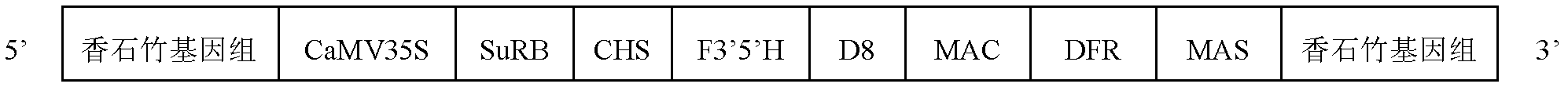Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Strain specificity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
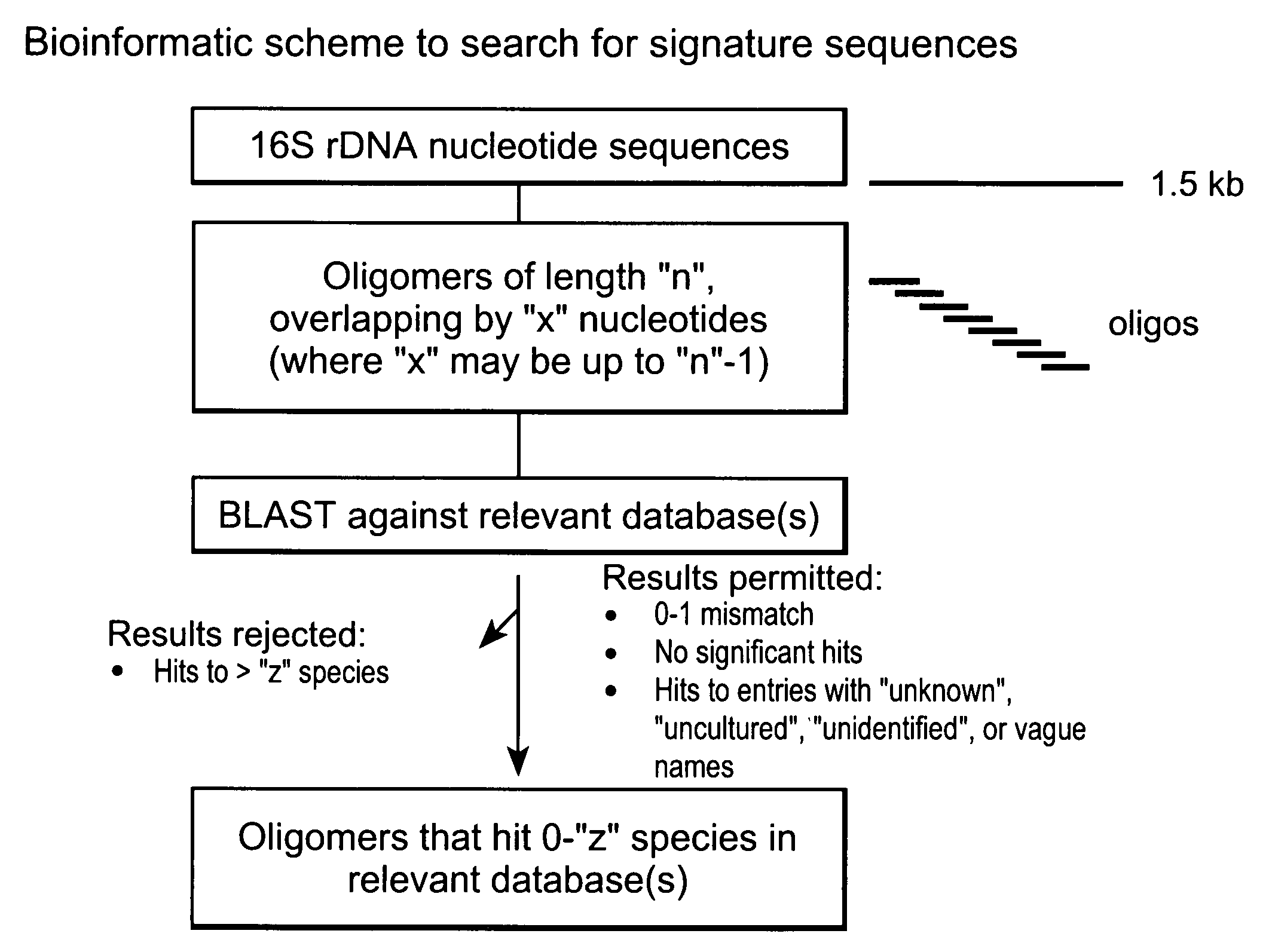
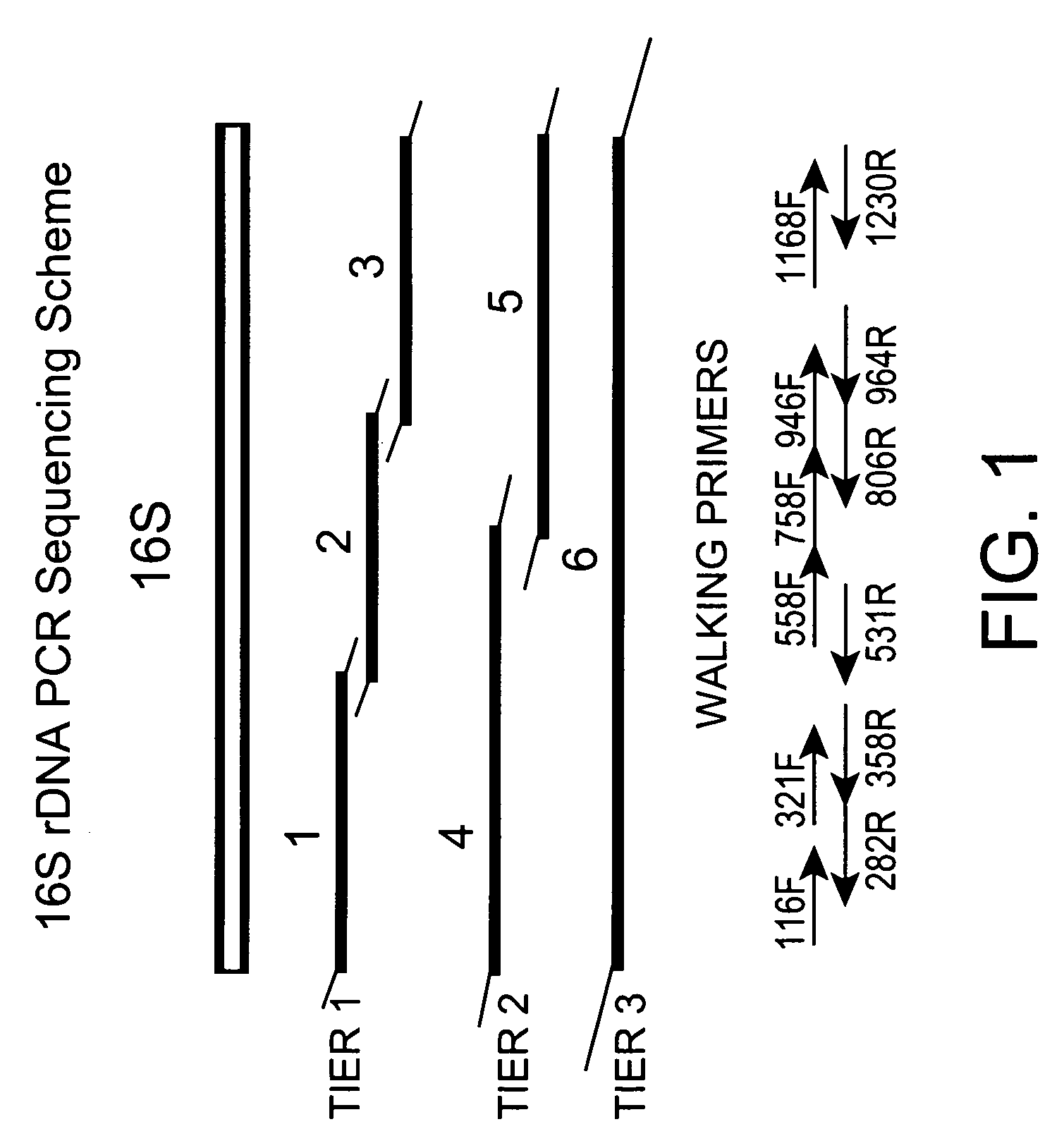
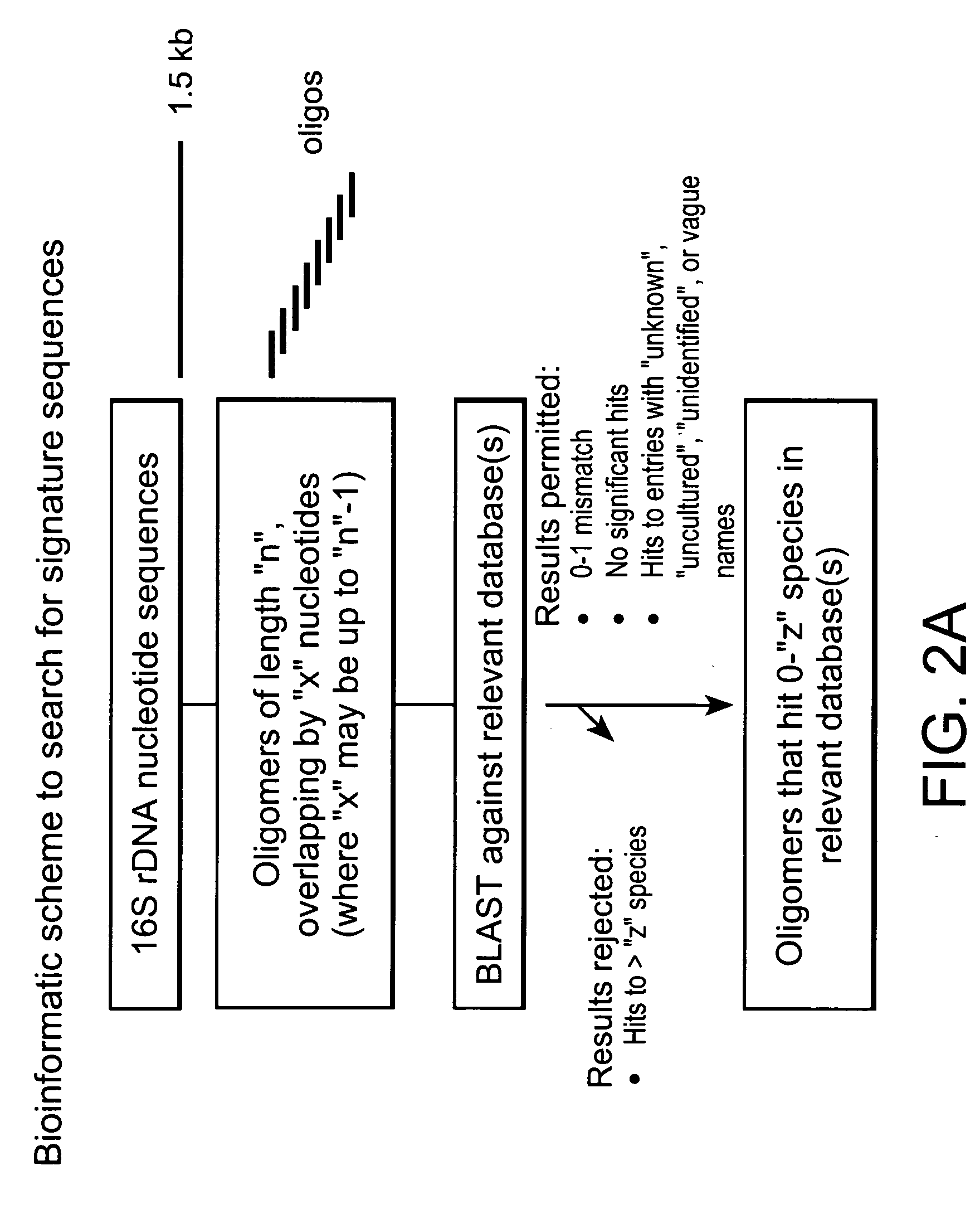
Genus, group, species and/or strain specific 16S rDNA sequences
InactiveUS20060046246A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismStrain specificity
Materials and methods for identifying unique sites in bacterial 16S and 23S rDNA are provided, as well as specific unique sequences of 16S rDNA in select bacteria. The distinguishing moieties will enable rapid differentiation between families, genera, groups, species, strains, subspecies, and isolates of microorganisms. Such differentiation can be performed by using rapid screening kits in combination with in silico analysis for diagnostic, prognastic, epidemiologic, phylogenetic, and other purposes.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC +1
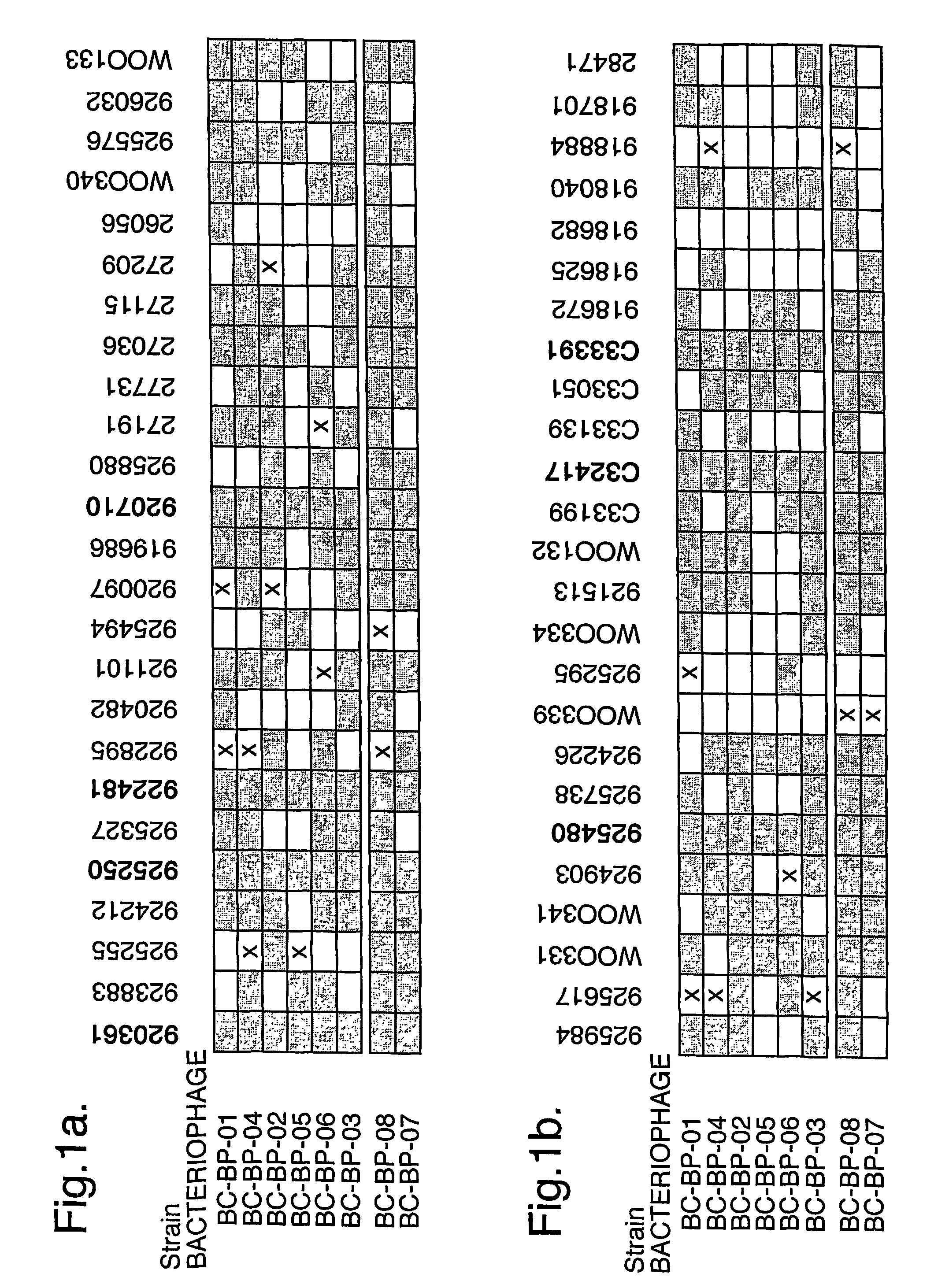
Bacteriophage-containing therapeutic agents
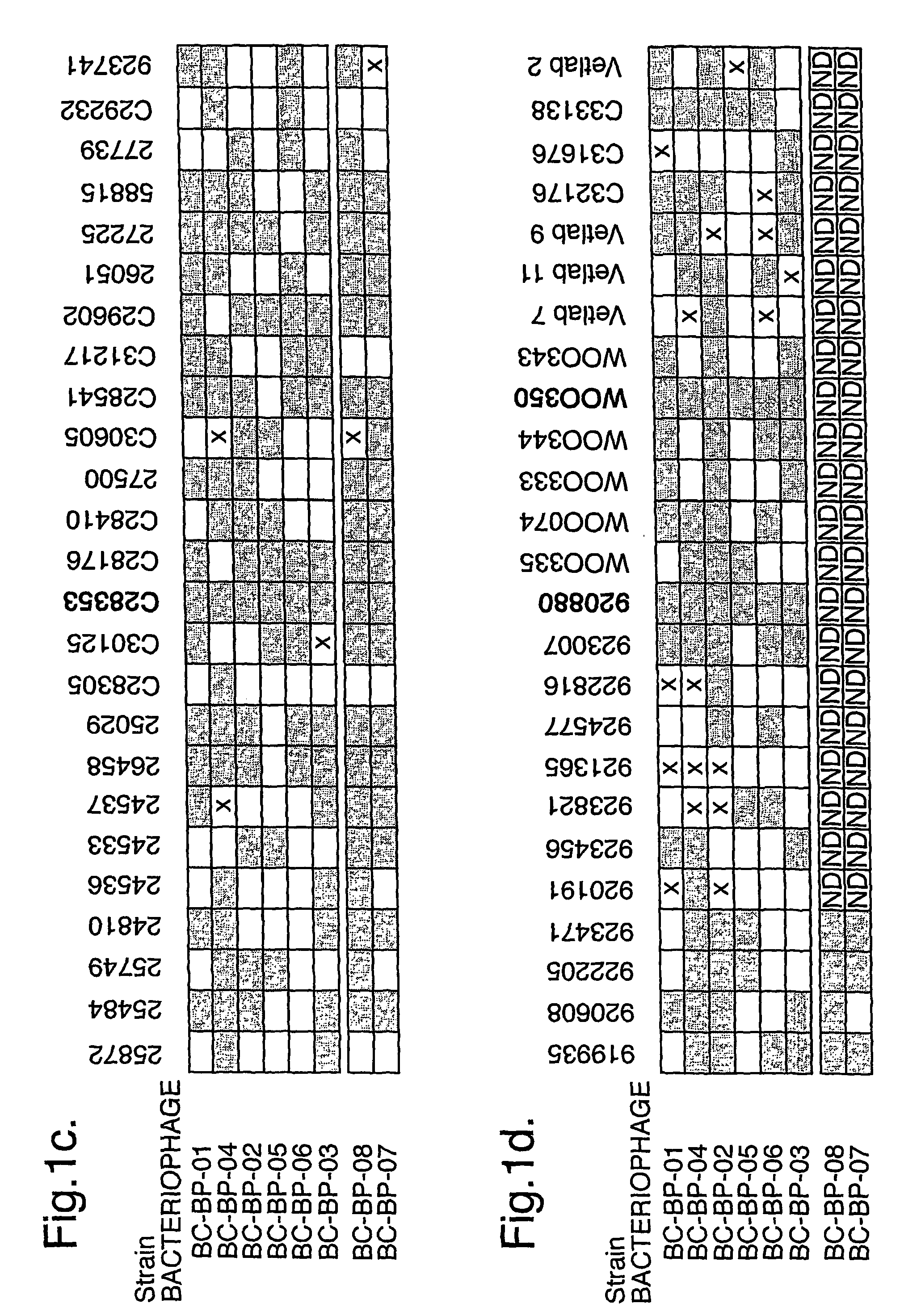
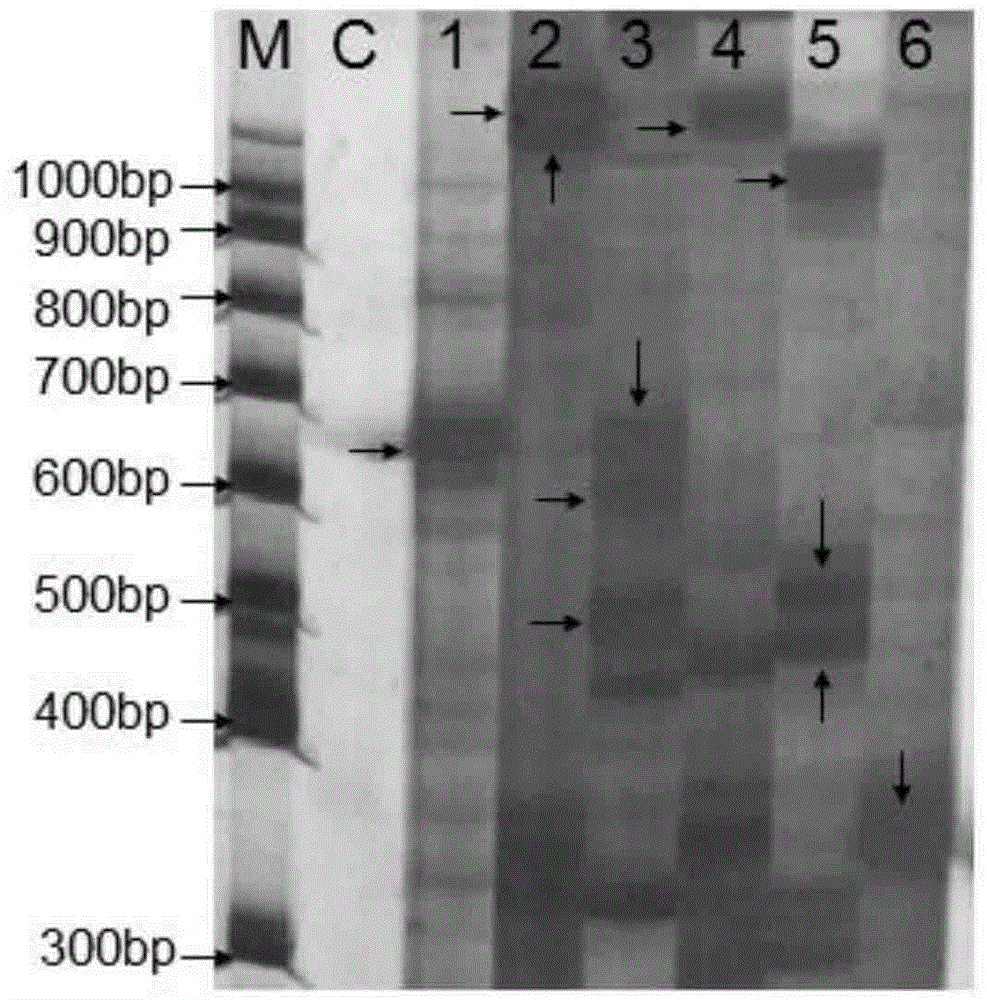
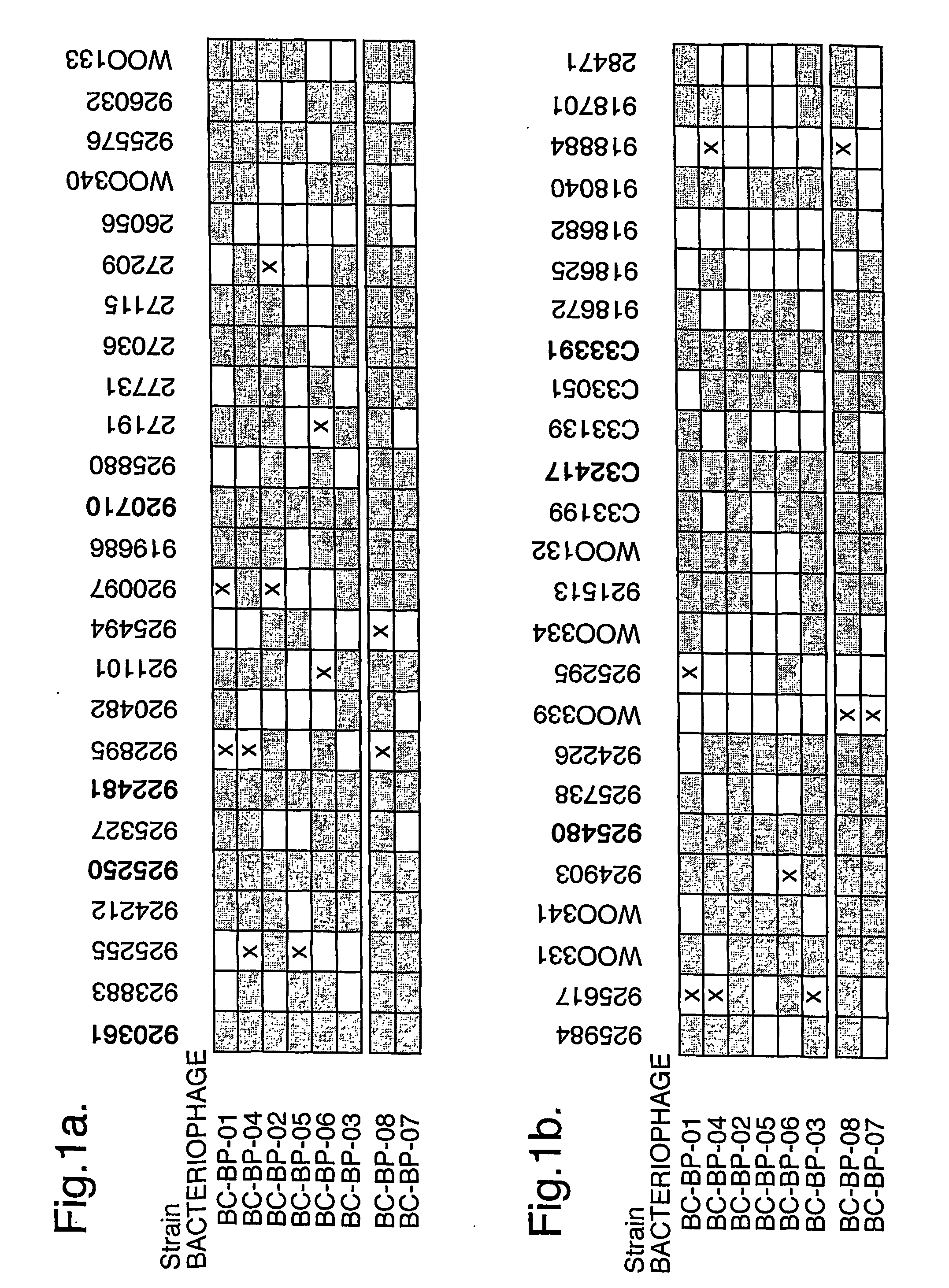
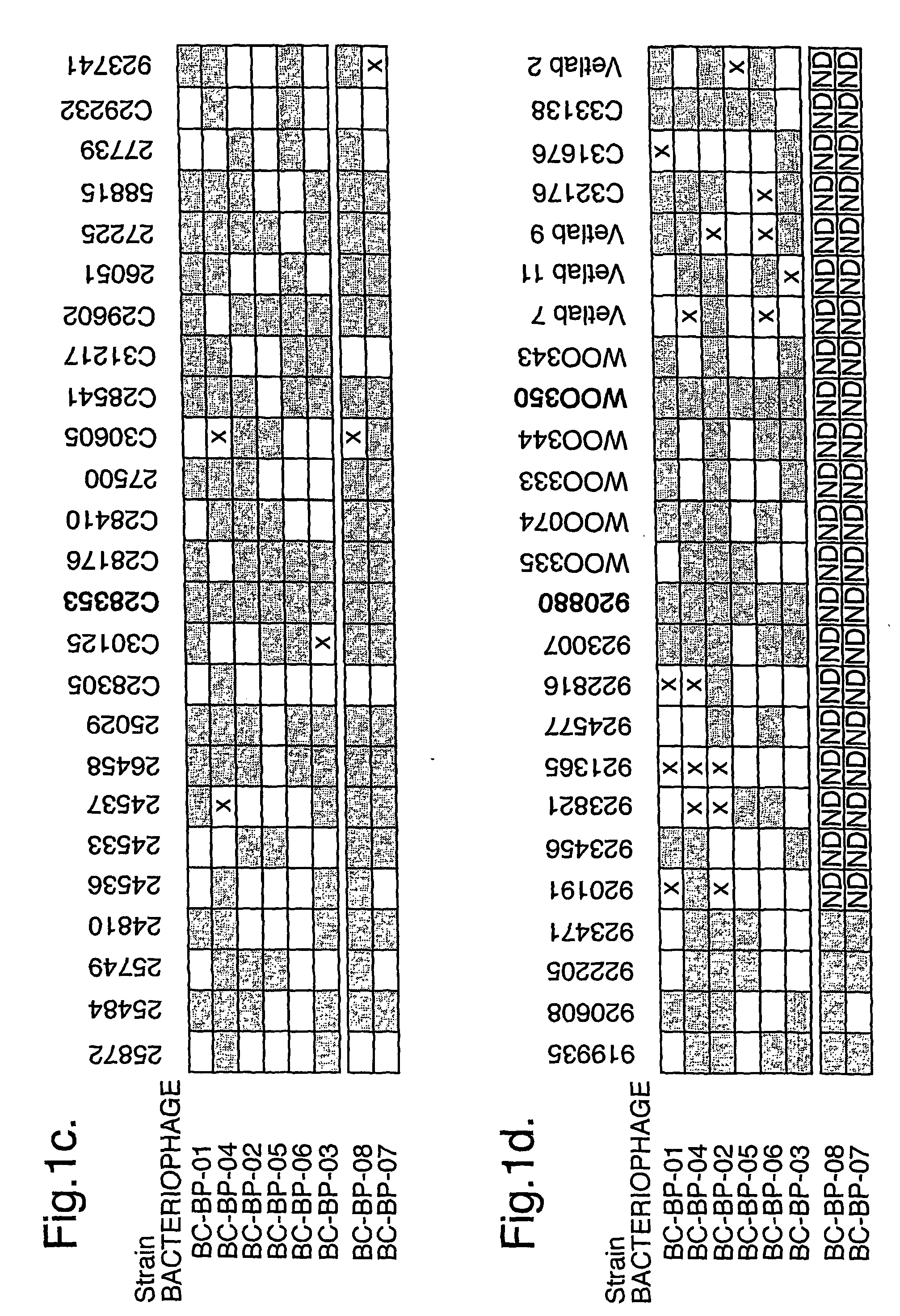
The present invention relates in its broadest aspect to combined phage / antibiotic therapy. More particularly, it relates to use of (i) one or more bacteriophages and (ii) one or more antibiotics in the manufacture of a combined product for simultaneous, separate or sequential administration of (i) and (ii) to treat a bacterial infection characterized by biofilm formation, for example an infection comprising or consisting of P. aeruginosa. Treatment in this context may be either therapeutic or prophylactic treatment. Also provided are deposited bacteriophages each exhibiting different strain specificity against P. aeruginosa and combinations of such bacteriophages, e.g. a panel of six deposited bacteriophages which was found to be effective against a high percentage of clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa from canine ear infections.
Owner:BIOCONTROL
SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom Minfeng No.1 strain, and application thereof
ActiveCN102851373AShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementStrain specificityAgricultural science
The invention relates to an SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom Minfeng No.1 strain, and an application thereof. The fingerprint is composed of 7 pairs of SSR-labeled specific allelic fragments developed according to a shiitake mushroom genomic sequence. The application comprises the steps that: SSR-labeled amplification is carried out upon a shiitake mushroom strain; and an obtained band type is compared with the fingerprint. If the band type is consistent with the fingerprint, the strain is a shiitake mushroom Minfeng No.1 strain. Compared with a conventional morphological detection method, an antagonistic test, and mushroom fruiting trials, the application provided by the invention has the advantages of short detection time, high accuracy, and good repeatability. In 25 collected nationally validated shiitake mushroom main cultivated strains of our nation, the fingerprint has shiitake mushroom Minfeng No.1 strain specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom Huaxiang No.5 strain, and application thereof
InactiveCN102851374AShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementStrain specificityAgricultural science
The invention relates to an SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom Huaxiang No.5 strain, and an application thereof. The fingerprint is composed of 7 pairs of SSR-labeled specific allelic fragments developed according to a shiitake mushroom genomic sequence. The application comprises the steps that: SSR-labeled amplification is carried out upon a shiitake mushroom strain; and an obtained band type is compared with the fingerprint. If the band type is consistent with the fingerprint, the strain is a shiitake mushroom Huaxiang No.5 strain. Compared with a conventional morphological detection method, an antagonistic test, and mushroom fruiting trials, the application provided by the invention has the advantages of short detection time, high accuracy, and good repeatability. In 25 collected nationally validated shiitake mushroom main cultivated strains of our nation, the fingerprint has shiitake mushroom Huaxiang No.5 strain specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized molecular marker and application thereof
InactiveCN103060322ARapid identificationQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFusarium oxysporumStrain specificity
The invention discloses a fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) marker (SEQ.ID.No.1), an SCAR (sequence characterized amplified region) marker (SEQ.ID.No.2) obtained by transforming the RAPD marker and application of the molecular markers in pathogenic bacteria identification and pathogenetic tissue detection. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention has fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized strain specificity, consistency and stability, can distinguish difference between the specialized strain and other specialized pathogenic bacteria, can identify fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized pathogens and plays an important role in identification of the fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized strain, so that a foundation is laid for building a special, quick, high-sensitivity, stable and reliable molecular detection technical system for fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized pathogenic bacteria. By applying the molecular marker disclosed by the invention, the defects that workload is high and cycle is long in the conventional fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized pathogenic bacterium identifying and distinguishing process can be overcome, and quick and accurate identification and detection on pathogens are realized.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
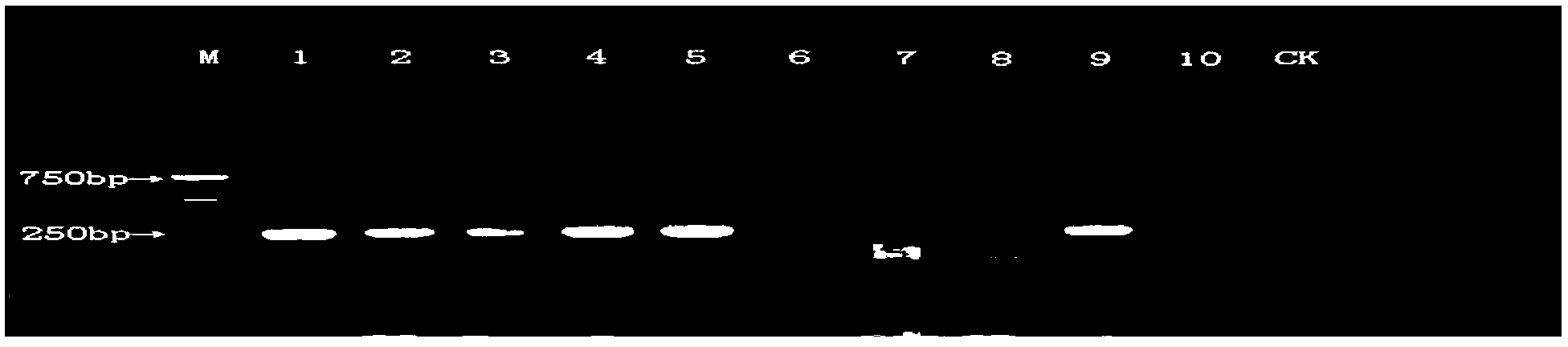
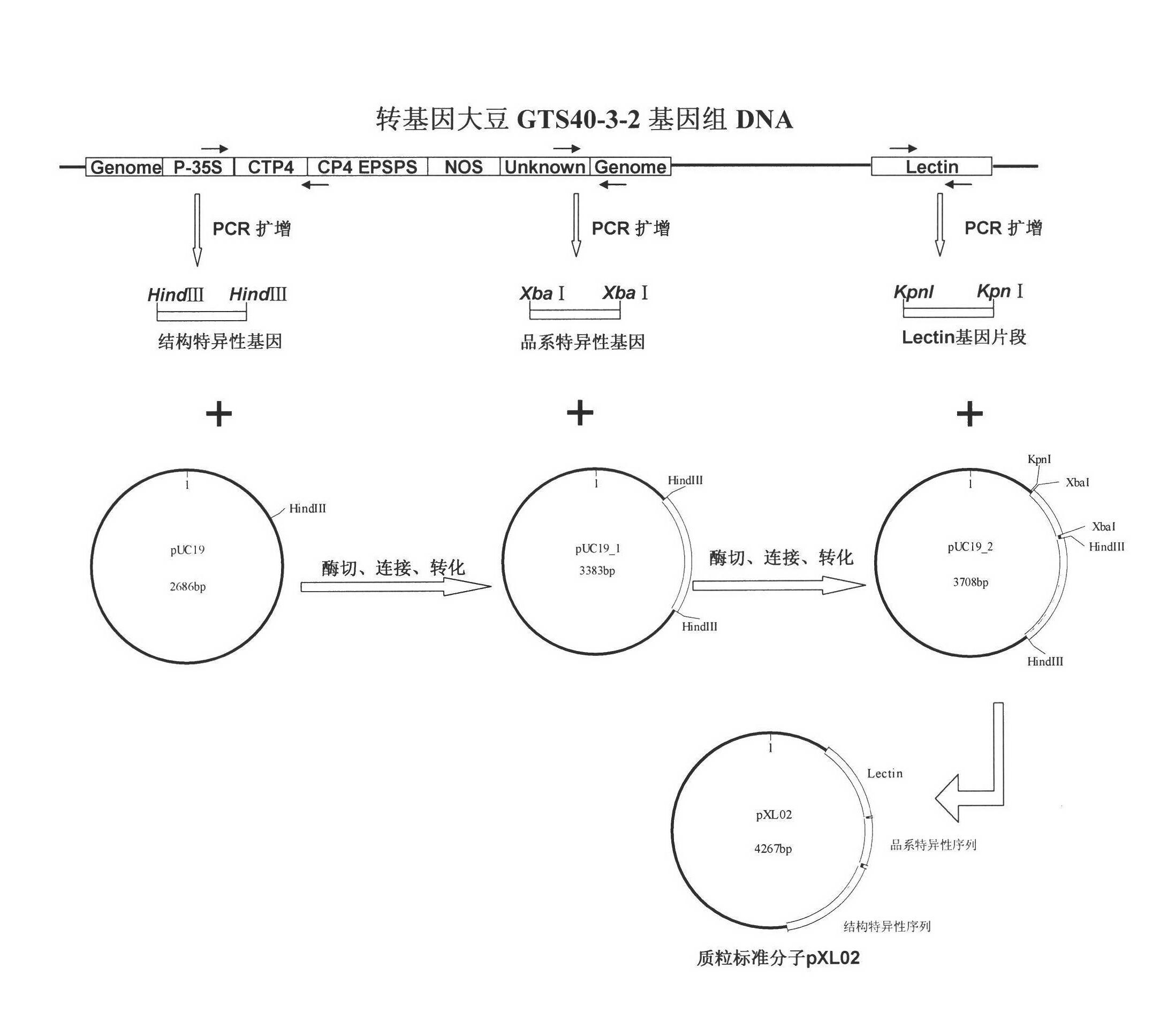
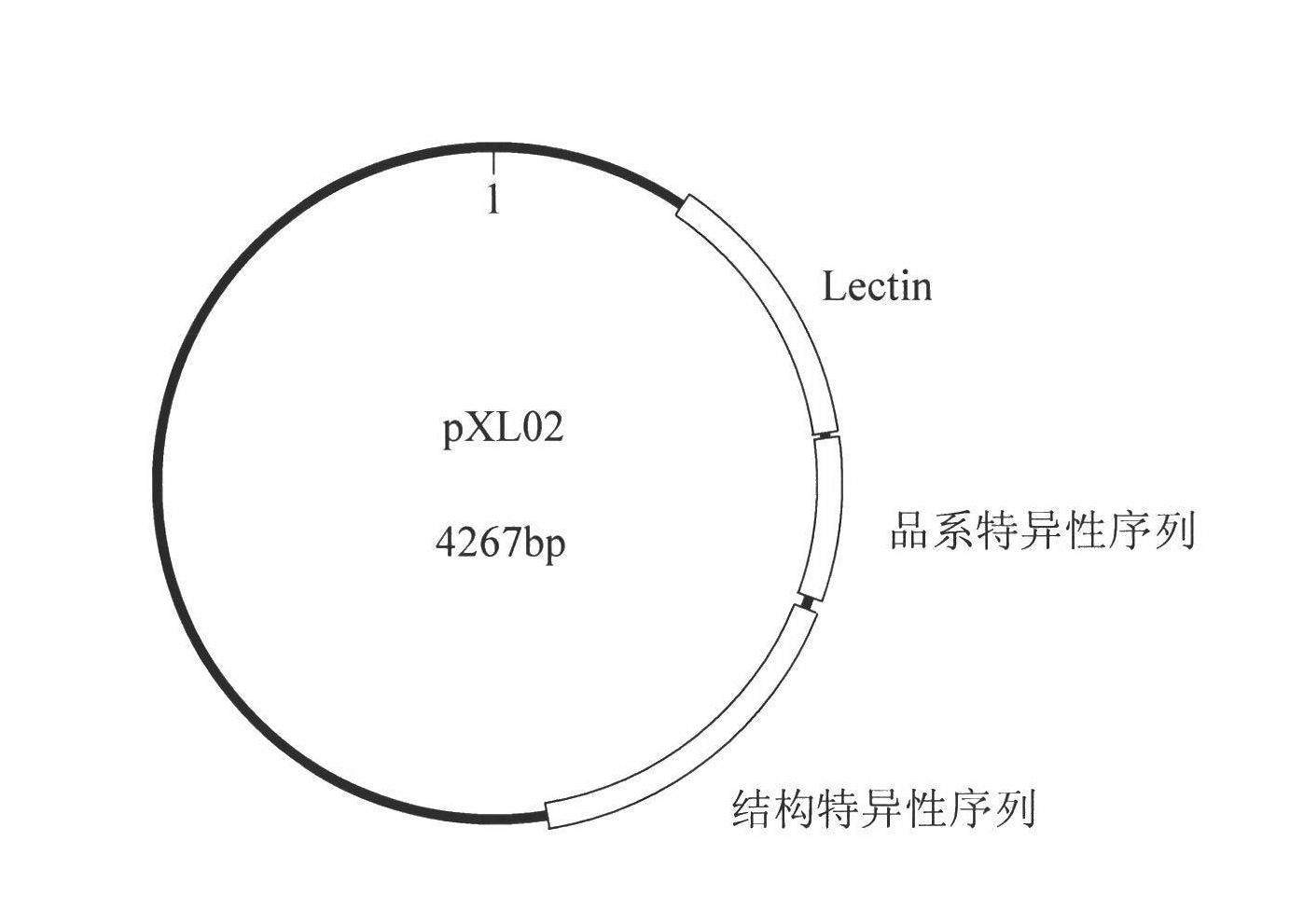
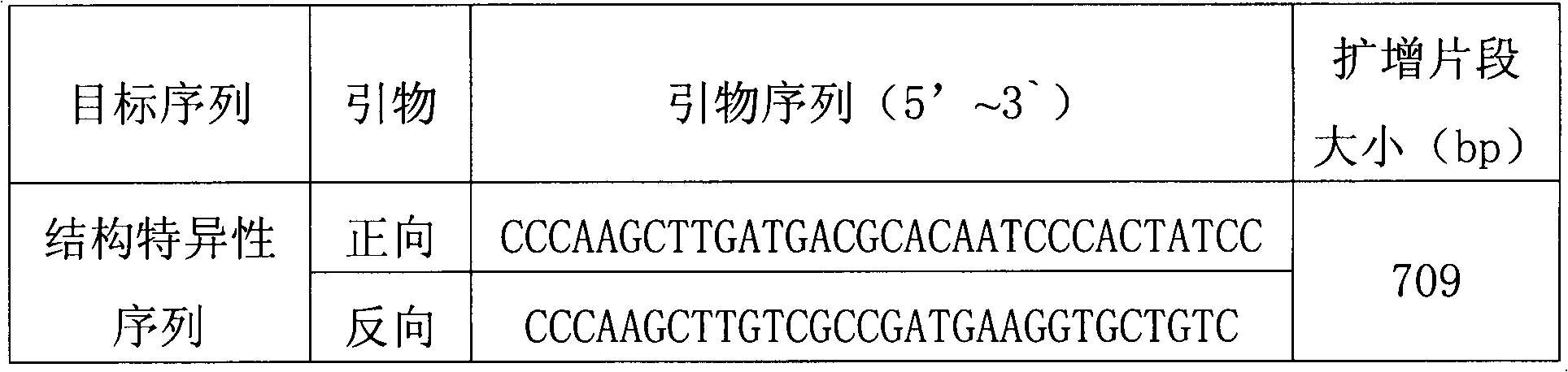
Plasmid reference molecule of quantitative determination of nucleic acids from transgenic soybean GTS40-3-2
InactiveCN102517393AAchieve traceabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionInductively coupled plasmaMass spectrometric
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MEASUREMENT & TESTING TECH
SSR marker fingerprint spectrum of needle mushroom Qinghe strain and application thereof
ActiveCN104152547AShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesStrain specificityMicrobiology
The invention relates to an SSR marker fingerprint spectrum of a flammulina velutipes Qinghe strain and application thereof. The SSR marker fingerprint spectrum of the flammulina velutipes Qinghe strain is combined by six pairs of peculiar allelic fragments, developed on the basis of a flammulina velutipes genomic sequence and marked with SSR. Application of the SSR marker fingerprint spectrum of the flammulina velutipes Qinghe strain comprises that SSR marker amplification is carried out on a flammulina velutipes strain, the obtained banding pattern is compared with the fingerprint spectrum, and if the banding pattern is consistent with the fingerprint spectrum, the flammulina velutipes strain is the flammulina velutipes Qinghe strain. Compared with the conventional morphological detection, the conventional antagonistic test and the conventional fruiting test, the SSR marker fingerprint spectrum of the flammulina velutipes Qinghe strain has the advantages of short detection time, high accuracy and good repeatability and has Qinghe strain specificity in 24 collected major flammulina velutipes strains in China.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Bacteriophage-containing therapeutic agents
The present invention relates in its broadest aspect to combined phage / antibiotic therapy. More particularly, it relates to use of (i) one or more bacteriophages and (ii) one or more antibiotics in the manufacture of a combined product for simultaneous, separate or sequential administration of (i) and (ii) to treat a bacterial infection characterized by biofilm formation, for example an infection comprising or consisting of P. aeruginosa. Treatment in this context may be either therapeutic or prophylactic treatment. Also provided are deposited bacteriophages each exhibiting different strain specificity against P. aeruginosa and combinations of such bacteriophages, e.g. a panel of six deposited bacteriophages which was found to be effective against a high percentage of clinical isolates of P. aeruginosa from canine ear infections.
Owner:BIOCONTROL
Strain specificity PCR detection method of heredity modified corn strain MON863
InactiveCN1724689AGood qualityImprove responseMicrobiological testing/measurementStrain specificityMicrobiology
The invention relates to strain specificity PCR testing method of improved corn strain MON863 that includes 5'end strain specificity testing method and 3'end strain specificity testing method. The process includes: analyzing external inserting carrier neighbor gene sequence of MON863 corn, designing primer of strain specificity PCR and ration PCR, and probe; building and optimizing strain specificity and ration PCR system; verifying the strain specificity and ration PCR testing method to build the testing platform of strain specificity PCR of improved corn strain MON863.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for identifying transgenic maize Bt176 strain specificity by RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification) technology
InactiveCN106801092AObvious amplification curveHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyStrain specificity
The invention discloses a method for identifying the transgenic maize Bt176 strain specificity by a RPA (recombinase polymerase amplification) technology. The method is characterized in that the DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample to be tested is firstly extracted as a template; screened primers and probes are used for performing RPA fast amplification and real-time fluorescence detection; if an amplification curve is obtained, the condition that the tested sample contains curve ingredients is proved. A large number of RPA primers are designed according to a connecting region of an exogenous inserted DNA sequence and a maize genome, a pair of primers and probe combinations capable of fast and effectively detecting the transgenic maize Bt176 ingredients are screened; a RPA detecting method of the transgenic maize Bt176 strain specificity is provided for the first time.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Standard plasmid molecule used for detecting genetically modified soybeans and cotton and building method thereof
ActiveCN102409081AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified cropsStrain specificity
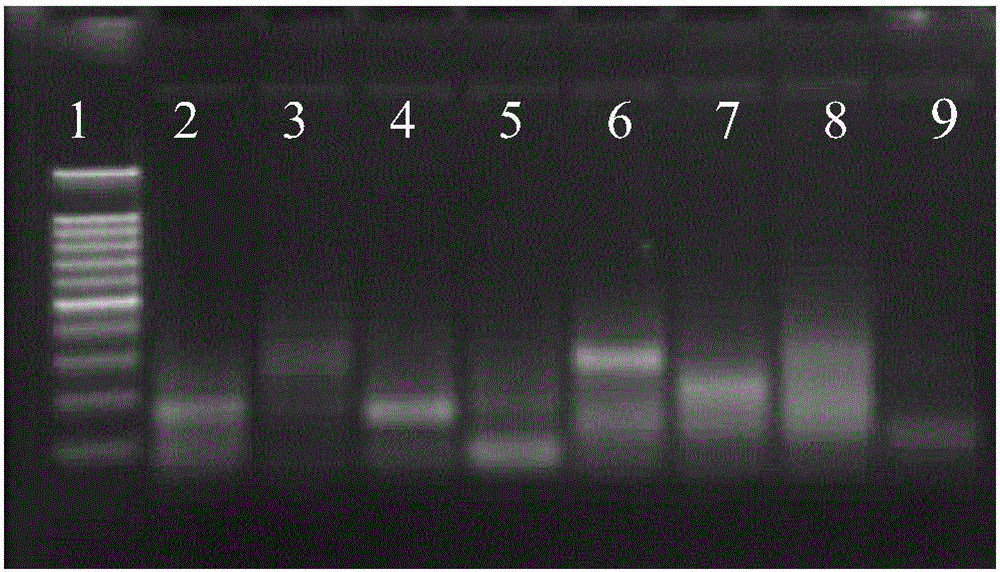
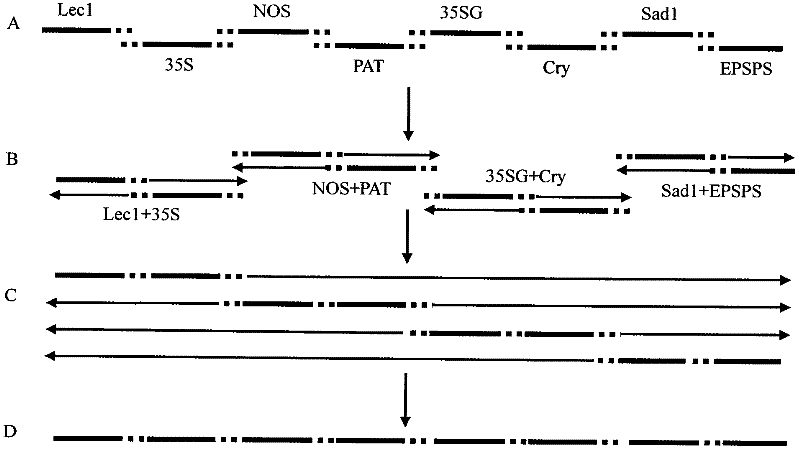
The invention discloses a standard plasmid molecule used for detecting genetically modified soybeans and cotton and a building method thereof. The standard plasmid molecule contains eight gene specific fragments (Lec1, 35S, NOS, PAT, Sad1, Cry1Ab / c and EPSPS) of soybeans and cotton. The standard plasmid molecule and the building method have the following beneficial effects: the eight genes are fused into a large fragment through fusion PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and the large fragment is cloned on a plasmid vector to obtain a recombinant plasmid molecule pTLE8; the standard plasmid molecule built in the invention can replace the positive controls and is suitable for the screening of the genetically modified soybean strain GTS40-3-2 and Bt cotton and the qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis and detection of the gene and strain specificity; and new exogenous gene fragments can be added on the basis of the original standard molecule if new genetically modified materials occur, thus meeting the increasing detection requirements of the genetically modified crop materials.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Molecular biological quantitative detecting method for pathogenicity paratypic hemolytic vibrio in aquatic products
InactiveCN1831139ALong test cycleHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesVibrio parahaemolyticusGel electrophoresis
The invention relates to a method to test pathogenicity vibrio parahaemolyticus in aquatic product that the feature is including the following steps: designing, filtering, and manufacturing the specificity primer of the testing strain, expanding PCR and testing, distilling DNA, PCR expanding of the testing strain specificity gene section, agarose gel electrophoresis of the PCR product and testing the specificity section; MPN method testing and calculating the testing result. The invention discloses a method to rapidly testing bacilli in testing sample.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
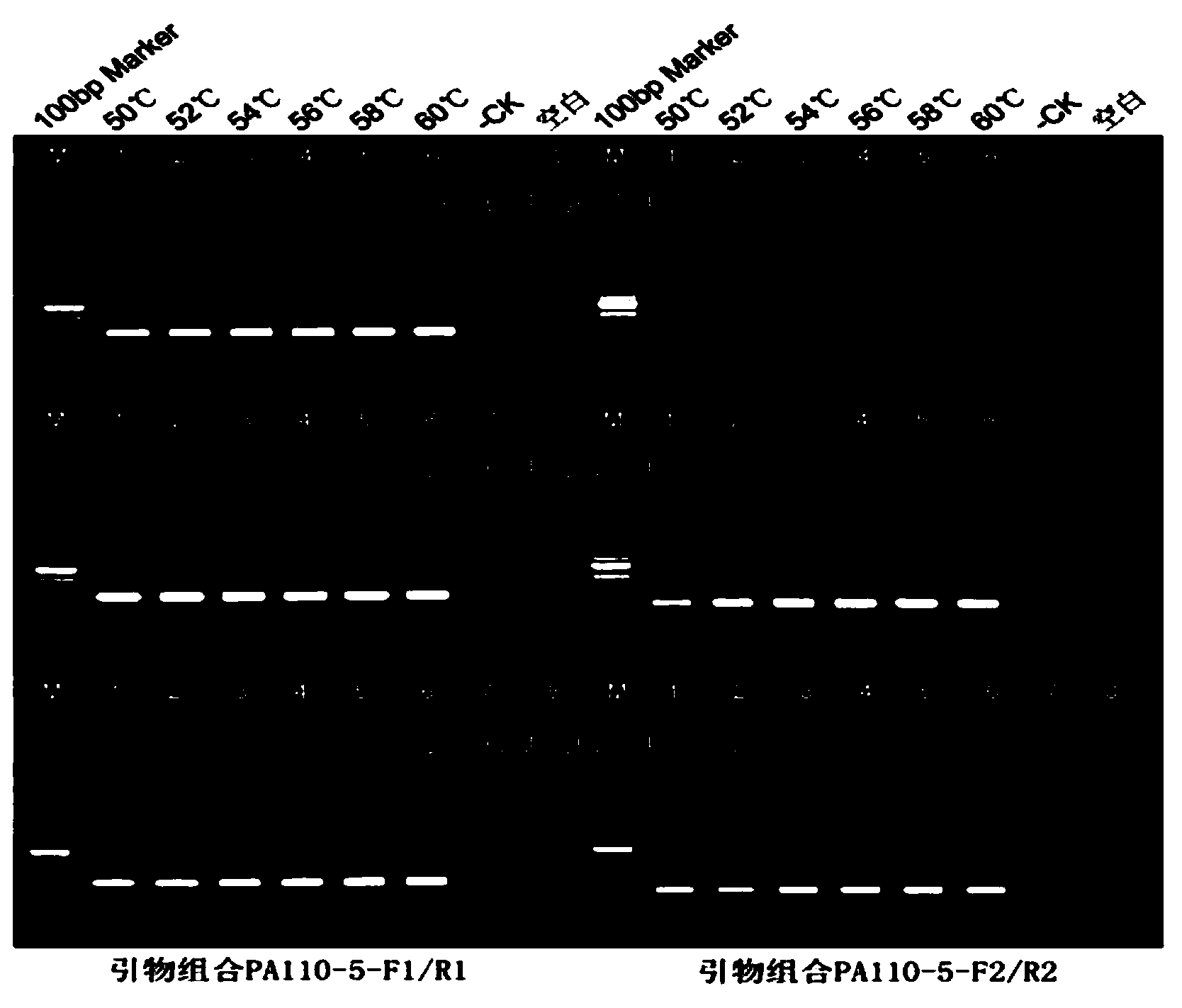
Transgenic rice PA110-15 foreign insert flanking sequence and application
ActiveCN103966208AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStrain specificityAgricultural science
The invention discloses a transgenic rice PA110-15 foreign insert flanking sequence and an application. According to the transgenic rice PA110-15 foreign insert flanking sequence, firstly, a 5' end sequence and a 3'flanking sequence of a transgenic rice PA110-15 strain foreign inserted gene are provided, and nucleotide sequences of the 5' end sequence and the 3'flanking sequence are represented by SEQID NO.1 and SEQID NO.2.The invention provides aPCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection primer for transgenic ricePA110-15(expressing lysine-rich storage protein gene)strain specificity and a strain specificityqualitative detection method with the flanking sequence used as a target gene. Specificityexperiments indicate that the establishedtransgenic rice PA110-15 strain specificityqualitative PCR detection method has the high specificity. Sensitivity test results indicate thatthe sensitivity of the established detection method reaches 0.1%.
Owner:RICE RES ISTITUTE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Transgenic maize T4-1-1 strain specific detection method and reagent kit
ActiveCN105177172AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationStrain specificitySpecific detection
The invention designs four pairs of PCR detection primers used for detecting the strain specificity of transgenic maize T4-1-1 and further provides a reagent kit containing the primers. Experiments indicate that by means of the detection primers, the PCR qualitative detection conducted on the strain specificity of the transgenic maize T4-1-1 is great in specificity and high in sensitivity.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Standard plasmid molecular used for detecting transgenic soybean, corn and cotton and construction of the standard plasmid molecular
ActiveCN102559854AImprove featuresGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionReference genesStrain specificity
The invention discloses a necessary standard plasmid molecular and a construction method of the standard plasmid molecular in the field of transgenic crop detection. The construction method comprises the following steps: modifying an octo-gene plasmid molecular pTLE8 (Patent Application No.201010286884.3), adding a fusion fragment of 3'-transformation event specific sequences of transgenic corn Bt176 strain and Mon810 strain and corn internal reference gene Hmg specific sequence, and modifying into a deca-gene plasmid molecular pTLH10 (Lec1, 35S, NOS, PAT, Sad1, Cry1, Ab / c, Bt176, Mon810 and Hmg). The standard plasmid molecular constructed by the invention can completely replace a positive standard sample, and is suitable for screening transgenic soybean GTS40-3-2 strain, transgenic corn Bt176 and Mon810 strains and transgenic Bt cottons, and qualitative and quantitative PCR analysis and detection of gene specificity and strain specificity.
Owner:FEED RESEARCH INSTITUTE CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
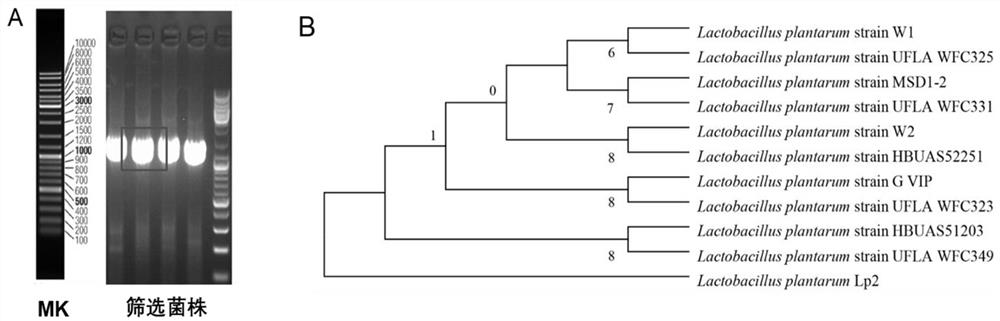
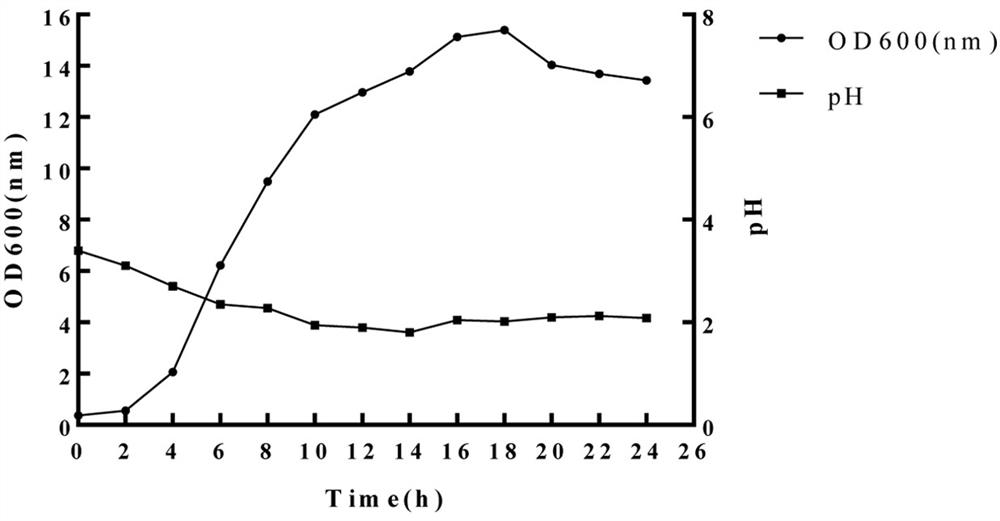
Lactobacillus plantarum Lp2 and application thereof
ActiveCN111925961AGood anti-inflammatory effectBacteriaDigestive systemBiotechnologyIsomaltooligosaccharide
The invention discloses a lactobacillus plantarum Lp2. The preservation number of the lactobacillus plantarum Lp2 is CCTCC NO: M 2019935. A probiotic solid beverage comprises the following componentsin parts by weight: 10 parts of lactobacillus plantarum freeze-dried powder, 5-10 parts of isomaltooligosacharide, 5-10 parts of soybean oligosaccharide and 5-15 parts of fruity powder. The preservation number of the lactobacillus plantarum is CCTCC NO: M 2019935. The invention also discloses application of the lactobacillus plantarum Lp2 in preparation of anti-enteritis drugs. Results show that the lactobacillus plantarum Lp2 has good acid stress tolerance, cholate stress tolerance, pathogenic bacteria infection resistance and high intestinal tract colonization capacity, and has a protectiveeffect on LPS-induced acute inflammation; the lactobacillus plantarum Lp2 strain is superior to other strains in in-vitro probiotic function evaluation and in-vivo indexes of mice, and it is shown that lactobacillus plantarum Lp2 shows obvious strain specificity in the aspect of anti-inflammation.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Two step genome comparison method for designing quantitative PCR specific primer of guizhouense NJAU 4742
ActiveCN108949908AImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGenome alignmentStrain specificity
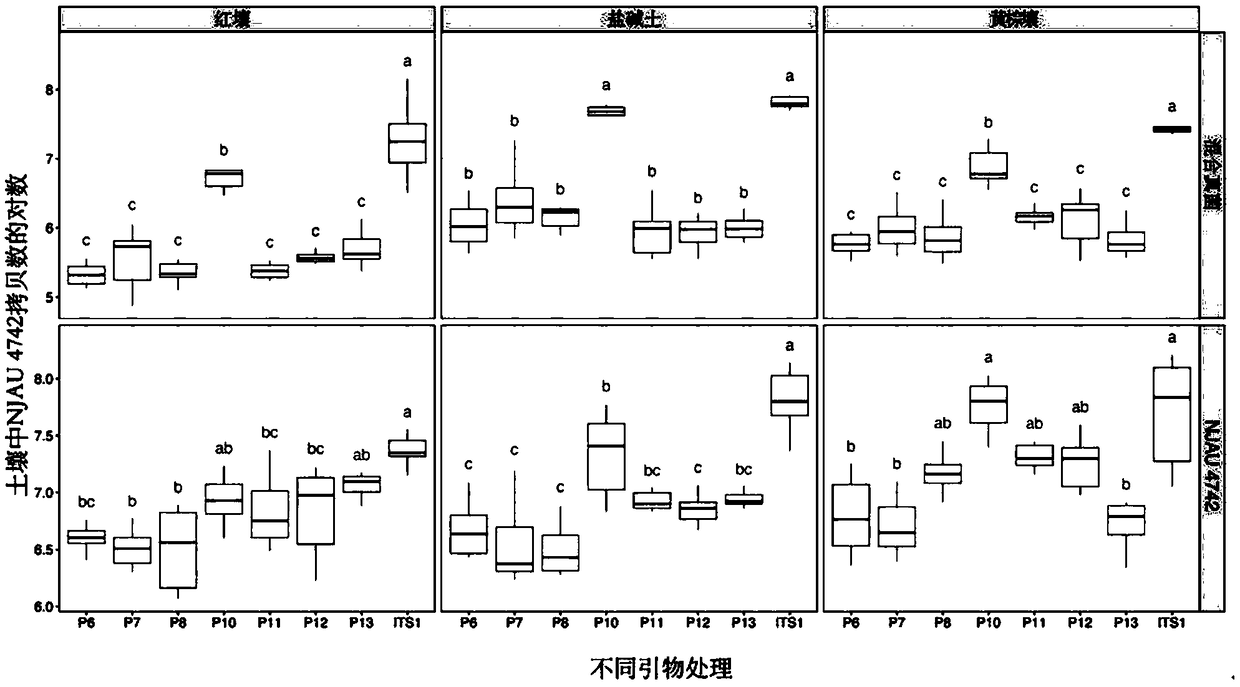
The invention discloses a two step genome comparison method for designing a quantitative PCR specific primer of guizhouense NJAU 4742. At first, full genome sequence of NJAU 4742 is compared in NCBI database and JGI database; genome segments, which are not matched and greater than 500 bp, are picked out; then the screened segments are compared with the full genome of a guizhouense strain 916; anda primer sequence with unique bases is designed. At the same time, three pairs of primers, which are prepared by inserting labeled segments into a gfp labeled strain (gfp-NJAU 4742), are used to examine the specificity of the primers designed based on the genome. By examining the amplification specificity of strains of same genus and different species, re-detecting the soil addition, and actuallydetecting the potting soil, an optimal quantitative PCR primer is screened out. The provided primer design method and design strain specific primer can be applied to quantitative PCR specific primer design of other strains and quantifying of guizhouense NJAU 4742.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
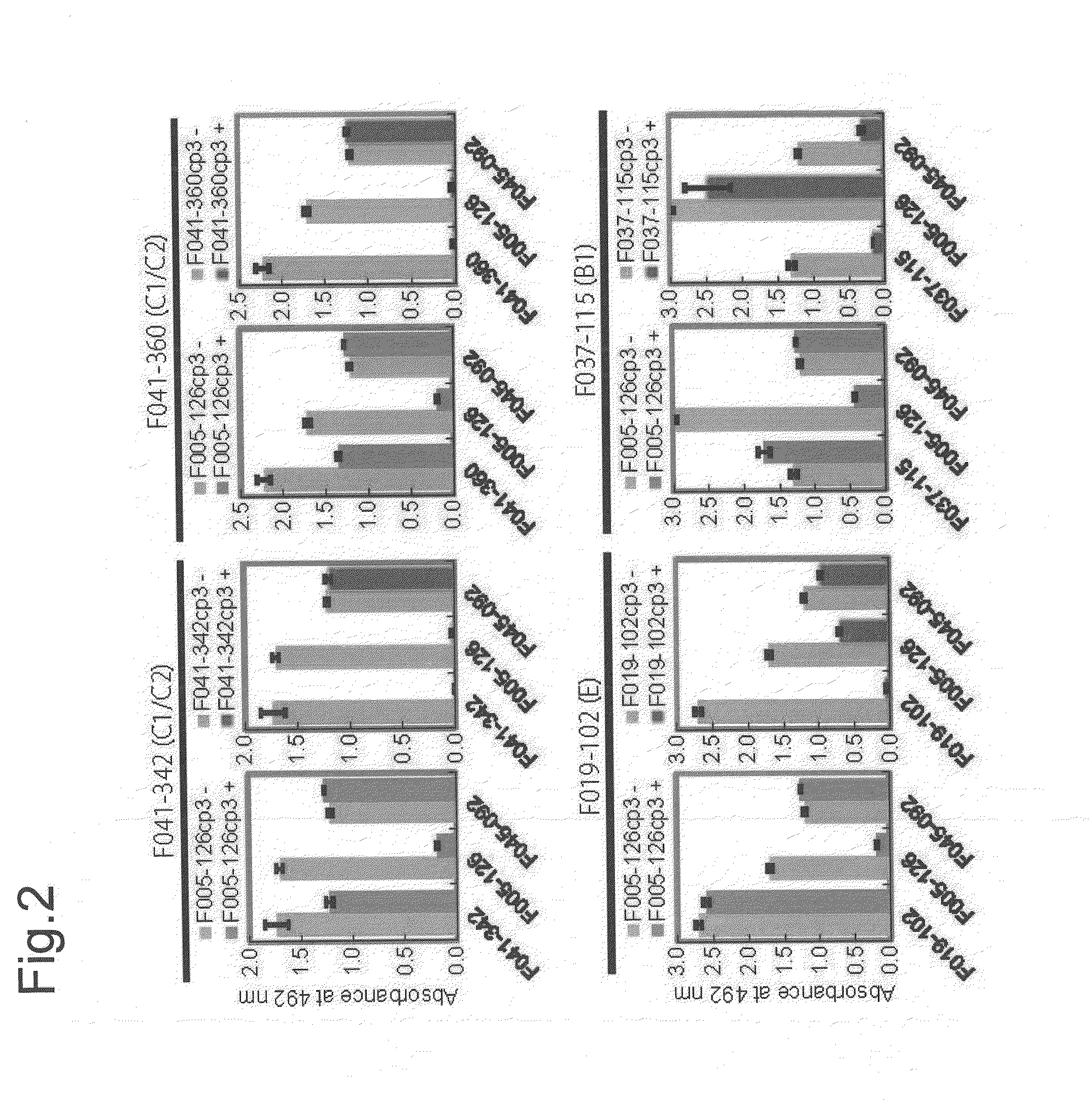
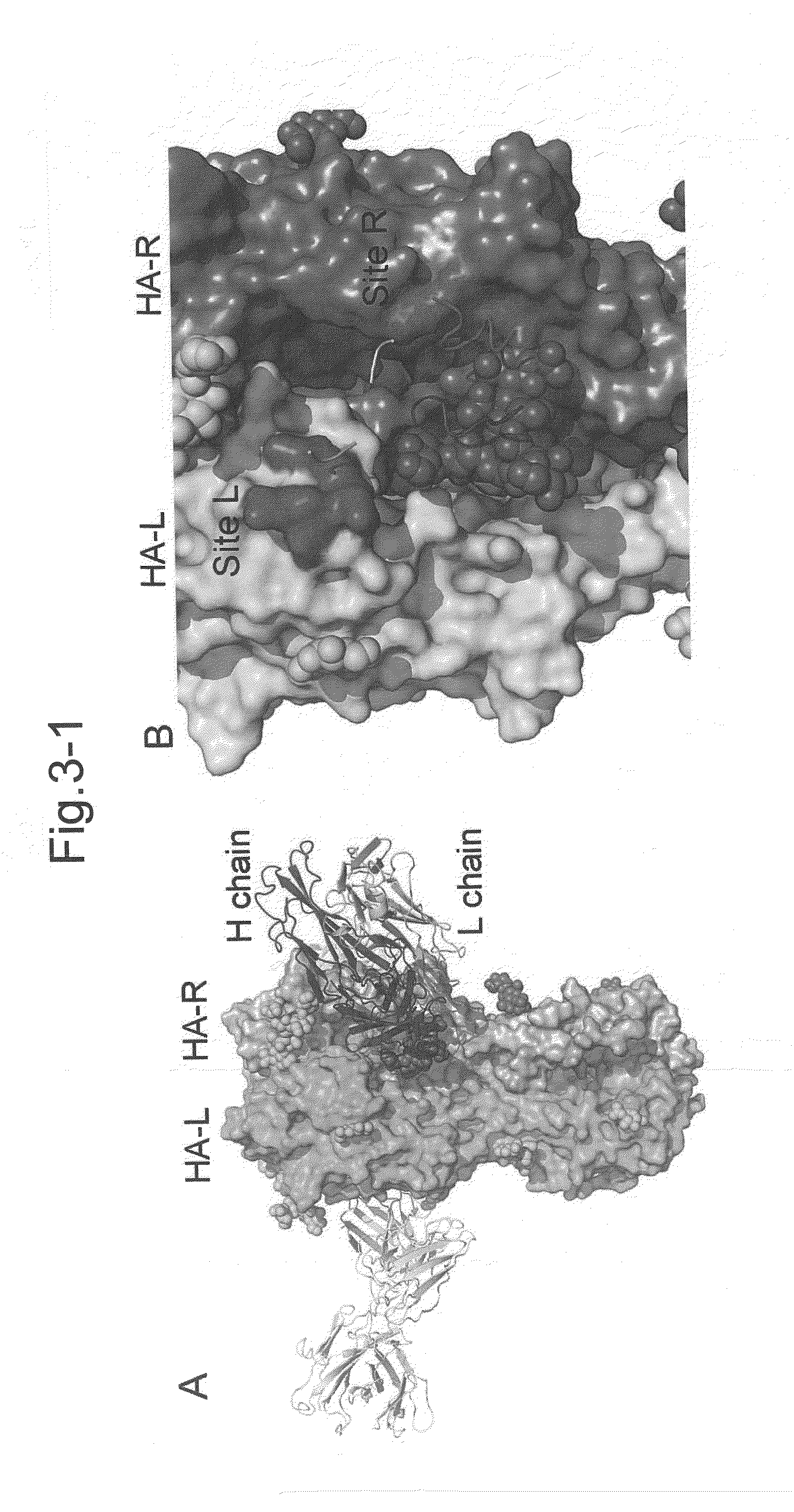
Novel epitope and mechanism of antigen-antibody interaction in an influenza virus
InactiveUS20140086927A1Molecular designMicrobiological testing/measurementHemagglutininNeutralizing antibody
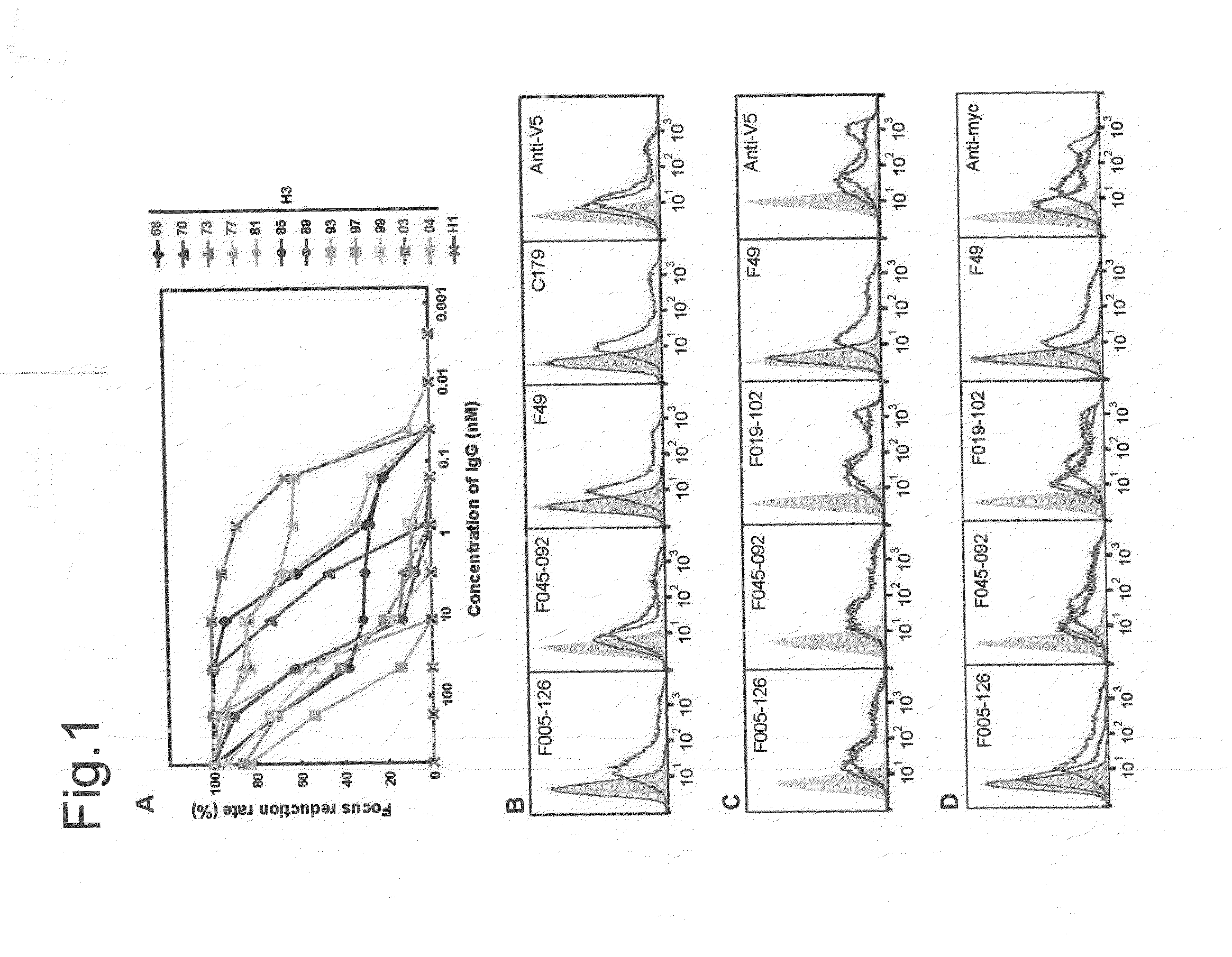
Antibodies (Abs) play roles in protection against influenza. Neutralizing Abs either inhibit the binding of hemagglutinin (HA) to cellular receptors or prevent the conformational change of HA induced by low pH. The former Ab binds to the regions near the sialic acid-binding pocket on the globular head formed by HA1 and generally shows narrow strain specificity. The latter Ab binds to the stem region formed mainly by HA2 and shows broad strain specificity. We isolated a broadly neutralizing Ab against H3N2 viruses. X-ray analysis of the HA / Ab complex indicated that the Ab binds to the valley formed by two neighboring HA monomers at the side of the globular head. The Ab shows neutralizing activity by preventing the conformational change of HA induced at low pH.
Owner:FUJITA HEALTH UNIVERSITY
A strain-specific qualitative and quantitative PCR detection method for transgenic carnation moonlite
InactiveCN102286624AGood qualityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementStrain specificityPcr method
The invention discloses a qualitative and quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method for strain specificity of transgenic carnation Moonlite, which comprises the following steps: 1) extraction of genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of the transgenic carnation Moonlite; 2) amplification and confirmation of the left boundary adjacent sequence of the transgenic carnation Moonlite exogenous gene insertion site; 3) establishment and verification of the qualitative PCR detection method for transgenic carnation Moonlite; and 4) establishment and verification of the quantitative PCRdetection method for transgenic carnation Moonlite. The invention successfully establishes the qualitative and quantitative PCR detection method for strain specificity of transgenic carnation Moonlite, and verifies the specificity and sensitivity of the detection method, thereby providing references for import detection, supervision and environmental safety evaluation of transgenic carnation.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom L9319 strain, and application thereof
ActiveCN102851377AShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementStrain specificityAgricultural science
The invention relates to an SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom L9319 strain, and an application thereof. The fingerprint is composed of 7 pairs of SSR-labeled specific allelic fragments developed according to a shiitake mushroom genomic sequence. The application comprises the steps that: SSR-labeled amplification is carried out upon a shiitake mushroom strain; and an obtained band type is compared with the fingerprint. If the band type is consistent with the fingerprint, the strain is a shiitake mushroom L9319 strain. Compared with a conventional morphological detection method, an antagonistic test, and mushroom fruiting trials, the application provided by the invention has the advantages of short detection time, high accuracy, and good repeatability. In 25 collected nationally validated shiitake mushroom main cultivated strains of our nation, the fingerprint has shiitake mushroom L9319 strain specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Authentication method of dairy products
The present invention relates to a new method of establishing the authenticity and origin of dairy products, more specifically to the use of lactic acid bacterial strains having strain-specific insertion sequence elements as tools for marking dairy products (such as cheese) and identification thereof. The invention also extends to new lactic acid bacterial strains, their use in the production of dairy products as well as the dairy products containing these bacterial strains.
Owner:EMMENTALER SWITZERLAND
SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom L9319 strain, and application thereof
ActiveCN102851377BShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementStrain specificityAgricultural science
The invention relates to an SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom L9319 strain, and an application thereof. The fingerprint is composed of 7 pairs of SSR-labeled specific allelic fragments developed according to a shiitake mushroom genomic sequence. The application comprises the steps that: SSR-labeled amplification is carried out upon a shiitake mushroom strain; and an obtained band type is compared with the fingerprint. If the band type is consistent with the fingerprint, the strain is a shiitake mushroom L9319 strain. Compared with a conventional morphological detection method, an antagonistic test, and mushroom fruiting trials, the application provided by the invention has the advantages of short detection time, high accuracy, and good repeatability. In 25 collected nationally validated shiitake mushroom main cultivated strains of our nation, the fingerprint has shiitake mushroom L9319 strain specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Size-variable strain-specific protective antigen for Potomac horse fever
InactiveUS20080069824A1Generate immune responseEffective vaccineSnake antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesProtective antigenAntigen
Owner:DUTTA SUKANTA +2
SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom Guangxiang strain, and application thereof
ActiveCN102851376AShort detection timeImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementStrain specificityAgricultural science
The invention relates to an SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom Guangxiang strain, and an application thereof. The fingerprint is composed of 7 pairs of SSR-labeled specific allelic fragments developed according to a shiitake mushroom genomic sequence. The application comprises the steps that: SSR-labeled amplification is carried out upon a shiitake mushroom strain; and an obtained band type is compared with the fingerprint. If the band type is consistent with the fingerprint, the strain is a shiitake mushroom Guangxiang strain. Compared with a conventional morphological detection method, an antagonistic test, and mushroom fruiting trials, the application provided by the invention has the advantages of short detection time, high accuracy, and good repeatability. In 25 collected nationally validated shiitake mushroom main cultivated strains of our nation, the fingerprint has shiitake mushroom Guangxiang strain specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for fast detection and identification of micro-organisms
ActiveUS20110287962A1Quick checkQuick filterMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningStrain specificitySpecific detection
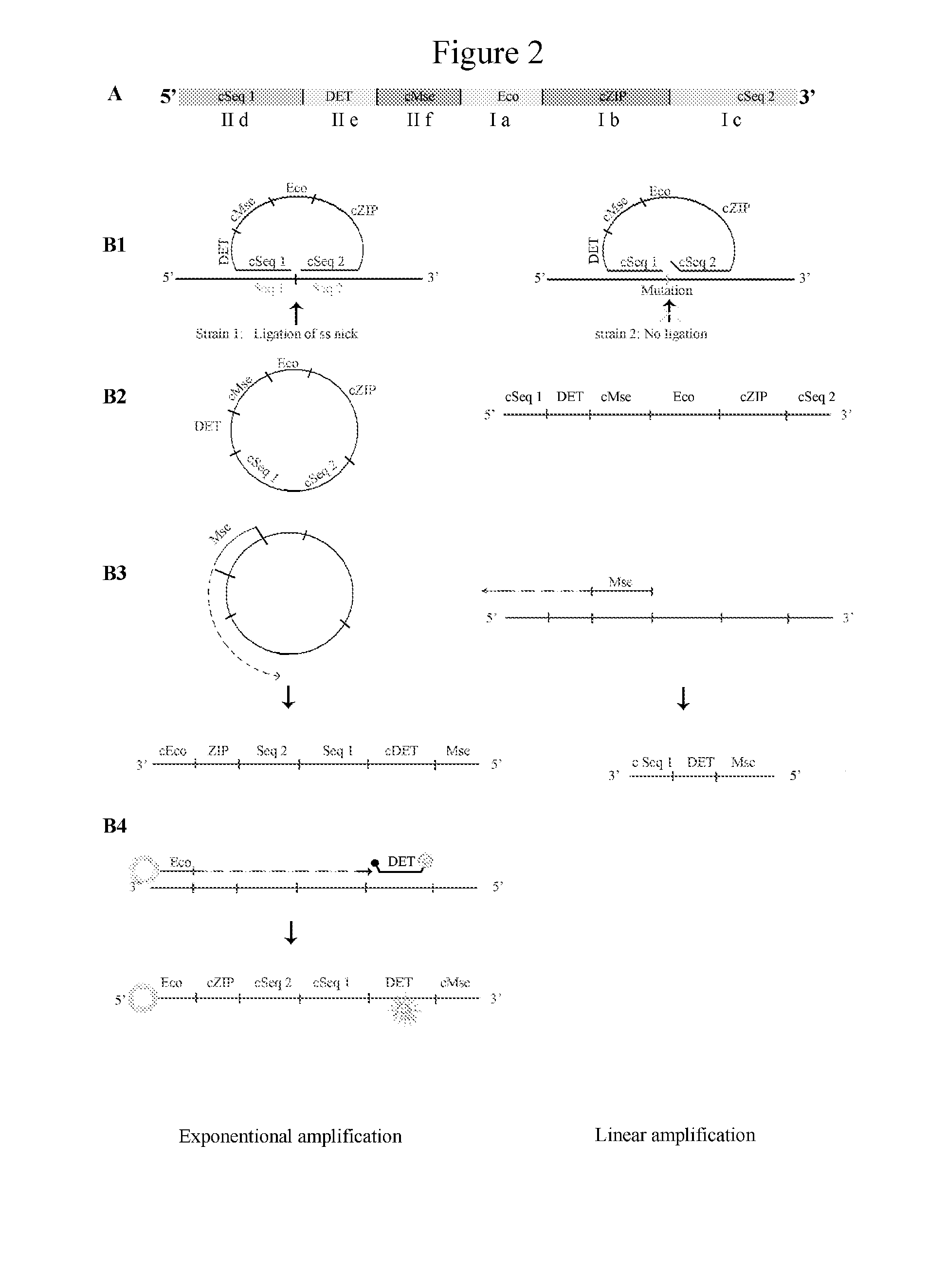
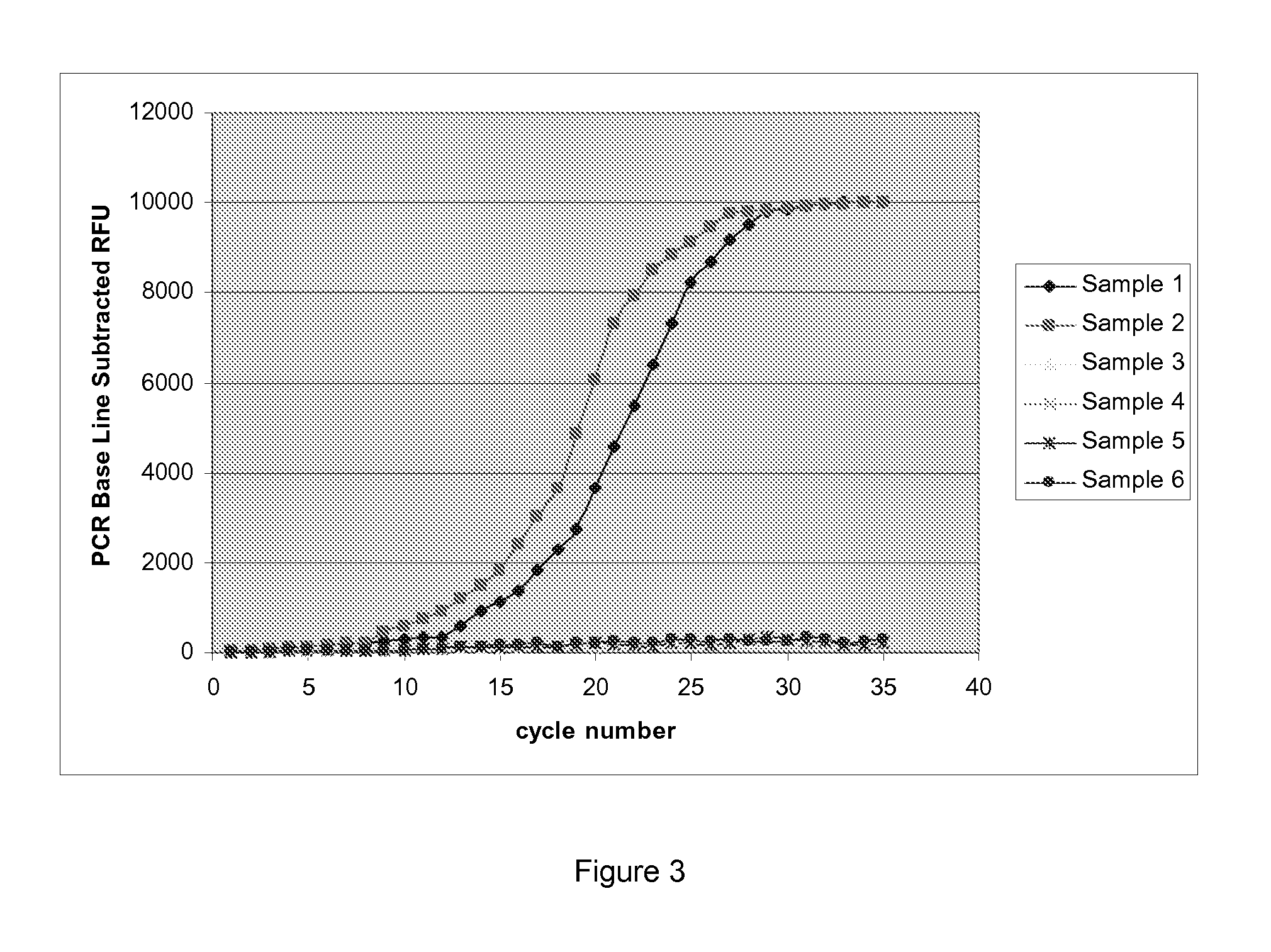
The present invention relates to a specific method accomplishing fast and specific detection, identification and characterization of contaminating micro-organisms in various samples. A method has been developed based on the detection of species-specific and / or strain-specific nucleotide sequences that are uniquely identified and amplified and subsequently detected on a microarray using addressable identifier ZIP oligonucleotides. By using a two step screening process, the method of the present invention enables in first instance the fast screening of a multitude of samples for the presence or the absence of specific micro-organisms in such samples, while in a second screening step the positive results of the first step are further processed to identify and characterize the detected micro-organisms.
Owner:CHECK POINTS HLDG
Target genes for strain-specific diagnostic of Ehrlichia ruminantium and use thereof
InactiveUS8206908B2Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementStrain specificitySpecific detection
The invention provides a combination of target genes that are useful as genetic markers for the strain-specific detection of Ehrlichia ruminantium. The invention also provides diagnostic methods using said combination of markers.
Owner:LE CENT DE COOPERATION INT & RES & DEV AGRONOMIQUE POUR LE DEVPEMENT CIRAD +1
SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom Guangxiang strain, and application thereof
ActiveCN102851376BShort detection timeImprove accuracyDermatological disorderAntibody medical ingredientsStrain specificityAgricultural science
The invention relates to an SSR-labeled fingerprint of shiitake mushroom Guangxiang strain, and an application thereof. The fingerprint is composed of 7 pairs of SSR-labeled specific allelic fragments developed according to a shiitake mushroom genomic sequence. The application comprises the steps that: SSR-labeled amplification is carried out upon a shiitake mushroom strain; and an obtained band type is compared with the fingerprint. If the band type is consistent with the fingerprint, the strain is a shiitake mushroom Guangxiang strain. Compared with a conventional morphological detection method, an antagonistic test, and mushroom fruiting trials, the application provided by the invention has the advantages of short detection time, high accuracy, and good repeatability. In 25 collected nationally validated shiitake mushroom main cultivated strains of our nation, the fingerprint has shiitake mushroom Guangxiang strain specificity.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Optimum Design Method of Pathogen Species-Specific PCR Primers
ActiveCN112634983BAvoid specificity issuesDetection and Analysis AdvantagesData visualisationProteomicsStrain specificityGenome
Owner:JIANGSU SIMCERE MEDICAL DEVICE CO LTD +1
Biocidal molecules, macromolecular targets and methods of production and use
InactiveUS20060240494A1Restrains essential movementInhibit activity of proteinCompound screeningBiocideScreening methodDirect binding
A method for identifying a compound that has a biocidal effect against a selected organism involves screening from among known or unknown peptide or non-peptide molecules, a test molecule that binds selectively to a target sequence of a multi-helical lid of a heat shock protein of the organism. The binding of the test compound inhibits the protein folding activity of the protein. A specific embodiment of such a method is useful for identifying or designing a pharmaceutical or veterinary biocidal or antibiotic compound, preferably a pathogen and / or strain-specific compound. For this purpose, the compound does not bind to a heat shock protein that is homologous to the mammalian subject to be treated with the compound. Screening methods can encompass direct binding or competitive assays. Molecules or compounds identified by these methods are employed as biocides for pharmaceutical, veterinary, pesticide, insecticide and rodenticide uses, among others.
Owner:THE WISTAR INST OF ANATOMY & BIOLOGY +1
Agaricus bisporus strain sporocarp color SCAR-PCR identification method
The invention belongs to the field of edible mushroom molecular marking assistant breeding and particularly relates to an agaricus bisporus strain sporocarp color SCAR-PCR identification method. According to the method, SCAR molecular marking is used for carrying out PCR specific amplification on agaricus bisporus brown strains, and accordingly strain sporocarp color is identified. According to the method, fruiting tests are of no need, agaricus bisporus strain sporocarp color is specifically identified, consumed time is short, operation is easy, specificity is high, the products of 1273 bp are obtained by specific amplifying of the agaricus bisporus brown strains, strain sporocarp color can be quickly identified in agaricus bisporus crossbreeding, and the efficiency of agaricus bisporus crossbreeding is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF EDIBLE FUNGI FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com