Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
70 results about "Deoxyribonucleoside" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A deoxyribonucleoside is a type of nucleoside including deoxyribose as a component. An example is deoxycytidine.
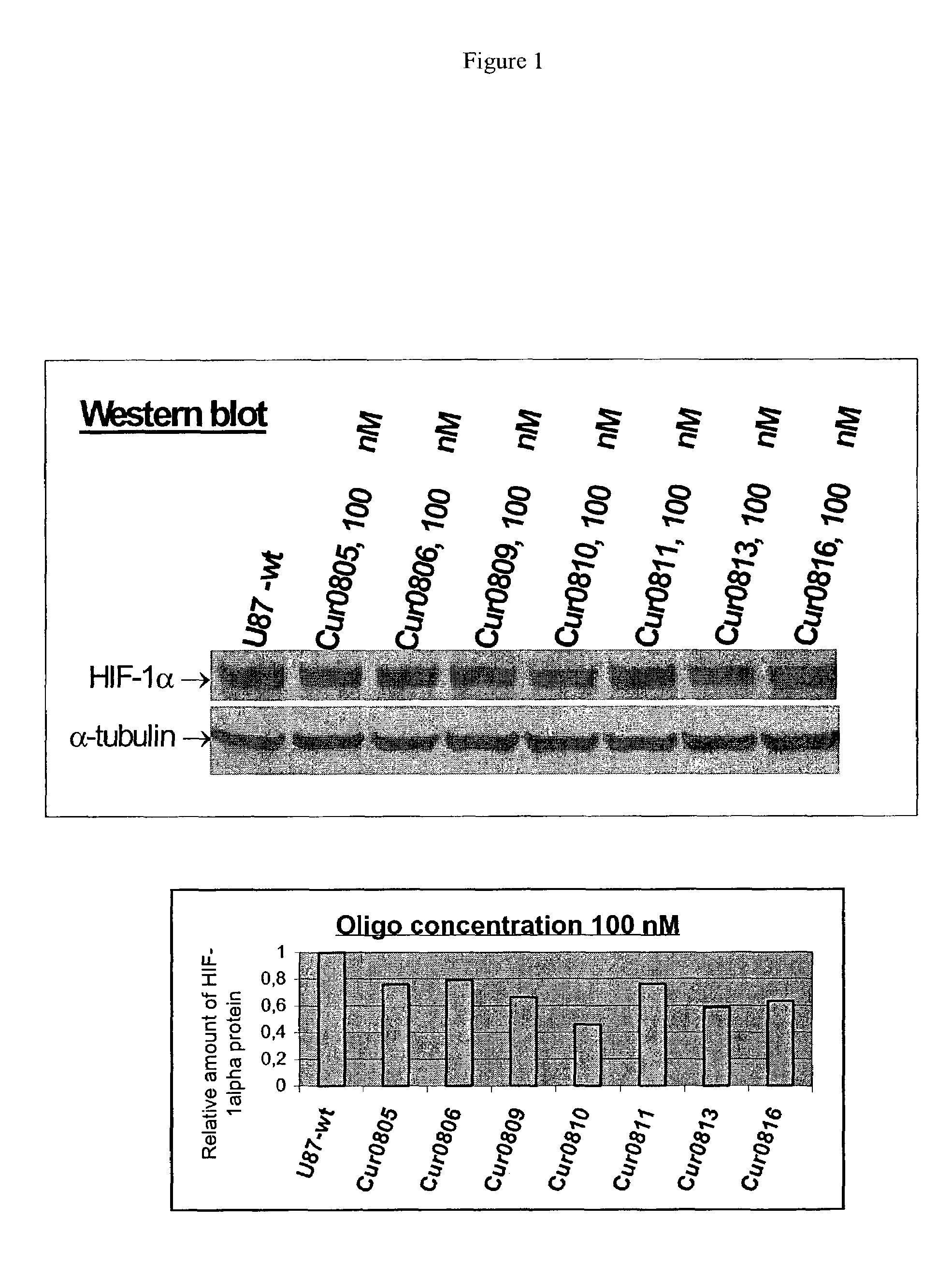
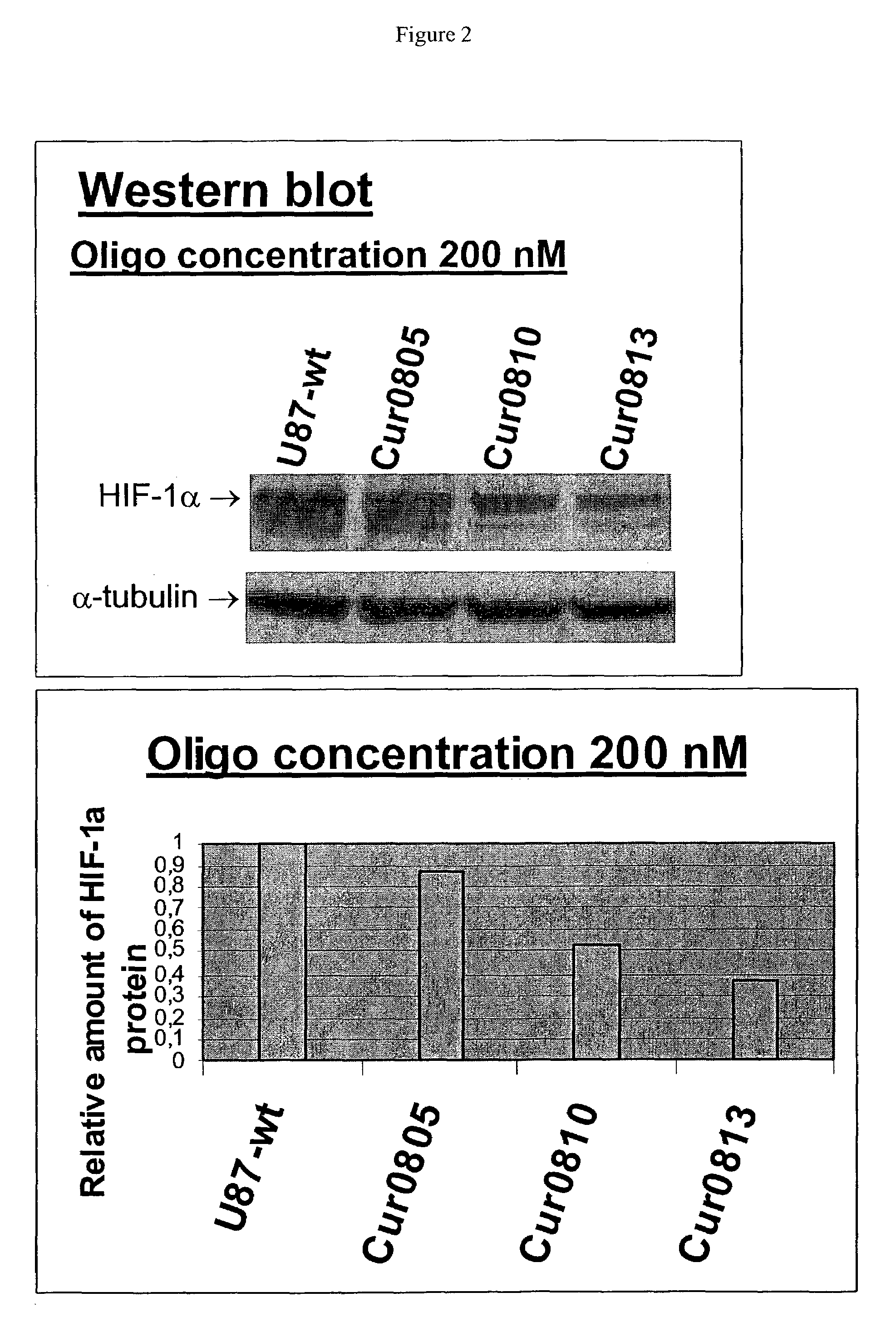
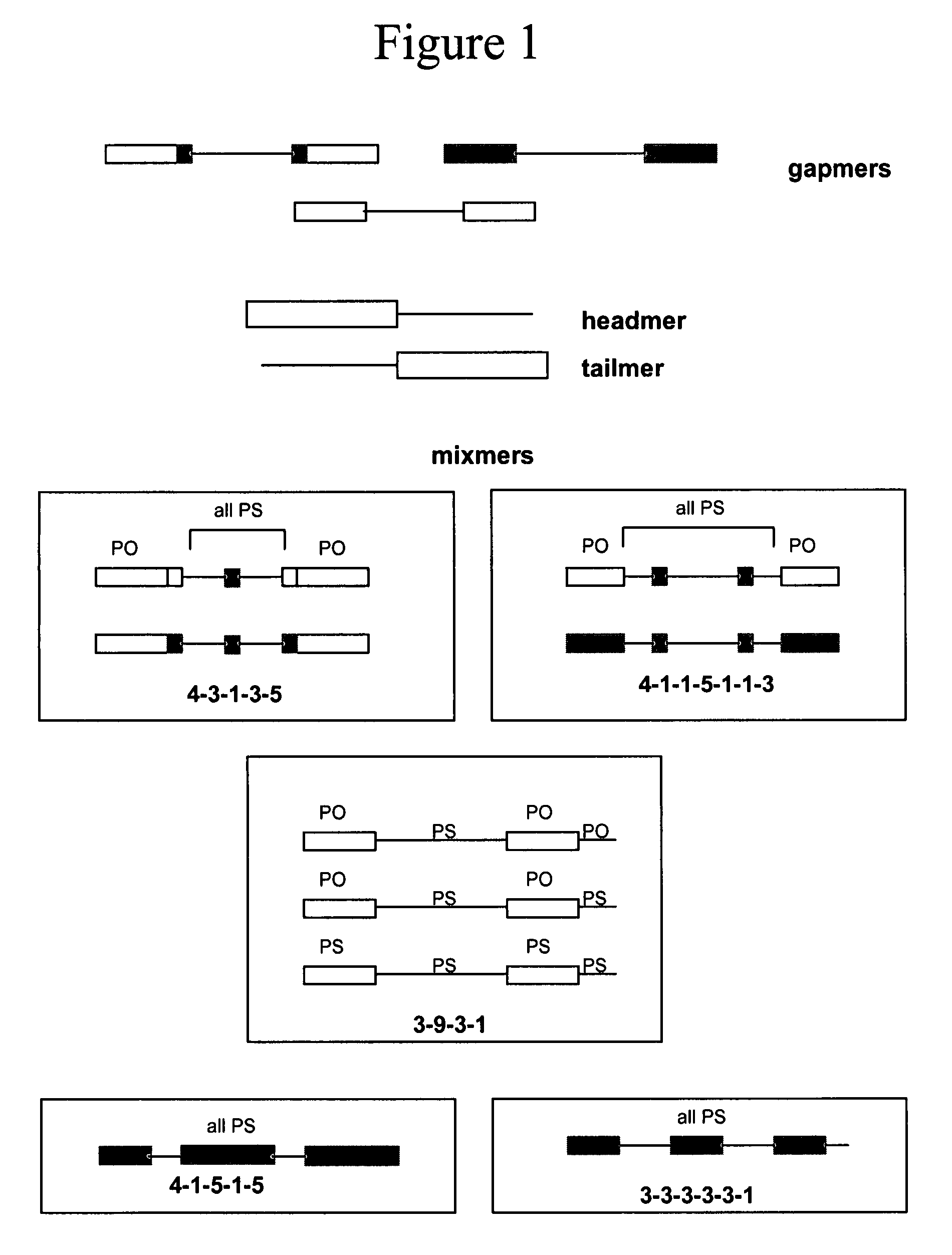
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation HIF-1α expression
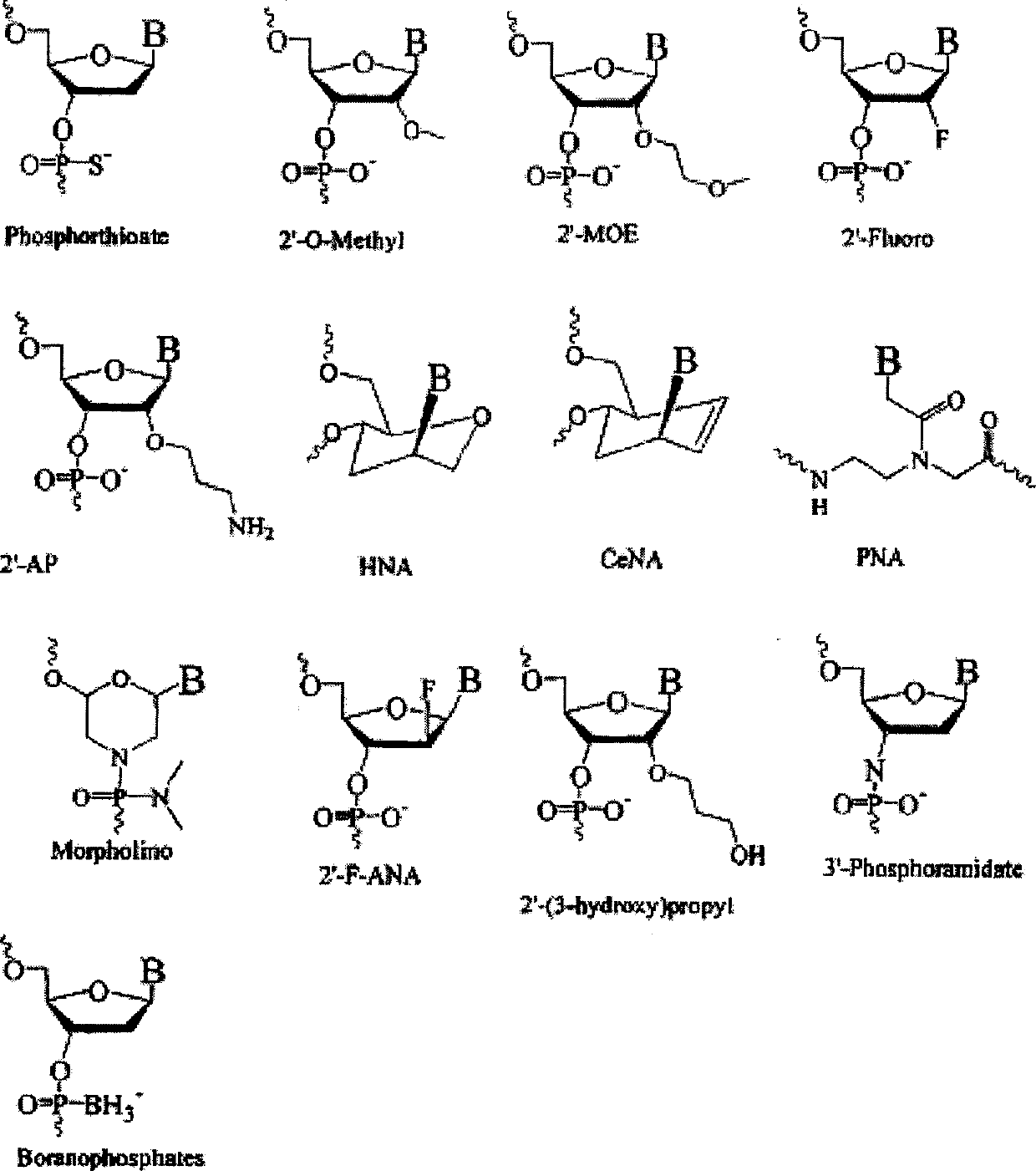
Oligonucleotides directed against the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) gene are provided for modulating the expression of HIF-1α. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the HIF-1α. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of HIF-1α expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer and pre-eclampsia. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides, a nucleic acid analogue, or Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) or a combination thereof.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
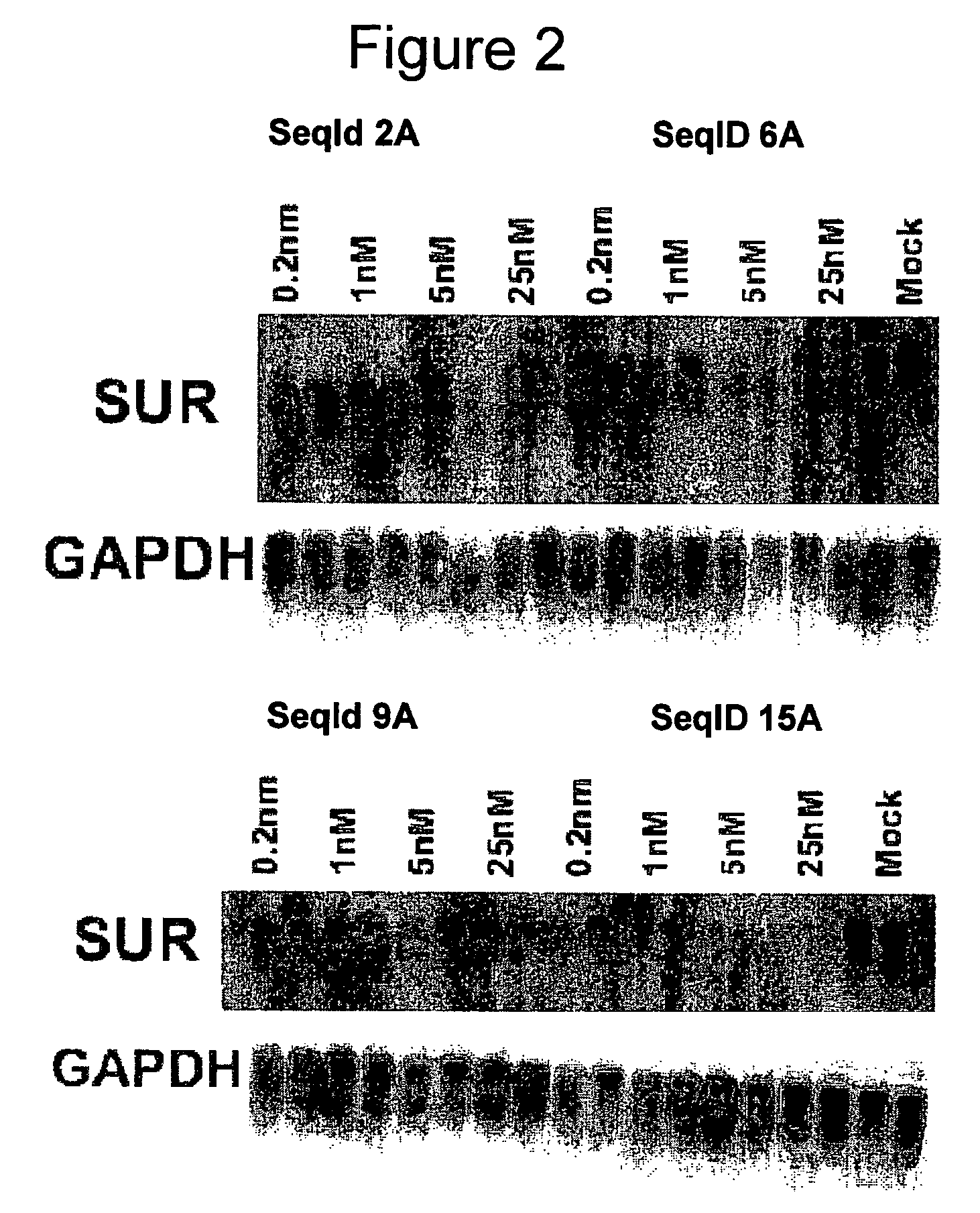
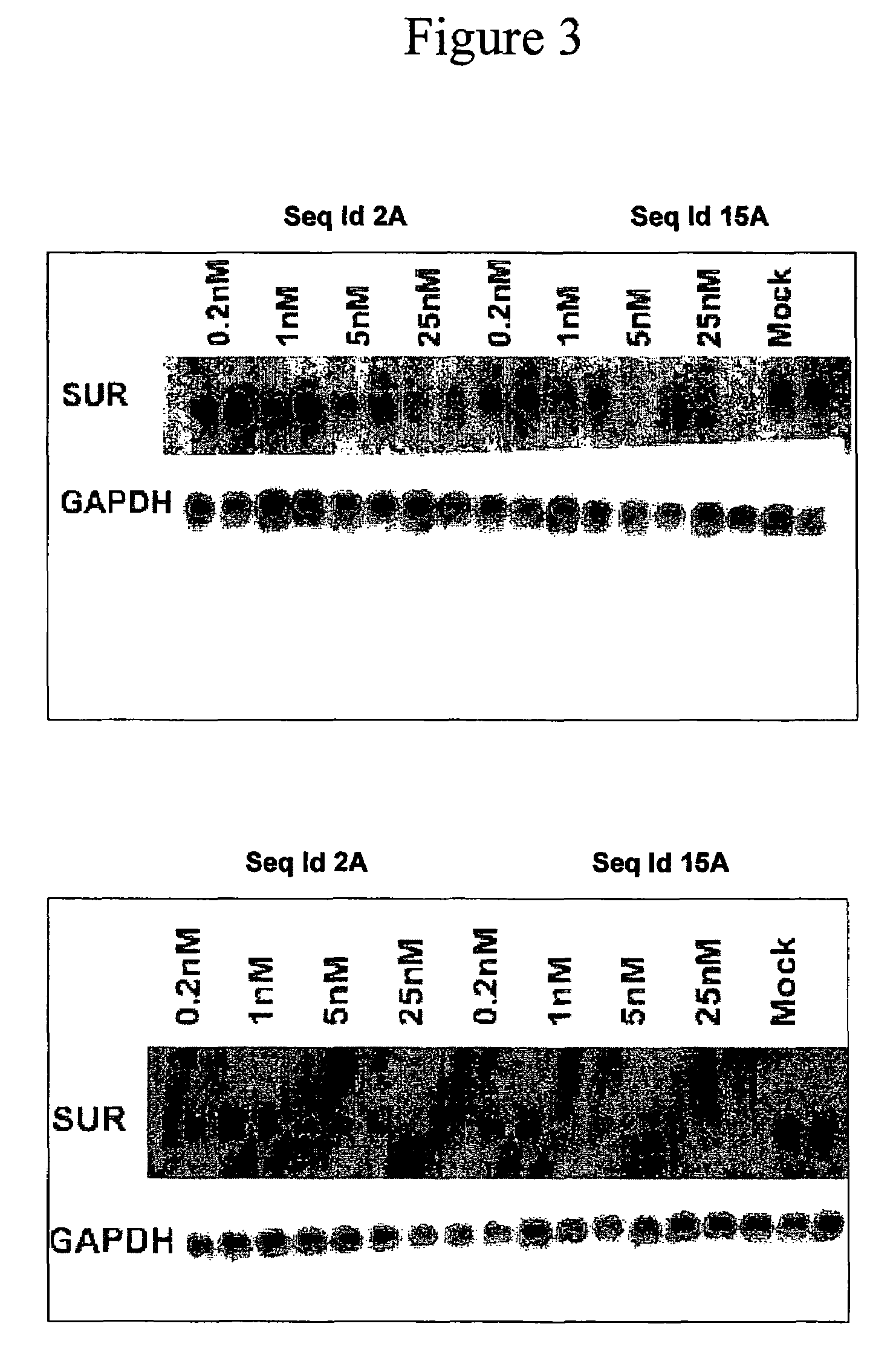
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC
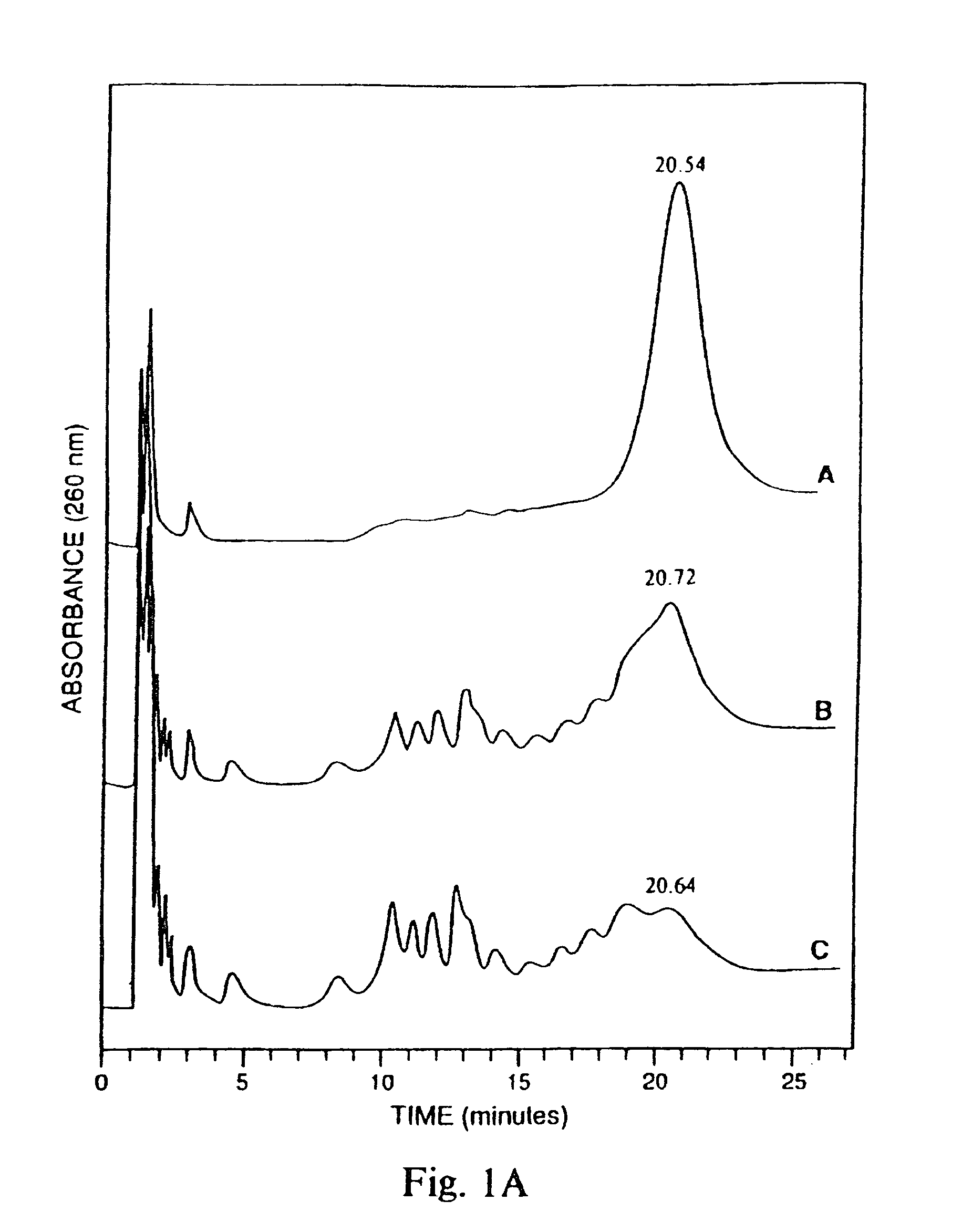
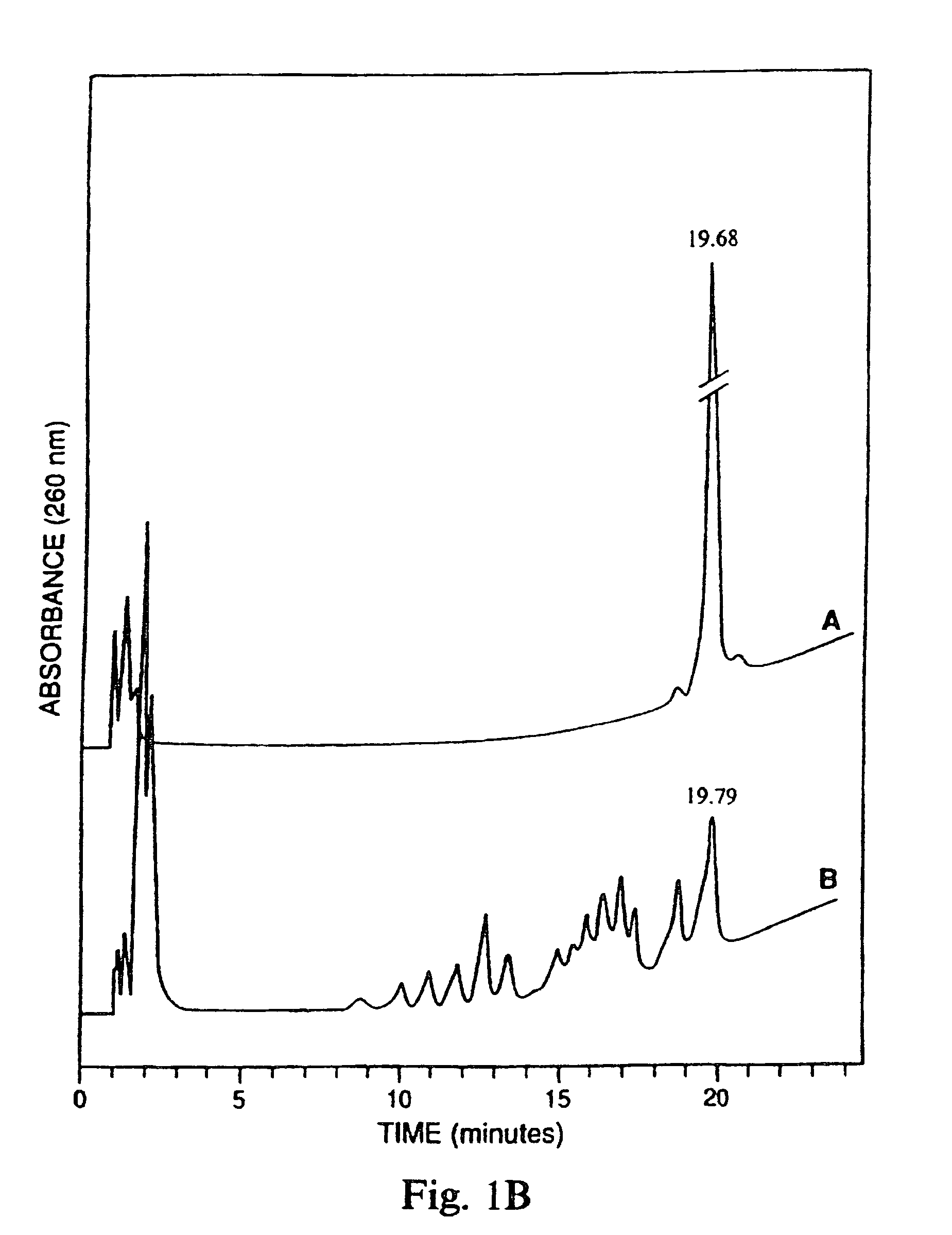
Hybrid oligonucleotide phosphorothioates
The invention provides hybrid oligonucleotides having phosphorothioate or phosphorodithioate internucleotide linkages, and both deoxyribonucleosides and ribonucleosides or 2′-substituted ribonucleosides. Such hybrid oligonucleotides have superior properties of duplex formation with RNA, nuclease resistance, and RNase H activation.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS WORCESTER
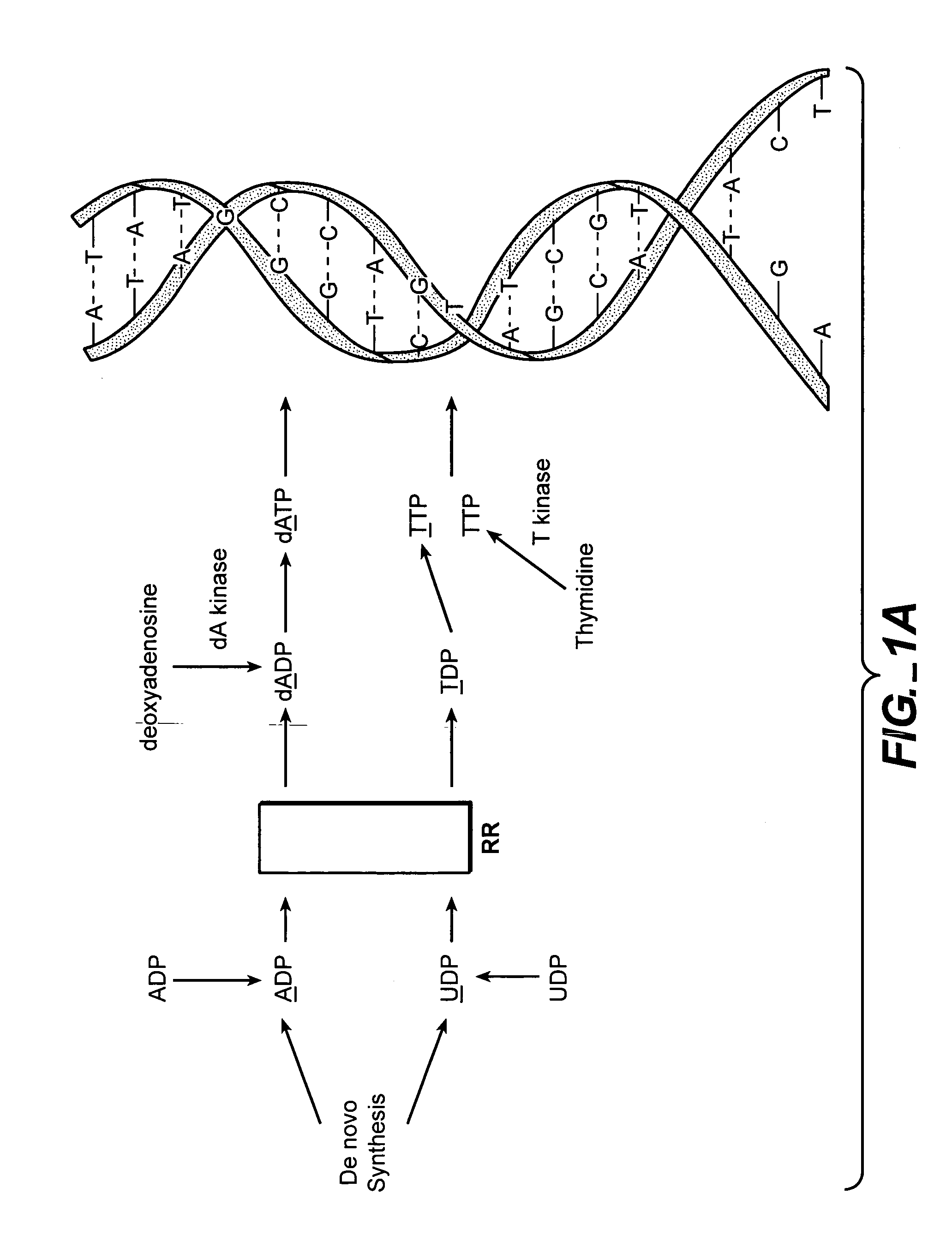
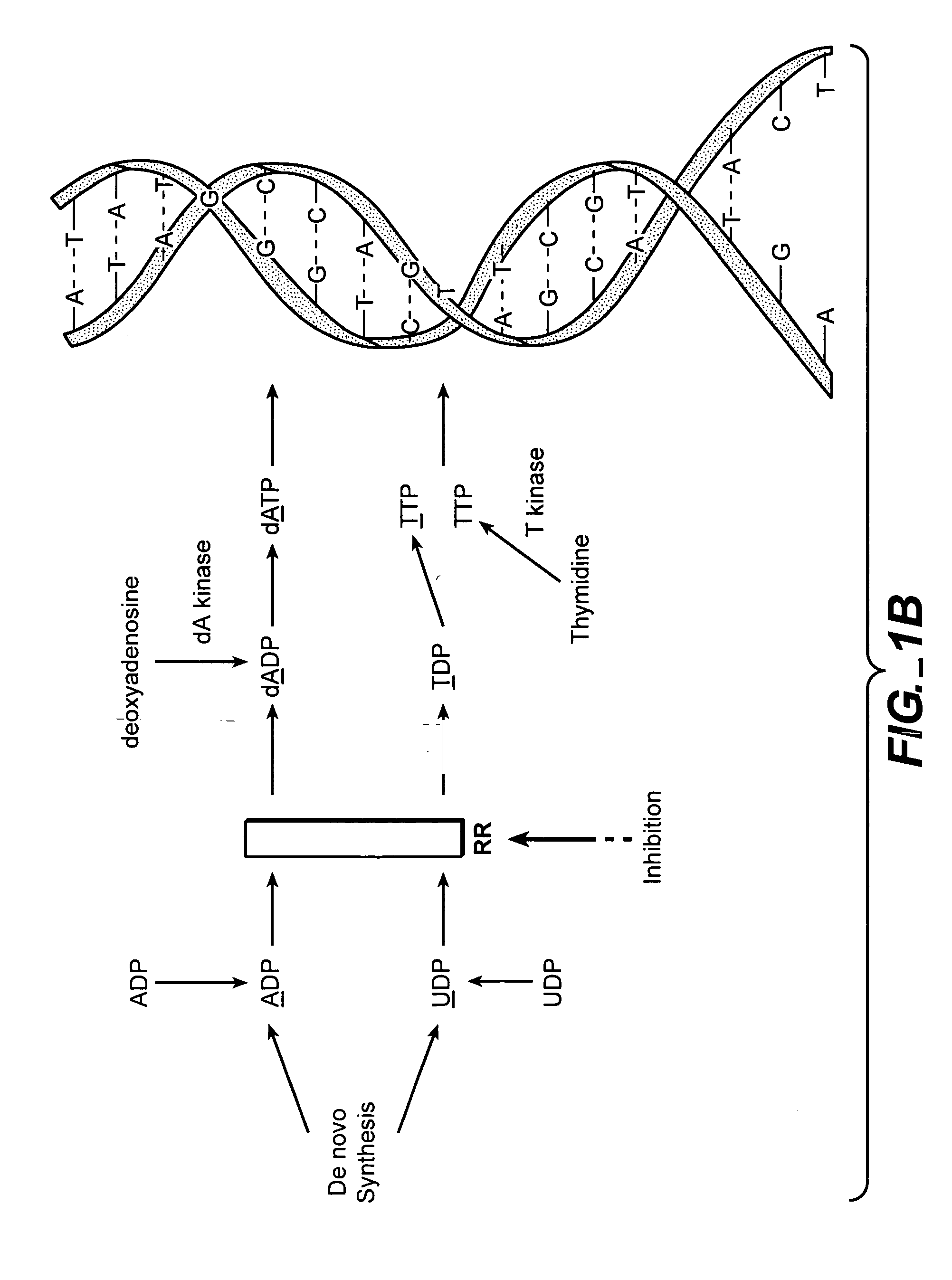
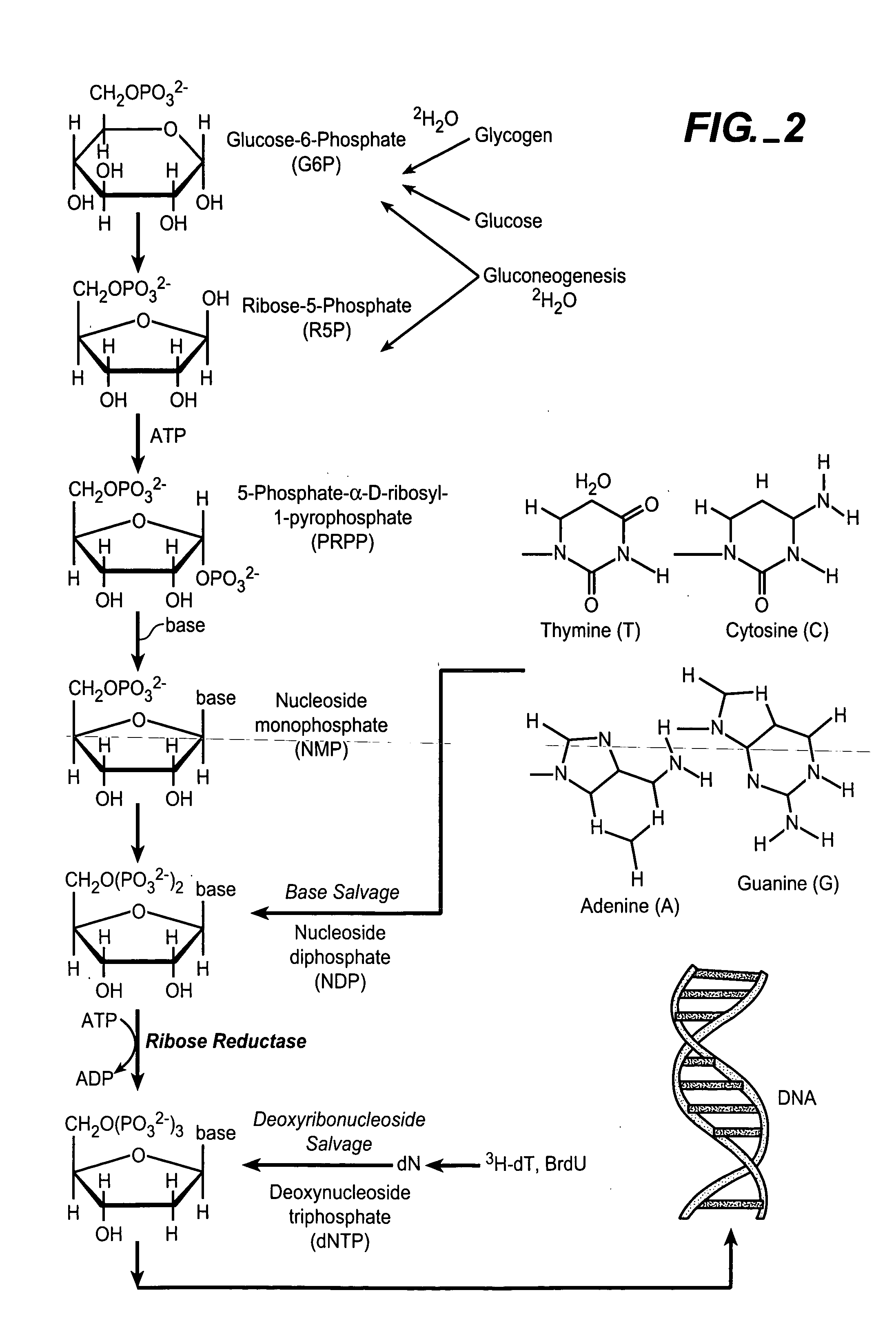
In vivo measurement of the relative fluxes through ribonucleotide reductase vs. deoxyribonucleoside pathways using isotopes
InactiveUS20050255509A1Increase salvageHigh activityCompound screeningApoptosis detectionRate-determining stepDeoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis
The methods of the present invention allow for the measurement of ribonucleotide reductase (RR) activity, an important enzyme in the de novo DNA synthesis pathway. Ribonucleotide reductase converts all four ribonucleotides to their deoxy form and is a rate-controlling step in this pathway. Biosynthetic pathways of deoxyribonucleotides (dN) have received considerable attention in the context of anti-proliferative chemotherapy. Inhibitors of various steps in dN biosynthesis, including inhibitors of RR are among the most useful chemotherapeutic agents in cancer, viral infections, and other therapeutic uses. DNA synthesis from the dN salvage pathway is also an important component to DNA replication. The relative contributions from RR vs. salvage pathways are critical to the actions and effectiveness of chemotherapeutic agents that act on nucleoside metabolic pathways. Until now, however, it has not been possible to study these metabolic processes in vivo. Disclosed within are methods of measuring RR activity in vivo and in vitro which find use, among other things, in drug discovery, development, and approval.
Owner:KINEMED
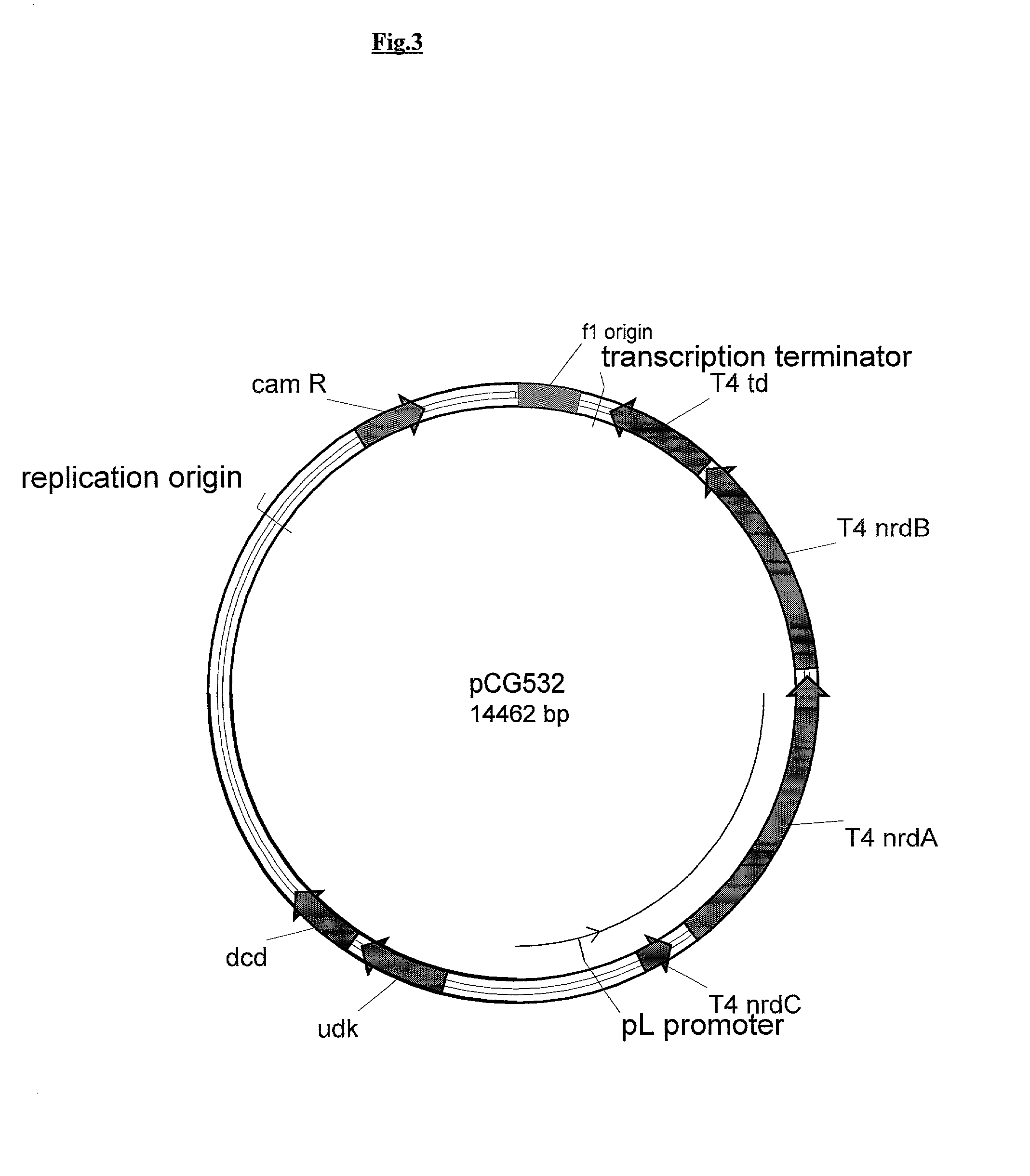
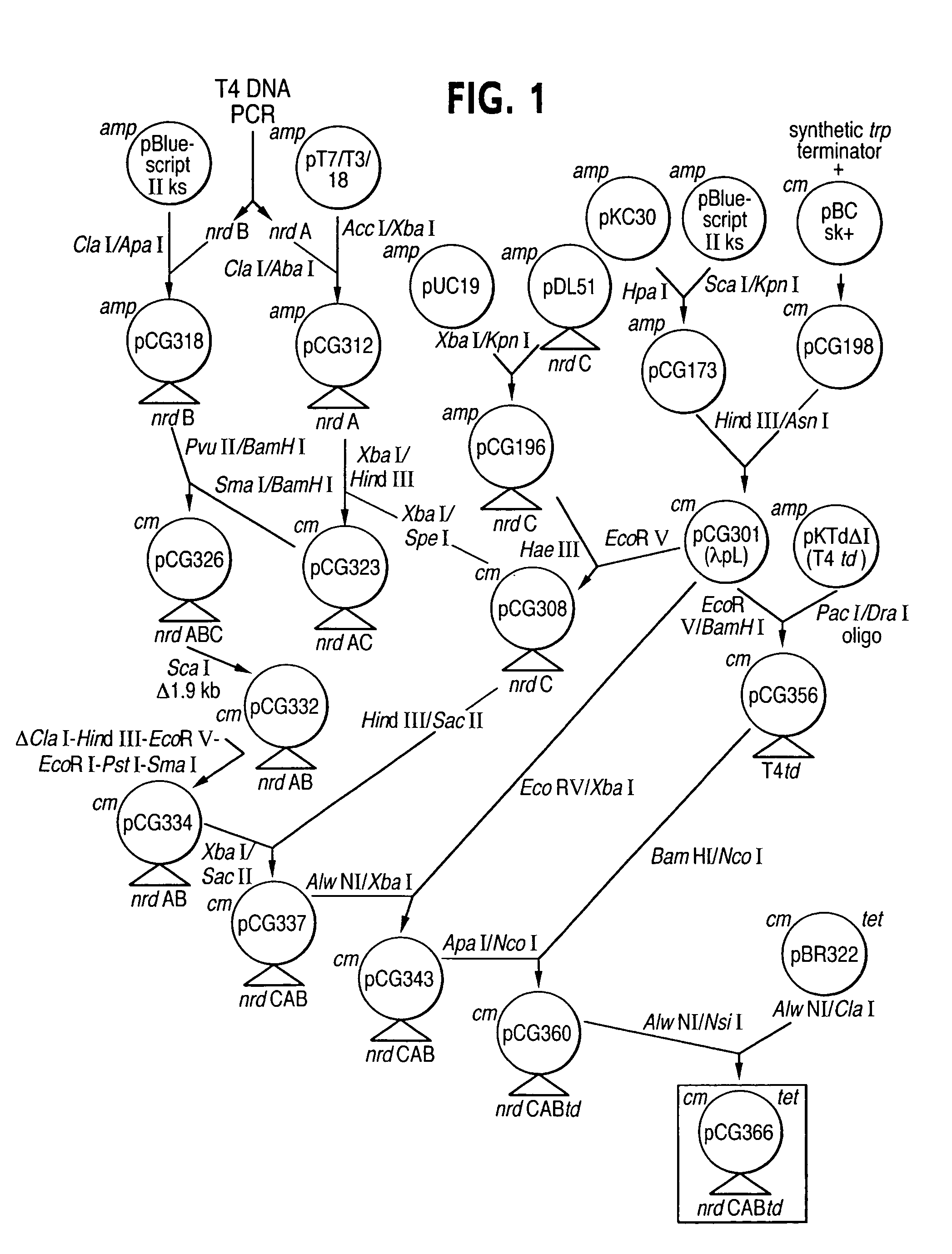
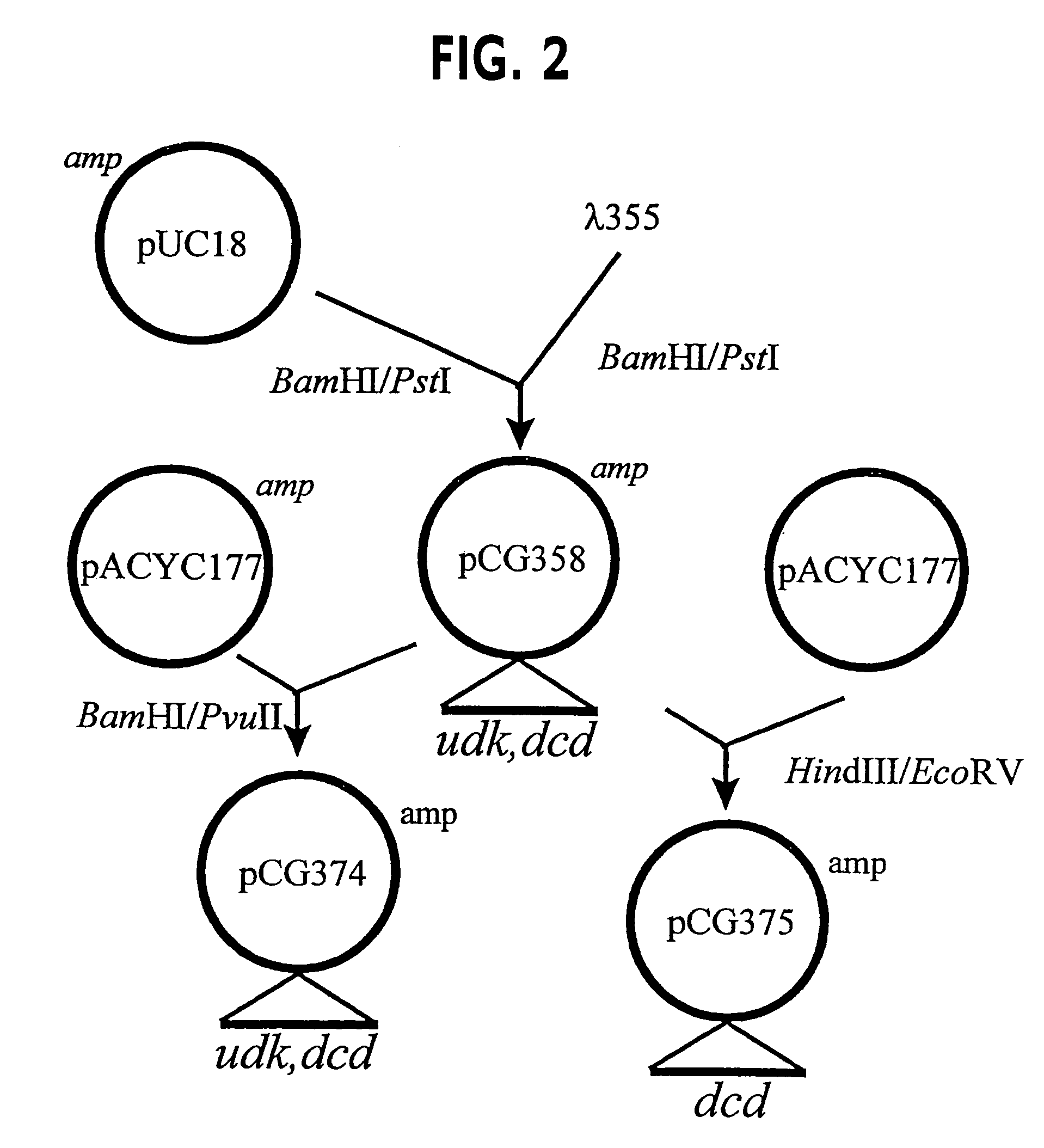
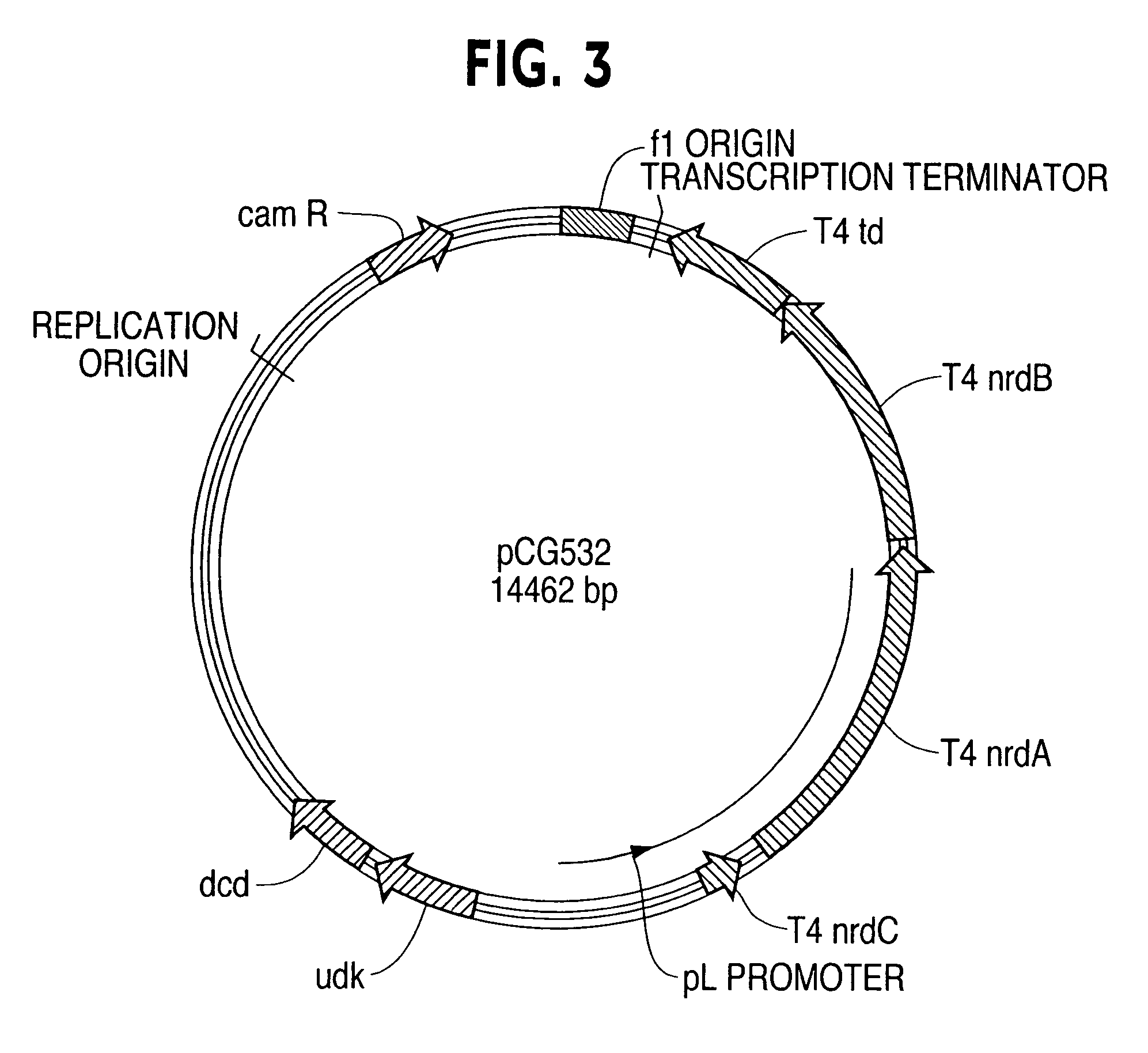
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin. In preferred embodiments, constructs further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, host cells comprising constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
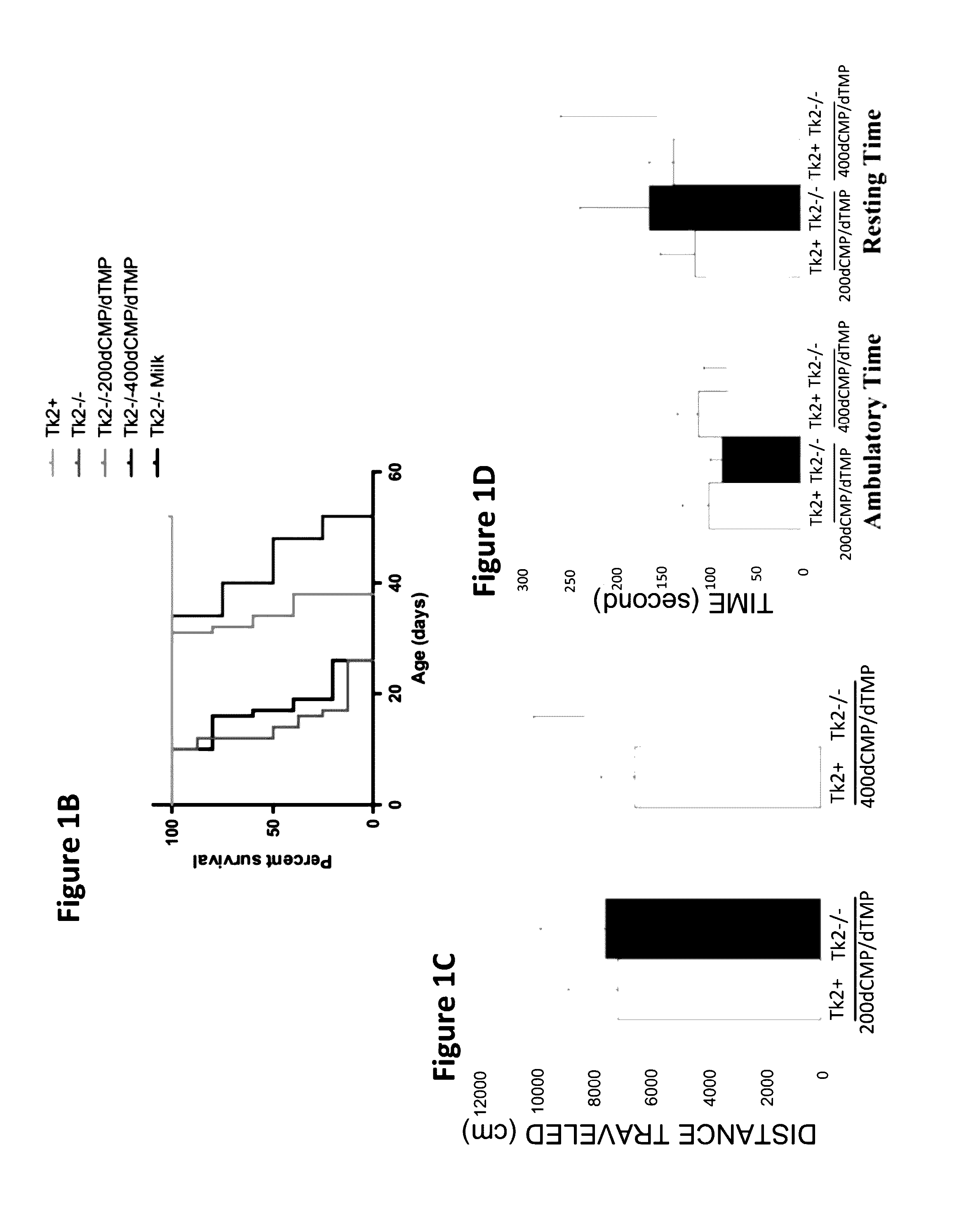
Deoxyribonucleoside monophospate bypass therapy for mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome
The invention relates generally to a pharmacological therapy for a human genetic diseases, specifically mitochondrial DNA depletion syndromes, and more specifically, thymidine kinase 2 (TK2) deficiency. The pharmacological therapy involves the administration of at least one deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate, or mixtures thereof. For the treatment of TK2 deficiency, the pharmacological therapy involves the administration of either deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP) or deoxycytidine monophosphate (dCMP), or mixtures thereof. This molecular bypass approach is applicable to other disorders of unbalanced nucleotide pools, especially those found in mitochondrial DNA depletion syndrome.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Reagents for reversibly terminating primer extension
This invention relates to the field of nucleic acid chemistry, more specifically to the field of compositions of matter that comprise triphosphates of modified 2'-deoxynucleosides and oligonucleotides that are formed when these are appended to the 3'-end of a primer, wherein said modifications comprise NH2 moiety attached to their 3'-hydroxyl group and a fluorescent species in a form of a tag affixed to the nucleobase via a linker that can be cleaved. Such compositions and their associated processes enable and improve the sequencing of oligonucleotides using a strategy of cyclic reversible termination, as outlined in US Patent 6,664,079. Most specifically, the invention concerns compositions of matter that are 5'-triphosphates of ribo- and 2'- deoxyribonucleosides carrying detectable tags and oligonucleotides that might be derived from them. The invention also concerns processes wherein a DNA polymerase, RNA polymerase, or reverse transcriptase synthesizes said oligonucleotides via addition of said triphosphates to a primer.
Owner:动态组合化学技术有限责任公司
Method for enhancing hematopoiesis with acyl deoxyribonucleosides
InactiveUS6103701AEfficiently enter circulationExcessive deliveryBiocideSugar derivativesWound healingTissue repair
Owner:VON BORSTEL REID WARREN +1
Antimutagenic compositions for treatment and prevention of photodamage to skin
InactiveUS6255290B1Reduce mutation frequencyReducing photagingCosmetic preparationsBiocideMedicineMutation frequency
A method of improving DNA repair and reducing DNA damage and for reducing mutation frequency in skin for the purpose of reducing consequences of exposure to solar or ultraviolet radiation is disclosed. The methods comprise administering to the skin a composition containing deoxyribonucleosides in concentrations sufficient to enhance DNA repair or reduce mutation frequency in a vehicle capable of delivering effective amounts of deoxyribonucleosides to the necessary skin cells.
Owner:PRO NEURON INC
Method for determining DNA nucleotide sequence
PCT No. PCT / JP95 / 02254 Sec. 371 Date May 5, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date May 5, 1997 PCT Filed Nov. 6, 1995 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 14434 PCT Pub. Date May 17, 1996Disclosed is a method for determining a nucleotide sequence of DNA product amplified by polymerase chain reaction not requiring removal of primers and / or 2'-deoxyribonucleoside-5'-triphosphates and / or derivatives thereof, which comprises reacting ribonucleoside-5'-triphosphates comprising ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP and derivatives thereof and one or more of 3'-deoxyribonucleotide-5'-triphosphates comprising 3'-dATP, 3'-dGTP, 3'-dCTP, 3'-dUTP and derivatives thereof in the presence of an RNA polymerase and a DNA product which has been amplified by polymerase chain reaction and contains a promoter sequence for the RNA polymerase to afford a nucleic acid transcription product, separating the obtained nucleic acid transcription product and determining a nucleic acid sequence from the resluting separated fractions.
Owner:RIKEN
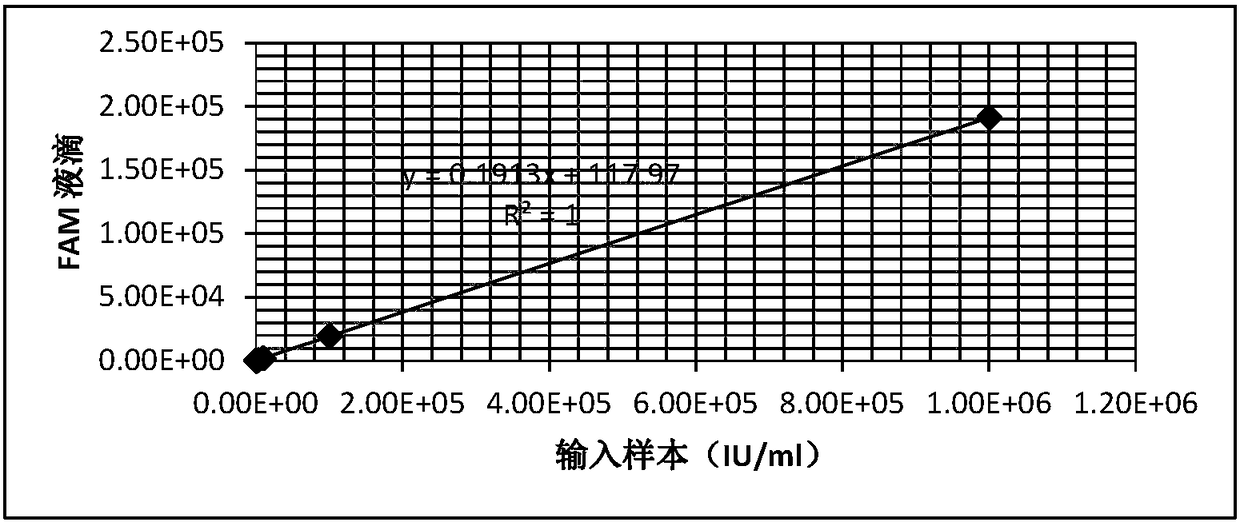
HBV nucleic acid quantitative detection system based on micro-droplet digital PCR technology
InactiveCN108342507AAccurate Absolute QuantificationMicrobiological testing/measurementHepatitis B virus DNAPcr ctpp
The invention provides a HBV nucleic acid quantitative detection system based on a micro-droplet digital PCR technology, the HBV nucleic acid quantitative detection system comprises an upstream primerand a downstream primer for amplifying hepatitis B virus DNA, a specific probe for detecting the hepatitis B virus DNA; a non-infected linearizing double-stranded plasmid quality control standard product and a probe for detecting the quality control standard product; and a buffer system comprising deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates dATP, dCTP, dGTP, and dUTP, and UNG. The HBV nucleic acid quantitative detection system is based on the micro-droplet digital PCR technology to realize the accurate absolute quantification of HBV DNA, faces the clinical actual demand, and has an important application prospect.
Owner:TARGETINGONE CORP +1
Use of base-modified deoxynucleoside triphosphates to improve nucleic acid detection
ActiveUS8349556B2Stable amplificationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesNucleic acid detectionPcr assay
Aspects of the invention provide novel and surprisingly effective methods for the detection of nucleic acids, comprising nucleic acid amplification using base-modified deoxynucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs). Particular aspects relate to methods for enhancing hybridization properties of oligonucleotide primers and probes in assays detecting nucleic acids, comprise amplifying target DNAs in presence of base-modified duplex-stabilizing deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates to provide for modified target DNAs, and thereby considerably improving performance of the detection assays. The disclosed methods allow for increasing of the reaction temperature in PCR-based detection systems or, alternatively, reducing the length of the oligonucleotide primers and probes. Certain aspects relates to improvement of real time PCR assays, wherein nucleic acids of interest are detected as the reaction proceeds using fluorescent agents or oligonucleotide FRET probes.
Owner:KUTYAVIN IGOR
Acyl deoxyribonucleoside derivatives and uses thereof
InactiveUS6348451B1Strengthen cellsPromote wound healingBiocideSugar derivativesWound healingTissue repair
The invention relates to compositions comprising acyl derivatives of 2'-deoxyribonucleosides. The invention also relates to methods of treating or preventing radiation, mutagen and sunlight-induced biological damage, and methods for improving wound healing and tissue repair, comprising administering the compositions of the present invention to an animal.
Owner:PRO NEURON INC
Kit and method for detecting Acinetobacter baumannii DNA
InactiveCN106434996AQuick destructionStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlAcinetobacter baumannii DNA
The invention discloses a kit and method for detecting Acinetobacter baumannii DNA; the kit comprises: a nucleic acid release agent, a PCR (polymerase chain reaction) liquid, an enzyme mixed liquid, an Acinetobacter baumannii positive control, and an Acinetobacter baumannii negative control, wherein the PCR liquid is made from PCR buffer solution, deoxyribonucleoside, primers for amplifying targeted polynucleotide, a probe for amplifying targeted polynucleotide, primers for amplifying internally labeled fragments and a probe for detecting an internal label. By optimizing conditions in the embodiment of the invention, primers for amplifying targeted polynucleotide and probes for amplifying the targeted polynucleotide, both having optimal amplification, are screened out, the kit is capable of detecting not pathogens of Acinetobacter baumannii but various infections of Acinetobacter baumannii but, is highly specific, and accordingly has greatly improved detection sensitivity, accuracy and stability.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
InactiveCN104293883ALow costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LSingle strand
The invention discloses a method for measuring activity of terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, synthesizing a primer according to a single stranded template, annealing the single stranded template, then performing a 3' end tailing reaction catalyzed by TdT enzyme in the presence of one of four deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates, after the 3' end tailing reaction is completed, performing a polymerization reaction in the presence of enough DNA polymerase without 3'-5 'excision enzyme activity to generate double stranded DNA, finally measuring the relative quantity of the double stranded DNA or single stranded DNA in the reaction system after the polymerization reaction is finished, and deducing the activity degree of the Poly (A) polymerase according to the detection result, wherein the basic group at the first site on the used single stranded template in the 3' direction and the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphate used in the tailing reaction are not complementary. Compared with the existing method, the method disclosed by the invention is free of radioactive pollution, simple and quick to operate, low in reagent preparation cost and high in sensitivity.
Owner:VAZYME BIOTECH NANJING
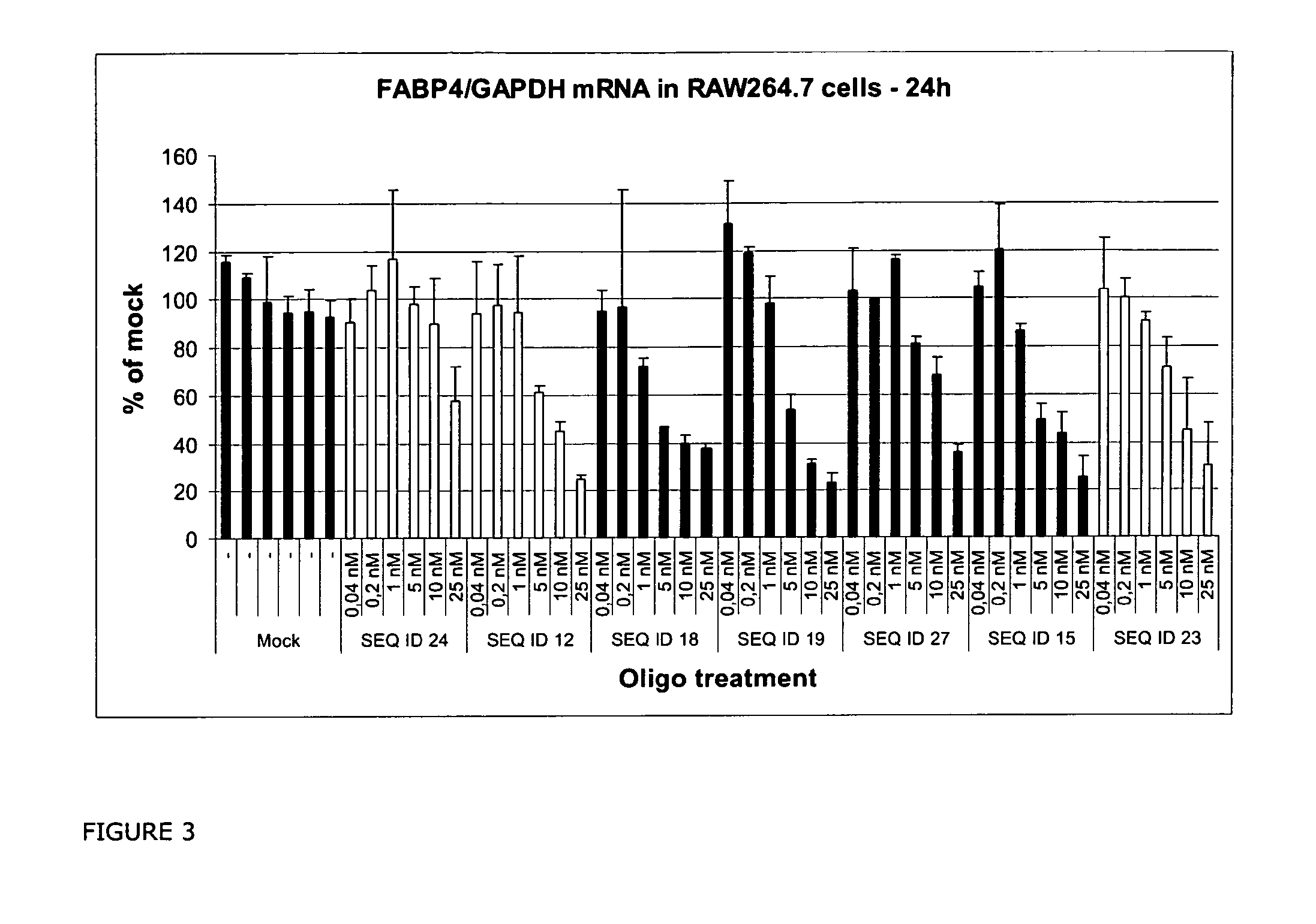
RNA Antagonist Compounds for the Modulation of FABP4/AP2
InactiveUS20110054011A1Lose weightHigh sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseArthritis
Oligonucleotides directed against the FABP4 gene are developed for modulating the expression of FABP4 protein. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding FABP4. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of FABP4 expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with over expression of FABP4 are provided. Examples of such diseases are the metabolic syndrome, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and inflammatory states such as arthritis. The oligomer may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid (LNA) or a combination thereof.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Immunocapture PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit of staphylococcus aureus and using method of kit
InactiveCN102304585AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesForward primerStaphyloccocus aureus
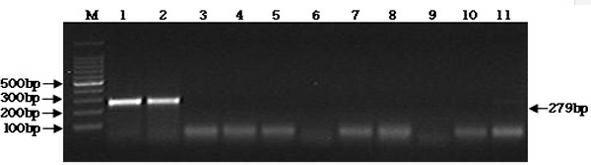
The invention relates to a gene detection kit of staphylococcus aureus, and the detection kit belongs to the field of detection of food-borne pathogenic bacteria and is specially used for detecting the staphylococcus aureus (SA). The immunocapture PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit of the staphylococcus aureus is mainly characterized by comprising 5 mu L of 10*PCR buffer, 2 mu L of dNTPs (deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates) (2.5 mmol / L), 0.25 mu L of Taq DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase (5 U / L), 2 mu L of forward primer (10 pmol / L) which refers to primer 5'-GCGATTGATGGTGATACGGTT-3', 2 mu L of reverse primer (10 pmol / L) which refers to primer 5'-AGCCAAGCCTTGACGAACTAAAGC-3' and 99%-100% of double-distilled water, as well as a detection PCR tube coated with a staphylococcus aureus polyclonal antibody, a positive control PCR tube coated with the staphylococcus aureus polyclonal antibody, namely inactivated staphylococcus aureus bacteria liquid, a negative control PCR tube coated with the staphylococcus aureus polyclonal antibody, namely sterilized PBS (phosphate-buffered solution), a positive control 1 tube and a negative control 1 tube. The immunocapture PCR detection kit has the advantages of being capable of quickly, simply and accurately detecting the pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:刘箐 +1
Antimutagenic compositions for treatment and prevention of photodamage to skin
InactiveUS20010044421A1Reduce frequencyReducing in skinBiocideCosmetic preparationsMutation frequencyMedicine
A method of improving DNA repair and reducing DNA damage and for reducing mutation frequency in skin for the purpose of reducing consequences of exposure to solar or ultraviolet radiation is disclosed. The methods comprise administering to the skin a composition containing deoxyribonucleosides in concentrations sufficient to enhance DNA repair or reduce mutation frequency in a vehicle capable of delivering effective amounts of deoxyribonucleosides to the necessary skin cells.
Owner:PRO NEURON INC
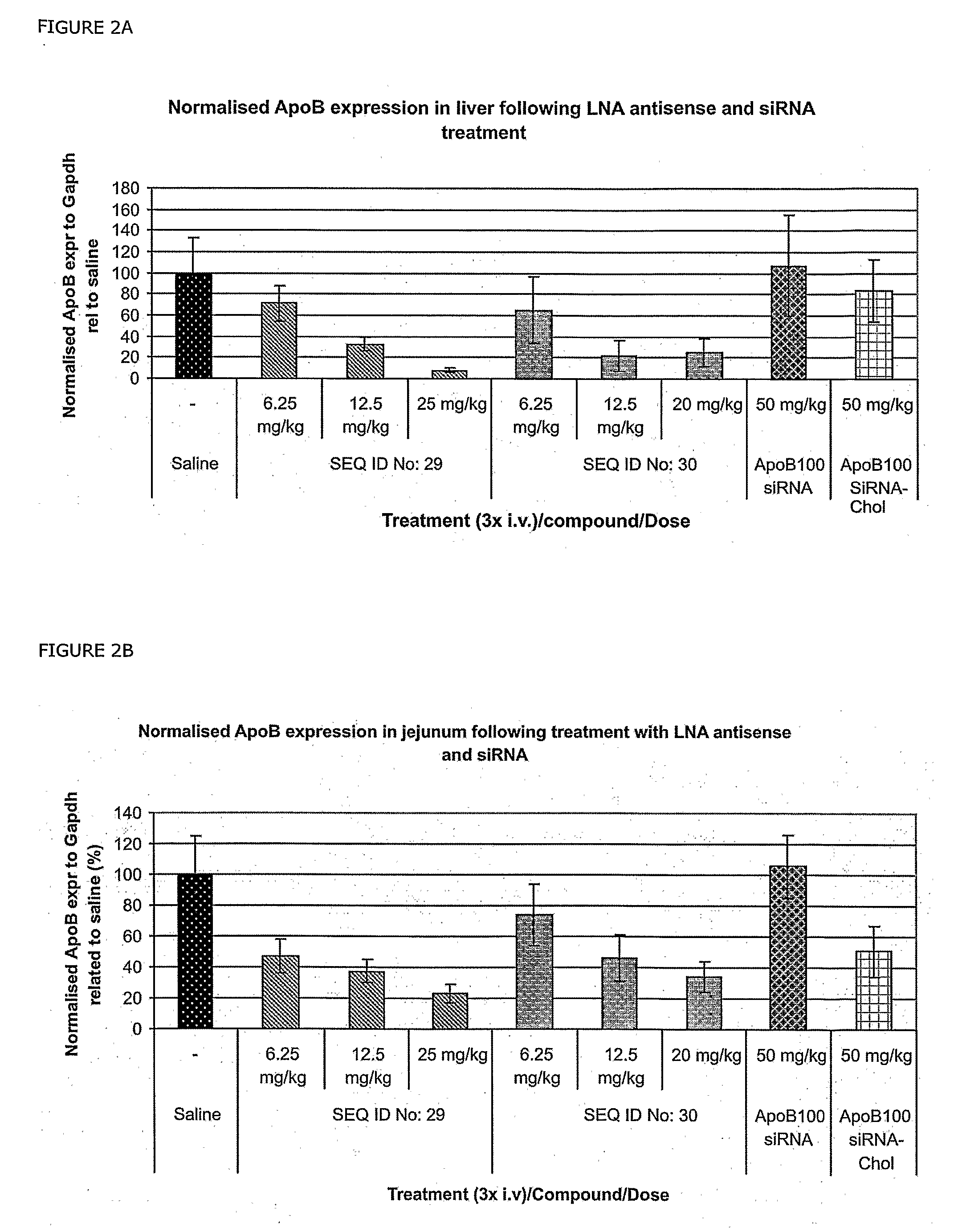
RNA antagonist compounds for the inhibition of apo-b100 expression
InactiveUS20090118213A1Lower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesIntestinal structureSpinal cord
Oligonucleotides directed against the Apo-B100 gene are provided for modulating the expression of Apo-B100. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the Apo-B100. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of Apo-B100 expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of Apo-B100, expression of mutated Apo-B100 or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
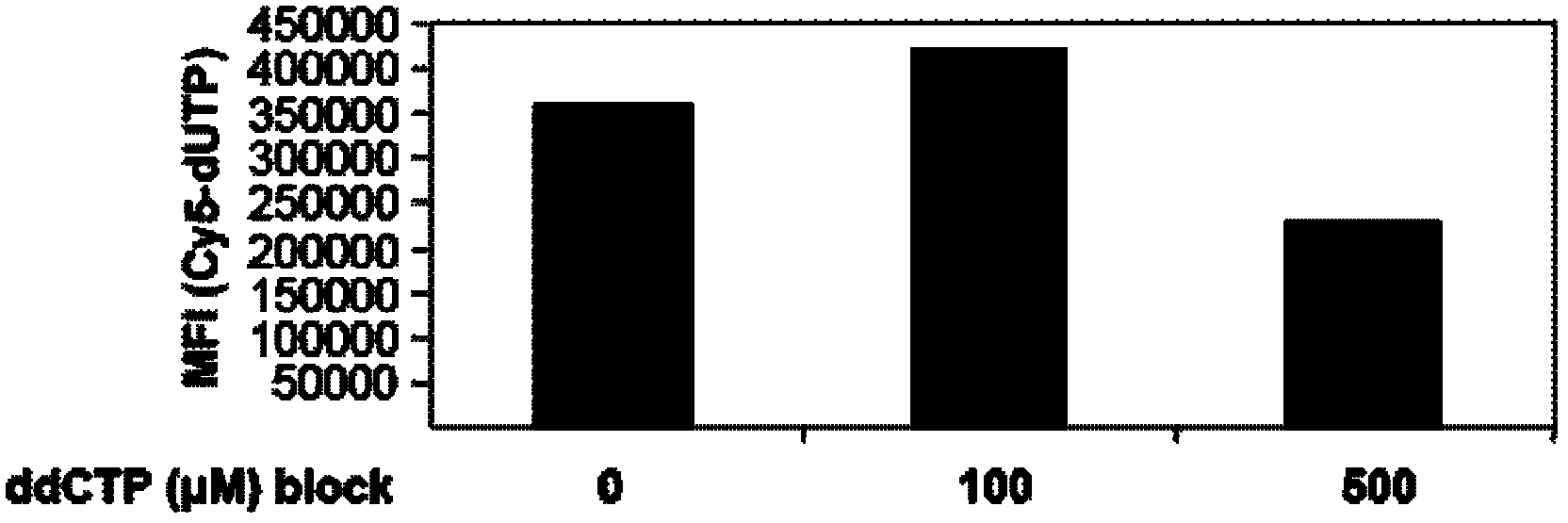
Specificity quantitive detection for cell apoptosis
InactiveCN102382893AStrong specificityReliable Guiding PrinciplesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideCell membrane
The invention discloses a cell pre-incubation reagent box for detecting cell apoptosis and is characterized in that the cell pre-incubation reagent box comprises a terminal transferase (TdT) for marking a terminal 3' of a DNA, and a dideoxy nucleotide triphosphoric acid (ddNTP) or a triphosphoric acid deoxyribonucleoside (dNTP); the dideoxy nucleotide triphosphoric acid (ddNTP) or the triphosphoric acid deoxyribonucleoside (dNTP) is not marked and is marked in advance as a basic group in a dideoxy nucleotide triphosphoric acid (ddNTP) pair or a triphosphoric acid deoxyribonucleoside (dNTP) pair is added at the terminal3' of a fractured DNA segment after a cell membrane is penetrated through. The method provides a more specific way for detecting cell apoptosis.
Owner:PERSONGEN BIOMEDICINESUZHOUCO +1
Isothermal PCR nucleic acid augmentative method based on dI modified primer and endonuclease V
InactiveCN101182514AIncrease compositing speedHigh synthesis efficiencyRecombinant DNA-technologyForward primerHelicase
The invention relates to an isothermal PCR nucleic acid amplification method based on dI modified primer and endonucleaseV. The amplified target nucleic acid primer is completely matched with the template; 1 to 5 dI nucleic acids are on the 10 to 30 site at the 5' end; 10 to 30 nucleic acids are at the downstream of the dI nucleic acids. The reaction components of isothermal PCR comprise dI modified forward primer and reverse primer, target nucleic acid template, four kinds of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates dATP, dTTP, dCTP and dGTP, DNA polymerase, endonucleaseV, single DNA chain binding protein and helicase. After the initial thermal denaturation and annealing hybridization, the mixture of isothermal PCR carries out the PCR reaction. During the amplification process, the circulation and regeneration of the primer-template compound is realized by endonucleaseV, which induces the DNA synthesis reaction; the single DNA chain binding protein and helicase can improve the efficiency of isothermal PCR. The amplification of the target nucleic acid of the invention does not rely on the thermal cycler; the invention has easy and convenient operation, which can be used for a large scale and high yield amplification of the target nucleic acid.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
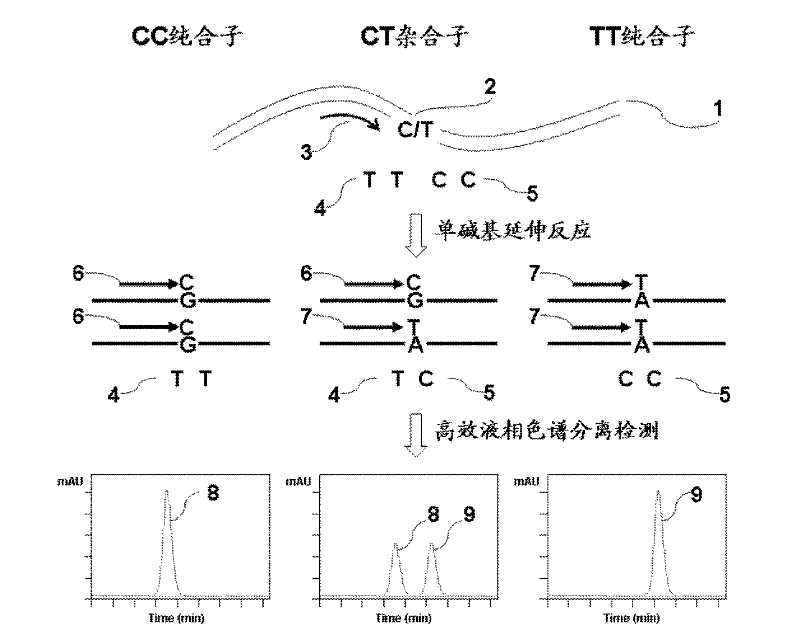
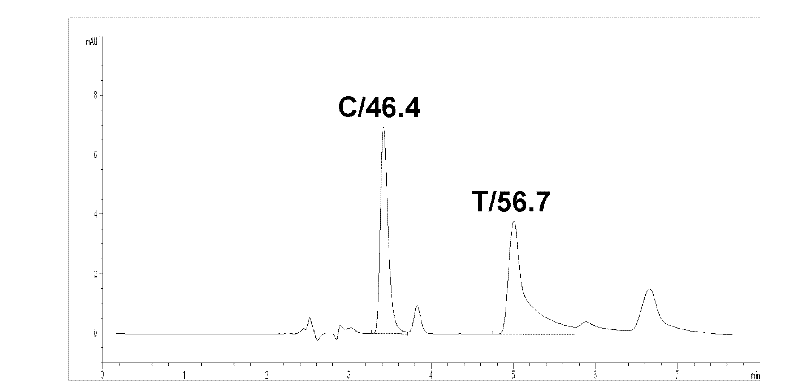
Method for polymorphism detection of gene based on single base extension reaction
InactiveCN102329881ASolve the shortcomings of gene polymorphism analysisQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymorphism Detection
The invention discloses a method for polymorphism detection of a gene based on single base extension reaction. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) designing and selecting a specific primer according to a gene sequence to be detected, adding the specific primer in a mixed liquid containing a sample to be detected, a dideoxynucleotide (ddNTP) pair or deoxynucleotide triphophate (dNTP) pair for single base extension reaction so that a base in ddNTP or dNTP is added at the terminal end of the specific primer, wherein the specific primer is positioned at the upstream of gene SPN (single nucleotide polymorphism) site to be detected, the 3'-terminal base of the primer is close to the SNP site to be detected, and a continuous nucleotide sequence is composed of 15-45 continuous nucleotides containing the gene sequence to be detected; and (2) detecting the amount of surplus ribonucleotides in an extended product, judging the type of the polymorphism of the target gene according to the amount of the ddNTP or dNTP in the extended product. The method has low cost and is simple to operate, and can rapidly detect the polymorphism of the gene in no need of complicated optimization steps.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Use of base-modified deoxynucleoside triphosphates to improve nucleic acid detection
ActiveUS20100151455A1Stable amplificationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesPcr assayFluorescence
Aspects of the invention provide novel and surprisingly effective methods for the detection of nucleic acids, comprising nucleic acid amplification using base-modified deoxynucleoside 5′-triphosphates (dNTPs). Particular aspects relate to methods for enhancing hybridization properties of oligonucleotide primers and probes in assays detecting nucleic acids, comprise amplifying target DNAs in presence of base-modified duplex-stabilizing deoxyribonucleoside 5′-triphosphates to provide for modified target DNAs, and thereby considerably improving performance of the detection assays. The disclosed methods allow for increasing of the reaction temperature in PCR-based detection systems or, alternatively, reducing the length of the oligonucleotide primers and probes. Certain aspects relates to improvement of real time PCR assays, wherein nucleic acids of interest are detected as the reaction proceeds using fluorescent agents or oligonucleotide FRET probes.
Owner:KUTYAVIN IGOR
Preparation of 5'-deoxynucleoside monophosphate
ActiveCN101503432AAdaptableReaction is easy to controlSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationOrganic solventPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a preparing method of 5'-deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate, which comprises the following steps: (1) mixing 2'-deoxyribonucleoside, phosphorus oxychloride and trialkyphosphate to obtain a crude solution containing 5'-deoxynucleotide; (2) hydrolyzing the 5'-deoxynucleotide crude solution obtained from the step (1) in a solution with pH higher than or equal to 8.0 so as to an obtain hydrolysis liquid; (3) mixing an organic solvent, i.e. halogenated hydrocarbon, with the hydrolysis liquid obtained from the step (2), and extracting the mixture to obtain an organic phase and an aqueous phase; (4) condensing the aqueous phase to obtain a condensed liquid; and (5) placing the condensed liquid obtained from the step(4) at a temperature of 10-15 DEG C to obtain the solid 5'-deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate.
Owner:SHANGHAI ZHAOWEI TECH DEV
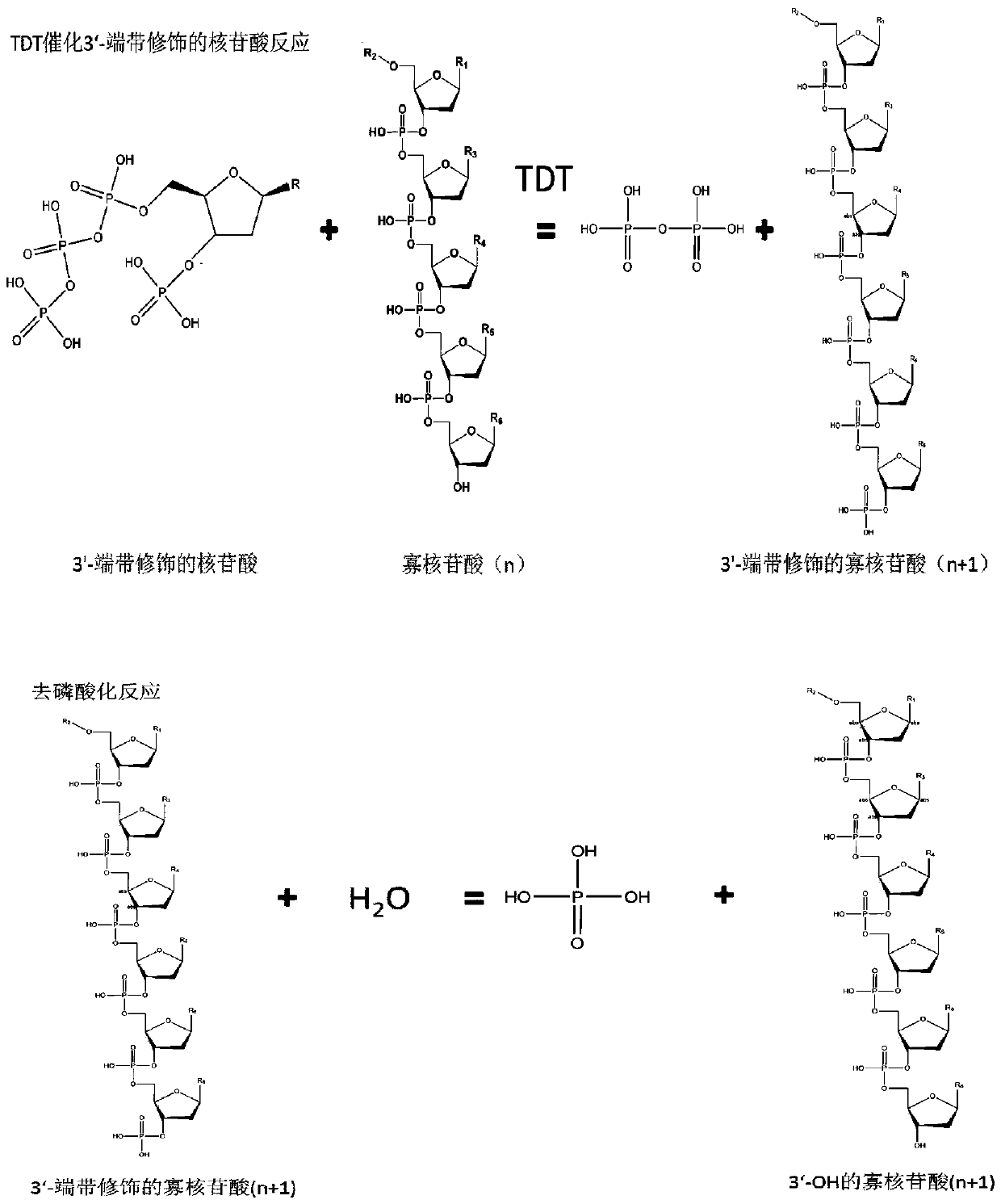
Terminal deoxyribonucleoside transferase variant and application thereof
ActiveCN110331136AImprove the efficiency of coupling 3'-OH modified nucleotidesTransferasesFermentationNucleotideWild type
The invention provides a terminal deoxyribonucleoside transferase variant and application thereof. The coupling efficiency of a nucleotide modified with a 3'-OH terminal is improved by introducing a mutation at a specific site in a wild type amino acid sequence, and nucleic acid molecules are synthesized by enzymatic reaction efficiently and controllably. The invention further provides a method for synthesizing the nucleic acid molecules without a template strand.
Owner:天津中合基因科技有限公司
Vectors, cells and processes for pyrimidine deoxyribonucleosides production
Novel DNA constructs and host cells comprising the same are disclosed. DNA constructs comprise a transcription unit (e.g. operon) comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin or a uridine kinase gene and / or a dCTP deaminase gene. In preferred embodiments the constructs comprising DNA sequences encoding for ribonucleotide reductase and thioredoxin further comprise DNA sequences encoding for thymidylate synthase and / or transcription units comprising sequences encoding for uridine kinase preferably together with dCTP deaminase. In particularly preferred embodiments, the host cells comprise constructs having all of the above characteristics wherein the host cell displays repressed or no uracil DNA glycosylase activity. This may be achieved by removal of the host cell ung gene. Use of host cells in the manufacture of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides e.g. thymidine is also disclosed.
Owner:GLAXO SMITHKLINE LLC
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
InactiveUS20090318362A1Modulate expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseIntestinal structure
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC +1
Antimutagenic compositions for treatment and prevention of photodamage to skin
InactiveUS20020006913A1Reduce frequencyReducing in skinCosmetic preparationsBiocideMutation frequencyMedicine
A method of improving DNA repair and reducing DNA damage and for reducing mutation frequency in skin for the purpose of reducing consequences of exposure to solar or ultraviolet radiation is disclosed. The methods comprise administering to the skin a composition containing deoxyribonucleosides in concentrations sufficient to enhance DNA repair or reduce mutation frequency in a vehicle capable of delivering effective amounts of deoxyribonucleosides to the necessary skin cells.
Owner:PRO NEURON INC
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:圣塔里斯·法尔马公司 +1
Antimutagenic compositions for treatment and prevention of photodamage to skin
InactiveUS20010044419A1Reduce frequencyReducing in skinBiocideCosmetic preparationsMedicineMutation frequency
Owner:WELLSTAT THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com