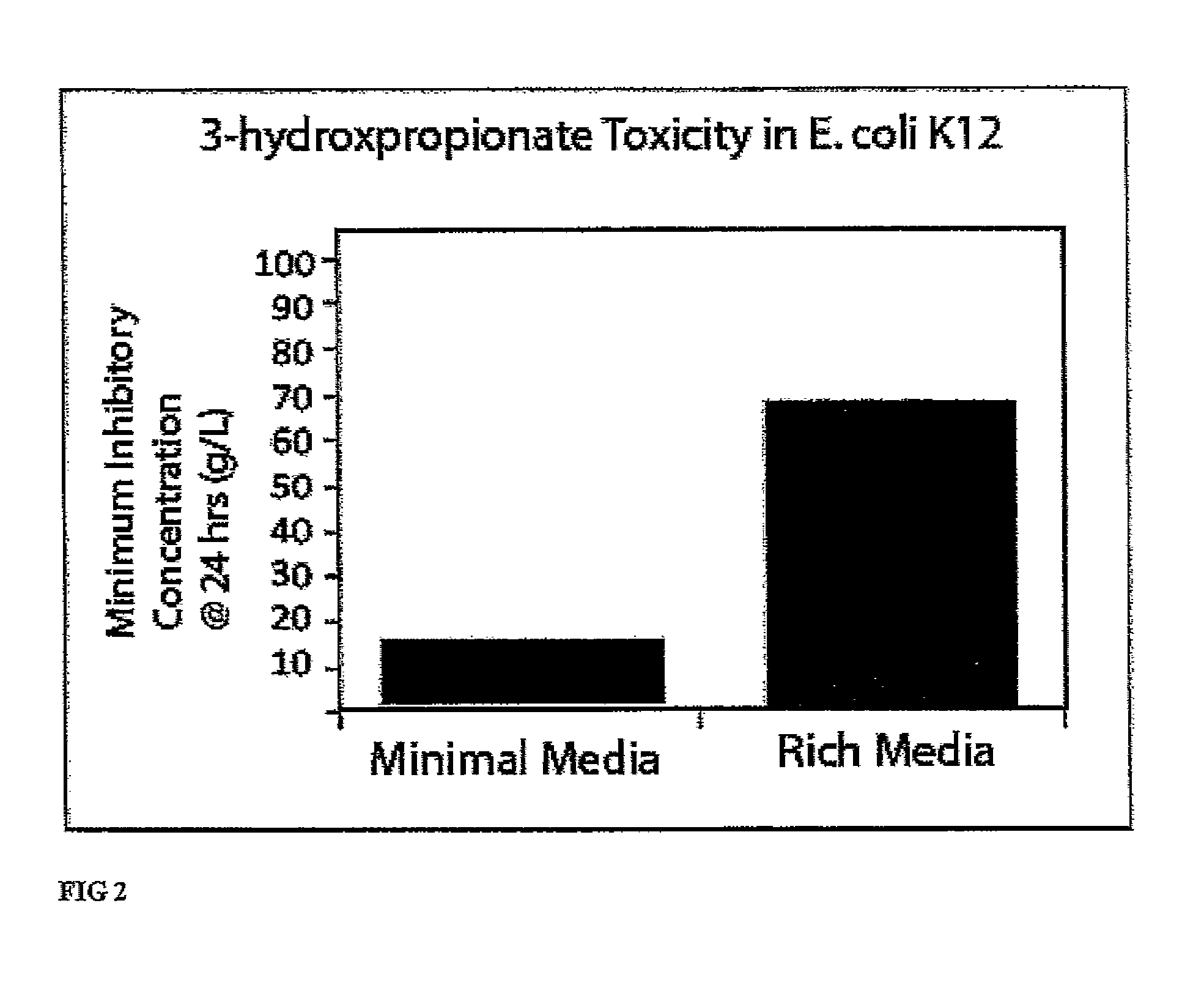
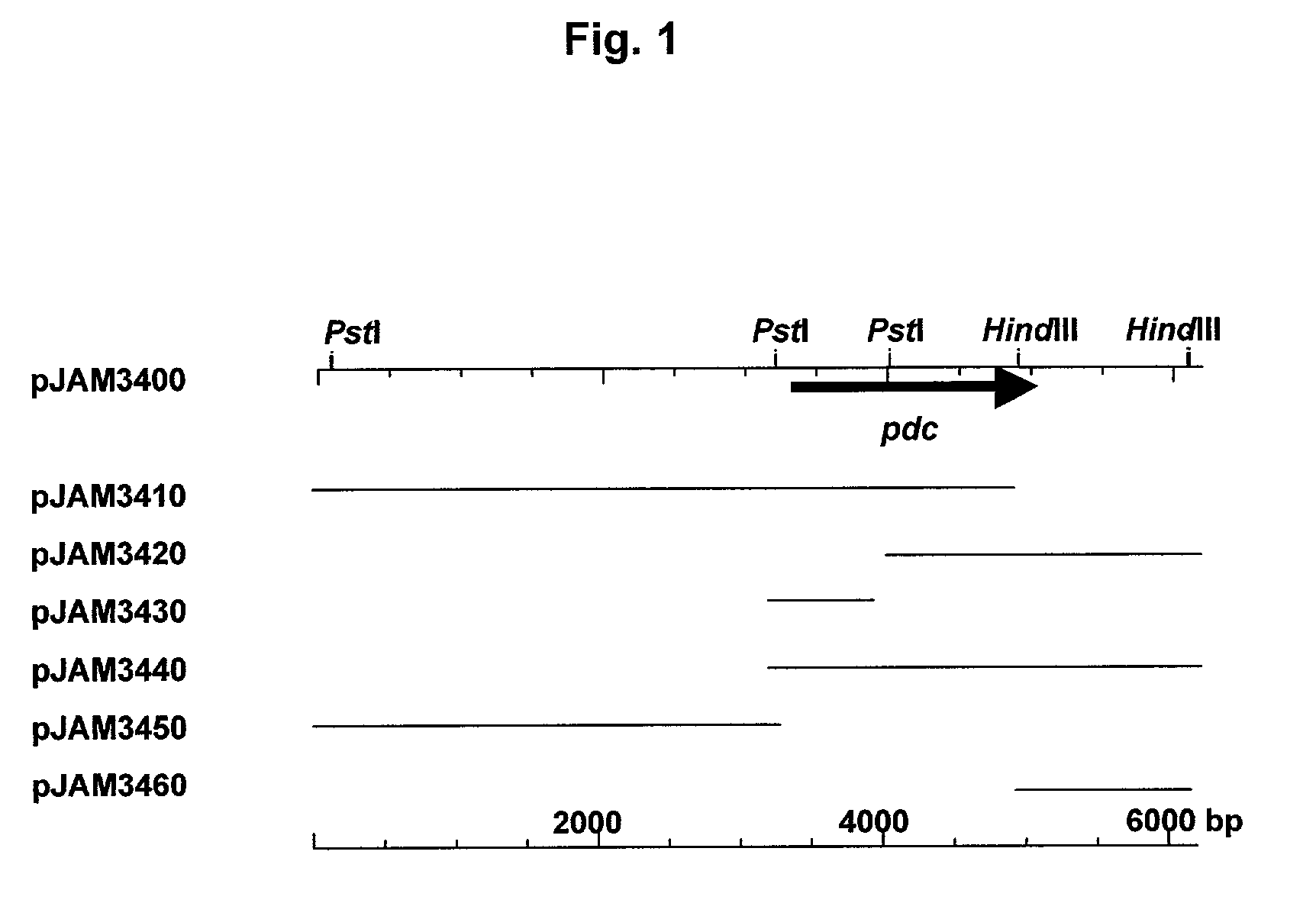
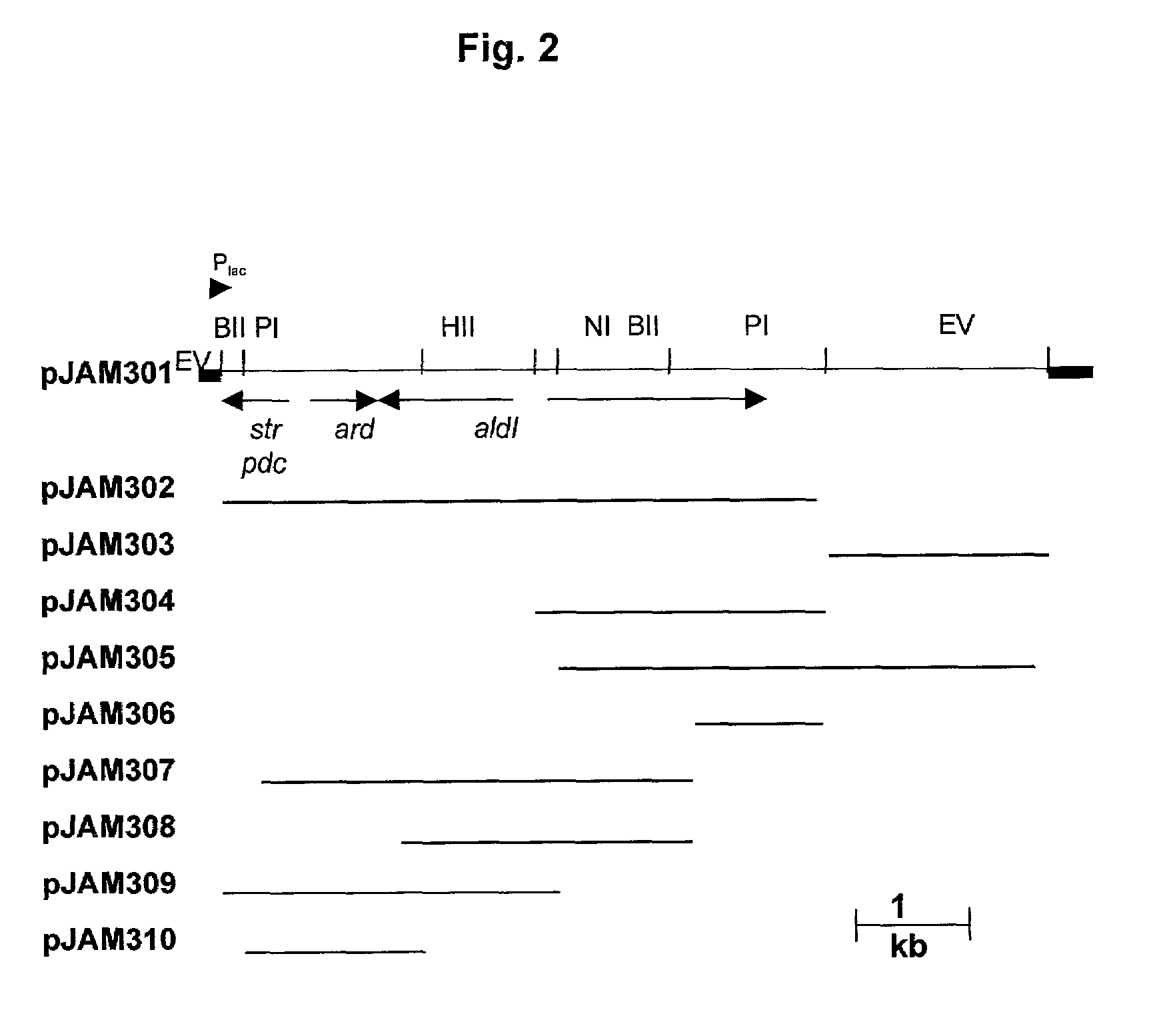
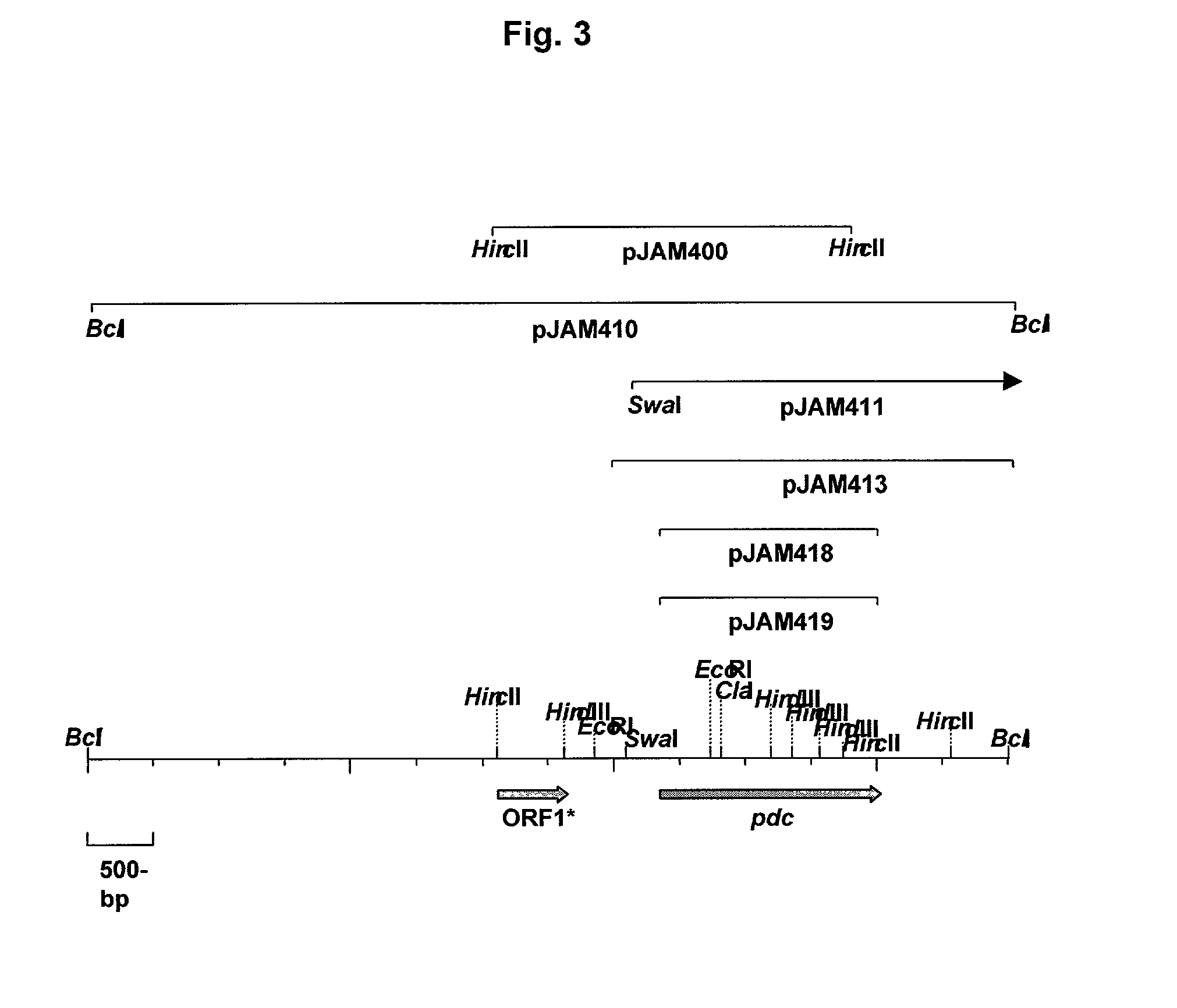
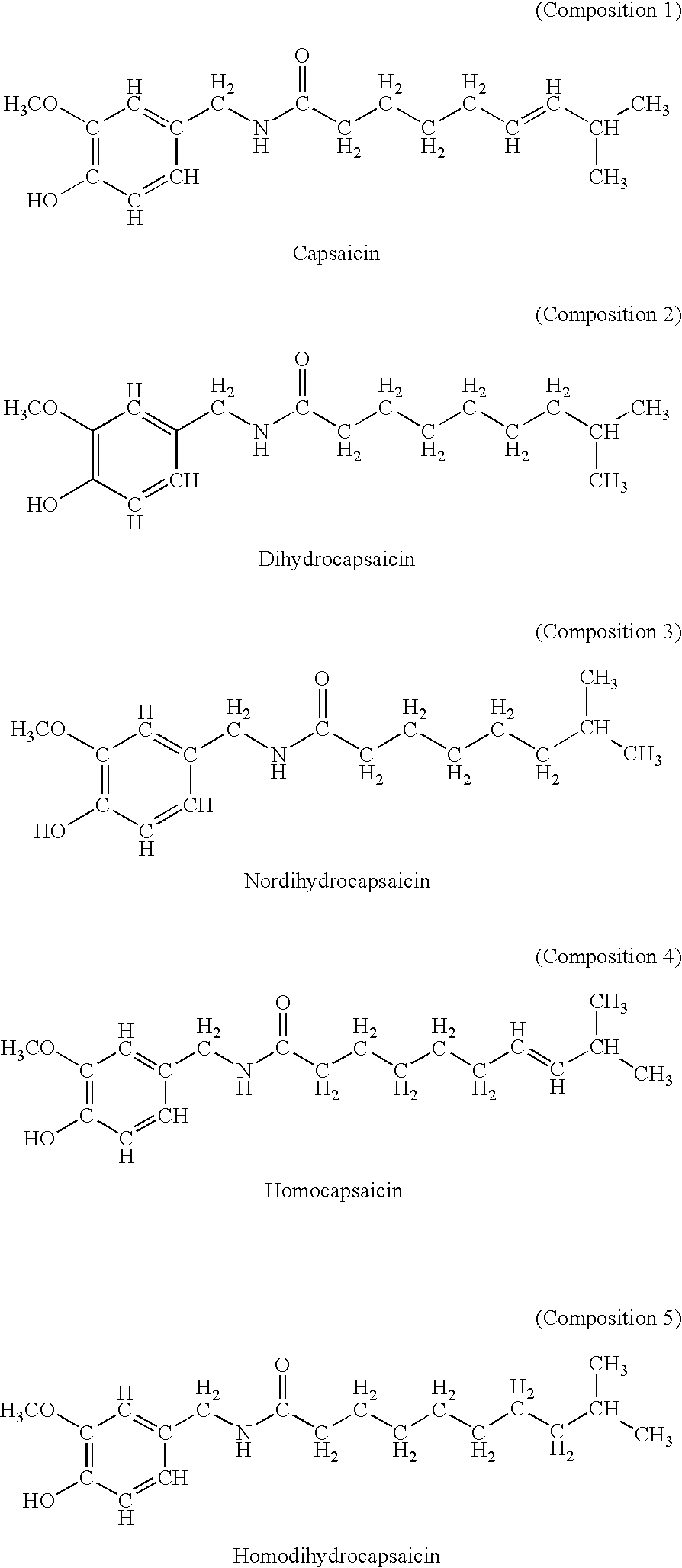
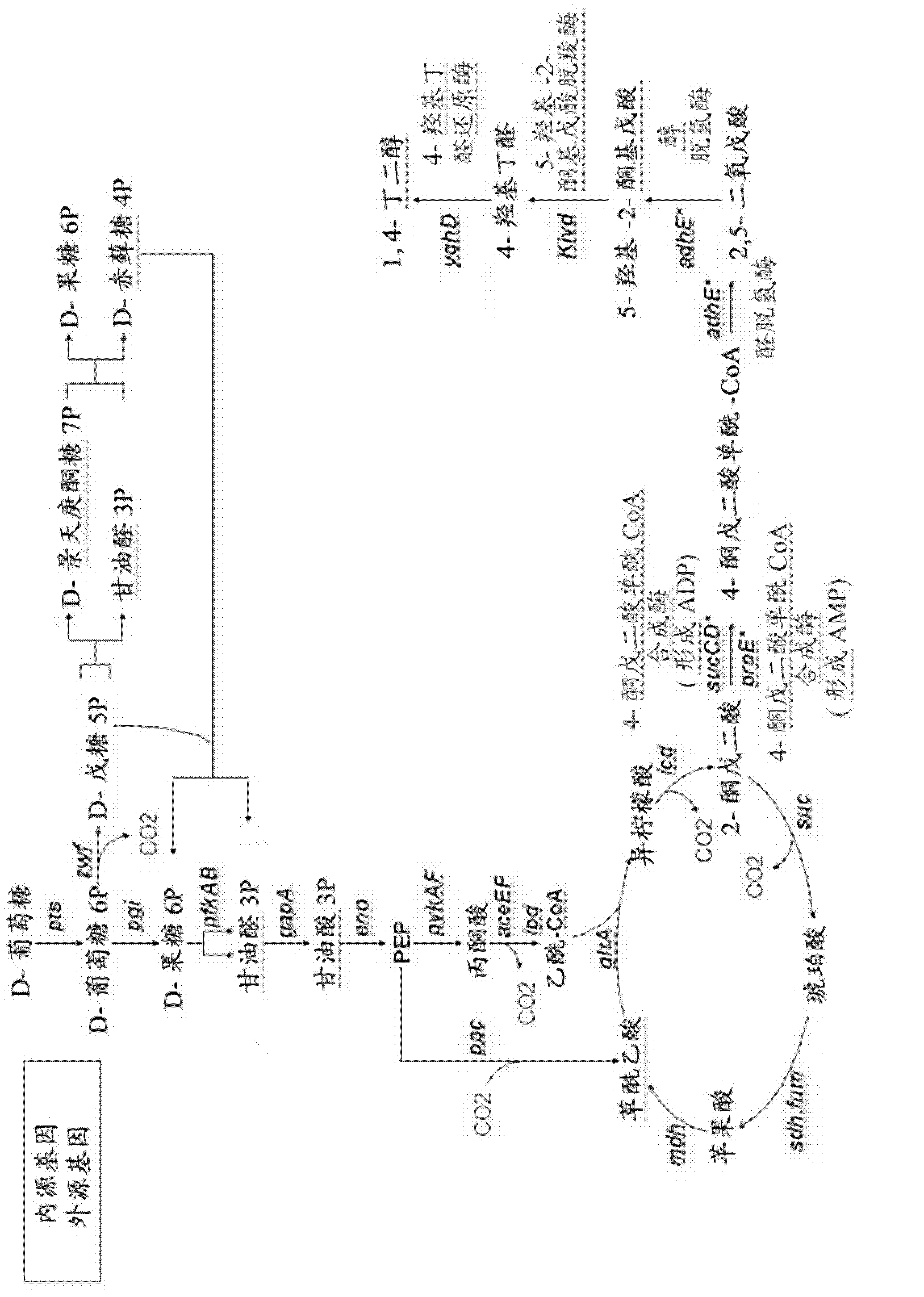
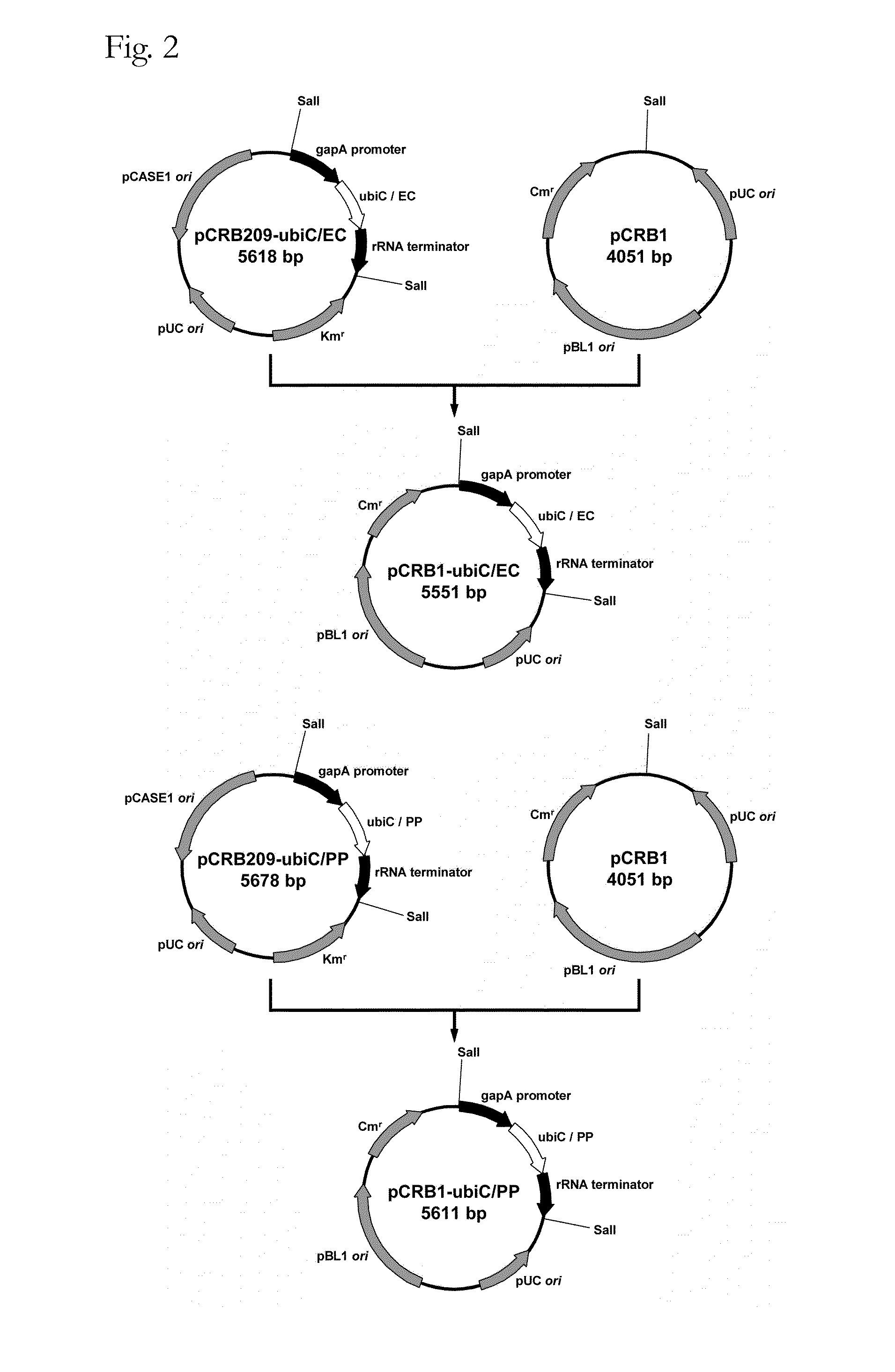
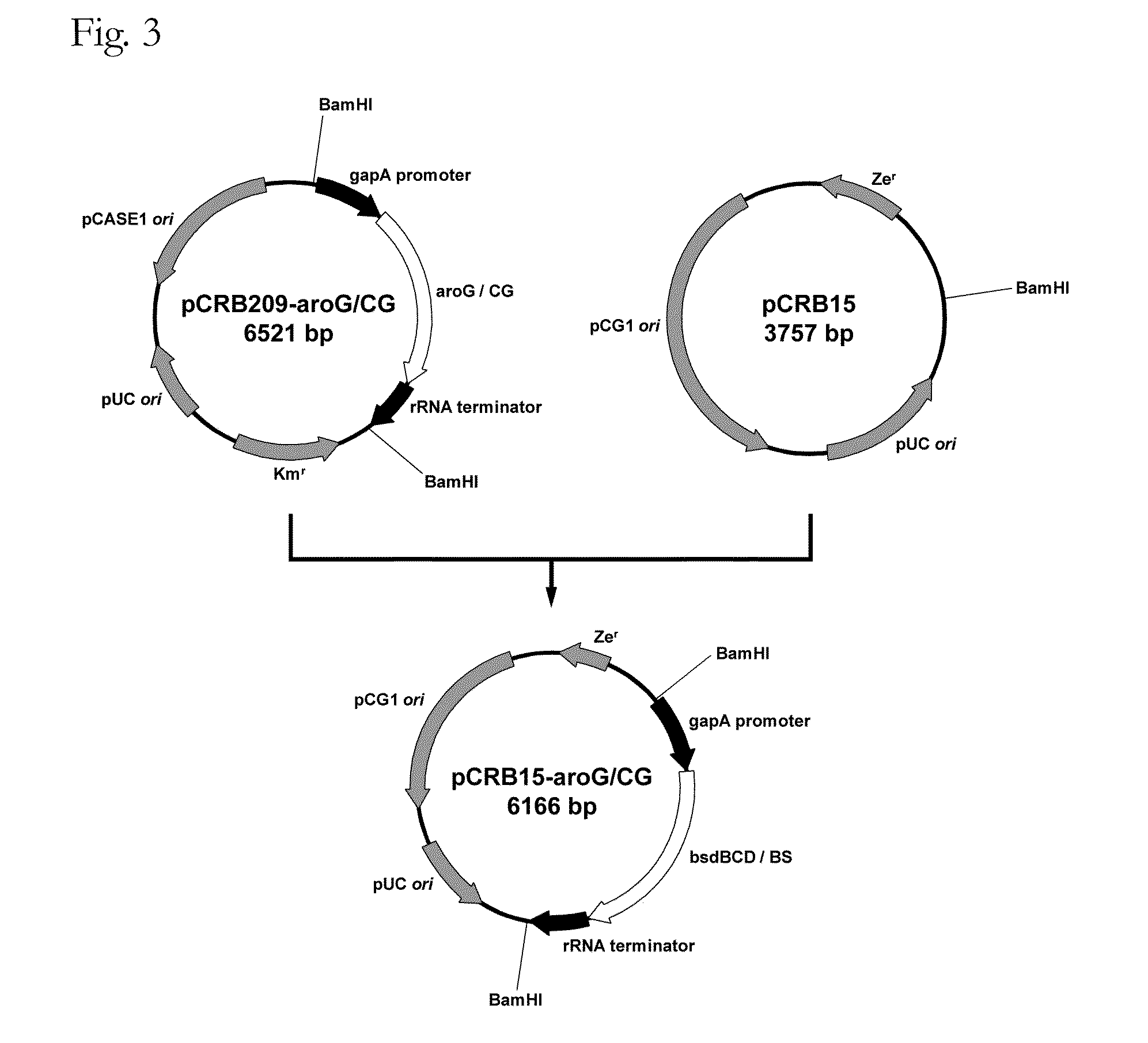
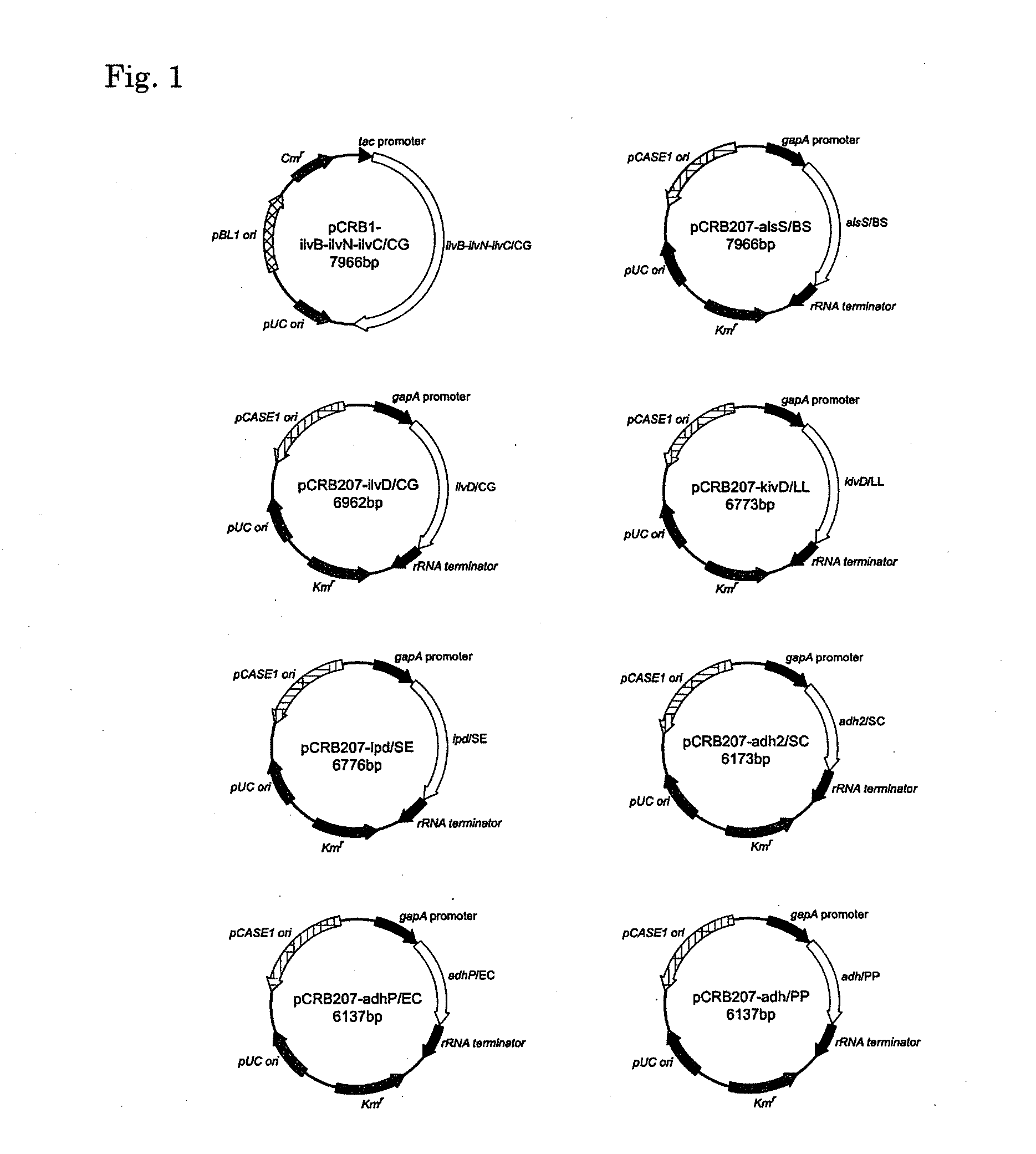
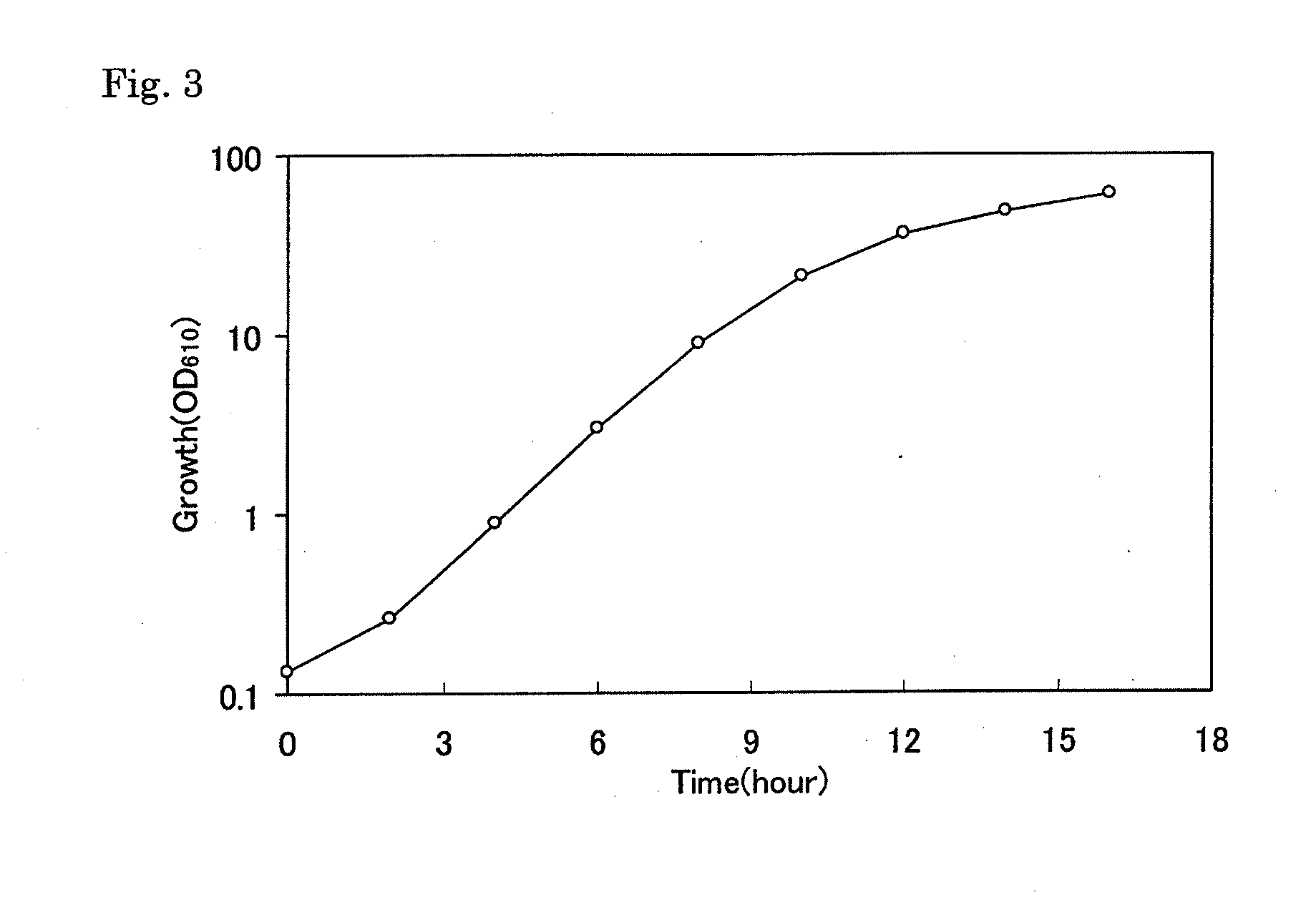
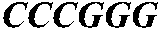Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
50 results about "Decarboxylase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Compositions and methods for 3-hydroxypropionate bio-production from biomass
ActiveUS8048624B1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurement3-Hydroxypropionic acidDecarboxylase activity
Methods of obtaining mutant nucleic acid sequences that demonstrate elevated oxaloacetate α-decarboxylase activity are provided. Compositions, such as genetically modified microorganisms that comprise such mutant nucleic acid sequences, are described, as are methods to obtain the same.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
Method for the preparation of diols
ActiveUS20110294178A1Increasing endogenous expressionHigh expressionFungiBacteriaMicroorganismMetabolite
The present invention concerns a new method for the biological preparation of a diol comprising culturing a microorganism genetically modified for the bioproduction of an aliphatic diol, wherein the microorganism comprises a metabolic pathway for the decarboxylation of a hydroxy-2-keto-aliphatic acid metabolite with an enzyme having a 2-keto acid decarboxylase activity, the product obtained from said decarboxylation step being further reduced into the corresponding aliphatic diol, and wherein the microorganism is genetically modified for the improved production of said hydroxy-2-keto-aliphatic acid metabolite.The invention also concerns a modified microorganism for the production of an aliphatic diol.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
Cloning and sequencing of pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) genes from bacteria and uses therefor
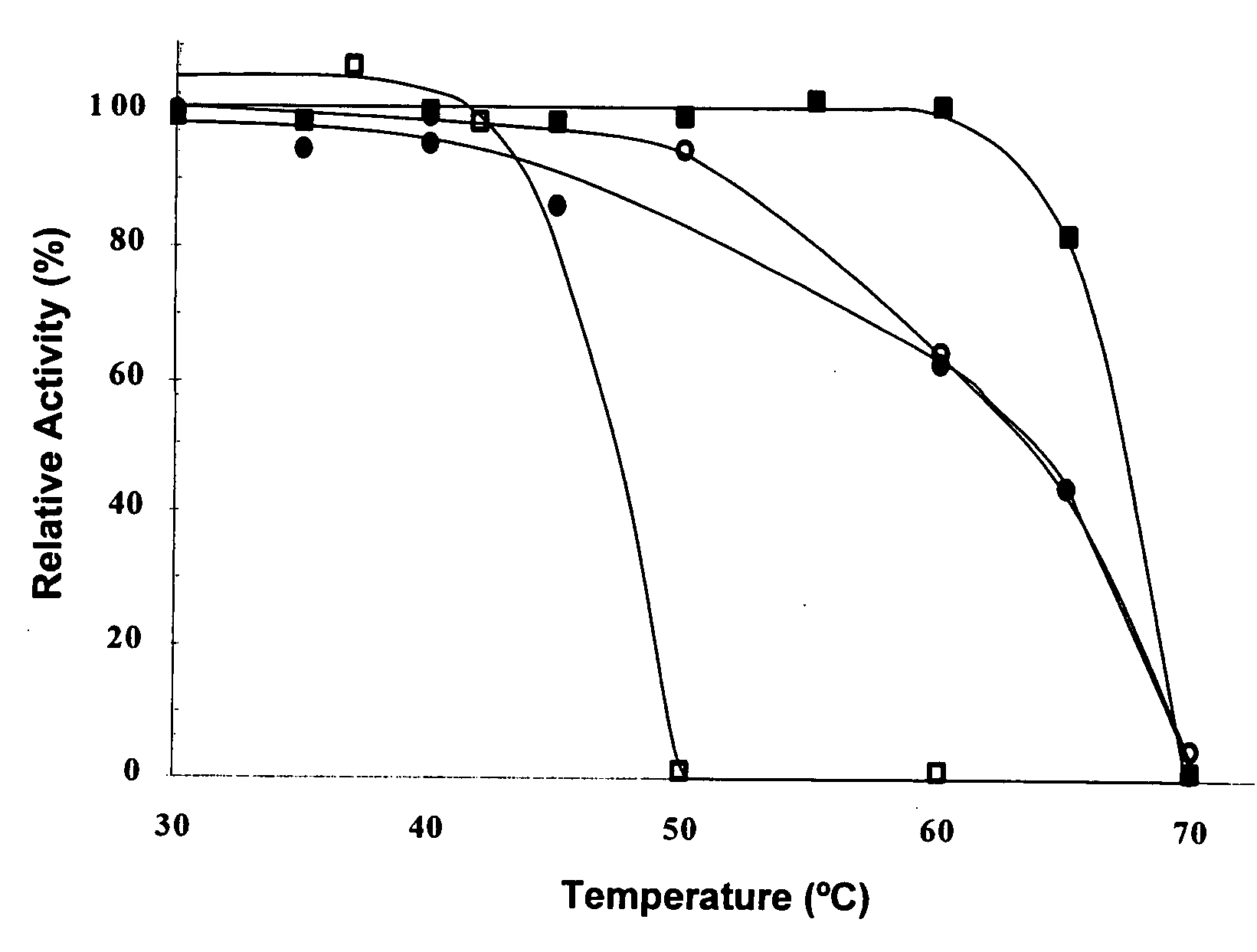
InactiveUS7326551B2Improve efficiencyImprove filtering effectFungiBacteriaBacteroidesPyruvate carboxylase
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules which encode pyruvate decarboxylase enzymes having improved decarboxylase activity, substrate affinity, thermostability, and activity at different pH. The nucleic acids of the invention also have a codon usage which allows for high expression in a variety of host cells. Accordingly, the invention provides recombinant expression vectors containing such nucleic acid molecules, recombinant host cells comprising the expression vectors, host cells further comprising other ethanologenic enzymes, and methods for producing useful substances, e.g., acetaldehyde and ethanol, using such host cells.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for production of l-amino acid
A bacterium which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family and has an ability to produce an L-amino acid such as L-lysine, L-threonine and L-tryptophan and is modified to enhance glutamic acid decarboxylase activity is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate the L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the bacterium. Then, the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or the cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Fermentation agent for low ergamine salami sausage and method of use thereof
InactiveCN101176559ALowers histamine levelsExcellent flavorMeat/fish preservation using acidsFood preparationFlavorDecarboxylase activity
The invention discloses a fermentation agent and the application method for processing low histamine salami sausage, comprising the followings: 1. The selected strains of fermentation agent are CGMCCNo.1923-pediococcus pentosaceus and CGMCCNo.1572-staphylococcus xylosus both without decarboxylase activity; 2. The matching proportion between the CGMCCNo.1923-pediococcus pentosaceus and the CGMCCNo.1572-staphylococcus xylosus is 1:1; 3. The fermentation agent dosage of the pediococcus pentosaceus and the staphylococcus xylosus are 100kg respectively every 100g of mince when processing, the inoculated-pathogen quantity can be up to 1 x 10<7>cfu / g. The adding method is as follow: to make fermentation liquid by mixing the pediococcus pentosaceus fermentation agent and the staphylococcus xylosus fermentation agent with equal ratio and being dissolved in 500g water, spread the fermentation liquid uniformly on the mix mince surface, and mix the mince and the fermentation liquid thoroughly; 4. The preserved preparation used is as follow: the mass ratio to the material mince is salt 3.0%, glucose 1.5%, sodium nitrite 0.015%, and ascorbic acid 0.08%; 5. Using the fermentation agent, preserved preparation and processing technology, the histamine content of salami product is reduced by more than 40% and meets with the food histamine content limitation requirement of the European Union. The invention is tested according to the regulated hygienic standards of cured meat products in the GB2730-2005 hygienic standard for cured meat products, the hygienic state of products meets with the standard, the product flavor and the hygienic safety are better than the traditional technologic product evidently. The invention has the advantages of good application prospect in the aspects of quality improvement and new product development of salami products.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Composition and method for neck skin firming
InactiveUS20070031367A1Soften sharp edgeSmooth appearanceBiocideCosmetic preparationsWrinkle skinBenzaldehyde
A topical composition and method for its use for reducing sagging or wrinkles in the neck area of human skin. The composition includes safe and effective amounts of a mild topical astringent (such as Camphor) for skin tightening, a topical antispasmodic (such as benzaldehyde or benzyl cinnamate) for skin smoothing, and a topical skin irritant to increase localized skin circulation. The composition can also optionally include palmitoyl oligiopeptides to stimulate production of collagen and elastin in skin, a mushroom or plant leaf ferment extract to increase the cell turnover rate skin, and to increase hydration, skin firmness and elimination of fine facial lines, a cocao ferment extract to inhibit lipid peroxidation, inhibit excess ornithine decarboxylase activity, and stimulate cutaneous blood flow to reduce lines and wrinkles, and a Lactobacillus lysate extract to stimulate collagen production. These ingredients are mixed in a dermatologically acceptable carrier for topical application.
Owner:BROWN VERA +1
Nucleotide sequences coding for cis-aconitic decarboxylase and use thereof
InactiveUS20110099670A1Maximizing numberMinimize the numberFungiSugar derivativesNucleotidePlant cell
The present invention relates to nucleotide sequences encoding polypeptides with cis-aconitic decarboxylase activity, the cells transformed with such nucleotide sequences, preferably fungal or plant cells, and to methods wherein such transformed cells are use for the production of itaconic acid.
Owner:KOOPS ANDRIES JURRIAAN +3
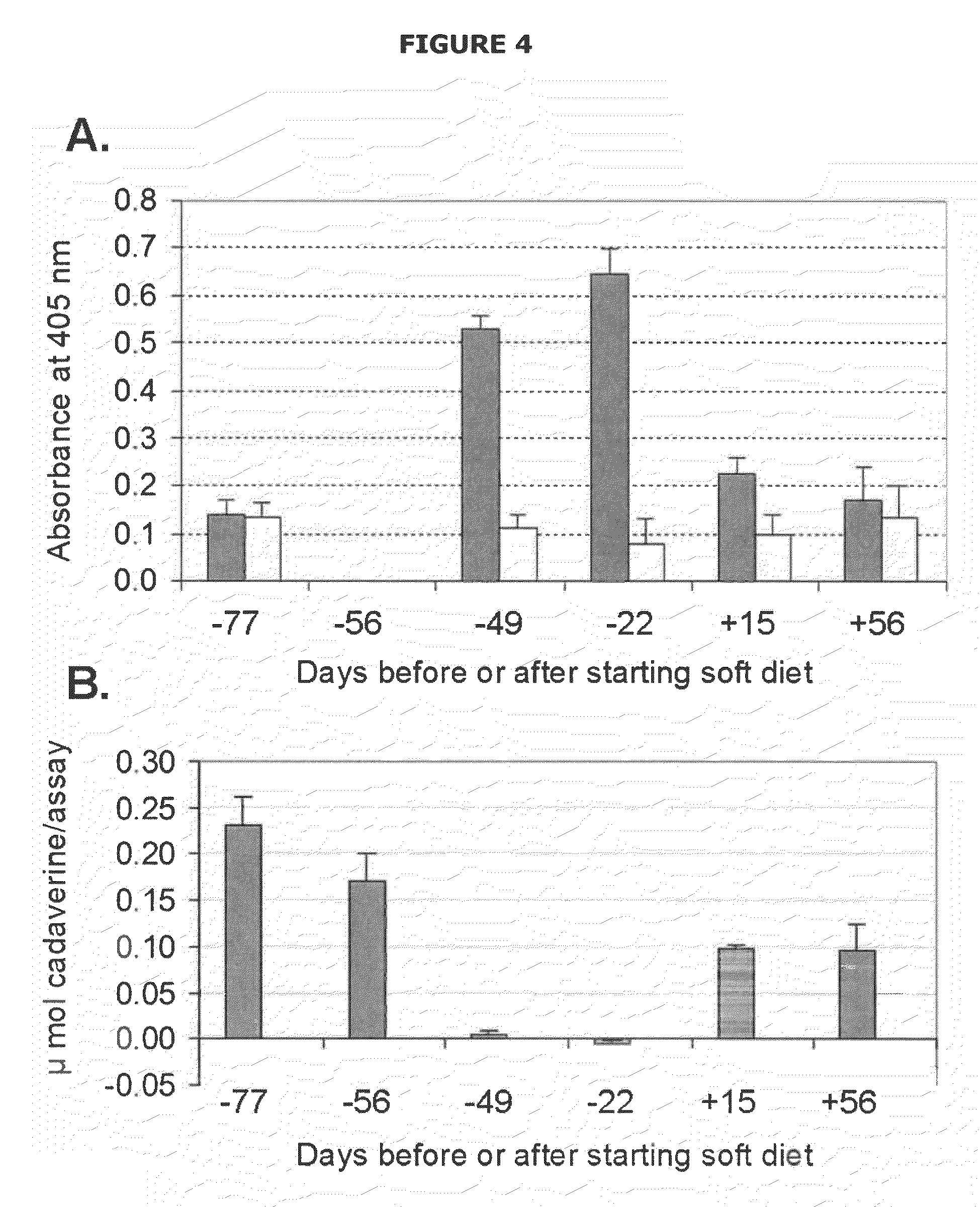
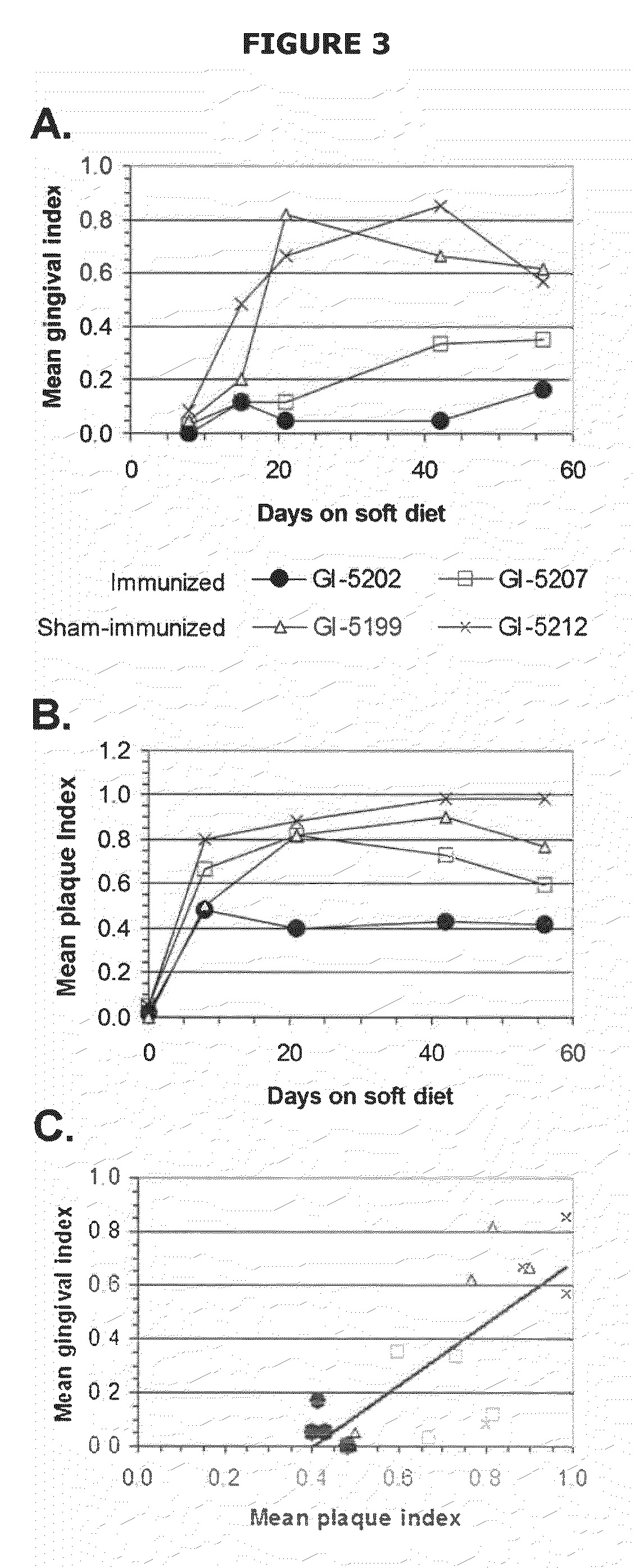
Mutants of lysine decarboxylase, vaccines for periodontitis, and methods of use
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Mutants of lysine decarboxylase, vaccines for periodontitis, and methods of use
InactiveUS20090155296A1Inhibiting and reducing developmentBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The present invention is directed to mutants of lysine decarboxylase, nucleic acids encoding the mutants, and vaccines comprising the mutants for inhibiting and reducing the development of periodontal diseases, including gingivitis and chronic periodontitis. The vaccine composition comprises a recombinant lysine decarboxylase mutant which is based on a native version of the enzyme from E. corrodens and induces production of antibodies that inhibit the activity of the lysine decarboxylase enzyme in the oral cavity. The recombinant lysine decarboxylase mutant, in one version, comprises a mutation at residue 365 or at other locations within the active site, and in a preferred embodiment is produced from E. coli in large amounts and to form inclusion bodies. The purified inclusion bodies can then be used in the vaccine composition to induce in vivo production of antibodies that inhibit the activity of native E. corrodens lysine decarboxylase.
Owner:THE BOARD OF RGT UNIV OF OKLAHOMA
Method for biotransformation production of gamma-aminobutyric acid with aquatic products and processing leftovers thereof as raw materials
ActiveCN103966274ALow costSuitable for industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationFreeze-dryingGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention specifically relates to a method for biotransformation production of gamma-aminobutyric acid by using aquatic products and processing leftovers thereof, which belongs to the technical field of bio-processing of aquatic products. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating 0.5 to 5% (V / V) of lactic acid bacteria with glutamic acid decarboxylase activity into a medium, carrying out fermentation culture at a fermentation temperature of 30 to 35 DEG C at a rotating speed of 100 to 500 r / min for 20 to 50 h so as to allow a viable count in fermentation broth to be as high as 10<6> to 10<7> cfu / ml and standing the fermented lactic acid bacteria for subsequent usage; carrying out centrifugation or filtering on transformation liquid, taking supernatant and subjecting the supernatant to reduced pressure concentration so as to prepare a GABA crude extract; and removing impurities in the crude extract with absolute ethyl alcohol by using a precipitation method, then carrying out separation and purification by successively using a macroporous resin, Sephadex gel and a cation exchange resin and subjecting a GABA product obtained after separation and purification to rotary evaporation and freeze drying so as to obtain a crystal. With the method, a novel application direction for aquatic products and processing leftovers thereof is opened up, and theoretical bases are provided for comprehensive and high-value utilization of aquatic products.
Owner:中科海洋生物研究院盘锦有限公司
Cloning and sequencing of pyruvate decarboxylase (PDC) genes from bacteria and uses therefor
InactiveUS20080009609A1Improve efficiencyImprove filtering effectFungiBacteriaBacteroidesPyruvate carboxylase
The invention provides isolated nucleic acids molecules which encode pyruvate decarboxylase enzymes having improved decarboxylase activity, substrate affinity, thermostability, and activity at different pH. The nucleic acids of the invention also have a codon usage which allows for high expression in a variety of host cells. Accordingly, the invention provides recombinant expression vectors containing such nucleic acid molecules, recombinant host cells comprising the expression vectors, host cells further comprising other ethanologenic enzymes, and methods for producing useful substances, e.g., acetaldehyde and ethanol, using such host cells.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Efficient production method of gamma-aminobutyric acid
ActiveCN104830745ASimplify separation and purification proceduresEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention discloses an efficient production method of gamma-aminobutyric acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. In the provided method, a twin-arginine signal peptide gene (torA) and a glutamic acid decarboxylase gene (gadB) are fused and transferred to a escherichia coil BL21(DE3) host so as to obtain a recombinant bacterium pET20b(+)-torA-gadB / E.coli BL21(DE3) that can secret and express glutamic acid decarboxylase. The extracellular glutamic acid decarboxylase activity level of the recombinant bacterium in a shaking bottle can reach 5.11 U / mL, and 15.82 U / mL in a fermentation tank. By using the system and a substrate (sodium glutamate monohydrate), the output of gamma-aminobutyric acid can reach 203.7 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Decarboxylase proteins with high keto-isovalerate decarboxylase activity
InactiveUS20150259710A1High level activityIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesMicroorganismIsobutanol
The present invention relates to recombinant microorganisms comprising an isobutanol producing metabolic pathway and methods of using said recombinant microorganisms to produce isobutanol. In various aspects of the invention, the recombinant microorganisms may comprise at least one nucleic acid molecule encoding a polypeptide with keto-isovalerate decarboxylase (KIVD) activity, wherein said polypeptide is at least about 65%, 70%, 75%, 80%, 85%, 90%, 91%, 92%, 93%, 94%, 95%, 96%, 97%, 98%, or 99% identical to a polypeptide selected from SEQ ID NOs: 1-214. Also provided are modified decarboxylases exhibiting an improved ability to utilize α-ketoisovalerate as a substrate in various beneficial enzymatic conversions.
Owner:GEVO INC
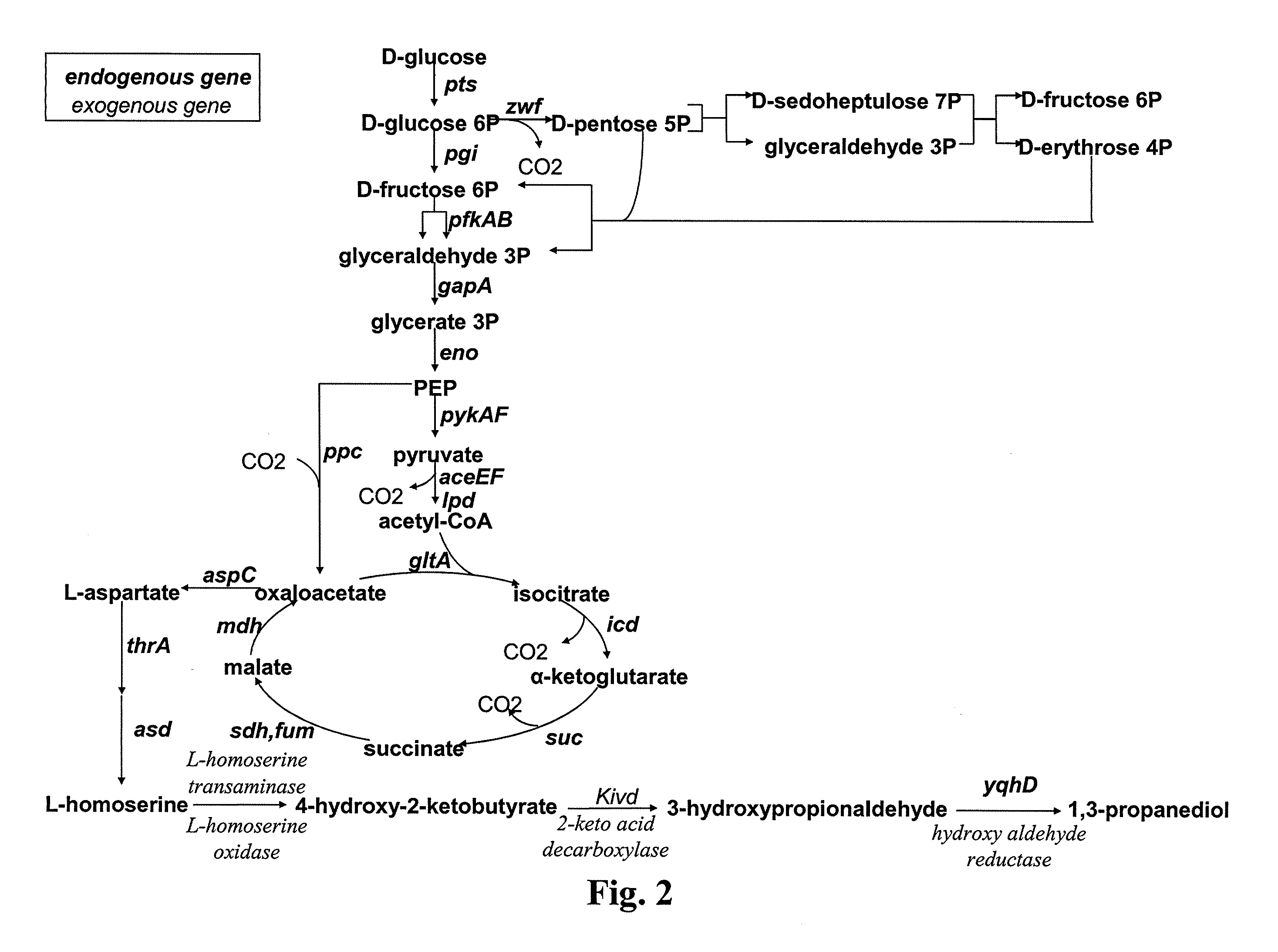
Method for the preparation of diols
The present invention concerns a new method for the biological preparation of a diol comprising culturing a microorganism genetically modified for the bioproduction of an aliphatic diol, wherein the microorganism comprises a metabolic pathway for the decarboxylation of a hydroxy-2-keto-aliphatic acid metabolite with an enzyme having a 2-keto acid decarboxylase activity, the product obtained from said decarboxylation step being further reduced into the corresponding aliphatic diol, and wherein the microorganism is genetically modified for the improved production of said hydroxy-2-keto-aliphatic acid metabolite. The invention also concerns a modified microorganism for the production of an aliphatic diol.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
A method for detecting amino acid decarboxylase activity of spoilage bacteria in food
InactiveCN102297864ALow costEasy to separateMaterial analysis by optical meansWater bathsLiquid medium
A method for detecting amino acid decarboxylase activity of spoilage bacteria in food belongs to the technical field of agricultural products. First, spoilage bacteria are isolated from food, fermented to obtain strain fermentation liquid, and then inoculated into a liquid medium containing amino acids to obtain biogenic amine detection. Use the spoilage bacteria fermentation liquid, and then obtain the supernatant of the sterile body by centrifugation, add Na2HPO4, NaOH and dansyl chloride to the supernatant and the mixed standard solution of biogenic amines, and obtain the derivatives of spoilage bacteria biogenic amines in a water bath under dark conditions. Derivative samples of samples and standard biogenic amines; after pointing and drying, put them into the development tank, wait for the developer to expand to 17cm from the sample point, take them out and dry them, then use automatic gel imaging analysis under ultraviolet light to take pictures respectively, and compare them Yes, determine the type of biogenic amine in the sample according to the Rf value, and judge the amino acid decarboxylase activity of the strain. The invention is convenient and quick, has low cost and can accurately realize the qualitative detection of biogenic amine.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Coryneform bacterium transformant and process for producing phenol using the same
ActiveUS20130273624A1Efficient productionSufficient efficiencyBacteriaFermentationChorismate pyruvate lyaseCorynebacterium amycolatum
Provided is a phenol-producing transformant constructed by transferring a gene which encodes an enzyme having chorismate-pyruvate lyase activity and a gene which encodes an enzyme having 4-hydroxybenzoate decarboxylase activity into a coryneform bacterium as a host. Also provided is a process for producing phenol, which comprises a step of allowing the transformant to react in a reaction mixture containing a saccharide under reducing conditions, and a step of collecting phenol from the reaction mixture.
Owner:GREEN CHEM
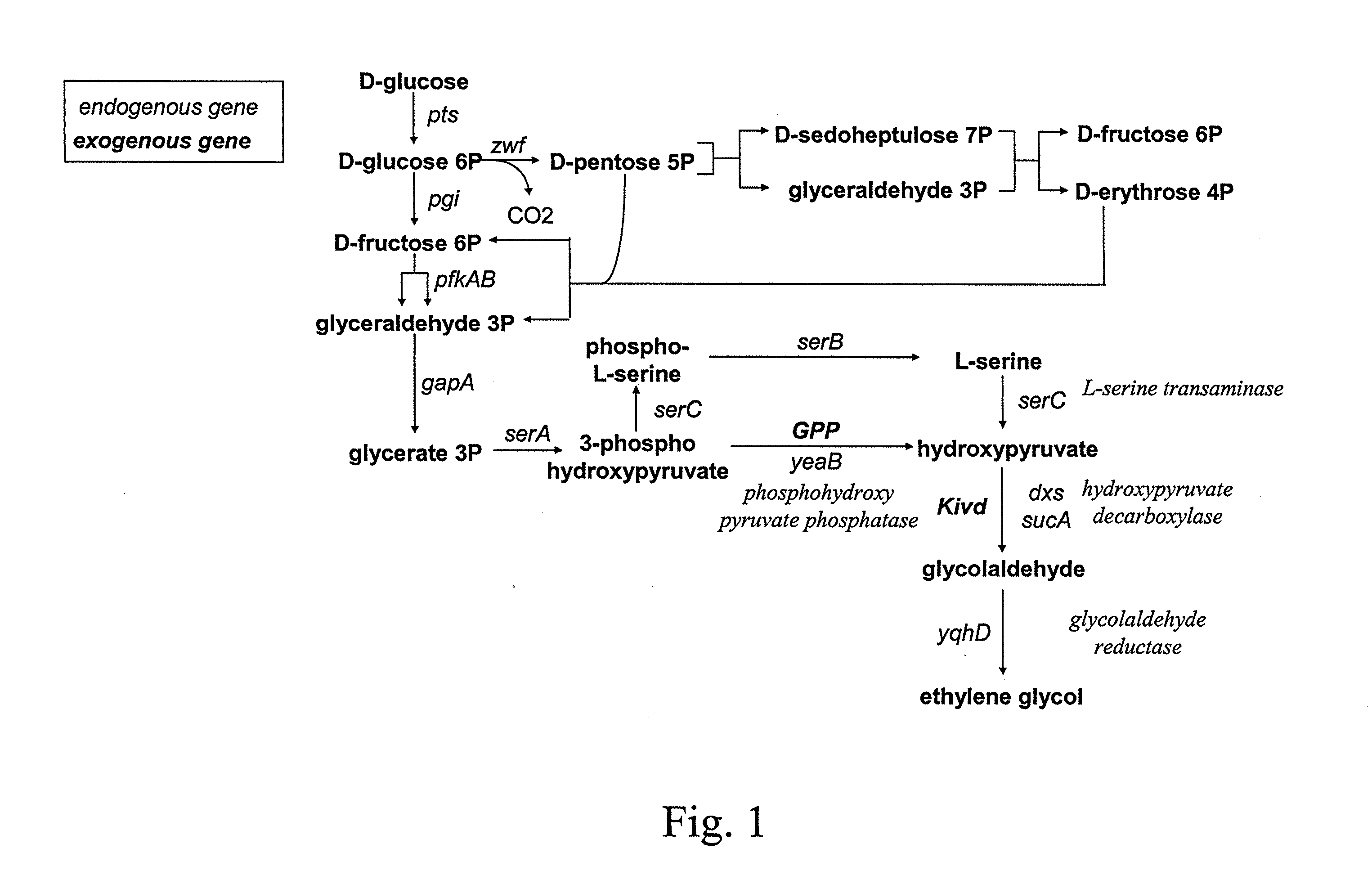
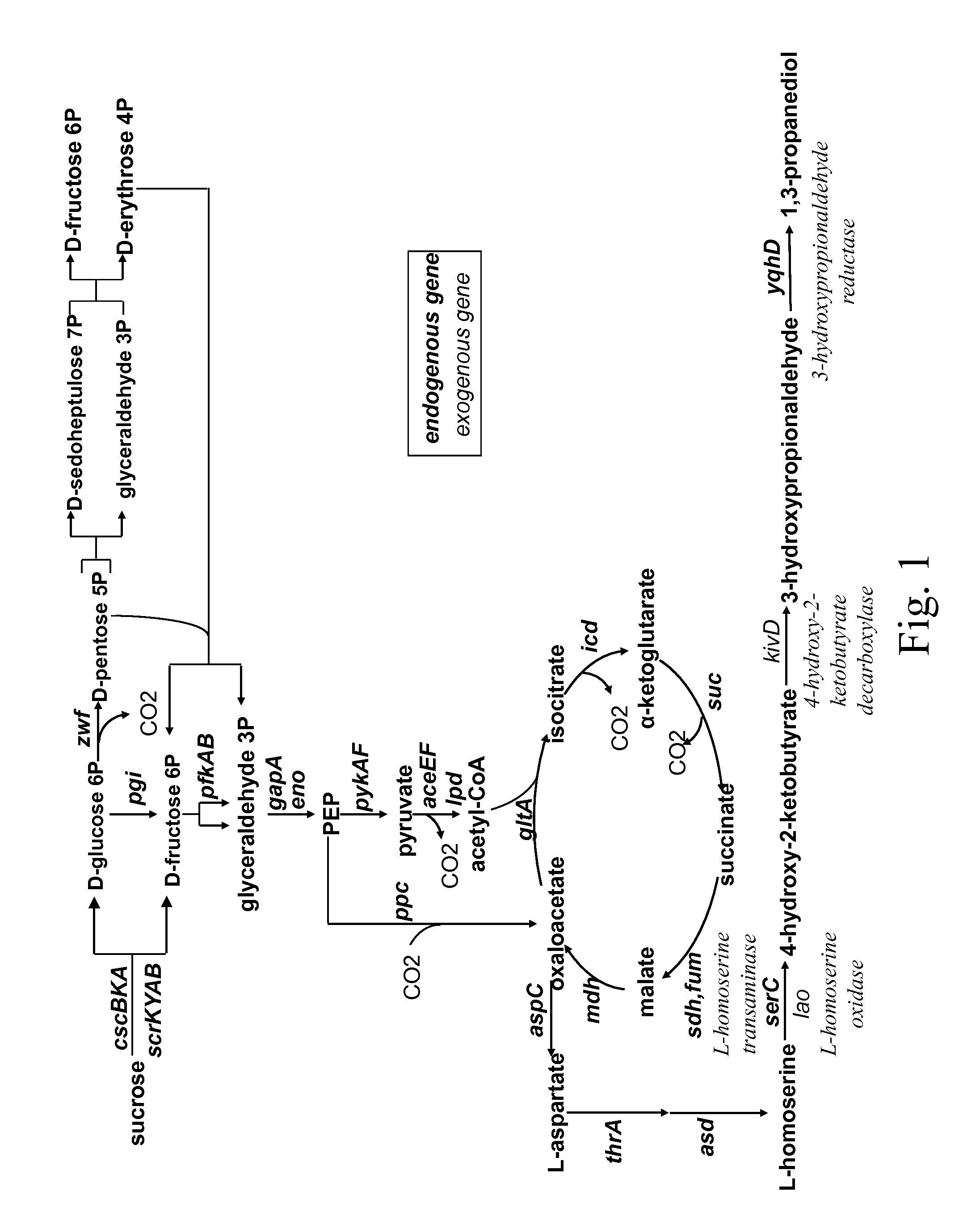
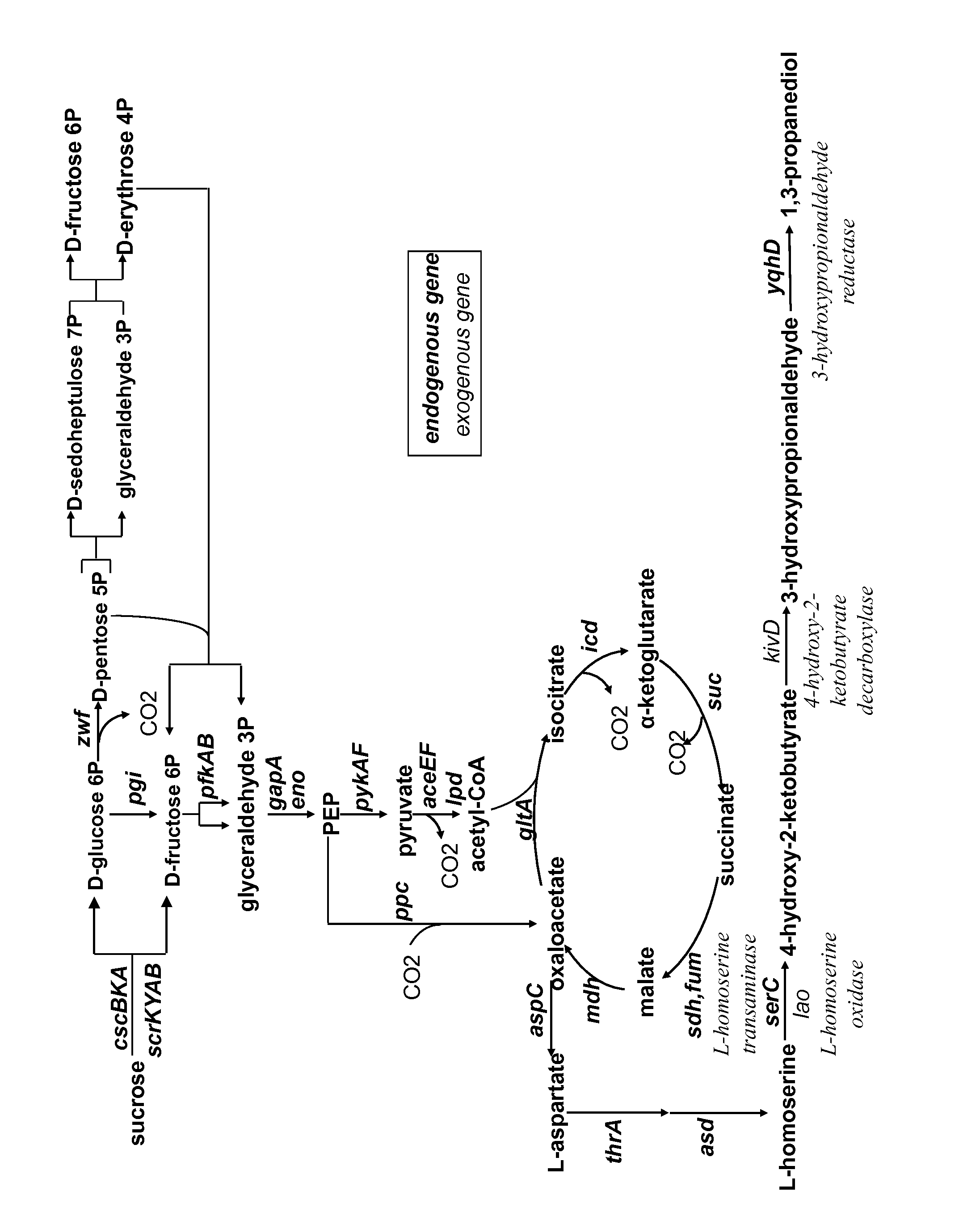
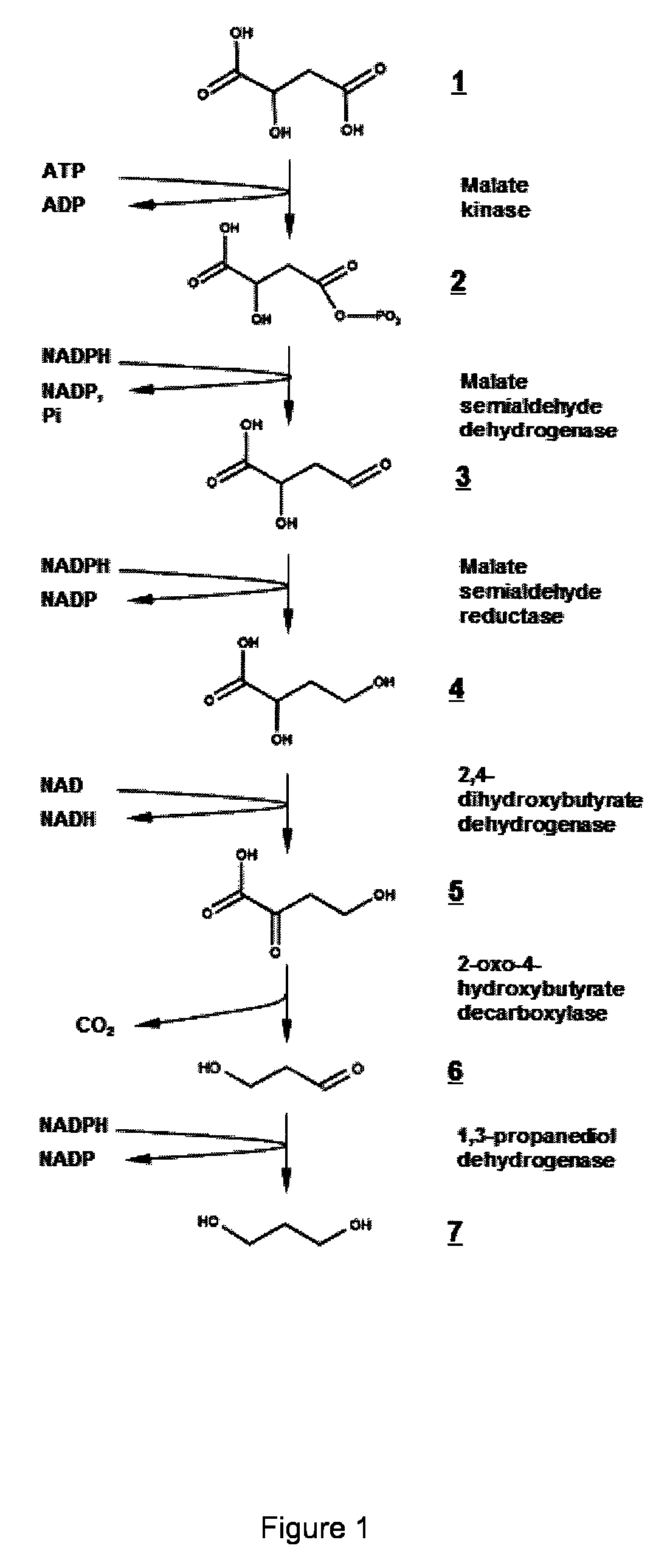
Method for the preparation of 1,3-propanediol from sucrose
The present invention concerns a microorganism genetically modified for the bioproduction of 1,3-propanediol from sucrose, wherein the microorganism comprises: a two-step metabolic pathway for the production of 1,3-propanediol, comprising a first step of decarboxylation of 4-hydroxy-2-ketobutyrate with an enzyme having a 2-keto acid decarboxylase activity, and a second step of reduction of the obtained 3 -hydroxypropionaldehyde with an enzyme having hydroxy aldehyde reductase activity, and genes enabling the microorganism to utilize sucrose as sole carbon source. The invention also concerns a new method for the biological preparation of 1,3-propanediol by fermentation, comprising cultivating said microorganism genetically modified, wherein the culture is performed in an appropriate medium comprising a source of sucrose, and recovering the 1,3 -propanediol being produced. In a preferred aspect of the invention, the source of sucrose is obtained from plant biomass.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
Method for production of L-amino acid
InactiveUS8367371B2Easy to useEfficient productionFermentationLyasesL-threonineGlutamate decarboxylase
A bacterium which belongs to the Enterobacteriaceae family and has an ability to produce an L-amino acid such as L-lysine, L-threonine and L-tryptophan and is modified to enhance glutamic acid decarboxylase activity is cultured in a medium to produce and accumulate the L-amino acid in the medium or cells of the bacterium. Then, the L-amino acid is collected from the medium or the cells.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for the preparation of 1,3-propanediol from sucrose
A microorganism genetically modified for the bioproduction of 1,3-propanediol from sucrose, wherein the microorganism includes:a two-step metabolic pathway for the production of 1,3-propanediol, including a first step of decarboxylation of 4-hydroxy-2-ketobutyrate with an enzyme having a 2-keto acid decarboxylase activity, and a second step of reduction of the obtained 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde with an enzyme having hydroxy aldehyde reductase activity, andgenes enabling the microorganism to utilize sucrose as sole carbon source.A method for the biological preparation of 1,3-propanediol by fermentation, including cultivating said microorganism genetically modified, wherein the culture is performed in an appropriate medium including a source of sucrose, and recovering the 1,3-propanediol being produced.
Owner:METABOLIC EXPLORER
Production of alpha-olefins
InactiveUS20180171252A1Specific decarboxylase activityFacilitates further identificationFermentationBase-materialsBiotechnologyDecarboxylase activity
The present invention relates to the biosynthesis of α-olefins. In particular, the invention provides methods for the production of medium-chain α-olefins, more particularly C11 α-olefins, using a polypeptide with decarboxylase activity on free fatty acids with 8 to 14 carbons, in particular on C8-C12 free fatty acids, more particularly on C12 free fatty acids, or a genetically engineered host cell expressing or overexpressing said polypeptide.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +2
Method for preparing imidazole derivatives
The present invention relates to methods for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of certain diseases modulated by the inhibition of the enzyme malonyl-coenzyme A decarboxylase (malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, MCD) by the administration of a composition containing as an active ingredient a compound according to Formula I. In particular, the invention relates to methods for the prophylaxis, management and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, acidosis, cancers, and obesity through the administration of a compound which inhibits malonyl-coenzyme A decarboxylase activity. The present invention also includes within its scope the novel process for the preparation of certain compounds
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Microbial conversion of glucose to para-hydroxystyrene
An in vivo method for the production of pHS via a recombinant host cell is disclosed. The host cell expresses at least one gene encoding a polypeptide having para-hydroxycinnamic acid decarboxylase activity in combination with either at least one gene encoding a polypeptide having tyrosine ammonia lyase activity or at least one gene encoding a polypeptide having phenylalanine ammonia lyase activity.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for increasing activity of GAD (Glutamate Decarboxylase) by using D101 macroporous adsorption resin
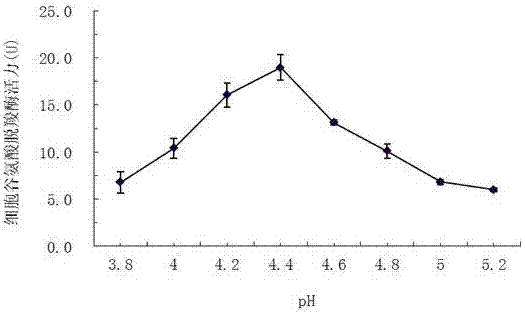
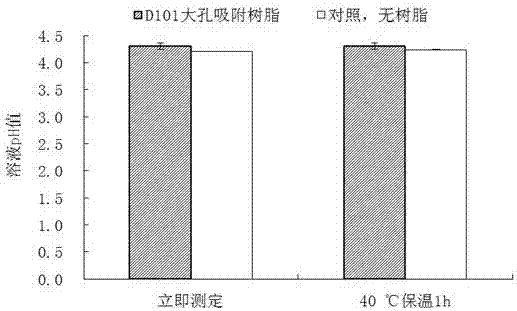
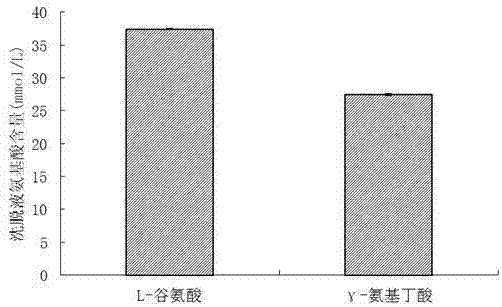
ActiveCN107326052AAvoid inactivationAccelerate the speed of leaving the active center of glutamic acid decarboxylaseMicroorganism based processesFermentationWater bathsGlutamate decarboxylase
The invention relates to a method for increasing the activity of enterococcus faecium Glutamate Decarboxylase by using D101 macroporous adsorption resin, and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the D101 microporous adsorption resin is used as an enzyme activity accelerator of enterococcus faecium GAD, and a D101 microporous adsorption resin-GAD composite catalytic system is constructed according to a proportion that the mass of the D101 macroporous adsorption resin to the volume of a substrate solution to the volume of an enterococcus faecium bacterial suspension solution or a GAD free enzyme solution is 1 to 1 to 1; when the D101 microporous adsorption resin-GAD composite catalytic system is subjected to reaction in a water bath oscillator of which the temperature is 37 to 43 DEG C at 80r / min or stirring reaction in a stirring tank at a low speed for 24 to 36 hours, the yield of GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid) can be increased by 18.54 to 149.11 percent; the D101 macroporous adsorption resin is capable of remarkably increasing the activity of the GAD, an exchange adsorption function of the D101 microporous adsorption resin on the GABA is also a purifying process of the GABA, a downstream extracting and purifying technology is simplified, and the production cost is reduced; the method is simple, green and environment-friendly.
Owner:LINGNAN NORMAL UNIV
Coryneform bacterium transformant and process for producing isobutanol using the same
ActiveUS20120115196A1Improve efficiencyEasy to collectBacteriaBiofuelsIsobutanolAcetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase
A Corynebacterium glutamicum transformant having the capability of producing isobutanol and the following genes (1) to (5):(1) a gene which encodes an enzyme having acetohydroxy acid synthase activity;(2) a gene which encodes an enzyme having acetohydroxy acid isomeroreductase activity;(3) a gene which encodes an enzyme having dihydroxy acid dehydratase activity;(4) a gene which encodes an enzyme having 2-keto acid decarboxylase activity; and(5) a gene which encodes an enzyme having alcohol dehydrogenase activity,at least one of the genes being endogenous, and at least one of the genes being exogenous, efficiently produces isobutanol.
Owner:RES INST OF INNOVATIVE TECH FOR THE EARTH
Method for preparing para-hydroxystyrene by biocatalytic decarboxylation of para-hydroxycinnamic acid in a biphasic reaction medium
A biocatalytic method for preparing para-hydroxystyrene from para-hydroxycinnamic acid is described. The method uses an enzyme source having para-hydroxycinnamic acid decarboxylase activity to catalyze the decarboxylation of para-hydroxycinnamic acid in a biphasic reaction medium to produce para-hydroxystyrene, which is extracted into the organic phase of the biphasic reaction medium. The method results in a high yield of para-hydroxystyrene due to the decreased exposure of the enzyme source to the inhibitory product. The product is readily recovered from the extractant, or may be chemically derivatized directly in the extractant before recovery.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Improved cytochrome p450 fatty acid decarboxylases
PendingUS20210292733A1High activityIncrease productionHydrolasesOxidoreductasesStaphylococcusCytochrome P450
The present invention relates to biocatalysts catalyzing the formation of α-olefins. In particular, the invention provides polypeptides with improved decarboxylase activity on C10-C16 free fatty acids, more particularly on C10 or C12 free fatty acids, as compared to the P450 fatty acid decarboxylase isolated from the Staphylococcus massiliensis strain S46 (Sm46). The invention further provides recombinant nucleic acids and vectors comprising the coding sequences encoding these polypeptides, genetically engineered host cells expressing said polypeptides and methods for the production of C9-C15 α-olefins, more particularly C9 or C11 α-olefins, using said polypeptides or said host cells.
Owner:TOTAL RAFFINAGE CHIM +2
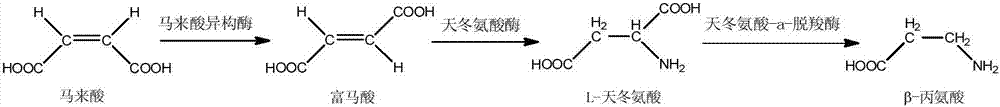
Method for preparing beta-alanine from maleic acid through multi-enzyme coupling
InactiveCN107012180AEasy to produceReduce manufacturing costCarbon-nitrogen lyasesCis-trans-isomerasesMaleopimaric acidAspartase activity
The invention specifically relates to a method for preparing beta-alanine from maleic acid through multi-enzyme coupling, belonging to the field of biotechnology. The method comprises the following steps: adjusting the pH value of an aqueous maleic acid solution with a certain concentration to 6 to 9 by using ammonia water; then separately adding bacterial cells respectively with maleate isomerase activity, aspartase activity and aspartate-alpha-decarboxylase activity or crude liquid of the three enzymes; carrying out enzymatic reaction at 30 to 50 DEG C; and separating and converting products by using isoelectric-point crystallization or a combination of isoelectric-point crystallization and ion exchange resin so as to obtain high-purity beta-alanine. The method provided by the invention uses maleic acid as a substrate for preparation of beta-alanine via multi-enzyme coupling and has the advantages of wide sources of raw materials, low price, simple operation, low production cost, suitability for large-scale industrial production, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
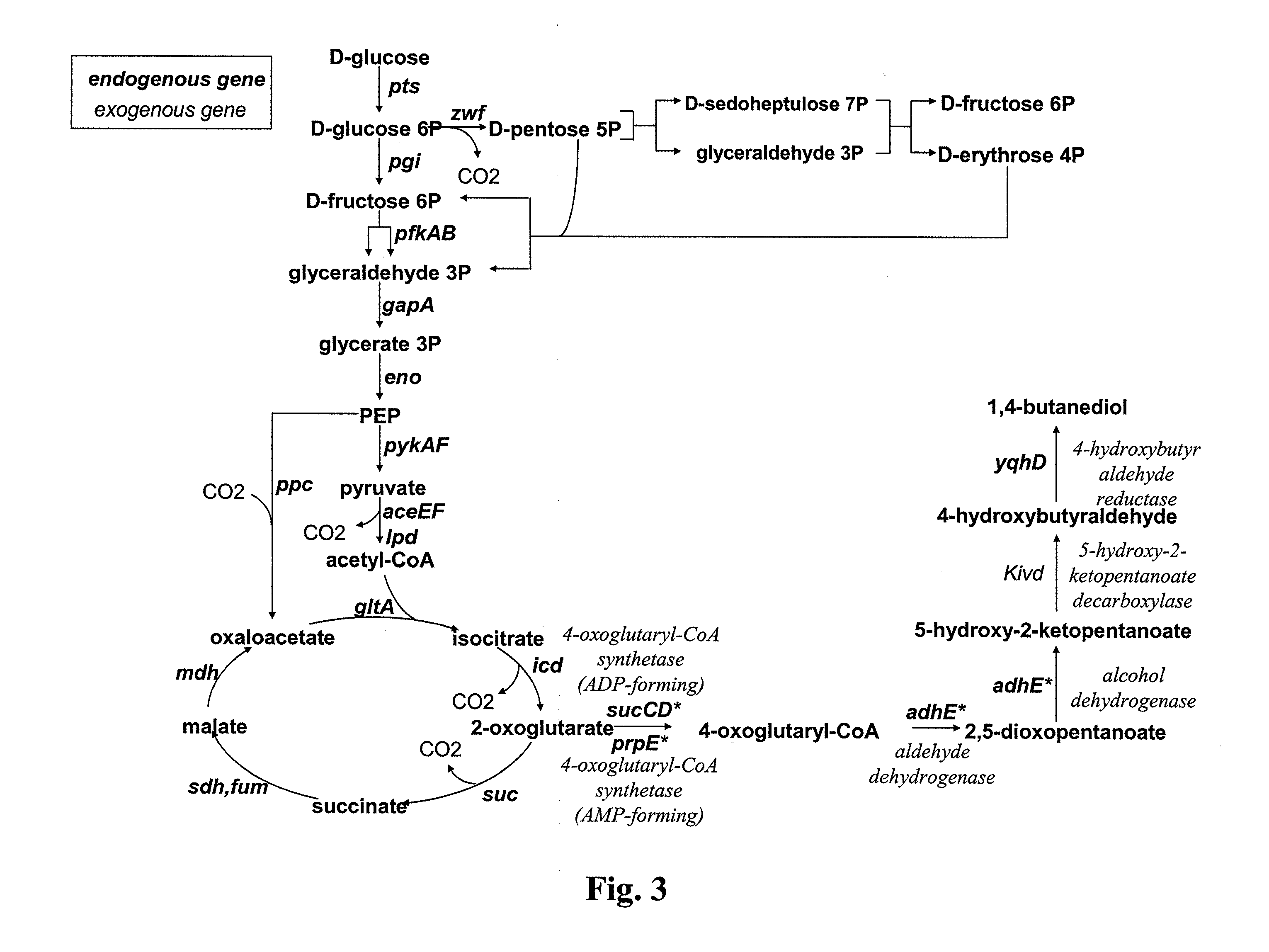
Microorganism modified for the production of 1,3-propanediol
The invention relates to a modified microorganism for the production of PDO from a carbon substrate wherein the microorganism includes a three-step metabolic pathway including a first step of conversion of 2,4-dihydroxybutyrate (DHB) to obtain 2-oxo-4-hydroxybutyrate (OHB) by an enzyme having 2,4-DHB dehydrogenase activity, a second step of decarboxylation of the OHB to obtain 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde by an enzyme having 2-oxo-4-hydroxybutyrate decarboxylase activity, and a third step of reduction of the obtained 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde to obtain PDO with an enzyme having 3-hydroxypropionaldehyde reductase activity and the genes enabling the microorganism for the synthesis of DHB.
Owner:INSTITUT NAT DES SCI APPLIQUEES INSA
Method for controlling content of histamine in aquatic products
InactiveCN106036564AMaintain textureMaintain nutritional contentMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingFood electrical treatmentHistamine ProductionAdditive ingredient
The invention relates to a method for controlling the content of histamine in aquatic products. The washed aquatic products are immersed in a treating fluid, fished out, drained, put into an insulating bag for high-voltage pulsed electric field treatment, added to a fermentation container and fermented at the controlled temperature of 23 DEG C for 20-35 days; the aquatic products are collected, packaged and put into freezing storage. Histamine produced in the transportation and storage processes of the aquatic products can be remarkably reduced while the specific texture and nutritional ingredients of the aquatic products are retained, growth and metabolism of bacterium colonies producing amino acid decarboxylase activity in the processing process of the aquatic products can be inhibited or prevented better, generation of amino acid decarboxylase is prevented fundamentally, accordingly, generation of histamine is prevented in the whole processing process and is further controlled, and the method has great social and economic benefits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG OCEAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com