Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43results about How to "High final concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for concentration of macromolecules
ActiveUS20060149042A1Reduce conductivityHigh final concentrationDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsCell culture supernatantOragene
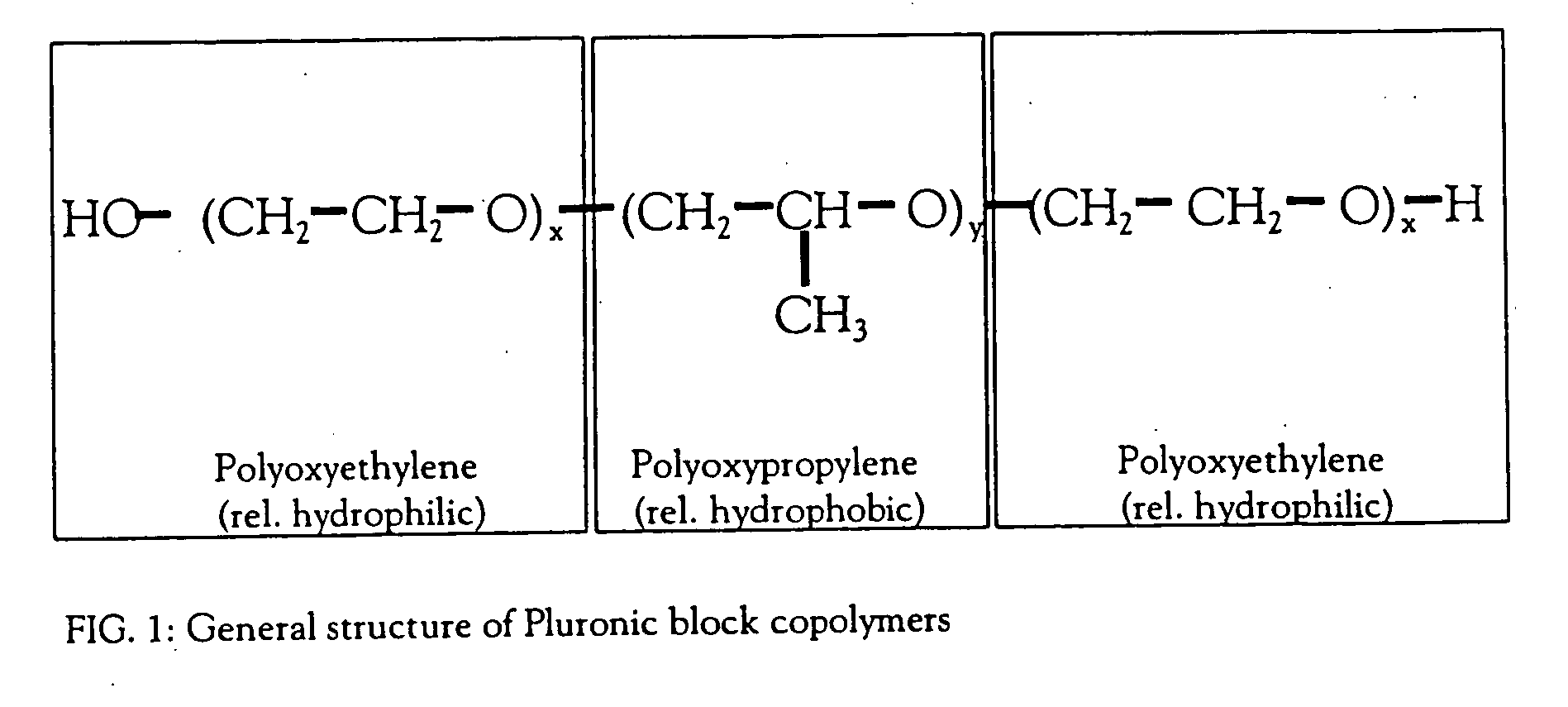
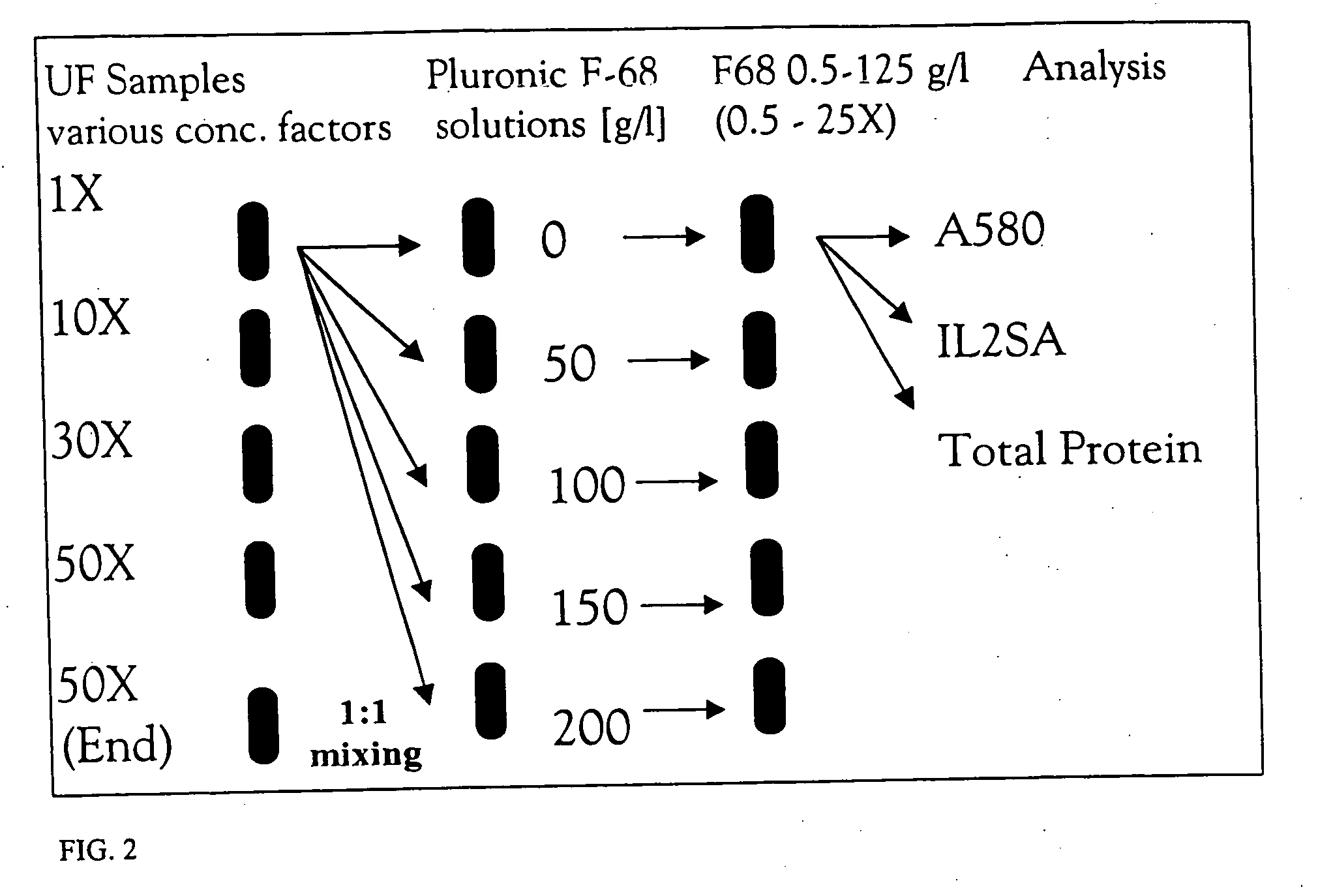
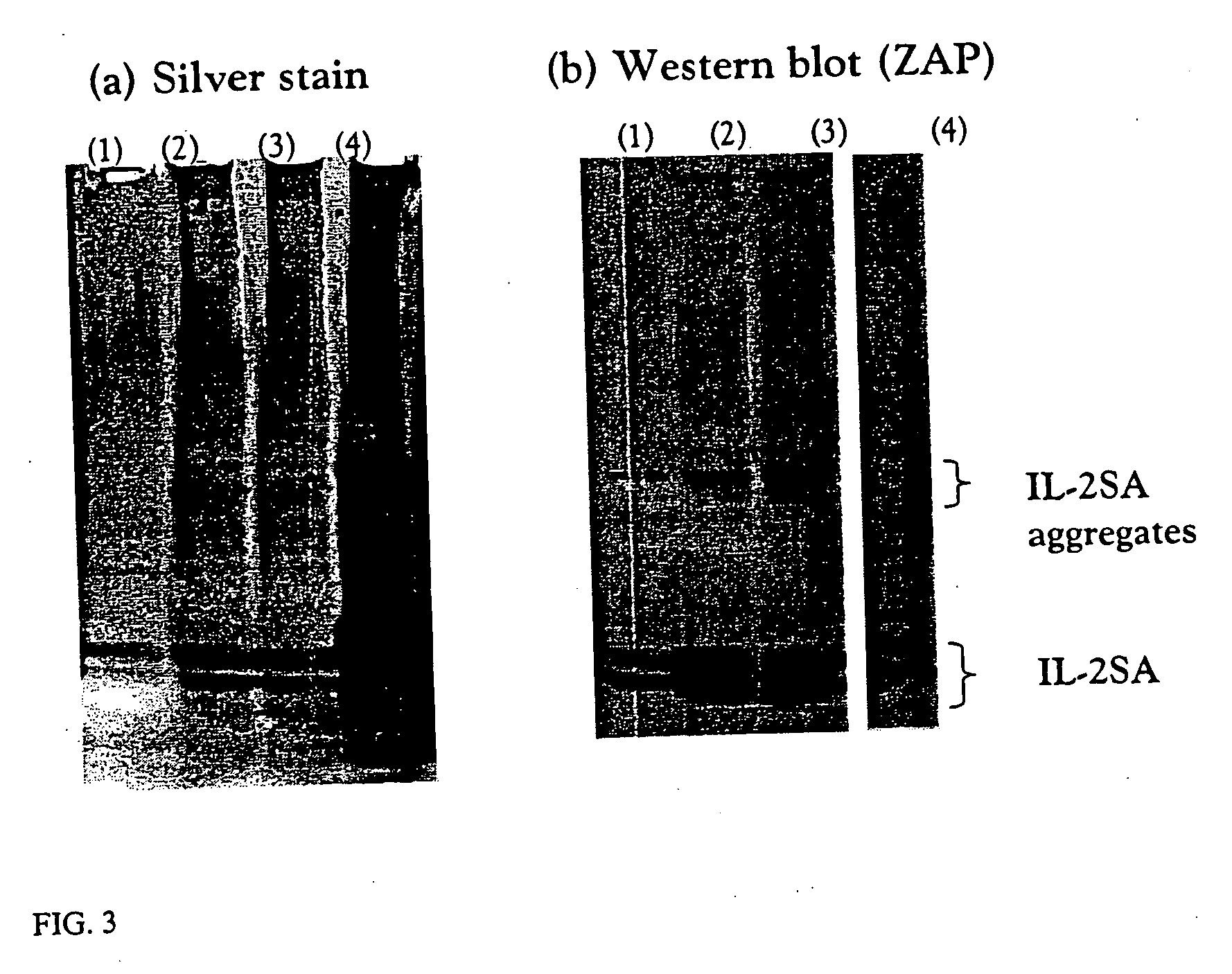
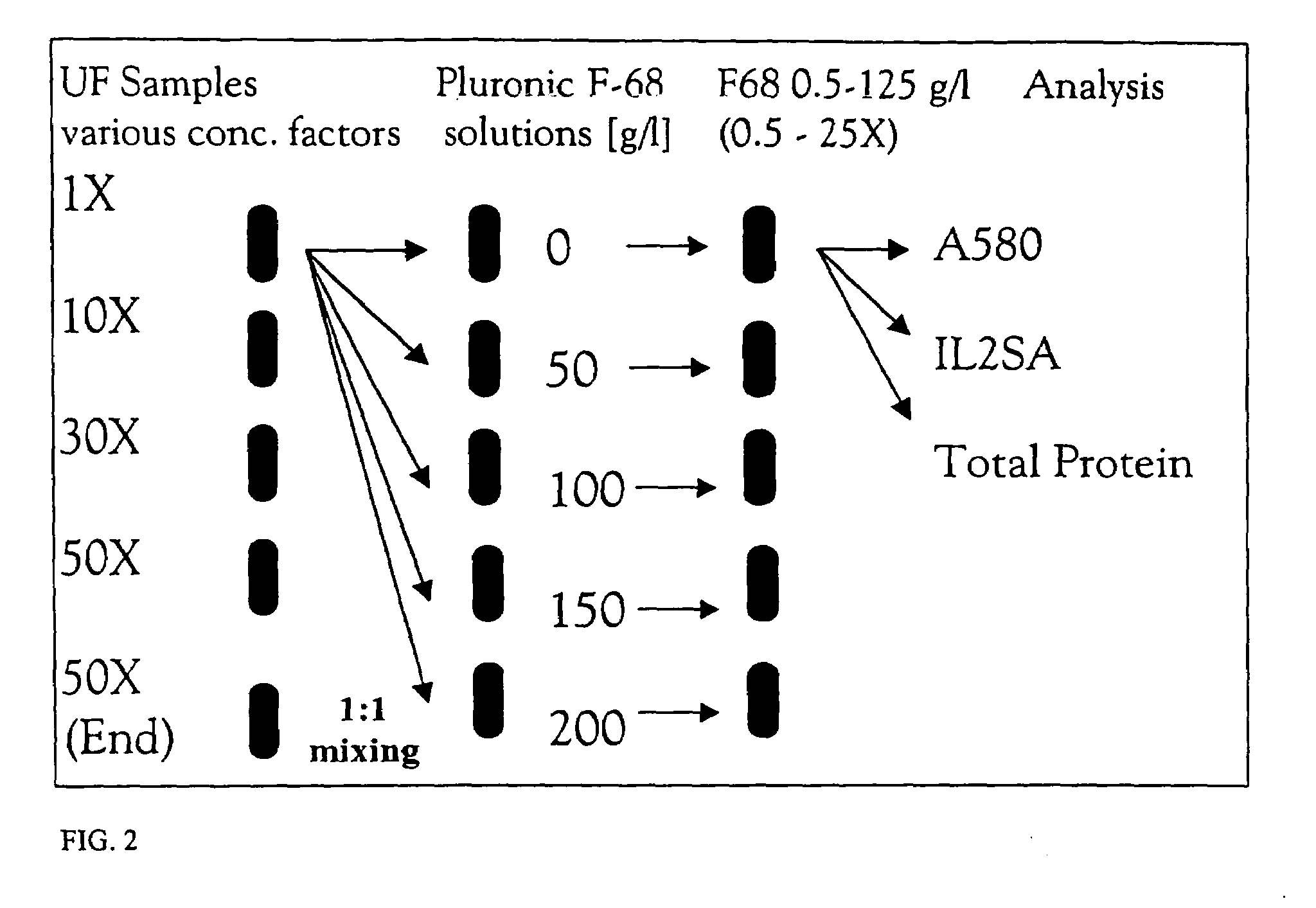
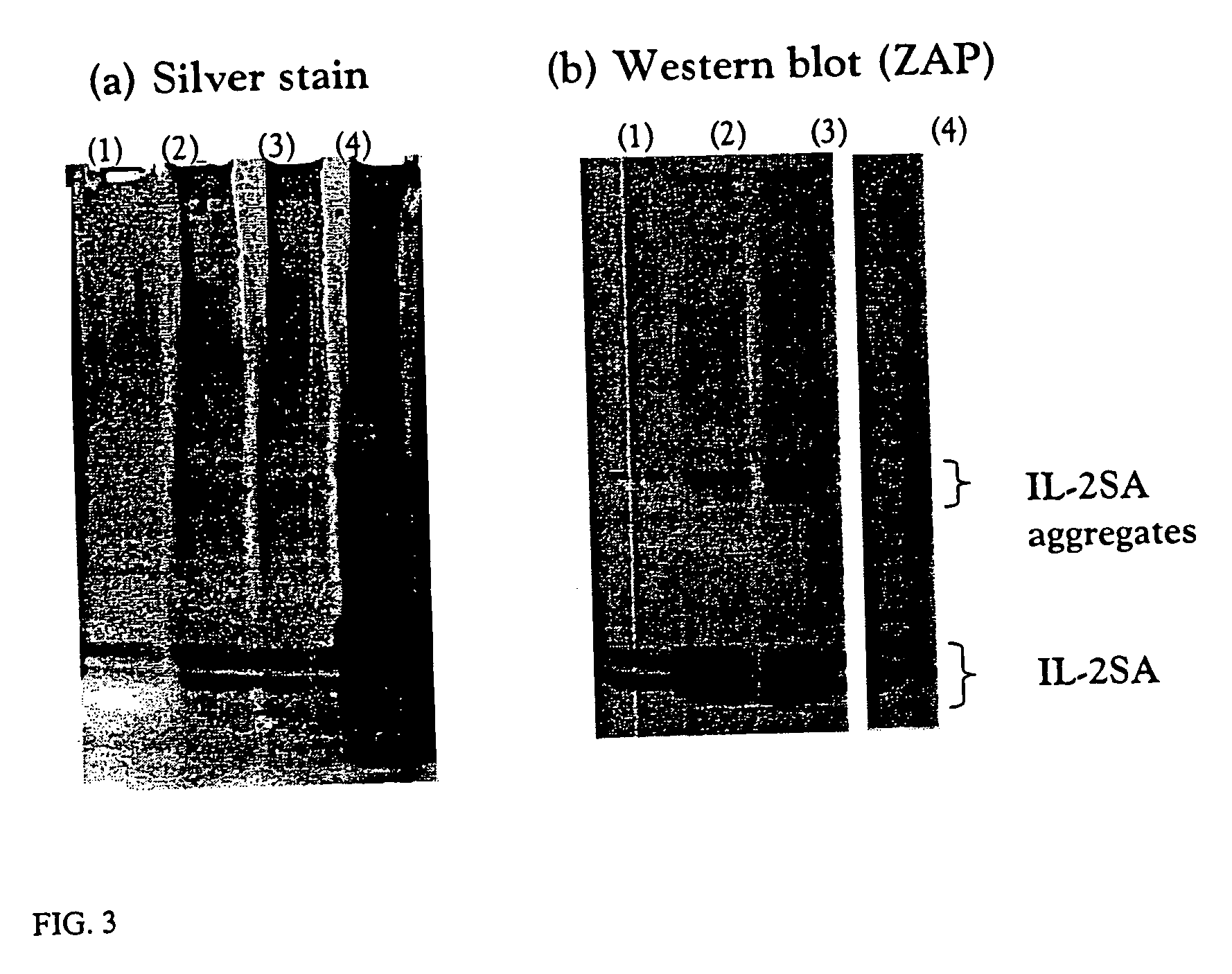
The invention provides methods for concentrating a macromolecule from a solution comprising the macromolecule and an organic polymer by first subjecting the solution to ultrafiltration to produce a first retentate solution, then adjusting the conductivity of the first retentate solution such that any protein precipitation induced by the organic polymer is essentially prevented to produce a second retentate solution, and then subjecting the second retentate solution to ultrafiltration. In a preferred embodiment, the conductivity is adjusted by diafiltration against water, suitable diluent or buffer. Preferably, the invention pertains to the concentration of solutions of native or recombinant proteins. The invention further pertains preferably to methods for the concentration of cell culture supernatant comprising a product protein and organic polymers of the Pluronic family of block co-polymers, and more preferably comprising Pluronic F-68 block co-polymer.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Method of adding reducing agent from extraneous sources for accelerating thallus to synthesize 1,3-propylene glycol
InactiveCN1446919AImprove conversion rateHigh final concentrationFermentationGlycerolEquivalent weight
A process for preparing 1,3-propanediol biologically features that in the culture medium for fermenting or in the anaerobic fermenting procedure, appropriate reducer is added to increase the accumulation of reduction equivalent weight in thallus for promoting metabolism of glycerine along the reductino approach, and increasing the concentration and transform rate of 1,3-propanediol. Its advantageis high biologic utilization rate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Process for producing 1,3-propylene glycol by microorganism aerobic fermentation
The present invention provides microbial aerobic fermentation process of producing 1, 3-propylene glycol, and belongs to the field of biochemical technology. Seed liquid is first added into industrial glycerin or initial fermentation culture medium of glycerin fermenting liquid with glycerin concentration of 20-50 g / L, and under fermentation condition of 30-40 deg.c, the culture medium is fermented with PDO producing Klebsiella pneumoniae or acid producing Klebsiella pneumoniae to produce PDO. During fermentation, air in 0.2-1.0 vvm is led in, the fermented matter is stirred in 50-250 rpm, glycerin and sodium hydroxide in certain amount are added to maintain certain glycerin concentration. The present invention has the advantages of lowered investment and power consumption, raised final PDO concentration, raised production strength and increased bacteria biomass.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Gene engineering bacterium for producing 1,3-propanediol and its preparation method and application
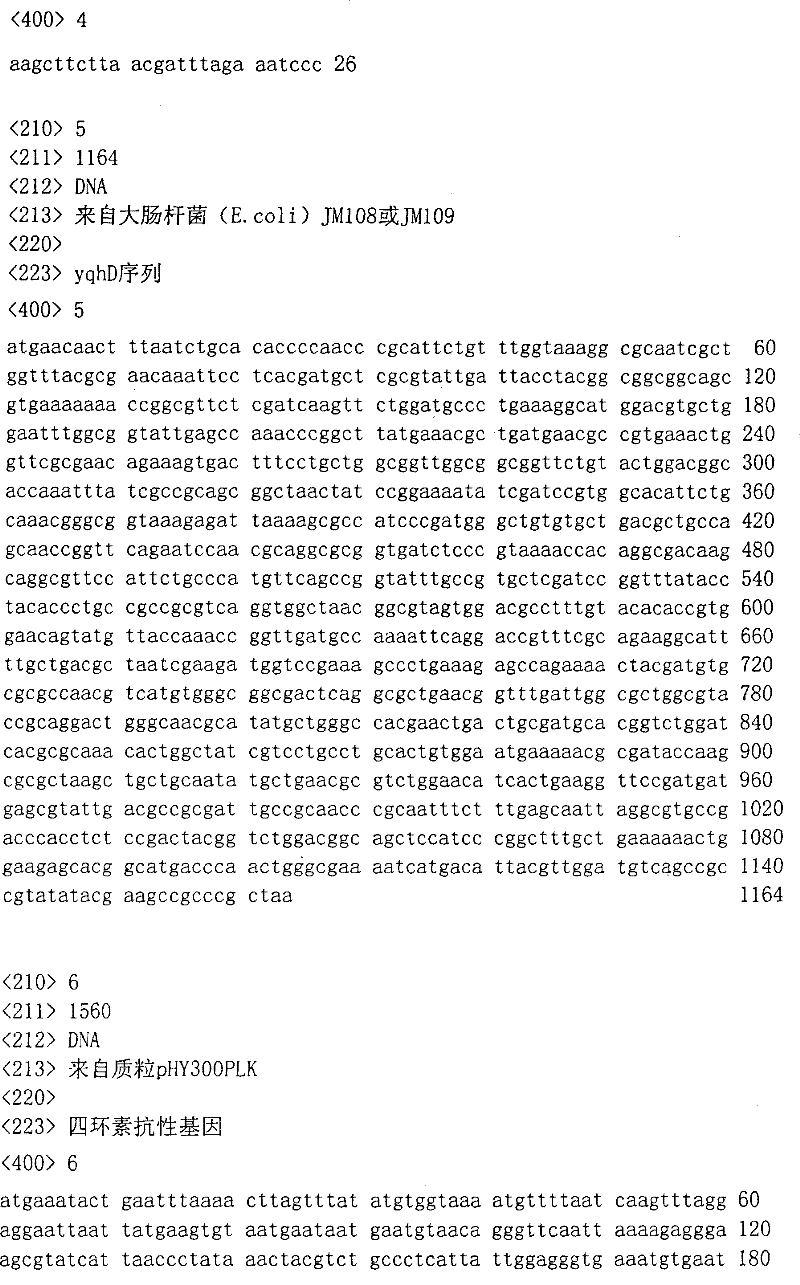
InactiveCN101260379AImprove stabilityHigh final concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsozymeGlycerol
The invention belongs to the biochemical field and discloses a 1, 3-propylene glycol genetic engineering bacterium and a preparation method and application thereof. The strain is classified and named as Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955-pUC18-yqhD-Tet<R>, and is obtained by connection of a 3-propylene redoxase isozyme gene yqhD from Escherichia coli and a tetracycline resistant gene Tet<R> from a plasmid pHY300PLK, insertion of a carrier pUC18 and conversion of Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955. The bacterium can obviously improve the capacity for conversion of glycerol into 1, 3-propylene glycol, improve the utilization ability and the conversion rate of the substrate glycerol and the final concentration of the final offspring 1, 3-propylene glycol, simultaneously shorten the fermentation time, and is convenient for industrial production of the 1, 3-propylene glycol through the microbial fermentation method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Genetic engineering strain for producing (R, R)-2,3-butanediol, as well as construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN102965324AStable in natureHigh final concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEngineering
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Quick extracting method for lotus rhizome tissue total RNA
InactiveCN1587405AQuality improvementHigh purityFermentationPlant genotype modificationTotal rnaUltraviolet
The quick extracting process of lotus rhizome tissue total RNA includes the steps of: compounding test chemical preparation and processing test articles; sampling tender leaf and leaf stalk; extracting, precipitating and centrifuging to obtain total RNA; identifying total RNA with ultraviolet spectrophotometer and formaldehyde denatured agarose gel electrophoresis detection. The obtained data and electrophoresis results show that the lotus rhizome tissue with complete total RNA has high purity and high yield. The present invention has simple test process, convenient and safe operation, accurate and effective result and high repeatability. The method is also suitable for the total RNA extraction of other plant tissue with rich polysaccharide and polyphenol.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for producing R-acetoin from klebsiella pneumoniae
ActiveCN103388009AImprove conversion rateHigh final concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationChemistryCarbon source
The invention discloses a method for producing R-acetoin from klebsiella pneumoniae. Under an aerobiotic condition, the R-acetoin is produced from the klebsiella pneumoniae which is deactivated by an acetoin reductase gene budC through fermentation. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the raw material is reproducible carbon source and the conversion rate of the raw material is high, the final concentration of the product R-acetoin is high, and the produced R-acetoin has very high optical purity and the content of R-isomers in the total acetoin is greater than 98%.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method and equipment for separating volatile organic matters from fermentation product in situ
InactiveCN101928200AEliminate Product InhibitionShorten the fermentation cycleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemistryPropanol
The invention discloses a method and equipment for separating volatile organic matters from a fermented product. In the method, in-situ separation of the volatile organic matters is realized by coupling fermentation with a gas stripping / vapor permeation process. The method and the equipment are characterized in that: inert gas is introduced from a gas distributor at the bottom of a fermentation tank; in-situ gas is extracted from the volatile organic matters and enters a vapor permeation device so as to separate water from the organic matters; dehydrated mixed gas enters a condenser to recycle the volatile organic matters; and non-condensable gas and a water vapor component containing a small number of organic matters can be recycled. The method and the equipment have the advantages of eliminating product inhibition, enhancing fermentation intensity, saving water and reducing energy consumption along with high in-situ movement efficiency of the volatile organic matters in a fermentation process. The volatile organic matters in the invention comprise ethanol, propanol, acetone, butanol and the like.
Owner:青岛生物能源与过程研究所
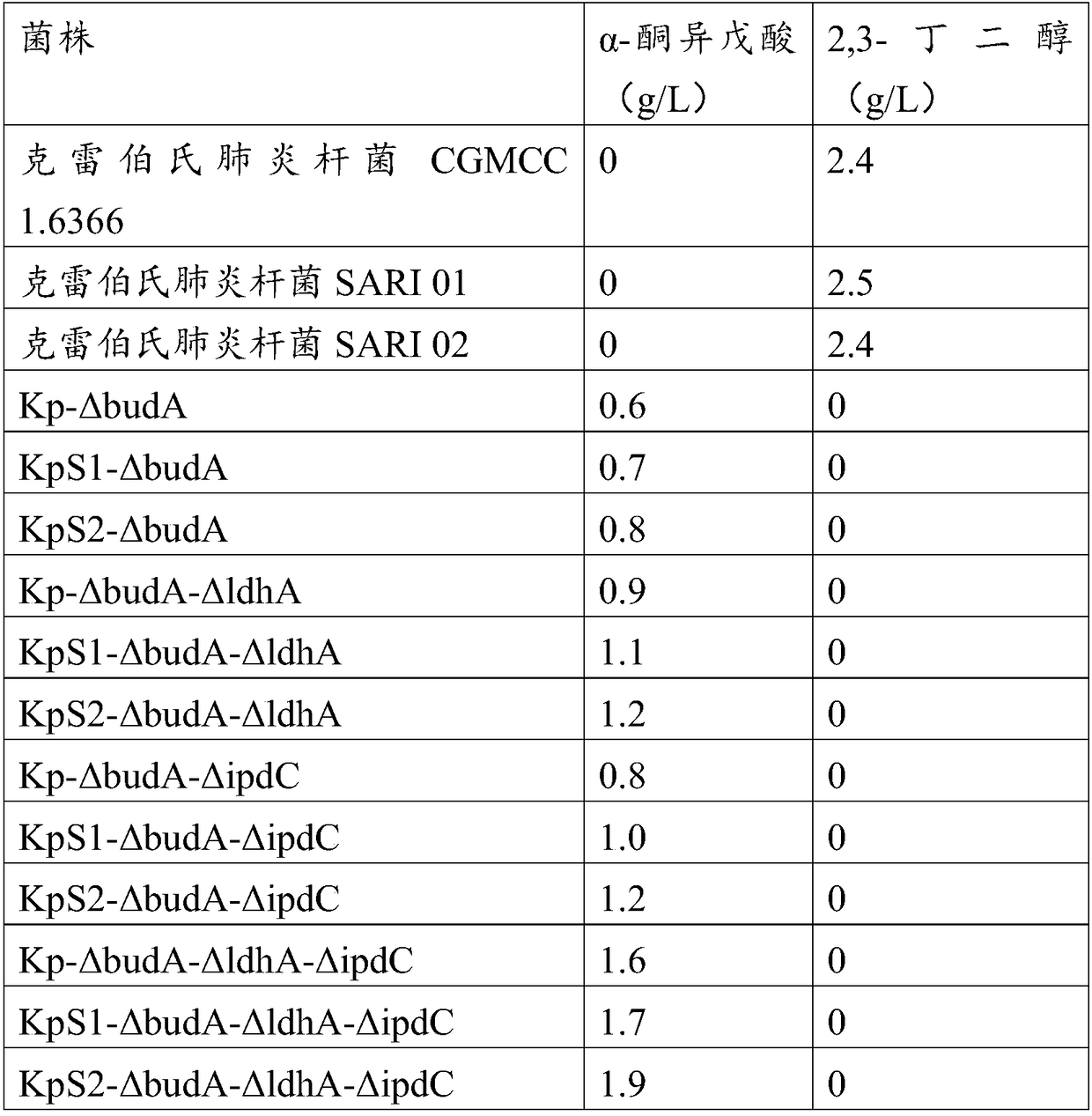
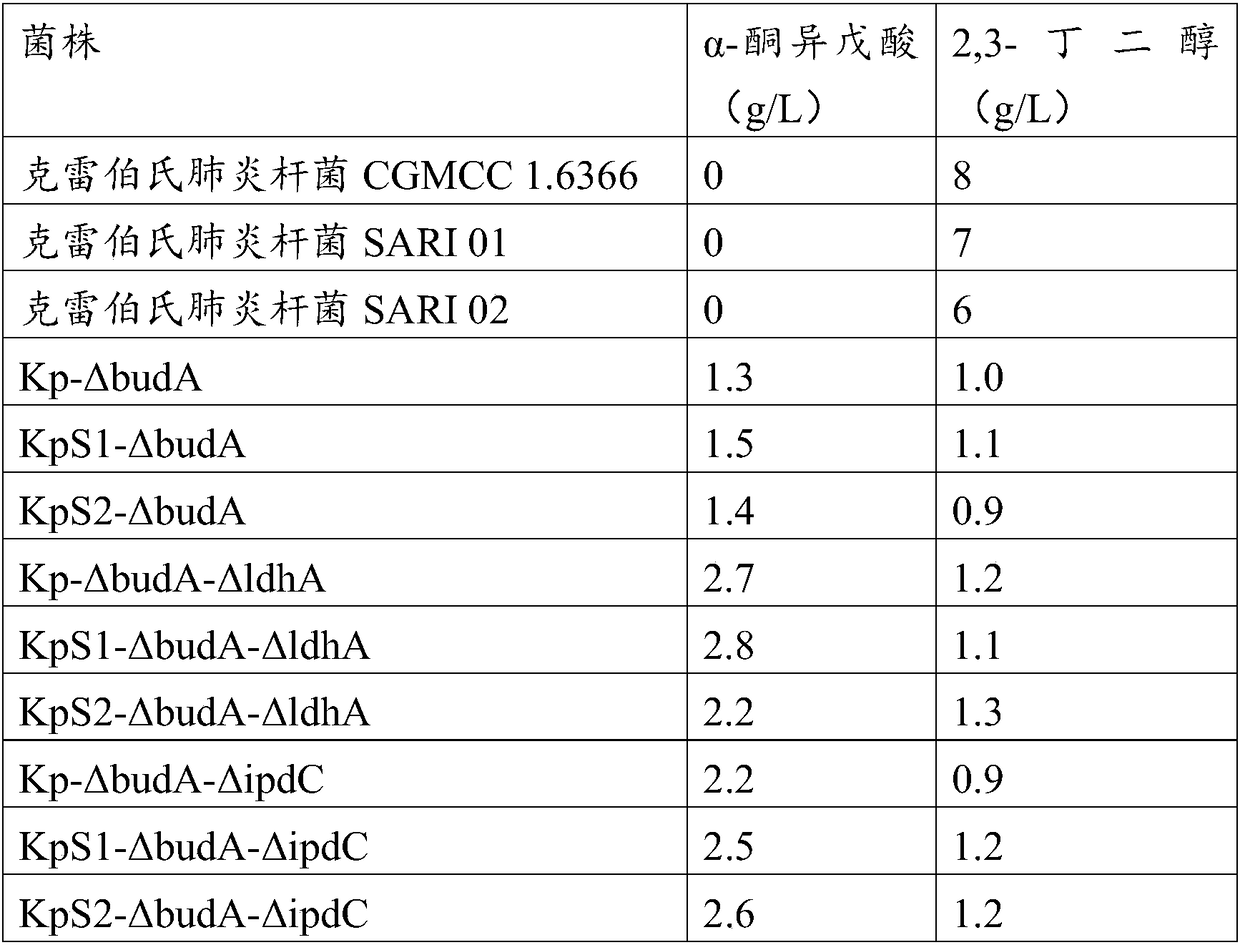
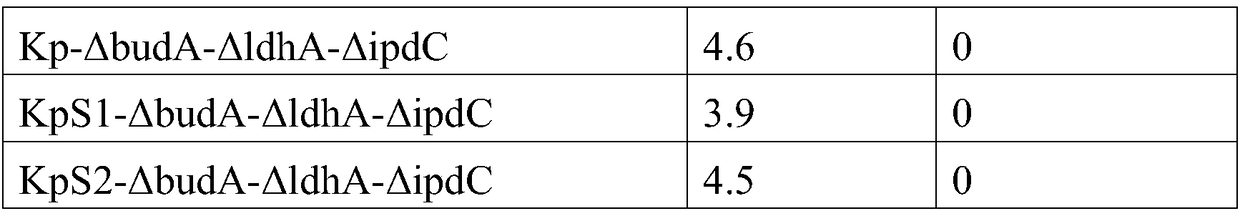
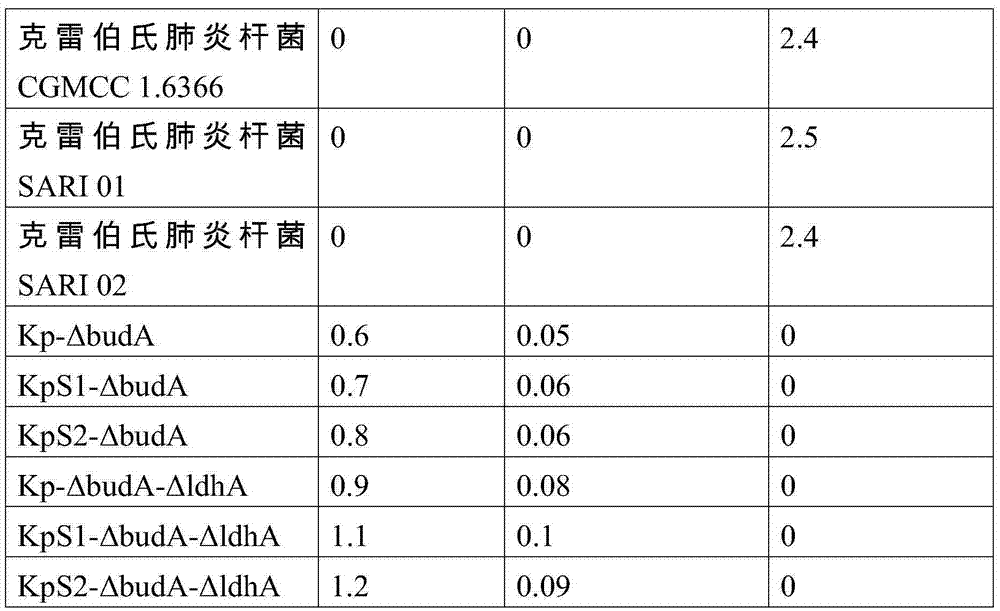
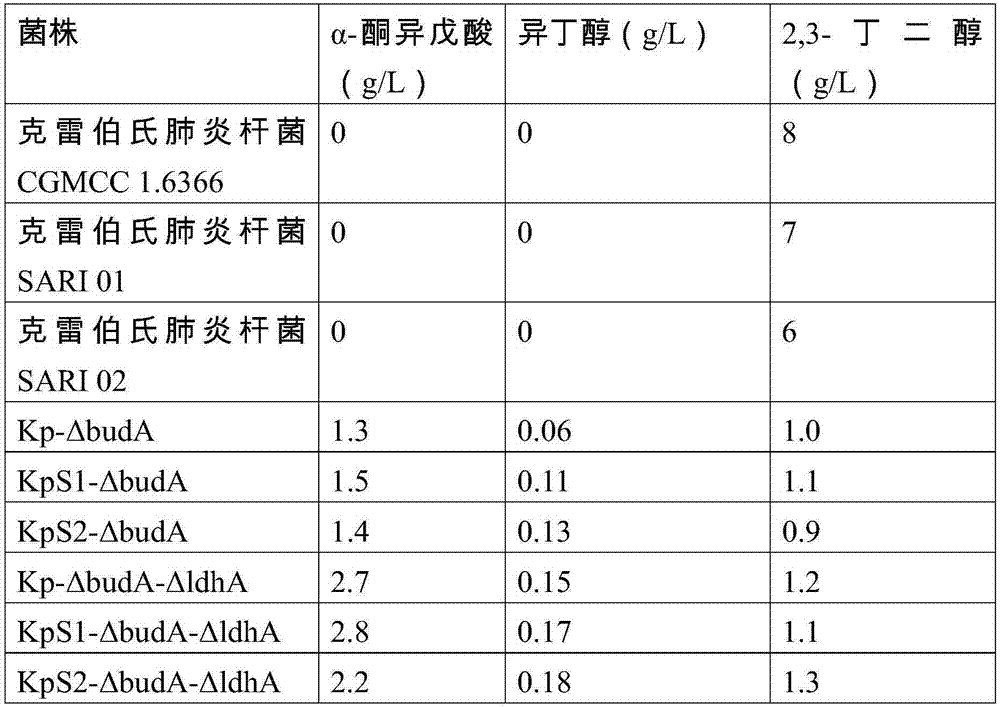
Method for improving alpha-ketoisovaleric acid yield of Klebsiella pneumoniae, and modified strain
ActiveCN108570438AHigh genetic stabilityRaw material conversion rate is highBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbon sourceAcetolactate decarboxylase
The invention discloses a method for improving the alpha-ketoisovaleric acid yield of Klebsiella pneumoniae, and a modified strain. The method comprises: inactivating acetolactate decarboxylase in Klebsiella pneumoniae, or simultaneously inactivating indole-3-pyruvate decarboxylase and / or lactate dehydrogenase, wherein the Klebsiella pneumoniae inactived with the enzyme is the modified strain; andinoculating the modified Klebsiella pneumoniae in a carbon source culture medium, and carrying out fermentation culture, wherein the carbon source in the culture medium is converted into alpha-ketoisovaleric acid by the modified Klebsiella pneumoniae during the fermentation culture. According to the present invention, with the method, the exogenous gene is not introduced into the modified strain,such that the strain has high genetic stability, the final concentration of the product is high, and the range of the raw material is wide.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for preparing alpha-ketoisovaleric acid and isobutanol by adopting klebsiella pneumoniae
ActiveCN106867922AHigh genetic stabilityHigh final concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIsobutanolLactate dehydrogenase
The invention discloses modified klebsiella pneumoniae and applications of modified klebsiella pneumoniae in producing alpha-ketoisovaleric acid and isobutanol. The modified klebsiella pneumoniae is klebsiella pneumoniae with deactivated acetolactate decarboxylase and deactivated lactic dehydrogenase. The modified klebsiella pneumoniae is adopted for carrying out fermentation production of alpha-ketoisovaleric acid and isobutanol under the neutral pH and micro-oxygen condition. For the method provided by the invention, no exogenous genes are introduced in strain production, thus the genetic stability of the strain is high, the final concentration of the product is high, and the range of the raw materials is wide.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method of improving concentration of butanol in process of acetone butanol fermentation
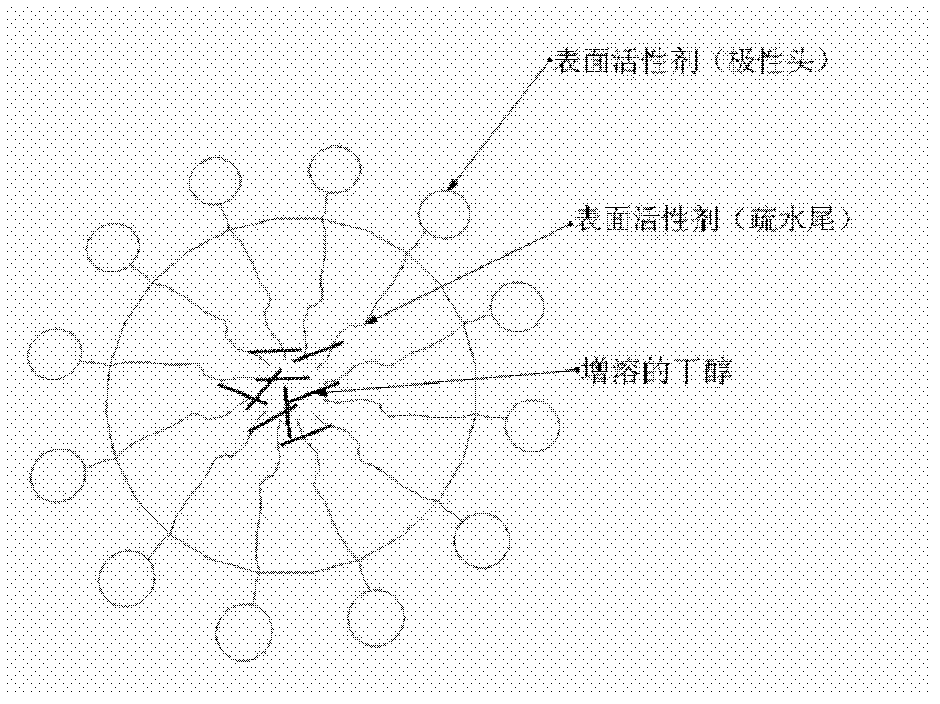
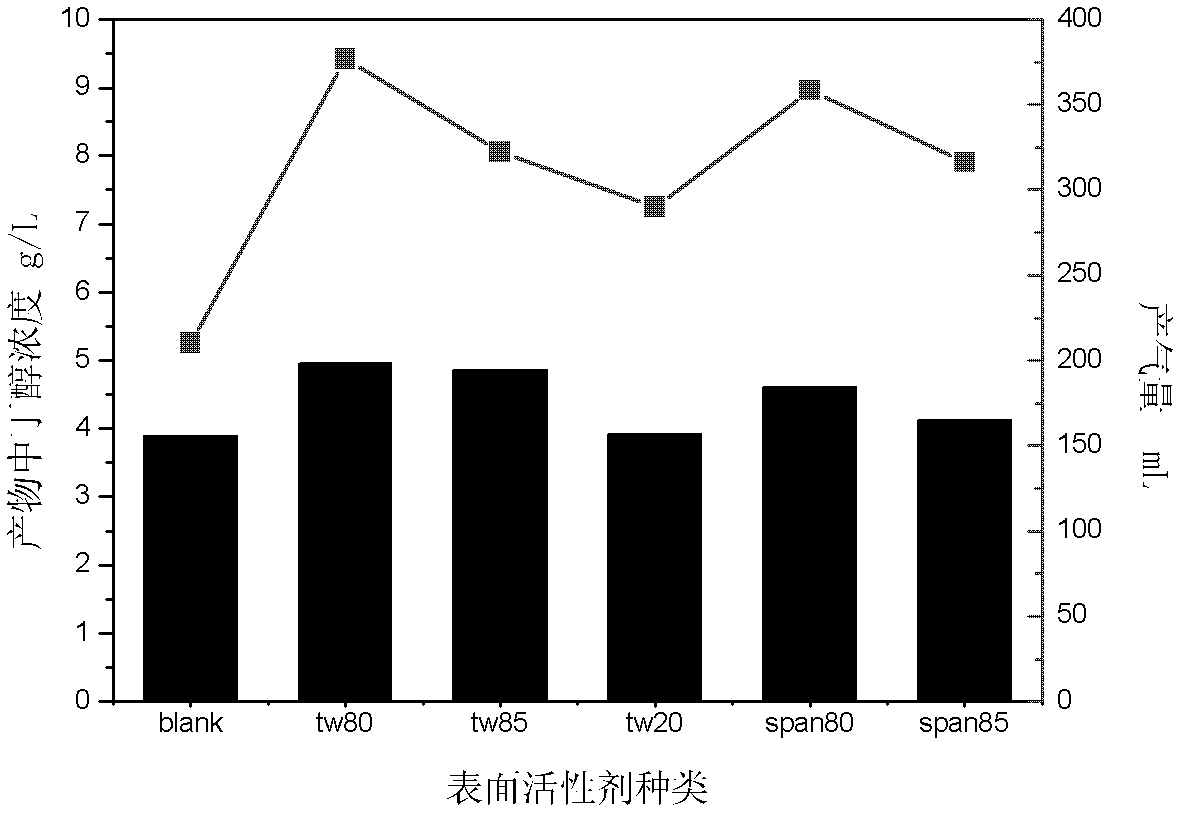
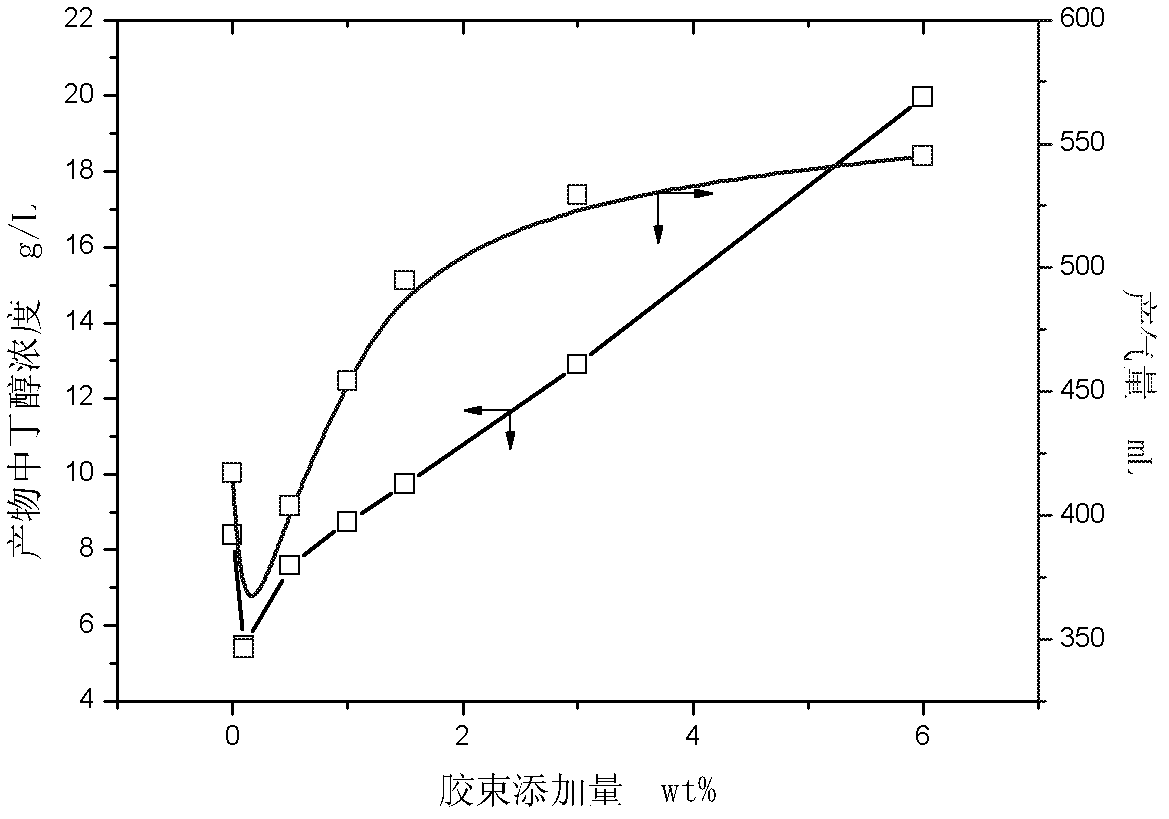
ActiveCN103131732AReduce dosageNon-toxicMicroorganism based processesFermentationN-ButanolSurface-active agents
The invention belongs to the field of the biochemical industry and particularly relates to a method of improving the concentration of butanol in the process of acetone butanol fermentation. The method of improving the concentration of the butanol in process of the acetone butanol fermentation includes the following steps of adding a surface active agent to a culture medium in the process of the acetone butanol fermentation and extracting and improving the concentration of the butanol by means of micelle formed by the surface active agent. The method of improving the concentration of butanol in the process of the acetone butanol fermentation is directed against the product inhibition effect existing in the process of the acetone butanol fermentation and extracts the butanol by means of the micelle formed by the surface active agent serving as an extraction agent, relieving the inhibition effect in the process of the acetone butanol fermentation, increases the final concentration of the butanol in fermentation liquor, and therefore energy consumption of rectification in a later period is reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A kind of 1,3-propanediol-producing genetically engineered bacteria and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101260379BImprove stabilityHigh final concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism1,3-Propanediol
The invention belongs to the field of biochemical industry and discloses a 1,3-propanediol-producing genetically engineered bacterium as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The strain is named Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC 25955-pUC18-yqhD-TetR, which is composed of the 1,3-propanediol oxidoreductase isoenzyme gene yqhD from Escherichia coli and the tetracycline resistance gene TetR from the plasmid pHY300PLK, and inserted into the vector pUC18 , obtained by transforming Klebsiella pneumoniae ATCC25955. The bacteria can significantly improve the ability of glycerol to convert 1,3-propanediol, improve the utilization ability and conversion rate of the substrate glycerol, increase the final concentration of the product 1,3-propanediol, and shorten the fermentation time, which is convenient for microbial fermentation. Industrial production of 1,3-propanediol.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
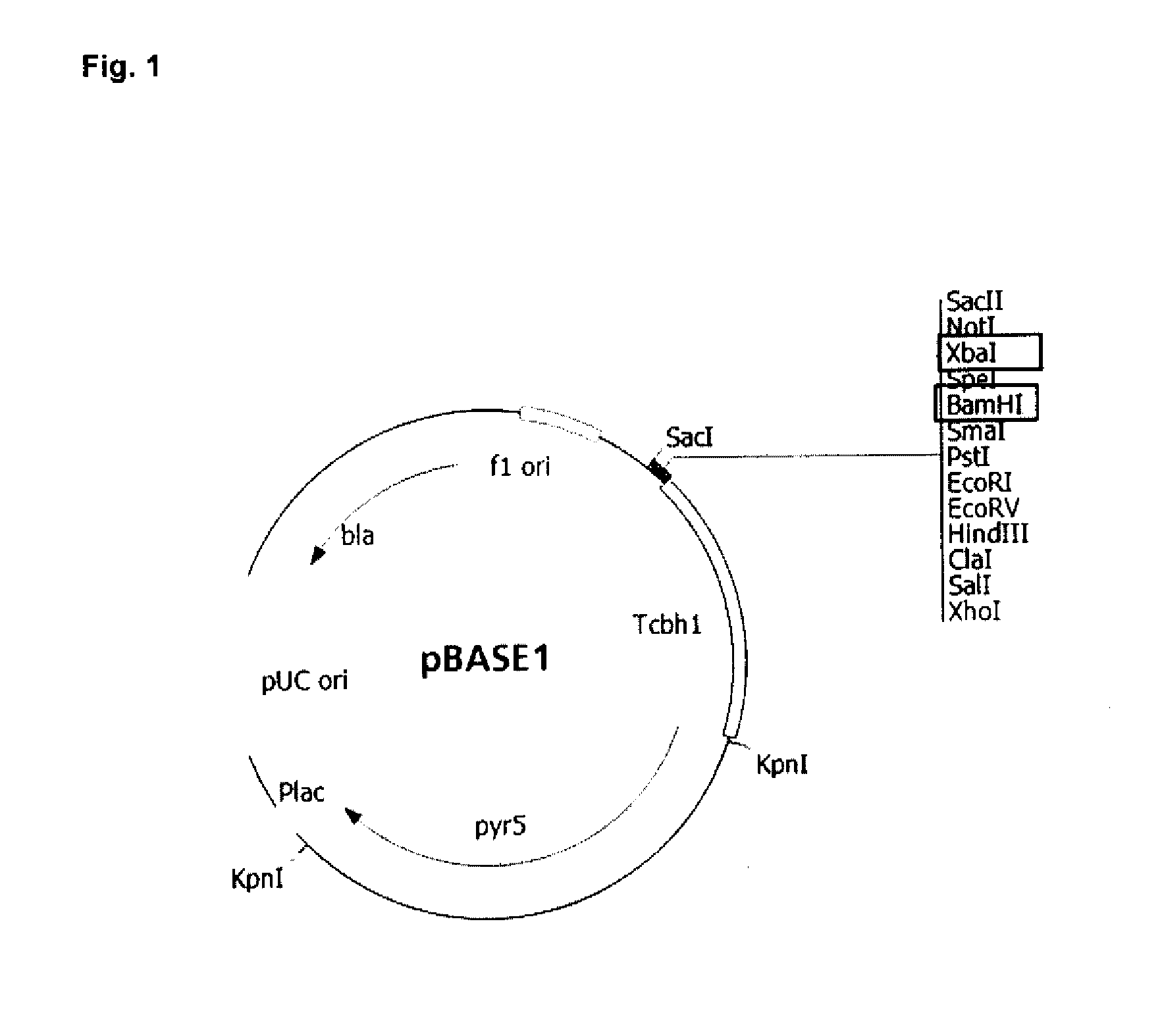
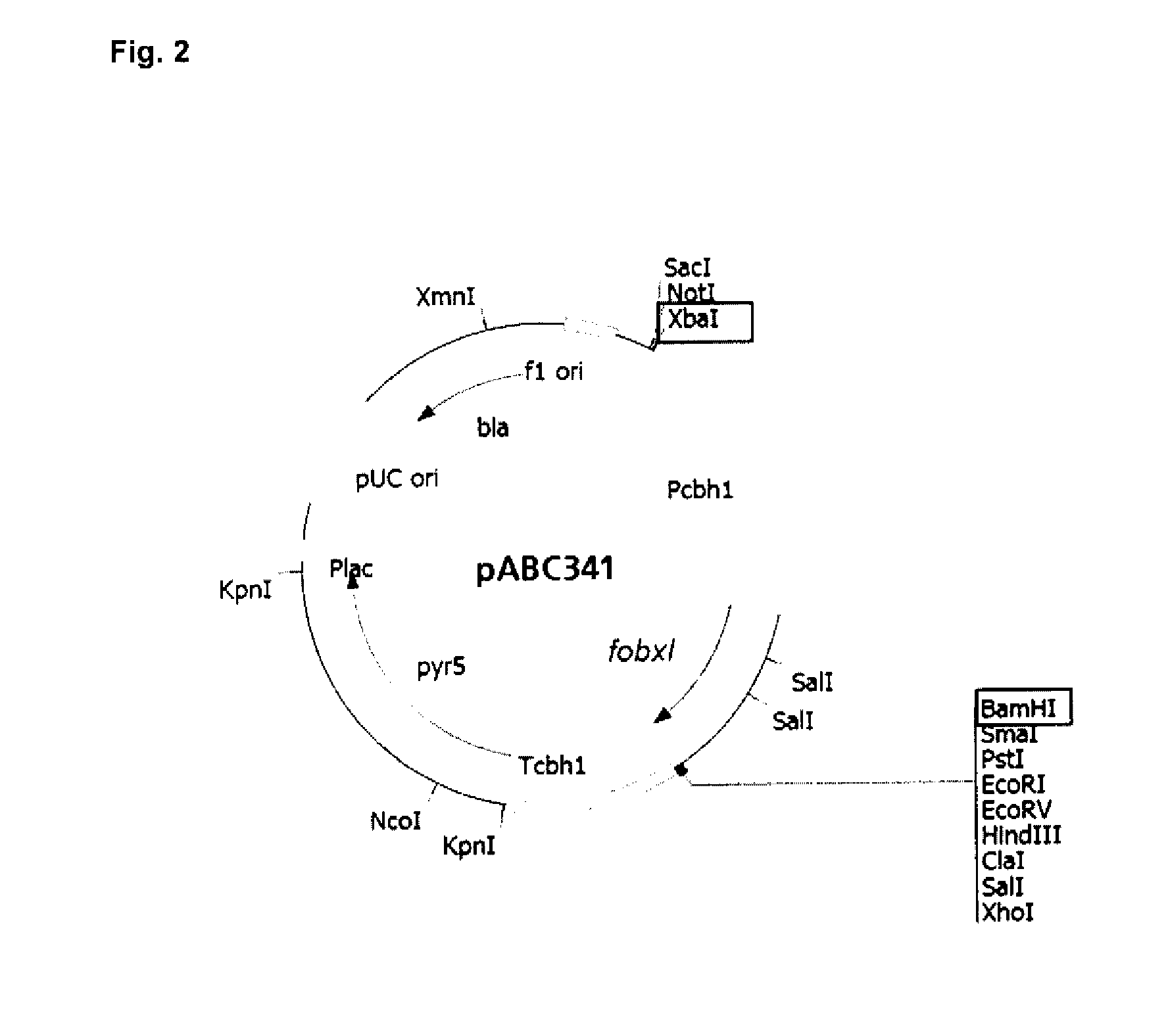
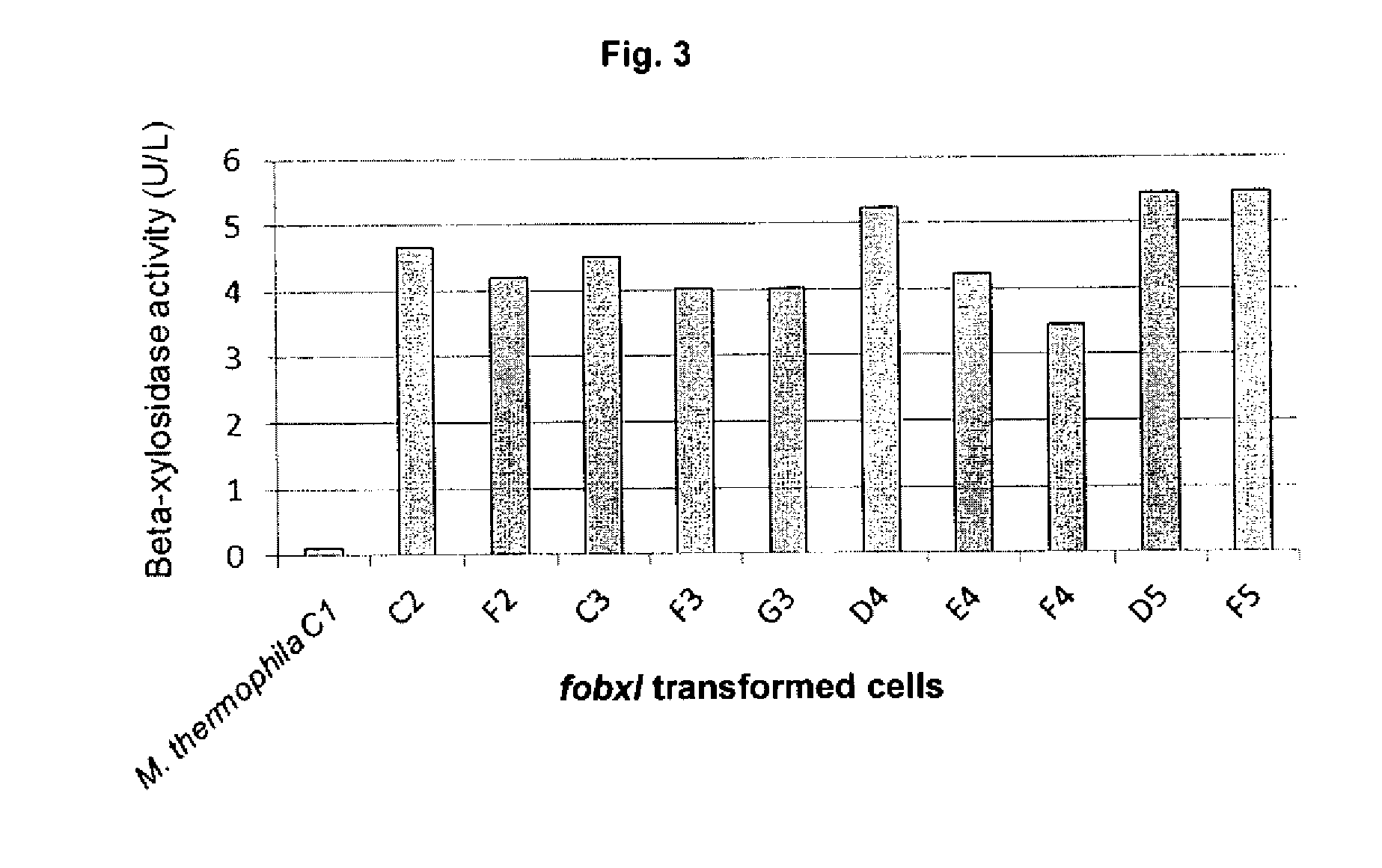
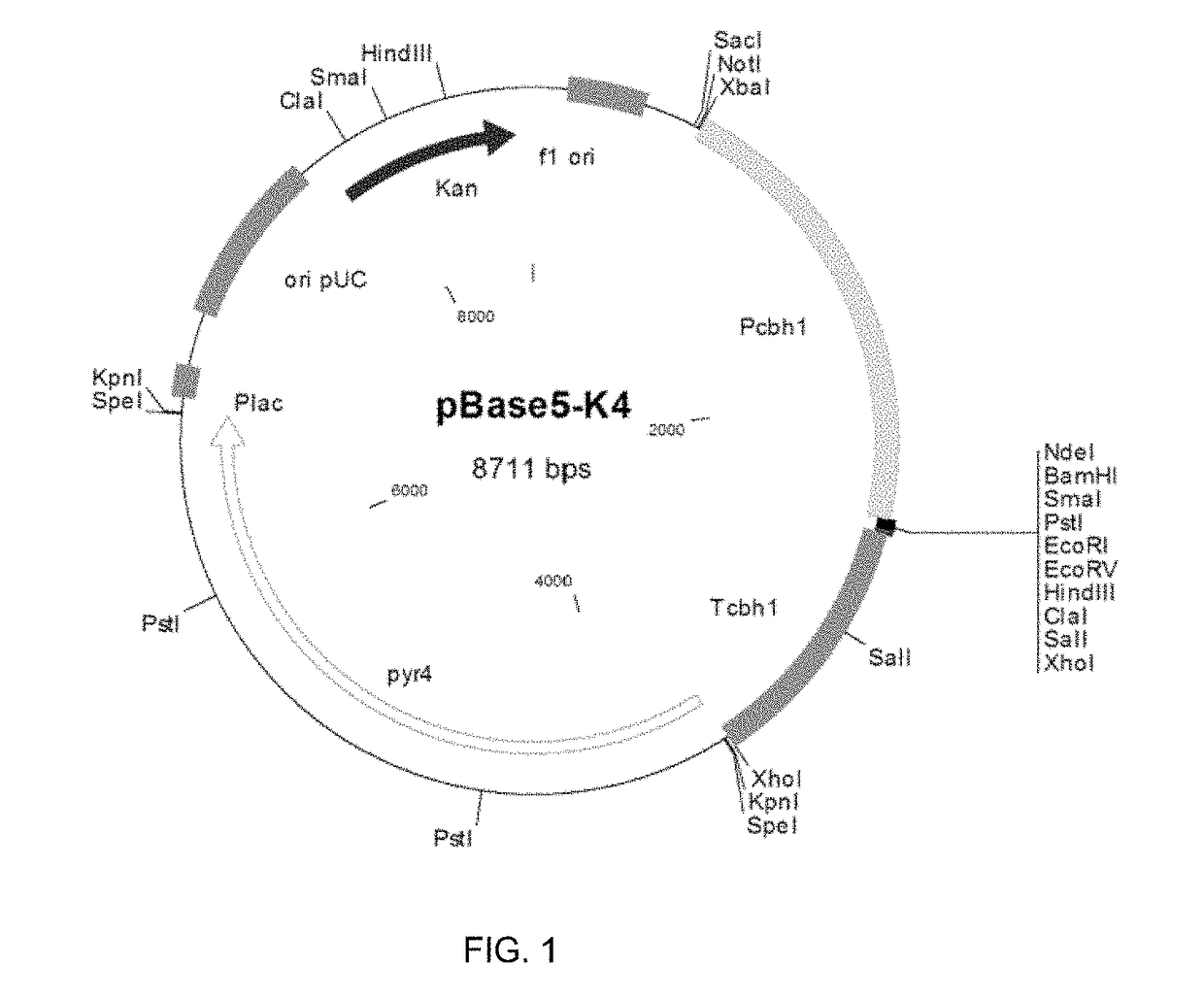
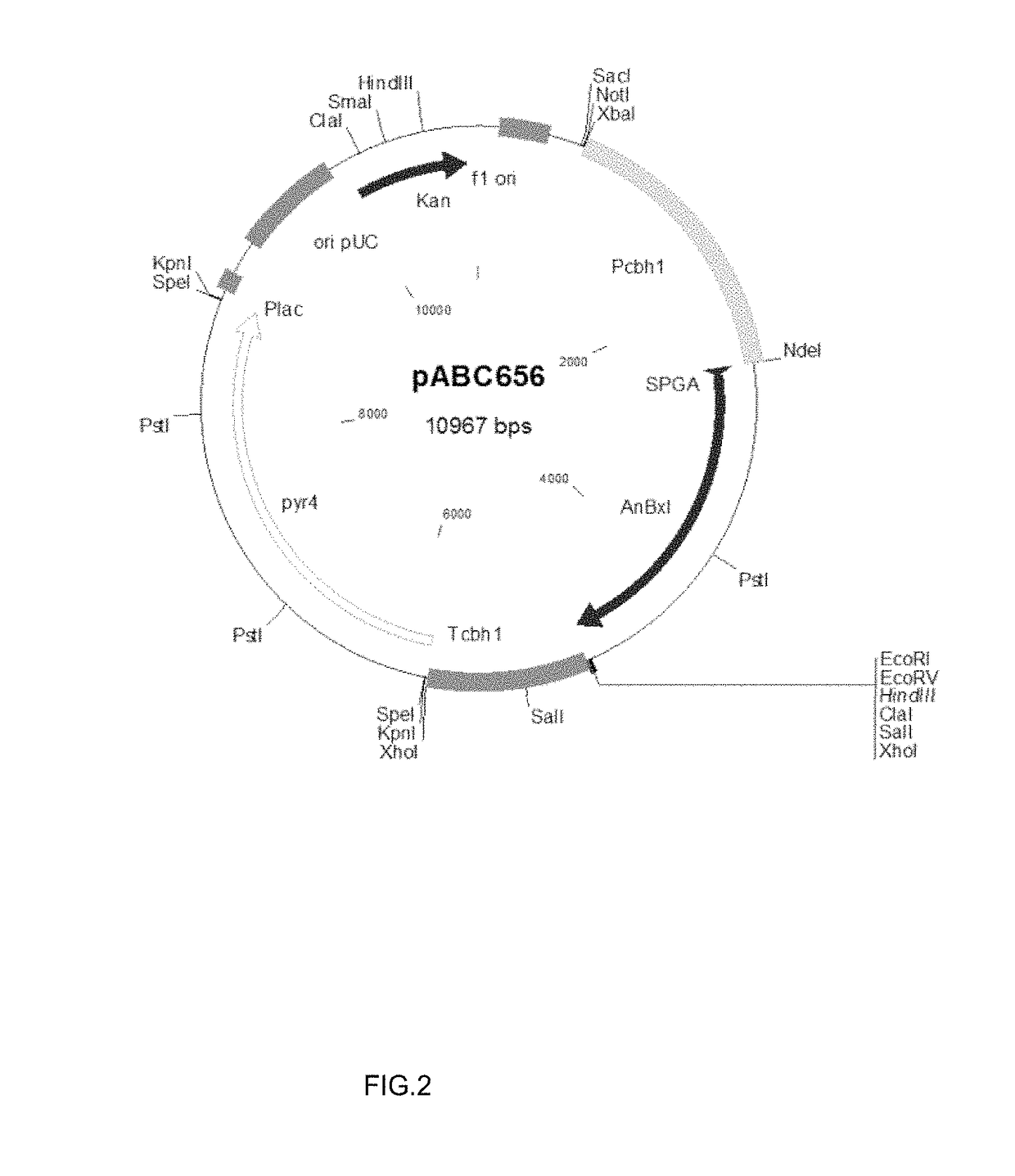
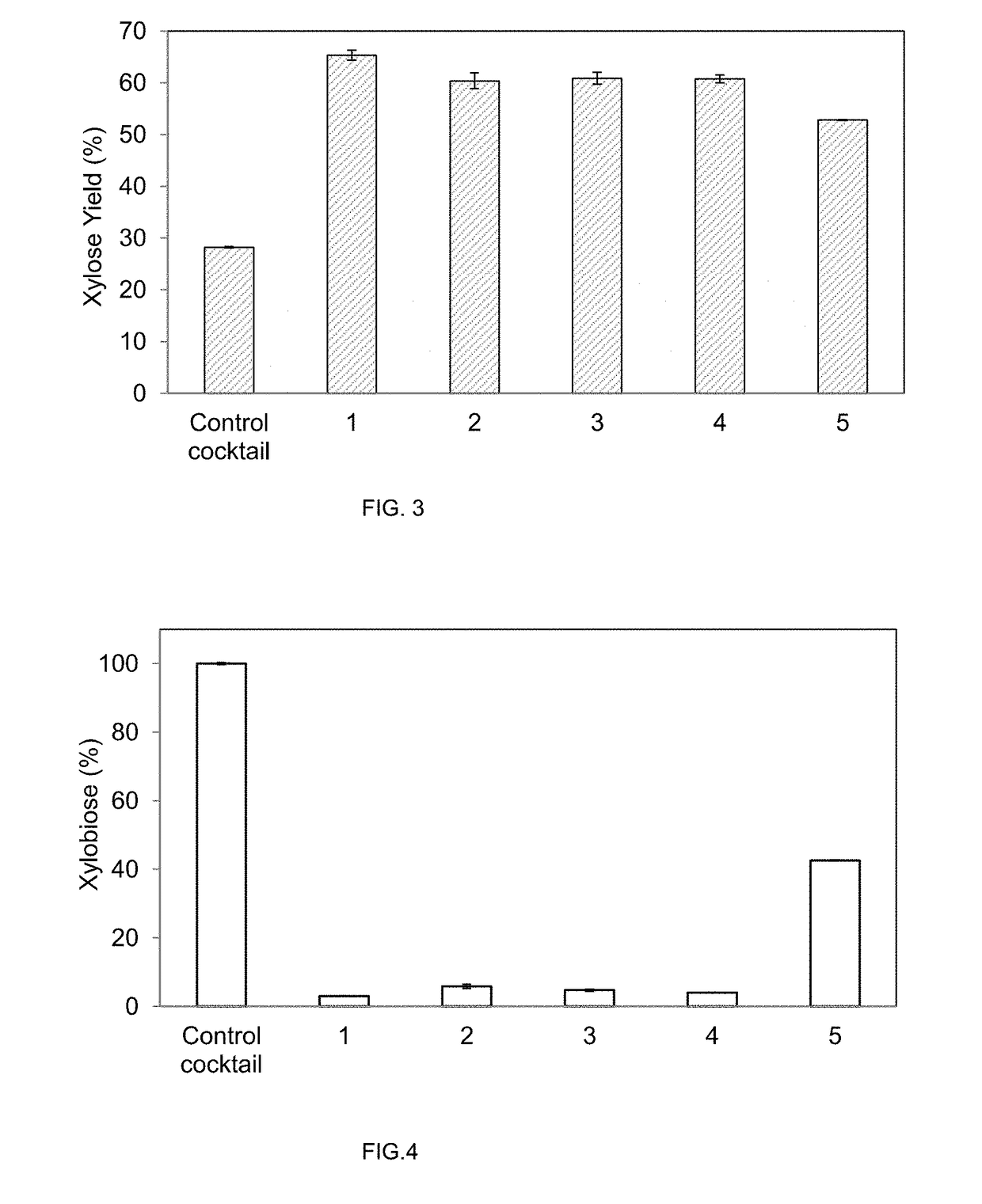
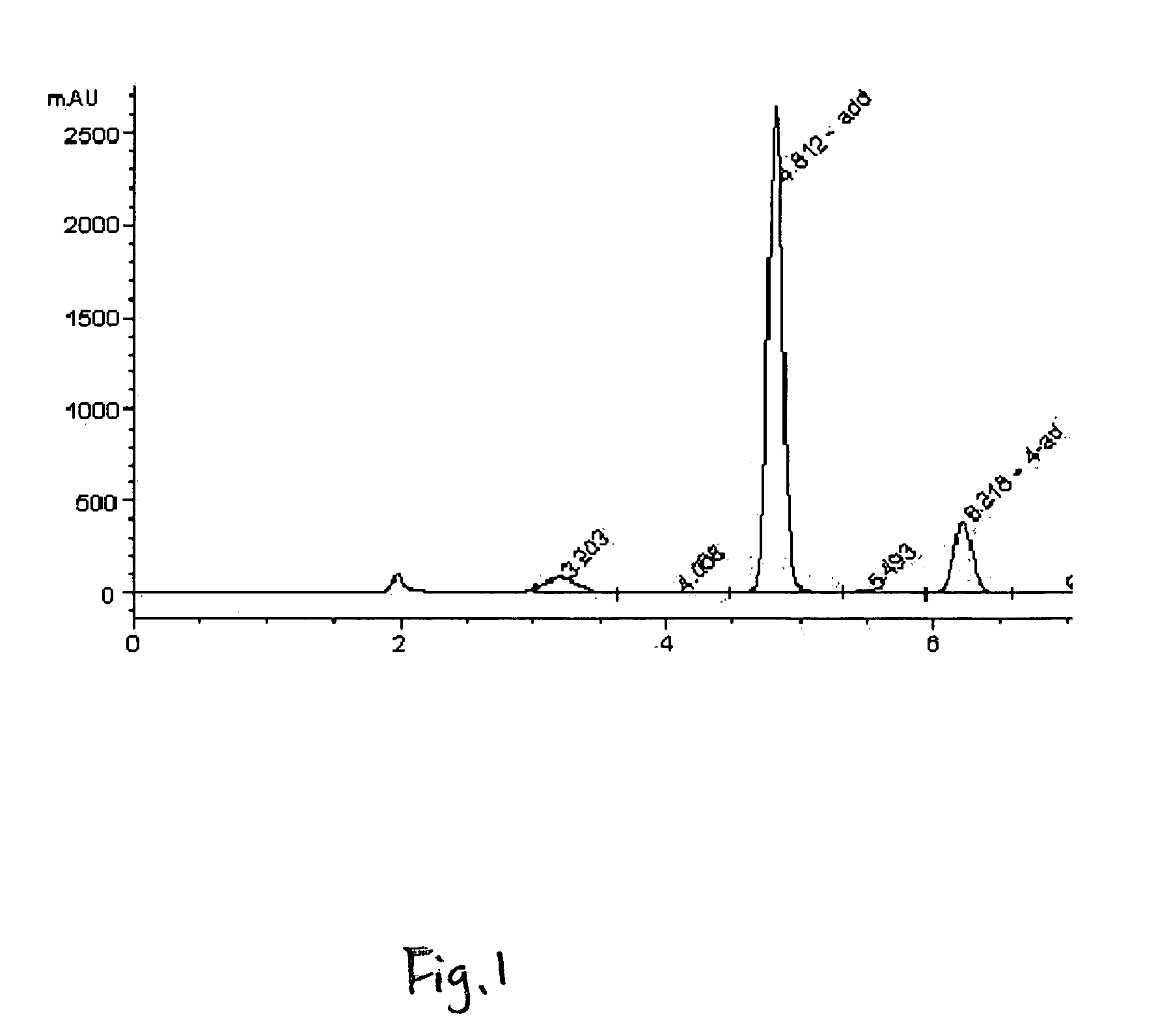
Expression of Recombinant Beta-Xylosidase Enzymes
InactiveUS20160272956A1Improve hydrolysis efficiencyIncrease productionBiofuelsFermentationBioproductsMyceliophthora thermophila
The present invention relates to a host cell, preferably Myceliophthora thermophila cell, which expresses recombinant enzymes with beta-xylosidase activity, an enzymatic composition comprising said cell and / or the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell, the use of this host cell, the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell or the composition for the degradation of biomass and a method of producing bioproducts, preferably bioethanol, which comprises the use of said host cell, the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell or said composition.
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGIA NUEVAS TECHAS
Method for producing peroxodisulfates in aqueous solution
ActiveCN100591805CNo costLow reduction lossCellsPeroxides/peroxyhydrates/peroxyacids/superoxides/ozonidesElectrolysisPeroxydisulfate
The invention describes a method for producing or regenerating persulfuric acid and the salts thereof by electrolysis of an aqueous solution containing sulfuric acid and / or metal sulfates on diamond-coated electrodes without using promoters. According to the inventive method, bipolar silicon electrodes are used which are diamond-coated on one side and whose uncoated silicon back is used as the cathode.
Owner:DEGUSSA INITIATORS GMBH & CO KG
Method for producing r-acetoin by Klebsiella pneumoniae
ActiveCN103388009BImprove conversion rateHigh optical purityMicroorganism based processesFermentationAcetoin reductaseMethods of production
The invention discloses a method for producing R-acetoin from klebsiella pneumoniae. Under an aerobiotic condition, the R-acetoin is produced from the klebsiella pneumoniae which is deactivated by an acetoin reductase gene budC through fermentation. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the raw material is reproducible carbon source and the conversion rate of the raw material is high, the final concentration of the product R-acetoin is high, and the produced R-acetoin has very high optical purity and the content of R-isomers in the total acetoin is greater than 98%.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process for concentration of macromolecules
ActiveUS7674885B2Reduce conductivityHigh final concentrationPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesDiluentCell culture supernatant
The invention provides methods for concentrating a macromolecule from a solution comprising the macromolecule and an organic polymer by first subjecting the solution to ultrafiltration to produce a first retentate solution, then adjusting the conductivity of the first retentate solution such that any protein precipitation induced by the organic polymer is essentially prevented to produce a second retentate solution, and then subjecting the second retentate solution to ultrafiltration. In a preferred embodiment, the conductivity is adjusted by diafiltration against water, suitable diluent or buffer.Preferably, the invention pertains to the concentration of solutions of native or recombinant proteins. The invention further pertains preferably to methods for the concentration of cell culture supernatant comprising a product protein and organic polymers of the PLURONIC family of nonionic block co-polymers, and more preferably comprising PLURONIC F-68 nonionic block co-polymer.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Peptide fractions promoting growth and synthesis of desired product(s) into cell and/or tissue culture
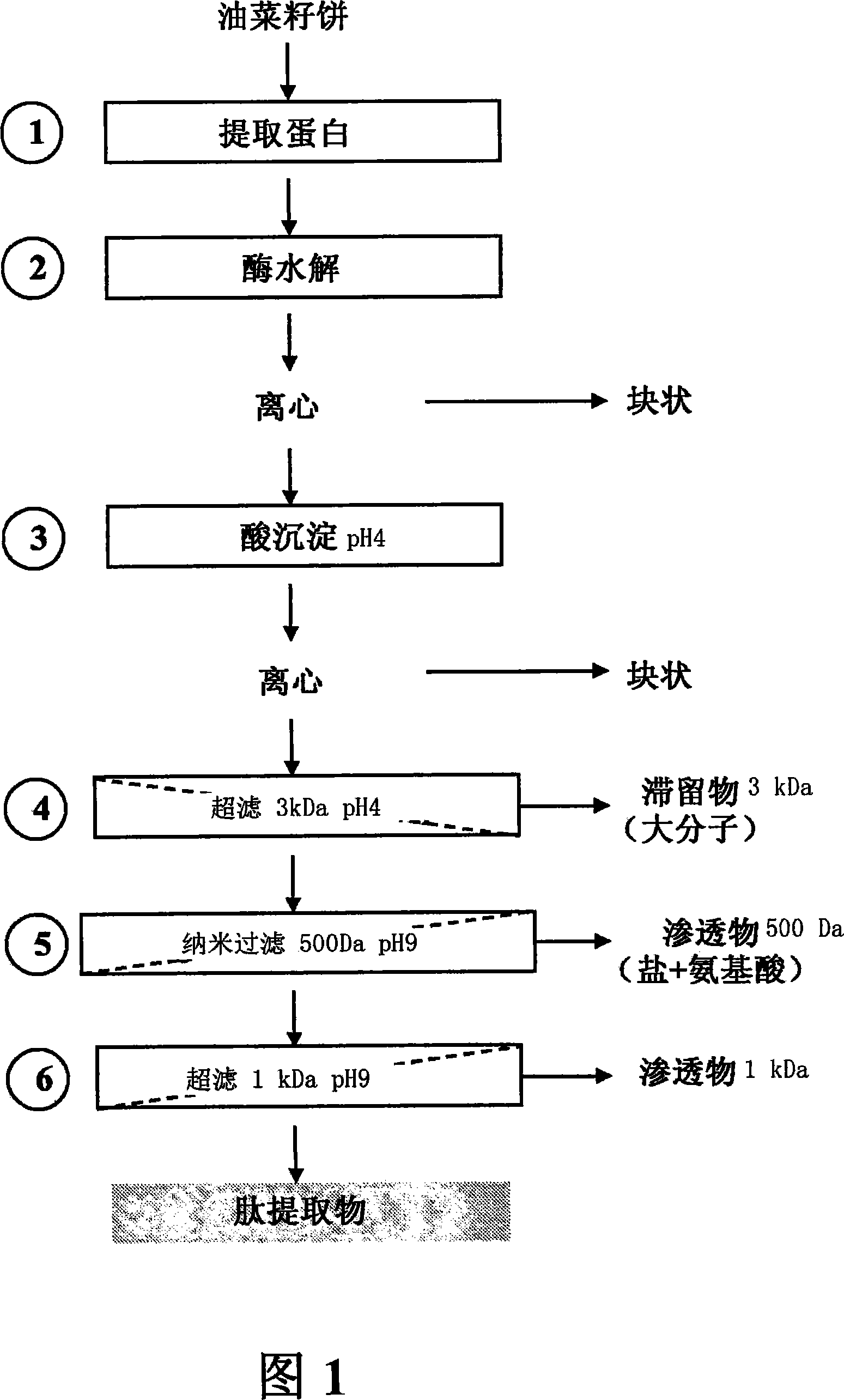
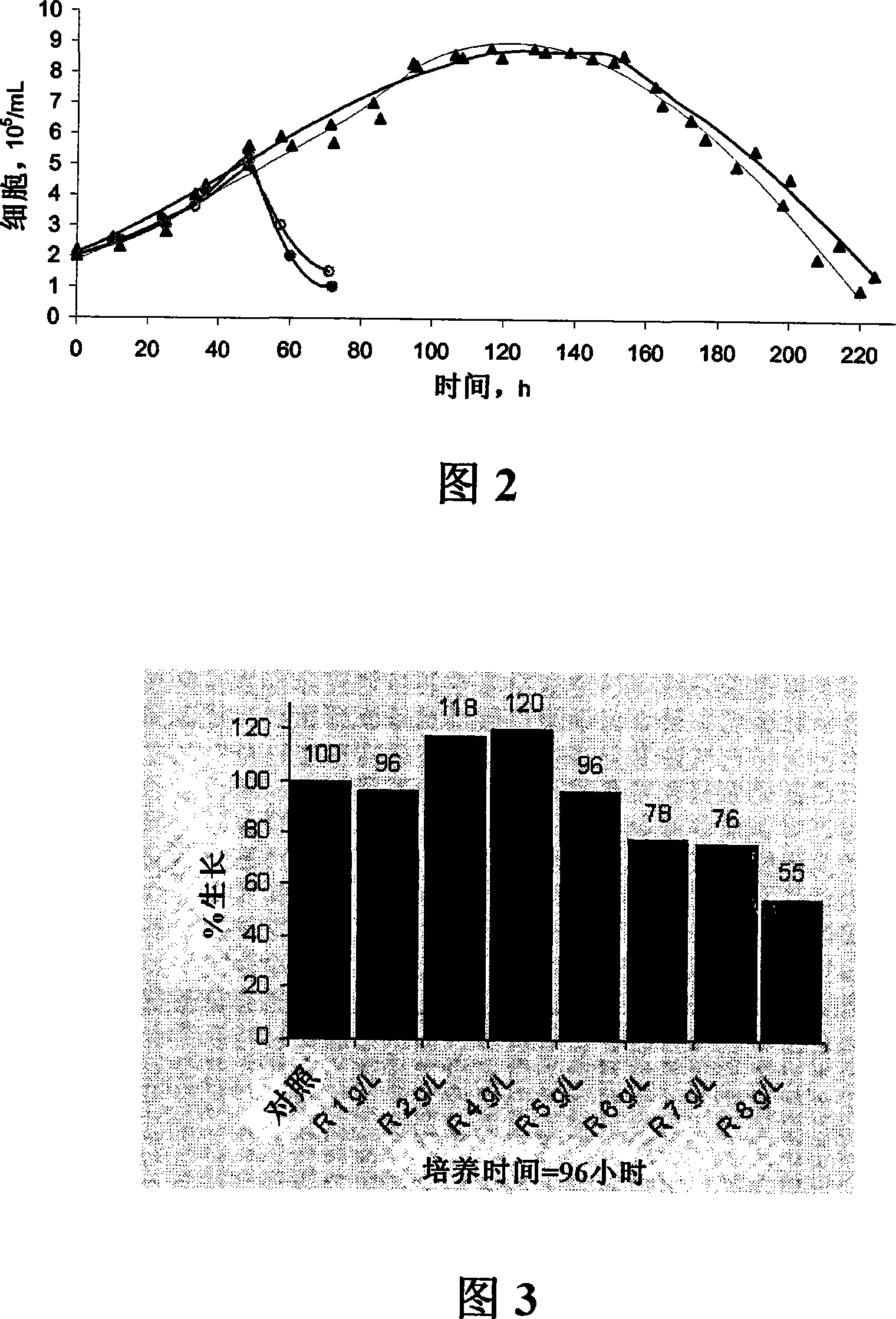
InactiveCN101084304AHigh final concentrationIncrease spawn rateAnimal cellsCulture processSerum freeCell culture media
The invention relates to preparing and / or supplementing a cell or tissue culture medium. In particular, said invention relates to a serum-free and / or protein-free cell culture medium comprising peptide fractions isolated from rapeseeds, in particular rapeseeds cakes. A method for the production of a cell culture comprising said peptide fractions and for the use thereof is also disclosed.
Owner:PIERRE FABRE MEDICAMENT SAS +1
Process for producing 1,3-propylene glycol by microorganism aerobic fermentation
The present invention provides microbial aerobic fermentation process of producing 1, 3-propylene glycol, and belongs to the field of biochemical technology. Seed liquid is first added into industrial glycerin or initial fermentation culture medium of glycerin fermenting liquid with glycerin concentration of 20-50 g / L, and under fermentation condition of 30-40 deg.c, the culture medium is fermented with PDO producing Klebsiella pneumoniae or acid producing Klebsiella pneumoniae to produce PDO. During fermentation, air in 0.2-1.0 vvm is led in, the fermented matter is stirred in 50-250 rpm, glycerin and sodium hydroxide in certain amount are added to maintain certain glycerin concentration. The present invention has the advantages of lowered investment and power consumption, raised final PDO concentration, raised production strength and increased bacteria biomass.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method of adding reducing agent from extraneous sources for accelerating thallus to synthesize 1,3-propylene glycol
InactiveCN1182249CImprove conversion rateHigh final concentrationFermentationGlycerolEquivalent weight
A process for preparing 1,3-propanediol biologically features that in the culture medium for fermenting or in the anaerobic fermenting procedure, appropriate reducer is added to increase the accumulation of reduction equivalent weight in thallus for promoting metabolism of glycerine along the reductino approach, and increasing the concentration and transform rate of 1,3-propanediol. Its advantage is high biologic utilization rate.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method of rebaudioside A, enzyme for preparing rebaudioside A, and use thereof
PendingCN109196110ALow costHigh yieldTransferasesGenetic engineeringGlucosyltransferasesIndustrial scale
The invention provides a preparation method of rebaudioside A, which comprises: preparing a reaction liquid by using a stevioside raw material as a substrate in the presence of uridine diphosphate glucose and glucosyltransferase, and adjusting the pH of the reaction solution to 6.0-8.0, after stirring reaction at a constant temperature of 20-45 DEG C, collecting rebaudioside A; the stevioside rawmaterial comprises stevioside, and the amino acid sequence of the glucosyltransferase comprises SEQ ID NO: 1 The amino acid sequence shown. The preparation method is a high-efficiency, simple, low-cost, high conversion rate, green and environmentally friendly biological enzymatic method, and can be widely applied to industrial scale production. The invention also provides an enzyme and applicationfor the preparation of rebaudioside A.
Owner:BONTAC BIO ENG SHENZHEN
Expression of recombinant beta-xylosidase enzymes
InactiveUS20180230446A1Improve hydrolysis efficiencyIncrease productionFungiBiofuelsNucleotideMyceliophthora thermophila
The present invention relates to a Myceliophthora thermophila cell, which expresses a nucleotide sequence that codifies a recombinant beta-xylosidase enzyme comprising an amino-acid sequence having at least 70% identity with SEQ ID NO: 1, an enzymatic composition comprising said cell and / or the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell, the use of this host cell, the recombinant enzyme with beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell or the composition for the degradation of biomass, and a method of producing biological products, preferably bioethanol, comprising the use of said host cell, the recombinant enzyme with the beta-xylosidase activity expressed by said cell or said composition.
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGIA NUEVAS TECHAS
Use of Cloud Point System in Biotransformation
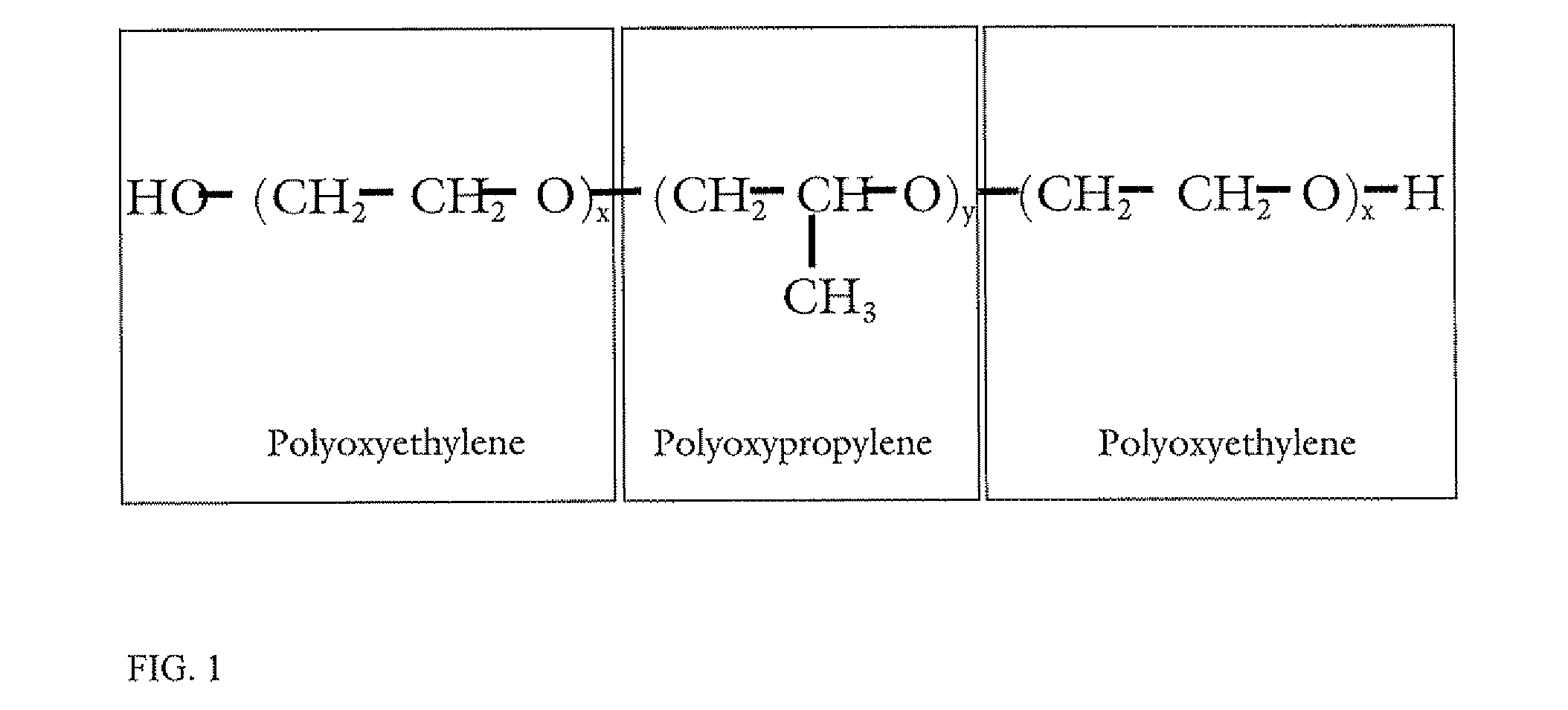
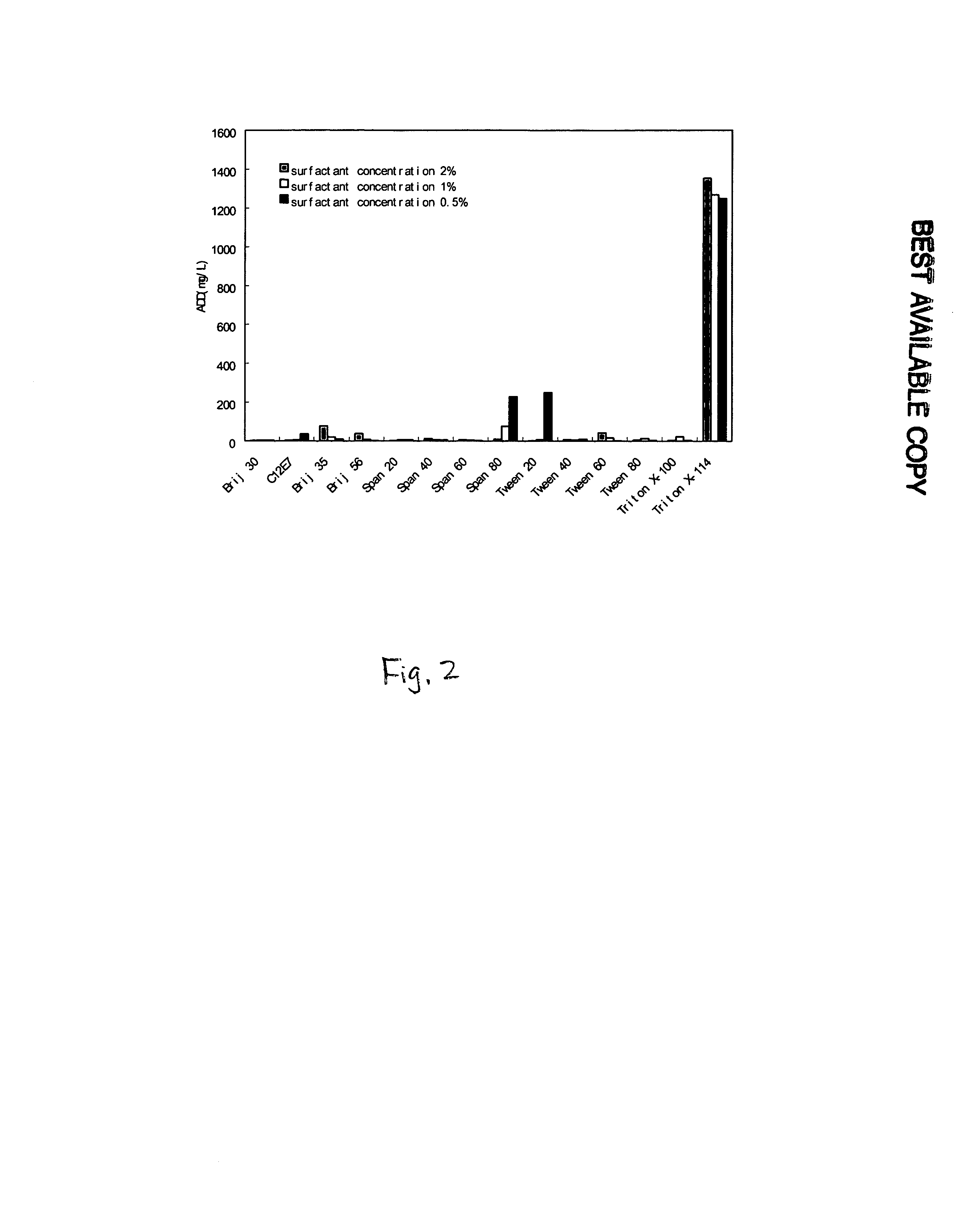
InactiveUS20070259428A1Increase mass transfer rateGood biocompatibilityBacteriaOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyMicrobial transformation
The invention relates to the field of microbial technology. It discloses a method to apply the cloud point system (CPS) in biotransformation by selecting one or more types of nonionic surfactant to form a aqueous system with a cloud point below the microbial transformation temperature, which serves as transformation medium. The method disclosed is suitable in particular for microbial transformation of hydrophobic compounds, for the system where substrate or product inhibits microbial growth or where product is further degraded by microbes. The CPS in the present invention forms a microemulsion of water-in-oil and oil-in-water, where the drops of surfactant is able to solubilize, serving as substrate reservoir and product extractant. This enhances bioavailability of substrates and elimination of product inhibition. The large water vesicles existing in the continuous surfactant phase provide aqueous environment to the cells where they can be sheltered from detrimental effects of surfactants, resulting in improvement of biocompatibililty.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
Method for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate through middle feeding fermentation
ActiveCN102899373AOvercoming inhibitory effectRemove inhibitionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBatch fermentationMicrobiology
The invention provides a method for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate through middle feeding fermentation. The method for producing cyclic adenosine monophosphate through middle feeding fermentation allows the cyclic adenosine monophosphate to be produced through batch fermentation in an intermittent uniform-speed feeding manner, fermentation strains are Arthrobacter sp having a preservation number of CGMCC No.3584, and a feeding carbon source is intermittently fed after the exponential phase of fermentation in a uniform speed manner each 3-10h 4-10 times. The method has the advantages of low concentration of the carbon source in the whole culture process, basic exhaustion of the carbon source after the fermentation ending, feedback inhibition reduction, and great increase of the output of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
A method for separating wheat high and low molecular weight glutenin subunit sds-page
InactiveCN108828049BReduce dosageHigh final concentrationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGluteninBiochemistry
The invention relates to an SDS-PAGE separation method for high-and-low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in wheat. The SDS-PAGE separation method comprises the following steps: removal of alcohol-soluble proteins; reduction of glutenin; mixed alkylation of glutenin subunits and a sample buffer; and SDS-PAGE. The method of the invention reduces the usage amount of a reagent, omits the preparationof a sample and shortens sample preparation time on the premise of maintaining sample separation effect.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
Method and equipment for separating volatile organic matters from fermentation product in situ
InactiveCN101928200BIncrease production capacityImprove separation efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsWater vaporDistributor
Owner:青岛生物能源与过程研究所
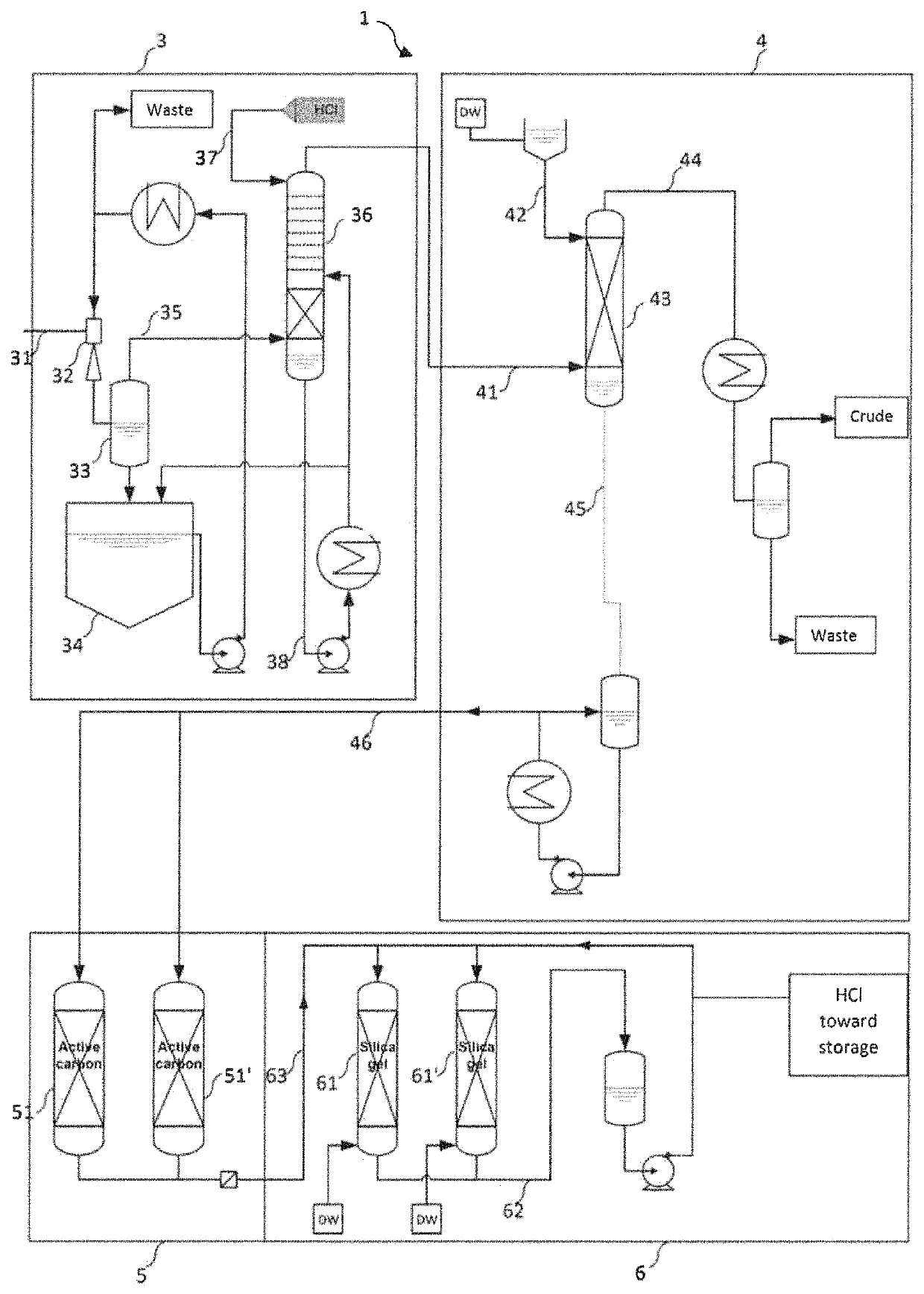
Hydrochloric acid purification process and plant
ActiveUS10576417B2Reduce contentHigh final concentrationChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationGas treatmentCatalytic pyrolysisActivated carbon
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
Quick extracting method for lotus rhizome tissue total RNA
InactiveCN1284852CReduce distractionsIncrease concentrationFermentationPlant genotype modificationExperimental drugTotal rna
The invention discloses a method for rapidly extracting total RNA from lotus root tissue. The steps are: first, the preparation of experimental medicines and the treatment of experimental supplies; second, the collection of materials, the young leaves of lotus root and the petioles connected with the leaves; the third, extraction, precipitation, and centrifugation to obtain total RNA; the fourth is The identification of total RNA was detected by UV spectrophotometer and formaldehyde-denatured agarose gel electrophoresis respectively. According to the obtained data and electrophoresis results, it was shown that the obtained lotus root tissue total RNA had good integrity, high purity and high yield. The invention has the advantages of simple and convenient experimental process, convenient and safe operation, accurate and effective results and good repeatability, and the method is also suitable for extracting total RNA from plant tissues of other species rich in polysaccharides and polyphenols.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
SDS-PAGE separation method for high-and-low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in wheat
InactiveCN108828049AReduce dosageHigh final concentrationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAlkyl transferAlcohol
The invention relates to an SDS-PAGE separation method for high-and-low-molecular-weight glutenin subunits in wheat. The SDS-PAGE separation method comprises the following steps: removal of alcohol-soluble proteins; reduction of glutenin; mixed alkylation of glutenin subunits and a sample buffer; and SDS-PAGE. The method of the invention reduces the usage amount of a reagent, omits the preparationof a sample and shortens sample preparation time on the premise of maintaining sample separation effect.
Owner:HEBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY SCI INST OF GENETICS & PHYSIOLOGY
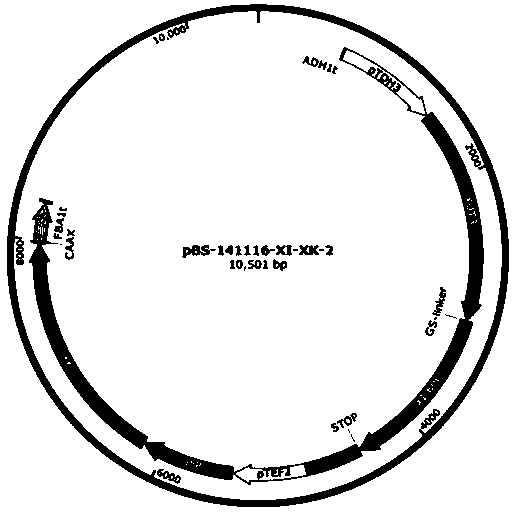
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain producing ethanol, its construction method and method for producing ethanol using the strain
The invention provides a recombined saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing ethyl alcohol, a construction method of the recombined saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a method for producing ethyl alcohol through the recombined saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. According to the recombined saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing ethyl alcohol, a wild type saccharomyces cerevisiae strain is used as an original strain, an XI xylose metabolism pathway is introduced into the original strain, the expression of four key genes in a PPP pathway is enhanced, meanwhile, the aldose reductase gene GRE3 is knocked out, the nitrobenzene phosphatase gene PHO13 is optionally knocked out, and XI protein and XK protein introduced exogenously are positioned to a yeast cell membrane through the membrane positioning effect of a membrane positioning group. The recombined saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing ethyl alcohol can efficiently carry out xylose metabolism, so that co-fermentation of C5 sugar and C6 sugar is achieved, and therefore the higher ethyl alcohol conversion rate is achieved.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
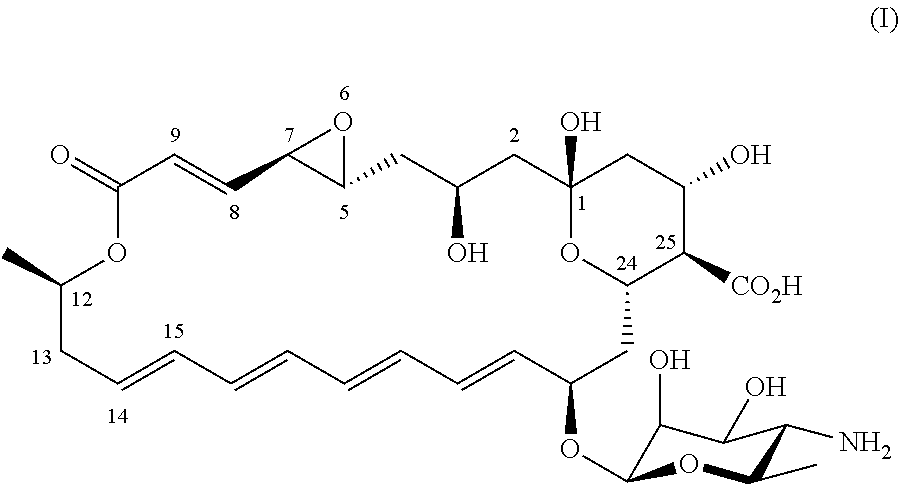
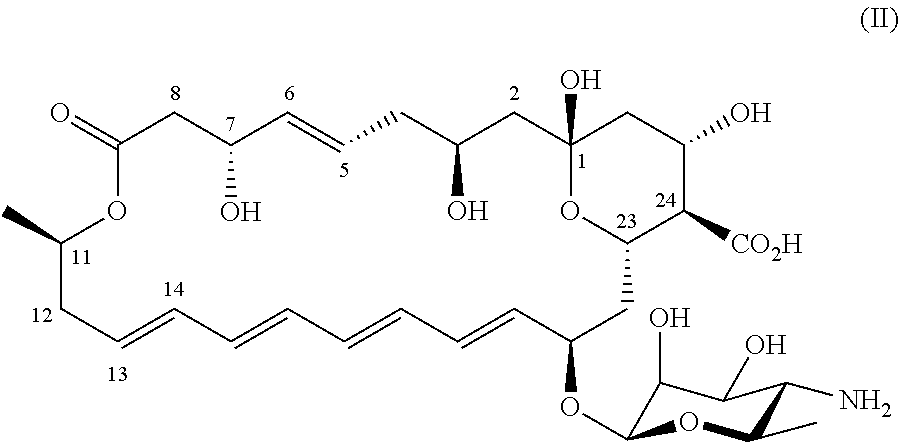
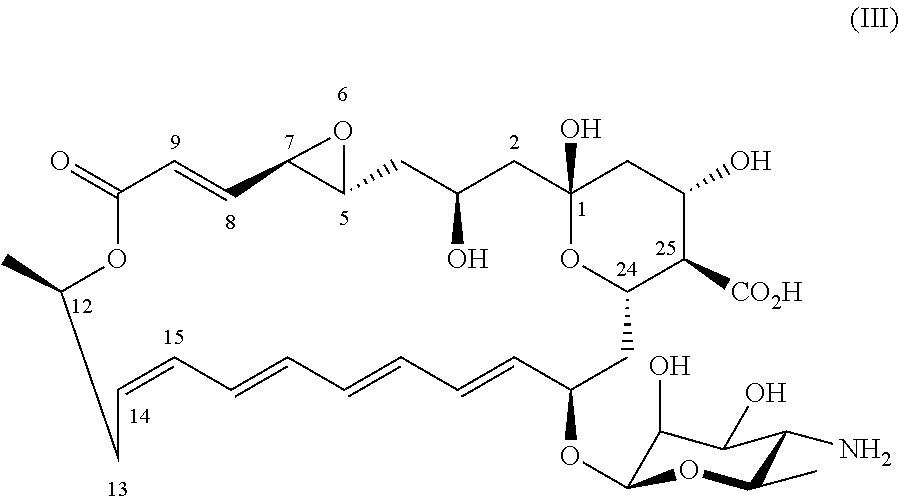
Novel all-trans polyene amphoteric macrolide
ActiveUS20210230207A1Improve stabilityDissolve fastSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationNatamycinePolyene
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com