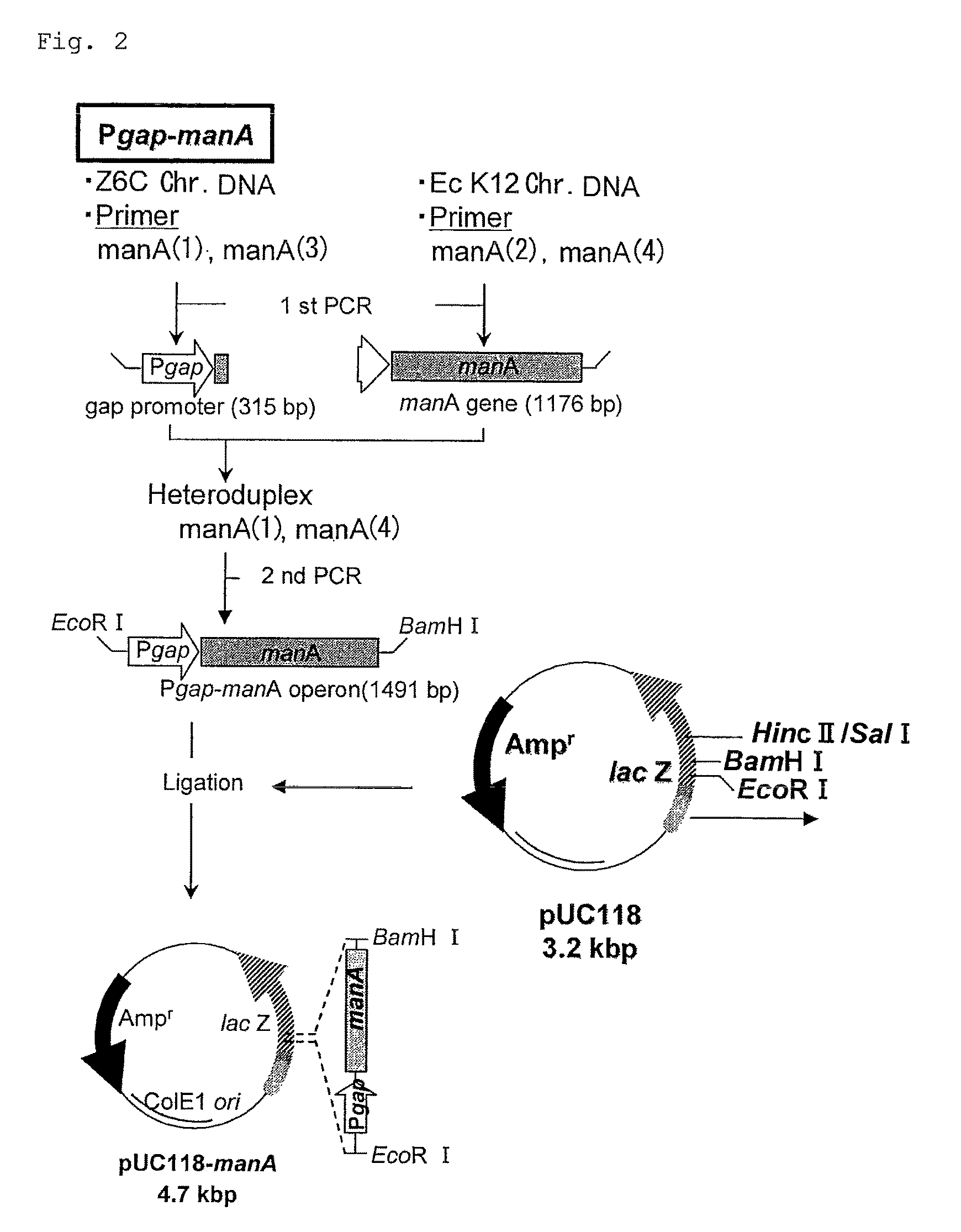
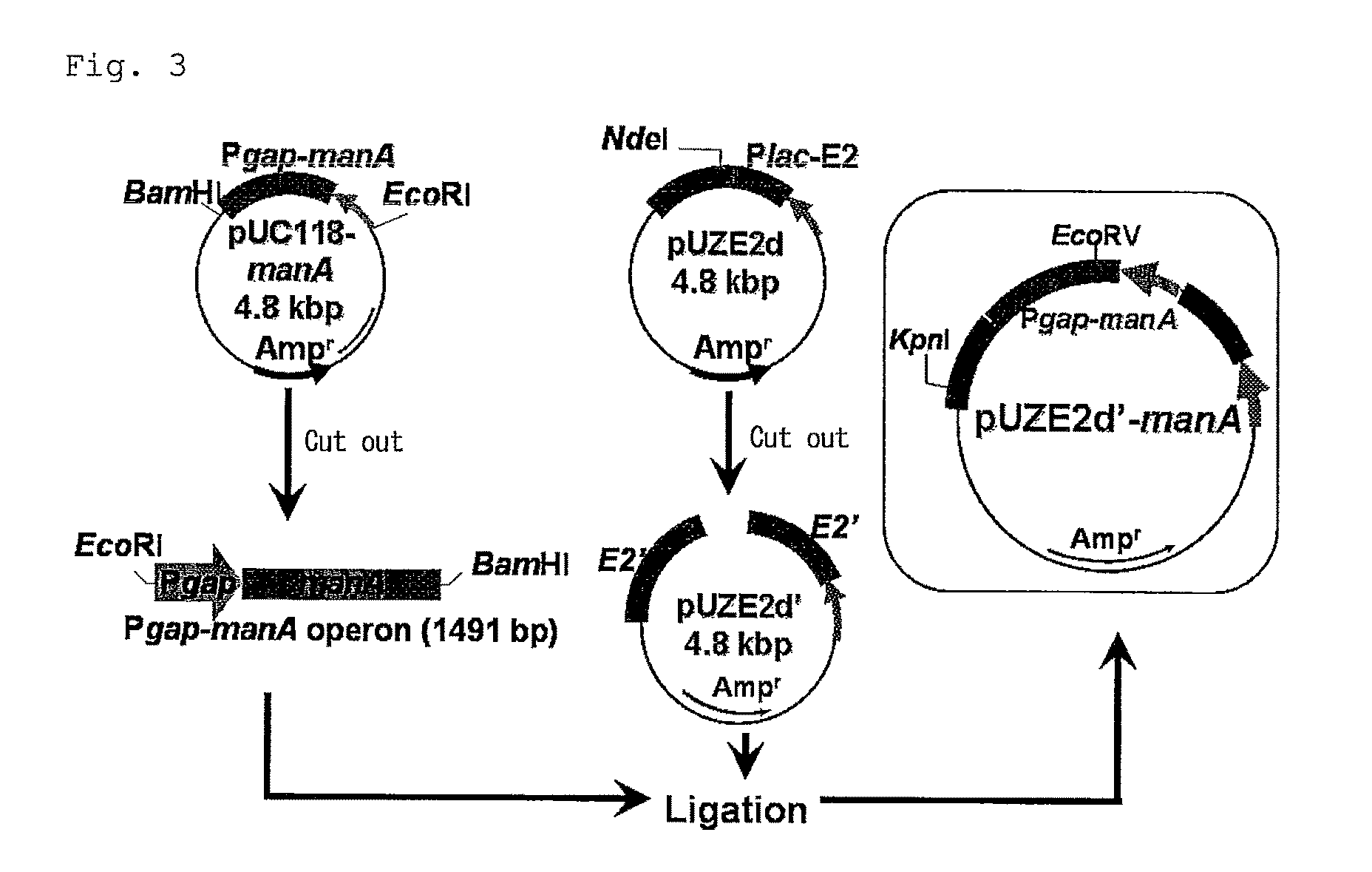
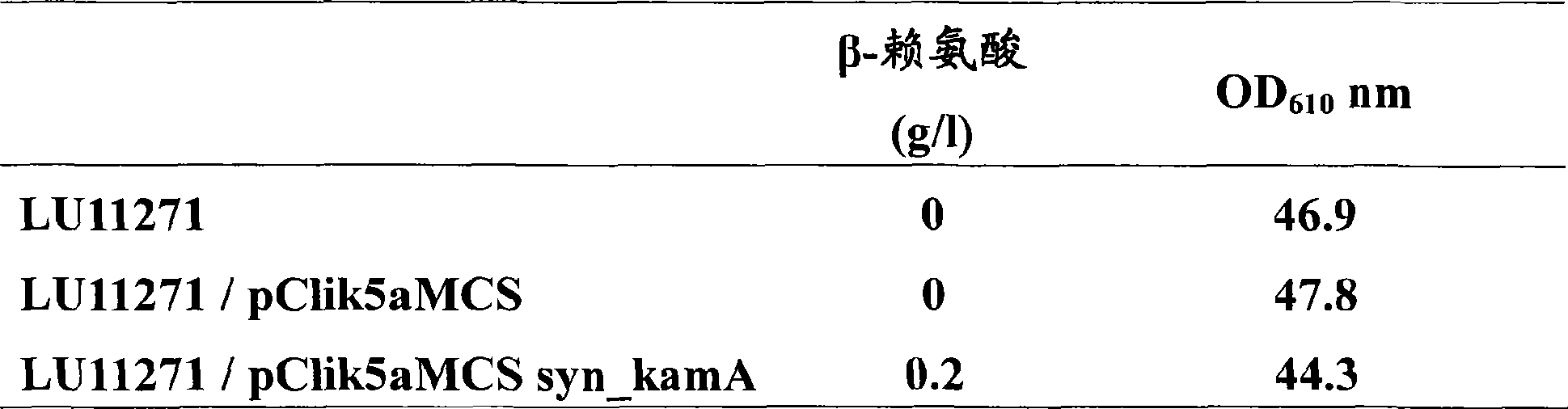
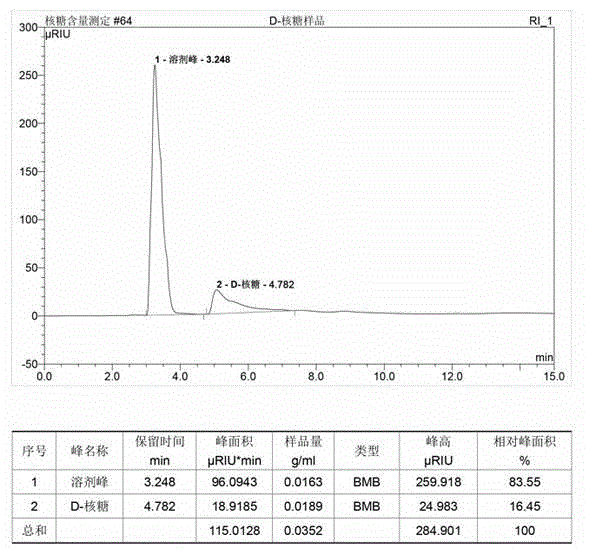
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Transketolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
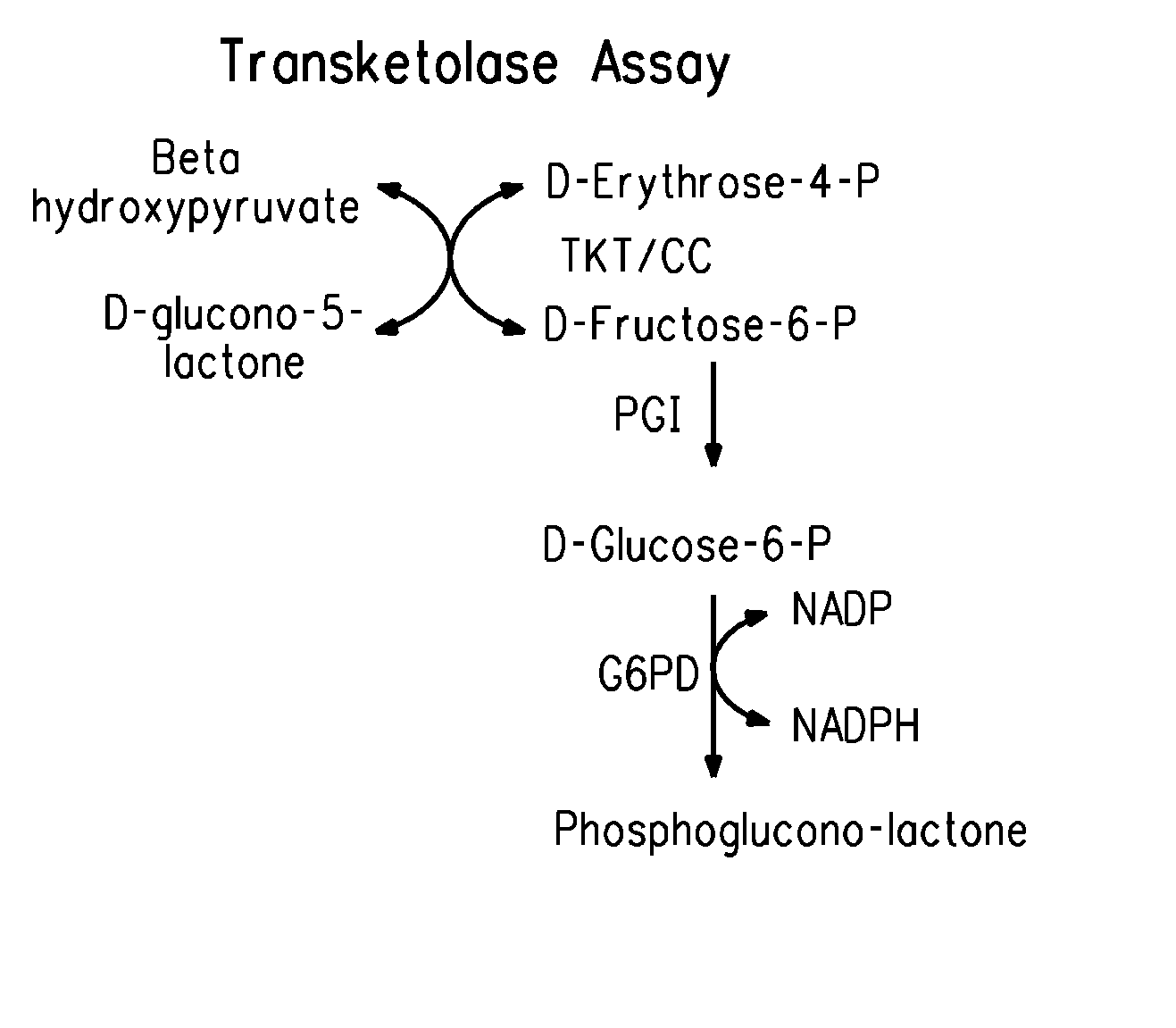
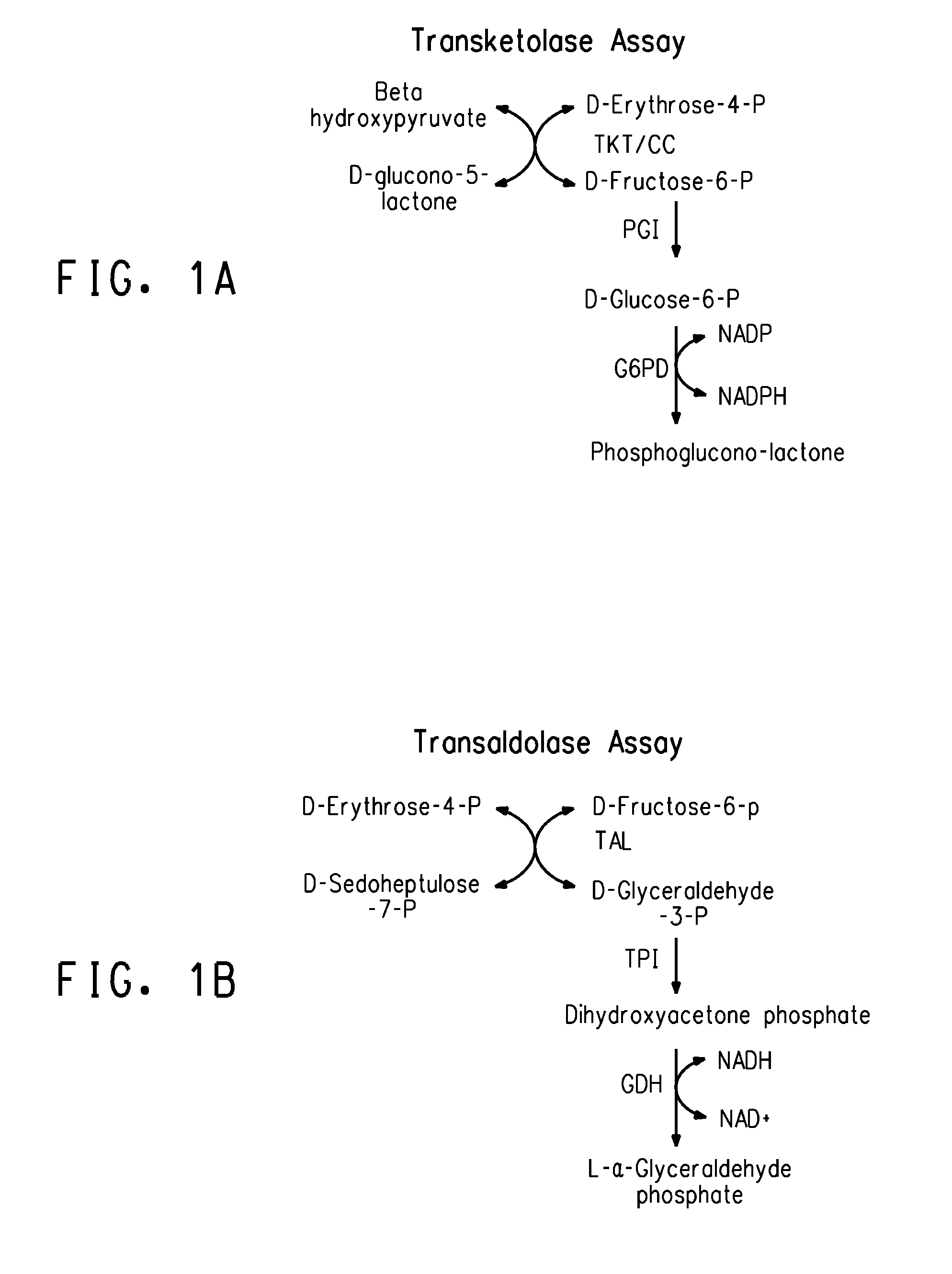
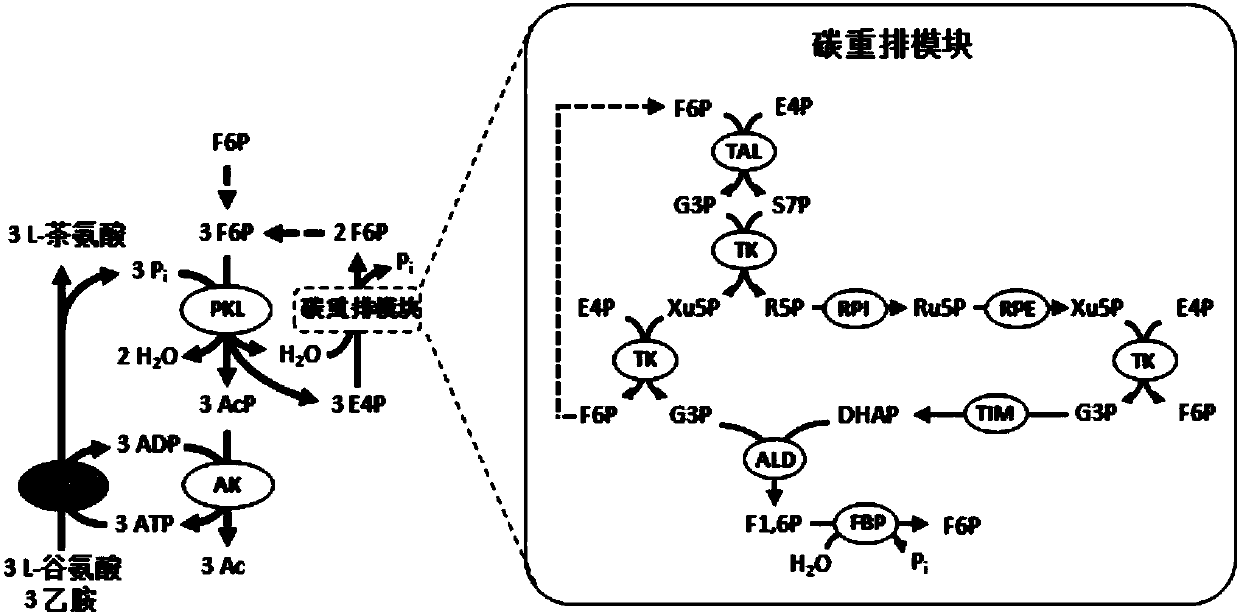
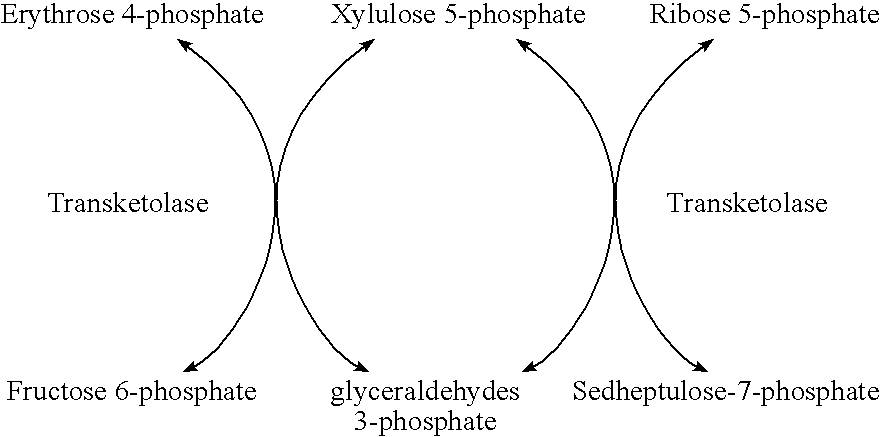
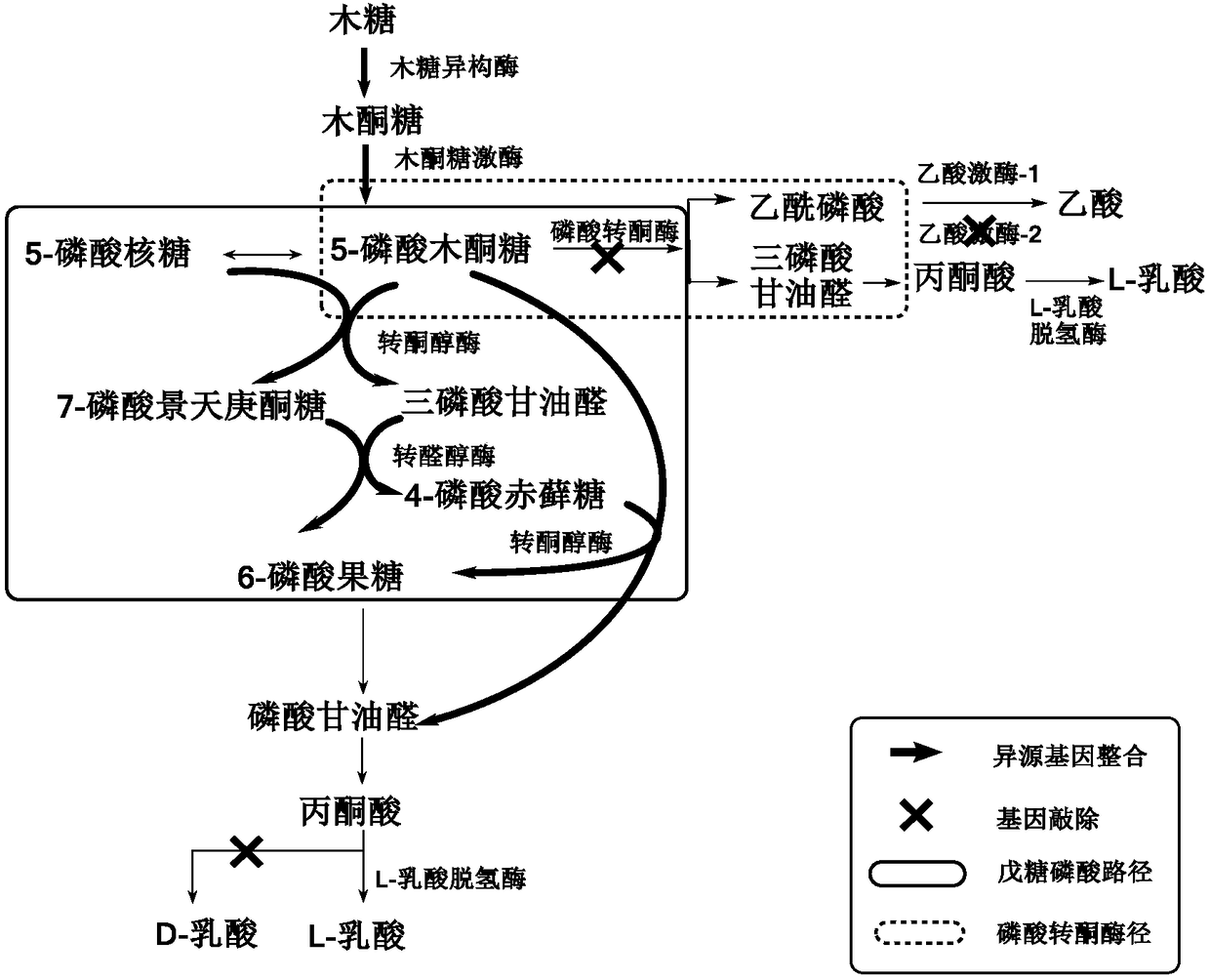
Transketolase encoded by the TKT gene is an enzyme of both the pentose phosphate pathway in all organisms and the Calvin cycle of photosynthesis. It catalyzes two important reactions, which operate in opposite directions in these two pathways. In the first reaction of the non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway, the cofactor thiamine diphosphate accepts a 2-carbon fragment from a 5-carbon ketose (D-xylulose-5-P), then transfers this fragment to a 5-carbon aldose (D-ribose-5-P) to form a 7-carbon ketose (sedoheptulose-7-P). The abstraction of two carbons from D-xylulose-5-P yields the 3-carbon aldose glyceraldehyde-3-P. In the Calvin cycle, transketolase catalyzes the reverse reaction, the conversion of sedoheptulose-7-P and glyceraldehyde-3-P to pentoses, the aldose D-ribose-5-P and the ketose D-xylulose-5-P.
Zymomonas with improved xylose utilization
ActiveUS20090246846A1High expressionImproved xylose utilizationSugar derivativesBacteriaTransketolaseGlyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Gene
Strains of Zymomonas were engineered by introducing a chimeric xylose isomerase gene that contains a mutant promoter of the Z. mobilis glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. The promoter directs increased expression of xylose isomerase, and when the strain is in addition engineered for expression of xylulokinase, transaldolase and transketolase, improved utilization of xylose is obtained.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
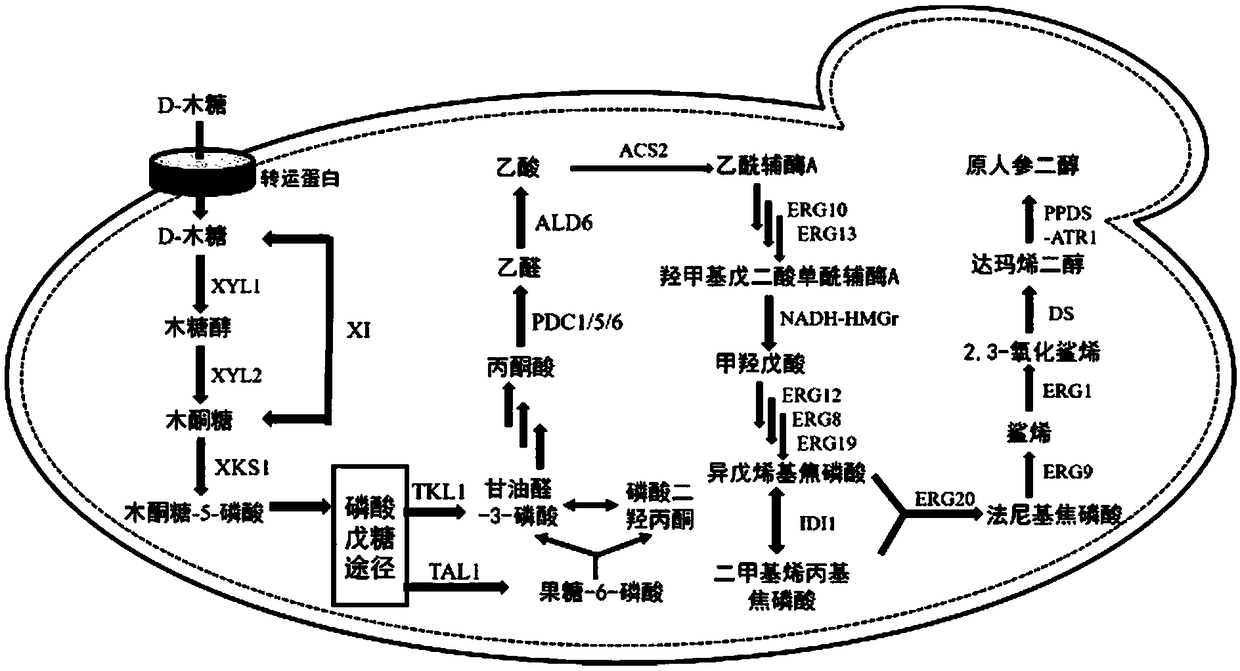
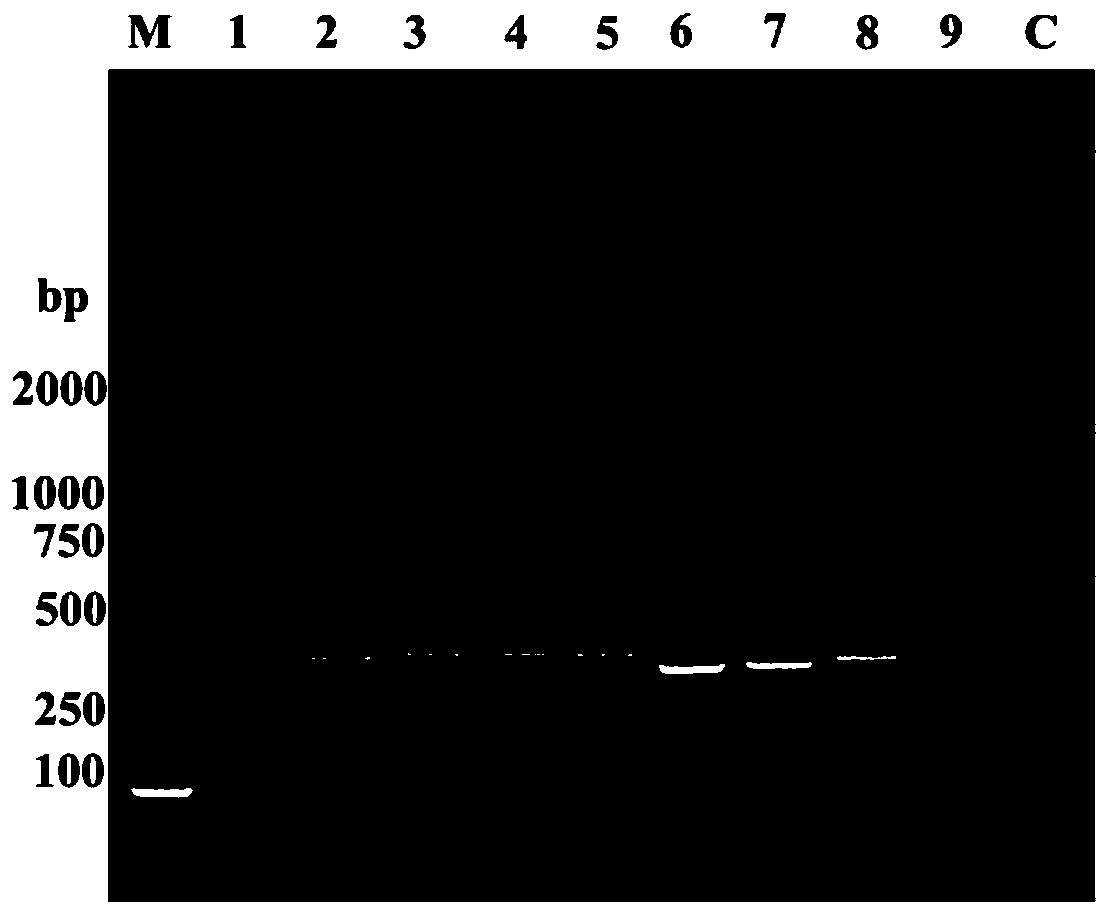
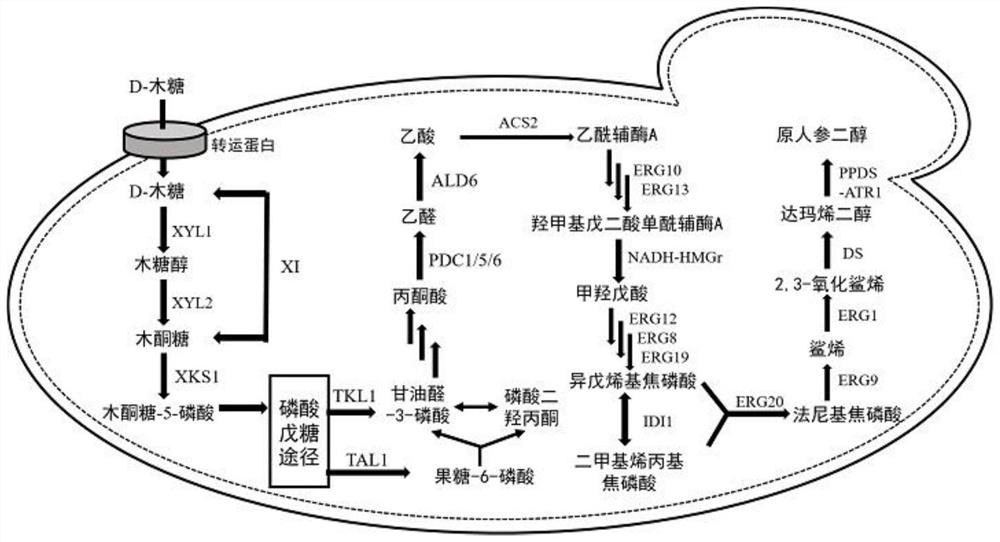
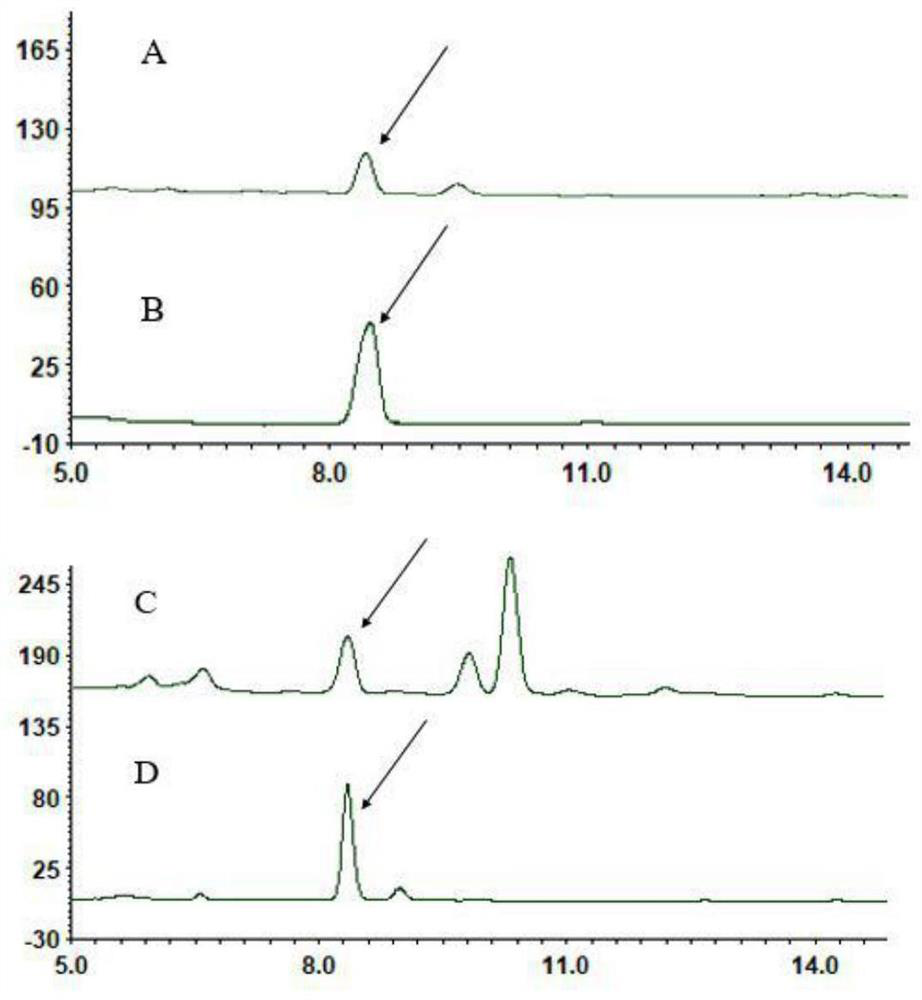
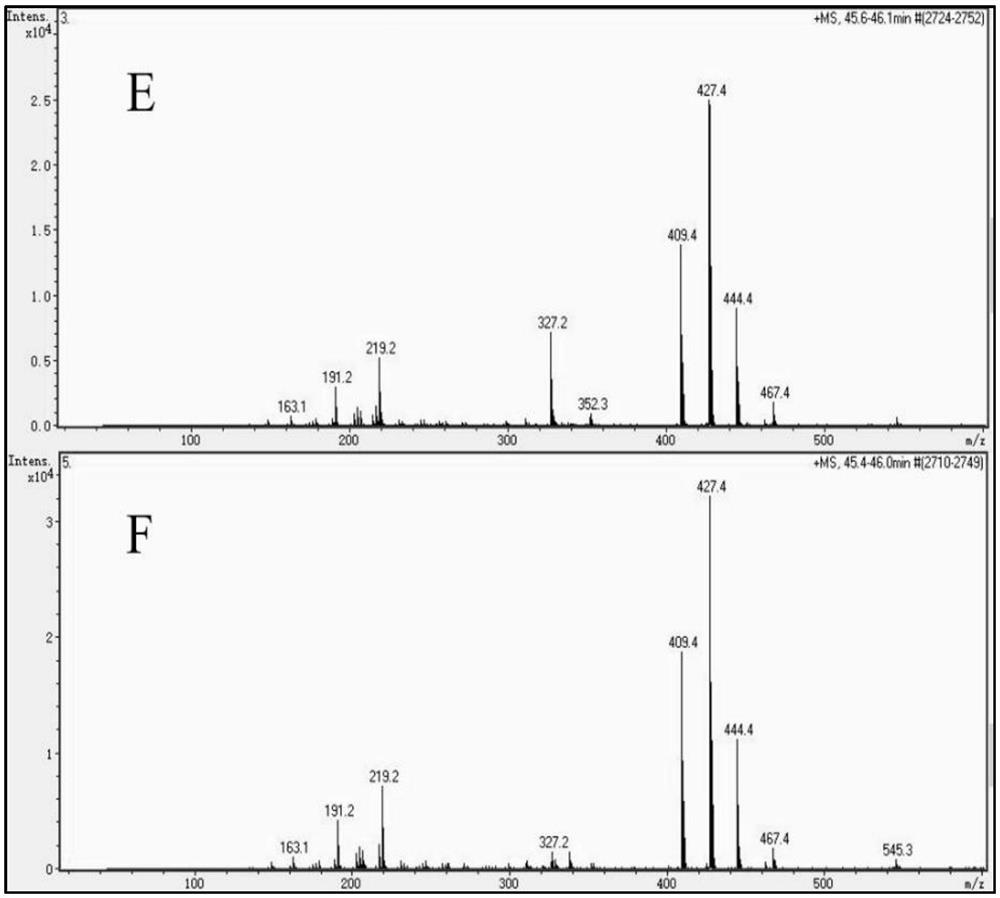
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and construction method
The invention discloses recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol using xylose and a construction method. The construction method comprises the steps of replacing a promoter of a saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 with a promoter PFBA1 by virtue of a homologous recombination method, introducing xylose reductase XYL1 and a xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassette, increasing the activities of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 1, introducing a farnesyl-diphosphate farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, a squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and a dammarenediol synthase gene DS into the recombinant bacteria 1 so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and introducing a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl diphosphatesynthase ERG20 and a protopanoxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 into the recombinant bacteria 2, so as to obtain recombinant bacteria 3. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae, dammarenediol and protopanoxadiol can be artificially synthesized by virtue of xylose.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN103074292AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and a method for producing the L-phenylalanine (Phe) by fermentation and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain C.glutamicum19AF / 99TP capable of being used for highly yielding the L-Phe is obtained in a corynebacterium glutamicum type strain ATCC13032 by carrying out induction expression on the following four genes: a 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase gene, a chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydratase gene which has resistance to feedback inhibition, a transketolase gene and a phosphoenolpyruvic acid synthetase gene. A shikimic acid metabolic pathway of an L-Phe synthetic metabolic pathway is over-expressed in the C.glutamicum ATCC13032; a key enzyme gene of a chorismic acid metabolic pathway enables the yield of the L-Phe to reach 3.47g / L; two enzyme genes which combines an expression center metabolic pathway to improve a precursor enables the highest yield of the L-Phe to reach 4.86g / L; and the original strain ATCC13032 which is used as a contrast strain cannot detect accumulation of the L-Phe in the integral fermenting process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and construction and applicaitons
InactiveCN107012161AHigh final concentrationHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolasePhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum for producing high-yield succinic acid by utilizing straw hydrolysate, and a construction and applications. The method comprises the following steps: (1) knocking out side products acetic acid and lactic acid formation pathway related genes from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032, and introducing anaplerotic pathway phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate carboxylase and phosphopentose pathway transketoaldehydase and transketolase on a strong promoter overexpression chromosome; and introducing xylose transport gene on the chromosome; and (2) expressing pyruvate carboxylase, succinic acid export protein and citrate synthase as well as xylose isomerase and xylulokinase on the corynebacterium glutamicum obtained in the step (1). 98.6gL<-1> of succinic acid can be anaerobically produced after 22.5h by utilizing mixed glucose and xylose in straw hydrolysate, with the yield of 0.98g succinic acid / g total sugar. The final concentration, yield and productivity of succinic acid achieve higher level, and the corynebacterium glutamicum has good industrial potential.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application
The invention provides a chassis system for ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) regeneration and application. The chassis system for ATP regeneration comprises the following five enzymes: alpha-glucan phosphorylase, glucophosphomutase, phosphoglucose Isomerase, phosphoketolase and acetokinase. In addition, the chassis system can further comprise the following seven enzymes: transaldolase, transketolase,ribose-5-phosphate isomerase, ribulose-3 epimerase, triosephosphate isomerase, fructose-bisphosphate aldolase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. The chassis system can be coupled to an enzymic catalyticreaction needing ATP, utilizes starch or maltodextrin as energy, is not added with any coenzyme, can efficiently regenerate the ATP at low cost through a one-pot reaction and is an economical, highlyefficient, stable and sustainable ATP regeneration system.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for producing high-activity and high-purity rifamycin SV
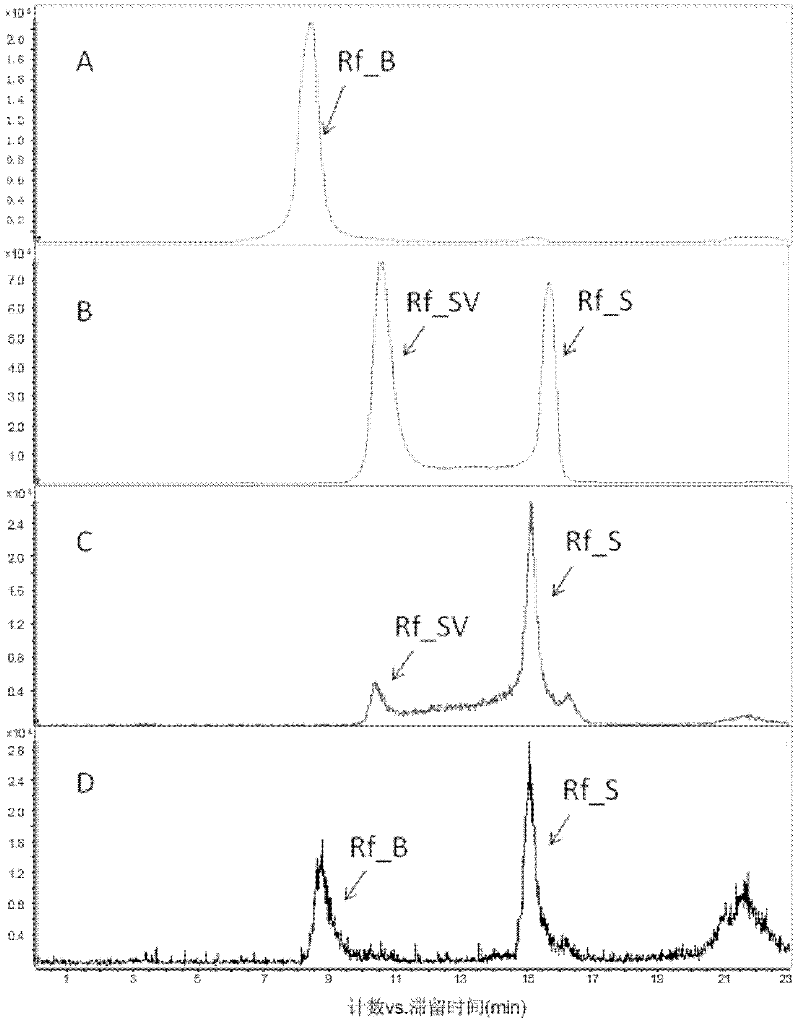
The invention relates to a method for producing high-activity and high-purity rifamyicn SV(Rf_SV). The invention particularly relates to the use of a cytochrome P450 gene or a transketolase gene or proteins coded by the cytochrome P450 gene and the transketolase gene in regulation of the conversion of rifamyicn SV into rifamyicn B. The method produces the high-activity and high-purity rifamyicn SV by deactivating two or one of key enzymes (Rif15 and Rif16) required for participating in conversion from Rf_SV into Rf_B in a rifamyicn synthesis process in a rifamyicn B (Rf_B) producing strain.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
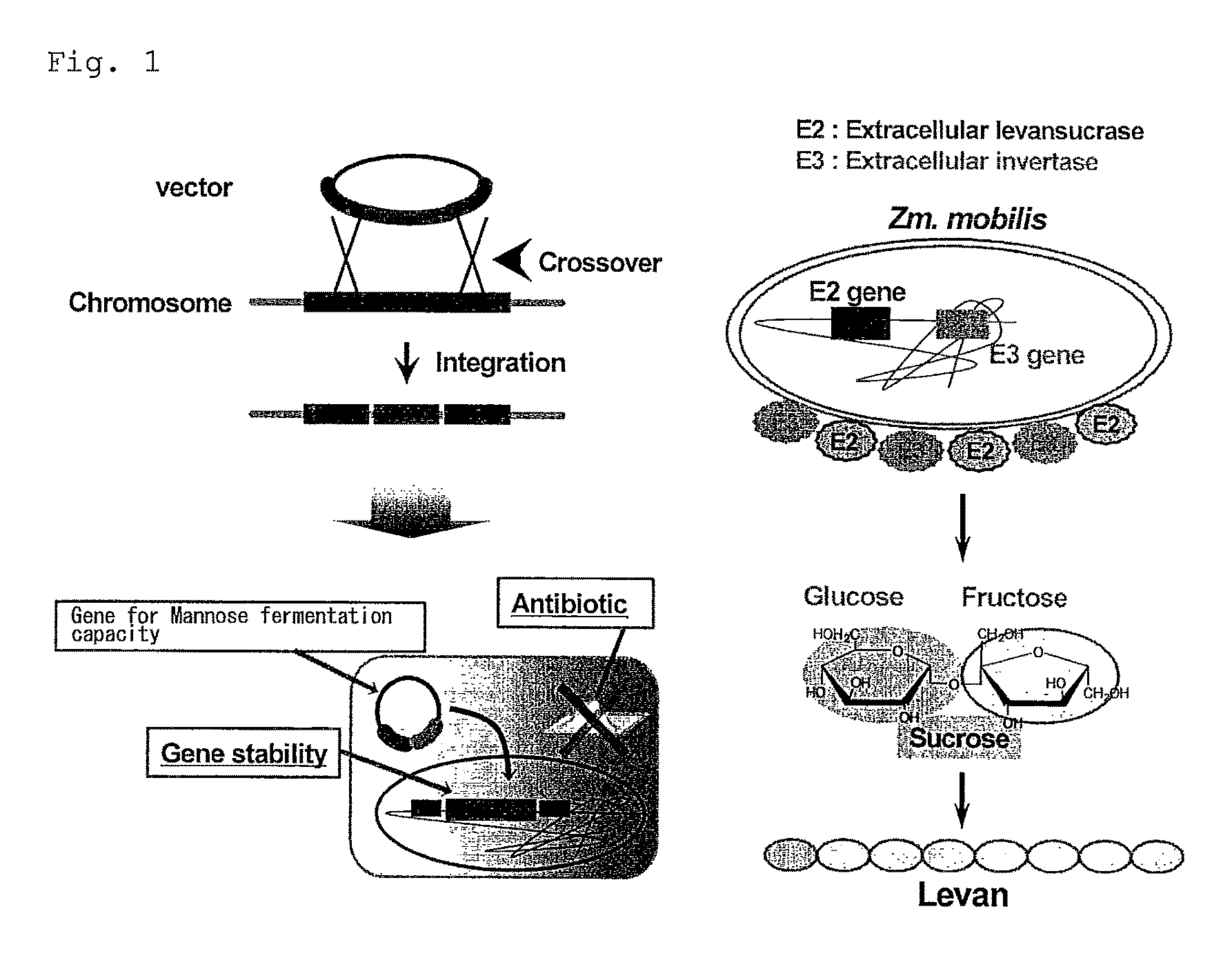
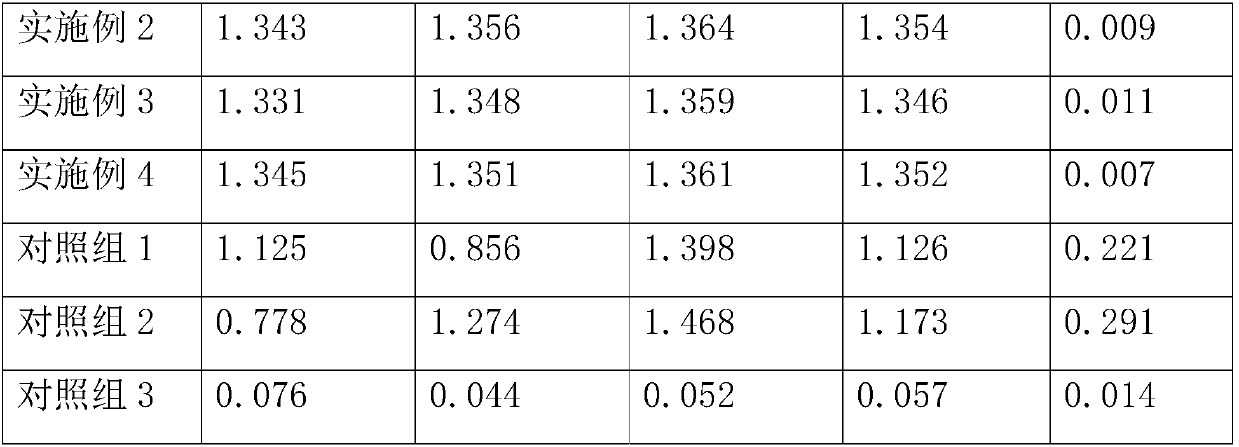
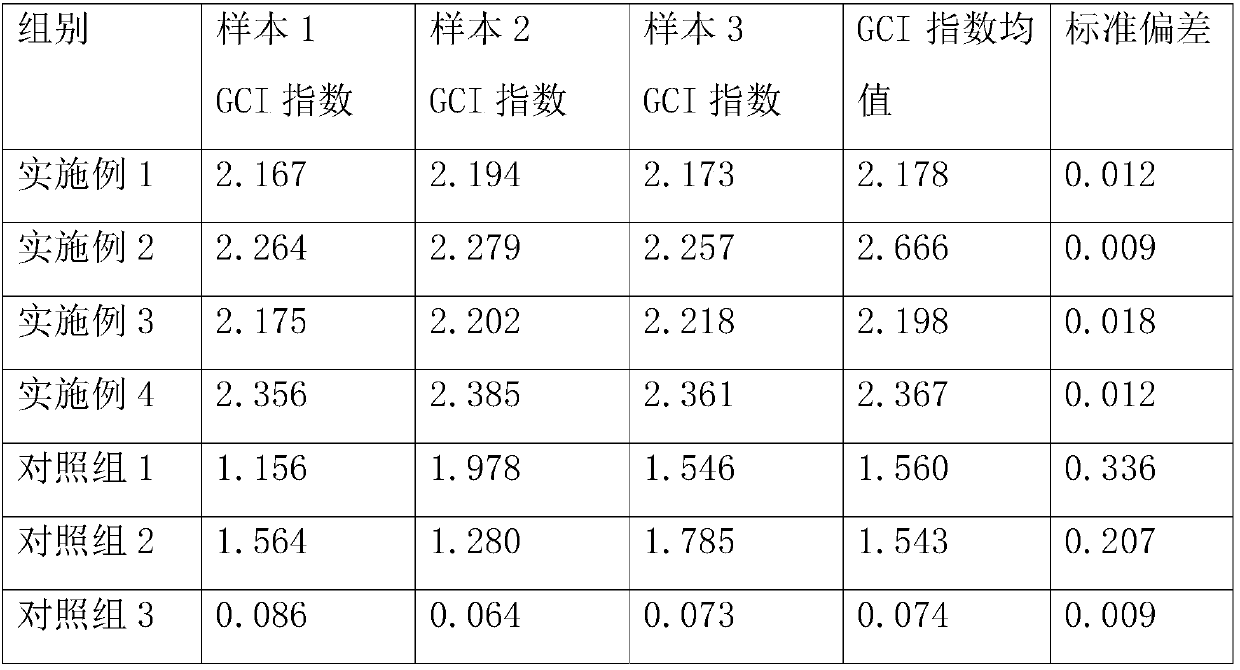
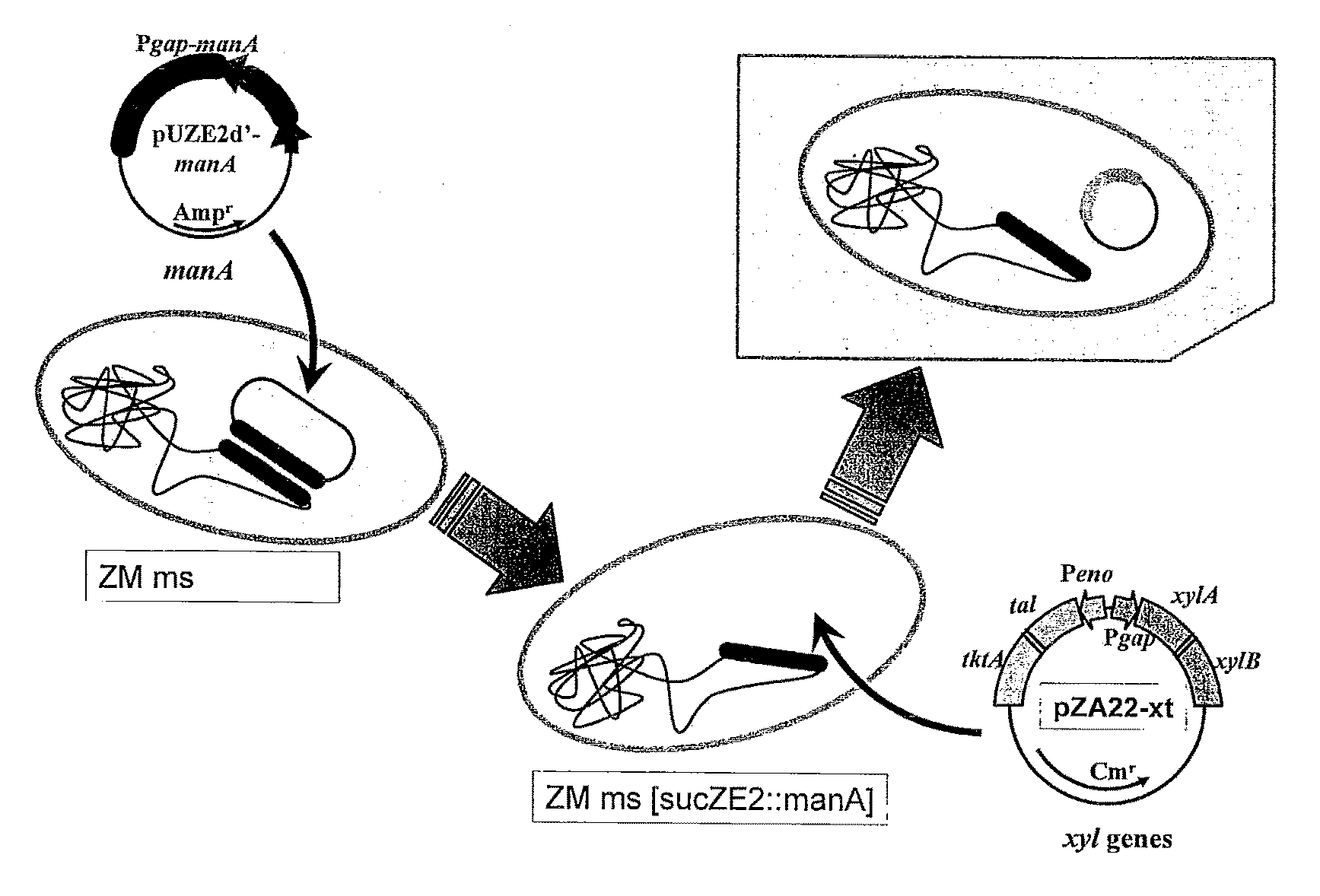
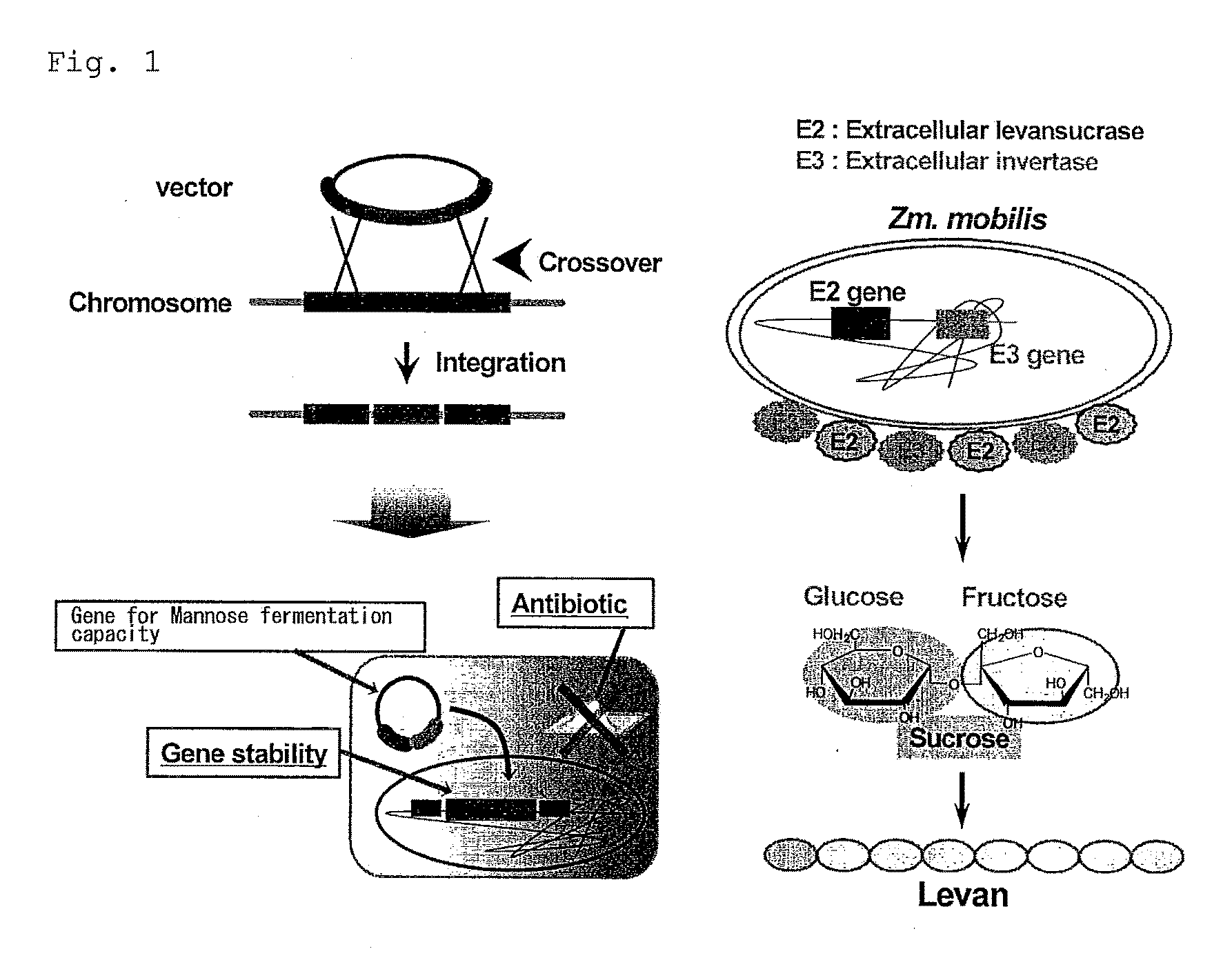
Bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, and method for production of bioethanol using the bacterium
InactiveUS8383377B2Strong glucose fermentation capacityImprove fermentation performanceBacteriaBiofuelsTransketolaseEscherichia coli
The object is to develop a bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, which can ferment a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type or lignocellulose-type biomass resource to produce ethanol, and to construct an energy-saving high-efficiency bioethanol conversion process. Thus, disclosed is Zymomonas mobilis bacterium which is prepared by integrating a gene encoding a phosphomannose isomerase derived from Escharichia coli into a levansucrase gene located on the chromosome by the double cross-over by means of a homologous recombsination method, and then introducing recombinant DNA prepared by binding a DNA fragment containing genes encoding a xylose isomerase, a xylulokinase, a transaldolase and a transketolase, respectively, all derived from Escherichia coli to a vector. Also disclosed is a method for producing ethanol by continuously fermenting a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type biomass resource in a system on which the Zymomonas mobilis bacterium is immobilized.
Owner:TOTTORI UNIVERSITY
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveCN101400799AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diaminopimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF SE
Bacillus subtilis and method for fermentation production of D- ribose
ActiveCN103146595APotential for industrial applicationGood genetic stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTransketolase
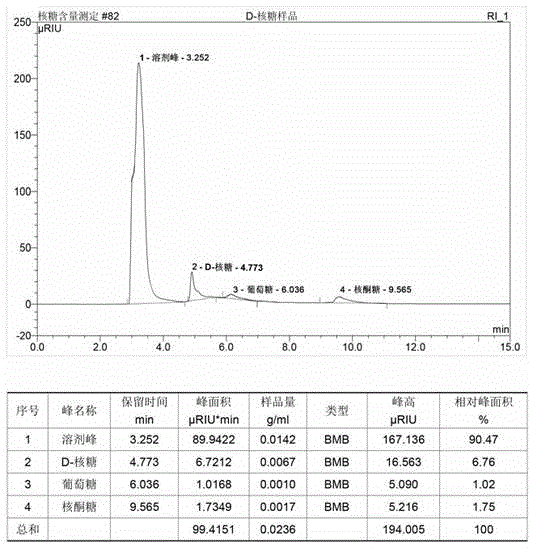
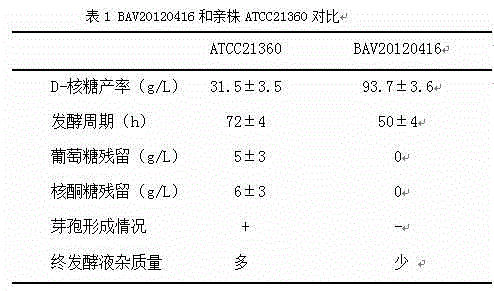
The invention discloses a bacillus subtilis BAV20120416 bacterial strain and a method for fermentation production of a D- ribose by the bacterial strain. The bacterial strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on April, 16th in 2012. The preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC NO.6013. The bacterial strain is a bacillus subtilis transketolase deletion mutation strain, has the advantages that hereditary stability is good, spores are difficult to generate and the like, and is capable of accumulating more than 90g / L of the D-ribose in a fermentation medium with glucose and corn steep liquor as main raw materials. The D-ribose accumulated by the bacterial strain is about third more than that accumulated by a parent strain of the bacterial strain, wherein the parent strain is bacillus subtilis ATCC21360. The fermentation time is short and generally controlled to be about 50 hours which is one-third lower than the time in the prior art. Particularly, impurities are few. Residual sugar of final fermentation liquid is reduced to 0. The bacterial strain is particularly applicable to the requirements for medicine production.
Owner:SHANDONG JINYANG PHARMA +1
Process for the production of beta-lysine
InactiveUS20090029425A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseTransketolase
Process for the production of -lysine by constructing a recombinant microorganism which has a deregulated lysine 2,3-aminomutase gene and at least one deregulated gene selected from the group (i) which consists of aspartokinase, aspartatesemialdehyde dehydrogenase, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydrodipicolinate reductase, tetrahydrodipicolinate succinylase, succinyl-amino-ketopimelate transaminase, succinyl-diamino-pimelate desuccinylase, diaminopimelate epimerase, diamino-pimelate dehydrogenase, arginyl-tRNA synthetase, diaminopimelate decarboxylase, pyruvate carboxylase, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, transketolase, transaldolase, 6-phosphogluconolactonase, fructose 1,6-biphosphatase, homoserine dehydrogenase, phophoenolpyruvate carboxykinase, succinyl-CoA synthetase, methylmalonyl-CoA mutase, provided that if aspartokinase is deregulated as gene (i) at least a second gene (i) other than aspartokinase has to be deregulated, and cultivating said microorganism.
Owner:BASF AG
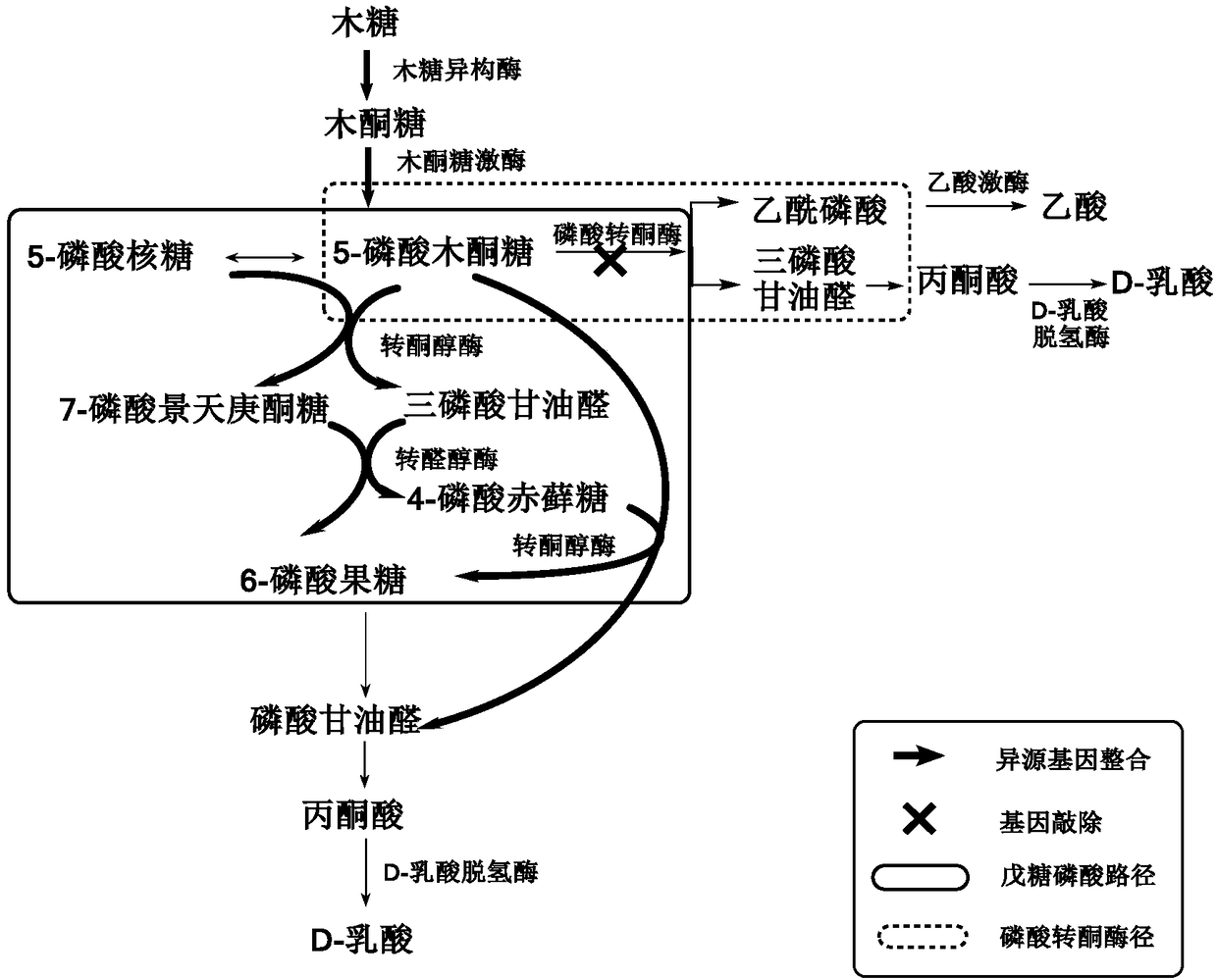
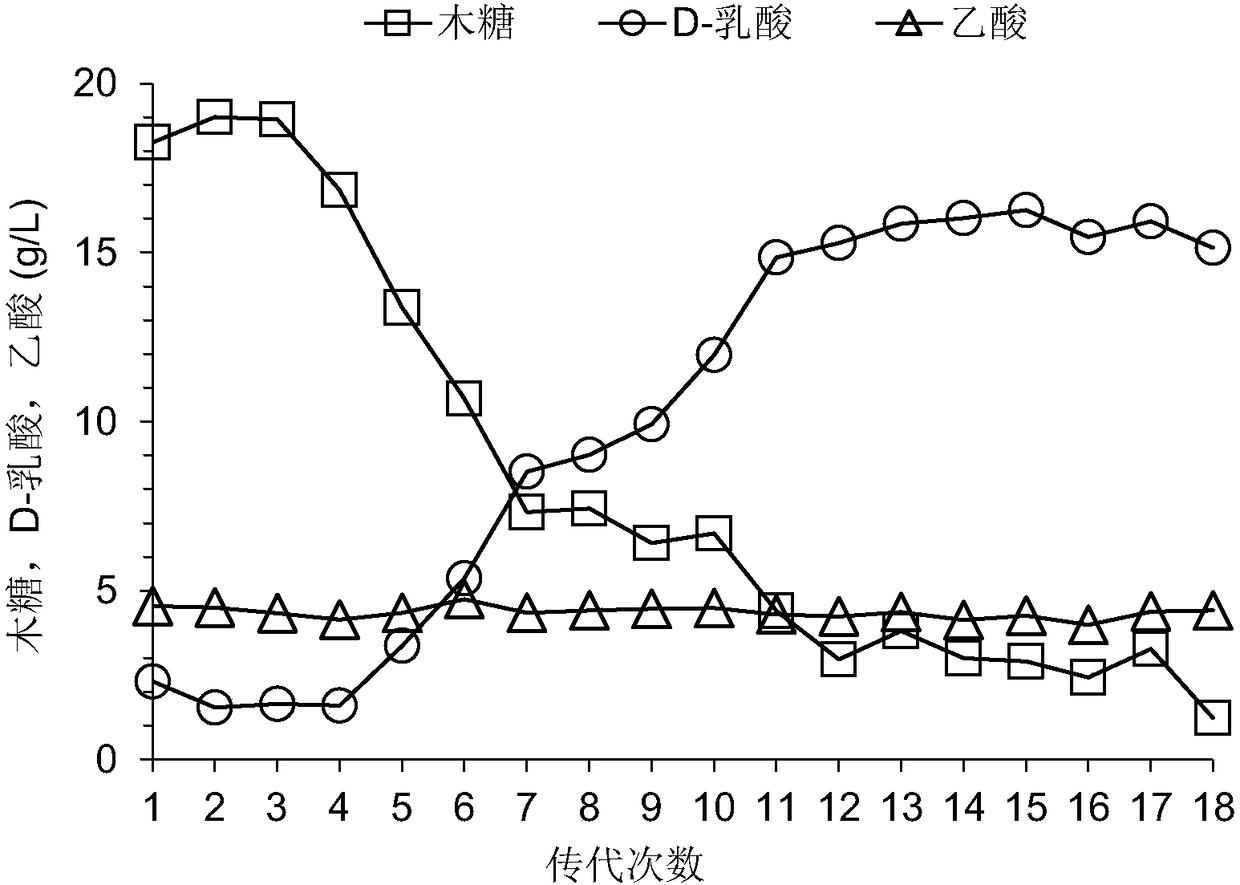
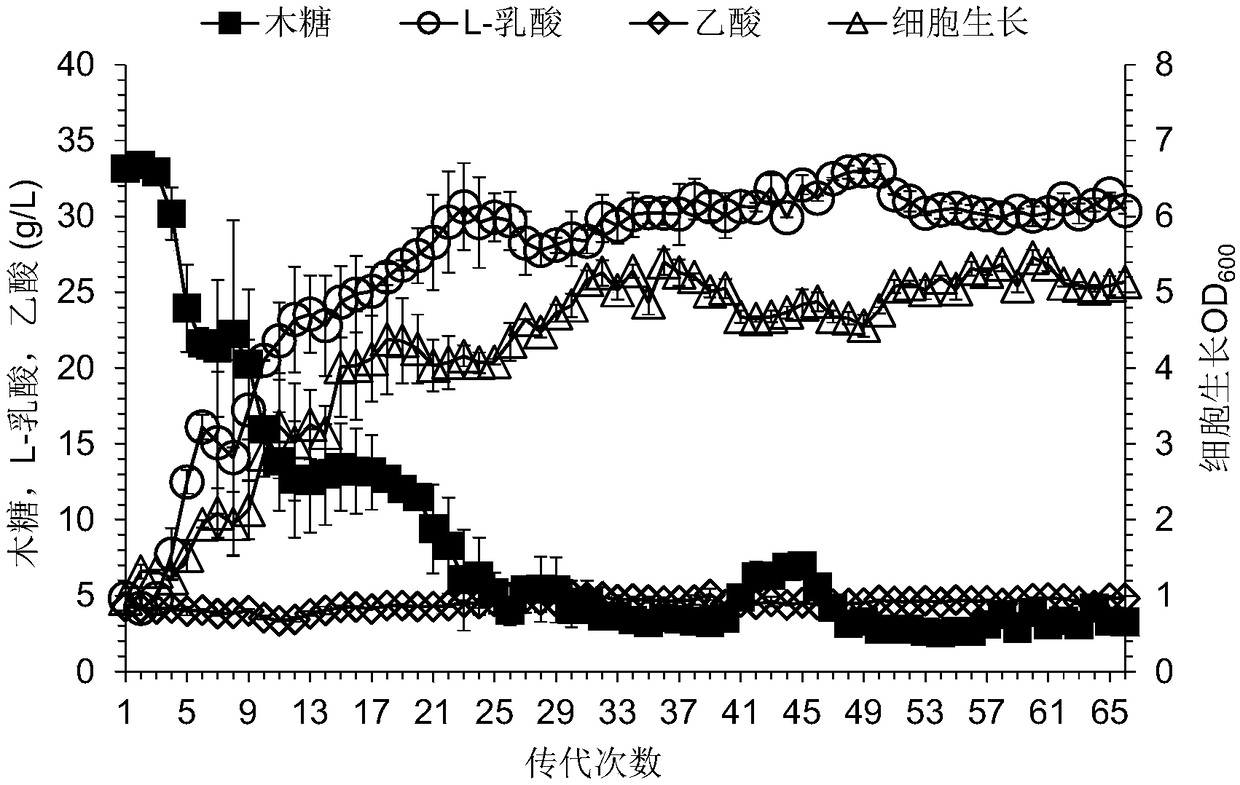
Building method of pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 for producing D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose
The invention discloses a building method of pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 for producing D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose, and belongs to the field of gene engineering. The method comprises the following building steps of integrating heterogenous xylose isomerase, xylulokinase, transketolase and transaldolase encoding genes onto pediococcus acidilactici ZP26 (with the preservationnumber being CGMCC NO.8665) genomes by using a thermosensitive knock-out system; knocking out phosphotransferase encoding genes so as to block the generation of byproducts of acetic acids; the capability of the engineering strain for co-fermenting glucose and xylose is obviously improved through an adaptive domestication strategy. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the building of the xylose metabolism path is successfully realized for the first time; the engineering strain for producing optical pure D-lactic acid by co-fermenting glucose and xylose at high efficiency is obtained, is named as P.acidilactici ZY15, and has the preservation number of CGMCC NO.13612.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
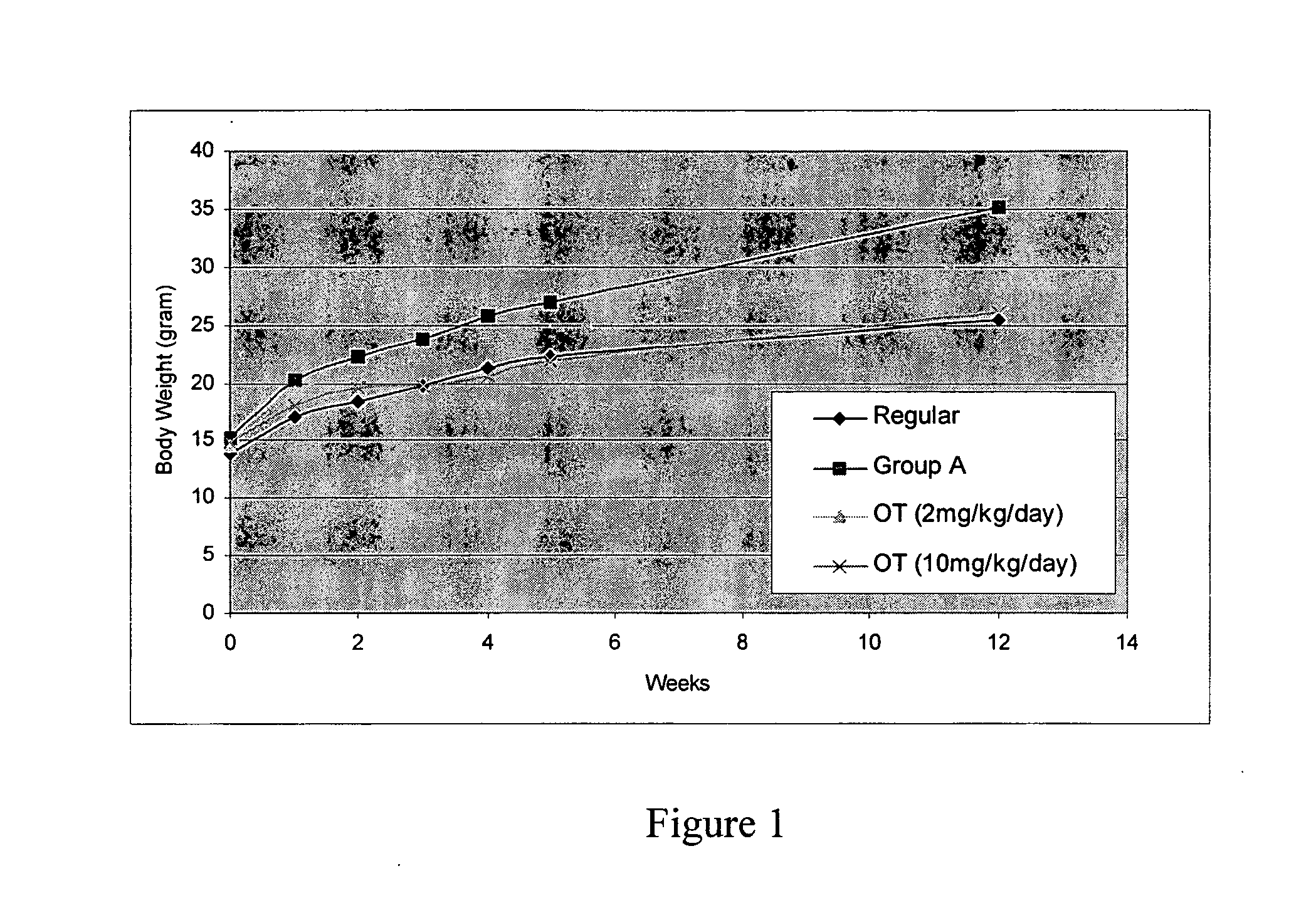
Method for preventing or treating obesity by modulating the activities of the pentose phosphate patway
Method for preventing or treating overweight or obesity, the method comprising administering to a patient in need thereof an antagonist that inhibits gene expression or activity of an enzyme that is involved or related to the pentose phosphate pathway. Preferably, the enzyme is a transketolase, and the antagonist is an antibody, an antisense molecule, an siRNA molecule, a molecule for forming a triplex nucleic acid molecule with the enzyme-encoding polynucleotide. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, and method for screening a substance that inhibits gene expression of a PPP enzyme or its function.
Owner:MINKON BIOTECH
Preparation method of 4-phosphoric acid erythrose
ActiveCN101875951ASimplify separation and purification stepsNot easy to infect bacteriaFermentationTransketolaseFructose phosphate
The invention relates to a preparation method of 4-phosphoric acid erythrose, comprising the following steps: immobilizing heat-resistant transketolase at the temperature of 55-65 DEG C; and then taking 6-fructose phosphate and 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate as raw materials to prepare the 4-phosphoric acid erythrose by enzymatic reaction. In the preparation method, the heat-resistant and specifically transformed transketolase of the 4-phosphoric acid erythrose is prepared by adopting a molecular biology technology, and the 6-fructose phosphate and the 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate are taken as the raw materials to efficiently prepare the 4-phosphoric acid erythrose by adopting an immobilized enzyme technology. The preparation method is simple and practical.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Broad host range plasmid carrying xylose metabolism related gene and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101475955AEfficient productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTransketolase
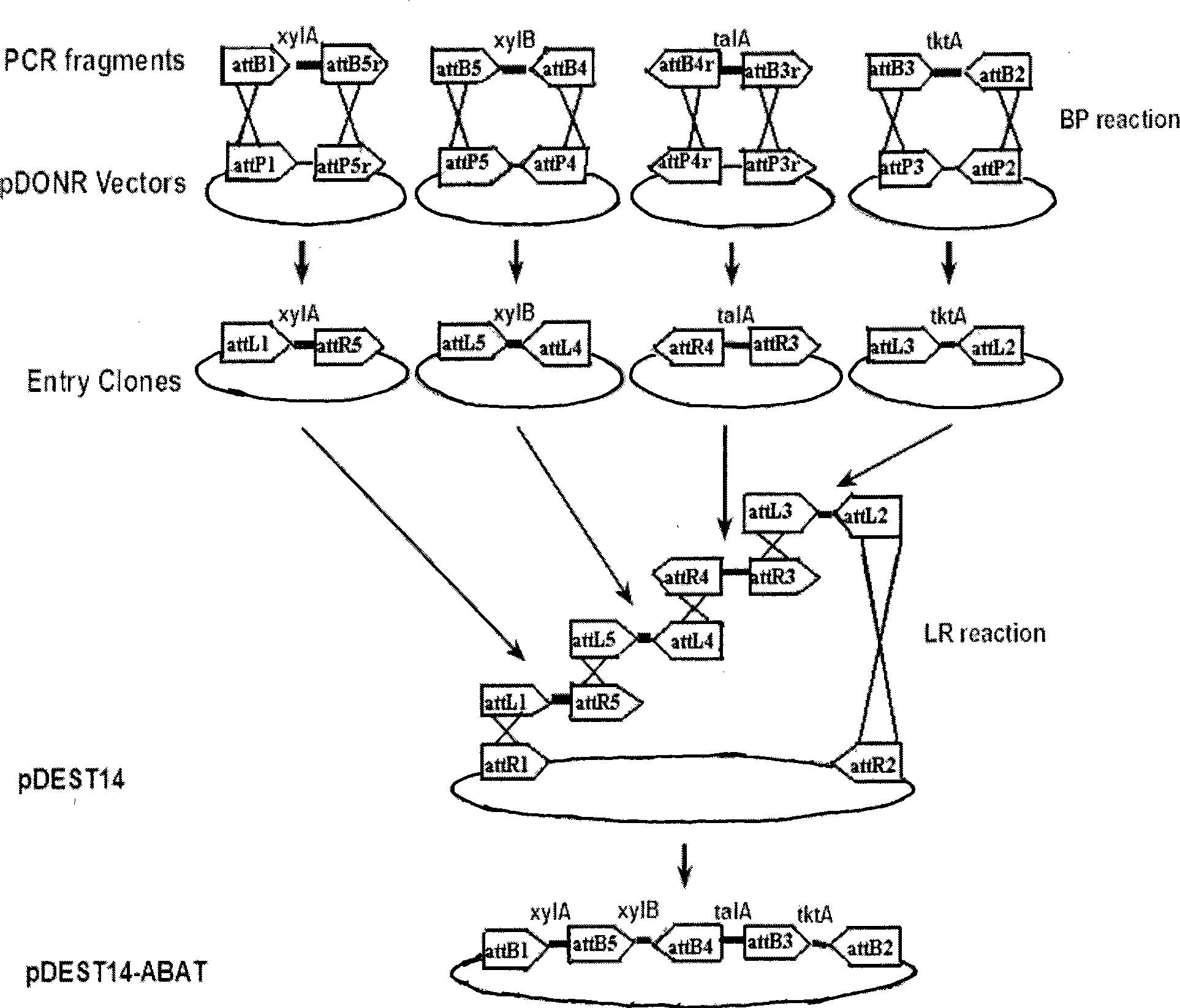
The invention discloses a wide host plasmid carrying xylose metabolism related genes and construction method thereof, belonging to the field of molecular biology techniques. The plasmid contains four xylose metabolism related enzyme genes, xylose isomerase (xylA), xylulokinase (xylB), transaldolase (talA) and transketolase (tktA), which are derived from E.coli DH5alpaha strain. The plasmid construction method uses the Gateway technology, to respectively design specific primers of four target genes xylA, xylB, talA and tktA, takes the E.coli DH5alpaha strain as the origin stain of the target genes to amplify the corresponding gene through the PCR; the PCR product performs BP recombination with the corresponding pDONR vector, and then the obtained Entry clones perform LR recombination with the pDEST14, to obtain the pDEST14-ABAT plasmid; the pDEST14-ABAT plasmid is connected to the Xha I single zyme cutting vector pBBR1MCS2 through the Xba I and Nhe I double zyme cutting product to obtained the recombinant plasmid pBBR1MCS2-ABAT. The superior strain shifted in the plasmid can greatly reduce production costs of cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
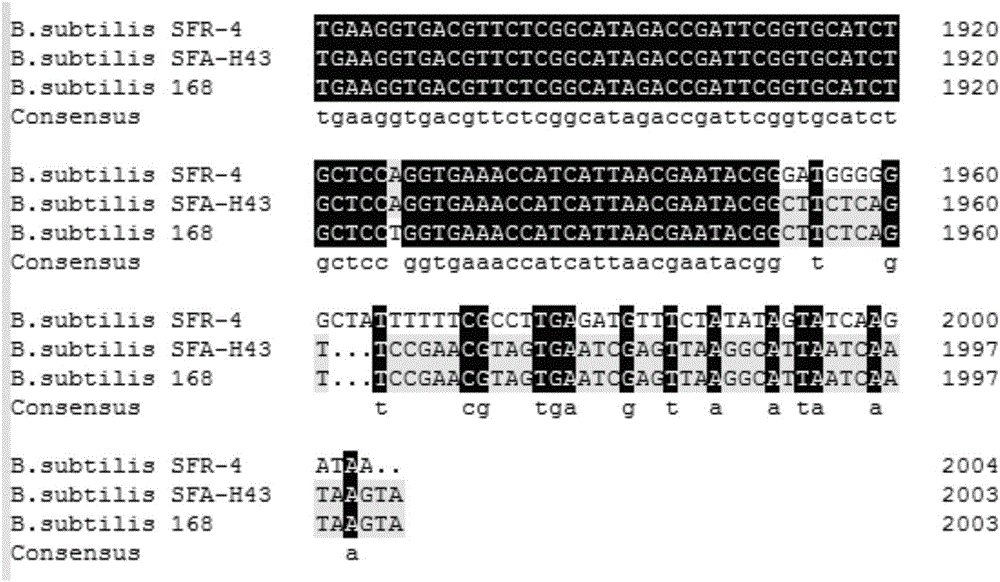
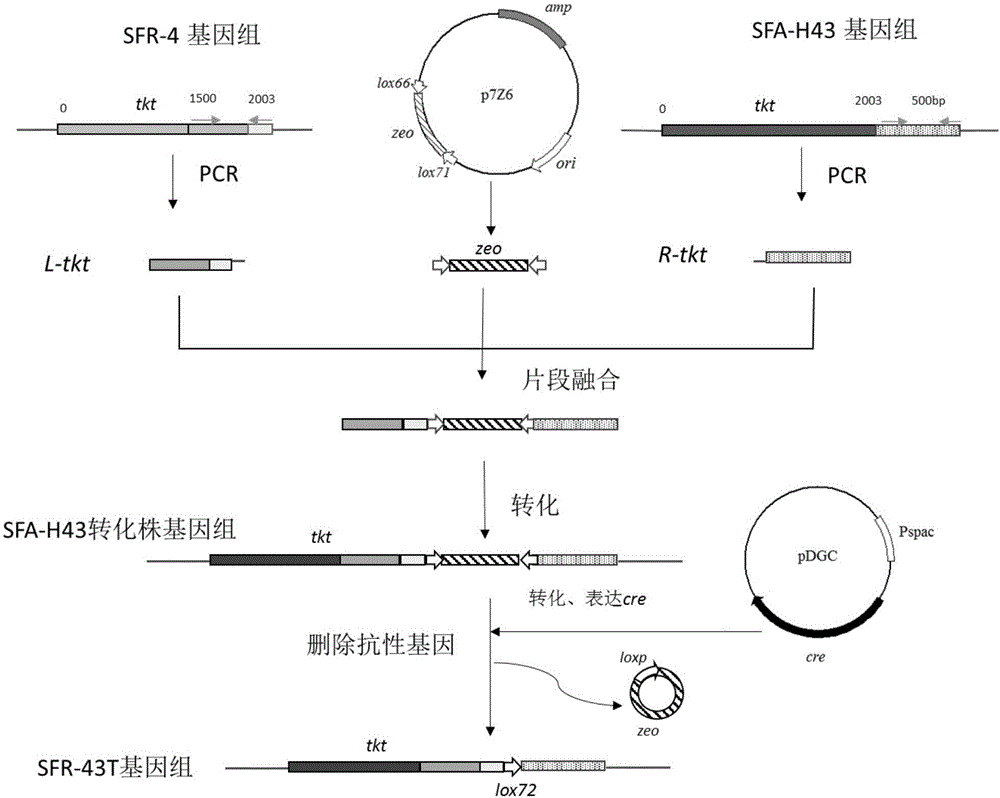
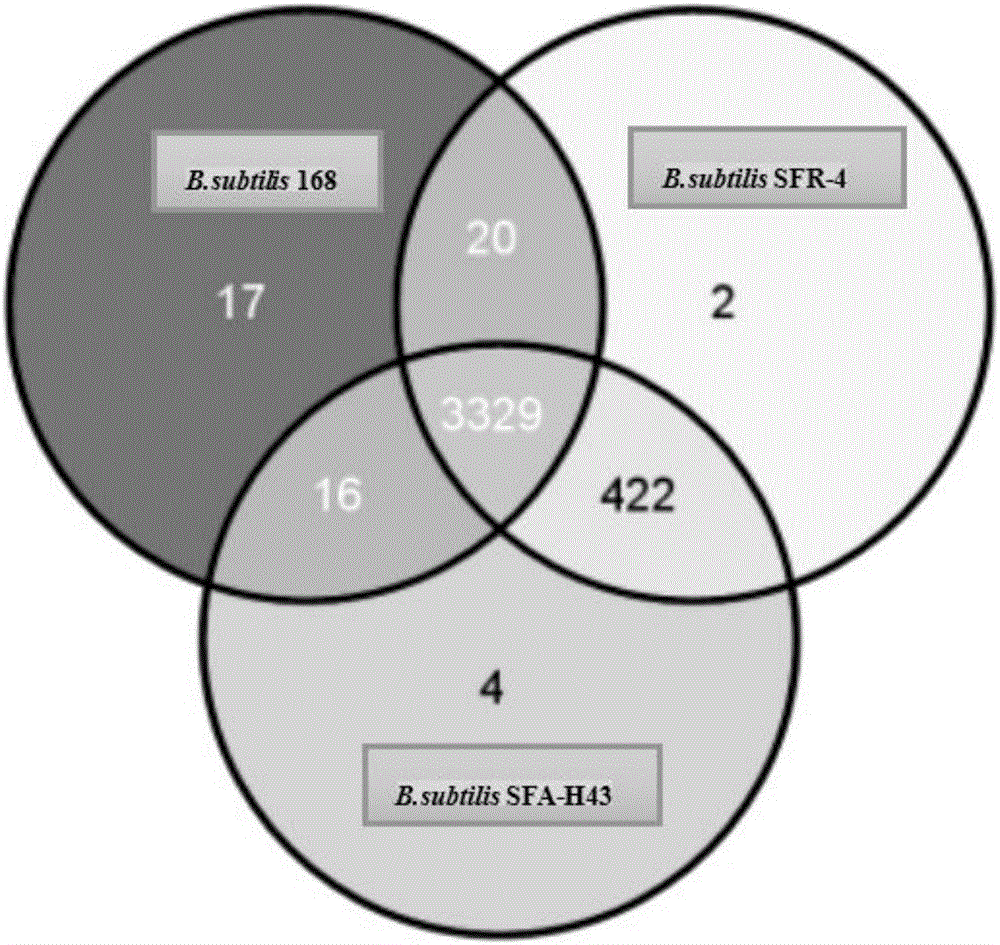
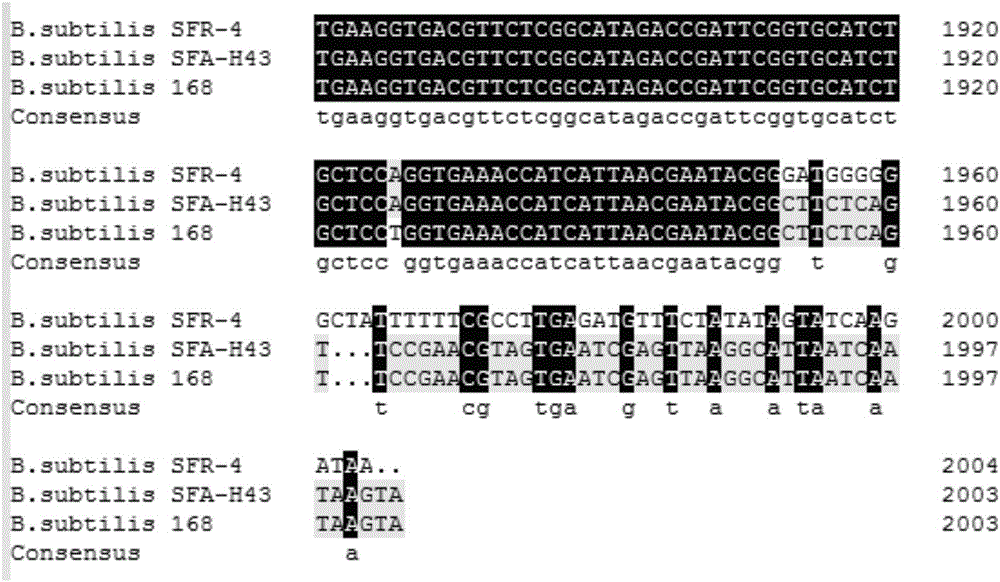
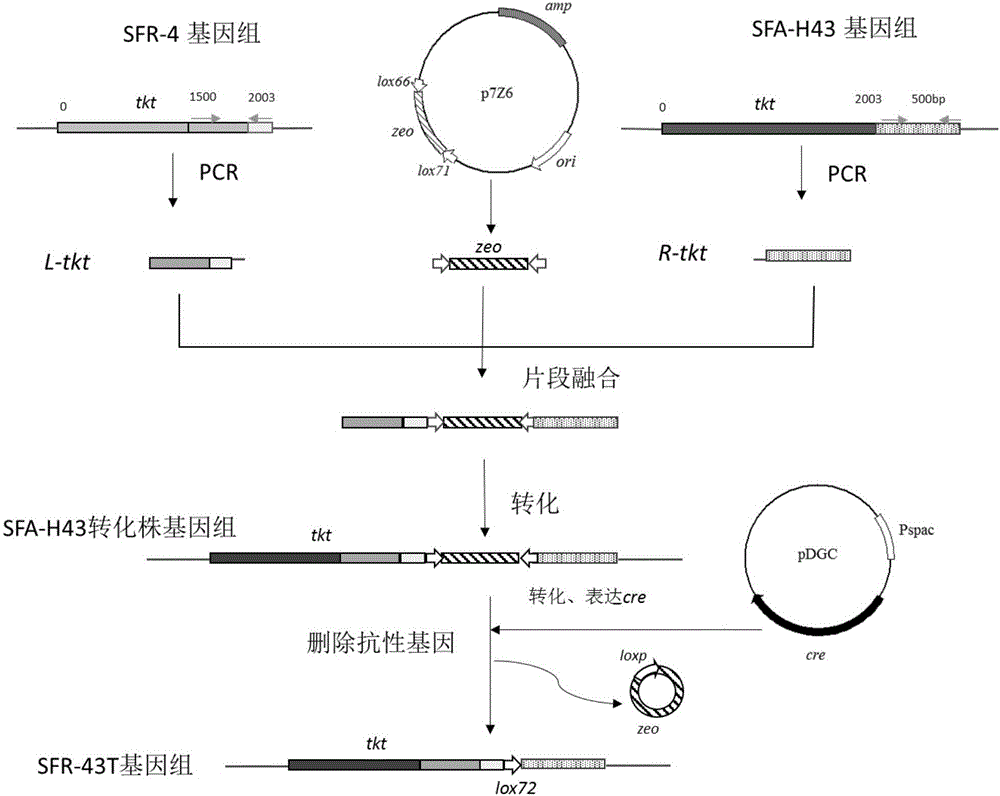
Bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria and application thereof
PendingCN106399218AImprove performanceImprove stress resistanceBacteriaTransferasesTransketolaseNucleotide
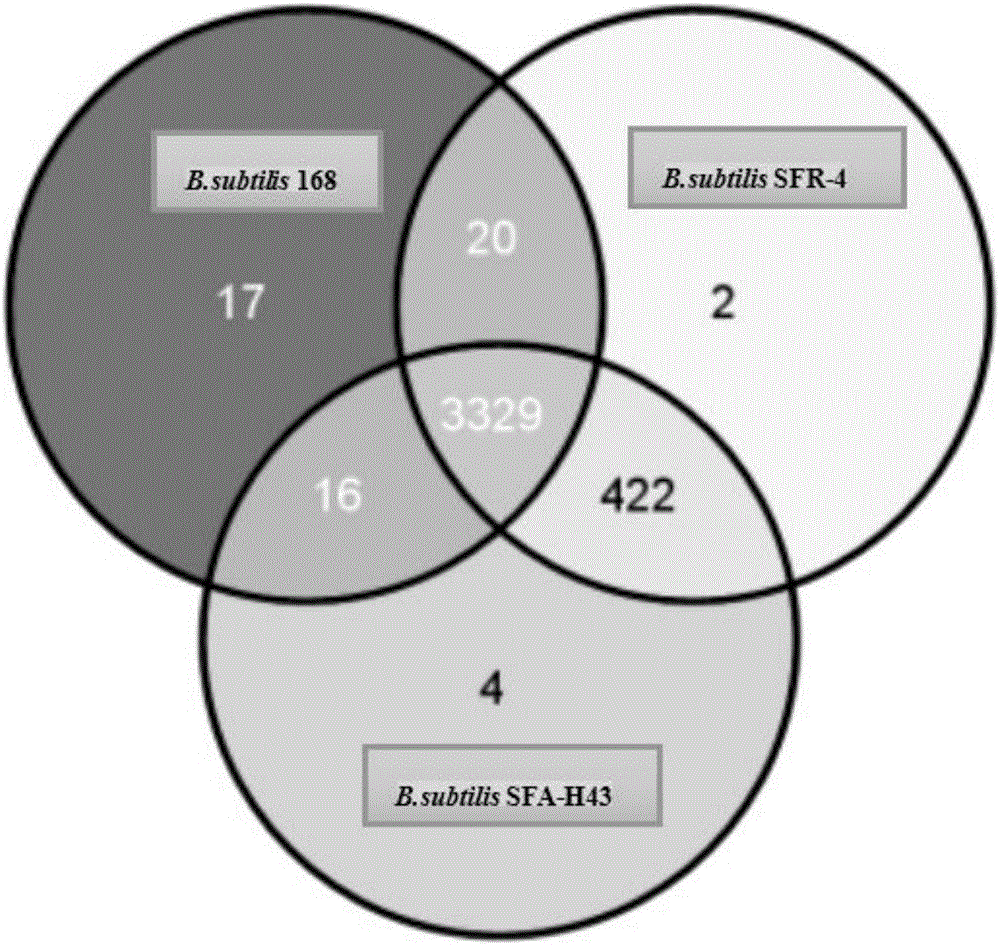
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria and application thereof. Whole genome sequencing comparative analysis shows that SFA-H43 and a D-ribose high-producing strain SFR-4 are higher in homology, and the nucleotide sequences of transketolase gene sequences except mutation sites are totally the same. According to the bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention, by adopting the way of homologous recombination, a transketolase gene mutation sequence of an SFR-4 strain is shifted into an SFA-43 strain so as to replace a normal sequence of transketolase genes of the SFA-43 strain, so that a transketolase mutant engineering strain SFR-43T is obtained; the transketolase mutant engineering strain SFR-43T not only maintains good fermentation properties (good stress resistance, fast glucose consumption speed, vigorous growth and difficulty in bacterial infection) of the SFA-43 strain, but also is capable of accumulating D-ribose, and the fermentation stress resistance is obviously increased.
Owner:SHANDONG FOOD & FERMENT IND RES & DESIGN INST
Method for producing D-ribose by fermenting bacillus subtilis
InactiveCN101338331AOvercoming the problem of low yieldEasy to separate and extractMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyTransketolase
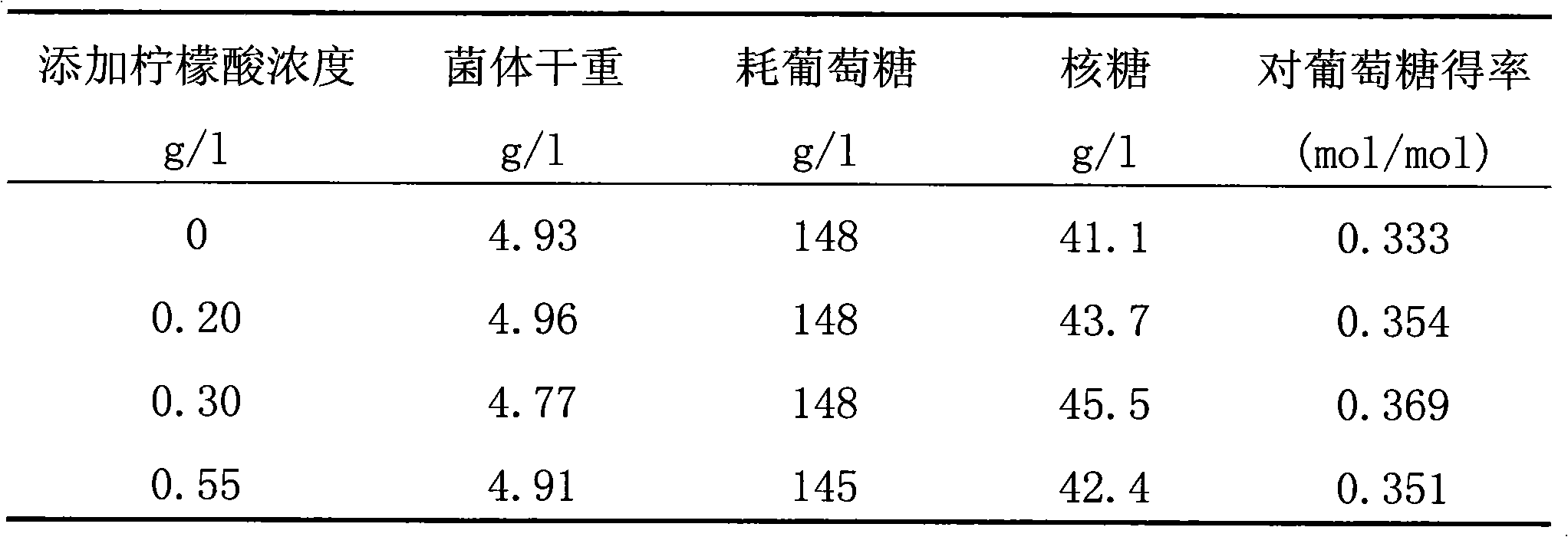
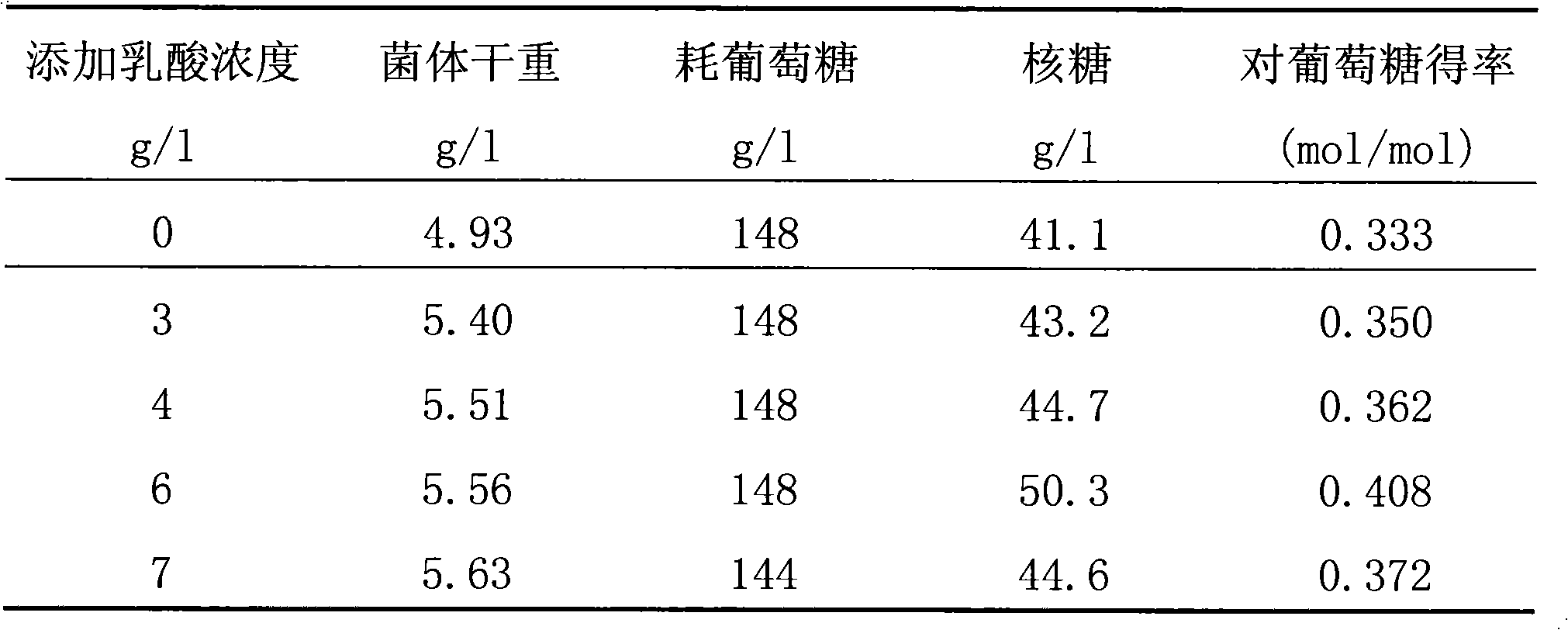
The invention relates to a method for producing D-plant nucleic acid by using Bacillus subtilis to ferment which includes the steps: (1) inoculating the production strain of transketolase defect Bacillus subtilis into a seed culture medium to activate to obtain a seed liquid; (2) preparing a fermentation culture medium which takes dextrose as a carbon source and adding organic acid such as citric acid or lactic acid; (3) inoculating the seed liquid into the fermentation culture medium to carry out fermentation. The method of the invention has the beneficial effects of: being capable of remarkably increasing the yield of the D-plant nucleic acid and improving the yield rate; reducing the outgrowths in the fermentation liquid, thus being beneficial to the separation and extraction of the D-plant nucleic acid; being simple and practical to control the fermentation metabolic process and being easily industrialized.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Construction method of pediococcus acidilactici for producing L-lactic acid through co-fermentation of glucose and xylose
The invention discloses a construction method of pediococcus acidilactici for producing L-lactic acid through co-fermentation of glucose and xylose, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. The construction method comprises the following construction steps: integrating heterogenous xylose isomerase, xylulokinase, transketolase and transaldolase coding genes on a genome of a strain pediococcus acidilactici TY112 (with the accession number of CGMCC NO.8664) for producing L-lactic acid by utilizing a thermosensitive knockout system; knocking out phosphoketolase and acetokinase coding genes; and carrying out adaptive evolution for improving the capacity of co-fermentation of glucose and xylose. With the construction method, an engineering strain capable of efficiently producingoptically pure L-lactic acid through co-fermentation of glucose and xylose is successfully obtained, the engineering strain is named P.acidilactici ZY271, and the accession number is CGMCC NO.13611.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Tumor antigen detection kit and tumor antigen detection method
The present invention relates to the field of tumor antigen level detection, particularly to a tumor antigen detection kit and a tumor antigen detection method. The tumor antigen detection kit comprises an antibody 1 and a substance for displaying the antibody 1, and / or an antibody 2 and a substance for displaying the antibody 2, wherein the antigen of the antibody 1 is TKTL1, and the antigen of the antibody 2 is DNASE1L1. The present invention further provides a tumor antigen detection method, wherein the tumor antigen information is obtained by detecting TKTL1 and DNASE1L1 in leukocyte lysates in the blood. According to the present invention, the tumor antigen level in the blood is obtained by detecting the TKTL1 (transketolase-sample 1) and the DNASE1L1 (deoxyribonuclease 1-sample 1) inthe blood, such that the detection results are stable, the specificity is high, and the detection is convenient.
Owner:北京金沐医疗科技有限公司
Bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, and method for production of bioethanol using the bacterium
InactiveUS20100311140A1Strong glucose fermentation capacityStable mannose fermentation capacityBacteriaBiofuelsTransketolaseEscherichia coli
The object is to develop a bacterium capable of fermenting glucose, mannose and xylose simultaneously, which can ferment a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type or lignocellulose-type biomass resource to produce ethanol, and to construct an energy-saving high-efficiency bioethanol conversion process. Thus, disclosed is Zymomonas mobilis bacterium which is prepared by integrating a gene encoding a phosphomannose isomerase derived from Escharichia coli into a levansucrase gene located on the chromosome by the double cross-over by means of a homologous recombsination method, and then introducing recombinant DNA prepared by binding a DNA fragment containing genes encoding a xylose isomerase, a xylulokinase, a transaldolase and a transketolase, respectively, all derived from Escherichia coli to a vector. Also disclosed is a method for producing ethanol by continuously fermenting a saccharified solution of a cellulose-type biomass resource in a system on which the Zymomonas mobilis bacterium is immobilized.
Owner:TOTTORI UNIVERSITY
Method for prodcuing D-ribose by inter mass fermentation
InactiveCN1814771ASimple ingredientsLow priceMicroorganism based processesFermentationTransketolaseAgricultural science
This invention relates to a method for producing D-ribose by supplementing substances characterizing in inducing, selecting and cultivating the type of transketolase defective Bacillus subtilis, cultivating them in the slope substrate, the seed liquid substrate and the fermentation substrate, in which, during the fermentation period, a feeding way of intermission degression and a way of quantitative feeding are applied to feed grape sugar supplementary solution and (NH4)2SO4 to get the D-ribose finally.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
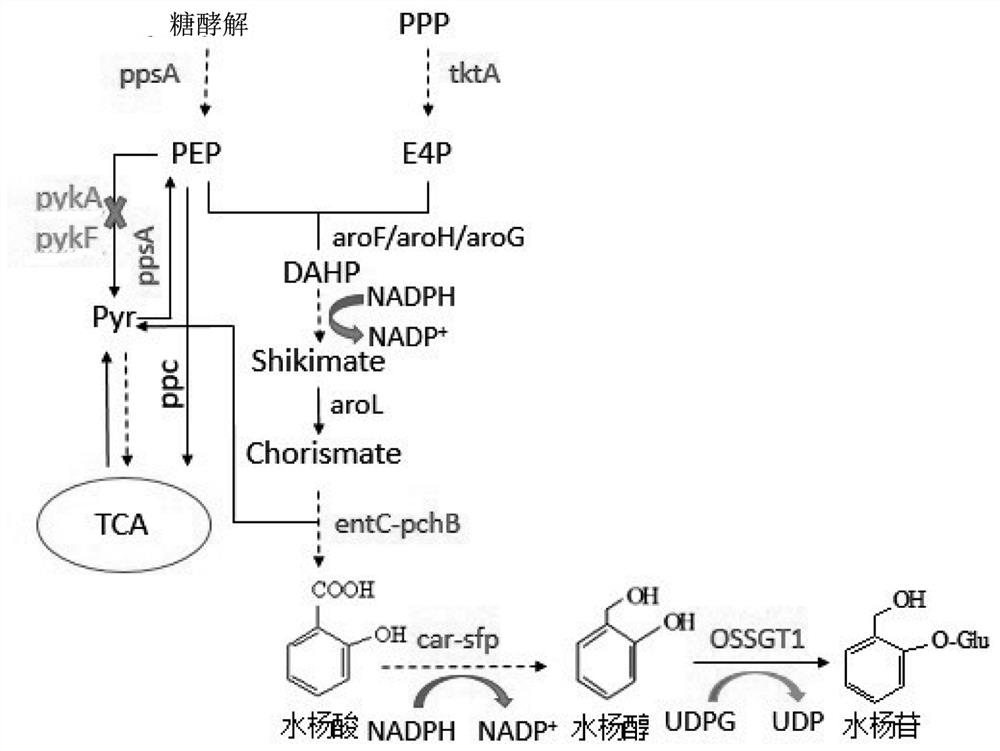
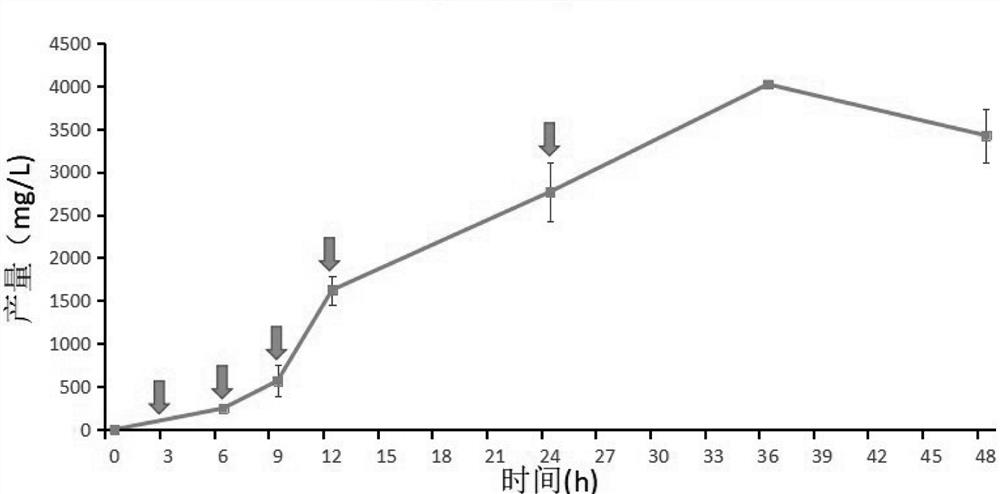
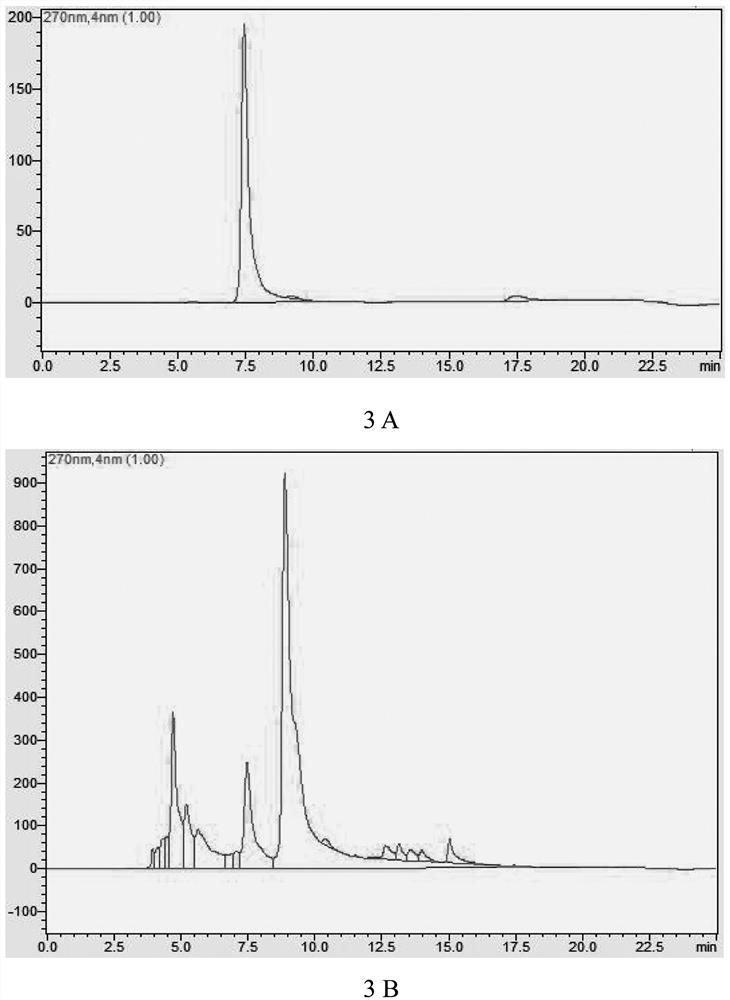
Engineering bacterium for synthesizing salicin as well as construction method and application of engineering bacterium
The invention provides an engineering bacterium suitable for salicin, which comprises a host and a recombinant plasmid vector, and the recombinant plasmid vector is connected with a gene for expressing and coding glucosyltransferase. The recombinant plasmid vector is also connected with a gene for coding carboxylic acid reductase and phosphoryl transferase, which is co-expressed with the gene for coding glucosyltransferase. The recombinant plasmid vector is also connected with genes for over-expressing and coding shikimic acid kinase, pyruvate kinase, transketolase, 3-deoxy-7-phosphoenanthate synthase, iso-chorismate pyruvate lyase and isochorismate synthase; and the host is also knocked out of genes for coding pykA and pykF, so that the yield of salicin is increased. The invention also provides a construction method and an application of the engineering bacterium for synthesizing salicin. By utilizing the engineering bacteria for synthesizing the salicin, the salicin is produced by using glucose and / or glycerol and other carbon sources, so that efficient biosynthesis of the salicin is realized.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
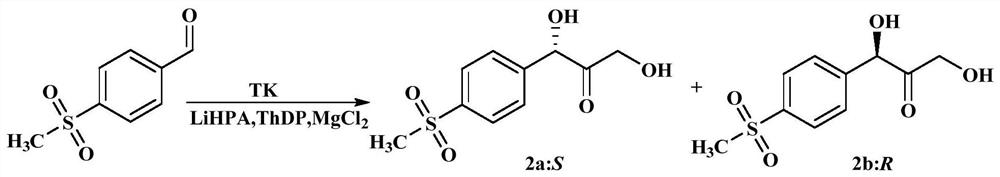
High-stereoselectivity R transketolase mutant as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a high-stereoselectivity R transketolase mutant as well as a coding gene and application thereof, and relates to the technical field of enzyme engineering, the amino acid sequence of the high-stereoselectivity R transketolase mutant is SEQ ID No.1, and the nucleotide sequence of the coding gene is SEQ ID No.2; a recombinant expression vector containing the encoding gene; a host cell containing the recombinant expression vector; a method for preparing the high stereoselectivity R transketolase mutant; the R transketolase mutant is applied to catalysis of aromatic aldehyde to form R-aromatic dihydroxy ketone with high stereoselectivity. The coding gene is applied to catalysis of aromatic aldehyde to form high-stereoselectivity R-aromatic dihydroxy ketone. The stereoselectivity of p-methylsulfonyl phenyl dihydroxy ketone generated by catalysis of the mutant EcTK1YYH is 95.2% ee (R), and the mutant EcTK1YYH has high activity and high stereoselectivity.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
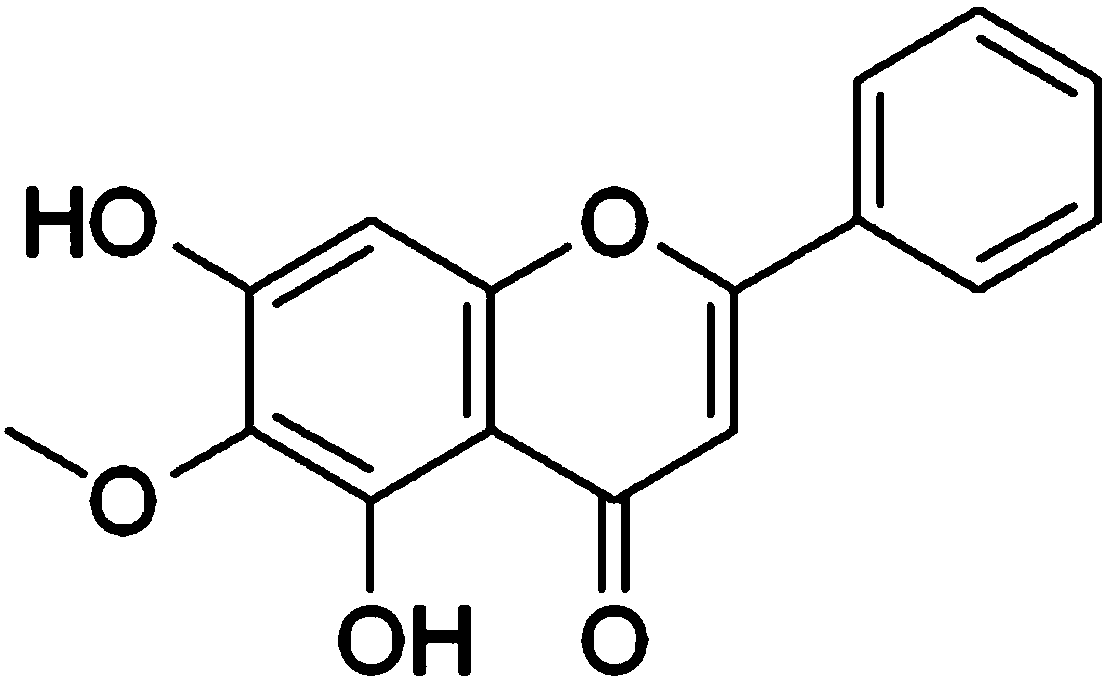
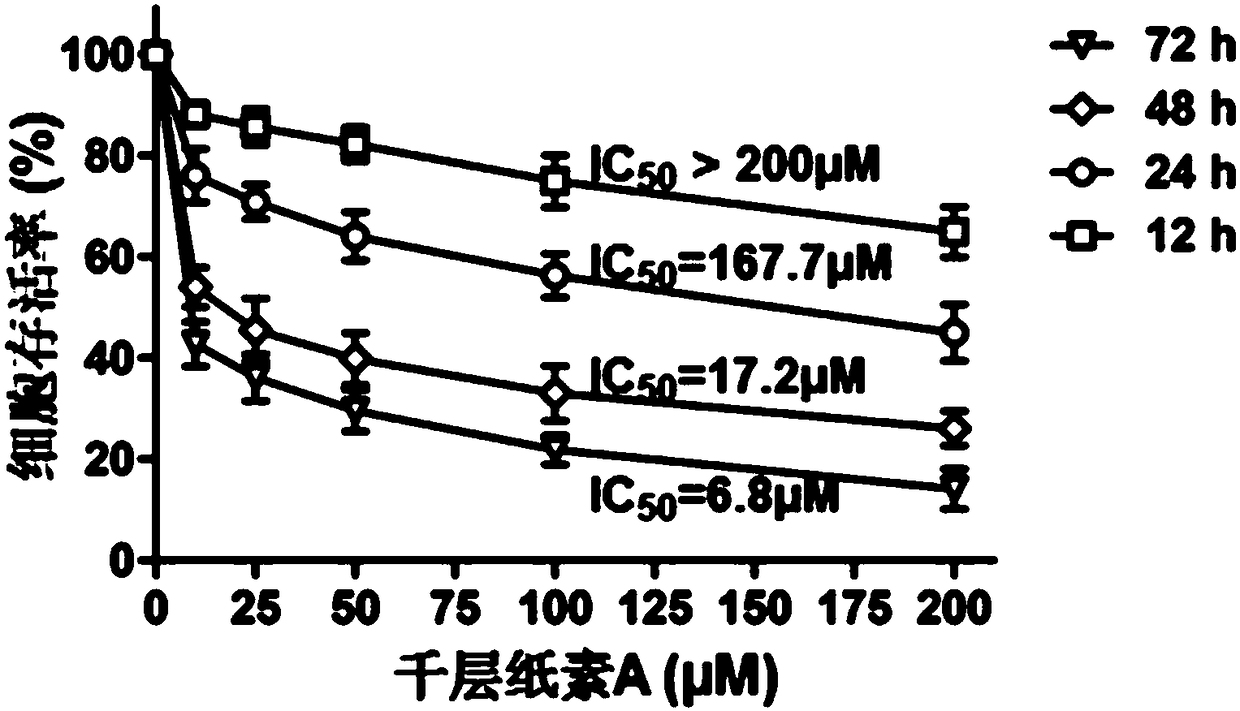
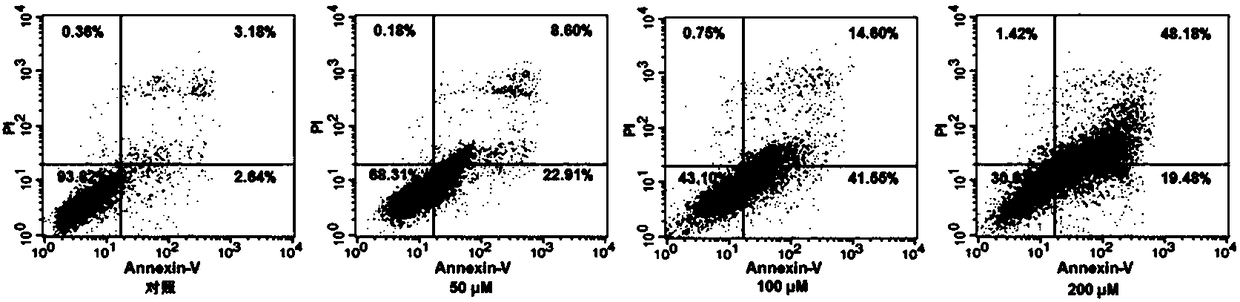
Use of oroxylin A as transketolase inhibitor
PendingCN108309966AStrong anti-liver cancer activityPrevent proliferationOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsTransketolaseProtein target
The invention discloses a use of oroxylin A as a transketolase inhibitor. The transketolase inhibitor is used for treating cancer. The use of the transketolase inhibitor for treating the cancer is realized by inhibiting the activity and expression of the transketolase to inhibit a non-oxidize pentose phosphate pathway and activate a p53 signal channel, thereby playing an antitumor effect. DARTS isused for identifying a target protein directly combined with oroxylin A in the human liver cancer cell HepG2, a key enzyme-transketolase of the non-oxidize pentose phosphate pathway is discovered andis a direct combined target point of the oroxylin A, a KD value is 11.2 microM, and the interactive effect is proved by virtue of the molecular docking, enzymatic activity determination, protein expression and the antitumor effect variation after the transketolase interference. The research result shows that the oroxylin A is an effective transketolase inhibitor.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
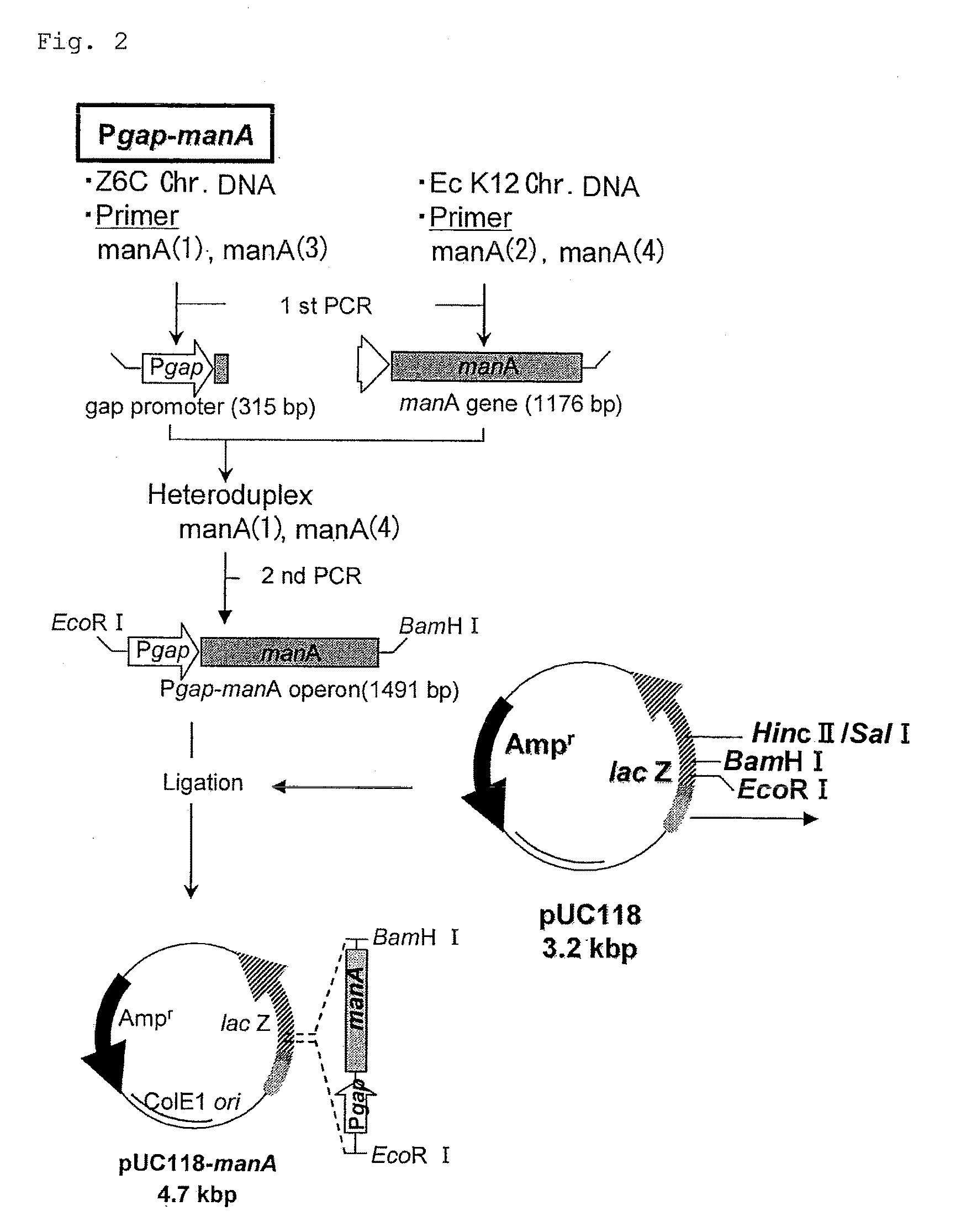
Method for expressing transketolase by applying pGAP regulation of Pichia pastoris
InactiveCN101698835AReduce manufacturing costEase of mass productionTransferasesMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseBiotechnology
The invention relates to a method for expressing transketolase by applying pGAP regulation of Pichia pastoris, belonging to the biotechnology field. Firstly, pGAP promoters are amplificated in Pichia pastoris, a Pichia pastoris expression vector of which xylose isomerase is regulated by the pGAP is built, and then the Pichia pastoris expression vector is transformed into Pichia pastoris genome. High copy recons are selected as engineering bacterial strain according to resistance genes on the Pichia pastoris expression vector, and the engineering bacterial strain is inoculated into liquid culture medium containing carbon source to ferment engineering bacteria for secreting and expressing the transketolase. The invention has the advantages of low production cost and short fermenting period. The using of the pGAP regulation of Pichia pastoris to express the transketolase is favorable to purifying the product, and the problems of high production cost and hard product purification caused by using natural bacterial strains produced transketolase to produce transketolase can be solved. The invention is favourable for mass production of transketolase.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method for producing D-ribose at high yield by using bacillus subtilis engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106636251AImprove performanceFast sugar consumptionBacteriaTransferasesTransketolaseHigh homology
The invention discloses a method for producing D-ribose at high yield by using bacillus subtilis engineering bacteria. On the basis of high homology between a D-ribose production strain SFR-4 and a strain SFA-H43 genome, a strain SFR-4 transketolase gene mutation sequence is transferred into a wild strain SFA-43 by a homologous recombination method, and a strain transketolase gene is substituted to obtain an engineering strain SFR-43T having a transketolase variation sequence; the engineering strain SFR-43T keeps superior fermentation performance (high stress resistance and high glucose consumption rate) of the strain SFA-43, and can accumulate the D-ribose at the same time. The initial sugar concentration is controlled, and a glucolactone feeding technology is adopted in a fermentation process, so that the yield and conversion rate of the engineering strain D-ribose can be increased greatly, and accumulation of 3-acetoin is controlled.
Owner:SHANDONG FOOD & FERMENT IND RES & DESIGN INST
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and application thereof
InactiveCN103074292BIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum capable of being used for highly yielding L-phenylalanine and a method for producing the L-phenylalanine (Phe) by fermentation and belongs to the field of metabolic engineering. According to the invention, a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering strain C.glutamicum19AF / 99TP capable of being used for highly yielding the L-Phe is obtained in a corynebacterium glutamicum type strain ATCC13032 by carrying out induction expression on the following four genes: a 3-deoxy-D-arabino-heptulosonate-7-phosphate synthase gene, a chorismate mutase / prephenate dehydratase gene which has resistance to feedback inhibition, a transketolase gene and a phosphoenolpyruvic acid synthetase gene. A shikimic acid metabolic pathway of an L-Phe synthetic metabolic pathway is over-expressed in the C.glutamicum ATCC13032; a key enzyme gene of a chorismic acid metabolic pathway enables the yield of the L-Phe to reach 3.47g / L; two enzyme genes which combines an expression center metabolic pathway to improve a precursor enables the highest yield of the L-Phe to reach 4.86g / L; and the original strain ATCC13032 which is used as a contrast strain cannot detect accumulation of the L-Phe in the integral fermenting process.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Preparation method of 4-phosphoric acid erythrose
ActiveCN101875951BSimplify separation and purification stepsNot easy to infect bacteriaFermentationTransketolaseFructose phosphate
The invention relates to a preparation method of 4-phosphoric acid erythrose, comprising the following steps: immobilizing heat-resistant transketolase at the temperature of 55-65 DEG C; and then taking 6-fructose phosphate and 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate as raw materials to prepare the 4-phosphoric acid erythrose by enzymatic reaction. In the preparation method, the heat-resistant and specifically transformed transketolase of the 4-phosphoric acid erythrose is prepared by adopting a molecular biology technology, and the 6-fructose phosphate and the 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate are taken as the raw materials to efficiently prepare the 4-phosphoric acid erythrose by adopting an immobilized enzyme technology. The preparation method is simple and practical.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Composition for detecting mycoplasma ovipneumoniae by taking transketolase gene as target kit and method thereof
ActiveCN110564877AGood technical effectOptimize the reaction systemMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesTransketolaseFluorescence
The invention discloses a composition for detecting mycoplasma ovipneumoniae by taking a transketolase gene as a target, a kit and a method thereof. A detection target of the composition is the transketolase gene of mycoplasma ovipneumoniae; various different fragments in the gene can be targeted, the experiments prove that the composition disclosed by the invention can be used for designing various specific combination situations so as to be applied to various amplification methods such as traditional PCR, basic RPA, nfo RPA and exo RPA; in addition, the experimental results can be observed by means of agarose gel electrophoresis, a lateral flow chromatography test strip and a constant-temperature fluorescence amplification instrument. The optimal reaction time and the optimal reaction temperature in the detection process and the specificity, the sensitivity, the repeatability and the stability of detection are explored; the optimal reaction condition is found, the mycoplasma ovipneumoniae rapid detection method which is good in specificity, high in sensitivity and capable of being stably repeated is established, and the composition has the advantages of being easy to operate, convenient to implement, and capable of saving time and free of large experimental instruments and equipment.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and construction method for producing dammarenediol and protopanaxadiol using xylose
The invention discloses a recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a construction method for producing dammarenediol and protopanaxadiol by using xylose. Through homologous recombination, the promoter of Saccharomyces cerevisiae xylulokinase gene XKS1 is replaced with a promoter Sub P FBA1 , and then introduce xylose reductase XYL1, xylitol dehydrogenase XYL2 expression cassettes, and then increase the activity of transketolase TKL1 and transaldolase TAL1 to obtain recombinant bacterium 1, and then introduce farnesyl diphosphate into recombinant bacterium 1 Farnesyltransferase gene ERG9, squalene monooxygenase gene ERG1 and dammarene diol synthase gene DS were obtained to obtain recombinant bacteria 2, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-hydroxymethyl was introduced into recombinant bacteria 2 Glutaryl-CoA reductase gene NADH-HMGr, farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase ERG20, protopanaxadiol synthase-cytochrome P450 reductase fusion protein gene PPDS-ATR1 were obtained to obtain recombinant bacteria 3, the recombinant brewing wine of the present invention Yeast uses xylose to synthesize dammarenediol and protopanaxadiol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
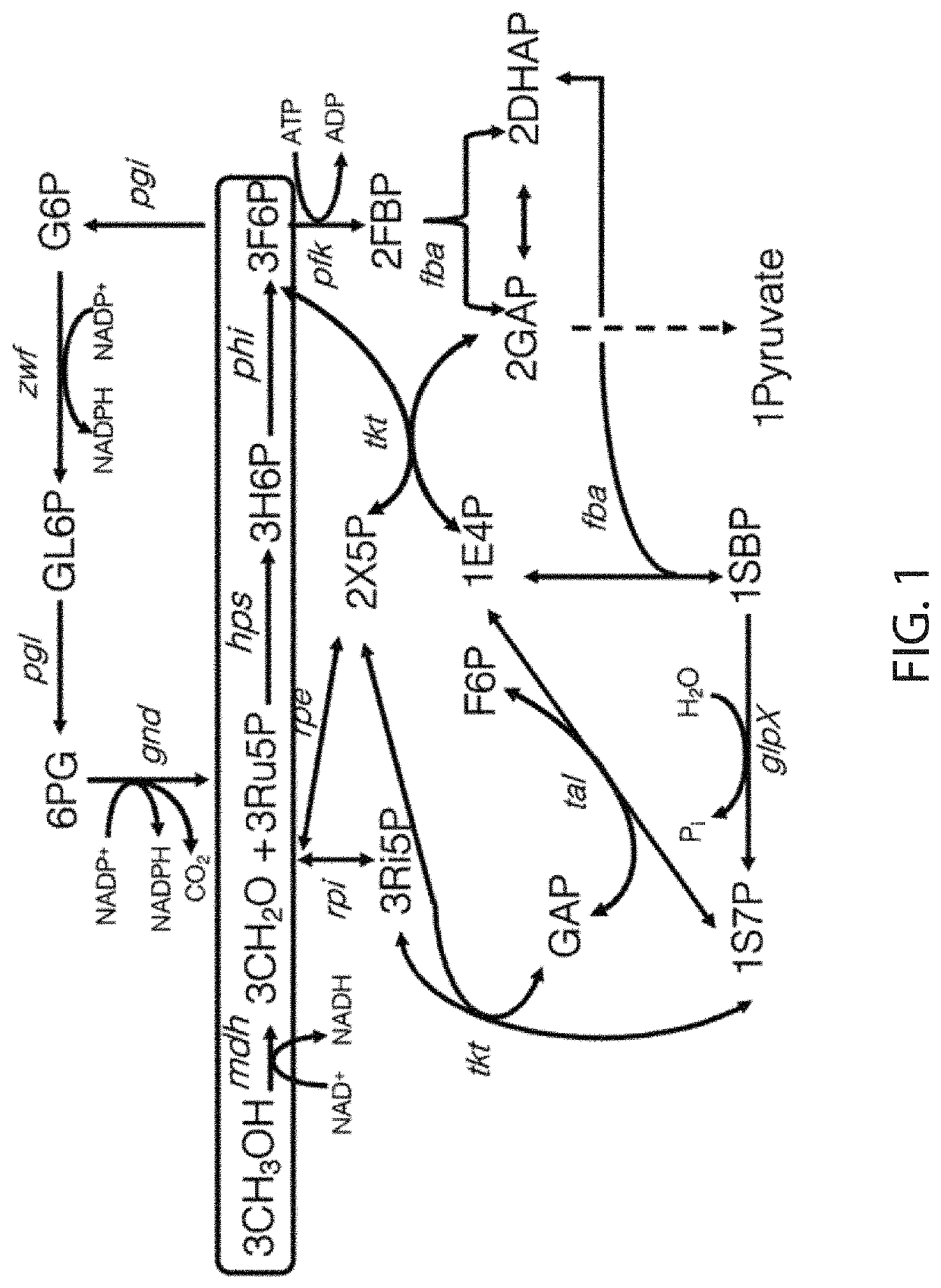
Methanol utilization
Described herein are enzymes, such as for example, methanol dehydrogenase (MDH), 3-hexulose-6-phosphate isomerase (PHI), 3-hexulose-6-phosphate synthase (HPS), ribose-5-phosphate isomerase (RPI), ribulose 5-phosphate 3-epimerase (RPE), transketolase (TKT), transaldolase (TAL) enzymes, phosphofructokinase (PFK), Sedoheptulose 1,7-Bisphosphatase (GLPX), fructose-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA), 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (GND), and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (ZWF); recombinant host cells expressing the enzymes; methods of producing methylotrophic cells; and methods of producing amino acids (e.g., lysine).
Owner:GINKGO BIOWORKS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com