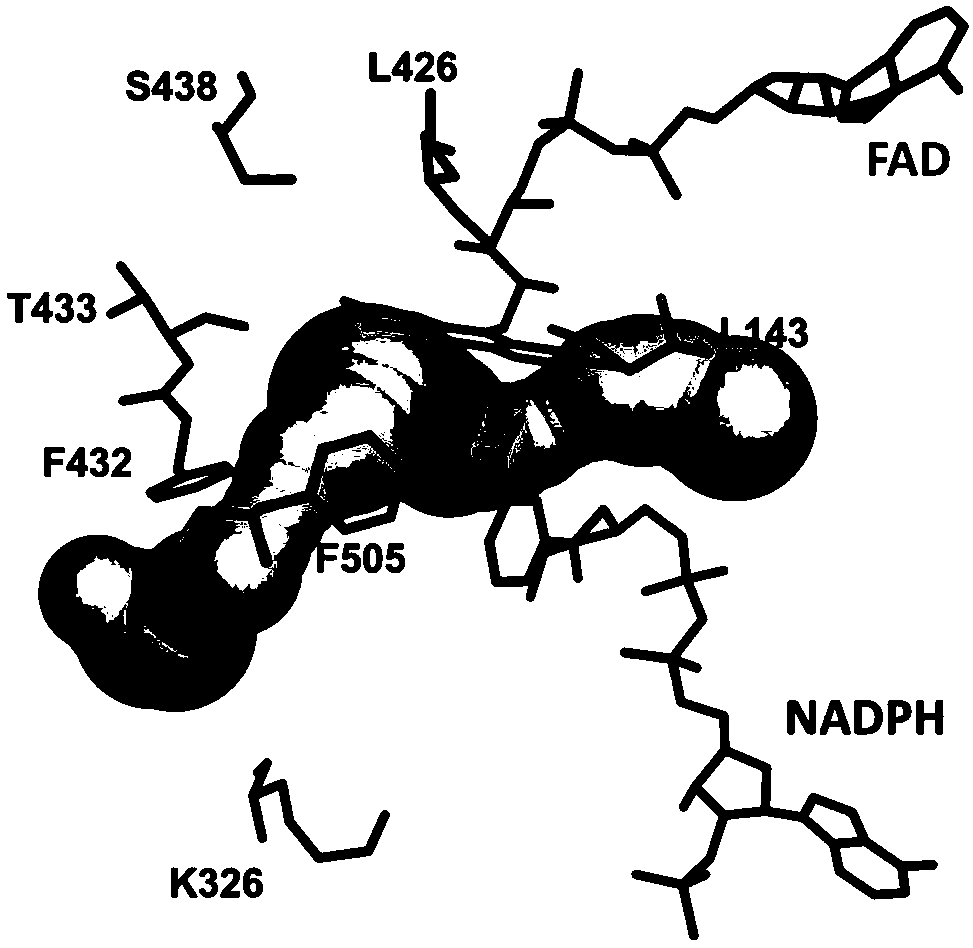
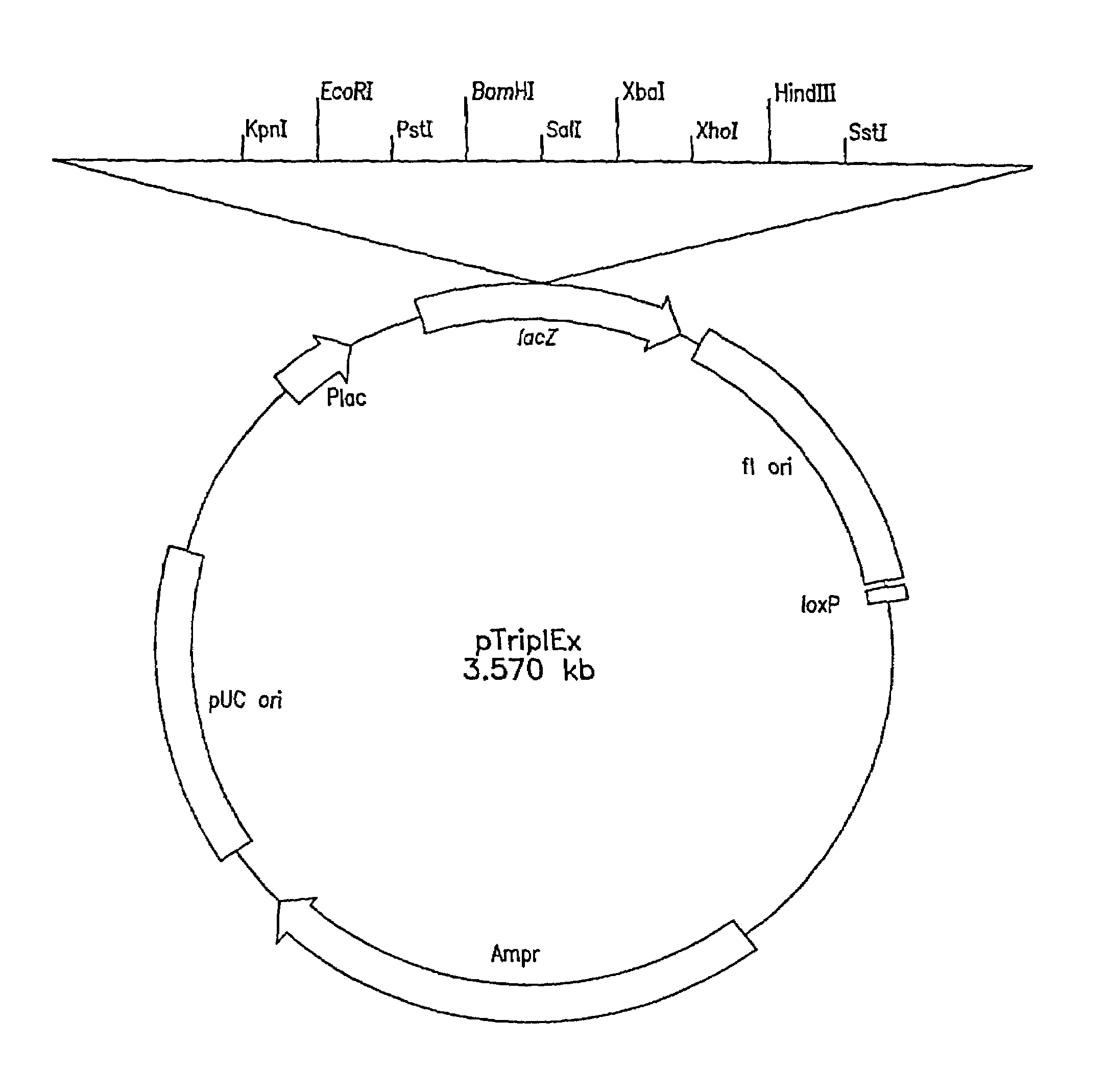
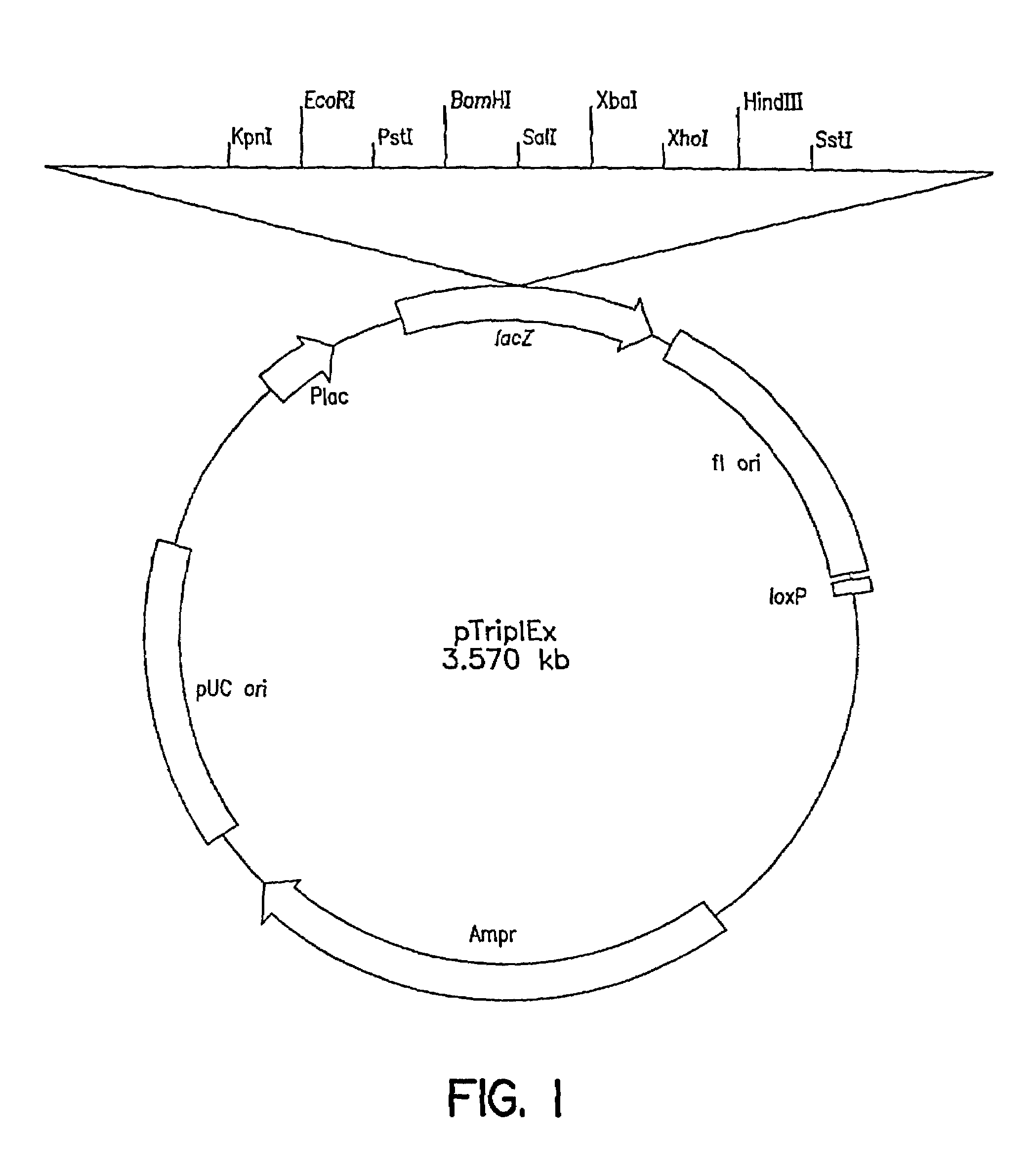
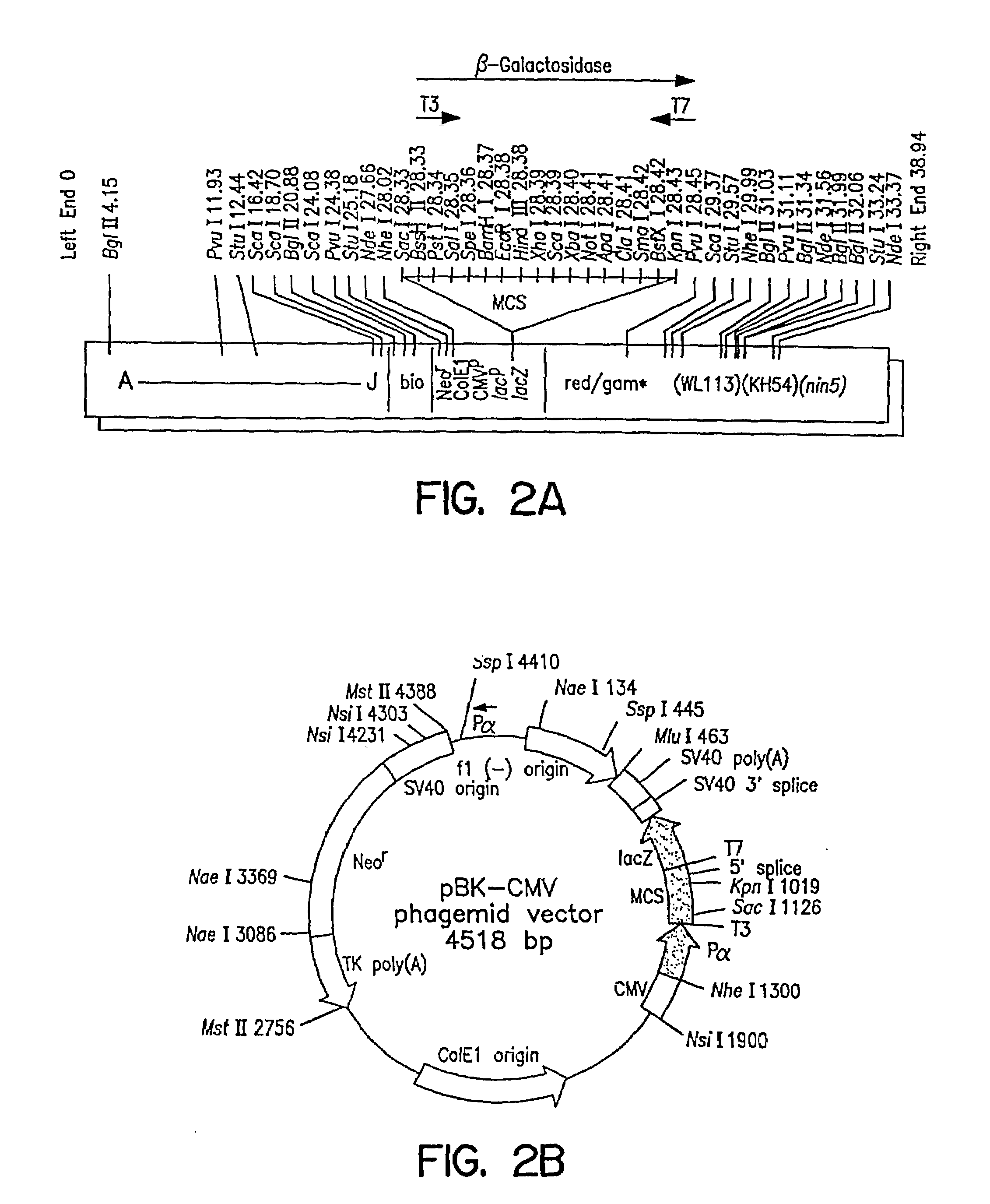
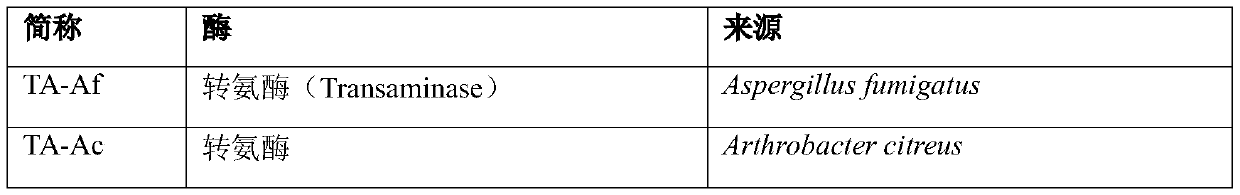
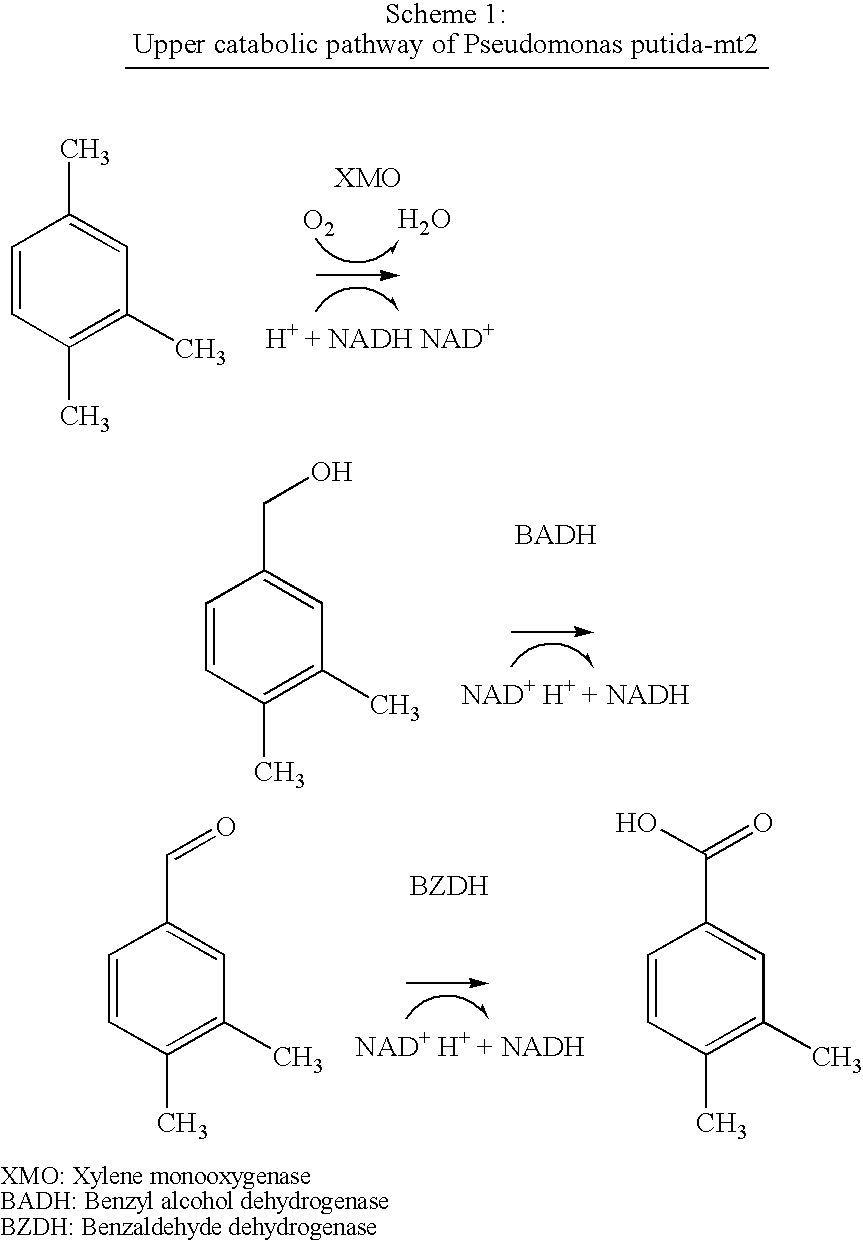
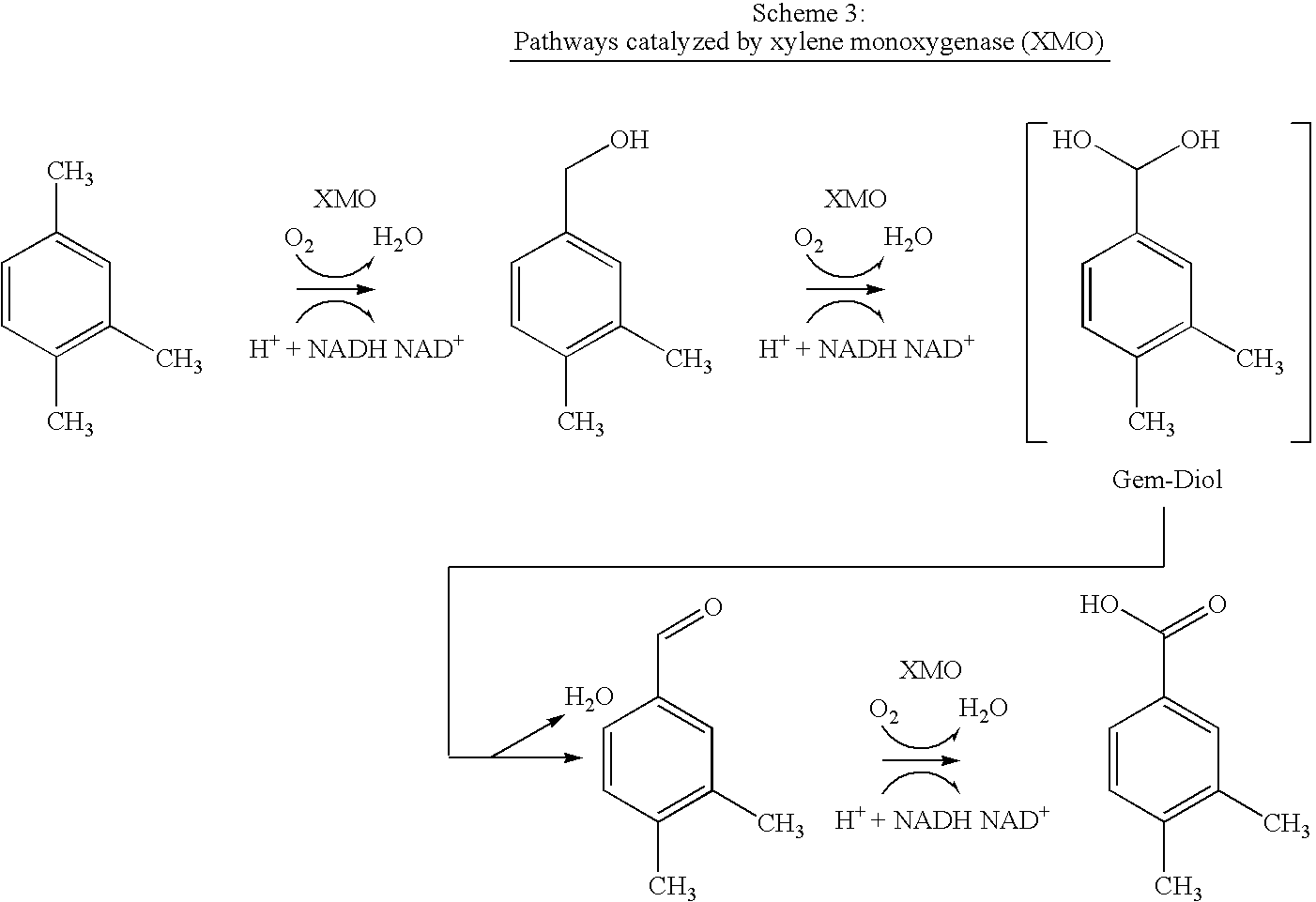
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
275 results about "Monooxygenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Monooxygenases are enzymes that incorporate one hydroxyl group into substrates in many metabolic pathways. In this reaction, the two atoms of dioxygen are reduced to one hydroxyl group and one H₂O molecule by the concomitant oxidation of NAD(P)H. One important subset of the monooxygenases, the cytochrome P450 omega hydroxylases, is used by cells to metabolize arachidonic acid (i.e. eicosatetraenoic acid) to the cell signaling molecules, 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid or to reduce or totally inactivate the activate signaling molecules for example by hydroxylating leukotriene B4 to 20-hydroxy-leukotriene B5, 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid to 5,20-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 5-oxo-eicosatetraenoic acid to 5-oxo-20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, 12-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid to 12,20-dihydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, and epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to 20-hydroxy-epoxyeicosatrienoic acids.
Modified DMO enzyme and methods of its use
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC +1
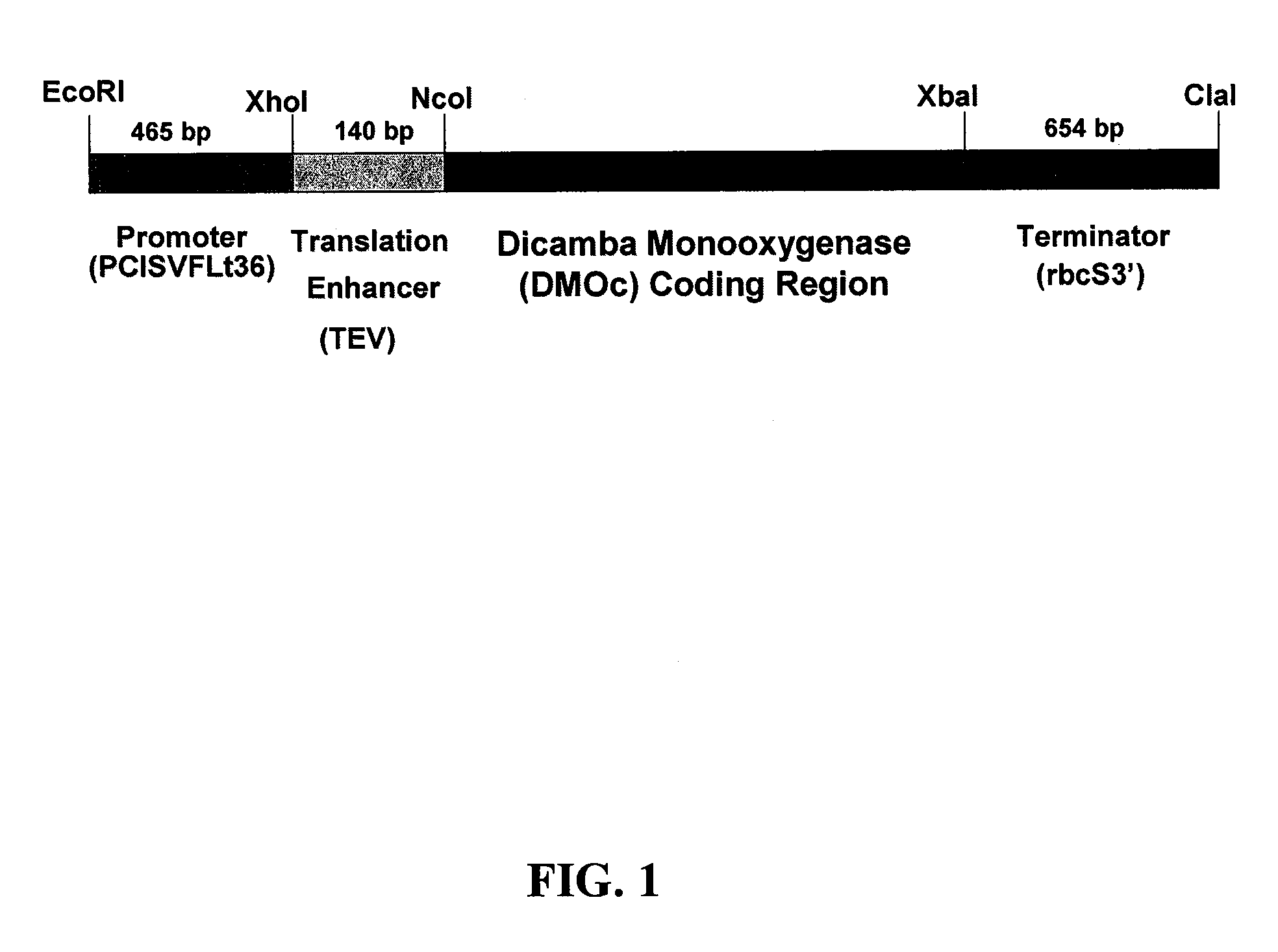
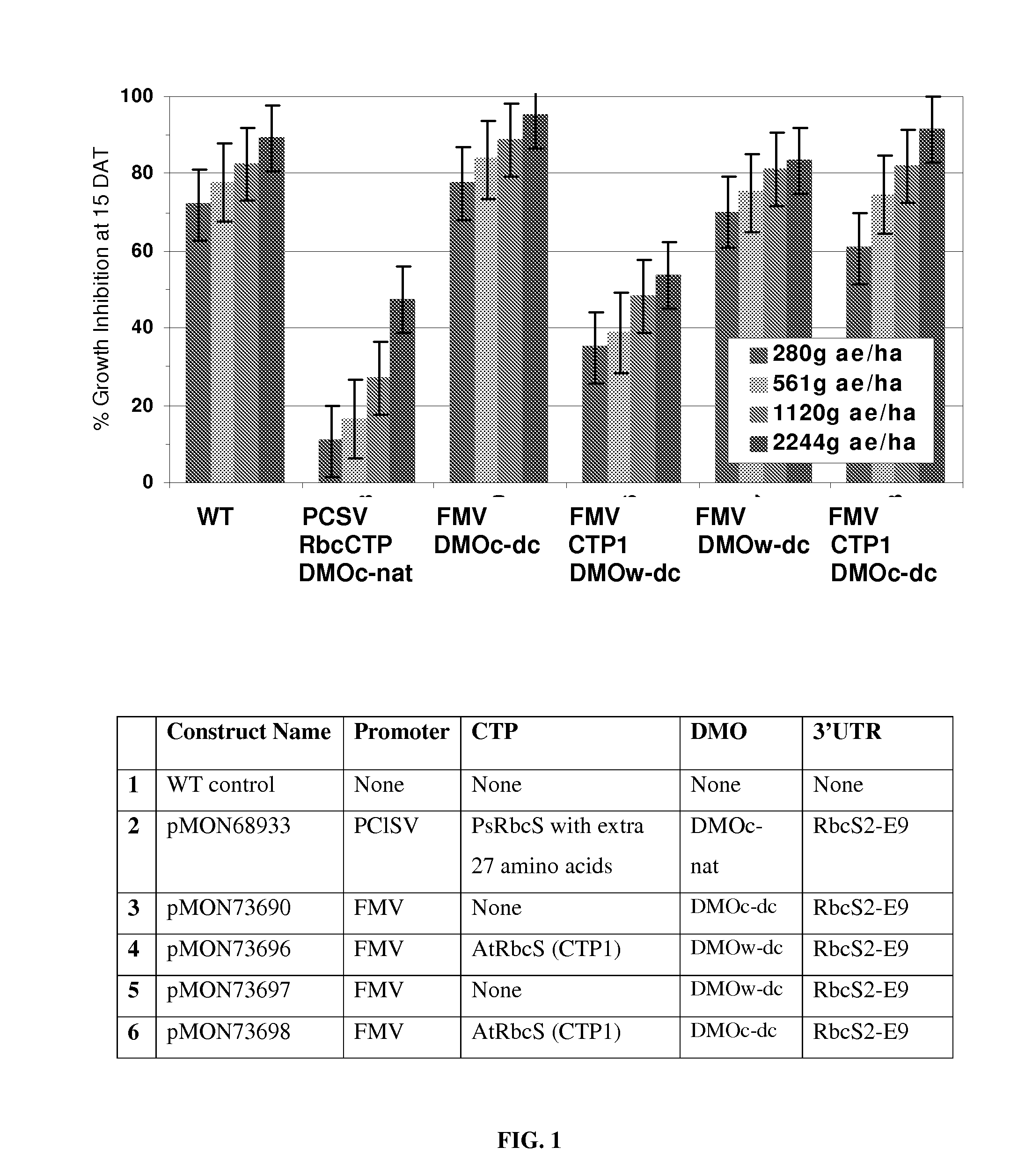
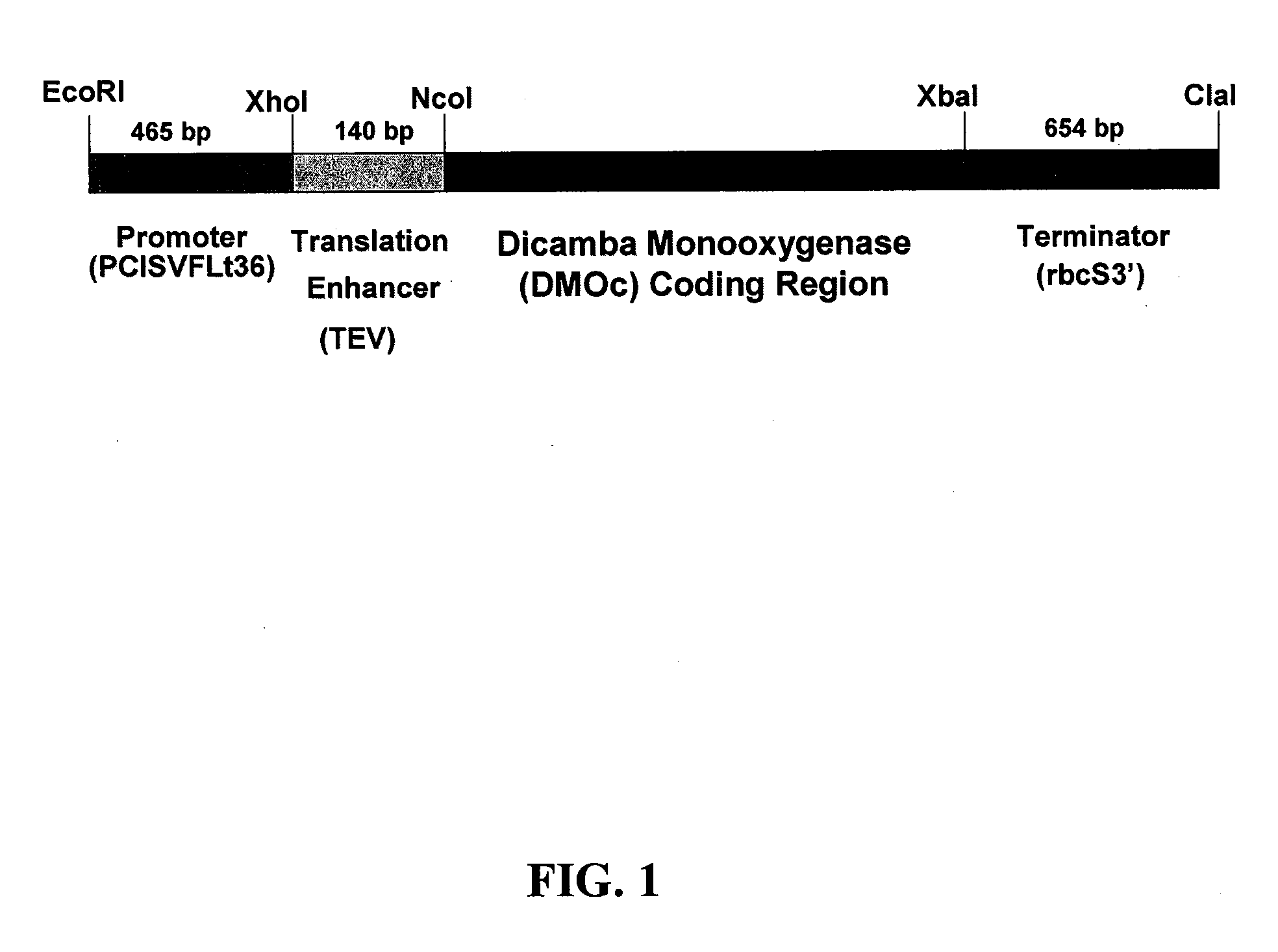
Chloroplast transit peptides for efficient targeting of DMO and uses thereof
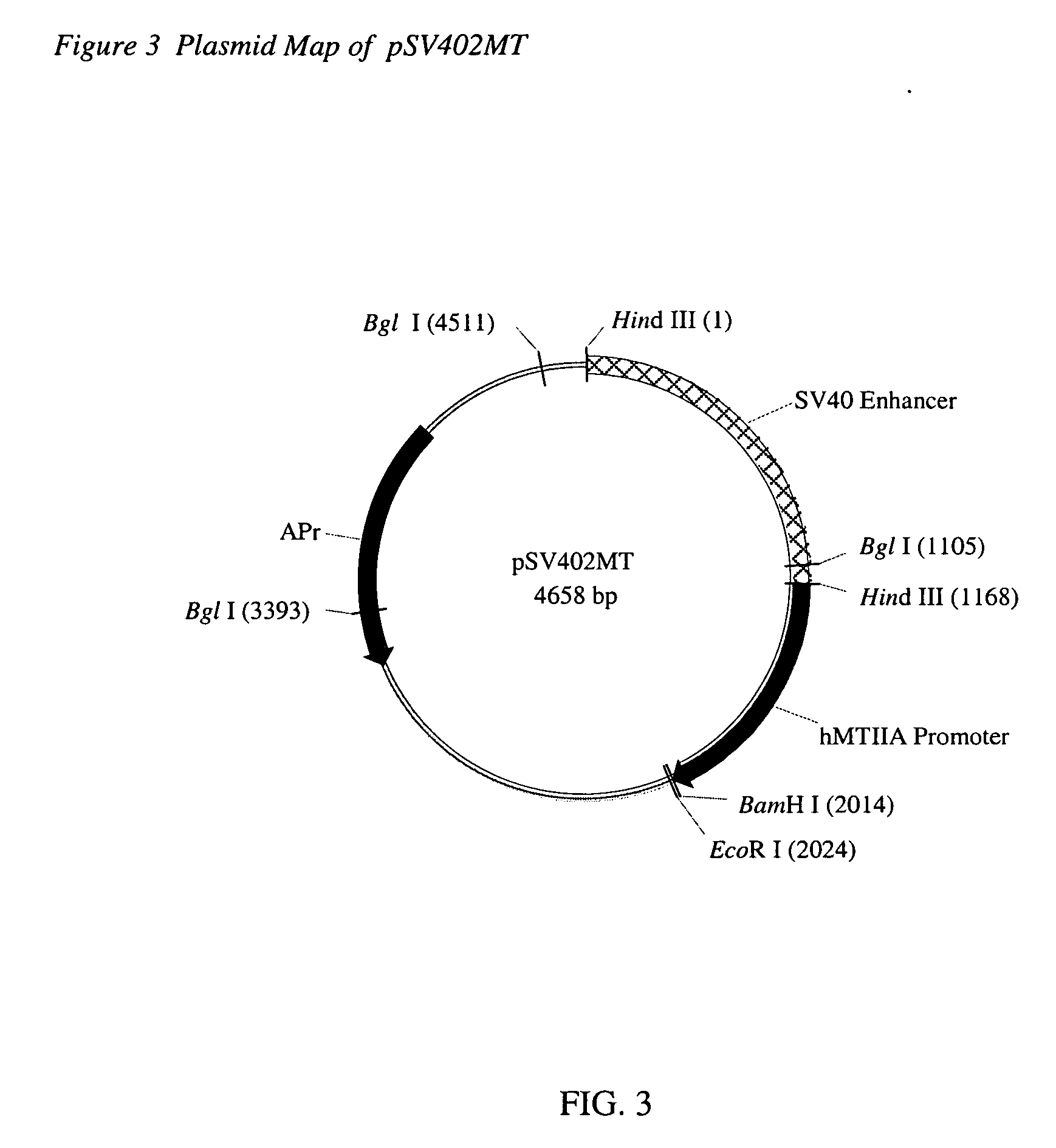
ActiveUS7838729B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesMonooxygenaseGMO Plants
The invention provides for identification and use of certain chloroplast transit peptides for efficient processing and localization of dicamba monooxygenase (DMO) enzyme in transgenic plants. Methods for producing dicamba tolerant plants, methods for controlling weed growth, and methods for producing food, feed, and other products are also provided, as well as seed that confers tolerance to dicamba when it is applied pre- or post-emergence.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
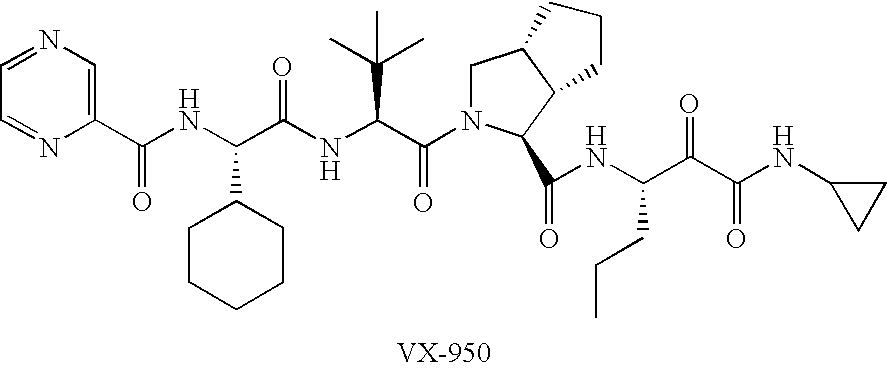
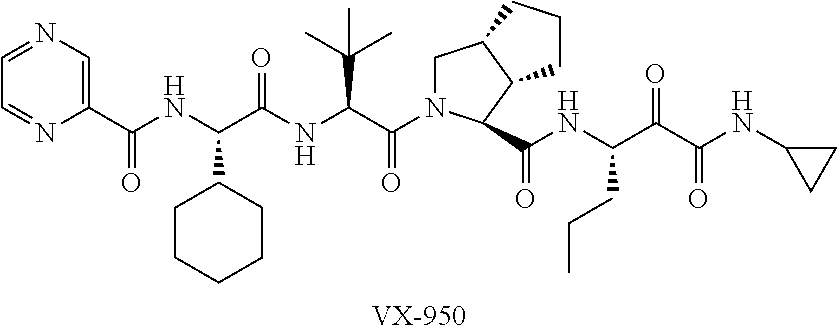
Combinations for HCV treatment
InactiveUS20060003942A1Improve pharmacokineticsImproving the pharmacokinetics of Hepatitis C NS3/4ABiocideOrganic active ingredientsHcv treatmentMonooxygenase
The present invention relates to co-administering a Hepatitis C virus NS3 / 4A protease inhibitor and a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase inhibitor. The combination acts by interfering with the life cycle of the hepatitis C virus and is therefore useful as an antiviral therapy. As such, the combination may be used for treating or preventing Hepatitis C infections in patients. The invention also relates to compositions comprising the combination of inhibitors. The invention also relates to kits and pharmaceutical packs comprising a Hepatitis C virus NS3 / 4A protease inhibitor and a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase inhibitor. The invention also relates to processes for preparing these compositions, combinations, kits, and packs.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
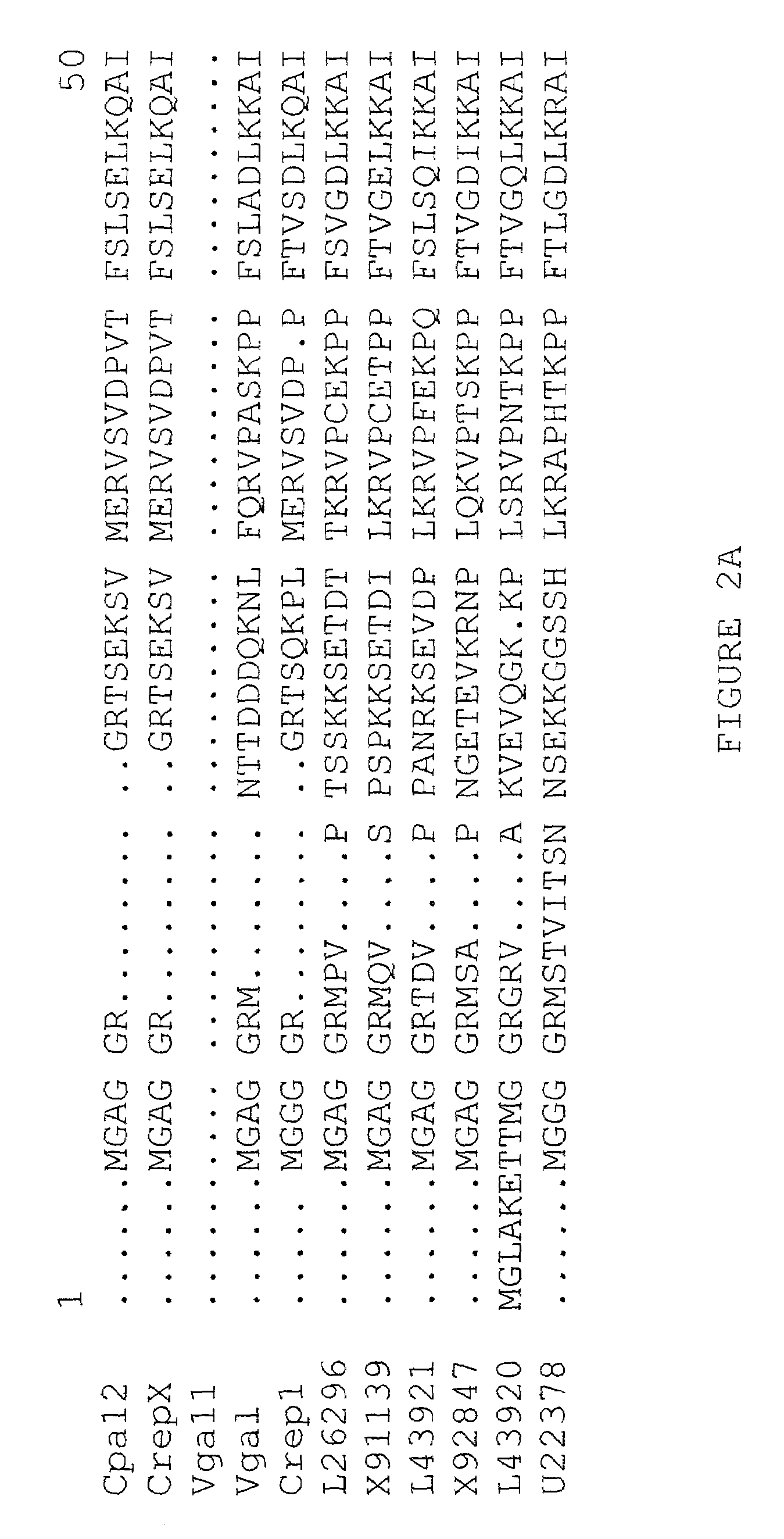
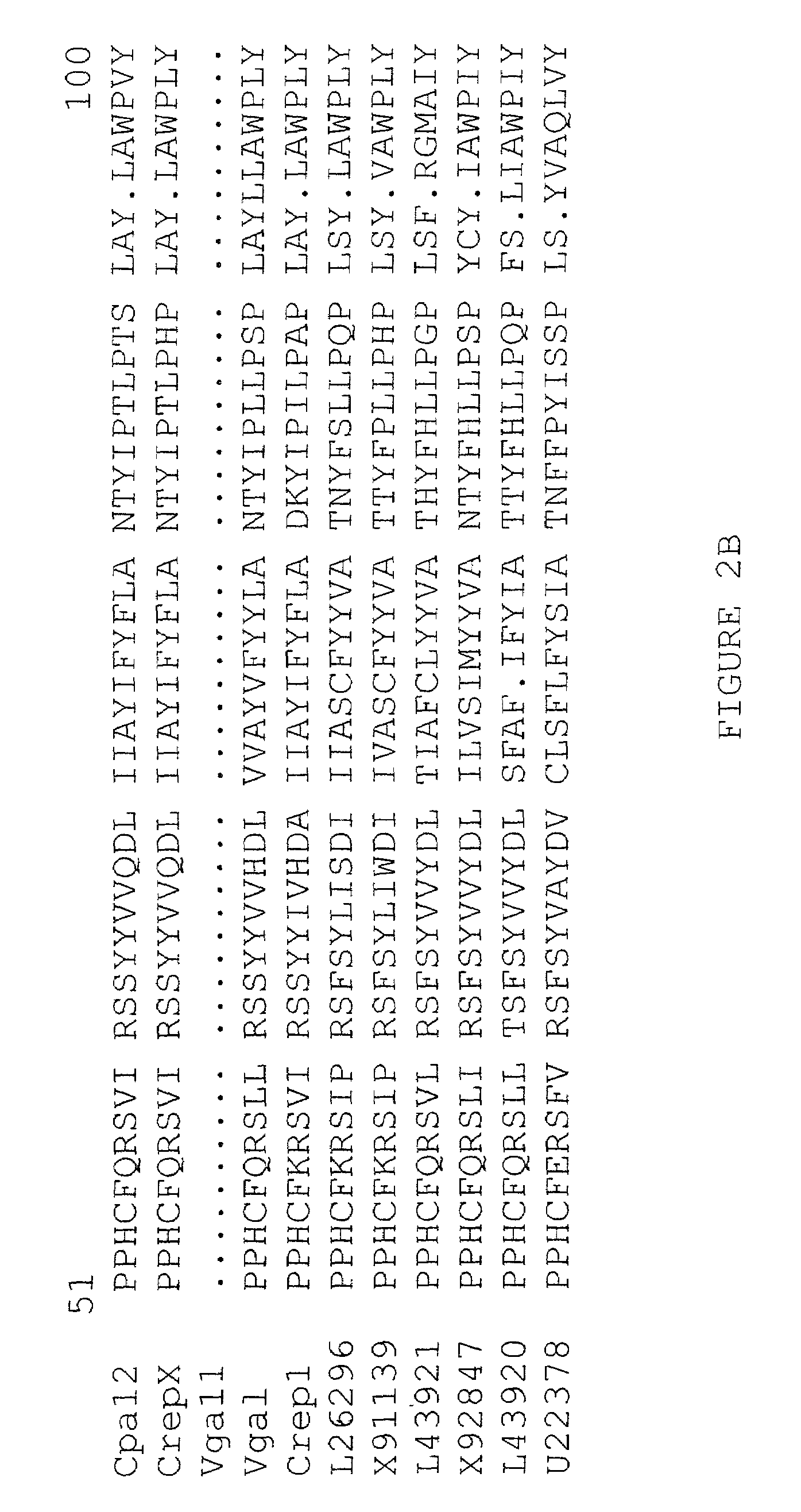
Fatty acid epoxygenase genes from plants and uses therefor in modifying fatty acid metabolism
The present invention relates generally to novel genetic sequences that encode fatty acid epoxygenase enzymes, in particular fatty acid Δ12-epoxygenase enzymes from plants that are mixed function monooxygenase enzymes. More particularly, the present invention exemplifies cDNA sequences from Crepis spp. and Vernonia galamensis that encode fatty acid Δ12-epoxygenases. The genetic sequences of the present invention provide the means by which fatty acid metabolism may be altered or manipulated in organisms, such as, for example, yeasts, moulds, bacteria, insects, birds, mammals and plants, and more particularly in plants. The invention also extends to genetically modified oil-accumulating organisms transformed with the subject genetic sequences and to the oils derived therefrom. The oils thus produced provide the means for the cost-effective raw materials for use in the efficient production of coatings, resins, glues, plastics, surfactants and lubricants.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
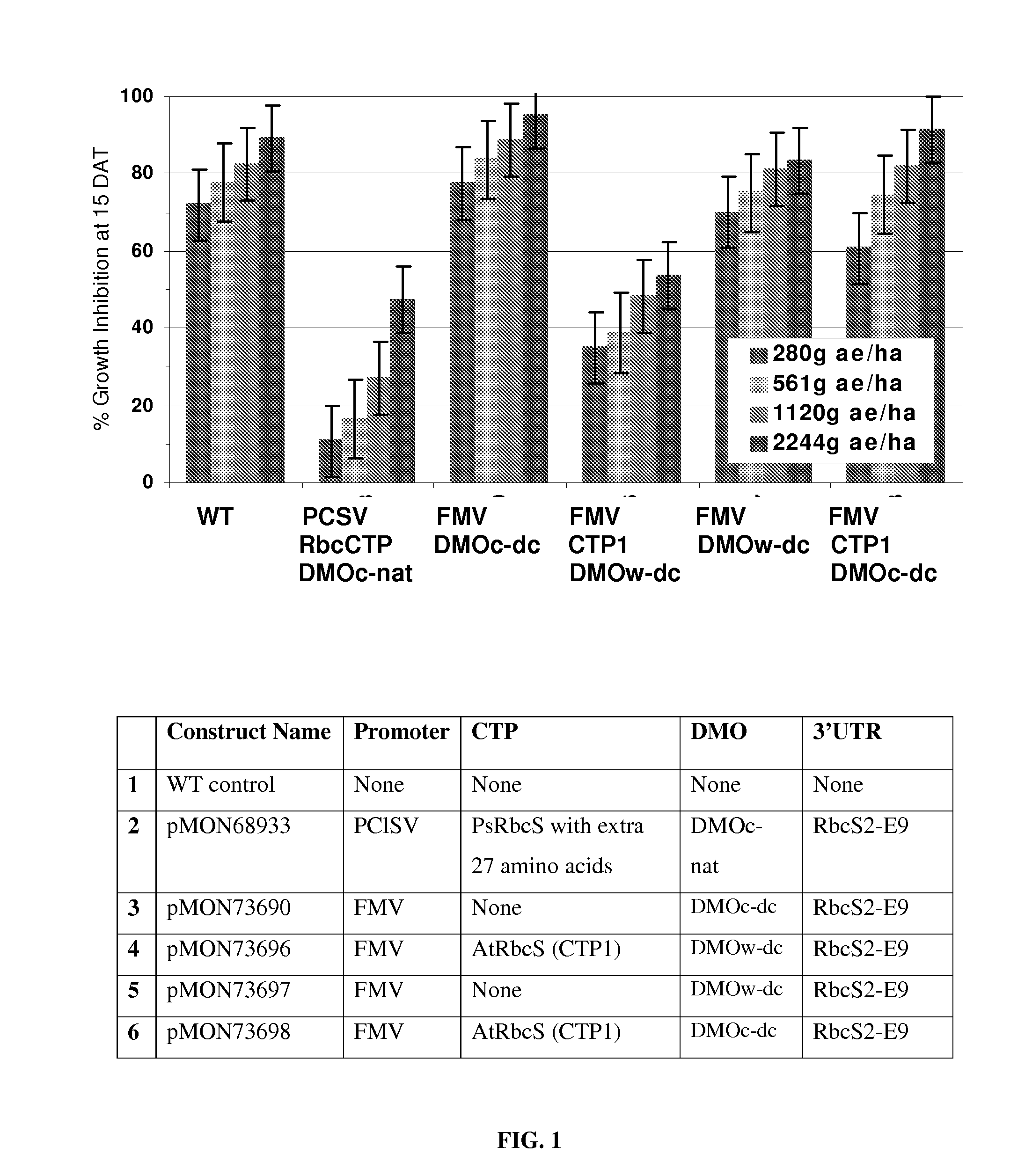
Modified dmo enzyme and methods of its use
The invention provides a modified variant of dicamba monooxygenase (DMO). The invention relates to the unexpected finding that cells expressing this DMO exhibit high levels of tolerance to the herbicide dicamba. Compositions comprising DMO-encoding nucleic acids and methods of use are provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC +1
Chloroplast transit peptides for efficient targeting of dmo and uses thereof
The invention provides for identification and use of certain chloroplast transit peptides for efficient processing and localization of dicamba monooxygenase (DMO) enzyme in transgenic plants. Methods for producing dicamba tolerant plants, methods for controlling weed growth, and methods for producing food, feed, and other products are also provided, as well as seed that confers tolerance to dicamba when it is applied pre- or post-emergence.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Cell lines for expressing enzyme useful in the preparation of amidated products
InactiveUS20060292672A1High expressionGood for survivalAnimal cellsSugar derivativesPeptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenaseChemical compound
Cell lines are provided for expressing peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase (PAM), or one of its two catalytic domains. High levels of enzyme expression are achieved while utilizing a non-animal source, low protein tissue culture medium. A robust two-step downstream purification results in high enzyme purity. Resulting PAM, or its PHM catalytic domain, is used to catalyze the enzymatic conversion of X-Gly to X-alpha-hydroxy-Gly or X—NH2 (X being a peptide or any chemical compound having a carbonyl group to which a glycine group can be covalently attached). Methods of preparing preferred cell lines are also set forth.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
Polynucleotides encoding choline monooxygenase and plants transformed therewith
A full length choline monooxygenase (CMO) cDNA was cloned from spinach and used to transform plants which do not naturally express CMO. A method is presented to improve stress tolerance of crops following engineering of CMO and BADH in plants that lack glycine betaine accumulation. Also provided are fragments useful as probes to isolate other CMO-type genes, and antisense sequences which inhibit the production of CMO. Reduction of glycine betaine as a consequence of antisense expression of CMO in species naturally accumulating glycine betaine, improves the transgenic plant's tolerance toward pathogens and pests and / or enhances its nutritional quality.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Plant fatty acid epoxygenase genes and uses therefor
The present invention relates generally to novel genetic sequences which encode fatty acid epoxygenase enzymes. In particular, the present invention relates to genetic sequences which encode fatty acid DELTA12-epoxygenase enzymes comprising mixed function monooxygenase enzymes. More preferably, the present invention provides cDNA sequences which encode plant fatty acid epoxygenases, in particular the Crepis palaestina DELTA12-epoxygenase and homologues, analogues and derivatives thereof. The genetic sequences of the present invention provide the means by which fatty acid metabolism may be altered or manipulated in organisms such as yeasts, moulds, bacteria, insects, birds, mammals and plants, in particular to convert unsaturated fatty acids to epoxygenated fatty acids therein. The invention extends to genetically modified oil-accumulating organisms transformed with the subject genetic sequences and to the oils derived therefrom. The oils thus produced provide the means for the cost-effective raw materials for use in the efficient production of coatings, resins, glues, plastics, surfactants and lubricants, amongst others.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +2
Enzymatic reactions in the presence of keto acids
ActiveUS7445911B2Efficient and high yieldImprove bioavailabilityCarbon-nitrogen lyasesOxidoreductasesLyaseKeto acid
Conversion in vitro of X-Gly to X-alpha-hydroxy-Gly or X—NH2 (X being a peptide or any other compound having a carbonyl group capable of forming a covalent bond with glycine) is accomplished enzymatically in the presence of keto acids, or salts or esters thereof, to provide a good yield without the necessity of catalase or similar enzymatic reaction enhancers. Peptidylglycine α-amidating monooxygenase (PAM) is a preferred enzyme for catalyzing the conversion. Alternatively, peptidylglycine α-hydroxylating monooxygenase (PHM) is utilized to convert X-Gly to X-alpha-hydroxy-Gly which may be recovered, or optionally may be simultaneously or sequentially converted to an amide by either a Lewis base or action of the enzyme peptidyl α-hydroxyglycine α-amidating lyase (PAL). Both PHM and PAL are functional domains of PAM.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
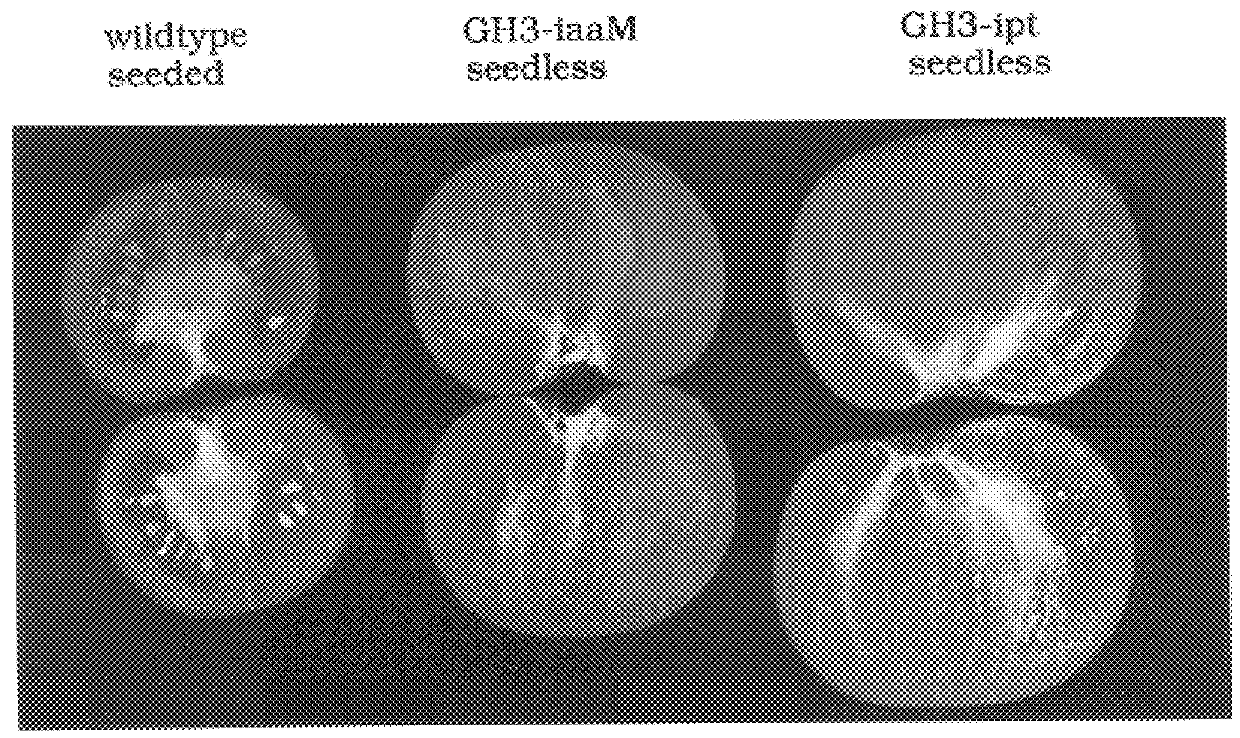
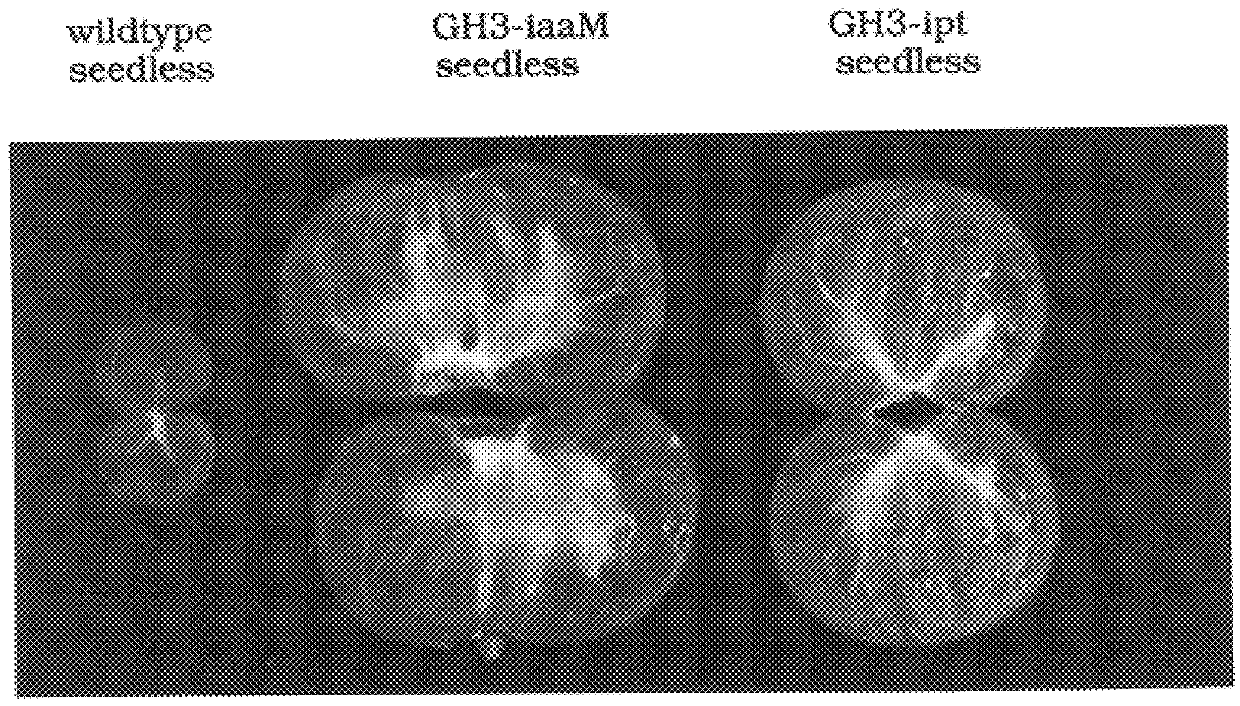
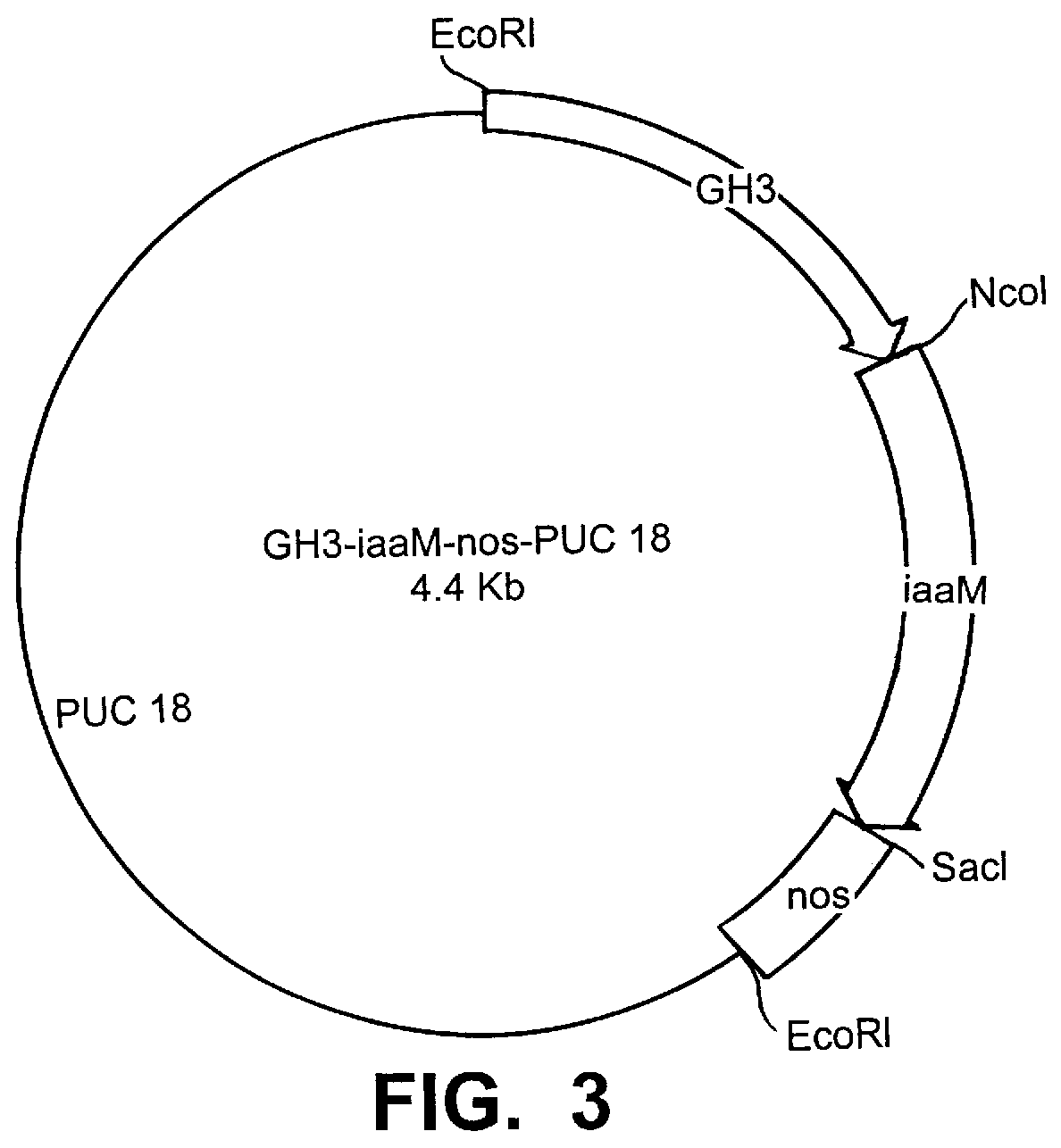
Transgenic seedless fruit comprising AGL or GH3 promoter operably linked to isopentenyl transferase or tryptophan monooxygenase coding DNA
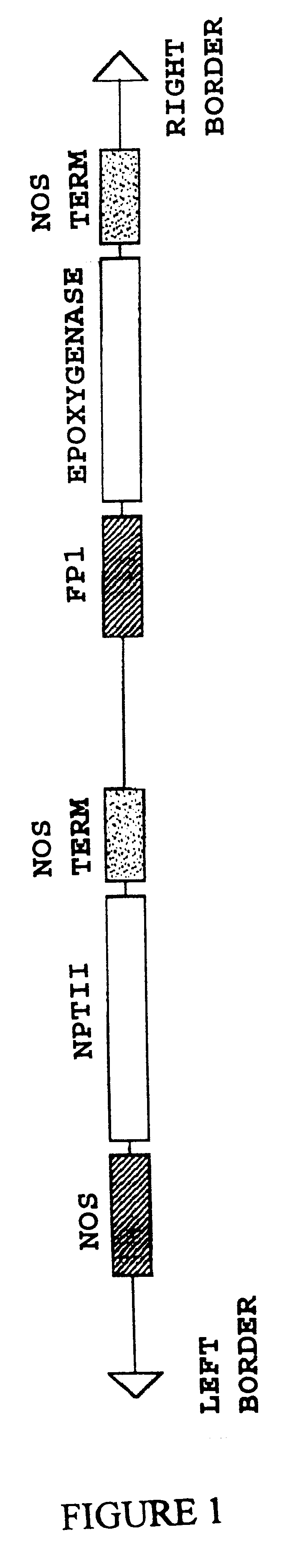
InactiveUS6268552B1TransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesBiosynthetic genesDNA construct
The present invention provides methods and DNA constructs for the genetic engineering of plant cells to produce plants which produce substantially seedless fruit in the absence of exogenous growth factors (auxins or cytokinins) and in the absence of pollination. The substantially seedless fruits produced by the methods described herein are about the size of wildtype seeded fruit (or somewhat larger) and these fruits are equal to or superior to the wildtype seeded fruit with respect to solid content and flavor. The seedless fruits of the present invention are produced in transgenic plants which contain and express auxin or cytokinin biosynthetic genes, e.g., tryptophan oxygenase or isopentenyl transferase coding sequences expressed under the regulatory control of GH3 or AGL promoter sequences directing preferential or tissue specific expression of a downstream gene in the ovaries or developing fruit.
Owner:LI YI
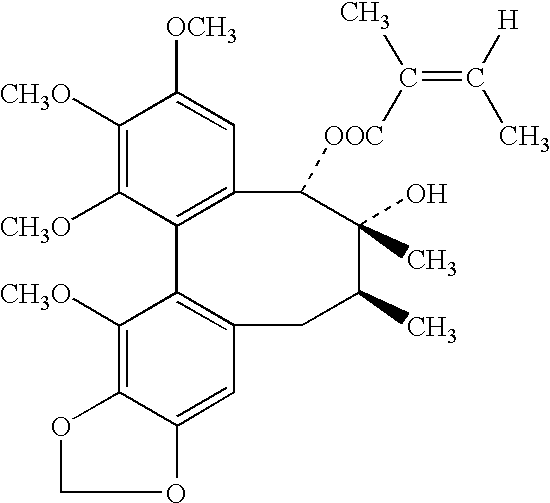
Plant drug for treatment of liver disease
The present invention related to safe plant drug for treatment of liver disease, specifically, this invention proves a safe plant drug Schisandrin and its preparation. Schisandrin has the following pharmaceutical functions: increasing tumor suppresson genes express activity, decreasing activity of oncogenes, increasing immune function, increasing liver DNA synthesis, decreasing serum alamine aminotransferase activity, increasing glutathione level, increasing glutathione reductase activity, decreasing lipid peroxidation of liver, increasing hepatic microsomal monooxygenases activity, increasing ATP content in liver, increasing energy metabolism activity, decreasing density lipoprotein oxidation, protecting gastrointestinal function, increasing killer cell activity, increasing complement activity, decreasing induced liver cancer activity and decreasing grown of cancer cells.
Owner:ZHAO XINXIAN
Directed evolution of recombinant monooxygenase nucleic acids and related polypeptides and methods of use
InactiveUS20060051782A1Improve abilitiesIncrease rangeBacteriaLibrary screeningNitrobenzeneMonooxygenase
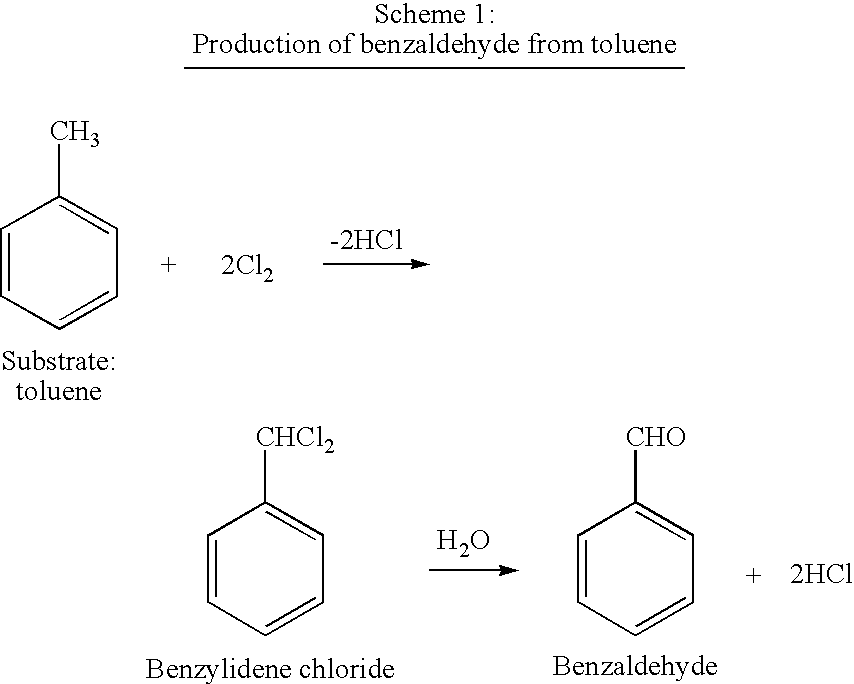
The present invention relates to novel monooxygenase nucleic acids and polypeptides created using mutagenesis, DNA shuffling, or both, in a single iteration or multiple iterations, and methods for their creation and use. The monooxygenase enzymes of the present disclosure have particular utility as biocatalysts in industrial chemical redox reactions, such as the oxidation of aromatic hydrocarbons, for example, toluene, benzene, or nitrobenzene, into industrially desirable products. The systems and processes of the present invention are especially useful for the coupled synthesis and recovery of catechols, methylcatechols, resorcinols, methylresorcinols, hydroquinones, methylhydroquinones, hydroxybenzenes, cresols, nitrobenzenes, and nitrohydroxyquinones.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Combinations for HCV Treatment
InactiveUS20100015090A1Improve pharmacokineticsImproving the pharmacokinetics of Hepatitis C NS3/4AOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHcv treatmentMonooxygenase
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
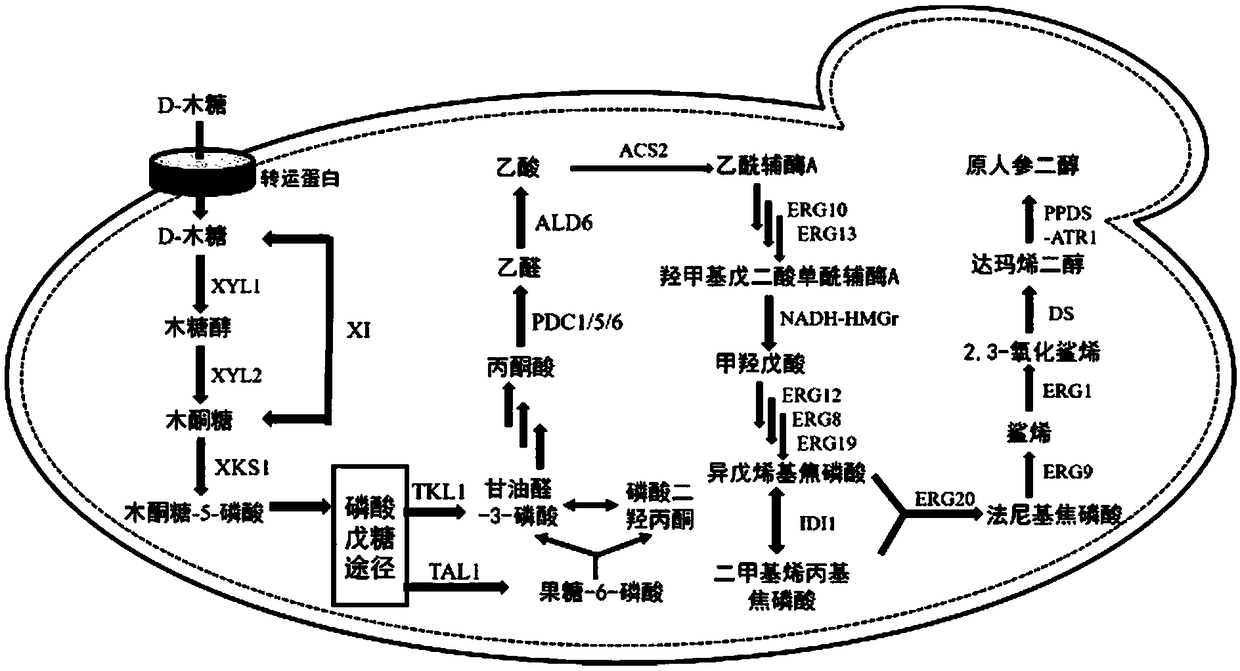
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and a construction method. The construction method comprises the steps of replacing a promoter of a saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 with a promoter PFBA1 by virtue of a homologous recombination method, introducing xylose reductase XYL1 and a xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassette, increasing the activities of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 1, introducing a farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, a squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and a dammarenediol synthase gene DS into the recombinant bacteria 1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and introducing a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl diphosphatesynthase ERG20 and a protopanoxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 into the recombinant bacteria 2, so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 3. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae, dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol can be artificially synthesized by virtue of xylose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Enzymatic reactions in the presence of keto acids
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
Flavin monooxygenase mutant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107384880AIncreased specific enzyme activityEasy to produceFungiMicroorganism based processesYeastRandom mutation
The invention belongs to the field of bioengineering and particularly relates to a flavin monooxygenase mutant and a preparation method thereof. The error-prone PCR technology is used to conduct random mutation on wild type flavin monooxygenase to obtain the flavin monooxygenase mutant. The specific enzyme activity of the flavin monooxygenase mutant is improved by 35% compared with that of the wild type flavin monooxygenase. Meanwhile, a yeast expression system is adopted, when the flavin monooxygenase is displayed on the surface of yeasts, yeast cells can serve as enzyme producers and can also serve as carriers in immobilized enzymes, operation of purification, fixation and the like of the enzymes are omitted, the production link is simplified, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Cytochrome P450BM-3 monooxygehase varient gene and its use
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for improving regeneration of mycobacterium coenzyme and for simultaneously promoting production of androstenedione
InactiveCN108913643APromote regenerationRaise the ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSterolTransformation efficiency
The invention belongs to the technical field of bio-catalysis, and in particular relates to a method for improving regeneration of mycobacterium coenzyme and for simultaneously promoting production ofandrostenedione. According to the method, sterol C27 site monooxygenase Cyp125 in a phytosterol metabolic pathway is introduced into steroid transformation microorganism, so as to improve androstenedione conversion efficiency of recombinant microorganism in a fermentation system; and therefore, a novel method for solving a problem of slow metabolism of mycelial phytosterol is offered. Through over-expression of the Cyp125, specific enzyme activity of the mycobacterium sterol C27 site monooxygenase is improved by 22.2%; regeneration of intracellular NAD+ is improved, and an intracellular NAD+ / NADH ratio is improved by 131%; and meanwhile, it is unexpectedly discovered that a bacterium biomass amount can be improved by 18.7% through the over-expression of the enzyme, and finally, effects ofshortening a conversion cycle by 24h and improving an AD(D) yield by 10.0% can be achieved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Novel cytochrome P450 monooxygenase
InactiveUS20060156430A1Improve the level ofAnimal feeding stuffOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationNucleotide
This invention relates to an isolated polynucleotide encoding a cytochrome P450 monooxygenase that in the presence of linoleic acid results in production of 1-octen-3-ol. The invention also relates to the construction of a recombinant DNA construct comprising all or a portion of the polynucleotide encoding the cytochrome P450 monooxygenases of the invention, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels 1-octen-3-ol in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Isoeugenol monooxygenase mutant and application thereof
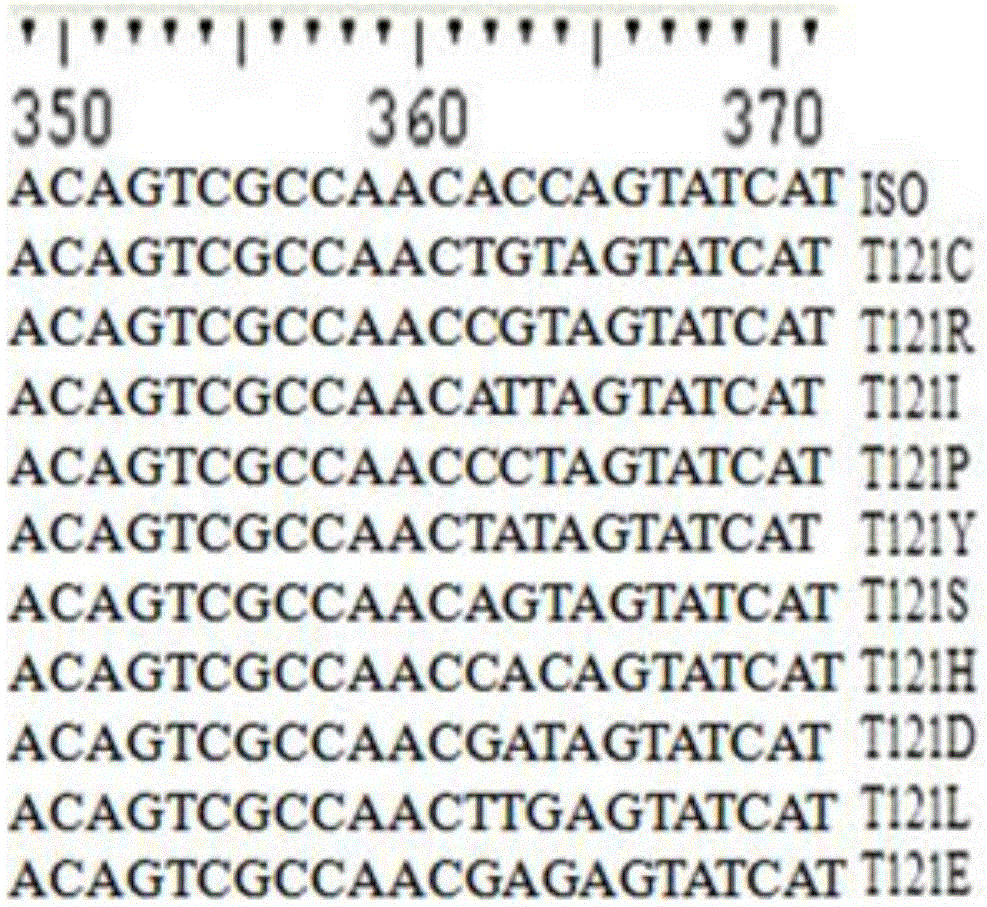
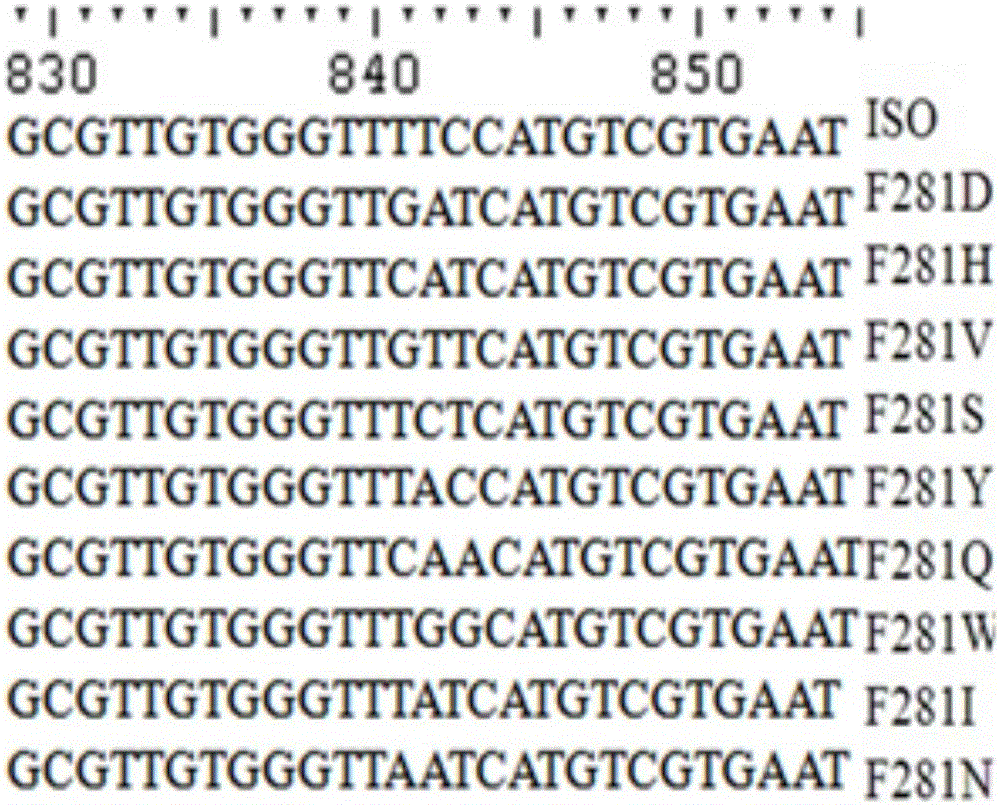
ActiveCN106754802AHigh catalytic activityGenerate efficientlyOxidoreductasesFermentationIsoeugenolBiology
The invention discloses an isoeugenol monooxygenase mutant and application thereof. The isoeugenol monooxygenase mutant comprises an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ 2, and the amino acid sequence has at least one mutant selected from a 120th site, a 121st site, a 281st site, a 298th site and a 470th site. The isoeugenol monooxygenase mutant with high catalytic activity is obtained by carrying out site-specific mutagenesis on an isoeugenol monooxygenase gene; the isoeugenol monooxygenase mutant can be efficiently catalyzed to generate vanillin by using isoeugenol as a substrate; by using the isoeugenol as the substrate, the isoeugenol monooxygenase mutant has the isoeugenol monooxygenase catalytic activity which is at least 117 percent higher than that of a parent.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Monooxygenase and application thereof in preparation of optically pure sulfoxide
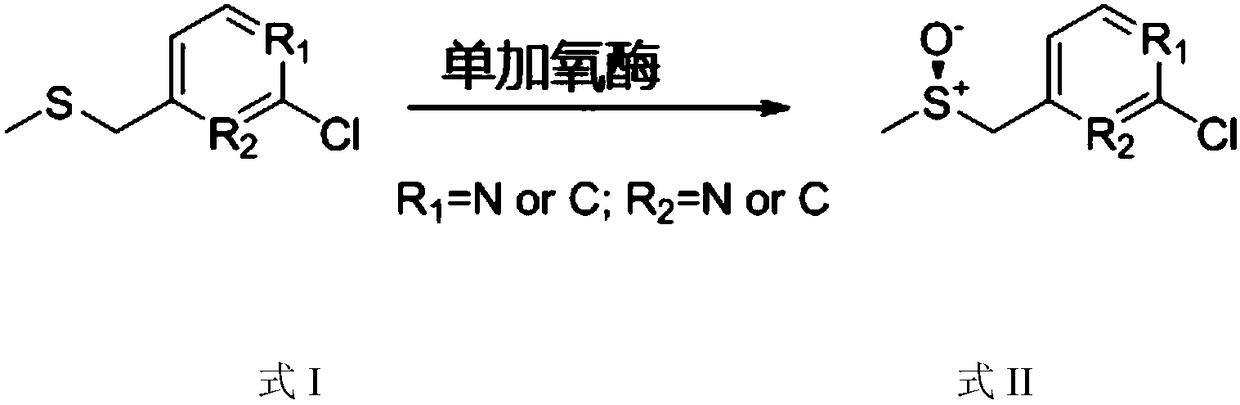
PendingCN111218431AMild reaction conditionsHigh yieldMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesMonooxygenaseMedicinal chemistry
The invention discloses monooxygenase. An amino acid sequence of the monooxygenase is obtained through mutation of an amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO:2. The monooxygenase is used for preparing chiral sulfoxide drugs, has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, environmental friendliness, high yield and product optical purity, few peroxidation products and the like and has very good industrial application prospects in production of a drug proton pump inhibitor for treating gastric ulcer.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Cytochrome P450 monooxygenase CYP52A2B from Candida tropicalis
InactiveUS7049112B2Increase productionHigh copy numberBacteriaSugar derivativesCandida tropicalisCandida famata
Novel genes have been isolated which encode cytochrome P450 and NADPH reductase enzymes of the ω-hydroxylase complex of C. tropicalis 20336. Vectors including these genes, transfected host cells and transformed host cells are provided. Methods of producing of cytochrome P450 and NADPH reductase enzymes are also provided which involve transforming a host cell with a gene encoding these enzymes and culturing the cells. Methods of increasing the production of a dicarboxylic acid and methods of increasing production of the aforementioned enzymes are also provided which involve increasing in the host cell the number of genes encoding these enzymes. A method for discriminating members of a gene family by quantifying the expression of genes is also provided.
Owner:COGNIS IP MANAGEMENT GMBH
Recombinant saccharomycetes for high yield of sandalwood oil as well as construction method and application thereof
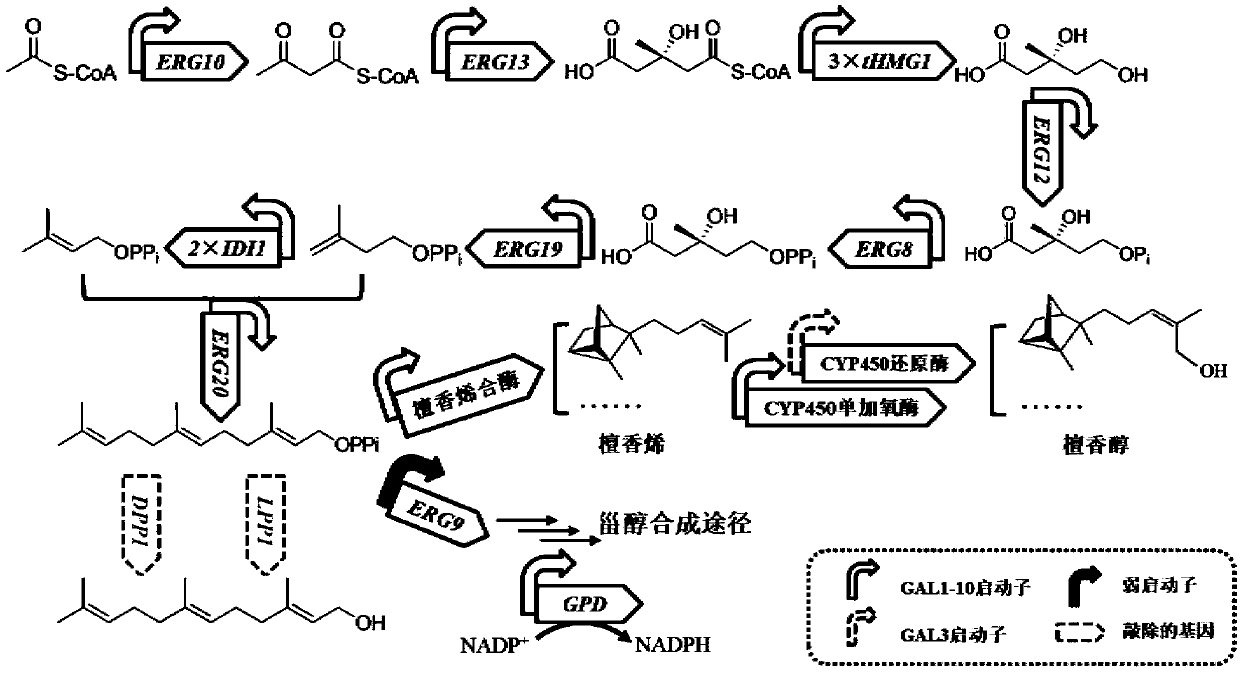
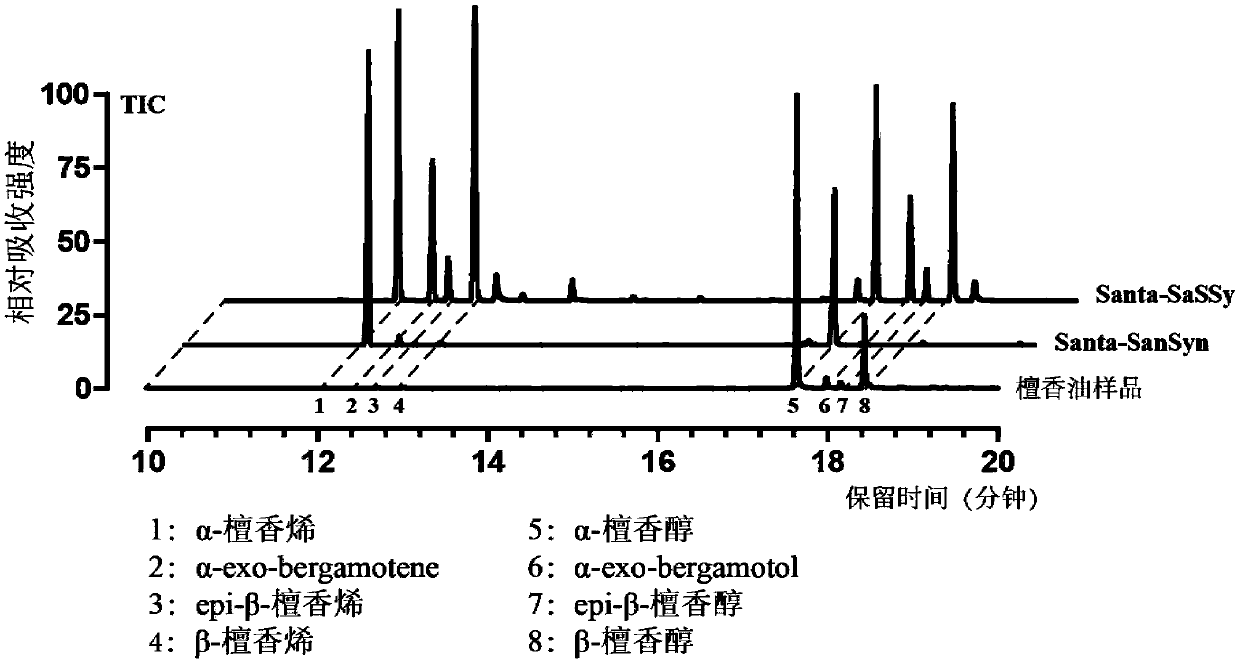
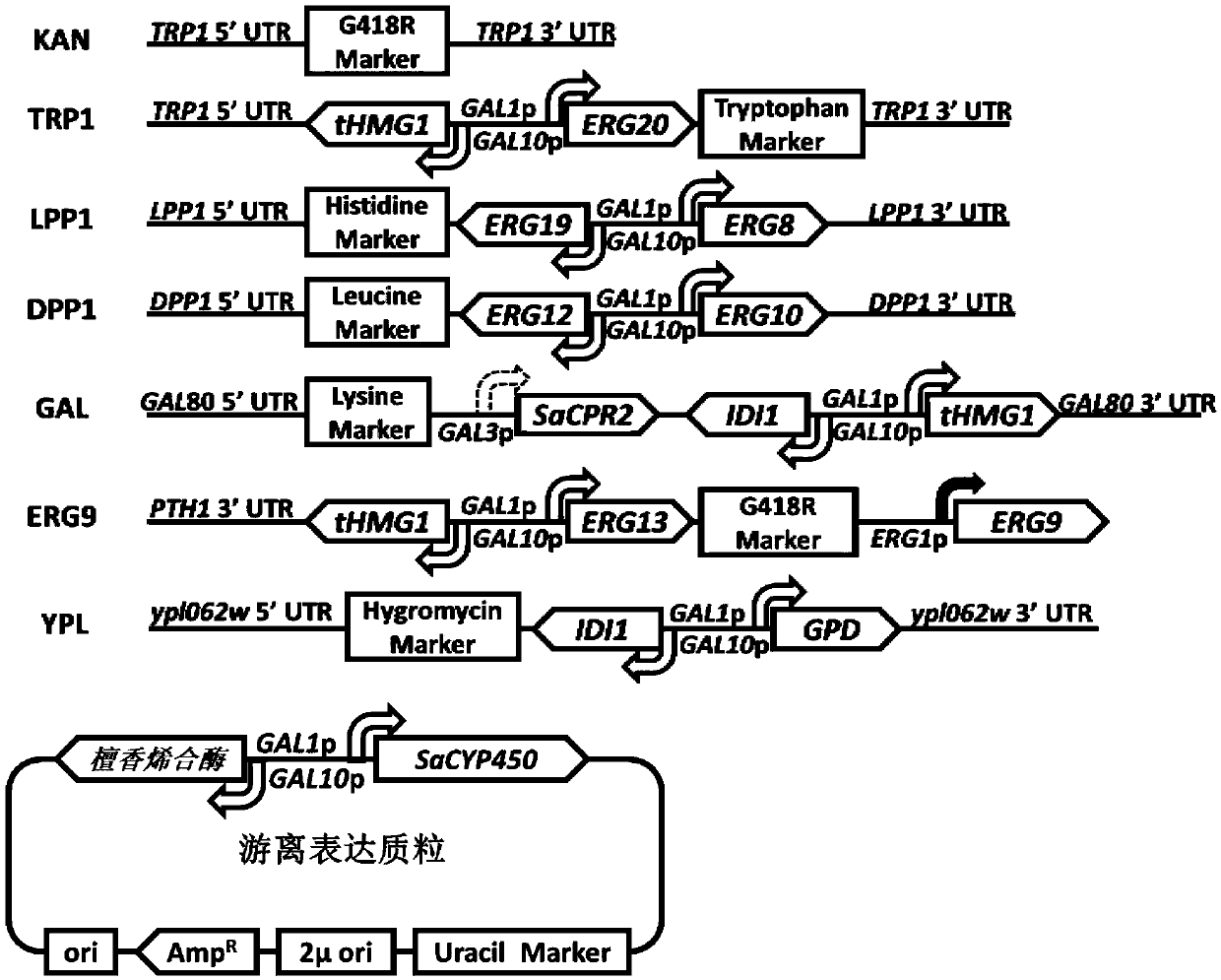
ActiveCN111434773AOvercoming extraction deficienciesMeet the level of industrial productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySandalwood oil
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomycetes for high yield of sandalwood oil as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant saccharomycetes. The method comprises the following steps: 1) integrating genes such as acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase gene and the like which are derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae and are driven by a strong promoter and CYP450 reductase gene whichis driven by a weak promoter into a saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 genome of an original strain in a homologous recombination manner; 2) replacing a promoter of a squalene synthase gene in the recombinant bacteria; knocking out genes such as galactose modulin 80 genes; and (3) inserting a sandalene synthase gene driven by a strong promoter and a CYP450 monooxygenase gene into the multi-copy freeplasmid to obtain an expression plasmid, and introducing the expression plasmid into the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae obtained in the step (2) to obtain the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for high yield of sandalwood oil. According to the method, the defect that sandalwood oil is extracted from sandalwood is overcome, and the yield of each liter of sandalwood oil of the recombinant yeast strain reaches 1g. Industrial production requirements can be met.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV +1
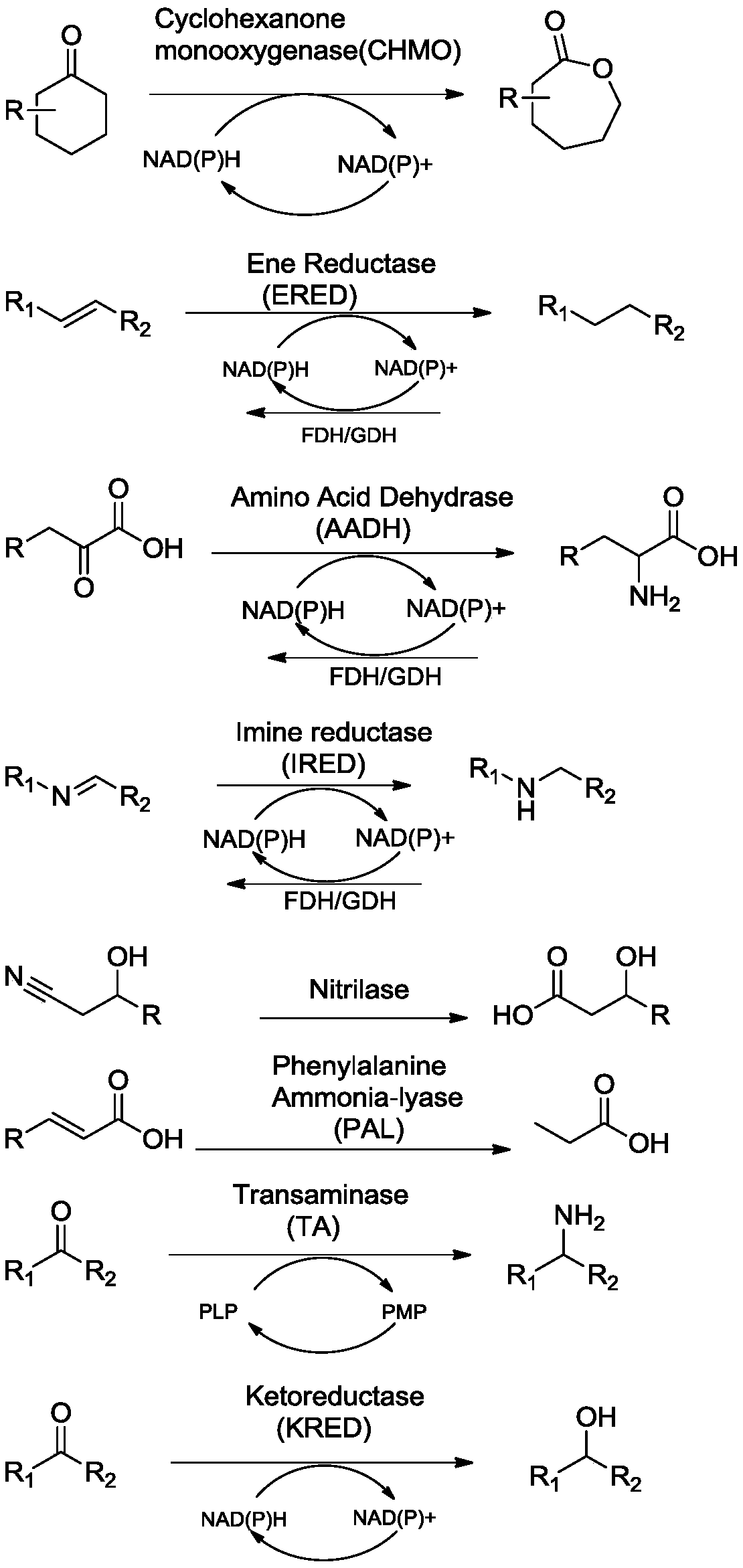
Immobilized enzyme as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110964710AEasy to fixImprove recycling efficiencyCarbon-nitrogen lyasesHydrolasesLyaseCross linker
The invention provides an immobilized enzyme as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The immobilized enzyme comprises an enzyme and an amino resin carrier for immobilizing the enzyme, the enzyme is selected from any one of transaminase, ketoreductase, monooxygenase, ammonia lyase, alkene reductase, imine reductase, amino acid dehydrogenase and nitrilase, the amino resin carrieris the cross-linking agent modified amino resin carrier, and a cross-linking agent is a cross-linking agent treated by a high polymer. The amino resin carrier is modified by adopting the cross-linking agent treated by the high polymer, so that enzymes immobilized on the amino resin carrier can form netted cross-linking, the immobilization effect of the enzymes is more stable, and the cyclic utilization efficiency of the enzymes is improved.
Owner:JILIN ASYMCHEM LAB CO LTD
Method for biological production of hydroxytyrosol
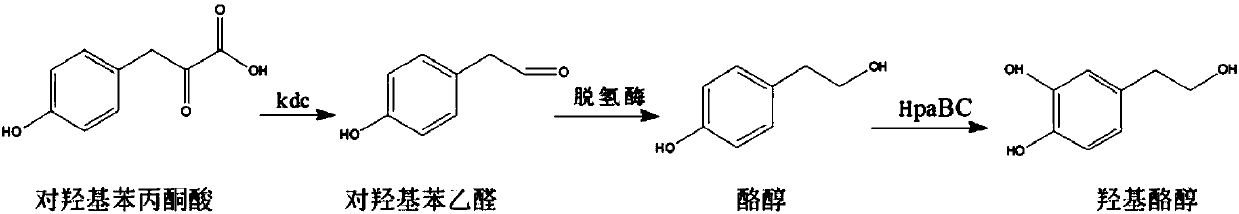
InactiveCN107723306AResolve source issuesReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliChemical synthesis
The invention discloses a method for biological production of hydroxytyrosol. The method comprises the following steps: performing complete chemical synthesis of a ketone group decarboxylase gene kdcwith a trc promoter and a 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid-3-monooxygenase gene hpaBC with a tac promoter, performing complete chemical synthesis of a carrier skeleton pBPE004, connecting the kdc and the hpaBC onto pBPE004 to obtain a recombinant vector pKB by using an enzyme digestion connection method, shifting the pKB into a base tray strain SyBE-002447 to obtain a SyBE-KB1 strain; integrating the kdc gene and the hpaBC gene onto a SyBE-002447 chromosome to obtain an SyBE-KB2 strain. Glucose is used as a precursor, and the SyBE-KB1 and SyBE-KB2 strains are fermented to produce the hydroxytyrosol.According to the method, engineering escherichia coli is used for producing the hydroxytyrosol, the source problem of the hydroxytyrosol can be solved, and the cost can be reduced.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Monooxygenase mutant and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a monooxygenase mutant and a preparation method and application thereof. The monooxygenase mutant is provided with any one of amino acid sequences as shown in formulas (I) and (II), wherein the amino acid sequence in the formula (I) reaches 80% consistency with the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; the amino acid sequence in formula (II) is obtained by modifying, substituting, decreasing or increasing one or some amino acid to 23 to 508 amino acid sites of the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; 1-34 amino acid is substituted; the mutant has the activity of monooxygenase. According to the method, a plurality of different sites, namely, 23-508 amino acid sites, are mutated; and the result shows that the mutants are capable of improving the activity, stability, soluble expression and selectivity of monooxygenase as well as decreasing the dosage of monooxygenase.
Owner:ASYMCHEM LAB TIANJIN
Method for the oxidation of aromatic compounds
InactiveUS20040106177A1Inhibitory activityEasy post-processingBacteriaMicroorganism based processesXylyleneMicrobiology
The invention relates to a process for the biocatalytic oxidation of aromatic compounds using recombinant xylene monooxygenase-expressing microorganisms in a biphasic reaction medium.
Owner:BASF AG
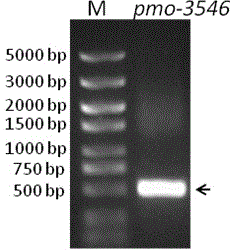
Thioether monooxygenase PMO-3546 and application thereof
The invention cloning expresses and discloses a thioether monooxygenase PMO-3546 and an application thereof. The size of the zymoprotein is 18 kD and the amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the corresponding coding gene length is 486 bp and the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The zymoprotein can effectively catalyze the thioether substrate to generate the sulfoxide after recombinant expression, and is high in conversion efficiency and stereoisomerism enantioselectivity and can be used for biosynthesizing the chiral sulfoxide medicine.
Owner:ZUNYI MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase and application of Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase
The invention discloses a Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase and an application of the Baeyer Villiger monooxygenase, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The invention provides another Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase aiming at the problems of reported Baeyer-Villiger monooxygenase, such as low catalytic activity to substrate thioether, poor thermal stability, low ee value of a product and the like. The enzyme shows high stereoselectivity to linear ketone, cyclic ketone and thioether substrates, has high catalytic activity to cyclohexanone and thioanisole, and can be used for preparing high-purity products. Therefore, the problems of the existing monooxygenase can be directly and effectively solved. When diphenyl sulfide is used as a substrate to prepare S-benzosulfoxide, the conversion rate can reach 95% or above, and the yield can reach 99.5%. According to the present invention, a new thought and a new method are provided for industrial production of the optically active sulfoxide.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com