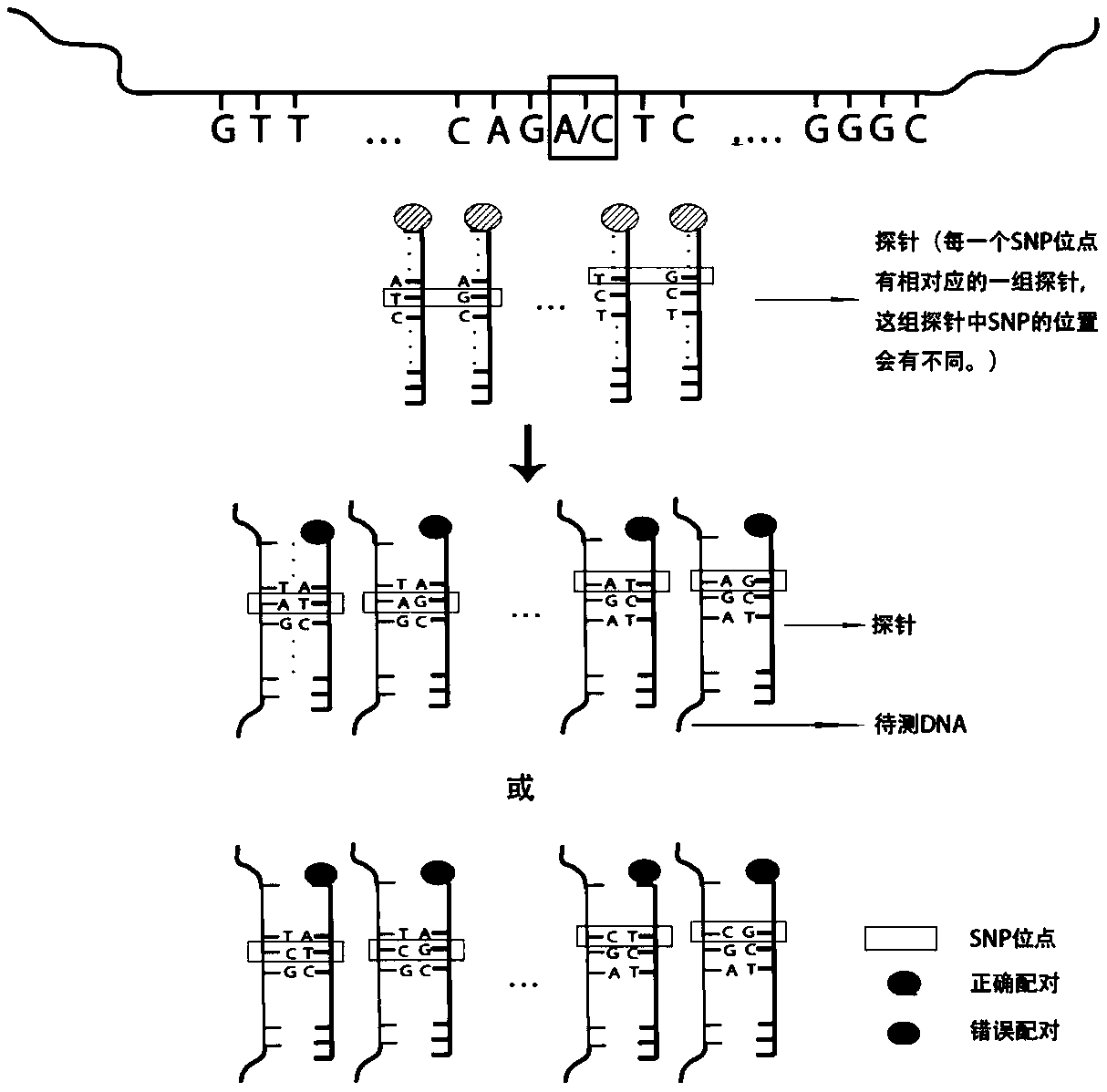
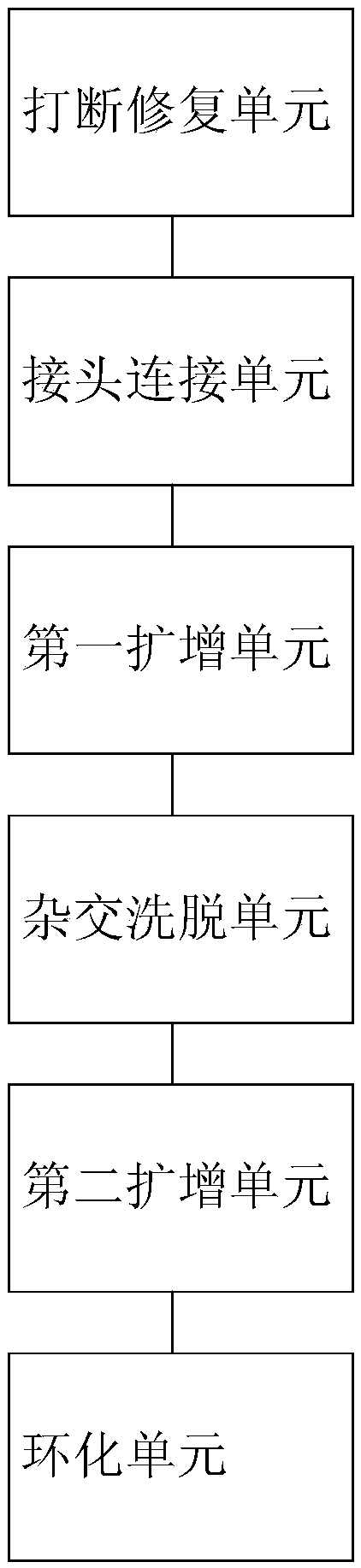
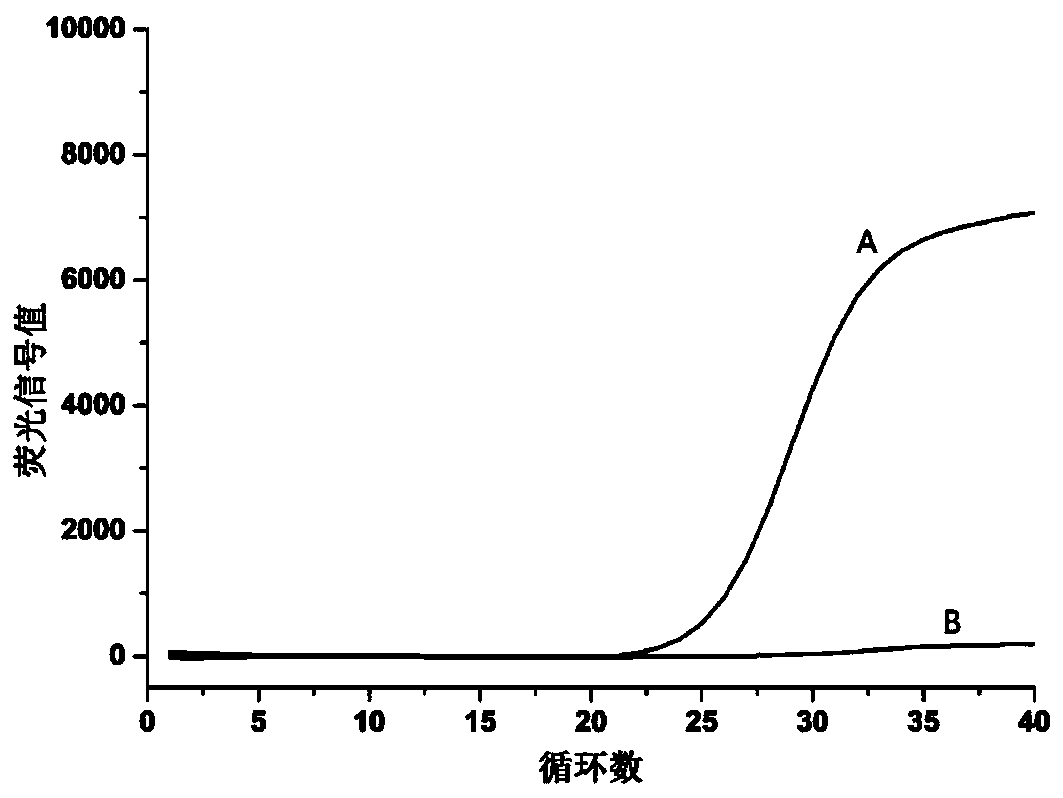
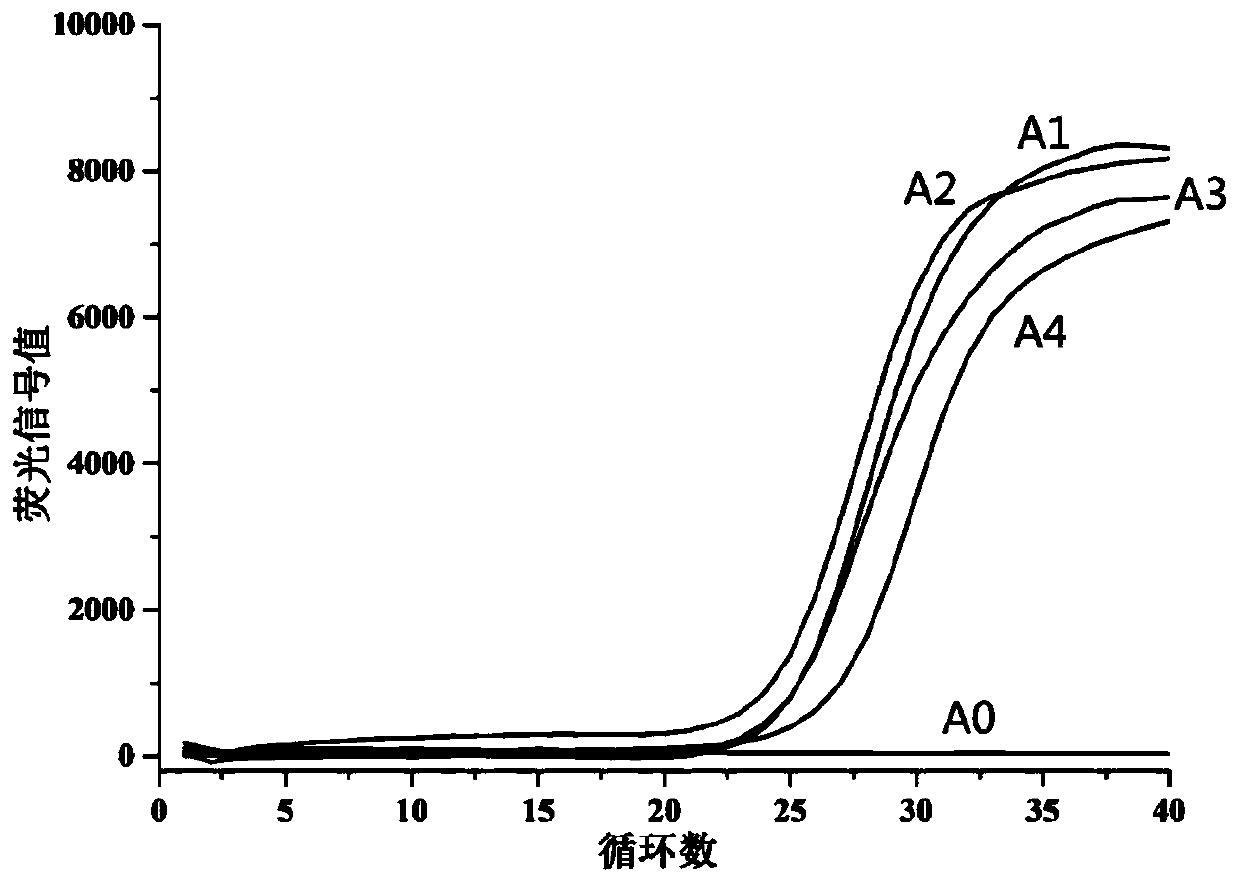
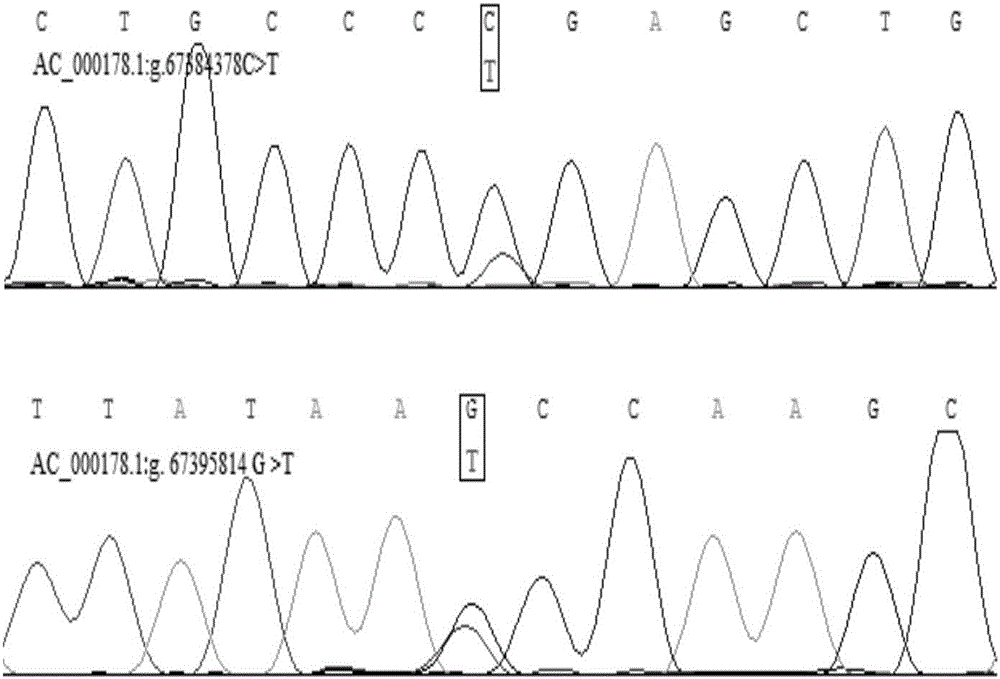
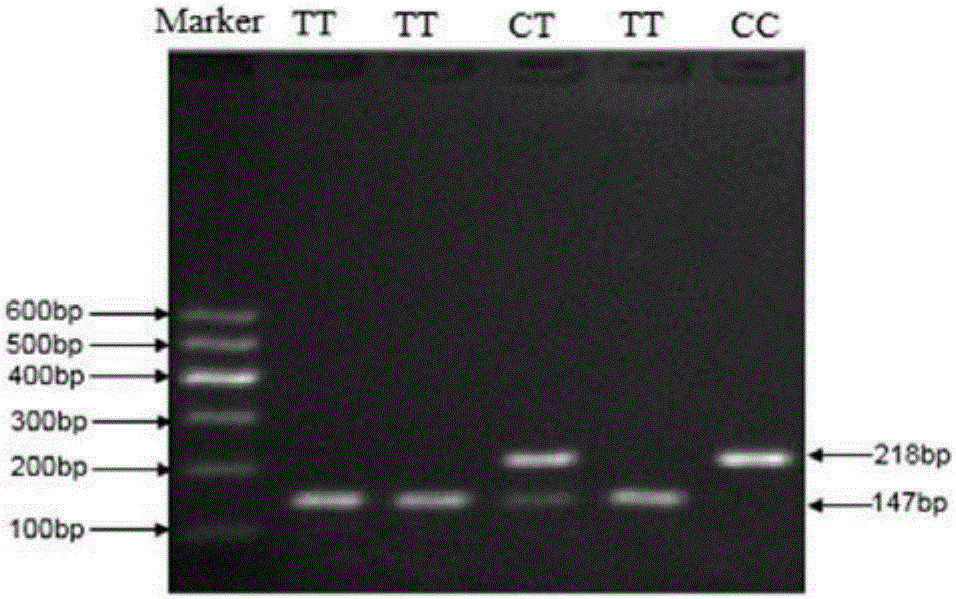
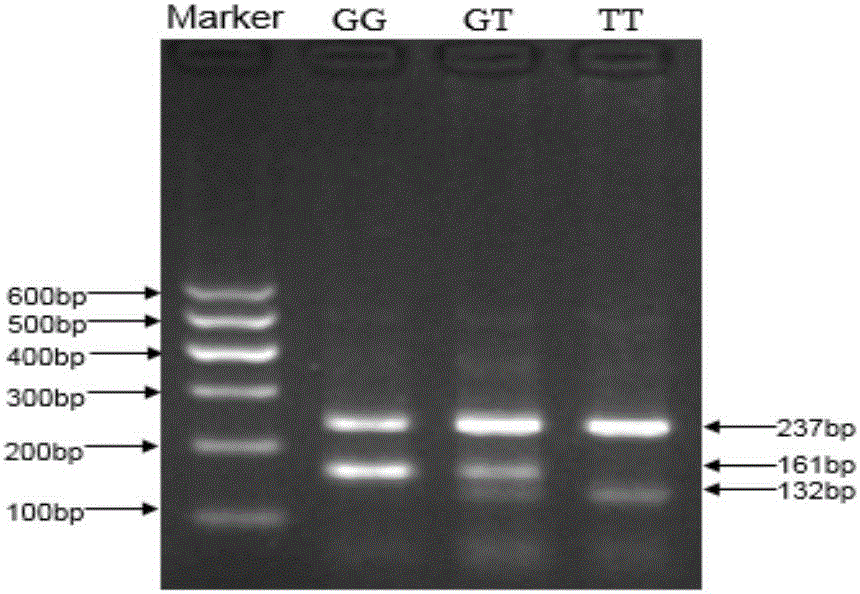
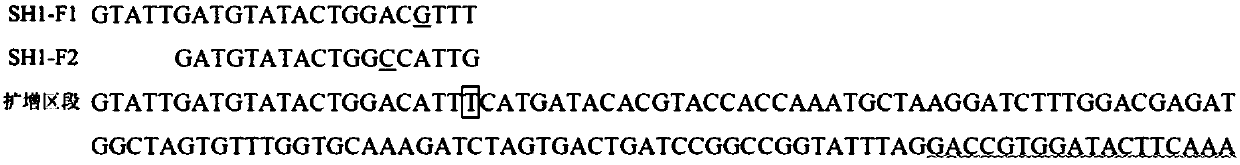Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
60 results about "Single nucleotide mutation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
SNP is the single nucleotide variation in a particular DNA sequence among the individuals. In SNPs, only one nucleotide difference can be observed at a particular location of the sequence. SNP is also a kind of a mutation known as point mutation as it changes DNA by changing one nucleotide from the considering sequence.
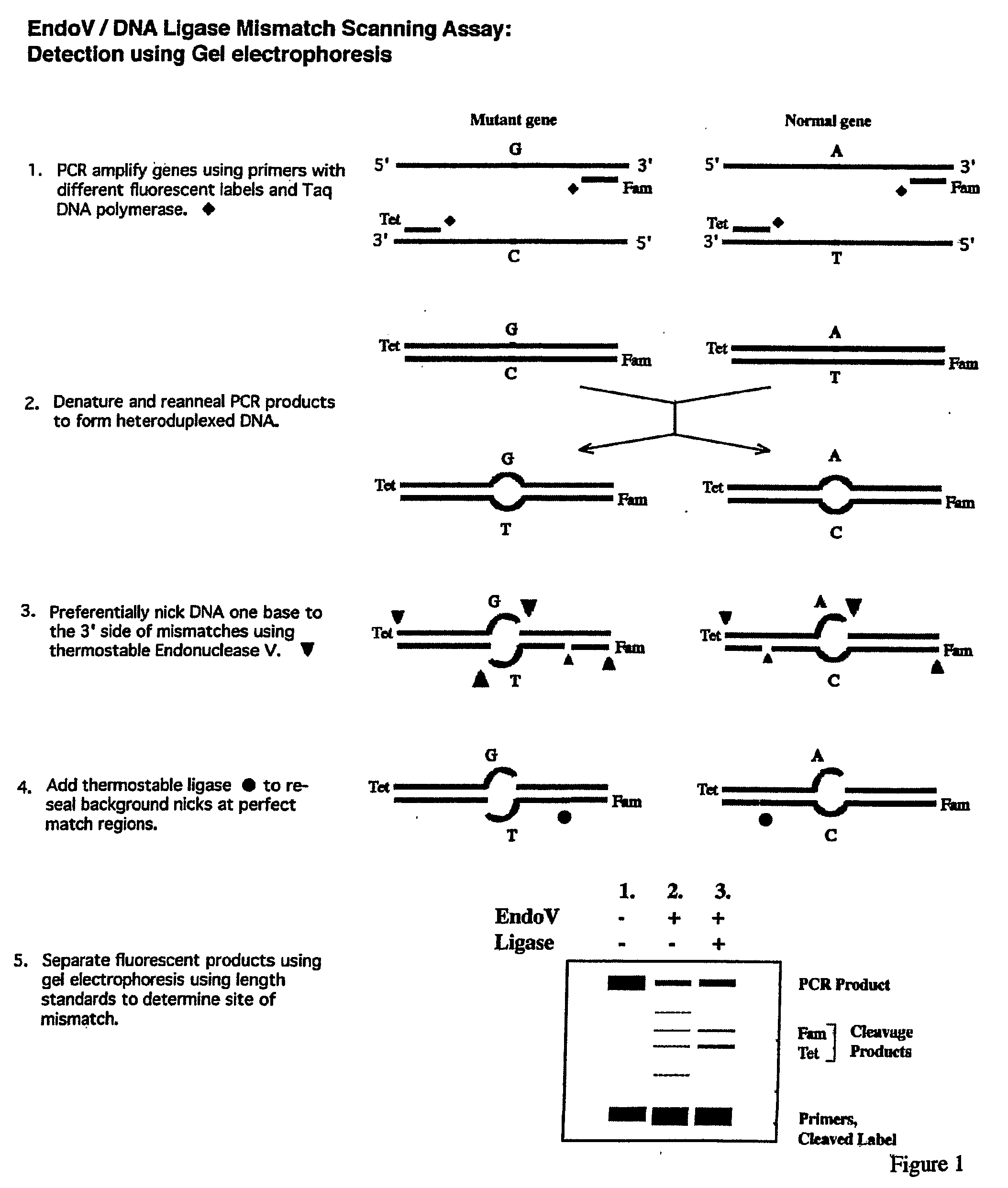
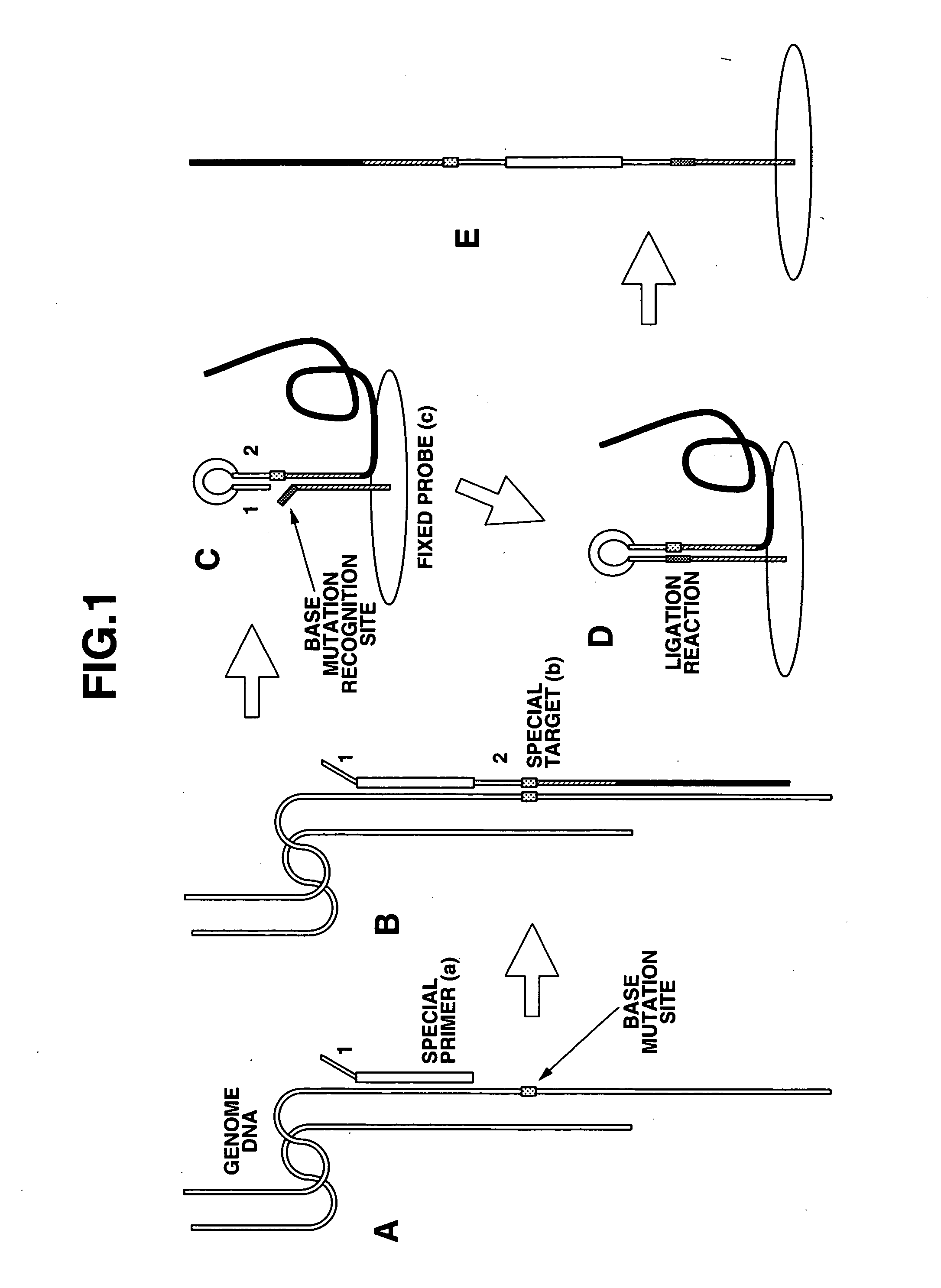
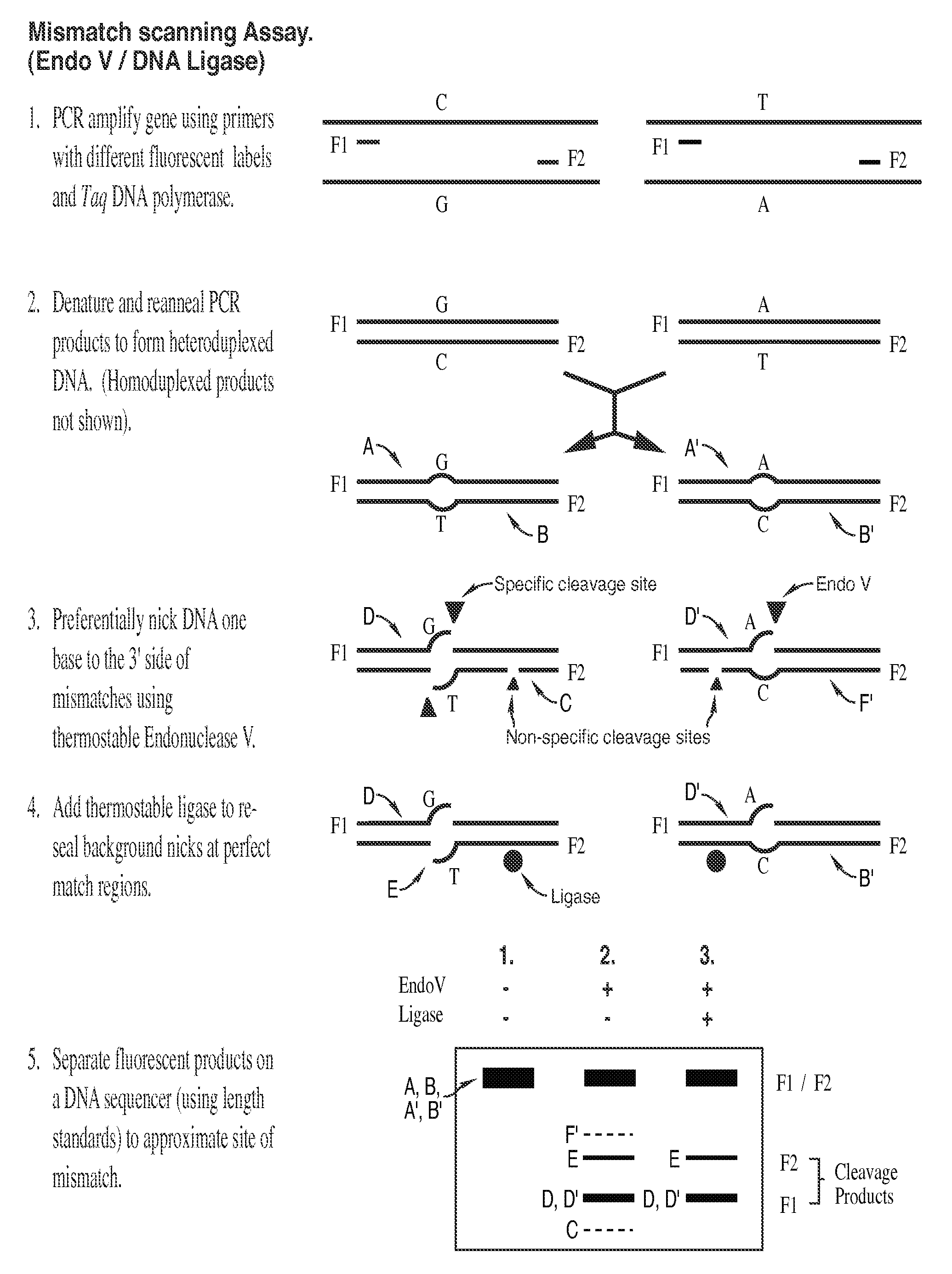
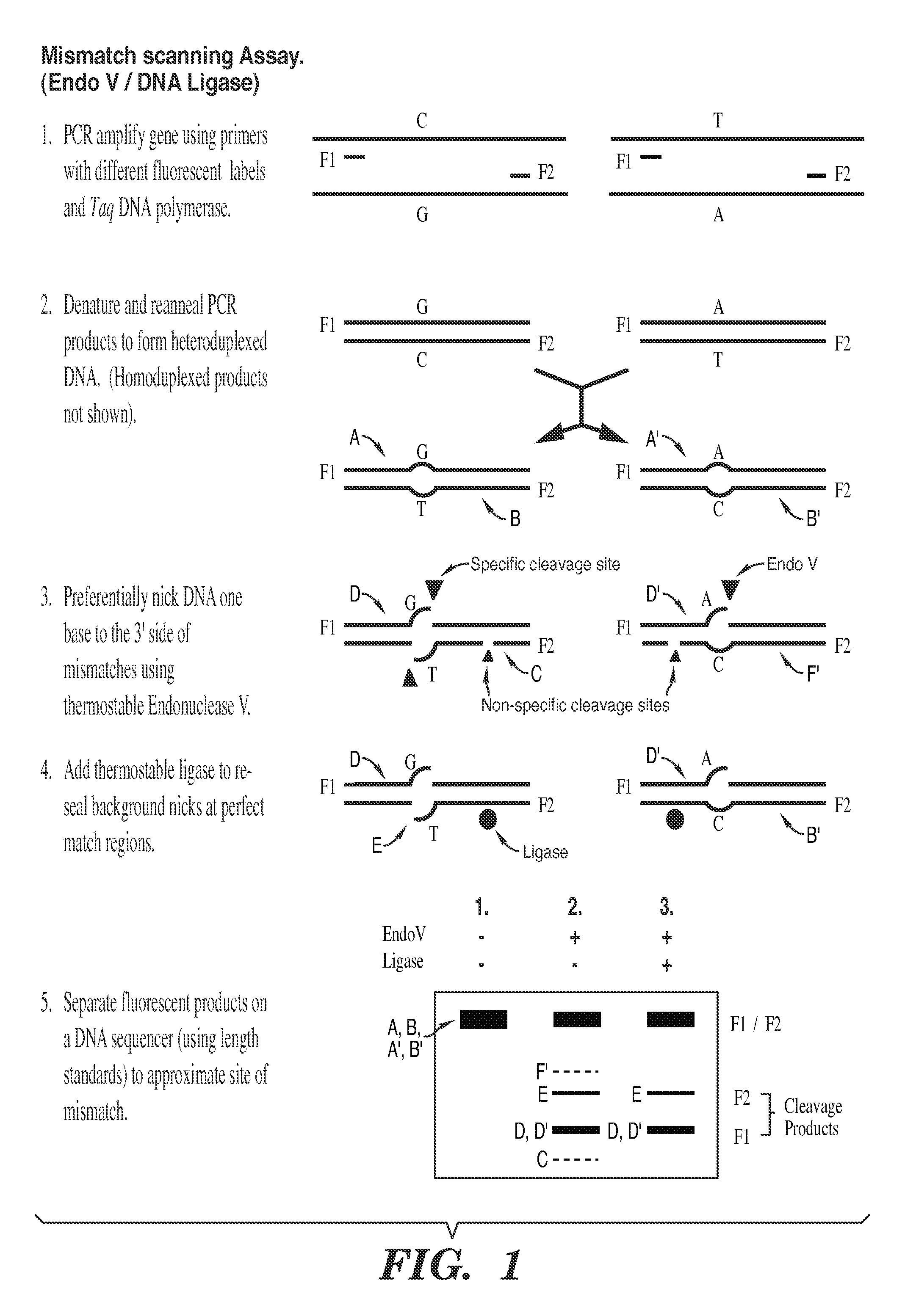
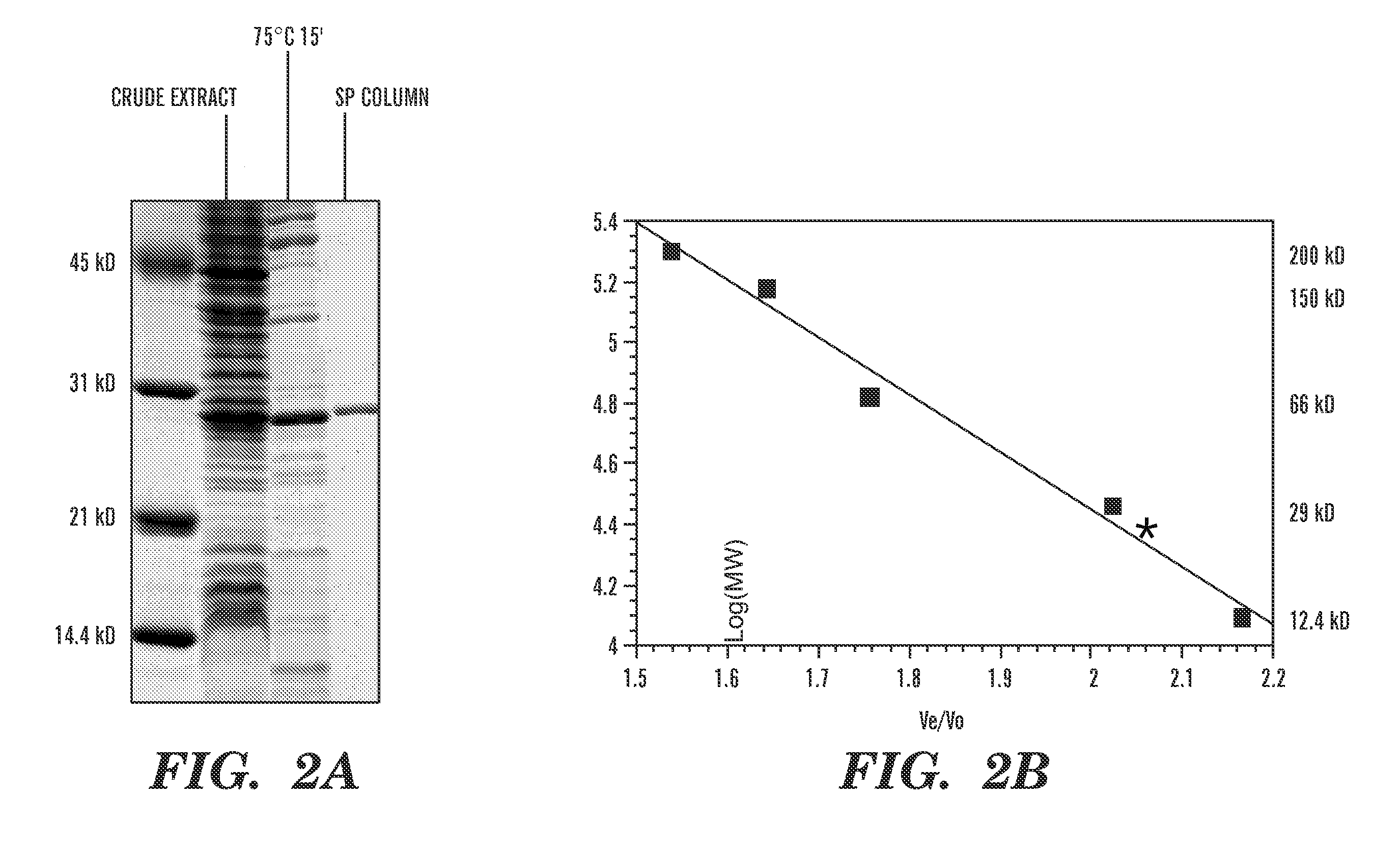
Detection of nucleic acid differences using combined endonuclease cleavage and ligation reactions
InactiveUS7807431B2Wide applicabilityImprove throughputSugar derivativesHydrolasesHeteroduplexSingle nucleotide mutation
The present invention is a method for detecting DNA sequence differences including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
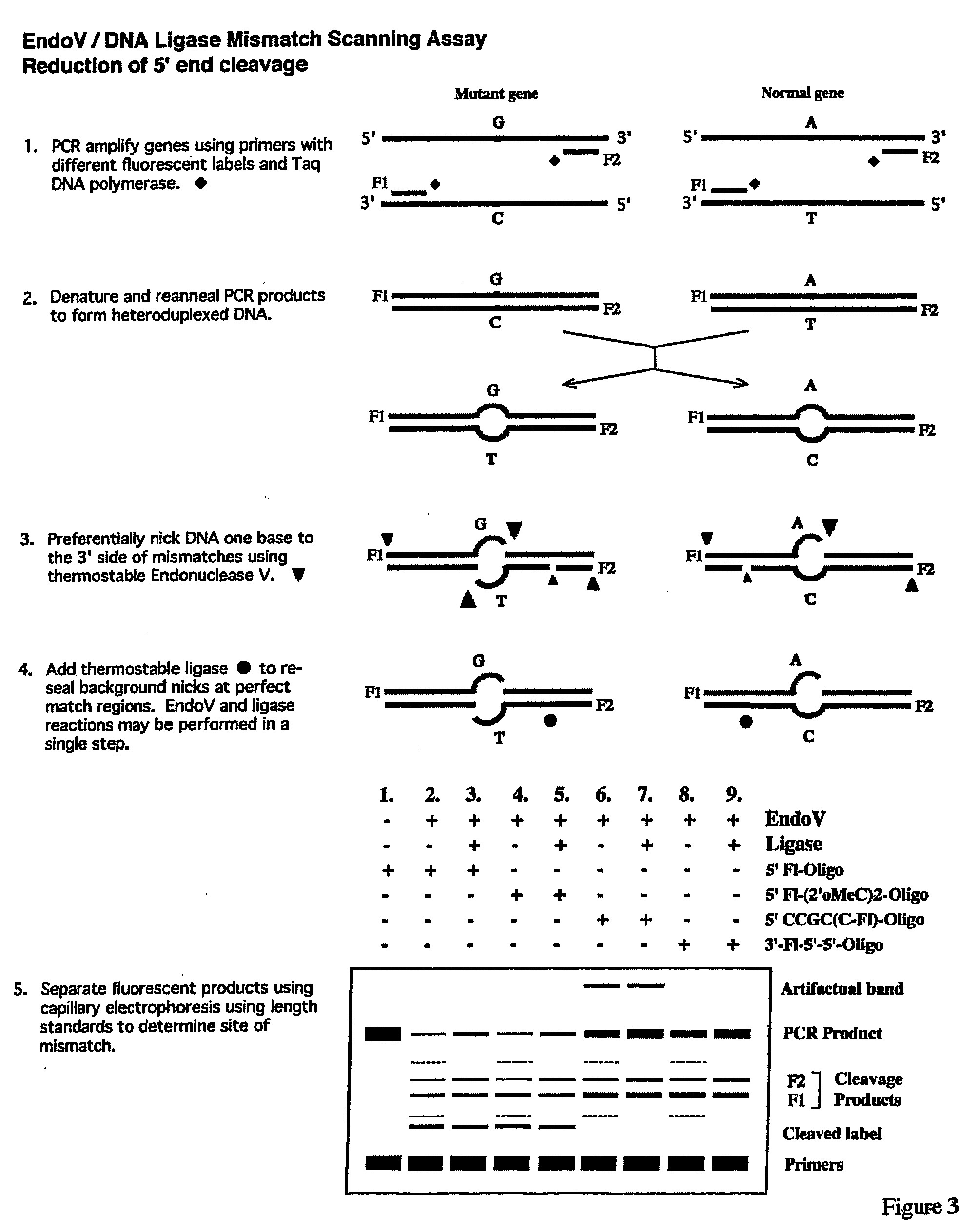
Detection of nucleic acid differences using endonuclease cleavage/ligase resealing reactions and capillary electrophoresis or microarrays
InactiveUS20090123913A1Reduce noiseObstruction is producedMicrobiological testing/measurementNanoinformaticsHeteroduplexA-DNA
The present invention is directed to various methods for detecting DNA sequence differences, including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and, to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
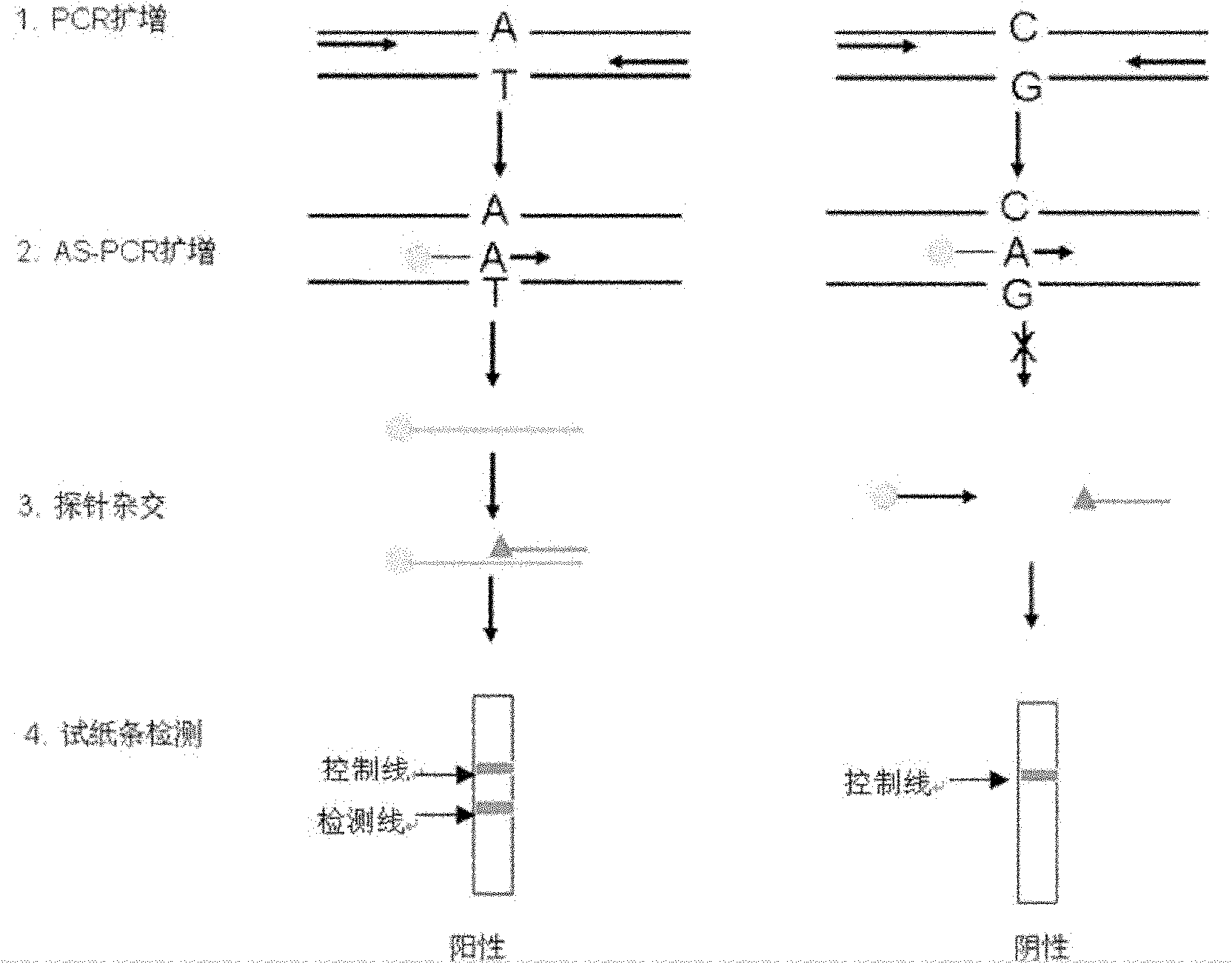
Method and kit for rapidly detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)
ActiveCN102618626AMicrobiological testing/measurementReceptor for activated C kinase 1Allele specific
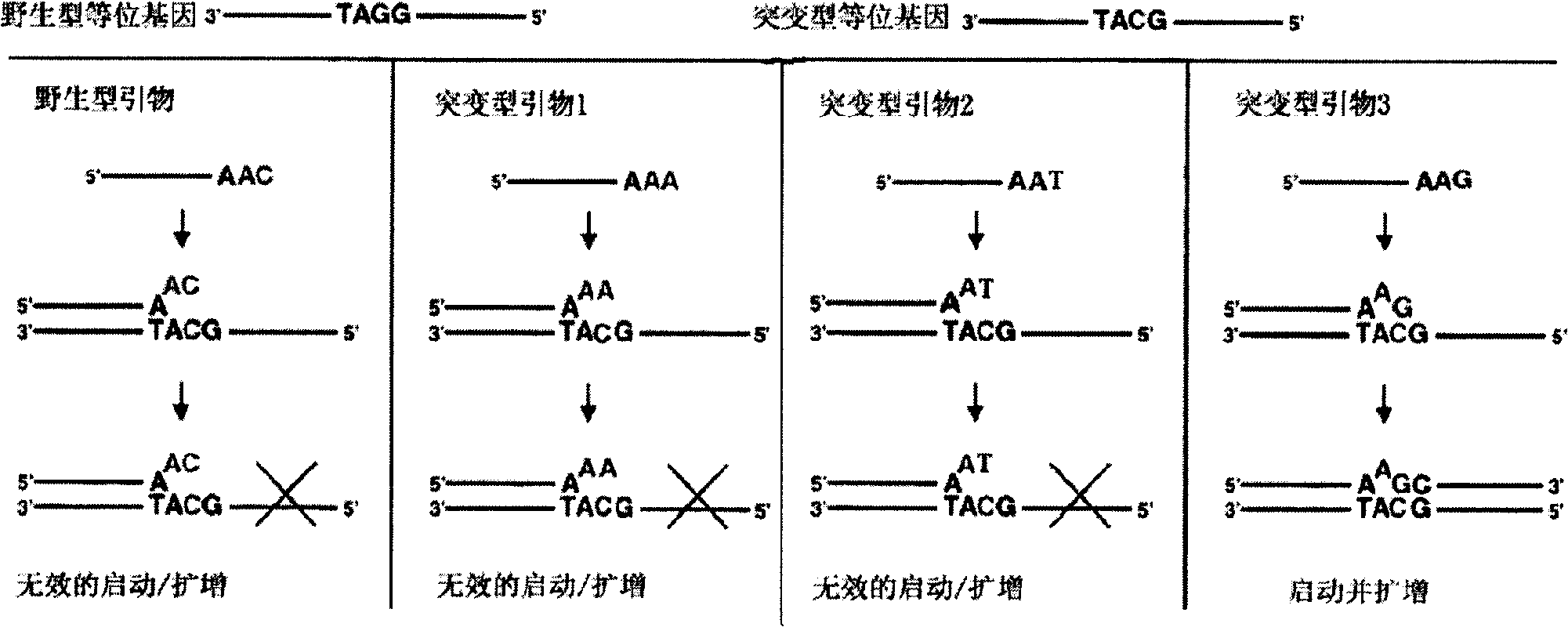
The invention relates to an SNPs detection method, and concretely relates to a method for detecting specifically amplified products through a one-step PCR reaction and a nucleic acid detection test paper strip in a same reaction system. The method comprises the following steps: nonspecifically amplifying fragments containing SNPs sites through first PCR temperature cycling; specifically amplifying bases containing the SNPs sites through AS-PCR (allele specific polymerase chain reaction); and detecting the specifically amplified products by the nucleic acid detection test paper strip. The method can also be used for detecting mononucleotide mutation. The method which has the characteristics of high sensitivity, strong specificity, simple operation, short time, and rapid and reliable detection result combines respective advantages of proteins and nucleic acids. The invention also relates to applications of a kit in the detection of known drug-resistant gene of pathogens, the mating selection of a donor and an acceptor in organ transplantation, and the discrimination of the identity of a criminal or paternity tests in forensic researches.
Owner:USTAR BIOTECHNOLOGIES (HANGZHOU) CO LTD
Method for detecting multiple mutation types of genome
InactiveCN109337957AHigh precisionIncrease linearlyMicrobiological testing/measurementLinear growthSingle nucleotide mutation
The invention relates to a method for detecting multiple mutation types of a genome. A BAM file is used as an input file, a tumor tissue sample is detected, multiple mutation information of differentsample types is detected, and detection of the tumor tissue sample comprises the steps as follows: 1) detection of mononucleotide mutation; 2) detection of insertion and deletion; 3) detection of structural variants; 4) detection of complex variants. According to the method for detecting multiple mutation types of the genome, insertion and deletion are detected with a GeneReader algorithm obtainedthrough combination of a supervised method and an unsupervised method, the local comparison precision is optimized, linear growth with increase of the sequencing depth is realized in the aspect of speed, the detection effect is good, the detection result is accurate, and actual application demands can be well met.
Owner:江苏医联生物科技有限公司
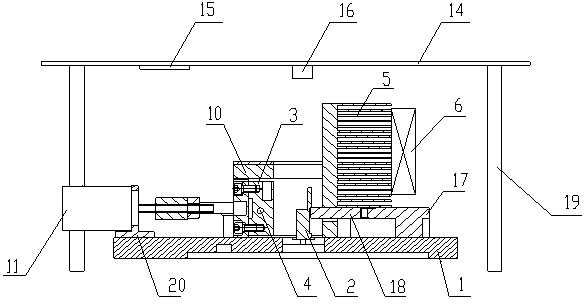
Rapid real-time DNA amplifying equipment and gene mutation detection method
ActiveCN103820306BRapid heating and coolingShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusGenes mutationNucleotide
The invention discloses a fast real-time DNA amplification instrument and a gene mutation detection method. The fast real-time DNA amplification instrument includes a reagent tank and a thermal cycle system. The reagent tank has at least one socket for placing a reaction tube. The thermal circulation system includes a heating body and a radiator, which are distributed on both sides of the reagent tank, and the heating body and the radiator can be driven by the driving mechanism to approach or move away from the reagent tank alternately. The rapid real-time DNA amplification instrument of the present invention realizes the rapid heating and cooling of the reagent by controlling the distance from the heating element and radiator to the reagent tank. This design is not only simple in structure, but also can help the reagent reach the set temperature point faster, Fast thermal cycle is realized, and at the same time, the gene mutation detection method of the present invention only takes 50 minutes from sampling to successful identification of single nucleotide mutations, while similar instruments on the market generally take 2-3 hours, which greatly improves the detection efficiency of gene mutations.
Owner:重庆京因生物科技有限责任公司
Primers and method for quickly detecting Takifugu obscurus young fish sex difference single base mutation
ActiveCN104372086AGender Accurate JudgmentOvercome the disadvantages of cumbersome operation and long time-consumingMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle nucleotide mutationTakifugu obscurus
The invention discloses primers and a method for quickly detecting Takifugu obscurus young fish sex difference single base mutation. According to the mononucleotide mutant sites on sex difference genes of Takifugu obscurus male and female individuals, a pair of external PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer and internal PCR primer containing mispaired base for the mutant sites are designed to respectively amplify the sex difference gene sequences. By utilizing the primers, different sexes of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) samples of Takifugu obscurus can obtain different amplification results, thereby judging the sex difference of Takifugu obscurus. The method has the advantages of high speed and high accuracy, is simple to operate and suitable for popularization and application, can quickly and accurately identify the sex of the Takifugu obscurus young fish on the basis of extracting genome DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of Takifugu obscurus under 1 year, and has important application values in accelerating the Takifugu obscurus unisexual breeding progress and researching the quick PCR detection method in the field of molecular biology.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
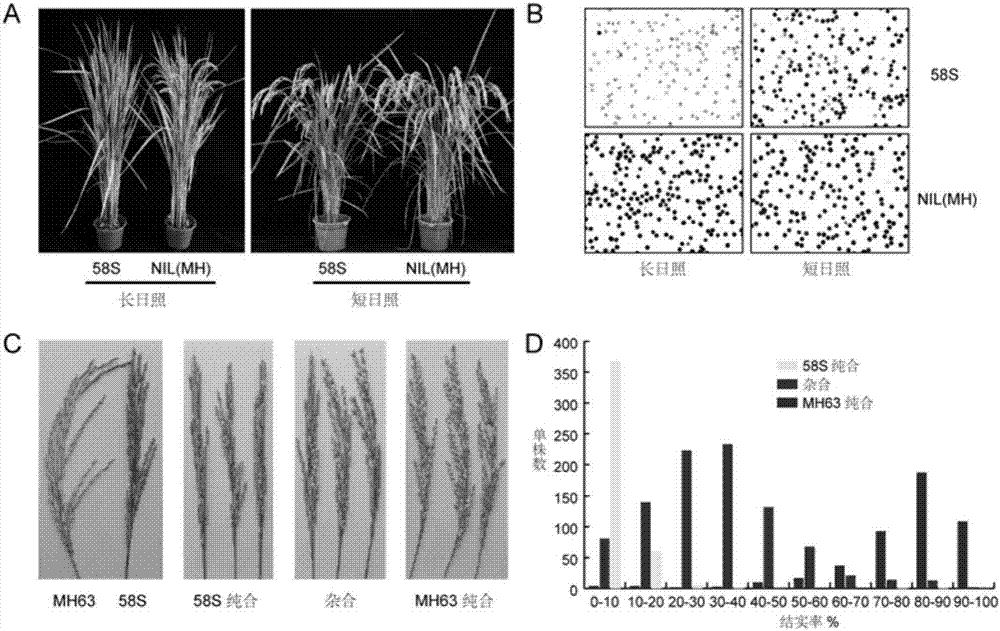
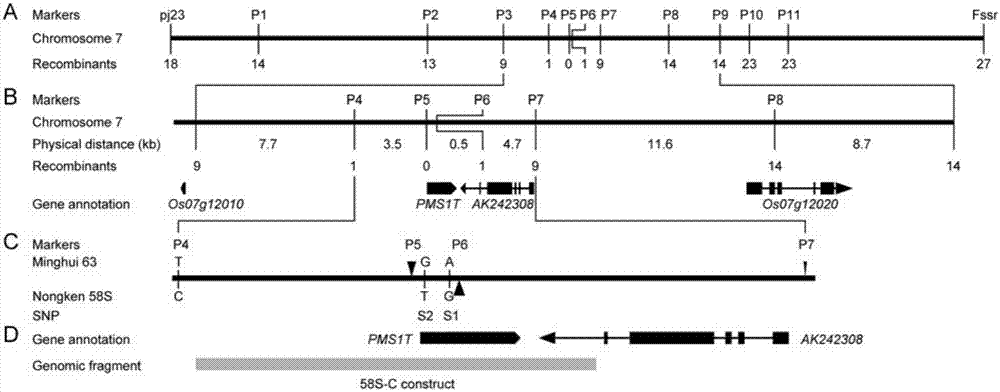
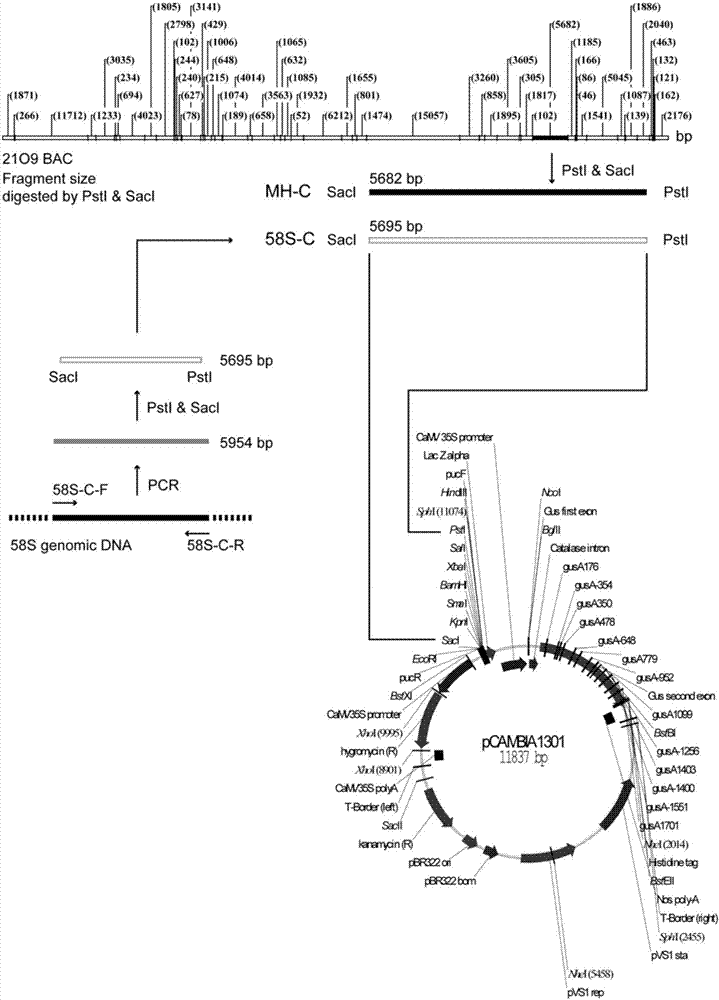
Isolation and cloning of paddy rice photoperiod sensitive genic male sterility gene pms1 and application thereof
The invention relates to isolation and cloning of paddy rice photoperiod sensitive genic male sterility gene pms1 and applications thereof. The pms1 gene has only one transcript PMS1T, which is a non-coding long-chain RNA. There are insertion / deletion variation as long as 65 bp and two mononucleotide mutations between different alleles of the gene, wherein the sequence of a dominant allele of the pms1 is represented as the SEQ ID No.4 and the sequence of a recessive allele is represented as the SEQ ID No.3. By means of the insertion / deletion variation and one mononucleotide mutation, two molecular markers of the paddy rice photoperiod sensitive genic male sterility gene pms1 are obtained. The dominant allele of the pms1 can reduce the setting rate of NIL (MH) under long-day condition, while excessive expression on total-length or shortcut PMS1T also can reduce the setting rate of NIL (MH) under long-day condition too, so that by inhibiting the expression of the PMS1T in a photoperiod sensitive genic male sterile line Nongken 58S, the fertility of the Nongken 58S can be recovered. The isolation and cloning of the gene has important utilization value for selective breeding and improvement of a novel paddy rice photoperiod sensitive genic male sterile line.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for detecting mutation and HRD scoring of tumor patient to guide medication
PendingCN112820351ACalculation speedEasy to detectDrug and medicationsBiostatisticsAllele ImbalanceWhite blood cell
The invention relates to a method for for detecting mutation and HRD scoring of tumor patient to guide medication, which comprises the following steps: detecting a tumor tissue sample and a control leukocyte sample thereof on the basis of taking a BAM file as an input file, and detecting mutation information of an HRR pathway in panels of different sample types and large-fragment chromosome abnormality HRD caused by gene recombination repair defects, the method for detecting the tumor tissue sample comprises the following steps: 1) detecting mononucleotide mutation of an HRR pathway; 2) detecting the loss of heterozygosity (LOH), telomere allele imbalance (TAI) and large fragment state transition (LST) of the HRR region, wherein the HRD score is equal to the weighted sum of LOH, TAI and LST scores; the invention provides a mutation and HRD scoring medication guidance method for tumor patients. According to the method, a traditional method that the HRD value score is calculated through whole genome detection and is not beneficial to clinical actual effect is optimized, the calculation speed is increased, the detection effect is good, the detection result is accurate, and the requirements of actual application can be well met.
Owner:江苏医联生物科技有限公司
Rapid real-time DNA amplifying equipment and gene mutation detection method
ActiveCN103820306ARapid heating and coolingShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenes mutationSingle nucleotide mutation
The invention discloses rapid real-time DNA amplifying equipment and a gene mutation detection method. The rapid real-time DNA amplifying equipment comprises a reagent tank and a thermal cycling system, wherein an inserting hole for placing a reaction tube is formed on the reagent tank; the thermal cycling system comprises a heating element and a radiator; the heating element and the radiator are distributed at two sides of the reagent tank; the heating element and the radiator can alternatively be close to or depart from the reagent tank under drive of a drive mechanism. The rapid real-time DNA amplifying equipment disclosed by the invention achieves rapid heating and cooling by controlling the distances from the heating element and the radiator to the reagent tank. The design not only is simple in structure, but also can help a reagent more rapidly achieve the set temperature point, and achieves rapid thermal cycle. Meanwhile, just 50 minutes are required from sampling to successful identification of mononucleotide mutation by adopting the gene mutation method disclosed by the invention while the similar instrument on the market generally needs 2-3 hours. Thus, the detection efficiency of the gene mutation is greatly improved.
Owner:重庆京因生物科技有限责任公司
Rice Gene, GS3, Exerting Primary Control Over Grain Length and Grain Weight
InactiveUS20100017919A1High yieldQuality improvementFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyNucleotide
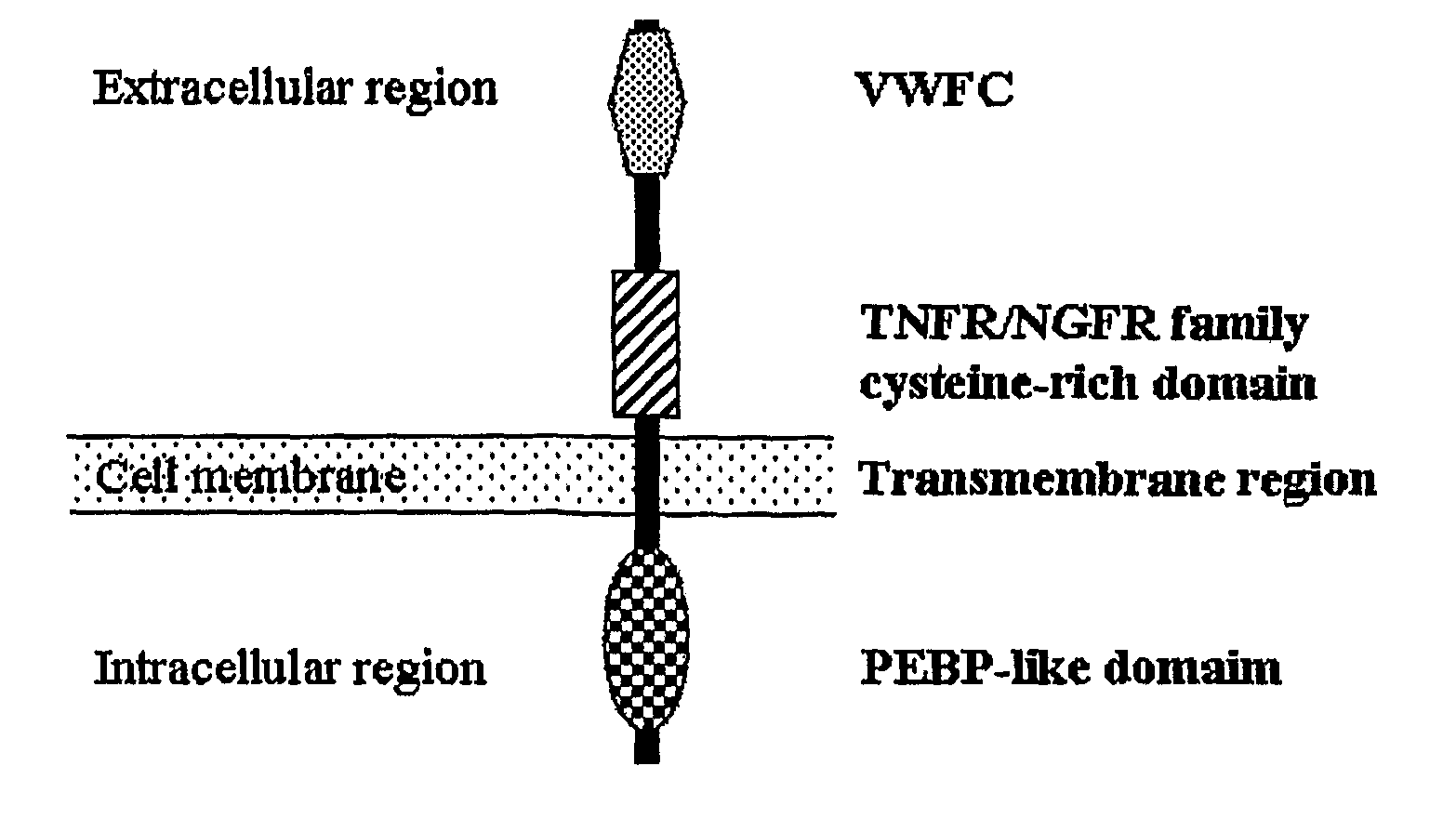
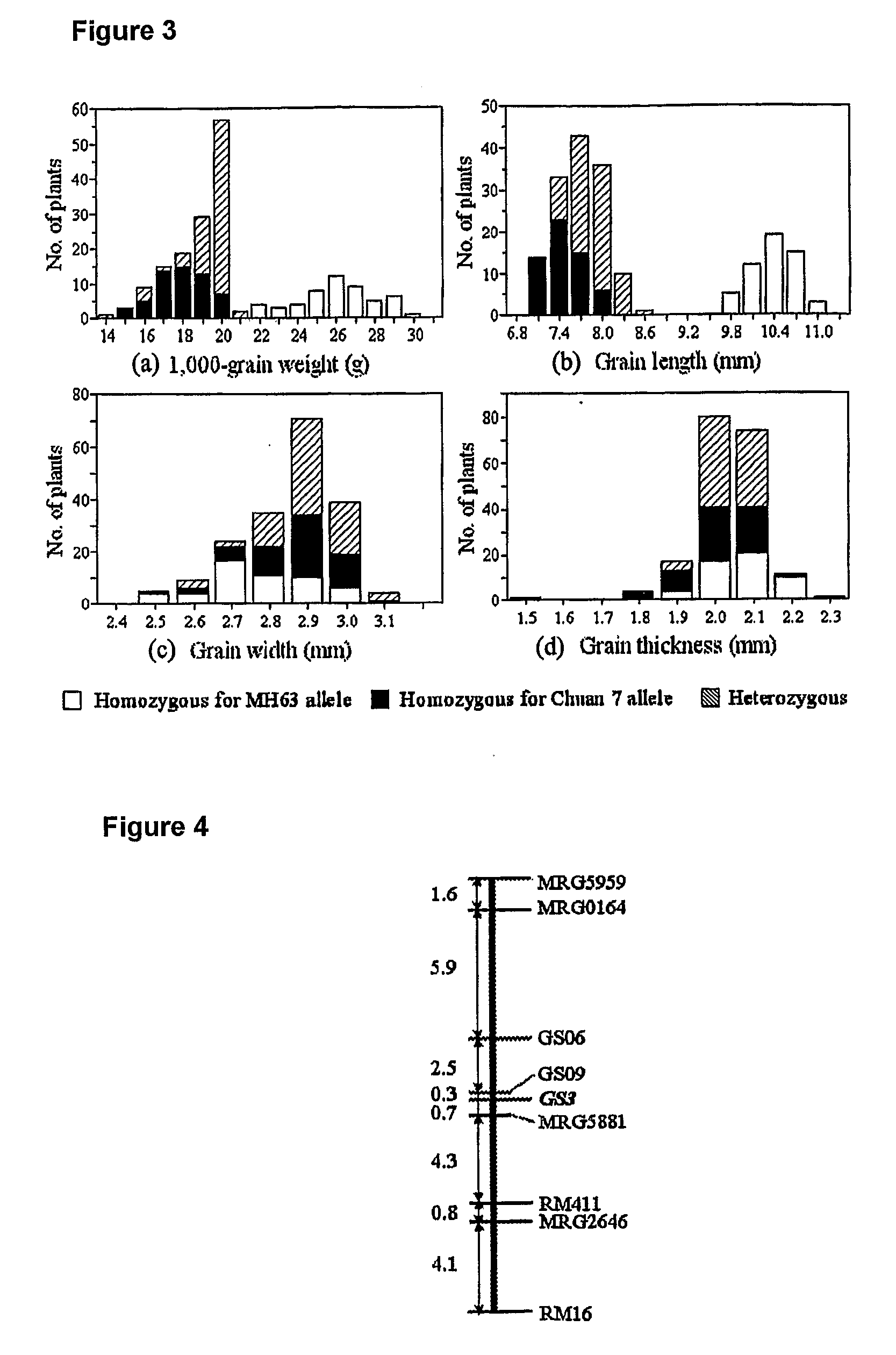
The present invention relates to an isolated major gene GS3 which regulates grain weight and grain length in the rice and the cloning of said gene. The DNA sequence of GS3 gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 and is 7883 bp in length. GS3 gene comprises 5 exons and encodes 232 amino acids. It is predicted based on bioinformatics analysis that said protein contains conserved domains including a PEBP-like domain, a transmembrane domain, a cysteine-rich domain of TNFR / NGFR and a VWFC domain. cDNA sequence of said gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. By sequence alignment between three large grain species and 3 small grain species of rice, it is revealed there is only one common single nucleotide mutation in a 7.9-kb region between the two different grain-length groups. Said nucleotide mutation is located at the second exon of the GS3 gene, in which a cysteine codon (TGC) in the small-grain group is mutated to a termination codon (TGA) in the large-grain group. This mutation causes a premature termination in the large-grain group, which leads to a 178-amino acids truncation (including part of the PEBP-like domain and all the other three conserved domains). The present invention also provides methods of producing transgenic plants comprising sequences disclosed herein.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Detection of two novel single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites of promoter region of sheep myostatin (MSTN) gene and establishment of detection method thereof
InactiveCN102181517ARepresentative of the groupSignificant technological progressMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionSingle nucleotide mutation
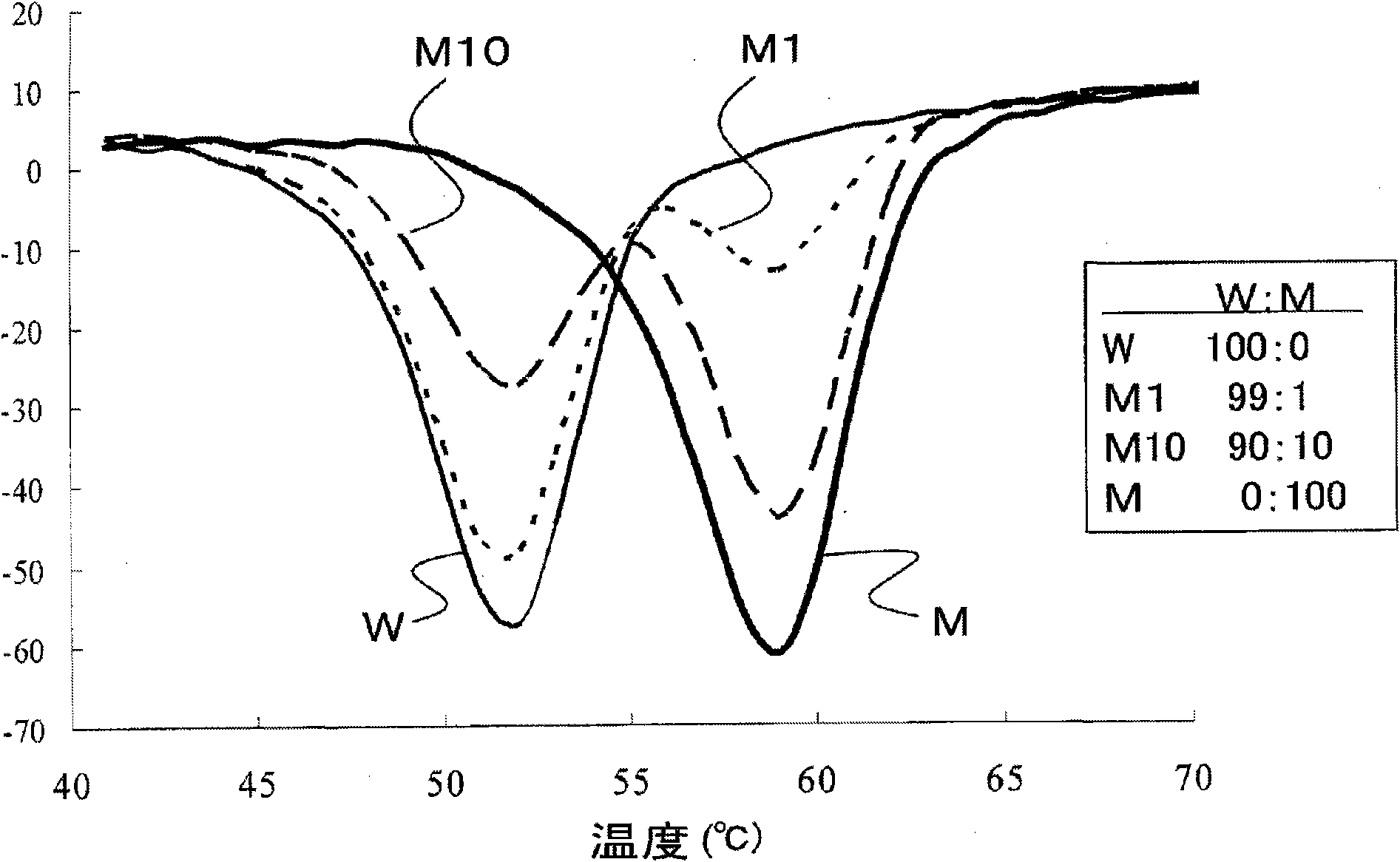
The invention discloses the detection of two novel single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) sites of a promoter region of a sheep myostatin (MSTN) gene, and the establishment of a detection method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, determining two mononucleotide mutational sites of the promoter region of the sheep myostatin gene, wherein the two mononucleotide mutational sites are positioned in a GeneBank sequence, the registry number is DQ530260, and the SNP sites (-959T / C, -784G / A) are positioned at -959th site and -784th site according to an initial codon ATG and comprise 6 genotypes (TT, TC, CC, GG, GA, AA); 2, detecting three specific primers of the mutant allele, wherein the lengths of the three specific primers are 22bp, 22bp and 21bp respectively, the first primer is used for the sequencing of the promoter region of the MSTN gene, and the second and third primers are bonded onto template strands of two mutant alleles respectively and are amplified to target genes obtained by the mutation of the alleles; and 3, performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification on genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of a sample by a designed oligonucleotide primer, performing enzyme digestion analysis on products which are amplified to 985bp and 121bp fragments by utilizing Psp1406I and Rsa I restriction enzymes, and establishing a PCR-RFLP detection system of the SNP sites so as to obtain the polymorphism of the two mononucleotide mutational sites.
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院中国-澳大利亚绵羊育种研究中心
Probe for detecting mutation in jak2 gene and use thereof
ActiveCN101622363AEasy to separateHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementCytosineSingle nucleotide mutation
It is intended to provide a probe for detecting a mutation in JAK2 gene capable of detecting a sequence to be detected having a single nucleotide mutation even when the sequence to be detected having such a mutation and a sequence not to be detected having no mutation are present together. At least one oligonucleotide which comprises the same sequence as that of a region up to the 17th to the 22nd base from a first base toward the 5' direction when a cytosine base (C) at position 84 in exon 12 of JAK2 gene composed of a nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 is determined to be the first base, and has the cytosine base (C) as the 3' end is used as the probe. By using such a probe in, for example, Tm analysis, even if a sample contains JAK2 gene having a mutation and JAK2 gene having no mutation, the former mutation can be detected. The probe is preferably labeled with a fluorescent dye.
Owner:ARKRAY INC
Strawberry anthocyanin regulatory gene functional marker
InactiveCN105734145AShorten the breeding periodImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFragariaAgricultural science
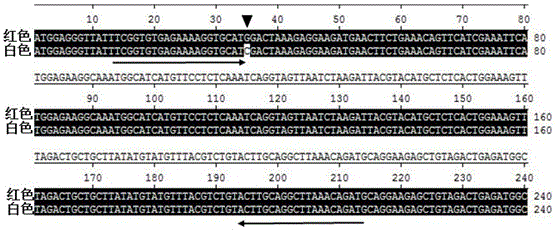
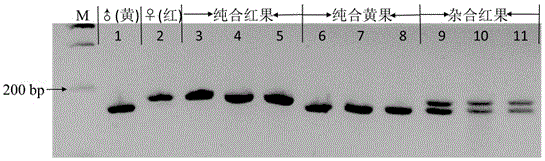
The invention provides a strawberry anthocyanin regulatory gene functional marker and belongs to the fields of fruit tree breeding and molecular genetics. The strawberry anthocyanin regulatory gene functional marker is characterized in that one mononucleotide mutation exists in coding regions by carrying out sequence comparison on a strawberry anthocyanin regulatory gene MYB10 in red and yellow strawberries, a dCAPS marker Fv-Ry is designed according to difference of the mononucleotide, the dCAPS marker can distinguish yellow, heterozygous red and homozygous red strawberries, and the marker and strawberry fruit colour character are in cosegregation. By utilizing the functional marker, a material carrying an anthocyanin regulatory gene can be rapidly and accurately screened and identified from a large number of strawberry germplasm resources, molecular marker early selective breeding is carried out, and progress of strawberry fruit colour breeding is greatly accelerated.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
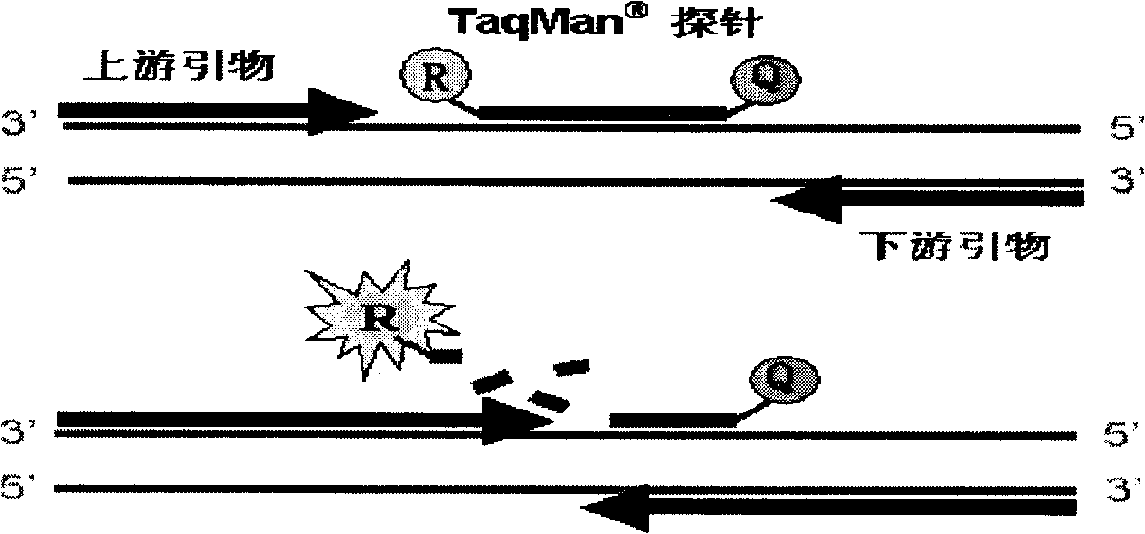
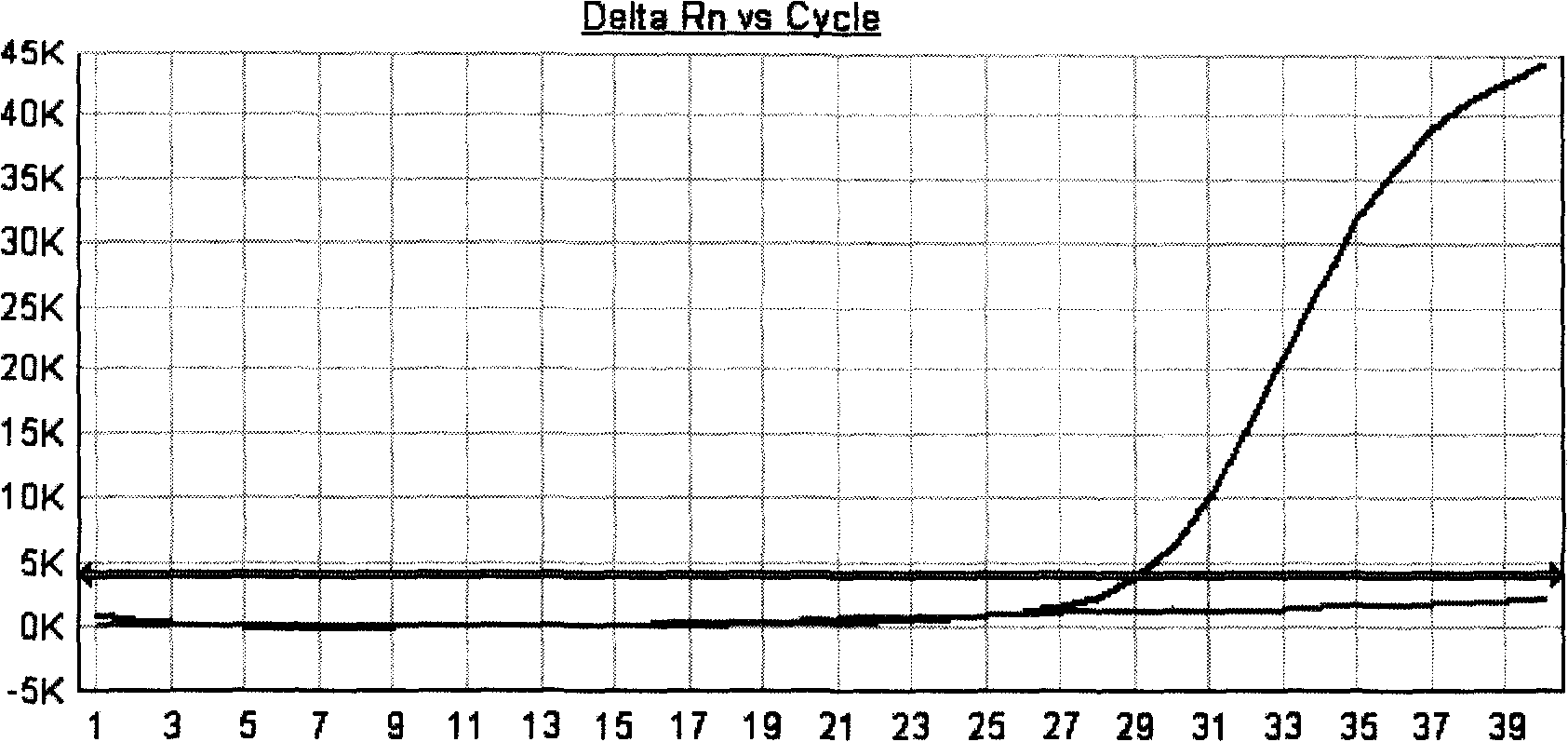
Fluorescent quantitative PCR method for real-time detecting mononucleotide polymorphism and reagent kit thereof
InactiveCN101354337AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansNucleotideFluorescence
The invention provides a real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR method for testing single nucleotide polymorphism. The method includes two sets of combinations of primers and probes, wherein, one set of quantitative primers and probes can determine the amount of initial nucleic acid of a sample to be tested, the other set of classifying-type primers and probes and the combination thereof can determinate whether single nucleotide polymorphism occurs or not; magnesium concentration of the system is 2 mM to 10 mM, the amount of Taq enzyme is 5U to 10U per reaction and the amount of UNG enzyme is 1U to 2U per reaction. A standard curve is made according to the Ct value of a quantitative standard; the Ct value of the sample to be tested is substituted into the standard curve to determine the copy number of an initial template; the deviation between quantitative Ct value and classifying-type Ct value of the sample is calculated, and then is compared with the wild-type and the mutant-type standards to determine whether single nucleotide mutant occurs or not. The invention also provides a kit of fluorescence quantitative PCR which adopts the method to test mutant of hepatitis B virus 1896.
Owner:CHANGZHOU ANBO BIO TECH
Method for detecting fetus father DNA mononucleotide difference from plasma in pregnaut women
InactiveCN1978668ALow costDetection of DNA contentMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisRelationship - FatherSingle nucleotide mutation
The invention relates to the method used to detect embryo paternal line DNA mononucleotide difference from pregnant woman's plasma. It includes the following steps: conventional PCR amplification, single basic group extending reaction marking target sequence, bead separating target sequence, and biologic bar code signal amplification and detecting. Its advantages are that it has low cost and is practicable; it can detect mononucleotide mutation and polymorphism in embryo paternal line DNA, and embryo DNA content.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
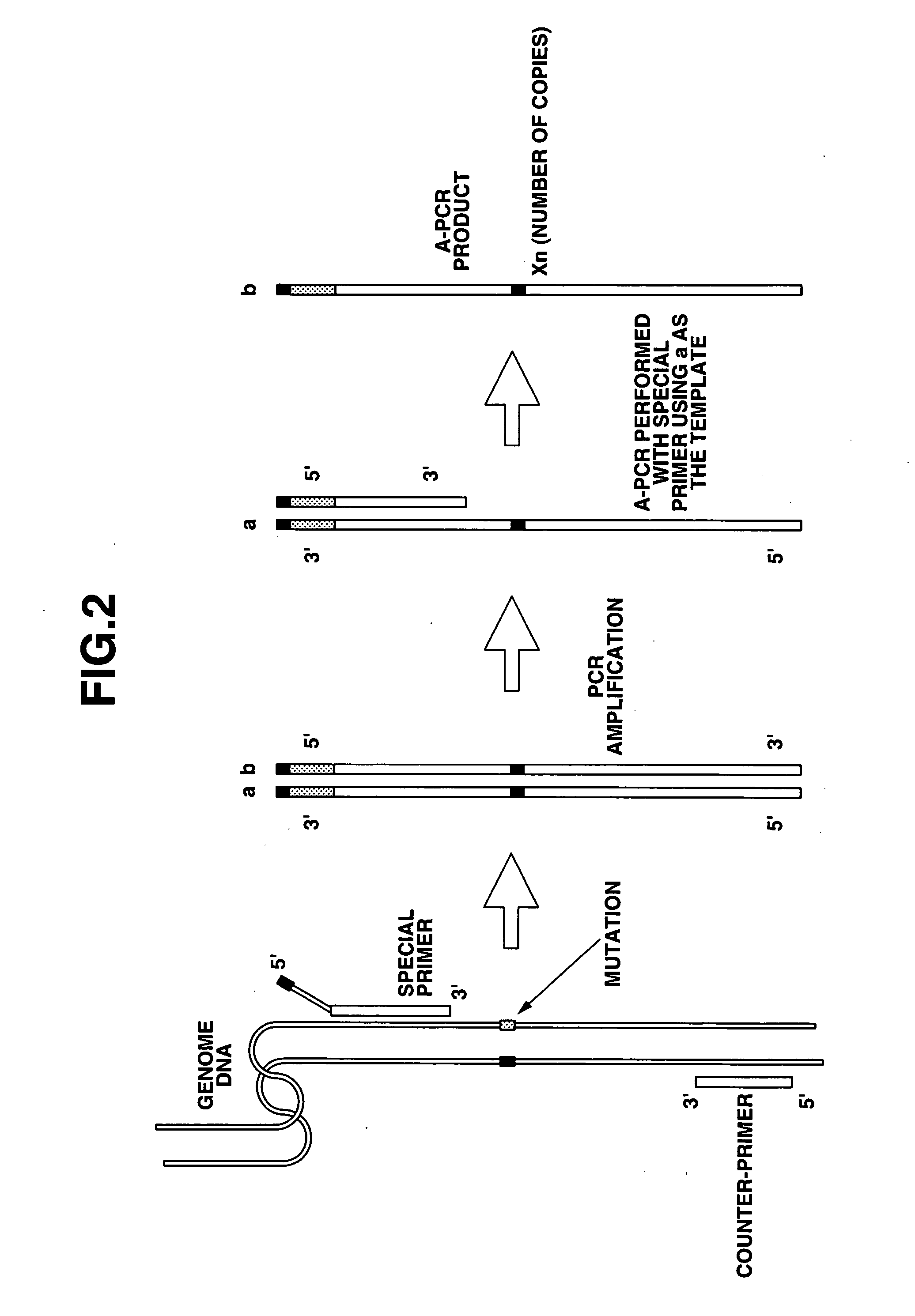
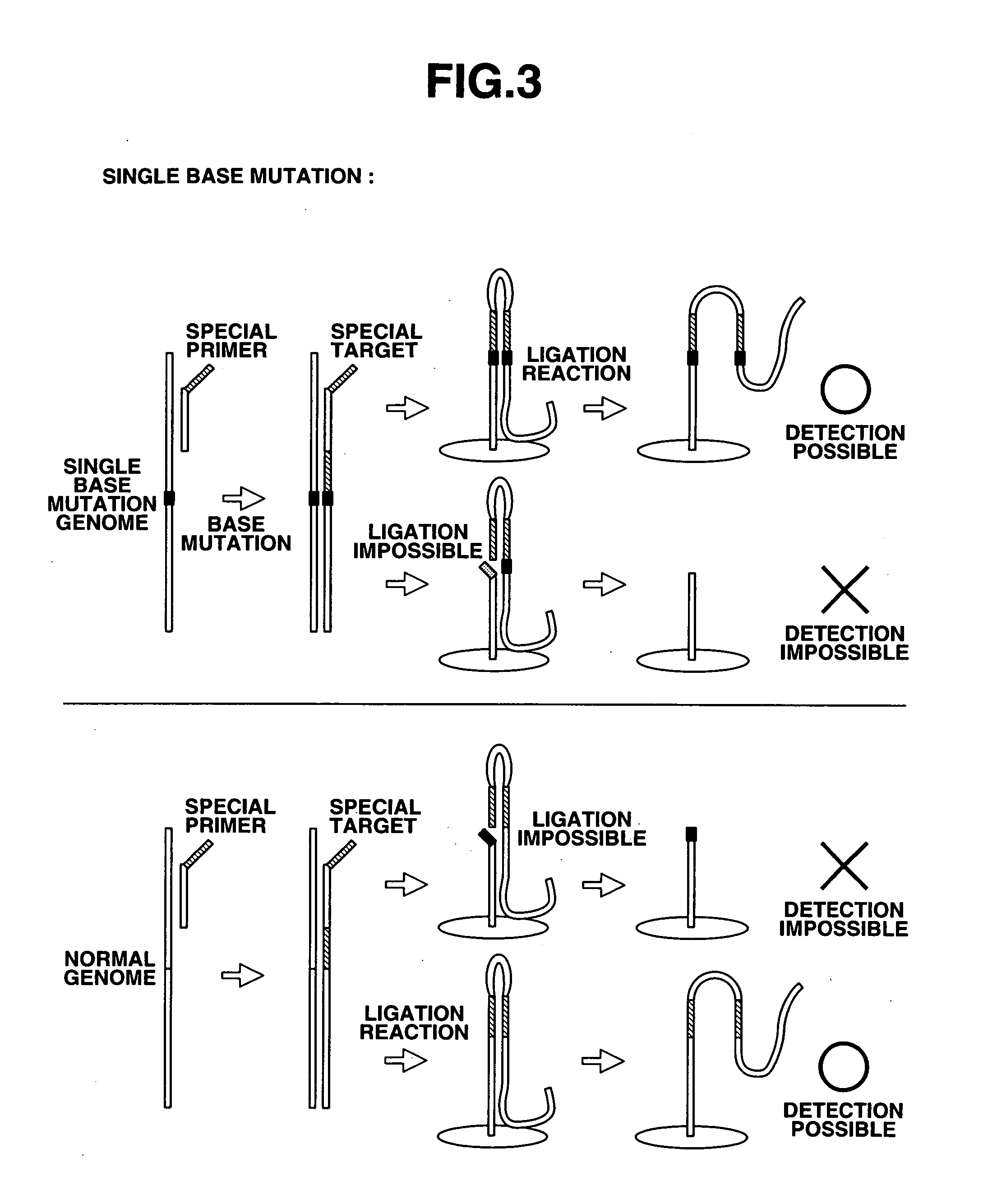
Method of detecting base mutation
InactiveUS20060003325A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolymerase LSingle strand
The present invention provides a nucleotide mutation detection method wherein primers having a nucleotide sequence complementary to part of the nucleic acids to be detected and also having a nucleotide sequence, which is complementary to the nucleotide sequence just upstream from a nucleotide site corresponding to the mutation site of the nucleotide sequence formed at the 3′ end, added to the 5′ end, are produced so that so that the nucleotide site corresponding to the mutation site of the nucleic acids to be detected including the nucleotide mutation is located within the nucleotide sequence formed at the 3′ end after elongation; a target is produced by subjecting the primers to an elongation reaction using polymerase or Klenow enzyme; the target is then denatured to a single strand, and is subjected to a hybridization reaction with a probe that has the nucleotide complementary to the mutation site of the nucleic acids present in the 3′ end region and then to a ligation reaction, whereby it is enable to determine and assay a nucleotide located at a specific position in a nucleotide sequence of DNA or RNA and to analyze rapidly a variety of mutations including single nucleotide mutations, short nucleotide tandem repeat mutations, nucleotide deletion mutations, nucleotide insertion mutations, translocation mutations and so on.
Owner:TOPPAN PRINTING CO LTD
Single nucleotide mutation site SNP and KASP markers significantly associated with soybean protein content and application thereof
ActiveCN112877467AHigh selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologySingle nucleotide mutation
The invention provides a single nucleotide mutation site SNP marker and a KASP marker remarkably associated with soybean protein content and application thereof, and belongs to the field of plant molecular breeding. According to the present invention, the SNP S14_73926 significantly associated with the soybean protein content is located at the No.14 chromosome 73,926bp position of the soybean genome v2.0, the base G-A replacement occurs, the phenotypic variation interpretation rate reaches 6.4%, the KASP marker is developed for the SNP site, and the SNP and KASP markers significantly associated with the soybean protein content provided by the present invention can be used for the molecular marker-assisted selection breeding of the soybean protein character, and have important theoretical and practical guiding significance for accelerating the genetic improvement process of soybean high-protein breeding and improving the breeding selection efficiency.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for identifying plant gene functions in total genome ranges
ActiveCN105734130AMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationSingle nucleotide mutationNucleotide
The invention relates to a method for identifying plant gene functions in total genome ranges.The method includes 1), mutating single nucleotide of starting plants and establishing plant mutant libraries; 2), detecting phenotypes of mutants in the plant mutant libraries and establishing plant mutant phenotype databases; 3), detecting genotypes of the mutants in the plant mutant libraries and establishing plant mutant genotype databases; 4), determining functions of genes where SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) sites caused by mutation of the single nucleotide in the starting plants by the aid of the plant mutant phenotype databases and the plant mutant genotype databases.The method has the advantages that the genes related to plant development procedures and biological procedures of stress-tolerant reaction or metabolic pathways or the like can be accurately and quickly found by the aid of the plant mutant phenotype databases and the plant mutant genotype databases which are established by the method, and novel ways can be created for plant functional genome research.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI +1
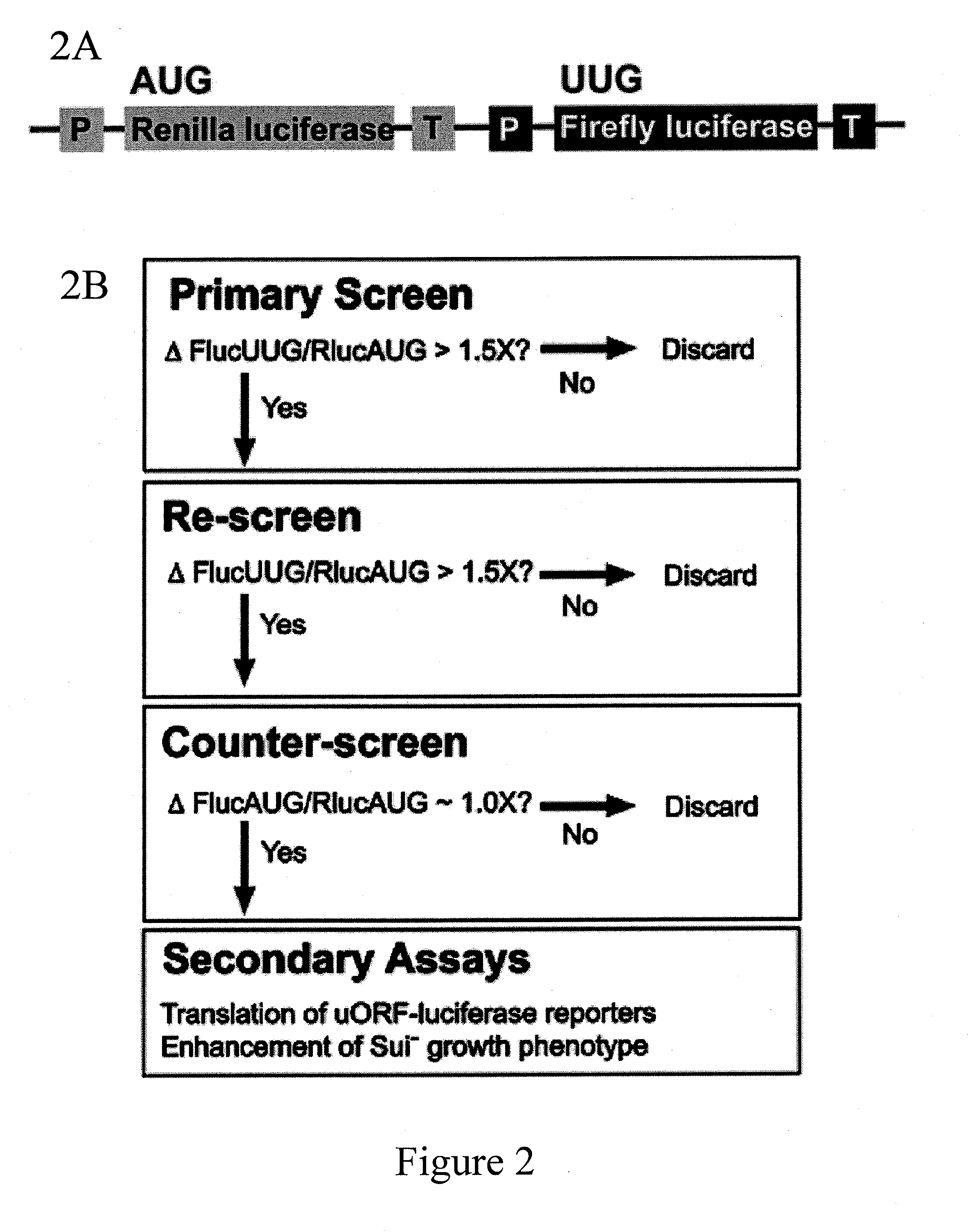
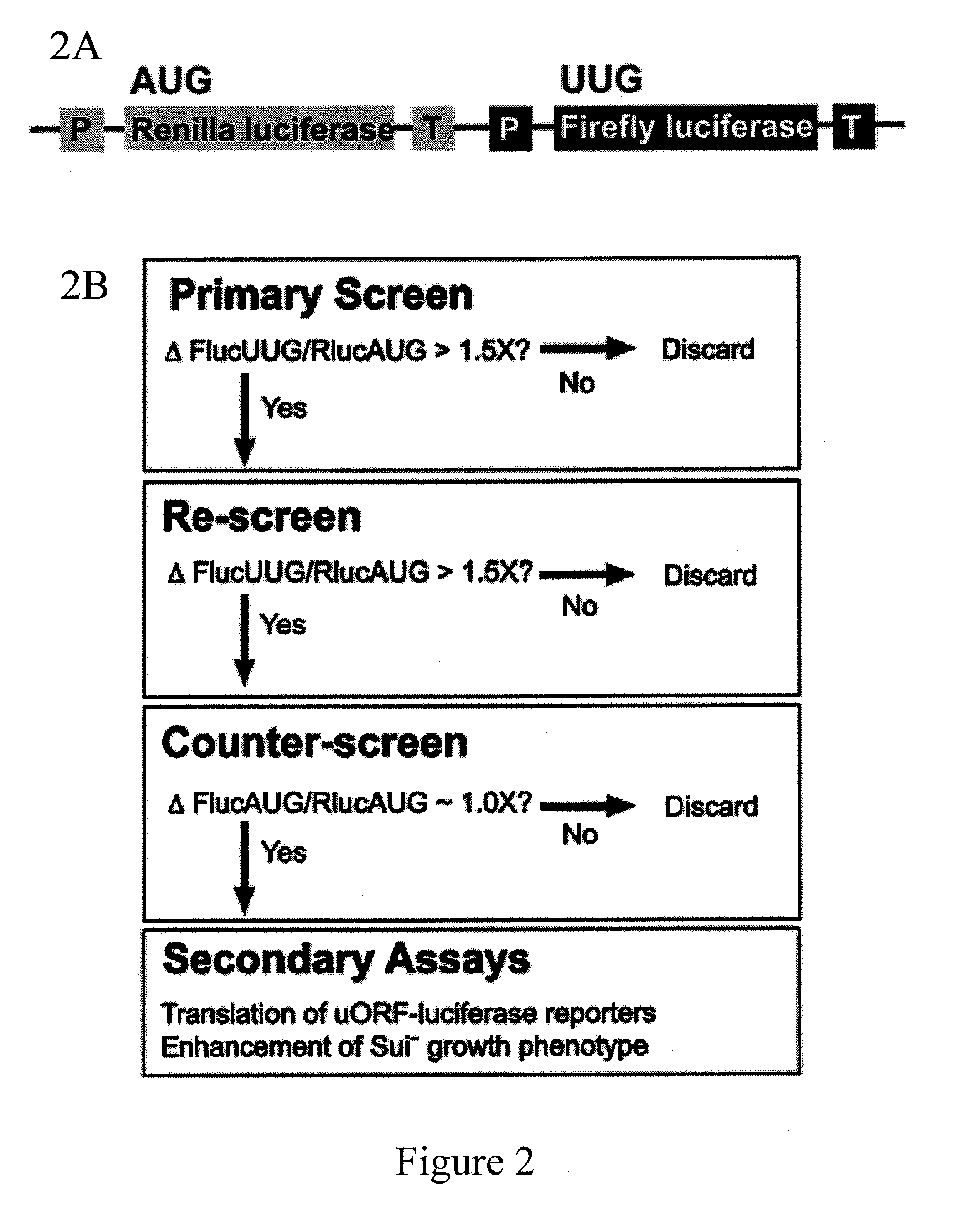
Identification and use of compounds that affect the fidelity of eukaryotic translation initiation codon selection
InactiveUS20110230451A1High expressionCompound screeningBiocideStart codonSingle nucleotide mutation
A screening method for identifying compounds that alter the fidelity with which the initiation codon in mRNAs is recognized by the translational apparatus in eukaryotes is disclosed. This screening method was used to identify compounds having such activity. Methods of altering the fidelity of initiation codon selection are also disclosed. Methods of treating disorders characterized by single nucleotide mutations in initiation codons using compounds identified by the screening method, as well as methods of treating fungal and parasitic infections and hyperproliferative disorders using compounds identified by the screening method are also disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
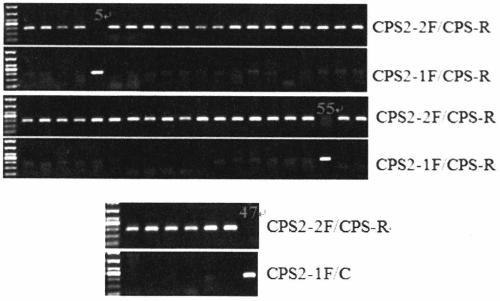
Specific primers and detection method for detecting the single nucleotide mutation of the key gene ntcps2 in tobacco abbitol synthesis
ActiveCN105177162BStrong specificityAvoid false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceAlcohol
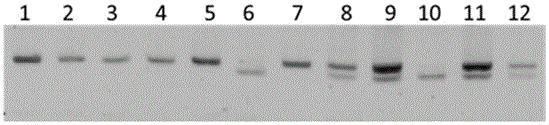
The invention discloses a specific primer for detecting a key gene NtCPS2 single nucleotide polymorphism for tobacco abienol synthesis and a detection method. The specific primer is characterized by comprising two upstream primers CPS2-1F and CPS2-2F and a downstream primer CPS2-R. The detection method comprises the following steps: based on the allele specific PCR (AS-PCR) principle, designing two complementary upstream primers at an SNP mutation site of the key gene NtCPS2 for abienol synthesis, and designing one shared downstream primer at the downstream of the mutation site; and by taking DNA of a tobacco variety to be detected as a template, performing PCR amplification by using two pairs of specific primers, performing electrophoresis detection on the PCR amplified product, and judging whether the PCR amplified product has a characteristic strip of 297bp. The primer pair disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, low expense, reliable result, rapid detection speed, distinguishable heterozygosis or homozygosis, and the like, the specific fragrance property breeding process of abienol can be greatly accelerated, the breeding period can be shortened, and the breeding efficiency can be improved.
Owner:TOBACCO RES INST CHIN AGRI SCI ACAD
Probe set and application thereof
PendingCN110527724AAccurate and effective captureEfficient constructionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationDiseaseBiotechnology
The invention relates to the biotechnology field, in particular to a probe set and application thereof. More particularly, the invention relates to one group of probe set, a method for constructing ahigh-throughput sequencing library, a method for determining single nucleotide mutation and haplotype of a sample to be detected, a device for constructing the high-throughput sequencing library and asystem for determining the single nucleotide mutation and the haplotype of the sample to be detected. The probe set can simultaneously detect the gene situations of various single gene inheritance diseases or genetic tumors, has good capture specificity, high sensitivity and wide coverage rate and can effectively realize the detection of 34 types of PGD (Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis).
Owner:MGI TECH CO LTD
Tiger-derived pseudorabies virus detection kit and tiger-derived pseudorabies virus detection method
PendingCN111560466ATime consumingIncrease costMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle nucleotide mutationNucleotide
The invention belongs to the field of animal epidemic disease molecular biological detection methods and detection reagents. The invention relates to a detection kit and a detection method for tiger-derived pseudorabies virus. A preparation method comprises the following steps: performing high-throughput sequencing on five tiger-derived pseudorabies viruses, and assembling to obtain a whole genomesequence of tiger-derived pseudorabies; comparing with a plurality of porcine pseudorabies viruses to find that a tiger-derived pseudorabies virus genome has a plurality of single nucleic acid mutations. The tiger-derived pseudorabies virus is used for detection aiming at one mononucleotide mutation; a pair of detection primers of the pseudorabies virus and a Cycling probe for detecting the tiger-derived pseudorabies virus are designed to form an inspection kit for detecting the tiger-derived pseudorabies virus, the detection method has the advantages of simplicity and convenience in operation, high sensitivity, strong specificity, good repeatability and the like, and a result can be judged according to an amplification curve immediately after the reaction is finished.
Owner:LONGYAN UNIV +2
Methods and reaction mixture reagent for increasing the specificity and fidelity of polymerase reactions
InactiveUS7312054B2High selectivityImprove fidelitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAcridineSingle nucleotide mutation
A method for reducing the efficiency of primer extension by polymerase enzymes when the 3′ end of a primer or growing nucleic acid chain does not hybridize perfectly with the target, for increasing the selectivity of single nucleotide mutation or gene analyses, for suppressing false positive results and for enhancing the fidelity of the amplification of nucleic acid fragments by avoiding the incorporation of mispairs, the method comprising the steps of: (a) obtaining a nucleic acid sample; (b) hybridizing said nucleic acid sample to a primer; (c) subjecting said nucleic acid sample hybridized to a extension reaction by extending a primer with a polymerizing enzyme; and (d) detecting the presence of extension products; wherein the reaction extension mixture medium contains an intercalating agent such as ethidium bromide, dihydroethidium, ethidium homodimer-1, ethidium homodimer-2, acridine, propidium iodide, YOYO®-1 or TOTO®-1. When the intercalating agent is ethidium bromide the concentration is about 1 to 7 g / ml.
Owner:BIODYNAMICS
Method for detecting MEG3 gene SNP related to cattle growth traits and application thereof
ActiveCN106755422ASimple and fast operationLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementAgricultural scienceMEG3
The invention discloses a method for detecting MEG3 gene SNP related to cattle growth traits and an application thereof. According to the position of a mononucleotide mutation site in an exon area of the cattle MEG3 gene, parting is carried out on a cattle individual by adopting the PCR-RFLP and Tetra-primer ARMS-PCR technology, and correlation analysis is carried out on a parting result and growth data. In the detection method disclosed by the invention, an SNP mark closely related to the cattle growth traits is detected on the DNA level, and the detection method can be used in the marker assisted selection of cattle variety growth traits in China so as to accelerate the establishment of high-quality cattle population.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Detection of nucleic acid differences using combined endonuclease cleavage and ligation reactions
InactiveUS20080003601A1Wide applicabilityImprove throughputHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexSingle nucleotide mutation
The present invention is a method for detecting DNA sequence differences including single nucleotide mutations or polymorphisms, one or more nucleotide insertions, and one or more nucleotide deletions. Labeled heteroduplex PCR fragments containing base mismatches are prepared. Endonuclease cleaves the heteroduplex PCR fragments both at the position containing the variation (one or more mismatched bases) and to a lesser extent, at non-variant (perfectly matched) positions. Ligation of the cleavage products with a DNA ligase corrects non-variant cleavages and thus substantially reduces background. This is then followed by a detection step in which the reaction products are detected, and the position of the sequence variations are determined.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Mononucleotide mutation and KASP specific primer of pepper phytoene synthase gene and application
PendingCN113999929AImprove efficiencyShorten identification timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLycoperseneGenes mutation
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a mononucleotide mutation and KASP specific primer of a pepper phytoene synthase gene and application. The nucleotide sequence of an SNP mutation site KASP marker of ae pepper Psy1 gene is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the 21st basic group of the sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.1 is A or T. The color of the fruit does not need to be confirmed after the pepper fruit is physiologically mature, the color of the mature fruit of the pepper material can be judged only by detecting the DNA of the pepper plant in the seedling stage, and the mononucleotide mutation and KASP specific primer can be widely applied to molecular marker-assisted breeding.
Owner:INST OF VEGETABLE & FLOWERS CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
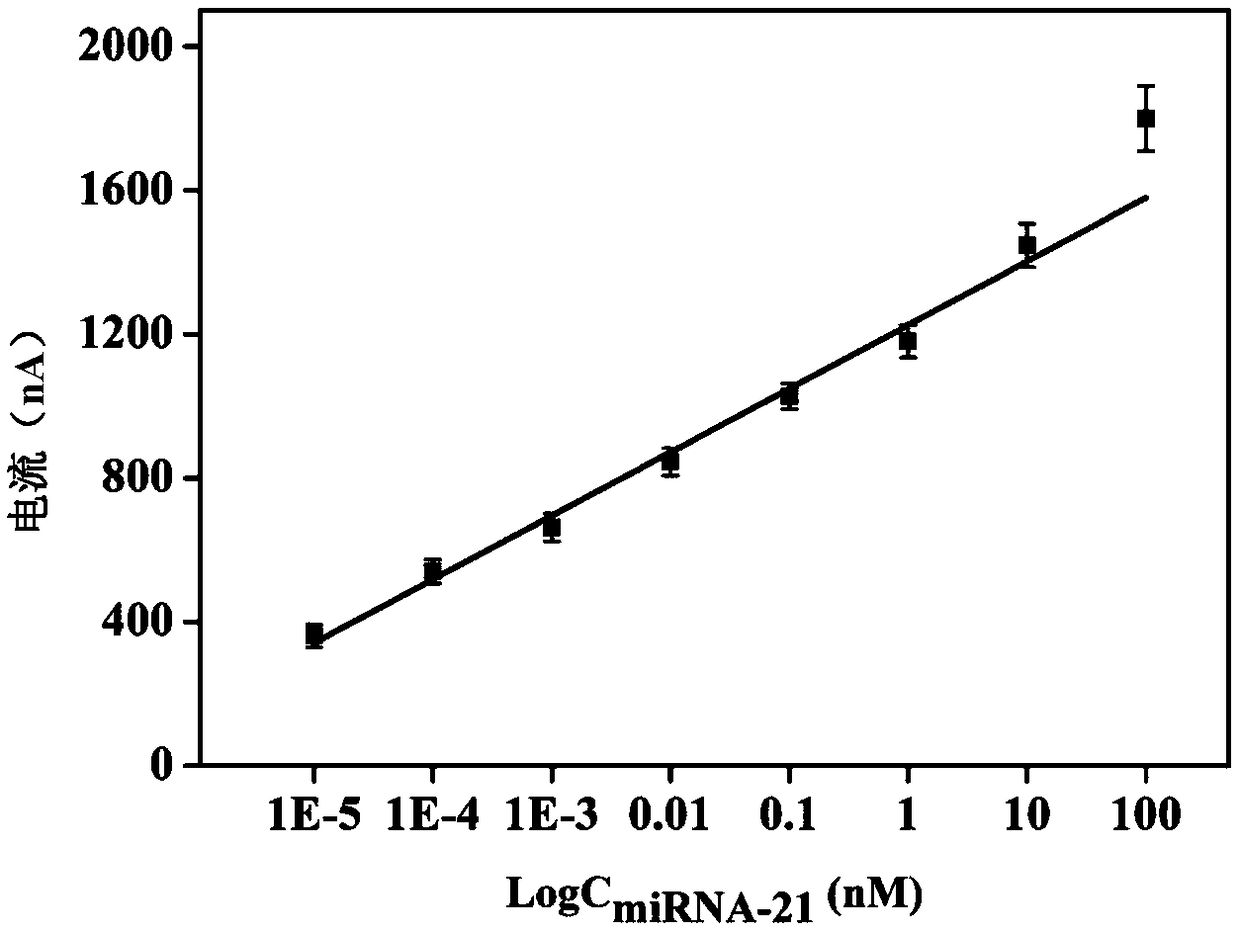
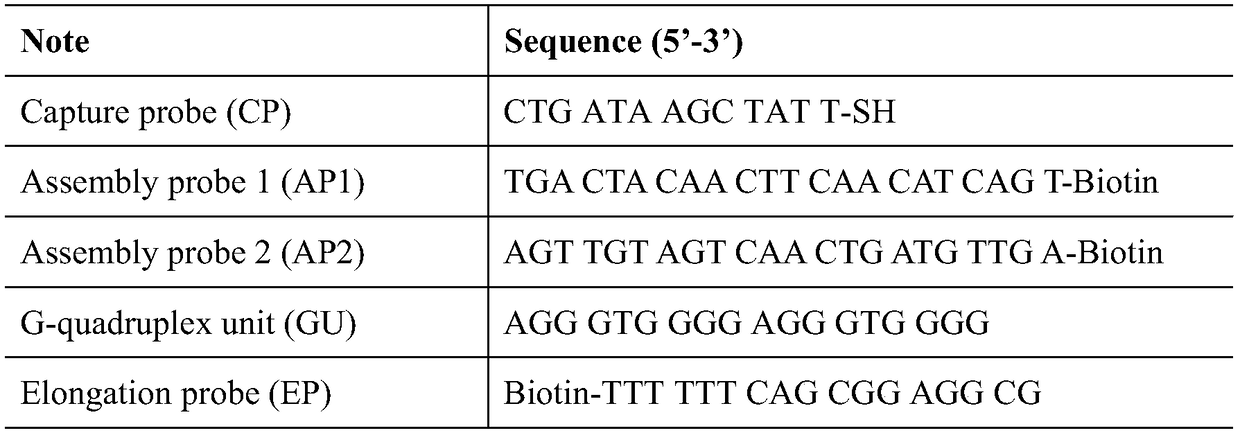
Electrochemical sensor for detecting microRNA-21, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109406596AHigh detection sensitivityStrong specificityMaterial electrochemical variablesBiotin-streptavidin complexHemin
The invention discloses an electrochemical sensor for detecting microRNA-21, a preparation method and application thereof. The method firstly anchors a DNA tandem with a biotin at the 5' end to the surface of an electrode, the DNA tandem is used as a main structure, and a G-rich quadruplex line is assembled by specific recognition of streptavidin-biotin as a branching structure; G tetra-chain monomer and G-quad-chain line pi-pi are stacked, self-assembly is conducted to form multi-branched DNA nanostructure, and the obtained DNA nano-assembly can be tightly combined with hemin to generate an oxidation reduction signal for electrochemical detection of miRNA-21. The method has good miRNA-21 detection sensitivity, has excellent specificity, can distinguish the single nucleotide mutation of the target nucleic acid analyte from the completely matched target RNA, analyzes an actual biological sample, and is a universal DNA nanometer biosensor platform.
Owner:安徽深蓝医疗科技股份有限公司
Functional marker of rice seed shattering gene qSH1, and application of functional marker
InactiveCN107603977ASpeed up the breeding processImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle nucleotide mutationAgricultural science
The invention discloses a functional marker of a rice seed shattering gene qSH1, and application of the functional marker. Three primers, namely SH1-F1, SH1-F2 and SH1-R, are designed and synthesizedaccording to mononucleotide mutation causing seed shattering gene qSH1 phenotypic difference; the three primers perform amplification on rice DNA in the same PCR system; and the amplification productis subjected to electrophoresis detection to detect the genotype of the seed shattering gene. The functional marker can screen and identify the seed shattering property of a large amount of rice germplasm resources rapidly and accurately, can improve the seed selection efficiency and can be used for performing early auxiliary selection on the seed shattering property of the rice so as to accelerate the seed selection progress.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Identification and use of compounds that affect the fidelity of eukaryotic translation initiation codon selection
A screening method for identifying compounds that alter the fidelity with which the initiation codon in mRNAs is recognized by the translational apparatus in eukaryotes is disclosed. This screening method was used to identify compounds having such activity. Methods of altering the fidelity of initiation codon selection are also disclosed. Methods of treating disorders characterized by single nucleotide mutations in initiation codons using compounds identified by the screening method, as well as methods of treating fungal and parasitic infections and hyperproliferative disorders using compounds identified by the screening method are also disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
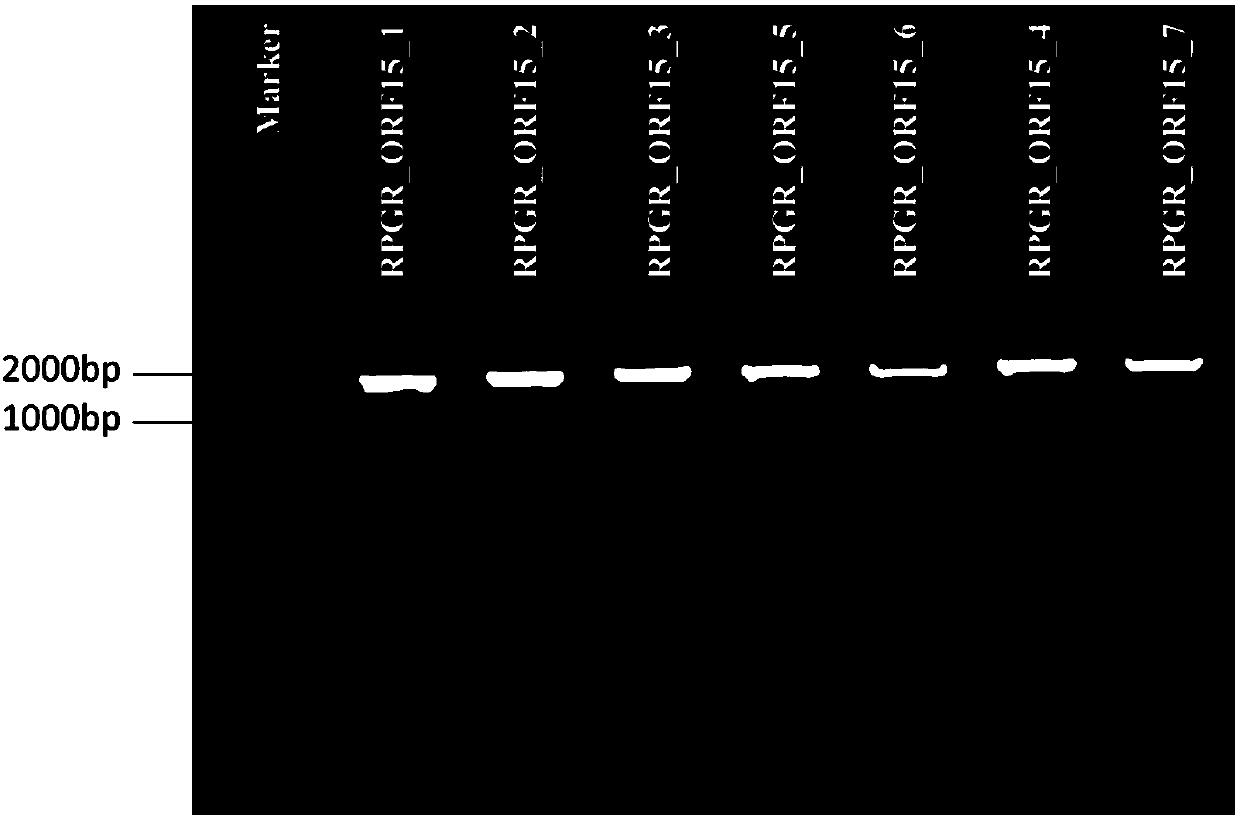
Method and primer for detecting mutation of ORF15 exon of RPGR gene
InactiveCN107619861AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle nucleotide mutationExon
The invention discloses a method and a primer for detecting mutation of an ORF15 exon of an RPGR gene. The primer for detecting the mutation of the ORF15 exon of the RPGR gene comprises a positive primer and a reverse primer for amplifying the ORF15 exon of the RPGR gene. The method for detecting the mutation of the ORF15 exon of the RPGR gene comprises the following steps of (1) extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of a sample; (2) utilizing a pair of amplification primers RPGR_ORF15_F3 and RPGR_ORF15_R6 to amplify the DNA in step (1), so as to obtain an amplification product; (3) at leastusing one type of sequencing primer to sequence the amplification product, so as to obtain a gene sequence of the amplification product; (4) comparing the sequence of the gene in step (3) and the wildtype reference sequence RPGR-ref of the RPGR gene, so as to determine whether the mutation site exists or not. The primer has the advantages that the specificity is strong, and the sensitivity is high. The detection method has the advantages that the mutation of mononucleotide can be accurately detected, and the frame-shift variation of homozygosis or heterozygosis can be effectively detected.
Owner:杭州科宁生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com