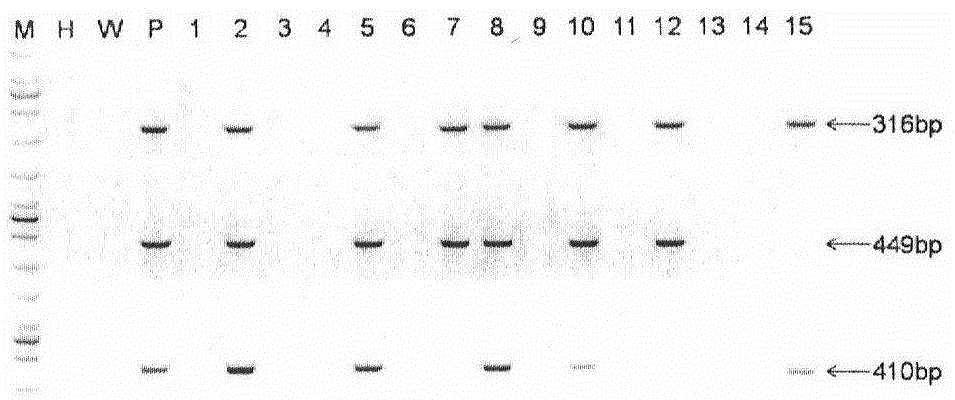
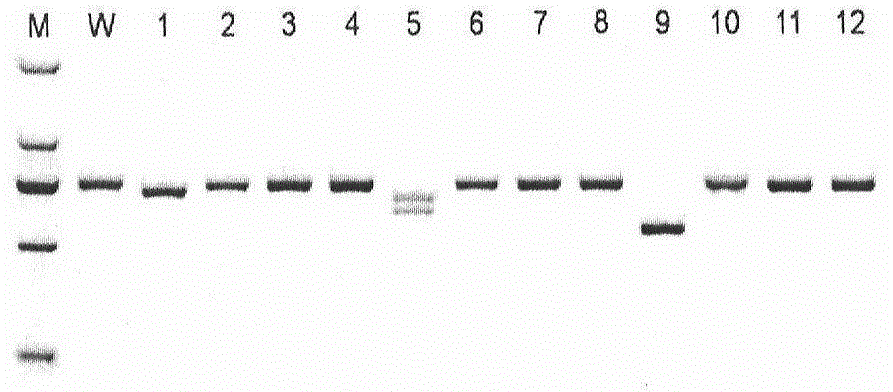
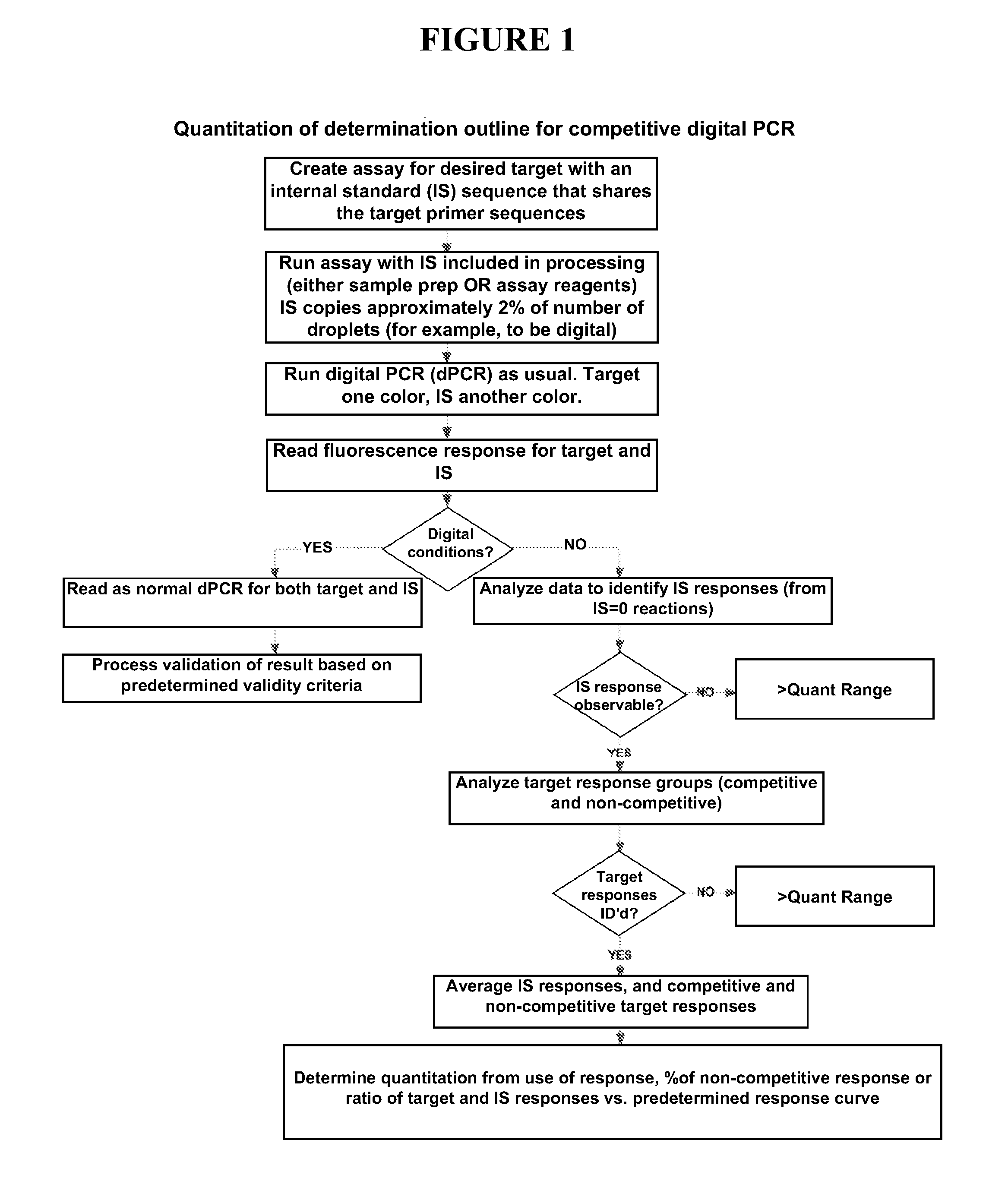
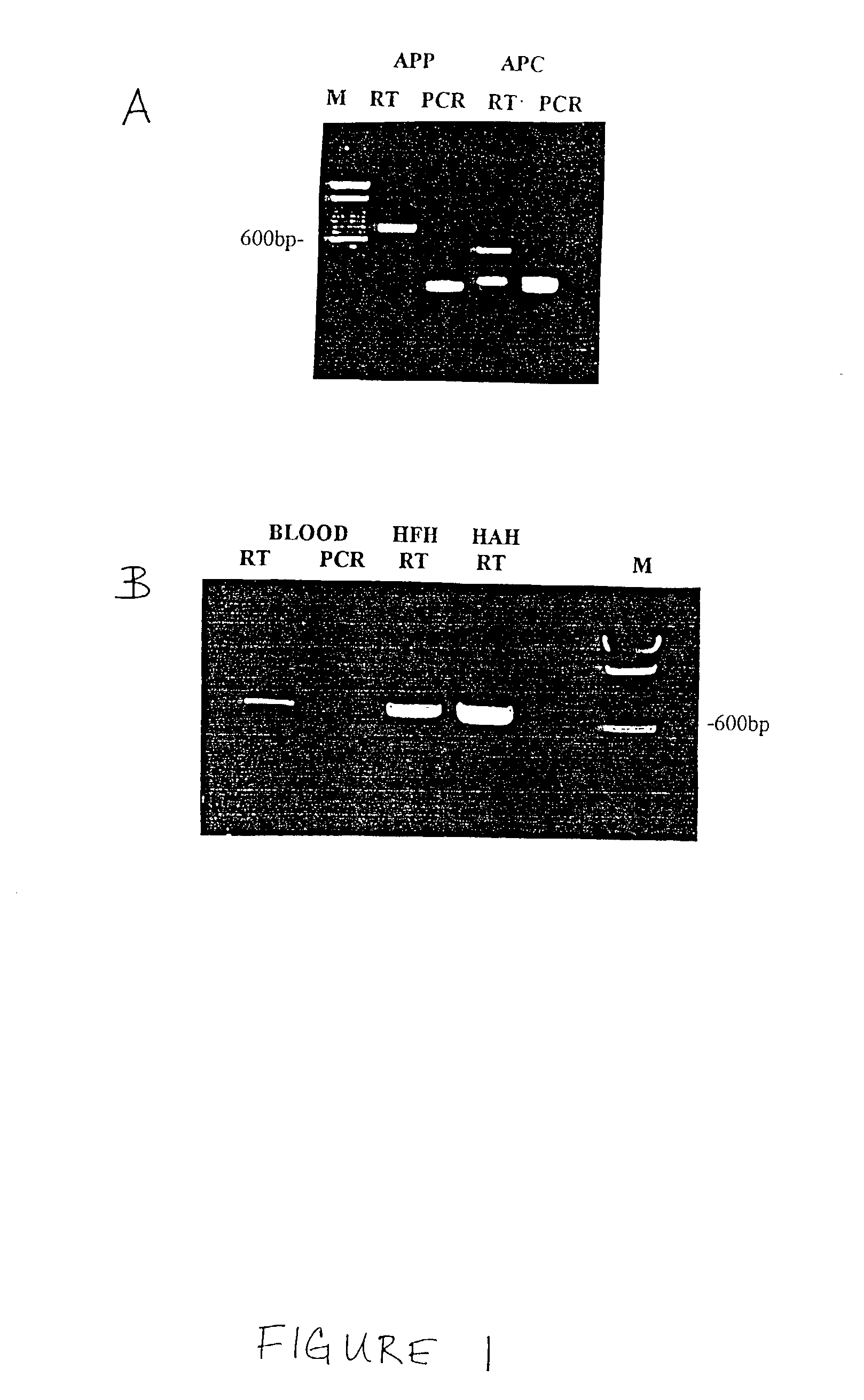
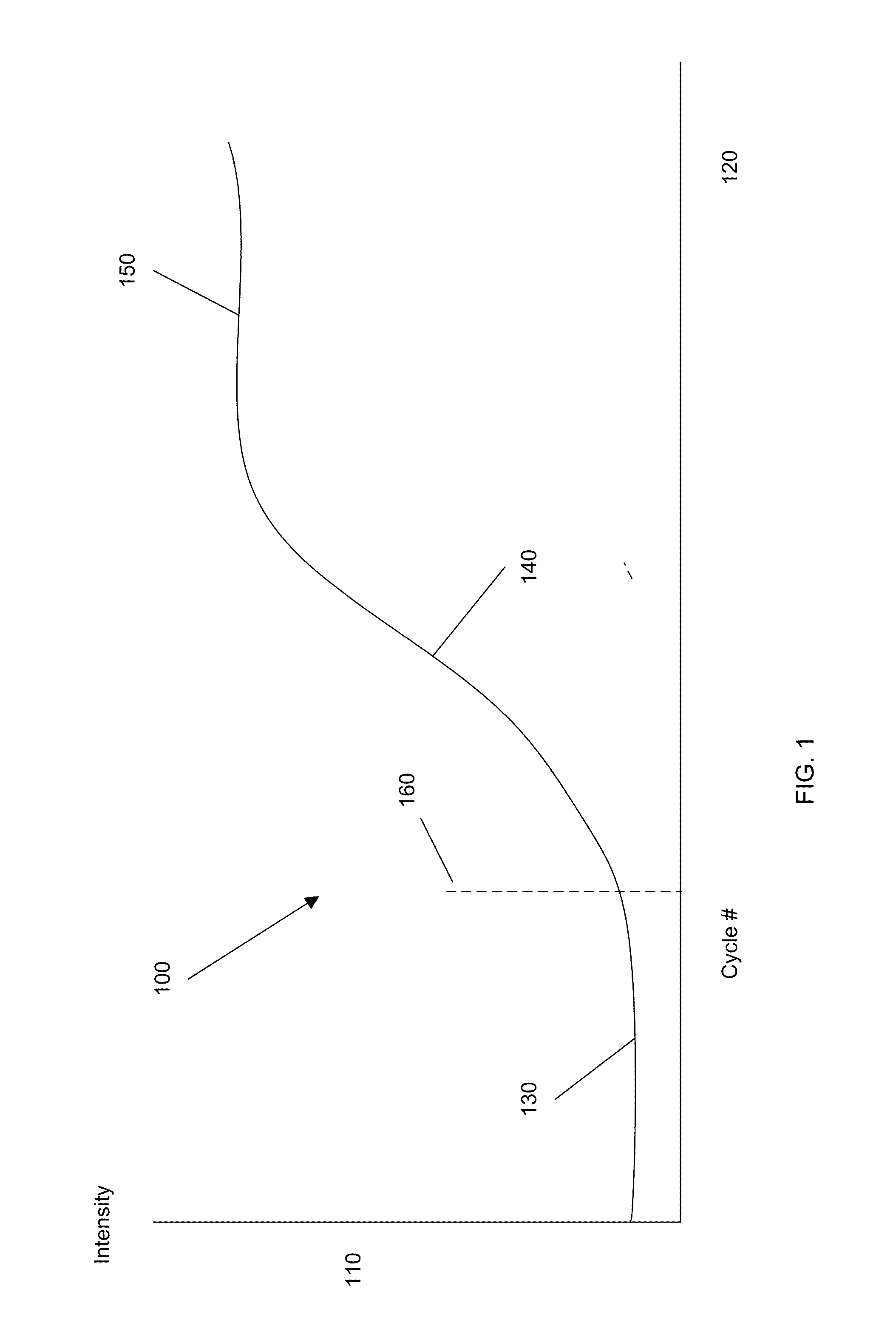
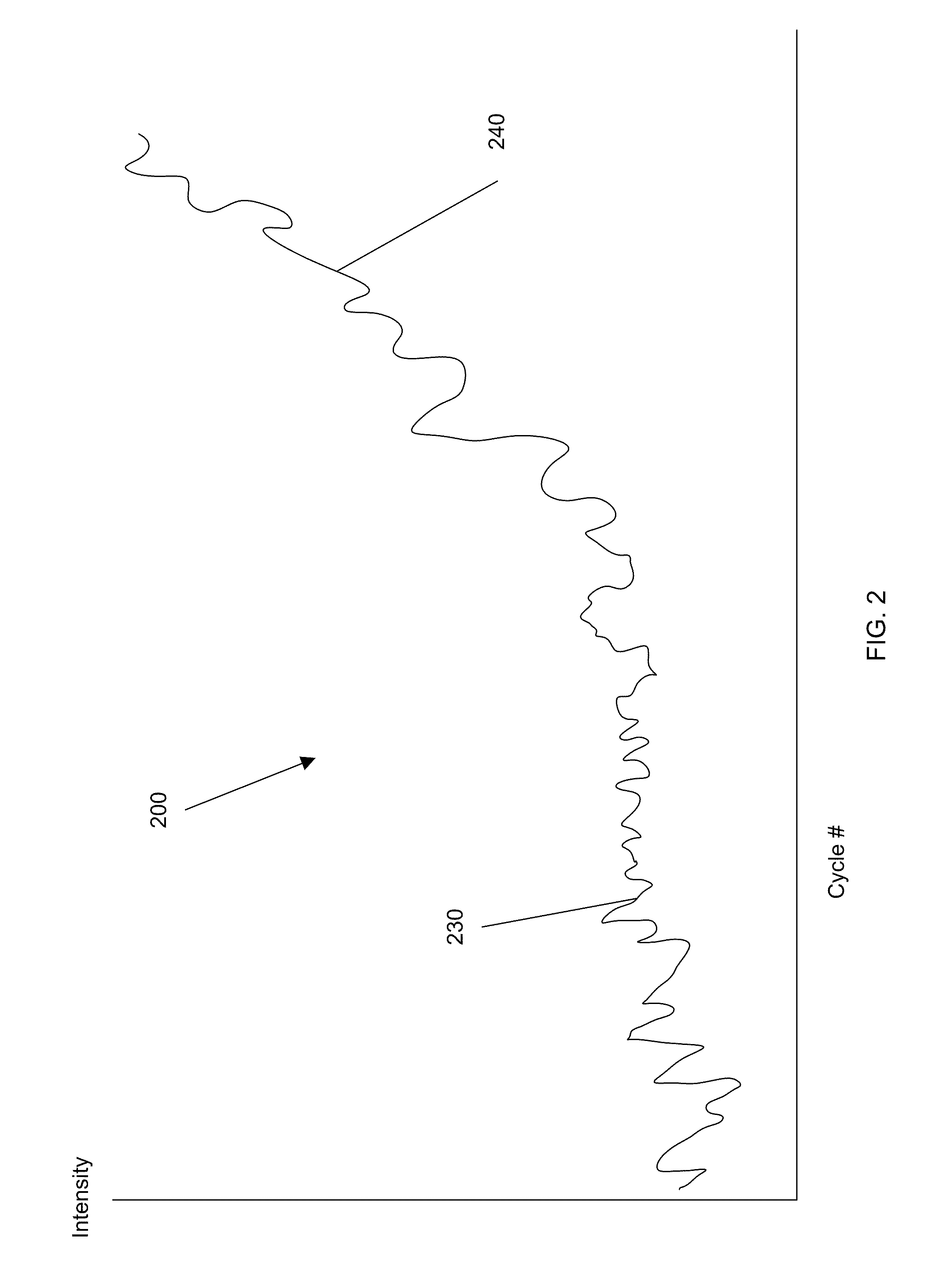
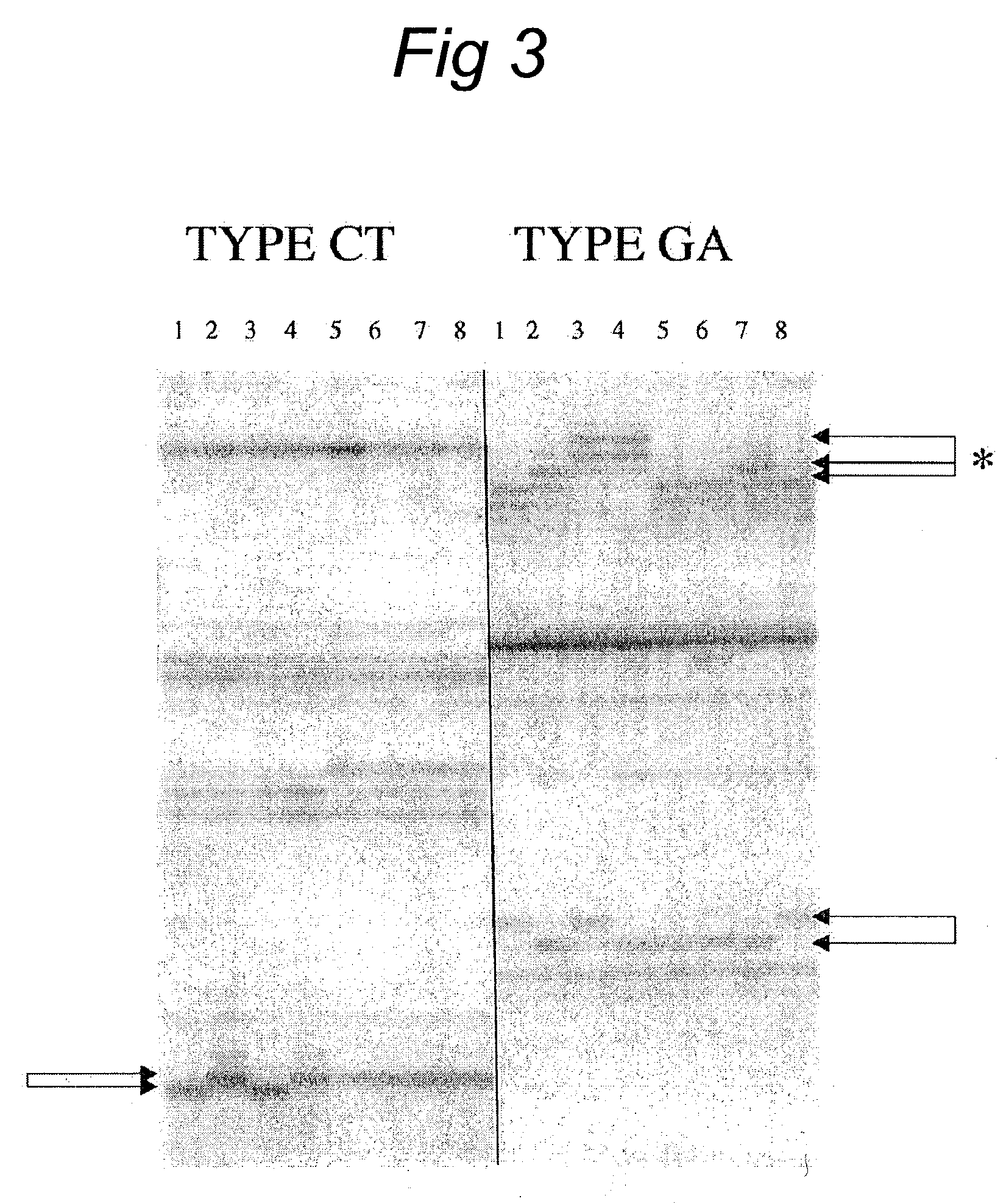
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
196 results about "Pcr analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pcr - Legal Definition. Stands for polymerase chain reaction, the newest (at this writing) method of DNA analysis. Using PCR technique, it is possible to analyze a biological specimen that is one-tenth the size of that required for the older RFLP method. It also gives quicker results, but the analysis is not as discriminating as RFLP.
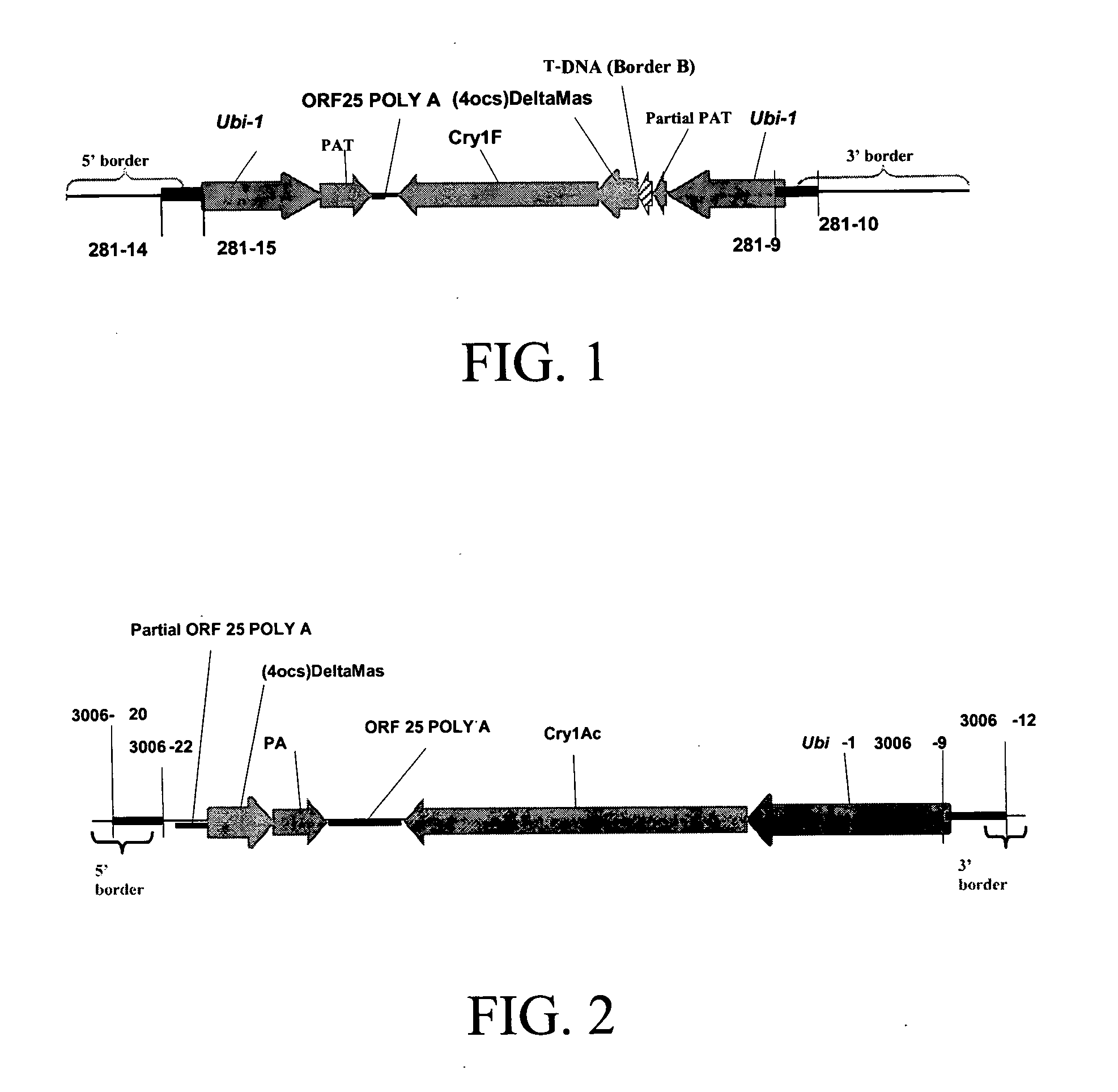
Cry1F and Cry1AC transgenic cotton lines and event-specific identification thereof
This invention relates to plant breeding and the protection of plants from insects. More specifically, this invention includes novel transformation events of cotton plants comprising one or more polynucleotide sequences, as described herein, inserted into specific site(s) within the genome of a cotton cell. In highly preferred embodiments, said polynucleotide sequences encode “stacked” Cry1F and Cry1Ac lepidopteran insect inhibitory proteins. However, the subject invention includes plants having single cry1F or cry1Ac events, as described herein. Additionally, the invention is related to cotton plants derived from that transformation event and to assays for detecting the presence of the event in a sample. More specifically, the present invention provides DNA and related assays for detecting the presence of certain insect-resistance events in cotton. The assays are based on the DNA sequences of recombinant constructs inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites. These sequences are unique. Based on these insert and border sequences, event-specific primers were generated. PCR analysis demonstrated that these cotton lines can be identified in different cotton genotypes by analysis of the PCR amplicons generated with these event-specific primer sets. Thus, these and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify these cotton lines. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. These materials and methods can also be used to assist breeding programs to further develop traits in cotton.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
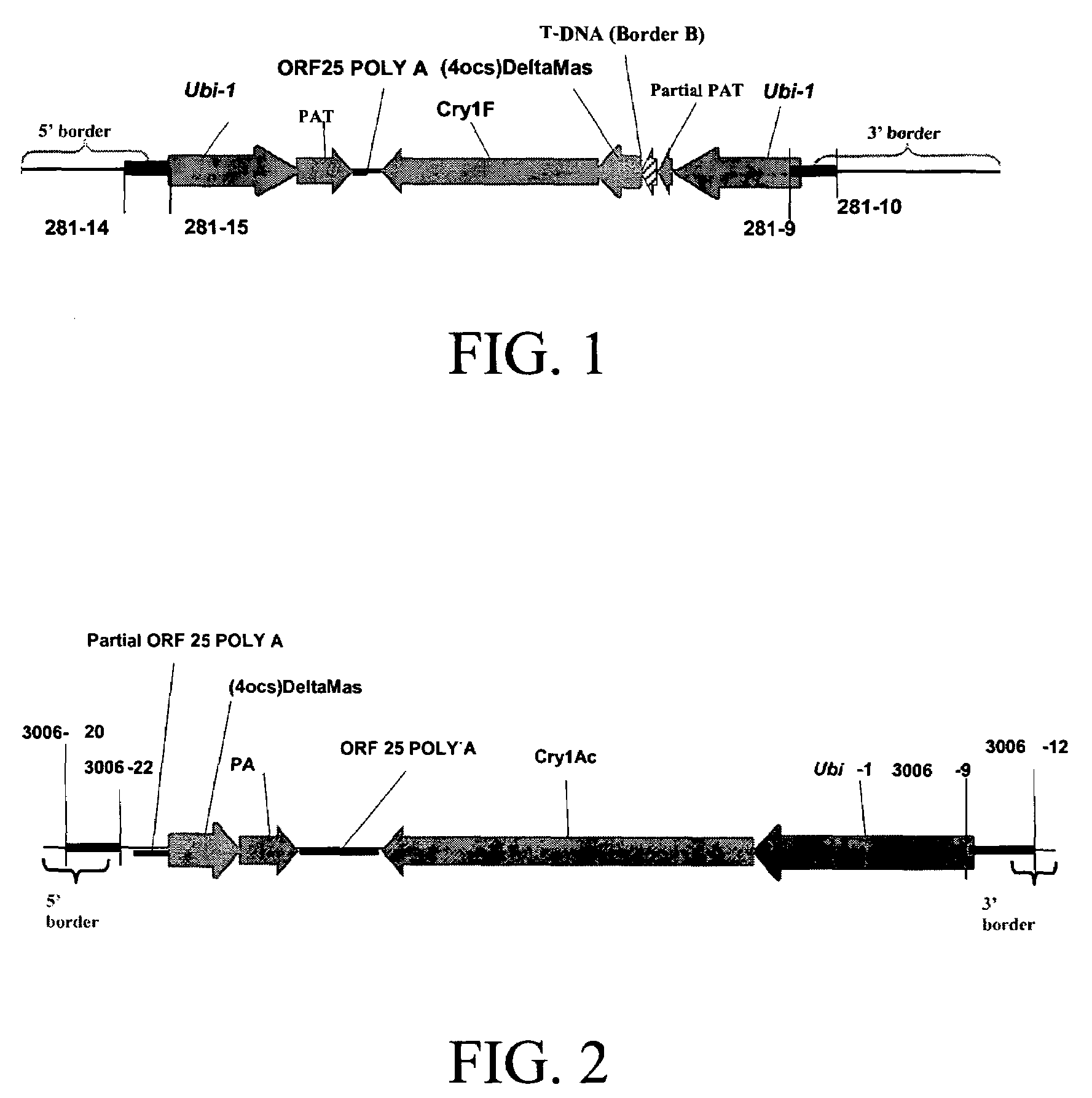
Cry1F and Cry1Ac transgenic cotton lines and event-specific identification thereof
This invention relates to plant breeding and the protection of plants from insects. More specifically, this invention includes novel transformation events of cotton plants comprising one or more polynucleotide sequences, as described herein, inserted into specific site(s) within the genome of a cotton cell. In highly preferred embodiments, said polynucleotide sequences encode “stacked” Cry1F and Cry1Ac lepidopteran insect inhibitory proteins. However, the subject invention includes plants having single cry1F or cry1Ac events, as described herein. Additionally, the invention is related to cotton plants derived from that transformation event and to assays for detecting the presence of the event in a sample. More specifically, the present invention provides DNA and related assays for detecting the presence of certain insect-resistance events in cotton. The assays are based on the DNA sequences of recombinant constructs inserted into the cotton genome and of the genomic sequences flanking the insertion sites. These sequences are unique. Based on these insert and border sequences, event-specific primers were generated. PCR analysis demonstrated that these cotton lines can be identified in different cotton genotypes by analysis of the PCR amplicons generated with these event-specific primer sets. Thus, these and other related procedures can be used to uniquely identify these cotton lines. Kits and conditions useful in conducting the assays are also provided. These materials and methods can also be used to assist breeding programs to further develop traits in cotton.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC
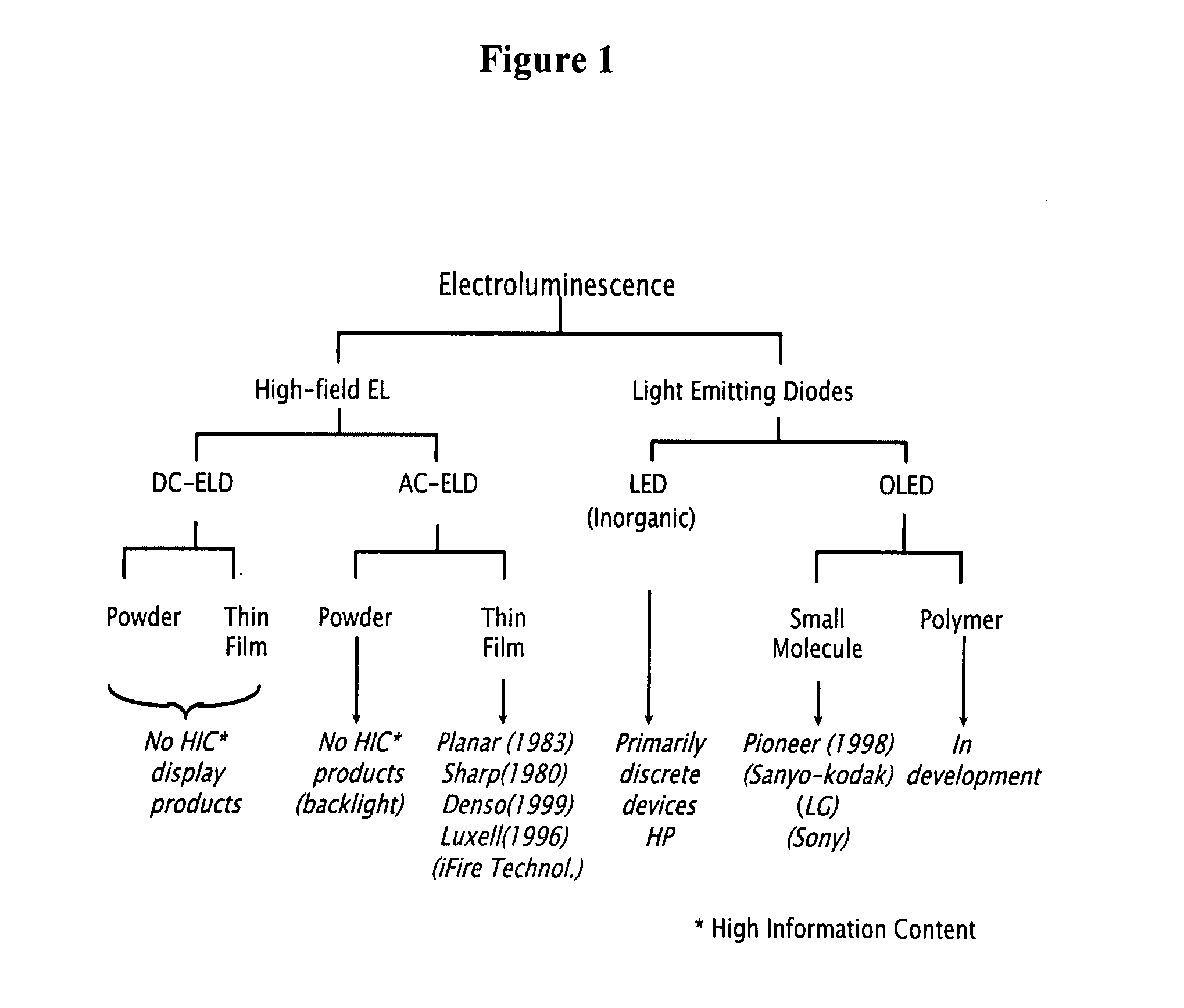
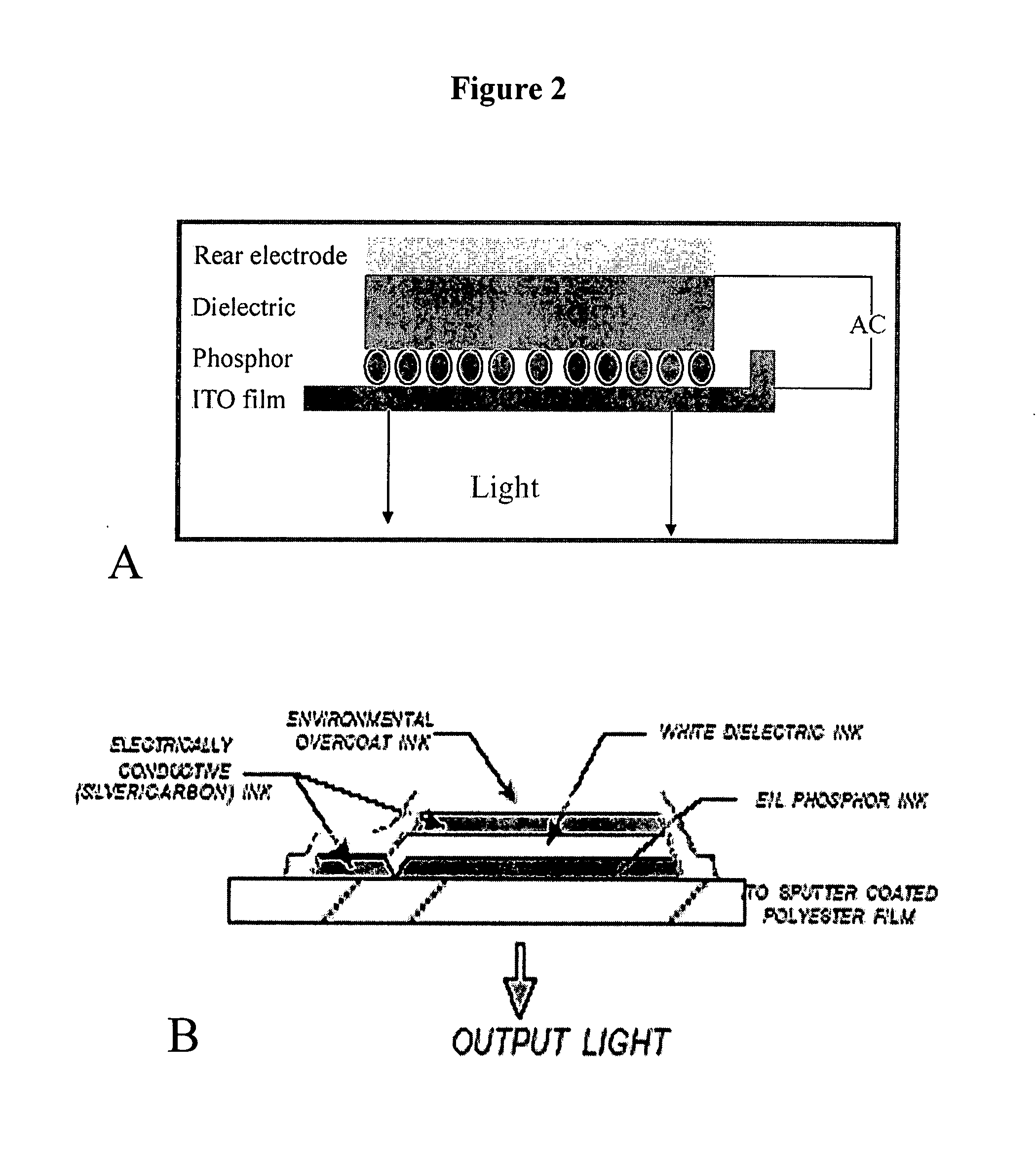
Electroluminescent-based fluorescence detection device
InactiveUS20100105035A1Quick identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElectricityFluorescence
The present invention provides compositions providing and methods using fluorescence detection device, comprising an electroluminescent light (EL) source, for measuring fluorescence in biological samples. In particularly preferred embodiments, the present invention provides an economical, battery powered and Hand-held device for detecting fluorescent light emitted from reporter molecules incorporated into DNA, RNA, proteins or other biological samples, such as a fluorescence emitting biological sample on a microarray chip. Further, a real-time hand-held PCR Analyzer device comprising an EL light source for measuring fluorescence emissions from amplified DNA is provided.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for establishing humanized rat drug evaluation animal model
InactiveCN104593418AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryLarge fragmentEngineered genetic
The invention provides a method for establishing a humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. According to the method, a multidrug resistance gene 1 (Abcb1)-knocked-out genetically engineered rat is obtained through a microinjection method by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology and 153kb bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) fragments containing a humanized Abcb1 promoter and cDNA is simultaneously inoculated into the rat genome through the microinjection method by virtue of a large fragment transgenic technology to obtain a transgenic rat capable of stably expressing human Abcb1 and the genetically engineered rat and the transgenic rat are hybridized to establish the humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. RT-PCR analysis shows that Abcb1 expression profiles of humanized Abcb1 rat are significantly different from those of the rat endogenous Abcb1. The method has the beneficial effects that the humanized rat capable of expressing human Abcb1 is obtained and the rat is used for expressing human Abcb1 genes and has closer expression profiles to those of human so that the model can be well used for the efficacy evaluation of newly developed drugs.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Quantitating high titer samples by digital PCR
ActiveUS20120164652A1Microbiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiologyHigh titer
The present invention provides systems, devices, methods, kits, and compositions for nucleic acid analysis using digital PCR. In particular, methods are provided to analyze high titer samples that cannot be divided into a sufficient number of partitions containing zero nucleic acid molecules per partition to allow for Poisson analysis (digital PCR analysis).
Owner:ABBOTT MOLECULAR INC
Method for the detection of gene transcripts in blood and uses thereof
InactiveUS20040014059A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationTissue specificGene transcript
The present invention is directed to detection and measurement of gene transcripts in blood. Specifically provided is a RT-PCR analysis performed on a drop of blood for detecting, diagnosing and monitoring diseases using tissue-specific primers. The present invention also describes methods by which delineation of the sequence and / or quantitation of the expression levels of disease-associated genes allows for an immediate and accurate diagnostic / prognostic test for disease or to assess the effect of a particular treatment regimen.
Owner:GENENEWS
Methods for the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis
ActiveUS20120264126A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismBacterial vaginosis
The present invention relates to methods for the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis based on an analysis of a patient sample. For example, patient test samples are analyzed for the presence or absence of one or more lactobacilli and two or more pathogenic organisms. The presence or absence of one or more lactobacilli and two or more pathogenic organisms may be detected using PCR analysis of nucleic acid segments corresponding to each target organism. The quantity of the target organisms can then be used to determine a score which is indicative of a diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS LLC
Integrated microfluidic analysis systems
InactiveUS8916375B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusChemical reactionMicrofluidic Analysis
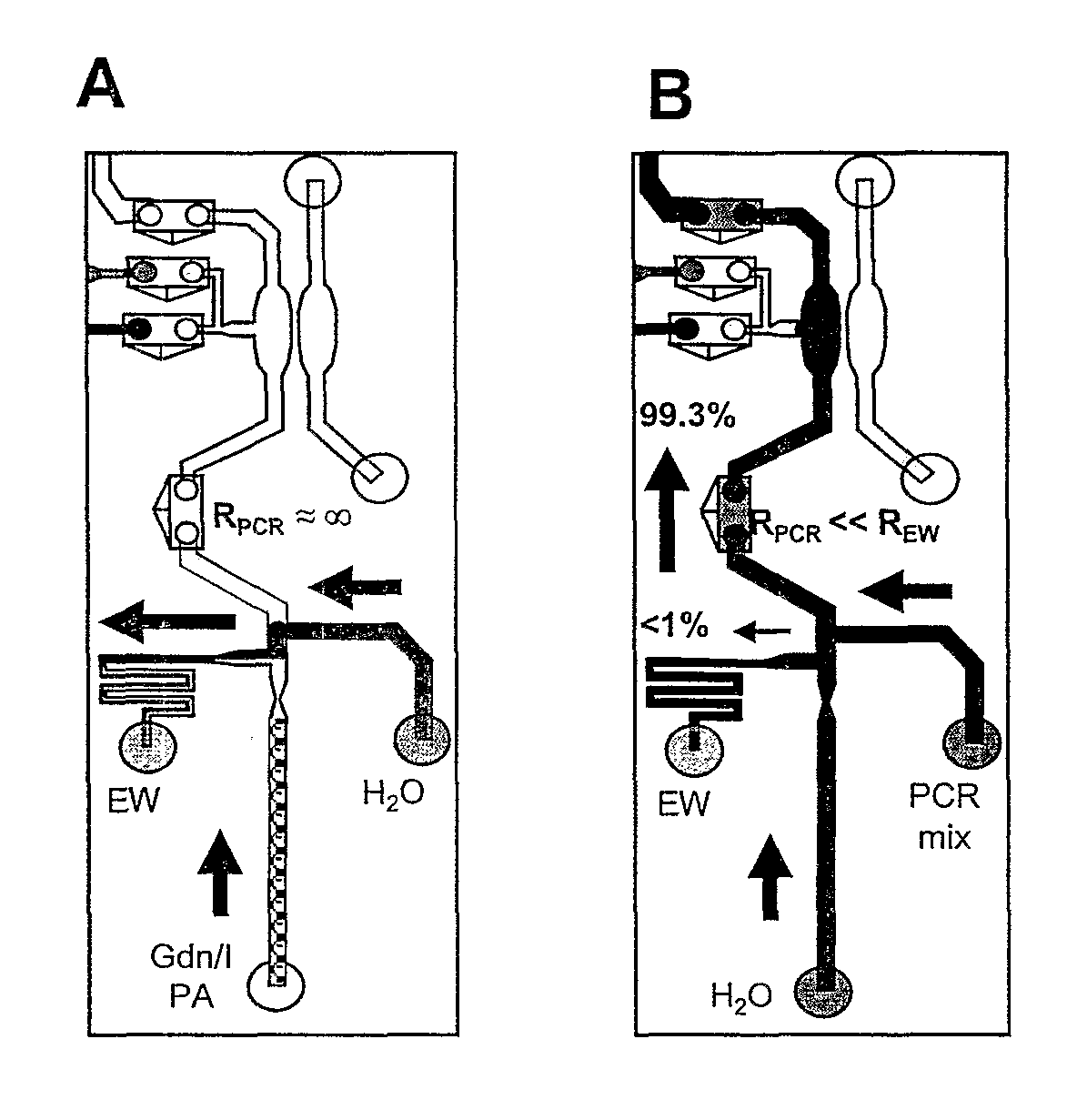
The present invention provides an integrated microfluidic analysis system. The system contains at least a first (pre-reaction treatment) domain for treating a sample prior to subjecting the sample to a chemical reaction. The following domains are optionally added to the first domain: a second (reaction) domain for reacting the chemical of interest in the sample; and a third (post-reaction separation) domain for separating products and reactants coming out of the reaction domain. The integrated microfluidic analysis system of the present invention is most applicable to PCR analysis.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Multi-stage, regression-based PCR analysis system
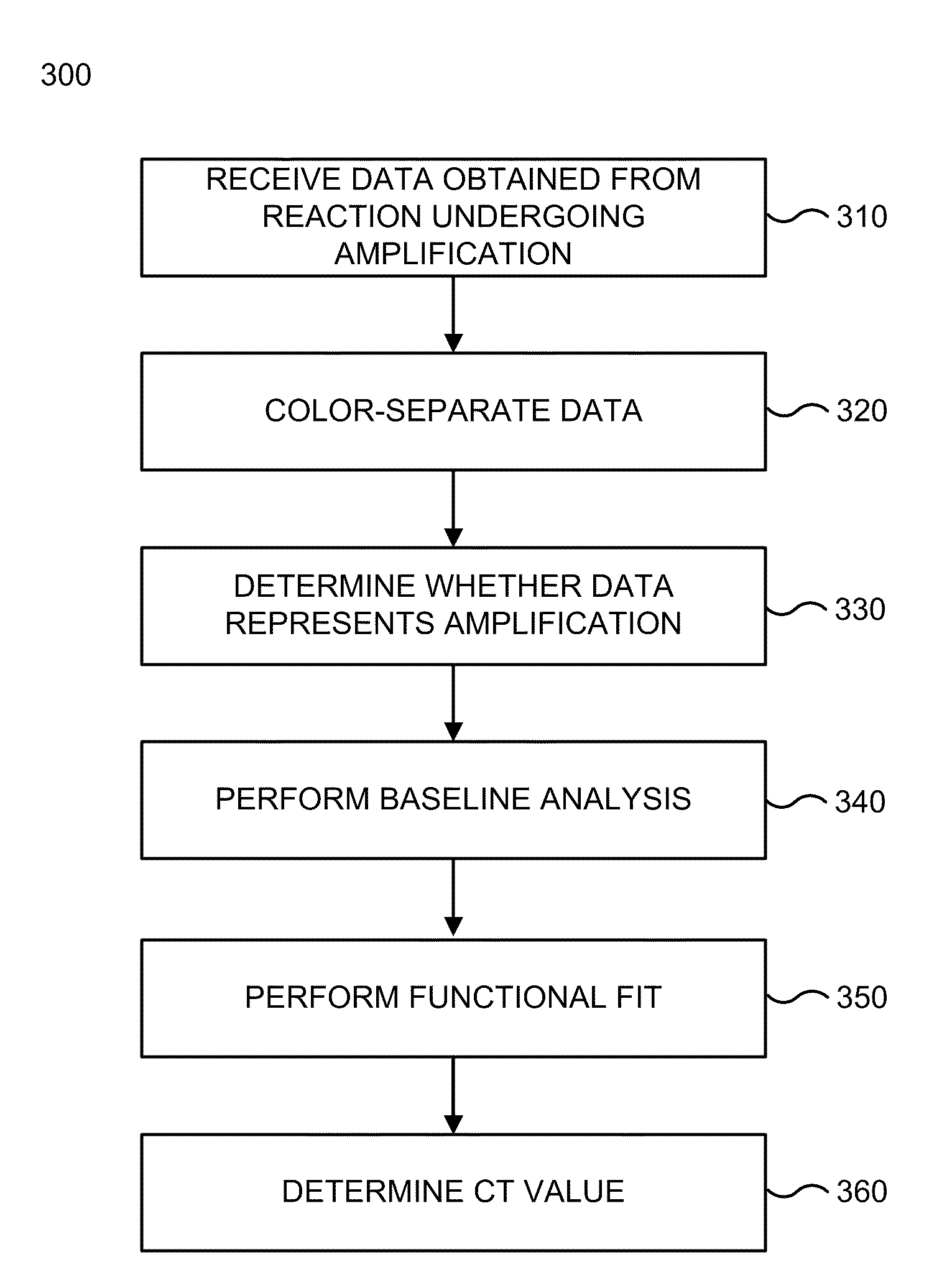
ActiveUS20100070190A1Improve accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalysis dataSigmoid function
Systems and methods are provided for analyzing data to determine properties of a PCR process or other process exhibiting amplification or growth. Data representing an amplification can be distinguished from data representing a jump or other error. A modified sigmoid function containing a drift term may be used in determining the properties. A multi-stage functional fit of the amplification data can provide increased accuracy and consistency of one or more of the properties. A baseline of the amplification data can be determined by analyzing an integrated area of a first derivative function of the data. A reference quantitation value can also be determined from locations of maxima of different derivative functions of the amplification data, e.g., a weighted average of the maxima locations for the second and third derivatives may be used.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Methods and kits comprising AFLP primers, and ramp primers with a part complementary to a compound microsatellite repeat and an anchor part complementary to nucleotides adjacent to the repeat
InactiveUS7217516B2Quick identificationReliable and powerfulMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSequence analysisNucleotide
The present invention discloses methods for identifying and analysing microsatellite-associated polymorphisms between different DNA samples. Different DNA samples, e.g. from different individuals, are analysed using a PCR based on the combination of a RAMP-primer and an AFLP-primer and polymorphisms between the different DNA samples are identified. The polymorphisms thus identified may be isolated and further analysed by e.g. DNA sequence analysis both upstream and downstream from the microsatellite-associated polymorphism. These sequences may subsequently be used to devise and synthesise new means for analysis of the polymorphic locus, such as e.g. PCR-primer pairs or oligonucleotide probes.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
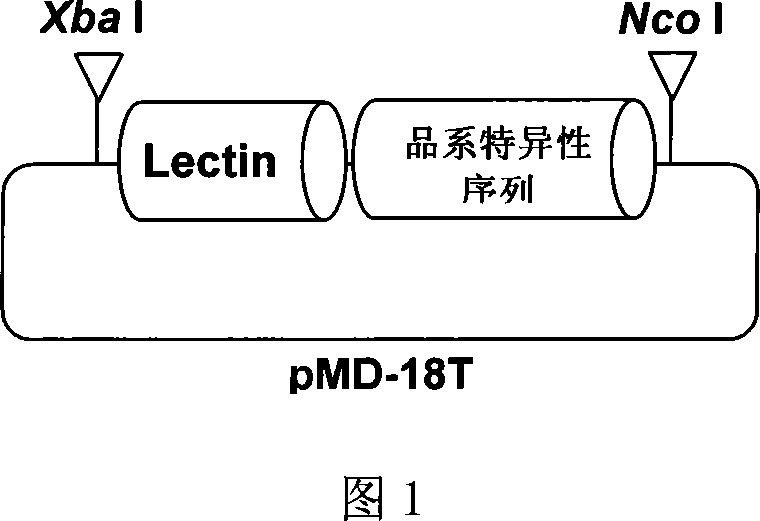
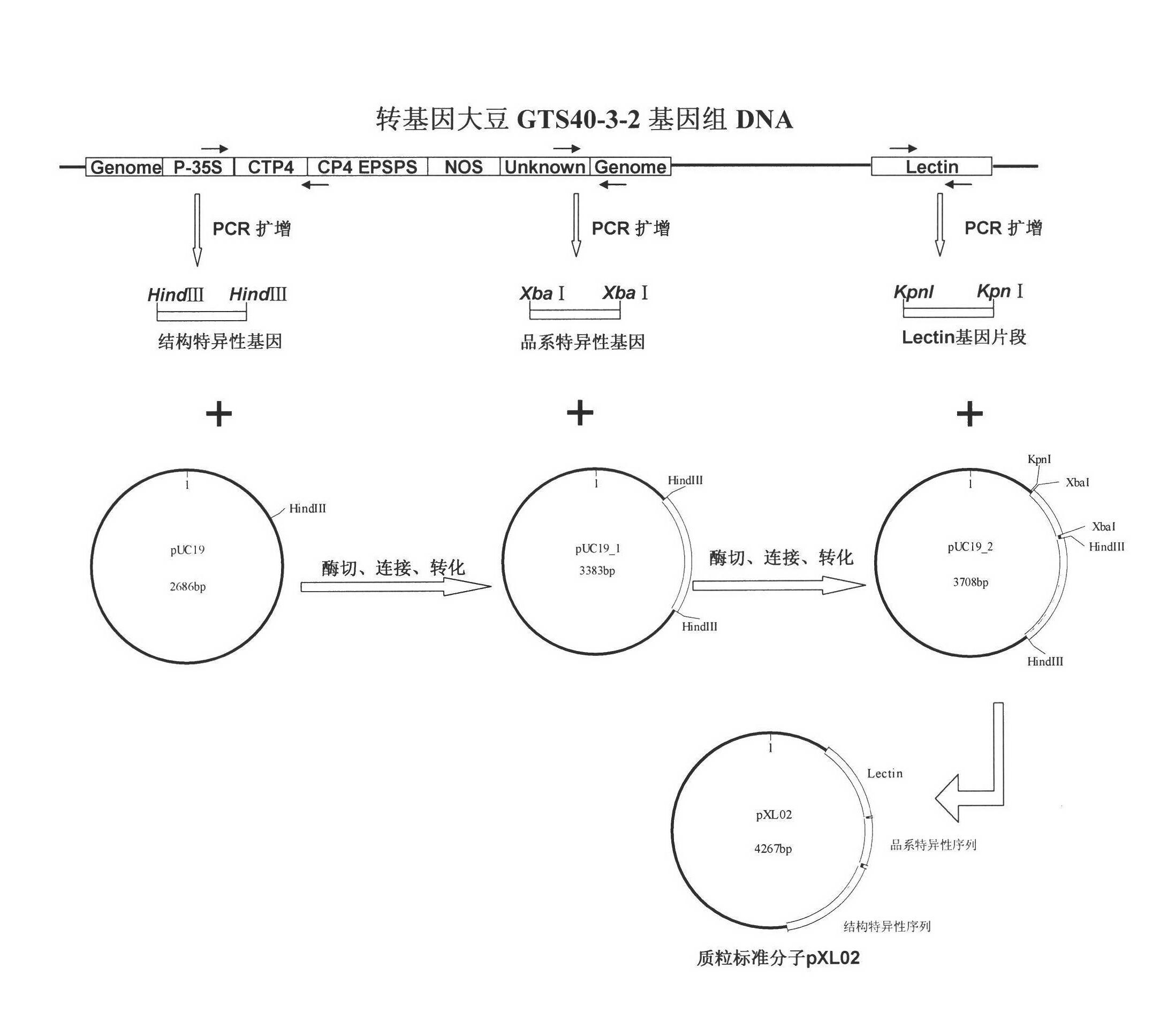
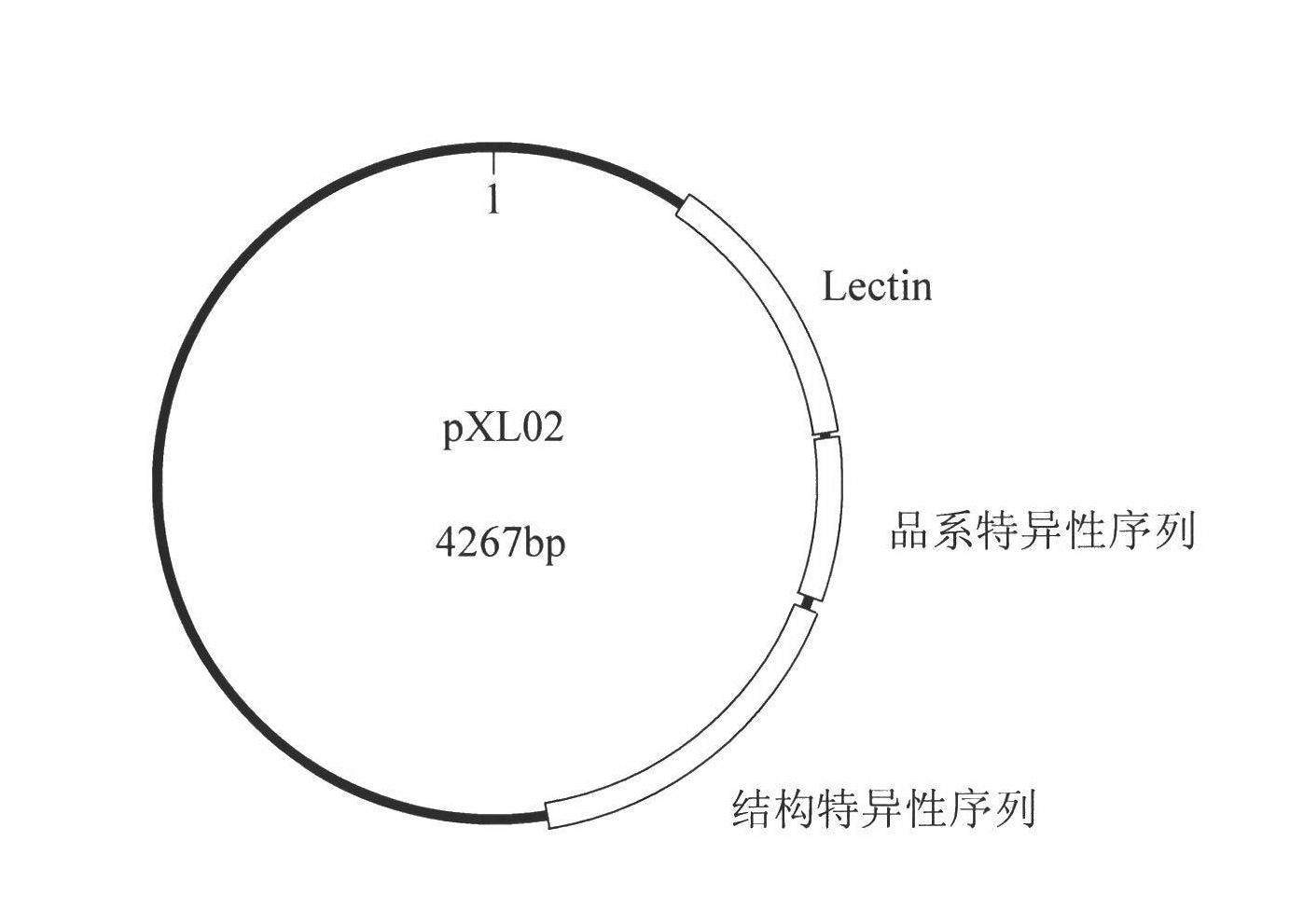
Standard plasmid molecule for detection of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and constructing method thereof
InactiveCN101063171AAvoid missingThe analysis result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringInternal standardPlasmid
The invention discloses a standard plasmid molecule to check genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and constructing method, which comprises the following steps: incorporating strain special fragment of the genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and special fragment of soybean internal standard gene Lectin; analyzing exogenesis inserting carrier by-pass ortho gene sequence of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2; designing strain special PCR primer; augmenting; getting strain special fragment of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and soybean internal standard gene special sequence; constructing into a plasmid molecule with molecular cloning method; getting artificial retooling plasmid molecule pMD-RRS. This standard plasmid molecule can be fit for strain special quantitative PCR analysis and check of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Capillary bioanalysis system, and analytical method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103409317AReduce volumeFast analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluid controlMedical equipment
The invention discloses a capillary bioanalysis system, and an analytical method and applications thereof, and belongs to the field of medical equipment and biological detection technologies. The capillary bioanalysis system comprises a three-dimensional movement sample injecting platform, a temperature control-optical detection module, a magnetic field control module, a fluid control unit and a capillary array. The three-dimensional movement sample injecting platform and the fluid control unit are arranged on the two sides of the capillary array, and the capillary array is provided with the temperature control-optical detection module and the magnetic field control module. According to the capillary bioanalysis system, the droplet technology and the magnetic bead technology are combined, and bioanalysis processes such as loop-mediated isothermal amplification, fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis and immunochemiluminometry are integrated in capillaries. Advantages of the capillary bioanalysis system are that: volume is small, analysis speed is fast, detecting flux is large, and automation degree of operation is high. The capillary bioanalysis system is flexible in application, is suitable for analysis of single sample, batches of samples and on-site rapid detection, is capable of reducing acquisition cost and operation cost of equipment significantly, and possesses excellent economic benefits.
Owner:广州市第一人民医院
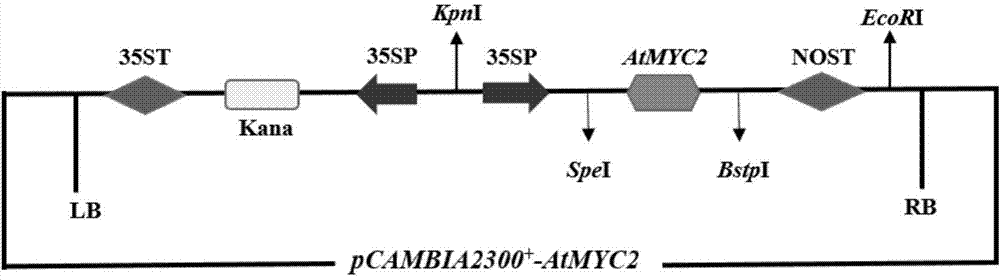
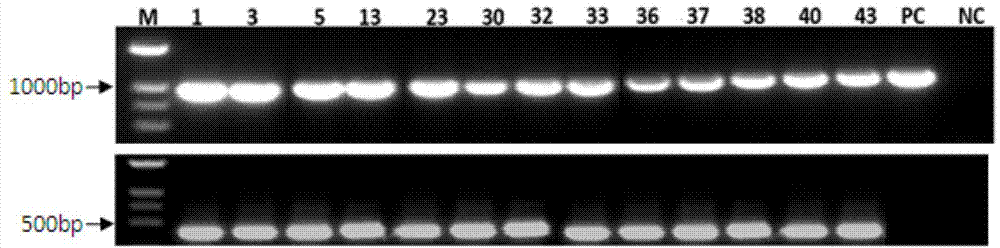
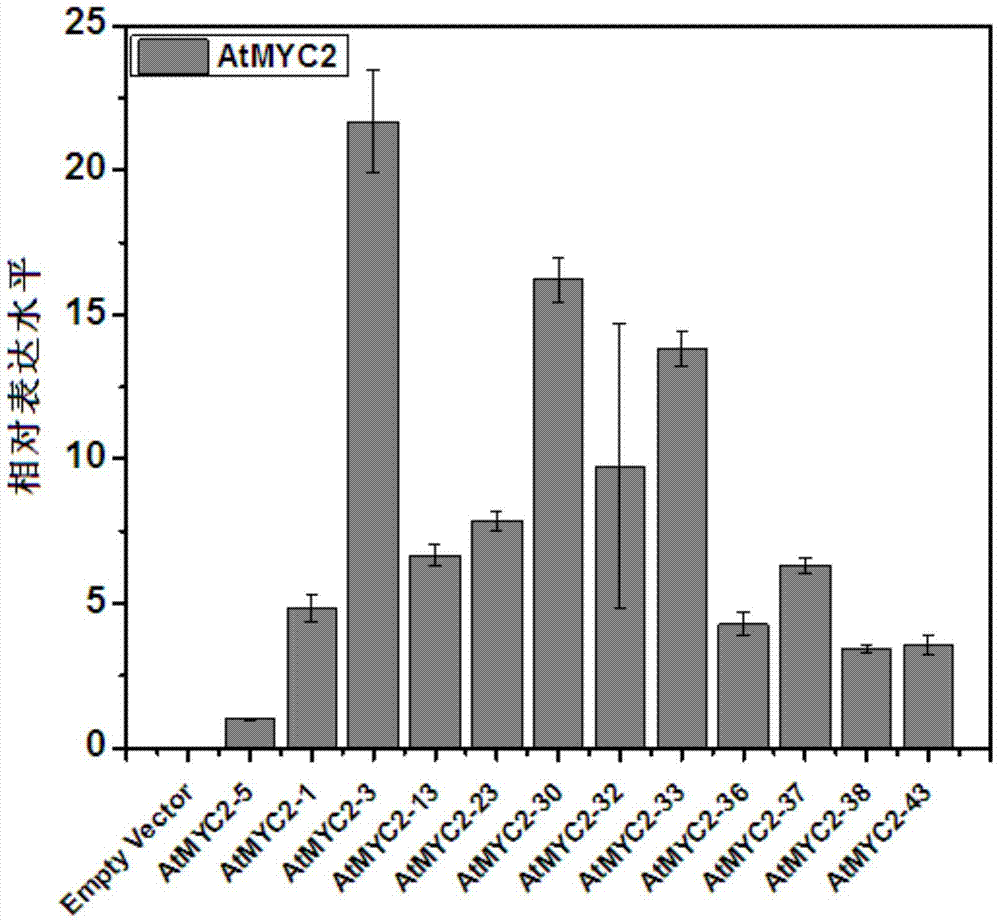
Method for increasing contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using transgene AtMYC2
InactiveCN104726485AIncrease contentGood effectFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSalvianolic acidBiology
The invention relates to a method for increasing the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in a salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a transgene AtMYC2, belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. The method comprises the steps of constructing a high-efficiency expression vector of a plant by using an arabidopsis transcription factor AtMYC2, and carrying out genetic transformation on salvia miltiorrhiza leaves to obtain a gene AtMYC2 overexpressed transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root; analyzing the expression of AtMYC2 in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root and related genes in biosynthetic pathways of tanshinone and salvianolic acid through qRT-PCR; measuring the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); and measuring the antioxidant activity of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in the transgenetic salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root by using a DPPH free radical scavenging method. The invention provides the method for simultaneously increasing the contents of tanshinone and salvianolic acid in salvia miltiorrhiza hairy root and also provides a novel high-quality raw material for producing tanshinone and salvianolic acid with important clinic demands so as to have the positive promoting significance and application value for relieving the problem that the drug resources of tanshinone and salvianolic acid are short.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Forensic swab and kit
InactiveUS20090098559A1Efficient releaseEasy to collectAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementForensic dnaDna recovery
The present invention relates to a high sensitivity crime scene swab device for maximal recovery of trace forensic DNA evidence left at a crime scene for DNA PCR analysis. More particularly, DNA recovery is obtained from fingerprints lifted from surfaces at the crime scene. The invention also relates to a high sensitivity method for DNA analysis of trace DNA obtained by generating small tandem repeat (STR) profiles using a polymerase chain reaction protocol.
Owner:CITY OF NEW YORK
Single molecule electronic multiplex SNP assay and PCR analysis
This invention provides methods of using labeled primers or probes for nucleic acid target detection and to detect the identity or presence of a nucleotide at certain positions in nucleic acid sequences with single molecule sensitivity using nanopore detection, and sets of oligonucleotide primers for use in such methods, as well as methods of quantitative PCR coupled with nanopore detection.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
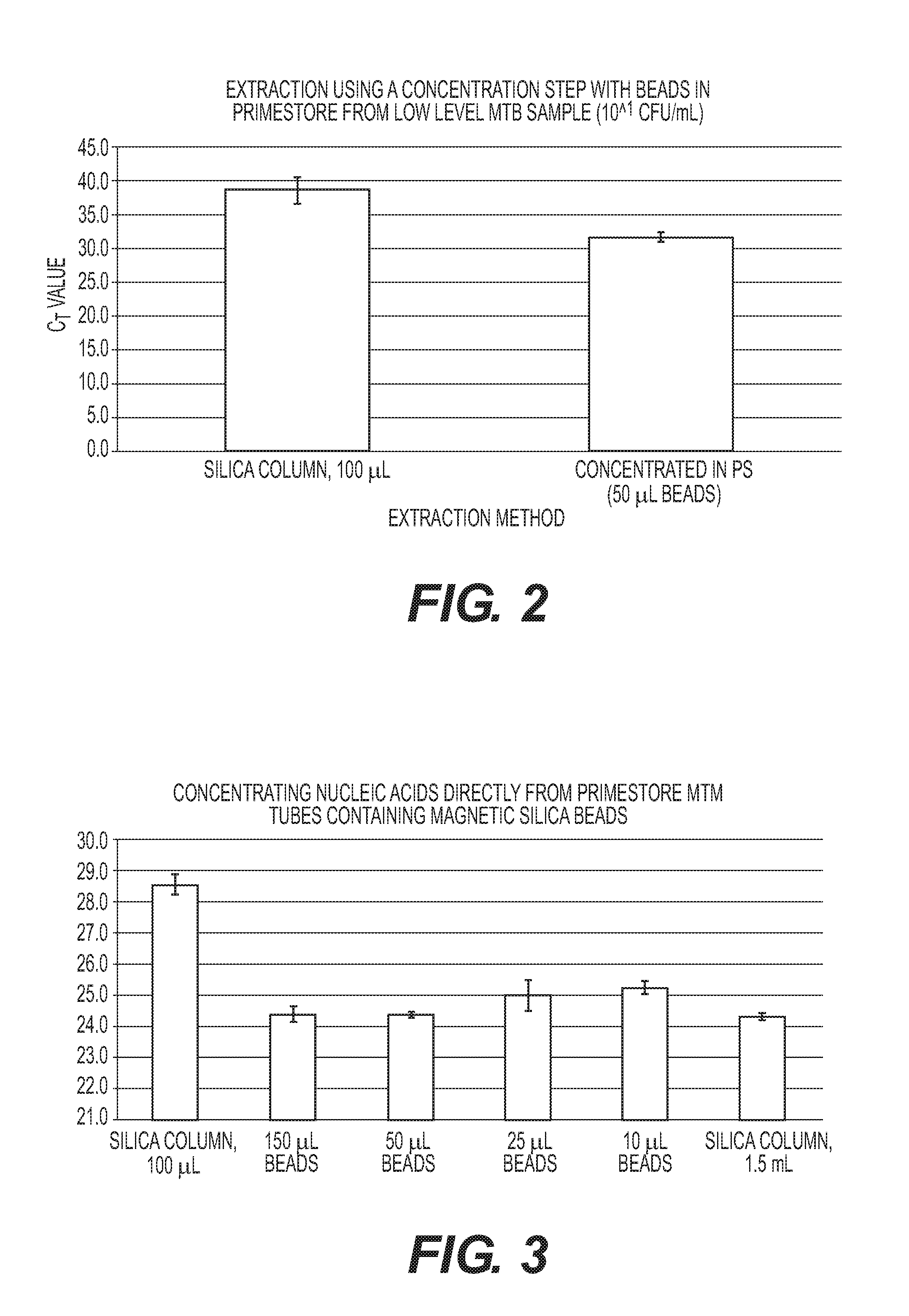
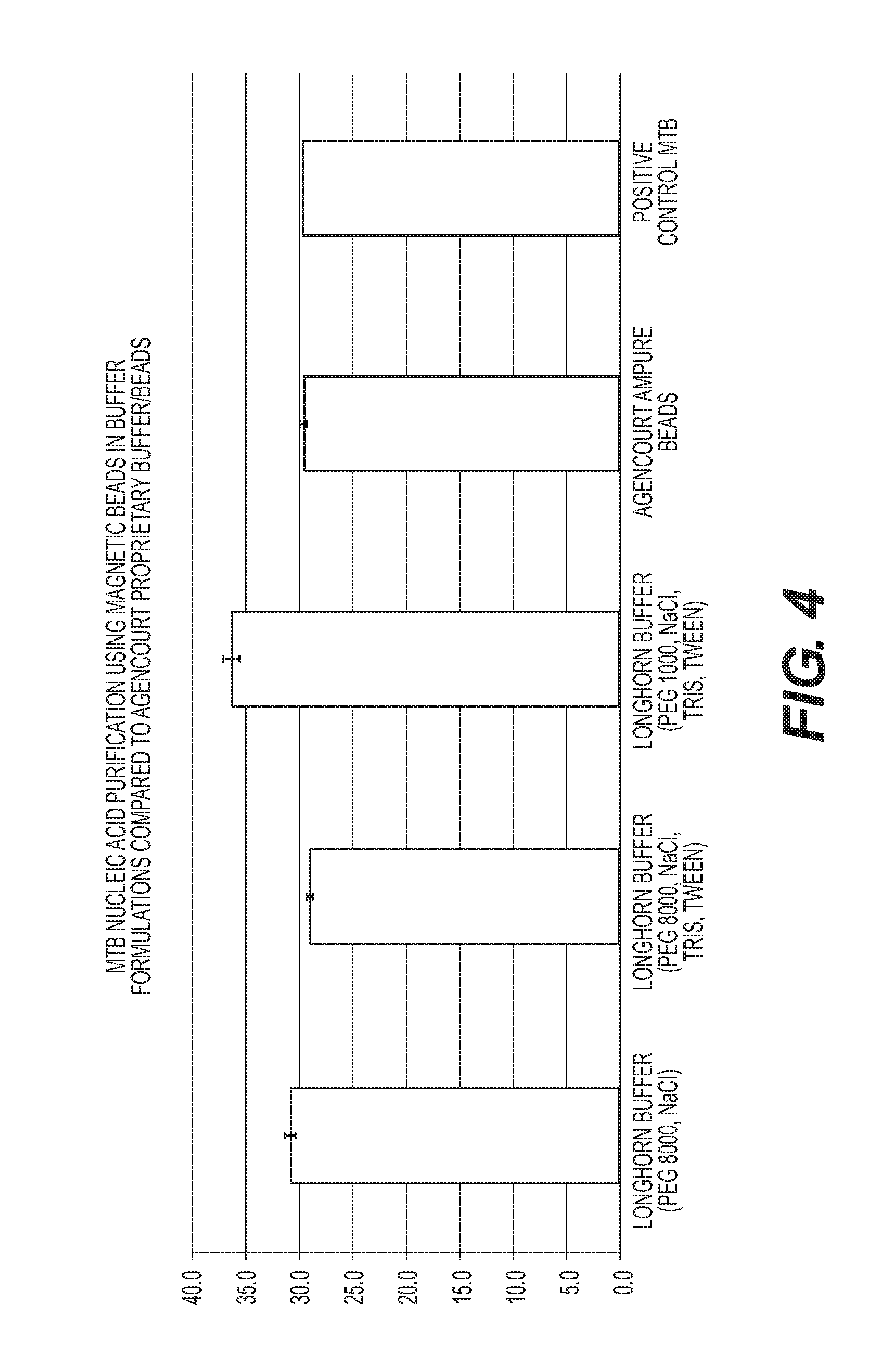
Rapid Methods for the Extraction of Nucleic Acids from Biological Samples
ActiveUS20160333339A1Rapidly and efficiently collecting and identifyingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationPcr analysisChemistry
The invention is directed to compositions and methods for rapidly and efficiently extracting nucleic acids and / or targeted nucleic acids sequences from biological samples. The methods of the invention comprise combining the sample with a buffer and magnetic silicon beads and concentrating the beads with a magnet or other electrical field. Liquid may be removed, or not, and an alkaline buffer is added followed by magnetic carboxy beads in a binding buffer so that nucleic acids transfer to the carboxy beads, which can be easily and quickly isolated once again with a magnet. Total nucleic acid extraction is greatly enhanced. Extracted nucleic acids can be analyzed, for example, by PCR wherein the nucleic acids can be identified and characterized. Carboxy beads may also contain a ligand so as to target specific nucleic acid sequences. The invention is also directed to kits comprising the tools and compositions for performing the methods of the invention.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
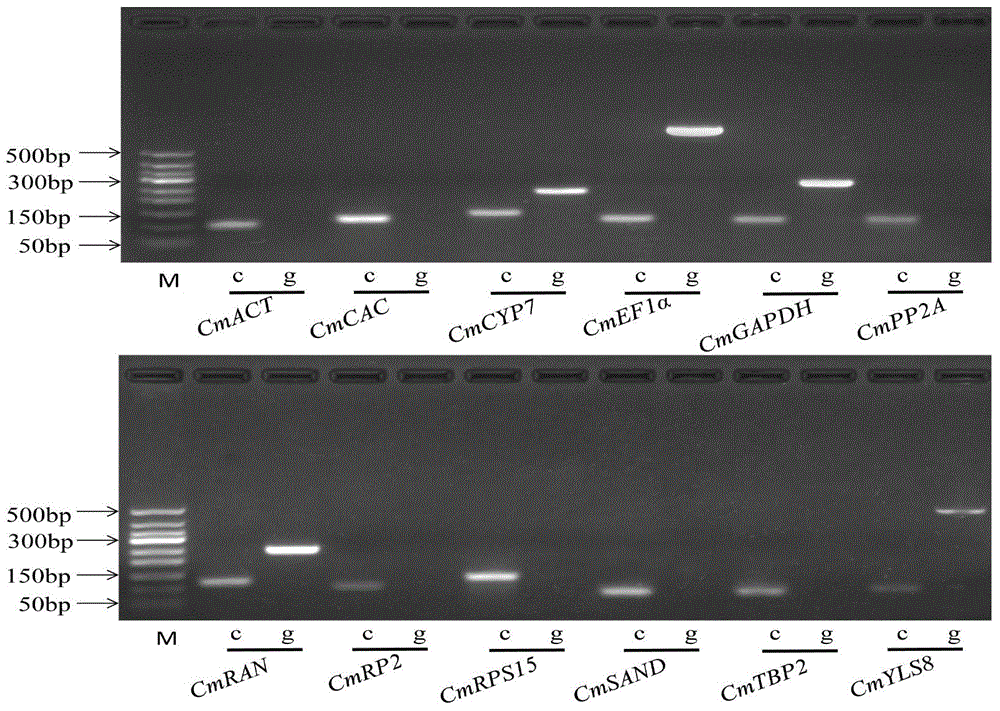
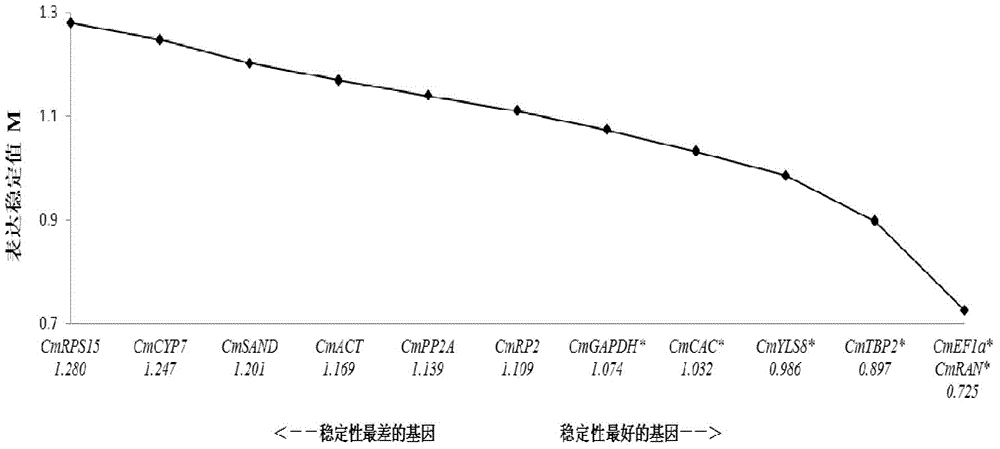
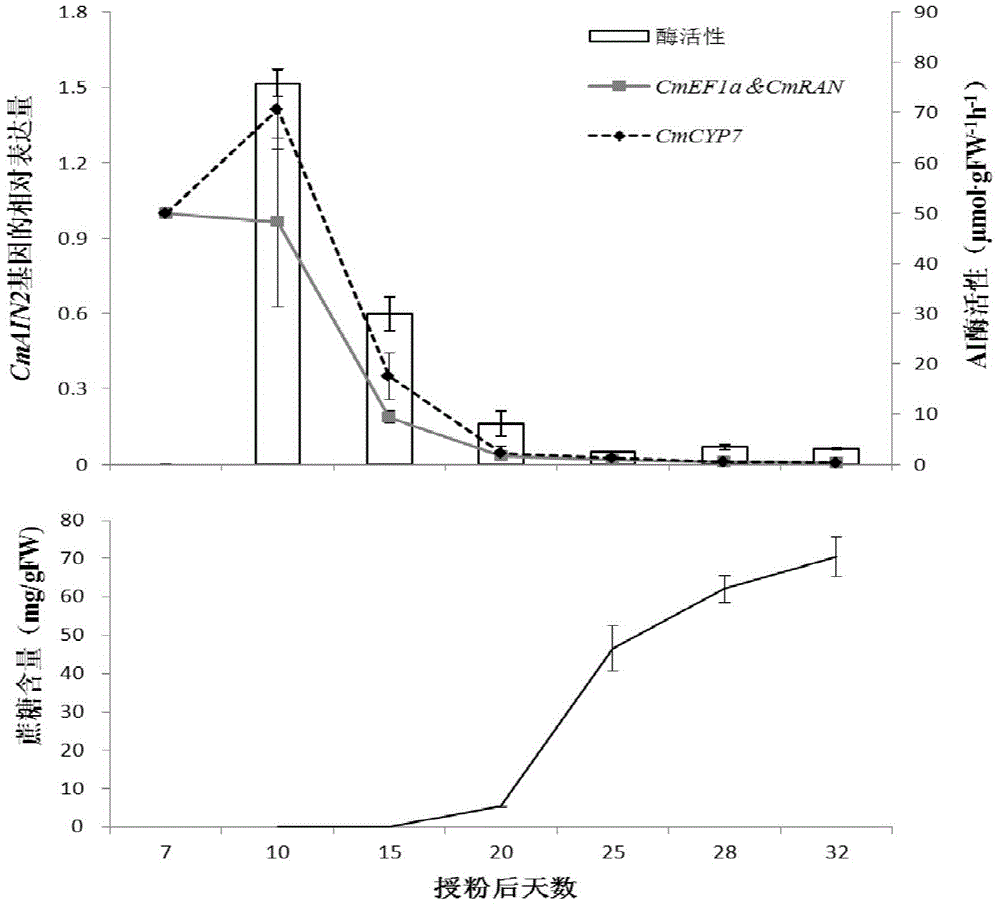
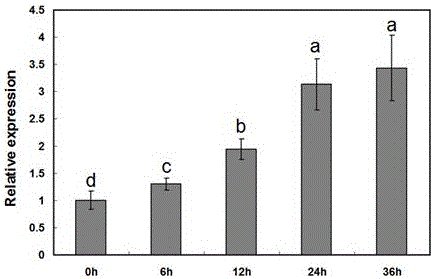
Application of CmEF1 alpha gene and CmRAN gene used as reference genes in analysis of genetic expression of Cucumis melo L. fruits
ActiveCN104357564AProven reliabilityWide applicabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDevelopmental stageReference genes
The invention belongs to the technical field of analysis of gene expression, and discloses application of a CmEF1 alpha gene and a CmRAN gene used as reference genes in analysis of genetic expression of Cucumis melo L. fruits. The nucleotide sequence of the CmEF1 alpha gene is shown in SEQ ID No:1; the nucleotide sequence of the CmRAN gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The invention further discloses a method for analyzing genetic expression of Cucumis melo L. fruits through adopting real-time fluorescence quantification PCR, and the method includes the step that the geometric mean of the gene combination of the CmEF1 alpha gene and the CmRAN gene is used as the reference genes in analysis of genetic expression of Cucumis melo L. fruits. According to the invention, the CmEF1 alpha gene and the CmRAN gene can be stably expressed in Cucumis melo L. fruits adopting different fruit bearing manners and at different developmental stages, so as to serve as a reliable reference gene combination in analysis of genetic expression during the development process of Cucumis melo L. fruits adopting the real-time fluorescence quantification PCR technology for detection.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
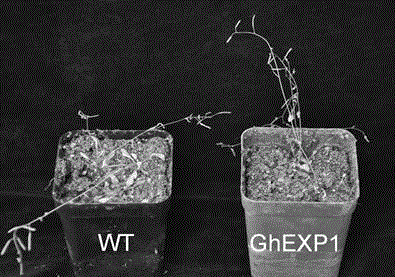
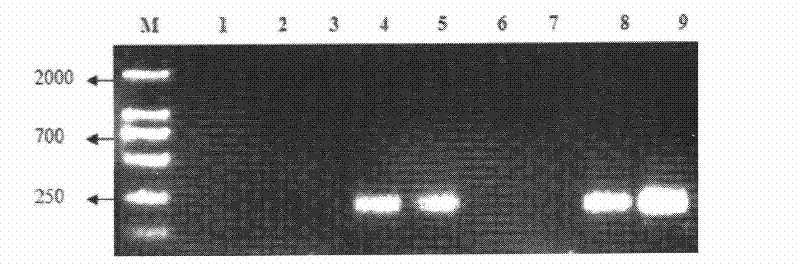
Cotton drought resistant gene GhEXP1 and applications thereof
InactiveCN104988159AReduced drought toleranceEasy to understandPlant peptidesFermentationAgricultural scienceResistant genes
The invention relates to a cotton drought resistant gene GhEXP1 and applications thereof, and belongs to the biology technical field. The related gene GhEXP1 is a cotton expansin gene and is reported for the first time. The gene is cloned from an upland cotton draught resistant species (Ao 3503), and through RT-PCR analysis, people find that the expression of GhEXP1 is up-regulated after a drought treatment. The drought resistant performance of strains containing silenced GhEXP1 gene is obviously reduced. The living rate of GhEXP1 transgene arabidopsis plants is 80% after a 30-day drought treatment; while the living rate of referential wild arabidopsis is 10%; and the result shows that the GhEXP1 gene can prominently improve the drought resistant performance of plants. The GhEXP1 gene is advantageously used for improving the plant drought resistance and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Citrus mature internode stems genetic transformation method
InactiveCN101250549AImprove disinfection effectLow pollution rateVector-based foreign material introductionPlant genotype modificationShootContamination rate
The invention relates to a method for genetically transforming citrus mature internode stems, which comprises following steps: firstly, disinfecting mature materials, selecting semi lignified new shoots in a greenhouse, using sodium hypochlorite solution 5wt% to wipe the shoots once every two days for a week before the shoots are sampled, wiping for 3-4 times together, then, cutting the shoots which are wiped with the sodium hypochlorite solution, cutting the shoots into stems of 4-5cm under the aseptic condition, using the sodium hypochlorite solution 10wt% which is added with tween 2-3 drops to dip for 20-35min, washing with sterilized water for 3-4 times, cutting the shoots into the internode stems of 1-1.5cm to preserve for use, secondly, transforming, thirdly, regenerating resistant buds, fifthly, grafting for the second time in the greenhouse, sixthly, identifying the resistant buds and resistant plants, and adopting a public-known PCR analysis method to identify. The citrus mature materials of the invention have good disinfection effect and low contamination rate, the adventitious bud induction frequency reaches 48%, the grafting survival rate of the resistant buds reaches more than 80%, and regenerated transformed plants do not have chimerism. The method is in particular suitable for genetically transforming mature internode stems of main cultivars of citrus such as crystal sugar oranges, navel orange, Ponkan and the like.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Pumpkin SSR labeled primers applied to multiplex PCR reaction and application of pumpkin SSR labeled primers
ActiveCN104694642AImprove analysis efficiencyReduce analysis costsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSize differenceHybrid seed
The invention discloses three groups of pumpkin SSR labeled primers applied to multiplex PCR reaction, belongs to the technical field of plant molecular biology DNA marks, and discloses an application of the primers to identification of pumpkin varieties and a pumpkin variety identification method. A batch of pumpkin SSR marks are developed by using pumpkin transcriptome sequencing results; three marks are selected from the marks and are characterized in that the polymorphism is high, the strip pattern is excellent, the size difference of amplification products is about 50bp, and primers cannot be matched with each other for forming hairpin structure SSR loca; by virtue of optimization of a PCR reaction system and an amplification program, a multiplex PCR analysis technical system with three SSR loca is built; the SSR marks are excellent in multiplex PCR amplification strip pattern, high in polymorphism and easily readable in results; the analysis efficiency of SSR is remarkably improved; the SSR marks can be applied to the fields of identification of pumpkin varieties, construction of fingerprint maps and identification of purity of hybrid seeds.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for extracting total DNAs of soil microorganisms at high purity
InactiveCN102643797AHigh yieldGood cracking effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFreeze and thawStructural composition
The invention discloses a method for extracting total DNAs of soil microorganisms at high purity. CTAB (Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide), lysozyme, protease and SDS (Sodium Dodecyl Sulfonate) act together to perform lysis of cells and simultaneously freeze and thaw the cells repeatedly; therefore, an excellent cell lysis effect is achieved; the humic acid is removed by utilizing PVP (Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone), CaC12 and BSA (Bull Serum Albumin); and the DNAs are precipitated by utilizing isopropanol so that the purity of the obtained DNAs is high. The method is simple and convenient; and without being purified, the DNAs obtained by the method can be used for subsequent PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analysis and DGGE (Denaturing Gradient Gel Electrophoresis) analysis. The purity of the extracted DNAs meets the requirement for directly performing subsequent molecular biological research; the extracted DNA segments can be subjected to 16SrDNA amplification and DGGE atlas analysis; glue cutting recovery and basic group sequencing can be performed on specific stripes of the DGGE band; unknown bacteria can be identified through comparison with the conventional sequences in an RDP (Ribosomal Database Project) database or by establishing a new sequence probe; and therefore, the structural composition of the microbial community can be determined, and a foundation can be laid for researching the structural diversity and ecological functions of the soil microorganisms in the rhizosphere of the mulberry in future.
Owner:INST OF ECONOMIC CROP HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for extracting total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of mulberry rhizosphere soil microorganisms by adopting plurality of measures
InactiveCN102643794AGood cracking effectHigh yieldMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFreeze and thawCommunity structure
The invention discloses a method for extracting total DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of mulberry rhizosphere soil microorganisms by adopting a plurality of measures, which can achieve a good cell lysis effect by utilizing PVP (polyvinyl pyrrolidone) prewashing to remove humic acid, the synergy of CTAB (cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide), lysozyme, protease and SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) to lyse cells and repetitively freezing and thawing the cells at the same time and utilizes PEG8000 to precipitate DNA, so that the purity of the obtained DNA is high. The adopted method is simple and convenient, and the DNA can be used in subsequent PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analysis and DGGE (denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis) analysis without needing to be purified. The extracted DNA is so pure as to meet the requirement of direct subsequent molecular biology research, an extracted DNA fragment can be used in the amplification and DGGE map analysis of 16SrDNA, moreover, the specific band gel extraction and base sequencing of a DGGE band can be carried out, comparison with the sequence existing in an RDP (ribosomal database project) database can be carried out, or a new sequence probe can be established to identify unknown bacteria, so that the composition of a microbial community structure can be determined, and thereby laying a foundation for the future research of the community structure diversity and the ecological functions of the mulberry rhizosphere soil microorganisms.
Owner:INST OF ECONOMIC CROP HUBEI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Nanopipette device and method for subcellular analysis
ActiveUS20160032275A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsChemical treatmentScanning ion-conductance microscopy
Described herein are devices and methods for extracting cellular material from living cells and then depositing them into to a receptacle in a nanoliter scale. Using a nanopipette integrated into a scanning ion conductance microscope (SICM), extraction of mitochondrial DNA from human BJ fibroblasts and Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) transcripts from HeLa / GFP cells was achieved with minimal disruption to the cellular milieu and without chemical treatment prior to obtaining the isolated sample. Success of the extraction was confirmed by fluorescence microscopy and PCR analysis of the extracted material. The method and apparatus may be applied to many different cell types and intracellular targets, allowing not only single cell analysis, but single subcellular compartment analysis of materials extracted in their native state.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for improving stress resistance of chrysanthemum through trans-CgHSP70 genes
InactiveCN102174566AImprove stress toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial thermal analysisFluorescencePlant genetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of plant gene engineering and transgenic breeding, and relates to a method for improving the stress resistance of cut chrysanthemum through trans-CgHSP70 genes. CgHSP70 established plant expression vectors obtained by cloning from Zhongshan purple cinnamon of the chrysanthemum are transferred into the cut chrysanthemum by using an agrobacterium-mediated method for cultivation so as to initially obtain resistant plants, and positively transferred plants are obtained through the screening of hygromycin resistance; PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis is performed on converted plants to prove that endogenous genes are transferred into genome DNA of transgenic plants and transcription occurs; and the resistance analysis on the offsprings of the transgenic plants proves that the resistance to high temperature, drought and high salt is obviously improved. In the invention, the stress resistance of the cut chrysanthemum is improved through the conversion of the endogenous CgHSP70 genes and normal transcription expression as well as the induction of the expression of the genes at an adverse environment; a novel and practical method is provided for selecting and breeding stress resistance varieties of chrysanthemum by using a gene engineering technology; and the breeding progress of the biotechnology of the chrysanthemum can be effectively accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
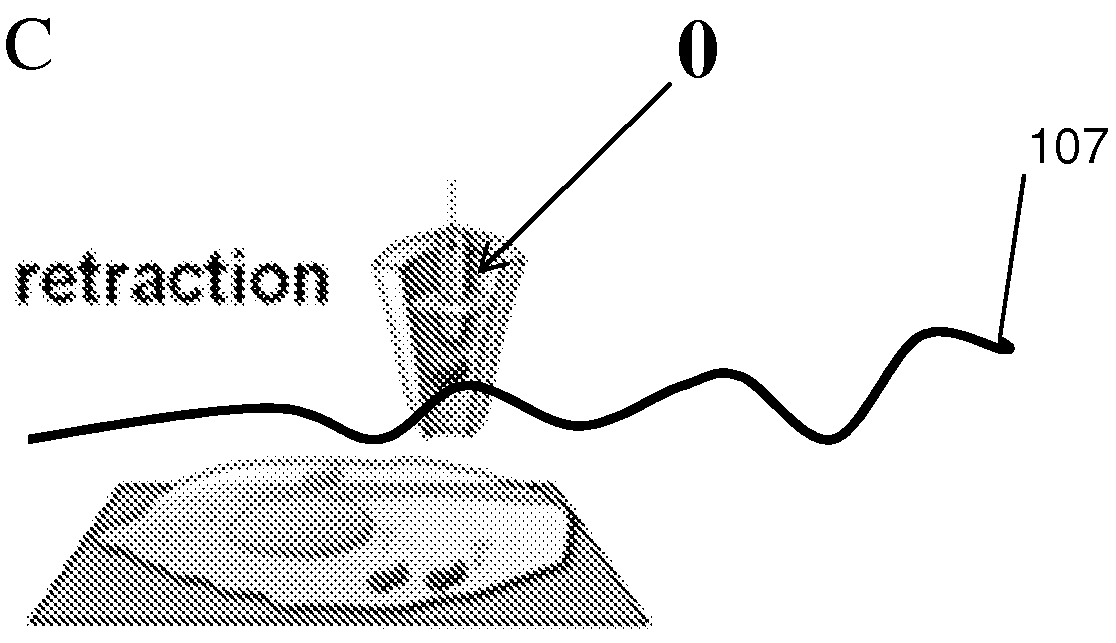
Six-color real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analyzer
ActiveCN104267009AReduce volumeReduce power consumptionFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLength wave
The invention relates to a six-color real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analyzer. The six-color real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR analyzer comprises a light source excitation part (A) and a light detector part (C), and is characterized in that the light source excitation part (A) is provided with six independent light source excitation passages, the light detector part (C) is provided with six independent detection passages, and a certain angle is formed between the light source excitation part (A) and the light detector part (C). A light path system adopts a fixed light path, light filters are superposed to realize the selection of wavelength coverage, and the wavelength coverage of each passage can be changed by changing the wavelength of the light filters so as to realize different wavelengths.
Owner:BEIJING GENOME BIOTECH
Method for extracting DNA from plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology and particularly relates to a method for extracting DNA from a plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol. The provided method for extracting DNA from the plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol comprises the following steps: using a specific lysis solution to lyse a cell, extracting the DNA with Tris phenol-chloroform mixed solution, chloroform and a sodium perchlorate combination solution, and purifying the extracted DNA through a self-made adsorption column membrane, thereby obtaining the high-quality genomic DNA. The purity of the DNA extracted through the method for extracting DNA from the plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol is high, the impurity is low, the DNA is further prevented from being damaged by asuperoxide anion free radical or active oxygen, the completeness of the extracted genomic DNA is guaranteed, and the method is favorable for the scientific researches like construction of the gene library, PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analysis, and Southern hybridization.
Owner:广州海思医疗科技有限公司
Variable-temperature metal module with precise temperature compensation and temperature compensating method
ActiveCN101974421AImprove temperature uniformityHigh precisionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringControl circuit
The invention relates to a variable-temperature metal module with precise temperature compensation and a temperature compensating method. Sample holes are arranged on the variable-temperature metal module. The variable-temperature metal module comprises temperature compensating heaters, the arrangement number of the temperature compensating heaters is less than or equal to the arrangement number of the sample holes, the temperature compensating heaters are connected with a control circuit, and each temperature compensating heater is singly arranged around the sample holes. The invention is used for a gene amplifying instrument and a full-automatic medical PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analytic system and can increase the temperature uniformity of the variable-temperature metal module to + / - 0.05 DEG C from + / -0.3 DEG C in the conventional technology.
Owner:上海宏石医疗科技有限公司
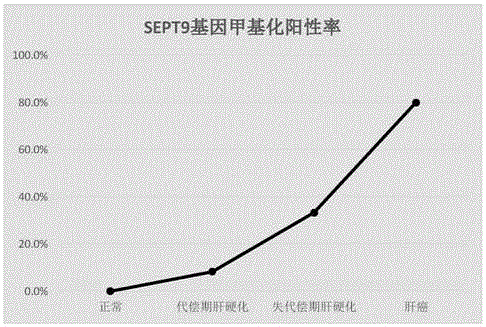
Composition for detecting liver cancer and application thereof
InactiveCN106222267AQuick judgmentEasy to judgeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBlood plasmaProtein C
The invention provides a composition for detecting liver cancer, which comprises a nucleic acid for detecting methylation status in at least one zone of SEPT9 gene and fragments thereof and a reagent for detecting concentration of alpha fetoprotein in serum, so as to detect the liver cancer by means of the methylation status of the gene and the fragments thereof and the concentration of the alpha fetoprotein. The invention also provides a kit comprising the composition and an in-vitro detection method for the liver cancer. In the invention, the DNA in a plasma sample is analyzed by real-time PCR, so as to conveniently detect the SEPT9 gene and the fragments thereof, and according to the circulating threshold value (Ct) of the real-time PCR, the sample is conveniently and quickly determined to be positive or negative; and furthermore, the invention provides the accurate in-vitro detection method by detecting the concentration of the alpha fetoprotein in the sample.
Owner:BIOCHAIN BEIJING SCI & TECH +1
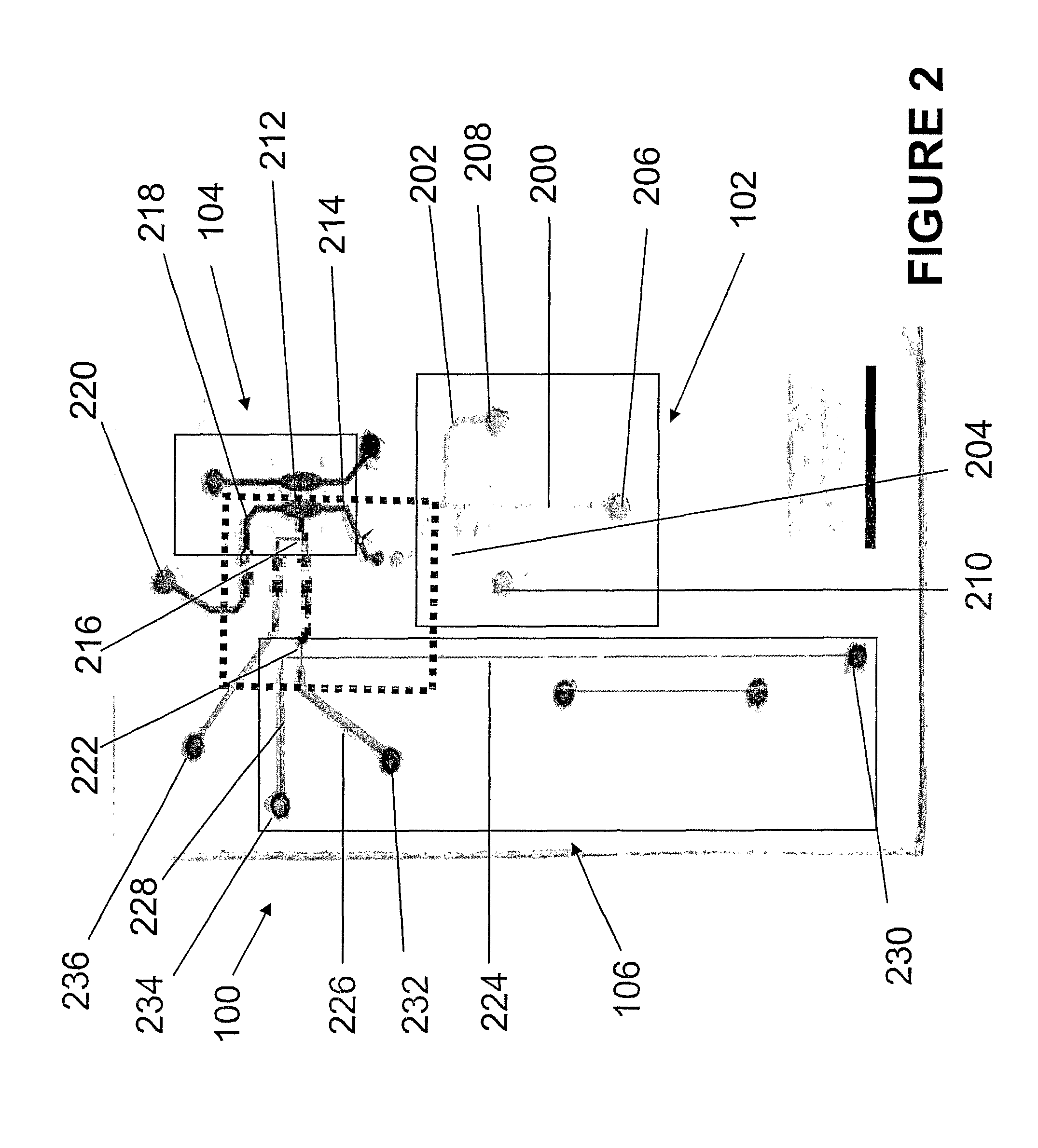
Sample preparation apparatus
The invention provides an apparatus for preparing a biological sample for PCR analysis has an inlet (4) for receiving the sample (15) and a sieve (13) through which the sample is forced by screwing down an inlet cap (16). A lysis solution between two rupturable seals (11 and 12) is effective to disrupt the cells of the sample and release nucleic acid. The apparatus is mounted releasably on a PCR machine (2) having a motor (2') releasably coupled with a drive mechanism (3, 36,40) in the apparatus to effect a rotary and a vertical up and down movement of its components (30, 31, 32, 42). The apparatus has a transparent cuvette (5) and a needle (71) extending to the lower end of the cuvette, by which the prepared sample is dispensed to the cuvette for PCR analysis.
Owner:SMITHS DETECTION WATFORD LTD
Plasmid reference molecule of quantitative determination of nucleic acids from transgenic soybean GTS40-3-2
InactiveCN102517393AAchieve traceabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionInductively coupled plasmaMass spectrometric
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com