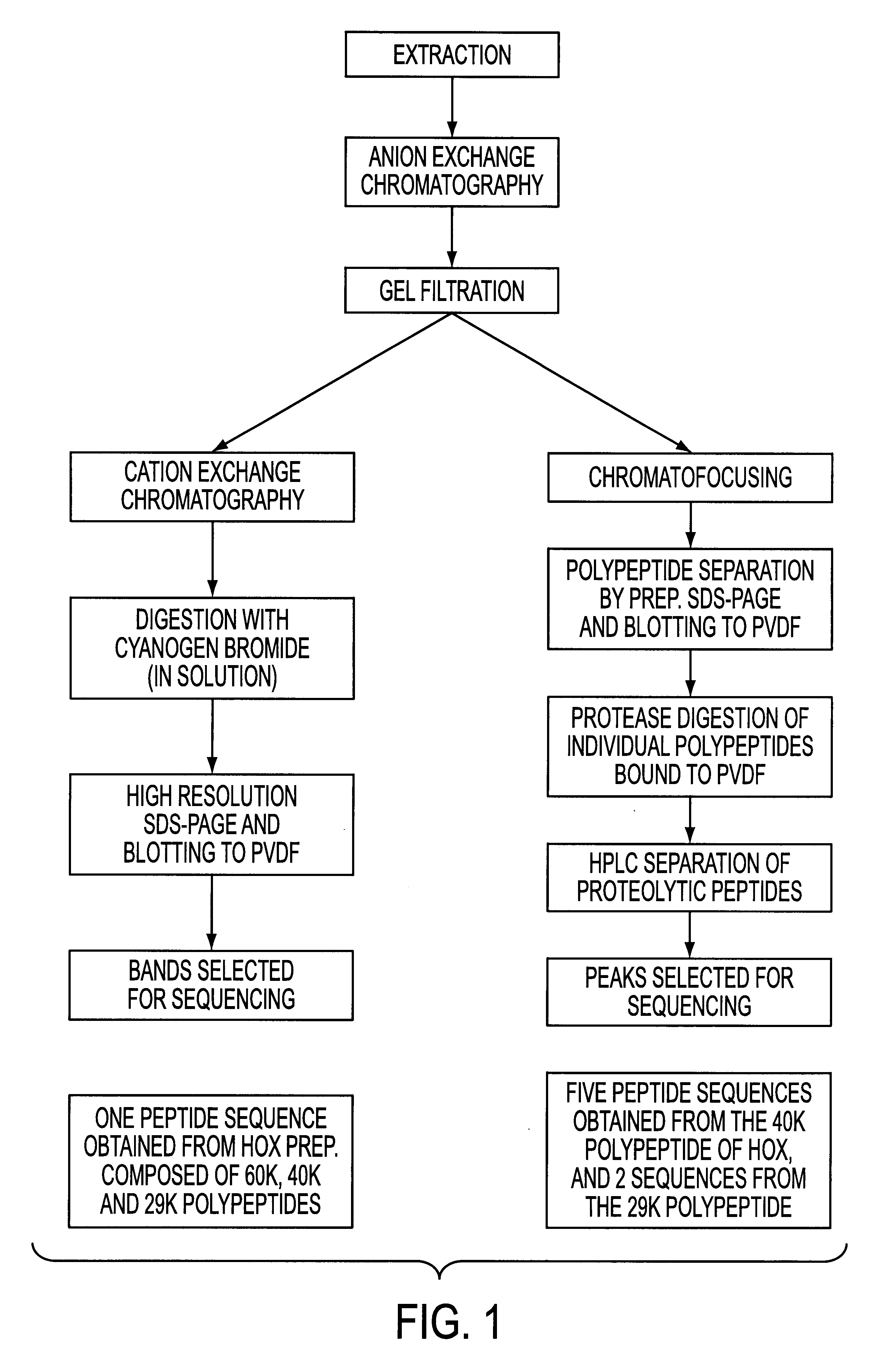
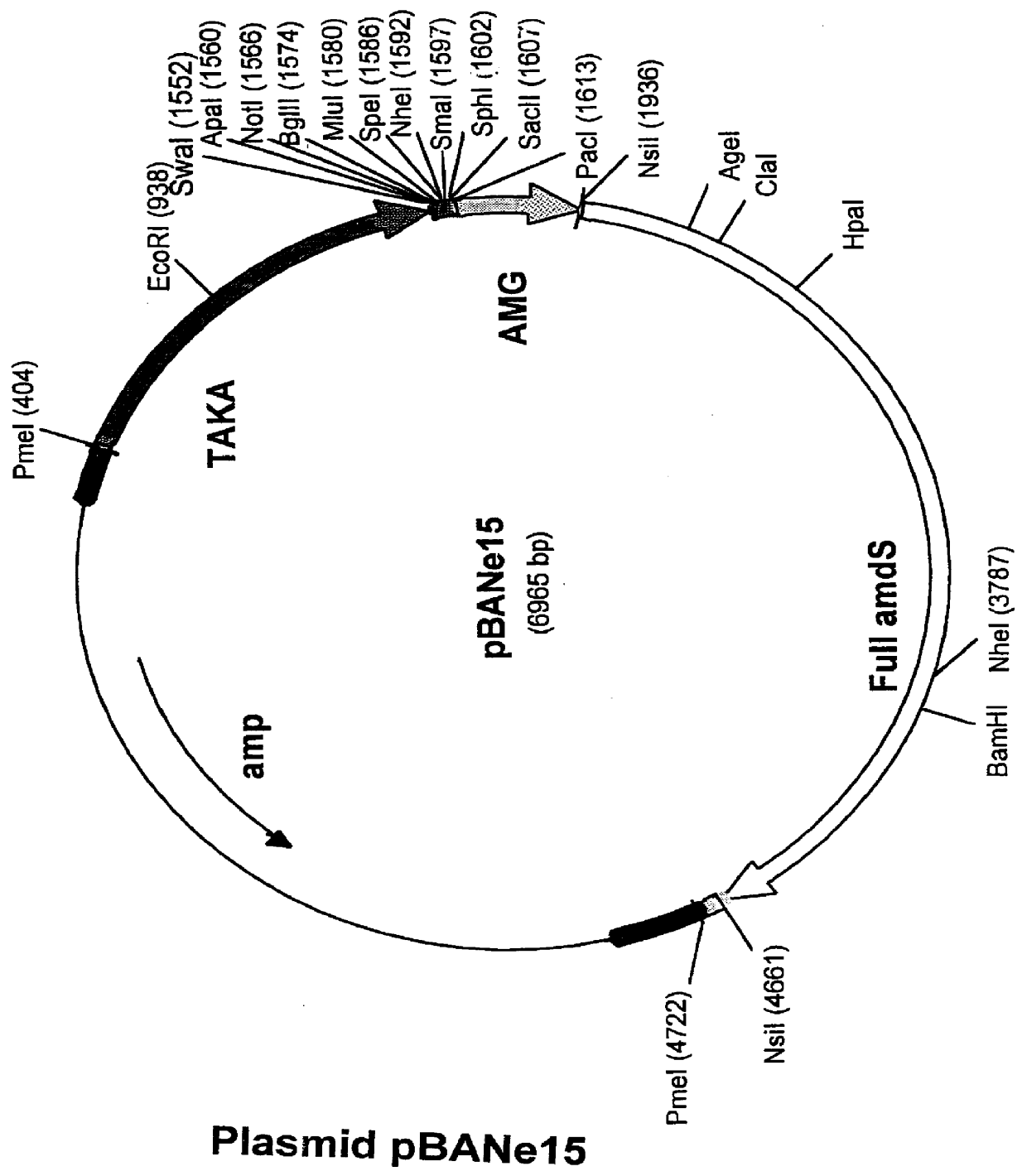
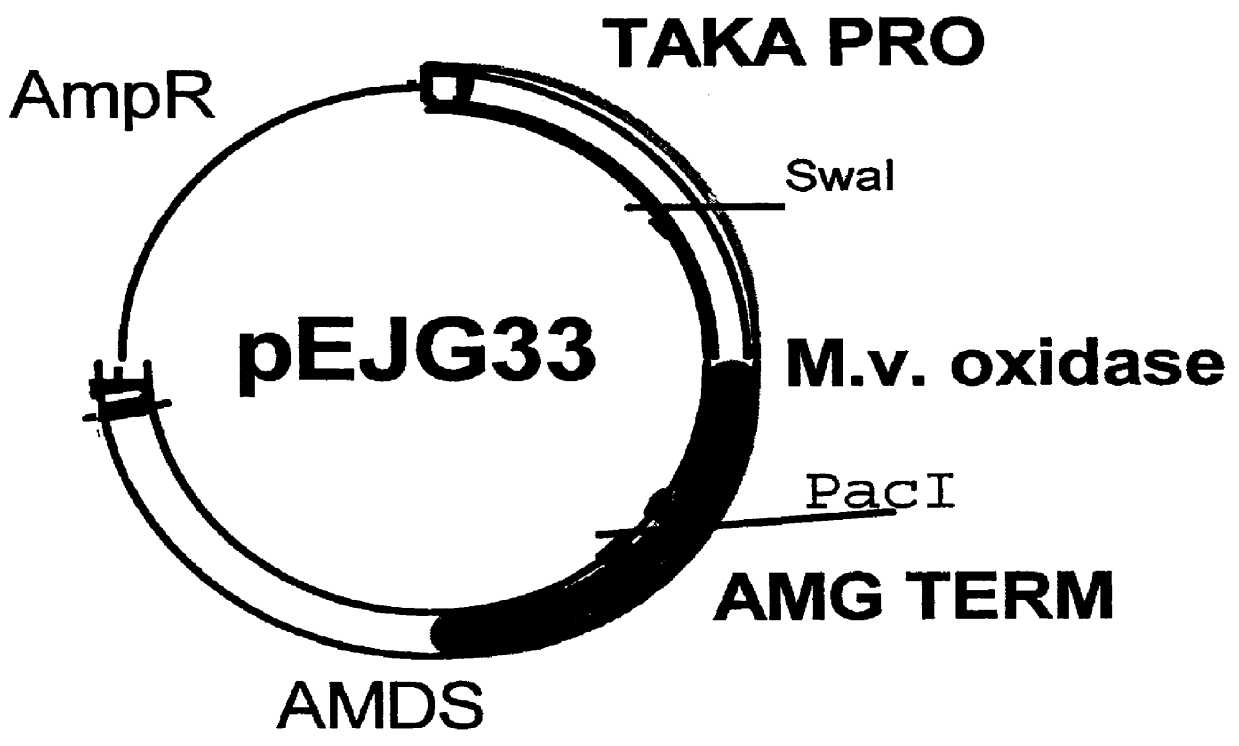
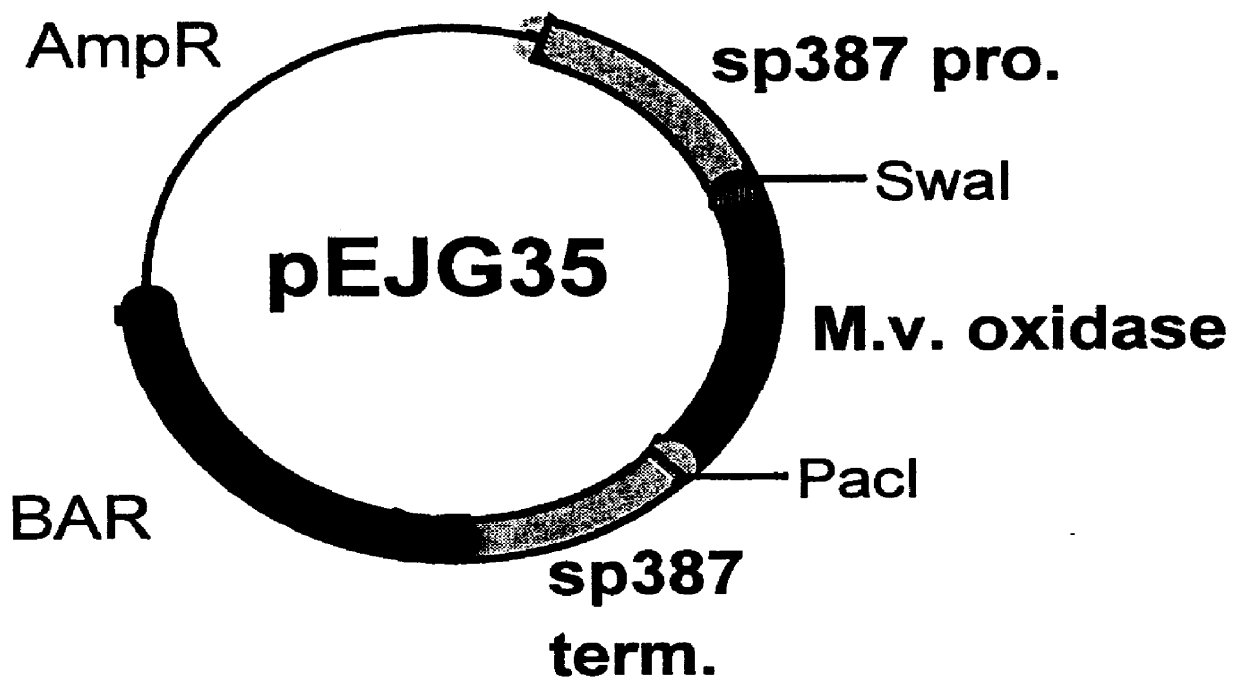
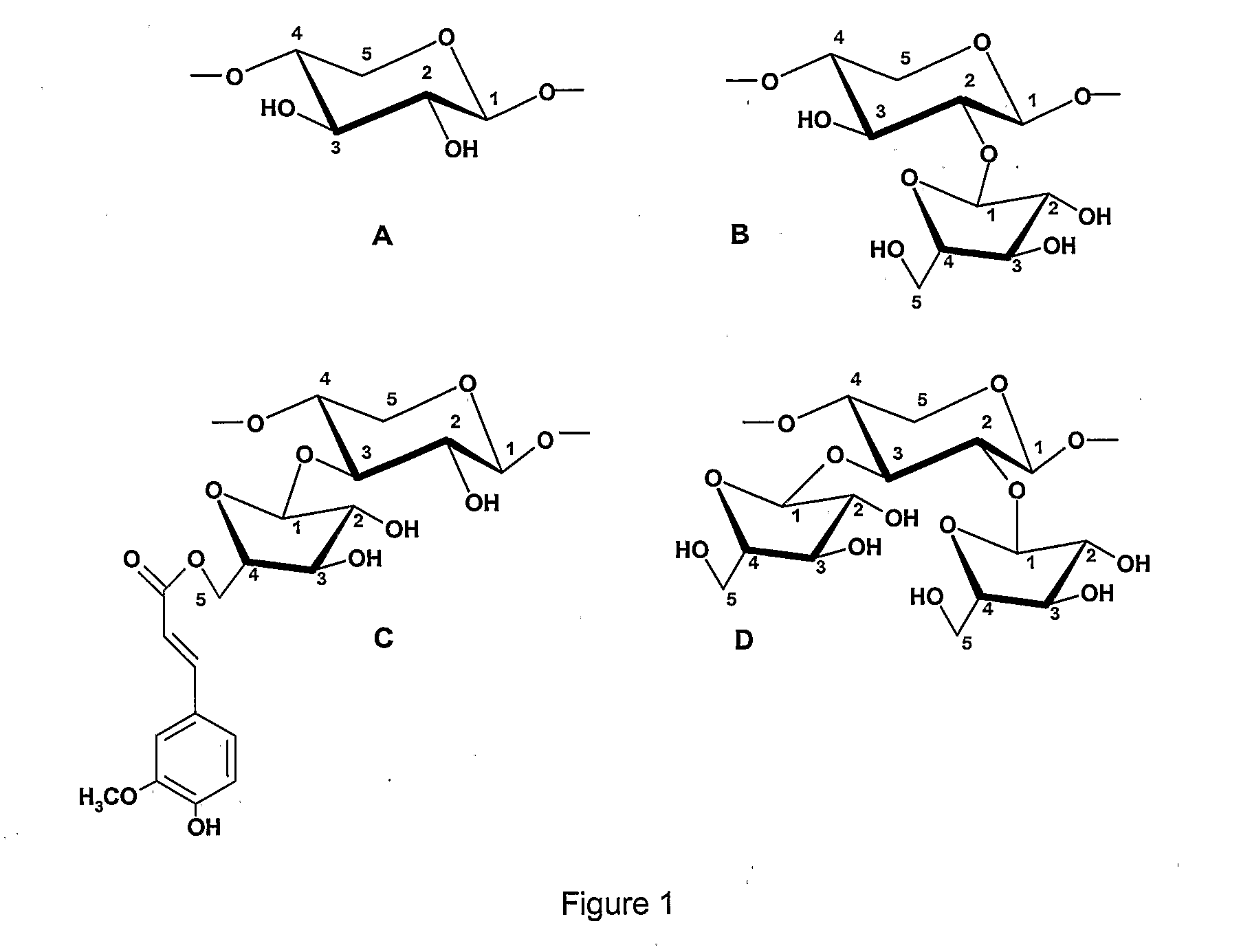
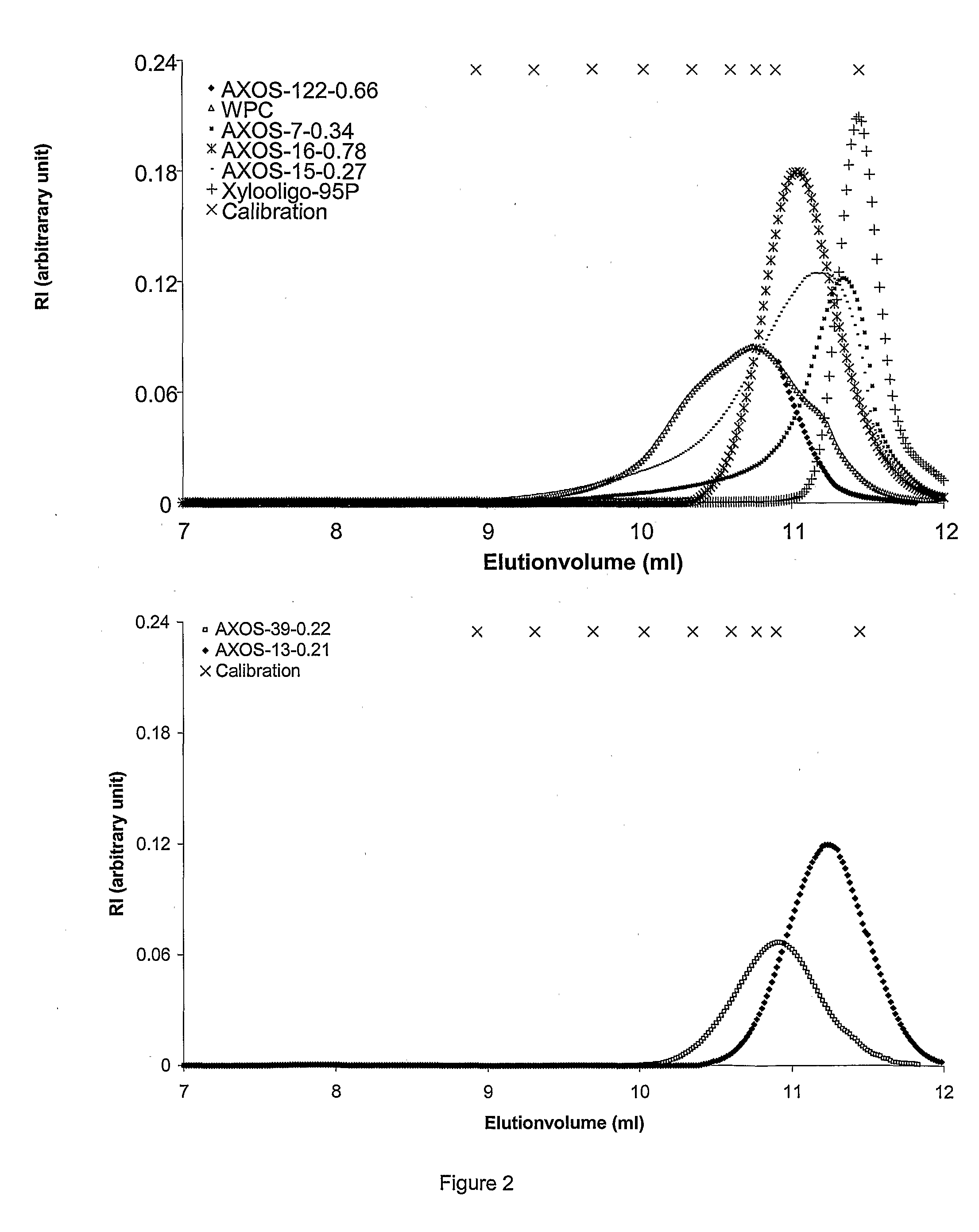
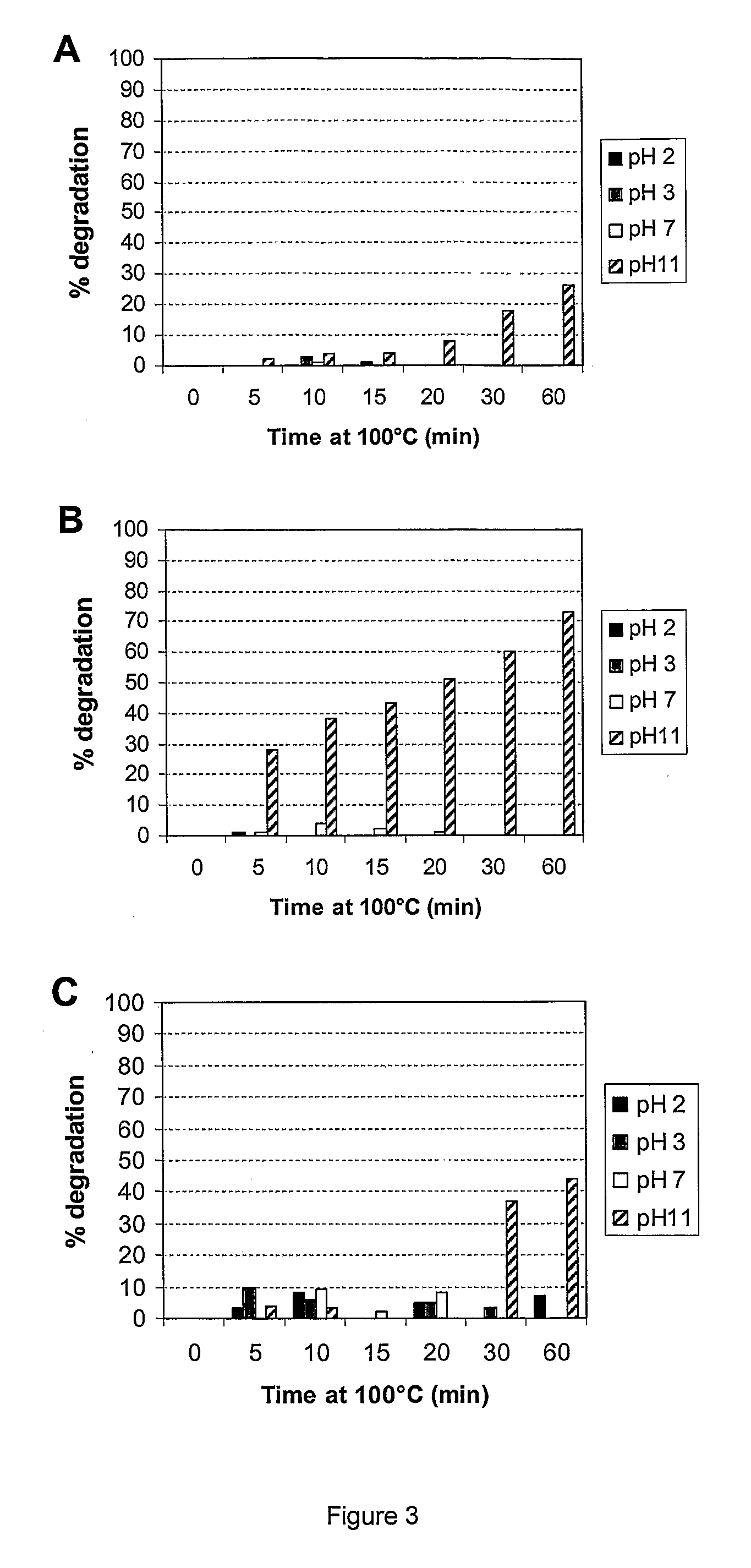
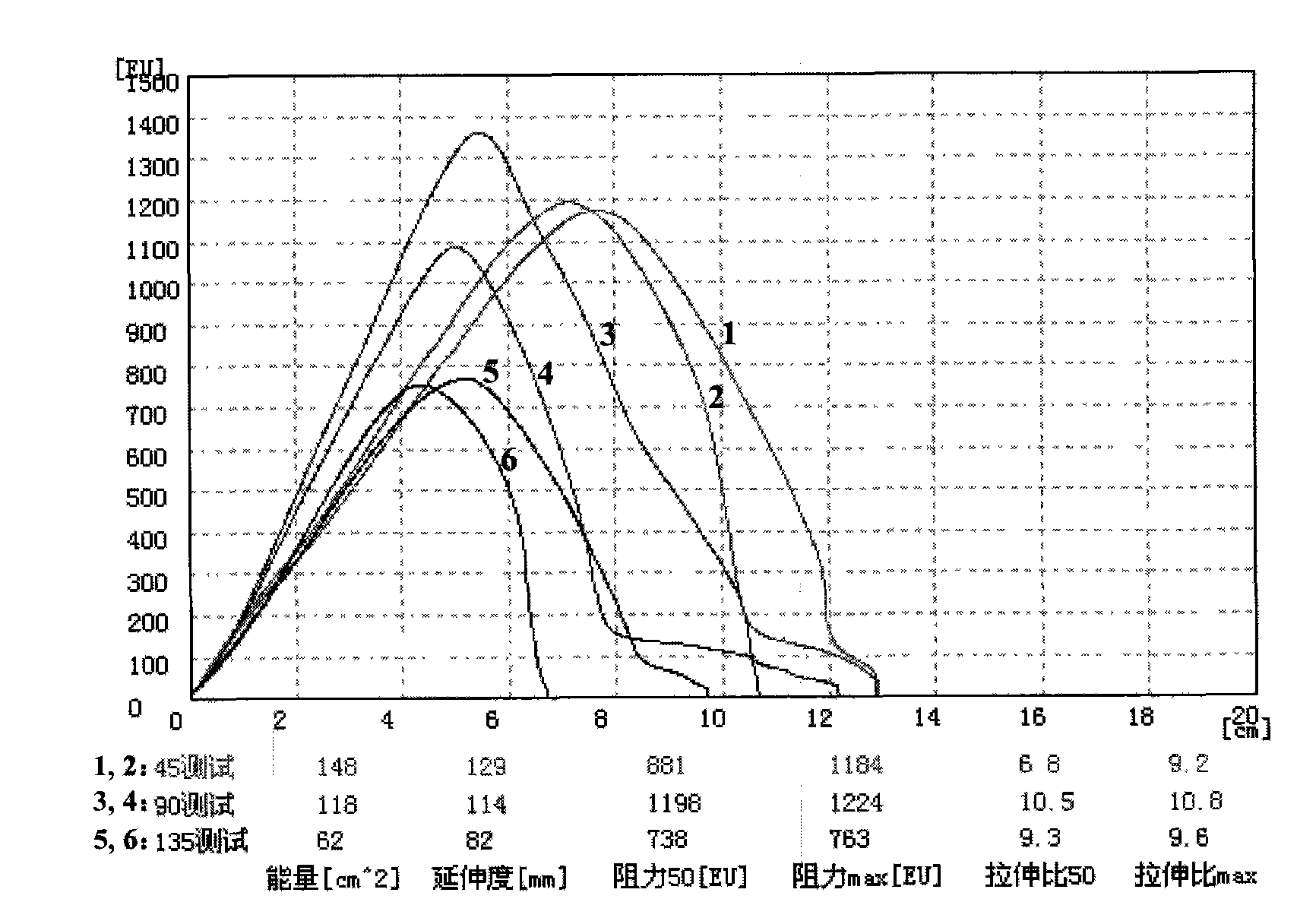
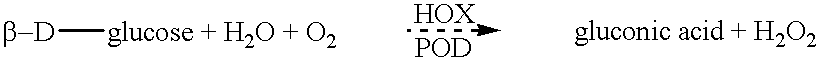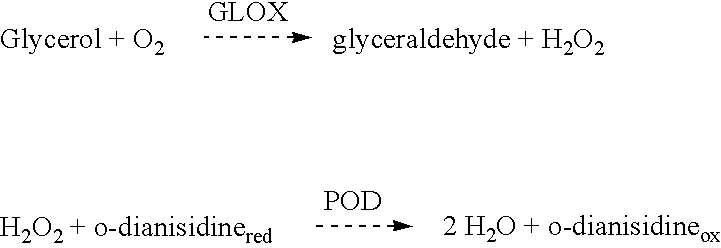Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2215results about "Pre-baking dough treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mixture of at Least 6 Species of Lactic Acid Bacteria and/or Bifidobacteria in the Manufacture of Sourdough
A mixture of at least 6 species of lactic acid bacteria and / or Bifidobacteria is disclosed for use in bakery and medical field. The preferred mixture comprises Streptococcus thermophilus, Bifidobacterium infantis, Bifidobacterium longum, Bifidobacterium breve, Lactobacillus acidophilus, Lactobacillus plantarum, Lactobacillus casei, Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus. Said mixture is useful for a sourdough, a leavening composition. Baked goods and other food products obtained therefrom are disclosed. These goods have low or no gluten content and are suitable for the integration of the diet of a subject suffering from celiac disease, for decreasing the risk of allergies due to wheat flour albumins and globulins, for the treatment of schizophrenic symptoms, in the preparation of products for enteric diet.
Owner:VSL PHARMA INC
Non-maltogenic exoamylases and their use in retarding retrogradation of starch
InactiveUS6667065B1Highly effective in retarding or reducing detrimental retrogradationImprove propertiesDough treatmentHydrolasesAmylosucrase activitySide chain
The present invention relates to a process for making a bread product. The process includes the addition of a non-maltogenic exoamylase that hydrolyses starch to a starch medium, and the application of heat to the starch medium. The non-maltogenic exomylase cleaves one or more linear malto-oligosaccharides, predominantly consisting of from four to eight D-glucopyranosyl units, from non-reducing ends of amylopectin side chains. The non-maltogenic exoamylase has an endoamylase activity of less than 0.5 endoamylase units (EAU) per unit of exoamylase activity.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Method of improving the properties of a flour dough, a flour dough improving composition and improved food products
InactiveUS6358543B1Reduce disadvantagesReduce stickinessDough treatmentHydrolasesIridophycus flaccidumEuthora cristata
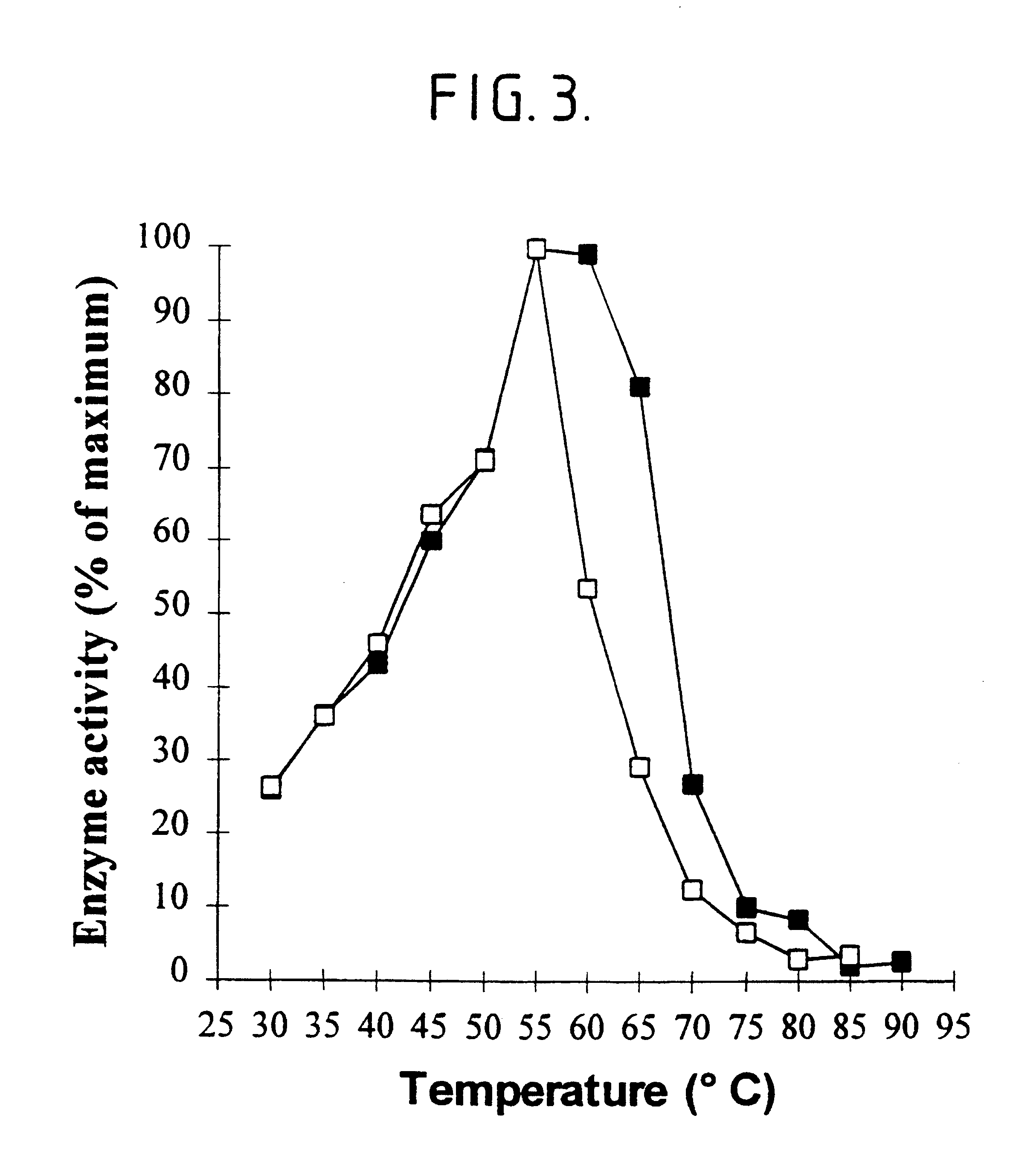
A method of improving the rheological properties of a flour dough and the quality of the finished product made from such a dough, including adding an effective amount of an oxido-reductase capable of oxidizing maltose, in particular a hexose oxidase, e.g. isolated from an algal species such as Iridophycus flaccidum, Chondrus crispus or Euthora cristata and a dough improving composition containing the oxidore-ductase.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Reduced Pigmentation Microalgae Strains and Products Therefrom
InactiveUS20100297292A1Reduced colorationIncrease rangeMilk preparationDough treatmentHypopigmentationCarotenoid
The invention provides unique and novel strains of microalgae that have been subjected to non-transgenic methods of mutation sufficient to reduce the coloration of biomass produced by the strains. Biomass produced from such strains can be used in the manufacture of baked goods, gluten free foods, beverages, high lipid algal flours, and other foods. Pigments such as carotenoids and chlorophyll can be undesirable for consumer acceptance when incorporated into foods such as mayonnaise, yogurt, and white sauces that are not traditionally associated with colors such as yellow, red, orange and green. Some pigments, such as chlorophyll, can also create undesirable taste profiles. Use of reduced pigment microalgal biomass expands the range of food products that can be manufactured with healthy lipid profiles. High protein containing biomass of the invention, also reduced in pigmentation, is also incorporated into products such as meat analogues, nutritional bars and meal replacement beverages. The reduced pigmentation microalgae also allow for incorporation of higher amounts of biomass into certain food products that could otherwise be achieved using highly pigmented microalgal biomass. Methods of generating novel reduced pigment microalgae are disclosed herein. The strains provided by the invention are also useful in the manufacture of healthy, neutral colored extracted triglyceride oils.
Owner:TERRAVIA HLDG INC
Thermostable amylase polypeptides, nucleic acids encoding those polypeptides and uses thereof
This invention relates to amylase polypeptides, and nucleic acids encoding the polpypeptides and uses thereof. The amylases of the present invention have been engineered to have more beneficial qualities. Specifically, the amylases of the current invention show an altered thermostability.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
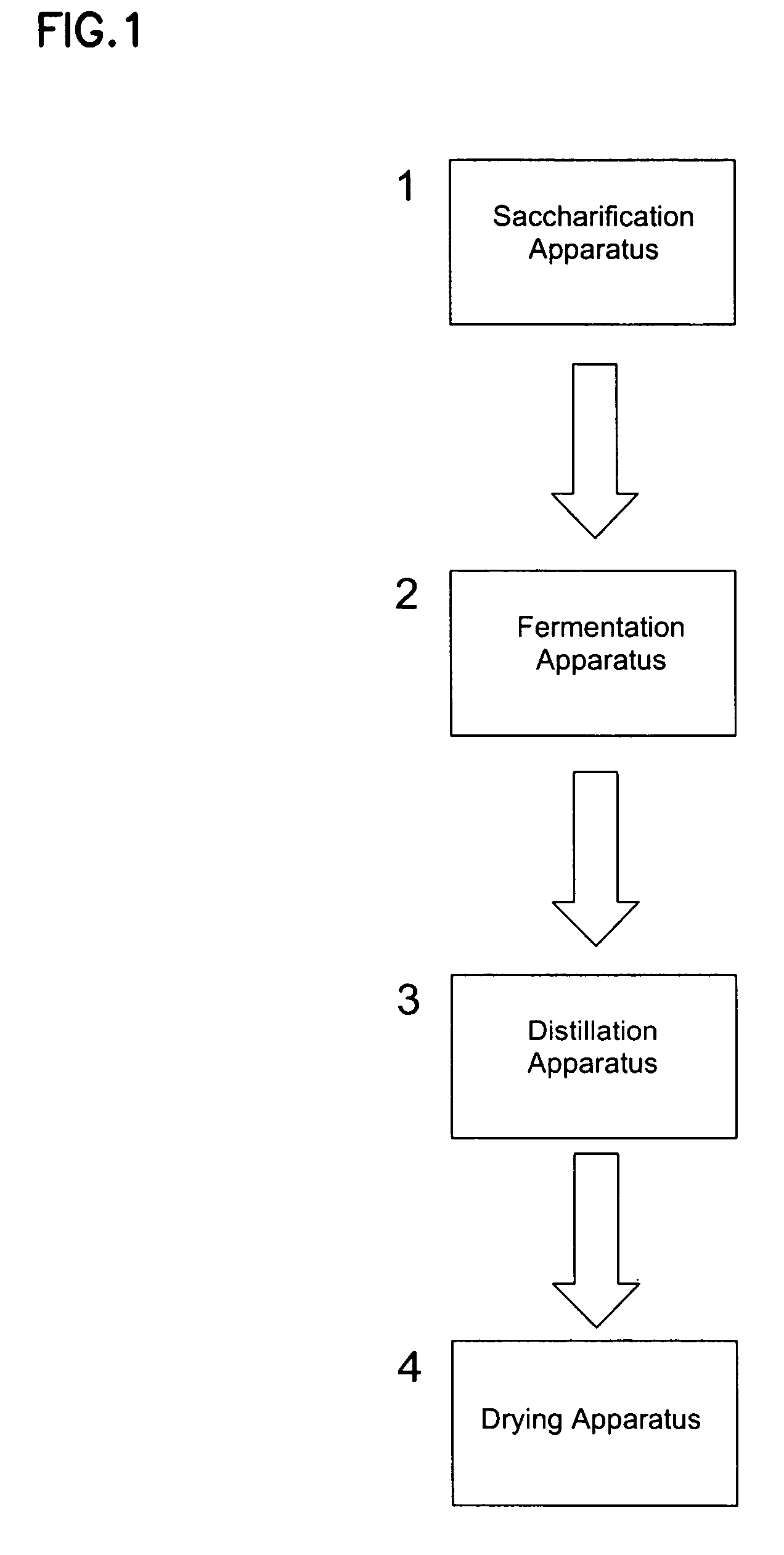
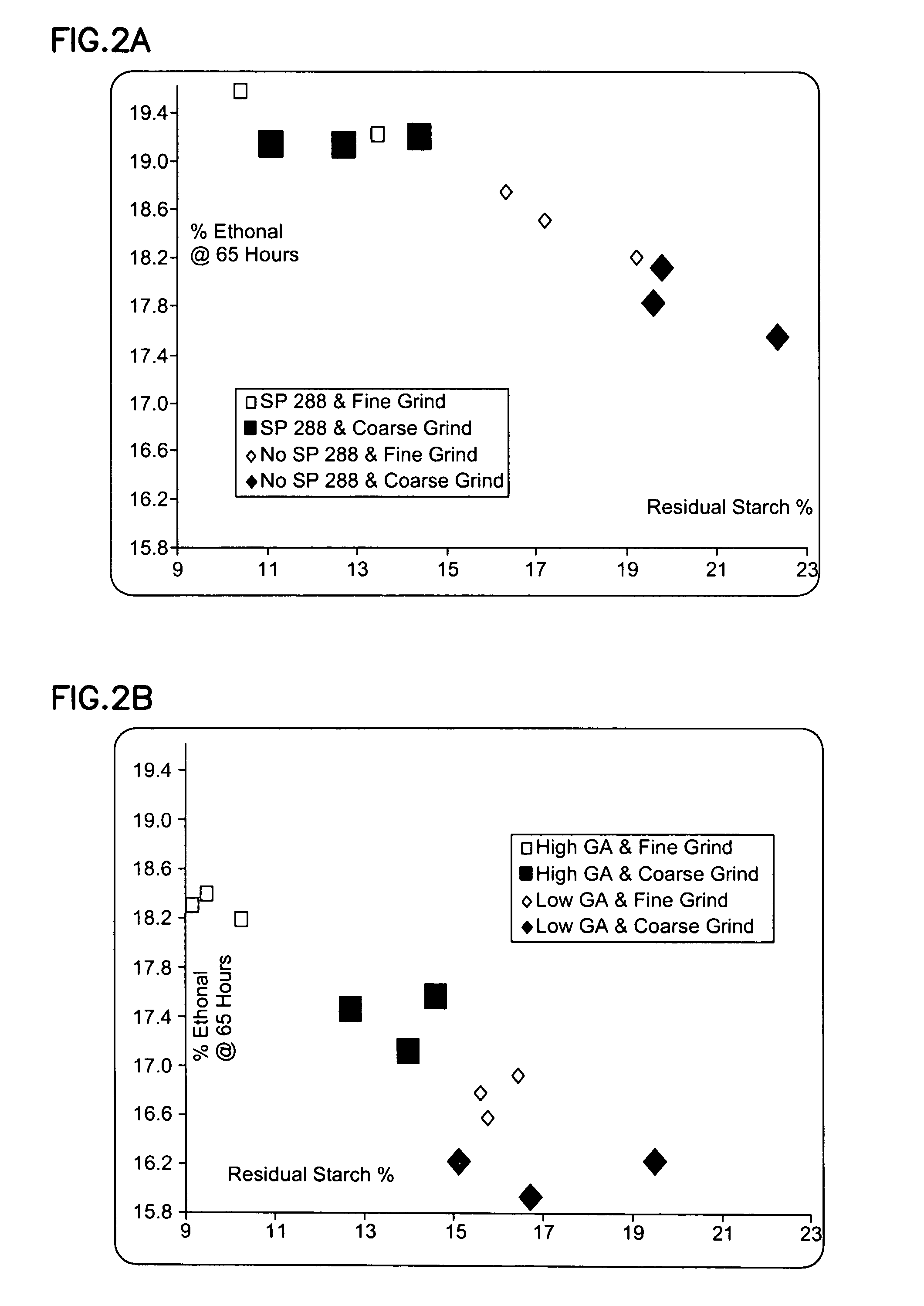
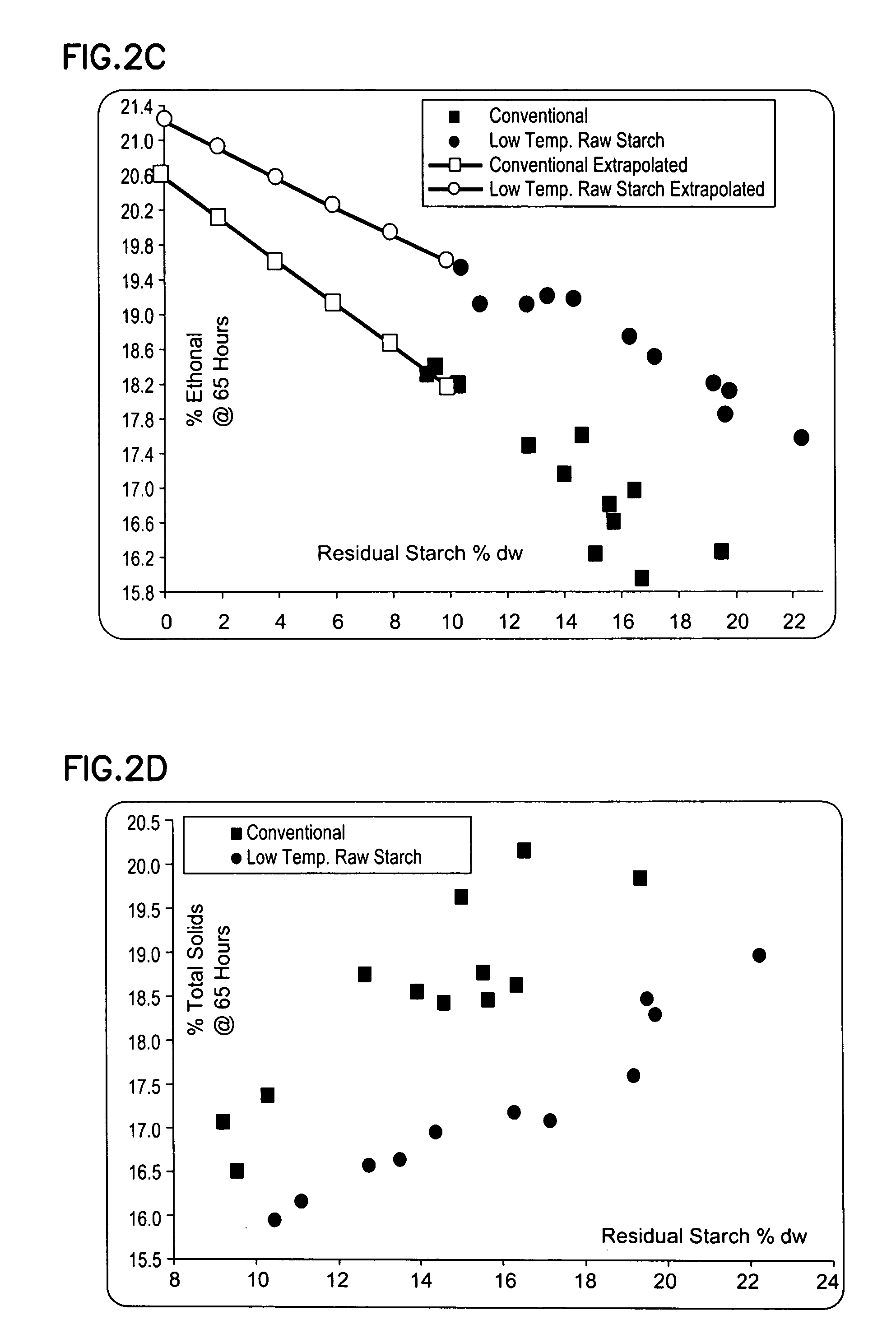
Methods and systems for producing ethanol using raw starch and selecting plant material
ActiveUS20070178567A1Improve the level ofDough treatmentWort preparationHigh alcohol beerStarch production
The present invention relates to methods for producing high levels of alcohol during fermentation of plant material, and to the high alcohol beer produced. The method can include selecting plant material. Selecting can include excluding plant material that has been exposed to high temperatures or that has had high moisture content.
Owner:POET RES INC
Method for preparing flour doughs and products made from such doughs using lipase
InactiveUS6852346B2Improve the immunityLess-prone to mechanical deformationFungiDough treatmentPore diameterSpecific volume
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Thermostable amylase polypeptides, nucliec acids encoding those polypeptides and uses thereof
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Whole grain non-dairy milk production, products and use
ActiveUS20070014892A1Increase coverageReserved functionDough treatmentWort preparationSlurryWhole milk
A method comprising selection of unbroken whole grain rice that are first washed, or whole grain corn that is first reduced in size, and then making an aqueous slurry that is subsequently wet milled to release all the protein, fat, fiber, and starch components normally held in the structure of the grain. The resulting slurry can be reacted with heat to gelatinize the starch and the subsequent product dried. Also, the heated slurry containing the liberated components can be treated to enzymatic hydrolysis via the process of liquefaction and optionally saccharification, producing whole grain rice milk products having diverse carbohydrate compositions. The whole grain milk products are characterized by a nutritional composition containing substantially all the nutritional components of the whole grain, being an opaque whole milk colloid, having smooth texture versus pulpiness, lacking in all bitterness normally associated with whole grain products, and having a variety of sweetness levels from non-sweet to very sweet.
Owner:STEUBEN FOODS
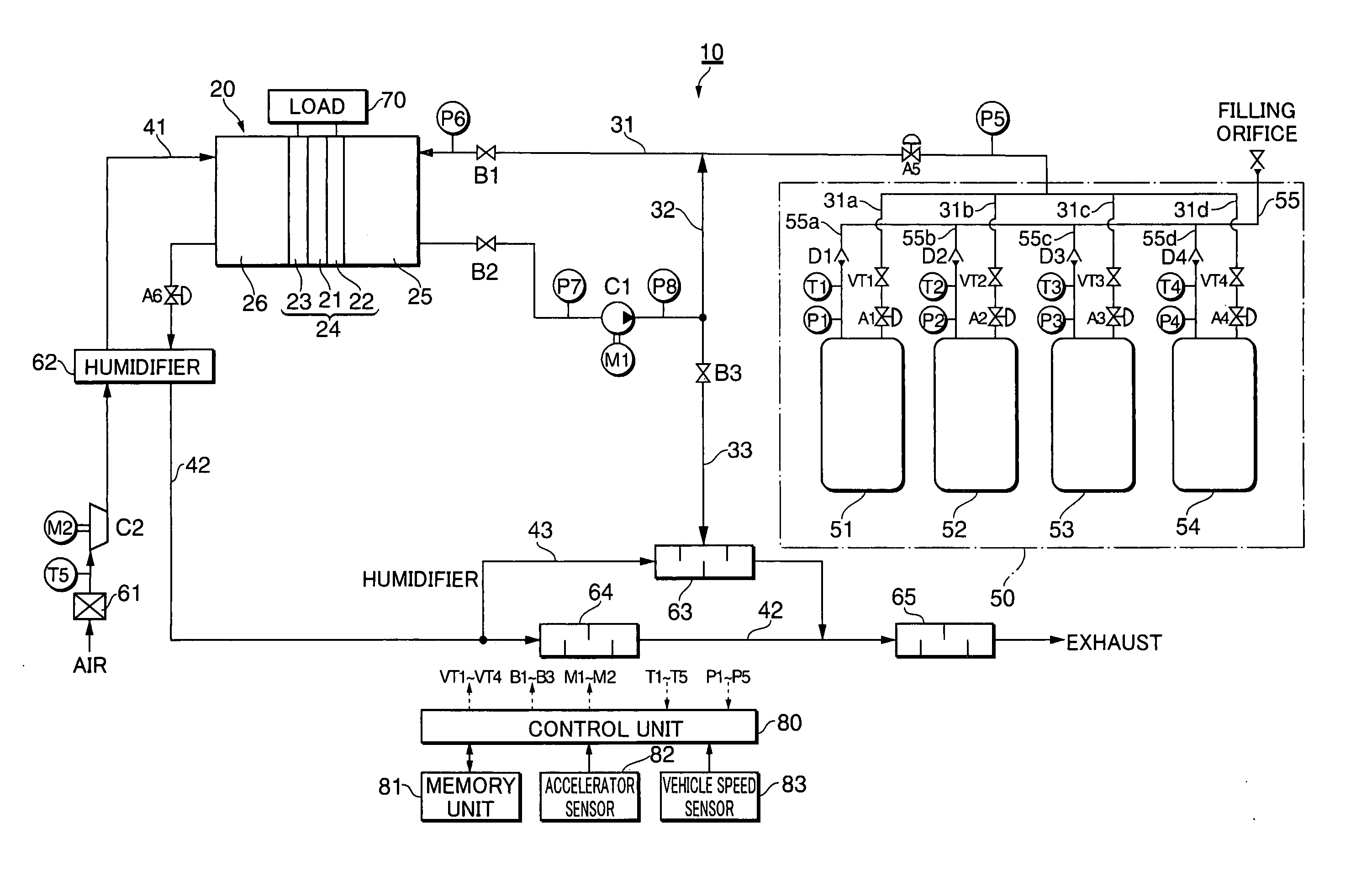
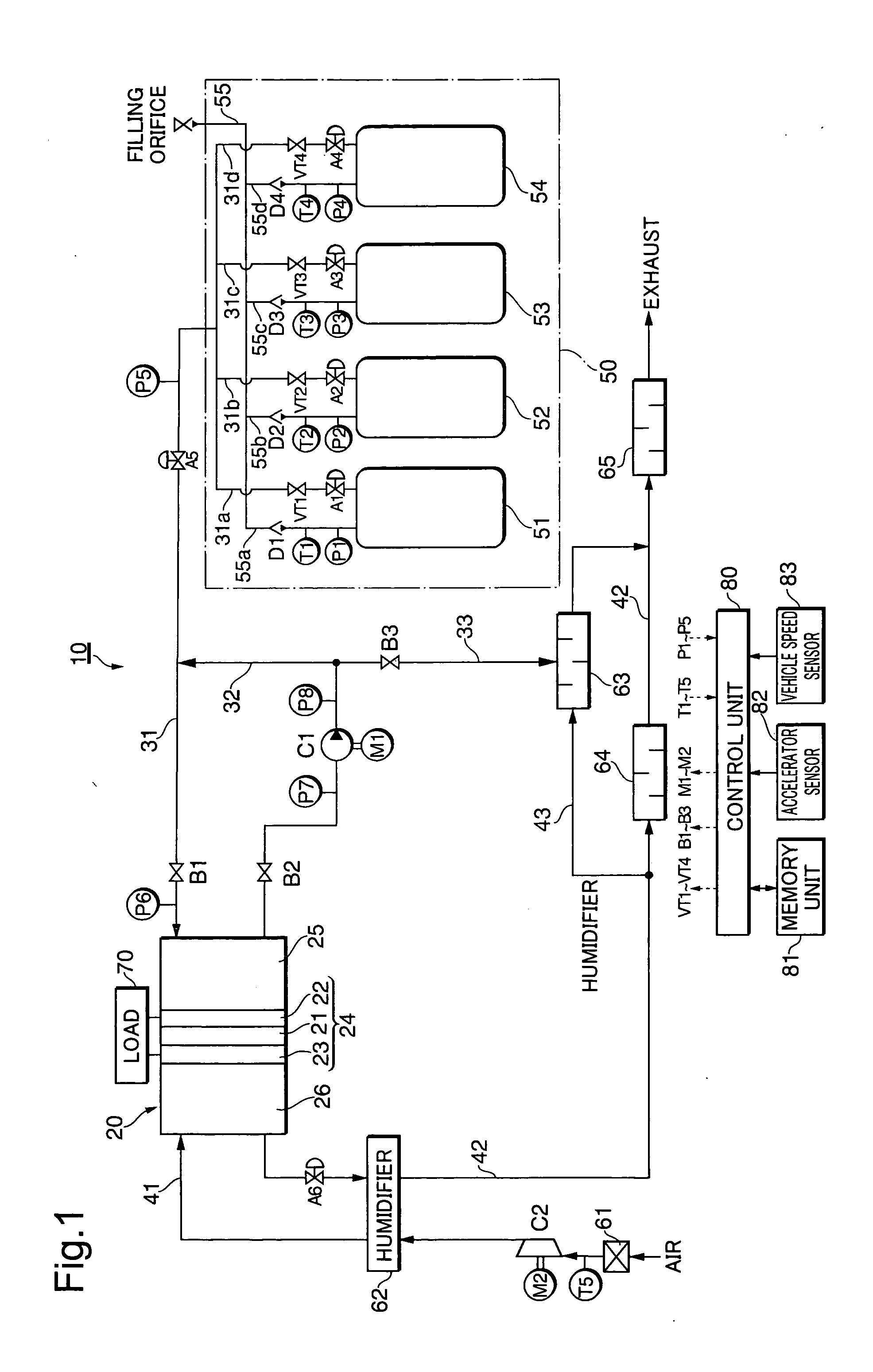
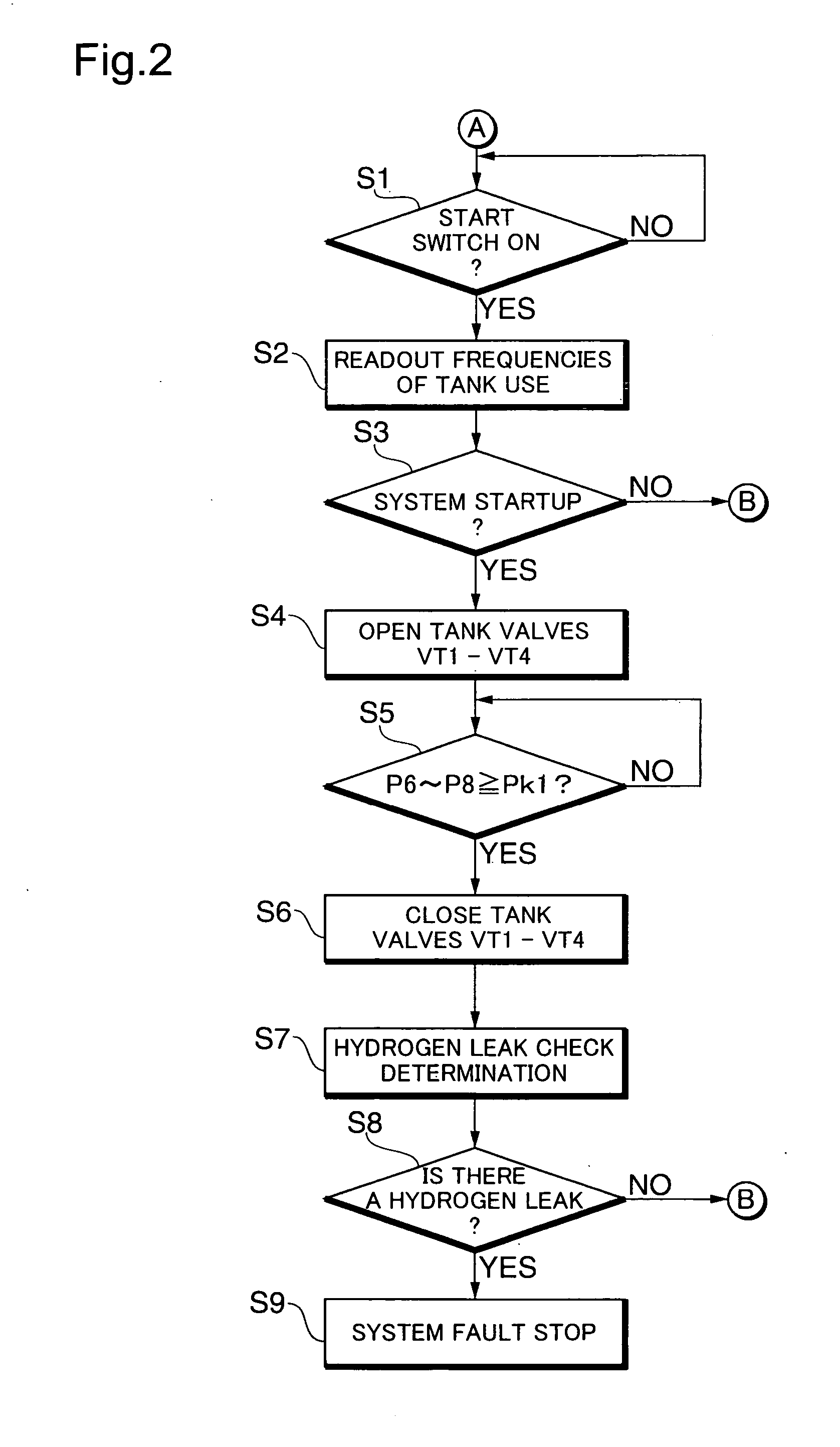
Gas supply apparatus
InactiveUS20060246177A1Reduce supplyReduce pressureGas handling applicationsSpecial dispensing meansProcess engineeringGas holder
A gas supply apparatus including: a tank unit that includes a tank storing a gas and a discharge mechanism discharging the stored gas to the outside of the tank at a reduced pressure of the stored gas; a temperature detector that detects a temperature of the tank; and a supply regulator that regulates supply of the gas from the tank according to the detected tank temperature.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Automated pizza preparation apparatus
InactiveUS20120185086A1Facilitate pizza-making processDough treatmentDough dividingAdditive ingredientEngineering
Automated apparatus for preparing pizza, and method of operating same. A customer selects a type of pizza, such as toppings or crust style. The apparatus slices and defrosts dough, applies cheese, slices and applies toppings, and cooks the pizza to order. The cooked pizza is packaged for delivery to the customer and may include a separate cutting apparatus. Proper temperature of hot and cold sections is maintained while ingredients are stored and as the pizza is cooked. The process is monitored and controlled by one or more processors.
Owner:K & G ENTERPRISES
Dough composition
InactiveUS20020094367A1Small sizeImprove the mixing effectMilk preparationDough treatmentLipid formationAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to a composition comprising i) an effective amount of one or more enzyme(s) encapsulated or coated by a lipid substance, wherein said lipid substance a) provides, at a temperature of less than 25° C., a barrier, which inhibits release of said enzyme(s) to the surrounding dough, and b) undergoes a phase transition in the temperature range from 25° C. to 60° C. to release said enzyme(s), and ii) flour and any additional, conventional dough ingredients, to methods for preparing said dough composition, to the use of one or more lipid-encapsulated or lipid-coated enzyme(s) in a dough composition, to a method for improving one or more properties of a dough, to a method for preparing a baked product, and to a dough and / or a baked product produced thereby.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Freezing flour-dough improver and uses thereof
ActiveCN101411344AOvercome stabilityOvercome volumeDough treatmentPre-baking dough treatmentYeastVitamin C
The invention discloses a frozen dough modifying agent, which is prepared by evenly mixing an enzyme preparation (including one or a plurality of alpha-amylase, cellulose, hemicellulase, pentosanase, lipase, glucose oxidase, glutamine transaminage and so on), vitamin C, an emulsifying agent, a thickening agent, wheat gluten powder, lecithin and stuffing according to certain proportion. The frozen dough modifying agent has the advantages that the frozen dough modifying agent can effectively improve the stability of dough during fermentation and roasting processes, improve the freezing resistance property of yeasts, increase the volume of finished products, improve the tissue of the finished products, reduce the loss of the vitality of the yeasts during the freezing process, and effectively delay the aging of the finished products.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
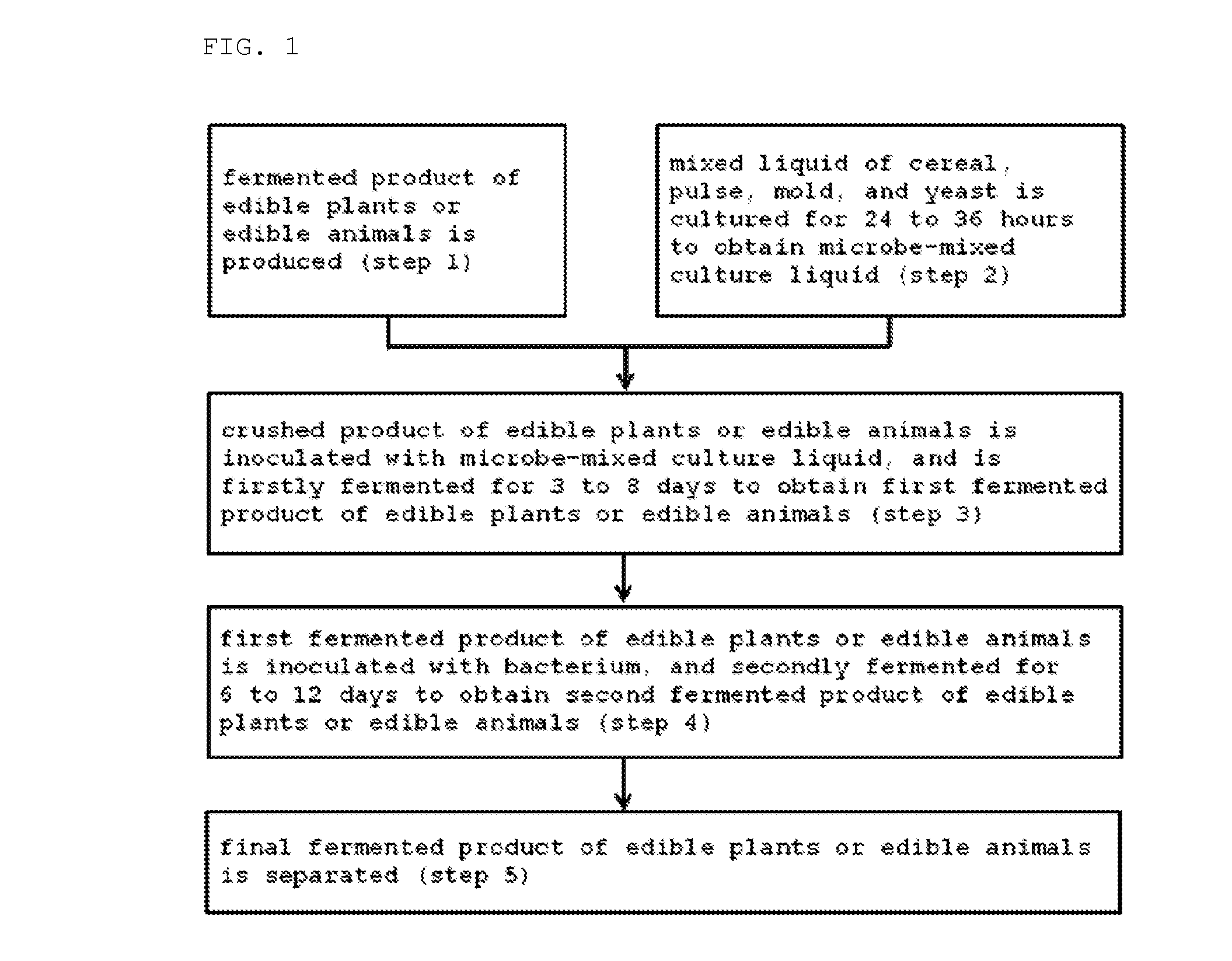
Method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal/plants, fermented edible plants or edible animal/plants produced by same, and foods containing same
ActiveUS20100316763A1Increase heightPrevent invasionDough treatmentEdible seed preservationFood flavorOrganism
The present invention relates to a method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants, to fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants produced by same, and to foods containing same. The method for producing fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants includes the steps of: producing crushed edible plants or edible animal / plants; culturing a liquid mixture of grains, saccharides, filamentous fungi, and yeast for 24 to 36 hours to produce a mixed microbial broth; inoculating the edible plants or edible animal / plants with the mixed microbial broth, and firstly fermenting the edible plants or edible animal / plants for 3 to 8 days to produce first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants; and inoculating the first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants with bacteria, and secondly fermenting the first fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants for 6 to 12 days to produce second fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants. Whereby, a fermentation period can be shortened, and food deterioration and the growth of pathogenic microorganisms can be suppressed. Further, adding the fermented edible plants or edible animal / plants produced by the above-described method into foods can provide storage stability, increase bioavailability, and improve flavor.
Owner:PHARVIS R&D KOREA
Method of improving the properties of a flour dough, a flour dough improving composition and improved food products
InactiveUS6936289B2Reduce certain disadvantageous effectsReduce stickinessDough treatmentHydrolasesFood productsRheology
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
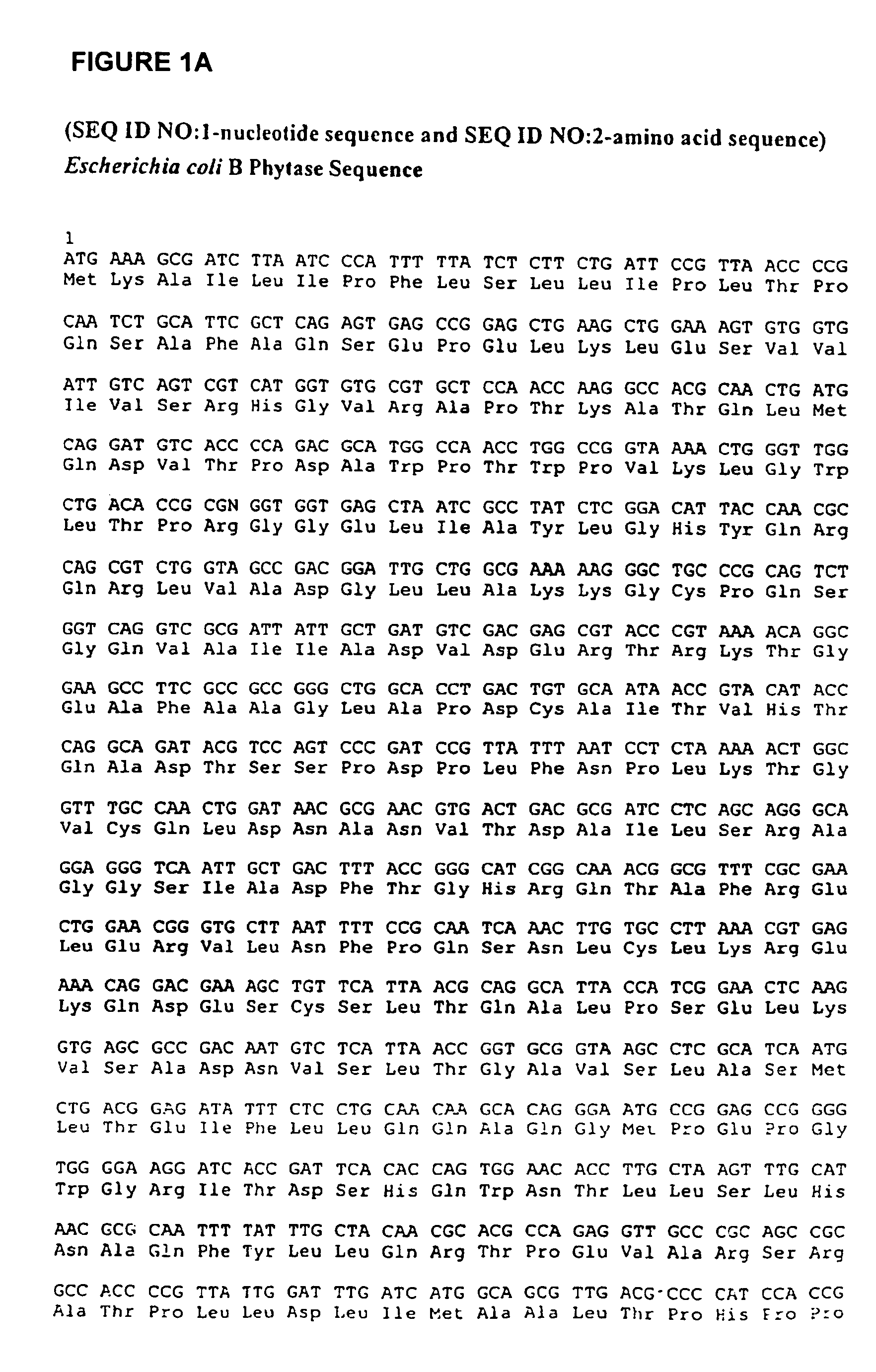
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS20050281792A1Improve publishing efficiencyHigh nutritional valueImmobilised enzymesBacteriaEscherichia coliAdditive ingredient
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified and modified phytase enzyme from Escherichia coli K12 appA phytase. The enzyme has phytase activity and improved thermal tolerance as compared with the wild-type enzyme. In addition, the enzyme has improved protease stability at low pH. Glycosylation of the modified phytase provided a further improved enzyme having improved thermal tolerance and protease stability. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells and can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In one aspect, the phytase of the present invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Method and Formulations For Gluten-Free Bakery Products
Provided herein are gluten-free compositions which can be made into a dough. The gluten-free dough can be subjected to a sheeting or pressing process and therefore can be prepared easily in commercial settings. The dough comprises gluten-free flour, modified starch, protein, leavening agents; oil and water.
Owner:RICH PRODUCTS
Method of improving dough and bread quality
InactiveUS6967035B2Increase gluten strengthDough is prevented from becoming too stiffDough treatmentHydrolasesMonoglycerideTriglyceride
A method of preparing a flour dough, said method comprising adding to the dough components an enzyme that under dough conditions is capable of hydrolysing a glycolipid and a phospholipid, wherein said enzyme is incapable, or substantially incapable, of hydrolysing a triglyceride and / or a 1-monoglyceride, or a composition comprising said enzyme, and mixing the dough components to obtain the dough.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Hybrid enzymes
InactiveUS20060147581A1Less riskImprove the baking effectDough treatmentBacteriaHybrid enzymeBiochemistry
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Phytases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS7078035B2Improve the immunityImprove heat resistanceImmobilised enzymesBacteriaPhytaseNucleotide
The invention provides isolated and recombinant phytase enzymes. In one aspect, the phytases are produced by modification of the wild type appA of E. coli. The enzyme can be produced from recombinant host cells. The phytases of the invention can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In particular, the phytases of the invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients. The phytases of the invention can be thermotolerant and / or thermostable. Also provided are methods for obtaining a variant polynucleotide encoding a phytase and for obtaining a phytase with thermostability or thermotolerant at high or low temperatures.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Phytase-containing foodstuffs and methods of making and using them
InactiveUS6720014B1High nutritional valueImprove release efficiencyFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliPhytase activity
A purified recombinant phytase enzyme derived from Escherichia coli B. The enzyme has a molecular light of about 47.1 kilodaltons and has phytase activity. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells and can be used to aid in the digestion of phytate where desired. In particular, the phytase of the present invention can be used in foodstuffs to improve the feeding value of phytate rich ingredients.
Owner:VERENIUM CORPORATION
Low lactose, low moisture shelf-stable, bakeable savory cheese product and process for preparing it
InactiveUS20020155198A1Good cheese flavorSuitable cheeseBaking mixturesConfectionerySmall dropletAdditive ingredient
A savory, smooth-textured, bakeable and shelf-stable product is prepared as a three-phase formulation, including an aqueous liquid phase, a dispersed fat phase and a solids phase, preferably containing cheese in significant proportion. The liquid phase is present in sufficient quantity to suspend and disperse the fat and solids phases. The dispersed fat must have sufficiently small droplet size raise the viscosity for this phase sufficiently to result in a creamy texture for the final product. The savory flavor ingredients are present as undissolved solids of sufficiently small particle size to provide the proper flavor release for the flavor and a texture consistent with the savory flavor. Preferred cheese products will have a lubricous, slippery, smooth mouthfeel and a flavor release that endures until the palate is essentially clean. The product can be applied to unbaked doughs prior to baking and retain their desired properties after baking. The product can also be packaged for use as is with any number of complimentary foods.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL GREAT BRANDS LLC
Recombinant hexose oxidase, a method of producing same and use of such enzyme
InactiveUS6251626B1Good effectLower pHCosmetic preparationsFungiIridophycus flaccidumEscherichia coli
A method of producing hexose oxidase by recombinant DNA technology, recombinant hexose oxidase and the use of such enzyme, in particular in the manufacturing of food products such as doughs and dairy products, animal feed, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, dental care products and in the manufacturing of lactones. Suitable sources of DNA coding for the enzyme are marine algal species including Chondrus crispus, Iridophycus flaccidum and Euthora cristata. In useful embodiments, the recombinant hexose oxidase is produced by Pichia pastoris, Saccharomyces cerevisiae or E. coli.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Carbohydrate oxidase and use thereof in baking
The properties of dough or bread can be improved by the addition of a carbohydrate oxidase which can oxidize the reducing end of an oligosaccharide more efficiently than the corresponding monosaccharide, e.g., preferentially oxidizing maltodextrins or cellodextrins over glucose. A novel carbohydrate oxidase having the capability to oxidize maltodextrins and cellodextrins more efficiently than glucose may be obtained from a strain of Microdochium, particularly M. nivale. The amino acid sequence of the novel carbohydrate oxidase has very low homology (<20% identity) with known amino acid sequences.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Low pressure refrigerated dough product
A refrigerated dough system is provided which includes a dough in a container flushed with a gas. The dough contains a leavening agent capable of generating gas in the dough after the dough is sealed in the container. The container is provided with a pressure release mechanism to release excess pressure generated within the container as the dough leavens and during storage. The dough system is capable of sustaining a leavened dough structure during storage so that upon baking the dough, the resulting baked product resembles a freshly prepared and baked dough.
Owner:GENERAL MILLS INC
Prebiotic Preparation
InactiveUS20080102162A1Extraordinary viscosity forming potentialSignificant positive effectOrganic active ingredientsDough treatmentArabinoxylanFood science
The present invention relates to a nutritional additive comprising arabinoxylans, which beneficially modulates the human intestinal flora. Furthermore, several food and beverage products comprising the additive are provided as well as methods to prepare the said additive.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV
Use of converted low-viscosity, high solids starch in foods
InactiveUS6896915B2Stable and low viscosityHigh glossDough treatmentConfectioneryViscosityFood products
Owner:CORN PROD DEV INC
Bread improver and application thereof in bread making
ActiveCN102113530AEasy to operateImprove anti-aging propertiesDough treatmentPre-baking dough treatmentFlavorAntioxidant
The invention relates to a bread improver and application thereof in bread making. The bread improver comprise the following ingredients in terms of the total weight of the improver: 0.9-2.3% of complex enzyme preparation, 0.5-4% of antioxidant, 10-30% of emulsifier, 15-40% of inactivated dried yeast and the balance of starch. The complex enzyme preparation comprises the following ingredients in terms of the total weight of the improver: 0.05-0.3% of alpha-amylase, 0.5-1% of hemicellulase, 0.3-0.7% of maltose amylase, and 0.05-0.3% of lipase. The improver provided by the invention is a composite additive for improving bread quality and can be used for improving the rheological properties and the processability of dough, effectively inhibiting dough aging and improving bread flavor.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
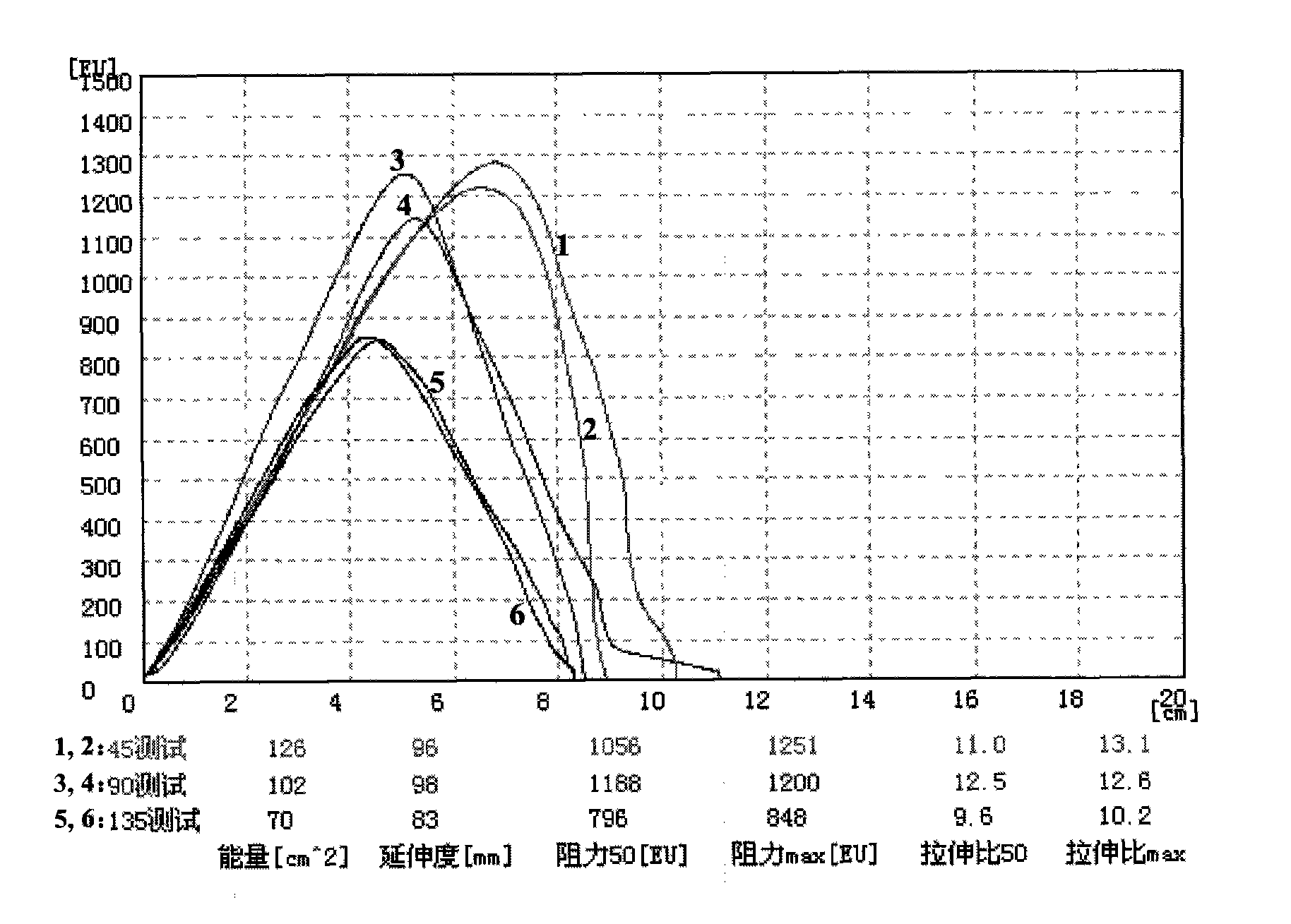
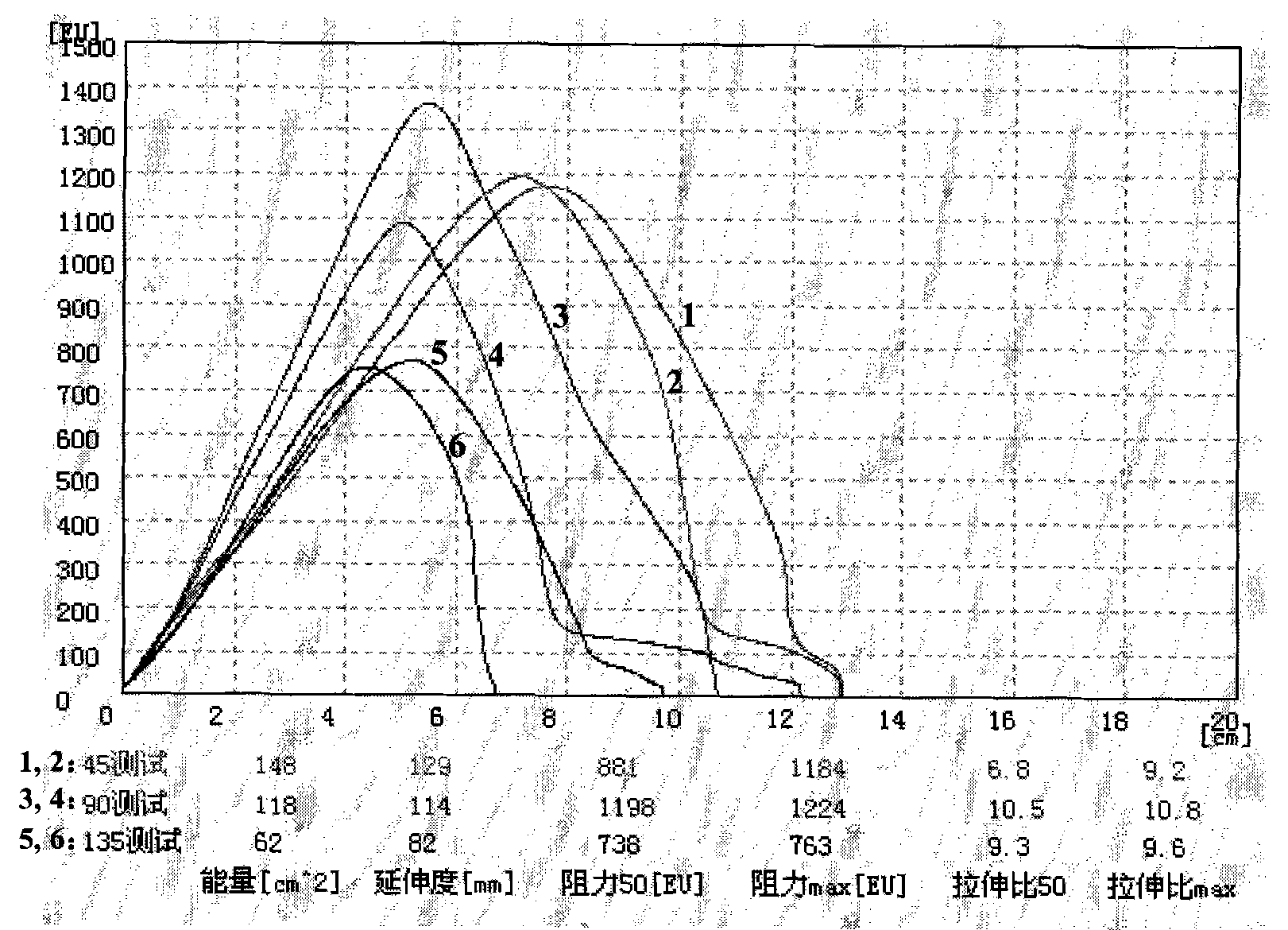
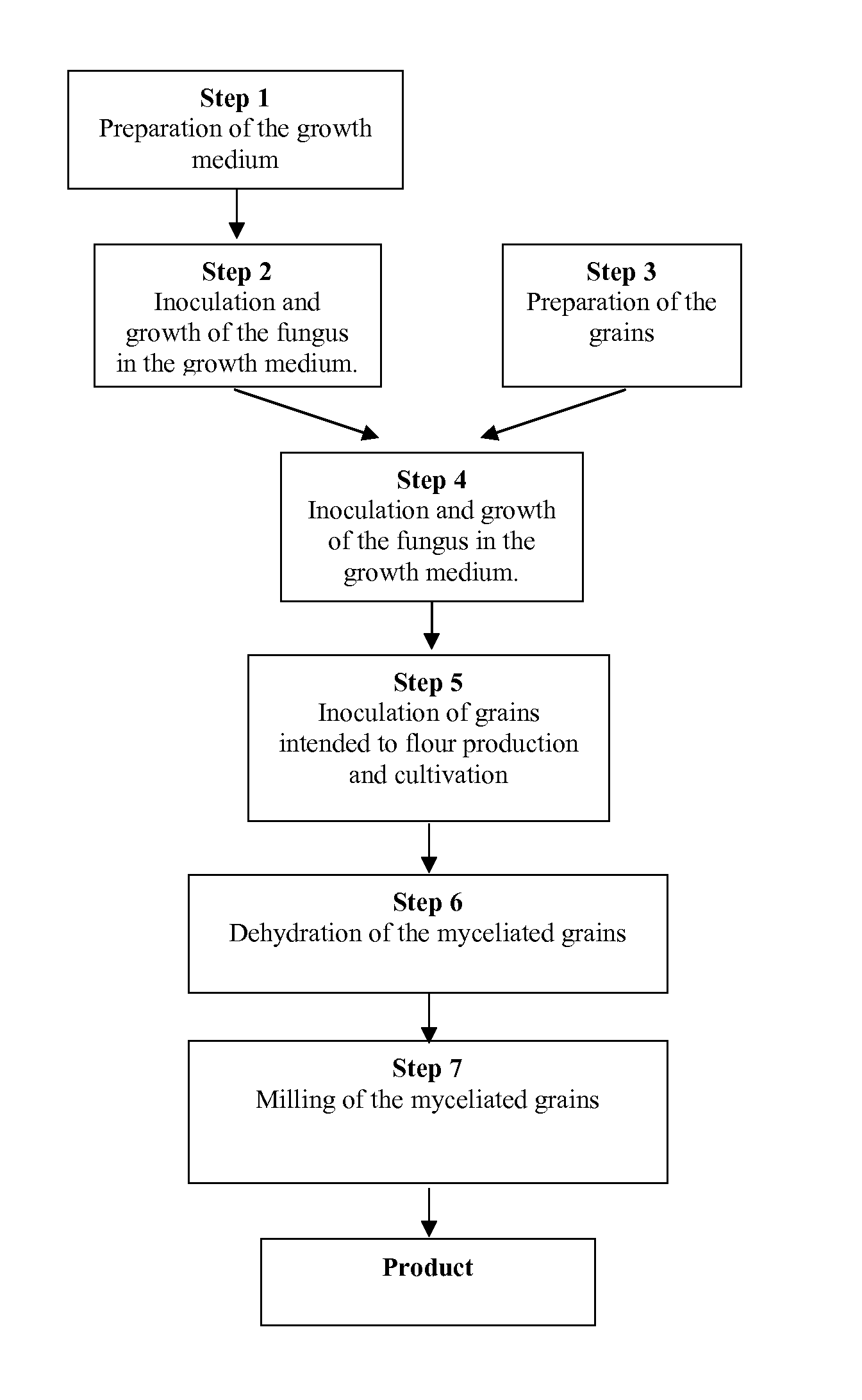
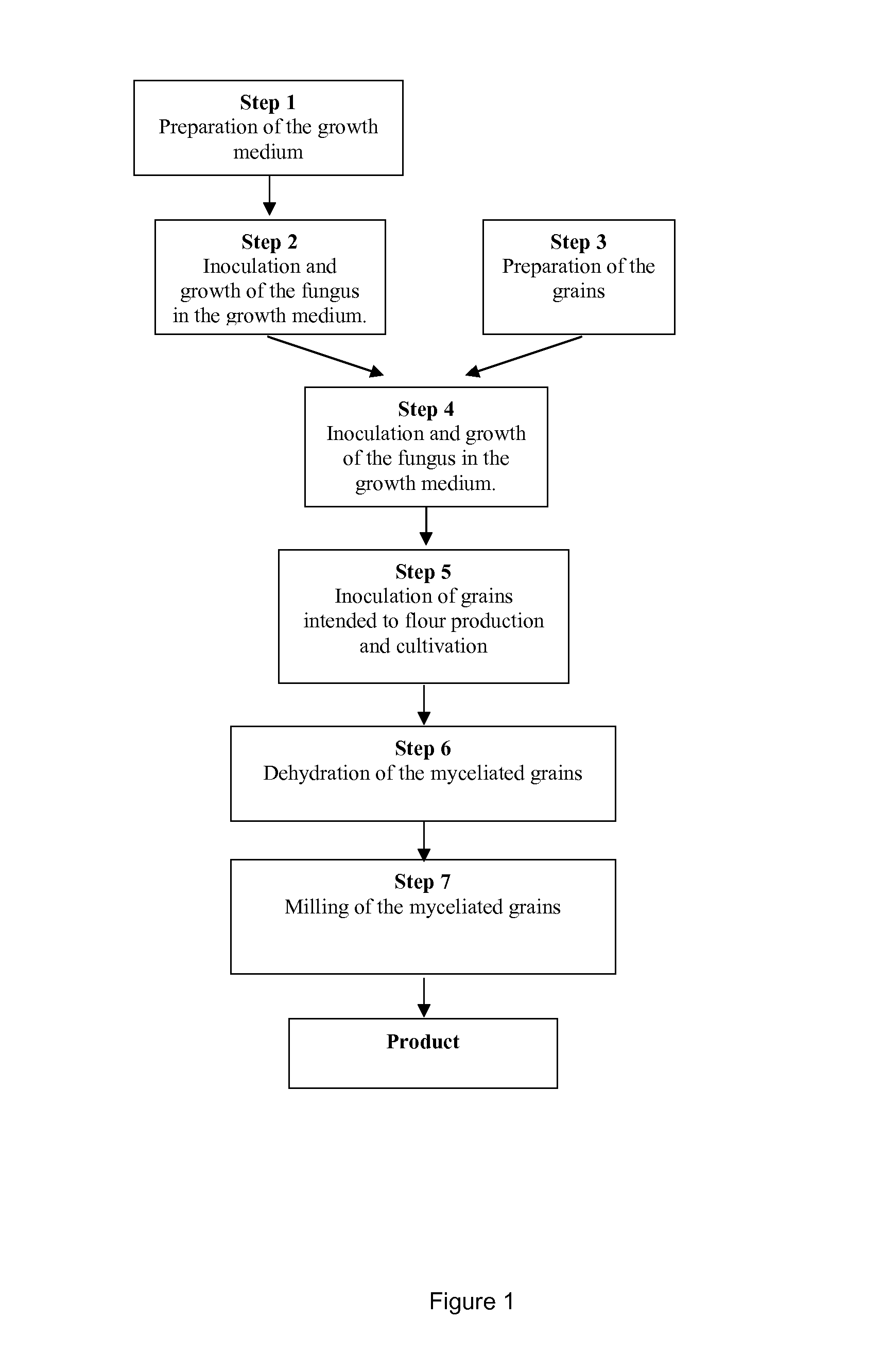
Flours produced from fungus myceliated grain
The present patent relates to a method for producing flours from grain myceliated with macroscopic fungi (mushrooms). These flours can be used to prepare food for human consumption, such as bread and biscuits, and for animal consumption, such as fodder. Active principles (ergosterol, beta glucan, linoleic and oleic acids, lectins), enzymes, proteins, amino acids, vitamins, mineral salts, inter alia, can also be extracted from these flours for use in the chemical, foodstuff and cosmetic industries, for producing phytotherapeutic agents, pharmaceuticals, textiles, paper products, pharmaceuticals and fodder for animals.
Owner:EMPRESA BRASILEIRA DE PESQUISA AGROPECUARIA EMBRAPA +2
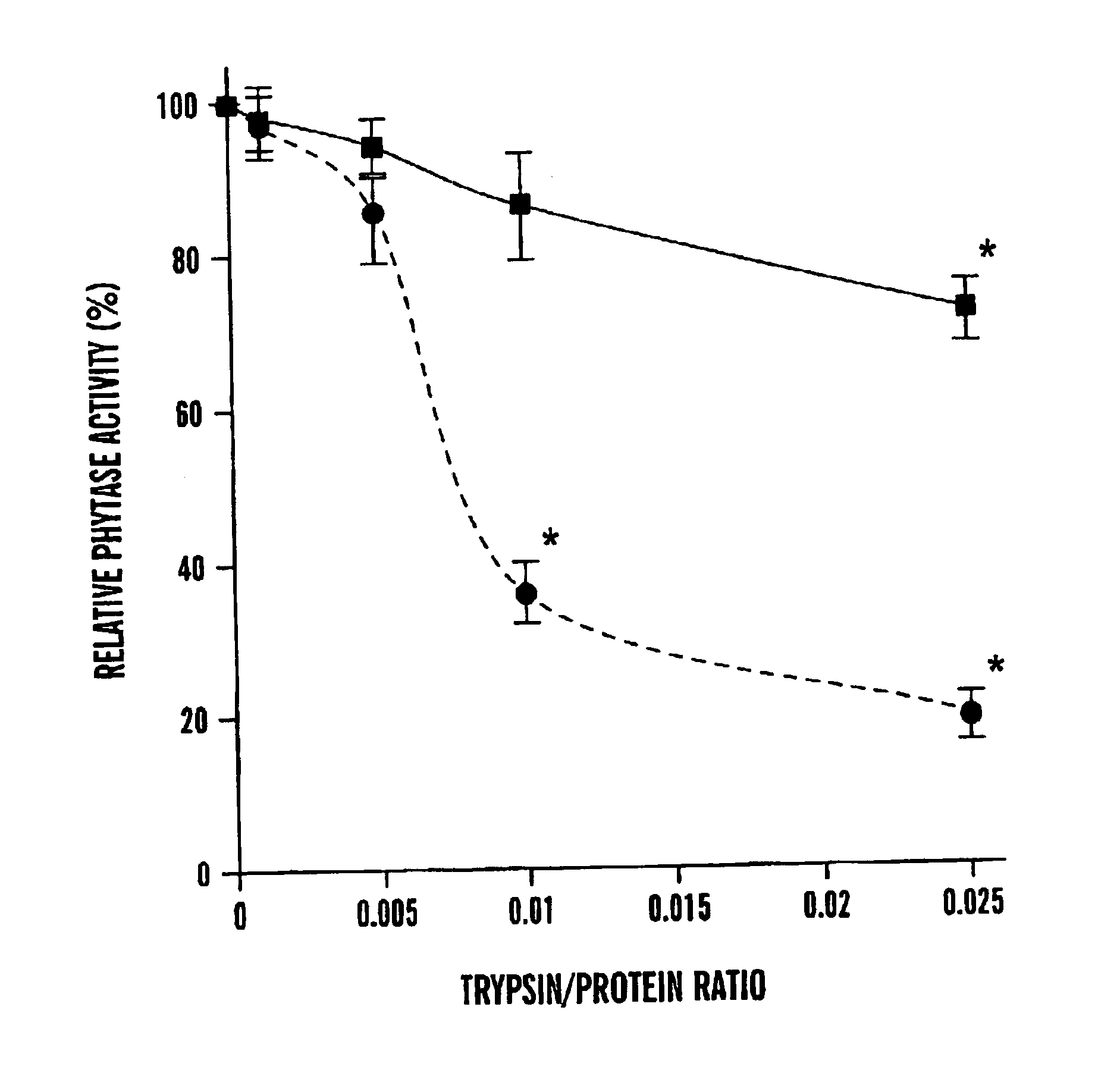
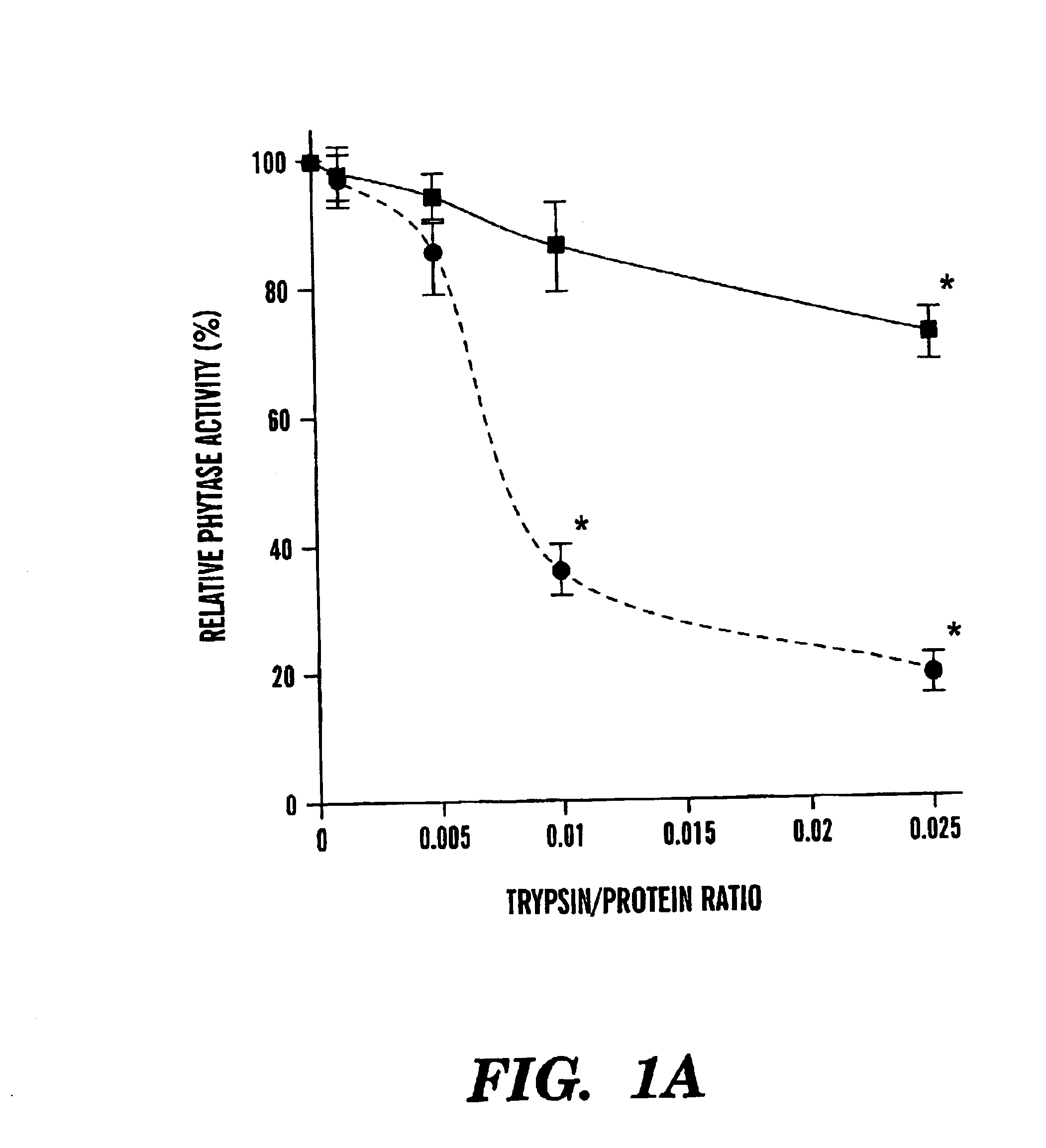
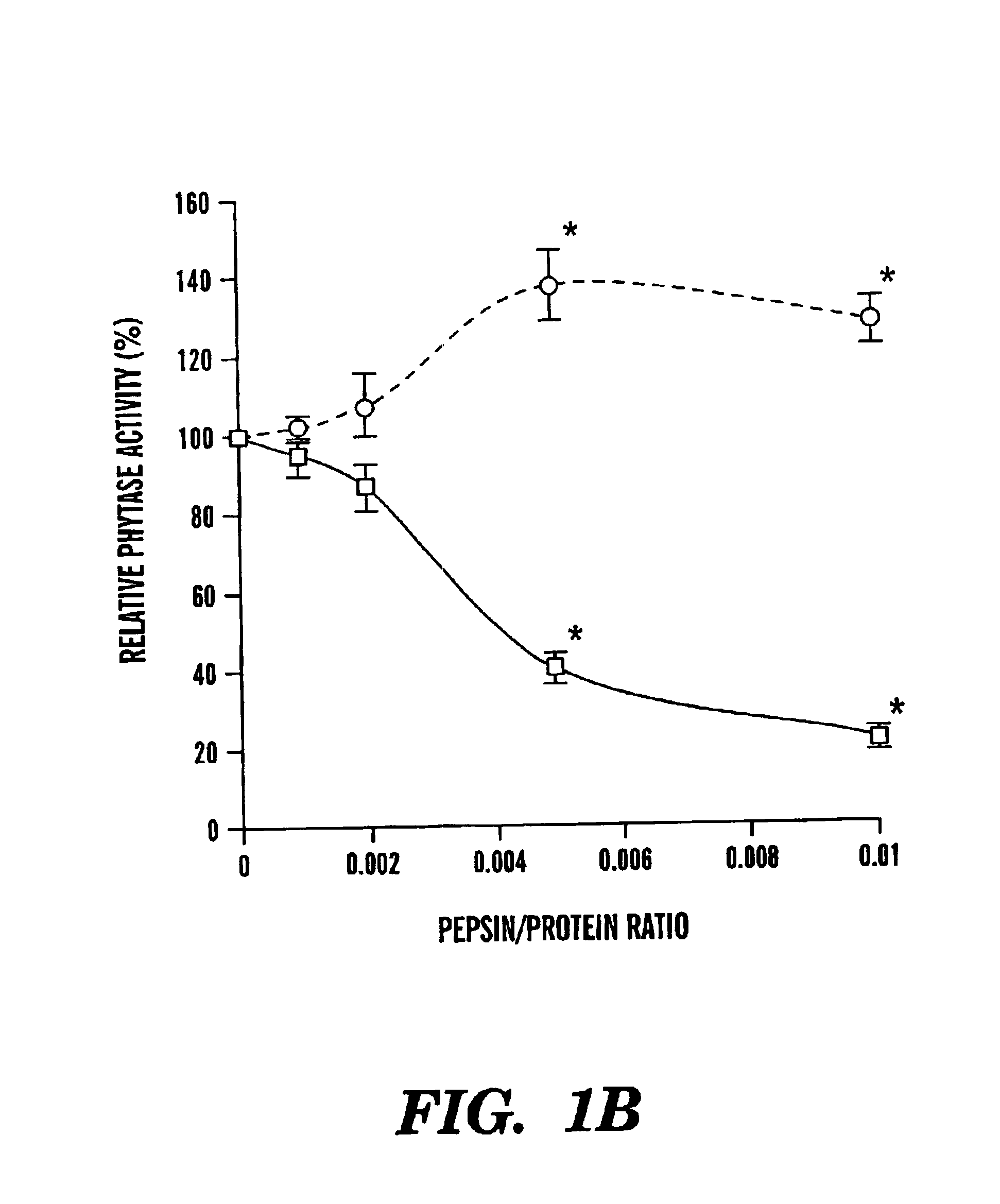
Phosphatases with improved phytase activity
InactiveUS6974690B2Improved phytase activityHigh activityDough treatmentBacteriaProteinase activityPhytase activity
The present invention provides phosphatases with improved phytase activity. The invention provides proteolytic fragments of phosphatase having improved phytase activity. A recombinant gene encoding a phosphatase fragment having improved phytase activity is also provided. The invention also includes a method of increasing the phytase activity of phosphatase by treating the phosphatase with a protease. In addition, the invention provides a new phosphatase, AppA2, having improved properties.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com