevention
The invention relates to effective parts of schisandra bee pollen and the application thereof in liver injury prevention. The effective parts are obtained through extracting the schisandra bee pollen using ethanol, and the active ingredients and the content are gallic acid 15.78+ / -1.64 mg / kg, protocatechuic acid 54.78+ / -5.09 mg / kg, vanillic acid 64.21+ / -5.13 mg / kg, p-coumaric acid 57.32+ / -5.25 mg / kg, quercetin 273.63+ / -20.84 mg / kg, hesperidin 741.56+ / -76.8 mg / kg, kaempferol 387.34+ / -35.65 mg / kg, and galangin 487.35+ / -47.24 mg / kg. The inventor has found that the antioxidant activity of the schisandra bee pollen is higher than that of all known commercial bee pollen, and that the schisandra bee pollen can be used for preparing medicine or health care food for preventing liver injury caused by carbon tetrachloride.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV +1
Paulownia 4-coumaric acid: coenzyme A ligase gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101434937AChange compositionChange physical and chemical propertiesFungiBacteriaPaulowniaCoumaric acid
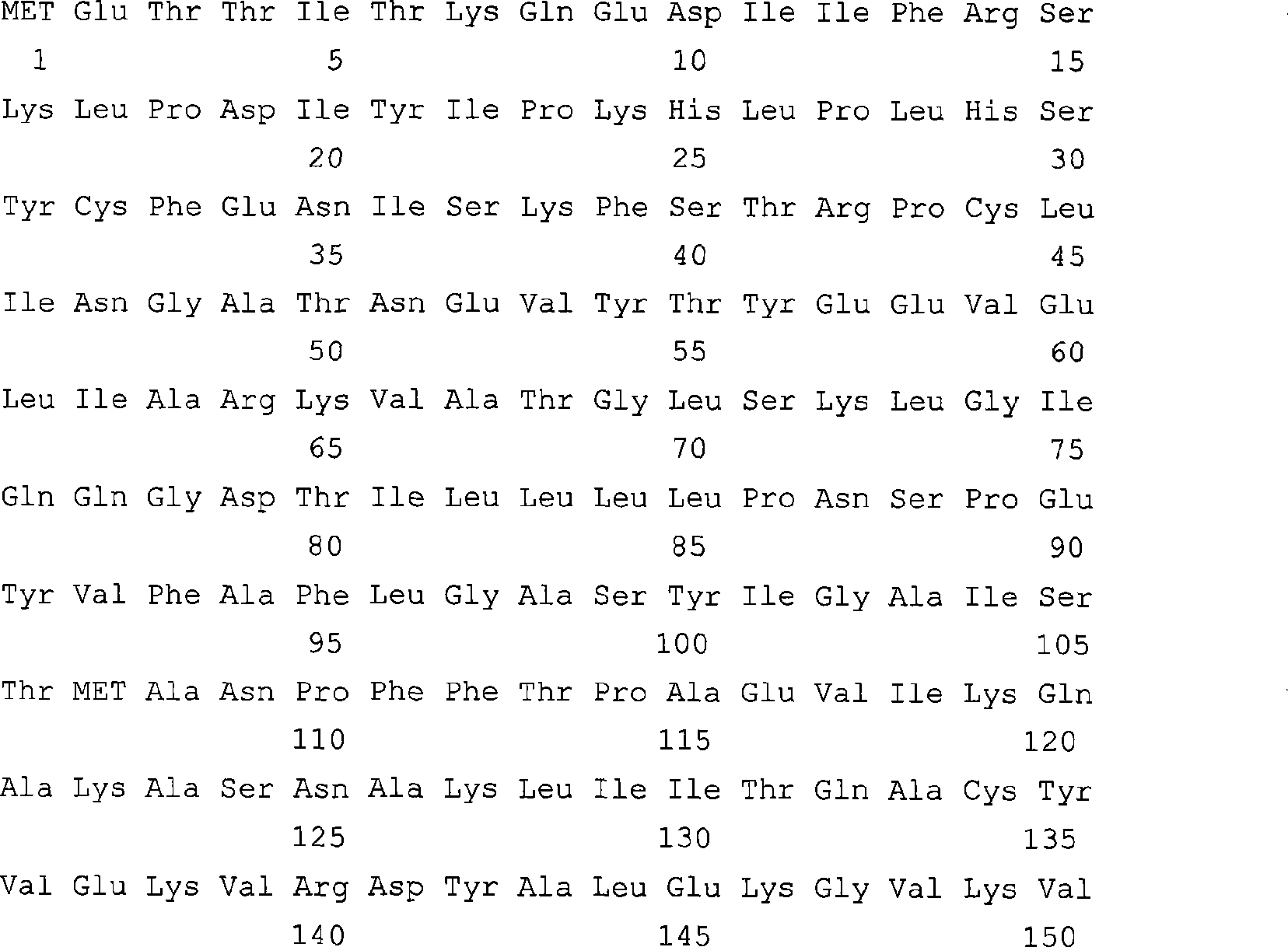
The invention discloses a paulownia 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase, encoding genes and application thereof. Amino acid residue sequence of the 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase is shown in SEQ ID No. of 1. The information can be used for constructing genes of the 4-coumaric-acid: coenzyme A ligase, or antisense genes and RNA disturbing mass of the genes, which can be used for improving plant materials and constructing new materials with higher or lower lignin content.
Owner:河南省绿士达林业新技术研究所
Alkali-soluble light-curing epoxy resin containing cinnamic acid or coumarin groups, preparation method of resin and solder resist prepared by using same
ActiveCN108034041AReduce dosageExcellent light curing propertiesInksPhotosensitive materials for photomechanical apparatusResistCoumaric acid
The invention provides alkali-soluble light-curing epoxy resin containing cinnamic acid or coumarin groups, a preparation method of the resin and a solder resist prepared by using the same, wherein the alkali-soluble light-curing epoxy resin containing the cinnamic acid or coumarin groups is obtained through the steps that epoxy resin undergoes a ring-opening reaction to introduce a cinnamic acidderivative or coumaric acid, and then the product undergoes an esterification reaction with an acid anhydride. Compared with the prior art, during the process of introducing unsaturated groups into the epoxy resin, the preparation method does not need addition of a polymerization inhibitor; and compared with the prior art, the solder resist prepared by using the alkali-soluble light-curing epoxy resin has a lower photoinitiator additive amount, thereby improving the performance and application effect of the solder resist.
Owner:广东炎墨方案科技有限公司
Method for producing verbascoside by using hairy roots of rehmannia
ActiveCN106148453AIncrease productionShort training periodMicroorganism based processesFermentationCoumaric acidSalicylic acid
The invention discloses a method for producing verbascoside by using hairy roots of rehmannia, and belongs to the technical field of bio-culture. The method comprises the following step: putting the hairy roots of the rehmannia into a salicylic acid-containing culture solution for inducing culture to obtain the verbascoside. The theory of the method is that the hairy roots, which are treated by salicylic acid, of the rehmannia can enhance the expression of key biosynthetic enzymes, such as phenylalnine ammonialyase (PAL), 4-coumaroyl-co-A ligase (4CL), cinnamate 4-hydroxylase (C4H), coumaric acid hydroxylase (C3H), copper amine oxidase (CuAO) and tyrosine carboxy-lyase (TyDC), for the verbascoside within a short time period (12 to 24 h) so as to complete gathering of the verbascoside and further increase the yield of the verbascoside. The method is easy and convenient to operate, short in culture period, convenient for industrial, large-scale and standardized implementation, and has a great significance for promotion of large-scale production of the verbascoside.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Trans-cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106754774AGood substrate specificityHigh regional selectivityOxidoreductasesGenetic engineeringRegioselectivitySubstrate Specificities
The invention relates to a trans-cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase and a coding gene and application thereof. The trans-cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase of lycoris aurea is disclosed for the first time; and the trans-cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase has good substrate specificity and regioselectivity, and hydroxylation of 4-bit C of trans-cinnamic acid can be catalyzed to generate p-cumaric acid. The invention further discloses a polynucleotide of coding the trans-cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase, a carrier and host cell for expressing the trans-cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase, and a method for producing the p-cumaric acid.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for biosynthesizing high-added-value compound by utilizing lignocellulose derivatives
ActiveCN112481336ASynthesis fastEfficient use ofBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydroxytyrosol
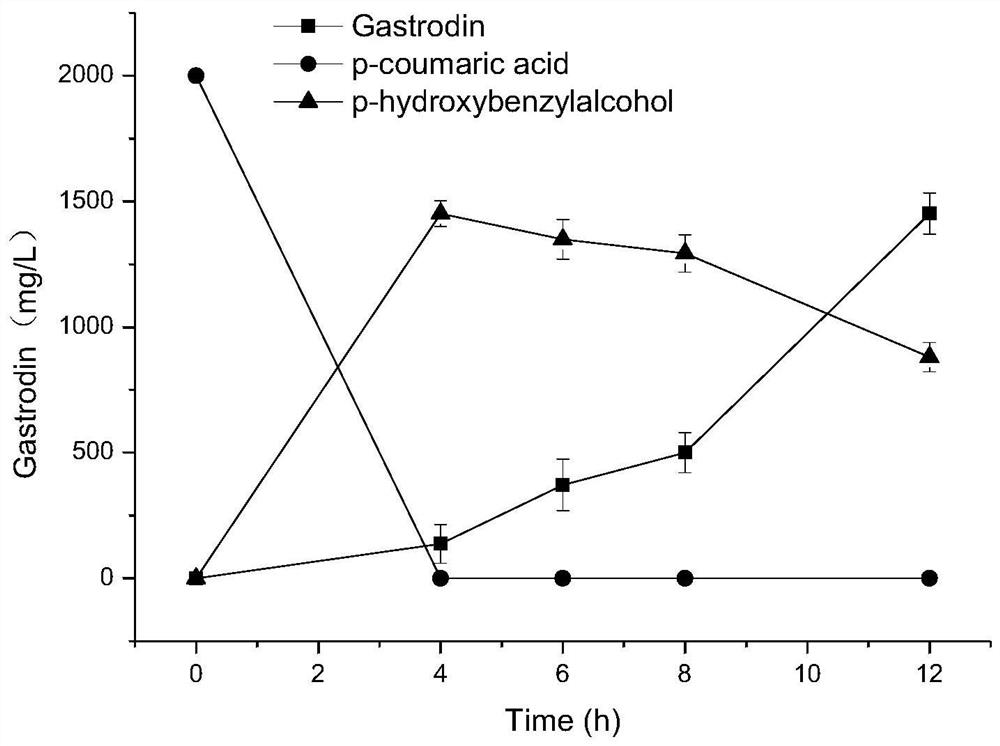
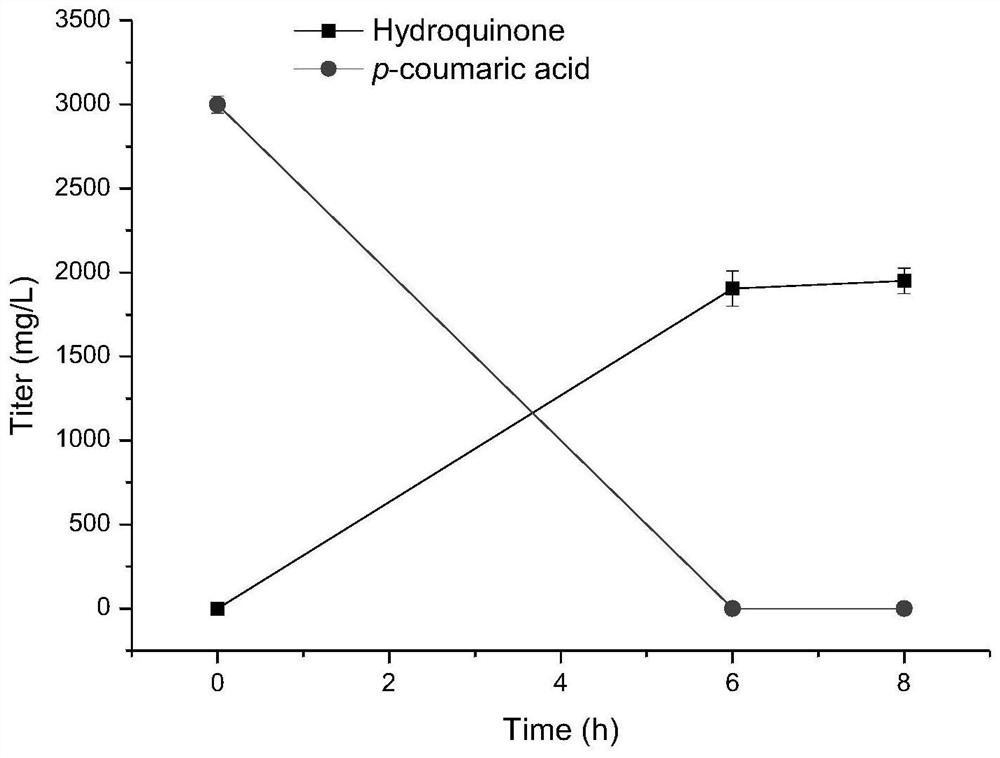
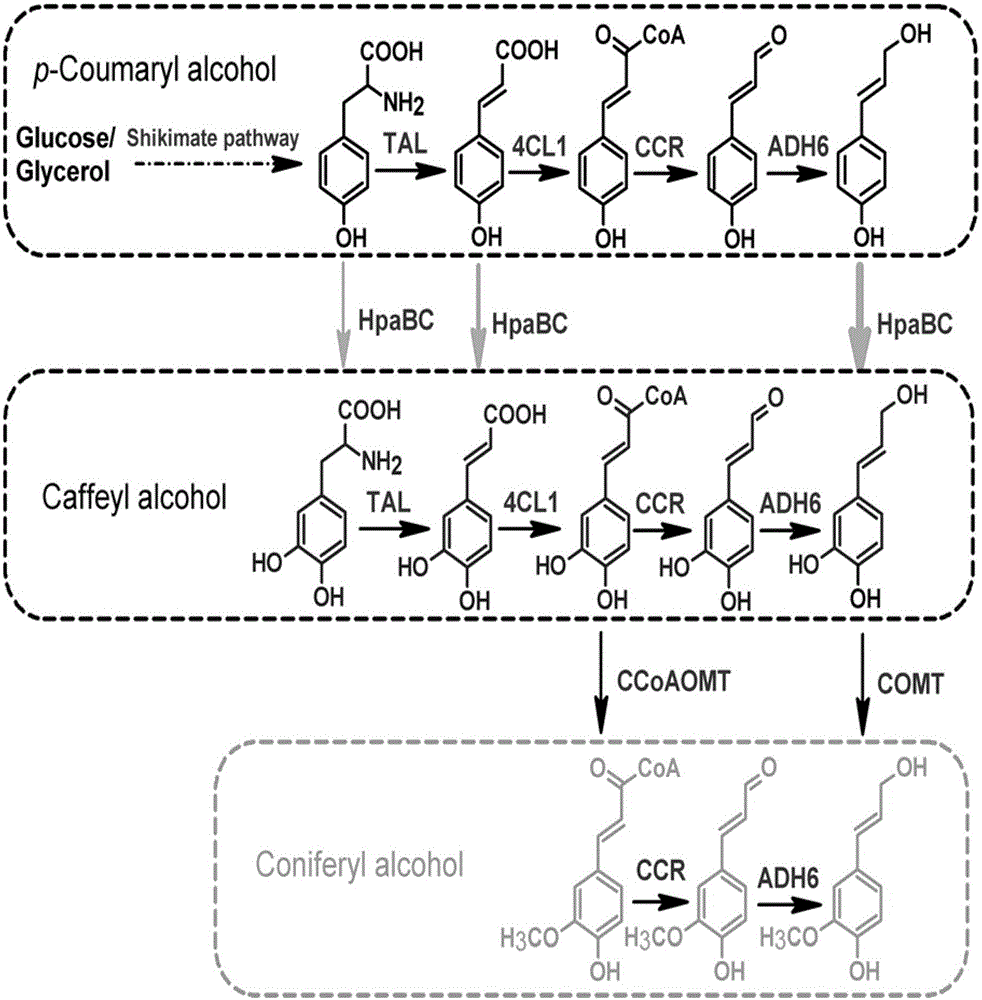
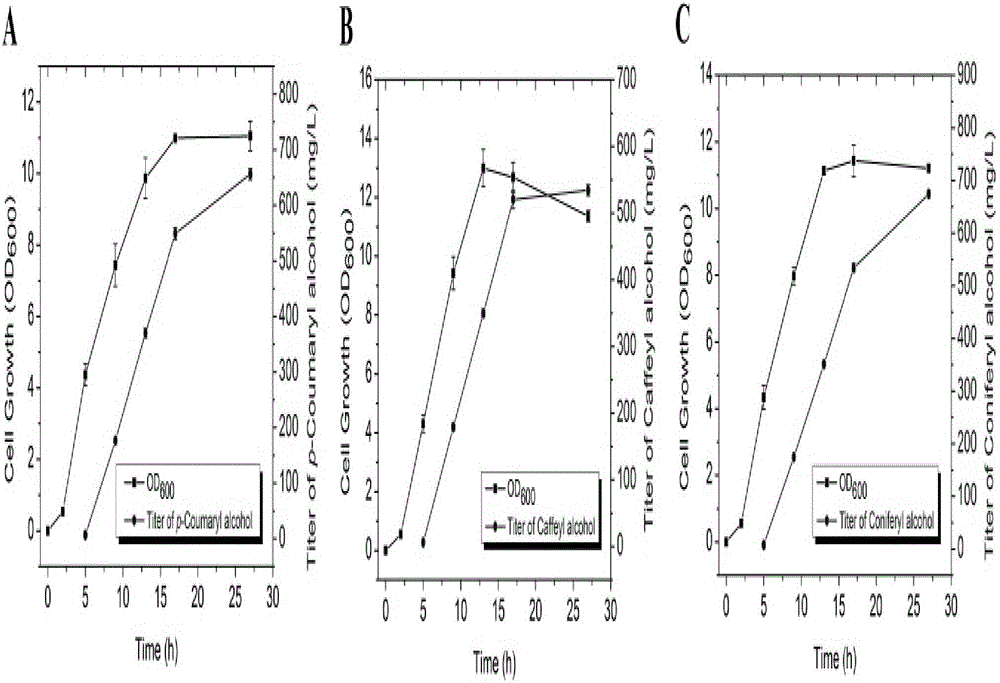
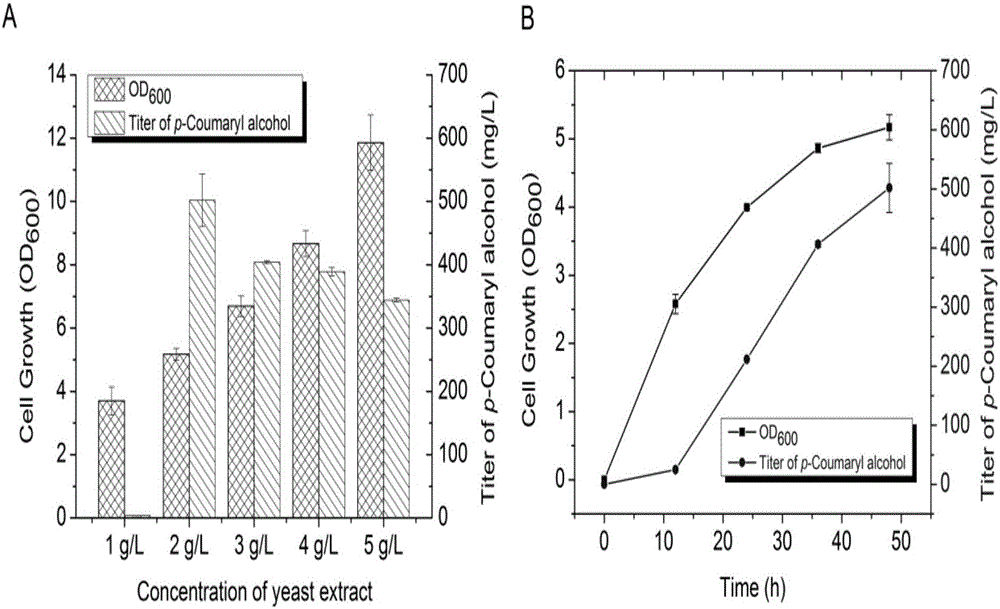
The invention discloses a method for biosynthesizing a high-added-value compound by using lignocellulose derivatives, which comprises the following steps: A, modifying Escherichia coli to obtain a biocatalyst; B, synthesizing a high-added-value compound by taking a lignocellulose derivative as an initial raw material through a biocatalyst, wherein the lignocellulose derivative comprises at least one of p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid, and the high-added-value compound comprises at least one of gastrodin, arbutin, salidroside and derivatives thereof such as hydroquinone, tyrosol, hydroxytyrosol and styracitol. According to the method, escherichia coli is modified through a genetic engineering means, three new enzymatic reaction ways are constructed, and various high-added-value compounds including gastrodin, arbutin, salidroside and the like are efficiently synthesized by utilizing lignocellulose derived aromatic compounds p-coumaric acid and ferulic acid, wherein the product yield reaches gram-level or above.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for heterologous biosynthesis of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol
InactiveCN105907804AEfficient productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCinnamoyl-CoA reductaseCoumaric acid
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and discloses a method for heterologous biosynthesis of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol. The metabolic pathway for production of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol is added into hosts. More precisely, tyrosine ammonia lyase, cinnamoyl-coA reductase, alcohol dehydrogenase and coumaric acid coA ligase are efficiently expressed in the host for producing tonquinol, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid3-monooxygenase is added to produce caffeol, coffee acyl coenzyme AO-methyl transferase or caffeic acid O-methyl transferase is added to produce ferulenol. Genes coded by the enzyme are guided into the host, and the production host of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol can be generated by means of glucose. The invention further discloses a method for co-culture of different hosts, and the caffeol and the ferulenol are produced more efficiently.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Method for Escherichia coli whole cell catalyzed production of phloretin
InactiveCN107805646ALow costPrevent extractionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaEscherichia coliSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a method for Escherichia coli whole cell catalyzed production of phloretin. The synthesis method is characterized in that the production of the phloretin is completed by adopting phenylalanine as a raw material and an Escherichia coli engineering bacterium as a host bacterium through catalysis of multiple enzymes in the host bacterium; and the host bacterium at least can express phenylalnine ammonialyase, cinnamic acid-4-hydroxylase, 4-coumaric acid coenzyme A ligase, double-bond reductase and chalcone synthetase. The method has the following advantages: 1, the phenylalanine is used as the raw material, so the raw material cost of the method is low; 2, catalytic synthesis of biological enzymes in microorganisms is carried out based on microorganism modification, solarge-scale extraction, separation and purification processes are avoided, and the production cost and the environmental protection are easy to control; 3, the size and the quantity of production devices used in the method are less than those of other methods, so the method can be easily industrially converted; and 4, only the final step in the production of the method contains separation and purification processes, so the product purifying process is simple, and the product has better quality and higher content than the product obtained through general methods.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
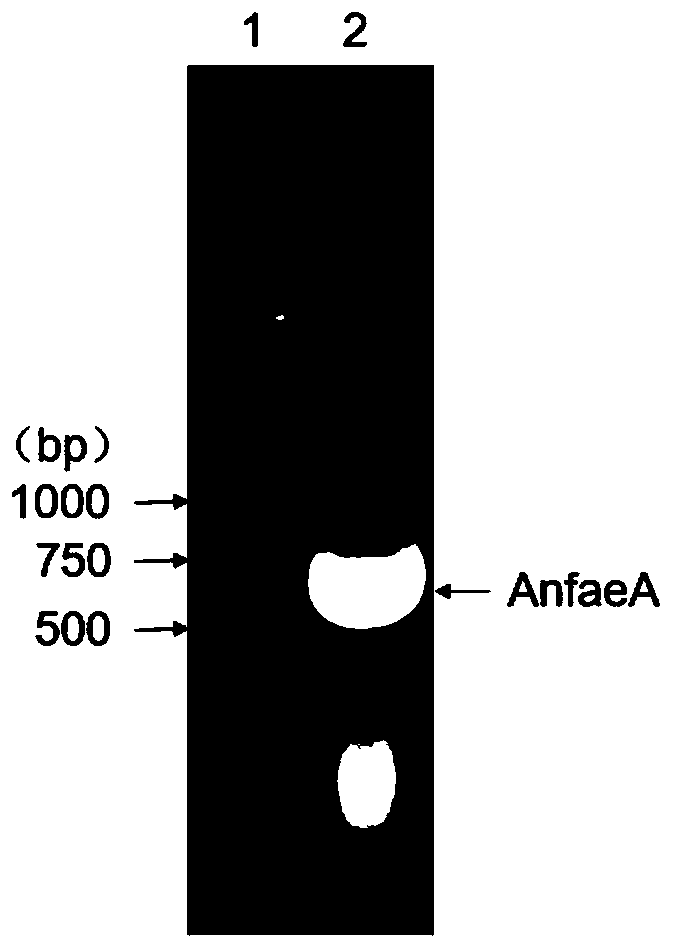
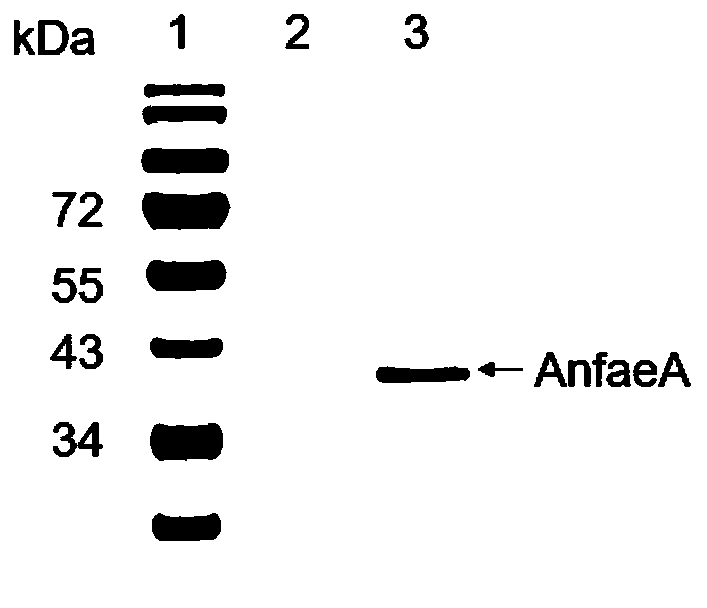
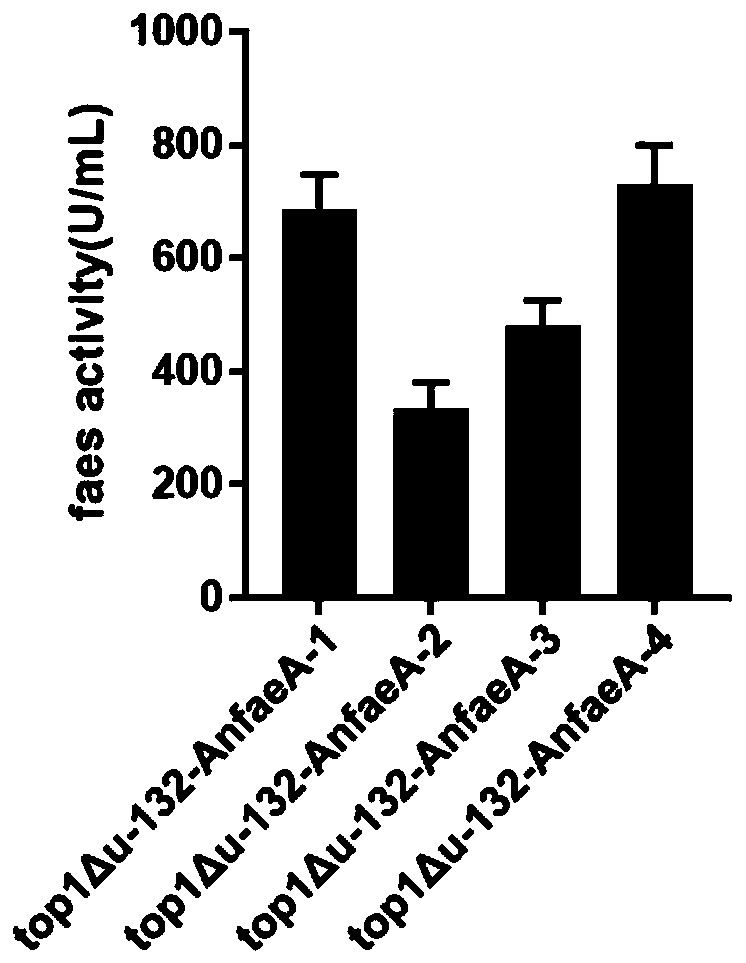
Recombinant expression strain of feruloyl esterase as well as preparation method and application of recombinant expression strain
The invention provides a Kluyveromyces marxianus recombinant strain capable of being used for preparing feruloyl esterase AnfaeA. The recombinant strain is constructed by cloning an aspergillus nigerferuloyl esterase AnfaeA gene with an optimized sequence to an expression vector and converting a Kluyveromyces marxianus host strain, and the yield of the feruloyl esterase obtained by high-density fermentation of the recombinant strain reaches 120000 U / ml. The invention also provides a method for preparing ferulic acid by hydrolyzing corncob powder with the feruloyl esterase. The feruloyl esterase AnfaeA prepared from the recombinant strain and xylanase have a synergistic effect, so that the corncob powder can be efficiently hydrolyzed to obtain the ferulic acid. The feruloyl esterase provided by the invention can be used for preparing phenolic substances such as ferulic acid, p-coumaric acid and the like through biodegradation of agricultural byproducts such as corncobs, rice bran, cornbran and the like, so that the feruloyl esterase has a wide application value in the fields of foods, papermaking, feeds, medicines and the like. Meanwhile, the preparation method is simple in process, high in yield and very suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
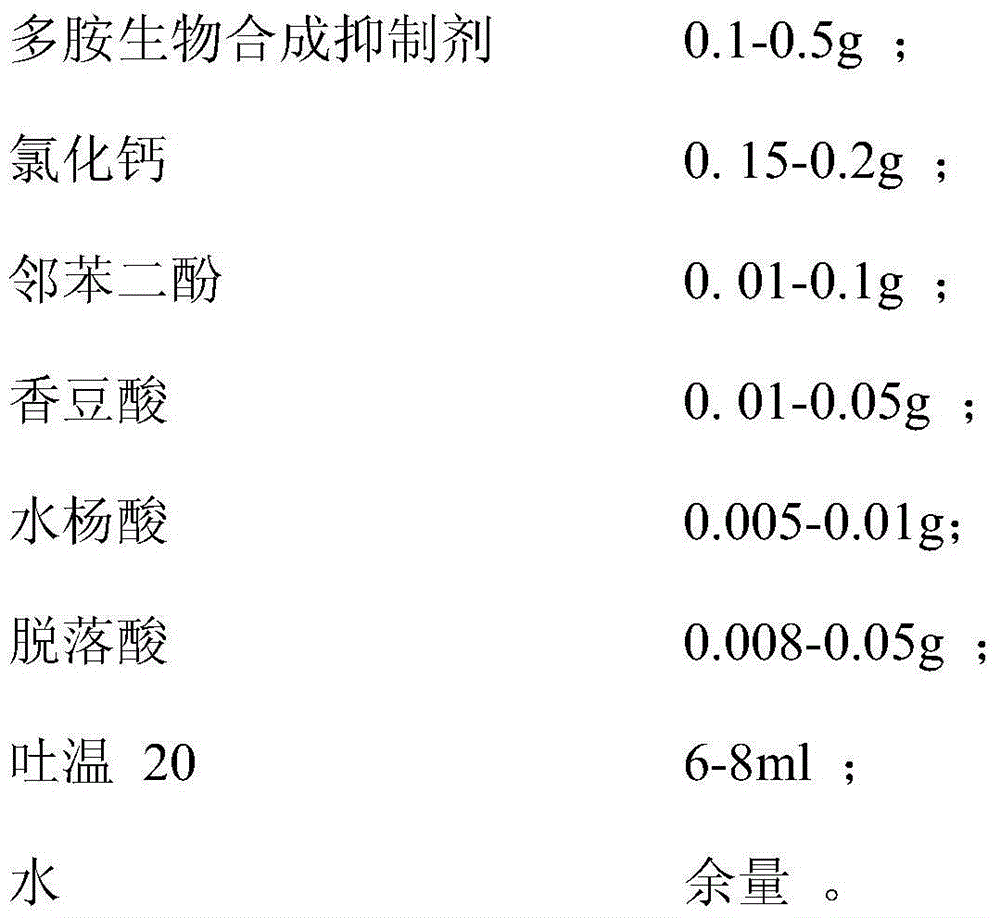
Dormancy agent for transplanting trees and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104782654ASlow down the rate of water metabolismDecrease breathing rateBiocidePlant growth regulatorsCoumaric acidSalicylic acid
The invention relates to the plant dormancy adjustment and control technical field, and discloses a dormancy agent for transplanting trees; each 1 L of the dormancy agent for transplanting the trees comprises the following components: 0.1-0.5 g of a polyamine biosynthetic inhibitor, 0.15-0.2 g of calcium chloride, 0.01-0.1 g of catechol, 0.01-0.05 g of coumaric acid, 0.005-0.01 g of salicylic acid, 0.008-0.05 g of abscisic acid, 6-8 ml of Tween 20, and the balance water. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the dormancy agent for transplanting the trees. The trees are subjected to dormancy induction before the trees are transplanted, seasonal restriction and technical barriers of tree full-year transplanting are overcome, and the transplanting survival rate of the trees is increased. The cost is low, the consumption is little, the trees restore quickly, the transplanting security coefficient is high, and the landscape effect is easy to form.
Owner:YUANCHENG ENVIRONMENT CO LTD
Cytochrome P450 reductase 1 of lycoris aurea as amaryllidaceae plant as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention relates to cytochrome P450 reductase as well as coding gene and application thereof. The invention discloses cytochrome P450 reductase 1 of lycoris aurea as an amaryllidaceae plant for the first time; the cytochrome P450 reductase 1 has favorable coenzyme specificity and can be used for assisting a cytochrome P450 enzyme in exerting catalytic activity to modify a synthetic product of a substrate of the cytochrome P450 enzyme in an oxidative manner. The invention also discloses a polynucleotide for coding the cytochrome P450 reductase, a carrier and a host cell for expressing the cytochrome P450 reductase and a method for producing p-coumaric acid.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Recombinant host cell for biosynthetic production
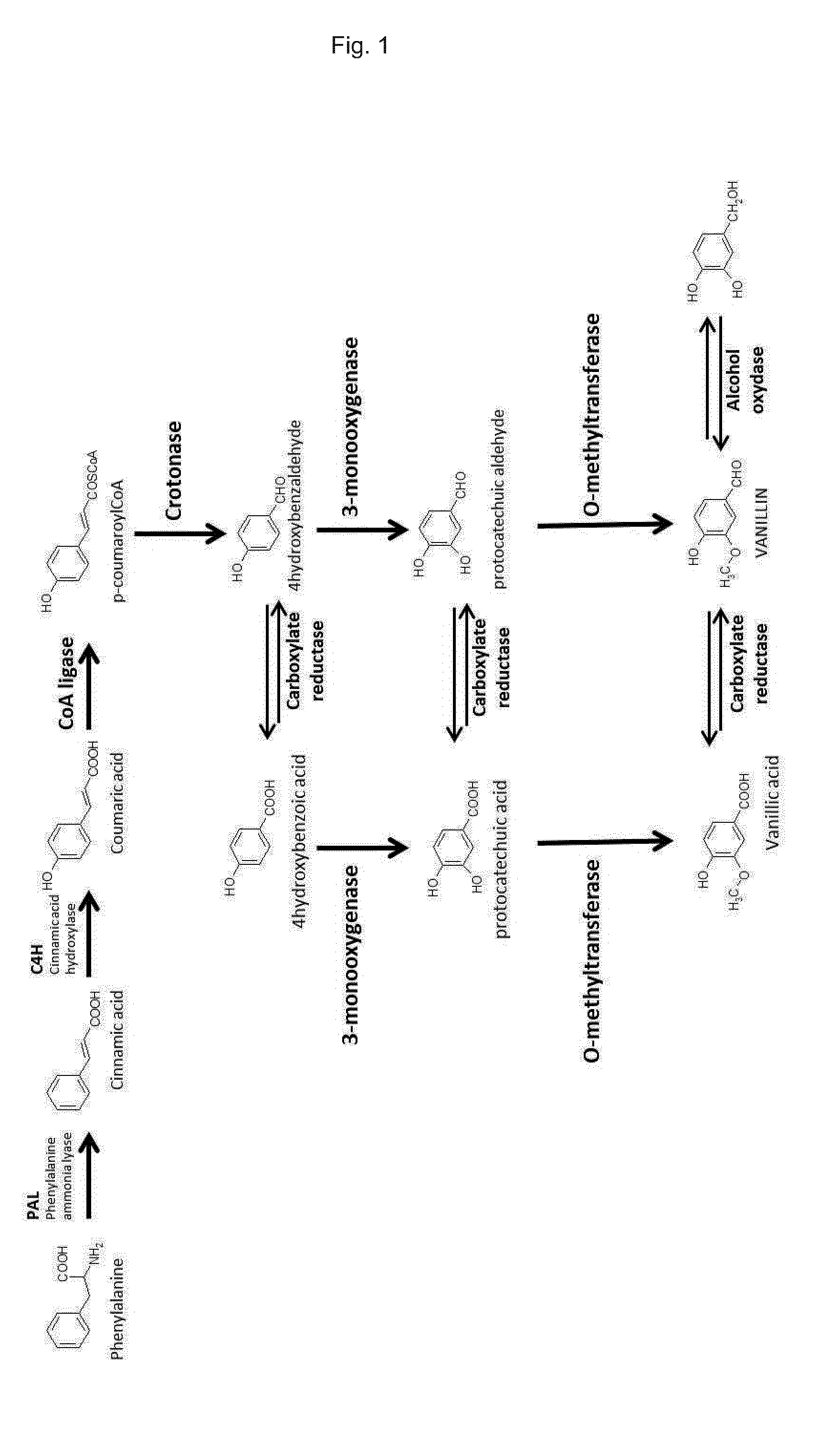
A cell may include heterologous polynucleotides encoding a multienzyme complex involved in the metabolic pathway of phenylpropanoids and biosynthesis of a vanilloid or a hydroxybenzaldehyde precursor thereof, which multienzyme complex comprises enzymes for the biosynthesis of coumaric acid and a crotonase.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com