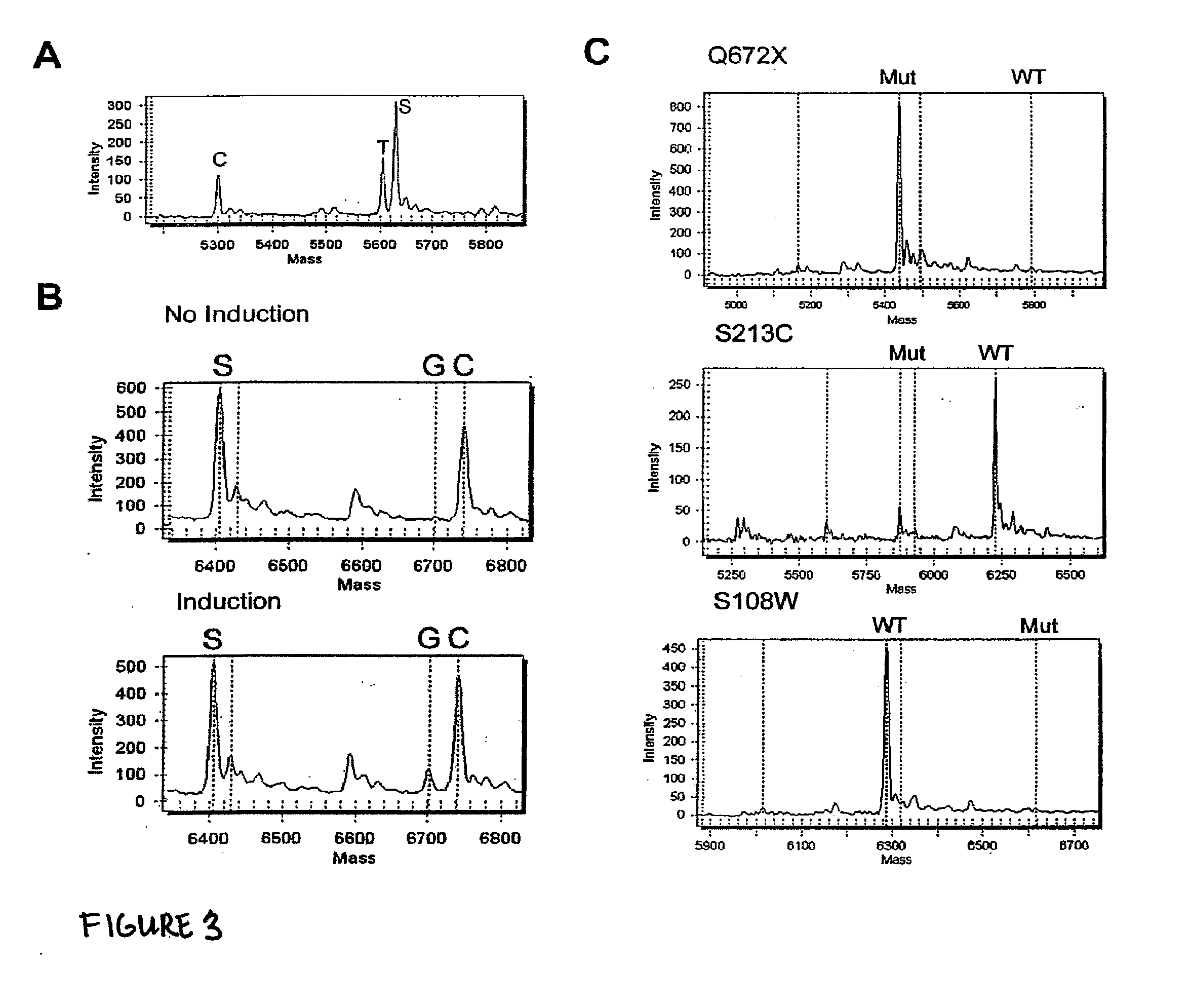
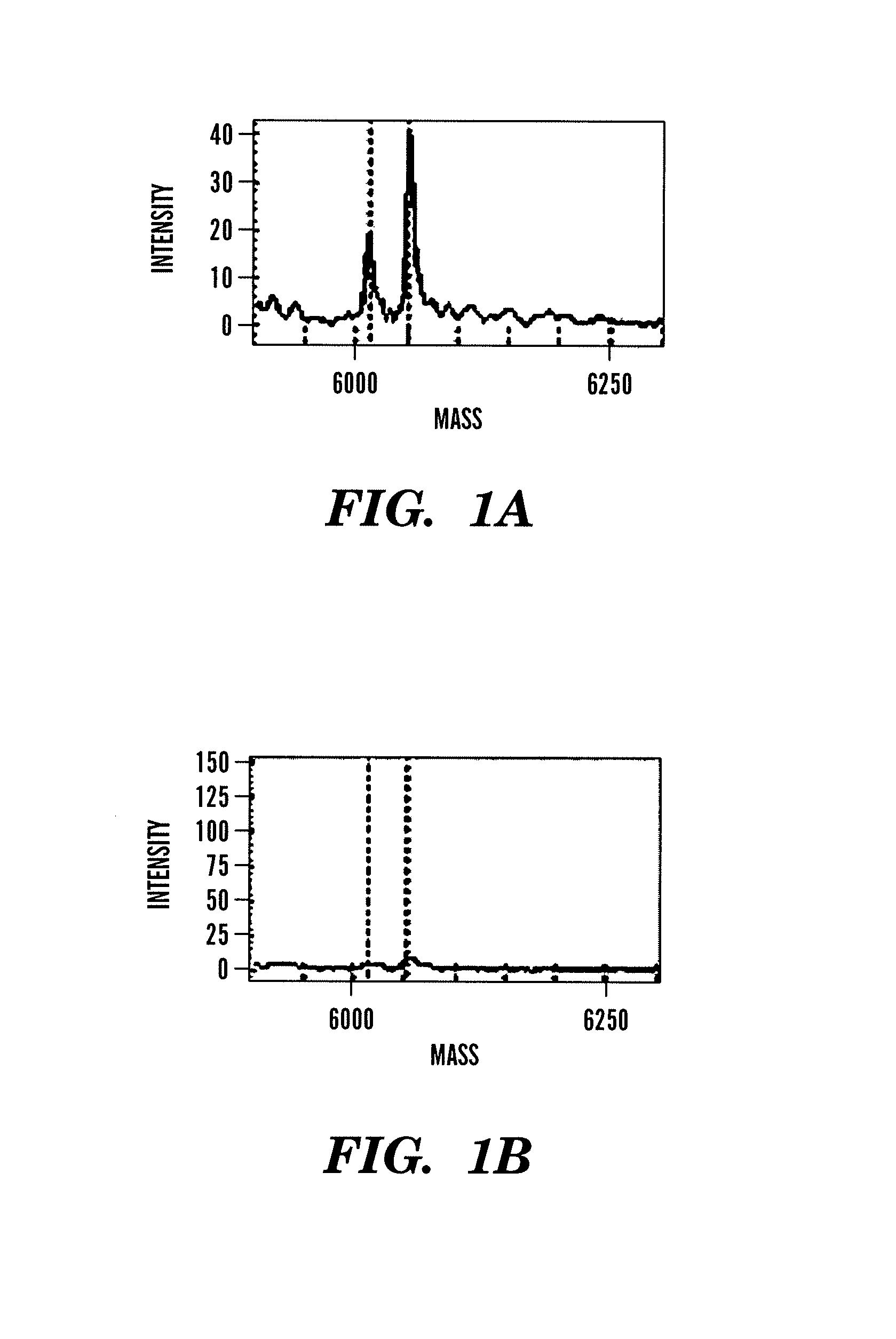
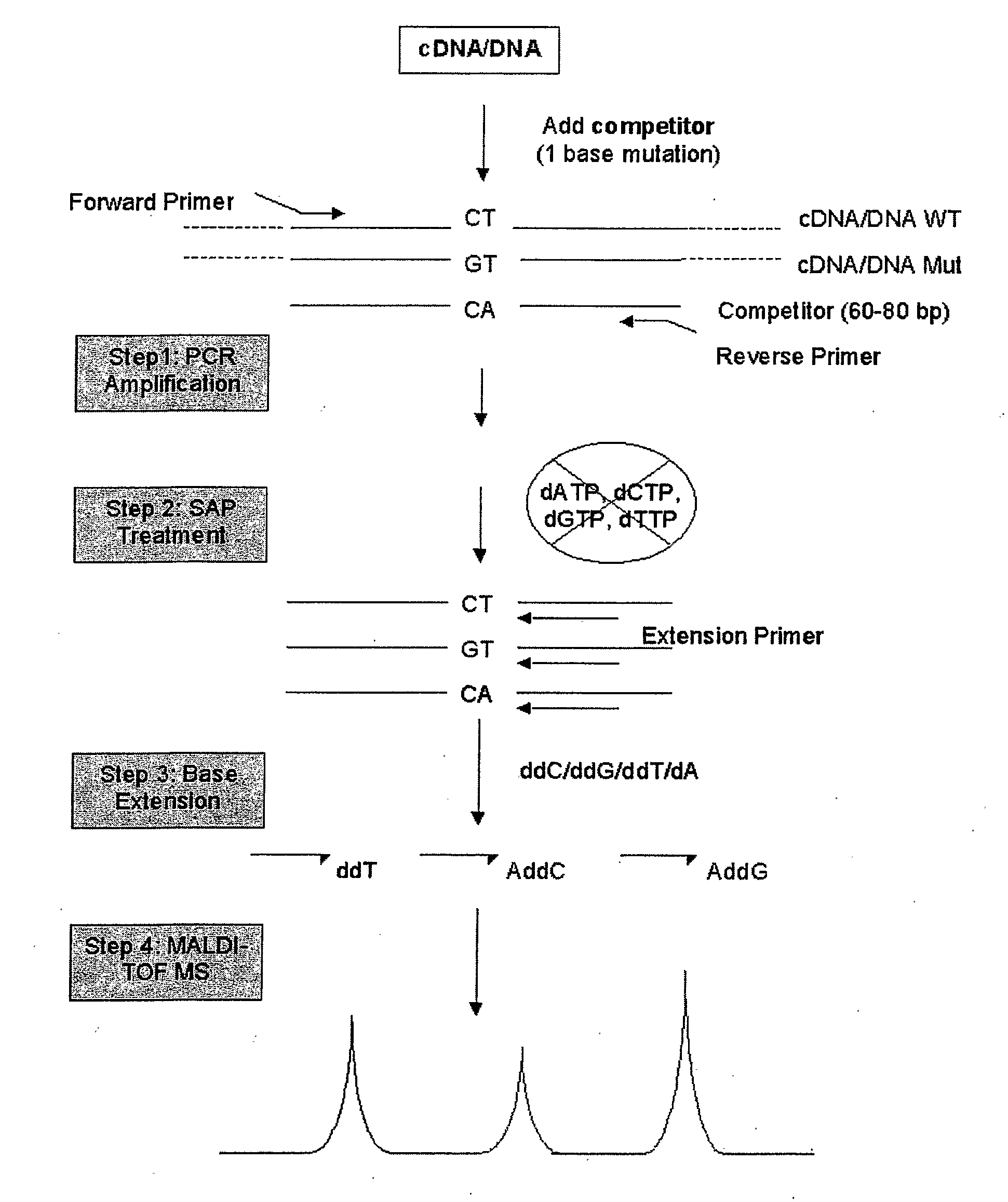
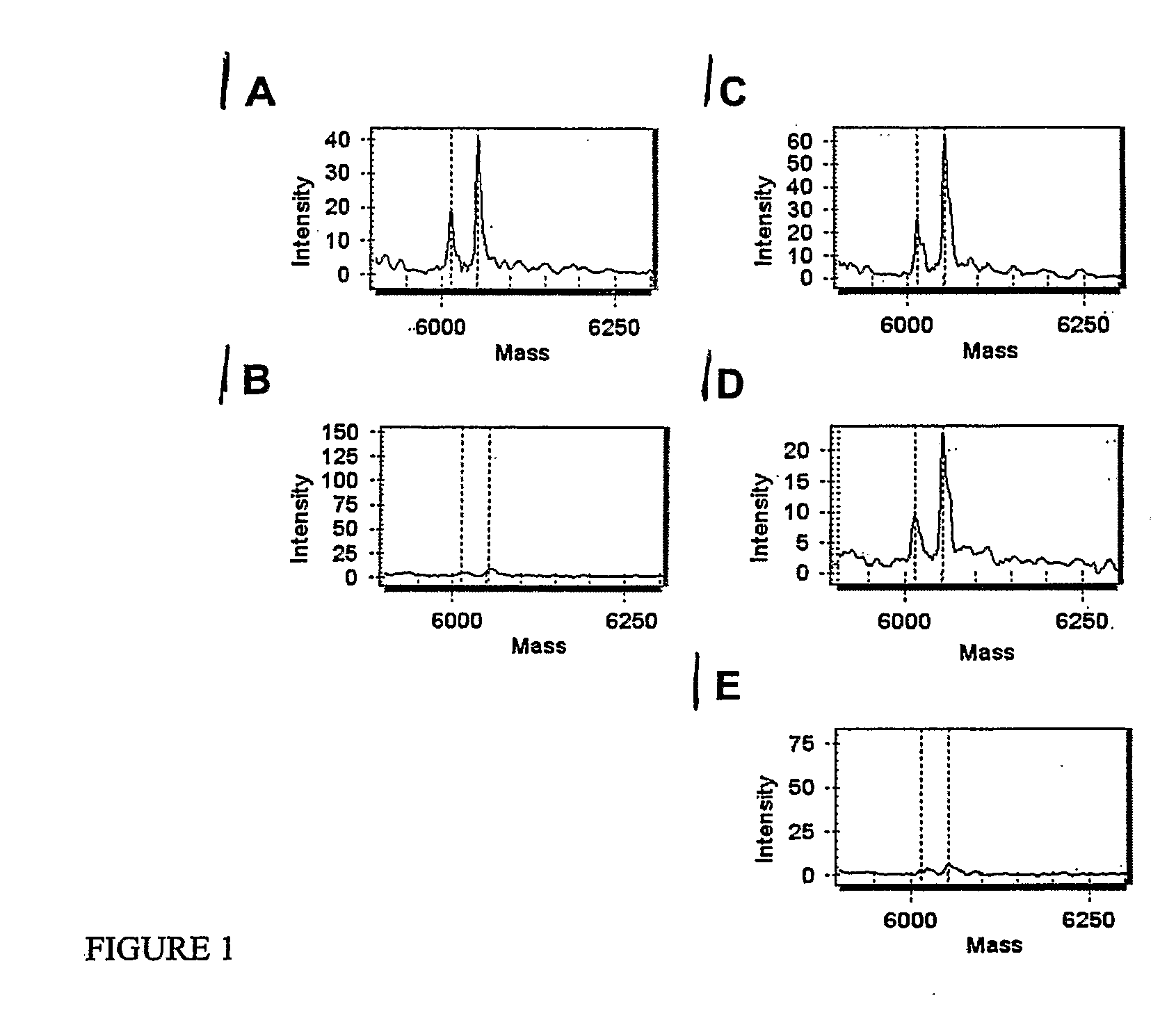
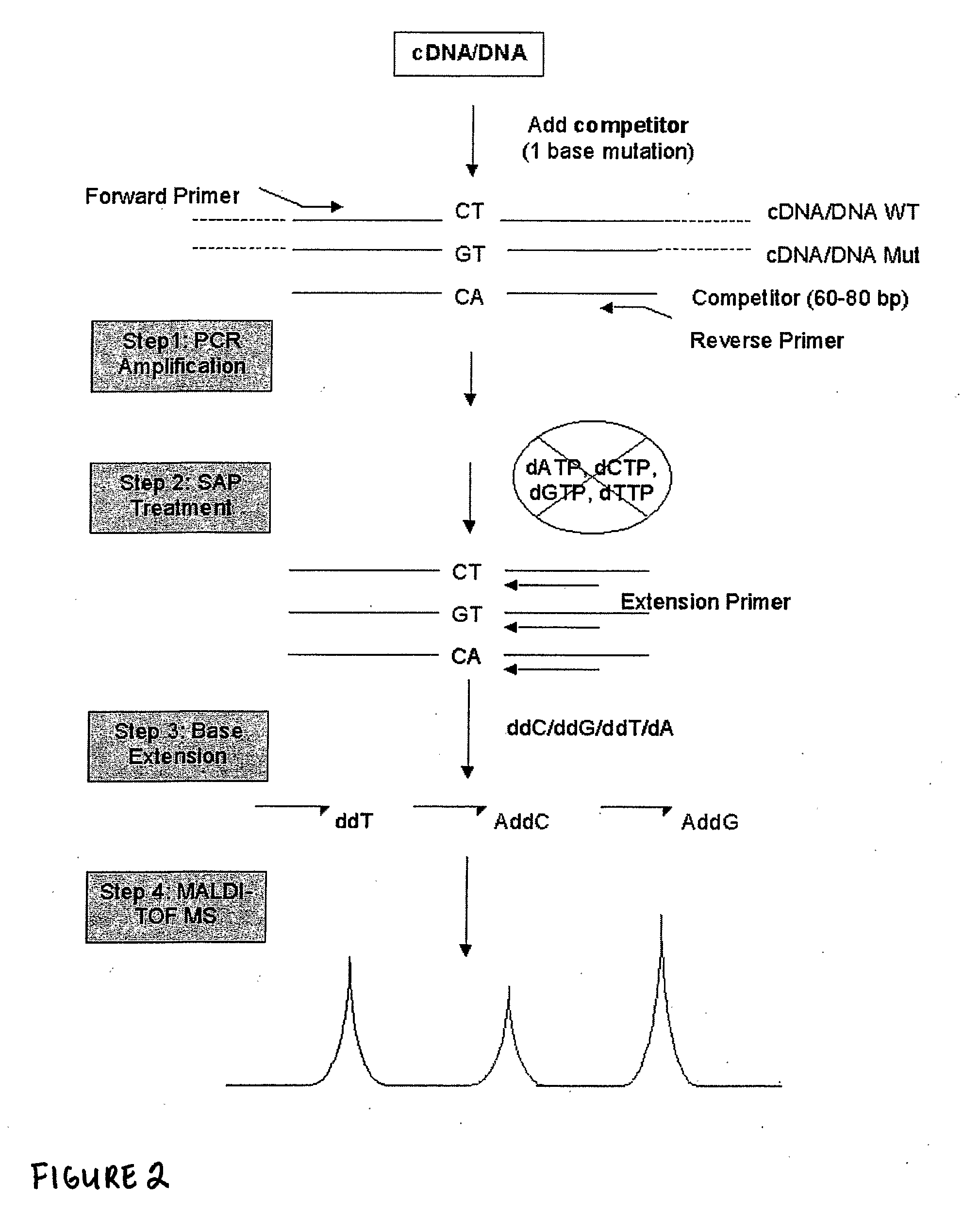
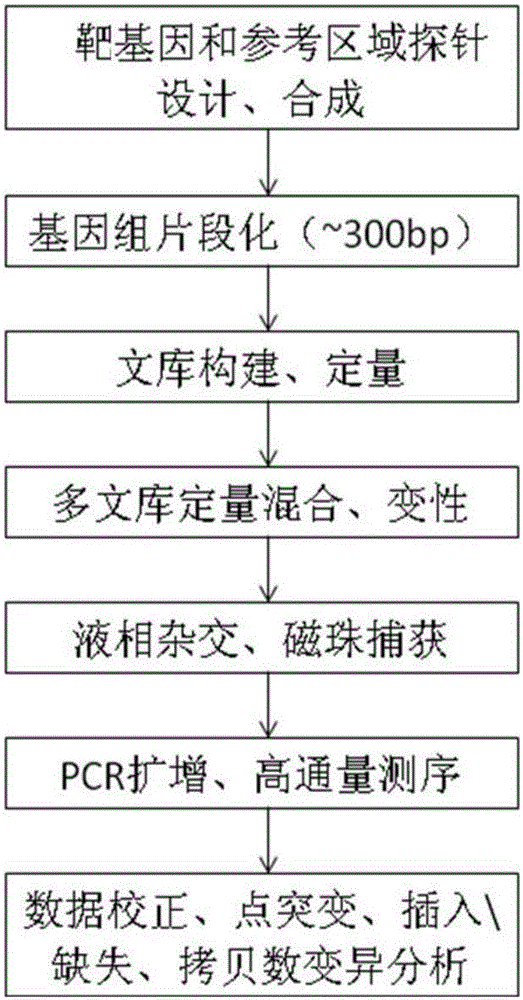
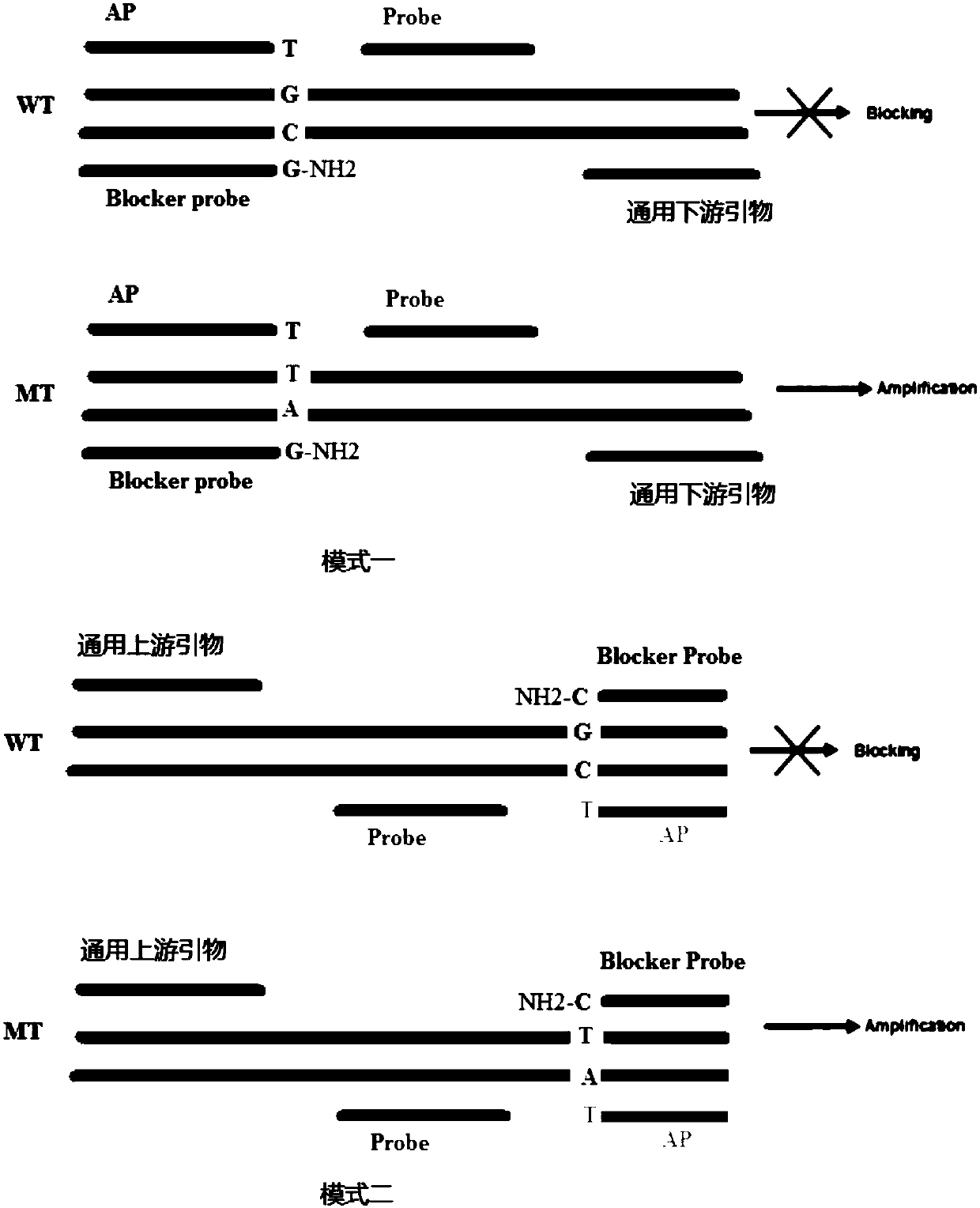
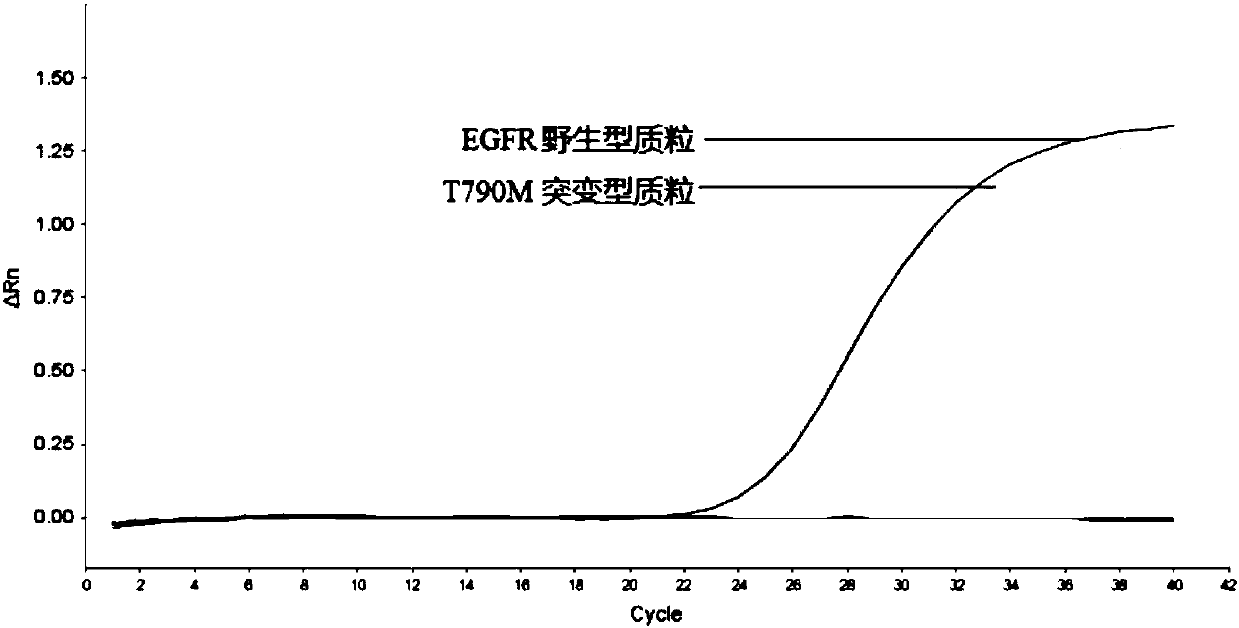
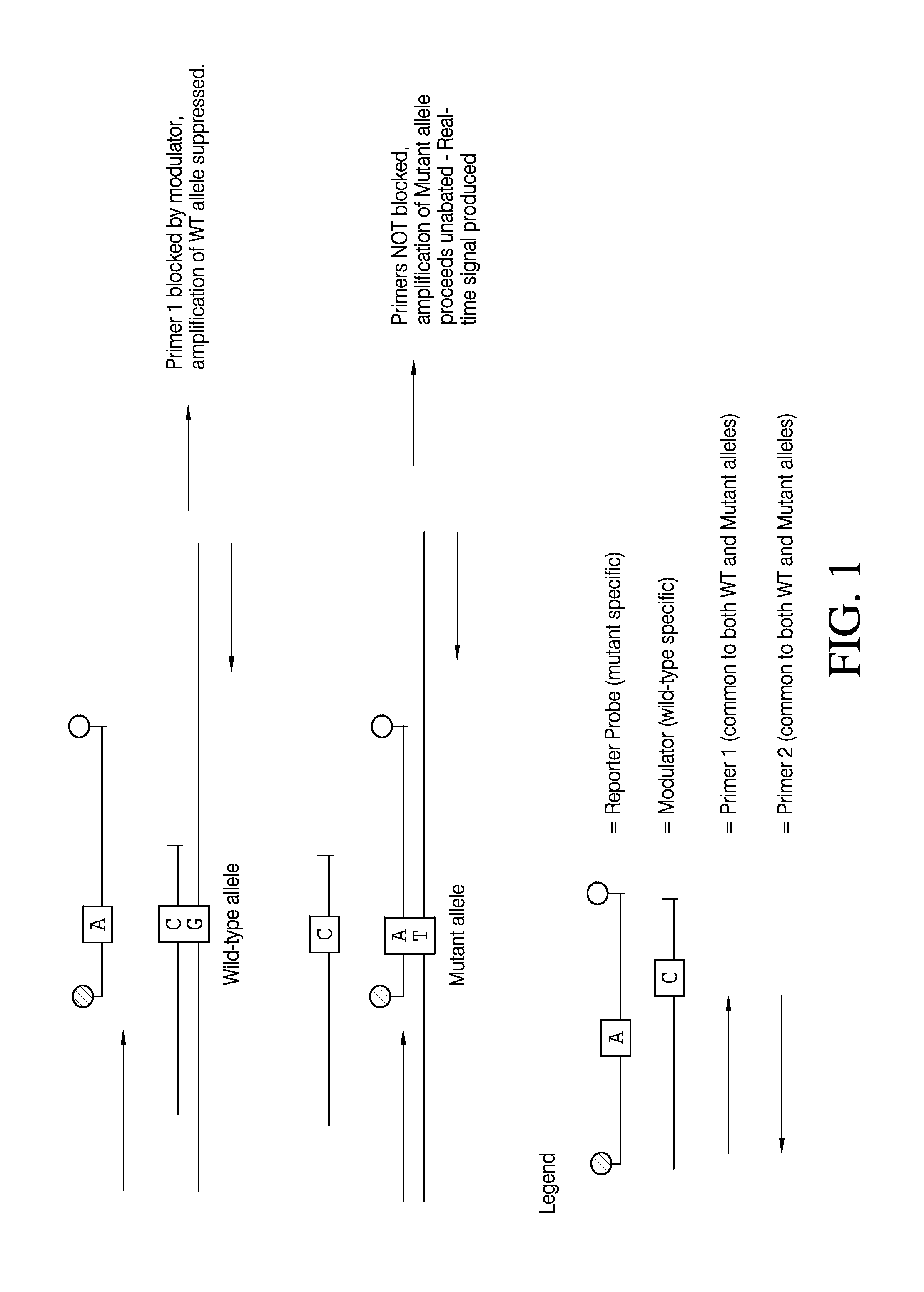
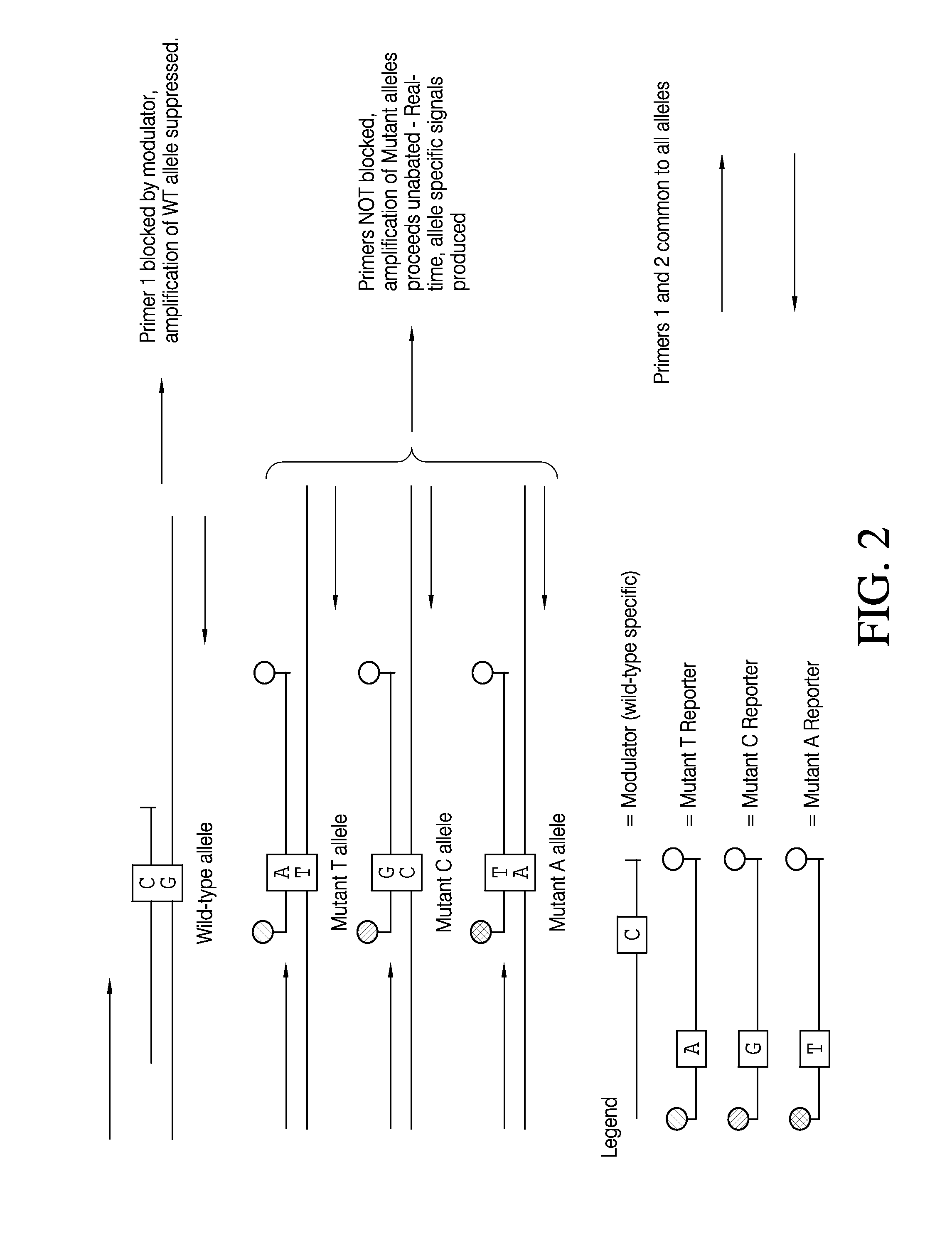
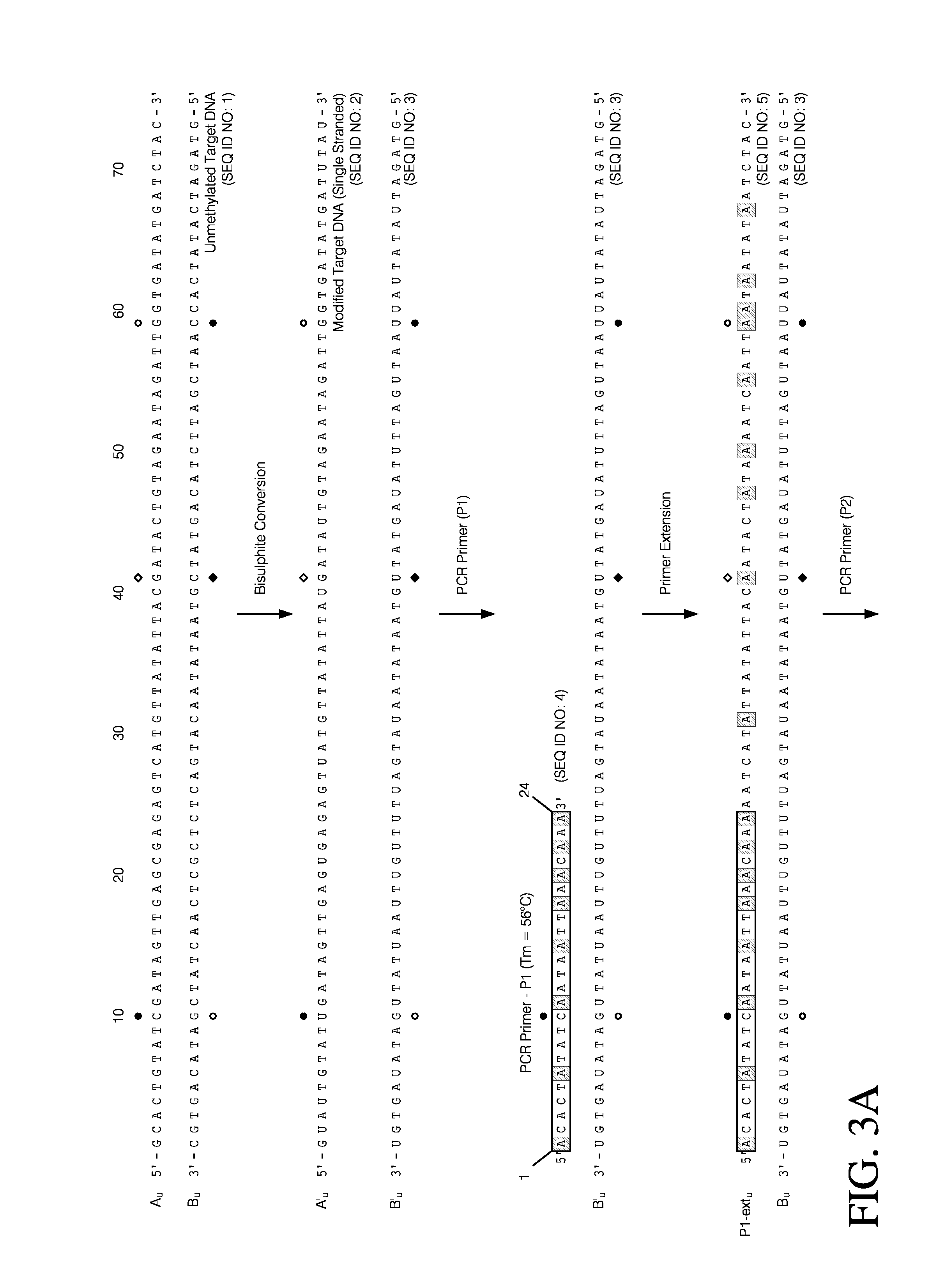
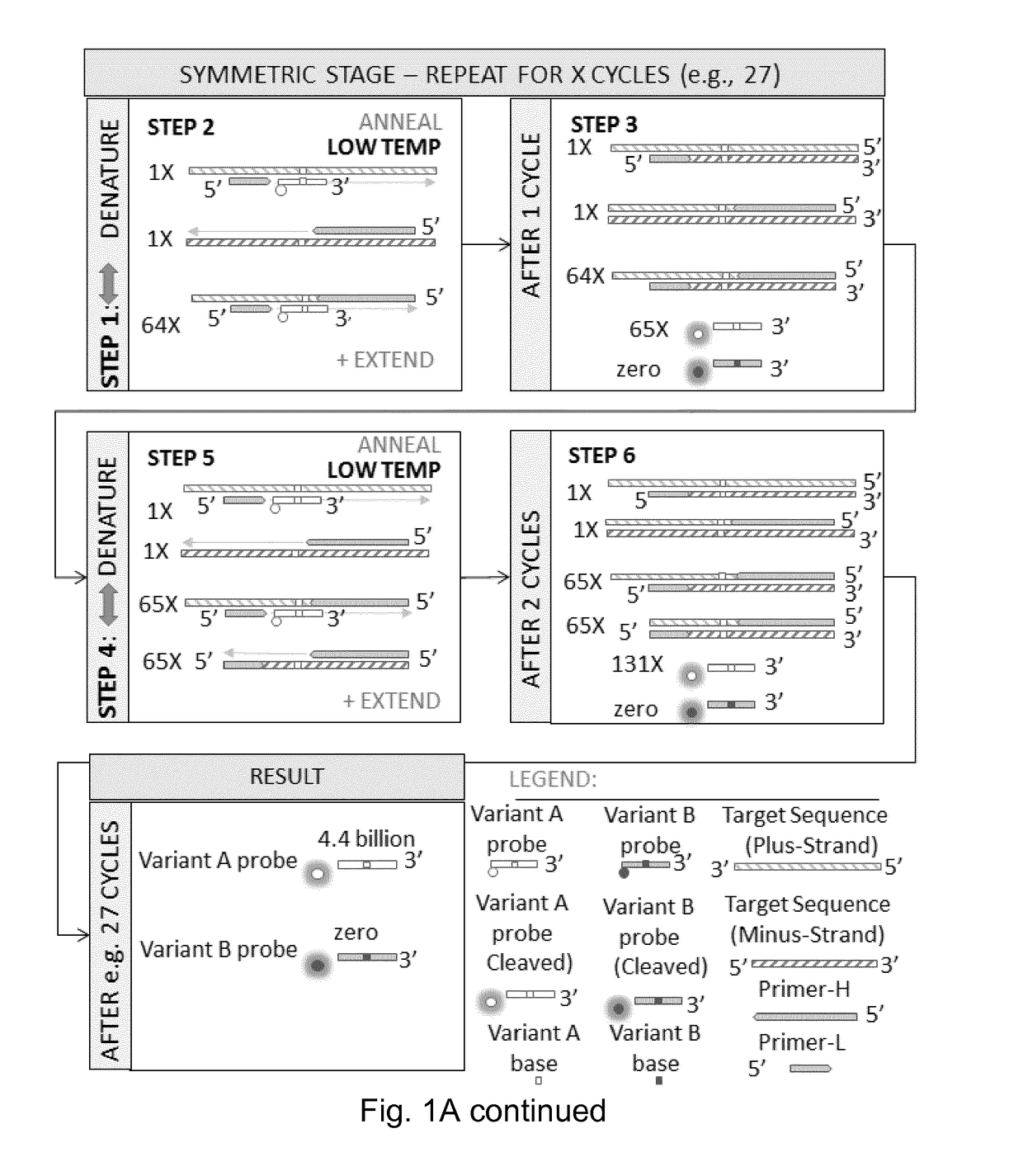
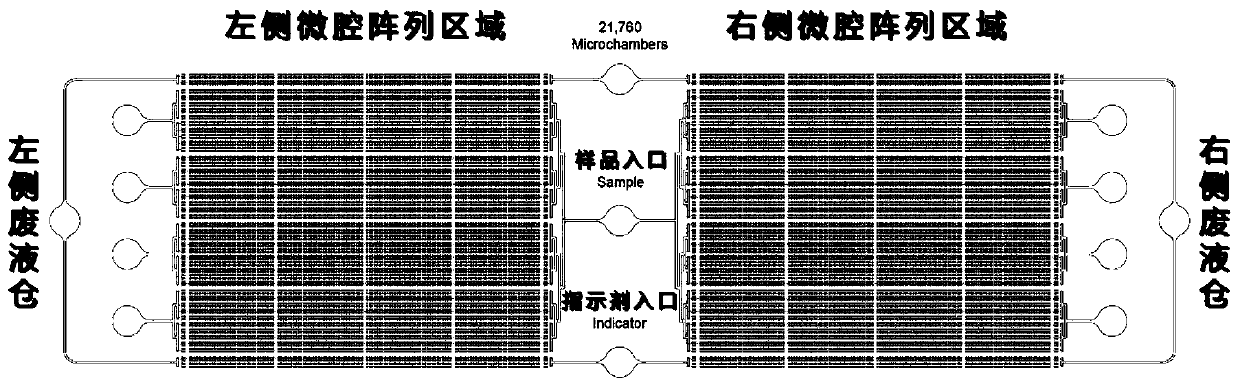
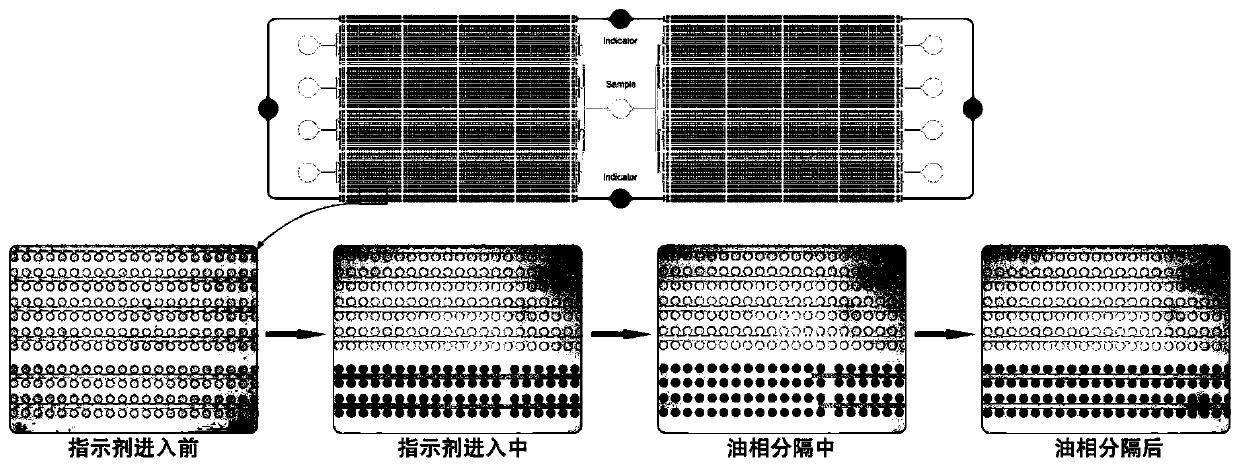
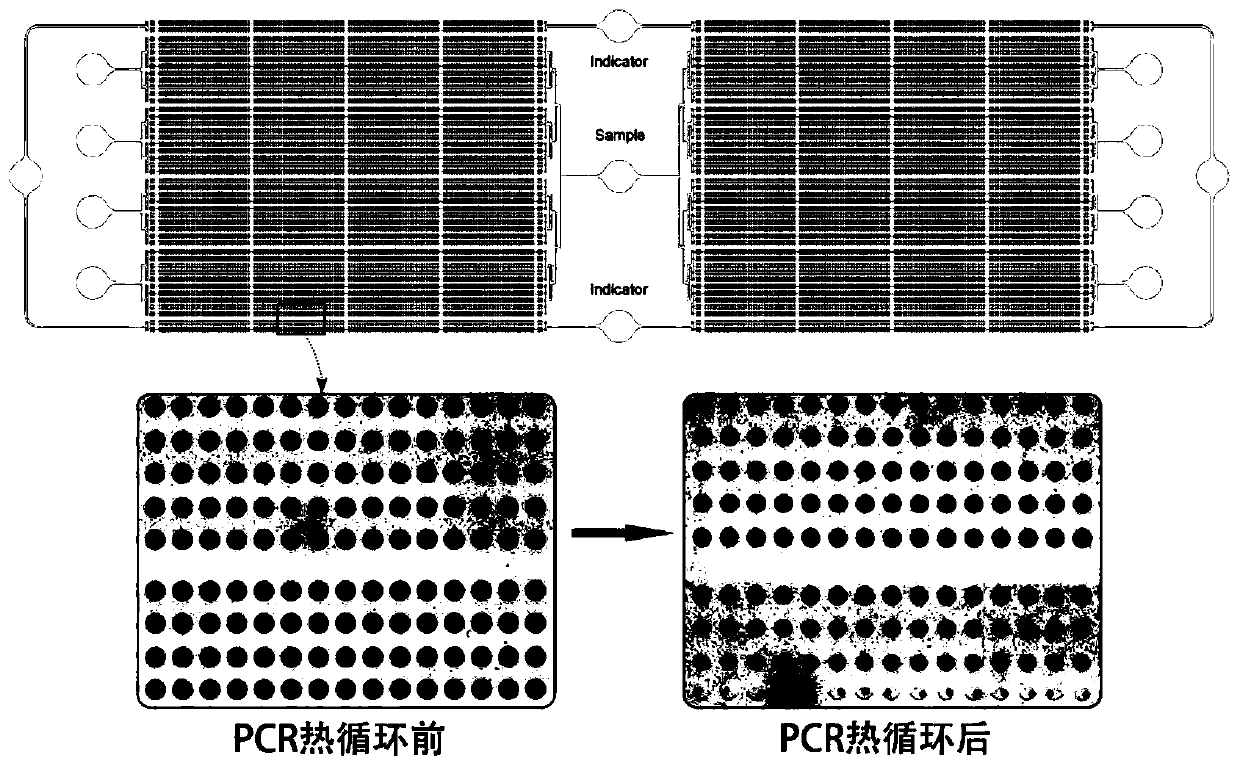
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "Rare mutations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mutations in the NTHL1 gene are very rare. A mutation in the NTHL1 gene only leads to cancer when the mutation is inherited from both parents.
Method and compositions for detection and enumeration of genetic variations
ActiveUS20070065823A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific populationFluorescence
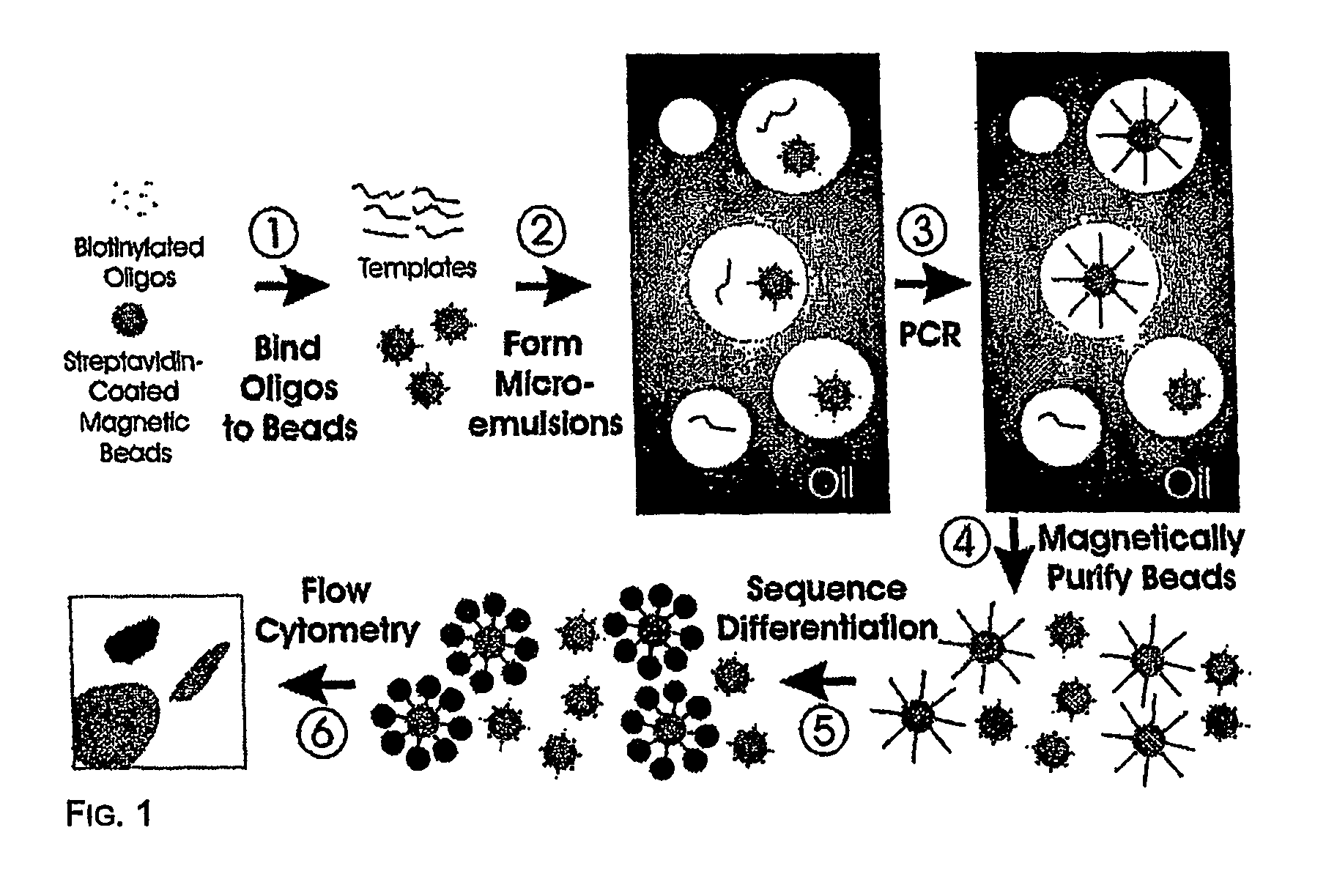
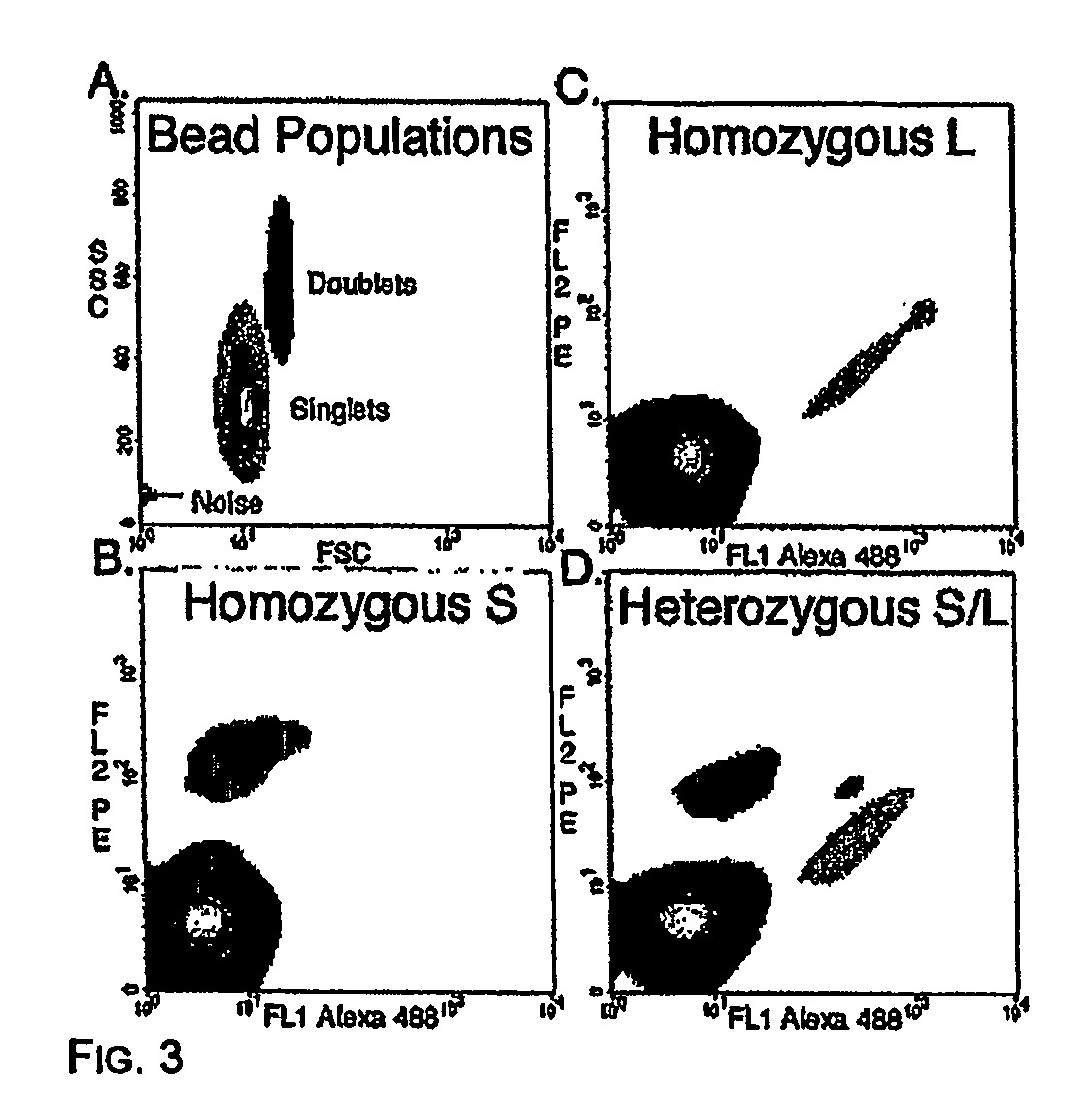
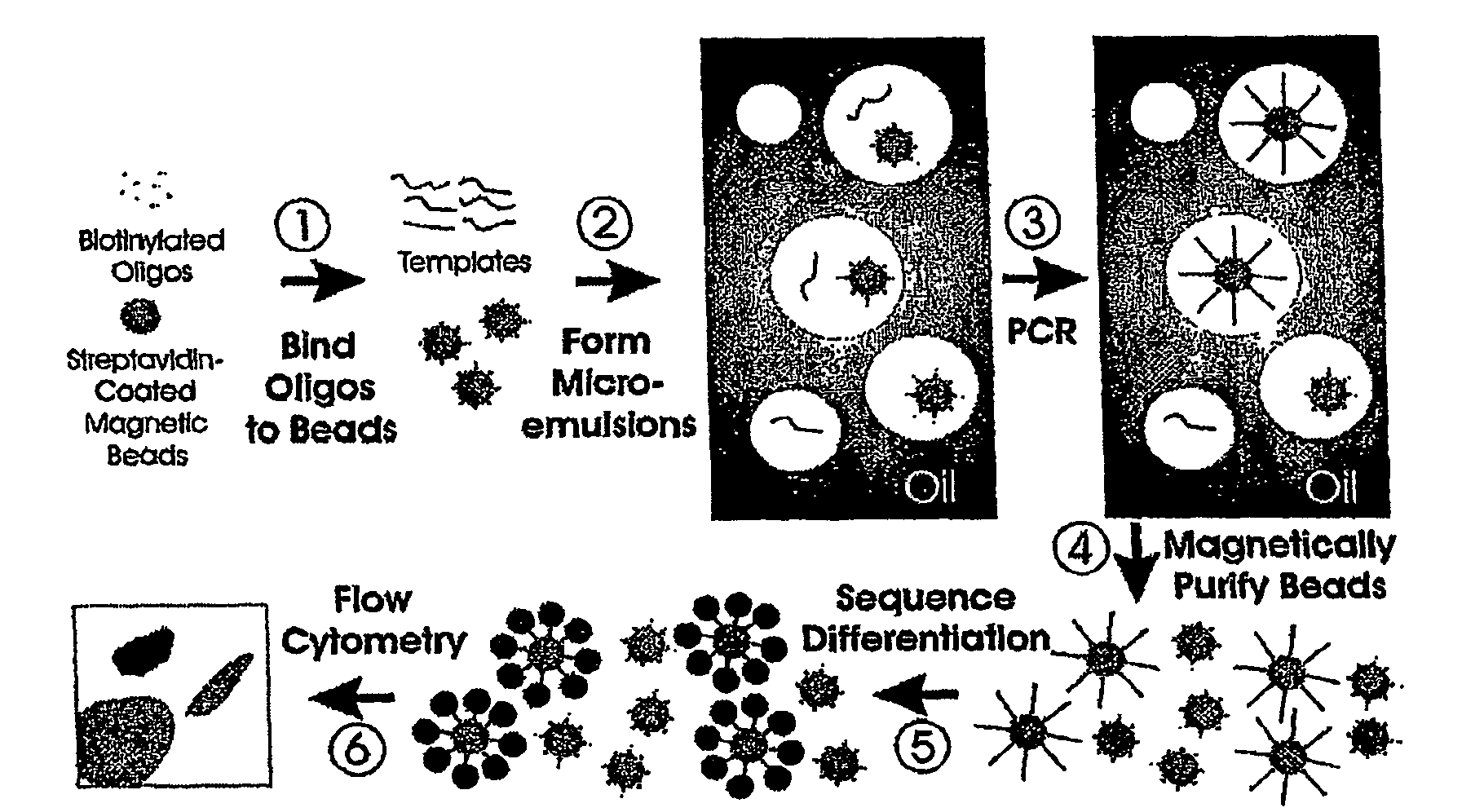
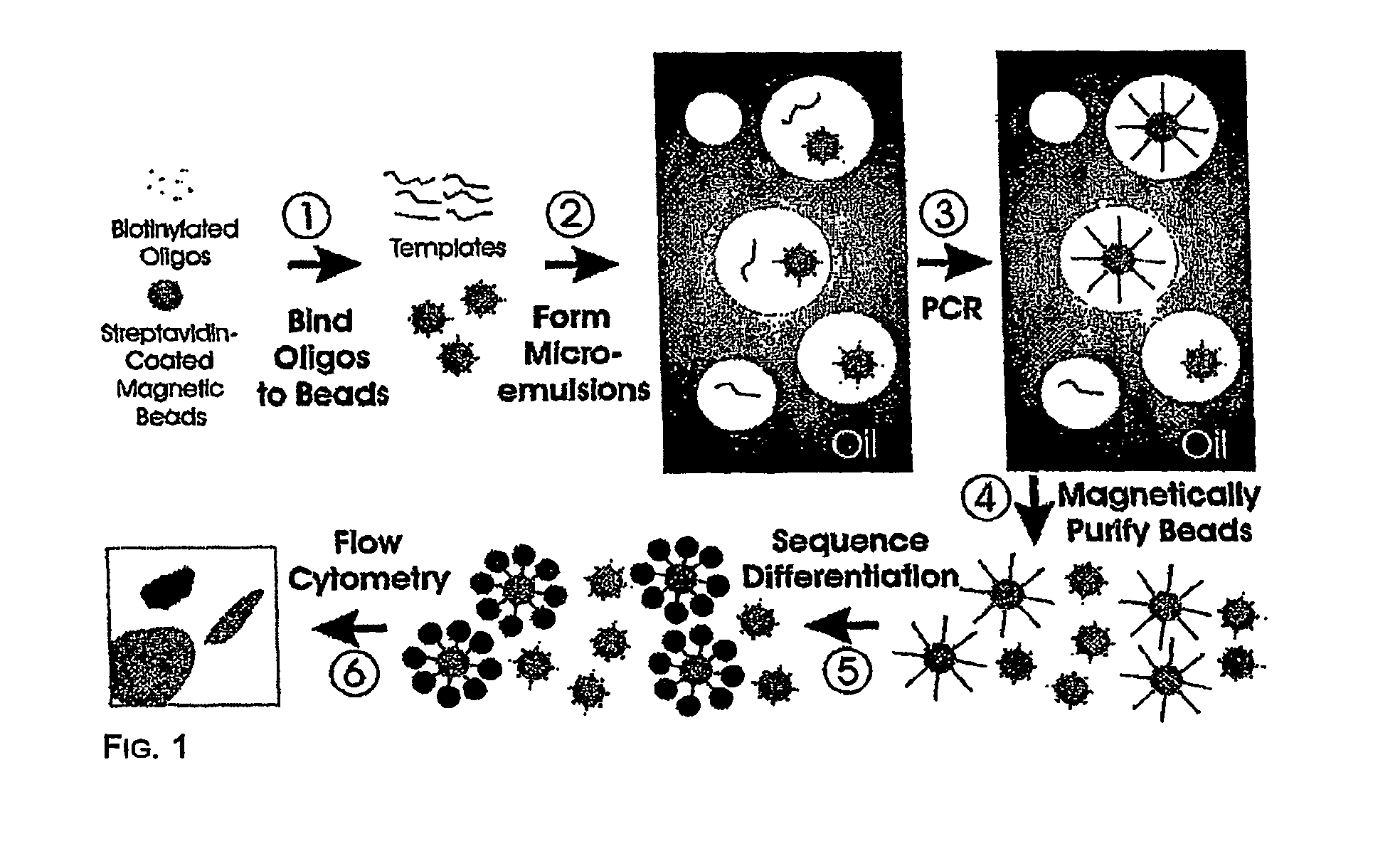
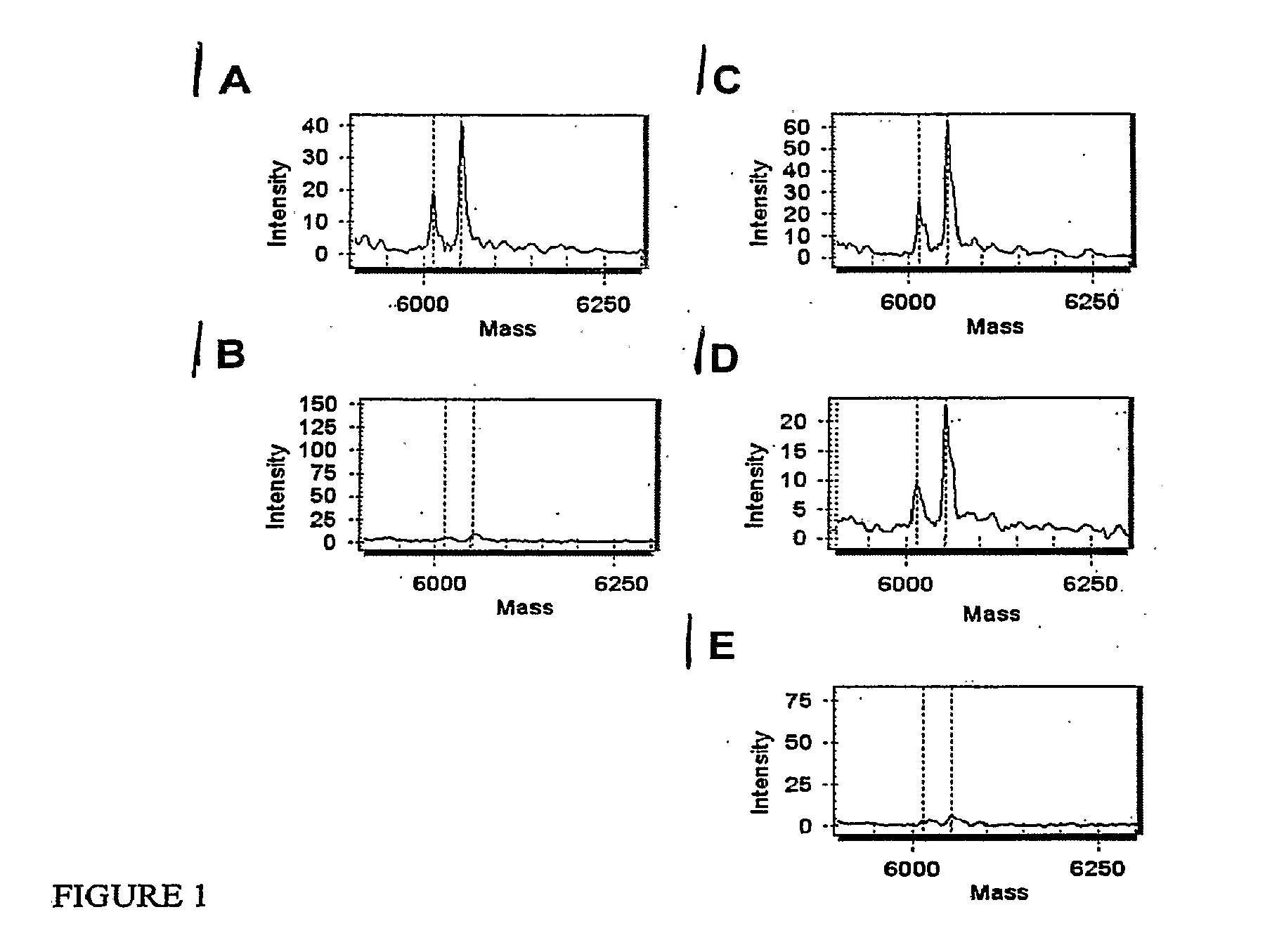
Many areas of biomedical research depend on the analysis of uncommon variations in individual genes or transcripts. Here we describe a method that can quantify such variation at a scale and ease heretofore unattainable. Each DNA molecule in a collection of such molecules is converted into a single particle to which thousands of copies of DNA identical in sequence to the original are bound. This population of beads then corresponds to a one-to-one representation of the starting DNA molecules. Variation within the original population of DNA molecules can then be simply assessed by counting fluorescently-labeled particles via flow cytometry. Millions of individual DNA molecules can be assessed in this fashion with standard laboratory equipment. Moreover, specific variants can be isolated by flow sorting and employed for further experimentation. This approach can be used for the identification and quantification of rare mutations as well as to study variations in gene sequences or transcripts in specific populations or tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method and Compositions for Detection and Enumeration of Genetic Variations
InactiveUS20090286687A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific populationIndividual gene
Many areas of biomedical research depend on the analysis of uncommon variations in individual genes or transcripts. Here we describe a method that can quantify such variation at a scale and ease heretofore unattainable. Each DNA molecule in a collection of such molecules is converted into a single particle to which thousands of copies of DNA identical in sequence to the original are bound. This population of beads then corresponds to a one-to-one representation of the starting DNA molecules. Variation within the original population of DNA molecules can then be simply assessed by counting fluorescently-labeled particles via flow cytometry. Millions of individual DNA molecules can be assessed in this fashion with standard laboratory equipment. Moreover, specific variants can be isolated by flow sorting and employed for further experimentation. This approach can be used for the identification and quantification of rare mutations as well as to study variations in gene sequences or transcripts in specific populations or tissues.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method for detecting and quantifying rare mutations/polymorphisms
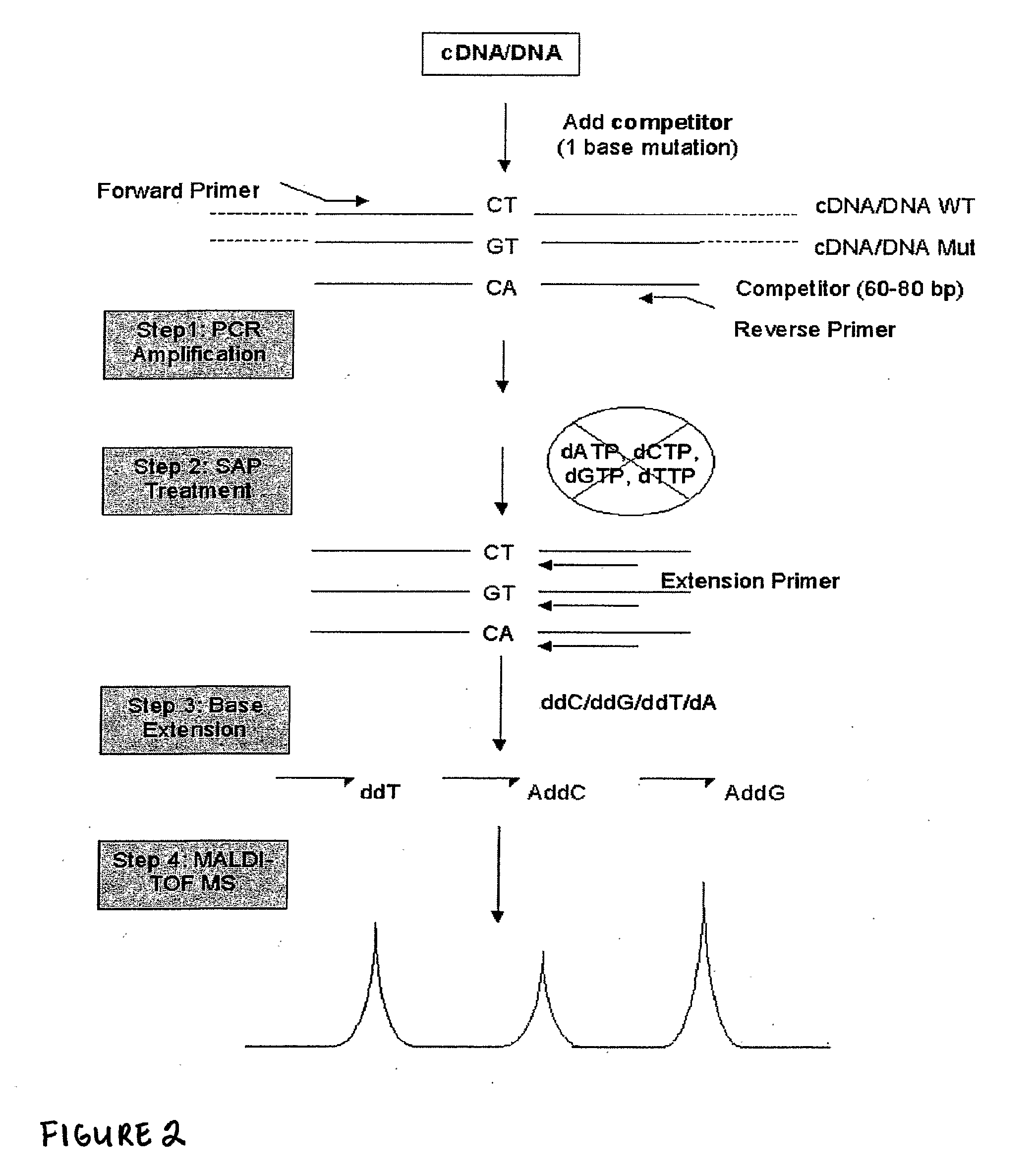
The present invention is directed to a method for detecting and quantifying rare mutations in a nucleic acid sample. The nucleic acid molecules under investigation can be either DNA or RNA. The rare mutation can be any type of functional or non-functional nucleic acid change or mutation, such as deletion, insertion, translocation, inversion, one or more base substitution or polymorphism. Therefore, the methods of the present invention are useful in detection of rare mutations in, for example, diagnostic, prognostic and follow-up applications, when the targets are rare known nucleic acid variants mixed in with the wildtype or the more common nucleic acid variant(s).
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
High sensitivity mutation detection using sequence tags
InactiveUS20160115532A1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideMutation detection
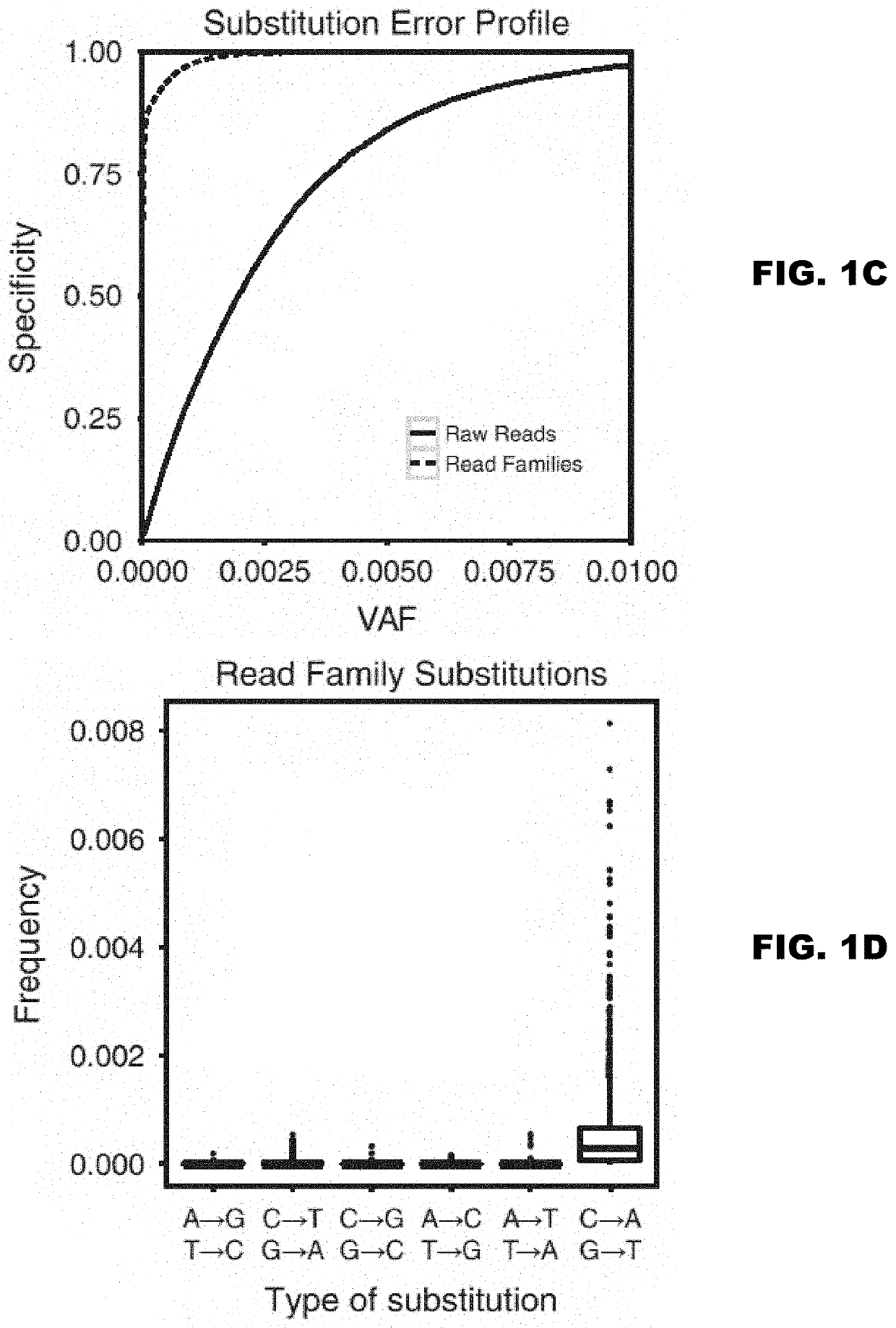
The invention is directed to methods for increasing the sensitivity of high throughput sequencing, particularly for distinguishing true rare mutations from amplification, sequencing and other sample processing errors that occur in sequencing techniques. In one aspect, methods of the invention includes steps of (a) preparing templates from nucleic acids in a sample; (b) labeling by sampling the templates to form tag-template conjugates, wherein substantially every template of a tag-template conjugate has a unique sequence tag; (c) linearly amplifying the tag-template conjugates; (d) generating a plurality of sequence reads from the linearly amplified tag-template conjugates; and (e) determining a nucleotide sequence of each of the nucleic acids based on the frequencies, or numbers, of each type of nucleotide at each nucleotide position of each plurality of sequence reads having identical sequence tags.
Owner:ADAPTIVE BIOTECH
Method for detecting and quantifying rare mutations/polymorphisms
The present invention is directed to a method for detecting and quantifying rare mutations in a nucleic acid sample. The nucleic acid molecules under investigation can be either DNA or RNA. The rare mutation can be any type of functional or non-functional nucleic acid change or mutation, such as deletion, insertion, translocation, inversion, one or more base substitution or polymorphism. Therefore, the methods of the present invention are useful in detection of rare mutations in, for example, diagnostic, prognostic and follow-up applications, when the targets are rare known nucleic acid variants mixed in with the wildtype or the more common nucleic acid variant(s).
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Method for Detecting and Quantifying Rare Mutations/Polymorphisms
InactiveUS20080032287A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingWild typeProtein translocation
The present invention is directed to a method for detecting and quantifying rare mutations in a nucleic acid sample. The nucleic acid molecules under investigation can be either DNA or RNA. The rare mutation can be any type of functional or non-functional nucleic acid change or mutation, such as deletion, insertion, translocation, inversion, one or more base substitution or polymorphism. Therefore, the methods of the present invention are useful in detection of rare mutations in, for example, diagnostic, prognostic and follow-up applications, when the targets are rare known nucleic acid variants mixed in with the wildtype or the more common nucleic acid variant(s).
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
Probes, method and chip for detecting alpha and/or beta-thalassemia mutation based on whole-gene capture sequencing and application of such probes, such method and such chip
ActiveCN106591441AEnables detection of deletions in large regionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBeta thalassemiaNew mutation
The invention provides primers, a method and a chip for detecting alpha and / or beta-thalassemia point mutation and deletion mutation based on whole-gene capture sequencing and application of such primers, such method and such chip. The primers, the method, the chip and application thereof have the advantages that through designing of capture probes, relevant genes involved in alpha-thalassemia and beta-thalassemia are enriched and all mutation information including SNP and indel in full-length sequences of genes is detected; through addition of autosome, X-chromosome and Y-chromosome regions as well as upstream and downstream regions of coded genes as references, structure variations such as SNV and CNV are detected; compared with existing various hotspot mutation site detection technologies, the method is capable of detecting hotspot mutation information as well as some rare mutations and undiscovered new mutation types to detect and analyze full-length sequence specificity of target genes, fully covers the mutation types and makes up the defect that a conventional detection method easily causes missing detection of low-frequency mutations and rare mutations greatly.
Owner:SHENZHEN E GENE TECH
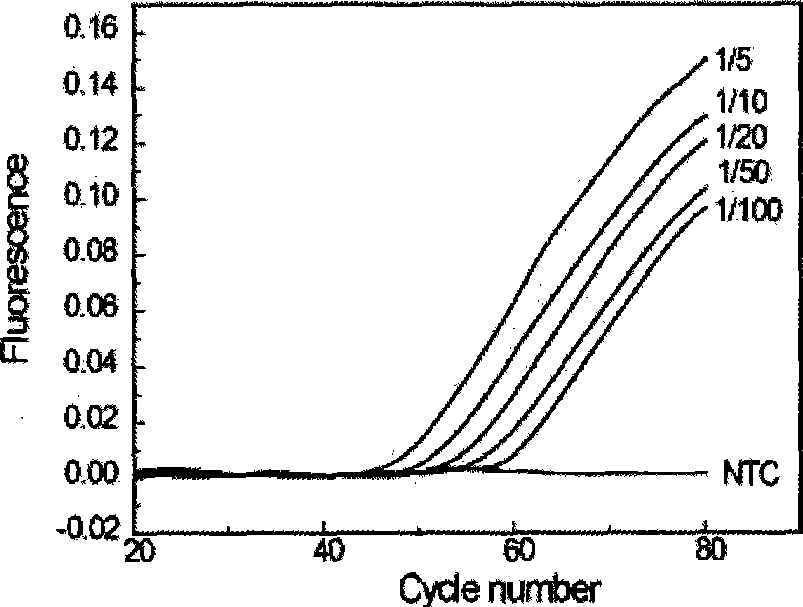
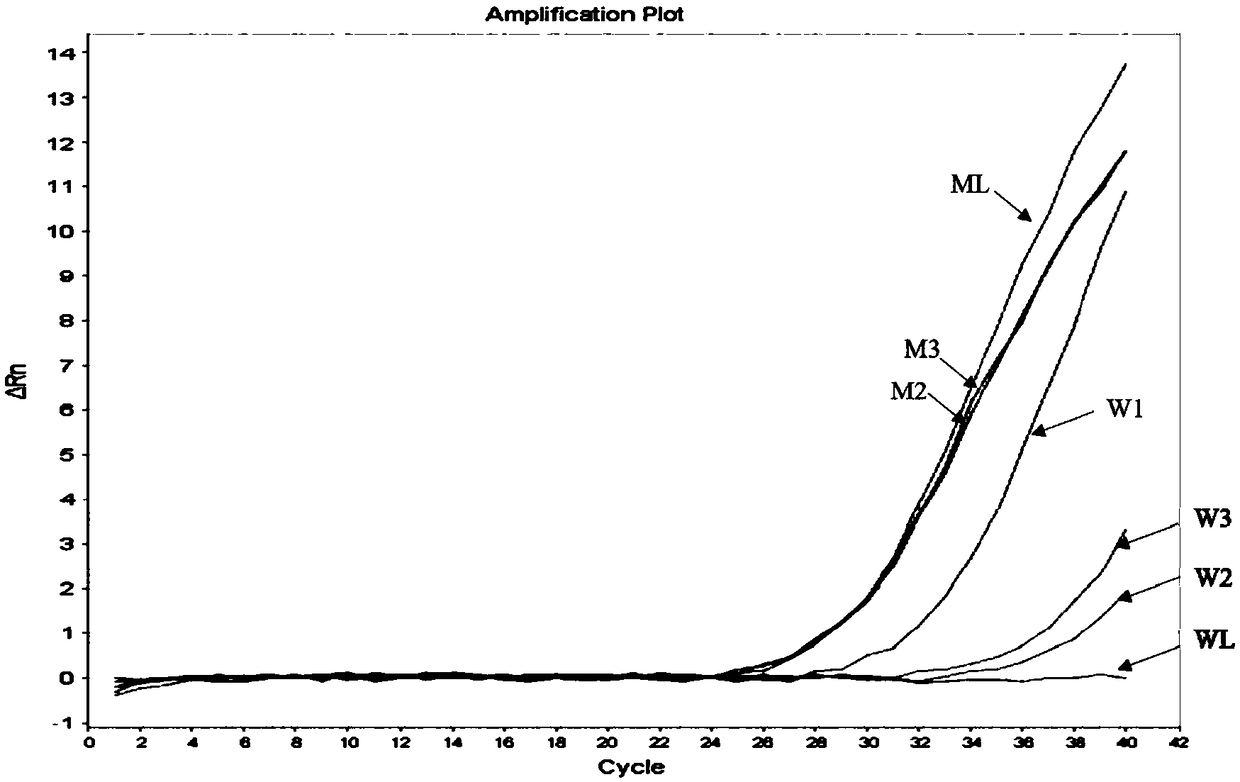
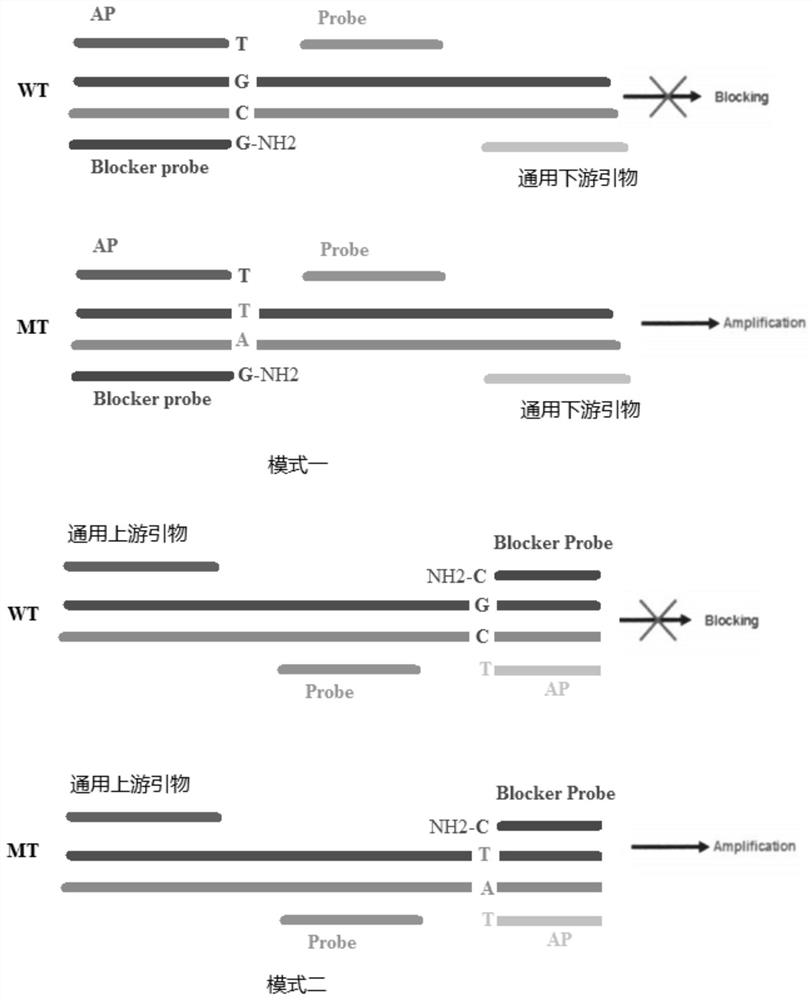
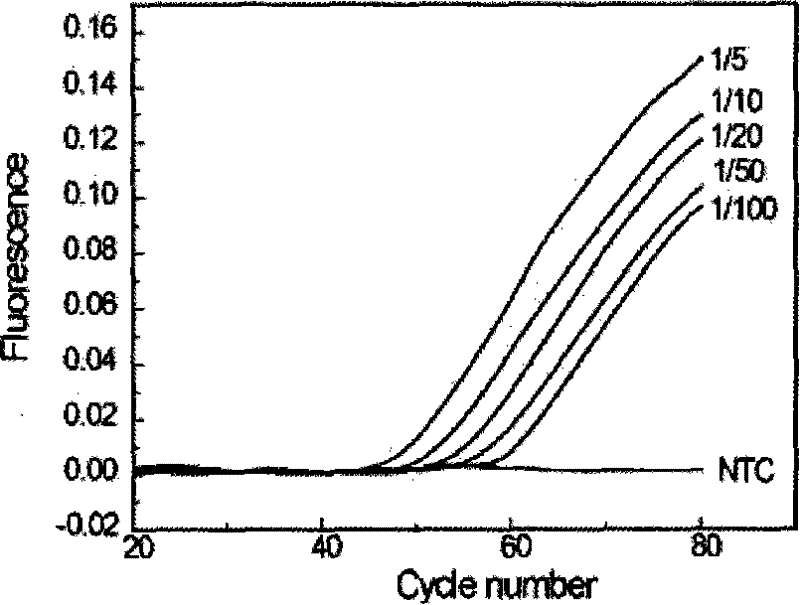
Hyper-blocking fluorescence quantitative PCR method with high sensitivity for detecting rare mutation
ActiveCN108048531ASpecific fastSpecificity does not affectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFluorescenceMutation detection
The invention discloses a hyper-blocking fluorescence quantitative PCR method with high sensitivity for detecting rare mutation. The invention adopts specific primers and a probe technology and can rapidly detect gene point mutation in a blood sample. The method has the advantage that (1) the conventional ARMS primers are modified by LNA or mismatched bases are introduced into 3' tail 2th site totail 3th site so that the sensitivity of the mutation detection is not influenced and the specificity of the single base mutation based on the mutation specific primers is guaranteed, (2) the modifiedblocker probe completely complementary to the wild type gene is introduced so that the wild type background interference is further reduced with keeping the efficiency of the mutant amplification, (3) based on the high specificity modified blocker probe, the ARMS primers can detect different base mutation forms at the same site at the same time so that multiple sites in the same gene can be detected by only a few systems, (4) sensitivity is high and (5) a detection rate is fast.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENEPHARMA CO LTD
Selective amplification and real-time PCR detection of rare mutations
InactiveUS20150315636A1Improved and efficientMicrobiological testing/measurementSpecific detectionGenetics
Provided herein are methods and kits for the improved detection of rare mutations within a high background. Exemplary embodiments relate to kits and methods that include amplification primers, a blocking oligonucleotide, and one or more allele-specific detector probes, useful in the specific detection of rare allelic variants or mutations.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Quantitative detection method of gene rare mutation
InactiveCN101381766ARealize real-time detectionAvoid pollutionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNucleotidePyrophosphate
The invention relates to a genetic detection method, in particular to a quantitative detection method for unusual genetic mutation. The quantitative detection method for unusual genetic mutation comprises the following steps: firstly, corresponding primer sequences are designed and prepared according to the unusual genetic mutation required for quantitative detection, wherein the 3' end of a primer is provided with a mutant site - special nucleotide; except for the final site of the nucleotide, all the other sequences can be synthesized by commercial means; and the final site of the nucleotide is modified nucleotide, so as to make the primer incapable of extending in the general PCR reaction; and the modified nucleotide is added to the tail of the primer; and secondly, in a reaction system which contains special DNA polymerase and pyrophosphate, the primer designed and prepared in the first step is adopted for amplifying the unusual genetic mutation for quantitative detection, and a real-time fluorescent PCR instrument is utilized for quantitative detection; and the quantitative detection information of the unusual genetic mutation can be acquired through analysis of an amplifying curve recorded by the real-time fluorescent PCR instrument.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
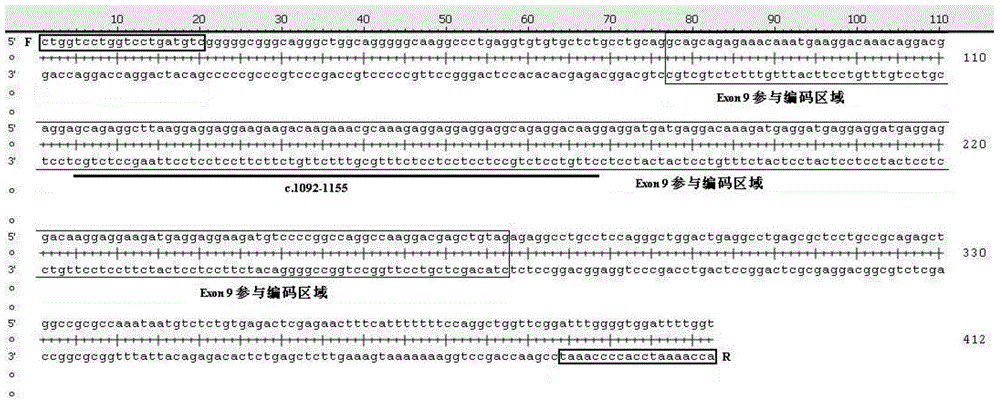
Reagent and method for detecting ninth exon mutation of CALR gene
The invention provides a reagent and a method for detecting the ninth exon mutation of a CALR gene by using a Sanger sequencing technology. The reagent and the method are high in detection specificity, and the mutation types of insertion and deficiency of the ninth exon of CALR can be specially analyzed, so that the false positive problem is eliminated, and missing inspection of rare mutation can also be avoided. The reagent and the method can be used for clinically screening genes of patients suffering from primary thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis.
Owner:南京艾迪康医学检验所有限公司
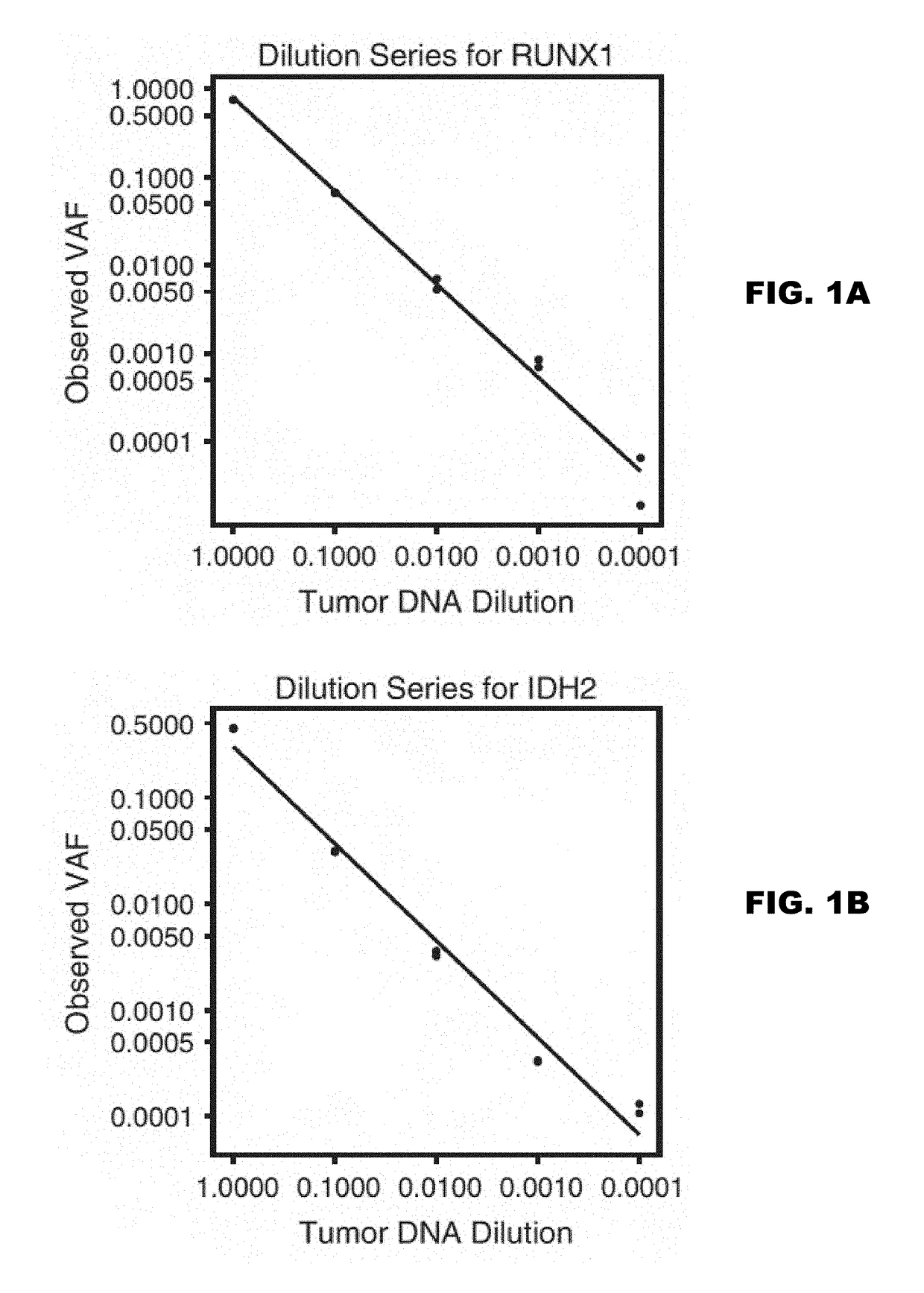
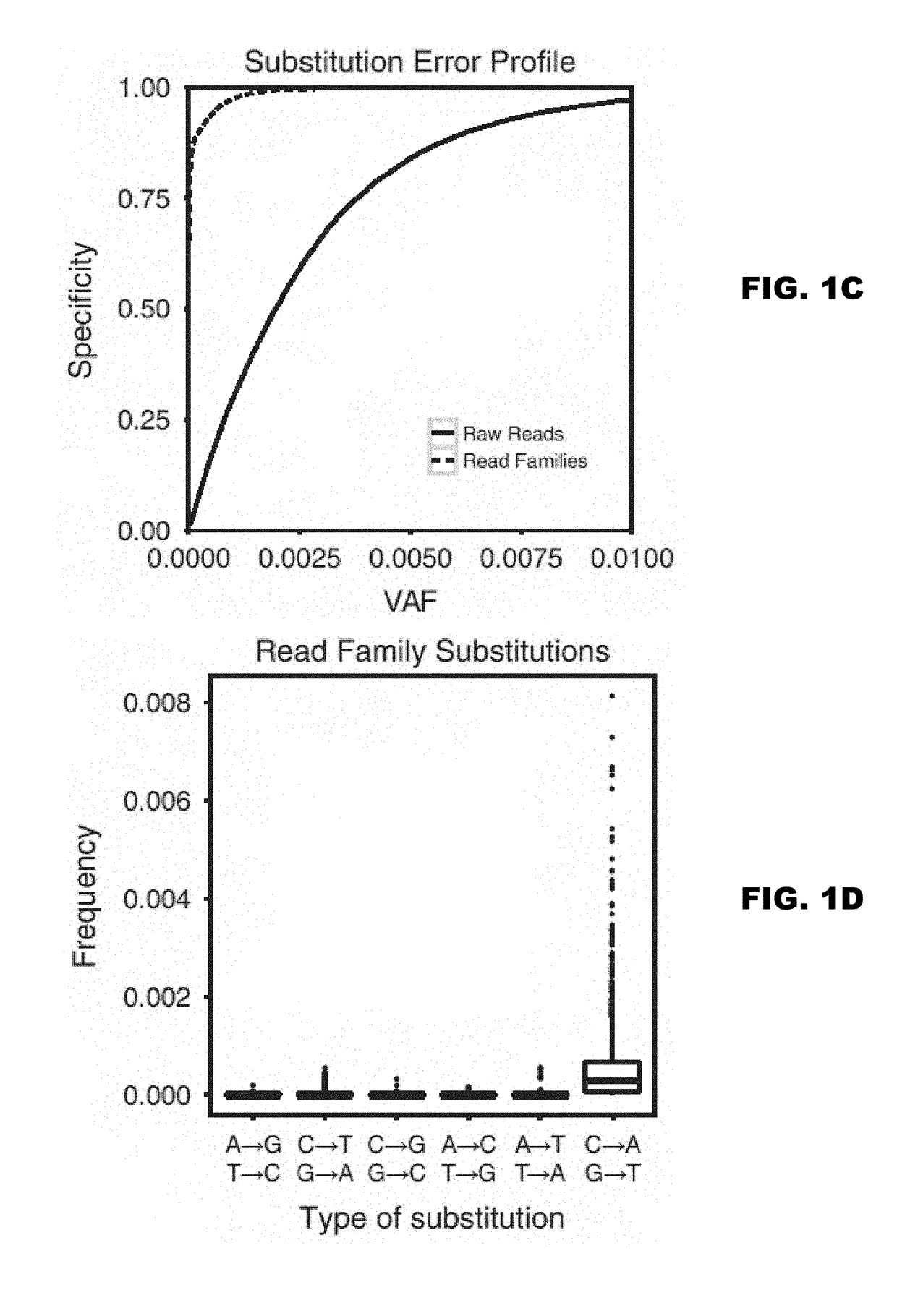
Detection of rare sequence variants, methods and compositions therefor
The present disclosure encompasses methods of error corrected sequencing (ECS) that enable detection of very rare mutations well below the error rate of convention next generation sequencing (NGS). Further, the methods disclosed herein enable multiplex targeting of genomic DNA.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Method of determining disease causality of genome mutations
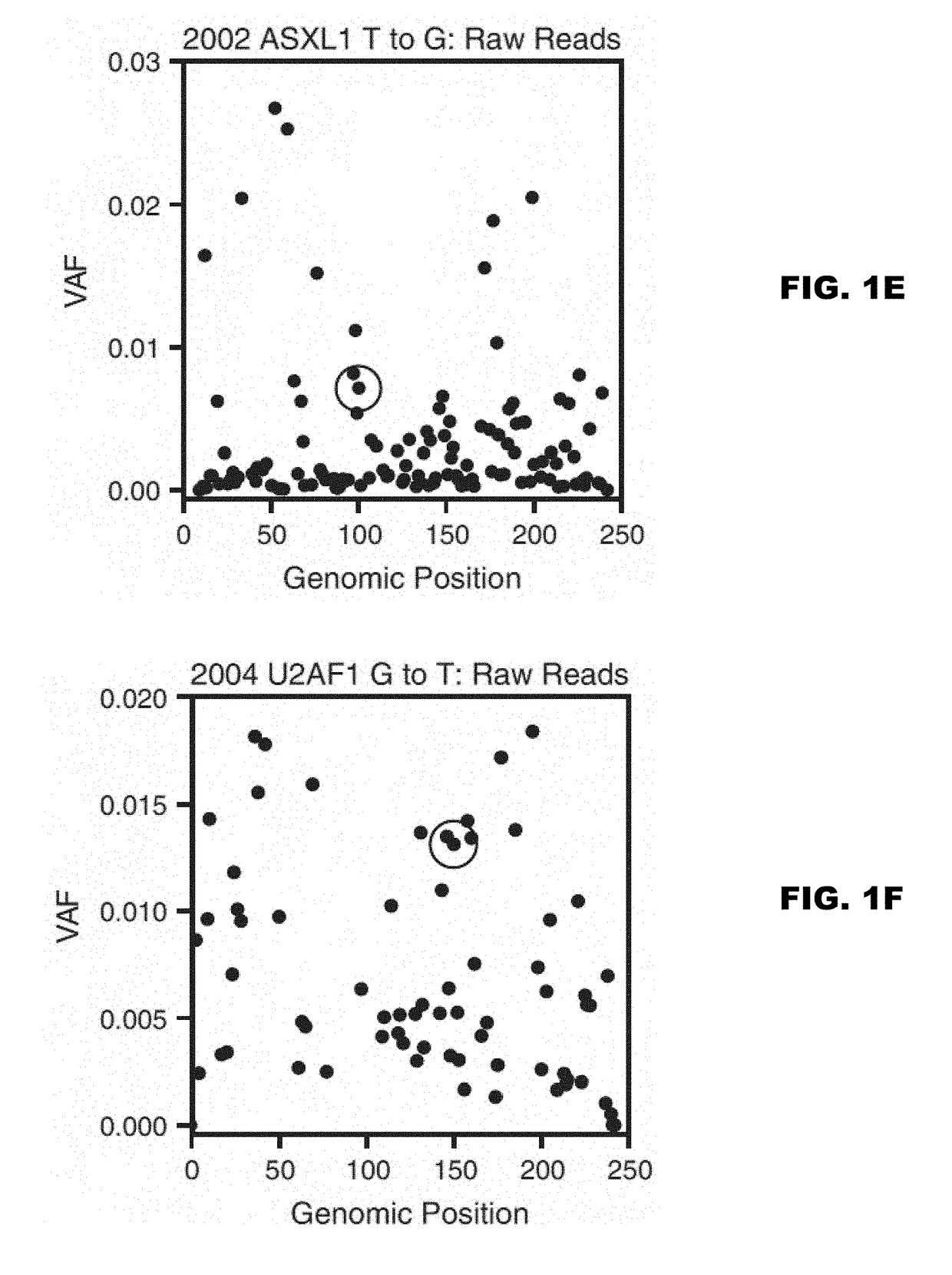
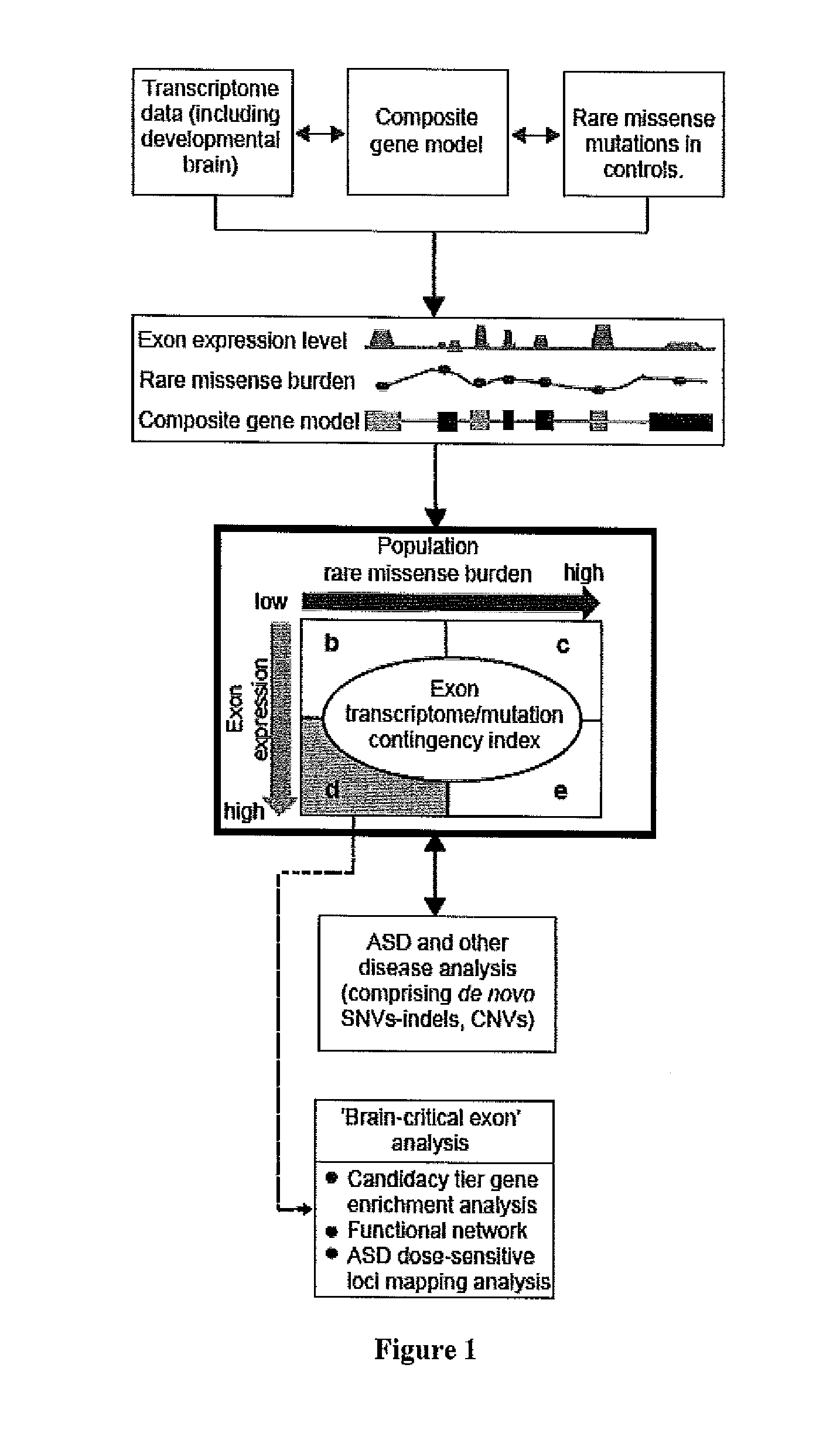
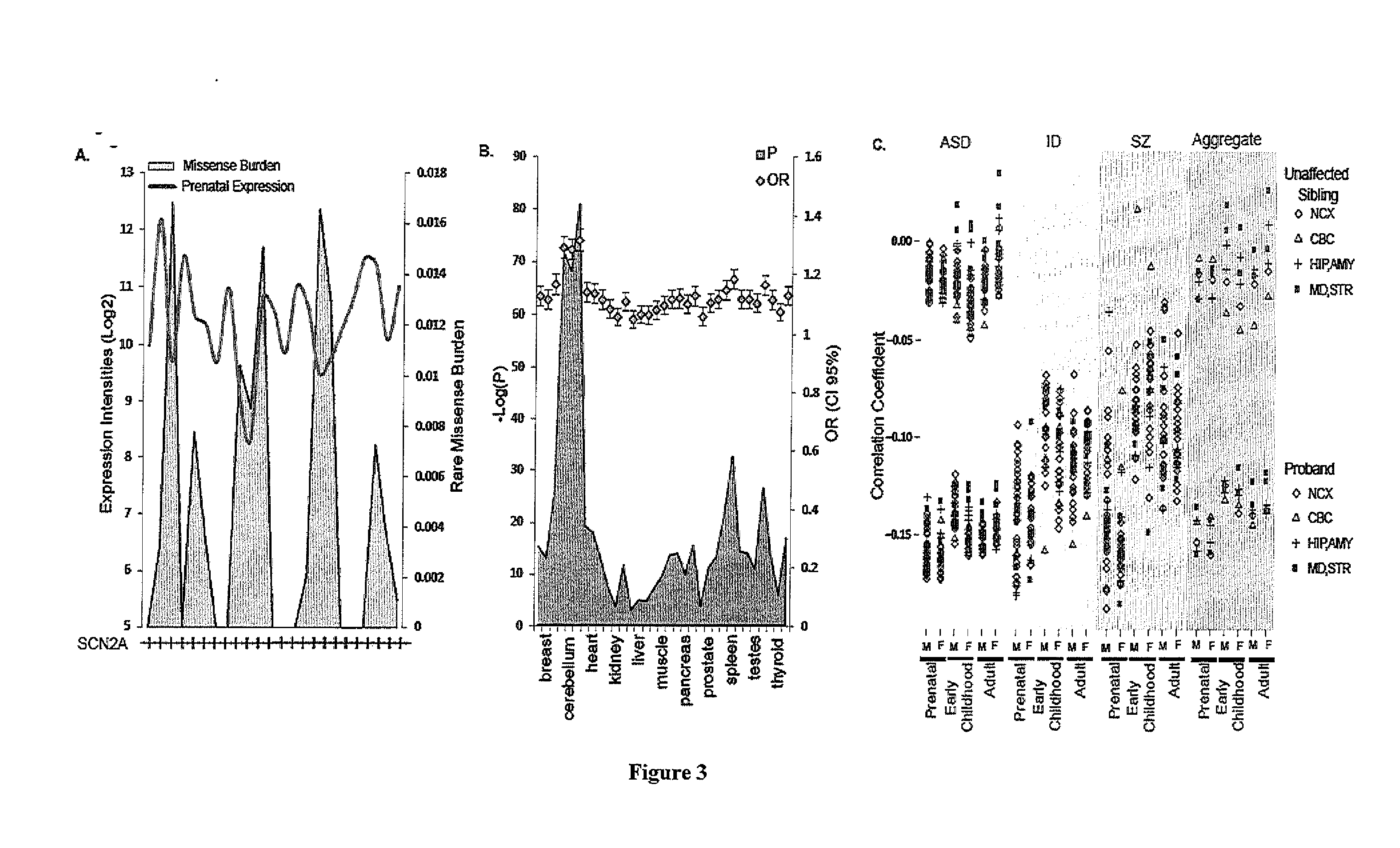
A method of identifying a gene or genomic mutation that is linked to causality of a neuropsychiatric disorder is provided. The method comprises identifying exons which exhibit an expression level that is at least within the 75th percentile of exon expression levels within a nucleic acid-containing sample from a mammal having a neuropsychiatric disorder; comparing the sequence of each identified exon to the sequence of a corresponding exon from a healthy control to identify rare or de novo sequence mutations within the identified exon; calculating the burden of rare or de novo mutations within the exon; and determining the correlation between expression level of the identified exon and burden of de novo or rare mutations in the exon, wherein an inverse correlation indicates that the exon gene is linked to causality of the neuropsychiatric disorder.
Owner:HOSPITAL FOR SICK CHILDREN
Rare mutation detection method, kit and application thereof
InactiveCN109266723AEasy to identifyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescenceMutation detection
The invention discloses a rare mutation detection method, a kit and an application thereof. The method is an ARMS method. The detection method provided by the invention combines ARMS and locking nucleic acid (LNA) mutation enrichment and Taqman-MGB fluorescence detection technology, using LNA to enhance the ability of base recognition, aRMS primers to mutation target sequence specific PCR amplification, a taqman-MGB probe detects that amplification product and identifies a specific mutation on the basis of fluorescent PCR. Compared with mutation detection technologies such as sanger sequence,chip detection and second generation sequencing, the method has the advantages of low cost, strong specificity, high sensitivity, simple and rapid operation and the like for gene mutation detection.
Owner:北京协和洛克生物技术有限责任公司
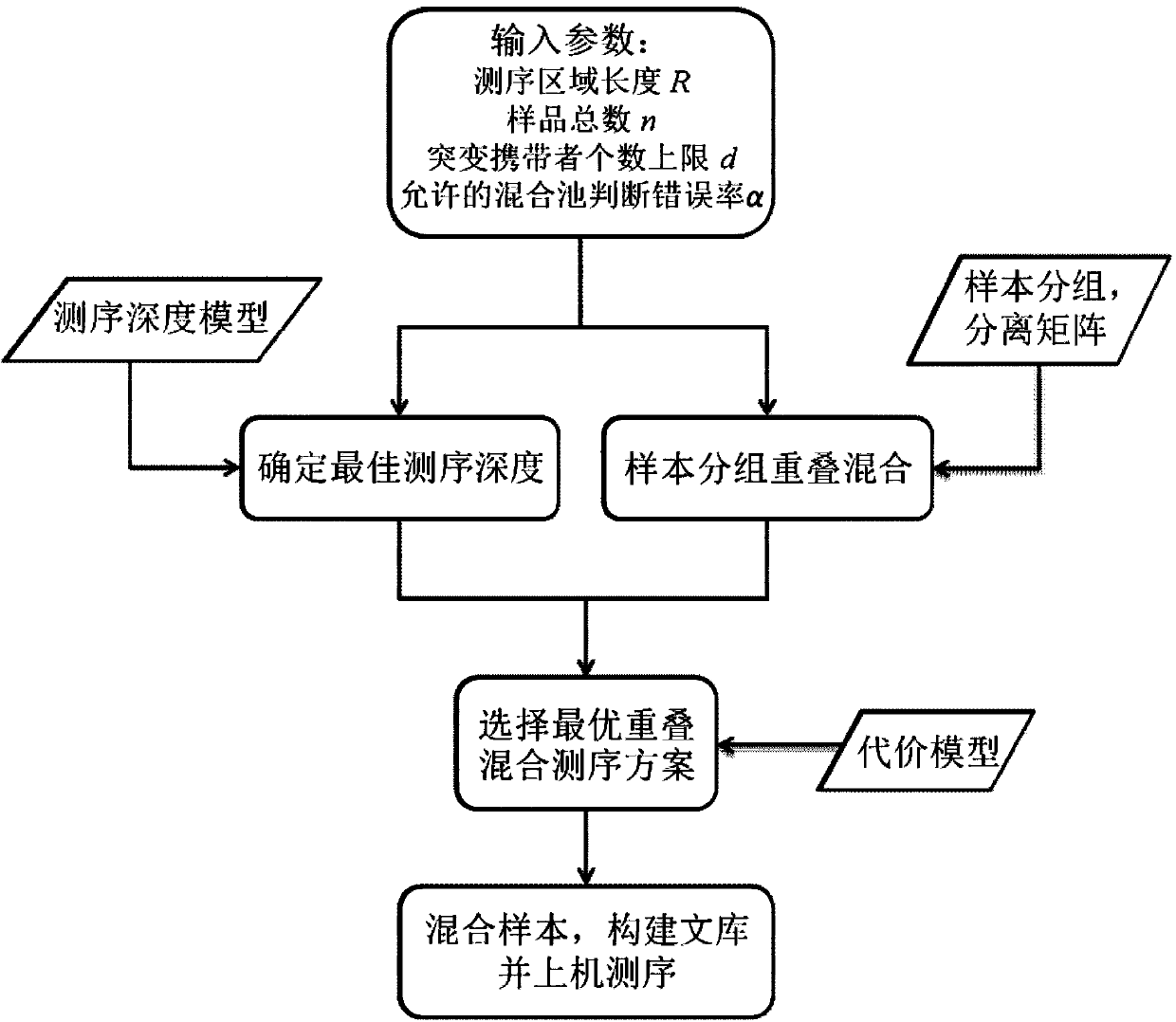
Optimized overlapping hybrid sequencing method
InactiveCN104217135AEffective observationCost controlSpecial data processing applicationsModel selectionDirect sequencing
The invention discloses an optimized overlapping hybrid sequencing method, which includes the following steps: on the basis of the general law that sequencing depth follows negative binomial distribution and sequencing errors follow binomial distribution in the process of sequencing, a depth model of hybrid sequencing is put forward, moreover, the optimal depth of hybrid sequencing is calculated and designed on the basis of the model, and sequencing cost is effectively reduced by reducing redundant sequencing depth; a grouped overlapping hybrid sequencing method based on rare mutation distribution probabilities is put forward, and compared with direct sequencing, the grouping strategy can greatly reduce the demand of sequencing on data volume and increase the efficiency of hybrid sequencing; a sequencing cost model is established, and on the basis of the model, an optimal overlapping hybrid sequencing scheme is chosen to screen rare mutation carriers. The optimized overlapping hybrid sequencing method reduces the sequencing cost of screening rare mutation carriers to the max.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Primers, method and kit for whole genome detection of human mitochondria
PendingCN110885880AImprove uniformityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRare mutationsMitochondrial mutation
The invention discloses primers, method and kit for whole genome detection of human mitochondria. The primers comprise forward and reverse primers for amplifying 37 gene coding regions of a mitochondrial whole genome (16569bp), and the base sequences of the forward and reverse primers are shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO: 3-222. A detection method based on the NGS technology comprises the following steps: combining specific primers and a target template DNA sequence, amplifying a target region of a to-be-detected sample by using universal primers, purifying a library by using magnetic beads,performing high-throughput sequencing on the obtained library, and analyzing mutation of the mitochondrial gene. According to the primers, the method and the kit disclosed by the invention, the raremutation of mitochondrial DNA can be accurately detected, a high cost performance, least manual operation and ultrahigh sensitivity are realized, guidance for drug selection of familial mitochondrialpatients and genetic susceptibility is provided, mitochondrial diseases caused by mitochondrial DNA mutation assists diagnosis and the onset risk is effectively reduced.
Owner:杭州联川基因诊断技术有限公司
Non-syndromic cleft lip related low-frequency/rare mutation and detection method thereof
PendingCN111334513APrecise positioningImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDiseaseCandidate Gene Association Study
The invention discloses a non-syndromic cleft lip related low-frequency / rare mutation and a detection method thereof. The TAF11 gene mutation is single point mutation c.G144C (chr6:34855591) in a first exon region, the amino acid is changed into p.L48F, and heterozygous mutation is pathogenic. The pathogenic mutation provided by the invention is not reported to be related to the occurrence and development of the non-synthetic cleft lip, and can provide a basis for the screening and detection of disease-causing genes and the formulation of treatment programs of non-syndromic cleft lip. At the same time, the invention constructs a disease-causing gene detection method. The method comprises the following steps: capturing and enriching DNA in a whole genome exon region by using a sequence capture technology, performing high-throughput sequencing, performing bioinformatics analysis and co-separation analysis to screen out candidate genes, and performing Sanger sequencing to verify the mutation.
Owner:AFFILIATED STOMATOLOGICAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MEDICAL UNIV
Methods and systems for RNA or DNA detection and sequencing
ActiveUS20190100793A1Microbiological testing/measurementFormalin fixed paraffin embeddedSanger sequencing
Disclosed are methods and systems for detecting RNA and sequencing RNA in a wide range of samples such as samples with low concentrations of nucleic acid, samples with degraded nucleic acid, samples that would not otherwise be amenable to conventional sequencing or RNA detection methods, poor quality samples, high quality samples in which rare mutations are sought, formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded samples, blood samples, etc. The methods of the present invention may use paired, large panels of primers to amplify many short fragments that overlap between but not within each panel. Each panel's amplicon set may fill the gaps between those of the opposing panel, thereby providing complete gene or genomic coverage. A preliminary, multiplex amplification step amplifies target nucleic acid for all downstream reactions such as Sanger sequencing, cloning, and Next Generation Sequencing (NGS).
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
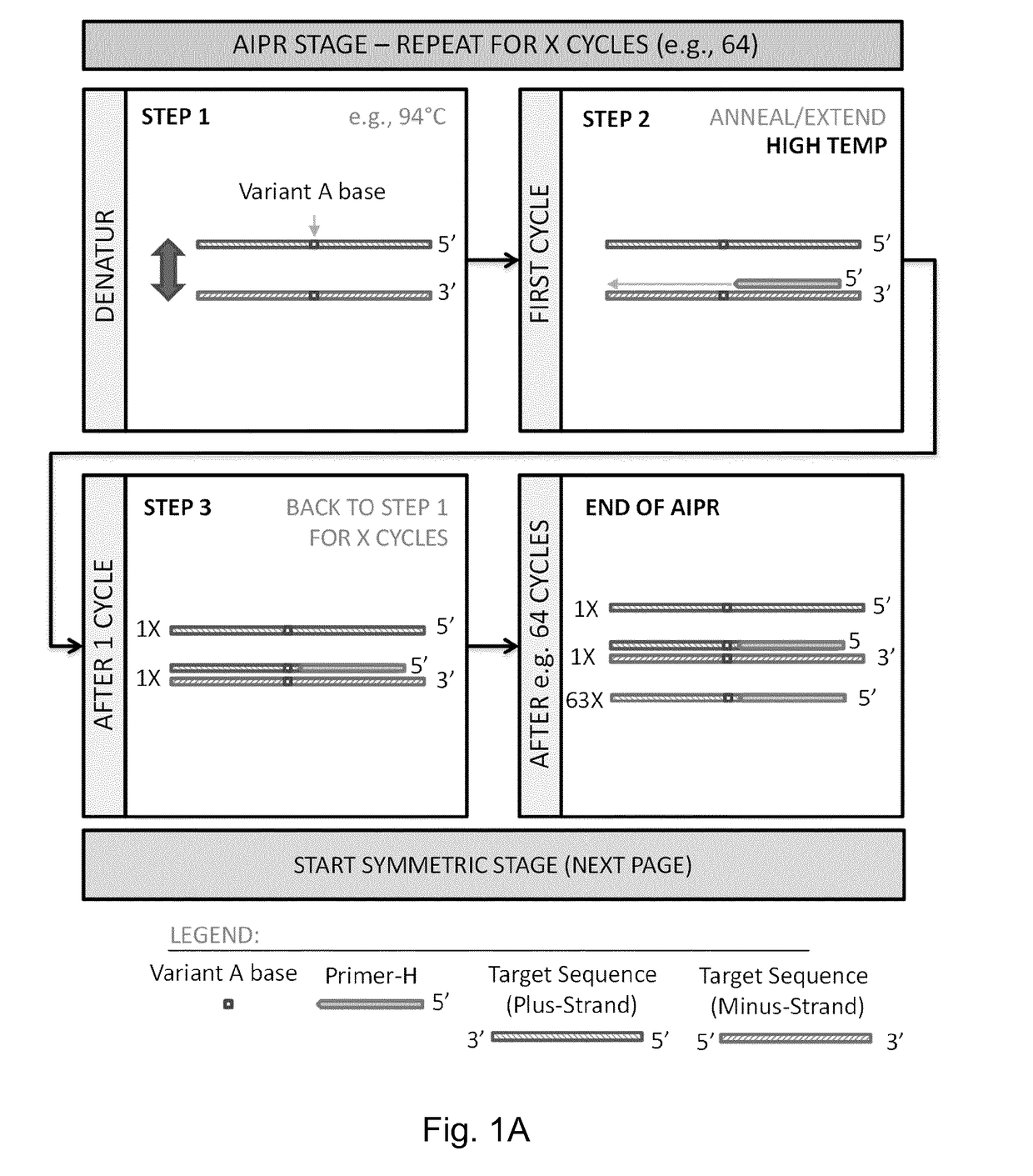
Detection of Target Nucleic Acid Variants
ActiveUS20180340230A1Improve analytical performanceHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LTrue positive rate
The present invention relates to highly sensitive and specific methods for detection of nucleic acids, which for example are useful for detection of rare mutations, or for detection of low-abundance variants in nucleic acids sequences. The methods involve an asymmetric incremental polymerase reaction (AIPR) followed by an exponential polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Owner:SAGA DIAGNOSTICS AB
Microcavity multicolor fluorescent digital PCR chip and application thereof
PendingCN109735444AProtection against external evaporationEase of useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPcr chipFluorescence
The invention relates to a microcavity multicolor fluorescent digital PCR chip and application thereof. The chip comprises a liquid inlet port, a double side microcavity array and a double side wasteliquid tank. The chip is used for rare cancer rare mutation analysis, differential gene expression analysis or high precision copy number variation analysis. The multicolor fluorescence detection is used, so that the detection flux of a single chip can be greatly improved, the reaction efficiency is greatly improved, the operation is convenient, the speed is high, extremely high detection sensitivity can be achieved compared with an existing real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR technology, and the application prospect is good.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
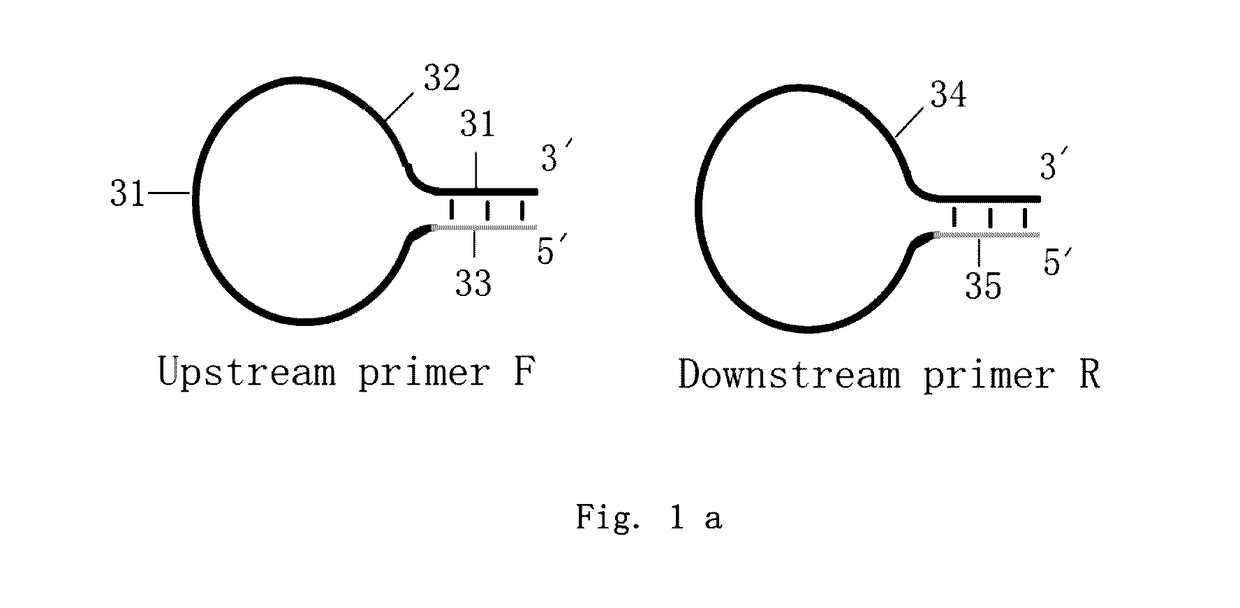
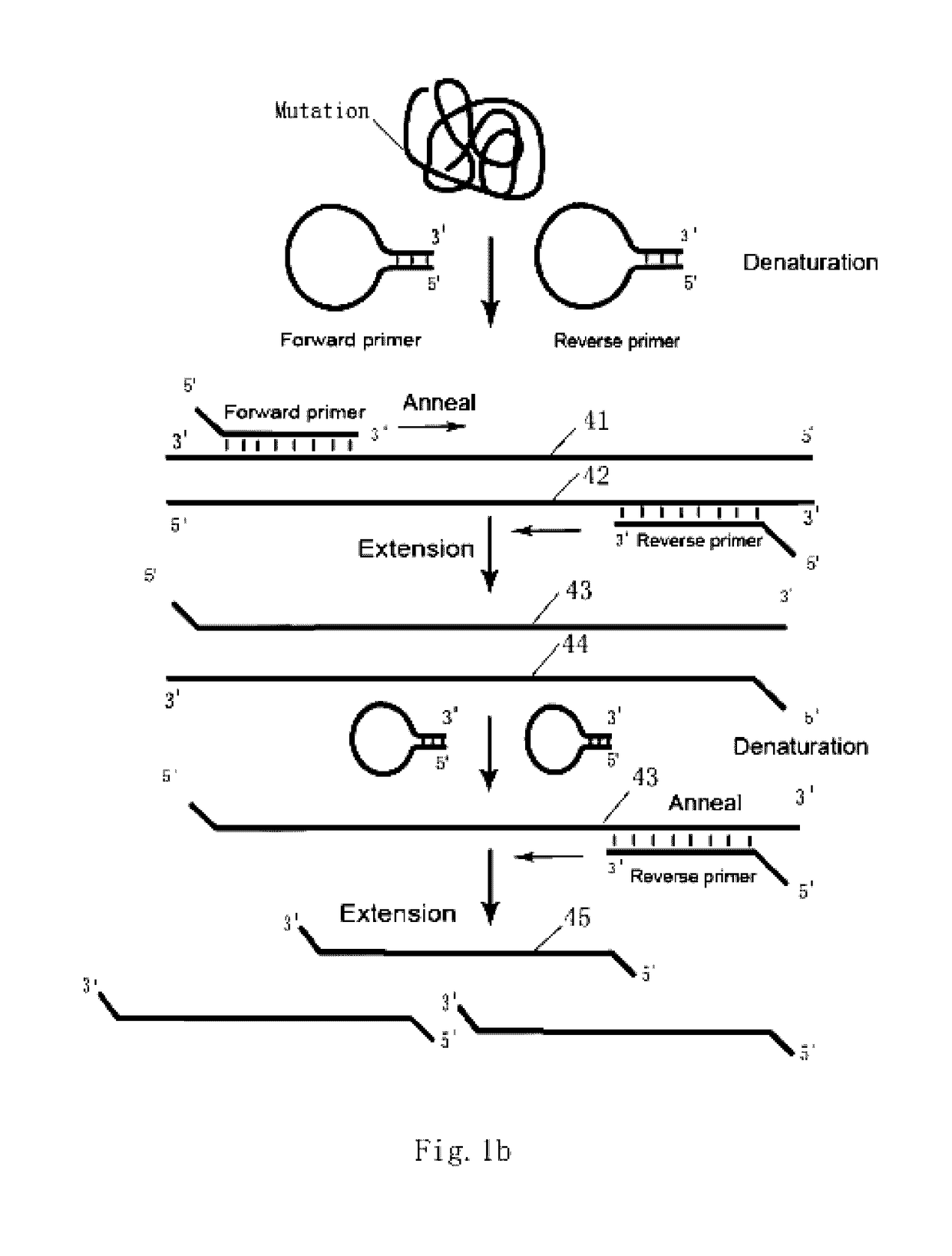
Loop-shaped primer used in nucleic acid amplification and the use thereof
Loop-shaped primer used in nucleic acid amplification is an oligonucleotide with 3-20 bases in both 3′ and 5′ ends which can be combined together to form a double-strand under appropriate conditions, resulting in the primer forming a stem-loop structure. The double-stranded structure is opened and the stem-loop structure dissolves when the primer recognizes and hybridizes with the target sequence. If the target sequence is not present the primer can form a stem-loop structure automatically by self-annealing. The primer can comprise a universal tag sequence or not. Together with universal tag sequence primer the primer comprising the universal tag sequence can be used for a second round of amplification. The primer has high specificity and does not form a primer dimmer. The primer is easy to design and is suitable for measuring gene expression and detecting features of nucleic acids such as SNPs and rare mutations.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
A super-blocking fluorescent quantitative PCR method for detecting rare mutations with high sensitivity
ActiveCN108048531BSpecific fastSpecificity does not affectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMutation detectionWild type
Owner:SHANGHAI GENEPHARMA CO LTD
Quantitative detection method of gene rare mutation
InactiveCN101381766BHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNucleotidePyrophosphate
The invention relates to a genetic detection method, in particular to a quantitative detection method for unusual genetic mutation. The quantitative detection method for unusual genetic mutation comprises the following steps: firstly, corresponding primer sequences are designed and prepared according to the unusual genetic mutation required for quantitative detection, wherein the 3' end of a primer is provided with a mutant site - special nucleotide; except for the final site of the nucleotide, all the other sequences can be synthesized by commercial means; and the final site of the nucleotide is modified nucleotide, so as to make the primer incapable of extending in the general PCR reaction; and the modified nucleotide is added to the tail of the primer; and secondly, in a reaction system which contains special DNA polymerase and pyrophosphate, the primer designed and prepared in the first step is adopted for amplifying the unusual genetic mutation for quantitative detection, and a real-time fluorescent PCR instrument is utilized for quantitative detection; and the quantitative detection information of the unusual genetic mutation can be acquired through analysis of an amplifying curve recorded by the real-time fluorescent PCR instrument.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Detection probe, method, chip and application of α and/or β-thalassemia mutation based on whole gene capture sequencing
ActiveCN106591441BEnables detection of deletions in large regionsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationChromosome regionsNew mutation
The present invention provides a detection primer, method, chip and application of α and / or β-thalassemia point mutations and deletion mutations based on whole gene capture sequencing. The present invention enriches all related genes involved in α and β thalassemia by designing capture probes, detects mutation information such as all SNPs and indels in the full-length sequences of each gene, and simultaneously increases The upstream and downstream regions of each coding gene are used as a reference to detect structural variations such as SNVs and CNVs. Compared with the current detection techniques of various hotspot mutation sites, the present invention can not only detect the information of hotspot mutations, but also detect some rare mutations and undiscovered new mutation types, and realize the specific detection and analysis of the full-length sequence of the target gene. Full coverage of types, greatly making up for the missed detection of low-frequency mutations and rare mutations by conventional detection methods.
Owner:高飞 +1
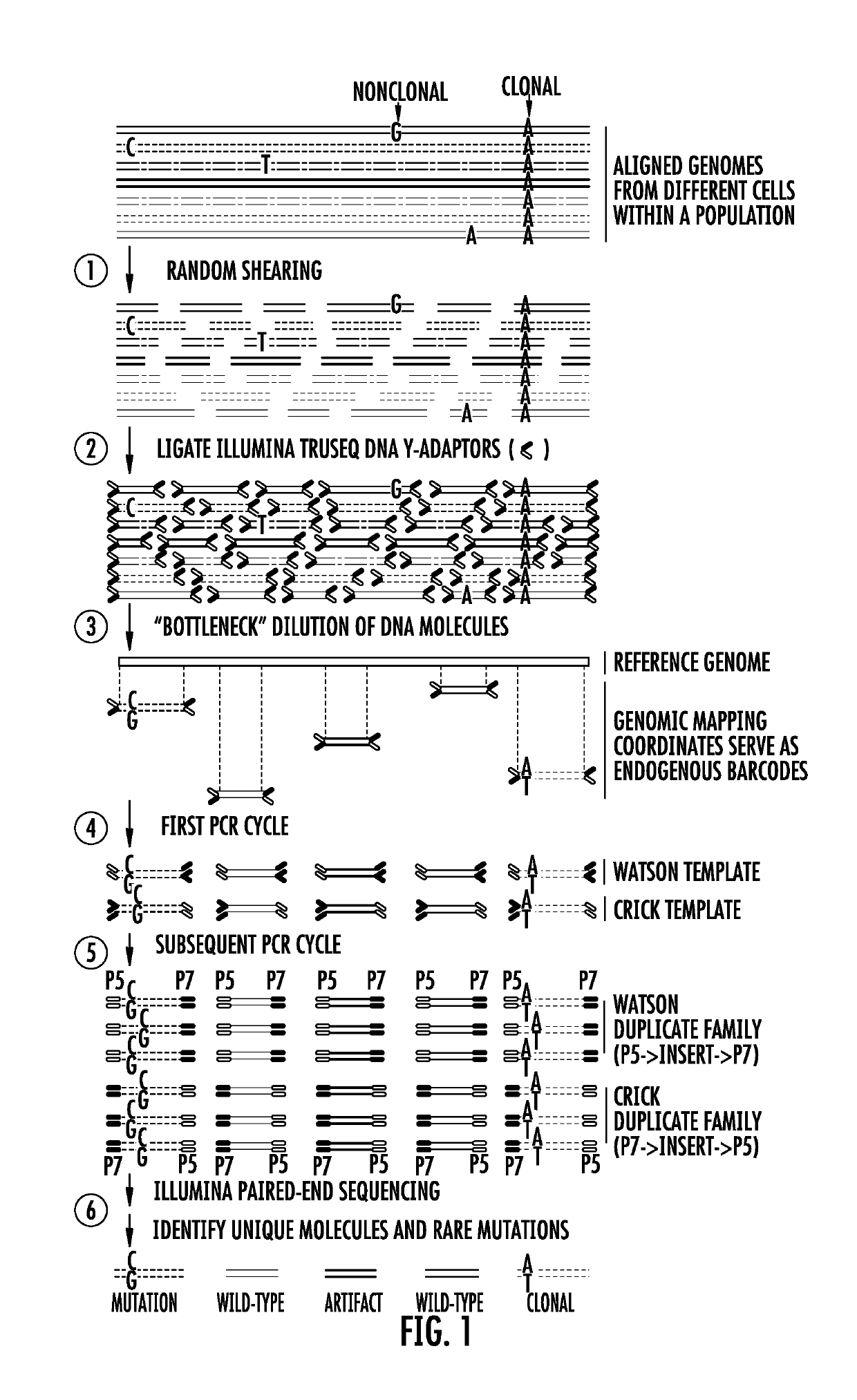
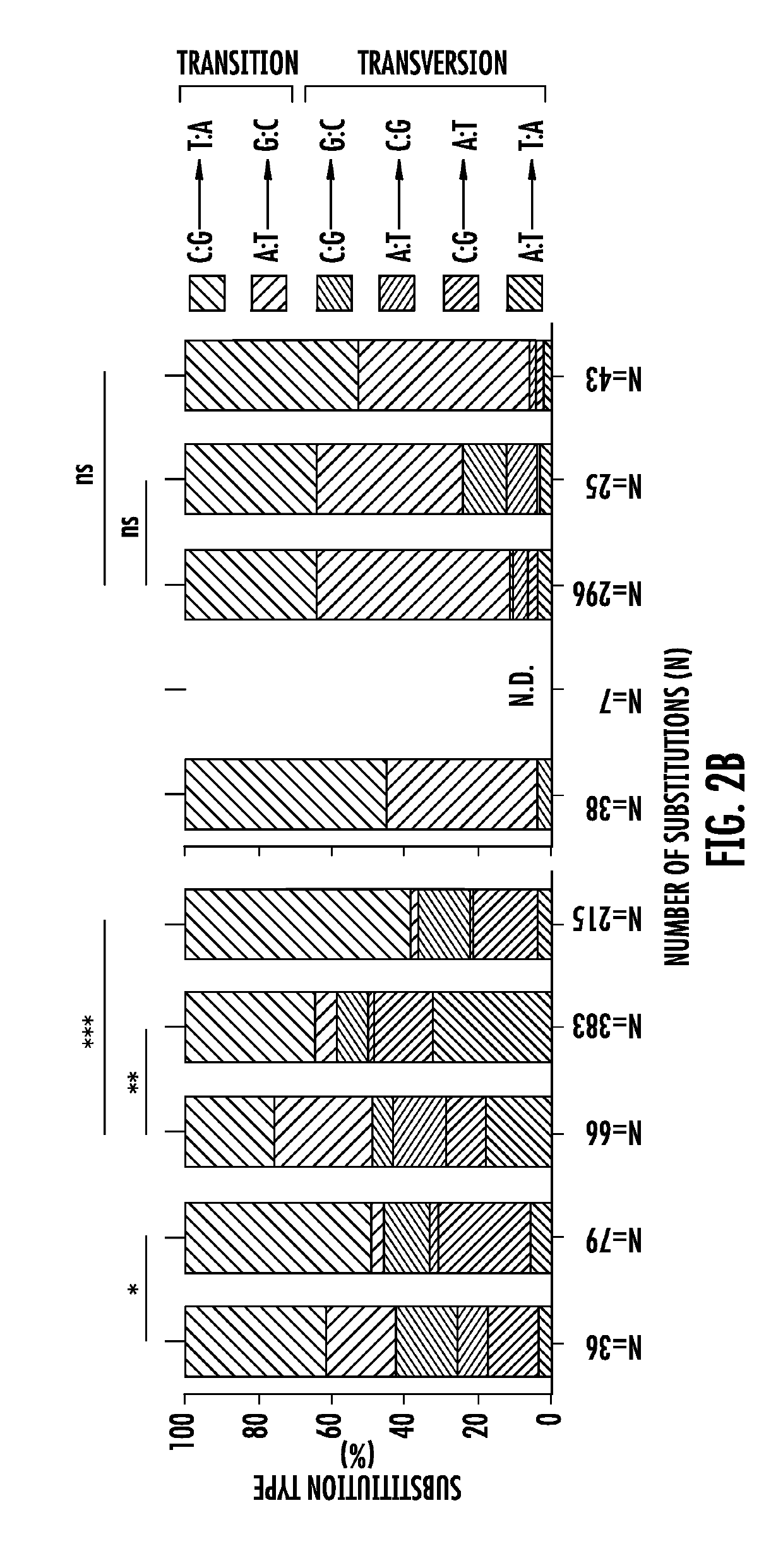
Bottleneck sequencing
PendingUS20190300946A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary member identificationNormal tissueSomatic cell
Bottleneck Sequencing System (BotSeqS) is a next-generation sequencing method that simultaneously quantifies rare somatic point mutations across the mitochondrial and nuclear genomes. BotSeqS combines molecular barcoding with a simple dilution step immediately prior to library amplification. BotSeqS can be used to show age and tissue-dependent accumulations of rare mutations and demonstrate that somatic mutational burden in normal tissues can vary by several orders of magnitude, depending on biologic and environmental factors. BotSeqS has been used to show major differences between the mutational patterns of the mitochondrial and nuclear genomes in normal tissues. Lastly, BotSeqS has shown that the mutation spectra of normal tissues were different from each other, but similar to those of the cancers that arose in them.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
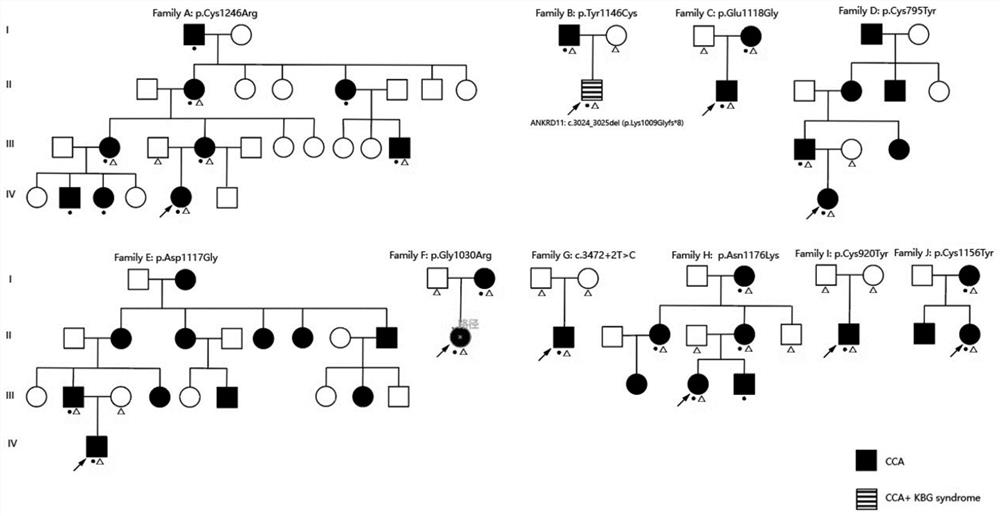
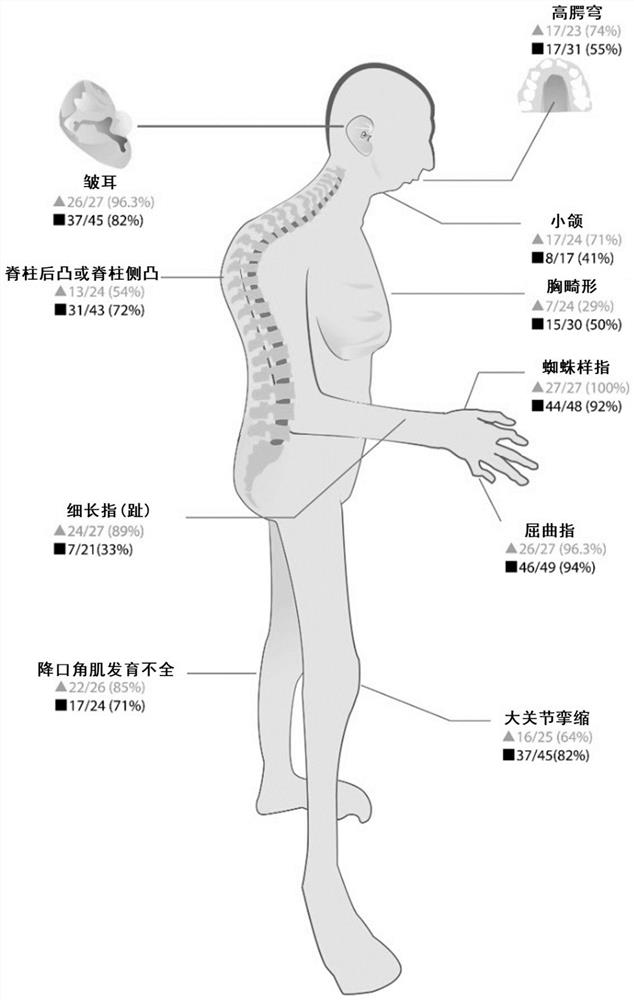
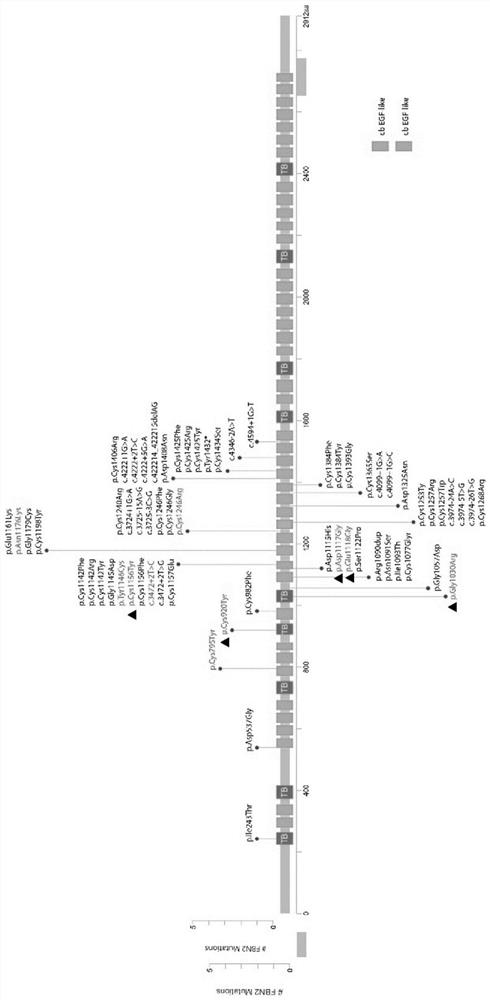
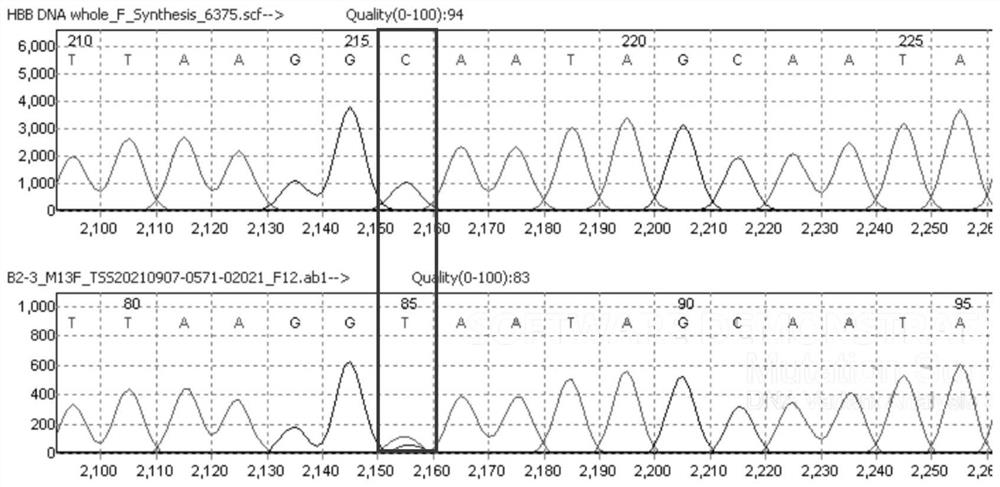
Novel FBN2 gene mutation marker and application thereof in CCA auxiliary diagnosis
ActiveCN113718027AProof of accuracyProven reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisPhysiologyGenetics
The invention discloses a novel FBN2 gene mutation marker and application thereof in CCA auxiliary diagnosis. According to the novel FBN2 gene mutation marker and the application thereof in the CCA auxiliary diagnosis, a whole exome sequencing analysis is carried out on 27 CCA patients of 10 families, it is found that the following rare mutations exist on FBN2: c.3353A > G, c.3350A > G, c.3088G > A, c.2759G > A and c.3467G > A, mutation sites are verified through a CCA clinical scoring system, the accuracy and reliability of the FBN2 gene mutation CCA diagnosis are proved, on one hand, the FBN2 gene mutation is beneficial to explaining the pathogenesis of a CCA patient, on the other hand, the mutation site can be used as a CCA biomarker for diagnosis or auxiliary diagnosis of CCA, assessment of the risk of suffering from CCA and pre-pregnancy early warning.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Detection of rare gene mutations
PendingCN108624662AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMutation detectionWild type
The invention relates to a method for detecting rare gene mutations. The method utilizes high-selectivity gene mutation detection primers and hinders, to achieve a purpose of enriching rare mutation products by specifically inhibiting wild-type amplification. The method, the primers and the hinders in the invention are particularly suitable for efficient and low-cost detection of rare gene mutations in cfDNA according to an NGS technology.
Owner:陈汉奎
Reagent, method and kit for detecting rare mutation of thalassemia gene
PendingCN114292908ALow costEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenes mutationBeta thalassemia
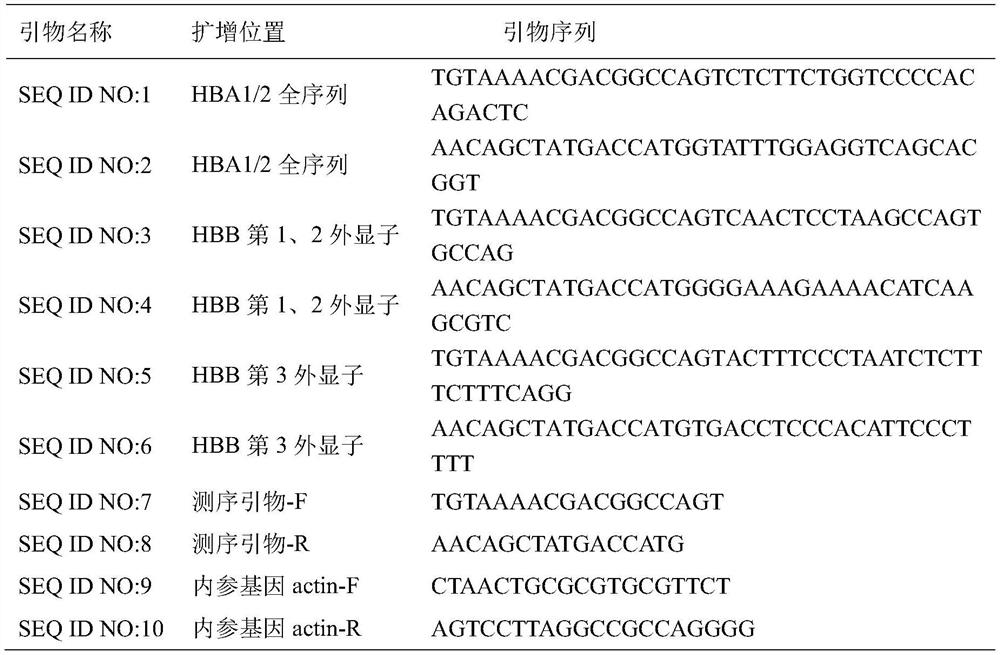
The invention discloses a reagent, a method and a kit for detecting rare gene mutation of thalassemia. The reagent comprises forward and reverse primers for specifically amplifying rare gene mutation of alpha thalassemia and beta thalassemia, an internal reference primer and a sequencing primer, the Sanger sequencing technology is combined, the rare gene mutation of the thalassemia is rapidly and accurately detected, the genotype of a patient can be clearly determined, and the omission ratio of the rare pathogenic mutation and the birth of severe children can be reduced in a high-incidence area of the thalassemia.
Owner:FUZHOU ADICON CLINICAL LAB INC
Detection of rare sequence variants, methods and compositions therefor
The present disclosure encompasses methods of error corrected sequencing (ECS) that enable detection of very rare mutations well below the error rate of convention next generation sequencing (NGS). Further, the methods disclosed herein enable multiplex targeting of genomic DNA.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Reagent kit for diagnosing mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and application
ActiveCN110452980AMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiologyRare mutations
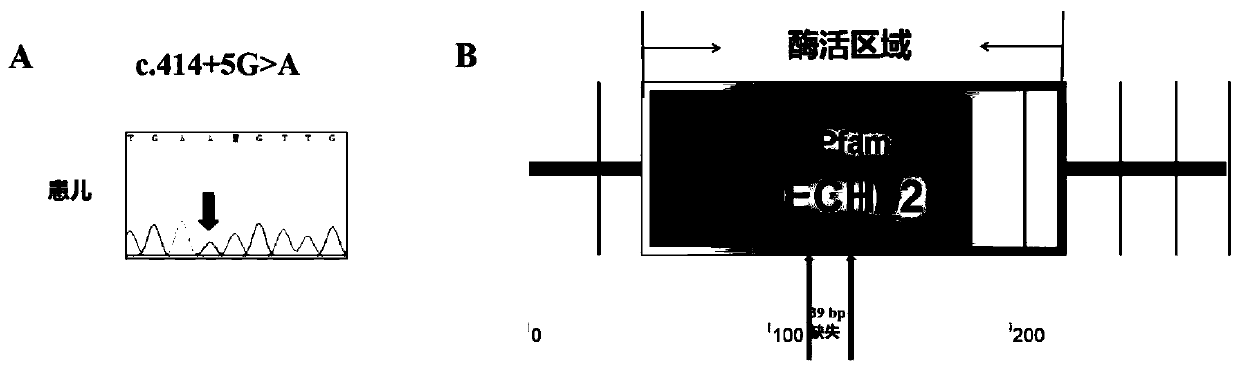
The invention discloses a reagent kit for diagnosing mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and an application. The reagent kit for diagnosing mitochondrial encephalomyopathy comprises an ECHS1 gene order detecting reagent, wherein the ECHS1 gene order detecting reagent is applied to the preparation of a mitochondrial encephalomyopathy diagnosis reagent. According to the reagent kit for diagnosing mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and the application of the reagent kit disclosed by the invention, through determining the incidence relation between an ECHS1 gene and the mitochondrial encephalomyopathy, particularly the situation that the mitochondrial encephalomyopathy is caused by rare mutation c.414+5G >A of an intron 3 of the ECHS1 gene, the reagent kit for diagnosing the mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and an application of the ECHS1 gene order detecting reagent are provided, and important genetic bases is provided for diagnosing and making a definite diagnosis for the mitochondrial encephalomyopathy.
Owner:WUHAN CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com