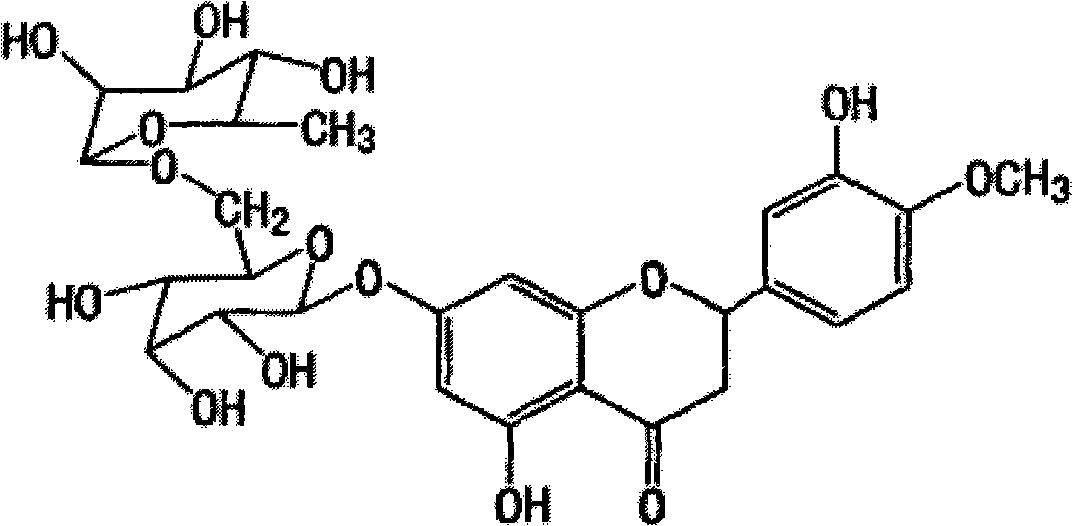
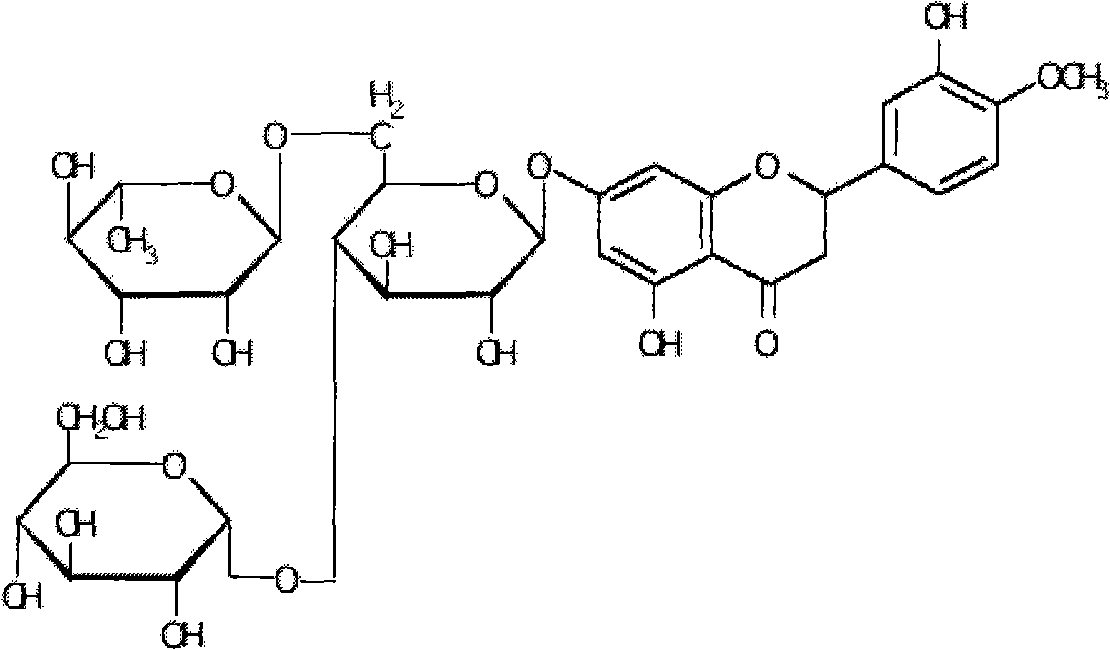
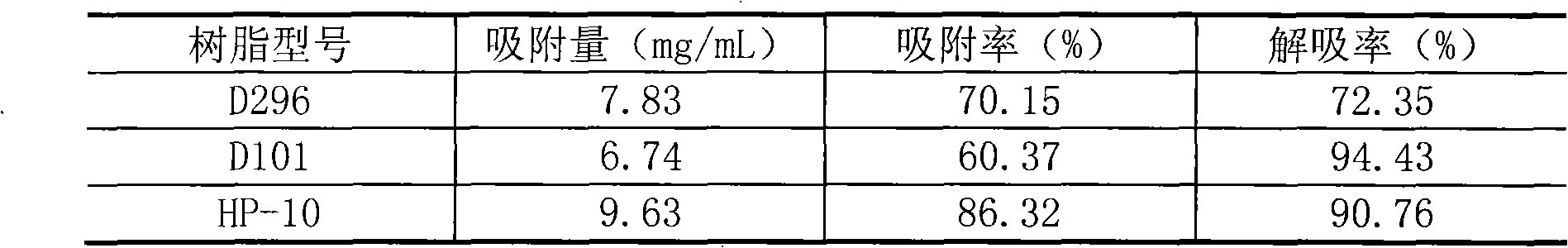
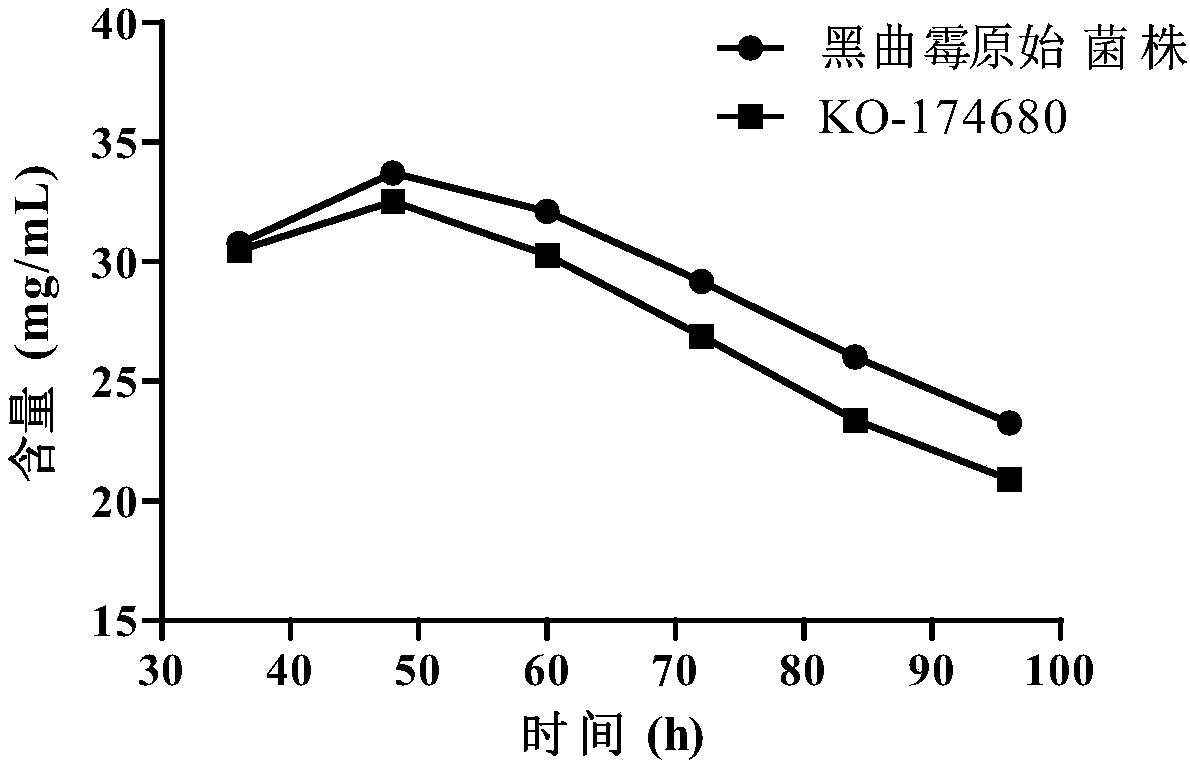
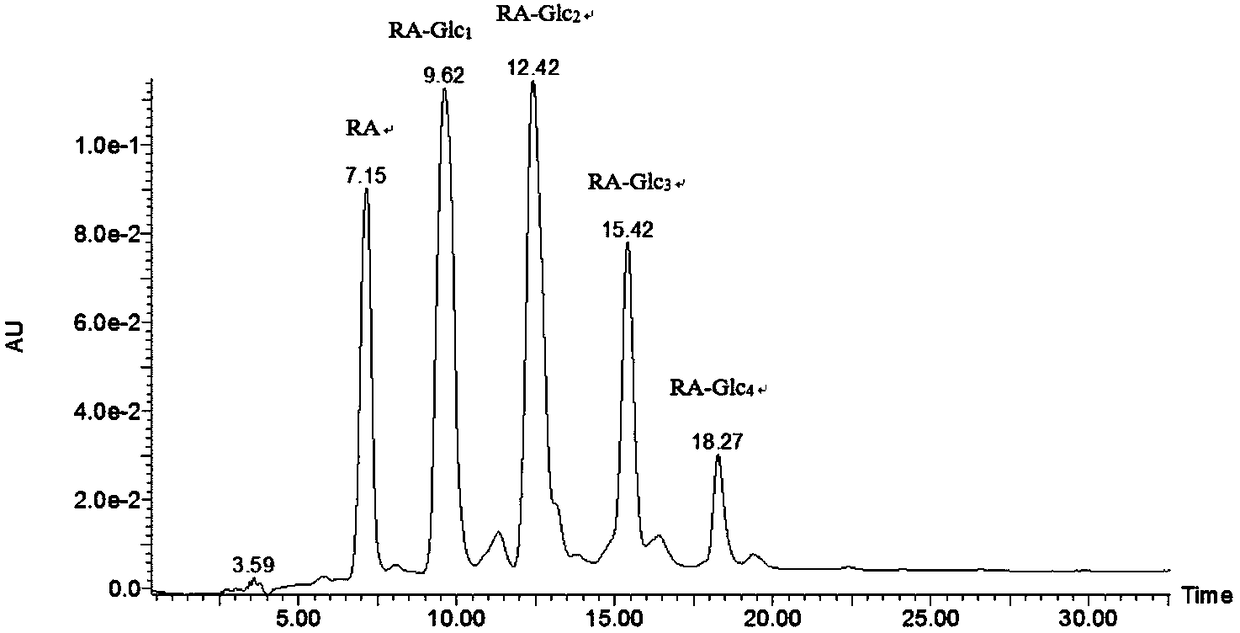
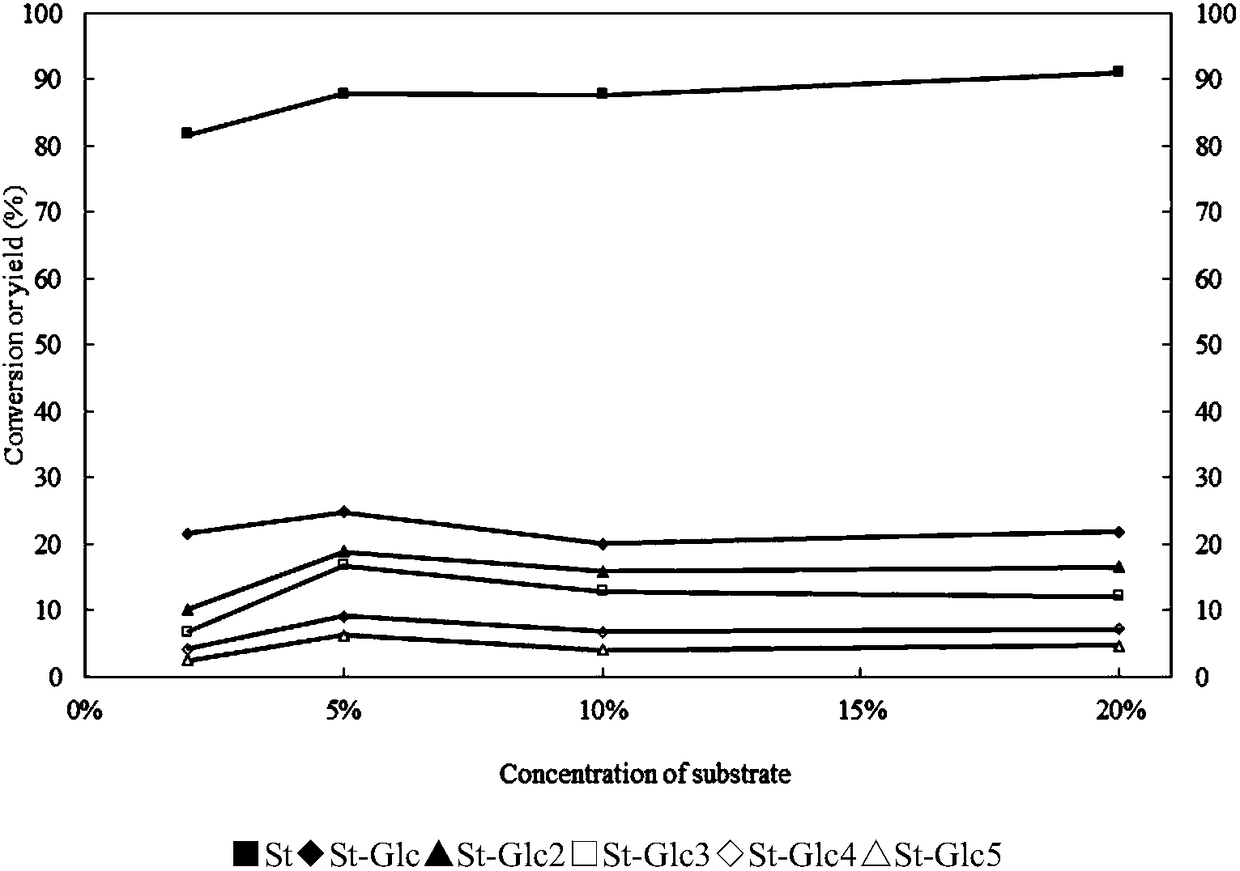
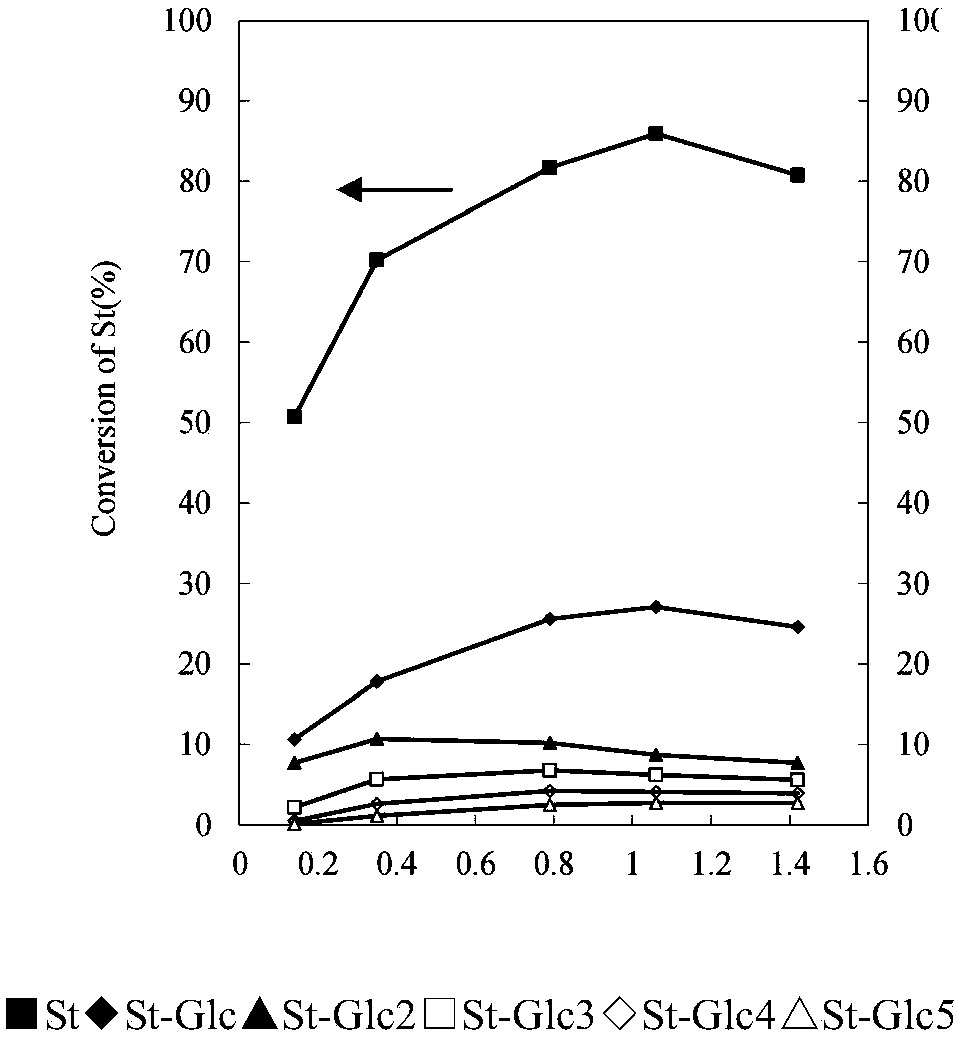
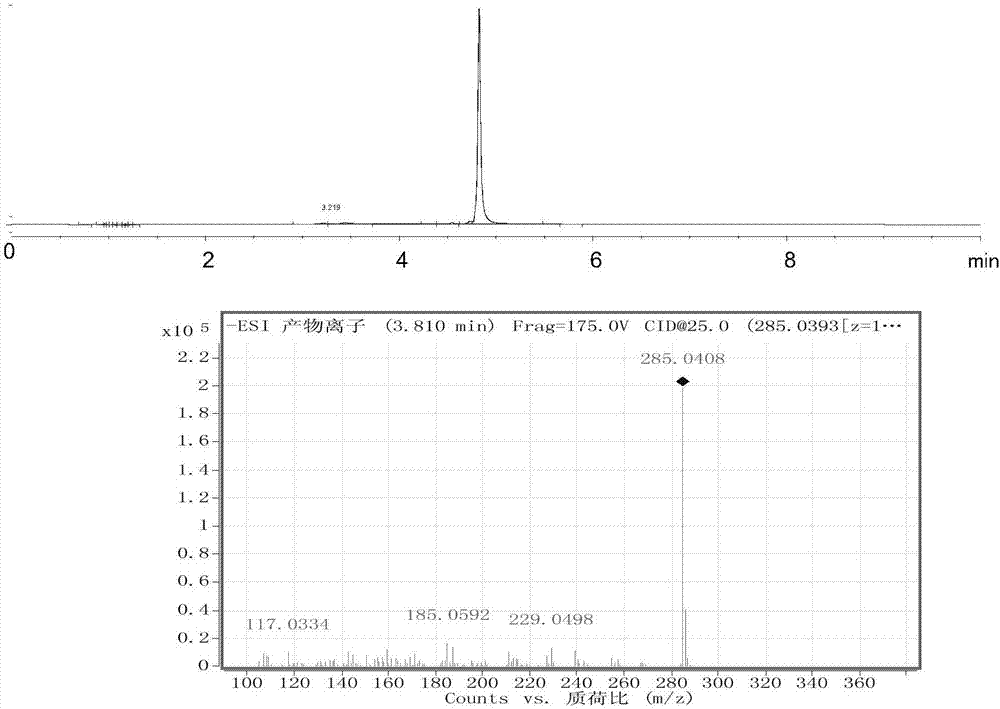
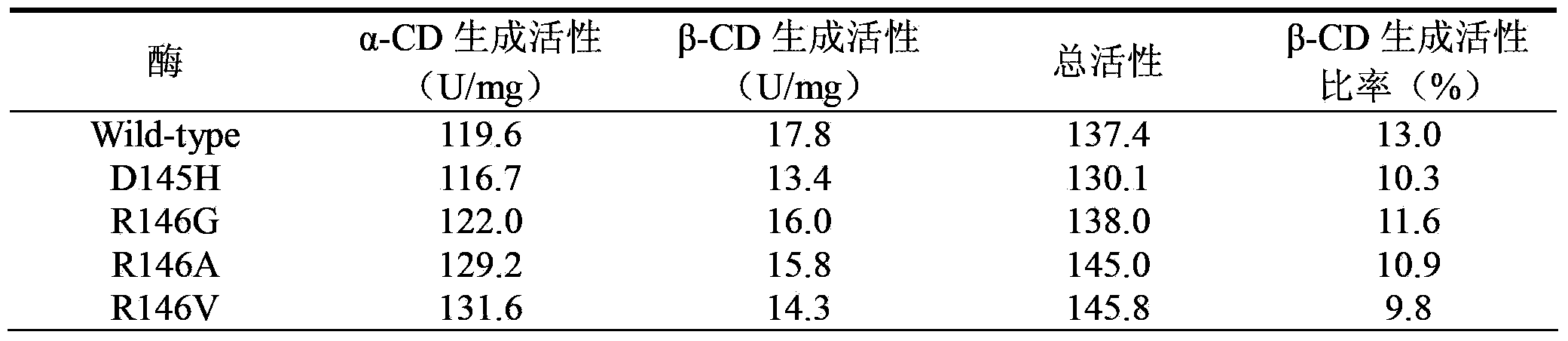
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
61 results about "Glucosyltransferases" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Enzymes that catalyze the transfer of glucose from a nucleoside diphosphate glucose to an acceptor molecule which is frequently another carbohydrate. EC 2.4.1.-.
High titer production of highly linear poly (alpha 1,3 glucan)
ActiveUS20130244287A1Improve mechanical propertiesMore amenable to preparing fibersTransferasesFermentationSucroseSaccharophagus degradans
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 4 INC
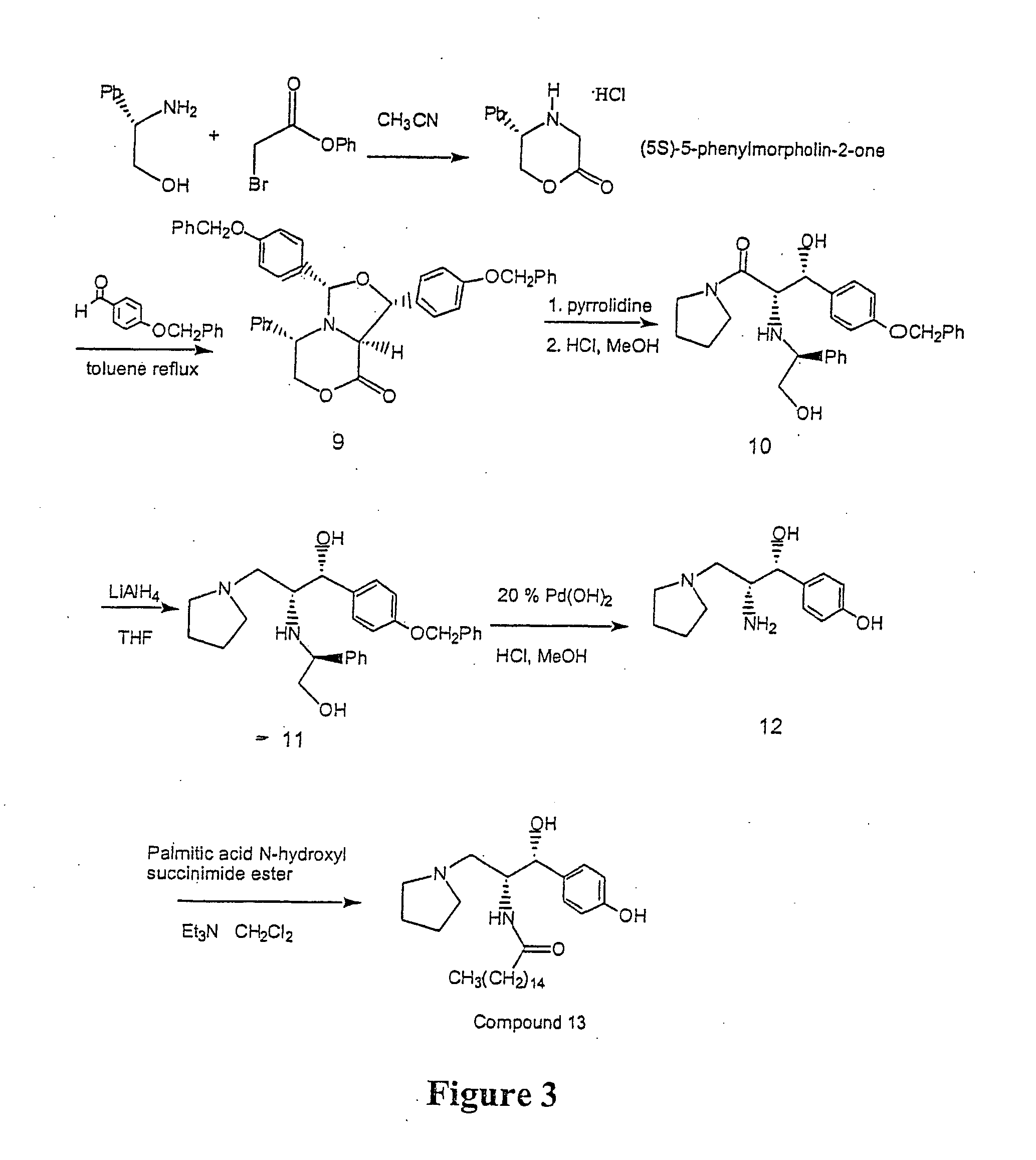
Synthesis of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase inhibitors
Disclosed is a novel enantiomeric synthesis ceramide-like inhibitors of UDP-glucose: N-acylsphingosine glucosyltransferase. Also disclosed are novel intermediates formed during the synthesis.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
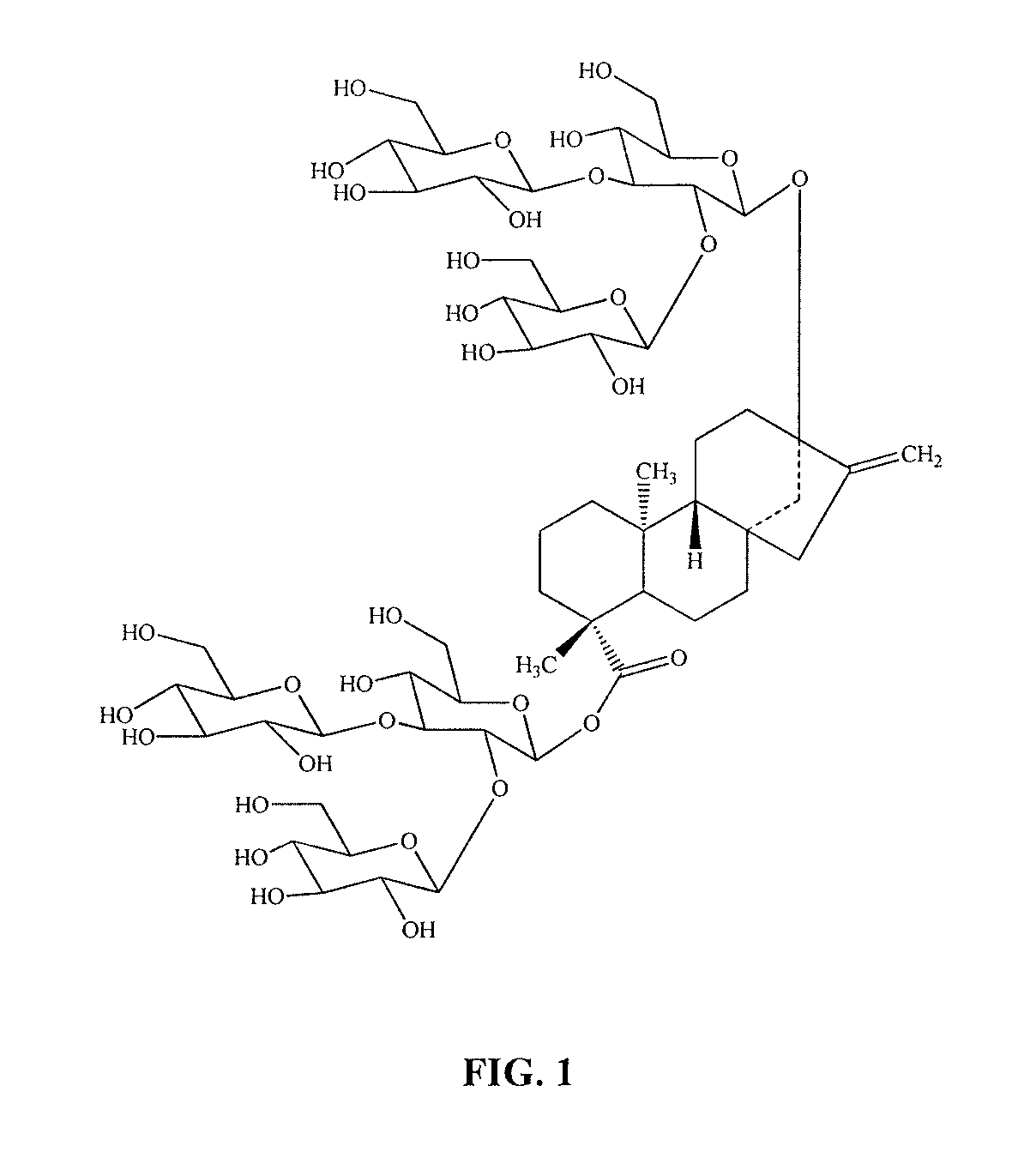
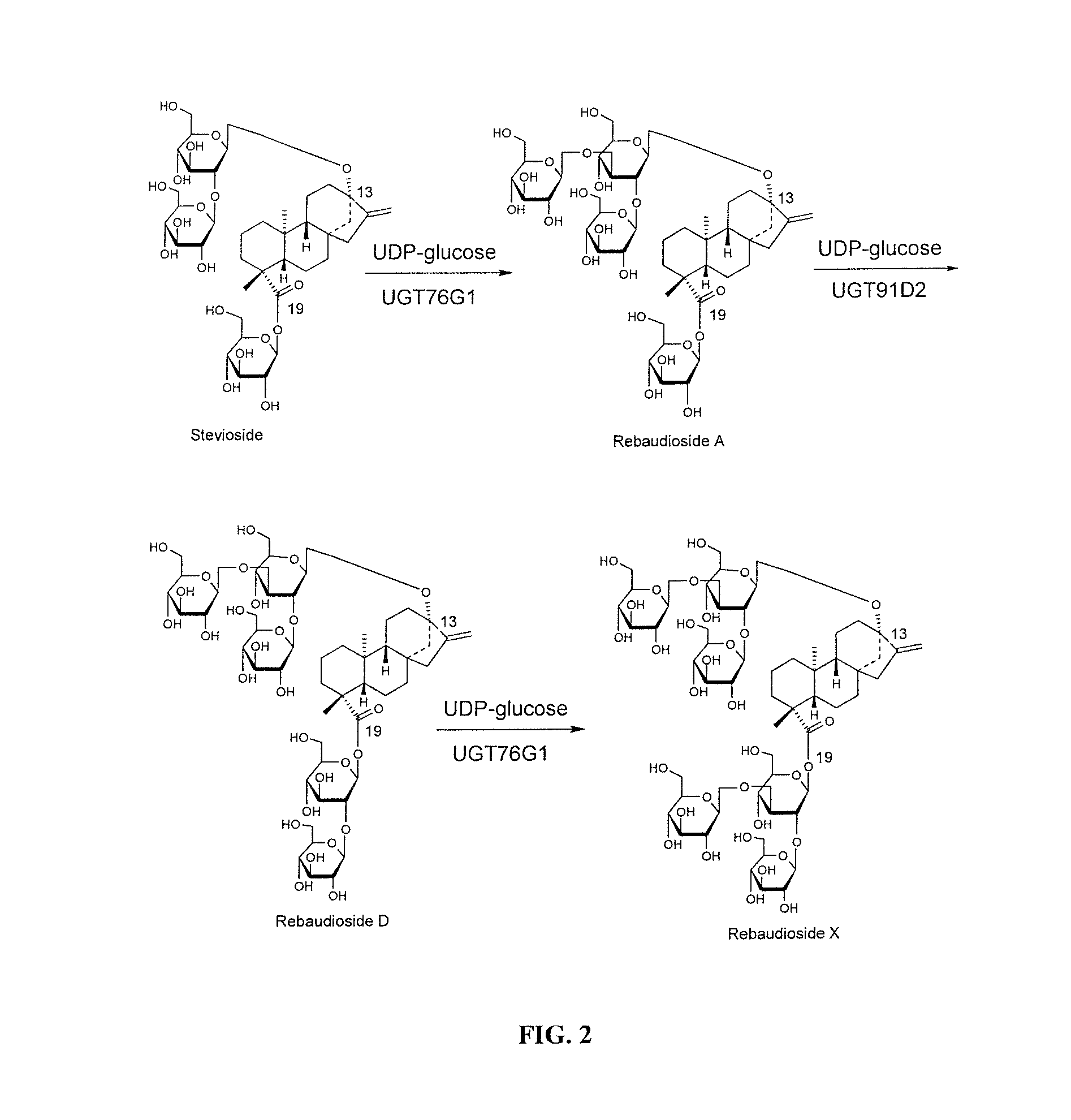
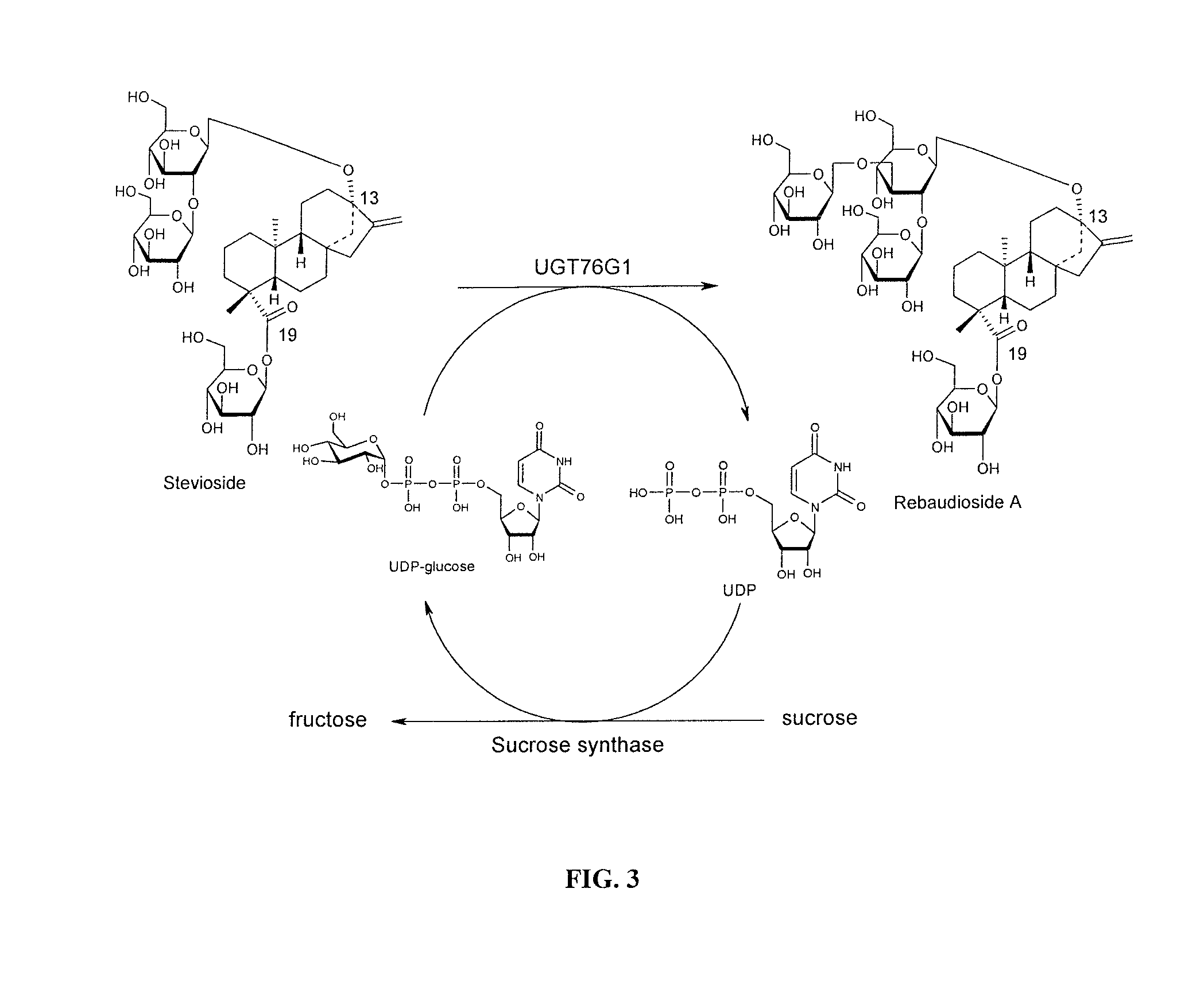
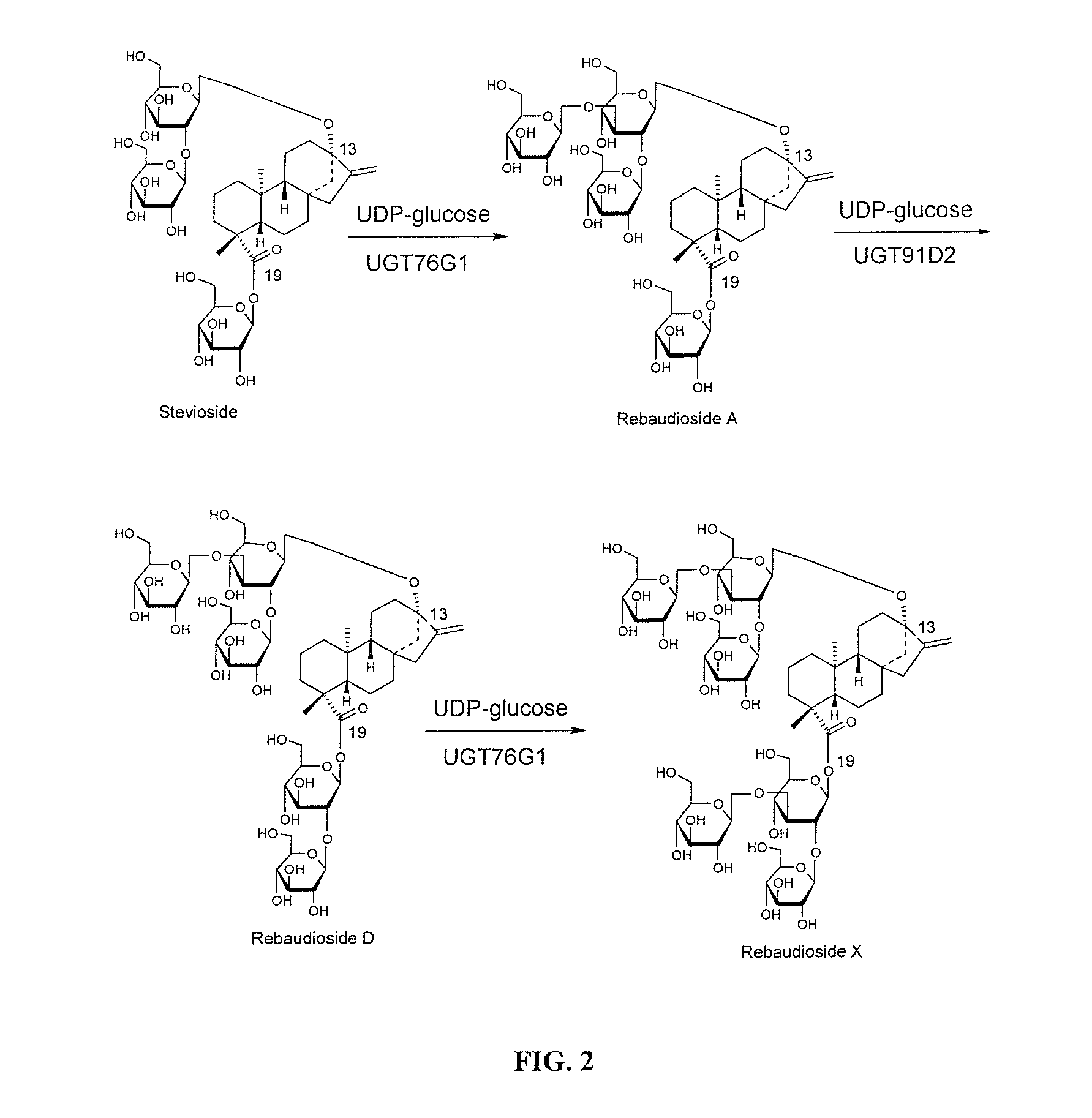
Method for making rebaudioside X
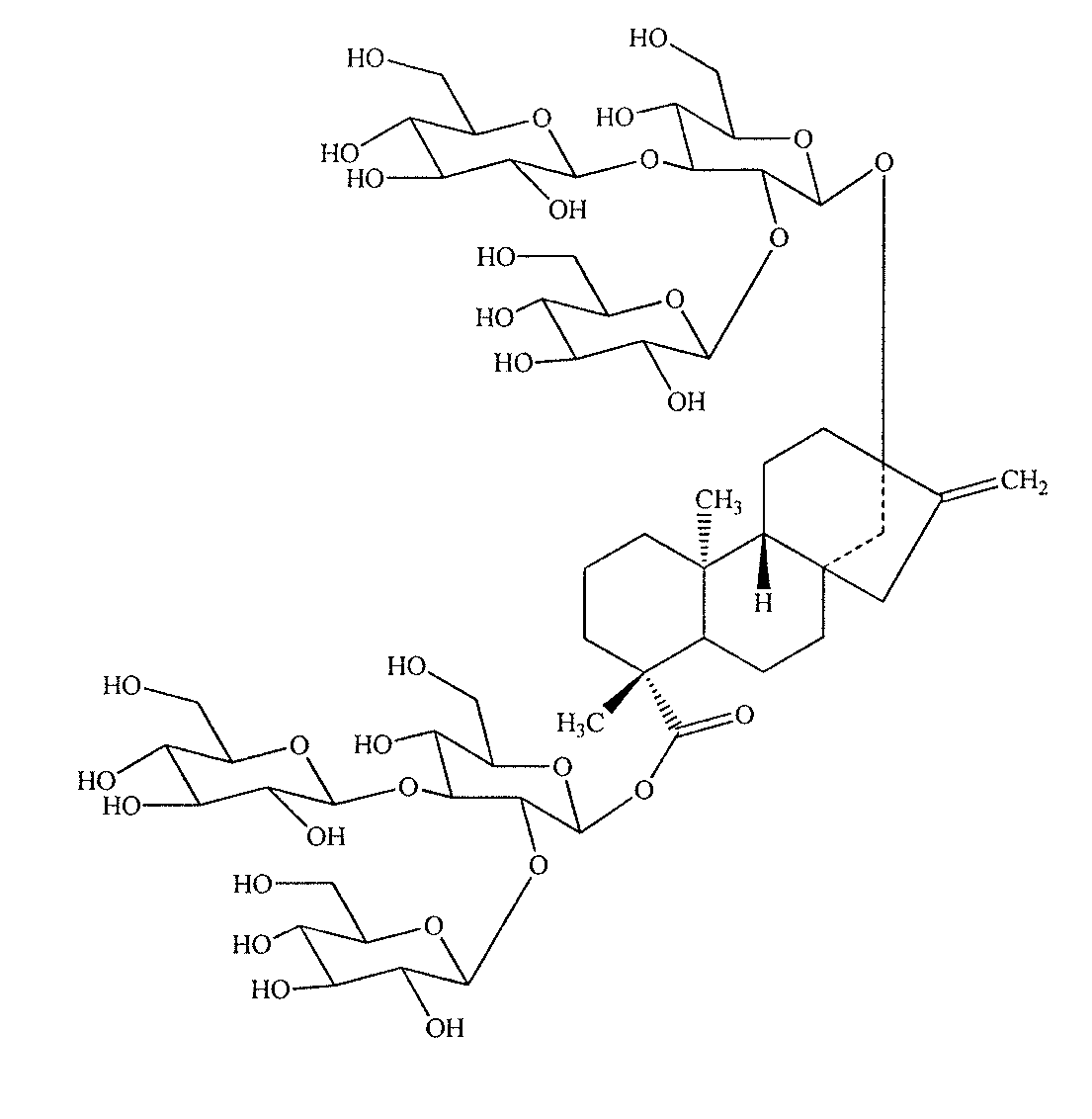
Methods of preparing highly purified steviol glycosides, particularly rebaudiosides A, D and X are described. The method includes expression of UDP-glucosyltransferases from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, which are capable converting certain steviol glycosides to rebaudiosides A, D and X. The highly purified rebaudiosides A, D and X, are useful as non-caloric sweetener in edible and chewable compositions such as any beverages, confectioneries, bakery products, cookies, and chewing gums.
Owner:PURECIRCLE SDN BHD
Method for producing isomaltulose by transforming sucrose by biological enzymatic method
ActiveCN101591689AHigh purityFast conversionMicroorganism based processesFermentationIon exchangeImpurity
Owner:GUANGXI INVESTMENT GROUP VECTOR BIOTECH
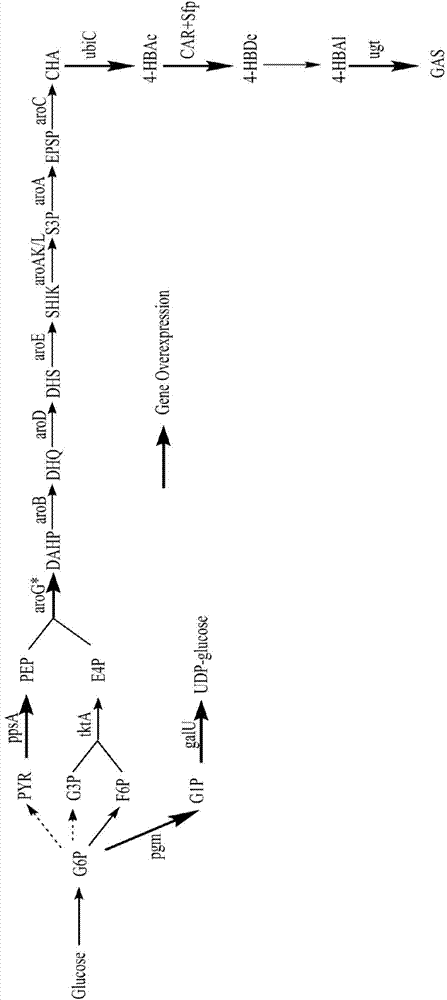
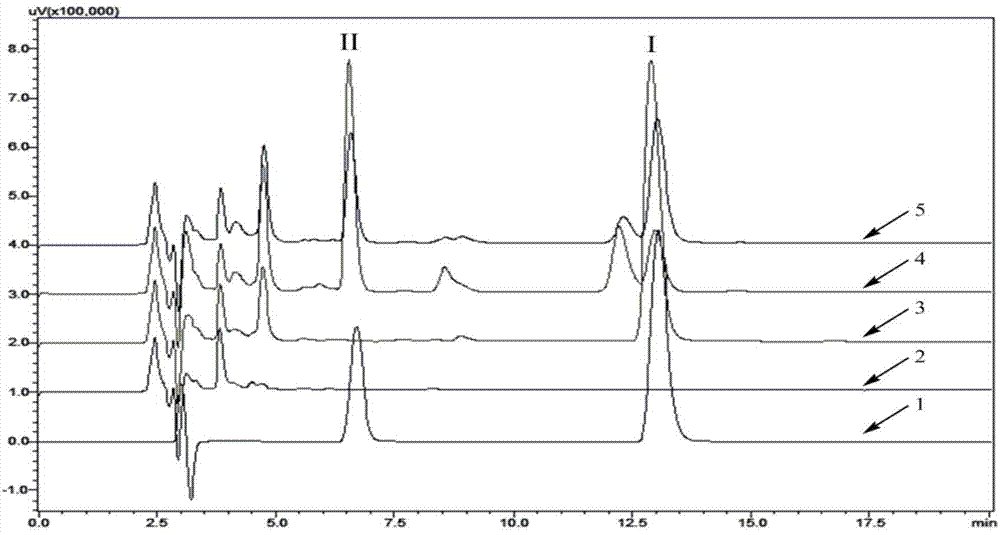
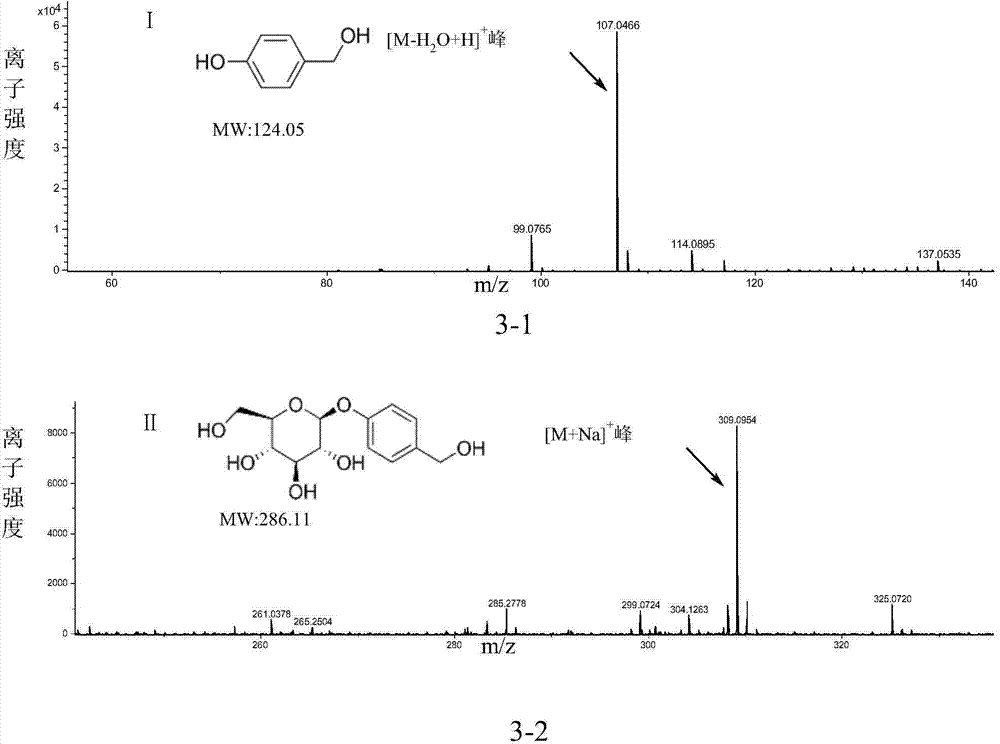
Recombinant escherichia coli for utilizing glucose to produce p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol or gastrodin and application
ActiveCN104846000AIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliUdp glucosyltransferase
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for utilizing glucose to produce p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol or gastrodin and application. The recombinant escherichia coli for utilizing glucose to produce the gastrodin comprises two expression vectors of pCDFDuet-aroG*-ppsA-pgm-galU and pETDuet-ubiC-CAR-Sfp-ugt73b6FS; the aro-G* gene is represented by SEQ ID NO:1. According to the invention, by constructing a new p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol synthetic pathway and regulating and controlling metabolic flux from glucose to tyrosine, the escherichia coli with high yield of gastrodigenin and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol is obtained; yield of p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol reaches 240mg / L; a high-efficiency UPD glucosyltransferase mutant is introduced; biosynthetic pathways of gastrodin and p-hydroxybenzyl alcohol are organically combined together; yield of gastrodin is obviously improved; the highest yield of gastrodin can reach 265mg / L.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Creation of chrysanthemum with blue flower color
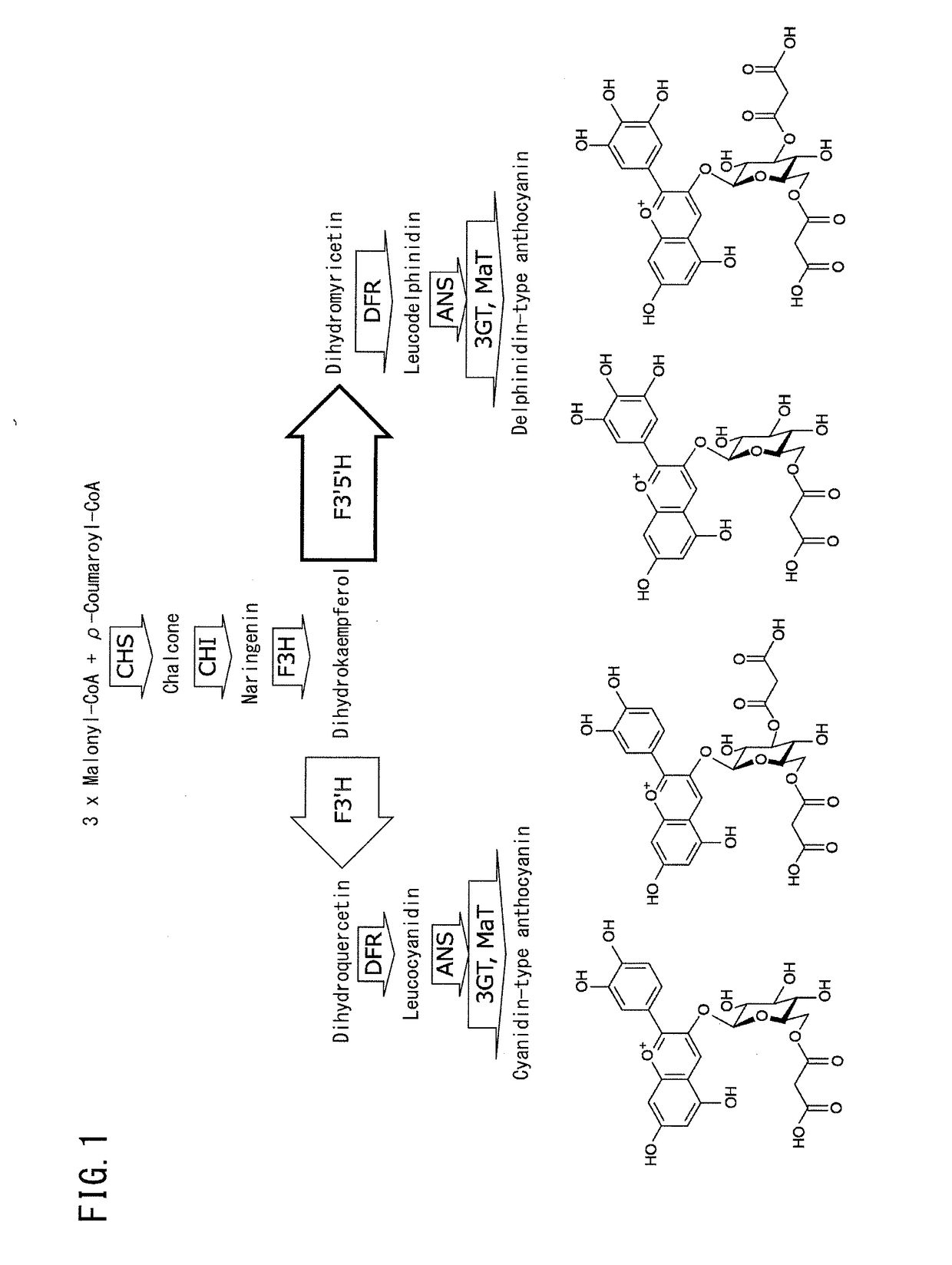
Provided are transformed chrysanthemum plants having blue flower color, their self-fertilized progenies or cross-fertilized progenies thereof, a vegetative propagated plants thereof, and a part, a tissue or a cell of the plant body. Anthocyanin 3′,5′-O-glucosyltransferase gene (CtA3′5′GT) derived from Clitoria ternatea and flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene derived from Campanula (CamF3′5′H) are coexpressed in chrysanthemum petals.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
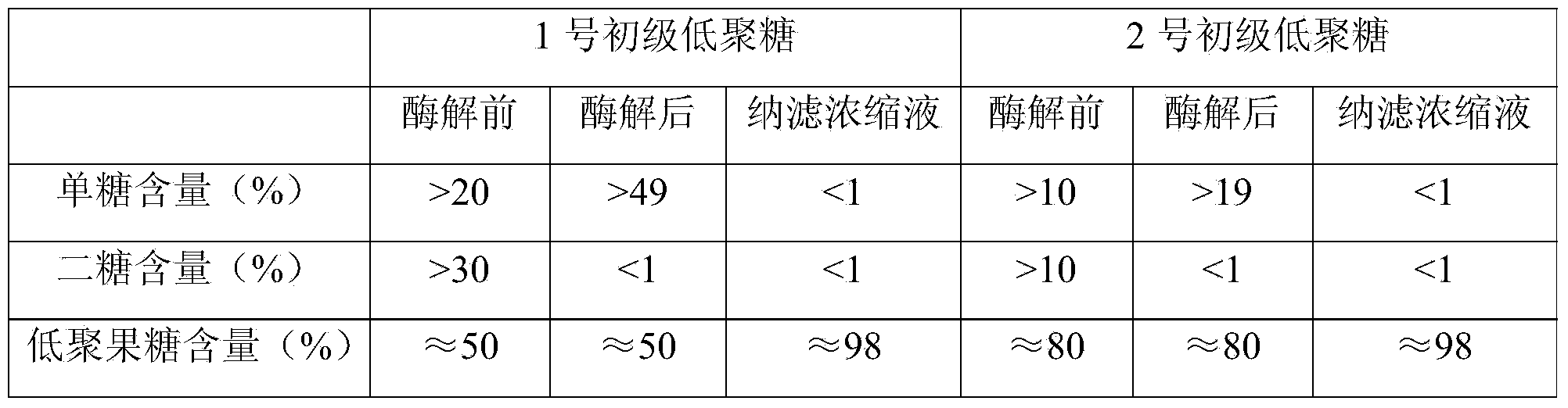
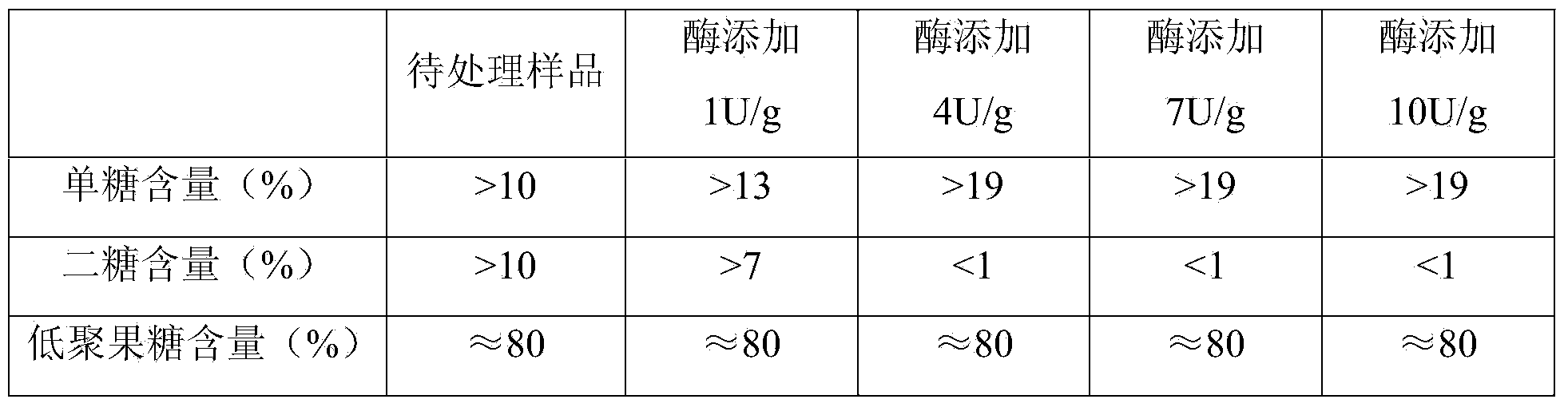
Method for purifying fructose oligosaccharide
ActiveCN103980382AHigh purityReduce removal rateSugar derivativesOligosaccharidesFiltration membraneFructan
The invention discloses a method for purifying fructose oligosaccharide. The method comprises the steps of performing enzymolysis on inulin by using inulase to obtain a primary fructose oligosaccharide mixed solution, putting the primary fructose oligosaccharide mixed solution into a reactor, adding a phosphate buffer of which the pH is 5.0-8.0 and a glucosyltransferase at 10-40 DEG C, performing enzymolysis for 1-20h, treating the enzymolysis solution through a nano-filtration membrane, and collecting the trapped solution to obtain a fructose oligosaccharide solution of which the purity is more than 98%. By adopting the method, saccharose is decomposed into monosaccharide, the monosaccharide is further removed through the nano-filtration membrane, and fructan of which the polymerization degree is more than 2, so that the purity of the fructose oligosaccharide can be greatly improved and can exceed 98%. Meanwhile, after the saccharose is decomposed into the monosaccharide, the saccharide in the nano-filtration permeate is monosaccharide which can be directly utilized by microbes and is applied in the fermentation industry as a byproduct, so that the market demand is huge.
Owner:完美(广东)日用品有限公司
Acidic heat-resisting isoamylase genetic engineering bacterium and application thereof
ActiveCN102559568AIncrease enzyme activityHas starch amylopectin hydrolysis activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisGenetic engineering
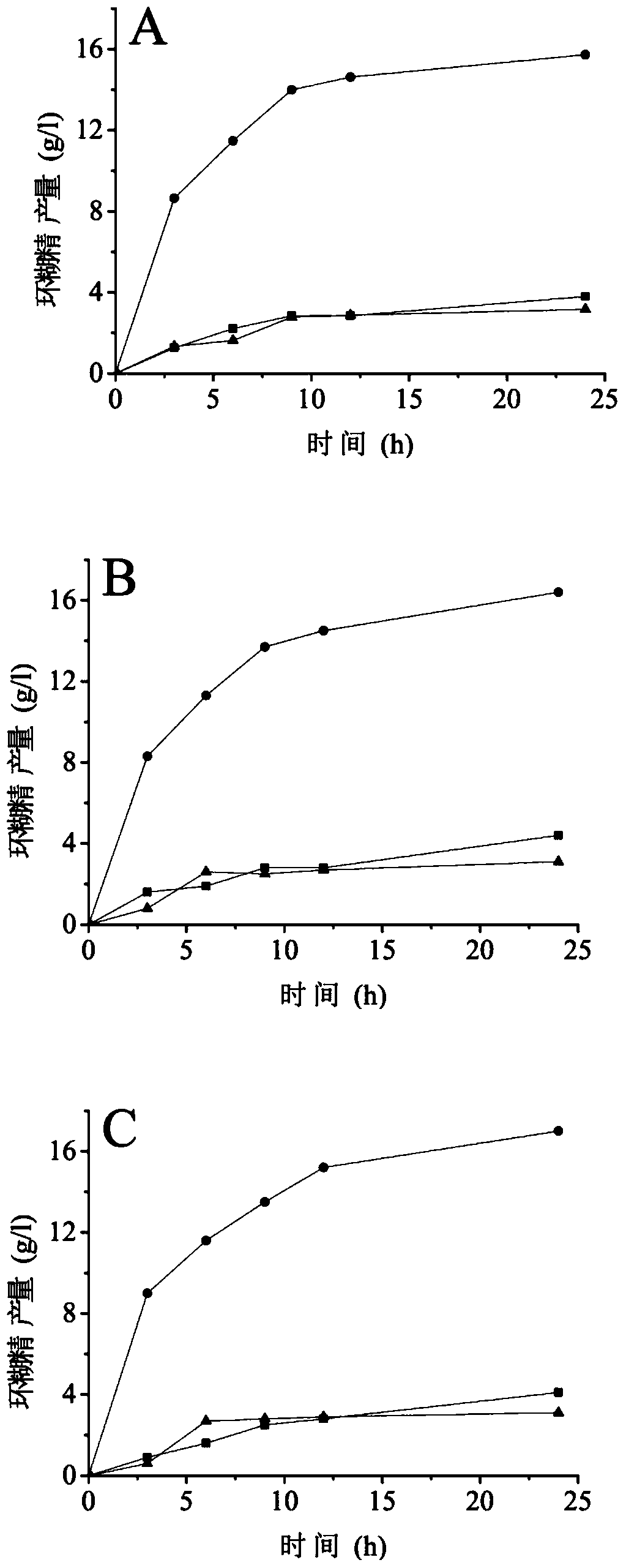
The invention relates to an acidic heat-resisting isoamylase genetic engineering bacterium and an application thereof, belonging to the field of enzyme engineering. According to the invention, a Tfu_1891 encoding gene sequence of isoamylase is obtained by chemical synthesis; culture is carried out in an industrial fermentation culture medium by taking pT7-7 as an expression vector and E.coli BL21 (DE3) as an expression host; and by virtue of inductive recombination, the fermentation vigor of the isoamylase reaches 3185U / mL. The recombinase has hydrolysis activity of a starch alpha-1,6 glucoside bond; the optimum temperature is 40-50 DEG C, and the optimum pH value is 5.5; after heat preservation is carried out for 30 hours at the temperature of 50 DEG C, the enzyme activity of the recombinase still maintains more than 50%; the recombinase has starch debranching activity and can hydrolyze branched starch in starch so as to form amylose; and the recombinase is combined with alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase to be used, thereby obviously improving the conversion rate of cyclodextrin and being suitable for industrial production of cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Production process for producing gamma-cyclodextrin by biological method
ActiveCN102827900AImprove conversion rateEasy to produceMicroorganism based processesFermentationOrganic solventGram
The invention relates to a production process for producing gamma-cyclodextrin by a biological method and belongs to the technical field of cyclodextrin production. The production process solves the technical problems to provide the process for producing gamma-cyclodextrin by the biological method, and the production cost of the gamma-cyclodextrin is reduced. The production process has the technical scheme that the gamma-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase from alkalophilic bacillus is adopted for producing the gamma-cyclodextrin, the starch pulp regulation is carried out according to the concentration being 10 percent, the materials are stirred for 5 to 15 minutes under the condition being 60 to 90 DEG C, the temperature is set to be 40 to 60 DEG C, the pH is regulated to be about 10.0, the gamma-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase is added according to a quantity of 1 to 10 units for one gram of starch, after 2 to 5 percent (w / v) organic solvents are added, the sufficient reaction is carried out for 8 to 10 hours, the organic solvents are recovered, and the gamma-cyclodextrin is obtained by adopting a crystallization method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene and application thereof
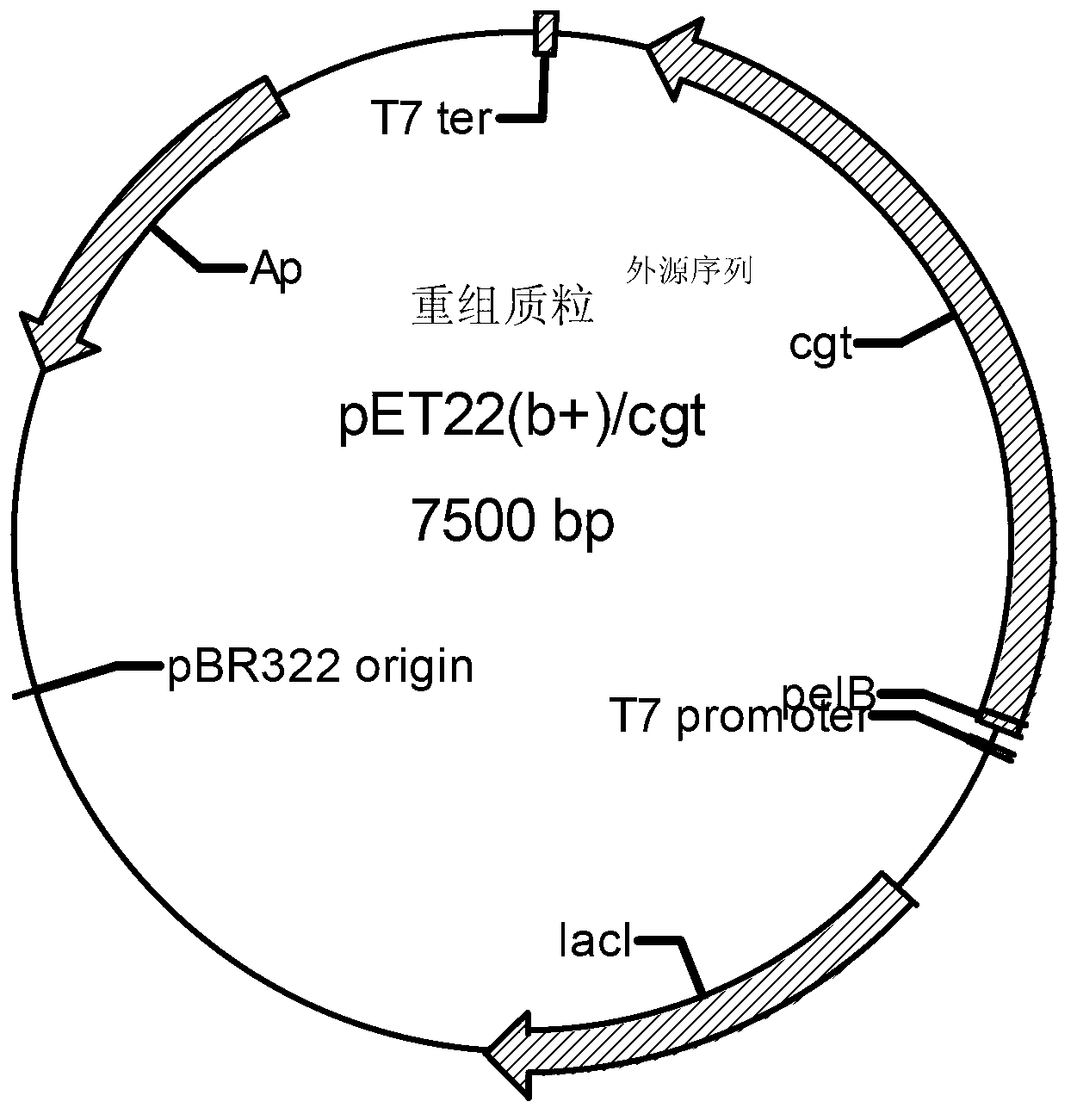
The invention discloses an alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene and the application thereof and relates to an alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene, an encoding enzyme, a carrier and an engineering bacterium which are extracted from paenibacillus macerans and the application thereof. The alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase gene can be connected with an expression vector to construct an expression recombinant plasmid (pET-20b(+) / cgt) containing the gene, the expression recombinant plasmid is then transferred into escherichia coli E.coil BL21, then recombinant escherichia coli is obtained, and the recombinant escherichia coli can secrete expression recombinant starch cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, so that cyclodextrin is prepared through biotransformation reaction with glucose polymer such as starch, glycogen and oligosaccharide as substrate.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for purifying gamma-cyclodextrin by utilizing cyclodextrin hydrolase
The invention discloses a method for purifying gamma-cyclodextrin by utilizing cyclodextrin hydrolase and belongs to the technical field of processing of cyclodextrin. The method comprises the following steps of using starch or dextrin as a substrate, using buffer solution to prepare substrate solution with certain concentration, adding a certain amount of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase with gamma-CD as a product, controlling reaction temperature and reaction time, and after reaction is ended, killing enzyme; using the reaction liquid as a substrate, adding a certain amount of cyclodextrin hydrolase, controlling reaction temperature and reaction time, and after reaction is ended, killing the enzyme. The method disclosed by the invention utilizes the cyclodextrin hydrolase with selectivedegradability to the cyclodextrin and utilizes a higher degradability of the cyclodextrin hydrolase to alpha-CD and beta-CD and a weaker degradability to gamma-CD to selectively remove the alpha-CD and the beta-CD and retain the gamma-CD so as to improve the purity of the gamma-CD. The method disclosed by the invention breaks through the original methods mostly adopting an organic solvent for precipitation in the industry, adopts the method for purifying the gamma-cyclodextrin by an enzymatic method, is simple in operation, is environment-friendly and has good application potential in the field of cyclodextrin processing.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing alpha-glucosylhesperidin
InactiveCN102051397AEasy to routeMild reaction conditionsFermentationInorganic saltsGlucosyltransferases
The invention relates to a method for preparing alpha-glucosylhesperidin. The method comprises the following steps of: (a) enzymatic conversion reaction: carrying out an alpha-glucosyl reaction on hesperidin and dextrin which are used as raw materials under the action of alpha-glucosyltransferase to generate alpha-glucosylhesperidin; (b) resin adsorption and purification: after the reaction of the step (a) ends, heating a reaction mixed solution to 80 DEG C to inactivate enzymes, placing over the night, filtering, taking a supernate and treating the supernate through an HP-10 macroporous resin column to remove sugar and inorganic salts; (c) decoloring: decoloring the supernate treated through the macroporous resin column with active carbon; and (d) concentration and crystallization: concentrating and crystallizing the liquid decolored with the active carbon in the step (c) to obtain a target product. The method has the advantages of simple route, moderate reaction condition and high yield.
Owner:成都丸荣易康科技有限公司
Method for increasing sugar utilization rate and yield of citric acid in citric acid fermentation and application
ActiveCN108018216AIncrease productionReduced reducing sugar contentFungiMicroorganism based processesIsomaltoseEconomic benefits
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering and particularly relates to a method for increasing sugar utilization rate and yield of citric acid in citric acid fermentation and an application. The method is implemented by knocking out glucosyltransferase genes in Aspergillus niger for citric acid production to construct genetic engineering strains and applying the genetic engineering strains to the citric acid fermentation. By means of knocking-out of the glucosyltransferase genes, content of reducing sugar can be reduced by 8.96%-9.89%, contentof total sugar is reduced by 9.78%-10.26%, content of isomaltose is reduced by 6.12%-7.01%, the yield of citric acid is increased by 10.28%-12.16%, at least 1,5000 tons of residual sugar can be reduced in a year, and the method has remarkable economic benefit.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Branched α-glucan, α-glucosyltransferase which forms the glucan, their preparation and uses
ActiveUS8324375B2Easy to solveReducing lipidCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsAcetic acidDietary fiber
The present invention has objects to provide a glucan useful as water-soluble dietary fiber, its preparation and uses. The present invention solves the above objects by providing a branched α-glucan, which is constructed by glucose molecules and characterized by methylation analysis as follows:(1) Ratio of 2,3,6-trimethyl-1,4,5-triacetyl-glucitol to 2,3,4-trimethyl-1,5,6-triacetyl-glucitol is in the range of 1:0.6 to 1:4;(2) Total content of 2,3,6-trimethyl-1,4,5-triacetyl-glucitol and 2,3,4-trimethyl-1,5,6-triacetyl-glucitol is 60% or higher in the partially methylated glucitol acetates;(3) Content of 2,4,6-trimethyl-1,3,5-triacetyl-glucitol is 0.5% or higher but less than 10% in the partially methylated glucitol acetates; and(4) Content of 2,4-dimethyl-1,3,5,6-tetraacetyl-glucitol is 0.5% or higher in the partially methylated glucitol acetates; a novel α-glucosyltransferase which forms the branched α-glucan, processes for producing them, and their uses.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
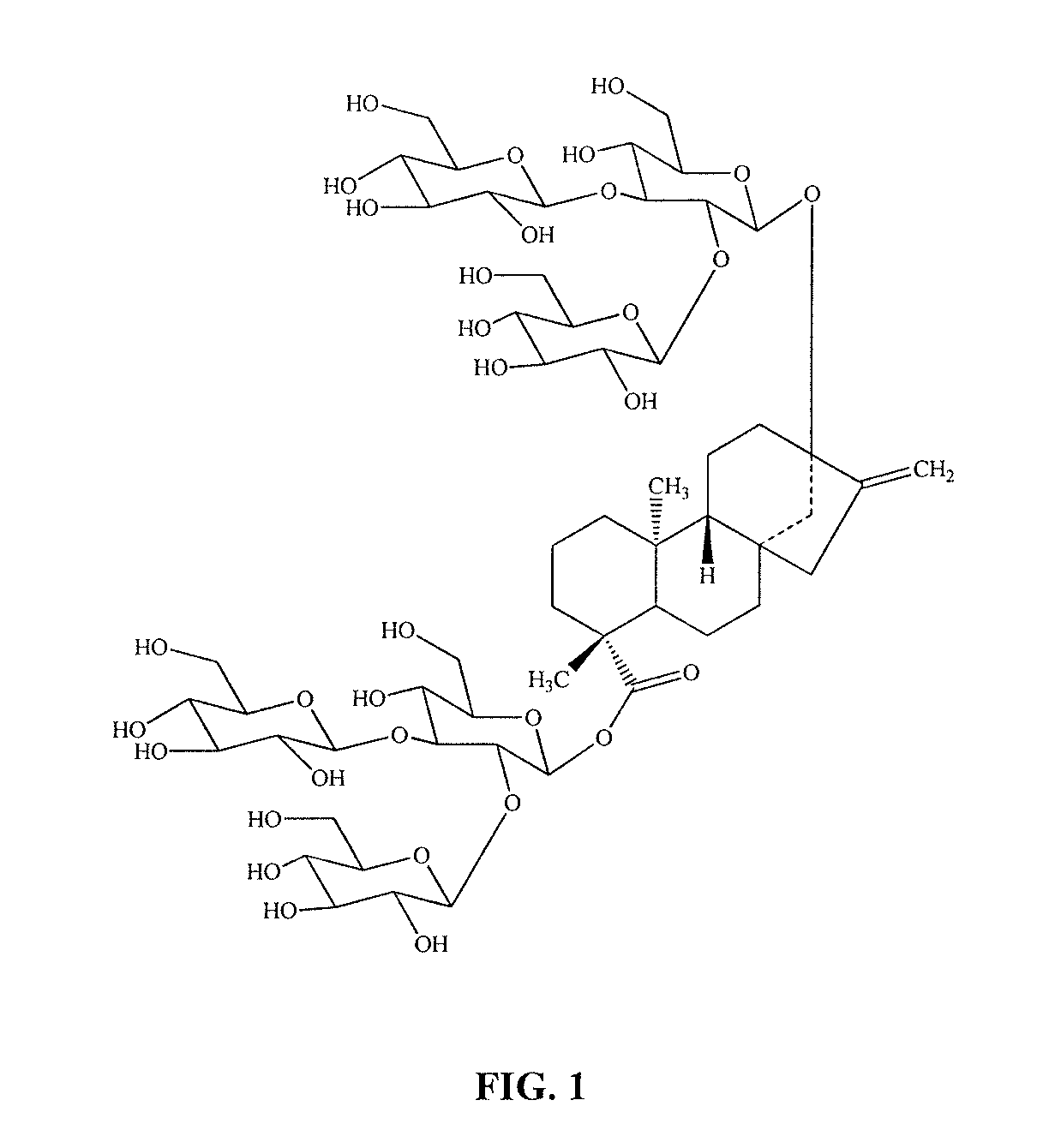
High-purity steviol glycosides
ActiveUS20150031869A1Sugar derivativesMetabolism disorderUdp glucosyltransferaseGlucosyltransferases
Methods of preparing highly purified steviol glycosides, particularly rebaudiosides A, D and X are described. The method includes expression of UDP-glucosyltransferases from Stevia rebaudiana Bertoni, which are capable converting certain steviol glycosides to rebaudiosides A, D and X. The highly purified rebaudiosides A, D and X, are useful as non-caloric sweetener in edible and chewable compositions such as any beverages, confectioneries, bakery products, cookies, and chewing gums.
Owner:PURECIRCLE SDN BHD
Preparation method of instant tea powder with high scent and low bitter
InactiveCN102138596AReduce moistureOvercome precipitationTea extractionInstant teaGlucose-Fructose Syrup
The invention relates to a preparation method of instant tea powder, in particular to the preparation method of the instant tea powder with high scent and low bitter by adopting enzymatical modification, and provides the preparation method for producing instant tea through an enzymatic method which can improve the bitter of the instant tea and the scent of the product, and needs low processing cost. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly extracting tea leaves for 30-60min through deionized water or pure water at the temperature of 25-80 DEG C; adding glucose or glucose syrup 1 / 2 to 1 / 8 the weight of the tea leaves and 10-60U of glucosyltransferase per glucose into the extract; reacting 2-8 hours at the temperature of 40-70 DEG C; and finally preparing the enzymatic reaction liquid into a powder-shaped product through steps of centrifugation, filtering, clarification, concentration, drying and the like. In the invention, the glucose serves as a donor; novel instant tea is produced by using a glucosyltransferase biological process; and the prepared product has the characteristics of having high scent, no bitter and good cold dissolubility.
Owner:DAMIN FOODSTUFF ZHANGZHOU CO LTD
Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant with improved cyclization activity
ActiveCN103966190AIncreased cyclization activityEase of industrial productionFermentationGlycosyltransferasesGlycineArginine
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant with improved cyclization activity, and belongs to the fields of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, through the adoption of a site-specific mutagenesis method, the 32nd aspartic acid (Asp) derived from beta-CGT enzyme of Bacillus circulans STB01 is mutated into alanine (Ala), glycine (Gly), glutamic acid (Glu), arginine (Arg), lysine (Lys) or glutamine (Gln) respectively. Compared with the cyclization activity of wild CGT enzyme, the cyclization activity of the mutant is obviously improved, so that the mutant is more suitable for industrial production of cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for detecting bacillus coli inducing diarrhoea and hydropsy during pig weaning period and reagent kit thereof
InactiveCN101118234AImprove accuracyGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingWeaningEnzyme Gene
The present invention relates to a gene chip, a testing method and a testing reagent case used for testing E.coli serological type and virulent gene that cause diarrhea and hydropsy of piglets in the ablactation period. The gene chip is fixed on an oligonucleotide probe of a solid phase support, the gene chip is mainly to select DNA fragments from UDPG-glucosyltransferase and Oligosaccharide unit treatment enzyme gene on E.coli serological type O-antigen gene cluster and main E.coil virulent factors that cause diarrhea and hydropsy of piglets in the ablactation period. The gene chip and the designed primer can be used for testing and can be made into the reagent case. The product and the method of the present invention can realize the purpose of testing test the common diarrhea and hydropsy of piglets in the ablactation period which are caused by E.coil serological type and virulent factors. The present invention has the advantages of simple operation, high accuracy and strong repetition; and is of great significance to the study and diagnosis of epidemiology.
Owner:TIANJIN BIOCHIP TECH CO LTD
Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant with high beta-cyclizing activity
ActiveCN104911158AIncreased β-cyclization activitySuitable for industrial productionFermentationGlycosyltransferasesGlycineArginine
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant with high beta-cyclizing activity, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant with high beta-cyclizing activity, the 89th tyrosine of beta-CGT enzyme from Bacillus circulans STB01 is mutated into glycine, aspartic acid and asparaginate respectively; double mutant means mutating the 89th tyrosine into the glycine, aspartic acid and asparaginate on the basis that the 577th aspartic acid of the CGT enzyme is mutated into arginine, and the obtained mutant is significantly improved in beta-cyclizing activity than wild CGT enzyme, thus being more applicable to the industrial production of cyclodextrin.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A group of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN102827815AIncrease productivityStrong specificityBacteriaTransferasesCyclodextrinGlucosyltransferases
The invention discloses a group of cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, and a coding gene and an application thereof. The cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase provided by the invention comes from Bacillus macerans, and is a protein obtained by mutating a protein as shown in a sequence 1 of a sequence table through the following two mutations: (a) mutating an amino acid residue at 536th site of N-end of the sequence 1 in the sequence table from alanine to valine, and (b) mutating an amino acid residue at 167th site of N-end of the sequence 1 in the sequence table. The protein provided by the invention is relatively high in specificity of producing alpha-CD, relatively high in production efficiency, and has great value to production.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Cyclodextrin Glucosyltransferase Mutant with Increased AA‑2G Conversion
ActiveCN104531629BIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationGlycosyltransferase activityArginine
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for improving AA-2G conversion rate and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant, the 228th lysine near the active center of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase of thermophilic fat bacillus (Bacillus stearotherm opilus NO2) is mutated into arginine to obtain a mutant K228R, the 367th aspartic acid is mutated into serine to obtain a mutant D367S and amphimutation is carried out on the basis to obtain a mutant D367S / K228R. The mutant can be used for realizing the improvement of the AA-2G conversion rate and has relatively high industrial value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing high-yield dye lignin glycosylated derivatives by using cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase
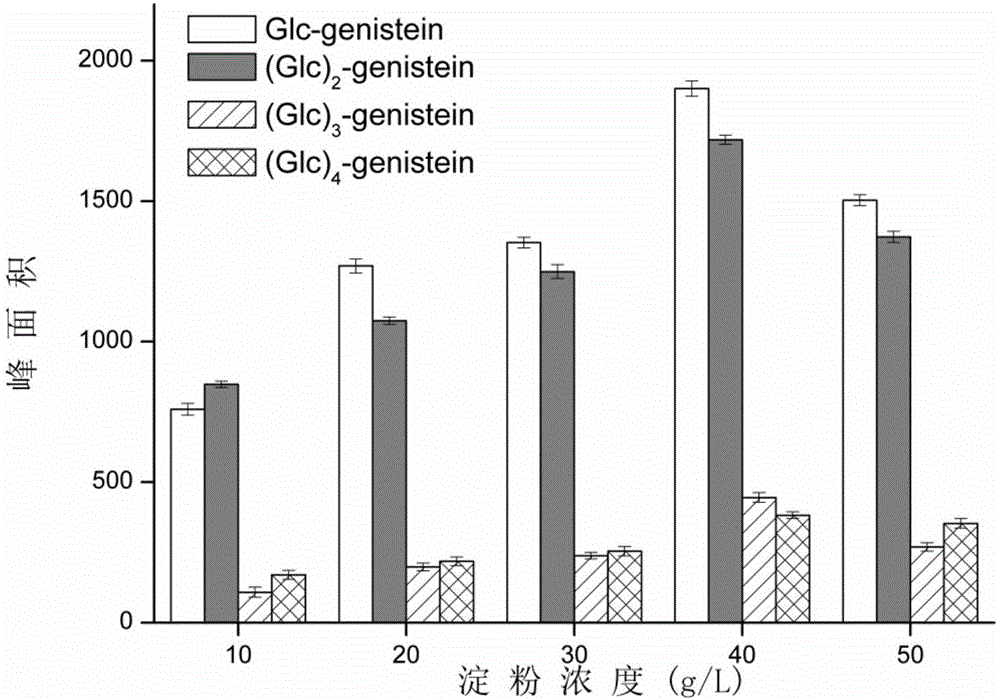
The invention discloses a method for producing high-yield dye lignin glycosylated derivatives by using cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. According to the method, the glycosyl donor type, the dye lignin solvent type, the substrate concentration and proportion, the enzyme concentration, reaction temperature, pH and time in a system for catalyzing glycosylation reaction of the dye lignin by cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase are optimized separately. Soluble starch and the dye lignin serve as a glycosyl donor and a receptor correspondingly, the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase serves as a catalyst, the yield of the glycosylated dye lignin products is maximized, and in particular for the main product (Glc)20genistein, the yield is increased by nearly 1.5 times compared with that before optimization.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
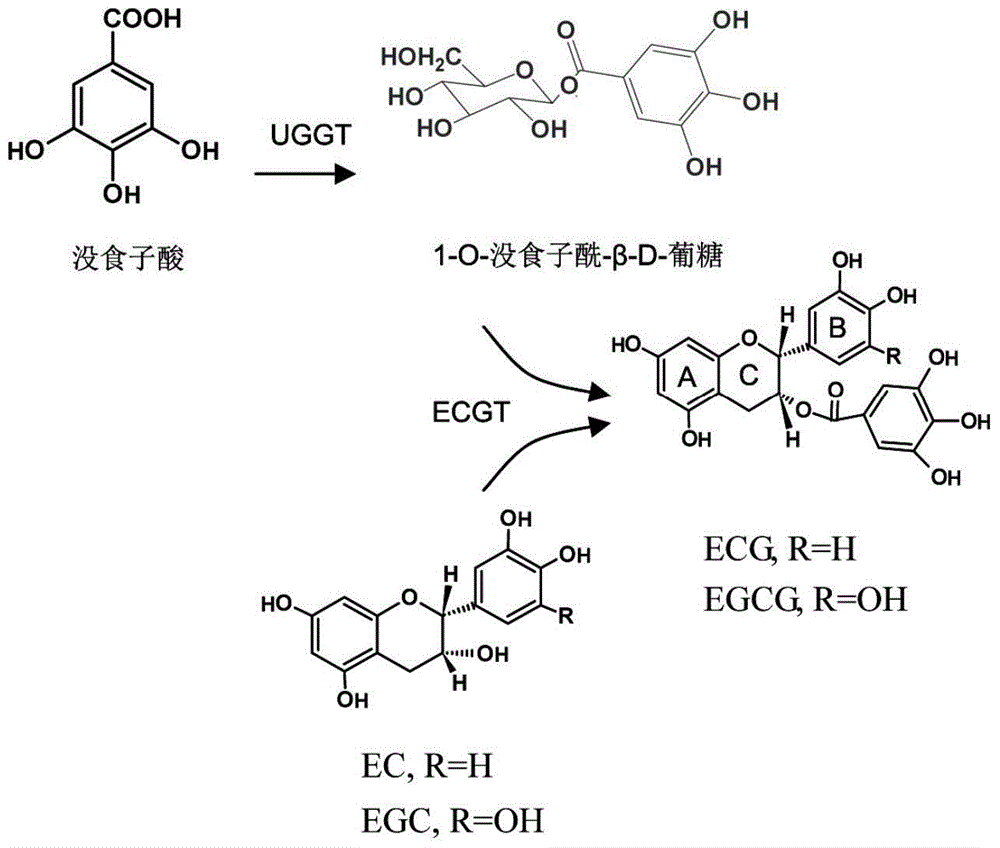
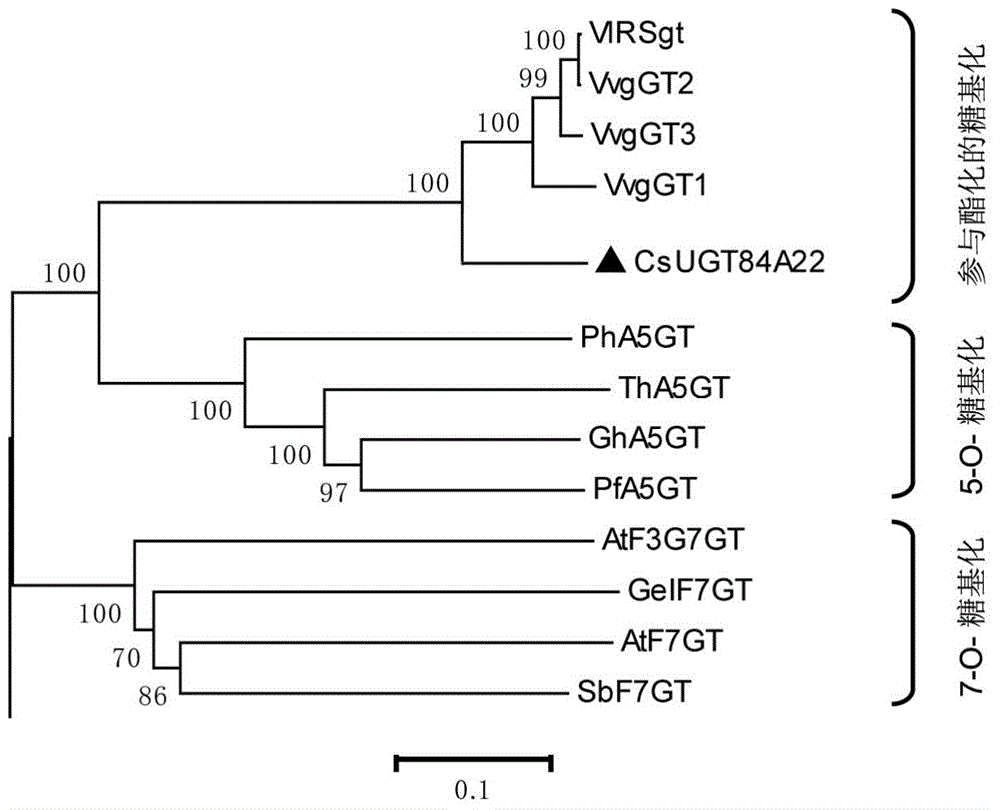
Galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene and encoded protein thereof and application
The invention discloses a galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene with a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. An encoded protein of the galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene is in an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. Compared with the prior art, the galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene has the advantages that the galloyl glucosyltransferase CsUGT84A22 gene for formation of uridine diphosphate glucose related to 1-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucoside are functionally cloned and verified for the first time, recombinant proteins, transgenic engineering bacteria and recombinant plasmids containing the CsUGT84A22 gene are provided, and mass synthesis of 1-O-galloyl-beta-D-glucoside is realized by means of bioengineering to lay the foundation for researches on biosynthesis regulation of ester catechins.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method using ocean alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase to convert starch so as to prepare alpha-cyclodextrin
InactiveCN106480133AUnique enzymatic propertiesThe method flow is simpleFermentationAlant starchChemistry
The invention relates to a method using ocean alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase to convert starch so as to prepare alpha-cyclodextrin. The method includes: performing starch gelatinization, adding the alpha-cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase at 55 DEG C, adding n-decanol to perform reaction, filtering reaction products, repeatedly washing filter cake with distilled water, and colleting the filter cake; adding anhydrous ethanol, performing stirring reaction under room temperature for 5 hours, performing static separatory filtration in a separating funnel, and evaporating lower liquid to obtain the alpha-cyclodextrin. The method has the advantages that the method is simple in flow, short in cycle and high in conversion rate, and the obtained alpha-cyclodextrin is high in purity and widely applicable to fields such as food, medicine, agriculture, spinning, environment protection, cosmetics, biotechnology and analytic chemistry.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Method for preparing glucose-based stevioside by enzymatic variable temperature and high-flux
The invention discloses a method for preparing glucose-based stevioside by enzymatic variable temperature and high-flux, and belongs to the technical field of sweetener biosynthesis. According to themethod for preparing the glucose-based stevioside by the enzymatic variable temperature and high-flux, cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase derived from geobacillus sp. is used as a catalyst, stevioside is used as a glycosyl acceptor, dextrin or oligosaccharide is used as a glycosyl donor, and a calcium barium ion salt bridge is used as a main stabilizer, and glycerol is combined with to adjust the conformation and binding domain opening degree of enzyme, the variable temperature utilizes the transesterification and hydrolysis activity of amylase by stages to prepare the glucose-based stevioside by enzymatic variable temperature and high-flux. The technology disclosed by the invention can improve the utilization rate of the enzyme, and obtain the glucose-based stevioside with excellent sweetness and good taste.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glucosyltransferase gene capable of participating in biosynthesis and biotransformation post modification
The invention provides glucosyltransferase. The glucosyltransferase can be used for glycosylation modification of flavonoid and polyketone compounds, and thereby directional biotransformation of the compounds is realized, and novel active compounds which are distinct from natural products in structure are obtained.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
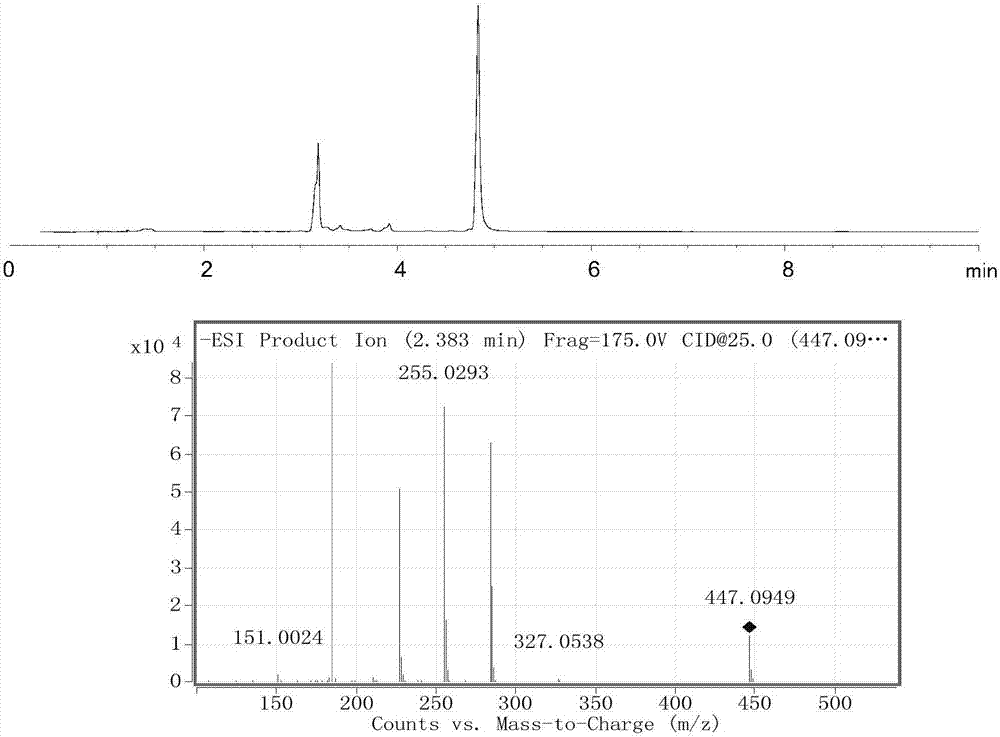
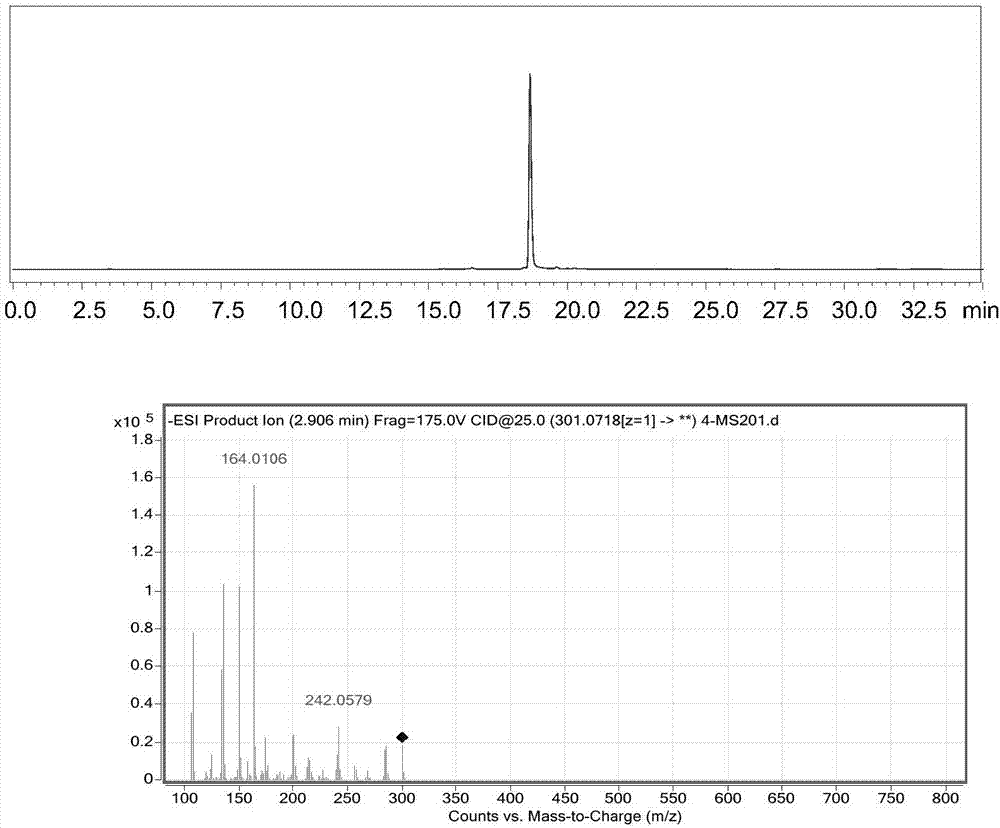
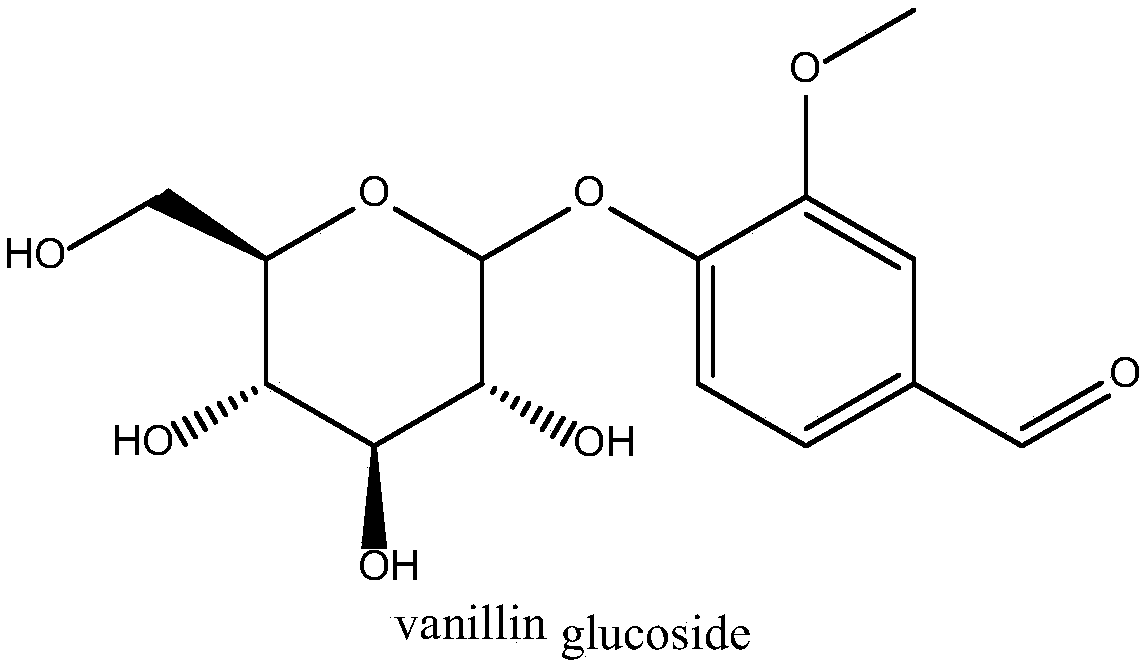
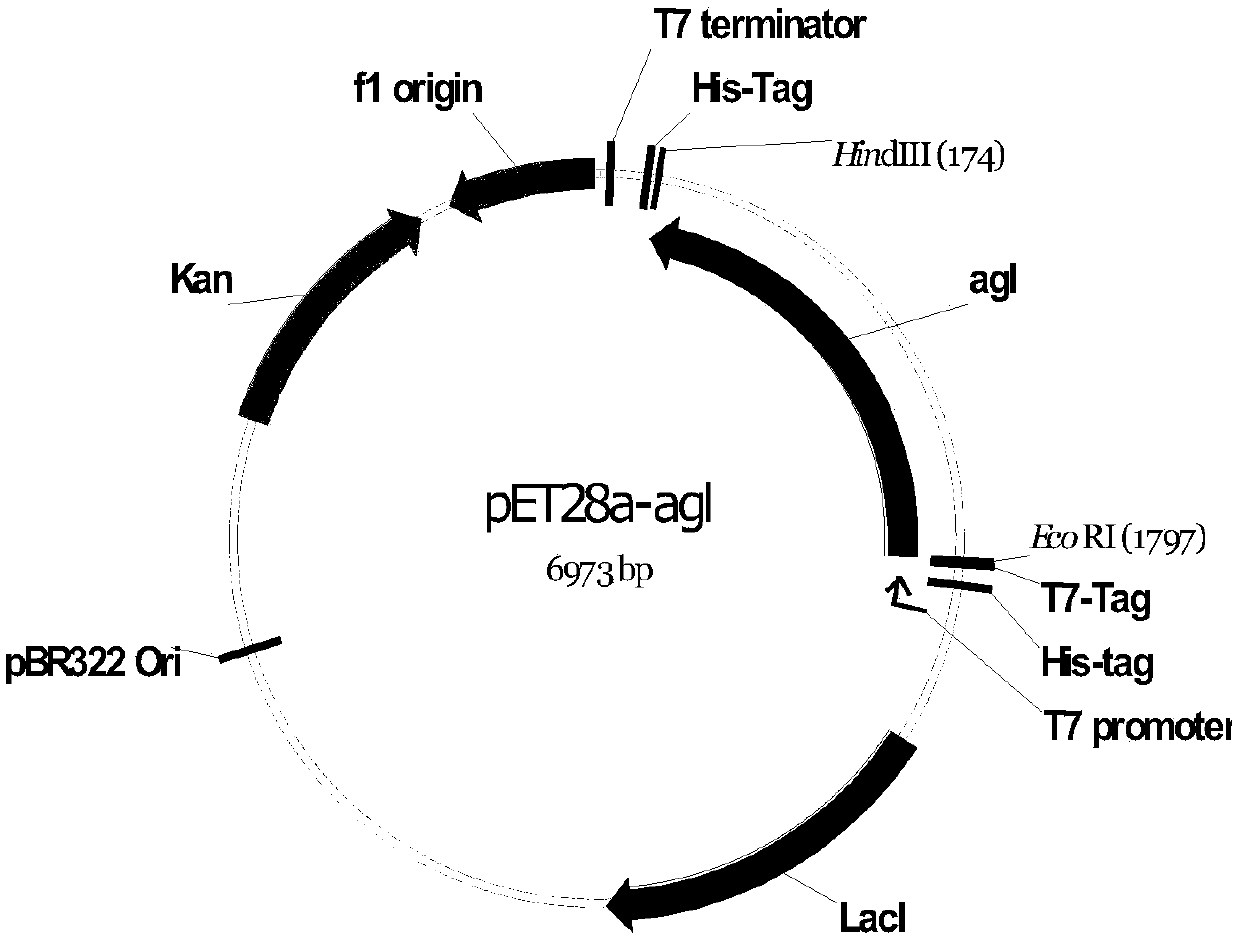
Glucosyltransferase and application thereof in producing vanillin-alpha-D-glucoside
ActiveCN109628420AImprove conversion rateHigh product concentrationBacteriaTransferasesGlucosyltransferasesFermentation
The invention discloses glucosyltransferase and application thereof in producing vanillin-alpha-D-glucoside. The amino acid sequence of glucosyltransferase is shown in SEQ NO.2. According to the application, fermentation liquid which is obtained by conducting fermentation cultivation on engineering bacteria containing glucosyltransferase coding genes serves as a bactericide, maltose and vanillin serve as a substrate, a conversion reaction is carried out with the pH value of 6.0-8.5 and at the temperature of 20-40 DEG C, and after the reaction is carried out completely, reaction liquid is separated and purified to obtain vanillin-alpha-D-glucoside. According to glucosyltransferase and the application thereof, vanillin-alpha-D-glucoside is produced through biological catalysis of the bactericide, after the reaction is carried out for 12 h, a vanillin-alpha-D-glucoside solution with the concentration lager than 10% can be obtained, the substrate conversion rate is larger than 60%, the yield concentration of vanillin-alpha-D-glucoside is high, and the conversion rate is high.
Owner:杭州佳嘉乐生物技术有限公司
Streptococcus mutans surface protein antigen (SpaP) and glucosyltransferase (GtfB) fused protein vaccine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104945513AImproving immunogenicityImprove developmentAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsGlucosyltransferasesStreptococcus mitis
The invention relates to a streptococcus mutans surface protein antigen (SpaP) and glucosyltransferase (GtfB) fused protein vaccine and a preparation method and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of a fused protein is SEQ ID NO:1. SpaP genes and GtfB genes are connected according to a Lingker sequence to obtain the fused protein which is used for preparing a caries prevention protein vaccine. The genetic engineering sigmasubunit vaccine is good in immunogenicity and can efficiently cause an immune response of an inoculum.
Owner:武汉第一口腔医院有限责任公司
Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for high-specificity production of alpha-cyclodextrin
ActiveCN103484439ARaise the ratioSimplify the subsequent purification processFungiBacteriaWild typeGlucosyltransferases
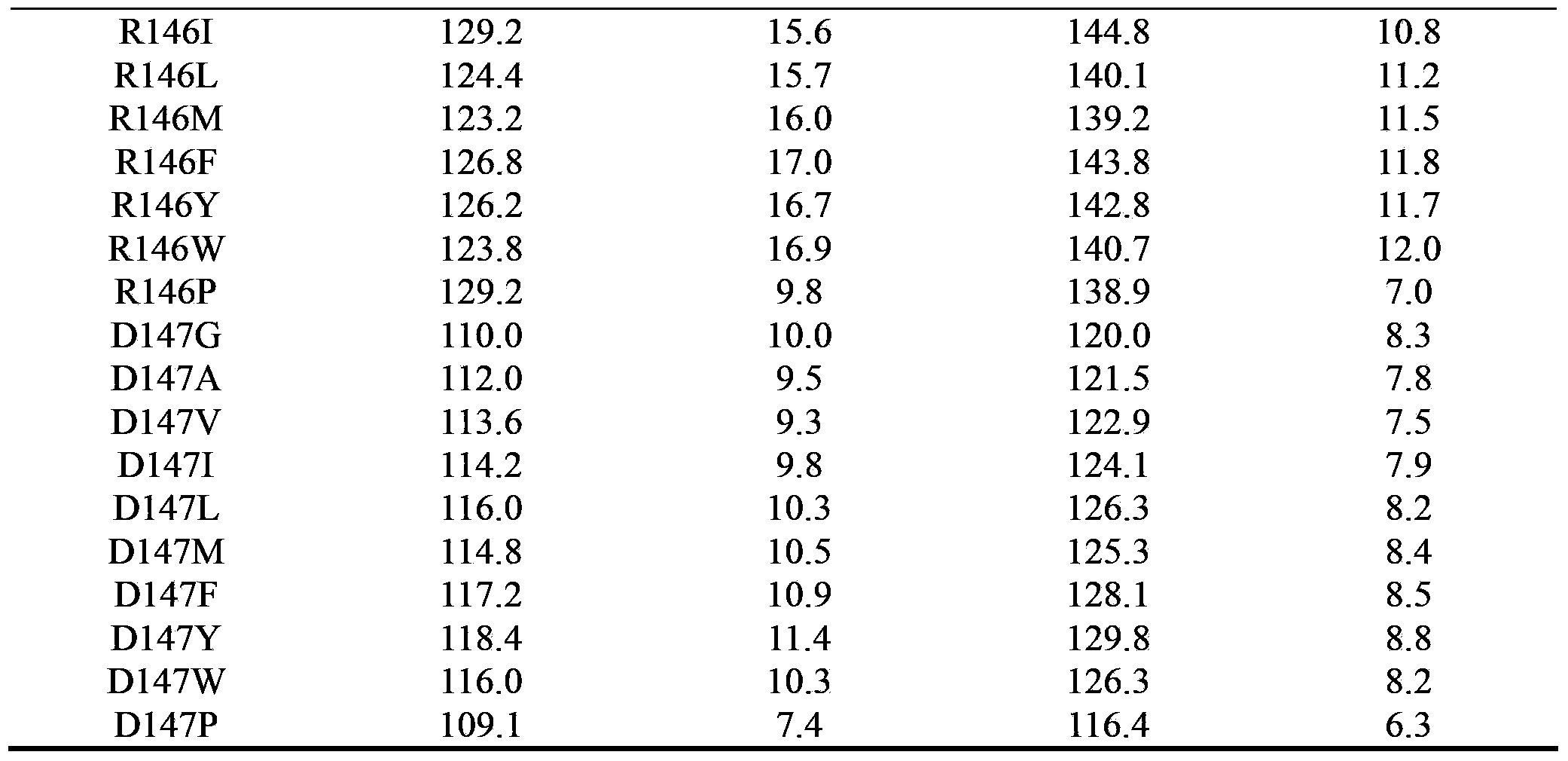
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for high-specificity production of alpha-cyclodextrin, belonging to the field of enzyme engineering. The cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant is prepared by transforming CGTase derived from Paenibacillus macerans JFB 05-01 and carrying out site-specific mutation on 145-site Asp,146-site Arg and 147-Asp of CGTase. The production capacity of beta-cyclodextrin of the prepared single mutant enzyme is lowered than that of wild-type CGTase, the production capacity of alpha-cyclodextrin is slightly increased, and the specificity of a principal product alpha-cyclodextrin is improved; double mutants and three mutants are obtained through combined mutation at the mutation sites of the CGTase; compared with the wild-type CGTase, the production capacity of the beta-cyclodextrin of the mutants is remarkably lowered, the production capacity of the alpha-cyclodextrin is slightly improved, the specificity of the principal product alpha-cyclodextrin is improved, and therefore, the industrial production of the alpha-cyclodextrin is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
A group of cyclodextrine glucosyltransferases and encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a group of cyclodextrine glucosyltransferases and an encoding gene and application of the group of cyclodextrine glucosyltransferases.. The cyclodextrine glucosyltransferases provided by the invention are characterized in that a protein as shown in a sequence 1 in a sequence table is the protein obtained by mutating as shown in (a) and (b): (a) mutating from tyrosine to histidine since the 167th amino acid residue at the N tail end as shown in the sequence 1 in the sequence table; and (b) mutating from the 195th amino acid residue at N tail end as shown in the sequence 1 in the sequence table. By adoption of the protein, the influence of the 195th amino acid in a catalytic center on the catalyzing specificity of Alpha-CGTase is researched, which brings a significant value for the study on the catalytic mechanism of the CGTase.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com