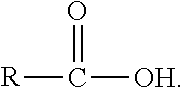
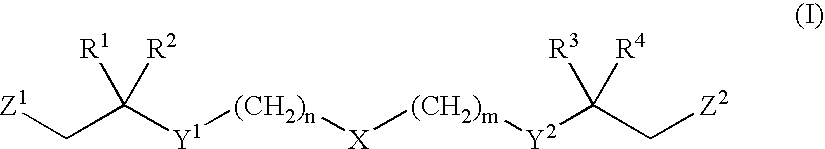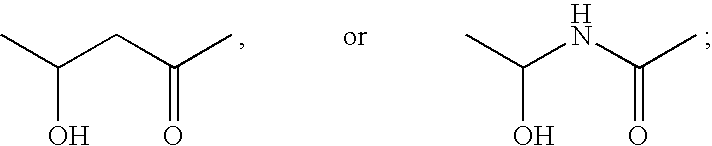Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Acyl coenzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant Genes Associated With Seed Oil Content And Methods Of Their Use
InactiveUS20110191904A1High oil contentRaise the ratioOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyReticulum cell
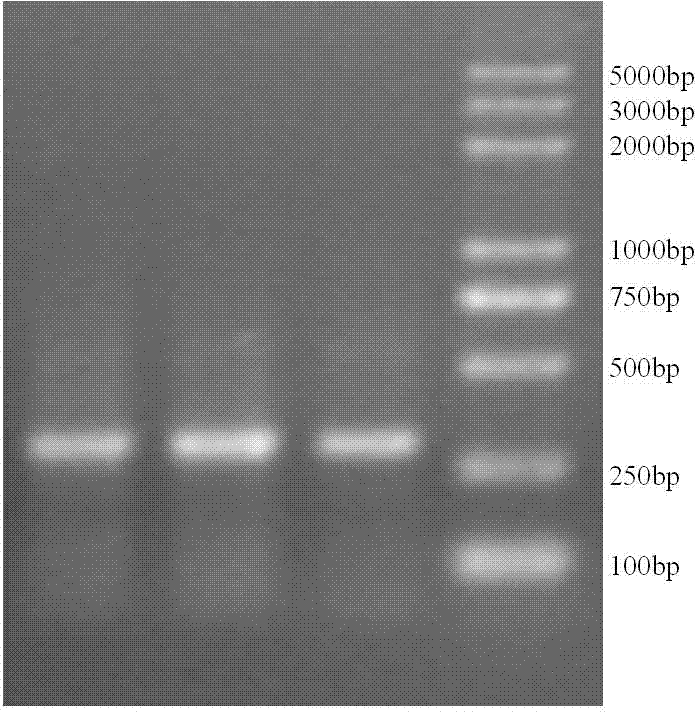
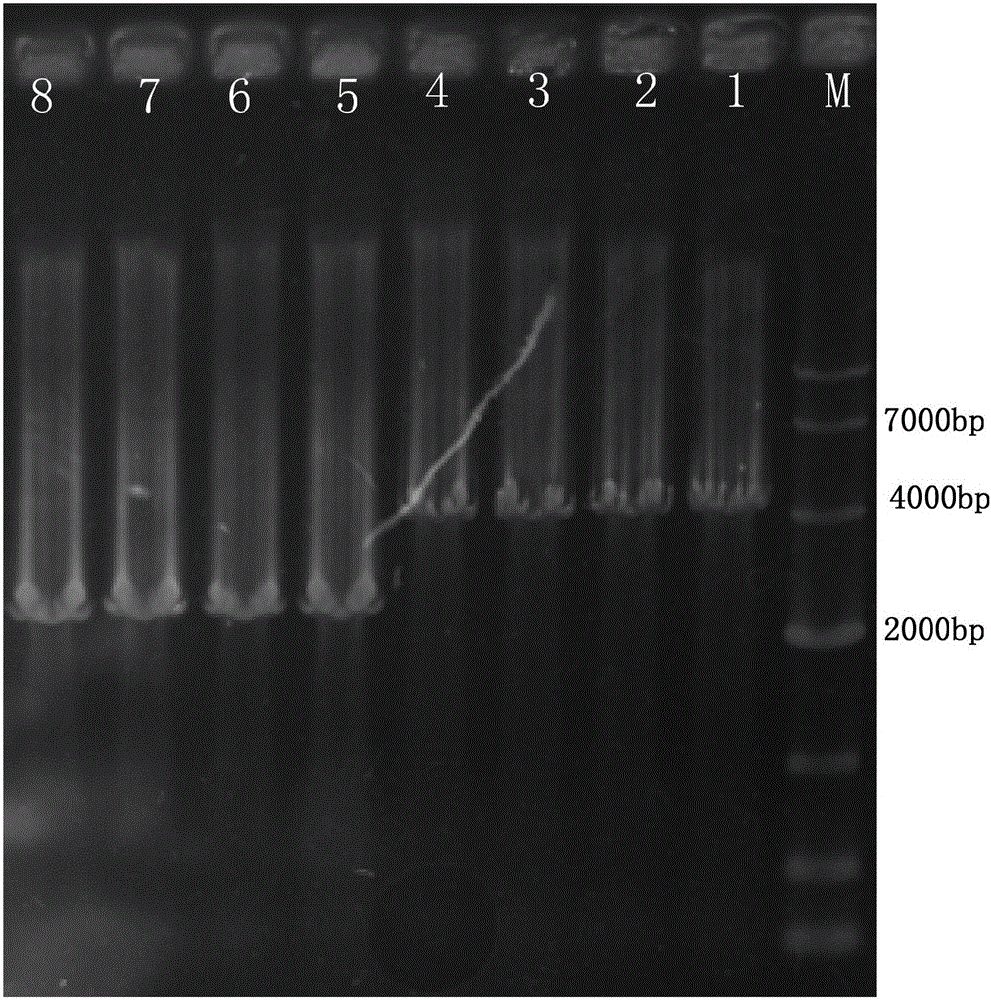
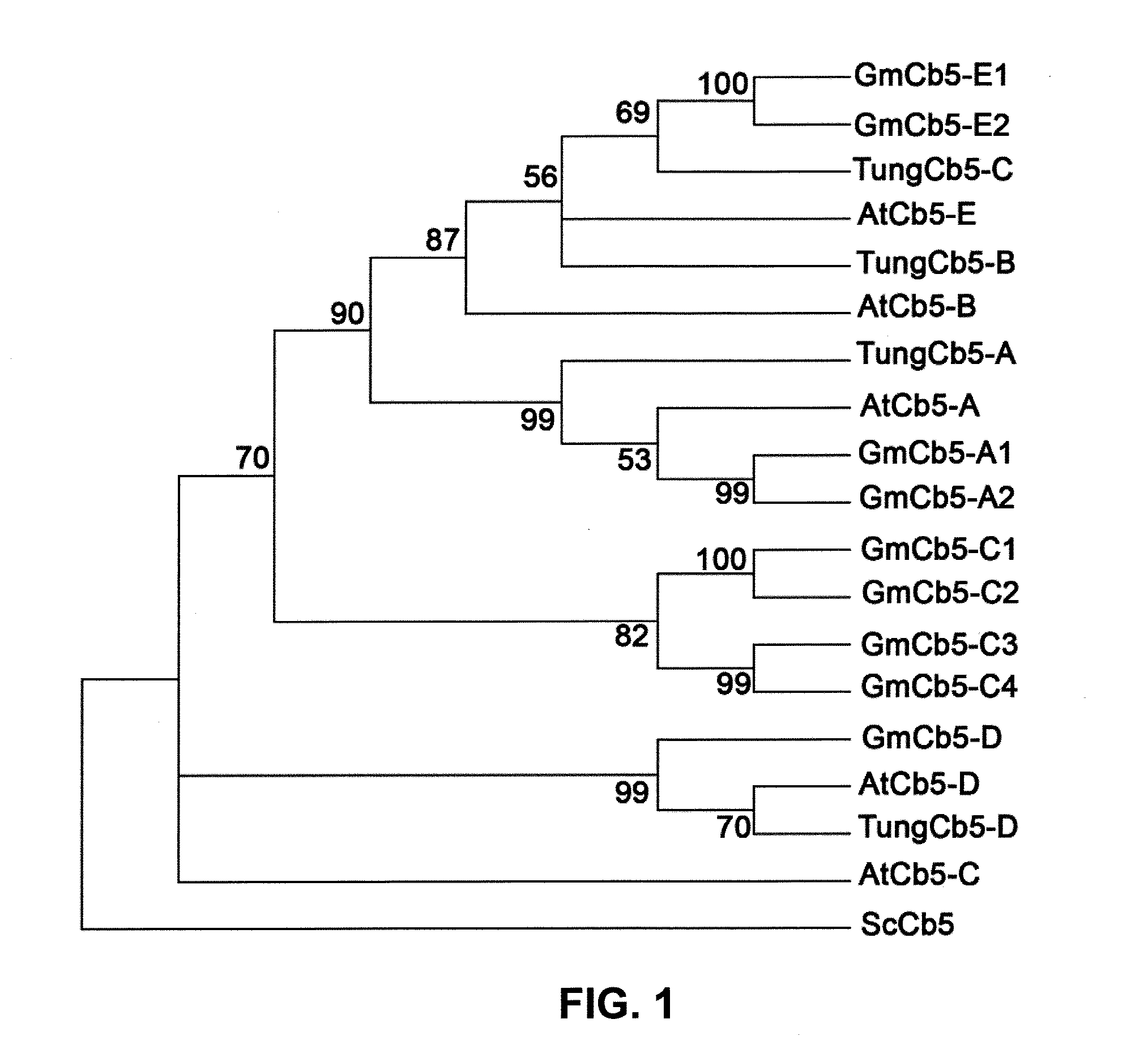
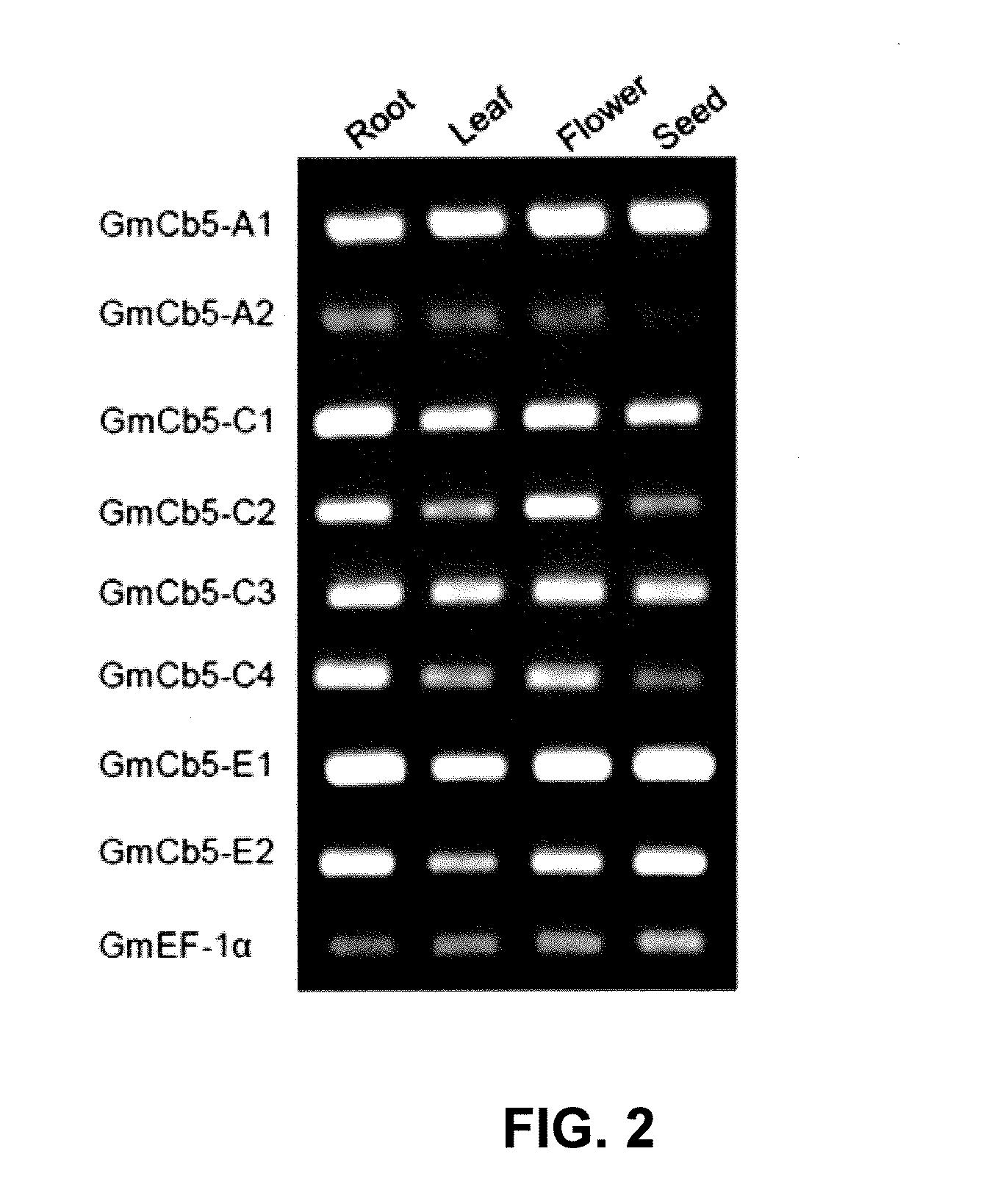
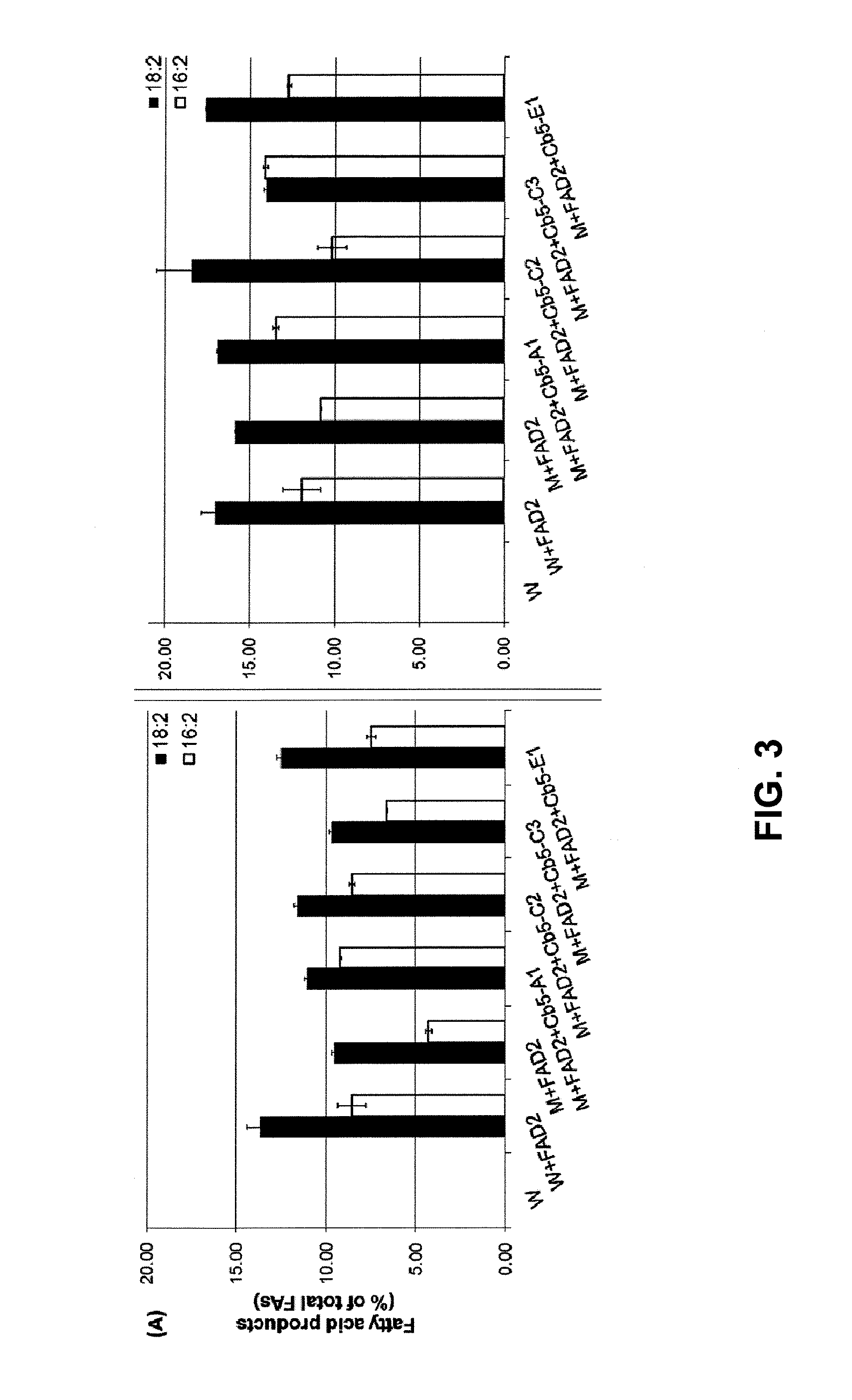
Cytochrome b5 (Cb5) is a haem-binding protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the outer mitochondrial membranes of higher eukaryotes. In higher plants, animals, and fungi, the ER resident Cb5 has been shown to play a role in desaturation of acyl CoA fatty acids. Higher plants Cb5 isoforms from plants such as soybean or Arabidopsis are capable of modulating omega-3 desaturation. Co-expression of certain Cb5 isoforms with FAD3 in a host plant results in increased production of seed oil content as well as altered ratio between different fatty acids. It is also disclosed here that overexpression of Yarrowia ACL enzymes in the plastids of a host plant helps boost the synthesis of acetyl CoA, which in turn, may lead to increased synthesis of fatty acids and enhanced oil accumulation in the seeds.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI
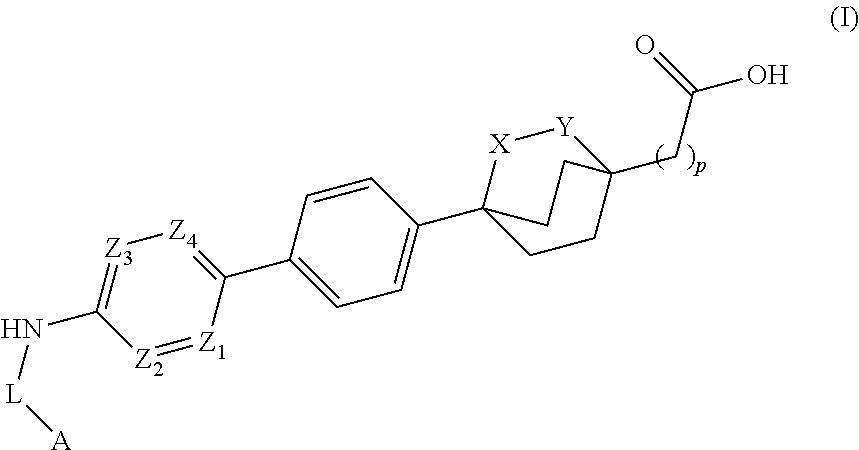
Urea derivatives having ACAT inhibitory activity, their preparation and their therapeutic and prophylactic use
Compounds of formula (I): wherein: R1 is alkyl; R2a, R2b, R2c and R2d are the same or different and each is hydrogen, optionally substituted alkyl or various other organic groups; R3 is alkyl; R4 is a group of formula (II), (III), (IV), (V), (VI), (VII), (VIII) or (IX): wherein: A1 is a single bond, alkylene or alkenylene; A2 is or alkenylene; A3 is a single bond, alkyleneor alkenylene; R5a and R5b are the same or different and each is hydrogen, alkyl or various other groups; R6 is alkyl or phenyl; R7 is hydrogen or alkyl; R8 is alkyl or various other groups; and n is 0 and pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof have valuable inhibitory activity against acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyl transferase.
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
Acyl-acp wax ester synthases
ActiveUS20130078684A1Enhance cell viabilityMore energy efficientBacteriaHydrolasesPhylum CyanobacteriaAlcohol
The invention relates to acyl-CoA-independent methods of producing a wax ester in recombinant host cells engineered to express an acyl-ACP wax ester synthase, and an alcohol-forming acyl-ACP reductase. The methods of the invention may take place in photosynthetic microorganisms, and particularly in cyanobacteria. Isolated nucleotide molecules and vectors expressing an acyl-ACP wax ester synthase and / or an alcohol-forming acyl-ACP reductase, recombinant host cells expressing an acyl-ACP wax ester synthase and optionally an alcohol-forming acyl-ACP reductase, and systems for producing a wax ester via an acyl-CoA-independent pathway, are also provided.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
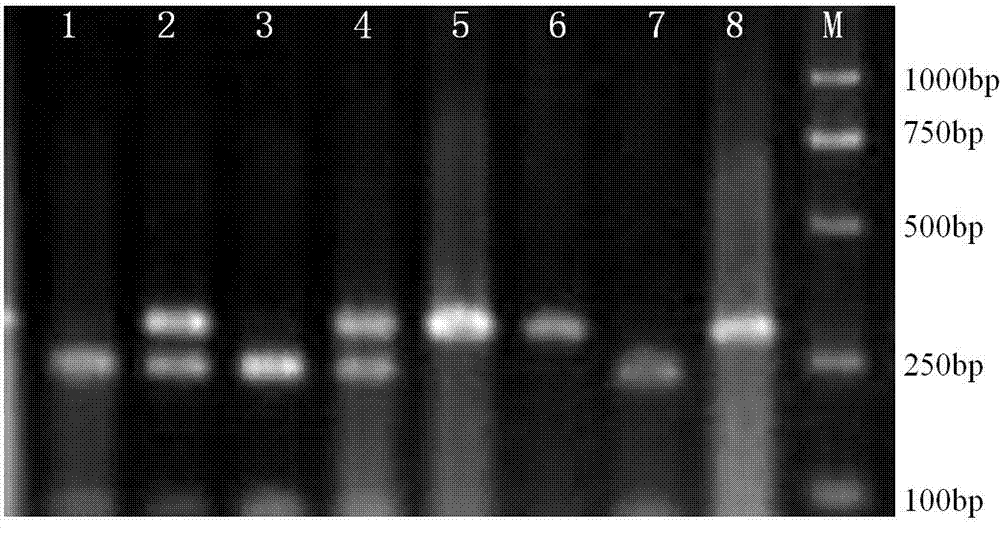
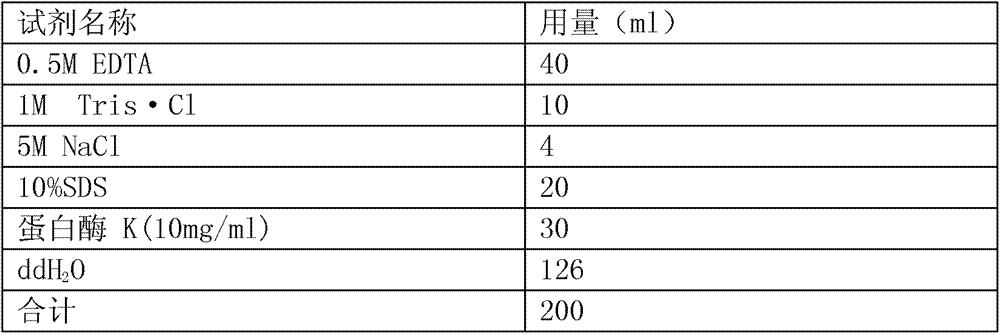
Molecule marking method for pig backfat thickness property
InactiveCN103497994ASolve the problems of high blindness and low selection accuracyShorten the generation intervalMicrobiological testing/measurementBOARAcyl coenzyme
The invention relates to a molecule marking method for pig backfat thickness property. The method comprises: extraction of pig genome DNA, design of a long-chain acyl-coenzyme Asynthetase 1 (ACSL1) gene seventh exon primer, amplification in vitro and genotype detection. For the first time, it is discovered that the polymorphism of the long-chain acyl-coenzyme Asynthetase 1 (ACSL1) gene seventeenth exon has significant correlation with the pig backfat thickness, and a method for detecting the restriction fragment polymorphism at mutation sites of the seventeenth exon is established. The molecule marking method is applicable to auxiliary selection on backfat thickness property during breeding of pigs, helps to realize early-stage breeding selection of boars, and even helps to accurately select breeding just when pigs are born, so that the generation interval is shortened, and the selection progress of the backfat thickness property is accelerated; and the method is simple in operation, condition requirements during a polymerase chain reaction are low, the length of amplified fragments is relatively short (292 bp), amplification is relatively easy, and the method helps to improve amplification efficiency and accuracy of genotype determining.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
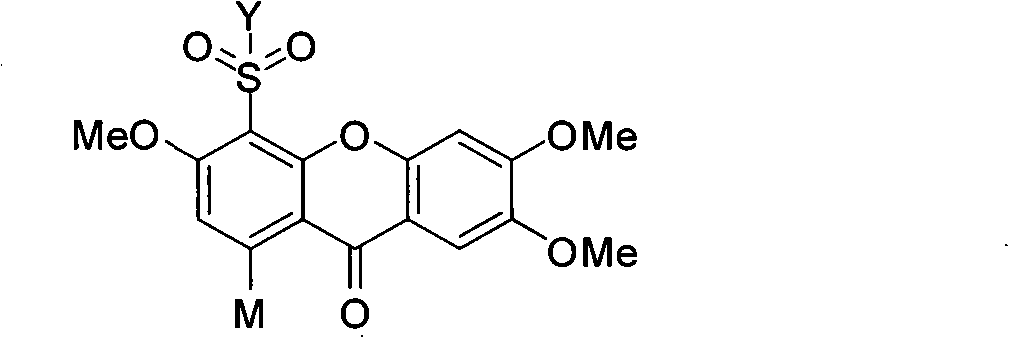
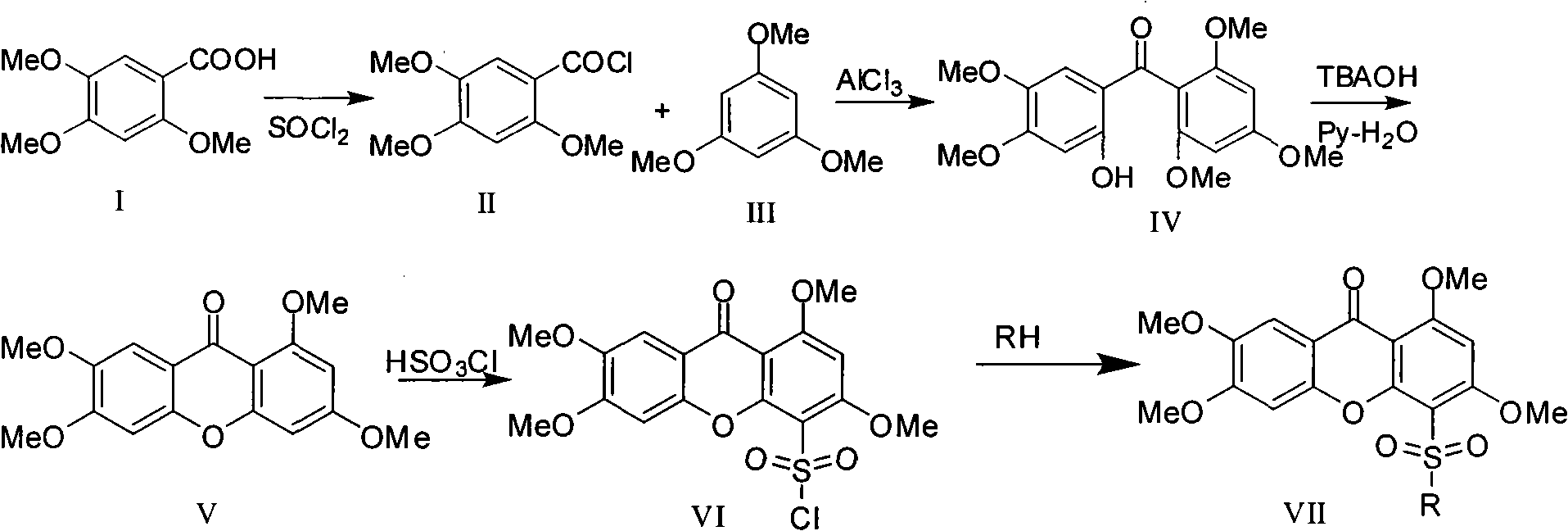
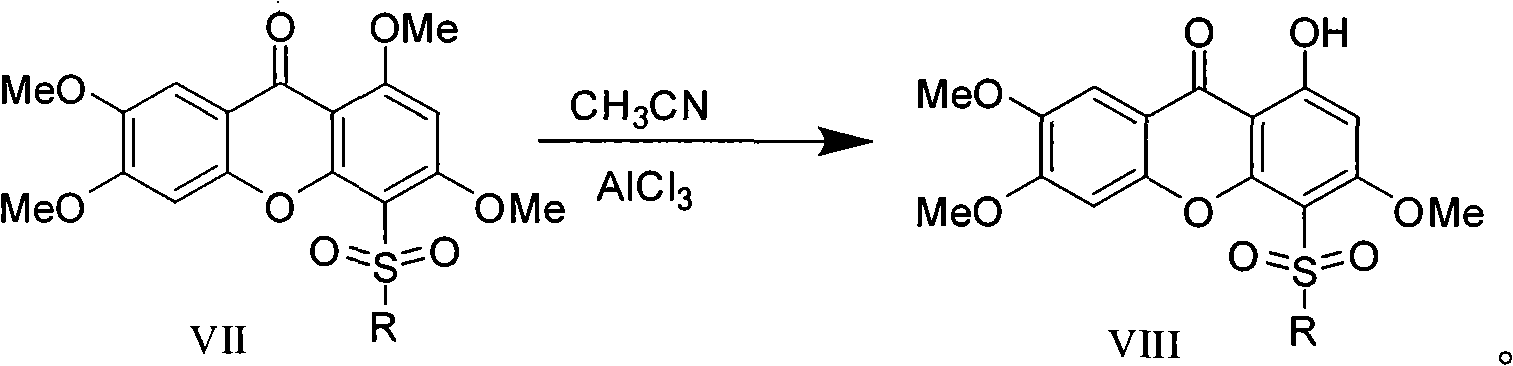
Novel sulfonyl substituted benzophenone oxide compounds, prepraring method and application thereof
InactiveCN101270110AGood inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseAcylcoenzyme A cholesterol acyltransferase
The present invention relates to the field of medical technology, and in particular relates to a category of novel sulphonyl substituted xanthene ketone compounds that have a structural formula as shown in the right, a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has high inhibitory activity for ACAT1 / ACAT2; most of the compounds have high inhibitory activity for acyl coenzyme A cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT). The compounds can be used for preparing anti-atherosclerosis drug combination. Furthermore, the compounds can be used as a preventive or a treating agent of such diseases as angina, myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, apoplexy, Alzheimer's disease, acute coronary syndrome, PTCA or restenosis of coronary artery after a bracket is arranged. The compounds can be used as a treating agent to adjust the function of sebaceous glands of the skin and inhibit the excessive generation of sebum. And the compounds can be used for treating such diseases as acne-like damage caused by oily skin, acne, seborrhea and corticosteroids.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Recombinant microbial cells that produce at least 28% eicosapentaenoic acid as dry cell weight
ActiveUS20140186906A1Reduce the amount presentDecreases the total amount of sugar alcoholsFungiAcyltransferasesPhosphatidic acidPolynucleotide
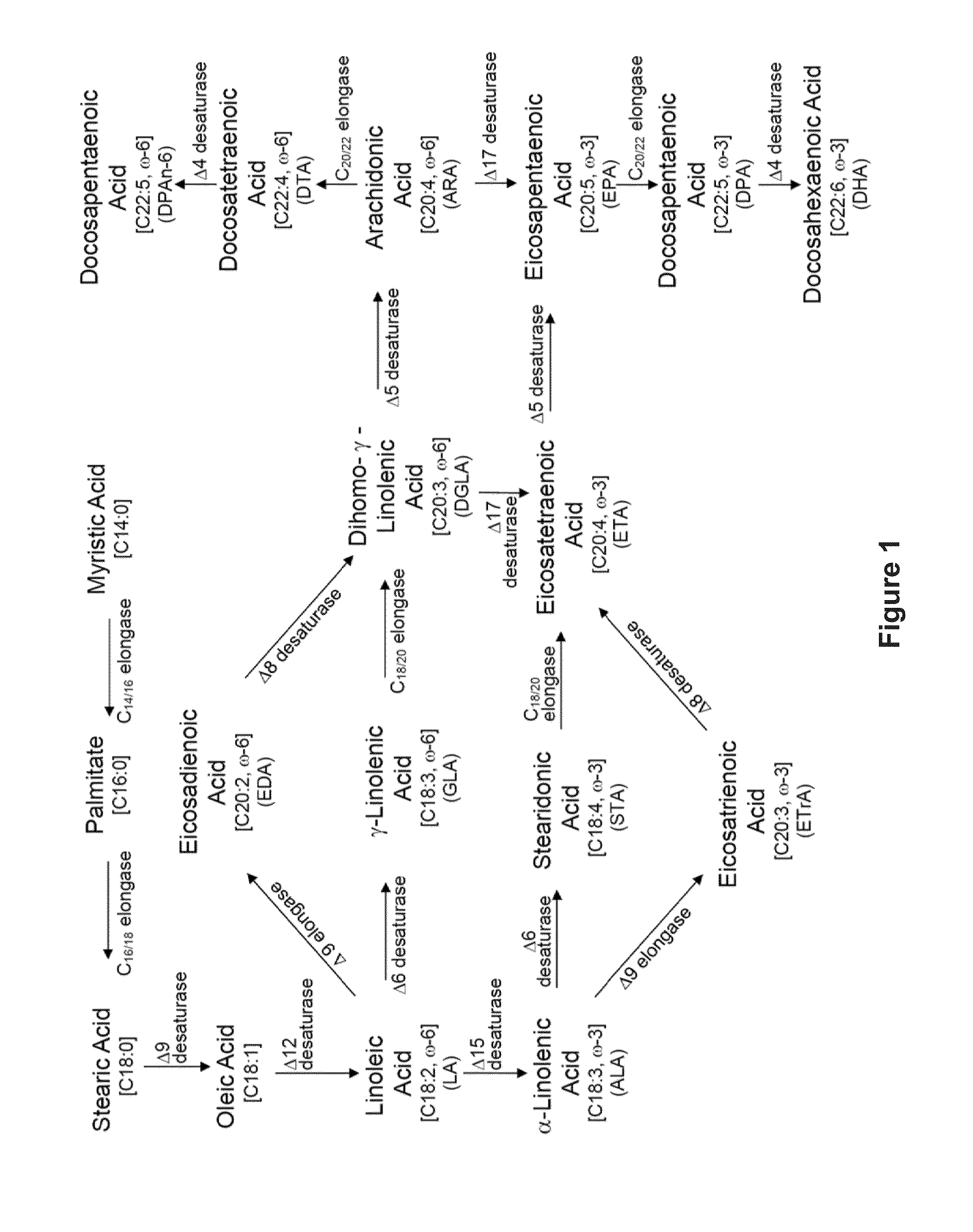
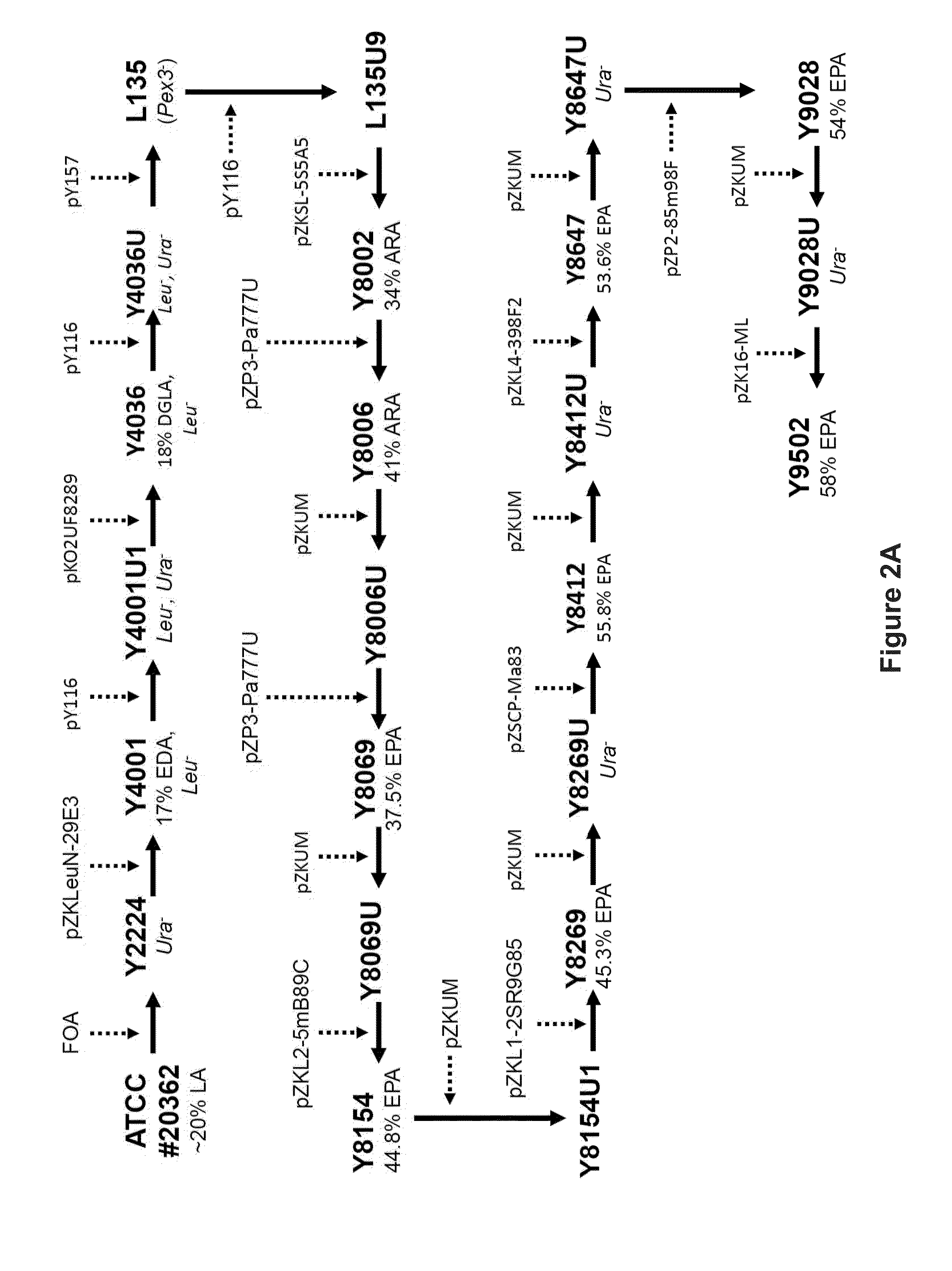
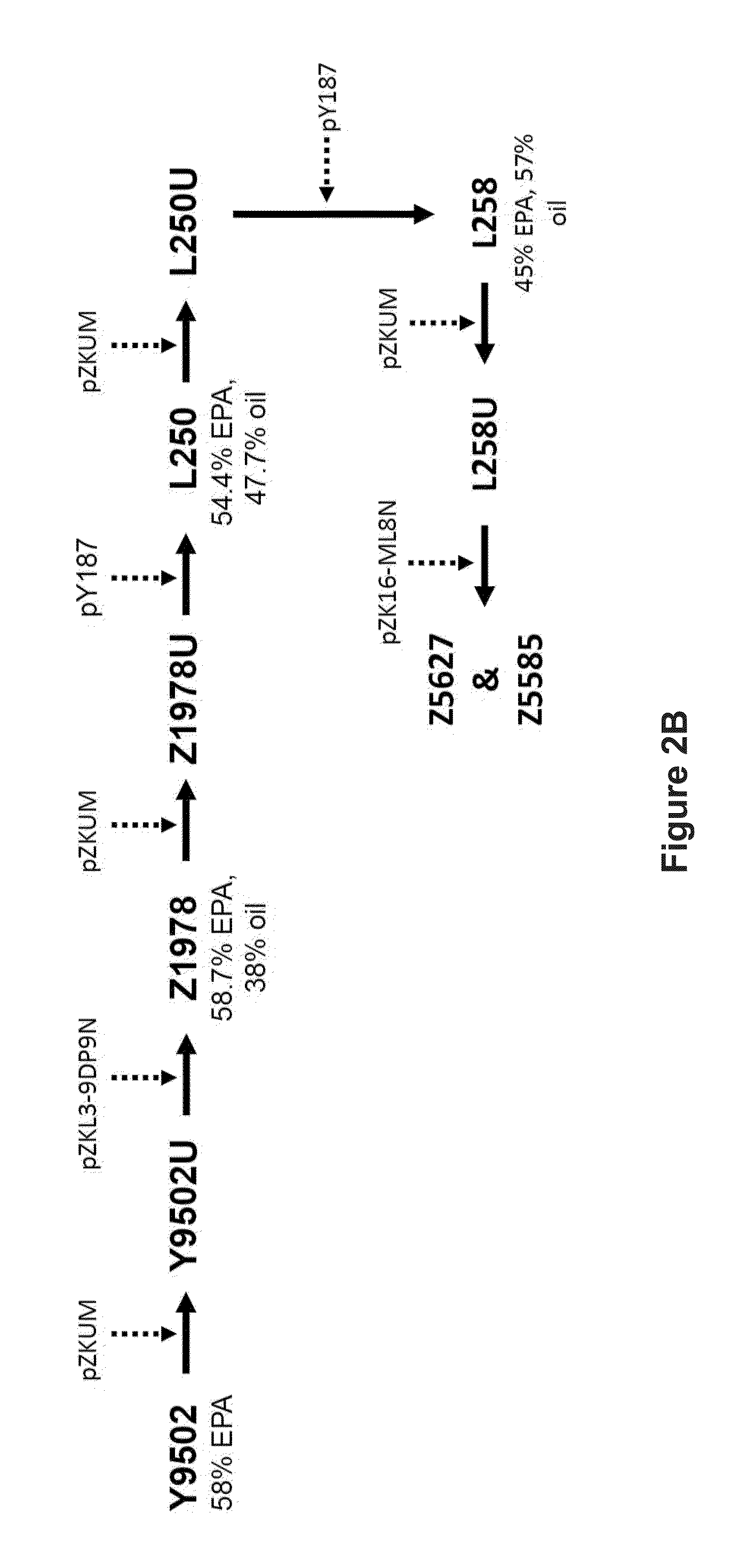
Recombinant microbial cells are disclosed herein that produce an oil comprising at least 28 percent eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) measured as a weight percent of dry cell weight. These cells may comprise a polynucleotide sequence encoding an active acyl-CoA:lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase (LPCAT) comprising at least one amino acid mutation in a membrane-bound O-acyltransferase motif. In addition, the cells may comprise a down-regulation of an endogenous polynucleotide sequence encoding Sou2 sorbitol utilization protein, and / or one or more polynucleotides encoding phospholipid:diacylglycerol acyltransferase (PDAT), delta-12 desaturase, a dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid (DGLA) synthase multizyme, delta-8 desaturase, malonyl-CoA synthetase (MCS), or acyl-CoA:lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase (LPAAT). Also disclosed are methods of using the recombinant microbial cells to produce oil containing omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids such as EPA.
Owner:DUPONT US HLDG LLC
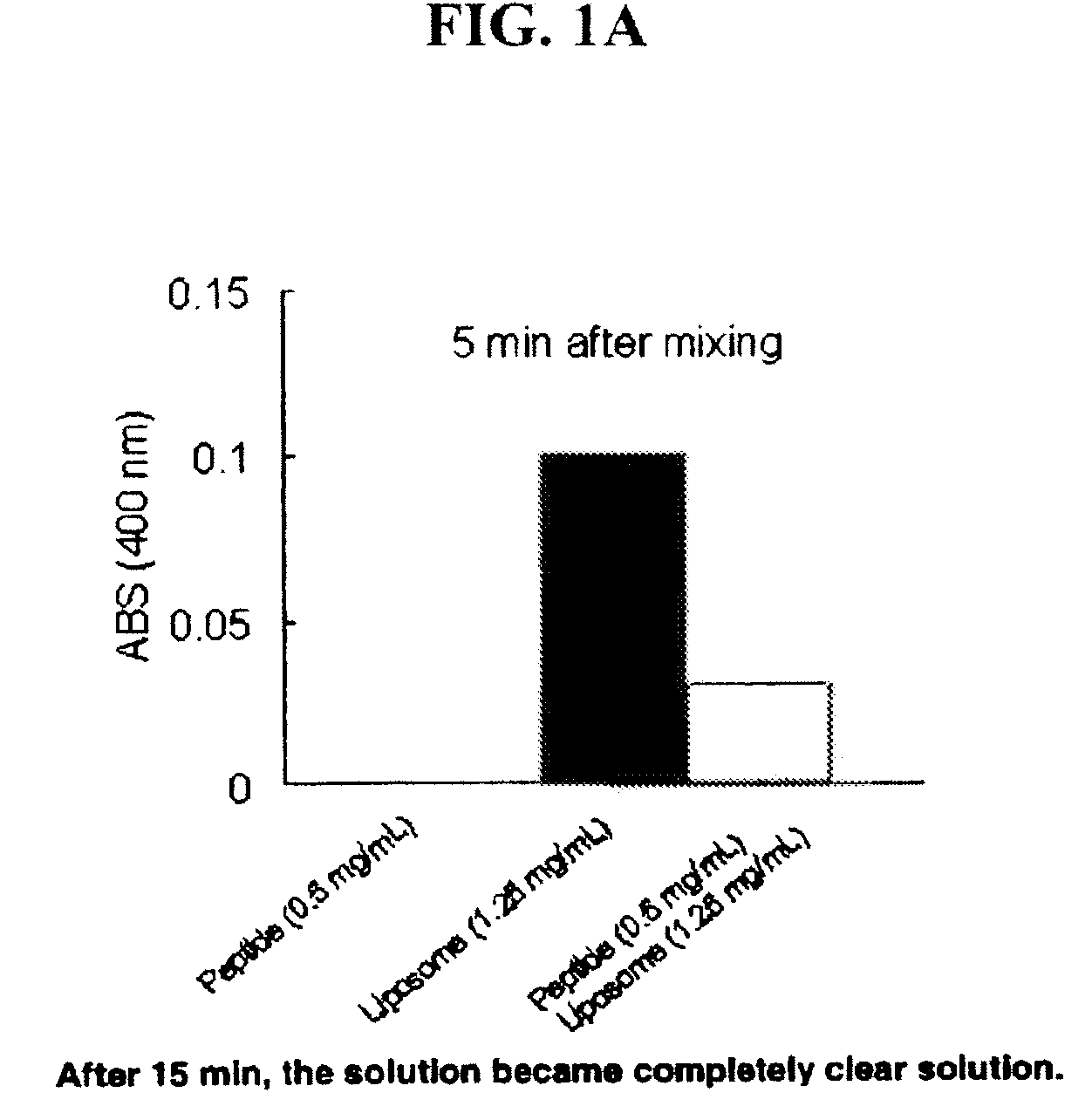
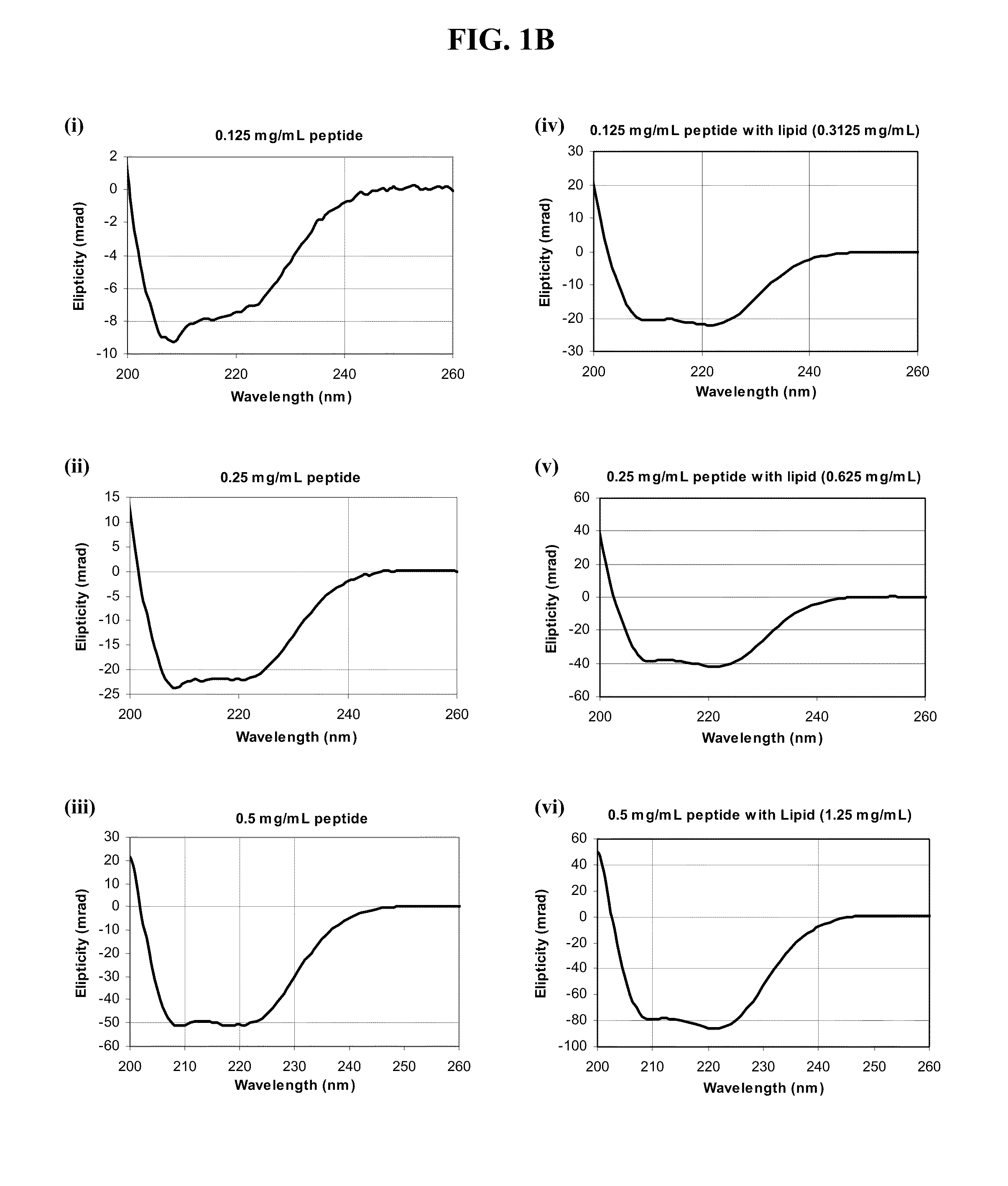
Sustained release of apo a-i mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20090081299A1Improve concentrationBiocidePowder deliveryReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
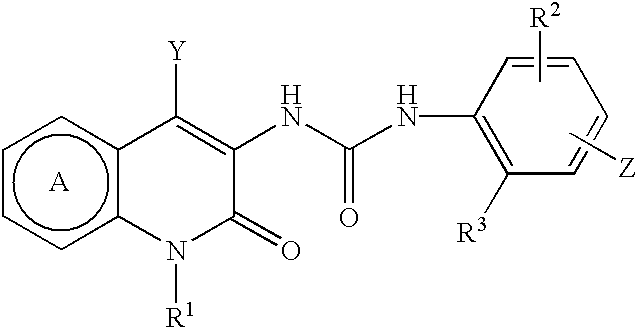
Naphthyridine derivatives
A compound of the formula (I):wherein Ring A is substituted or unsubstituted pyridine ring, Y is substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, etc., R1 is hydrogen, or substituted or unsubstituted alkyl, etc., R2 is hydrogen or lower alkyl, R3 is lower alkyl, Z is1) -D1-Q [D1 is direct bond or divalent C1-8 hydrocarbon, etc., Q is hydroxy, carboxyl, etc.], or2) -D2M-E-W [D2 is direct bond or divalent C1-8 hydrocarbon, etc., M is oxygen, sulfur, etc., E is direct bond or divalent C1-8 hydrocarbon, etc., W is hydroxyl, carboxyl, etc.],or a prodrug thereof, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of the same, which exhibits acyl-CoA: cholesterol acyl transferase (ACAT) inhibitory activity, and is useful as an agent for treatment of hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis.
Owner:SUMITOMO DAINIPPON PHARMA CO LTD
Sustained release of apo a-i mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS20090081298A1Improve concentrationPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsSterol transportReverse cholesterol transport
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
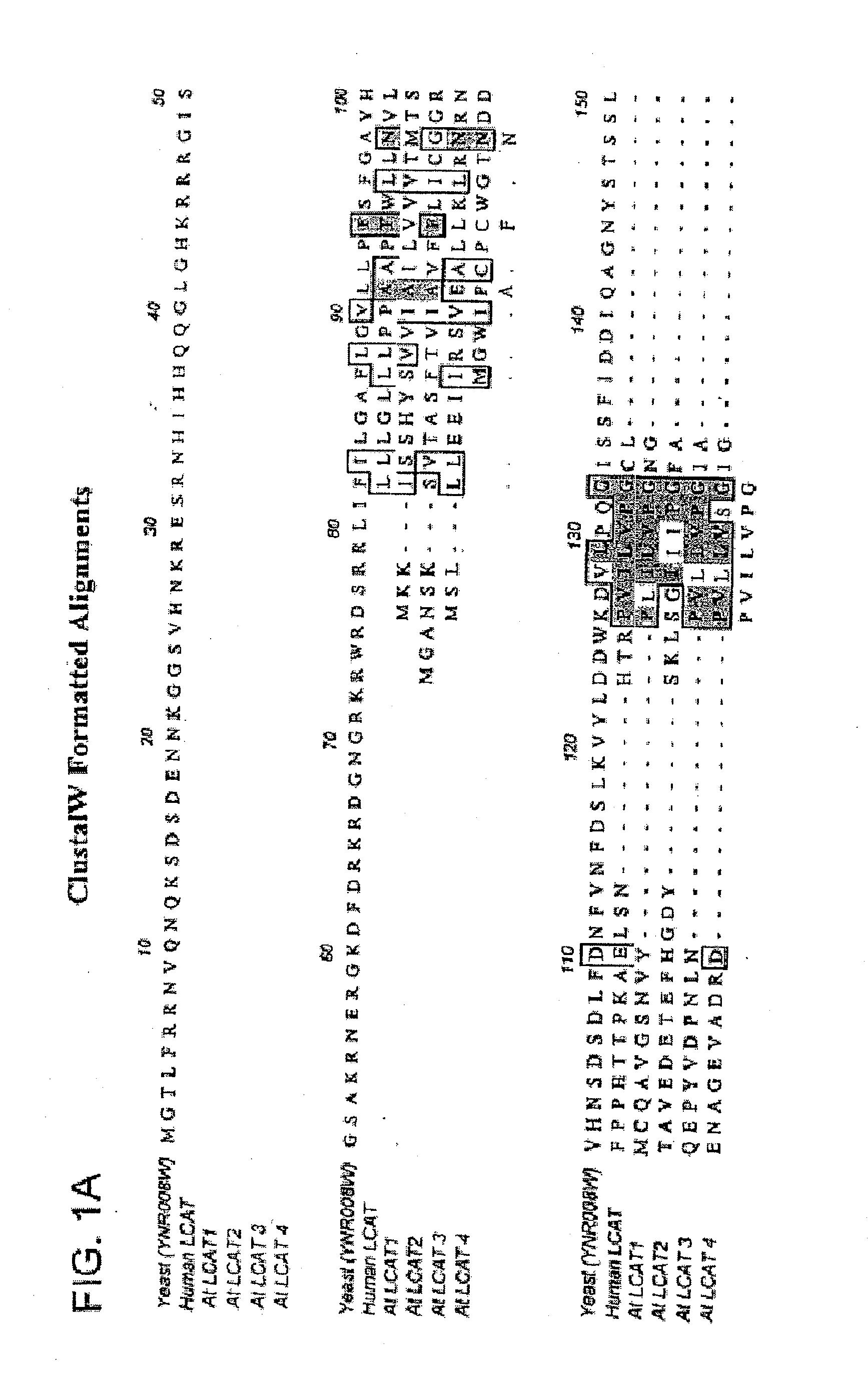
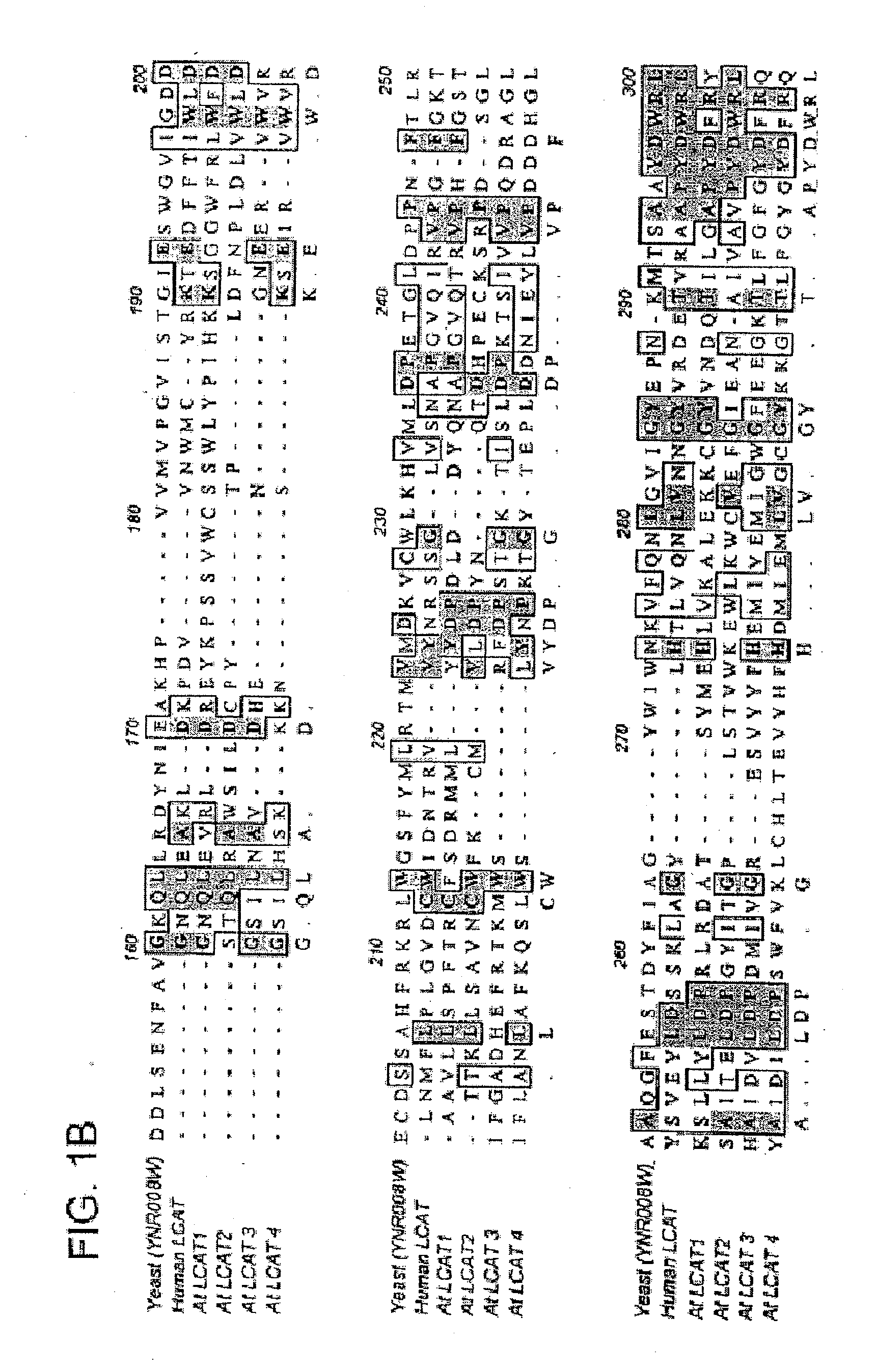
Plant sterol acyltransferases
The present invention is directed to lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase-like polypeptides (LCAT) and acyl CoA:cholesterol acyltransferases-like polypeptides (ACAT). The invention provides polynucleotides encoding such cholesterol:acyltransferases-like polypeptides, polypeptides encoded by such polynucleotides, and the use of such polynucleotides to alter sterol composition and oil production in plants and host cells. Also provided are oils produced by the plants and host cells containing the polynucleotides and food products, nutritional supplements, and pharmaceutical composition containing plants or oils of the present invention. The polynucleotides of the present invention include those derived from plant sources
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Sustained release of apo A-I mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
InactiveUS8044021B2Organic active ingredientsPowder deliveryReverse cholesterol transportCholesterol
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
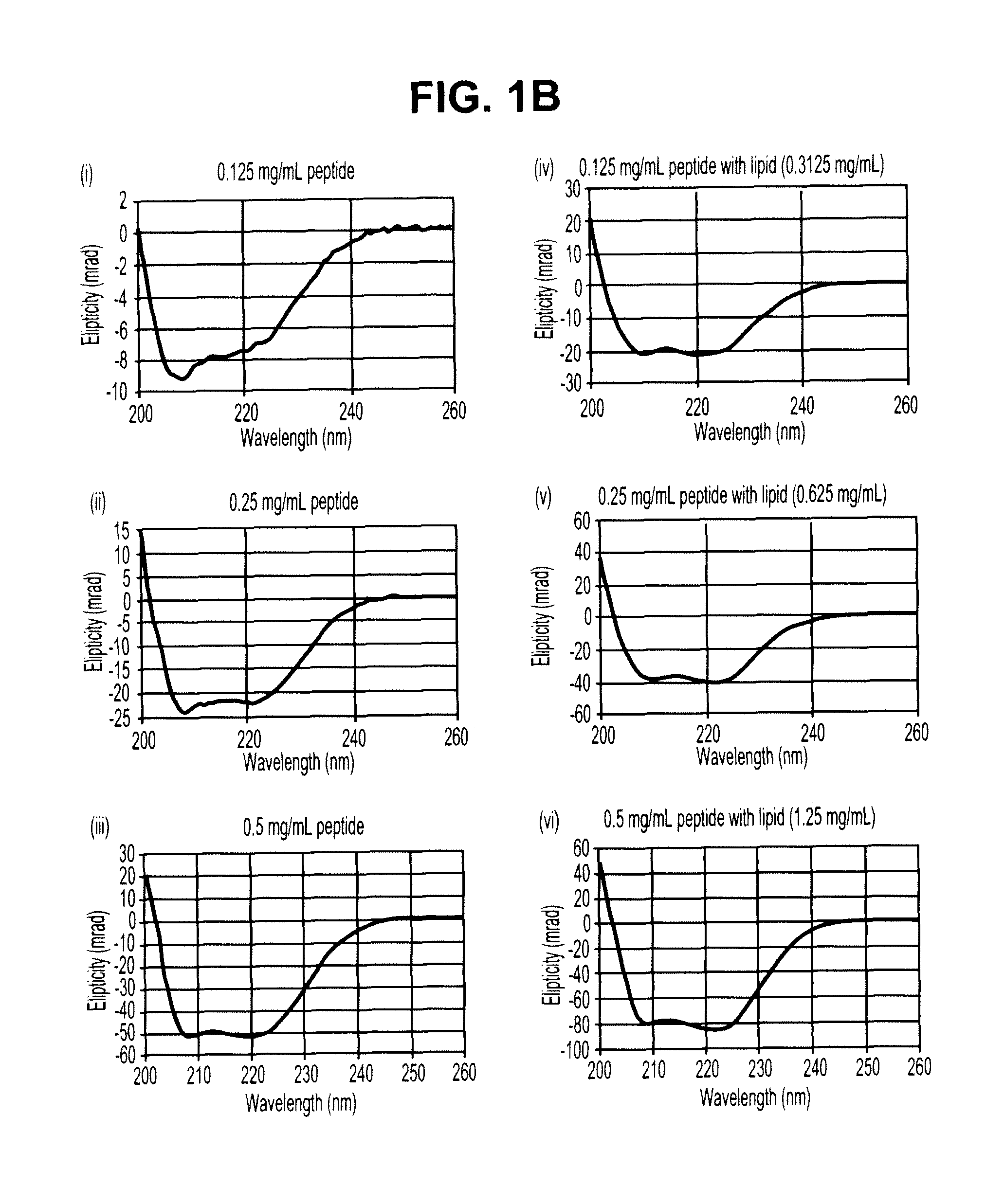
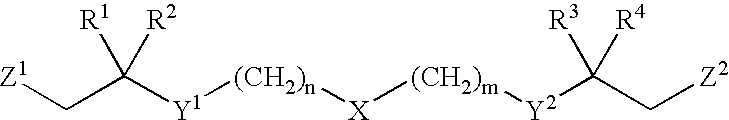
Functionalized long chain derivatives as acyl coenzyme-A mimics, compositions thereof, and methods of cholesterol management and related uses
InactiveUS20030236212A1Increase level of HDL cholesterolInhibit synthesisAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDyslipidemiaAcyl coenzyme A
The invention relates to novel Acyl coenzyme-A mimics, compositions comprising ketone compounds, and methods useful for treating and preventing cardiovascular diseases, dyslipidemias, dysproteinemias, and glucose metabolism disorders comprising administering a composition comprising a ketone compound. The Acyl coenzyme-A mimics, compositions, and methods of the invention are also useful for treating and preventing Alzheimer's Disease, Syndrome X, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-related disorders, septicemia, thrombotic disorders, obesity, pancreatitis, hypertension, renal disease, cancer, inflammation, bacterial infection and impotence. In certain embodiments, the Acyl coenzyme-A mimics, compositions, and methods of the invention are useful in combination therapy with other therapeutics, such as hypocholesterolemic and hypoglycemic agents.
Owner:ESPERION THERAPEUTICS
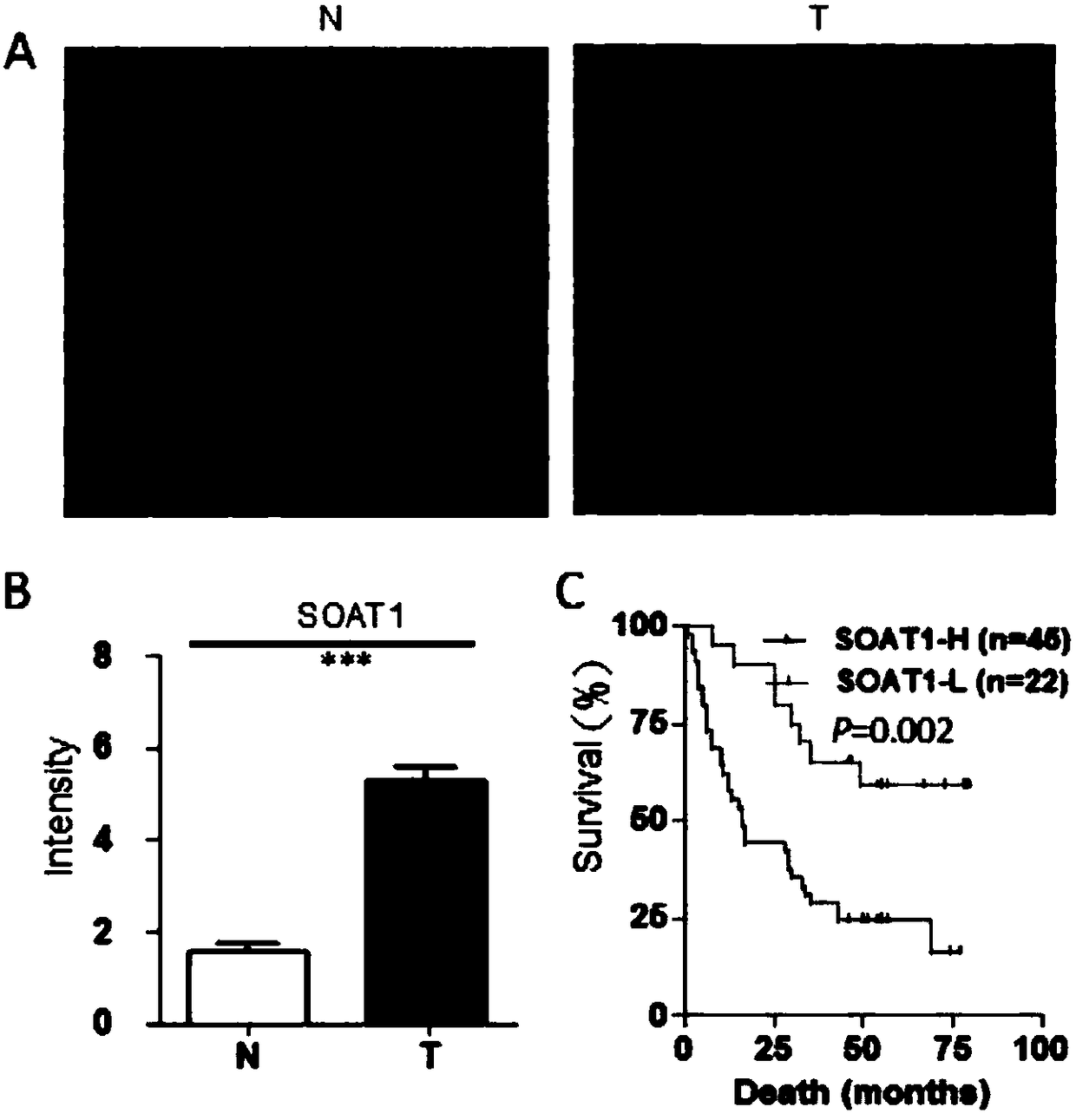
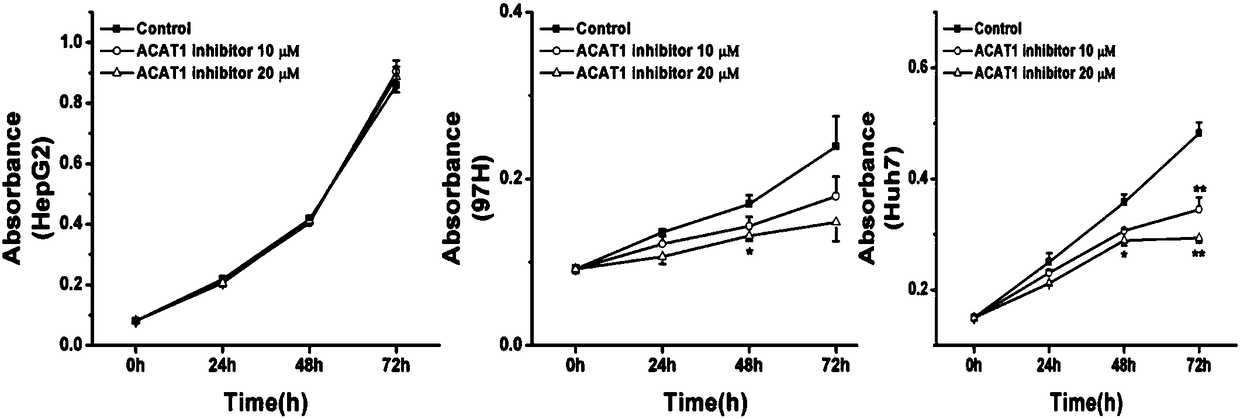
New application of acyl coenzyme A/cholesterol acyltransferase-1 inhibitor
InactiveCN109125324APrevention and/or treatment of metastasesOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsApoptosisAcyl coenzyme A
The invention discloses new application of a substance for inhibiting genetic expression and / or protein activity of acyl coenzyme A / cholesterol acyltransferase-1. According to the application, the inhibitor can be used for preparing drugs for preventing and / or treating cancer; the inhibitor can be used for preparing drugs for preventing and / treating cancer spreading and metastasis; the inhibitor can be used for preparing drugs for promoting apoptosis of cancer cells; the inhibitor can be used for preparing drugs for inhibiting cancer cells from being transformed into cancer; the inhibitor canbe used for preparing drugs for inhibiting in vitro proliferation growth of the cancer cells. Through experiments, the inventor proves that the acyl coenzyme A / cholesterol acyltransferase-1 (ACAT1 / SOAT1) is obviously highly expressed in liver cancer tissue, and the high enrichment value of the acyl coenzyme A / cholesterol acyltransferase-1 shows that prognosis of a liver cancer patient is poor. TheACAT1 / SOAT1 inhibitor can effectively inhibit growth of human liver cancer cells and other cancer cells in the cellular level, and the inhibitor can used as a candidate drug target of cancers, especially the liver cancer.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEOME RES CENT +1
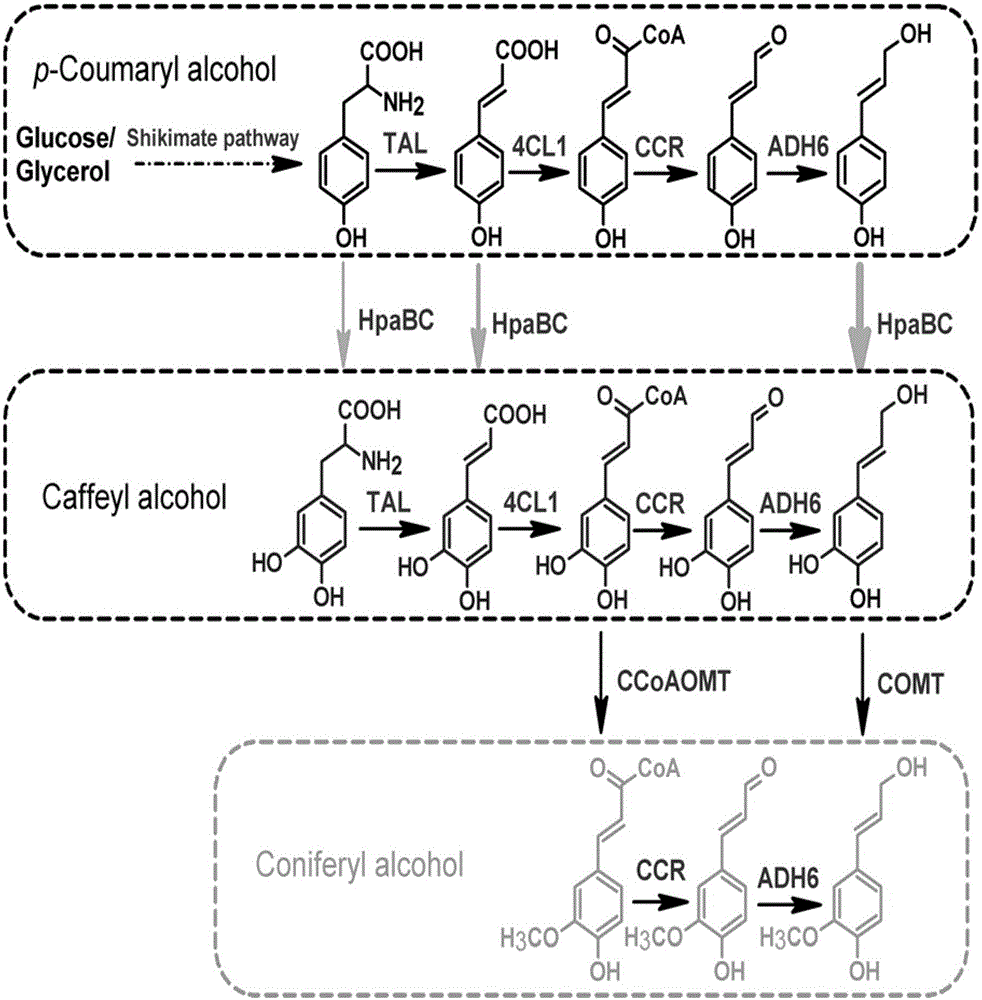
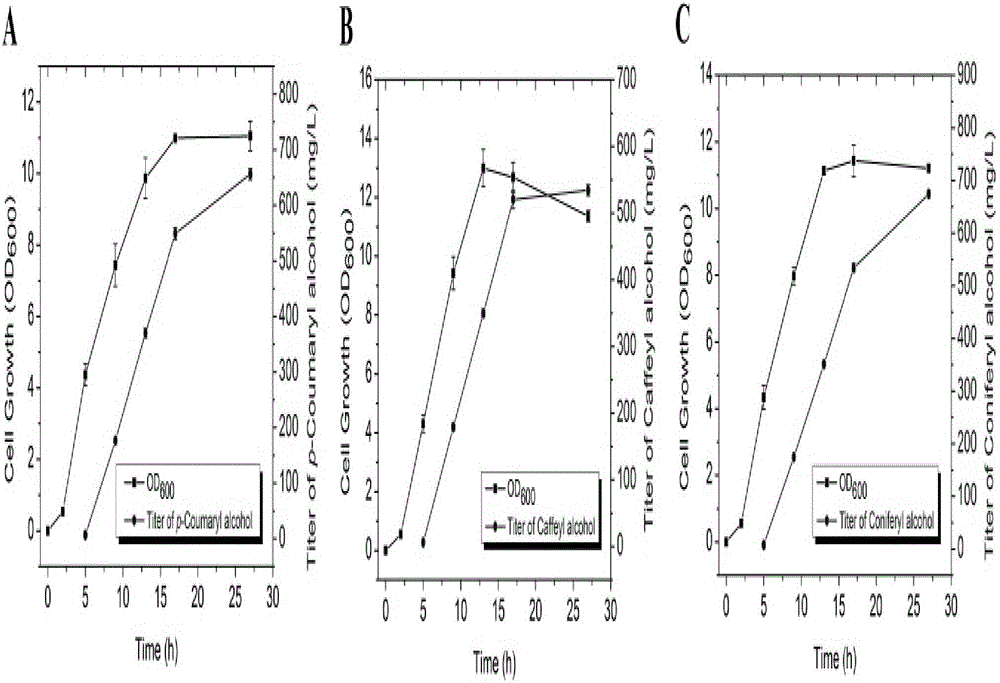
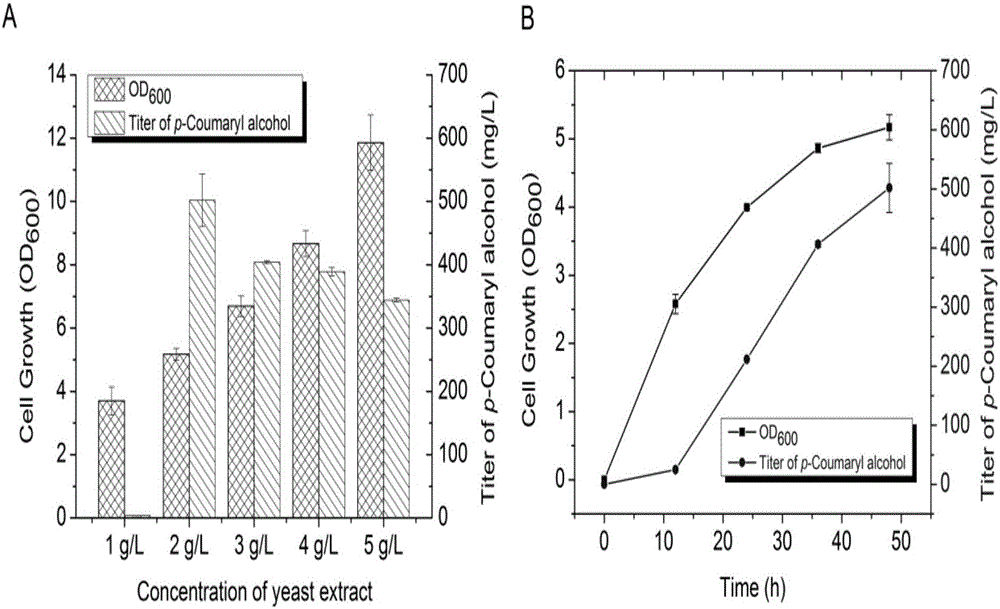
Method for heterologous biosynthesis of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol
InactiveCN105907804AEfficient productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCinnamoyl-CoA reductaseCoumaric acid
The invention relates to the technical field of biology and discloses a method for heterologous biosynthesis of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol. The metabolic pathway for production of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol is added into hosts. More precisely, tyrosine ammonia lyase, cinnamoyl-coA reductase, alcohol dehydrogenase and coumaric acid coA ligase are efficiently expressed in the host for producing tonquinol, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid3-monooxygenase is added to produce caffeol, coffee acyl coenzyme AO-methyl transferase or caffeic acid O-methyl transferase is added to produce ferulenol. Genes coded by the enzyme are guided into the host, and the production host of tonquinol, caffeol and ferulenol can be generated by means of glucose. The invention further discloses a method for co-culture of different hosts, and the caffeol and the ferulenol are produced more efficiently.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
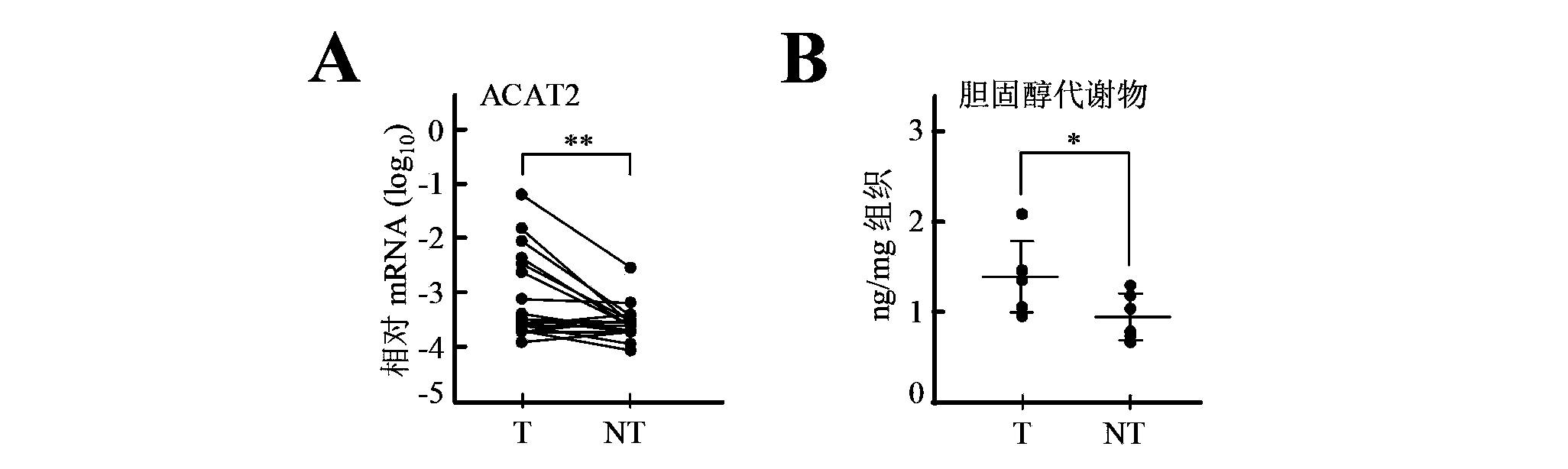
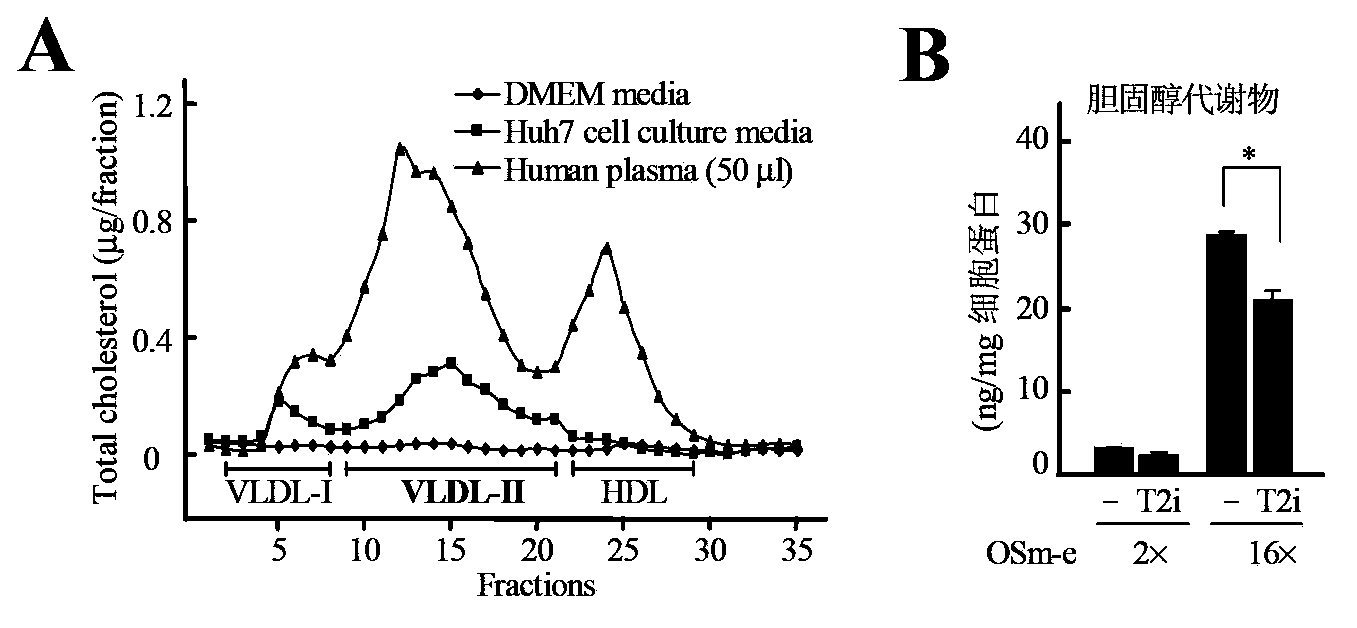
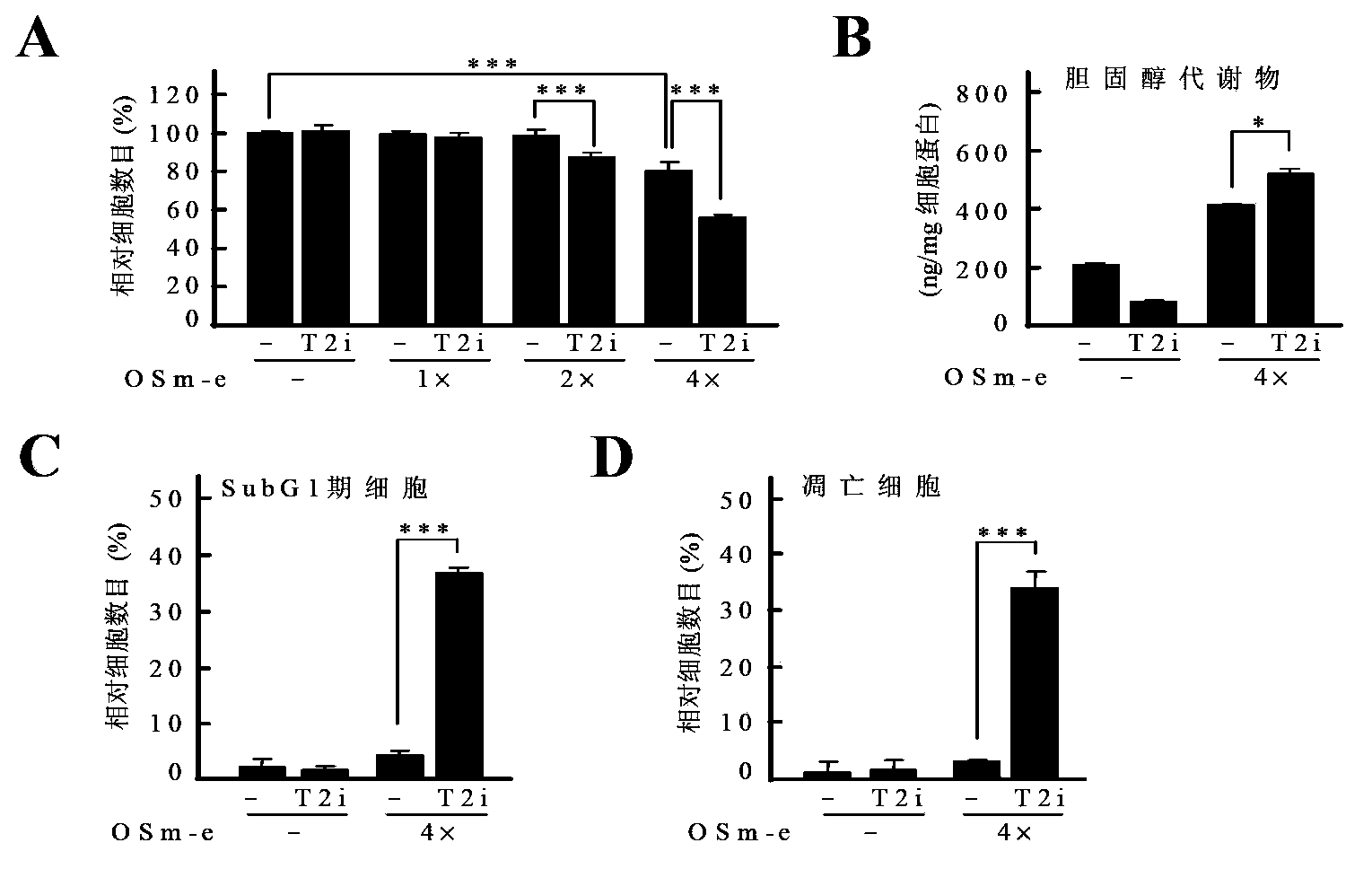
Application of acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase-2 (ACAT2) inhibitor in liver cancer growth inhibition
ActiveCN103536922AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteIntracellular cholesterol
The invention relates to application of an acyl-coenzyme A: cholesterol acyltransferase-2 (ACAT2) inhibitor in liver cancer growth inhibition. Concretely, the inhibition of the activity of the ACAT2 can effectively inhibit the growth of human liver cancer cells and transplanted tumors respectively in cellular and animal levels, and the inhibitory effect is generated through accumulating intracellular cholesterol metabolites by blocking the secretion and excretion of ACAT2-mediated cholesterol metabolites. The accumulation of the cholesterol metabolites has effects on promoting the apoptosis of liver cancer cells and inhibiting the growth of liver cancer; the excretion of the cholesterol metabolites can remove the inhibitory effect.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Oleaginous microalgae having an LPAAT ablation
Recombinant DNA techniques are used to produce oleaginous recombinant cells that produce triglyceride oils having desired fatty acid profiles and regiospecific or stereospecific profiles. Genes manipulated include those encoding stearoyl-ACP desaturase, delta 12 fatty acid desaturase, acyl-ACP thioesterase, ketoacyl-ACP synthase, lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase, ketoacyl-CoA reductase, hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydratase, and / or enoyl-CoA reductase. The oil produced can have enhanced oxidative or thermal stability, or can be useful as a frying oil, shortening, roll-in shortening, tempering fat,cocoa butter replacement, as a lubricant, or as a feedstock for various chemical processes. The fatty acid profile can be enriched in midchain profiles or the oil can be enriched in triglycerides of the saturated-unsaturated-saturated type.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC
Sustained release of Apo A-I mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
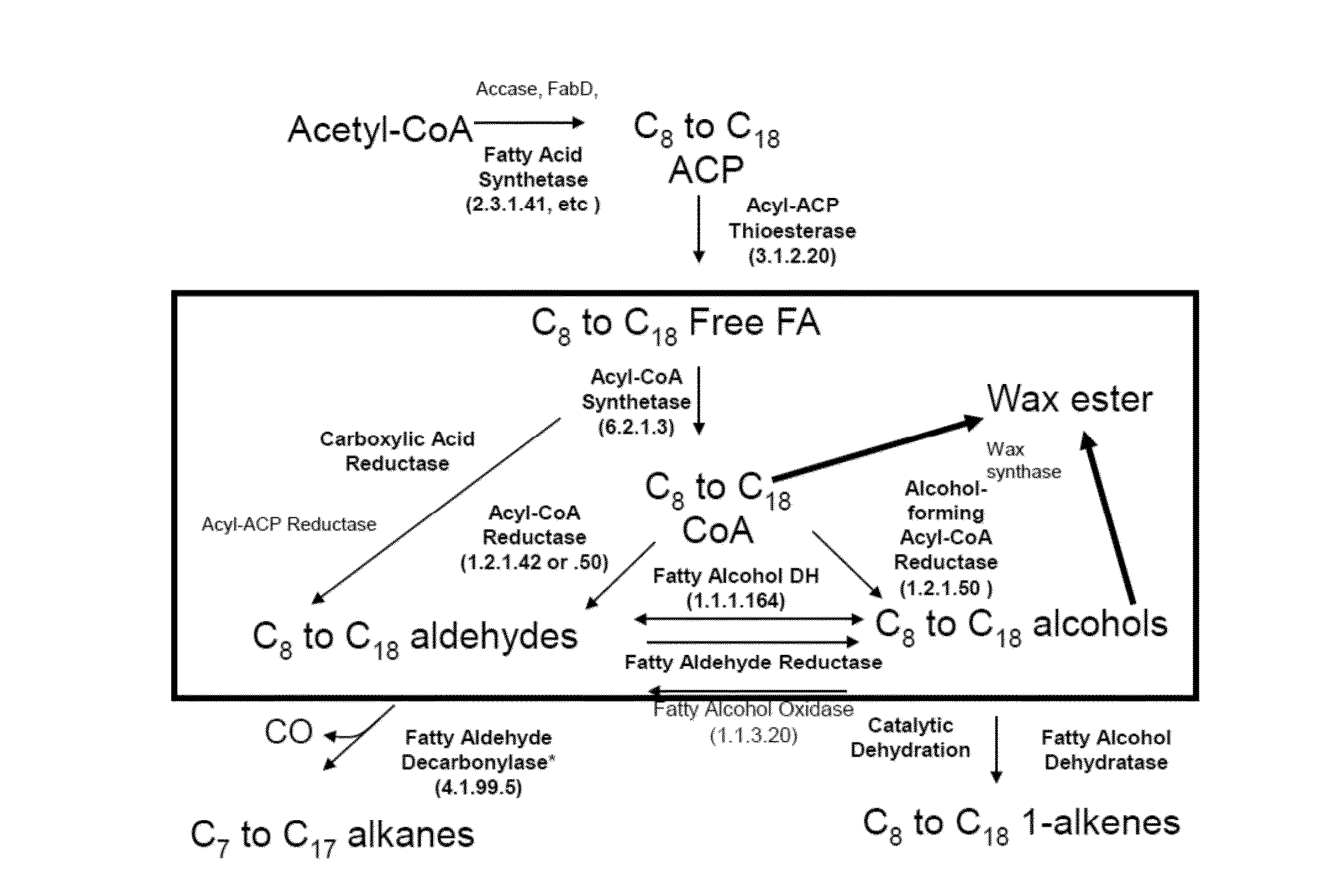
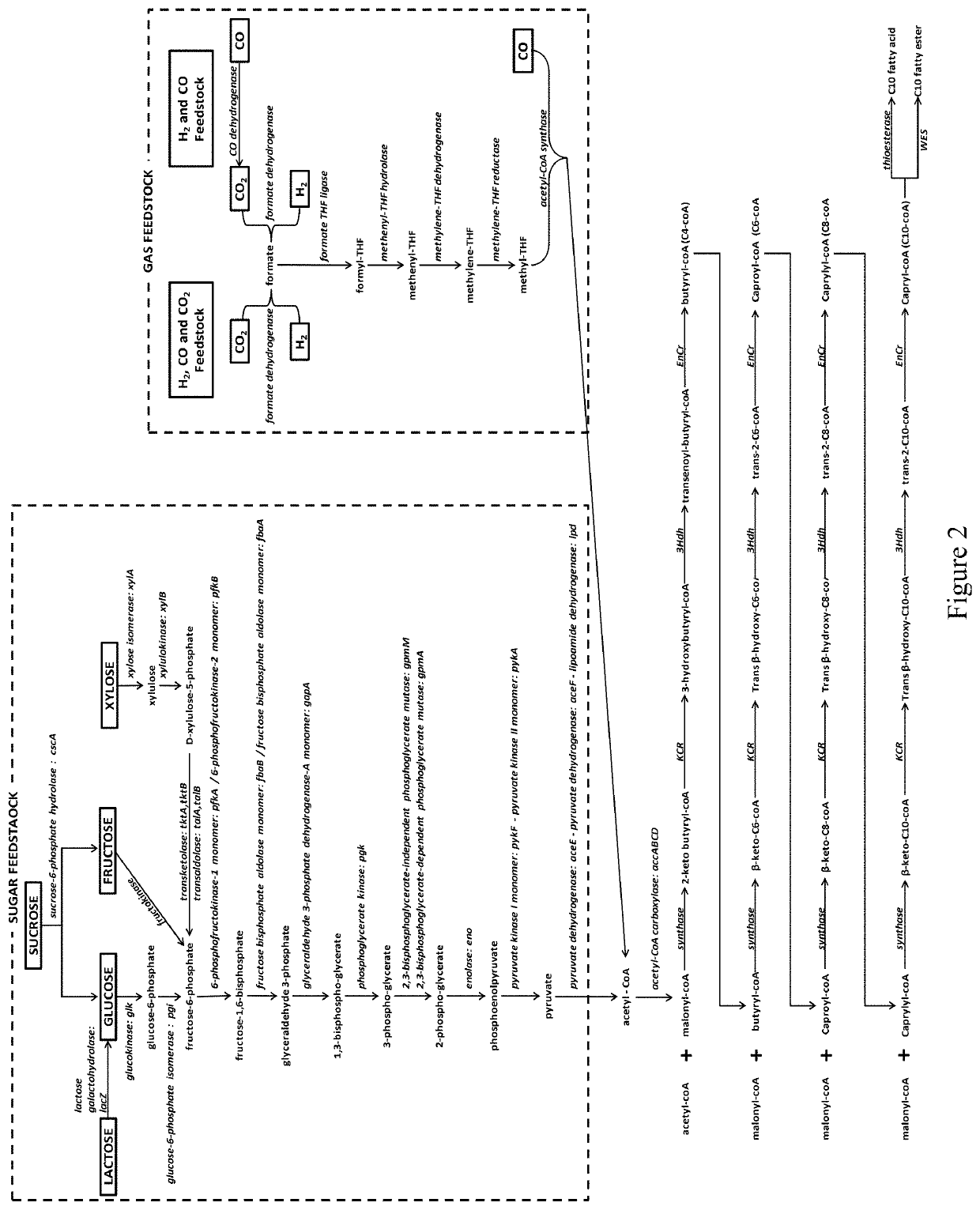
Microorganisms and methods for the production of fatty acids and fatty acid derived products
This invention relates to metabolically engineered microorganism strains, such as bacterial strains, in which there is an increased utilization of malonyl-CoA for production of a fatty acid or fatty acid derived product, wherein the modified microorganism produces fatty acyl-CoA intermediates via a malonyl-CoA dependent but malonyl-ACP independent mechanism.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Cyclic bridgehead ether DGAT1 inhibitors
The invention relates to compounds of formula (I):useful for treating disorders mediated by acyl coA-diacylglycerol acyl transferase 1 (DGAT1), e.g. metabolic disorders. The invention also provides methods of treating such disorders, and compounds and compositions etc. for their treatment.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Breeding method of laying hen with low egg yolk cholesterol content
InactiveCN103122384AIncrease production capacityImprove qualityMicrobiological testing/measurementYolkAnimal science
The invention discloses a breeding method of a laying hen with low egg yolk cholesterol content. The breeding method comprises the following steps of (1) taking a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence including chicken HMGCR (Hydroxymethyl glutaric acyl coenzyme) gene as a template, designing a pair of primers, and carrying out sample chicken individual gene parting by a PCR-RFLP (polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism) method; (2) utilizing a genetic effect analysis model to determine selected and remained genetype; (3) building a family from individual bodies of cocks and hens according with the selected and remained genetype; (4) extracting the DNA in later generation of the selected and remained family hen, carrying out PCR-RFLP analysis on the pair of primers in step (1), selecting and remaining the hens with selected and remained genetype in step (2); and (5) repeating steps (3) and (4) to continuously breed for at least three generations, so as to obtain the laying hen with low egg yolk cholesterol content. The HMGCR gene molecular marker is adopted to assist and select the breeding method; the generation interval is shortened; the breeding accuracy is improved; the breeding flock feeding capacity is reduced; and the feeding cost is also reduced.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microorganism and application thereof
ActiveCN103194419AFast growthGrowth rate can be adjustedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsFungiEthanol dehydrogenaseEnzyme Gene
The invention provides a microorganism and an application thereof. The microorganism is used for preparing aliphatic ester. The microorganism comprises a first nucleotide sequence, a second nucleotide sequence, a third nucleotide sequence and a fourth nucleotide sequence, wherein the first nucleotide sequence is used for encoding acyltransferase AT genes or a functional equivalent thereof, and the second nucleotide sequence is used for encoding 2-keto acid decarboxylase ARO10 gene or a functional equivalent of the 2-keto acid decarboxylase ARO10 gene, ethanol dehydrogenase ADH2 genes or a functional equivalent of the ethanol dehydrogenase ADH2 gene and acyl coenzyme A reductase FAR genes or a functional equivalent of the acyl coenzyme A reductase FAR gene; the third nucleotide sequence is used for encoding endoglucanase gene or a functional equivalent of the endoglucanase gene and beta-glucosaccharase gene B-GL or a functional equivalent of the beta-glucosaccharase gene, and the fourth nucleotide sequence is used for encoding acyl-coenzyme A reductase FAR gene or a functional equivalent of the acyl-coenzyme A reductase FAR gene. By utilizing the microorganism, the preparation efficiency of the aliphatic ester can be effectively improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
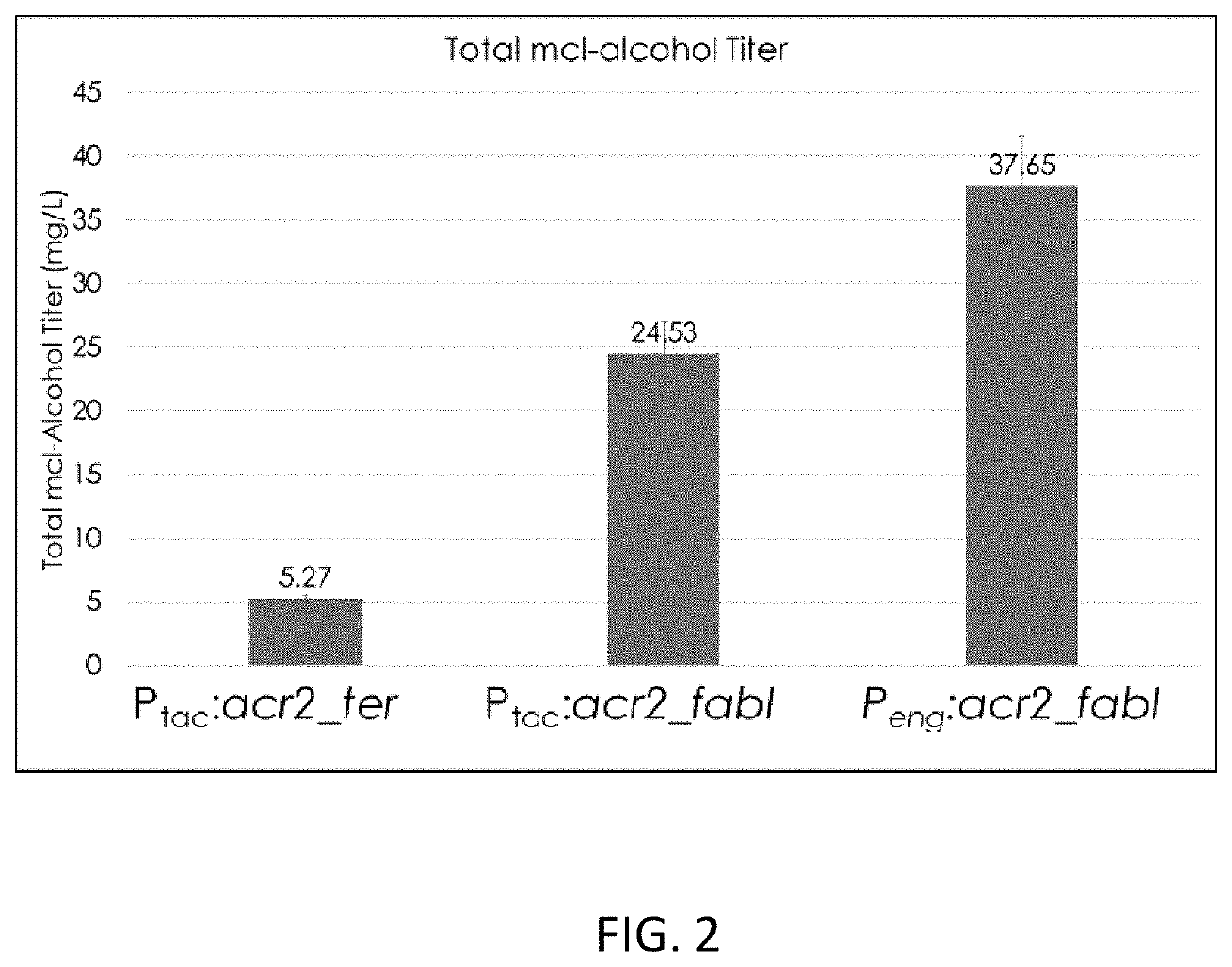
Engineered microbes for conversion of organic compounds to medium chain length alcohols and methods of use
This disclosure provides a genetically-modified bacterium from the genus Pseudomonas that comprises an exogenous nucleic acid encoding an enoyl-CoA reductase and an exogenous nucleic acid encoding an acyl-CoA reductase that produces medium chain length alcohols. The disclosure further provides methods for producing medium chain alcohols using such genetically-modified bacterium. This disclosure provides a renewable, bio-based production platform for valuable mcl-alcohols that have a wide range of industrial applications. Current production of mcl-alcohols typically occurs through the hydrogenation of plant oils and waxes. This process leads to issues of deforestation and is largely unsustainable. Utilizing waste lignin streams as the carbon source provides a more sustainable feedstock that can be generated from plant waste like corn stover. Along with this, the use of lignin avoids competition with food resources as traditional starch and sugar feedstocks.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Acyl coenzyme A-reductase gene phsR and application thereof
ActiveCN106434705AHigh purityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideAcyl coenzyme A
The invention discloses an acyl coenzyme A-reductase gene phsR and the application thereof. The acyl coenzyme A-reductase gene phsR has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 1. The invention also provides an engineering strain with deletion of the acyl coenzyme A-reductase gene phsR. The engineering strain is named as Mycobacterium neoaurum Delta phsR, and has a collection number of CCTCC NO. M2016321. The engineering strain disclosed by the invention is capable of effectively eliminating 4-BNA by-products in the sterol degradation process, obviously improving the purity and the yield of AD, ADD, 9-OH-AD and other series of steroid products prepared by depending on the sterol degradation, reducing the cost of raw materials for producing steroid drugs and the energy consumption, improving the utilization rate of prodrugs and greatly simplifying the preparation process of AD and other steroid drugs, and has a high industrial application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XIANJU PHARMA
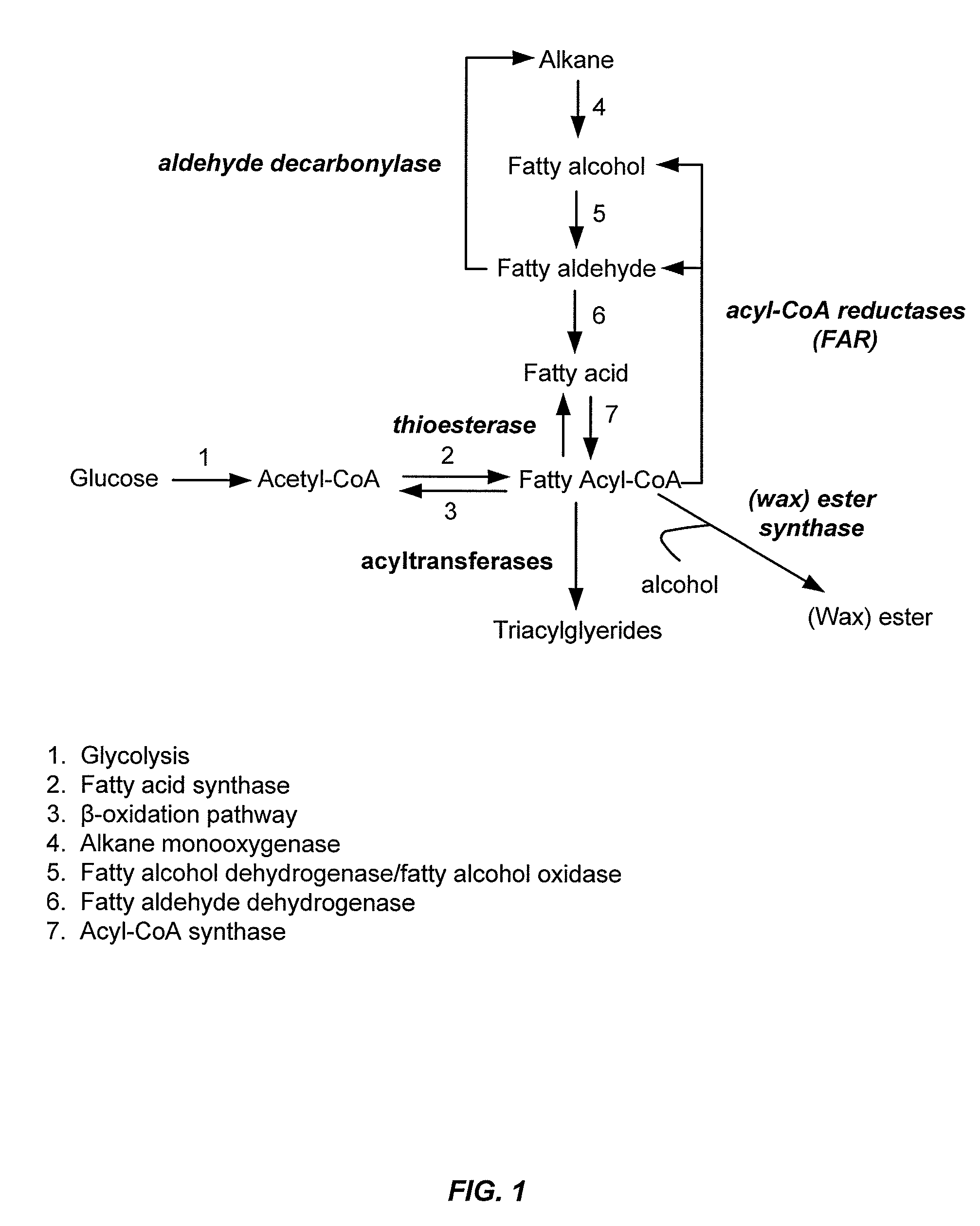
BIOTECHNOLOGICAL PRODUCTION OF omega-FUNCTIONALISED CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND ESTERS THEREOF
There is provided a microbial cell for producing at least one omega-functionalized carboxylic acid ester from at least one alkane, wherein the cell is genetically modified to increase the expression relative to the wild type cell of(i) Enzyme E1 capable of converting the alkane to the corresponding 1-alkanol;(ii) Enzyme E2 capable of converting the 1-alkanol of (i) to the corresponding 1-alkanal;(iii) Enzyme E3 capable of converting the 1-alkanal of (ii) to the corresponding alkanoic acid;(iv) Enzyme E4 capable of converting the alkanoic acid of (iii) to the corresponding alkanoic acid ester; and(iv) Enzyme E5 capable of converting the alkanoic acid ester of (iv) to the corresponding omega-hydroxy-alkanoic acid ester,and wherein the cell does not comprise a genetic modification that increases the expression relative to the wild type cell of at least one of the following enzymes E20-E24 selected from the group consisting of:E20 Acyl-ACP thioesterase, of EC 3.1.2.14 or EC 3.1.2.22,E21 Acyl-CoA thioesterase, of EC 3.1.2.2, EC 3.1.2.18, EC 3.1.2.19, EC 3.1.2.20 or EC 3.1.2.22,E22 Acyl-CoA:ACP transacylase,E23 Polyketide synthase, andE24 Hexanoic acid synthase
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
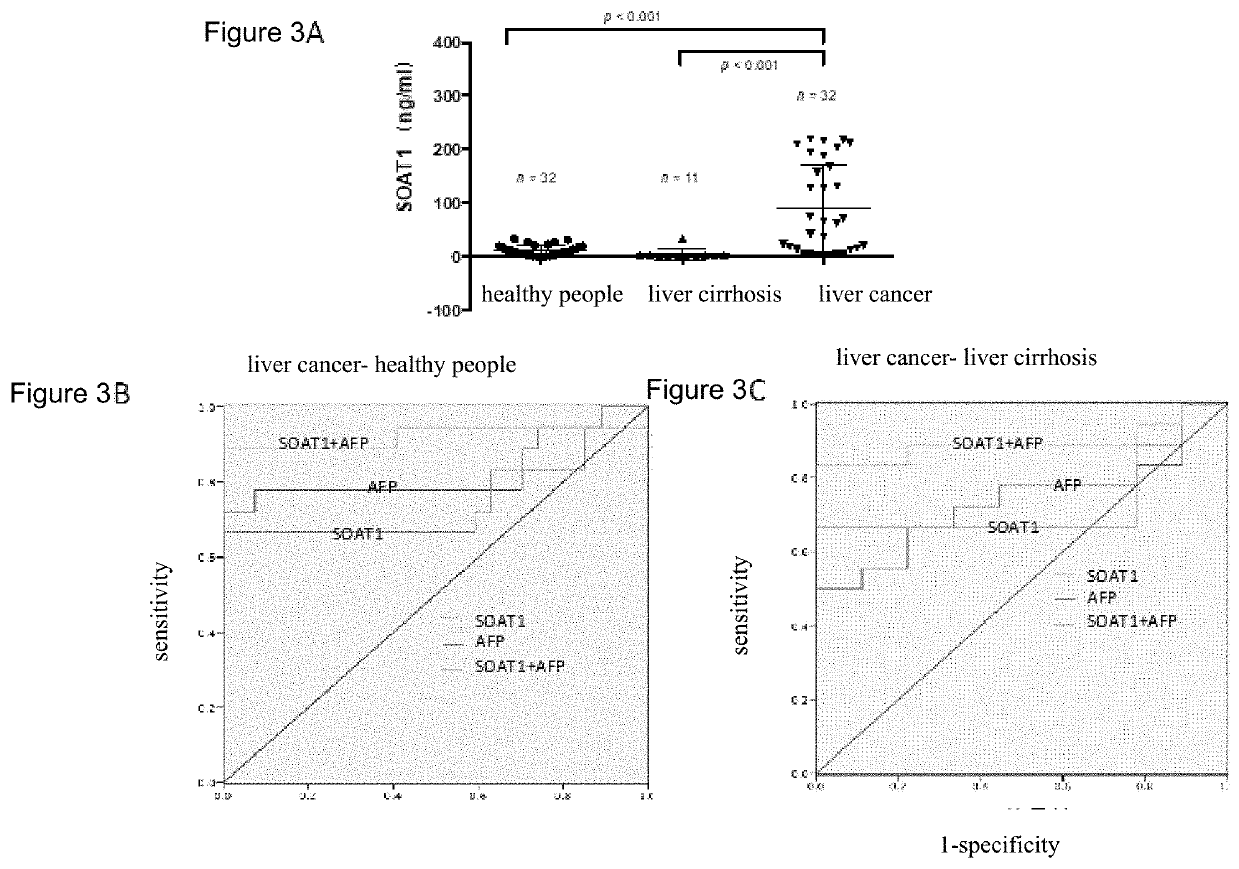
Use of acyl coenzyme a: cholesterol acyltransferase-1 in diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer
PendingUS20220034891A1Improve accuracyStrong complementarityOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCholesterolApoptosis
A use of a substance for inhibiting SOAT1 gene expression and / or protein activity. The use is selected from at least one of: (a) Preparation of kits for liver cancer diagnosis; (b) Preparation of kits for liver cancer prognosis; (c) Preparation of companion diagnostic kits for treatment of liver cancer; (d) For the preparation of drugs for the prevention and / or treatment of cancer; (e) For the preparation of drugs for the prevention and / treatment of cancer spread and metastasis; (f) For the preparation of drugs that promote the apoptosis of cancer cells; (g) For the preparation of drugs for inhibiting cancer cell formation; (h) For the preparation of drugs that inhibit the proliferation and growth of cancer cells in vitro. Experiments have shown that SOAT1 is highly expressed in liver cancer tissues and serum, and its high abundance indicates poor prognosis of liver cancer patients.
Owner:BEIJING PROTEOME RES CENT
Saccharomyces cerevisiae highly producing C6-C10 ethyl esters and construction method and purpose of saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN110804561AHigh yieldGood yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesEthyl groupAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
The invention discloses saccharomyces cerevisiae highly producing C6-C10 ethyl esters and a construction method and purpose of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Through overexpressing acetaldehyde dehydrogenase ALD6 and acetyl-CoA synthase ASC1 in an original strain, synthesis of acetyl-CoA is strengthened, through overexpressing acetyl-CoA carboxylase ACC1**, malonyl CoA is strengthened, through overexpressing fatty acid synthetase FAS1 and fatty acid synthetase FAS2, medium-chain acyl-CoA is strengthened, more metabolism flows flow to medium-chain acyl groups CoA, alcohol acyl-transferase genes SAAT in strawberries are further exogenously introduced, and a reformed strain C-ald6acs1A*F1F2S is obtained. Under the condition of fermentation,the yield of ethyl caproate is 7.53mg / L which is 2.72 times of that of an original strain C-ald6acs1A*F1F2, and 26.89 times of that (only 0.27mg / L) of an original strain CA, the yield of ethyl caprylate is 13.65mg / L which is 9.11 times of that of the original strain CA, the yield of ethyl decanoate is 13.89mg / L which is 7.27 times of that of the original strain, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae has potential application prospects in improving flavor of wine and improving the quality of the wine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Sustained release of Apo A-I mimetic peptides and methods of treatment
A method including advancing a delivery device through a lumen of a blood vessel to a particular region in the blood vessel; and introducing a composition including a sustained-release carrier and an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic mimetic peptide into a wall of the blood vessel at the particular region or a perivascular site, wherein the peptide has a property that renders the peptide effective in reverse cholesterol transport. A composition including an apolipoprotein A-I (apo A-I) synthetic peptide, or combination of an apo A-I synthetic mimetic peptide and an Acyl CoA cholesterol: acyltransferase (ACAT) inhibitor in a form suitable for delivery into a blood vessel, the peptide including an amino acid sequence in an order reverse to an order of various apo A-I mimetic peptides, or endogenous apo A-I analogs, or a chimera of helix 1 and helix 9 of endogenous apo A-I.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
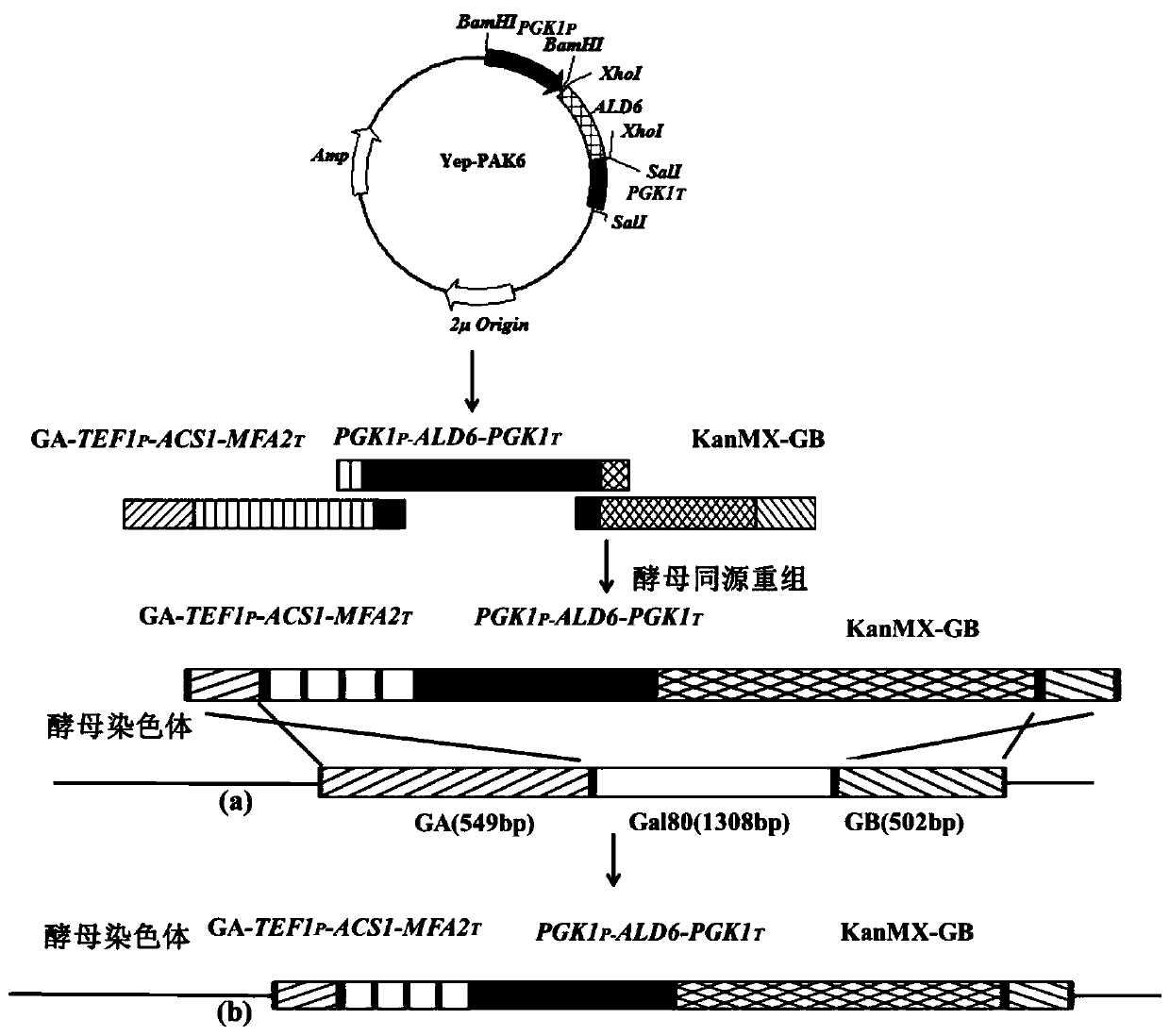
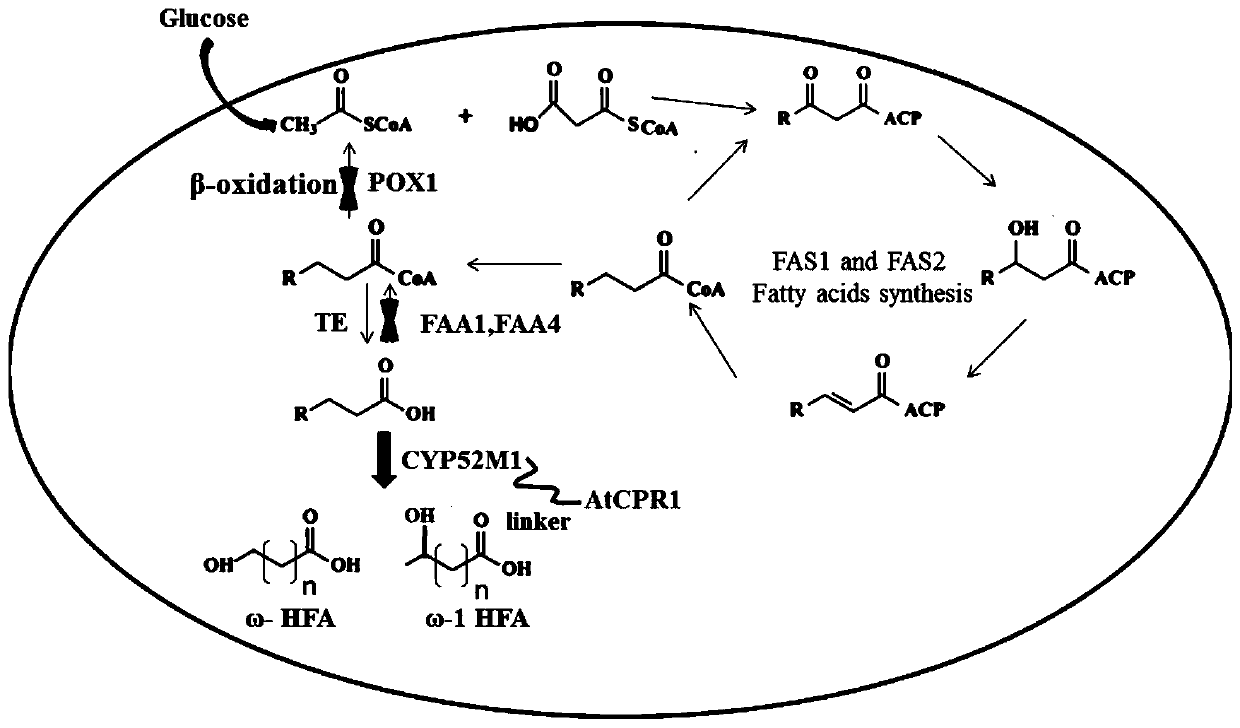
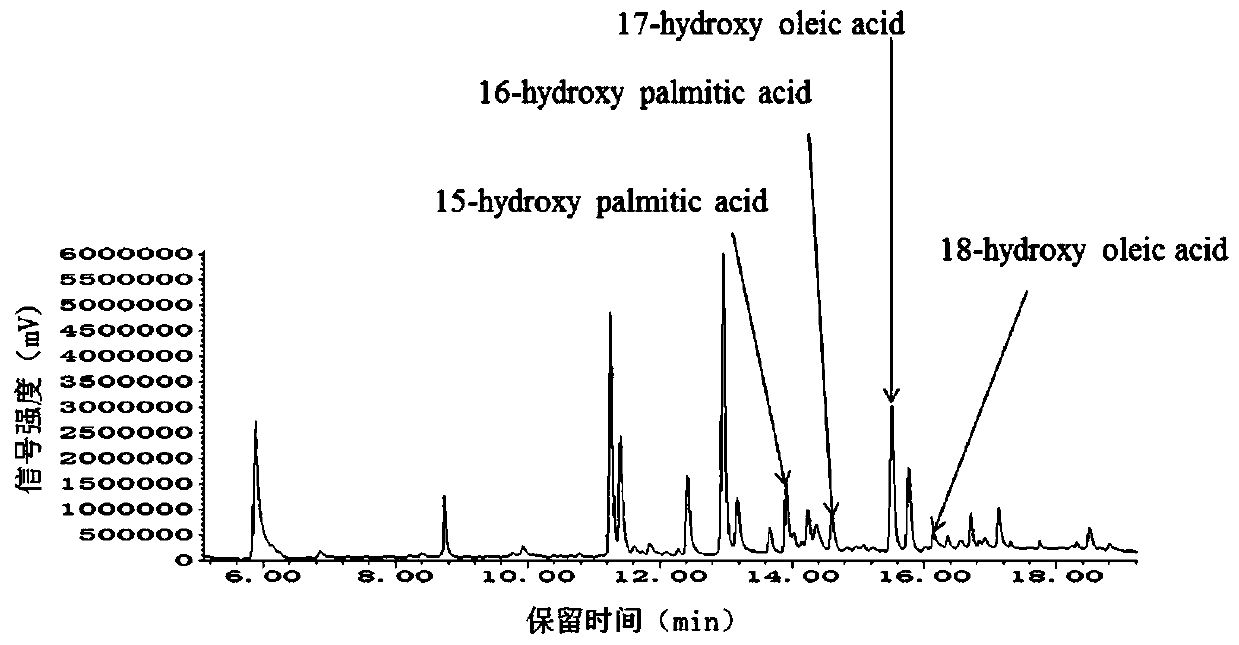
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes, construction methods of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes and applications of recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes in production of hydroxy fatty acids
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes, construction methods of the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes and applications of the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiaes in production of hydroxy fatty acids. Through a homologous recombination method, the recombinant fungi (1) are obtained by knocking out key gene acyl coenzyme A oxidase POX1 in a beta-oxidation pathway relatedto fatty acid catabolism in saccharomyces cerevisiaes and knocking out acyl coenzyme A activating enzymes FAA1 and FAA4, recombinant fungi (2) are obtained by introducing cytochrome P450 oxidase CYP52M1 and cytochrome P450 reductase SbCPR into the recombinant fungi (1), or the recombinant fungi (3) are obtained by introducing cytochrome P450 oxidase CYP52M1 and cytochrome P450 reductase AtCPR1 into the recombinant fungi (1), or the recombinant fungi (4) are obtained by introducing cytochrome P450 oxidase and cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene CYP52M1-AtCPR1 into the recombinant fungi (1).
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Use of a class of enzymes and their encoding genes to increase the oil content in transgenic organisms
The present invention relates to the use of a novel enzyme and its encoding gene for transformation. More specifically, the invention relates to the use of a gene encoding an enzyme with acyl-Co A: diacylglycerol acyltransferase activity. This gene expressed alone in transgenic organisms will increase the total amount of oil, i.e. triacylglycerols, that is produced.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com