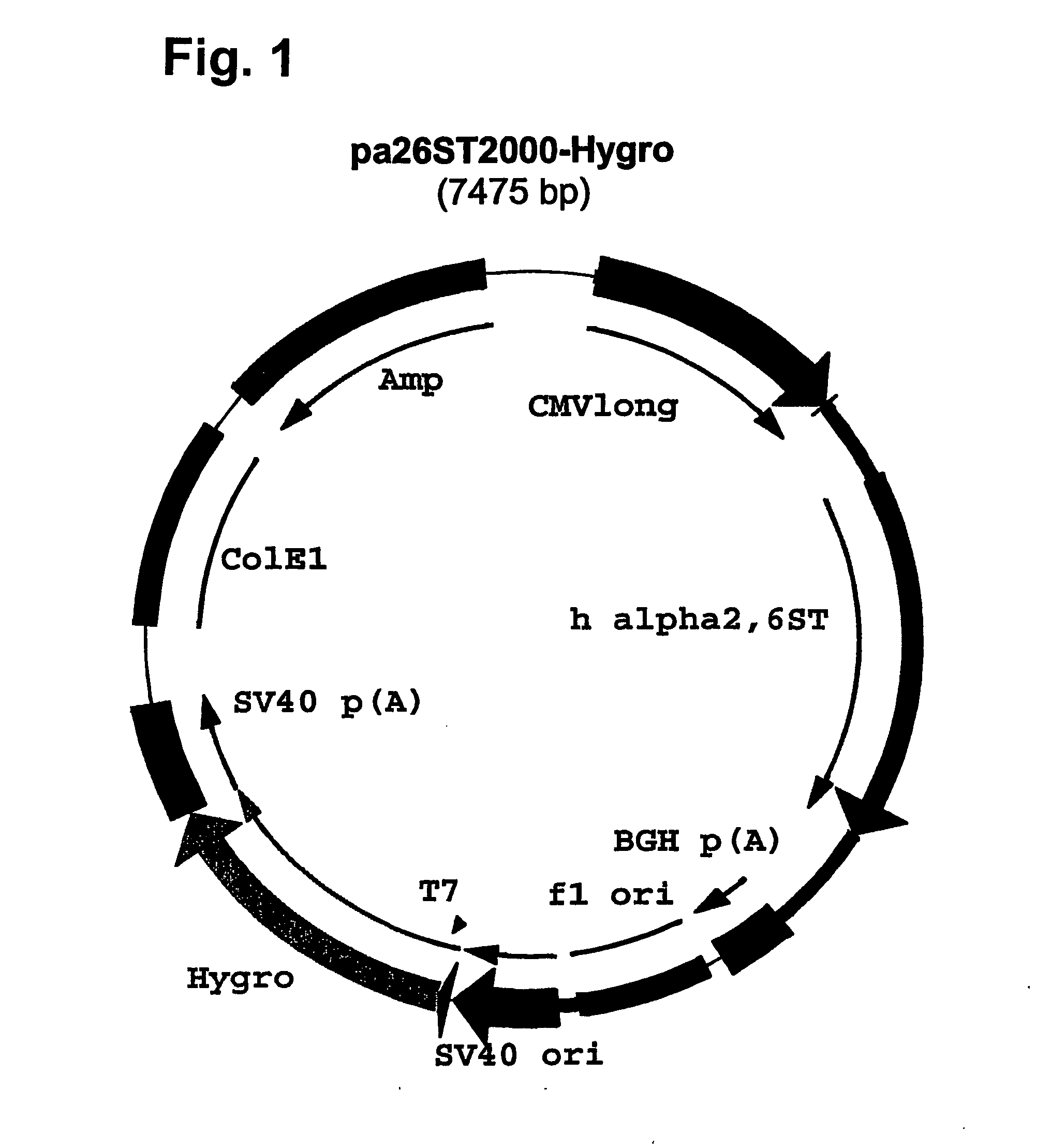
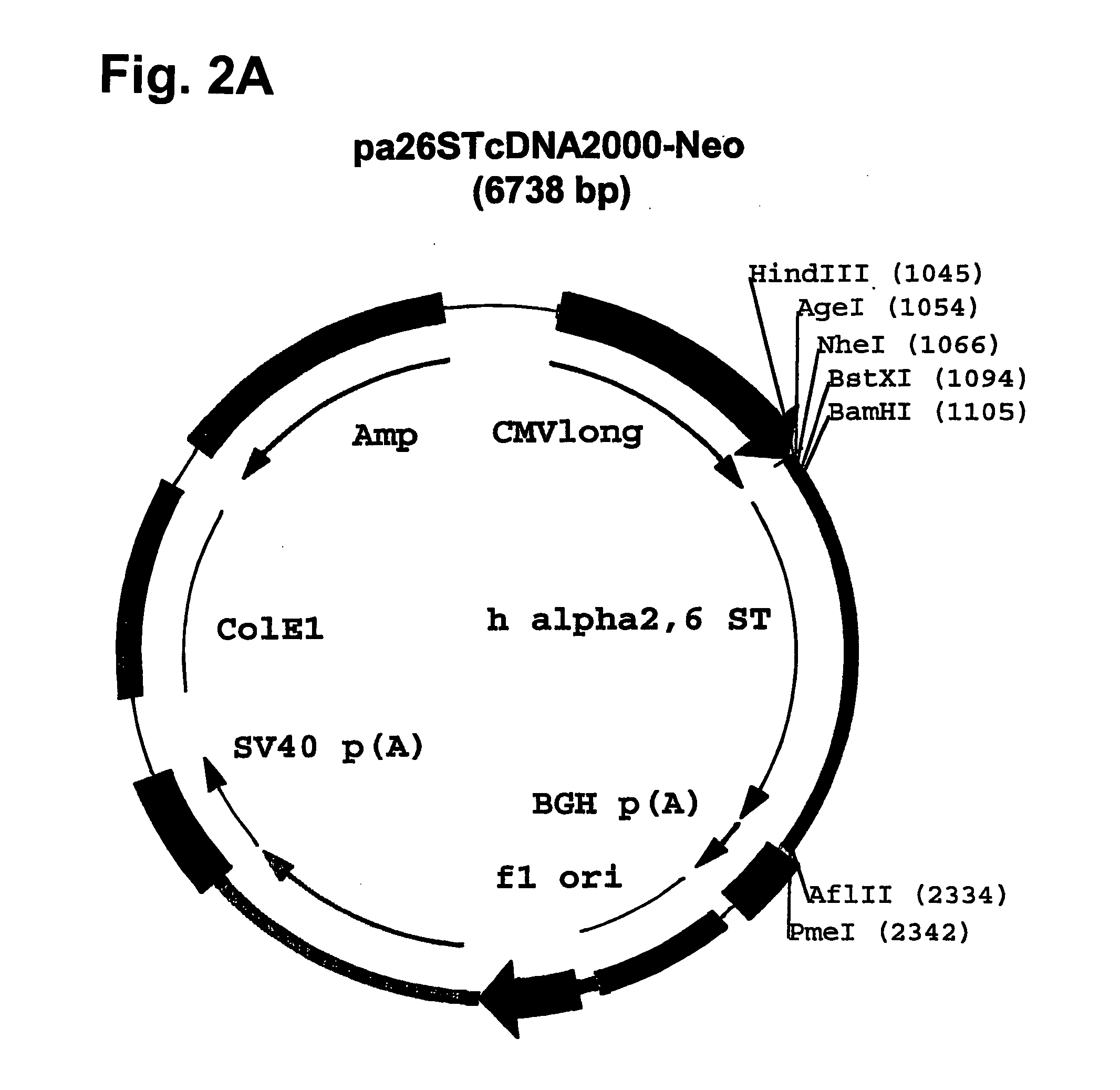
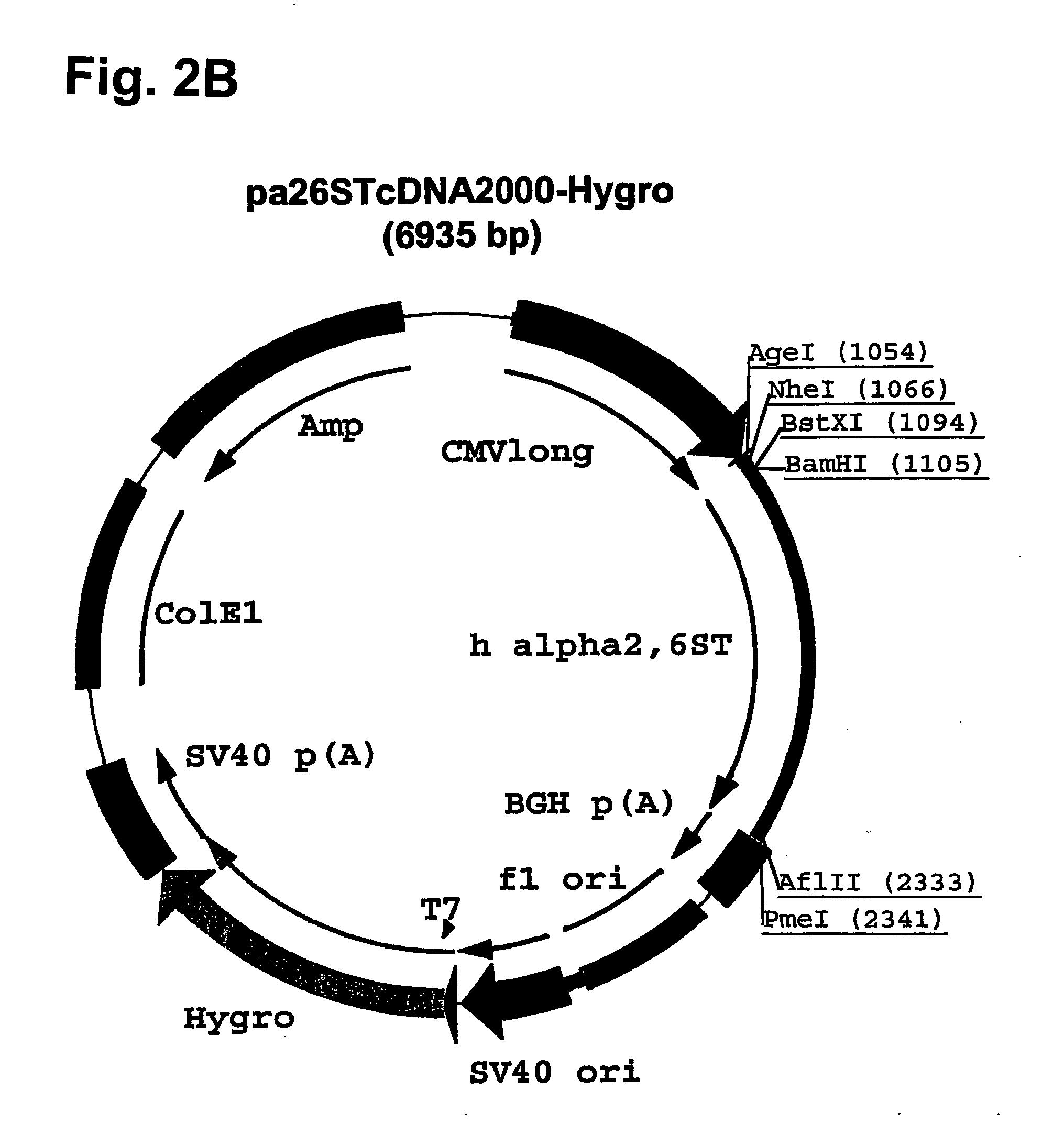
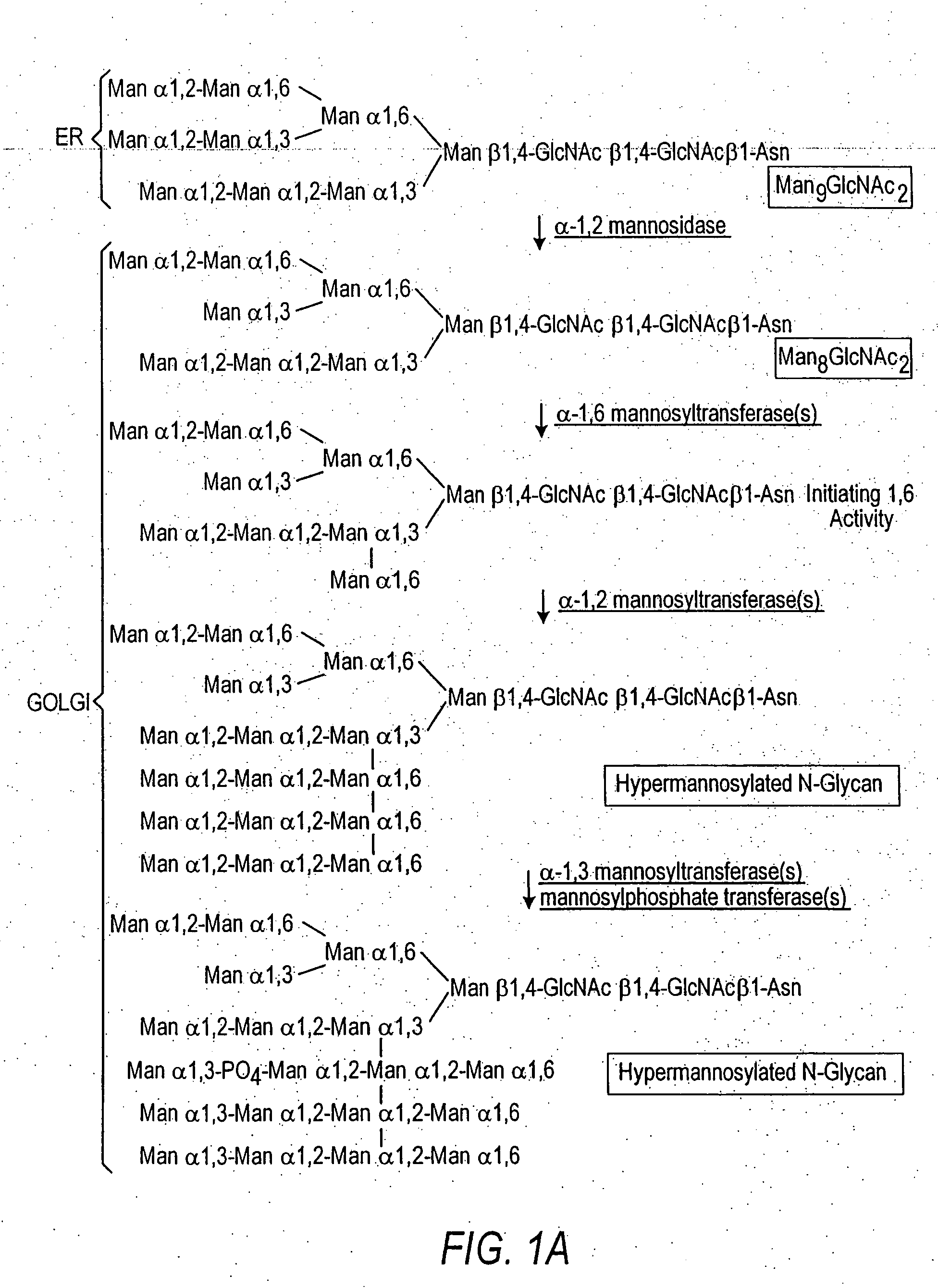
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
79 results about "Sialyltransferase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
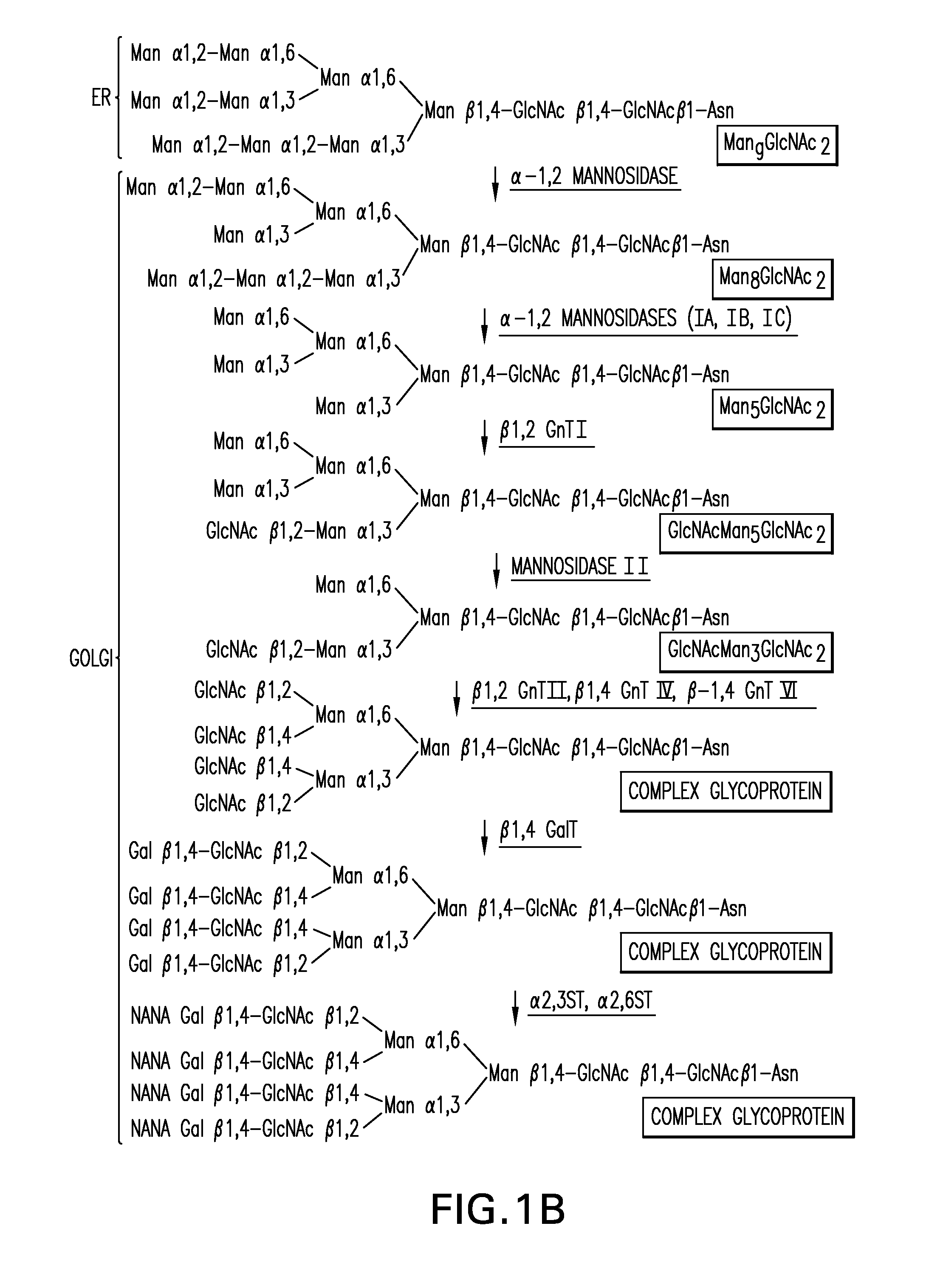
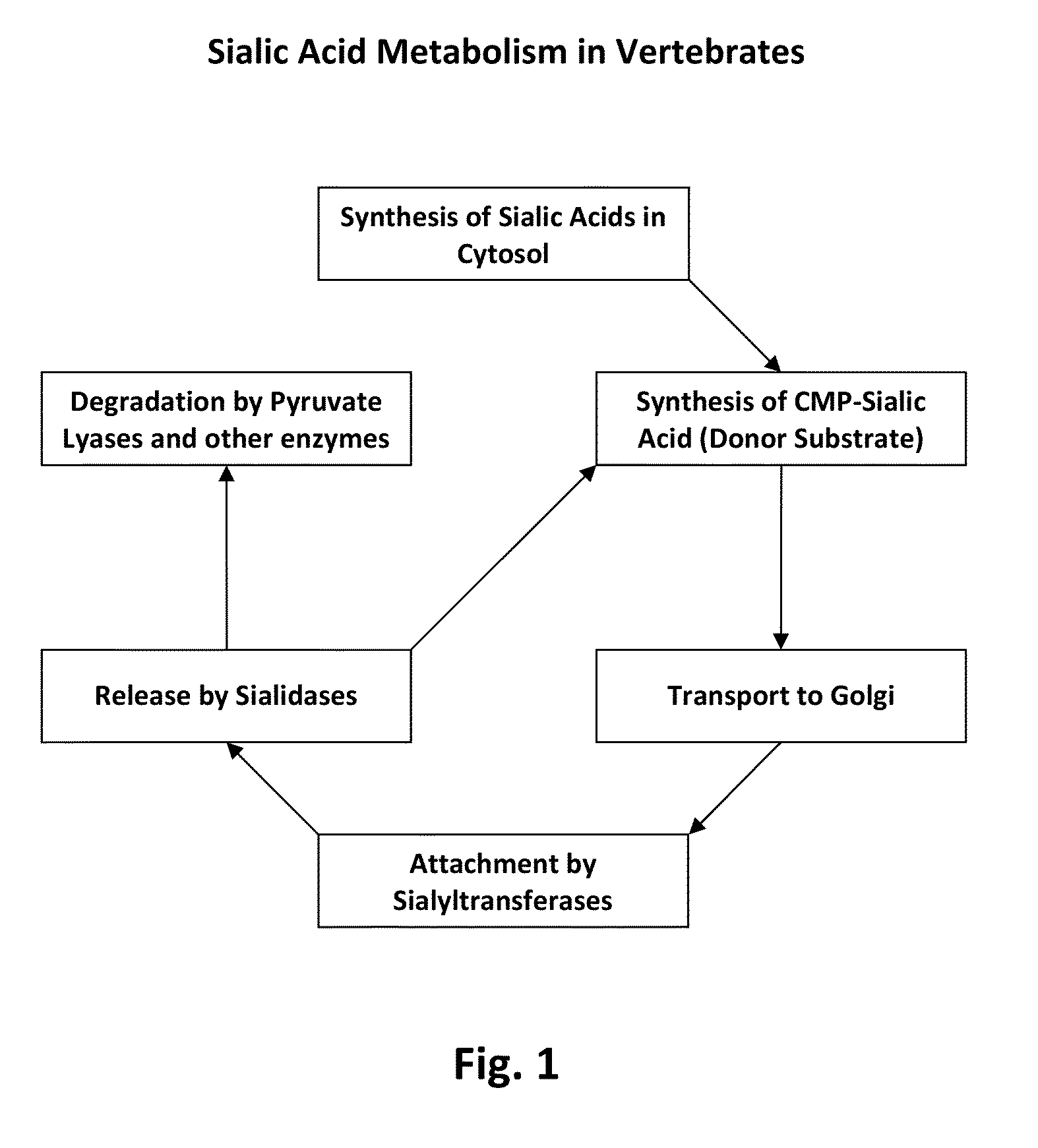
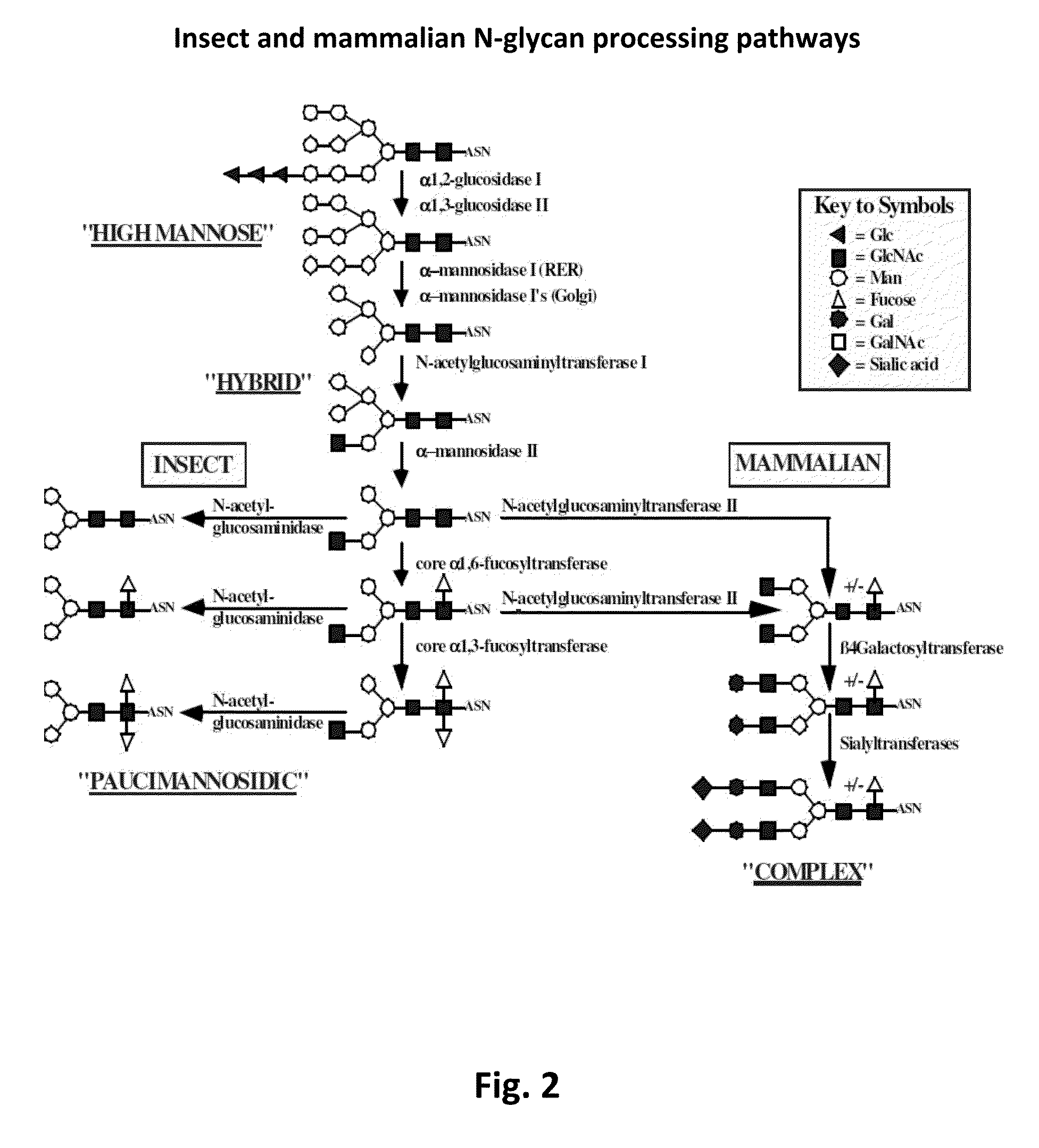
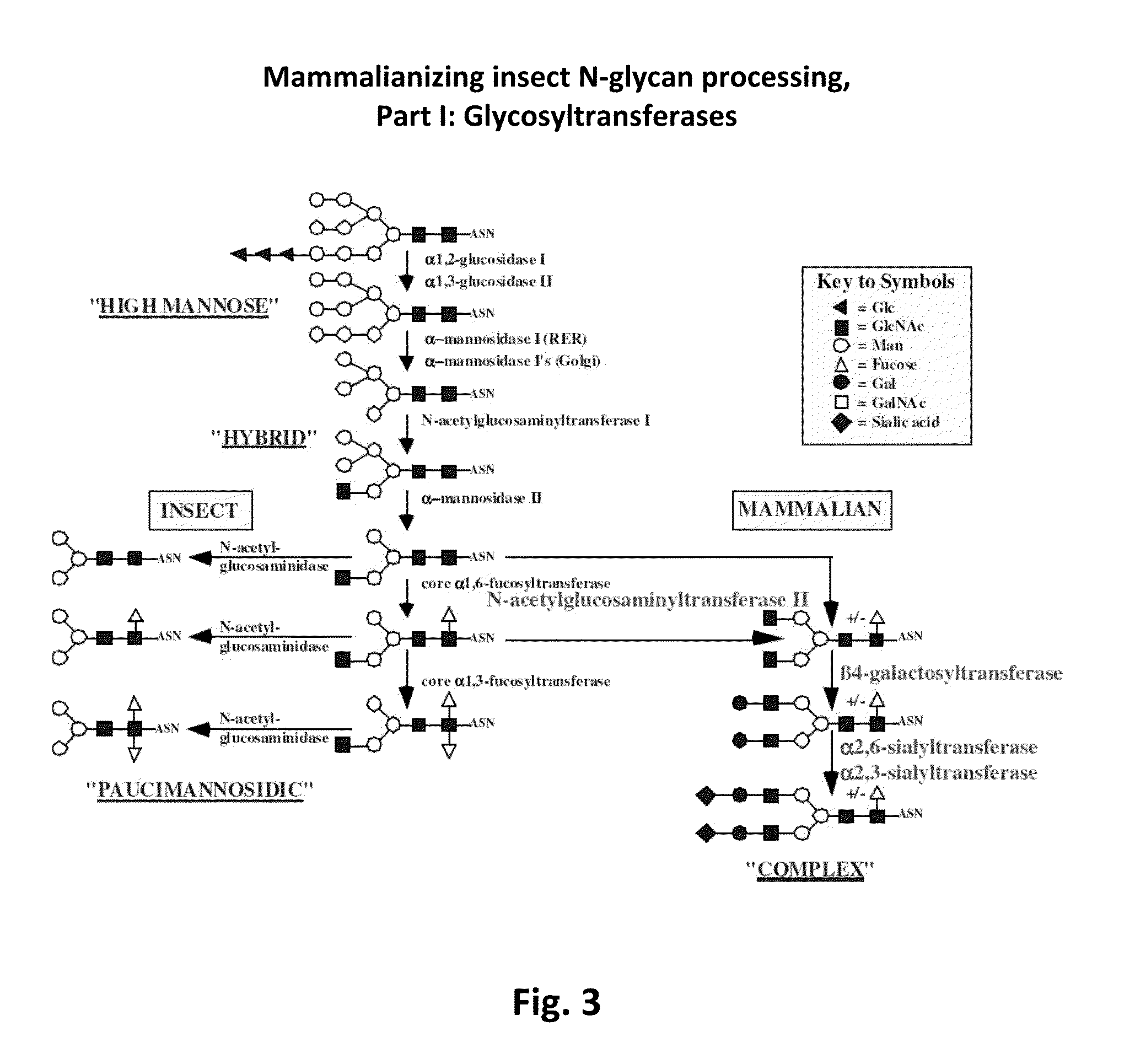
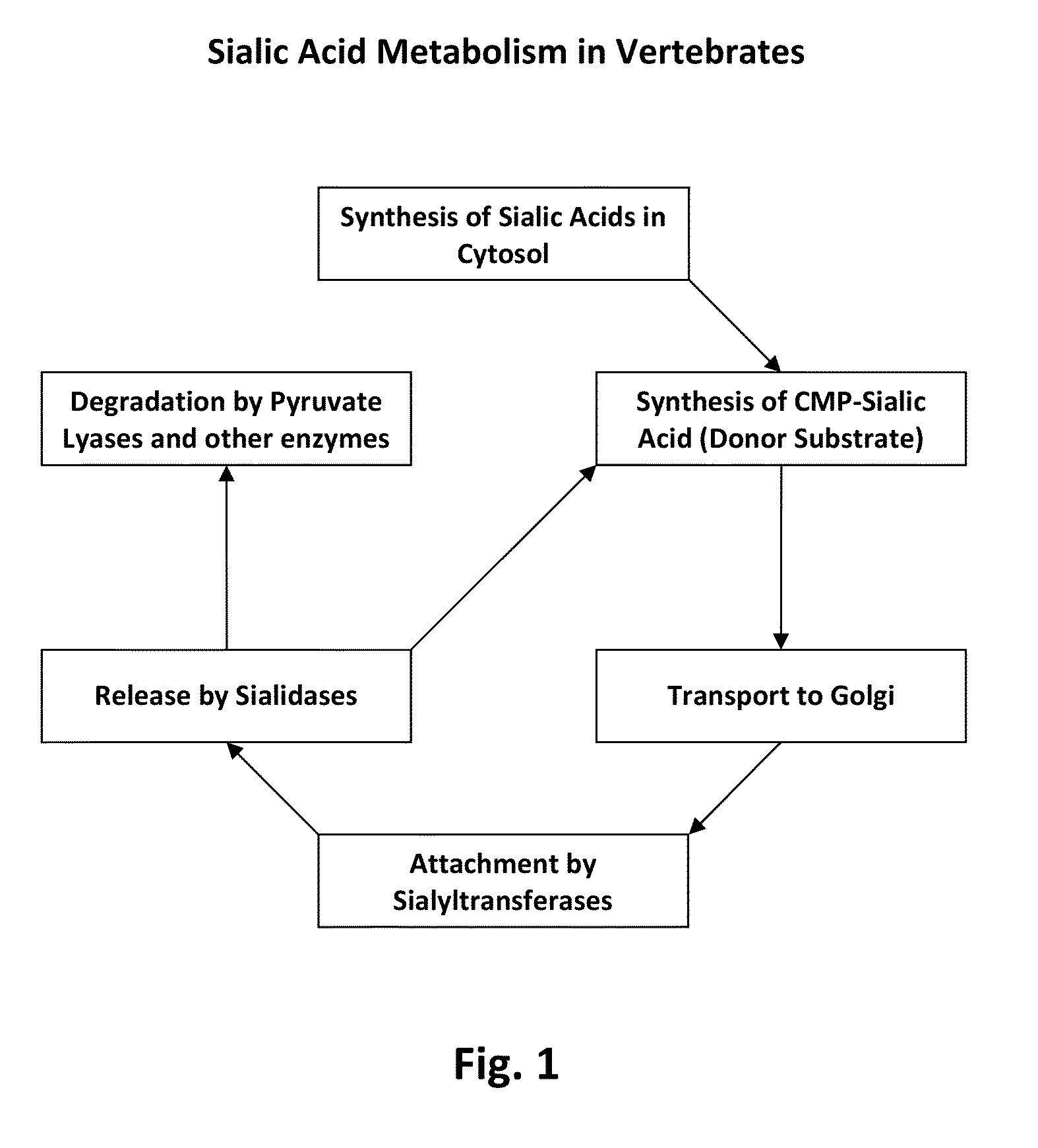
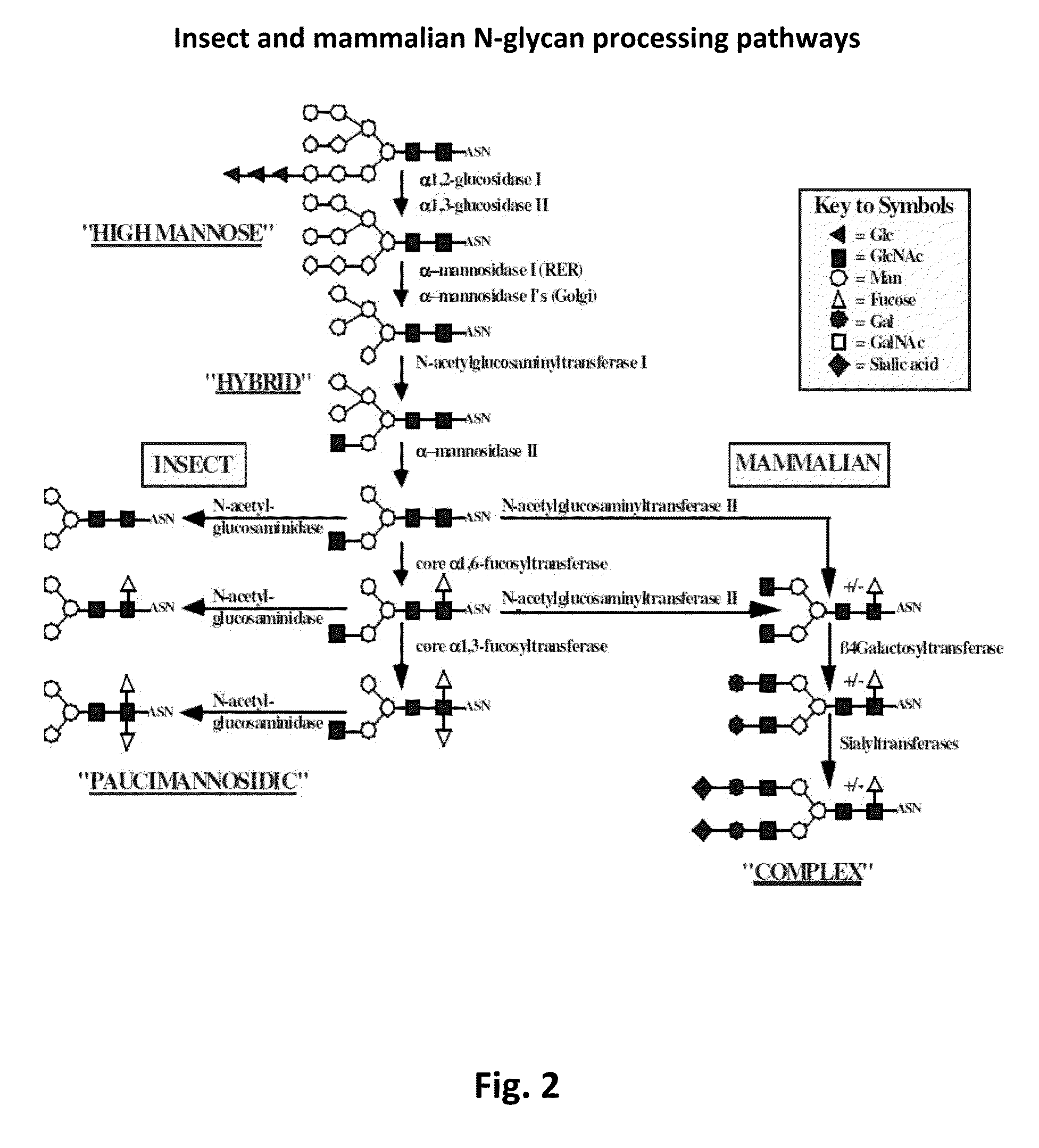
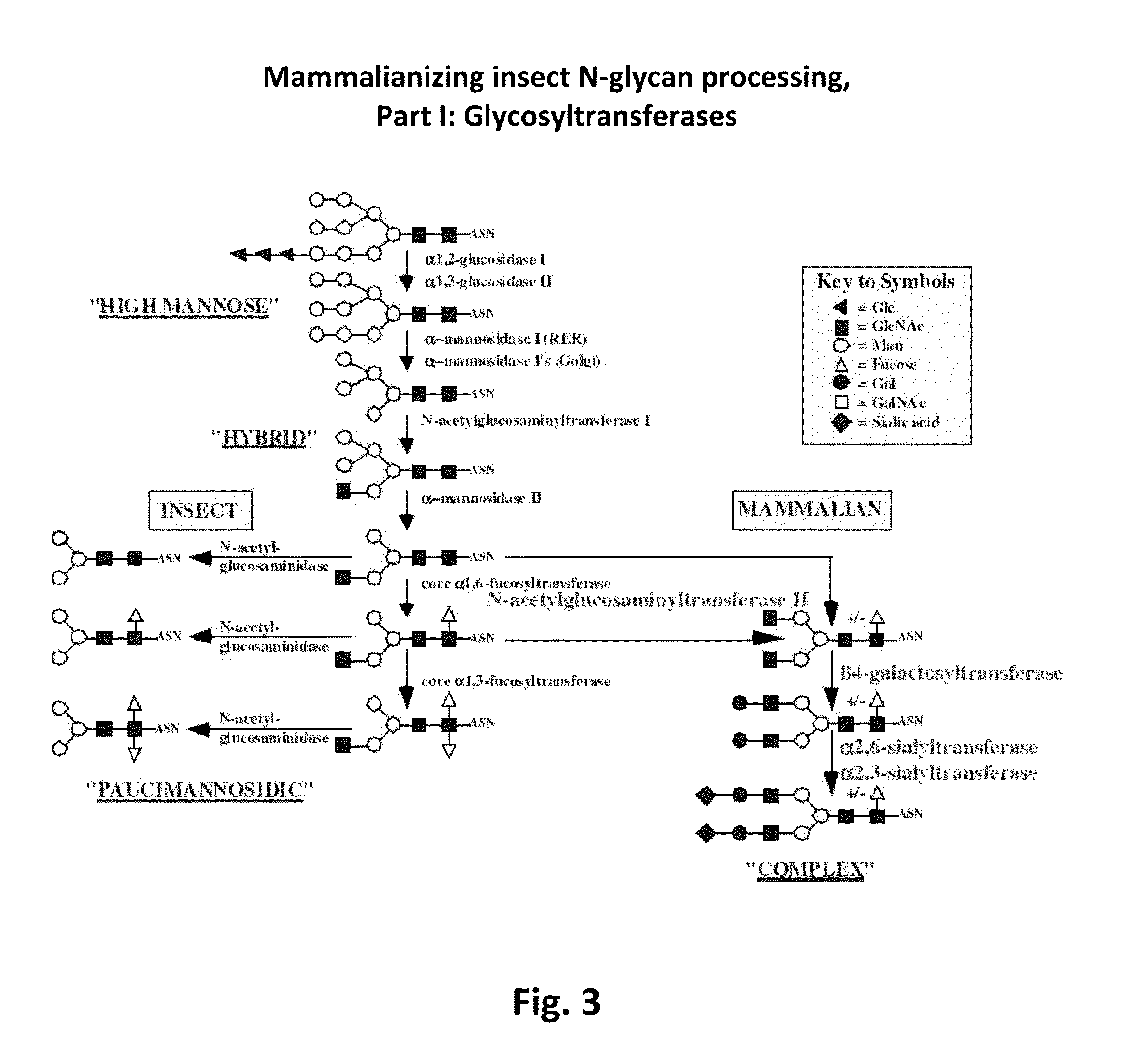
Sialyltransferases are enzymes that transfer sialic acid to nascent oligosaccharide. Each sialyltransferase is specific for a particular sugar substrate. Sialyltransferases add sialic acid to the terminal portions of the sialylated glycolipids (gangliosides) or to the N- or O-linked sugar chains of glycoproteins.
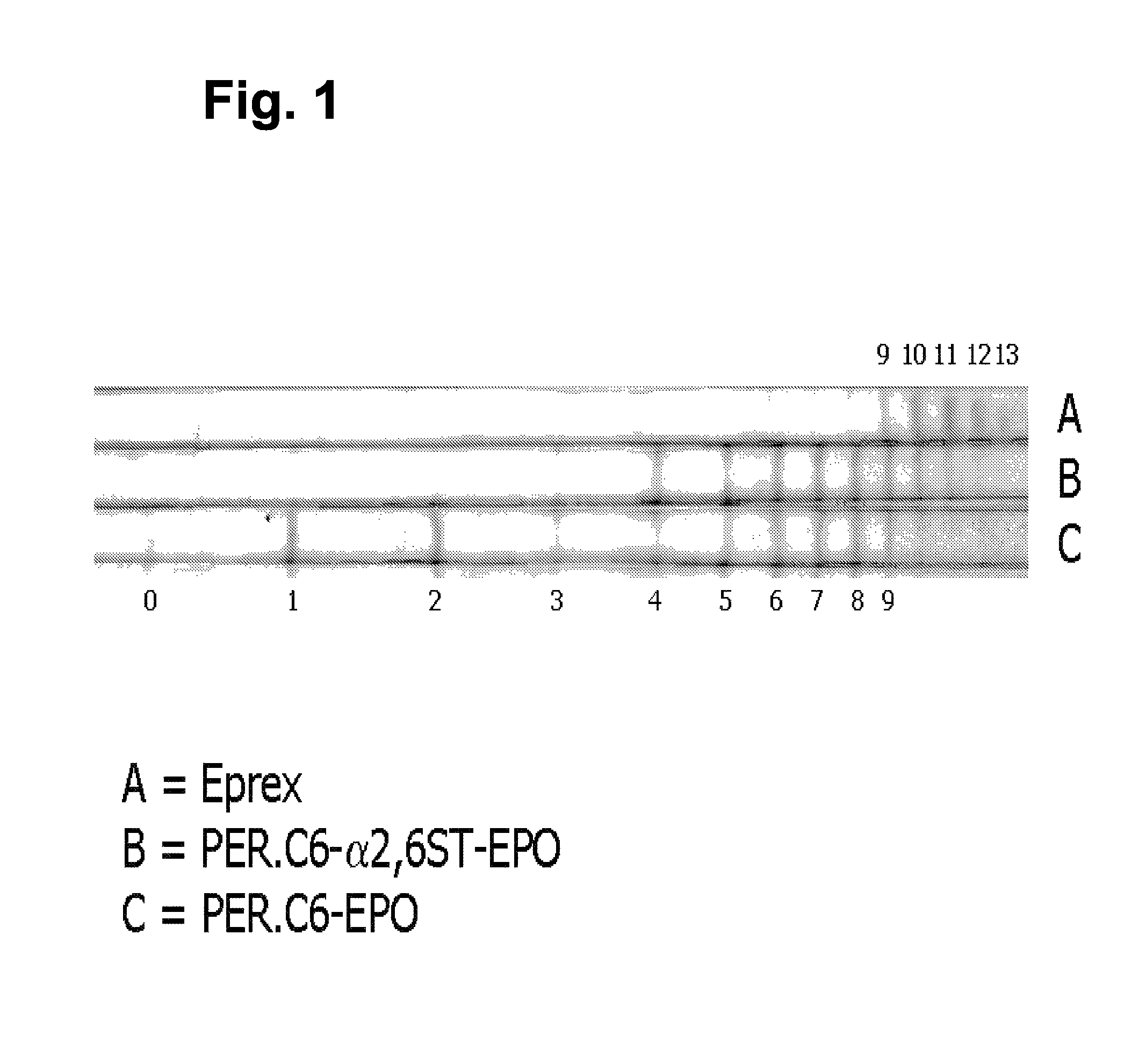
Compositions of erythropoietin isoforms comprising Lewis-X structures and high sialic acid content
InactiveUS20050181359A1Presence can be undesiredImprove system reliabilityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideHeterologousE1A Protein
Disclosed are immortalized human embryonic retina cells, having a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein integrated into the genome of the cells, and further comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding an enzyme involved in post-translational modification of proteins, such as a sialyltransferase, wherein said nucleic acid sequence encoding the enzyme involved in post-translational modification of proteins is under control of a heterologous promoter. Methods for producing recombinant proteins from such cells and obtaining such recombinant proteins having increased sialylation are provided as are novel compositions of isoforms of erythropoietin .
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Production of sialylated N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20060286637A1Improve efficiencyReducing competitive product inhibitionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTransferasesHeterologousSialic acid aldolase
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells which have been modified to produce sialylated glycoproteins by the heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferase and / or trans-sialidase, to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. Novel eukaryotic host cells expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities (such as those involved in sialylation) to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
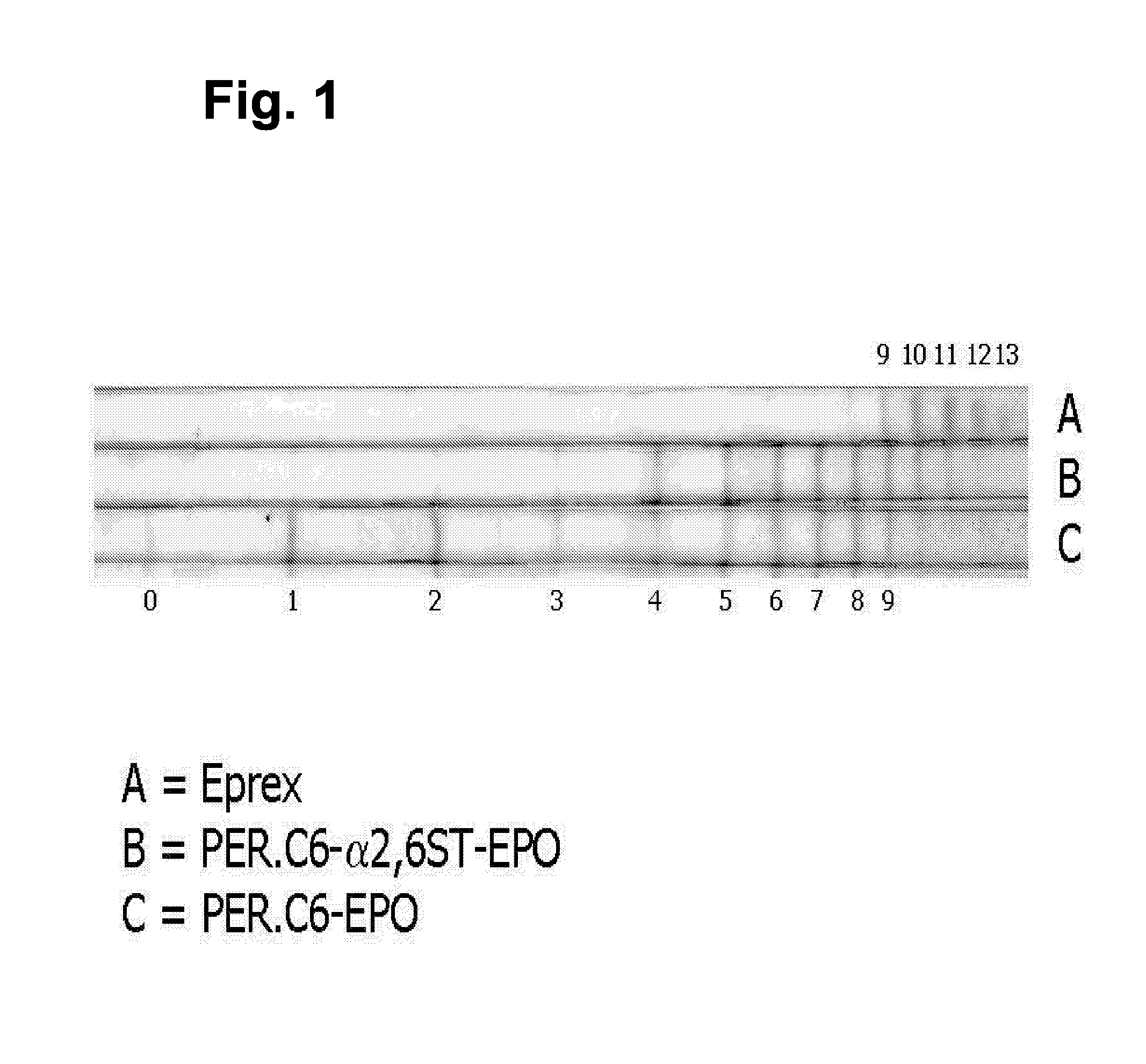
Compositions of erythropoietin isoforms comprising Lewis-X structures and high sialic acid content
InactiveUS7297680B2Improve system reliabilitySimplifies isolationOrganic active ingredientsVirusesHeterologousE1A Protein
Disclosed are immortalized human embryonic retina cells, having a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein integrated into the genome of the cells, and further comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding an enzyme involved in post-translational modification of proteins, such as a sialyltransferase, wherein said nucleic acid sequence encoding the enzyme involved in post-translational modification of proteins is under control of a heterologous promoter. Methods for producing recombinant proteins from such cells and obtaining such recombinant proteins having increased sialylation are provided as are novel compositions of isoforms of erythropoietin.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Method of producing sialylated oligosaccharides
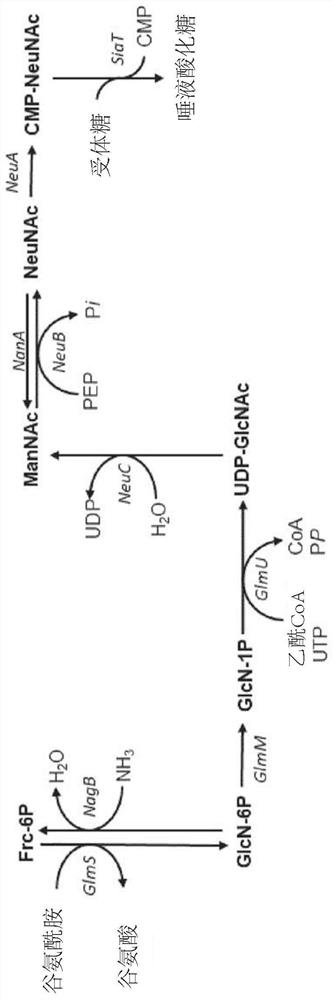
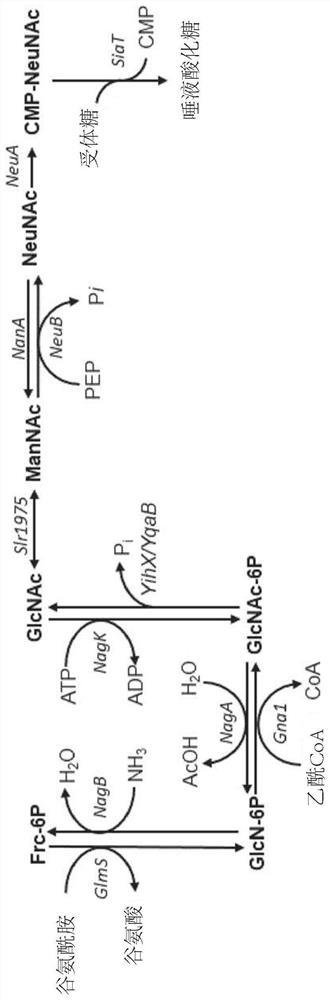
The present invention relates to a method for the large scale in vivo synthesis of sialylated oligosaccharides, culturing a microorganism in a culture medium, optionally comprising an exogenous precursor such as lactose, wherein said microorganism comprises heterologous genes encoding a CMP-Neu5Ac synthetase, a sialic acid synthase, a GlcNAc-6-phosphate 2 epimerase and a sialyltransferase, and wherein the endogenous genes coding for sialic acid aldolase (NanA) and for ManNac kinase (NanK) have been deleted or inactivated. The invention also relates to these micoorganisms which are capable of producing internally activated sialic acid.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Labeled substrate conjugates for identifying enzyme inhibitors
ActiveUS20060057658A1Sufficient quantityChange detectionEsterified saccharide compoundsCompound screeningNeuraminidaseSialyltransferase
This invention provides labeled-substrate conjugates for assaying enzymes, particularly neuraminidases. Also provided are assays that are useful for identifying compounds that inhibit sialyltransferases or neuraminidases and may be useful in treating subjects with influenza. In particular, the present invention relates to methods of using such labeled substrate conjugates to screen for enzyme inhibitors, particularly in a high-throughput format.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Prevention of atherosclerosis and undesired blood clotting by reducing von Willebrand factor
InactiveUS7192914B1Preventing and treating blood clottingPreventing or treating blood clottingFactor VIIBiocideFactor VIII vWFMammal
This invention provides methods and compositions for treating and preventing atherosclerosis other undesired blood clotting. The methods for treating and preventing atherosclerosis and related conditions involve administering to a mammal an agent that reduces activity of an ST3Gal IV sialyltransferase, which results in enhanced clearance of von Willebrand Factor (vWF) from the mammal.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Production of sialylated N-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS7863020B2High yieldImprove efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesHeterologousNucleic acid molecule
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells which have been modified to produce sialylated glycoproteins by the heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferase and / or trans-sialidase, to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. Novel eukaryotic host cells expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities (such as those involved in sialylation) to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Method of treating inflammation with inhibitors of sialyl transferases
Provided herein are a methods of reducing a level of activity of a sialyl transferase enzyme, a sialidase enzyme or a combination thereof using inhibitors of these enzymes, for example specific inhibitory compound or antibodies directed against the enzymes. The methods are effective to treat an inflammatory disease or disorder or a primary or metastatic cancer. Also provided is a method for screening potential inhibitors of sialyl transferase enzymes.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF THE BALTIMORE
Synthetic method of double-sialylated tetrasaccharide
ActiveCN103555796AHigh reactivityHigh substrate reactivitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationChemical synthesisGlycopeptide
The invention discloses a synthetic method of synthesizing double-sialylated tetrasaccharide by a chemically controllable enzyme method. The invention further provides two intermediates, which are used for synthesizing and preparing the double-sialylated tetrasaccharide, are compounds respectively as shown in formulas IV and V. According to the synthetic method disclosed by the invention, the flexibility of a chemical synthetic method and the high-area selectivity and high efficiency of the enzyme synthetic method are combined together, so that synthesis of the double-sialylated tetrasaccharide by using a chemical intervention method is firstly realized, defects such as low substrate reaction activity, multiple synthetic steps and low yield facing in existing chemical synthesis of the double-sialylated tetrasaccharide are solved, as well as a problem that sialyl transferase is difficult to obtain and only glycopeptides is identified in the enzyme method is solved; the synthetic method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high substrate reaction activity and high yield, and therefore, the synthetic method has important significance in researching biological functions of sialic acid glucoside on molecular level and developing carbohydrate drugs based on the biological functions.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method of producing sialylated oligosaccharides
The present invention relates to a method for the large scale in vivo synthesis of sialylated oligosaccharides, culturing a microorganism in a culture medium, optionally comprising an exogenous precursor such as lactose, wherein said microorganism comprises heterologous genes encoding a CMP-Neu5Ac synthetase, a sialic acid synthase, a GlcNAc-6-phosphate 2 epimerase and a sialyltransferase, and wherein the endogenous genes coding for sialic acid aldolase (NanA) and for ManNac kinase (NanK) have been deleted or inactivated. The invention also relates to these micoorganisms which are capable of producing internally activated sialic acid.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECH SCI (C N R S)
Self-priming polysialyltransferase
The invention relates to a fusion protein comprising a bifunctional sialytransferase and a poly-sialytransferase and methods to use the fusion proteins for production of poly-sialylated end products, e.g. oligosaccharides and glycoproteins.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
IgG antigen epitope and application thereof as target
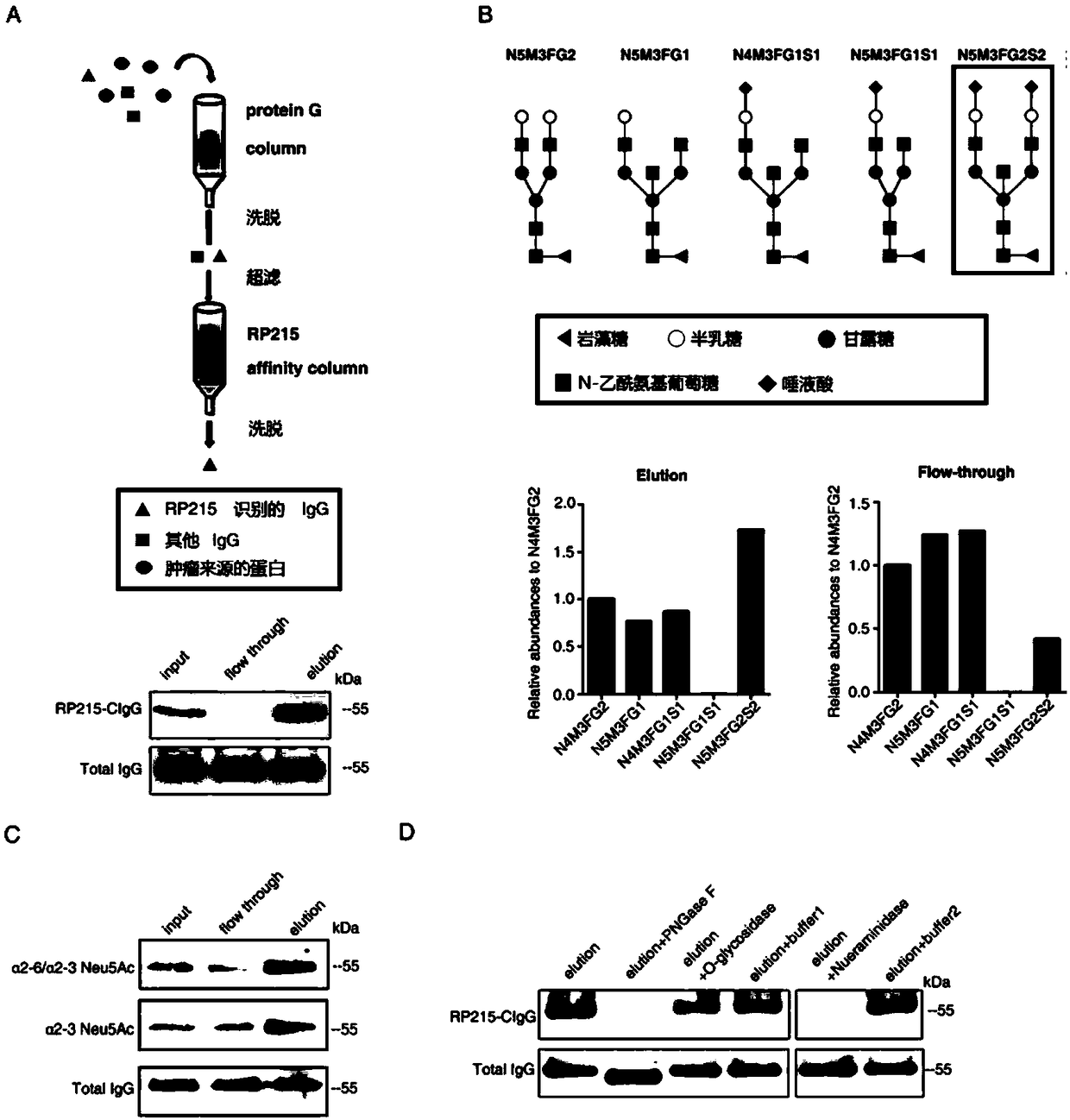
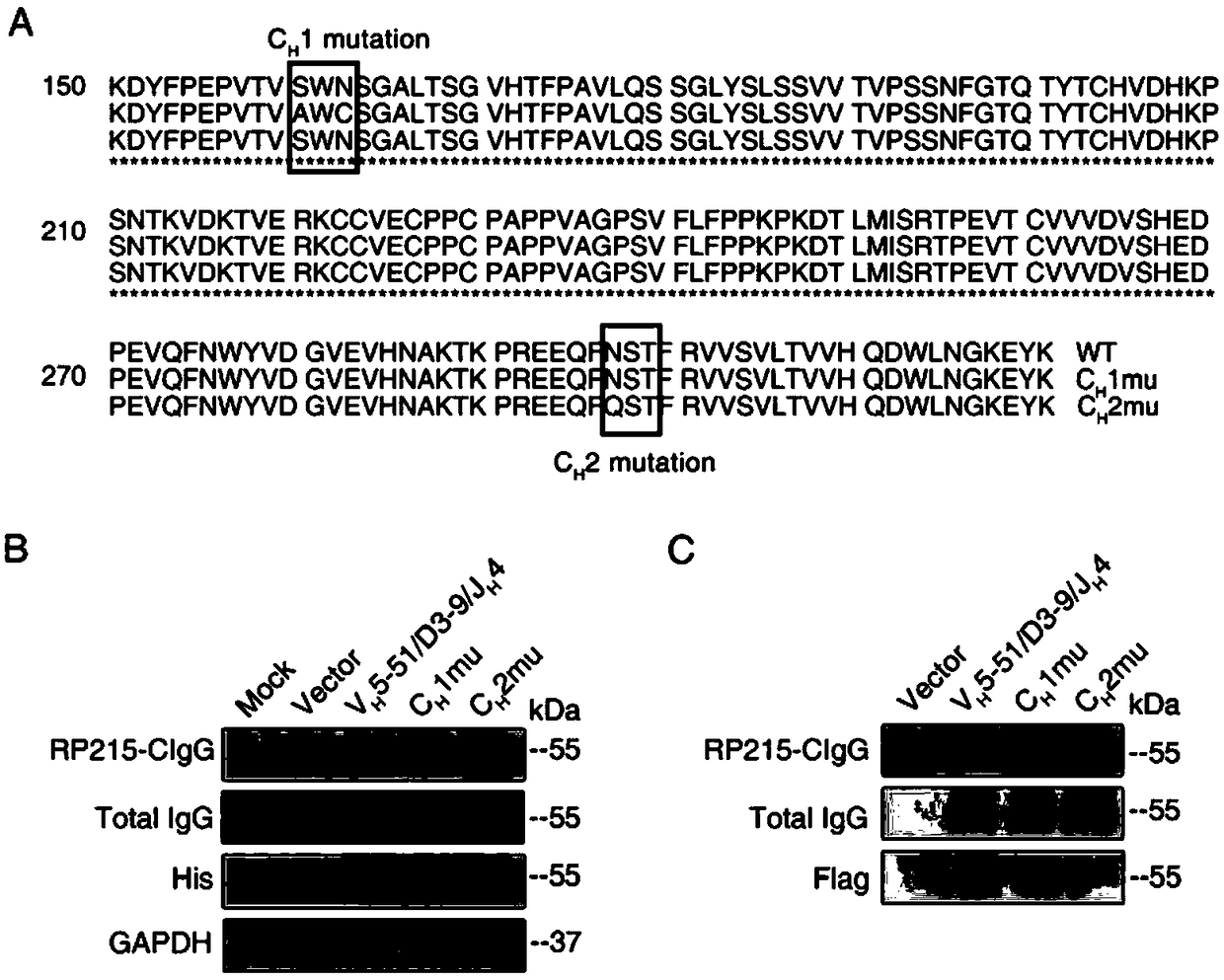
ActiveCN108610414AEffective drug targetBiological material analysisAntibody ingredientsEpitopeSialic acid aldolase
The invention discloses an IgG antigen epitope and an application thereof as a target. The IgG antigen epitope is a CH1 structural domain of non-B-cell-derived IgG, and an Asn162 site of the structural domain is modified by N-glycosylated sialic acid, and realization of an antigenic function needs to depend on the sialylation of the site. The invention also provides an application of the IgG antigen epitope as a drug action target in preparation of drugs for diagnosis and / or treatment of epithelial tumors. In addition, research results show that the function of the antigen as the drug target depends on the sialylation of the Asn162 site, the sialylation of the Asn162 site also needs to depend on a sialic acid transferase ST3GAL4, the enzyme is suggested to be used as a drug action target for preparation of tumor therapy drugs. In addition, integrin beta 4 is co-expressed and co-localized with IgG containing the antigen epitope. In view of the function of IgG, the IgG antigen epitope can be used as a marker for preparation of drugs for aided detection of epithelial tumors.
Owner:BEIJING SIG BIOPHARMACEUTICAL TECH CO LTD
Production of sialylated n-glycans in lower eukaryotes
InactiveUS20100279356A1High yieldImprove efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiHeterologousBiology
The present invention relates to eukaryotic host cells which have been modified to produce sialylated glycoproteins by the heterologous expression of a set of glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferase and / or trans-sialidase, to become host-strains for the production of mammalian, e.g., human therapeutic glycoproteins. Novel eukaryotic host cells expressing a CMP-sialic acid biosynthetic pathway for the production of sialylated glycoproteins are also provided. The invention provides nucleic acid molecules and combinatorial libraries which can be used to successfully target and express mammalian enzymatic activities (such as those involved in sialylation) to intracellular compartments in a eukaryotic host cell. The process provides an engineered host cell which can be used to express and target any desirable gene(s) involved in glycosylation.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Β-galactoside-α2,6-sialyltransferase, a gene encoding thereof, and a method for enhancing enzyme activity
The present invention provides an extremely useful and novel β-galactoside-α2,6-sialyltransferase having an optimum reaction pH in a neutral to alkaline range, and a nucleic acid encoding the sialyltransferase. The present invention further provides a vector carrying a nucleic acid encoding the sialyltransferase, and a host cell transformed with the vector, as well as a method for producing a recombinant β-galactoside-α2,6-sialyltransferase.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
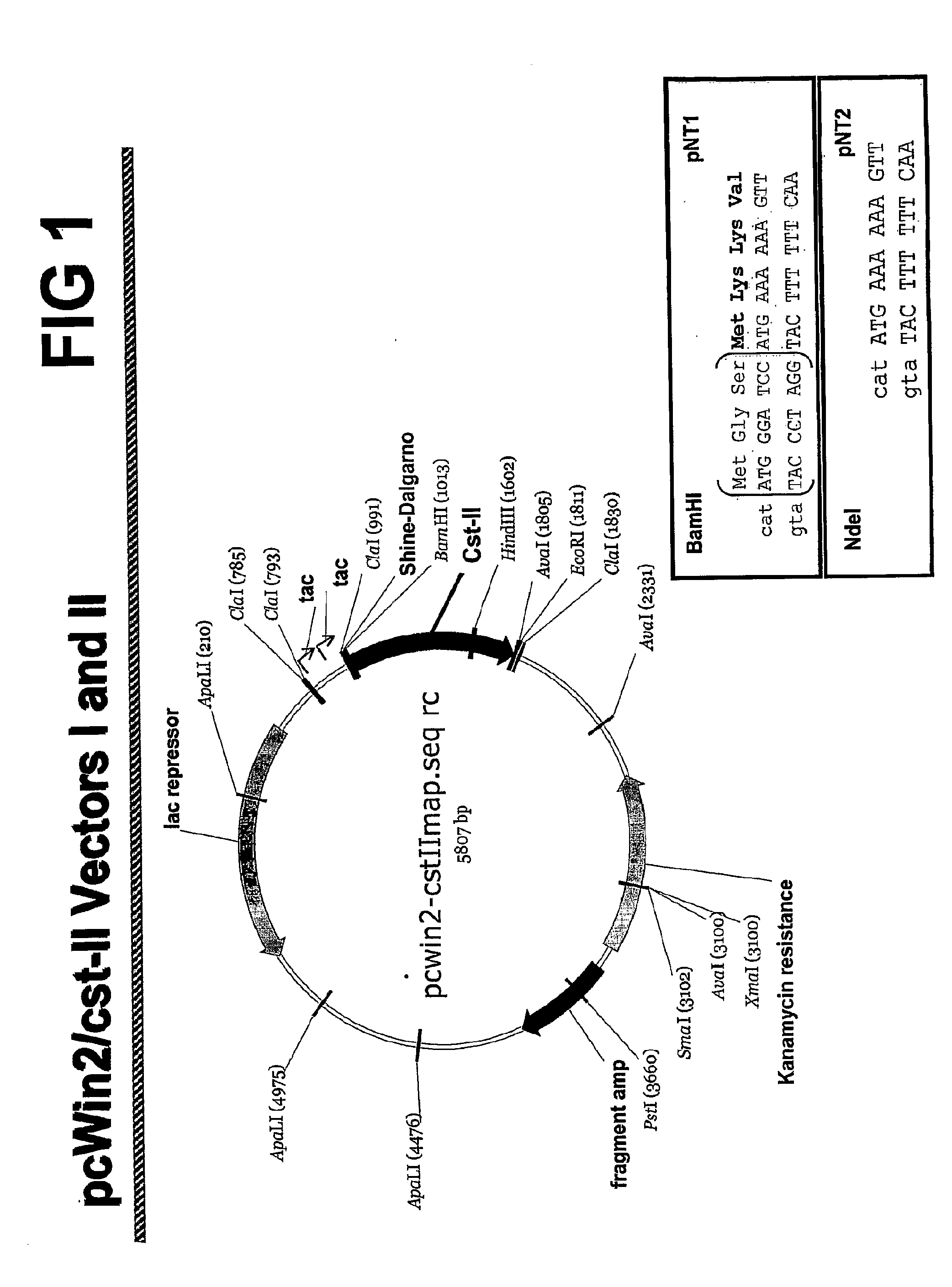
Modifications of cst-ii for increased protein expression
The present invention provides modified Campylobacter sialyltransferase proteins that exhibit enhanced expression as compared to its unmodified form. Nucleic acids that encode the sialyltransferase proteins are also included, as are methods to produce and use the sialyltransferase proteins.
Owner:RATIOPHARM GMBH
Method for preparing sialyllactose
InactiveCN110396532ASimple ingredientsClear ingredientsFermentationSialyltransferaseCMP-Sialic Acid Synthetase
The invention discloses a method for preparing sialyllactose, and relates to the technical field of preparation of sialyllactose. The method for preparing sialyllactose disclosed by the invention comprises the steps of adding kinase to a reaction system containing a substrate, and performing an enzyme catalysis reaction to prepare the sialyllactose, wherein the kinase comprises CMP kinase, polyphosphate sialic acid synthase and sialytransferase; and the substrate comprises CMP, polyphosphate, sialic acid and lactose. The method adopts various kinase namely the CMP kinase, the polyphosphate kinase, the CMP-sialic acid synthetase and sialytransferase to catalyze the corresponding substrate to prepare the sialyllactose. The method has the characteristics of being high in yield, low in cost, short in cycle and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Haemophilus influenzae sialyltransferase and methods of use thereof
The present invention is directed to sialytransferases, such as SiaA sialytransferases isolated from Haemophilus influenzae. Further provided herein are methods for producing sialylated lipooligosaccharides, vaccines, and host cells and systems for the production of sialylated lipooligosaccharides.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND +1
Synthesis method of tetrasaccharide MAG antagonist
ActiveCN103525888AHigh substrate reactivityHigh yieldSugar derivativesFermentationChemical synthesisSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a synthesis method of a disialic acid tetrasaccharide MAG antagonist by a chemical enzyme process. The invention also discloses two intermediates for synthesizing and preparing a tetrasaccharide MAG antagonist, which are respectively compounds disclosed as general formulae IV and V. By combining the flexibility of the chemical synthesis process and the regioselectivity and high efficiency of the enzyme synthesis process, the method overcomes the defects of low substrate reaction activity, multiple synthesis steps and low yield in the chemically synthesized disialic acid tetrasaccharide MAG antagonist at present, and the defects of difficulty in obtaining sialyl transferase, only recognition of glycopeptide and the like in the enzyme process, and has the advantages of high substrate reaction activity and high yield. Therefore, the method has important meanings in researching interactions between the sialic acid antagonist and the myelin related glycoprotein on the molecular level.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
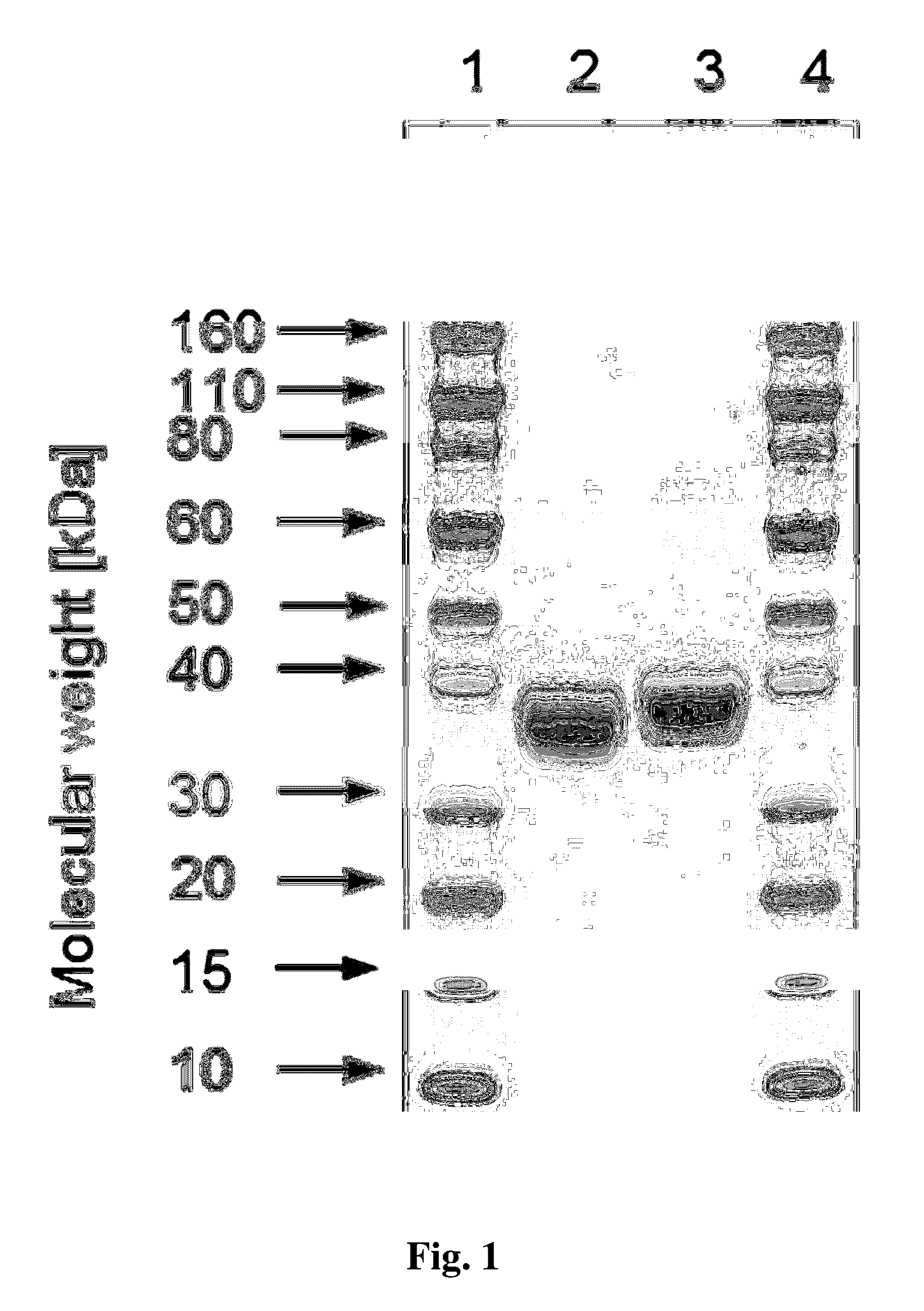
Methods to obtain recombinant proteins with increased sialylation from cells that express adenovirus E1A protein, and proteins obtained thereby
InactiveUS7642078B2Reduce contentIncrease contentDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsHeterologousE1A Protein
The invention provides compositions comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (EPO) comprising glycans linked thereto, characterized in that said glycans comprise LewisX structures and on average at least 6 sialic acid moieties per EPO molecule. The invention further provides methods for obtaining a composition comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (EPO) comprising glycans linked thereto wherein said glycans comprise on average at least 6 sialic acids per EPO molecule and from 0 to 2 Lewis x structures, said method comprising: a) providing a eukaryotic cell containing a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein in expressible format and further containing a nucleic acid encoding an EPO in expressible format, wherein said cell further contains a nucleic acid sequence encoding a sialyltransferase, preferably an alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase or an alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase, under control of a heterologous promoter; b) culturing said cell in a serum-free culture medium and allow expression of an EPO in said cell; c) harvesting the expressed EPO from said cell and / or from the culture medium; and d) purifying and fractionating the EPO to obtain fractions which have an increased average sialic acid content of the N-linked glycans per EPO molecule, to obtain a composition comprising one or more iso forms of an EPO comprising glycans linked thereto wherein said glycans comprise on average at least 6 sialic acids per EPO molecule and from 0 to 2 Lewis x structures.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Quantitative control of sialylation and specific mono-sialylation
ActiveUS9481902B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsSialic acid aldolaseControl manner
The present disclosure is directed to the use of certain glycosyltransferase variants having N-terminal truncation deletions. It was found that the combination of two different truncation variants of human β-galactoside-α-2,6-sialyltransferase I (hST6Gal-I) exhibited different specific sialyltransferase enzymatic activities. In one example, under conditions wherein the first variant Δ89 hST6Gal-I catalyzed formation of bi-sialylated target molecules the second variant Δ108 hST6Gal-I catalyzed formation of mono-sialylated target molecules. Thus, disclosed are variants of mammalian glycosyltransferase, nucleic acids encoding the same, methods and means for recombinantly producing the variants of mammalian glycosyltransferase and use thereof, particularly for sialylating in a quantitatively controlled manner terminal acceptor groups of glycan moieties being part of glycoproteins such as immunoglobulins.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Methods to obtain recombinant proteins with increased sialylation from cells that express adenovirus E1A protein, and proteins obtained thereby
InactiveUS8524477B2Reduce contentIncrease in sialic acid contentOxidoreductasesErythropoietinHeterologousE1A Protein
Provided are compositions comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (“EPO”) comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans have Lewis x structures and on average at least six sialic acid moieties per EPO molecule. Further provided are methods for obtaining a composition comprising one or more isoforms of EPO comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans comprise on average at least six sialic acids per EPO molecule and from zero to two Lewis x structures, the method comprising: a) providing a eukaryotic cell containing a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein in expressible format and a nucleic acid encoding EPO in expressible format, wherein the cell further contains a nucleic acid sequence encoding a sialyltransferase, e.g., an α-2,6-sialyltransferase or an α-2,3-sialyltransferase, under control of a heterologous promoter; b) culturing the cell in a serum-free culture medium and allowing expression of EPO in the cell; c) harvesting the expressed EPO from the cell and / or from the culture medium; and d) purifying and fractionating the EPO to obtain fractions that have an increased average sialic acid content of the N-linked glycans per EPO molecule, to obtain a composition comprising one or more isoforms of an EPO comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans comprise on average at least six sialic acids per EPO molecule and from zero to two Lewis x structures.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Methods To Obtain Recombinant Proteins With Increased Sialylation From Cells That Express Adenovirus E1a Protein, And Proteins Obtained Thereby
InactiveUS20070275439A1Reduce contentIncrease contentPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesHeterologousE1A Protein
The invention provides compositions comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (EPO) comprising glycans linked thereto, characterized in that said glycans comprise LewisX structures and on average at least 6 sialic acid moieties per EPO molecule. The invention further provides methods for obtaining a composition comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (EPO) comprising glycans linked thereto wherein said glycans comprise on average at least 6 sialic acids per EPO molecule and from 0 to 2 Lewis x structures, said method comprising: a) providing a eukaryotic cell containing a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein in expressible format and further containing a nucleic acid encoding an EPO in expressible format, wherein said cell further contains a nucleic acid sequence encoding a sialyltransferase, preferably an alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase or an alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase, under control of a heterologous promoter; b) culturing said cell in a serum-free culture medium and allow expression of an EPO in said cell; c) harvesting the expressed EPO from said cell and / or from the culture medium; and d) purifying and fractionating the EPO to obtain fractions which have an increased average sialic acid content of the N-linked glycans per EPO molecule, to obtain a composition comprising one or more iso forms of an EPO comprising glycans linked thereto wherein said glycans comprise on average at least 6 sialic acids per EPO molecule and from 0 to 2 Lewis x structures.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
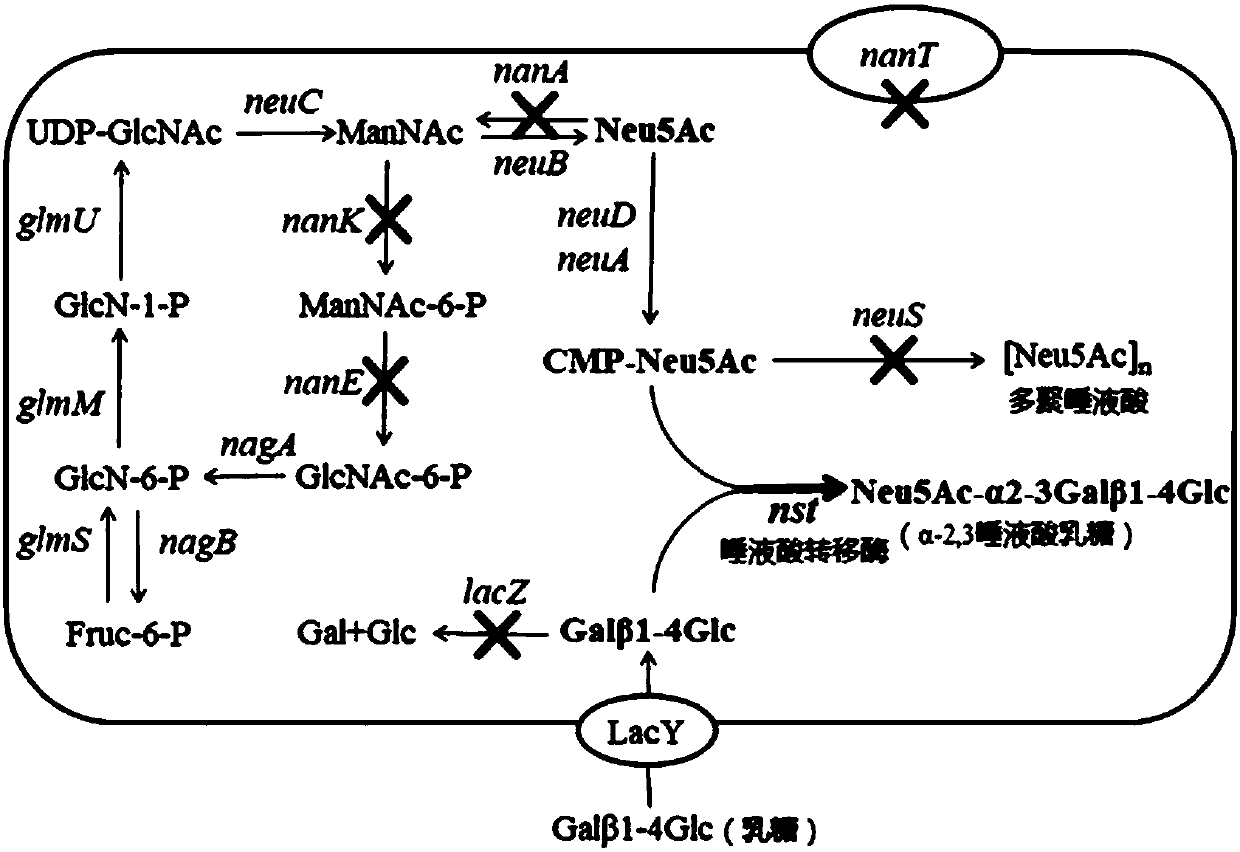
Construction method for engineered Escherichia coli strain capable of producing sialyllactose
InactiveCN107904253ASimple production methodReduce disturbanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismGene cluster
The invention discloses a construction method for an engineered Escherichia coli strain capable of producing sialyllactose. The construction method comprises the following steps: knocking out a polysialytransferase gene (neuS) and beta-galactosidase gene (lacZ) in Escherichia coli so as to obtain a Delta neuS-Delta lacZ double-defective strain; knocking out a gene cluster (nanKETA) related to decomposition of N-acetylneuraminic acid so as to obtain a Delta neuS-Delta lacZ-Delta nanKETA defective strain; and transferring a recombinant plasmid pXC1k-Nst into the Delta neuS-Delta lacZ-Delta nanKETA defective strain so as to obtain a K1-KETA-pNst strain. The Escherichia coli strain K1-KETA-pNst provided by the invention is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, No. 3, Yard 1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City, China, on October 16, 2017, with an accession number of CGMCC No. 14825. The construction method has the advantages that introductionof genes for synthesis and activation of sialic acid is not needed; the resources of cells are directly used; and the method is simple and practical to implement, low in cost and high in yield.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Preparation method of sialyl enteromorpha oligosaccharide promoting intestinal probiotics proliferation
ActiveCN105603023APromote proliferationImprove product valueOrganic active ingredientsDisinfectantsSialyltransferaseGut flora
The invention discloses a preparation method of sialyl enteromorpha oligosaccharide promoting intestinal probiotics proliferation. Enteromorpha is dried and subjected to superfine grinding, and by means of an ethanol reflux extraction technology, the dried and degreased enteromorpha powder is obtained; the enteromorpha oligosaccharide is obtained through microwave-assisted extraction, deproteinization and polysaccharide and pigment removing; sialyltransferase is added into a reaction system containing enteromorpha oligosaccharide, a glycosylation reaction is conducted, and the sialyl enteromorpha oligosaccharide is prepared. The oligosaccharide can significantly increase the number of intestinal probiotics and can be used for preparing drugs or health-care products which improve intestinal flora.
Owner:SHAANXI NIANQINGBAO PHARMA CO LTD
Method for preparing recombinant glycoproteins with high sialic acid content
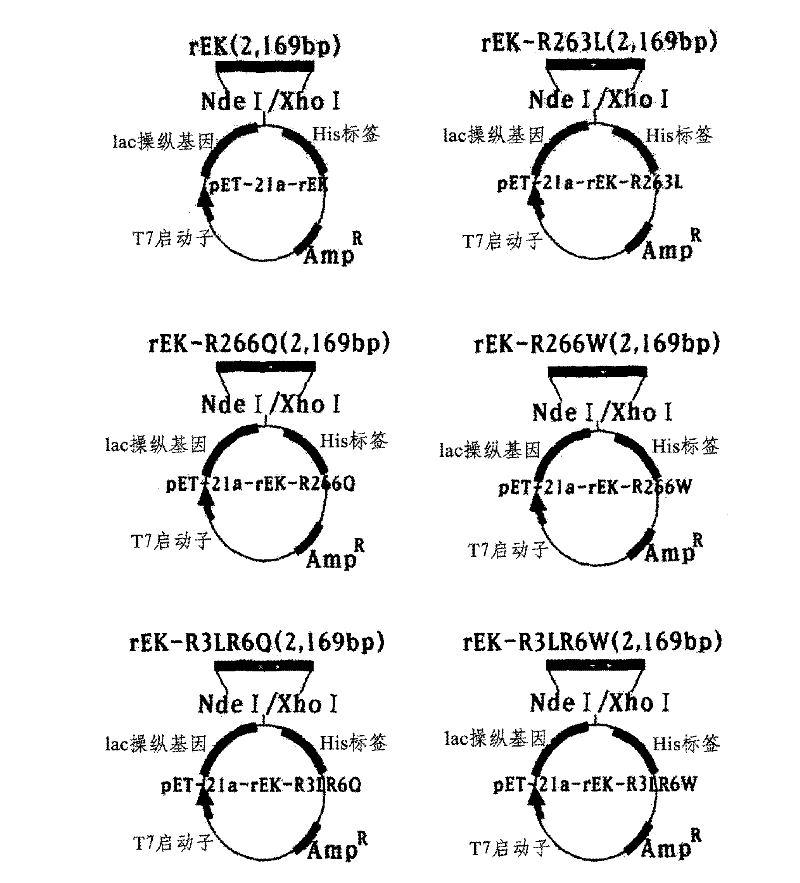
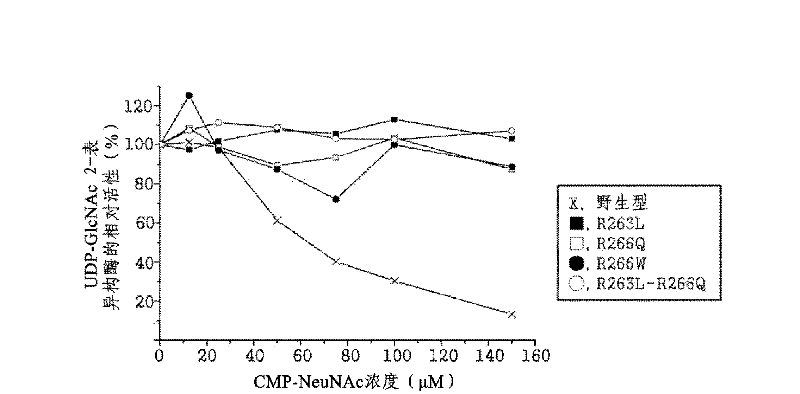
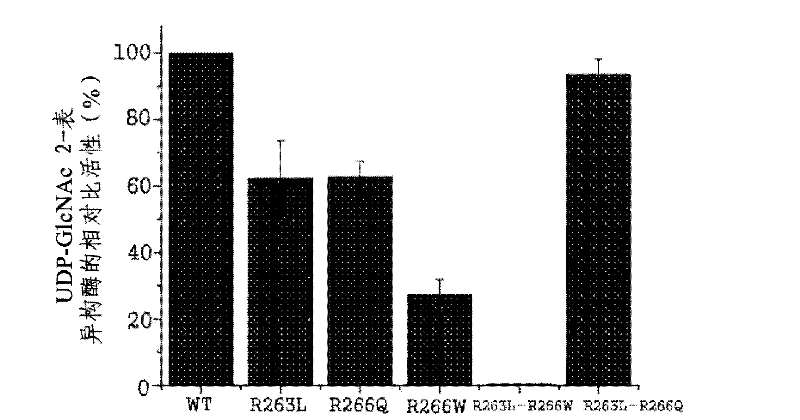
ActiveCN102482674AIncreased sialic acid contentThrombopoietinCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsArginineTert-leucine
The present disclosure relates to a method for preparing recombinant glycoproteins with high sialic acid content. More specifically, for UDP-GlcNAc 2-epimerase / ManNAc kinase (GNE / MNK) enzyme where point mutation was induced by substituting arginine at position 263 by leucine only or by further substituting arginine at position 266 by glutamine, epimerase activity is constantly maintained, and overexpressed cells thereof experience an increase in intracellular cytidine monophosphate (CMP)-sialic acid content, irrespective of CMP-sialic acid concentration.,Particularly, since in an glycoprotein(such as, erythropoietin and thrombopoietin)-producing host cell where point mutationinduced GNE / MNK, human alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase and a CMP-sialic acid transporter gene are simultaneously overexpressed, intracellular content of CMP-sialic acid and sialic acid in glycoprotein increases in cells, overexpression in a host cell producing a sialylated recombinant glycoprotein the three genes above may be useful for preparing glycoprotein with increased sialic acid content.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Methods of using a bacterial GlcNAc-6-P 2'- epimerase to promote sialylation of glycoconjugates
The present invention relates to new methods to promote sialylation of glycoconjugates, including recombinant glycoproteins, in glycoconjugate production systems. The invention relates to methods to promote efficient glycoconjugate sialylation in recombinant expression systems, by providing simpler and more economical ways to produce large intracellular pools of sialic acid precursors. The invention is directed to nucleic acids, vectors, and cells harboring vectors comprising nucleic acids encoding enzymes involved in the synthesis of sialic acid precursors, and cells harboring these nucleic acids in combination with nucleic acids encoding glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferases, to facilitate the production of humanized recombinant glycoproteins in bacterial, fungal, plant, and animal cell expression systems. The engineered cells can be used to produce glycosylated proteins in virally-infected, transiently-transformed, or stably-transformed host cells, including lepidopteran insects and cultured cell lines derived from Spodoptera frugiperda, Trichoplusia ni, and Bombyx mori that can be infected by baculovirus expression vectors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Sialyltransferases and their use in producing sialylated oligosaccharides
Disclosed are methods, genetically engineered cells, sialyltransferases and nucleic acid molecules encoding said sialyltransferases for producing sialylated oligosaccharides as well as the use of saidsialylated oligosaccharides for providing nutritional compositions.
Owner:CHR HANSEN HMO GMBH
Methods of Using a Bacterial GlcNAc-6-P 2'- Epimerase to Promote Sialylation of Glycoconjugates
The present invention relates to new methods to promote sialylation of glycoconjugates, including recombinant glycoproteins, in glycoconjugate production systems. The invention relates to methods to promote efficient glycoconjugate sialylation in recombinant expression systems, by providing simpler and more economical ways to produce large intracellular pools of sialic acid precursors. The invention is directed to nucleic acids, vectors, and cells harboring vectors comprising nucleic acids encoding enzymes involved in the synthesis of sialic acid precursors, and cells harboring these nucleic acids in combination with nucleic acids encoding glycosyltransferases, including sialyltransferases, to facilitate the production of humanized recombinant glycoproteins in bacterial, fungal, plant, and animal cell expression systems. The engineered cells can be used to produce glycosylated proteins in virally-infected, transiently-transformed, or stably-transformed host cells, including lepidopteran insects and cultured cell lines derived from Spodoptera frugiperda, Trichoplusia ni, and Bombyx mori that can be infected by baculovirus expression vectors.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Novel Beta-Galactoside Alpha 2,6-Sialyltransferase, Gene Coding For The Transferase And Process For Producing The Same
InactiveUS20090291471A1Improve production efficiencyWide rangeBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismBeta-galactoside
The present invention provides a novel β-galactoside-α2,6-sialyltransferase having high productivity and / or high activity, and a nucleic acid encoding the sialyltransferase. The present invention also provides a microorganism producing the sialyltransferase. The present invention further provides a vector carrying a nucleic acid encoding the sialyltransferase, and a host cell transformed with the vector, as well as a method for producing a recombinant β-galactoside-α2,6-sialyltransferase.
Owner:JAPAN TOBACCO INC
Fermentative production of sialylated saccharides
Disclosed are methods for the fermentative production of a sialylated saccharide and genetically engineered microbial cells for use in said method, wherein the genetically engineered microbial cells comprise (i) a sialic acid biosynthesis pathway comprising a glucosamine-6-phosphate N-acetyltransferase, (ii) a cytidine 5'-monophospho- (CMP)-N- acetylneuraminic acid synthetase; and (iii) a sialyltransferase, for producing sialylated saccharides, as well as the use of said sialylated oligosaccharides for providing nutritional compositions.
Owner:CHR HANSEN HMO GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com