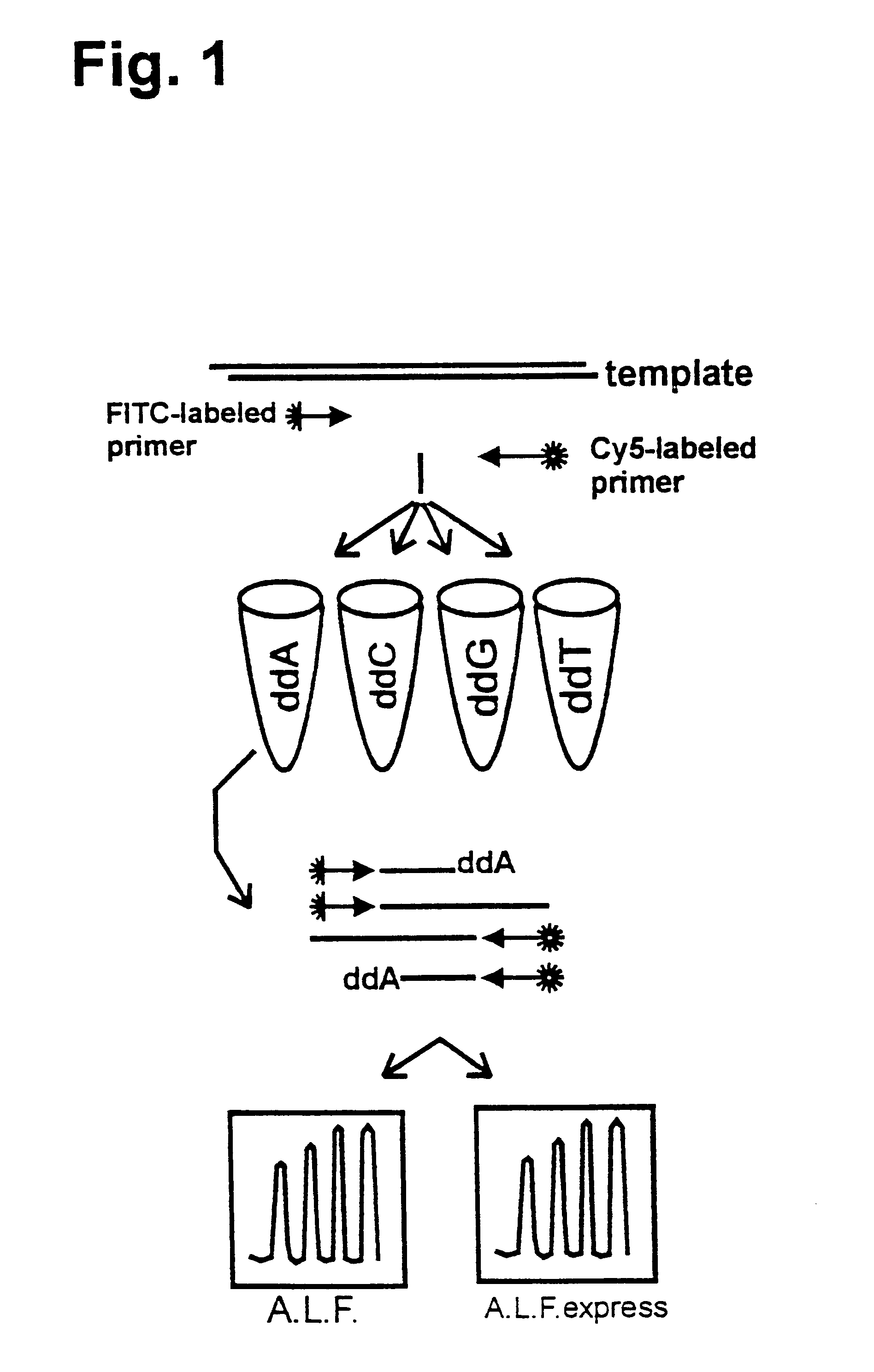
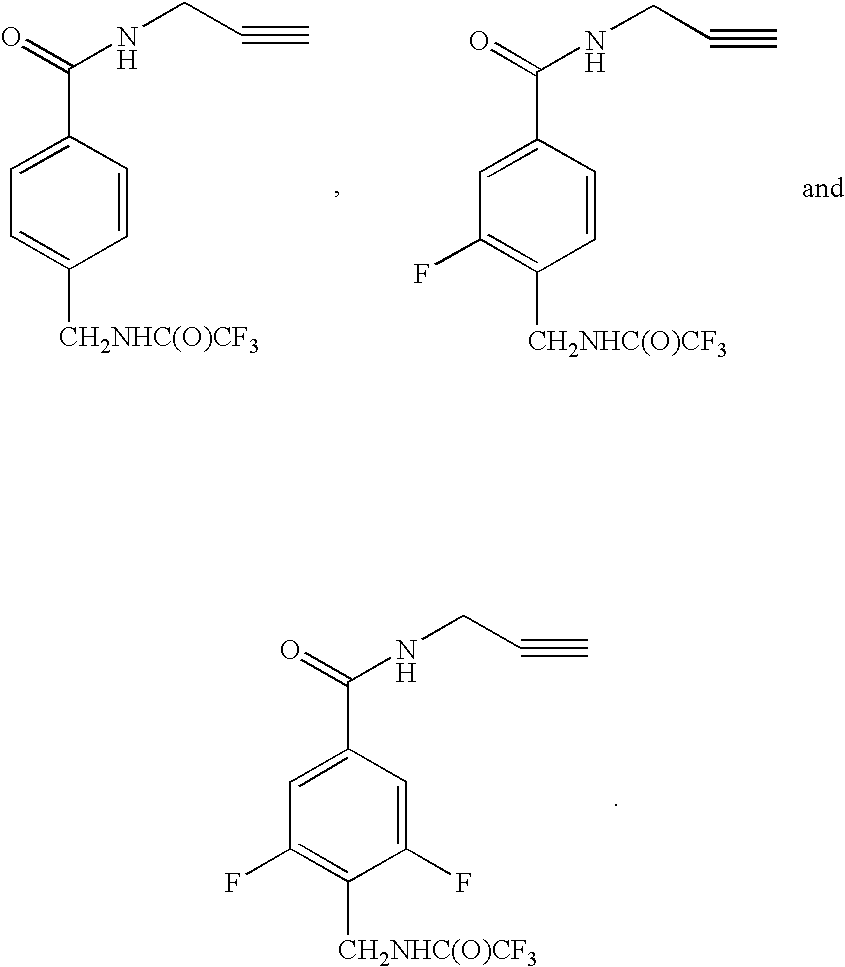
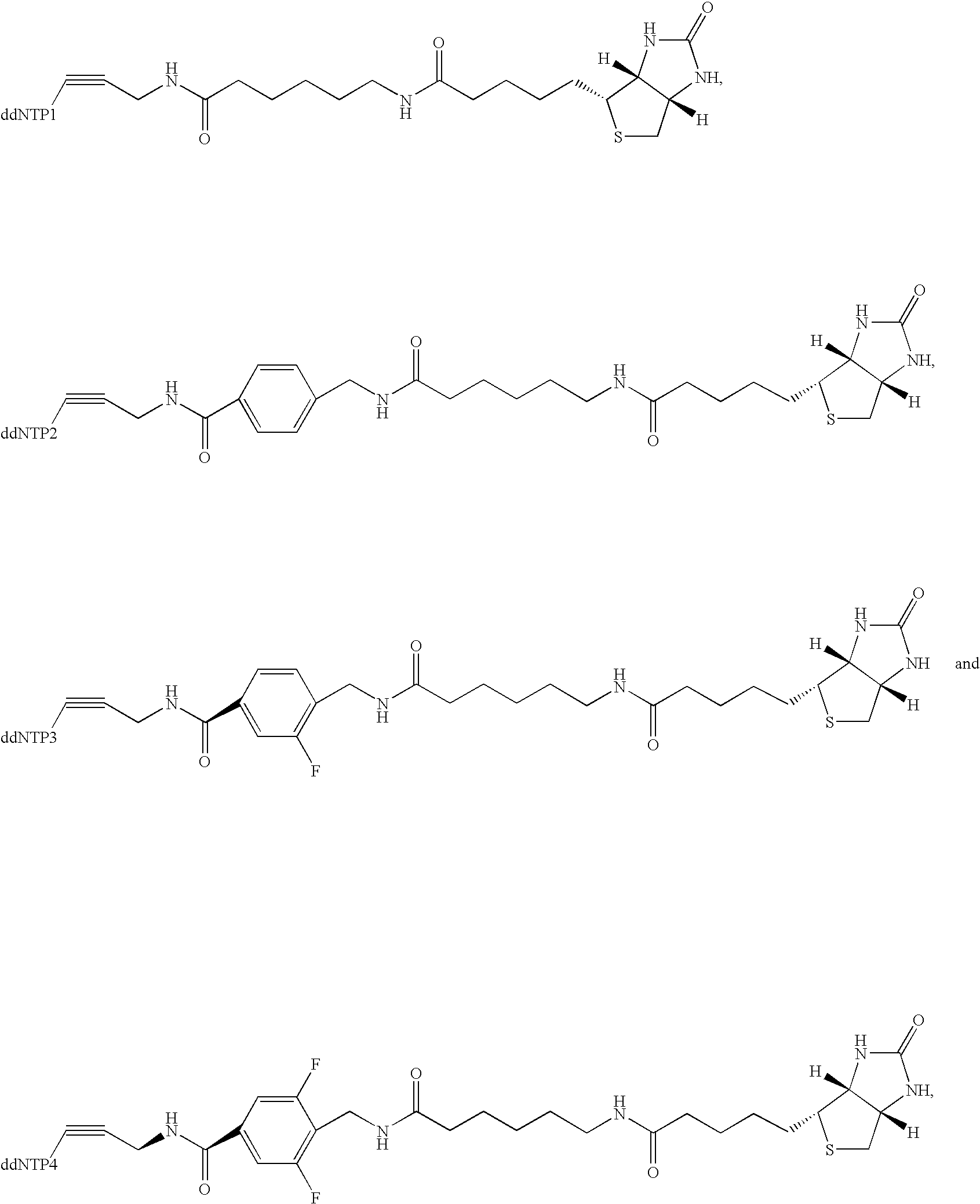
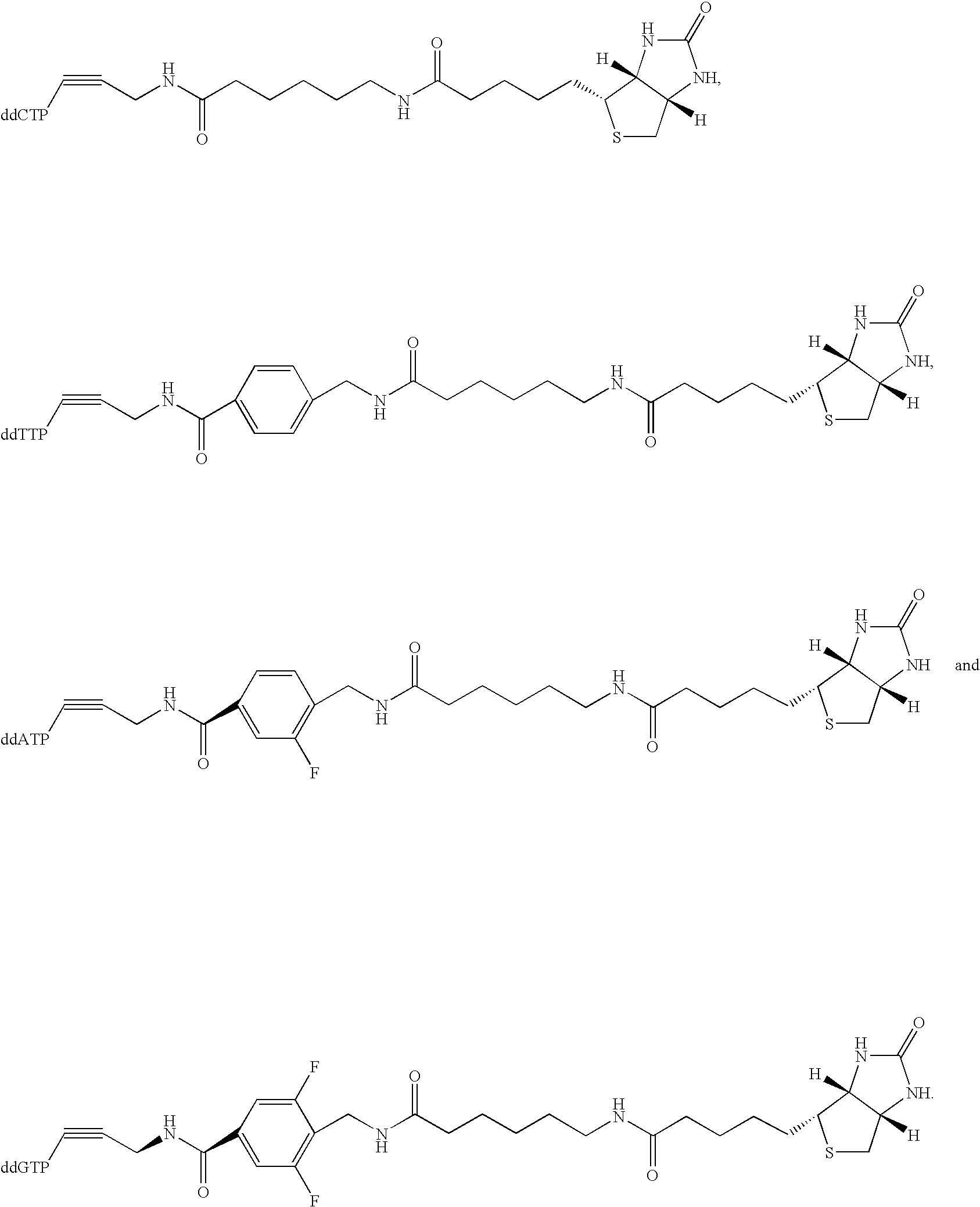
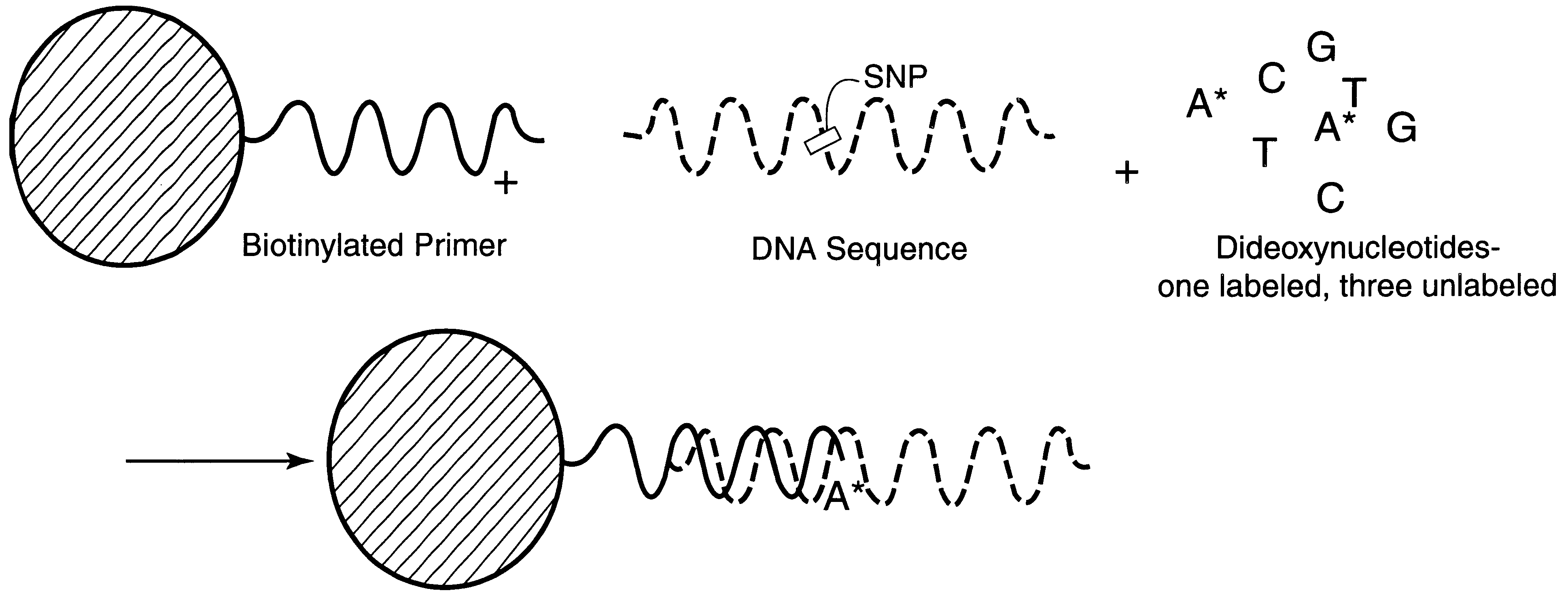
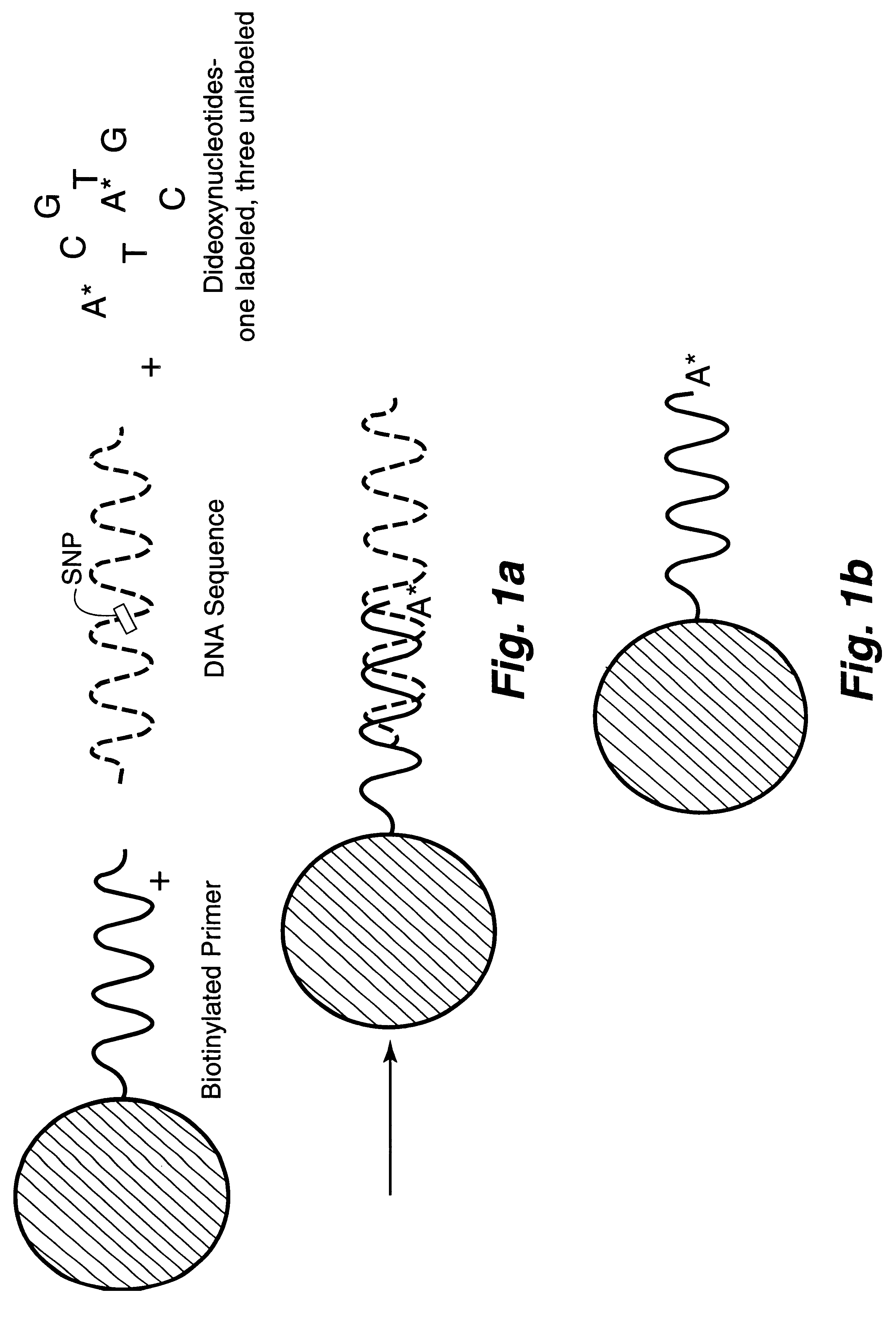
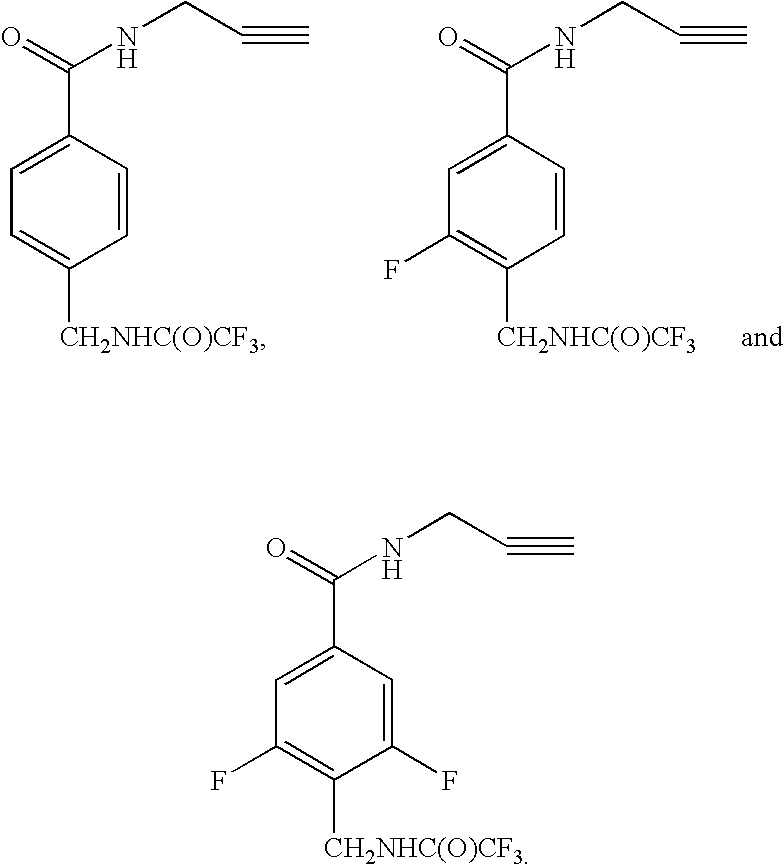
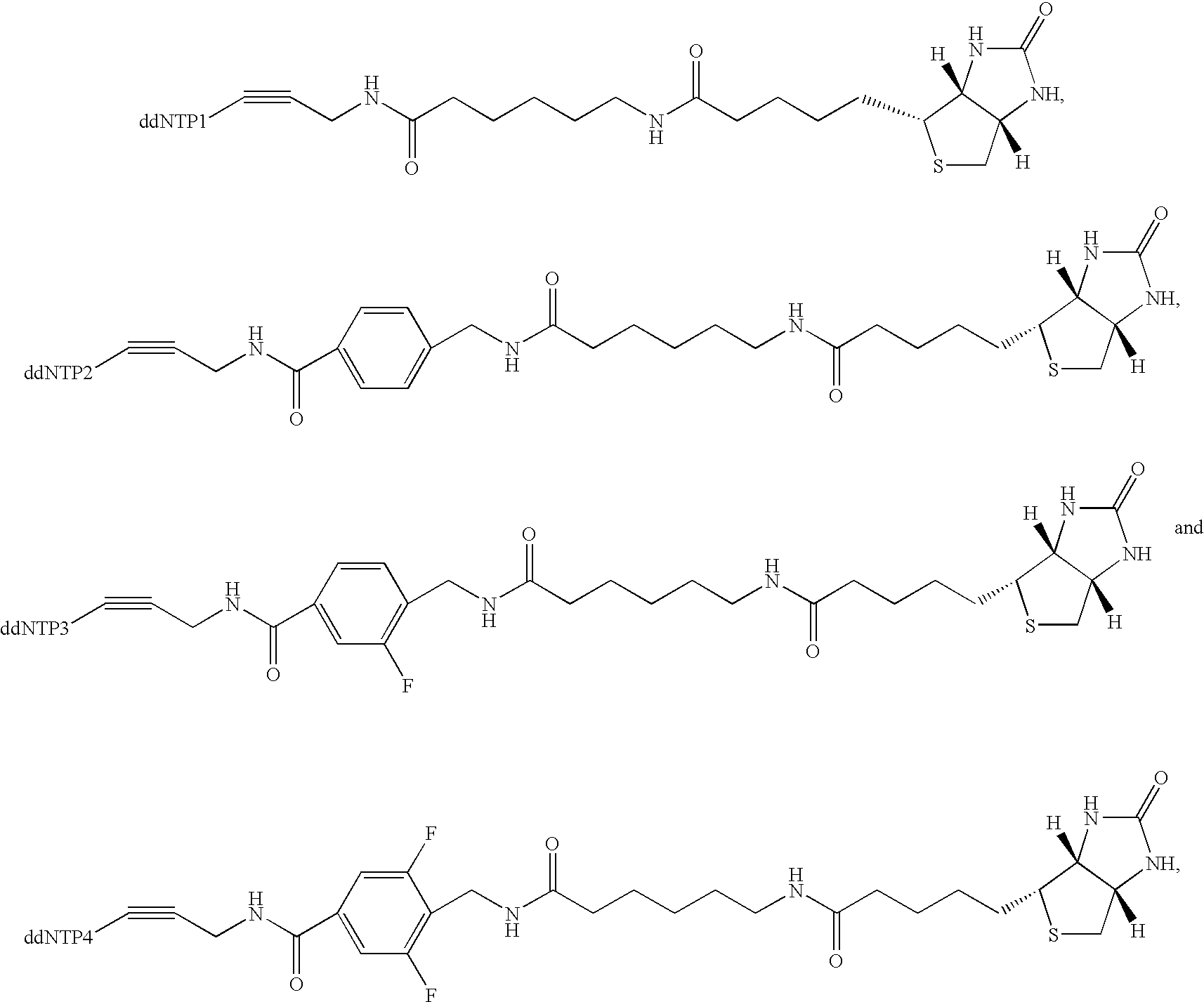
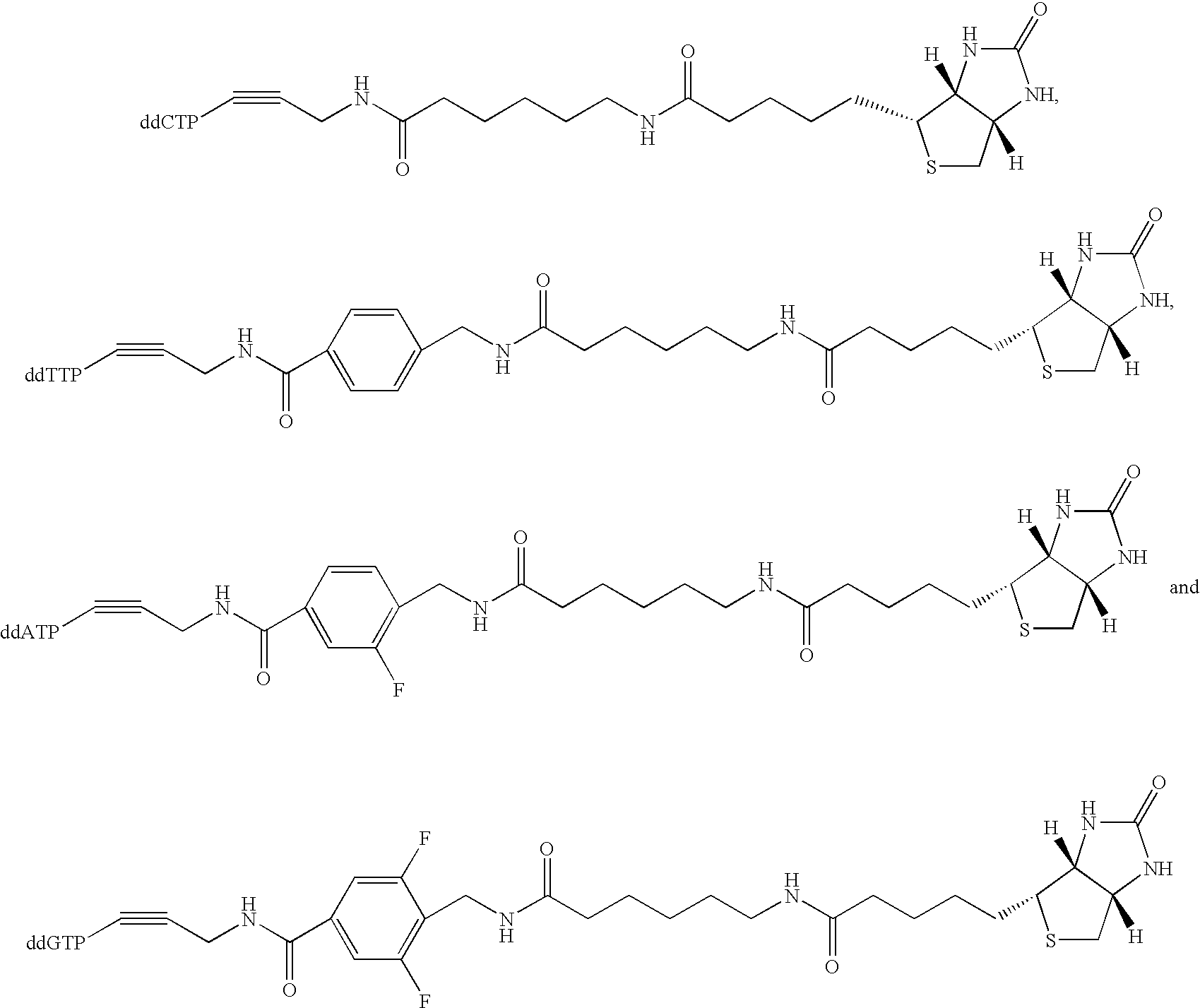
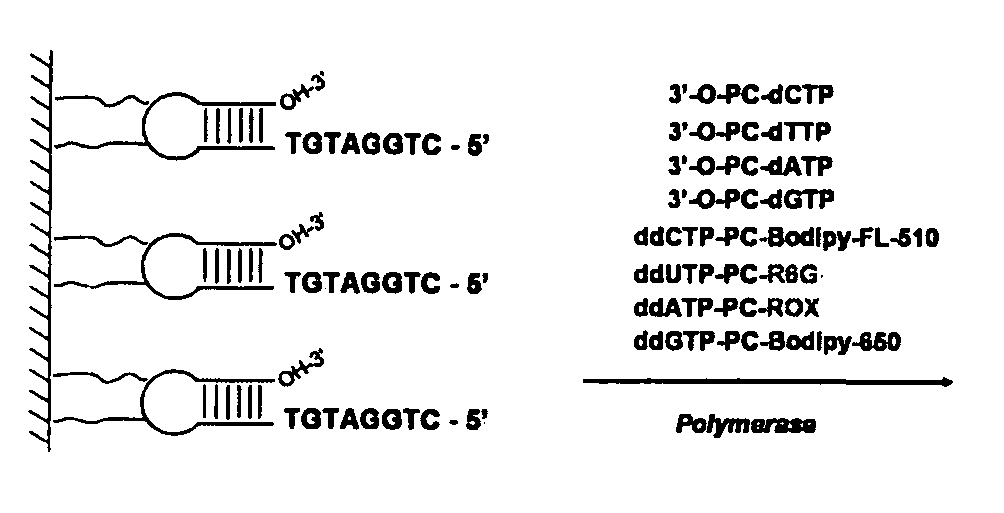
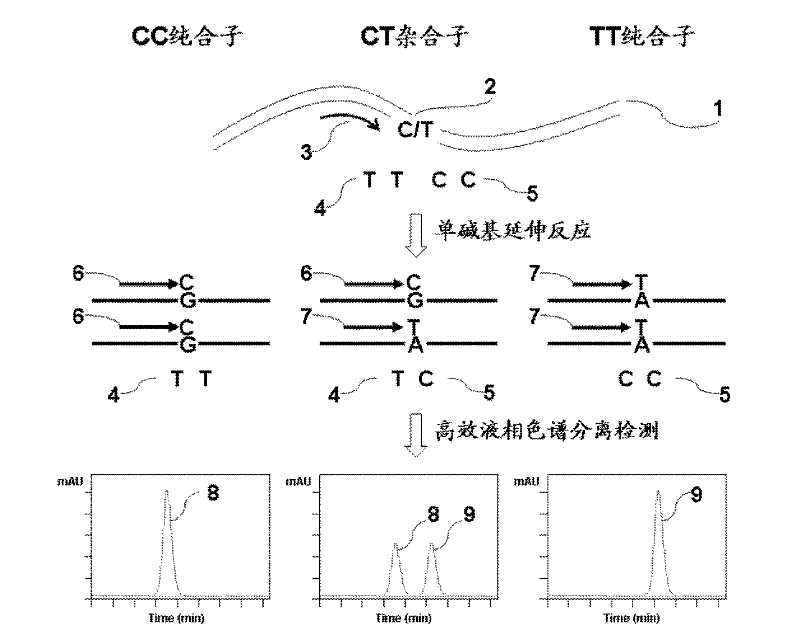
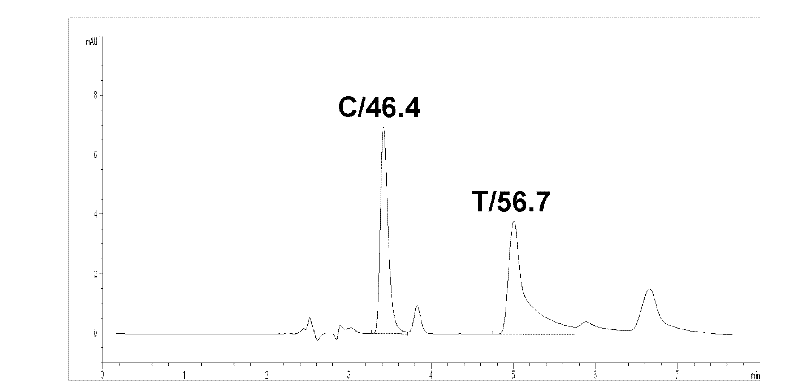
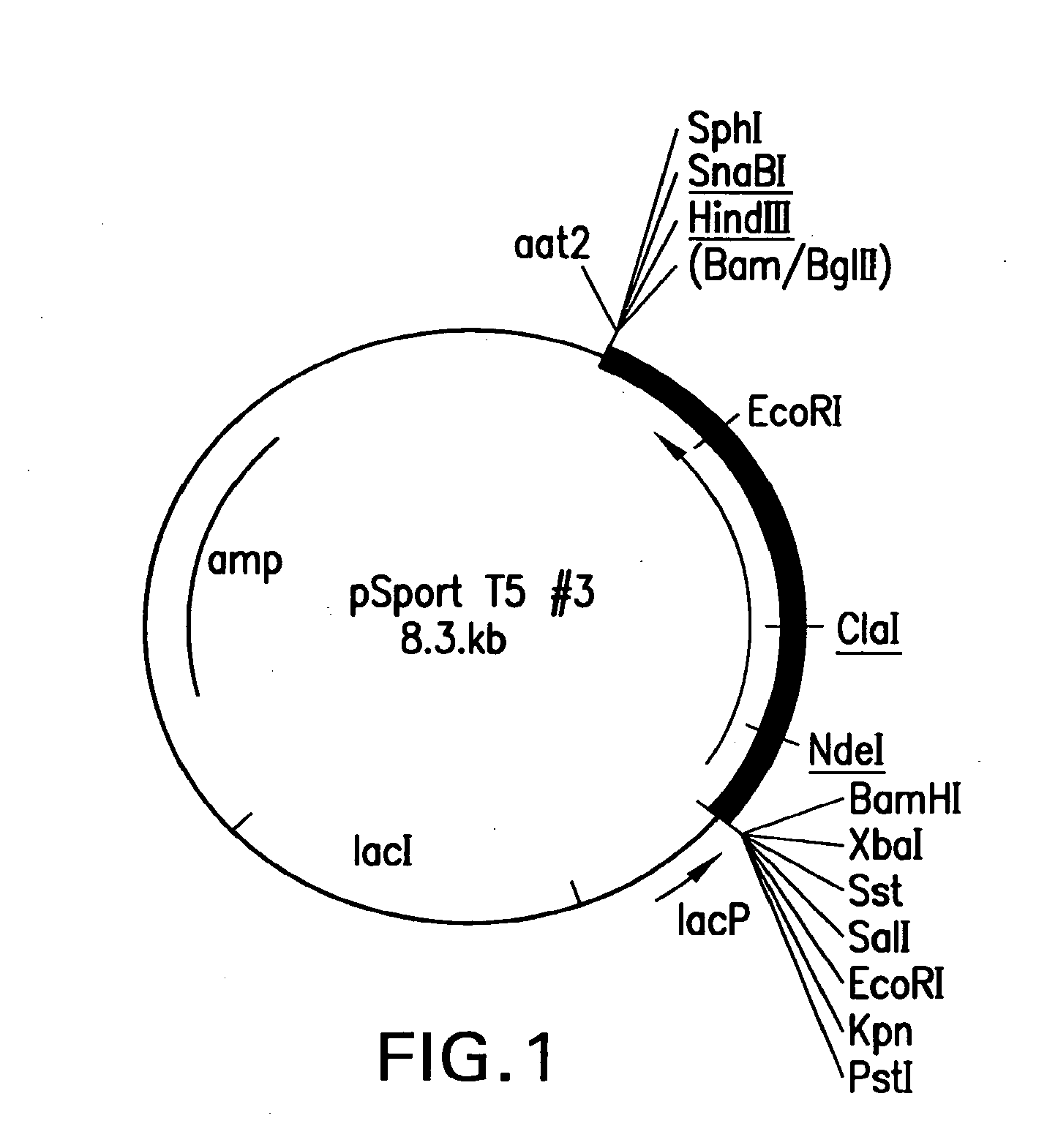
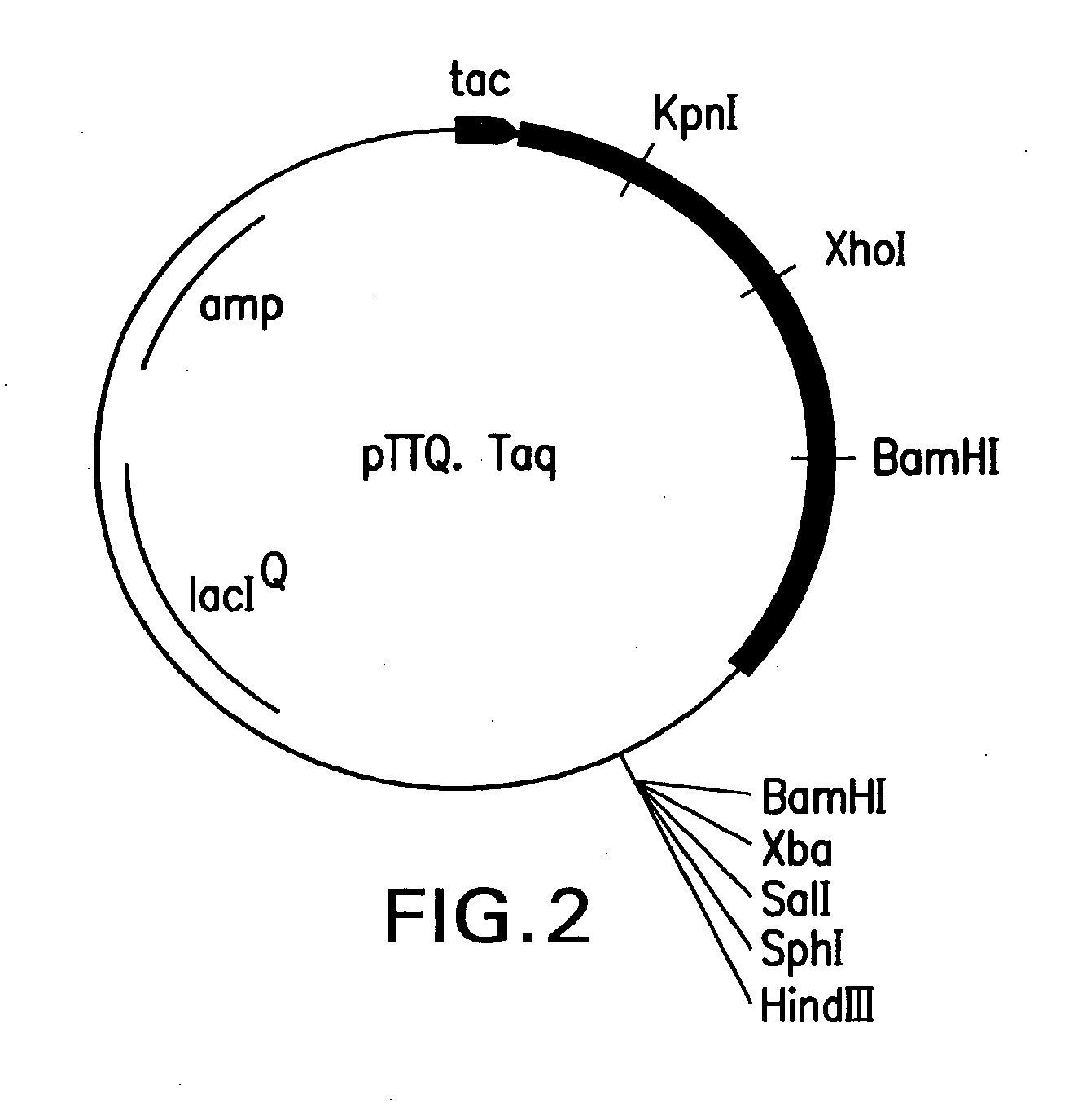
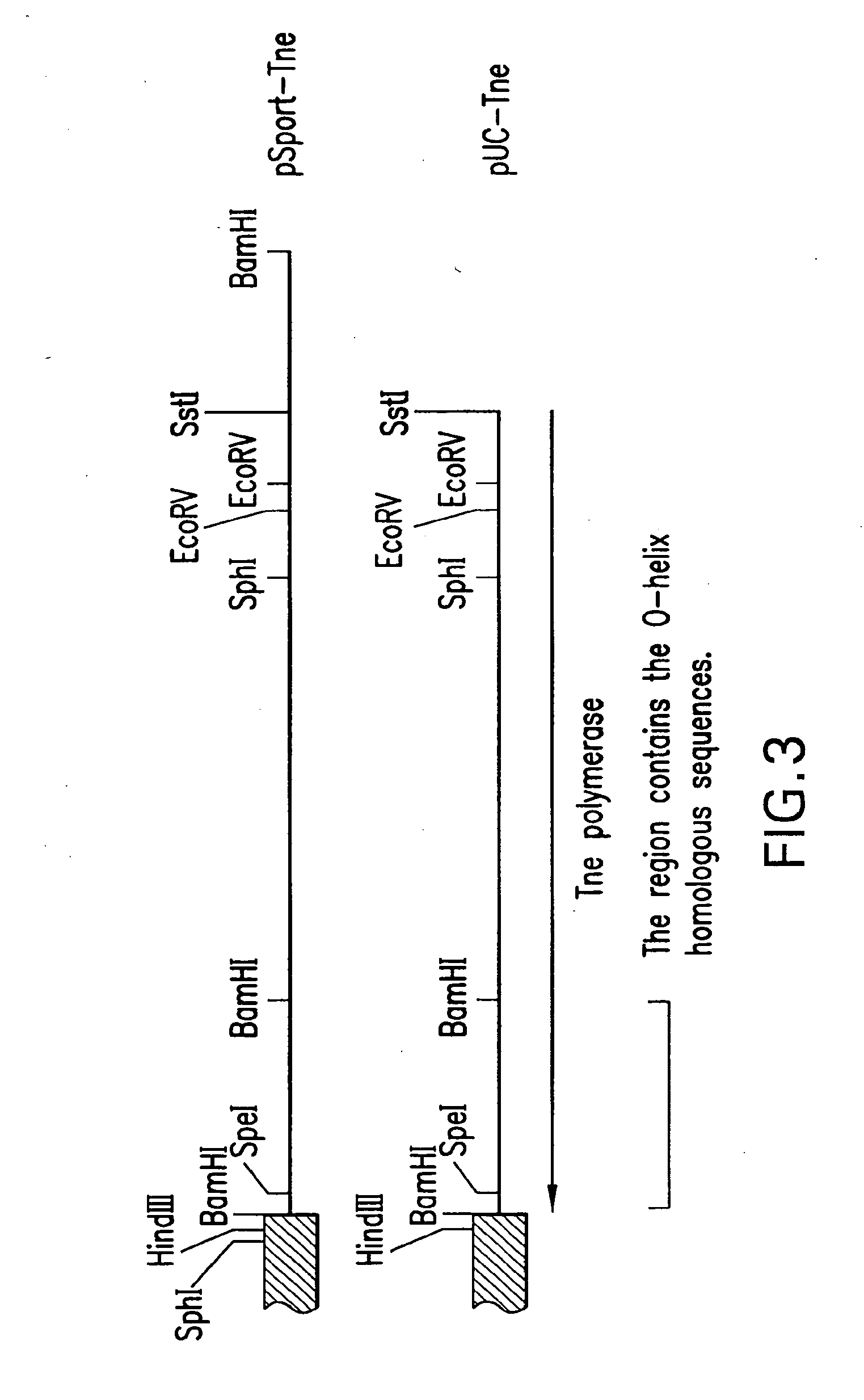
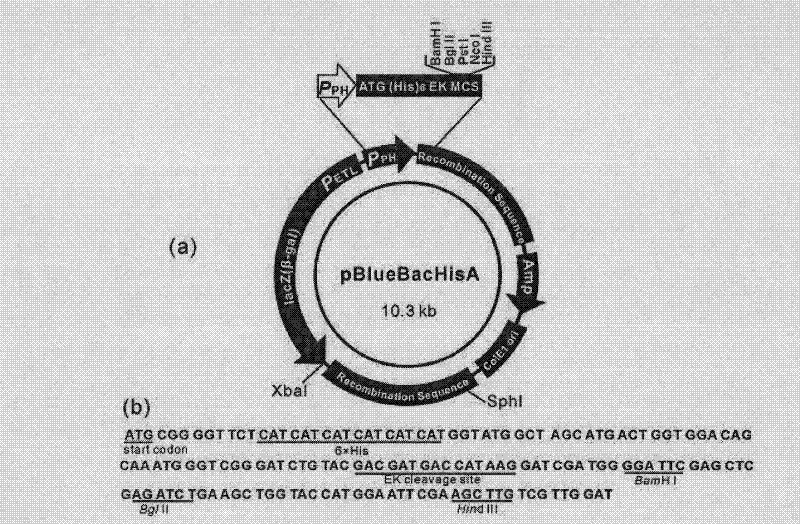
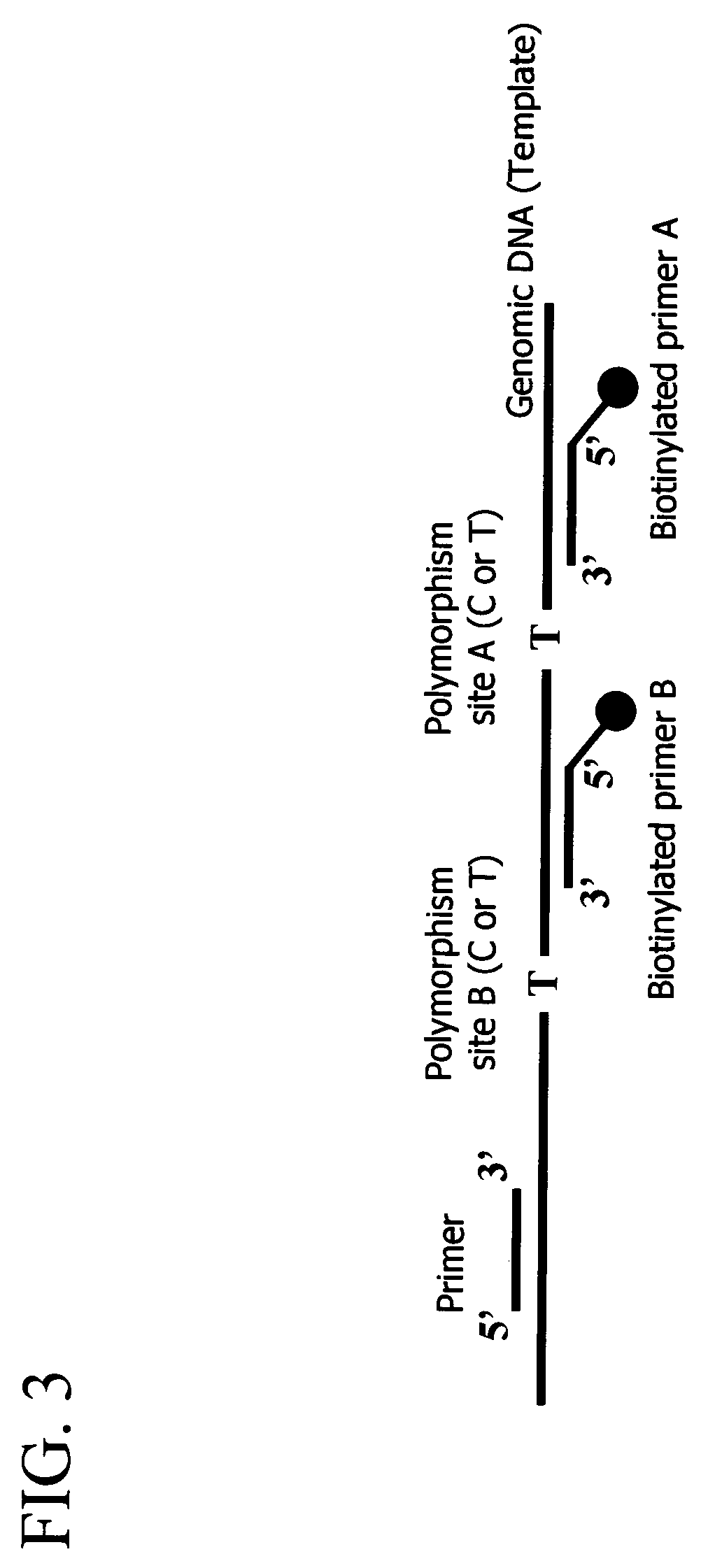
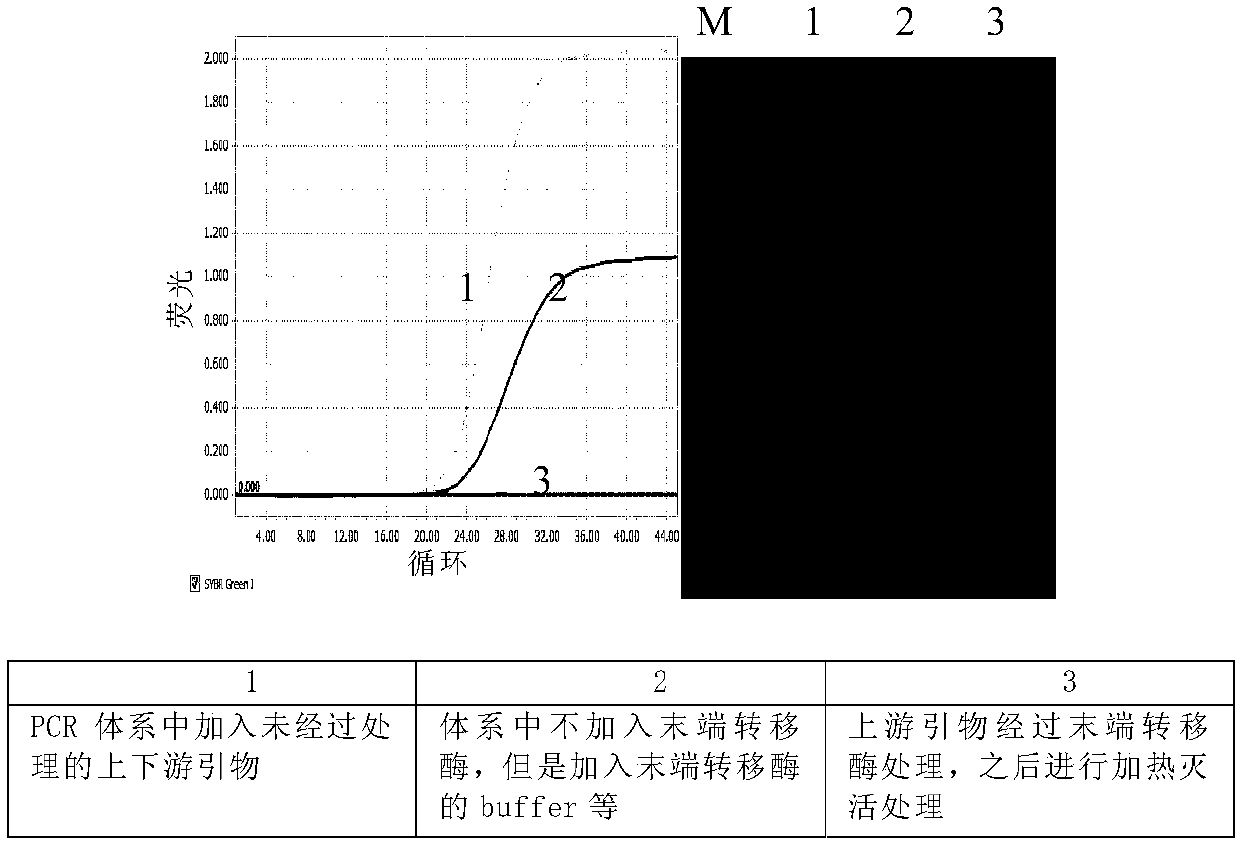
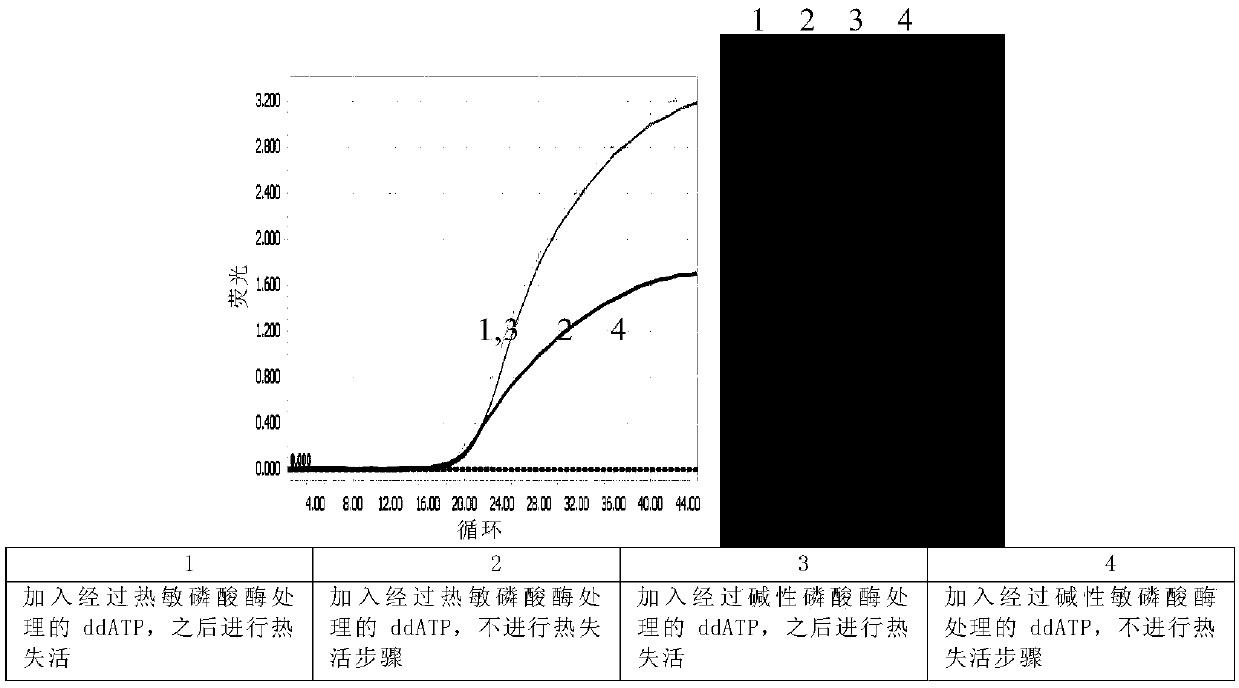
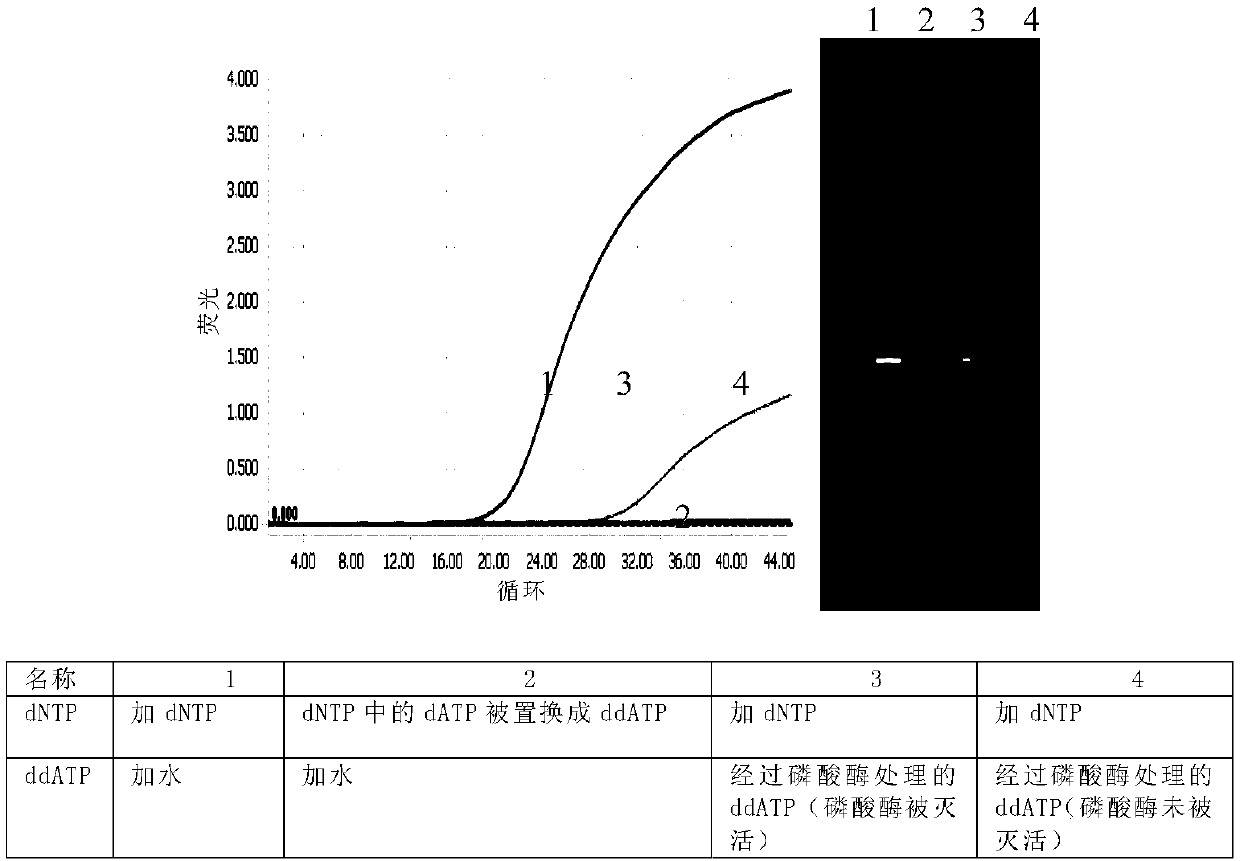
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Dideoxynucleotide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
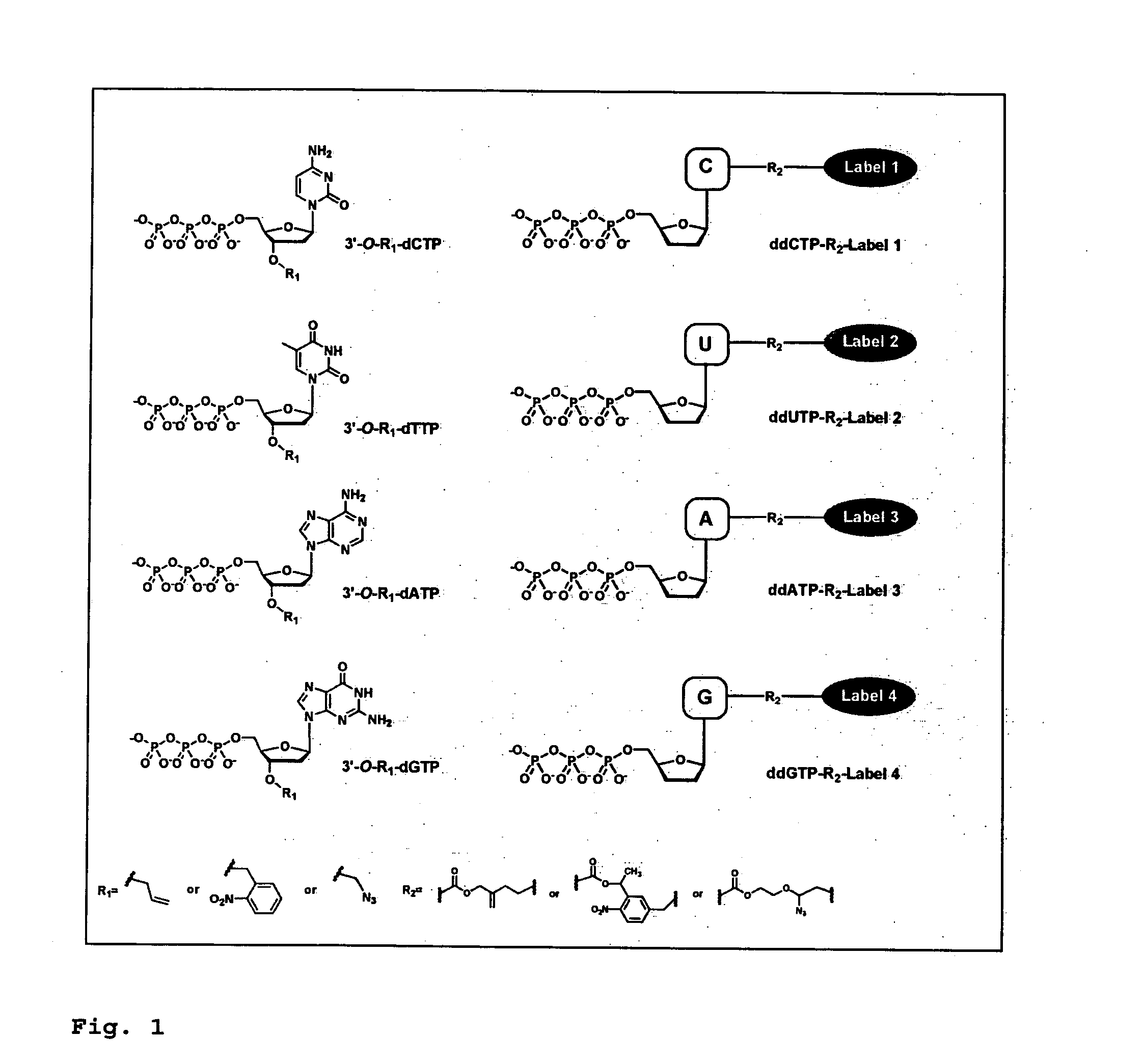
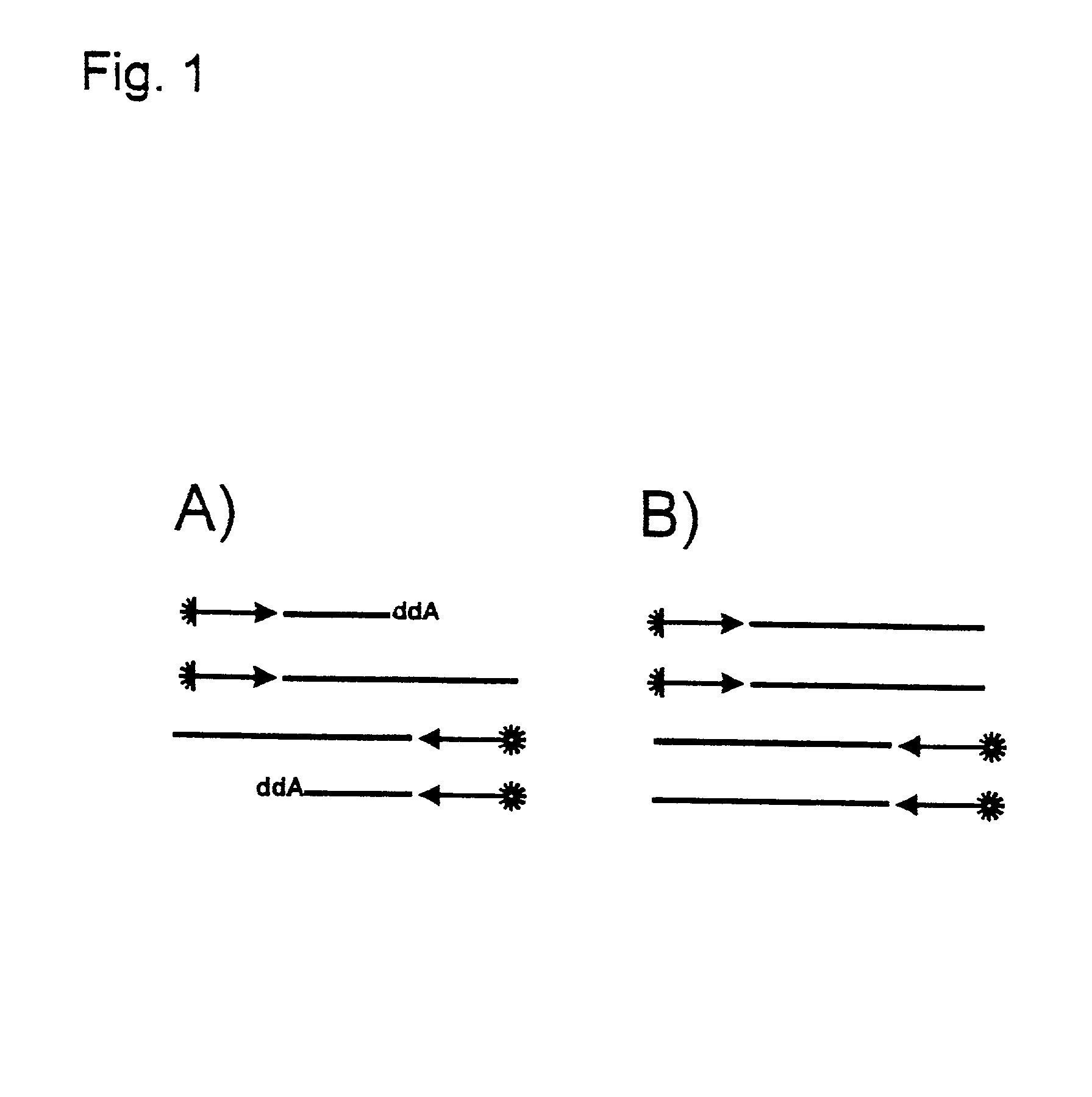
Dideoxynucleotides are chain-elongating inhibitors of DNA polymerase, used in the Sanger method for DNA sequencing. They are also known as 2',3' dideoxynucleotides, and abbreviated as ddNTPs (ddGTP, ddATP, ddTTP and ddCTP).
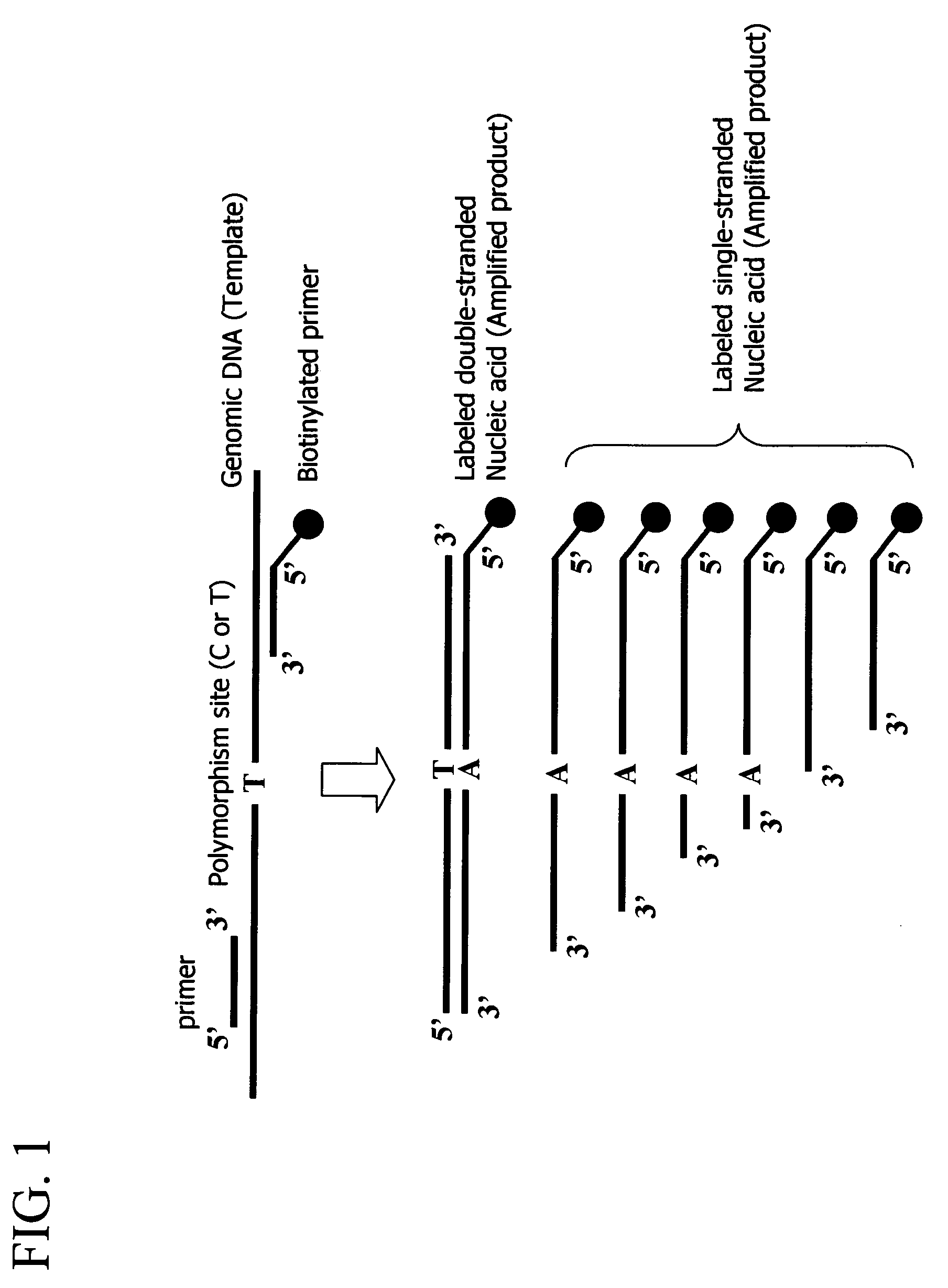
Method for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules and its application
InactiveUS6605428B2Improved and rapid and reliable methodReduction of initial amountSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
A method is described for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing ("DEXAS") of a DNA molecule from a complex mixture of nucleic acids, wherein truncated DNA molecules as well as DNA molecules of full length are synthesized simultaneously and exponentially between two positions on the said DNA molecule, which initially contains a DNA molecule in a thermocycling reaction, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a thermostable DNA polymerase, a thermostable pyrophosphatase (optionally), deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed using one polymerase having a Tabor-Richardson mutation, or a functional derivative thereof, and reverse transcriptase activity. In a more preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed in one step, in one vessel.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Multiplex genotyping using solid phase capturable dideoxynucleotides and mass spectrometry
InactiveUS7074597B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMultiplex genotyping
This invention provides methods for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms and multiplex genotyping using dideoxynucleotides and mass spectrometry.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry
InactiveUS6287766B1Sensitive, homogenous, and flexibleSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereDideoxynucleotide Triphosphates
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry. Primers designed to be immobilized on microspheres are allowed to anneal to the DNA strand under investigation, and are extended by either DNA polymerase using fluorescent dideoxynucleotides or ligated by DNA ligase to fluorescent reporter oligonucleotides. The fluorescence of either the dideoxynucleotide or the reporter oligonucleotide attached to the immobilized primer is measured by flow cytometry, thereby identifying the nucleotide polymorphism on the DNA strand.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Multiplex genotyping using solid phase capturable dideoxynucleotides and mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060252038A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMultiplex genotyping
This invention provides methods for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms and multiplex genotyping using dideoxynucleotides and mass spectrometry.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
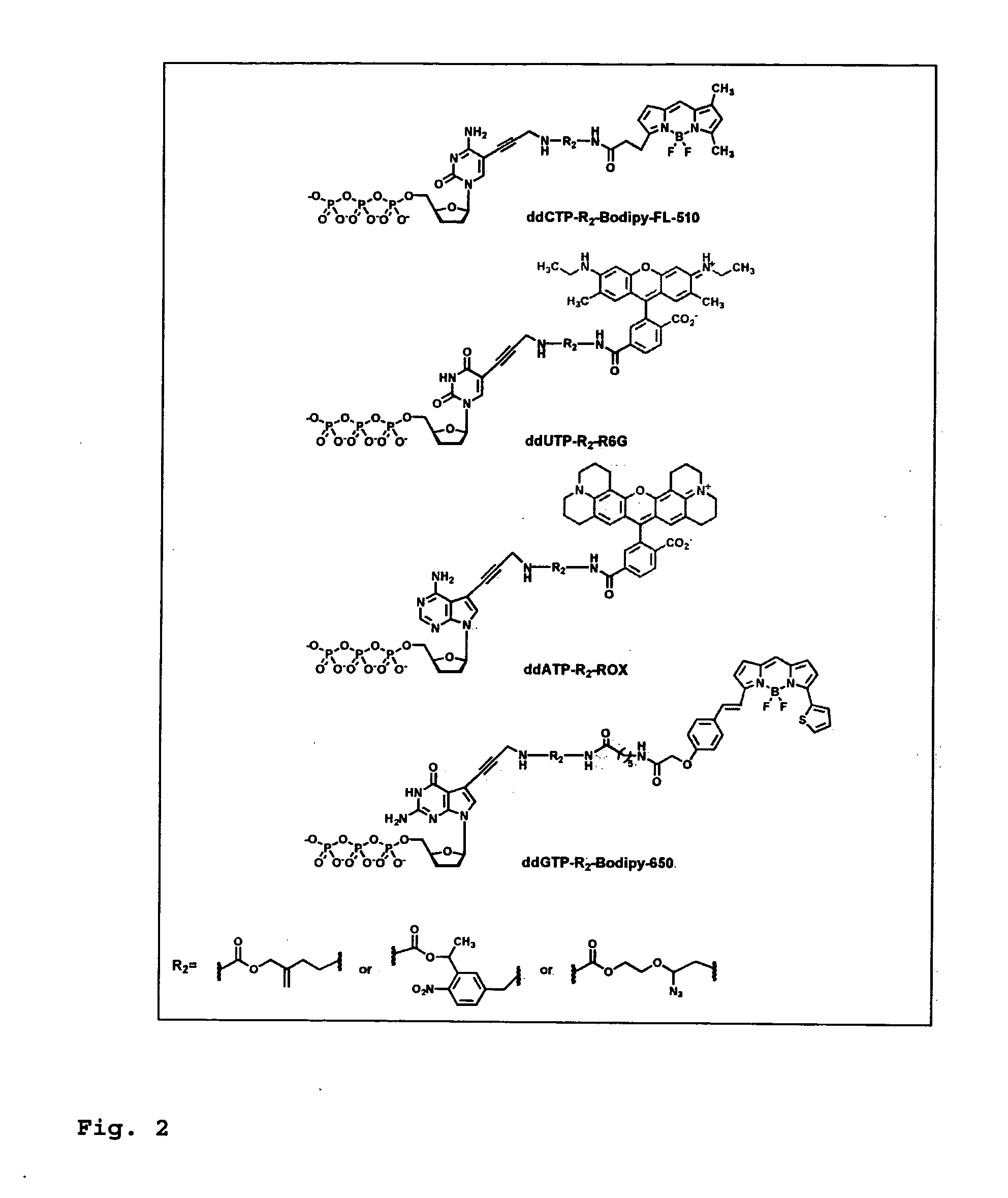
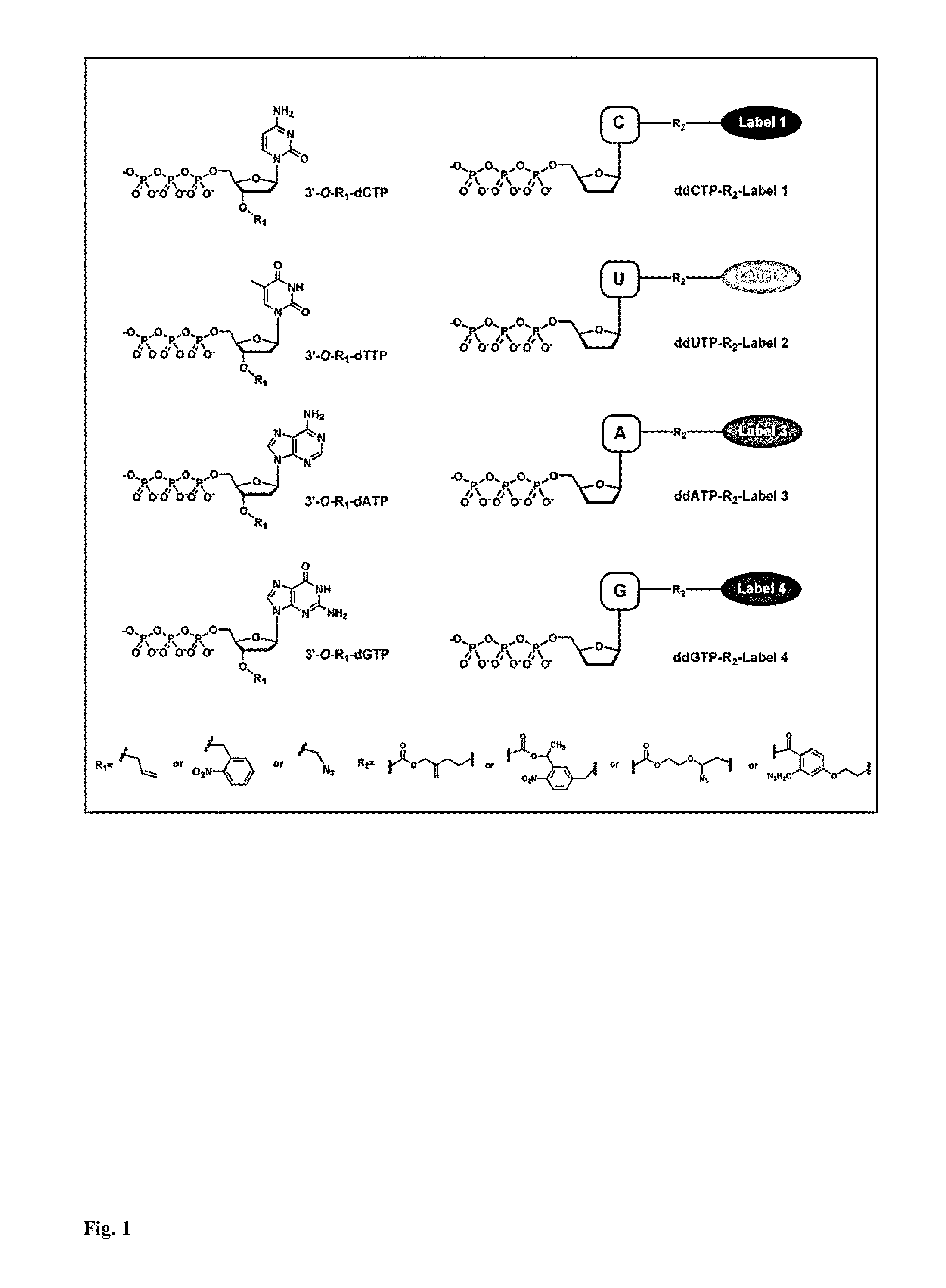
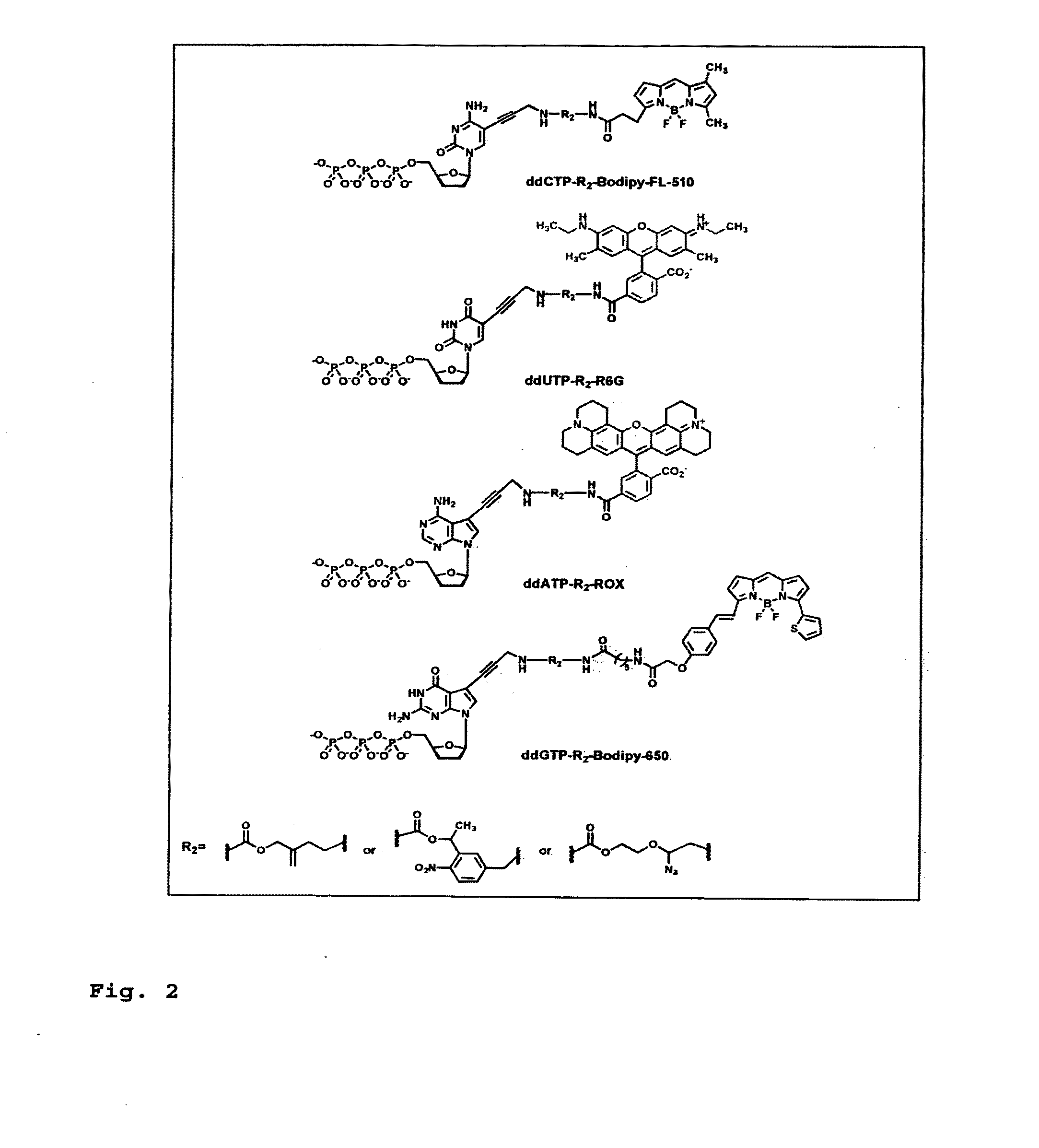
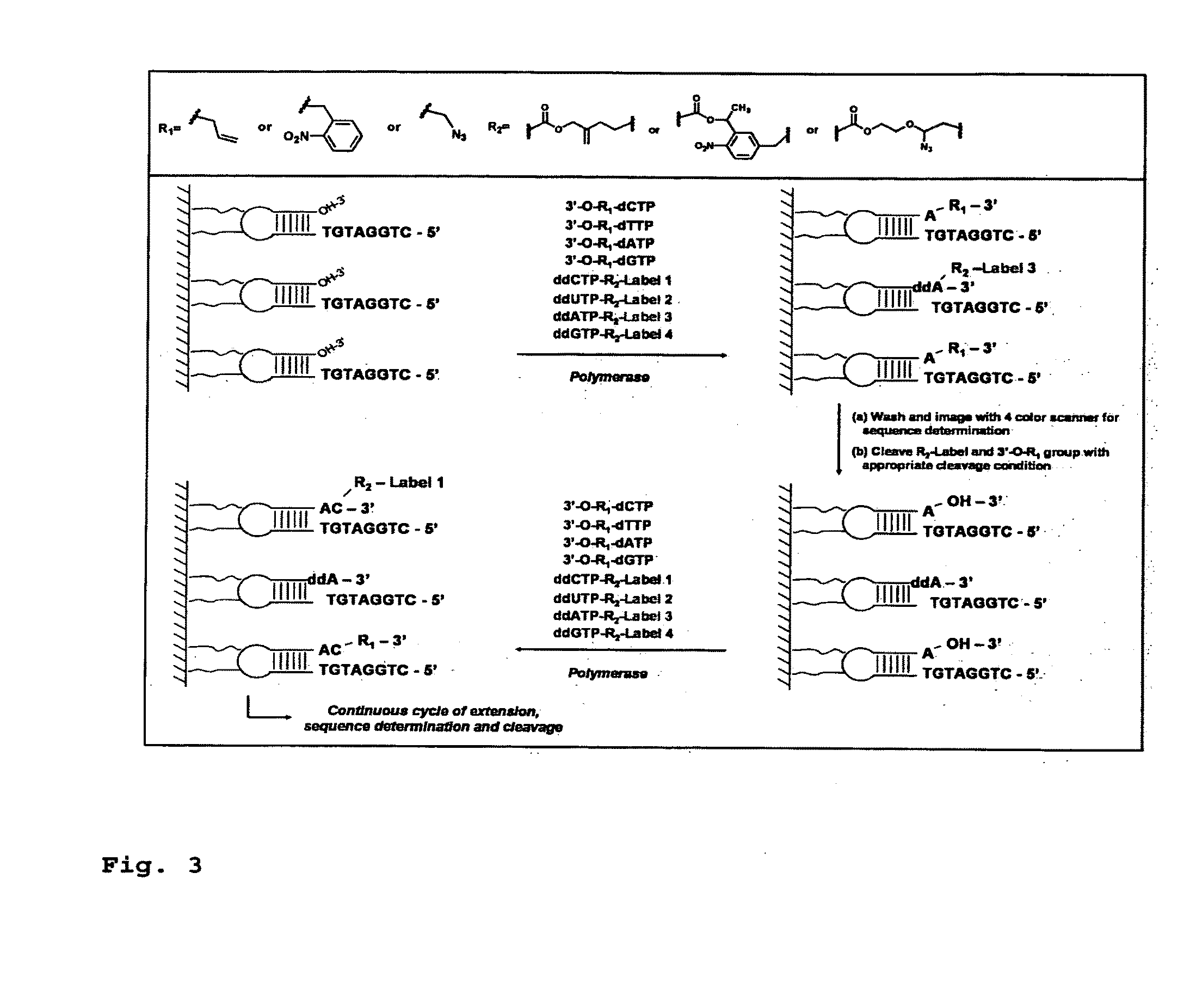
DNA sequence with non-fluorescent nucleotide reversible terminators and cleavable label modified nucleotide terminators
ActiveUS20110039259A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesDNA
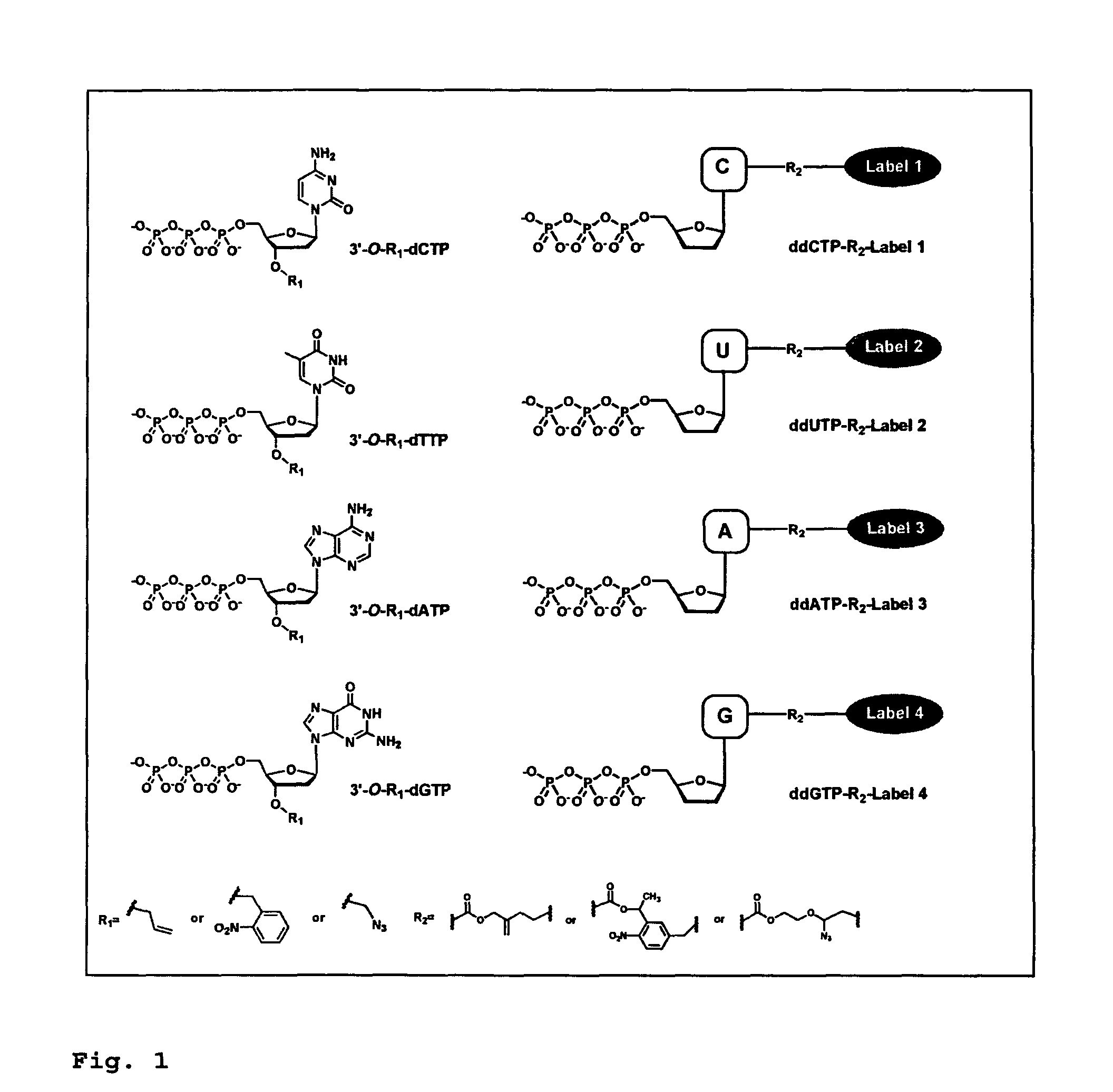
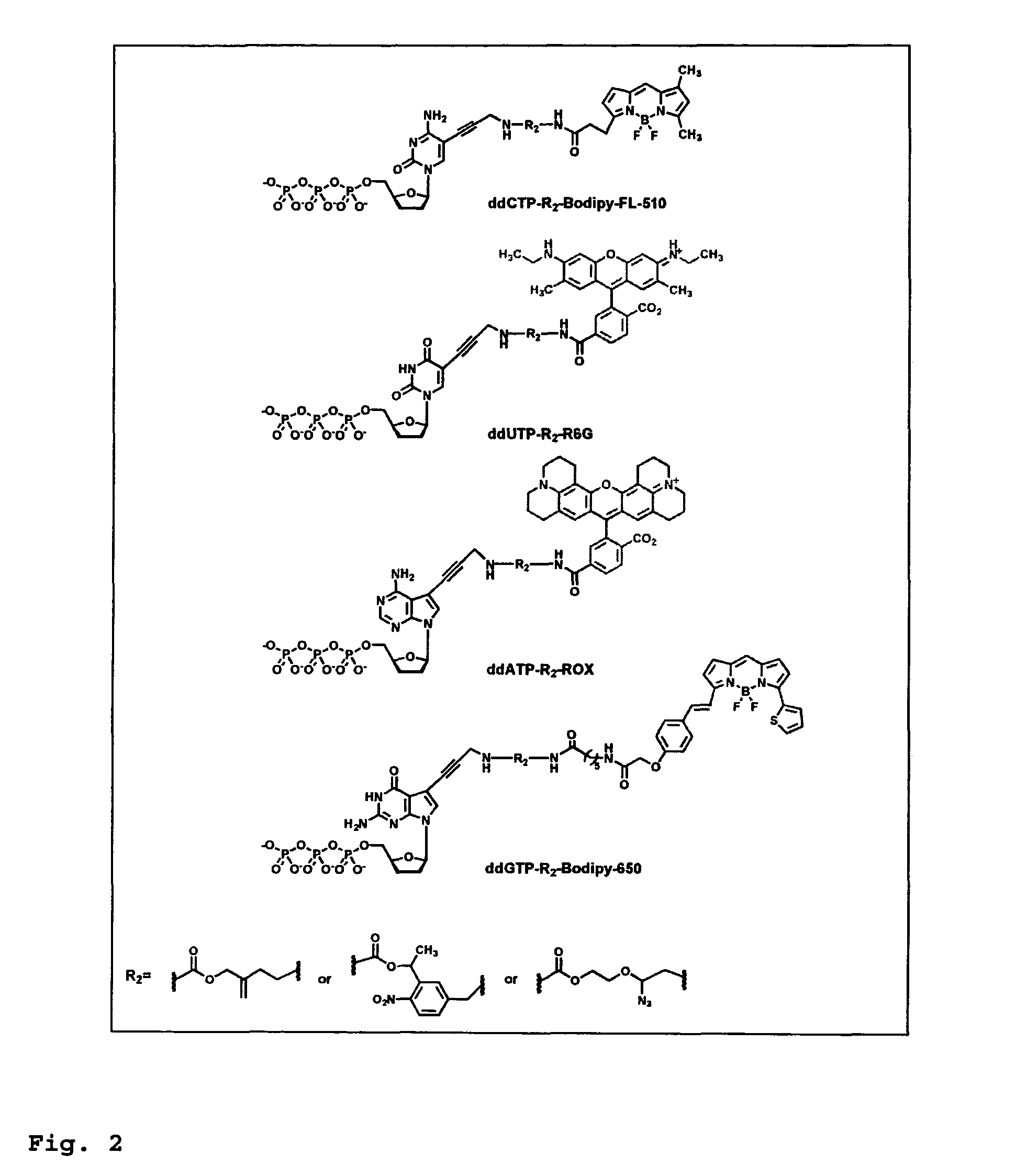
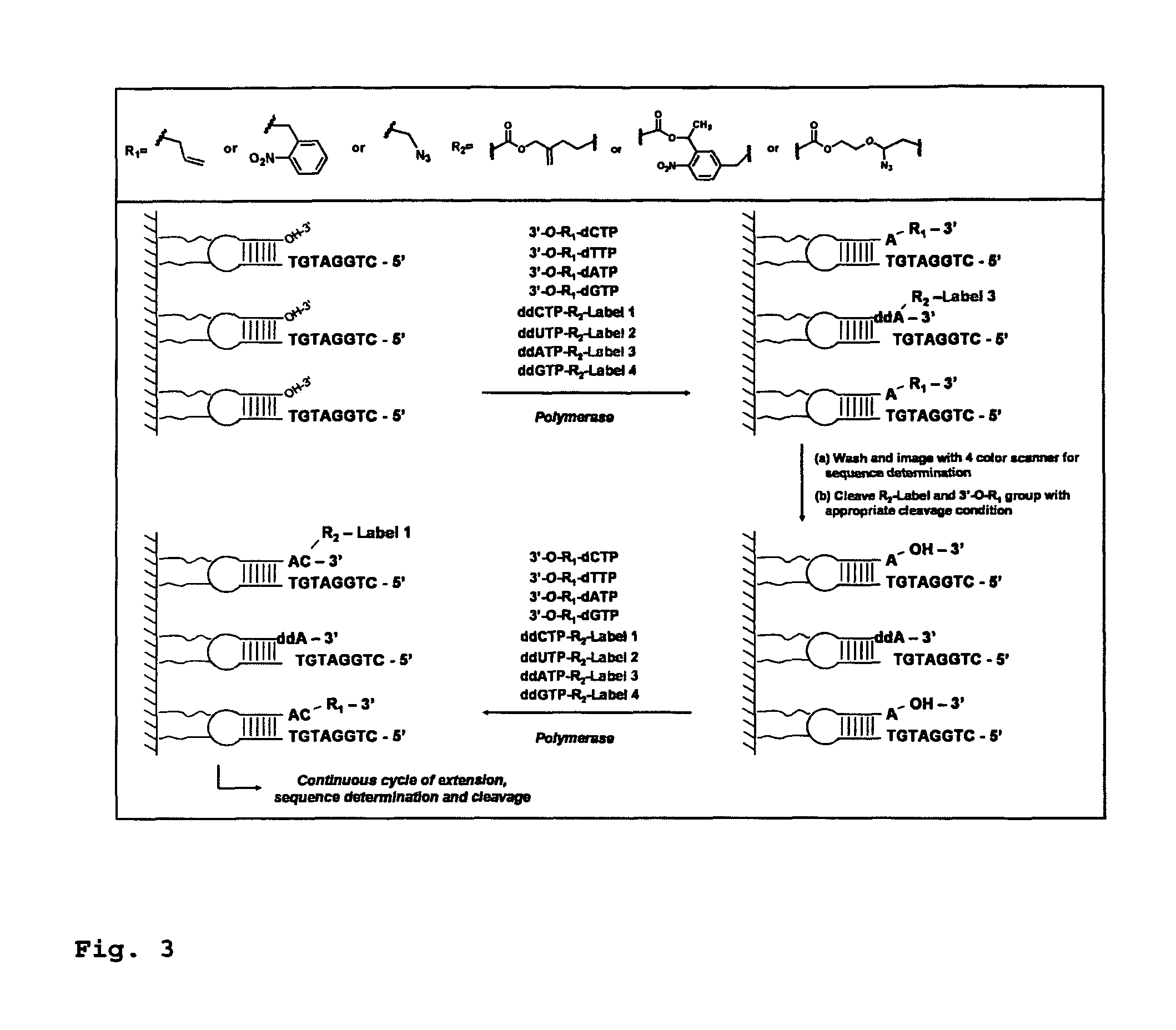
This invention provides a process for sequencing nucleic acids using 3′ modified deoxynucleotide analogues or 3′ modified deoxyinosine triphosphate analogues, and 3′ modified dideoxynucleotide analogues having a detectable marker attached to a base thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Dideoxynucleotide-triphosphate utilization by the hyper-thermophilic DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus
InactiveUS6333183B1High sensitivityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaSugar derivativesDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesBinding site
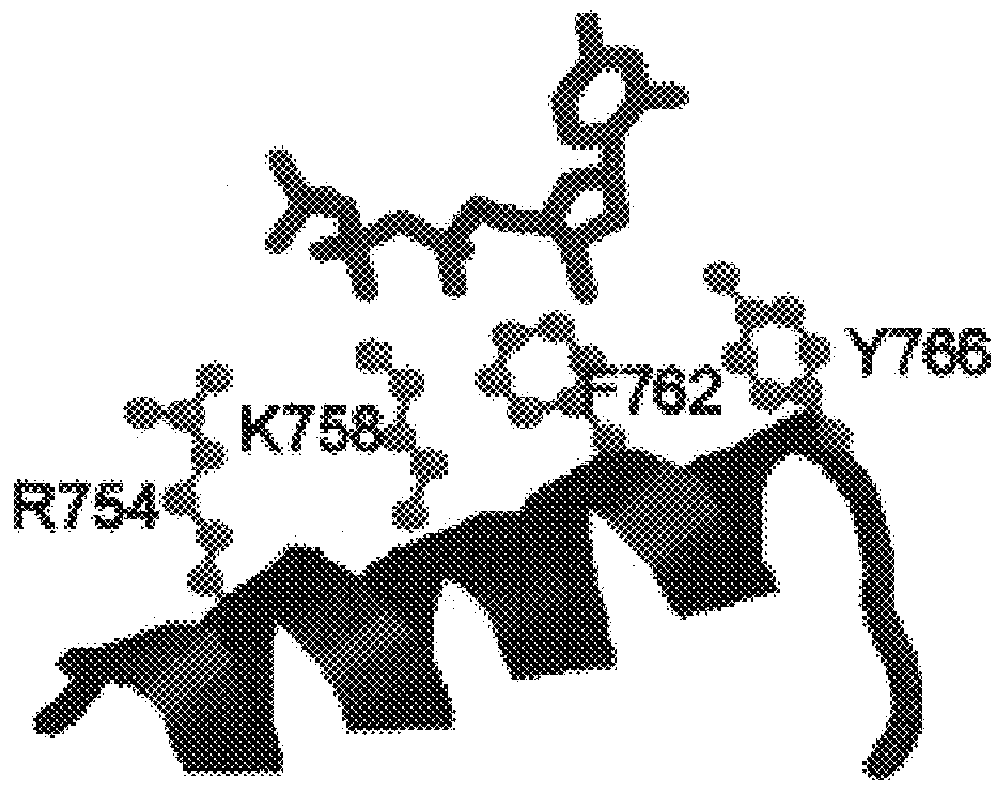
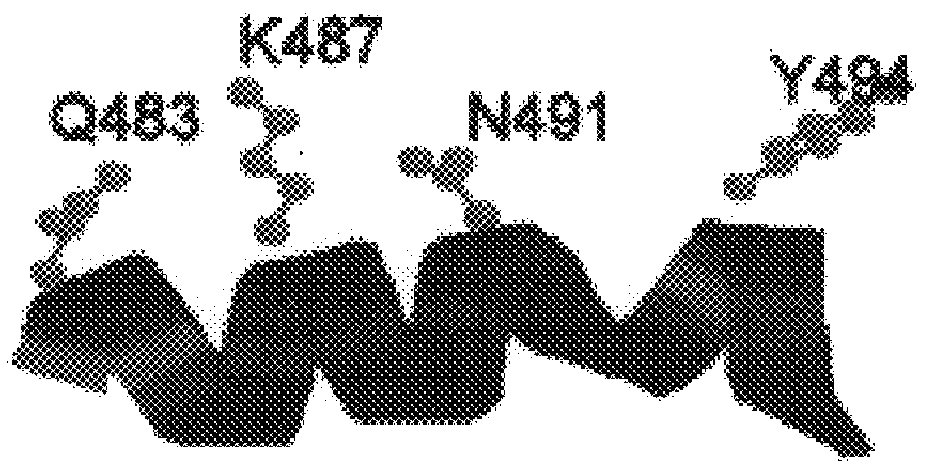
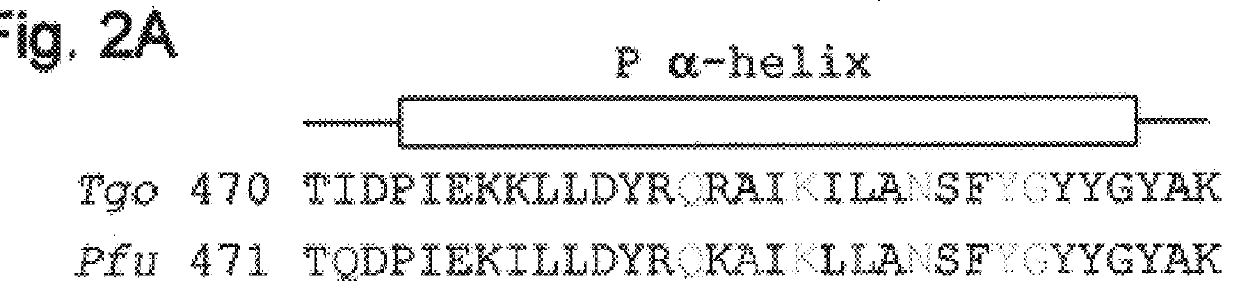
Polymerases from the Pol I family which are able to efficiently use ddNTPs have demonstrated a much improved performance when used to sequence DNA. A number of mutations have been made to the gene coding for the Pol II family DNA polymerase from the archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus with the aim of improving ddNTP utilisation. "Rational" alterations to amino acids likely to be near the dNTP binding site (based on sequence homologies and structural information) did not yield the desired level of selectivity for ddNTPs. However, alteration at four positions (Q472, A486, L490 and Y497) gave rise to variants which incorporated ddNTPs better than the wild type, allowing sequencing reactions to be carried out at lowered ddNTP:dNTP ratios. Wild type Pfu-Pol required a ddNTP:dNTP ratio of 30:1; values of 5:1 (Q472H), 1:3 (L490Y), 1:5 (A486Y) and 5:1 (Y497A) were found with the four mutants; A486Y representing a 150-fold improvement over the wild type. A486, L490 and Y407 are on an alpha-helix that lines the dNTP binding groove, but the side chains of the three amino acids point away from this groove; Q472 is in a loop that connects this alpha-helix to a second long helix. None of the four amino acids can contact the dNTP directly. Therefore, the increased selectivity for ddNTPs is likely to arise from two factors: 1) Small overall changes in conformation that subtly alter the nucleotide triphosphate binding site such that ddNTPs become favoured; 2) interference with a conformational change that may be critical both for the polymerisation step and discrimination between different nucleotide triphosphates.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
DNA sequence with non-fluorescent nucleotide reversible terminators and cleavable label modified nucleotide terminators
ActiveUS9115163B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesDNA
This invention provides a process for sequencing nucleic acids using 3′ modified deoxynucleotide analogues or 3′ modified deoxyinosine triphosphate analogues, and 3′ modified dideoxynucleotide analogues having a detectable marker attached to a base thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for the uncoupled, direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules with the addition of a second thermostable DNA polymerase and its application
InactiveUS20020034792A1Increases exponential amplificationReduction of initial amountMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesDNA
Method for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule in a thermocycling reaction which initially comprises a nucleic acid molecule, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a first thermostable DNA polymerase, (optionally) a thermostable pyrophosphatase, deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or a derivative thereof and which is characterized in that the thermocycling reaction additionally contains a second thermostable DNA polymerase which, in comparison to the said first thermostable DNA polymerase, has a reduced ability to incorporate dideoxynucleotides as well as the use of the said method.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
DNA sequencing with non-fluorescent nucleotide reversible terminators and cleavable label modified nucleotide terminators
This invention provides a process for sequencing nucleic acids using 3′ modified deoxynucleotide analogues or 3′ modified deoxyinosine triphosphate analogues, and 3′ modified dideoxynucleotide analogues having a detectable marker attached to a base thereof.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method for the uncoupled, direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules with the addition of a second thermostable DNA polymerase and its application
InactiveUS6828094B2Increases exponential amplificationReduction of initial amountMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesDNA
Method for sequencing a nucleic acid molecule in a thermocycling reaction which initially comprises a nucleic acid molecule, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a first thermostable DNA polymerase, (optionally) a thermostable pyrophosphatase, deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or a derivative thereof and which is characterized in that the thermocycling reaction additionally contains a second thermostable DNA polymerase which, in comparison to the said first thermostable DNA polymerase, has a reduced ability to incorporate dideoxynucleotides as well as the use of the said method.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
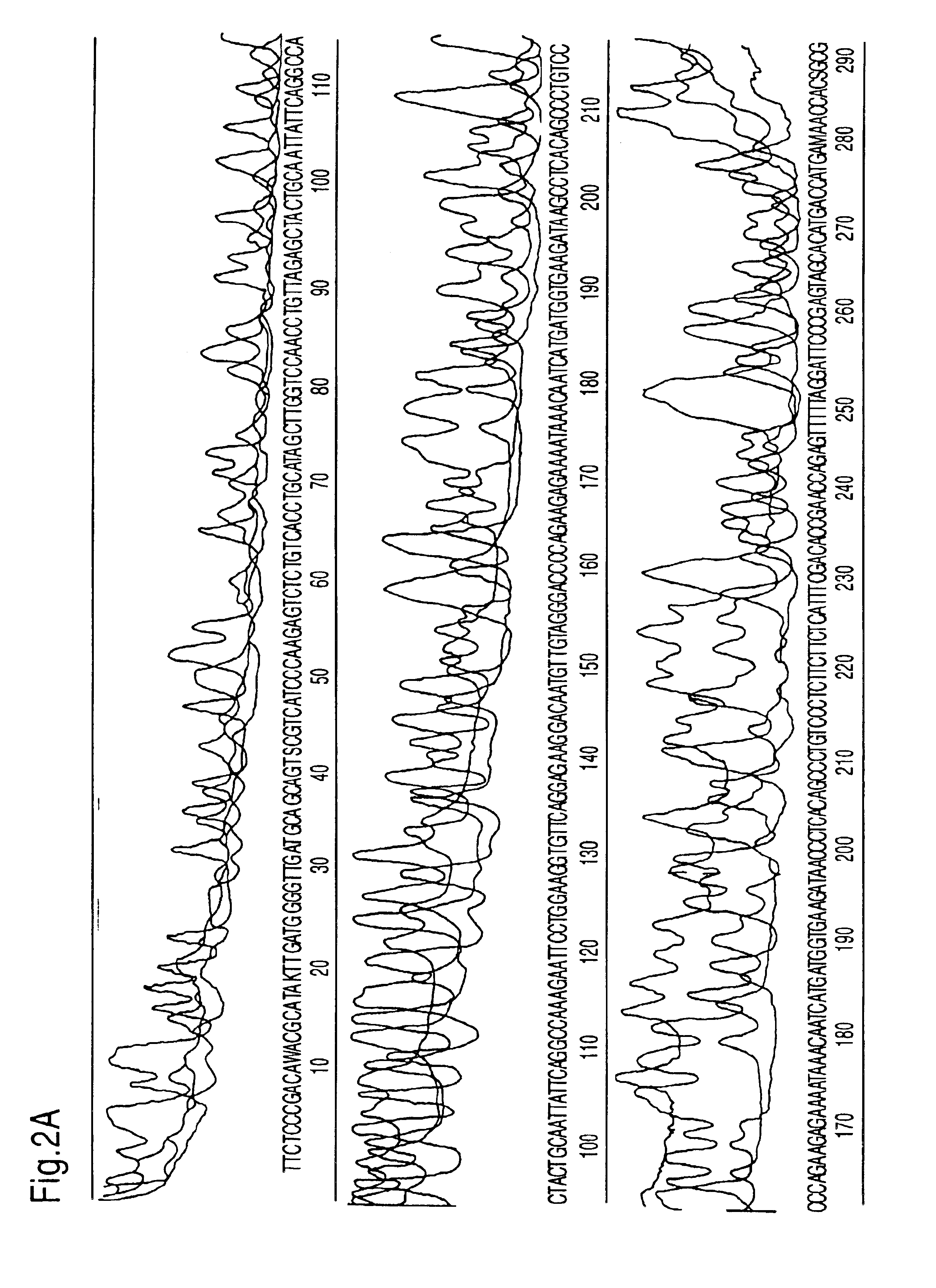
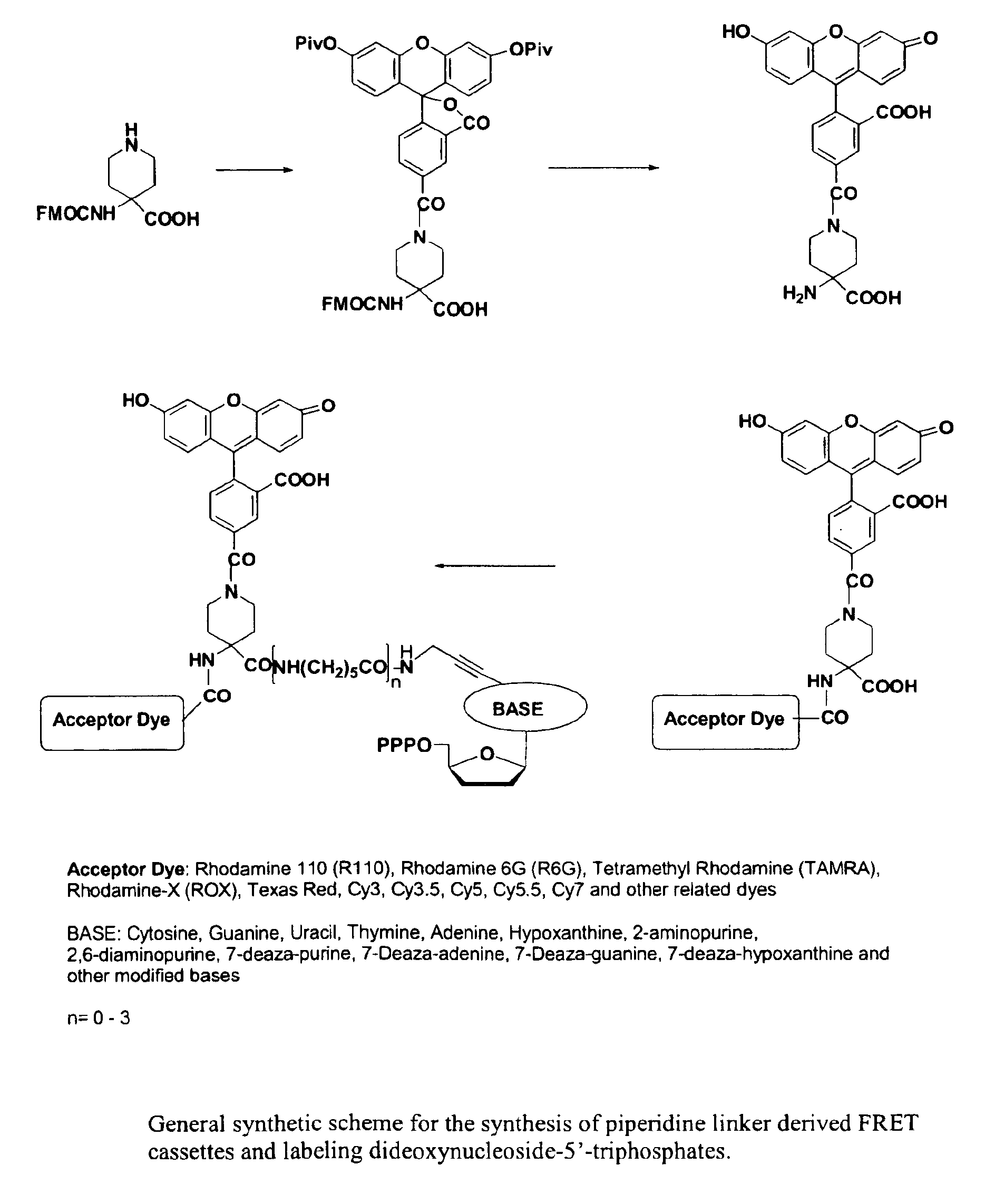
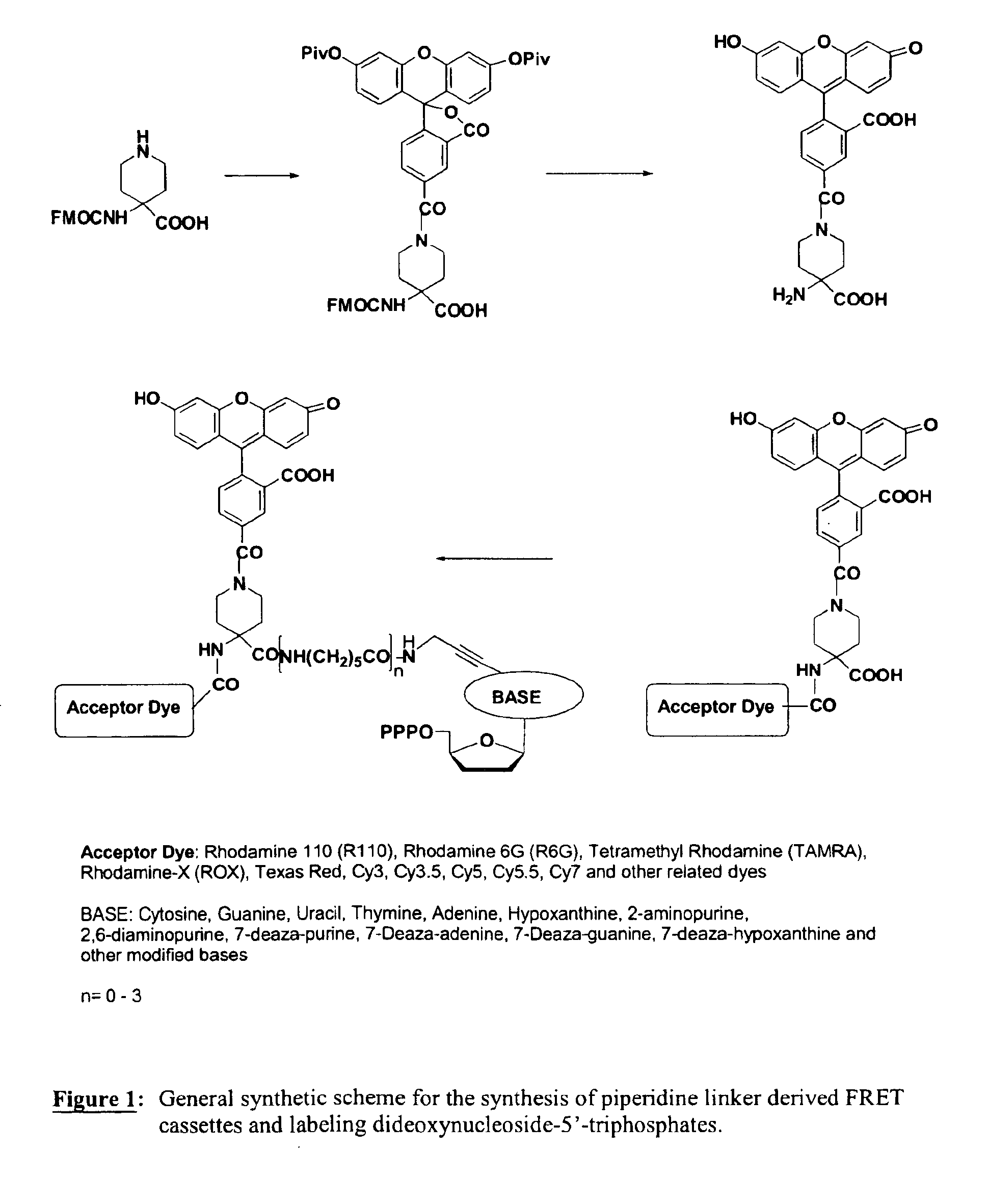
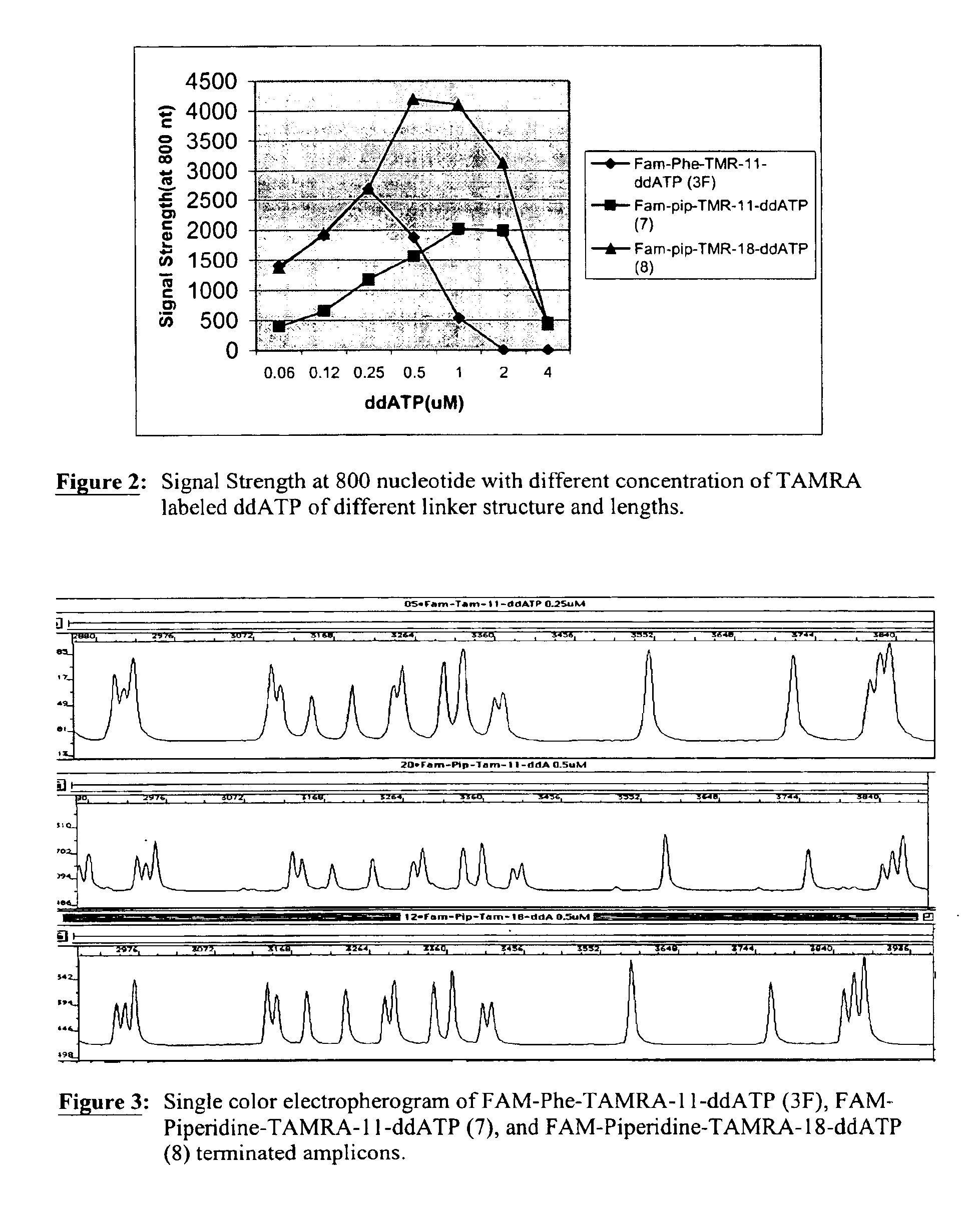
Heterocyclic FRETdye cassettes for labeling biological molecules and their use in DNA sequencing
InactiveUS6855503B2Methine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesEnergy transferDideoxynucleotide Triphosphates
Exploitation of suitably functionalized heterocyclic molecules, in the design and synthesis of Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) cassettes and their corresponding dideoxynucleotide terminators culminated into efficient reagents for DNA sequencing. Additionally, these FRET cassettes / terminators, of the present invention, derived from different classes of heterocyclic systems have high potential to be used for general labelling of biological molecules to generate highly sensitized signals. Their preparation, energy transfer efficiency, and use as labels, specifically, in DNA sequencing reactions is disclosed.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Heterocyclic FRETdye cassettes for labeling biological molecules and their use in DNA sequencing
Exploitation of suitably functionalized heterocyclic molecules, in the design and synthesis of Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) cassettes and their corresponding dideoxynucleotide terminators culminated into efficient reagents for DNA sequencing. Additionally, these FRET cassettes / terminators, of the present invention, derived from different classes of heterocyclic systems have high potential to be used for general labelling of biological molecules to generate highly sensitized signals. Their preparation, energy transfer efficiency, and use as labels, specifically, in DNA sequencing reactions is disclosed.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Use of extremely thermophilic DNA-polymerases
InactiveUS6251637B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesCycle sequencing
Cycle sequencing of DNA with marker-labeled dideoxynucleotides is performed using extremely thermophilic DNA polymerases in a one-lane technique in which dideoxynucleotides labeled with a dye as a marker are used to obtain sequence ladders of more 500 bases. Chain elongation is performed at a temperature of 65 to 75° C. Surprisingly, it was found that chain elongation temperatures of substantially more than 60° C. could be used in cycle sequencing of DNA with marker labeled dye dideoxynucleotides when using extremely thermophilic DNA polymerases.
Owner:GSF FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR UMWELT & GESUNDHEIT
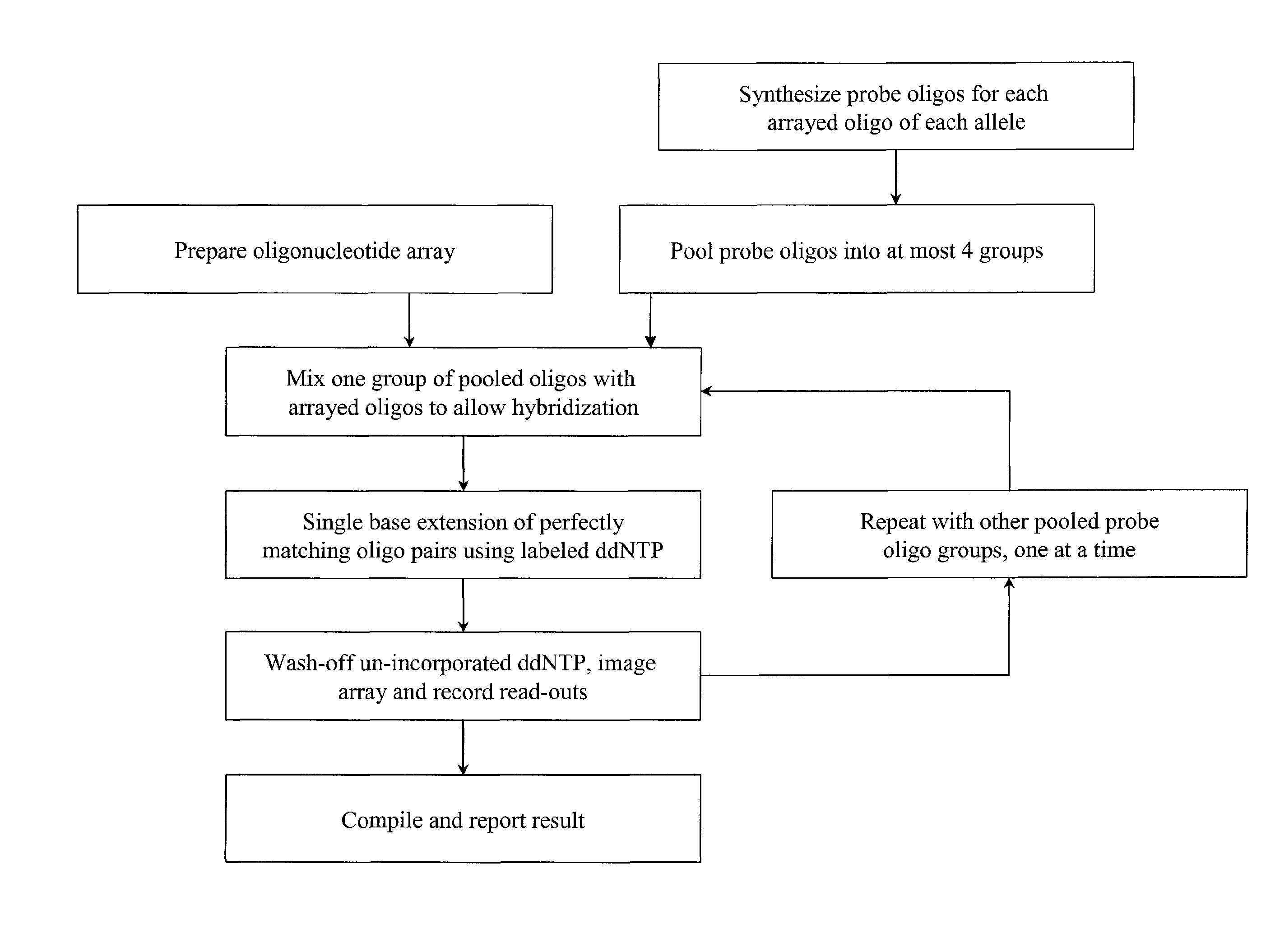
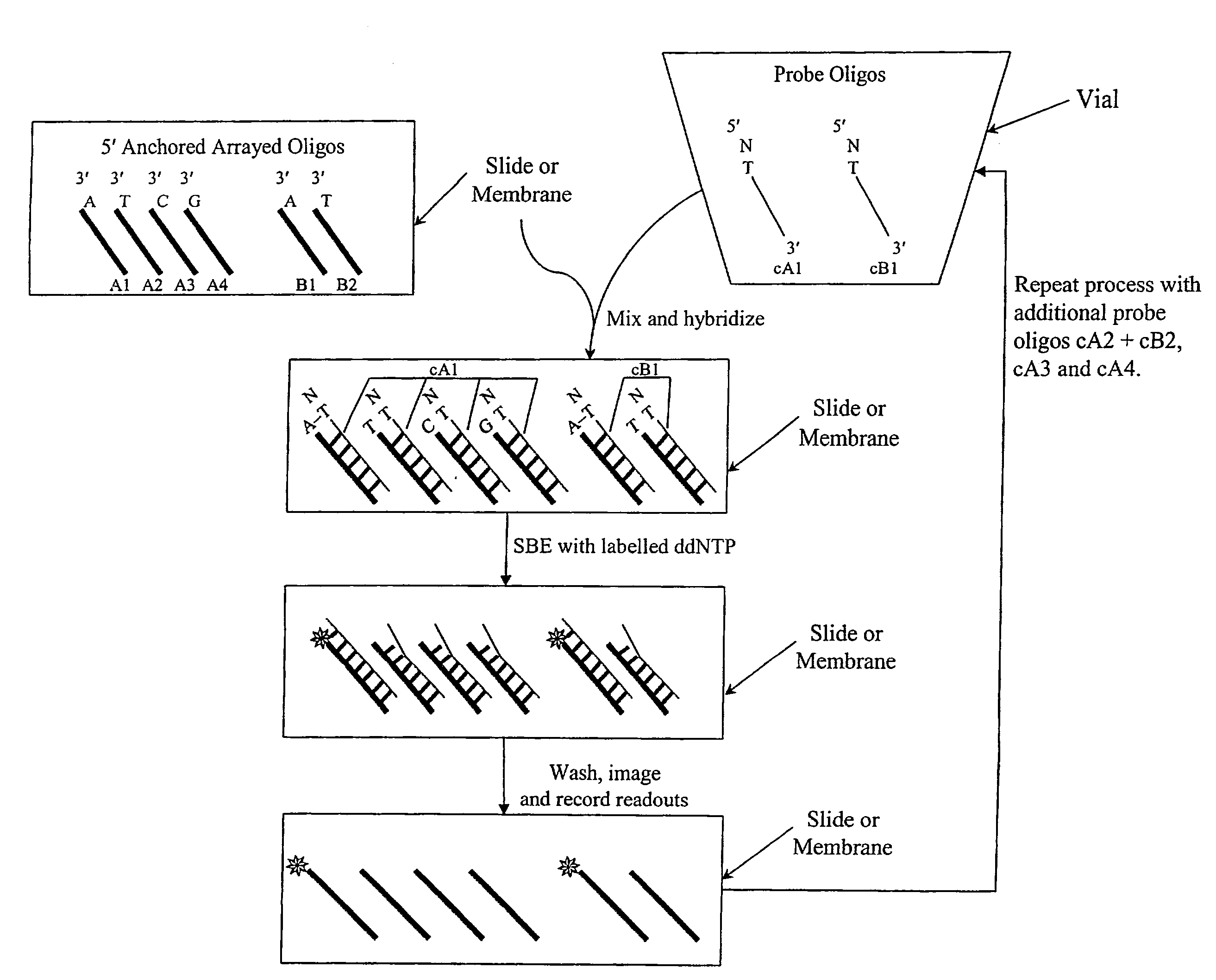
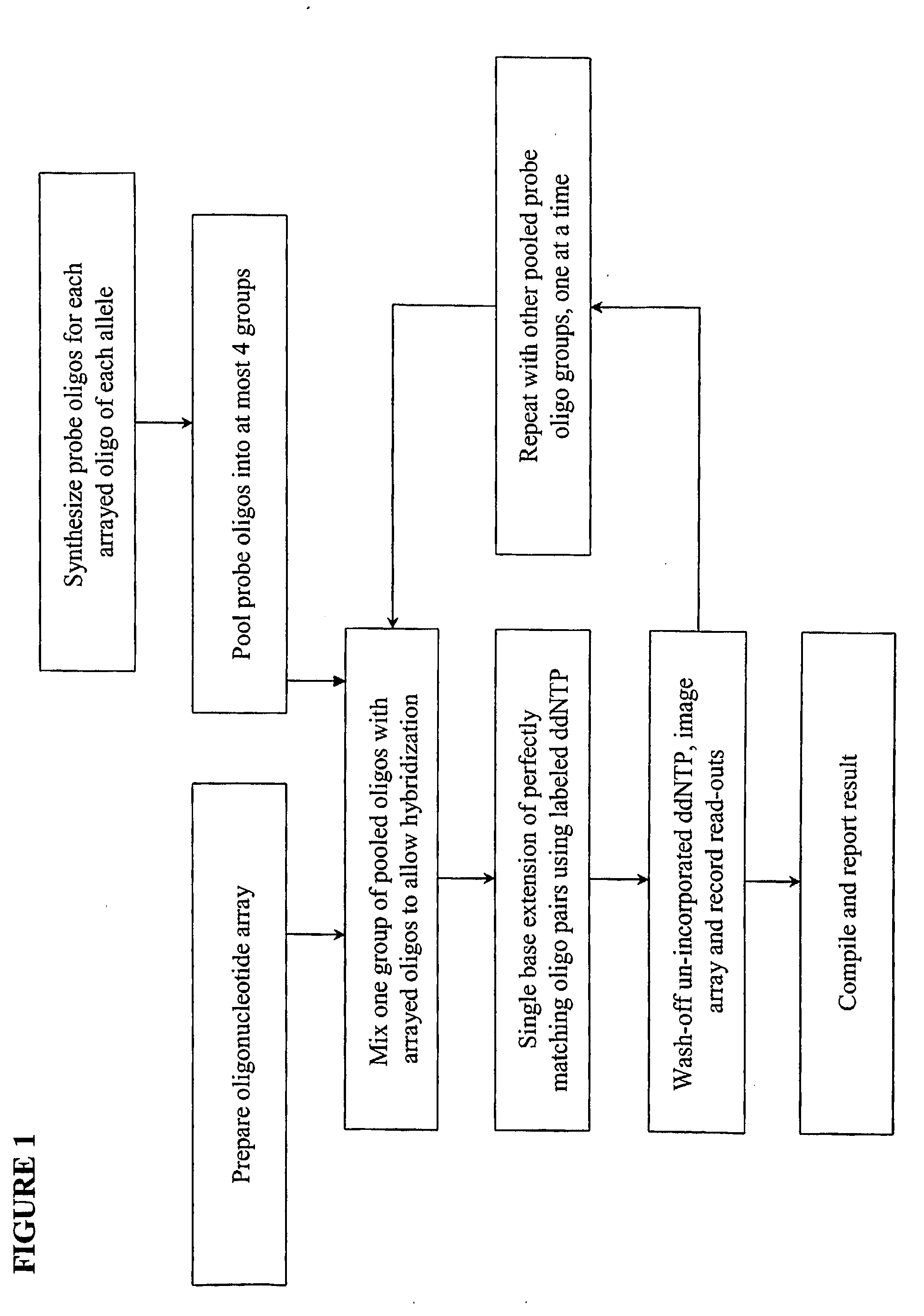
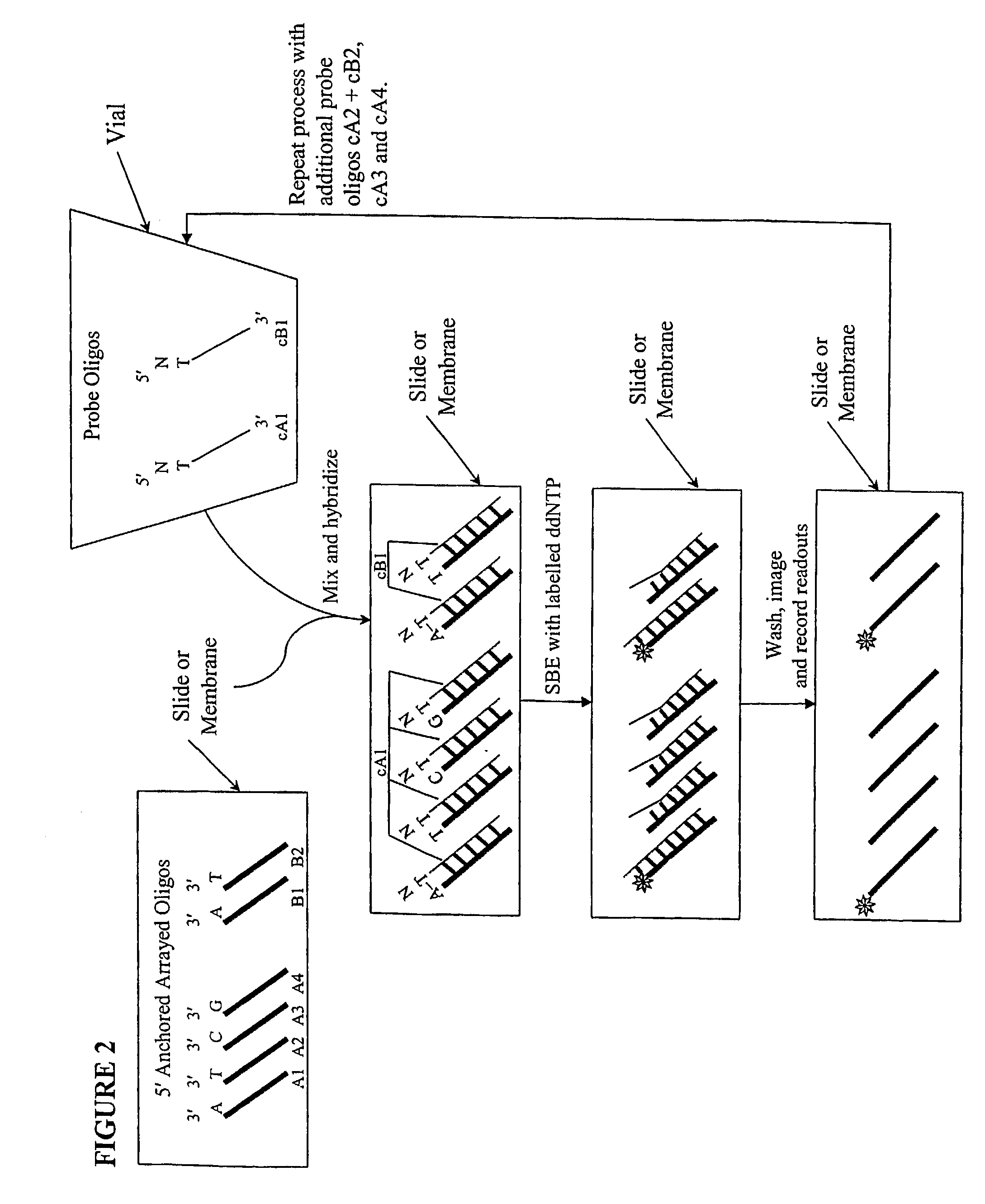
Quality control methods for arrayed oligonucleotides
InactiveUS8507197B2Quick and accurate verificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesQuality control
We disclose quality controls methods that allow quick and accurate verification of a test oligonucleotide deposited on a solid support. It is especially useful for the verification of oligonucleotides representing alleles of a multi-allelic locus. It employs single base extension, with labeled dideoxynucleotides, to locate and verify the identity of test oligonucleotides. This approach involves synthesizing a complement probe oligonucleotide for each oligonucleotide being tested. Probe oligonucleotides are optionally grouped. They are then hybridized to test oligonucleotides, and the hybridized pair is subject to single base extension and detection. It requires the presence of one unique base, either in the last two bases at the free hanging end of the test oligonucleotide—as opposed to the end anchored to the solid support surface, or in the last two bases at one end of the probe oligonucleotide.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Enrichment method for peripheral blood free tumor DNA, kit and application thereof
ActiveCN108251502AGuaranteed specificityGuaranteed purityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyPeripheral blood
The invention discloses an enrichment method for peripheral blood free tumor DNA, a kit and application thereof. The enrichment method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: capturing a tumor DNA fragment from a cfDNA library by adopting a PAP probe, and performing amplification by taking the PAP probe as a primer and taking the captured tumor DNA fragment as a template, whereinthe PAP probe comprises generic primer sequences and specific recognition sequences from the end 5' to the end 3'; the end 3' of the specific recognition sequence comprises at least 30 bp of sequences which are hybridized and complemented with the tumor DNA fragment; the terminus 3' of the PAP probe is dideoxy nucleotide. According to the enrichment method disclosed by the invention, the PAP probe is used for capturing the target tumor DNA fragment, and extension is carried out by using the PAP probe; the PAP probe is high in specificity and high in capturing efficiency; the purity of an enriched product is guaranteed, and a guarantee is provided for subsequent sequencing. The enrichment method disclosed by the invention provides a novel free tumor DNA enrichment scheme for clinical detection of cfDNA.
Owner:BGI GENOMICS CO LTD +3
Quality control methods for arrayed oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20090143234A1Quick and accurate verificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesQuality control
We disclose quality controls methods that allow quick and accurate verification of a test oligonucleotide deposited on a solid support. It is especially useful for the verification of oligonucleotides representing alleles of a multi-allelic locus. It employs single base extension, with labeled dideoxynucleotides, to locate and verify the identity of test oligonucleotides. This approach involves synthesizing a complement probe oligonucleotide for each oligonucleotide being tested. Probe oligonucleotides are optionally grouped. They are then hybridized to test oligonucleotides, and the hybridized pair is subject to single base extension and detection. It requires the presence of one unique base, either in the last two bases at the free hanging end of the test oligonucleotide—as opposed to the end anchored to the solid support surface, or in the last two bases at one end of the probe oligonucleotide.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
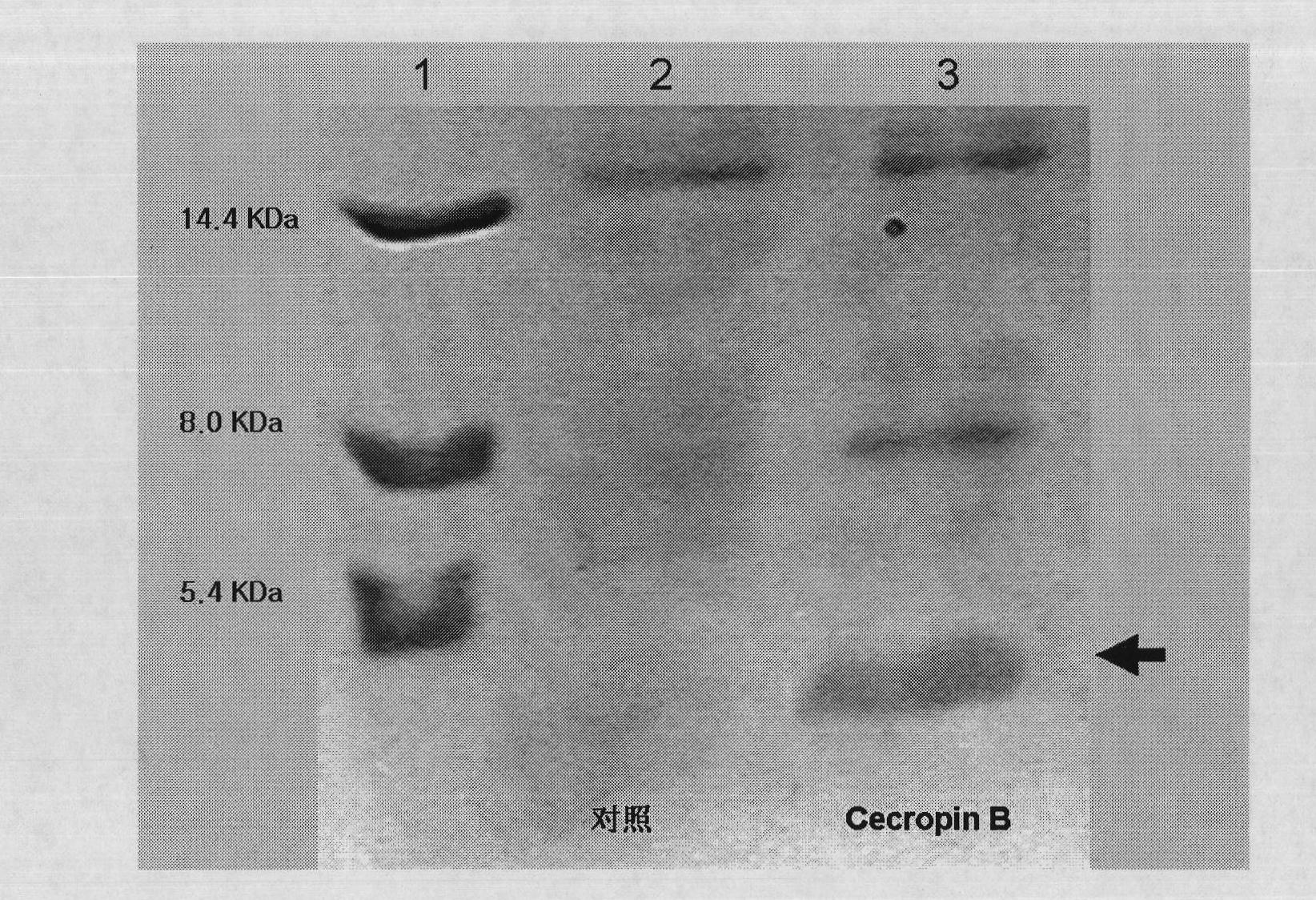
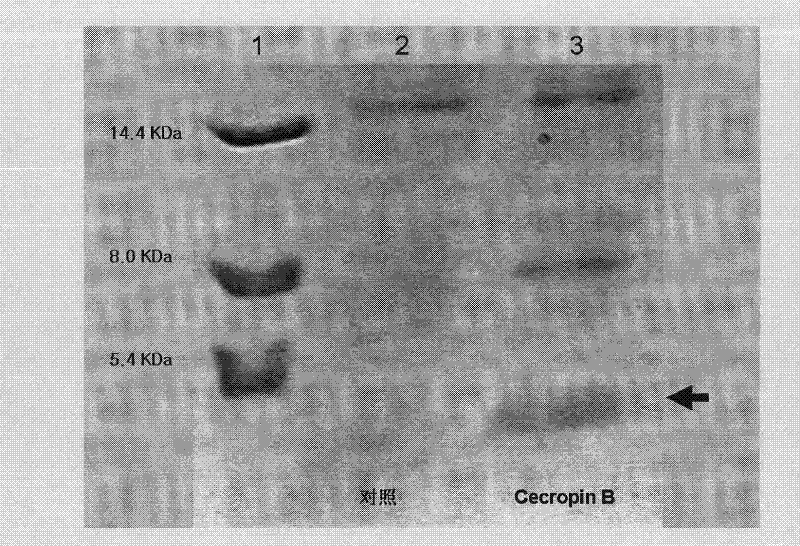
Method for using silkworm cultured cell to express antibacterial peptide Cecropin B
InactiveCN101845439ASolve operational problemsFix stability issuesViruses/bacteriophagesGenetic engineeringDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesTotal rna
The invention discloses a method for using silkworm cultured cell to express antibacterial peptide Cecropin B. The method comprises the following steps: (1) using the total RNA extracted from the fat body cells of wild silkworm chrysalis as template, adopting RT-PCR amplification to obtain wild silkworm antibacterial peptide Cecropin B gene; using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to perform PCR product analysis to the antibacterial peptide Cecropin B gene, using a PCR purification kit of Qiagene for purification, then cloning the purified PCR product to TA vector pCR2.1 to obtain pCR2.1-Cecropin B, utilizing the dideoxynucleotide chain termination to confirm the correctness of cloned gene order; using restriction endonuclease BamHI and HindIII to digest pCR2.1-Cecropin B and obtain Cecropin B genetic fragments, then cloning rhabdovirus transfer vector pBlueBacHisa in the genetic fragments to obtain reconstituted transfer vector; performing cotransfection of the reconstituted transfer vector and silkworm wild-type nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV DNA in silkworm cultured cell, performing homologous recombination to generate recombinant virus; and (3) inoculating the recombinant virus containing wild silkworm antibacterial peptide Cecropin B gene in the silkworm cultured cell, infecting at 27 DEG C for three days to express the infection, and centrifuging to collect silkworm cultured cell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for polymorphism detection of gene based on single base extension reaction
InactiveCN102329881ASolve the shortcomings of gene polymorphism analysisQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymorphism Detection
The invention discloses a method for polymorphism detection of a gene based on single base extension reaction. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) designing and selecting a specific primer according to a gene sequence to be detected, adding the specific primer in a mixed liquid containing a sample to be detected, a dideoxynucleotide (ddNTP) pair or deoxynucleotide triphophate (dNTP) pair for single base extension reaction so that a base in ddNTP or dNTP is added at the terminal end of the specific primer, wherein the specific primer is positioned at the upstream of gene SPN (single nucleotide polymorphism) site to be detected, the 3'-terminal base of the primer is close to the SNP site to be detected, and a continuous nucleotide sequence is composed of 15-45 continuous nucleotides containing the gene sequence to be detected; and (2) detecting the amount of surplus ribonucleotides in an extended product, judging the type of the polymorphism of the target gene according to the amount of the ddNTP or dNTP in the extended product. The method has low cost and is simple to operate, and can rapidly detect the polymorphism of the gene in no need of complicated optimization steps.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Mutant DNA polymerases and uses thereof
The present invention relates to mutant DNA polymerases which incorporate dideoxynucleotides with about the same efficiency as deoxynucleotides. The present invention also related to mutant DNA polymerases which also have substantially reduced 5′-to-3′ exonuclease activity or 3′-to-5′ exonuclease activity. The invention also relates to DNA molecules coding for the mutant DNA polymerases, and hosts containing the DNA molecules.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
DNA sequencing method based on primer array chip
InactiveCN102643893AImprove accuracyAvoid false negativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesA-DNA
The invention relates to a DNA sequencing method based on a primer array chip, and is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: fixing a group of primers with known sequences on a chip, respectively putting four same chips into four reaction systems which contain different dideoxynucleotides with fluorescent tracers, performing annealing hybridization with DNA to be detected to allow the primers to extend 1 nucleotide, detecting the fluorescence signals of the chips to obtain a group of short sequences composed of primer end sequences and extended nucleotides, splicing the short sequences overlapped with each other to obtain a complete sequence of the DNA to be detected.
Owner:陈国燕
DNA polymerase having ability to reduce innate selective discrimination against fluorescent dye-labeled dideoxynucleotides
InactiveUS20050089910A1Reduced discriminationIncrease ratingsSugar derivativesBacteriaModified dnaFluorescence
The invention relates to genetical modification of DNA polymerase to reduce its innate selective sequence-related discrimination against incorporation of fluorescent dye-labeled ddCTP and ddATP in the enzymatic reaction for preparation of samples for automated florescent dye-labeled terminator DNA sequencing. The modified DNA polymerases are more resistant to heat inactivation and are more effective in dideoxynucleotide incorporation than current DNA polymerases.
Owner:HONG GUOFAN +1
Method for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing of DNA molecules and its application
InactiveUS20030134276A1Reduction of initial amountIncreases the exponential amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
A method is described for the direct, exponential amplification and sequencing ("DEXAS") of a DNA molecule from a complex mixture of nucleic acids, wherein truncated DNA molecules as well as DNA molecules of full length are synthesized simultaneously and exponentially between two positions on the said DNA molecule, which initially contains a DNA molecule in a thermocycling reaction, a first primer, a second primer, a reaction buffer, a thermostable DNA polymerase, a thermostable pyrophosphatase (optionally), deoxynucleotides or derivatives thereof and a dideoxynucleotide or derivatives thereof. In a preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed using one polymerase having a Tabor-Richardson mutation, or a functional derivative thereof, and reverse transcriptase activity. In a more preferred embodiment of the method of the invention, direct sequencing of RNA can be performed in one step, in one vessel.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Mutant DNA polymerases and uses therof
InactiveUS20090191560A1BacteriaSugar derivativesDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesDeoxyribonucleotide synthesis
The present invention relates to mutant DNA polymerases which incorporate dideoxynucleotides with about the same efficiency as deoxynucleotides. The present invention also related to mutant DNA polymerases which also have substantially reduced 5′-to-3′ exonuclease activity or 3′-to-5′ exonuclease activity. The invention also relates to DNA molecules coding for the mutant DNA polymerases, and hosts containing the DNA molecules.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
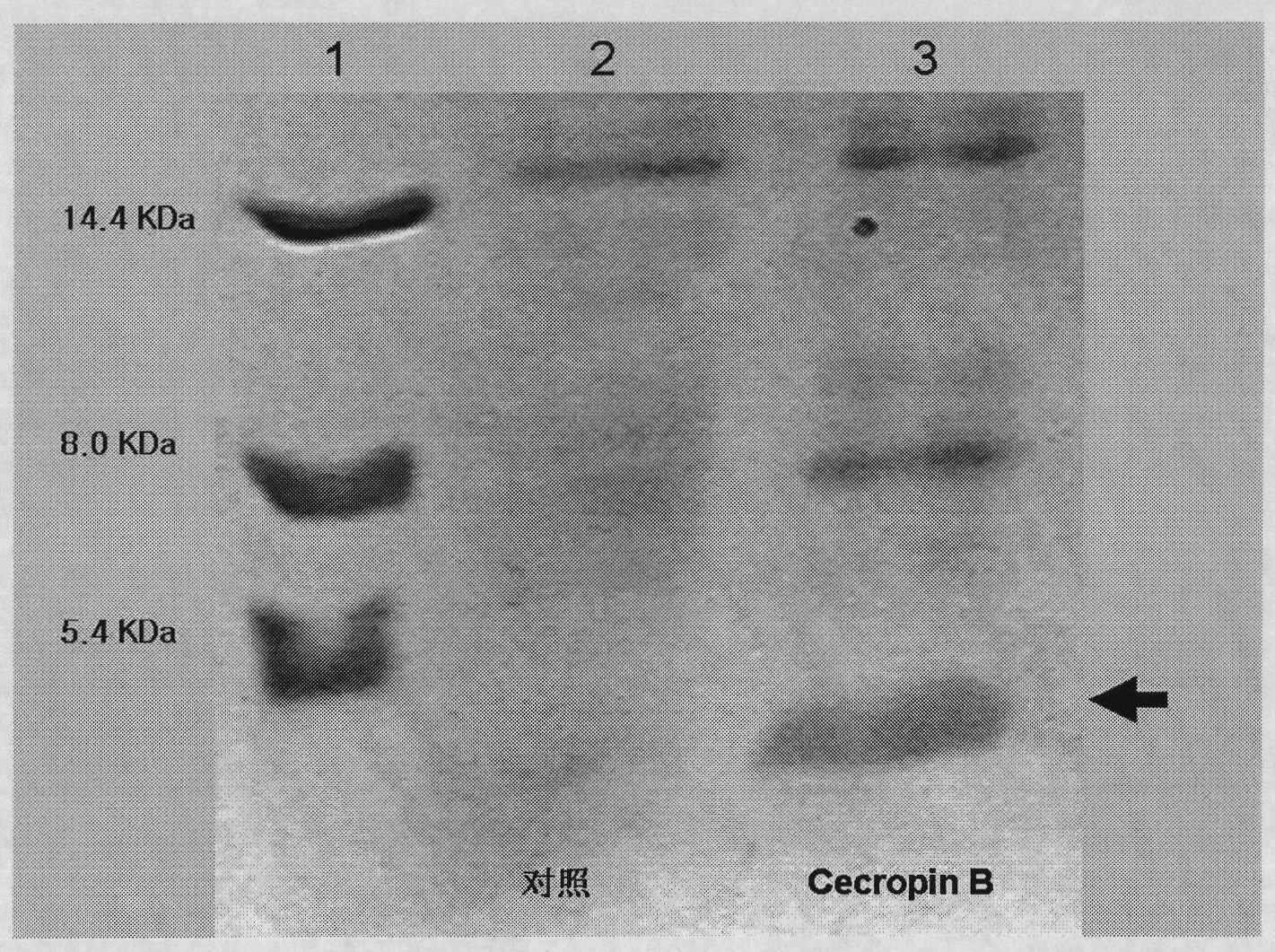
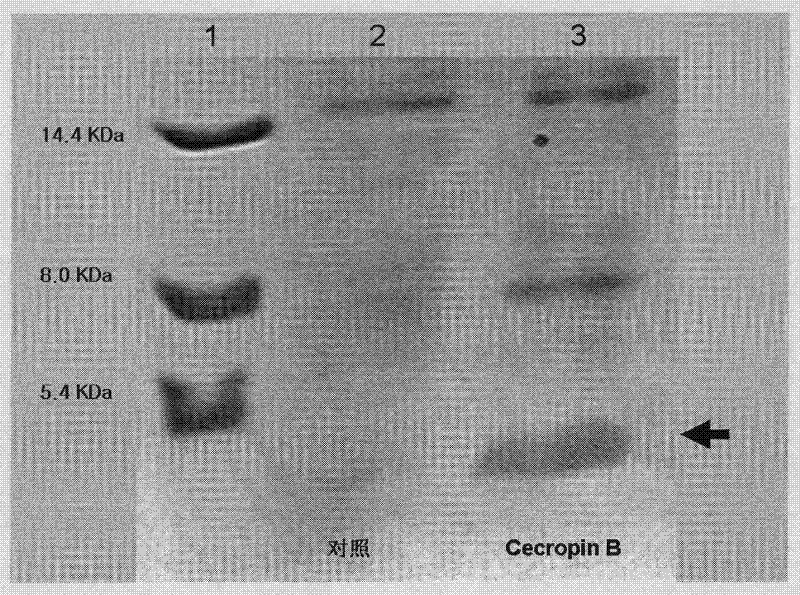
Method for using silkworm cultured cell to express antibacterial peptide Cecropin B
InactiveCN101845439BQuick extractionImprove biological activityViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesTotal rna
The invention discloses a method for using silkworm cultured cell to express antibacterial peptide Cecropin B. The method comprises the following steps: (1) using the total RNA extracted from the fat body cells of wild silkworm chrysalis as template, adopting RT-PCR amplification to obtain wild silkworm antibacterial peptide Cecropin B gene; using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to perform PCR product analysis to the antibacterial peptide Cecropin B gene, using a PCR purification kit of Qiagene for purification, then cloning the purified PCR product to TA vector pCR2.1 to obtain pCR2.1-Cecropin B, utilizing the dideoxynucleotide chain termination to confirm the correctness of cloned gene order; using restriction endonuclease BamHI and HindIII to digest pCR2.1-Cecropin B and obtain CecropinB genetic fragments, then cloning rhabdovirus transfer vector pBlueBacHisa in the genetic fragments to obtain reconstituted transfer vector; performing cotransfection of the reconstituted transfer vector and silkworm wild-type nuclear polyhedrosis virus BmNPV DNA in silkworm cultured cell, performing homologous recombination to generate recombinant virus; and (3) inoculating the recombinant virus containing wild silkworm antibacterial peptide Cecropin B gene in the silkworm cultured cell, infecting at 27 DEG C for three days to express the infection, and centrifuging to collect silkworm cultured cell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
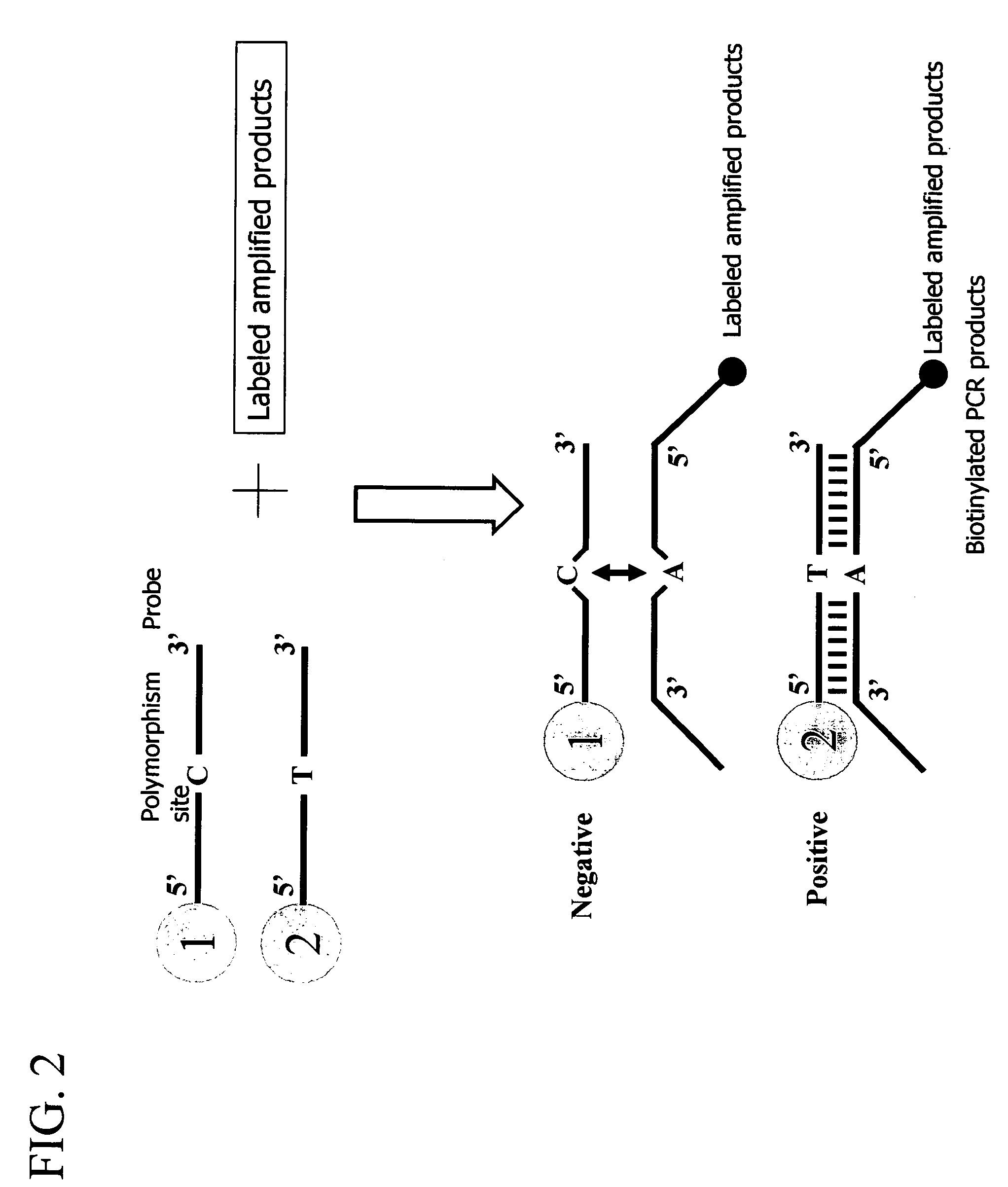
Method for detecting a nucleic acid comprising asymmetrical amplification
InactiveUS7101673B2High sensitivityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesBiology
A method for detecting amplified nucleic acid fragments is provided. The method comprises the steps of carrying out amplification reaction to amplify a predetermined region of a nucleic acid in a reaction solution comprising the nucleic acid as a template, a pair of primers, deoxynucleotides, and dideoxynucleotides; hybridizing the amplified products of the reaction solution to a probe; and then detecting the hybridization between the amplified products and the probe.
Owner:HITACHI SOFTWARE ENG
Preparation method and application of oligonucleotide with closed dideoxyribonucleoside
The invention provides a preparation method and application of an oligonucleotide with a closed dideoxyribonucleoside. The method specifically comprises the steps that a terminal transferase (TdT) isfirstly used for catalyzing deoxyribonucleotides (dNTPs) or dideoxynucleotides (ddNTPs) in combination with the characteristics of a 3'hydroxyl terminal of a DNA molecule, so that a primer is mixed with any one of four dideoxynucleotides (ddATP, ddTTP, ddCTP or ddGTP), the TdT can add the dideoxynucleotides to the 3'hydroxyl terminal of the primer, and the obtained primer modified by the ddNTP cannot be catalytically extended by a DNA polymerase. The prepared oligonucleotide (primer) with the closed dideoxyribonucleoside can be used in combination with amplification methods such as allele PCR,proof-reading PCR for detecting mutation.
Owner:INST PASTEUR OF SHANGHAI CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
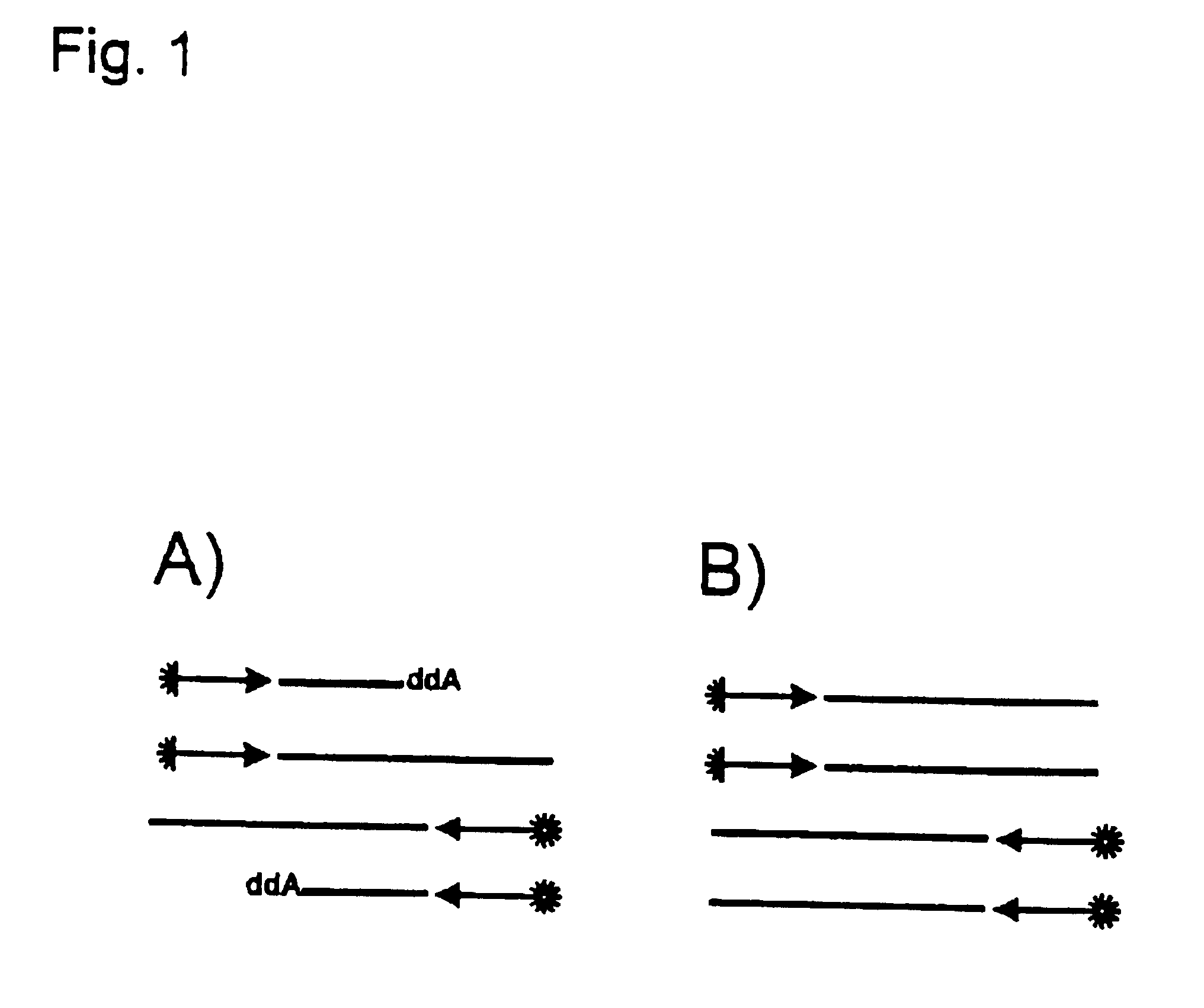
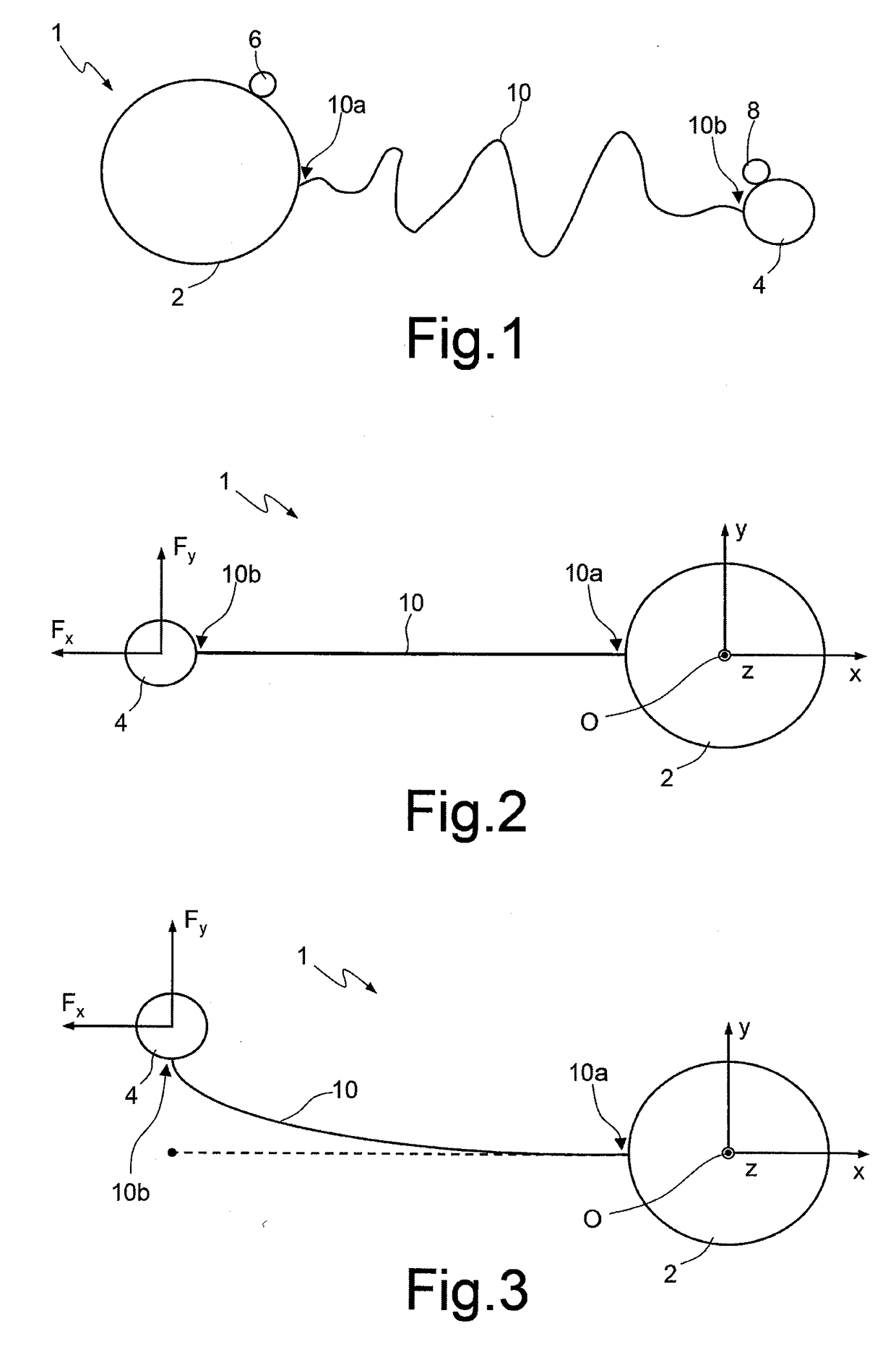
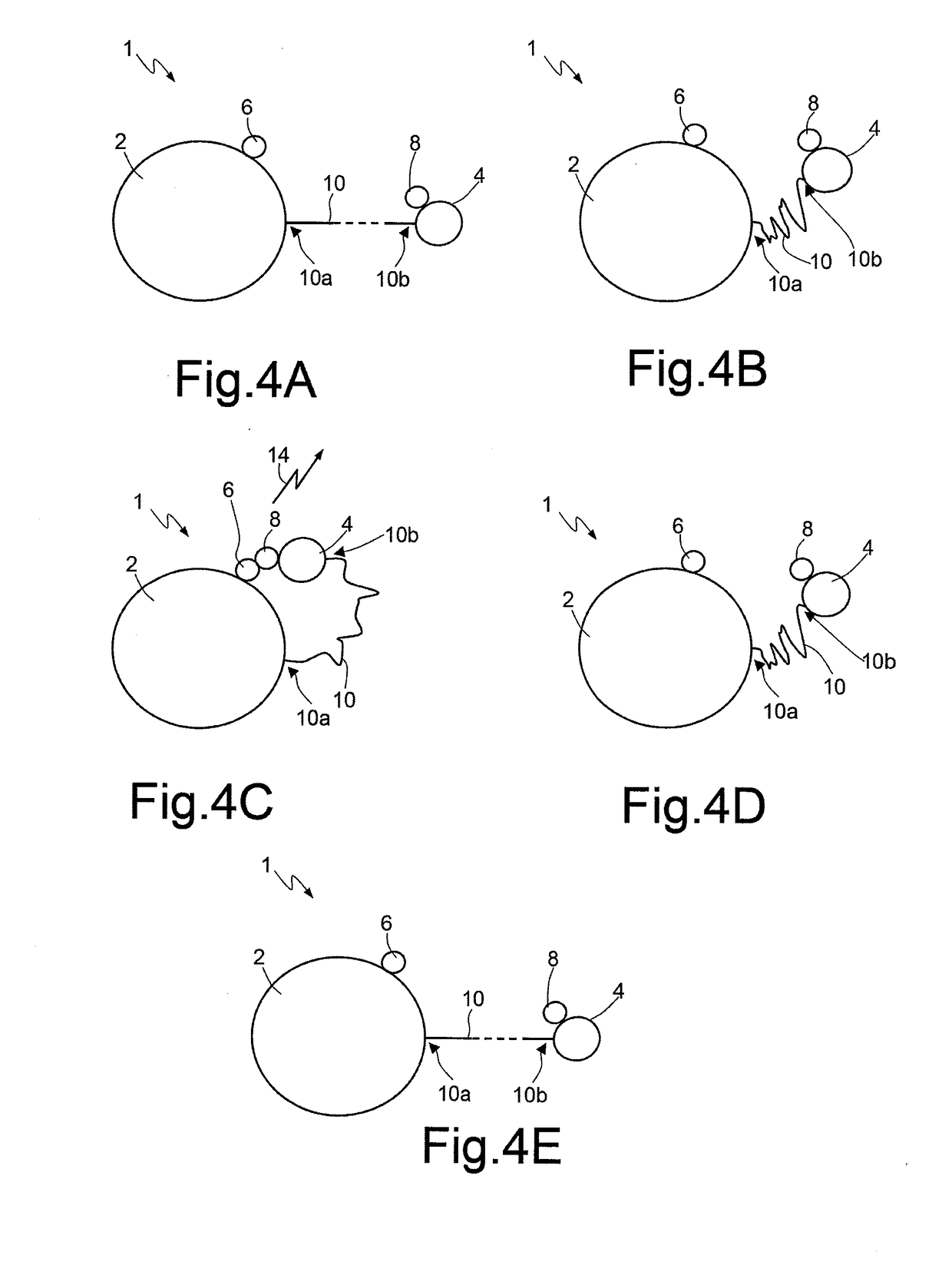
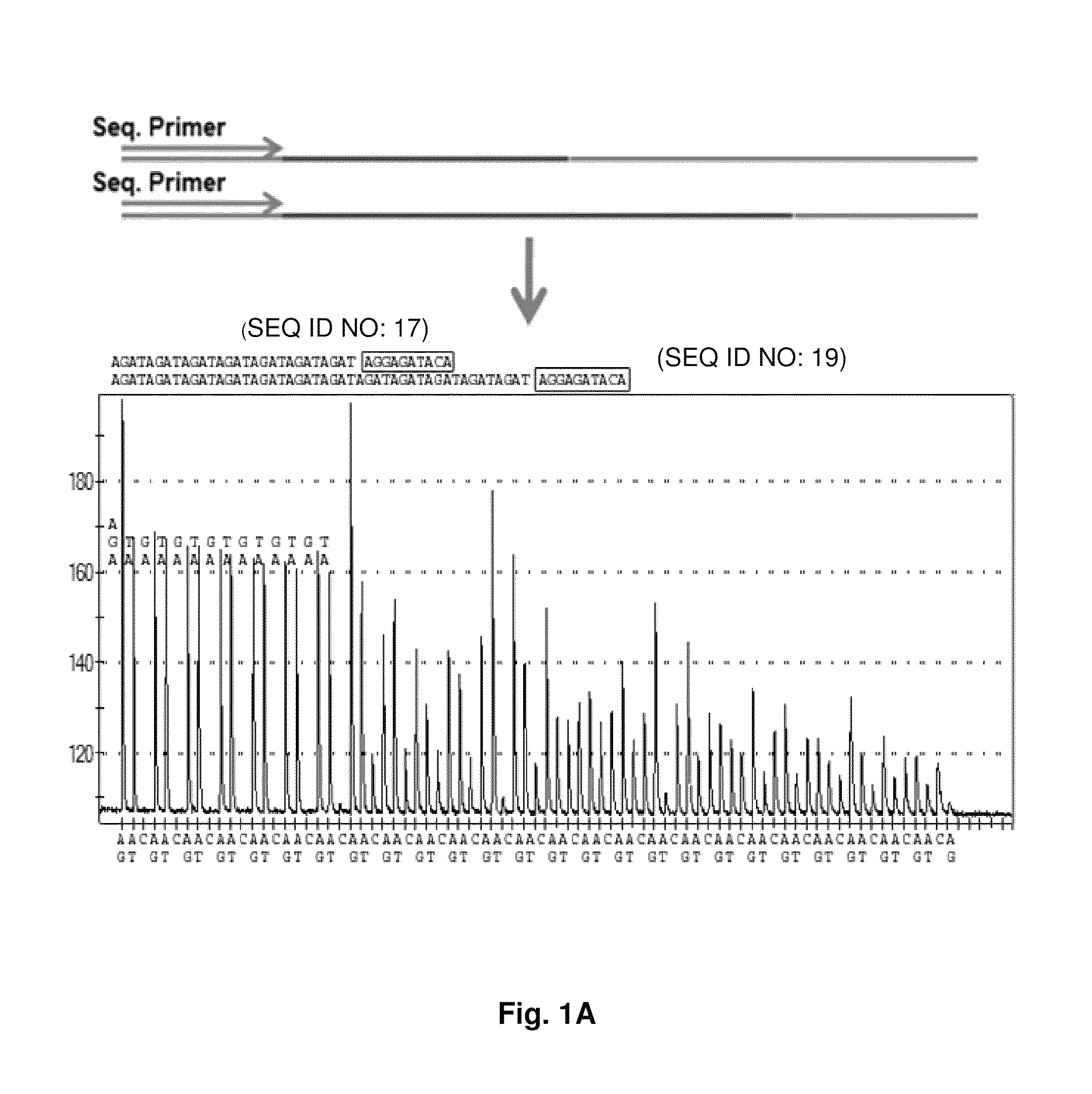
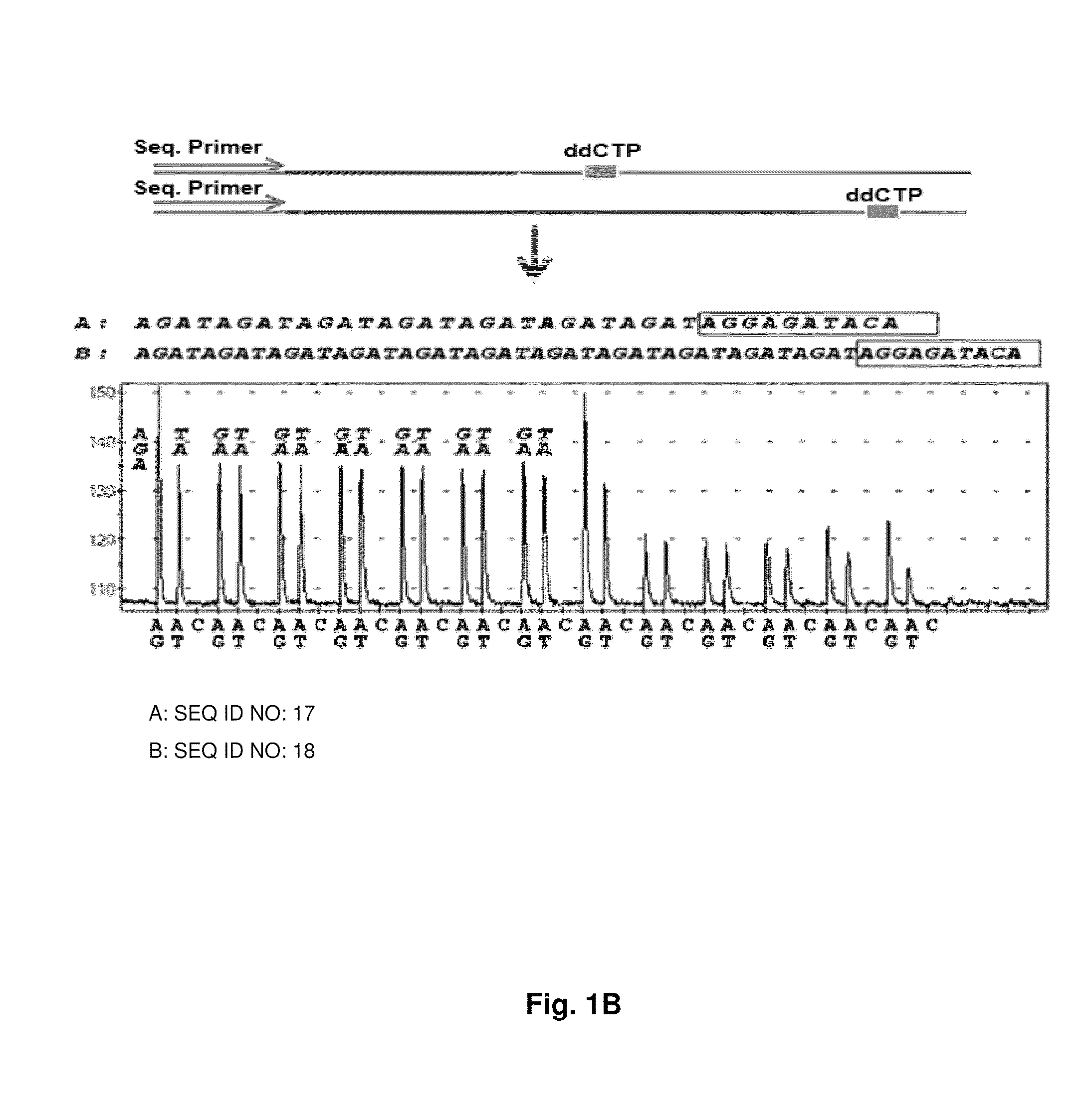
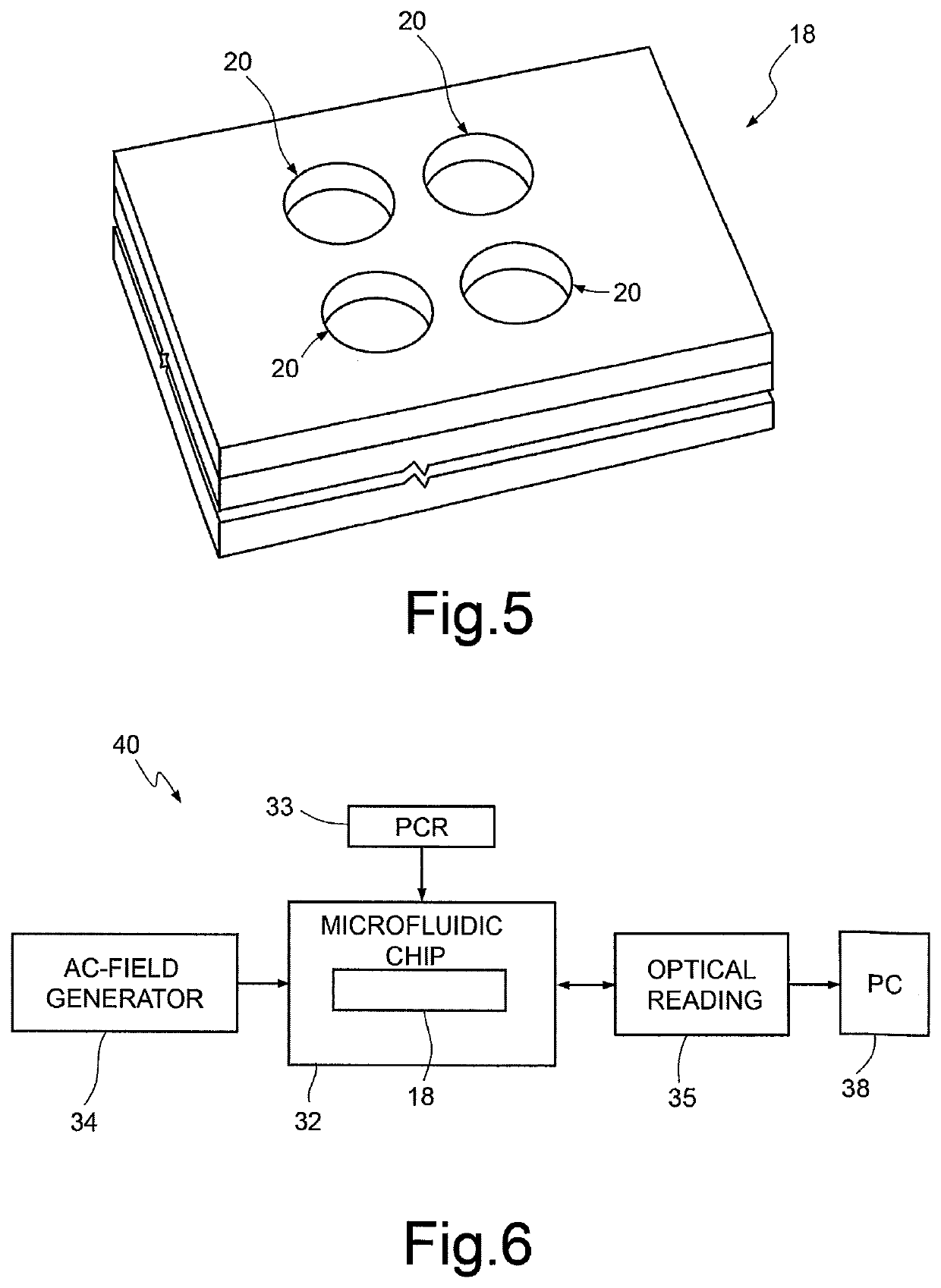
Method and device for nucleic acid sequencing
ActiveUS20170369943A1Microbiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesNucleic acid sequencing
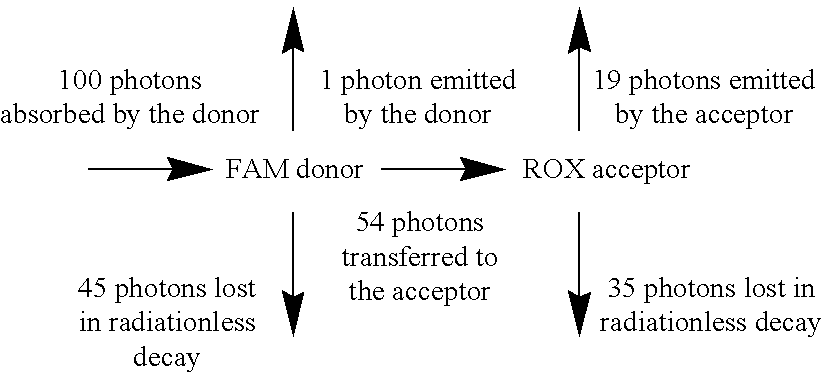
A method for sequencing a nucleic acid strand, comprising the steps of: providing a solution containing truncated strands having lengths different from one another terminating with a respective dideoxynucleotide from among ddATP, ddTTP, ddGTP, and ddCTP; functionalizing first masses by a donor molecule and second masses by an acceptor molecule such as to generate a light emission when they come into mutual contact; coupling a first mass to a first end of each truncated strand; coupling the second masses to a respective terminal dideoxynucleotide of each strand; applying an AC electrical field having variable frequencies that are such as to generate, on each second mass, a net movement directed towards the first mass; acquiring a plurality of light radiations for each frequency value; and associating each light radiation acquired to a respective dideoxynucleotide and, thus, to a respective nucleotide base.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
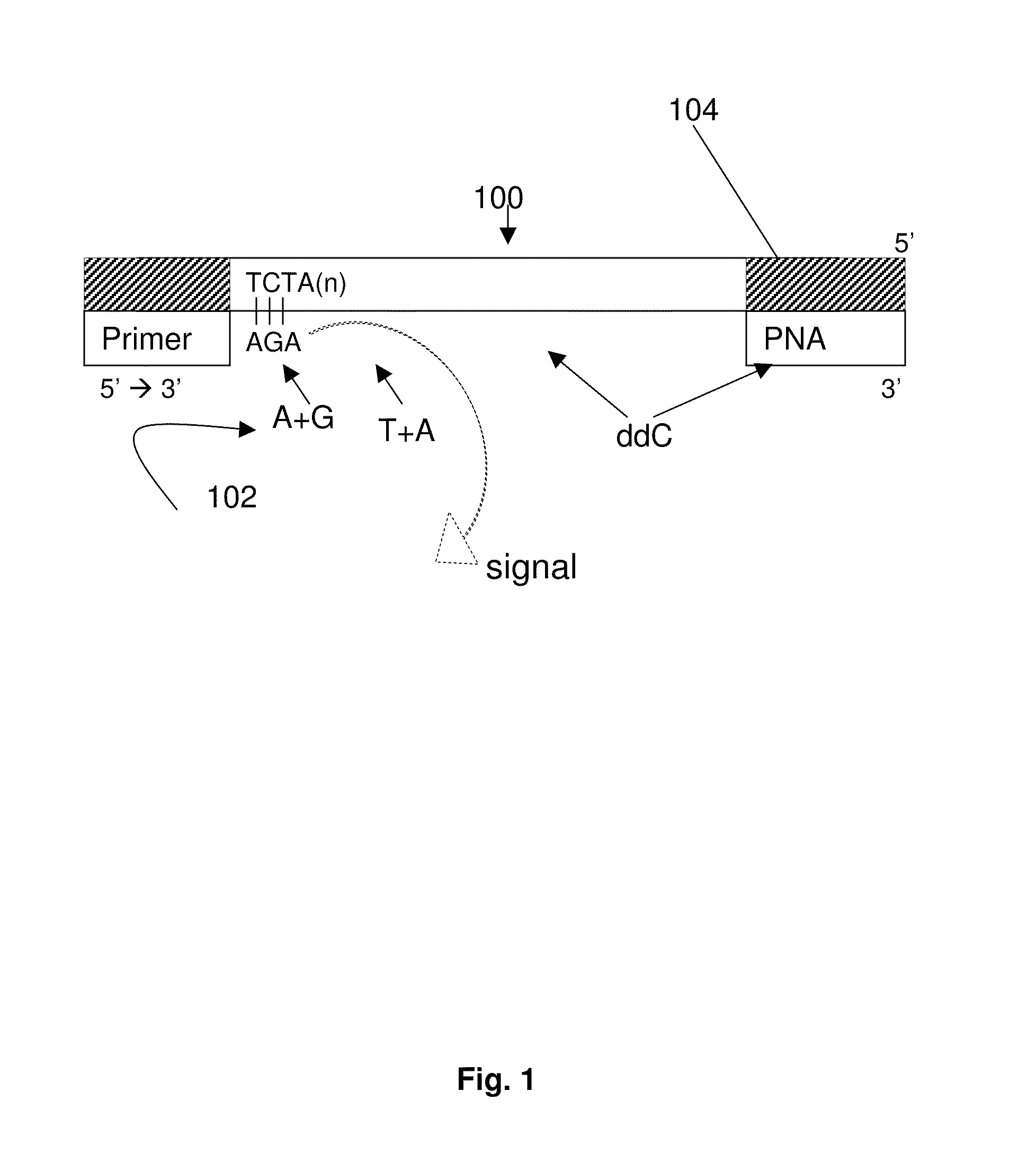
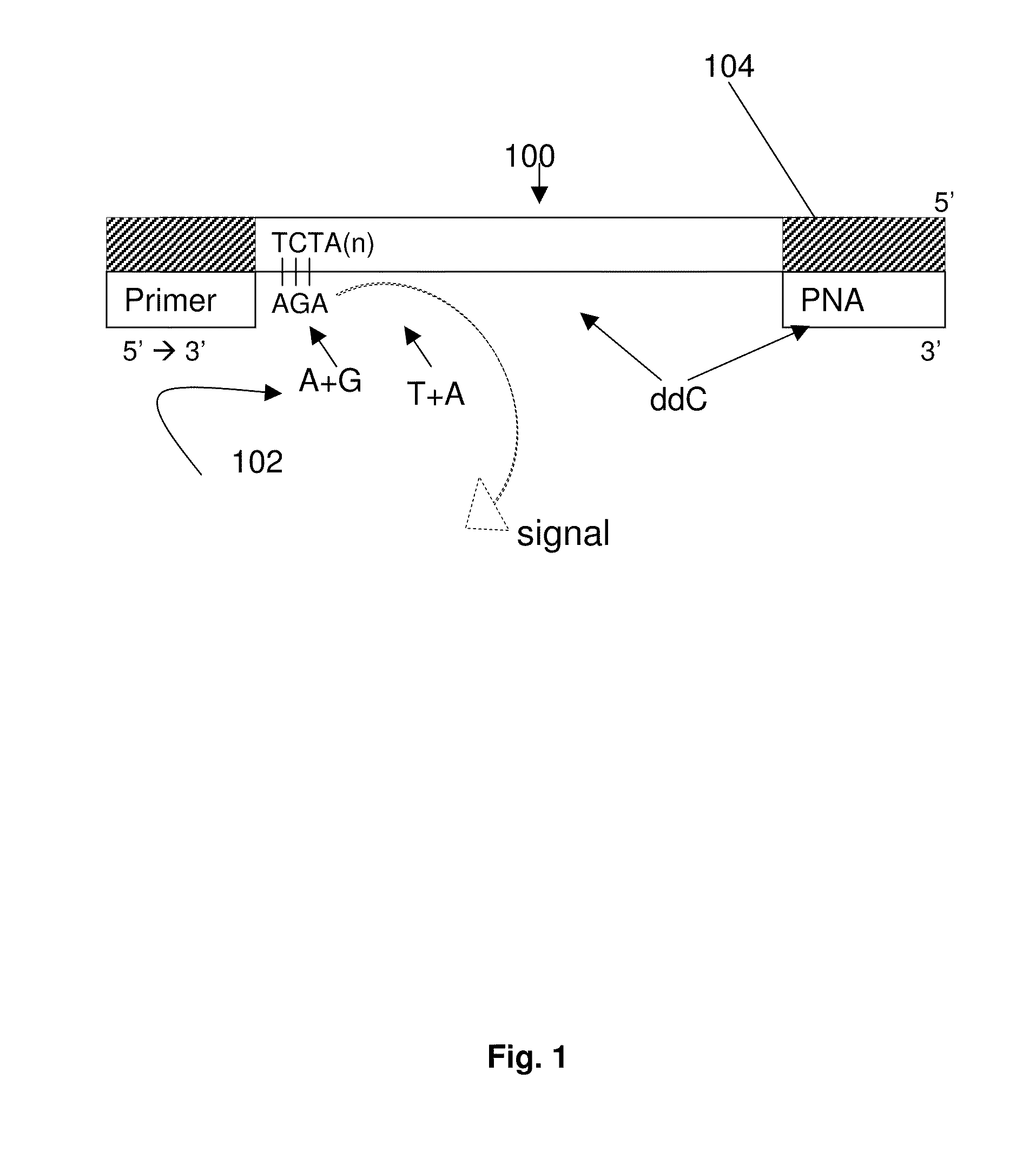
DNA template tailoring using PNA and modified nucleotides
ActiveUS9187782B2Reliable and rapid and information-rich and cost-effective approachQuick measurementSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
Disclosed is a method whereby a repetitive nucleic acid sequence, such as a short tandem repeat (STR), may be characterized as to its length. Pyrosequencing is used to sequence an STR repetitive region to measure the length of STRs in a rapid manner. A combinatorial approach is disclosed for the addition of multiple nucleotides (e.g., two mononucleotides) at a time by the polymerase, which reduces the sample analysis time by half. In addition, modified nucleic acids, such as peptide nucleic acids, are used as blocking probe to stop polymerization on the flanking region which makes it possible to use pyrosequencing for DNA length measurement both in the case of homozygous or heterozygous samples for varying repeat patterns of different markers. Further, dideoxynucleotides are added to stop polymerization in the flanking region of the STR.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Device for nucleic acid sequencing
ActiveUS10597716B2Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationOptical radiationNucleic acid sequencing
A method for sequencing a nucleic acid strand, comprising the steps of: providing a solution containing truncated strands having lengths different from one another terminating with a respective dideoxynucleotide from among ddATP, ddTTP, ddGTP, and ddCTP; functionalizing first masses by a donor molecule and second masses by an acceptor molecule such as to generate a light emission when they come into mutual contact; coupling a first mass to a first end of each truncated strand; coupling the second masses to a respective terminal dideoxynucleotide of each strand; applying an AC electrical field having variable frequencies that are such as to generate, on each second mass, a net movement directed towards the first mass; acquiring a plurality of light radiations for each frequency value; and associating each light radiation acquired to a respective dideoxynucleotide and, thus, to a respective nucleotide base.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
DNA template tailoring using pna and modified nucleotides
ActiveUS20110207118A1Reliable and rapid and information-rich and cost-effective approachShorten analysis timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDideoxynucleotide TriphosphatesPolymerase L
Disclosed is a method whereby a repetitive nucleic acid sequence, such as a short tandem repeat (STR), may be characterized as to its length. Pyrosequencing is used to sequence an STR repetitive region to measure the length of STRs in a rapid manner. A combinatorial approach is disclosed for the addition of multiple nucleotides (e.g., two mononucleotides) at a time by the polymerase, which reduces the sample analysis time by half. In addition, modified nucleic acids, such as peptide nucleic acids, are used as blocking probe to stop polymerization on the flanking region which makes it possible to use pyrosequencing for DNA length measurement both in the case of homozygous or heterozygous samples for varying repeat patterns of different markers. Further, dideoxynucleotides are added to stop polymerization in the flanking region of the STR.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com