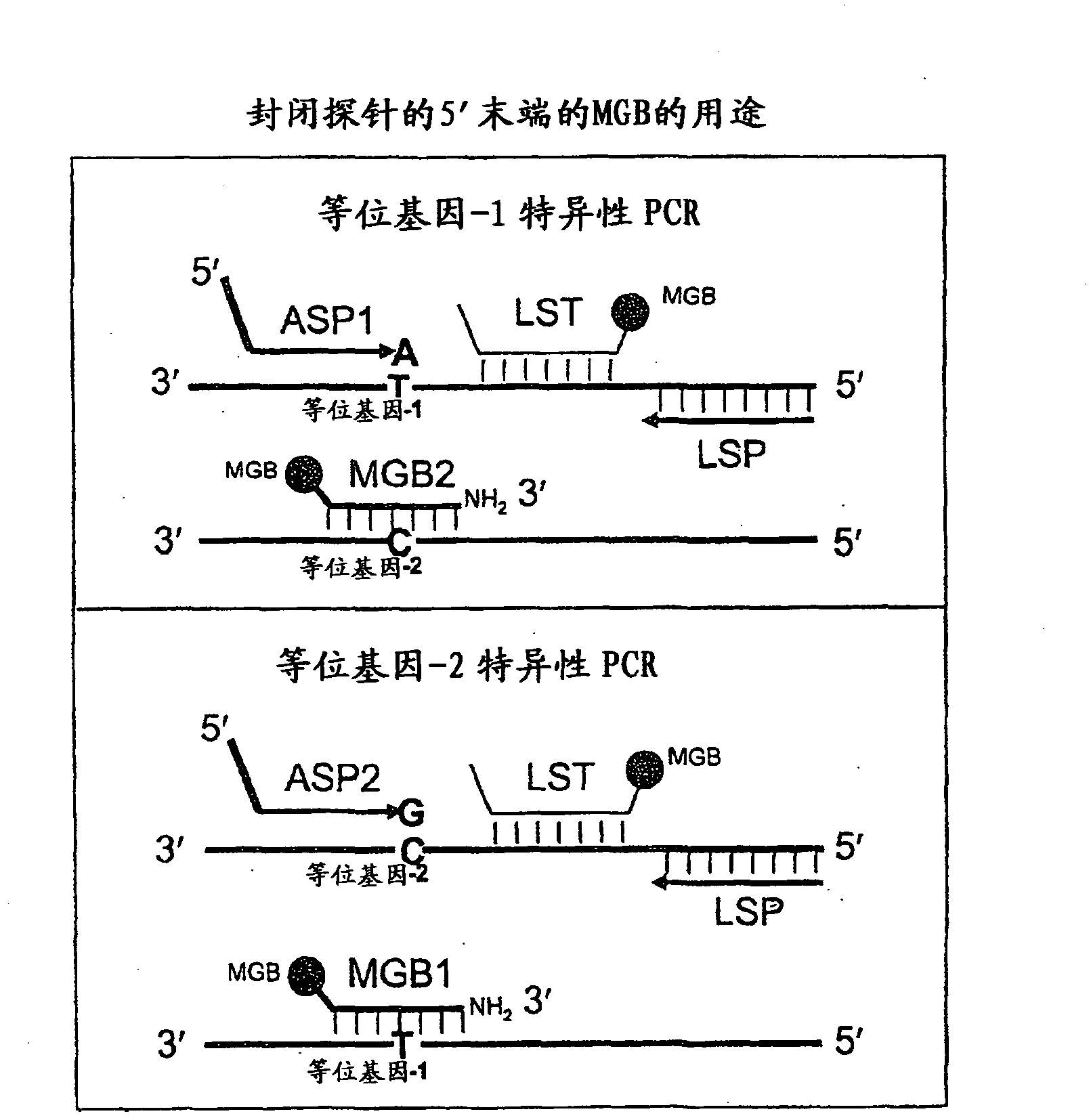
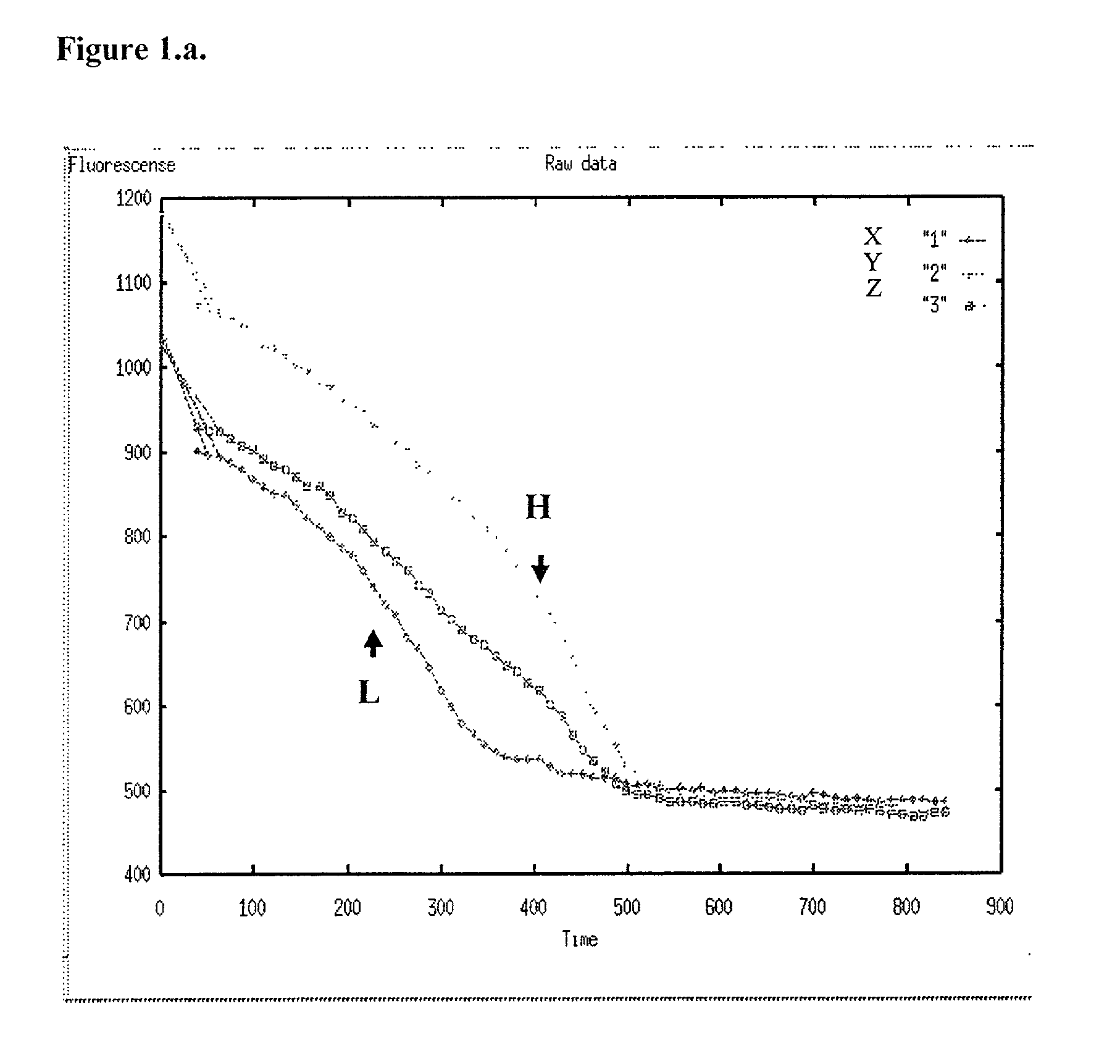
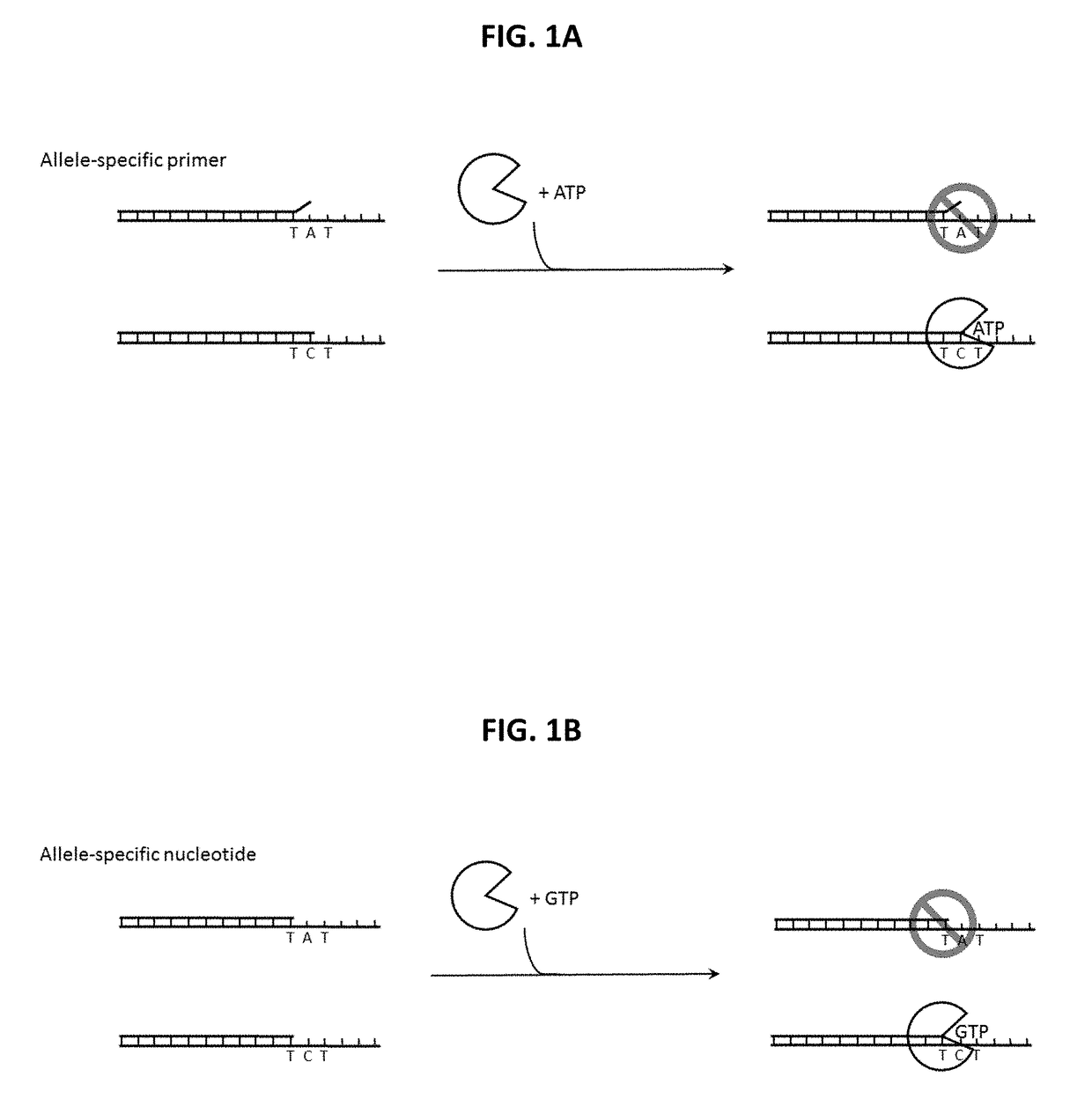
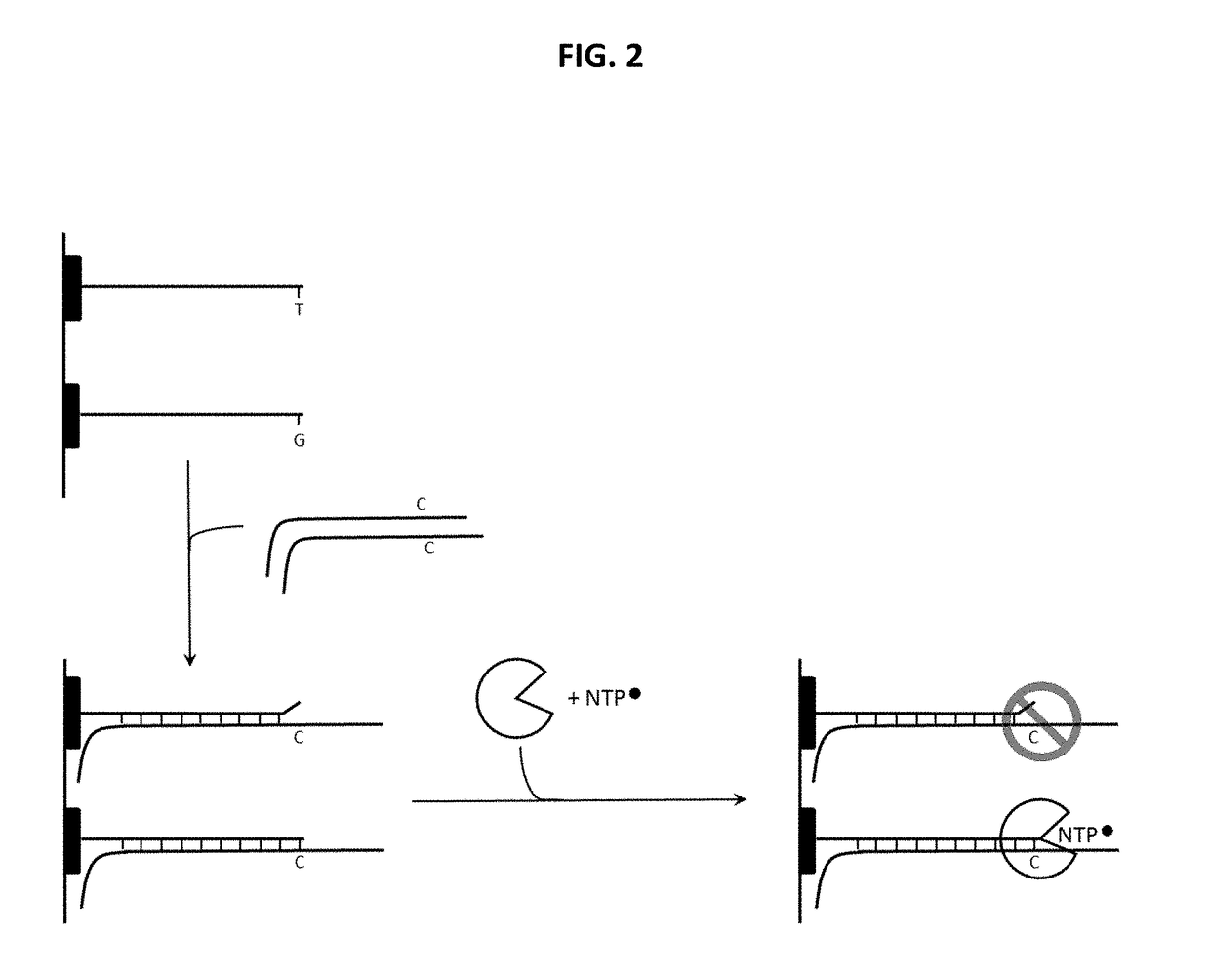
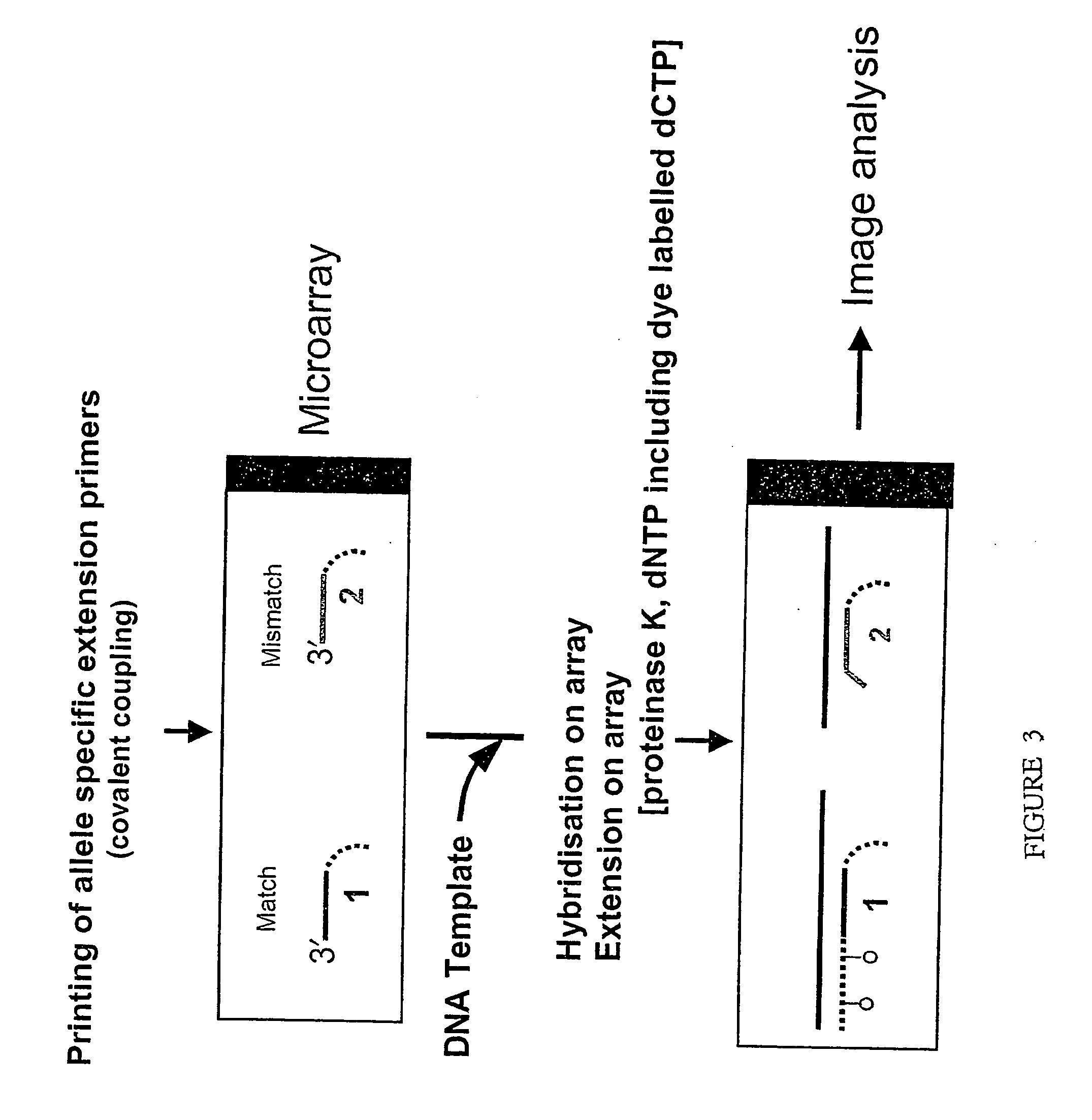
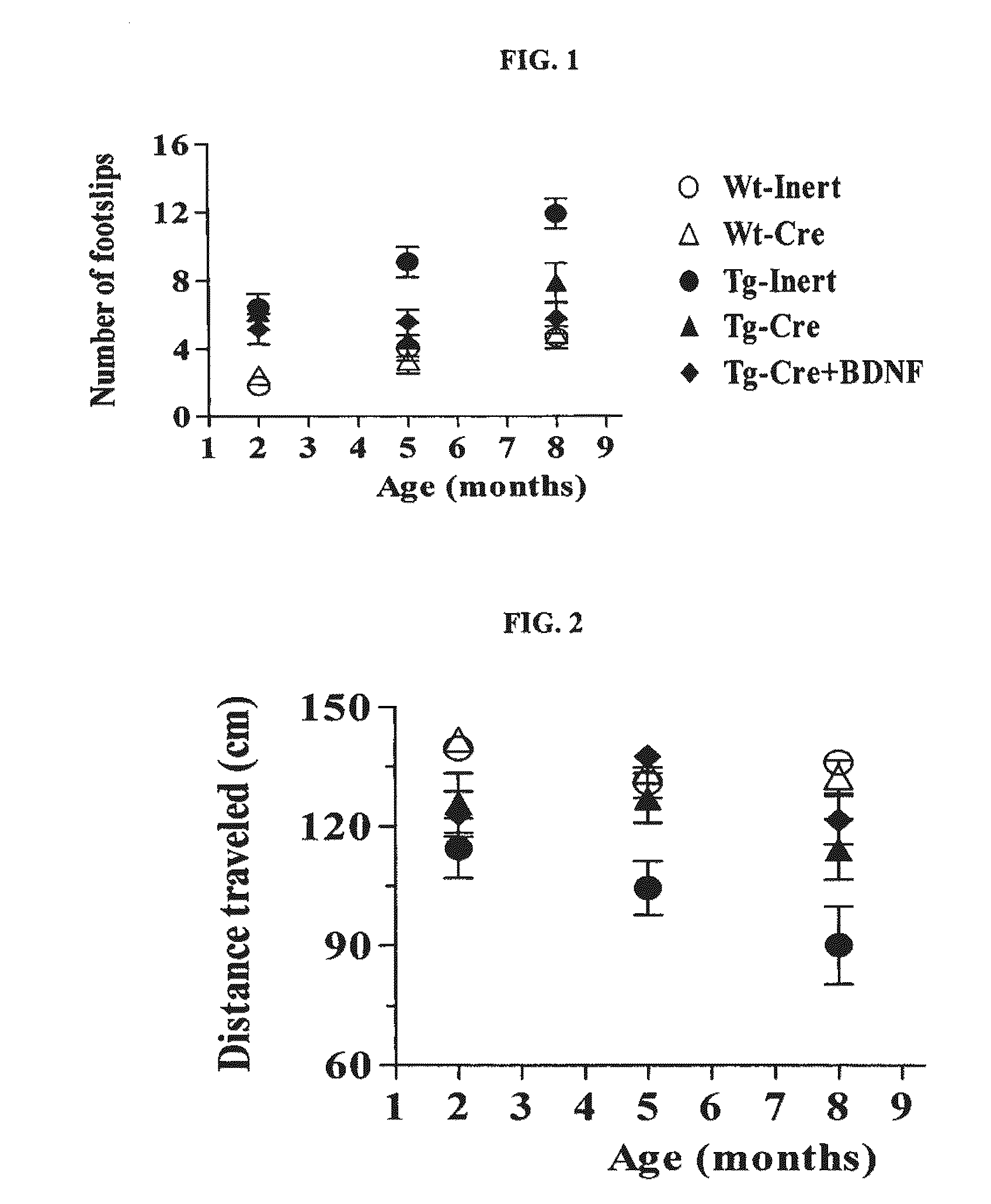
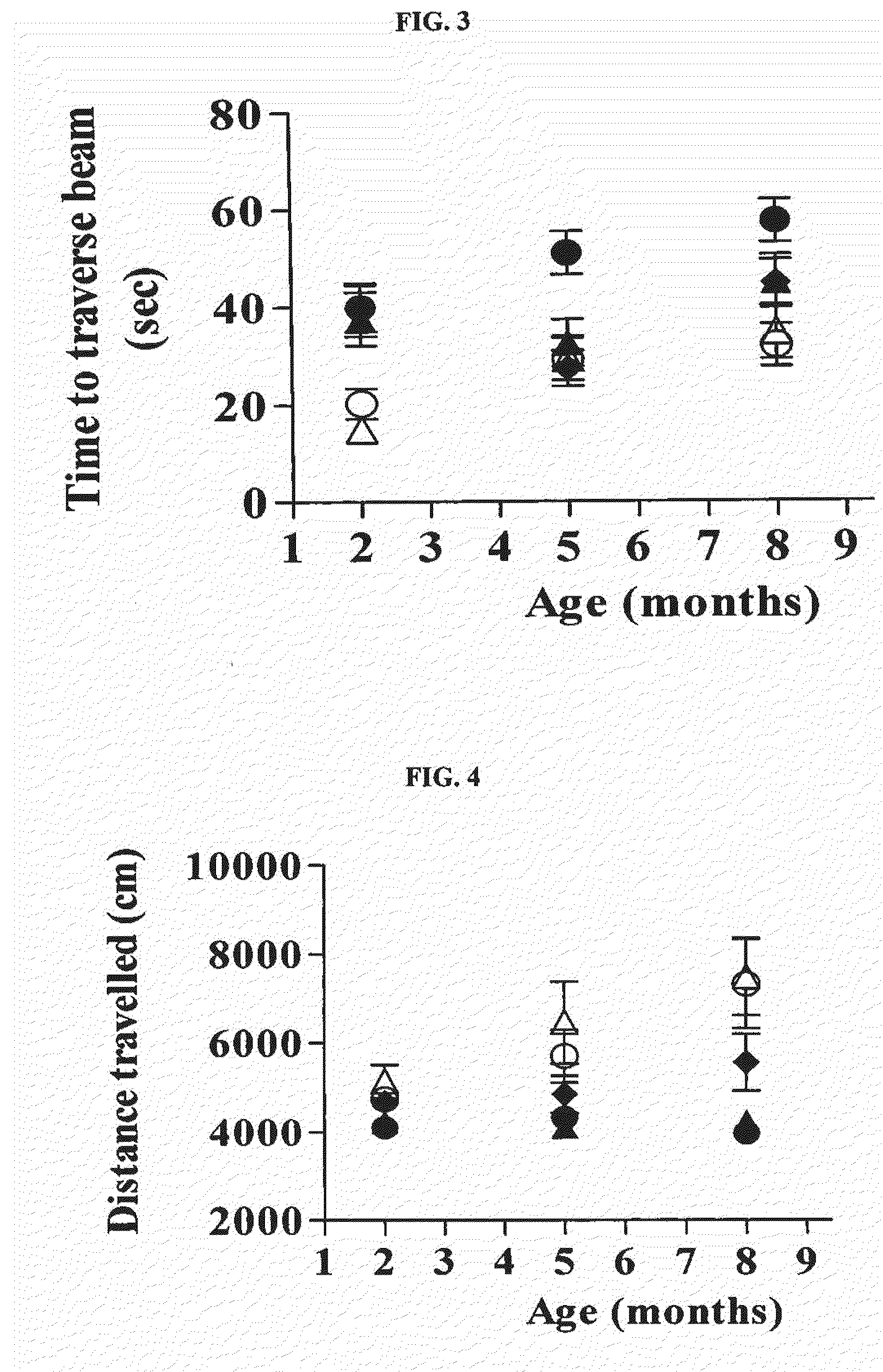
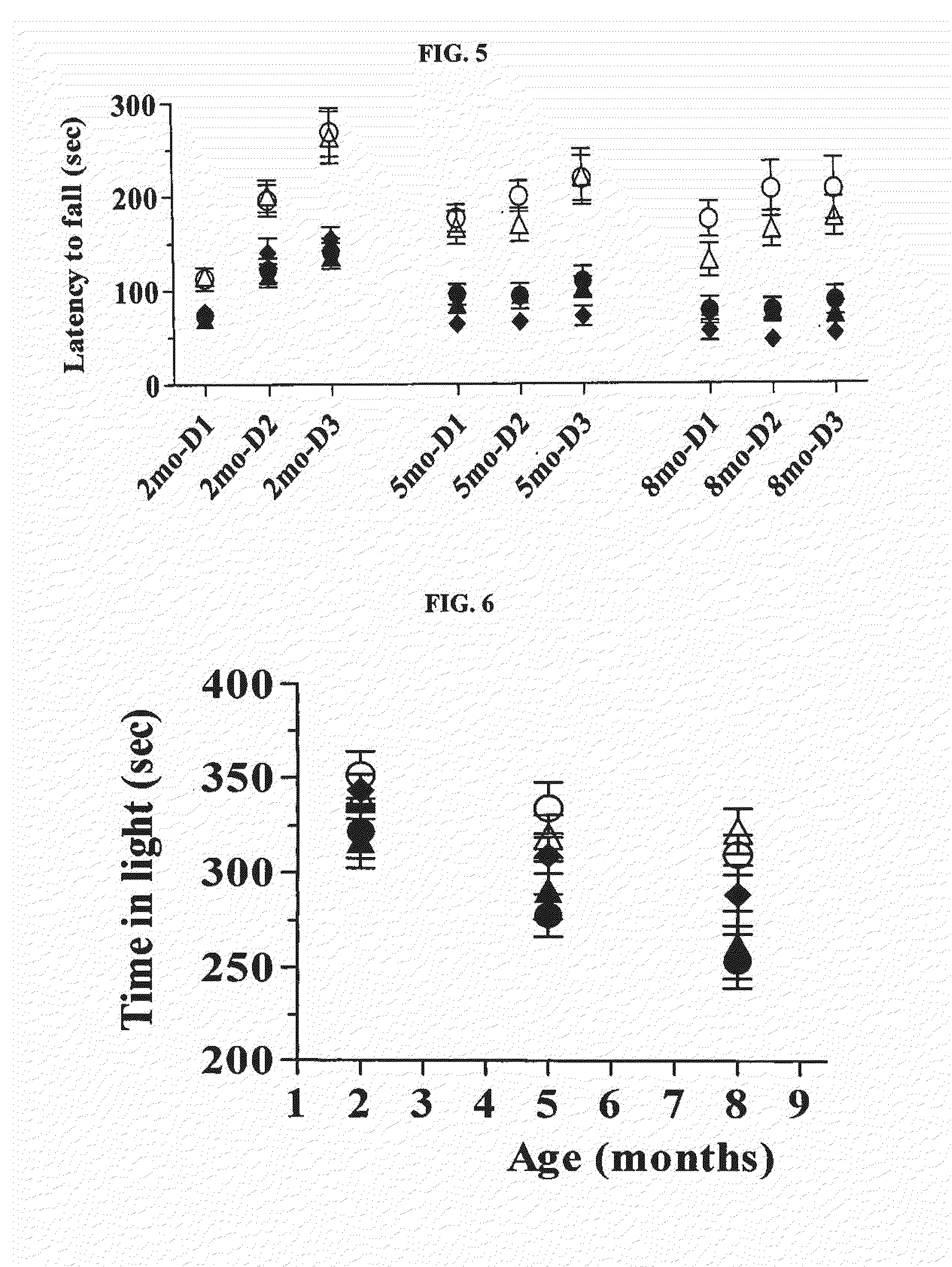
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
451 results about "Allele specific" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An allele is specific variation of a gene. Bacteria, because they have a single ring of DNA, have one allele per gene per organism. In sexually reproducing organisms, each parent gives an allele for each gene, giving the offspring two alleles per gene.
Primers and methods for the detection and discrimination of nucleic acids
InactiveUS7537886B1Reduced background fluorescenceEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyNucleic acid sequencingNucleic acid sequence
The present invention provides novel primers and methods for the detection of specific nucleic acid sequences. The primers and methods of the invention are useful in a wide variety of molecular biology applications and are particularly useful in allele specific PCR.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
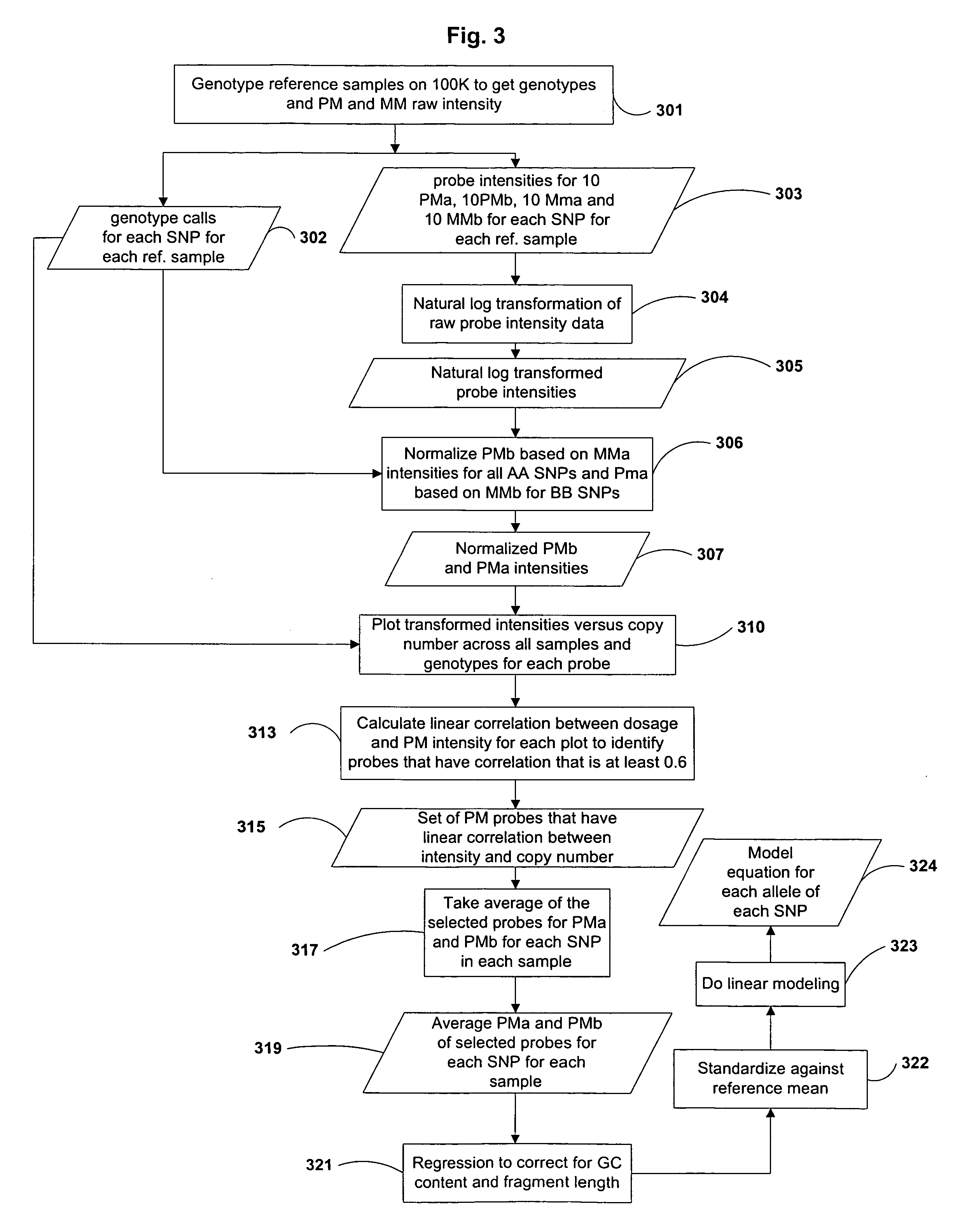
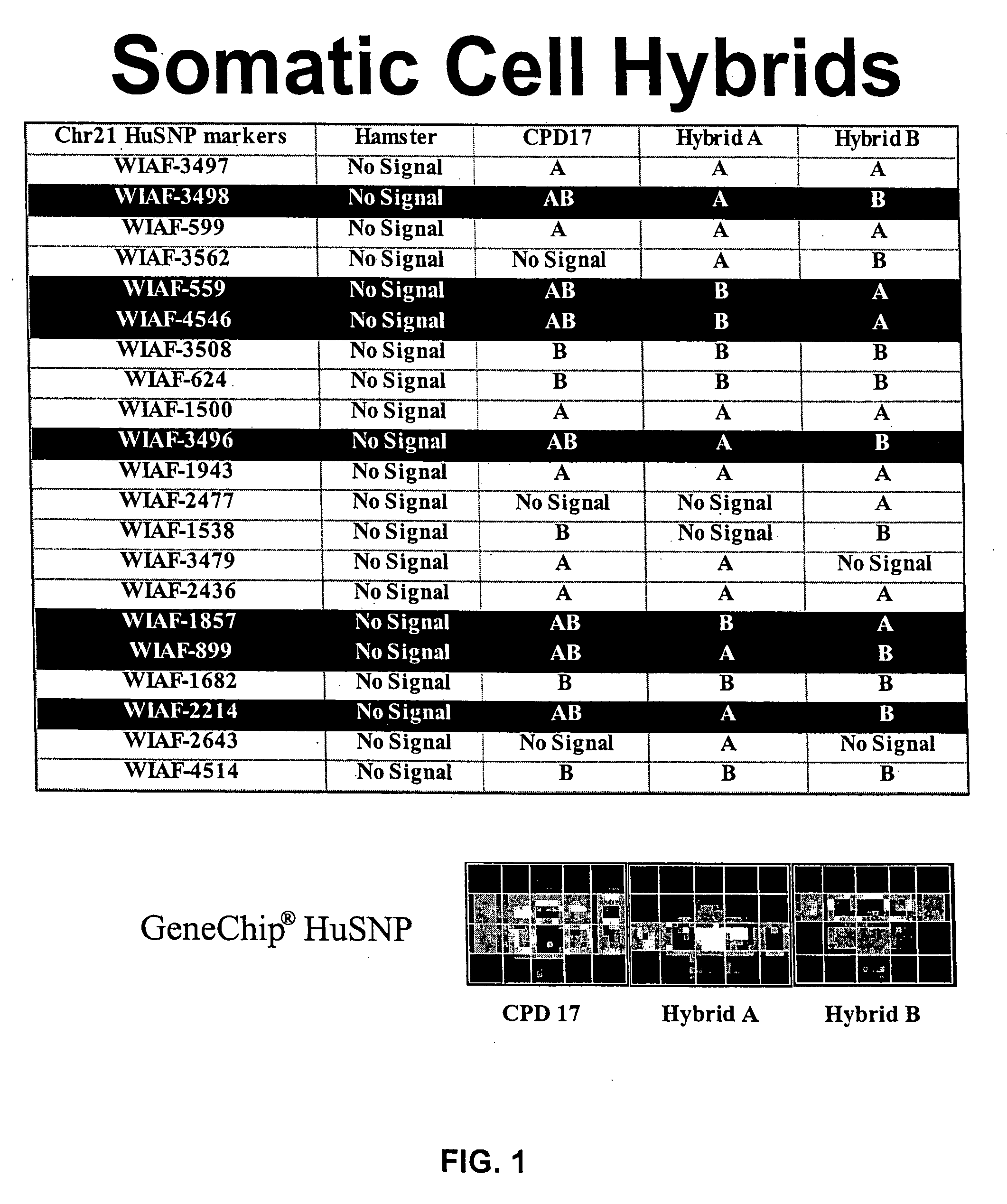
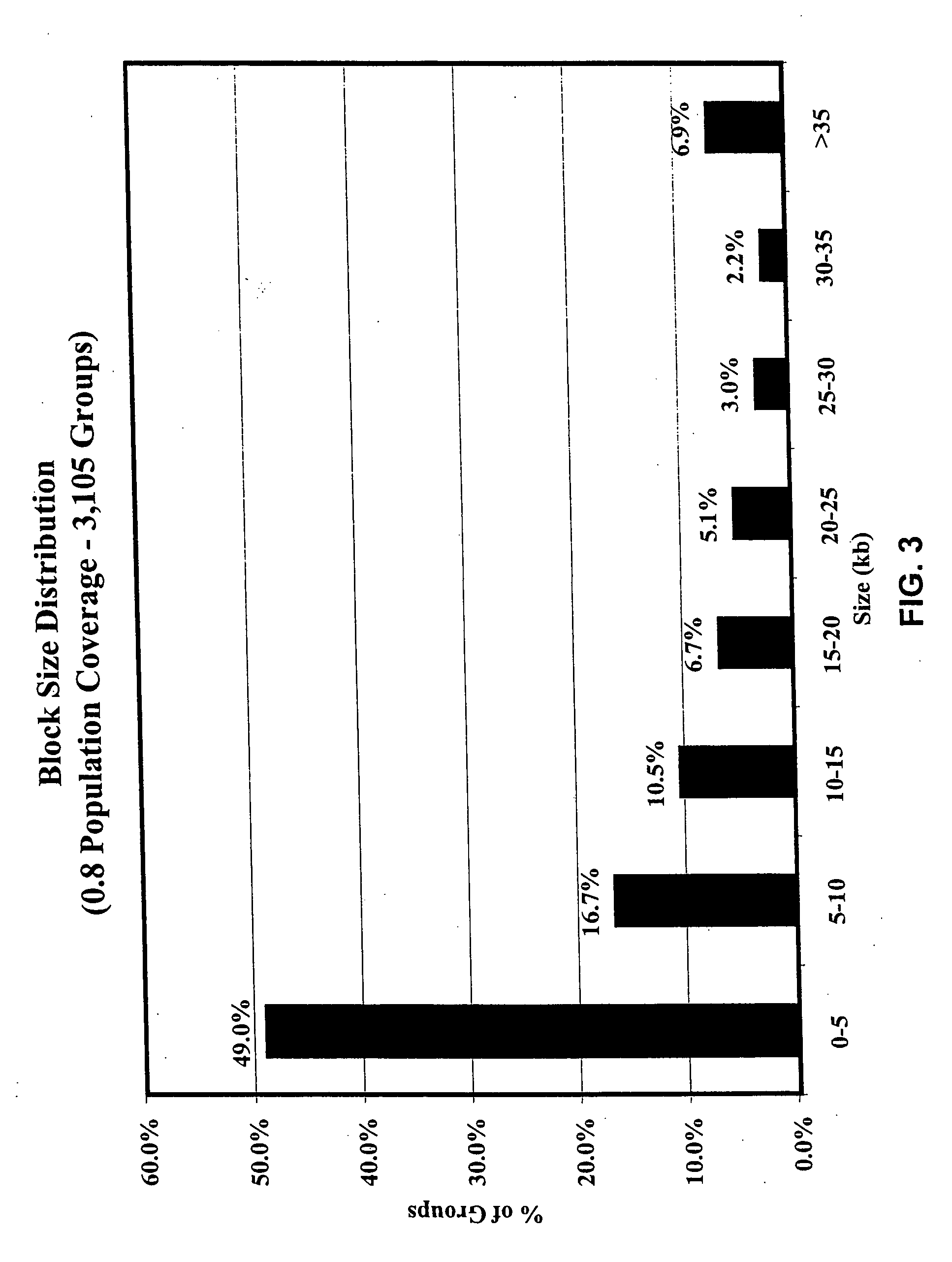
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Allele specific primer extension
InactiveUS20040048301A1Rapid rise in fluorescenceEnhanced signalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphateNucleotide
A method of characterizing a nucleic acid sample is provided that includes the steps of: (a) conducting a DNA polymerase reaction that includes the reaction of a template, an allele specific primer, at least one terminal phosphate-labeled nucleotide, DNA polymerase, and optionally an enzyme having 3'->5' exonuclease activity when the primer is non-hydrolyzable, which reaction results in the production of labeled polyphosphate; (b) permitting the labeled polyphosphate to react with a phosphatase to produce a detectable species; (c) detecting the detectable species; and (d) characterizing the nucleic acid sample based on such detection.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Human genomic polymorphisms
InactiveUS20060188875A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingInformative snps
The invention provides nucleic acid segments of the human genome including polymorphic sites, SNP haplotype blocks, SNP haplotype patterns for each block and informative SNPs for each pattern. Allele-specific primers and probes hybridizing to regions flanking these sites are also provided. The nucleic acids, primers and probes are used in applications such as association studies and other genetic analyses.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
Methods for identifying DNA copy number changes
Methods of identifying allele-specific changes in genomic DNA copy number are disclosed. Methods for identifying homozygous deletions and genetic amplifications are disclosed. An array of probes designed to detect presence or absence of a plurality of different sequences is also disclosed. The probes are designed to hybridize to sequences that are predicted to be present in a reduced complexity sample. The methods may be used to detect copy number changes in cancerous tissue compared to normal tissue. The methods may be used to diagnose cancer and other diseases associated with chromosomal anomalies.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Allele-specific expression patterns
The invention provides methods of analyzing genes for differential relative allelic expression patterns. Haplotype blocks throughout the genomes of individuals are analyzed to identify haplotype patterns that are associated with specific differential relative allelic expression patterns. Haplotype blocks that contain associated haplotype patterns may be further investigated to identify genes or variants of genes involved in differential relative allelic expression patterns.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
Tgfbr1 HAPLOINSUFFICIENCY MODIFIES RISK FOR CANCER
ActiveUS20100267028A1High riskReduce expressionMicrobiological testing/measurementHaploinsufficiencyRisk haplotype
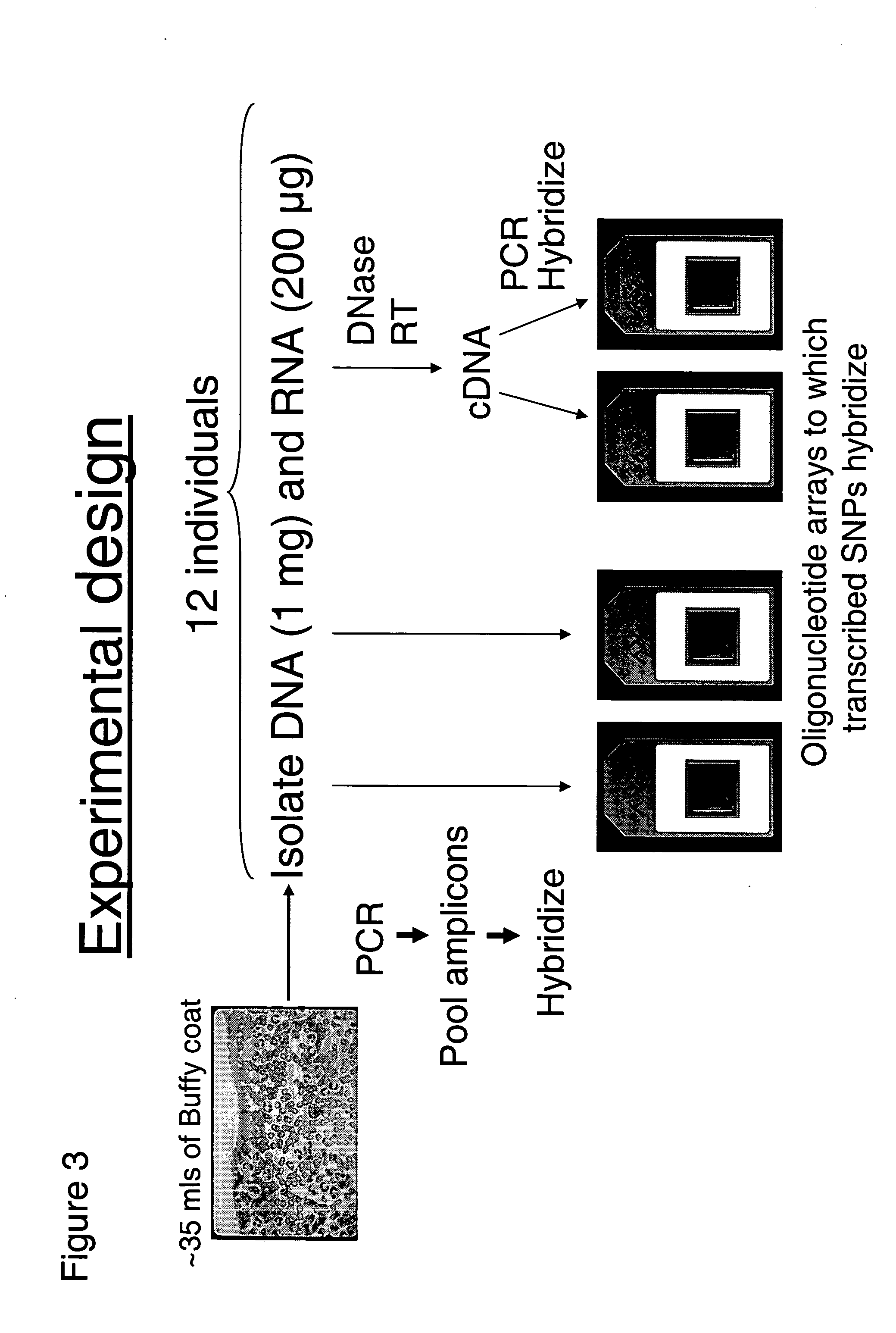
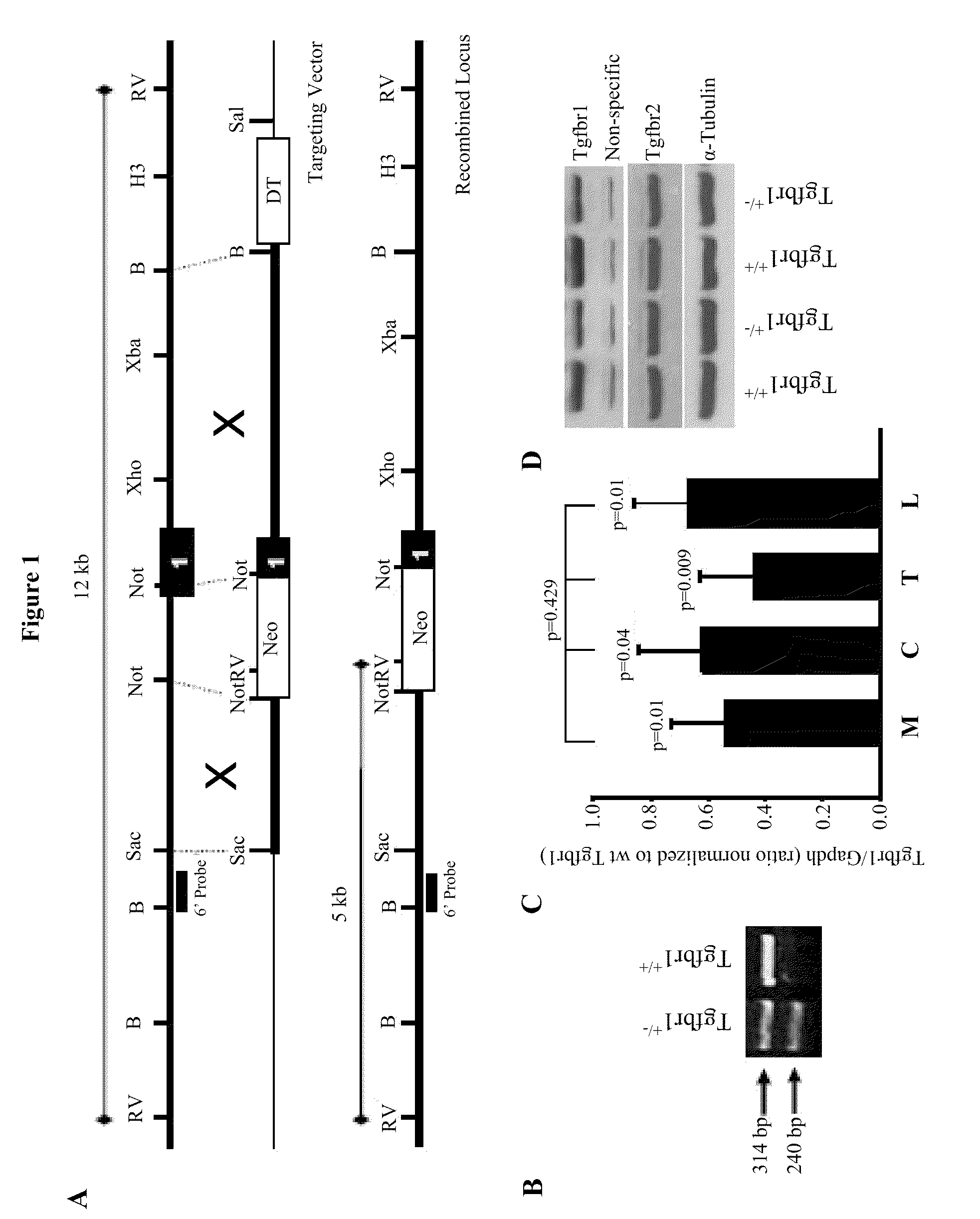
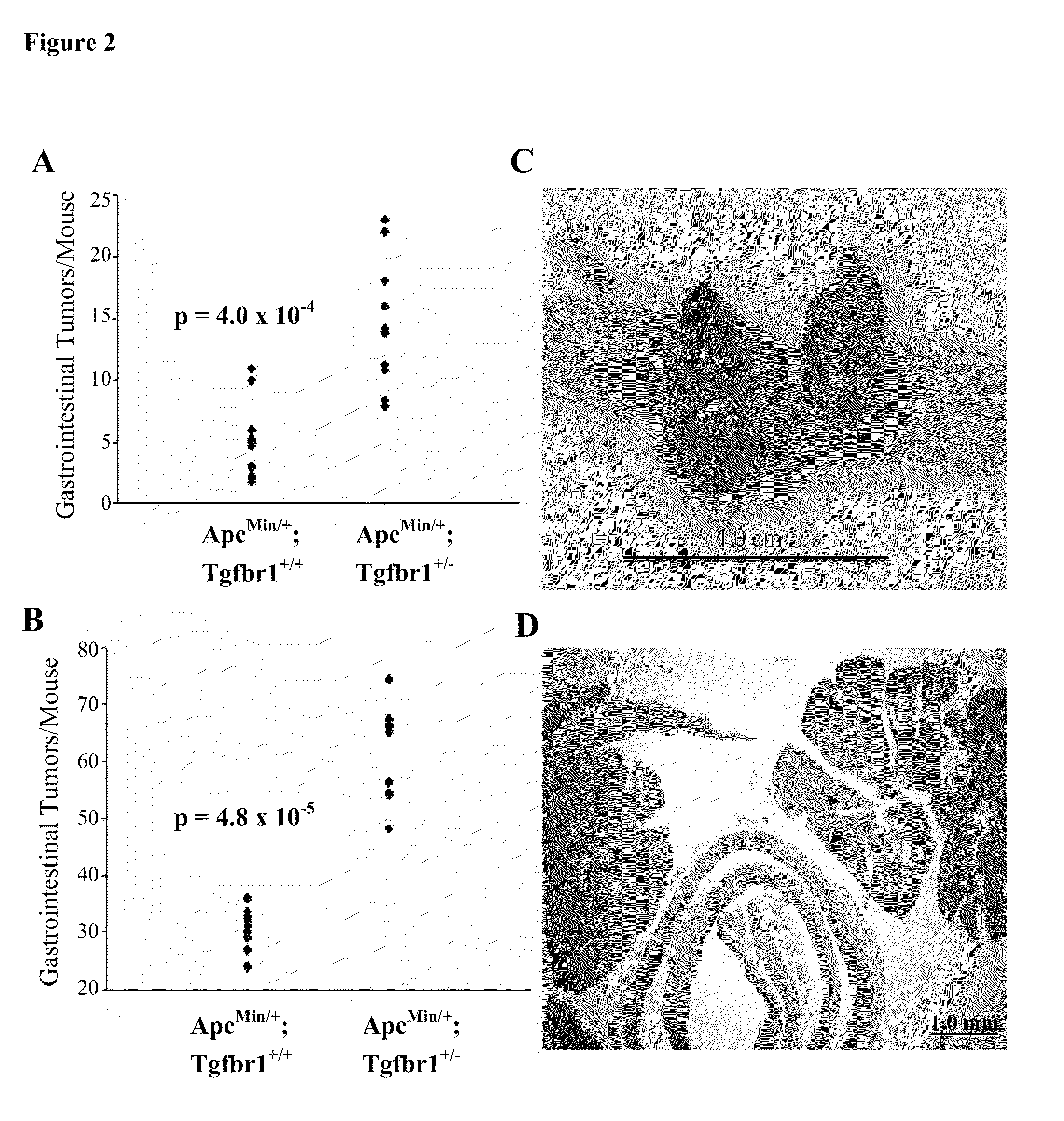
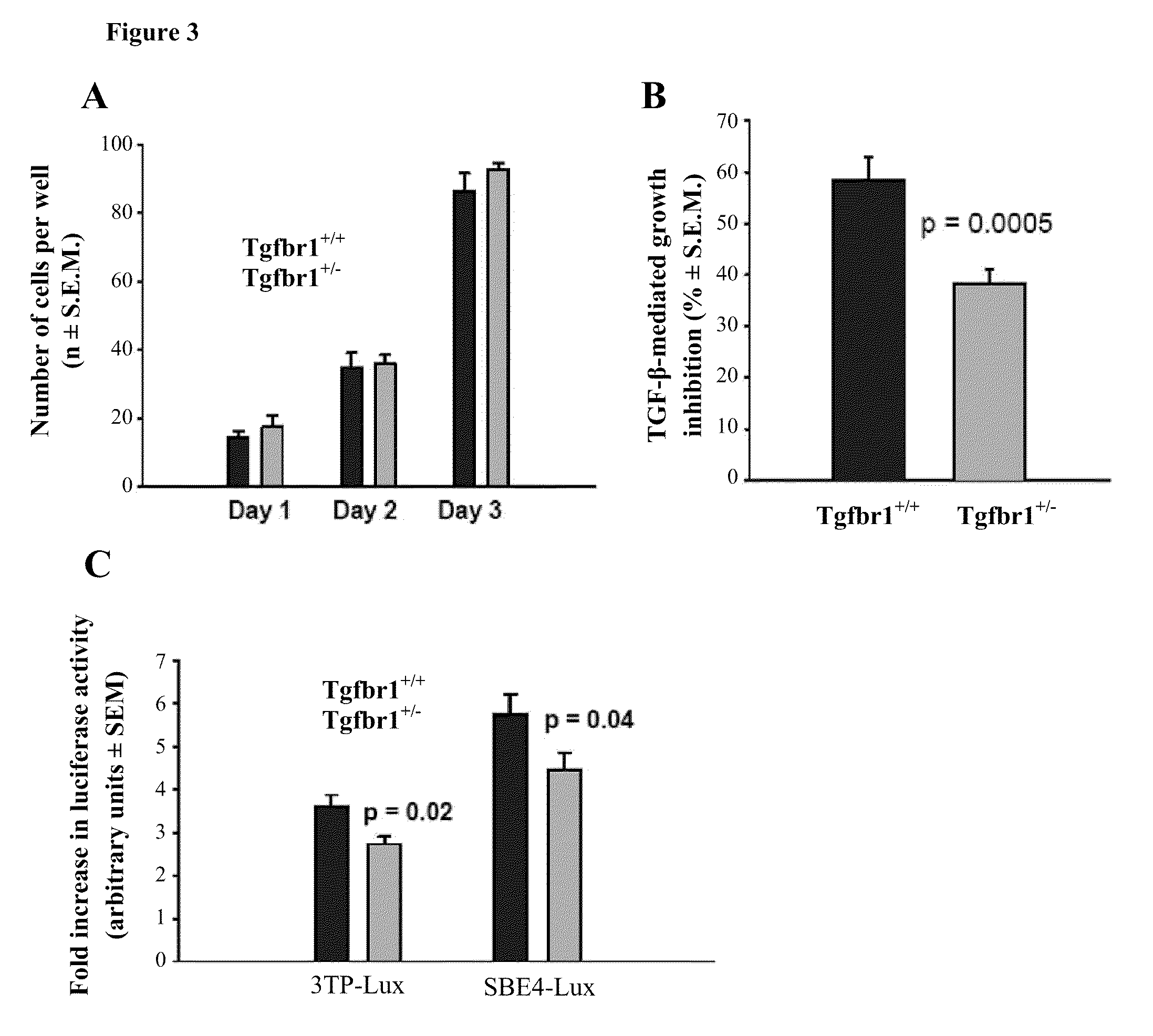
The present invention provides methods for assessing a genetic susceptibility to cancer in a subject which includes measuring allele specific expression or presence of at-risk haplotypes of TGFBR1, where a difference in expression or the presence of at-risk haplotypes is indicative of a cancer or susceptibility to a cancer. Methods to screen for agents that modify expression of TGRBR1 are also provided.
Owner:PASCHE BORIS
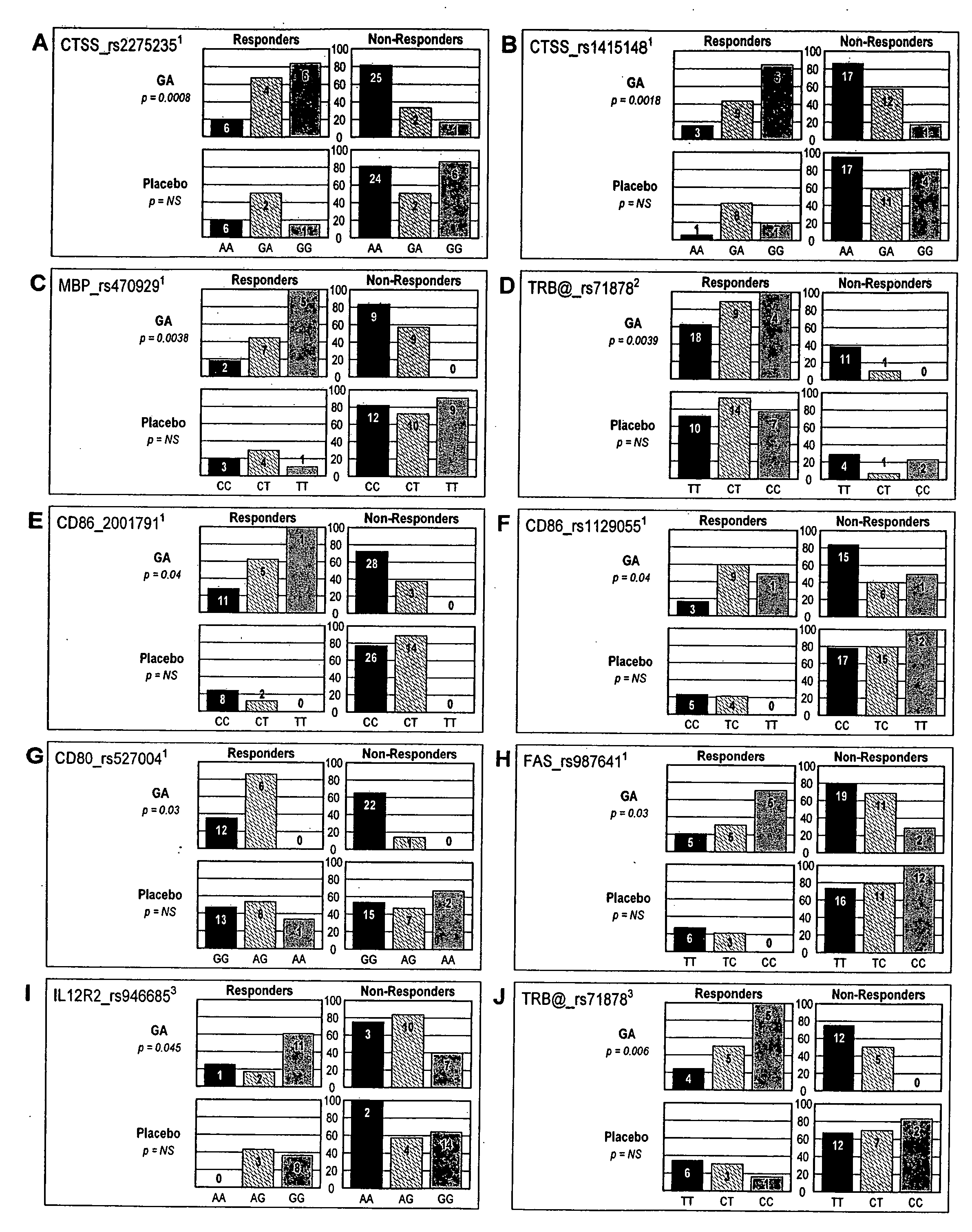
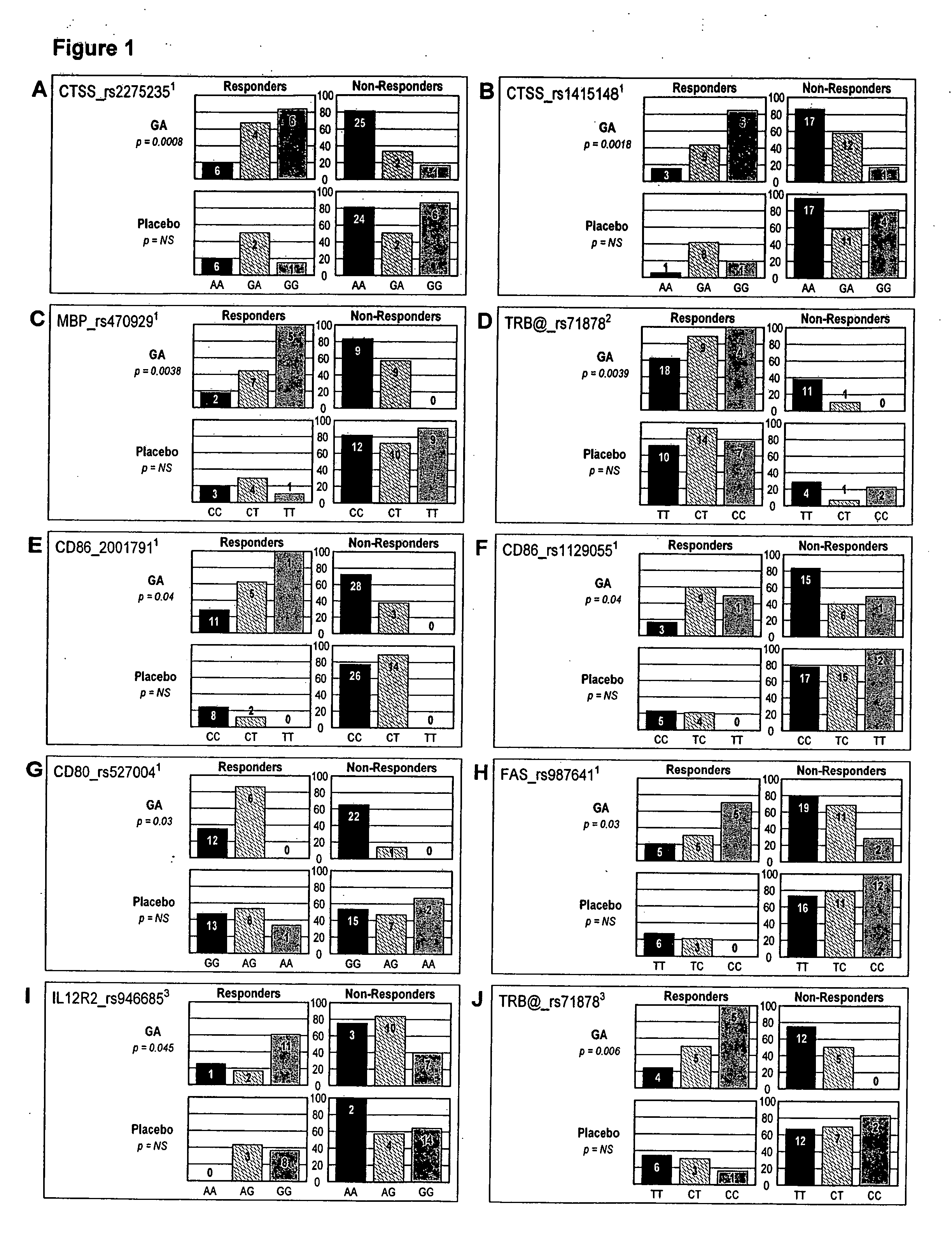
Markers associated with the therapeutic efficacy of glatiramer acetate
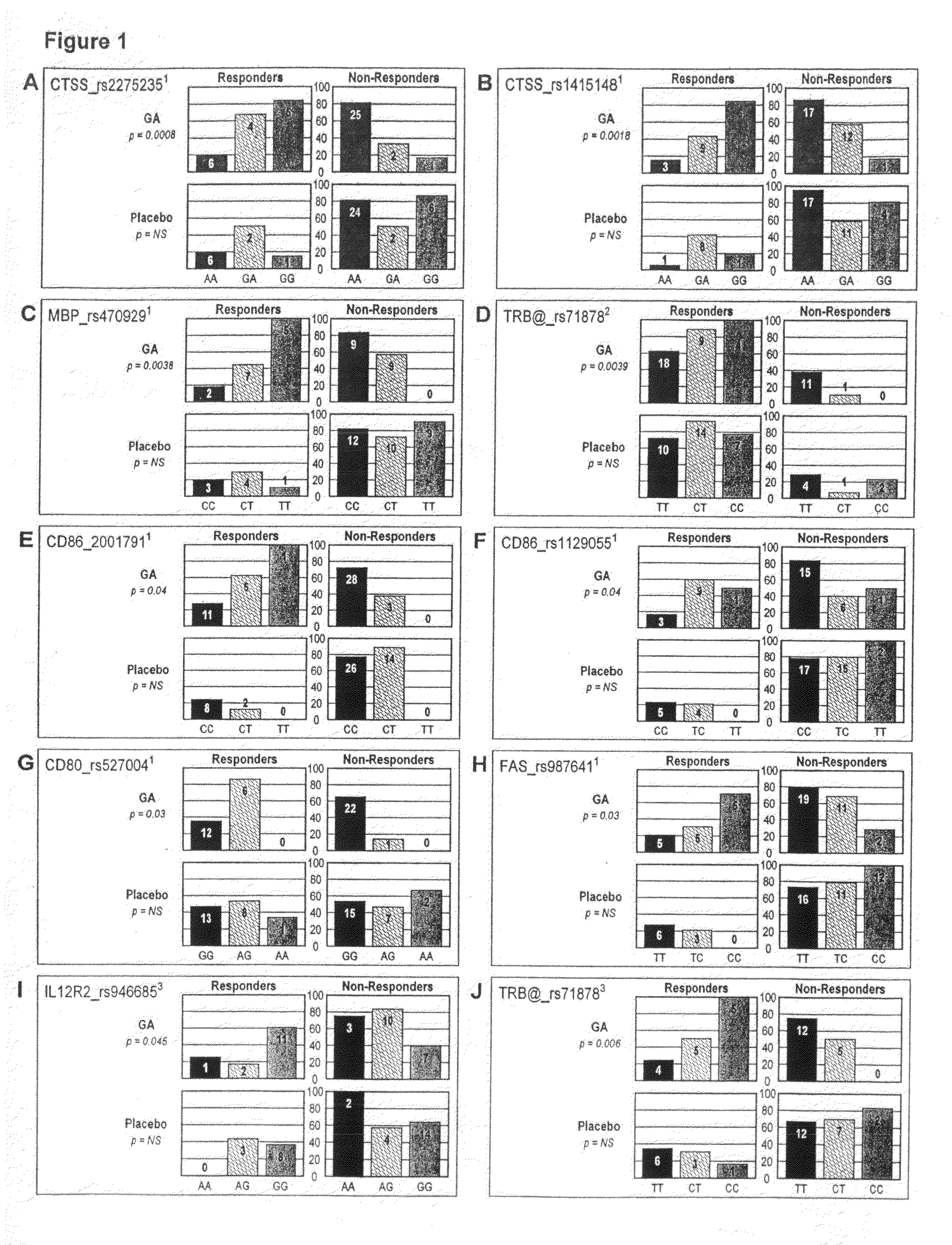
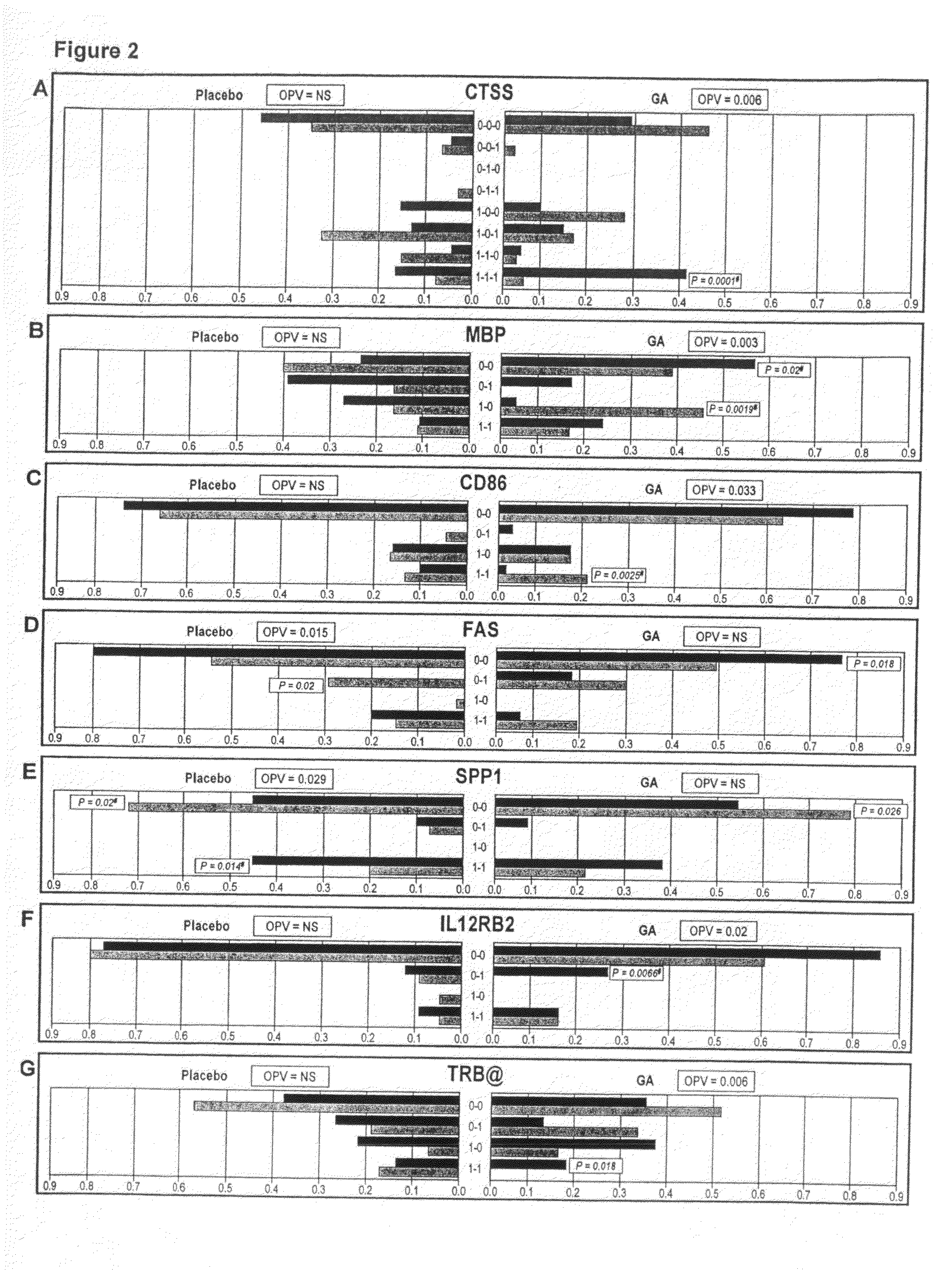
The present invention is directed to methods and kits based, at least in part, on the identification of allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness to glatiramer acetate for the treatment of immune disorders, such as relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. The allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness is based on polymorphisms in the following genes, CTSS, MBP, TCRB, CD95, CD86, IL-1R1, CD80, SCYA5, MMP9, MOG, SPP1 and IL-12RB2.
Owner:RAPPAPORT FAMILY INSTITUTE FOR RESEACH IN THE MEDICAL SCIENCES +2
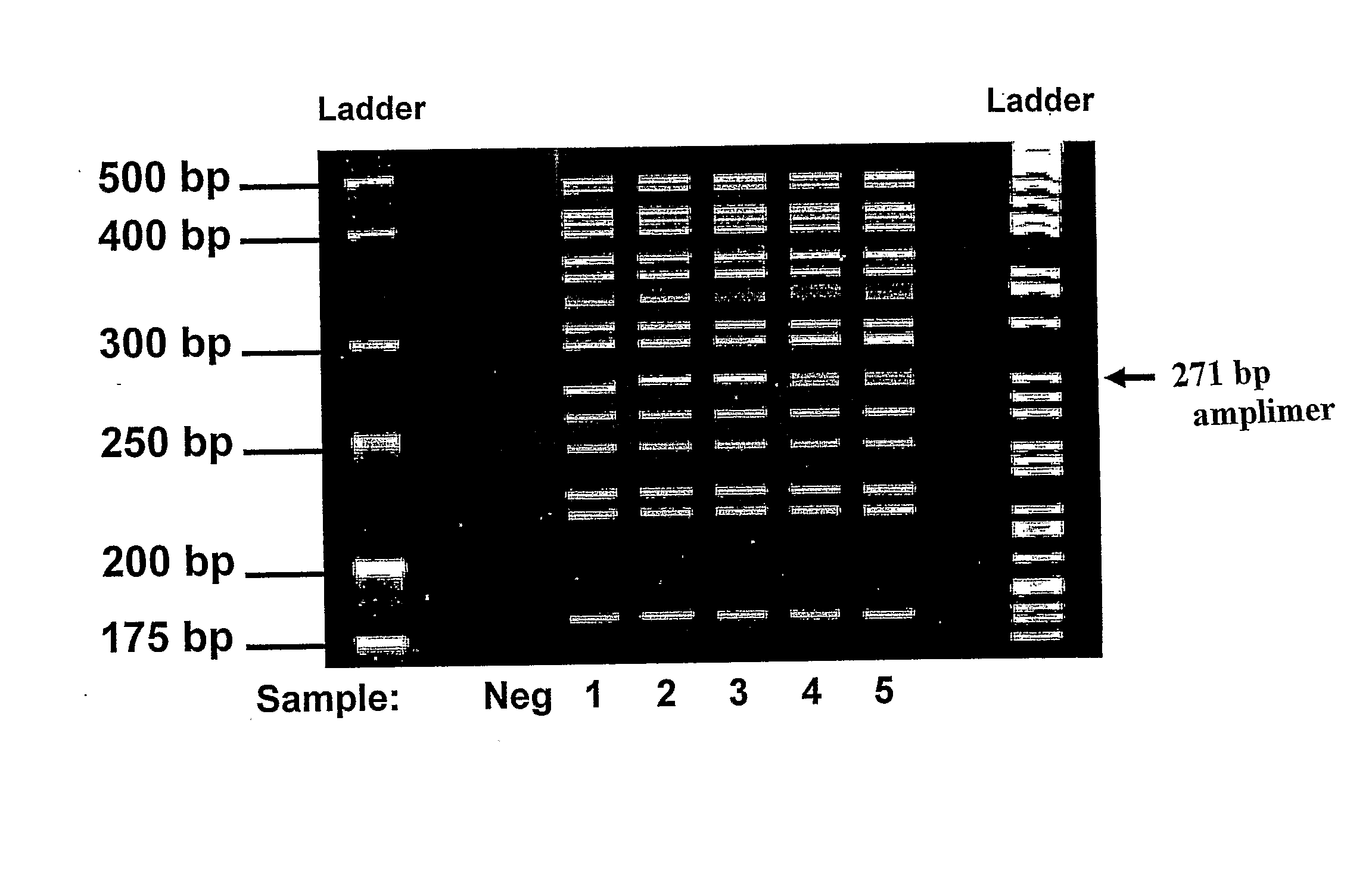
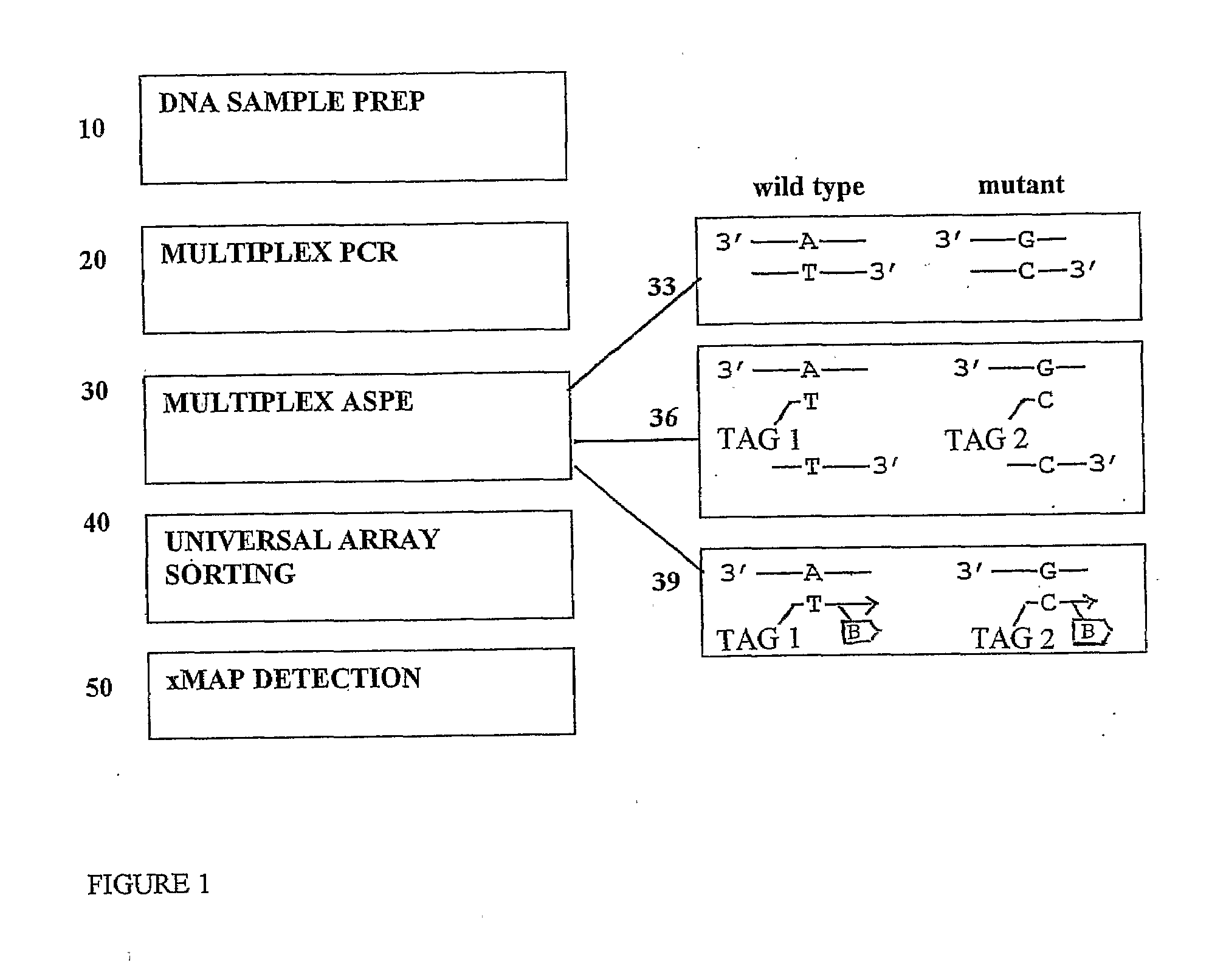
Method of Detecting Cystic Fibrosis Associated Mutations
InactiveUS20080138803A1Microbiological testing/measurementNucleotide sequencingCystic fibrosis lungs
The present invention describes a method for the simultaneous identification of two or more single base changes, insertions, deletions or translocations in a plurality of target nucleotide sequences that are markers associated with cystic fibrosis. Multiplex detection is accomplished using multiplexed tagged allele specific primer extension (ASPE) and hybridization of such extended primers to a probe, preferably an addressable anti-tagged support.
Owner:LUMINEX MOLECULAR DIAGNOSTICS
Methods for Genotyping
InactiveUS20070269817A1Reduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotidePolymerase L
The present invention provides for methods for discriminating between alleles at polymorphic positions in a genome. In general the methods employ allele specific extension of oligonucleotides that are complementary to one of the alleles at the 3′ end of the oligonucleotide. The allele specific oligonucleotides are resistant to proof reading activity from a polymerase and may be extended in an allele specific manner by a DNA polymerase with a functional 3′ to 5′ exonuclease activity. The allele specific oligonucleotides may be attached to a solid support such as a chip or a bead.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Methods and compositions for analyzing AHASL genes
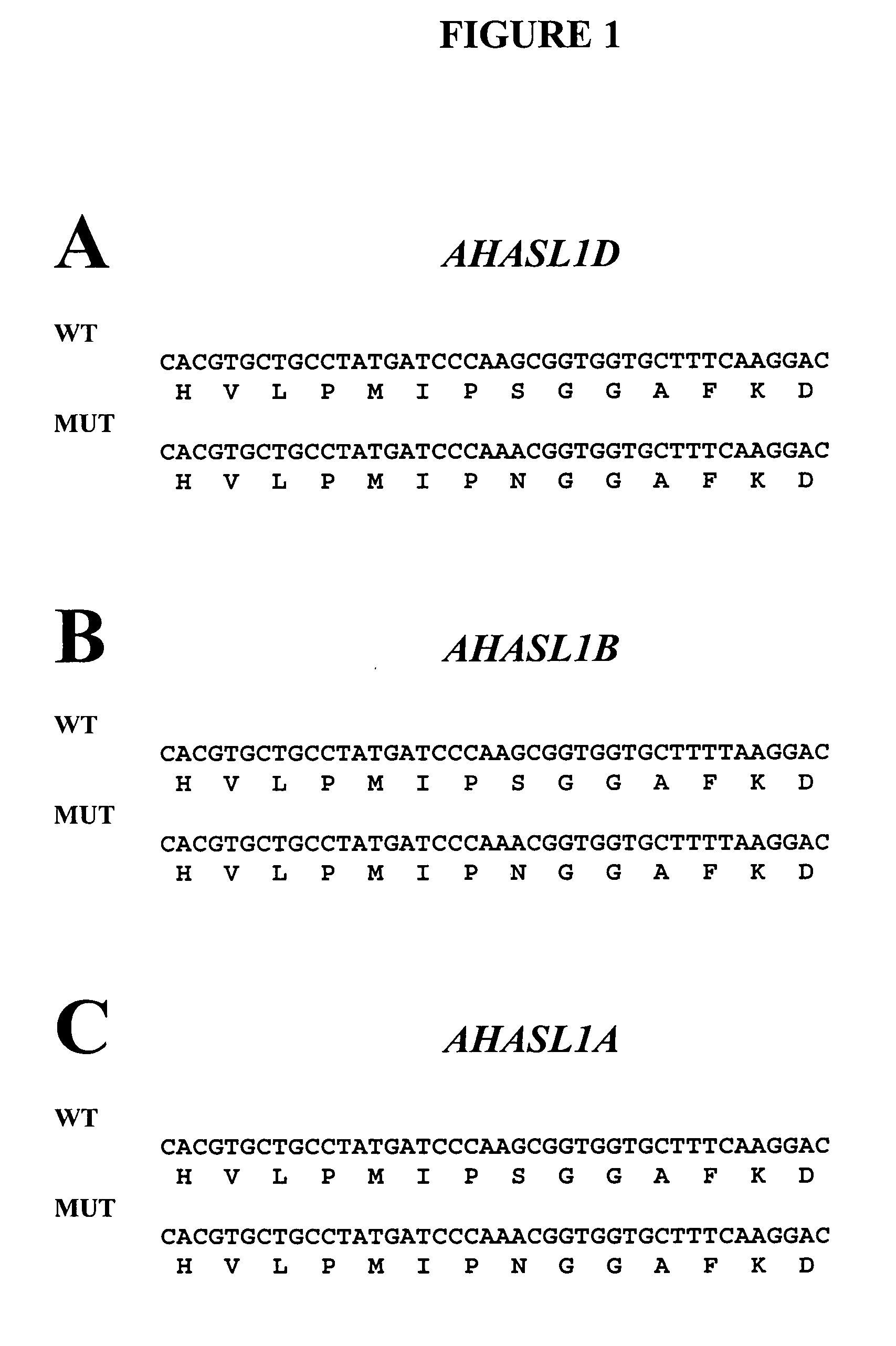
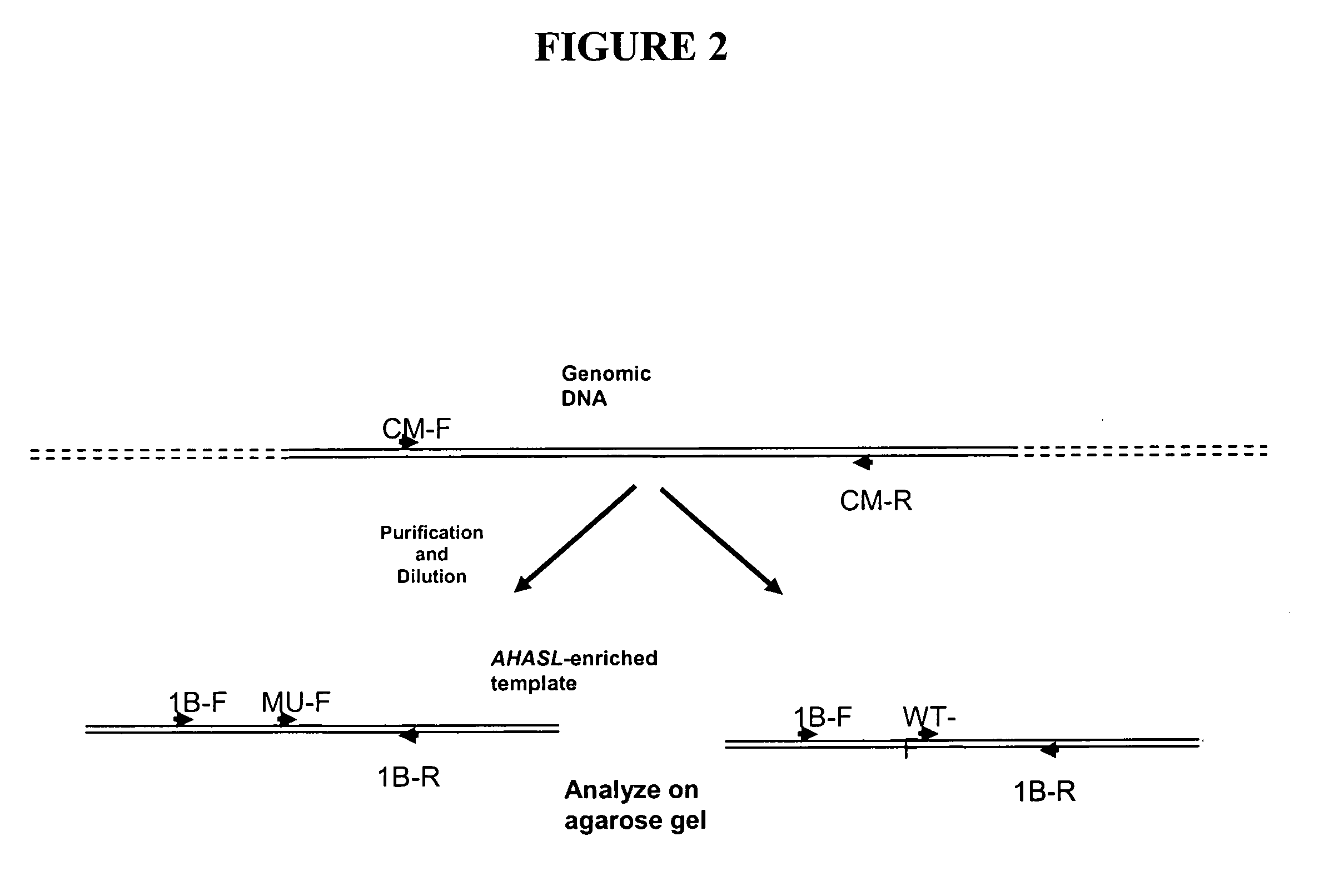
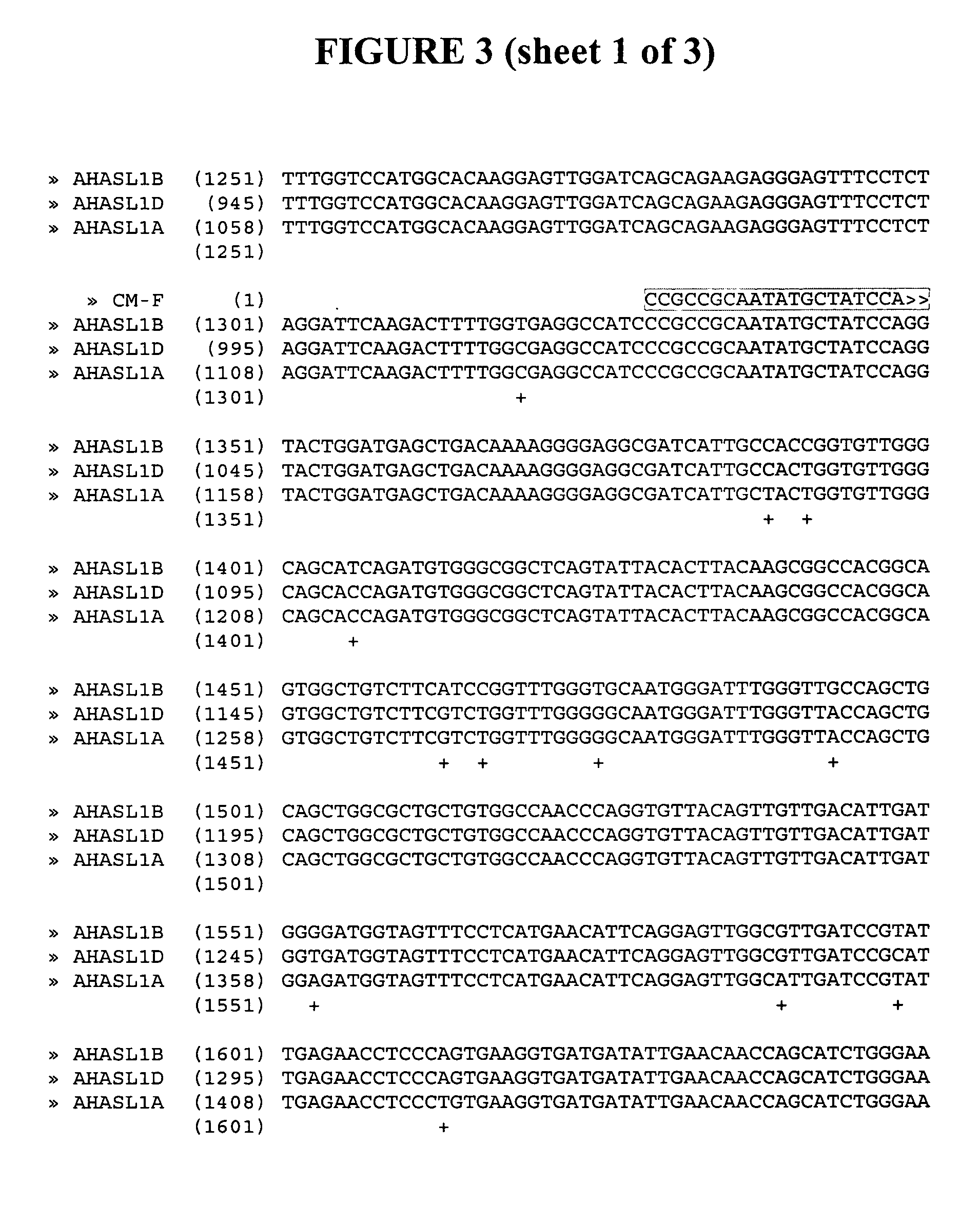
The invention relates to methods and compositions for analyzing plant acetohydroxy acid synthase large subunit (AHASL) genes. In particular, the invention relates to methods for the detection of wild-type AHASL alleles and mutant AHASL alleles that encode imidazolinone-tolerant AHASL proteins. The methods involve the use of PCR amplification and novel compositions comprising allele-specific and gene-specific primers to detect the presence of mutant and / or wild-type alleles present at the individual AHASL genes of a plant. Specifically, the methods and compositions are useful for analyzing the three AHASL genes of Triticum aestivum and the two AHASL genes of Triticum turgidum ssp. durum.
Owner:BASF AG
Allele-Specific Amplification
ActiveUS20100099110A1Simple methodSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAllele-specific oligonucleotideGenetics
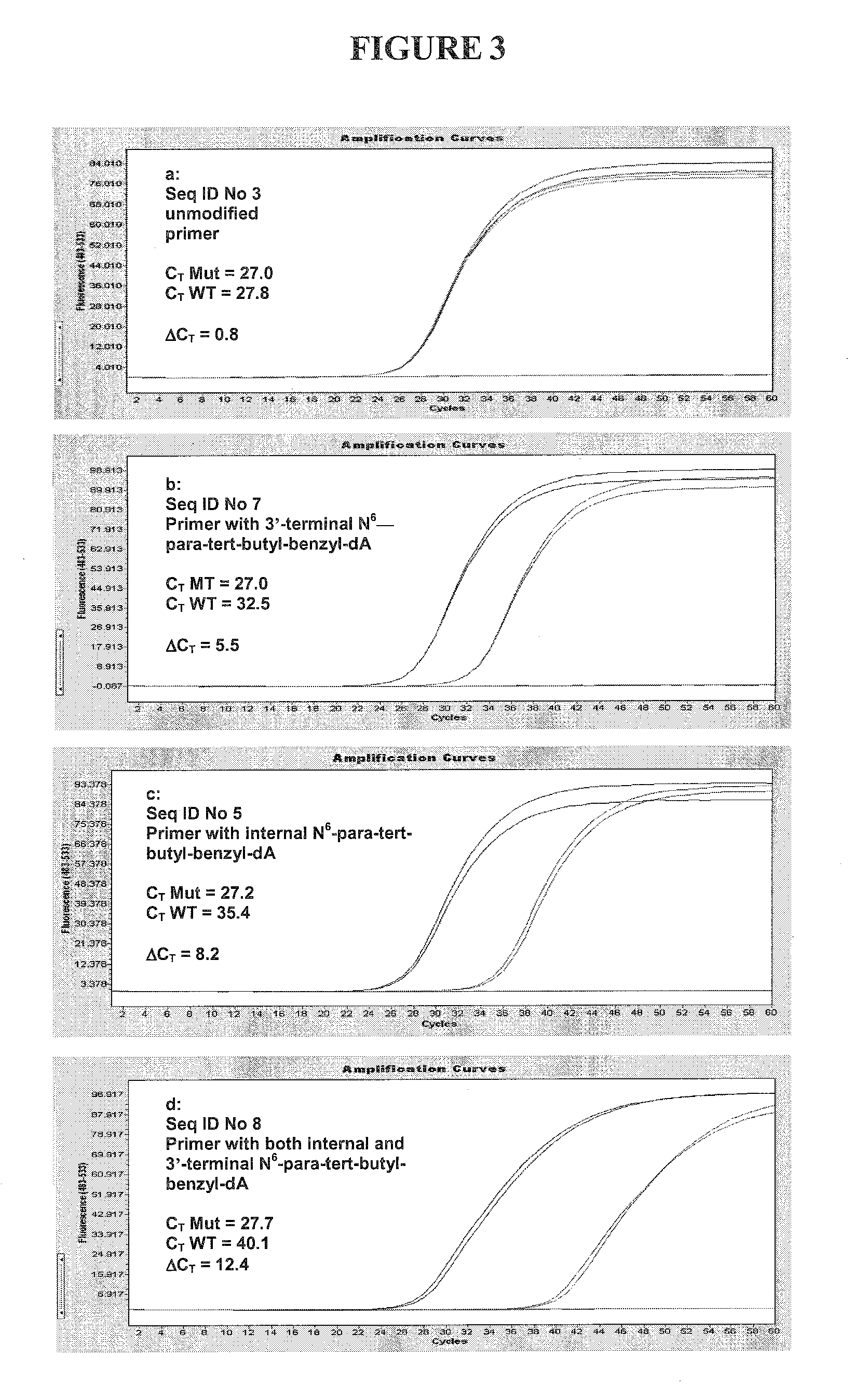
The present invention includes a method of allele-specific amplification, utilizing an allele-specific oligonucleotide, at least partially complementary to more than one variant of the target sequence, but having a 3′-terminal nucleotide complementary to only one variant of the target sequence and having at least one nucleotide with a base covalently modified at the exocyclic amino group, wherein the allele-specific oligonucleotide is extended by a nucleotide-incorporating biocatalyst predominantly when hybridized to the variant of the target sequence for which it has said complementary 3′-terminal nucleotide.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Method of detection of allelic variants of SCA2 gene
InactiveUS6623927B1Reduce riskHigh riskSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular diagnosticsGenetic analysis
The present invention relates to allelic variants of human Spinocerebellar ataxia 2 (SCA2) gene and provides allele-specific primers and probes suitable for detecting these allelic variants for applications such as molecular diagnosis, prediction of an individual's disease susceptibility, and / or the genetic analysis of SCA2 gene in a population.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for long range allele-specific PCR
InactiveUS20070184457A1Enhanced hybridizationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LA-DNA
The present invention is directed to a method and kit for determining the molecular haplotype of a gene in a diploid DNA sample. The method discriminates between two haplotypes on the basis of a difference of one or more nucleotides using allele-specific PCR amplification in combination with long range PCR, using a DNA polymerase enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity, using annealing temperature conditions sufficiently greater than the predicted annealing temperature (Tm) to effect selective hybridization and extension of an allele-specific extension primer to the target allele relative to the variant allele. The present invention is particularly useful, for example, to determine the haplotype of a gene having multi-allelic genetic loci separated by a distance in which accurate PCR amplification of a single fragment containing the multiple genetic loci cannot be performed without using a DNA polymerase enzyme having 3′→5′ exonuclease activity, generally about 5 kilobases or more.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer
ActiveCN105112546AImprove throughputImprove detection efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses a primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on the basis of a KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of the set primer. The primer set comprises totally 14 groups of KASP primers. The KASP primers are respectively designed for the 14 functional genes of the wheat, and particular nucleotide sequences of the KASP primers are sequences 1-42 in sequence tables. The primer set and the application have the advantages that the functional genes of different wheat varieties can be quickly detected by the aid of the KASP primer set, methods for detecting the functional genes of the wheat are simple, convenient and speedy, and detection results are accurate and reliable; the primer set has an important theoretical significance and important economic value in assistant selection of the wheat varieties by the aid of molecular markers.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
c-KIT gene mutation detection liquid-phase chip
ActiveCN101984070AImprove signal-to-noise ratioImplement parallel detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Mutation detection
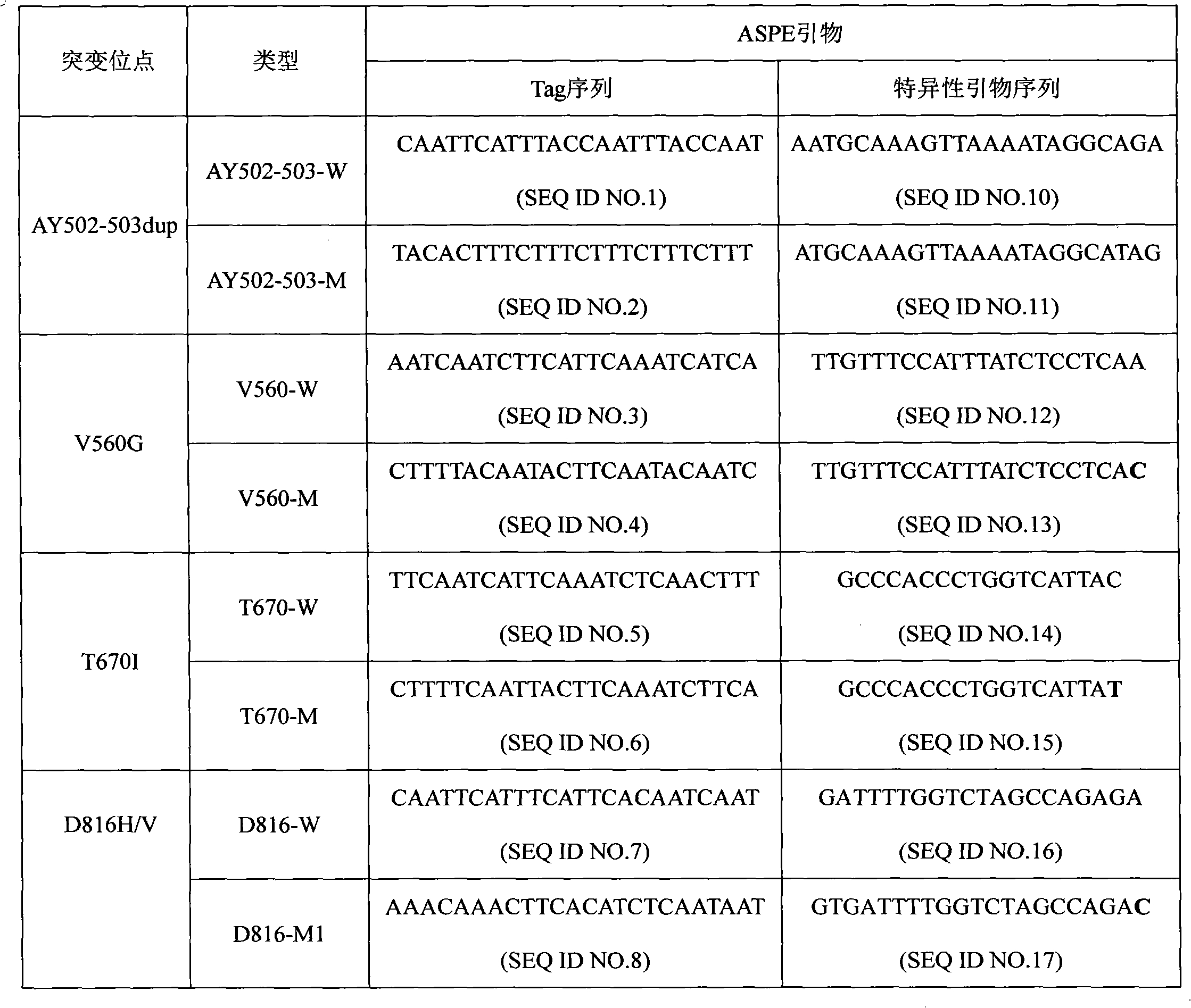
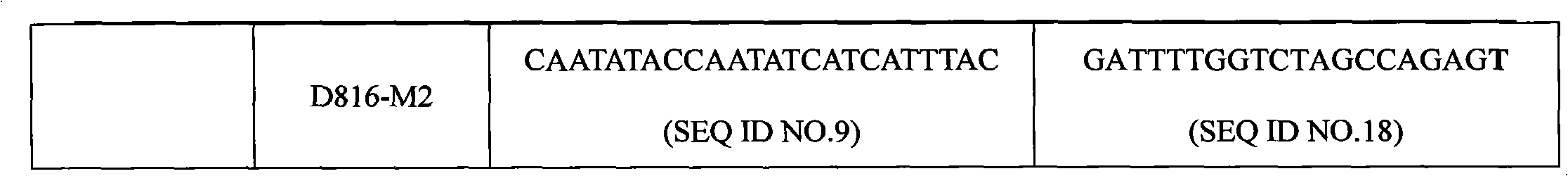
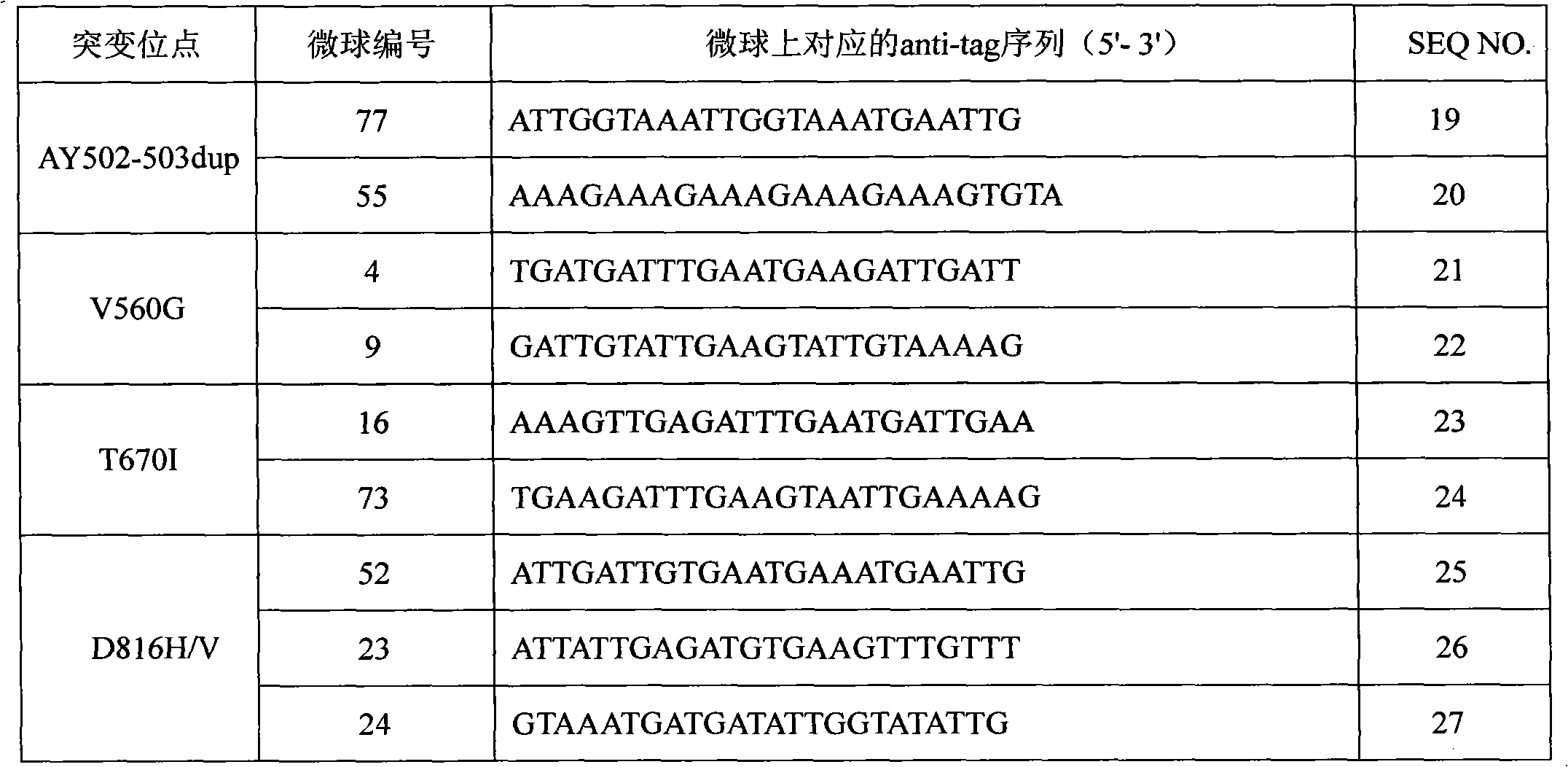
The invention discloses a c-KIT gene mutation detection liquid-phase chip, which comprises tag sequence at 5' terminal and ASPE (Allele Specific Primer Extension) primers consisting of specific primers specific to mutational sites at 3' terminal. The specific primers consist of sequences shown in SEQ ID No.10 and SEQ ID No.11 specific to AY502-503dup mutational sites, sequences shown in SEQ ID No.12 and SEQ ID No.13 specific to V560G mutational site, sequences shown in SEQ ID No.14 and SEQ ID No.15 specific to T670I mutational site and / or sequences shown in SEQ ID No.16-SEQ ID No.18specific to D816H / V mutational site, the tag sequence which is selected from sequences shown in SEQ ID No.1-SEQ ID No.9, microballoons which have different color codings and are respectively enveloped with a specific anti-tag sequence and amplification primers. The coincidence ratio of the result of sequencing method with that of the c-KIT gene mutation detection liquid-phase chip reaches up to 100 percent. The c-KIT gene mutation detection liquid-phase chip can simultaneously detect a plurality of mutational sites with excellent signal to noise ratio.
Owner:SUREXAM BIO TECH
Nucleic acid sequence detection using multiplexed oligonucleotide PCR
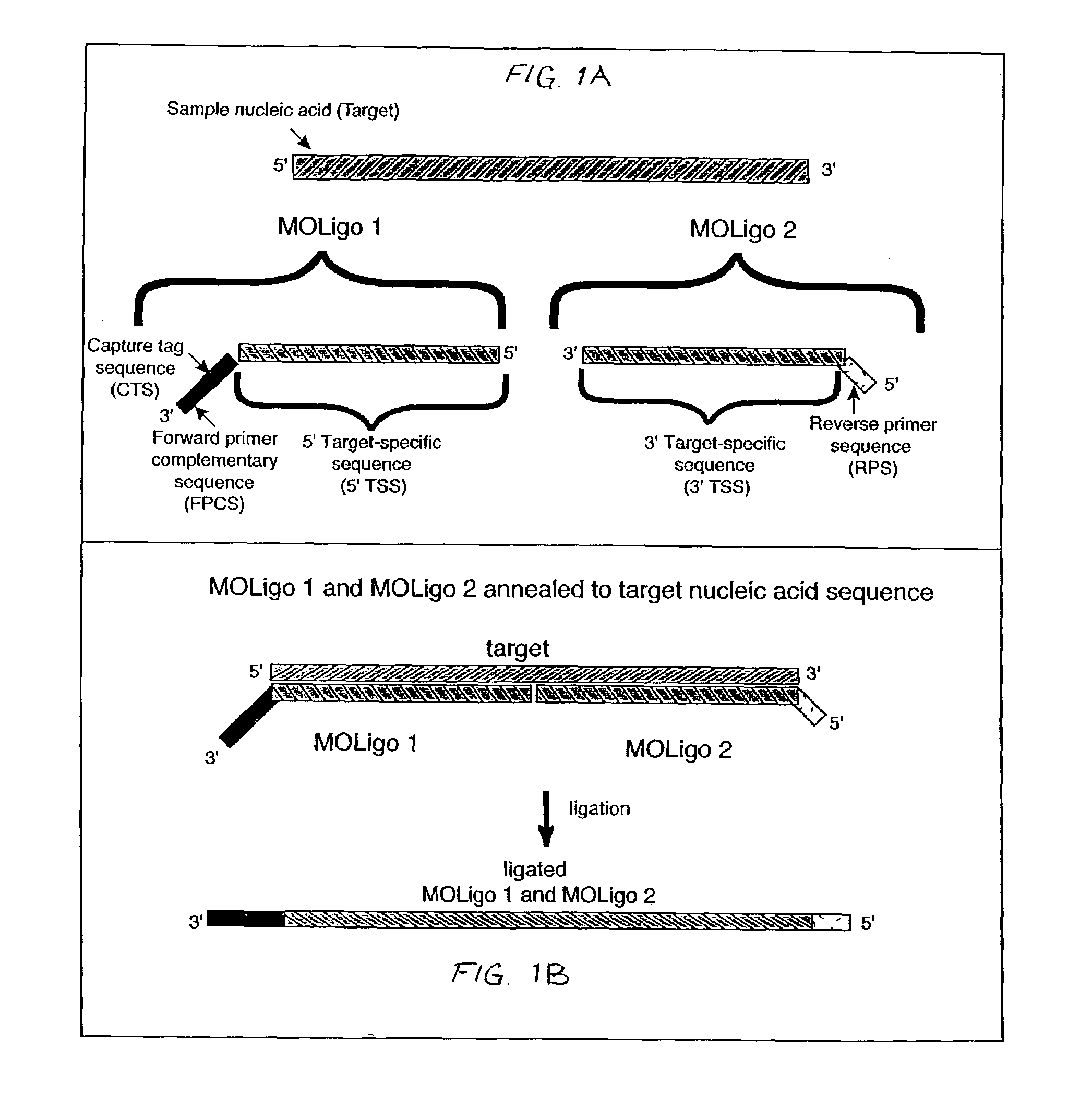
InactiveUS7153656B2Provides redundancyRedundancy in allele discriminationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereBiology
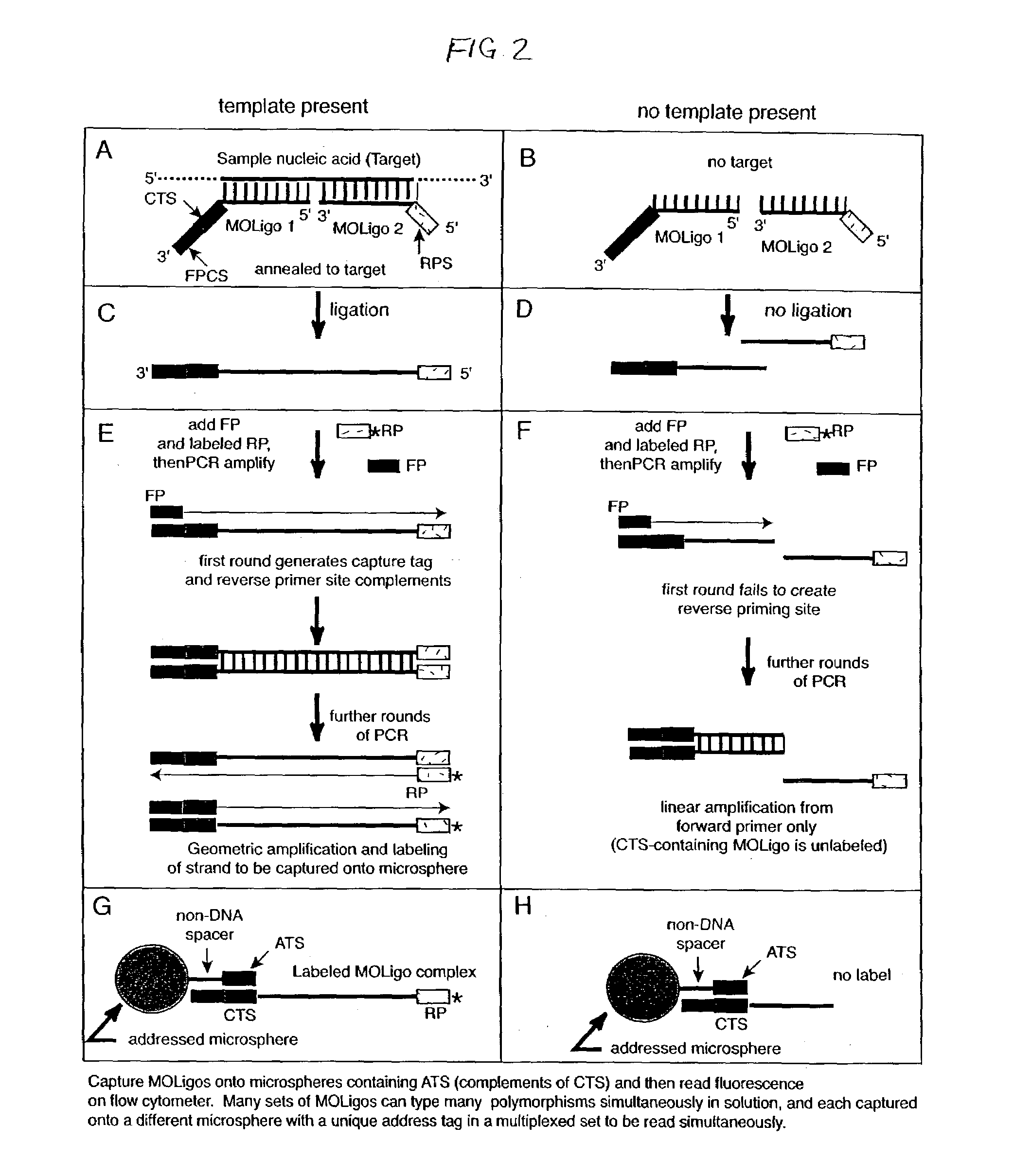
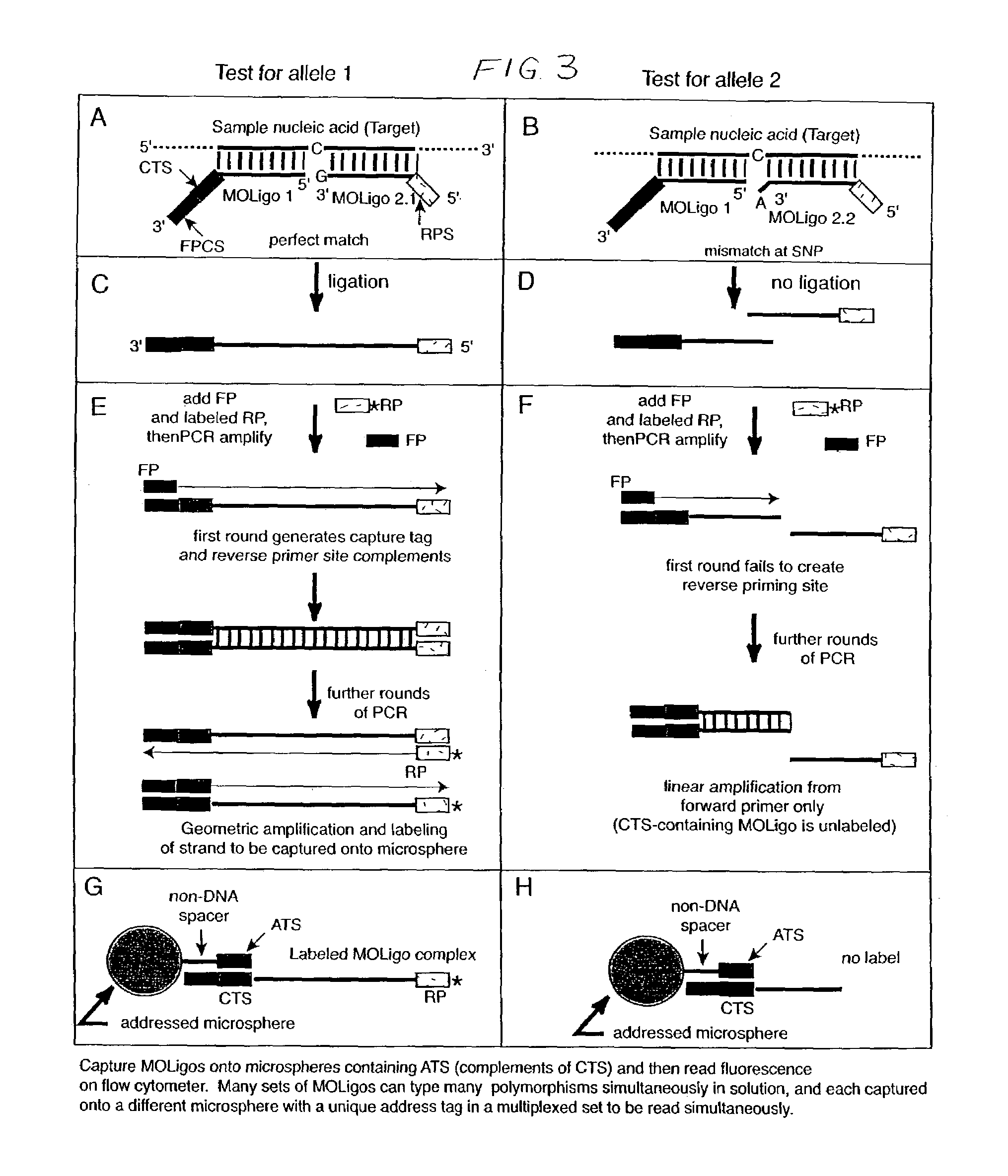
Methods for rapidly detecting single or multiple sequence alleles in a sample nucleic acid are described. Provided are all of the oligonucleotide pairs capable of annealing specifically to a target allele and discriminating among possible sequences thereof, and ligating to each other to form an oligonucleotide complex when a particular sequence feature is present (or, alternatively, absent) in the sample nucleic acid. The design of each oligonucleotide pair permits the subsequent high-level PCR amplification of a specific amplicon when the oligonucleotide complex is formed, but not when the oligonucleotide complex is not formed. The presence or absence of the specific amplicon is used to detect the allele. Detection of the specific amplicon may be achieved using a variety of methods well known in the art, including without limitation, oligonucleotide capture onto DNA chips or microarrays, oligonucleotide capture onto beads or microspheres, electrophoresis, and mass spectrometry. Various labels and address-capture tags may be employed in the amplicon detection step of multiplexed assays, as further described herein.
Owner:LOS ALAMOS NATIONAL SECURITY
Genotyping methods
InactiveUS20050042654A1Minimizing chanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenomic DNAGenotyping
Methods for amplifying genomic DNA and genotyping amplified genomic DNA samples are provided. The genotyping methods use genotyping arrays of probes that are allele specific probes for single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The methods also relate to methods for amplifying a plurality of genomic DNA samples from a plurality of individuals in a manner that minimizes the potential for contamination of samples that have not been amplified by amplicons from samples that have already been amplified.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Nucleic acid testing method for point-of-care diagnostics and genetic self-monitoring
InactiveUS20080050735A1The testing process is simpleSpecial trainingMicrobiological testing/measurementPoint of careGenomic DNA
This invention describes a nucleic acid testing procedure in a form of portable device or a test kit for the purposes of clinical genetic testing, infectious disease diagnostics, biodefense, forensic analysis, paternity testing, pet and cattle breeding, food testing, etc. This testing does not include toxic chemicals and is simple enough to be used by an average individual without any special laboratory training. The procedure includes collecting the sample, potential isothermal amplification of the whole genomic DNA or a fragment of genomic DNA, denaturing double-stranded DNA into single-stranded form, hybridizing the denatured sample DNA to single-stranded allele-specific tester oligonucleotides complementary to the analyzed DNA sequence of interest, selective removal of single-stranded DNA from DNA hybrids, and finally detecting the label in double-stranded hybrids to determine the presence or absence of a particular sequence in the initial sample.
Owner:PUSHNOVA ELENA
Methods and products related to genotyping and DNA analysis
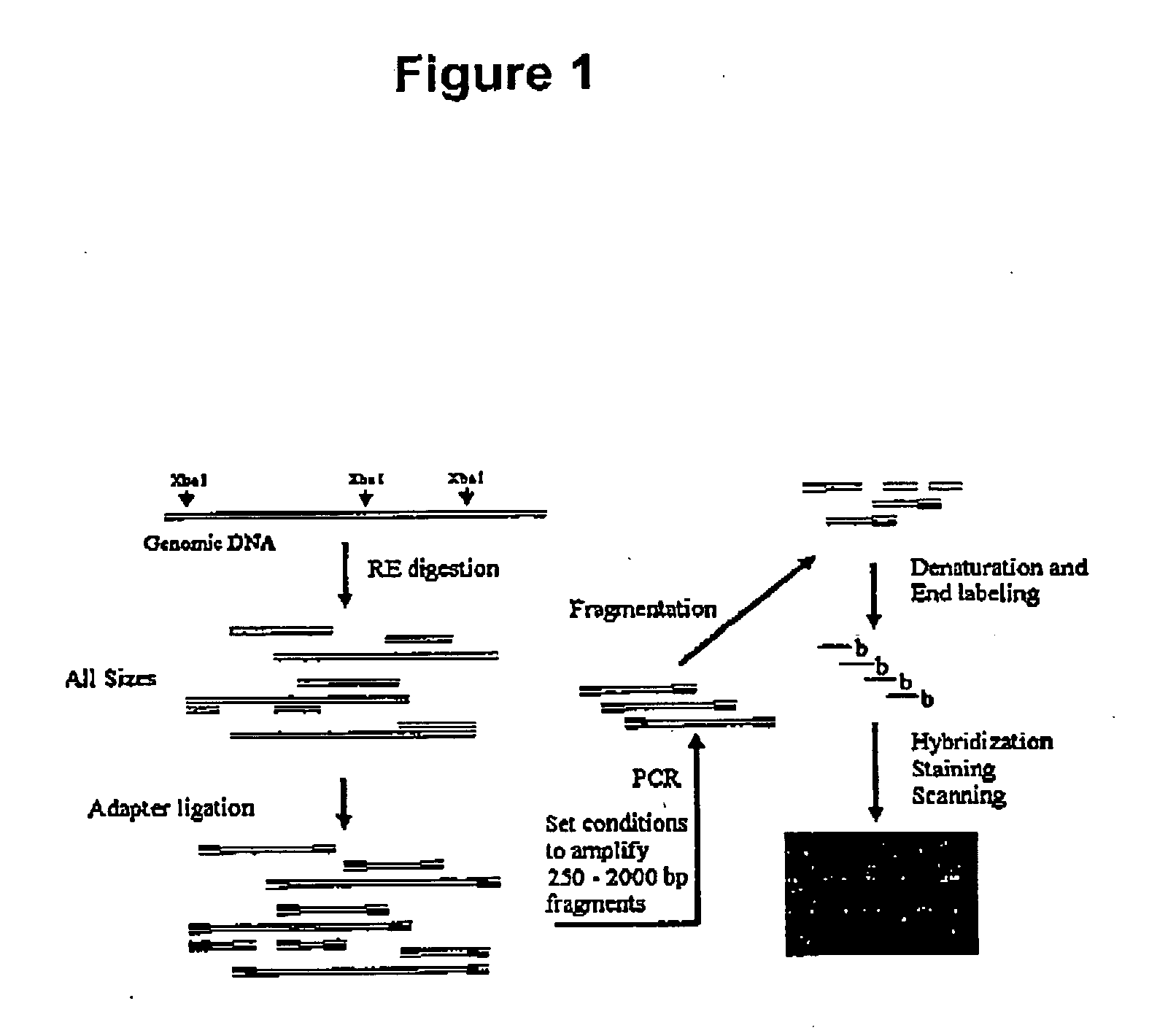
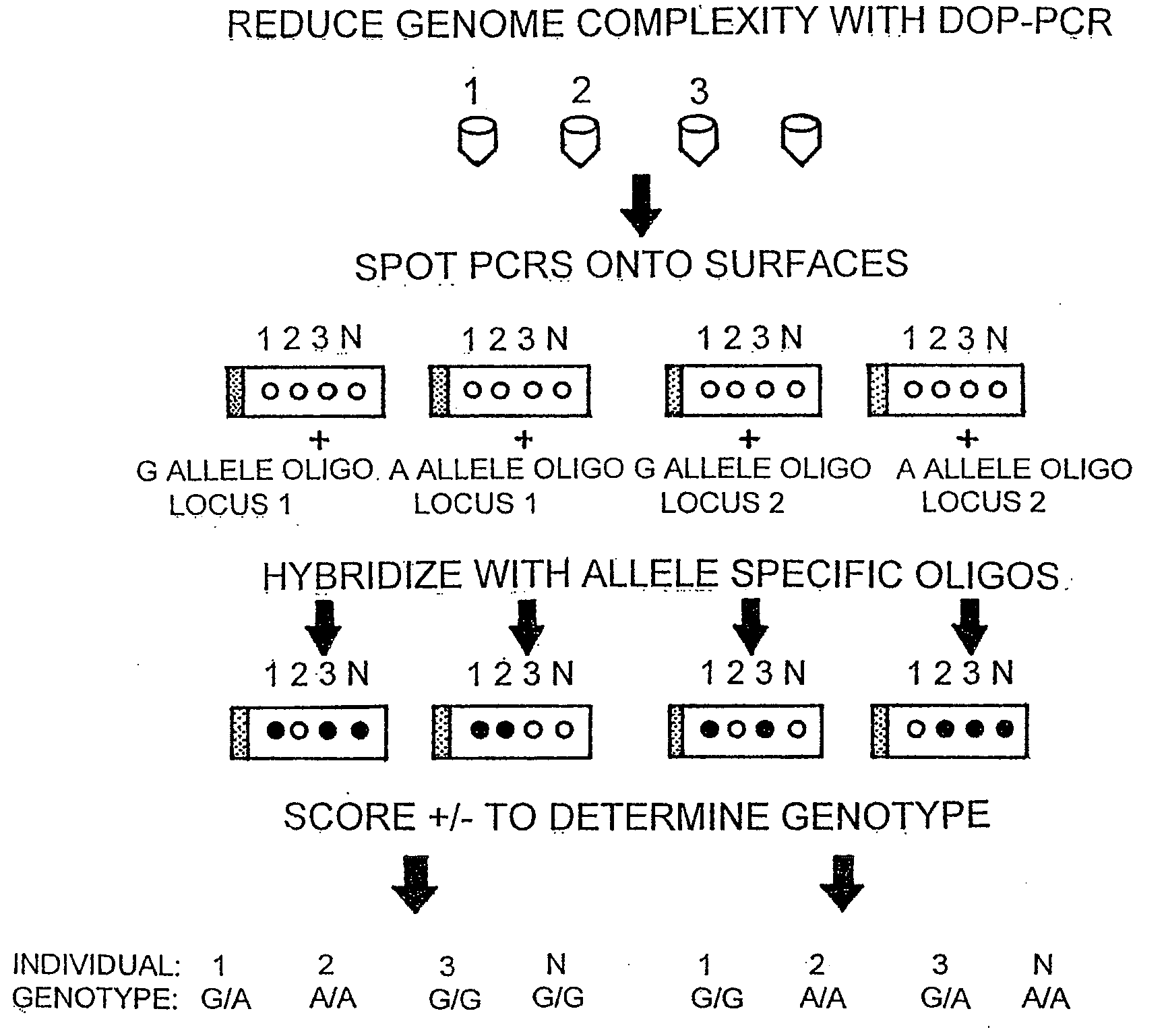
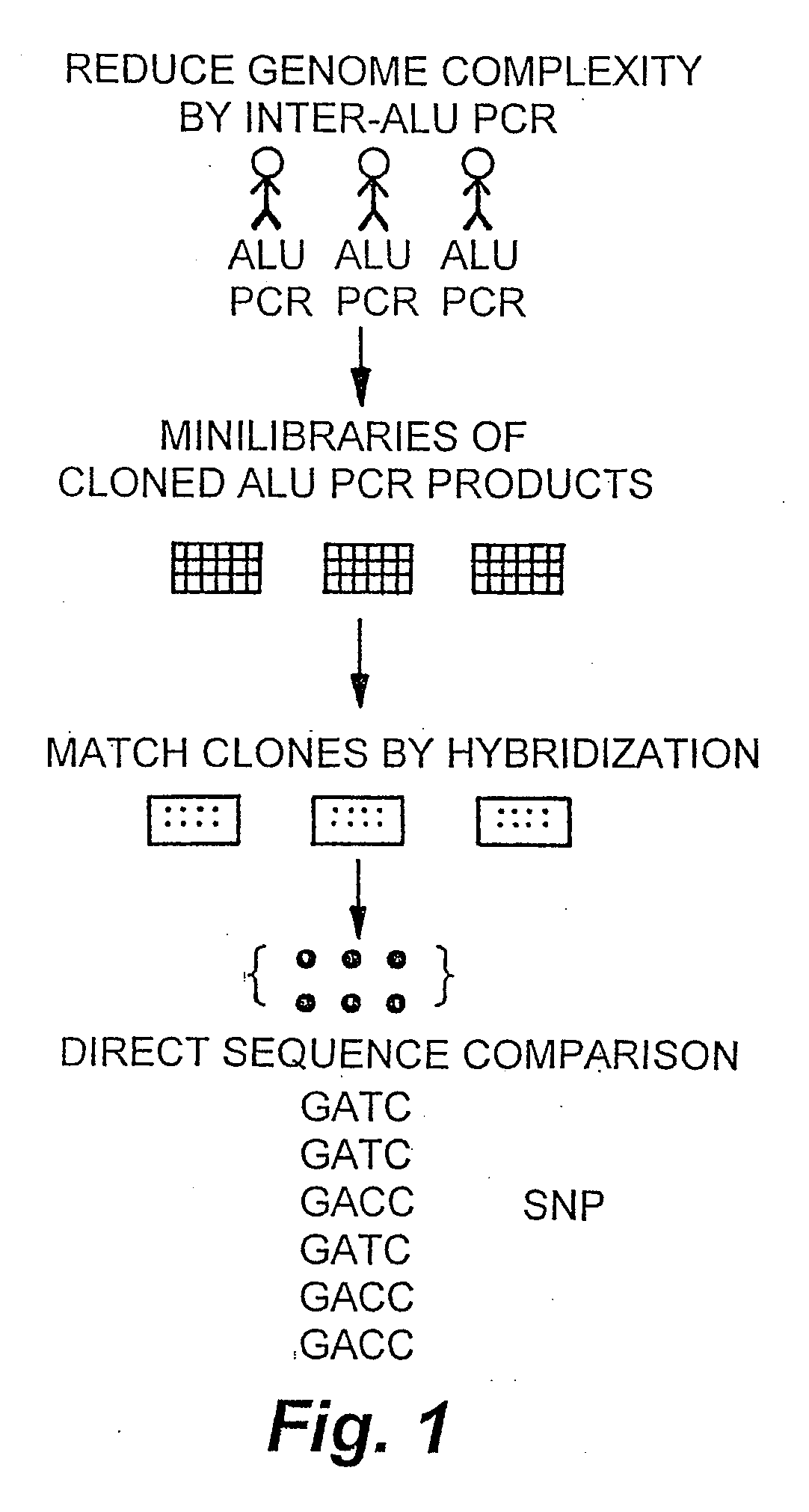
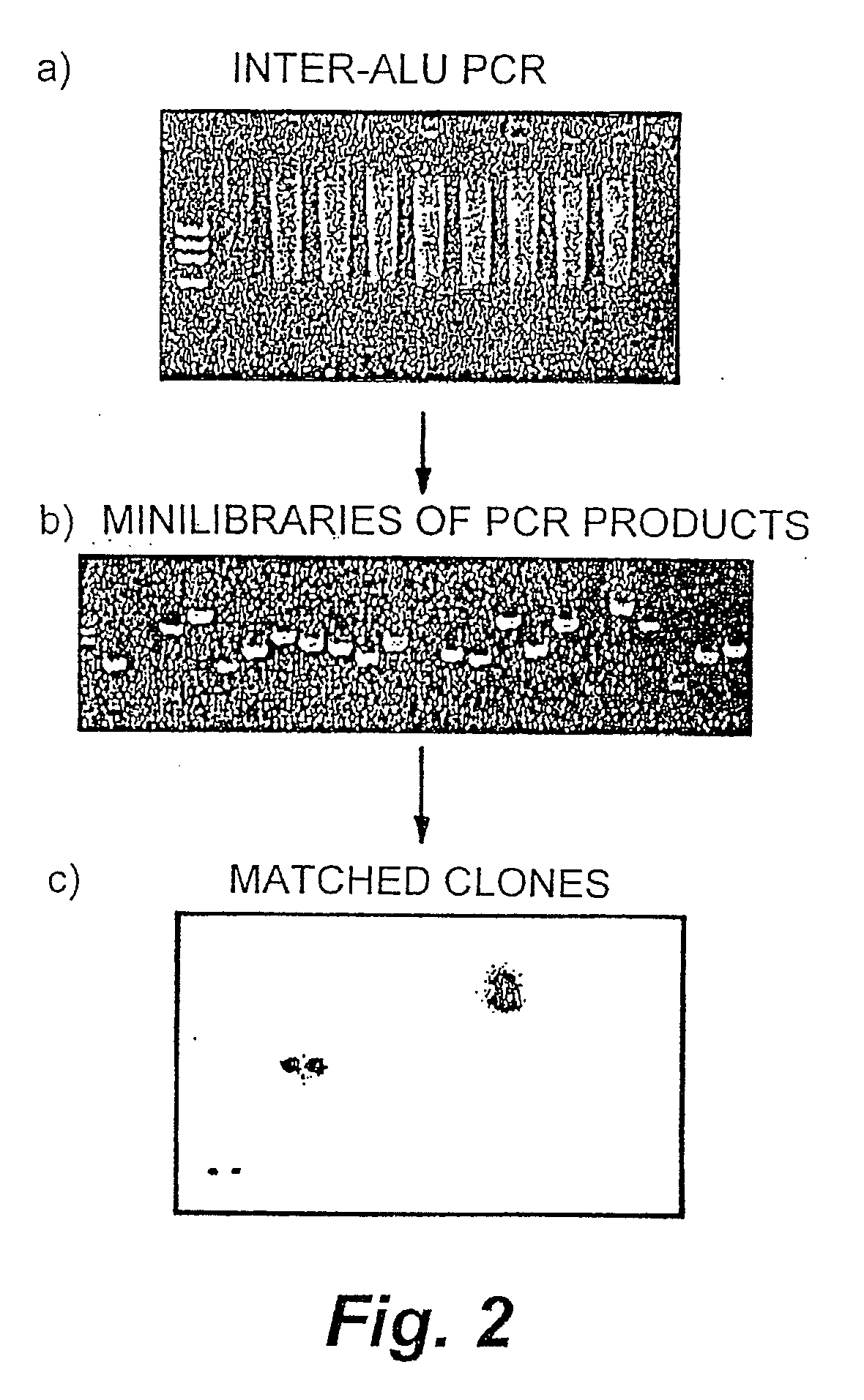
InactiveUS20090098551A1Improve throughputReduce complexityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGenome ScanAllele-specific oligonucleotide
The invention encompasses methods and products related to genotyping. The method of genotyping of the invention is based on the use of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to perform high throughput genome scans. The high throughput method can be performed by hybridizing SNP allele-specific oligonucleotides and a reduced complexity genome (RCG). The invention also relates to methods of preparing the SNP specific oligonucleotides and RCGs, methods of fingerprinting, determining allele frequency for a SNP, characterizing tumors, generating a genomic classification code for a genome, identifying previously unknown SNPs, and related compositions and kits.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Kit for diagnosing gene of Leber optic neuropathy in heredity and detecting method
InactiveCN1661116ASolve difficult collection problemsShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseLesion
A reagent kit for the gene diagnosis of Leber's hereditary optical nerve (LHON) lesion which is caused by the mutations on 3 primary pathogenic sites (G11778A, G3460A and T14484C) is disclosed. Its detecting process includes such steps as designing and synthesizing the site specific PCR primer, using whole blood as DNA template, PCR amplification, and detecting said mutant sites of LHON patient.
Owner:FUJIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Methods, compositions, and kits for detecting allelic variants
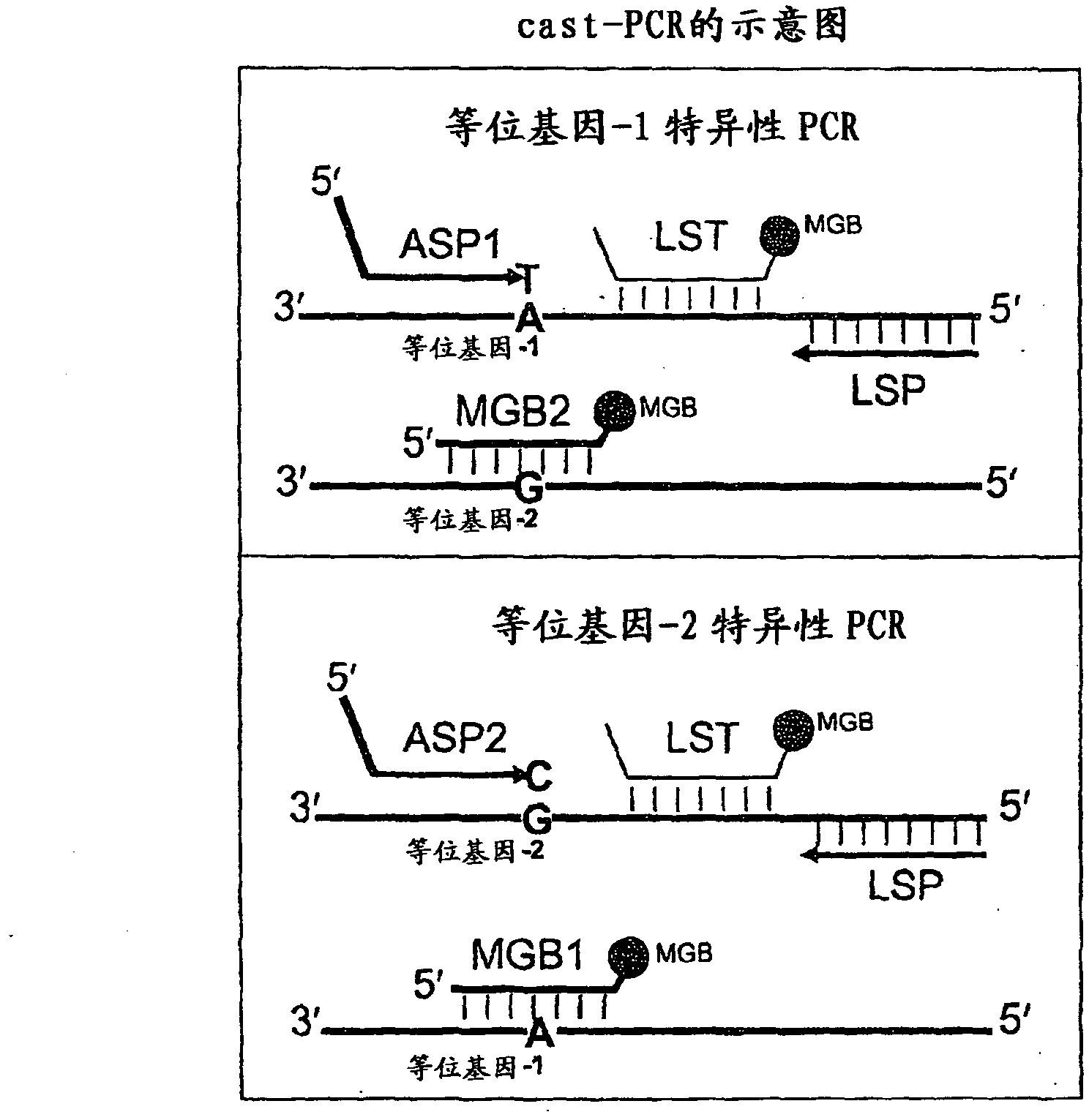
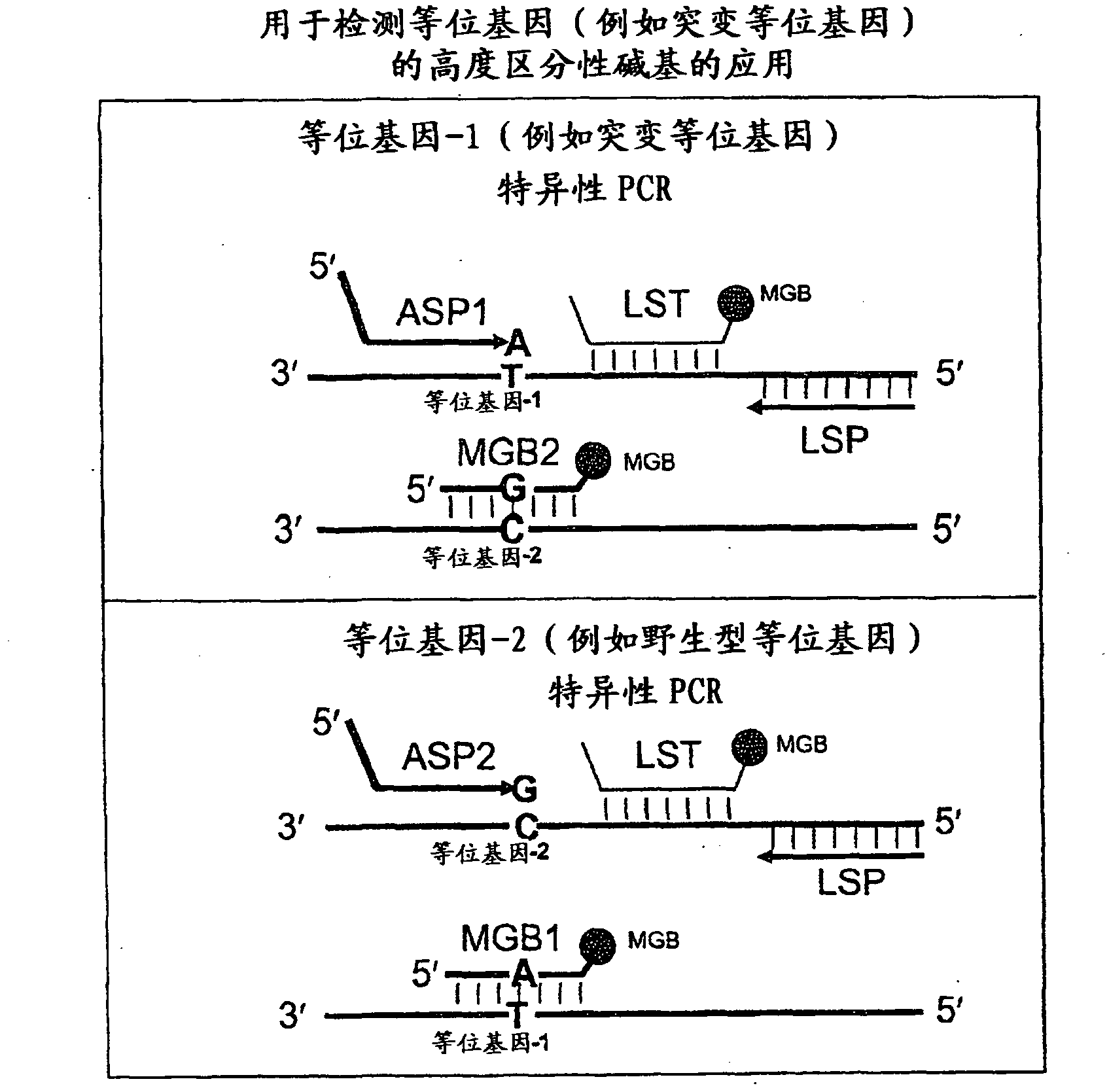
ActiveCN102428190AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNucleotideMutation detection
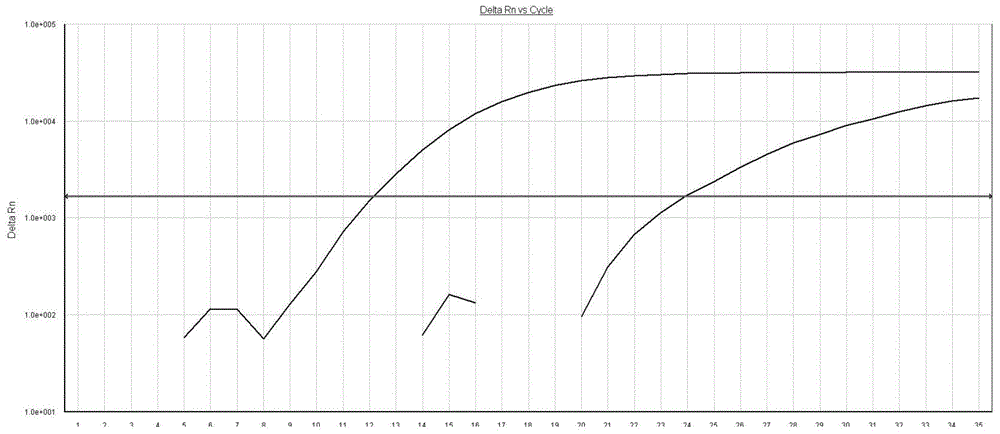
In some embodiments, the present inventions relates generally to compositions, methods and kits for use in discriminating sequence variation between different alleles. More specifically, in some embodiments, the present invention provides for compositions, methods and kits for quantitating rare (e.g., mutant) allelic variants, such as SNPs, or nucleotide (NT) insertions or deletions, in samples comprising abundant (e.g., wild type) allelic variants with high specificity and selectivity. In particular, in some embodiments, the invention relates to a highly selective method for mutation detection referred to as competitive allele-specific TaqMan PCR ('cast-PCR').
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Detection of nucleic acid polymorphism
InactiveUS20010046670A1Increases Tm distinctionOptimizes potential for allele discriminationMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyNucleotideFluorescence
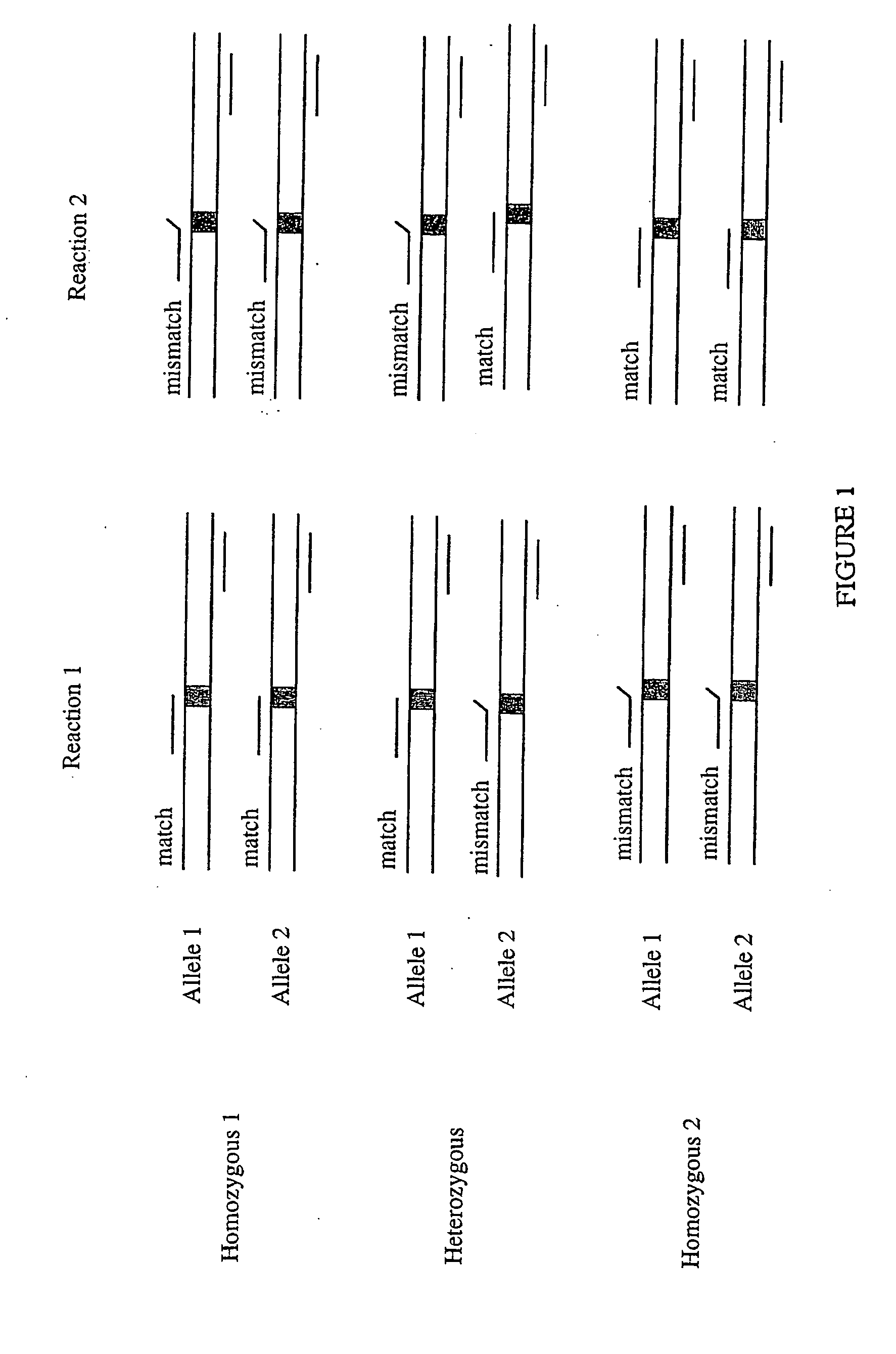
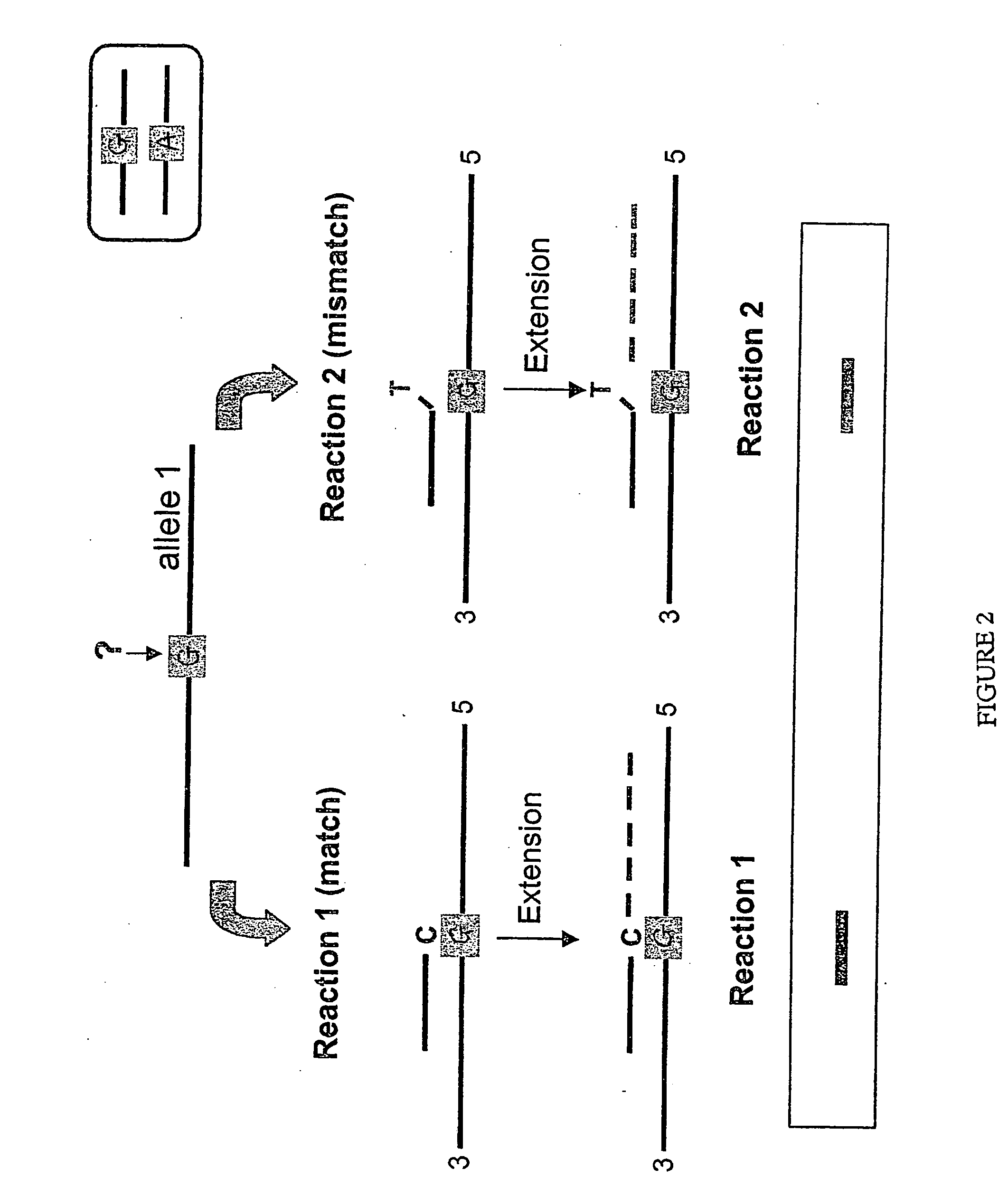
This document describes a method of detecting DNA variation by monitoring the formation or dissociation of a complex consisting of: (a) a single strand of a DNA sequence containing the locus of a variation, (b) an oligonucleotide or DNA analogue probe specific for one allele of the variation and capable of hybridizing to the single strand (a) to form a duplex, a marker specific for the duplex structure of (a) plus (b) which forms a complex with the said duplex and reacts uniquely when interacting within the duplex, which comprises continually measuring an output signal indicative of interaction of the marker with duplex formed from the strand (a) and probe (b) and recording the conditions at which a change in reaction output signal occurs which is attributable to formation or dissociation of the complex and is thereby correlated with the strength with which the probe (b) has hybridized to the single strand (a). The method, termed Dynamic Allele Specific Hybridization (DASH), scores nucleotide differences in DNA sequences. Fluorescent markers are convenient as markers to underline variations in fluorescence resulting from denaturization or hybridization of the complex.
Owner:DYNAMETRIX
Genotyping by polymerase binding
A method for identifying target alleles, that includes steps of (a) forming a plurality of stabilized ternary complexes at a plurality of features on an array, wherein the stabilized ternary complexes each has a polymerase, a template nucleic acid having a target allele of a locus, a primer hybridized to the locus, and a next correct nucleotide having a cognate in the locus, wherein either (i) the primer is an allele-specific primer having a 3′ nucleotide that is a cognate nucleotide for the target allele, or (ii) the primer is a locus-specific primer and the next correct nucleotide hybridizes to the target allele; and (b) detecting stabilized ternary complexes at the features, thereby identifying the target alleles.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Markers associated with the therapeutic efficacy of glatiramer acetate
InactiveUS20100285600A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingImmunologic disordersCD86
The present invention is directed to methods and kits based, at least in part, on the identification of allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness to glatiramer acetate for the treatment of autoimmune disorders, such as relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. The allele-specific responsiveness or non-responsiveness is based on polymorphisms in the following genes, CTSS, MBP, TCRB, CD95, CD86, IL-1R1, CD80, SCYA5, MMP9, MOG, SPP1 and IL-12RB2.
Owner:TEVA PHARMA IND LTD
Allele-specific mutation detection assay
InactiveUS20060088872A1Rapid responseDifference in efficiencyHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific detectionOligomer
The present invention relates to a method of detecting a base at a pre-determined position in a nucleic acid molecule by performing enzymatic detection reactions using base-specific detection oligomers, where each oligomer is specific for a particular base at the predetermined position, and then comparing the enzymatic detection reactions to determine which base is present at the position, with an enzyme-disabling agent being present during the enzymatic detection reaction. In preferred embodiments the enzymatic detection reaction is an oligomer elongation extension reaction, catalysed by, among others, polymerase or ligase. Also disclosed are methods of performing the assay in a liquid phase and on microarrays.
Owner:AHMADIAN AFSHIN +1
Compositions and Methods for Making Therapies Delivered by Viral Vectors Reversible for Safety and Allele-Specificity
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Double-probe gene mutation detecting method based on allele special amplification as well as special chip and kit thereof
ActiveCN101619352AEasy to detectAvoid the hassle of markingMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotypeOligonucleotide
The invention relates to a method for identifying gene mutation types in the field of gene analysis as well as a special chip and a kit thereof. The gene mutation detecting method comprises the following steps: taking a genome to be detected from a human tissue as a template, carrying out multiple allele special PCR amplification by a primer group that is designed aiming at special mutant sites and DNA polymerase without 3'-5' end exonclease activity, then hybridizing the obtained PCR product and an oligonucleotide probe (allele special probe) on the gene chip, and confirming mutation types of all gene sites according to the hybridizing result. The allele special probe is designed aiming at special gene types of gene mutant sites to be detected. The invention can detect gene mutations in comprehensive, systemic and high-flux ways and has light environmental pollution as well as simple and rapid operation compared with PCR-RFLP and a sequencing method.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Allele-specific sequence variation analysis
InactiveUS20050089904A1Reduce leakageImprove allele-specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationGenomic DNAMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
Fragmentation-based methods and systems, particularly mass spectrometry based methods and systems, for the analysis of sequence variations including haplotypes are provided. Also provided are methods for obtaining a specific allele from a nucleic acid mixture, such as genomic DNA.
Owner:AGENA BIOSCI
AS-PCR (allele-specific polymerase chain reaction) primer design method, gene mutation detection method and kit
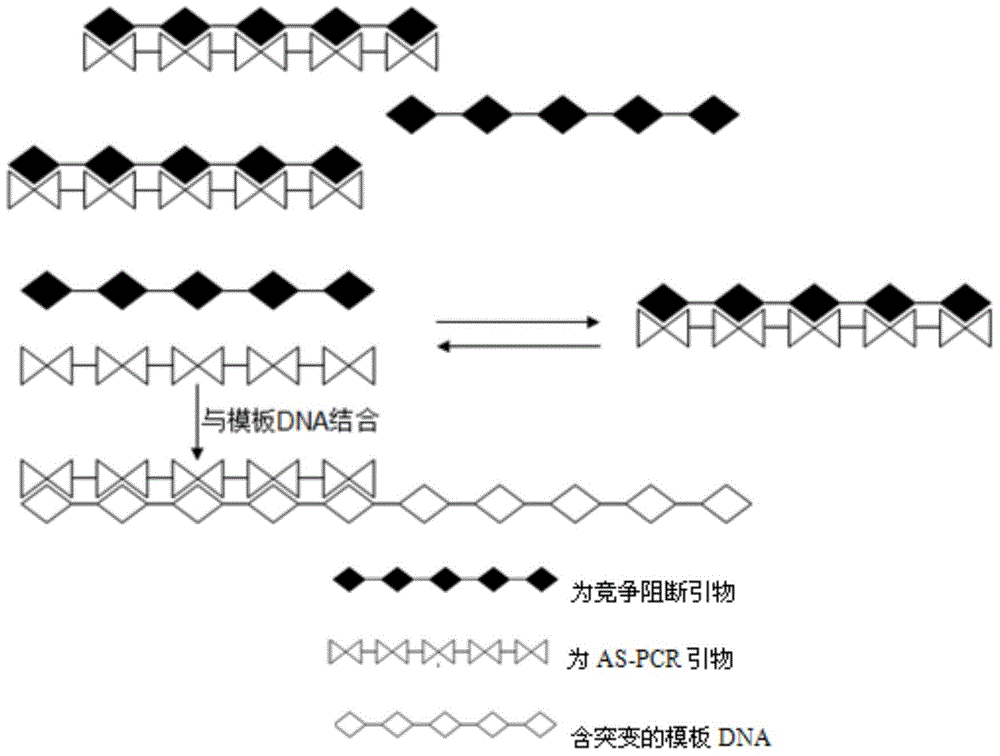
InactiveCN104611427AStrong specificityImprove featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPolymerase LOligonucleotide
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to an AS-PCR (allele-specific polymerase chain reaction) primer design method, a gene mutation detection method and a kit. The AS-PCR primer design method comprises the following steps: (1), an AS-PCR primer is designed for a target sequence containing a to-be-detected allele mutation region; (2), a competition blocking primer is designed for the AS-PCR primer and adopts oligonucleotide in reverse complement with the AS-PCR primer. According to the gene mutation detection method, the AS-PCR primer and the competition blocking primer have a PCR amplification reaction. The kit comprises the AS-PCR primer, the competition blocking primer, a TaqMan probe, an internal control primer, an internal control probe, polymerase, dNTP (deoxynucleotide) and a buffer solution. The AS-PCR primer design method, the gene mutation detection method and the kit have the advantage that the difference of specificity of the AS-PCR primers on mutation sites due to strong and weak mismatch of the mutation sites is reduced effectively.
Owner:江苏宏泰格尔生物医学工程有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
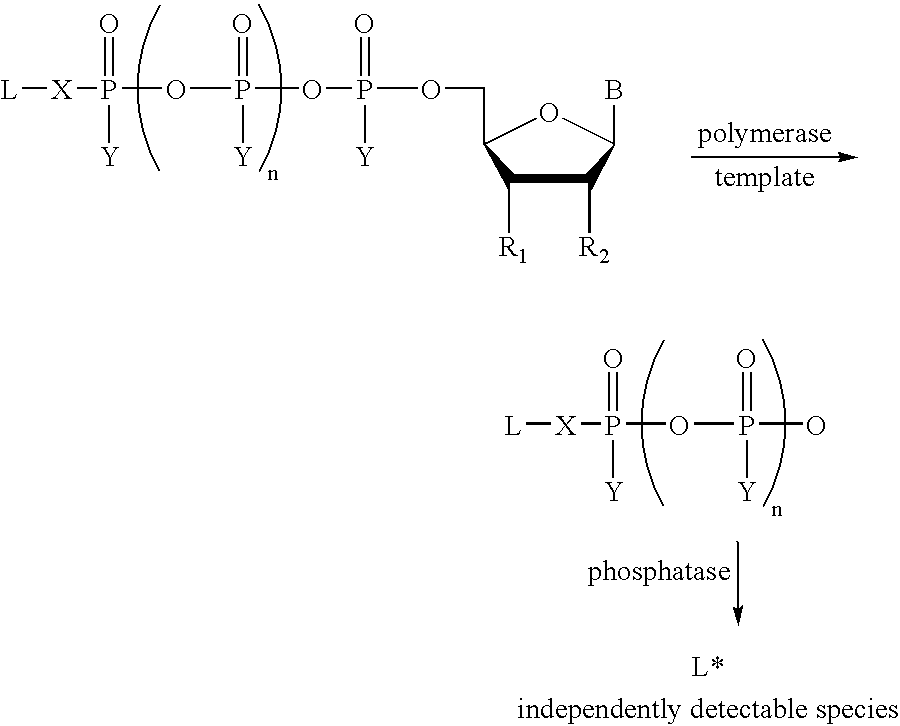







![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000011.PNG)
![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000012.PNG)
![Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer Primer set for detecting functional genes of wheat on basis of KASP [competitive allele specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction)] technology and application of set primer](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/935db461-2e79-4d64-a703-4ba19d999536/HDA0000809386820000013.PNG)