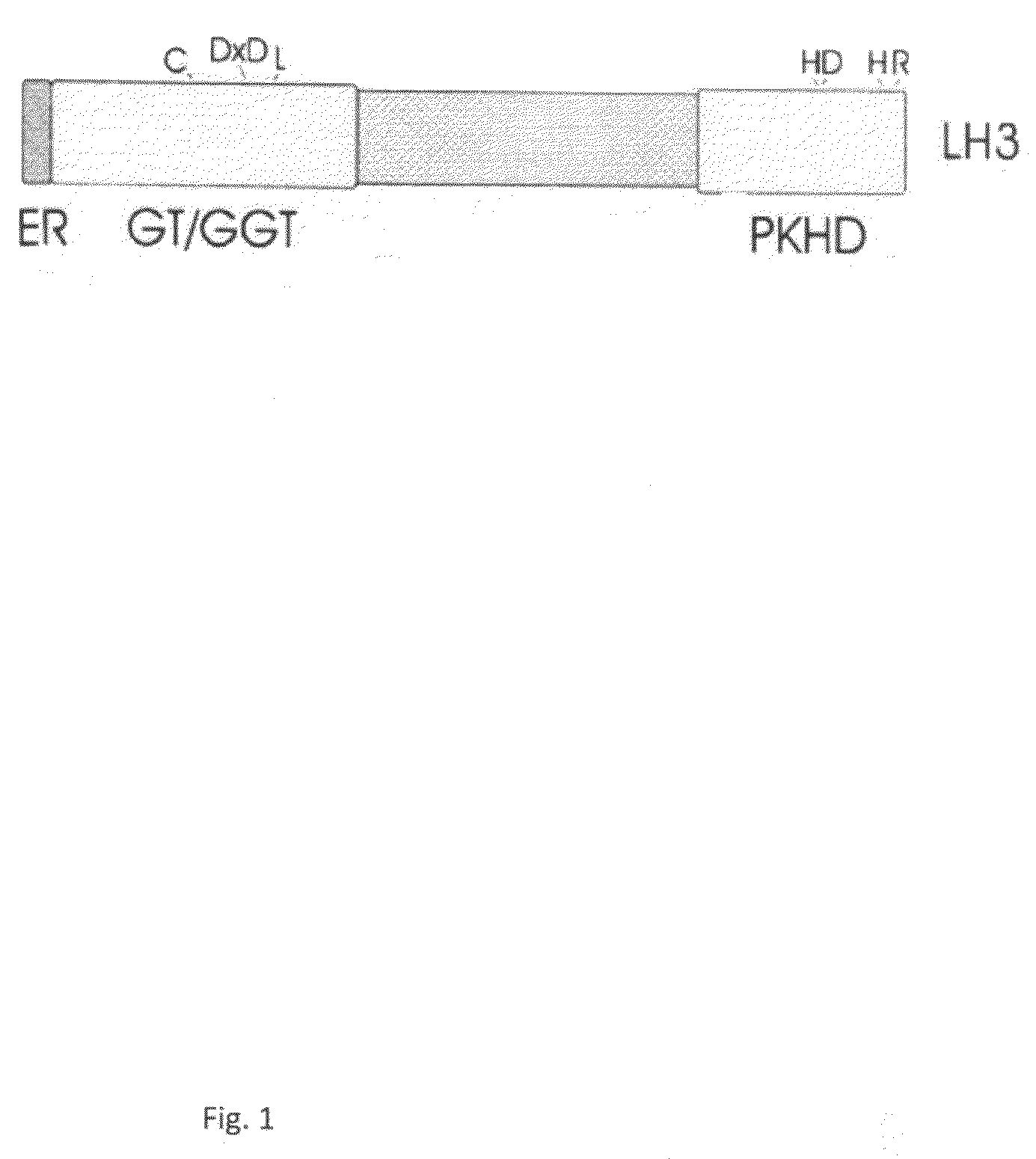Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
53 results about "Glycosyltransferase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glycosylated protein expression in prokaryotes
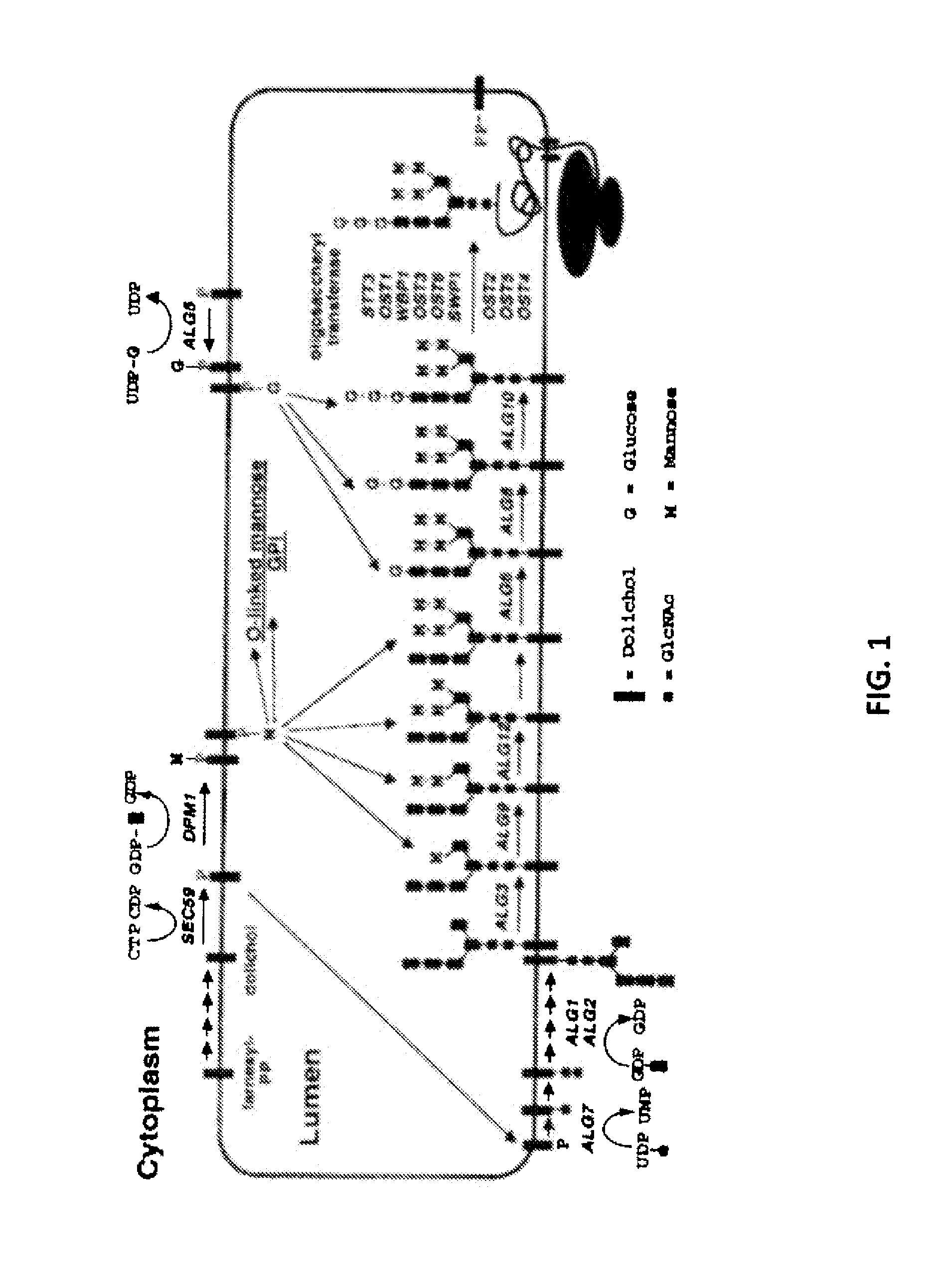
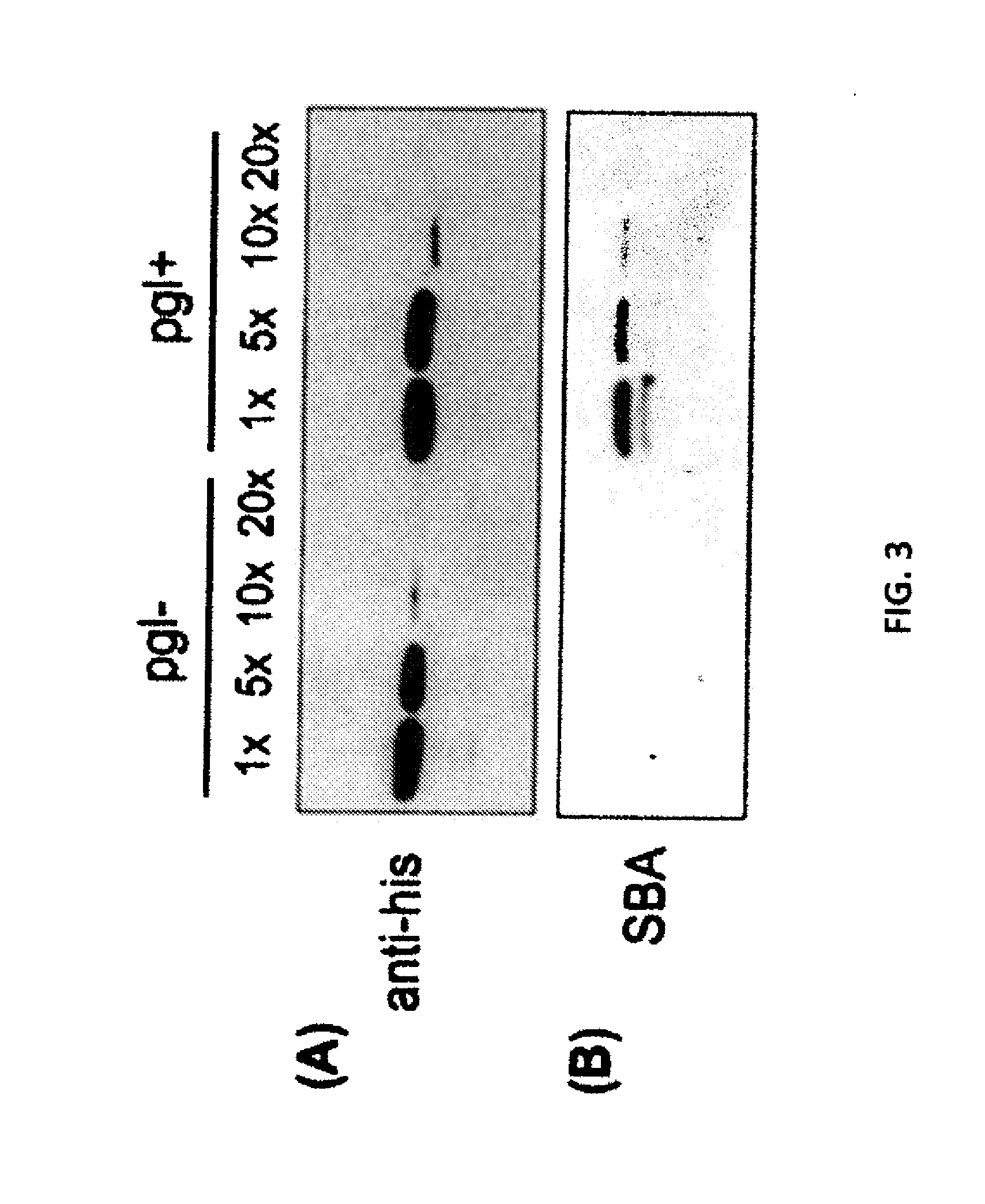
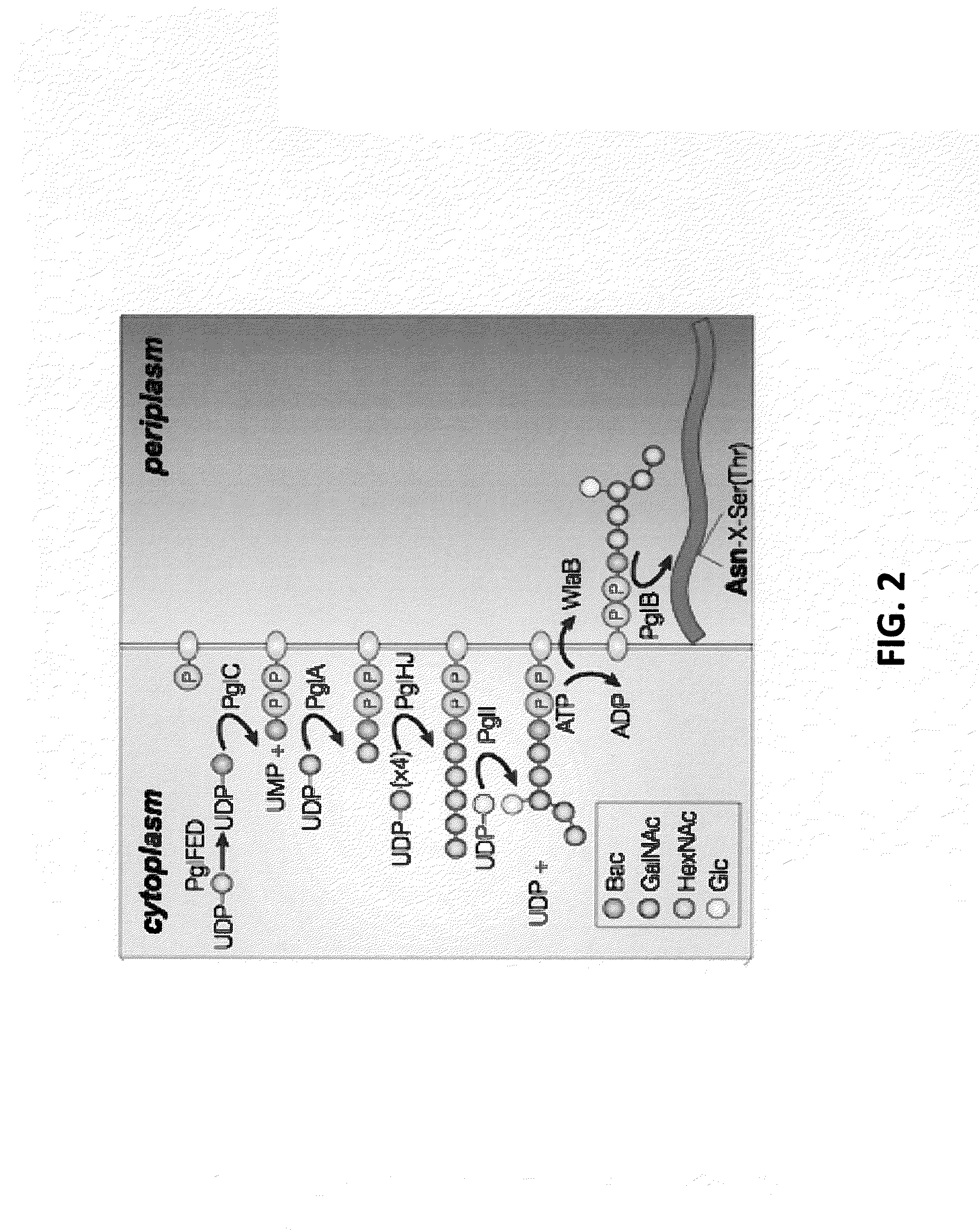
The present invention relates to a prokaryotic host cell comprising eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity, where the eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity is eukaryotic dolichyl-linked UDP-GlcNAc transferase activity and eukaryotic mannosyl-transferase activity. Also disclosed is a method of producing a glycosylated protein by providing a prokaryotic host cell comprising the eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity and culturing the prokaryotic host cell under conditions effective to produce a glycosylated protein. Another aspect of the present invention pertains to a method for screening bacteria or bacteriophages by expressing one or more glycans on the surface of a bacteria, attaching a label on the one or more glycans on the surface of the bacteria or on the surface of a bacteriophage derived from the bacteria, and analyzing the label in a high-throughput format. A glycosylated antibody comprising an Fv portion which recognizes and binds to a native antigen and an Fc portion which is glycosylated at a conserved asparagine residue is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Glycosyltransferase gene
The present invention provides an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer sugar to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of chalcones and a gene thereof, and preferably an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer glucose to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of the chalcones. Furthermore, the invention provides a plant whose flower color has been changed using the glycosyltransferase. Using probes corresponding to conservative regions of the glycosyltransferase, some tens of glycosyltransferase genes having nucleotide sequences corresponding to the conservative regions were cloned from flower petal cDNA libraries of carnation and the like. Furthermore, each of the glycosyltransferase genes was expressed in Escherichia coli, activity to transfer glucose to position 2′ of the chalcone, i.e., the glycosyltransferase activity at position 2′ of chalcone was confirmed in an extract solution of the Escherichia coli, and it was confirmed that cloned genes encoded the glycosyltransferase at position 2′.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
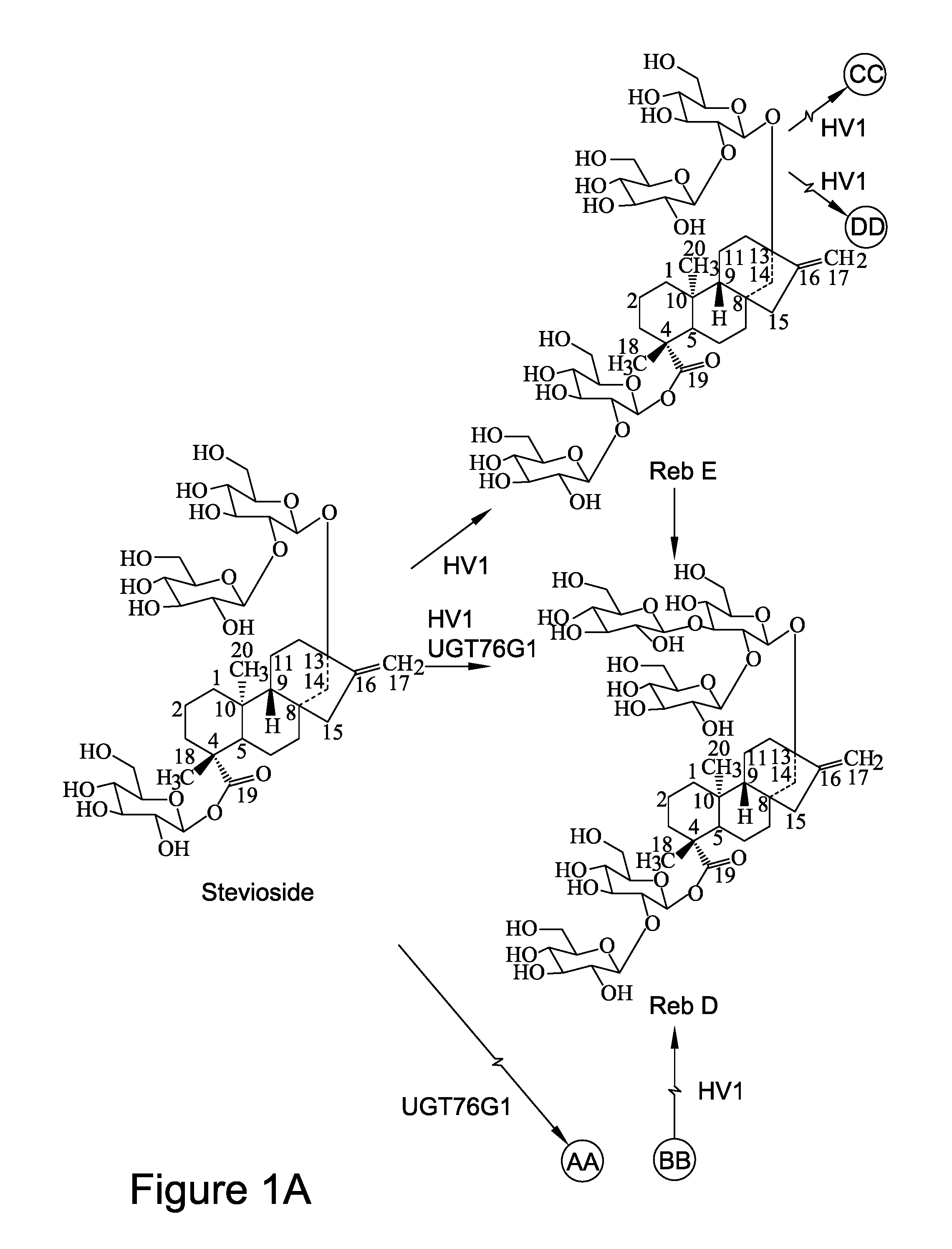
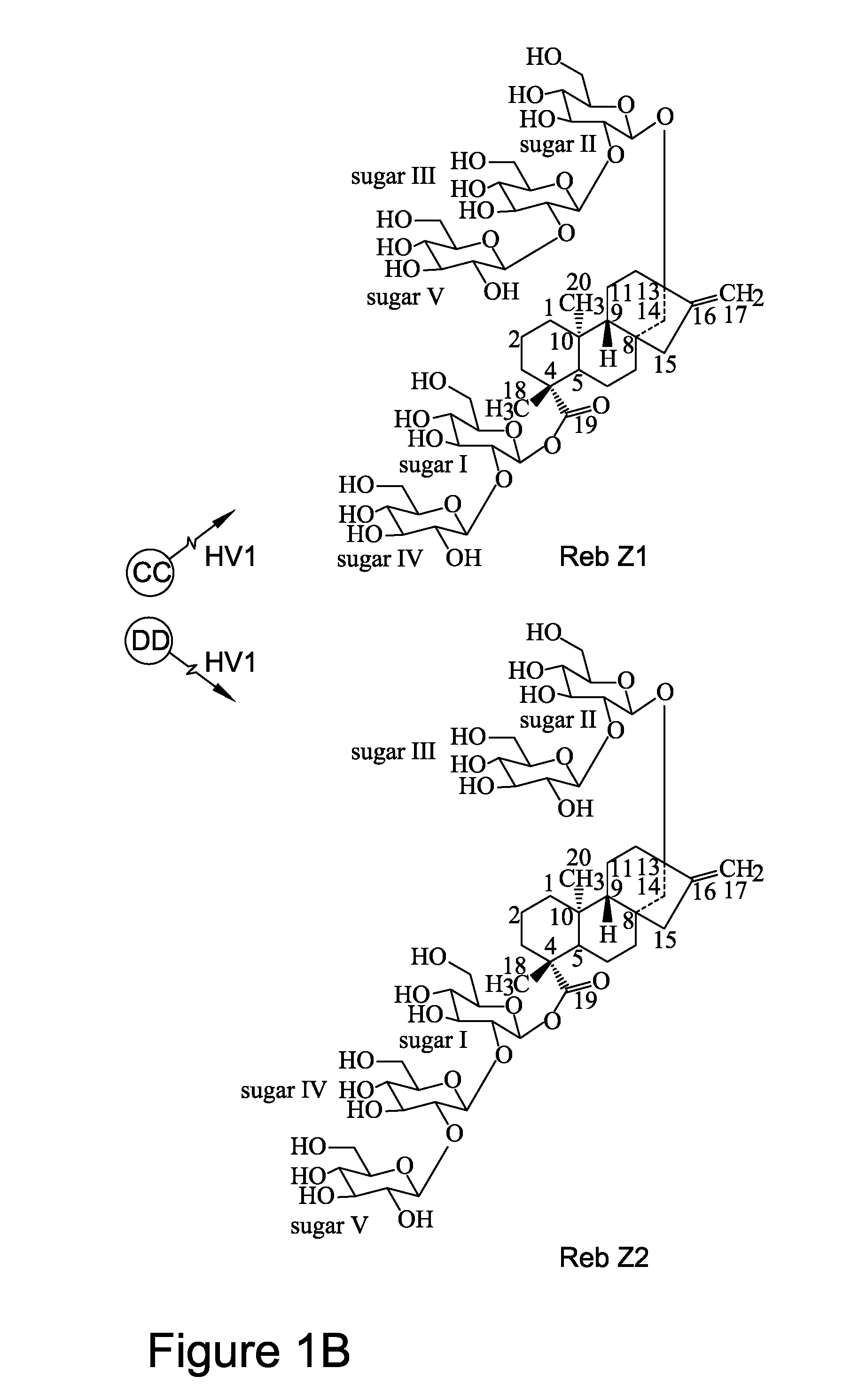
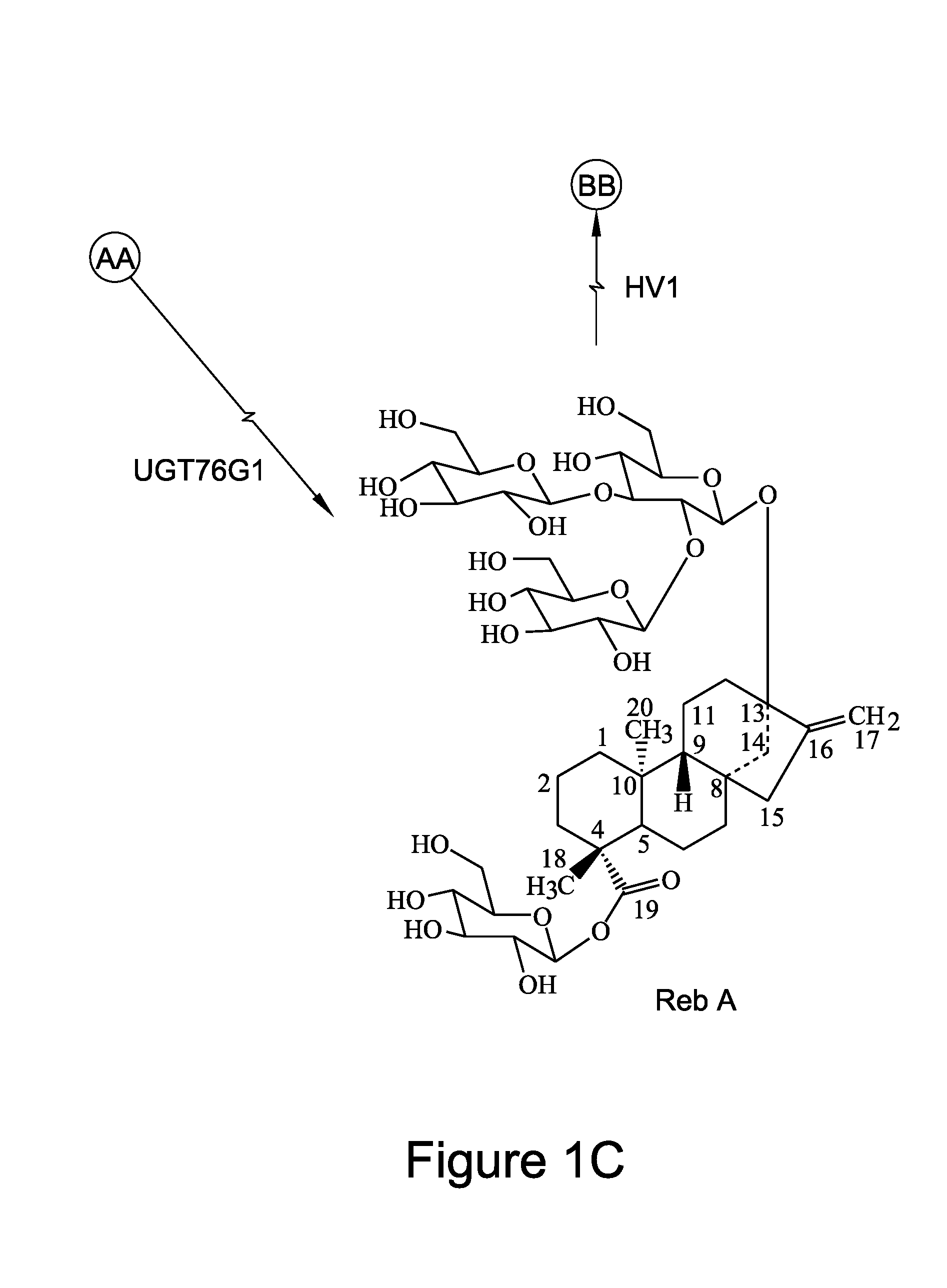
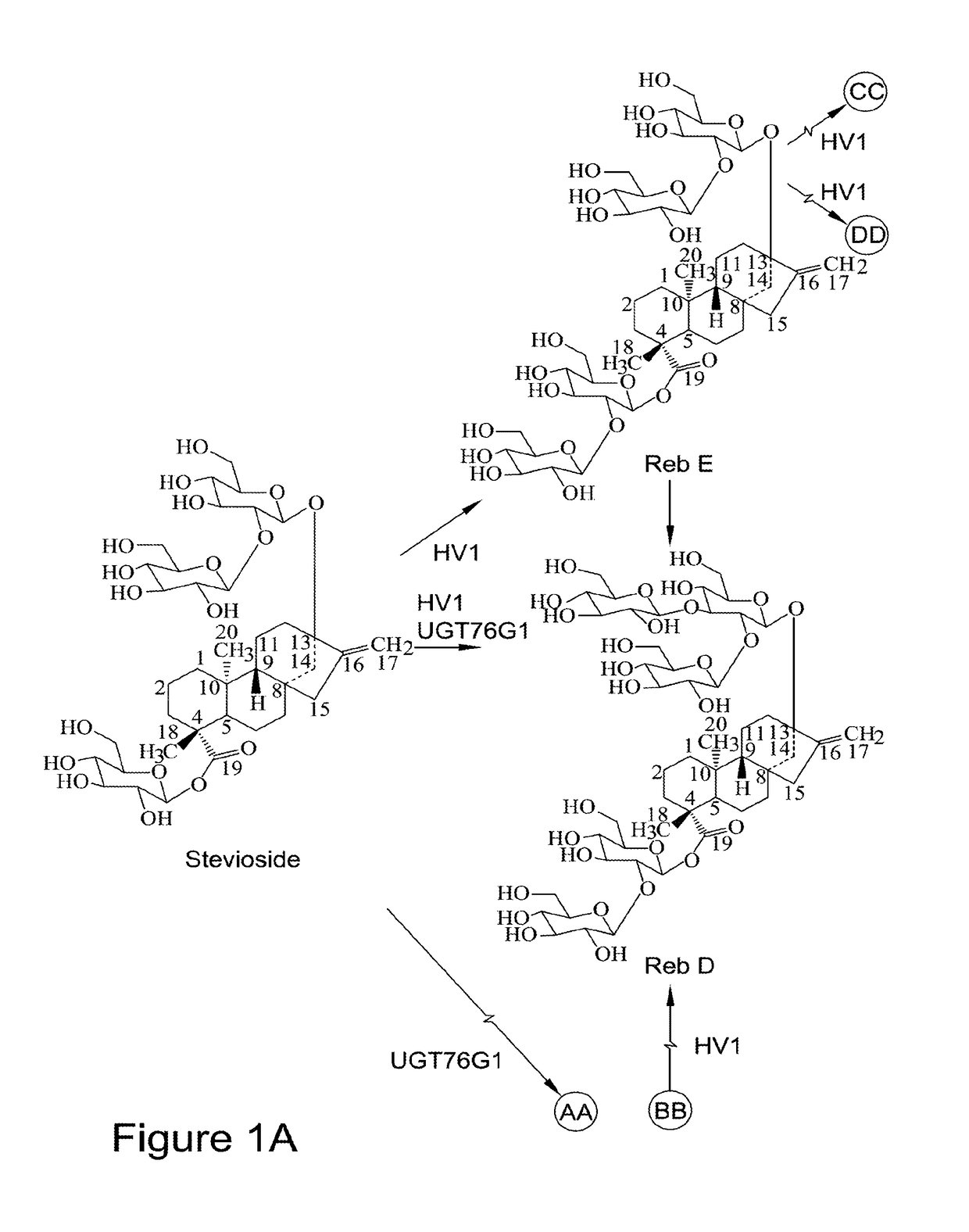
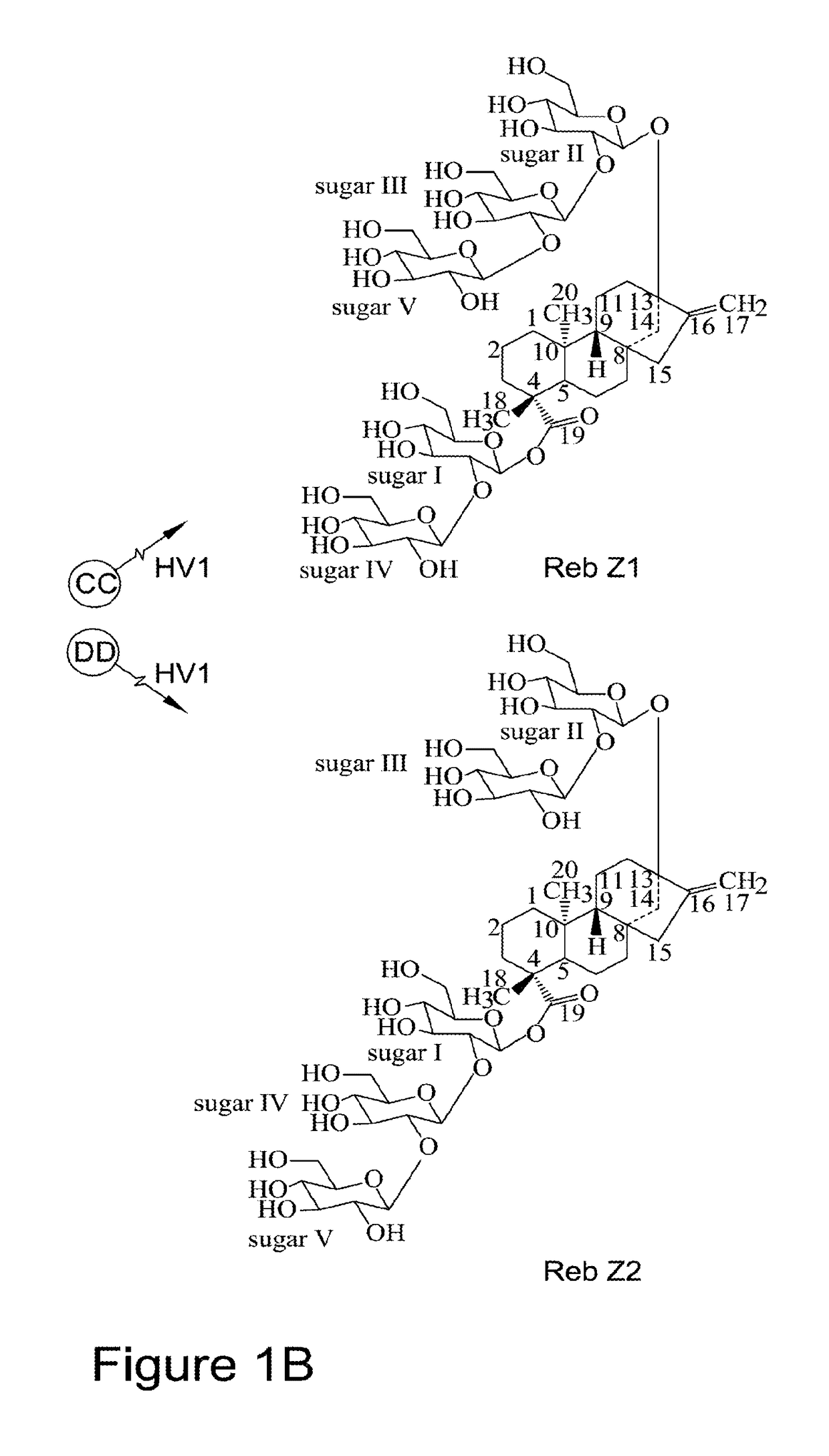
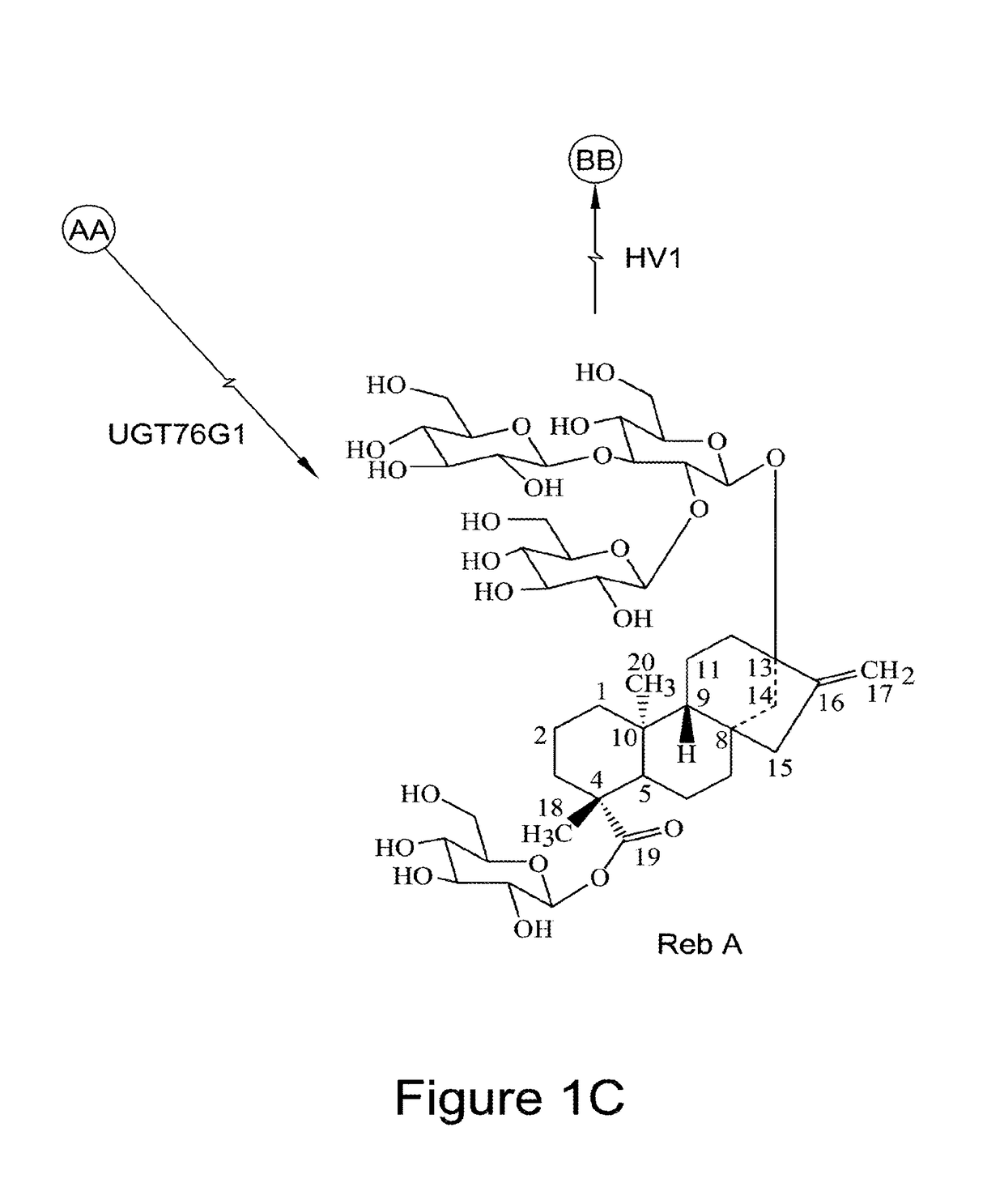
Recombinant production of steviol glycosides
InactiveUS20160251635A1Sugar derivativesConfectioneryGlycosyltransferase activityUdp glycosyltransferase
Recombinant polypeptides having UDP-glycosyltransferase activities, including a 1,2-19-O-glucose glycosylation activity and a 1,2-13-O-glucose glycosylation activity for synthesizing of steviol glucosides, are provided. A method of producing a steviol glycoside composition using such recombinant polypeptide is also provided. Also disclosed are steviol glycosides referred to as rebaudioside Z1 and rebaudioside Z2.
Owner:CONAGEN INC
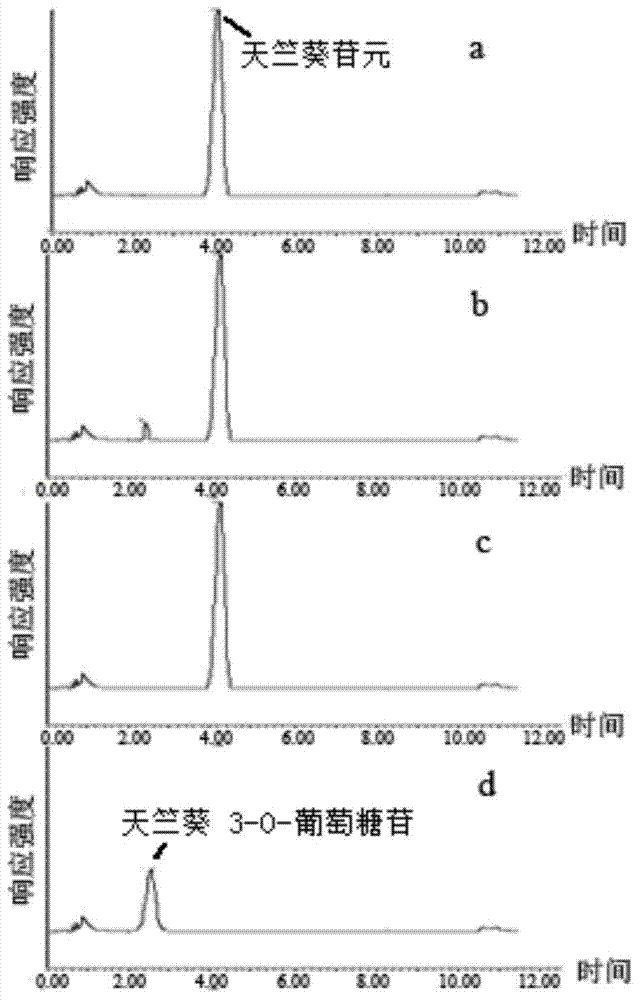
Tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT protein and coding gene thereof
InactiveCN103695382AImprove viewing valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGlycosyltransferase activityTransgene
The invention discloses a tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT protein and a coding gene thereof. The protein is a protein composed of amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2, or a protein with tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase activity obtained by substitution, deletion or addition of one or more amino acids on the basis of the amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO.1 for coding the protein. When the tulip flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase Tf3GT gene is expressed in Escherichia coli cells, the recombinant flavonoid 3-O-glucosyltransferase protein can promote anthocyanin and UDP-glucose to react and generate the anthocyanin. The Tf3GT coding sequence has application value in modification of varieties by a transgenic technique.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for improving AA-2G conversion rate
ActiveCN104531629AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationGlycosyltransferase activityArginine
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for improving AA-2G conversion rate and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant, the 228th lysine near the active center of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase of thermophilic fat bacillus (Bacillus stearotherm opilus NO2) is mutated into arginine to obtain a mutant K228R, the 367th aspartic acid is mutated into serine to obtain a mutant D367S and amphimutation is carried out on the basis to obtain a mutant D367S / K228R. The mutant can be used for realizing the improvement of the AA-2G conversion rate and has relatively high industrial value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
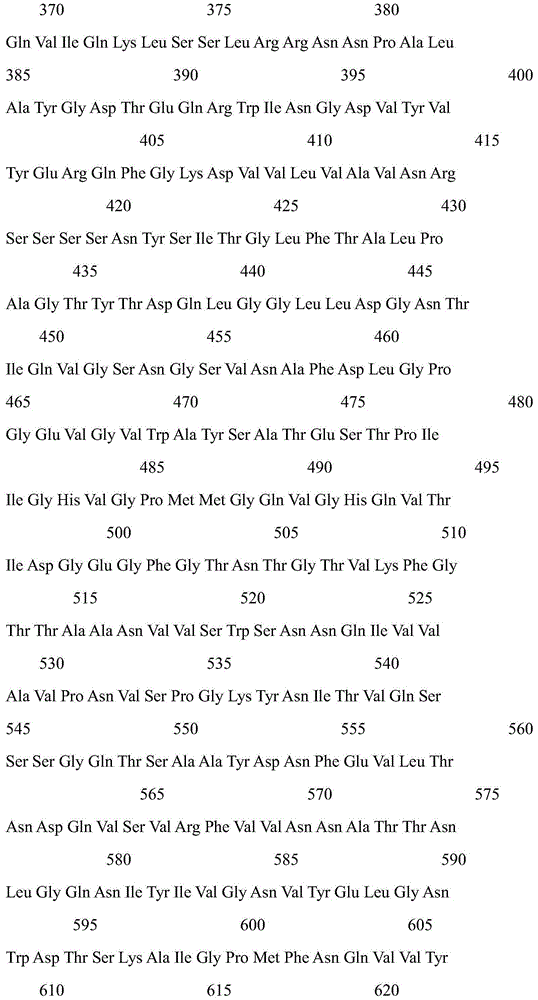
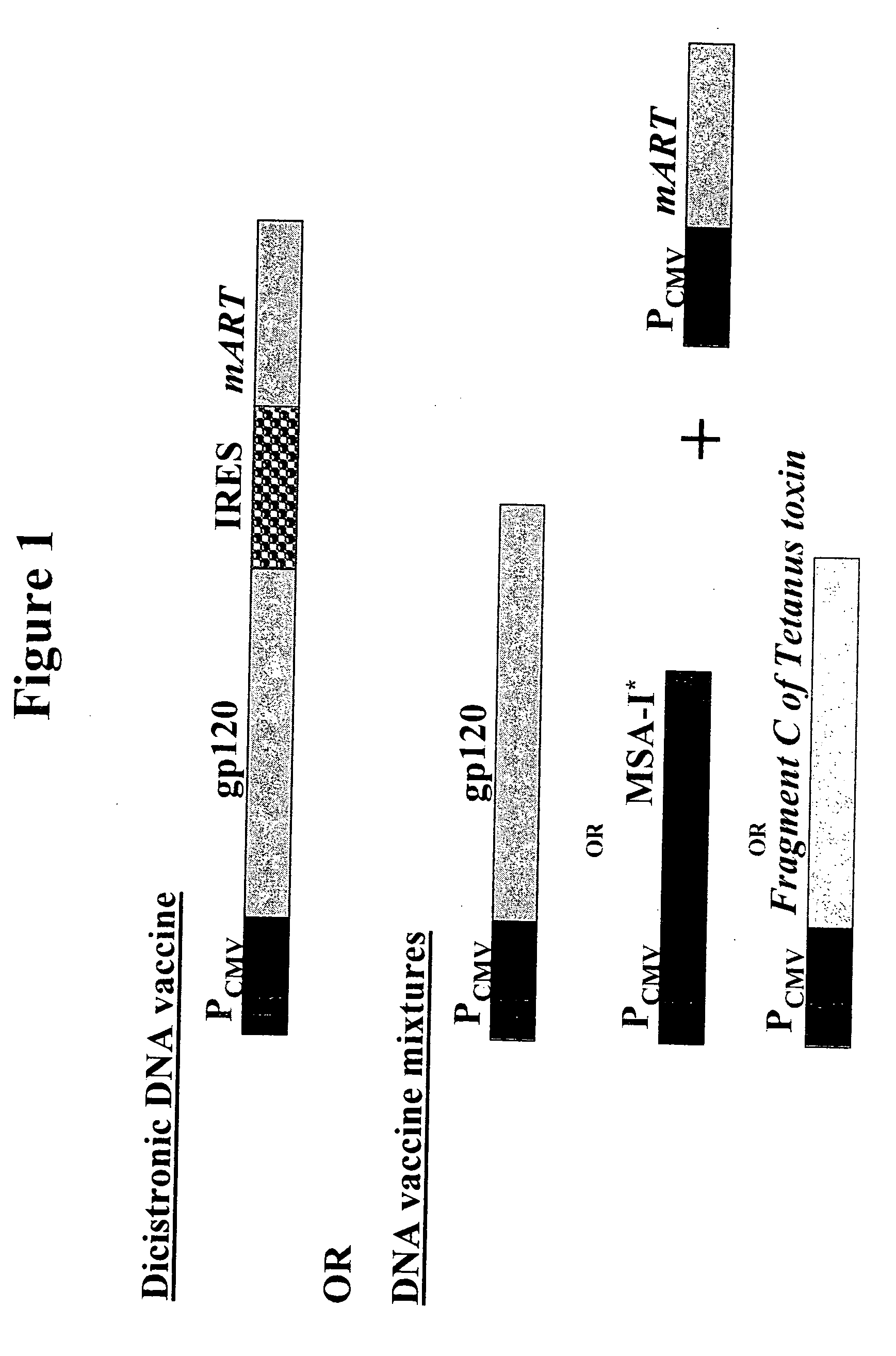
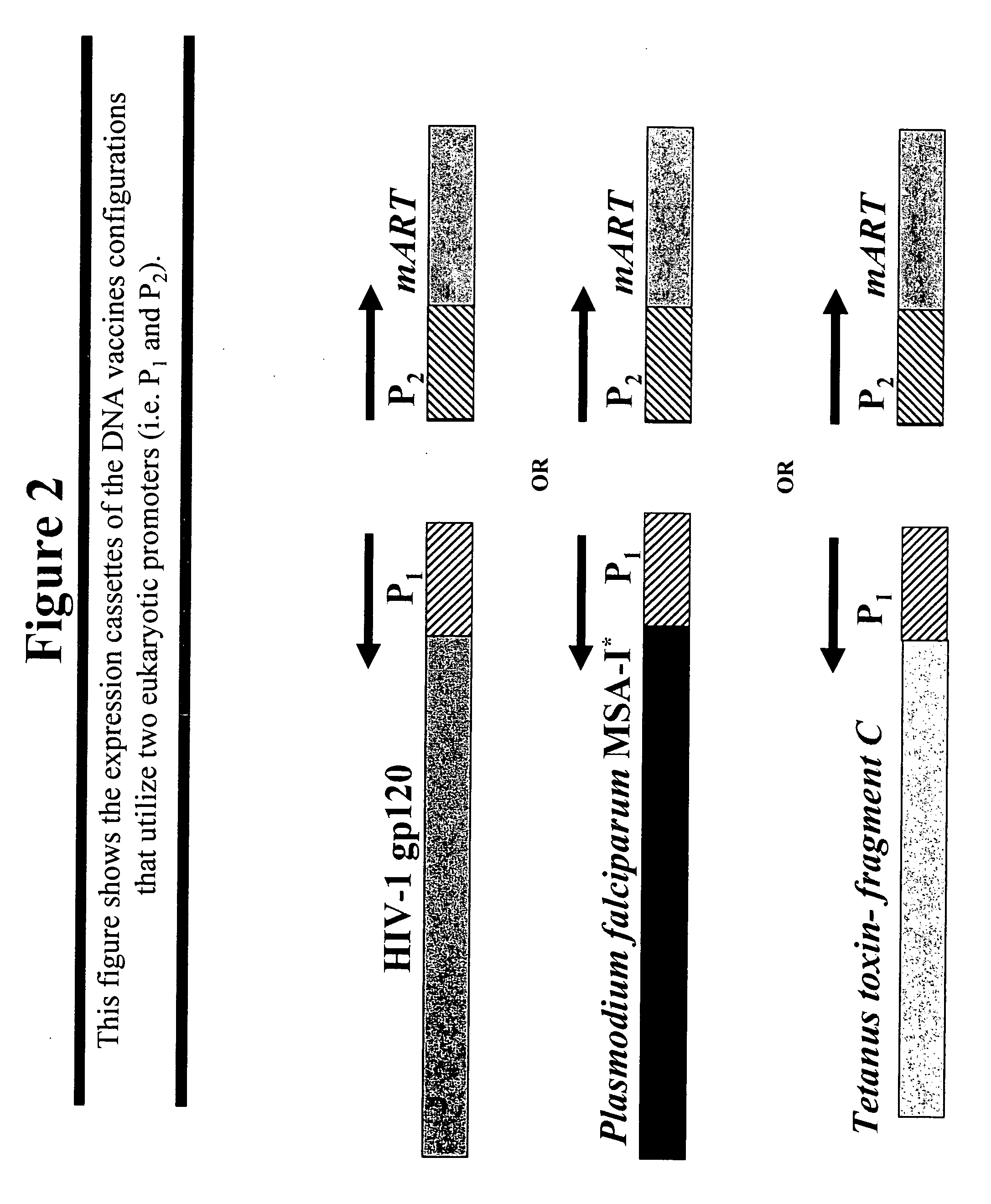
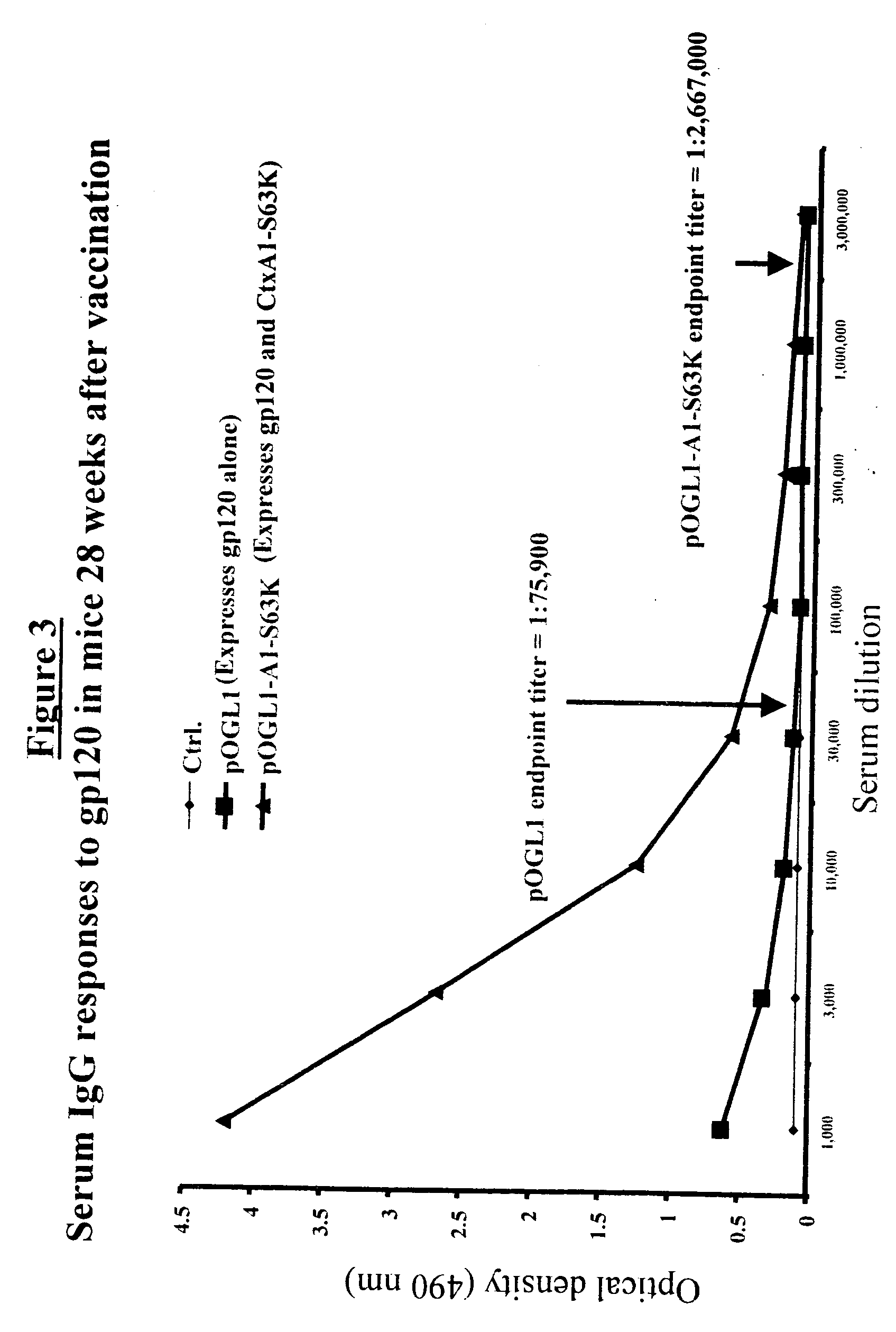
DNA vaccines that expresses mutant ADP-ribosyItransferase toxins which display reduced, or are devoid of, ADP-ribosyltransferase activity
InactiveUS20060069052A1Lack of activityDevoid of ADP-ribosyltransferaseGenetic material ingredientsWhole-cell/virus/DNA/RNA ingredientsGlycosyltransferase activityADP-ribosyltransferase activity
The present invention provides DNA vaccines that direct the coincident expression of vaccine antigens coincidently with mutant ADP-ribosyltransferase toxins (mARTs), which display reduced, or are devoid of, ADP-ribosyltransferase activity, and methods for vaccinating animals with the same. In particular, the present invention provides DNA vaccines that direct the coincident expression of vaccine antigens and mARTs that are useful for vaccinating against viral, bacterial, parasitic pathogens, autoimmune antigens and transplantation antigens.
Owner:AERAS GLOBAL TB VACCINE FOUND
Preparation method of protein UGTCs4
The invention discloses a preparation method of protein UGTCs4. The protein UGTCs4 has the croctin acid glycosyl transferase activity. The preparation method comprises the following step of culturing engineering bacteria, so as to obtain the protein UGTCs4, wherein the engineering bacteria is a recombinant bacteria which is obtained by importing a recombinant expression carrier into host bacteria, and the recombinant expression carrier is a recombinant plasmid which is obtained by inserting the expression carrier into an encoding gene of the protein UGTCs4. After proofing by experiments, the preparation method of the protein UGTCs4 has the advantages that the croctin acid can be sequentially glycosylated to form crocin 5 and crocin 3; the important application value is realized for the production of crocin 5 and / or crocin 3, preparation of products with croctin acid glycosyl transferase functions, or catalyzing on glycosylation of croctin acids.
Owner:ECONOMIC CROPS RES INST XINJIANG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Novel glycosyltransferase gene
The present invention provides an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer sugar to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of chalcones and a gene thereof, and preferably an enzyme which catalyzes a reaction to transfer glucose to a hydroxyl group at position 2′ of the chalcones. Furthermore, the invention provides a plant whose flower color has been changed using the glycosyltransferase. Using probes corresponding to conservative regions of the glycosyltransferase, some tens of glycosyltransferase genes having nucleotide sequences corresponding to the conservative regions were cloned from flower petal cDNA libraries of carnation and the like. Furthermore, each of the glycosyltransferase genes was expressed in Escherichia coli, activity to transfer glucose to position 2′ of the chalcone, i.e., the glycosyltransferase activity at position 2′ of chalcone was confirmed in an extract solution of the Escherichia coli, and it was confirmed that cloned genes encoded the glycosyltransferase at position 2′.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Glycosyltransferases, Polynucleotides Encoding These And Methods Of Use
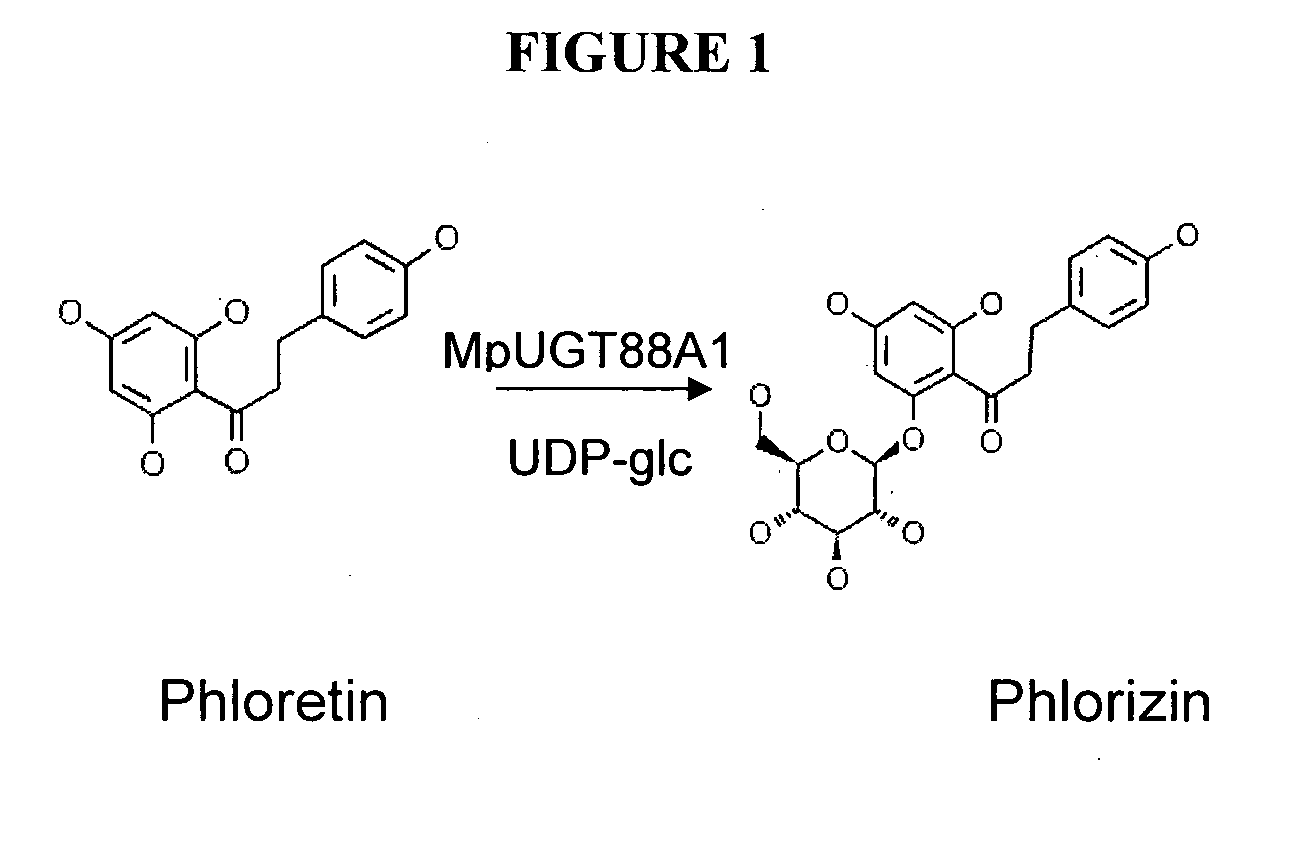
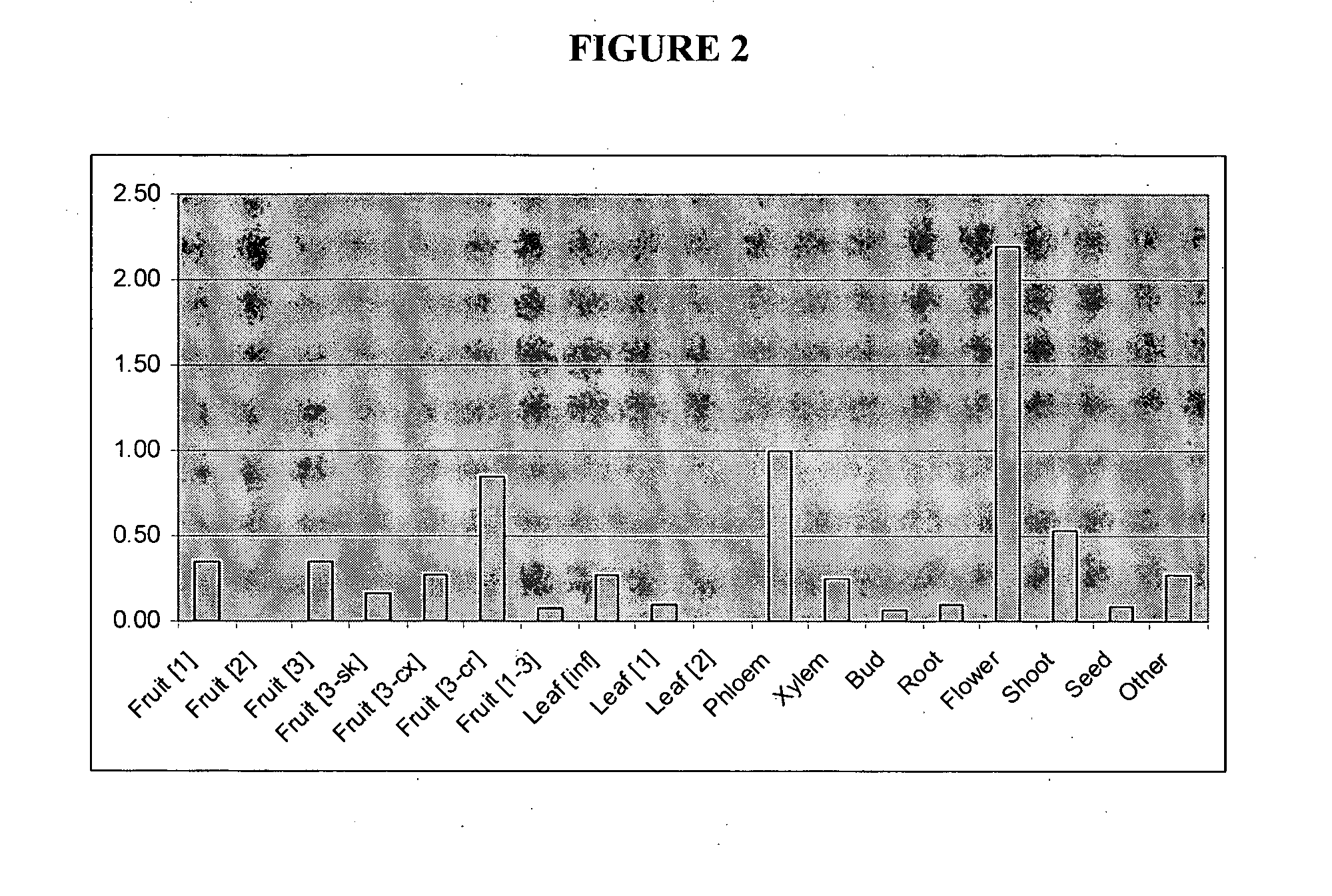
The invention provides method for producing a plant cell or plant with increased phlorizin or phloretin glycosyltransferase activity, the method comprising transformation of a plant cell or plant with a polynucleotide encoding a polypeptide with phloretin glycosyltransferase activity. The invention also provides host cells, plant cells and plants, genetically modified to contain and or express the polynucleotides.
Owner:THE NEW ZEALAND INST FOR PLANT & FOOD RES LTD
Glycosylated protein expression in prokaryotes
ActiveUS8999668B2Efficient productionRevolutionize enterpriseHydrolasesMicroorganismsAntigenBacteroides
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Phloretin glycosyltransferases, polynucleotides encoding these and methods of use
Owner:THE NEW ZEALAND INST FOR PLANT & FOOD RES LTD
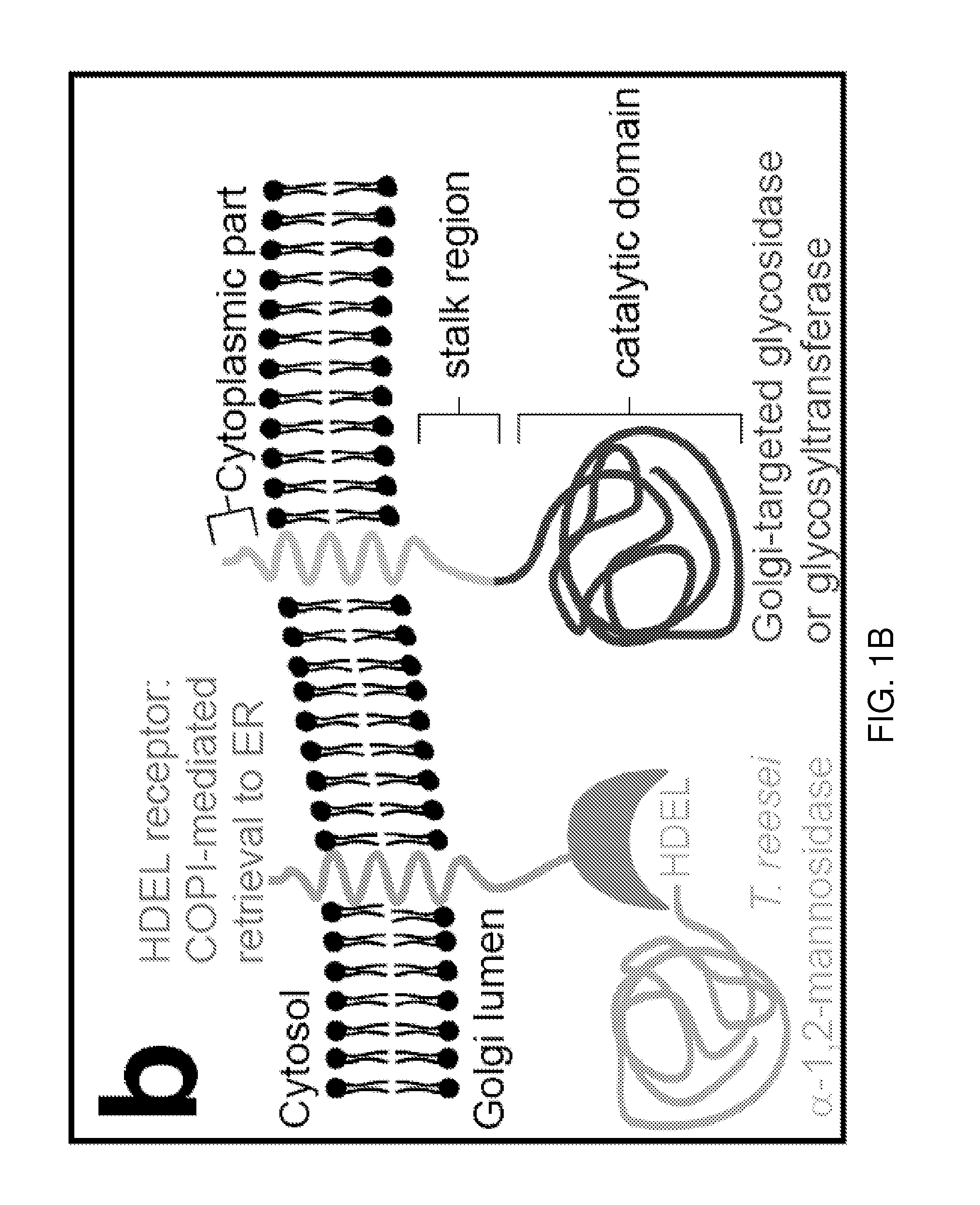
Methods for producing substantially homogeneous hybrid or complex n-glycans in methylotrophic yeasts
InactiveUS20120029174A1Highly efficient and effective engineeringDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsYeastBiotechnology
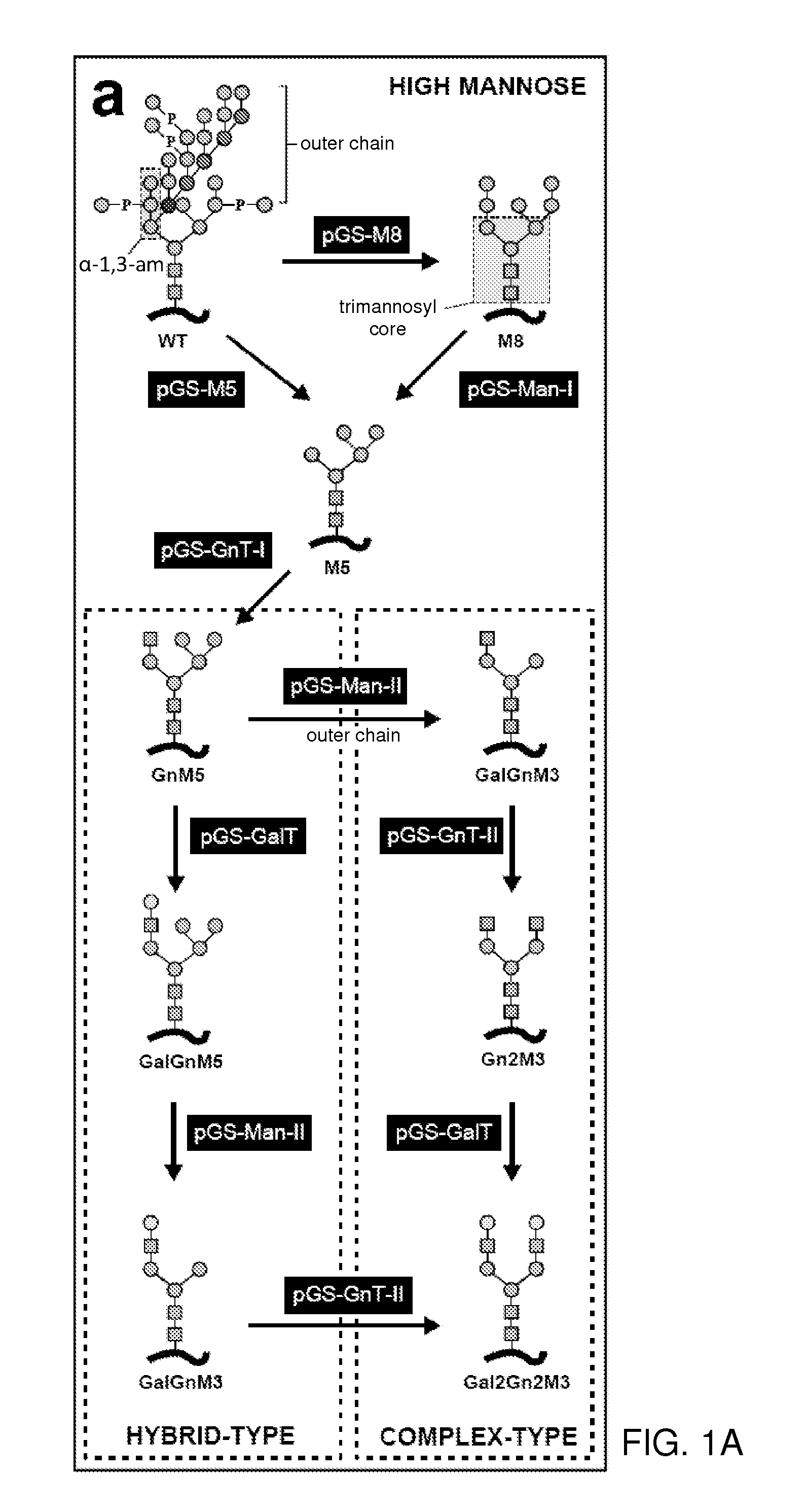
The present invention provides methods for effectively and efficiently converting methylotrophic yeast's heterogeneous high mannose-type N-glycosylation to mammalian-type N-glycosylation by disruption of an endogenous glycosyltransferase gene (OCH1) and step-wise introduction of heterologous glycosidase and glycosyltransferase activities. Each engineering step includes a number of stages: transformation with an appropriate vector, cultivation of a number of transformants, performance of sugar analysis and heterologous protein expression analysis, and selection of a desirable clone. The selected clone is then subjected to the next engineering step.
Owner:VLAAMS INTERUNIVERSITAIR INST VOOR BIOTECHNOLOGIE VZW +2
Emodin glycosyltransferase protein FtUGT75R2 and coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses an emodin glycosyltransferase protein FtUGT75R2 and coding gene and application thereof. The protein is one protein of the following a) or b): a) protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2 in the sequence table; and b) protein which is derived from a) obtained by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of theamino acid sequence shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table and has emodin 6-O-glucoside glycosyltransferase activity. According to the emodin glycosyltransferase protein FtUGT75R2, an emodin glycosyltransferase sequence is obtained mainly based on a tartary buckwheat genome, and FtUGT75R2 can catalyze emodin to produce emodin 6-O-glucoside by prokaryotic expression of recombinant protein.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
A Cyclodextrin Glucosyltransferase Mutant with Increased AA‑2G Conversion
ActiveCN104531629BIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationGlycosyltransferase activityArginine
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant for improving AA-2G conversion rate and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase mutant, the 228th lysine near the active center of the cyclodextrin glucosyltransferase of thermophilic fat bacillus (Bacillus stearotherm opilus NO2) is mutated into arginine to obtain a mutant K228R, the 367th aspartic acid is mutated into serine to obtain a mutant D367S and amphimutation is carried out on the basis to obtain a mutant D367S / K228R. The mutant can be used for realizing the improvement of the AA-2G conversion rate and has relatively high industrial value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant production of steviol glycosides
ActiveUS20170081691A1Sugar derivativesConfectioneryUdp glycosyltransferaseGlycosyltransferase activity
Recombinant polypeptides having UDP-glycosyltransferase activities, including a 1,2-19-O-glucose glycosylation activity and a 1,2-13-O-glucose glycosylation activity for synthesizing of steviol glucosides, are provided. A method of producing a steviol glycoside composition using such recombinant polypeptide is also provided. Also disclosed are steviol glycosides referred to as rebaudioside Z1 and rebaudioside Z2.
Owner:CONAGEN INC
Electrochemical sensing detection method of protein O-GlcNAc glycosyltransferase activity
ActiveCN107462618AEasy to operateImprove throughputMaterial electrochemical variablesGlycosyltransferase activityElectrochemical biosensor
The invention discloses an electrochemical sensing detection method of protein O-GlcNAc glycosyltransferase activity. The electrochemical sensing detection method comprises the following steps that a membrane of substrate polypeptide molecules of OGT is formed on the surface of an electrode; the obtained electrode fixed with the membrane of the polypeptide molecules on the surface and a glycosylation reaction fluid are incubated through OGT catalysis to obtain an electrode fixed with the membrane of the glycosylated polypeptide molecules on the surface; the electrode fixed with the membrane of the polypeptide molecules on the surface and the electrode fixed with the membrane of the glycosylated polypeptide molecules on the surface are sequentially subjected to the treatment in the steps 1-3 as follows: 1, the electrodes are put in a protease reaction fluid for hydrolysis; 2, the electrodes are cleaned with water; 3, a tyrosine residue serves as an electrochemical signal probe, and the electrodes perform electrochemical oxidation reaction; tyrosine residue electrocatalytic oxidized currents in the obtained systems are respectively determined, and OGT activity can be quantitively analyzed according to the obtained catalyzed and oxidized currents. By adopting the method, simple, quick and non-marked OGT activity detection is achieved through an electrochemical biosensor.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
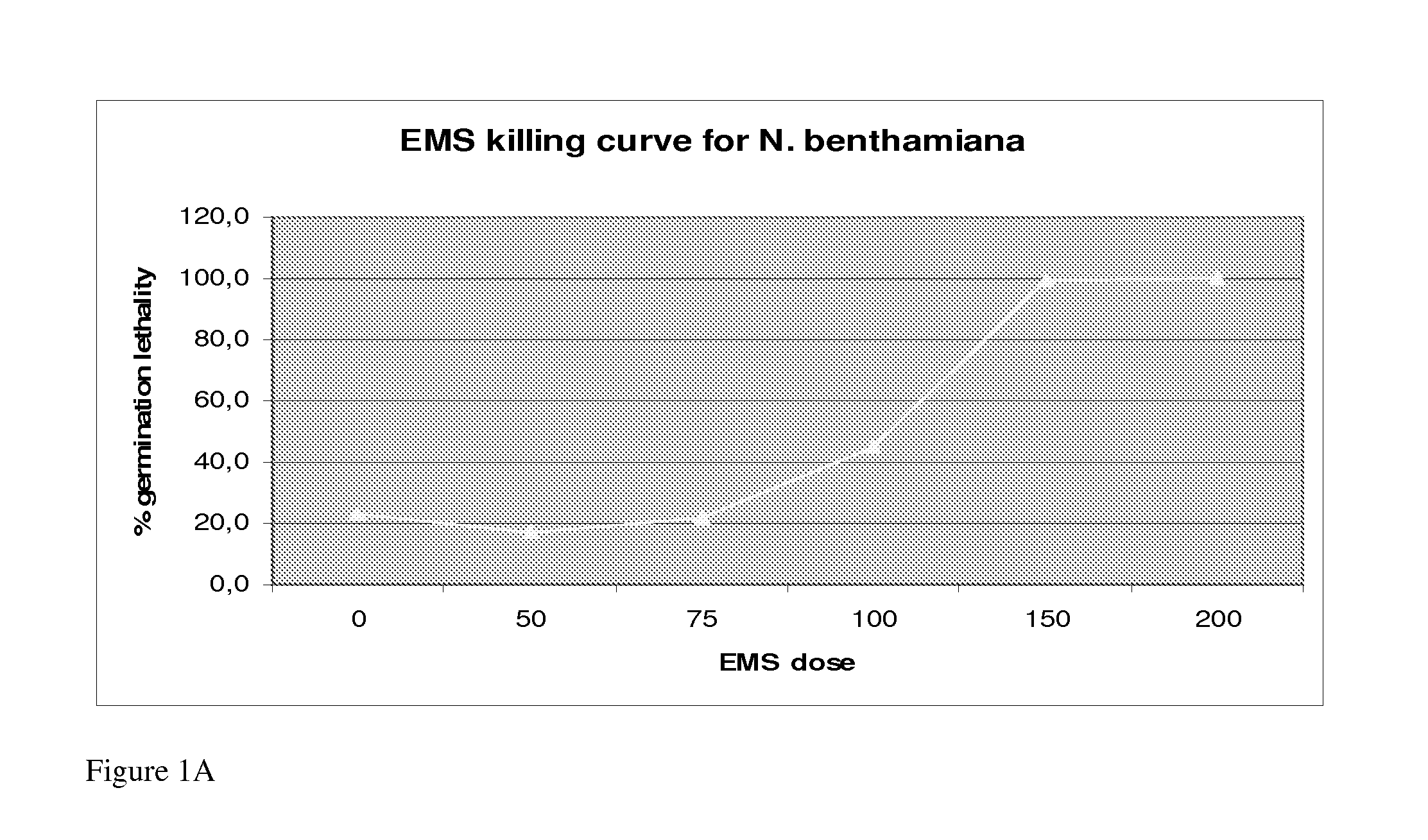
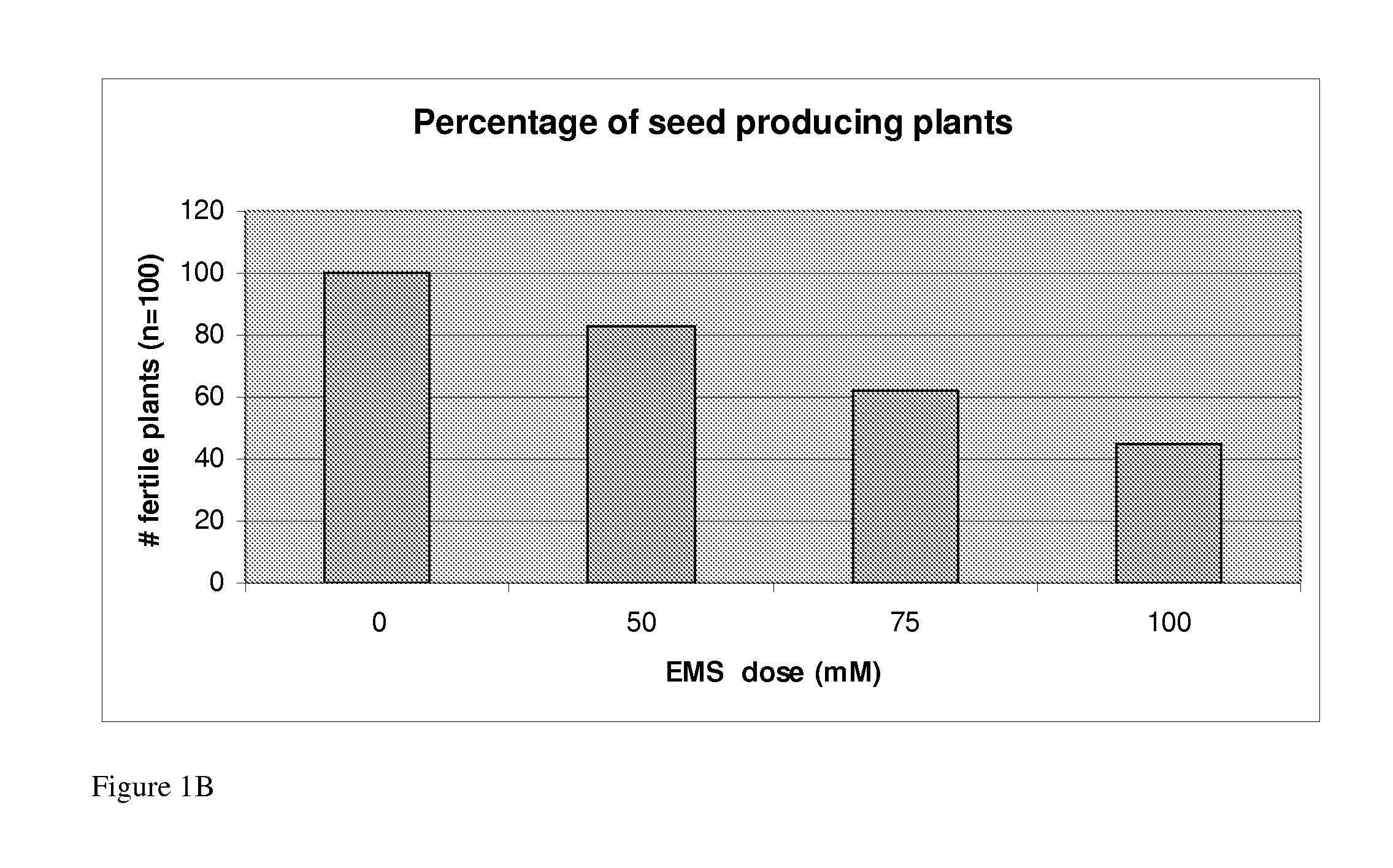
Nicotiana Benthamiana Plants Deficient in Xylosyltransferase Activity
The invention provides Nicotiana benthamiana mutant plants which are incapable of forming xylosyl-structures on glycoproteins. In addition, the invention provides methods for the production of heterologous glycoproteins in said mutant plants.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
Process for producing starch-containing food, and enzyme preparation for modification of starch-containing food
A starch-containing food can be improved in its quality by using an enzyme having a glycosyltransferase activity which can covert an a-1,4 bond to an a-1,6 bond and a transglutaminase.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Pharmaceutical product
InactiveUS20100124548A1Increase heightImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesGlycosyltransferase activityLysyl hydroxylase
The present invention relates to methods and products for the treatment of any disorder or condition, which is associated with abnormal amount of non-collagenous protein, or abnormal oligomerization or dysfunction of non-collagenous protein, such as adiponectin in the blood circulation and / or tissue of a patient. The treatment comprises that functional form of the non-collagenous protein is adjusted in the blood circulation and / or tissue of the patient substantially to the level it is in the blood circulation and / or tissue of a healthy person, by using lysyl hydroxylase and / or glycosyl-transferase activities of LH3 or other lysyl hydroxylase to modify the non-collagenous protein to HMW or other functional form.
Owner:OULU UNIV OF
Esculin and fraxin glycosyltransferase protein as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses aesculin and fraxin glycosyl transferase protein as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The esculetin and fraxin glycosyl transferase protein provided by the invention is a protein as shown in a) or b): a) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; b) a protein which is obtained by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table, has the activity of aesculin and / or fraxin glycosyltransferase and is derived from a). Based on related results of high-throughput sequencing of aesculus chinensis, a key enzyme UGTs in the last step of synthesis of fraxin and aesculin is found and identified by using a reverse genetics method, the terminal blank of a coumarin biosynthesis pathway is filled, and glycosyl transferase protein and a coding sequence thereof are provided for further biosynthesis of fraxin and aesculin.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
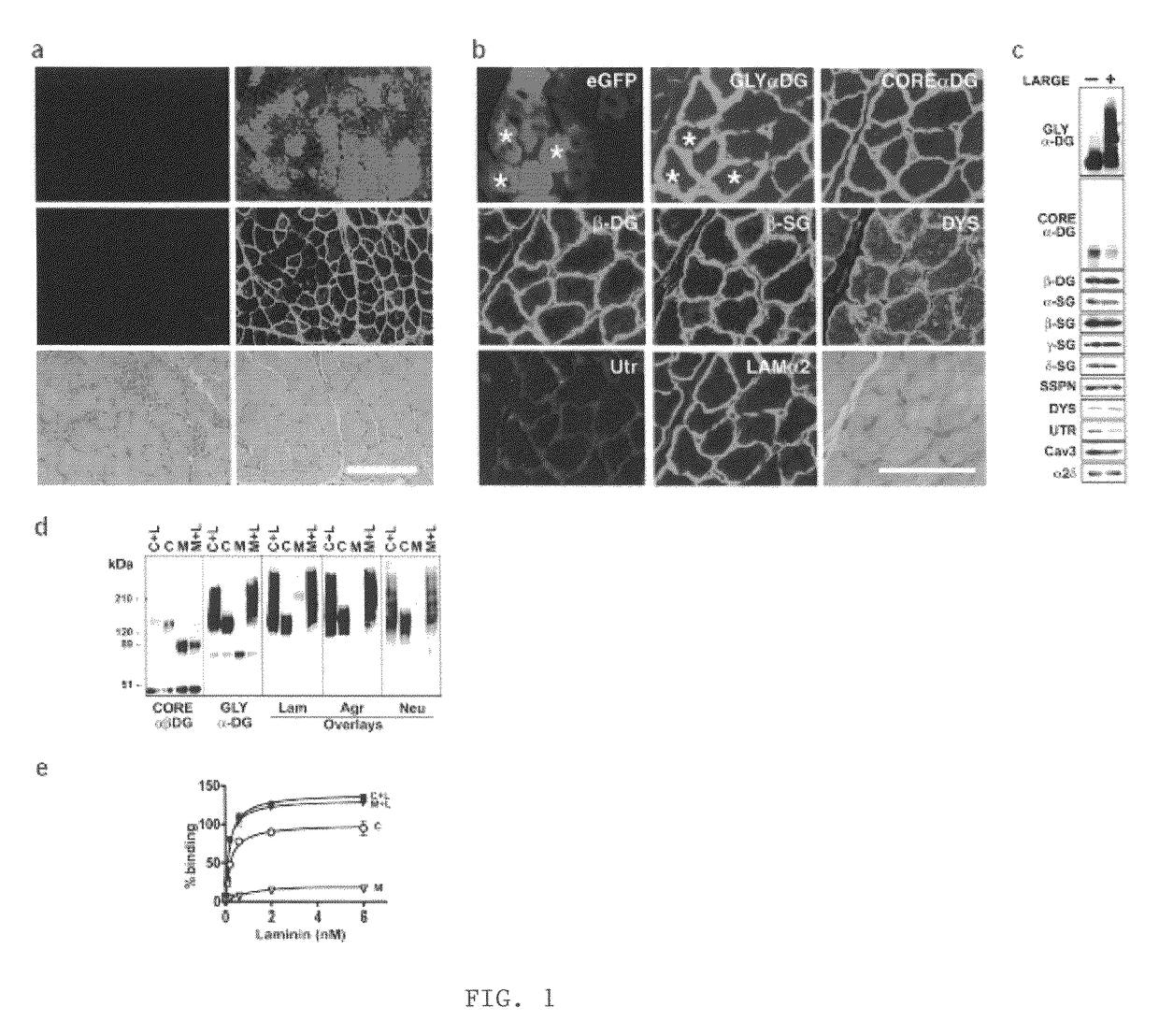
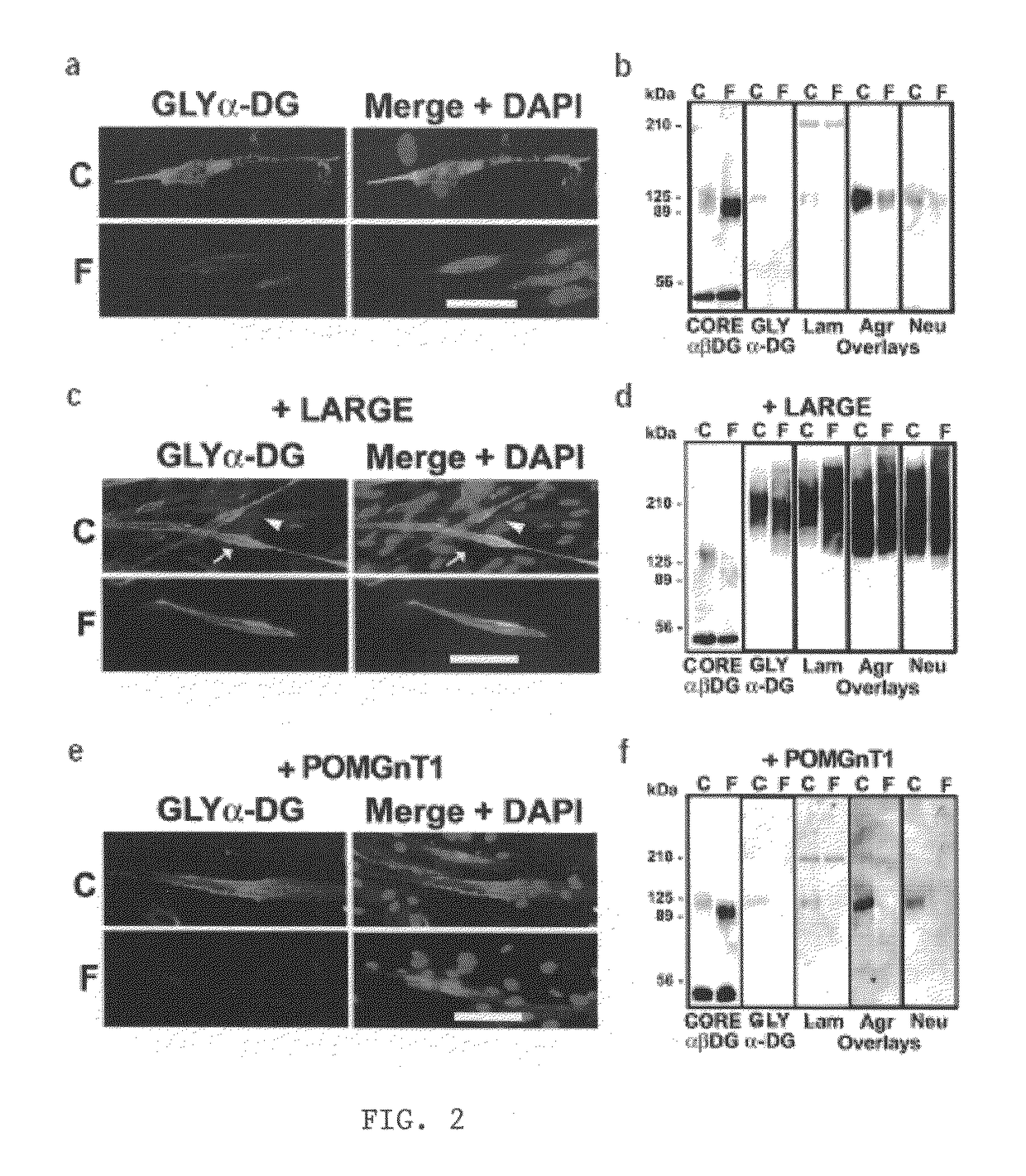
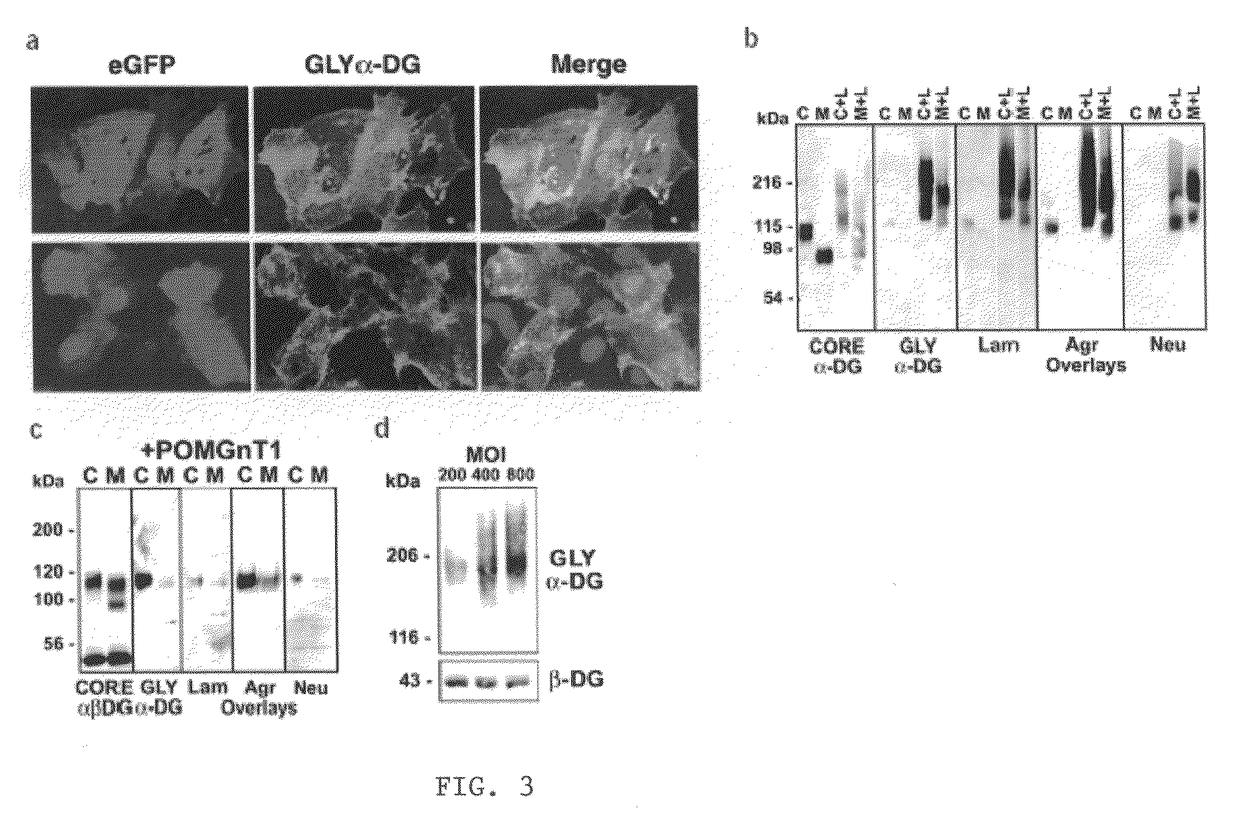
Increasing functional glycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan in the treatment of muscle degeneration
ActiveUS20060276376A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsAlpha-DystroglycanGlycosyltransferase activity
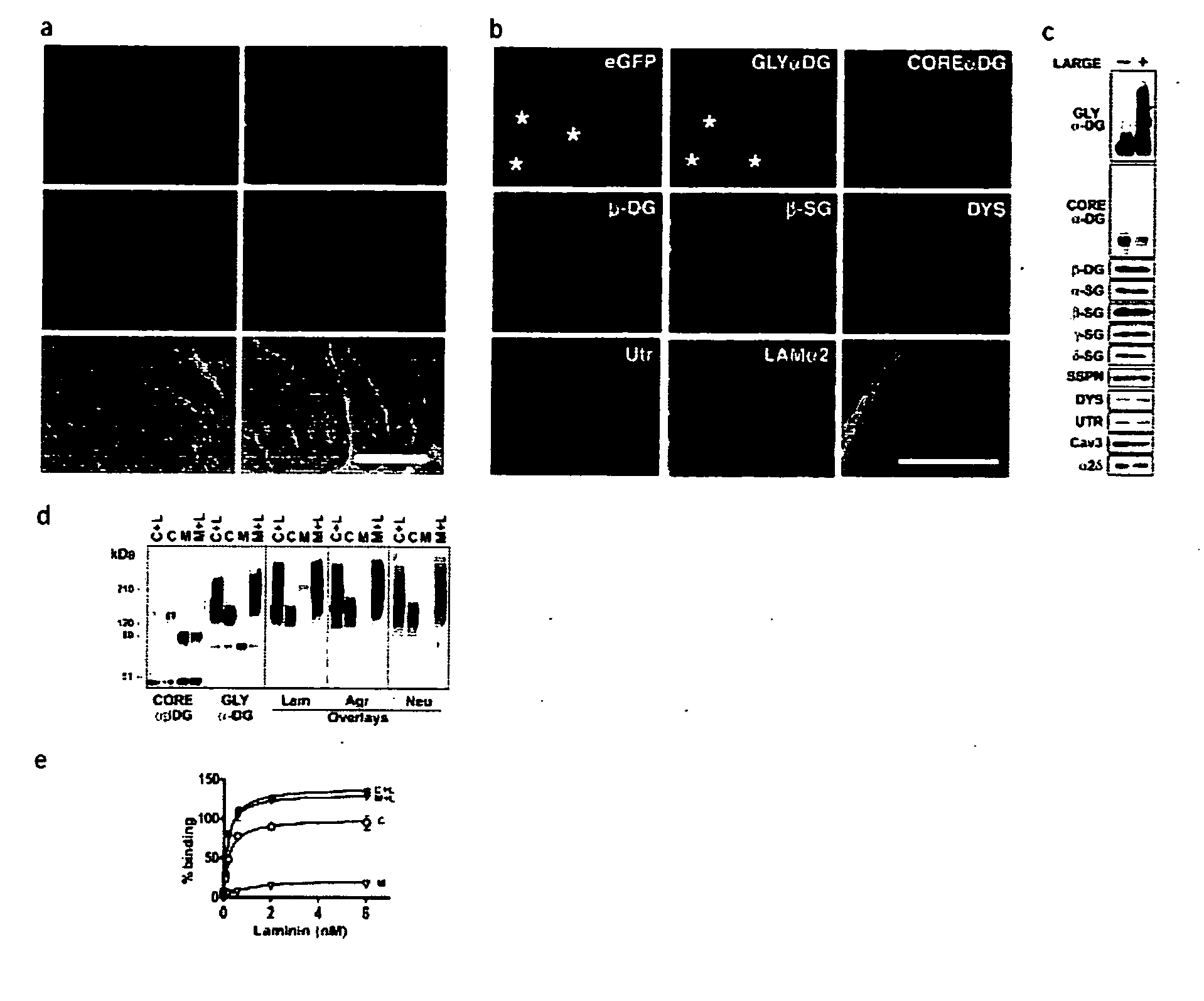
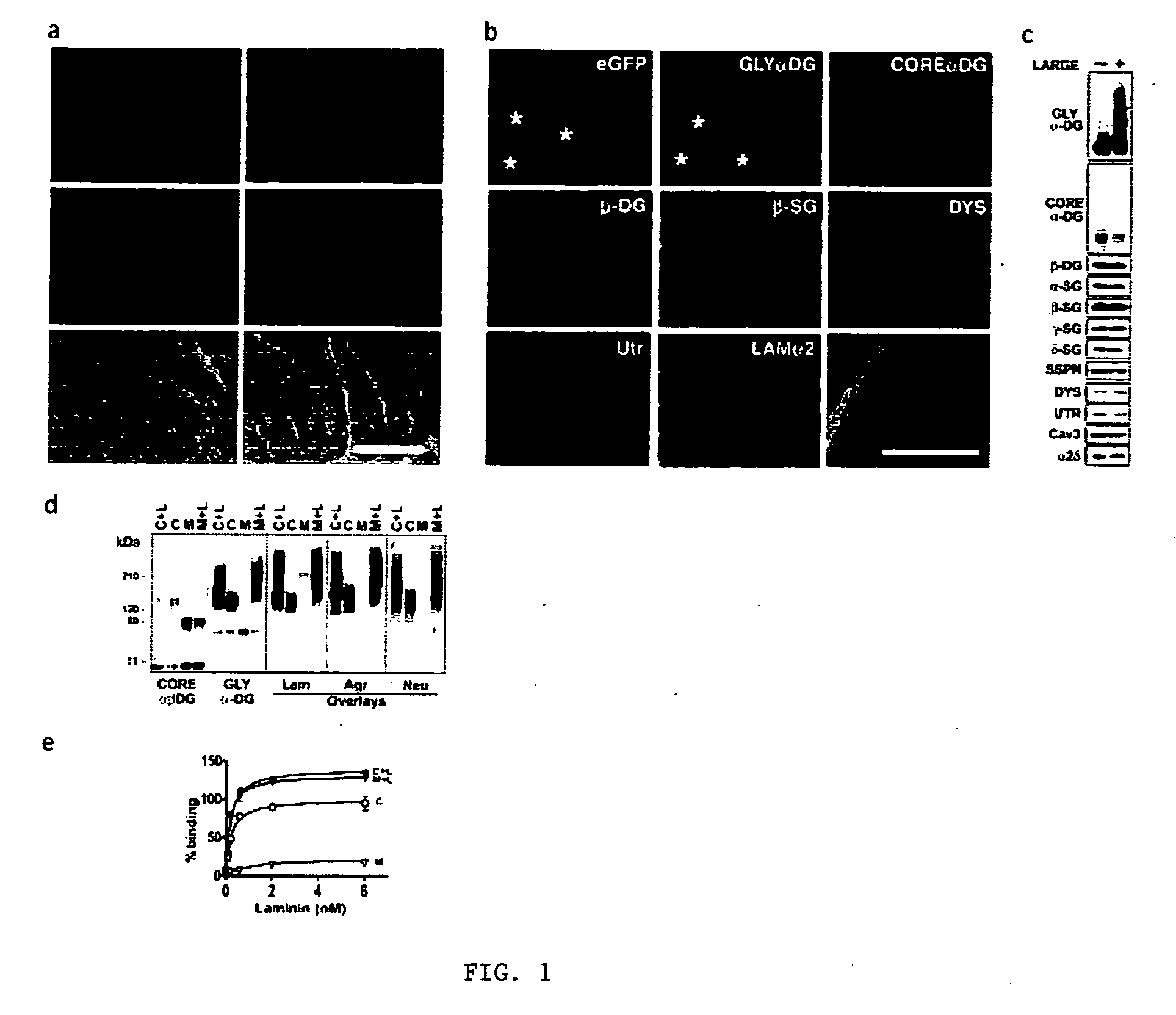
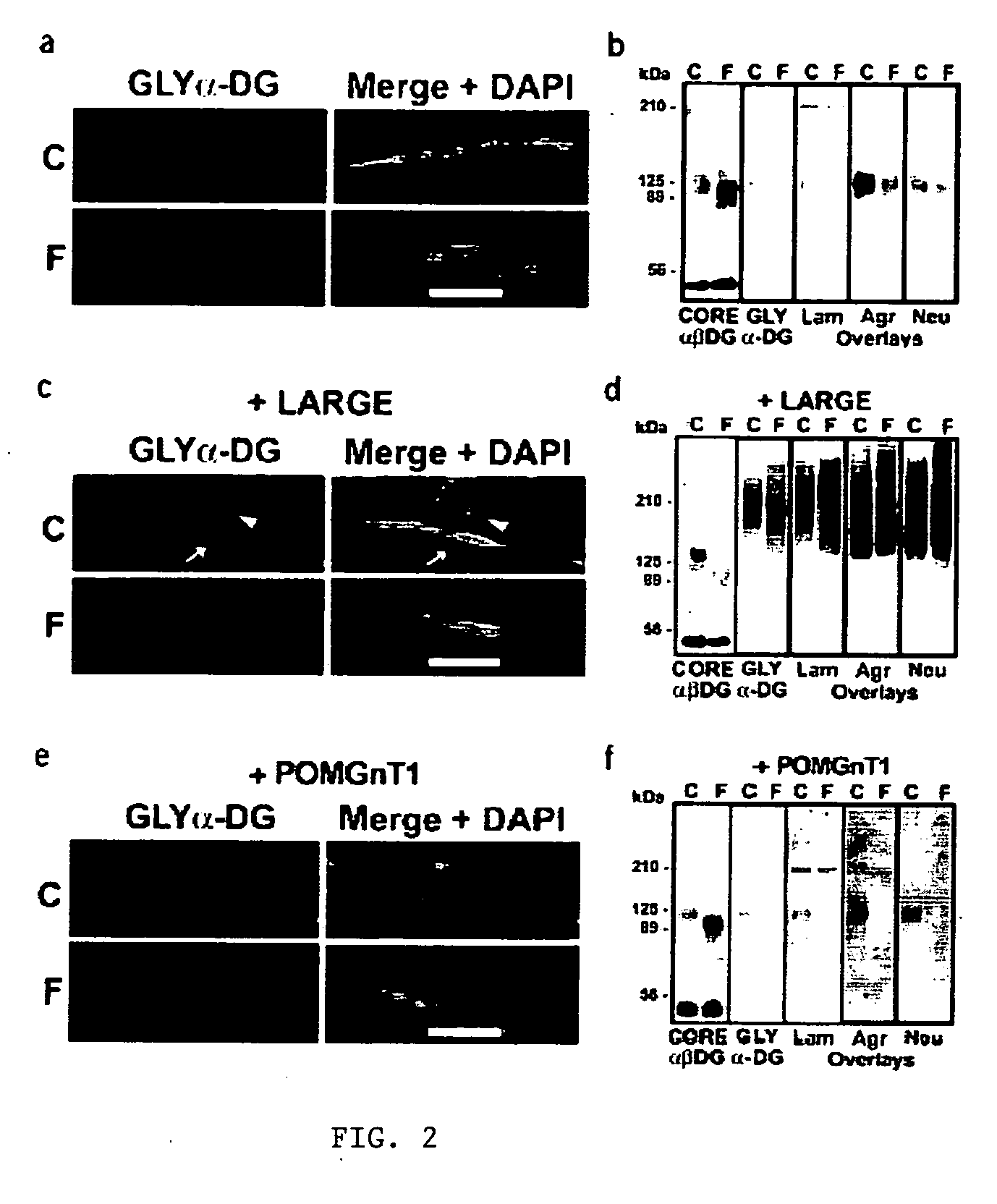
Disclosed is a method for the prevention and / or treatment of muscle degeneration. In this method, a subject recognized as having muscle degeneration is treated with a composition effective to increase functional glycosylation of α-dystroglycan in an affected tissue in the subject. Functional glycosylation is to be increased to an extent wherein the binding of α-dystroglycan to its ligands in the affected tissue is rescued to levels substantially similar to those in an evenly matched tissue unaffected by degeneration. One effective means for increasing functional glycosylation of α-dystroglycan in a subject includes increasing glycosyltransferase activity, such as LARGE or LARGE2 activity, in the muscle of the subject. Therapeutic glycosylated peptide compositions are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF IOWA +1
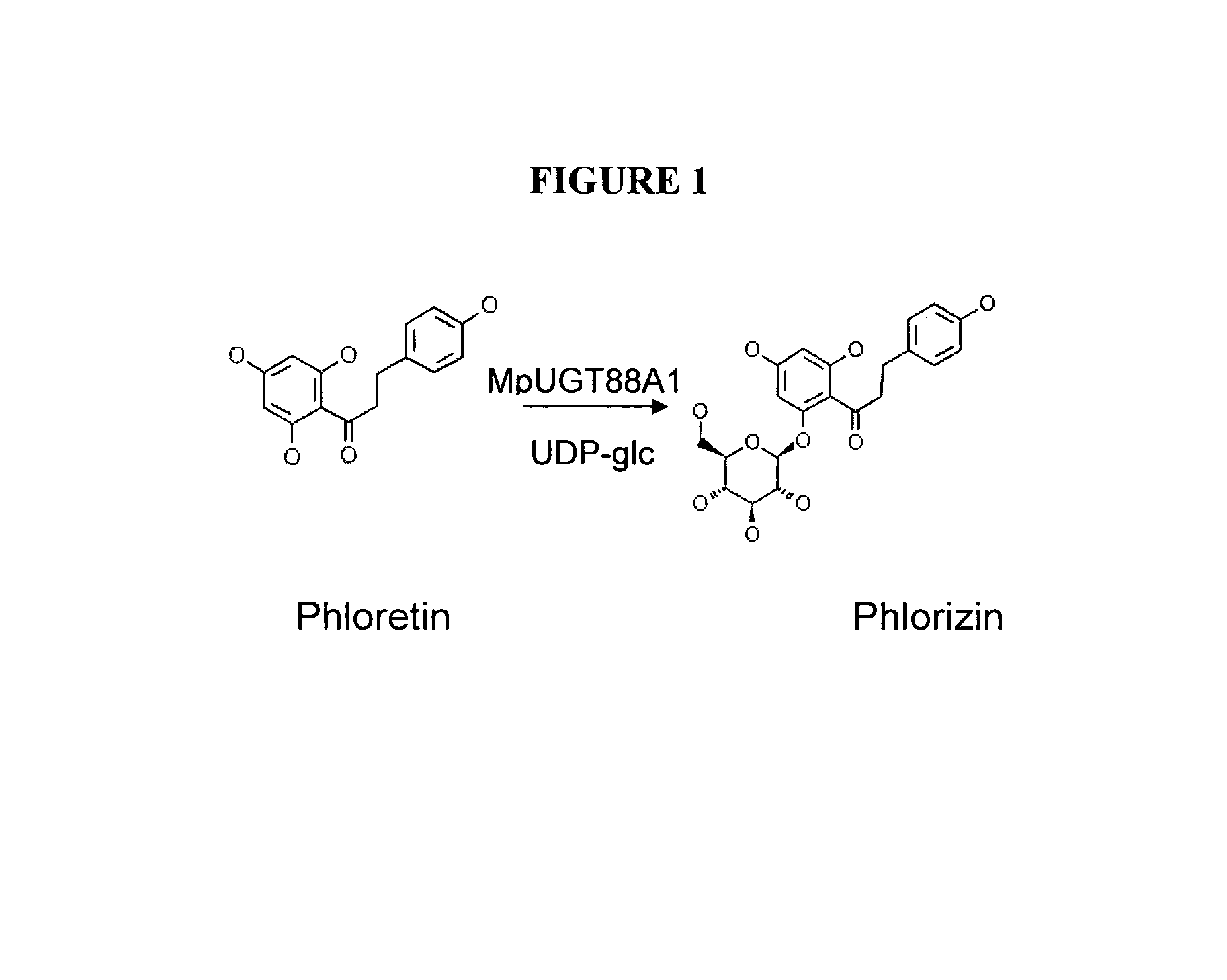
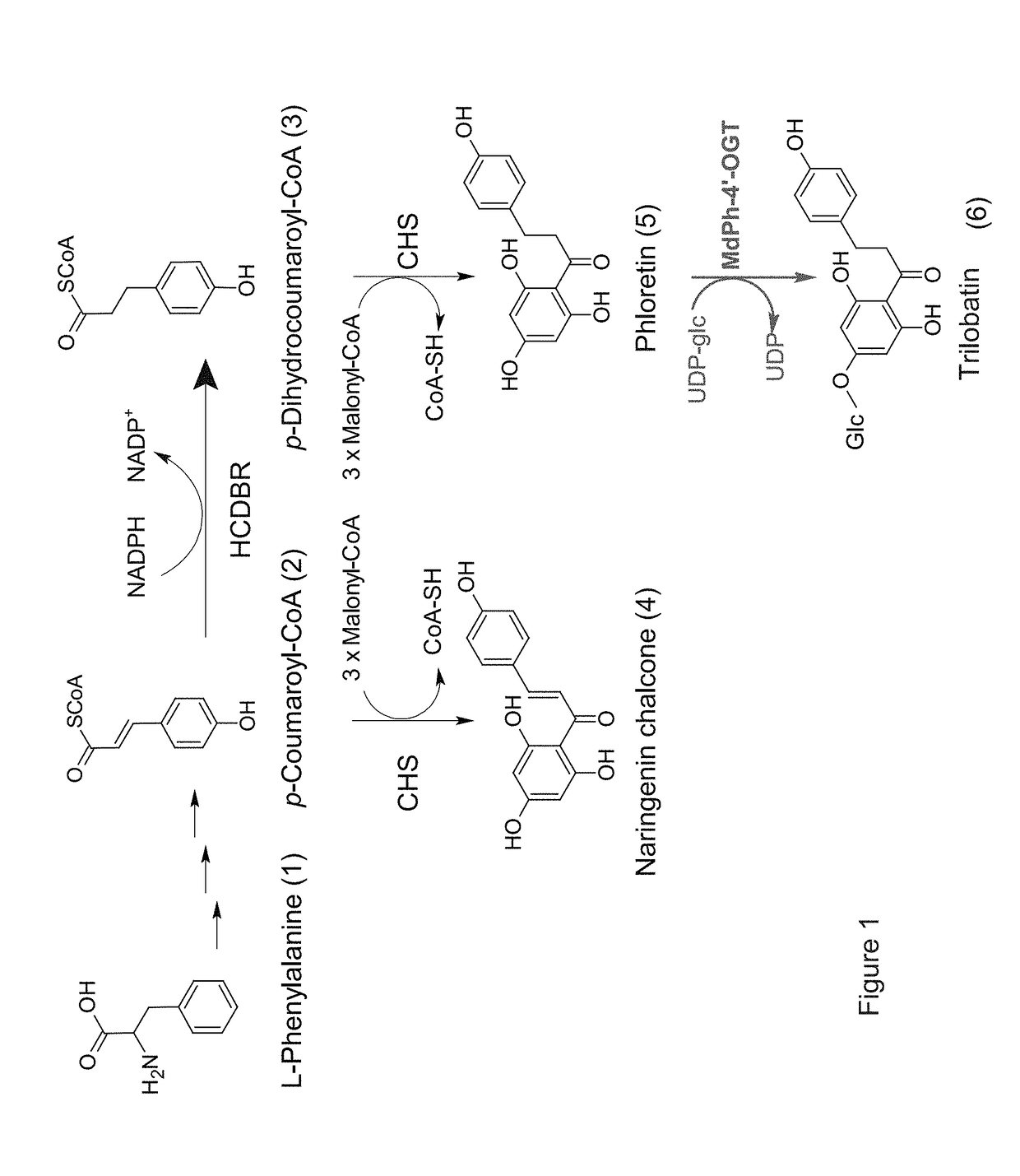
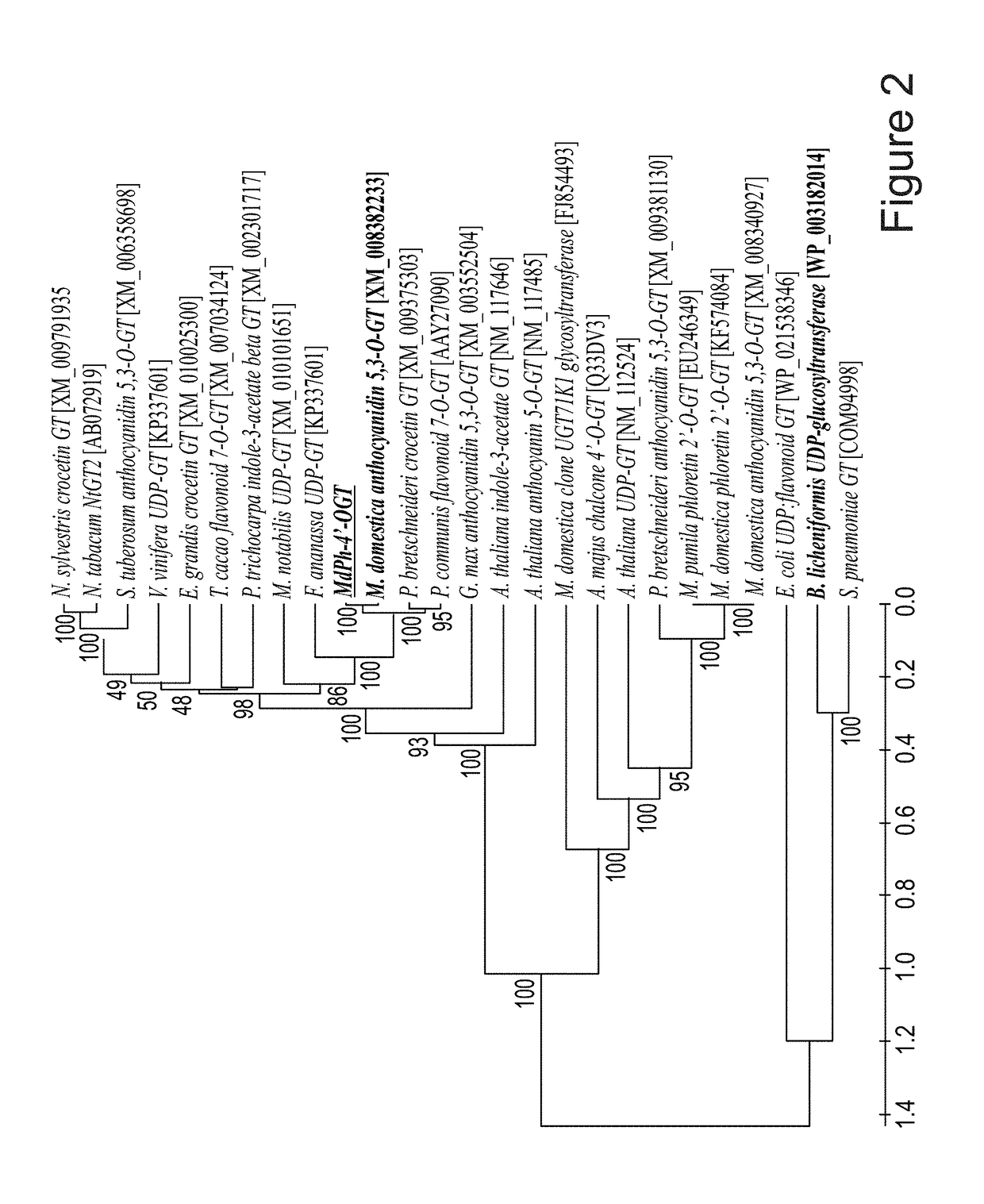
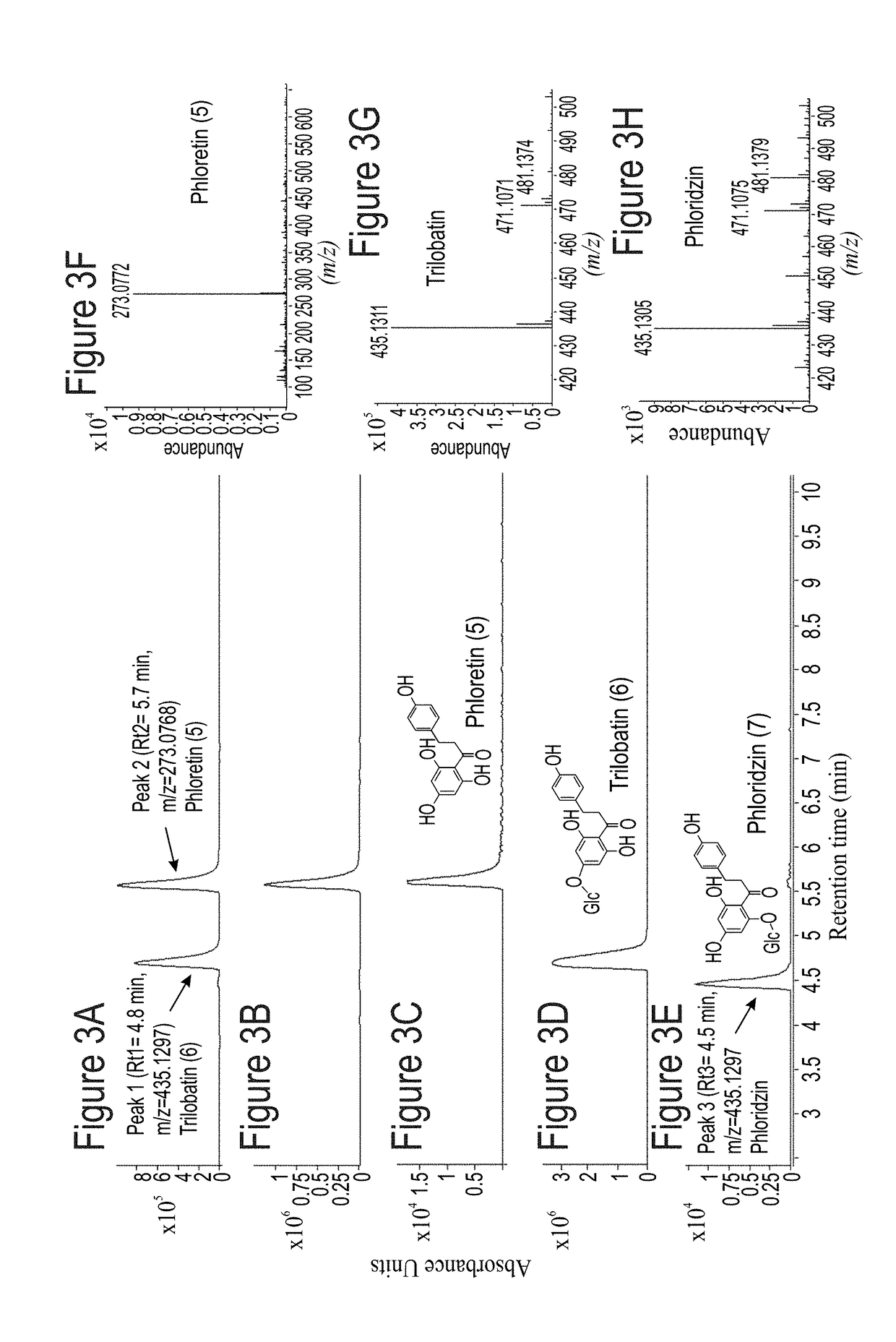
Identification and characterization of udp-glucose:phloretin 4'-o-glucosyltransferase from malus x domestica borkh
ActiveUS20190062768A1Nervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsGlycosyltransferase activityPlant cell
A method of producing trilobatin is disclosed. The method comprising contacting a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence at least 90% identical to SEQ ID NO: 8 and having a 4′-O-glycosyltransferase activity with phloretin and UDP-glucose under conditions which allow the formation of trilobatin, thereby producing trilobatin. A method of producing a plant which produces trilobatin, transgenic plant or plant cell and methods of producing transgenic plants are disclosed. Composition comprising trilobatin are also disclosed.
Owner:STATE OF ISRAEL MINIST OF AGRI & RURAL DEV AGRI RES ORG (A R O) (VOLCANI CENT)
Xanthomonas campestris and application thereof
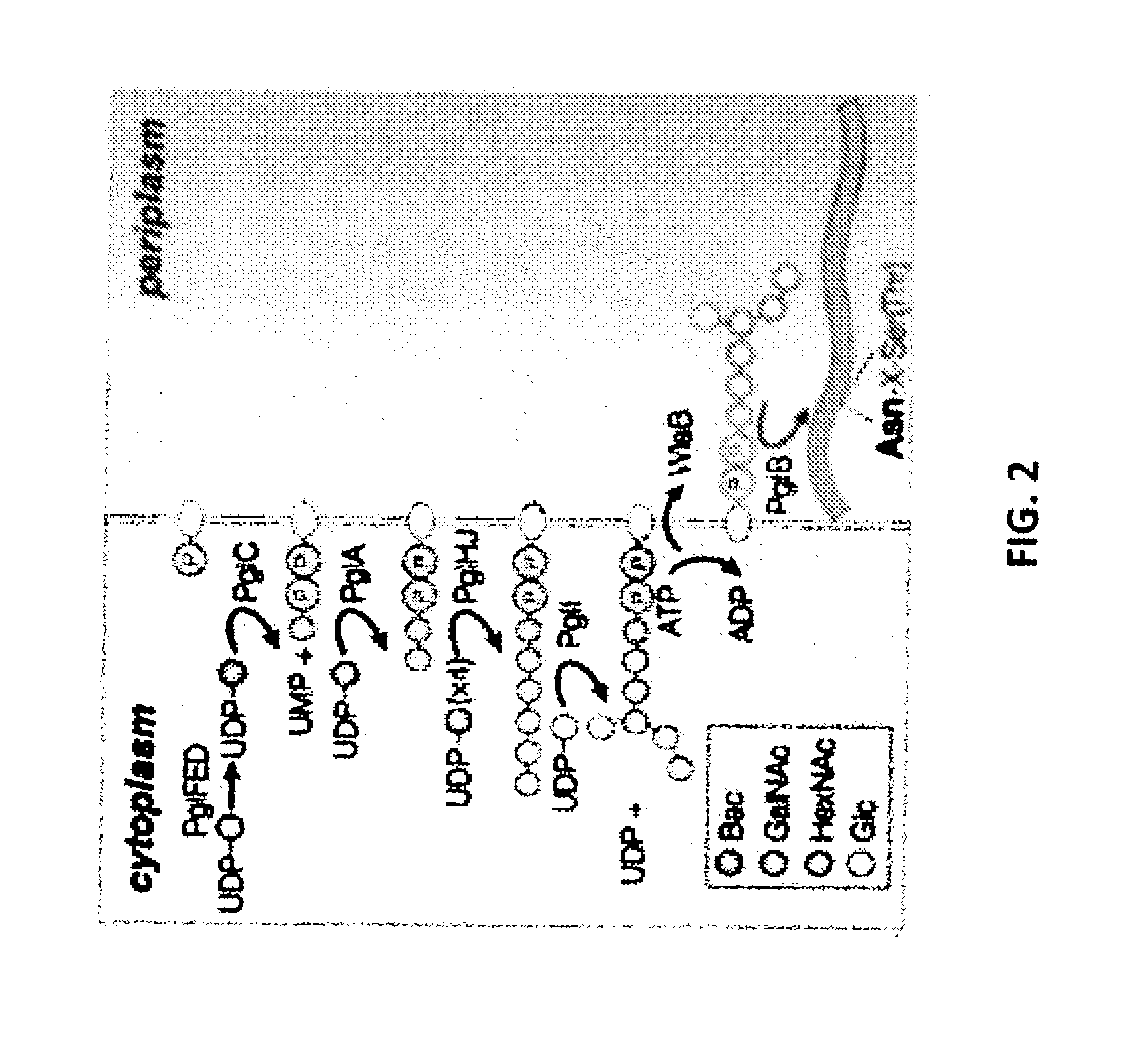
InactiveCN107446844AHighly active glycosyltransferase activityPossess active glycosyltransferase activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesXanthomonas campestrisGlycosyltransferase activity
The invention discloses Xanthomonas campestris and application thereof. The strain has high-activity glycosyltransferase activity, so that glycosylation can be effectively performed on various small molecule compounds such as hydroquinone, L-menthol, eugenol and isoeugenol.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Emodin glycosyltransferase protein FtUGT73BE5 as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses emodin glycosyltransferase protein FtUGT73BE5 as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. The protein is as shown in the following a) or b): a) protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown in the sequence 2 in a sequence table; b) protein which consists of the amino acid sequence shown in sequence 2 in the sequence table by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues, has emodin 6-O-glucoside glycosyltransferase activity and is derived from a). The emodin glycosyltransferase sequence is mainly obtained on the basisof Fagopyrum tataricum genome, and prokaryotic expression of recombinant protein confirms that FtUGT73BE5 can catalyze generation of emodin 6-O-glucoside from emodin. Meanwhile, the gene can be overexpressed in hairy roots through agrobacterium mediation by means of FtUGT73BE5, and finally, emodin 6-O-glucoside is obtained.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Regulation of glucose and insulin levels by gnt-4 glycosyltransferase activity
InactiveUS20070259379A1Reduce transportationIncrease metabolic ratePeptide/protein ingredientsPancreatic cellsGlycosyltransferase activityPre diabetes
The invention is based on the discovery that the gylcosylation enzyme GnT-4 increases glyocsylation and the stability of glucose transporter (Glut) family members, e.g., by increasing lectin binding. Modulators of GnT-4 activity can therefore be identified and used for the treatment of diabetes or pre-diabetes. In addition, inhibitors of GnT-4 activity can be used for the treatment of cancer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
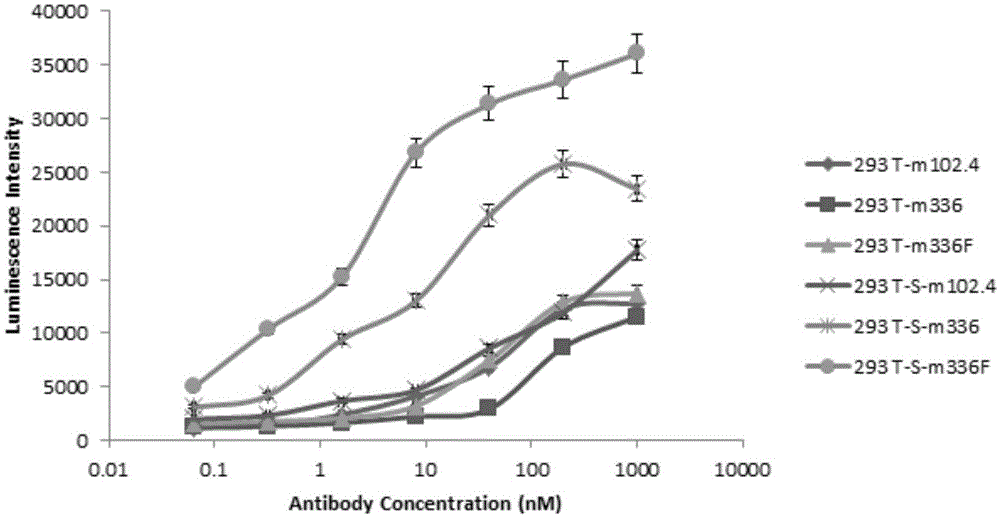
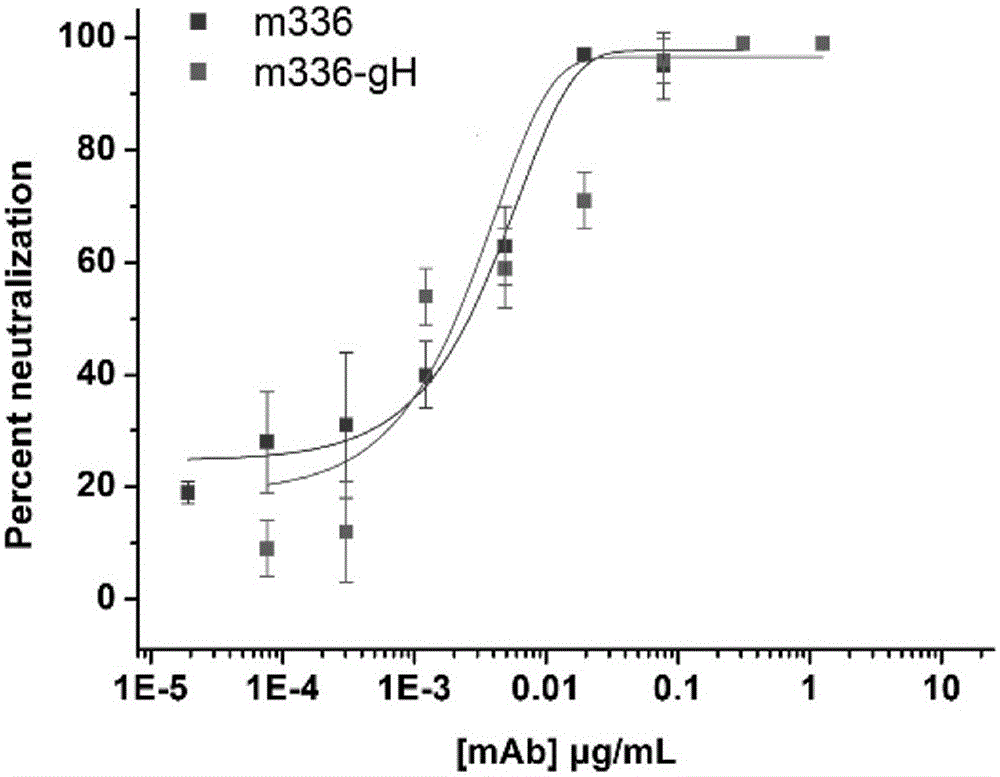
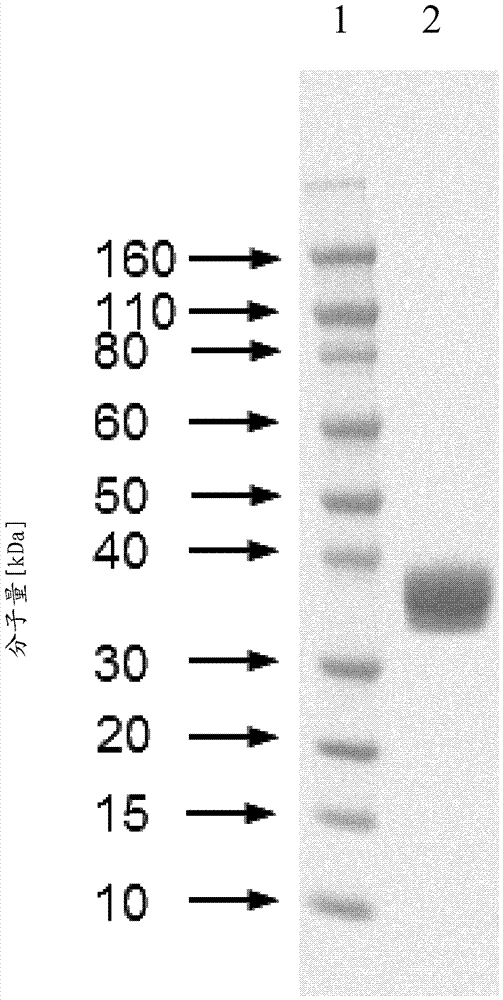
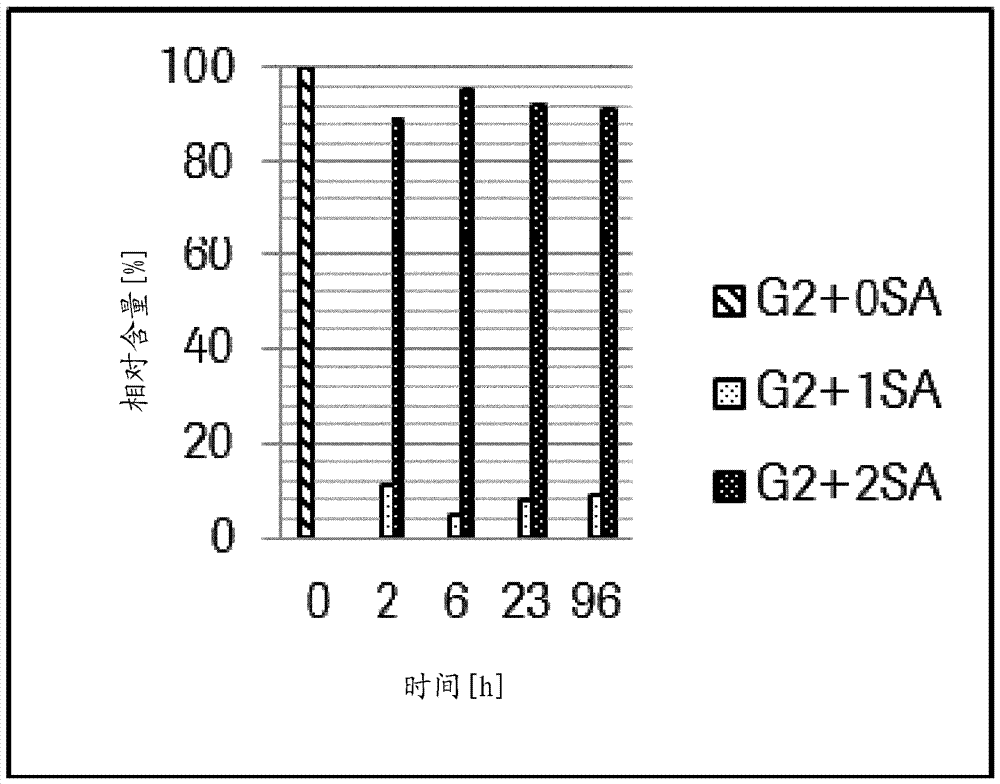
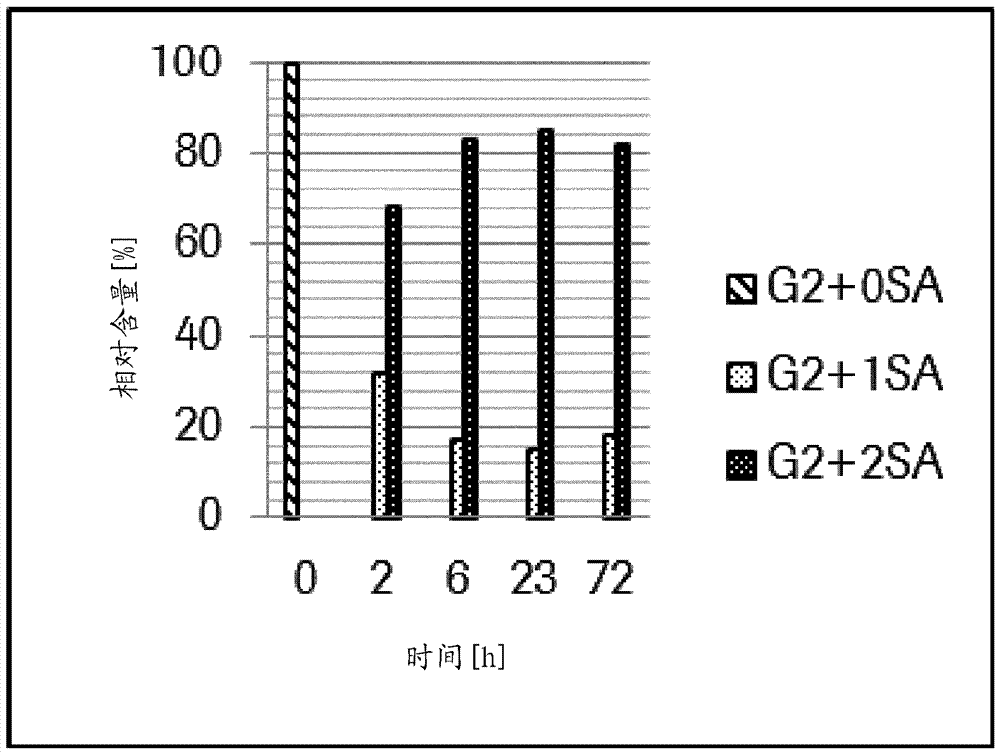
De-fucosylated fully humanized monoclonal antibody and applications thereof
InactiveCN106478814AStrong cytotoxicityImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsFucosylationGlycosyltransferase activity
The present invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to a de-fucosylated fully humanized monoclonal antibody for Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV), an antigen binding fragment, and applications thereof, wherein the de-fucosylated fully humanized monoclonal antibody is mainly characterized in that the de-fucosylated fully humanized monoclonal antibody has an enhanced antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) effect, wherein the effect comprises cleaving the cells expressing MERS-CoV S protein. The present invention further relates to a method for making cells express the de-fucosylated MERS-CoV fully humanized monoclonal antibody by inhibiting fucosyltransferase activity. According to the present invention, by using the antibody, the Middle Eastern respiratory syndrome can be clinically prevented or treated.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
CMP-dependent sialidase activity
The present disclosure is directed to the properties of certain glycosyltransferase variants having N-terminal truncation deletions or internal deletions. Any of the mutants disclosed in here exhibit alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase enzymatic activity in the presence of CMP-activated sialic acid as co-substrate, and in the presence of a suitable acceptor site. A fundamental finding documented in the present disclosure is that such enzyme are not only capable of catalyzing transfer of a sialidyl moiety but they are also capable of catalyzing hydrolytic cleavage of terminally bound sialic acid from a glycan. Particularly it was found that in the presence of cytidine 5'-monophosphate (CMP) glycosyltransferase activity is inhibited, and sialidase activity is stimulated. Sialidase activity was found to be dependent on the presence of a particular stretch of amino acids (position 90 to 108) in the polypeptide sequence of the reference (wild type) hST6Gal-I polypeptide. Deletion of this sequence portion in an N-terminal truncation variant was found to abolish sialidase activity, notably both in the presence and in the absence of CMP. Thus, disclosed are compositions, uses and methods employing the CMP-mediated feed-back regulation documented herein.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
Increasing functional glycosylation of alpha-dystroglycan in the treatment of muscle degeneration
ActiveUS8119766B2Increased glycosylationPrevent degradationSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsGlycosyltransferase activityMedicine
Disclosed is a method for the prevention and / or treatment of muscle degeneration. In this method, a subject recognized as having muscle degeneration is treated with a composition effective to increase functional glycosylation of α-dystroglycan in an affected tissue in the subject. Functional glycosylation is to be increased to an extent wherein the binding of α-dystroglycan to its ligands in the affected tissue is rescued to levels substantially similar to those in an evenly matched tissue unaffected by degeneration. One effective means for increasing functional glycosylation of α-dystroglycan in a subject includes increasing glycosyltransferase activity, such as LARGE or LARGE2 activity, in the muscle of the subject. Therapeutic glycosylated peptide compositions are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF IOWA +1
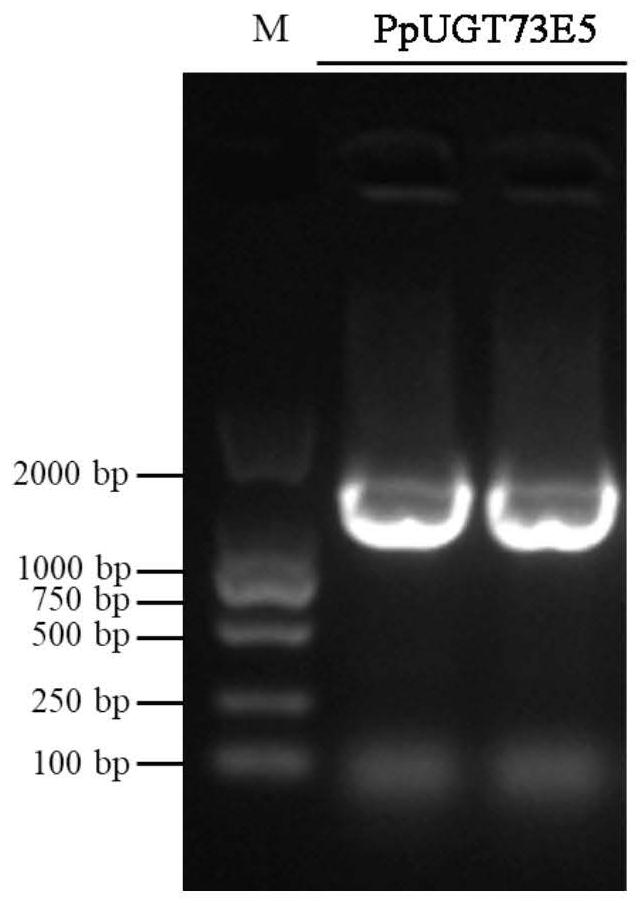
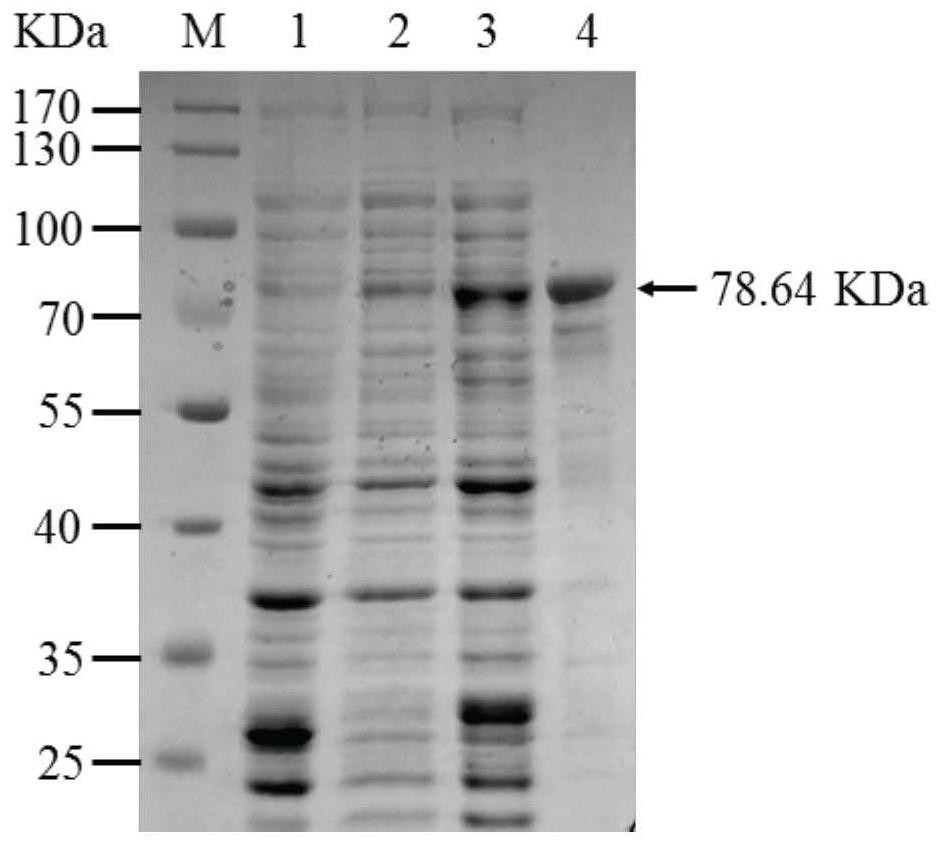
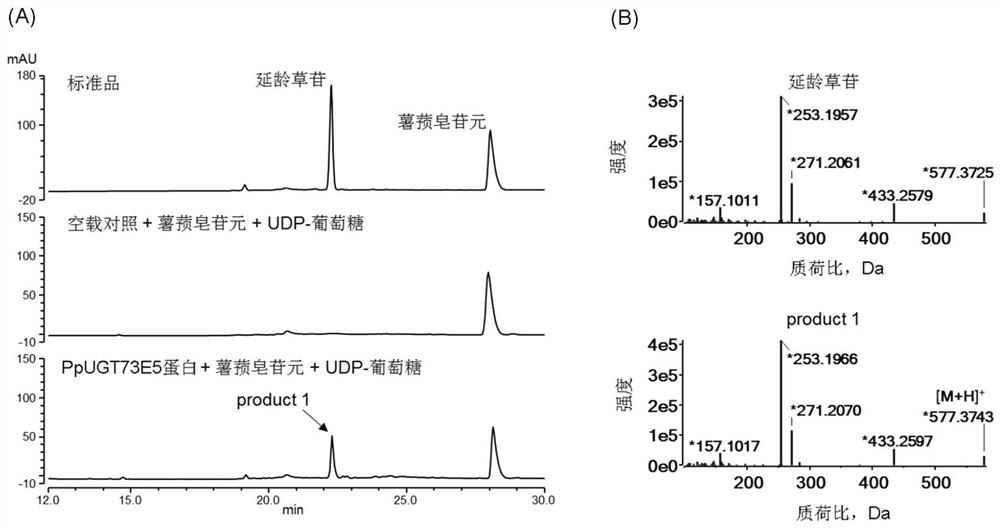
Glycosyl transferase PpUGT73E5 and application thereof in synthesis of polyphyllin
The invention relates to a saponin metabolic pathway, in particular to glycosyl transferase PpUGT73E5 and application of the glycosyl transferase PpUGT73E5 in synthesis of polyphyllin. The glycosyl transferase is a protein as shown in a1 or a2: a1, a protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; a2, a protein with glycosyl transferase activity, which is formed by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. The glycosyltransferase can catalyze glycosylation of steroid sapogenin, and a gene resource is provided for subsequent obtaining of multiple polyphyllin.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Epicatechin glucosyltransferase
ActiveUS20100064387A1Increased proanthocyanidin biosynthesisTransferasesImmunoglobulinsGlycosyltransferase activityBetacyanins
The invention provides methods and compositions for the modulation of epicatechin glucosyltransferase activity in plants. Increased expression of epicatechin glucosides, and ultimately anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins, in plants may be used to increase the nutritional value of food plants for both human and animal consumption. Increased proanthocyanidin content also reduces the potential for bloat in animals fed certain forage plants low in condensed tannin content.
Owner:NOBLE RES INST LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com