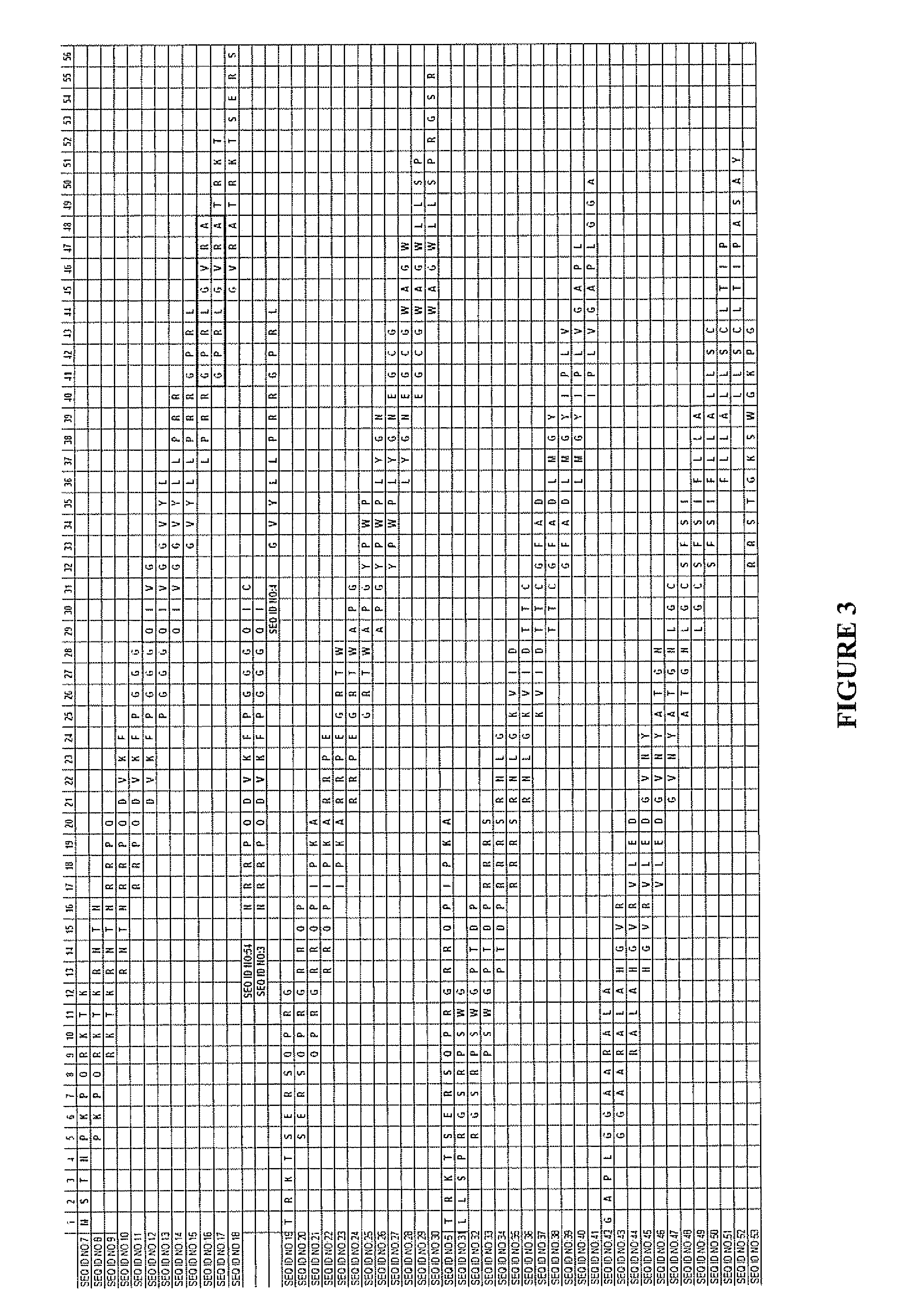
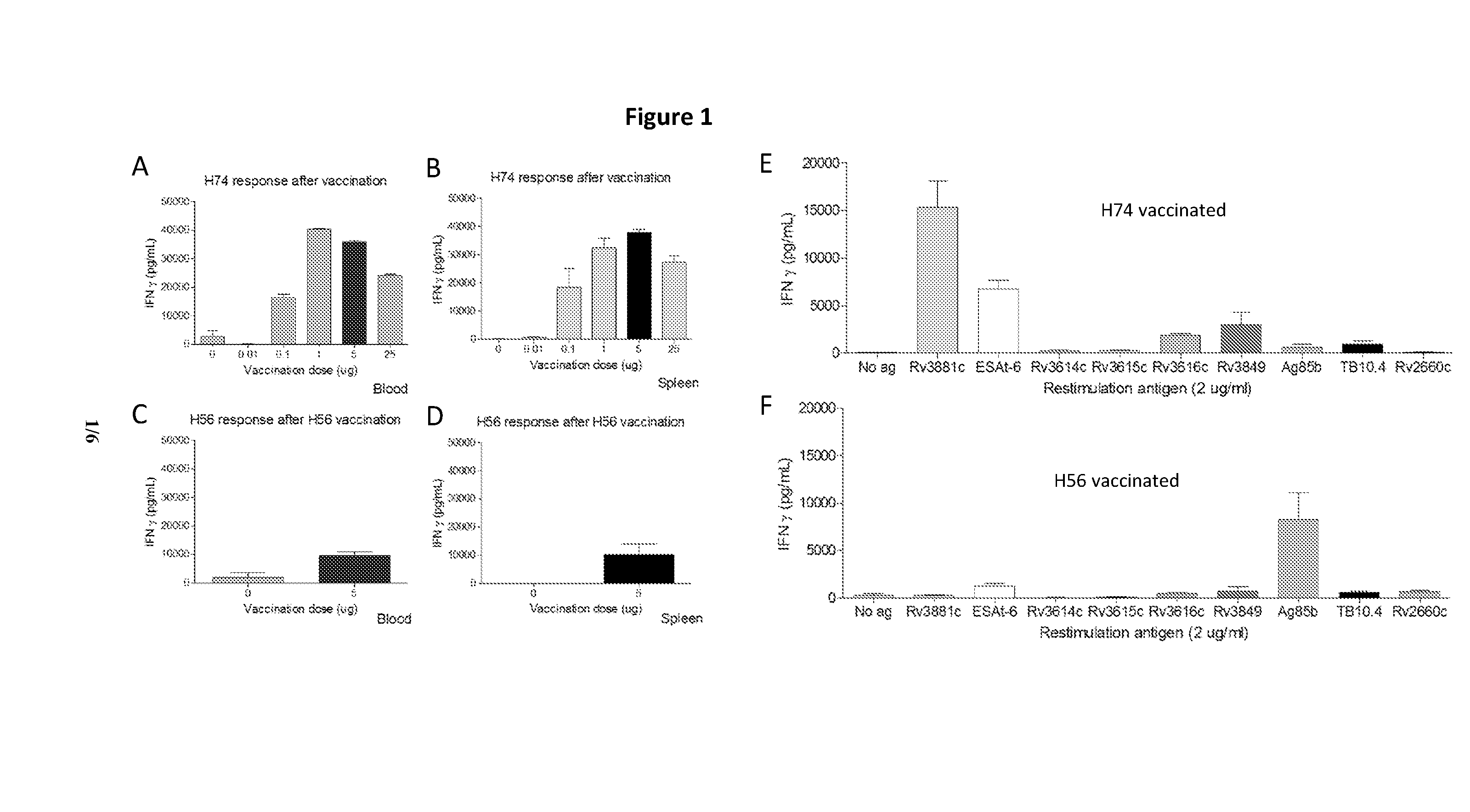
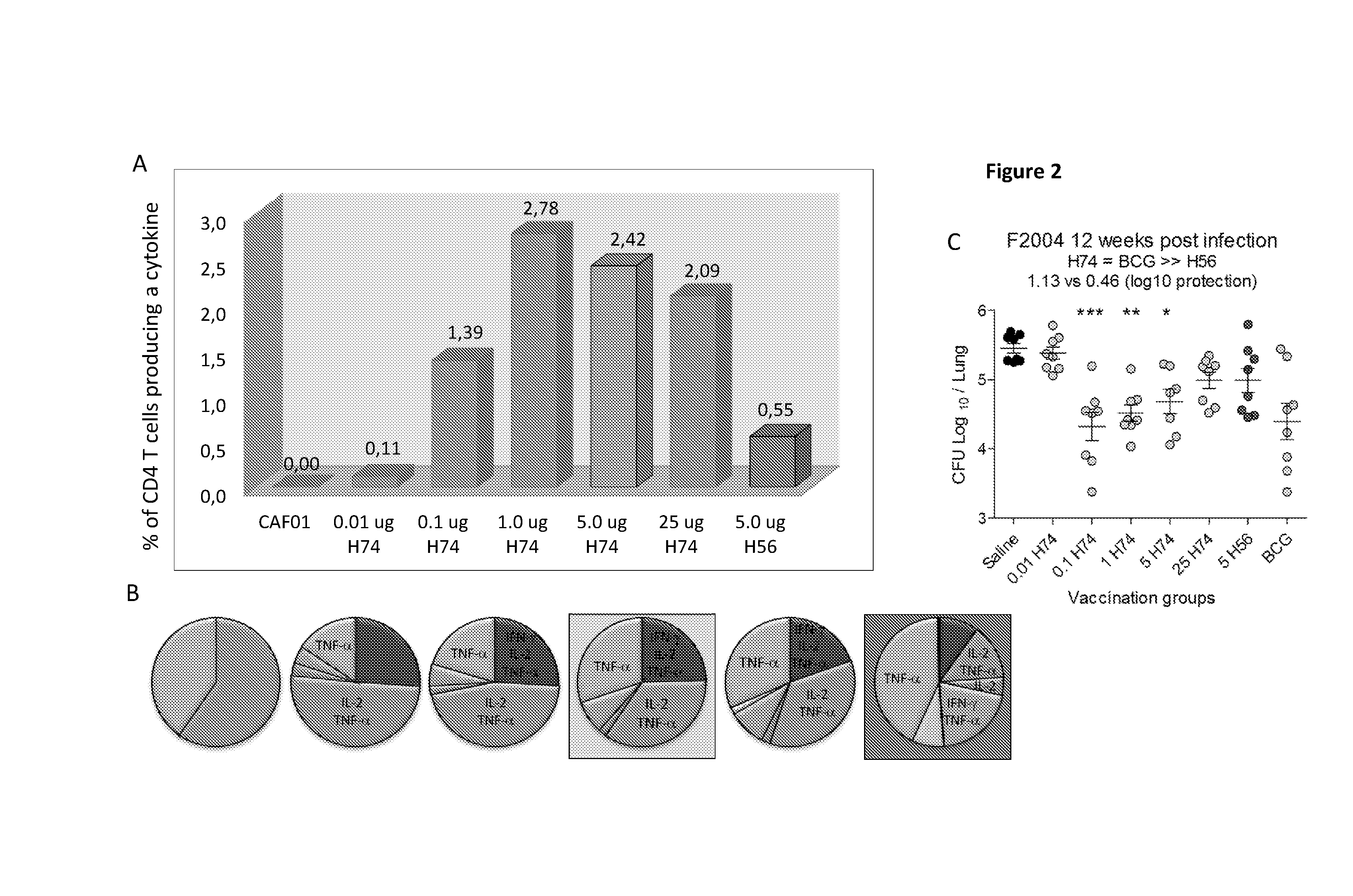
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
78 results about "Immunodominance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Immunodominance is the immunological phenomenon in which immune responses are mounted against only a few of the antigenic peptides out of the many produced. That is, despite multiple allelic variations of MHC molecules and multiple peptides presented on antigen presenting cells, the immune response is skewed to only specific combinations of the two. Immunodominance is evident for both antibody-mediated immunity and cell-mediated immunity. Epitopes that are not targeted or targeted to a lower degree during an immune response are known as subdominant epitopes. The impact of immunodominance is immunodomination, where immunodominant epitopes will curtail immune responses against non-dominant epitopes. Antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, can have up to six different types of MHC molecules for antigen presentation. There is a potential for generation of hundreds to thousands of different peptides from the proteins of pathogens. Yet, the effector cell population that is reactive against the pathogen is dominated by cells that recognize only a certain class of MHC bound to only certain pathogen-derived peptides presented by that MHC class. Antigens from a particular pathogen can be of variable immunogenicity, with the antigen that stimulates the strongest response being the immunodominant one. The different levels of immunogenicity amongst antigens forms what is known as dominance hierarchy.
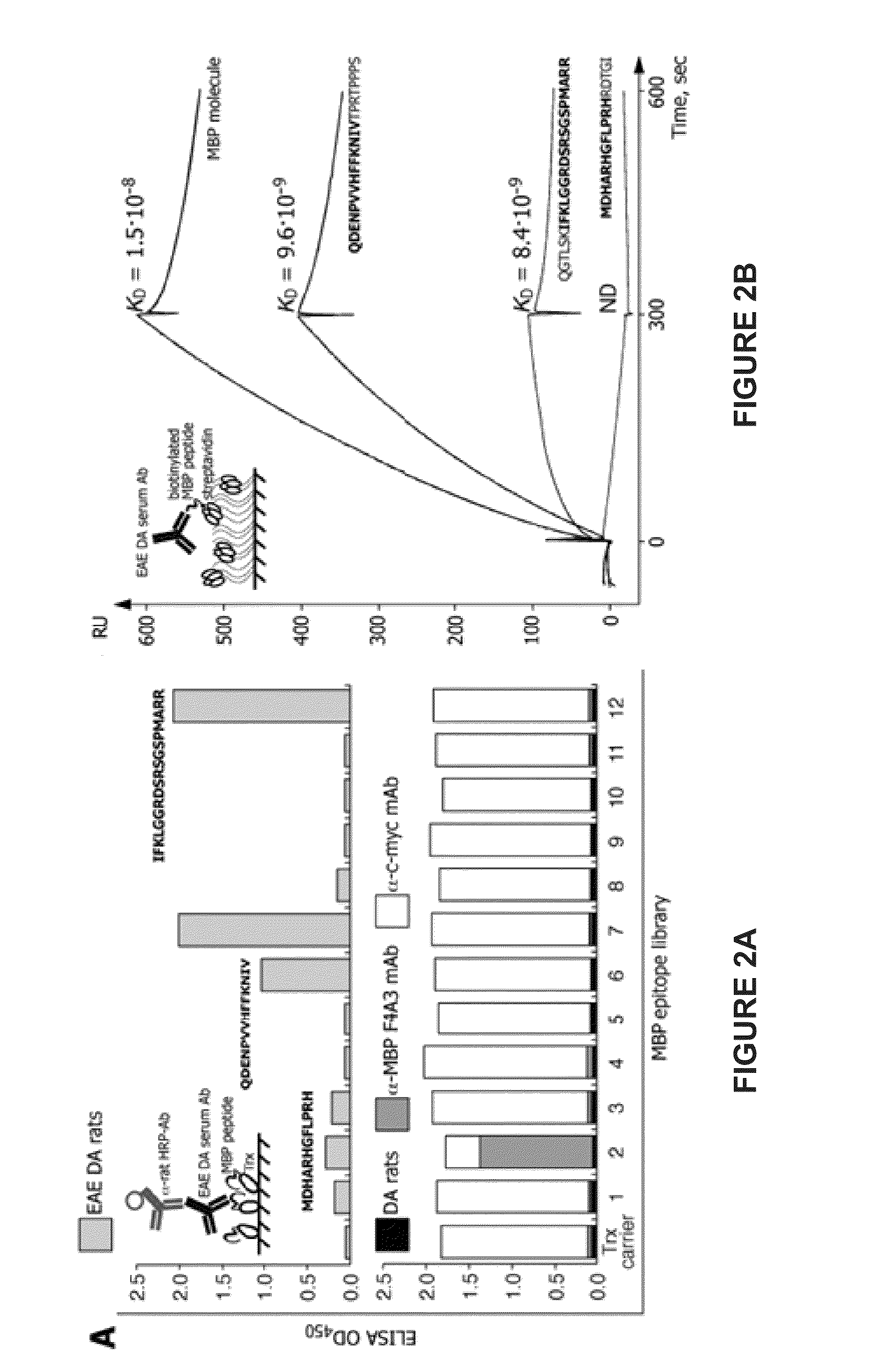
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with Her-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080177046A1Good curative effectImprove efficiencyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The Predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
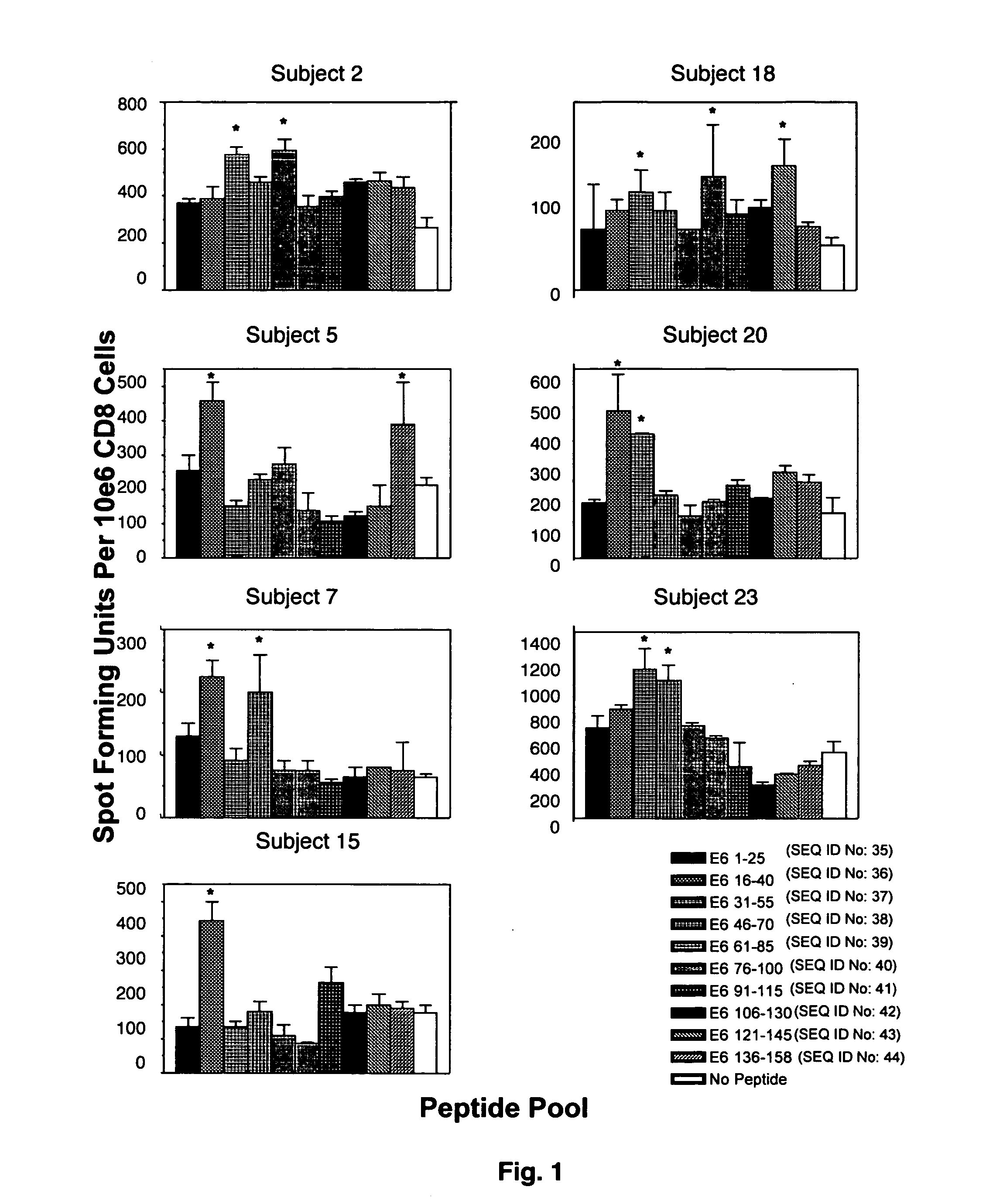
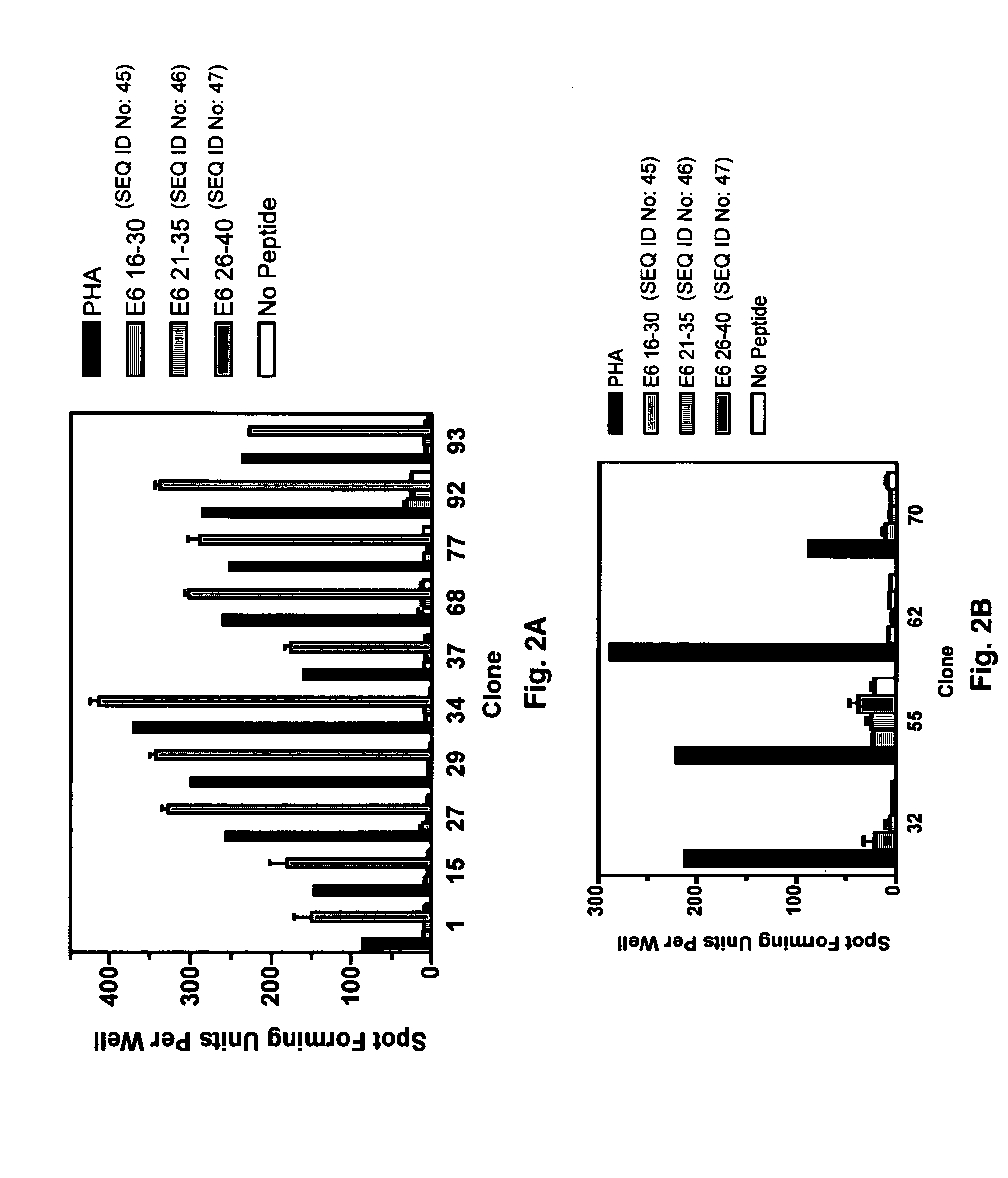
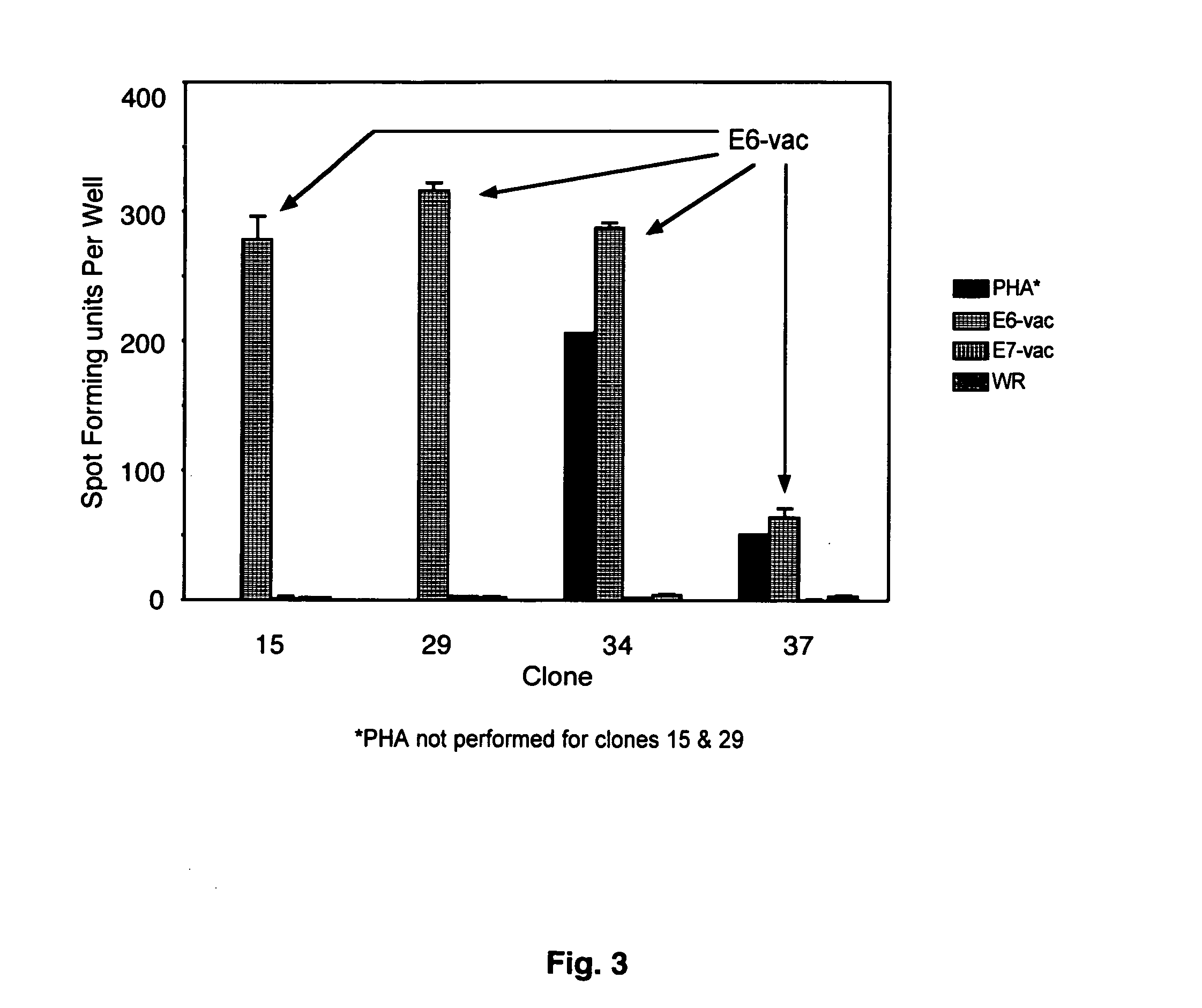
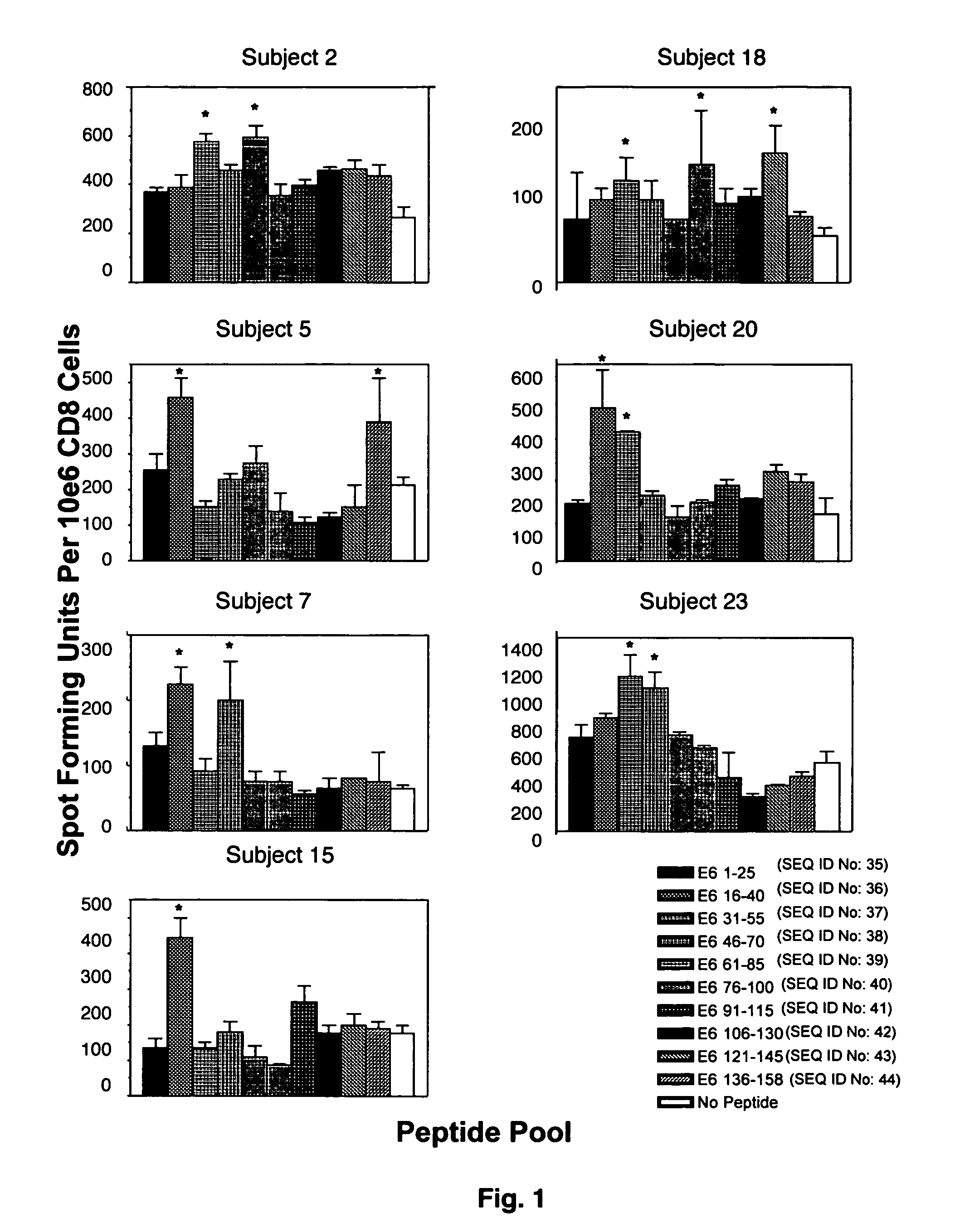
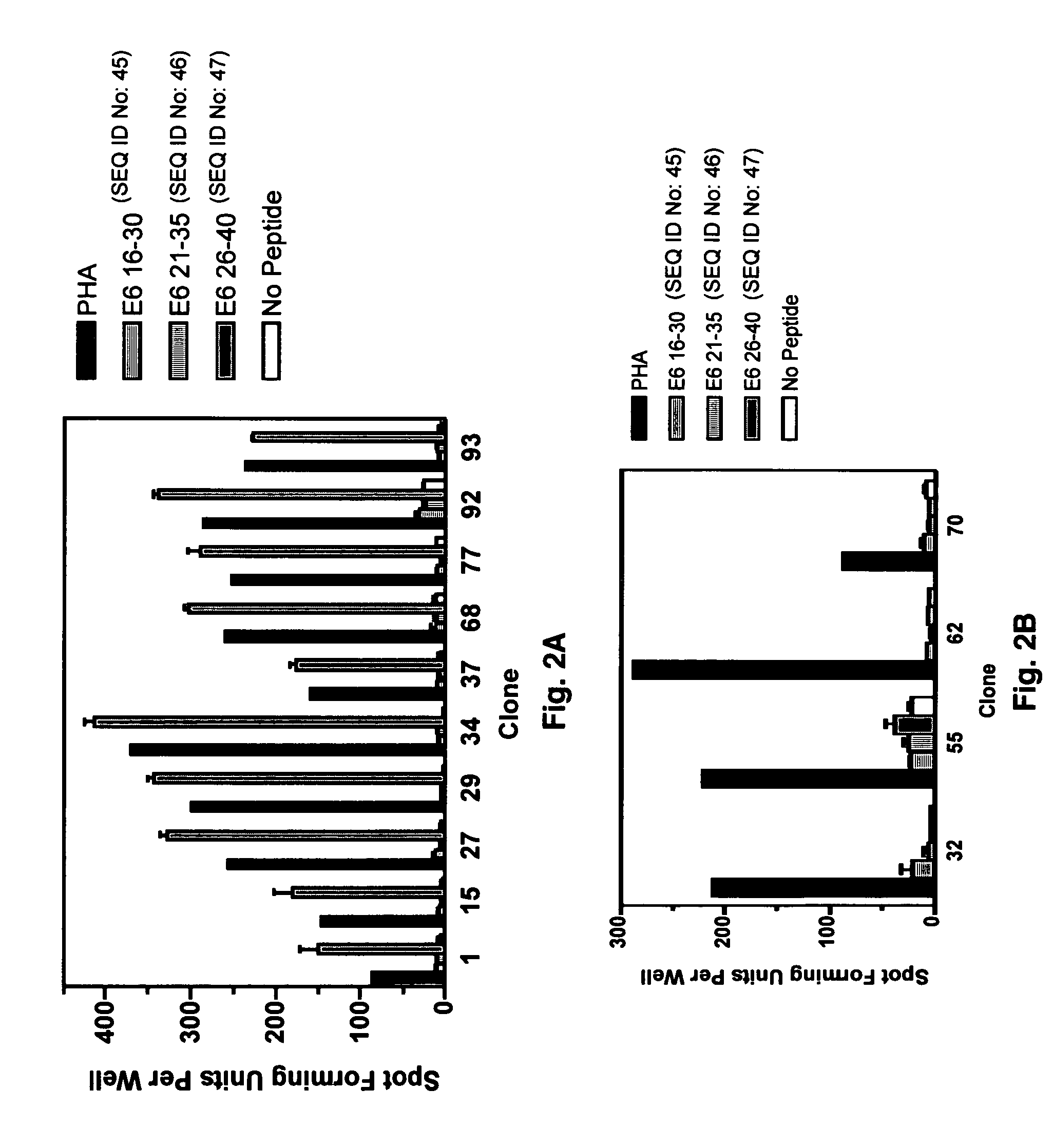
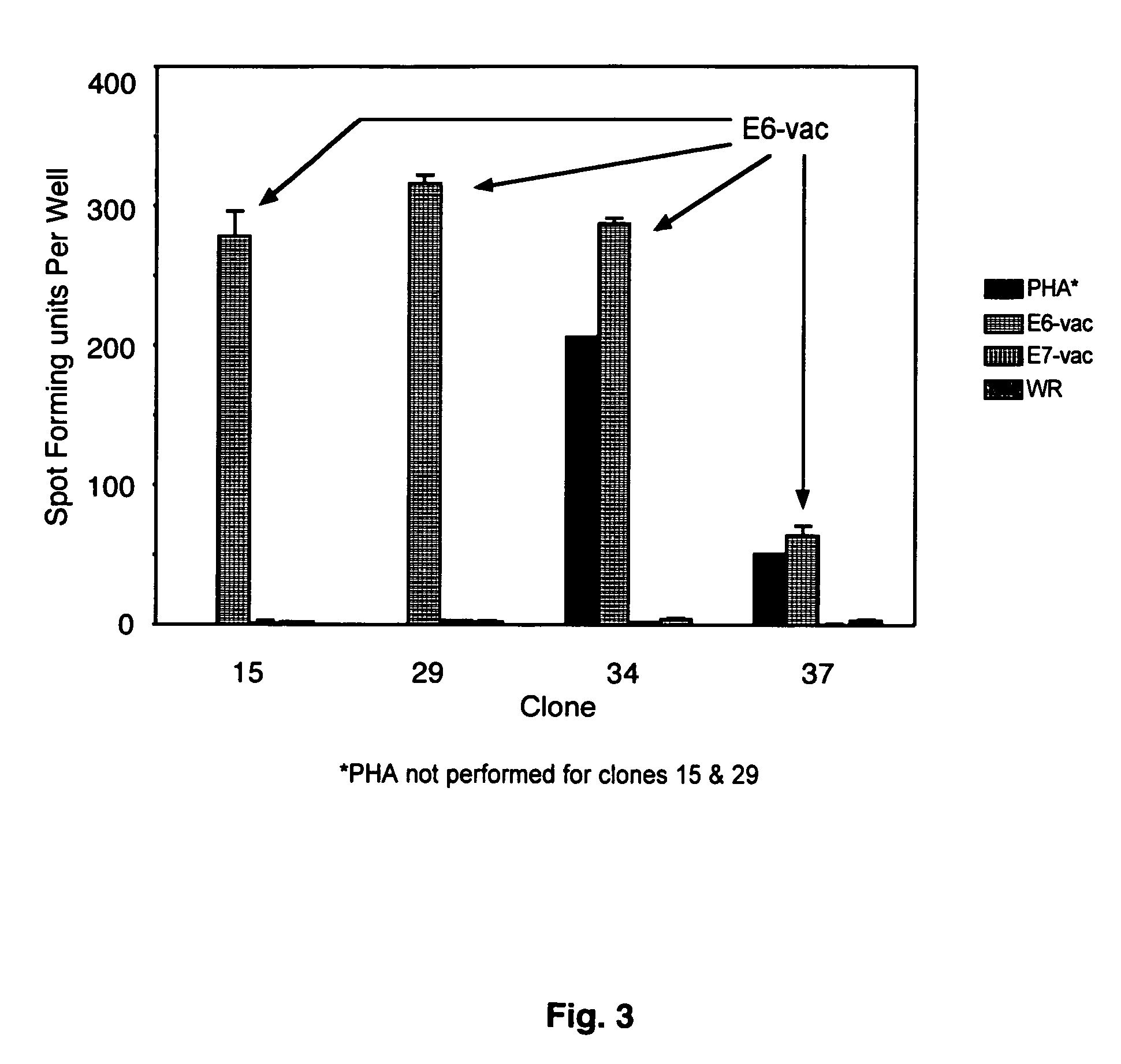
CD8 T cell epitopes in HPV 16 E6 and E7 proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060182763A1Peptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsHuman papillomavirusDendritic cell
The present invention is directed to the examination of the pattern of immunodominant CD8 T cell epitopes in the E6 and E7 protein of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its further characterization in terms of its amino acid sequence and HLA restriction. These epitopes are identified based on their ability to induce strong CD8 T cell response and therefore, are important as sources of antigens for dendritic cell immunotherapy to treat cervical cancer. The present invention contemplates identifying a number of similar epitopes restricted by a wide variety of HLA types so that they can be used in concert to develop a preventative vaccine, which can be used for general population.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
Method for down-regulating GDF-8 activity using immunogenic GDF-8 analogues
InactiveUS7070784B1Small sizeQuality improvementAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsMyostatinVaccination
Disclosed are novel methods for increasing muscle mass by means of immunization against Growth Differentiation Factor 8 (GDF-8, myostatin). Immunization is preferably effected by administration of analogues of GDF-8 which are capable of inducing antibody production against homologous GDF-8. Especially preferred as an immunogen is homologous GDF-8 which has been modified by introduction of one single or a few foreign, immunodominant and promiscuous T-cell epitopes while substantially preserving the tertiary structure of the homologous GDF-8. Also disclosed are nucleic acid vaccination against GDF-8 and vaccination using live vaccines as well as methods and means useful for the vaccination. Such methods and means include methods for identification of useful immunogenic GDF-8 analogues, methods for the preparation of analogues and pharmaceutical formulations, as well as nucleic acid fragments, vectors, transformed cells, polypeptides and pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:PHARMEXA
Vaccine composition
InactiveUS20060216307A1UpregulationReducing lipid A toxicityAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderProtective antigenBacteroides
The present invention relates to an immuno-protective and non-toxic Gram-negative bleb vaccine suitable for paediatric use. Examples of the Gram-negative strains from which the blebs are made are N. meningitidis, M. catarrhalis and H. influenzae. The blebs of the invention are improved by one or more genetic changes to the chromosome of the bacterium, including up-regulation of protective antigens, down-regulation of immunodominant non-protective antigens, and detoxification of the Lipid A moiety of LPS.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Combination hepatitis c virus antigen and antibody detection method
InactiveUS20080113339A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsWhole blood productHepatitis C virus core
An in vitro method that allows detection of hepatitis C by detecting hepatitis C virus (HCV) core protein and antibodies to HCV core protein (anti-core antibodies) in a single assay is provided. Cross-reactivity is eliminated in the method preferably by utilizing short peptides, each of which has an amino acid sequence that corresponds to an immunodominant region of the native core protein but which does not wholly encompass the epitope bound by the antibodies utilized in the method. The method can be used to detect the presence of HCV in a subject, and / or to determine the suitability of donor blood or blood products for transfusion purposes. Also provided are diagnostic kits for carrying out the method and a process for selecting suitable capture peptides and monoclonal antibodies for use in the combination method.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
CD8 T cell epitopes in HPV 16 E6 and E7 proteins and uses thereof
The present invention is directed to the examination of the pattern of immunodominant CD8 T cell epitopes in the E6 and E7 protein of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its further characterization in terms of its amino acid sequence and HLA restriction. These epitopes are identified based on their ability to induce strong CD8 T cell response and therefore, are important as sources of antigens for dendritic cell immunotherapy to treat cervical cancer. The present invention contemplates identifying a number of similar epitopes restricted by a wide variety of HLA types so that they can be used in concert to develop a preventative vaccine, which can be used for general population.
Owner:BIOVENTURES LLC
Preparation method and application of Qbeta-2aa phage virus-like particle protein
ActiveCN101921733AImproving immunogenicityEfficient inductionAntiinfectivesViruses/bacteriophagesEscherichia coliPeptide antigen
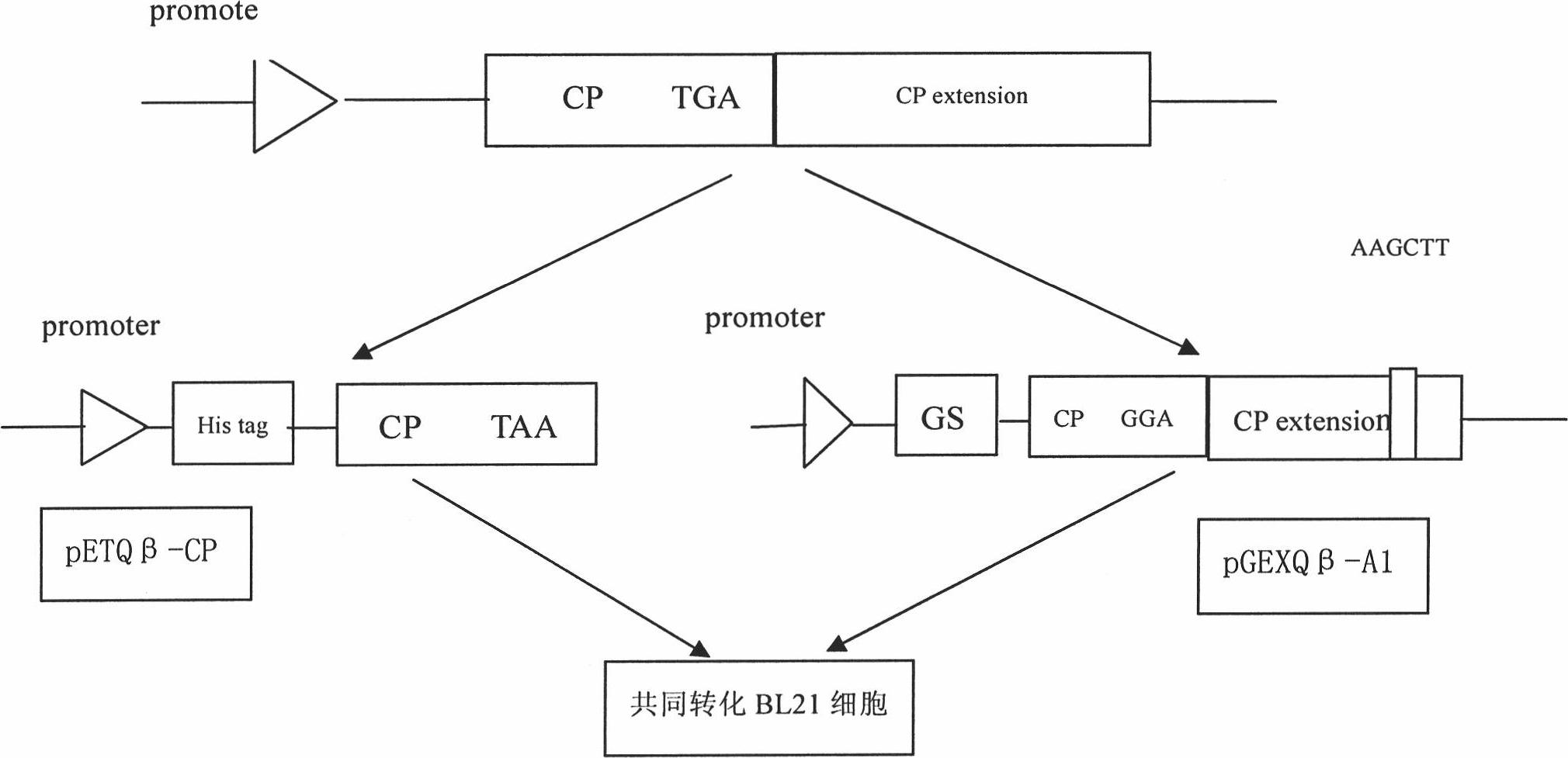
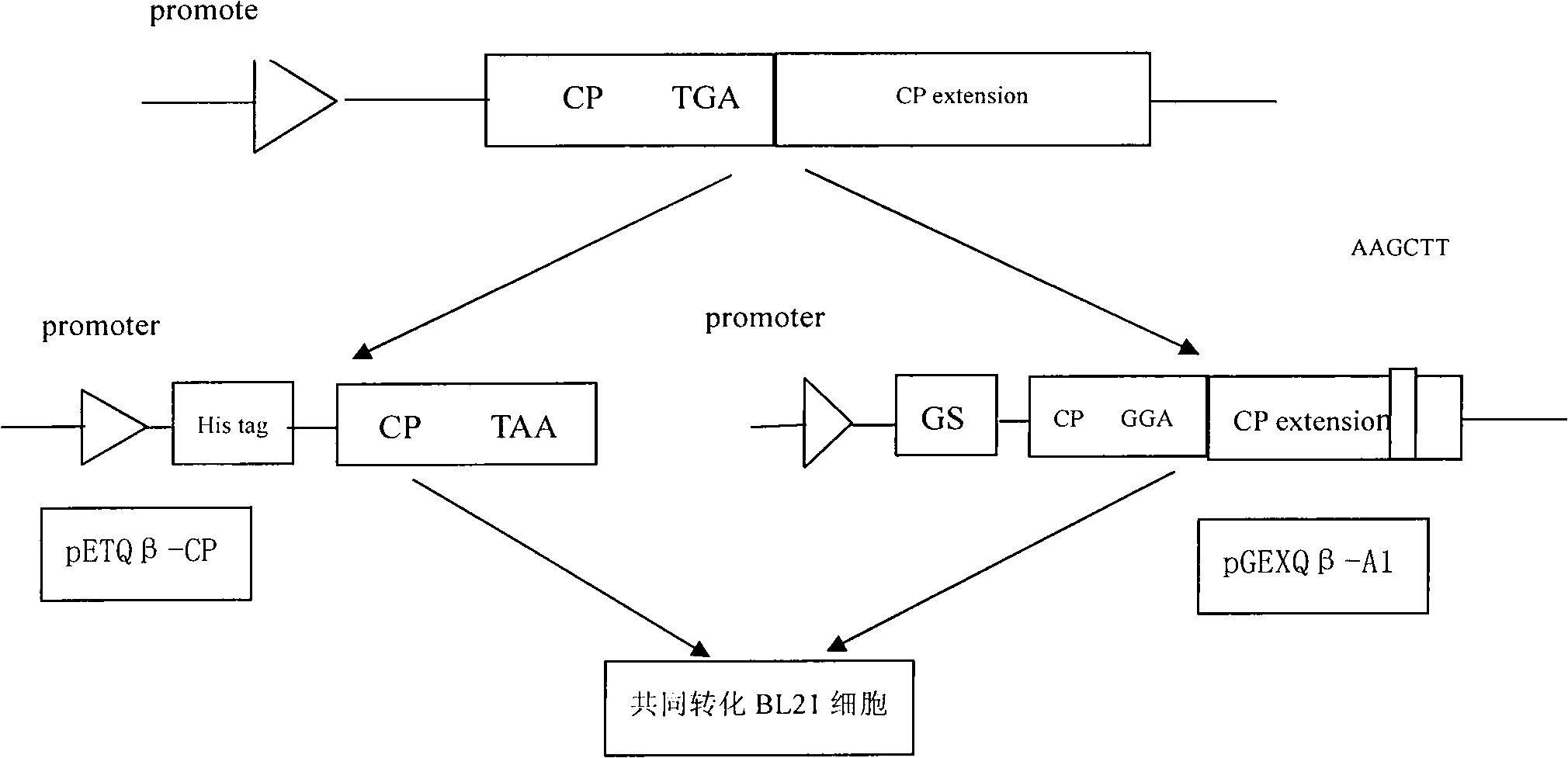
The invention relates to a Qbeta-2aa phage virus-like particle protein which is prepared according to a method comprising the following steps of: (1) mutating a Qbeta phage CP (coat protein) gene terminator codon into a strong terminator codon TAA from TGA and then cloning the strong terminator codon into a protokaryon expression vector pET28a(+) to obtain a coding CP plasmid pETQB-CP; (2) inserting the nucleotides AAGCTT of coding lysine and leucine at the coding immunodominance determining region position in a Qbeta phage CP extension protein gene, i.e. between the 72th codon and the 73th codon of the Qbeta phage CP extension protein gene, and mutating the CP gene terminator codon into GGA from TGA and then cloning the GGA into a protokaryon expression vector PGEX4T-2 to obtain a codingA1 protein plasmid pGEXQbeta-A1; (3) jointly converting the mutated coding Qbeta phage CP plasmid and the A1 protein plasmid into escherichia coli, and inducing and then expressing to obtain the virus-like particle protein Qbeta-2aa; and (4) coupling a short peptide antigen to Qbeta-2aa phage virus-like particles by using a iso-bifunctional cross-linking agent.
Owner:WUHAN HUAJIYUAN BIOTECH DEV
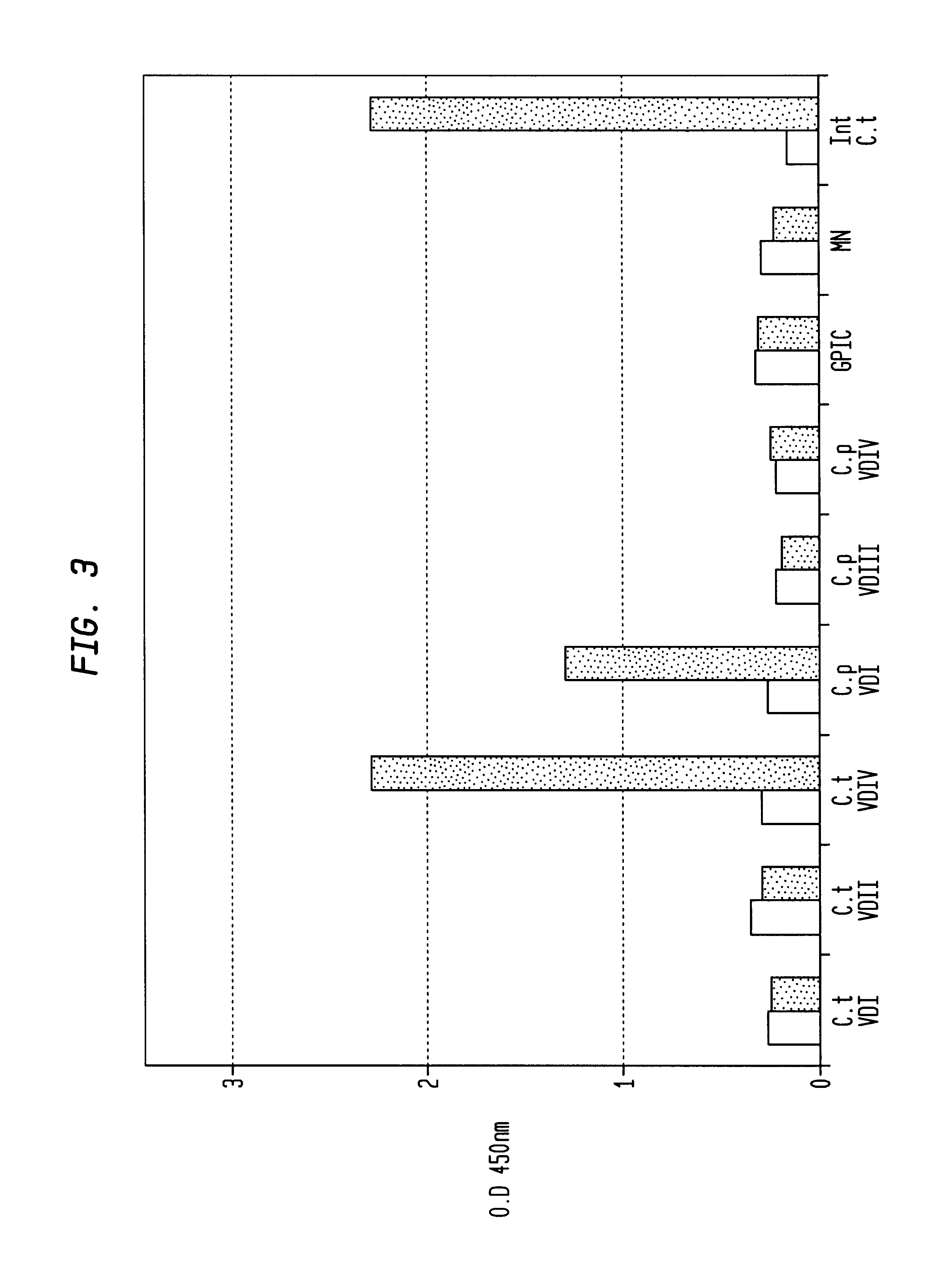
Chlamydia trachomatis specific peptides and their use in diagnostic assays
InactiveUS6699678B1High sensitivityStrong specificityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsAntiendomysial antibodiesDrug biological activity
Disclosed are peptides or a mixture of peptides, or analogs thereof, derived from the variable domains of the Chlamydia trachomatis (C. trachomatis) immunodominant major outer membrane protein (MOMP). The peptides or mixtures of peptides are characterized by having specificity only to C. trachomatis anti-MOMP antibodies and being non-cross reactive with anti-MOMP antibodies of other Chlamydia species Specific peptides are described (SEQ ID Nos. 1 to 8) as well as their analogs, which have essentially the same biological activity.
Owner:SAVYON DIAGNOSTICS
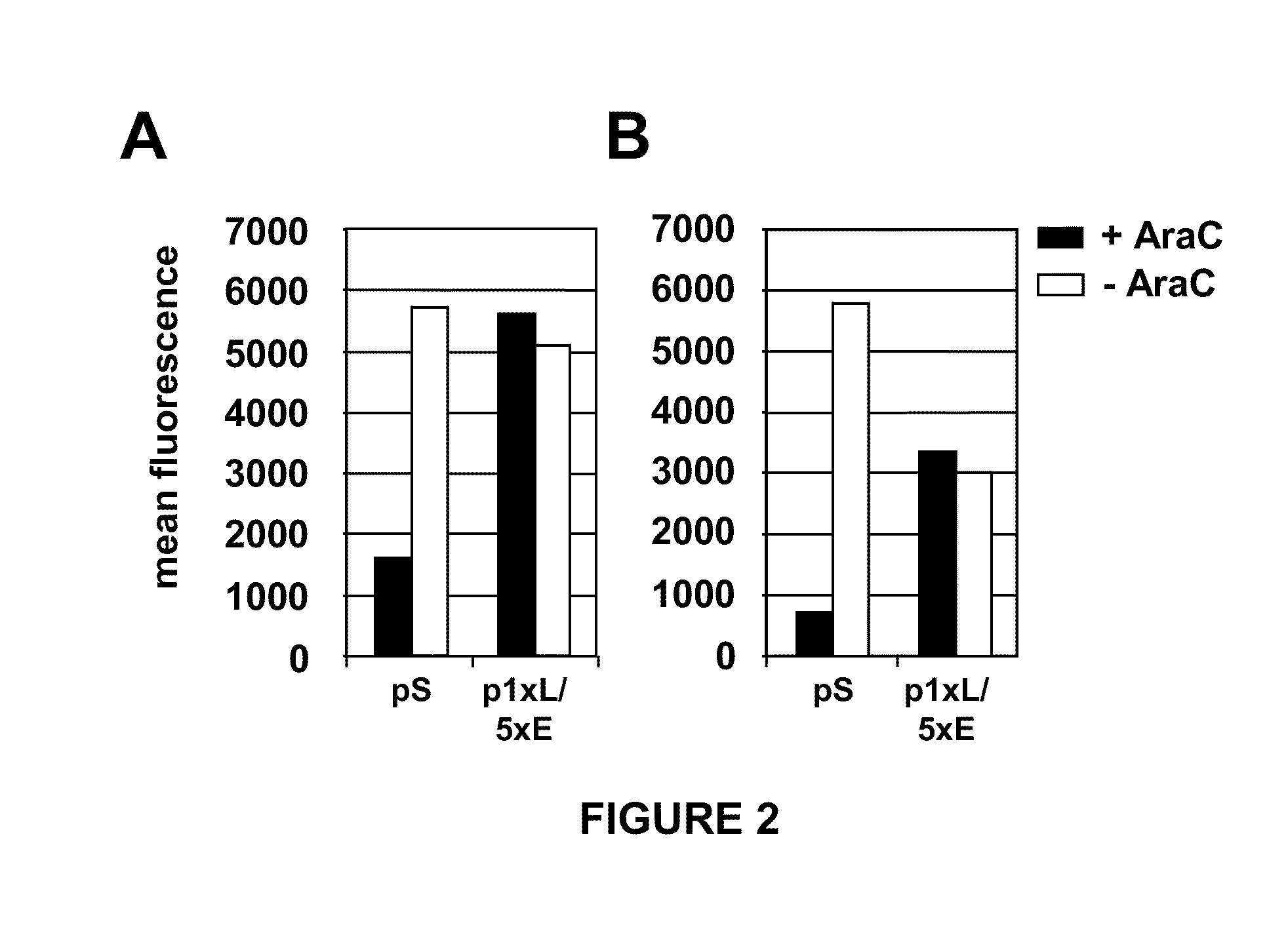
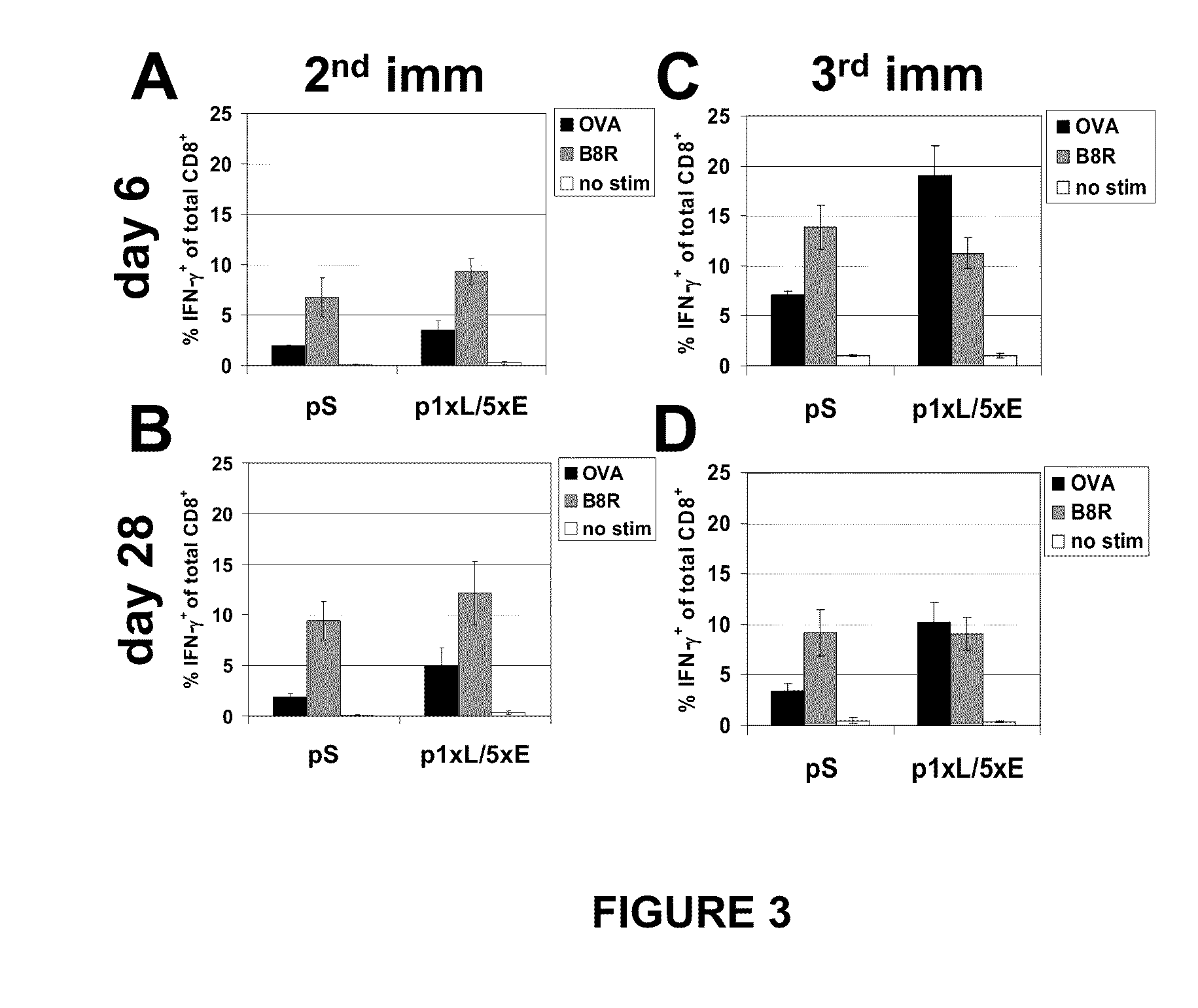
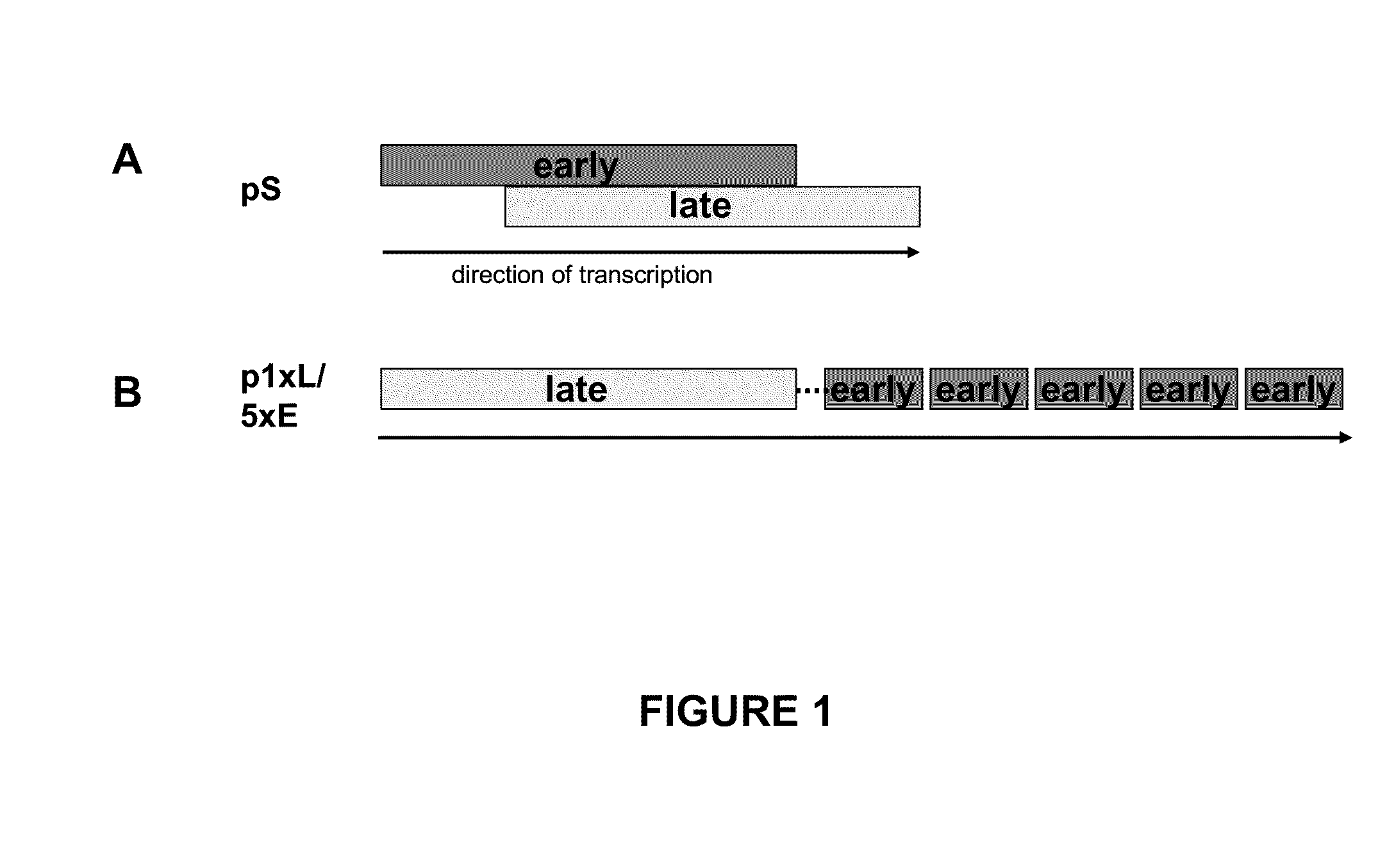
Optimized early-late promoter combined with repeated vaccination favors cytotoxic T cell response against recombinant antigen in MVA vaccines
The invention is drawn to compositions and methods for the induction of a strong CD8 T cell response to a specific antigen(s). The combination of an early / late hybrid promoter directing strongly enhanced early expression of a neoantigen with at least three immunization rounds resulted in a highly efficient neoantigen-specific CD8 T cell response. This combination reversed the immunodominance hierarchy and converted a moderately immunogenic and subdominant CD8 T cell epitope into the immunodominant epitope.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
High molecular weight surface proteins of non-typeable haemphilus
High molecular weight surface proteins of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae which exhibit immunogenic properties and genes encoding the same are described. Specifically, genes coding for two immunodominant high molecular weight proteins, HMW1 and HMW2, have been cloned, expressed and sequenced, while genes coding for high molecular proteins HMW3 and HMW4 have also been cloned, expressed and sequenced.
Owner:BARENKAMP STEPHEN J
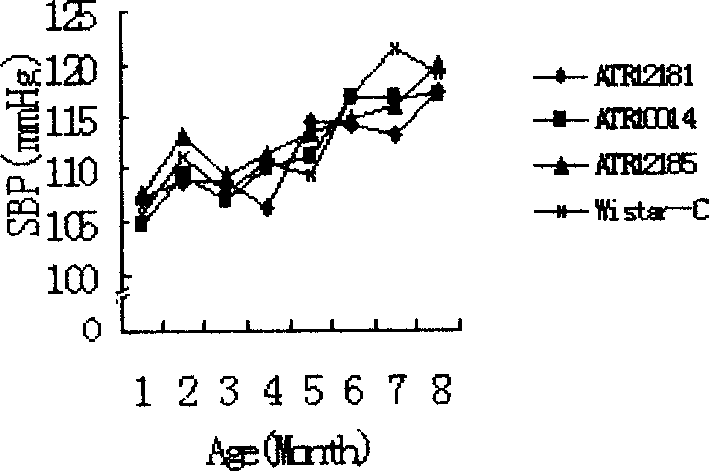
Angiotensin II receptors I immunogenic peptide section and its use
ActiveCN1896094AImprove complianceEffective blood pressure controlPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesImmunogenic peptideImmunogenicity
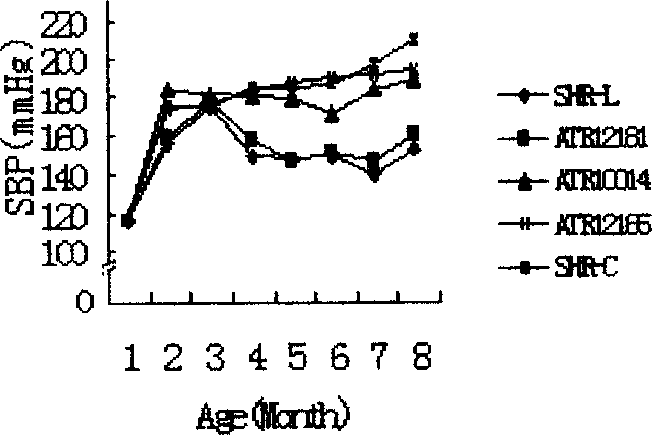
An angiotensin IIreceptorI-type immune peptide section and its use are disclosed. The peptide section is selected from the amino-acid sequence as following: SEQ ID NO:181-187, amino-acid sequence of peptide section is Ala-Phe-His-Tyr-Glu-Ser-Arg; its analog is Ala-Phe-His-Tyr-Glu-Ser-Gln. It has excellent treatment performance, antigenicity and / or immunodominance. The use is carried out by feeding medicine by injecting for 0-8weeks. It can be used to treat primary hypertension as vaccine or medicinal composition.
Owner:WUHAN HUAJIYUAN BIOTECH DEV
Preparation method and application of Qbeta-2aa phage virus-like particle protein
ActiveCN101921733BImproving immunogenicityEfficient inductionAntiinfectivesViruses/bacteriophagesEscherichia coliPeptide antigen
Owner:WUHAN HUAJIYUAN BIOTECH DEV
HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN101579528AExtensive cross-reactivityShow feasibilityGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsCtl epitopeVaccination
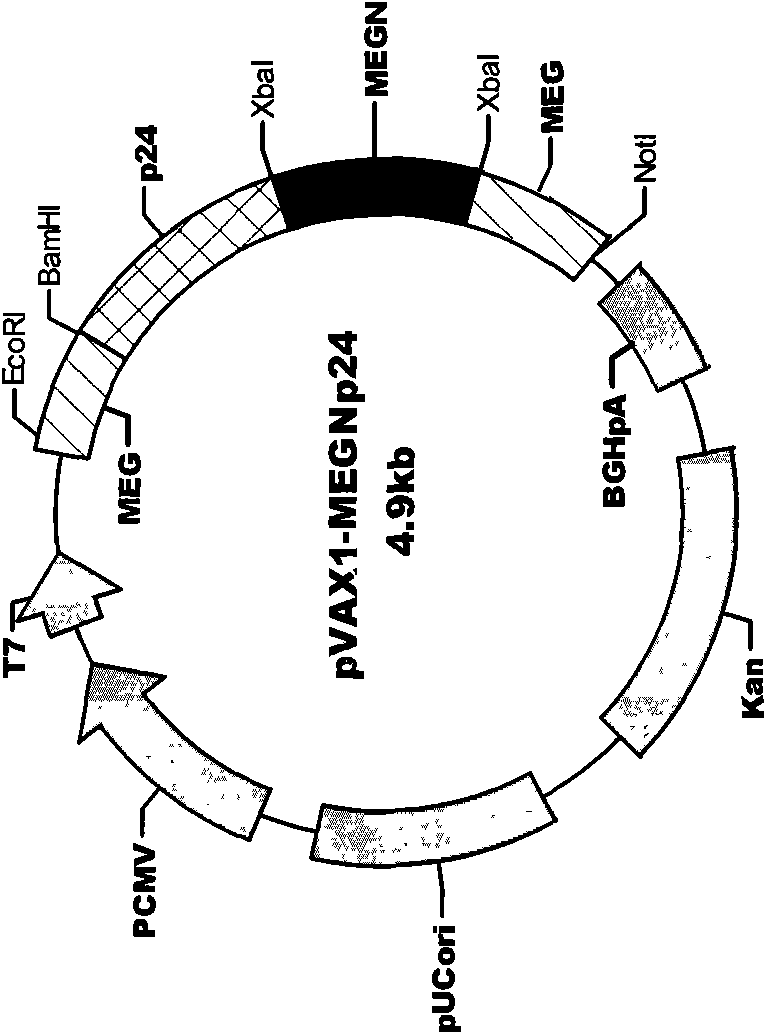
The invention discloses an HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine which takes HIV-1 capsid protein p24 as a vector backbone molecule and ER signal peptide as a homing sequence, and contains twenty-six highly conservative immunodominant epitopes in an HIV genome; wherein, the HIV composite multi-epitope DNA vaccine comprises twenty-nine epitopes which are three neutralizing antibody epitopes, twenty-three CTL epitopes, one HIV-1 isolate common antibody epitope, one MHC nonrestrictive T helper lymphocyte epitope and one spasmotoxin B cell epitope. The vaccine can be used for vaccination of healthy people and immunization therapy of people who are infected by AIDS virus, thus having double effects of prevention and treatment.
Owner:MILITARY VETERINARY RES INST PLA MILITARY MEDICAL ACAD OF SCI
Helicobacter pylori antigen HLA restrictive immunodominance epitope peptide and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102746381AImproving immunogenicityReduce the risk of useAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesImmunodominance
The invention relates to Helicobacter pylori antigen HLA restrictive immunodominance epitope peptide as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The dominance epitope peptide has the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:63, 74, 95 and 105. The invention also provides a preparation method of the epitope peptide, and further provides application of the epitope peptide to preparation for preventing or treating Helicobacter pylori infection.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
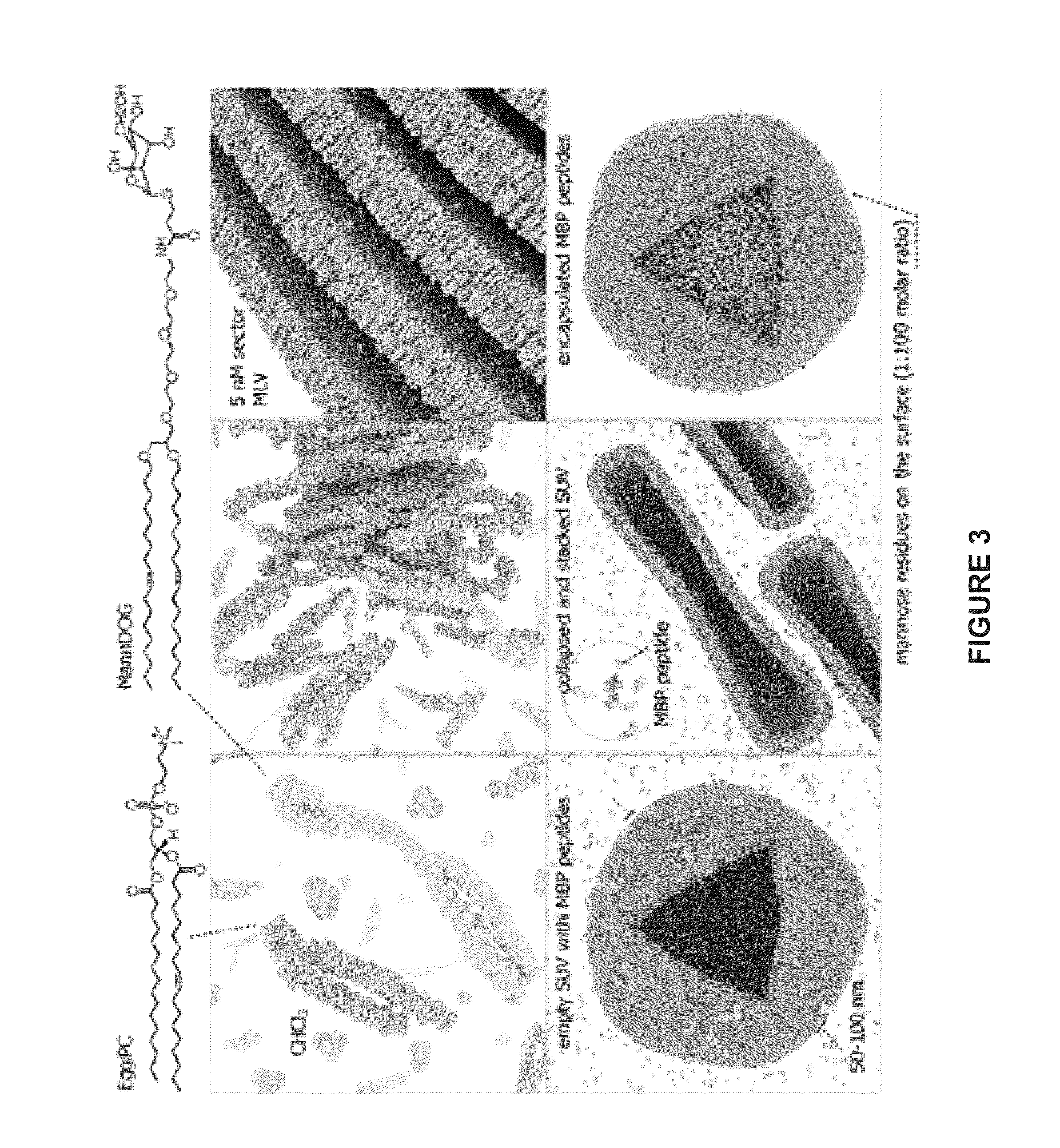
Liposomes containing oligopeptide fragments of myelin basic protein, a pharmaceutical composition and a method for treatment of multiple sclerosis
InactiveUS20130058994A1Reduce paralysisReduce deliveryNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineOligopeptide
The present invention provides compositions and methods for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Among others, the invention provides compositions of immunodominant peptides of myelin basic protein encapsulated in mannosylated liposomes. In a specific embodiment, the compositions comprise mylein basic protein (MBP) peptides MBP(46-62), MBP(124-139), and MBP(147-170).
Owner:LIPOXEN TECHNOLOGIES LTD
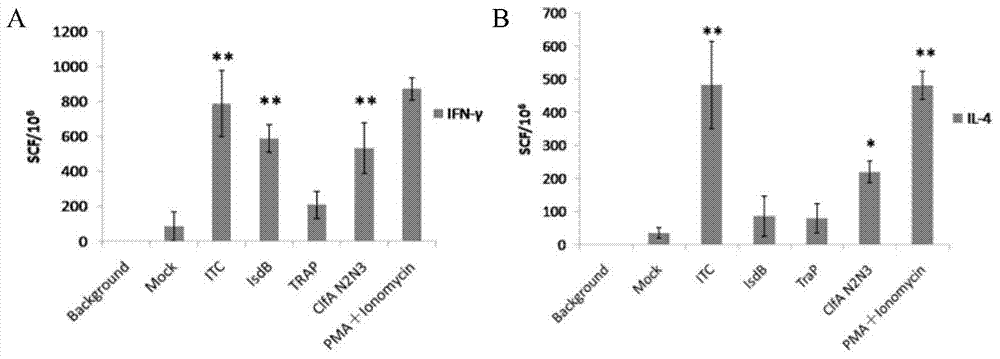
Staphylococcus aureus ITC (Inverse Transition Cycling) fusion protein as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103570835AGood immune effectImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsAntibody medical ingredientsAntigenStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses a staphylococcus aureus ITC (Inverse Transition Cycling) fusion protein which is a protein formed by fusing IsdB immunodominance fragments (IsdBid) and Trap as well as a ClfA immunodominance fragment N3 area (ClfAN3); an amino acid sequence of the fusion protein is as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention further provides a coding gene, a preparation method and application of the fusion protein in preparing a vaccine for preventing staphylococcus aureus infection. The ITC fusion protein disclosed by the invention contains various antigens, and therefore, immune effect is good, protective effect of preventing staphylococcus aureus infection is improved; compared with the immune result of any of ClfA, IsdB and TraP, the ITC fusion protein immune effect is better than that of single protein; moreover, the ITC contains Trap with smaller molecular weight and has an immunodominance fragment with two antigens, so that peptide chain length is not lengthy, and therefore, the fusion protein is beneficial to in-vitro expression and has important value in developing and applying a novel vaccine for preventing staphylococcus aureus.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
New m.tuberculosis vaccines
InactiveUS20170043003A1High expressionReduce bacterial loadAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsAntigenMycobacterium microti
The present invention is directed to a fusion protein, antigen cocktails and immunological compositions such as vaccines against infections caused by virulent mycobacteria, e.g. by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Mycobacterium africanum, Mycobacterium bovis, Mycobacterium microti, Mycobacterium canettii, Mycobacterium pinnipedii or Mycobacterium mungi. The fusion protein, antigen cocktails and immunological compositions are based on proteins secreted by the ESAT-6 secretion system 1 (ESX-1) and are among the most immunodominant M. tuberculosis (MTB) antigens.
Owner:STATENS SERUM INST
Modulated Immunodominance Therapy
InactiveUS20140099341A1Substantial therapeutic benefitAlter immunodominance hierarchyAntipyreticAnalgesicsBiological bodyCellular homeostasis
The invention involves generating a T cell response to subdominant antigens and using the cells to therapeutically change the cellular homeostasis and nature of the immune response. In a preferred embodiment, the cells are generated outside of the patient avoiding the influence of the patient's immunologic milieu. By stimulating and growing the T cells from a patient in a tissue culture to one or more subdominant antigens and the transplanting them into the patient, if enough cells are expanded and transplanted, the transplanted cells overwhelm the endogenous dominant T cells in the response to either break or induce immune tolerance or otherwise modify the immune response to the cells or organism expressing that antigen. When the memory cells are established they are then reflective of this new immunodominance hierarchy so that the desired therapeutic effect is long lasting. In effect, the transplantation exogenously generated T cells reactive to the subdominant antigens is recapitulating priming and rebalancing the patient's immune response to target previously subdominant antigens in the cells or organism to produce a therapeutic benefit.
Owner:GENEIUS BIOTECH
Optimized early-late promoter combined with repeated vaccination favors cytotoxic t cell response against recombinant antigen in mva vaccines
ActiveUS20100233203A1Increasing early gene expressionBiocideGenetic material ingredientsAntigenImmunodominant Epitopes
The invention is drawn to compositions and methods for the induction of a strong CD8 T cell response to a specific antigen(s). The combination of an early / late hybrid promoter directing strongly enhanced early expression of a neoantigen with at least three immunization rounds resulted in a highly efficient neoantigen-specific CD8 T cell response. This combination reversed the immunodominance hierarchy and converted a moderately immunogenic and subdominant CD8 T cell epitope into the immunodominant epitope.
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
Helicobacter pylori immunodominance epitope peptide and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102924576AGood immune protectionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunodominant EpitopesImmunodominance
The invention relates to helicobacter pylori immunodominance epitope peptide and a preparation method and the application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the dominance epitope peptide is shown as SEQ ID NO: 97, 100, 108 and 115. A preparation method and application of the dominance epitope peptide in prevention or treatment of helicobacter pylori infection are further provided.
Owner:中国人民解放军第三军医大学药学院
Human streptococcus mutans genetic engineering vaccine for decayed tooth and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101474400AHigh titerGood immune protectionBacterial antigen ingredientsDigestive systemProtective antigenGenetic engineering
The invention belongs to the biopharmaceutical field and relates to a method for constructing and preparing human streptococcus mutans gene engineering vaccine for tooth decay. In the method, the genes at a glucan binding domain at the end of glucosyltransferase C and at an N end immunodominance domain of glucan-binding protein B which are major protective antigens of streptococcus mutans of human primary cariogenic bacteria and the mucous membrane immunologic adjuvant heat-labile toxin B subunit are used for constructing fusion engineering bacteria by a gene recombination method, and fusion protein molecular vaccine with high purity is obtained by high density fermentation and a series of purifying procedures. The technology for preparing the vaccine is simple and easy for amplifying and has good repeatability; the obtained protein has high purity; primary animal experiments prove that the fusion protein can stimulate body to produce efficient immunity response; and the fusion protein is approved as good candidate antigens of gene engineering vaccine for tooth decay and has good application prospect.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Helicobacter pylori dominant antigen assembly based on CD4+T cell immunity and screening method
InactiveCN106480003AImprove cleanlinessMild immunopathological damageAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsProtective antigenScreening method
The invention relates to a helicobacter pylori dominant antigen assembly based on CD4+T cell immunity and a preparation method. The dominant antigen assembly comprises the following three components and homologous protein of the three components: inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, type II citrate synthase and urease B subunit, wherein the amino acid sequences are shown as SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.2 and SEQ ID NO.3. The screened dominant antigen assembly based on CD4+T cell immunity has the obvious immune protection effect, has the protection effect superior to that of H.pylori holoprotein antigen, has strong capacity of scavenging helicobacter pylori, and causes extremely slight pathological injuries. The three immunity dominant antigens provided by the invention can induce the body to generate strong immune response reaction aiming at antigens, therefore, through the means of inducing the body to generate the response aiming at the immunoprotecive dominant antigens, or directly immunizing the body by adopting the protective antigens, the effective immune protection effect can be achieved on the helicobacter pylori infection, and the scheme can be used for the further study on the preventive and therapeutic polyvaccines of helicobacter pylori.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
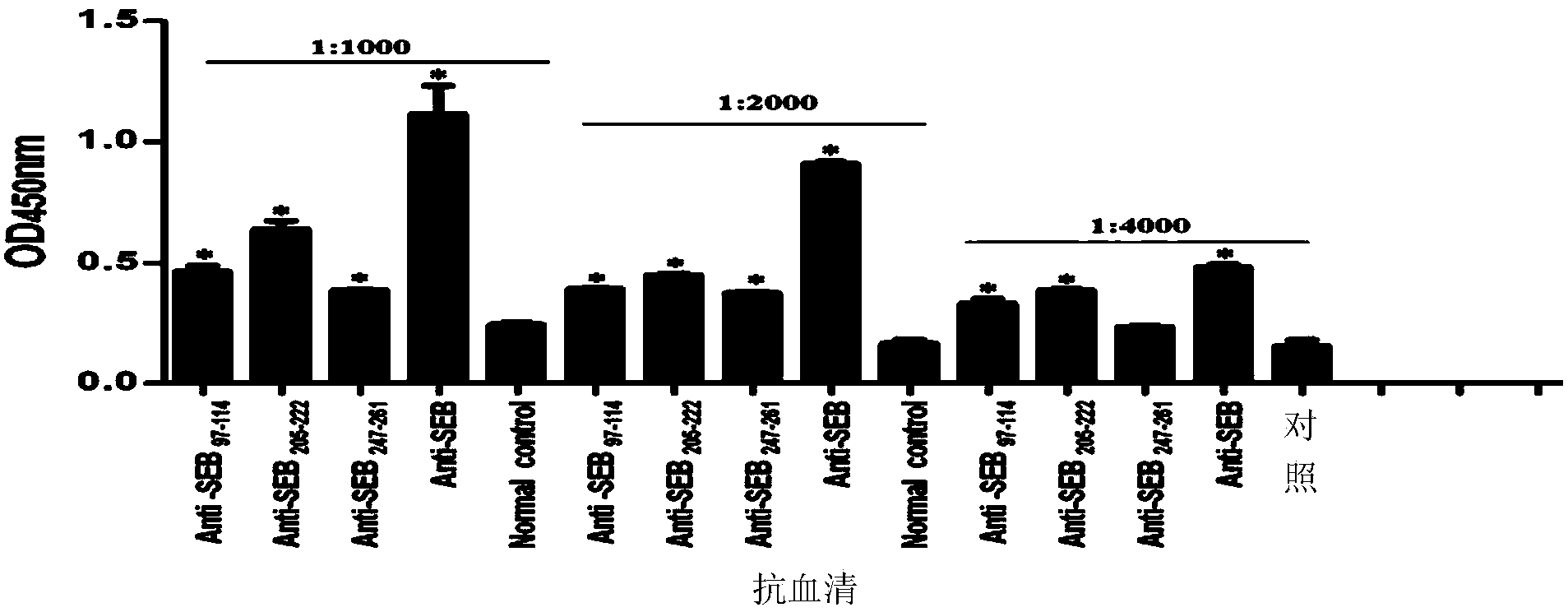
B cell immunodominant epitope peptide of staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103772493AImproving immunogenicitySimple methodAntibacterial agentsBiological material analysisStaphylococcus aureus enterotoxin BImmunodominance
The invention relates to a B cell immunodominant epitope peptide of staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B and a preparation method and application thereof, and concretely provides a B cell immunodominant epitope peptide of staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B. Amino acid sequences of the B cell immunodominant epitope peptide are shown in SEQ ID NO: 17, 35 and 42. Corresponding amino acid sequences of core epitopes of the B cell immunodominant epitope peptide are respectively shown in SEQ ID NO: 48, 54 and 69. According to the preparation method, the B cell immunodominant epitope peptide of the staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B is assayed by an overlapping peptide binding titration method, so that the screening method is simple, convenient, quick and accurate and is free from omission. The immunodominant epitope peptide does not contain unnecessary or even harmful parts, so that the risk of vaccines prepared from the immunodominant epitope peptide during use is lowered; the immunodominant epitope peptide has a relatively high vaccine application value and can be applied to the preparation of epitope vaccines and / or prevention vaccines of the staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for identifying and validating dominant T helper cell epitopes using an HLA-DM-assisted class II binding assay
ActiveUS8916340B2SsRNA viruses negative-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseImmunotherapeutic agent
Rational design of immunotherapeutics relies on clear knowledge of the immunodominant epitopes of antigens. Current methods for identifying kinetically stable peptide-MHC complexes are in many cases inadequate for a number of reasons. Disclosed herein is a reductionistic system incorporating known participants of MHC class II antigen processing in solution to generate peptide pools from antigens, including those for which no immunodominant epitope has yet been identified, that are highly enriched for proteolytic fragments containing their immunodominant epitopes. HLA-DM-mediated editing contributes significantly to immunodominance and is exploited in discovering immunodominant epitopes from novel or previously uncharacterized antigens, particularly antigens associated with pathogens, tumors or autoimmune diseases.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Novel method for down-regulation of amyloid
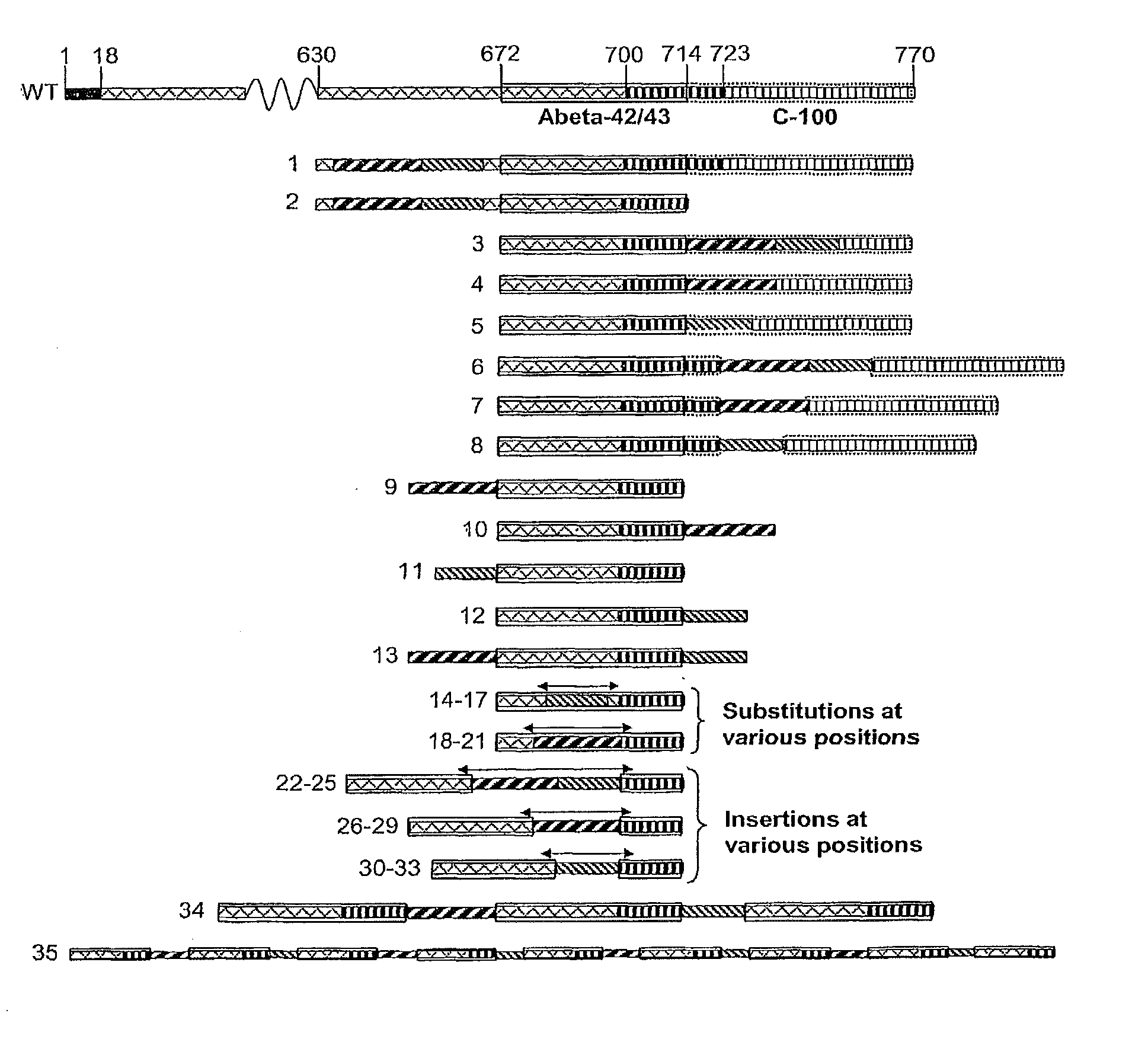
Disclosed are novel methods for combating diseases characterized by deposition of amyloid. The methods generally rely on immunization against amyloidogenic proteins (proteins contributing to formation of amyloid) such as beta amyloid (Aβ). Immunization is preferably effected by administration of analogues of autologous amyloidogenic polypeptides, said analogues being capable of inducing antibody production against the autologous amyloidogenic polypeptides. Especially preferred as an immunogen is autologous Aβ which has been modified by introduction of one single or a few foreign, immunodominant and promiscuous T-cell epitopes while substantially preserving the majority of Aβ's B-cell epitopes. Also disclosed are nucleic acid vaccination against amyloidogenic polypeptides and vaccination using live vaccines as well as methods and means useful for the vaccination. Such methods and means include methods for identification of useful immunogenic analogues of the amyloidogenic proteins, methods for the preparation of analogues and pharmaceutical formulations, as well as nucleic acid fragments, vectors, transformed cells, polypeptides and pharmaceutical formulations.
Owner:H LUNDBECK AS
Compositions and methods for modifying blood cell carbohydrates
InactiveUS7767415B2BacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementWhole blood productRed blood cell enzymes
This invention relates to enzymatic removal of type A and B antigens from blood group A, B, and AB reactive cells in blood products, and thereby converting these to non-A and non-B reactive cells. The invention further relates to using unique αN-acetylgalactosaminidases and α-galactosidases with superior kinetic properties for removing the immunodominant monosaccharides of the blood group A and B antigens and improved performance in enzymatic conversion of red blood cells. The preferred unique α-N-acetylgalactosaminidases and α-galactosidases exhibit the following characteristics:(i) exclusive, preferred or no less than 10% substrate specificity for the type A and B branched polysaccharide structures relative to measurable activity with simple mono- and disaccharide structures and aglycon derivatives hereof; (ii) optimal performance at neutral pH with blood group oligosaccharides and in enzymatic conversion of cells; and (iii) a favorable kinetic constant Km with mono- and oligosaccharide substrates. The conversion methods of the invention use significantly lower amounts of recombinant glycosidase enzymes than previous and result in complete sero-conversion of all blood group A and B red cells.
Owner:VELICO MEDICAL
Mhc class II haplotype specific immunodominancy of peptides derived from rsv fusion (f) and attachement (g) proteins
InactiveUS20050249744A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsVaccinationAttachment protein
The present invention relates immunodominant peptides derived from human respiratory syncytial virus (H-RSV) that may be used in ex vivo diagnosis of immune responses to H-RSV The immunodominant peptides are derived from the H-RSV Fusion (F) and Attachment (G) proteins and are capable of inducing an antigen specific CD4+ T cell response ex vivo in a MHC class 11 haplotype restricted manner. The immunodominant H-RSV-derived peptides may further be used in methods for vaccination against H-RSV, preferably in a MHC class 11 haplotype specific manner.
Owner:DE STAAT DER NEDERLANDEN VERT DOOR DE MINIST VAN VWS
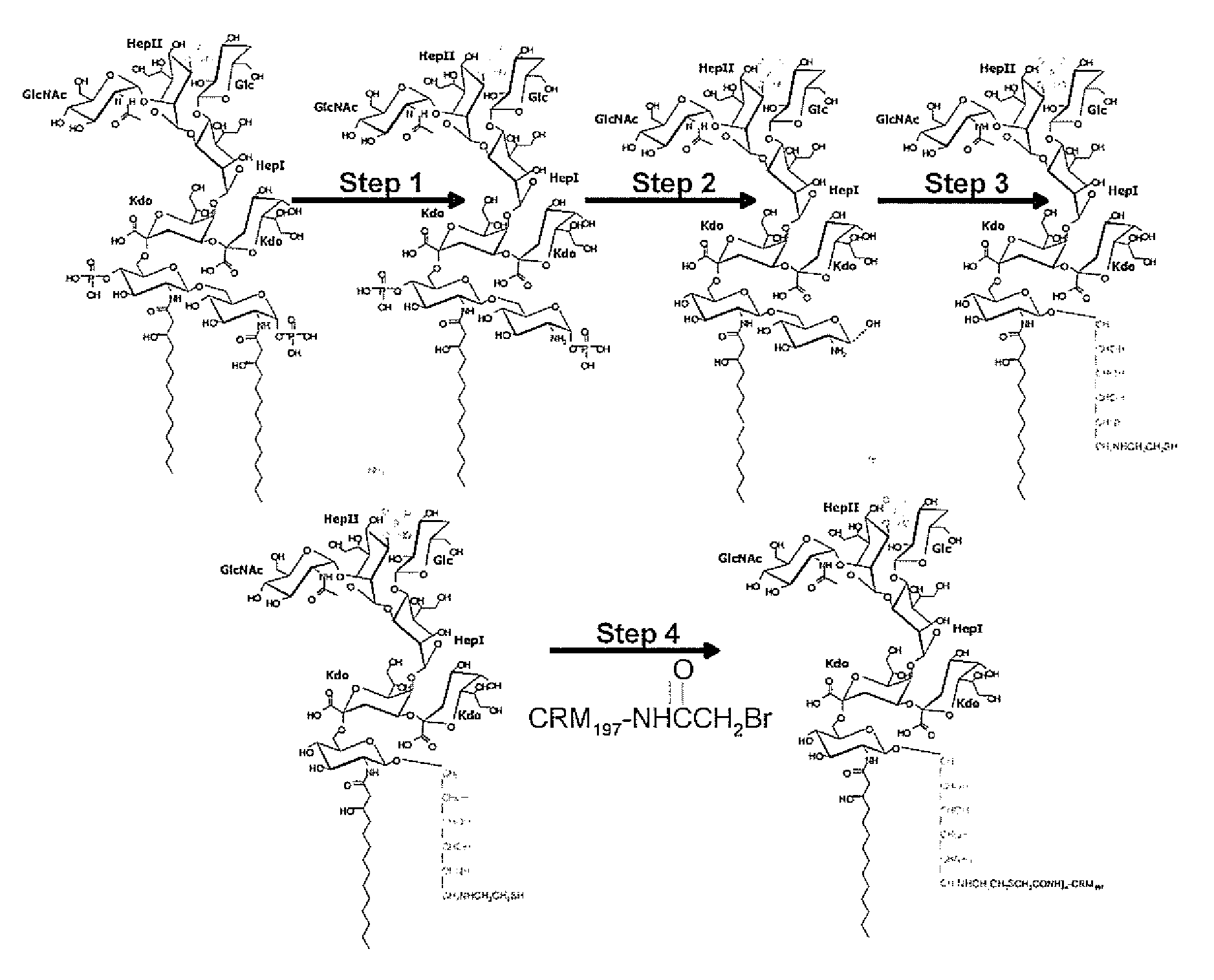
LPS Based Vaccines
The removal of the glycosidic phosphate from the reducing end of the derived LPS molecule creates an aldehydo functionality which causes the formation of an immunologically dominant neo-epitope. Conjugation to the reducing end of a carbohydrate molecule following removal of the glycosidic phosphate traps the reducing glucosamine residue in an open-chain form which surprisingly was found to dominate the immune response. We therefore modified our conjugation strategy to avoid this open-chain form, by utilising the amino functionality created by the isolated amidase activity from Dictyostelium discoideum, concomitant with a unique blocking and un-blocking strategy to protect the immunologically important phosphoethanolamine inner core residue. These antigenic structures are useful in producing vaccines and compounds helpful in combating Gram-negative bacteria. Also described are specific structures of the carbohydrate molecules derived from a variety of Gram-negative bacteria, which when presented appropriately as a glycoconjugate will facilitate a functional immune response to the target core oligosaccharide region.
Owner:COX ANDREW D +3
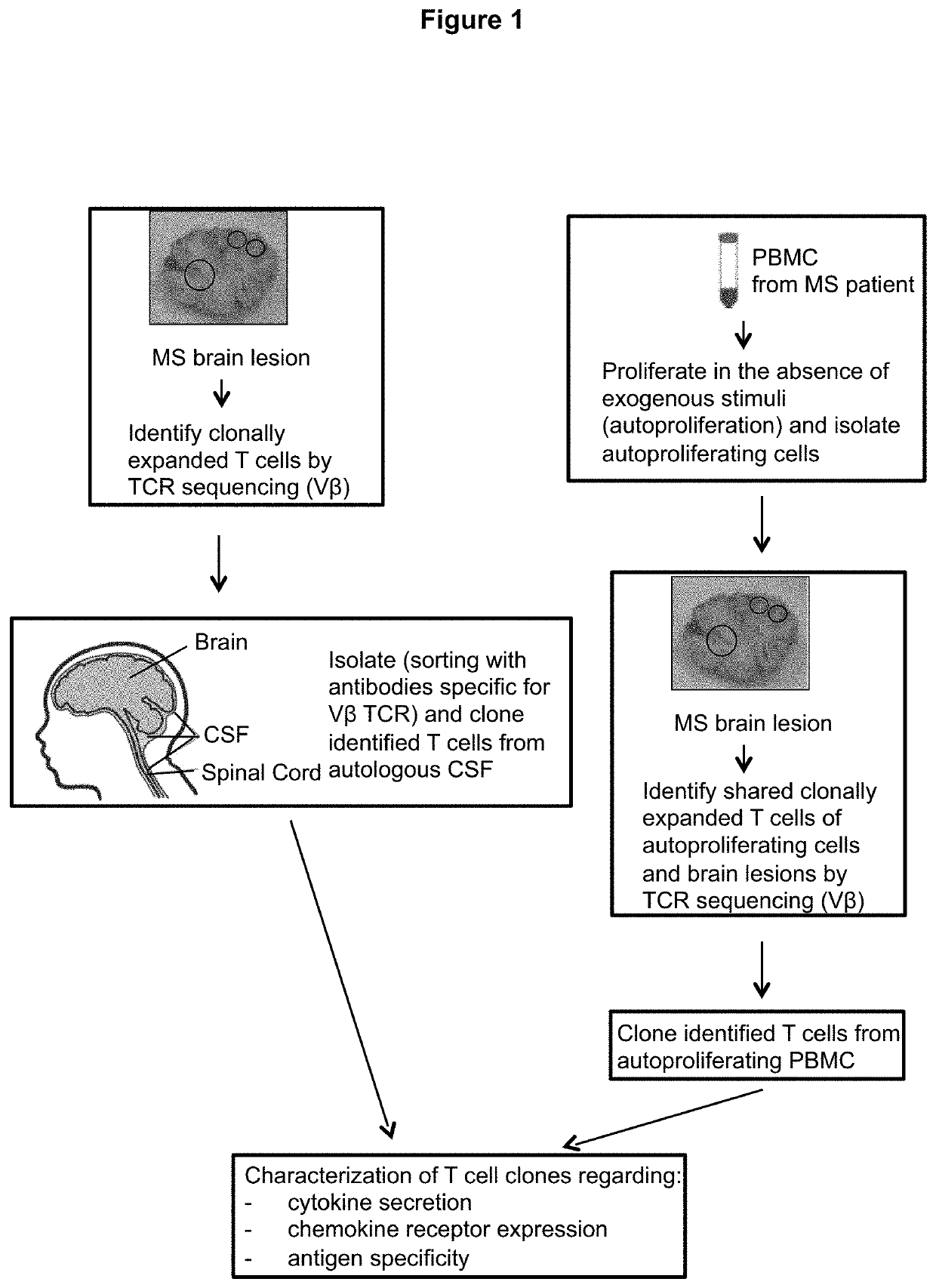
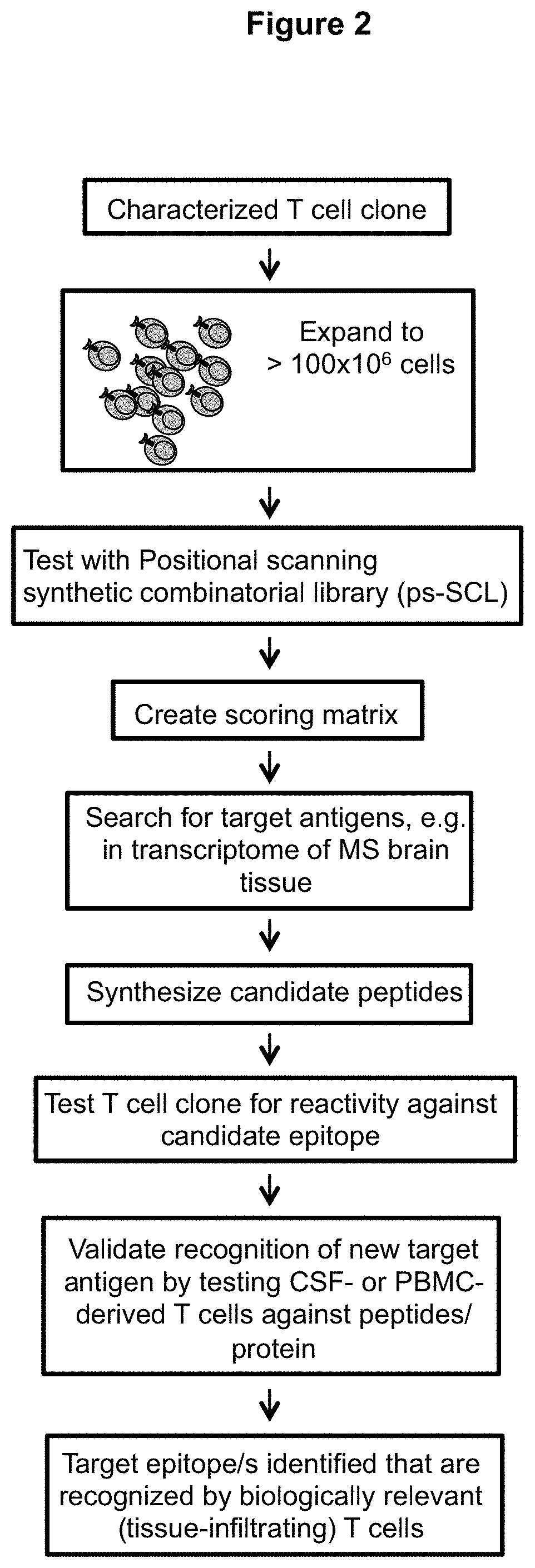
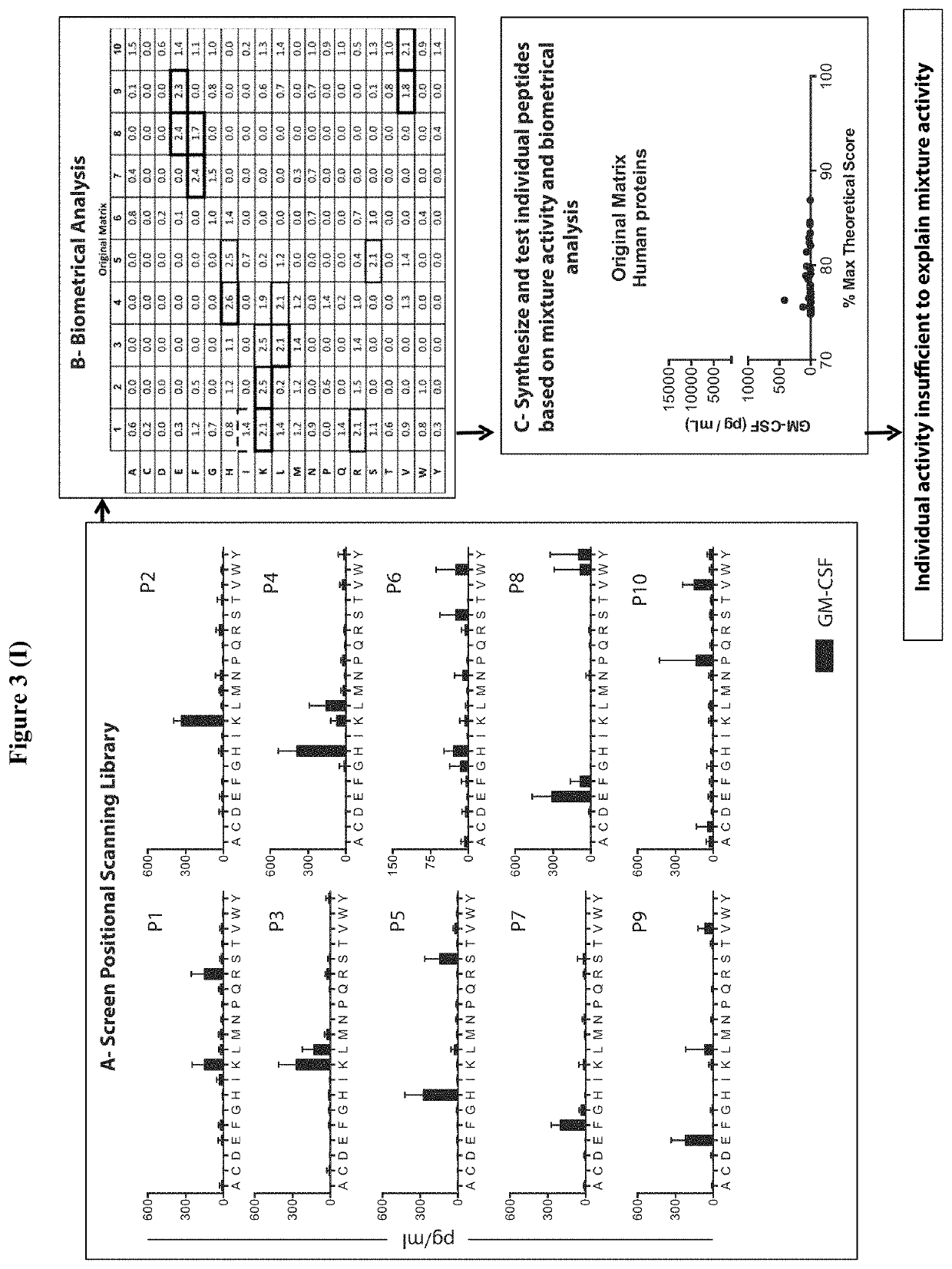
Immunodominant proteins and fragments in multiple sclerosis
PendingUS20210162019A1Peptide/protein ingredientsDisease diagnosisMS multiple sclerosisImmunodominance
The disclosure relates to the treatment, diagnosis and / or prevention of multiple sclerosis (MS) by using an immunodominant protein or peptide. More particular the invention relates to the field of antigen specific immunotherapies, such as the induction of tolerance.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
Helicobacter pylori antigen hla-restricted immunodominant epitope peptide and its application
ActiveCN102276697AImproving immunogenicityReduce the risk of useAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsImmunogenicityTGE VACCINE
The invention relates to a helicobacter pylori antigen HLA restricted immuno-dominant epitope peptide and an application thereof. The helicobacter pylori HpaA antigen immuno-dominant epitope polypeptide has amino acid sequences as shown in SEQ ID No:8, 22, 30 and 42. The polypeptide of the invention has high immunogenicity, and can initiate strong immune response. Additionally, the immuno-dominant epitope polypeptide does not contain unnecessary or even harmful parts, and thus application risk of vaccines prepared by the polypeptide is reduced. Superiority combination of the immuno-dominant epitope polypeptide with other vaccine components can be realized, which extends the width of immune response. Vaccines prepared by the immuno-dominant epitope polypeptide not only have prevention effect on helicobacter pylori infection, but also can be used as therapeutic vaccines.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com