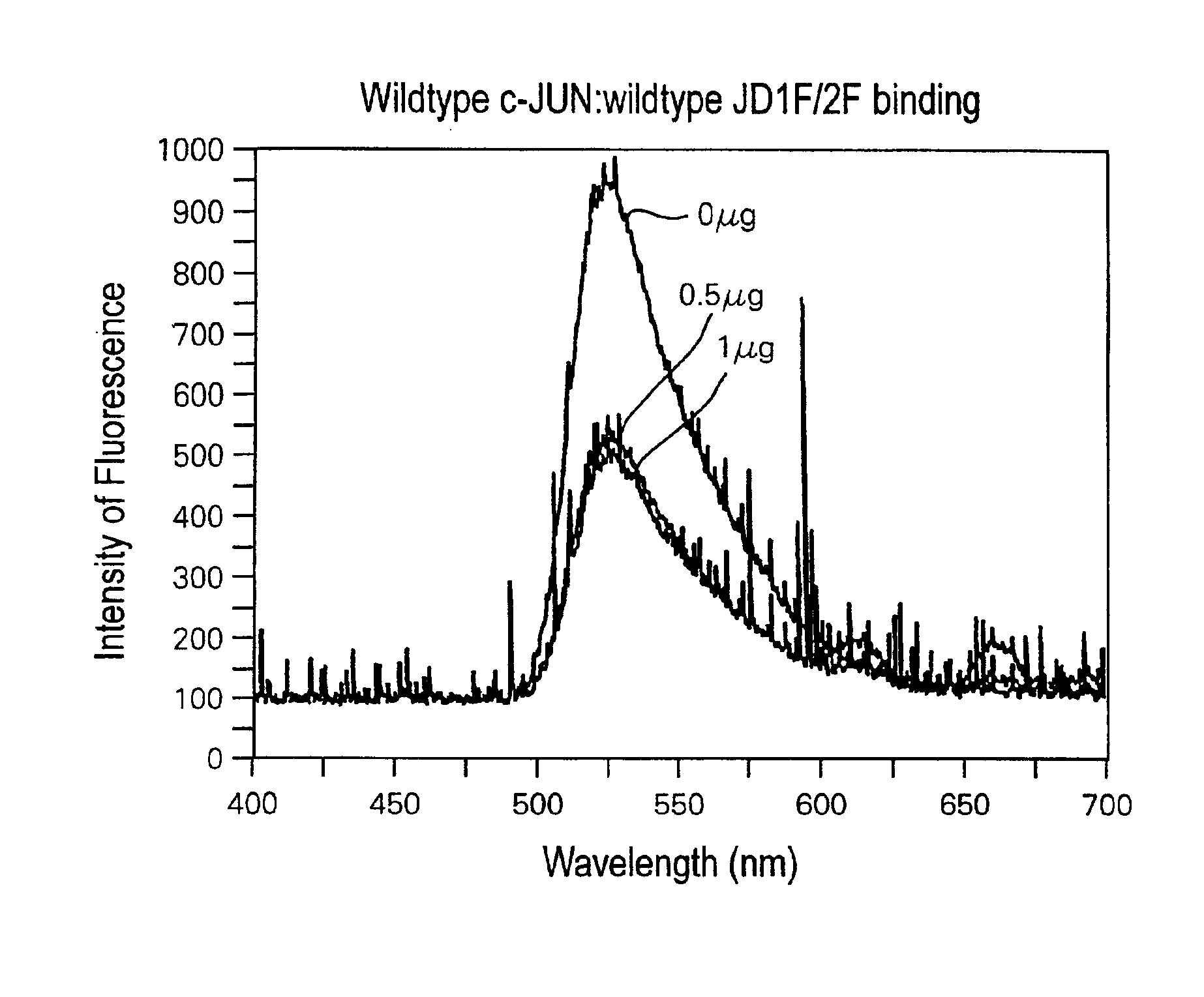
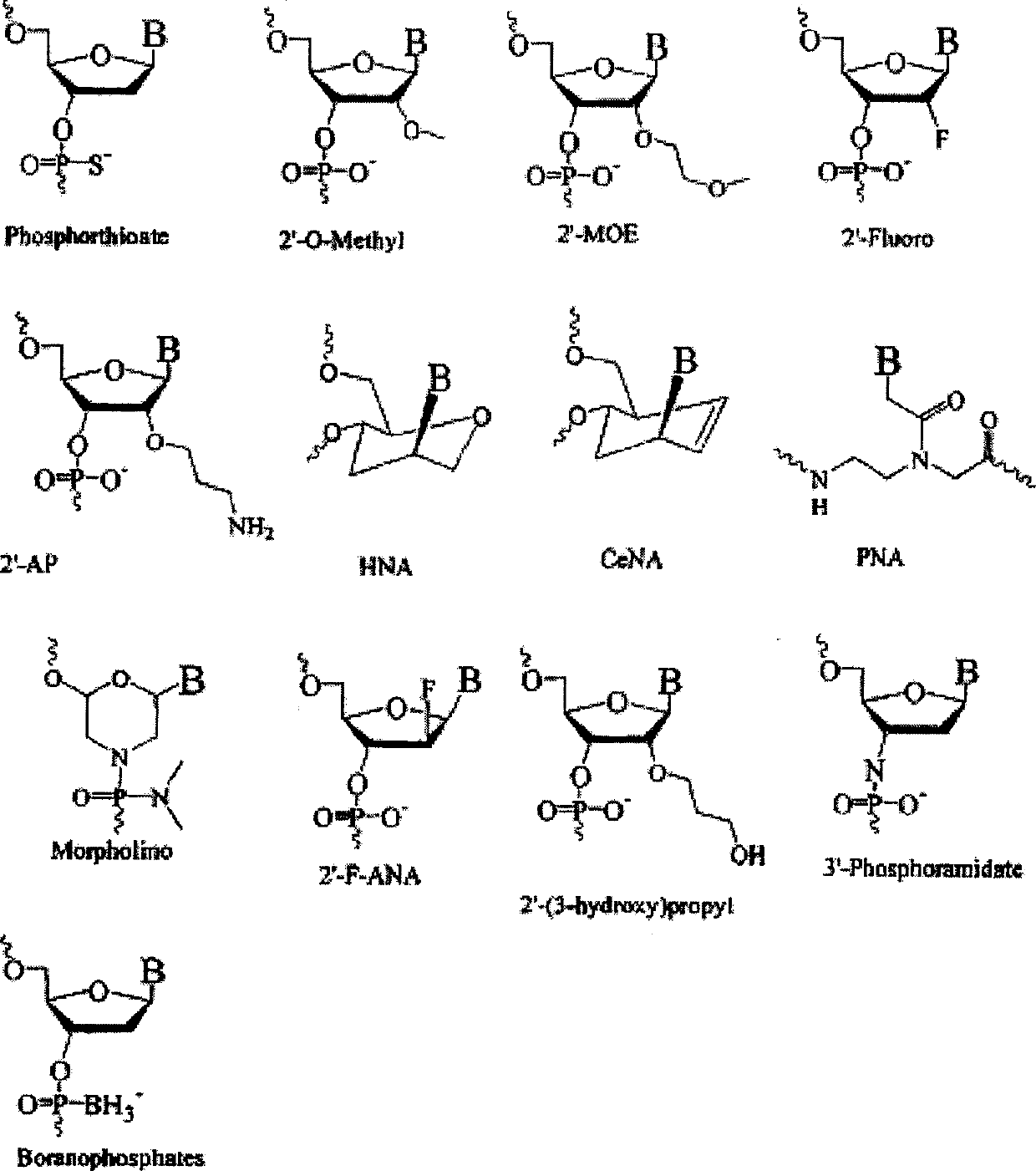
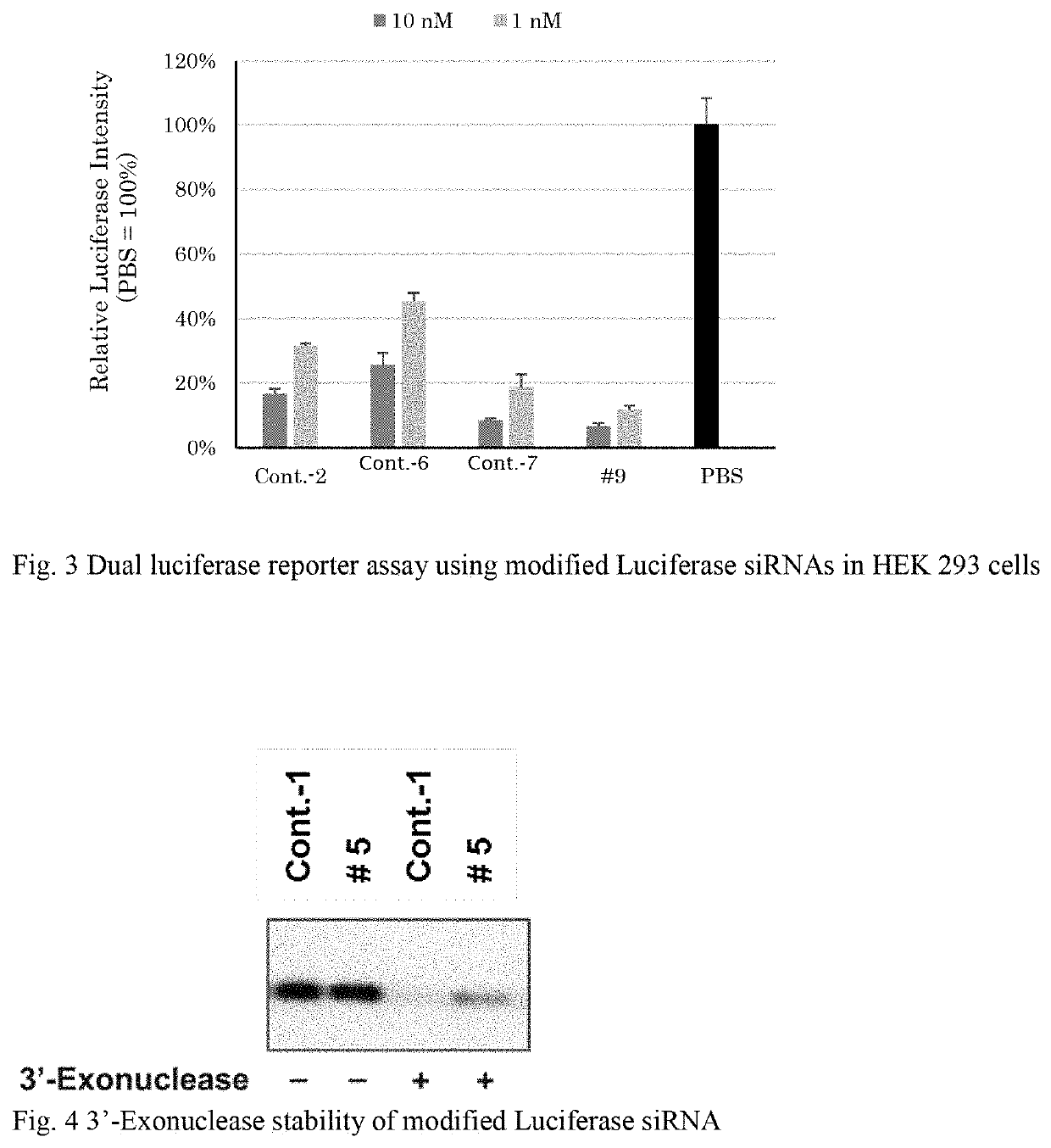
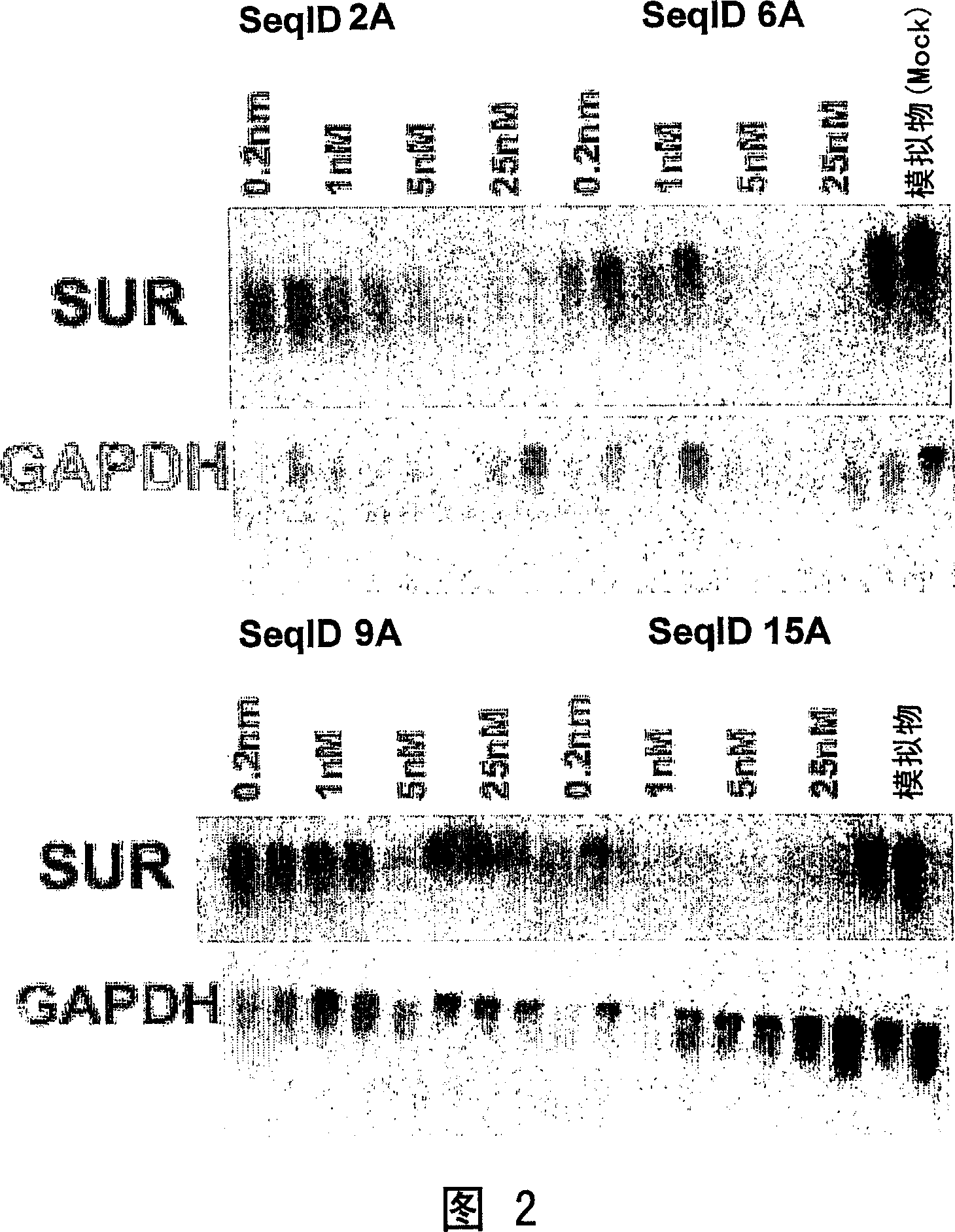
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Nucleic acid analogue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research. Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases. An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix). Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.
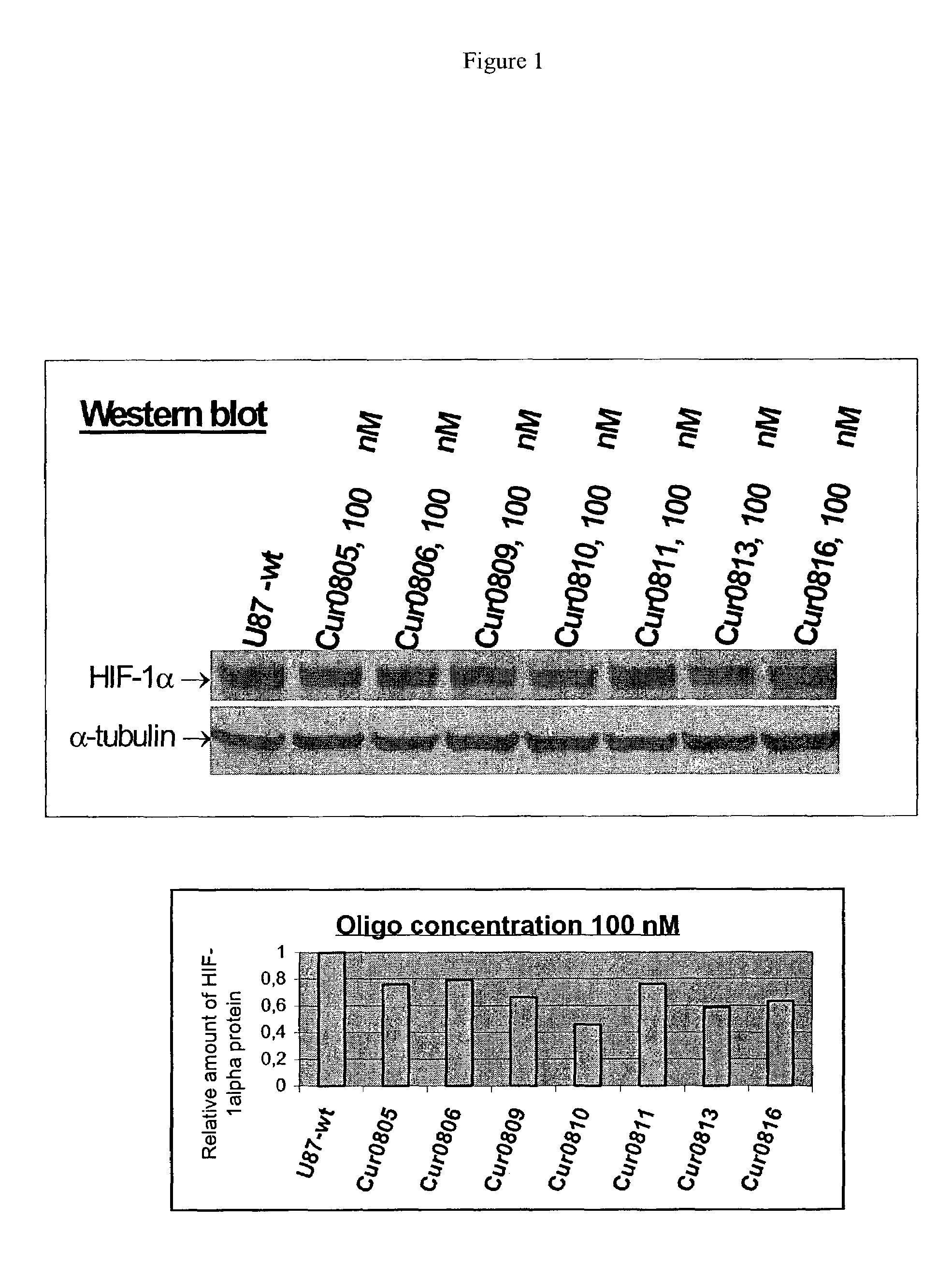
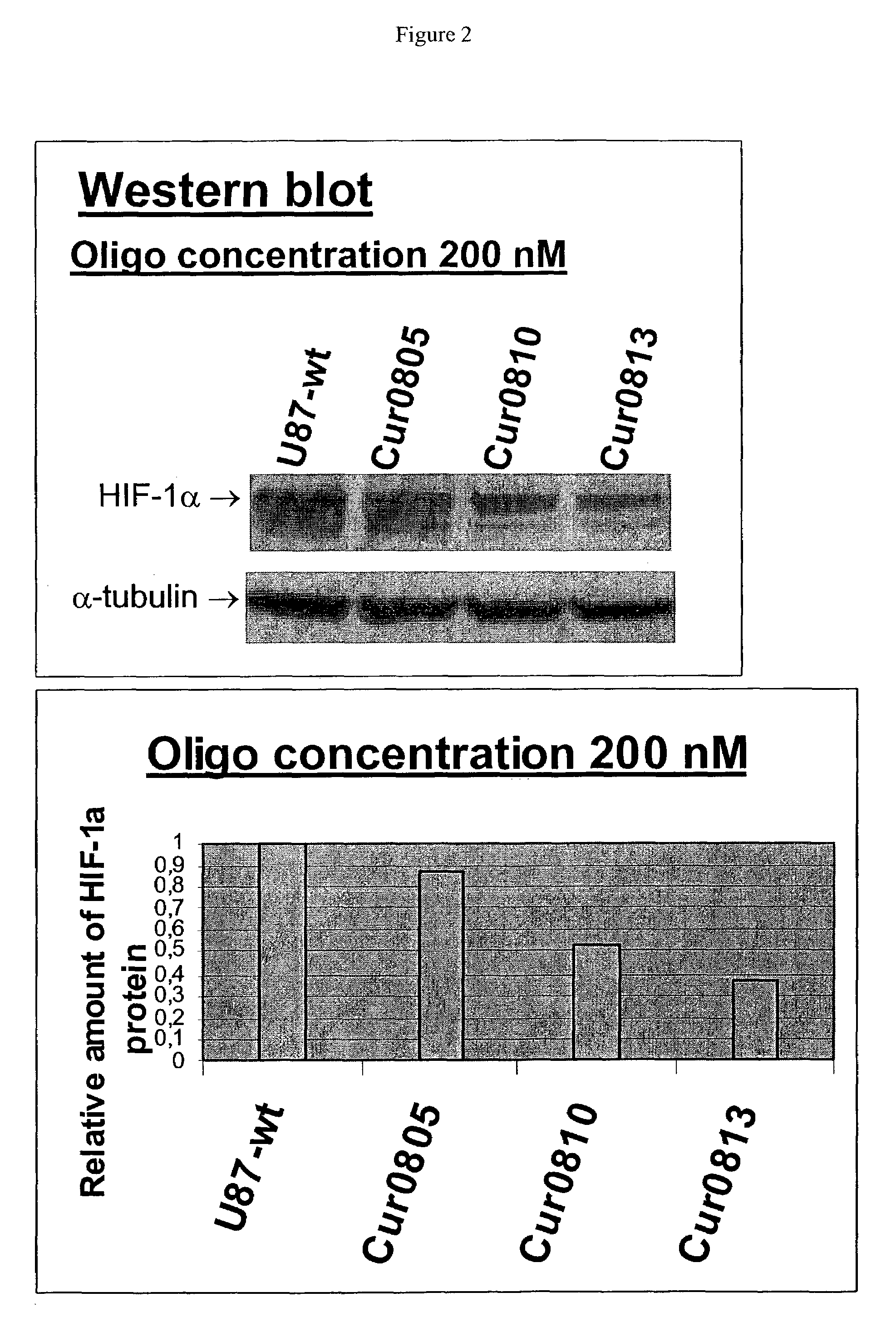
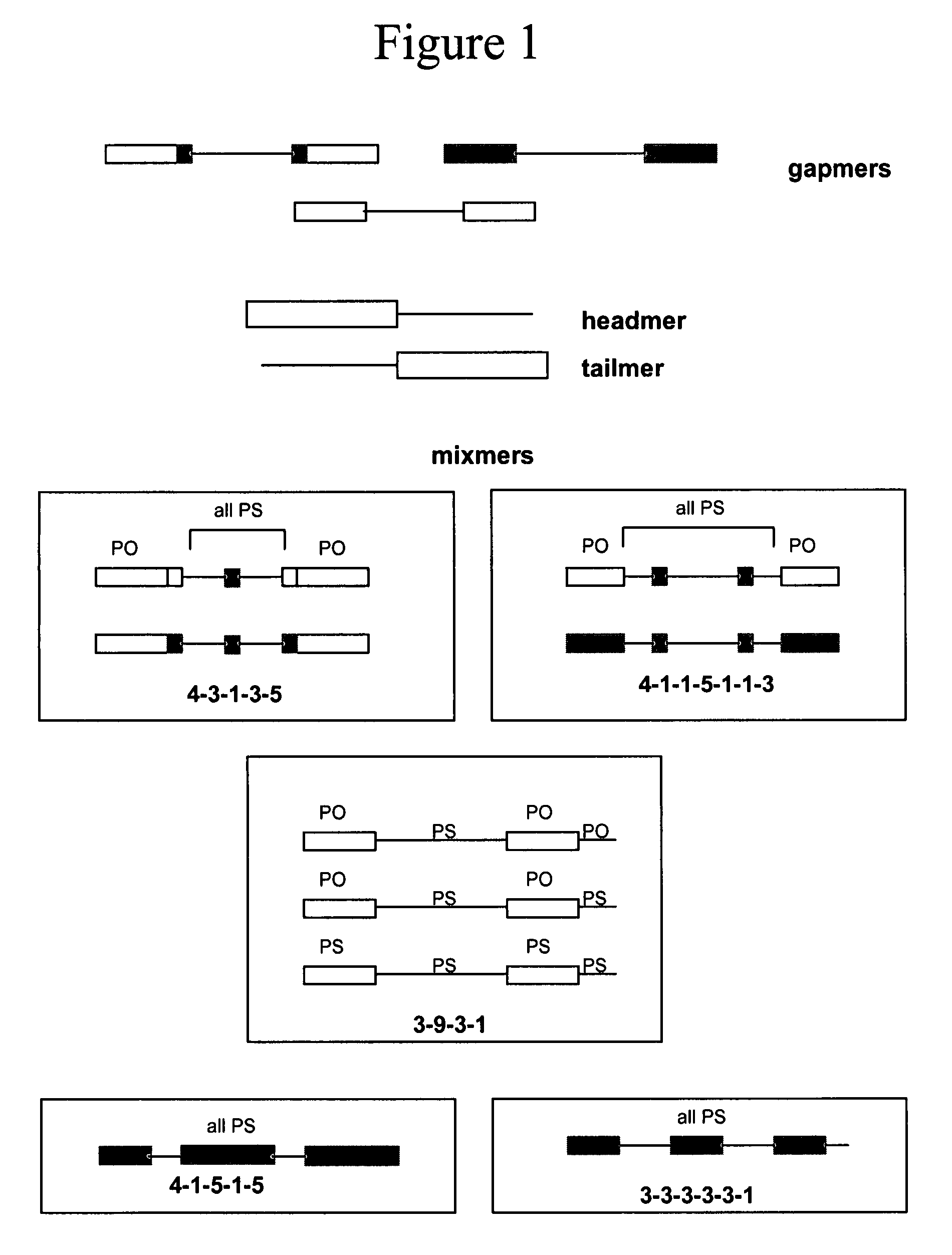
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation HIF-1α expression
Oligonucleotides directed against the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) gene are provided for modulating the expression of HIF-1α. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the HIF-1α. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of HIF-1α expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer and pre-eclampsia. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides, a nucleic acid analogue, or Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) or a combination thereof.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
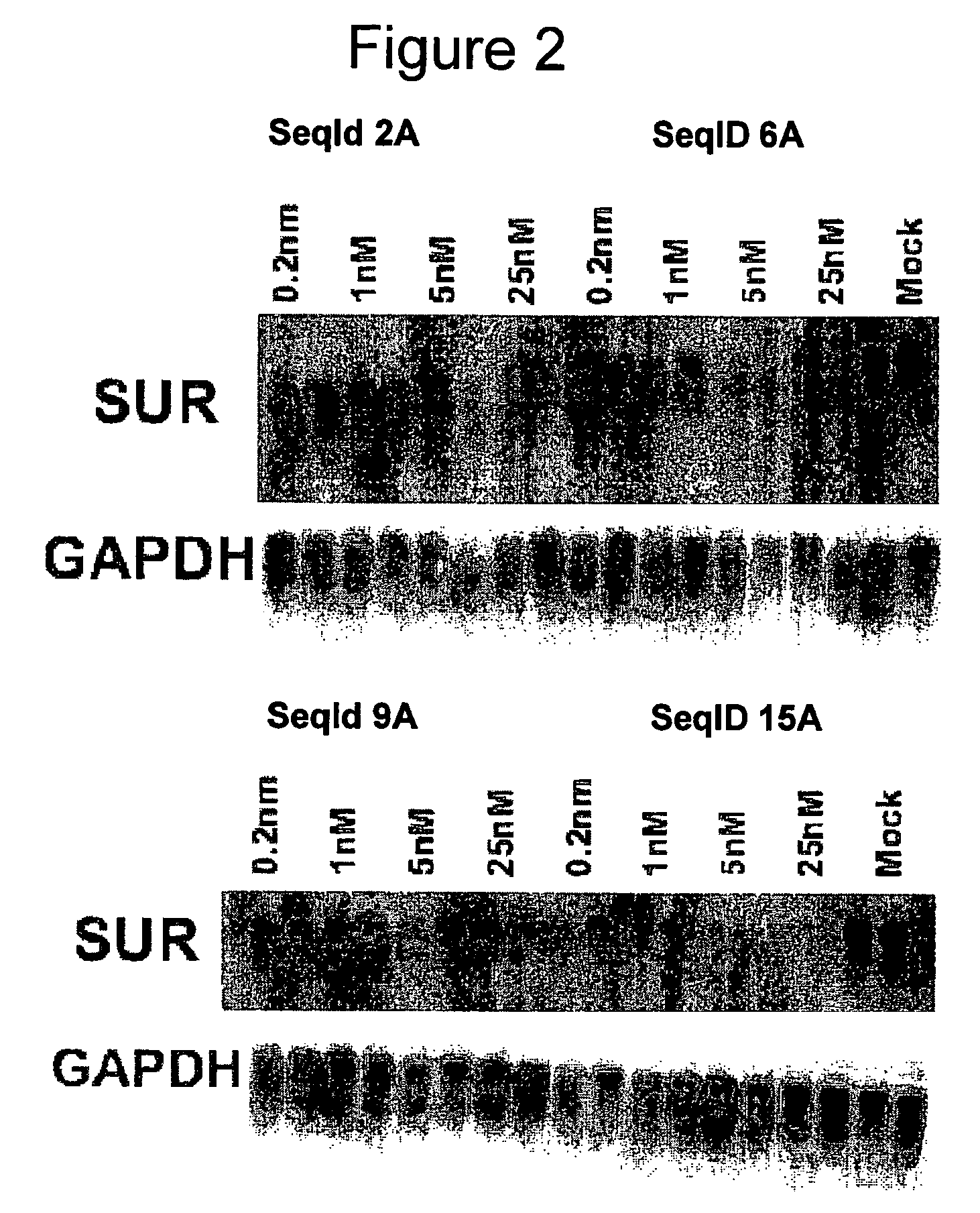
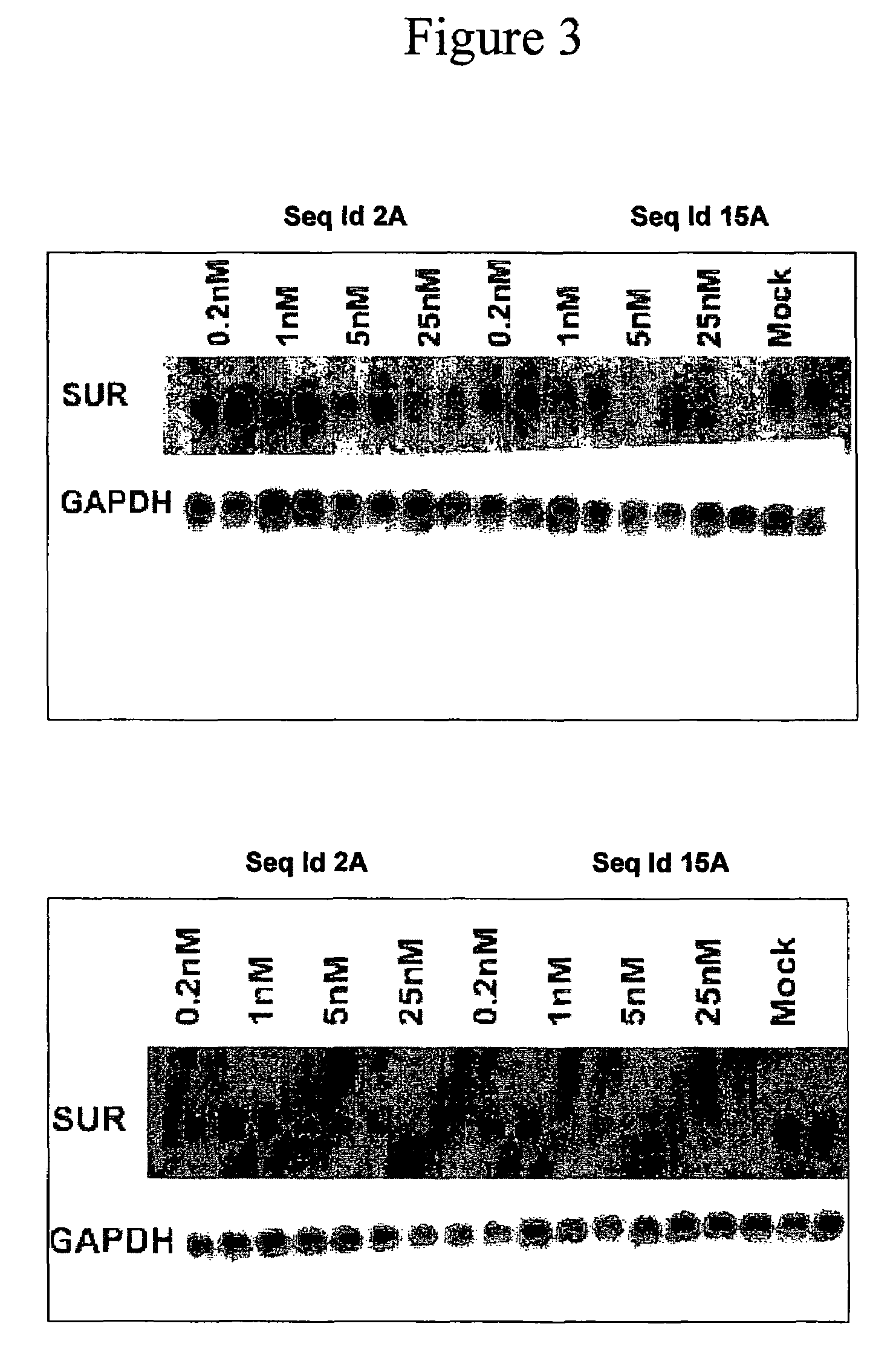
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC
Pseudonucleotide comprising an intercalator
InactiveUS20060014144A1Strong specificityHigh melting temperatureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleobaseNucleic acid analogue
The present invention relates to intercalator pseudonucleotides. Intercalator pseudonucleotides according to the invention are capable of being incorporated into the backbone of a nucleic acid or nucleic acid analogue and they comprise an intercalator comprising a flat conjugated system capable of co-stacking with nucleobases of DNA. The invention also relates to oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues comprising at least one intercalator pseudo nucleotide. The invention furthermore relates to methods of synthesising intercalator pseudo nucleotides and methods of synthesising oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues comprising at least one intercalator pseudonucleotide. In addtition, the invention describes methods of separating sequence specific DNA(s) from a mixture comprising nucleic acids, methods of detecting a sequence specific DNA (target DNA) in a mixture comprising nucleic acids and / or nucleic acid analogues and methods of detecting a sequence specific RNA in a mixture comprising nucleic acids and / or nucleic acid analogues. In particular said methods may involve the use of oligonucleotides comprising intercalator pseudo nucleotides. The invention furthermore relates to pairs of oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues capable of hybridising to one another, wherein said pairs comprise at least one intercalator pseudonucleotide. Methods for inhibiting a DNAse and / or a RNAse and methods of modulating transcription of one or more specific genes are also described.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Gradient resolved information platform
InactiveUS20030055233A1Easy to identifyEasy to quantifyMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNucleic Acid ProbesVolumetric Mass Density
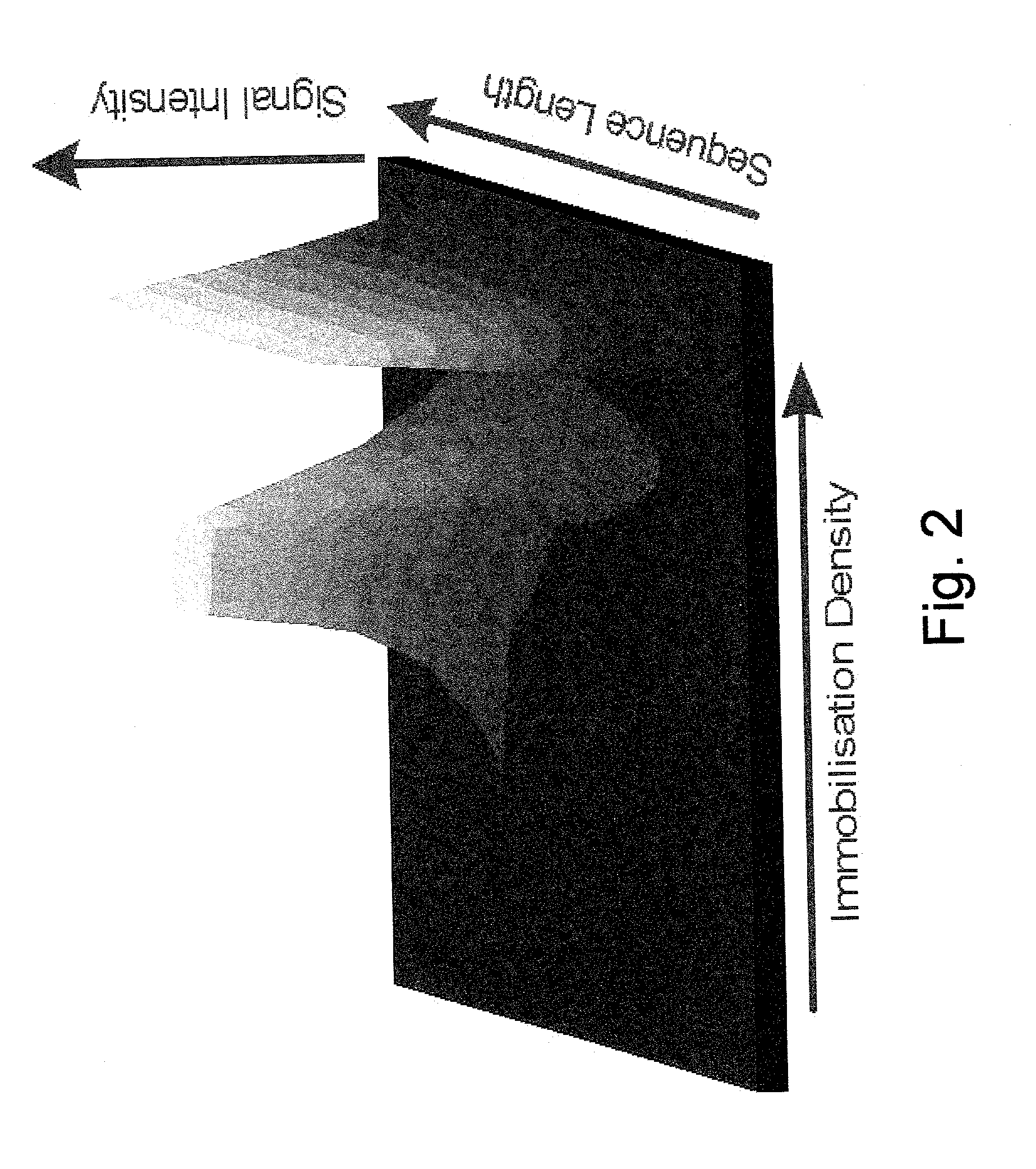
The invention provides improved methods and devices for the detection and identification in a sample of one or more target molecules which bind to probe molecules, particularly to nucleic acid probe molecules. The improved method is based on contacting the sample with a surface that is coated with one or more gradients of probe molecules, particlarly nucleic acid or nucleic acid analog probe molecules that serve to bind target molecules in the sample, particularly nucleic acids having sequences that are complementary or partially complementary to one or more probe molecules. A probe gradient generated on the surface is formed by the variation of a physical, structural or functional property of the probes on the surface. The gradient is generated, e.g., by varying density of probe molecules bound to the surface, by varying probe sequence length, by varying probe sequence, by varying probe sequence type, by varying the orientational structure of probes, and by varying the concentration of label associated with probes. Determination of the location, speed and / or extent of hybridisation of a nucleic acid on such a gradient surface is useful to identify target molecules bound to probes and / or to quantitatively measure the amount of the target in a sample. Hybridisation of target molecules to a gradient of nucleic acid probe can be examined as a function of time and / or hybridisation conditions (e.g., temperature, salt concentration, etc.) The methods and devices of this invention employ gradient surfaces to bind to one or more target molecules, particularly nucleic acids (or target sequences) in a sample, detecting their presence in the sample and quantitating the amount of one or more of such targets in a sample.
Owner:KRULL ULRICH J
Pseudonucleotide comprising an intercalator
InactiveUS20100121056A1Strong specificityHigh melting temperatureSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleobase
The present invention relates to intercalator pseudonucleotides. Intercalator pseudonucleotides according to the invention are capable of being incorporated into the backbone of a nucleic acid or nucleic acid analogue and they comprise an intercalator comprising a flat conjugated system capable of co-stacking with nucleobases of DNA. The invention also relates to oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues comprising at least one intercalator pseudo nucleotide. The invention furthermore relates to methods of synthesising intercalator pseudo nucleotides and methods of synthesising oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues comprising at least one intercalator pseudonucleotide. In addition, the invention describes methods of separating sequence specific DNA(s) from a mixture comprising nucleic acids, methods of detecting a sequence specific DNA (target DNA) in a mixture comprising nucleic acids and / or nucleic acid analogues and methods of detecting a sequence specific RNA in a mixture comprising nucleic acids and / or nucleic acid analogues. In particular said methods may involve the use of oligonucleotides comprising intercalator pseudo nucleotides. The invention furthermore relates to pairs of oligonucleotides or oligonucleotide analogues capable of hybridising to one another, wherein said pairs comprise at least one intercalator pseudonucleotide. Methods for inhibiting a DNAse and / or a RNAse and methods of modulating transcription of one or more specific genes are also described.
Owner:HUMAN GENETIC SIGNATURES PTY LTD
Gradient resolved information platform
InactiveUS7183050B2Easy to identifyEasy to quantifyMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNucleic Acid ProbesMolecular binding
Methods and devices for the detection and identification in a sample of one or more target molecules which bind to nucleic acid probe molecules are provided. The method includes contacting the sample with a surface that is coated with one or more gradients of nucleic acid or nucleic acid analog probe molecules that bind target molecules in the sample. Gradients are formed by varying a physical, structural or functional property of the probes on the surface; for example, the density of probe molecules bound to the surface. The coating layer or immobilization layer in which the gradient is formed is preferably continuous Determination of the location, speed and / or extent of hybridisation of a nucleic acid on a gradient surface is useful to identify target molecules bound to probes and / or to quantitatively measure the amount of the target in a sample.
Owner:KRULL ULRICH J
Method for Selective Labeling and Detection of Target Nucleic Acids Using Immobilized Peptide Nucleic Acid Probes
InactiveUS20100248980A1Raise the ratioStrong specificityLibrary tagsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic Acid ProbesNucleic acid analogue
Disclosed are a method for selective labeling of target nucleic acids on an array having nucleic acid analogue, e.g. PNA (peptide nucleic acid), probes immobilized on a support or supports, comprising adding to the array a detectable label and an agent for introducing the label into the target nucleic acids, after hybridization between the target nucleic acids and the nucleic acid analogue probes, and a method for detection of target nucleic acids using the same.
Owner:PANAGENE INC
Drug delivery system of small interfering RNA drug and preparation
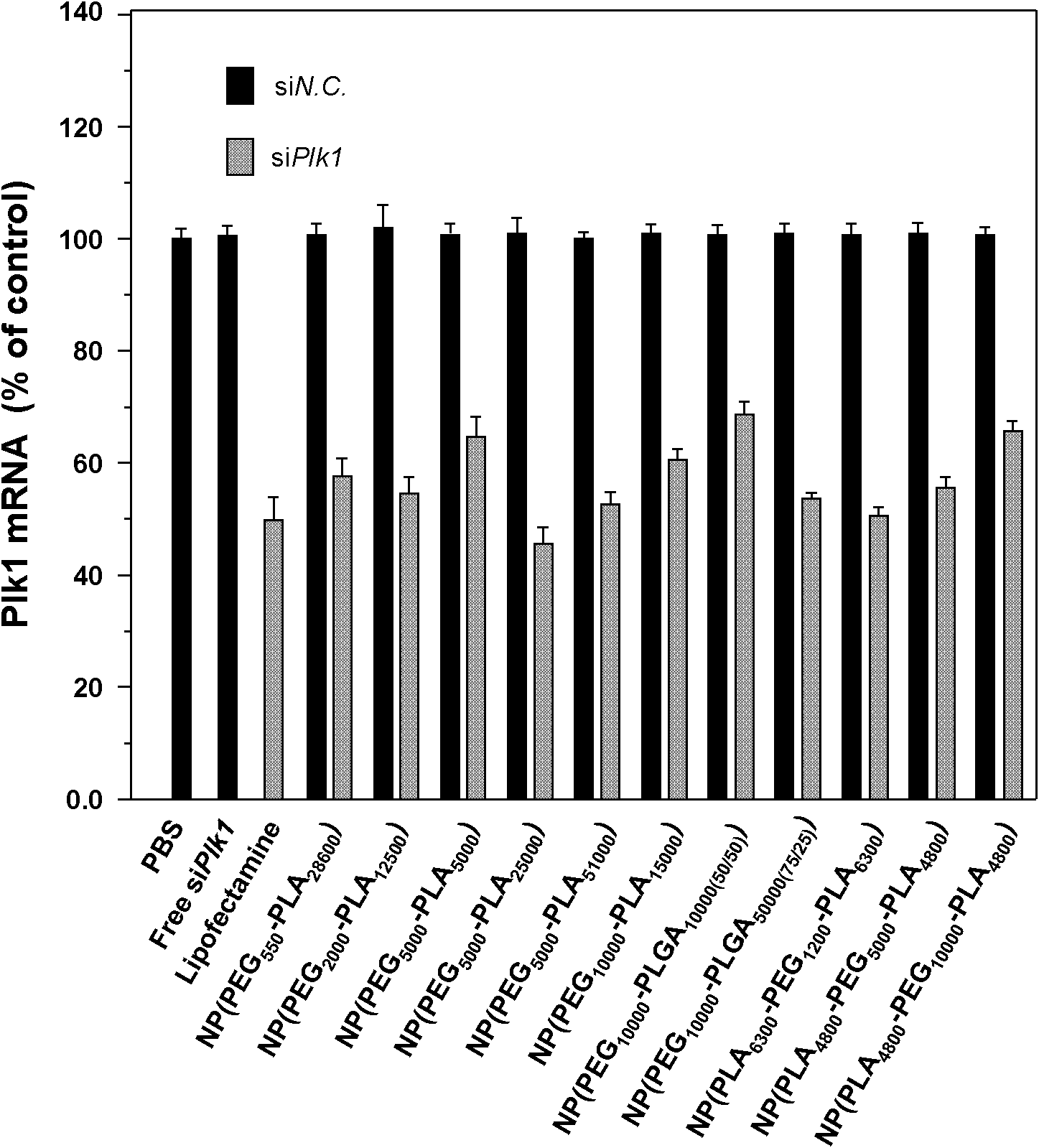
InactiveCN102727907AHigh encapsulation efficiencyEfficient packagingMicroencapsulation basedGenetic material ingredientsDiseasePolyethylene glycol
The invention discloses a drug delivery system of siRNA and a preparation. The active component of the drug delivery system is siRNA-loaded nanoparticles formed by a polymer and cationic lipid. The polymer can be a two-block copolymer or three-block copolymer of polyethylene glycol-polylactic acid or polyethylene glycols-polvlactic-co-glycolic acid. The cationic lipid can be N,N-dihydroxyethyl-N-methyl-N-2-(cholesteryloxycarbonylamino)ethyl ammonium bromide or N-[1-(2,3-dioleyloxy)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethylammonium chloride. The nanoparticles and the preparation can well transport siRNA into cells and play an effective role in the silence of target gene expression. In addition, after ligand or antibody modification, the siRNA drug delivery system can be used for better silence of the target gene on a cellular level and on an animal level. Therefore, the drug delivery system has a good prospect in drug delivery of siRNA and small nucleic acid analogues drugs for treating diseases.
Owner:SUZHOU RIBO LIFE SCIENCE CO LTD
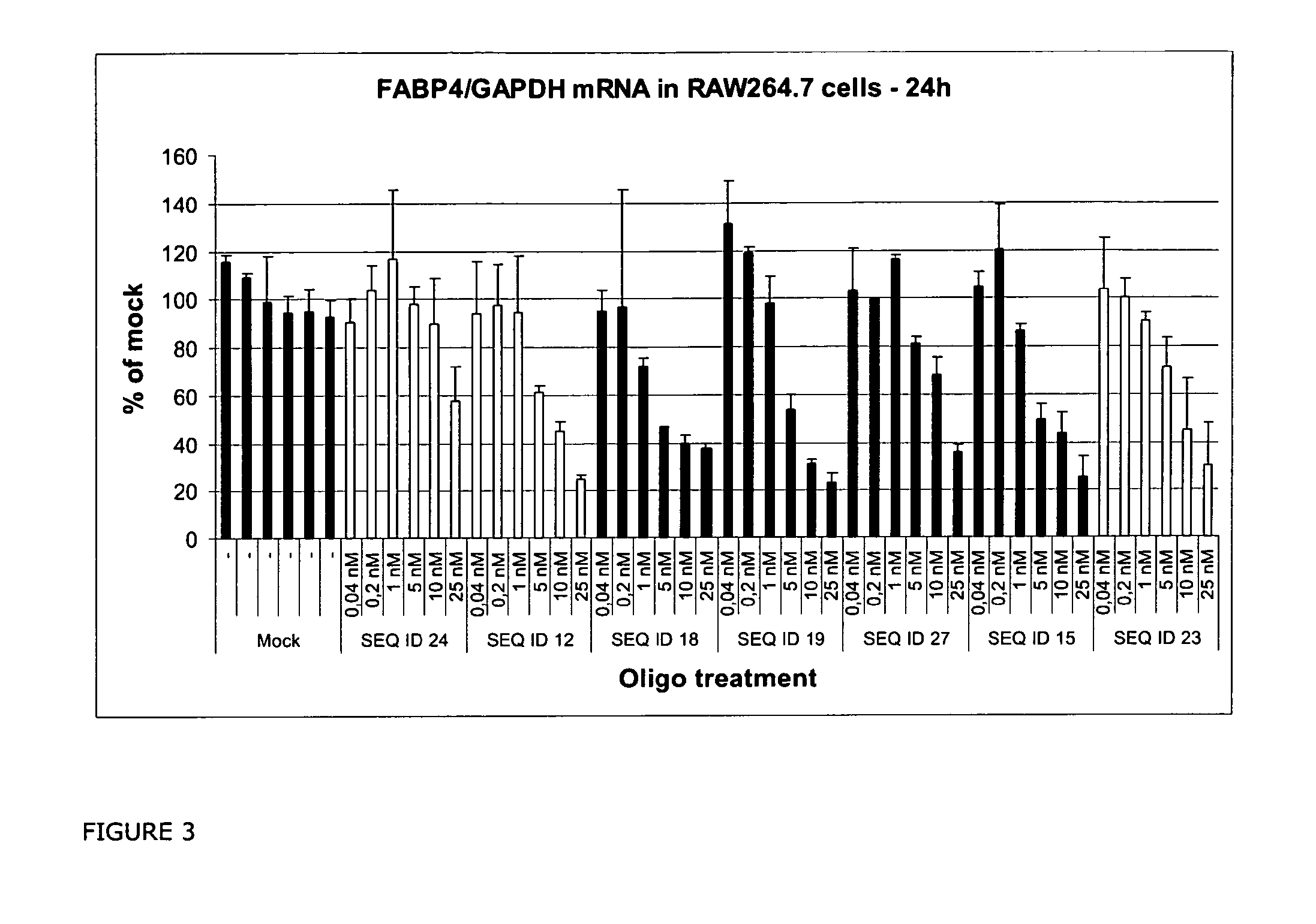
RNA Antagonist Compounds for the Modulation of FABP4/AP2
InactiveUS20110054011A1Lose weightHigh sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseArthritis
Oligonucleotides directed against the FABP4 gene are developed for modulating the expression of FABP4 protein. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding FABP4. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of FABP4 expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with over expression of FABP4 are provided. Examples of such diseases are the metabolic syndrome, diabetes, atherosclerosis, and inflammatory states such as arthritis. The oligomer may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid (LNA) or a combination thereof.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Method for enriching nucleic acids with target sequence from nucleic acid sample
The invention provides a method for enriching nucleic acids with a target sequence from a nucleic acid sample, wherein the method comprises the following steps: providing the nucleic acid sample which contains a the target nucleic acid sequence or a bait sequence which is consistent with the target nucleic acid sequence or has characteristics to the target sequence; conducting in vitro transcription by taking the bait sequence as a template so as to prepare a nucleic acid analogue, wherein the nucleic acid analogue has a binding part; fragmenting the nucleic acid sample; hybridizing the nucleic acid analogue with the nucleic acid sample, so that a nucleic acid analogue / DNA hybrid complex is formed by the nucleic acid analogue and the nucleic acid with the target sequence; and by virtue of the binding part, separating the nucleic acid analogue / DNA hybrid complex from non-specific hybrid nucleic acids, so that the nucleic acids with non-target sequences are removed. According to a preferred embodiment, the method further comprises a step of amplifying the nucleic acid analogue / DNA hybrid complex, so that the purpose of enriching the nucleic acids with the target sequence is achieved.
Owner:艾吉泰康(嘉兴)生物科技有限公司
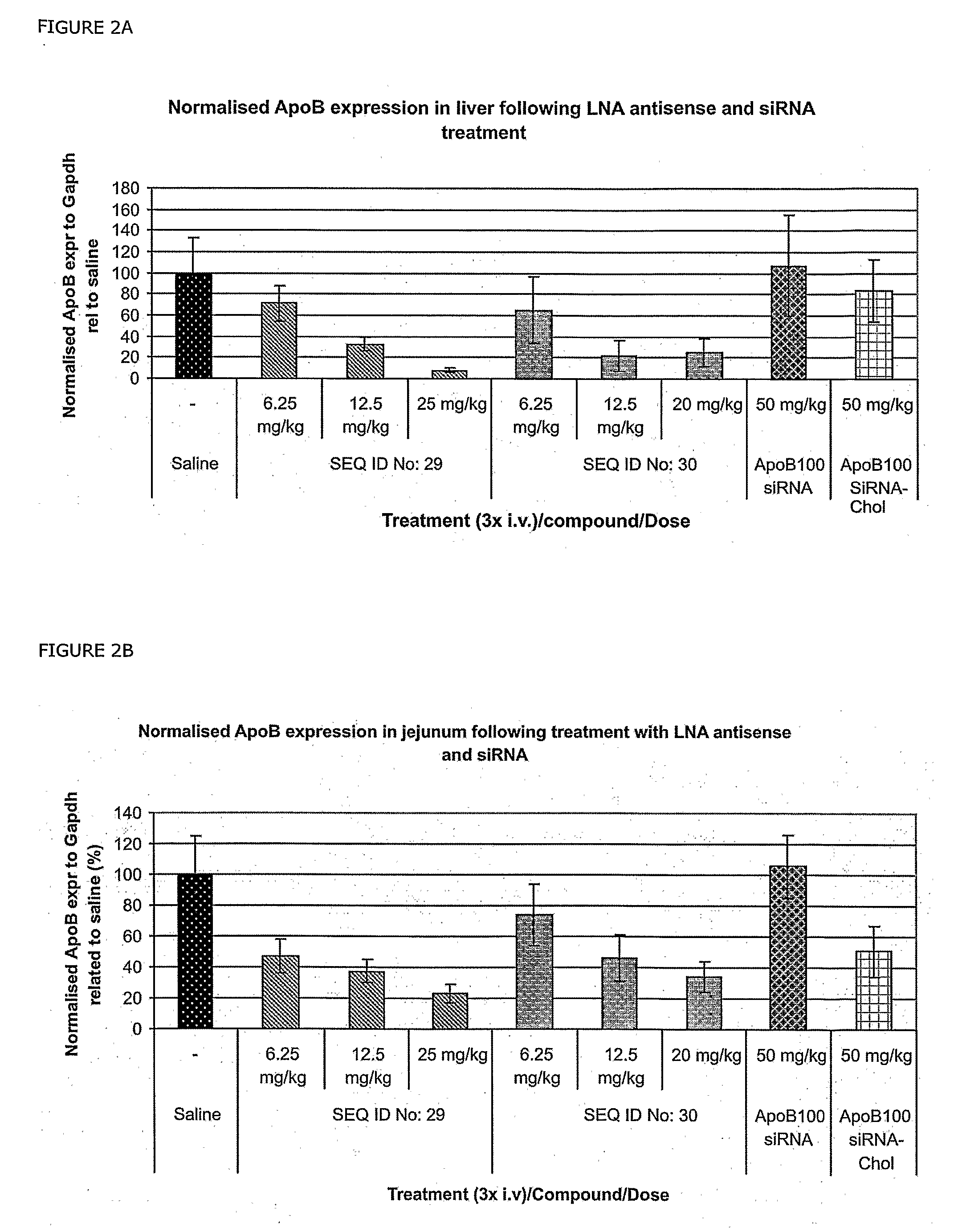
RNA antagonist compounds for the inhibition of apo-b100 expression
InactiveUS20090118213A1Lower Level RequirementsOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesIntestinal structureSpinal cord
Oligonucleotides directed against the Apo-B100 gene are provided for modulating the expression of Apo-B100. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the Apo-B100. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of Apo-B100 expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of Apo-B100, expression of mutated Apo-B100 or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
Methods of capturing bindable targets from liquids
InactiveCN103354904AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBiotin-streptavidin complexEpitope
A bindable target such as a bacterial cell, virus, or molecule is captured from a liquid by contacting the liquid with magnetically attractable particles have an affinity for the target, and causing said particles to move repeatedly through said liquid to at least one solid support zone by attractive magnetic forces to capture the target onto said particles. The particles may be ferromagnetic, paramagnetic or superparamagnetic particles and may bear antibody, antibody binding fragments, a substance having an epitope capable of reacting in a specific manner with an antibody, an aptamer, a nucleic acid sequence or a nucleic acid analogue sequence, biotin, avidin or streptavidin. The particles may be moved back and forth in the liquid between separated solid support zones by attractive magnetic forces which attract the particles temporarily to different solid support zones in turn.
Owner:MATRIX MICROSCI
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
InactiveUS20090318362A1Modulate expressionSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseIntestinal structure
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:ENZON PHARM INC +1
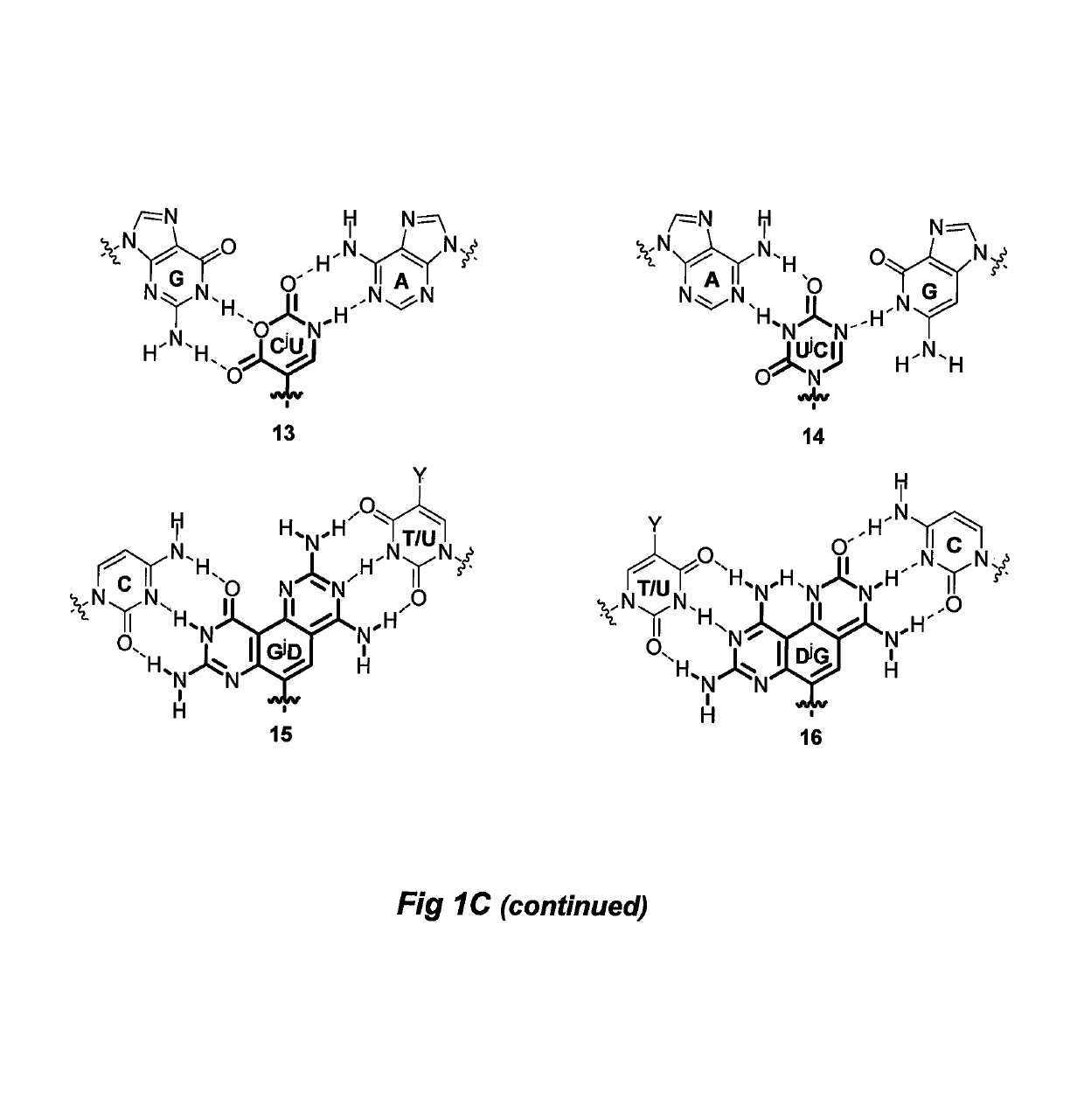
Divalent nucleobase compounds and uses therefor
Described herein are novel divalent nucleobases that each bind two nucleic acid strands, matched or mismatched when incorporated into a nucleic acid or nucleic acid analog backbone (a genetic recognition reagent, or genetic recognition reagent). In one embodiment, the genetic recognition reagent is a peptide nucleic acid (PNA) or gamma PNA (?PNA) oligomer. Uses of the divalent nucleobases and monomers and genetic recognition reagents containing the divalent nucleobases also are provided.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Aptamers containing sequences of nucleic acid or nucleic acid analogues bound homologously, or in novel complexes
InactiveUS6858390B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsOrganic active ingredientsNucleobaseNucleic acid sequencing
An aptamer contains at least two parallel or antiparallel heteropolymeric nucleobase-containing sequences bonded together by Watson-Crick complementary base interaction or by homologous base interaction, provided that: (a) when the aptamer is single-stranded, the at least two sequences are bonded together by homologous base interaction; and (b) when the aptamer is a duplex and the at least two sequences are antiparallel to each other, the at least two sequences are bonded together by homologous base interaction. The aptamer can be used to bind ligands or to catalyze reactions when functioning as an aptazyme.
Owner:INGENEUS INC
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:圣塔里斯·法尔马公司 +1
Application of miR-325 nucleic acid analog in preparation of sinusoid endothelial cell pathologic dysfunction treatment related product
PendingCN112402440AAdjust quicklyRelieve inflammationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderPTPRMYWHAQ
Owner:XIAN TISSUE ENG & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE RES INST
Enhancer of activity of nucleic acid analogue
InactiveCN102458417AHigh activityImprove liver reserve functionDigestive systemAntiviralsValineNucleic acid analogue
Disclosed are: an enhancer of the activity of a nucleic acid analogue preparation; and others. Specifically disclosed is an enhancer of the activity of an nucleic acid analogue, which is characterized by comprising at least one branched amino acid selected from isoleucine, leucine and valine or a salt thereof and has an antiviral activity.
Owner:EA PHARMA CO LTD
Morphatides: novel shape and structure libraries
InactiveUS6838238B1Effectively “ evolve ”Simple structureSilicon organic compoundsSugar derivativesBiologyNucleic acid analog
This invention provides a method for identifying one or more complexes from a library of complexes, wherein said complex or complexes are selected for their ability to perform a preselected or desired function on a target molecule or by having a pre-selected structure, each complex being designated a morphatide, said method comprising: (a) preparing a library of morphatides, comprised of: (i) a scaffolding component selected from the group consisting of nucleic acid, nucleic acid like molecule or nucleic acid analog having one or more regions of randomized sequence; (ii) one or more linker components; and (iii) one or more agent molecules or type of agent molecules, linked to the scaffolding component by one or more type of linker components; and (b)screening the library of morphatides prepared in step (a) by contacting, binding, or associating the morphatides with one or more suitable target molecules upon which a morphatide performs a preselected or desired function or to which a morphatide binds or associates through a pre-selected structure of said morphatide under conditions permitting said morphatide to perform said preselected or desired function on said target molecules or permitting said morphatide to bind or associate with said target molecules through the preselected structure; (c) separating the morphatides performing the preselected or desired function or binding or associating through the preselected structure, from the library of morphatides and target molecules; thereby identifying one or more complexes from a library of complexes, wherein said complex or complexes are selected for their ability to perform a preselected or desired function on a target molecule or by having a pre-selected structure.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
High-sensitivity gene mutation detection method and kit used in same
InactiveCN106755489AAccurate detectionHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementExonuclease IWild type
The invention discloses a high-sensitivity gene mutation detection kit which comprises a PCR buffer solution, DNA polymerase without exonuclease activity, an LNA modified ARMS-like primer, a conventional primer, dNTP mixed liquid, nucleic acid dye and reference dye. The end 3' of the LNA modified ARMS-like primer is nucleic acid analogue; methylene is introduced to the sites of 2' oxygen atom and 4' carbon atom of the carbon ring of the nucleic acid analogue to form a lock structure, so that the LNA remarkably enhances the oligonucleotide identifying capability. The invention also provides a high-sensitivity gene mutation detection method adopting the kit, wherein if the result of PCR reaction has an amplification curve, the to-be-detected sample is a mutant sample; otherwise, if the result of PCR reaction does not have an amplification curve, the to-be-detected sample is a wild sample.
Owner:HANGZHOU JINXI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Transiently bonding drag-tags for separation modalities
ActiveUS20100213059A1Low applicabilityGood effectElectrolysis componentsComponent separationHydrodynamic radiusElectrophoresis
The invention relates transiently attaching drag-tags to molecules during electrophoresis. The invention includes running buffers having drag-tags that transiently attach to lipophilic moieties attached to the molecules. The lipophilic moieties can be covalently or ionically bonded to the molecules. One particular aspect of the invention is a nucleoside analog or a nucleic acid analog comprising a lipophilic moiety. The invention is also directed to methods of separating molecules that comprise a lipophilic moiety. The methods generally comprise transiently attaching a drag-tag to the lipophilic moiety during a separation modality. These methods can be used to separate the molecules by size or weight, to measure a hydrodynamic radius of a drag-tag, or to separate a plurality of drag-tag by their hydrodynamic radius.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Modified nucleic acid monomer compound and oligonucleic acid analog
ActiveUS11208429B2Good biological stabilityTarget gene silencing activityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsOrganic active ingredientsMeth-Ethyl group
The present invention provides a modified nucleic acid monomer compound having a specific backbone such as 2-ethylglycerol or methoxymethyl-1,3-propanediol backbone instead of a ribose or deoxyribose backbone of a nucleoside, and an oligonucleic acid analogue containing the monomer compound as at least one of building blocks. The oligonucleic acid analogue containing the nucleic acid monomer compound of the present invention allows provision of an oligonucleic acid analogue having excellent biological stability and / or target gene silencing activity.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Nucleic acid supported protein complementation
ActiveUS7662554B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSugar derivativesIn vivoNucleic acid analogue
The present invention is directed to novel methods for in vitro and in vivo detection of target nucleic acid molecules, including DNA and RNA targets, as well as nucleic acid analogues. The present invention is based on protein complementation, in which two individual polypeptides are inactive. When the two inactive polypeptide fragment are brought in close proximity during hybridization to a target nucleic acid, they re-associate into an active, detectable protein.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Method for purification of cytidinediphosphoric choline
A method for purification of cytidinediphosphoric choline comprises the steps of contacting a cytidinediphosphoric choline solution having a pH of 0.5 to 5.0 (inclusive) and containing a nucleic acid analogue with a H-type strongly acidic cation exchange resin, and eluting cytidinediphosphoric choline adsorbed on the resin with water or an aqueous solution having an ion concentration of 0.1 mol / L or lower to thereby isolate and purify cytidinediphosphoric choline.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
Liposome composition and method for producing the same
InactiveUS20180243215A1Great leakage rateImprove leakageOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsLiposomeNiosome
An object of the present invention is to provide a liposome composition containing a liposome having an excellent leakage rate of a nucleic acid analog anticancer agent, and a method for producing the same. According to the present invention, there are provided a liposome composition containing a liposome which (1) contains a nucleic acid analog anticancer agent and in which (2) a content ratio of a lysophospholipid contained in a lipid forming the liposome with respect to a total amount of phospholipids other than the lysophospholipid contained in the lipid forming the liposome is 0.01 mol % to 5 mol % and (3) a nucleic acid analog anticancer agent / lipid ratio is 2 mass % to 10 mass %, and a method for producing the same.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Methods for detecting chromosome aberrations
ActiveUS20060078904A1Easy to useFast resultsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBioinformaticsNucleic acid analog
The present invention relates to methods for detecting a change in chromosomal structure. These methods employ labeled probes that bind nucleic acids. For example, these probes may be comprised of nucleic acids or nucleic acid analogs and a detectable label.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation ras expression
InactiveUS20080188432A1Inhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseIntestinal structure
Oligonucleotides directed against the Ha-ras gene are provided for modulating the expression of Ha-ras. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the Ha-ras. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of Ha-ras expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of Ha-ras, expression of mutated Ha-ras or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
OLIGOMERIC COMPOUNDS FOR THE MODULATION OF HIF-1alpha EXPRESSION
InactiveUS20100093839A1Modulate expressionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseFhit gene
Oligonucleotides directed against the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIP-1α) gene are provided for modulating the expression of HIF-1α. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the HIF-1α. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of HIF-1α expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer and pre-eclampsia. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides, a nucleic acid analogue, or Locked Nucleic Acid (LNA) or a combination thereof.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Method for purification of cytidinediphosphoric choline
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO BIO CO LTD
Oligomeric compounds for the modulation of survivin expression
Oligonucleotides directed against the survivin gene are provided for modulating the expression of survivin. The compositions comprise oligonucleotides, particularly antisense oligonucleotides, targeted to nucleic acids encoding the survivin. Methods of using these compounds for modulation of survivin expression and for the treatment of diseases associated with either overexpression of survivin, expression of mutated survivin or both are provided. Examples of diseases are cancer such as lung, breast, colon, prostate, pancreas, lung, liver, thyroid, kidney, brain, testes, stomach, intestine, bowel, spinal cord, sinuses, bladder, urinary tract or ovaries cancers. The oligonucleotides may be composed of deoxyribonucleosides or a nucleic acid analogue such as for example locked nucleic acid or a combination thereof.
Owner:圣塔里斯·法尔马公司 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com