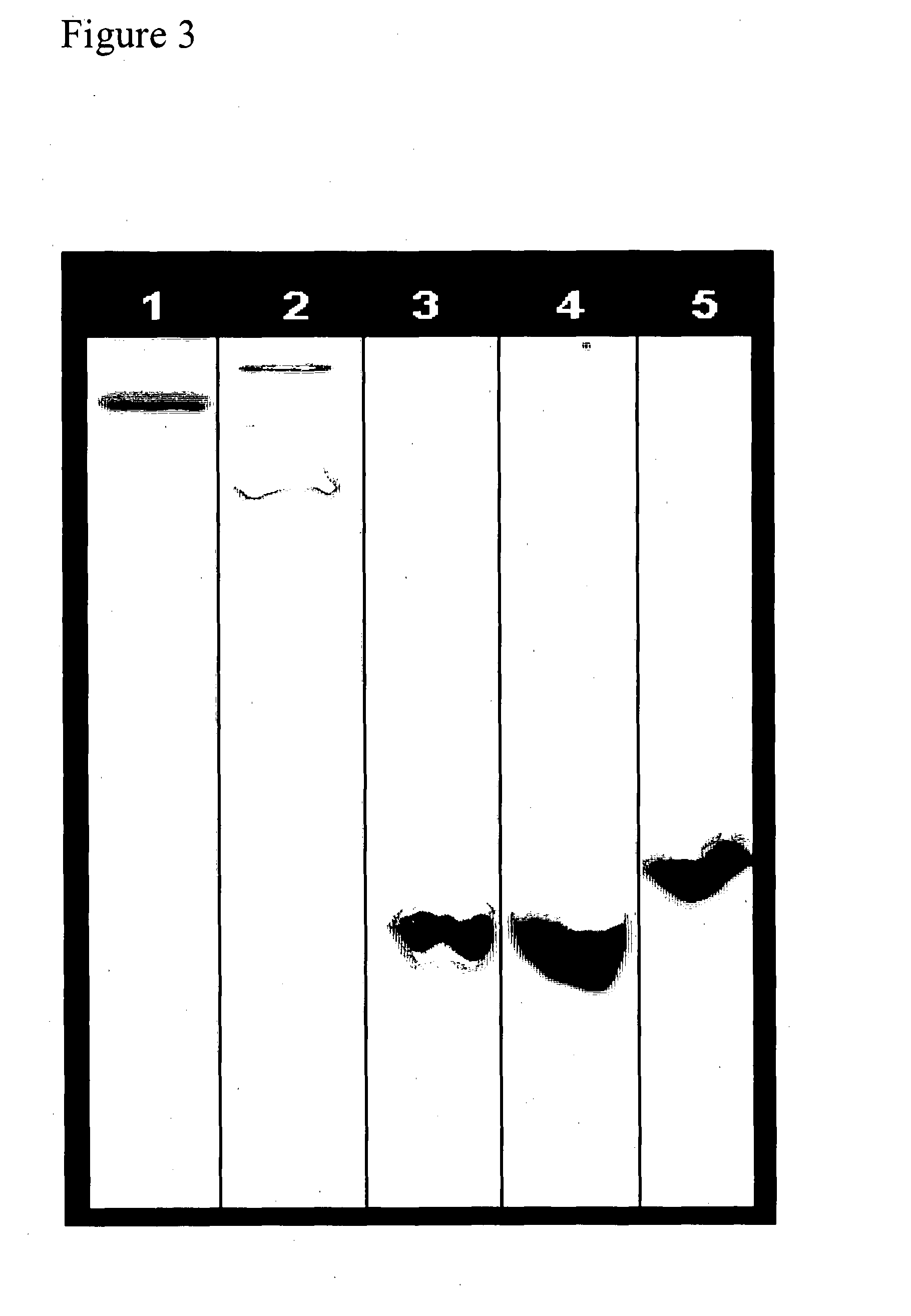
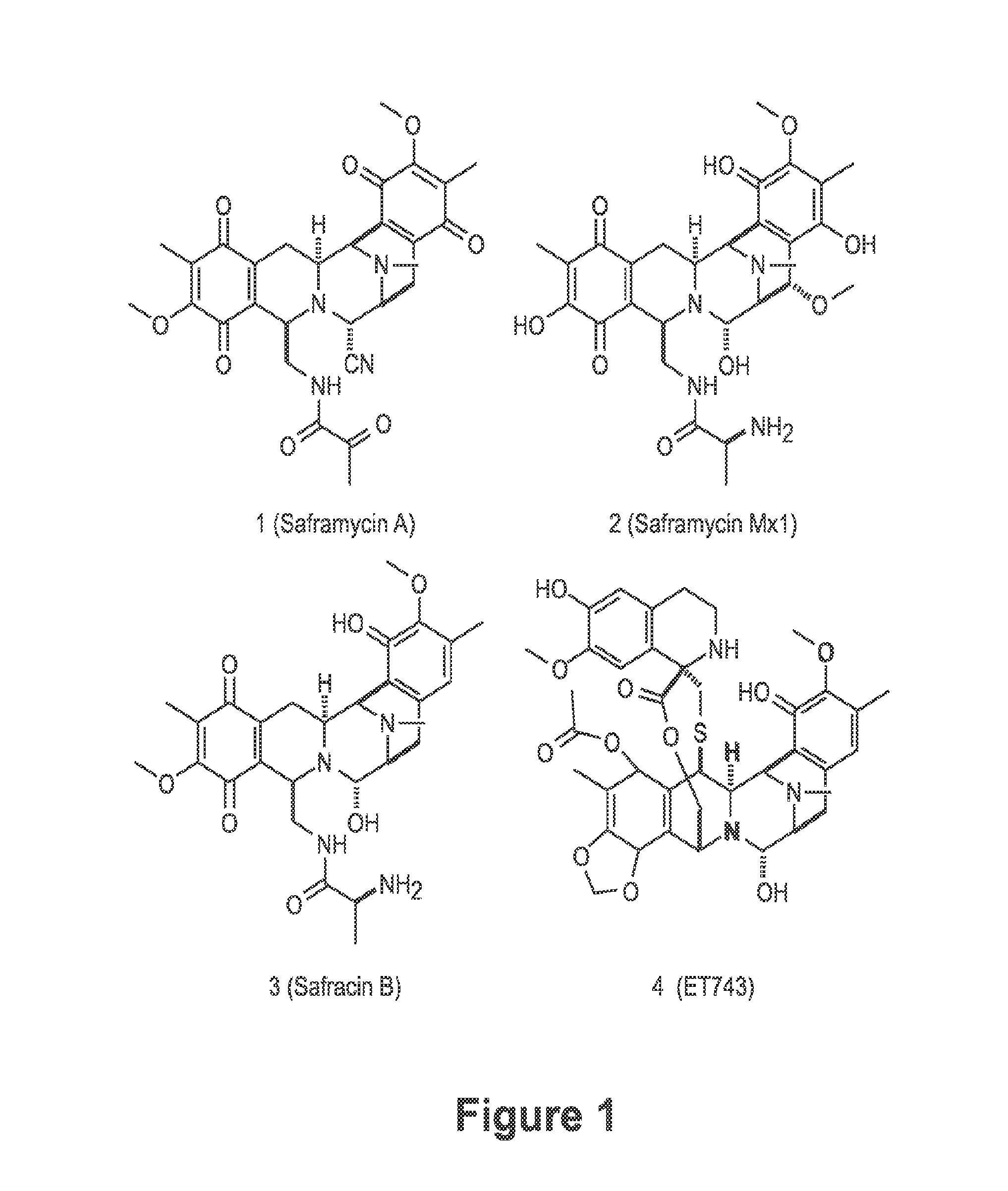
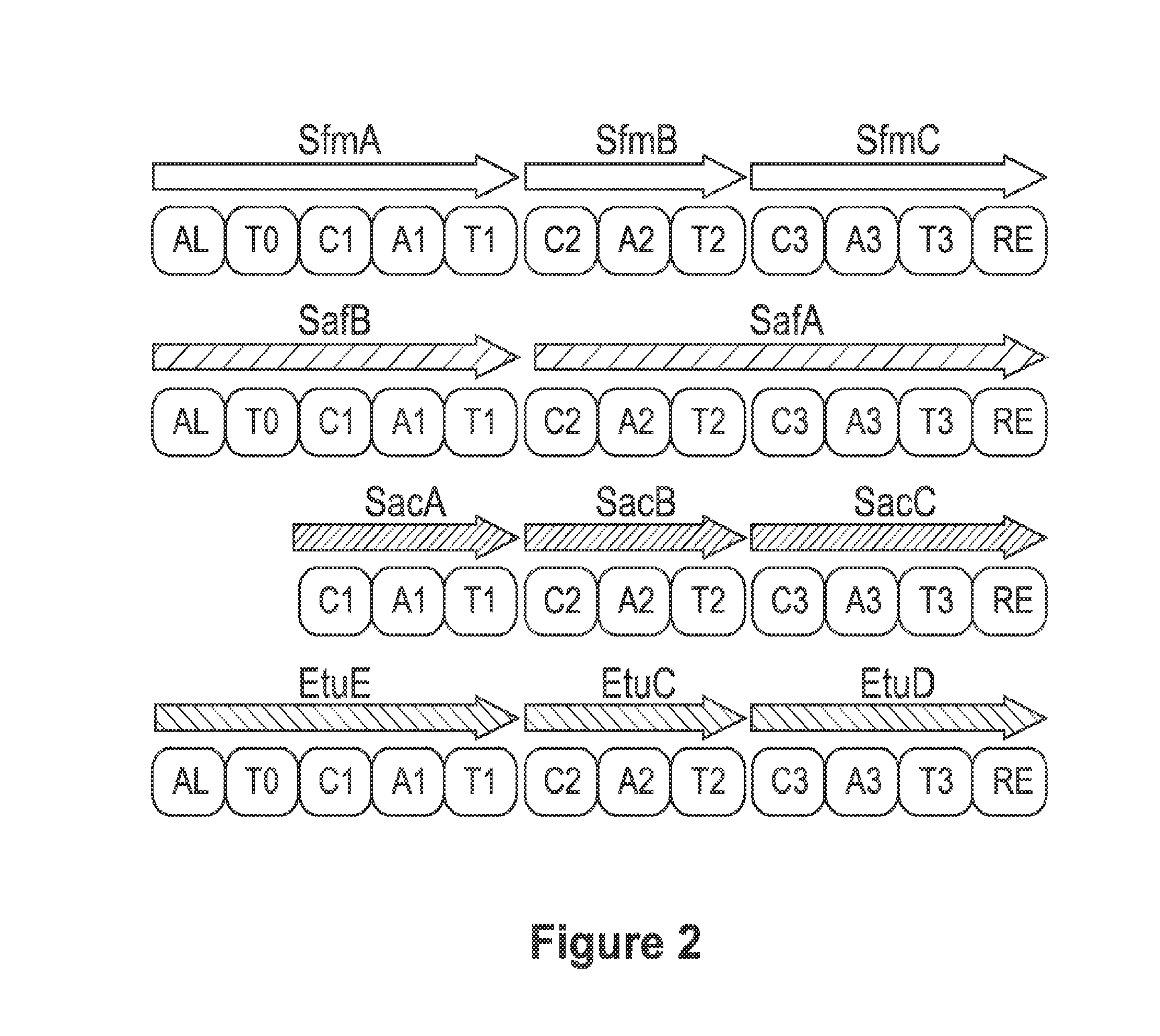
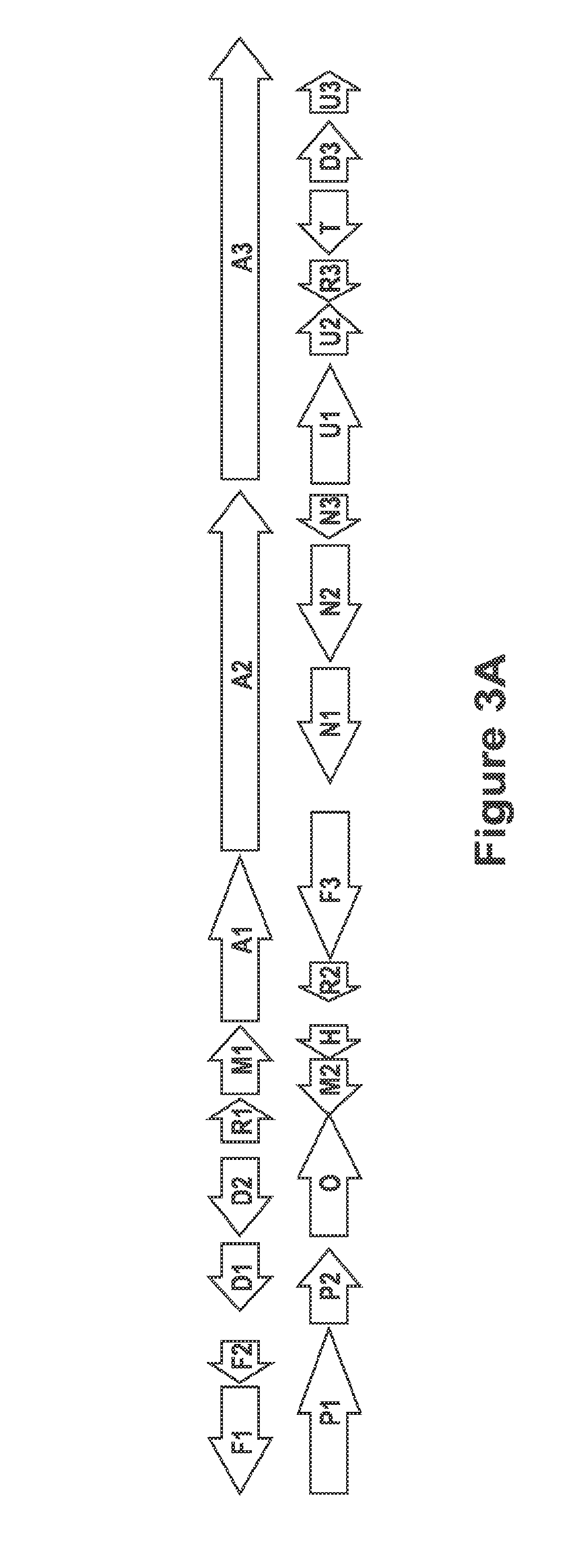
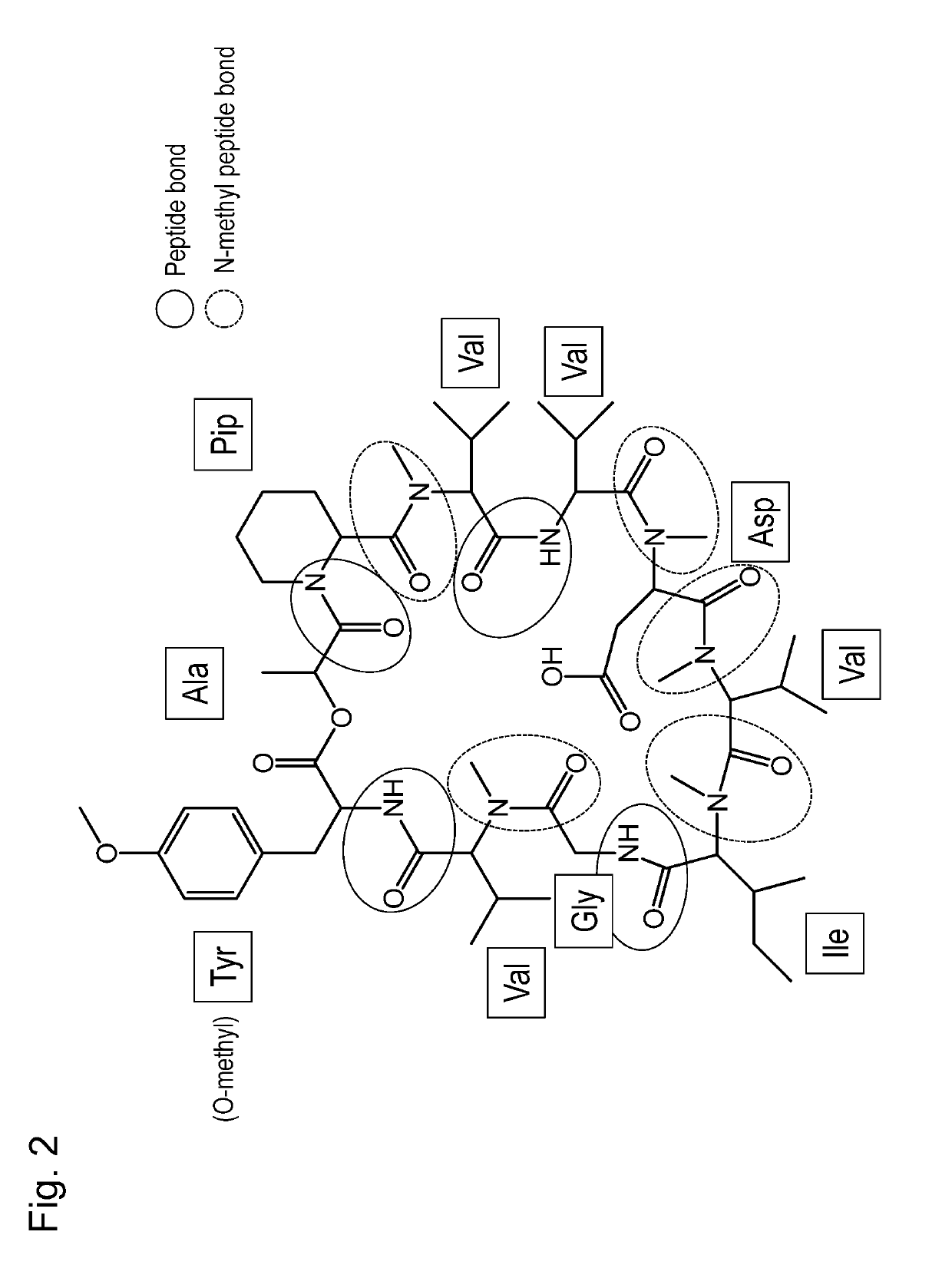
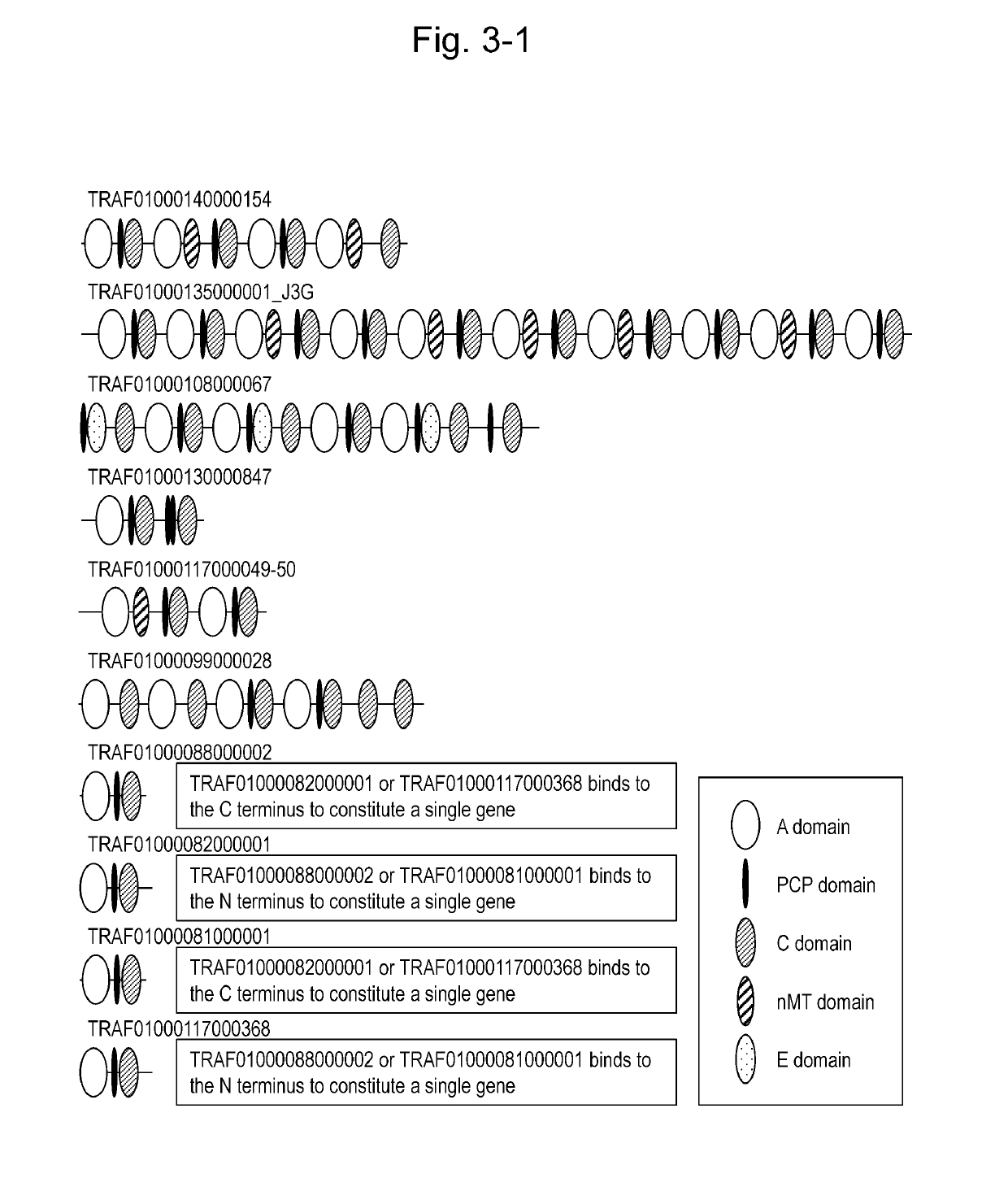
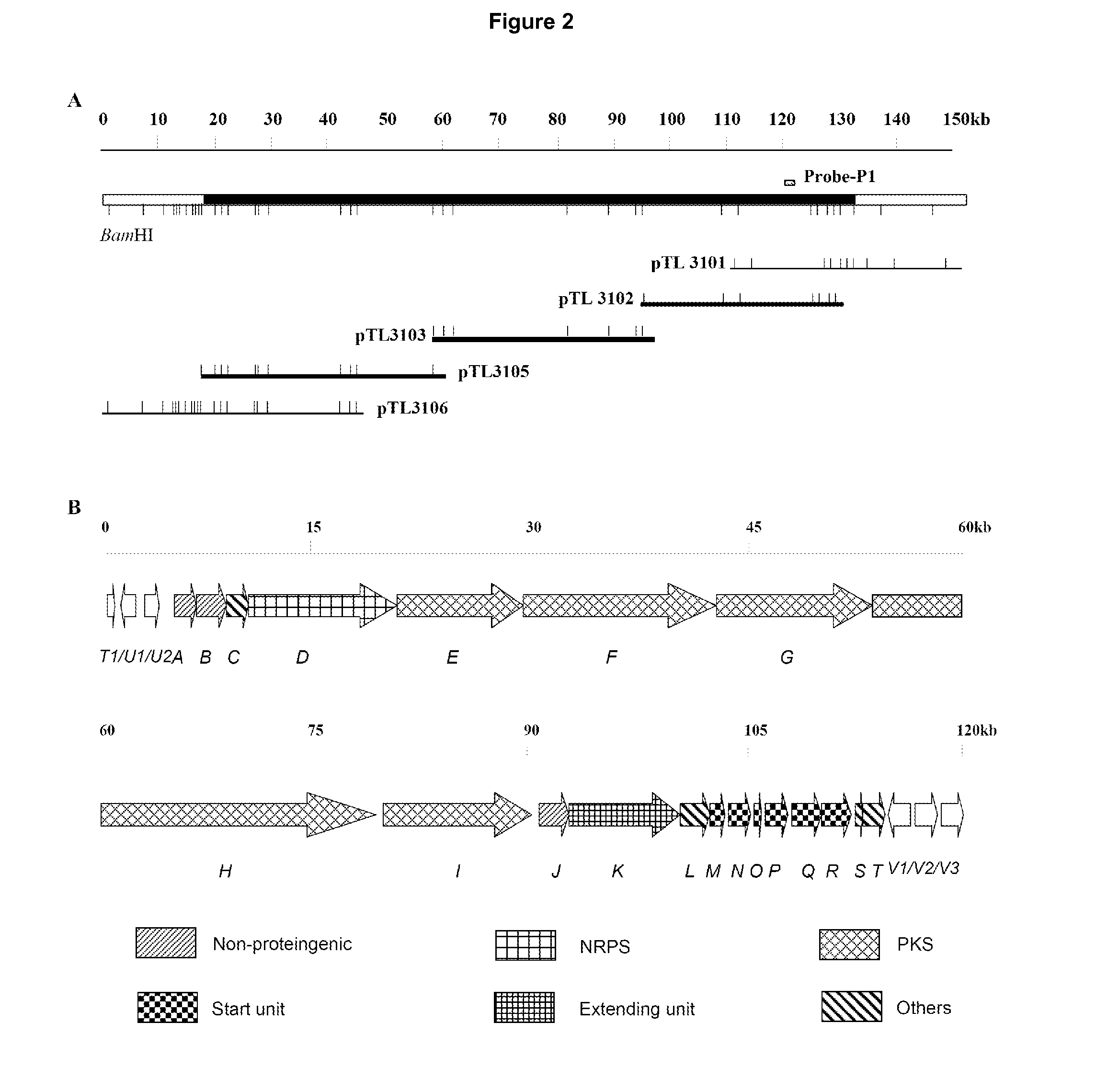
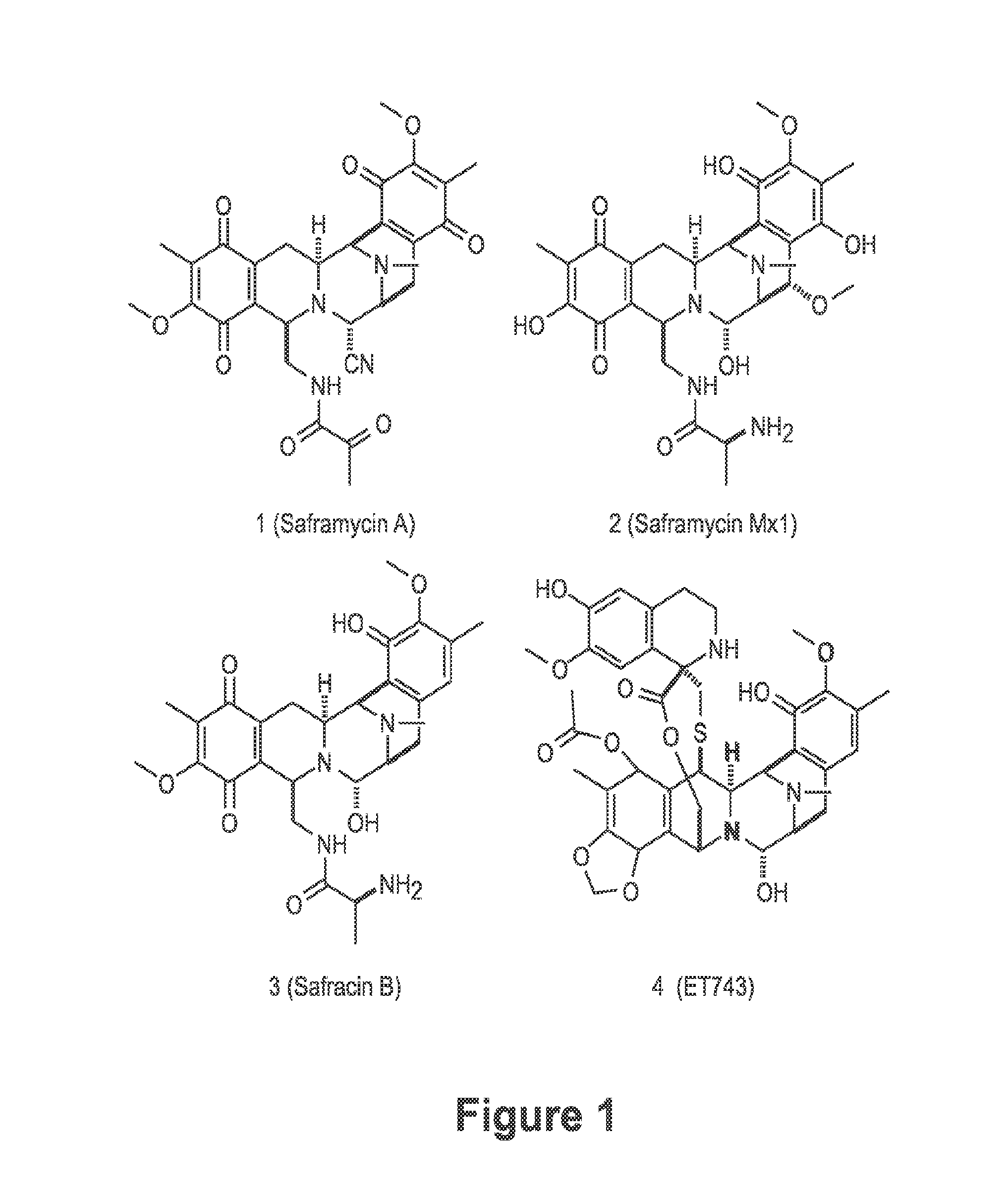
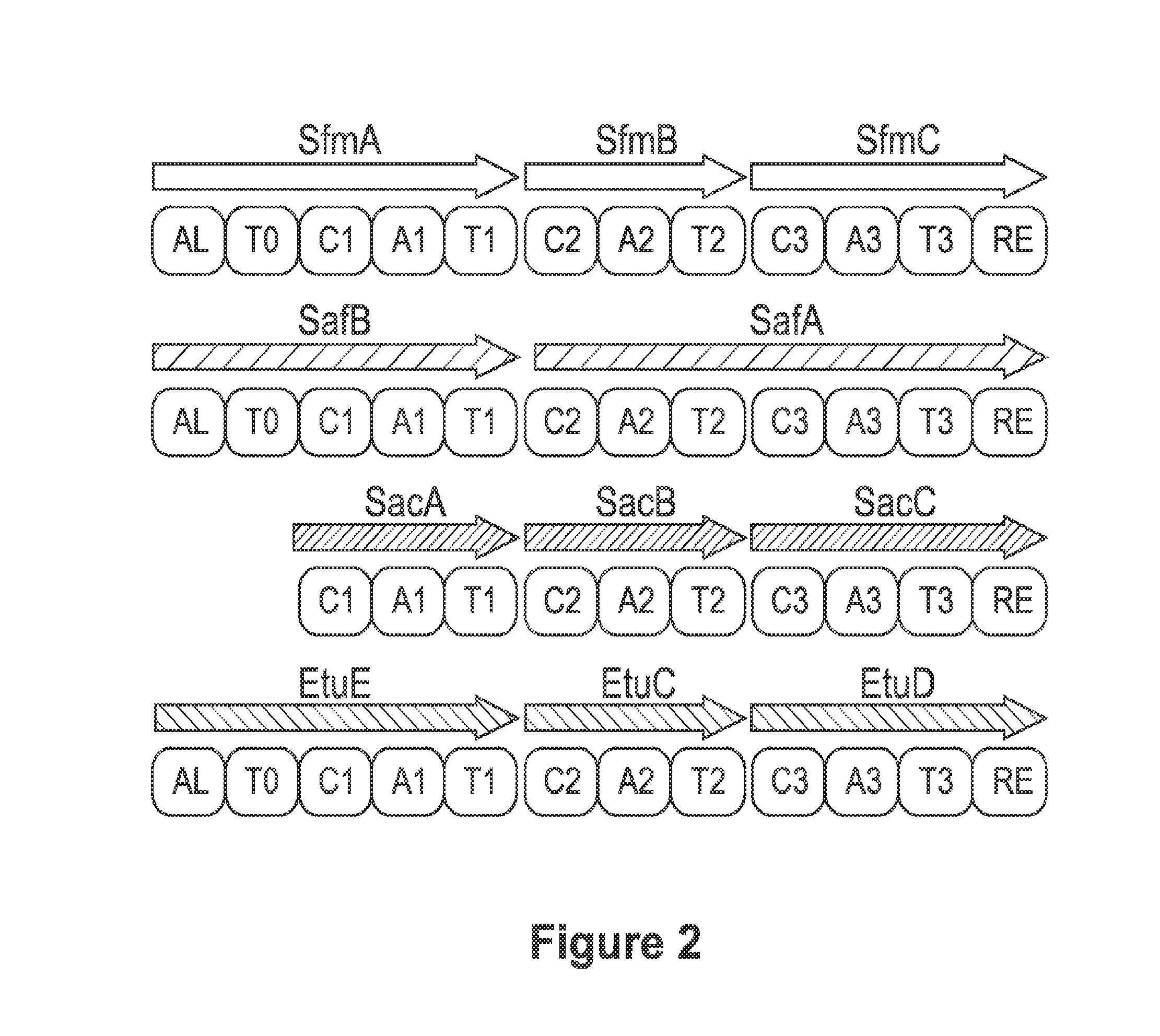
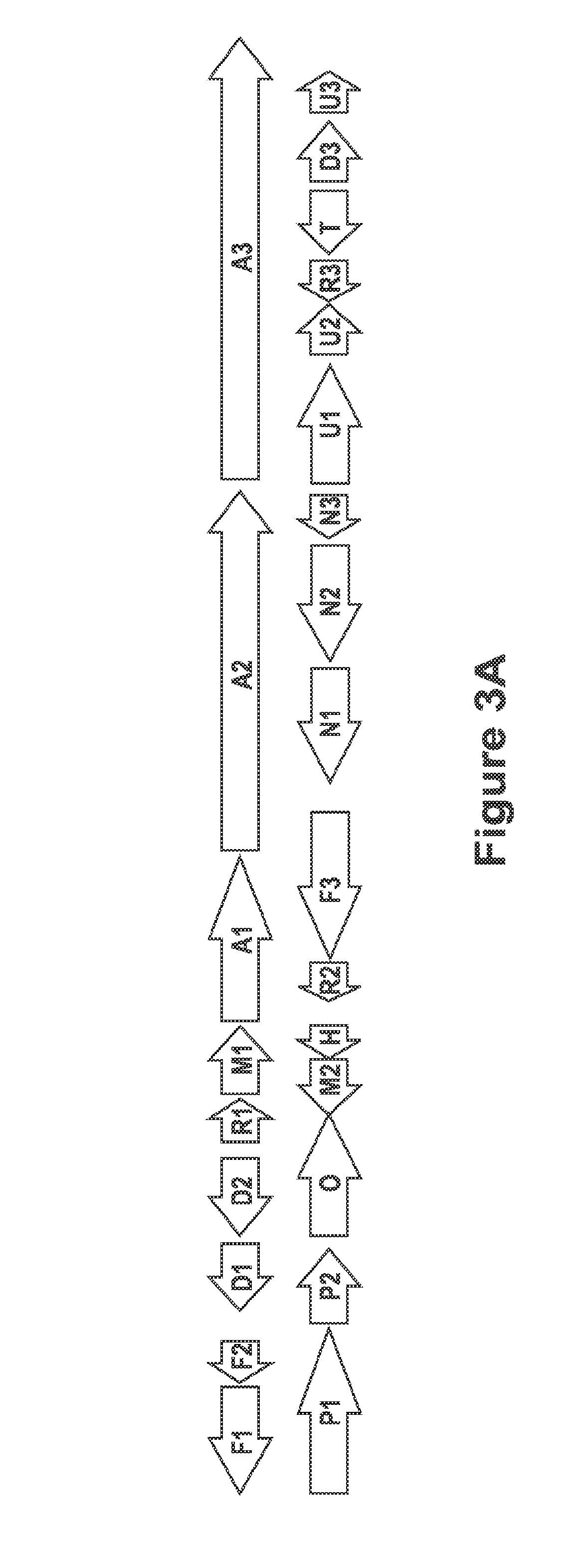
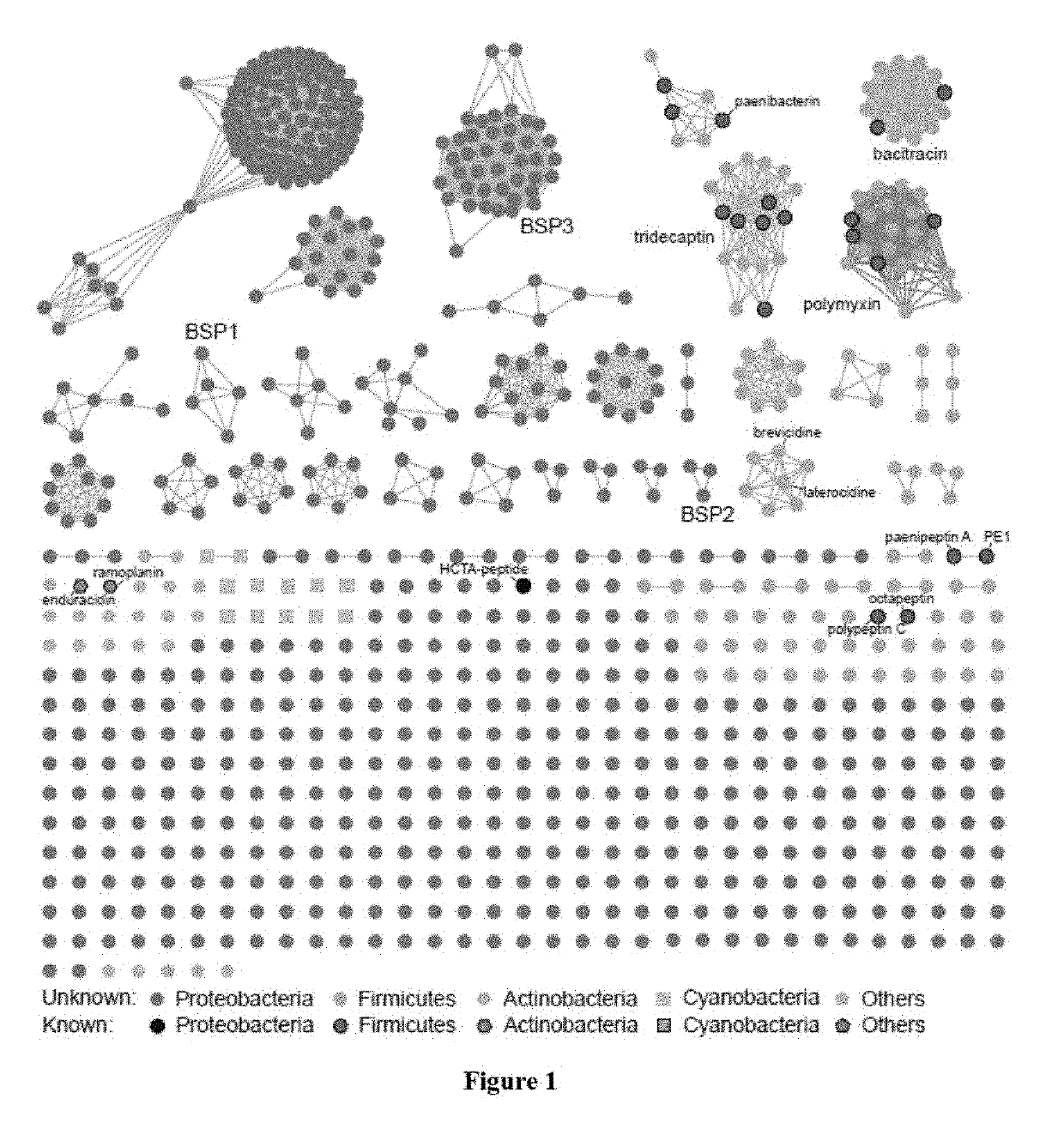
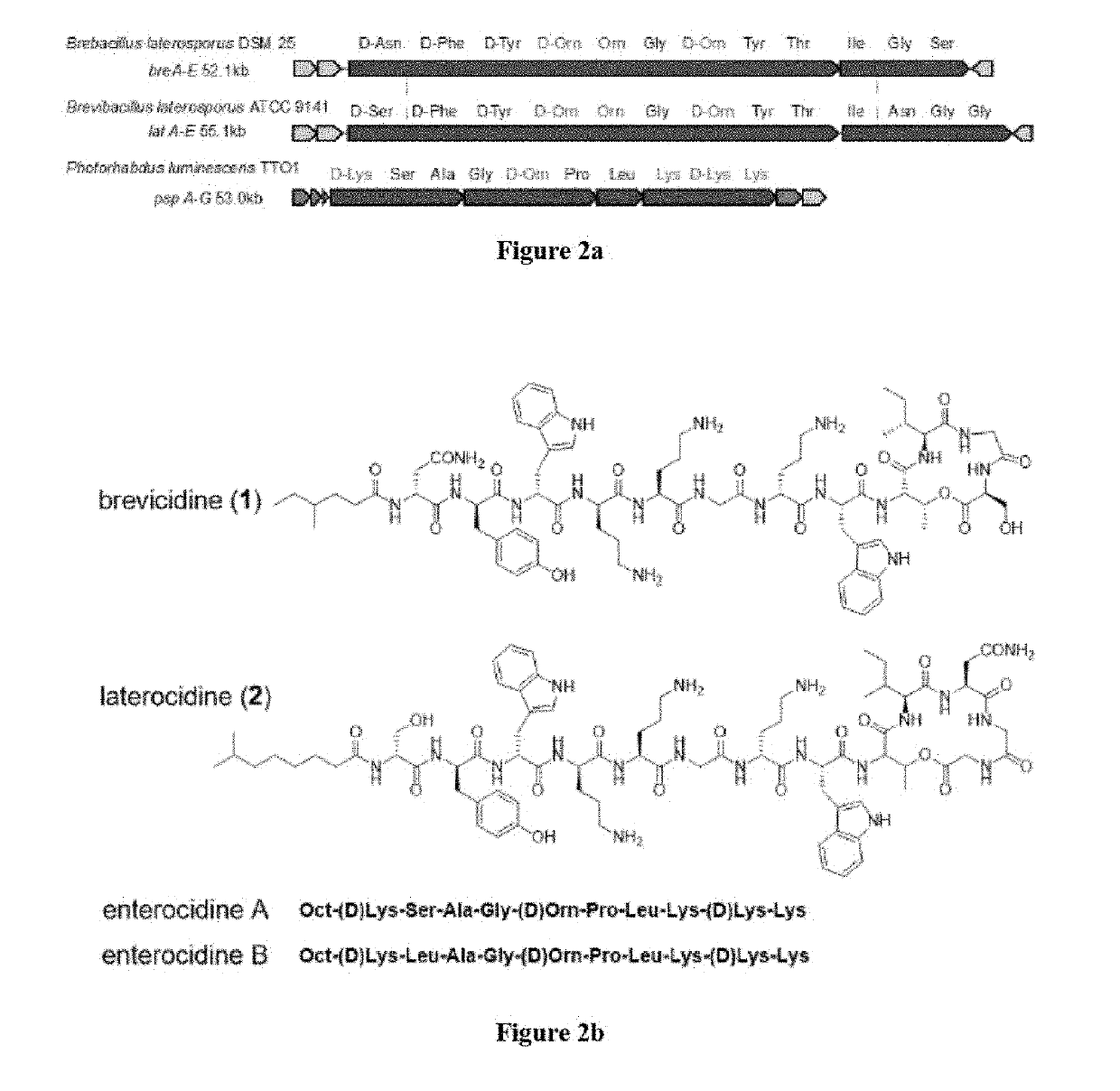
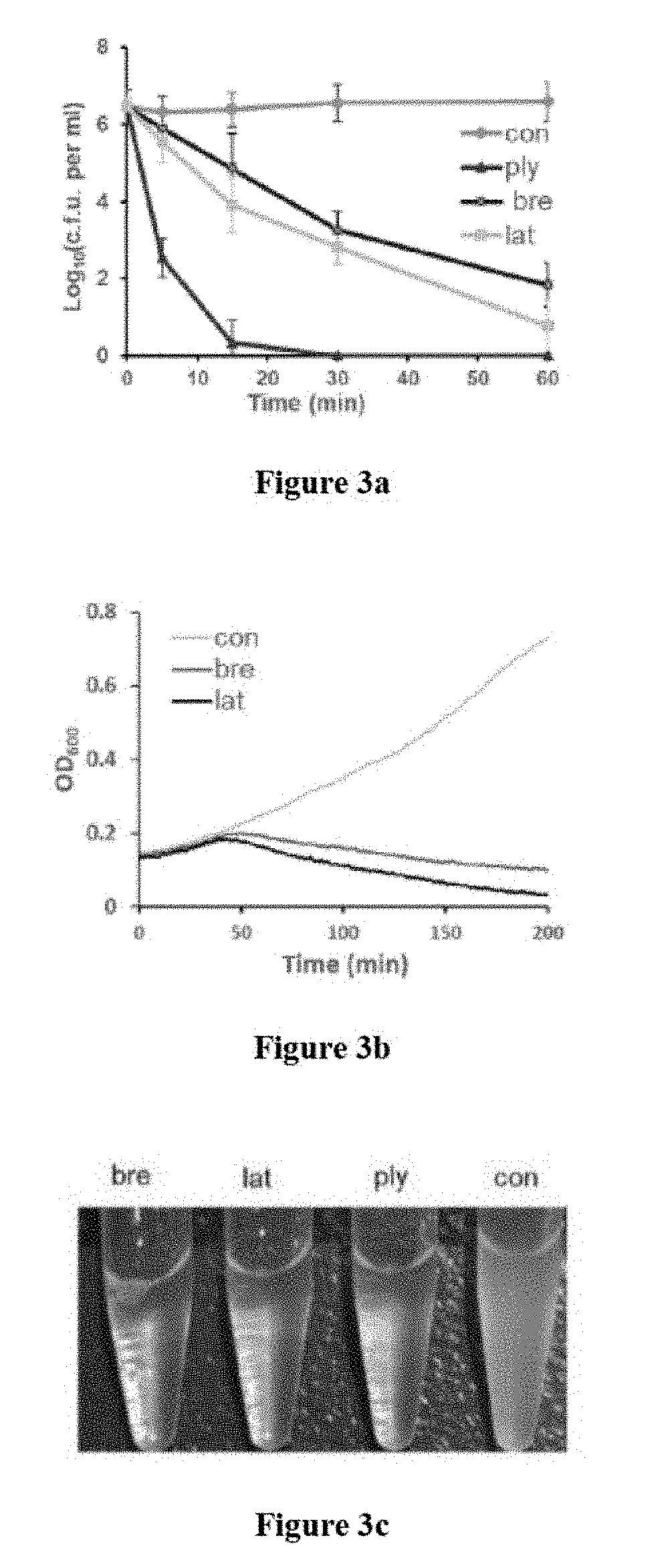
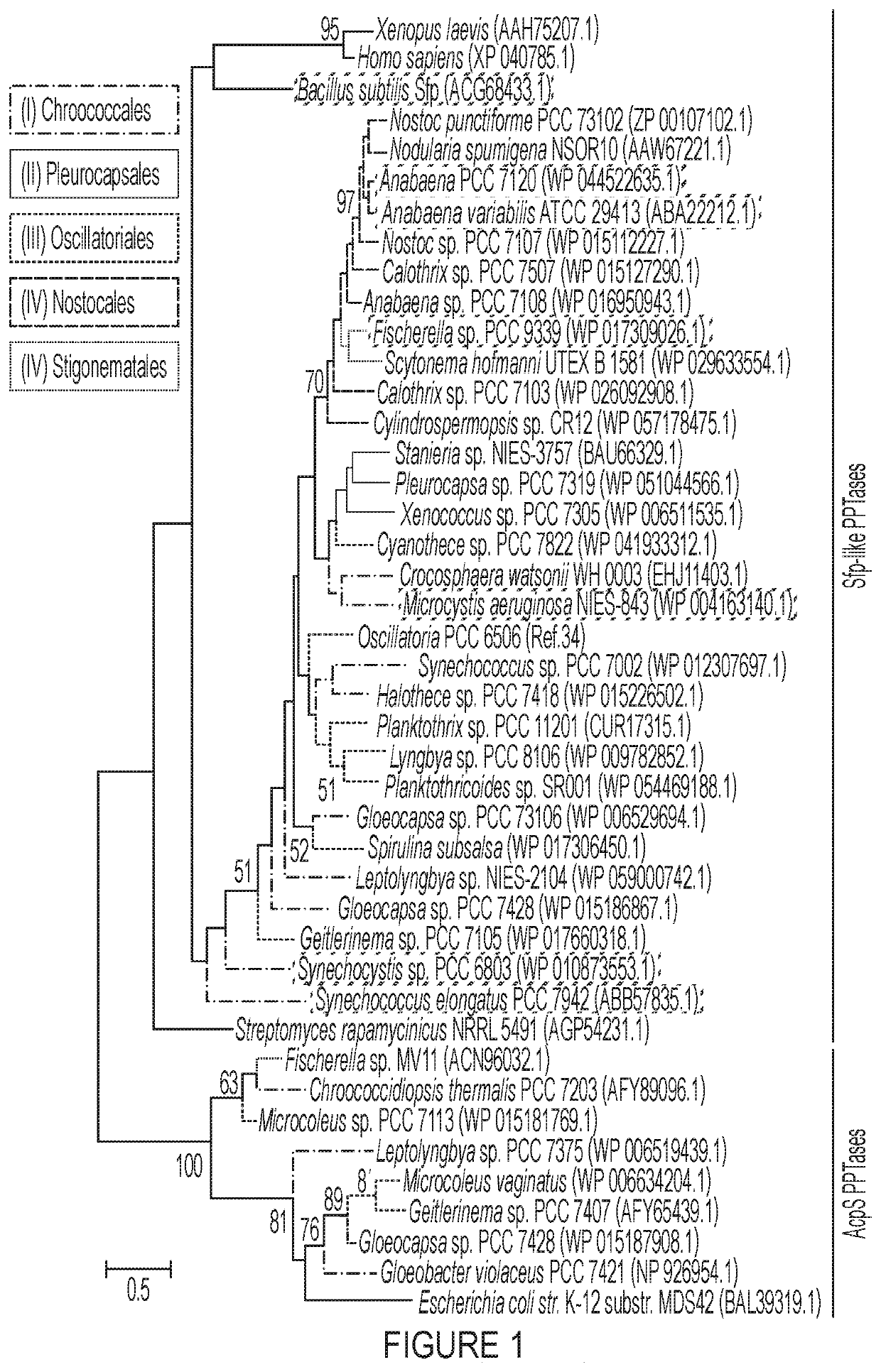
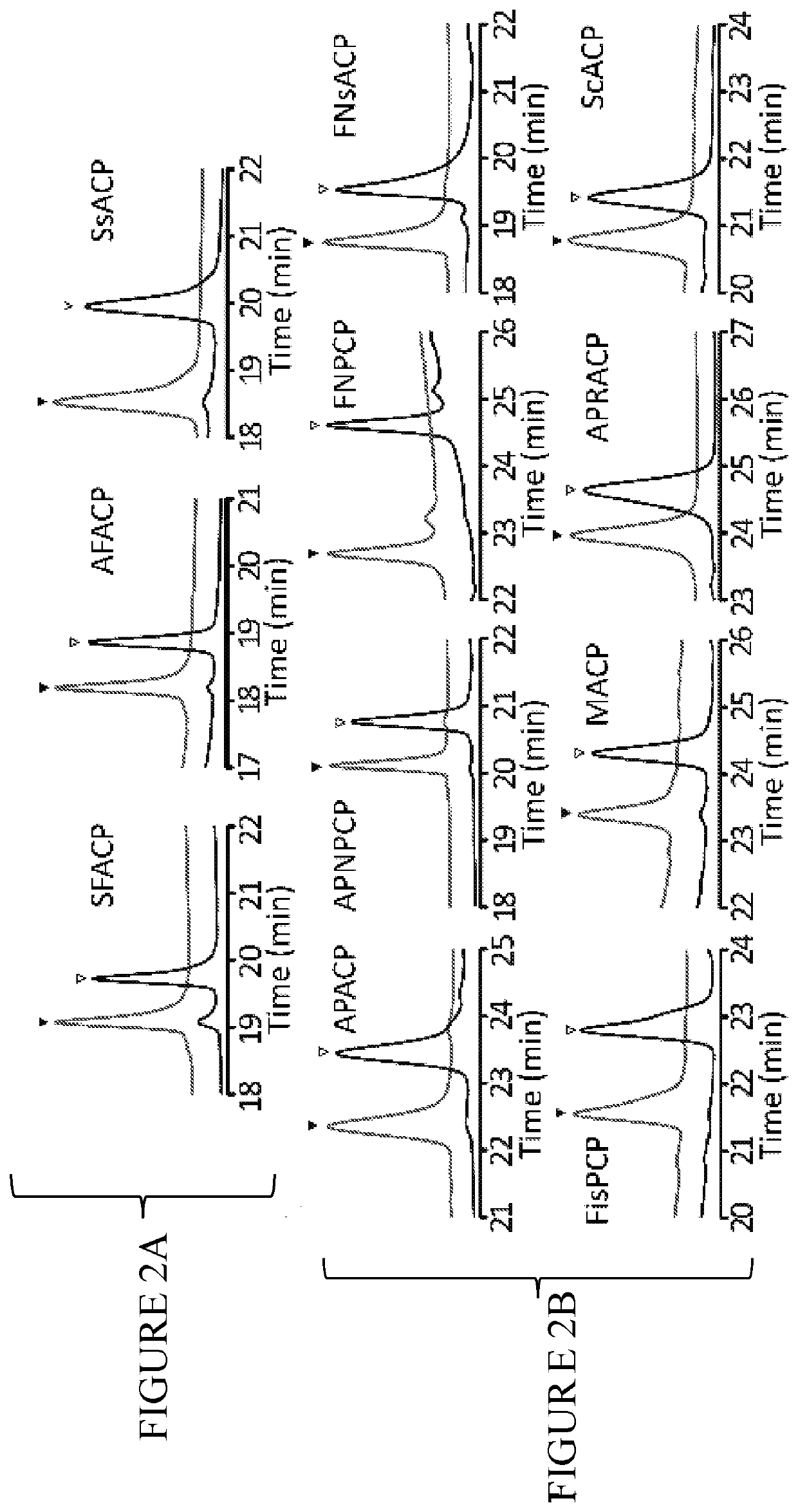
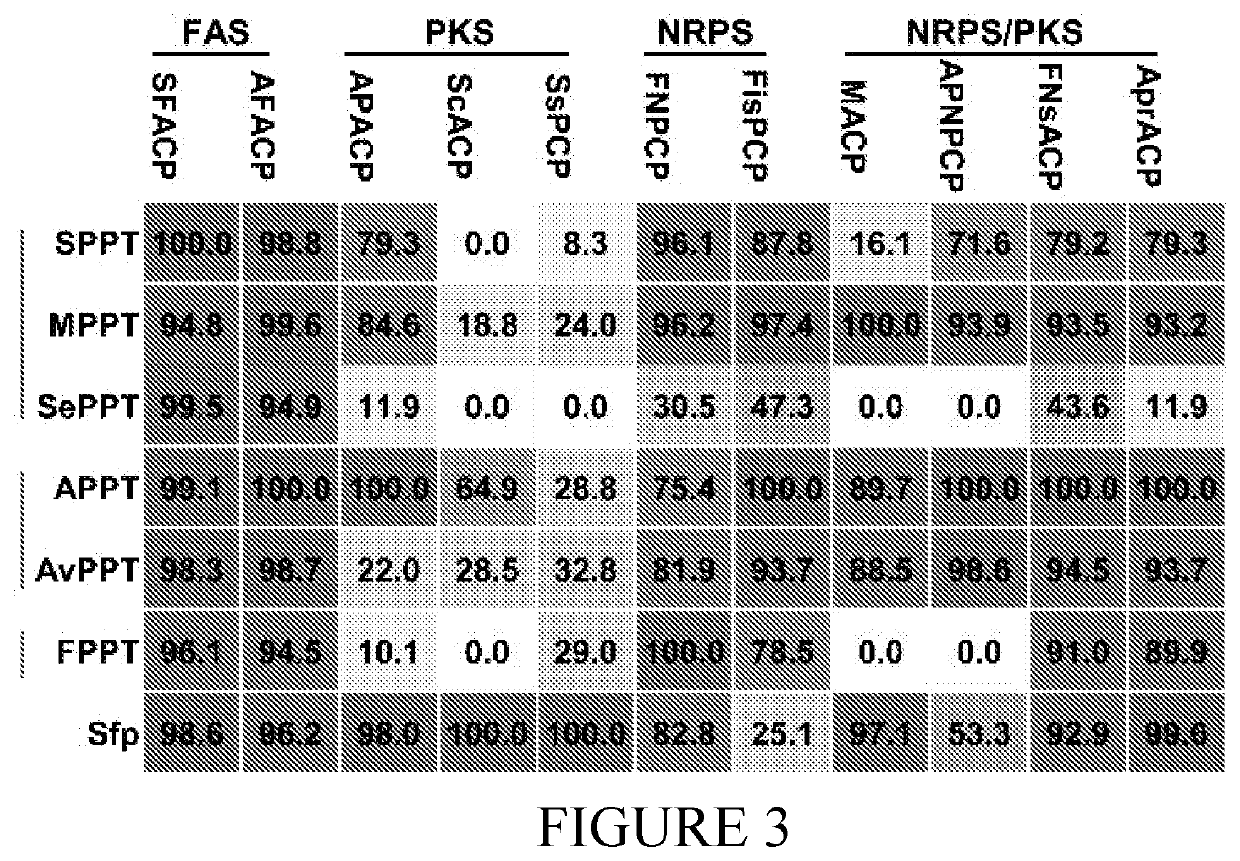
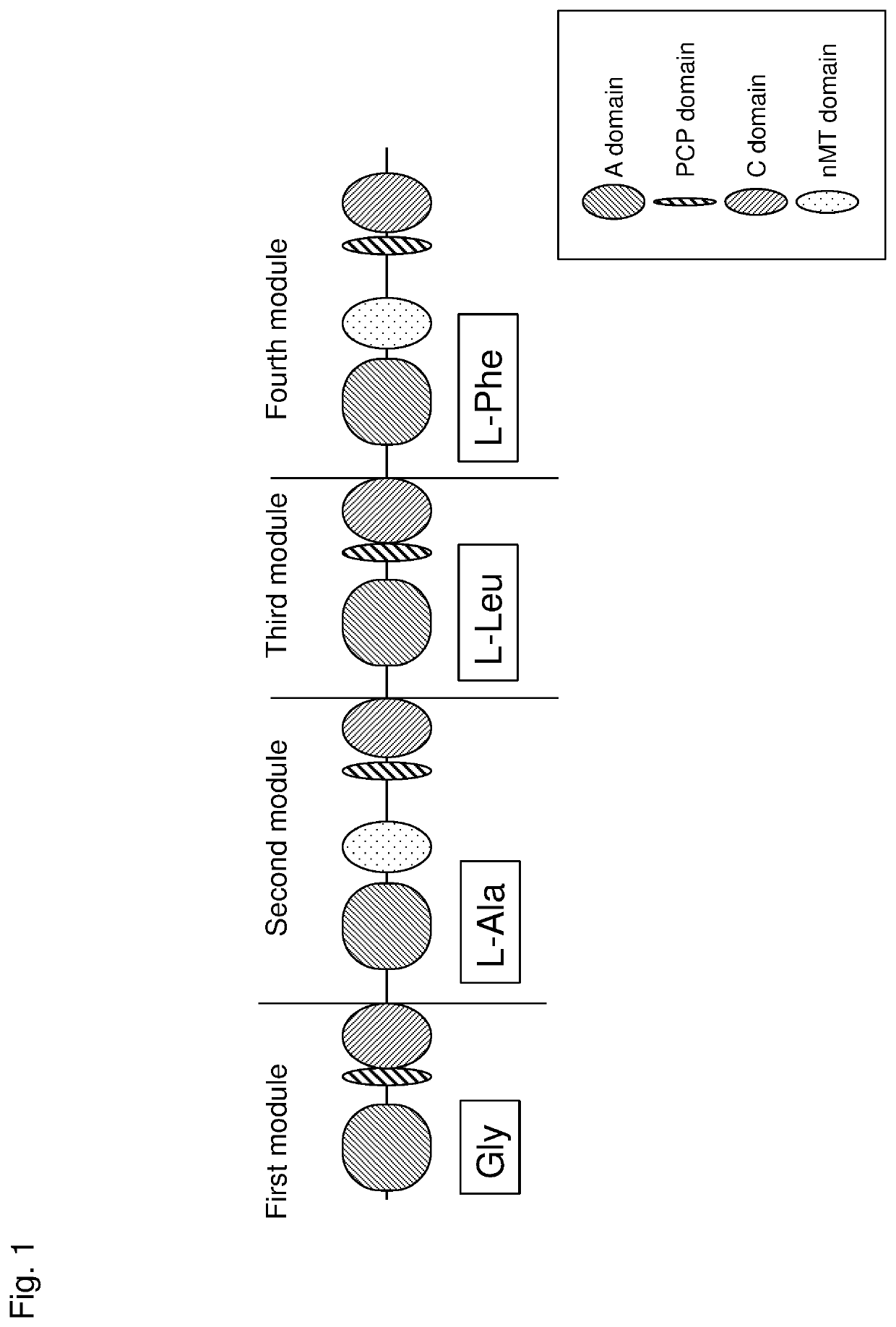
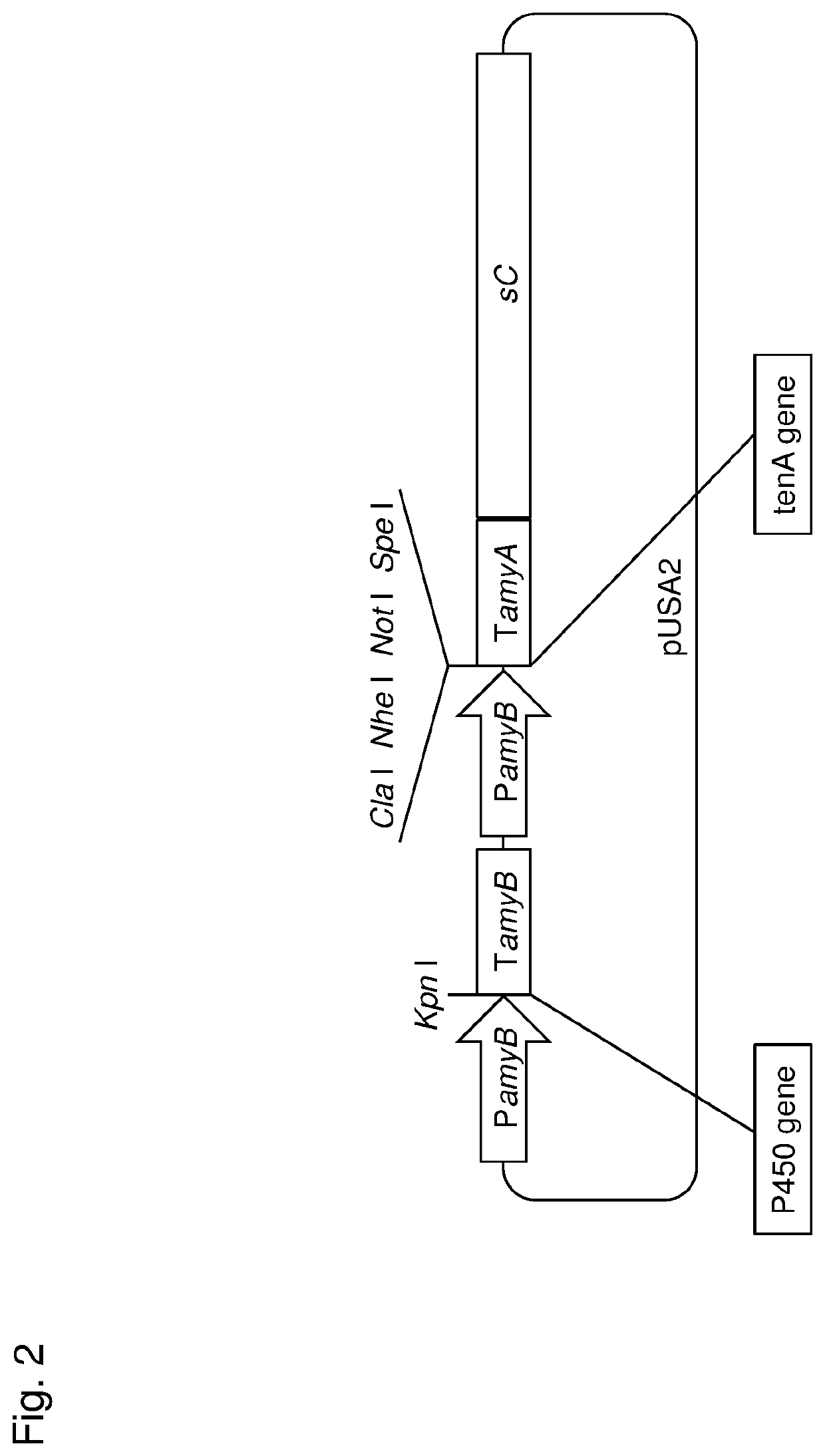
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Nonribosomal peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
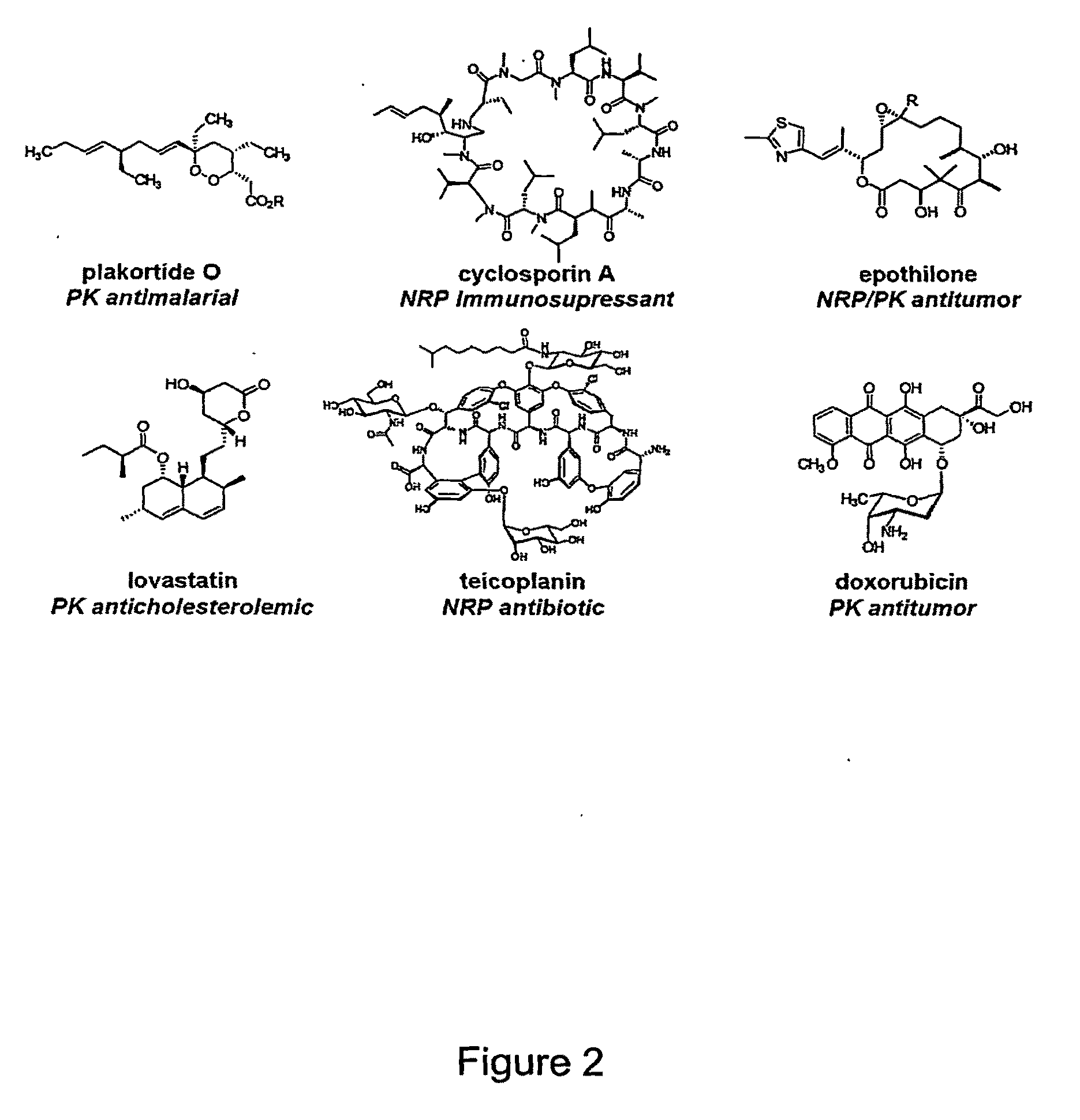
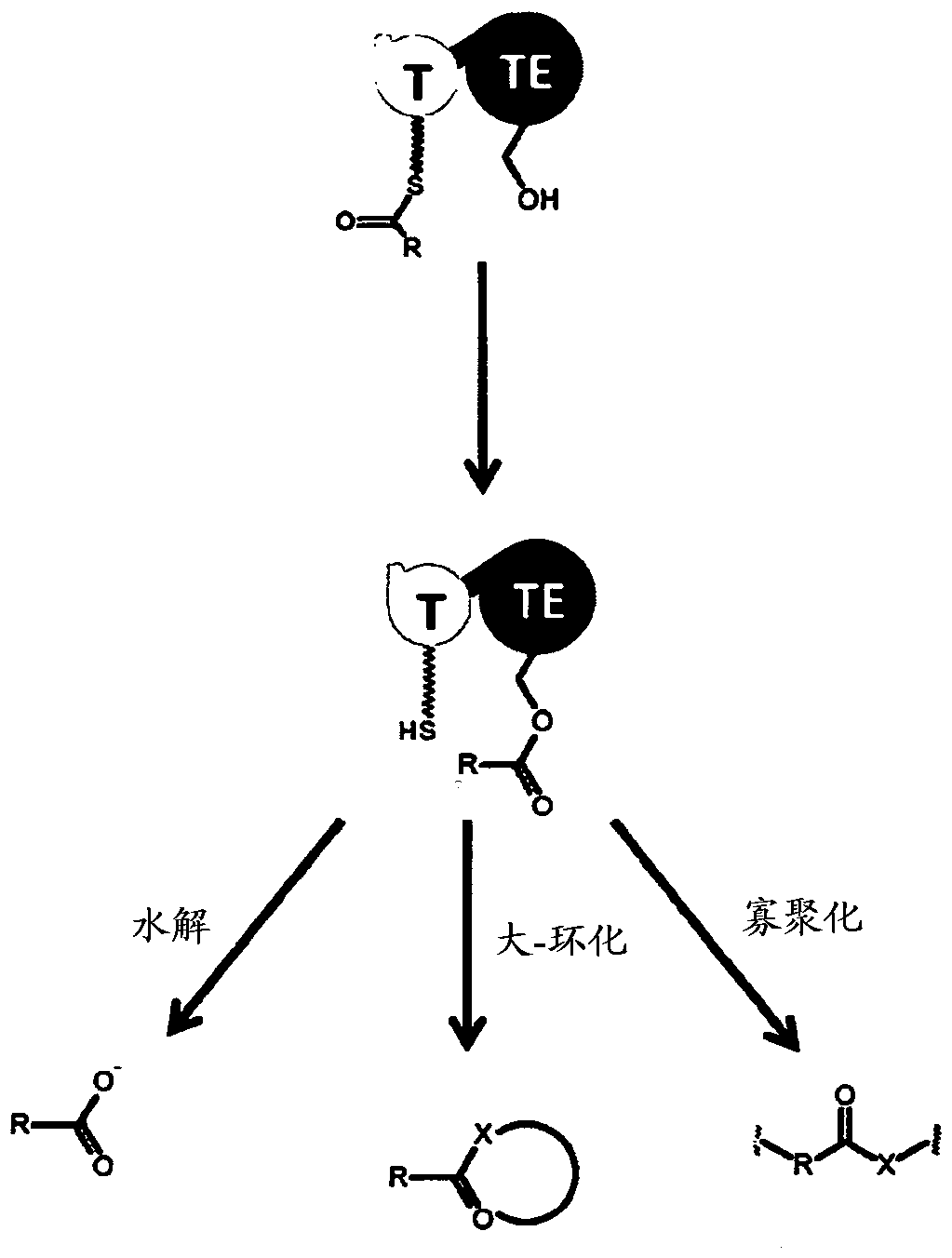
Nonribosomal peptides (NRP) are a class of peptide secondary metabolites, usually produced by microorganisms like bacteria and fungi. Nonribosomal peptides are also found in higher organisms, such as nudibranchs, but are thought to be made by bacteria inside these organisms. While there exist a wide range of peptides that are not synthesized by ribosomes, the term nonribosomal peptide typically refers to a very specific set of these as discussed in this article.
Construction method and use of Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria
ActiveCN102146414AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRibosomal protein E-L30
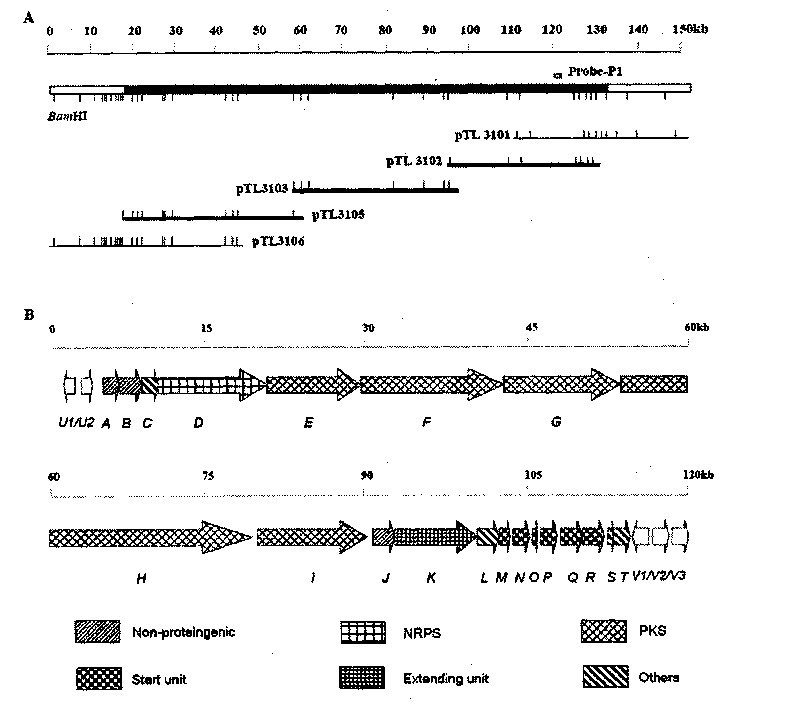
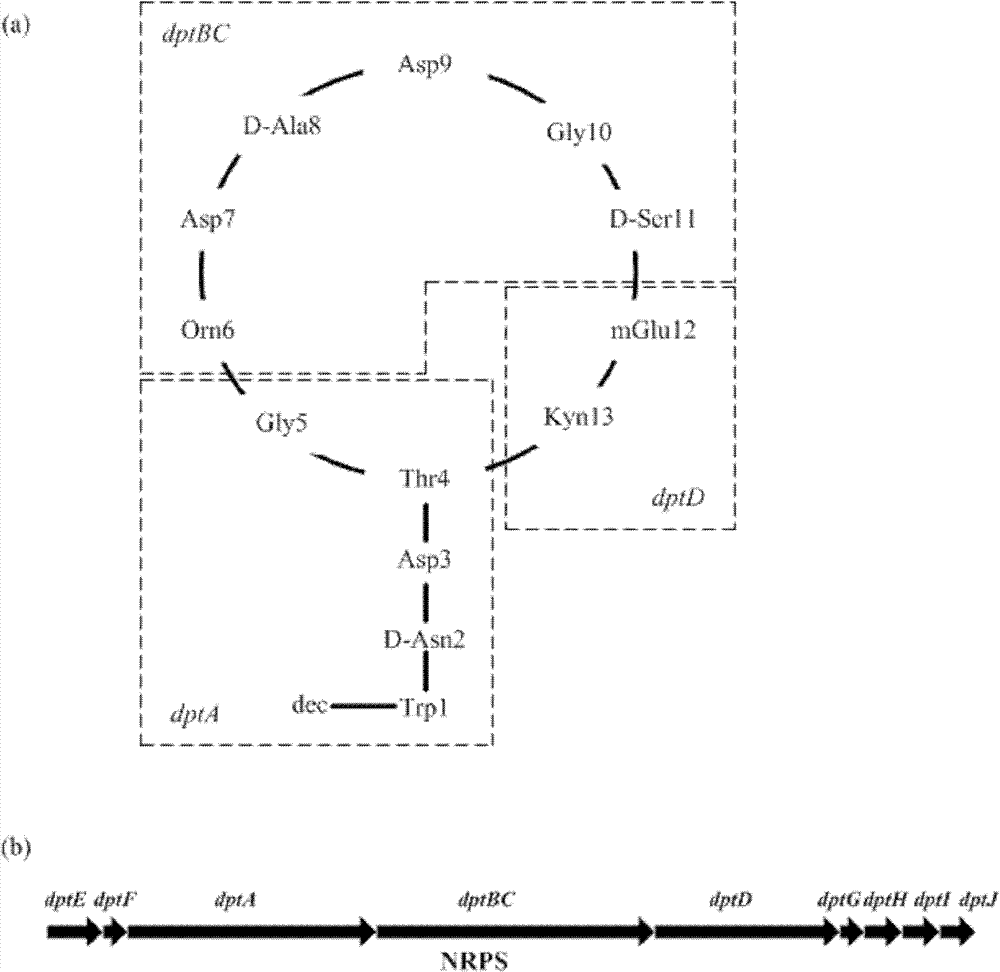
The invention provides a construction method and use of Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria. The construction method comprises: cloning upstream and downstream accessory key genes dptE, dptF, dptG, dptH, dptI and dptJ of a nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) gene in a daptomycin gene cluster; and constructing recombinant plasmids by using an Escherichia coli-Streptomyces shuttle expression vector. The recombinant plasmids are transferred into Escherichia coli ET12567 to culture the ET12567 and the Streptomyces roseosporus together, the Streptomyces roseosporus is transformed by a combined transfer method, a transformant is screened by brulamycin resistance and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is performed for further confirmation. The Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria constructed by the invention can be directly used in the industrial production of daptomycin and can improve yield and reduce cost.
Owner:NANTONG YIKAI MEDICAL DEVICES CO LTD
Biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and application thereof
ActiveCN106434702ABiosynthetic gene cluster activationHas antitumor activityOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryCyclasePolyketide
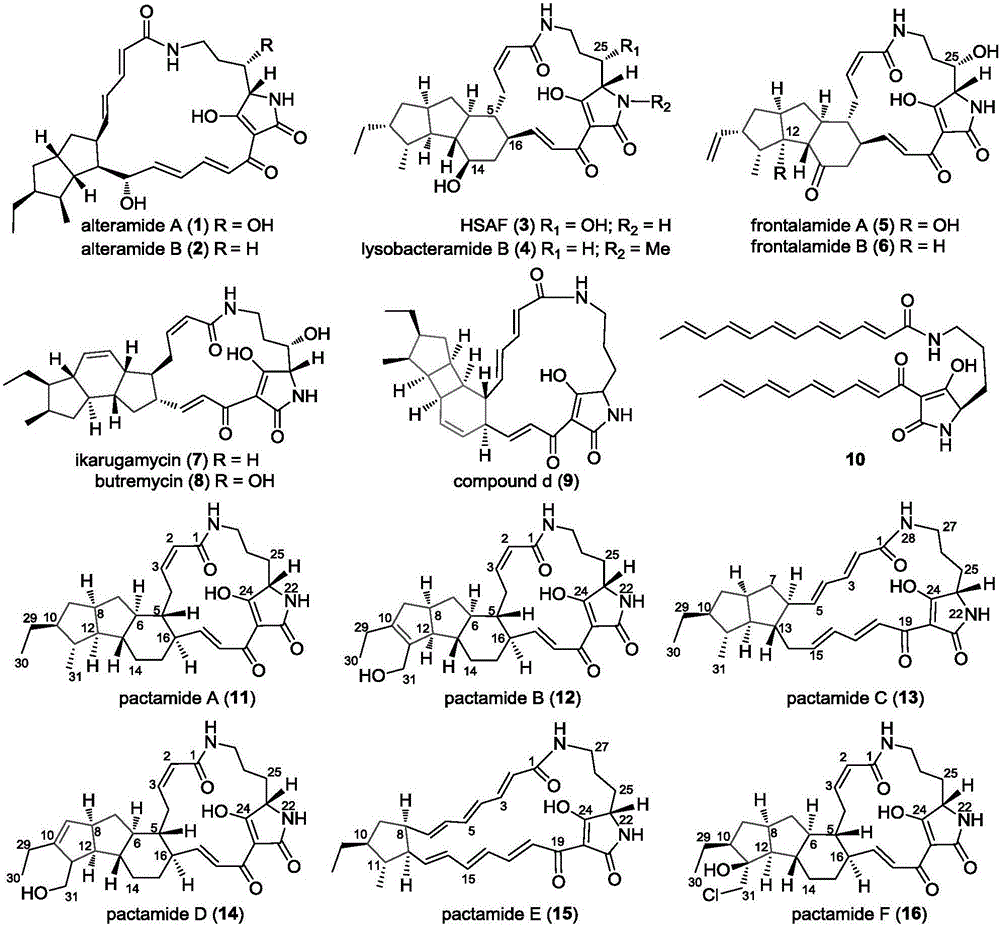
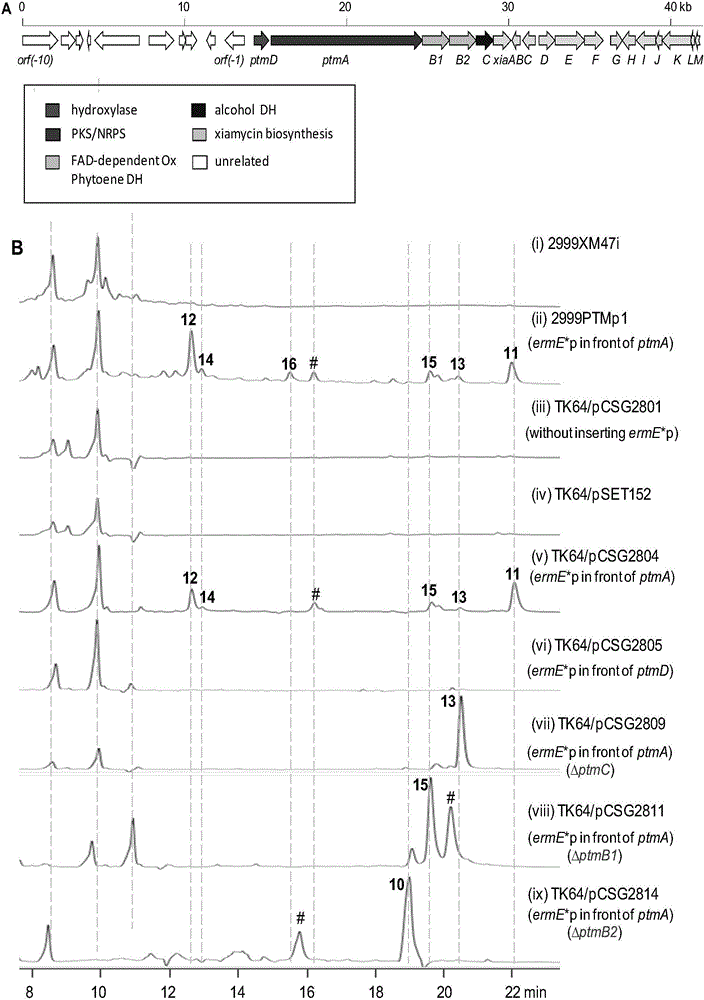
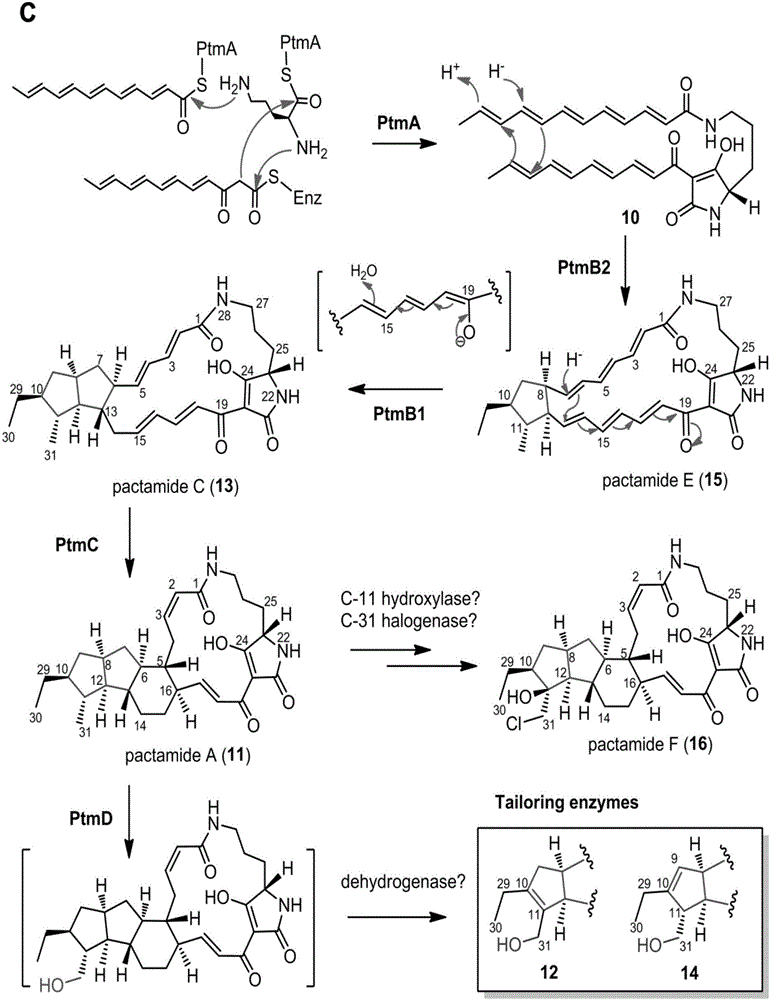
The invention discloses a biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and an application thereof. The biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide comes from (Streptomyces pactum)SCSIO 02999, and the cluster comprises five genes including heterozygous polyketone / nonribosomal peptide synthetases genes ptmA, FAD dependent redox enzyme genes ptmB1, phytoene dehydrogenase genes ptmB2, cyclase genes ptmC and hydroxylase genes ptmD. According to the biosynthetic gene cluster of paquete amide and the application thereof, information in genes and proteins related to biosynthesis of the paquete amide provides theoretical foundations and materials for conducting genetic modification on the biosynthesis of multi-ring tetramate macrocylic lactam family. By conducting genetic modifications on the biological synthetic genes, 6 new structures antineoplastic paquete amide compounds pactamide A-F are obtained, and thus effective compound entities are provided for research and development of antineoplastic drugs.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
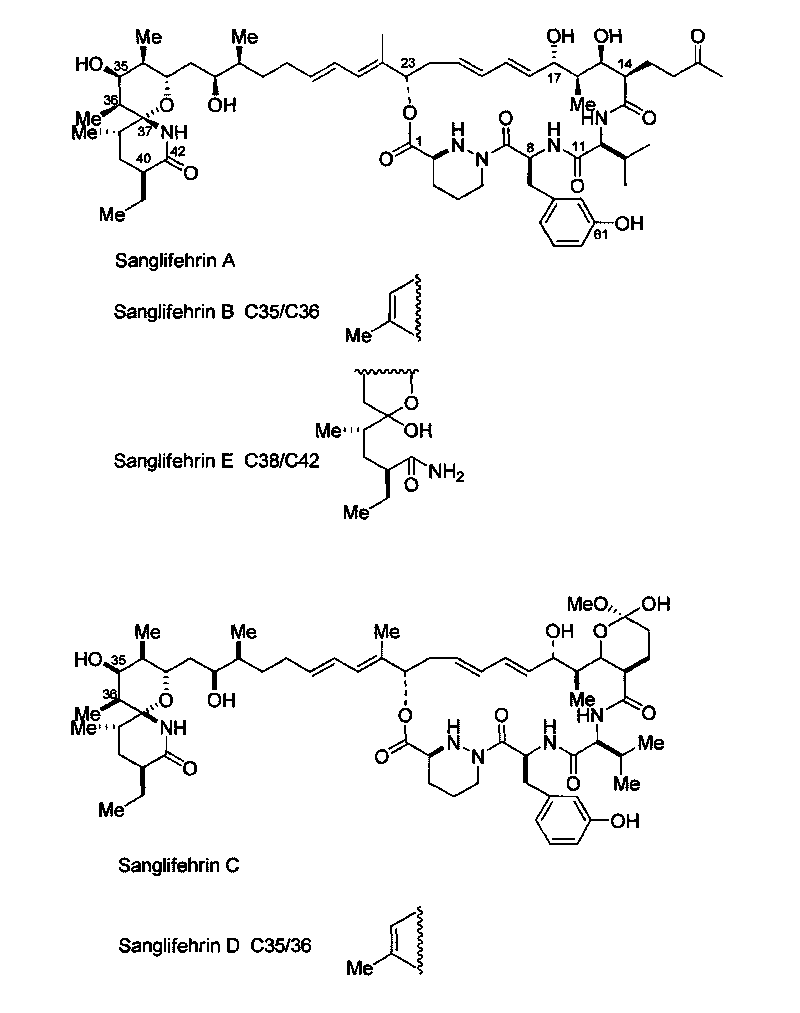
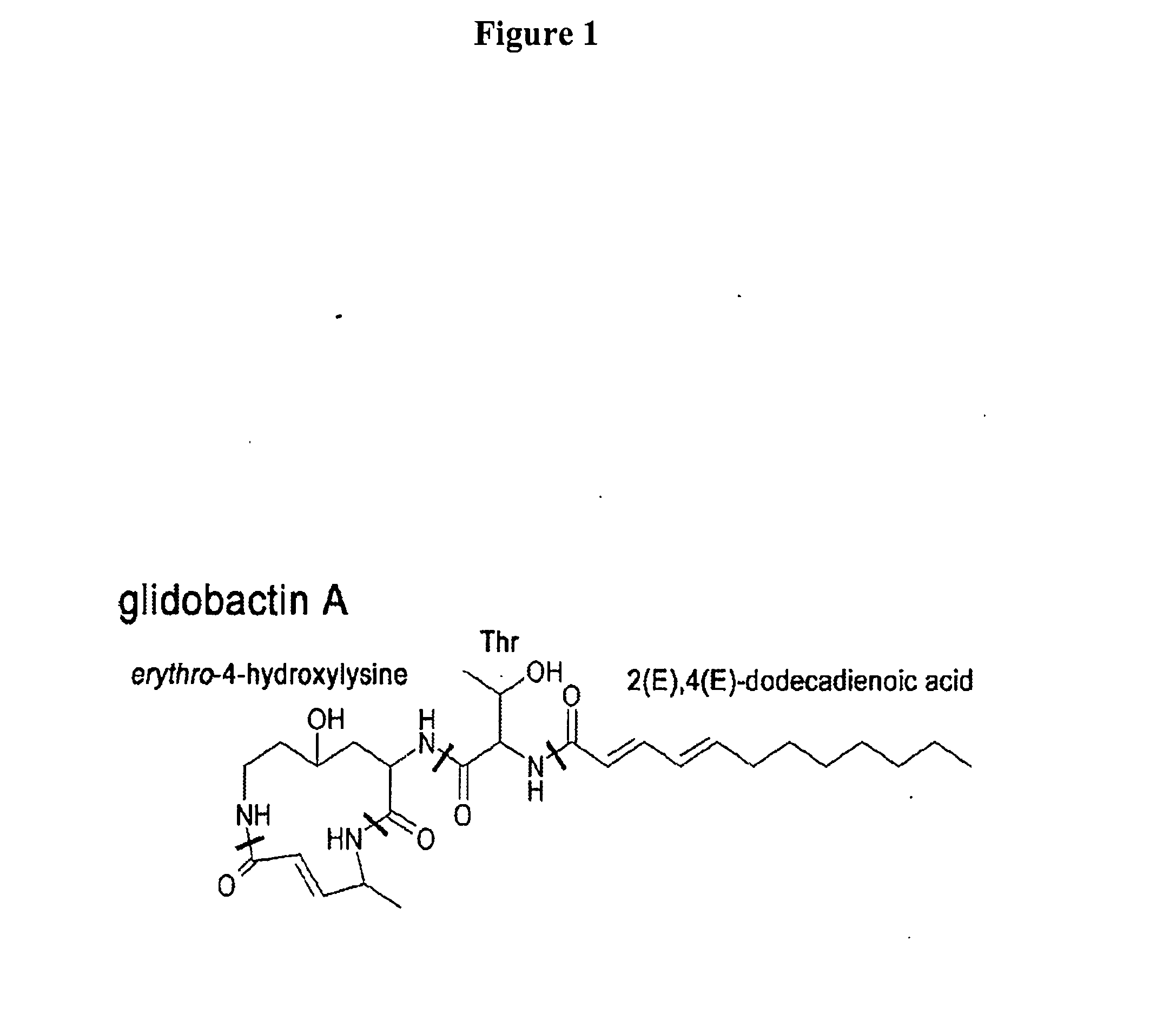
Biosynthetic gene cluster of sanglifehrin
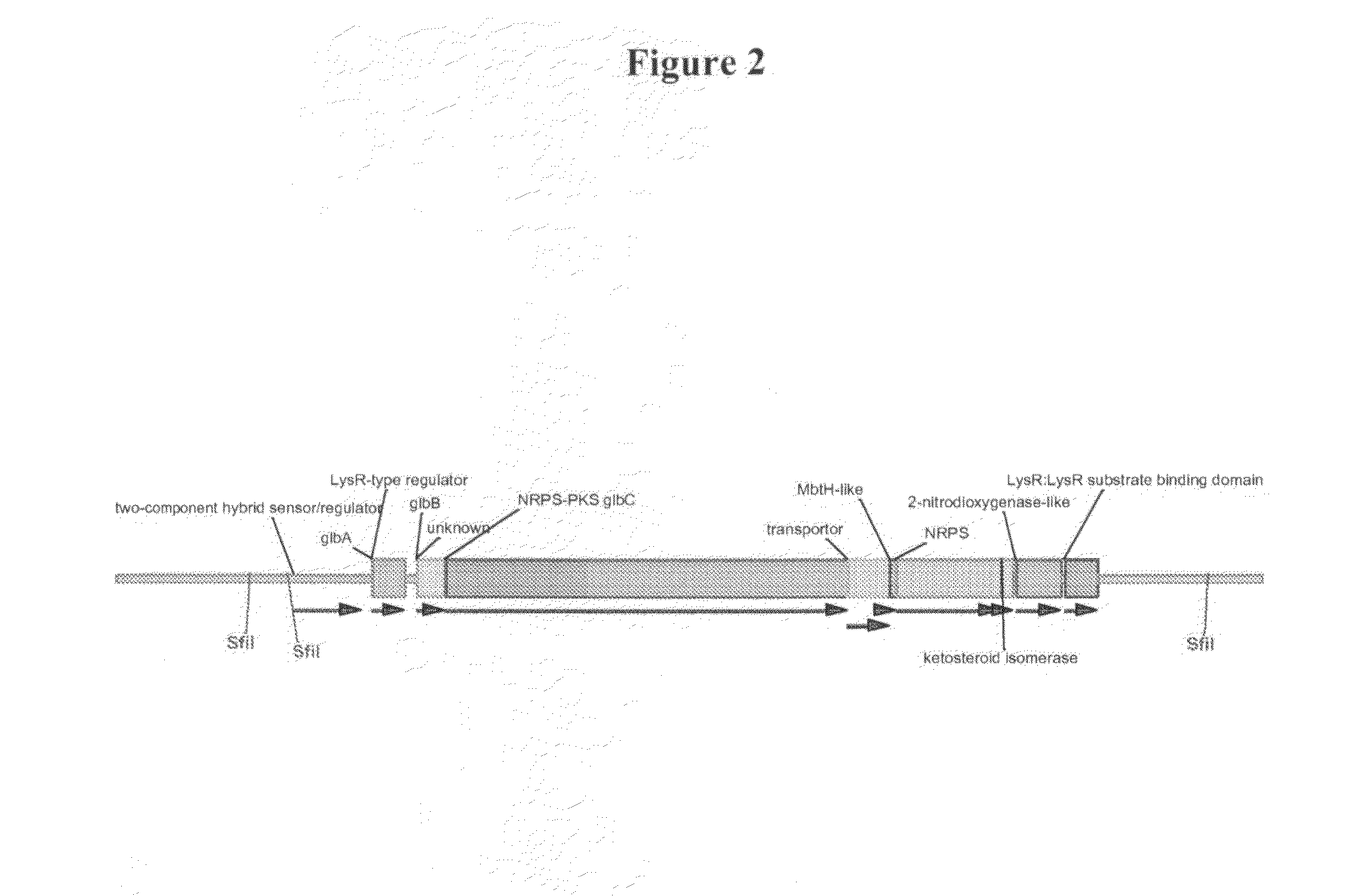
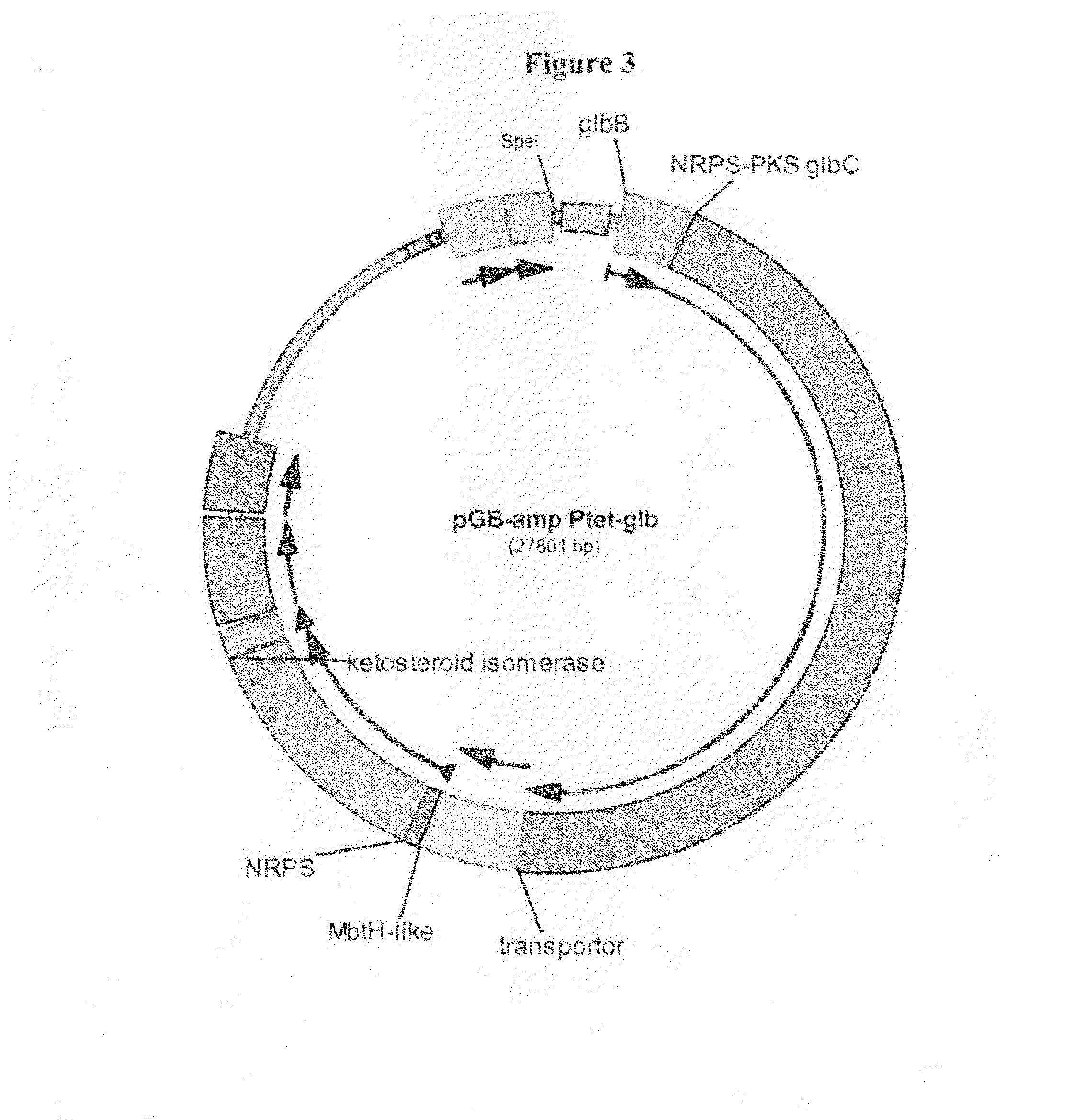
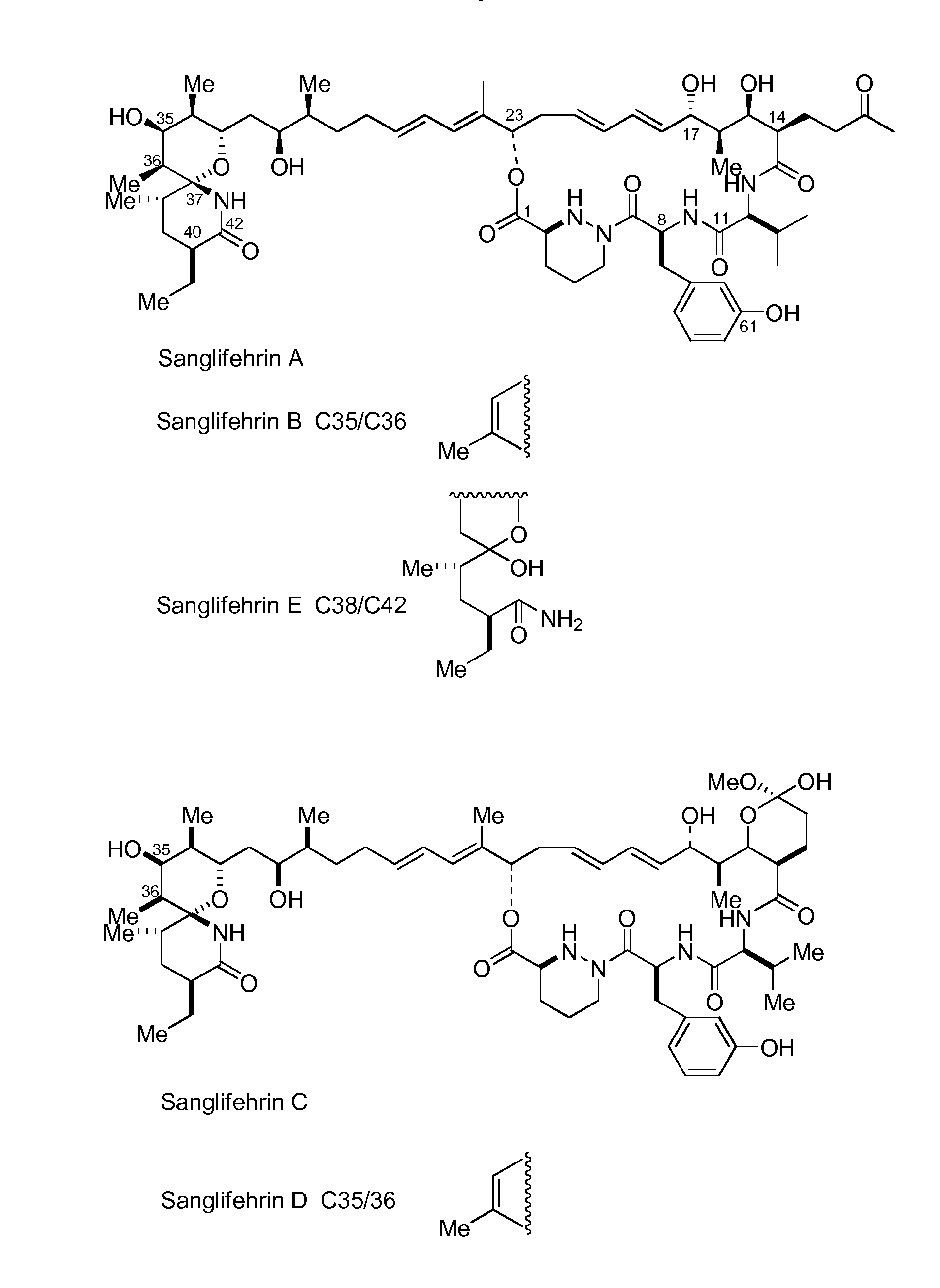
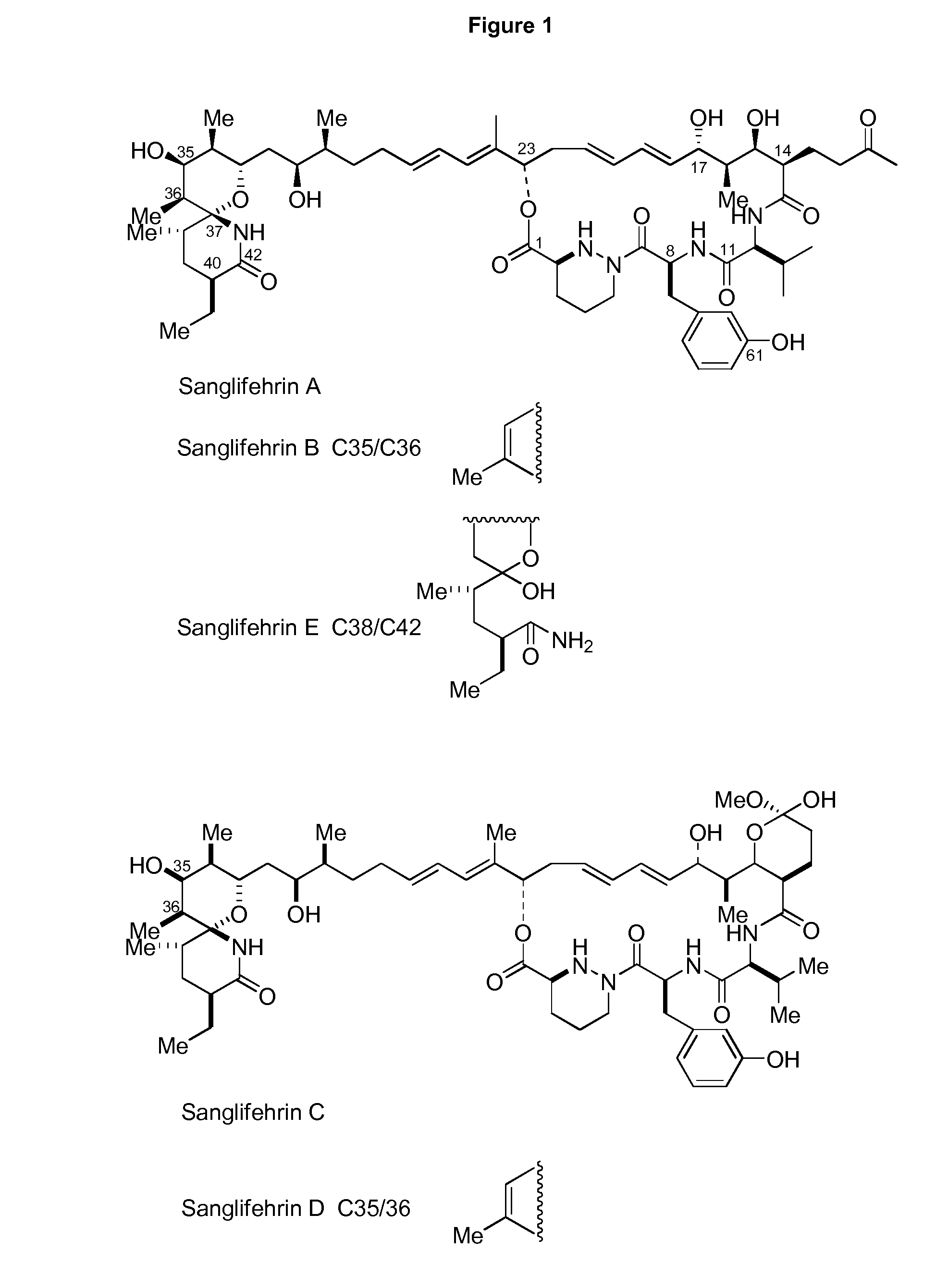
The invention relates to a biosynthetic gene cluster of sanglifehrin, which relates to related information of clone, whole sequencing, sequence analysis, gene function research, in vitro biochemical research and application thereof of a natural product sanglifehrin which is produced by streptomyces flavolus and has immunosuppressive activity. The whole gene cluster can contain 24 genes, namely 1 NRPS gene, 7 type-I linear PKS genes, 1 type-I repeated PKS gene, 8 precursor synthetic genes, 2 regulatory genes and 5 functional unknown genes. The generation of the sanglifehrin can be blocked by operating the genetics of the core functional genes. Genes and protein provided by the invention can be used for research and development of new medicine or research and development of other products with industrial and agricultural application prospects.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
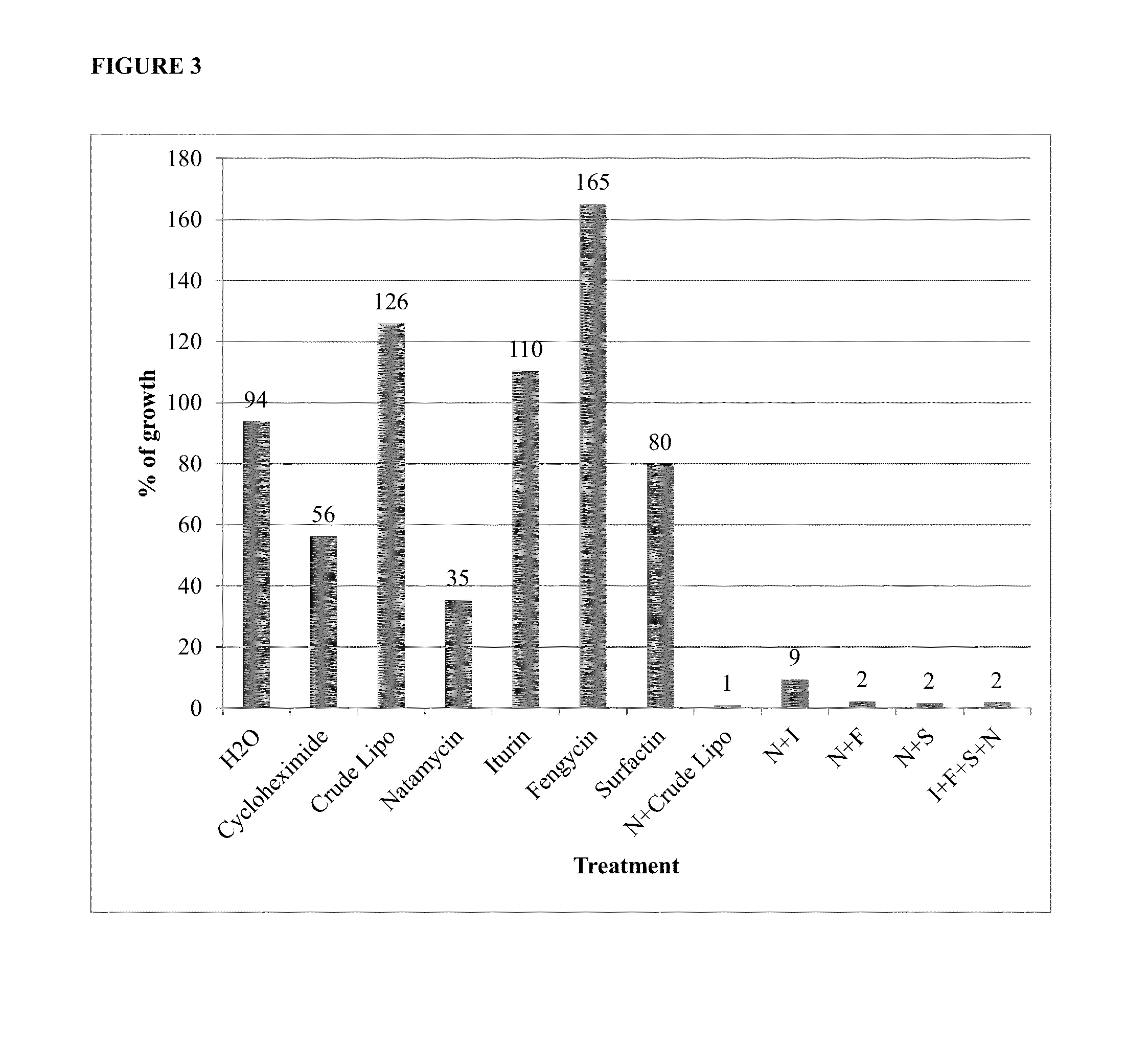
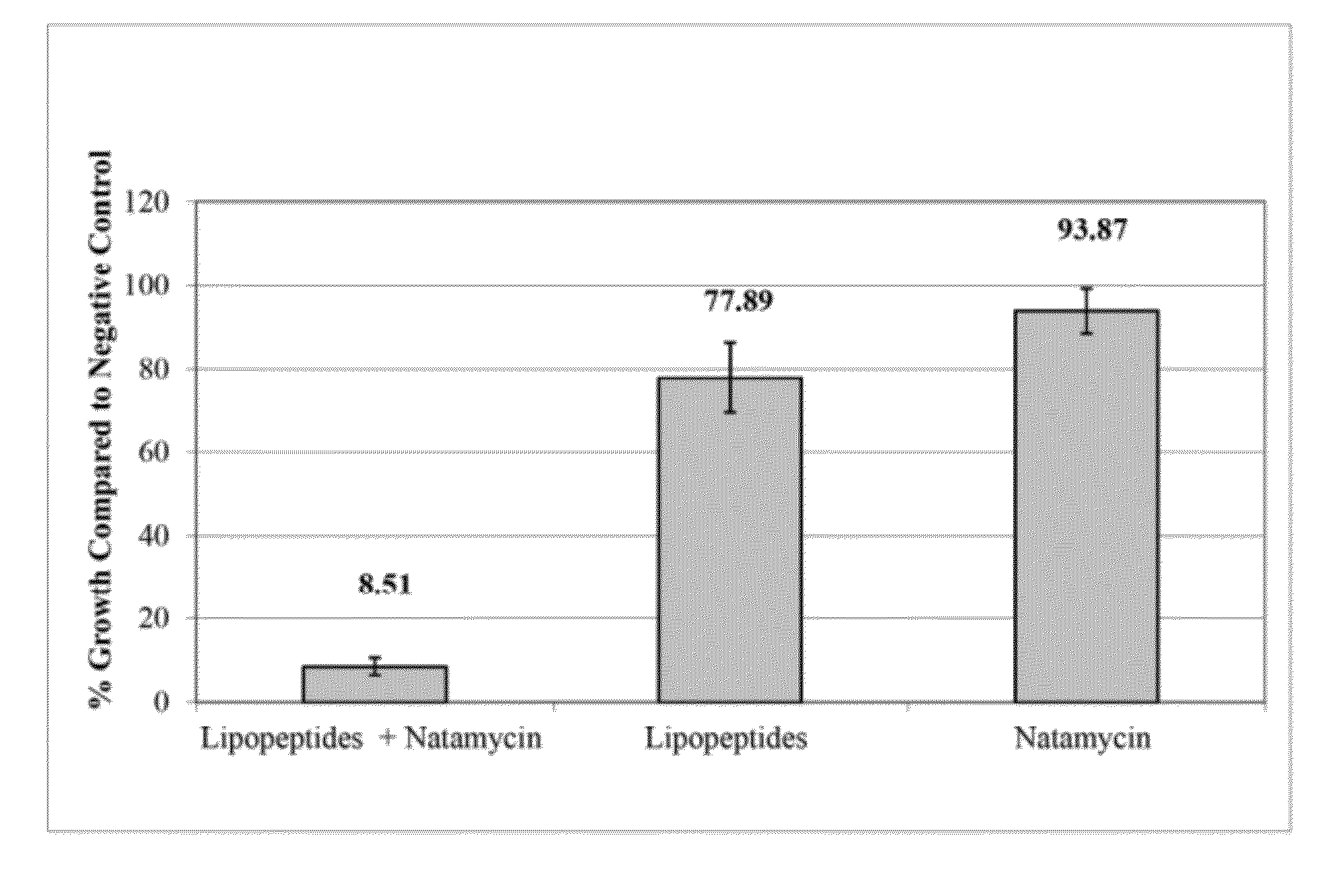
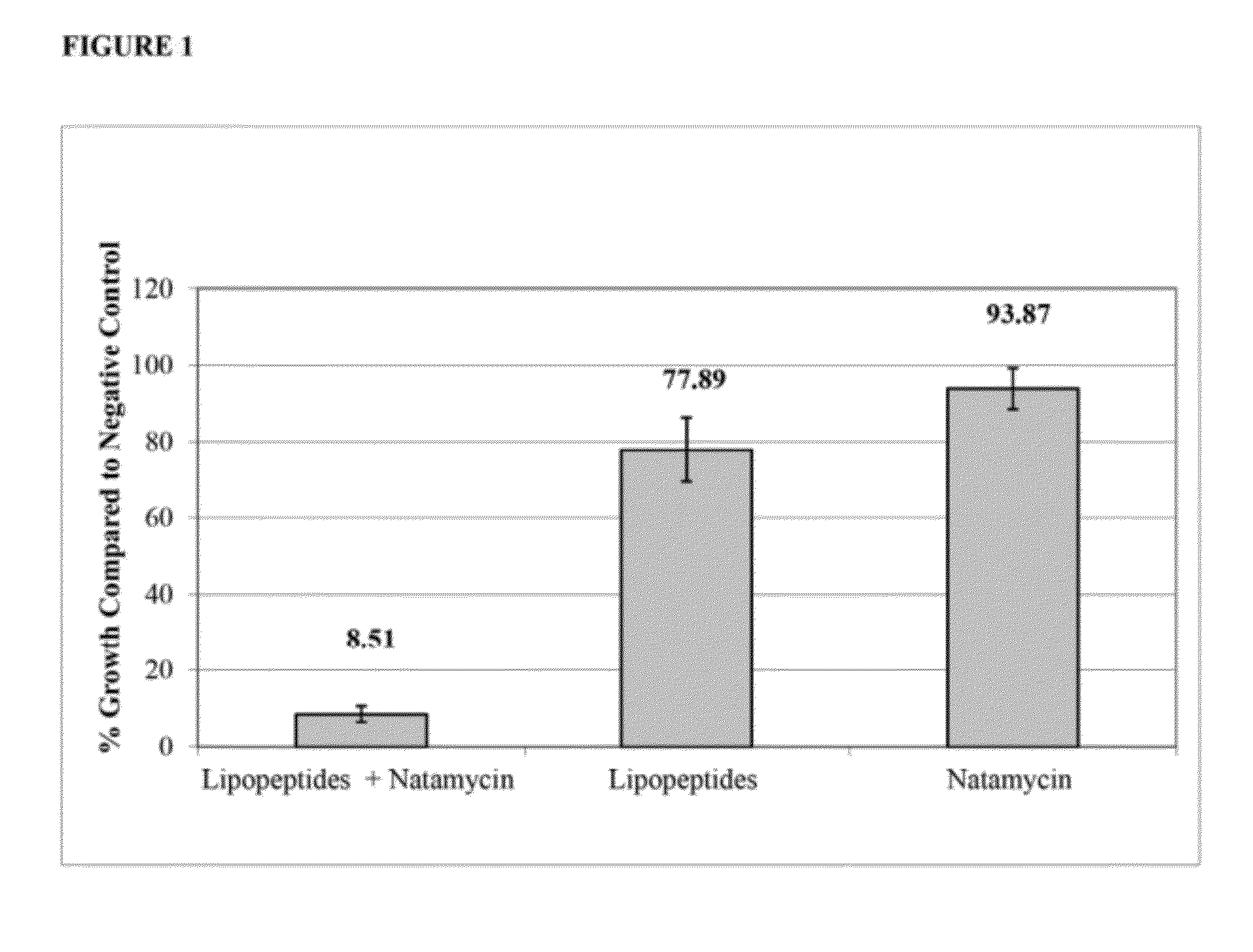
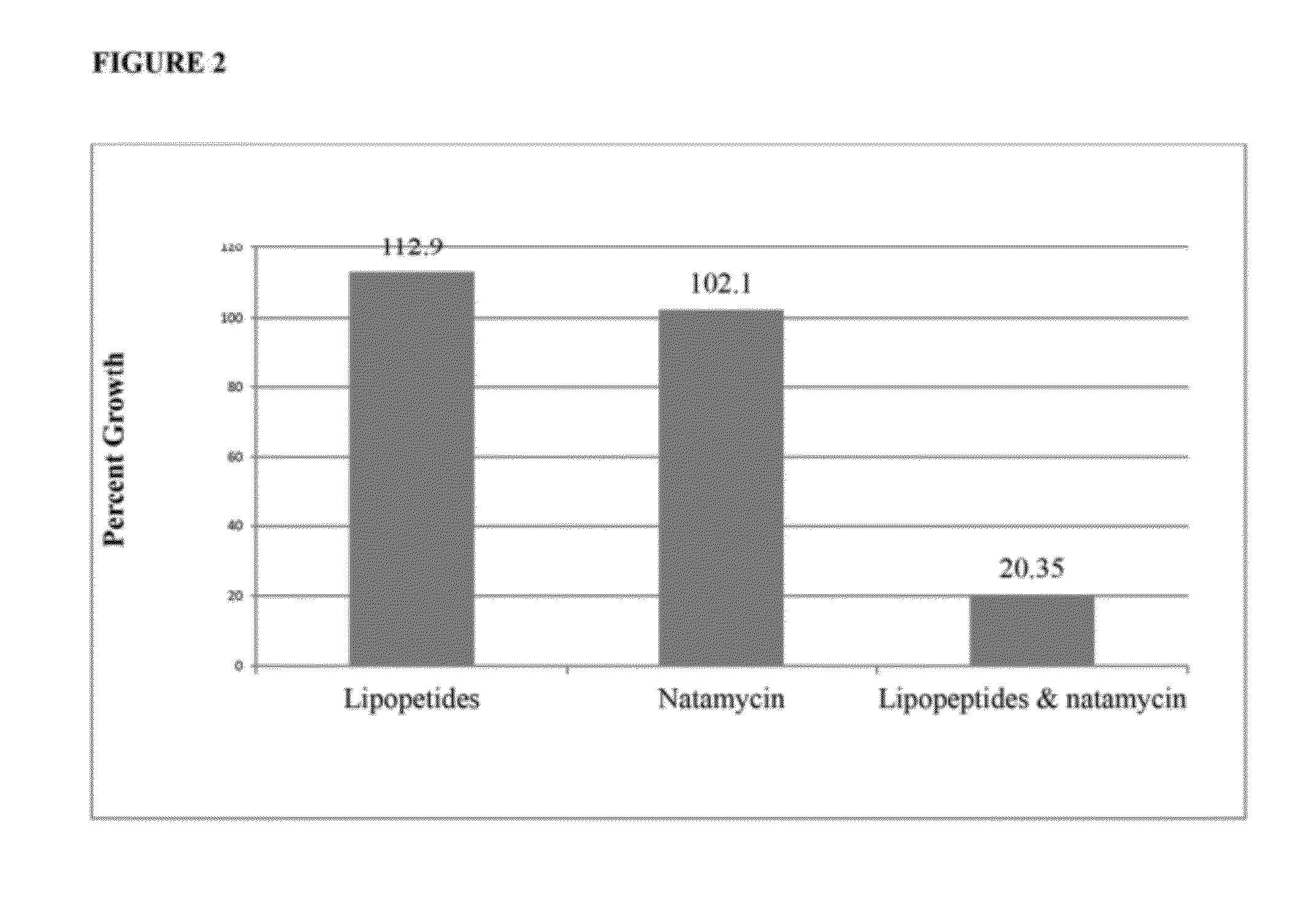
Synergistic Combinations of Polyene Fungicides and Non-Ribosomal Peptides and Related Methods of Use
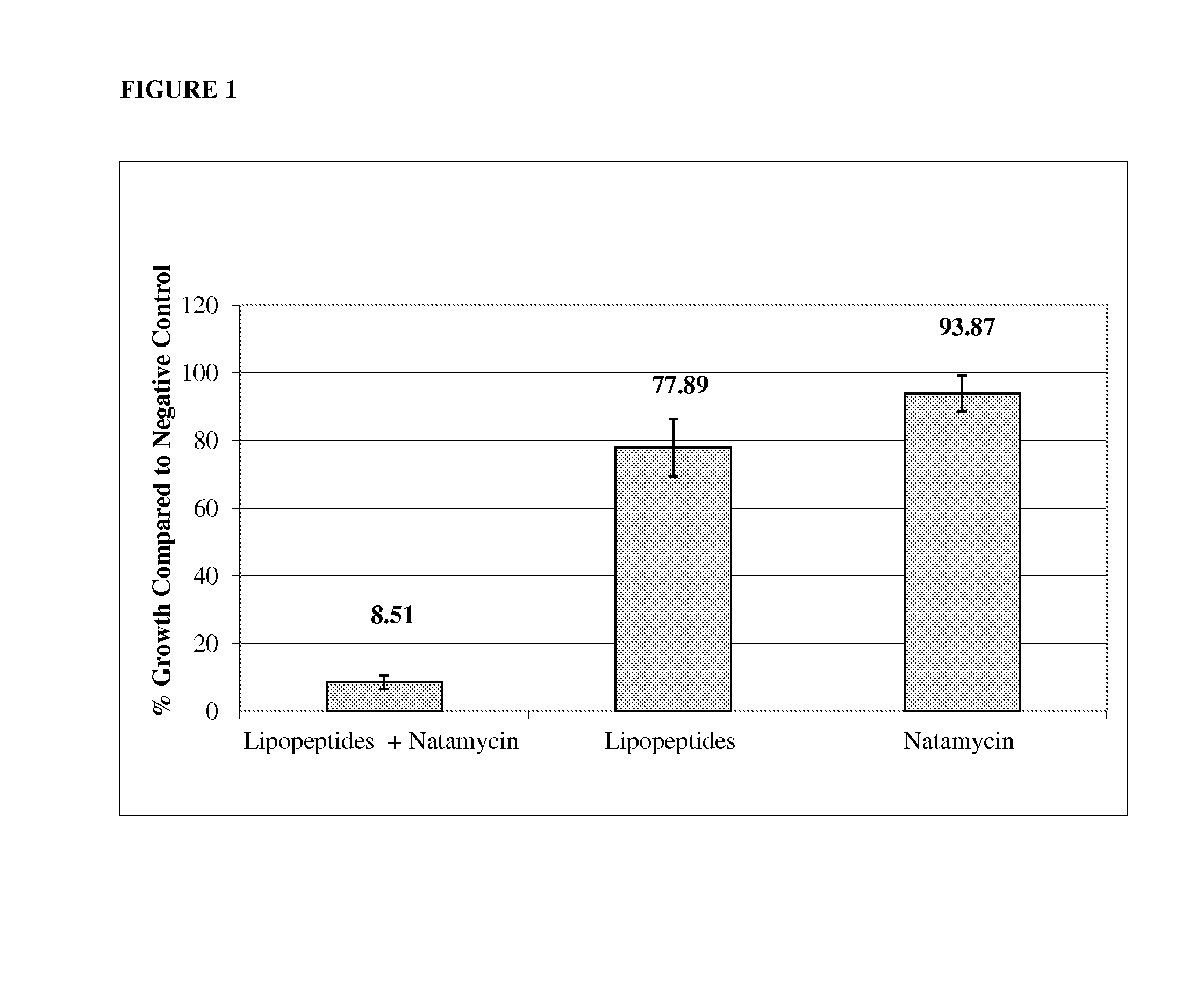
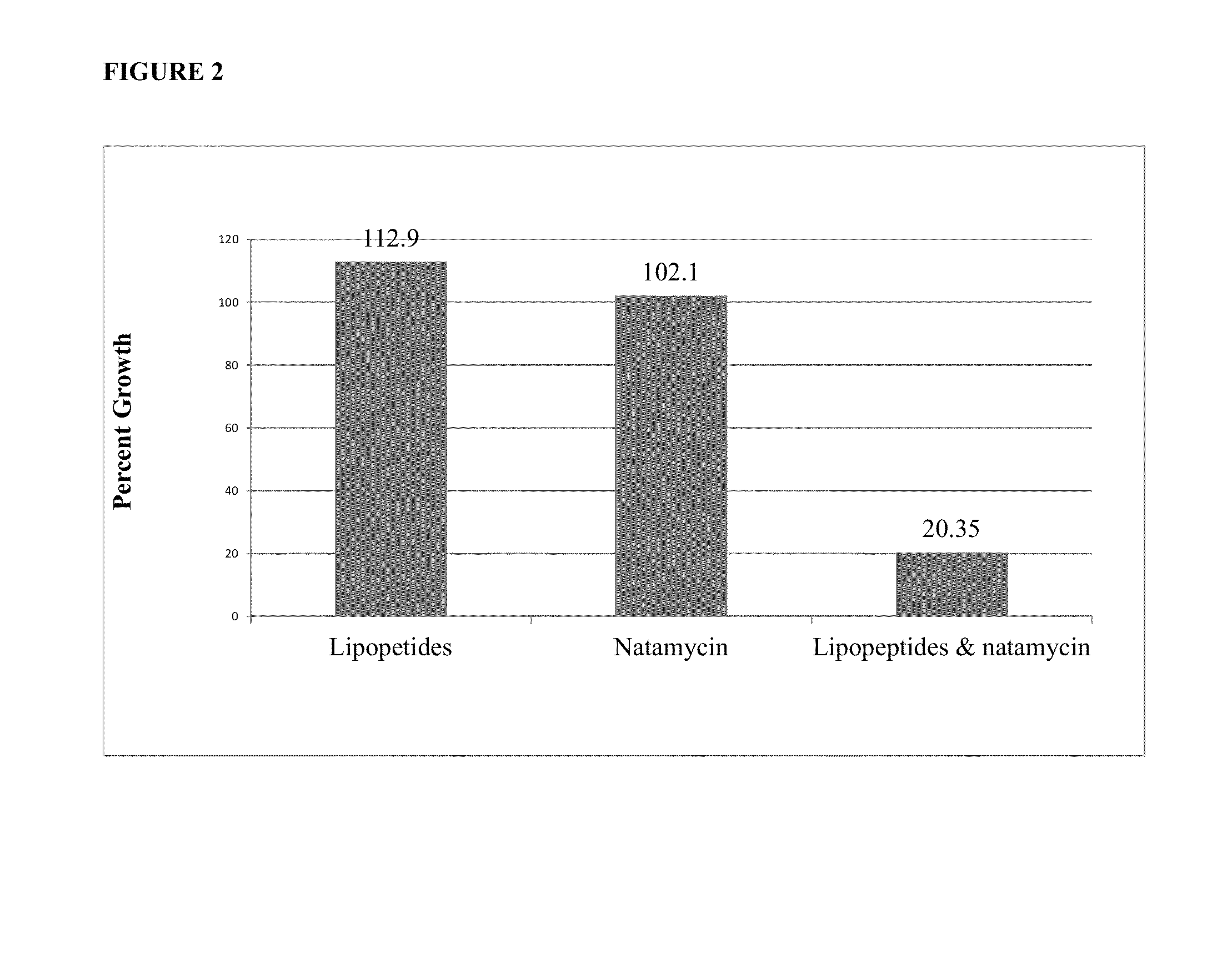
The present invention includes compositions comprising a synergistic fungicidal combination of a polyene fungicide and at least one lipopeptide and methods for using such compositions in controlling fungal pathogens.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCI LP
Synergistic combinations of polyene fungicides and non-ribosomal peptides and related methods of use
ActiveUS20120302494A1Toxic reductionLow resistance-inducingBiocideOrganic active ingredientsFungicideToxicology
The present invention includes compositions comprising a synergistic fungicidal combination of a polyene fungicide and at least one lipopeptide and methods for using such compositions in controlling fungal pathogens.
Owner:BAYER CROPSCI LP
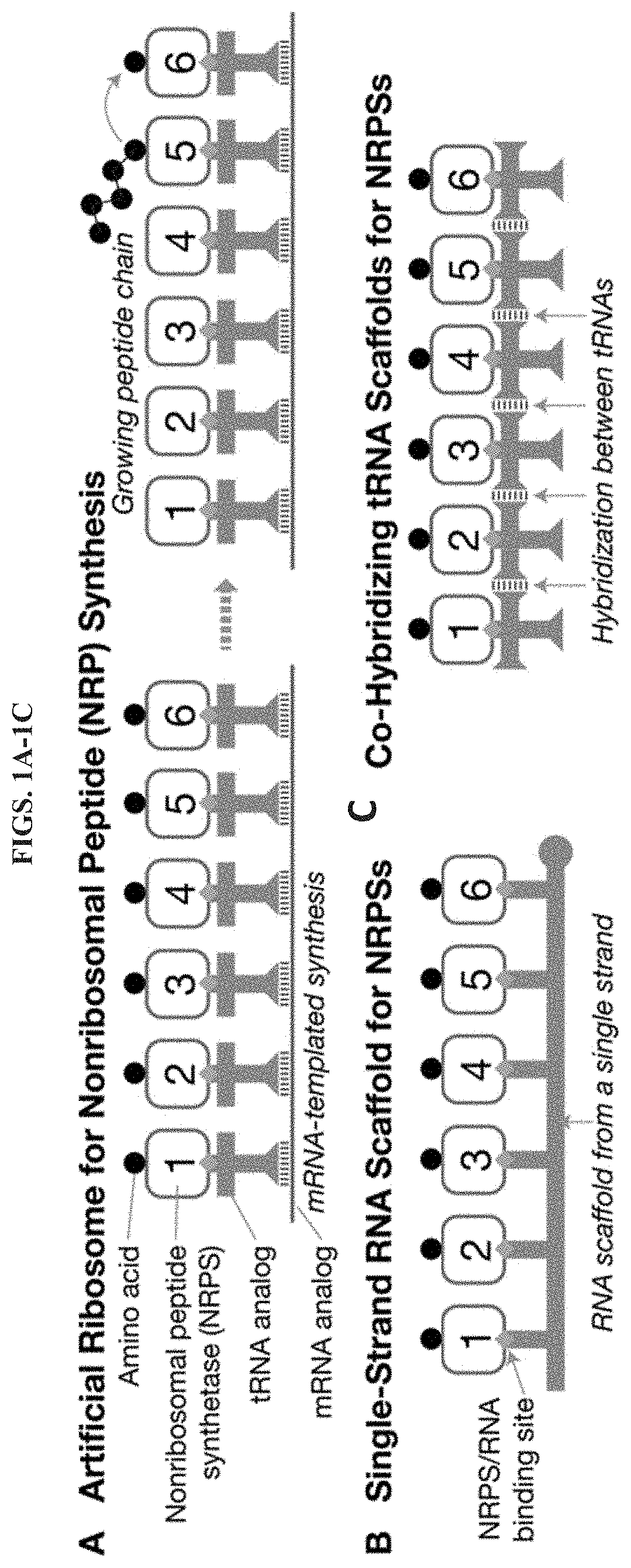
Artificial Ribosomes for Fully Programmable Synthesis of Nonribosomal Peptides
Provided herein, in some embodiments, are artificial ribosomes that synthesize nonribosomal peptides, polyketides, and fatty acids with full control over peptide sequence. Also provided herein are methods for programmed synthesis of nonribosomal peptides, polyketides, and fatty acids. In particular, provided herein are methods for scalable synthesis of a wide range of antibacterial, antifungal, antiviral, and anticancer compounds.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
Methods of Producing Modified Assembly Lines and Related Compositions
The present invention provides a method producing a modified assembly line, such as those that produce non-ribosomal peptides and polyketides. The modified assembly lines of the invention can be used to produce novel compounds with therapeutic activities. The invention also provides organisms containing modified assembly lines and libraries of modified assembly lines.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
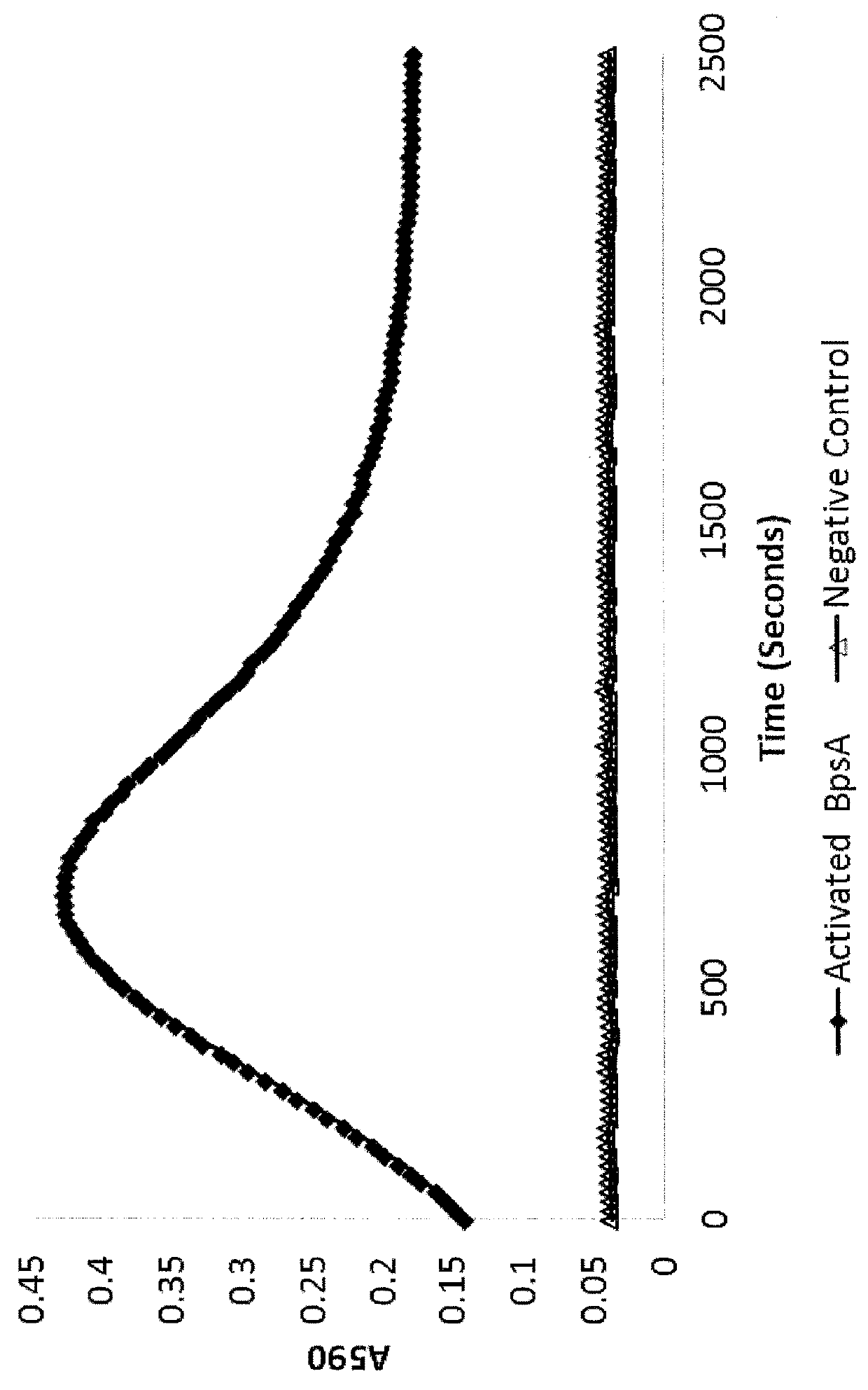
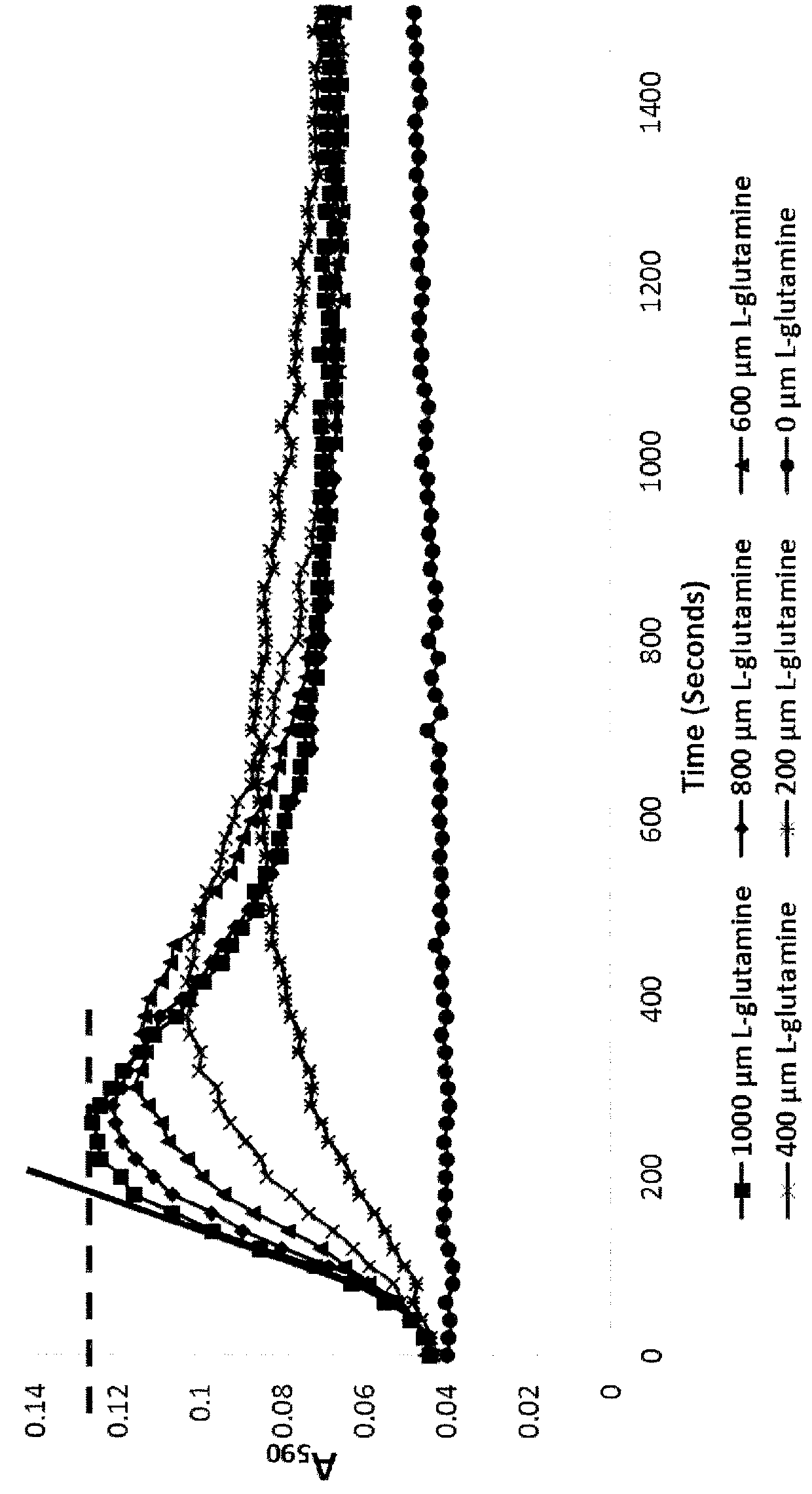
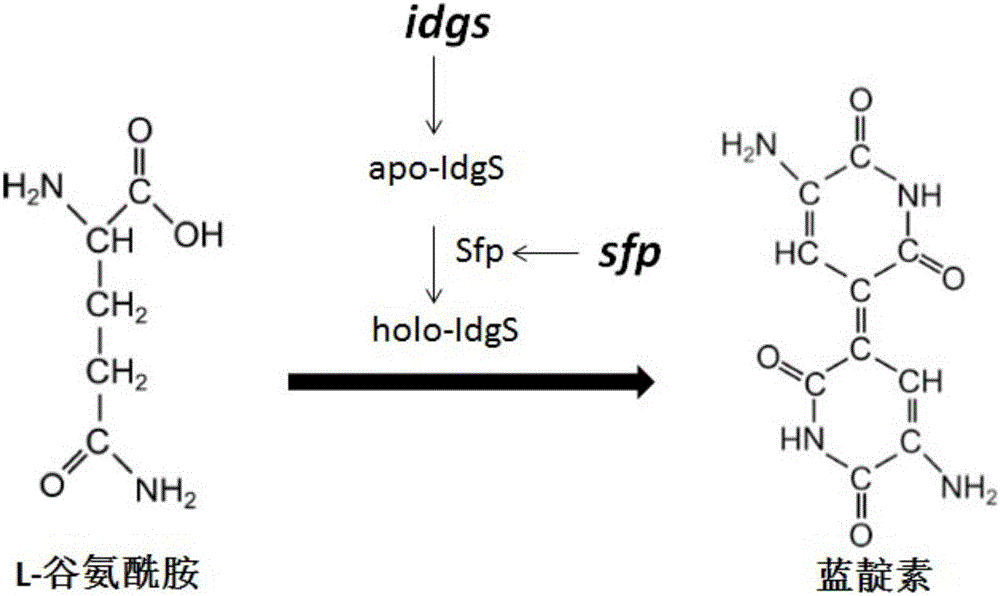
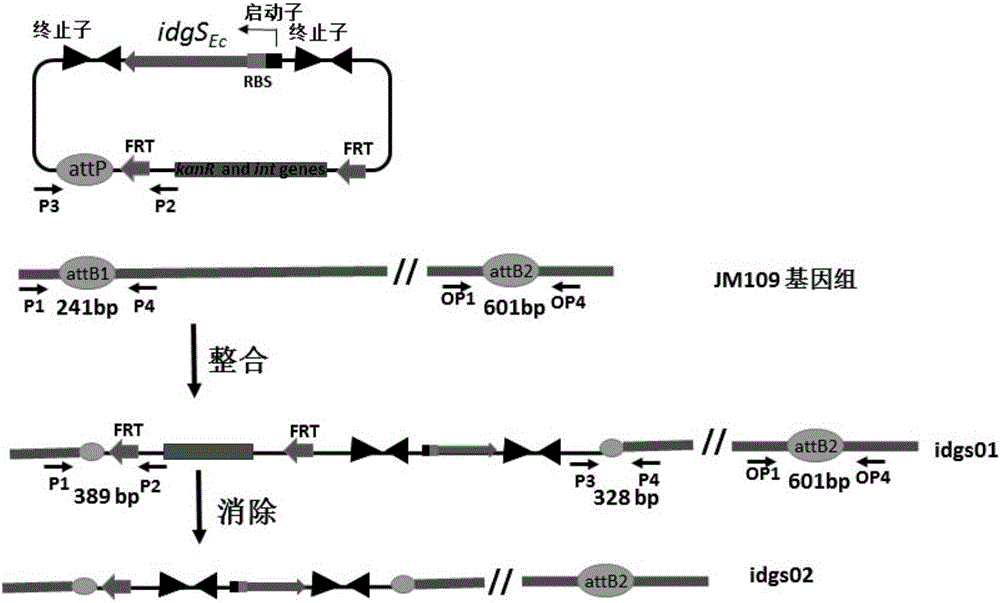
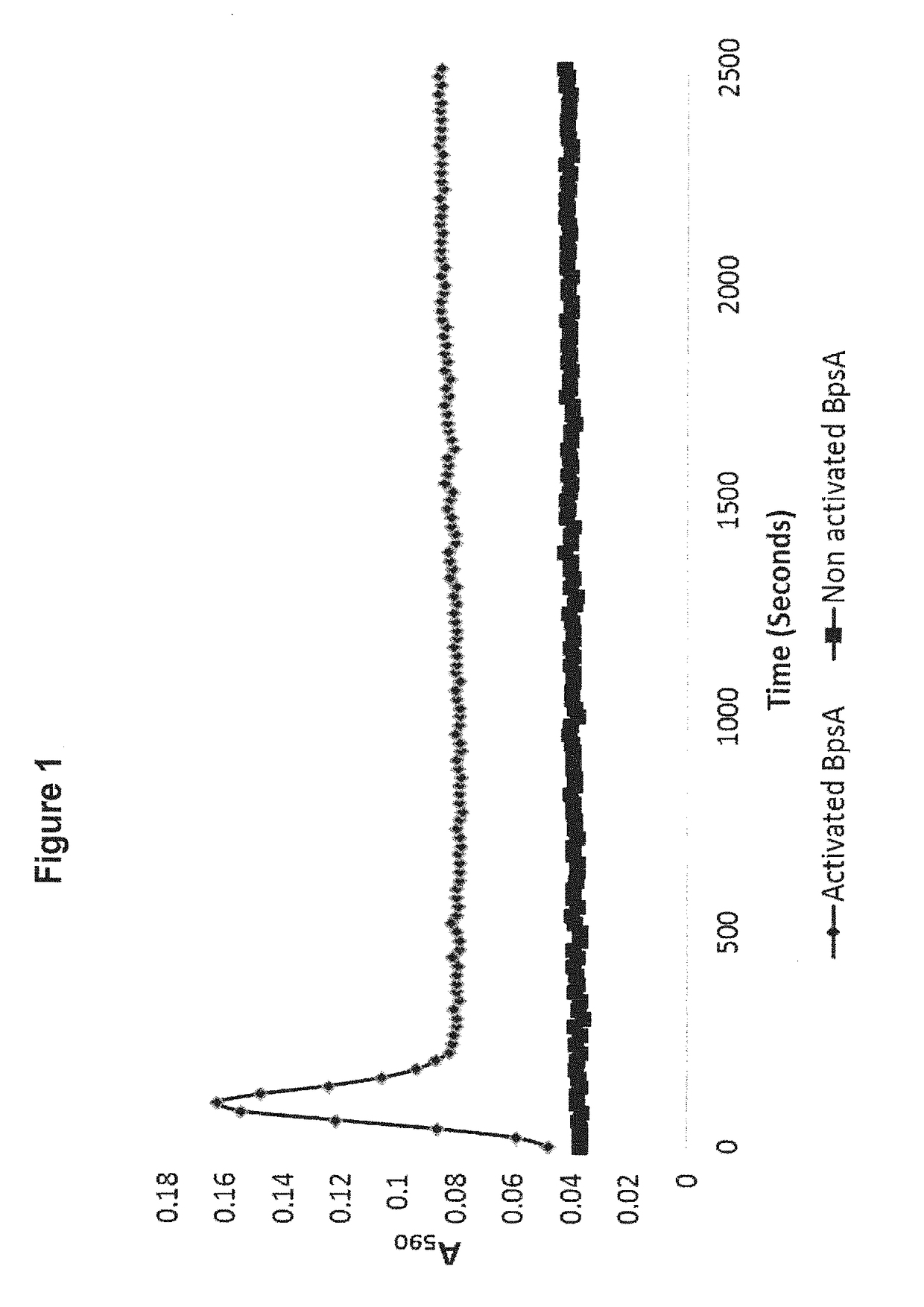
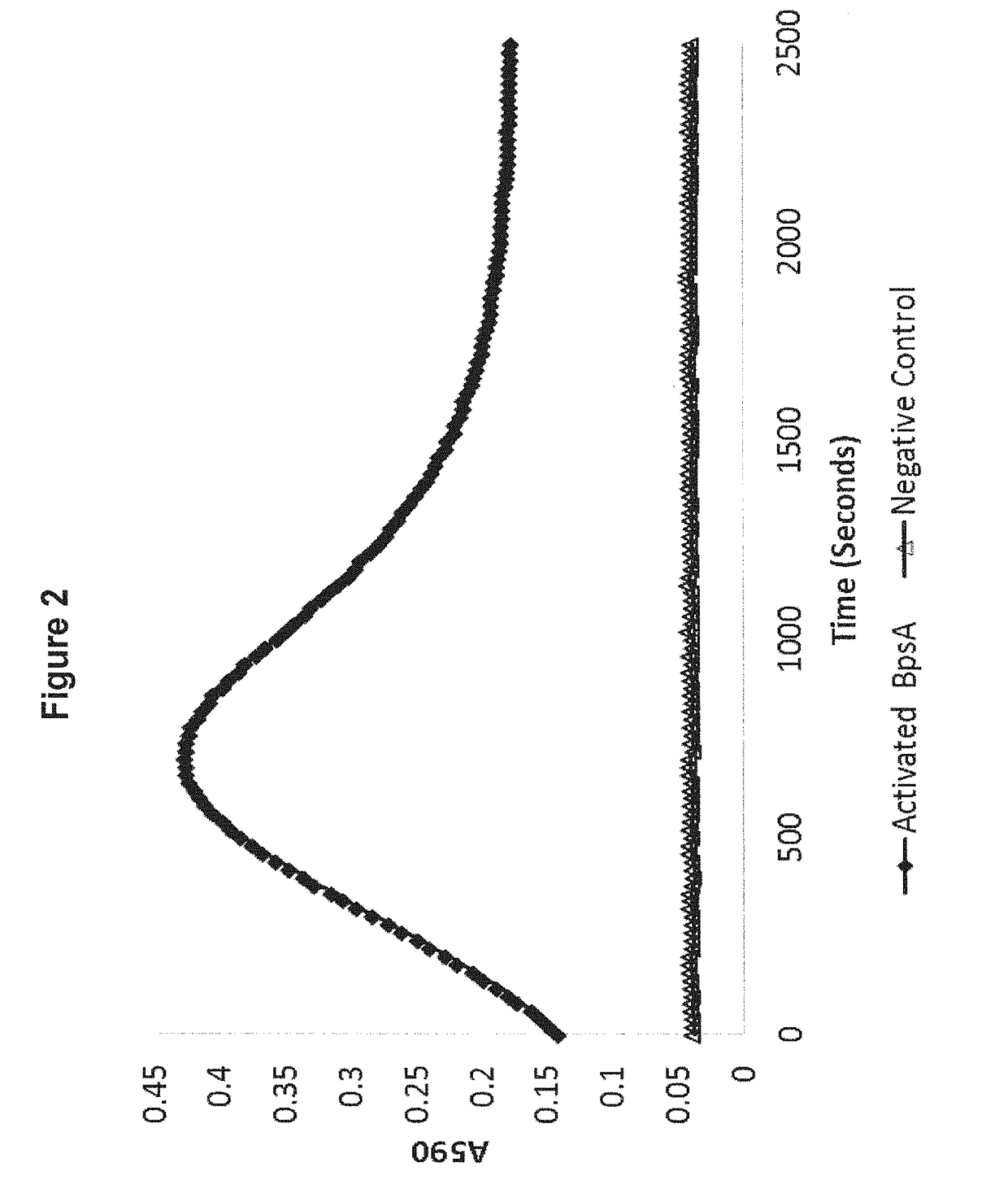
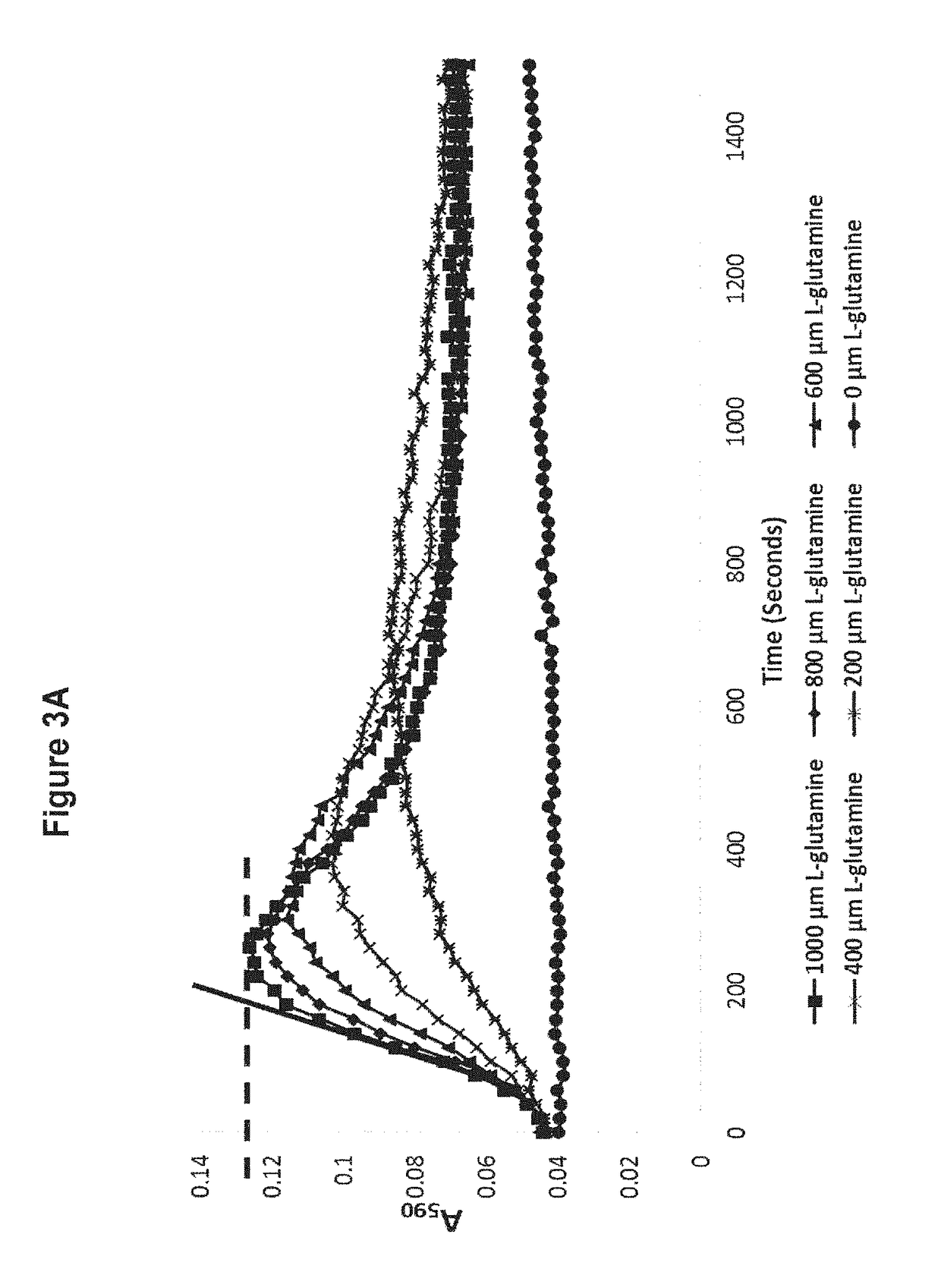
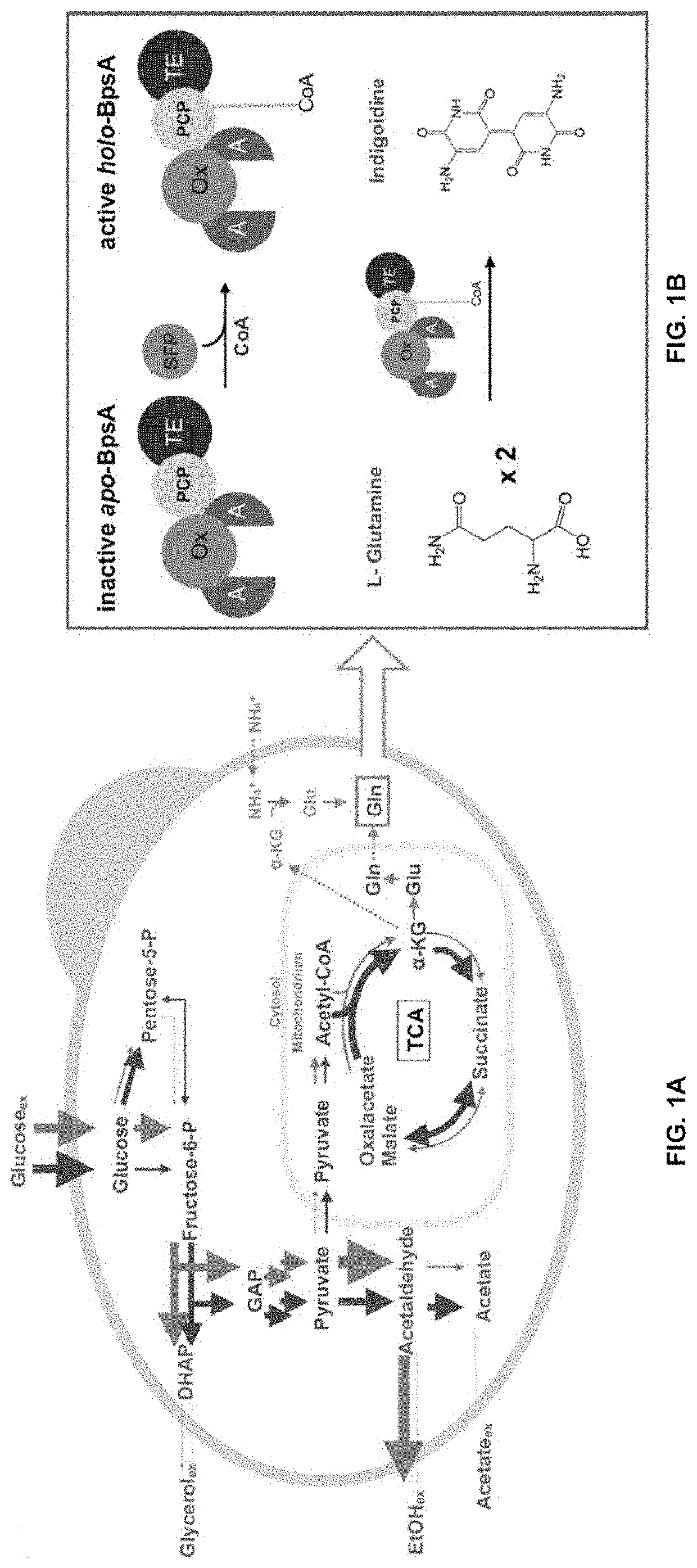
Methods of detecting and measuring glutamine and analogues thereof, and methods related thereto
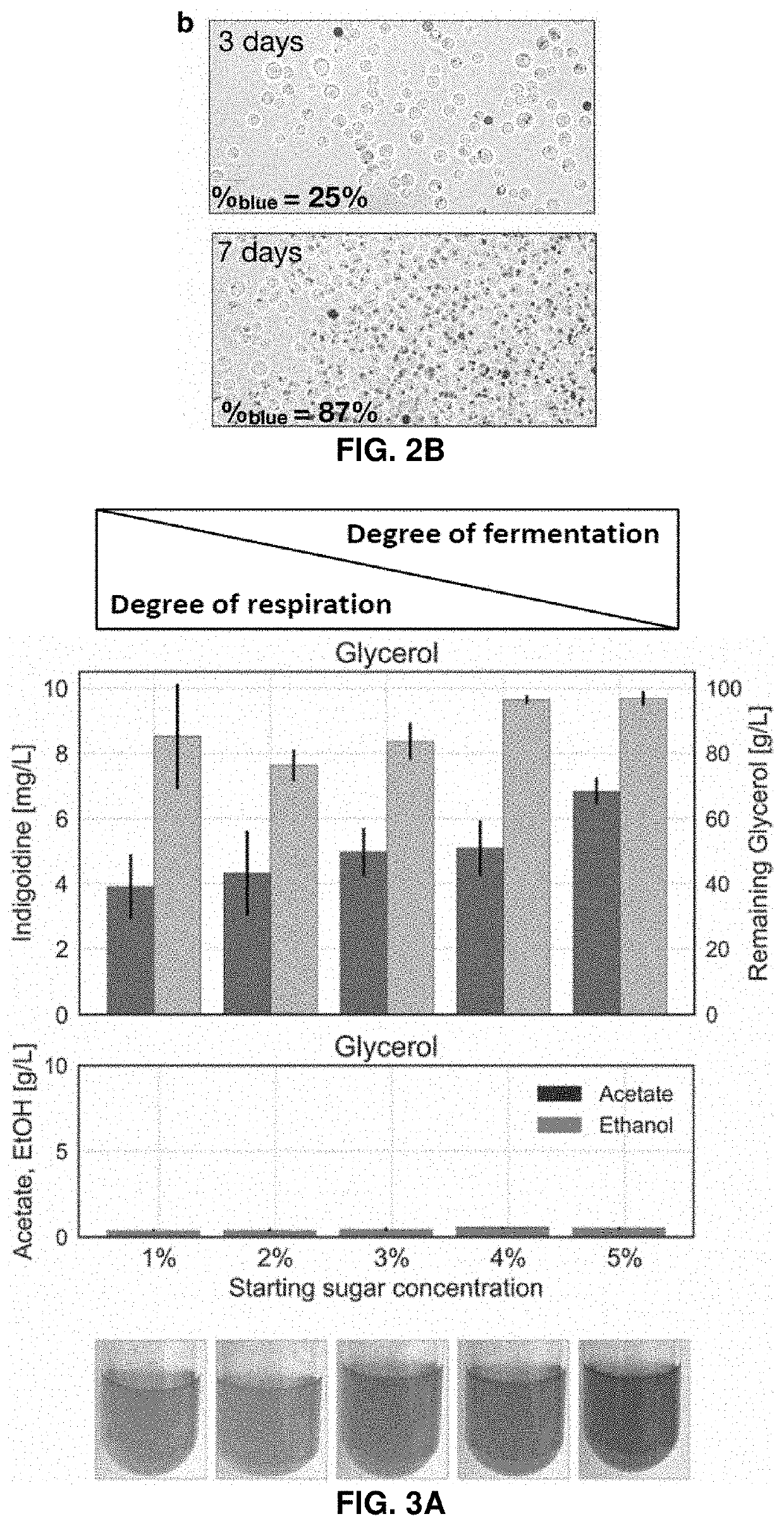
ActiveUS9995750B2Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisGlutamine analogIndigoidine
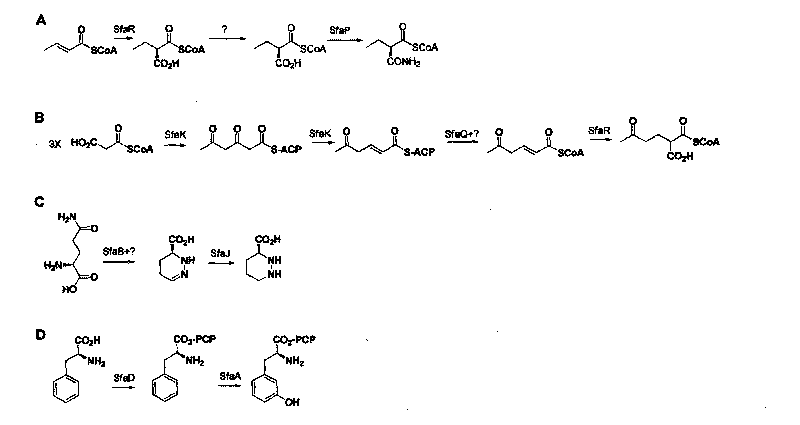
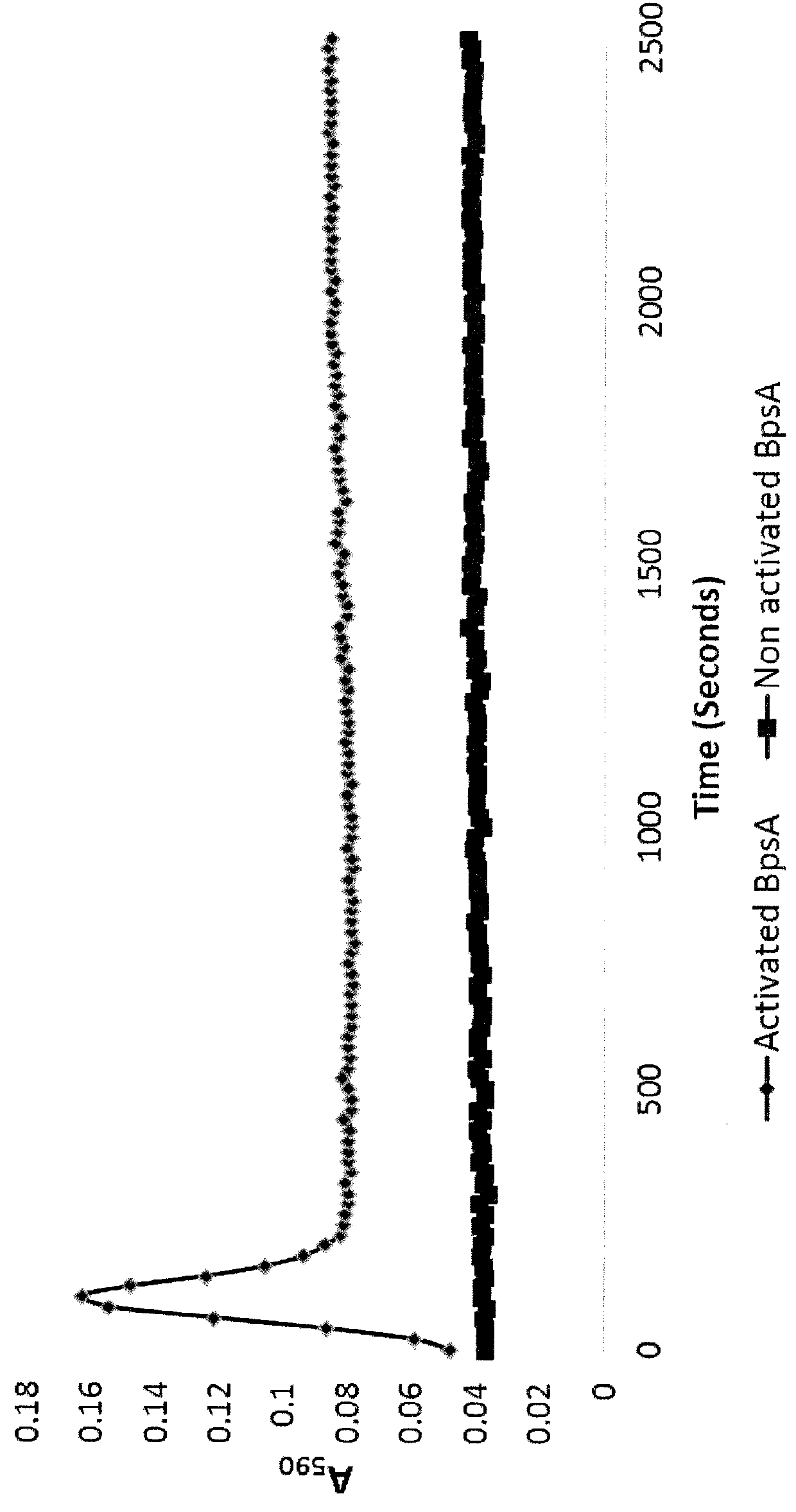
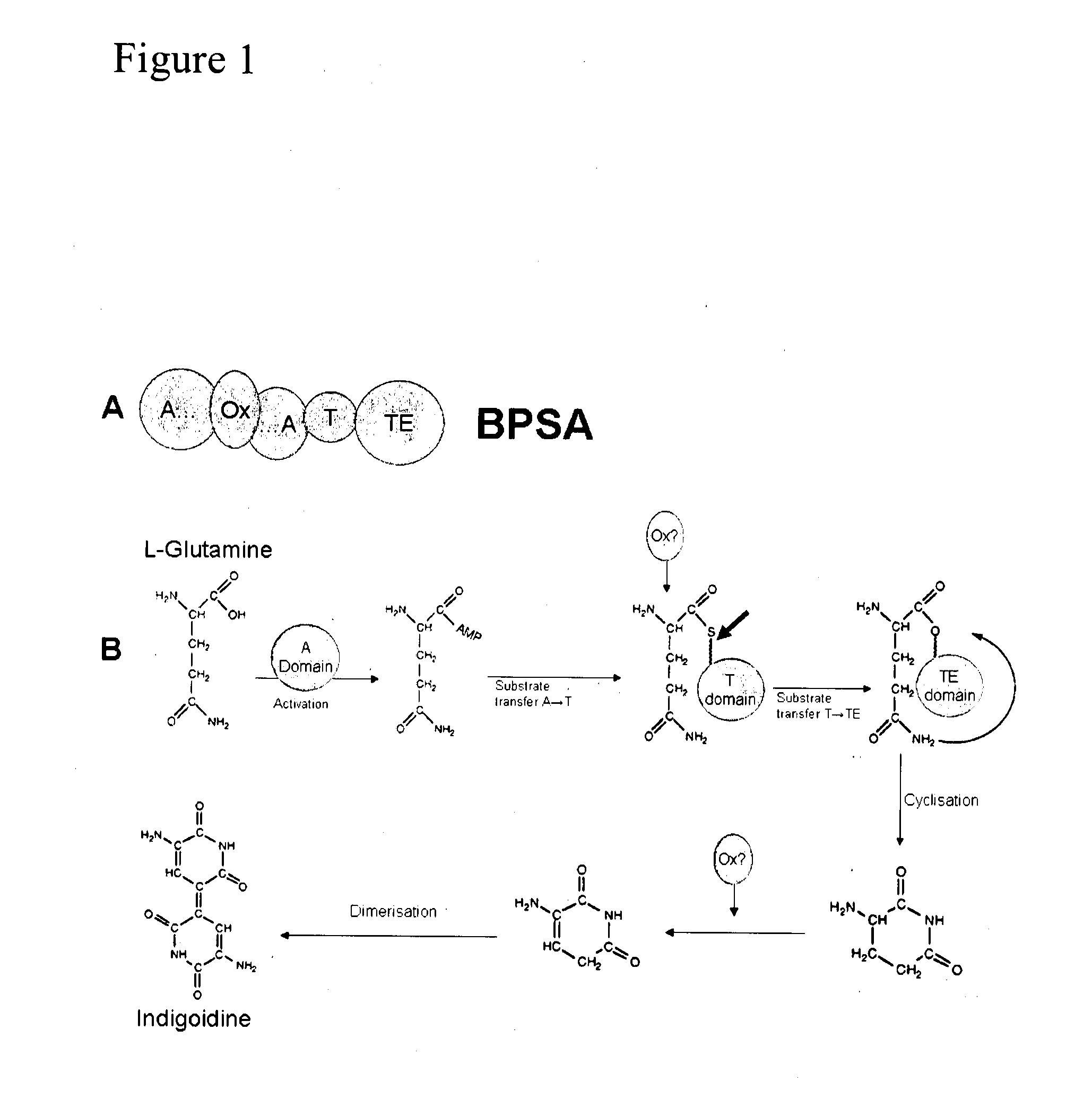
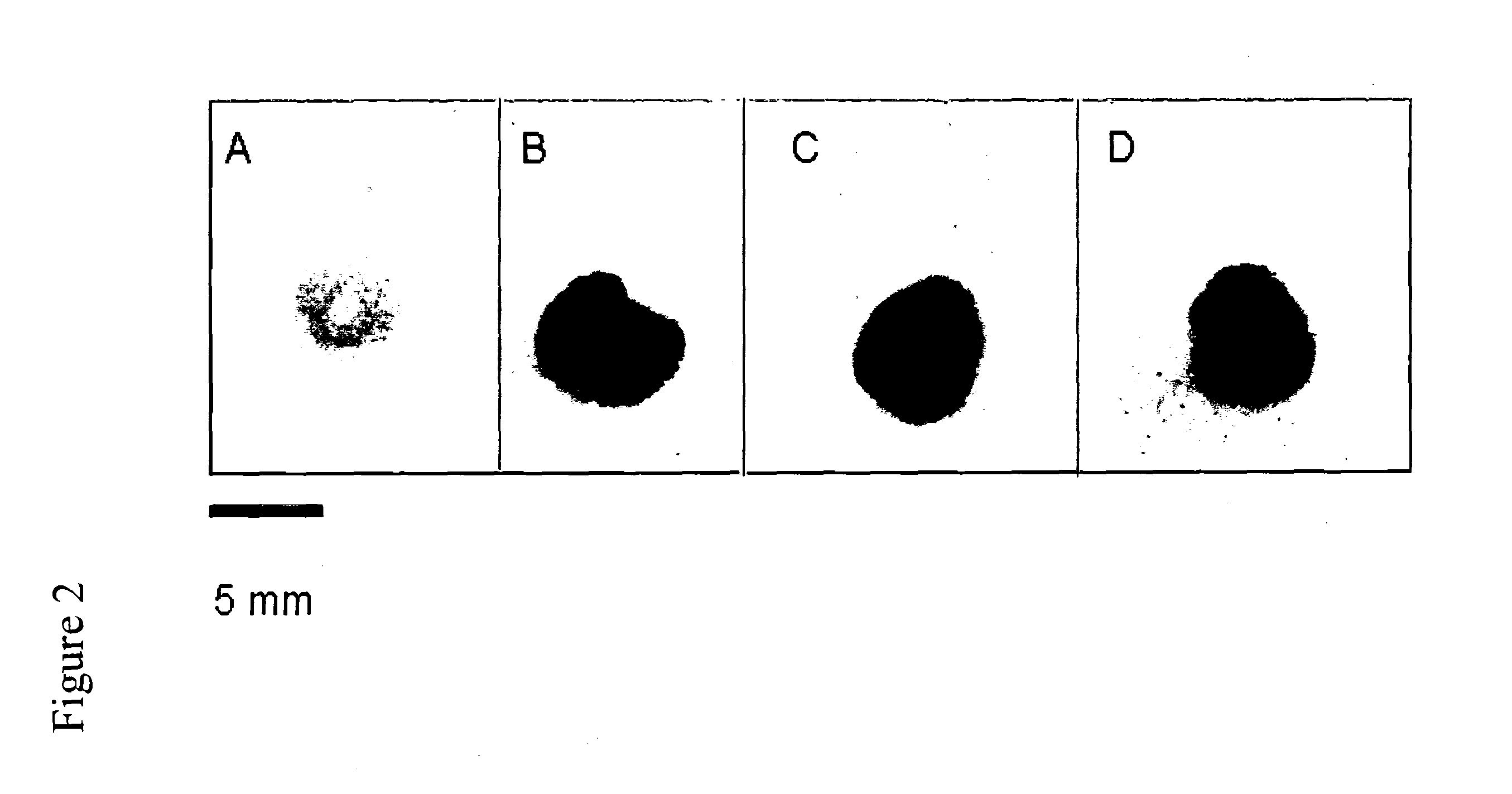
Method for the detection of glutamine and its analogs are provided by the present disclosure. Also provided are methods for measuring the levels of glutamine and its analogs, including diagnostic methods. Further provided are methods that utilize glutamine analogs for the synthesis of colored pigments and other useful agents. The methods comprise the use of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) under conditions to produce an indigoidine or indigoidine-related pigment.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Methods of Identifying and Characterizing Natural Product Gene Clusters
InactiveUS20130260436A1Rapid and reproducible assessmentHigh detection sensitivityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSecondary metabolite biosynthesisADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to methods and compositions for identifying a candidate nucleic acid (CNA) comprising a polynucleotide sequence encoding at least a part of a natural product gene cluster (NPGC), a secondary metabolite biosynthesis cluster (SMBC), a non ribosomal peptide (NRP), a polyketide (PK) biosynthesis cluster, a protein involved in NRP and / or PK biosynthesis, a protein involved in other secondary metabolite biosynthesis, and / or a phosphopantetheinyl transferase (PPTase), by expressing the candidate nucleic acid (CNA) to form at least one PPTase, incubating the PPTase with a non ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS), and detecting activation of the NRPS, wherein activation indicates that said CNA comprises a polynucleotide sequence encoding at least one of the above.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Biosynthetic pathway for heterologous expression of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase drug and analogs
The present invention is directed to the biosynthetic pathway for a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) derived drug and analogs thereof. The invention also discloses polynucleotide sequences useful for heterologous expression in a convenient microbial host for the synthesis of the NRPS derived drug.
Owner:ALLEGHENY SINGER RES INST +2
Biosynthetic Systems Producing Fungal Indole Alkaloids
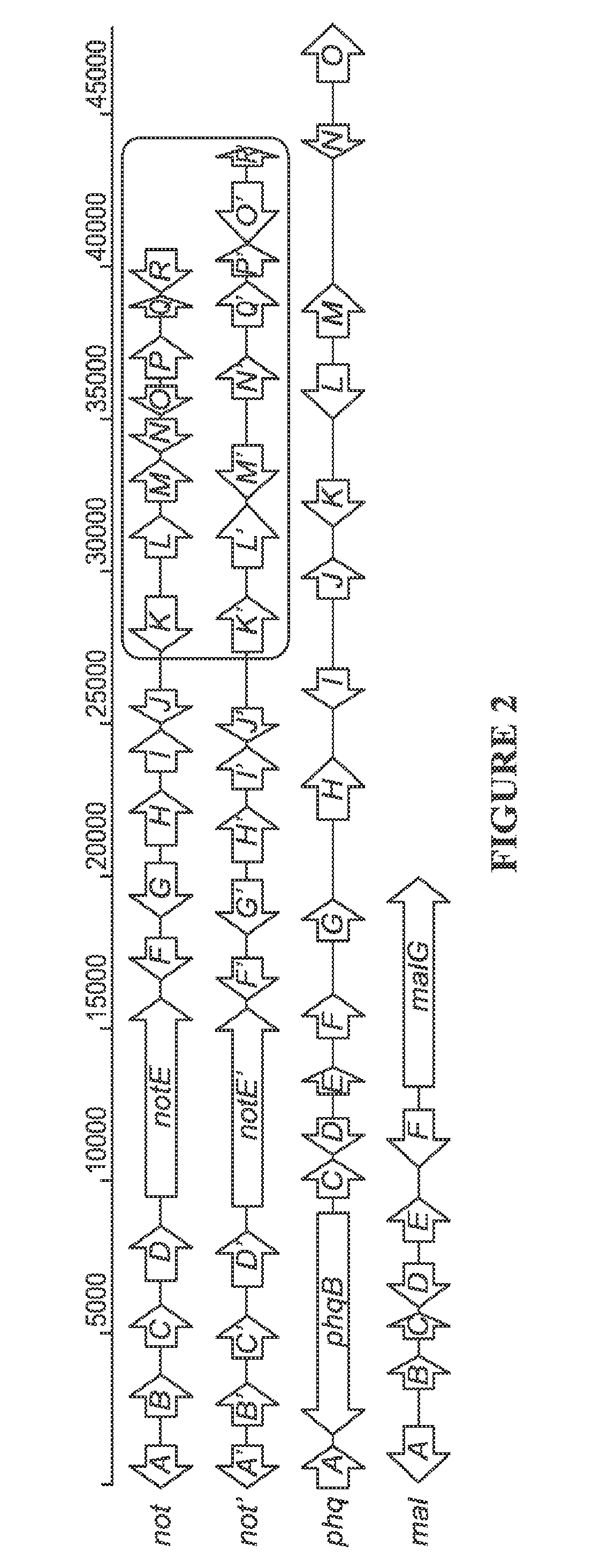
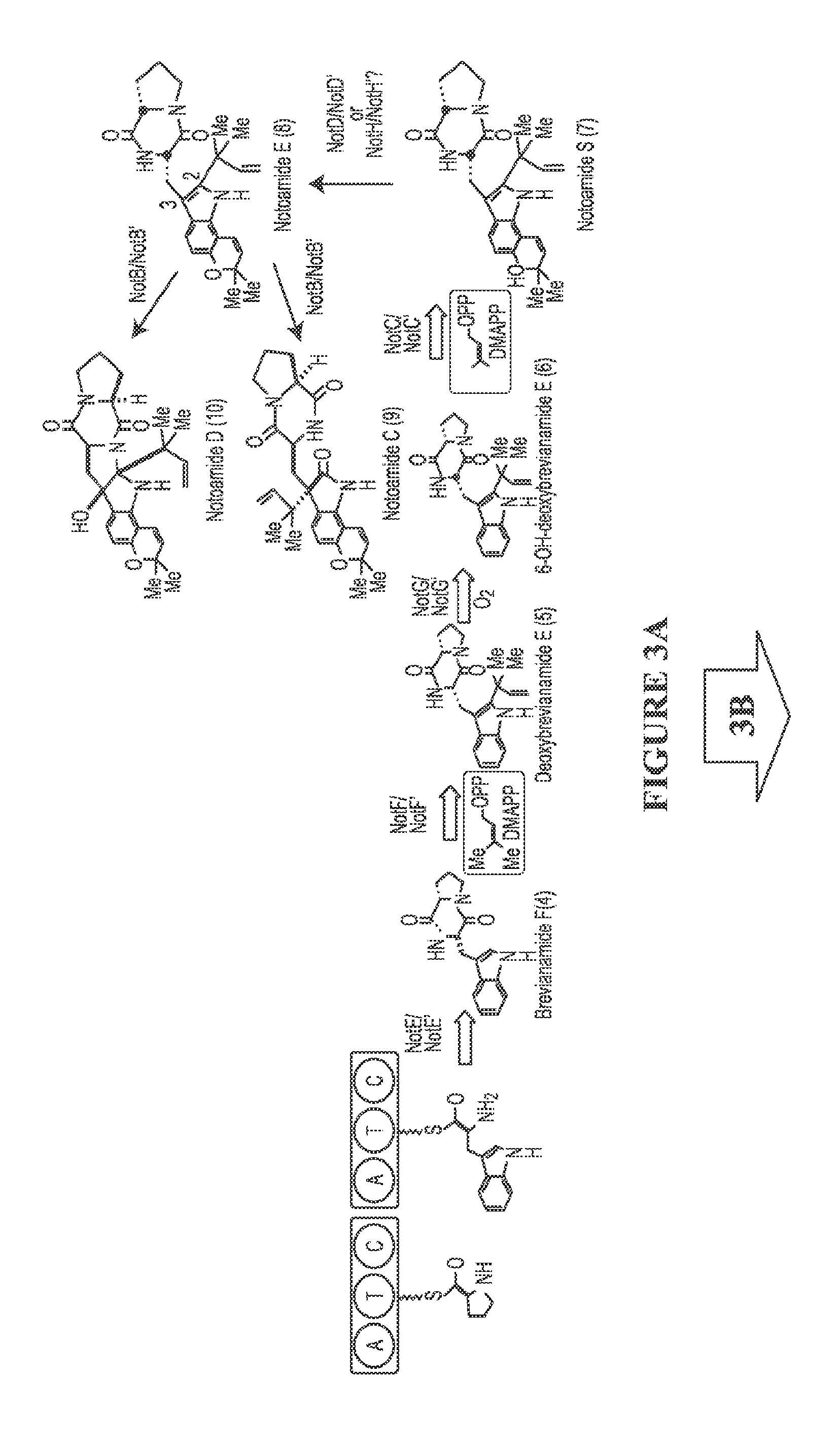
The biosynthesis of fungal bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane indole alkaloids with a wide spectrum of biological activities have attracted increasing interest. Their intriguing mode of assembly has long been proposed to feature a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase, a presumed intramolecular Diels-Alderase, a variant number of prenyltransferases, and a series of oxidases responsible for the diverse tailoring modifications of their cyclodipeptide-based structural core. Until recently, the details of these biosynthetic pathways have remained largely unknown due to lack of information on the fungal derived biosynthetic gene clusters. Herein, we report a comparative analysis of four natural product metabolic systems of a select group of bicyclo[2.2.2]diazaoctane indole alkaloids including (+) / (−)-notoamide, paraherquamide and malbrancheamide, in which we propose an enzyme for each step in the biosynthetic pathway based on deep annotation and on-going biochemical studies.
Owner:COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY +1
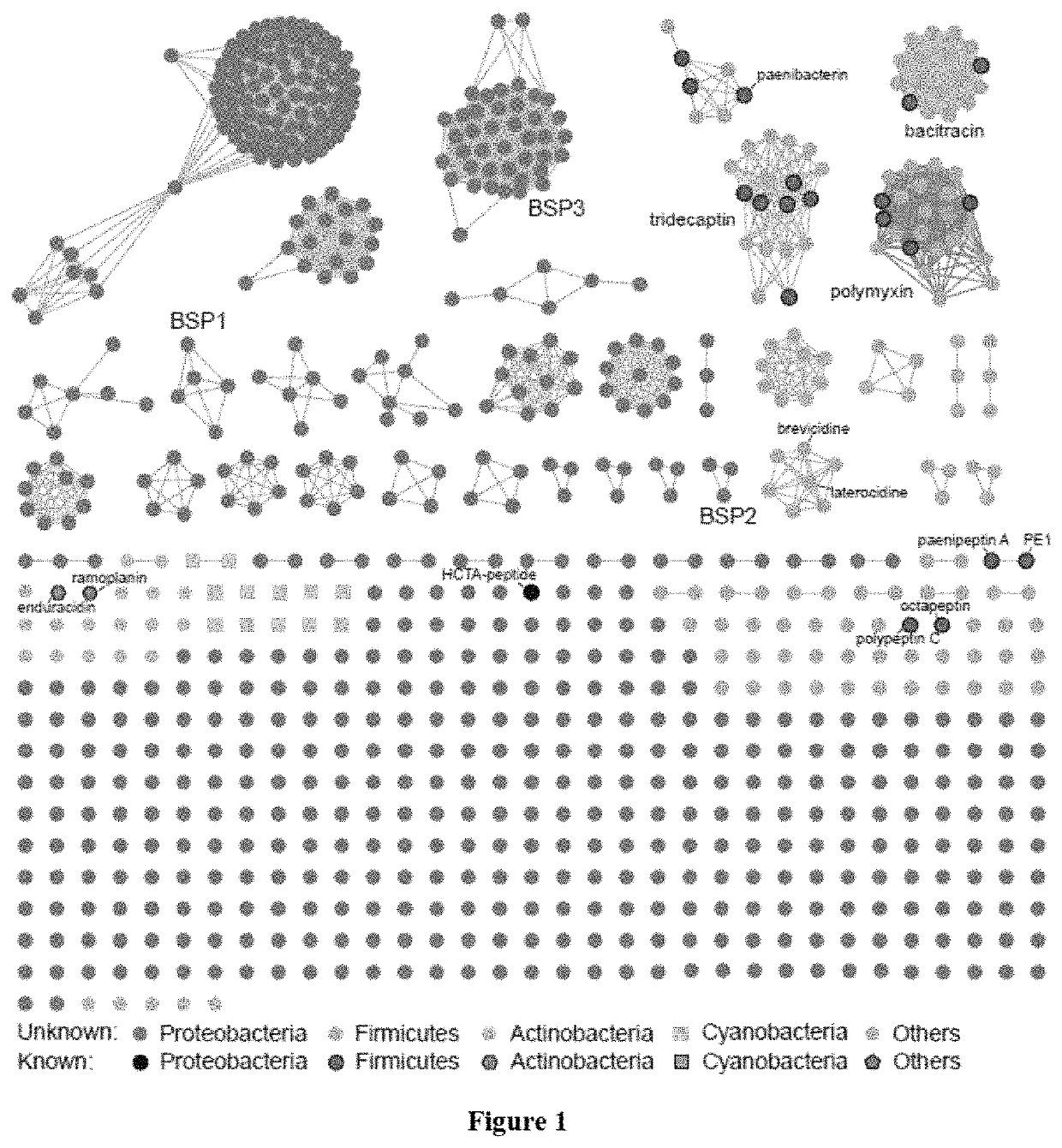
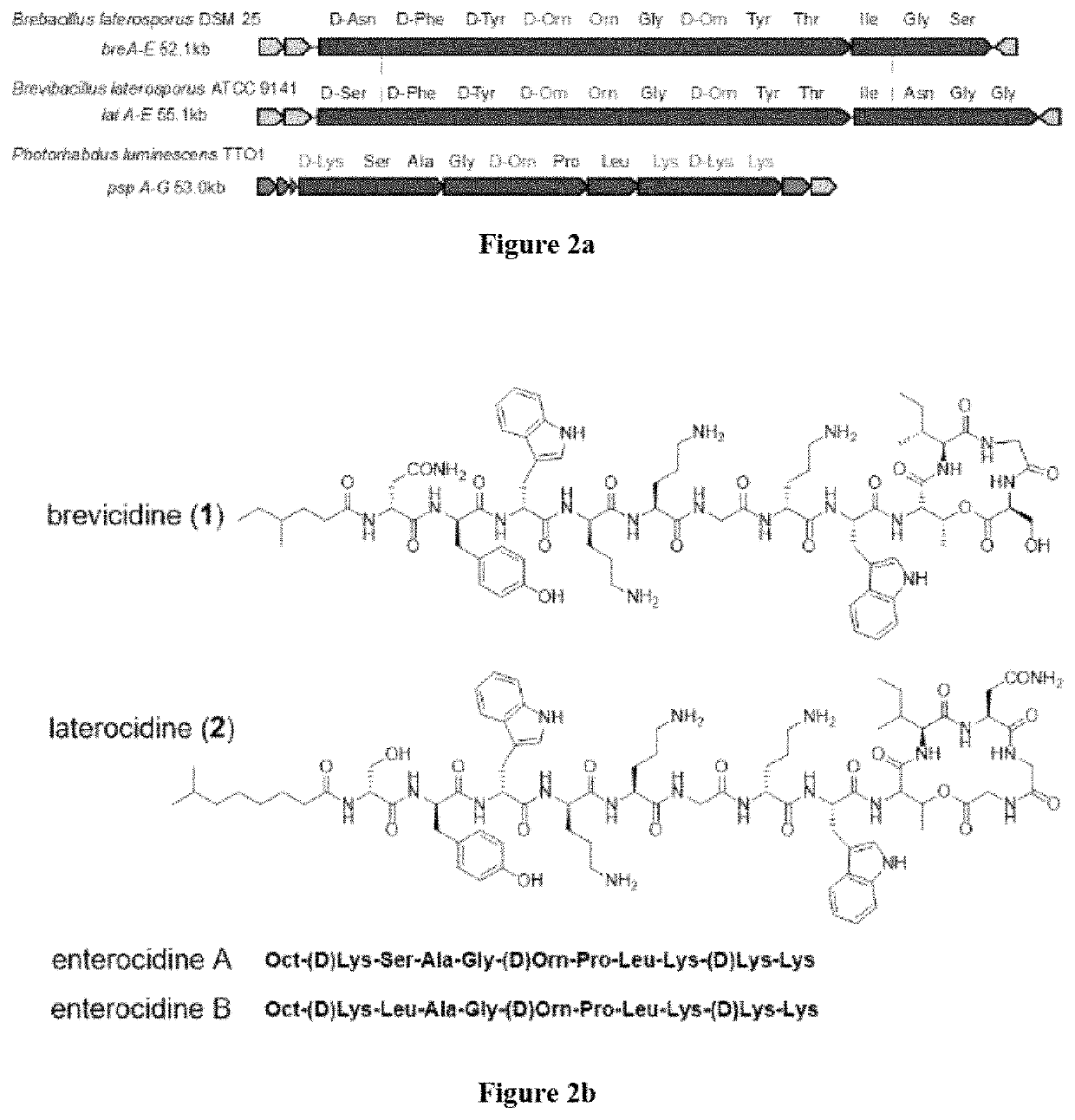
Discovery of cationic nonribosomal peptides as Gram-negative antibiotics through global genome mining
ActiveUS10738093B2Facilitate genome-guided discoveryHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmacometricsBiochemistry
Pharmacological compositions comprising a cationic nonribosomal peptide (CNRP) or a salt thereof are described. Further, methods of treating a bacterial infection in a subject by administering to the subject a CNRP or a salt thereof are provided.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
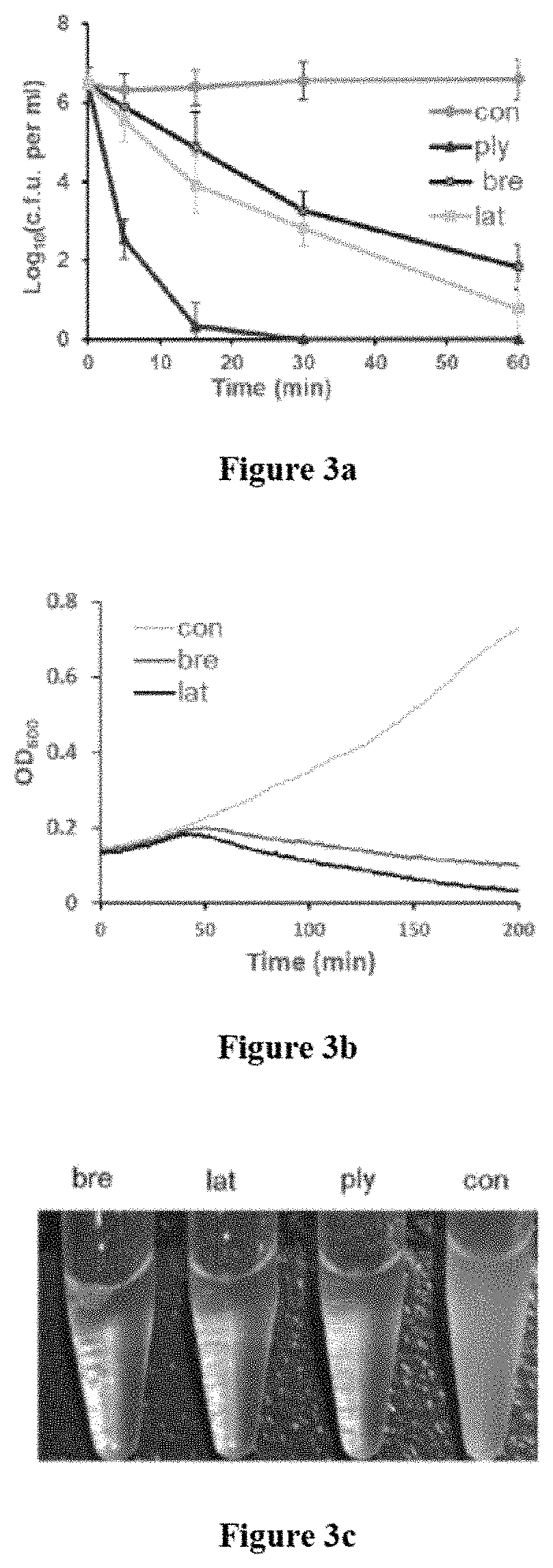
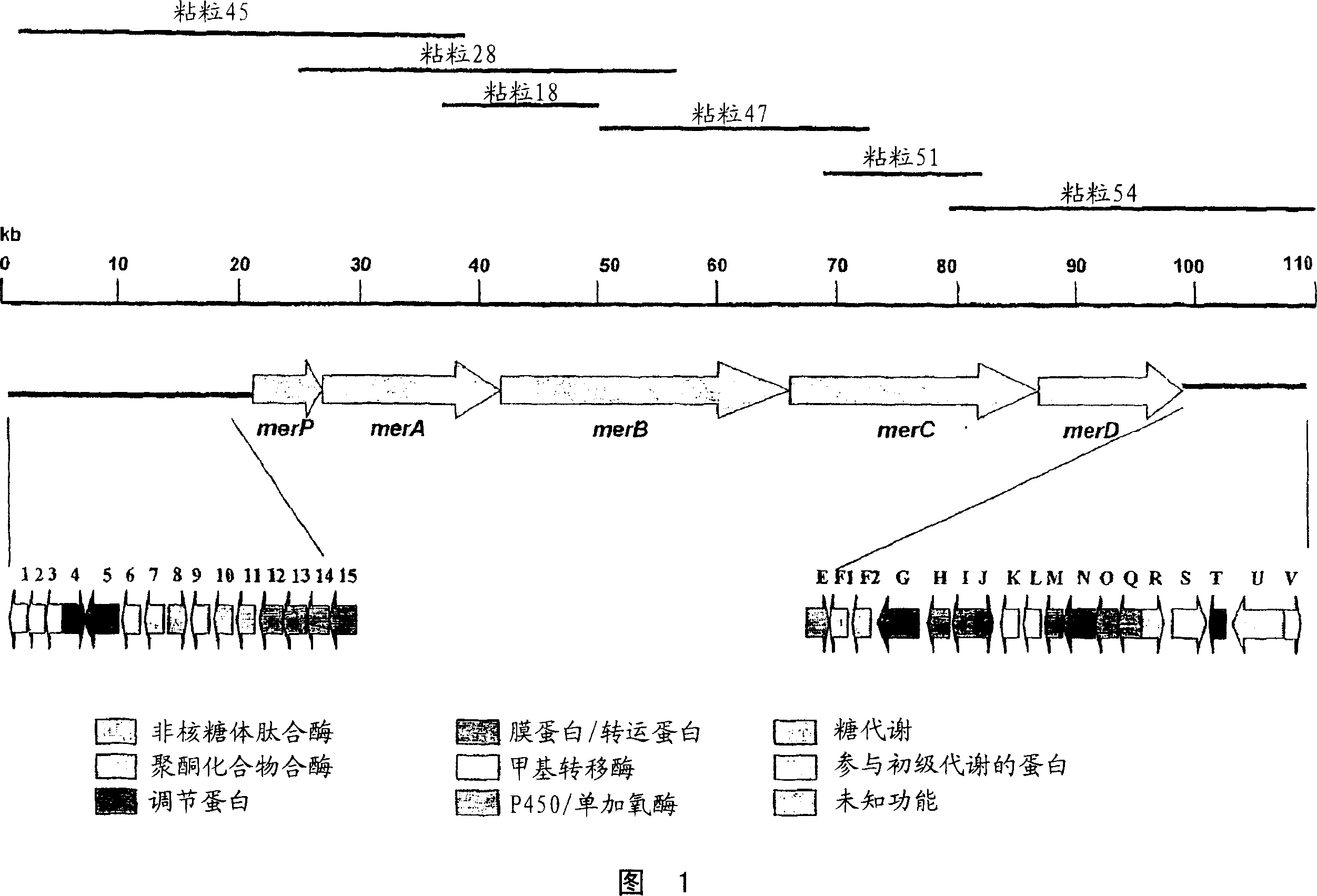
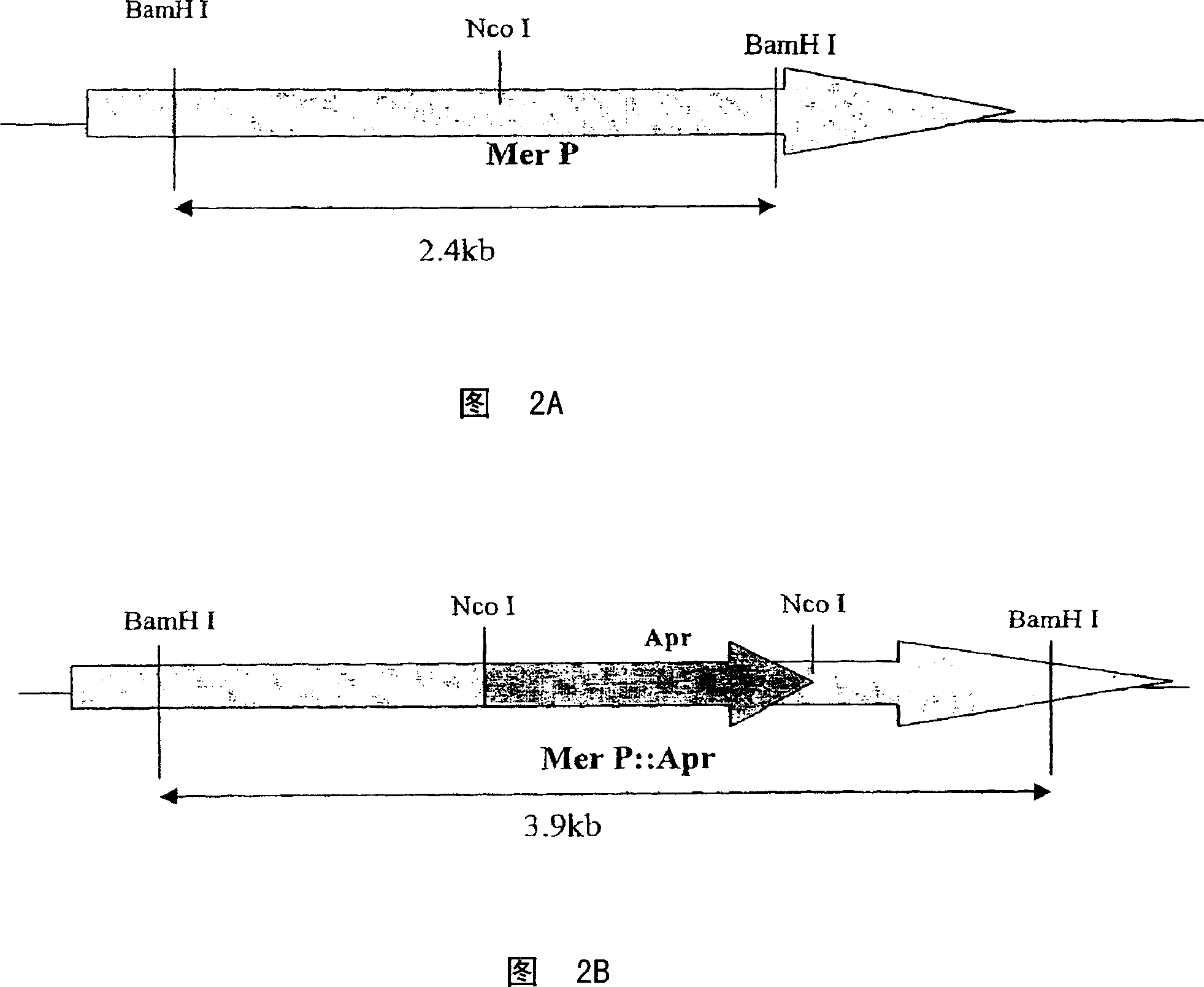
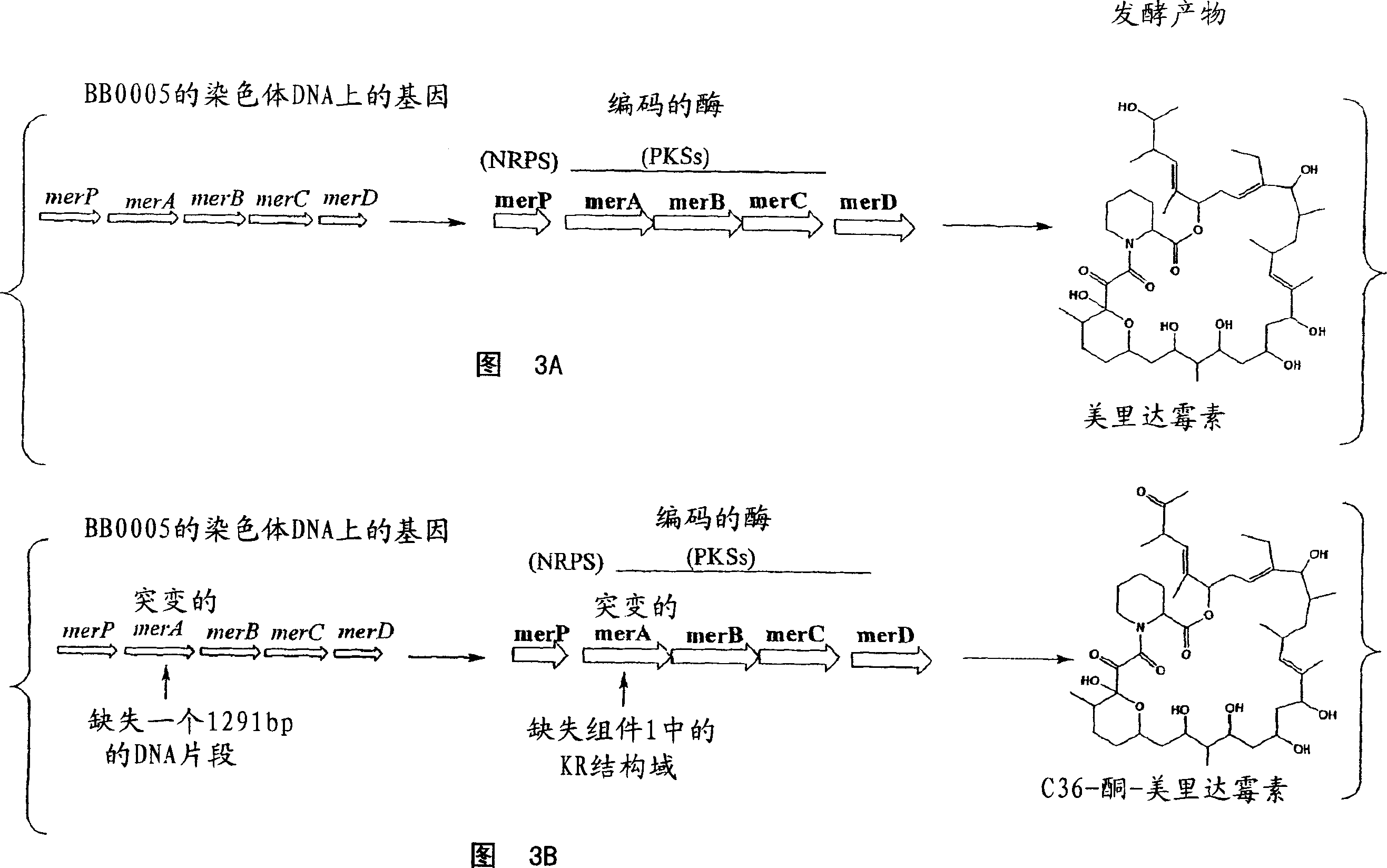
Biosynthetic gene cluster for the production of a complex polyketide
A polyketide synthase complex composed of polyketide synthase with 15 total modules, a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase with I module, and a cytochrome P450 hydroxylase is described. Also provided are novel Streptomyces species and methods of modified Streptomyces species. Further described are novel compounds, 36-ketomeridamycin, C9-deoxomeridamycin, and C9-deoxoprolylmeridamcyin and uses thereof.
Owner:WYETH LLC
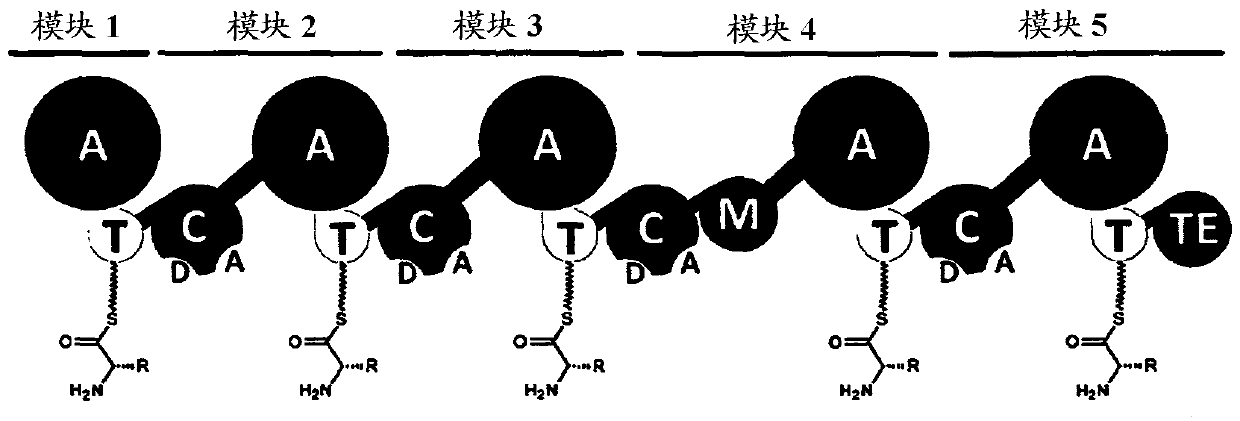
Novel non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene and cloning and expression of adenylylation structural domains thereof
The invention discloses a novel non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene named NRPS114. The nucleotide sequence of the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene is shown in SEQ ID NO 1. Besides, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene, a plasmid pCC1FOS<TM> Fosmid-NRPS114 containing the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene and an expression vector of a recombinant plasmid pET28a-A-2his of five adenylylation structural domains in the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene. Additionally, the invention further discloses the five adenylylation structural domains and a preparation method thereof. Recombinant adenylylation structural domains are obtained by means of over-expression of the adenylylation structural domains A1, A2, A3, A4 and A5 in an escherichia coli prokaryotic expression system, and the non-ribosomal peptide synthetase gene has high activity enabling amino acid to undergo adenylylation, provides more genetic manipulation materials for study of combinatorial biology and has a huge application prospect in research and development of new drugs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Gene involved in synthesis of cyclic peptide compound, method for producing cyclic peptide compound using the same, and transformant comprising the same
This invention is intended to identify a gene cluster involved in biosynthesis of a cyclic peptide compound produced by a filamentous fungus of the Curvularia species and to establish a system for synthesizing such cyclic peptide compound. The gene is composed of a first module to a tenth module and encodes a protein having activity of synthesizing a nonribosomal peptide constituting a basic peptide backbone of a cyclic peptide compound produced by a filamentous fungus of the Curvularia species.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH +2
Recombinant cell screening system and building method thereof
The invention relates to a recombinant cell screening system and a building method thereof. The recombinant cell screening system comprises the receptor cells of constitutive expression non-ribosomal peptide synthetase encoding genes and plasmids containing phosphopantetheine transferase encoding genes. The recombinant cell screening system has the advantages that exogenous substrate needs not to be added, special detecting equipment is not needed, and a screening process can be completed fast, simply, economically and efficiently. The application example, namely clone screening of gene segments, of the system is specifically elaborated in the embodiment of the invention, and the application example proves that the system can be effectively used for screening recombinant cells.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
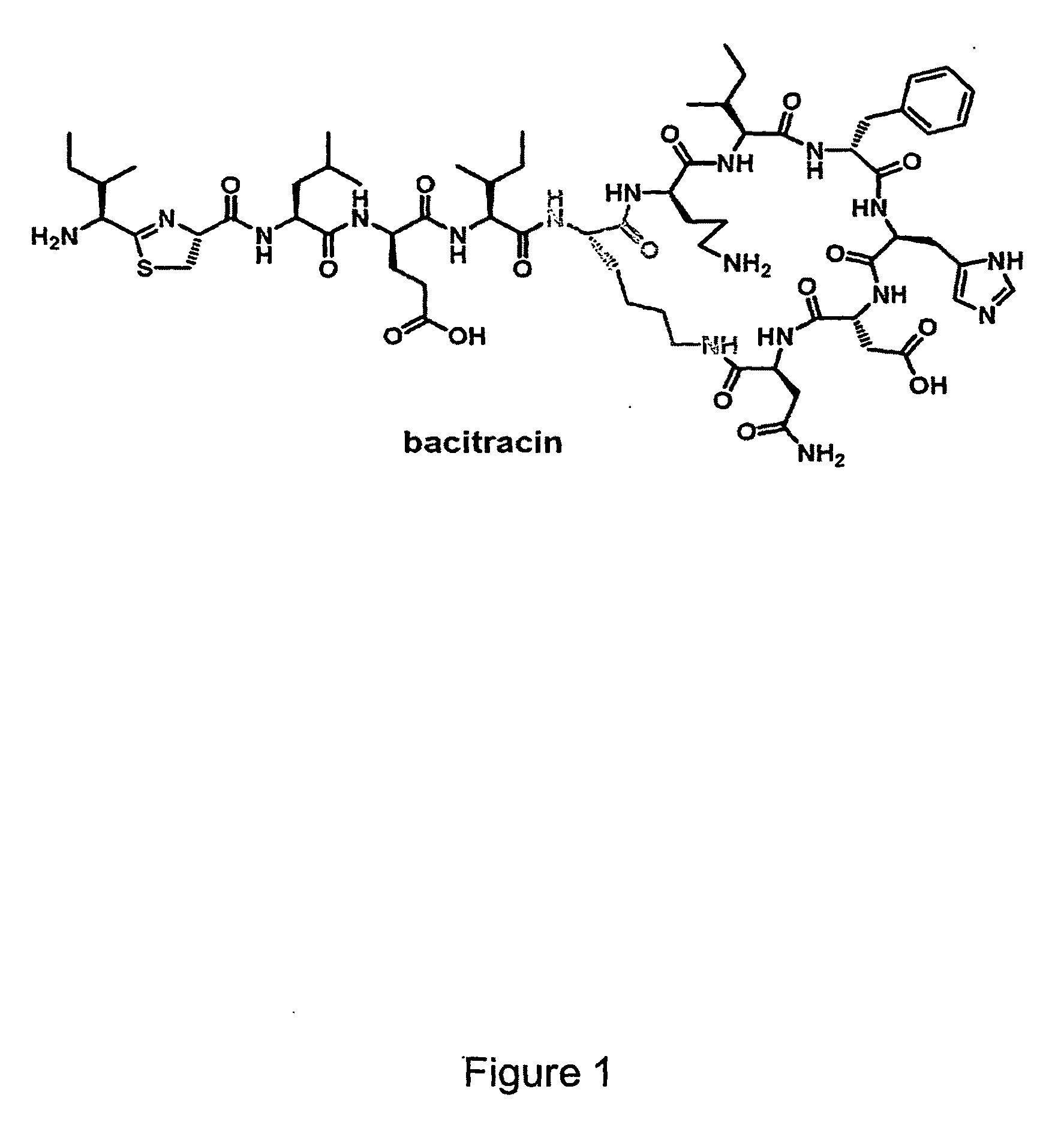
Production of beta-lactam antibiotics
ActiveUS20100009404A1High specific activitySimple reaction conditionsSugar derivativesBacteriaBeta lactam antibioticSide chain
The present invention describes a process for the production of an N-α-amino-hydroxyphenylacetyl or an N-α-aminophenylacetyl β-lactam antibiotic comprising an IPNS-catalysed conversion of a precursor tripeptide hydroxyphenylglycyl-cysteinyl-valine (HpgCV) or phenylglycyl-cysteinyl-valine (PgCV), respectively, to the N-hydroxyphenylglycyl or the N-phenylglycyl β-lactam antibiotic, respectively. The tripeptide HpgCV or the tripeptide PgCV may further be prepared by contacting the amino acids hydroxyphenylglycine (Hpg) or phenylglycine (Pg), cystein (C) and valine (V) with a non-ribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) to effect formation of the tripeptide HpgCV or the tripeptide PgCV, the NRPS comprising a first module M1 specific for Hpg or Pg, a second module M2 specific for C and a third module M3 specific for V An IPNS is further provided having an improved activity in this conversion, as well as an NRPS catalysing the formation of the tripeptides. Also a host cell is provided capable of fermentatively producing β-lactam antibiotics with N-α-amino-hydroxyphenylacetyl or an N-α-aminophenylacetyl side chains.
Owner:DSM SINOCHEM PHARMA NETHERLANDS
Chaperone-assisted protein expression and methods of use
InactiveUS20110086388A1Increase success rateWide applicabilityDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsBiotechnologyBiosynthetic genes
The present disclosure provides methods of utilizing chaperone proteins for the production of active protein such as those encoded by the genes of natural biosynthetic clusters. The methods provided herein have applicability for a wide variety of genes ranging from small fatty acid biosynthetic genes to large non-ribosomal peptide synthetase genes.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Methods of detecting and measuring glutamine and analogues thereof, and methods related thereto
ActiveUS20180246116A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisGlutamine analogGlutethimide
Method for the detection of glutamine and its analogues are provided by the present disclosure. Also provided are methods for measuring the levels of glutamine and its analogues, including diagnostic methods. Further provided are methods that utilise glutamine analogues for the synthesis of coloured pigments and other useful agents. The methods comprise the use of a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) under conditions to produce an indigoidine or indigoidine-related pigment.
Owner:VICTORIA LINK LTD
Heterologous hosts
InactiveUS20130089522A1Minimise cell deathIncrease cell densityBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyHeterologous
This invention is related to bacterial engineering and the heterologous expression of useful compounds. In particular, the invention relates to a heterologous host that has been engineered for expression of a gene which is capable of polyketide or non-ribosomal peptide synthesis. Methods of treating cancer are also disclosed.
Owner:GENE BRIDGES GMBH
Novel Gene Cluster
Novel isolated DNA sequences which comprise all or part of a gene cluster encoding sanglifehrin synthase, processing and regulatory genes involved in the biosynthesis of a mixed non-ribosomal peptide / polyketide compound, or mutants having altered biosynthetic capability, polypeptides or mutants thereof encoded by DNA or the mutants, vectors containing the DNA or the mutants thereof, host cells transformed with the DNA, the mutants thereof, or the vector, and a method for producing sanglifehrin compounds. Compounds with cyclophilin inhibition activity used as immunosuppressants, antivirals or cardiac protection agents.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Biosynthetic Pathway for Heterologous Expression of a Nonribosomal Peptide Synthetase Drug and Analogs
The present invention is directed to the biosynthetic pathway for a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS) derived drug and analogs thereof. The invention also discloses polynucleotide sequences useful for heterologous expression in a convenient microbial host for the synthesis of the NRPS derived drug.
Owner:ALLEGHENY SINGER RES INST +2
Discovery of Cationic Nonribosomal Peptides as Gram-Negative Antibiotics Through Global Genome Mining
ActiveUS20190225663A1Facilitate genome-guided discoveryStrong antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsGramMedicine
Certain embodiments of the invention pertain to pharmaceutical compositions comprising a cationic nonribosomal peptide (CNRP) or a salt thereof. Certain other embodiments of the invention pertain to methods of treating a bacterial infection in a subject by administering to the subject a CNRP or a salt thereof.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Cyanobacterial hosts and methods for producing chemicals
The present invention relates to recombinant cyanobacterial cells for the production of a chemical compound of interest. In particular, the present invention relates to genetic modifications that introduce one or more heterologous phosphopantetheinyl transferases (PPTases) into a cyanobacterial cell. These cells can, optionally, further comprise heterologous carrier protein and nucleic acid constructs that provide the cyanobacterial cells with the capability of producing chemicals of interest or compounds of interest, such secondary metabolites polyketides, nonribosomal peptides and their hybrids, the three major families of bioactive natural products, of cyanobacteria and other bacterial phyla, secondary metabolites analogs, and unnatural compounds.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
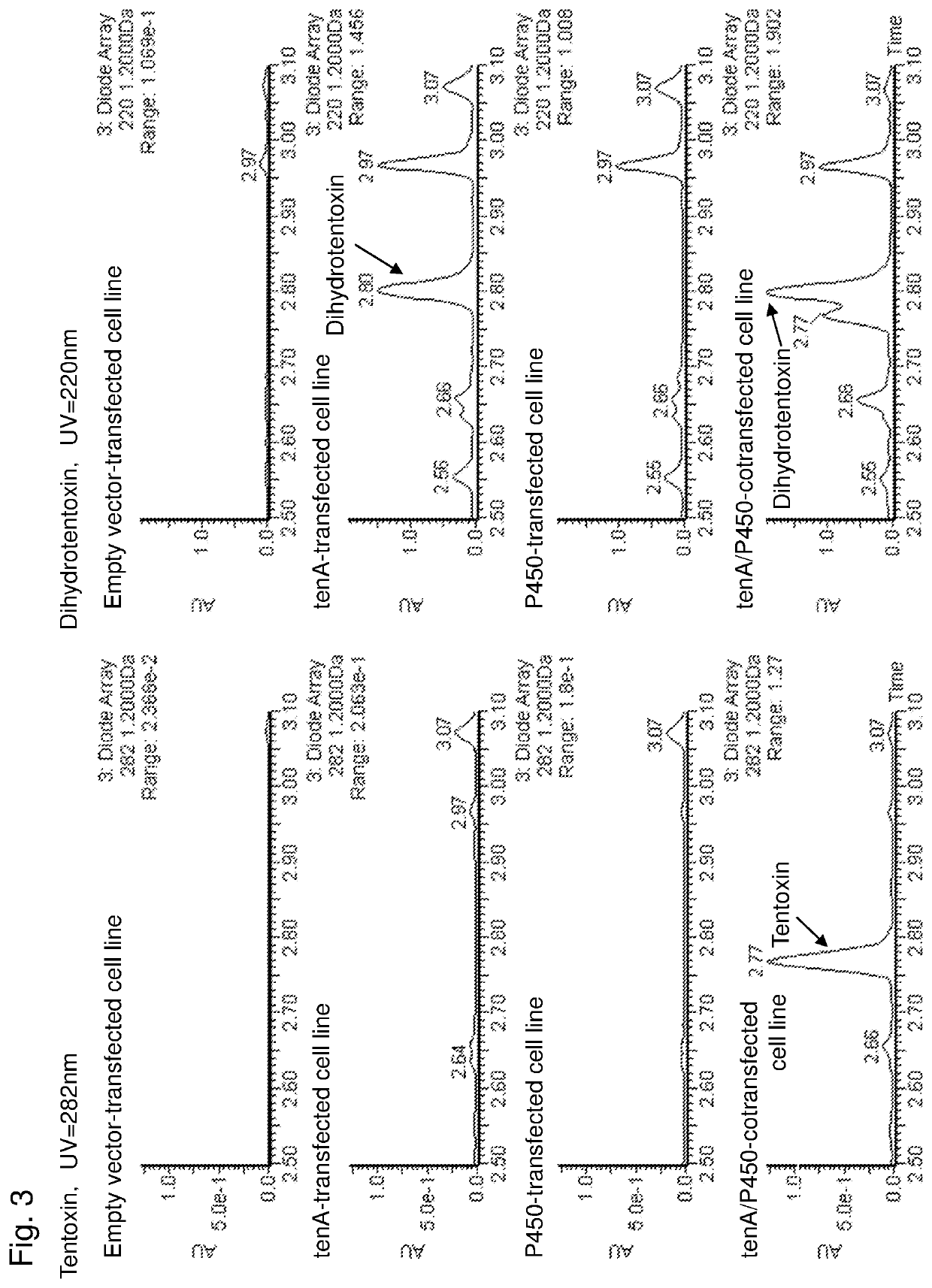
Tentoxin synthesis gene, a method for producing tentoxin or dihydrotentoxin using the same, and a transformant comprising the same
An object of the present invention is to identify an enzyme having activity of synthesizing dihydrotentoxin that is a tentoxin precursor and an enzyme having activity of synthesizing tentoxin using dihydrotentoxin as a substrate. The present invention concerns a tentoxin synthesis-related gene encoding a protein comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 16 and having activity of nonribosomal peptide synthesis of dihydrotentoxin and a tentoxin synthesis-related gene encoding a protein comprising the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 18 and having activity of converting dihydrotentoxin to tentoxin.
Owner:KUMIAI CHEM IND CO LTD
Construction method and use of Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria
ActiveCN102146414BIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRibosomal protein E-L30
The invention provides a construction method and use of Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria. The construction method comprises: cloning upstream and downstream accessory key genes dptE, dptF, dptG, dptH, dptI and dptJ of a nonribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPS) gene in a daptomycin gene cluster; and constructing recombinant plasmids by using an Escherichia coli-Streptomyces shuttle expression vector. The recombinant plasmids are transferred into Escherichia coli ET12567 to culture the ET12567 and the Streptomyces roseosporus together, the Streptomyces roseosporus is transformed by a combined transfer method, a transformant is screened by brulamycin resistance and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is performed for further confirmation. The Streptomyces roseosporus gene engineering bacteria constructed by the invention can be directly used in the industrial production of daptomycin and can improve yield and reduce cost.
Owner:NANTONG YIKAI MEDICAL DEVICES CO LTD
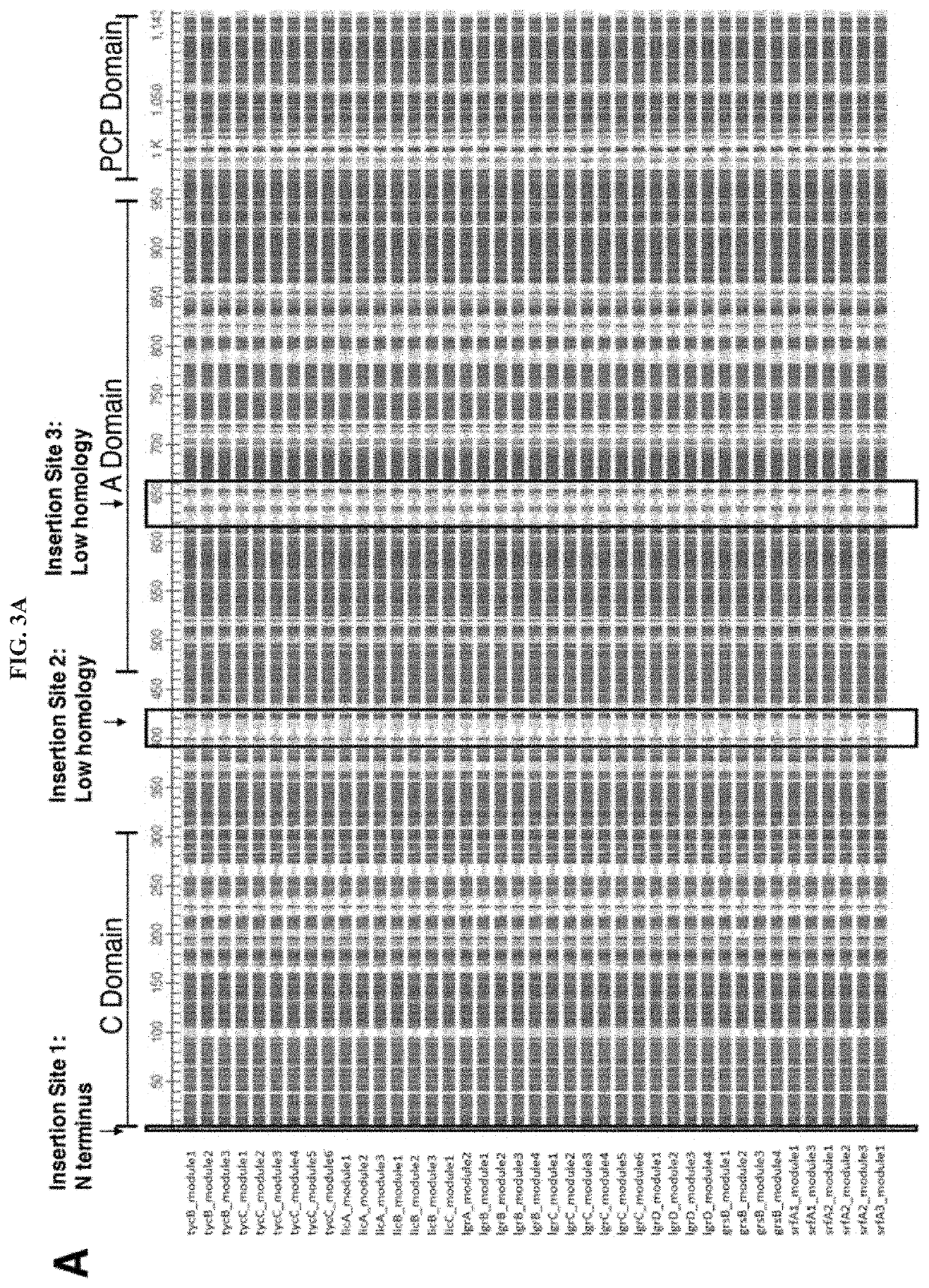
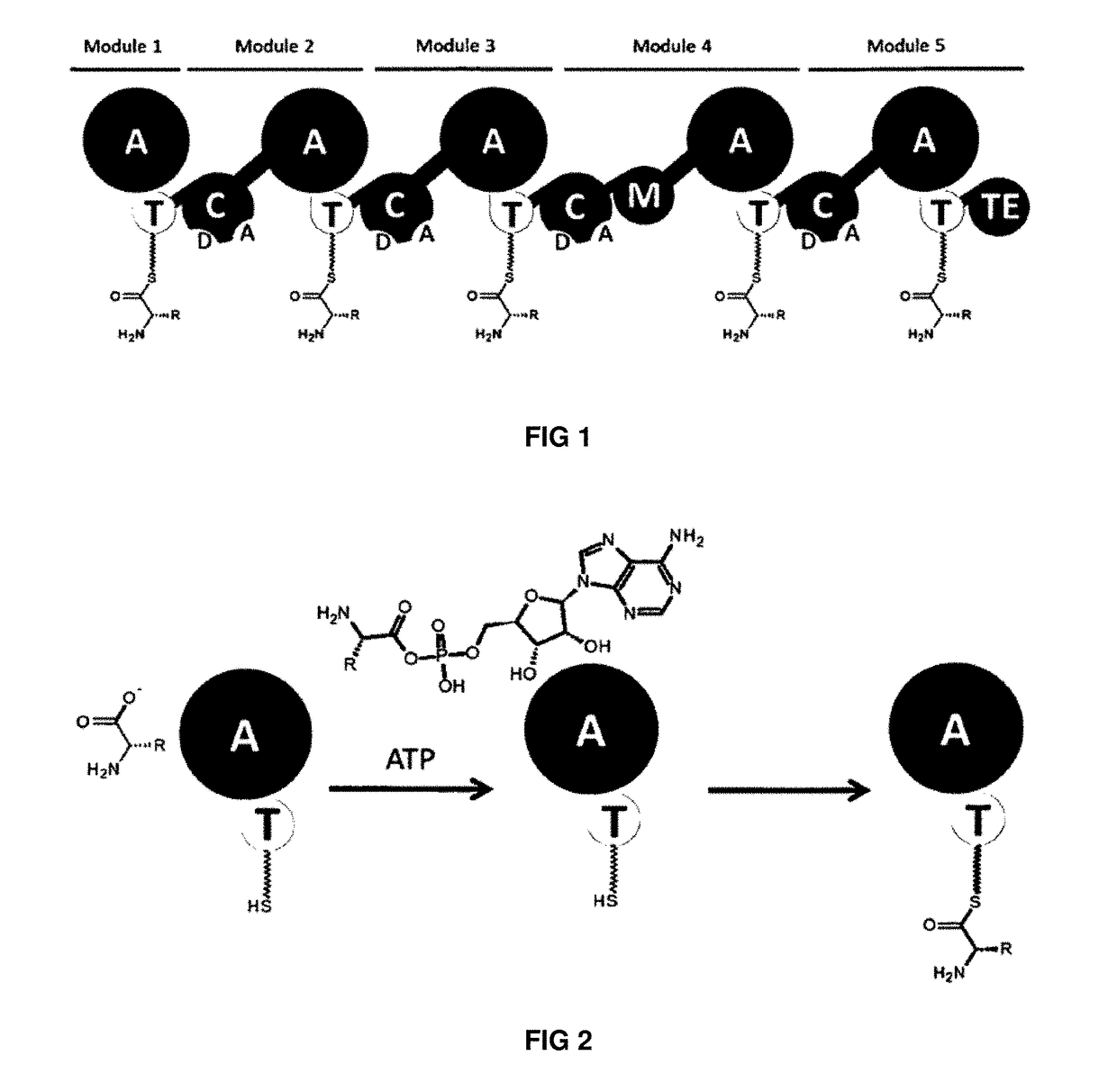
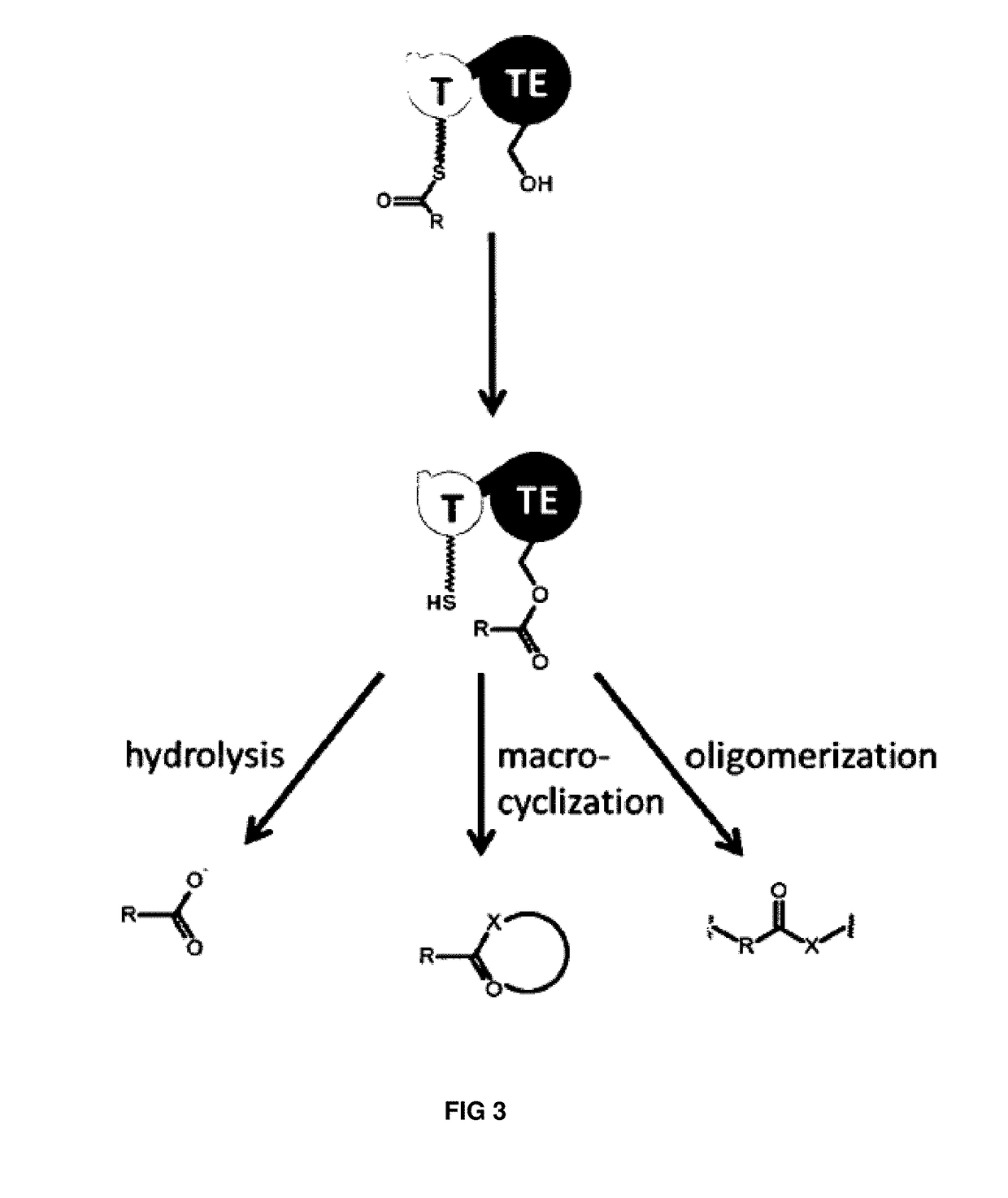
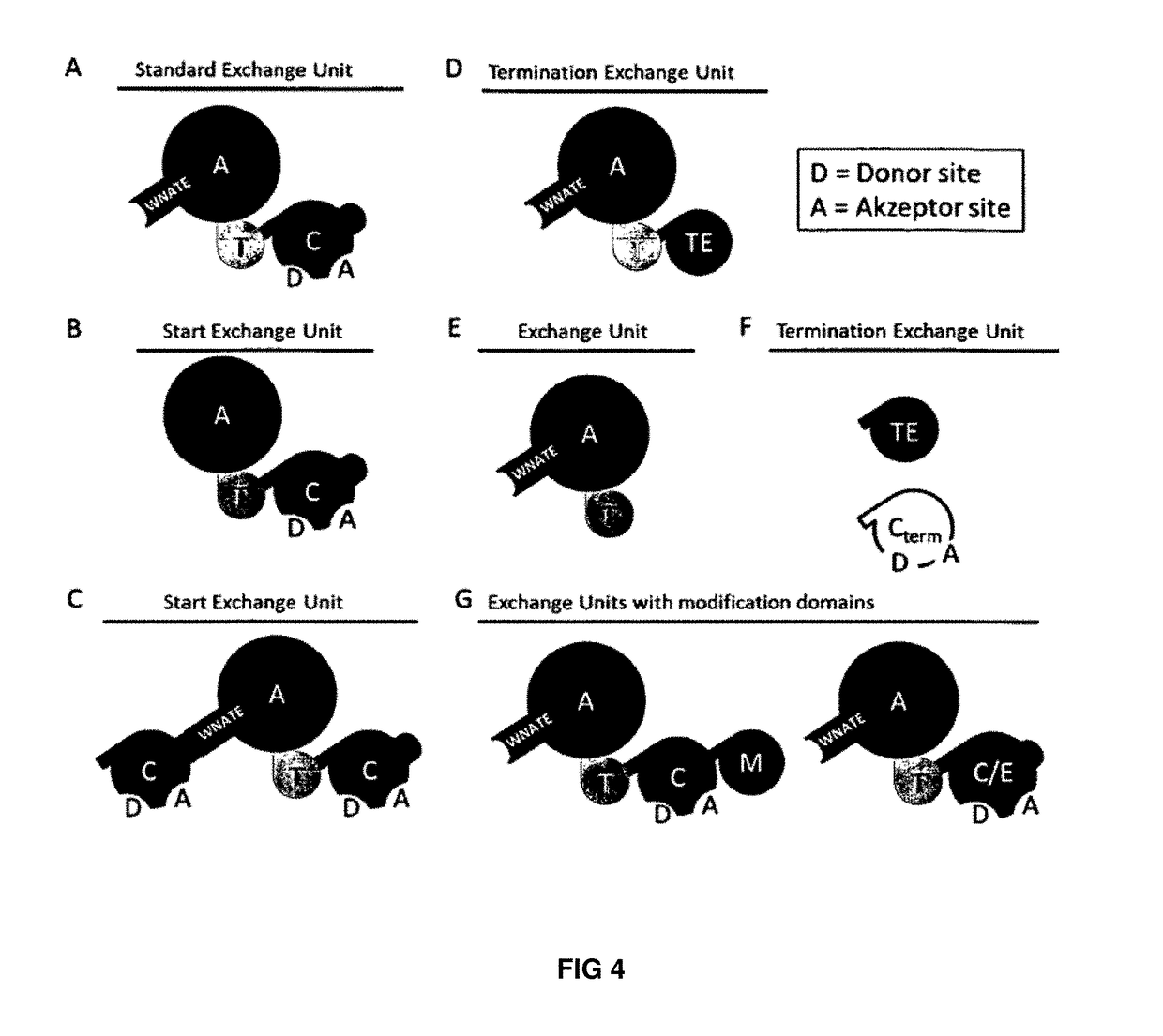
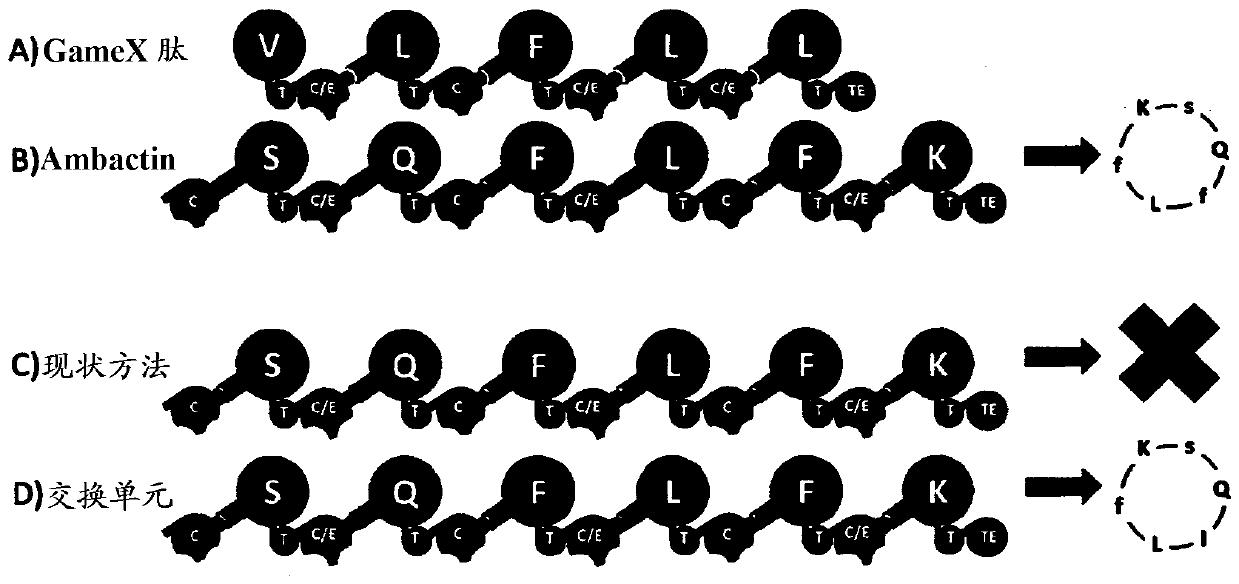
Artificial non-ribosomal peptide synthetases
The present invention concerns a novel method for the modification and / or custom-made design of artificial non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) from naturally available NRPSs. The artificial NRPSs are of predetermined length and amino acid composition and sequence. Via fusion of well-defined NRPS units (so-called “exchange units”) in a certain manner, using a specific sequence motif in the linker areas it is possible to construct artificial and / or modified NRPS assembly lines, which have the ability of synthesizing peptides of a desired structure.
Owner:JOHANN WOLFGANG GOETHE UNIV FRANKFURT AM MAIN
Host yeast cells and methods useful for producing indigoidine
PendingUS20220112531A1High titer productionHigh productMicroorganism based processesLigasesYeastIndigoidine
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Artificial non-ribosomal peptide synthetases
The present invention concerns a novel method for the modification and / or custom-made design of artificial non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) from naturally available NRPSs. The artificial NRPSs are of predetermined length and amino acid composition and sequence. Via fusion of well-defined NRPS units (so-called "exchange units") in a certain manner, using a specific sequence motif in the linker areas it is possible to construct artificial and / or modified NRPS assembly lines, which have the ability of synthesizing peptides of a desired structure.
Owner:JOHANN WOLFGANG GOETHE UNIV FRANKFURT AM MAIN
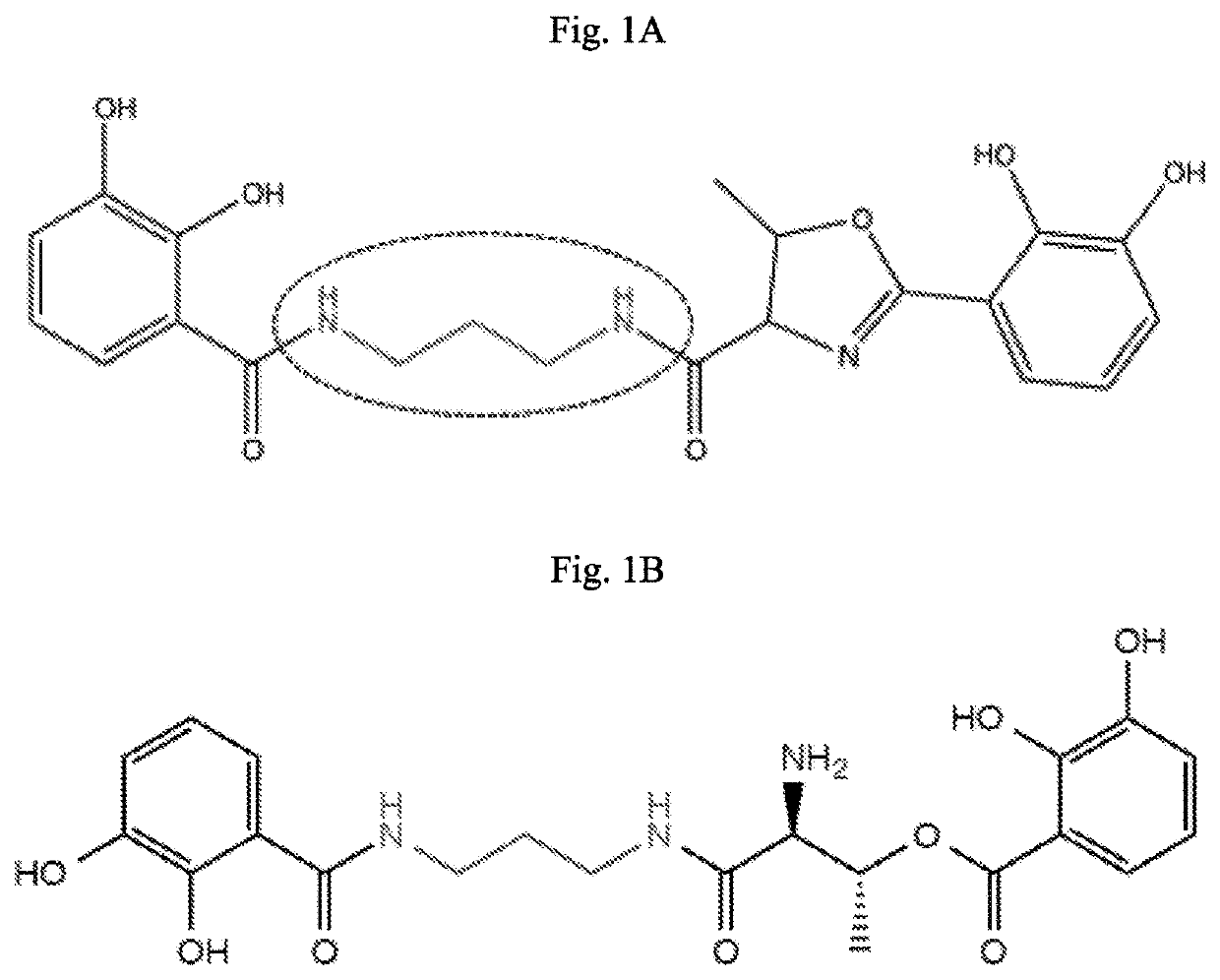
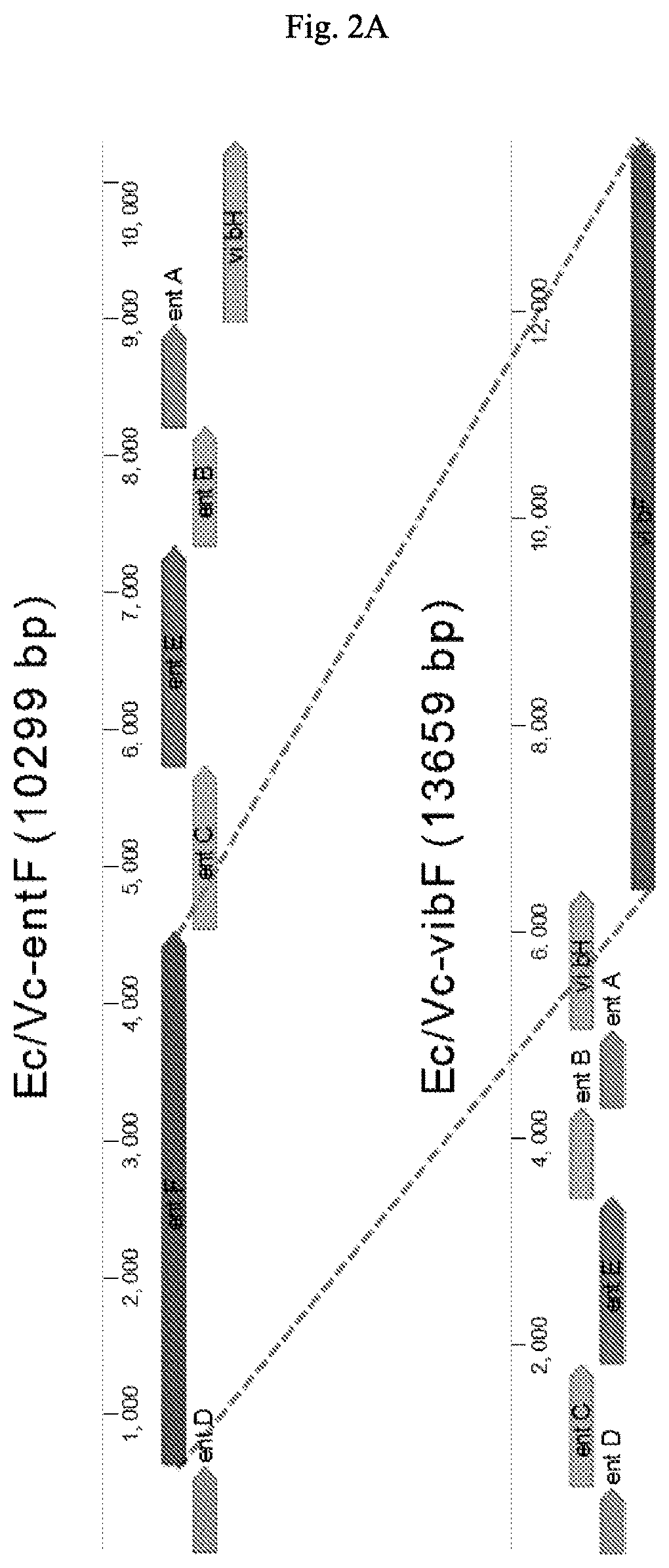
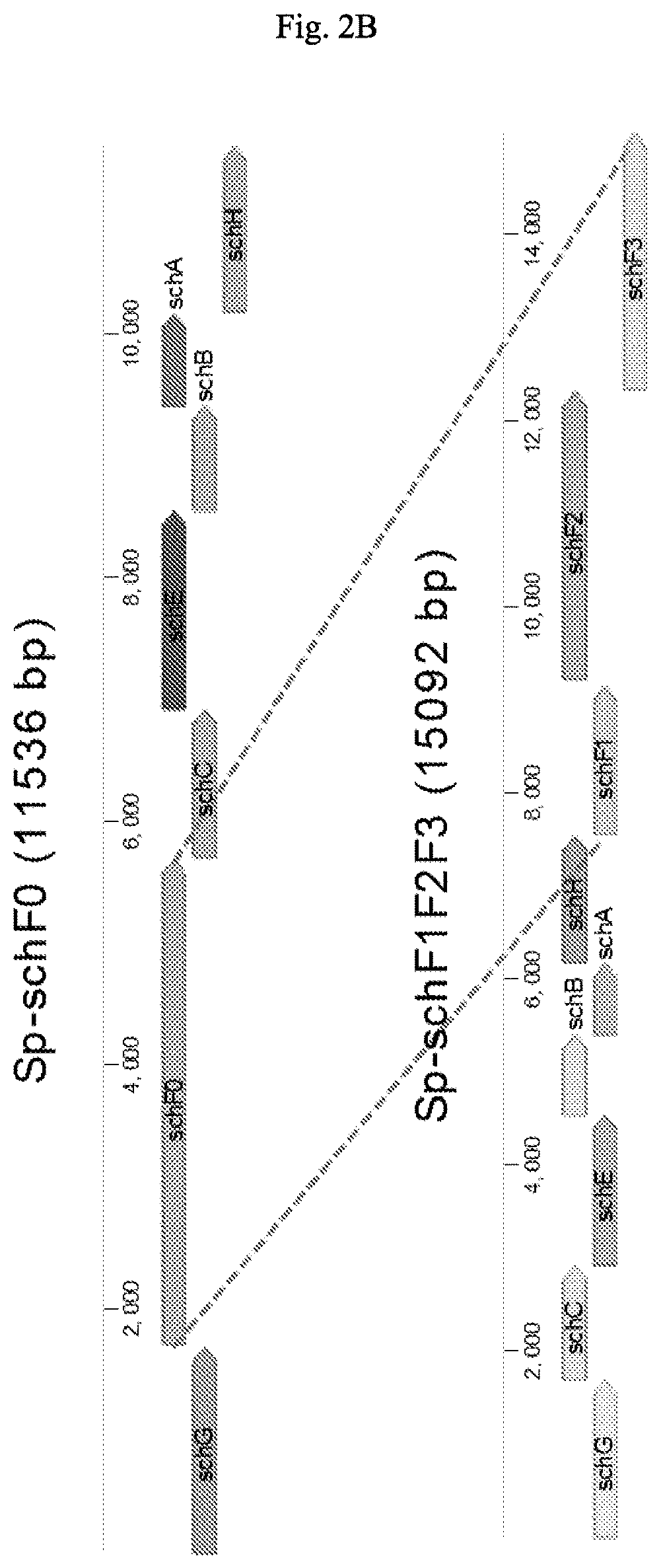
Compressed pathways for nonribosomal molecular biosynthesis
Provided herein are synthetic pathways from Escherichia coli and Vibrio cholerae genes for the production of new, synthetic nonribosomal peptides, and methods and compositions comprising the same. Some aspects of the present disclosure are directed to modified bacterial cells comprising a compressed biosynthetic pathway that comprises (a) biosynthetic genes obtained from one species encoding enzymes active in the bioassembly of a nonribosomal molecule, (b) biosynthetic genes obtained from another species encoding enzymes active in the bioassembly of a nonribosomal molecule that is different from the nonribosomal molecule of (a). In some embodiments, the biosynthetic genes of (a) are Escherichia coli biosynthetic genes and may include entD gene, an entC gene, an entE gene, an entB gene and an entA gene. In some embodiments, the biosynthetic genes of (b) are Vibrio cholera biosynthetic genes and may include a vibH gene and a vibF gene.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com