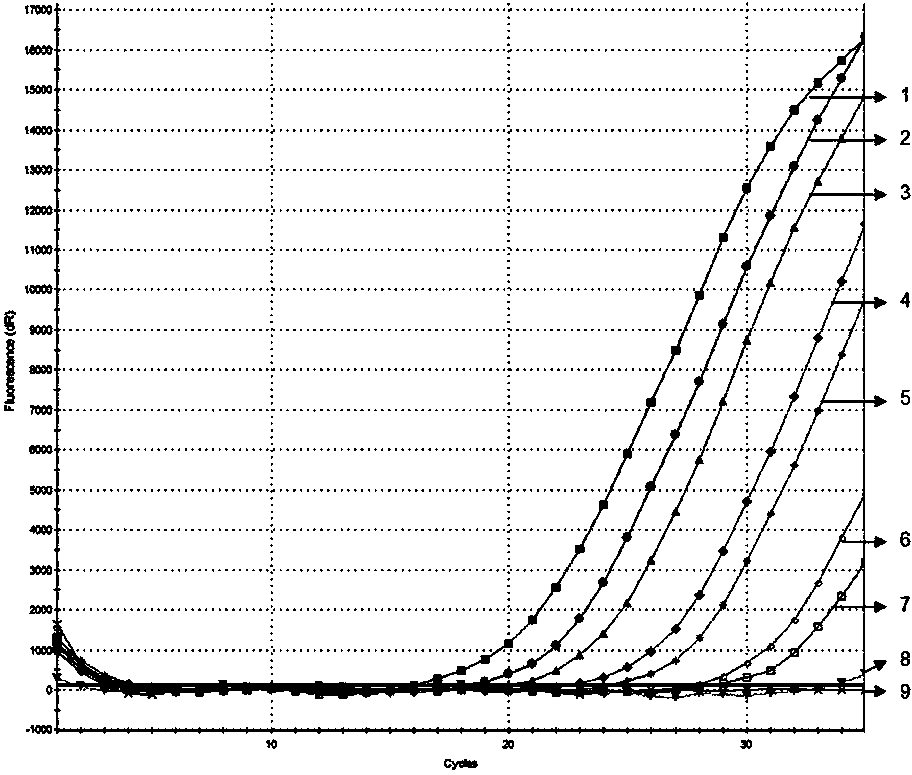
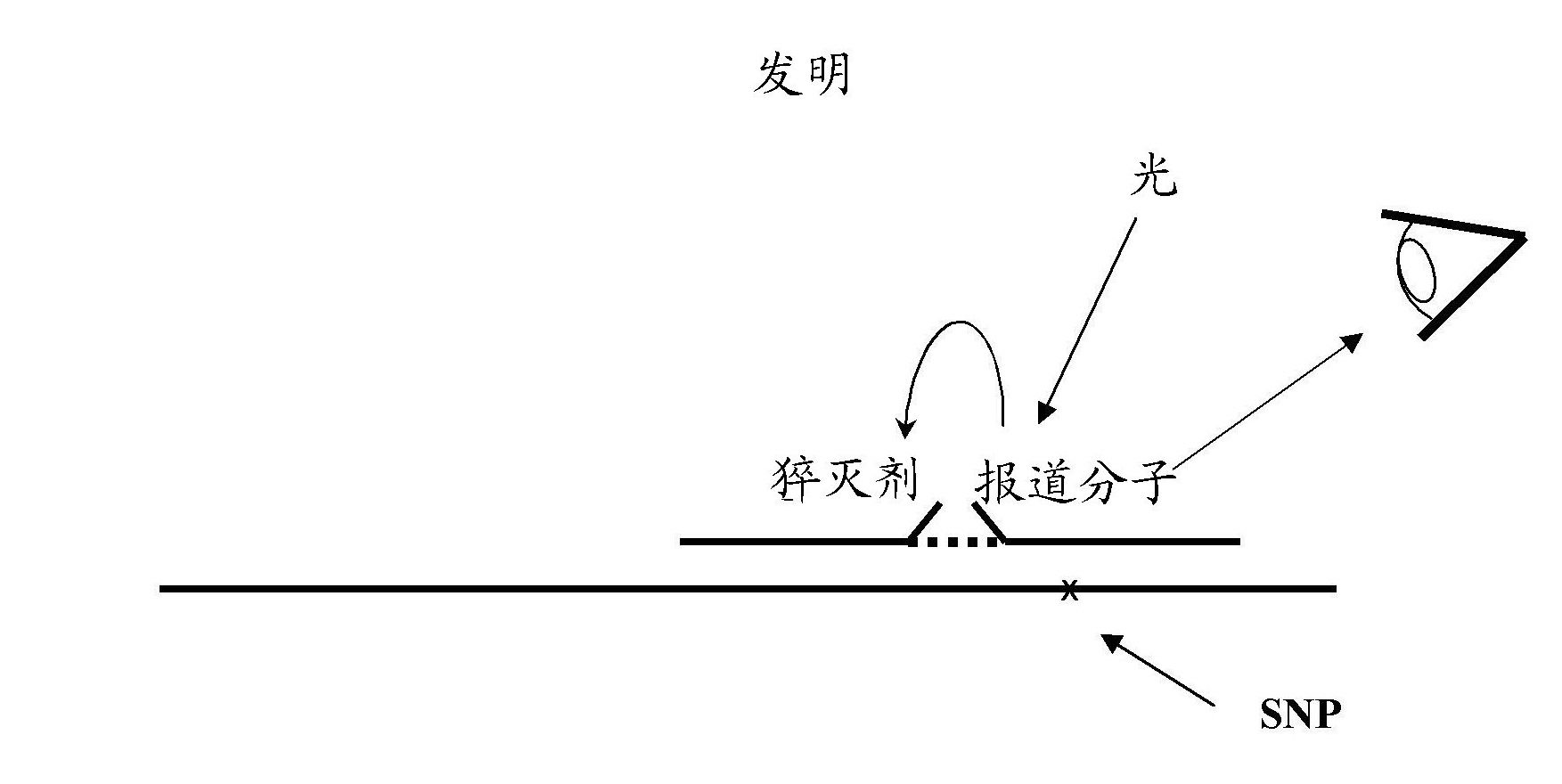
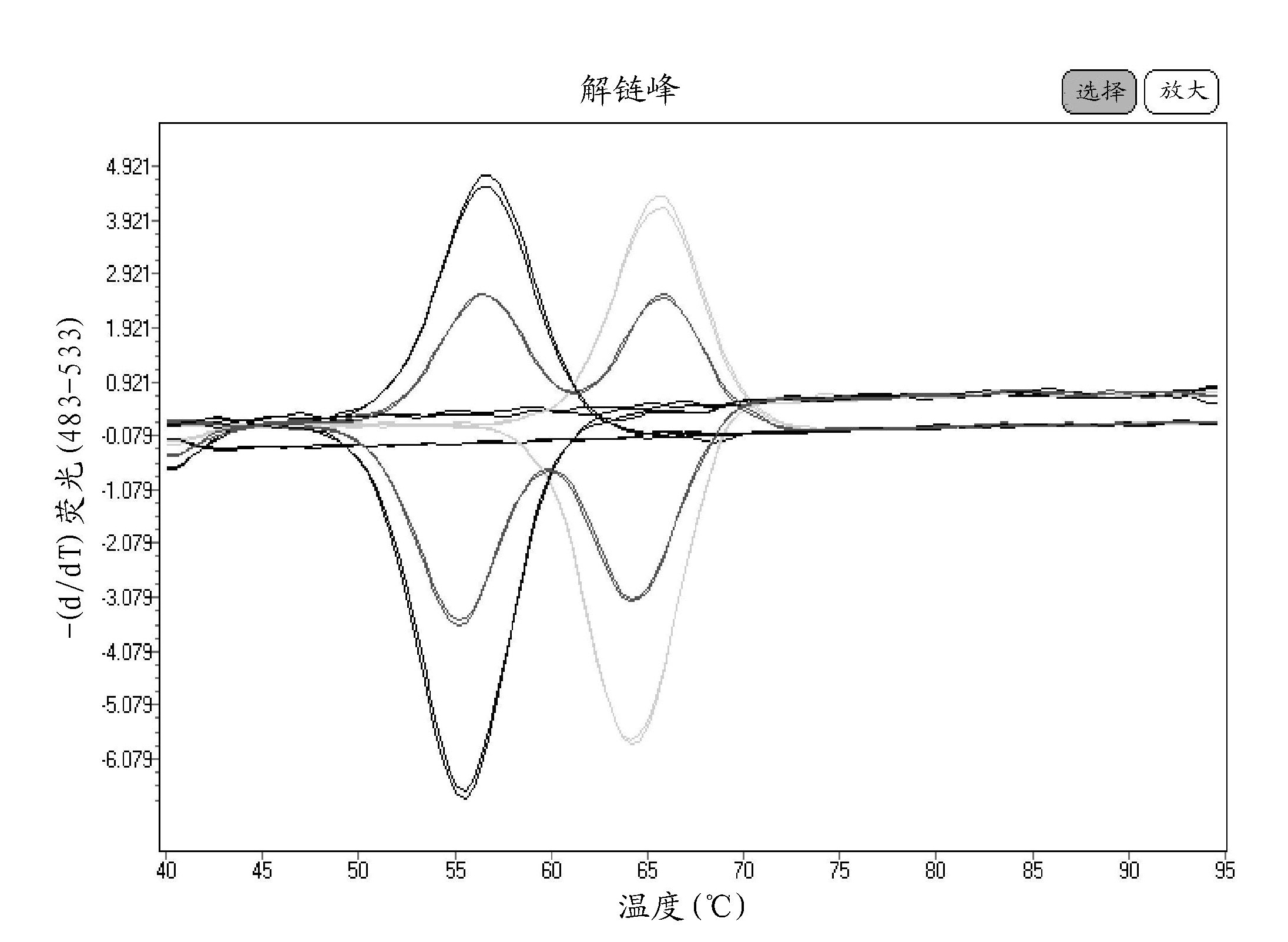
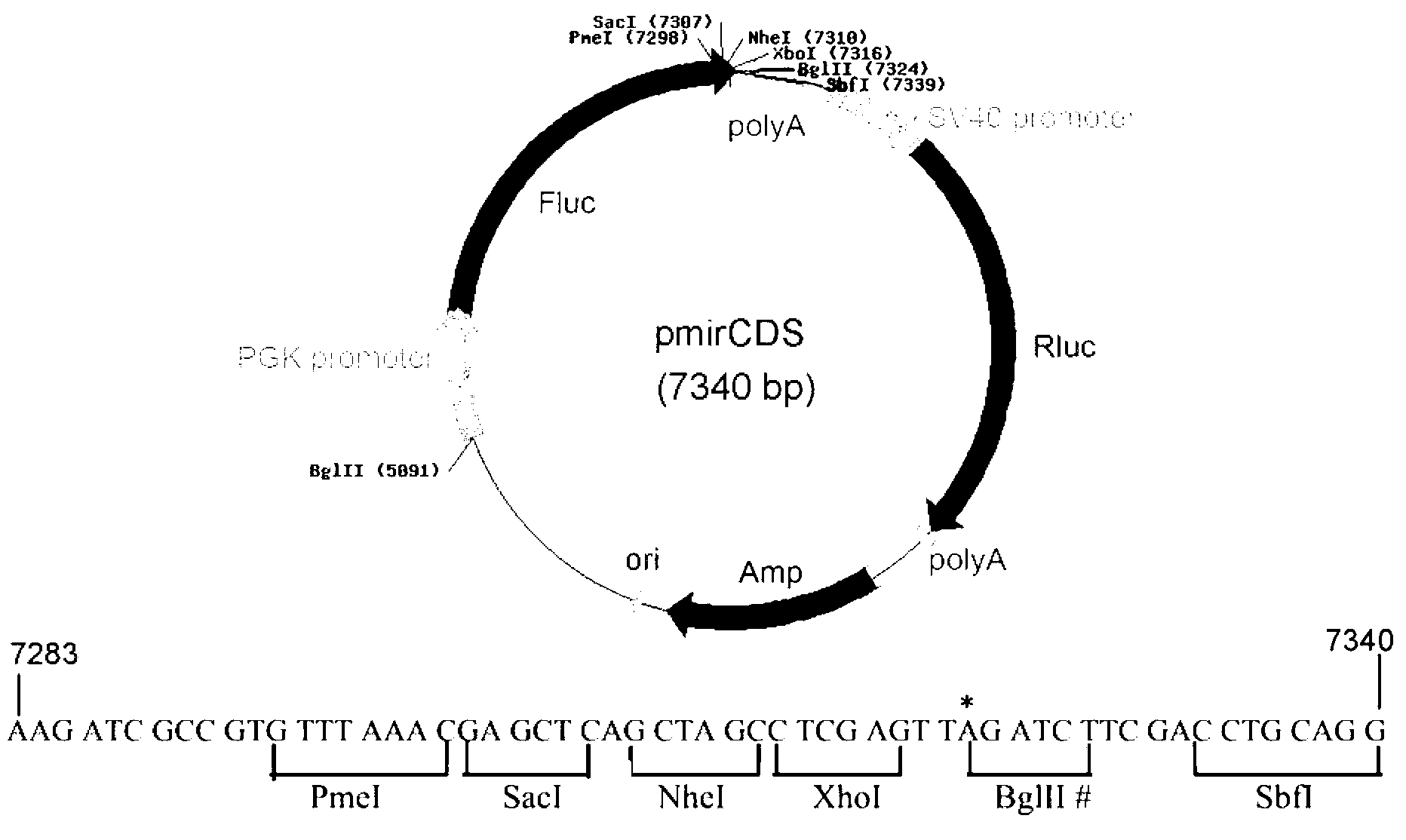
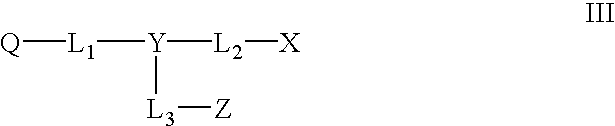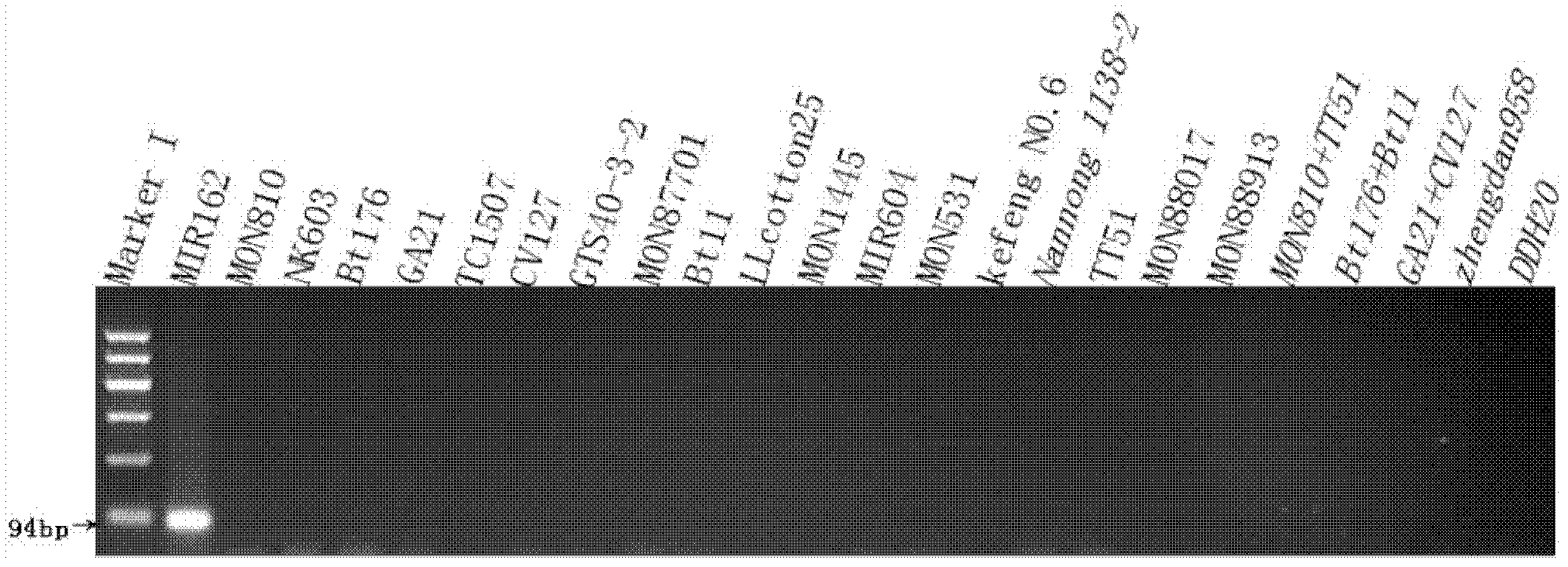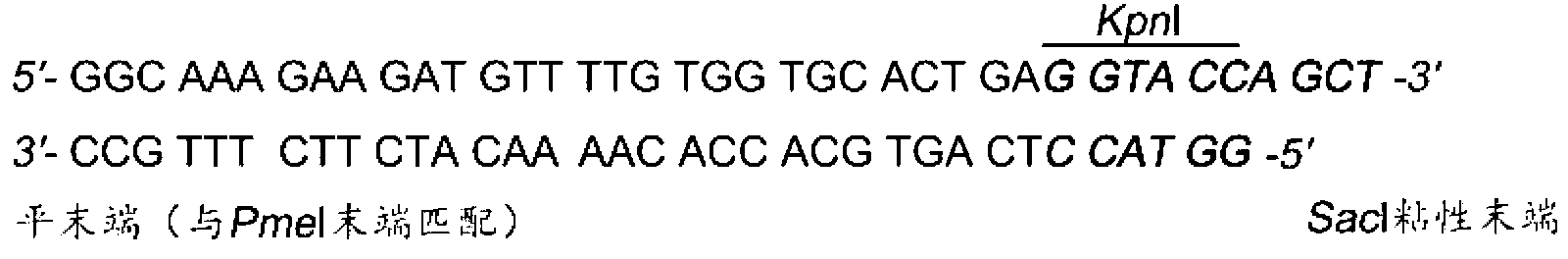Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
191 results about "Fluorescent reporter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
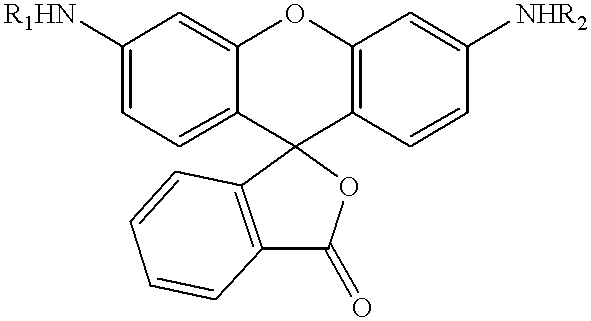
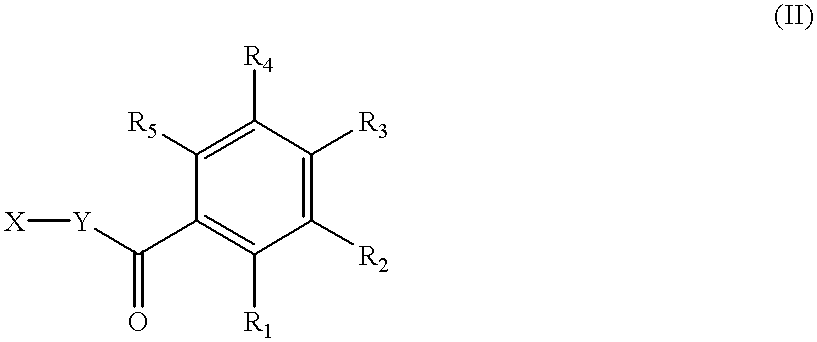
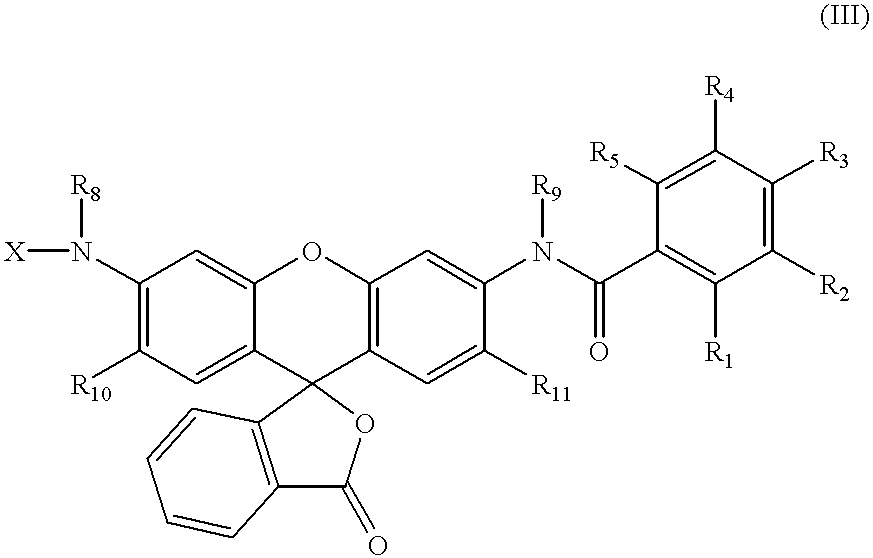
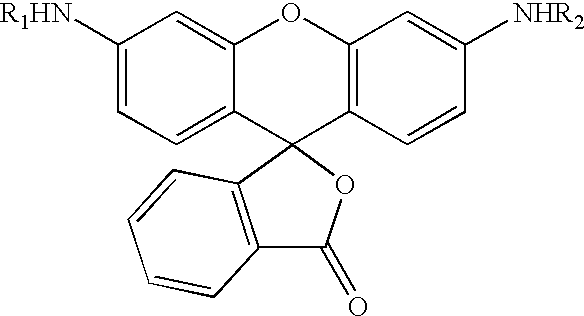
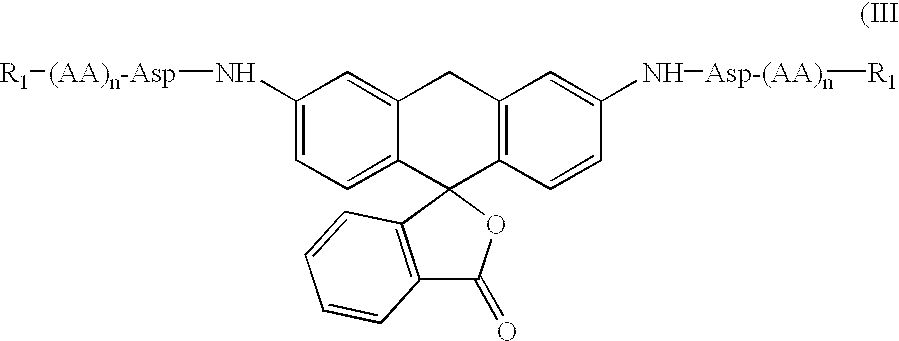
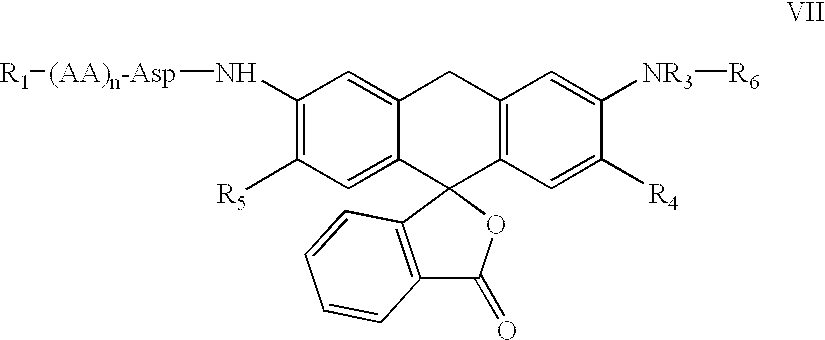
Fluorogenic or fluorescent reporter molecules and their applications for whole-cell fluorescence screening assays for caspases and other enzymes and the use thereof
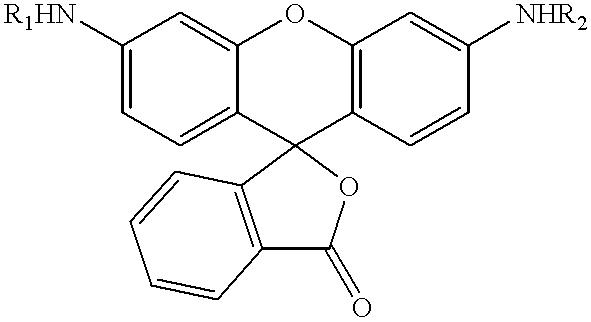
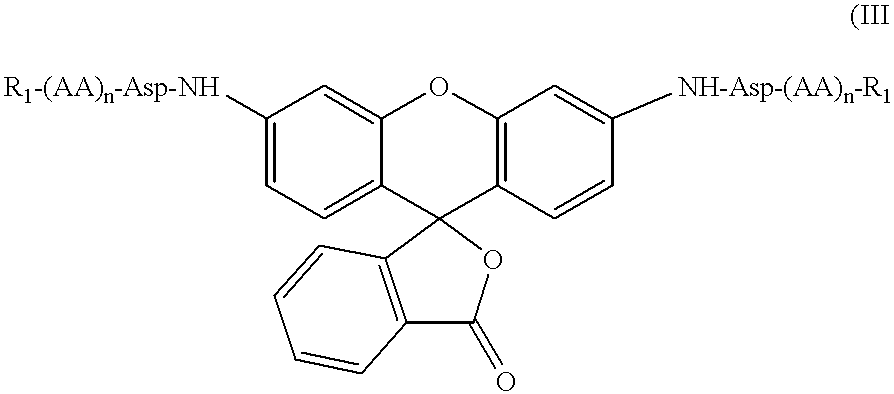
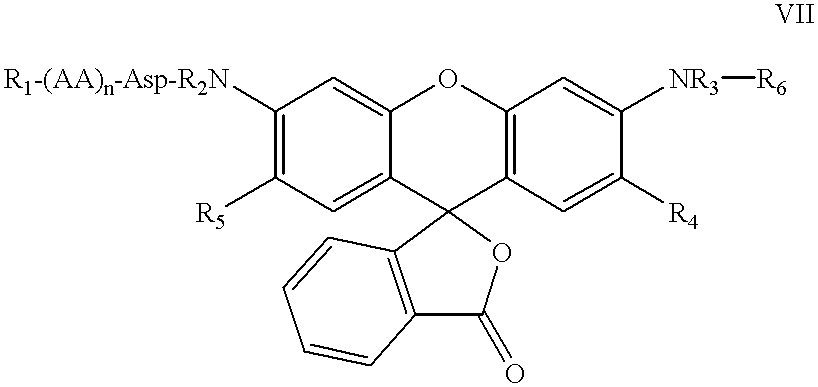
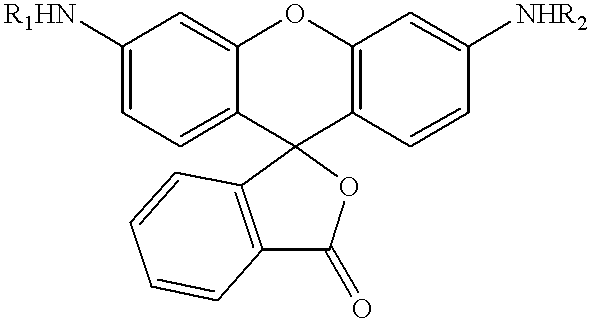
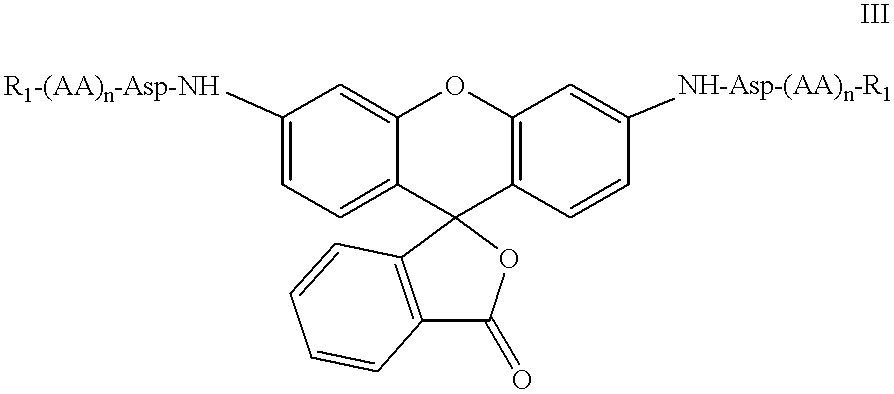
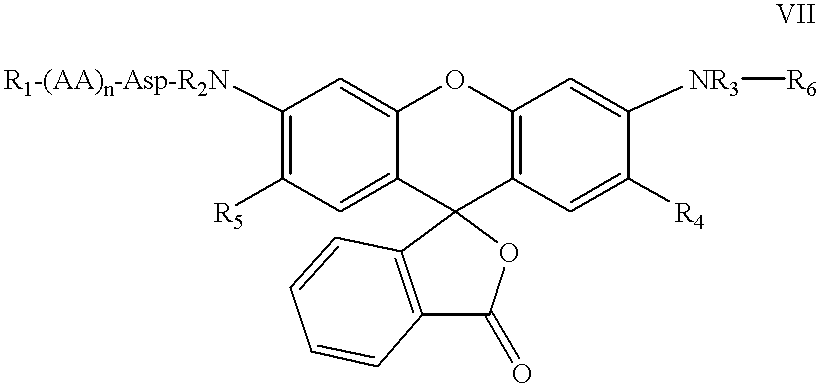
The present invention relates to novel fluorescent dyes, novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of caspases and other enzymes involved in apoptosis in whole cells, cell lines and tissue samples derived from any living organism or organ. The reporter molecules and assay processes can be used in drug screening procedures to identify compounds which act as inhibitors or inducers of the caspase cascade in whole cells or tissues. The reagents and assays described herein are also useful for determining the chemosensitivity of human cancer cells to treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs. The present invention also relates to novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of type 2 methionine aminopeptidase, dipeptidyl peptidase IV, calpain, aminopeptidase, HIV protease, adenovirus protease, HSV-1 protease, HCMV protease and HCV protease.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
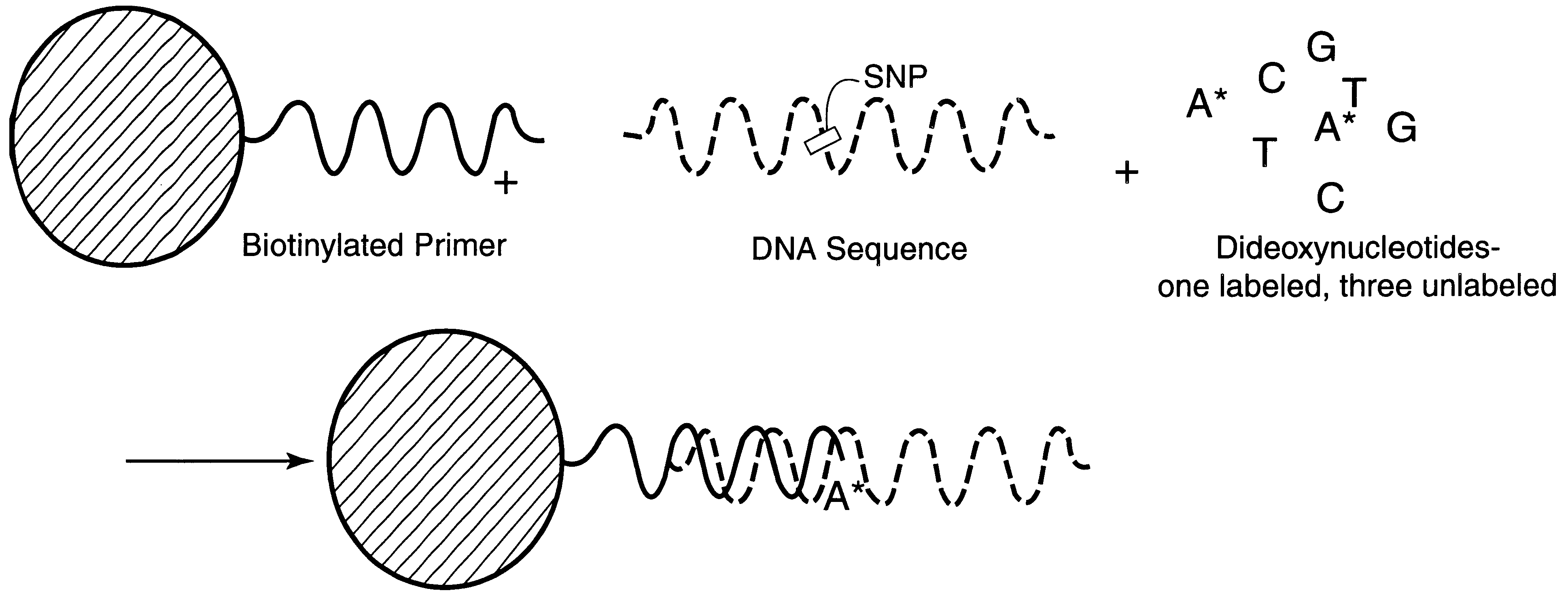
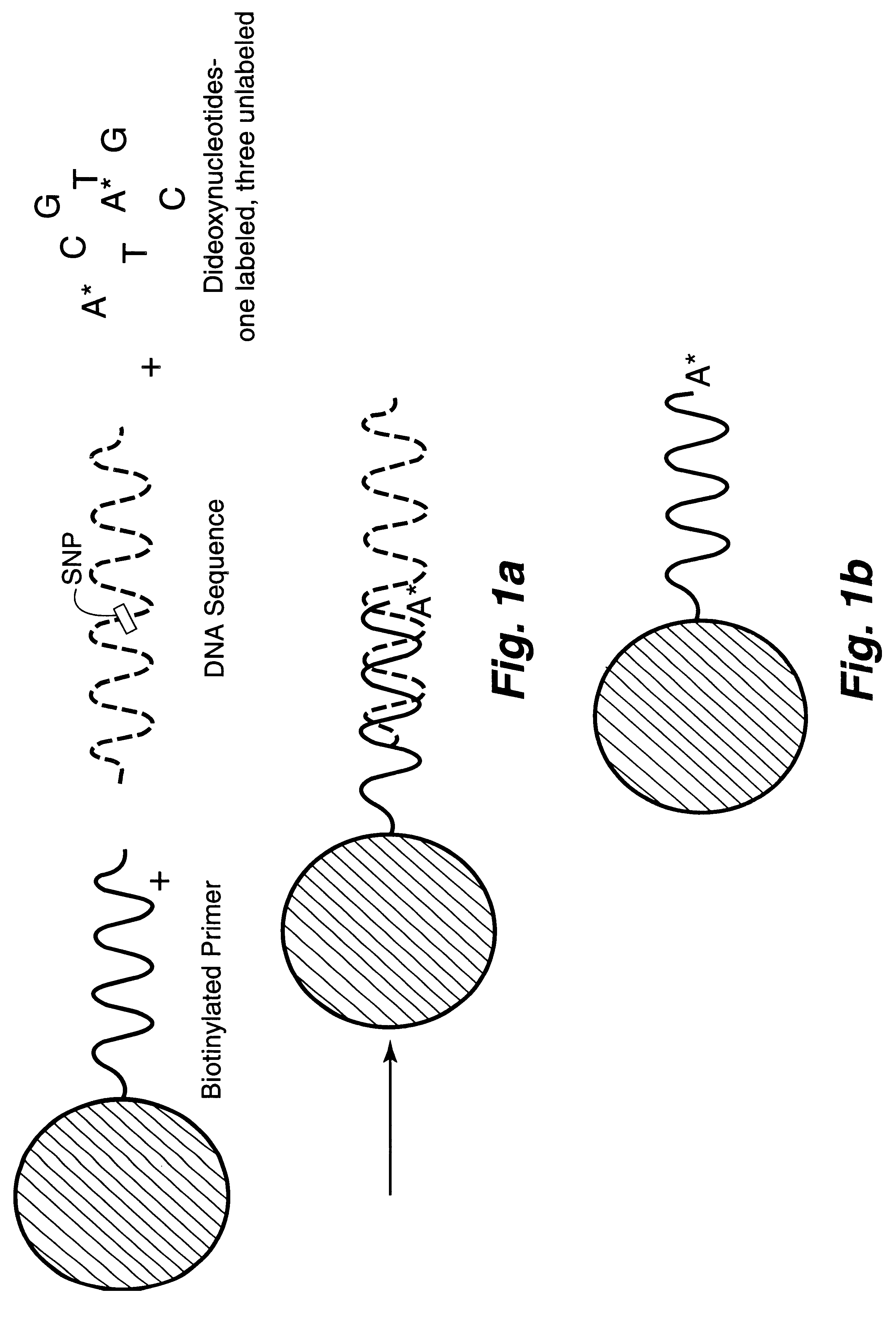
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry
InactiveUS6287766B1Sensitive, homogenous, and flexibleSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereDideoxynucleotide Triphosphates
DNA polymorphism identity determination using flow cytometry. Primers designed to be immobilized on microspheres are allowed to anneal to the DNA strand under investigation, and are extended by either DNA polymerase using fluorescent dideoxynucleotides or ligated by DNA ligase to fluorescent reporter oligonucleotides. The fluorescence of either the dideoxynucleotide or the reporter oligonucleotide attached to the immobilized primer is measured by flow cytometry, thereby identifying the nucleotide polymorphism on the DNA strand.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Fluorogenic or fluorescent reporter molecules and their applications for whole-cell fluorescence screening assays for capsases and other enzymes and the use thereof
InactiveUS6342611B1Organic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening proceduresApoptosis
The present invention relates to novel fluorescent dyes, novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of caspases and other enzymes involved in apoptosis in whole cells, cell lines and tissue samples derived from any living organism or organ. The reporter molecules and assay processes can be used in drug screening procedures to identify compounds which act as inhibitors or inducers of the caspase cascade in whole cells or tissues. The reagents and assays described herein are also useful for determining the chemosensitivity of human cancer cells to treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs. The present invention also relates to novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of type 2 methionine aminopeptidase, dipeptidyl peptidase IV, calpain, aminopeptidase, HIV protease, adenovirus protease, HSV-1 protease, HCMV protease and HCV protease.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
Fluorescence dyes and their applications for whole-cell fluorescence screening assays for caspases, peptidases, proteases and other enzymes and the use thereof
InactiveUS6248904B1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingScreening proceduresCancer cell
The present invention relates to novel fluorescent dyes, novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of caspases and other enzymes involved in apoptosis in whole cells, cell lines and tissue samples derived from any living organism or organ. The reporter molecules and assay processes can be used in drug screening procedures to identify compounds which act as inhibitors or inducers of the caspase cascade in whole cells or tissues. The reagents and assays described herein are also useful for determining the chemosensitivity of human cancer cells to treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs. The present invention also relates to novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of type 2 methionine aminopeptidase, HIV protease, adenovirus protease, HSV-1 protease, HCMV protease and HCV protease.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
Non-fluorescent quencher compounds and biomolecular assays
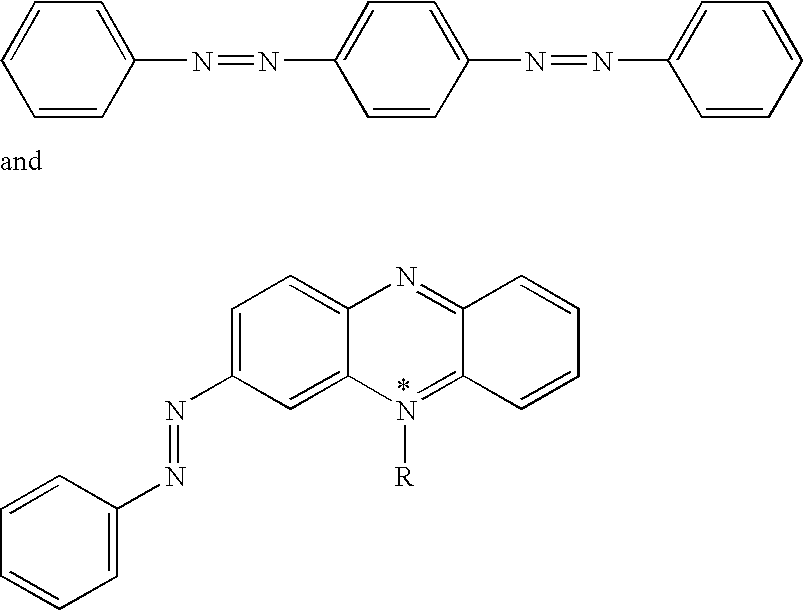
Bis-diazo,triaryl and aryldiazo-N-arylphenazonium quencher moieties, substituted with electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents which induce polarity in the delocalized aryl / diazo ring systems, are useful as labels when attached to biomolecules such as polynucleotides, nucleosides, nucleotides, and polypeptides. The quencher moieties are non-fluorescent and accept energy from fluorescent reporter labels by any energy-transfer mechanism, such as FRET. Fluorescence quencher compositions are useful in preparing quencher labelled biomolecules for various molecular biology assays based on fluorescence detection.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
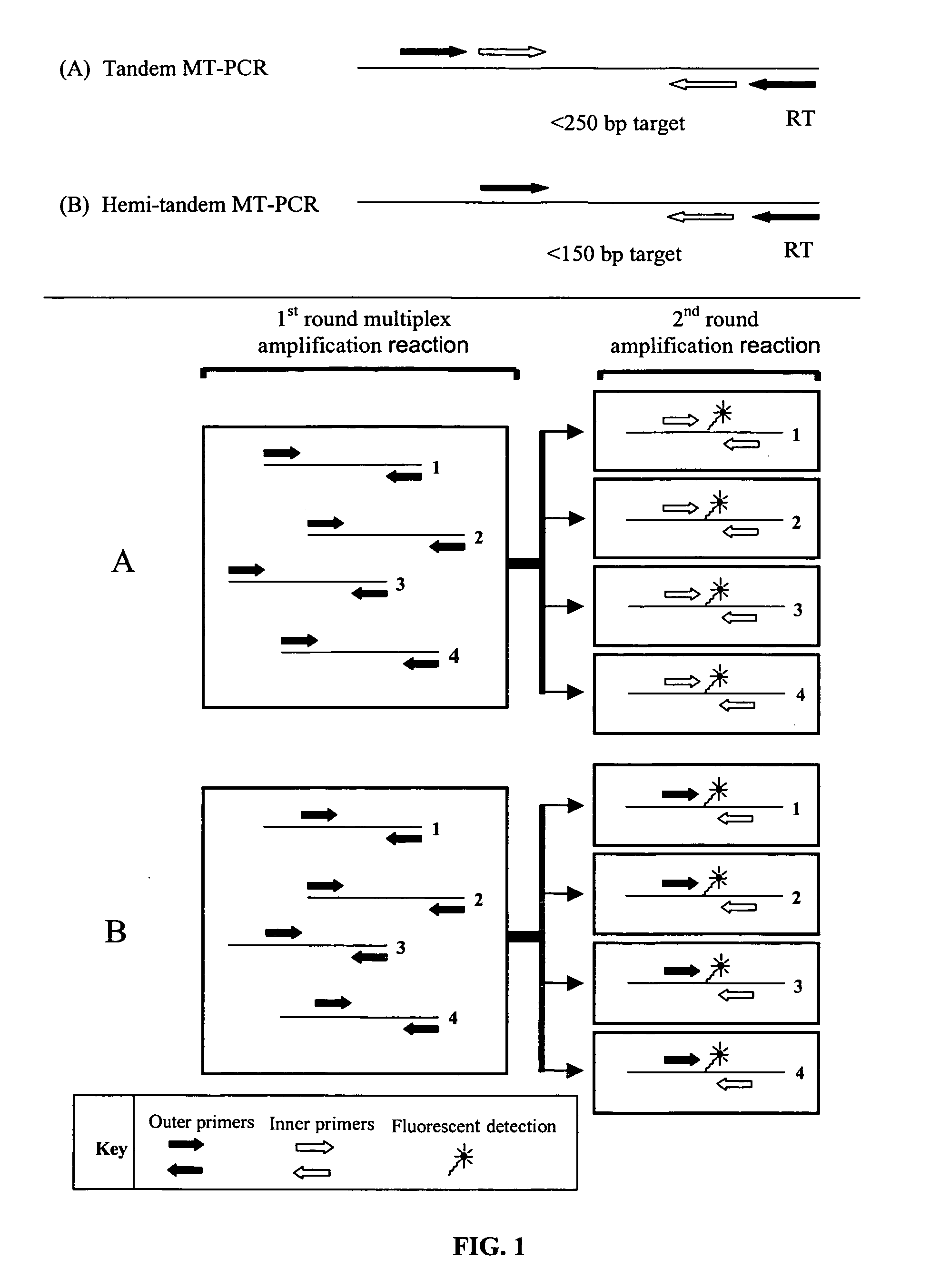
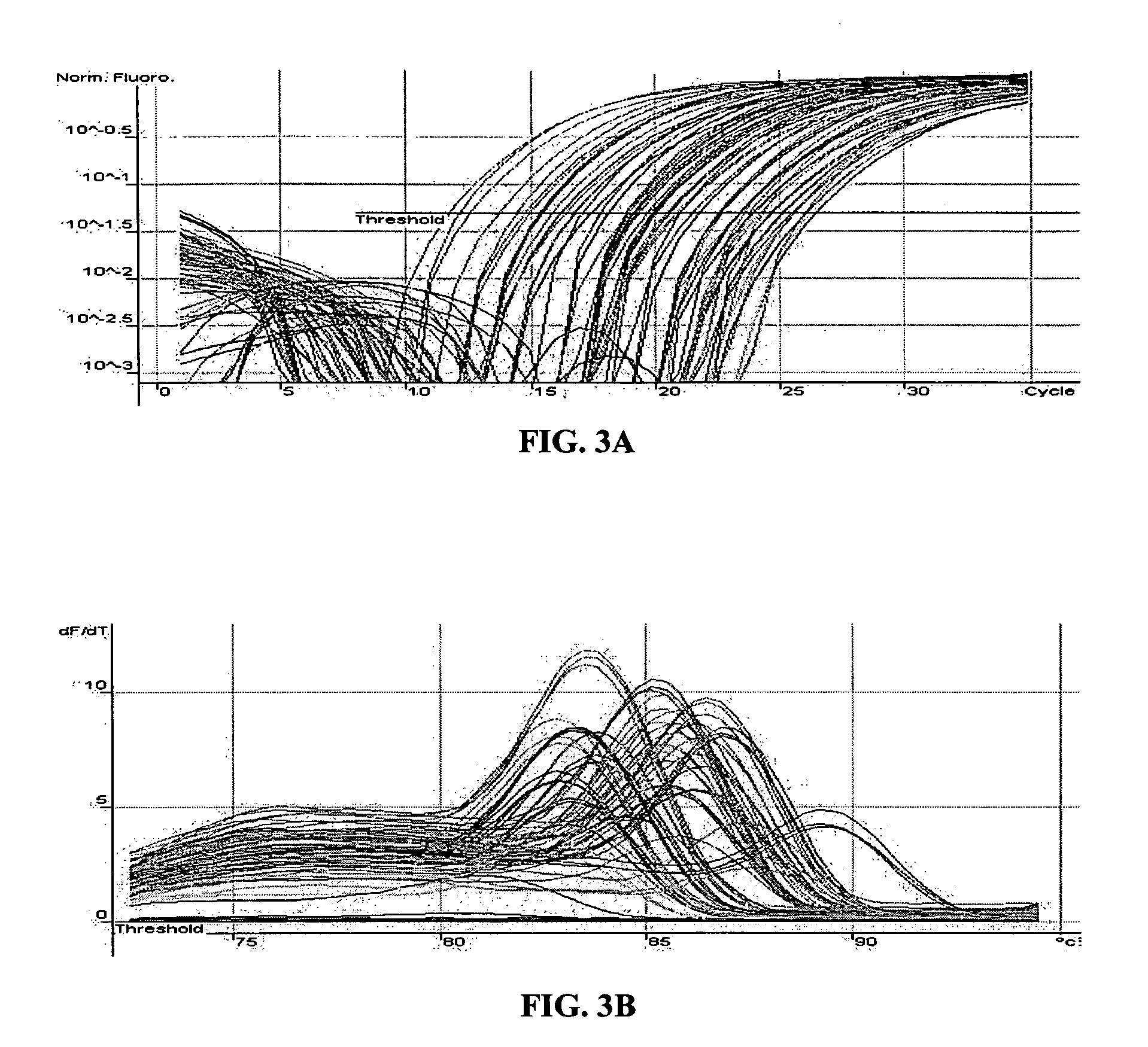
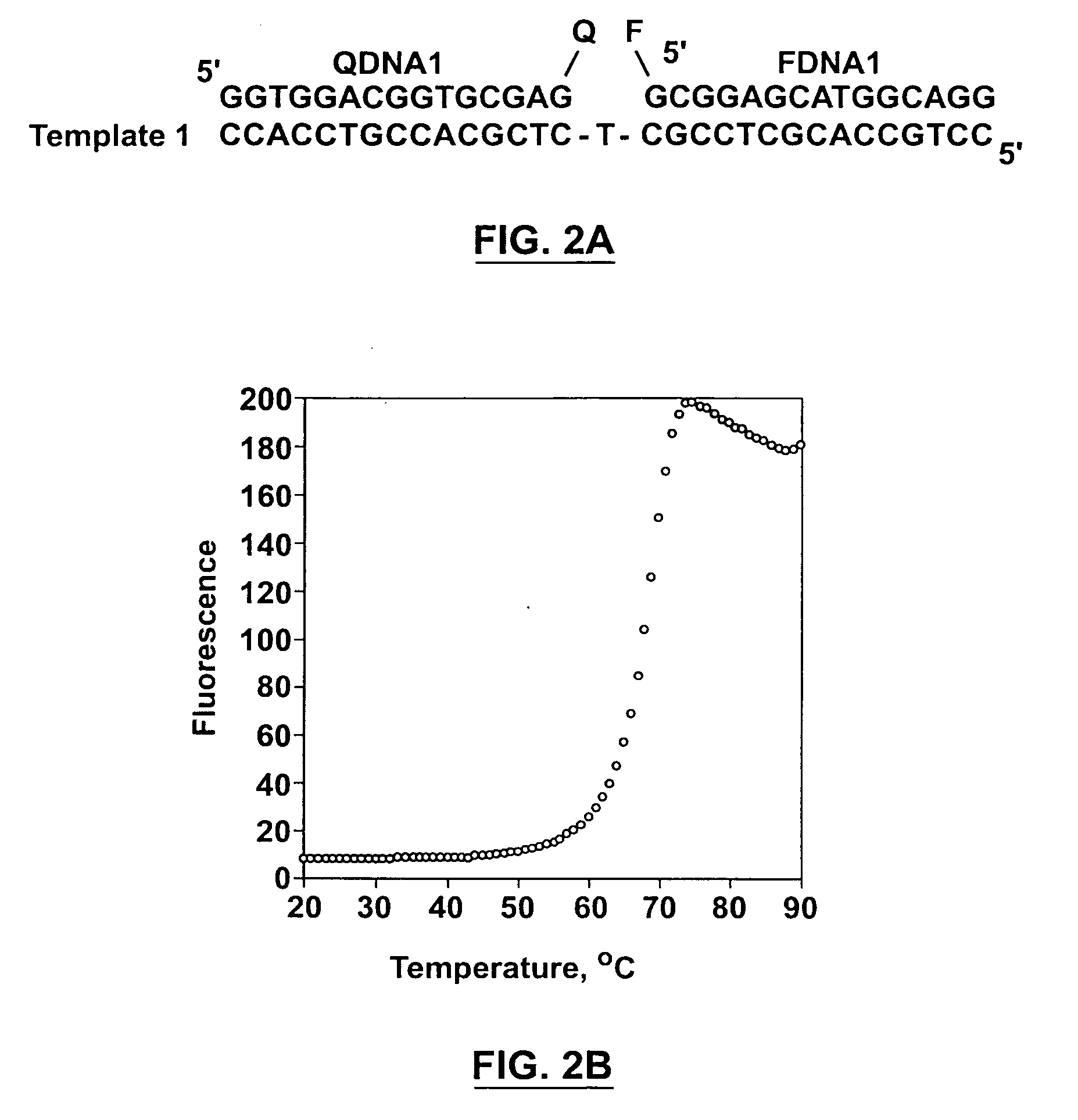
Methods for the amplification, quantitation and identification of nucleic acids
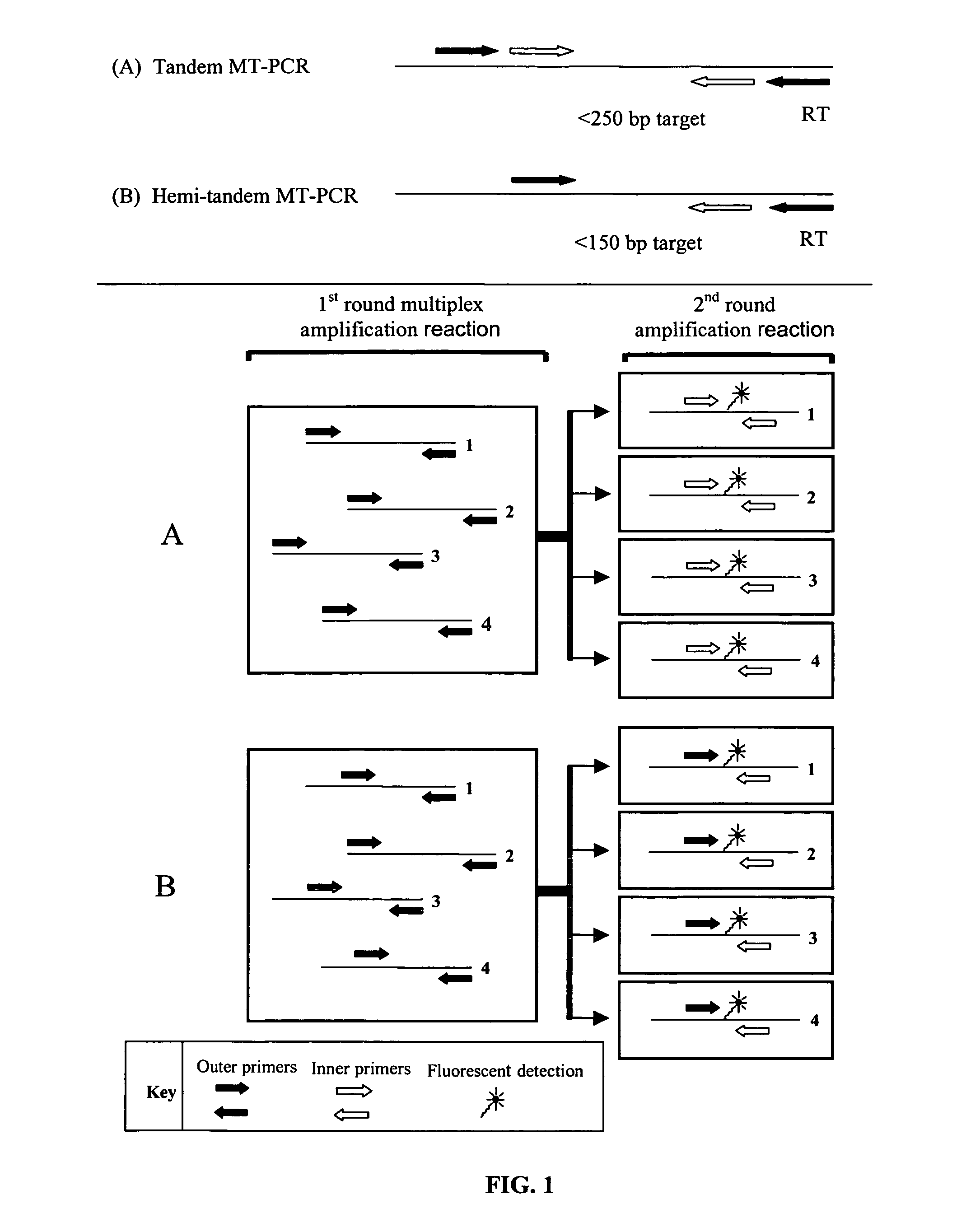
ActiveUS20070190540A1Avoid pollutionPromote digestionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingFluorescent reporter
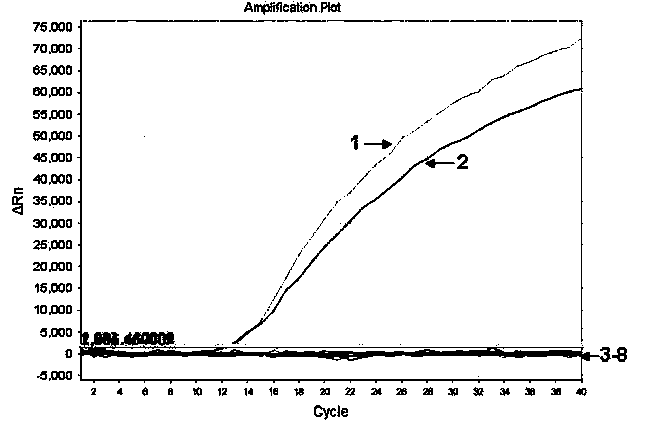
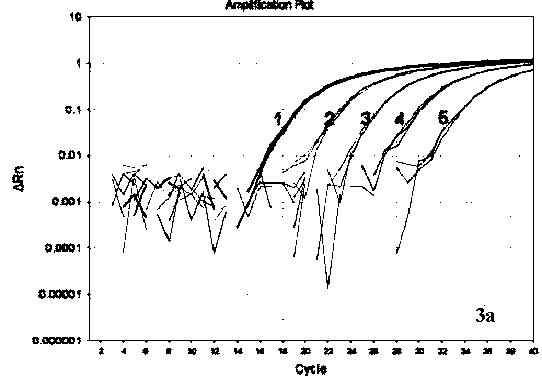
The invention relates to improved methods of amplifying and optionally quantifying and / or identifying a plurality of selected nucleic acid molecules from a pool of nucleic acid molecules. A first round of multiplex amplification used where the amplification reaction is allowed to proceed to a point prior to that at which significant competition between amplicons for reaction components has occurred. This is the followed by a second round of amplification that typically includes a fluorescent reporter to allow for each of the selected nucleic acid sequences to be quantified. The methods are useful for the amplification and quantification of nucleic acids from a variety of sources, such as gene expression products, whereby many such products may be amplified and quantified from very limited samples and from degraded archival samples.
Owner:AUSDIAGNOSTICS
Signalling aptamer complexes
Aptamer based fluorescent reporters that function based on a switch from DNA / DNA duplex conformation to DNA / target conformation are provided. The DNA / DNA duplex is formed between the aptamer DNA sequence and an oligonucleotide carrying a reporter moiety. When the aptamer target is present, the aptamer assumes a tertiary structure for binding to the target. The formation of the tertiary structure forces the dissociation of the duplex structure and a signal is generated. The signal is preferably a fluorescent signal due to spatial separation of a fluorophore / quencher pair.
Owner:MCMASTER UNIV
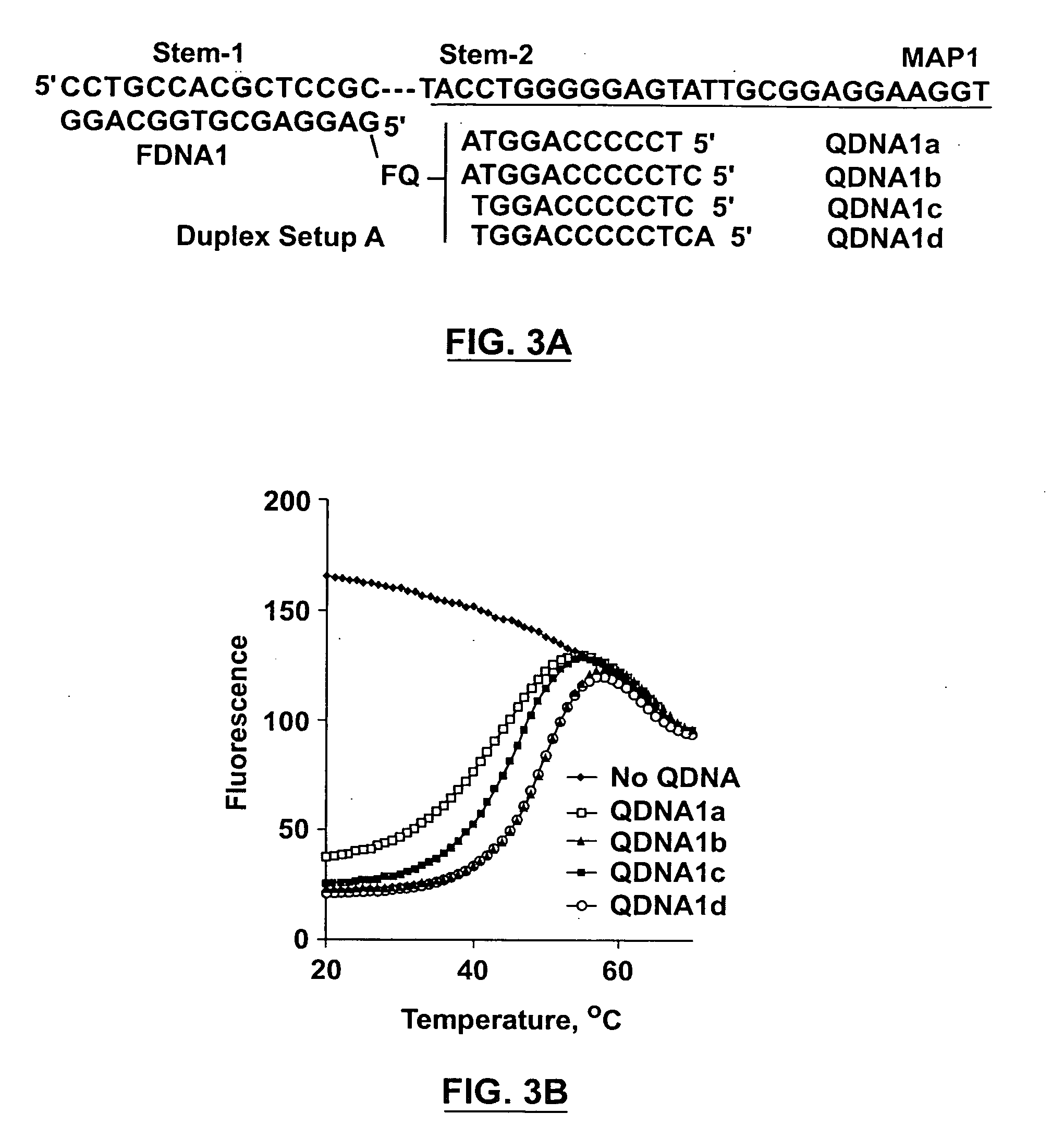
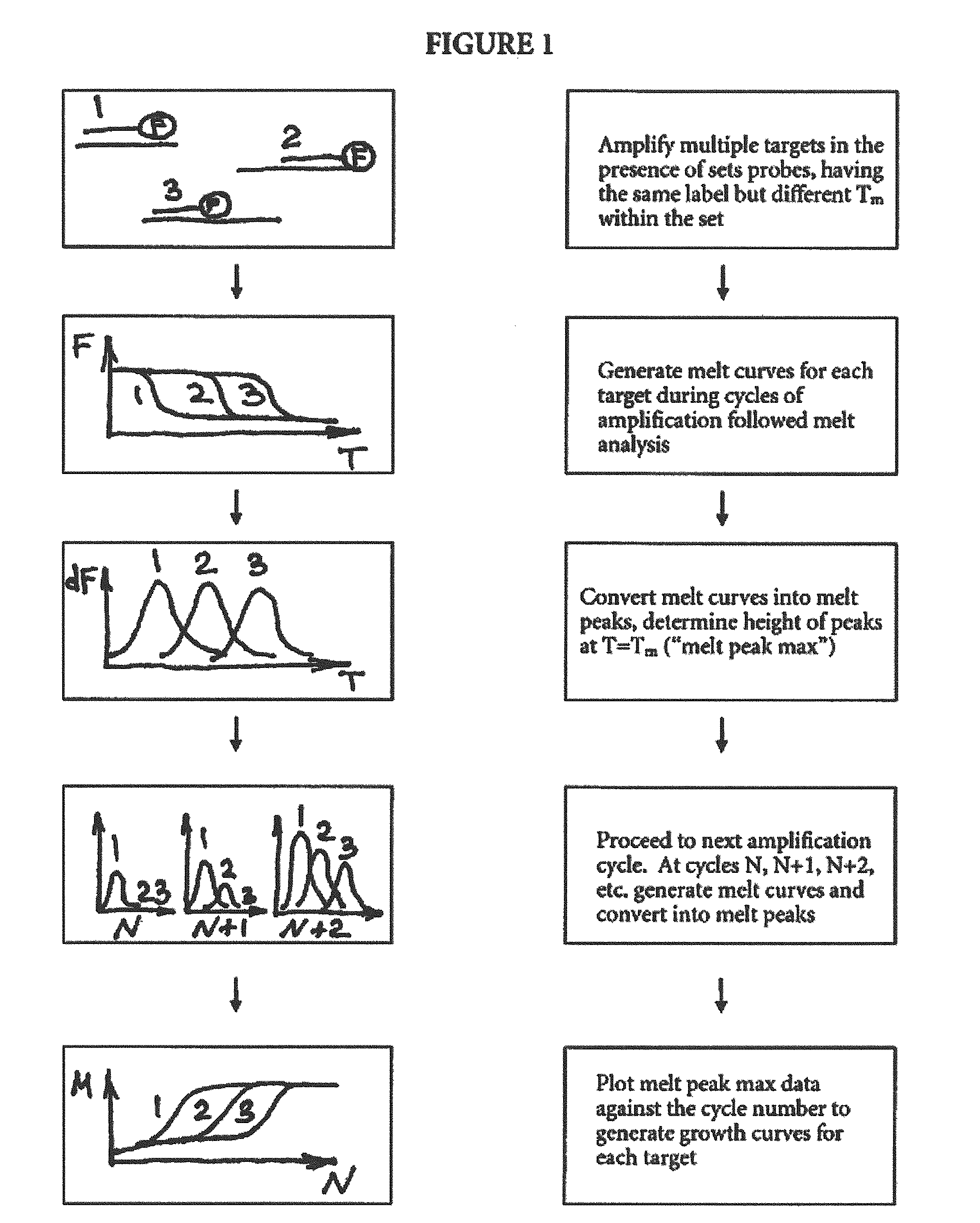
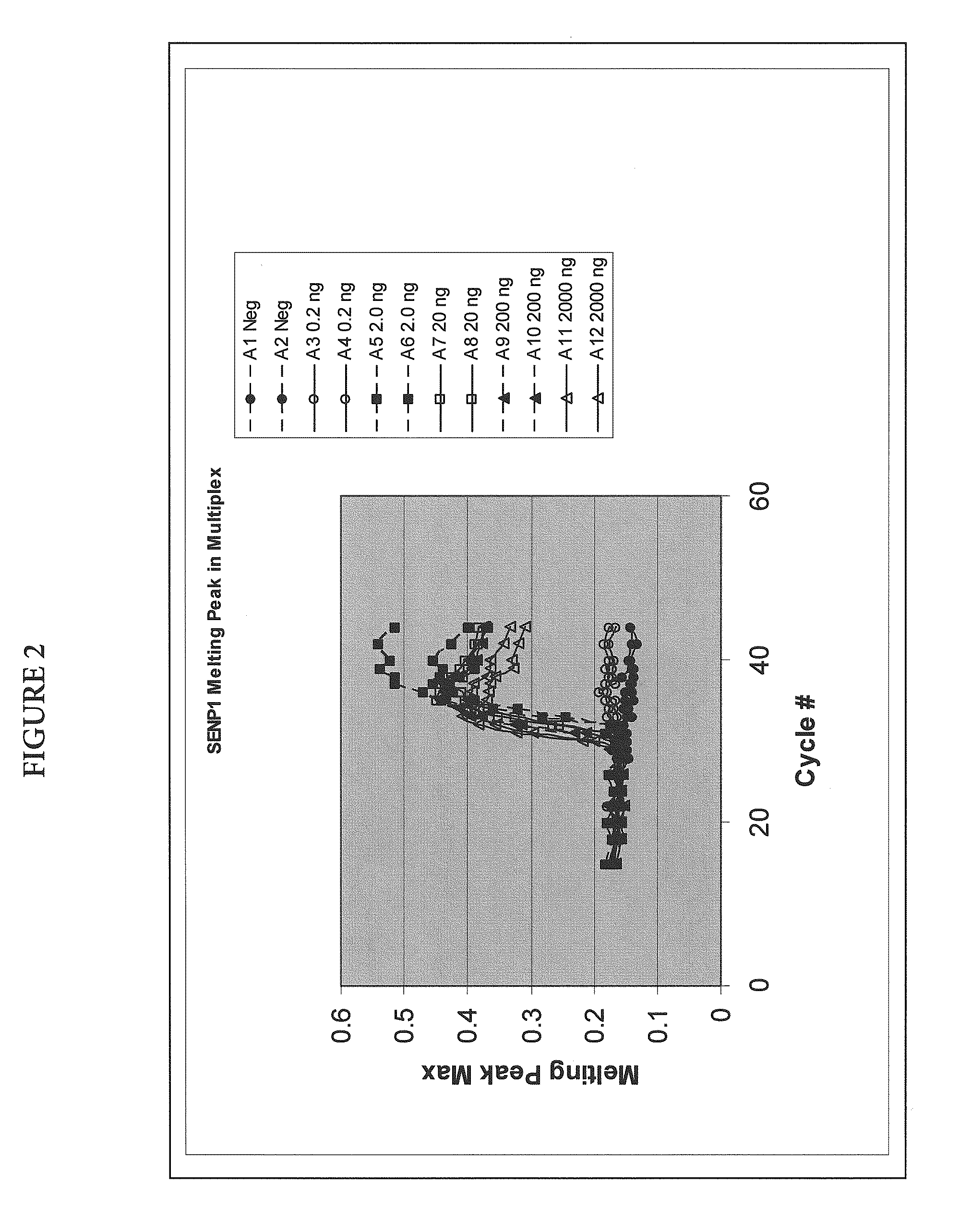
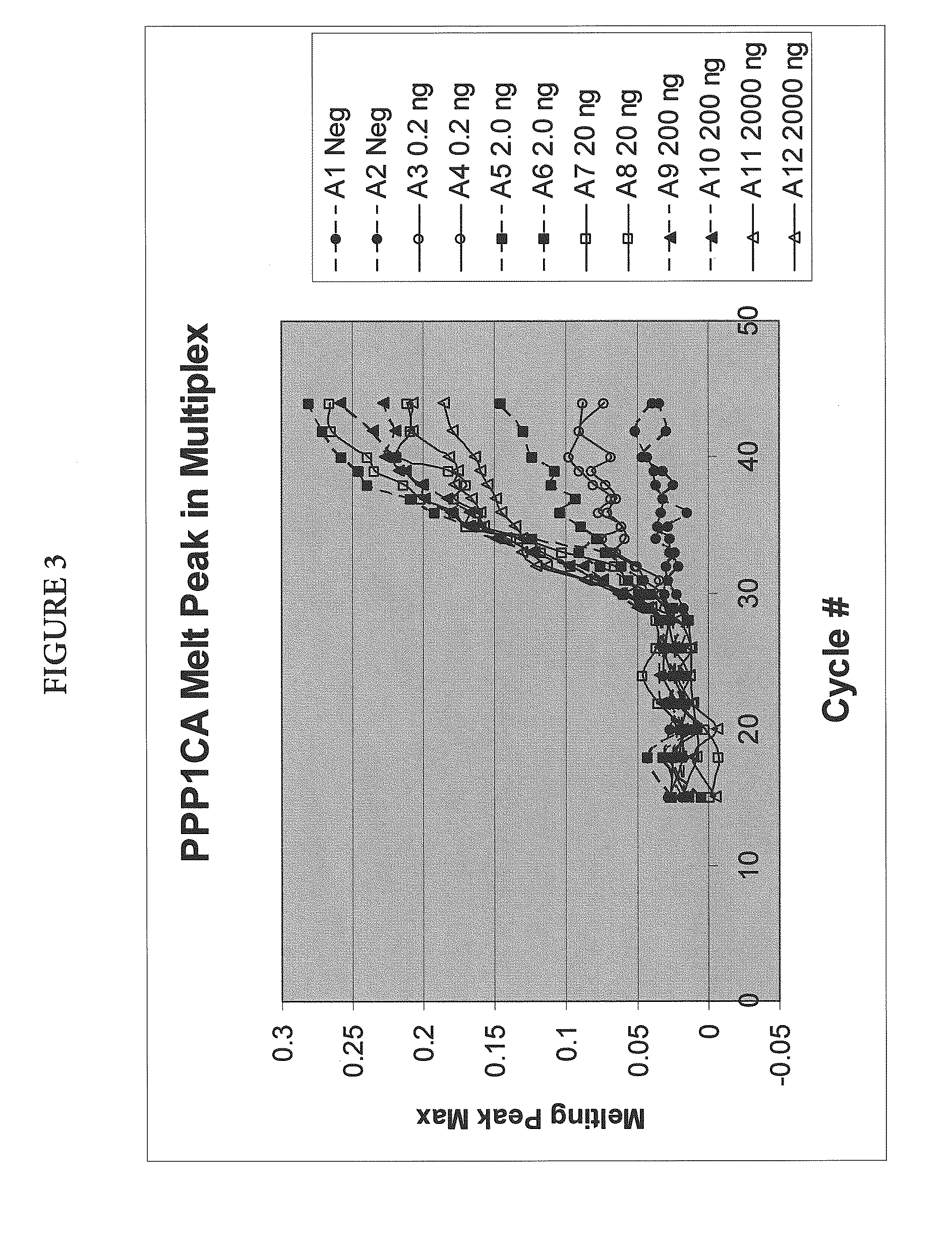
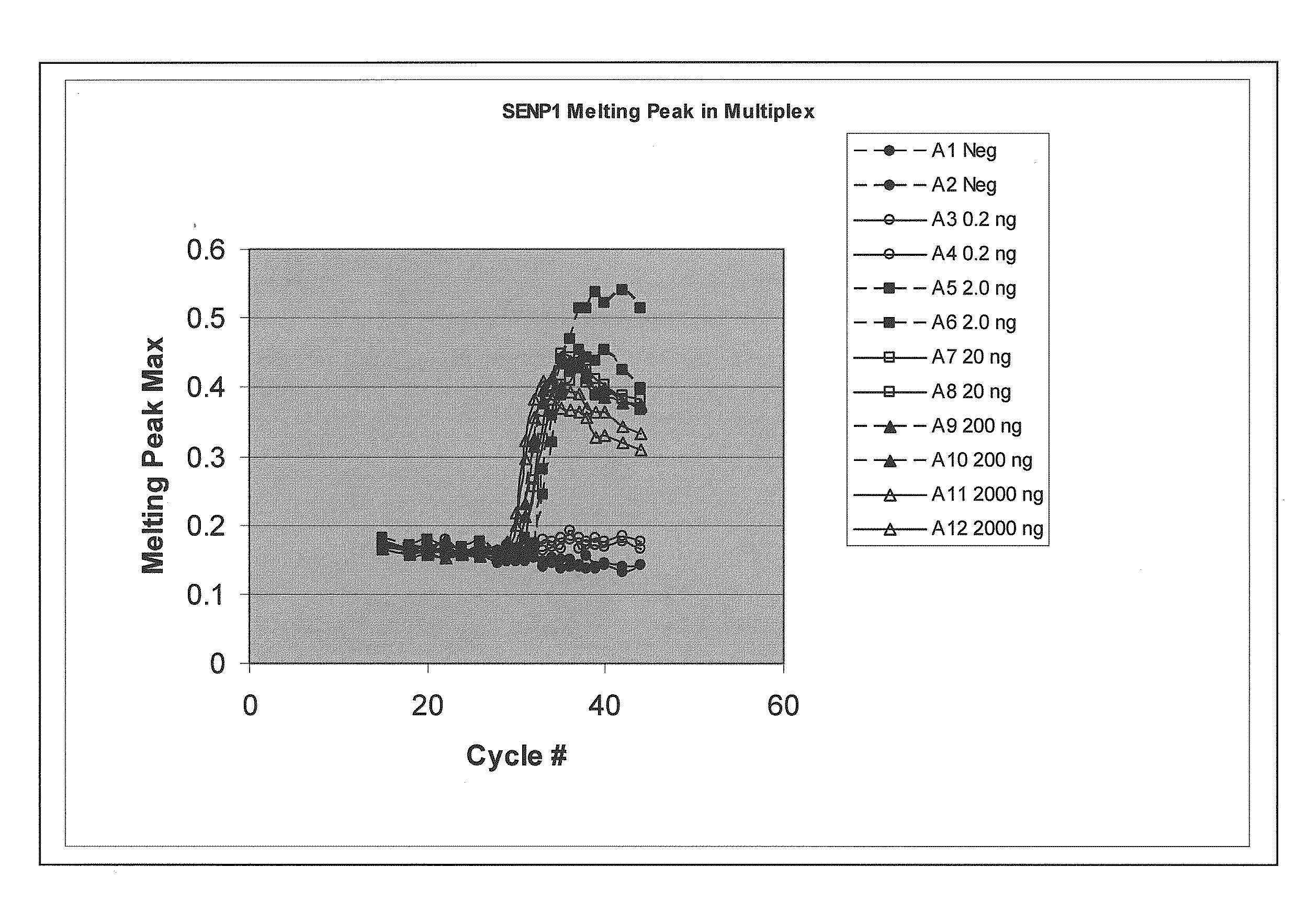
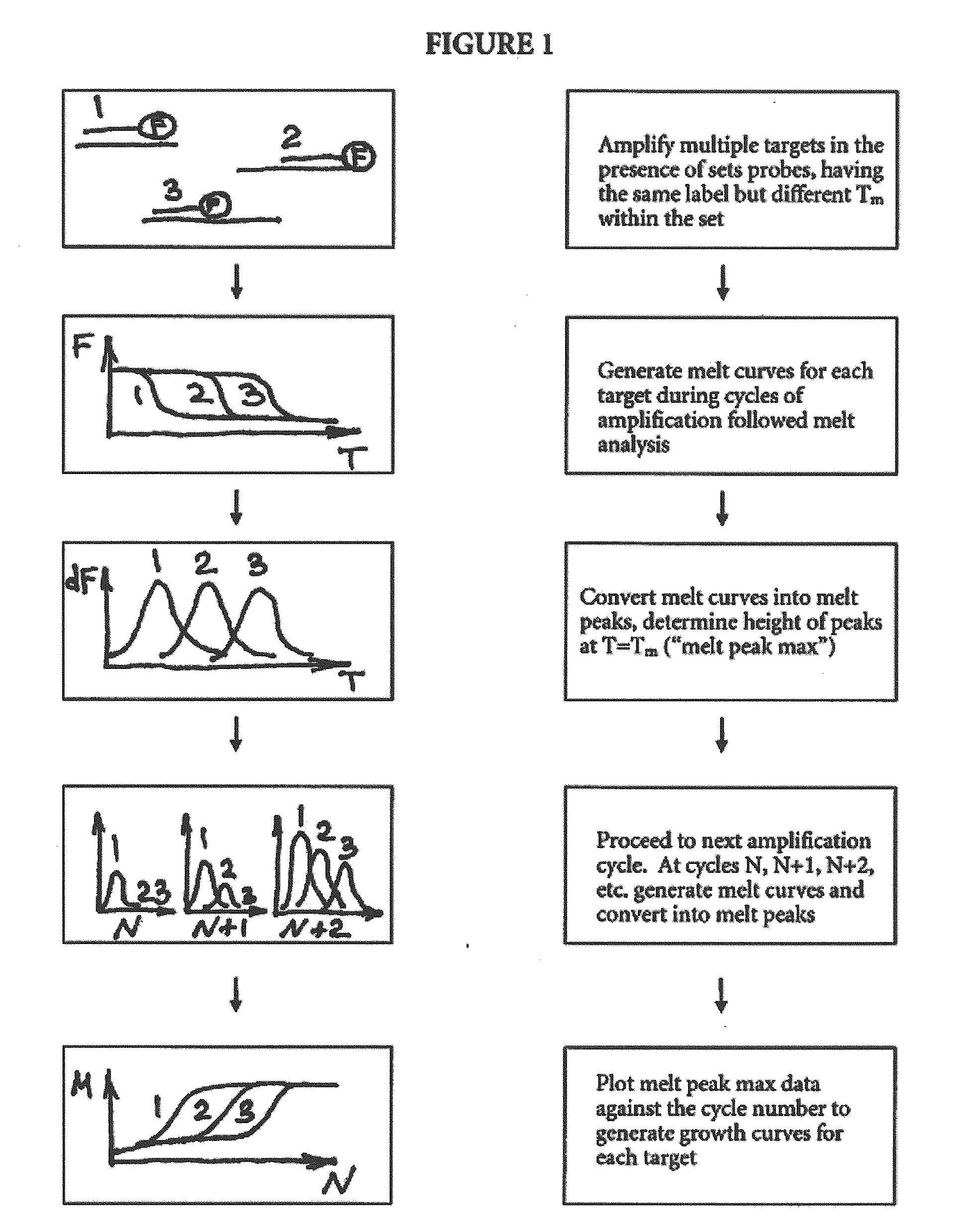
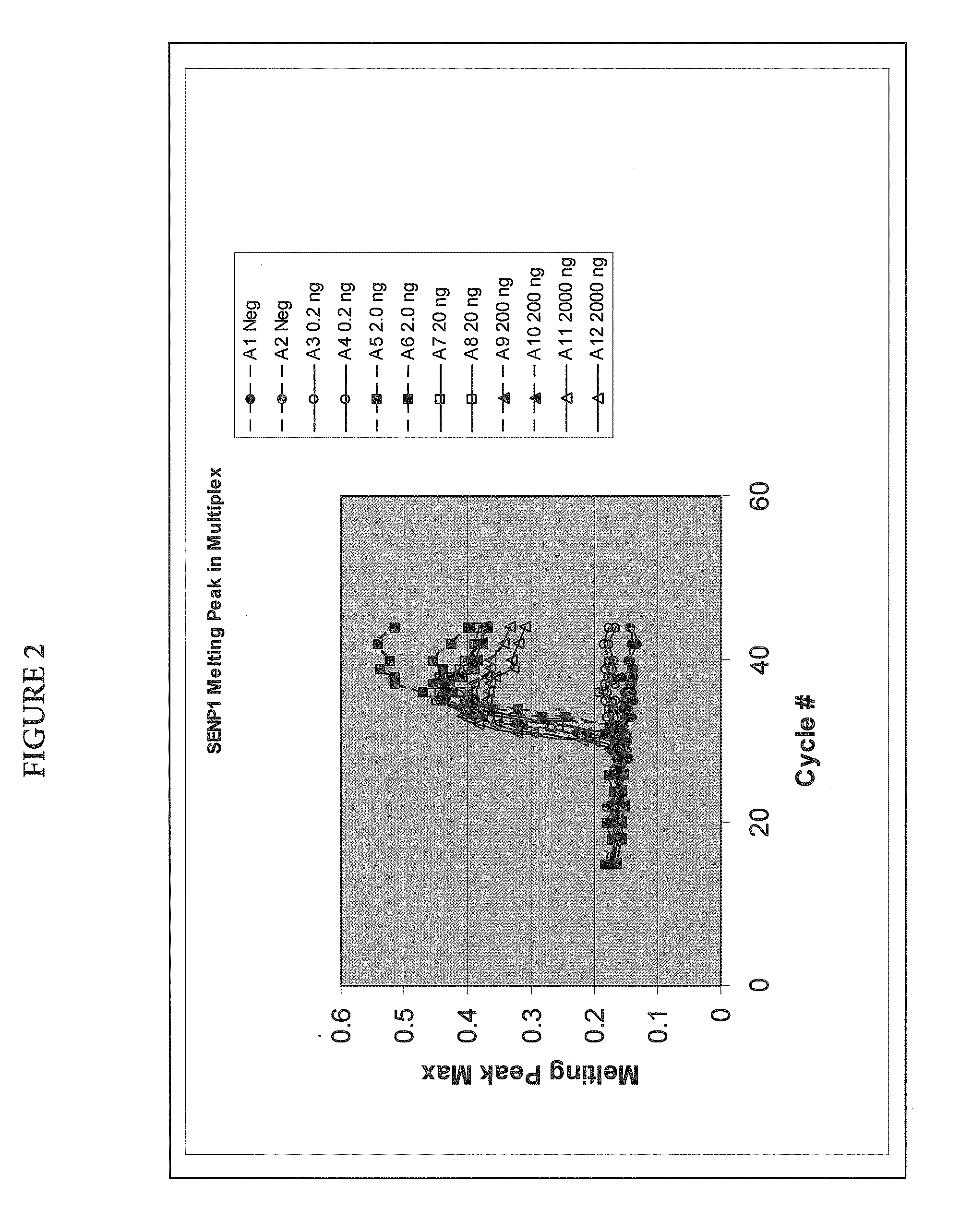
Multiplex quantitative nucleic acid amplification and melting assay
ActiveUS8039215B2Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationHybridization probeMelting temperature
The invention is a single-tube multiplex assay, capable of simultaneously amplifying, detecting and quantifying multiple nucleic acid targets, using multiple hybridization probes, labeled with the same fluorescent reporter label, but each having a distinct melting temperature. The assay can be further multiplexed with the use of multiple sets of hybridization probes, each set labeled with a separate fluorescent reporter label.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Novel fluorogenic or fluorescent reporter molecules and their applications for whole-cell fluorescence screening assays for caspases and other enzymes and the use thereof
InactiveUS20020150885A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceScreening proceduresApoptosis
The present invention relates to novel fluorescent dyes, novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of caspases and other enzymes involved in apoptosis in whole cells, cell lines and tissue samples derived from any living organism or organ. The reporter molecules and assay processes can be used in drug screening procedures to identify compounds which act as inhibitors or inducers of the caspase cascade in whole cells or tissues. The reagents and assays described herein are also useful for determining the chemosensitivity of human cancer cells to treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs. The present invention also relates to novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of type 2 methionine aminopeptidase, dipeptidyl peptidase IV, calpain, aminopeptidase, HIV protease, adenovirus protease, HSV-1 protease, HCMV protease and HCV protease.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
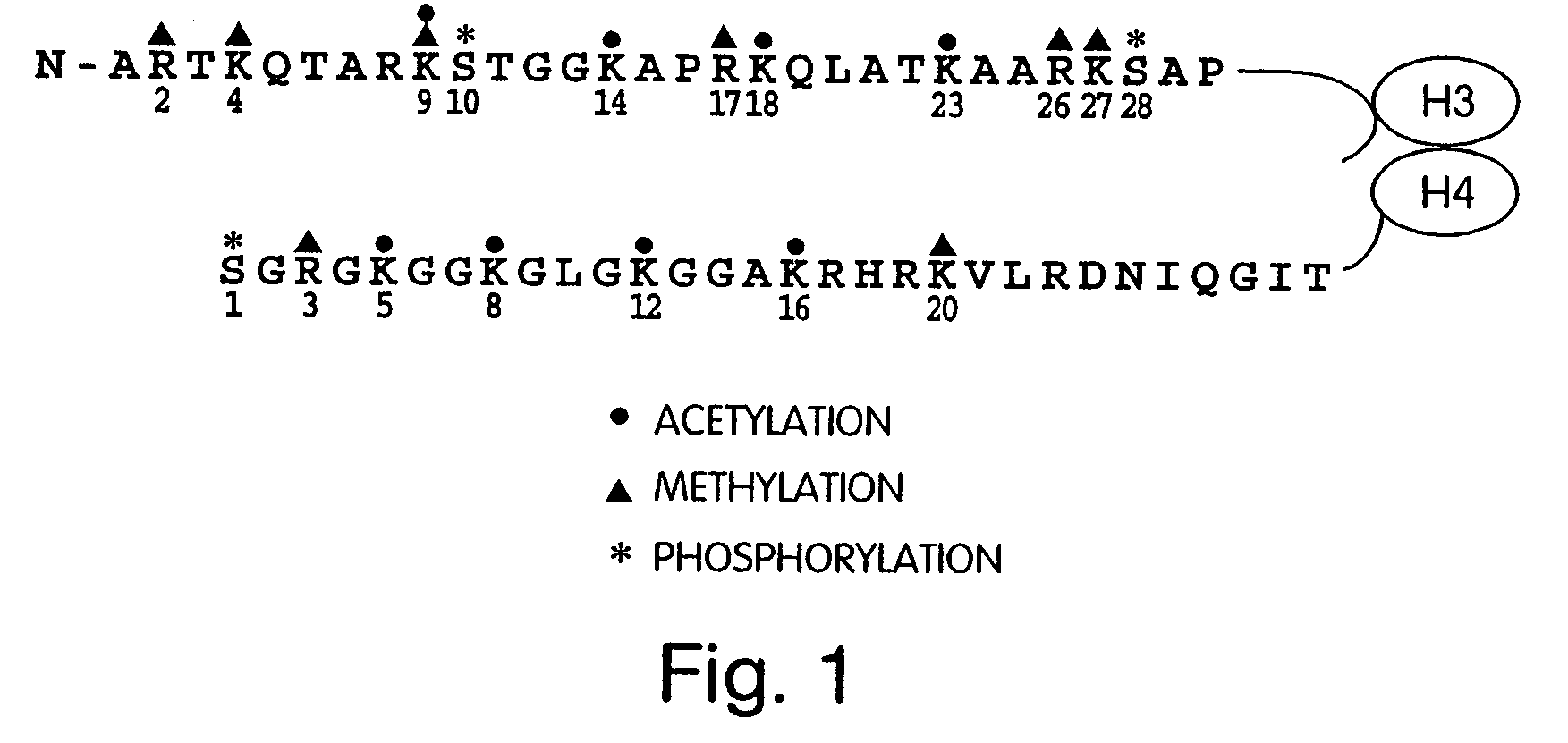
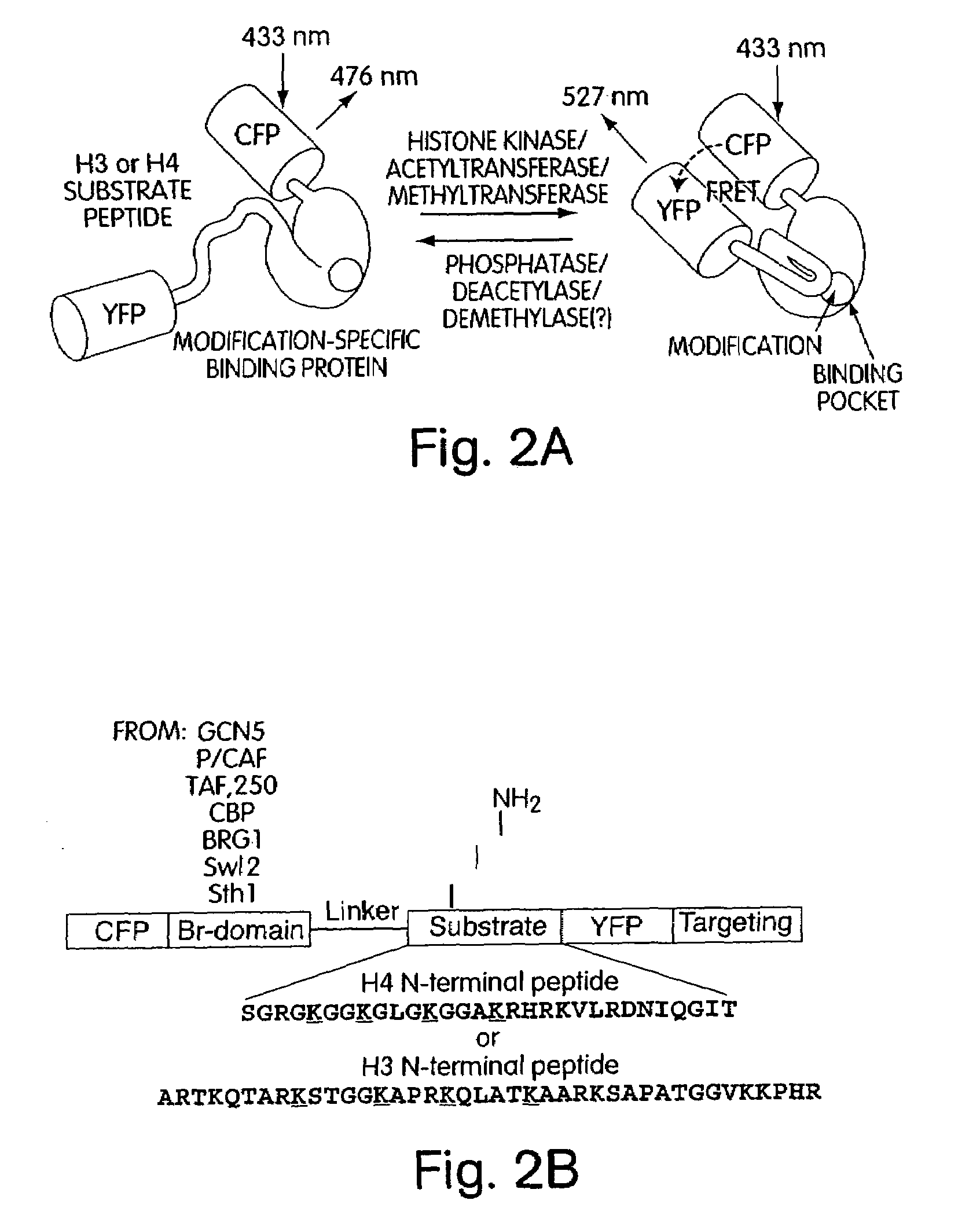
Genetically encoded fluorescent reporters of kinase, methyltransferase, and acetyl-transferase activities
InactiveUS7056683B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesMolecular diagnosticsFhit gene
The invention provides fusion protein reporter molecules that can be used to monitor protein modifications (e.g., histone modifications) in living cells, and methods of using the fusion reporter molecules for diagnosing protein-modification-associated disorders (e.g. histone-modification-associated disorders). The invention also provides methods of using the fusion protein reporters to identify candidate pharmaceutical agents that effect protein modification in cells and tissues, thus permitting identification of candidate pharmaceutical agents for treatment of protein-modification-associated disorders.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Multiplex Quantitative Nucleic Acid Amplification and Melting Assay
ActiveUS20100233686A1Microbiological testing/measurementFermentationHybridization probeFluorescent reporter
The invention is a single-tube multiplex assay, capable of simultaneously amplifying, detecting and quantifying multiple nucleic acid targets, using multiple hybridization probes, labeled with the same fluorescent reporter label, but each having a distinct melting temperature. The assay can be further multiplexed with the use of multiple sets of hybridization probes, each set labeled with a separate fluorescent reporter label.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Methods to increase the capacity of high content cell-based screening assays
InactiveUS7085765B2Increase capacityMaintaining “ hit ” rateCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCell basedBiology
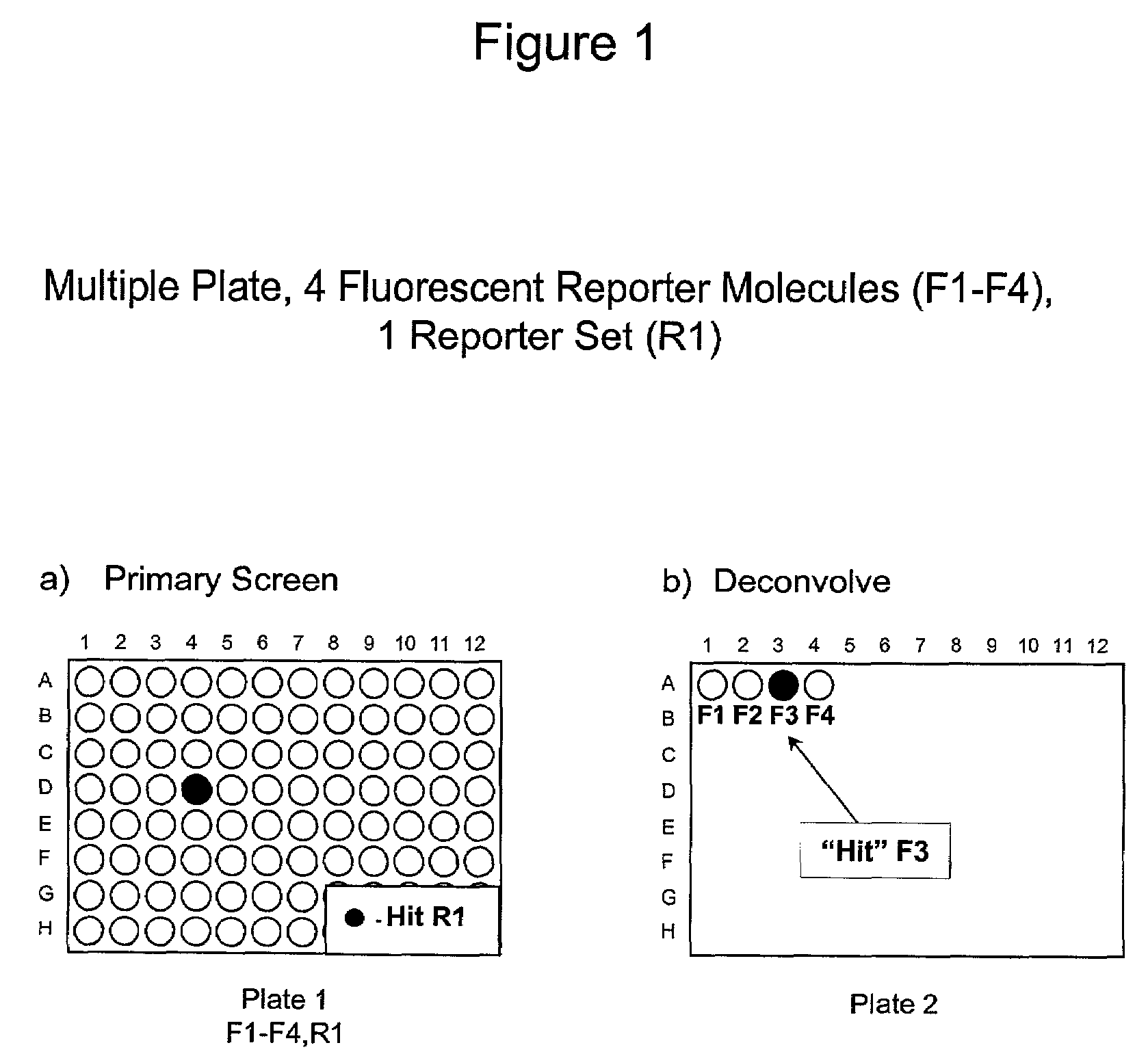
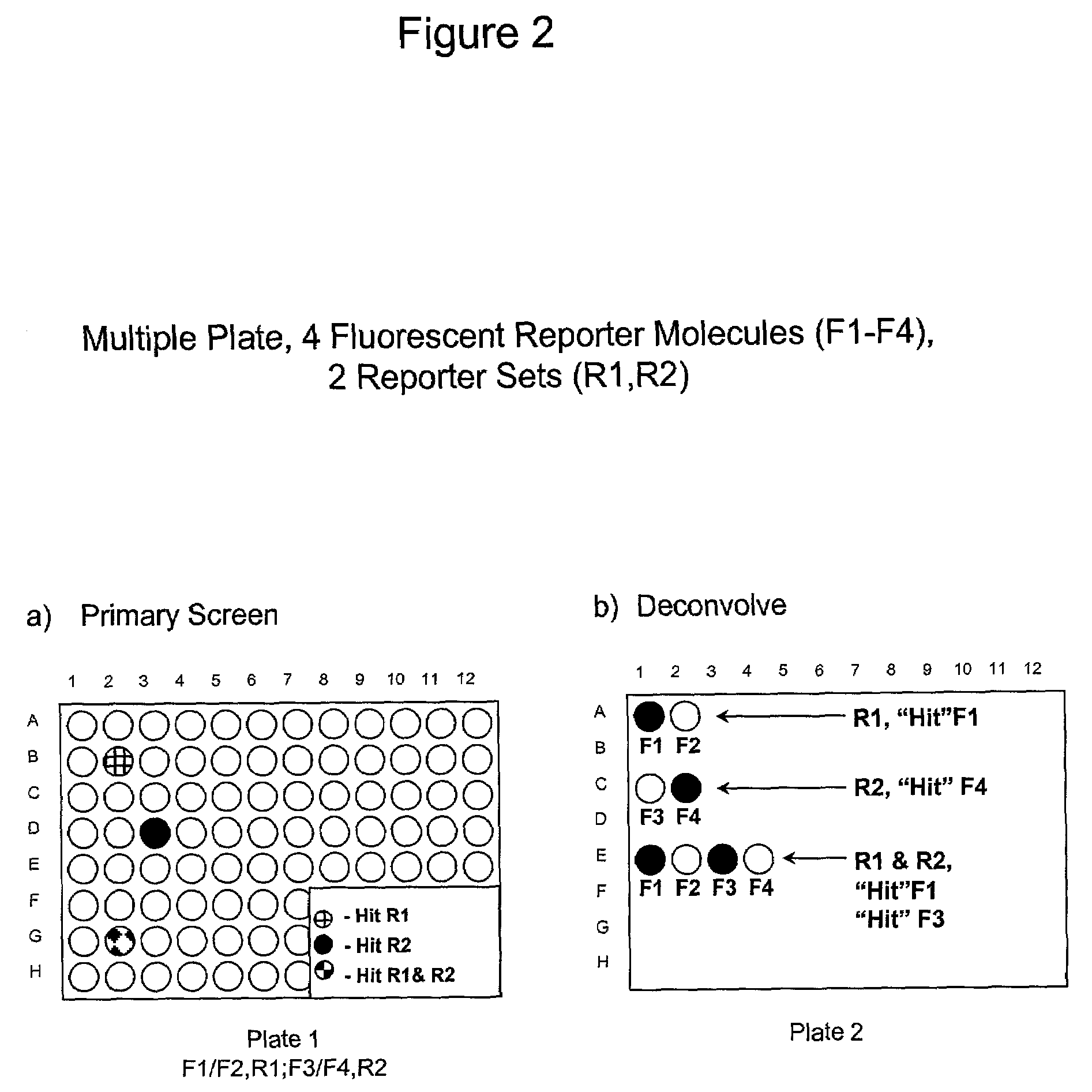
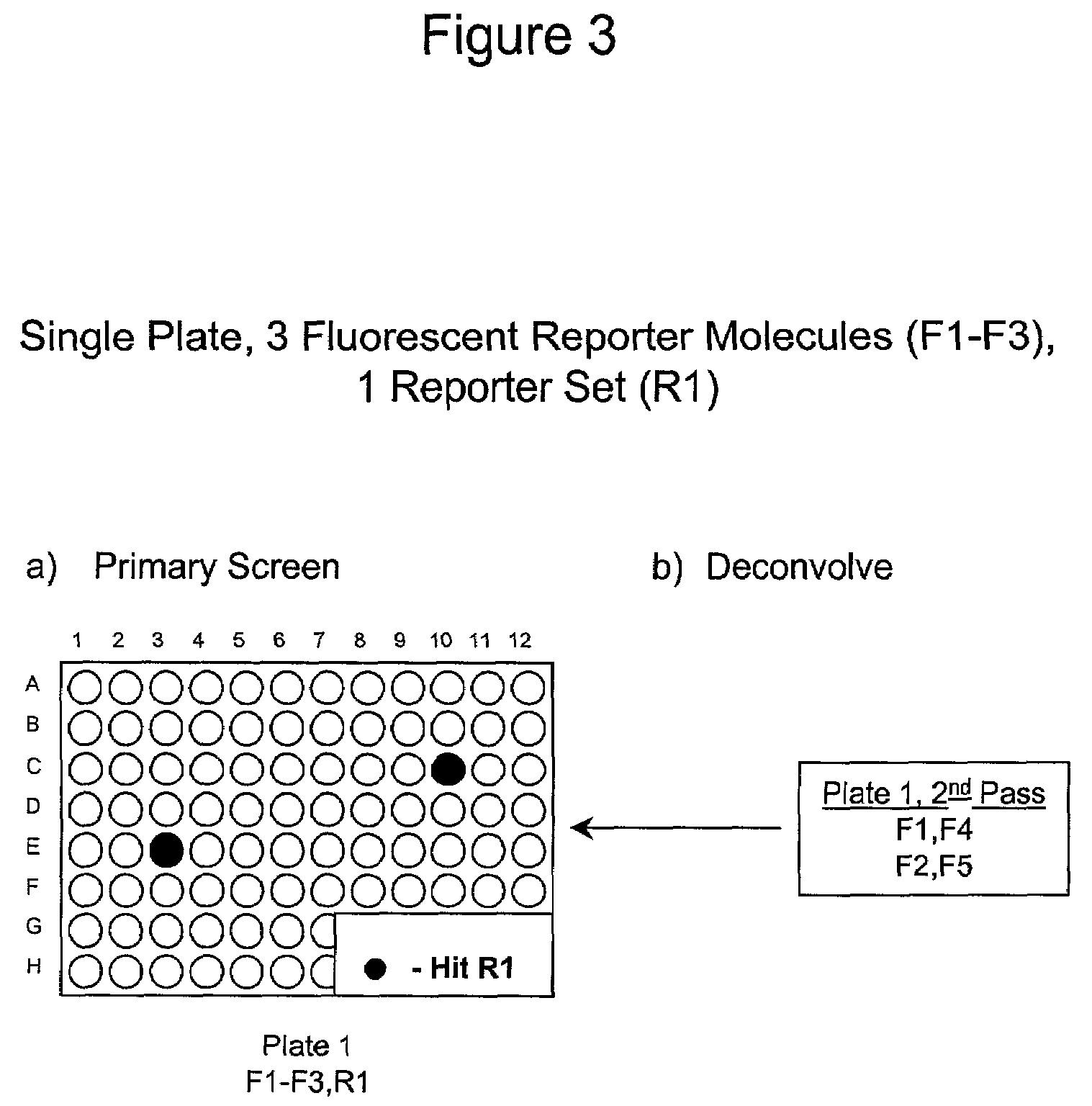
The present invention involves the pooling of multiple high content cell-based screening assays, and carrying out a primary screen in a one or more channels of a fluorescence detection device, which drastically increases the number of simultaneous high content cell-based screening events that can be carried out. Subsequent deconvolution of primary screen “hits” (ie: those wells or locations on an array of locations in which the one or more test compounds caused a change in the fluorescence signal(s) from the fluorescent reporter molecules in the cells) enables much more rapid generation of high content cell screening data than was previously possible, and at significantly reduced costs.
Owner:CELLOMICS
Fluorescent quantitative PCR primers and probes for porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses
ActiveCN103509882AImprove featuresHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesEpidemic diarrheaFluorescent quenching
The invention discloses fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primers and probes for porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses. An upstream primer and a downstream primer are shown as SEQIDNO: 1-2; a probe P1 is shown as SEQIDNO: 3; a probe P2 is shown as SEQIDNO: 4; the 3' end of sequences of the probe 1 and the probe 2 are combined with a fluorescent quenching group; and the 5' end of sequences of the probe 1 and the probe 2 are combined with different fluorescent reporter groups. The primers are relatively high in specificity and sensitivity, can detect out variant PEDV (porcine epidemic diarrhea viruses), and can detect and differentiate a variety of clinical samples so as to quickly differentiate epidemic PEDV strains; the operation is simple and practical.
Owner:WENS FOODSTUFF GRP CO LTD
Non-fluorescent quencher compounds and biomolecular assays
Bis-diazo,triaryl and aryldiazo-N-arylphenazonium quencher moieties, substituted with electron-withdrawing and electron-donating substituents which induce polarity in the delocalized aryl / diazo ring systems, are useful as labels when attached to biomolecules such as polynucleotides, nucleosides, nucleotides, and polypeptides. The quencher moieties are non-fluorescent and accept energy from fluorescent reporter labels by any energy-transfer mechanism, such as FRET. Fluorescence quencher compositions are useful in preparing quencher labelled biomolecules for various molecular biology assays based on fluorescence detection.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Low Level Fluorescence Detection at the Light Microscopic Level
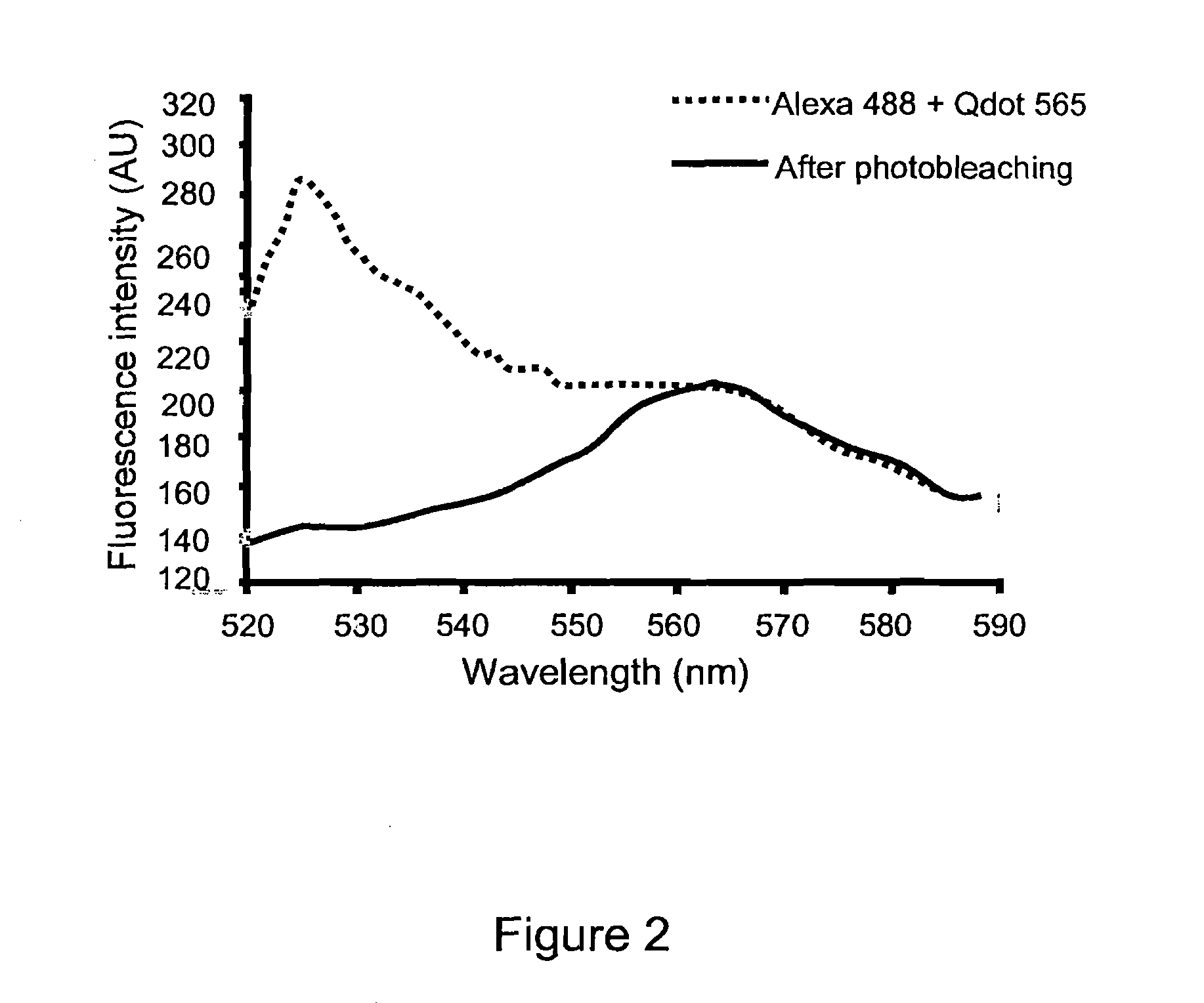
InactiveUS20100216652A1Microbiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMicroscopic levelPolynucleotide
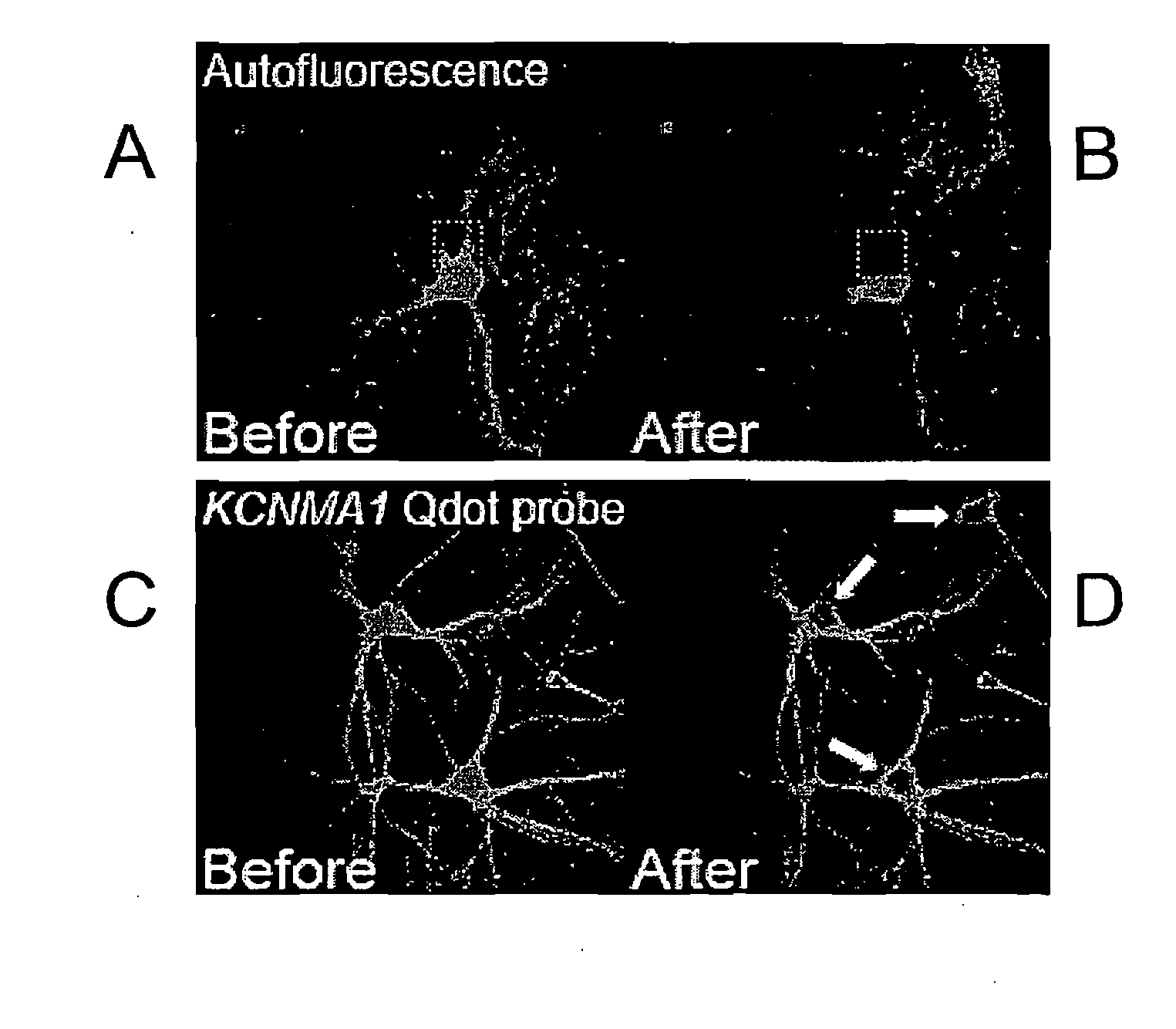
The present invention discloses methods of removing unwanted fluorescence from a sample by photobleaching said sample to enhance detection of proteins and fragments thereof, polynucleotides and fragments thereof, and biomolecules and fragments thereof in a sample by contacting said proteins, polynucleotides and biomolecules with a fluorescent reporter, wherein said fluorescent reported comprises a fluorescent semiconductor crystal or SCN, wherein said SCN further comprises a targeting moiety.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods for the amplification, quantitation and identification of nucleic
ActiveUS8962250B2Avoid pollutionPromote digestionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleic acid sequencingFluorescent reporter
Owner:AUSDIAGNOSTICS
Specific primer and probe for assaying genetically modified corn MIR162 and application thereof
InactiveCN102586442ABroad application valueBroad market prospectMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceAgricultural scienceFluorescent reporter
The invention discloses a specific primer for assaying genetically modified corn MIR162, the sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. The invention also discloses a fluorescently labeled probe for assaying genetically modified corn MIR162, the sequence of which is shown as SEQ ID NO:3, the 5' end of the probe is connected with a fluorescent reporter FAM, and the 3' end of the probe is connected with a fluorescent quencher Eclipse. The invention also discloses an assay method which utilizes the primer and the probe to carry out gene-specific qualitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), SYBR Green I real-time fluorogenic quantitative PCR and TaqMan probe real-time fluorogenic quantitative PCR to assay whether corn and related products thereof contain MIR162 transformation events, and an experiment proves that the assay method is sensitive, accurate, simple and reliable, and has a high application value and a wide market prospect.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SHANDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Fluorescent detection kit and detection method for Klebsiellapneumoniae carbapenamase
InactiveCN102002529AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceK pneumoniaeForward primer
The invention provides a fluorescent detection kit and a detection method for Klebsiellapneumoniae carbapenamase. The sequences of specific primers and a fluorescent probe in the kit are as follows: a forward primer: 5'-ACT GGG CGC GCACCTA-3'; a reverse primer: 5'-TCG CTGTGC TTG TCATCC TT-3'; and the fluorescent probe: 5'-FAM-CCG TCT ACACCCGGG CGC C-TAMRA-3', wherein the FAM is a fluorescent reporter, and the TAMRA is a fluorescent quencher. The invention has the advantages that: the detection kit has high sensitivity and good specificity for the Klebsiellapneumoniae carbapenamase, and reduces the false positive rate of the conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification; and quick, accurate and specific detection for the Klebsiellapneumoniae carbapenamase can be realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Fluorescence quantitative PCR kit used for detecting PRV, and application thereof
ActiveCN103509877AStrong specificityQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescent reporterVaccine strain
The invention relates to a fluorescence quantitative PCR rapid detection kit used for specifically detecting pig pseudorabies virus (PRV) infection, and an application thereof. The kit comprises a specific primer pair used for amplifying PRV gE gene conserved region, and a specific TaqMan fluorescent-labeled probe. An upstream primer sequence of the specific primer pair is 5'-GAGGACGACGGGCTGTAC-3', and a downstream primer sequence of the specific primer pair is 5'-GGACATCAACAGGCGGTTG-3'. The sequence of the TaqMan probe is 5'-TGGGTCCATTCGTCACTTCCG-3'. The 5' end of the TaqMan probe is labeled with a fluorescent reporter group FAM. The 3' end of the TaqMan probe is labeled with a fluorescence quenching group BHQ1 which is not intrinsically fluorescent. The kit can be used for rapid qualitative and quantitative detections of PRV infection, and can be used in identification detections of PRV gE gene-deleted vaccine strains and / or PRV wild strains.
Owner:WUHAN CHOPPER BIOLOGY
Methods and reagents for in vivo imaging of cancer cell lines
InactiveUS20090311193A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansCancer cellCell type specific
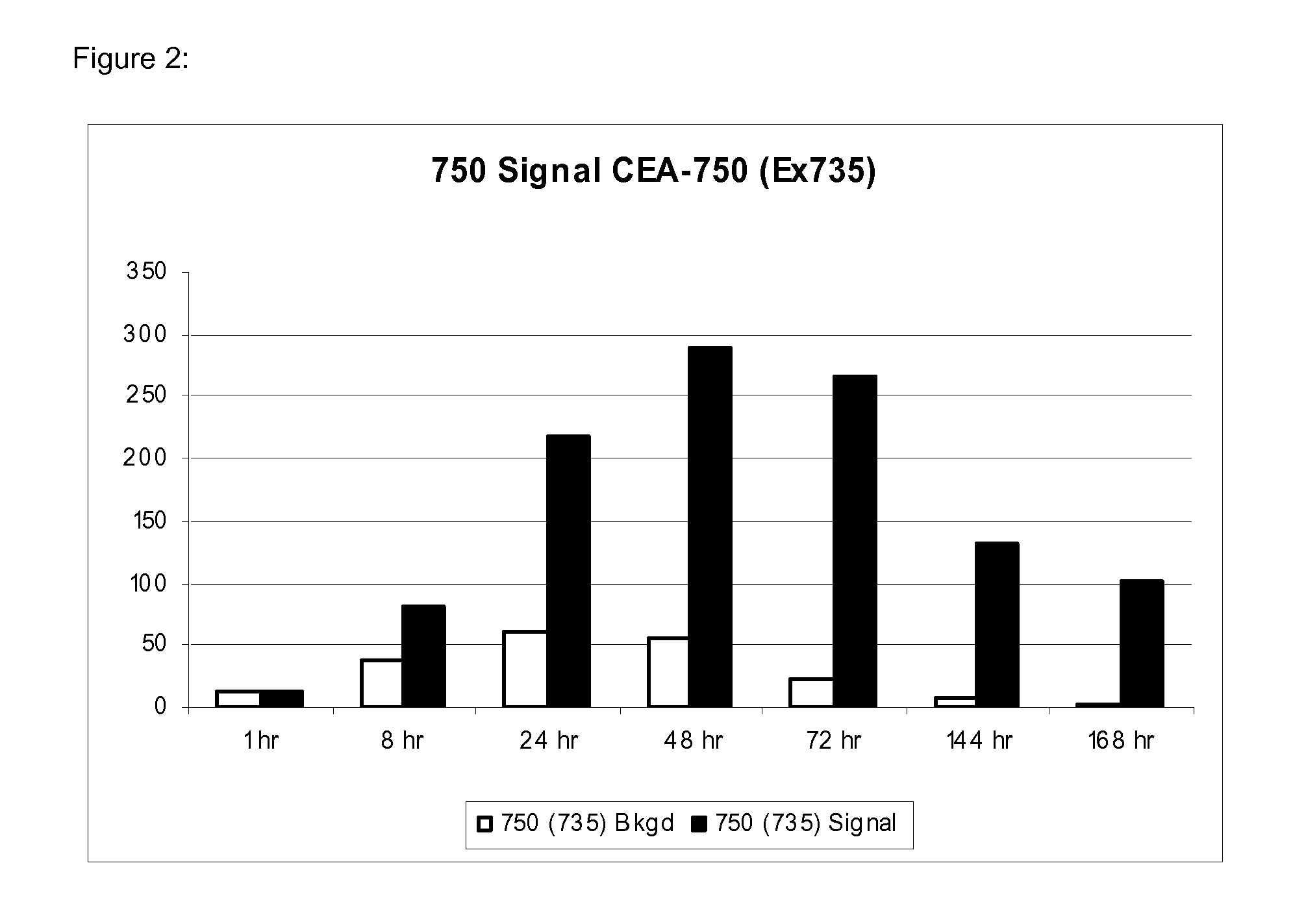
Provided are reagents and methods for non-invasive in vivo imaging wherein the reagents comprise targeted carrier molecules conjugated to a NIR reporter molecule. In one aspect the targeted carrier molecule is an antibody, or fragment thereof that has specificity for an antigen in a living body, animal or human. In one embodiment the antibodies are anti-cancer / tumor marker antibodies, organ specific antibodies, tissue specific antibodies, cell type specific antibodies, cell surface specific antibodies, anti-viral antibodies, anti-bacterial antibodies and anti-pathogenic antibodies. The NIR reporter molecules are any fluorescent reporter molecule compatible with in vivo imaging and generally having an excitation wavelength of at least 580 nm.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
DNA construct and method for transgene expression
InactiveUS20160040186A1Easy to identifyRapidly and conveniently performVectorsMicroorganismsGene PositionDNA construct
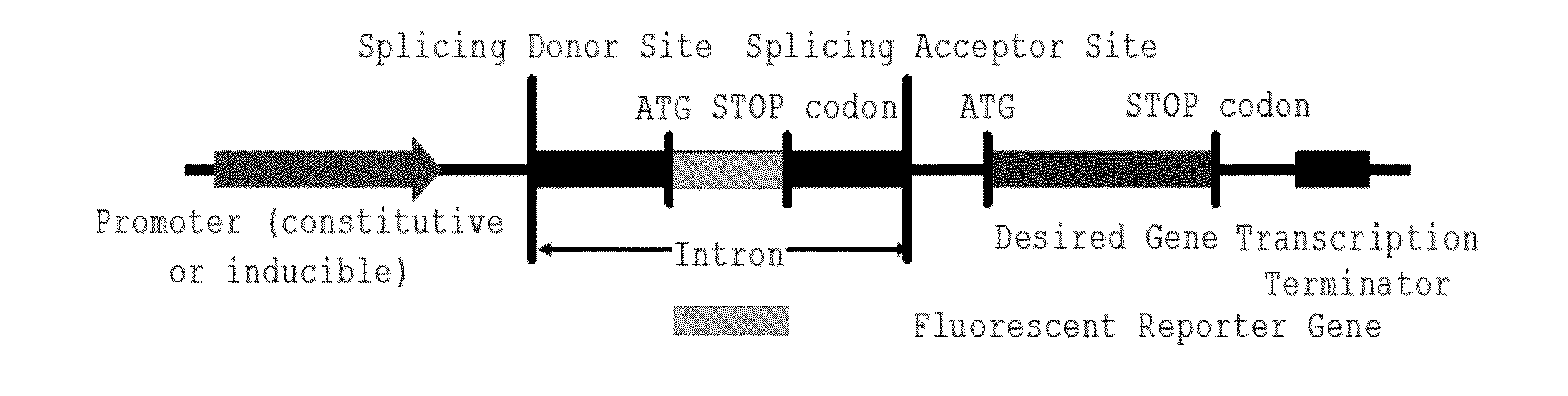
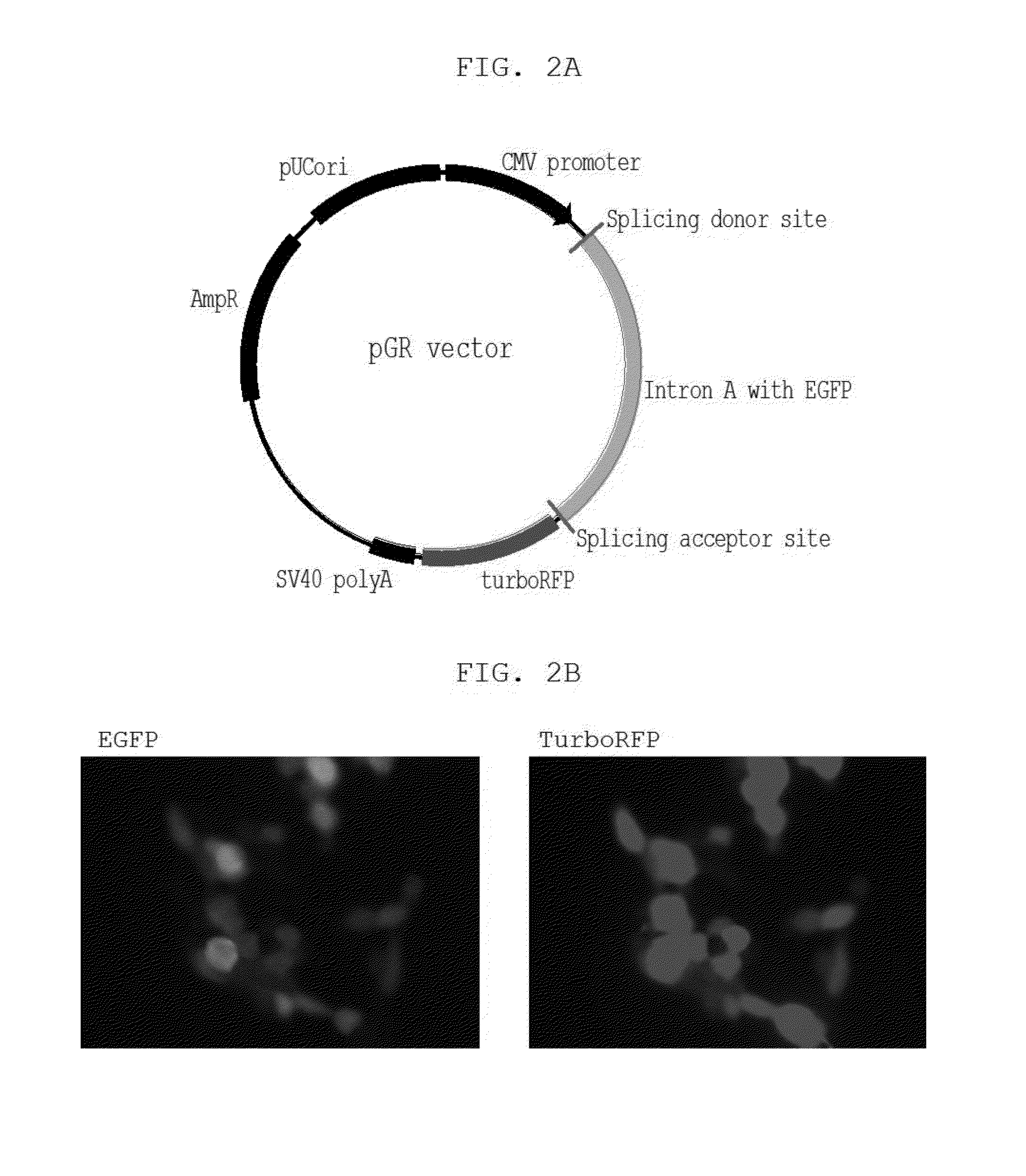
This invention relates to a DNA construct that is capable of expressing a desired transgene in a trackable manner. The construct comprises in 5′ to 3′ downstream direction: a promoter; a fluorescent reporter gene positioned within an intron defined by a 5′-donor splice site comprising a splice donor sequence and a 3′-acceptor splice site comprising a splice acceptor sequence; a desired gene and a transcription terminator. A method of producing a transgenic host cell having a desired product is also disclosed.
Owner:LIU XIAOYUN
Fluorescent quantitative detection kit of H1N1 influenza virus A and detection method thereof
ActiveCN101649356AStrong specificitySensitive detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesReverse transcriptasePolymerase L
The invention provides a nucleic-acid fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR detection kit of H1N1 influenza virus A and a detection method thereof. The detection kit mainly comprises a specific primer, a fluorescent probe, a PCR buffer solution, a deoxidized nucleoside triphosphate compound, a DNA polymerase, a reverse transcriptase and an RNA enzyme inhibitor, wherein the specific primer and the fluorescent probe have the following sequences: an upstream primer H1N1 A-FP:5'-AGGTTTGAGATATTCCCCAAGACA-3'; a downstream primer H1N1 A-RP:5'-AATTTTTGTAGAAGCTTTTTGCTCC-3'; and a specific probe H1N1 A-P:5'-F-CATGGCCCAATCATGACTCGAACA-Q-3', wherein F is a fluorescent reporter group; and Q is a fluorescent quenching group. The invention has the advantages that the nucleic-acid fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR detection kit of the H1N1 influenza virus A and the detection method thereof can be applied to the emergent detection and the monitoring of a lab where the H1N1 influenza virus A causes an outbreakepidemic.
Owner:ZHEJIANG CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Novel fluorescence dyes and their applications for whole-cell fluorescence screening assays for caspases, peptidases, proteases and other enzymes and the use thereof
The present invention relates to novel fluorescent dyes, novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of caspases and other enzymes involved in apoptosis in whole cells, cell lines and tissue samples derived from any living organism or organ. The reporter molecules and assay processes can be used in drug screening procedures to identify compounds which act as inhibitors or inducers of the caspase cascade in whole cells or tissues. The reagents and assays described herein are also useful for determining the chemosensitivity of human cancer cells to treatment with chemotherapeutic drugs. The present invention also relates to novel fluorogenic and fluorescent reporter molecules and new enzyme assay processes that can be used to detect the activity of type 2 methionine aminopeptidase, HIV protease, adenovirus protease, HSV-1 protease, HCMV protease and HCV protease.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
Optical biomodule for detection of diseases at an early onset
An optical biomodule for detecting a disease specific biomarker, utilizing an enhanced fluorescence emission (due to integration of one or more three-dimensional (3-D) protruded structures) in a fluidic container, upon chemical binding of a disease specific biomarker binder with its corresponding disease specific biomarker is disclosed. The three-dimensional (3-D) protruded structure can be coupled with a photonic crystal / metamaterial / metamaterial of Epsilon-Near-Zero (ENZ) of a suitable wavelength range. Furthermore, an enhanced fluorescence emission can be modulated by a synthetic Cas13 protein chemically coupled with a CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and a quenched fluorescent reporter. Alternatively, a suitable synthetic substitute of a synthetic Cas13 protein chemically coupled with a CRISPR RNA (crRNA) containing a targeting sequence can also be utilized.
Owner:MAZED MOHAMMAD A
Primer pair for identifying plectropomus leopardus, probe, kit and detection method
InactiveCN103589802AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLeopardus colocoloBiochemistry
The invention discloses a primer pair for identifying plectropomus leopardus, a probe, a kit and a detection method. The primer pair comprises primers F289 and R380 with sequences as shown in SEQ ID No:1 and SEQ ID No:2 respectively; the probe P309 has a sequence as show in SEQ ID No:3, a fluorescent reporter group FAM is connected with the 5' end of the probe sequence, and a fluorescent quenching group TAMRA is connected with the 3' end of the probe sequence. The invention further discloses the kit comprising the primer pair and the probe as well as the detection method for identifying the plectropomus leopardus by the primer pair, the probe or the kit. The method has the advantages of quickness, accuracy and sensitiveness.
Owner:陈双雅
Method for detecting a target nucleic acid in a sample
The invention relates to a method for detecting a target nucleic acid in a sample using fluorescent probe pairs which include fluorescent reporter and quencher molecules which may be used in hybridization assays and in nucleic acid amplification reactions, especially fluorescent reporter molecules and quencher molecules of polymerase chain reactions (PCR).
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
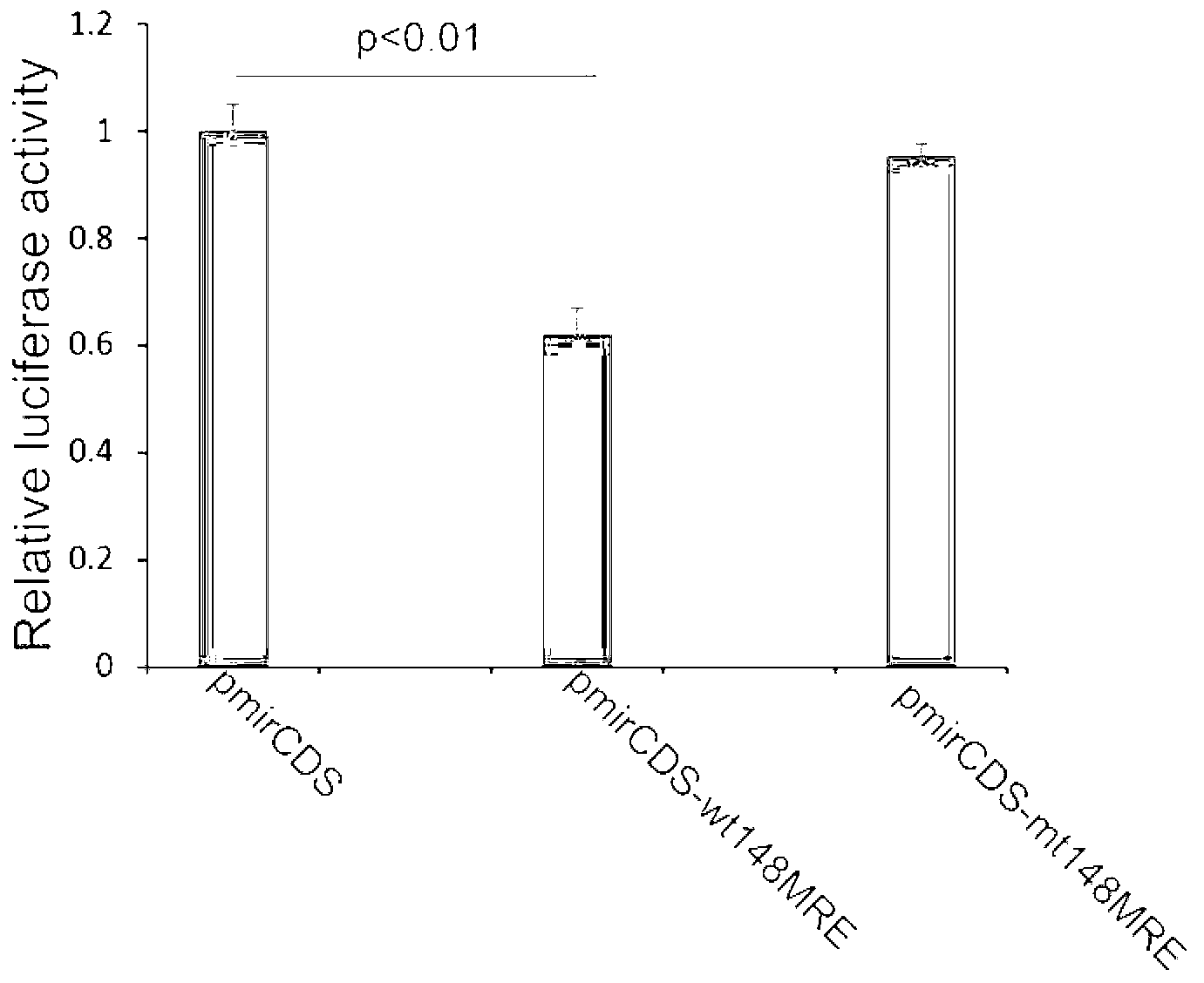
Dual fluorescent reporter gene vector for identifying miRNA targets, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103266120AEasy to operateShort experiment cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRenilla luciferaseMultiple cloning site
The invention discloses a dual fluorescent reporter gene vector for identifying miRNA targets, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof in identifying the miRNA targets in coding regions and detecting functions of the miRNA on the coding regions. The carrier has a renilla luciferase gene and a firefly luciferase gene, and multiple cloning sites (MCS) are located between a terminal amino acid codon and a stop codon of a firefly luciferase reporter gene, thereby facilitating insertion of the miRNA targets into the coding regions of the firefly luciferase reporter gene, so as to identify the miRNA targets in coding regions and detect the functions of the miRNA on the coding regions. The preparation method of the carrier provided by the invention does not require a special treatment for terminals of the carrier or target fragments, is free of connection reaction and PCR amplification, and is simple to operate, short in experiment period and high in efficiency.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
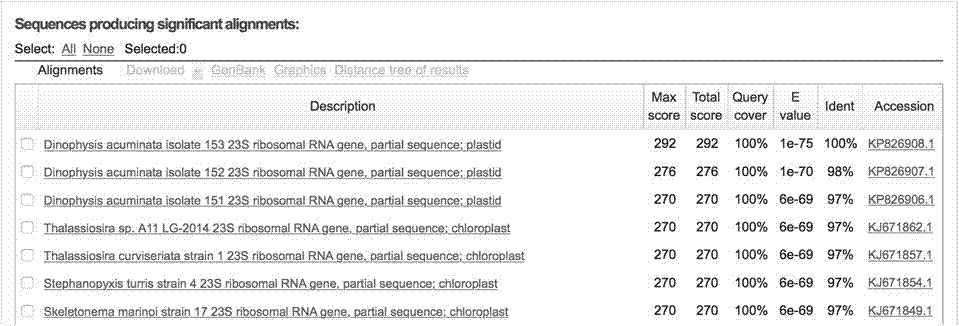
Diatom UPA (universal plastid amplicon) gene analyzing method and application thereof in legal medical expert detection
The invention discloses application of a diatom UPA (universal plastid amplicon) gene in judging whether the drowned dead really die of drowning. The invention provides a pair of primer pairs for detecting the diatom UPA gene and further provides a diatom UPA gene analyzing method. The analyzing method comprises the steps of extracting diatom nucleic acid, utilizing the primer pair shown in the right of claim 2 to amplify the UPA gene in the nucleic acid, utilizing an amplified product to prepare a sample to be tested and performing nucleic acid analysis on the sample to be tested. Furthermore, a used probe is 5''-CGGAGGCGTACAAAG-3'', the 5'' end of the probe is marked by an FAM fluorescent reporter group, and the 3'' end of the probe is marked by an NFQ-MGC MGB fluorescent quencher group. The invention further provides application of the diatom UPA gene analyzing method in legal medical expert detection. The application of the diatom UPA gene analyzing method in legal medical expert detection comprises the steps of extracting the diatom nucleic acid in organs of the drowned dead, amplifying the diatom nucleic acid through a PCR technology, then detecting and comparing the diatom nucleic acid with diatom nucleic acid in a water sample. Through comparison of relevance ratio and a sequencing result of the diatom UPA gene, whether the drowned dead really die of the drowning can be judged. Meanwhile, the application of the diatom UPA gene analyzing method in legal medical expert detection is beneficial to finding out a real drowned area.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CRIMINAL SCI & TECH RES INST
African swine fever virus wild strain and vaccine strain identification and detection kit
InactiveCN111876527AHigh utility valueIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesClassical swine fever virus CSFVAfrican swine fever
The invention discloses an African swine fever virus wild strain and vaccine strain identification and detection kit and application thereof. The kit provided by the invention comprises three groups of primers and probes, and the first group of primers and probes is completely paired with a specific sequence of an African swine fever virus B646L gene conserved region and is used for detecting theAfrican swine fever virus; the second group of primers and probes is completely paired with a specific sequence of an African swine fever virus EP402R gene conserved region and is used for detecting the African swine fever virus wild strain; and the third group of primers and probes is completely paired with the specific sequence of a red fluorescent protein mCherry gene and is used for detectingthe African swine fever virus vaccine strain. Different fluorescent reporter groups are respectively marked on the three probes. The African swine fever virus wild strain and vaccine strain identification and detection kit is high in detection sensitivity, capable of detecting target DNA with the minimum concentration of 100 copies / [mu] L, good in specificity, easy and convenient to operate and capable of effectively distinguishing African swine fever vaccine immune animals from wild virus infected animals.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL HEALTH & EPIDEMIOLOGY CENT
A nucleic acid detection method
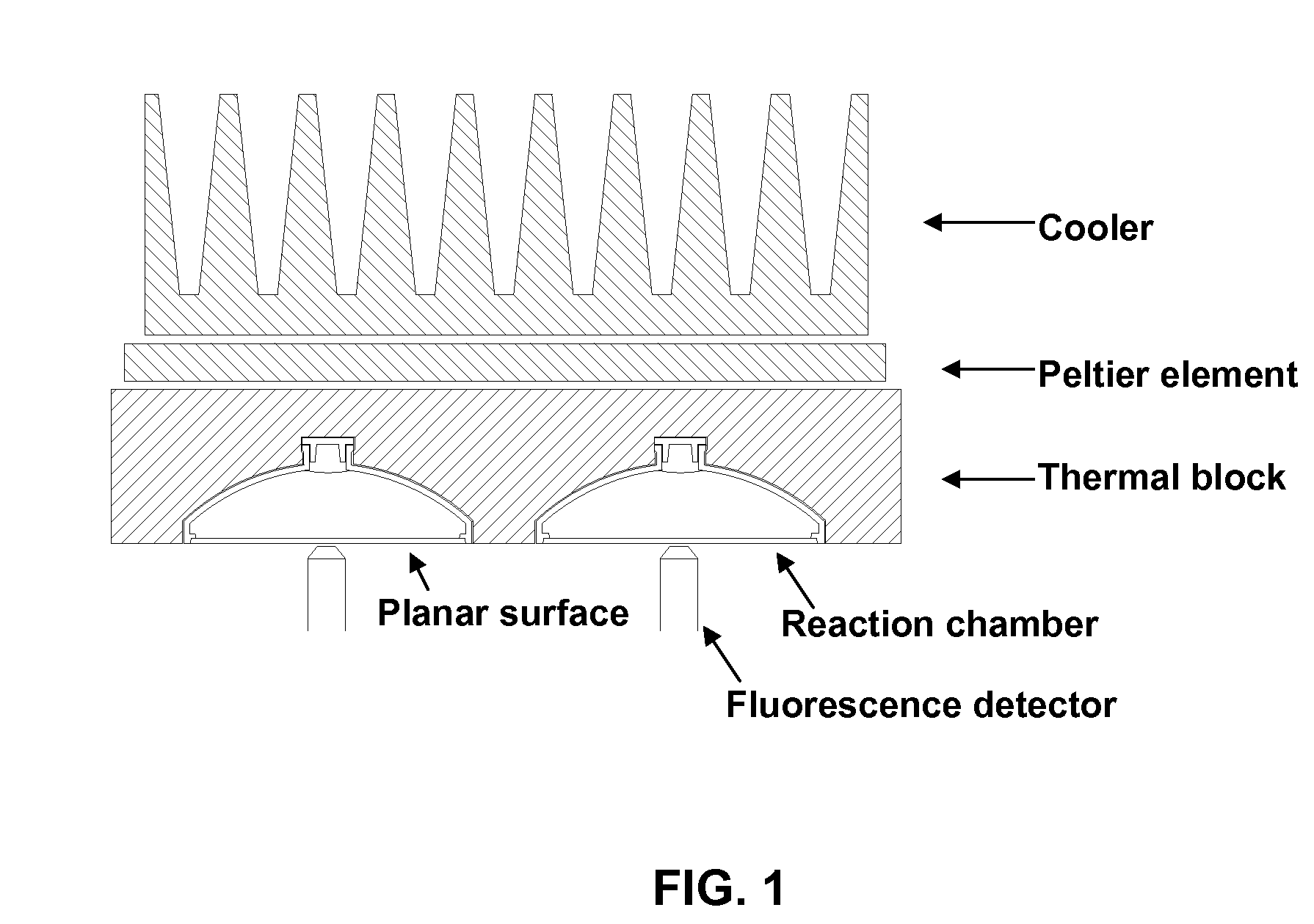
InactiveUS20070254284A1Simplify and facilitateEliminating pre-assay manipulationHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid detectionFluorescent reporter
A nucleic acid detection method utilizing fluorescent reporter for real-time monitoring of amplification in a solid state where both forward and reverse primers are attached to a array with a plurality of primers.
Owner:ZHAO BIWEI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com