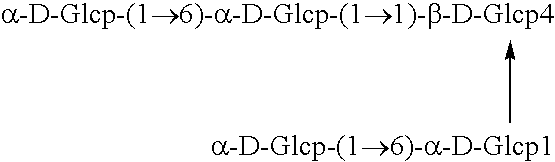Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
163 results about "A-transferase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for the production of polyunsaturated fatty acids
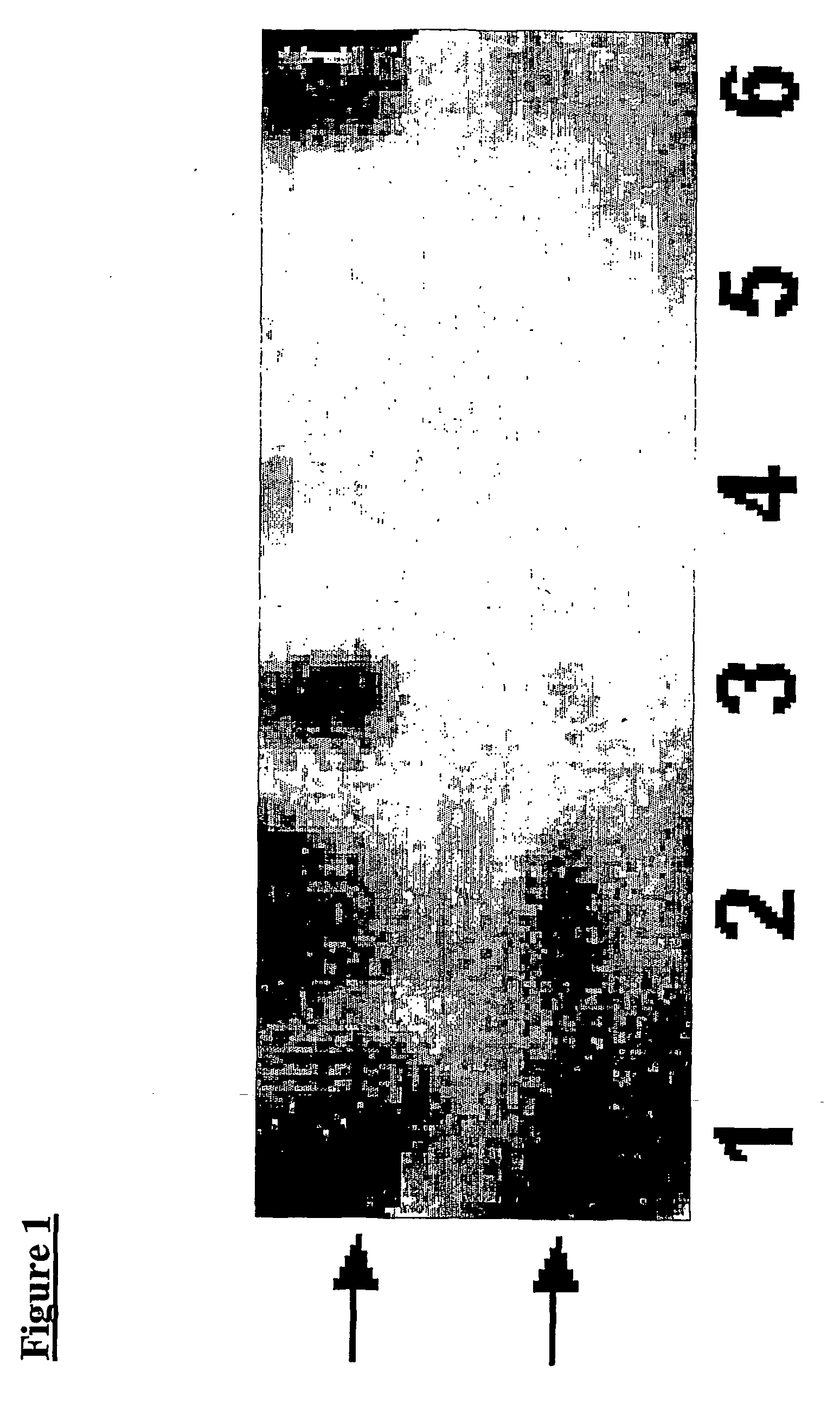
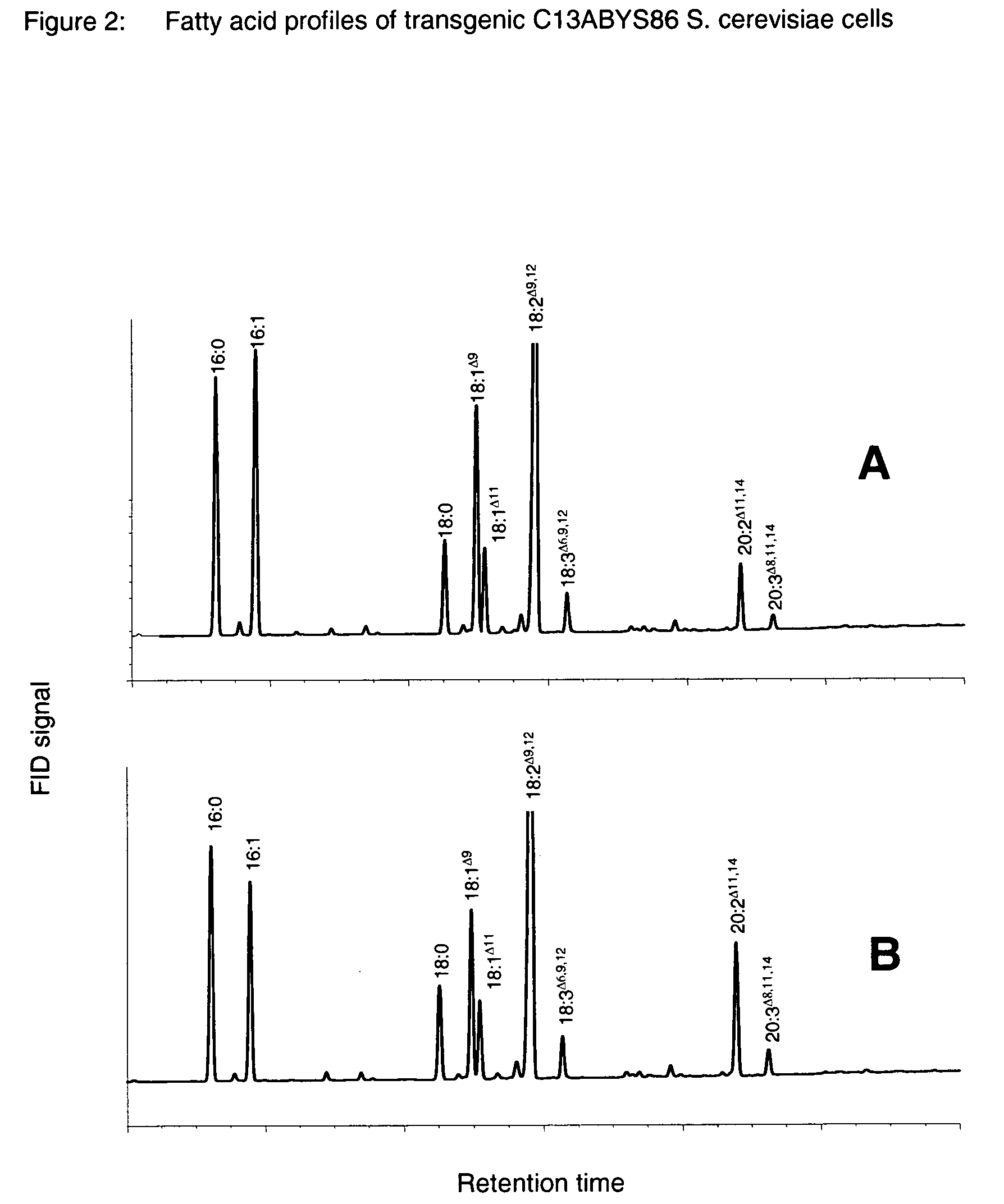
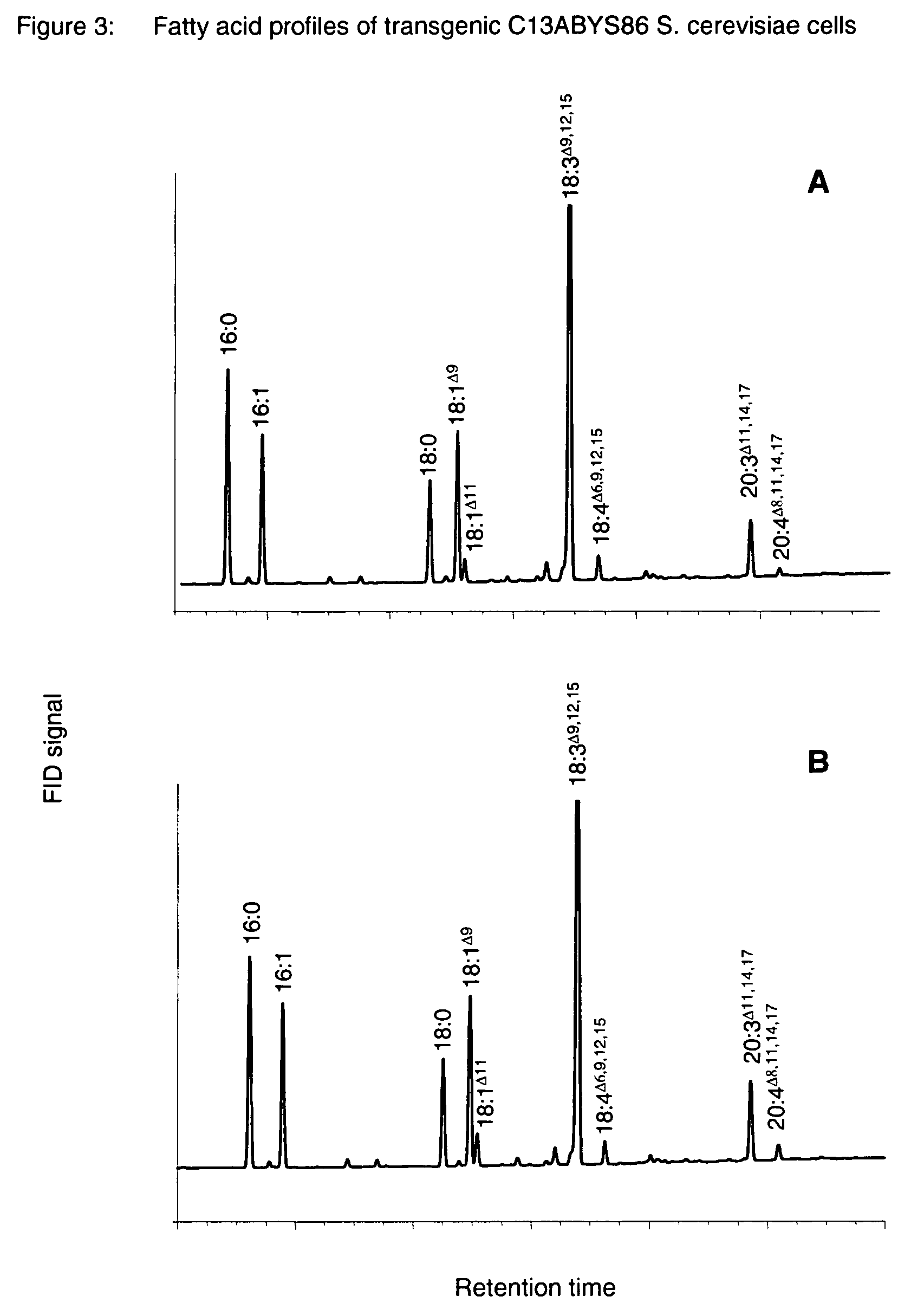
The present invention relates to a process for producing polyunsaturated fatty acids in an organism by introducing nucleic acids into the organism which code for polypeptides having acyl-CoA:lysophospholipid a cyltransferase activity. Advantageously, these nucleic acid sequences may, if appropriate together with further nucleic acid sequences coding for biosynthesis polypeptides of the fatty acid or lipid metabolism, be expressed in the transgenic organism. The invention furthermore relates to the nucleic acid sequences, to nucleic acid constructs comprising the nucleic acid sequences of the invention, to vectors comprising the nucleic acid sequences and / or the nucleic acid constructs and to transgenic organisms comprising the abovementioned nucleic acid sequences, nucleic acid constructs and / or vectors. A further part of the invention relates to oils, lipids and / or fatty acids produced by the process of the invention and to their use.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI
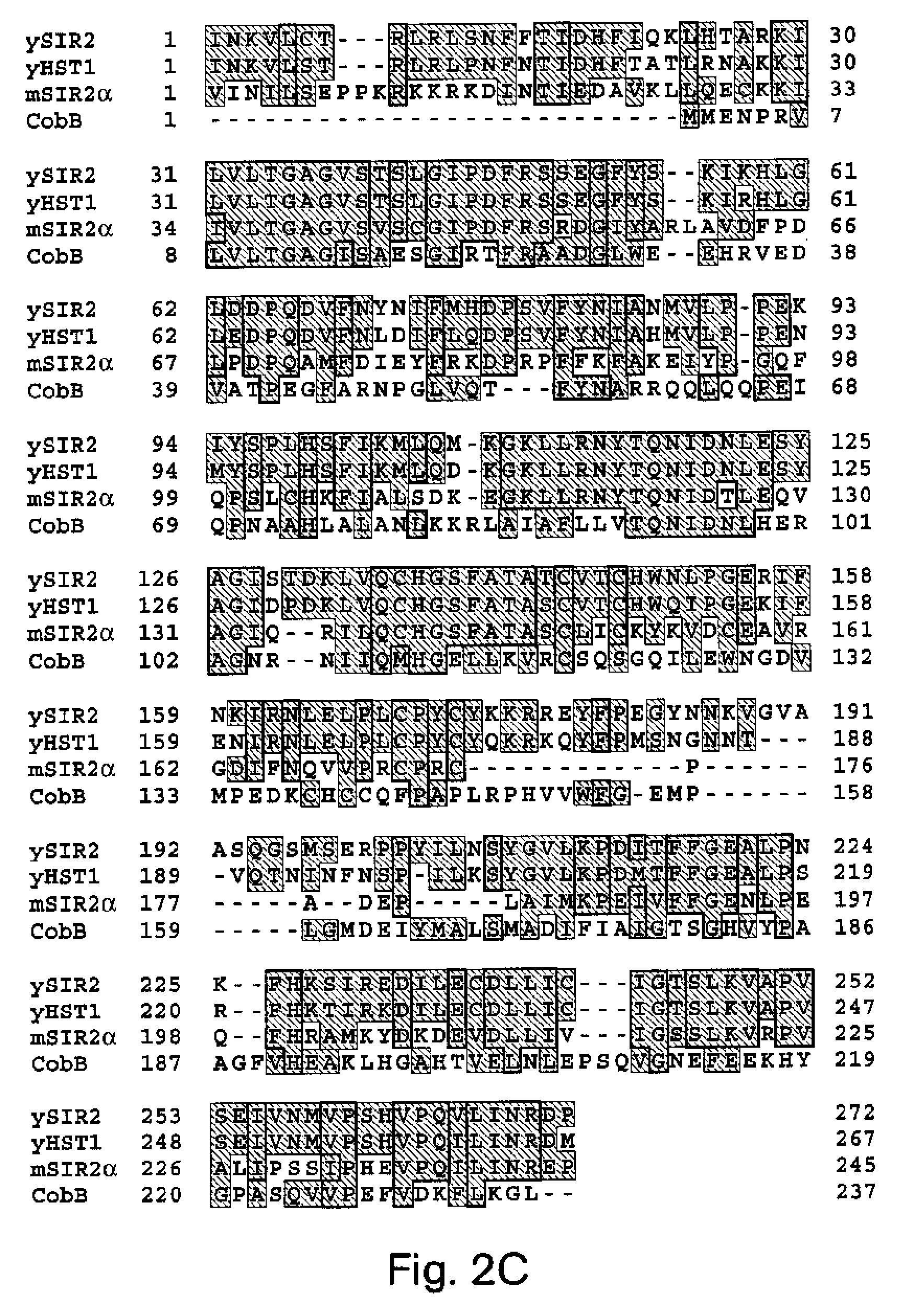
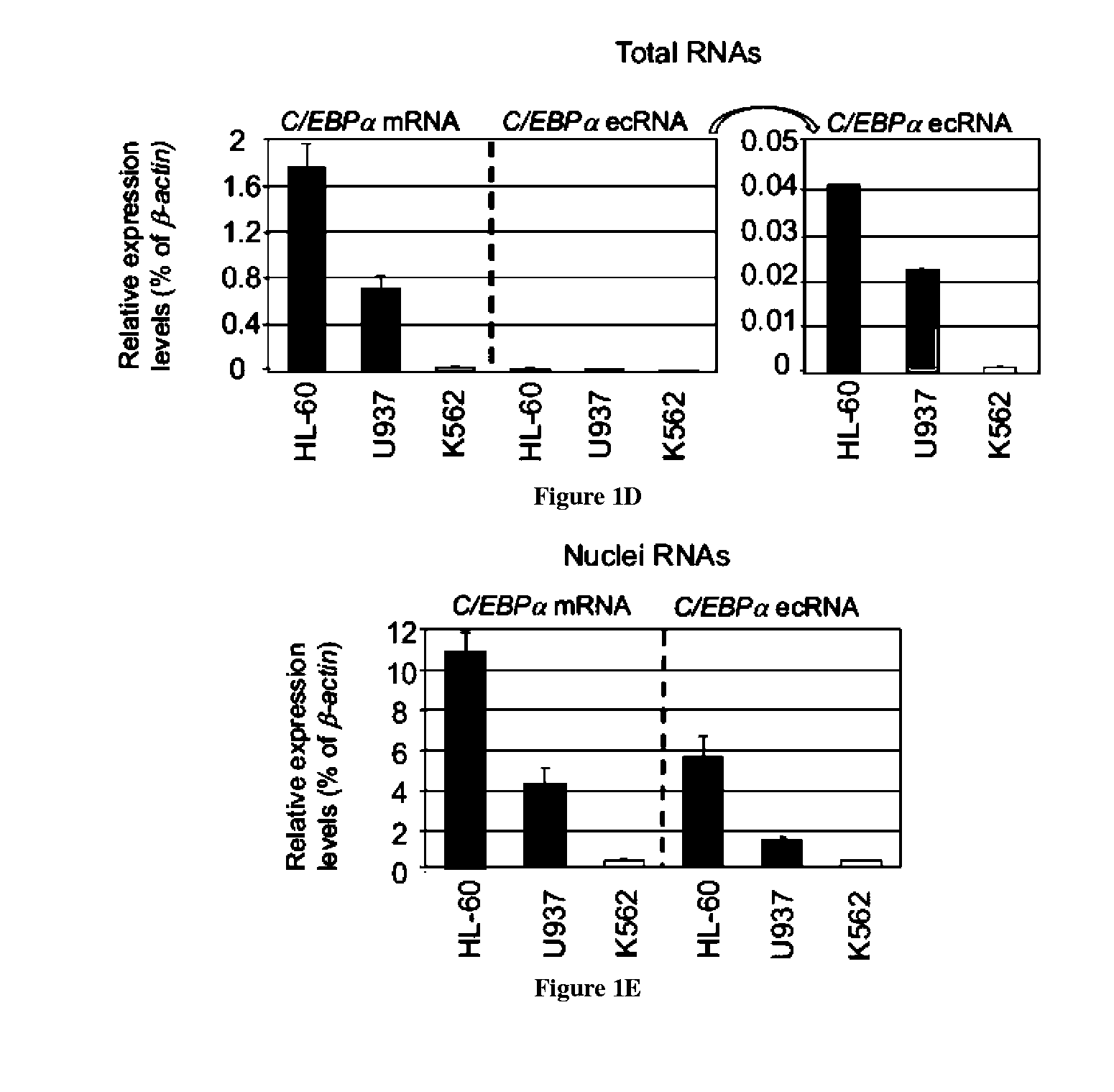
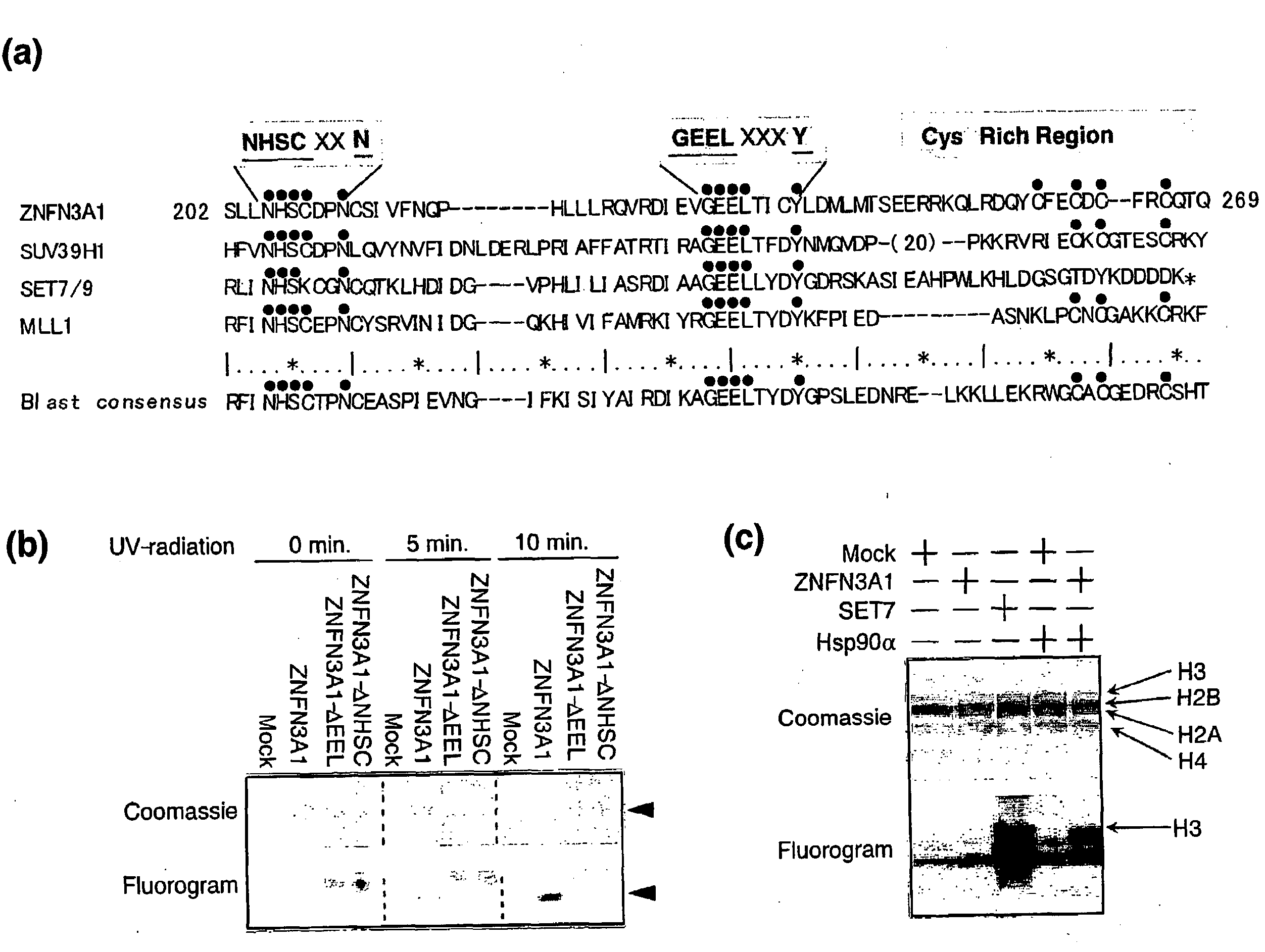
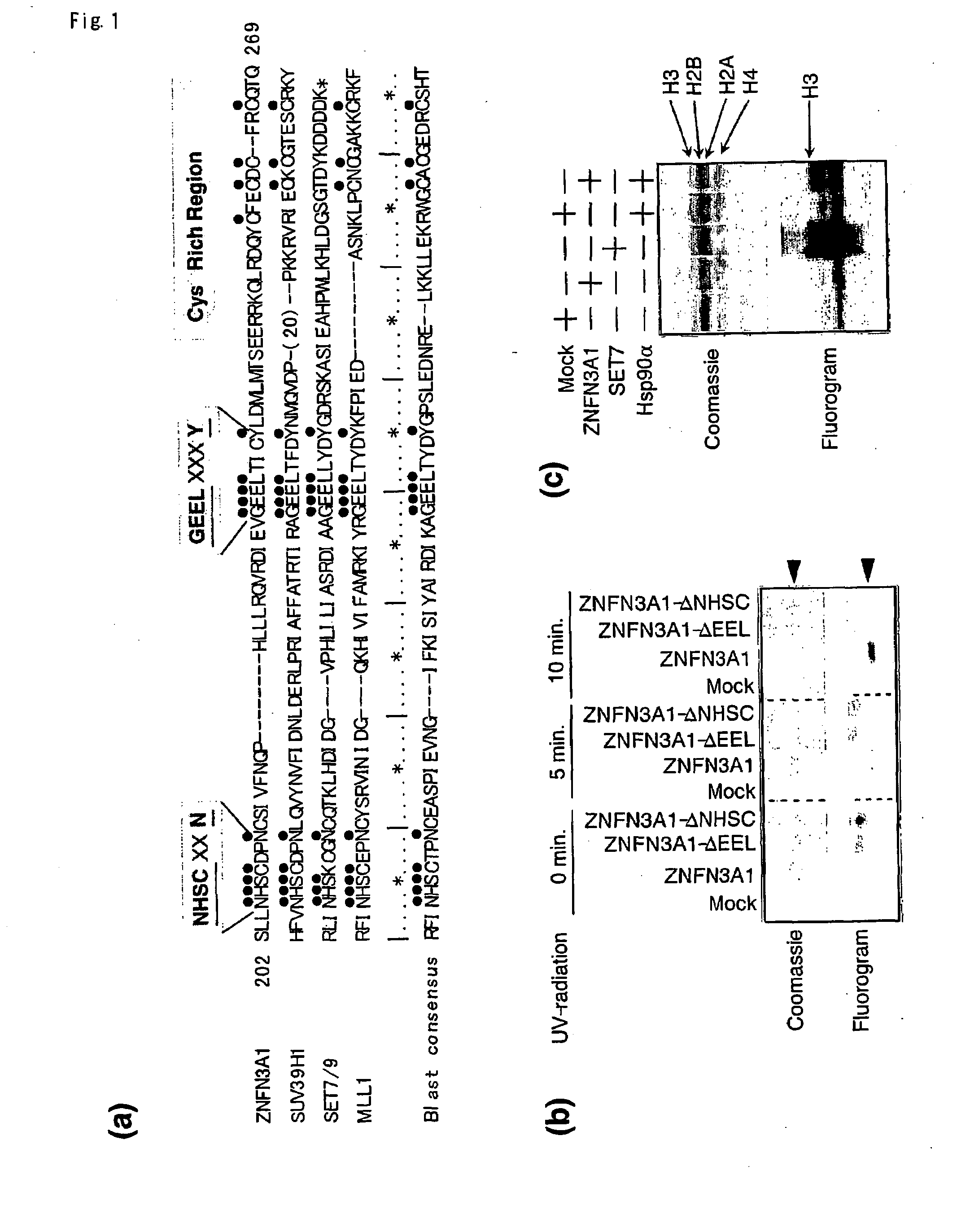
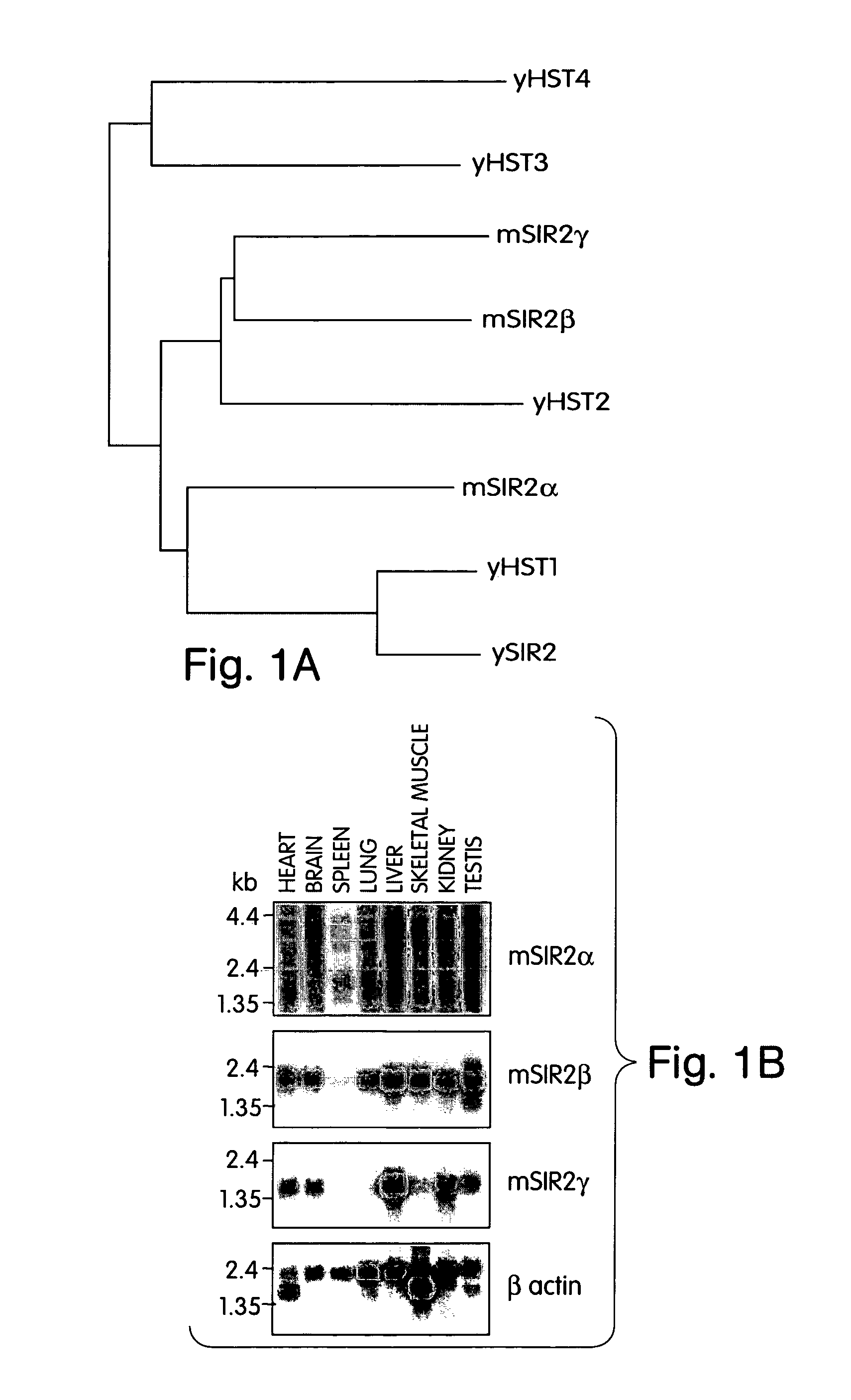
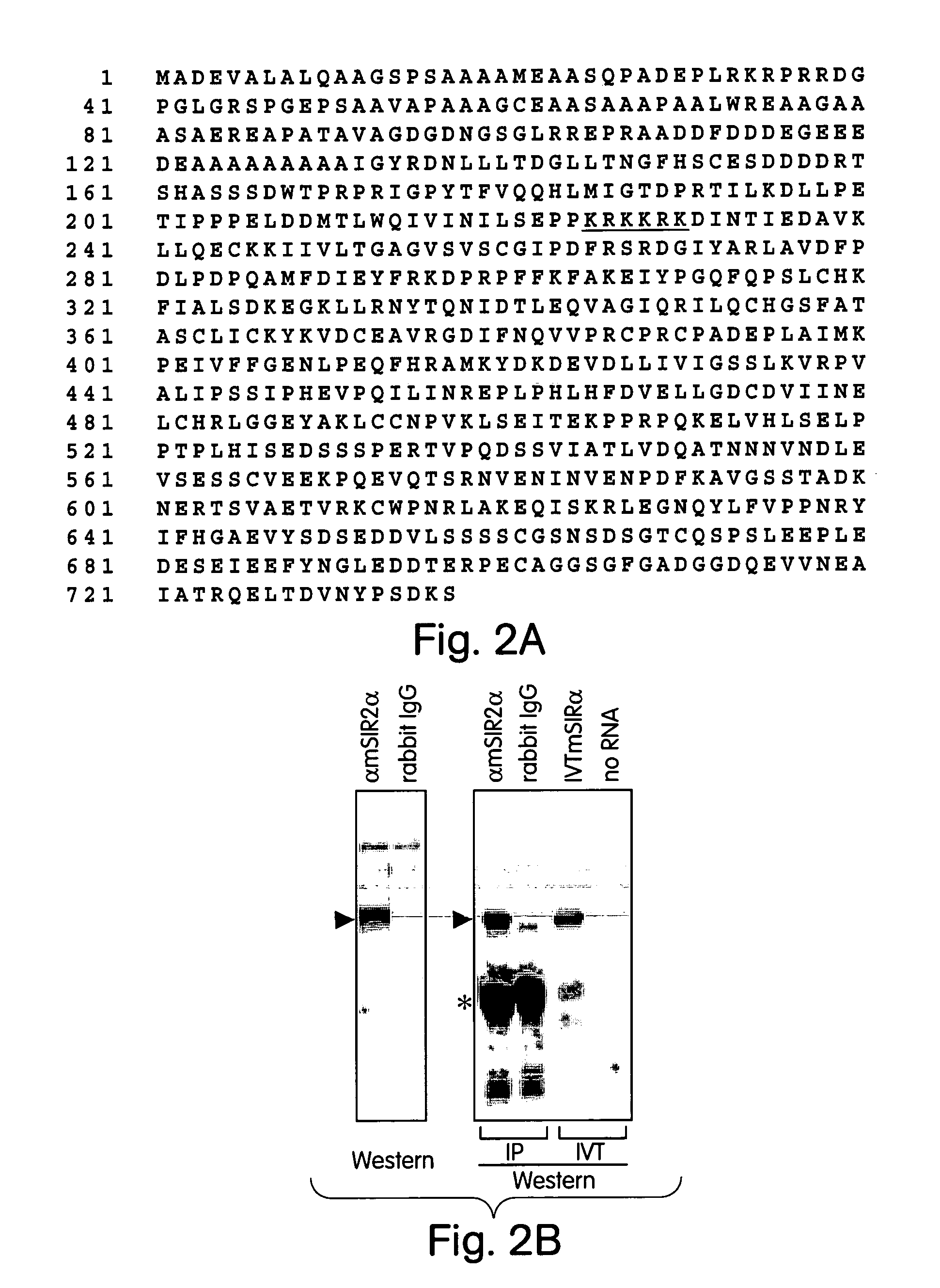
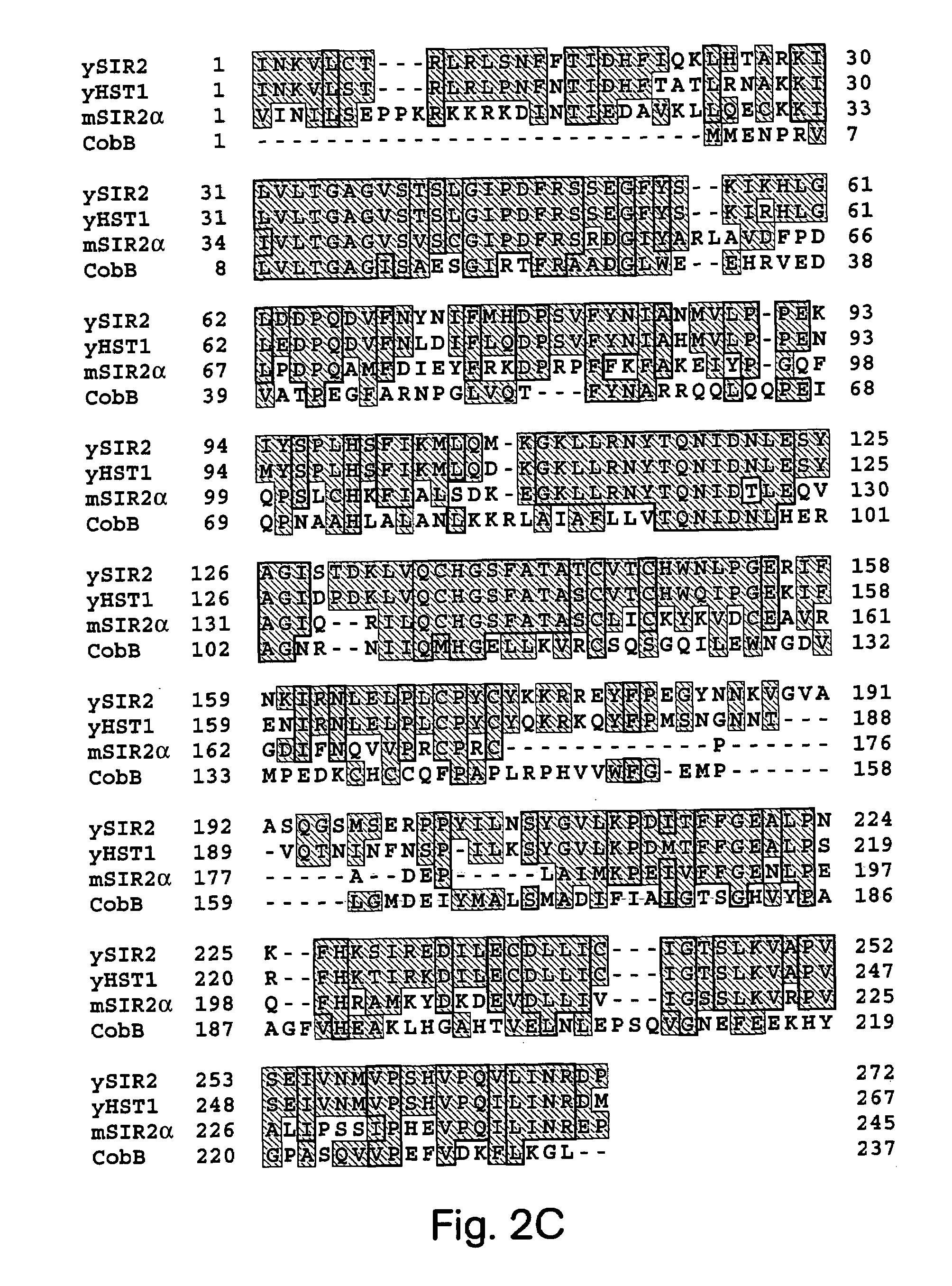
Methods for identifying agents which alter histone protein acetylation, decrease aging, increase lifespan
InactiveUS20030207325A1Extend your lifeEasy to identifyCompound screeningSenses disorderADPRibosylationNad dependent
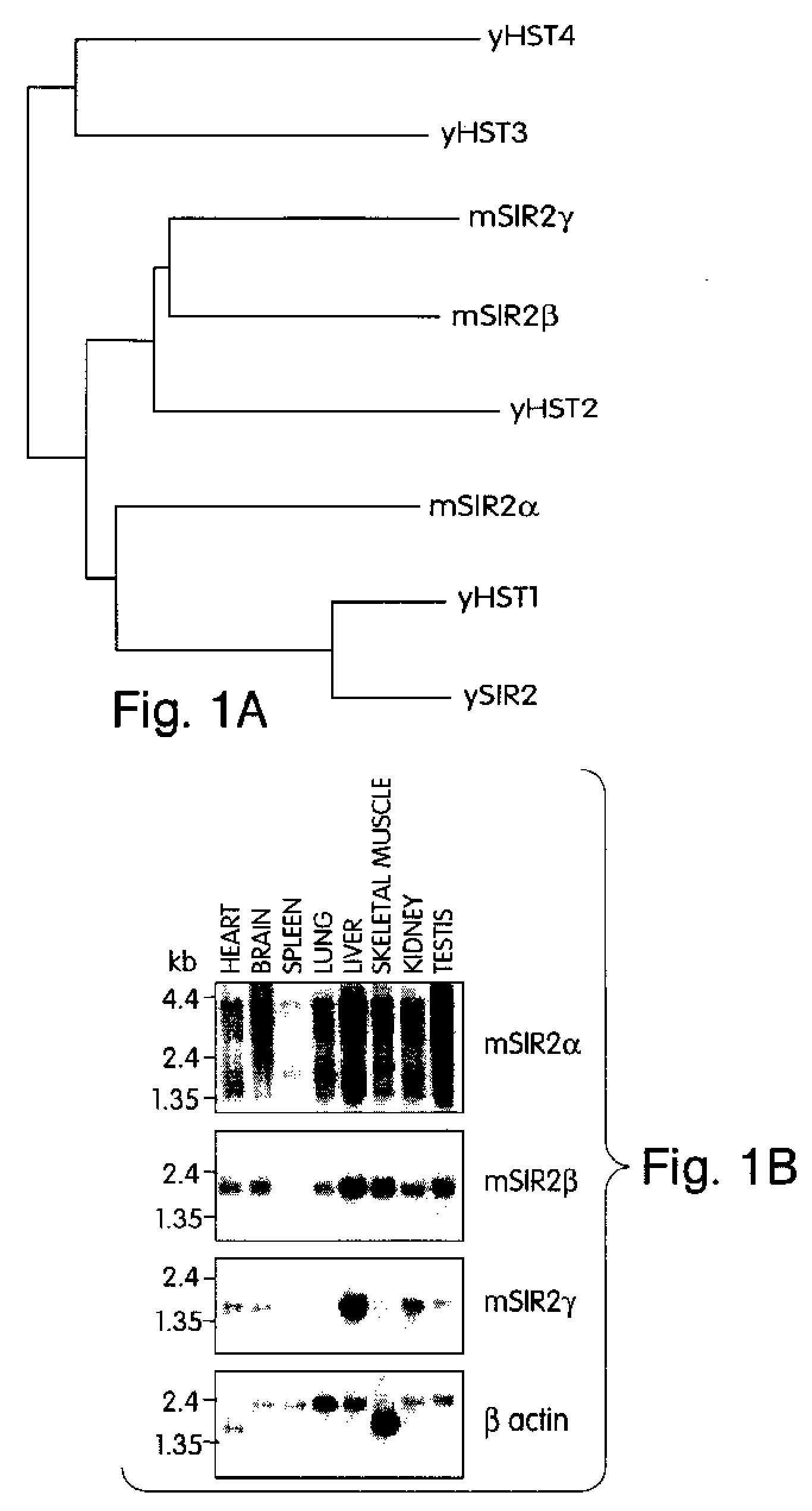
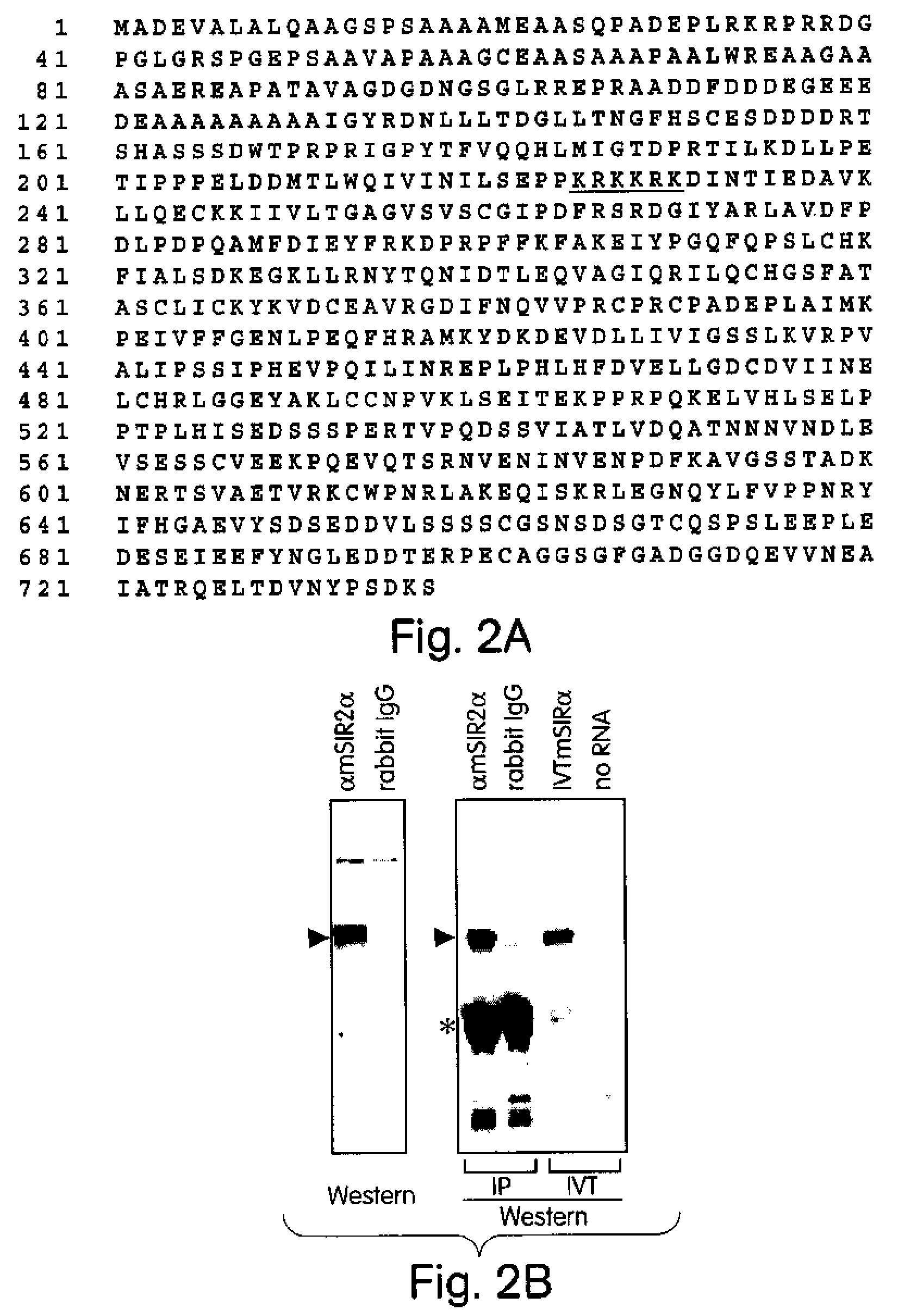
Abstract of the Disclosure Methods of identifying agents which alter the NAD-dependent acetylation status and mono-ADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins are disclosed. The methods further include identifying agents which alter the life span or aging of a cell or an organism by determining the level of NAD-dependent acetylation and / or ADP ribosylation of a nuclear protein. The invention also relates to a mammalian Sir2 protein which acetylates or deacetylates nuclear proteins in a NAD-dependent manner and has mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Host cells producing the Sir2 protein and antibodies to the Sir2 protein are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
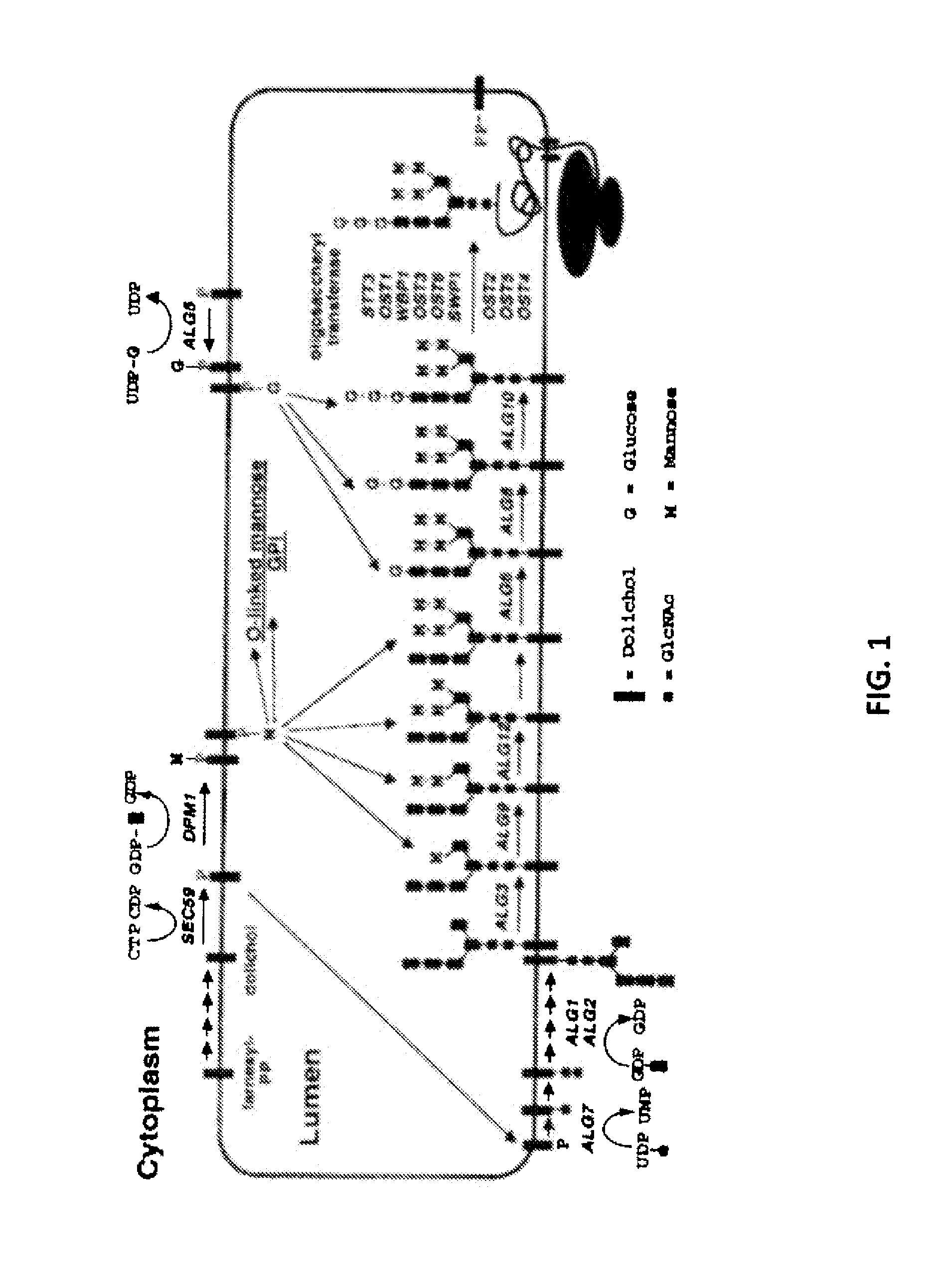
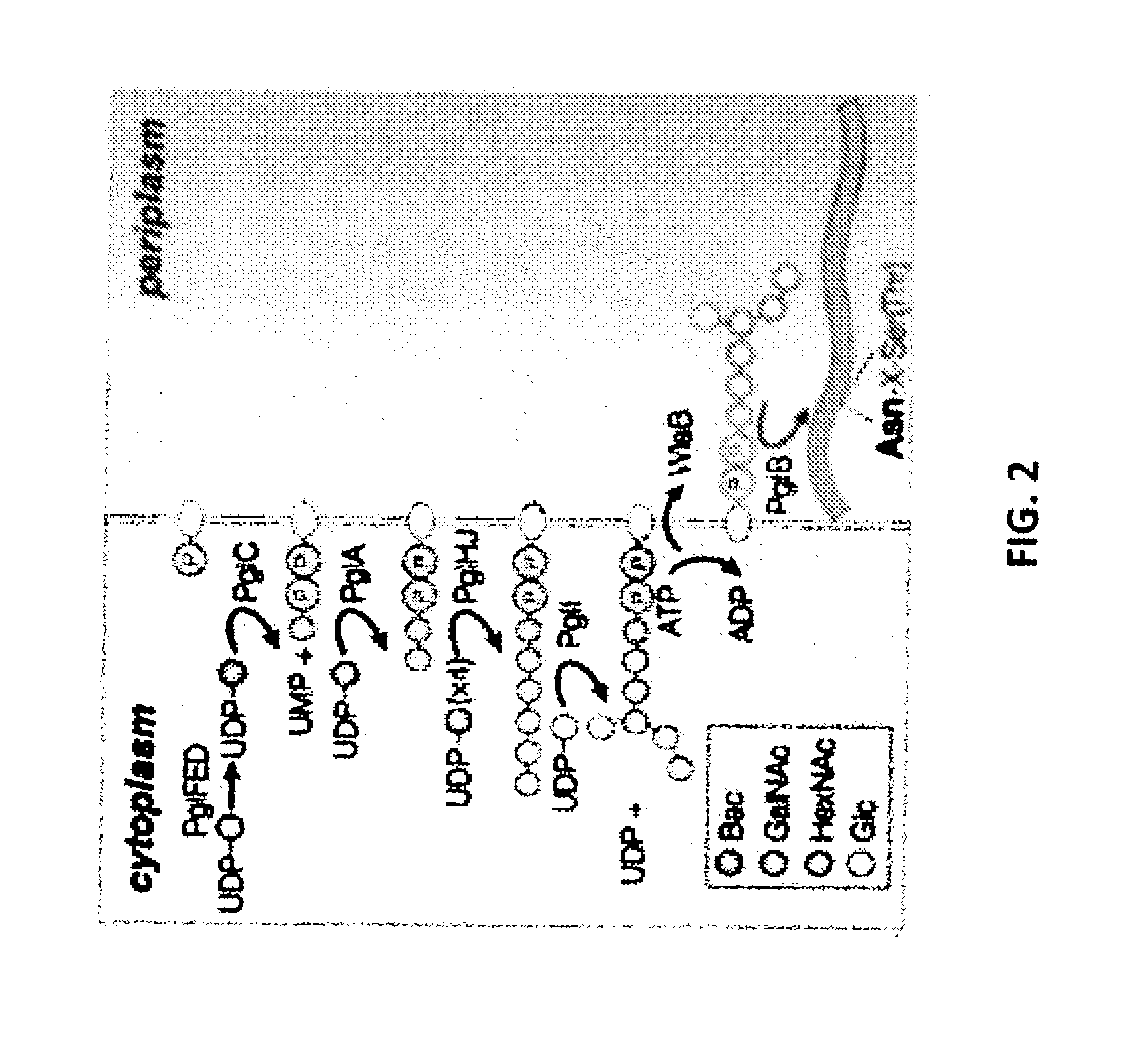
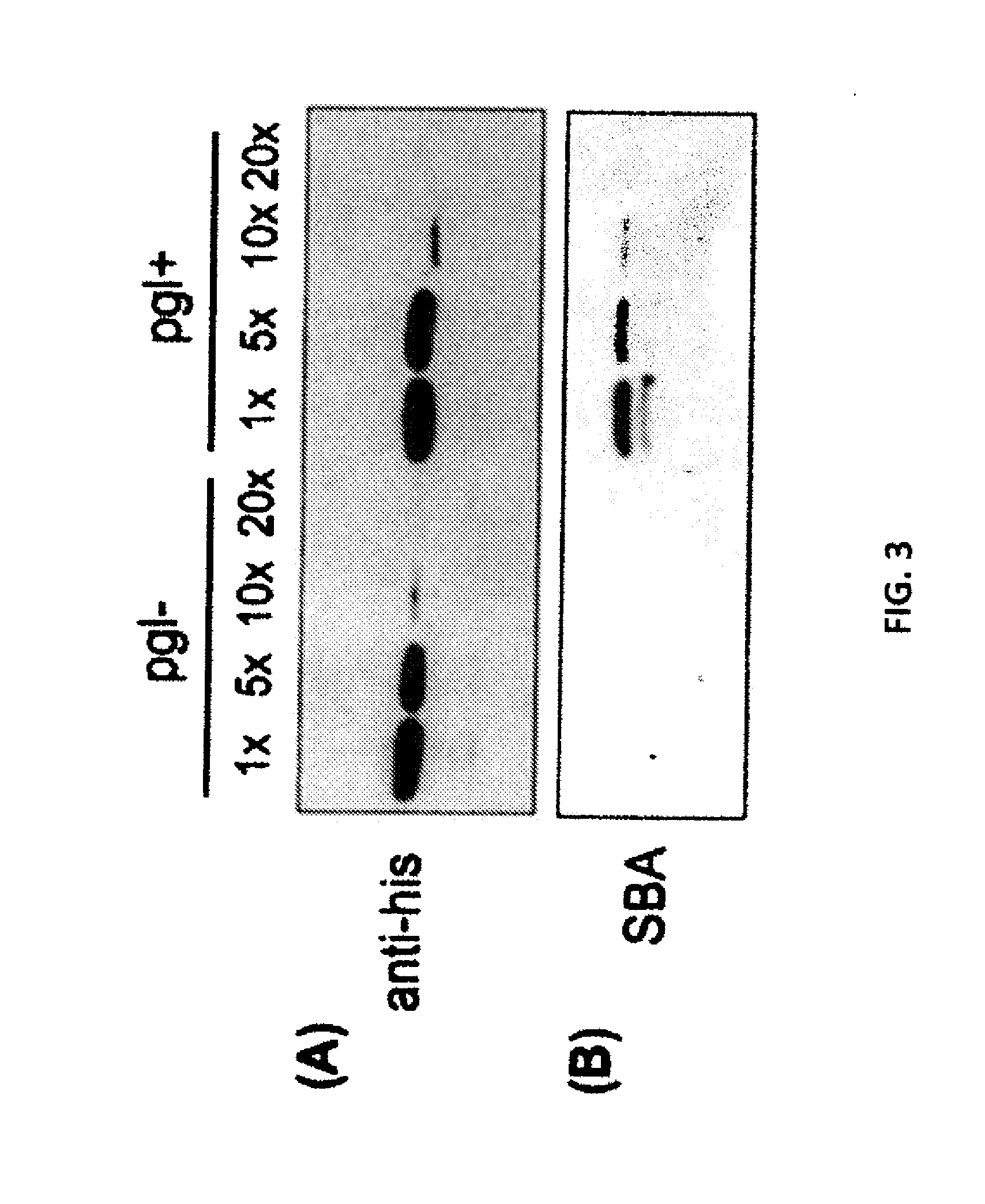
Glycosylated protein expression in prokaryotes
The present invention relates to a prokaryotic host cell comprising eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity, where the eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity is eukaryotic dolichyl-linked UDP-GlcNAc transferase activity and eukaryotic mannosyl-transferase activity. Also disclosed is a method of producing a glycosylated protein by providing a prokaryotic host cell comprising the eukaryotic glycosyltransferase activity and culturing the prokaryotic host cell under conditions effective to produce a glycosylated protein. Another aspect of the present invention pertains to a method for screening bacteria or bacteriophages by expressing one or more glycans on the surface of a bacteria, attaching a label on the one or more glycans on the surface of the bacteria or on the surface of a bacteriophage derived from the bacteria, and analyzing the label in a high-throughput format. A glycosylated antibody comprising an Fv portion which recognizes and binds to a native antigen and an Fc portion which is glycosylated at a conserved asparagine residue is also disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Genetically Modified Host Cells And Use Of Same For Producing Isoprenoid Compounds
ActiveUS20080171378A1Improve the level ofLower Level RequirementsMicroorganismsTransferasesPrenylationSqualene synthase activity
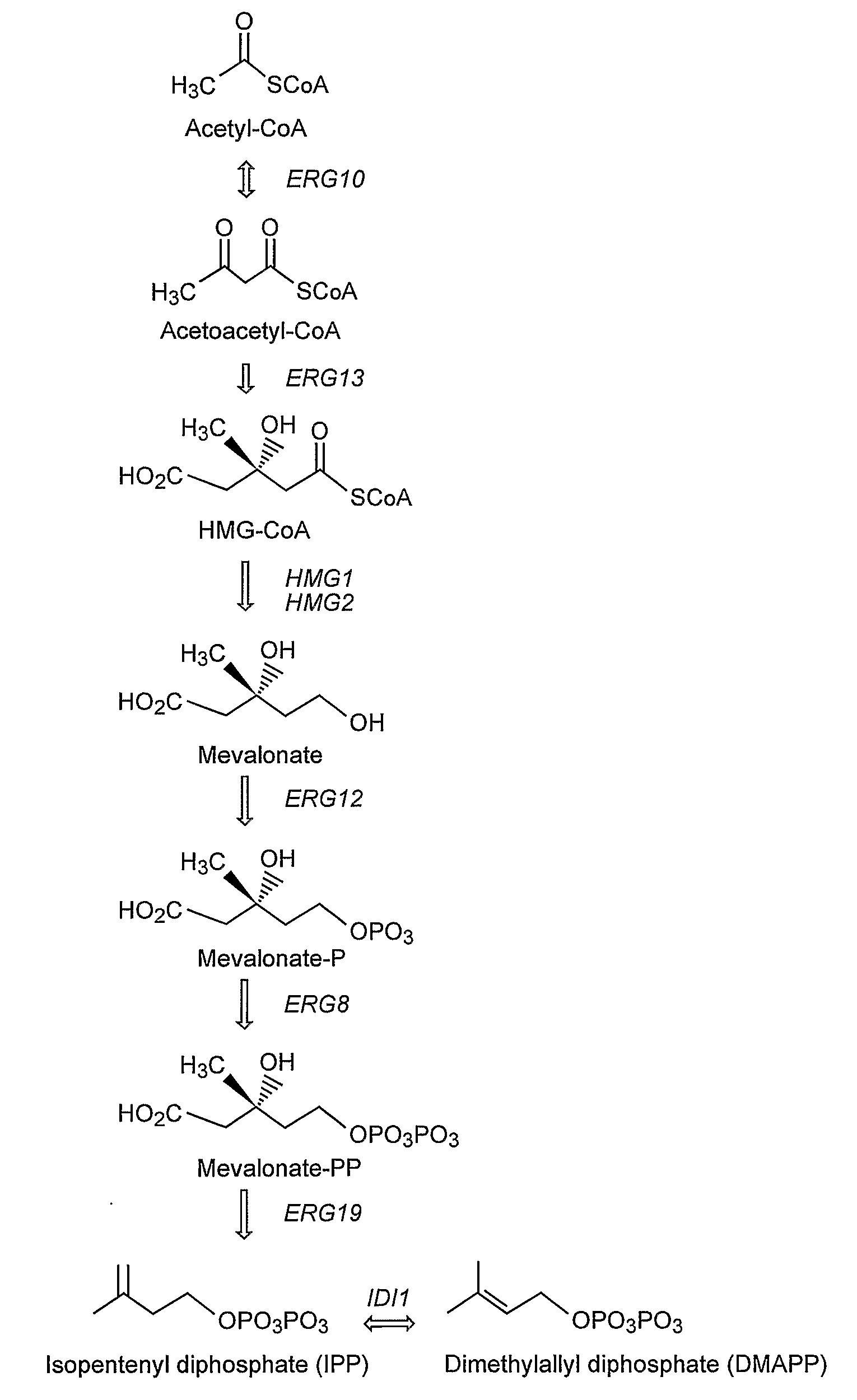
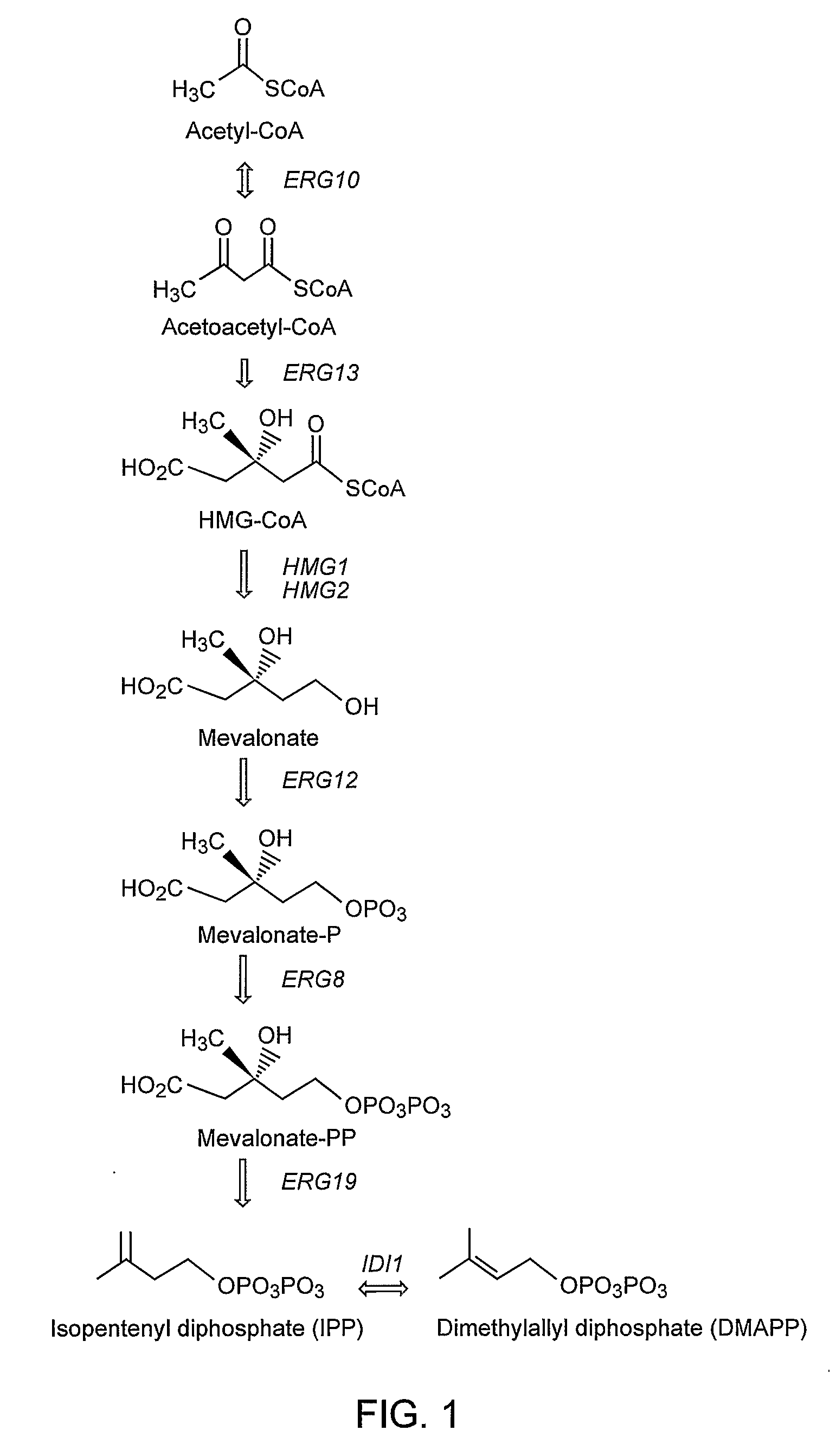
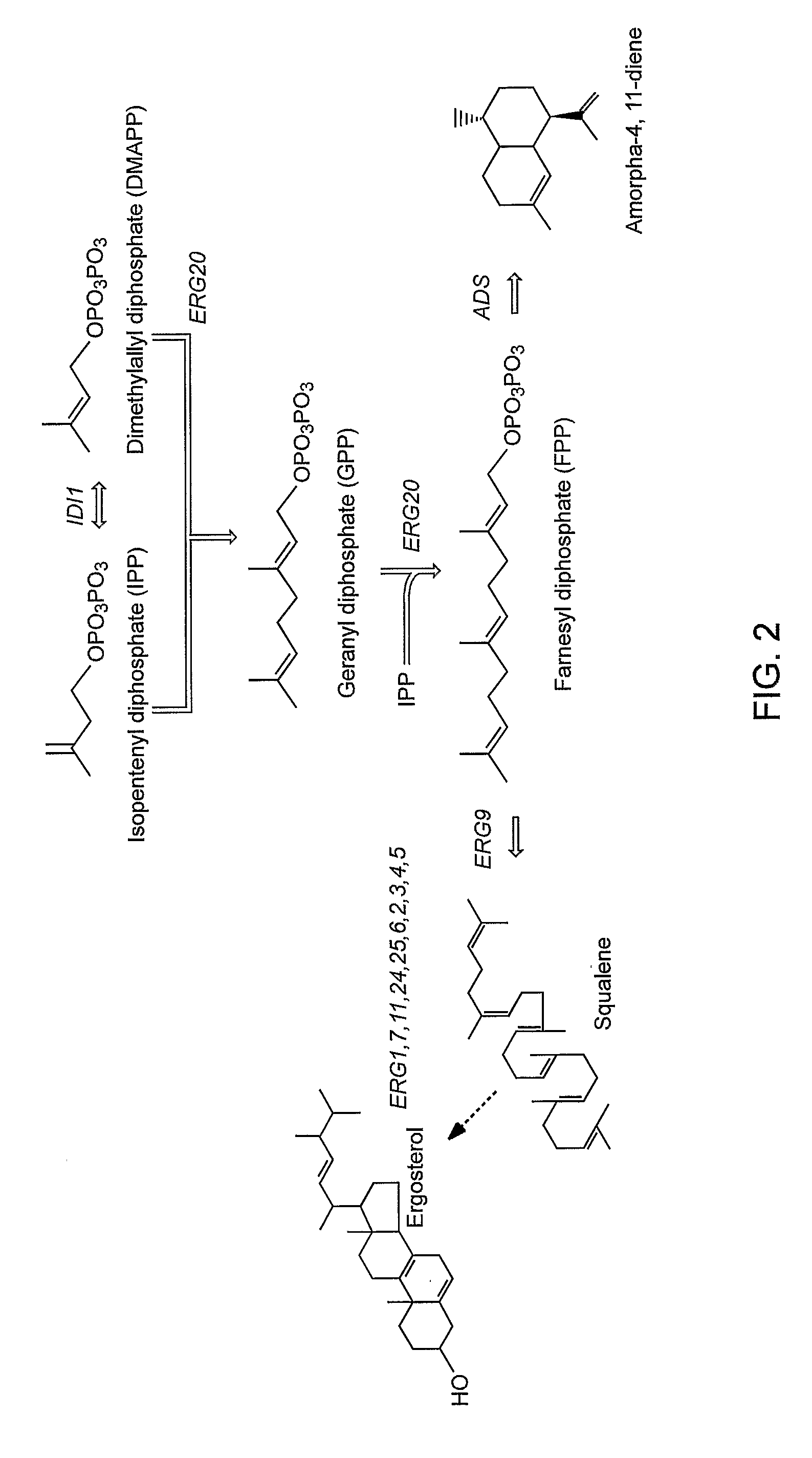
The present invention provides genetically modified eukaryotic host cells that produce isoprenoid precursors or isoprenoid compounds. A subject genetically modified host cell comprises increased activity levels of one or more of mevalonate pathway enzymes, increased levels of prenyltransferase activity, and decreased levels of squalene synthase activity. Methods are provided for the production of an isoprenoid compound or an isoprenoid precursor in a subject genetically modified eukaryotic host cell. The methods generally involve culturing a subject genetically modified host cell under conditions that promote production of high levels of an isoprenoid or isoprenoid precursor compound.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
L-amino acid-producing microorganism and a method for producing an l-amino acid
ActiveUS20090104667A1Efficient productionHigh activityBacteriaUnicellular algaeMicroorganismOrotate phosphoribosyltransferase
An L-amino acid is produced by culturing a microorganism which belongs to the family Enterobacteriaceae and is able to produce an L-amino acid, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance orotate phosphoribosyltransferase activity is enhanced, in a medium to produce and cause accumulation of an L-amino acid in the medium or cells, and collecting the L-amino acid from the medium or the cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Chondroitin synthetase and dna encoding the enzyme
A human-derived novel chondroitin synthase, which is an enzyme for synthesizing a fundamental backbone of chondroitin and has both glucuronic acid transferase activity and N-acetylgalactosamine transferase activity.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD +1
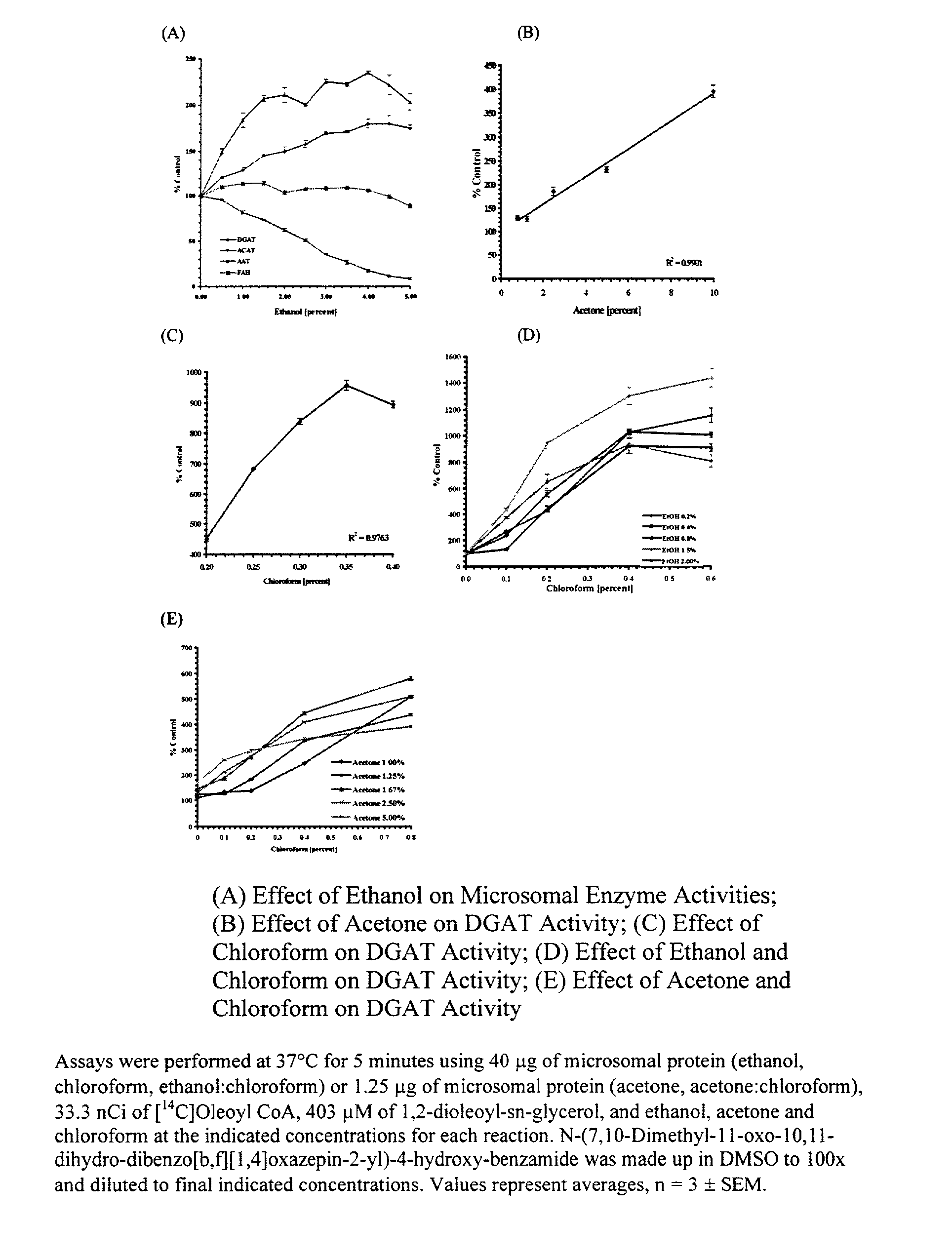
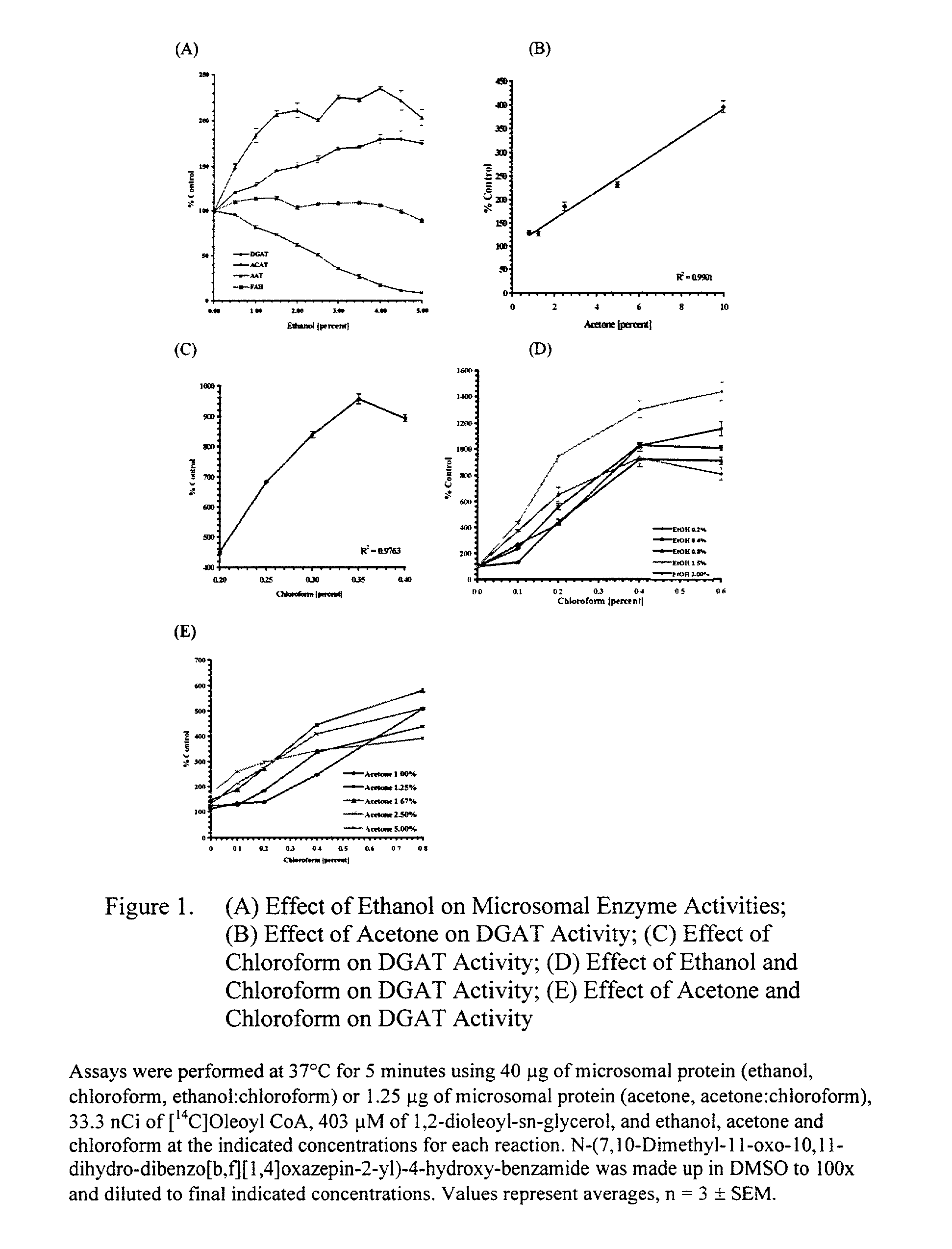
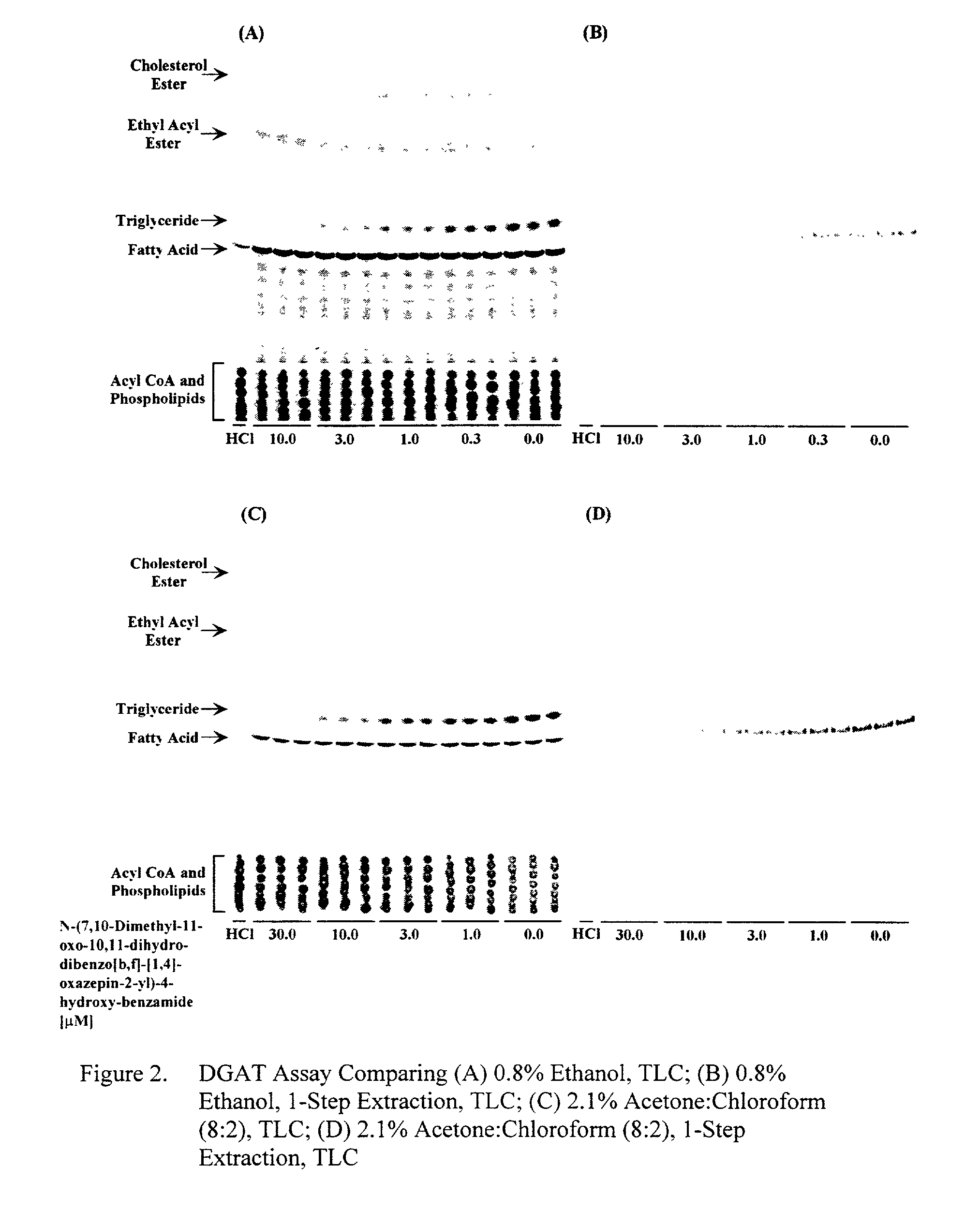
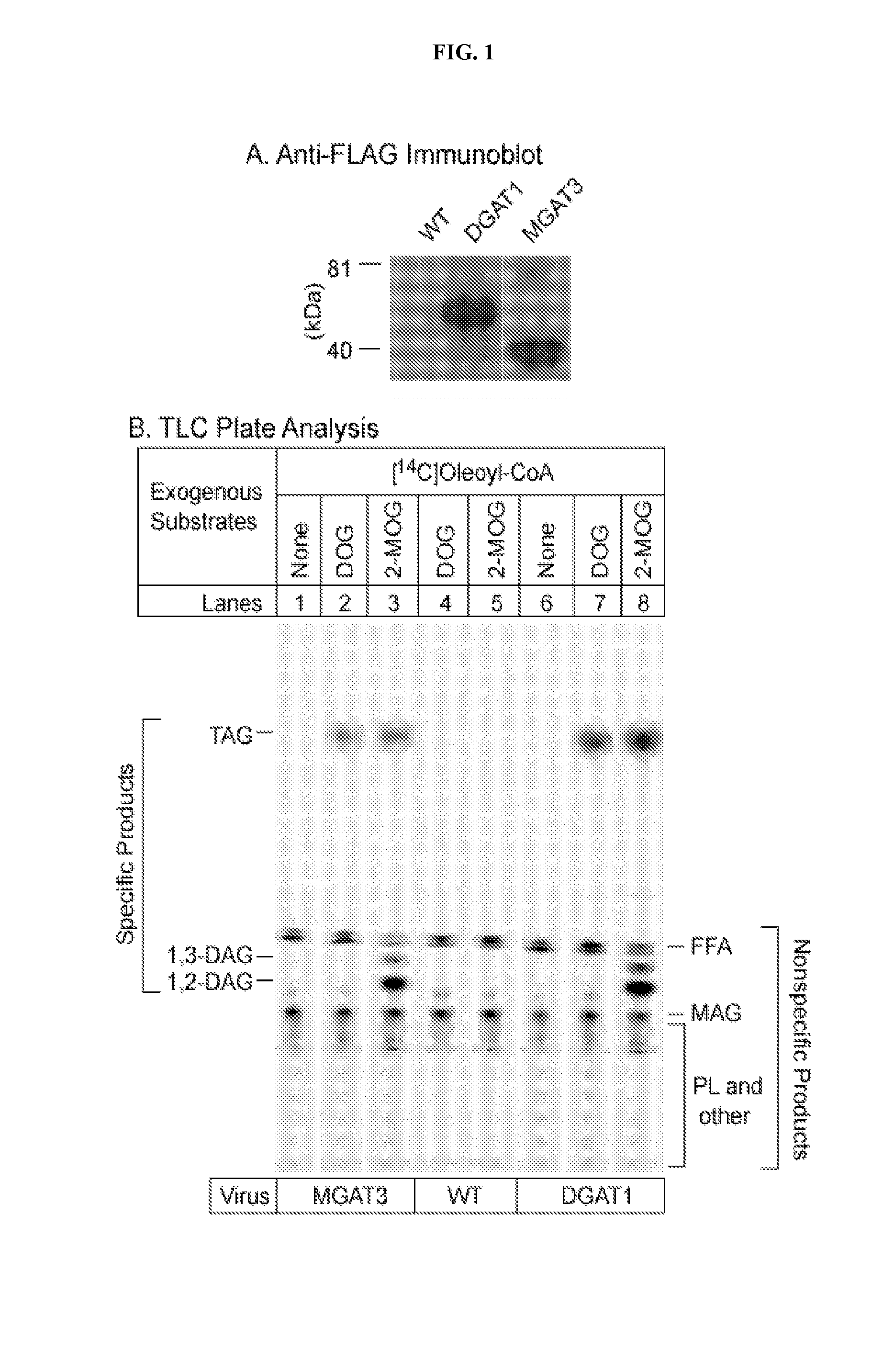
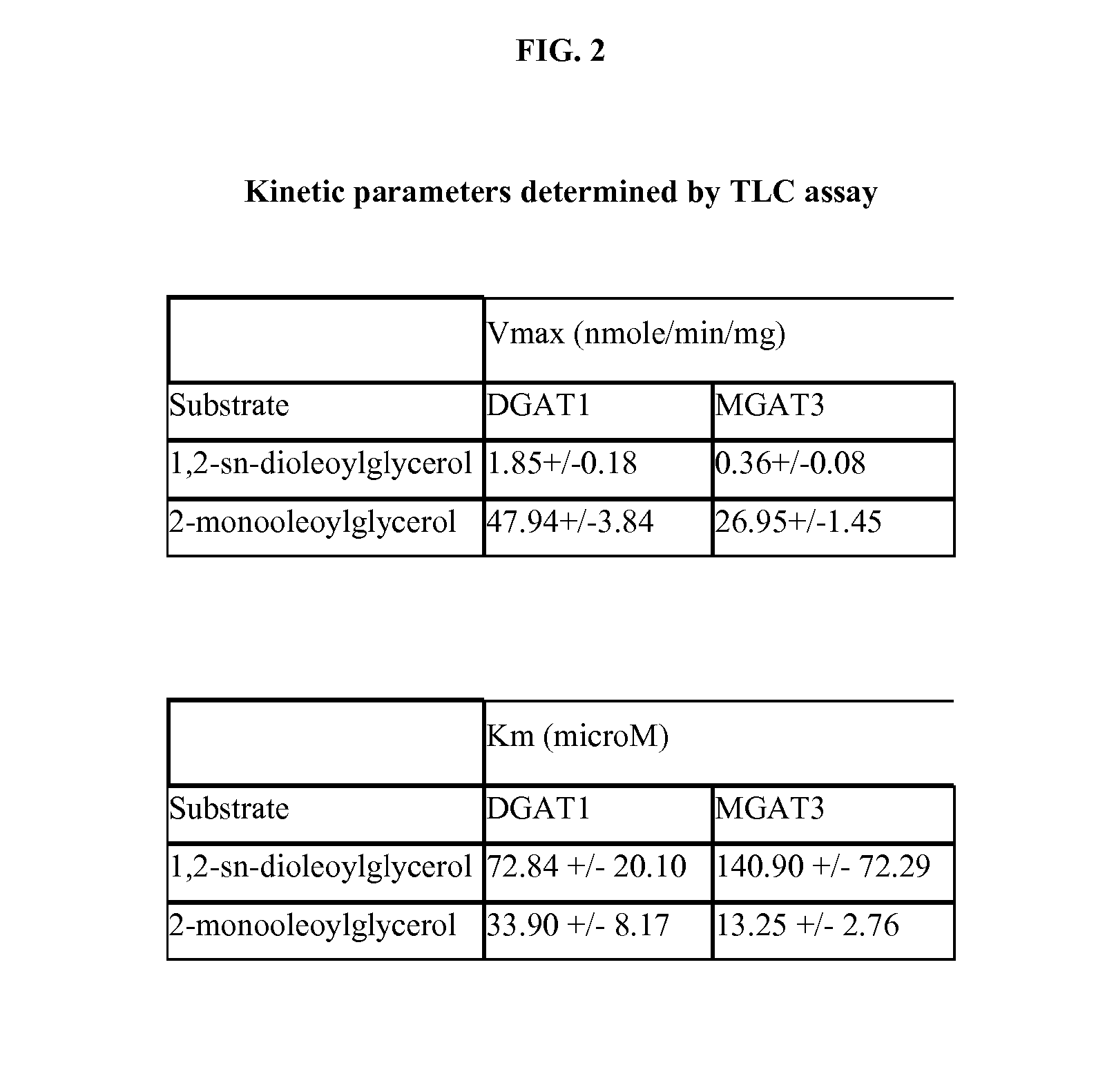
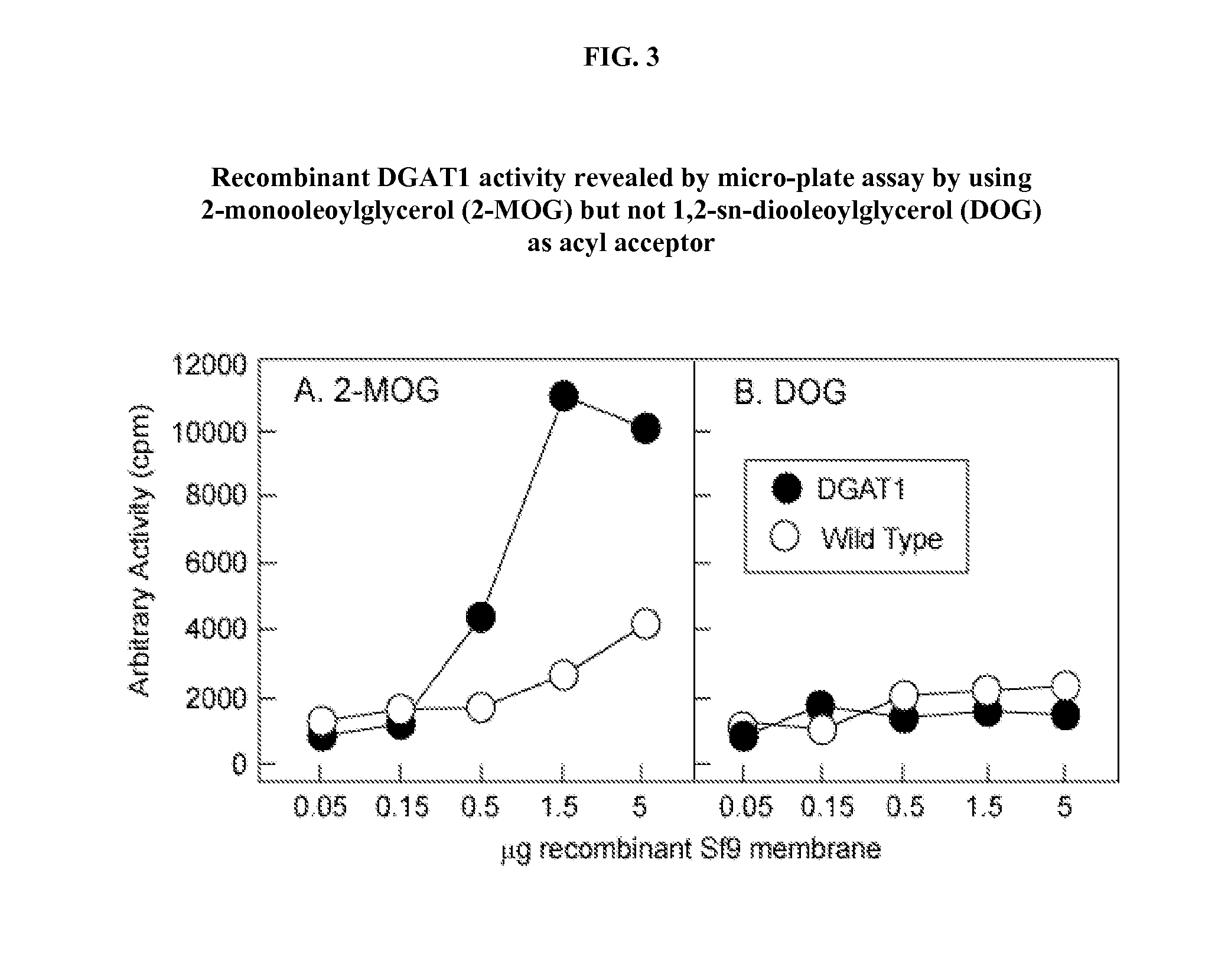
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase (DGAT) assay
InactiveUS20020127627A1Reduce eliminate activityUseful biological activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionAcetyltransferaseDrug biological activity
The present invention provides a method for measuring diacylglycerol acetyltransferase (DGAT) activity which utilizes a novel solvent system to reduce and / or eliminate the activities of related compounds. The present invention also discloses a method for determining whether a compound is useful for modulating DGAT biological activity. The method is capable of being utilized for mass screening of compounds as modulators of the biological activity of DGAT.
Owner:WARNER-LAMBERT CO
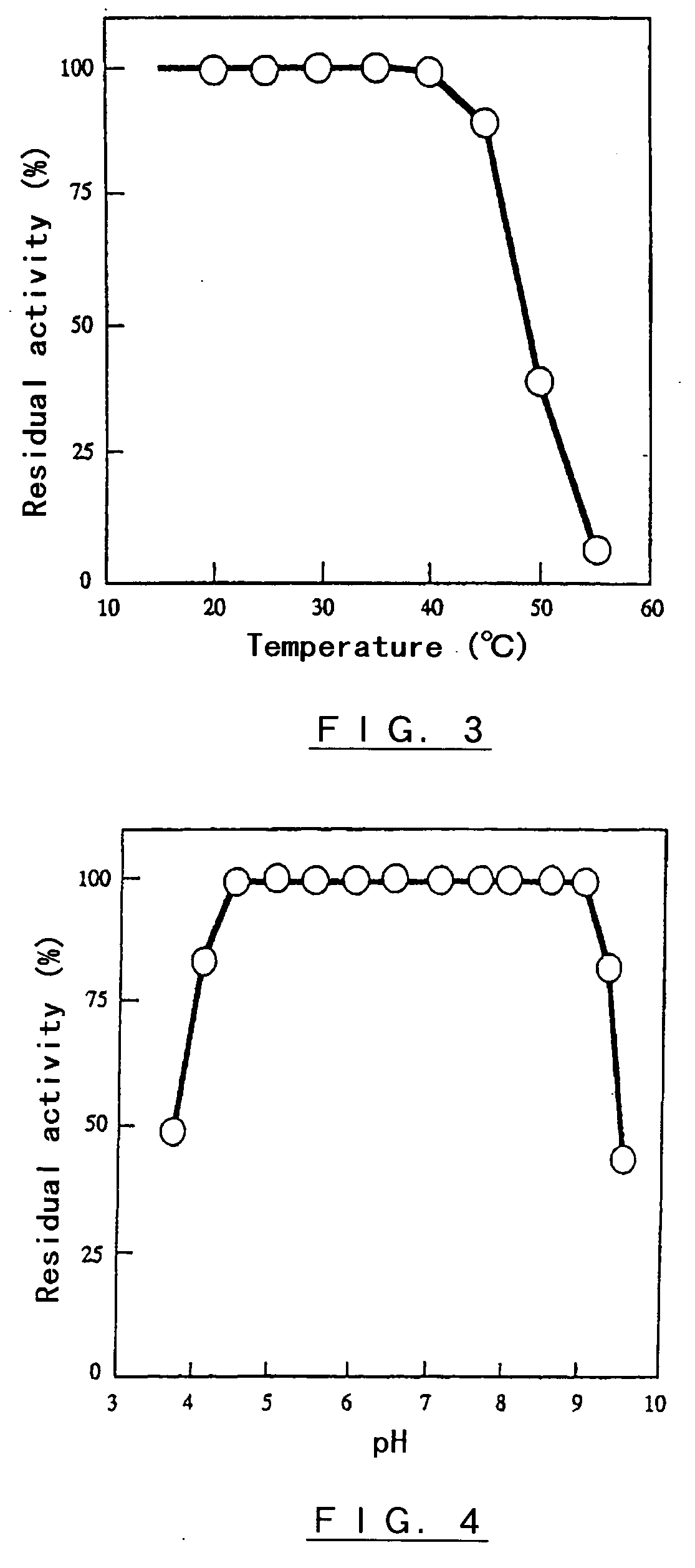
Process
A process of water degumming an edible oil (preferably a crude edible oil) comprising the steps of: a) admixing approximately 0.1-5% w / w water with an edible oil (preferably a crude edible oil) and a lipid acyltransferase, b) agitating the admixture for between about 10 minutes and 180 minutes at about 45 to about 900 C, and c) separating the oil phase and the gum phase. Preferably said lipid acyltransferase is a polypeptide having lipid acyltransferase activity which polypeptide is obtained by expression of the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 49 or a nucleotide sequence which as has 70% or more identity therewith; and / or is obtained by expression of a nucleic acid which hybridises under medium stringency conditions to a nucleic probe comprising the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ No. 49; and / or is a polypeptide having lipid acyltransferase activity which polypeptide comprises the amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID No. 68 or an amino acid sequence which as has 70% or more identity therewith. In one embodiment the lipid acyltransferase is preferably used in combination with a phospholipase C enzyme. A process for modifying the gum phase of a degummed oil using a lipid acyltransferase is also taught herein.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
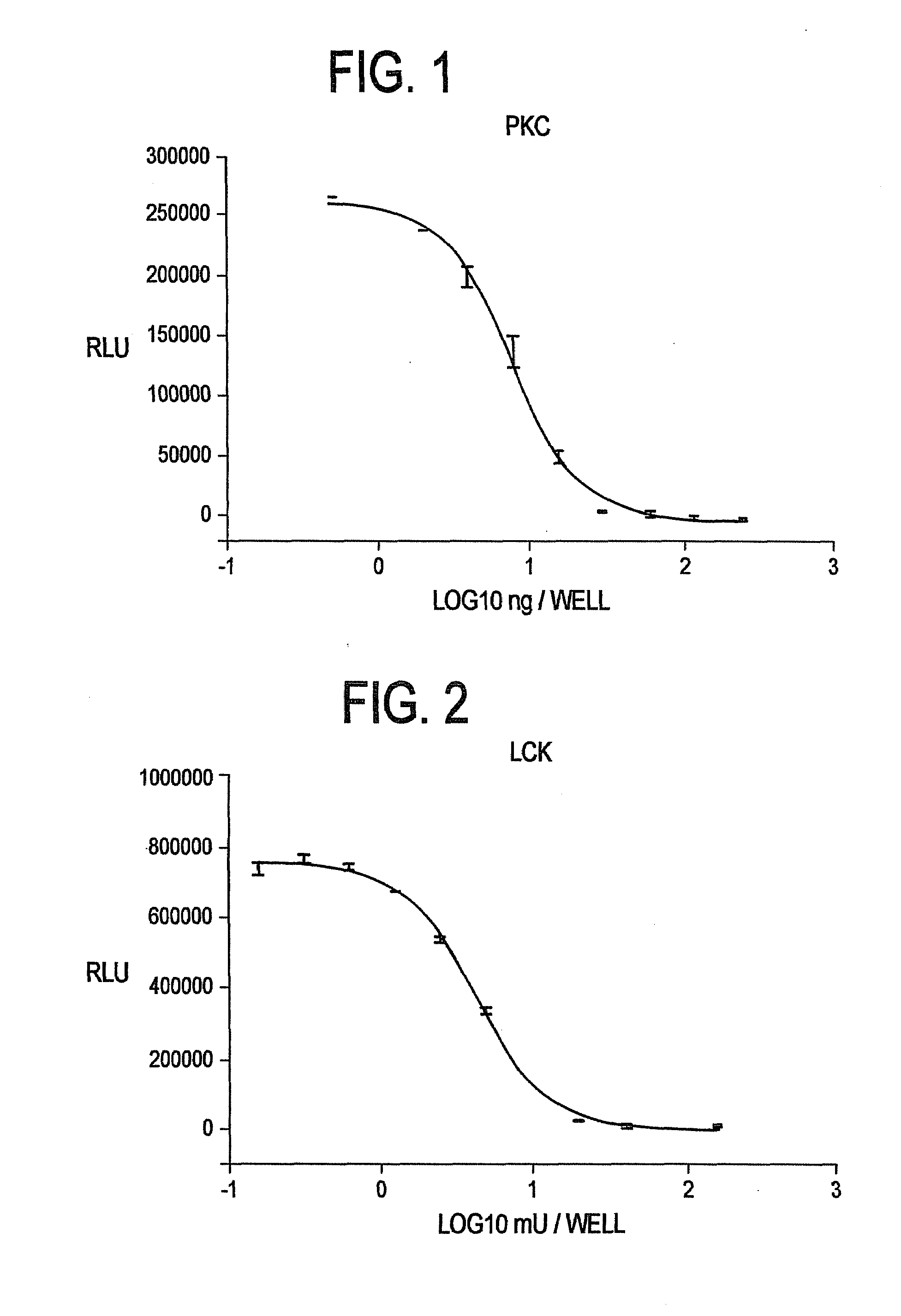
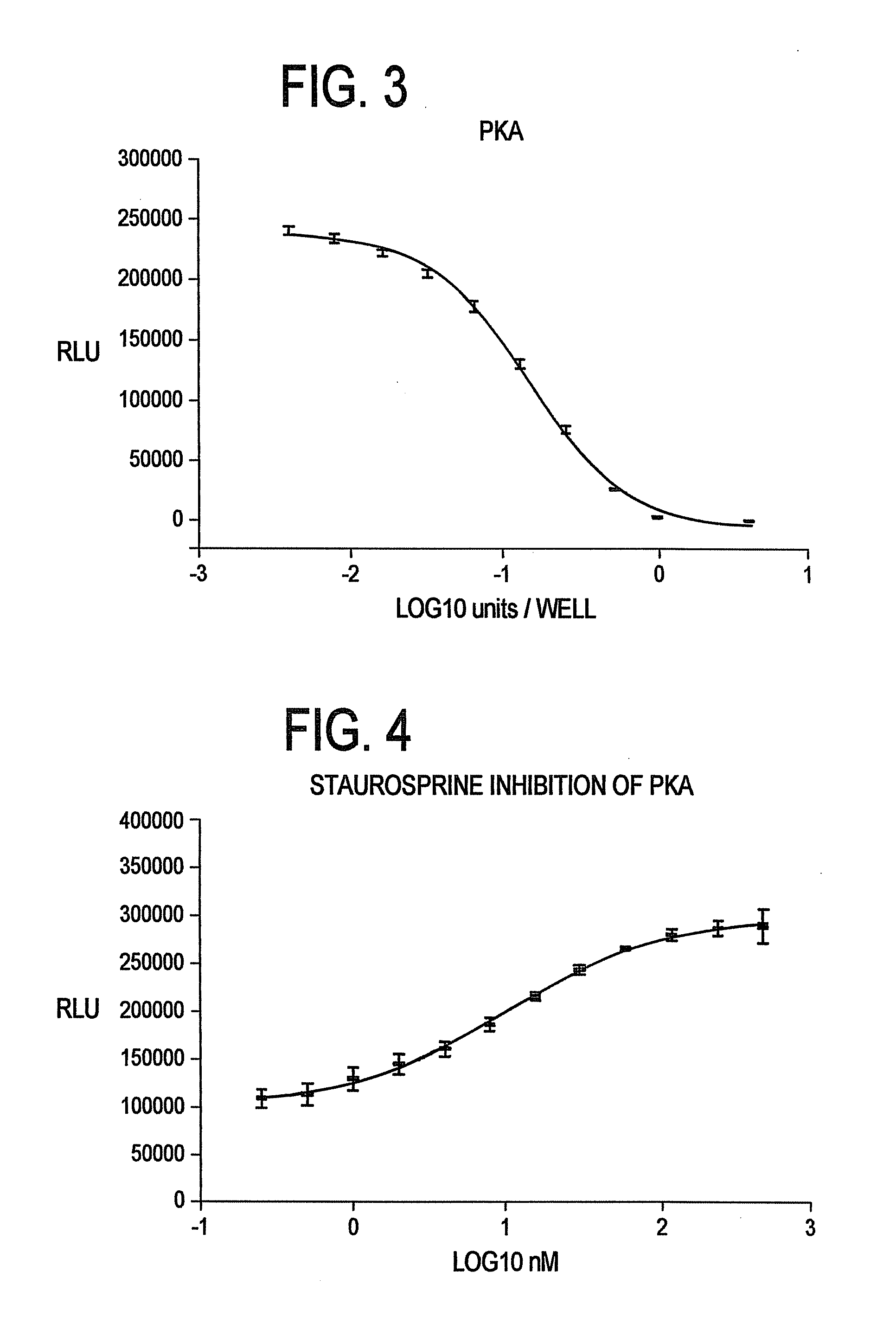
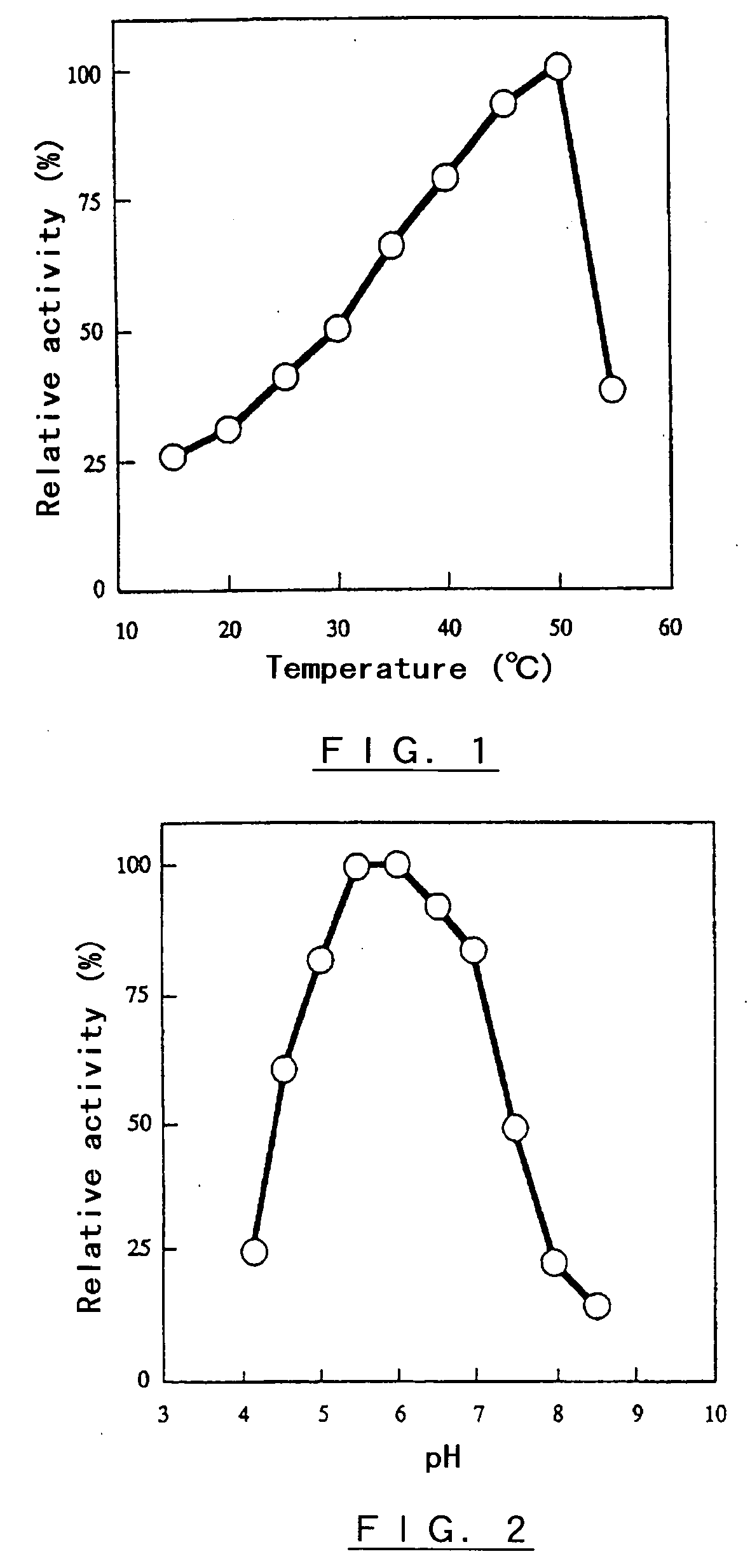
Method for Detecting Transferase Enzymatic Activity
InactiveUS20100021949A1Easy to measureEliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingQuenchingTransferase
Methods and kits for detecting transferase activity in a sample by measuring ATP using a composition comprising an ATP-dependent bioluminescence-generating enzyme, a luminogenic molecule and one or more transferase quenching agents.
Owner:PROMEGA
Gene encoding a protein having acyl group transfer activity
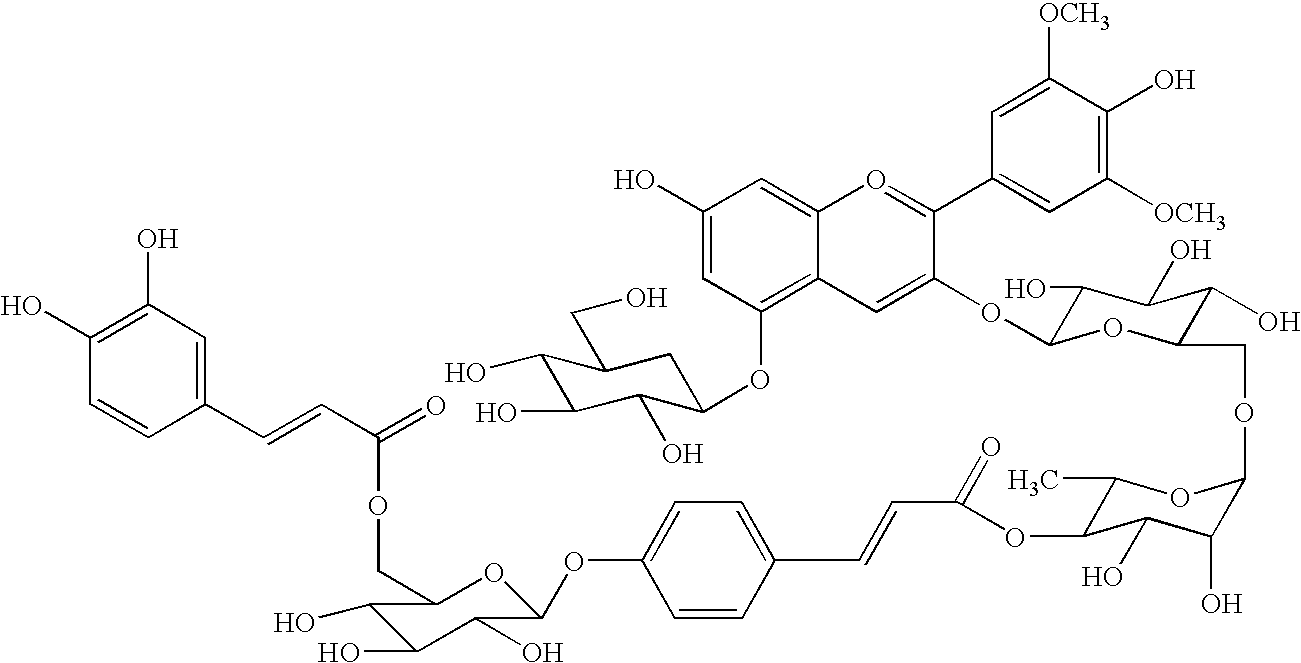
The invention relates to isolated polynucleotides encoding a protein having aromatic acyltransferase activity, vectors comprising aromatic acyltransferase polynucleotides, and methods of transforming plants with anthocyanin acyltransferase polynucleotides to alter flower colors. The invention also relates to transformed host cells, plants, and flower cuts expressing proteins having anthocyanin acyltransferase activity.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Chimeric RNA oligonucleotides and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140171492A1Reduce the frequency of occurrenceReduce severitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic disorderDna methyl transferase
The present invention relates to chimeric RNA oligonucleotides that are single-stranded oligonucleotides. These compounds are capable of targeting particular genes and reducing DNA methyltransferase activity. Accordingly, these compounds are particularly useful in the treatment of disease associated with aberrant DNA methyltransferase activity, such as cancer or a genetic disorder.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
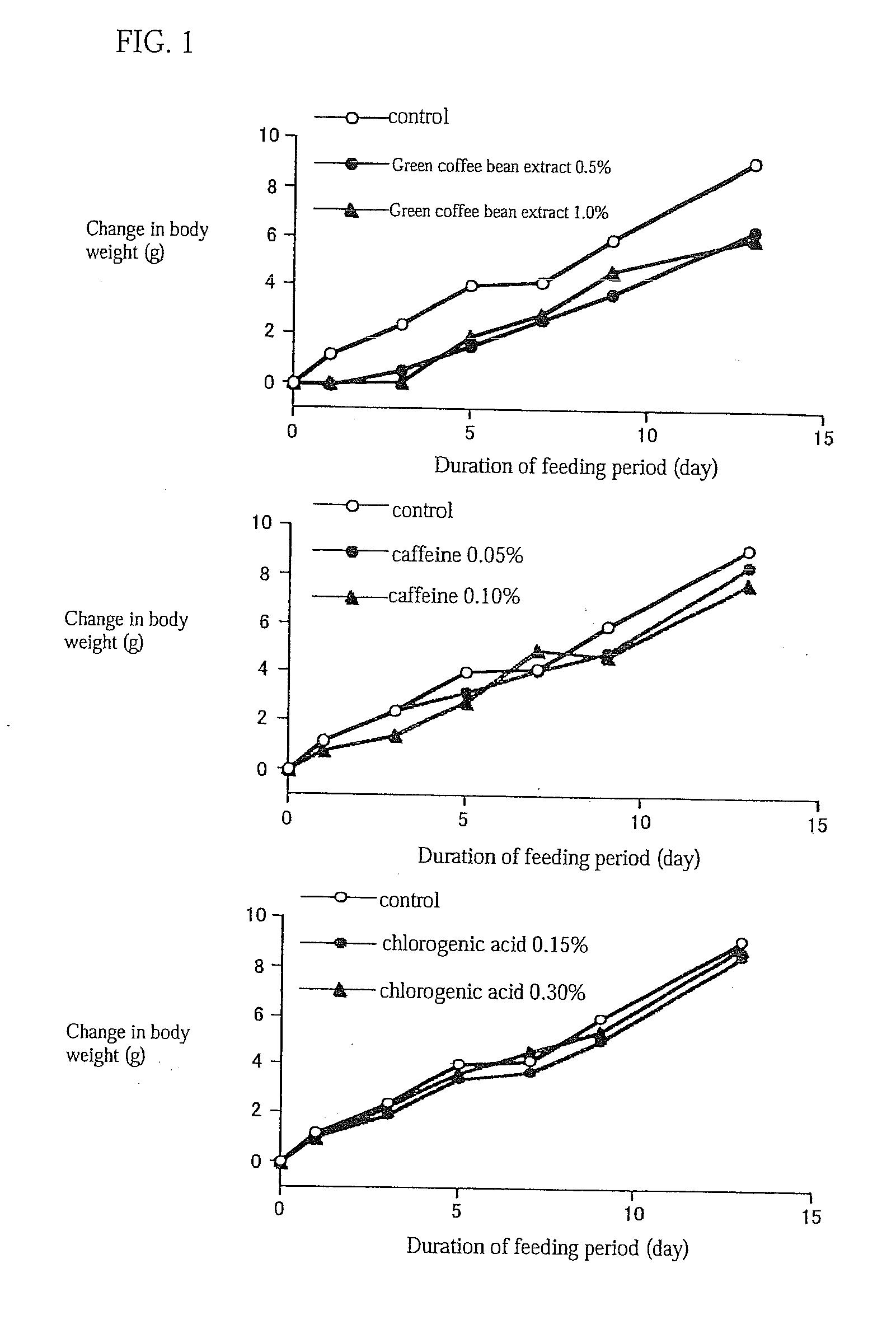
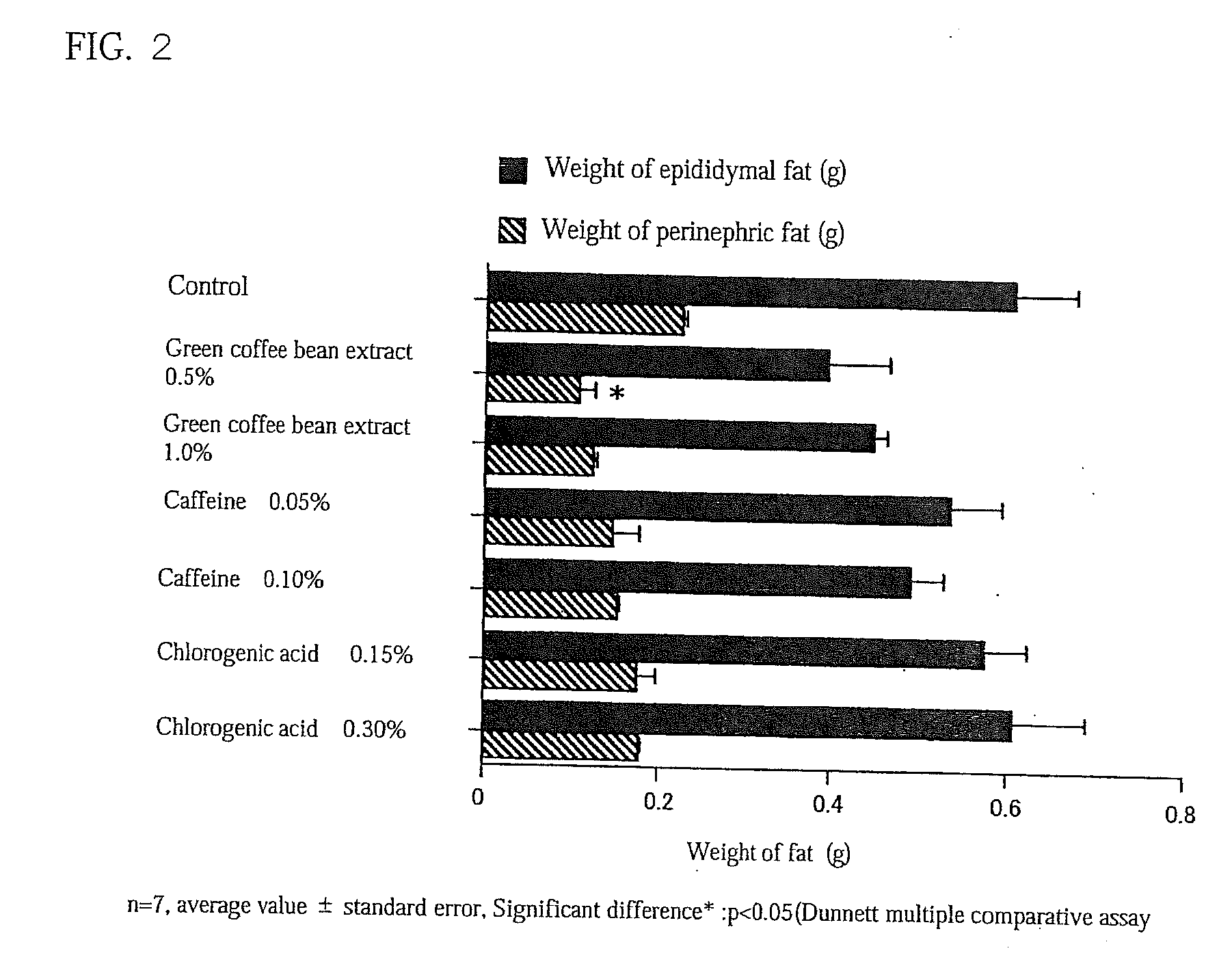
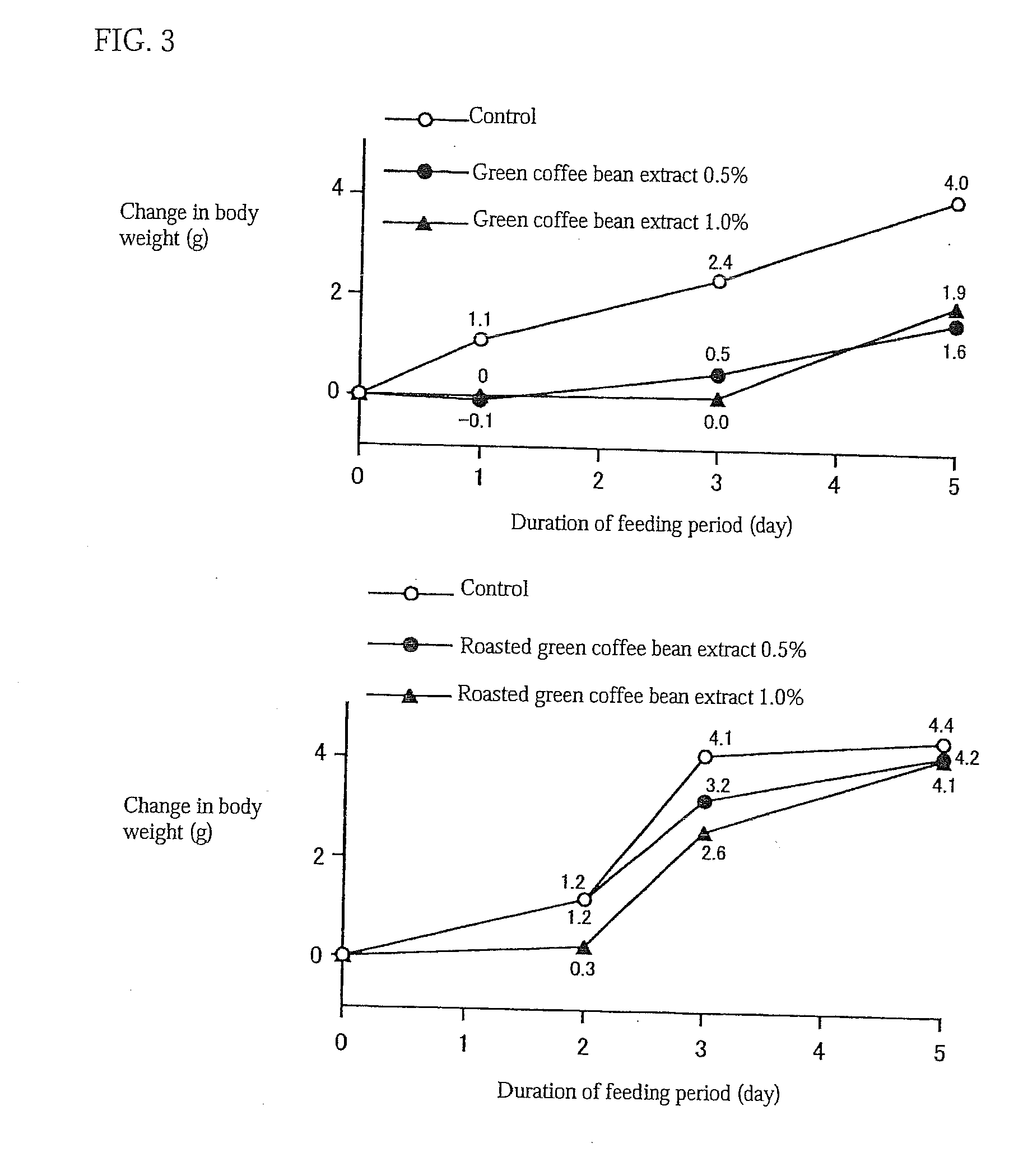
Method of using a green coffee bean extract to promote carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity
InactiveUS20110189313A1Improve securitySimple compositionCosmetic preparationsBiocideDiseaseAdditive ingredient
(Problems) To provide a highly safe dietetic composition originating in green coffee beans by which excellent dietetic effects can be obtained and which contributes to the prevention and treatment of life style-related diseases such as diabetes.(Means for Solving Problems) A dietetic composition characterized by comprising, as the active ingredient, a polar solvent extract of defatted green coffee beans. It is preferable that the above-described polar solvent extract is an extract obtained by using water-containing ethanol, still preferably water-containing ethanol having an ethanol concentration of from 40 to 90% (wt / wt). It is preferable that the above-described defatted green coffee beans are those obtained by extracting green coffee beans with N-hexane to thereby separate oily components therefrom. It is recommended to combine the above-described dietetic composition with one or more members selected from among salacia extract, evening primrose extract, sesamine and garcinia. This dietetic composition is usable as a material for foods, drinks, drugs, or skin preparations for external use.
Owner:ORIZA YUKA KK
N-acetylglucosaminlytransferase and polynucleotide encoding the same
The present invention relates to an enzyme having novel N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase (OMGnT) activity, a polynucleotide encoding the enzyme, a recombinant polynucleotide comprising the polynucleotide, a host cell comprising the recombinant polynucleotide, a method for producing an enzyme protein having OMGnT activity by culturing the host cell in a medium, and a method for modifying a sugar chain structure with the enzyme and a carbohydrate having a sugar chain structure modified by the method. This enzyme enables the production of complex carbohydrates, which could not be formed with conventional glycosyltransferases.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Novel aromatic prenyltransferases, nucleic acids encoding same and uses therefor
ActiveUS20060183211A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPrenyltransferase activityIsoprene
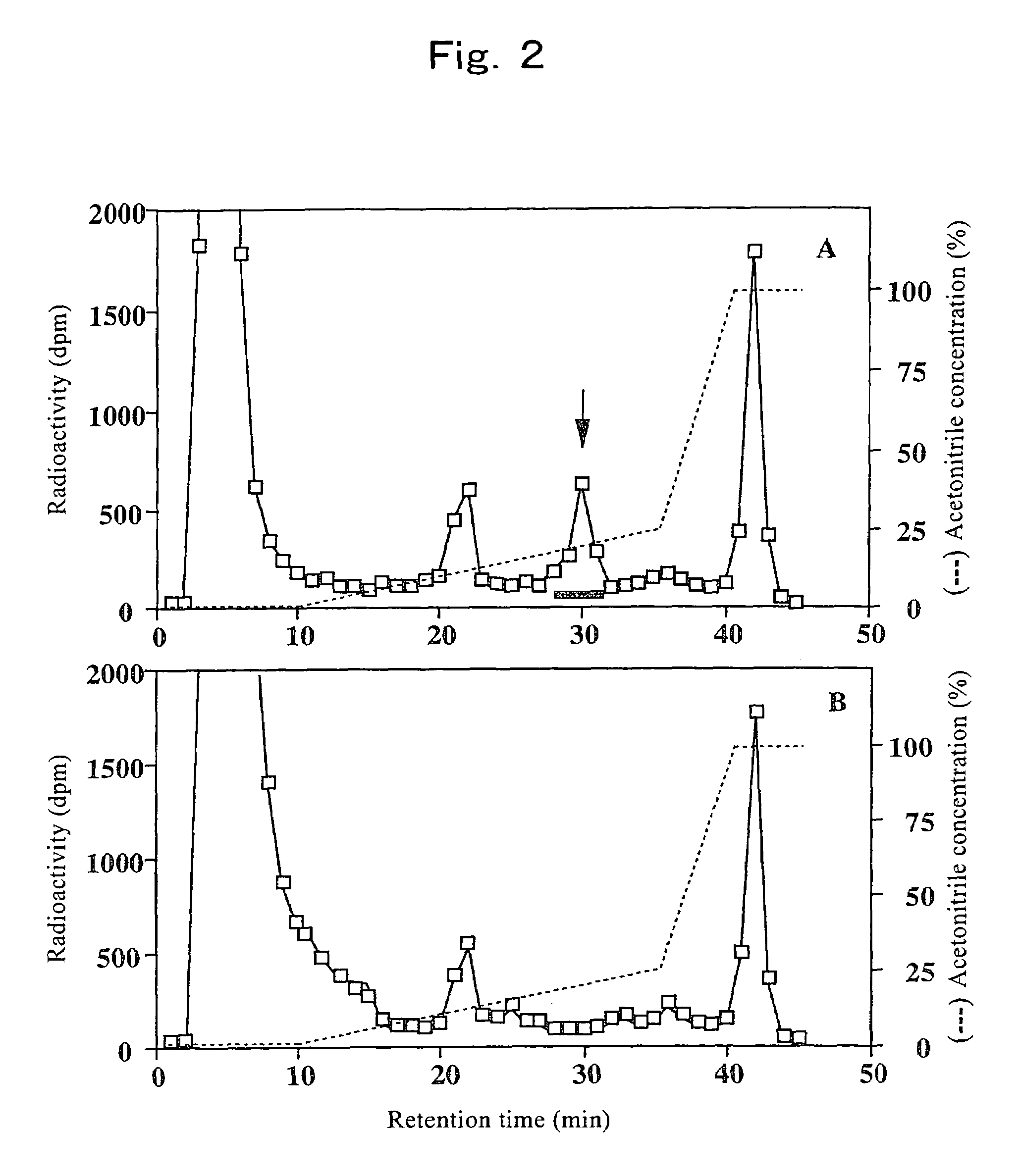
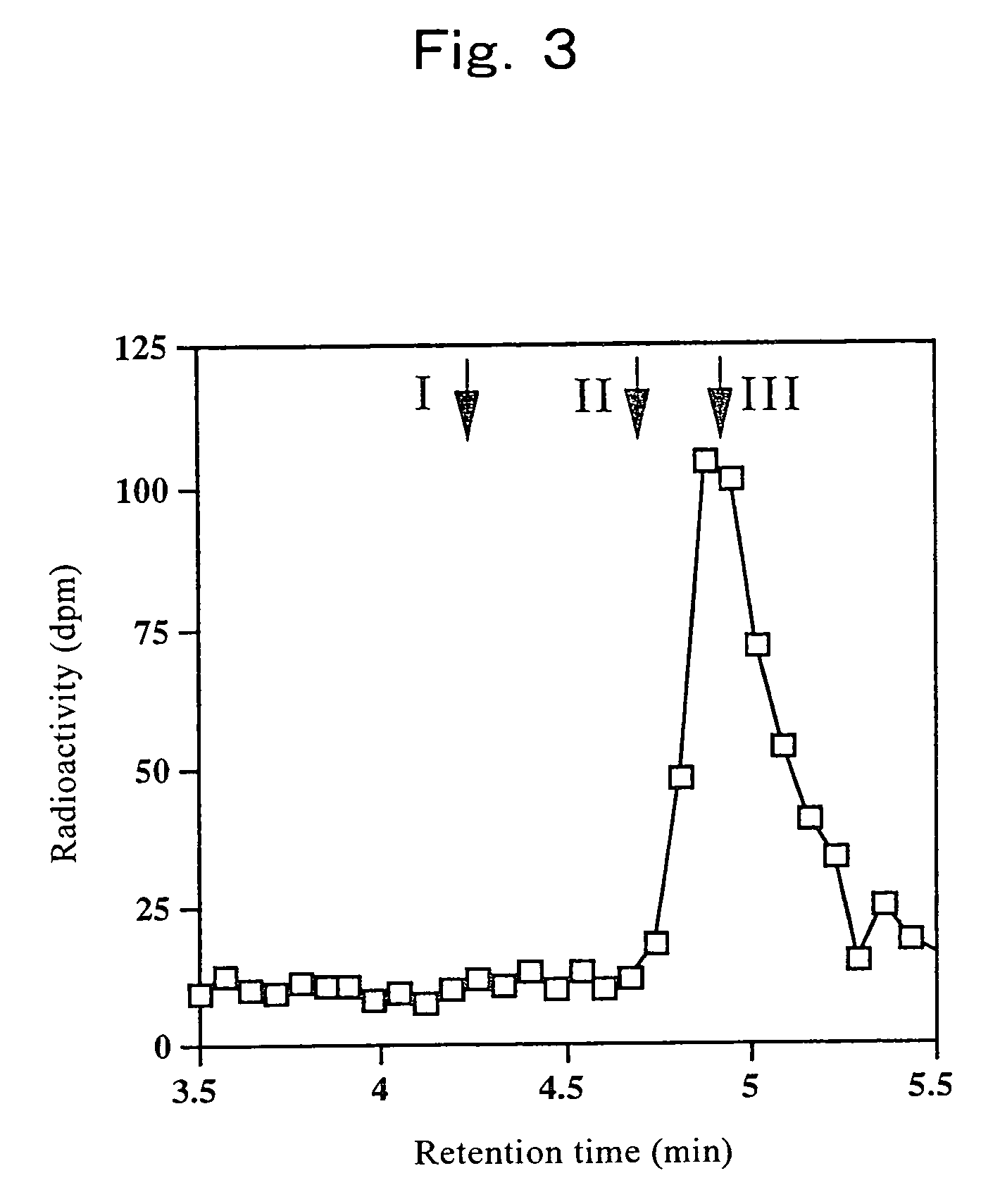
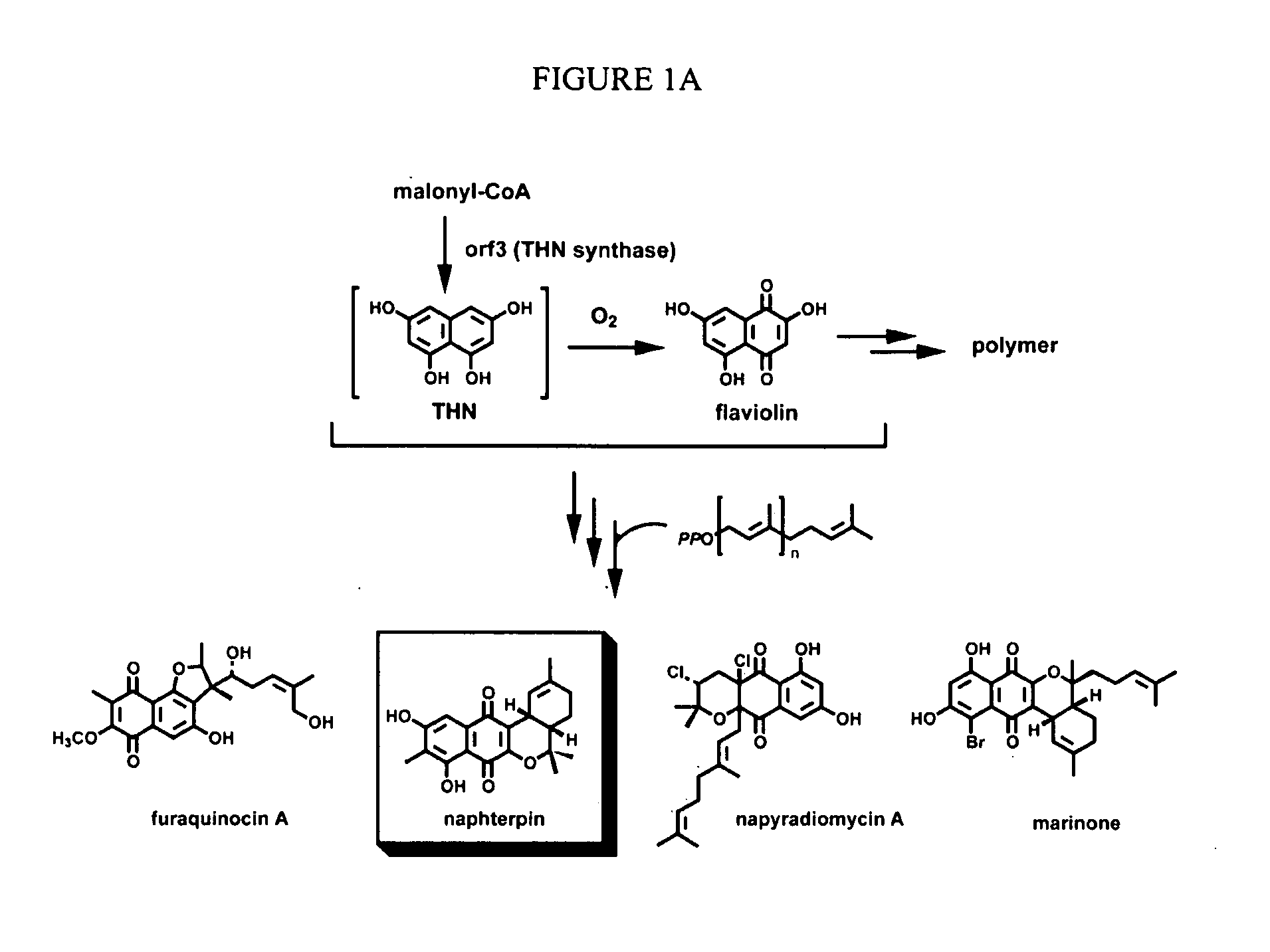
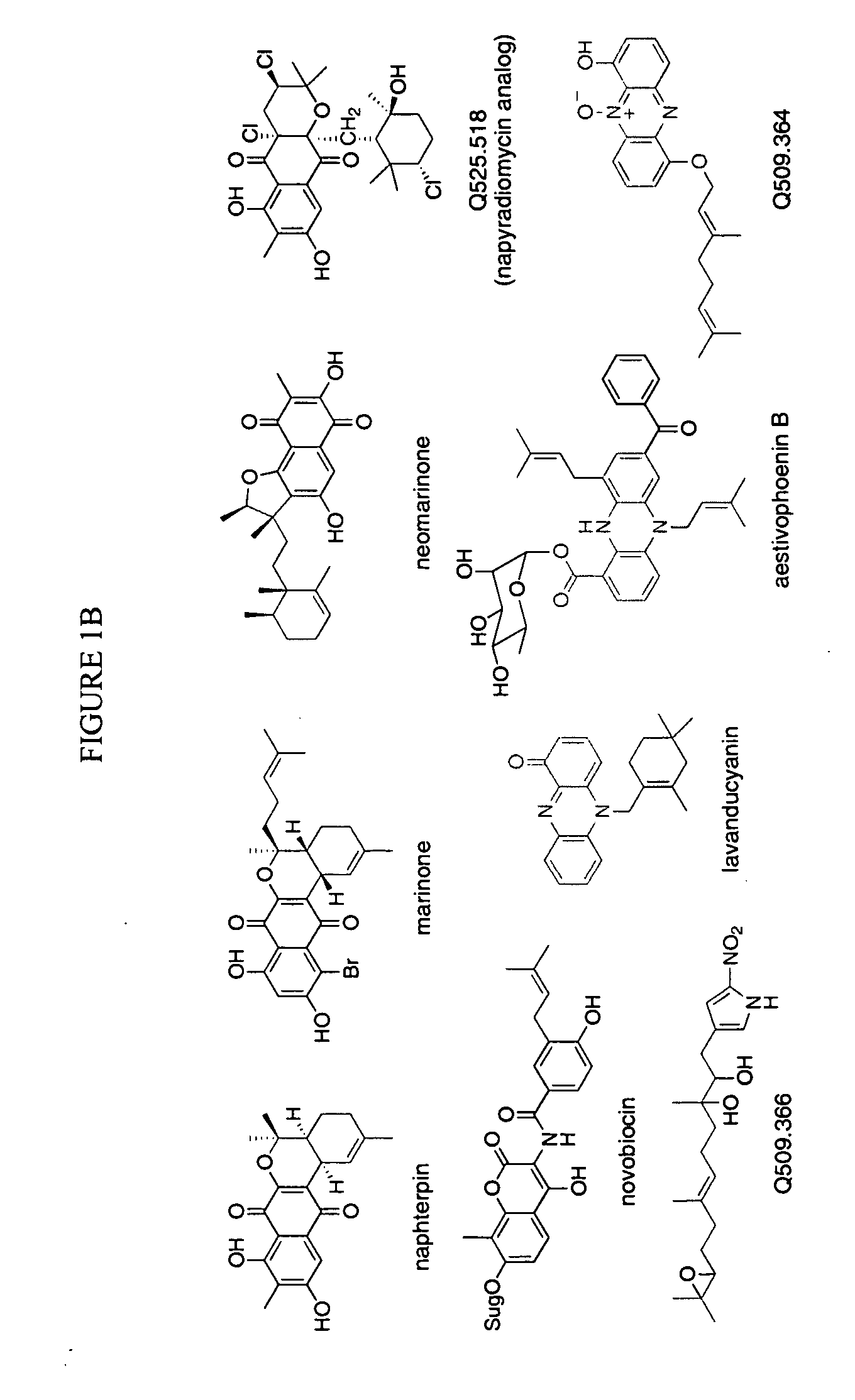
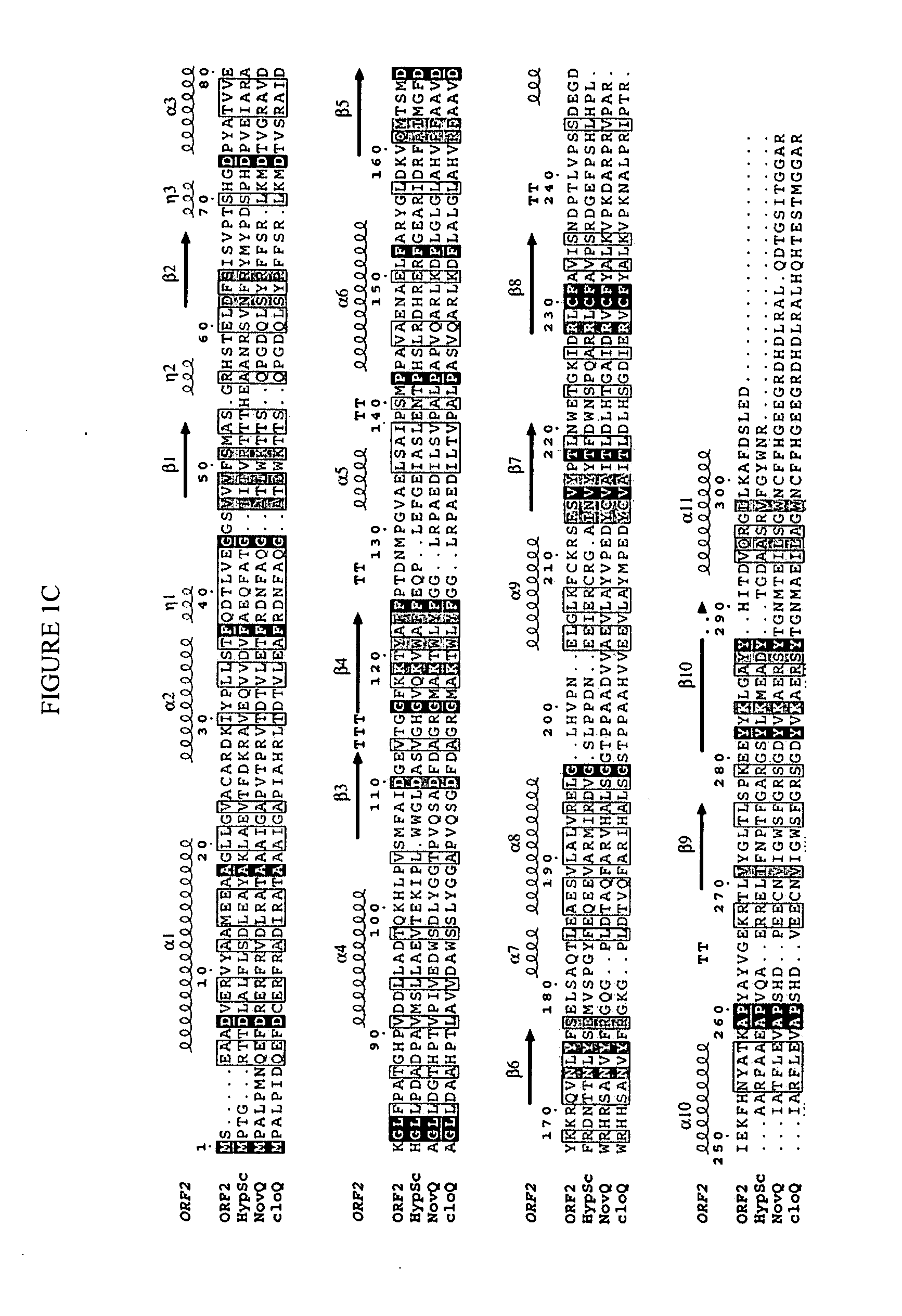
In accordance with the present invention, a novel aromatic prenyltransferase, Orf2 from Streptomyces sp. strain CL190, involved in naphterpin biosynthesis has been identified and the structure thereof elucidated. This prenyltransferase catalyzes the formation of a C—C bond between a prenyl group and a compound containing an aromatic nucleus, and also displays C—O bond formation activity. Numerous crystallographic structures of the prenyltransferase have been solved and refined, e.g., (1) prenyltransferase complexed with a buffer molecule (TAPS), (2) prenyltransferase as a binary complex with geranyl diphosphate (GPP) and Mg2+, and prenyltransferase as ternary complexes with a non-hydrolyzable substrate analogue, geranyl S-thiolodiphosphate (GSPP) and either (3) 1,6-dihydroxynaphthalene (1,6-DHN), or (4) flaviolin (i.e., 2,5,7-trihydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone, which is the oxidized product of 1,3,6,8-tetrahydroxynaphthalene (THN)). These structures have been solved and refined to 1.5 Å, 2.25 Å, 1.95 Å and 2.02 Å, respectively. This first structure of an aromatic prenyltransferase displays an unexpected and non-canonical (β / α)-barrel architecture. The complexes with both aromatic substrates and prenyl containing substrates and analogs delineate the active site and are consistent with a proposed electrophilic mechanism of prenyl group transfer. These structures also provide a mechanistic basis for understanding prenyl chain length determination and aromatic co-substrate recognition in this structurally unique family of aromatic prenyltransferases. This structural information is useful for predicting the aromatic prenyltransferase activity of proteins.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Methods of detecting methyl transferase activity and methods of screening for methyl transferase activity modulators
The invention features a method for determining methyl transferase activity of a polypeptide and screening for modulators of methyl transferase activity. The invention further provides a method or pharmaceutical composition for prevention or treating of colorectal cancer or hepatocellular carcinoma using the modulator.
Owner:ONCOTHERAPY SCI INC
Prevention of atherosclerosis and undesired blood clotting by reducing von Willebrand factor
InactiveUS7192914B1Preventing and treating blood clottingPreventing or treating blood clottingFactor VIIBiocideFactor VIII vWFMammal
This invention provides methods and compositions for treating and preventing atherosclerosis other undesired blood clotting. The methods for treating and preventing atherosclerosis and related conditions involve administering to a mammal an agent that reduces activity of an ST3Gal IV sialyltransferase, which results in enhanced clearance of von Willebrand Factor (vWF) from the mammal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
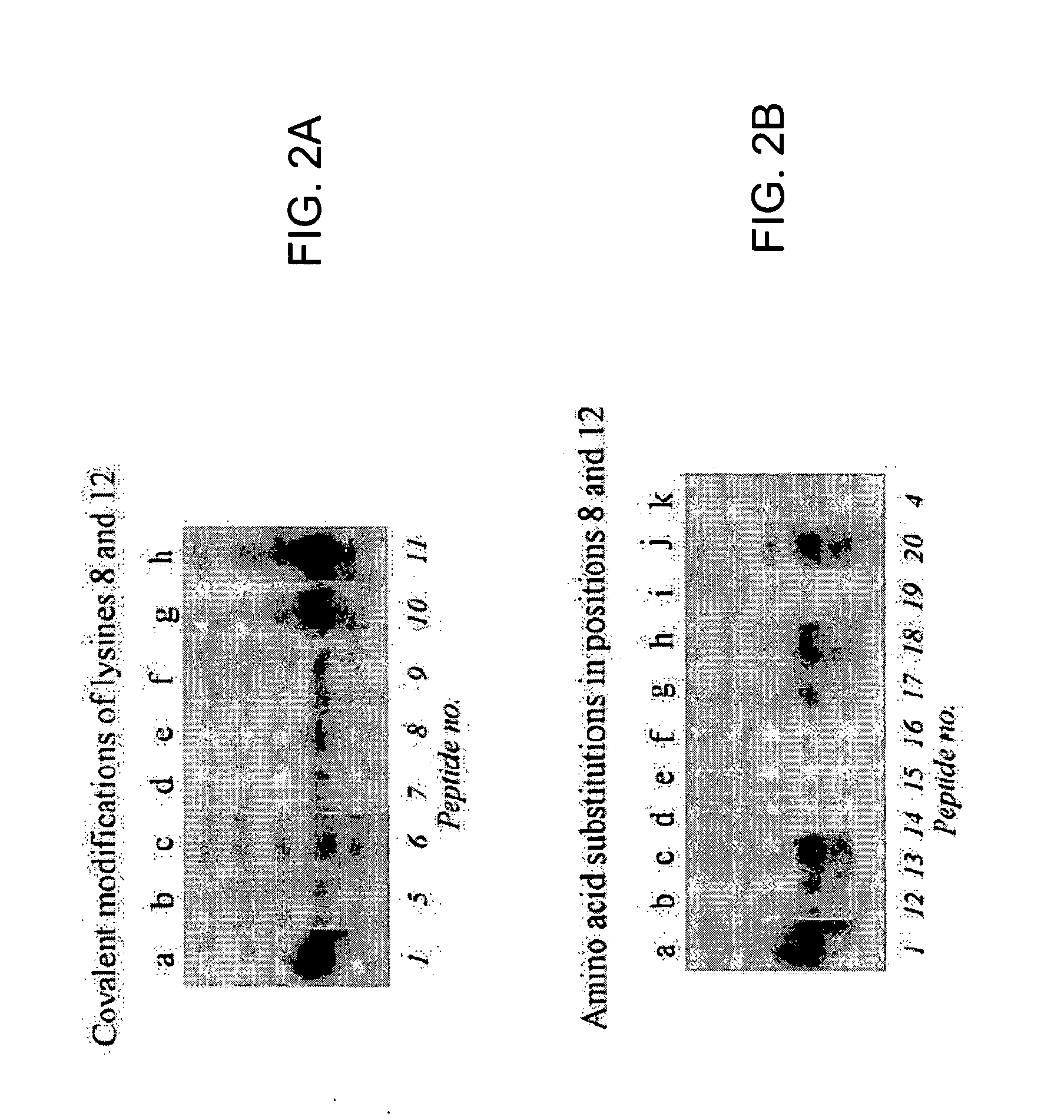
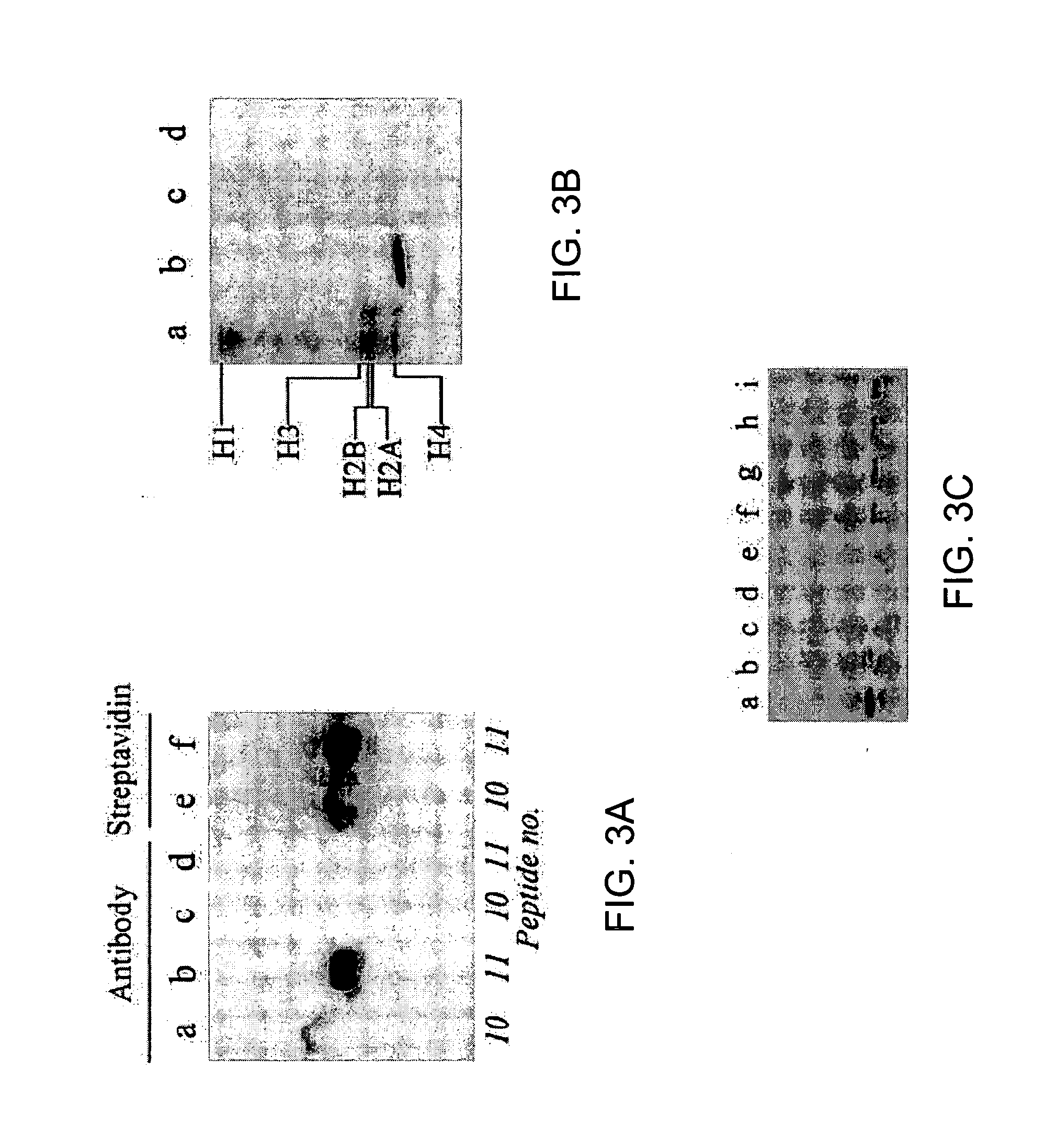
Antibodies against biotinylated histones and related proteins and assays related thereto
InactiveUS20060286611A1Enhancer of histone biotinylationMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansHistone biotinylationAntiendomysial antibodies
Described are specific biotinylation sites in histones, polypeptide fragments of histones comprising such biotinylation sites, and antibodies that selectively bind to such biotinylated sites. Also described are methods to detect biotinylation in a sample, to detect biotinyl transferase activity in a sample, to identify regulators of biotinylation, and to detect activities associated with histone biotinylation. Also described is an assay to detect or measure histone debiotinylation.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF NEBRASKA
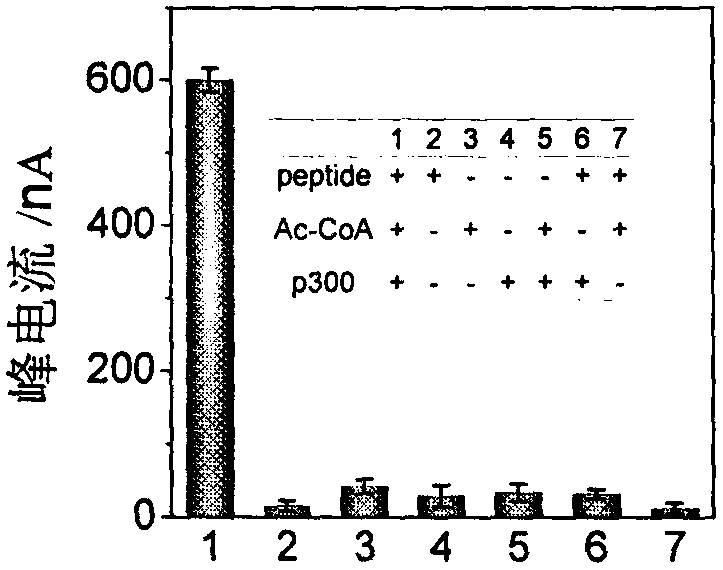
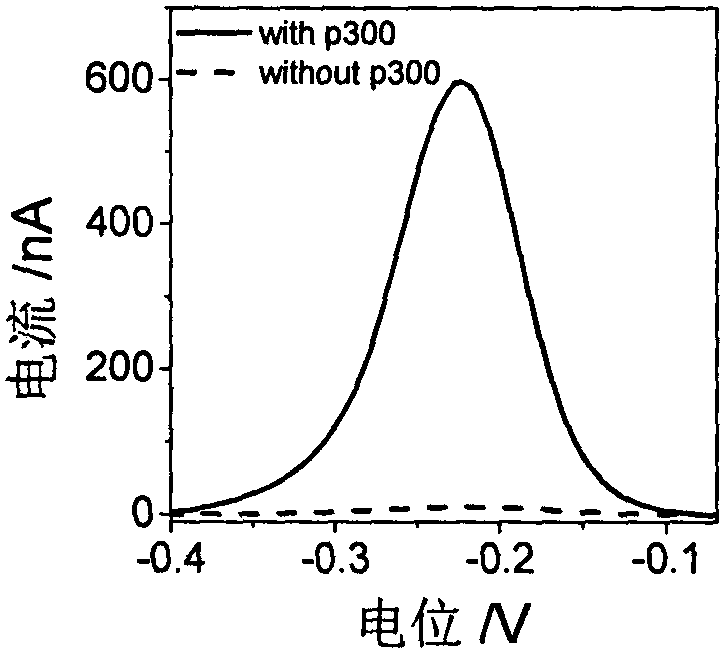
Electrochemical method for detecting activity of protein acetyltransferase
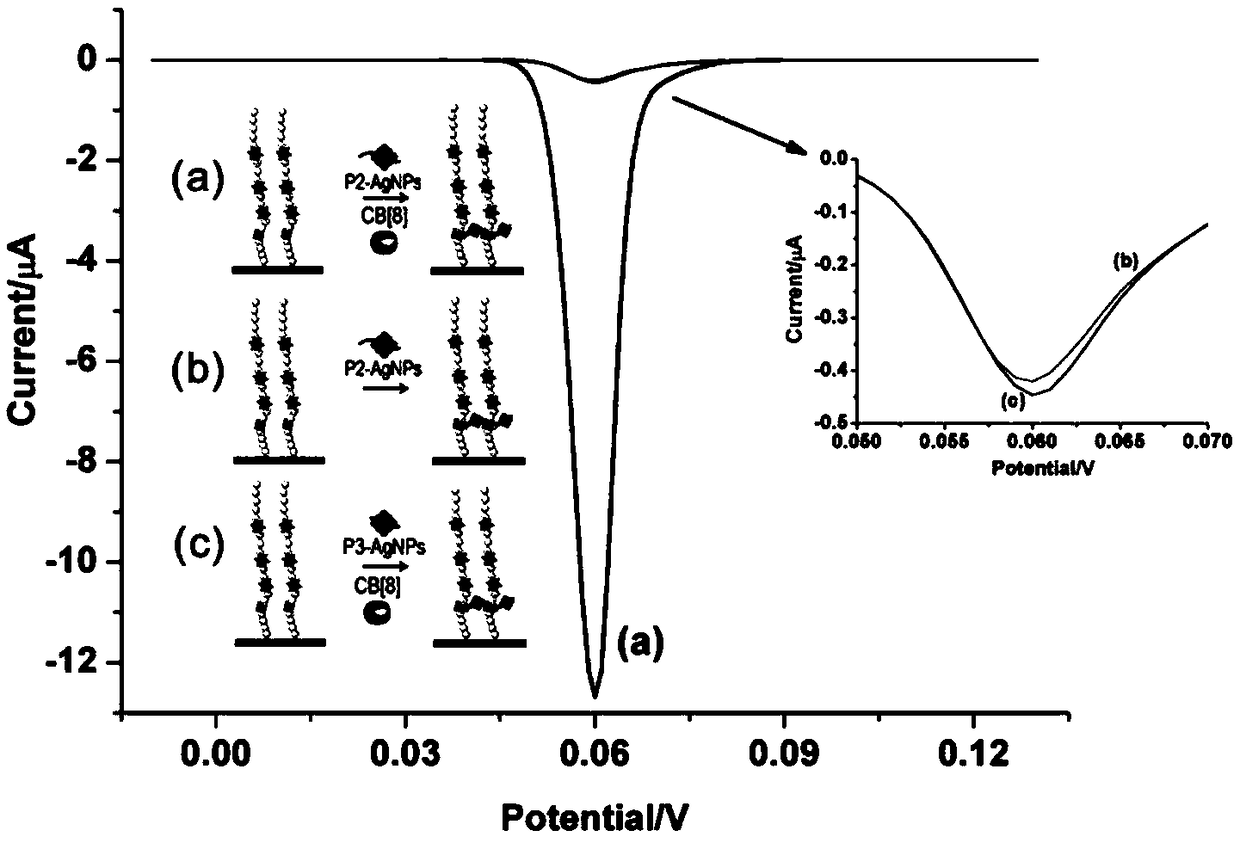
ActiveCN109187708AGood choiceGood repeatabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesCholine acetyltransferaseAmino acid
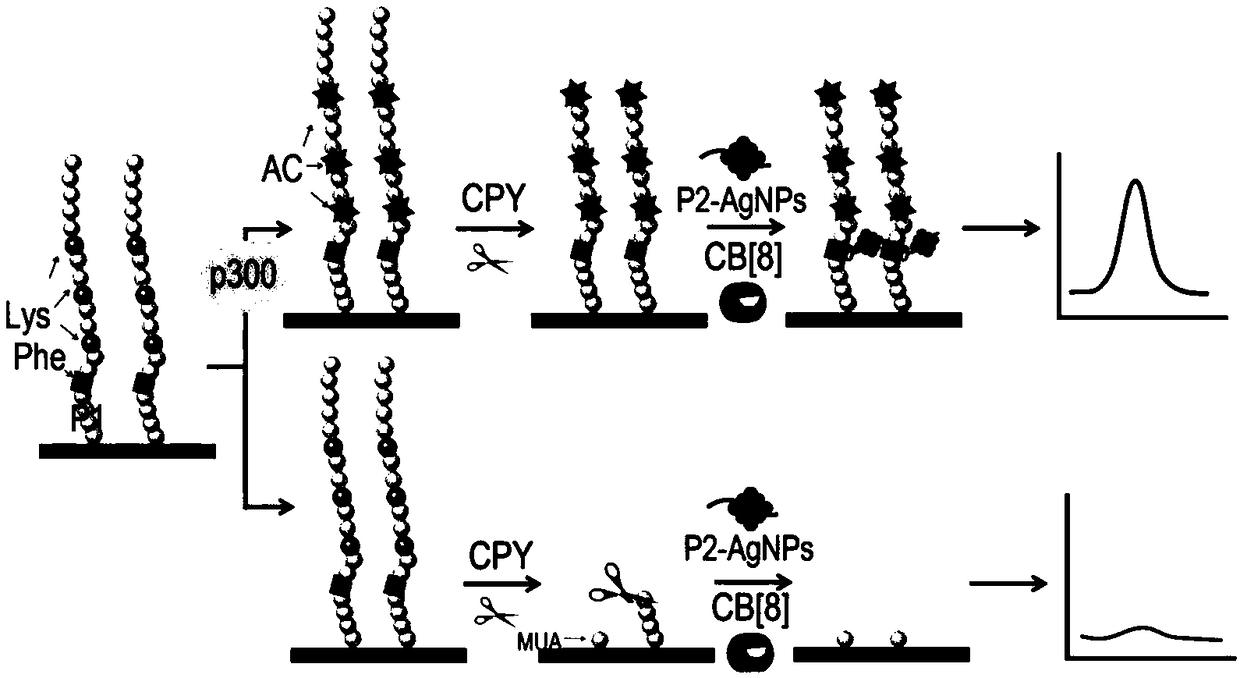
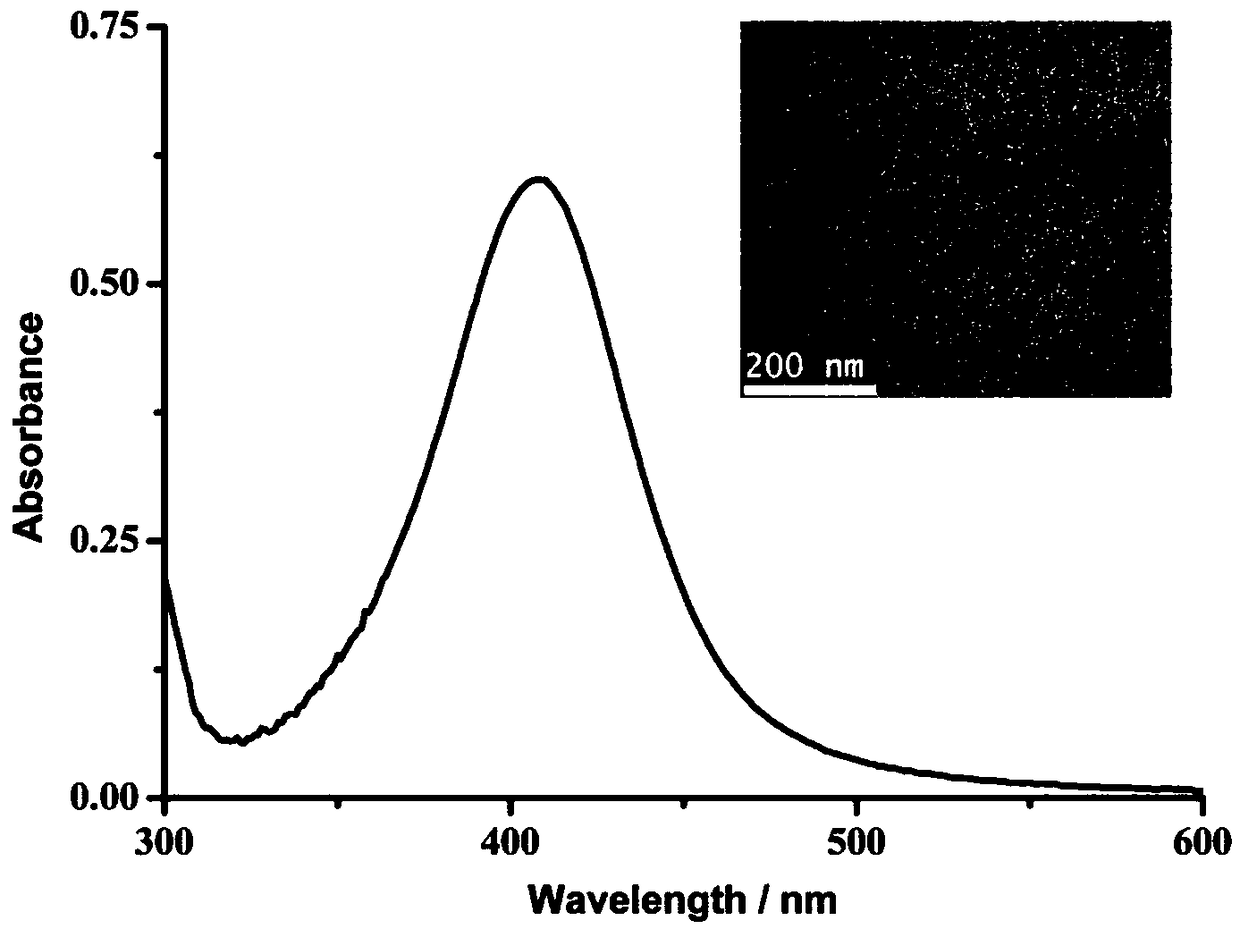
The invention discloses an electrochemical method for detecting the activity of protein acetyltransferase. P2 templated silver nanoparticles and cucurbit [8] urea are added into a P1 modified gold electrode and a detection system of a p300 protein, the activity of the p300 protein is detected by electrochemical measurement, and the protein transferase activity is obtained; the amino acid sequenceof P1 is 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid (MUA)-GGGFRGKGGKGLGKGGAKA; and the amino acid sequence of P2 is FGGGASLWWSEKL. p300 is used as a model, and the silver nanoparticles are synthesized by a signal template P2, and assembled with a sensing template P1 through a cavity, so that the sensitivity of detection is ensured, high design flexibility is achieved, and meanwhile, the selectivity of HATs is enhanced. The development of the simple and practical electrochemical method capable of detecting HATs activity is expected to help early diagnosis of major diseases.
Owner:SUZHOU CHIEN SHIUNG INST OF TECH
Process for producing sugar chains using beta1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase
The present invention provides a novel polypeptide having a β1,3-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase activity, an agent for synthesizing a sugar chain comprising the polypeptide, a process for producing a sugar chain or a complex carbohydrate using the agent for synthesizing a sugar chain, DNA encoding the polypeptide, a process for producing the polypeptide, an antibody against the polypeptide, and a diagnosis method and a medicament for treatment for inflammation, cancer or tumor metastasis using the DNA or the antibody. The present invention is useful for synthesis of a useful sugar chain and diagnosis and treatment for inflammatory diseases, cancer or tumor metastasis.
Owner:HISASHI NARIMATSU +1
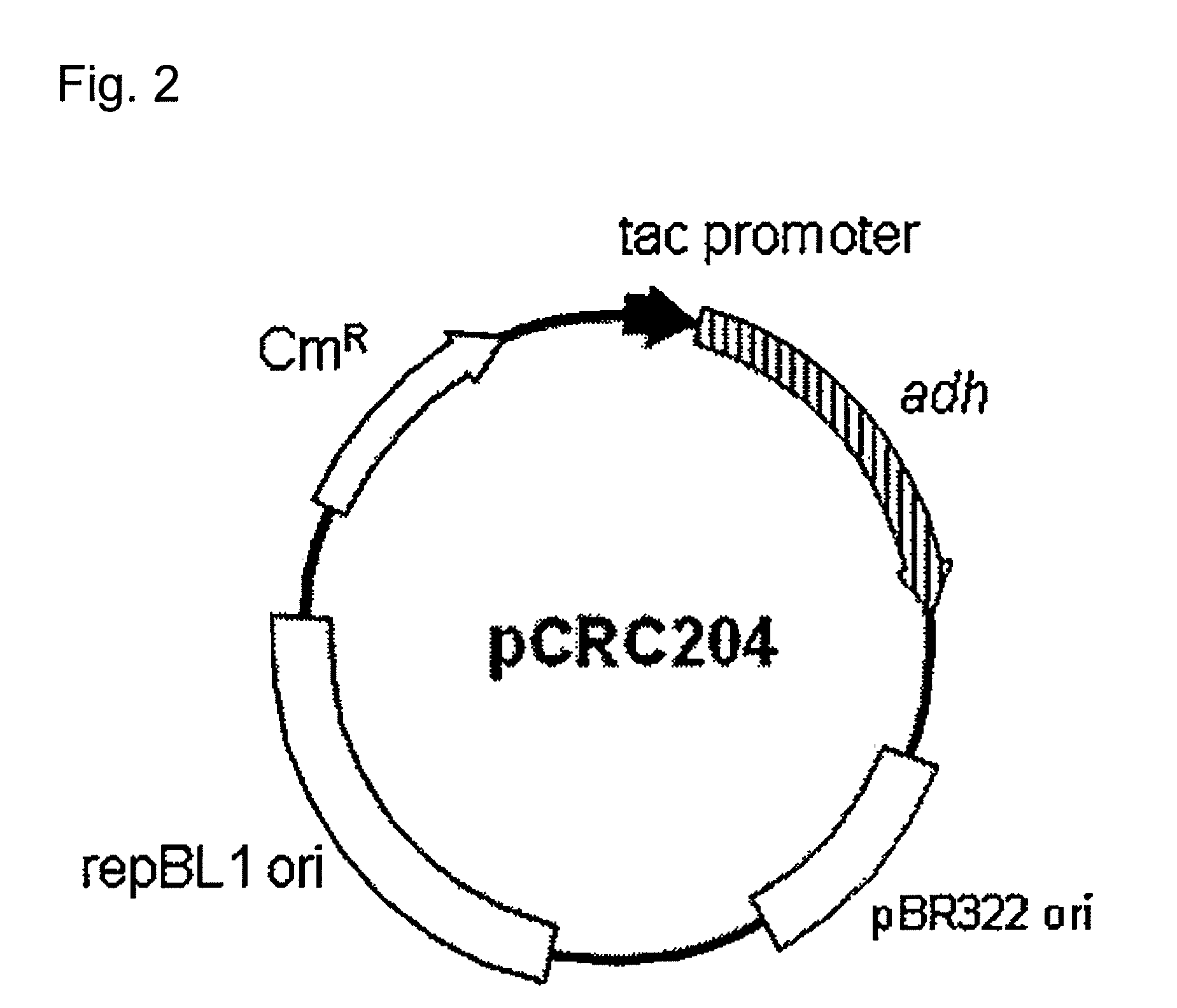
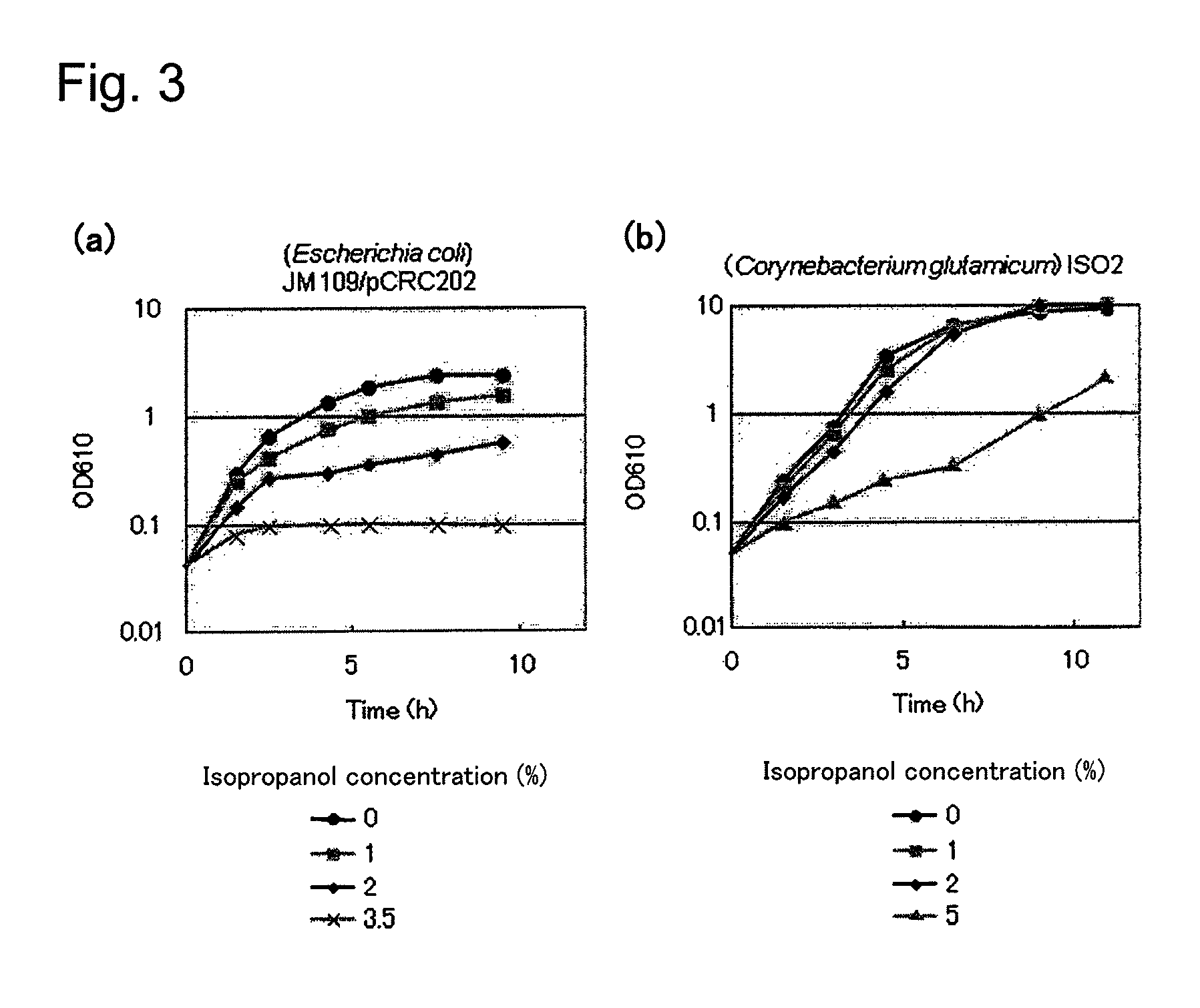
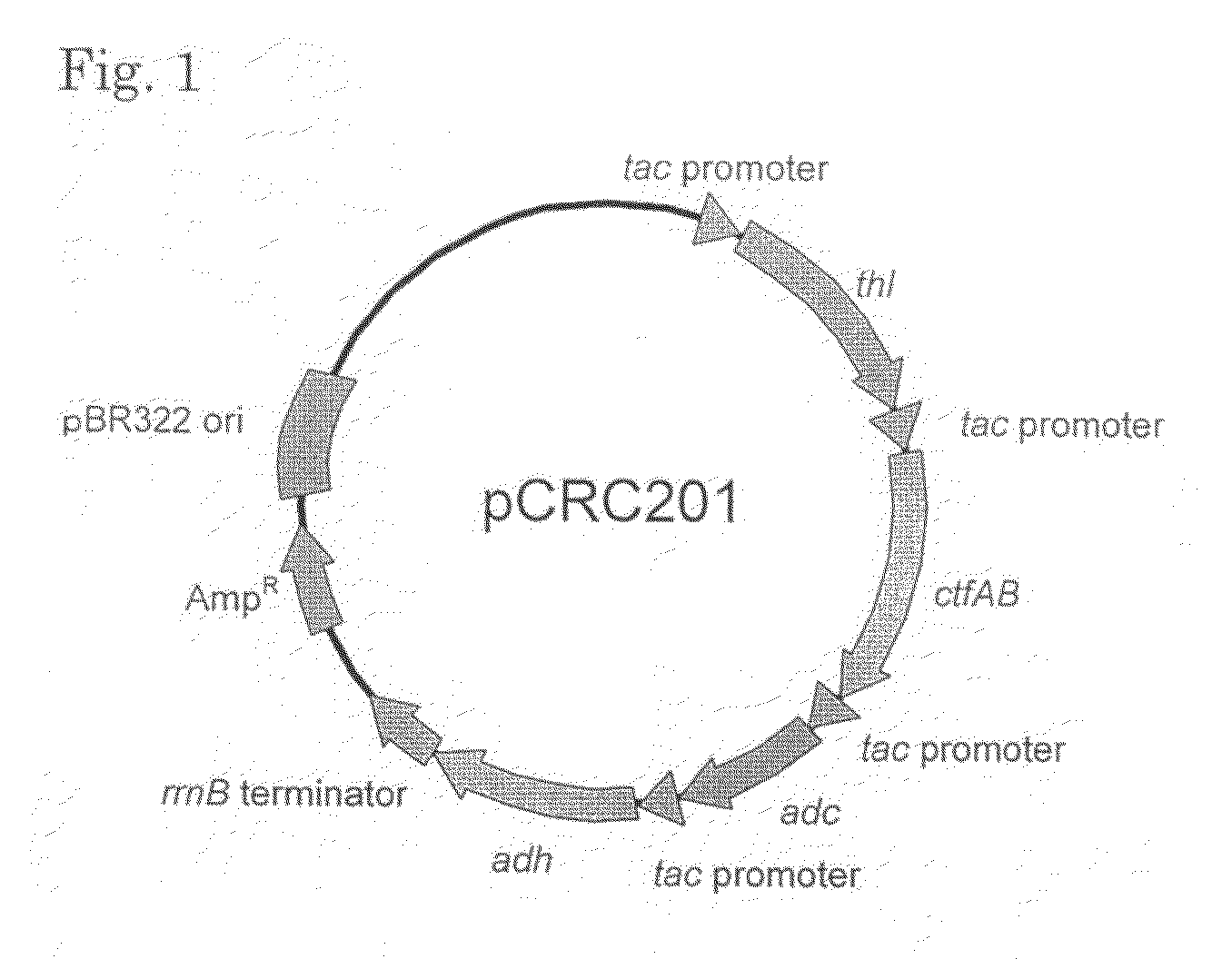
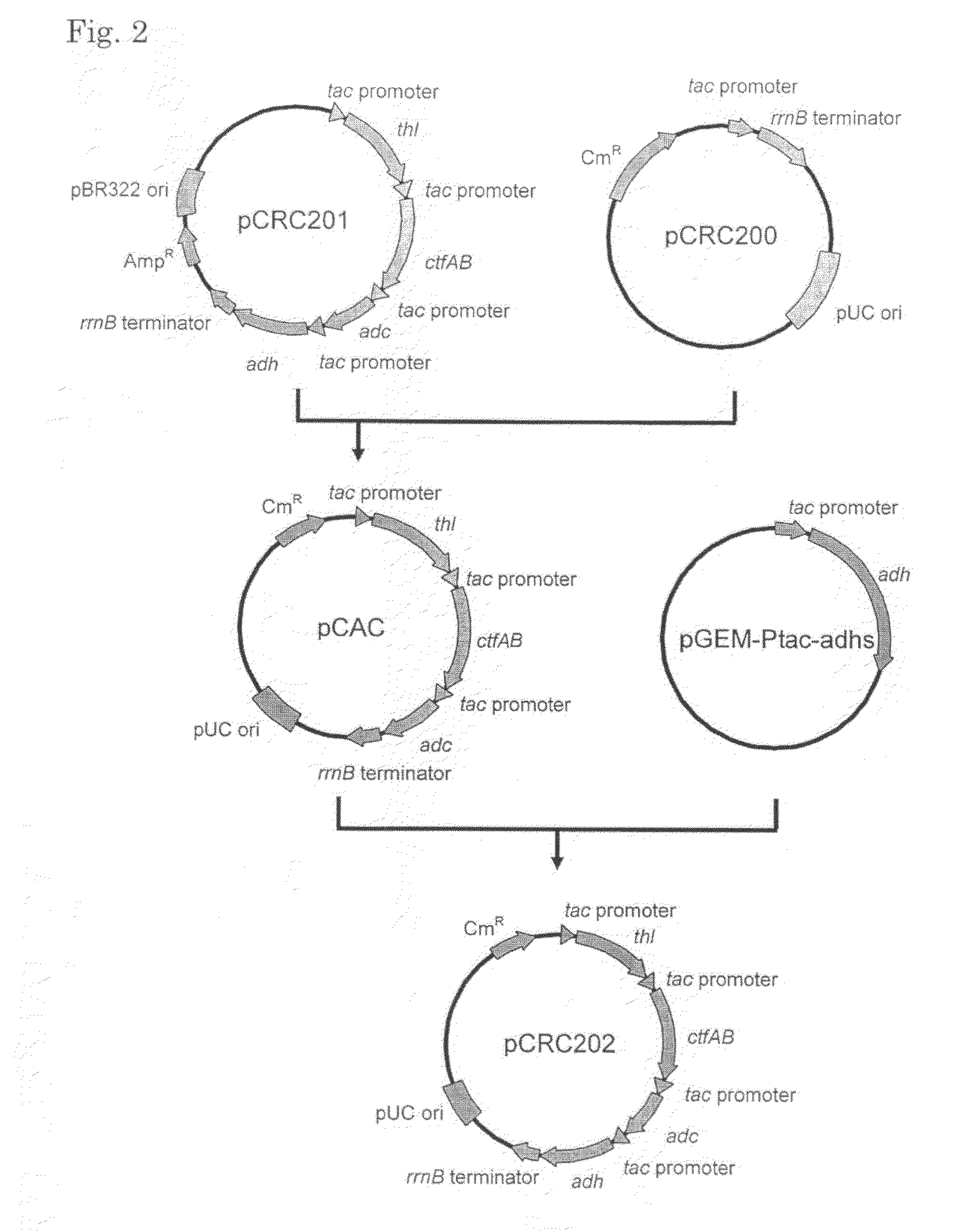
Transformant of coryneform bacteria capable of producing isopropanol
ActiveUS8216820B2Efficient productionBacteriaFermentationCorynebacterium efficiensAcetoacetate decarboxylase activity
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Transformant capable of producing isopropanol
ActiveUS20100203604A1Efficient productionBacteriaTransferasesAcetyltransferase activityFacultative anaerobic organism
A transformant capable of producing isopropanol which is constructed by transferring the following genes (a) to (d) into an aerobic bacterium or a facultative anaerobic bacterium:(a) a foreign gene which encodes an enzyme having acetyl-CoA acetyltransferase activity;(b) a foreign gene which encodes an enzyme having acetoacetyl CoA:acetate CoA-transferase activity;(c) a foreign gene which encodes an enzyme having acetoacetate decarboxylase activity; and(d) a foreign gene which encodes an enzyme having isopropanol dehydrogenase activity.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Preparation of wild cactus polysaccharide extract and high-efficient serum cholesterol-reducing function
InactiveCN101474235AImprove developmentImprove utilizationMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsCoenzyme A biosynthesisIn vivo
The invention relates to the preparation of a wild cactus polyoses extract and the highly effective function thereof for reducing serum cholesterase. The extract is a polyoses extracted from the natural wild cactus polyoses, and can reduce the total cholesterol content in the hypercholesterolemia and obviously improve the lipid metabolic disturbance by improving the activity of in vivo lipid metabolic key enzyme lecithin cholesterin acylase and reducing the activity of synthetical rate-limiting enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methyl pentane diacid coenzyme A reductase of liver cholesterin; the invention has no obviouse adverse reaction and can be used for preparing medicines used for lowering the cholesterin.
Owner:ZHANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
Construction method and application of electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor for detecting activity of histone acetyltransferase
ActiveCN108593751AHigh sensitivityAchieving High Sensitivity DetectionMaterial electrochemical variablesWater bathsUltrasonic dispersion
The invention discloses a construction method and an application of an electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor for detecting the activity of histone acetyltransferase. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing peptide / Au: respectively taking acetyltransferase p300, polypeptide and acetyl-CoA, fully mixing the taken substances in PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.0), incubating the obtained solution in a constant-temperature water bath, taking and dropwise applying a catalytic reaction to the surface of a gold electrode, and incubating the gold electrode in a 4 DEG C refrigerator; (2) preparing MB&AuNPs@GO-Ab: mixing HAuCl4 and CTAB with water, adding ascorbic acid to the obtained reaction mixture, adding NaOH to obtain CTAB covered AuNPs, centrifuging and purifying the CTAB covered AuNPs, dispersing the purified CTAB covered AuNPs in an equal amount of water, adding GO to the obtained solution, performing ultrasonic dispersion, standing the dispersed solution for later use,adding an acetyl antibody, performing incubation, adding MB, and performing vibration and uniform mixing; and (3) producing the electrochemical Faraday cage immunosensor: taking and dropwise applyingthe MB&AuNPs@GO-Ab to the surface of the peptide / Au, performing incubation at room temperature, and placing the produced sensor in the PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.0) to carry out electrochemical SWV test.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Laundry detergent and/or fabric care compositions comprising transferase
The present invention relates to laundry detergent and / or fabric care compositions comprising a transferase, preferably an alkaline transferase, wherein when said transferase is a xyloglucan transferase, said xyloglucan transferase exhibits greater transferase activity than hydrolytic acitivity and / or exhibits higher reaction rates for donor substrates with higher molecular weight than for donor substrates with lower molecular weight.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
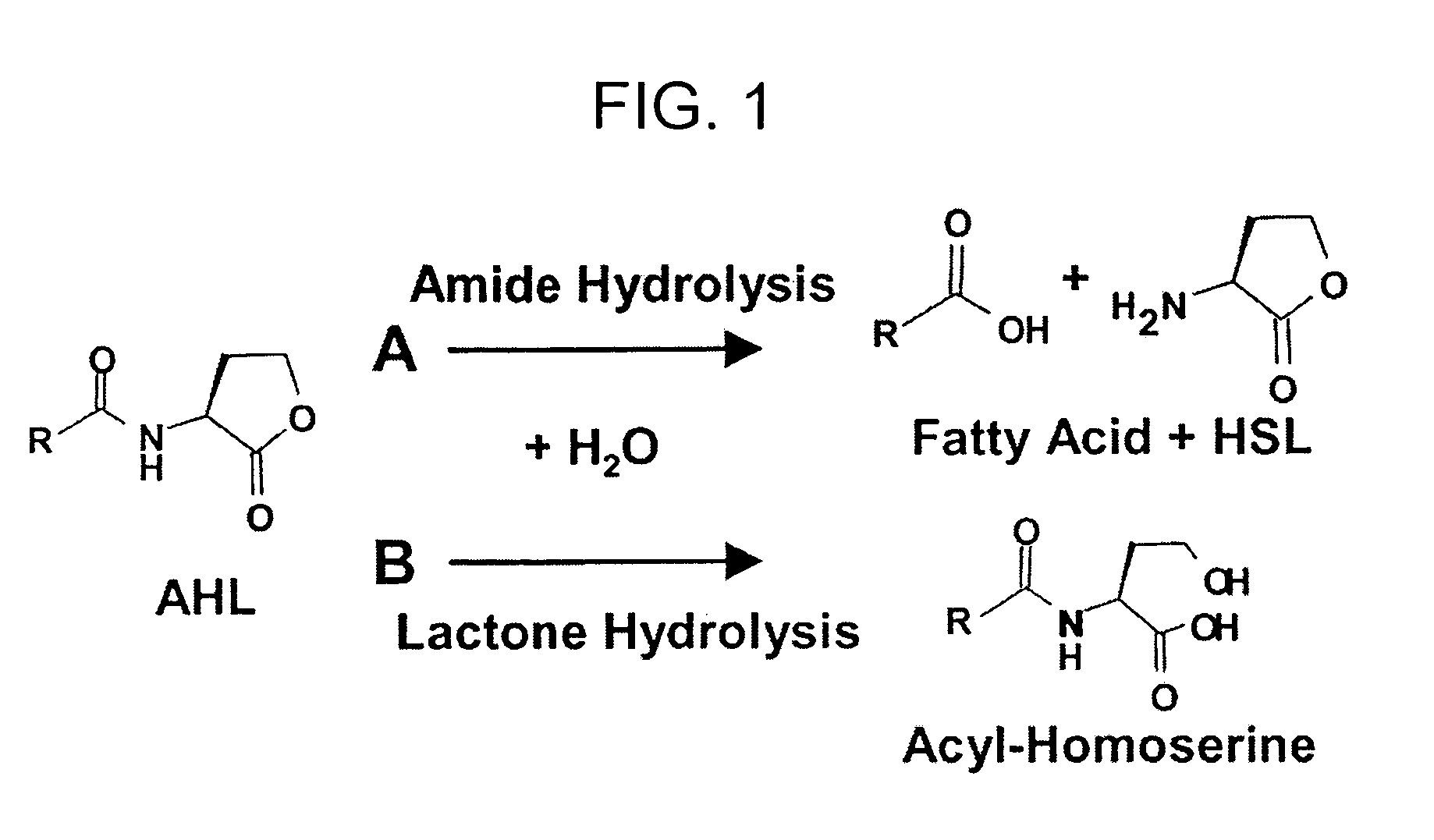
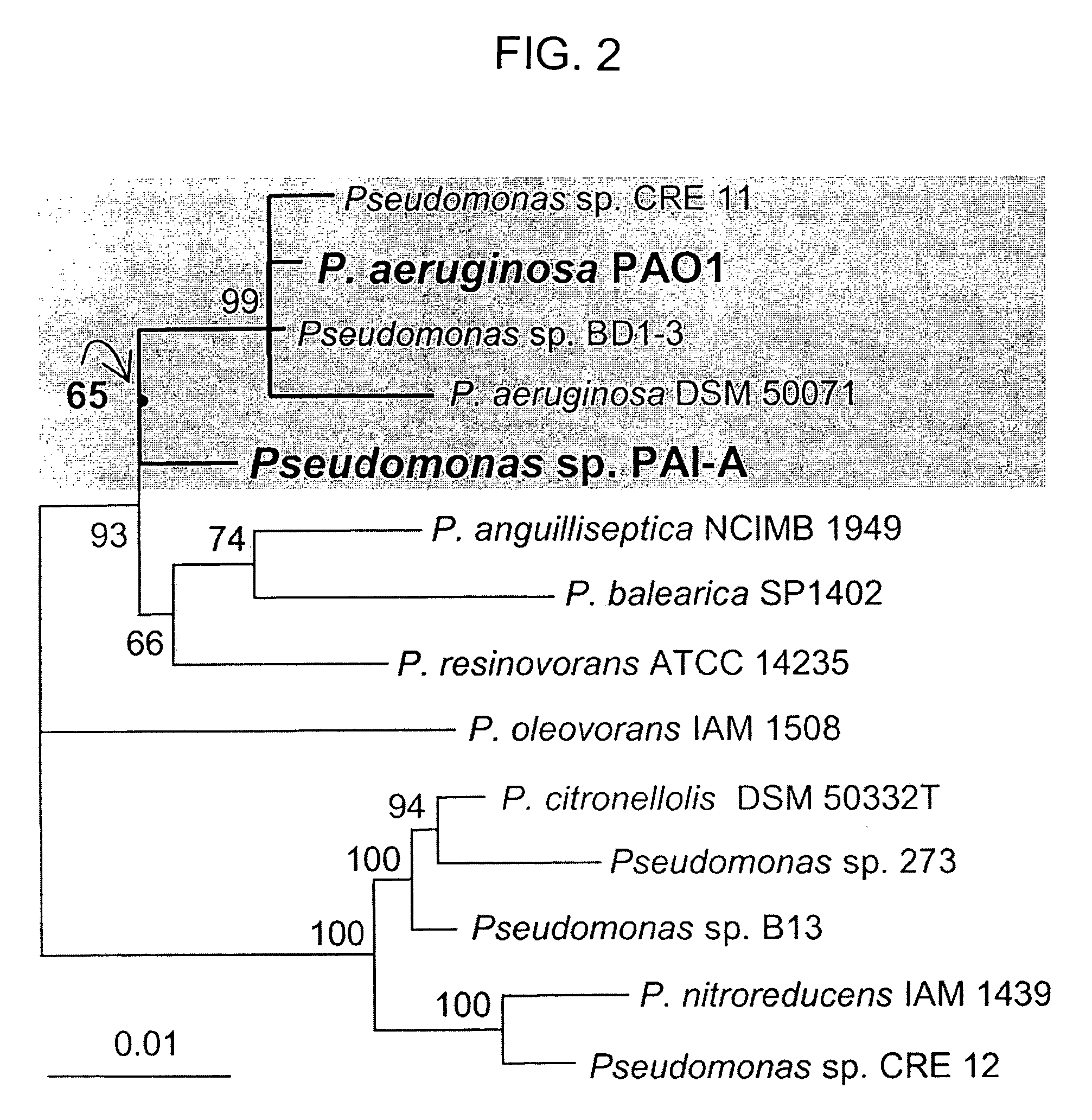
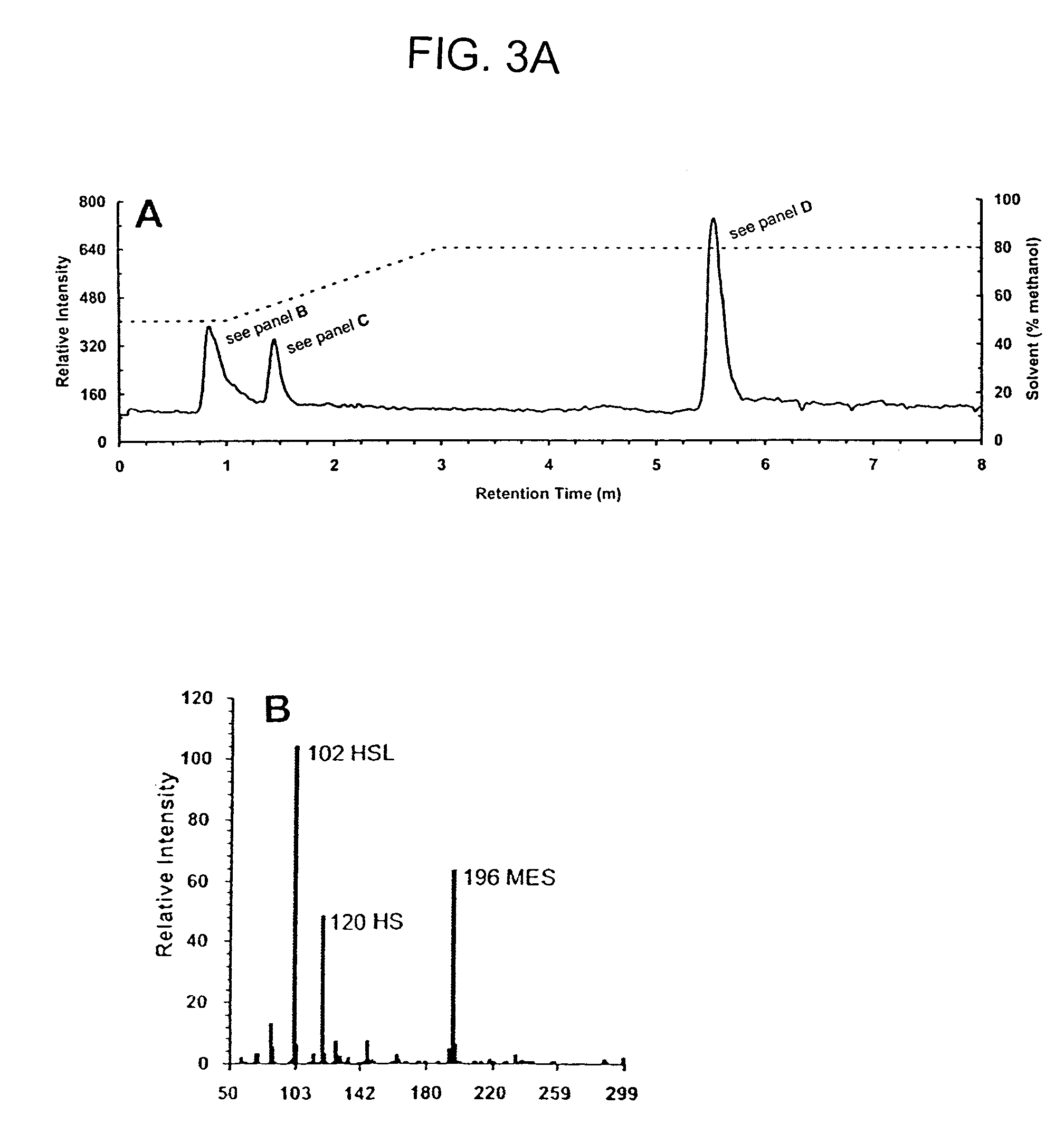
Method of identifying agents that inhibit quorum sensing activity of gamma-proteobacteria
InactiveUS7335352B1High throughput screeningImprove throughputBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesGamma proteobacteria
Screening assays that allow for the identification of agents that increase acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) acylase expression and / or AHL acylase activity in γ-proteobacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Such agents are useful, for example, for inhibiting quorum sensing activity of such bacteria by increasing degradation of long chain, but not short chain, AHLs and, therefore, can be useful for treating infections by such bacteria.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
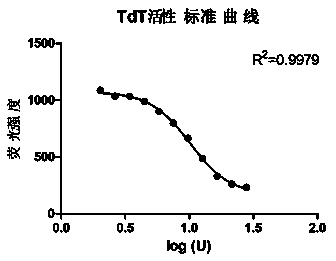
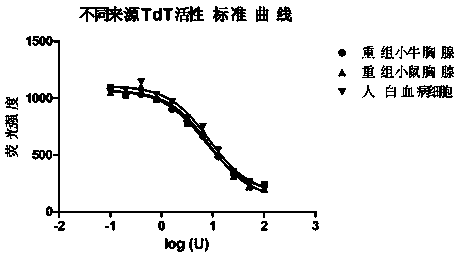
Method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
InactiveCN104293883ALow costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSingle strand
The invention discloses a method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, synthesizing a primer according to a single stranded template, annealing the single stranded template, then performing a 3' end tailing reaction catalyzed by TdT enzyme in the presence of one of four deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, after the 3' end tailing reaction is completed, performing a polymerization reaction in the presence of enough DNA polymerase without 3'-5 'excision enzyme activity to generate double stranded DNA, finally measuring the relative quantity of the double stranded DNA or single stranded DNA in the reaction system after the polymerization reaction is finished, and deducing the activity degree of the Poly (A) polymerase according to the detection result, wherein the basic group at the first site on the used single stranded template in the 3' direction and the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate used in the tailing reaction are not complementary. Compared with the existing method, the method disclosed by the invention is free of radioactive pollution, simple and quick to operate, low in reagent preparation cost and high in sensitivity.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
Methods for identifying agents which alter histone protein acetylation
InactiveUS7452664B2Alters agingAccelerated agingCompound screeningSenses disorderLife spanAnticentromere antibodies
Methods of identifying agents which alter the NAD-dependent acetylation status and mono-ADP-ribosylation of nuclear proteins are disclosed. The methods further include identifying agents which alter the life span or aging of a cell or an organism by determining the level of NAD-dependent acetylation and / or ADP ribosylation of a nuclear protein. The invention also relates to a mammalian Sir2 protein which acetylates or deacetylates nuclear proteins in a NAD-dependent manner and has mono-ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Host cells producing the Sir2 protein and antibodies to the Sir2 protein are also provided.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Assay for measuring acyltransferase activity
InactiveUS20070292906A1High throughput screeningOvercome obstaclesCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSubject matterObesity
The subject matter disclosed and claimed herein relates to a high-throughput assay, and components thereof, for measuring the activity of acyltransferases. The high-throughput assay allows for rapid and accurate screening and identification of compounds that are modulators (e.g., inhibitors or activators) of acyltransferases, that may be used, for example, for the treatment of diabetes, diabetes-related disorders, obesity, cardiovascular disease, and other diseases or disorders attributed to acyltransferase activity.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO
Polypeptide having alpha-isomaltosyl-transferase activity
The object of the present invention is to provide a polypeptide which can be used to produce a saccharide having a structure of cyclo{->6)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->3)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->3)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->}, a DNA encoding the polypeptide, and uses thereof. The present invention solves the above object by establishing a polypeptide which has an enzymatic activity to produce a saccharide having a structure of cyclo{->6}-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->3)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->6)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->3)-alpha-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->} from a saccharide with a glucose polymerization degree of 3 or higher and bearing both the alpha-1,6 glucosidic linkage as a linkage at the non-reducing end and the alpha-1,4 glucosidic linkage other than the linkage at the non-reducing end by catalyzing the alpha-isomaltosyl-transfer, and having an amino acid sequence of either SEQ ID NO:1 or SEQ ID NO:2, or that which is a member selected from the group consisting of amino acid sequences having deletion, replacement, or addition of one or more amino acid residues therein or thereto, a DNA encoding the polypeptide, and uses thereof.
Owner:HAYASHIBARA BIOCHEMICAL LAB INC
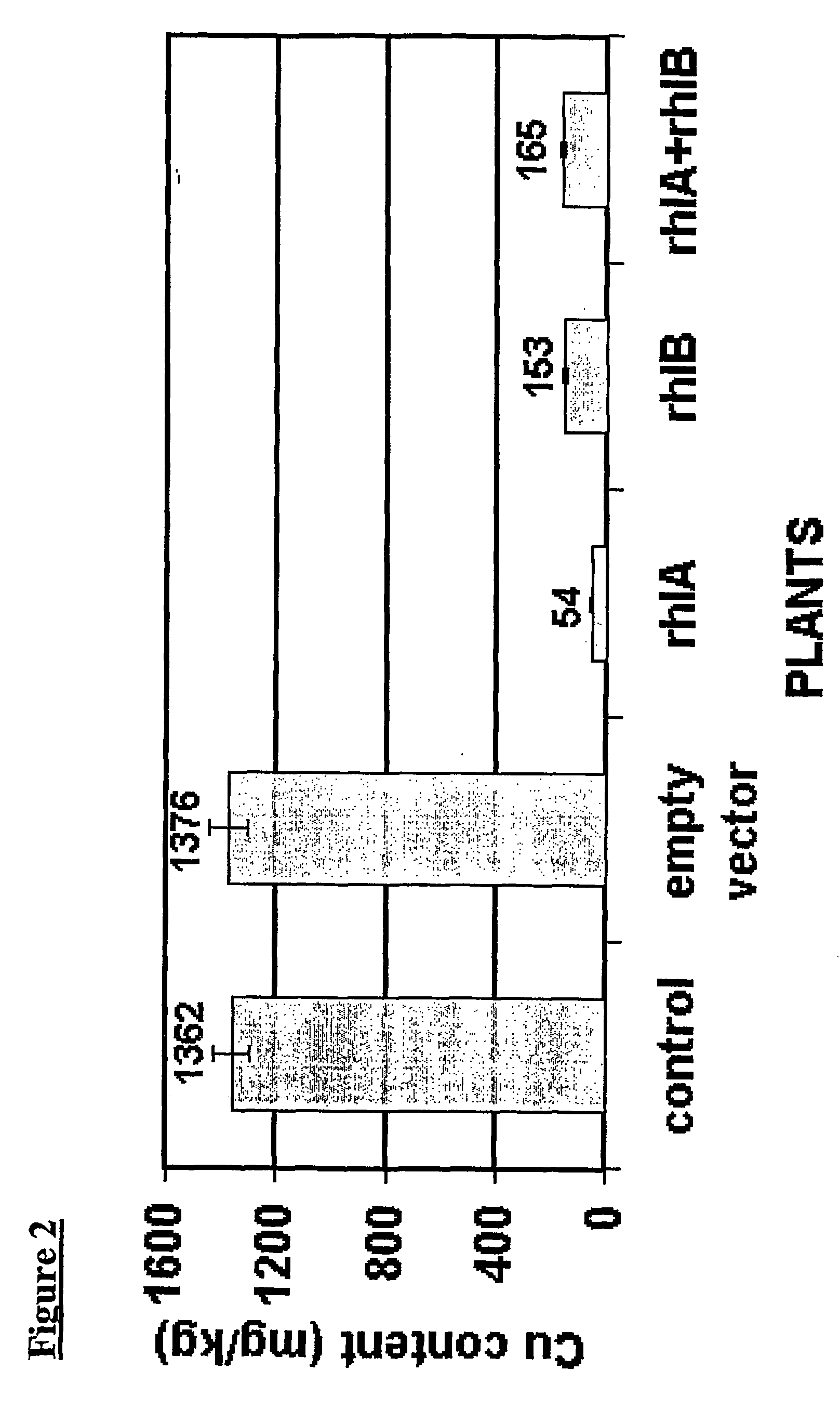
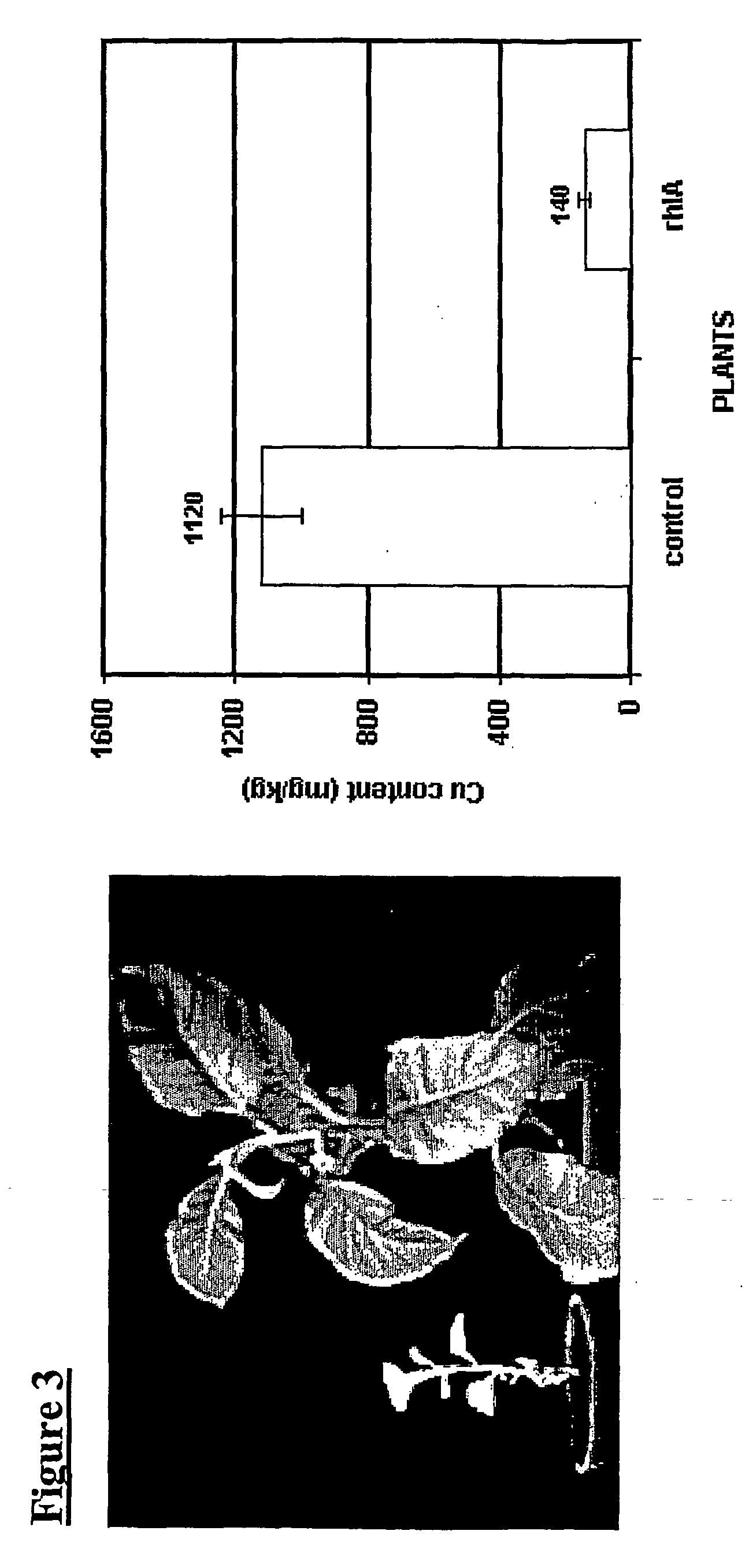
Bioremediation with transgenic plants
InactiveUS20060150279A1Improve efficiencyEffective instrument for their phytoremediationTransferasesContaminated soil reclamationBiotechnologyPseudomona aeruginosa
Methods are provided for phytoremediating environments contaminated with at least one heavy metal or oil hydrocarbon (or both), the methods comprising use of transgenic plants which express one or more enzymes having rhamnosyltransferase activity (e.g. encoding the rh1A and rh1B genes derived from Pseudomonas aeruginosa). Also provided are related methods, materials and processes for producing and using such transgenic plants.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com