Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Quantitative PCR analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
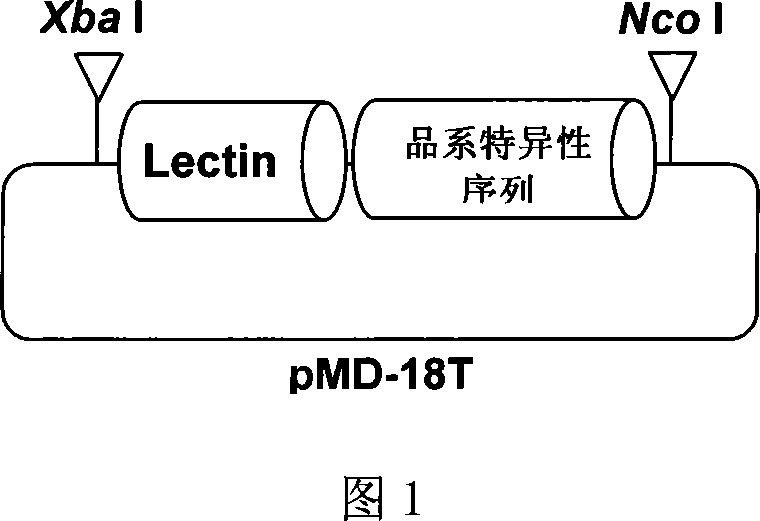
Plasmid control molecule for detection of transgenic soybean and building method thereof
InactiveCN101775440AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionEnzyme digestionPositive control
The invention relates to a plasmid control molecule for detection of transgenic soybean and a building method thereof. The plasmid control molecule contains a control gene lectin specific sequence in soybean, a 3' end transformant specific sequence and a 5' end transformant specific sequence of transgenic soybean MON89788. Through designing a specific qualitative PCR primer, the lectin gene specific sequence, the 3' end transformant specific sequence and the 5' end transformant specific sequence of the MON89788 are obtained through amplification. Through molecular cloning techniques such as enzyme digestion, connection, transformation and the like, the three specific sequence segments are built into a plasmid molecule to obtain an artificially recombined plasmid control molecule pMD-LM3M5. According to tests, the plasmid control molecule built in the invention can fully substitute for the positive control of the transgenic soybean MON89788 and is suitable for the transformant specific qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis and detection of the MON89788 soybean.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
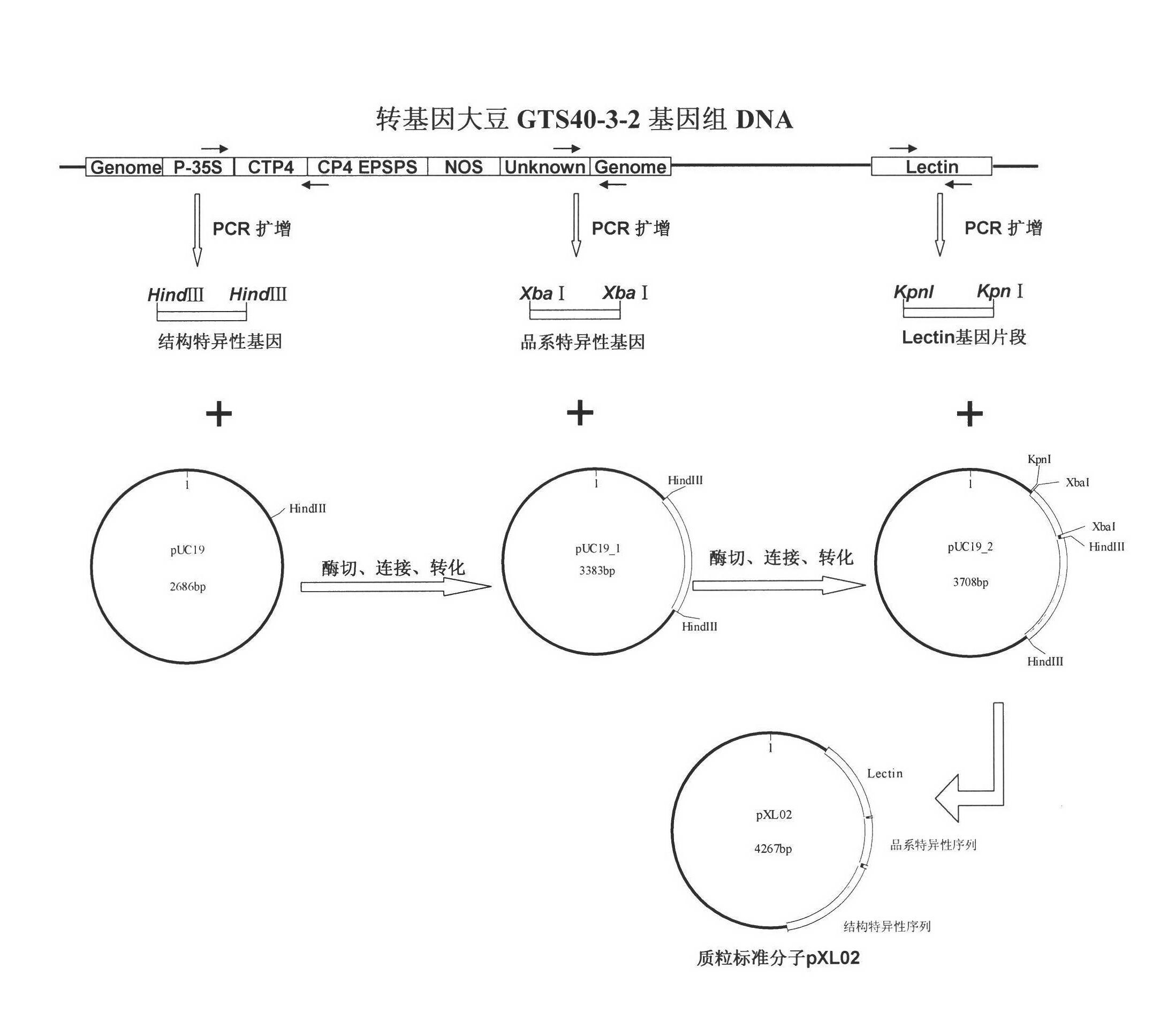
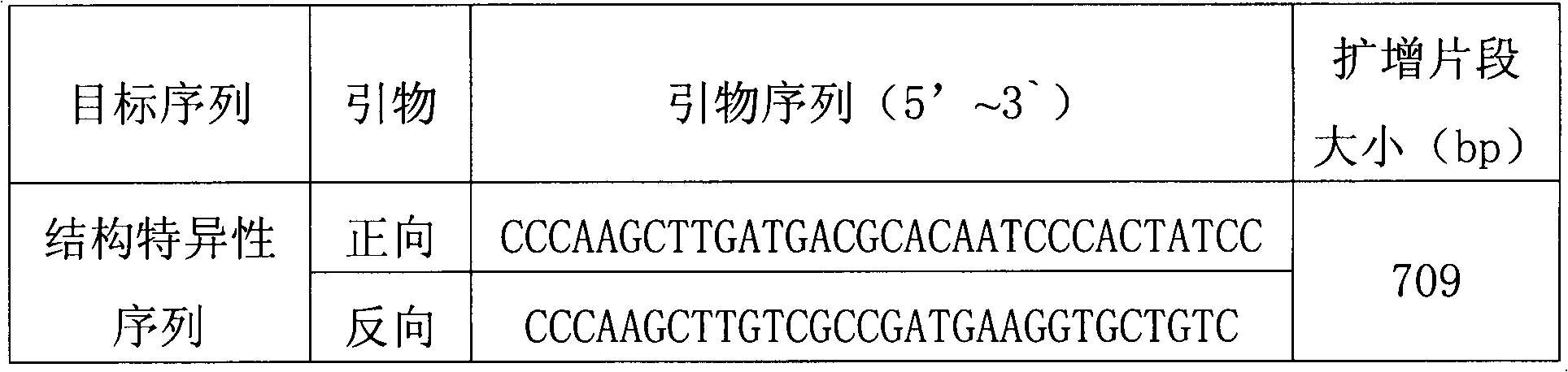
Standard plasmid molecule for detection of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and constructing method thereof
InactiveCN101063171AAvoid missingThe analysis result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringInternal standardPlasmid
The invention discloses a standard plasmid molecule to check genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and constructing method, which comprises the following steps: incorporating strain special fragment of the genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and special fragment of soybean internal standard gene Lectin; analyzing exogenesis inserting carrier by-pass ortho gene sequence of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2; designing strain special PCR primer; augmenting; getting strain special fragment of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and soybean internal standard gene special sequence; constructing into a plasmid molecule with molecular cloning method; getting artificial retooling plasmid molecule pMD-RRS. This standard plasmid molecule can be fit for strain special quantitative PCR analysis and check of genetic improved soybean strain GTS40-3-2 sample.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Capillary bioanalysis system, and analytical method and applications thereof
ActiveCN103409317AReduce volumeFast analysisBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluid controlMedical equipment
The invention discloses a capillary bioanalysis system, and an analytical method and applications thereof, and belongs to the field of medical equipment and biological detection technologies. The capillary bioanalysis system comprises a three-dimensional movement sample injecting platform, a temperature control-optical detection module, a magnetic field control module, a fluid control unit and a capillary array. The three-dimensional movement sample injecting platform and the fluid control unit are arranged on the two sides of the capillary array, and the capillary array is provided with the temperature control-optical detection module and the magnetic field control module. According to the capillary bioanalysis system, the droplet technology and the magnetic bead technology are combined, and bioanalysis processes such as loop-mediated isothermal amplification, fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis and immunochemiluminometry are integrated in capillaries. Advantages of the capillary bioanalysis system are that: volume is small, analysis speed is fast, detecting flux is large, and automation degree of operation is high. The capillary bioanalysis system is flexible in application, is suitable for analysis of single sample, batches of samples and on-site rapid detection, is capable of reducing acquisition cost and operation cost of equipment significantly, and possesses excellent economic benefits.
Owner:广州市第一人民医院
Method and device for quantitative PCR multi-wavelength fluorescence detection
ActiveCN101705280ANo crosstalkOvercome the effects of decay and degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLength wave
The invention discloses a method and a device for quantitative PCR multi-wavelength fluorescence detection. N fluorescence wavelength detection passages with the mutual interval as a module standard hole site are arranged, each fluorescence wavelength detection passage is provided with a light source exciting optical fiber path and a fluorescence receiving optical fiber path, the light sources of the n light source exciting optical fiber paths respectively pass through a collimating lens and an exciting light filter so as to obtain exciting light with required wavelength, and then the exciting light is irradiated onto n test tube exciting reagent samples through focusing; the fluorescence of the n test tube exciting reagent samples respectively enters the fluorescence receiving optical fiber paths, the fluorescence with the required wavelength is obtained through the collimating lens and the exciting light filter, is irradiated onto a plane reflecting mirror and is then refracted onto n working surfaces of the same polyhedral reflecting mirror through the plane reflecting mirror, and the fluorescence of the n fluorescence wavelength detection passages is converged onto a photoelectric surface of an optical sensor through the polyhedral reflecting mirror so as to realize the real-time synchronous detection of the multi-wavelength fluorescence. The invention can greatly improve the detection efficiency, no exciting light interference is generated in detection, and quantitative PCR analysis results are exact.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOER TECH CO LTD
Method for improving stress resistance of chrysanthemum through trans-CgHSP70 genes
InactiveCN102174566AImprove stress toleranceMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial thermal analysisFluorescencePlant genetic engineering
The invention belongs to the field of plant gene engineering and transgenic breeding, and relates to a method for improving the stress resistance of cut chrysanthemum through trans-CgHSP70 genes. CgHSP70 established plant expression vectors obtained by cloning from Zhongshan purple cinnamon of the chrysanthemum are transferred into the cut chrysanthemum by using an agrobacterium-mediated method for cultivation so as to initially obtain resistant plants, and positively transferred plants are obtained through the screening of hygromycin resistance; PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis is performed on converted plants to prove that endogenous genes are transferred into genome DNA of transgenic plants and transcription occurs; and the resistance analysis on the offsprings of the transgenic plants proves that the resistance to high temperature, drought and high salt is obviously improved. In the invention, the stress resistance of the cut chrysanthemum is improved through the conversion of the endogenous CgHSP70 genes and normal transcription expression as well as the induction of the expression of the genes at an adverse environment; a novel and practical method is provided for selecting and breeding stress resistance varieties of chrysanthemum by using a gene engineering technology; and the breeding progress of the biotechnology of the chrysanthemum can be effectively accelerated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Multi-microbe solid fermentation ethanol and acetic acid production key microbe quantitative analysis method
ActiveCN107523625AStable amplificationAmplification results are clearMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesAcetic acidMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of liquor production, particularly to a multi-microbe solid fermentation ethanol and acetic acid production key microbe quantitative analysis method. The method comprises performing quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) analysis on HIS3 genes of saccharomyces cerevisiae, AHD1 genes of schizosaccharomyces pombe and 16S rRNA (ribonucleic acid) fragments of lactobacillus to analyze the change tendency of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, the schizosaccharomyces pombe and the lactobacillus in liquor yeasts and fermented grains and accordingly to predict the yield of ethanol. The multi-microbe solid fermentation ethanol and acetic acid production key microbe quantitative analysis method has the advantages of being high in detecting speed and sensitivity, good in accuracy and specificity and free from cultivation.
Owner:KWEICHOW MOUTAI COMPANY
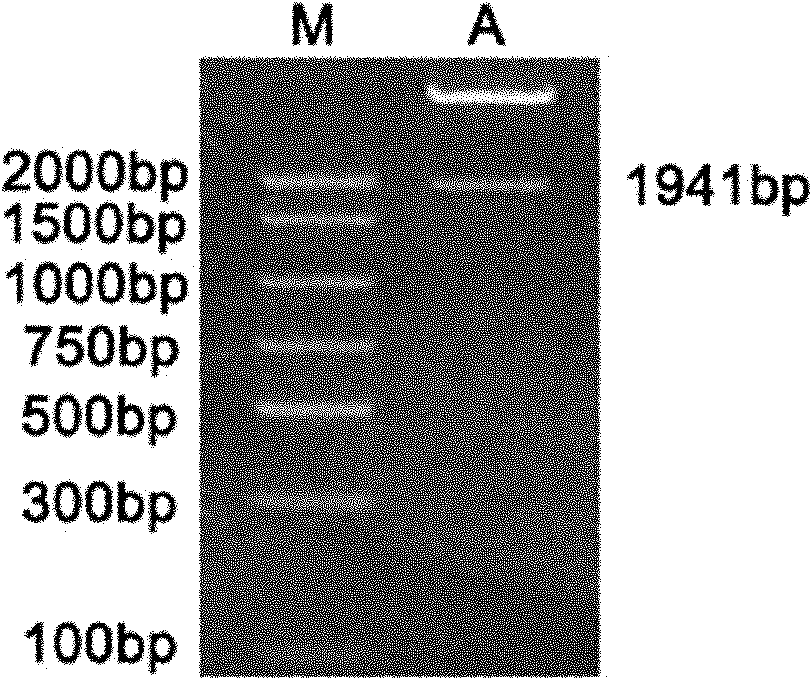
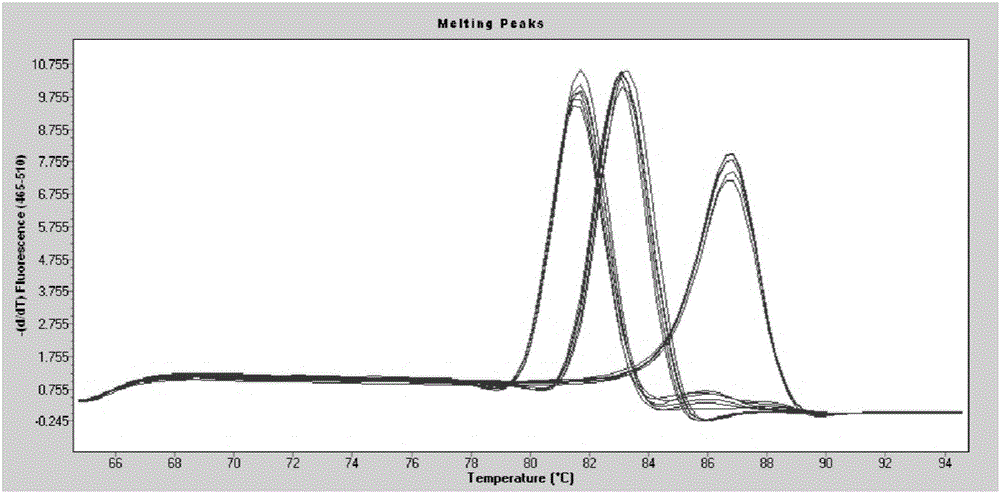
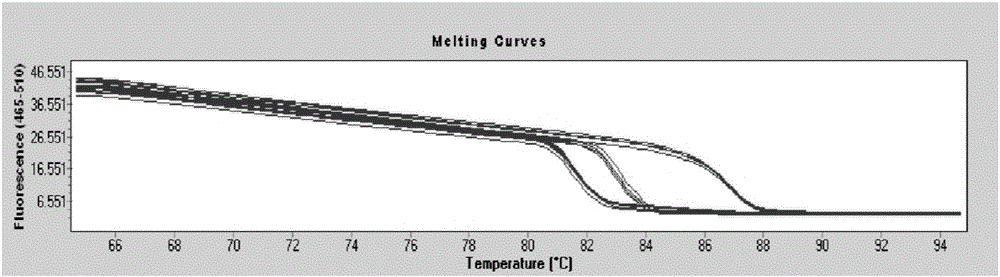
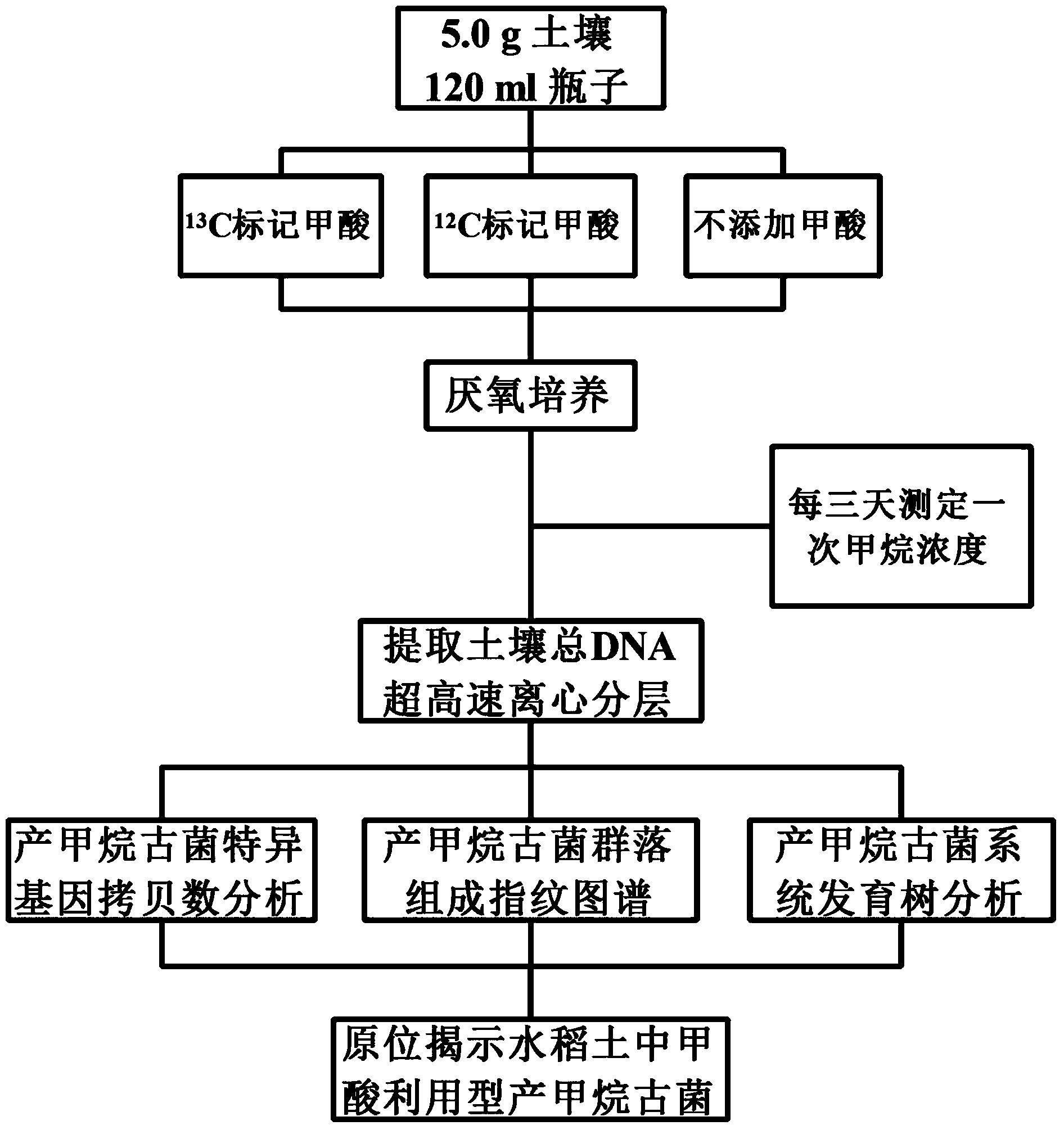
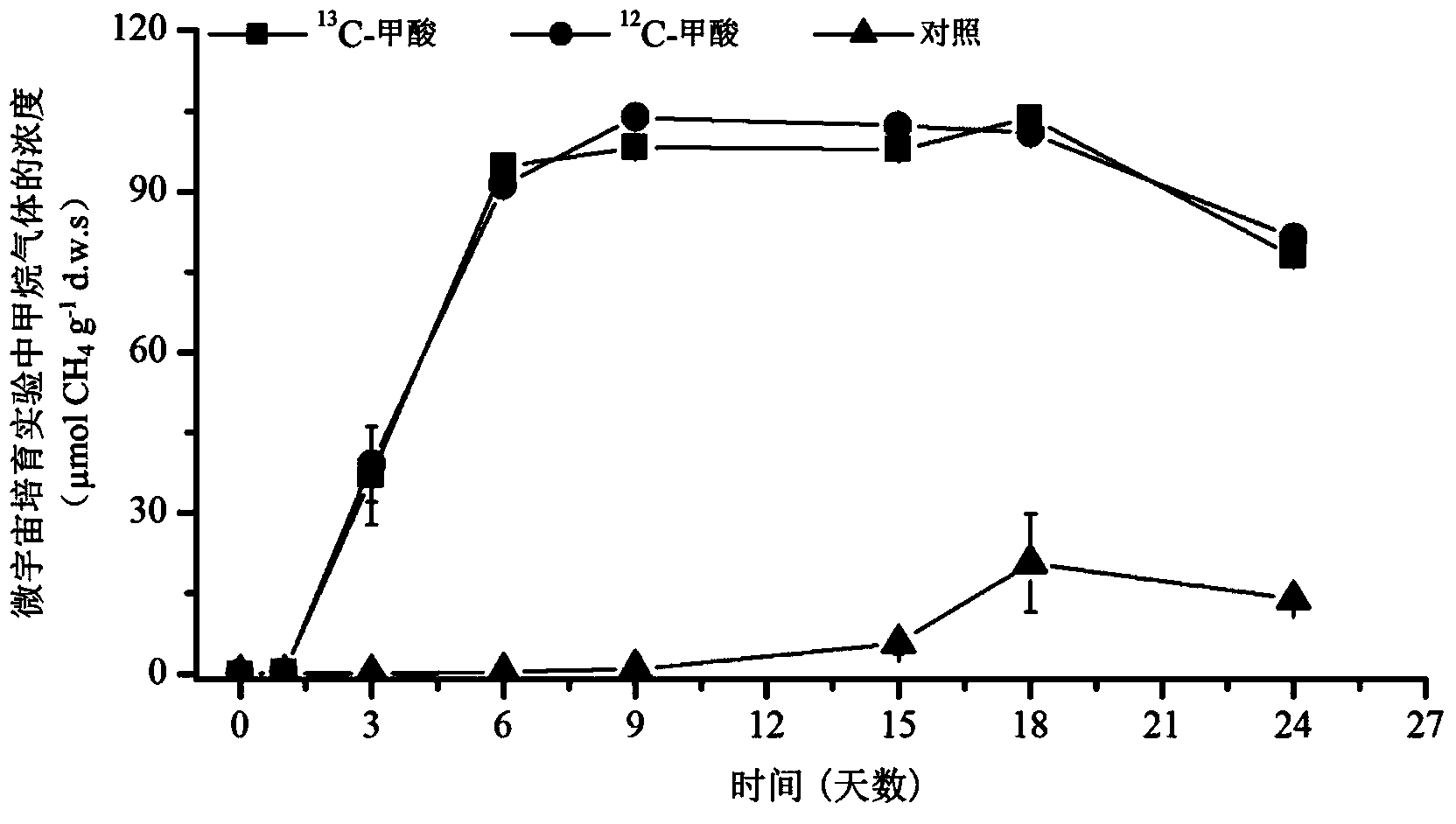
Method for revealing and distinguishing paddy field formic acid utilization type methanogenic archaea in situ by adopting DNA-based stable isotope probing technology
A method for revealing and distinguishing paddy field formic acid utilization type methanogenic archaea in situ by adopting DNA-based stable isotope probing technology comprises the followings steps: (1), collecting a paddy soil sample; (2), performing a micro universe cultivation experiment of <13>C-formic acid; (3), performing centrifugation layering on the microbe total DNA of <13>C-formic acid cultivation soil by using an ultracentrifuge; (4), performing real-time quantitative PCR analysis and finger-print analysis on methanogenic archaea genes in layers of multiple buoyant densities after layering to judge whether the paddy soil contains the formic acid utilization type methanogenic archaea with metabolic activity. Therefore, the method can be used for keenly revealing the paddy field formic acid utilization type methanogenic archaea in situ based on the DNA-based stable isotope probing technology, and has great significance on the understanding of the paddy field nutrient cycling process driven by microbes and the cognition of the ecological functions of paddy field methanogenic archaea functional groups.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Plasmid reference molecule of quantitative determination of nucleic acids from transgenic soybean GTS40-3-2
InactiveCN102517393AAchieve traceabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionInductively coupled plasmaMass spectrometric
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
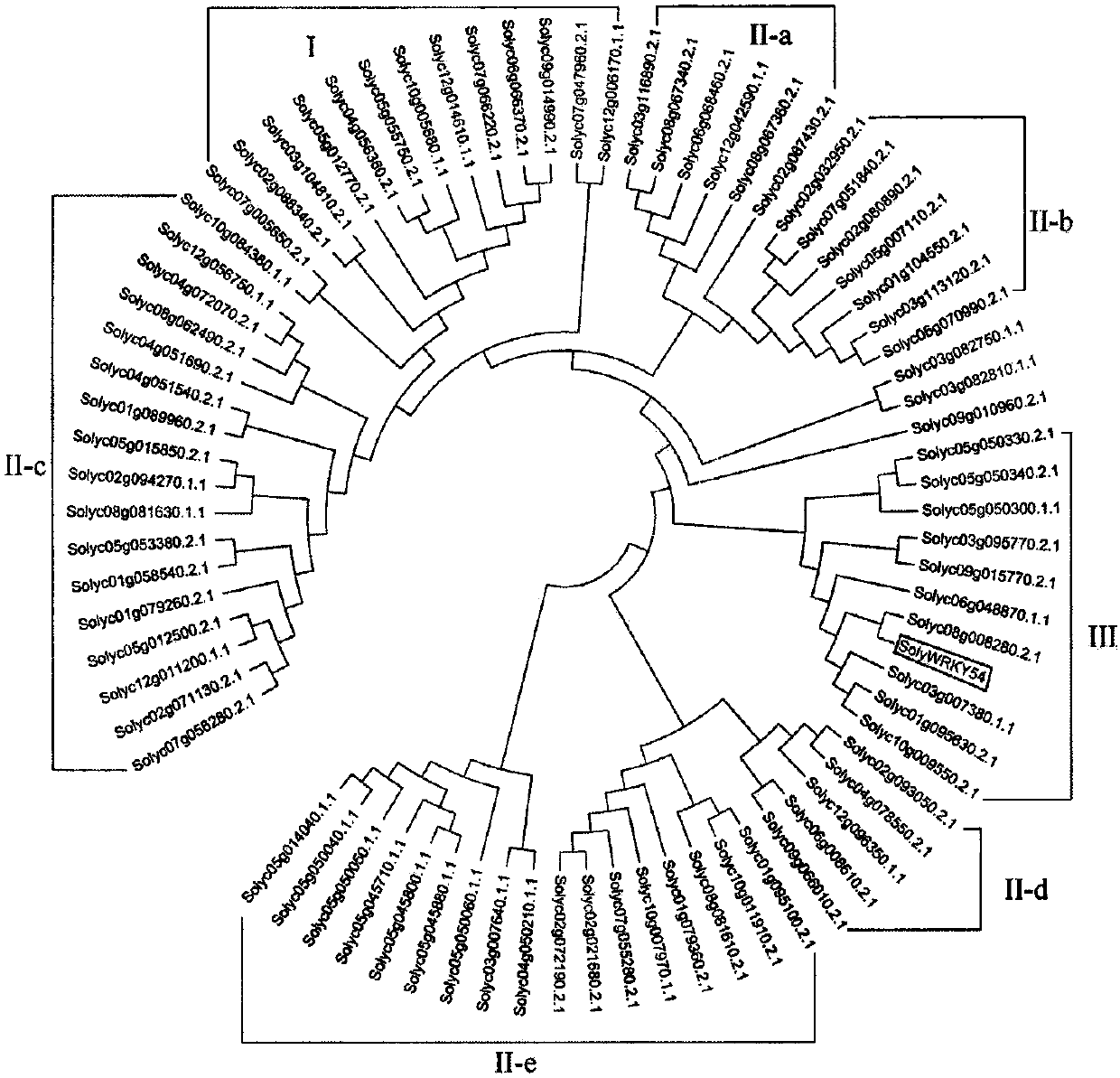
Identification and application of tomato SolyWRKY54 transcription factor in regulating and controlling tomato yellow leaf curl virus
The invention discloses identification and an application of a tomato SolyWRKY54 transcription factor in regulating and controlling tomato yellow leaf curl virus. According to the invention, a WRKY transcription factor gene SolyWRKY54, which responds to the tomato yellow leaf curl virus, is identified from tomatoes; protein coded by the gene belongs to III sub-family in a WRKY transcription factorfamily. A semiquantitative PCR result shows that a susceptible variety, namely 'Jinpeng No.1', is higher than a disease-resistant variety, namely 'Zheza 301', in virus accumulation. Based upon fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis, it is indicated that the expression amount of the SolyWRKY54 gene is reduced in the disease-resistant tomato variety, namely 'Zheza 301'. Through a virus-induced genesilencing experiment, it further provides a negative regulation function of the SolyWRKY54 gene in a process of responding to the tomato yellow leaf curl virus. The SolyWRKY54 transcription factor gene, which is identified by the invention, is beneficial to analyzing and researching a resistance mechanism of tomatoes responding to the tomato yellow leaf curl virus; and the SolyWRKY41 transcriptionfactor is applicable to tobacco disease-resistance breeding.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
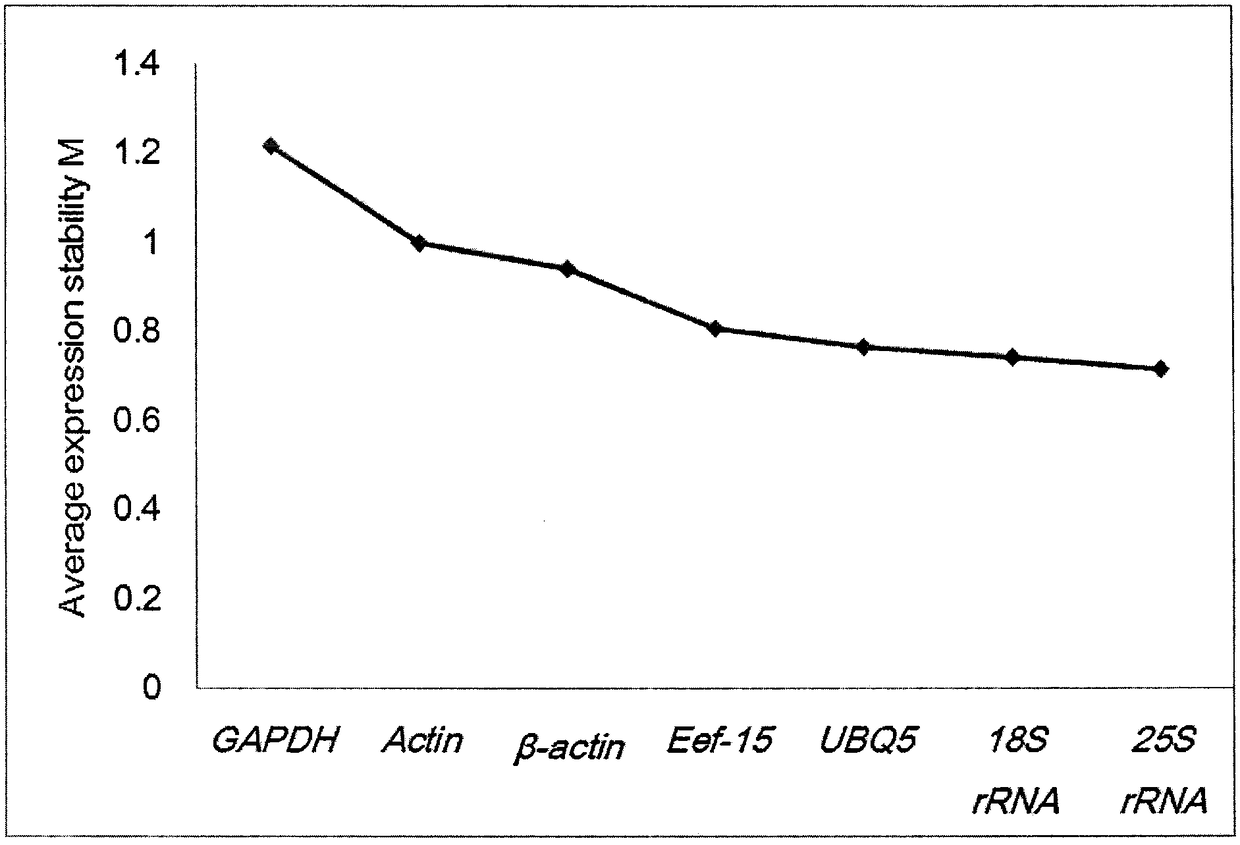
Selection method of reference genes in quantitative real-time PCR analysis of jerusalem artichoke
InactiveCN108588191AStable expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative Real Time PCRReference genes
The invention discloses a selection method of reference genes in quantitative real-time PCR analysis of jerusalem artichoke, and relates to the field of quantitative PCR. The method comprises the following steps: taking different tissues (radicles, immature stems, leaves, stem blocks and petals) of the jerusalem artichoke as materials, and carrying out expression analysis of the reference genes of18S ribosomal RNA gene (18S rRNA), transcription elongation factor gene (Ef-1a), actin gene (Actin and beta-actin), 3-glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH), 25S ribosomal RNA gene (25S rRNA)and poly-ubiquitin enzyme gene (UBQ)7 by using a q PCR technology; carrying out statistical assessment on the obtained data and analyzing expression change of all housekeeping genes by utilizing GeNorm and NormFinder software, so as to screen out relatively-stable genes as the reference genes of the jerusalem artichoke, which are used for studying the gene dosage changes of the jerusalem artichoke.
Owner:青海大学农林科学院
Method for evaluating soil health through quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analysis of microorganisms
InactiveCN101974631ACompliance with validityCompliance sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismPlasmid
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and in particular relates to a method for evaluating soil health through the quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analysis of microorganisms. The method of the invention comprises the following steps of: synthesizing a suitable quantitative PCR primer according to microorganism parameters for evaluating the soil health; constructing standard product plasmids of all the parameters and establishing a standard curve; and extracting sample DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and detecting the copy numbers of all the types of microorganism genes in the samples through quantitative PCR so as to judge the soil health state. The invention integrates various molecular biology methods needed for evaluating the soil health till now into a whole and is rapid, simple, convenient and effective.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for reprogramming spinal marrow astrocytes into motor neurons through induction
ActiveCN110283788ANervous system cellsCell culture active agentsTransdifferentiationStatistical analysis
The invention provides a method for reprogramming spinal marrow astrocytes into motor neurons through induction. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) primary rat astrocytes are subjected to pure culture; (2) 7 small molecule drugs including SB431542, LDN-193189, RA, bFGF, Purmorphamine, Forskolin and VPA are selected according to substances required in the stages of neuron induction and motor neuron formation and development, and the astrocytes are induced and reprogrammed in vitro through the small molecule drugs; (3) the reprogramming and differentiation conditions of the astrocytes to the motor neurons are analyzed through observation of morphologic change of cells and methods of chemical technology analysis of immunofluorescent cells, real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis and statistical analysis. The rat astrocytes can be successfully induced and reprogrammed into the motor neutrons in vitro through small molecular drug composition, and the transdifferentiation exceeds 75%; in-situ direct reprogramming of the astrocytes to the neurons is a possibly comparatively feasible thought in SCI (spinal cord injury) repairing and functional reconstruction treatment.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
Five-gene standard plasmid molecule for transgenic soybean detection and construction thereof
ActiveCN102409082AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionPlasmid VectorPcr method
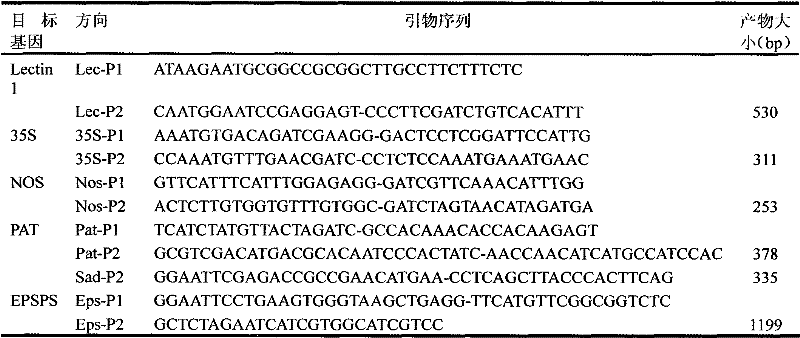
The invention discloses a standard plasmid molecule necessary for transgenic crop detection and a construction method thereof, and particularly discloses a standard plasmid molecule for transgenic soybean detection and a construction method thereof. The standard plasmid molecule comprises a soybean endogenous gene Lectin-specific fragment, a 35S promoter and NOS terminator-specific fragment, a transgenic soybean line A2704-12 foreign gene PAT-specific fragment, and a transgenic soybean line GTS40-3-2 foreign gene EPSPS-specific fragment. By analyzing the specific sequences of the above five genes, specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primers are designed, and five target gene fragments are obtained by amplification. By a fusion PCR method, the five genes are fused to form a long fragment, and the long fragment is cloned to plasmid vector pMDTM19-T Simple to obtain a recombinant plasmid molecule pTLE5. The standard plasmid molecule constructed in the invention can completely substitute for a positive standard product, and is completely suitable for screening as well as structural-gene-specific qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis and detection of transgenic soybean lines GTS40-3-2 and A2704-12. If a new transgenic material emerges, a new foreign gene fragment can be added to an original standard molecule, thus the detection requirements of increasing transgenic crop materials are met.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method for identifying traditional strain and highly pathogenic strain of PRRSV (porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus)
InactiveCN102653798AIncreased sensitivityEasy to optimizeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesHighly pathogenicPorcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus
The invention discloses a fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method for identifying the traditional strain and highly pathogenic strain of PRRSV (porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus). In order to accurately and quickly detect the nsp2 gene-deleted PRRSV, an upstream primer and two downstream primers are designed on the nucleotide sequence of the nsp2 gene, wherein one of the downstream primers is designed in a base sequence-deleted area. A PCR method for identifying the traditional strain and the highly pathogenic nsp2 gene-deleted strain is established through condition optimization; and a fluorescent quantitative PCR method for identifying the nsp2-deleted variant strain according to a melting curve is created by applying the optimal condition to the SYBR Green fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis, wherein the sensitivity is enough to detect 3-6 gene copies. Compared with the conventional PCR, the fluorescent quantitative PCR method disclosed by the invention can quickly and accurately detect the traditional strain and the deleted strain, and the sensitivity is 10 times higher than that of the conventional PCR.
Owner:天津市动物疫病预防控制中心
Standard plasmid molecular used for detecting transgenic soybean, corn and cotton and construction of the standard plasmid molecular
ActiveCN102559854AImprove featuresGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionReference genesStrain specificity
The invention discloses a necessary standard plasmid molecular and a construction method of the standard plasmid molecular in the field of transgenic crop detection. The construction method comprises the following steps: modifying an octo-gene plasmid molecular pTLE8 (Patent Application No.201010286884.3), adding a fusion fragment of 3'-transformation event specific sequences of transgenic corn Bt176 strain and Mon810 strain and corn internal reference gene Hmg specific sequence, and modifying into a deca-gene plasmid molecular pTLH10 (Lec1, 35S, NOS, PAT, Sad1, Cry1, Ab / c, Bt176, Mon810 and Hmg). The standard plasmid molecular constructed by the invention can completely replace a positive standard sample, and is suitable for screening transgenic soybean GTS40-3-2 strain, transgenic corn Bt176 and Mon810 strains and transgenic Bt cottons, and qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis and detection of gene specificity and strain specificity.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Enrichment culture method of whole-process nitrifying bacteria
ActiveCN111635862AGood growing mediumRaise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationBiotechnologyMicrobiology
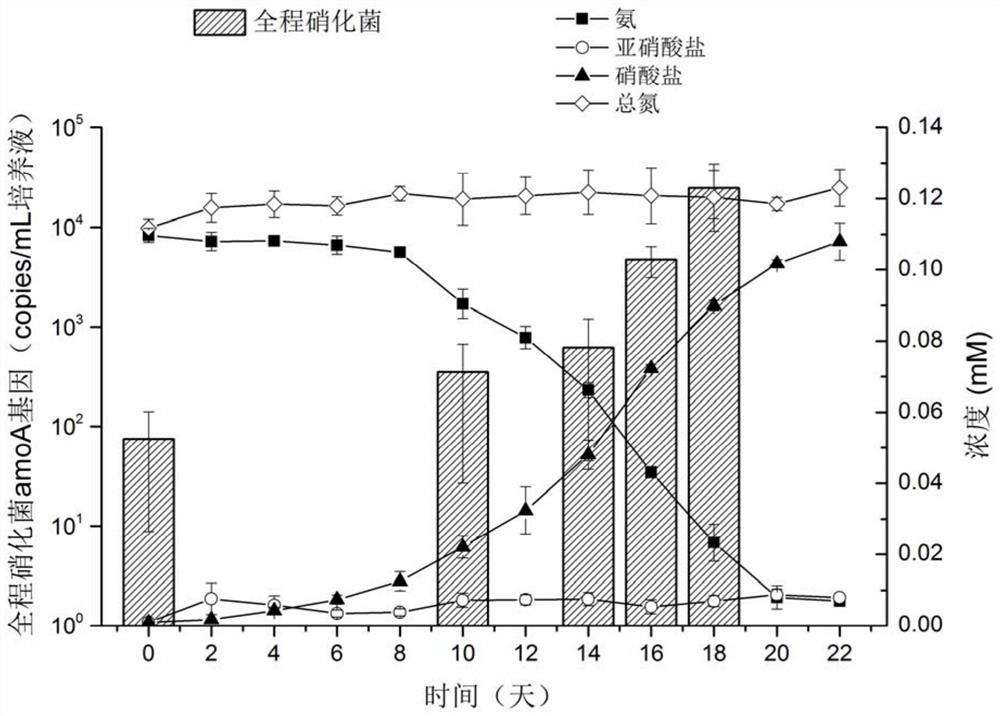
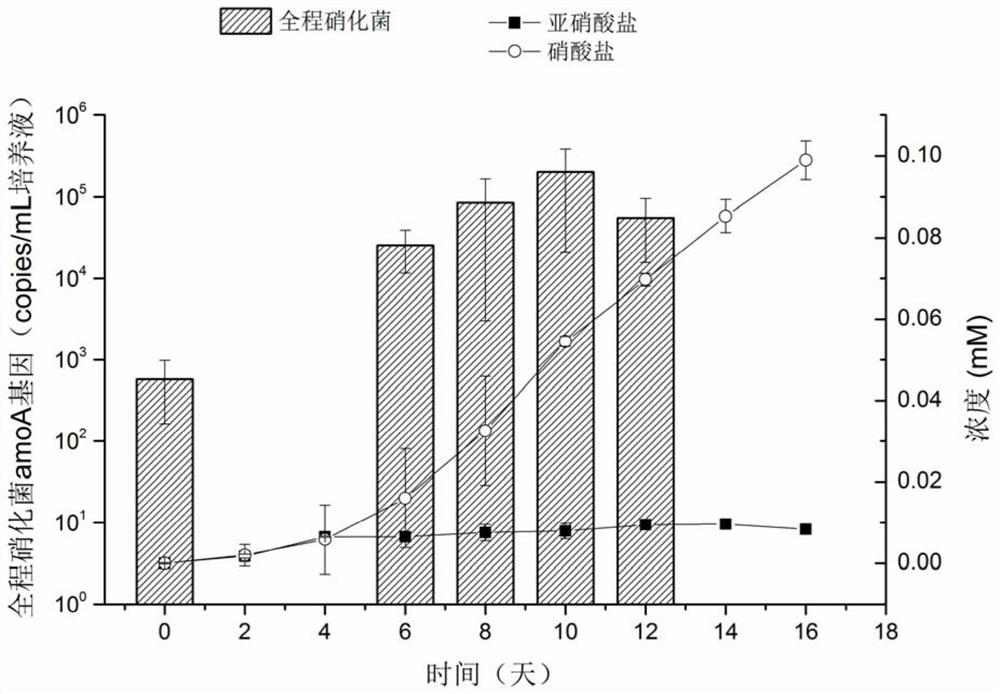
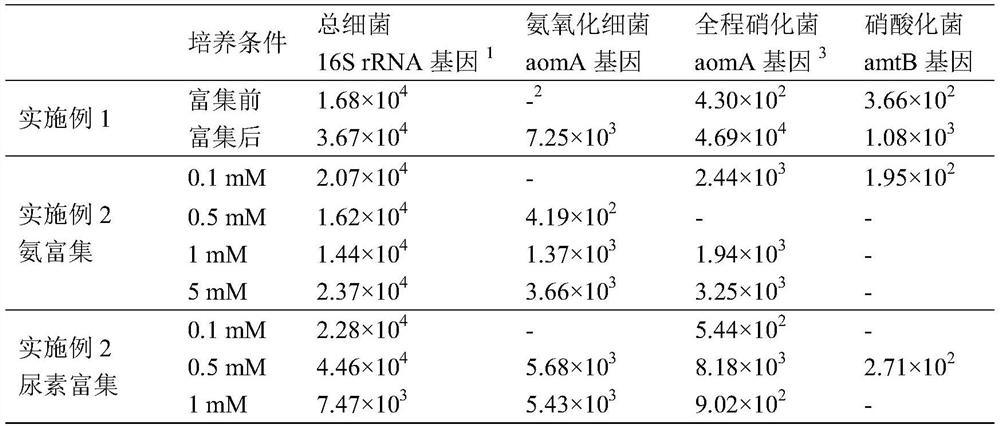
The invention discloses an enrichment culture method of whole-process nitrifying bacteria. The enrichment culture method comprises the following steps of S1, filtering a water body sample by adoptinga sterile filter membrane; S2, culturing the sterile filter membrane in an enrichment culture medium added with a substrate to obtain a filter membrane subjected to enrichment culture, wherein the substrate comprises ammonia or urea; S3, adopting a new sterile filter membrane as a transfer filter membrane, culturing the transfer filter membrane and the filter membrane subjected to enrichment culture in a new enrichment culture medium added with the substrate, and making the transfer filter membrane contact with the filter membrane subjected to enrichment culture, so that the whole-process nitrifying bacteria are transferred to the transfer filter membrane from the filter membrane subjected to enrichment culture; S4, taking out the transfer filter membrane, and culturing the transfer filtermembrane in a new enrichment culture medium added with the substrate; and S5, continuously transferring the whole-process nitrifying bacteria on the transfer filter membrane for multiple times by adopting the filter membrane, so as to achieve the purpose of enrichment culture of the whole-process nitrifying bacteria. In the culture process, part of the filter membrane is taken out regularly to extract DNA, and quantitative PCR analysis is carried out to confirm the enrichment condition of the whole-process nitrifying bacteria.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for analyzing hypoxia stress on shrimps by detecting HURP1 gene expression
InactiveCN106591471AEasy to judgeQuick judgmentMicrobiological testing/measurementOpen reading frameTotal rna
The invention provides a method for analyzing hypoxia stress on shrimps by detecting HURP1 gene expression. The method comprises the steps as follows: step one, acquiring the sequence of an open reading frame of an HURP1 gene of litopenaeus vannamei, and designing and synthesizing a sequence-specific fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer; step two, acquiring to-be-detected blood lymphocytes of litopenaeus vannamei, extracting the total RNA (ribose nucleic acid) of the blood lymphocytes, reversely transcribing the total RNA into cDNA, and preparing a fluorescent quantitative PCR template; step three, performing fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis to analyze expression of HURP1 in the blood lymphocytes of litopenaeus vannamei. With the adoption of the method, whether litopenaeus vannamei is in a low-oxygen stress state is judged more conveniently, more quickly and more accurately by detecting expression of the HURP1 gene.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
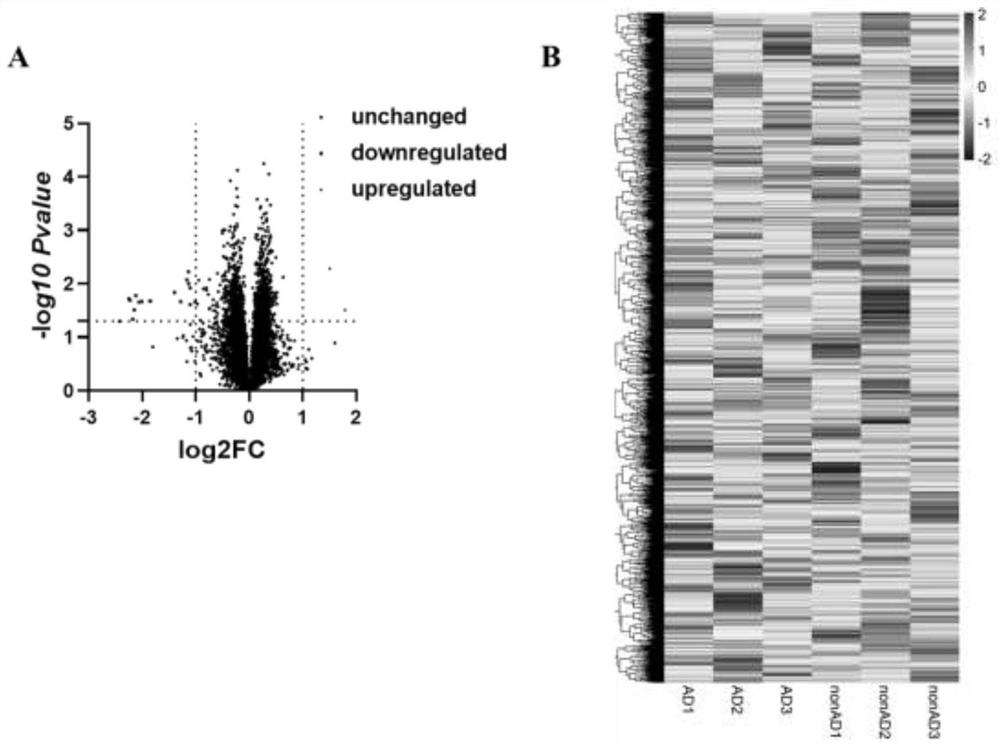
Application of brain cell-derived exosome circular RNA in serum as Alzheimer's disease diagnostic marker
ActiveCN113774058AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesDisease patientHigh throughput sequence
The invention discloses application of brain cell-derived exosome circular RNA in serum as an Alzheimer's disease diagnostic marker. The invention relates to application of a reagent for detecting any one or more of hsa_circ_0029426 and hsa_circ_0044837 in preparing an Alzheimer's disease auxiliary diagnostic reagent. High-throughput sequencing and quantitative PCR analysis in nearly 100 patients finds that two kinds of circular RNA in exosome in serum can effectively distinguish Alzheimer's disease patients from normal people and non-Alzheimer's disease patients with clinical symptoms similar to Alzheimer's disease, and the area under an ROC curve is greater than 0.90. Therefore, the two kinds of circular RNA or a combination thereof can be used as detection markers for Alzheimer's disease diagnosis.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
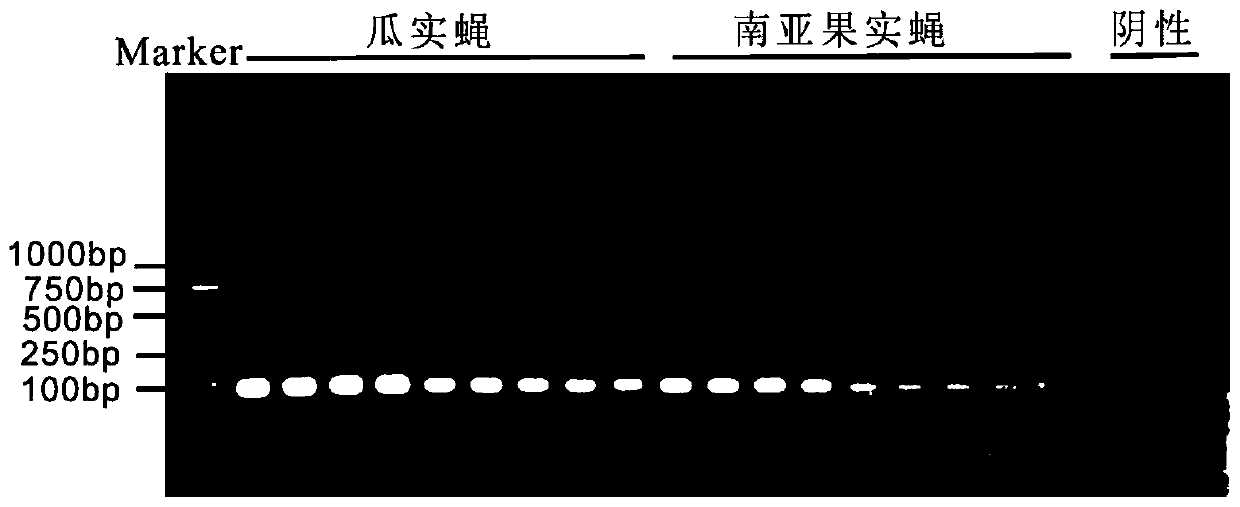
HRM primer, kit and method for rapidly identifying bactrocera cucurbitae and South Asia fruit flies
PendingCN110885890AAccurate identificationStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyRapid identification
The invention discloses an HRM primer, a kit and a method for rapidly identifying bactrocera cucurbitae and South Asia fruit flies. The method comprises the steps of firstly, designing and synthesizing a HRM specific primer for distinguishing two kinds of fruit flies based on mitochondrial genomes of bactrocera cucurbitae and South Asia fruit flies; respectively extracting genome DNAs of bactrocera cucurbitae and South Asia fruit flies; carrying out high-resolution real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis by taking the extracted DNAs as templates and EvGreen as a dye; and distinguishingtwo types of bactrocera cucurbitae according to peak difference of melting temperature curves. According to the invention, the problem of rapid identification of two kinds of bactrocera cucurbitae and South Asia fruit flies which are co-hosted and have similar larvae is solved; the HRM method for identifying the two kinds of bactrocera cucurbitae based on mitochondrial genes is established; bactrocera cucurbitae and South Asia fruit flies which are mixed on melon vegetables can be quickly, efficiently and simply distinguished; and the HRM primer, the kit and the method have the advantages ofhigh accuracy, high flux, good repeatability and low cost.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION GUANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
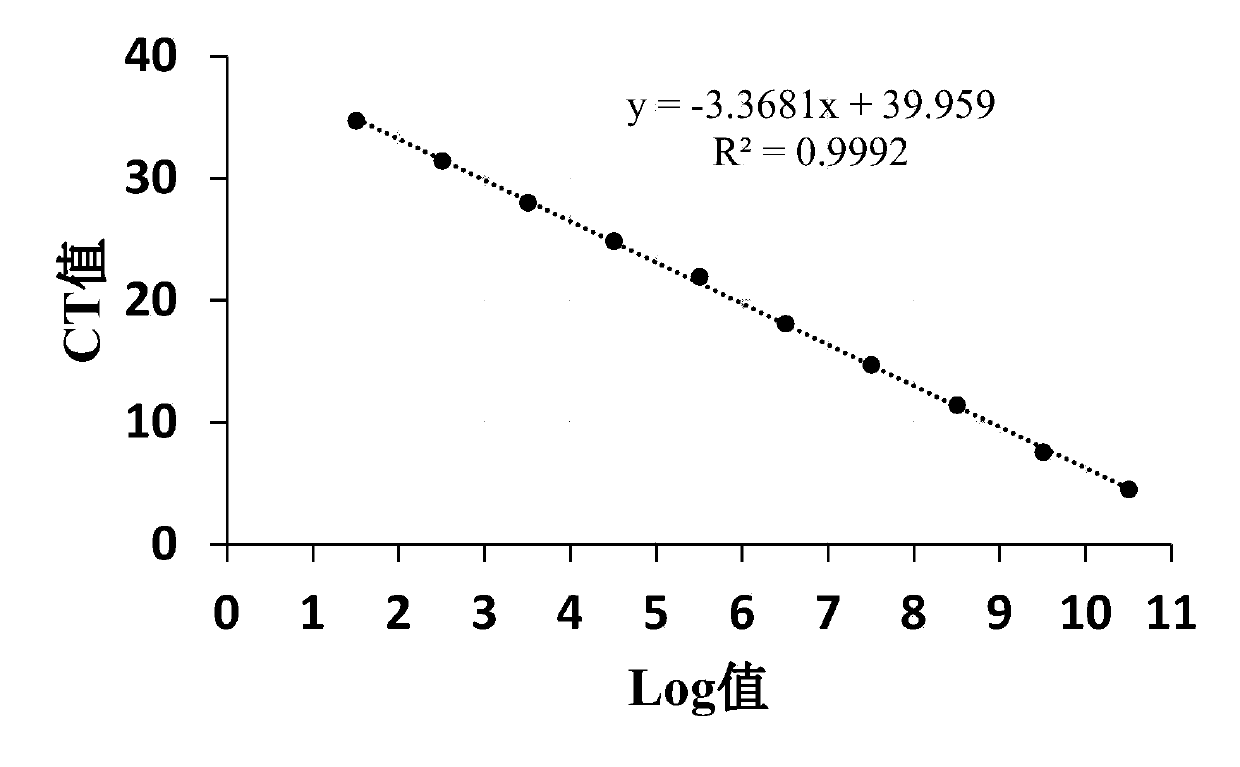
Quantitative analysis method of Zygosaccharomyces bailii
PendingCN111560455AStrong specificityStable amplificationMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyYeast
The invention relates to the technical field of white spirit brewing, in particular to a quantitative analysis method of important saccharomycetes Zygosaccharomyces bailii in a white spirit solid-state fermentation process. According to the invention, a specific primer is adopted to carry out quantitative PCR analysis on 26S rRNA of Zygosaccharomyces bailii, so as to analyze the variation trend ofZygosaccharomyces bailii in Daqu and fermented grains and predict the alcohol yield. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high detection speed, high sensitivity, good accuracy,good specificity and no culture.
Owner:KWEICHOW MOUTAI COMPANY
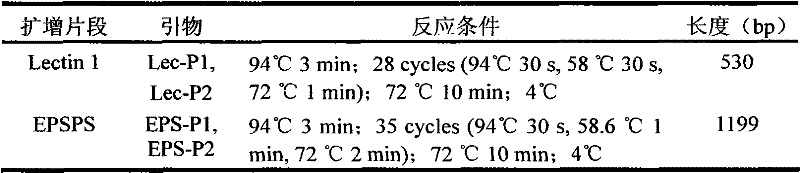
Two-gene standard plasmid molecule used for detecting genetically modified soybeans and building method thereof
InactiveCN102409080AVerify validityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyGenetically modified crops
The invention discloses an essential standard plasmid molecule used for detecting genetically modified crops and a building method thereof. The standard plasmid molecule contains specific fragments of a soybean endogenous gene Lectin and specific fragments of an exogenous gene EPSPS in the genetically modified soybean strain GTS40-3-2. The standard plasmid molecule and the building method have the following beneficial effects: the two target gene fragments are obtained by analyzing sequences, designing primers and amplifying the genes; the standard artificial recombinant plasmid molecule pTLE2 is obtained through such gene cloning technologies as fusion PCR (polymerase chain reaction), link, transform and the like; the standard plasmid molecule built in the invention can absolutely replace the positive controls and is suitable for qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis and detection of the specificity of the structural genes in the genetically modified soybean strain GTS40-3-2; and new exogenous gene fragments can be added on the basis of the original standard molecule if new genetically modified materials occur, thus meeting the increasing detection requirements of the genetically modified crop materials.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method and device for quantitative PCR multi-wavelength fluorescence detection
ActiveCN101705280BImprove detection efficiencyNo crosstalkMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceLength wave
The invention discloses a method and a device for quantitative PCR multi-wavelength fluorescence detection. N fluorescence wavelength detection passages with the mutual interval as a module standard hole site are arranged, each fluorescence wavelength detection passage is provided with a light source exciting optical fiber path and a fluorescence receiving optical fiber path, the light sources ofthe n light source exciting optical fiber paths respectively pass through a collimating lens and an exciting light filter so as to obtain exciting light with required wavelength, and then the exciting light is irradiated onto n test tube exciting reagent samples through focusing; the fluorescence of the n test tube exciting reagent samples respectively enters the fluorescence receiving optical fiber paths, the fluorescence with the required wavelength is obtained through the collimating lens and the exciting light filter, is irradiated onto a plane reflecting mirror and is then refracted onton working surfaces of the same polyhedral reflecting mirror through the plane reflecting mirror, and the fluorescence of the n fluorescence wavelength detection passages is converged onto a photoelectric surface of an optical sensor through the polyhedral reflecting mirror so as to realize the real-time synchronous detection of the multi-wavelength fluorescence. The invention can greatly improve the detection efficiency, no exciting light interference is generated in detection, and quantitative PCR analysis results are exact.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOER TECH CO LTD
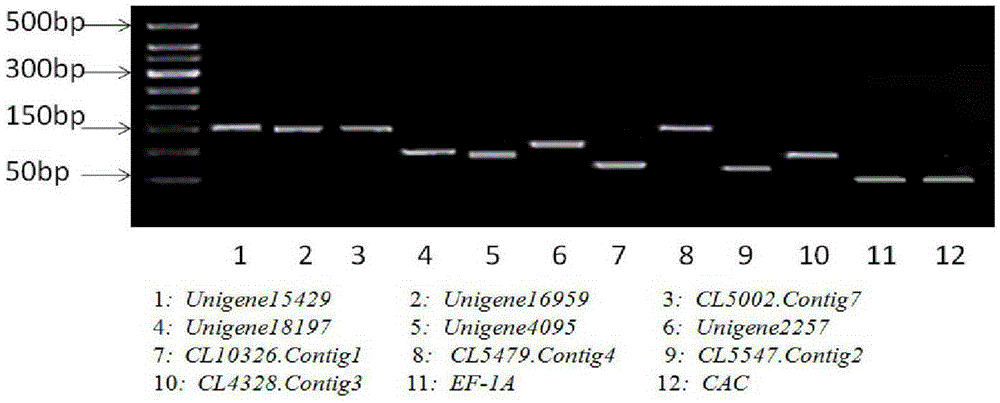
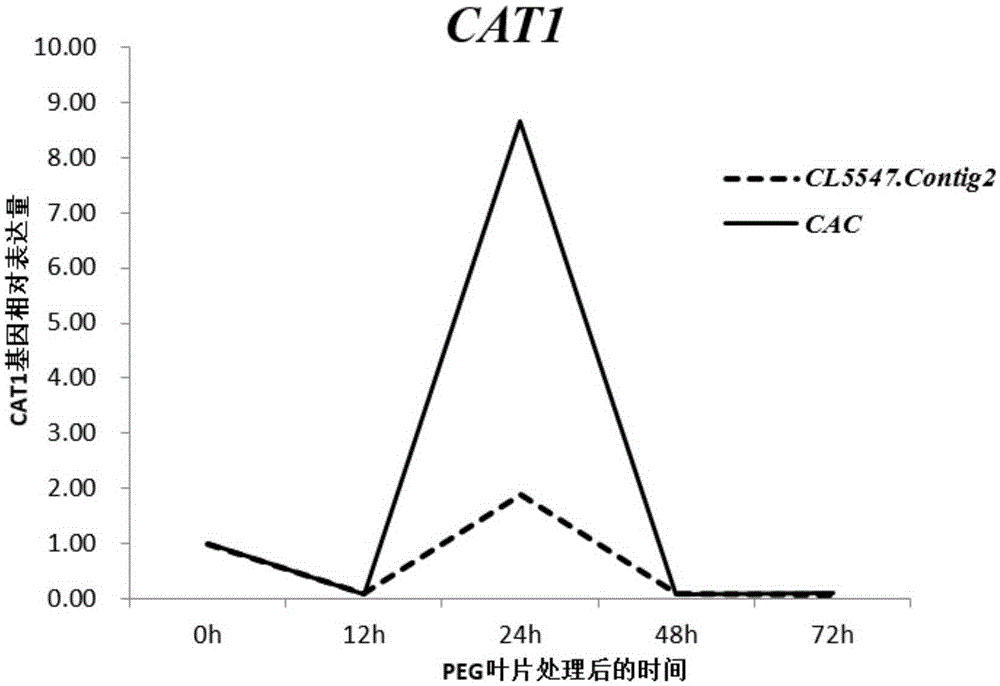
Application of CL5547.Contig2 gene to pumpkin gene expression real-time fluorogenic quantitative PCR analysis as reference gene
ActiveCN105274219AHigh expression stabilityExcellent expression stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementGene expression levelPlant growth
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene expression analysis, and concretely relates to application of CL5547.Contig2 gene to pumpkin gene expression real-time fluorogenic quantitative PCR analysis as a reference gene. The gene expression level and stability are compared at whole genome level by utilizing pumpkin transcriptome data, 10 genes with stable expression are selected, also 2 commonly-used conventional reference genes in pumpkin are selected as contrast, and the expression stability of the 12 genes in different tissue organs of two pumpkin varieties under conditions of abiotic stress, biotic stress and plant-growth regulator processing (GA3, ABA, NAA and ETH), and CAT1 gene and CAT2 gene are used to perform verification, so that the CL5547.Contig2 gene is confirmed to have the highest expression stability, and is an optimum reference gene for pumpkin gene expression real-time fluorogenic quantitative PCR analysis.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Screening method and application of reference genes in real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analysis of plum blossom
ActiveCN114457187AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesReference genesQuantitative assay
The invention discloses application of GAPDH, UBQ, Actin7, PP2A and Actin1 genes as reference genes and special primers thereof in real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) analysis of plum blossom. The invention also discloses a screening method of the reference gene in real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis of plum blossom, which can provide theoretical basis and technical guarantee for molecular level research of plum blossom.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for screening reference gene in real-time quantitative PCR analysis of heterodera glycines infected wild soybean root tissue
InactiveCN107338322AExploring the mechanism of resistanceMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesHigh resistance
The invention provides a method for screening a reference gene in the real-time quantitative PCR analysis of a heterodera glycines infected wild soybean root tissue, and relates to the fields of biology and genetics. A high-resistance high-sensitive wild soybean germplasm is taken as a test material, the condition of gene expression of 24 candidate housekeeping genes in a wild soybean root system in different heterodera glycines infection periods is detected, the expression abundance and the expression stability are evaluated so as to screen the reference gene suitable for studying the expression of the gene in the heterodera glycines infected wild soybean root system, and the method is used for exploring the resistance mechanism of the wild soybean to the heterodera.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
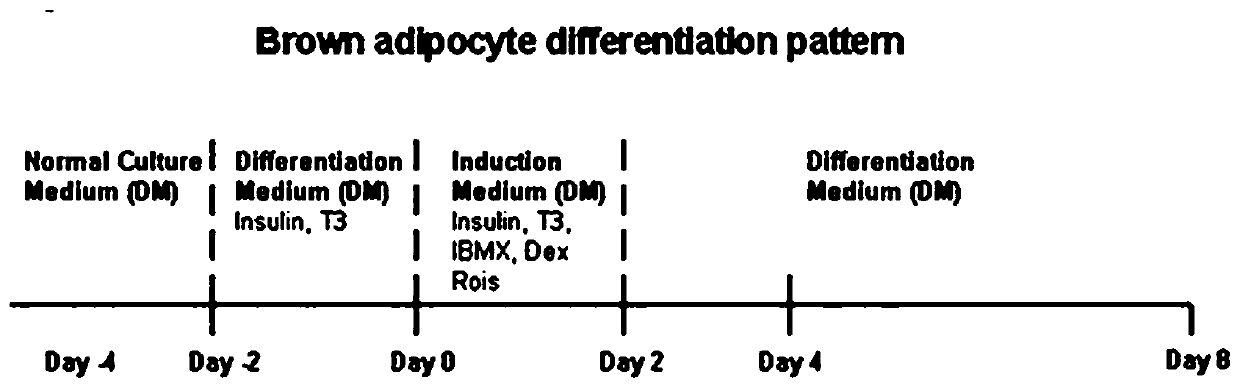
Method for promoting brown adipose differentiation through SFRP4 and application
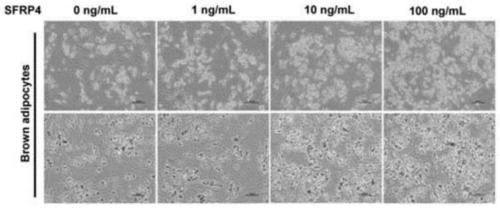
ActiveCN111548989APromote differentiationImprove expression levelSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsBrown adipose cellStaining
The invention discloses a method for promoting brown adipose tissue differentiation through SFRP4 and an application. The method comprises treating precursor adipose cells for differentiation by usingSFRP4 active proteins (with different concentrations of 0, 1, 10, 100ng / mL), when the cells grow to 80%, culturing with a cell differentiation induction culture medium I until the cells are fused, adding an induction culture medium II into the cells, inducing for 2-8 days, and replacing the culture medium in the culture bottle with an induction culture medium III, inducing for 2-8 days, observingunder a microscope, after dyeing with oil red O, observing under the microscope again, collecting cells with different differentiation days, extracting total RNA of the cells, detecting expression levels of marker genes UCP-1 and SFRP4 of brown adipose cells by using a real-time quantitative PCR analysis technology after the purity and integrity of the RNA are detected to be qualified, and finally, carrying out statistical analysis. The experimental process is uniform in sampling, and the result reliability is high.
Owner:XIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Clone, expression and use of Schistosoma Japonicum signal transduction protein Sjwnt-4 gene
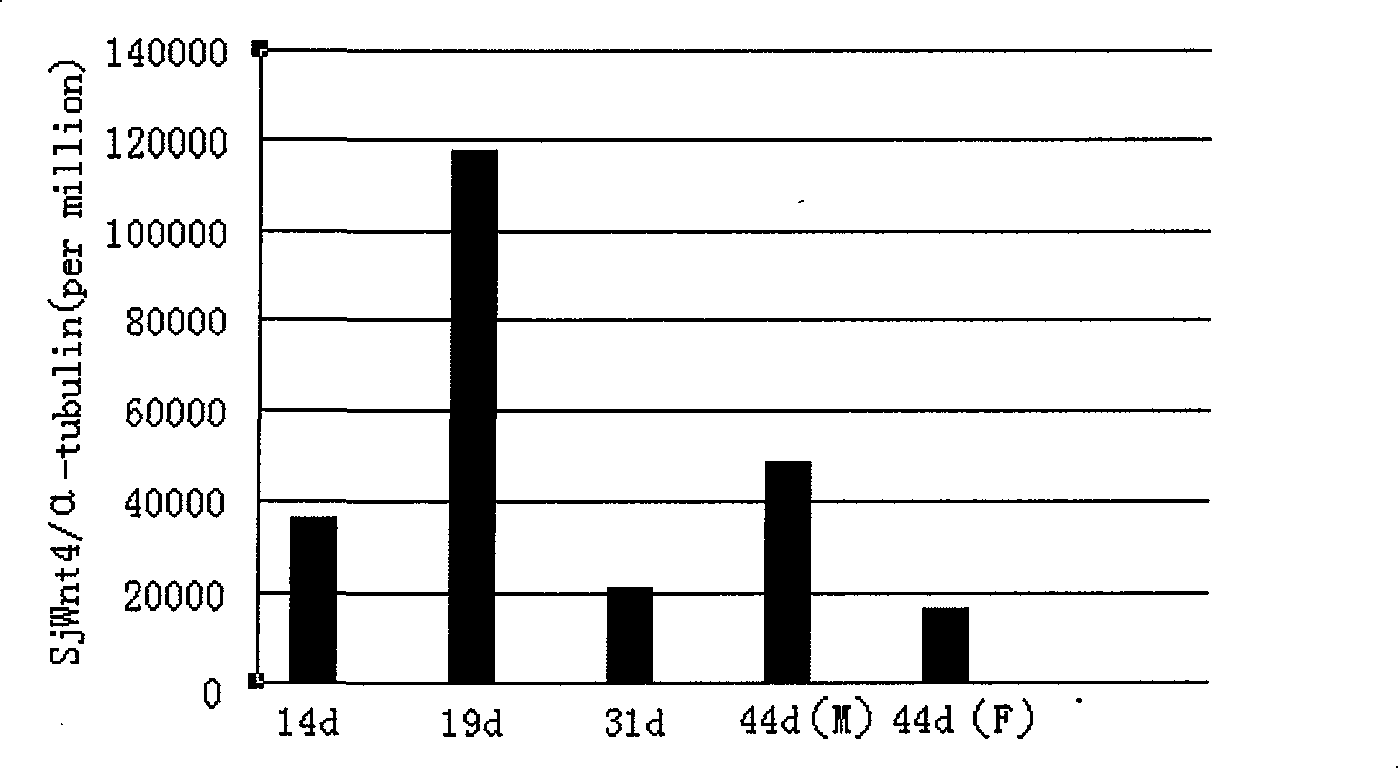
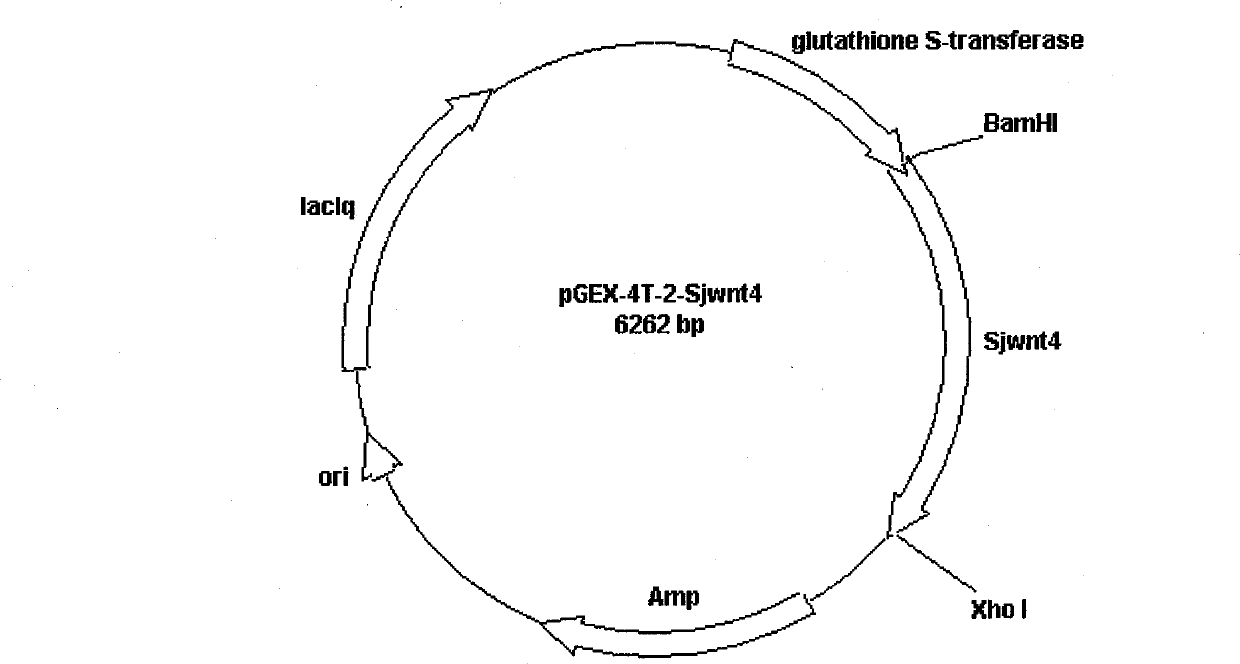
The invention discloses a Wnt family gene which is amplified for the first time from Schistosoma japonicum 19-day schistosomulum by utilization of RACE technology, wherein, sequence analysis indicates that: a complete coding frame of the gene comprises 1311bp, 436 amino acids coded; and theoretical molecular weight of 49.6kD. Homology analysis results indicate that: amino acid sequences of the gene have typical Wnt family protein characteristics; similarity of the amino acid sequences with amino acid sequences of Dugesia japonica and human Wnt4 is relatively 43 percent and 37 percent; the gene is presumed to be a Wnt4 gene of schistosome and named as Sjwnt4 (GenBanK Log-On No.: DQ643829). Real-time quantitative PCR analysis indicates that: the gene is expressed all in 14-day schistosomulum, 19-day schistosomulum, 31-day imago, 44-day female worms and 44-day male worms. The invention constructs a pronucleus expression vector pGEX-4T-2-Sjwnt4 of the gene and applies an Escherichia coli system for expression; expression proteins exist in the form of inclusion bodies; Western blottings indicate that expression products can be identified by crude antigen immune serums of Schistosoma japonicum imago.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Gene and method for rapidly judging brassica plants with low cadmium accumulation
ActiveCN107130036AImprove identification efficiencyFast wayMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSequence analysisBrassica
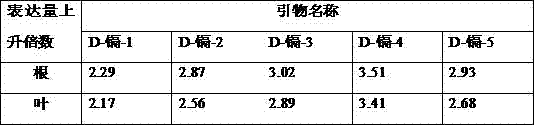
The invention discloses a method for rapidly judging brassica plants with low cadmium accumulation by detecting the up-regulated expression of cadmium inhibition genes. Mustard type rape with low cadmium accumulation is taken as the material, the transcriptomes of roots and leaves of the cadmium processed material and a control material are subjected to sequencing analysis, the mRNA sequences, whose expression amount in leaves and roots is increased by 2.00 times or more, are selected, the functions of the genes corresponding to the mRNA sequences are analyzed, and the genes that can inhibit the absorption and transportation of heavy metals such as cadmium are screened out, namely cadmium inhibition genes. Quantitative PCR is used to analyze the relationship between the gene expression change and the cadmium processing concentrations, 5 cadmium inhibition genes are determined, and the expression amounts of the five genes in the leaves and roots of all processed groups are all increased by 2.00 times or more. The primer of the five genes is utilized to detect the change of gene expression of a brassica plant in a MS culture medium under the induction of cadmium with a concentration of 5-25 mg / kg. If the expression amounts of the five cadmium inhibition genes in roots and leaves are all increased by 2.00 times or more compared with the control group, the brassica plant is a plant with low cadmium accumulation.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Clone, expression and use of Schistosoma Japonicum signal transduction protein Sjwnt-4 gene
The invention discloses a Wnt family gene which is amplified for the first time from Schistosoma japonicum 19-day schistosomulum by utilization of RACE technology, wherein, sequence analysis indicates that: a complete coding frame of the gene comprises 1311bp, 436 amino acids coded; and theoretical molecular weight of 49.6kD. Homology analysis results indicate that: amino acid sequences of the gene have typical Wnt family protein characteristics; similarity of the amino acid sequences with amino acid sequences of Dugesia japonica and human Wnt4 is relatively 43 percent and 37 percent; the gene is presumed to be a Wnt4 gene of schistosome and named as Sjwnt4 (GenBanK Log-On No.: DQ643829). Real-time quantitative PCR analysis indicates that: the gene is expressed all in 14-day schistosomulum, 19-day schistosomulum, 31-day imago, 44-day female worms and 44-day male worms. The invention constructs a pronucleus expression vector pGEX-4T-2-Sjwnt4 of the gene and applies an Escherichia colisystem for expression; expression proteins exist in the form of inclusion bodies; Western blottings indicate that expression products can be identified by crude antigen immune serums of Schistosoma japonicum imago.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Standard plasmid molecule for transgenic maize Mon810 detection and construction method thereof
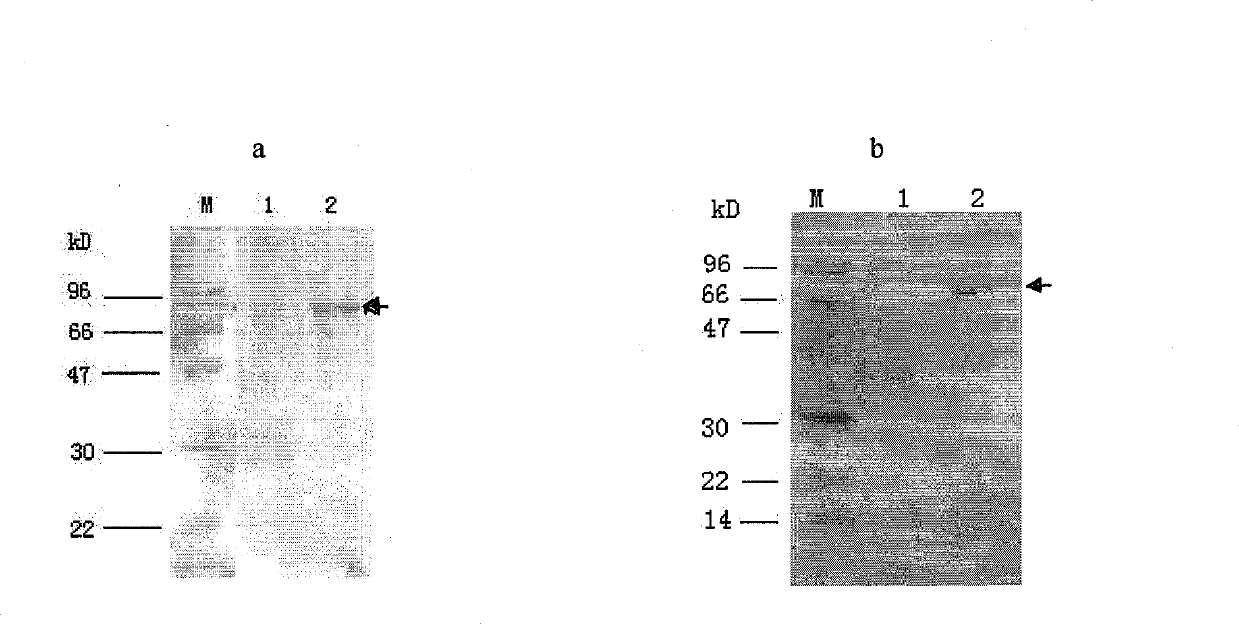
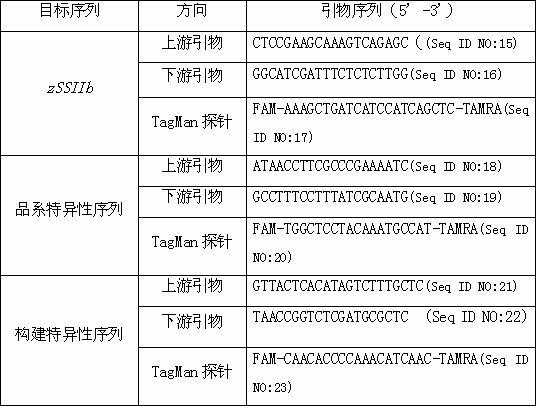
InactiveCN102492777AAvoid missingThe analysis result is accurateMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionSequence analysisTransgene
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological detection, and particularly relates to a standard plasmid molecule for genetically modified maize strain Mon810 detection and a construction method thereof. The standard plasmid molecule comprises a strain specific sequence, a construction specific sequence and a maize internal standard gene zSSIIb specific segment of genetically modified maize strain Mon810; by analyzing an exogenous insertion vector border sequence of the genetically modified maize strain Mon810 and a sequence of a joining region of two elements Hsp70 and cryIA (b), strain specific and construction specific PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) primers are designed, amplification is performed to obtain the strain specific segment and the construction specific segment of the genetically modified maize strain Mon810 and the maize internal standard gene specific sequence; and an artificial recombinant plasmid molecule pMHZ is obtained by constructing the sequences and the segment into the plasmid molecule through a molecular cloning method. A positive standard sample of the genetically modified maize strain Mon810 can be fully substituted by the constructed standard plasmid molecule; and the plasmid molecule is used for quantitative PCR analysis and detection of the genetically modified maize strain Mon810 sample.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com