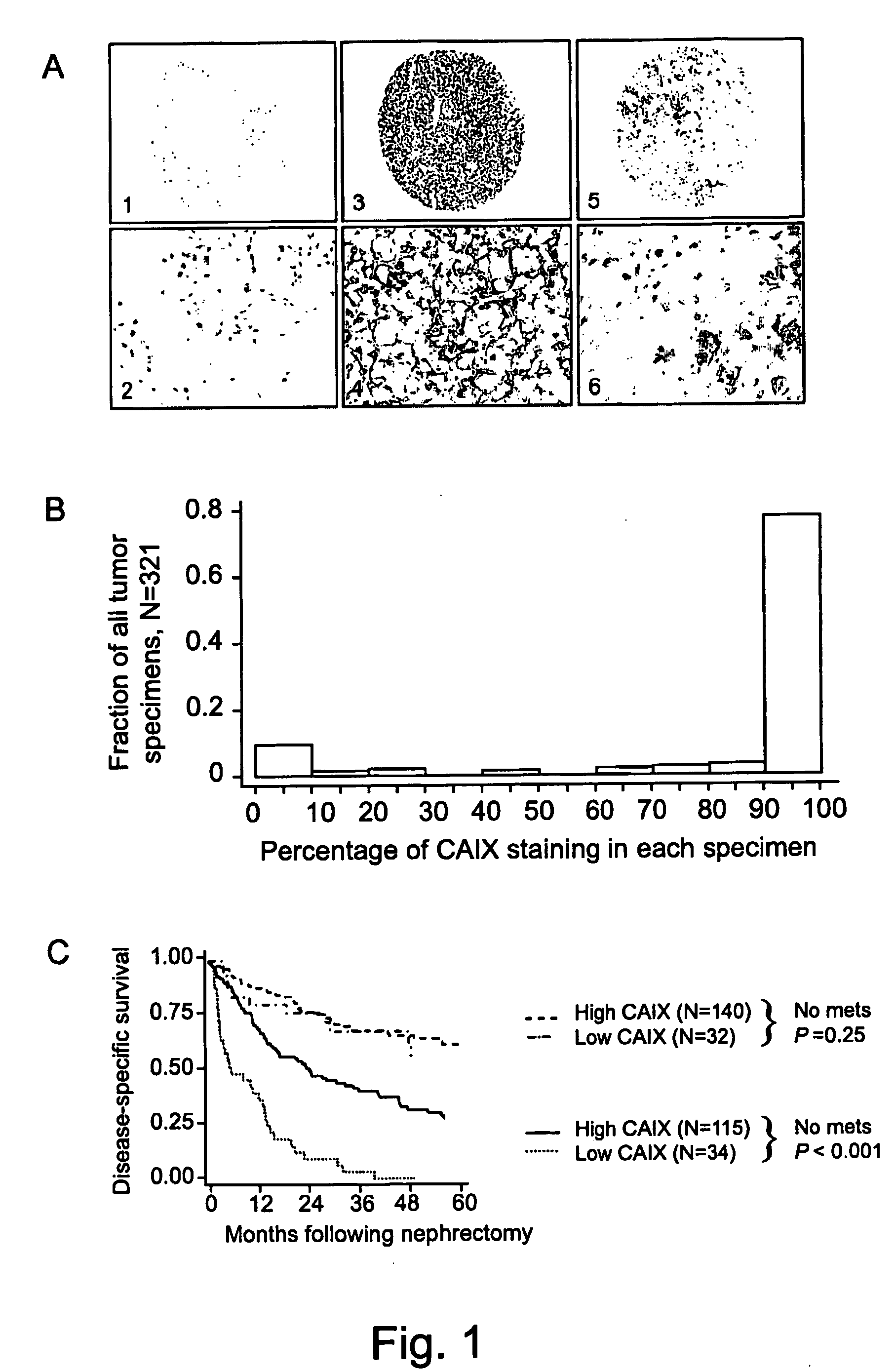
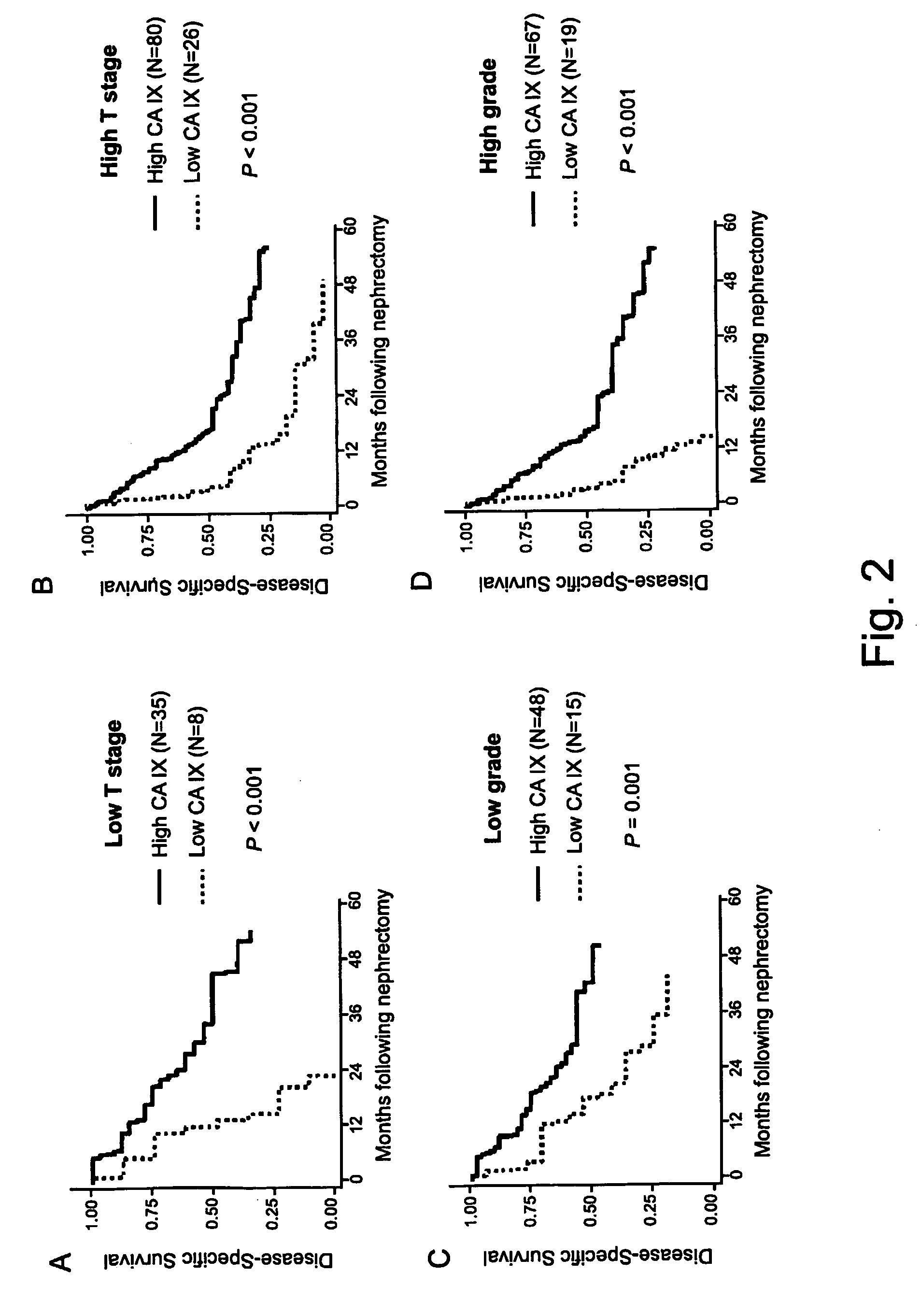
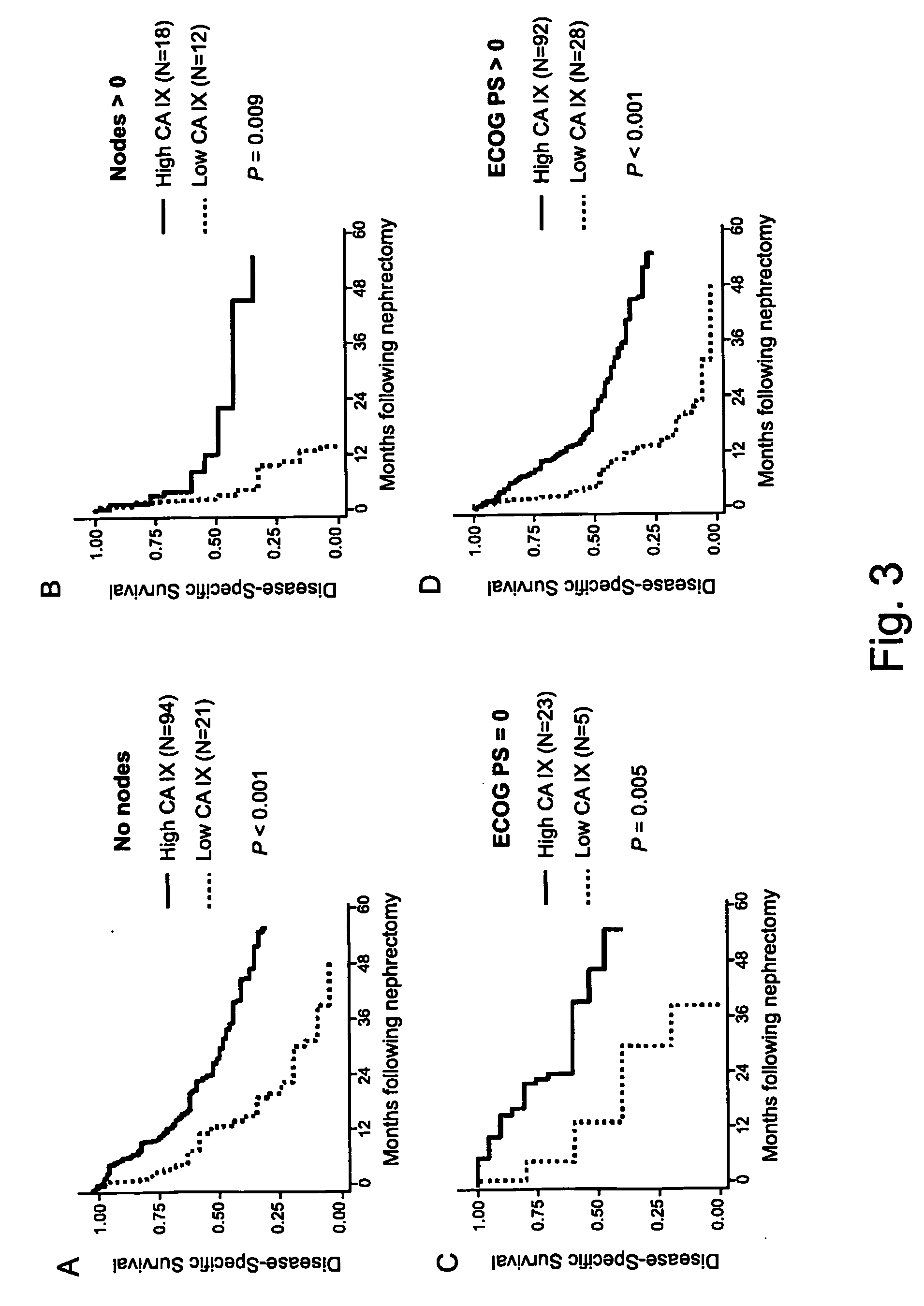
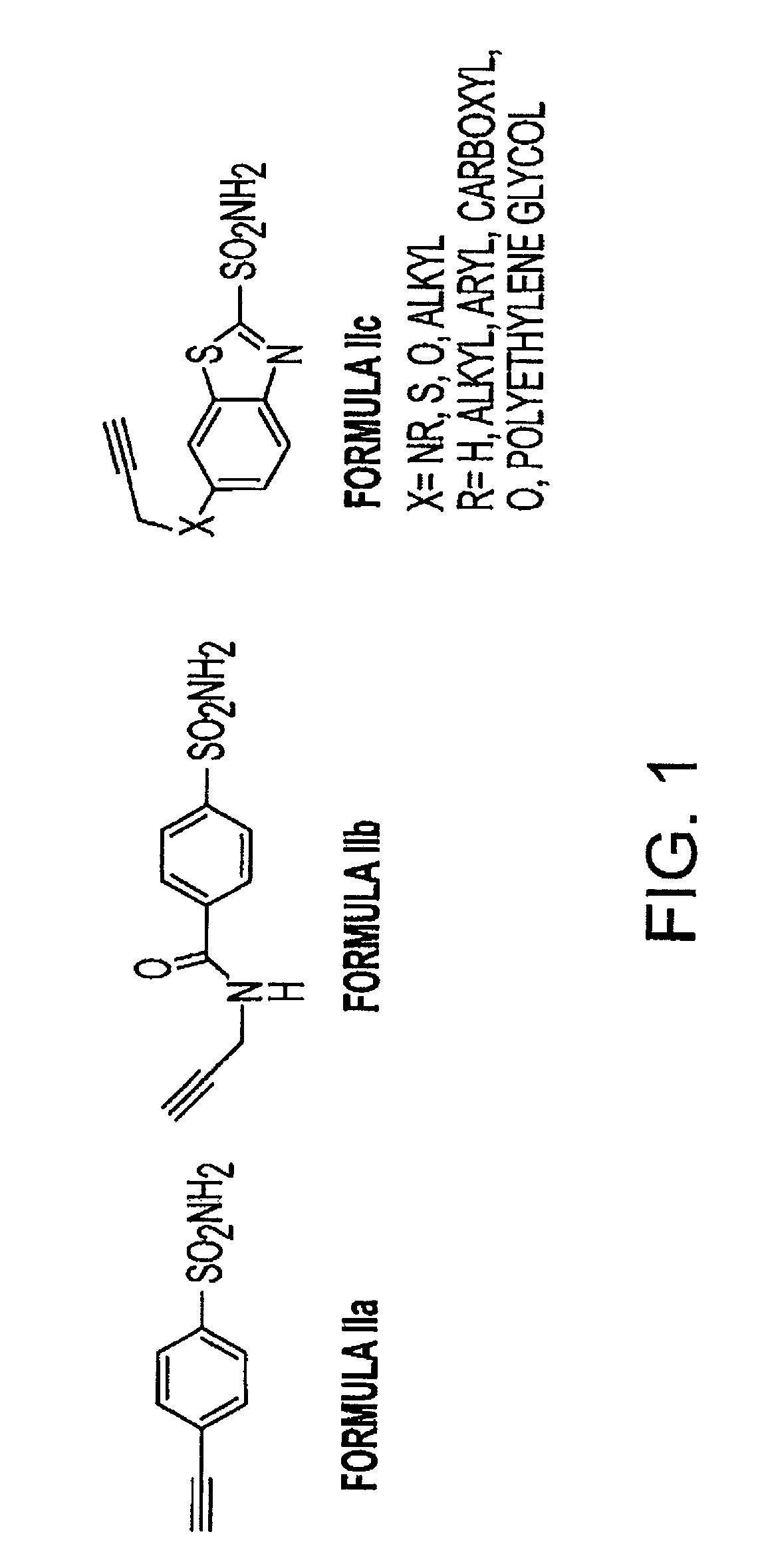
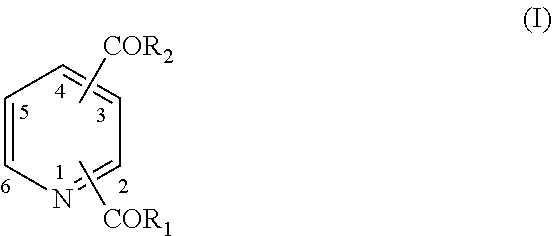Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Carbonic Anhydrase IX" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Carbonic anhydrase IX overexpression is associated with esophageal cancer. Studies indicate that HIF-1alpha, CAIX and VEGF were expressed in OSCC. COX-2/CA-IX interplay promotes the aggressive behaviour of colorectal cancer cells. High carbonic anhydrase IX is associated with recurrence in breast cancer.
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176258A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesImmunodominant EpitopesMonoclonal antibody
Disclosed herein among other MN / CA IX-related inventions are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Subsets of the new antibodies are to either the proteoglycan-like (PG) domain or to the carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain of MN / CA IX, and methods are provided by which antibodies can be prepared to the other MN / CA IX domains. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080176310A1Improve efficiencyIncrease resourcesOxidoreductasesFermentationKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Soluble Form of Carbonic Anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), Assays to Detect s-CA IX, CA IX's Coexpression with Her-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-Specific Monoclonal Antibodies to Non-Immunodominant Epitopes
InactiveUS20080177046A1Good curative effectImprove efficiencyImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological material analysisKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The Predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Antibodies against carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) tumor antigen
InactiveUS7378091B2Reduce and eliminate biological activityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseMonoclonal antibody
The present invention relates generally to the generation and characterization of anti-CA IX monoclonal antibodies. The invention further relates to the use of such anti-CA IX antibodies in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders associated with increased activity of CA IX, in particular, tumors such as colorectal cancer, renal cell carcinoma (RCC), cervical and other cancers of epithelial origin.
Owner:ABQENIX INC
Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (S-CA IX), assays to detect s-CA IX, CA IX'S coexpression with HER-2/NEU/C-ERBB-2, and CA IX-specific monoclonal antibodies to non-immunodominant epitopes
InactiveUS7816493B2Good curative effectSugar derivativesBiological material analysisKilodaltonC erbb 2
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) found in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Soluble CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer / cancer that detect or detect and quantitate s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 that provides potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer / cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer / precancer. Preferred are new antibodies, specific for non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, useful to detect soluble CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, preferably in combination with antibodies specific to immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
Inhibitors of carbonic anhydrase IX
InactiveCN102083427AOrganic chemistryRadioactive preparation carriersTherapeutic treatmentIsrapafant
Novel radiopharmaceuticals that are useful in diagnostic imaging and therapeutic treatment of disease characterized by over expression of CA-IX comprise a complex that contains a sulfonamide moiety which is capable of binding the active catalytic site of CA- IX, and a radionuclide adapted for radioimaging and / or radiotherapy.
Owner:分子洞察制药股份有限公司
Camel-derived nano antibody capable of being specifically combined with carbonic anhydrase IX and application of camel-derived nano antibody
The invention relates to the field of biological medicine, in particular to a camel-derived nano antibody capable of being specifically combined with carbonic anhydrase IX (CA IX) and application of the camel-derived nano antibody. According to the invention, through eukaryotic expression of extracellular region of CA IX antigen, a camel is immunized, and the nano antibody for resisting the extracellular region of the CA IX antigen is prepared and identified, so that a foundation is laid for a next step of targeted imaging and treatment.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军特色医学中心
Methods and compositions for diagnosis and prognosis of renal injury and renal failure
InactiveUS20120231476A1Eliminate needEasy to adaptDisease diagnosisBiological testingCathepsin BDipeptidyl peptidase
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for monitoring, diagnosis, prognosis, and determination of treatment regimens in subjects suffering from or suspected of having a renal injury. In particular, the invention relates to using a one or more assays configured to detect a kidney injury marker selected from the group consisting of Cathepsin B, Renin, Dipeptidyl Peptidase IV, Neprilysin, Beta-2-microglobulin, Carbonic anhydrase IX, and C-X-C motif chemokine 2 as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in renal injuries.
Owner:ASTUTE MEDICAL
Methods of renal cell carcinoma prognosis and treatment selection with carbonic anhydrase IX
The present invention provides methods of aiding in a renal cell carcinoma prognosis that include quantifying expressed carbonic anhydrase in samples derived from renal cell carcinoma patients. The methods also identify patients that are likely to respond positively to selected courses of treatment. The invention further provides related computer program products.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
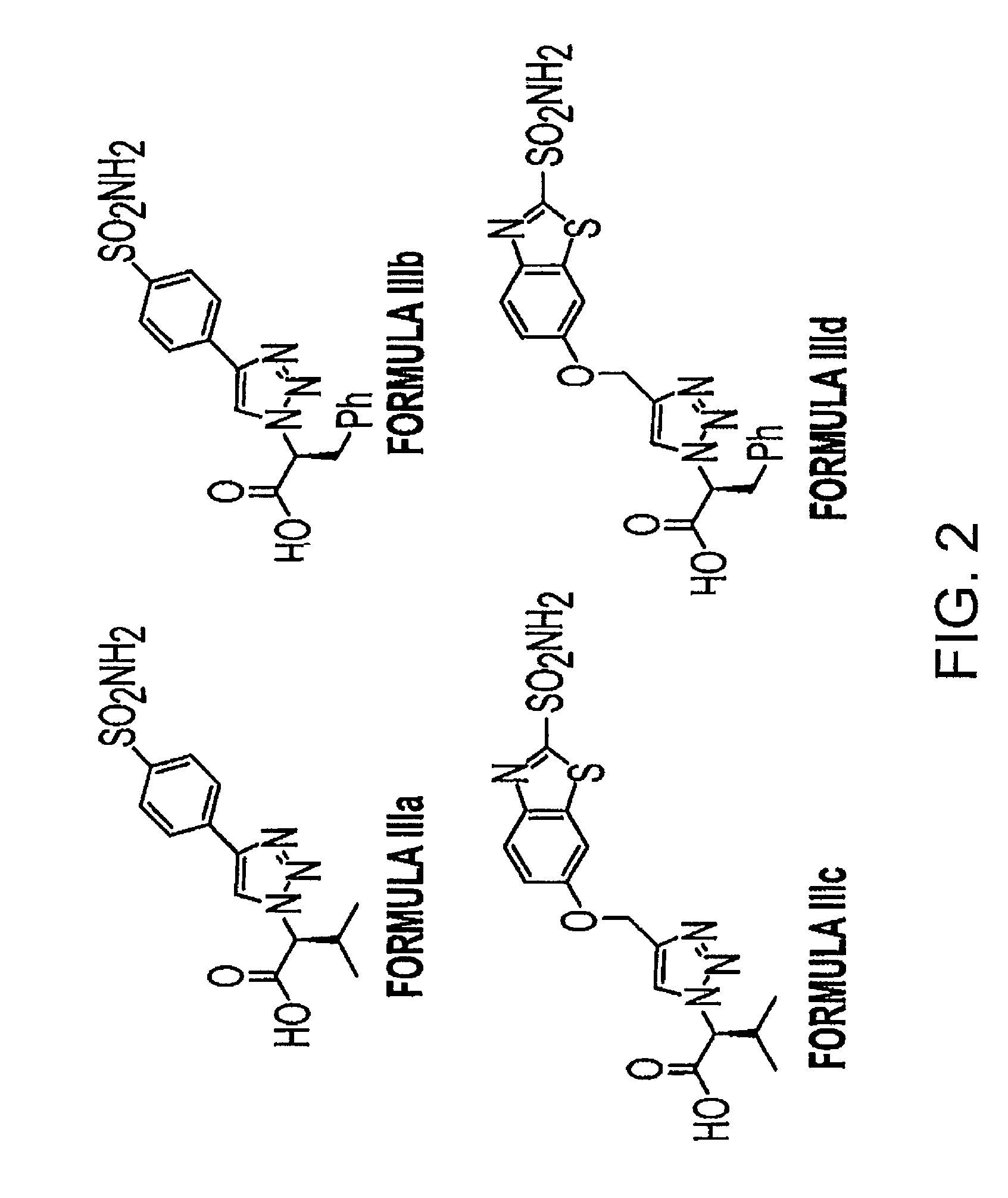
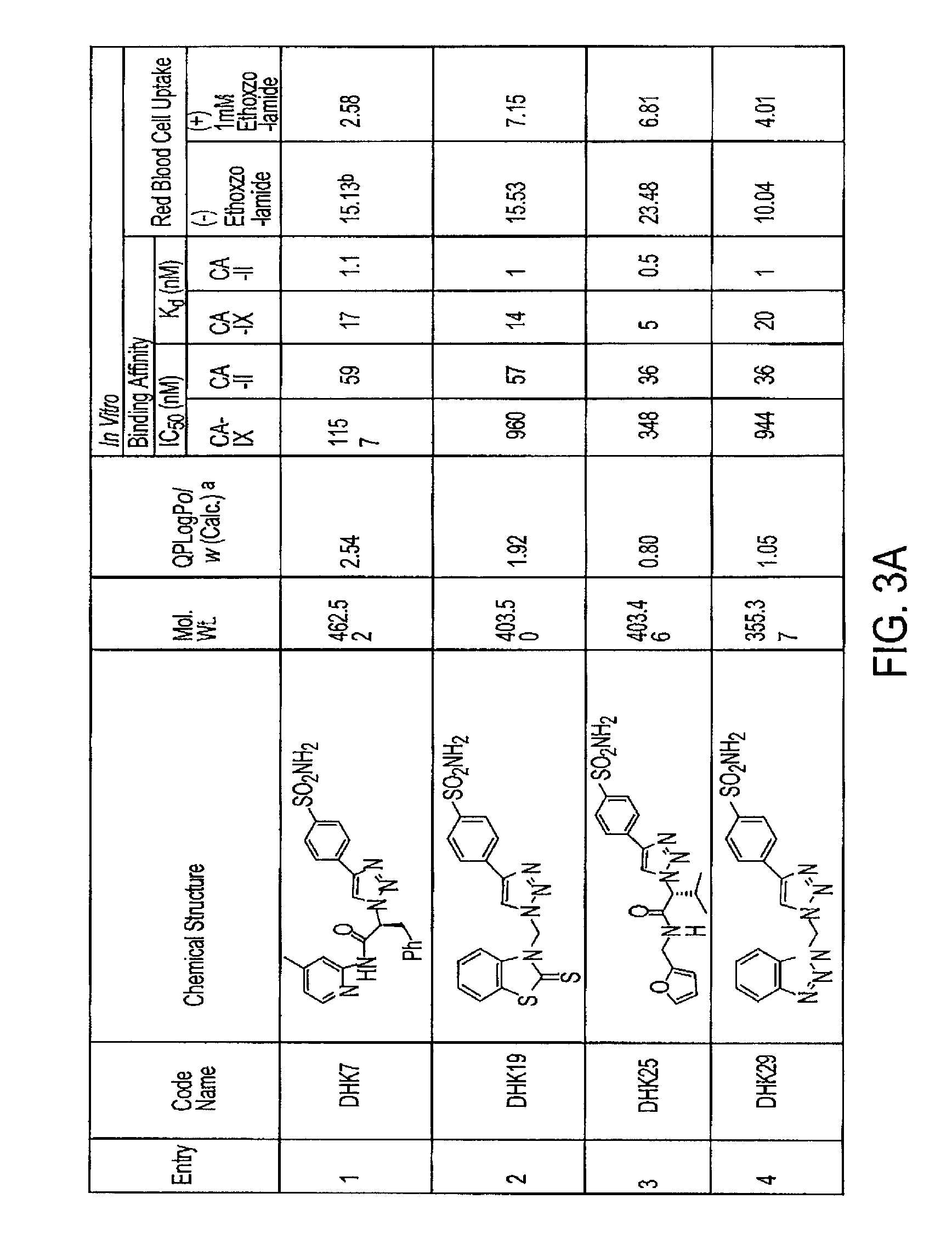
Development of molecular imaging probes for carbonic anhydrase-IX using click chemistry
The present application discloses methods for identifying inhibitors with high binding-affinity for the carbonic anhydrase-IX (CA-IX) enzyme using click chemistry and uses the candidates thereof as positron emission tomography (PET) imaging agents.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Soluble form of carbonic anhydrase IX (s-CA IX), assays to detect s-CA IX, CA IX's coexpression with HER-2/neu/c-erbB-2, and CA IX-specific monoclonal antibodies to non-immunodominant epitopes
InactiveUS7833728B2Good curative effectBiological material analysisDepsipeptidesKilodaltonWestern blot
Disclosed herein is the discovery of a soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, such as, urine and serum. Said s-CA IX comprises the extracellular domain of CA IX or portions thereof. The predominant s-CA IX species is the extracellular domain comprising a proteoglycan-like (PG) domain and carbonic anhydrase (CA) domain, and having a molecular weight of about 50 / 54 kilodaltons (kd) upon Western blot. A smaller s-CA IX form of about 20 to about 30 kd comprising the CA domain or parts thereof, not linked to the PG domain, has also been found in body fluids. Diagnostic / prognostic methods for precancer and cancer that detect or detect and quantitate said s-CA IX in body fluids, are described. Also disclosed herein is the coexpression of CA IX and HER-2 / neu / c-erbB-2 that provides parallel, alternative and potentially synergistic diagnostic / prognostic and therapeutic strategies for precancer and cancer. Further disclosed are new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies generated from MN / CA IX-deficient mice, preferably monoclonal antibodies and immunoreactive fragments and engineered variants thereof. Such new MN / CA IX-specific antibodies, fragments and variants are useful diagnostically / prognostically and therapeutically for cancer and precancer. Particularly preferred are the new monoclonal antibodies, fragments and variants that are specific for the non-immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, which antibodies are, among other uses, useful to detect soluble MN / CA IX (s-CA IX) in body fluids, alone but preferably in combination with antibodies specific to the immunodominant epitopes of MN / CA IX, for example, in a sandwich assay.
Owner:BIOMEDICAL RES CENT OF THE SLOVAK ACADEMY OF SCI
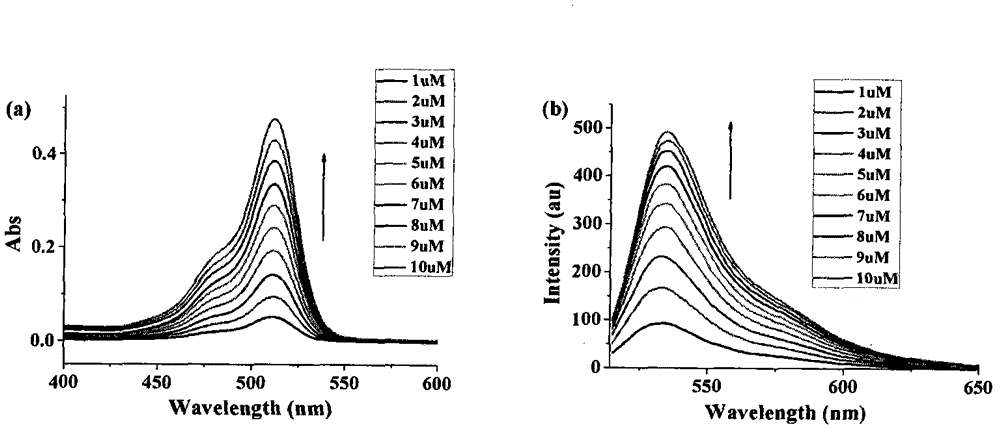
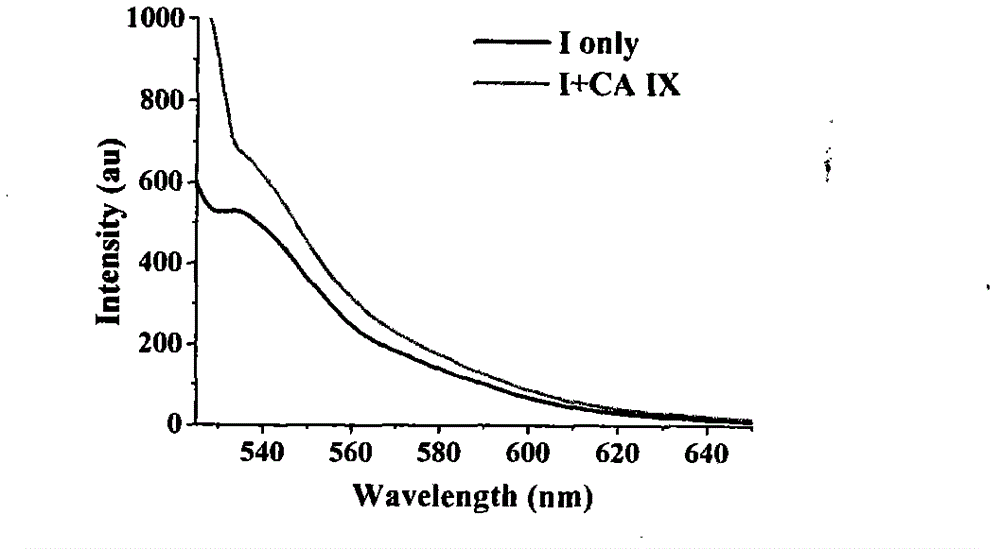
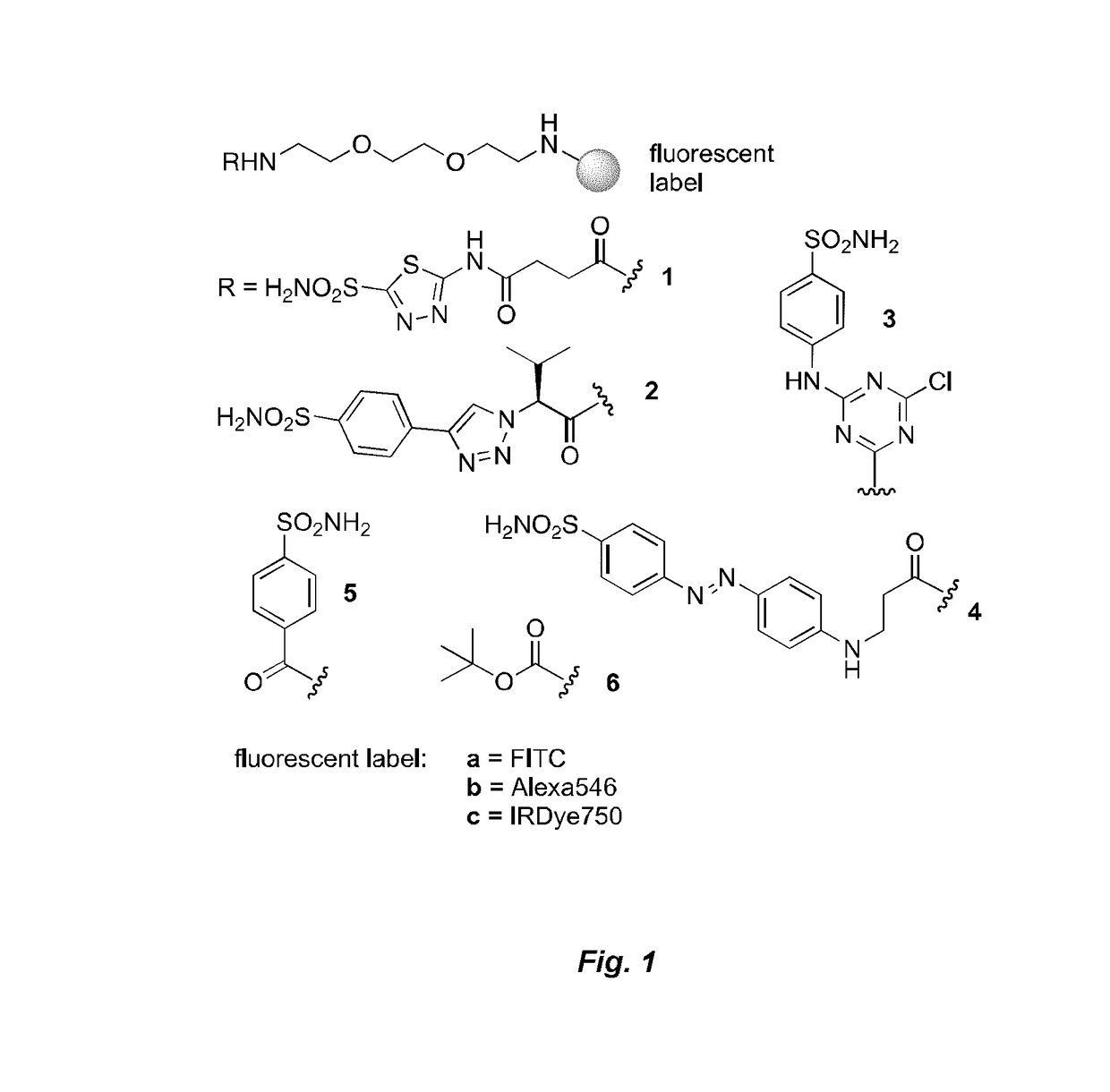
Dihalofluorescein derivative and application thereof
InactiveCN102796094AHigh selectivityStrong specificityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceMedicinal chemistry
The invention relates to a dihalofluorescein derivative and application thereof. The dihalofluorescein derivative is a compound shown as a formula I or a pharmacologically acceptable salt thereof. The dihalofluorescein derivative is used for preparing label-free carbonic anhydrase IX fluorescent probes. In the formula I, R1 and R2 are respectively one of Cl and Br, and X is NH or O.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and method of their production
ActiveUS20140303390A1High yieldHeavy metal active ingredientsInorganic boron active ingredientsBoron clustersMedicinal chemistry
Derivatives of boron cluster compounds of general formula I and their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and solvates, and their specific inhibition effect on the enzyme carbonic anhydrase IX, a protein overexpressed in cancer tissues. Methods of synthesis and the use of the novel derivatives. These inhibitors of human carbonic anhydrase IX can be used as active compounds of pharmaceuticals for diagnostics and / or therapy of cancer diseases.
Owner:USTAV ORGANICKE CHEM A BIOCHEM AKADE VED CR V V I +3
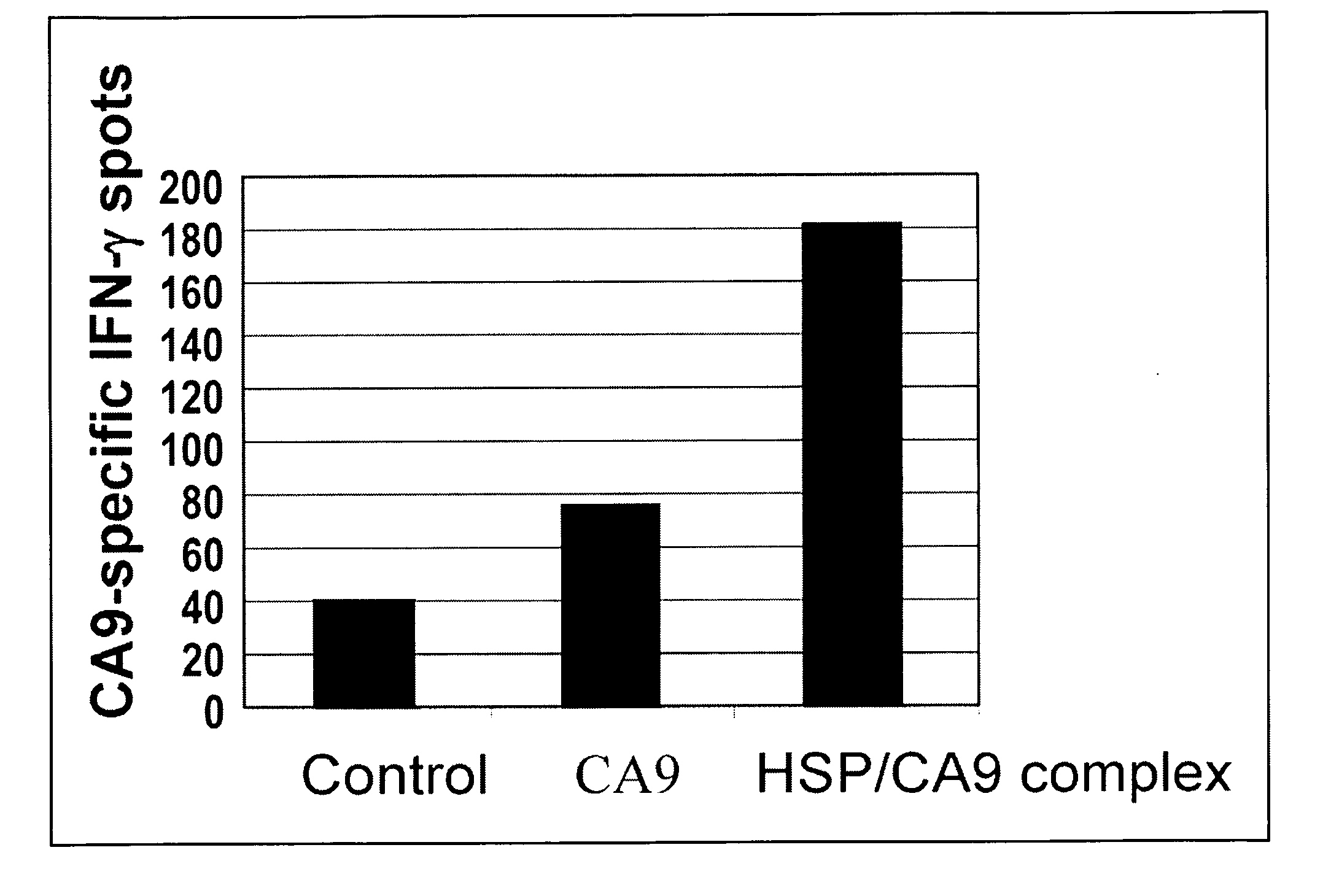
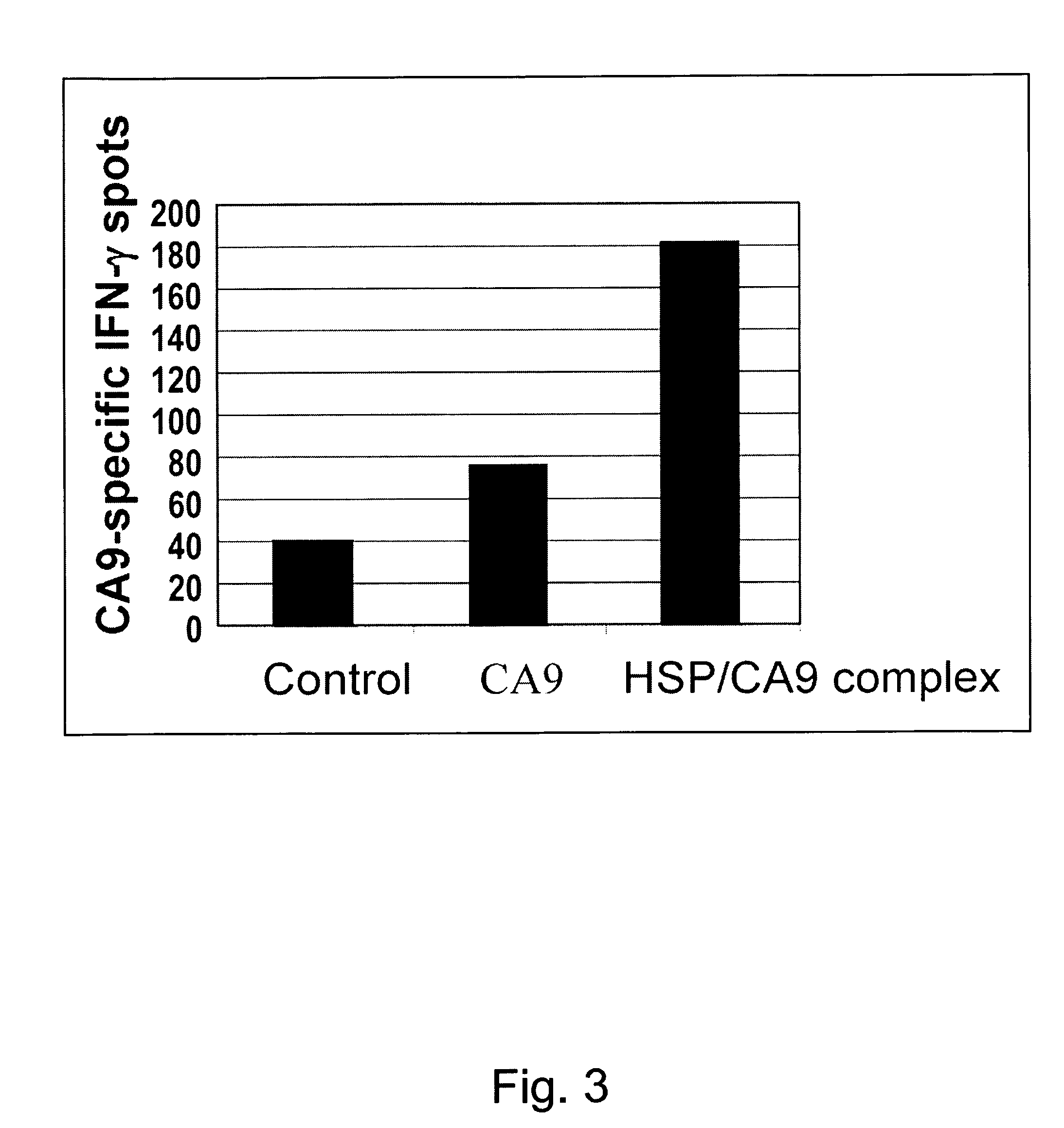
Use of recombinant heat shock protein complexed to kidney cancer antigen
A heat shock protein in combination with carbonic anhydrase IX and a method for improving immune response to carbonic anhydrase IX in a mammal by complexing it with a heat shock protein prior to administration to the mammal.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
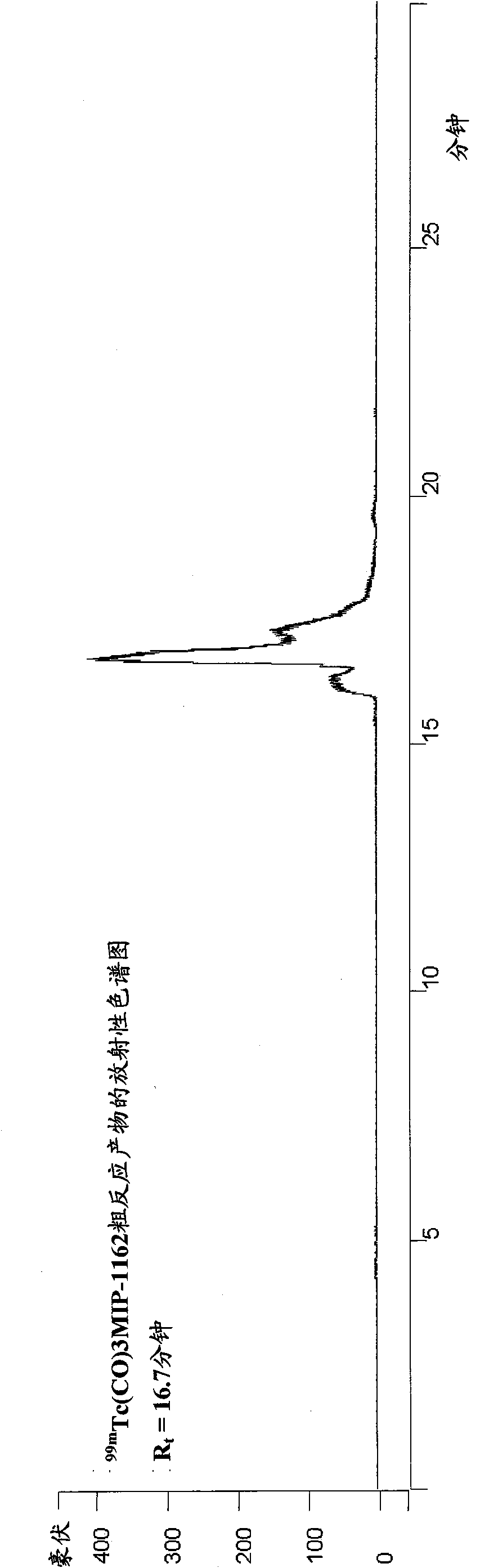
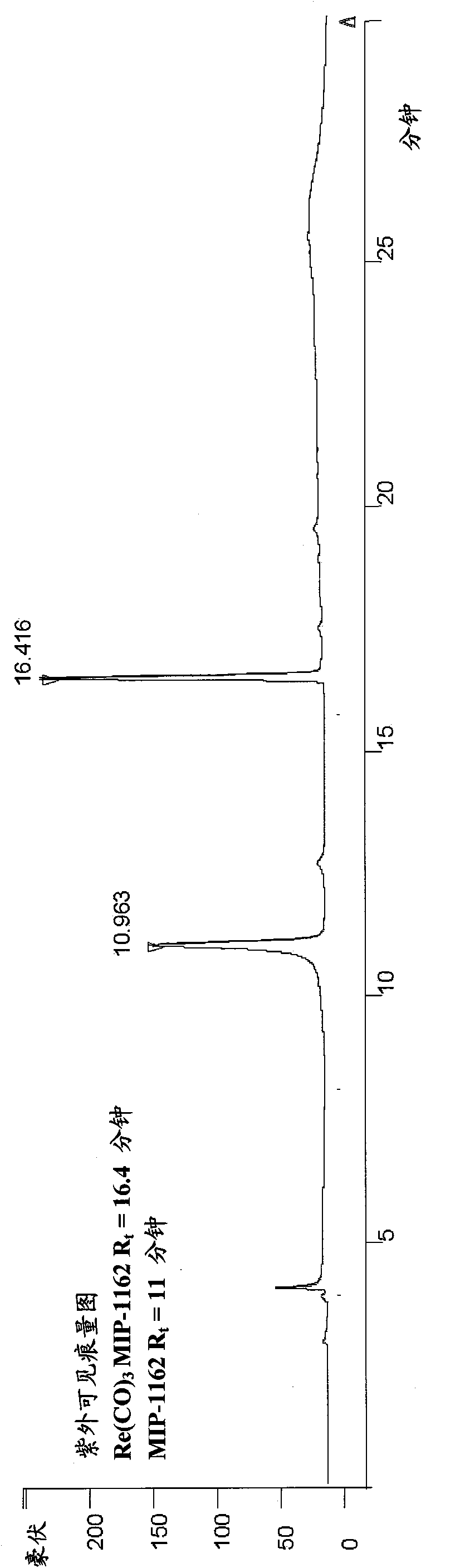
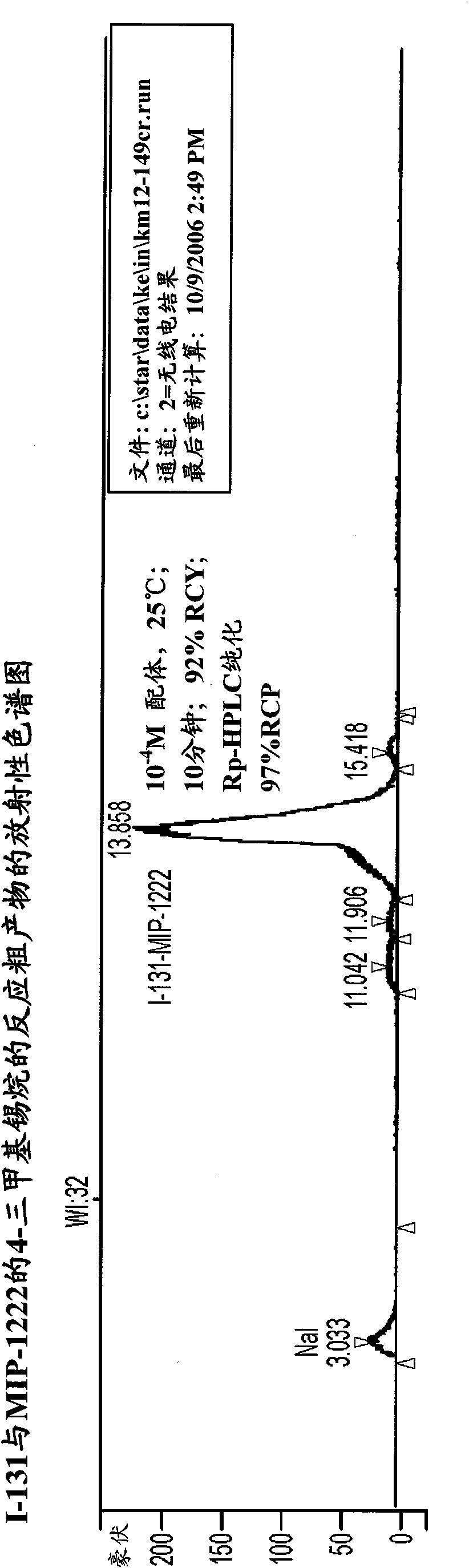
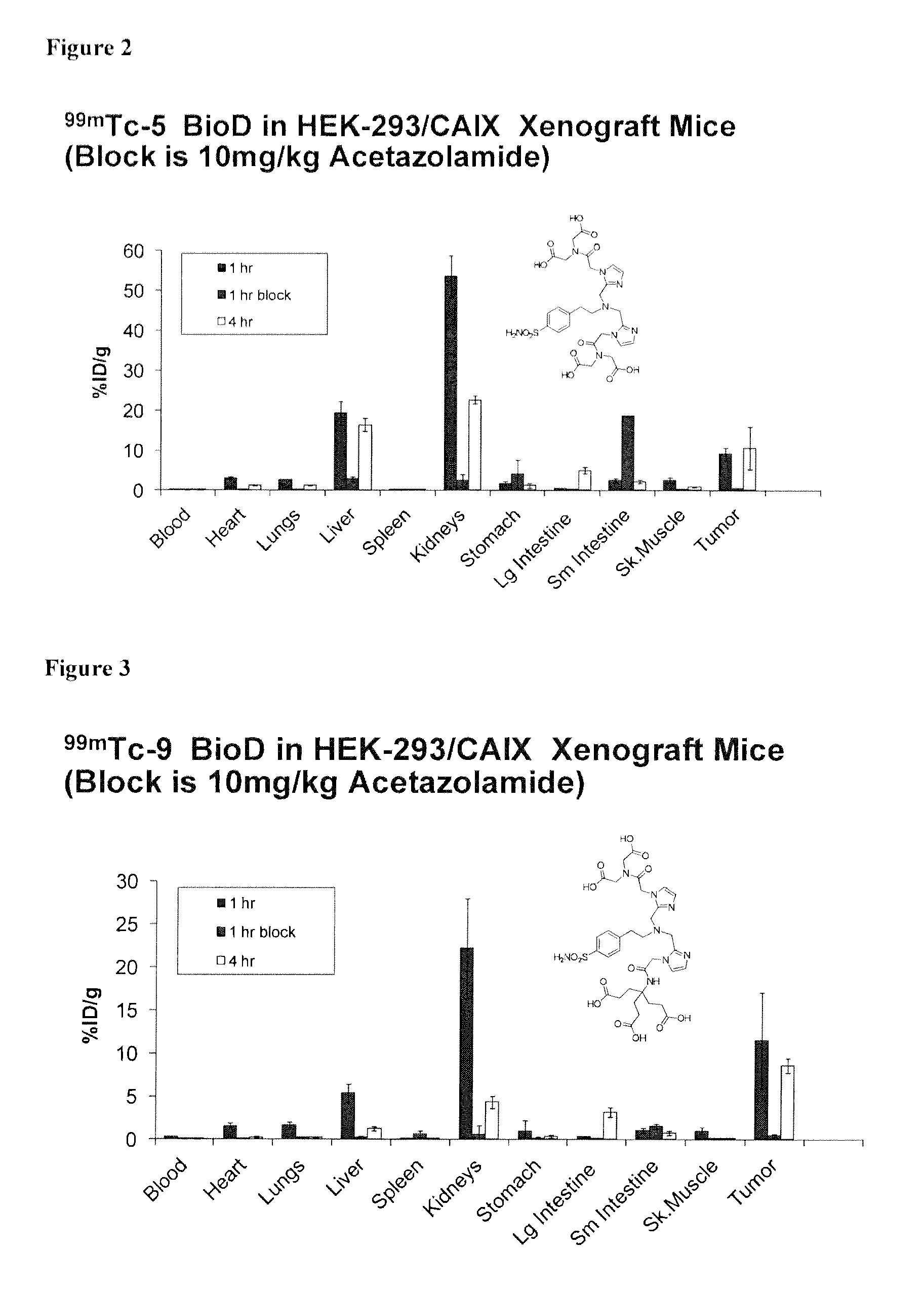
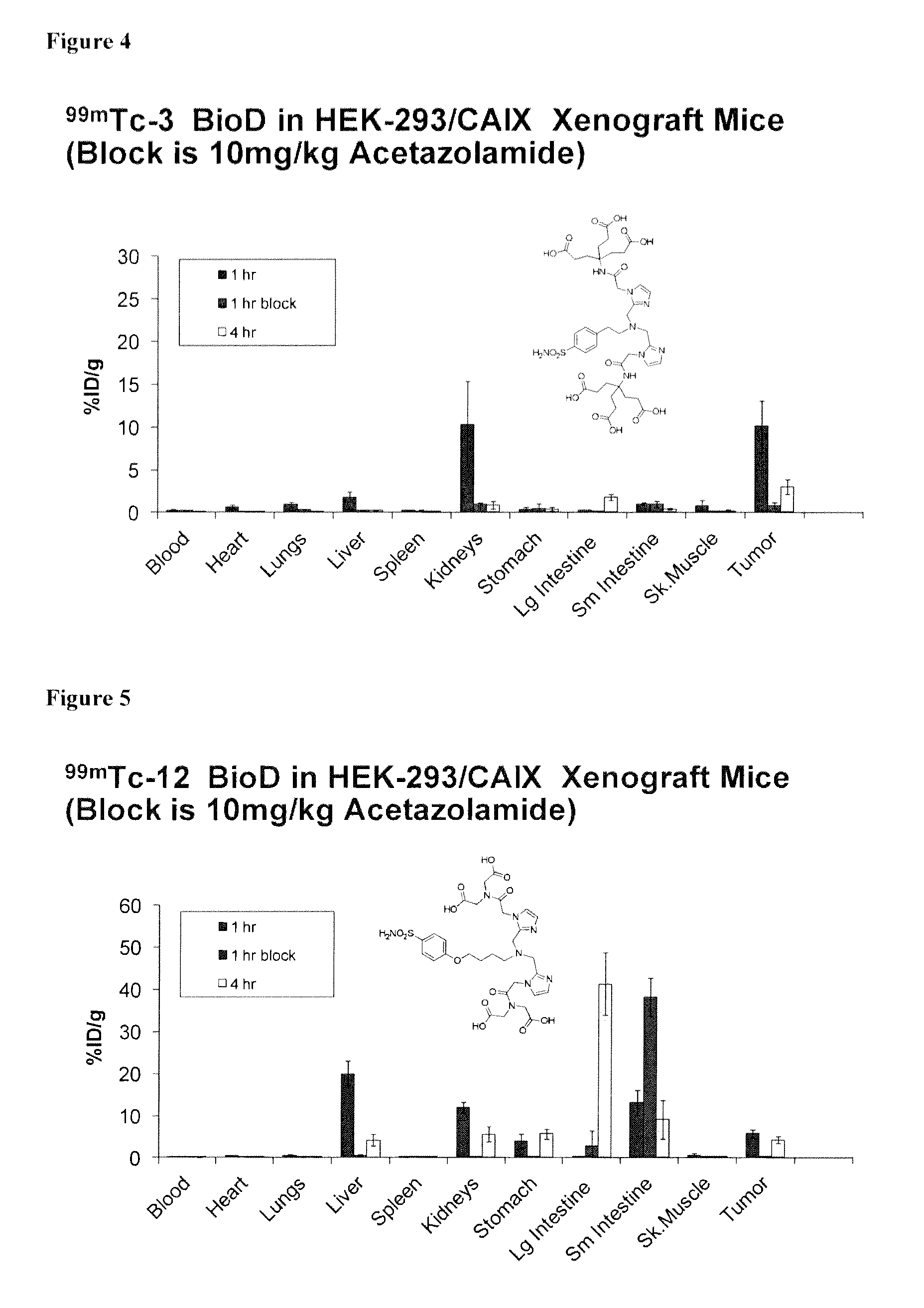
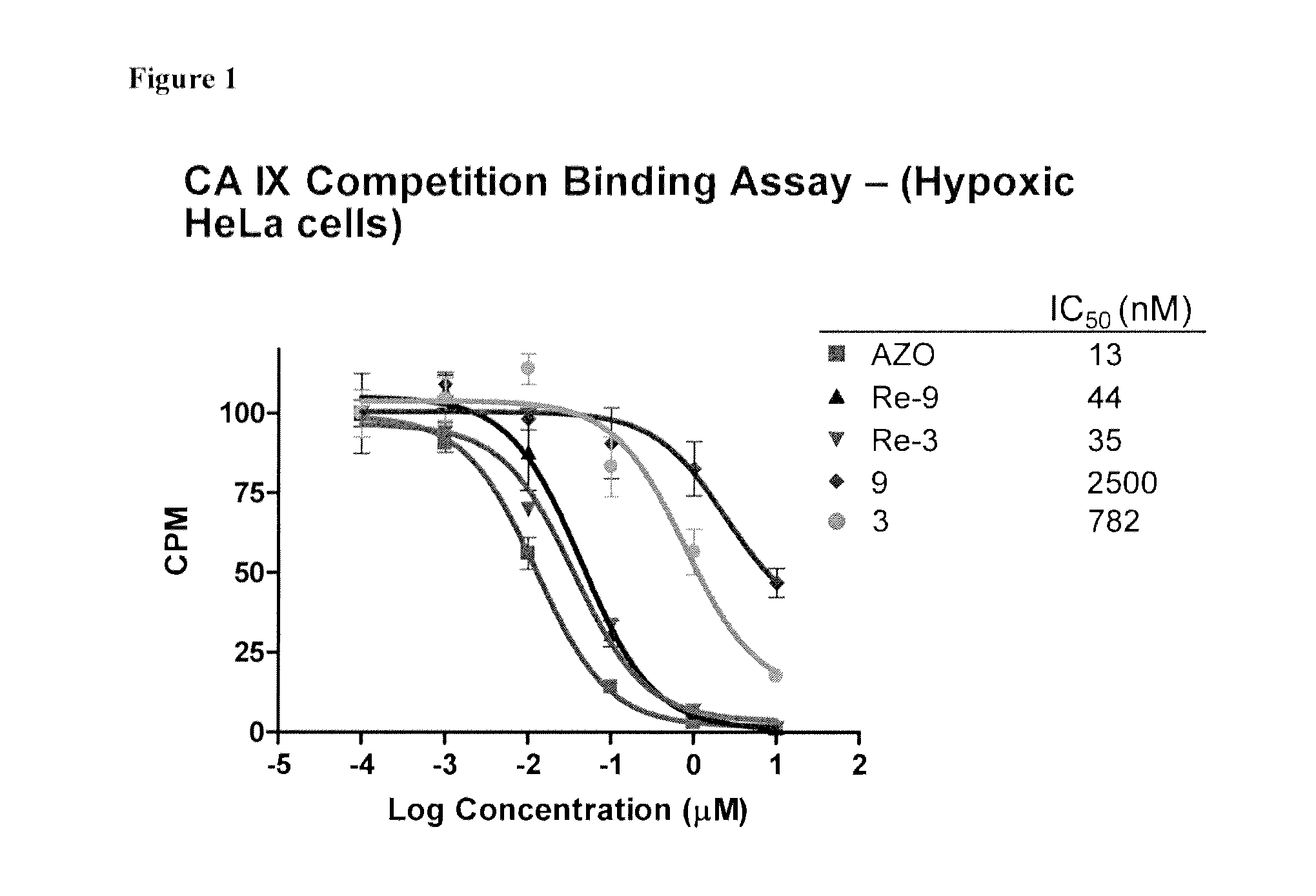
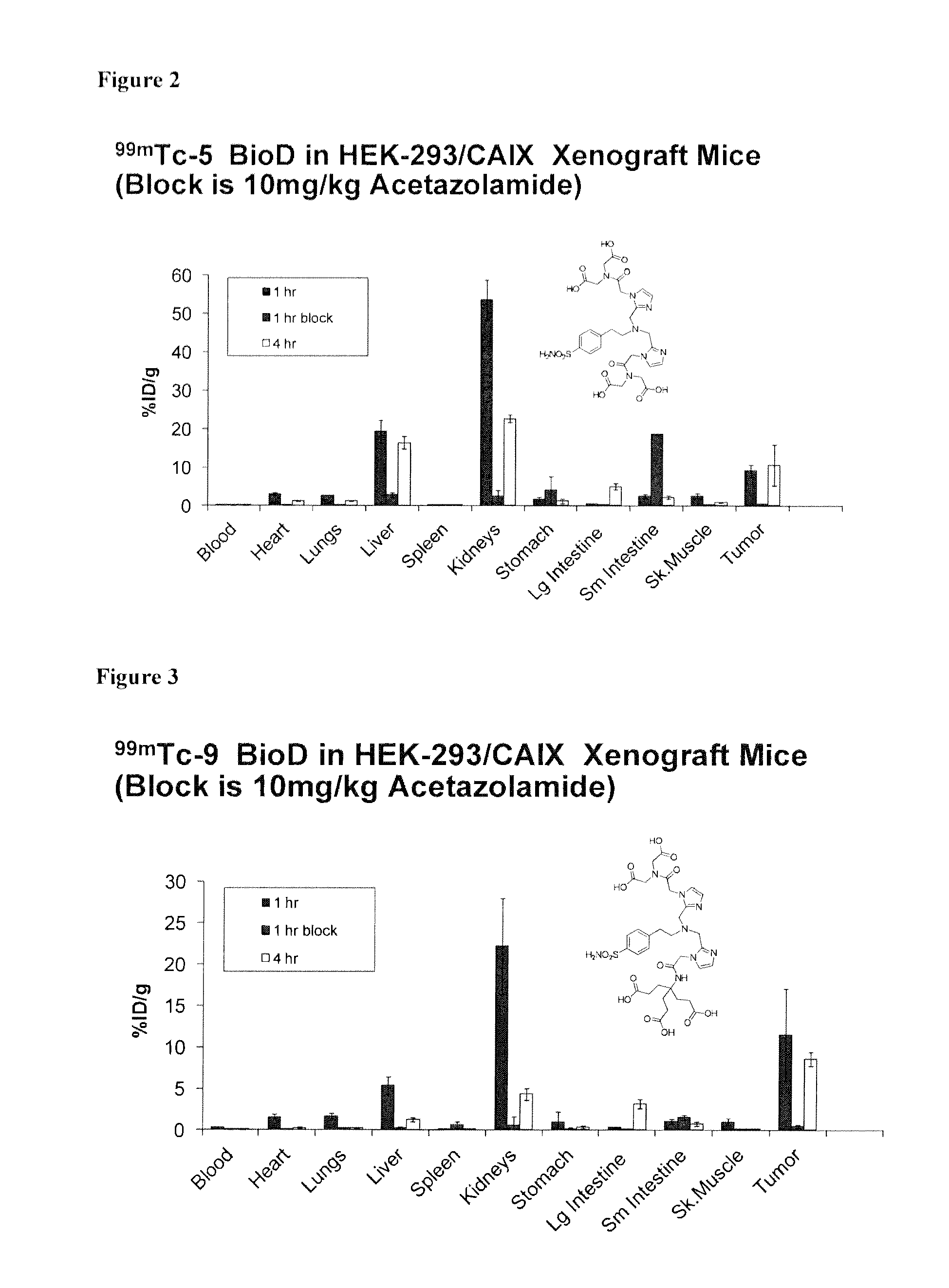
Metal complexes of poly(carboxyl)amine-containing ligands having an affinity for carbonic anhydrase IX
The present invention is directed to CA IX inhibitors that conform to Formula I where the substituents X, A, B, D, E, E′ and G are as defined above.Also described are Pt, 64Cu, 186Re, 188Re and 99mTc metal complexes of Formula I compounds which find use as candidate agents for imaging tumors.
Owner:MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMA
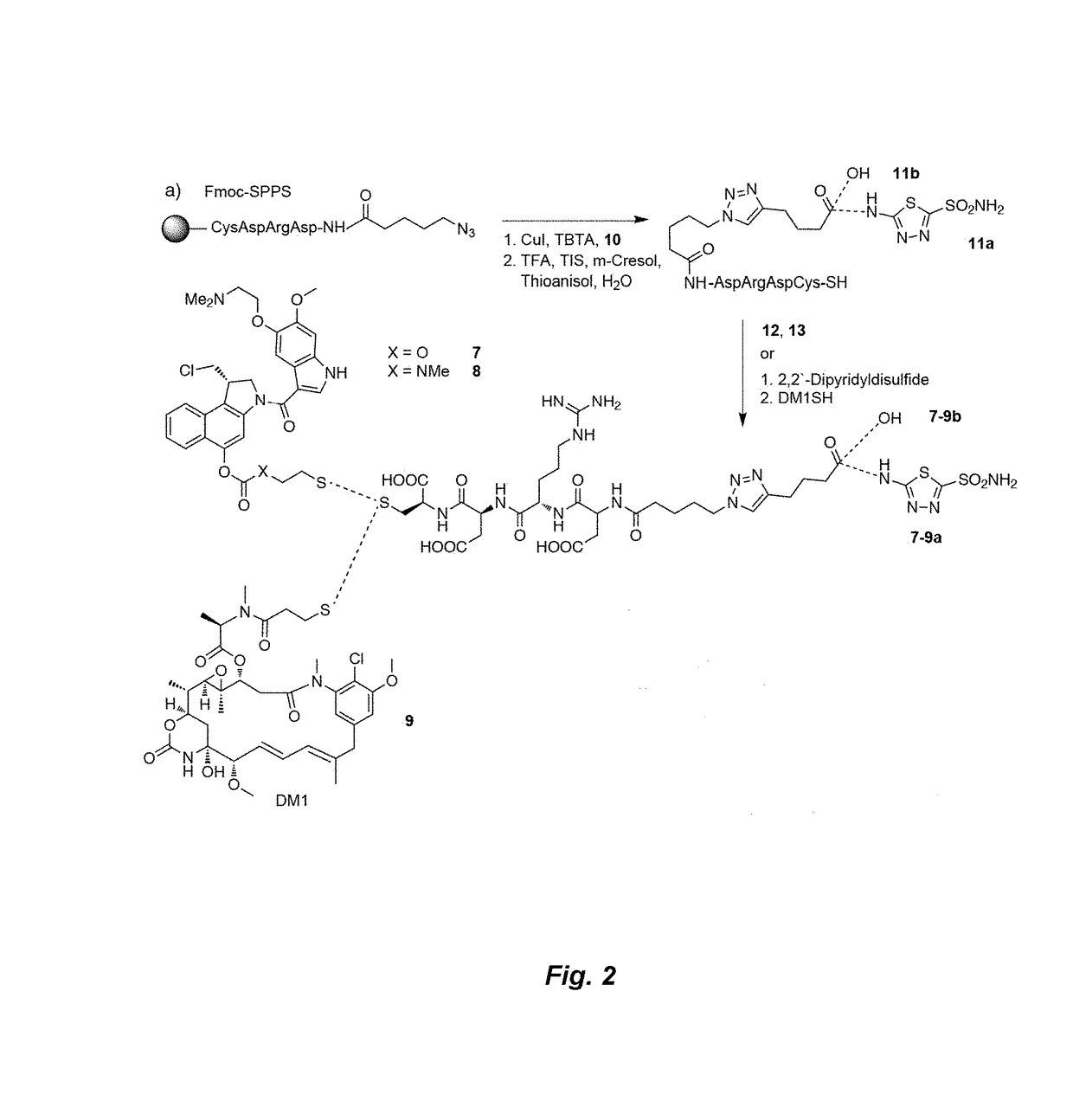
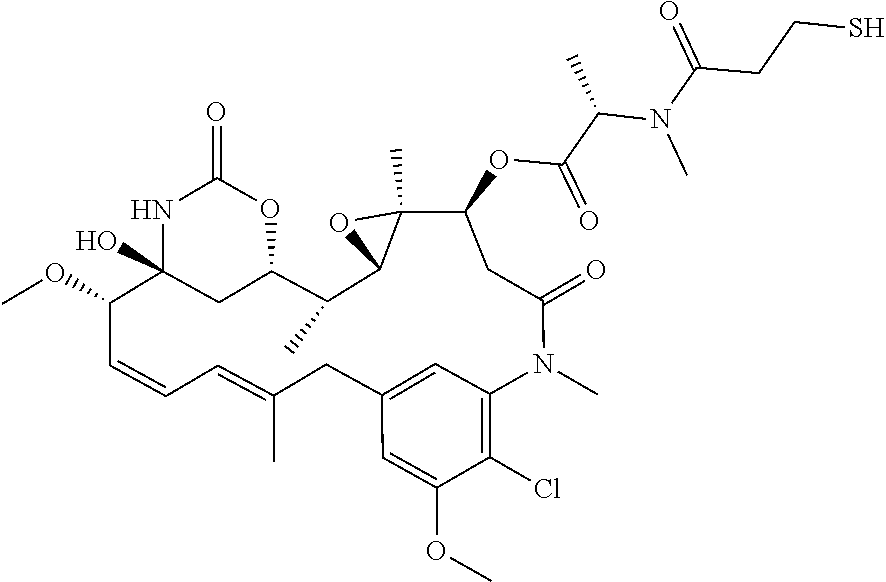
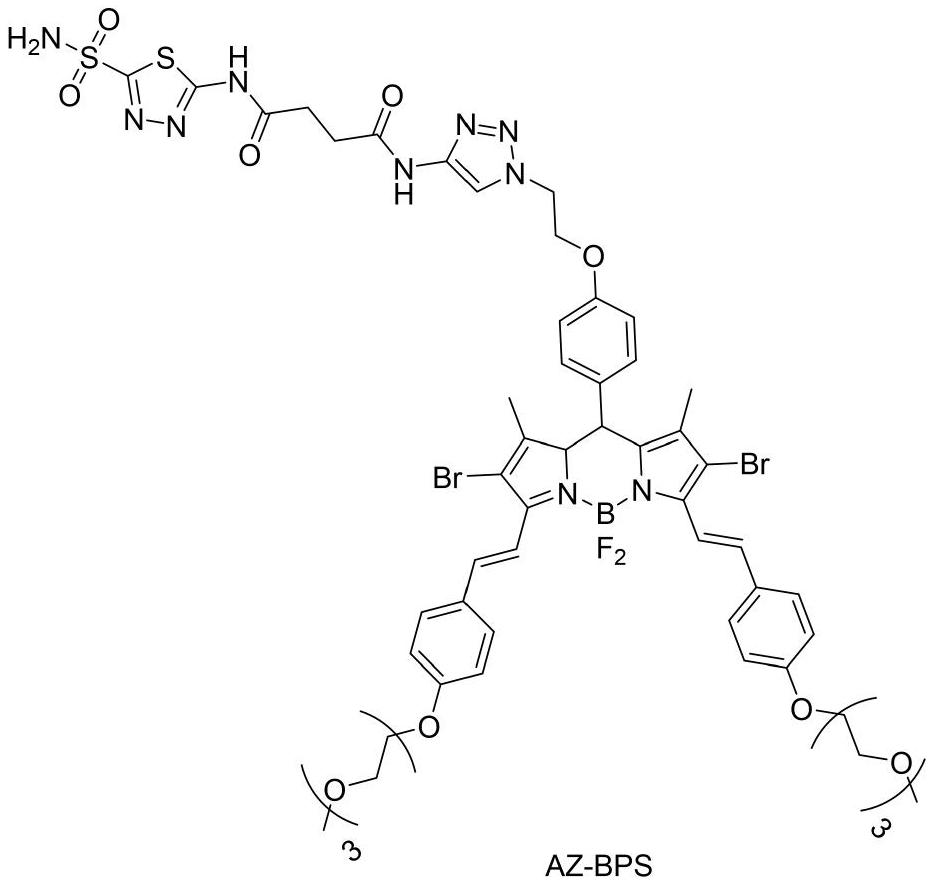
Small Molecule Drug Conjugates
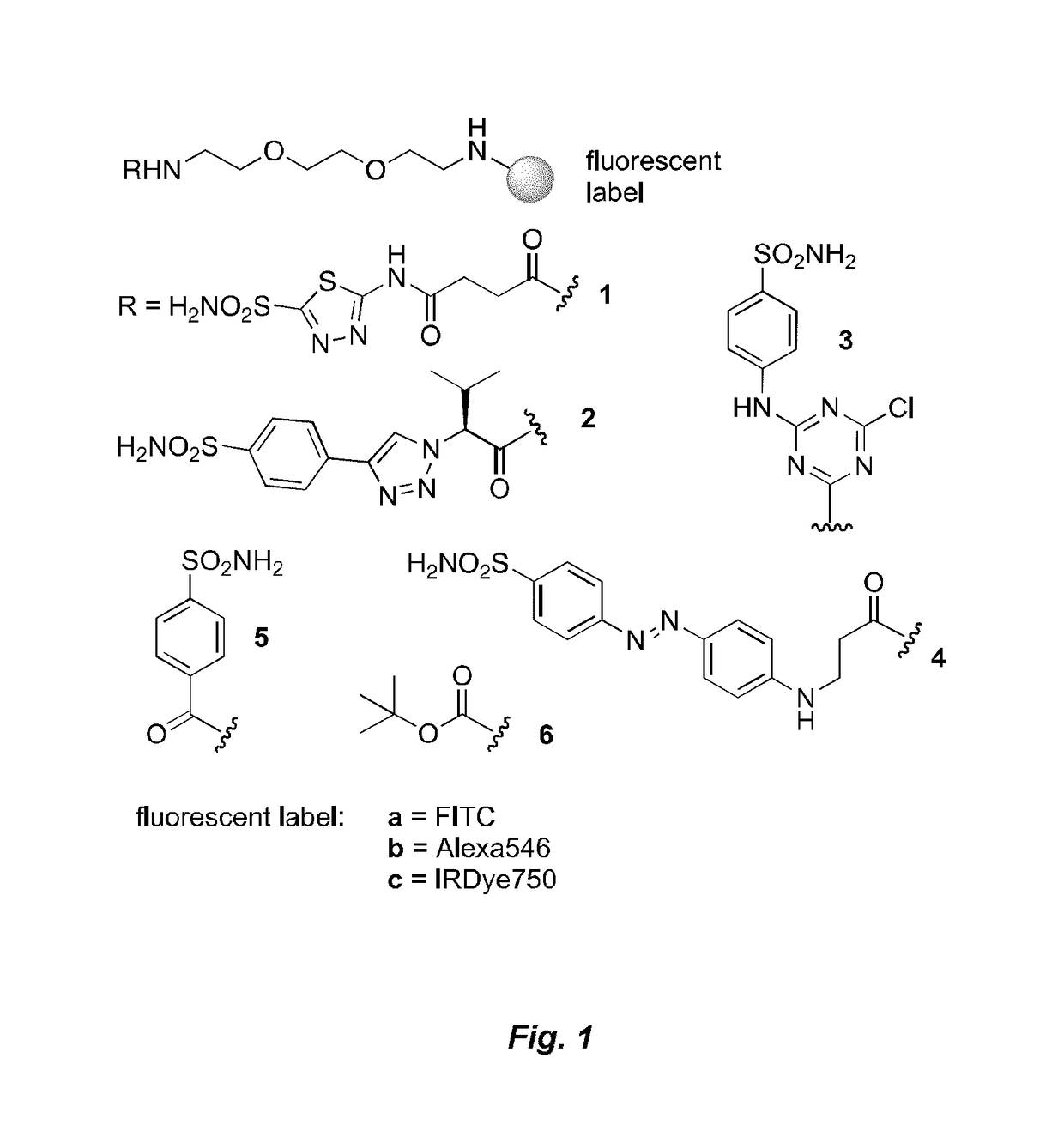
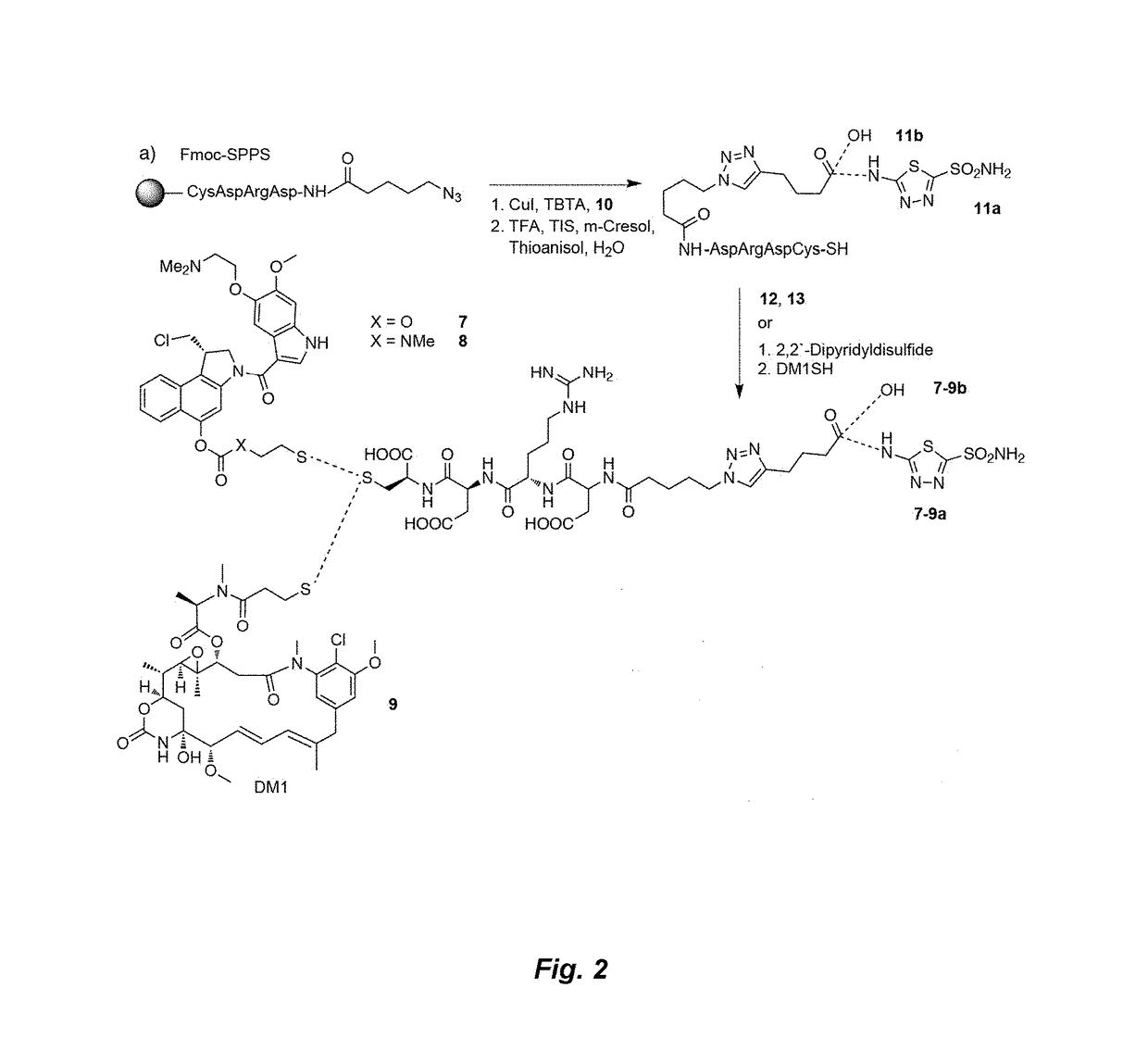
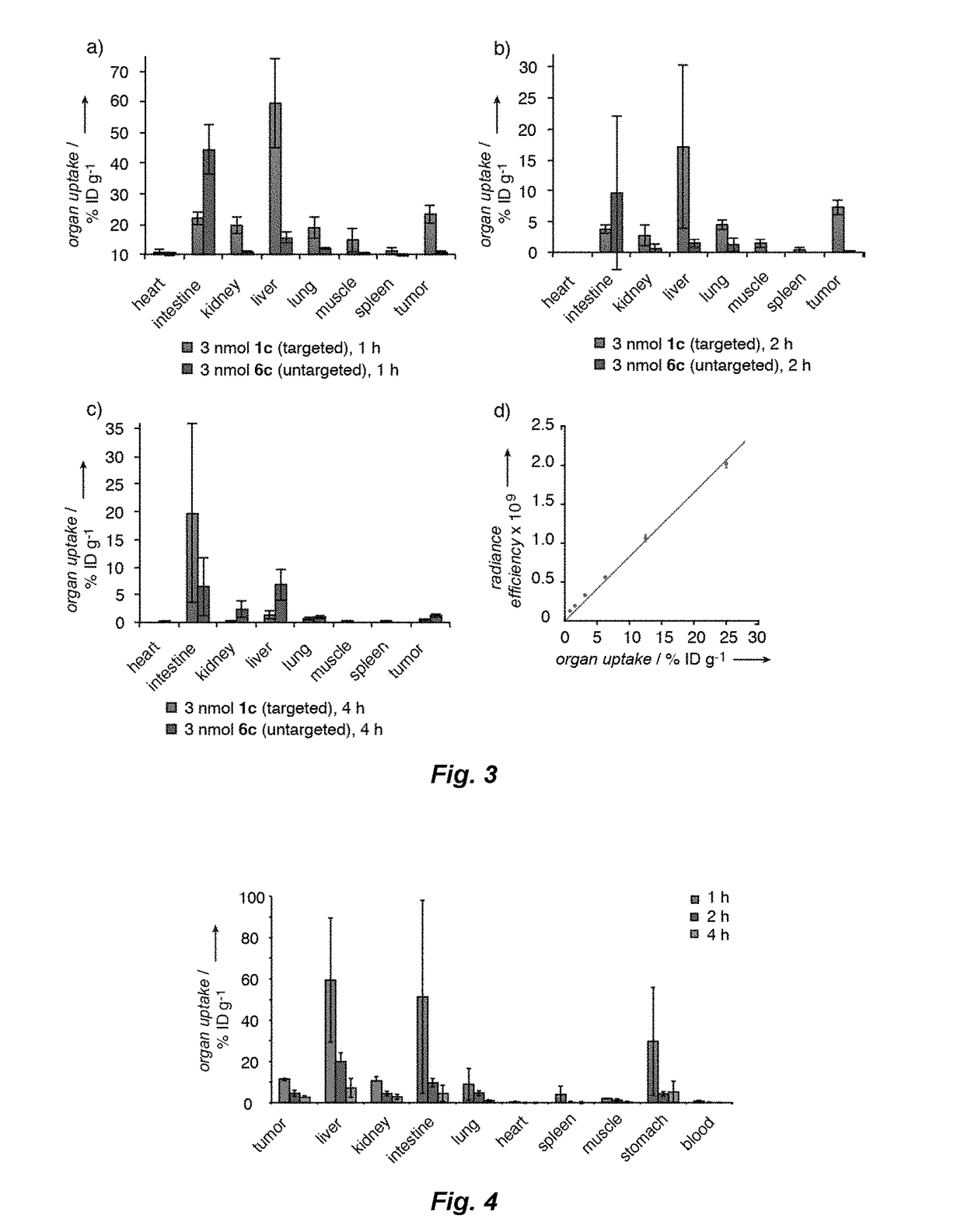
ActiveUS20170224831A1Faster and deep and efficient drug targetingOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsDiseaseTargeted therapy
A binding moiety (B) for Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CAIX), the binding moiety comprising:The binding moiety is univalent, bivalent, or multivalent. A targeted therapeutic agent may comprise the binding moiety. The invention also includes a method for treating a disease expressing elevated levels of CAIX by administering the targeted therapeutic agent.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
Dual-targeted carbonic anhydrase ix complex and contrast agent thereof
ActiveUS20210154334A1In-vivo radioactive preparationsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsBinding peptidePharmaceutical drug
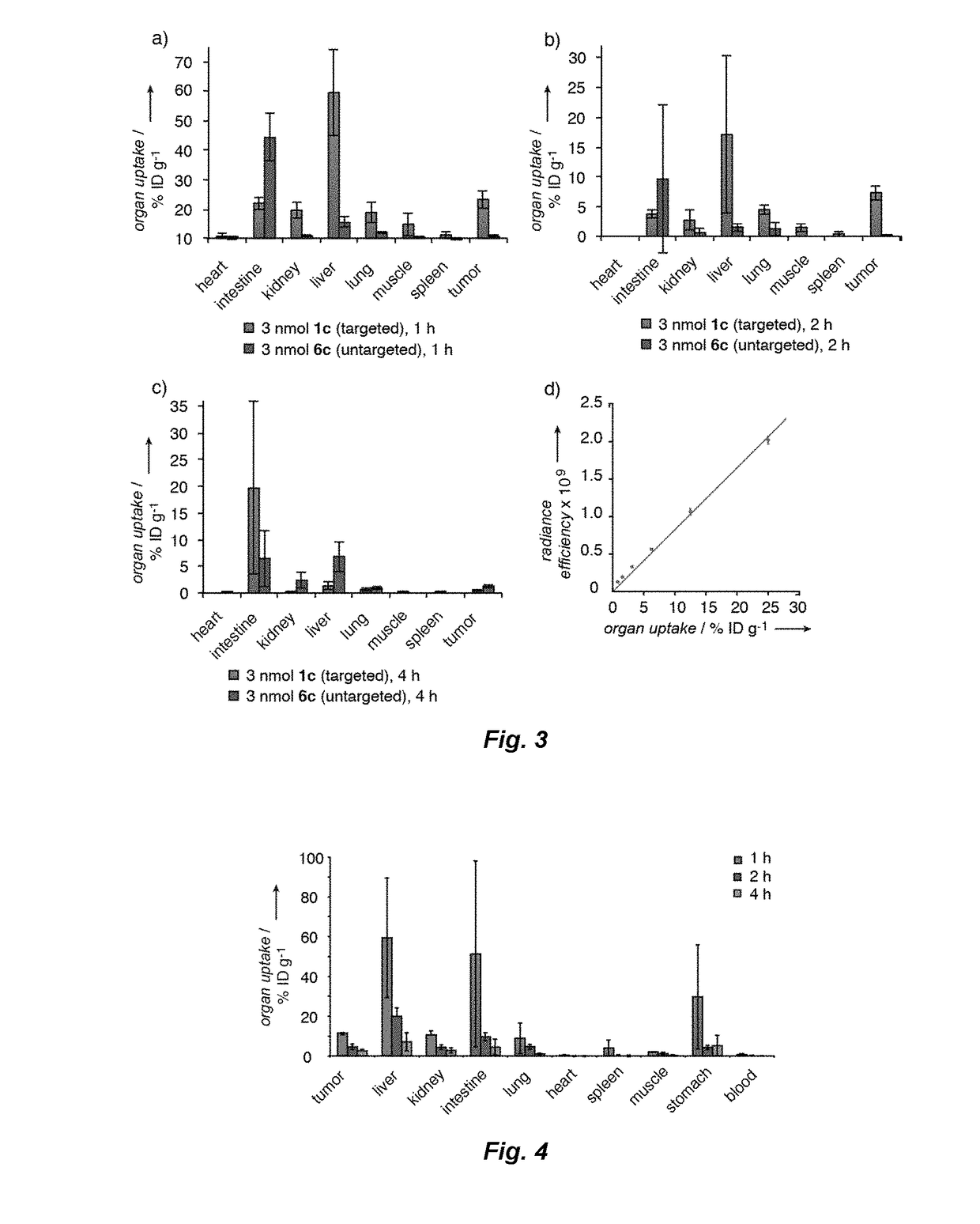
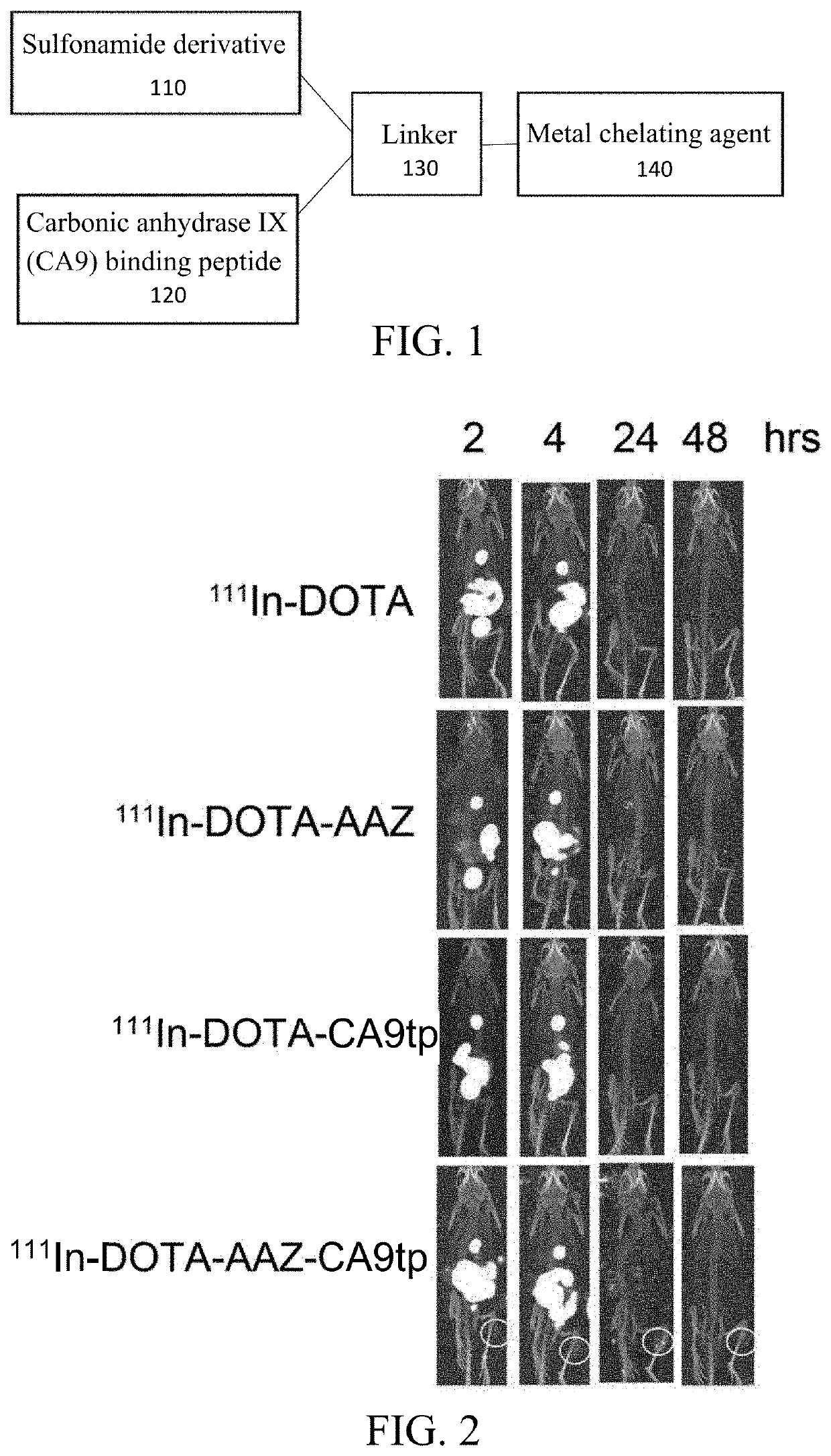
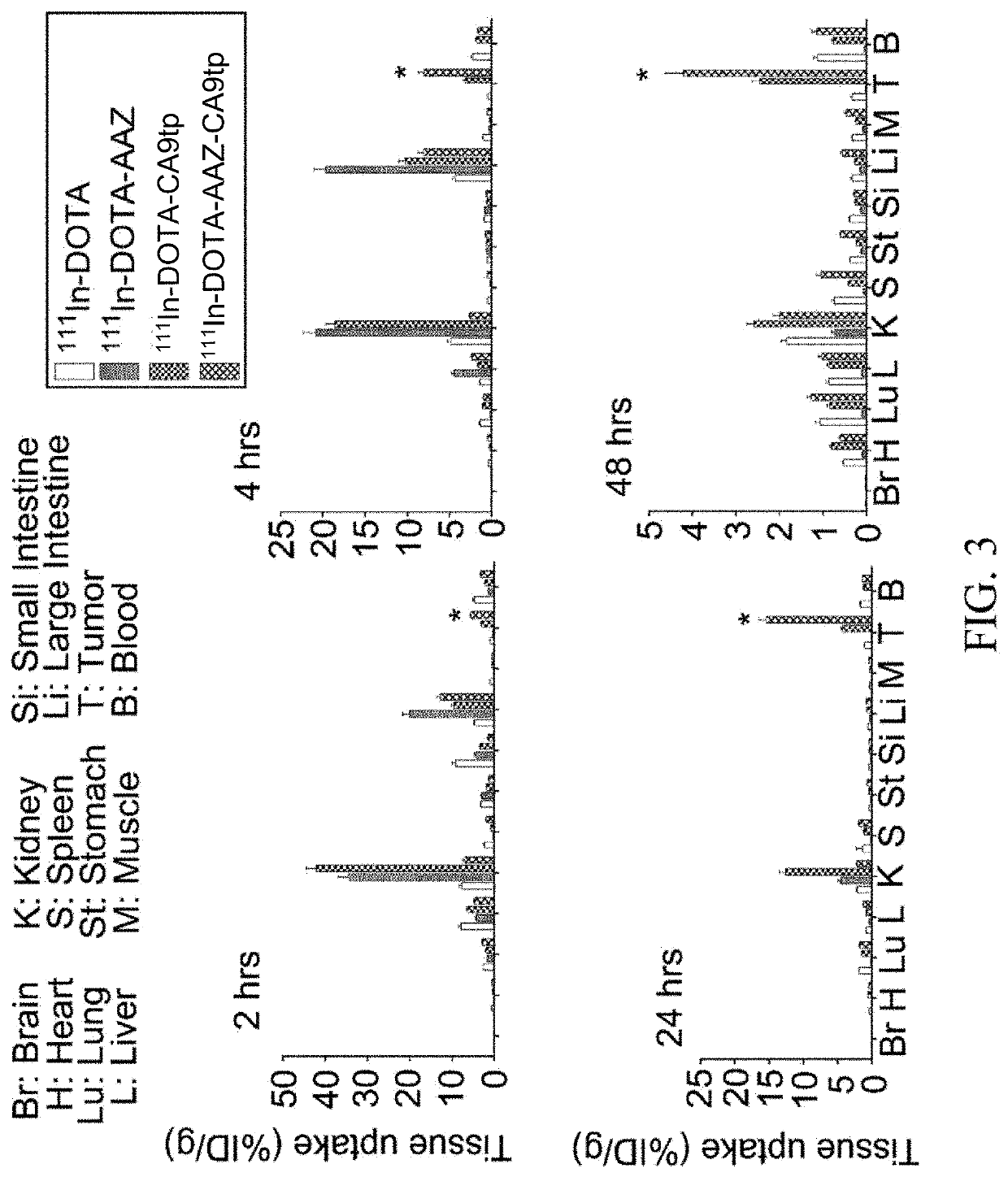
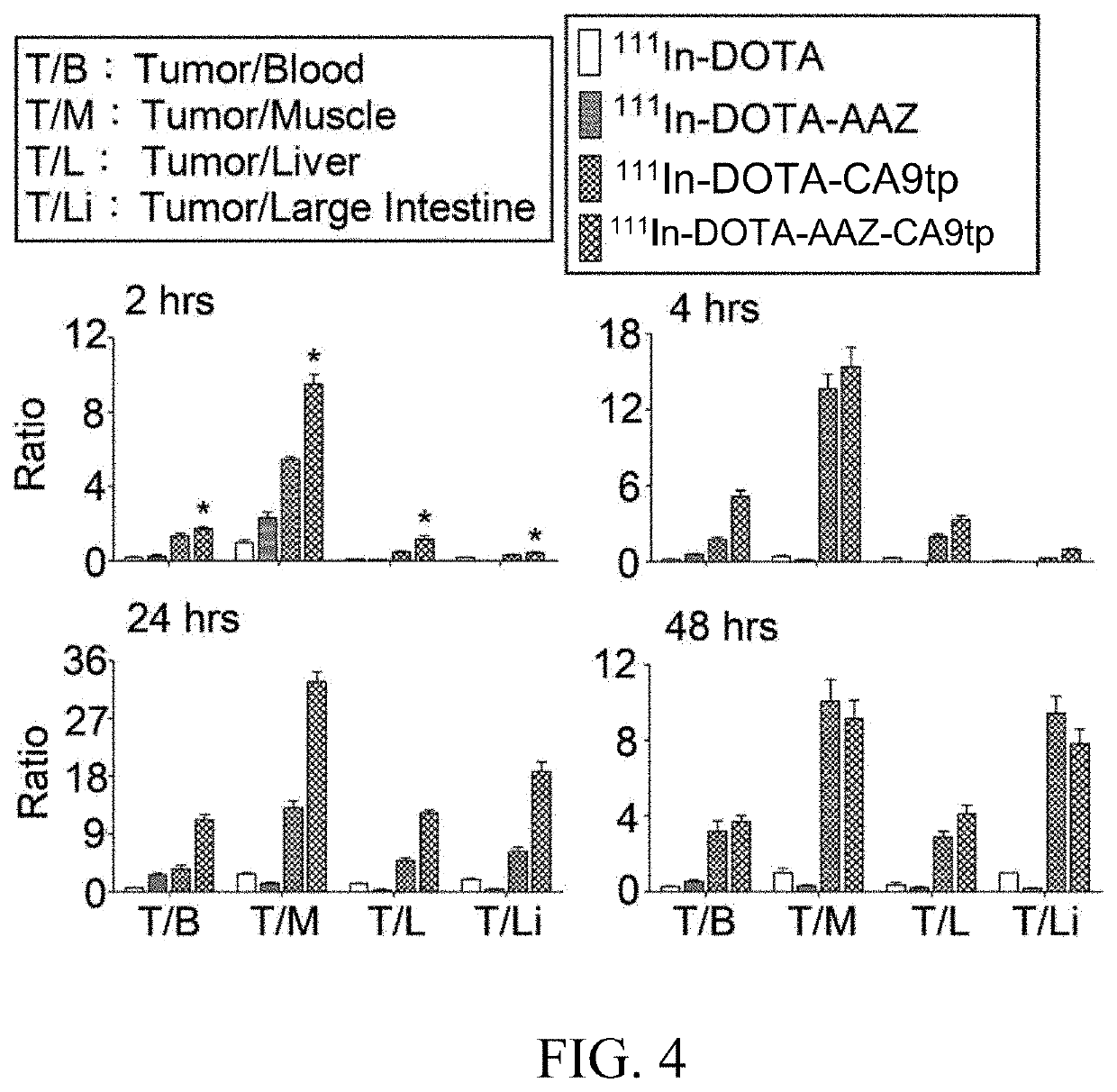
Disclosed herein are a dual-targeted carbonic anhydrase IX complex, a contrast agent comprising the same, and a synthesizing method thereof. The dual-targeted carbonic anhydrase IX complex includes a carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) binding peptide, a sulfonamide derivative, and a metal chelating agent. The dual-targeted carbonic anhydrase IX complex has potential for use as a molecular nuclear drug.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
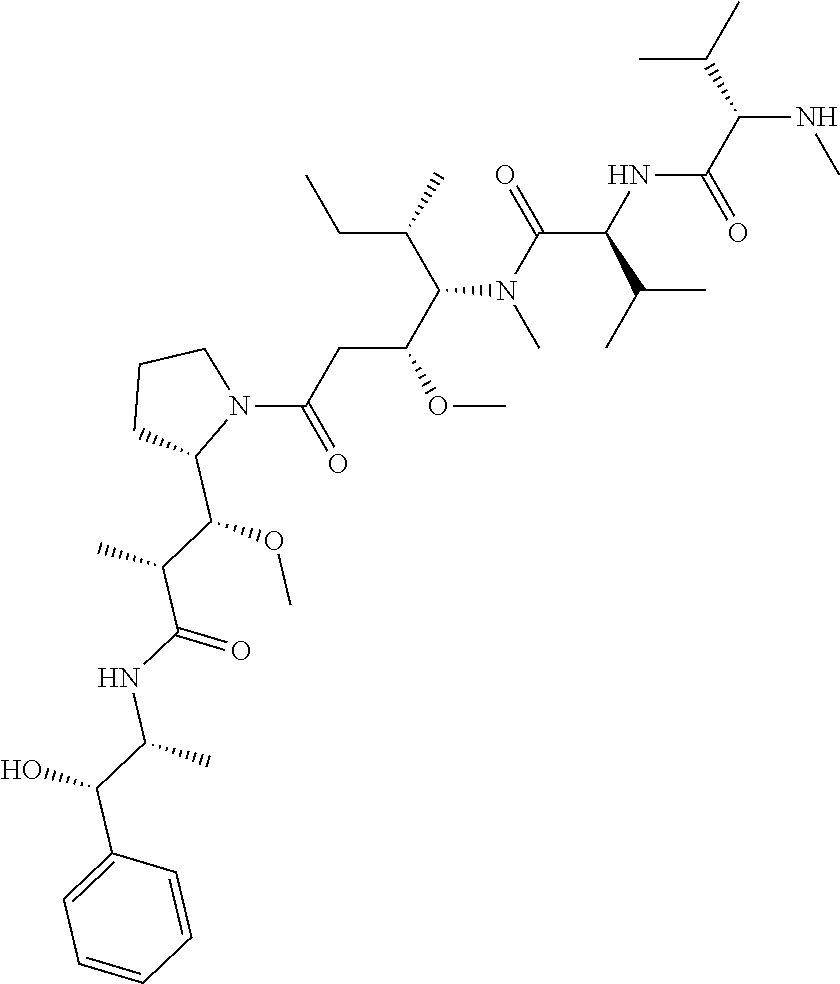
Small molecule drug conjugates
ActiveUS9884122B2Faster and deep and efficient drug targetingOrganic active ingredientsDipeptide ingredientsCancer cellIn vivo
A targeted therapeutic agent comprising a compound of formula I:B-L-D (I),wherein: B is a low molecular weight binding moiety for Carbonic Anhydrase IX (CAIX); D is a drug moiety; and L is a linker group that undergoes cleavage in vivo for releasing said drug moiety in an active form. The drug moiety is suitably a cytotoxic agent for targeted delivery to cancer cells expressing CAIX. The binding moiety B suitably comprises a sulfonamidothiadiazole moiety. The binding moiety B may comprise one, two or more groups capable of binding to CAIX. The linker group suitably comprises a disulfide bond and / or a triazole group and / or a cleavable peptide group.
Owner:ETH ZZURICH
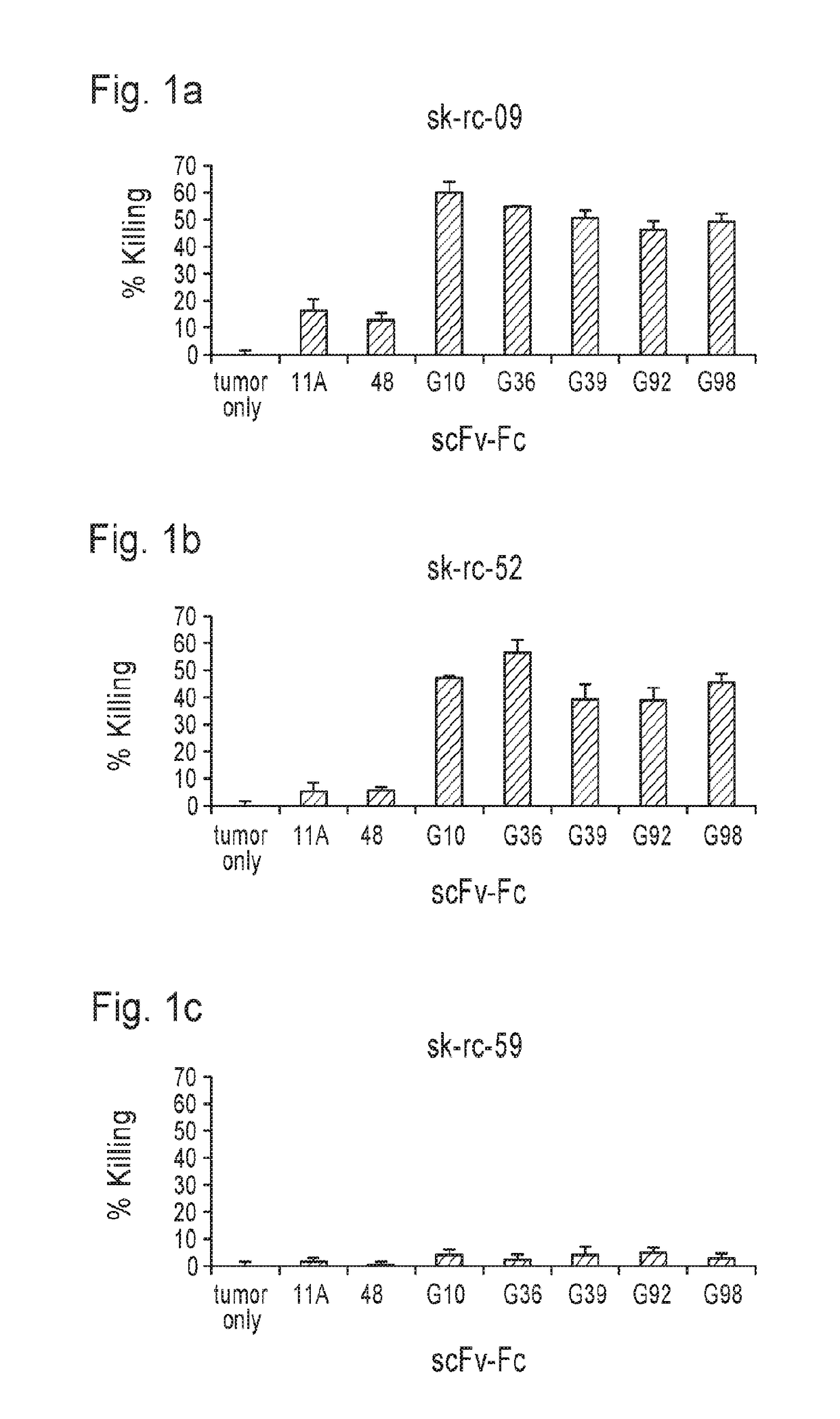
Carbonic anhydrase ix specific chimeric antigen receptors and methods of use thereof
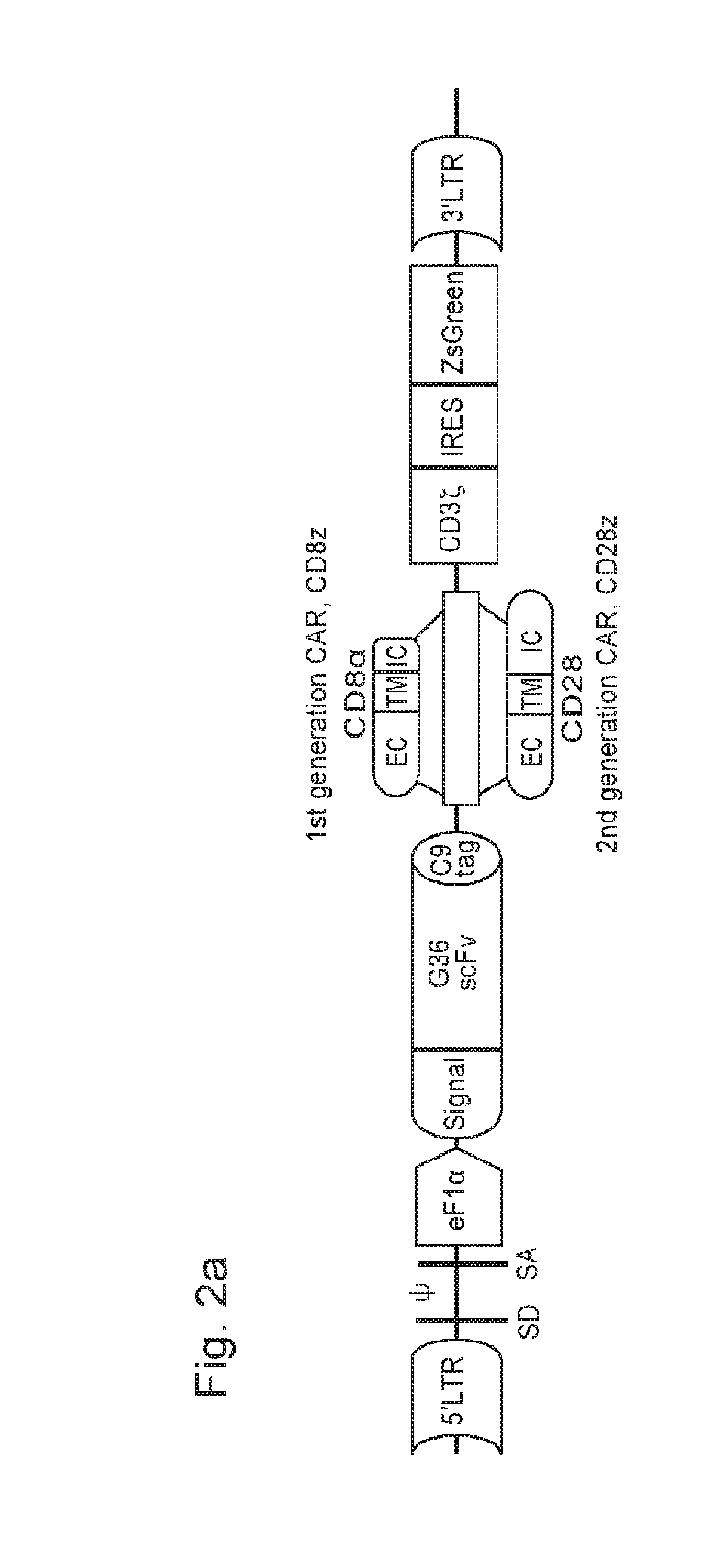
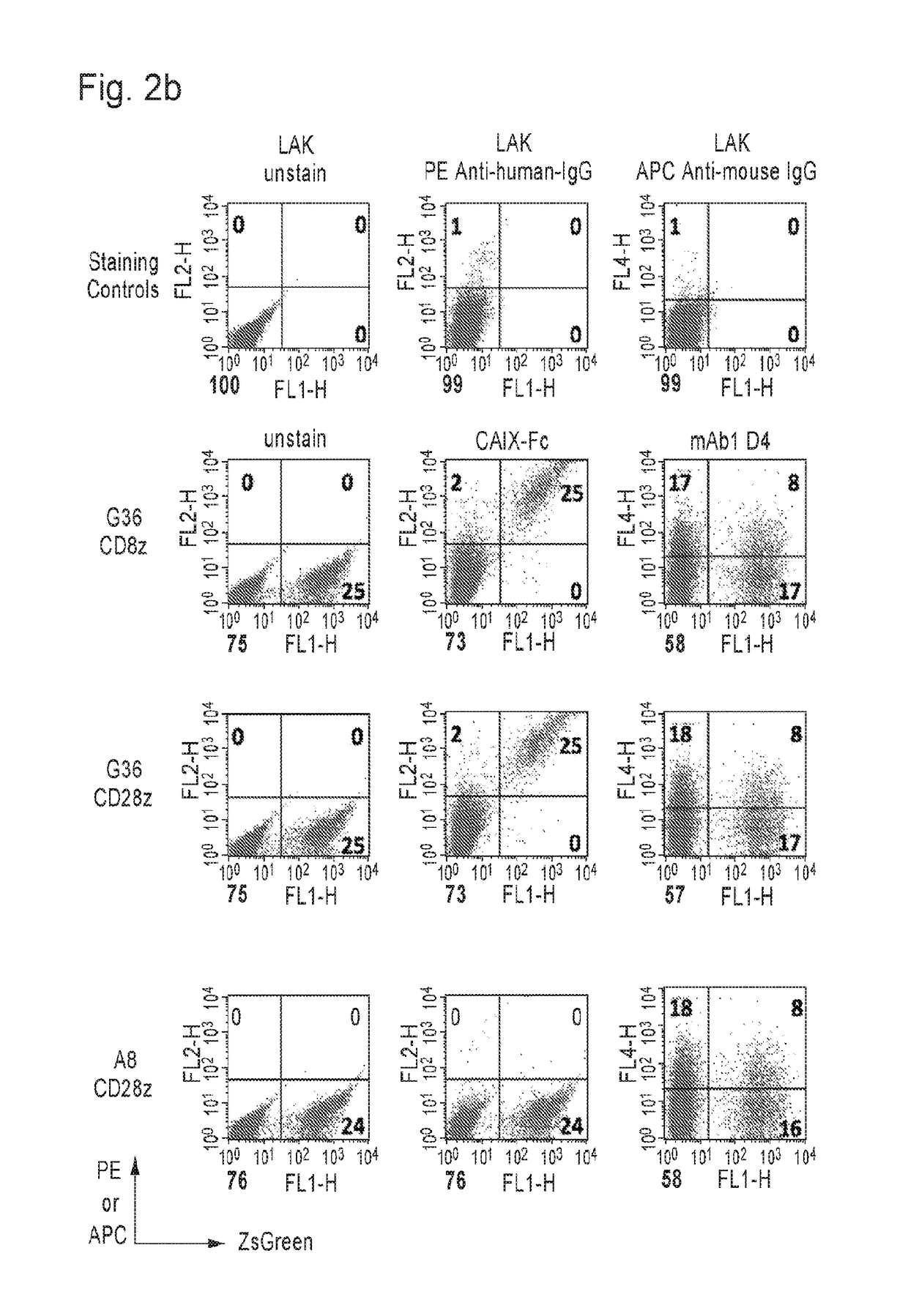
ActiveUS20180030147A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntigen receptorsChimeric antigen receptor
The present invention provides chimeric antigen receptor cells specific for carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX) and methods of using same for treatment of CAIX expressing cancers such as renal cell carcinoma.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Carbonic anhydrase ix-specific antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180186893A1High degree of internalizationBiological material analysisRadioactive preparation carriersSpecific antibodyAcid anhydride
The present invention relates to isolated or purified antibodies or fragments thereof specific for Carbohydrate Anhydrase IX (CA-IX) and their use as therapeutic tools. Specifically, the present invention is directed to high-affinity Carbohydrate Anhydrase IX-specific antibodies and fragments thereof and their use as antibody-drug conjugates. Compositions for use in therapy as well as therapeutic methods are also described.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Carbonic anhydrase ix-related markers and use thereof
The present disclosure provides methods for detecting the presence of a cancer stem cell and their use in cancer prognosis, evaluating risk of cancer metastasis, identifying or validating drug candidates, and determining treatment efficacy. It also provides kits useful for detecting the presence of cancer stem cells as well as methods of treating cancer using CAIX inhibitors.
Owner:SIGNALCHEM LIFESCI +1
Bicyclic peptide ligands specific for caix
PendingUS20220088118A1Preventing and suppressing and treating diseasePeptidesCyclic peptide ingredientsCyclic peptidePeptide ligand
The present invention relates to polypeptides which are covalently bound to non-aromatic molecular scaffolds such that two or more peptide loops are subtended between attachment points to the scaffold. In particular, the invention describes peptides which are high affinity binders of carbonic anhydrase IX (CAIX). The invention also includes drug conjugates comprising said peptides, conjugated to one or more effector and / or functional groups, to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said peptide ligands and drug conjugates and to the use of said peptide ligands and drug conjugates in preventing, suppressing or treating a disease or disorder mediated by CAIX.
Owner:BICYCLETX LTD
Use of recombinant heat shock protein complexed to kidney cancer antigen
A heat shock protein in combination with carbonic anhydrase IX and a method for improving immune response to carbonic anhydrase IX in a mammal by complexing it with a heat shock protein prior to administration to the mammal.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Camelid-derived nanobodies capable of specifically binding to carbonic anhydrase IX and applications thereof
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军特色医学中心
Cell membrane carbonic anhydrase IX fluorescent probe with high brightness and high stability
ActiveCN111333605AImprove photostabilityIncrease brightnessOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh cellFluoProbes
The invention provides a cell membrane carbonic anhydrase IX fluorescent probe with high brightness and high stability. The probe is based on a rhodamine 6G fluorescent parent, is connected with a benzenesulfonamide targeting group, has a structural formula shown in (1), has high cell membrane impermeability, and realizes no-clean imaging of the cell membrane carbonic anhydrase IX by utilizing rapid coordination combination of benzenesulfonamide and zinc atoms in the human carbonic anhydrase IX. The probe is simple in structure, cheap and easily available in raw materials and convenient to synthesize, and has a wide prospect in research in the field of cell membrane carbonic anhydrase IX.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Carbonic anhydrase IX-specific antibodies and uses thereof
ActiveUS10487153B2High degree of internalizationBiological material analysisRadioactive preparation carriersSpecific antibodyAntibody-drug conjugate
The present invention relates to isolated or purified antibodies or fragments thereof specific for Carbohydrate Anhydrase IX (CA-IX) and their use as therapeutic tools. Specifically, the present invention is directed to high-affinity Carbohydrate Anhydrase IX-specific antibodies and fragments thereof and their use as antibody-drug conjugates. Compositions for use in therapy as well as therapeutic methods are also described.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Novel carbonic anhydrase IX targeted photosensitizer and application thereof in field of medicine
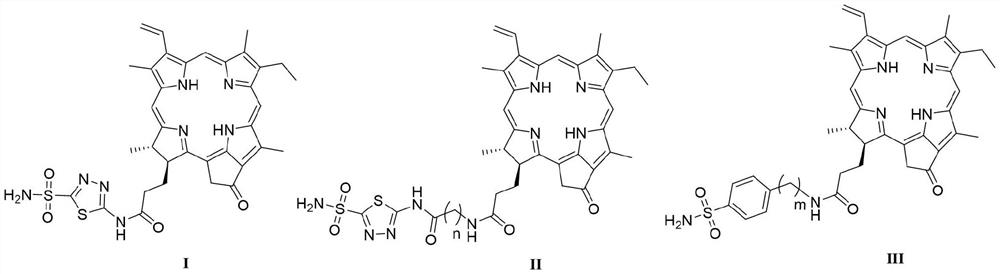
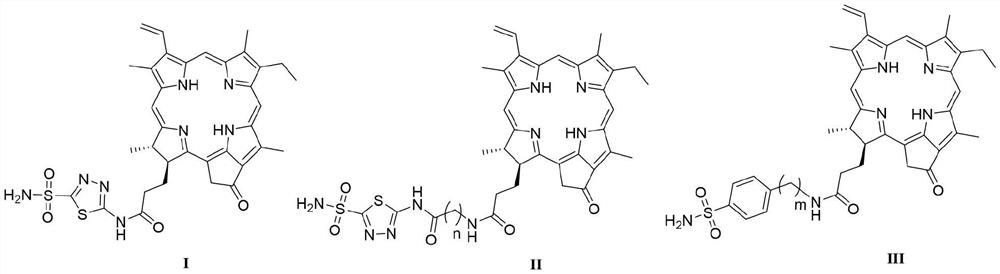
PendingCN114315842AStrong targetingSignificant photodynamic activitySenses disorderOrganic chemistryDiseaseRetinal
The invention relates to novel pyropheophorbide amide derivatives (I, II and III) targeting carbonic anhydrase IX and application of the novel pyropheophorbide amide derivatives (I, II and III) in the field of medicines. The compounds have the following structures: the invention relates to the field of photosensitive medicines and photodynamic therapy, and particularly relates to novel pyropheophorbide amide derivatives (I, II and III). In particular to a novel pyropheophorbide amide derivative targeting carbonic anhydrase IX and application of the pyropheophorbide amide derivative in the field of medicine. The compound prepared by the invention is single in component, stable in property, controllable in quality, simple and convenient in preparation method and relatively good in photodynamic activity, and can be used as a photodynamic therapeutic drug for diseases such as tumors, retina macular degeneration, actinic keratosis, nevus flammeus and condyloma acuminata.
Owner:SHANGHAI XIANHUI MEDICAL TECH
Sulfa compounds, intermediates, preparation and application targeting carbonic anhydrase ⅸ
ActiveCN106278963BThe synthesis steps are simpleHigh yieldRadioactive preparation carriersSulfonic acid amide preparationStructural formulaMedicinal chemistry
Owner:SHANGHAI ATOM KEXING PHARMA
Process for evaluating active agent(s) capable of preserving the functionality of epithelial stem cells
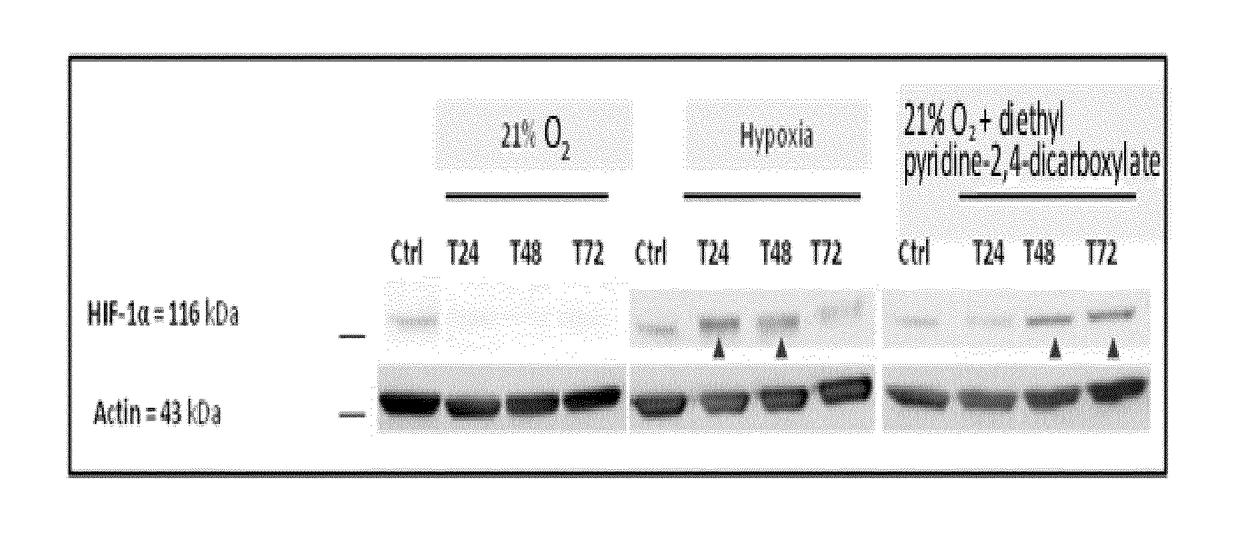
The present invention relates to a process for evaluating in vitro at least one active agent capable of preserving the functionality of epithelial stem cells, in particular of maintaining or stimulating the growth and / or the density and / or the renewal of a keratin material, consisting in determining the ability of the active agent(s) to mimic a hypoxic state in the keratin material, the active agent(s) being capable of increasing the expression of at least carbonic anhydrase IX as biological marker of hypoxia, in the keratin material treated with the active agent(s) compared with the keratin material not treated with the active agent(s). It also relates to the use of such a process.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Metal complexes of poly(carboxyl)amine-containing ligands having an affinity for carbonic anhydrase ix
InactiveUS20130216477A1BiocideRadioactive preparation carriersCoordination complexCarbonic anhydrase
The present invention is directed to CA IX inhibitors that conform to Formula I where the substituents X, A, B, D, E, E′ and G are as defined above.Also described are Pt, 64Cu, 186Re, 188Re and 99mTc metal complexes of Formula I compounds which find use as candidate agents for imaging tumors.
Owner:MOLECULAR INSIGHT PHARMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com