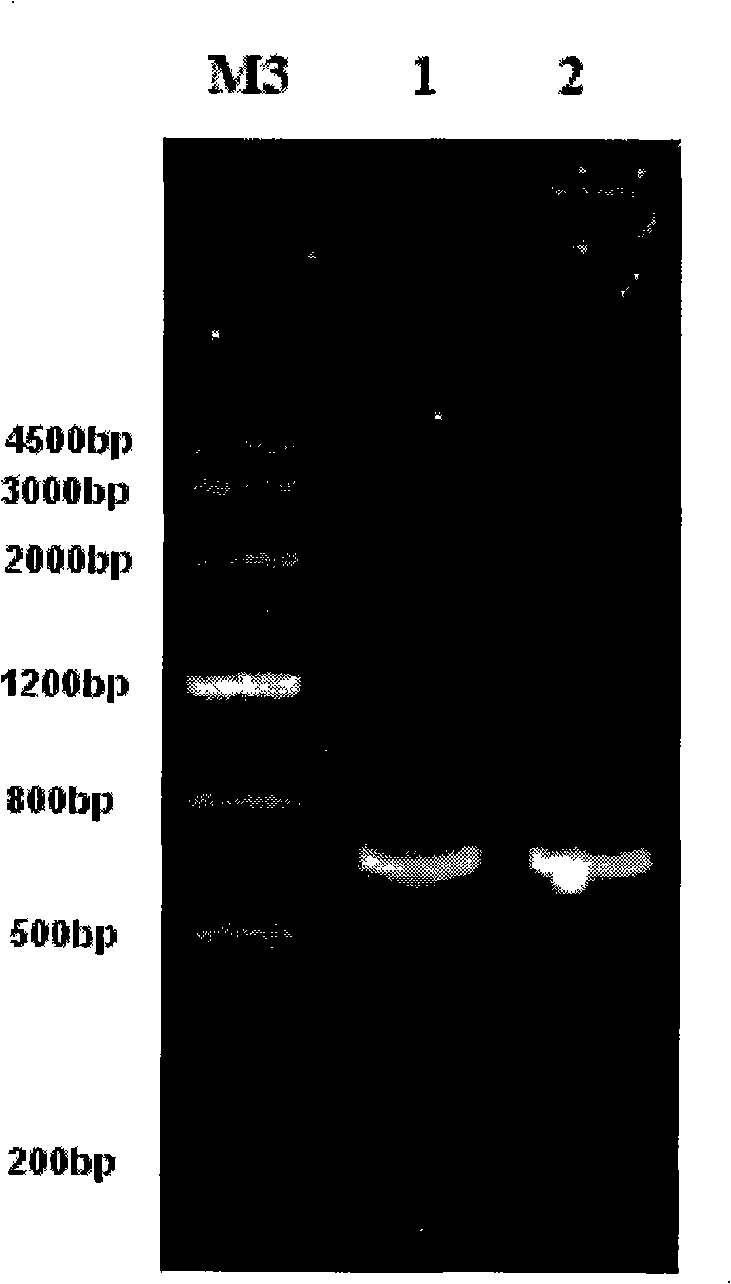Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
787 results about "Evolutionary biology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes that produced the diversity of life on Earth, starting from a single common ancestor. These processes include natural selection, common descent, and speciation.
Polypeptide compositions toxic to diabrotic insects, and methods of use
InactiveUS6468523B1Easy to storeInhibit microbial growthBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDelta endotoxinPolynucleotide
Disclosed is a novel Lepidopteran- and Coleopteran-active delta-endotoxin polypeptide, and compositions comprising the polypeptide, peptide fragments thereof, and antibodies specific therefor. Also disclosed are vectors, transformed host cells, and transgenic plants that comprise nucleic acid segments encoding the polypeptide. Also disclosed are methods of identifying related polypeptides and polynucleotides, methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel sequences of the invention, as well as methods for controlling an insect population, such as the Western Corn Rootworm and Colorado potato beetle, and for conferring to a plant population resistance to the target insect species.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Seed specificity highly effective promoter and its application
InactiveCN101063139AReduce adverse effectsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousNucleotide
The invention discloses a special promoter separated from millet, expressing carrier with nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 host with the expressing carrier and appliance of the promoter, which is characterized by the following: utilizing Tail-PCR (colored body step moving method); getting the special promoter from gene group DNA; possessing nucleic acid sequence of SEQ ID No. 1; ;linking downstream of the promoter to non-homologous or homologous gene; constructing plant expressing carrier; transferring host plant; driving the downstream gene to high effective and special express goal protein in the seed; realizing genetic modification of plant; or using as effective tool for studying plant and biological reactor.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
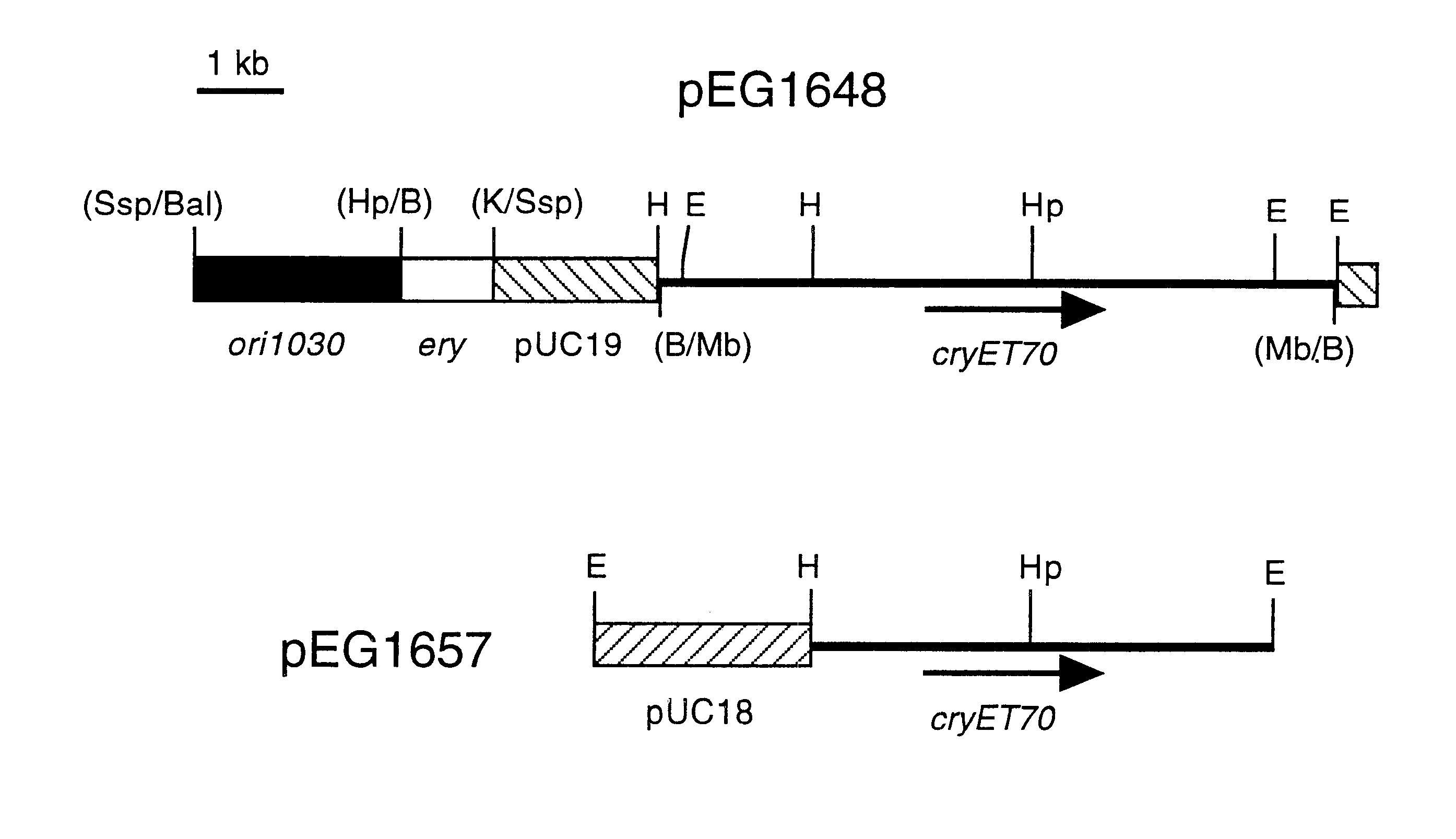
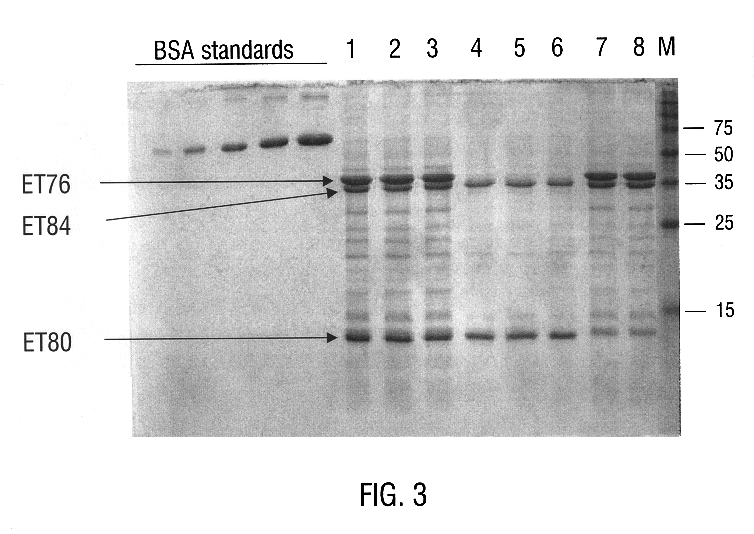
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET33 and CryET34 compositions and uses therefor
Disclosed are Bacillus thuringiensis strains comprising novel crystal proteins which exhibit insecticidal activity against coleopteran insects including red flour beetle larvae (Tribolium castaneum) and Japanese beetle larvae (Popillia japonica). Also disclosed are novel B. thuringiensis crystal toxin genes, designated cryET33 and cryET34, which encode respectively the coleopteran-toxic proteins, CryET33 (29-kDa) crystal protein, and CryET34 (14-kDa) crystal protein. Also disclosed are methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel nucleic acid sequences of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Bacillus thuringiensis cryET33 and cryET34 compositions and uses therefor
Disclosed are Bacillus thuringiensis strains comprising novel crystal proteins which exhibit insecticidal activity against coleopteran insects including red flour beetle larvae (Tribolium castaneum) and Japanese beetle larvae (Popillia japonica). Also disclosed are novel B. thuringiensis crystal toxin genes, designated cryET33 and cryET34, which encode the colepteran-toxic crystal proteins, CryET33 (29-kDa) crystal protein, and the cryET34 gene encodes the 14-kDa CryET34 crystal protein. The CryET33 and CryET34 crystal proteins are toxic to red flour beetle larvae and Japanese beetle larvae. Also disclosed are methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising the novel nucleic acid sequences of the invention.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Transgenic plant event detection
ActiveUS8700336B2Reduce in quantityExtension of timeMicrobiological testing/measurementClimate change adaptationGenetic MaterialsTransgene
The present invention relates to detection of materials derived from transgenic plant events. In particular, the invention provides methods, reagents, kits and reference materials for detecting the presence or absence in a sample of genetic material derived from and attributable to select transgenic plant events.
Owner:SCIENSANO
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6093695ARemarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaBacillus thuringiensisCtenocephalides felis felis
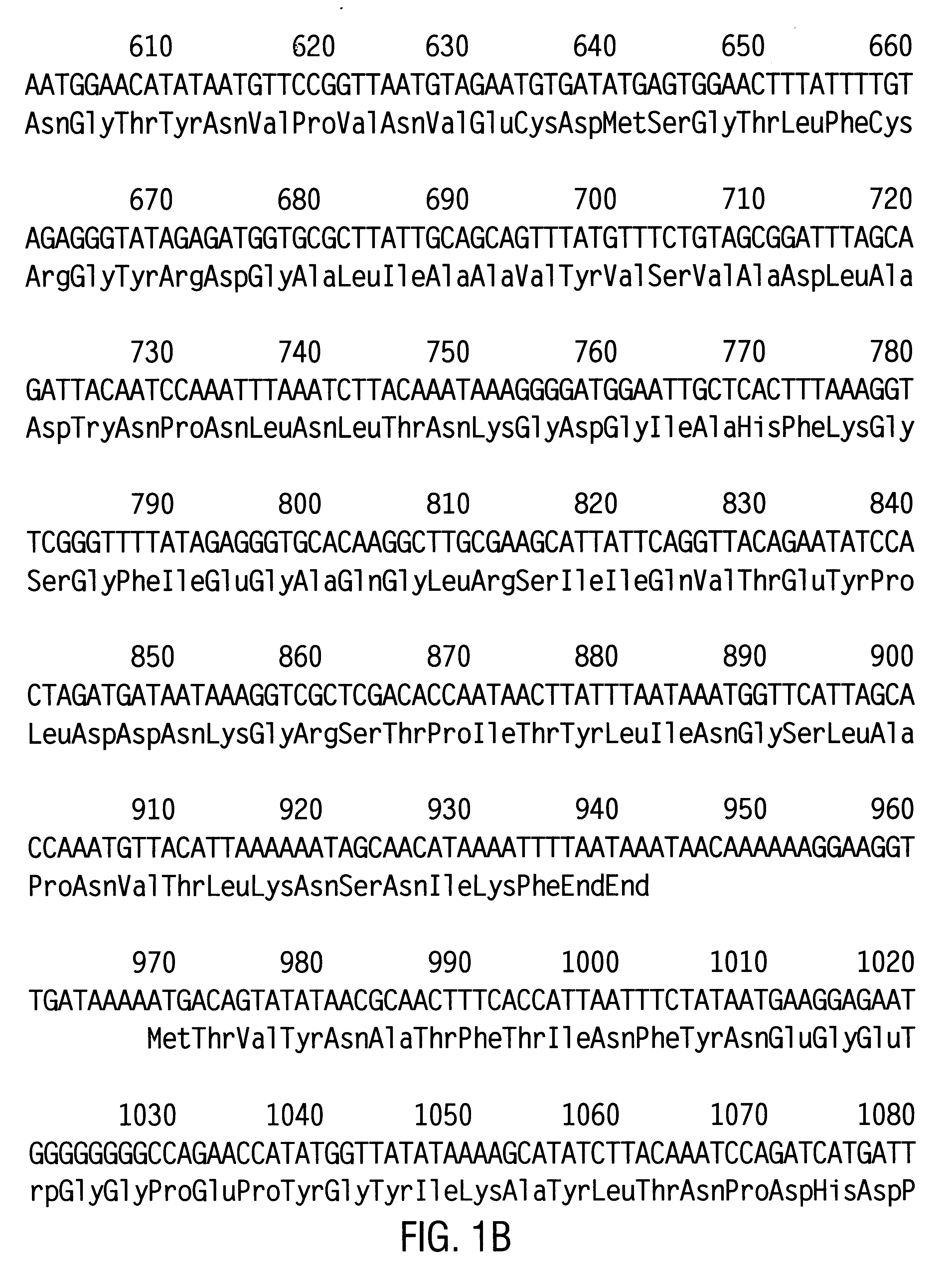
Disclosed is a novel delta -endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against colcopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneur). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Bacillus thuringiensis CryET29 compositions toxic to coleopteran insects and Ctenocephalides SPP
InactiveUS6537756B1Remarkable insecticidal activityGood reproducibilityBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinCtenocephalides felis felis
Disclosed is a novel delta-endotoxin, designated CryET29, that exhibits insecticidal activity against siphonapteran insects, including larvae of the cat flea (Ctenocephalides felis), as well as against coleopteran insects, including the southern corn rootworm (Diabrotica undecimpunctata), western corn rootworm (D. virgifera), Colorado potato beetle (Leptinotarsa decemlineata), Japanese beetle (Popillia japonica), and red flour beetle (Tribolium castaneum). Also disclosed are nucleic acid segments encoding CryET29, recombinant vectors, host cells, and transgenic plants comprising a cryET29 DNA segment. Methods for making and using the disclosed protein and nucleic acid segments are disclosed as well as assays and diagnostic kits for detecting cryET29 and CryET29 sequences in vivo and in vitro.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
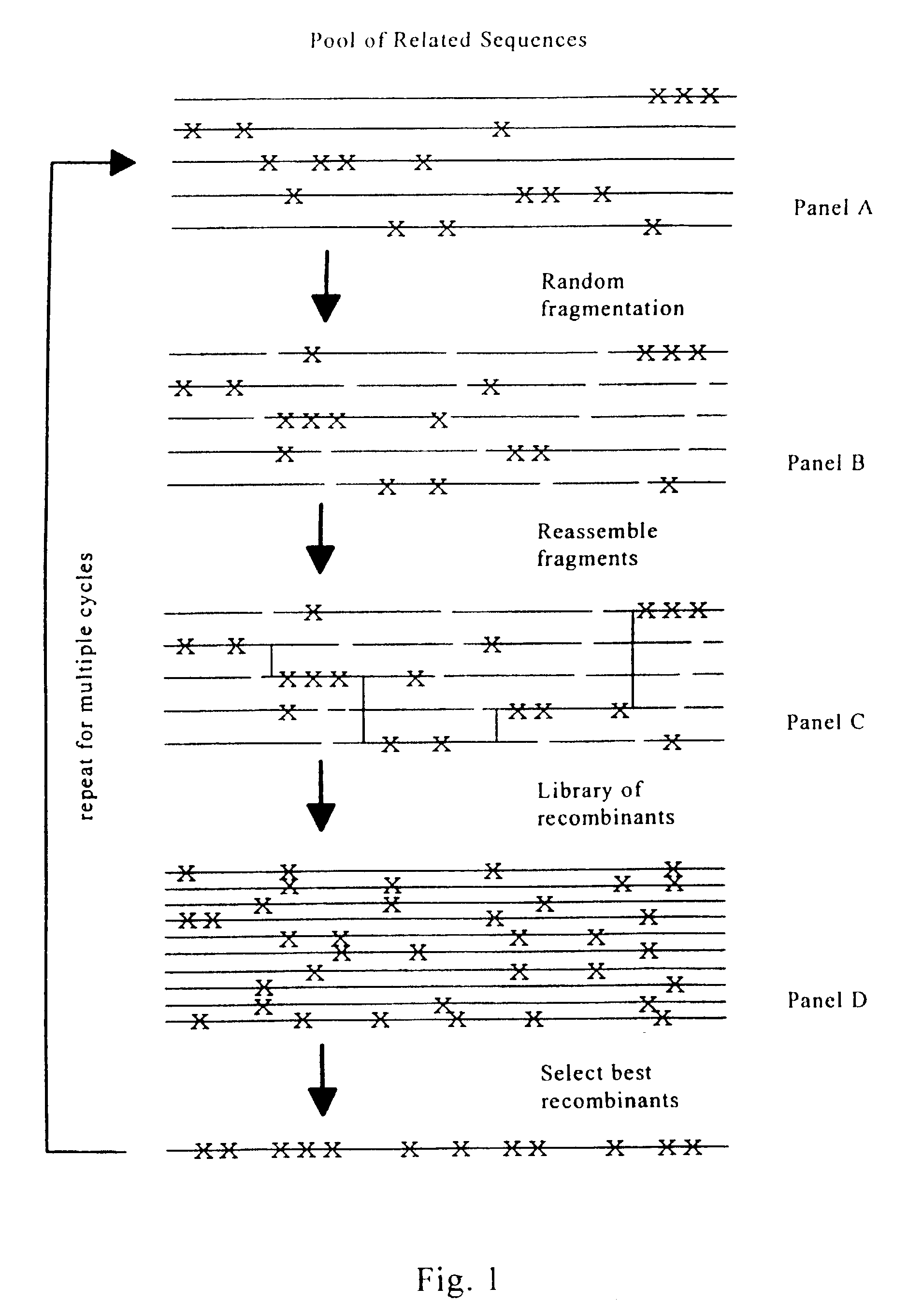
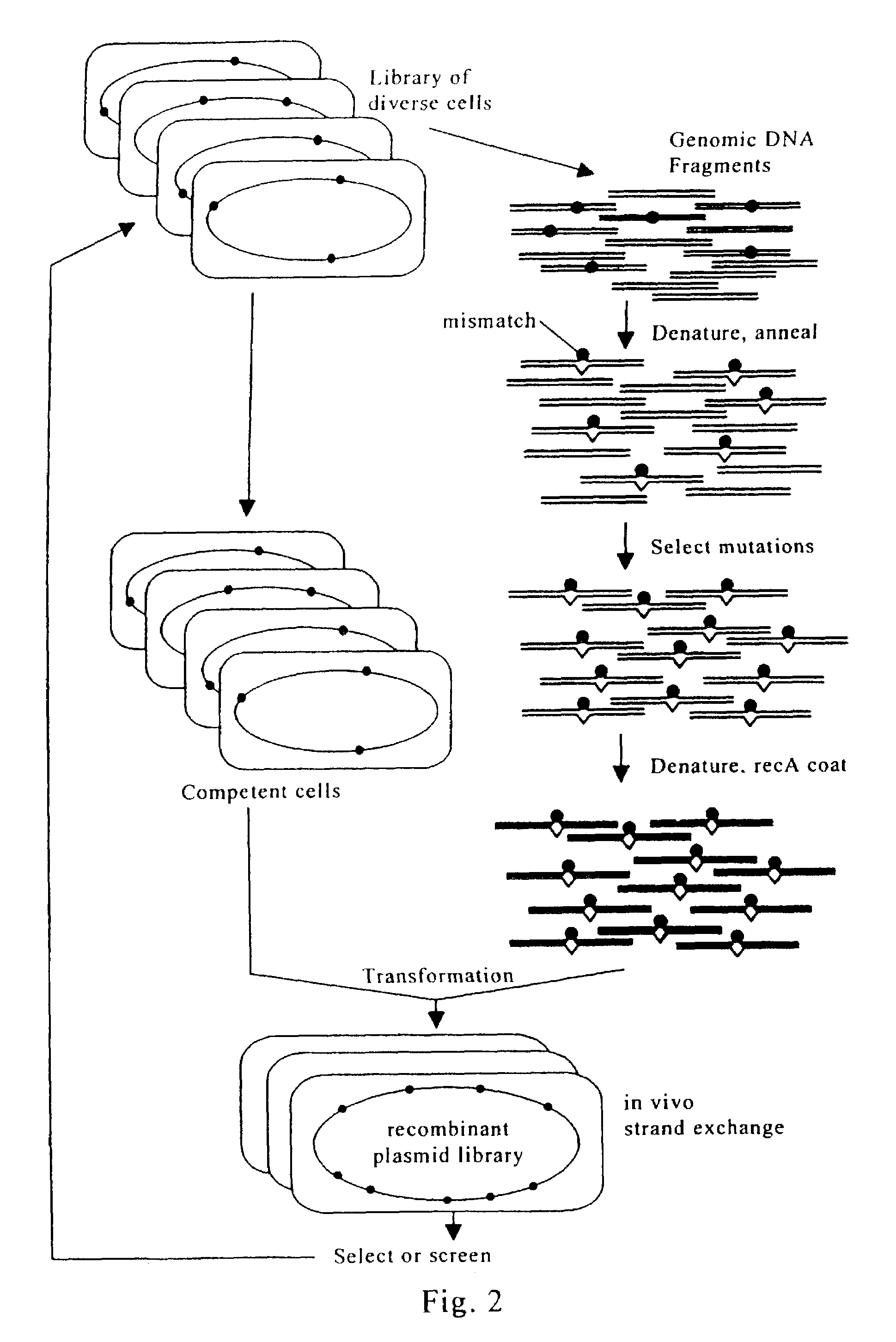
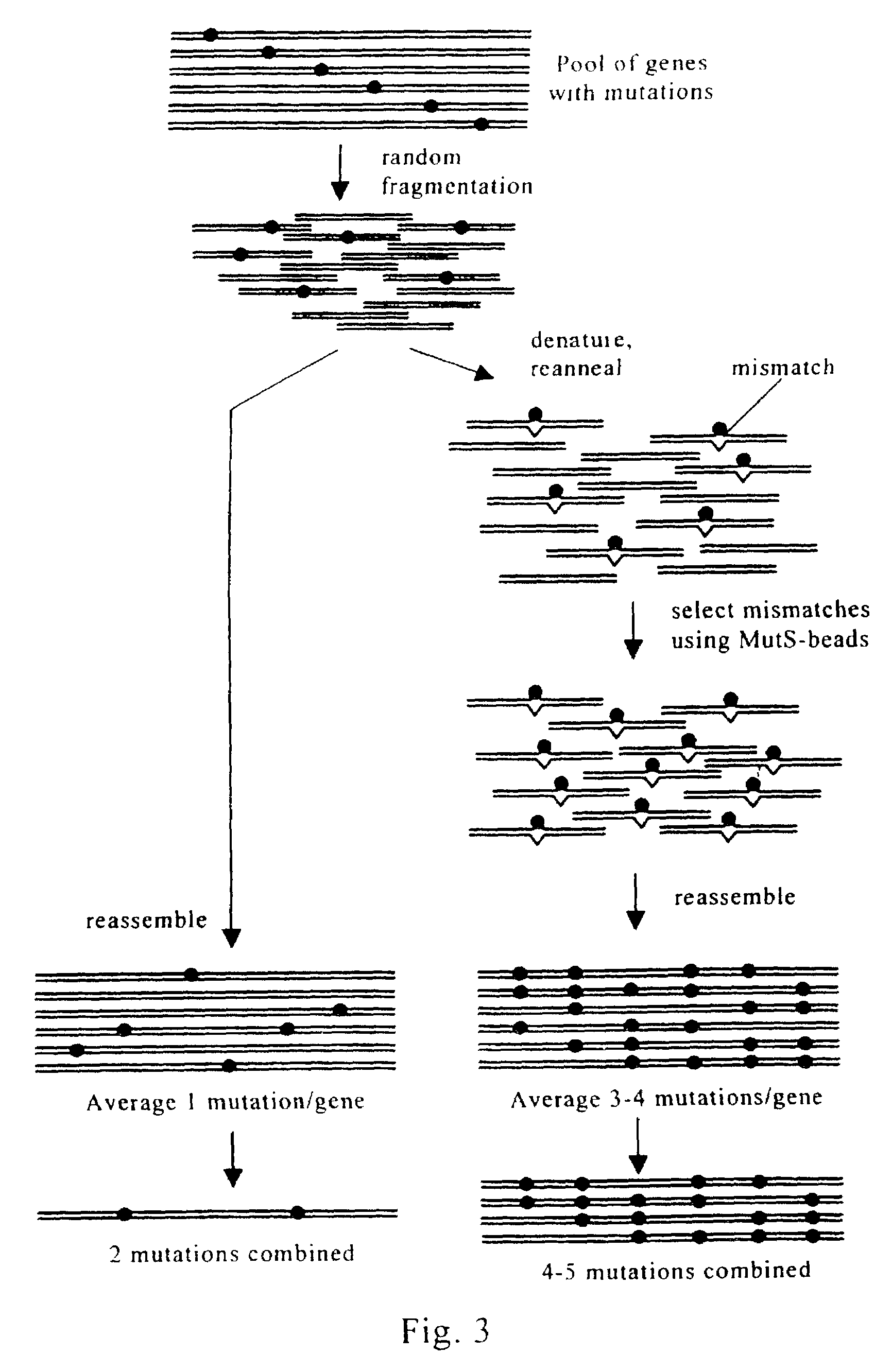
Evolution of whole cells and organisms by recursive sequence recombination
InactiveUS7148054B2Increase diversityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteSecondary metabolite
The invention provides methods employing iterative cycles of recombination and selection / screening for evolution of whole cells and organisms toward acquisition of desired properties Examples of such properties include enhanced recombinogenicity, genome copy number, and capacity for expression and / or secretion of proteins and secondary metabolites.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Coleopteran-toxic polypeptide compositions and insect-resistant transgenic plants
InactiveUS6555655B1Easy to storeInhibit microbial growthBiocideBacteriaDelta endotoxinPolynucleotide
Disclosed are novel insecticidal polypeptides, and compositions comprising these polypeptides, peptide fragments thereof, and antibodies specific therefor. Also disclosed are vectors, transformed host cells, and transgenic plants that contain nucleic acid segments that encode the disclosed delta-endotoxin polypeptides. Also disclosed are methods of identifying related polypeptides and polynucleotides, methods of making and using transgenic cells comprising these polynucleotide sequences, as well as methods for controlling an insect population, such as Colorado potato beetle, southern corn rootworm and western corn rootworm, and for conferring to a plant resistance to a target insect species.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
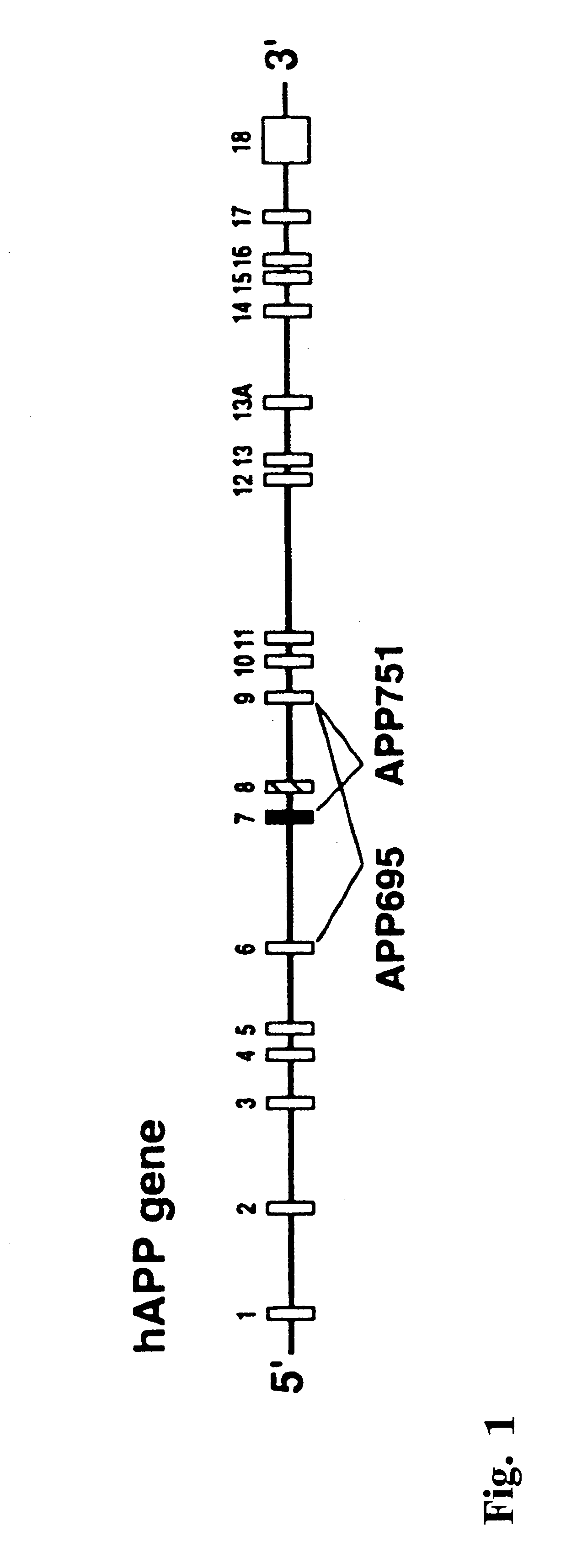
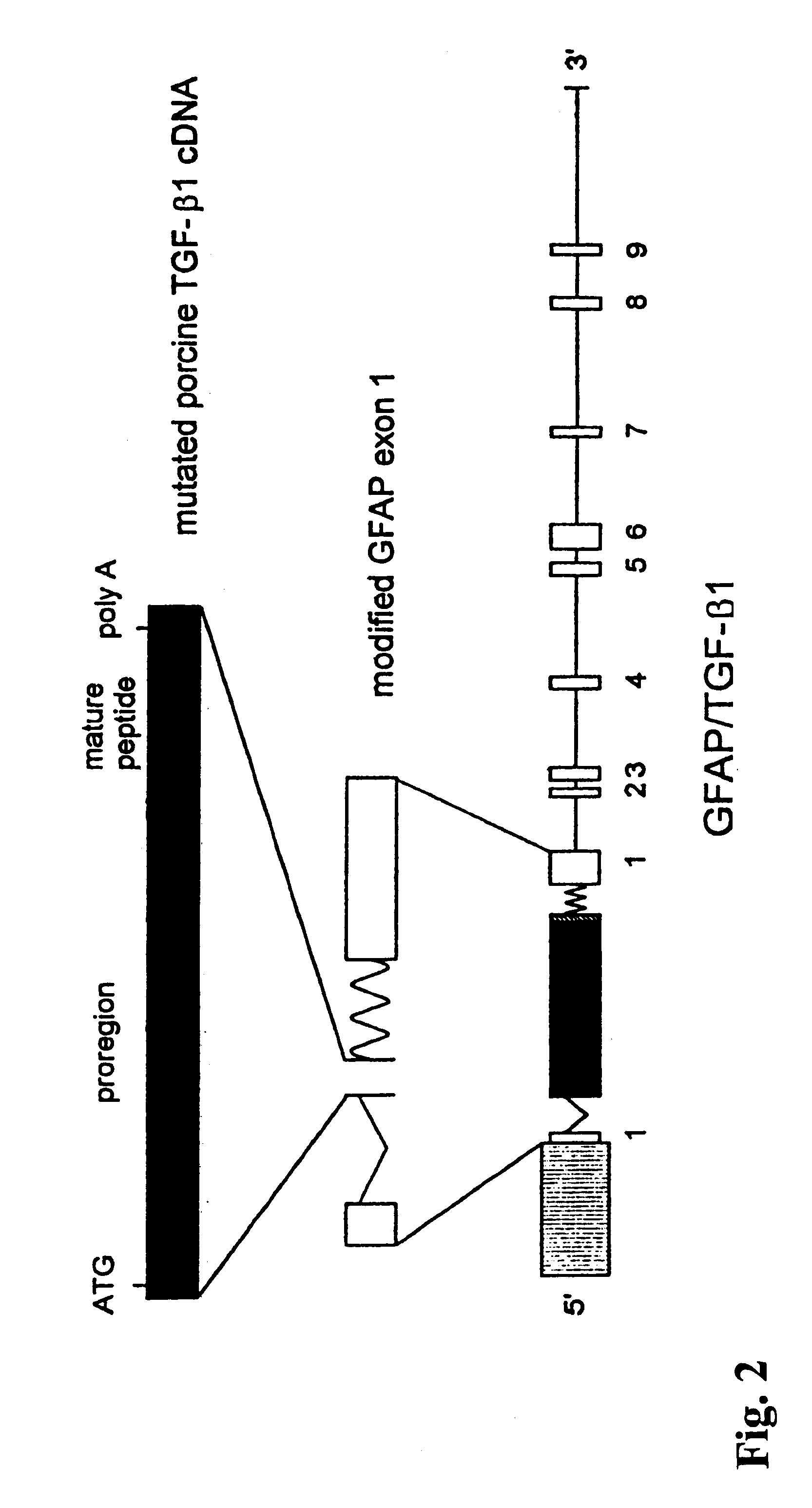
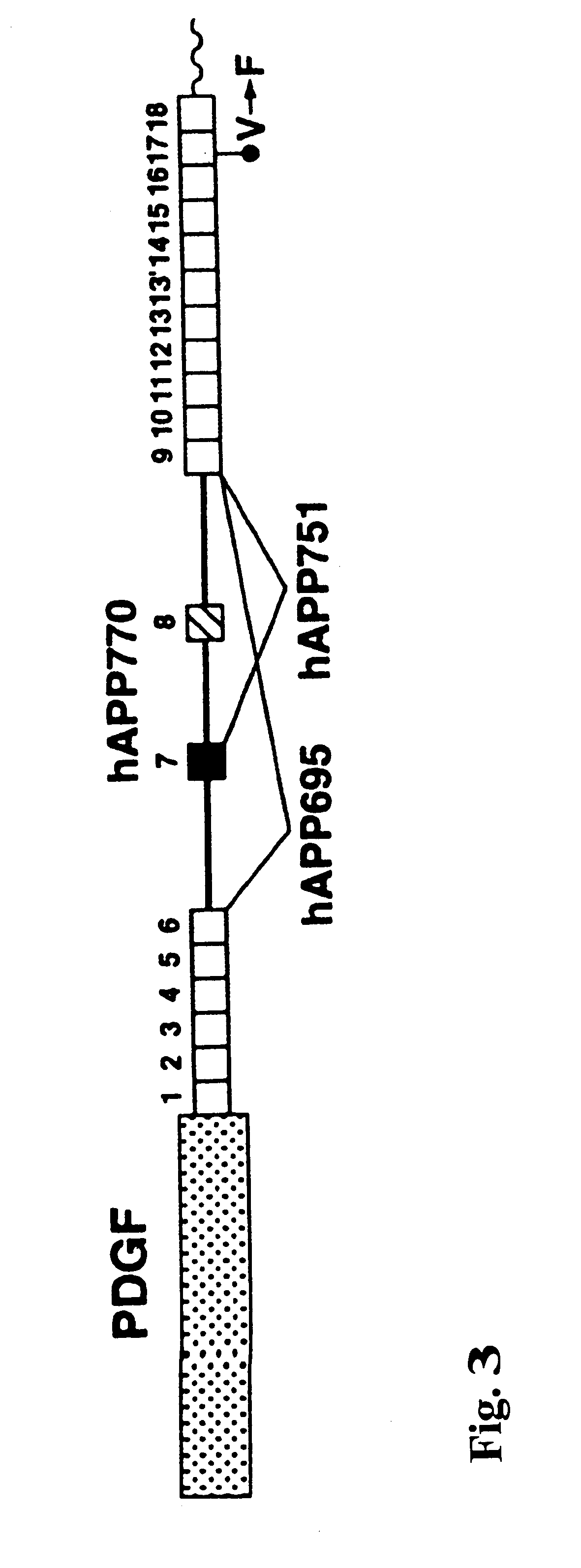
Transgenic mouse model of alzheimer's disease and cerebral amyloid angiopathy
InactiveUS6175057B1Lower Level RequirementsConvenient treatmentVectorsIn-vivo testing preparationsOrganismTgf beta1
The present invention features non-human transgenic animal models for Alzheimer's disease (AD) and CAA, wherein the transgenic animal is characterized by 1) overexpression of bioactive transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-beta1) or 2) both overexpression of bioactive TGF-beta1 and expression of a human amyloid beta precursor protein (APP) gene product. The transgenic animals may be either homozygous or heterozygous for these alterations. Bigenic animals are further characterized by development of AD-associated and / or CAA-associated pathology within about two to three months of age.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Expression vector for animal cell
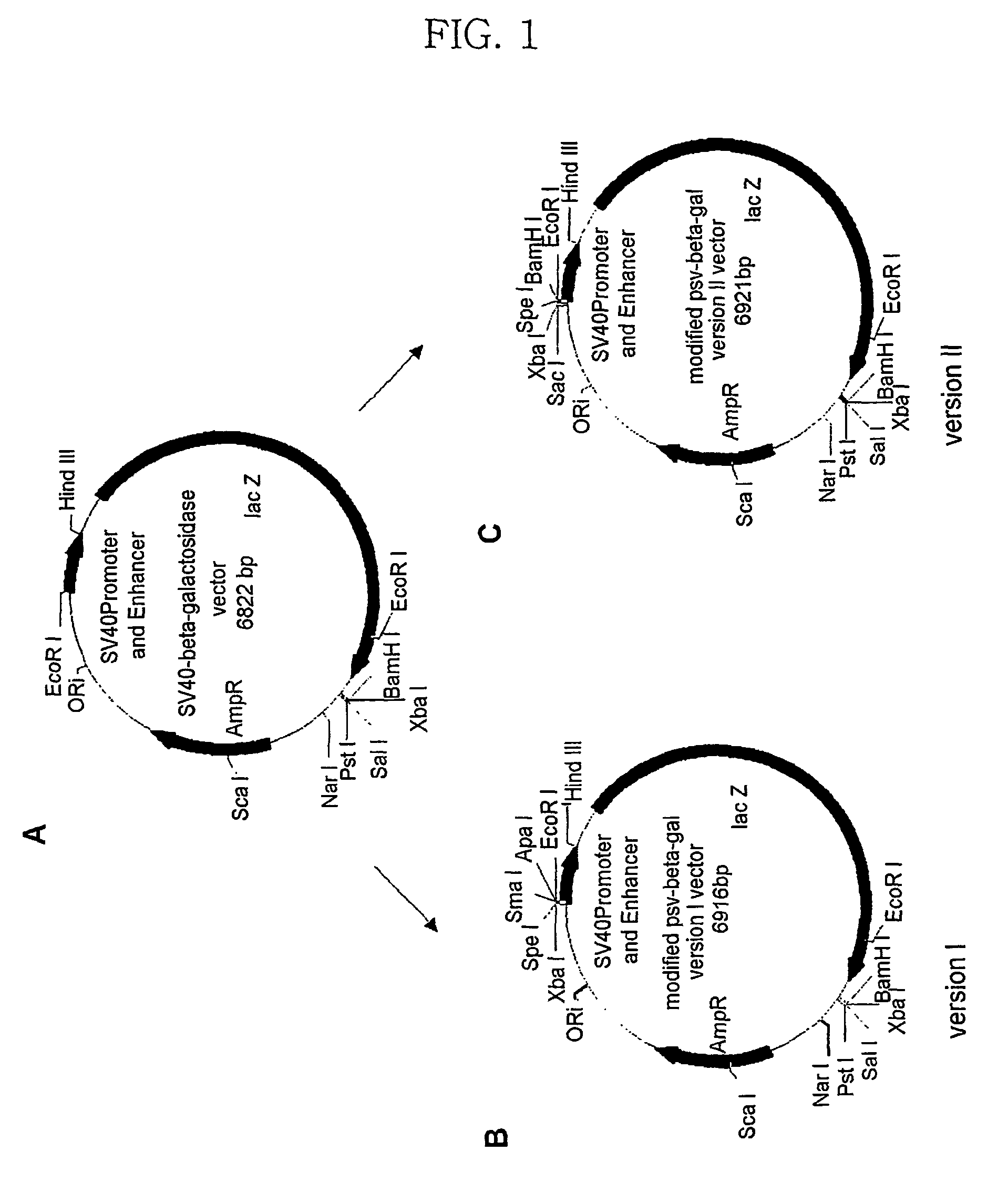
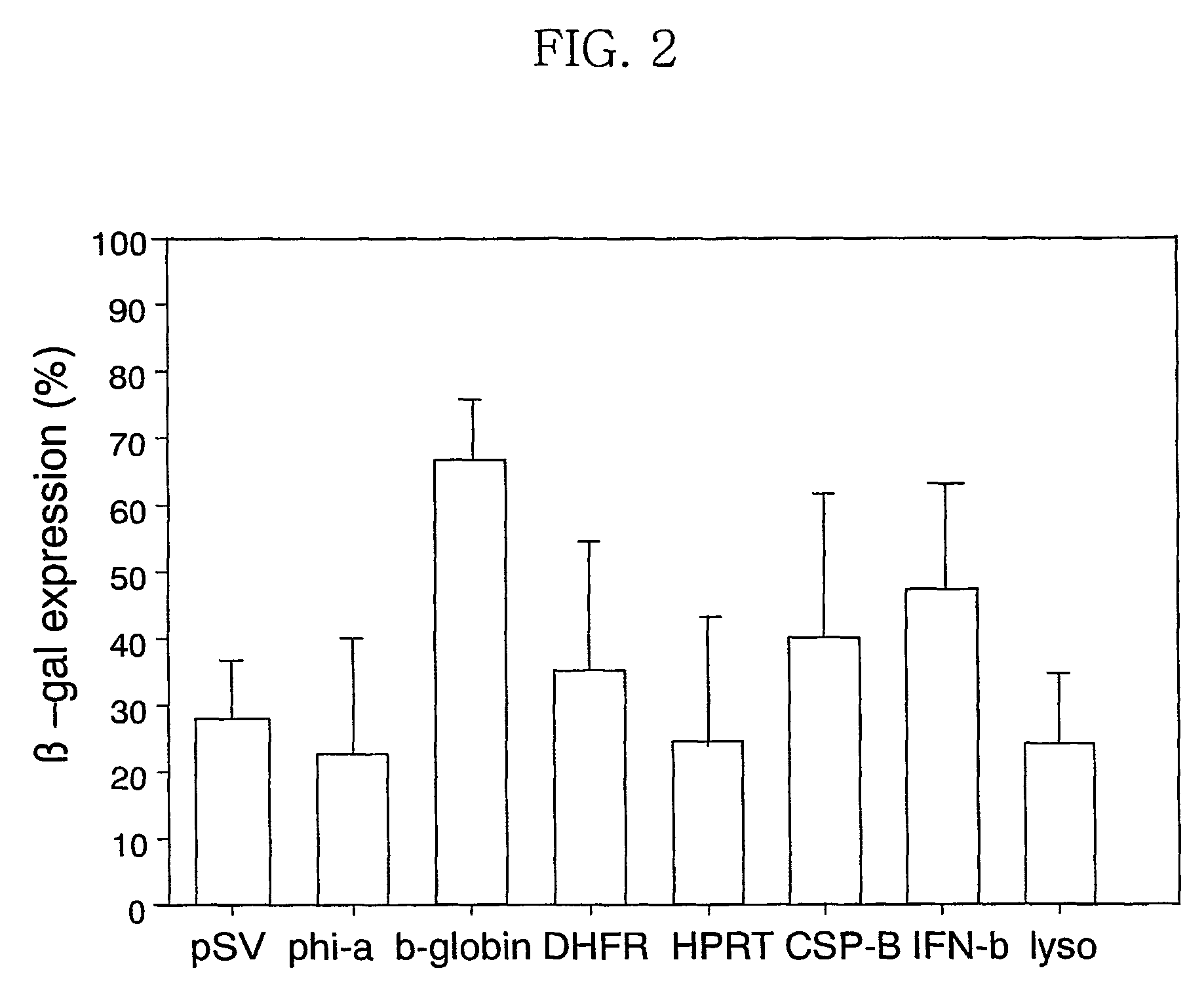
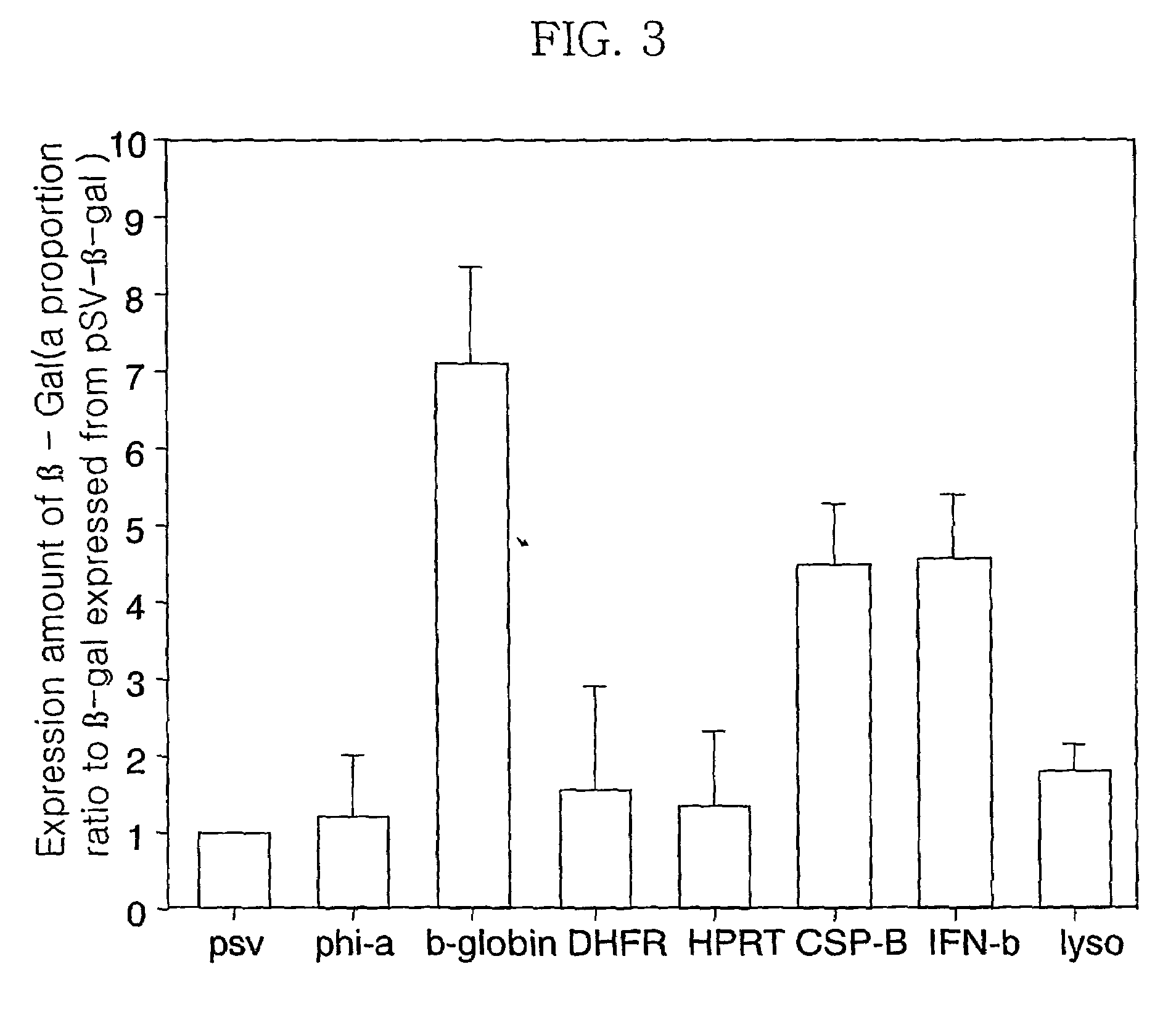
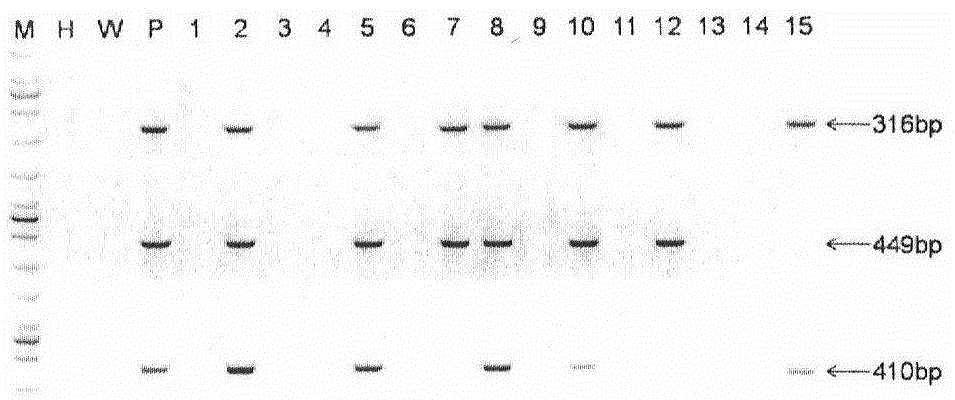
InactiveUS7422874B2Increased expression efficiency and levelVectorsSugar derivativesGastrin GeneEvolutionary biology
The present invention relates to an expression vector for animal cells. Specifically, the present invention relates to an expression vector, pMS vector, pSG vector and pMSG vector, including the human β-globin 5′ MAR complementary sequence or / and the transcription termination site of the gastrin gene. An expression system using an expression vector of the present invention can successfully produce recombinant proteins in various animals cells and recombinant protein having a unique structure and function.
Owner:MOGAM BIOTECH RES INST +1
Method for establishing humanized rat drug evaluation animal model
InactiveCN104593418AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryLarge fragmentEngineered genetic
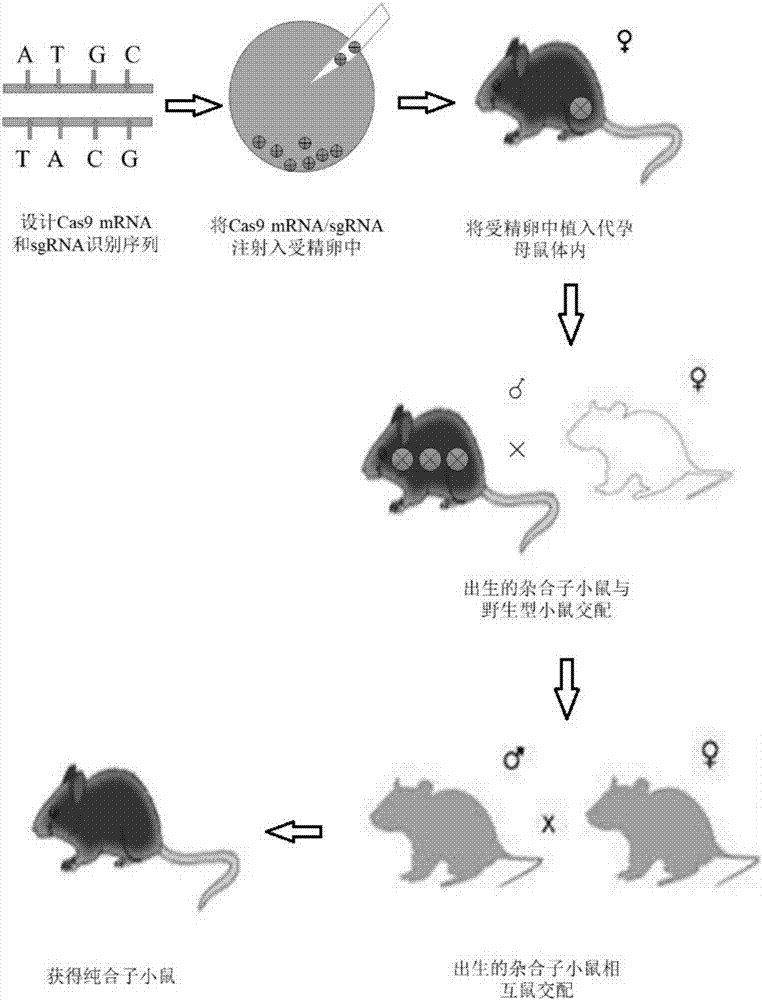
The invention provides a method for establishing a humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. According to the method, a multidrug resistance gene 1 (Abcb1)-knocked-out genetically engineered rat is obtained through a microinjection method by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology and 153kb bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) fragments containing a humanized Abcb1 promoter and cDNA is simultaneously inoculated into the rat genome through the microinjection method by virtue of a large fragment transgenic technology to obtain a transgenic rat capable of stably expressing human Abcb1 and the genetically engineered rat and the transgenic rat are hybridized to establish the humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. RT-PCR analysis shows that Abcb1 expression profiles of humanized Abcb1 rat are significantly different from those of the rat endogenous Abcb1. The method has the beneficial effects that the humanized rat capable of expressing human Abcb1 is obtained and the rat is used for expressing human Abcb1 genes and has closer expression profiles to those of human so that the model can be well used for the efficacy evaluation of newly developed drugs.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
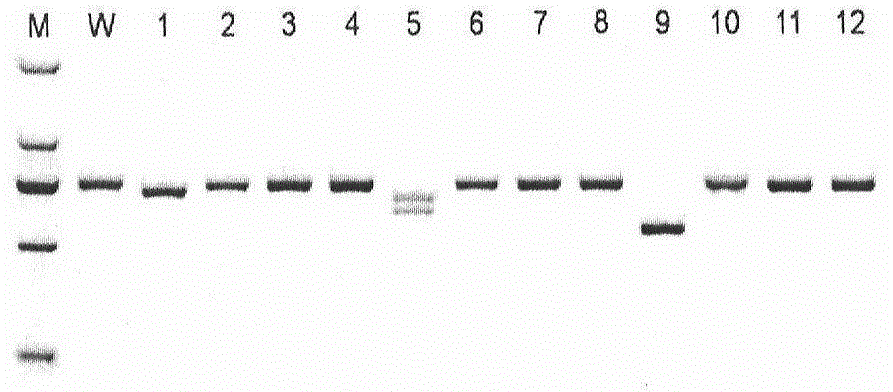
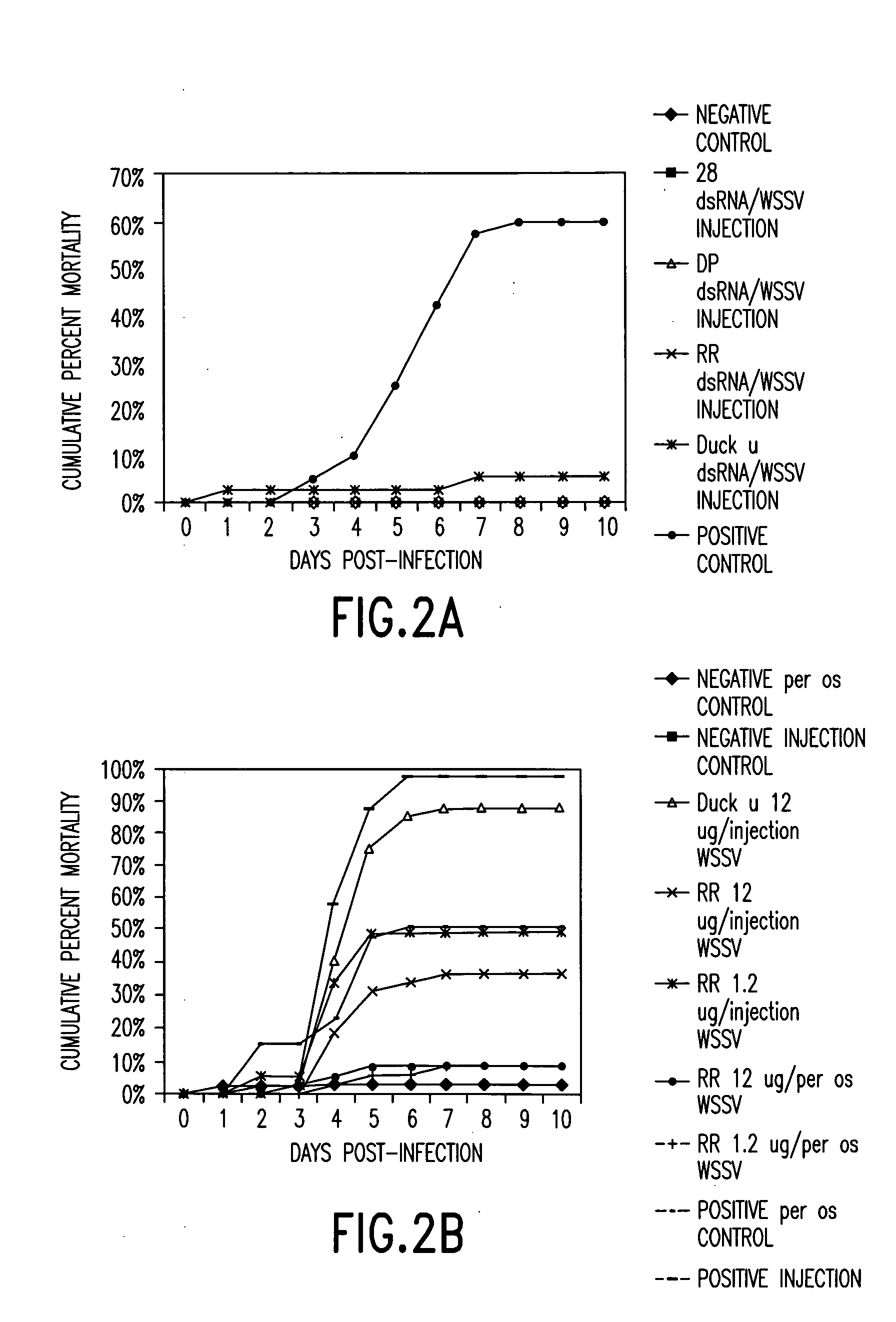
dsRNA induced specific and non-specific immunity in crustaceans and other invertebrates and biodelivery vehicles for use therein
InactiveUS20050080032A1Easy to understandGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsWhole bodyMarine invertebrates
Methods for inducing systemic, non-specific and / or sequence specific immune responses in invertebrates, e.g., marine invertebrates such as mollusks, porifera, ctenophora, echinodermas, marine worms, cnideria and preferably crustaceans, by the administration of at least one dsRNA, that confers immunity against a pathogen, or modulates expression of gene that affects growth, reproduction, and general health or "robustness" are provided. Also provided are methods of identifying invertebrate genes, e.g., crustacean genes, the expression of which is involved in the induction of non-specific (systemic) immune responses against pathogens. Also disclosed are preferred delivery systems and methods for stably administering at least one dsRNA to a crustacean whereby the dsRNA is administered via injection, immersion, in a feed or nutrient medium or comprised in a microorganism, e.g., yeast or microalgae, that expresses said dsRNA and is ingestible by said crustacean, e.g., a shrimp.
Owner:MUSC FOUND FOR RES DEV
Method for establishing obese rat animal model based on CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) gene knockout technology
InactiveCN103614415AImprove the level ofDeepen understanding of gene regulationVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryDiseaseLepr gene
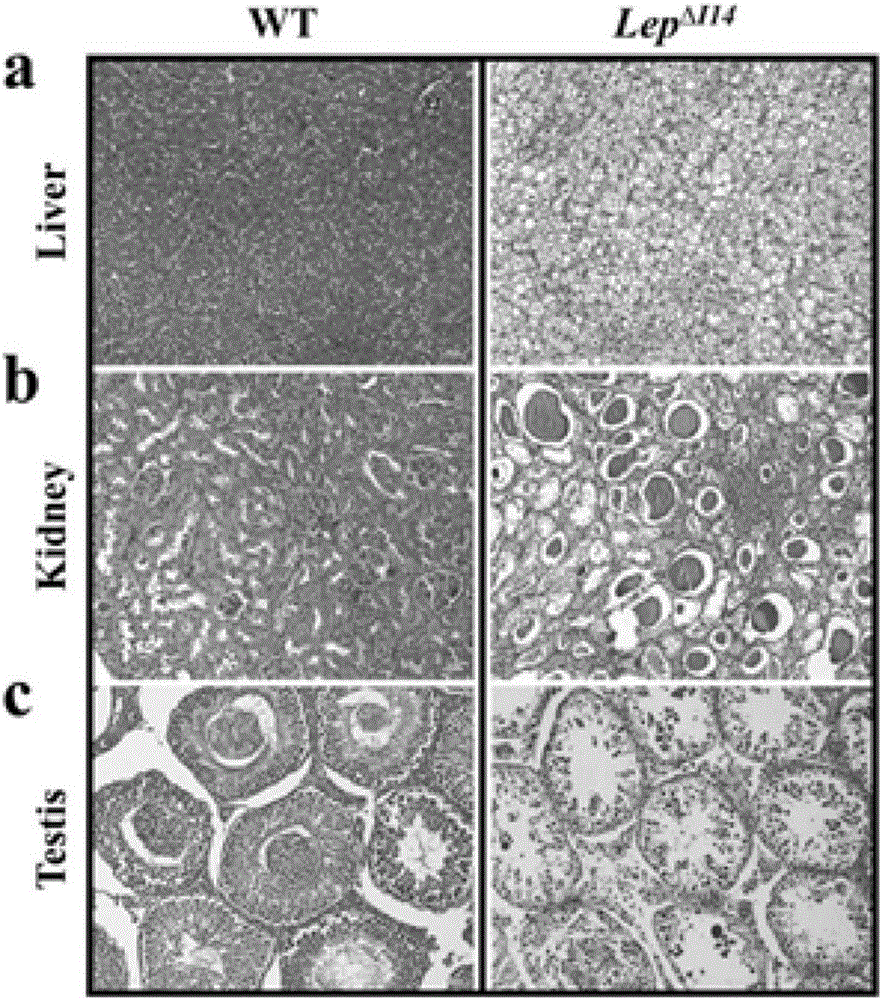
The invention provides a method for establishing an obese rat animal model based on a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) gene knockout technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing an Lep / Lepr gene knockout rat model; (2) carrying out the authentication and related analysis on the obese rat animal model; (3) evaluating the energy metabolism and the body fat rate of the obese rat animal model. According to the method, a CRISPR / Cas system is used for respectively or simultaneously knocking out Lep and LepR genes so as to obtain the rat model modified by a corresponding target gene, so that the understanding of gene regulation in the obesity morbidity process can be deepened, and the high-level animal model can be provided for the translational medicine and the new medicine research and development.
Owner:SUZHOU TONGSHAN BIO TECH
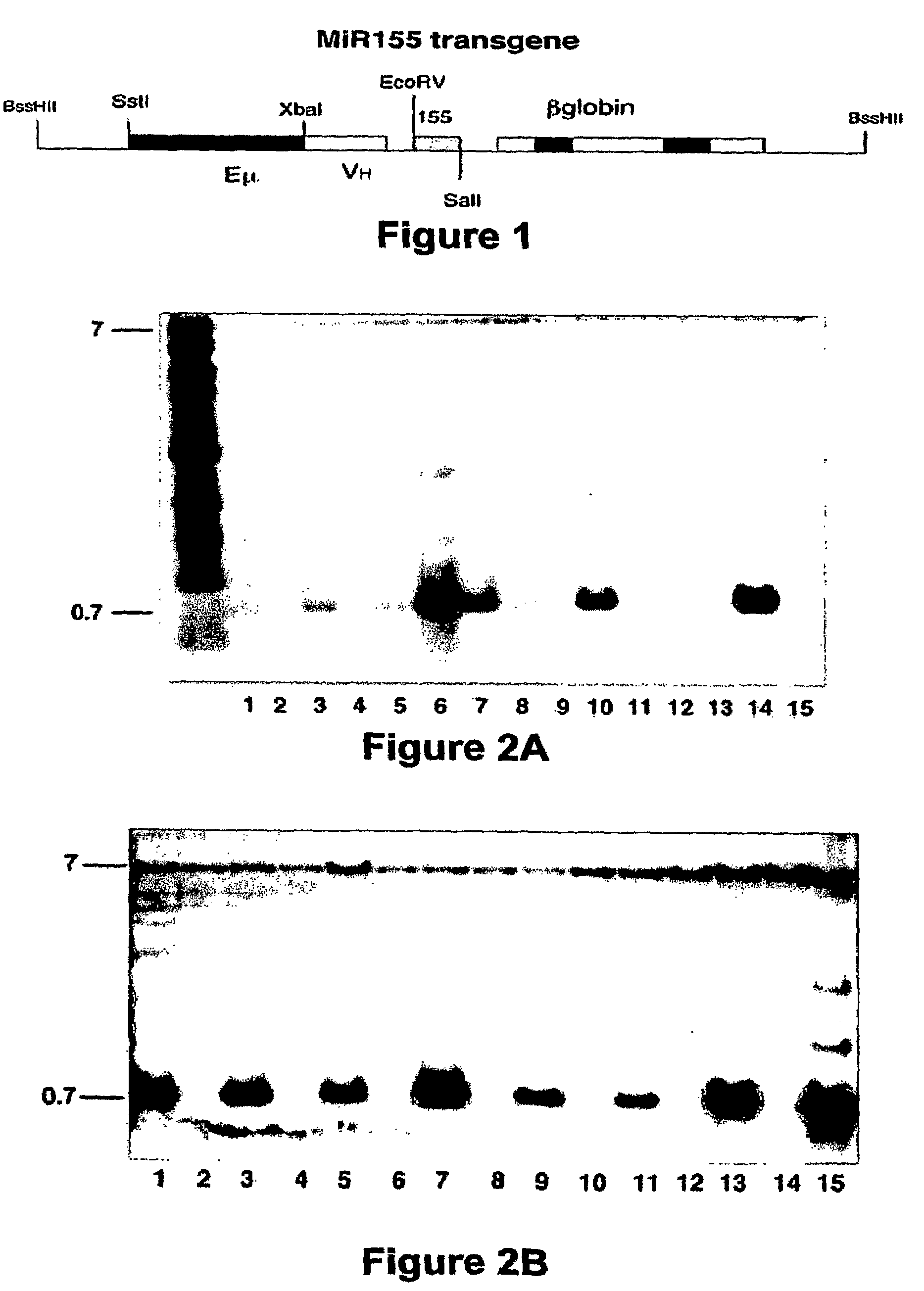
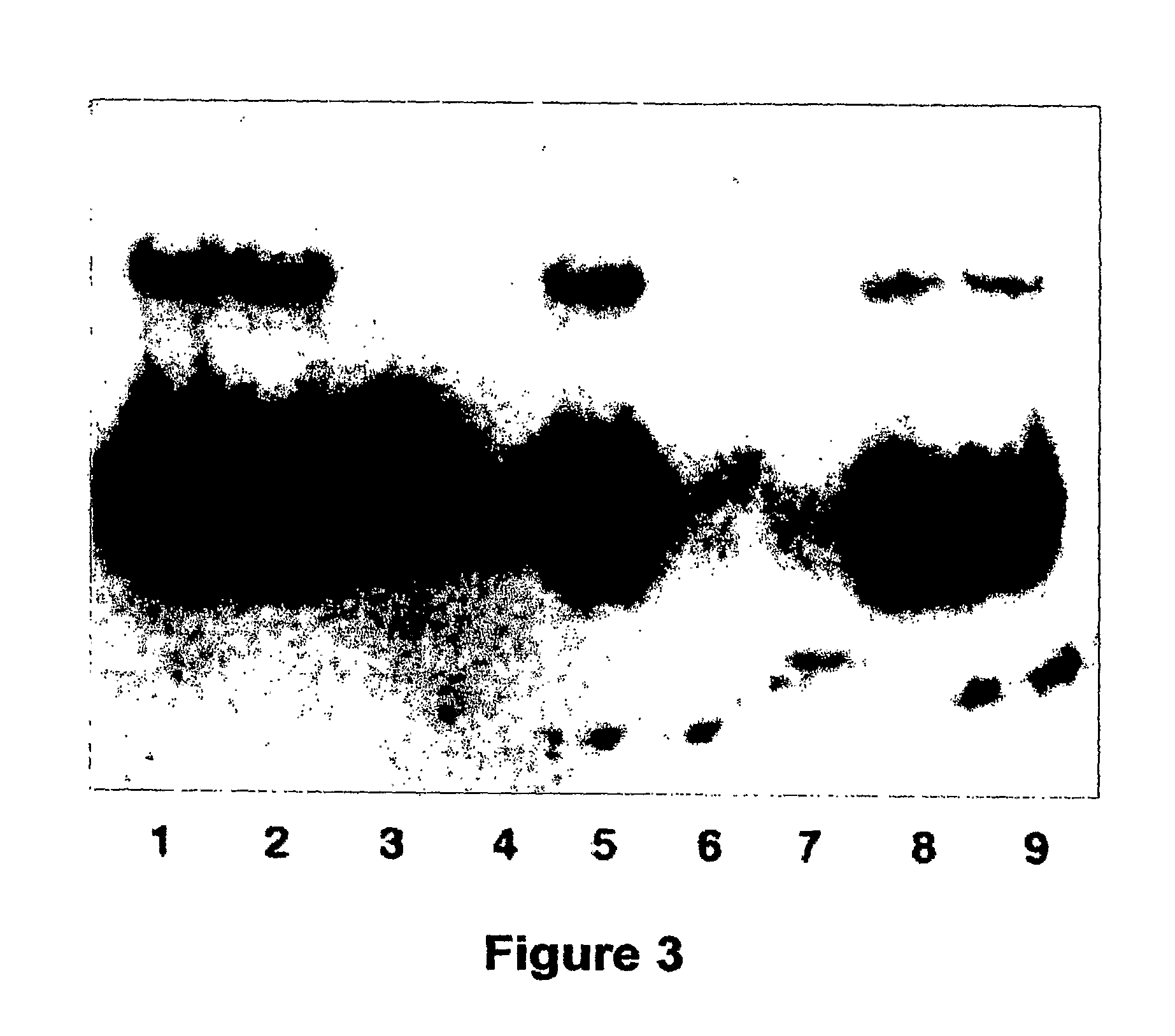
Transgenic mouse model of B cell malignancy
A transgenic non-human animal, such as a mouse, has a genome that include a nucleic acid construct having at least one transcriptional regulatory sequence capable of directing expression in B cells of the animal, wherein the transcriptional regulatory sequence is operably linked to a nucleic acid encoding a miR155 gene product. A method of testing the therapeutic efficacy of an agent in treating or preventing a lymphoproliferative condition includes assessing the effect(s) of the agent on a transgenic non-human animal.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Construction method and application of Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model
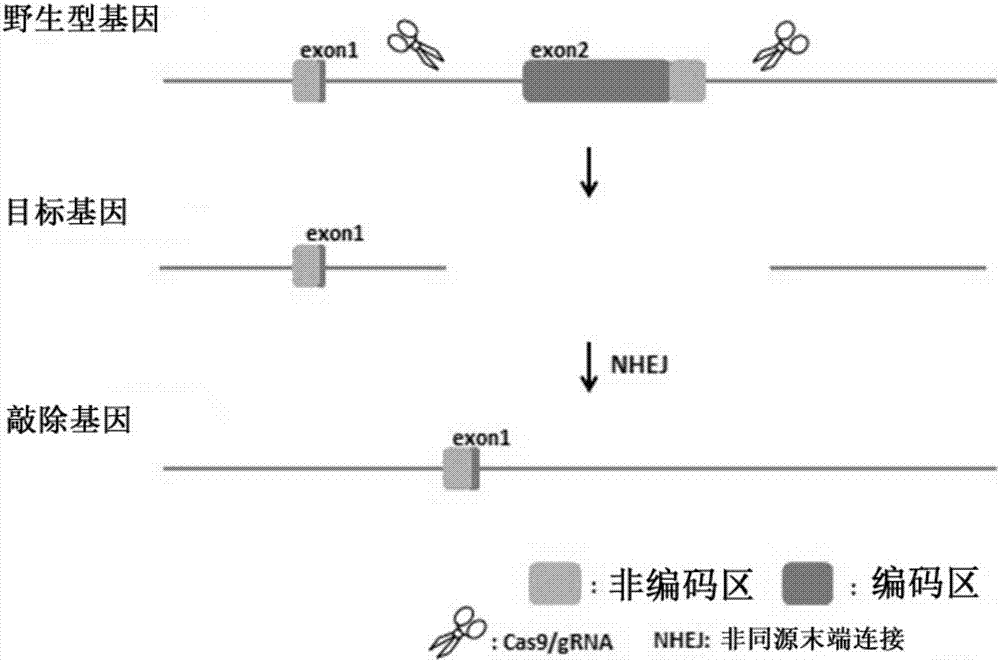
The invention relates to a method of constructing an Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model and belongs to the biotechnical field. The method comprises the following steps: S1, determining specific target sites sgRNA1 and sgRNA2 of a to-be-knocked out gene of an Ifit3-eKO1 mouse, and performing in vitro transcription with Cas9 nuclease to mRNA; and S2, micro-injecting active sgRNA and Cas9RNA into an oosperm of the mouse to obtain the Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse. The method has the advantages that by using the CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology, the Ifit3-eKO1 gene knockout mouse animal model is constructed for the first time, thereby providing a convenient, reliable and economical animal model for researching action of Ifit3 in tumorigenesis and development.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGJI HOSPITAL
Method for establishing fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model on basis of CRISPR gene knockout technology
InactiveCN103642836APredictive effectReduce the risk of research and developmentVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryDiseaseFragile X chromosome
The invention discloses a method for establishing a fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model on the basis of a CRISPR gene knockout technology. The method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a FMR1 gene knockout machin model; (2) carrying out identification and related functional analysis on the machin model; (3) carrying out tests on the nerve characteristics and learning and memorizing ability of the machin model. The method utilizes a CRISPR gene knockout technology to establish a fragile X-syndrome non-human primate model. The model fills the blank of non-human primate model, can effectively stimulate the pathological process of human diseases, can be used as an optimum animal model for researching human diseases, can effectively predict the effect of novel vaccine, novel drug or novel diagnostic reagent in clinical applications, and thus greatly reduces the risk of novel drug development.
Owner:SUZHOU TONGSHAN BIO TECH
Methods and compositions for the generation of humanized mice
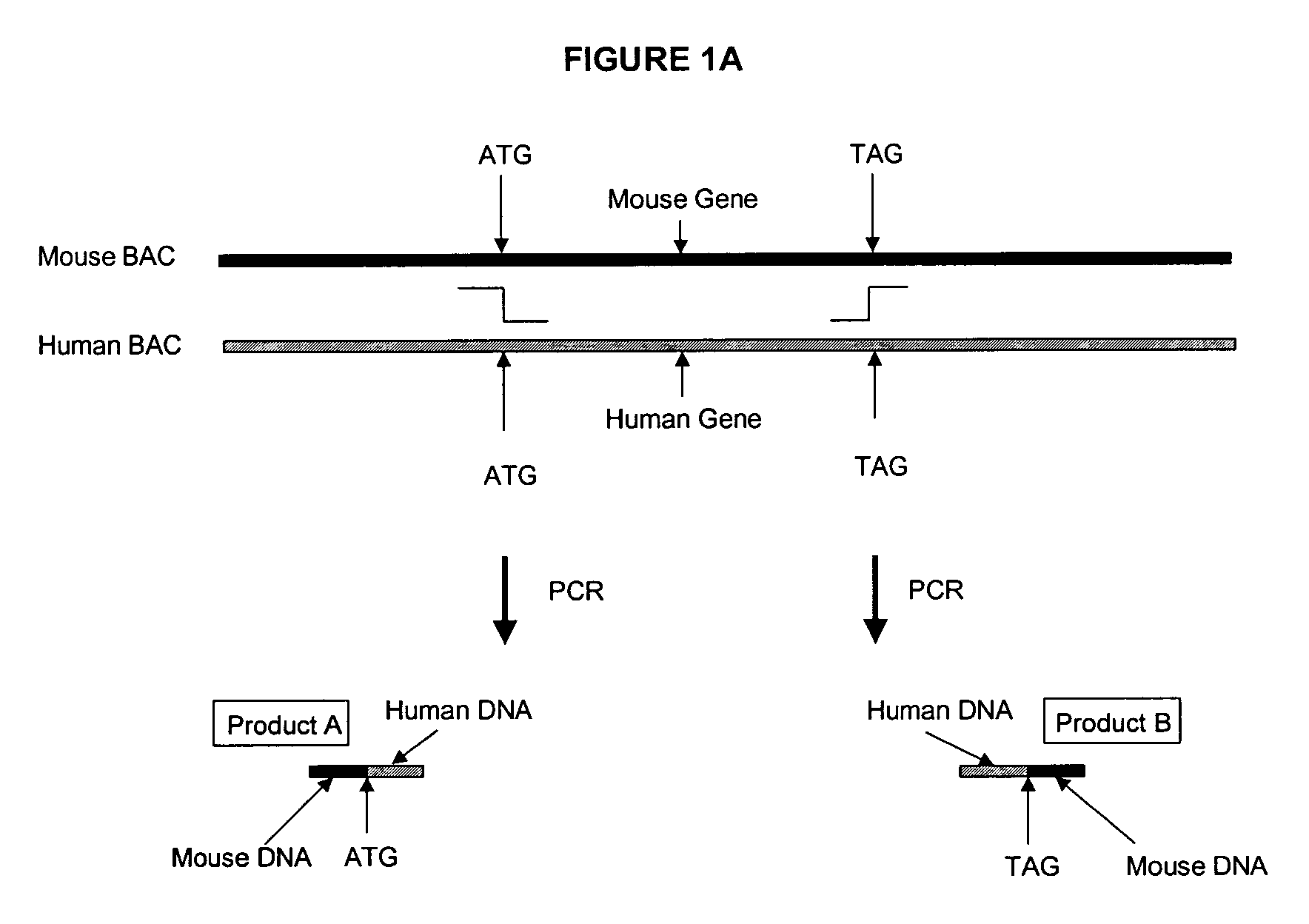
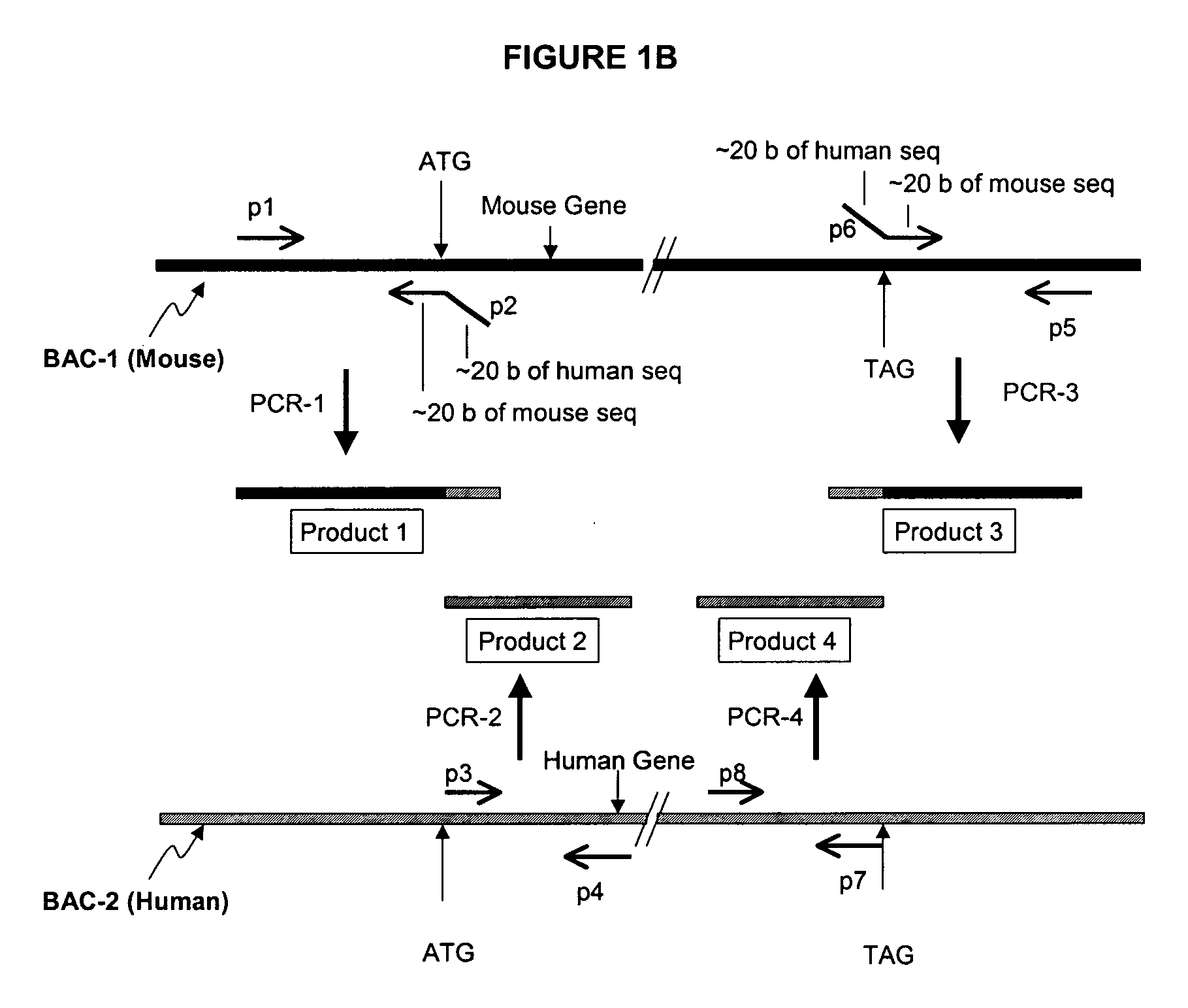
The invention provides methods and compositions for generating non-human transgenic animals that are humanized at one or more gene sequences. According to the methods of the invention, a DNA construct containing a human DNA sequence flanked by sequences from the non-human animal is generated by recombination in a bacterial cell, for example, in E. coli. The DNA construct that is produced can then be introduced into a non-human embryogenic stem cell where it can recombine with the genomic DNA of the non-human animal.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method for deleting selection marker gene of transgenic rice
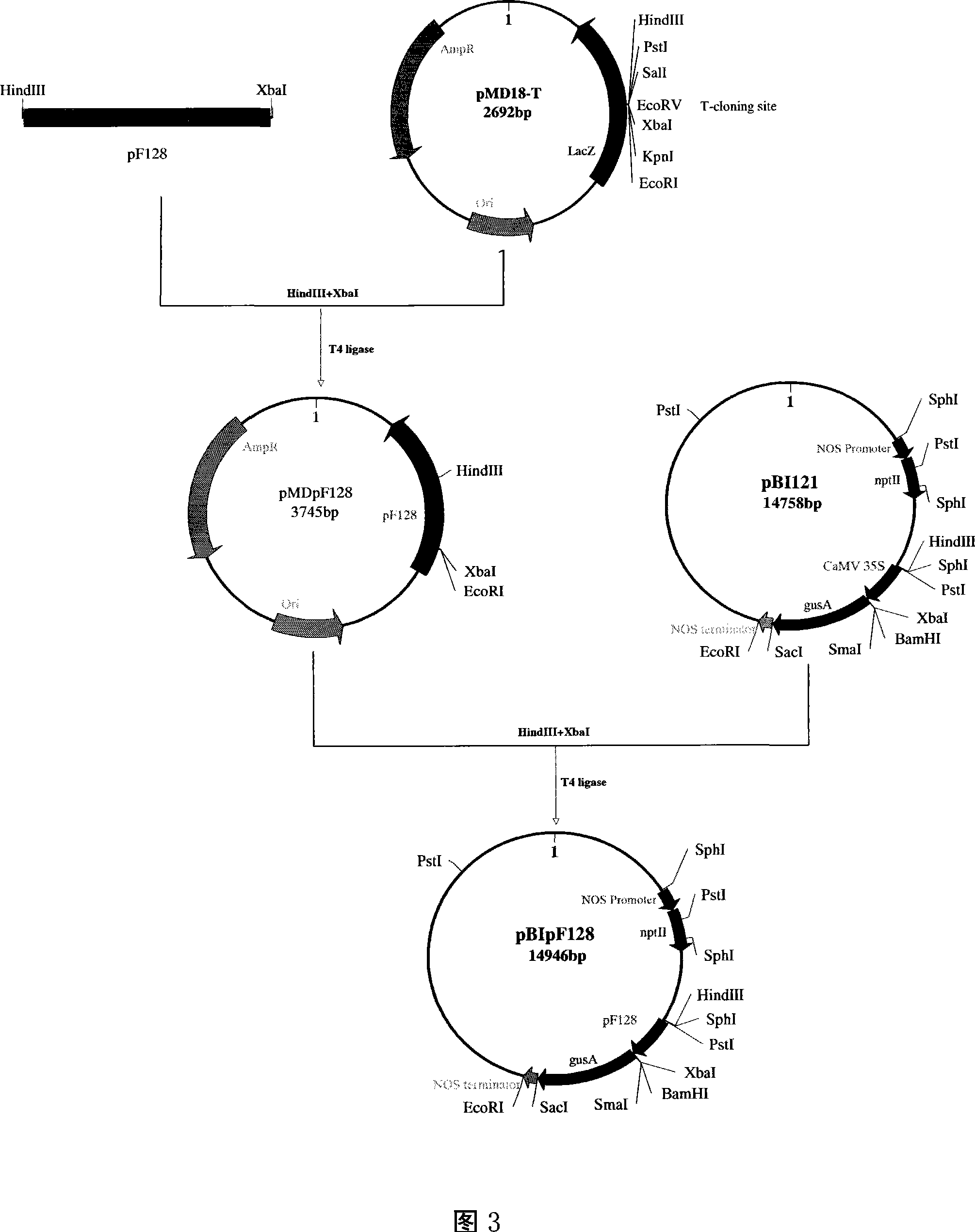
ActiveCN104846010AHigh distribution frequencyEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsGenetically modified ricePlant genetic engineering
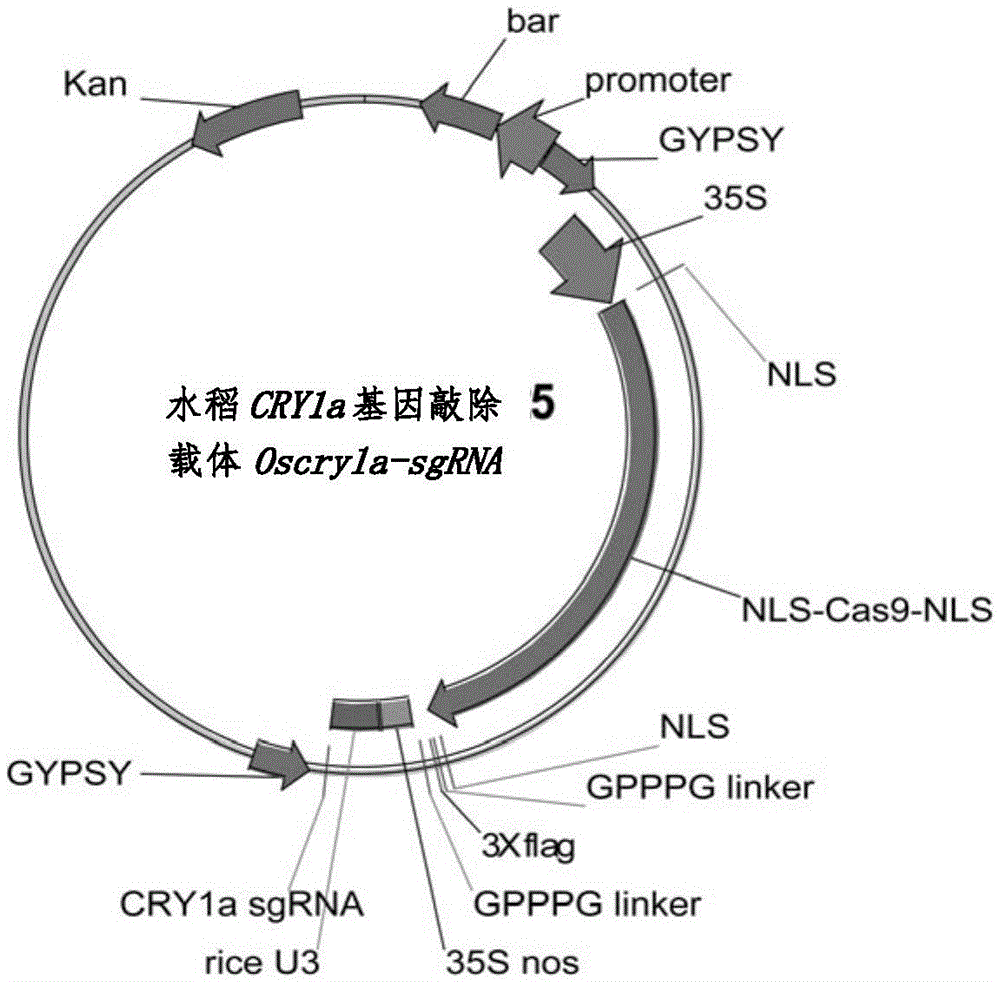
The invention provides a method for deleting a selection marker gene of transgenic rice and belongs to the field of plant gene engineering. The method for efficiently deleting the marker gene of the transgenic rice in a plant level is established by utilizing a genome fixed-point editing technology mediated by a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The whole segment of the marker gene can be effectively deleted by utilizing the method, and only an expression frame of the marker gene is deleted pointedly without change of the expression of other components in the transgenic rice. Thus, the transgenic rice without the selection marker gene can be efficiently bred by utilizing the method, so that the safety doubt of people about the selection marker gene can be completely removed.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Compositions and methods for 3-hydroxypropionate bio-production from biomass
ActiveUS8048624B1BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurement3-Hydroxypropionic acidDecarboxylase activity
Methods of obtaining mutant nucleic acid sequences that demonstrate elevated oxaloacetate α-decarboxylase activity are provided. Compositions, such as genetically modified microorganisms that comprise such mutant nucleic acid sequences, are described, as are methods to obtain the same.
Owner:OPX BIOTECH
Nucleotide sequences for regulating gene expression in plant trichomes and constructs and methods utilizing same
InactiveUS20060260002A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesNucleotide sequencingPolynucleotide
Novel plant derived regulatory sequences and constructs and methods of using such sequences for directing expression of exogenous polynucleotide sequences in trichomes are provided
Owner:EVOGENE LTD
Method for feeding dsRNA restraint insect gene expression
InactiveCN101343637ALow costSimple methodBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme GeneBacteria coliforms
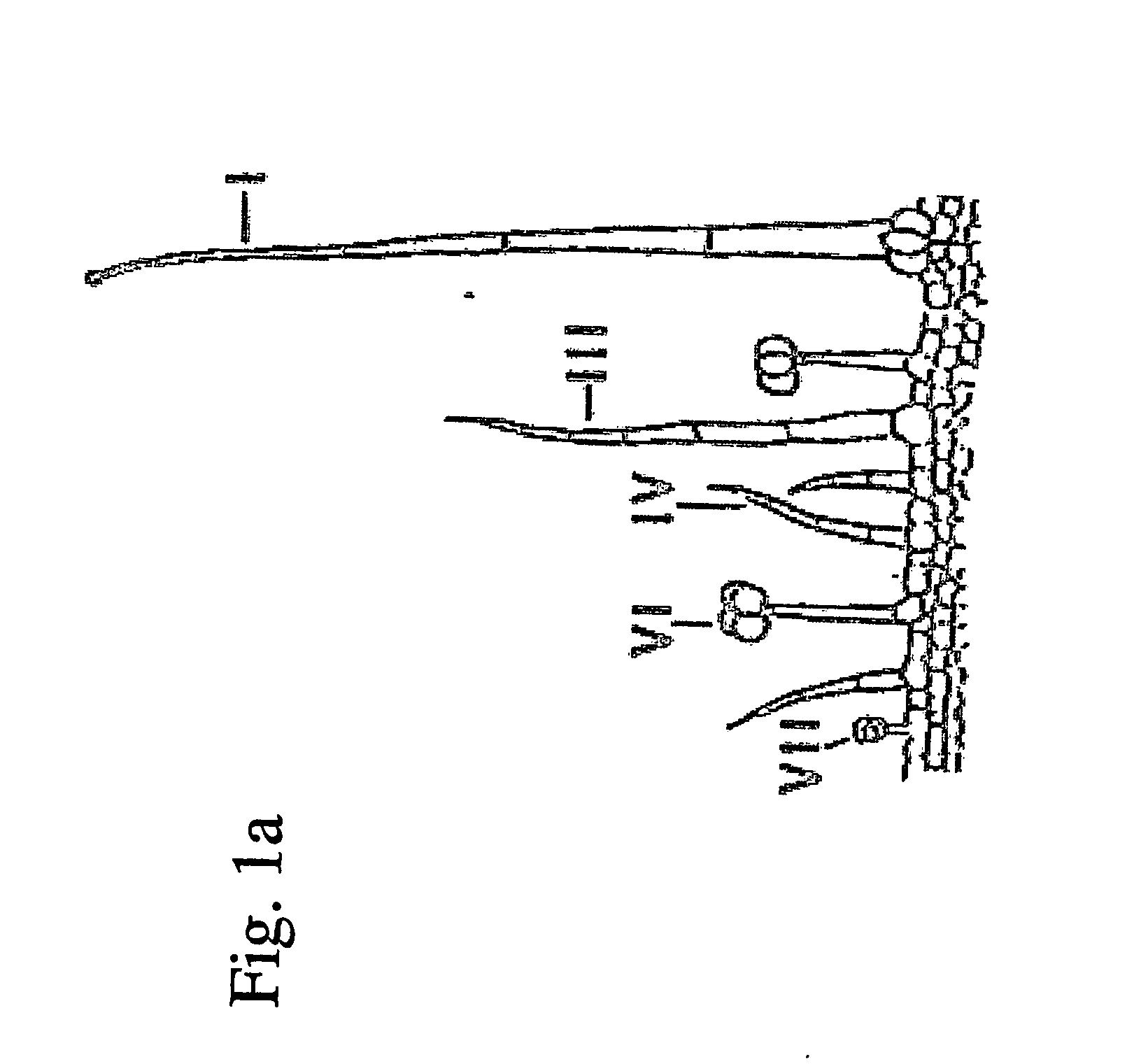
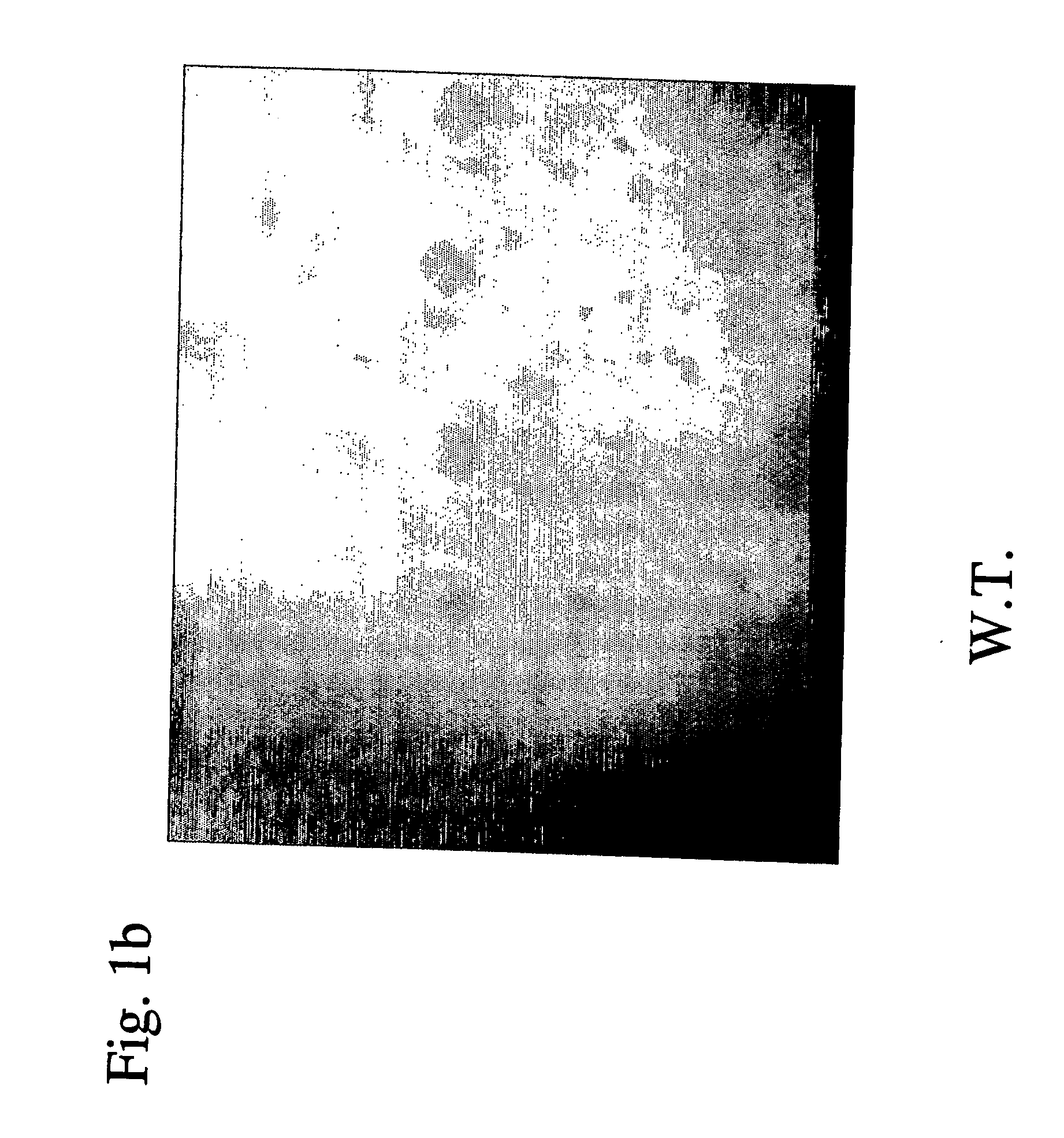
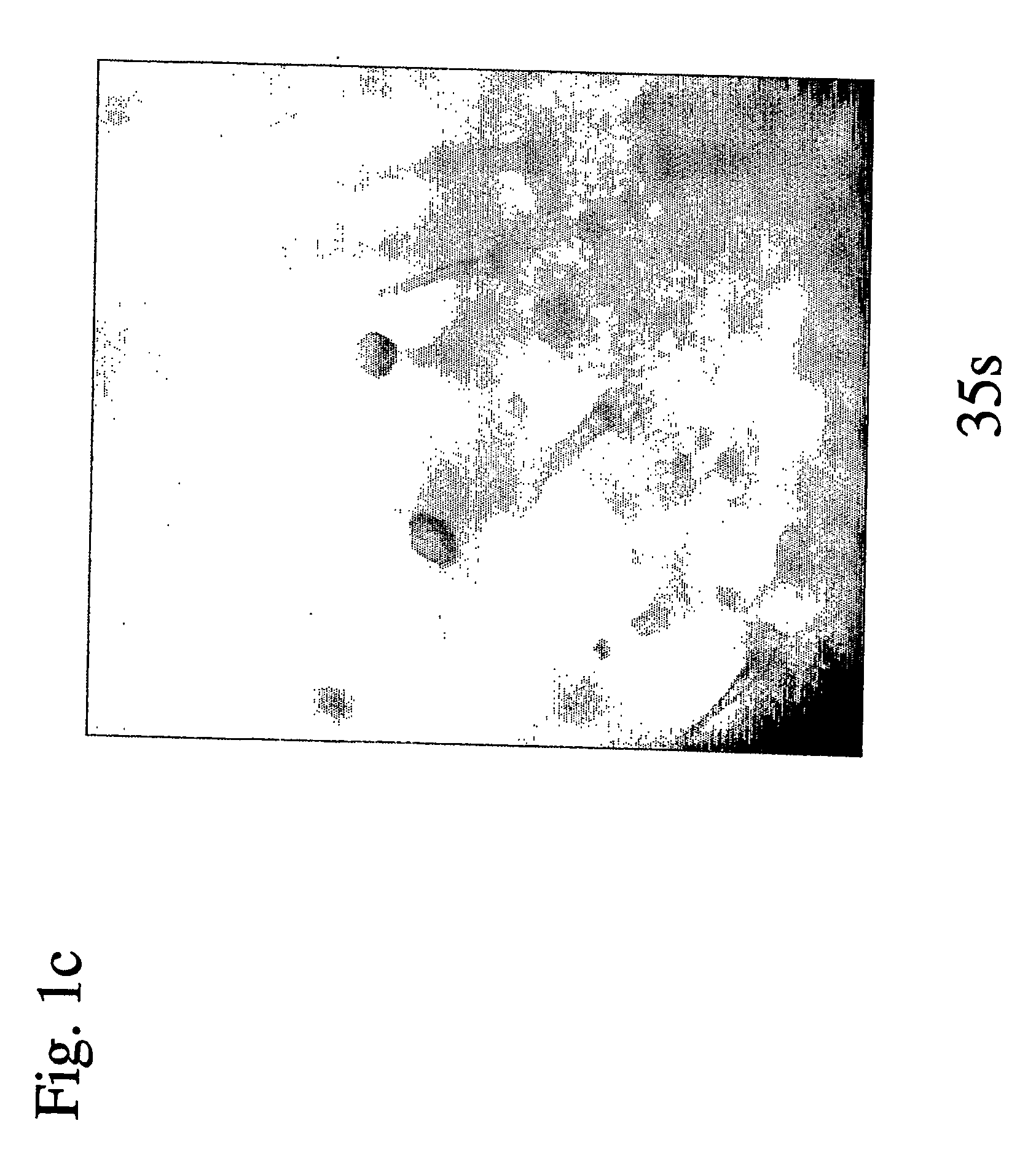
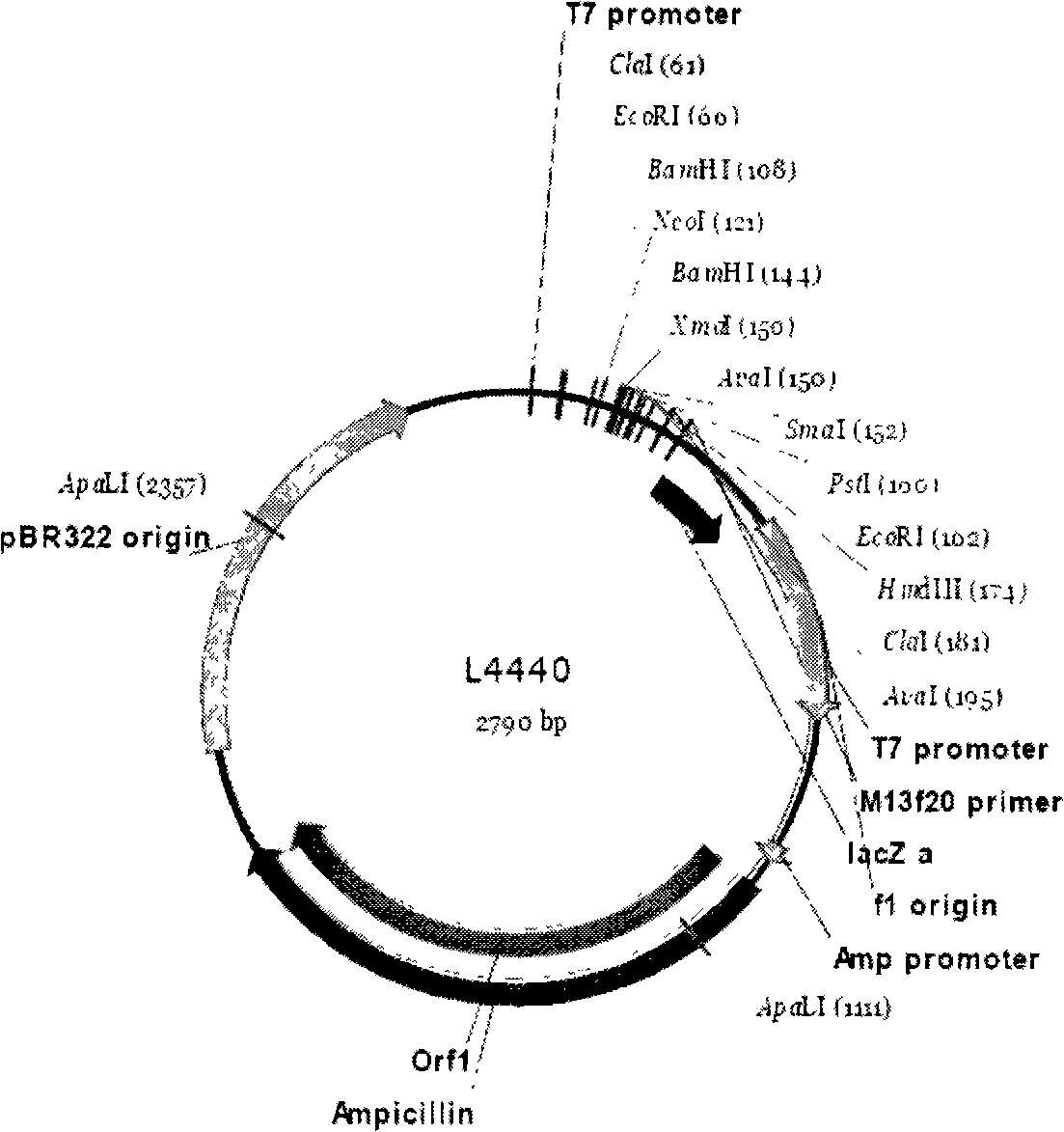
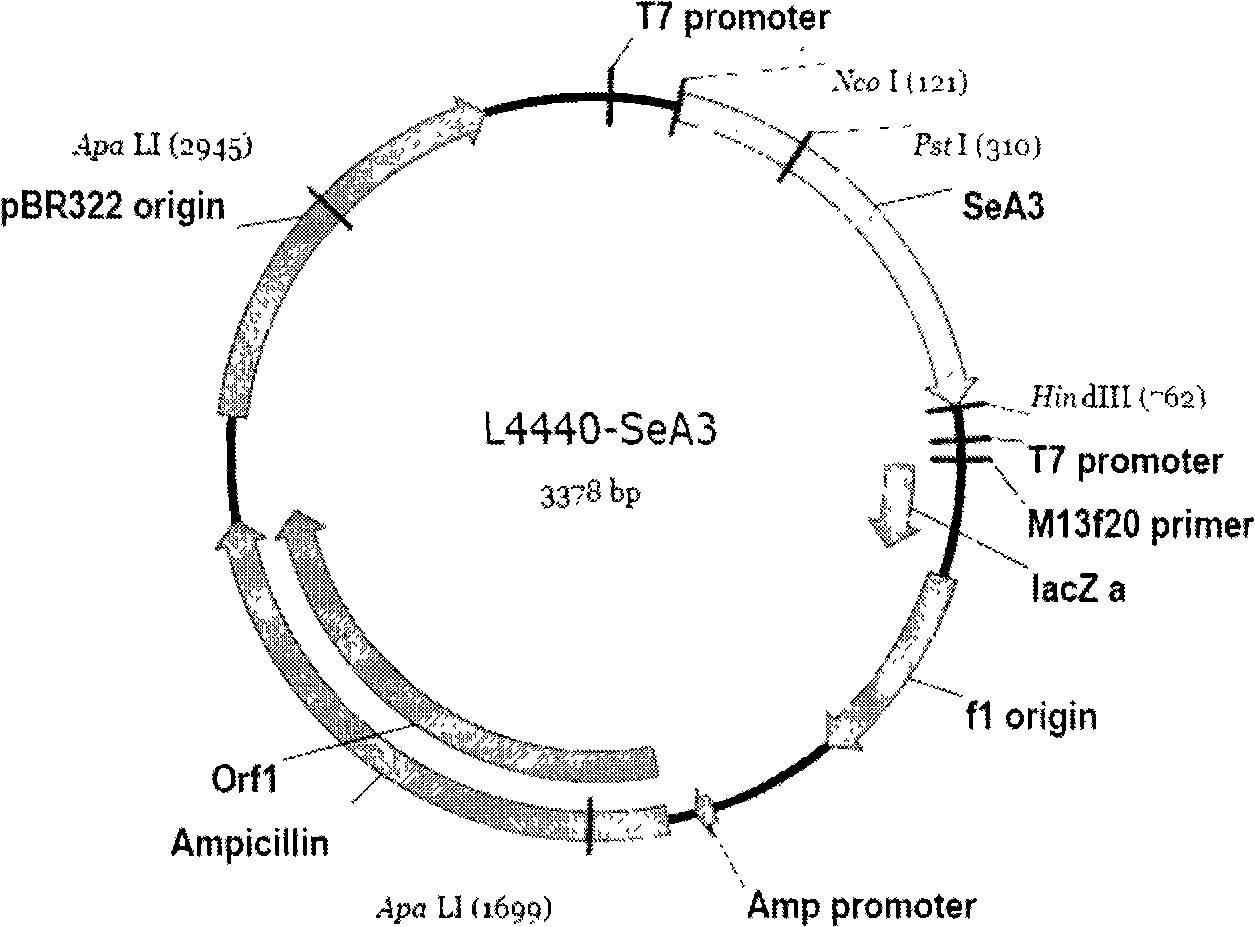
The invention provides a method for suppressing the gene expression of insects through feeding dsRNA, which belongs to the growth development field of adjusting and controlling insects through naturally feeding the dsRNA of the silenced and specific gene. The method selects a gene fragment SeA3 on chitin synthetase enzyme gene SeCHS-A, and studies the impact on the insects after the natural feeding. The method mainly comprises the steps: a proper expression vector L4440 is selected to construct a recombinant expression vector L4440-SeA3 with a purpose gene fragment SeA3; the recombinant vector is induced and expressed in specific recipient cell coliform bacteria HT115 (DE3) under vitro adaptive condition; and the recipient bacterium htLSA3 which expresses dsRNA is added into the feedstuff of the insects, the insect larvae are naturally fed with the feedstuff, the situation of the insects suppressing the gene expression is detected after the feeding, and the change of the phenotype of the insects is recorded. By adopting natural feeding to suppress the expression of the insect genes, the method explores new paths for controlling the insects.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Fixed-point gene editing method based on intratestis injection
InactiveCN105296537AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryMatingGene Modification
The invention discloses a simple, convenient and efficient fixed-point gene editing method relating to the fields of transgenic animal preparation, gene functional study and biomedicines. A testis injection method is a sperm-mediated gene transferring method developed by utilizing the sperm capacity of actively combining, transferring and integrating an exogenous DNA. By using the method disclosed by the invention, an animal testis injection method is optimized, a carrier constructed by utilizing a clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat system (CRISPR / Cas9) is integrated with a sperm chromosome through multi-point testis injection or seminiferous tubule microinjection, so that the aims of deleting, replacing and inserting genes are achieved. Then, a transgenic animal descendant is obtained through various approaches such as natural mating and artificial insemination. According to the method, the advantages of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing system are sufficiently utilized, and the existing transgenic animal system is combined, so that the complexity of in-vitro cell operation and requirement on expensive precise instruments / equipment are avoided while the gene modification animal obtaining efficiency is greatly increased.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Double resistance CRISPR/Cas9 carrier and application
The invention relates to a double resistance CRISPR / Cas9 carrier and application. The invention provides the double resistance carrier having both hygromycin B resistance and Basta resistance at the same time; the double resistance carrier is obtained by inserting sequences and fragments derived from multiple different carriers into a sequence of a carrier pFGC5941 by enzyme-cutting and linking up, and constructing. Hygromycin B is used for screening in a conversion process, and Basta is used for screening offspring transgenic plants not containing an external source T-DNA sequence in offspring plants. Two resistances, i.e., the hygromycin B and the Basta are used to respectively serve as screening marks of the transgenic plants for the first time, a feasible manner is provided for screening transgenic offspring not containing the external source T-DNA sequence, determining the existence of external source T-DNA by a complex molecular biology detection experiment is avoided, and the offspring transgenic plants not containing the external source T-DNA sequence can be obtained by directly screening the Basta resistance and performing phenotype combination.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for acquiring Nogo-B knockout mode mouse based on CRISPR/Cas9 technology and application thereof
The invention relates to a method for acquiring a Nogo-B knockout mode mouse based on CRISPR / Cas9 technology and an application thereof, the method for acquiring the Nogo-B knockout mode mouse comprises the following steps of: designing a high-efficiency sgRNA for identifying EGE-ZXH-007 of a specific gene; connecting the sgRNA to a plasmid vector and then carrying out in-vitro transcription to obtain a Ca9 / sgRNA capable of being subject to microinjection; injecting the Ca9 / sgRNA capable of being subject to microinjection into a mouse fertilized egg, and then carrying out genotype detection and identification on the born mouse, and finally obtaining the Nogo-B knock-out mode mouse. According to the invention, the Nogo-B knockout mode mouse is obtained by using the CRISPR / Case9 technology,and compared with the traditional gene knockout technology, the operation is easy and the efficiency is higher, and the homozygous mutation is more easily obtained, thus laying a good foundation for further researching the function of Nogo-B.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Animal model for obese rats and establishing method
The invention relates to an animal model for obese rats and an establishing method, and belongs to the field of animal genetic engineering and genetic modification. The animal model for obese rats and the establishing method are characterized in that rats with LEP and LEPR genes knocked out are obtained through the CRISPR / Cas9 technology. The rats with LEP and LEPR genes knocked out have a typical obesity characteristic, the reliable animal model can be provided for studying the obesity disease of people, and the rats with LEP and LEPR genes knocked out are expected to become a standard experiment animal of obese rats.
Owner:SUZHOU RUIQI BIO PHARMA CO LTD
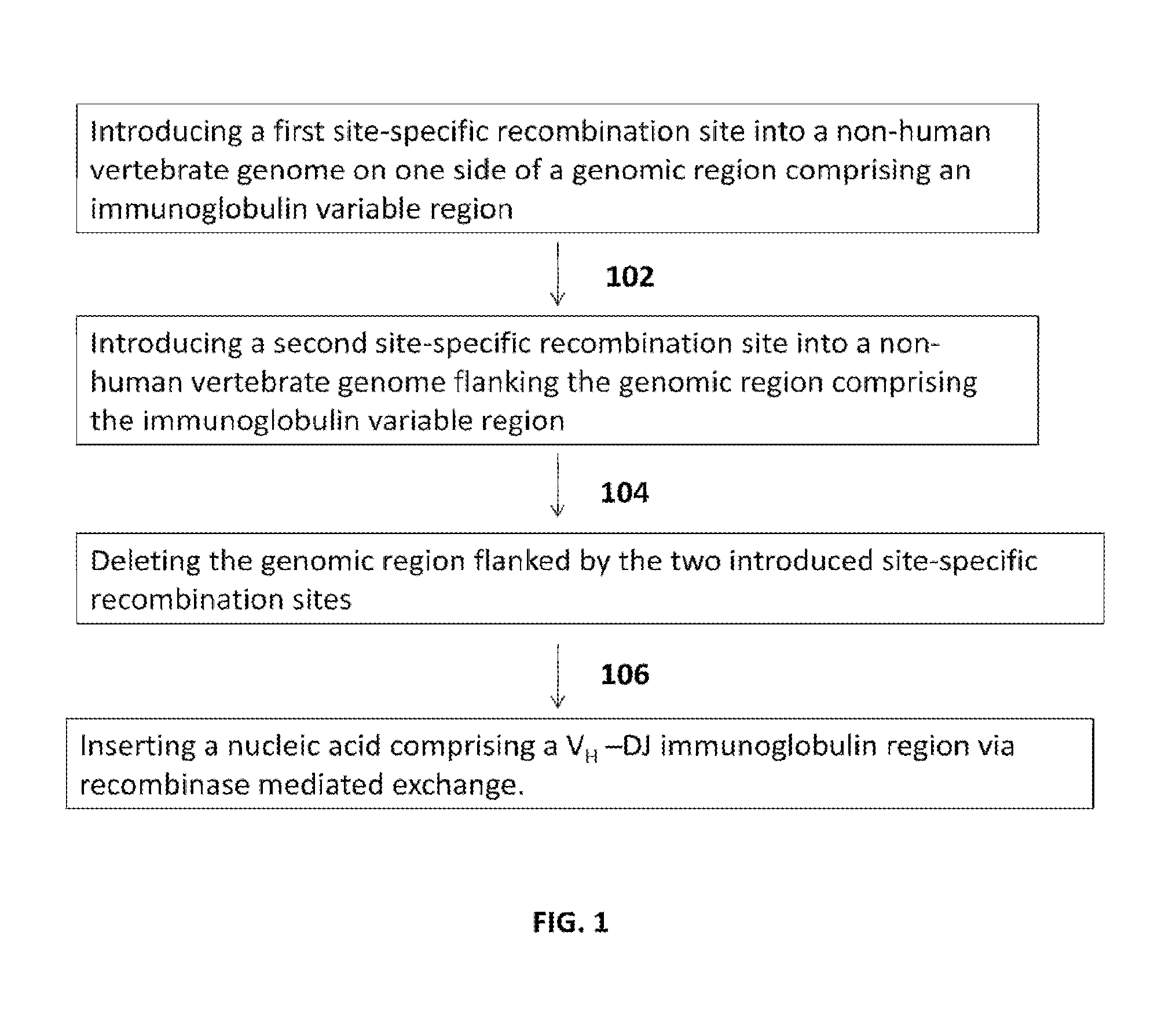
Transgenic animals and methods of use
The present invention comprises non-human vertebrate cells and non-human mammals having a genome comprising an introduced partially human immunoglobulin region, said introduced region comprising human VH coding sequences and non-coding VH sequences based on the endogenous genome of the non-human mammal.
Owner:TRIANNI INC
Transgenic animal and methods
InactiveUS20020066117A1Easy to useCompounds screening/testingAnimal cellsNeurological disorderPathology diagnosis
A transgenic animal, preferably a mouse, that expresses human antichymotrypsin (ACT) in brain tissues is provided, together with animal tissue-derived cell lines and progeny animals of said transgenic animal. Progeny are obtained by mating the transgenic animal with select animal strains used as models of Alzheimer's disease, related neurological disorders, or amyloidogenic diseases. Methods utilizing the parent and progeny animals and cells derived therefrom are disclosed for testing compounds for use as anti-inflammatory drugs, inhibitors of amyloidogenesis, and / or inhibitors of tau protein pathology associated with Alzheimer's disease, in the treatment of a variety of neurological diseases.
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
Methods of screening compositions for potential insect control activity
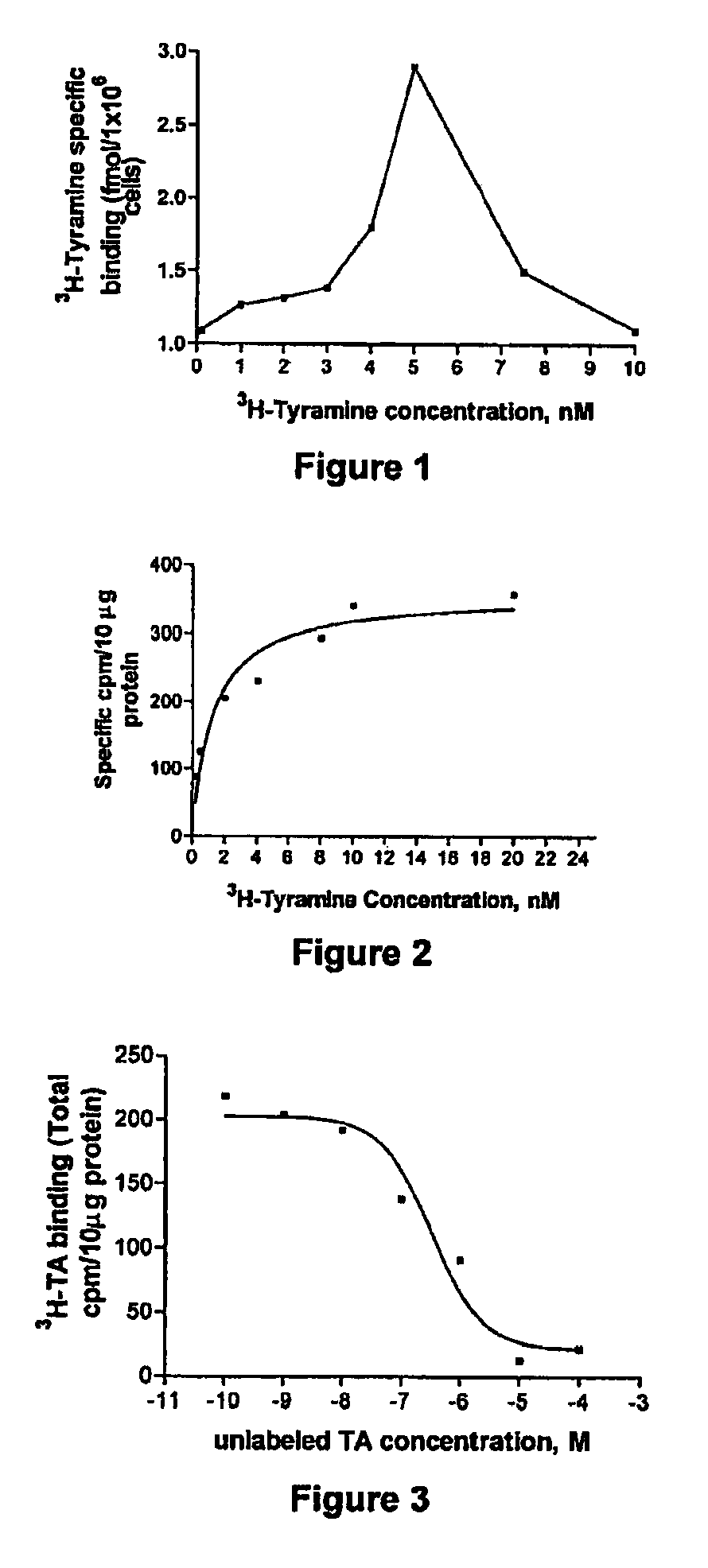
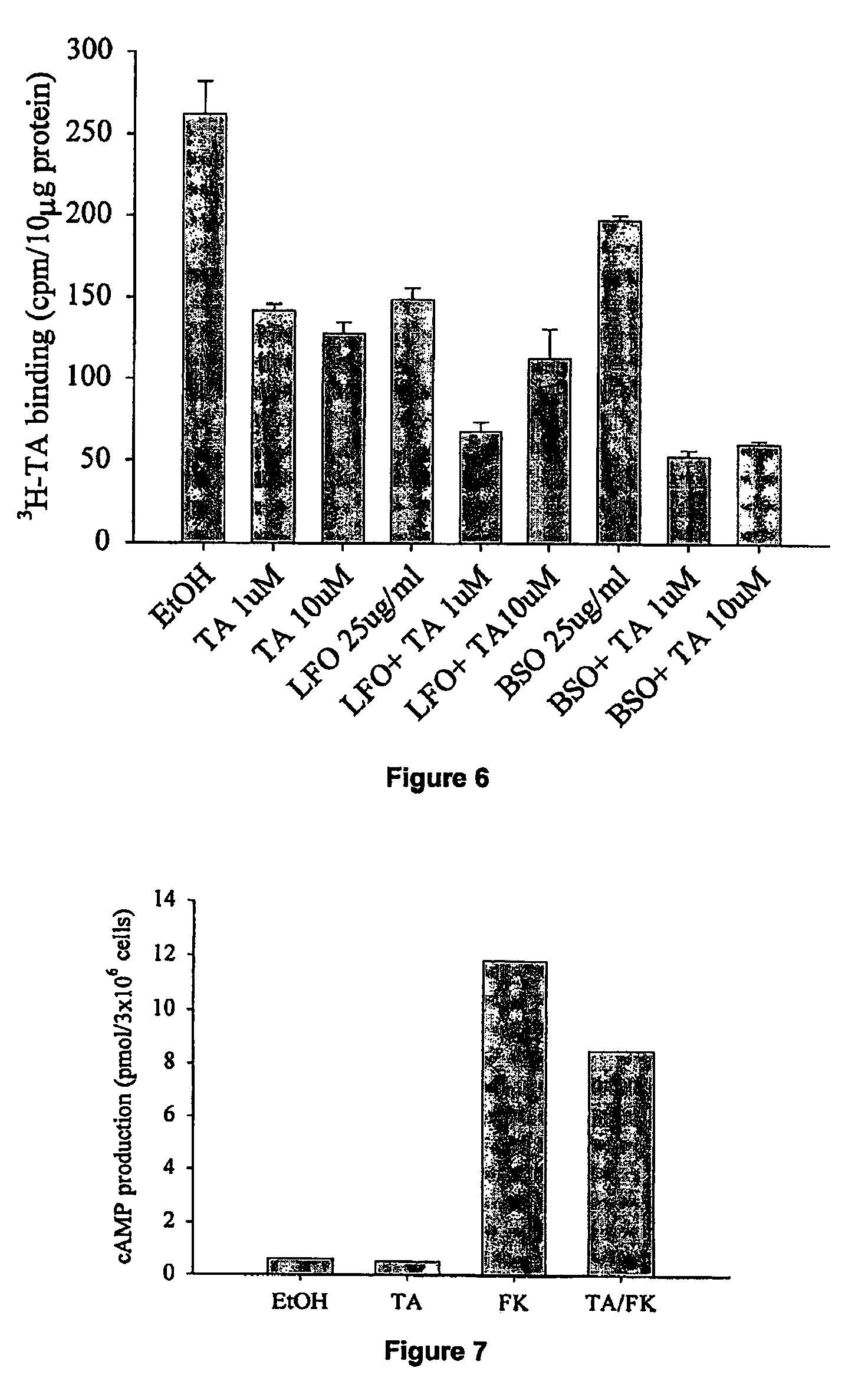
ActiveUS7541155B2BiocideBiological material analysisTyramine receptorsReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The present invention comprises compositions, methods and cell lines related to controlling insects. An embodiment of a composition comprises a plant essential oil and targets at least one receptor of insects chosen from tyramine receptor, Or83b olfactory receptor, and Or43a olfactory receptor, resulting in a change in the intracellular levels of cAMP, Ca2+, or both in the insects.
Owner:TYRATECH
Transgenic non-human mammals producing fibrinogen in their milk
A transgenic, non-human mammalian animal is capable of expressing a heterologous gene for human or other recombinant physiologically functional fibrinogen holoprotein or individual subunit chain polypeptides thereof or a modified or fusion fibrinogen in mammary glands of the animals and secreting the expressed product into a body fluid. Methodology employing such a mammal yields recombinant physiologically functional fibrinogens, subunit chain polypeptides thereof, and modified or fusion fibrinogens.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL UNIVERSTIY OF THE +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com