Method for producing isomaltulose by transforming sucrose by biological enzymatic method
A technology of isomaltulose and bio-enzyme method is applied in the field of bio-enzymatic conversion of sucrose to produce isomaltulose, which can solve the problems of low bacterial cell concentration, large tolerance, insufficient contact between materials and bacterial cells, etc., and achieve High reaction conditions, good product quality, and not easy to infect bacteria
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1 prepares the technological process of isomaltulose:
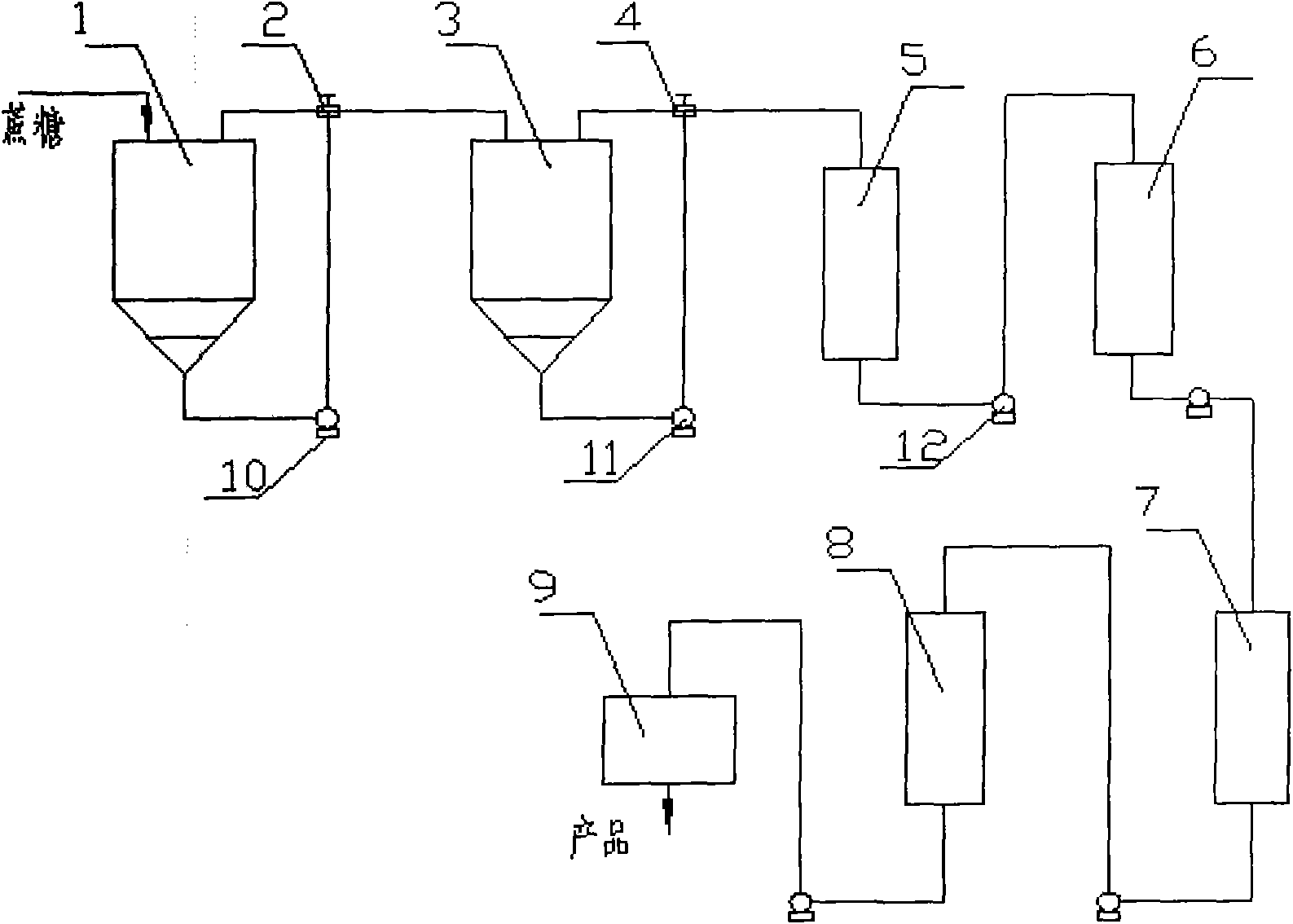
[0029] (1) Circulating the sucrose solution through a transformation tank equipped with immobilized cells with α-glucosyltransferase for transformation, the reaction temperature is 26-32°C, and the reaction produces isomaltulose and other miscellaneous sugars containing more than 85% (such as sucrose, glucose, fructose, etc.) conversion solution;
[0030] (2) Circulate the obtained transformation liquid into the reaction tank for removing miscellaneous sugars equipped with immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and transform by aeration under the condition of 28-32°C for 24-36 hours, until no bubbles are generated to show miscellaneous sugars has been consumed, and the conversion solution of removing miscellaneous sugars is obtained;
[0031] (3) The conversion solution after removing impurities is subjected to ion exchange to remove impurities to obtain a clear liquid containing isomaltulose, and the cl...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment two prepares the technological process of immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae:
[0034] Immobilized Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) cultivation can adopt the following specific preparation process: a. medium (mass%): 1-3% yeast extract, 2-6% sucrose, 0.05~0.1% defoamer (peanut oil or poly Silicone oil), pH4~7, sterilized at 120~125℃, sterilized for 25~30min. Cool to 32.5-35.5°C, inoculate yeast strains according to the inoculum amount of 2-10%, and cultivate them with an aeration rate of 0.3-10% (air volume per minute: fermentation volume) and a stirring speed of 100-200rpm 48±12h, put in the tank; b. Centrifuge the fermented liquid through a tube centrifuge at 16,000rpm to collect the wet yeast; c. Dissolve the wet yeast with sterile water, filter, and add 7-12% pre-dissolved sodium alginate solution , and make the concentration of wet yeast in the solution 10-20%, mix well; d. put the above yeast emulsion and sodium alginate mixture in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com