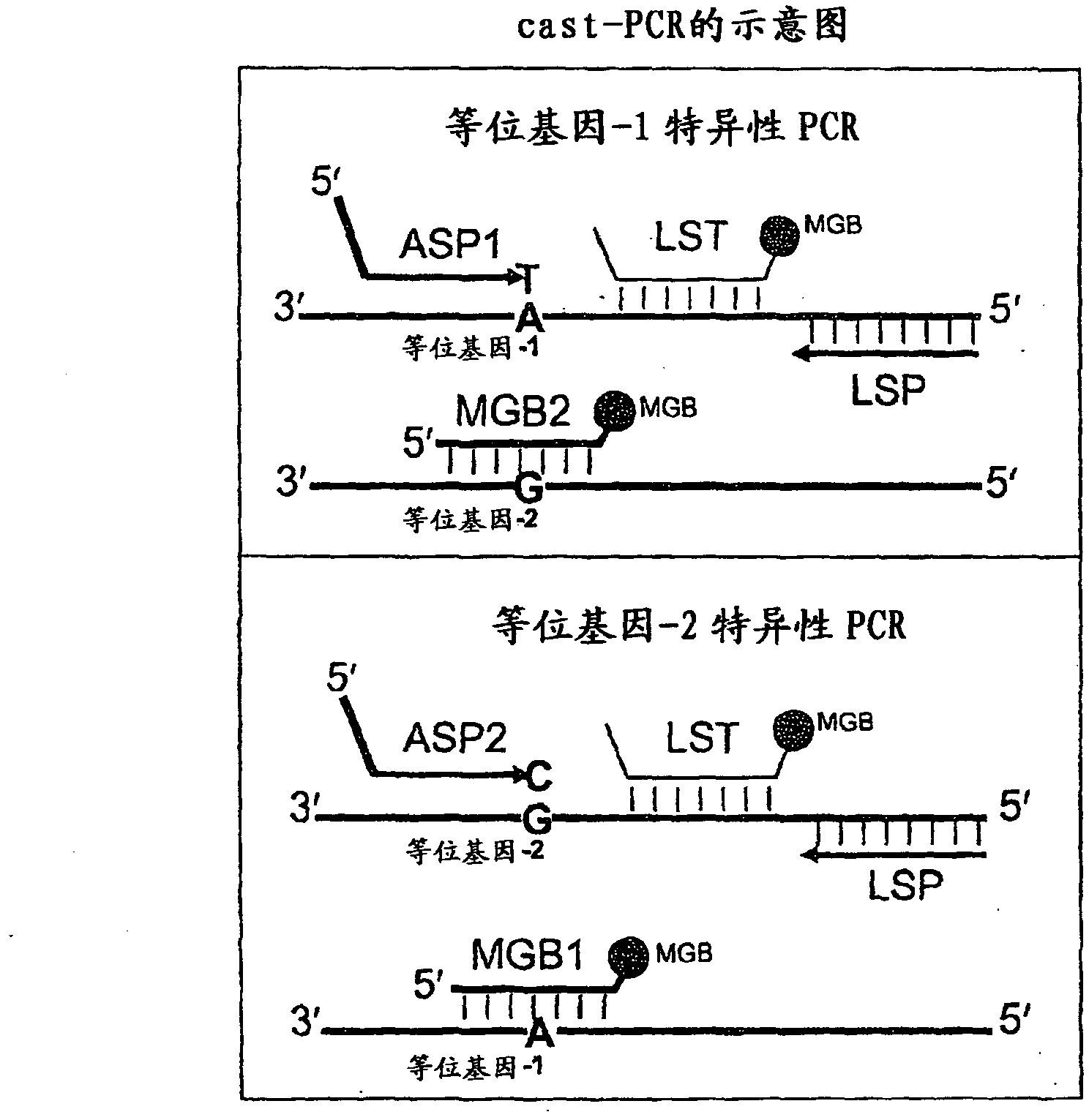
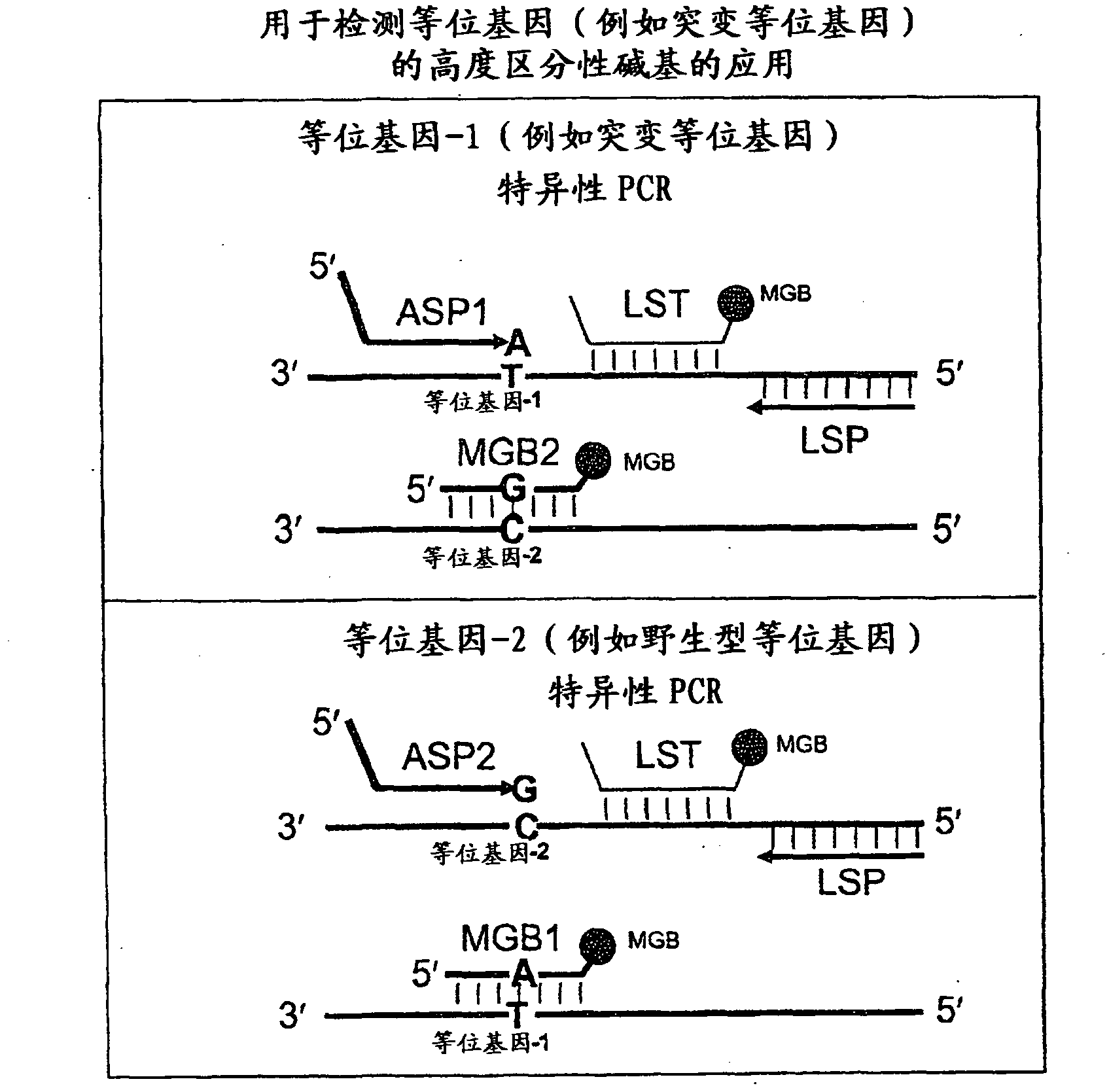
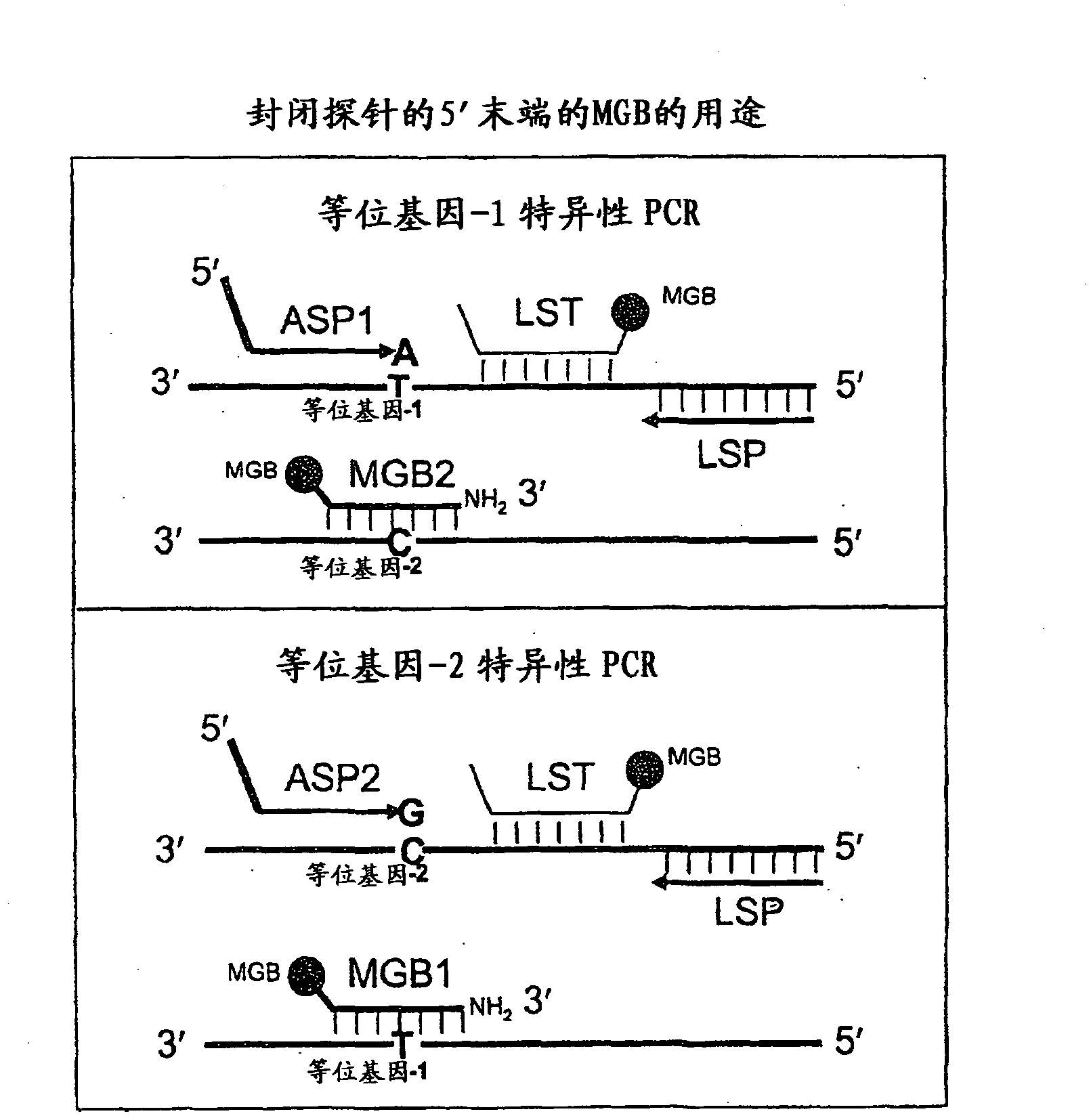
Methods, compositions, and kits for detecting allelic variants
An allele, allele-specific technology, applied in the field of detection of allelic variants, compositions and kits, can solve the problems of limited selectivity and inappropriateness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0240] Example 1: Tailed primers improve discrimination of allelic variants
[0241] The following examples demonstrate that the use of tail-containing allele-specific primers significantly improves discrimination of allelic variants.
[0242] In traditional AS-PCR, discrimination of 3' nucleotide mismatches is highly dependent on the sequence surrounding the SNP and the nature of the allele. The ΔCt varies between amplification reactions with matched and mismatched primers. To improve the discrimination between the amplification of matched and mismatched sequences, allele-specific primers were designed to contain a tail at their 5' end and then tested for their suitability in the AS-PCR assay.
[0243] Assays were performed using the general experimental design and reaction conditions described above (except that blocking probes were not included and tailed or non-tailed allele-specific primers were added), using 0.5 ng / uL of genomic DNA as A nucleic acid template, the geno...
Embodiment 2
[0255] Example 2: Low primer concentrations improve discrimination of allelic variants
[0256] Using the general experimental design and reaction conditions described above, in the presence of 1,000,000 copies of plasmid DNA containing multiple SNP target sequences (see Table 1) and 200 nM or 800 nM tailed ASP (as indicated), To measure. according to Figure 11A Design assay primers and probes with the indicated sequences.
[0257] The effect of tailed ASP concentration on discrimination of allelic variants is summarized in Table 5. The ΔCt between amplification reactions of matched and mismatched primers demonstrates that lower tailed ASP concentrations improve discrimination of allelic variants.
[0258] Table 5: Assay results using different concentrations of tailed allele-specific primers
[0259]
Embodiment 3
[0260] Example 3: Primers designed with reduced Tm improve discrimination of allelic variants
[0261] Using the general experimental design and reaction conditions as described above, tailing with a higher Tm (~57°C) was used in the presence of 1,000,000 copies of plasmid DNA containing multiple SNP target sequences (see Table 1). or tailed ASP with a lower Tm (~53°C). according to Figure 11B Design assay primers and probes for sequences indicated in -E (for higher Tm ASPs, see Figure 11B ; for lower Tm ASP, see Figure 11C ).
[0262] The effect of Tm of allele-specific primers on discrimination of allelic variants is summarized in Table 6. The ΔCt of allele-specific primers with lower Tm was significantly higher than that of allele-specific primers with higher Tm. Allele-specific primers designed with reduced Tm improved discrimination of the allelic variants by up to 118-fold in some cases, with an average of about 13-fold difference.
[0263] Table 6: [Delta]Ct va...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com