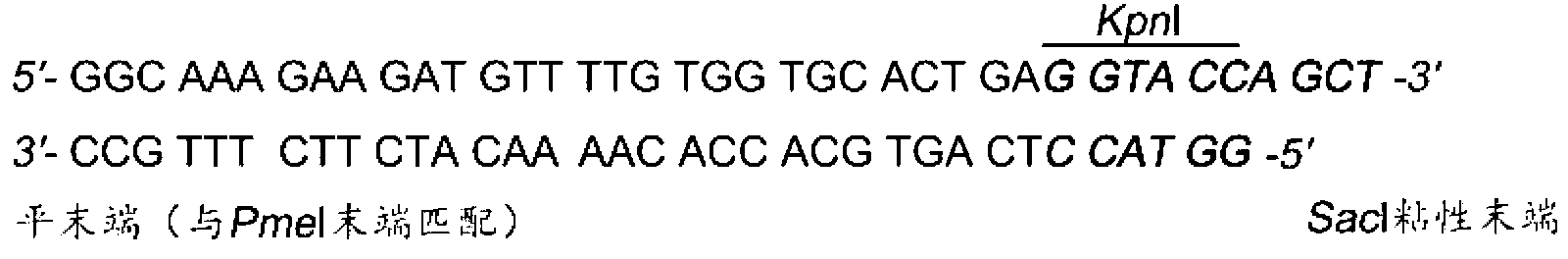Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
251 results about "Stop codon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
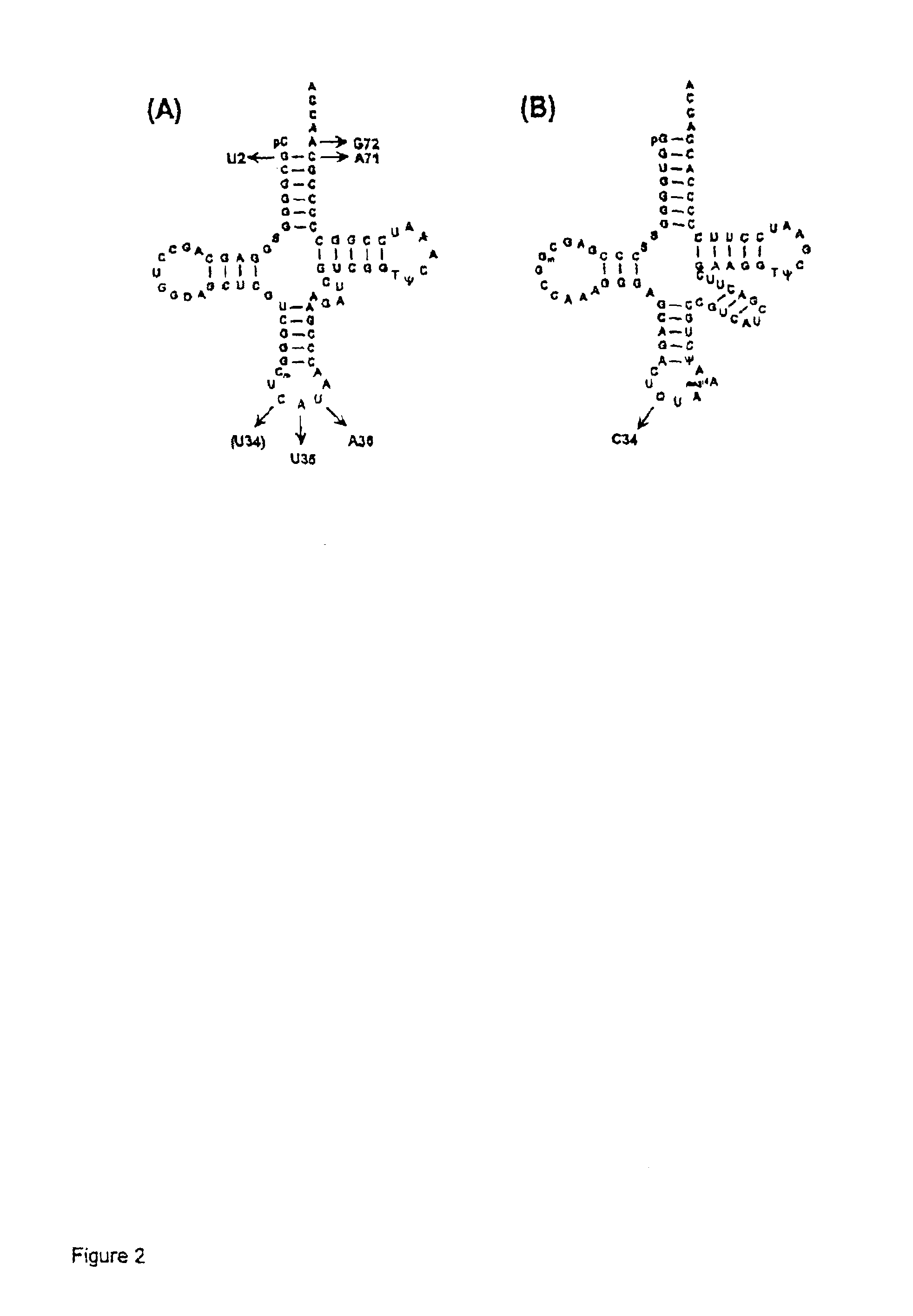
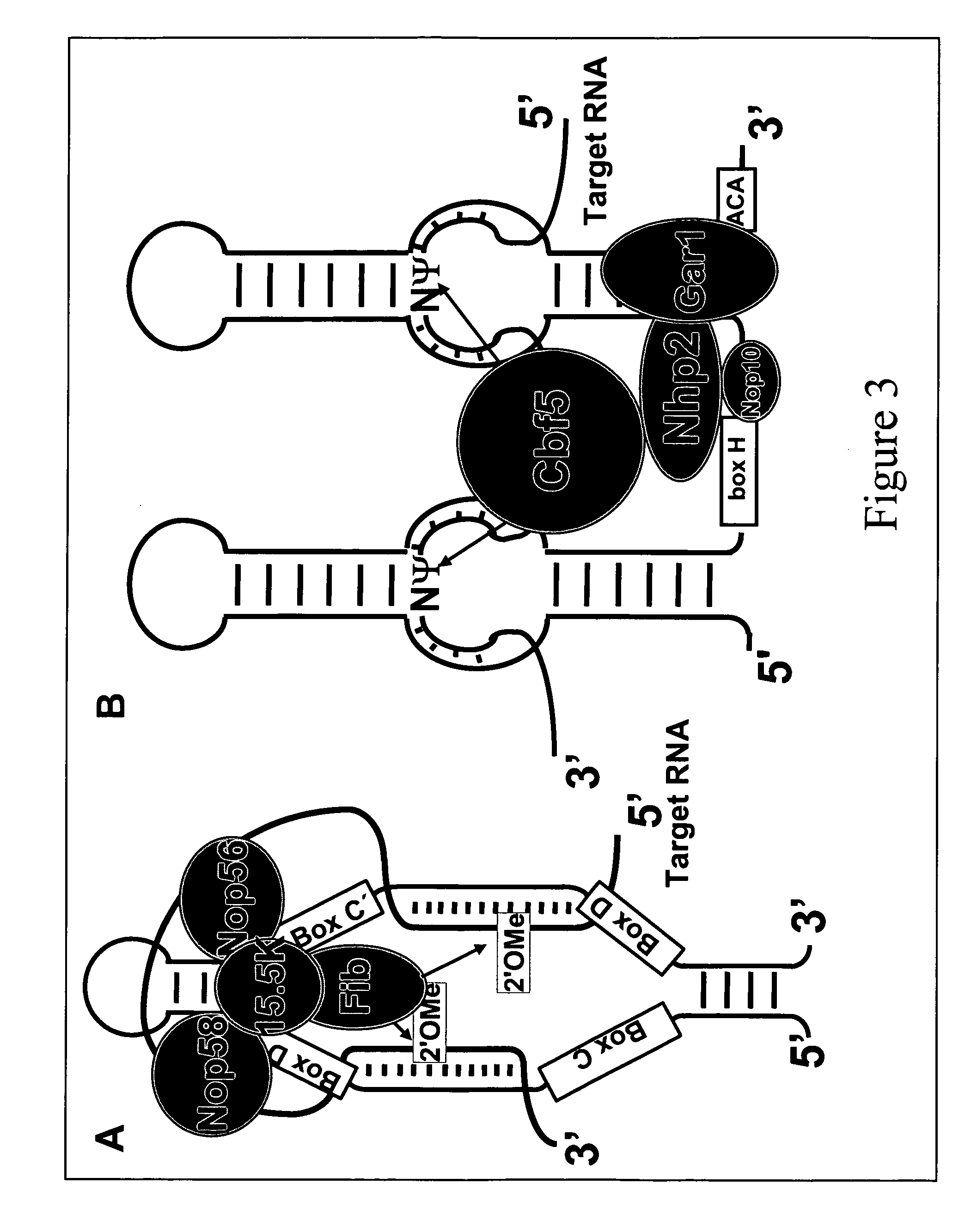
In the genetic code, a stop codon (or termination codon) is a nucleotide triplet within messenger RNA that signals a termination of translation into proteins. Proteins are based on polypeptides, which are unique sequences of amino acids. Most codons in messenger RNA (from DNA) correspond to the addition of an amino acid to a growing polypeptide chain, which may ultimately become a protein. Stop codons signal the termination of this process by binding release factors, which cause the ribosomal subunits to disassociate, releasing the amino acid chain. While start codons need nearby sequences or initiation factors to start translation, a stop codon alone is sufficient to initiate termination.
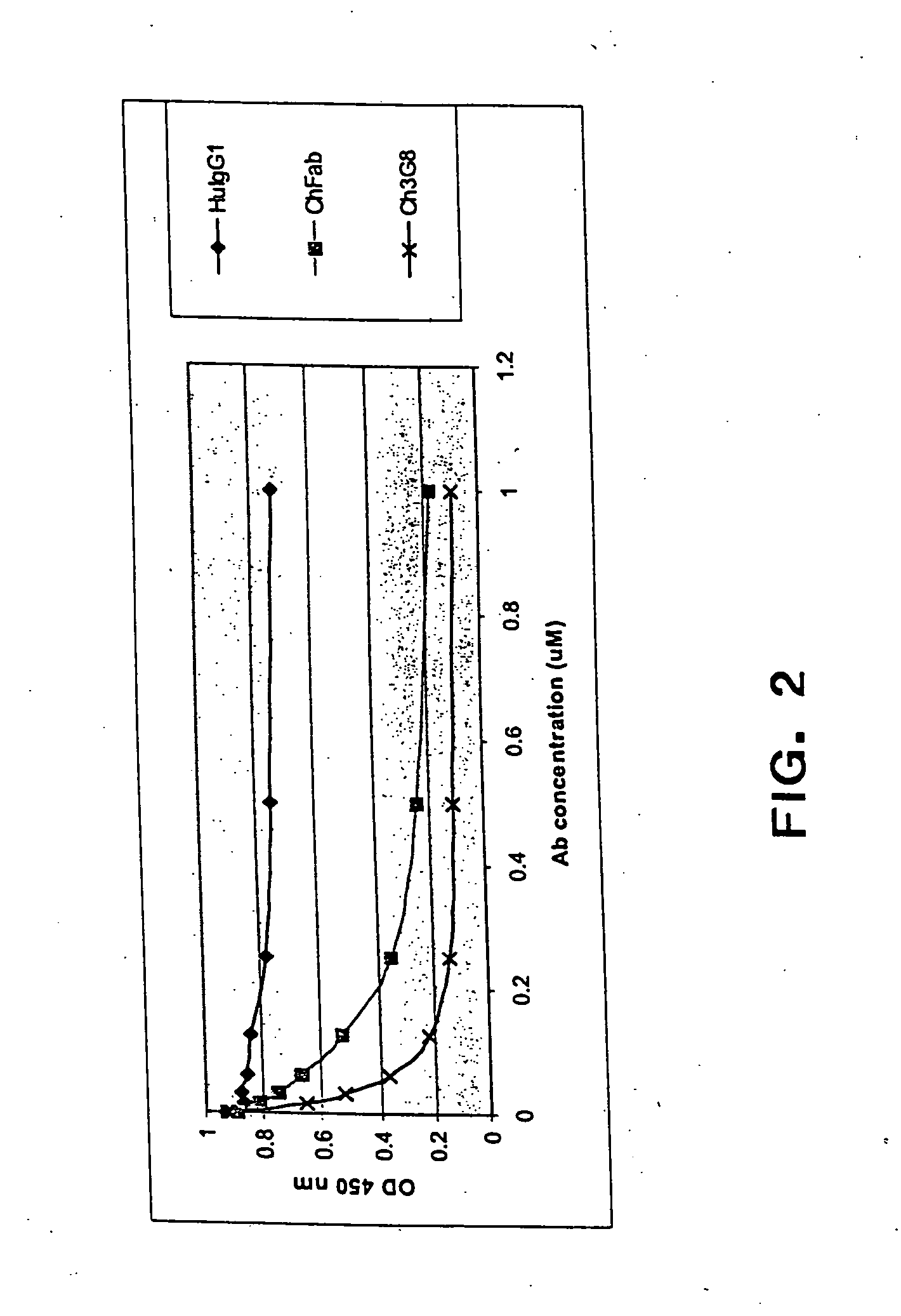
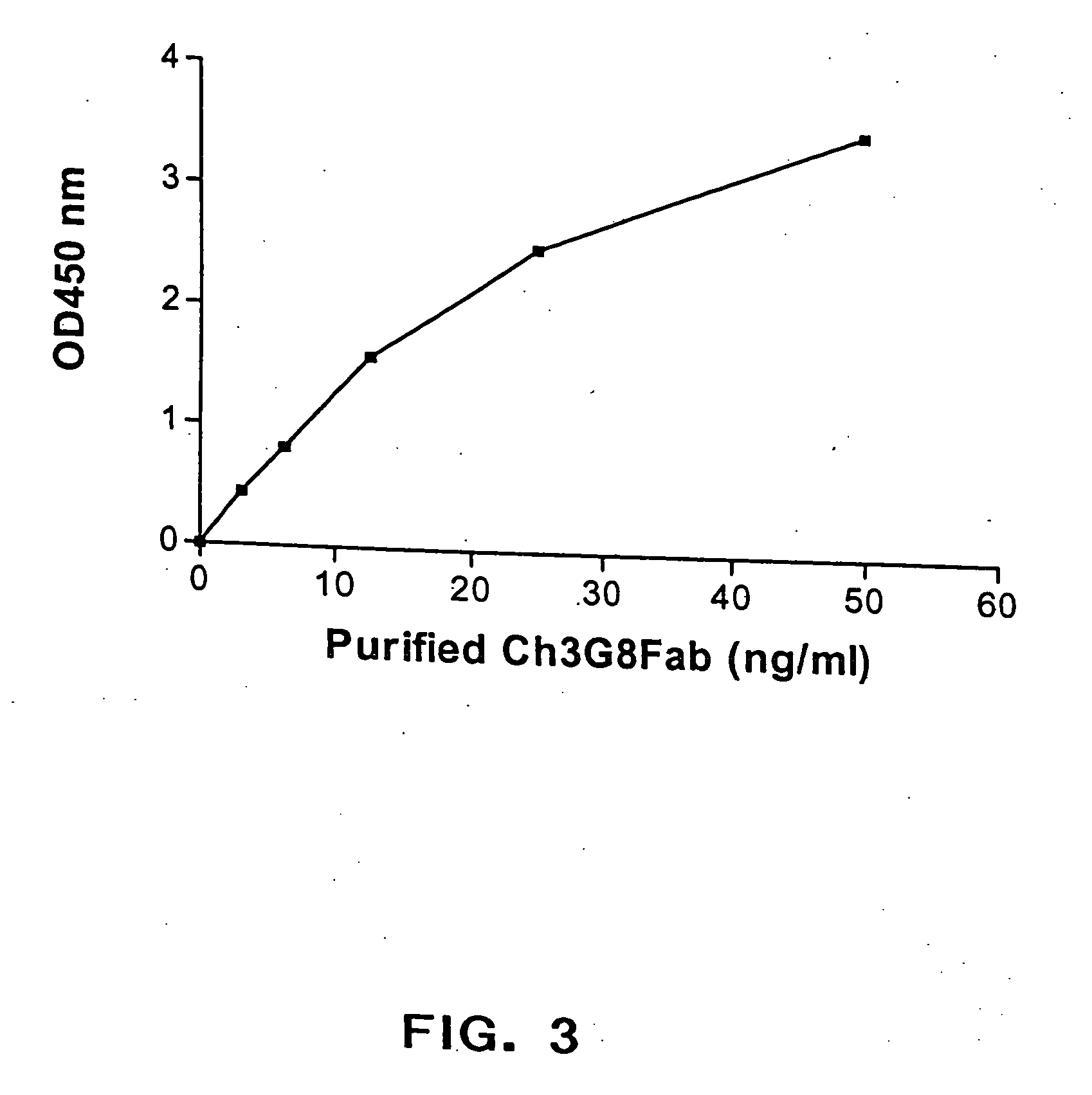
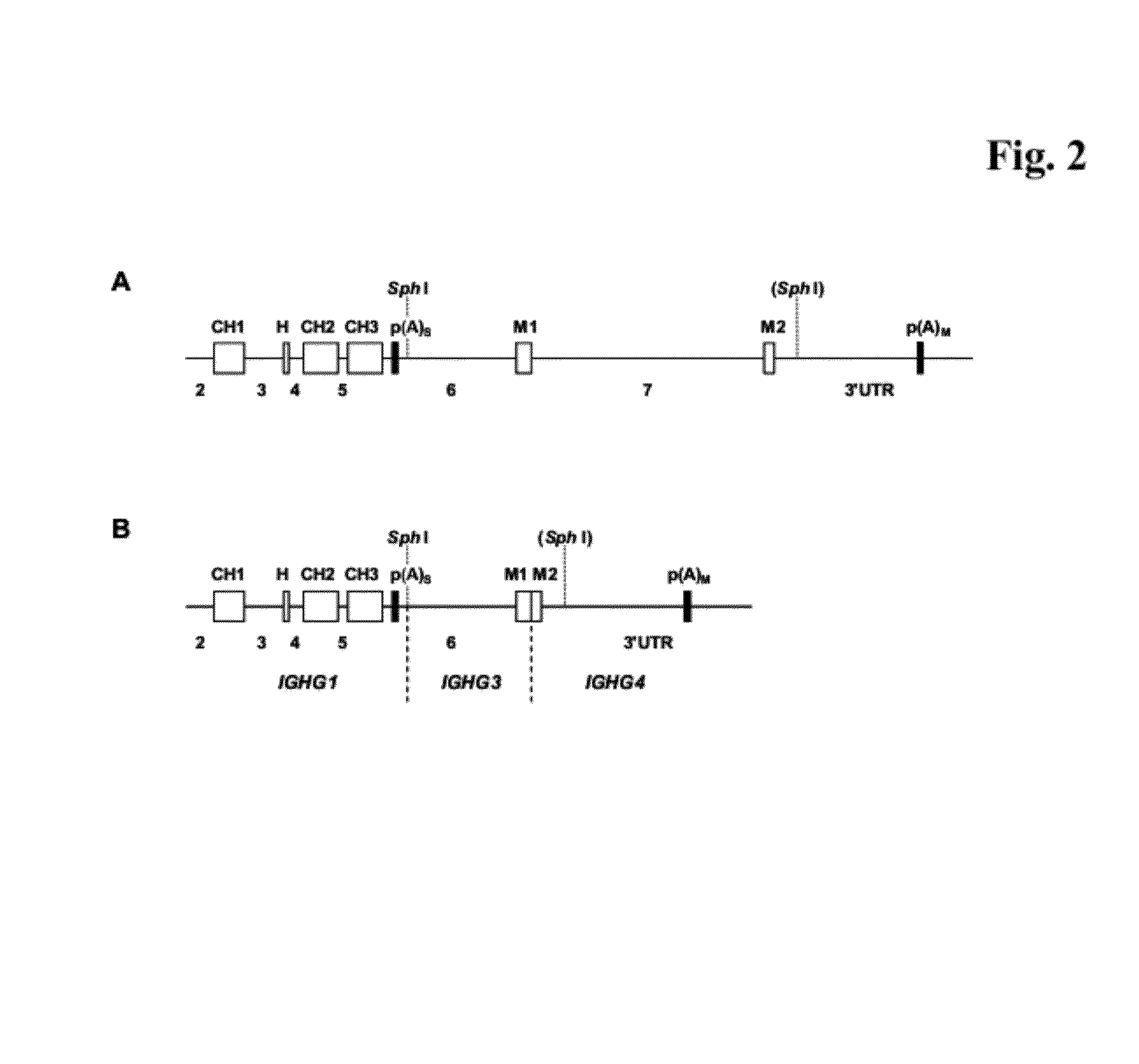
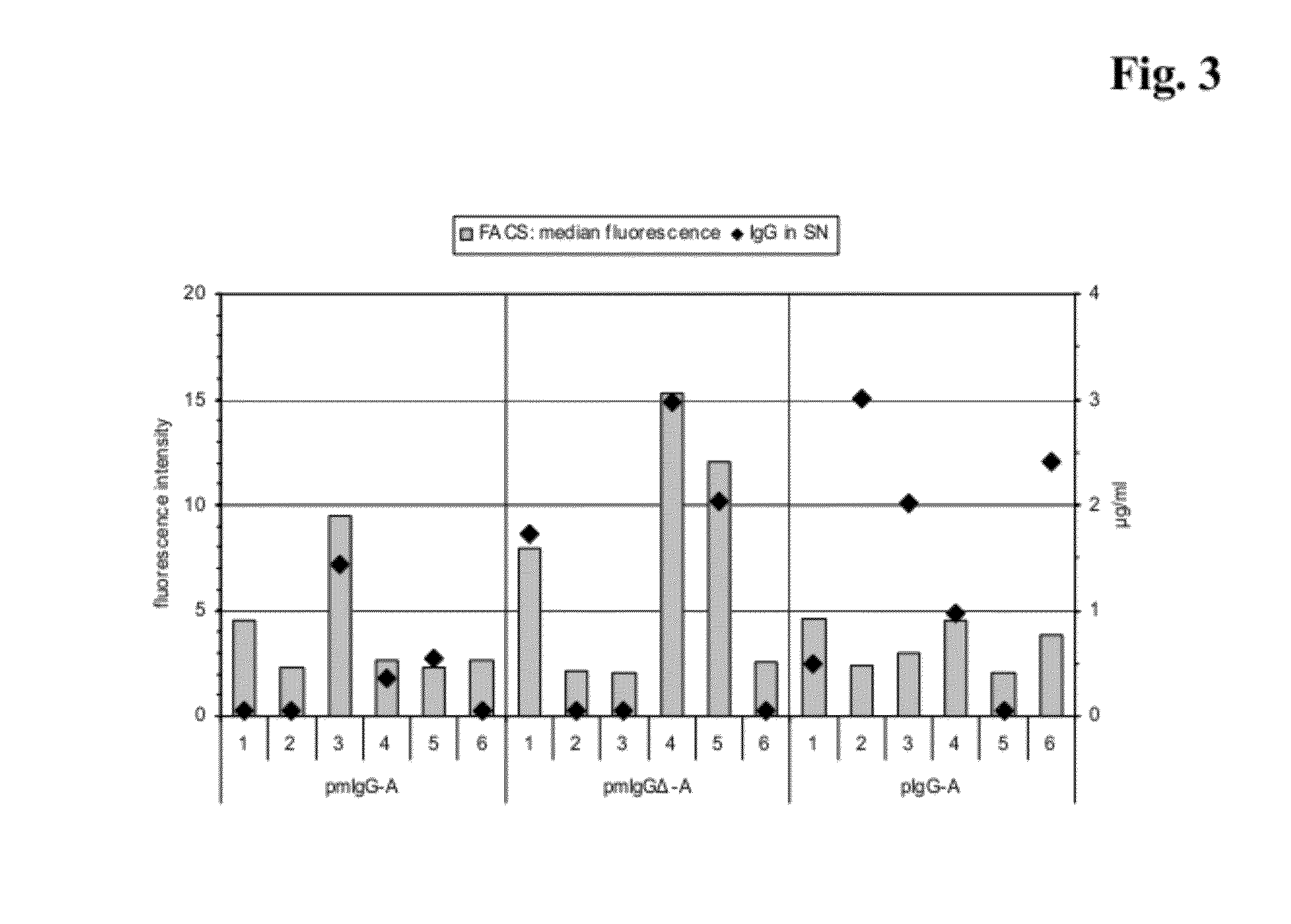
Dual expression vector system for antibody expression in bacterial and mammalian cells
ActiveUS7112439B2Maintaining their functionalityEasy to identifyAnimal cellsBacteriaAntigenBacteroides
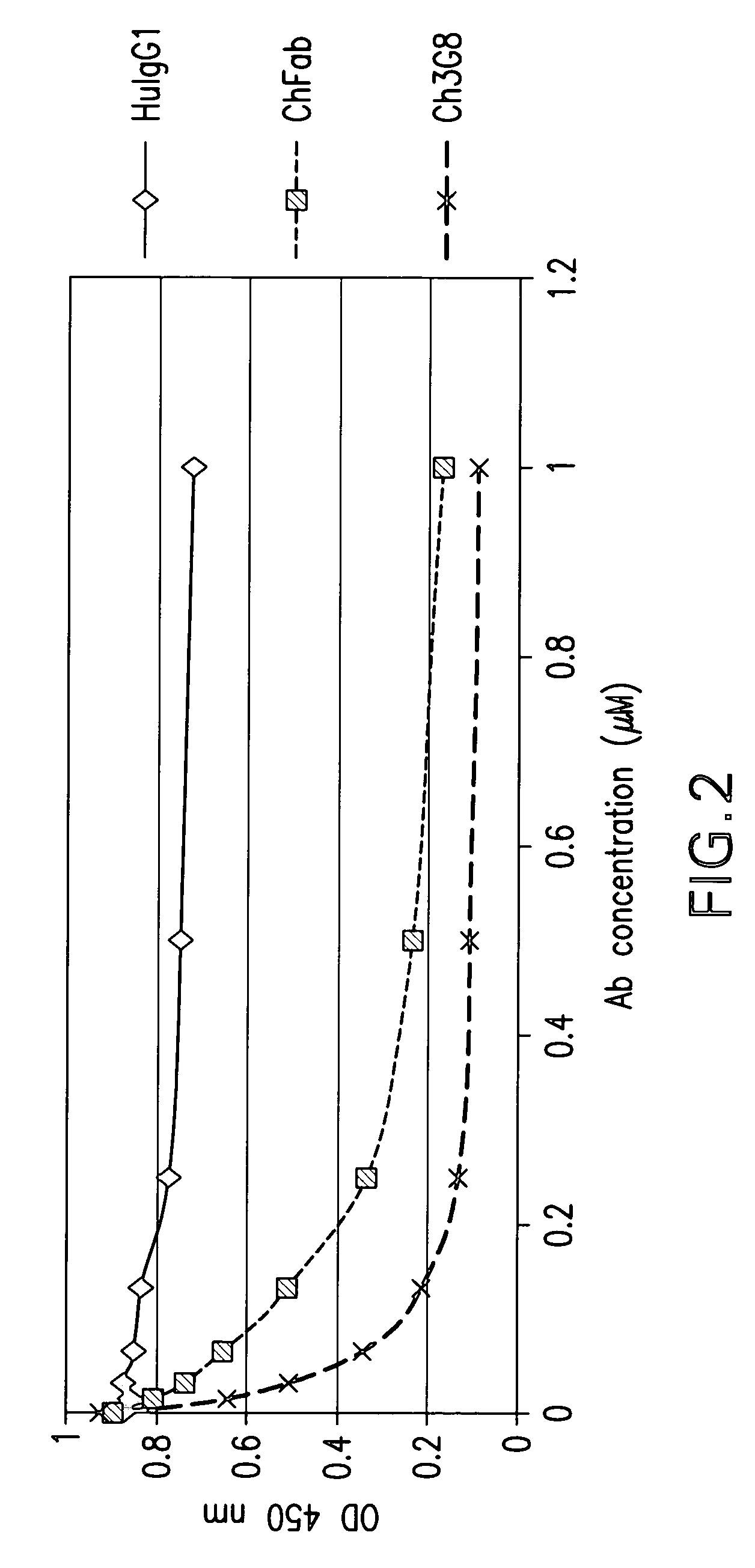
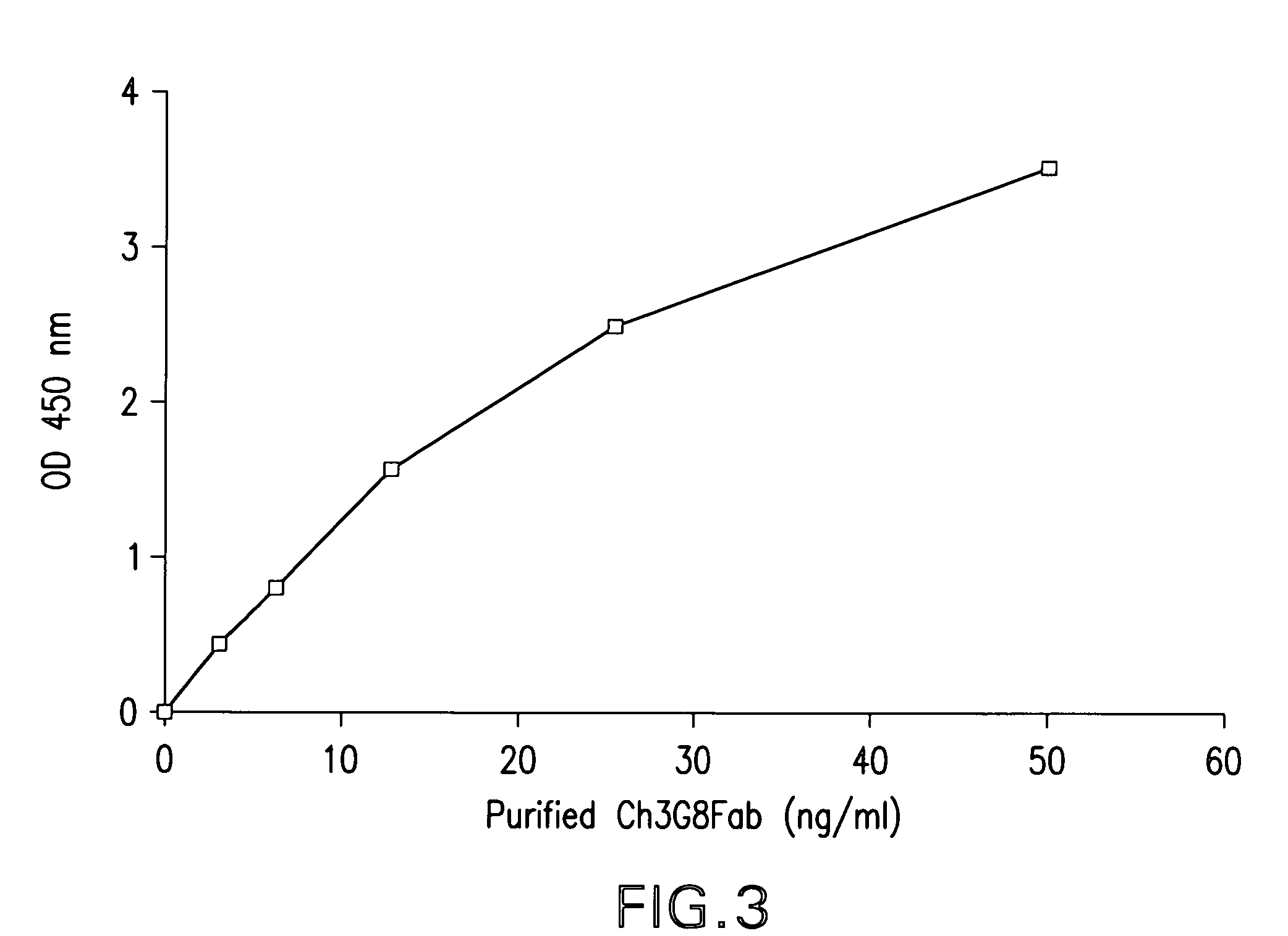
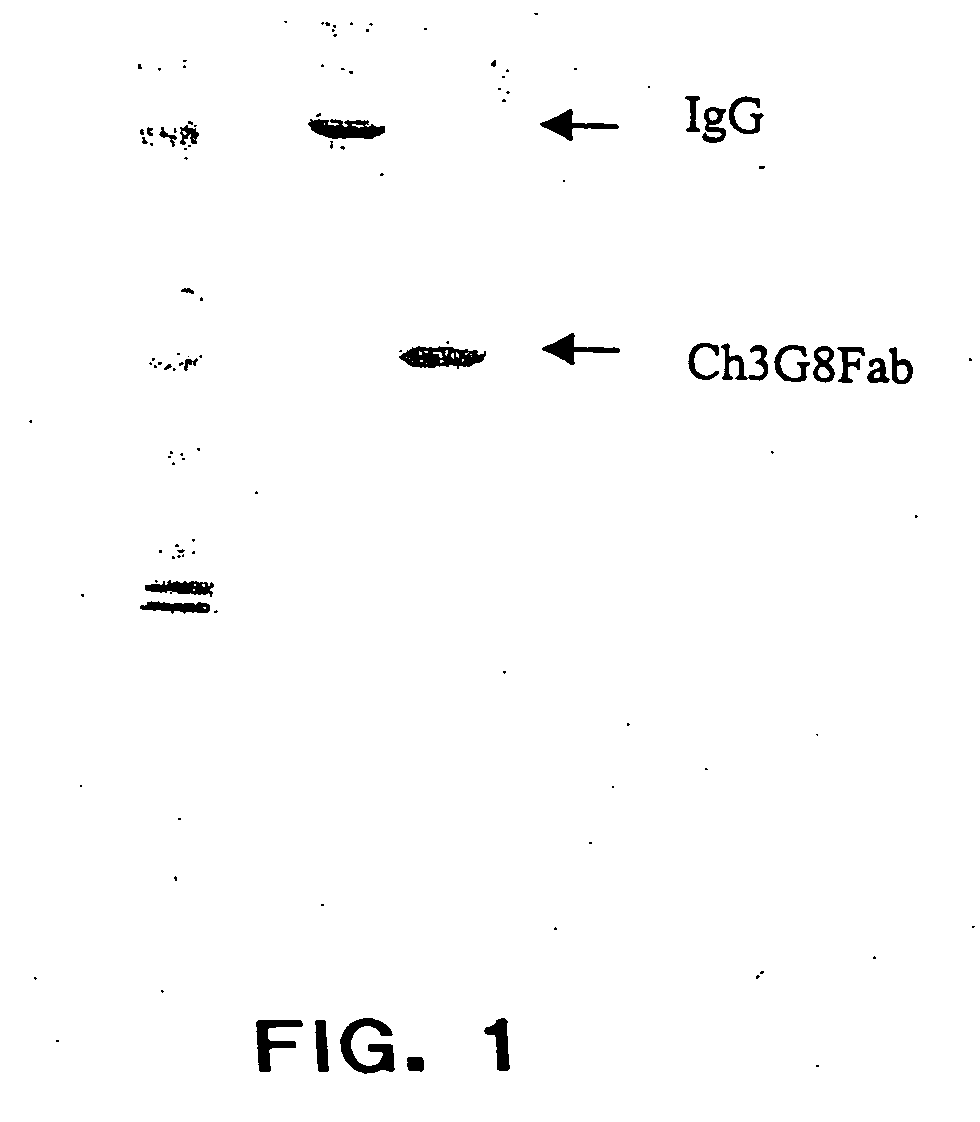
The present invention provides a dual expression vector, and methods for its use, for the expression and secretion of a full-length polypeptide of interest in eukaryotic cells, and a soluble domain or fragment of the polypeptide in bacteria. When expressed in bacteria, transcription from a bacterial promoter within a first intron and termination at the stop codon in a second intron results in expression of a fragment of the polypeptide, e.g., a Fab fragment, whereas in mammalian cells, splicing removes the bacterial regulatory sequences located in the two introns and generates the mammalian signal sequence, allowing expression of the full-length polypeptide, e.g., IgG heavy or light chain polypeptide. The dual expression vector system of the invention can be used to select and screen for new monoclonal antibodies, as well as to optimize monoclonal antibodies for binding to antigenic molecules of interest.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
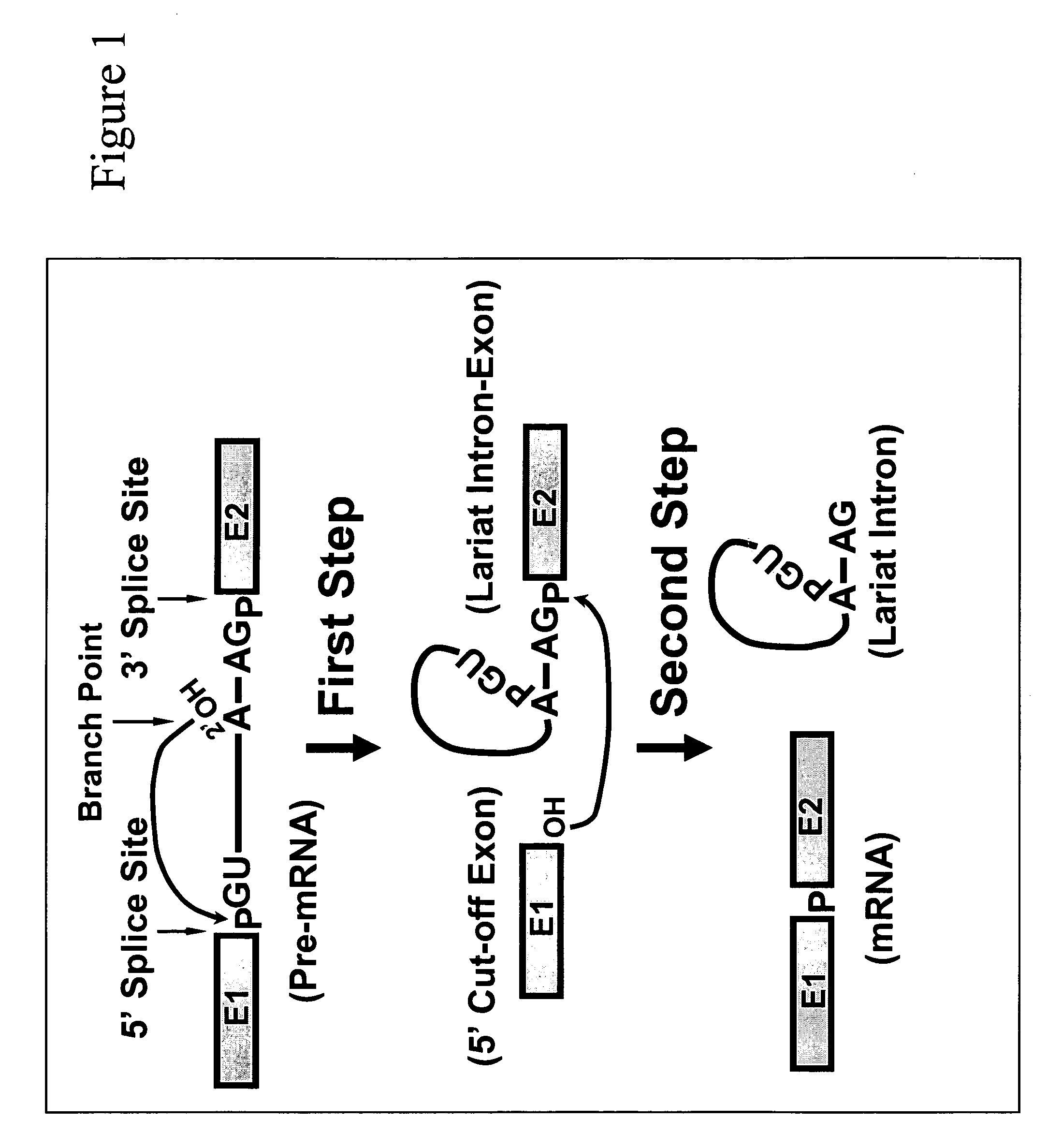
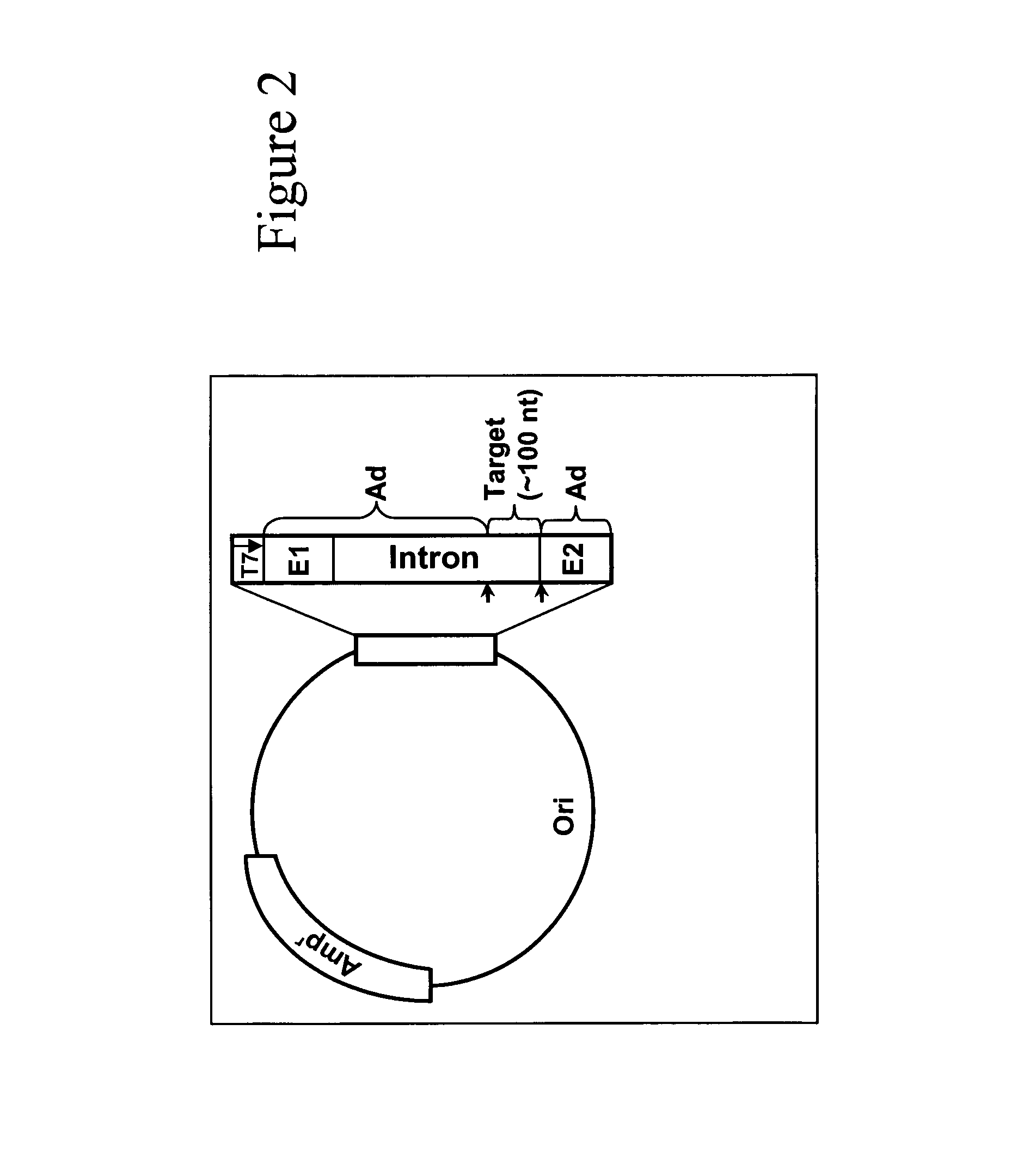
Targeted pre-mRNA/mRNA modification and gene regulation
ActiveUS20070141030A1Easy to identifyLarge productionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAdenosinePrecursor mRNA
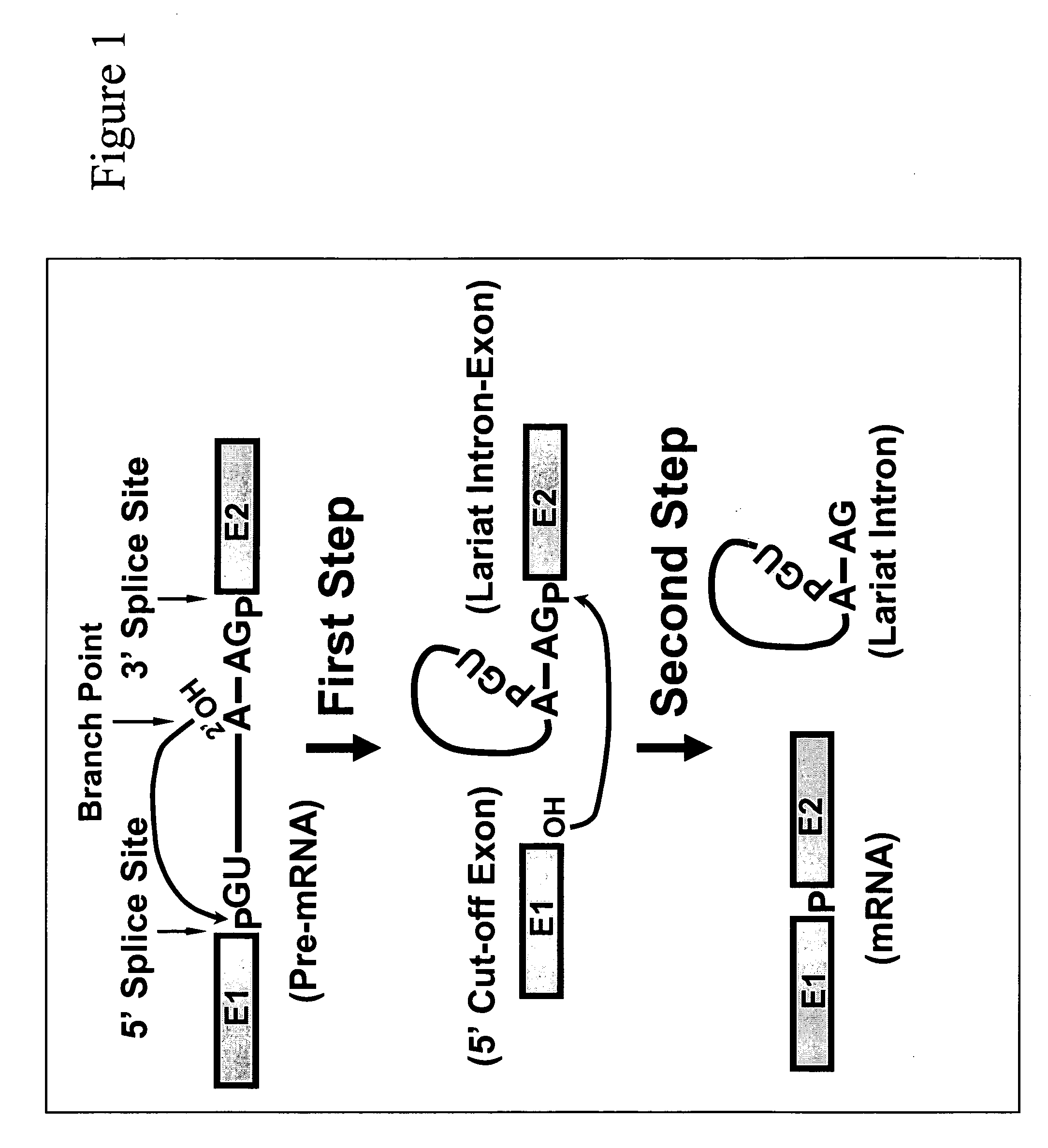
Methods for affecting mRNA expression or translation through the modification of pre-mRNA or mRNA transcripts are described. In one embodiment of the methods of the present invention, the branch point adenosine of a pre-mRNA transcript is 2′-O-methylated to block splicing and subsequent expression of the protein encoded by the transcript. In another embodiment, a uridine residue in a nonsense stop codon may be modified to pseudouridine, causing the translation machinery to read through the nonsense stop codon and translate a full length protein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
Dual expression vector system for antibody expression in bacterial and mammalian cells
The present invention provides a dual expression vector, and methods for its use, for the expression and secretion of a full-length polypeptide of interest in eukaryotic cells, and a soluble domain or fragment of the polypeptide in bacteria. When expressed in bacteria, transcription from a bacterial promoter within a first intron and termination at the stop codon in a second intron results in expression of a fragment of the polypeptide, e.g., a Fab fragment, whereas in mammalian cells, splicing removes the bacterial regulatory sequences located in the two introns and generates the mammalian signal sequence, allowing expression of the full-length polypeptide, e.g., IgG heavy or light chain polypeptide. The dual expression vector system of the invention can be used to select and screen for new monoclonal antibodies, as well as to optimize monoclonal antibodies for binding to antigenic molecules of interest.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
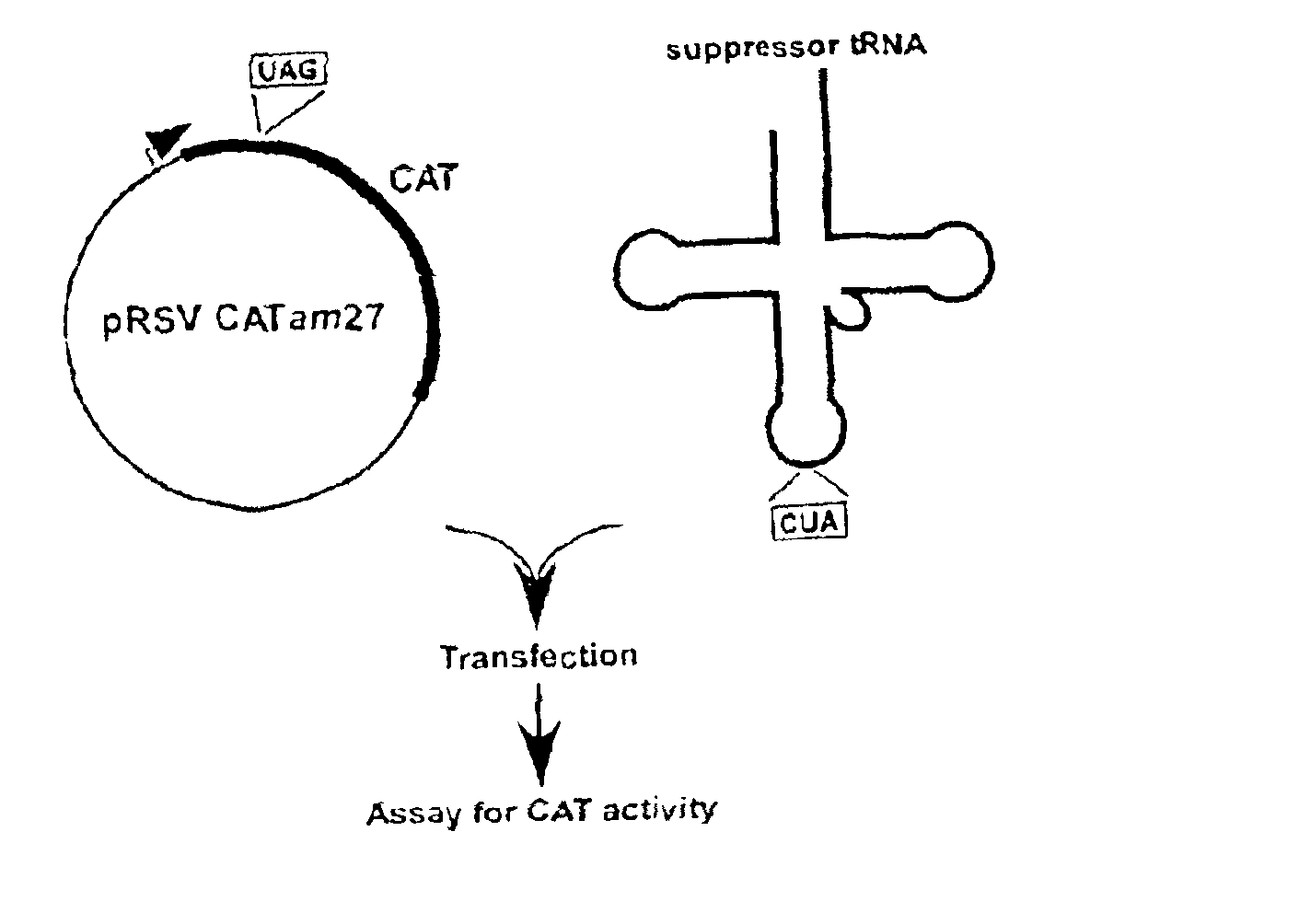
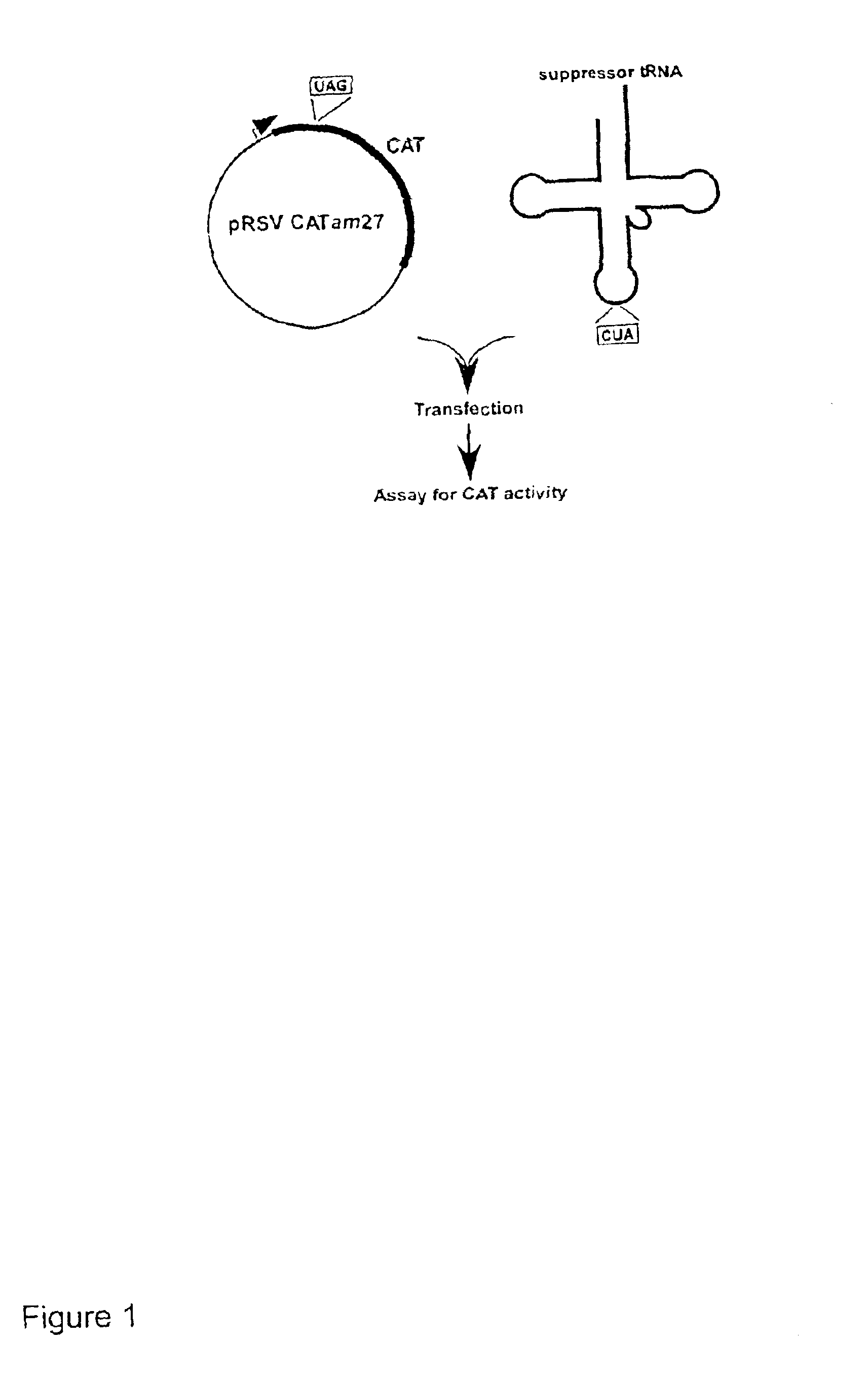
Suppressor tRNA system
The present invention provides techniques and reagents for read-through of stop codons in mammalian cells. In certain embodiments, the invention provides methods in which a mammalian cell is contacted with a synthesized tRNA so that the tRNA is taken up into the cell at levels that allow read-through of stop codons. Preferably, the synthesized suppressor tRNA is aminoacylated, optionally with an unnatural amino acid. In certain preferred embodiments, the inventive system is utilized to generate proteins containing two or more unnatural amino acids.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
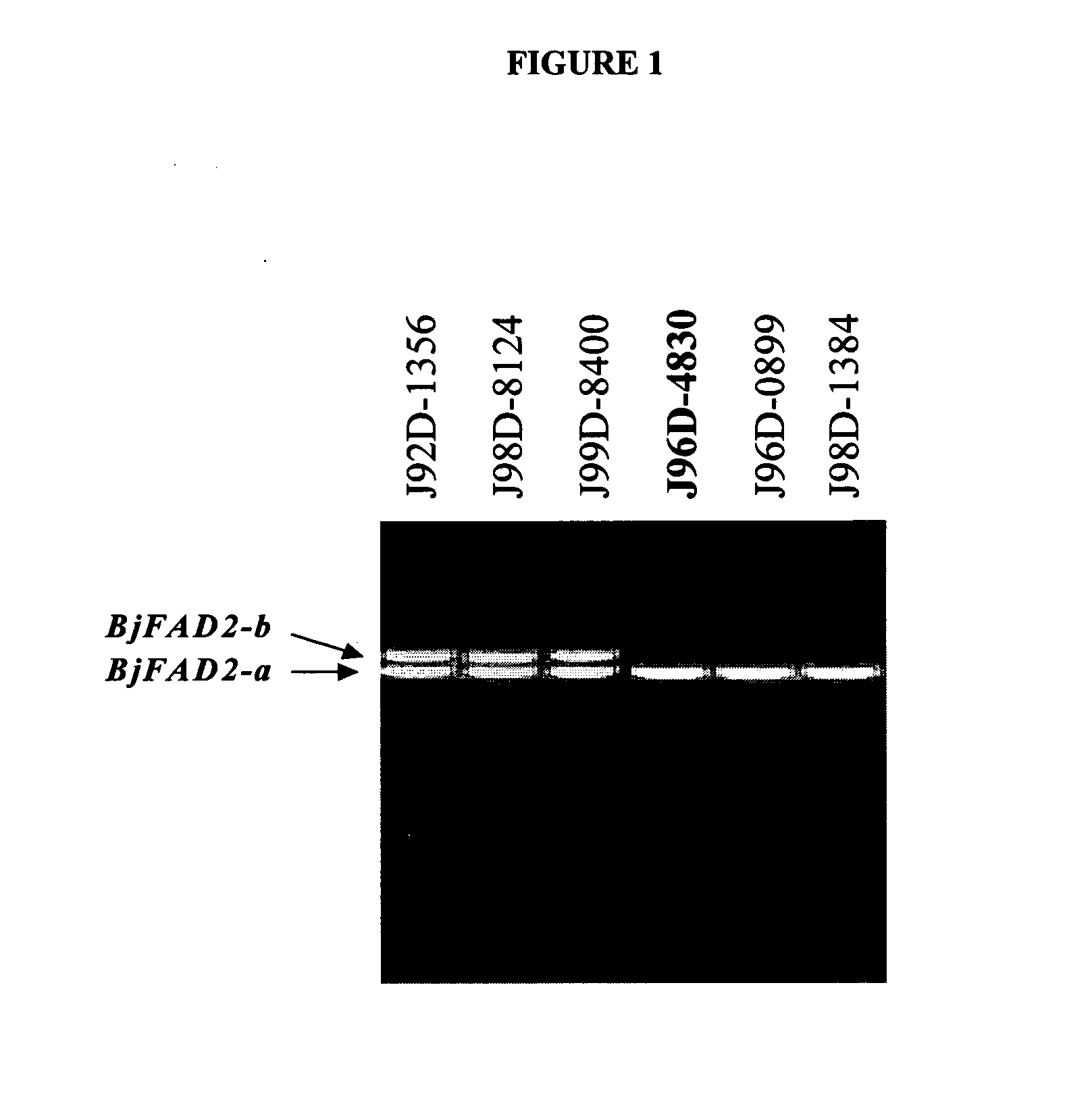
High oleic acid Brassica juncea
ActiveUS20050039233A1High oleic acid contentOther foreign material introduction processesOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyPremature Stop Codon
In various aspects, the invention provides Brassica juncea plants, seeds, cells, nucleic acid sequences and oils. Edible oil derived from plants of the invention may have significantly higher oleic acid content than other B. juncea plants. In one embodiment, the B. juncea line MJ02-086-3 contains a mutant allele MJ02-086-3 / BjFAD2-a at the BjFAD2-a gene locus, having a premature stop codon, so that there are no functional copies of the FAD2 gene in MJ02-086-3 plants. Seeds from MJ02-086-3 plants may for example yield an oil having oleic acid content of greater than about 70% by weight.
Owner:SASKATCHEWAN WHEAT POOL +1
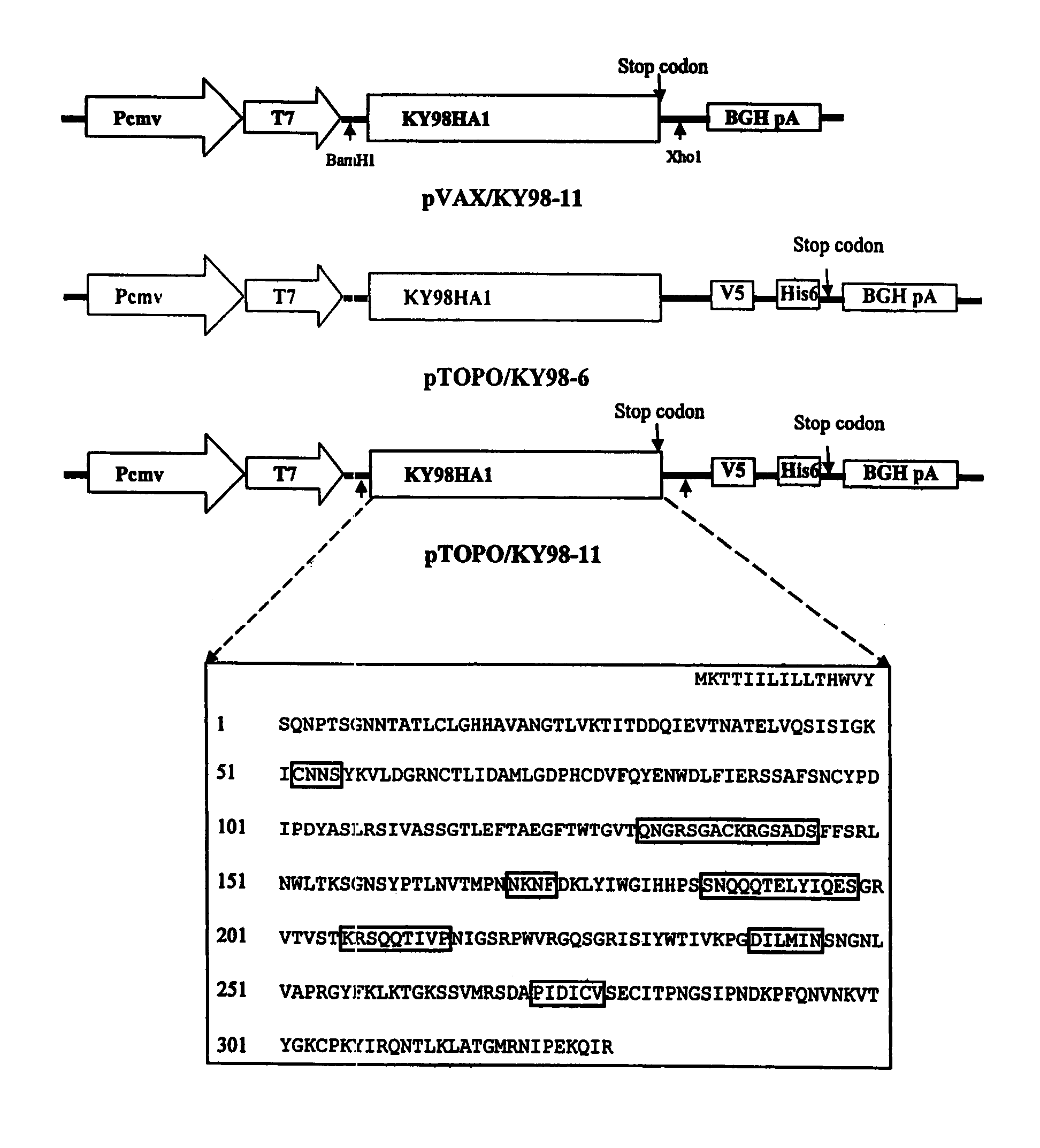
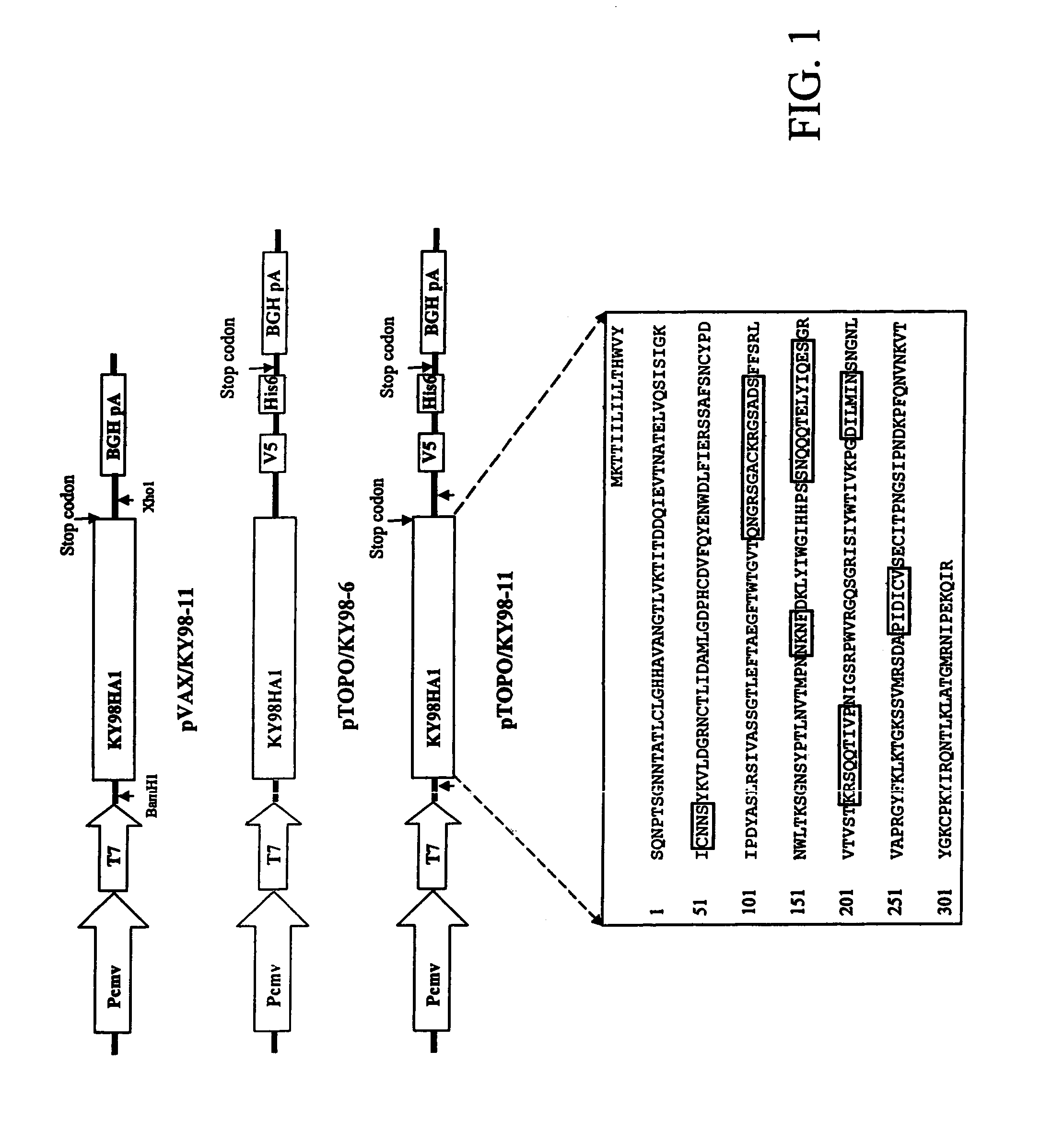
DNA vaccine expressing HA1 of equine-2 influenza virus
InactiveUS7244435B2Reduce riskReduce dosageSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHemagglutininA-DNA
The invention is for a DNA vaccine expressing the hemagglutinin (HA1) gene of equine-2 influenza virus. By engineering a stop codon within HA1, expression of HA1 is ensured. By encapsulation of the DNA vaccine in liposome and by intranasal inoculation, it is sufficient to elicit protective immunity at a significantly lower dosage compared to a DNA vaccine expressing the full length HA gene. Lower dosage reduces the risk of induction of anti-DNA antibodies. Intranasal inoculation directly to the respiratory epithelial cells reduces the risk of DNA integration. The inventive vaccine is advantageous over current inactivated or live attenuated vaccines, as updating of the vaccine requires only the replacement of the encoding sequence with the new virus.
Owner:BOARD OF REGENTS FOR OKLAHOMA STATE UNIVERSITY
Human soluble neuropilin-1 primary polyadenylation signal and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050175591A1Easy to transportImprove translationBiocideGenetic material ingredientsPoly-A RNANucleotide
The human soluble neuropilin-1 (sNRP) polyadenylation signal (sNRP-poly(A)), situated downstream of the GT splice donor site of intron 12 of the full-length neuropilin-1 gene, also functions as the termination codon for sNRP. This 17 nucleotide sequence efficiently facilitates addition of poly(A) tails to RNAs expressed in cells. The present invention shows that this optimally succinct sequence has similar activity to the SV40 polyadenylation signal that is currently used in expression vectors. By using this shorter dual termination / polyadenylation signal and avoiding the need for large and cumbersome polyadenylation signals, expression vectors may be engineered to carry considerably larger genes.
Owner:OREGON HEALTH & SCI UNIV
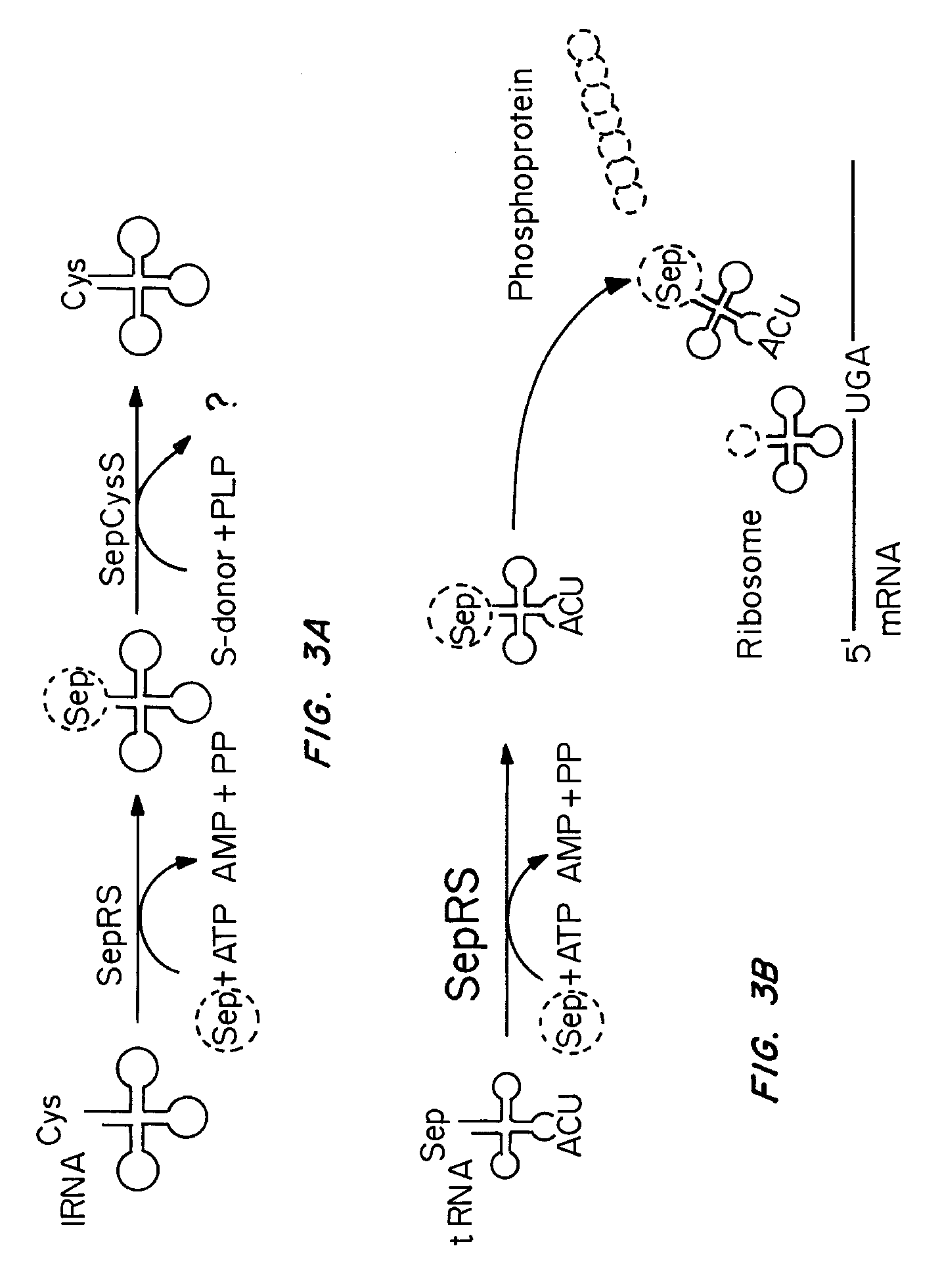
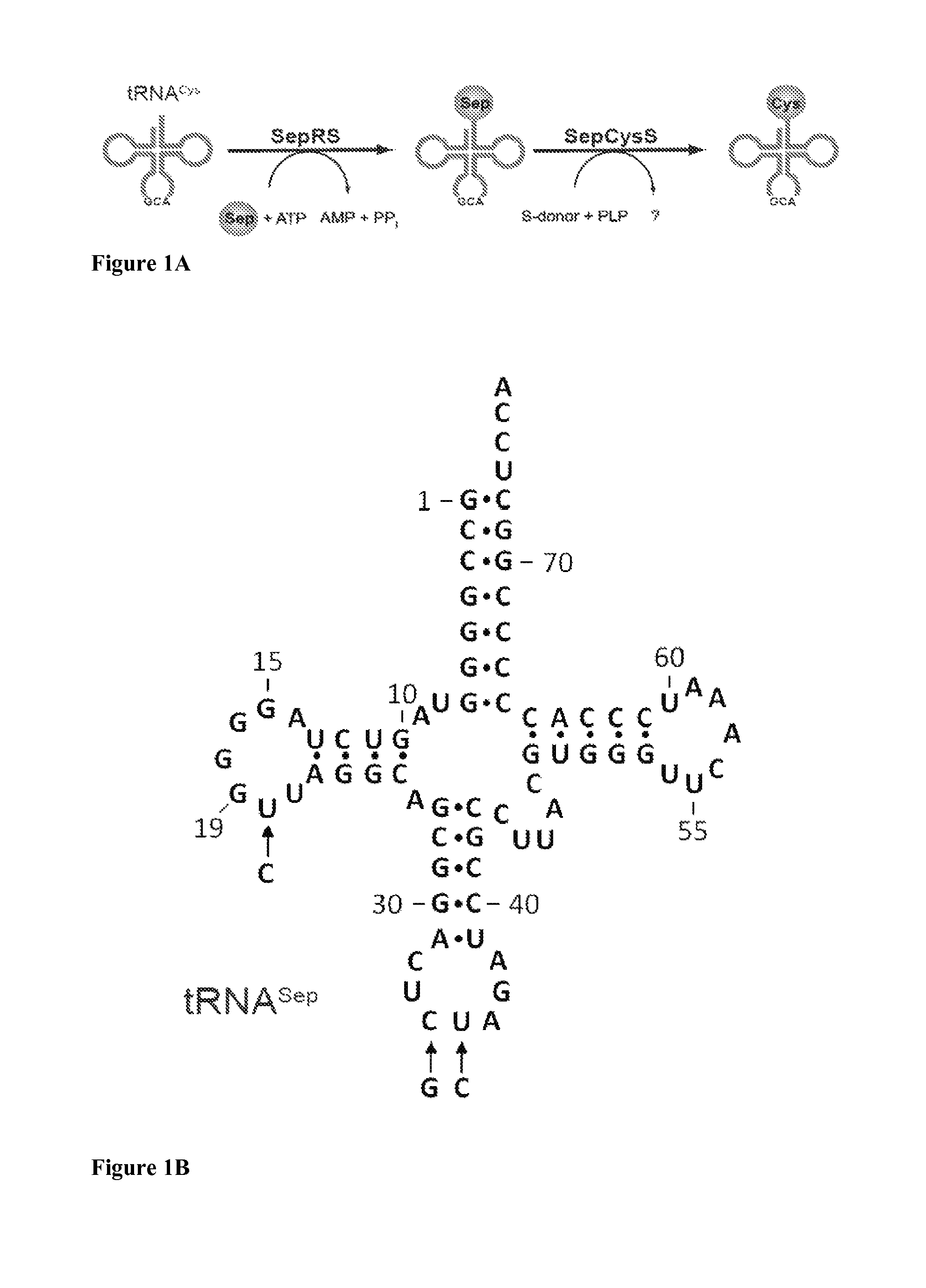
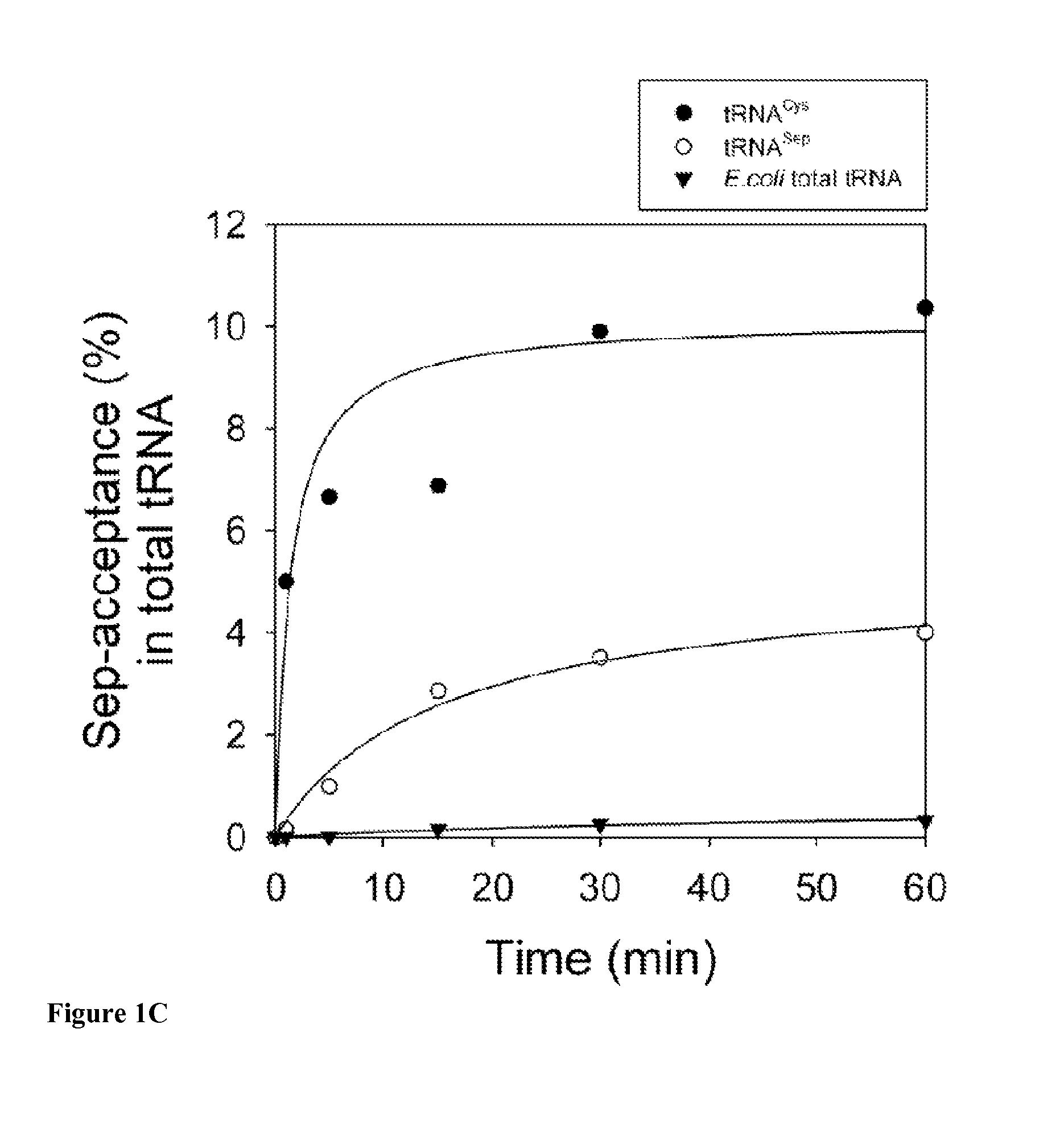
Site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into polypeptides using phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase
Nucleic acids encoding genes with SepRS and tRNASep activity for site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into a protein or polypeptide and methods of use thereof are described. Typically, SepRS preferentially aminoacylates tRNASep with O-phosphoserine and the tRNASep recognizes at least one codon such as a stop codon. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acids are on vectors. In one embodiment, the vectors are expressed in cells such as bacterial cells, archeaebacterial cells, and eukaryotic cells. In an alternative embodiment, the vectors are expressed in an in vitro transcription / translation system. Proteins or polypeptides containing phosphoserine produced by the methods described herein can be used for a variety of applications such as research, antibody production, protein array manufacture and development of cell-based screens for new drug discovery.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Preparation method and application of Qbeta-2aa phage virus-like particle protein
ActiveCN101921733AImproving immunogenicityEfficient inductionAntiinfectivesViruses/bacteriophagesEscherichia coliPeptide antigen
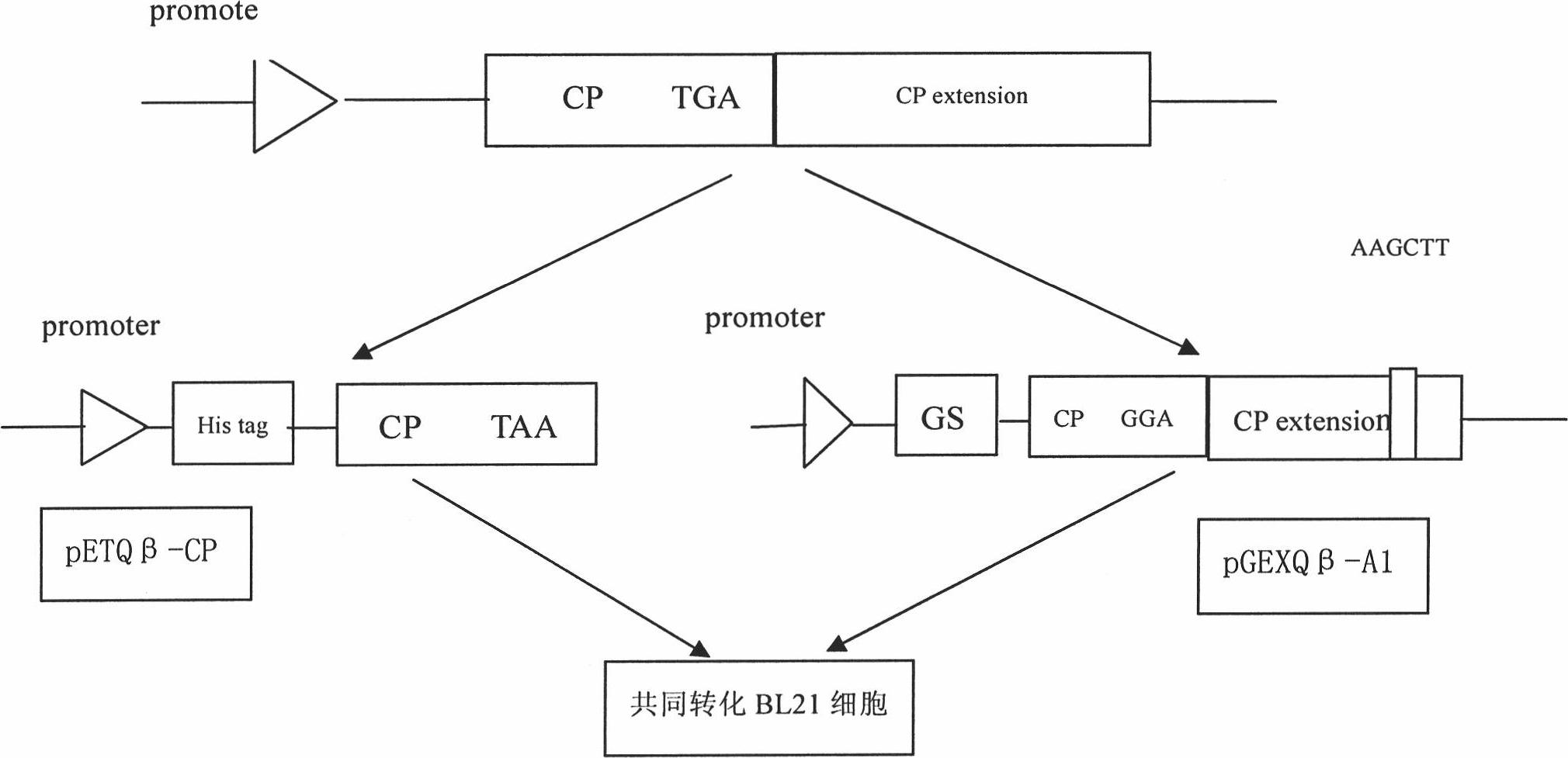
The invention relates to a Qbeta-2aa phage virus-like particle protein which is prepared according to a method comprising the following steps of: (1) mutating a Qbeta phage CP (coat protein) gene terminator codon into a strong terminator codon TAA from TGA and then cloning the strong terminator codon into a protokaryon expression vector pET28a(+) to obtain a coding CP plasmid pETQB-CP; (2) inserting the nucleotides AAGCTT of coding lysine and leucine at the coding immunodominance determining region position in a Qbeta phage CP extension protein gene, i.e. between the 72th codon and the 73th codon of the Qbeta phage CP extension protein gene, and mutating the CP gene terminator codon into GGA from TGA and then cloning the GGA into a protokaryon expression vector PGEX4T-2 to obtain a codingA1 protein plasmid pGEXQbeta-A1; (3) jointly converting the mutated coding Qbeta phage CP plasmid and the A1 protein plasmid into escherichia coli, and inducing and then expressing to obtain the virus-like particle protein Qbeta-2aa; and (4) coupling a short peptide antigen to Qbeta-2aa phage virus-like particles by using a iso-bifunctional cross-linking agent.
Owner:WUHAN HUAJIYUAN BIOTECH DEV
Cyclic RNA and protein production method
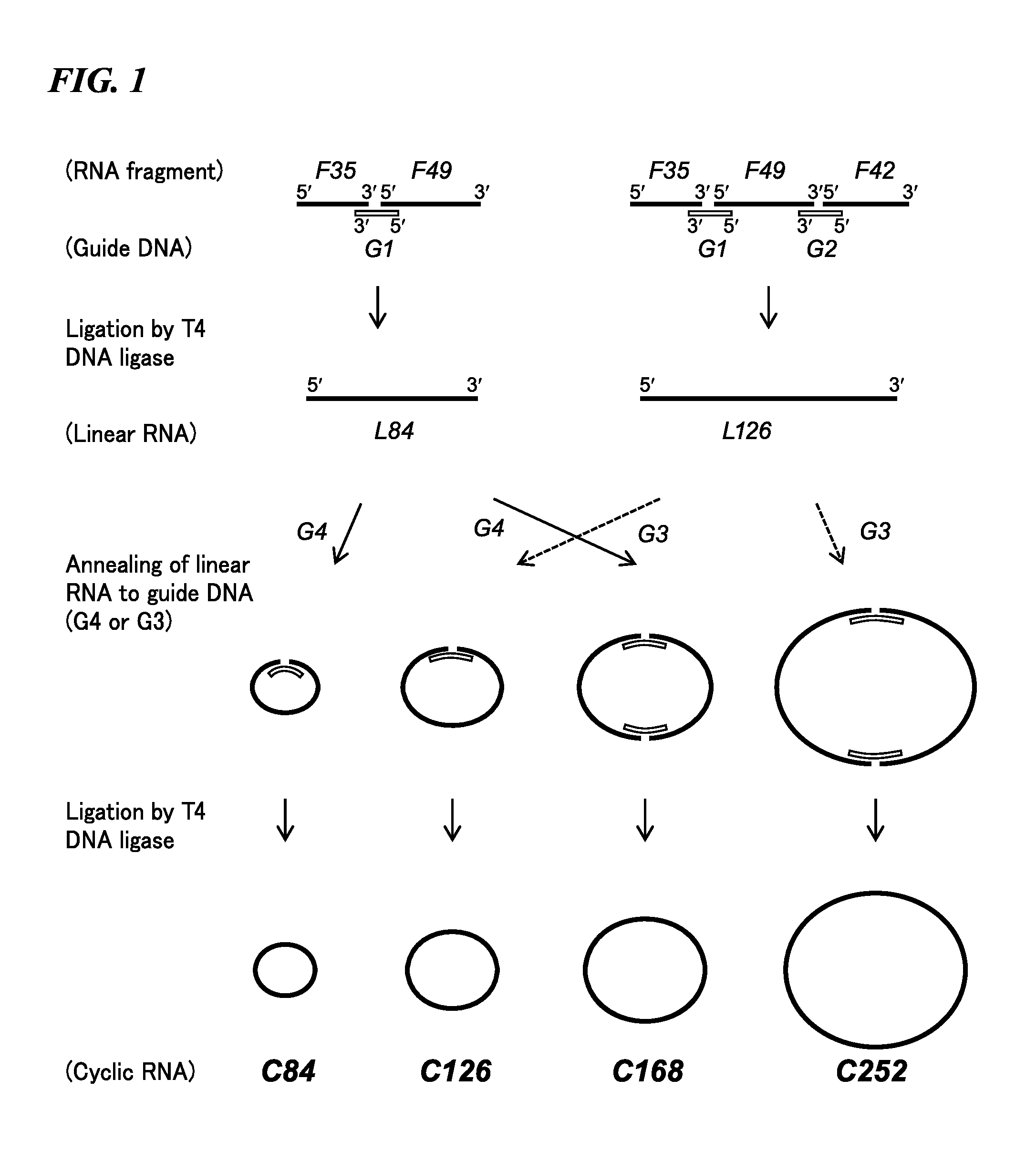
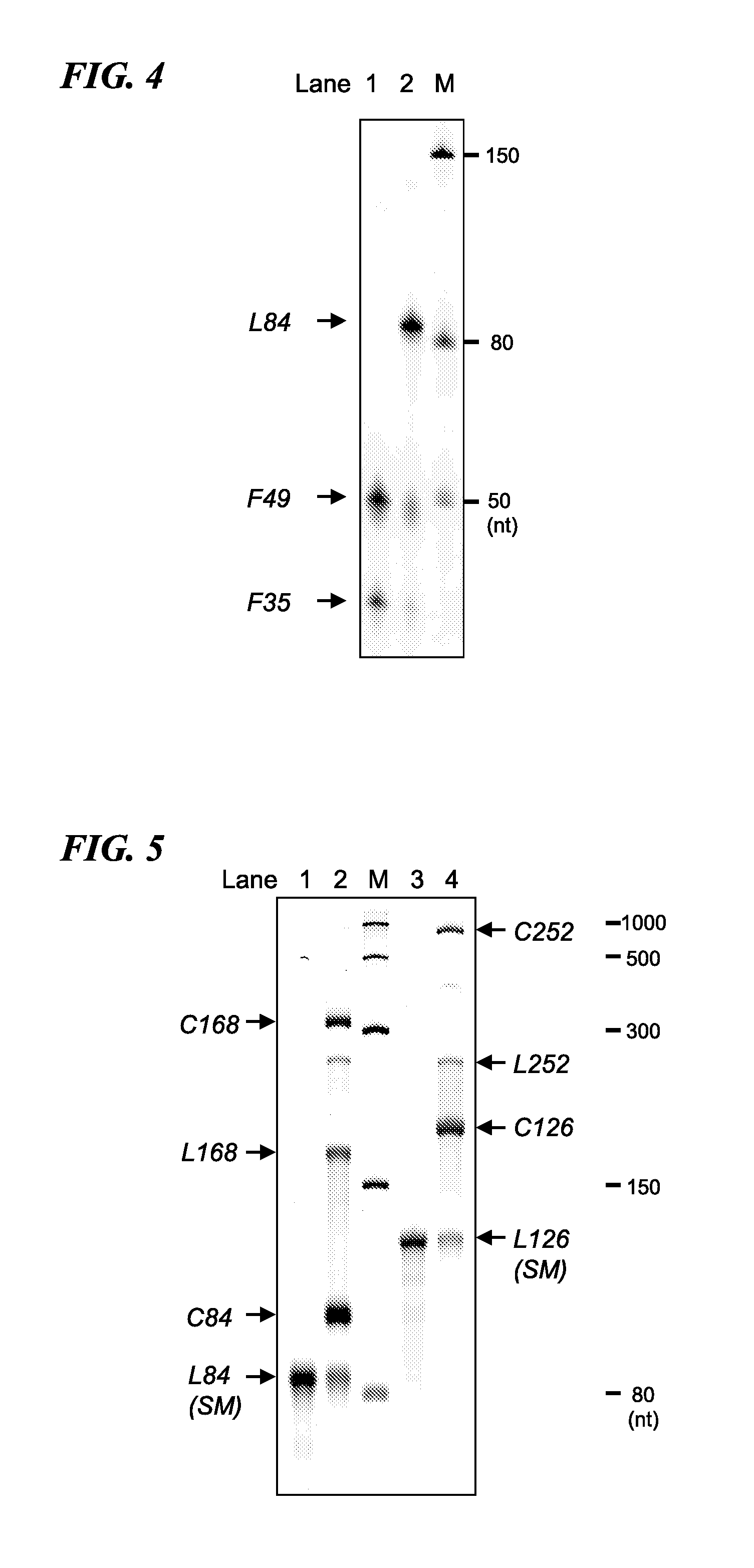
The present invention provides a cyclic RNA preferable for carrying out rotary protein translation in which translation domains other than that of the target protein are sufficiently short and translation efficiency is high, and a method for producing protein that uses this cyclic RNA as template. More specifically, the present invention provides a cyclic RNA that encodes a protein, has a full-length number of bases that is equal to or greater than 102 and is a multiple of 3, has at least one start codon, does not have a stop codon in the same reading frame as the start codon, and does not contain an internal ribosome entry site (IRES). In addition, the present invention provides a method for producing protein in a eukaryotic cell expression system that consists of using the aforementioned cyclic RNA as template and expressing a protein encoded by that cyclic RNA.
Owner:RIKEN
Polynucleotides encoding interferon gamma peptide variants
InactiveUS20050201982A1Reducing or avoiding C-terminal heterogeneity of an IFNG polypeptideSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideNucleotide level
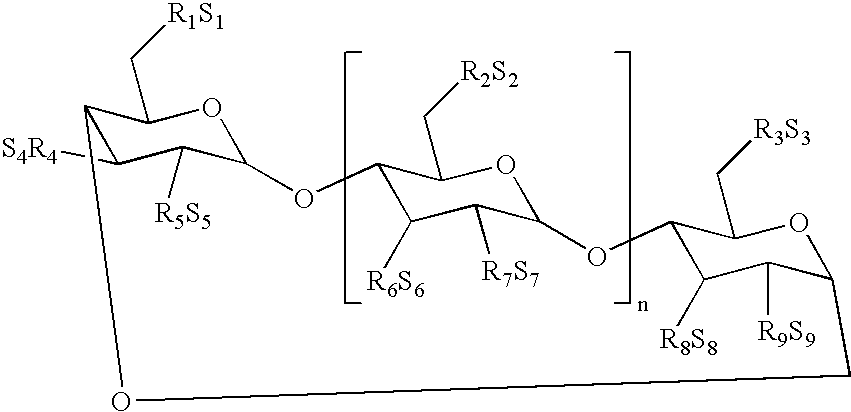
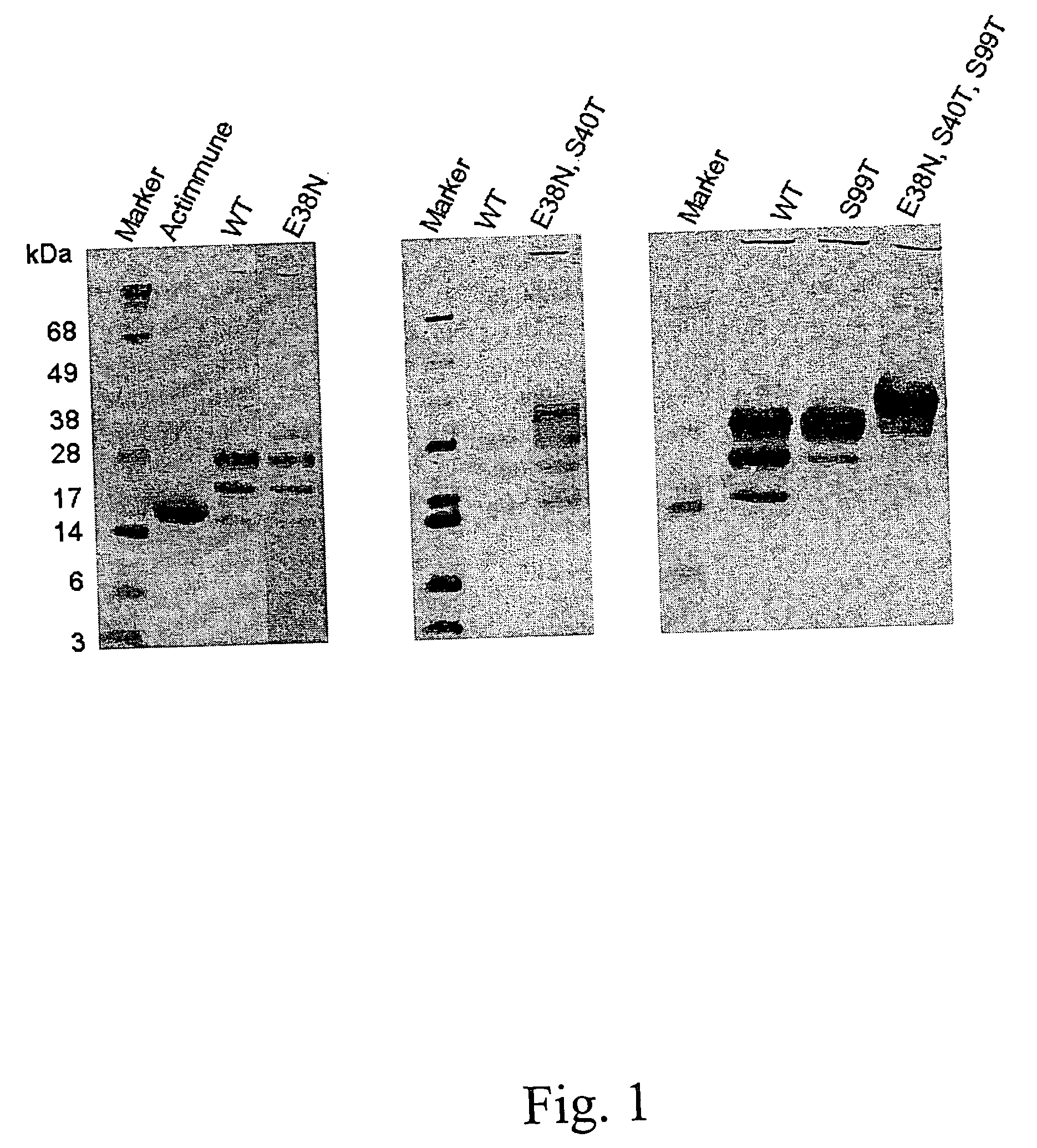
When interferon gamma (IFNG) is produced in mammalian cell lines a heterogenous population of IFNG polypeptides is obtained due to C-terminal processing of the IFNG polypeptide. Clearly, this constitutes a severe problem in that valuable polypeptide material is lost and, further, it is necessary to carry out time-consuming and cumbersome purification in order to obtain a homogenous population of active IFNG polypeptides having the desired length. It has now been found that an IFNG fragment containing 132 amino acid residues (truncated at the nucleotide level by introducing a stop-codon after the codon encoding amino acid residue no. 132) does not undergo C-terminal truncation or, at least, is not significantly C-terminally truncated. Furthermore, as the IFNG fragment containing 132 amino acid residues is active, this opens up the possibility of producing a homogenous active IFNG polypeptide in eukaryotic host cells, such as CHO cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to an IFNG polypeptide variant exhibiting IFNG activity and having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:12. In a highly preferred embodiment of the invention, the variant comprises at least one further modification, such as 1-10 further modifications, relative to the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:12. A particular preferred further modification is E38N+S40T.
Owner:PERSEID THERAPEUTICS
Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae fusion gene and application
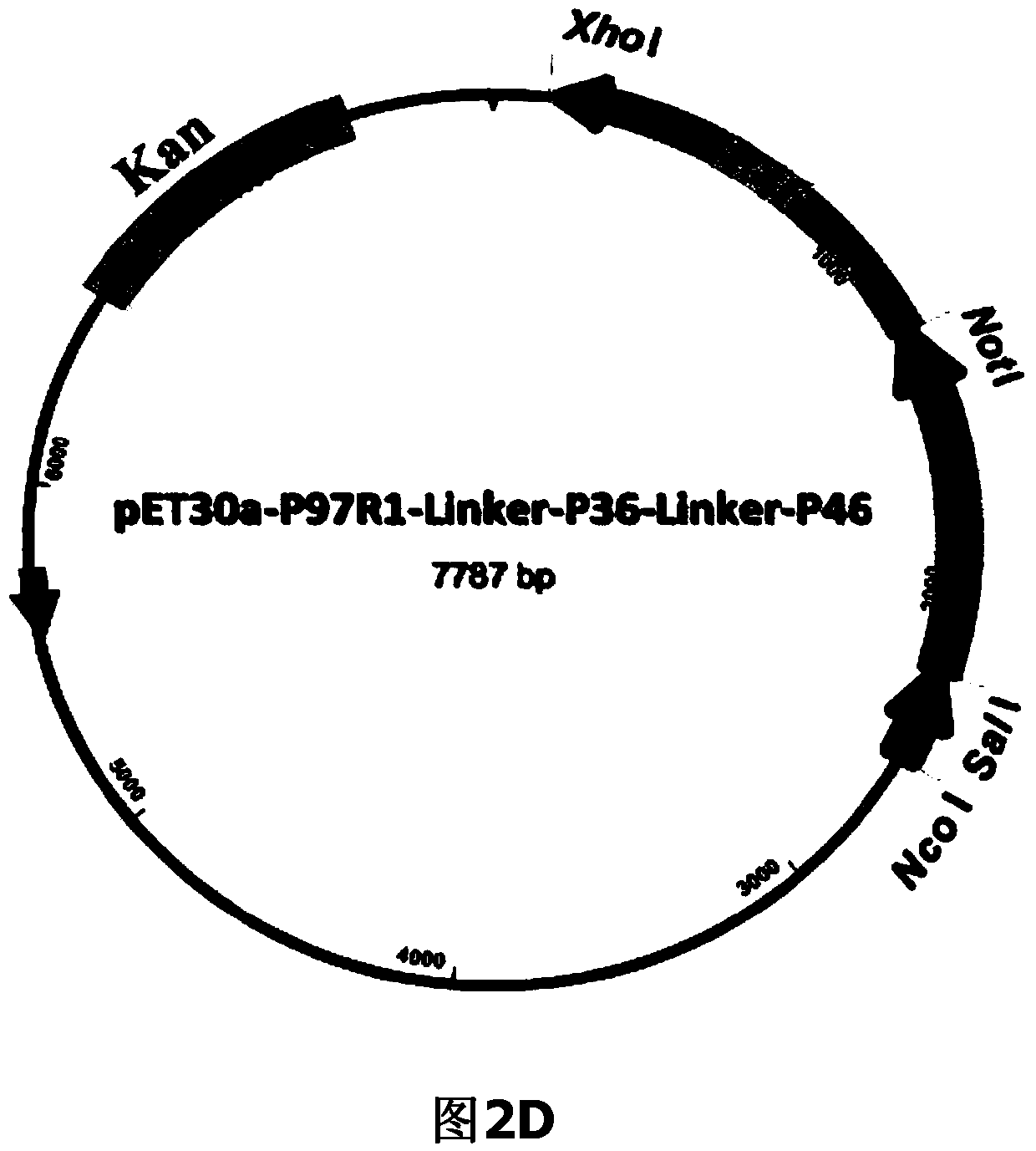
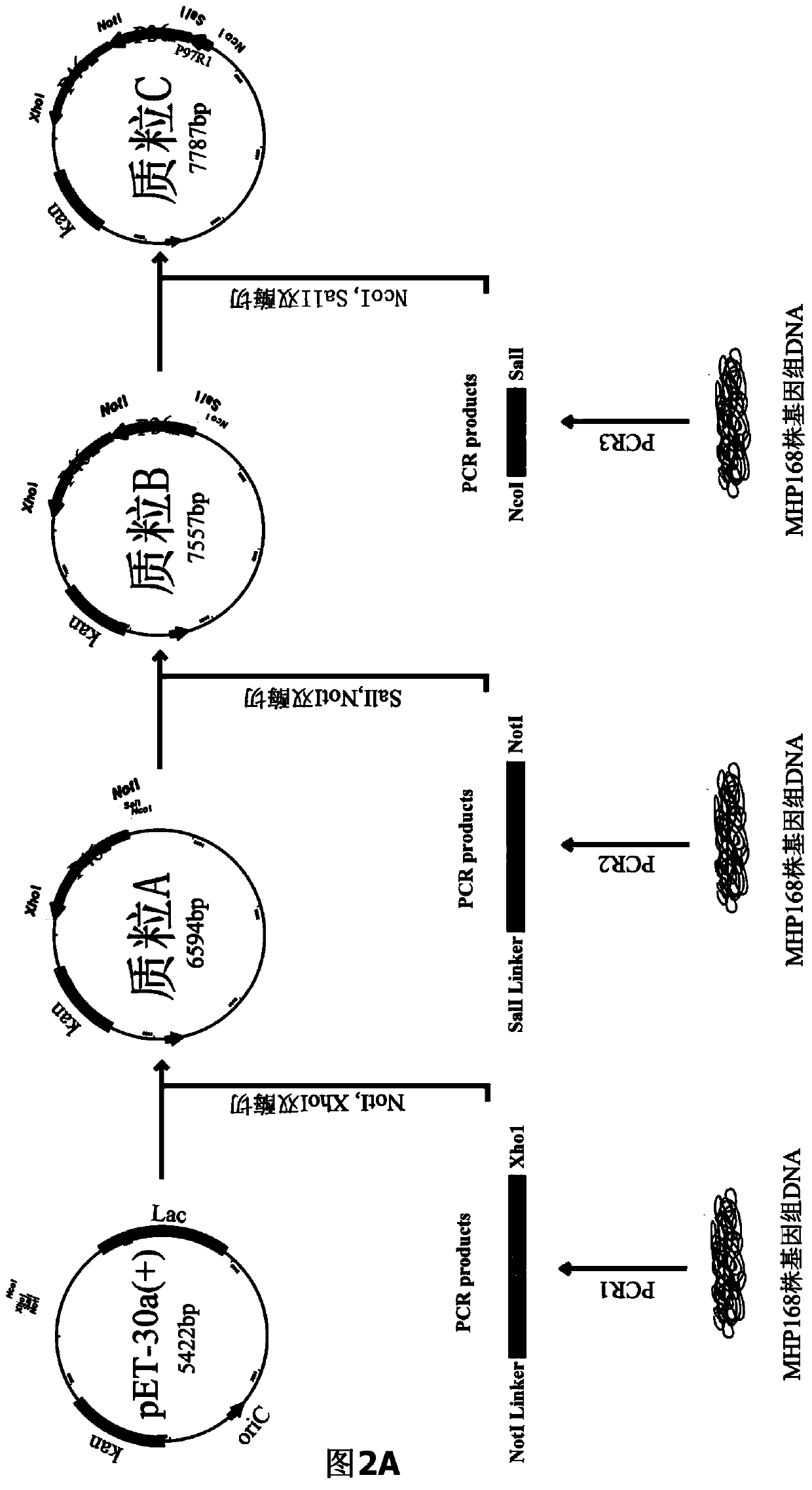
ActiveCN104293816AImproving immunogenicityHigh expressionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsEscherichia coliNucleotide
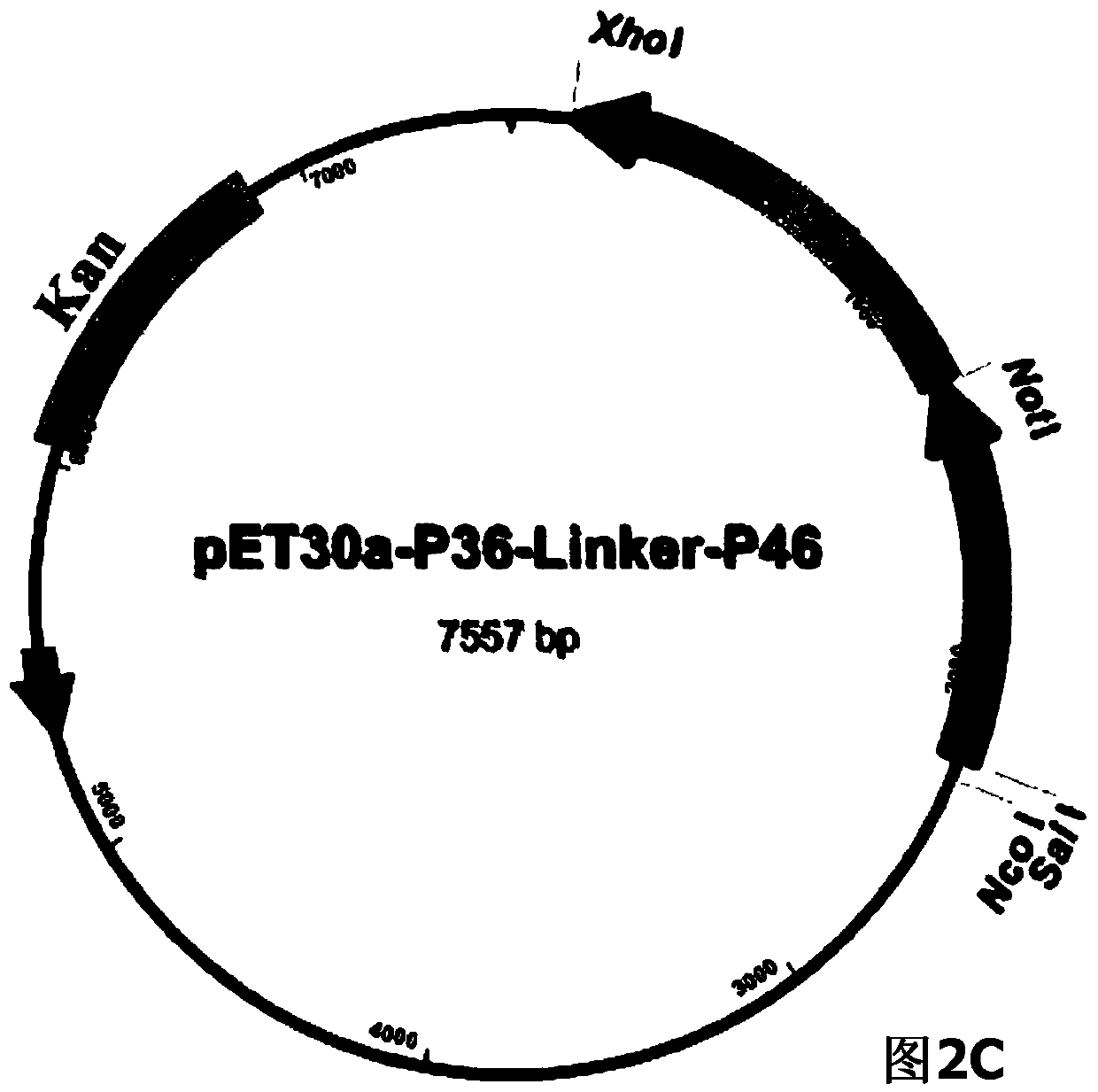
The invention belongs to the field of animal gene engineering, and in particular relates to a synthetic fusion gene for expressing mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and application. The fusion gene is characterized in that a mycoplasma hyopneumoniae P97R1 gene is connected in series with a P36 gene through a Linker, the termination codon of the P36 gene is deleted, the P46 gene with signal peptide removed is fused at the C end of the P36 gene through Linker, and then the fusion gene P97R1-P36-P46 is obtained, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the fusion gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The fusion gene is included in a prokaryotic expression plasmid, and escherichia coli BL21 / pET30a-P97R1-Linker-P36-Linker-P46 containing the plasmid is collected in CCTCC with the collection number CCTCC NO: M2014269. The invention further discloses immune efficacy evaluation of the fusion gene and application of the fusion gene in a novel vaccine.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Nonsense suppression and genetic codon alteration by targeted modification
ActiveUS8603457B2Easy to identifyLarge productionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAdenosineGenetics
Methods for affecting mRNA expression or translation through the modification of pre-mRNA or mRNA transcripts are described. In one embodiment of the methods of the present invention, the branch point adenosine of a pre-mRNA transcript is 2′-O-methylated to block splicing and subsequent expression of the protein encoded by the transcript. In another embodiment, a uridine residue in a nonsense stop codon may be modified to pseudouridine, causing the translation machinery to read through the nonsense stop codon and translate a full length protein.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER
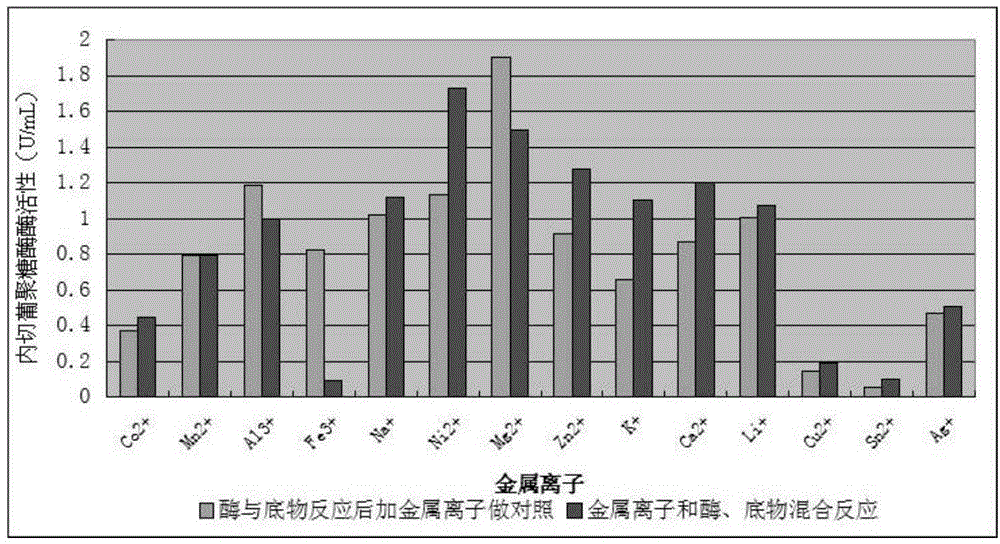
Neutral endoglucanase as well as encoding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a neutral endoglucanase as well as an encoding gene and an application thereof. An H31 gene sequence is an intact open reading frame (ORF), wherein the open reading frame begins from an initiation codon ATG and is terminated by a termination codon TAG, and comprises 762 nucleotides; the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No:1; an amino acid sequence of protein encoded by the neutral endoglucanase H31 gene is shown in SEQ ID No.2. The invention further discloses an application of the neutral endoglucanase H31 in industries such as washing and papermaking.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Polypeptide producing cells
ActiveUS8354516B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSugar derivativesPolyadenylationPoly-A RNA
The current invention describes a nucleic acid comprising in a 5′ to 3′ direction a) a first nucleic acid encoding a heterologous polypeptide without an in frame stop codon, b) a second nucleic acid beginning with a 5′ splice donor site and terminated by a 3′ splice acceptor site comprising an in frame translational stop codon and a polyadenylation signal, and c) a nucleic acid encoding i) at least a fragment of a transmembrane domain, or ii) a signal peptide for a GPI-anchor.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Manually-combined Newcastle diseases virus F gene and recombining expression vector and application thereof
InactiveCN101629178APrevent proliferationEffective controlViral antigen ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsWild typeRestriction site
The invention discloses a manually-combined Newcastle diseases virus F gene and a recombining expression vector and an application thereof. Codons of NDVF gene OFR are all replaced into chicken bias codons, EcoR V restriction sites and Kozak sequences are added upstream, Xbal I restriction sites and TGA stop codons are added downstream, and downstream bases A of the stop codons are changed into G, obtained genes (SEQ, ID NO: 2) can be efficiently expressed in eukaryotic cells, and the expression efficiency of the obtained genes is higher than that of wild type genes. Expressed genes have immunogenicity and biologic activity of natural protein of Newcastle diseases virus, can stimulate chicken to generate body fluid stronger immunologic response and stronger cell immunologic response than the wild F gene DNA vaccine so as to enable immunized chicken to obtain 100 percent of resistance to fatal attack of high-pathogenicity Newcastle strains, and can effectively inhibit the propagation of the virus in the chicken.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Alkaline endo glucanase gene, recombinase and applications thereof
InactiveCN101182527AImprove toleranceNo significant loss of residual enzyme activityRecombinant DNA-technologyDetergent compounding agentsStart codonGlucanase
The invention discloses an alkaline endoglucanase gene. The gene sequence is a complete open reading frame, which begins with ATG start codon and concludes with TAA stop codon. The whole sequence comprises 2502 nucleic acids. The invention also discloses the application of the recombinant alkaline endoglucanase in detergent industry etc. The recombinant alkaline endoglucanase has good resistance for SDS, which is preserved in the detergent with 0.2 percent final concentration for ten minutes without significant activity loss of the residue enzyme. The recombinant alkaline endoglucanase suits for the detergent and textile industries etc.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Premature-termination-codons readthrough compounds
ActiveUS20150051251A1Increase transcriptionIncrease productionBiocideNervous disorderCombinatorial chemistryPremature Termination Codon
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
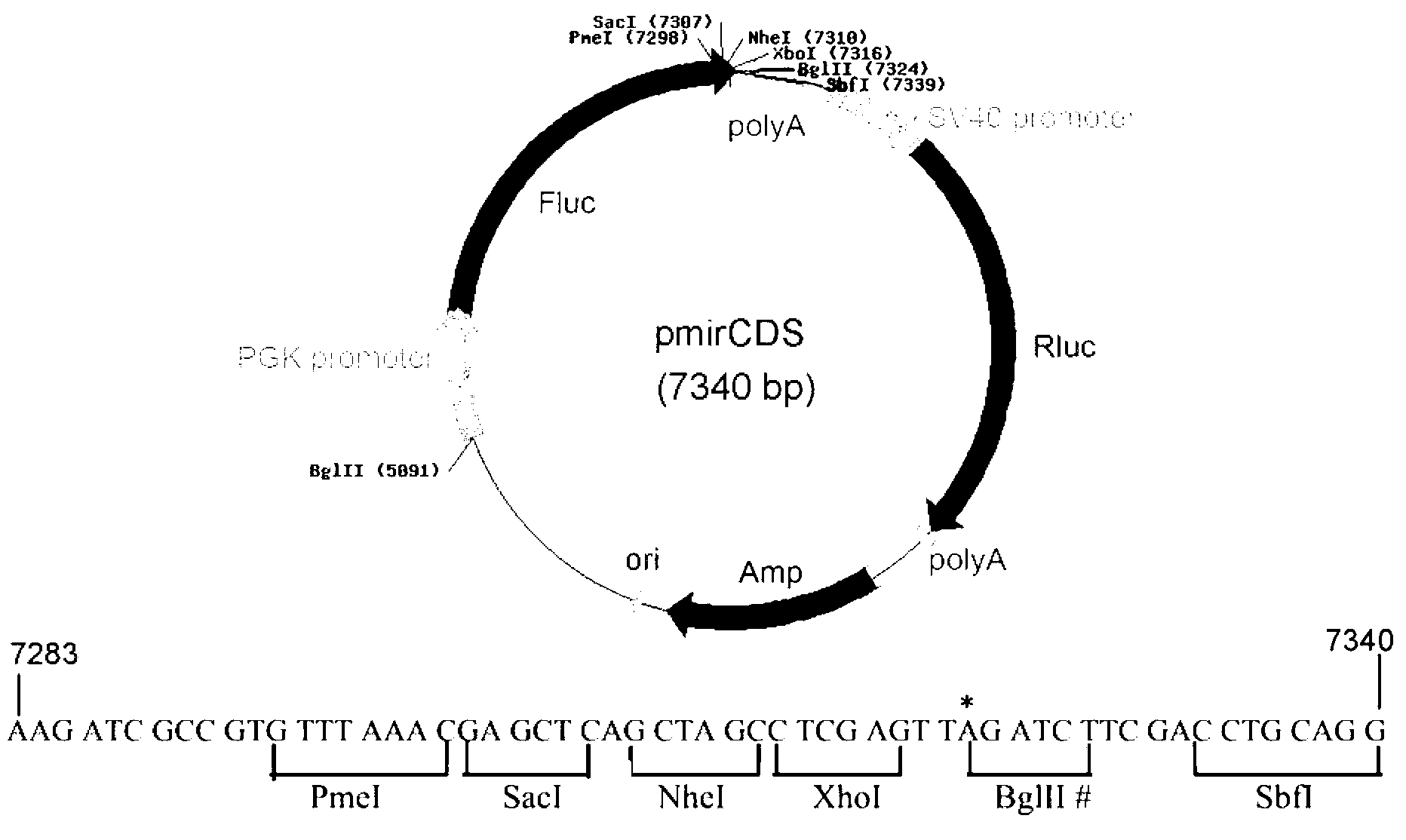
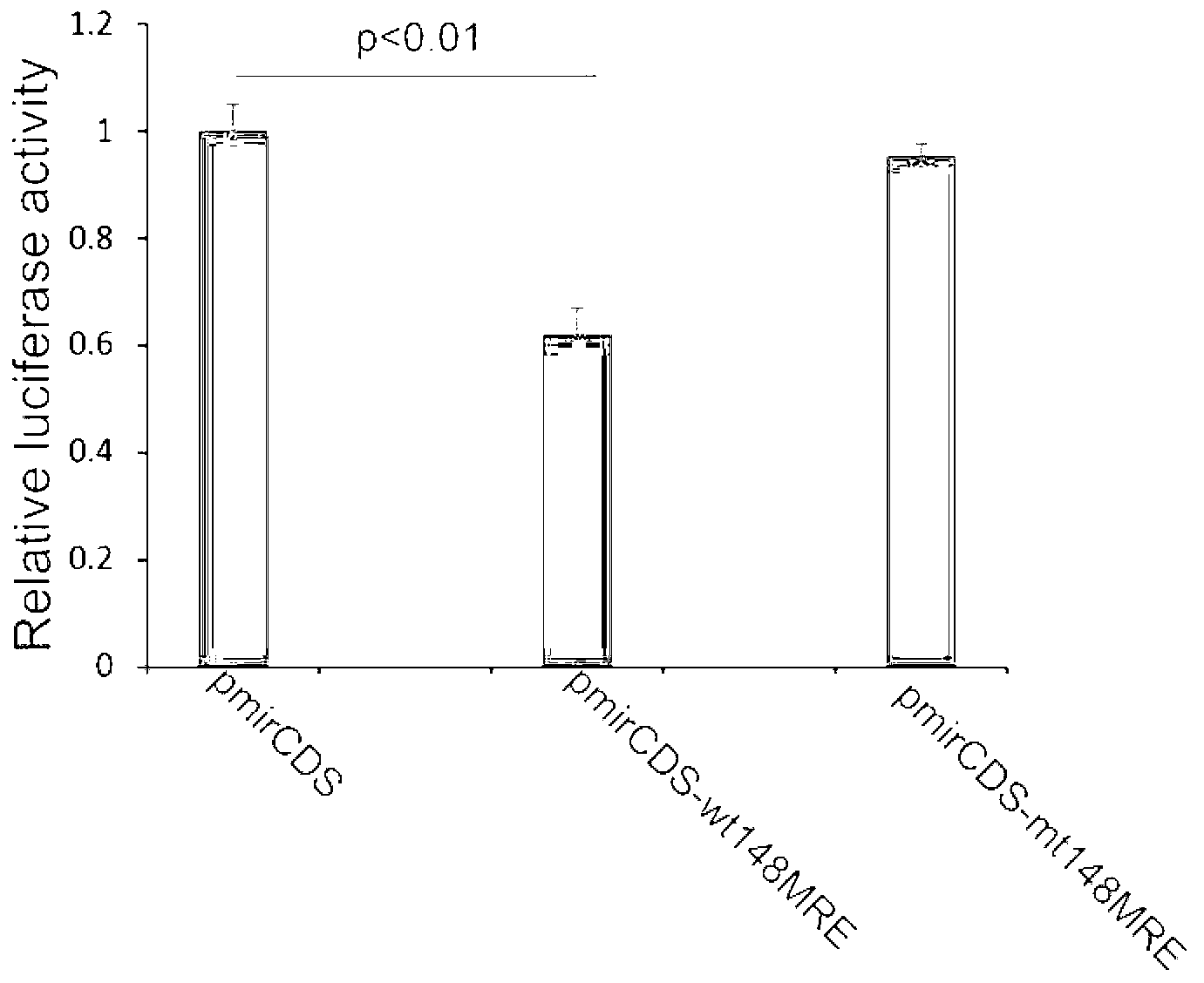
Dual fluorescent reporter gene vector for identifying miRNA targets, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103266120AEasy to operateShort experiment cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionRenilla luciferaseMultiple cloning site
The invention discloses a dual fluorescent reporter gene vector for identifying miRNA targets, a preparation method thereof, and an application thereof in identifying the miRNA targets in coding regions and detecting functions of the miRNA on the coding regions. The carrier has a renilla luciferase gene and a firefly luciferase gene, and multiple cloning sites (MCS) are located between a terminal amino acid codon and a stop codon of a firefly luciferase reporter gene, thereby facilitating insertion of the miRNA targets into the coding regions of the firefly luciferase reporter gene, so as to identify the miRNA targets in coding regions and detect the functions of the miRNA on the coding regions. The preparation method of the carrier provided by the invention does not require a special treatment for terminals of the carrier or target fragments, is free of connection reaction and PCR amplification, and is simple to operate, short in experiment period and high in efficiency.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Site-specific incorporation of phosphoserine into proteins in Escherichia coli
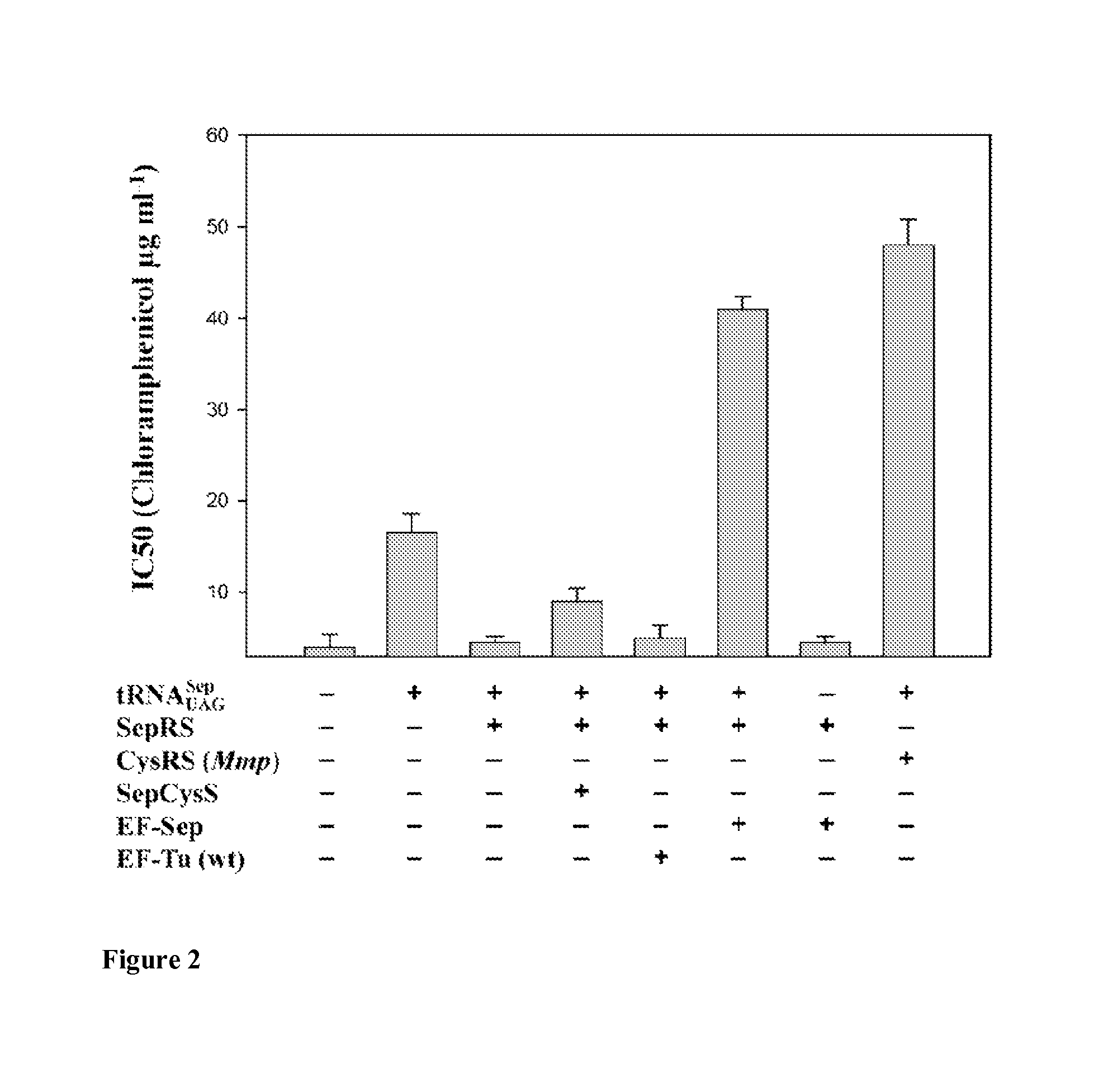
Nucleic acids encoding mutant elongation factor proteins (EF-Sep), phosphoseryl-tRNA synthetase (SepRS), and phosphoseryl-tRNA (tRNASep) and methods of use in site specific incorporation of phosphoserine into a protein or polypeptide are described. Typically, SepRS preferentially aminoacylates tRNASep with O-phosphoserine and the tRNASep recognizes at least one codon such as a stop codon. Due to the negative charge of the phosphoserine, Sept-tRNASep does not bind elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu). However, mutant EF-Sep proteins are disclosed that bind Sep-tRNASep and protect Sep-tRNASep from deacylation. In a preferred embodiment the nucleic acids are on vectors and are expressed in cells such as bacterial cells, archeaebacterial cells, and eukaryotic cells. Proteins or polypeptides containing phosphoserine produced by the methods described herein can be used for a variety of applications such as research, antibody production, protein array manufacture and development of cell-based screens for new drug discovery.
Owner:YALE UNIV
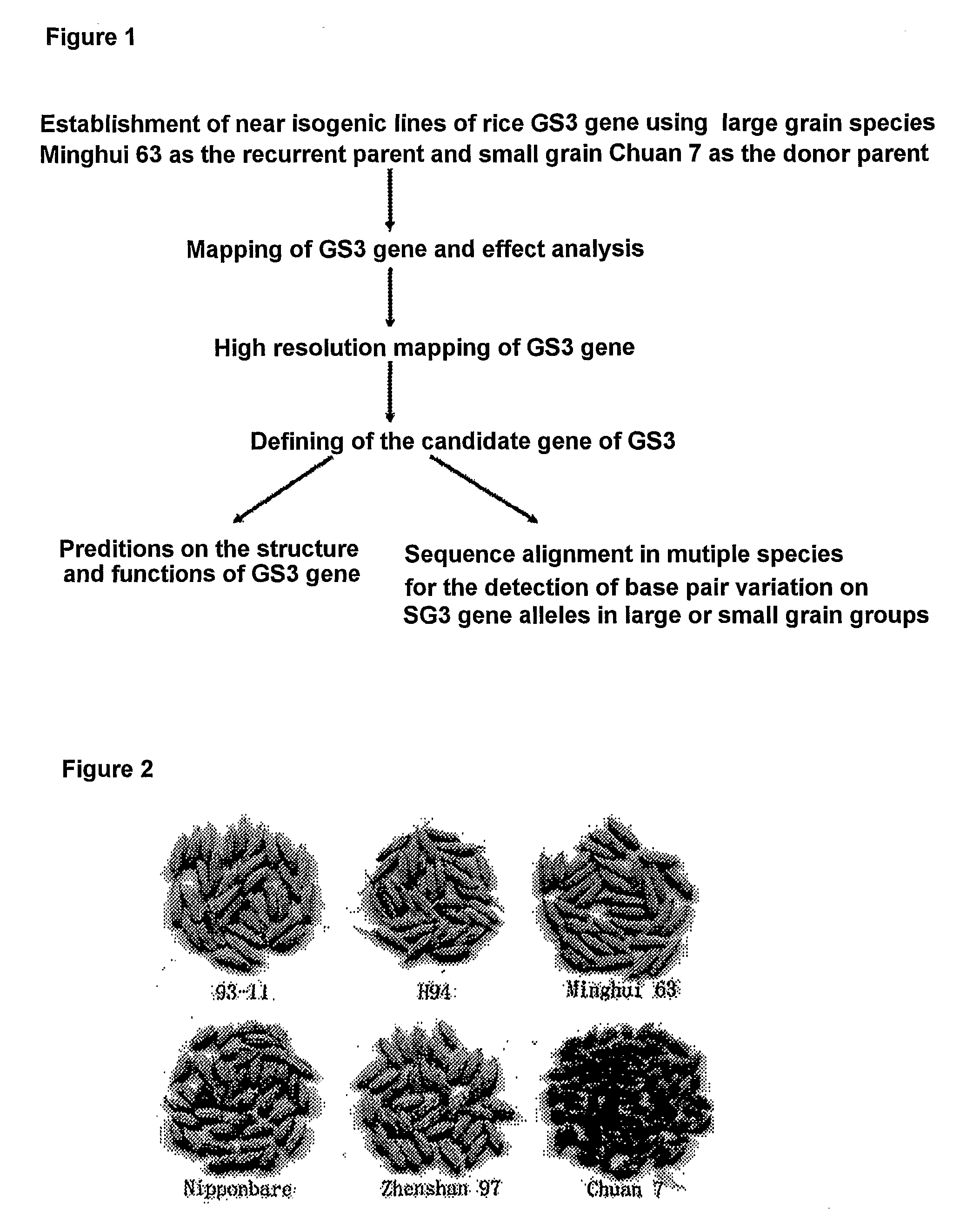
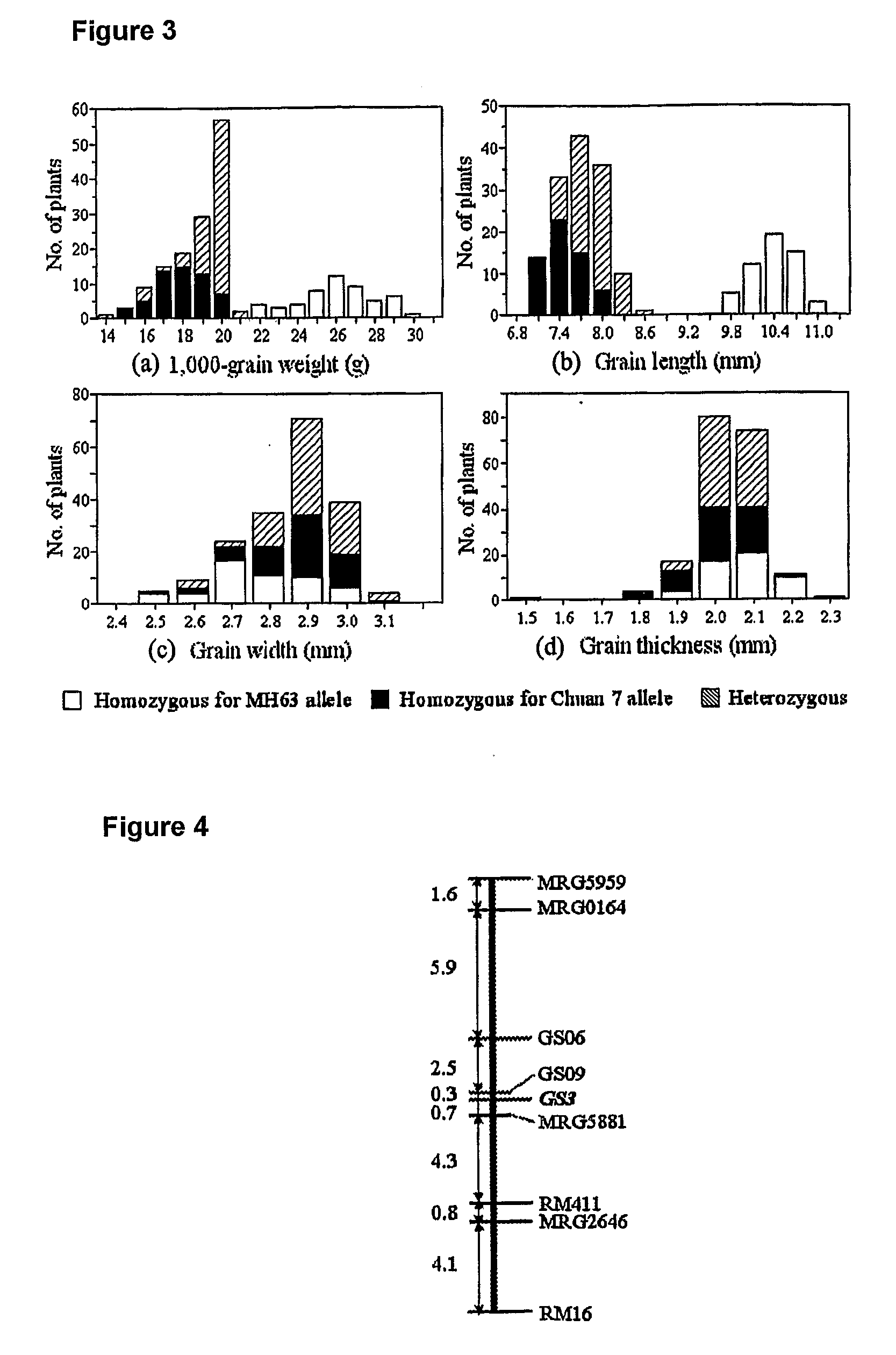
Rice Gene, GS3, Exerting Primary Control Over Grain Length and Grain Weight
InactiveUS20100017919A1High yieldQuality improvementFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleotide
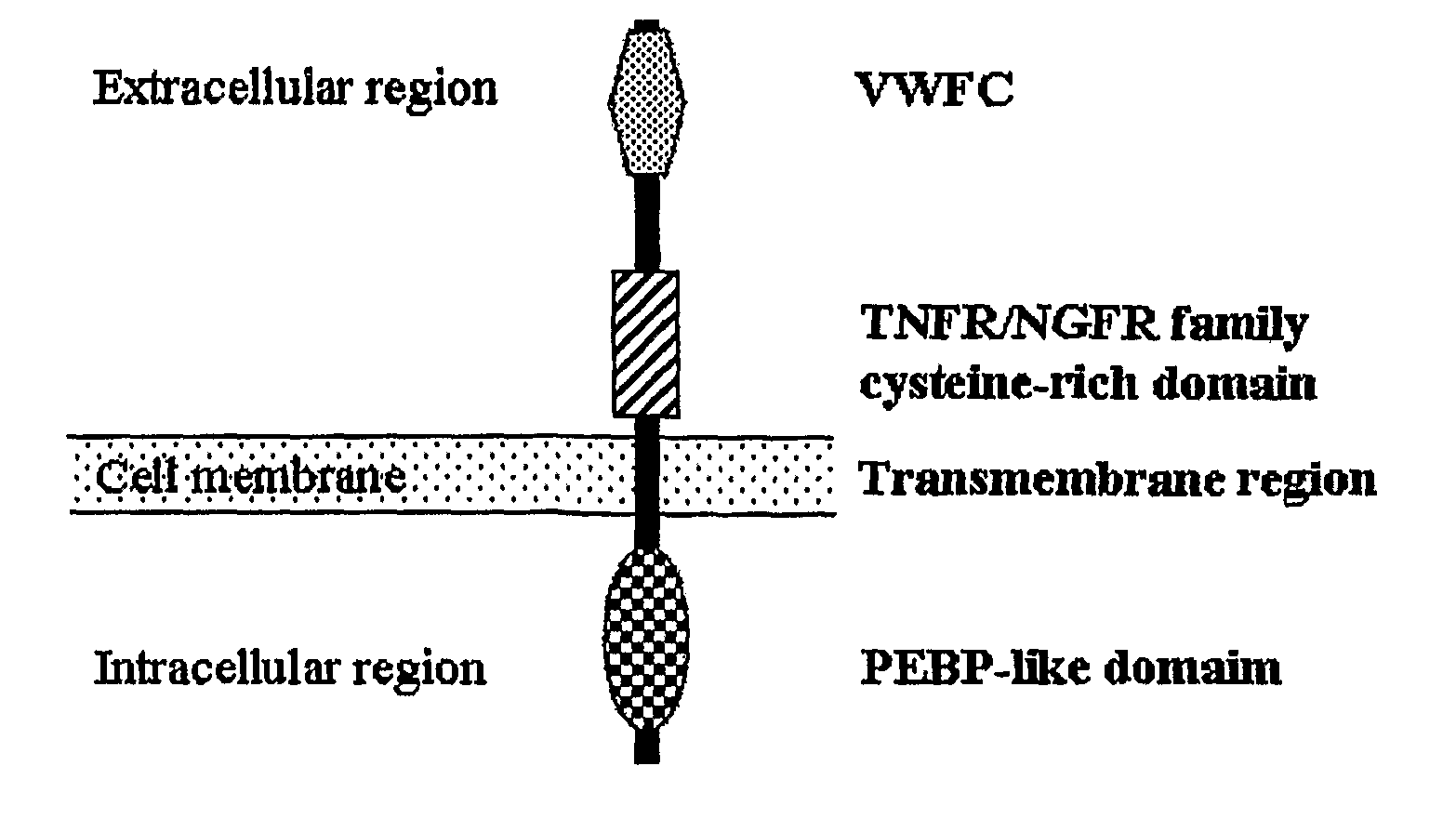
The present invention relates to an isolated major gene GS3 which regulates grain weight and grain length in the rice and the cloning of said gene. The DNA sequence of GS3 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and is 7883 bp in length. GS3 gene comprises 5 exons and encodes 232 amino acids. It is predicted based on bioinformatics analysis that said protein contains conserved domains including a PEBP-like domain, a transmembrane domain, a cysteine-rich domain of TNFR / NGFR and a VWFC domain. cDNA sequence of said gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. By sequence alignment between three large grain species and 3 small grain species of rice, it is revealed there is only one common single nucleotide mutation in a 7.9-kb region between the two different grain-length groups. Said nucleotide mutation is located at the second exon of the GS3 gene, in which a cysteine codon (TGC) in the small-grain group is mutated to a termination codon (TGA) in the large-grain group. This mutation causes a premature termination in the large-grain group, which leads to a 178-amino acids truncation (including part of the PEBP-like domain and all the other three conserved domains). The present invention also provides methods of producing transgenic plants comprising sequences disclosed herein.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
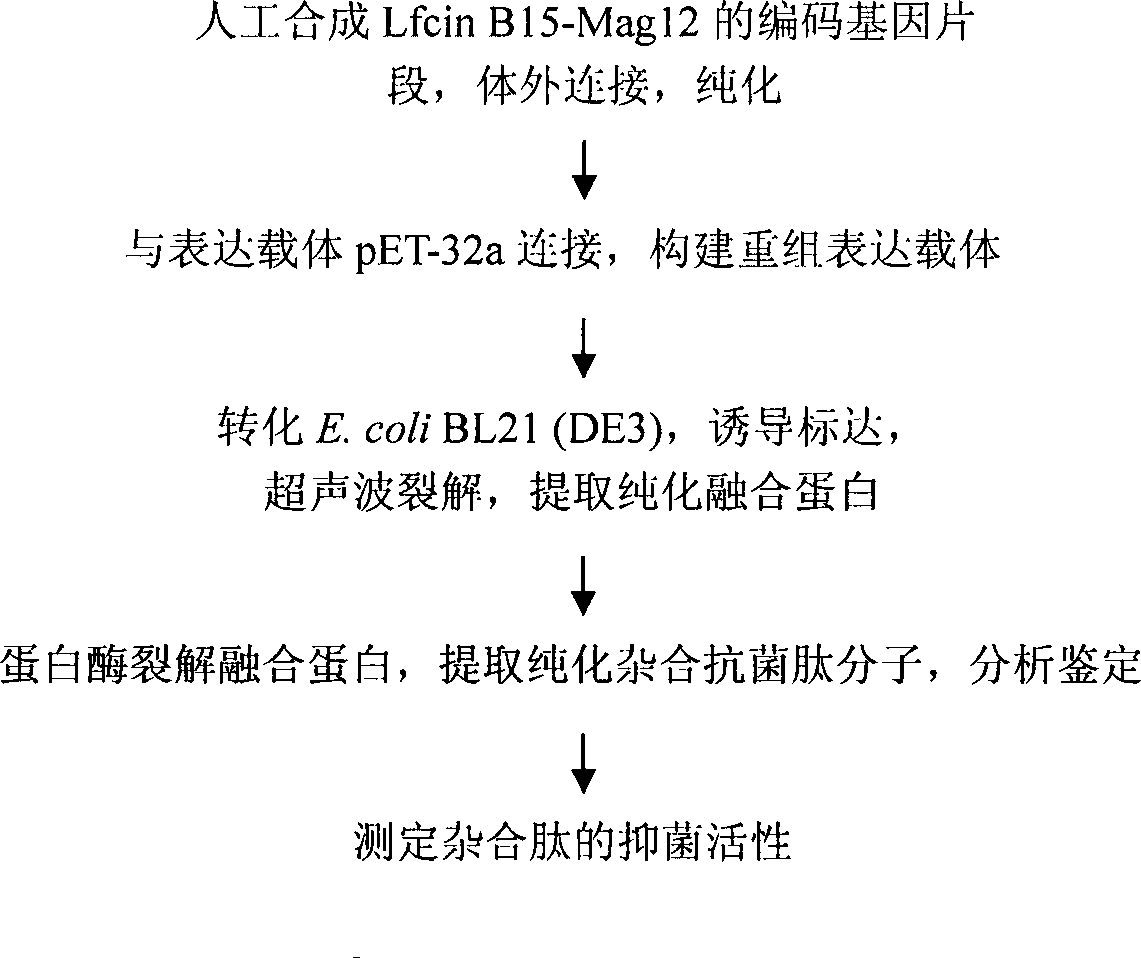
Synthesis of LfcinB15-Mag12 encoding gene and expression method in colon bacillus
InactiveCN101509007AHybrid peptidesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliMultiple cloning site
The invention provides a method for synthesizing an LfcinB15-Mag12 encoding gene and expressing the same in colon bacillus. Active gene fragments enconding LfcinB 1-15 amino acid and active gene fragments of Magainin from 1 to 12 are designed according to E. coli codon preference, a recombinant expression vector pET-32a-Lfcin B15-Mag12 is constructed by an expression vector pET-32a, codon encoding 6 histidine labels exists before multiple cloning sites of pET-32a, and stop codon TAG and TAA are added. The method successfully expresses the LfcinB15-Mag12 in the colon bacillus by a gene engineering method, establishes basis of theory and practice for scale production of hybrid peptide and other noble peptides by the gene engineering method, and is significant for establishing peptide gene engineering strains and commonness technology of antibacterial peptide research.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
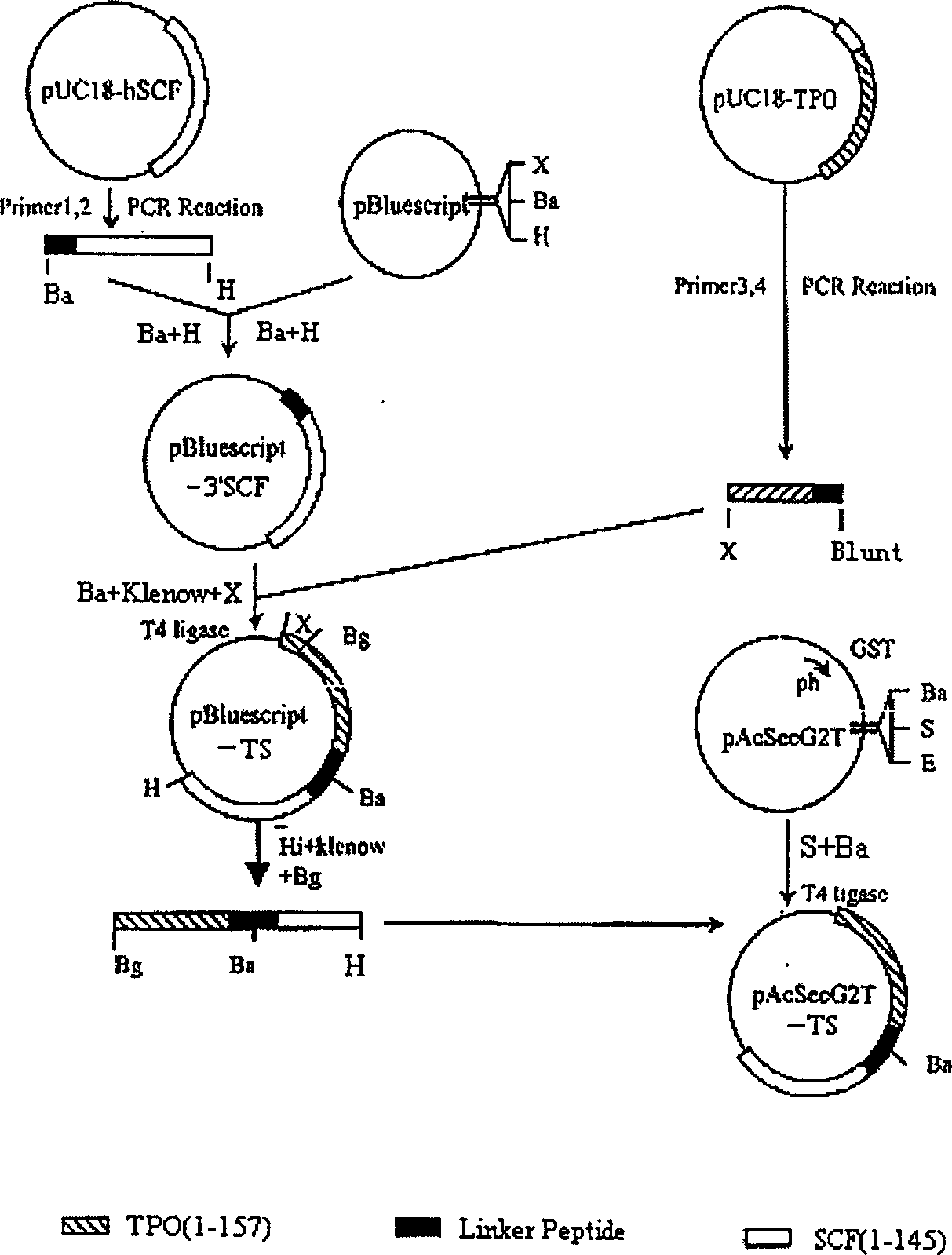
Recombinant human platelet auxin/dry cell factor fusion protein and preparation thereof
The invention is the gene engineering preparation polypeptide remedy technology field of biology technology. The aid is to build a double function fusion albumen gene of rhTPO / SCF, express and prepare with more biology activityú¼less side-effect rhTPO / SCF in insect cell. The gene of rhTPO / SCF includes 1-157 amino acids coding sequence with TPO, 16 amino acids continual peptide coding sequence, 1-145 amino acids coding sequence of SCF and codoní»s DNA fragments. By taking the rhTPO / SCF into TF1 cells experiment, which preparation from the infect recombination virus growing in adherence S19 cell, it mensurates that the specific activity is 2.0 í10 to the power 5 units / mg; by Mo7e cells experiment, the specific activity is 8.3í10 to the power 5 units / mg. It can be used to cure low blood platelet cause by radiotherapy, chemotherapy, bone marrow transplantationíú
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Recombinant expression cassettes with a fungal 3′ termination sequence that function in plants
InactiveUS7344885B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyHeterologous
The present invention provides recombinant expression cassettes comprising a fungal 3′ termination sequence which is functional in a plant. The recombinant expression cassettes comprise a plant promoter operably linked to a coding sequence having a stop codon, and the fungal 3′ termination sequence. The fungal 3′ termination sequence is heterologous to the coding sequence. The fungal 3′ termination sequence comprises structural features including a cleavage site, a positioning element, and an upstream element. The present invention also comprises methods for construction of the plant expression cassettes and introducing the cassettes into plant cells.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
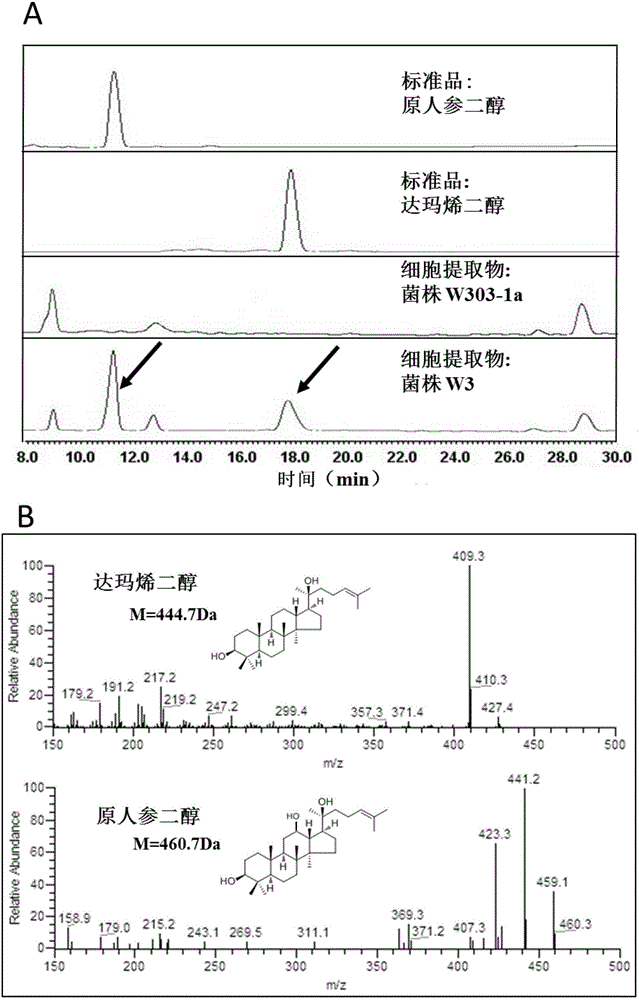
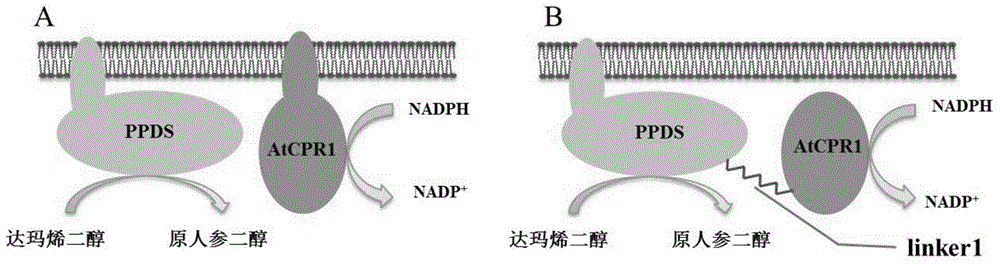
Fusion protein capable of improving dammarenediol conversion efficiency, construction method and application
ActiveCN104611303AImprove conversion efficiencyEfficient synthesisMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesProtopanaxadiolTransformation efficiency
The invention discloses fusion protein capable of improving dammarenediol conversion efficiency, a construction method and application. The construction steps comprise: excising first 138 bases at 5' end of arabidopsis thaliana cytochrome-NADPH-reductase 1 gene AtCPR1, so as to obtain a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2; (2) removing a termination codon TAA at 3' end of ginseng protopanaxadiol synthase gene PPDS with a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 3, and connecting with the base sequence which at 5' end of the sequence shown as SEQ ID NO. 2 and used for coding polypeptide GSTSSGSG, so as to construct a gene member of fusion protein; and (3) connecting the gene member of the fusion protein with saccharomyces cerevisiae cell endogenous promoter and terminator, so as to construct a fusion protein gene expression cassette, and transforming into saccharomyces cerevisiae cell for expression. The fusion protein constructed by the method is capable of improving the conversion rate of dammarenediol to protopanaxadiol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Alkaline xylanase as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses alkaline xylanase as well as a coding gene and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biology. The gene sequence of WMN-3 is a complete ORF (open readingframe), wherein the ORF starts with start codon ATG, stops with stop codon TAA and totally contains 1476 nucleotides, and the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. An amino acid sequence of a protein coded by a gene of alkaline xylanase WMN-3 is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The invention further discloses the application of the alkaline xylanase WMN-3 to industries such as papermaking and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
A method for cloning the complete sequence of goat mc4r gene coding region
InactiveCN102268437AClear lengthReduce workloadFermentationPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyMuscle tissue
The invention discloses a method for cloning the complete sequence of goat MC4R gene coding region, comprising the following steps: A1, extracting total RNA in goat eye muscle tissue, and then reverse-transcribing the total RNA into cDNA; A2, designing primers and PCR Reaction: The upstream primer is designed in the upstream region of the start codon, and the downstream primer is designed in the downstream region of the stop codon; the designed primers are: upstream primer P1: 5′-CTCTCCGCCGCCTAACTTTCGTTT-3′ downstream primer P2: 5′-GTGCCTATAACCTGTGATGTGGAT- 3'. A3, recovery and purification of PCR products; A4, cloning. The invention provides a simple and fast method for obtaining the complete coding region sequence of goat MC4R gene, fills in the blank of the gene in goat, and lays the foundation for further research on the gene of goat.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
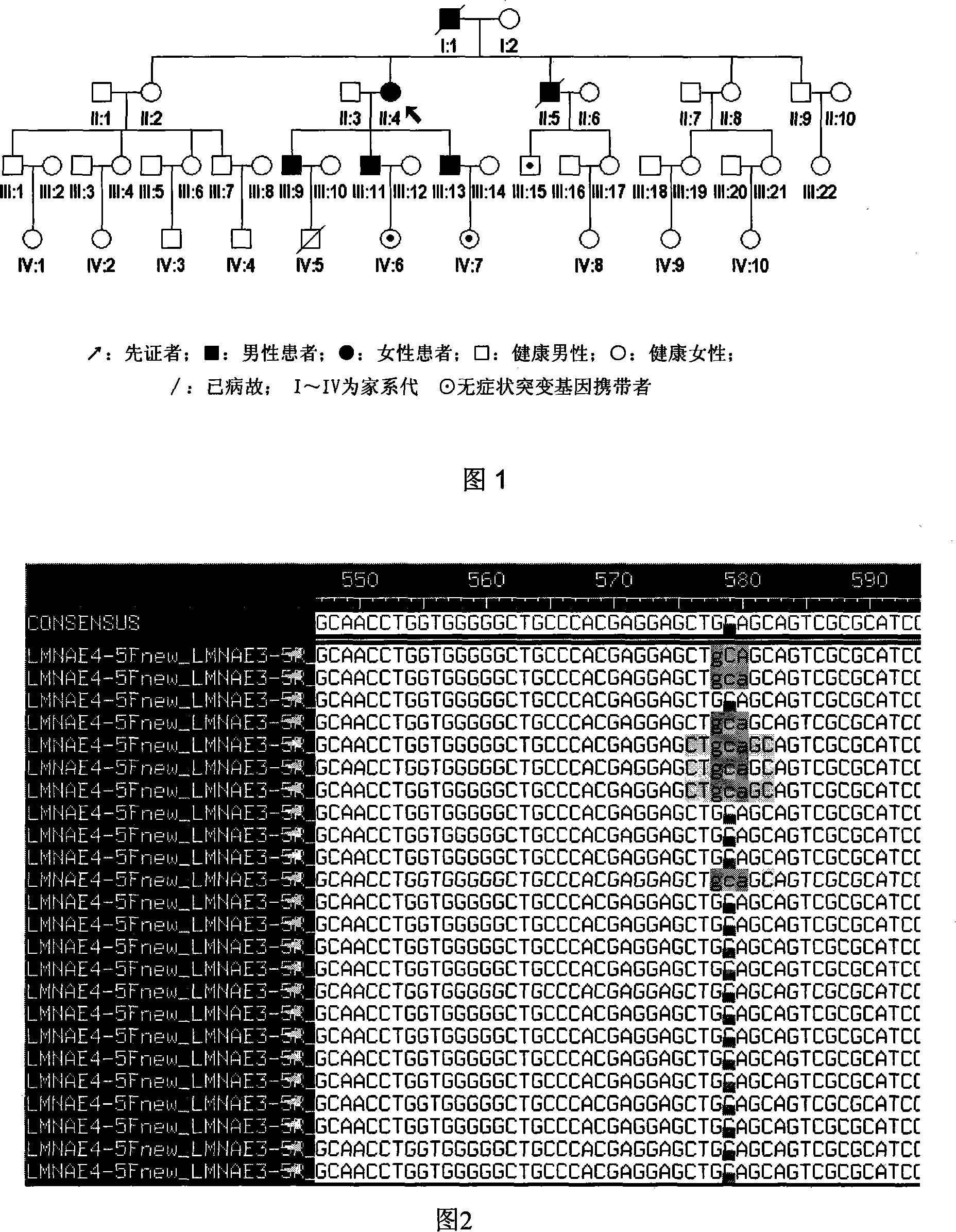
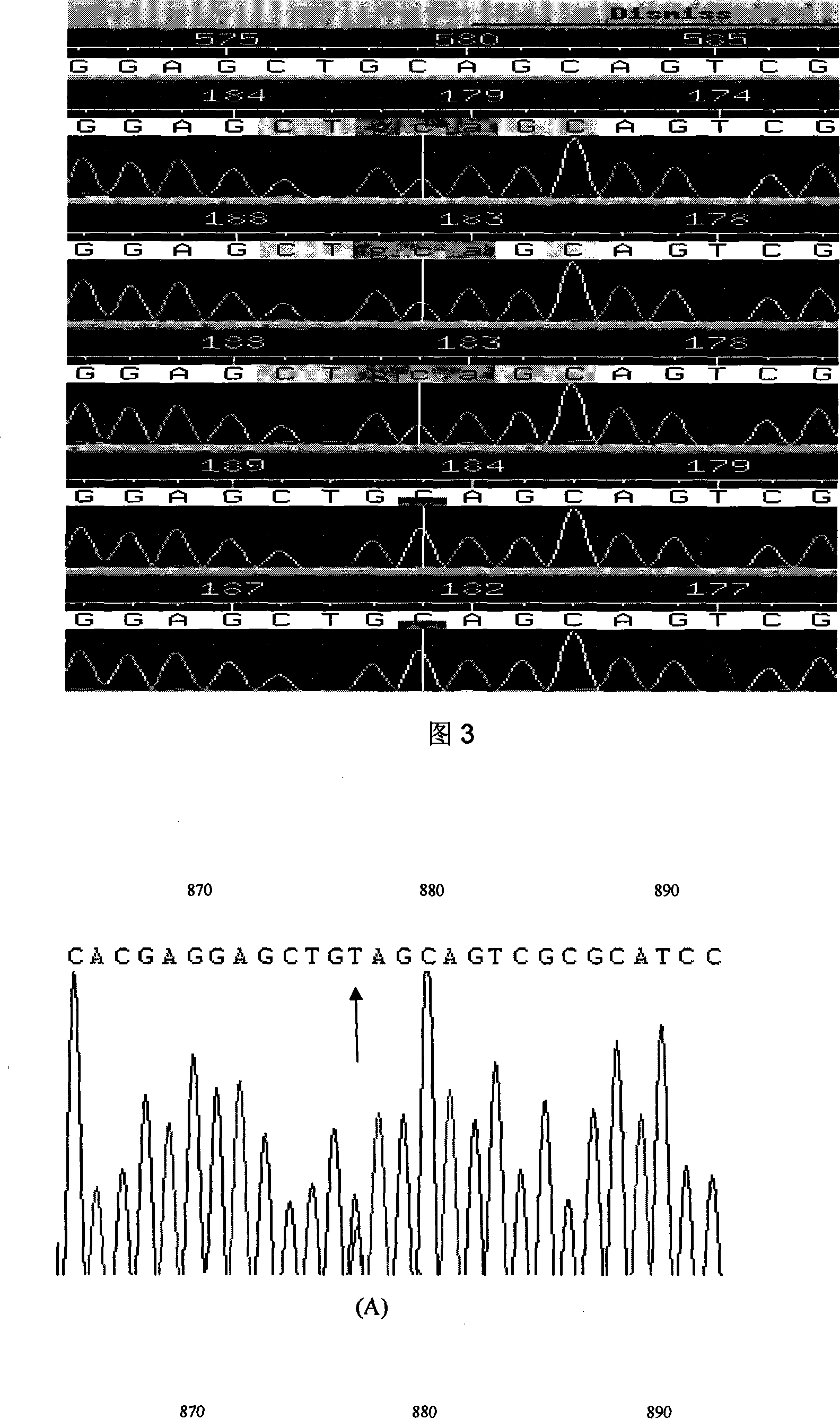
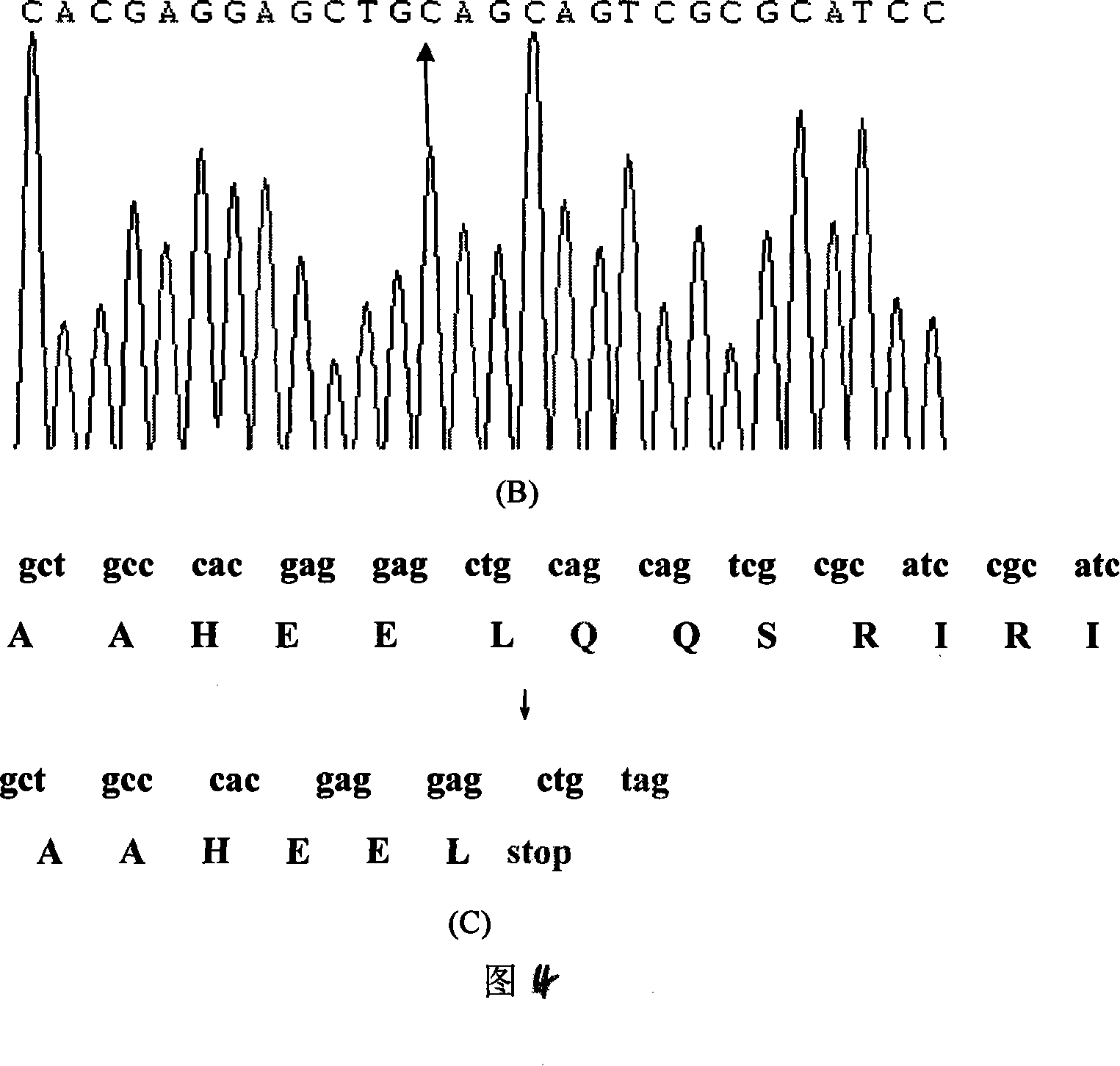
Expanding cardiomyopathy LMNA gene mutation and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN101134960AMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMolecular geneticsConducting system
The present invention relates to LMNA gene mutation of dilated cardiomyopathy and its detection method. The LMNA gene mutation is the C-->T heterozygous mutation of the No. 877 place base in the 5th exon of LMNA gene, and causes the coded amino acid in No. 293 place to change from glutamine (Q) to termination codon (X). Its detection method includes the following steps: 1. extracting peripheral blood DNA; 2. in vitro PCR amplification of LMNA gene exon; and 3. DNA sequencing analysis. The discovery of the LMNA gene mutation can define the molecular genetic mechanism of dilated cardiomyopathy combined with conducting system abnormality further.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY +1
alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase capable of improving filtration performance of wort
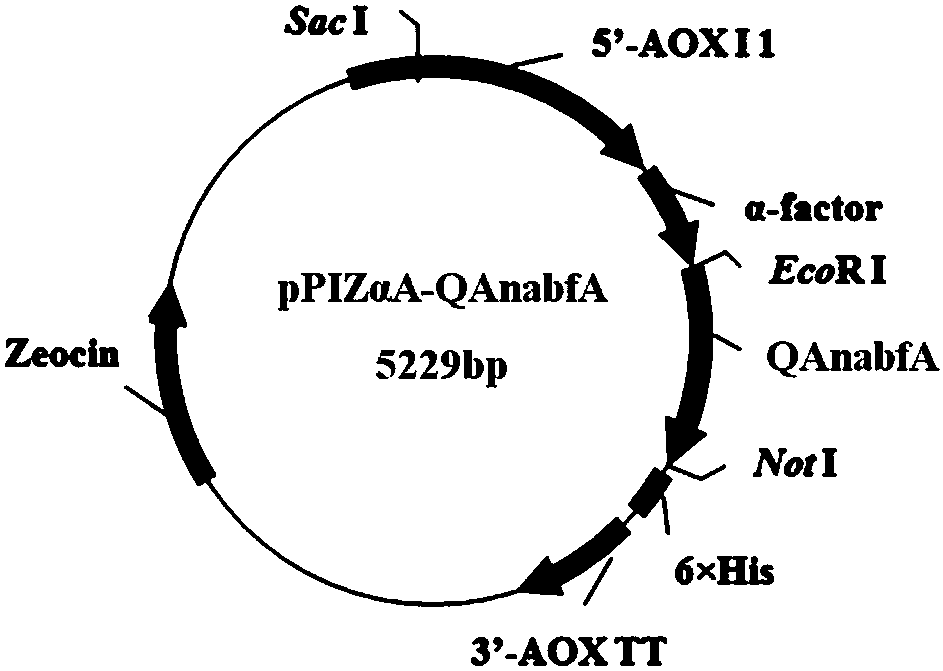
InactiveCN108587932ASpeed up filteringLow viscosityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisSequence signal
The invention discloses an alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase capable of improving the filtration performance of wort, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the present invention, the gene of alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase is modified, wherein the intron, the signal peptide and the stop codon sequence are removed, the sequence of the modified alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase gene isrepresented by SEQ ID NO.4, and the corresponding amino acid sequence is represented by SEQ ID NO.2; the sequence of the modified alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase gene is linked to an expression vector pPIZ[alpha]A to construct a recombinant expression vector pPIZ[alpha]A-QAnabfA, and expression is performed in Pichia pastoris X33 to obtain recombinant alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase; and with the application of the recombinant alpha-L-arabinofuranosidase in the production of wort, the filtration speed of the wort can be improved.
Owner:JIANGSU NONGKEN MALT +1
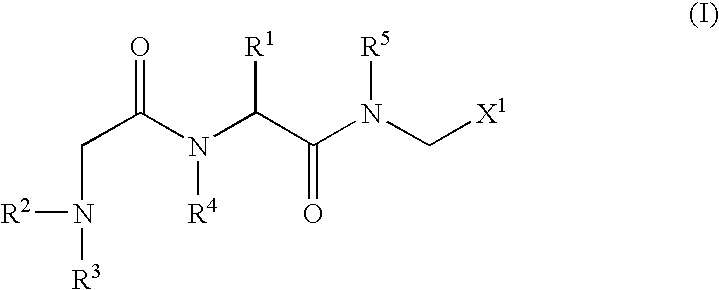
Method Of Treating Genetic Disease Caused By Nonsense Mutation
An object of the present invention is to provide compounds having read-through activity for use in treatment methods of genetic diseases caused by nonsense mutation, to provide pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compound, and to provide a treatment method of genetic diseases caused by nonsense mutation comprising administering the compound.The present invention can provide a method of producing wild type normal protein in a living body of a mammal from a gene with a premature termination codon being generated by a mutation, wherein the method comprises administering a compound expressed by the following formula (VI):(wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 and X1 in the formula are as defined in description) or the like to the mammal.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com