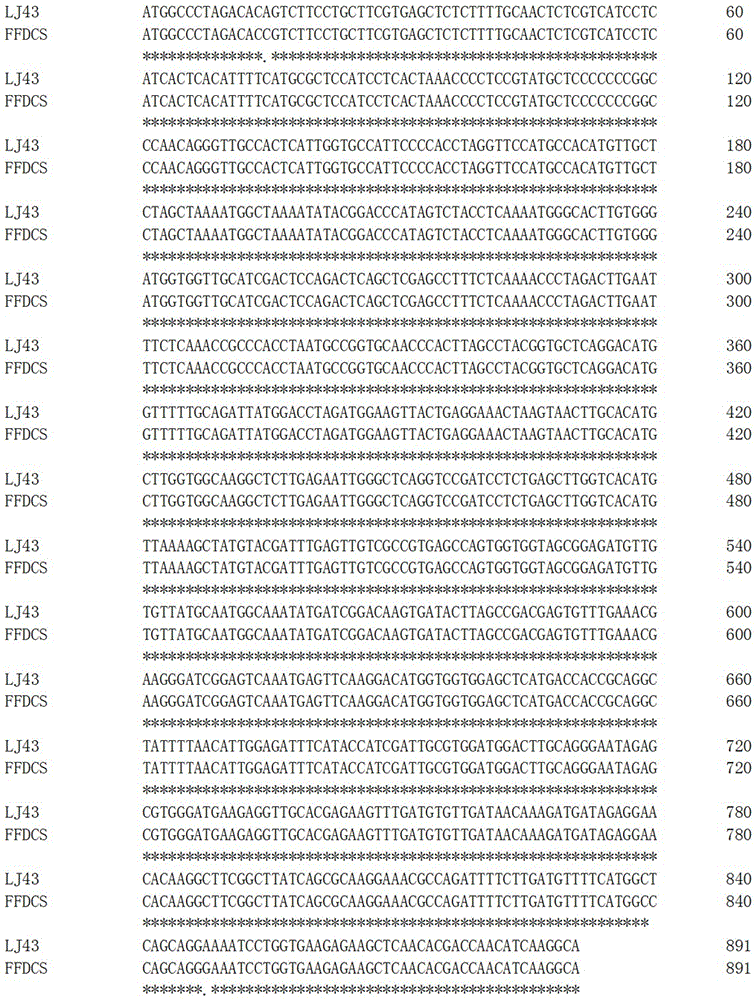
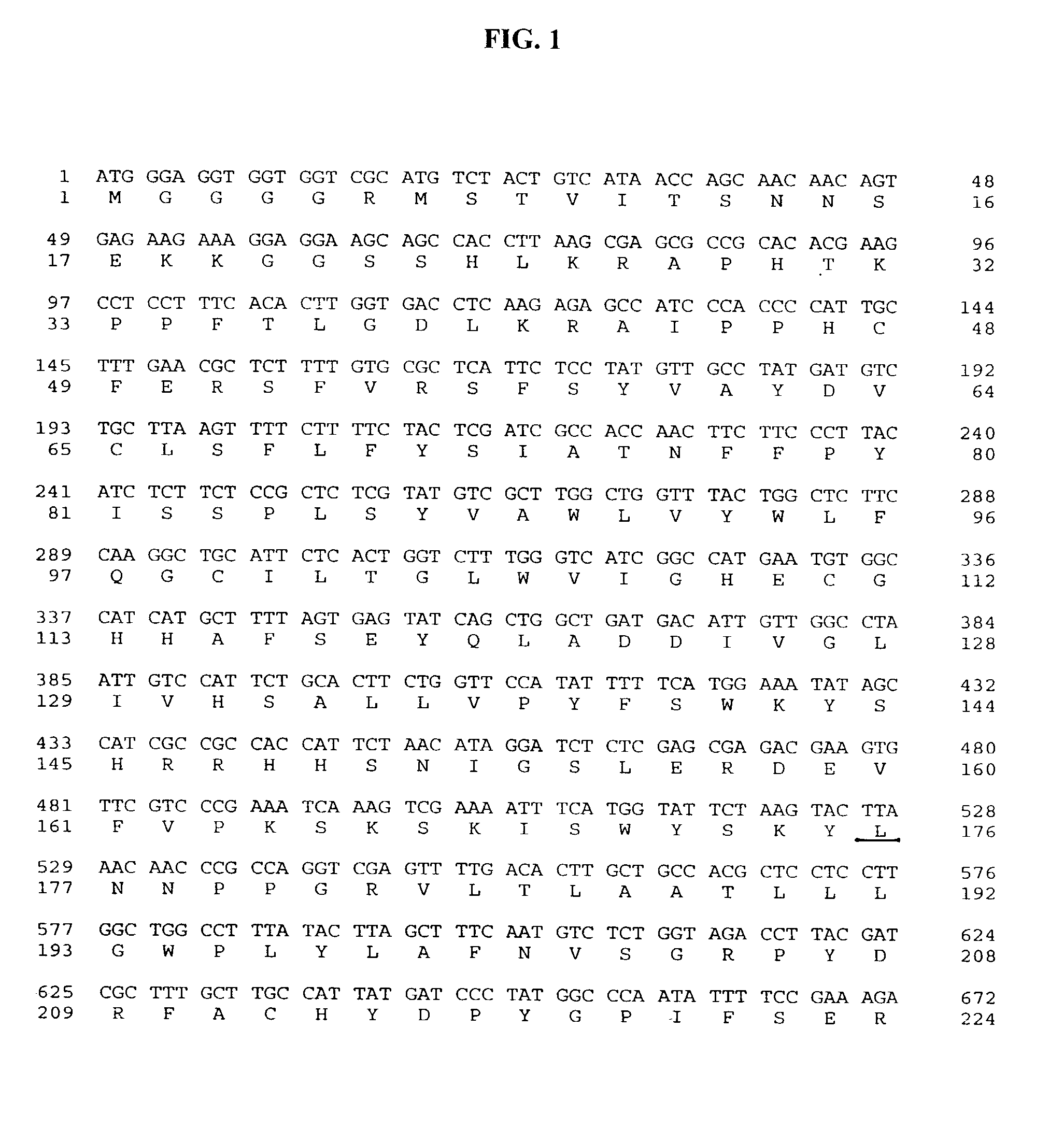
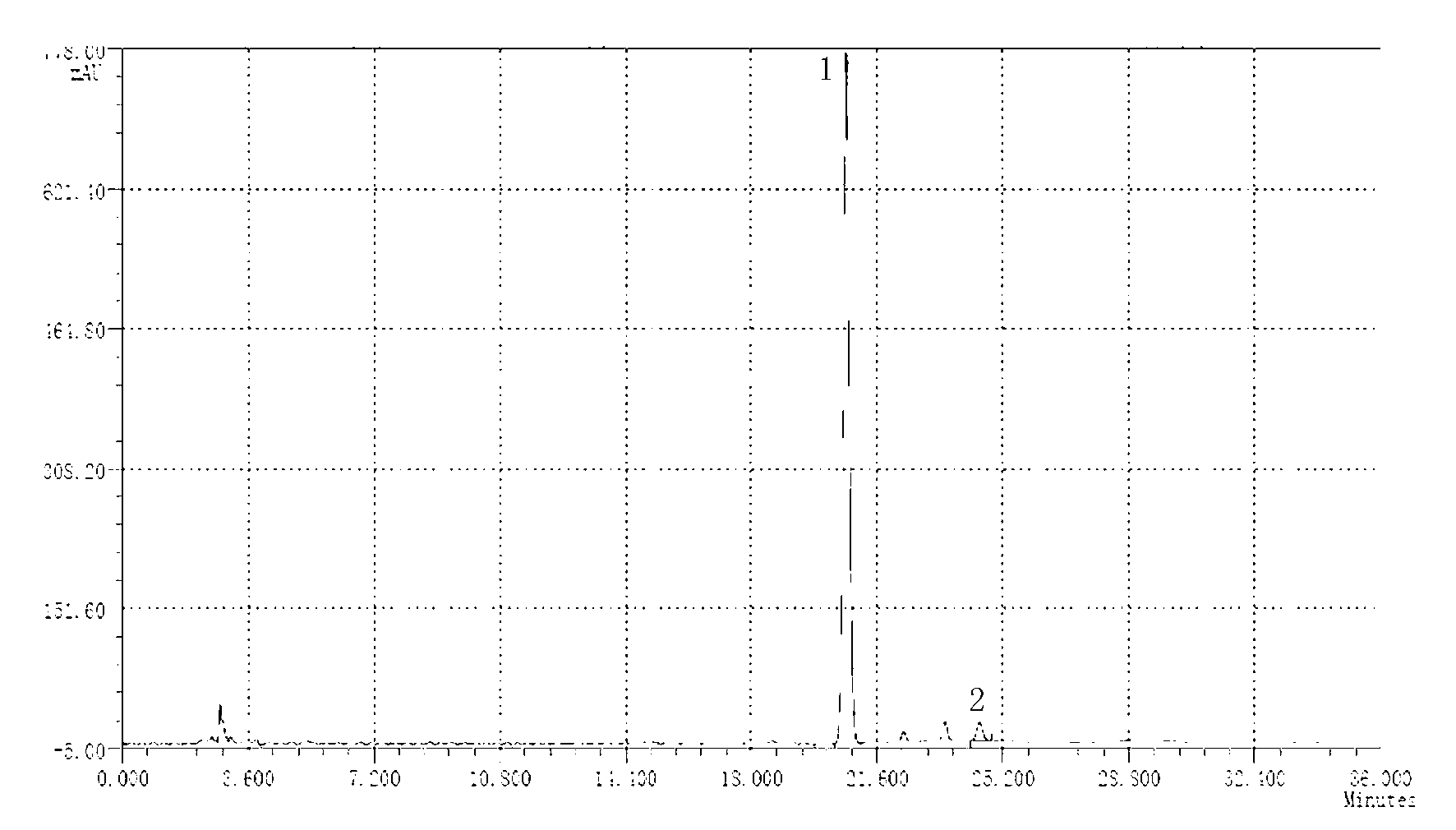Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
170 results about "Hydroxylase gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene functional marker for screening high-dihydroxyl catechin-content tea plant, as well as application and application method thereof
ActiveCN106755308AQuick filterAccelerate the pace of breedingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHydroxylase genePlant variety
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, particularly relates to a flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene functional marker for screening a high-dihydroxyl catechin-content tea plant, as well as application and an application method thereof, and discloses a functional marker for identifying the high-dihydroxyl catechin-content tea plant. The functional marker is applied to molecular marker-assisted selection, and can be used for rapidly screening a tea plant material with high dihydroxyl catechin content, thereby accelerating cultivation of a high-quality team plant variety. The functional marker has great theoretical significance and high economic value for molecular marker-assisted selection of a high-dihydroxyl catechin-content tea plant variety.
Owner:TEA RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Isoform of castor oleate hydroxylase
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Isoform of castor oleate hydroxylase
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Fermentation of pravastatin
InactiveUS20100048938A1Increase synthesisReduce consumptionFungiOrganic chemistryMicroorganismHydroxylase gene
The present invention provides a microorganism containing a compactin biosynthesis gene and a gene for conversion of compactin into pravastatin. In a preferred example, said compactin biosynthesis gene is mIcA and / or mIcB and / or mIcC and / or mIcD and / or mIcE and / or mIcF and / or mIcG and / or mIcH and / or mIcR and said gene for conversion of compactin into pravastatin is a hydroxylase gene. Furthermore, the present invention provides a method for producing a compound of interest such as a statin. In a preferred example said statin is pravastatin.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
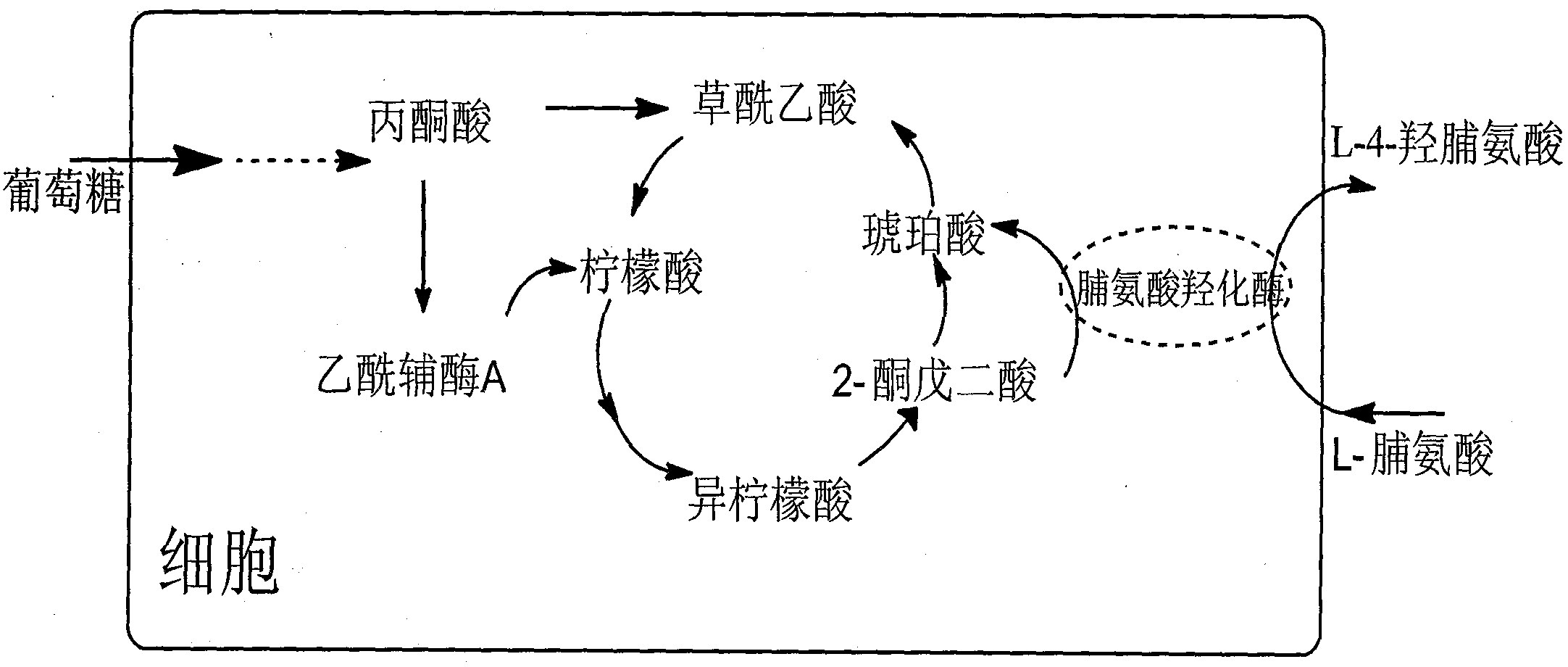
Method for production of L-4-hydroxyproline by using recombinant escherichia coli fermentation
InactiveCN103509813AImportant industrial application valueGood prospects for industrial developmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliHydroxyproline
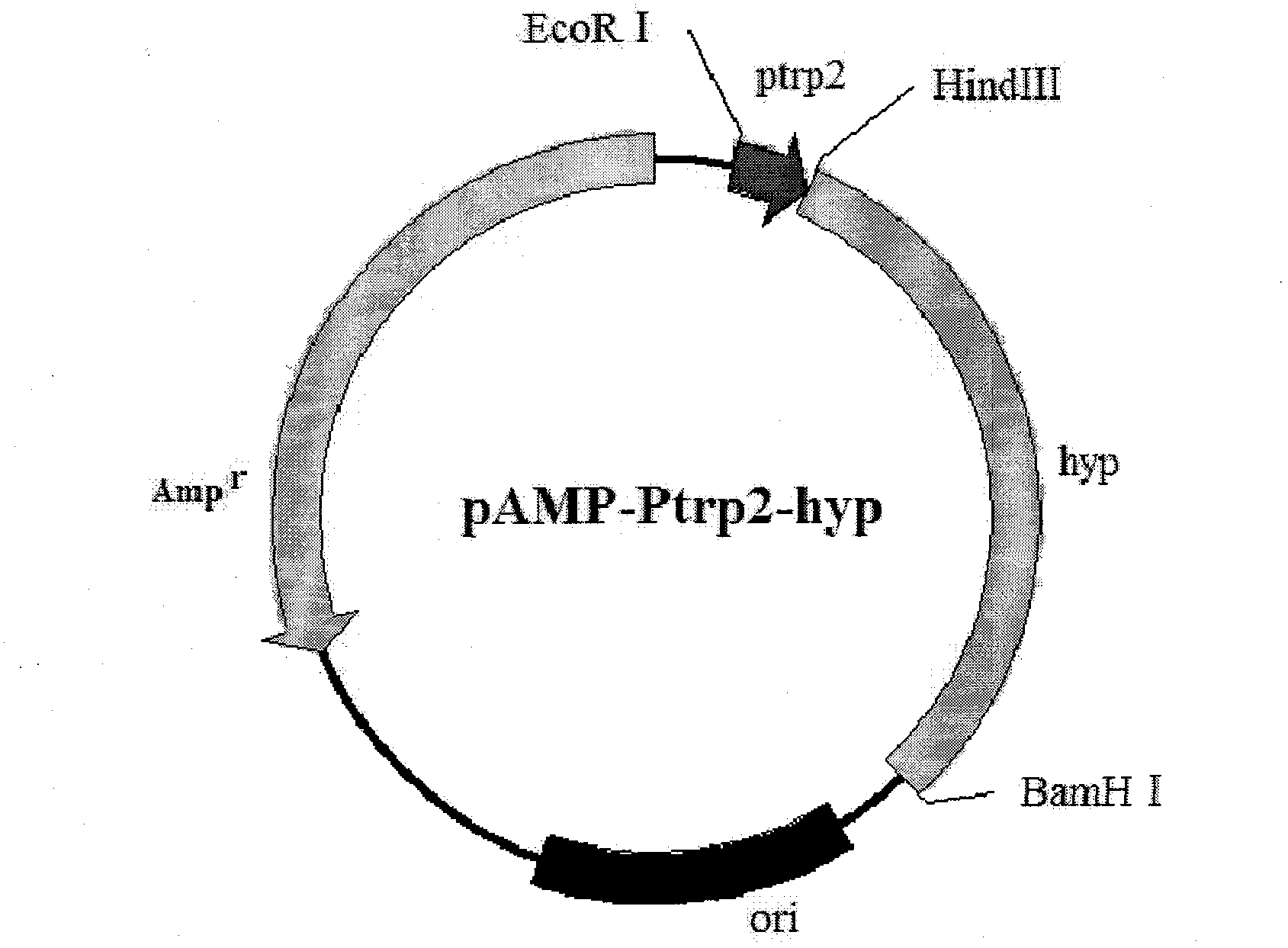
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and discloses a method for production of L-4-hydroxyproline by using recombinant escherichia coli fermentation. Recombinant escherichia coli is constructed by the following method: according to a published proline-4-hydroxylase gene and tryptophan promoter sequence, first optimally designing a tryptophan tandem promoter and a proline-4-hydroxylase structure gene, then after the total gene synthesis of the tryptophan tandem gene promoter and the proline-4-hydroxylase structure gene, connecting the promoter and the structure gene to pAMP plasmid to construct recombinant plasmid pAMP-P2trp-Hyp for overexpression of proline-4-hydroxylase. The invention also discloses the application of the escherichia coli in the production of the 4-hydroxyproline, the shake flask fermentation results show that the 4-hydroxyproline prepared by the recombinant escherichia coli has a yield reached 0.31g / L, and suggest that the recombinant escherichia coli has good industrial development prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Gene segment with coded and highly-active trans-4-hydroxyl-L-prolyl hydroxylase and application thereof
ActiveCN103275998AImprove conversion rateIncrease enzyme activityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEscherichia coliDactylosporangium
The invention discloses a gene segment provided with coded and highly-active trans-4-hydroxyl-L-prolyl hydroxylase and an application thereof. Gene codons of trans-4-hydroxyl-L-prolyl hydroxylase (GenBank ID: BAA 20094.1) in Dactylosporangiumsp. RH1 are optimized to obtain a p4hyd gene; the optimized p4hyd gene is truncated to obtain a P4Hyd1-257 gene; recombinant plasmids including pET-M-3C-P4Hyd and pET-M-3C-P4Hyd1-257 are built respectively, prokaryotic expression is performed through escherichia coli, and trans-4-hydroxyl-L-proline is produced in a conversion manner by utilizing thalli as an enzyme source. An experimental result shows that L-proline is taken as a substrate, compared with pET-M-3C-P4Hyd, the highest conversion rate of trans-4-hydroxyl-L-proline generated by pET-M-3C-P4Hyd1-257 in the conversion manner is increased from 91.4% to 97.4%, the conversion time is shortened from 80 hours to 60 hours, so that the conversion rate is improved remarkably, and the conversion time is shortened remarkably. The gene segment provided with coded and highly-active trans-4-hydroxyl-L-prolyl hydroxylase and the application thereof can be used for producing L-proline by a bioconversion method, and have better industrial application prospect.
Owner:HEBEI BOLUNTE PHARMA +1
Method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering
ActiveCN103865864AReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
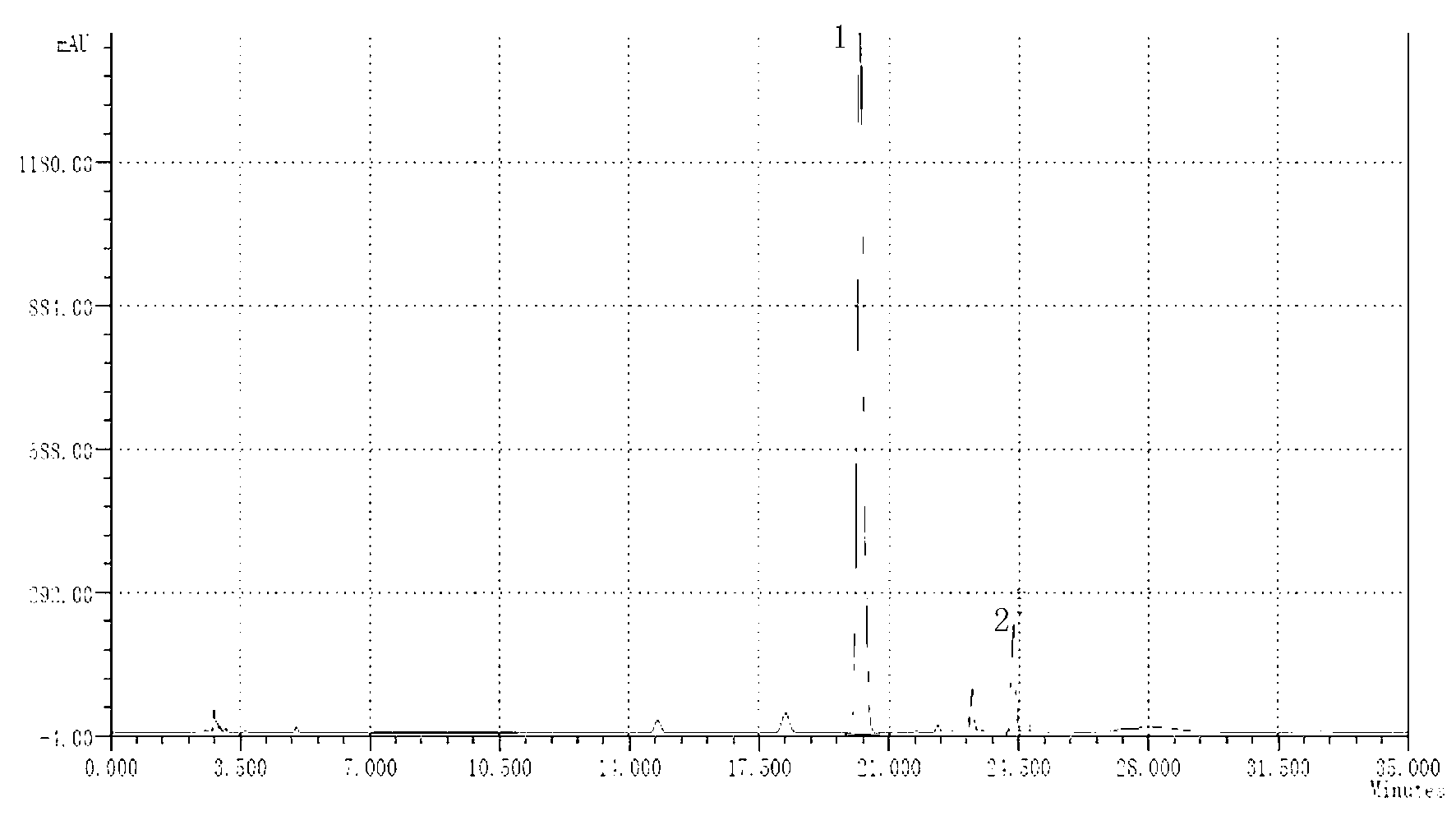
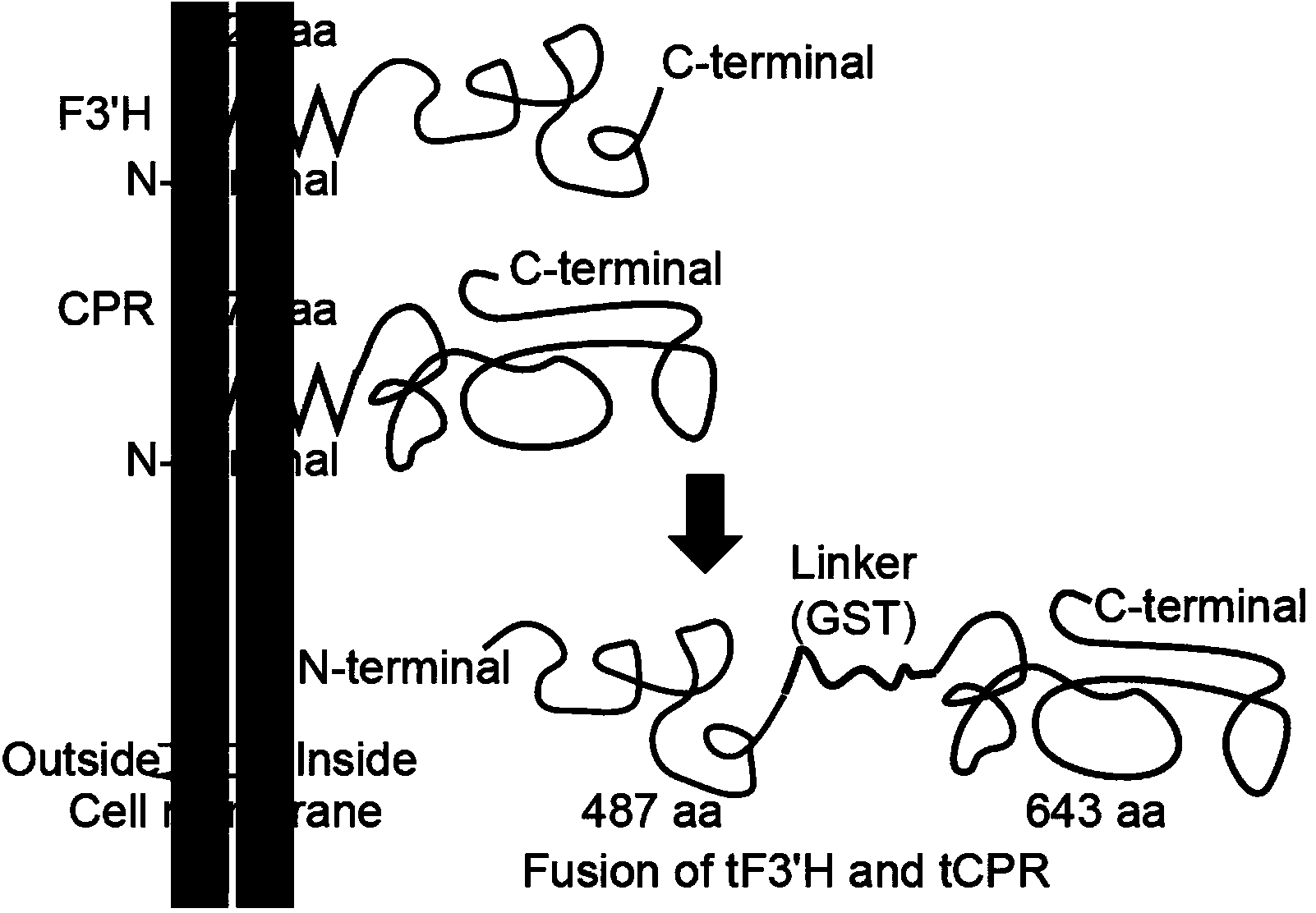
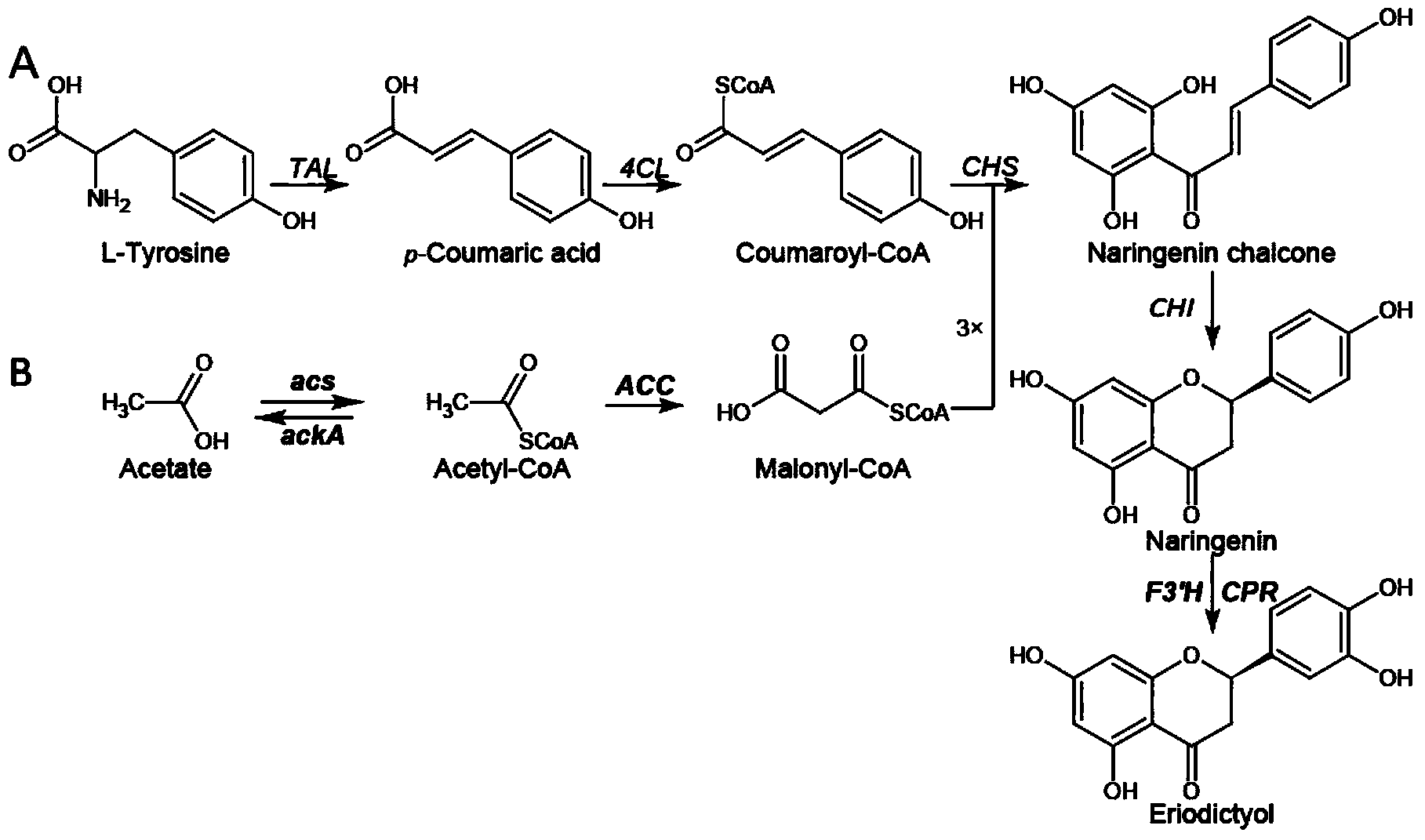
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione by microbial fermentation
InactiveCN104232722AImprove conversion rateHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention provides a method for producing 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione by microbial fermentation. Recombinant Mycobacterium smegmatis is fermented to convert phytosterin to produce the 9-alpha-hydroxyandrostenedione. The method comprises the following steps: constructing a recombinant expression vector pMV261-ksh; constructing a recombinant strain; and carrying out culture propagation and fermentation conversion. Gene engineering means are utilized to obtain the gene engineering strain for overexpressing 3-sterone-9-alpha-hydroxylase gene (ksh); after the strain is fermented for 120 hours, the conversion rate of the phytosterin is up to 95% above; and the method has the characteristics of high yield, fewer byproducts, short fermentation time simple extraction, small pollution, low pressure for environmental protection and the like, and has huge advantages in industrial production.
Owner:宋浩雷
Method for producing cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline through recombinant escherichia coli
InactiveCN104894152AFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliHydroxyproline
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering and discloses a method for producing cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline through recombinant escherichia coli. The recombinant escherichia coli is constructed by a method comprising the following steps: optimizing the known gene sequence of L-proline-cis-4-hydroxylase; performing total gene synthesis of the optimized L-proline-cis-4-hydroxylase gene; connecting the gene to a carrier containing a proper promoter to construct a recombinant plasmid which can over-express L-proline-cis-4-hydroxylase; then introducing the recombinant plasmid into escherichia coli to obtain recombinant escherichia coli which can convert free L-proline into cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline. The invention further discloses application of the recombinant escherichia coli in production of cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline. The shake-flask fermentation result shows that the output of cis-4-hydroxy-L-proline produced by the recombinant escherichia coli is up to 47.33mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106086102AIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseGlutamate 5-kinase
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the engineering bacteria provided by the invention includes the steps of A1) and A2): A1) introducing a L-proline-4-hydroxylase gene, a glutamate-5-kinase gene and a glutamate-5-semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene into a receptor cell; and A2) knocking an alpha-ketoglutaricdehydrogenase gene, an isocitratlyase gene or a proline dehydrogenase gene of the receptor cell out, or replacing a pyruvic oxidase gene of the receptor cell with an acetylcoenzyme A synthetase gene; and carrying out a reaction of the recombinant cell and a substrate to obtain the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline. Experiments prove that the production method of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline can be used for production of the trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Creation of chrysanthemum with blue flower color
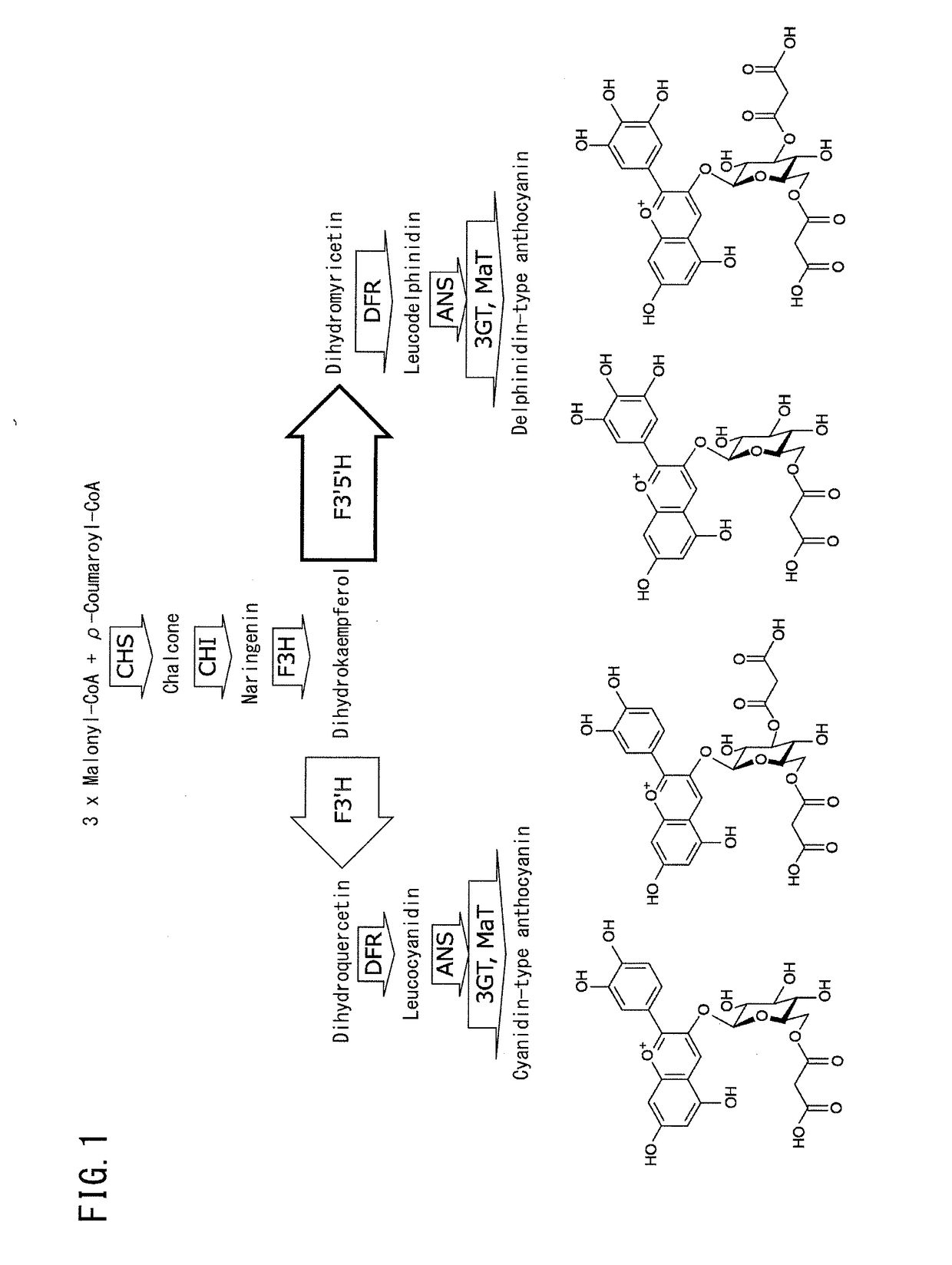
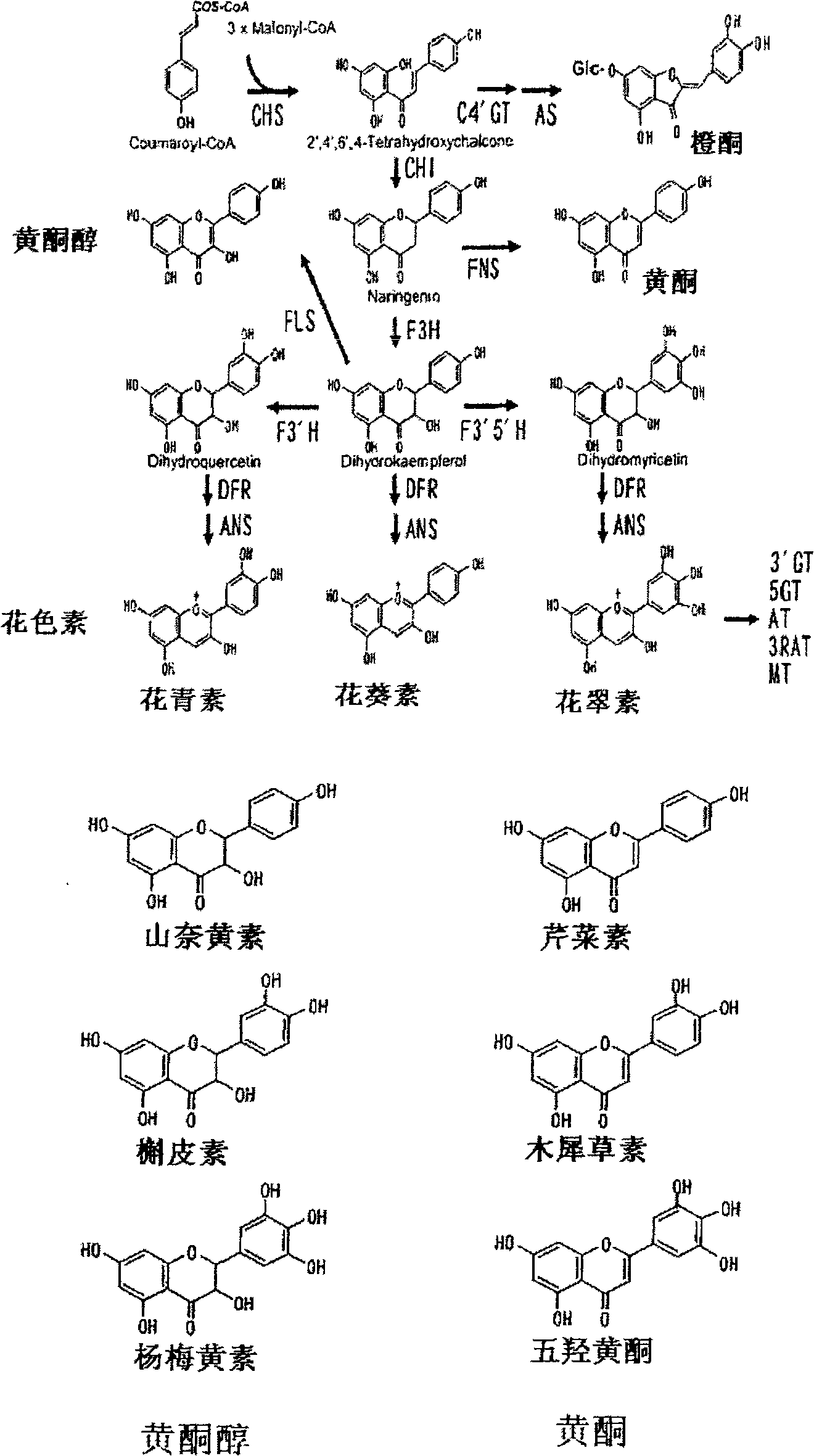
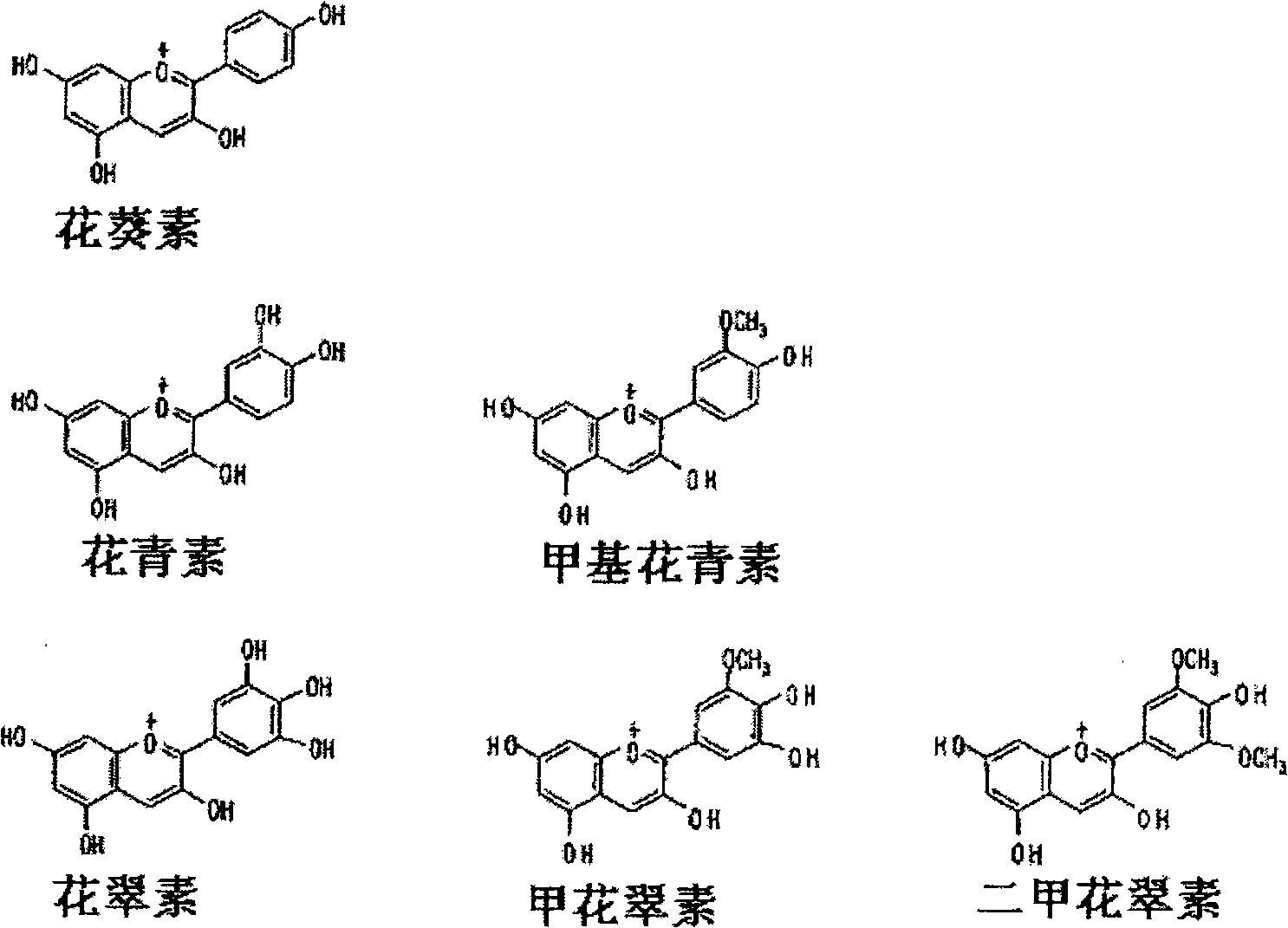
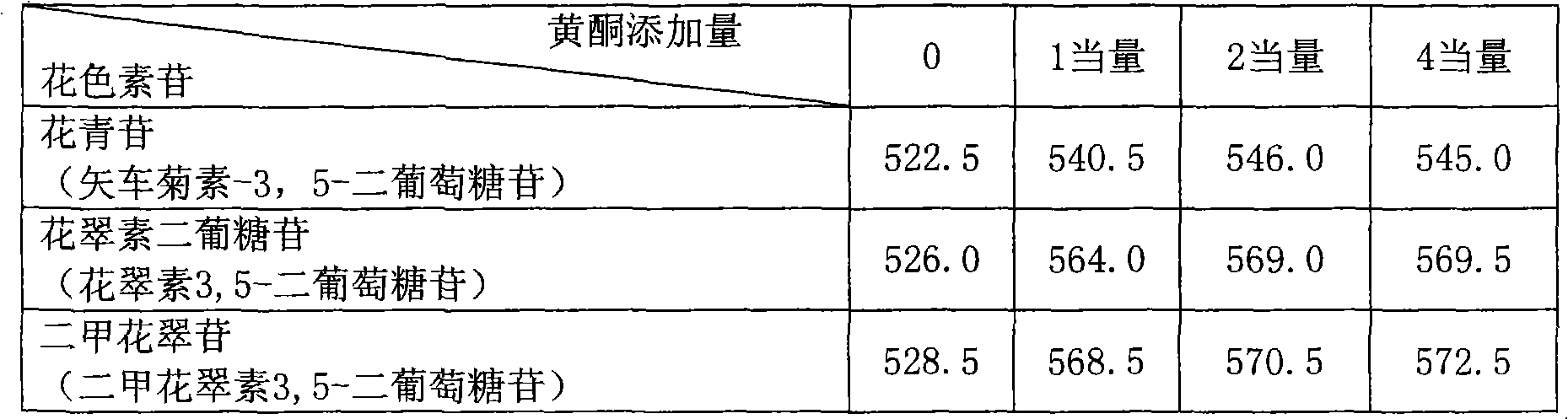
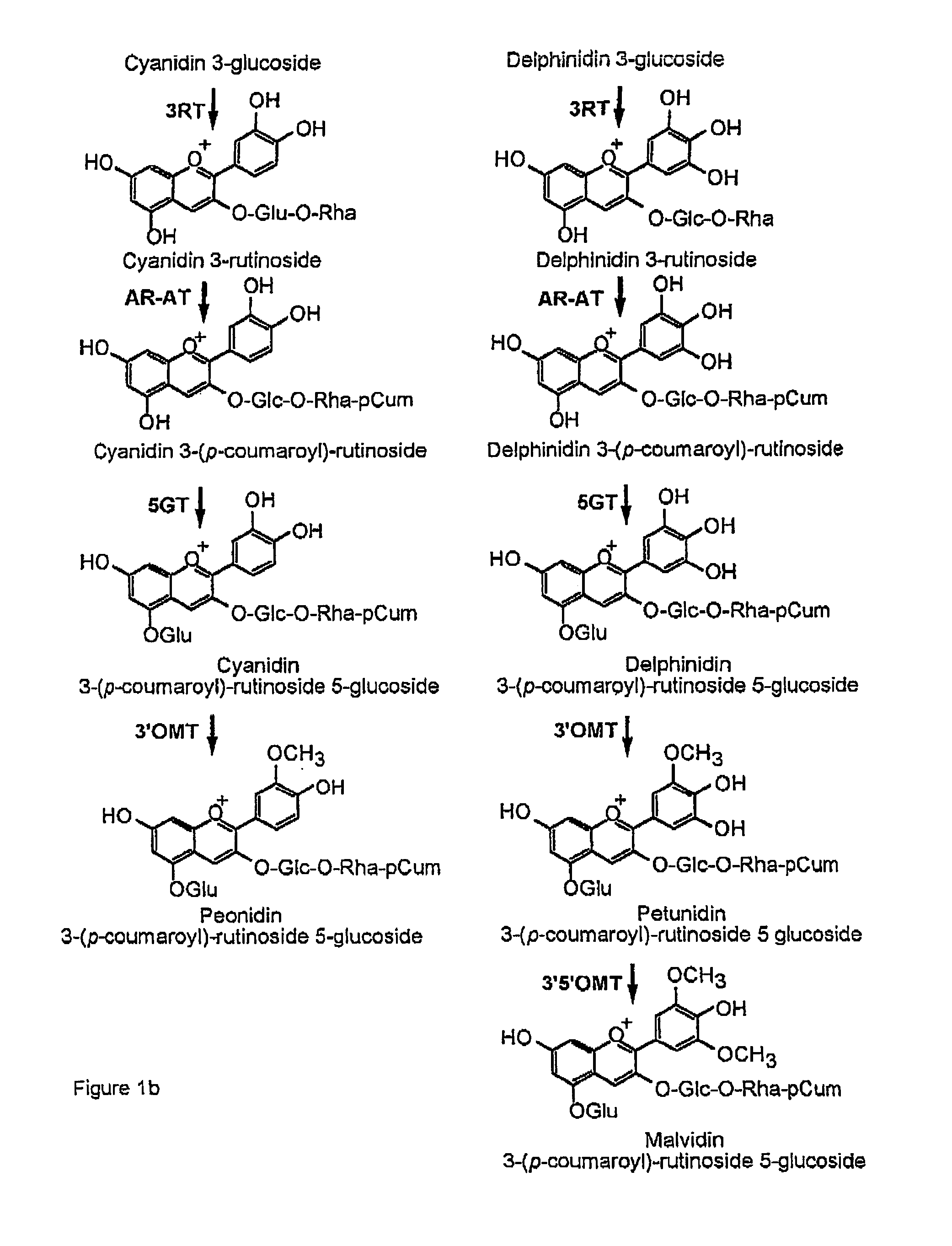
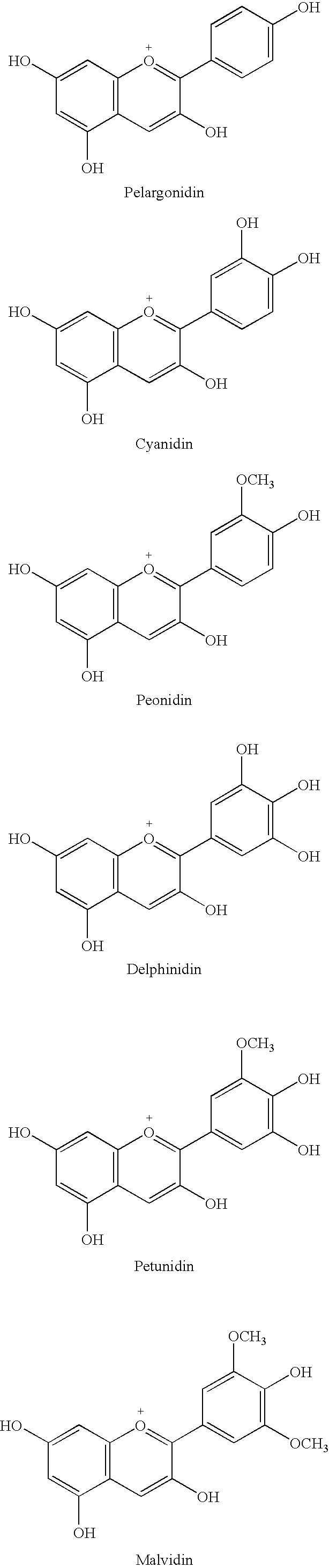
Provided are transformed chrysanthemum plants having blue flower color, their self-fertilized progenies or cross-fertilized progenies thereof, a vegetative propagated plants thereof, and a part, a tissue or a cell of the plant body. Anthocyanin 3′,5′-O-glucosyltransferase gene (CtA3′5′GT) derived from Clitoria ternatea and flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene derived from Campanula (CamF3′5′H) are coexpressed in chrysanthemum petals.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
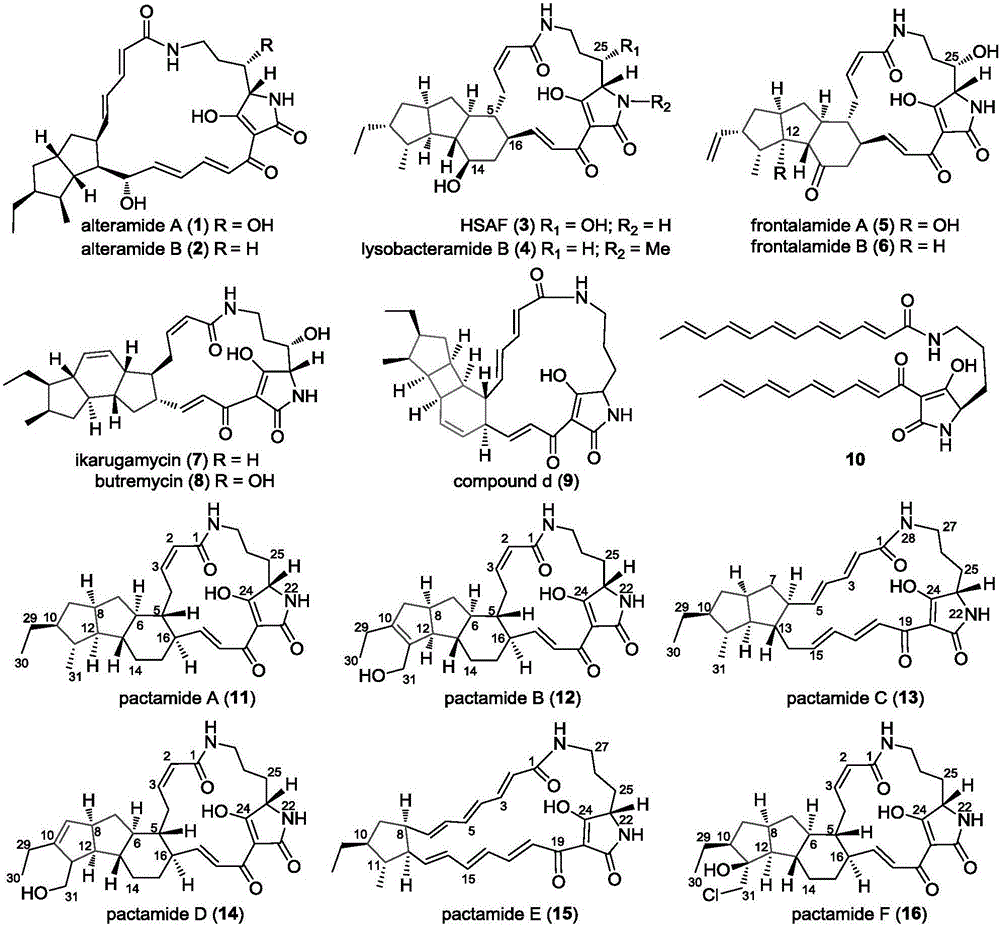
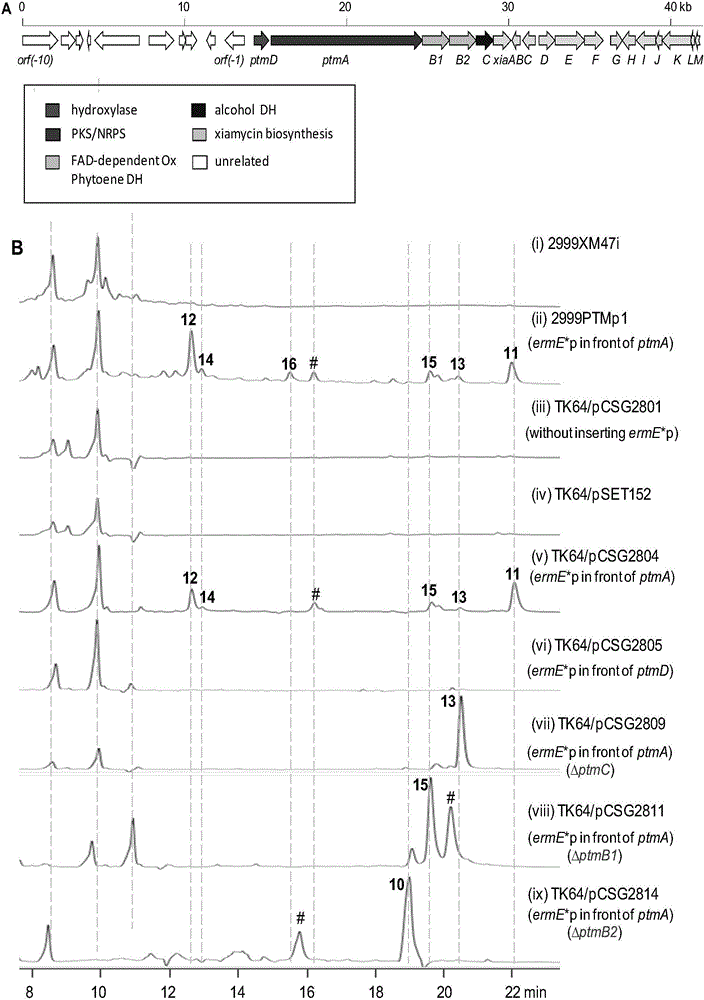
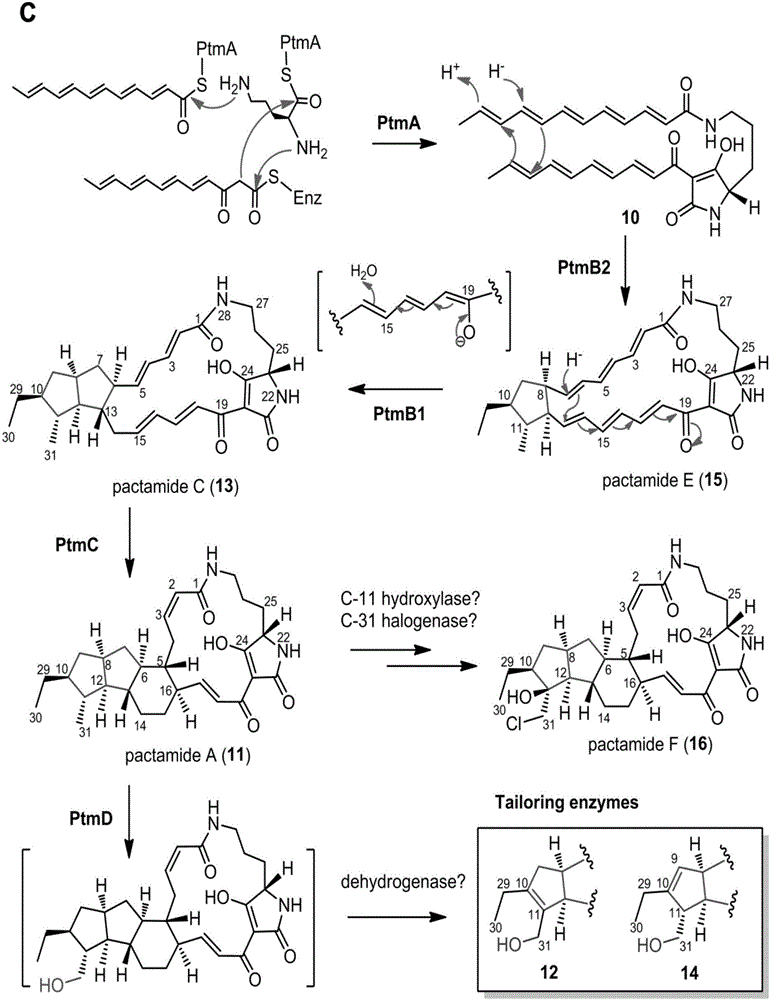
Biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and application thereof
ActiveCN106434702ABiosynthetic gene cluster activationHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclasePolyketide
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gene sequence related to flavone composite in radix scutellariae and application thereof
The invention discloses a gene related to flavone composite in radix scutellariae. The gene includes one or several in flavone synthetase gene with a sequence shown in SEQ ID No.1, flavone 6-site hydroxylase gene with a sequence shown in SEQ ID No.3 and flavone 8-site hydroxylase gene with a sequence shown in SEQ ID No.5. The invention further provides primer composite for amplifying the gene, protein encoded by the gene, a recombinant vector, host cell or transgenic cell line containing the gene and application thereof. The protein encoded by the gene disclosed by the invention can participate in synthesizing baicalein and wogonin and catalyzing synthesis and hydroxylation reaction of flavone matters of the similar structures, can provide very good basis for producing effective active matters, provides theoretical basis for producing baicalein, wogonin and aglycone of the baicalein and the wogonin in a large scale and establishes solid basis for industrially producing other related flavonoid compound.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHENSHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN
Rose containing flavone and malvidin, and method for production thereof
The invention provides a rose characterized by comprising a flavone and malvidin added by a genetic modification method. The flavone and malvidin are typically produced by expression of a transferred flavone synthase gene, pansy flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene and anthocyanin methyltransferase gene. The flavone synthase gene is, for example a flavone synthase gene of the family Scrophulariaceae,and specifically, the invention may be the flavone synthase gene of snapdragon of the family Scrophulariaceae, or the flavone synthase gene of torenia of the family Scrophulariaceae. The flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene is, for example, the pansy flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene. The anthocyanins methyltransferase gene is, for example, the methyltransferase gene of torenia of the family Scrophulariaceae.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
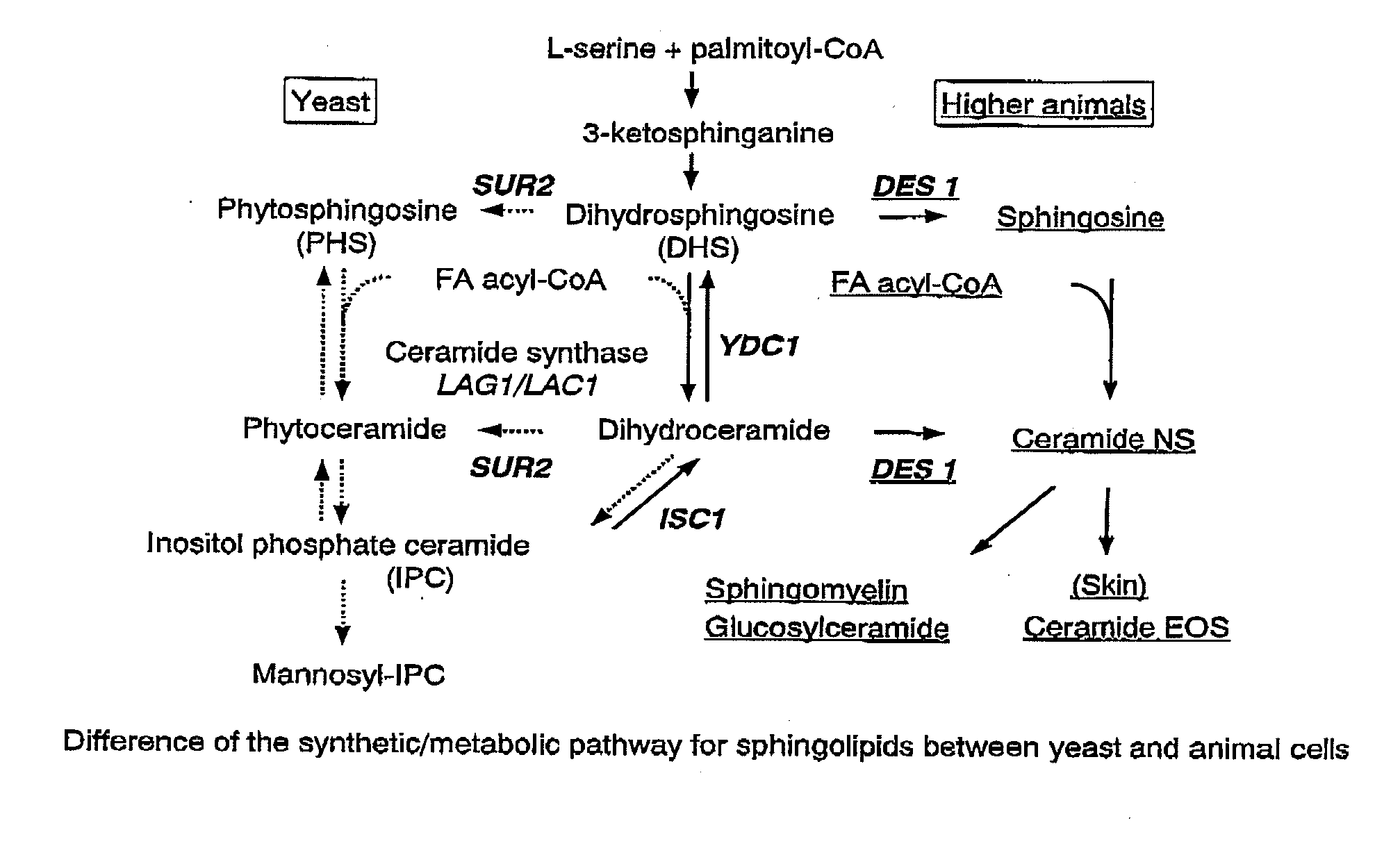
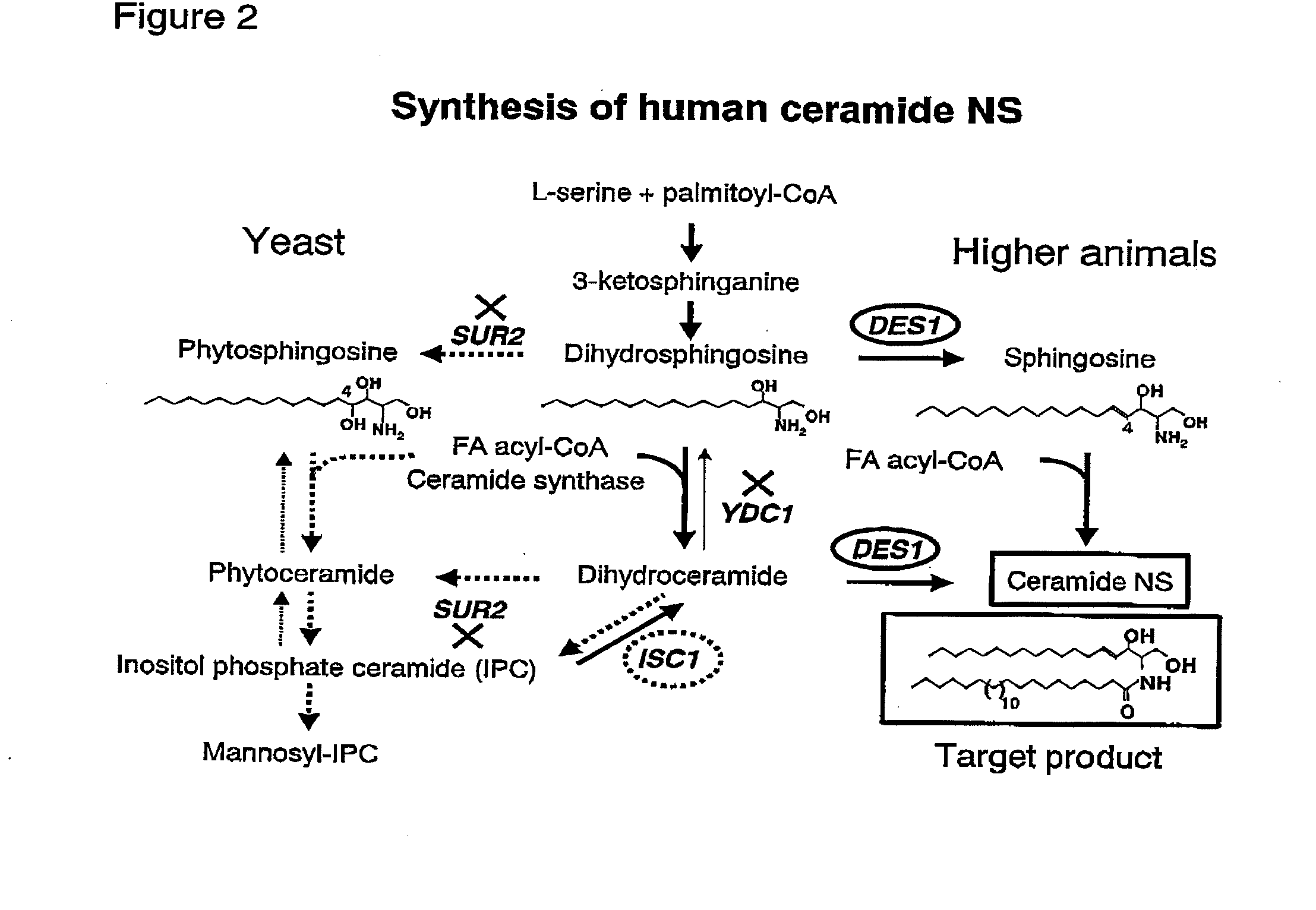
Methods for producing ceramide using transformed yeast
InactiveUS20090325247A1FunctionalLow production costRecombinant DNA-technologyFermentationYeastEnzyme Gene
The present invention provides methods for producing human ceramide in a yeast cell.The methods of the present invention comprise:1) introducing the sphingoid Δ4-desaturase gene (DES1) by transformation of the yeast cell; and2) abolishing the expression of the yeast sphinganine C4-hydroxylase gene (SUR2) by transformation of the yeast cell.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD +1
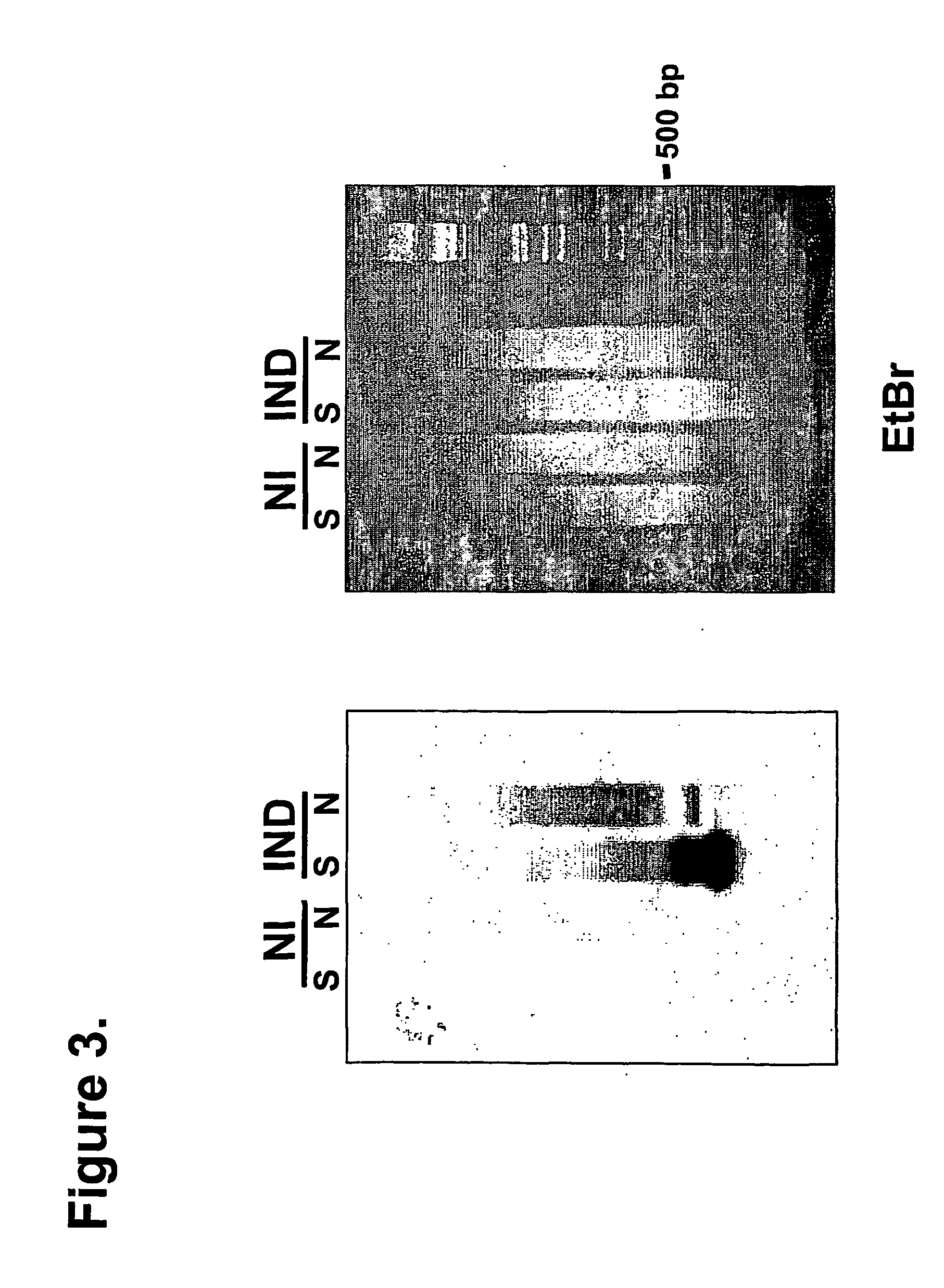
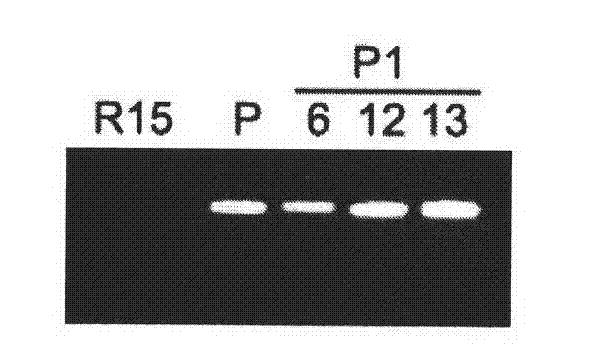
Flavonoid-3,5'-hydroxylase gene cloned from moth orchid, its coded sequence and application
The present invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and gene technology, and is especially the nucleotide coding sequence of flavoid-3', 5'-hydroxylase gene expressed in butterfly orchid, and its application in changing flower color. The present invention relates to the recombinant expression vector including the said gene, the transgenic plant, nucleotide primer sequence for obtaining the gene, the oligonucleotide sequence probe for detecting endogenous expression mode and method of analyzing and identifying the expression mode of the endogenous gene in butterfly orchid. Transforming the gene into petunia obtains transgenic plant with differentially expressed flavoid-3', 5'-hydroxylase gene and altered flower color.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for producing trans-4-hydroxyproline from glucose in fermentation manner
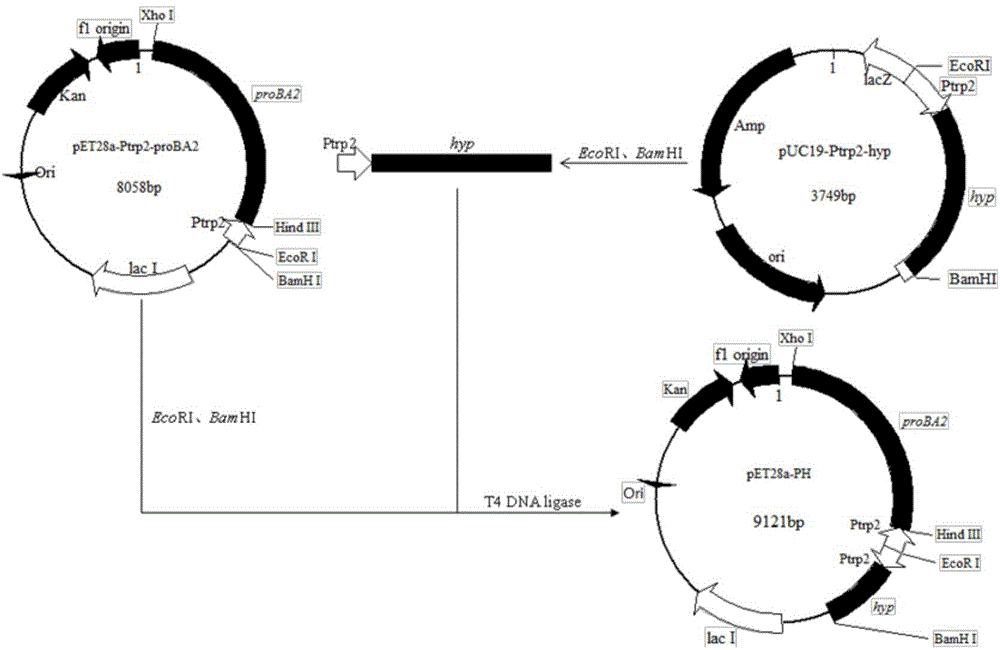
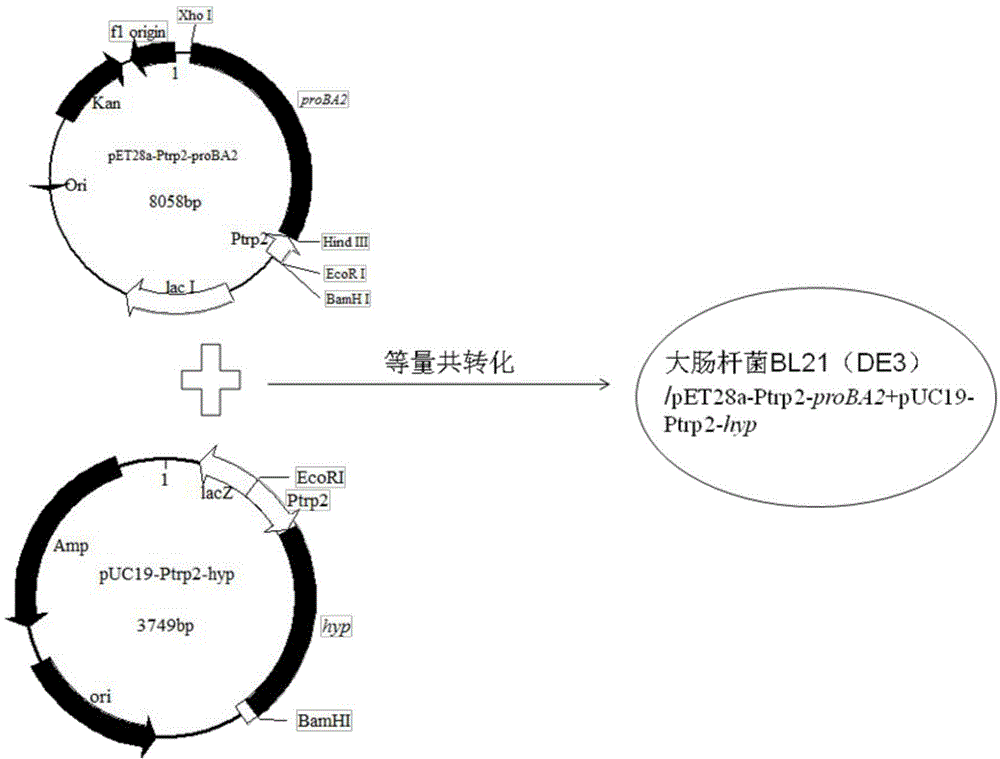
The invention discloses a method for producing trans-4-hydroxyproline from glucose in a fermentation manner by virtue of recombinant Escherichia coli without adding exogenous L-proline. A recombinant plasmid carried by the recombinant Escherichia coli has a mutant gene proBA2 and hyp (4-hydroxyproline), wherein proBA2 is mutated on a glutamyl kinase encoding gene proB, and the inhibition effect of L-proline on glutamyl kinase encoded by the mutated gene is remarkably reduced. proBA2 and hyp are co-expressed, and trans-4-hydroxyproline can be produced directly from glucose in the fermentation manner without adding exogenous L-proline. The recombinant plasmid is obtained by recombining proBA2 and hyp onto the same expression plasmid or by co-transforming recombinant plasmids which contain the two genes respectively and have different resistances. The invention further discloses the application of the Escherichia coli to the production of hydroxyproline.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
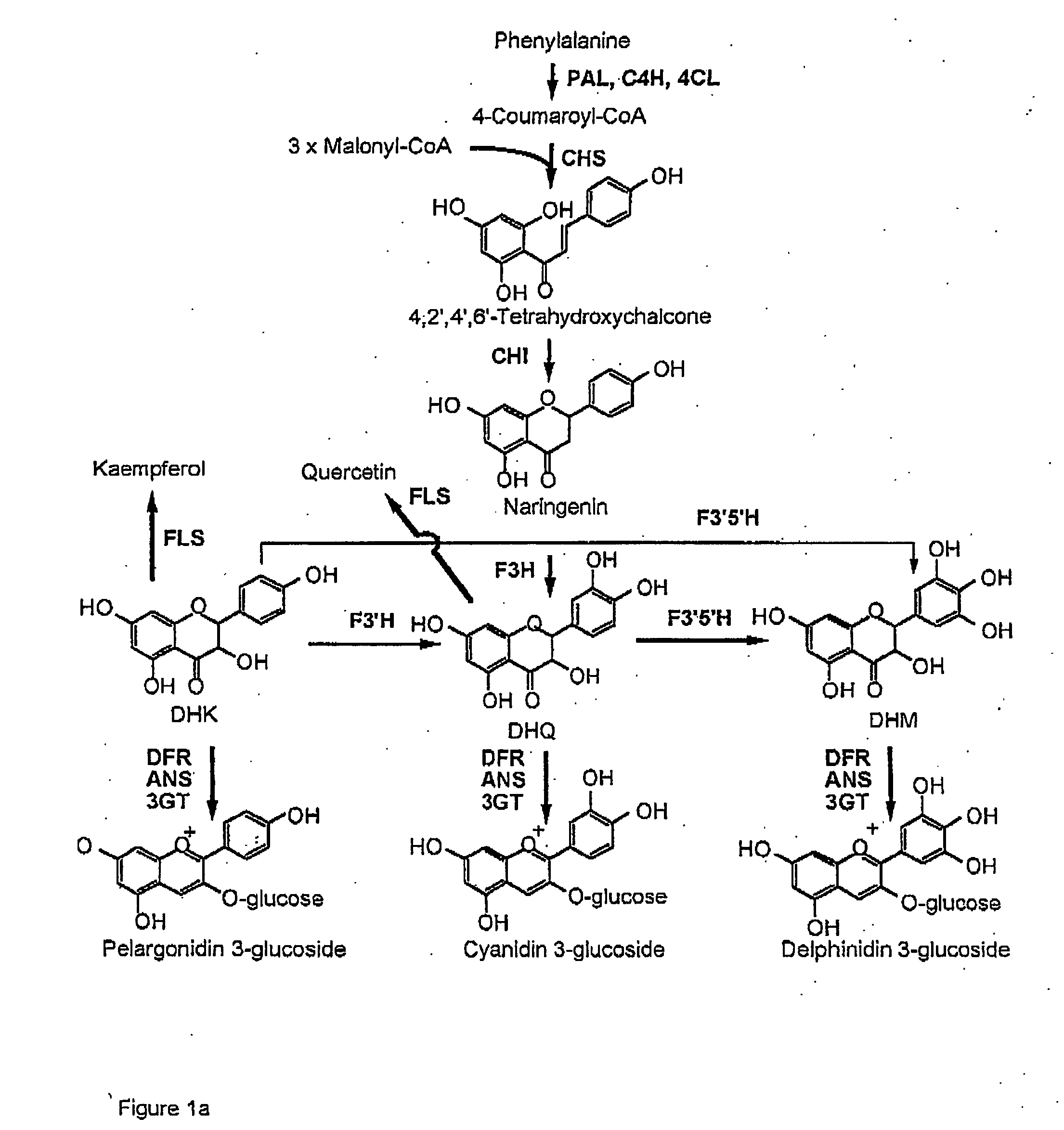
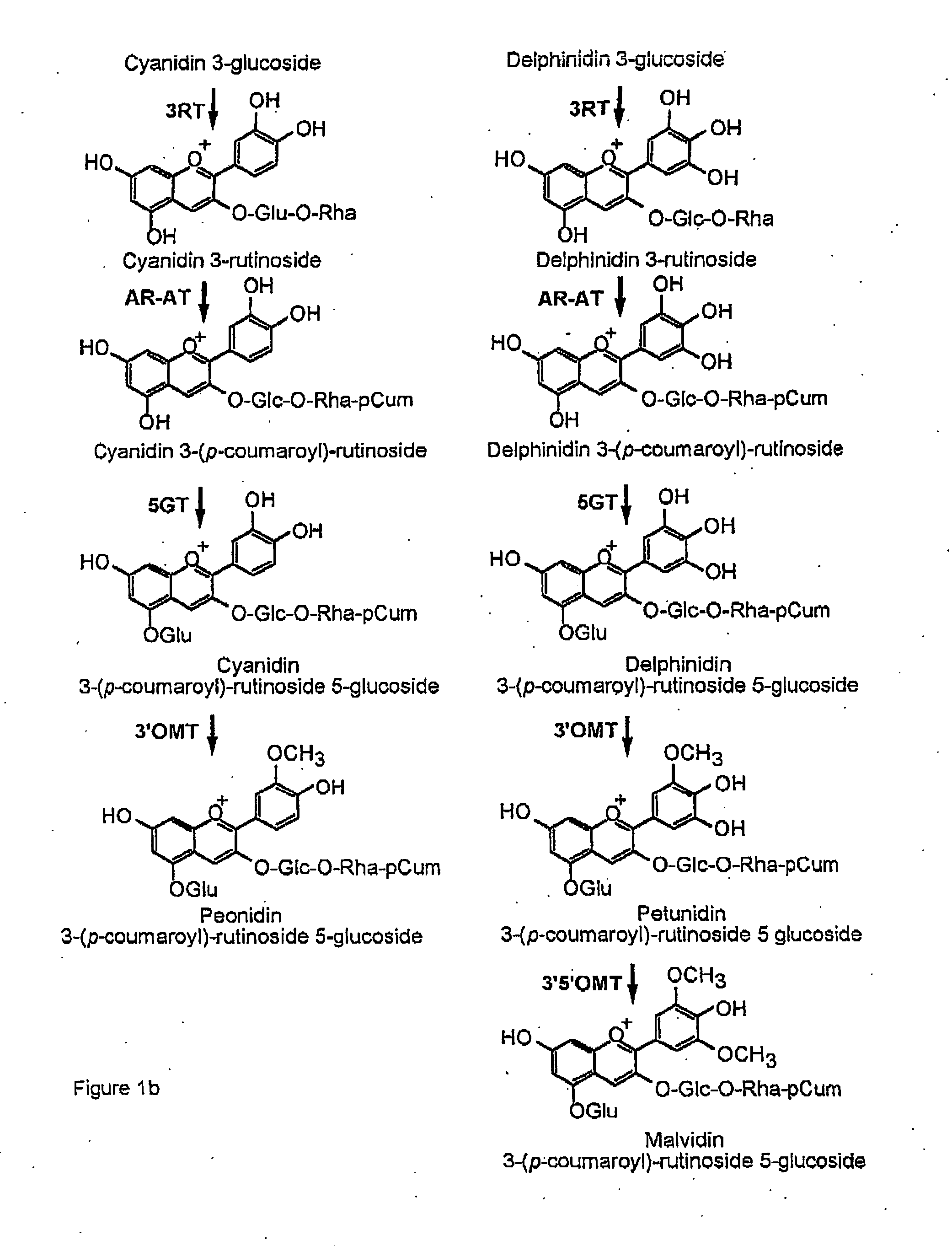
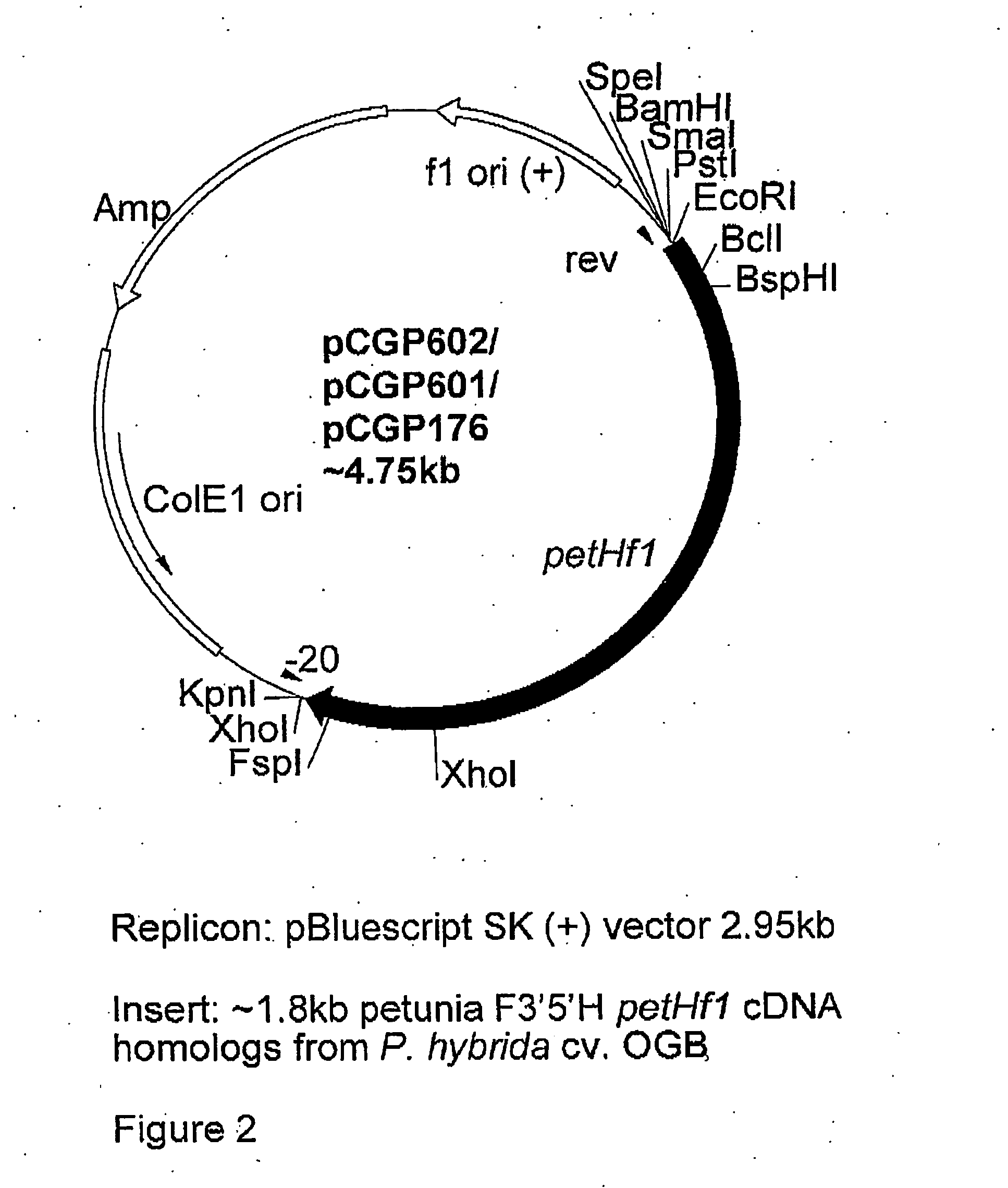
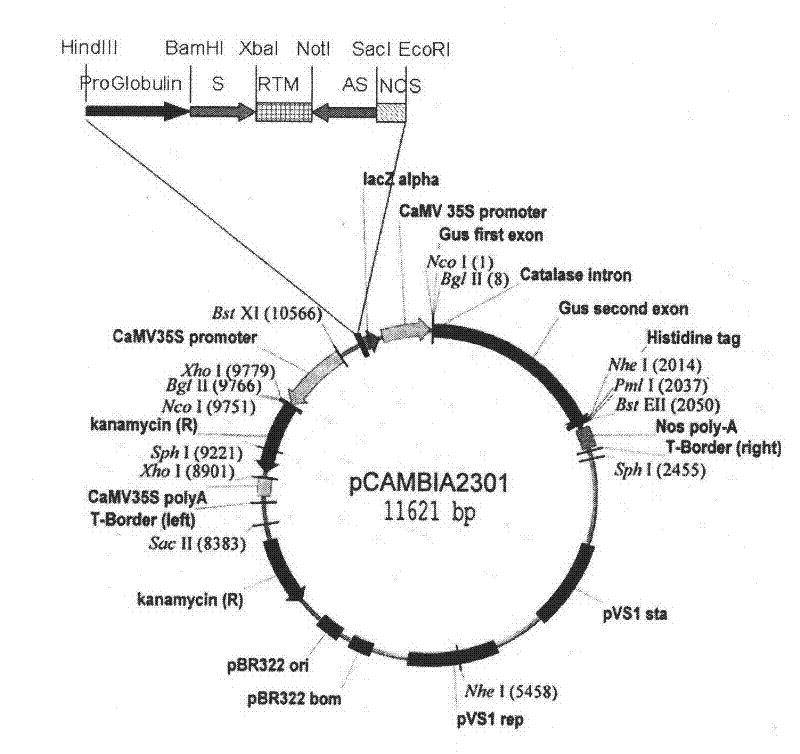
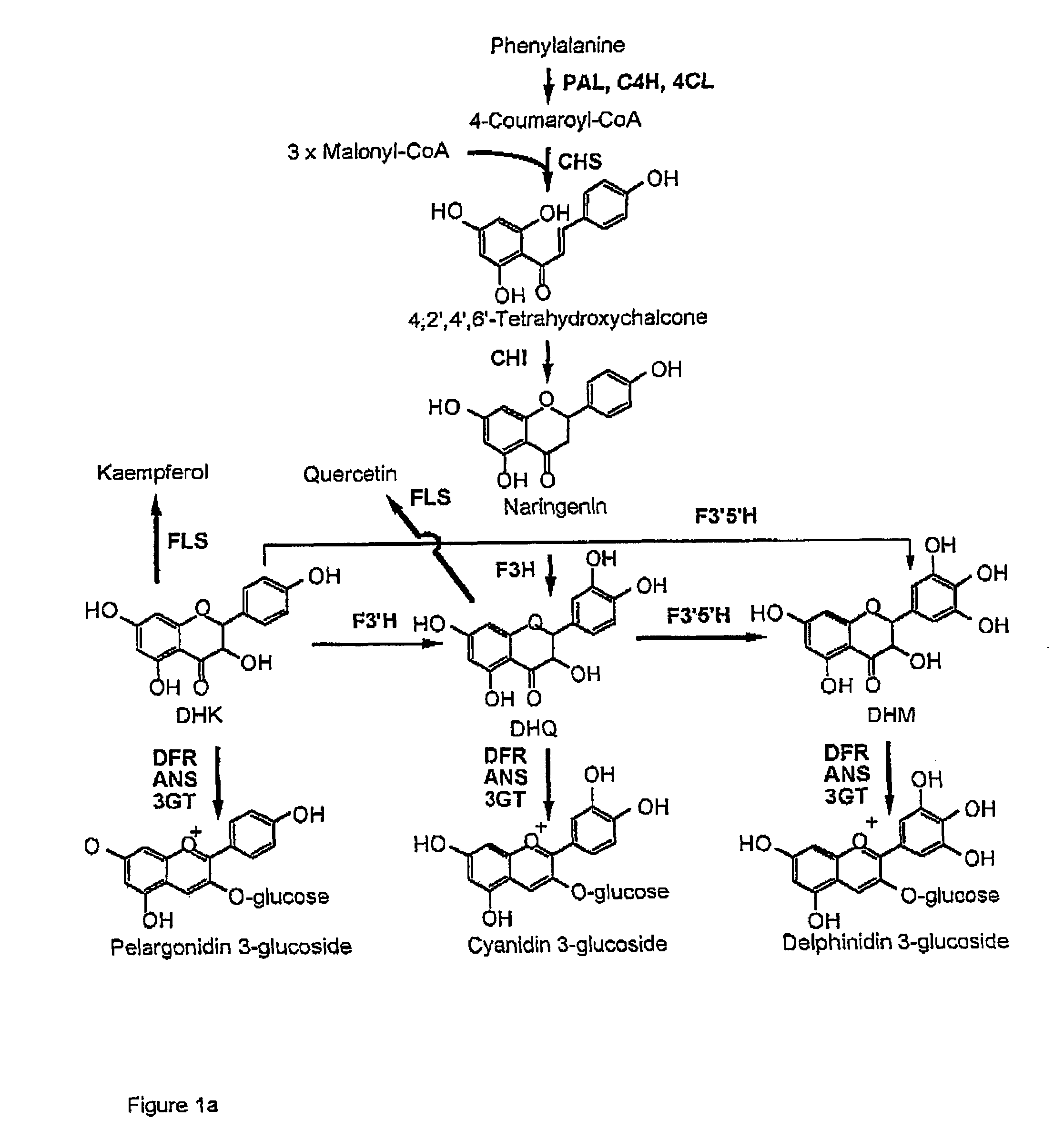
Flavanoid 3',5' hydroxylase gene sequences and uses therefor
ActiveUS20070033674A1Easy to operateSufficient levelTransferasesOxidoreductasesPlant tissueEriodictyol
The present invention relates generally to a genetic sequence encoding a polypeptide having flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase (F3′5′H) activity and to the use of the genetic sequence and / or its corresponding polypeptide thereof inter alia to manipulate color in flowers or parts thereof or in other plant tissue. More particularly, the F3′5′H has the ability to modulate dihydrokaempferol (DHK) metabolism as well as the metabolism of other substrates such as dihydroquercetin (DHQ), naringenin and eriodictyol. Even more particularly, the present invention provides a genetic sequence encoding a polypeptide having F3′5′H activity when expressed in rose or gerbera or botanically related plants. The instant invention further relates to antisense and sense molecules or RNAi-inducing molecules corresponding to all or part of the subject genetic sequence or a transcript thereof. The present invention further relates to promoters which operate efficiently in plants such as rose, gerbera or botanically related plants.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Genes for microsomal delta-12 fatty acid desaturases and hydroxylases from plants
InactiveUS7105721B2Analysis using chemical indicatorsOther foreign material introduction processesLipidomeHydroxylase gene
The preparation and use of nucleic acid fragments encoding fatty acid desaturase enzymes are described. The invention permits alteration of plant lipid composition. Chimeric genes incorporating such nucleic acid fragments with suitable regulatory sequences may be used to create transgenic plants with altered levels of unsaturated fatty acids.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for using 4-hydroxyisoleucine to produce plasmids and strains and synthesizing method of 4-hydroxyisoleucine
ActiveCN107475267AEliminate the need for crushingReduce utilizationBacteriaOxidoreductasesSynthesis methodsTransmembrane domain
The invention relates to a synthesizing method of 4-hydroxyisoleucine. According to the method, isoleucine hydroxylase genes are screened out, recombinant expression plasmid is constructed, and fusion protein having an amino acid deaminase transmembrane domain and isoleucine hydroxylase is expressed, so that isoleucine hydroxylase is anchored to the surface of cells; then a complete cell catalysis technology is utilized to replace a cell thawing and breaking technology, a cell freezing technology is omitted, and freezing processing equipment is not needed; meanwhile, product separation difficulty caused when inclusion of the cells is spread to reaction liquid after the cells are broken is avoided, the production procedure is simplified, the energy consumption, the material consumption and the production cost are lowered by a large margin, the conversion ratio of 4-hydroxyisoleucine produced through the method reaches up to 99.0% or above, and the synthesizing method is more beneficial to industrialized production.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Abscisic acid 8'-and 7'-hydroxylase genes and related sequences from plants
InactiveUS20040103451A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention relates to plant enzymes responsible for hydroxylation of abscisic acid, said enzymes capable of 7'- and 8'-hydroxylation of abscisic acid, and polynucleotides encoding the same. The invention further relates to methods for using said polynucleotides to alter plant metabolism, in particular metabolism of abscisic acid. The invention further relates to plants exhibiting altered characteristics as a result of the alteration of abscisic acid metabolism.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Method for improving characters of gossypol in cotton, and use thereof
InactiveCN102242118AThe content of gossypol in the plant is normalPlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsHydroxylase geneGossypol
The invention relates to a method for improving characters of gossypol in cotton, and a use thereof. In the invention, expression of a cadinene-8-hydroxylase gene CYP 706 B 1 in cotton seeds is down-regulated specifically thus synthesis of gossypol in cotton seeds is inhibited effectively without an influence on synthesis of gossypol in other tissues. Through the method, characters of gossypol ina cotton plant are improved and an integrated utilization value of cotton is increased greatly.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Flavonoid 3′,5′ hydroxylase gene sequences and uses therefor
ActiveUS7612257B2Sufficient levelAvoid insufficient lengthBryophytesSugar derivativesPlant tissueEriodictyol
The present invention relates generally to a genetic sequence encoding a polypeptide having flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase (F3′5′H) activity and to the use of the genetic sequence and / or its corresponding polypeptide thereof inter alia to manipulate color in flowers or parts thereof or in other plant tissue. More particularly, the F3′5′H has the ability to modulate dihydrokaempferol (DHK) metabolism as well as the metabolism of other substrates such as dihydroquercetin (DHQ), naringenin and eriodictyol. Even more particularly, the present invention provides a genetic sequence encoding a polypeptide having F3′5′H activity when expressed in rose or gerbera or botanically related plants. The instant invention further relates to antisense and sense molecules or RNAi-inducing molecules corresponding to all or part of the subject genetic sequence or a transcript thereof. The present invention further relates to promoters which operate efficiently in plants such as rose, gerbera or botanically related plants.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method for obtaining 5-hydroxytryptophane by fermenting engineering bacterial strain BL 21-DE3
InactiveCN101864466ARaw materials are easy to getLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProcess optimizationBiotechnology
The invention provides a technology for obtaining 5-hydroxytryptophane by fermenting an engineering bacterial strain BL 21-DE. The engineering bacterial strain is prepared by utilizing a reported rabbit Oryctolagus cuniculus trptophan hydroxylase gene to build and reconstruct an expression vector and carrying out plasmid conversion. The bacterial strain is utilized for one-step fermentation process optimization; and under the condition of not purifying tryptophan hydroxylase, substrate tryptophan is added in the fermentation mature period to obtain the final product of 5-hydroxytryptophane. The invention has easily obtained raw material and low cost, conversion rate is more than 70%, and yield is more than 80%.
Owner:CHENGDU KAISHENG BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
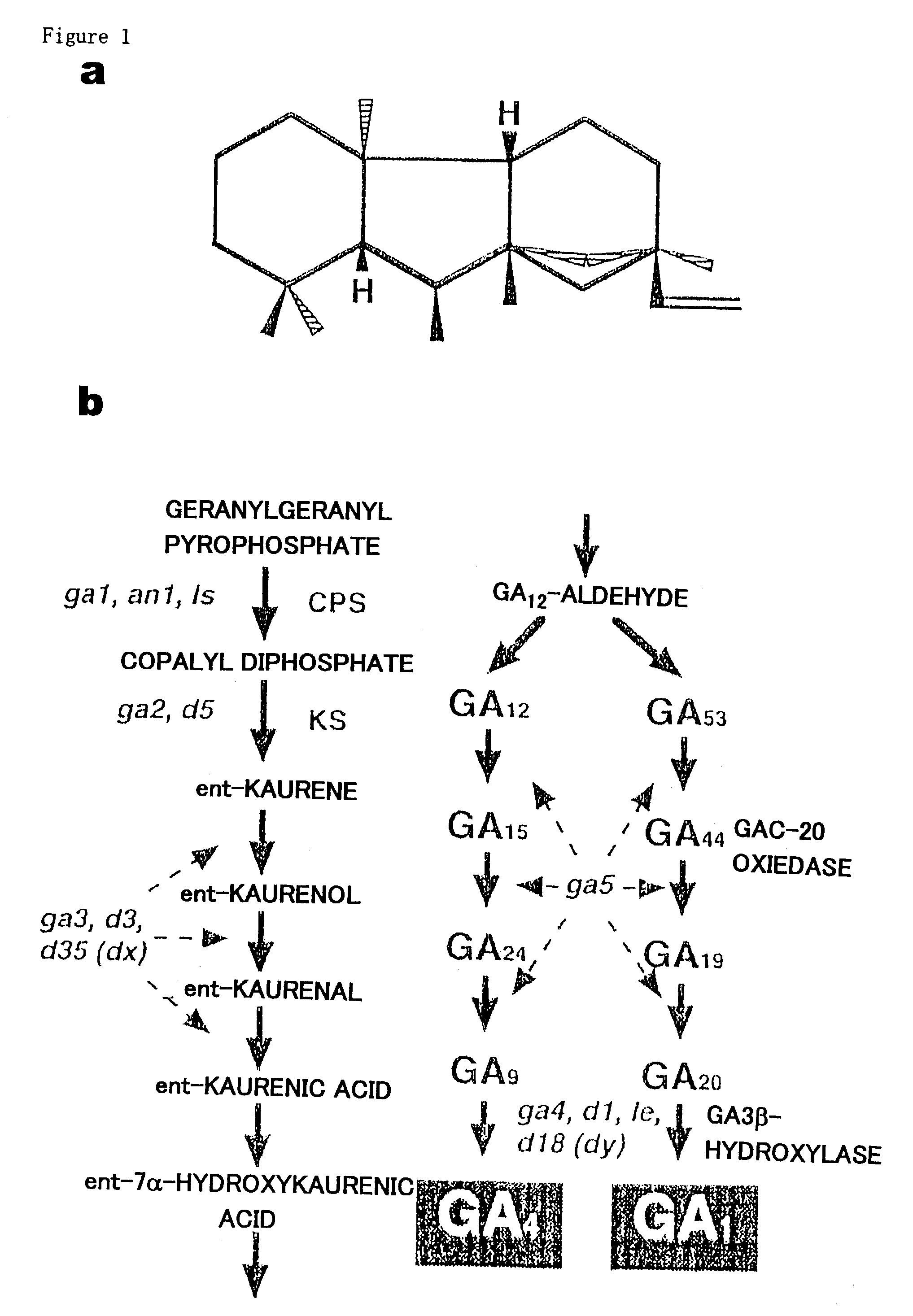
Gibberellin 3β-hydroxylase genes of rice and uses thereof
InactiveUS7049490B2Shortened statureIncrease fruit weightSugar derivativesHydrolasesRice plantsGenomic DNA
Genomic DNA and cDNA encoding GA 3β-hydroxylase were isolated from rice. When the expression of these genes was suppressed in rice plants, the plants became dwarfed compared with the wild type plants.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
Method for converting indole by phenol hydroxylase genetic engineering strains to prepare indigotine
InactiveCN101851649AImprove conversion abilityBroad substrate spectrumBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDry weight
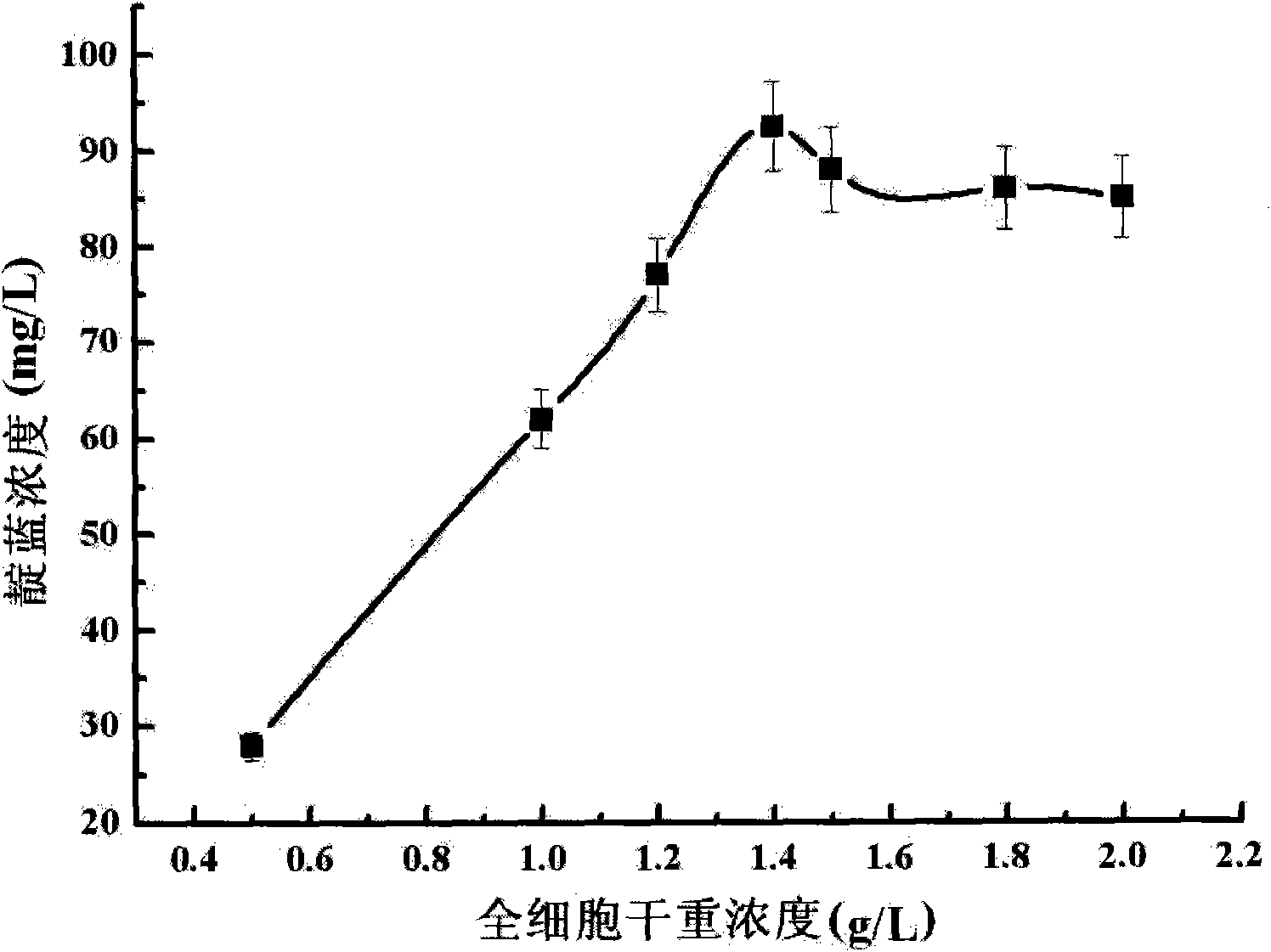
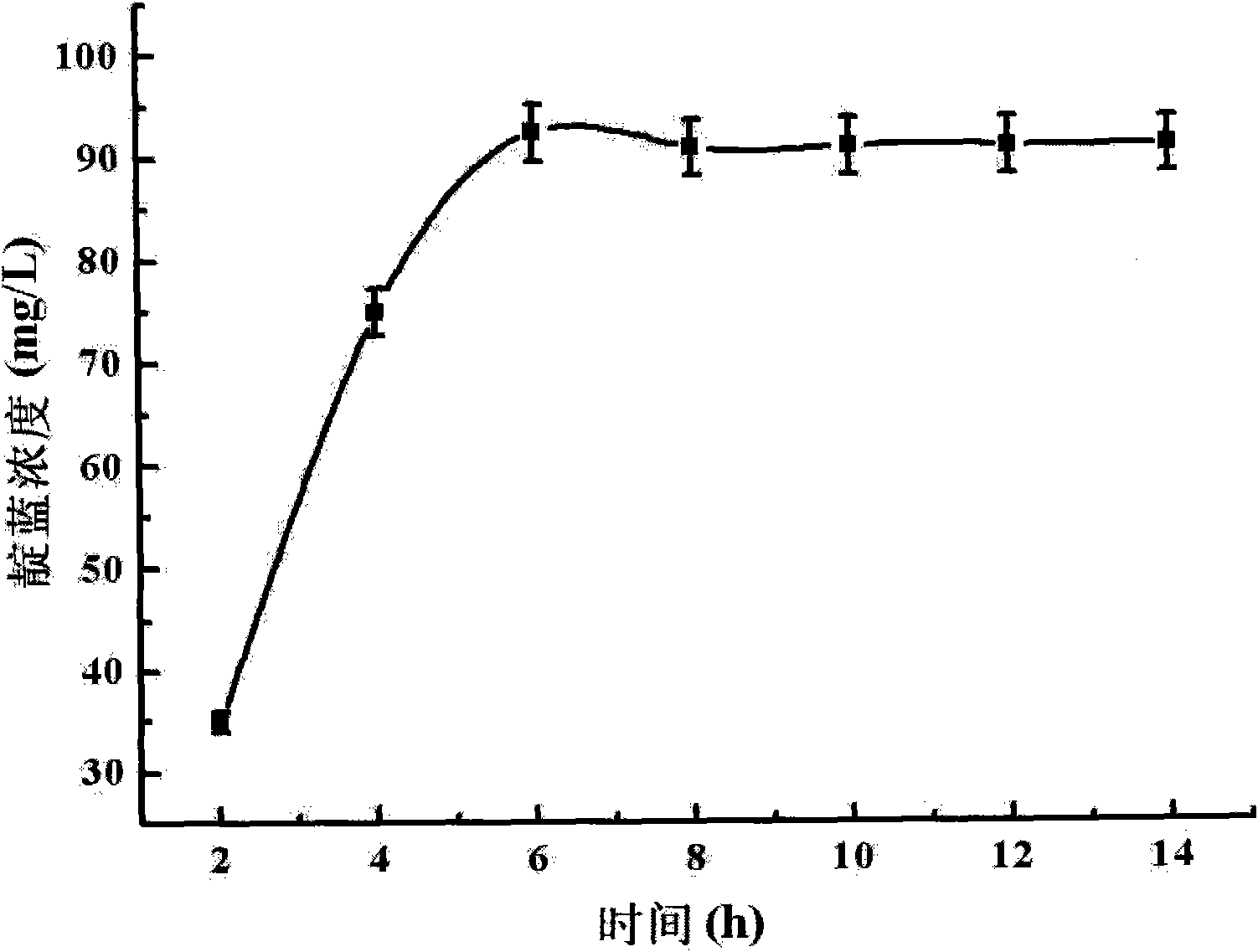
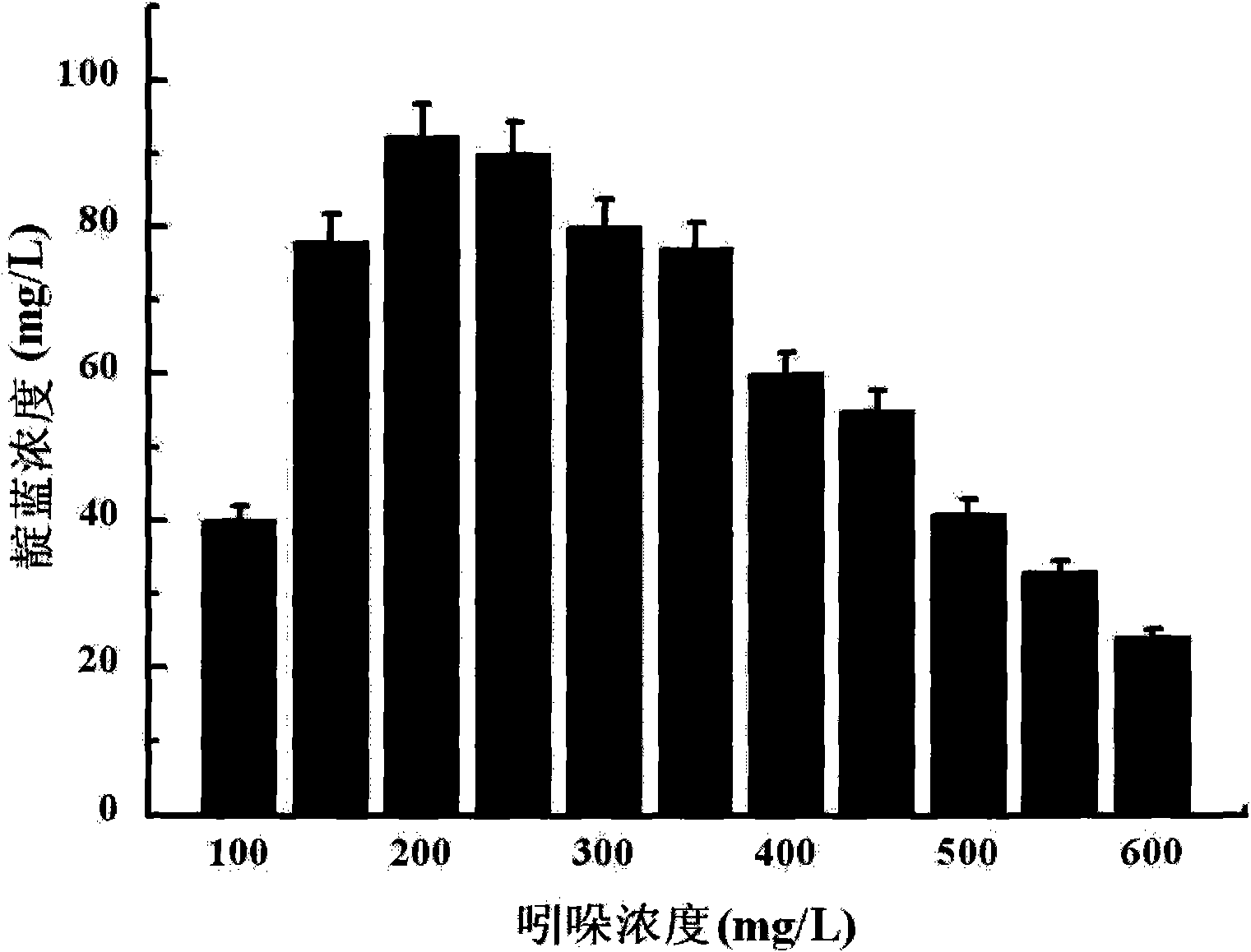
The invention relates to a method for converting indole to prepare indigotine by engineering strains formed by recombining phenol hydroxylase genes into colon bacillus, which belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining phenol hydroxylase gene full-length sequences with the total length of 5490bp and the Genbank registration number of FJ610336 in high-efficient phenol-degrading bacteria Arthrobacter sp.W1 with the GenBank registration number of EU339930; connecting the phenol hydroxylase gene full-length sequences to carrier plasmids (pET28a (+) Vector); and converting the phenol hydroxylase gene full-length sequences into host cell colon bacillus to construct phenol hydroxylase genetic engineering strains. The full-cell dry weight concentration of the phenol hydroxylase genetic engineering strains in a biological conversation reaction solution is between 1 and 2 g / L, the indole concentration is between 100 and 600 mg / L, the glucose concentration is between 0.5 and 2 mmol / L, the rotation speed of a shaking table is controlled between 50 to 200 r / min at a temperature between 20 and 40 DEG C, and the oscillating reaction lasts 2 to 14 hours. The biological conversation method of the invention has the advantages of mild reaction condition, high product concentration and short production period, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Rose containing flavone and delphinidin, and method for production thereof
The invention provides a rose characterized by comprising a flavone and delphinidin added by a genetic modification method. The flavone and delphinidin are typically produced by expression of a transferred flavone synthase gene and flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene, respectively. The flavone synthase gene is, for example, a flavone synthase gene of the family Scrophulariaceae, and specifically it may be the flavone synthase gene of snapdragon of the family Scrophulariaceae, or the flavone synthase gene of torenia of the family Scrophulariaceae. The flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene is, for example, the pansy (Viola×wittrockiana) flavonoid 3′,5′-hydroxylase gene.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Preparation method of gallic acid and protocatechuic acid, and preparation method of reaction catalyst thereof
PendingCN110184288AResolve source issuesReduce manufacturing costOxidoreductasesFermentationGallic acid esterGlucose polymers
The invention discloses a preparation method of gallic acid and protocatechuic acid as well as a preparation method of a reaction catalyst thereof. According to the preparation method of the gallic acid and the protocatechuic acid, a catalytic enzyme solution is prepared by carrying out construction of aroZ fragments of 3-dehydroshikimate dehydratase genes or pobA fragments of hydroxybenzoate hydroxylase genes; and then, biosynthesis reaction is carried out so as to synthesize the gallic acid and the protocatechuic acid. The preparation method of the gallic acid and the protocatechuic acid hasthe following beneficial effects: by taking glucose, which is affordable in price and wide in source, as a raw material, the whole process is simplified so as to have environmental pollution reducedwith production cost of gallic acid decreased.
Owner:南京趣酶生物科技有限公司 +1
Astaxanthin-producing Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae gene engineering strain
ActiveCN111454854AFast high density growthHelp with pollution controlFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses an astaxanthin-producing Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae gene engineering strain which contains a nucleotide sequence of beta-carotene hydroxylase gene crtZ shown as SEQ ID NO:1,and a nucleotide sequence of beta-carotene ketolase gene crtW shown as SEQ ID NO:3. The beta-carotene ketolase gene crtW and beta-carotene hydroxylase gene crtZ are transformed into Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae YM25235 through an agrobacterium-mediated method for construction of the Rhodosporidium kratochvilovae gene engineering strain YM25235 / pRHcrtW-crtZ; and the crtZ and crtW genes expressedby the strain can further transform the beta-carotene in the YM25235 strain into astaxanthin, after fermentation culturing is carried out and comparing with a starting strain is carried out, the astaxanthin output of the engineering strain can reach 0.637 mg / g dry strain body, and a foundation is laid for large-scale commercial production of astaxanthin.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Phenol hydroxylase gene and uses thereof
The present invention relates to phenol hydroxylase gene and its use. The present invention provides metabolic encoding gene capable of converting phenol into catechol; constitutes HF conjugal transfer plasmid; and obtains genetic engineering strain capable of degradation to phenol or enlarging degradation range of substrate. When the phenol hydroxylase gene is transferred to immobile calcium acetate bacillus PHEA-2, the phenol degrading capacity of the strain will be raised. When the hydroxylase gene is transferred to toluene degrading bacillus, the bacillus strain will obtain phenol degrading capacity and enlarged substrate degrading range.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com