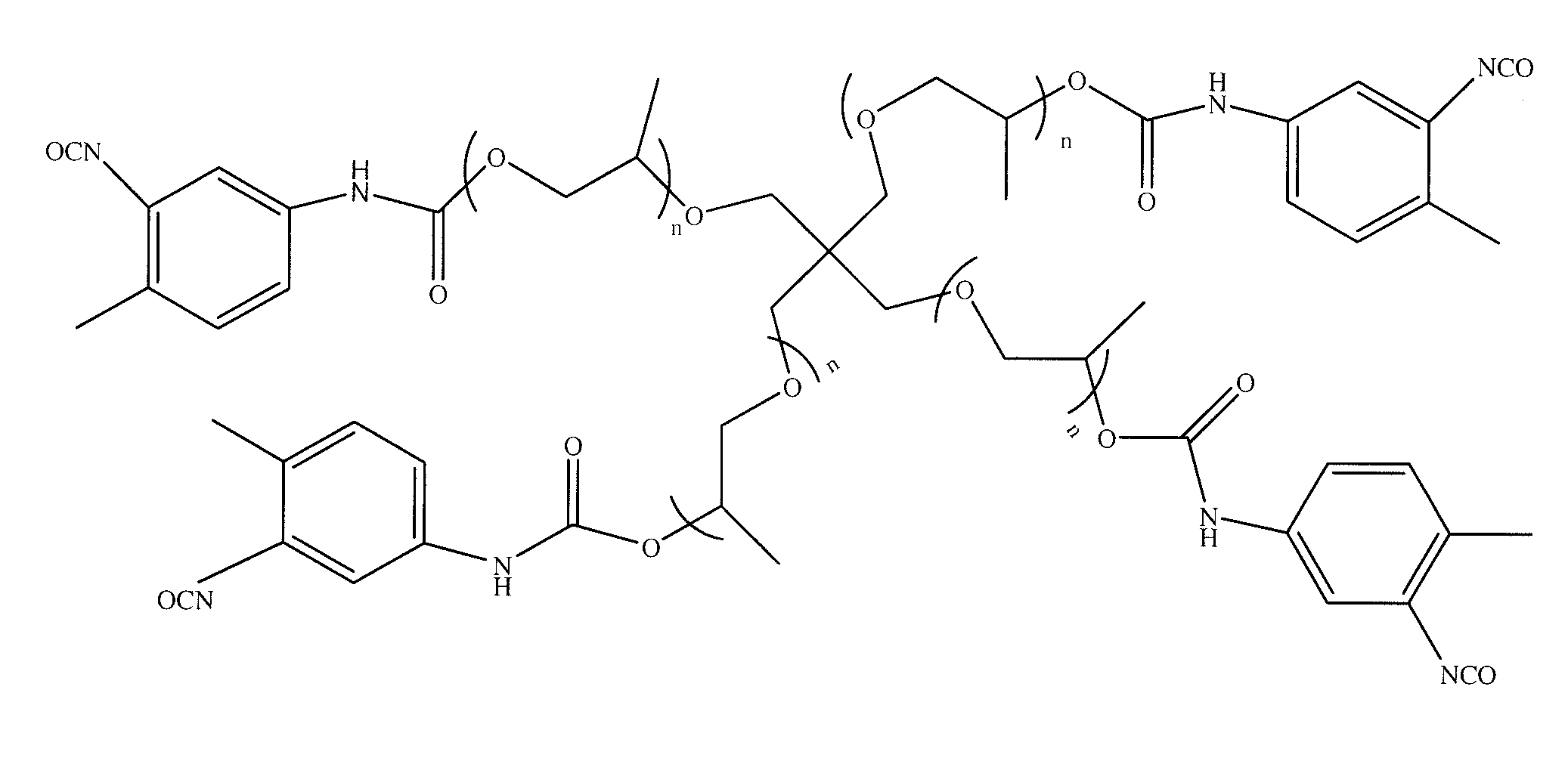
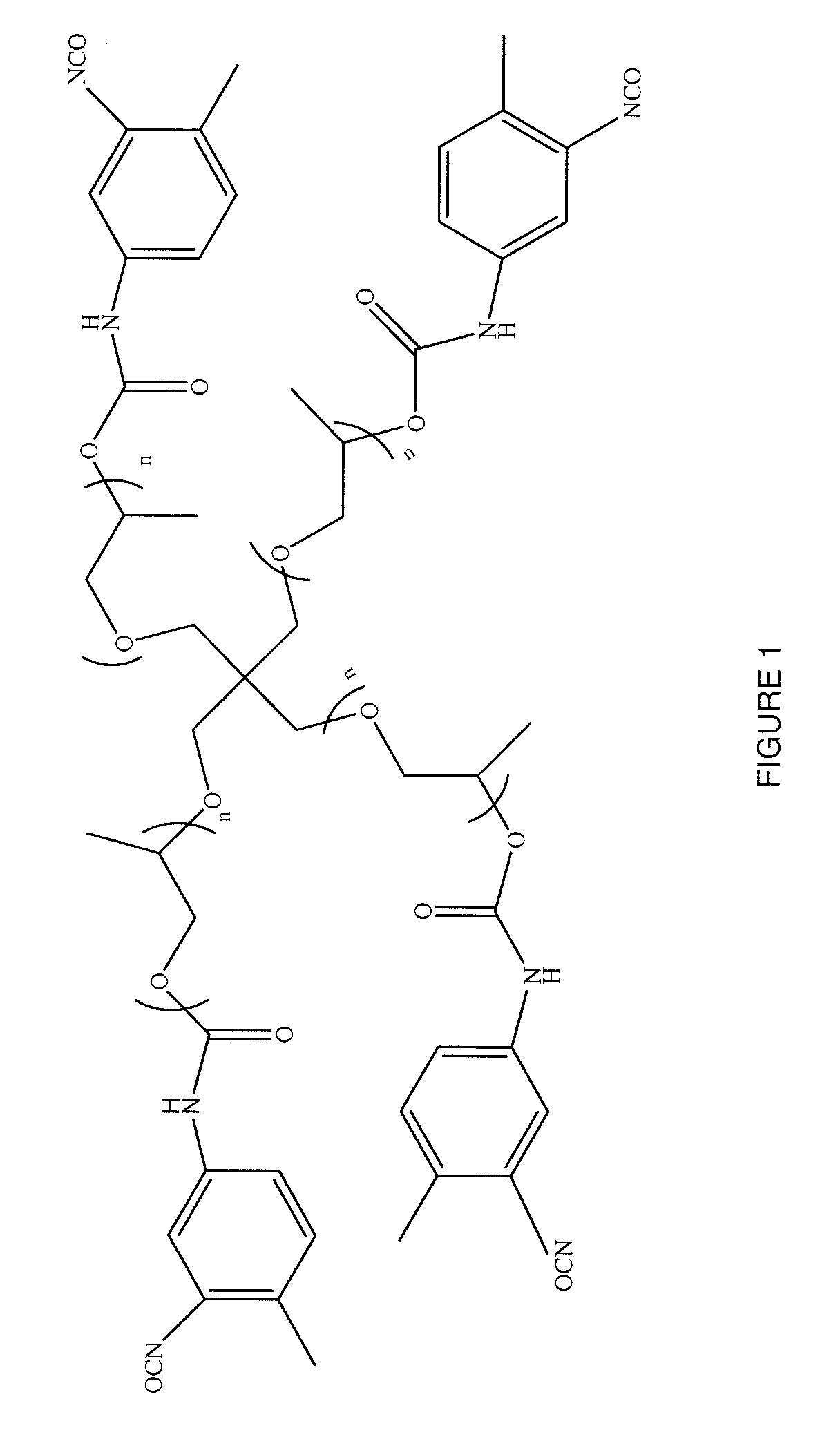
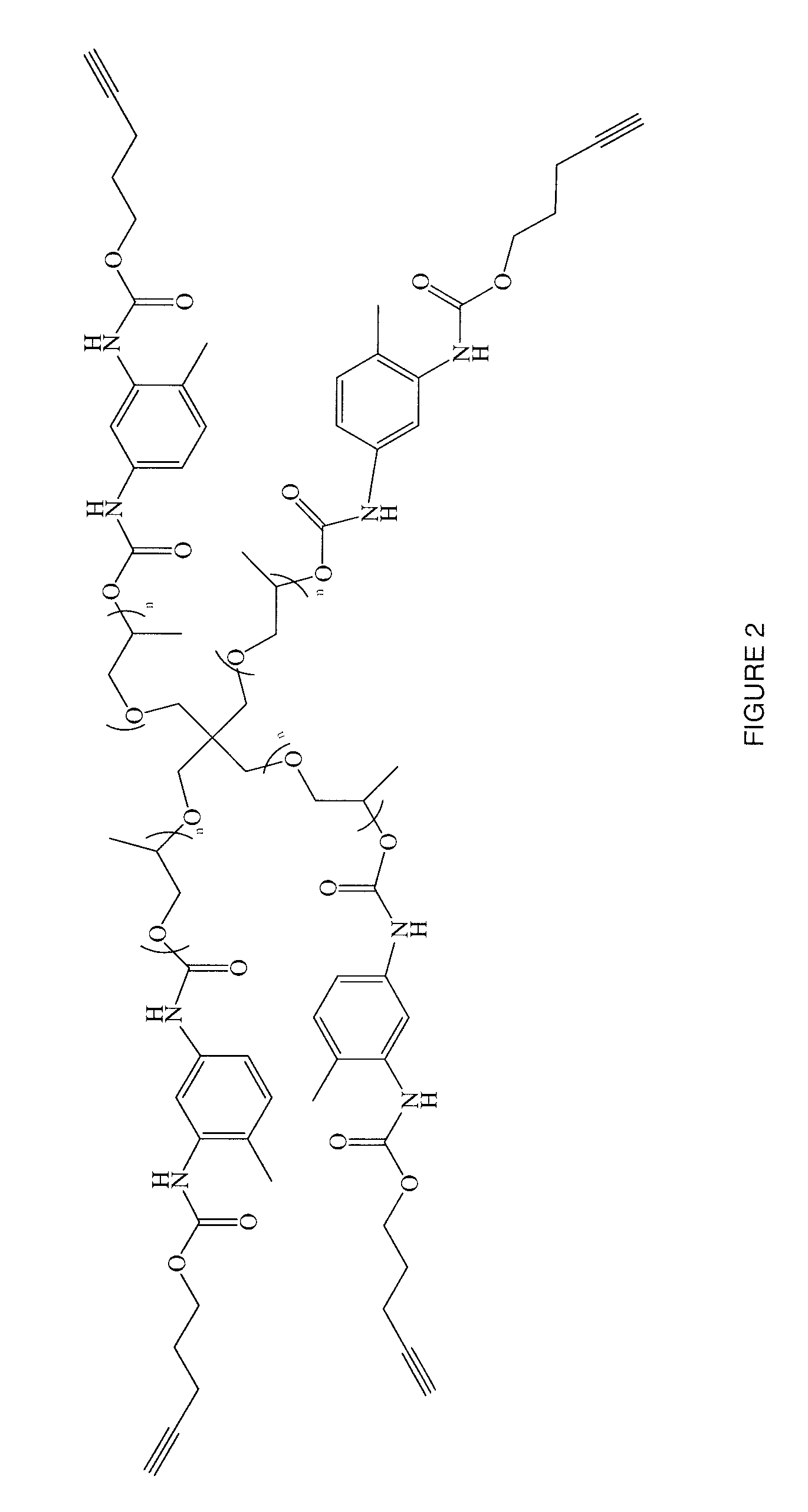
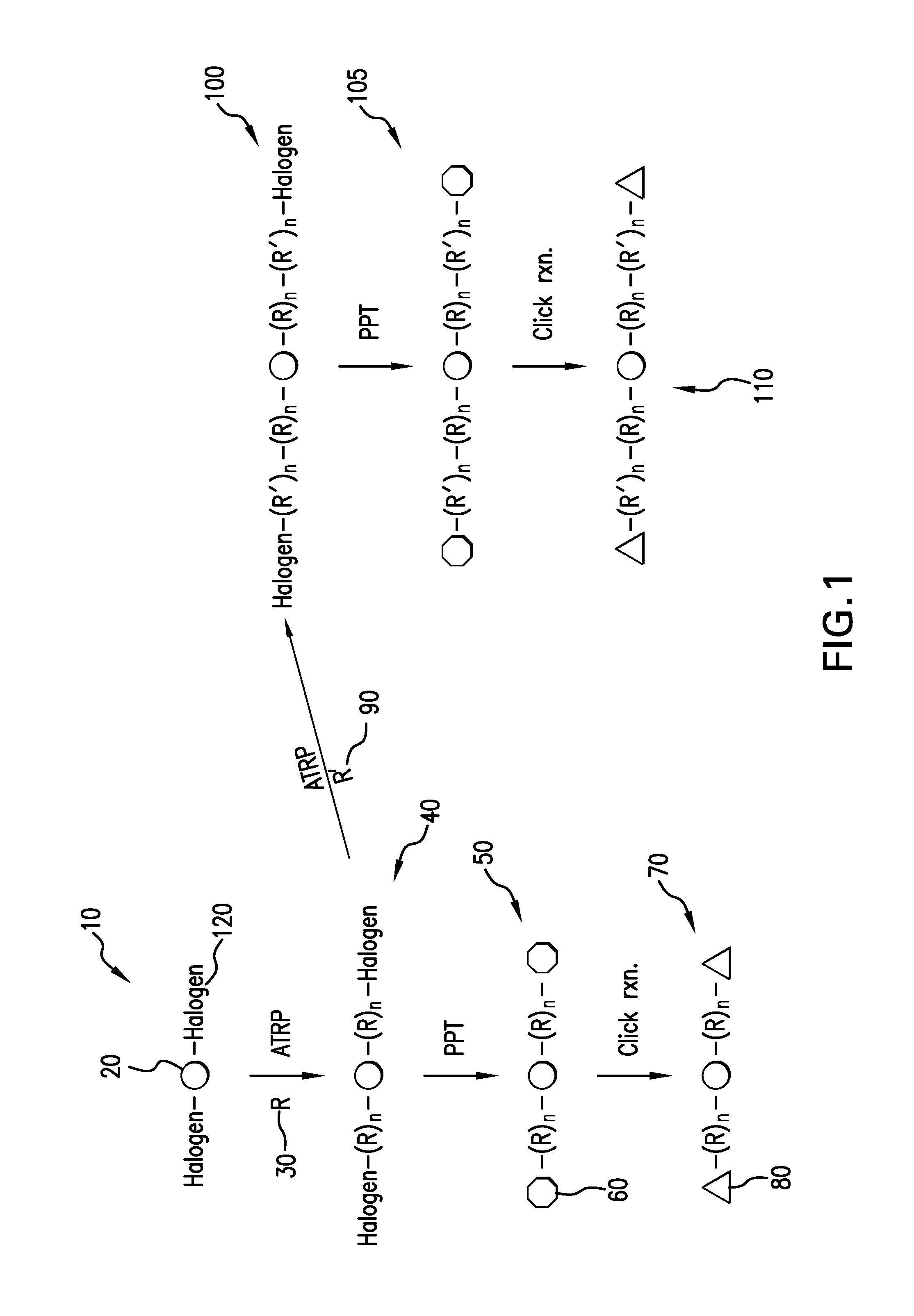
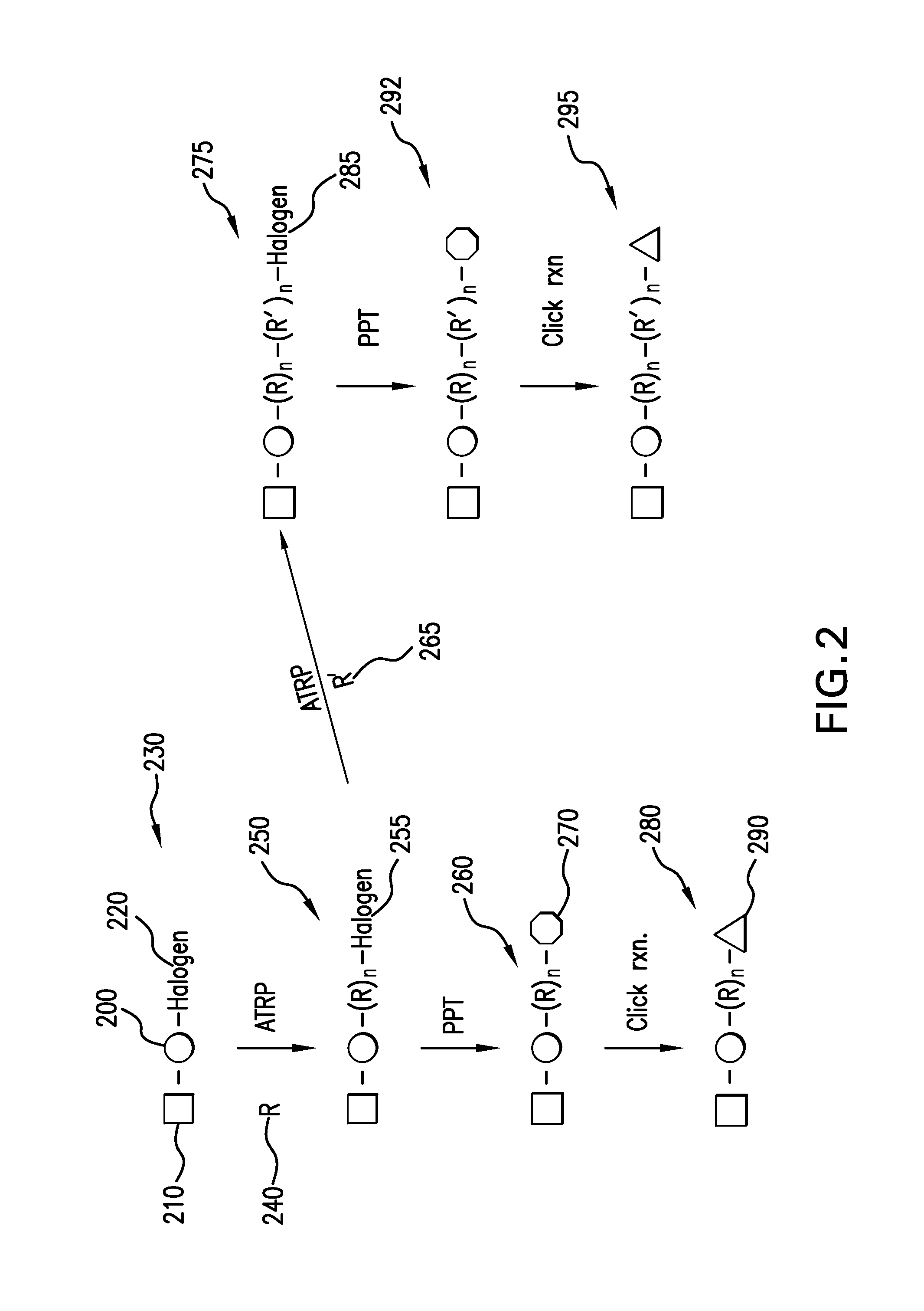
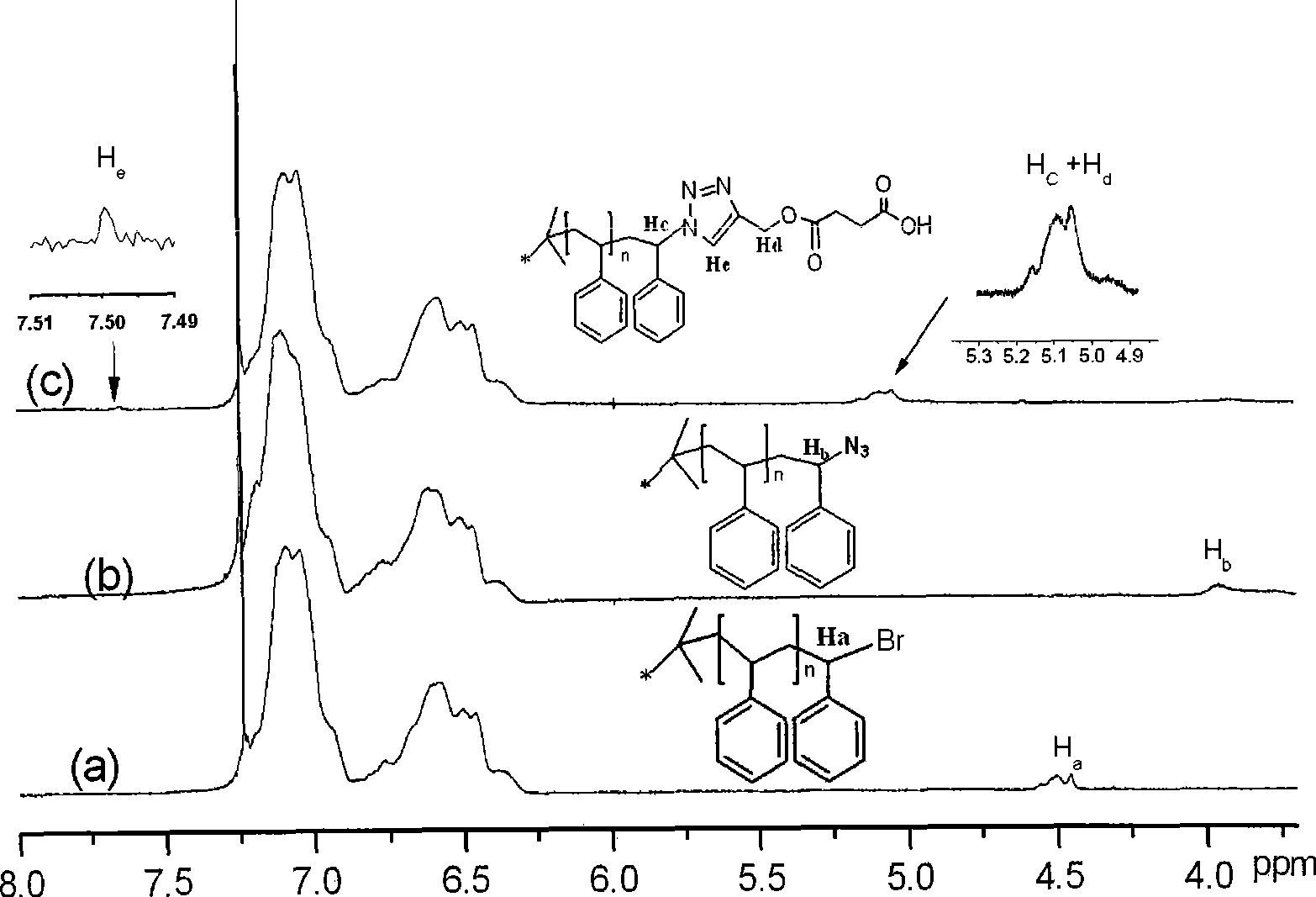
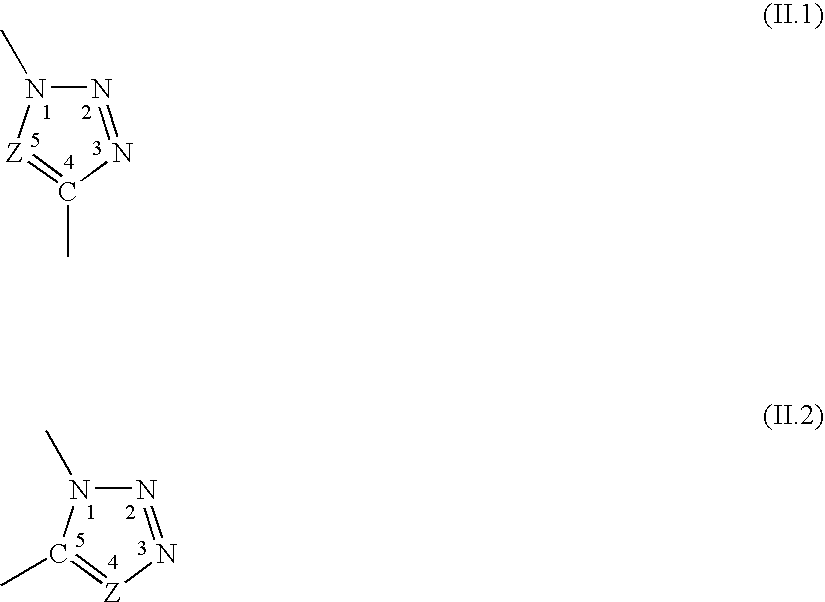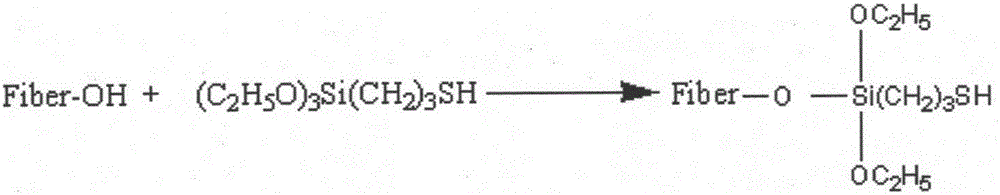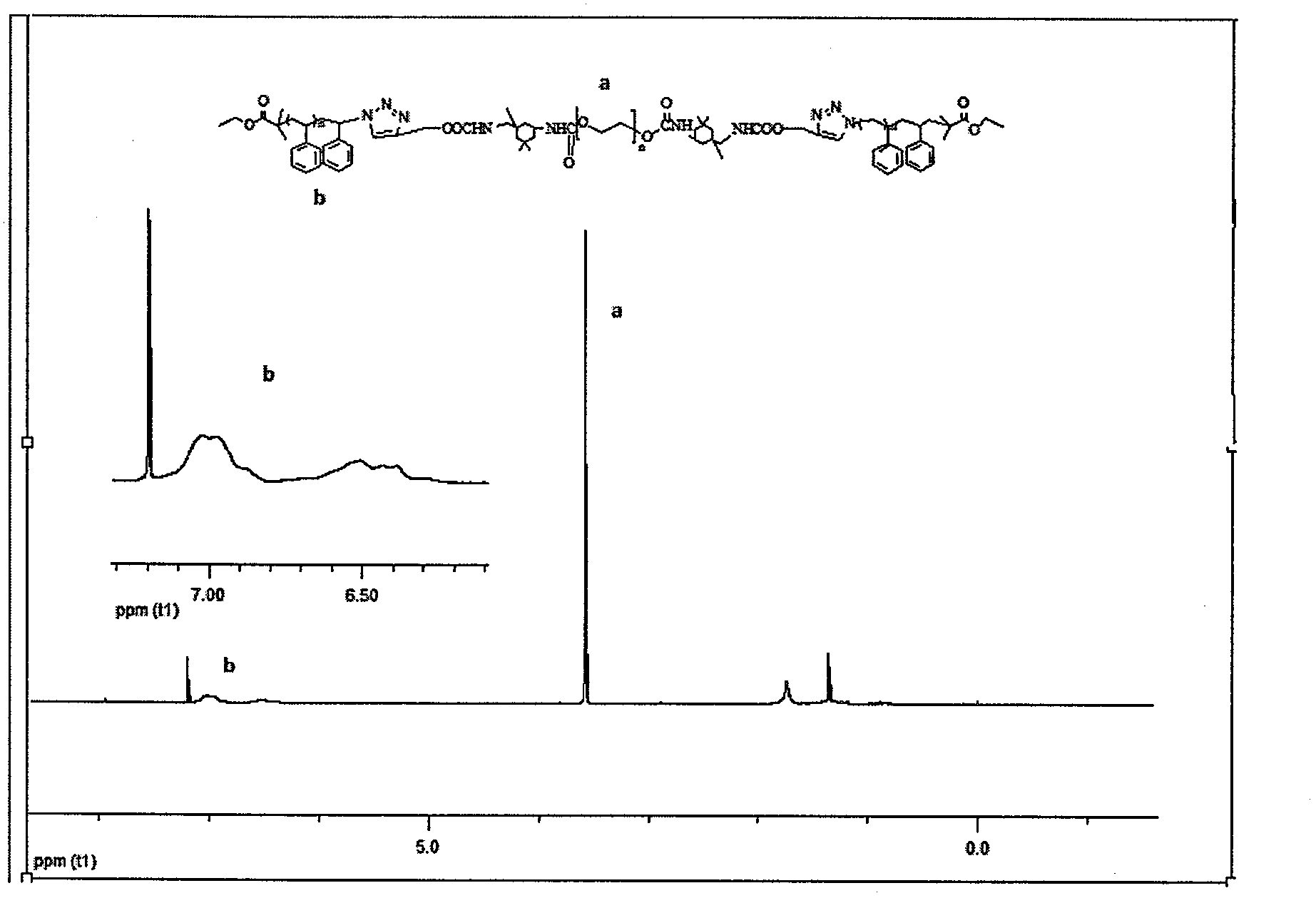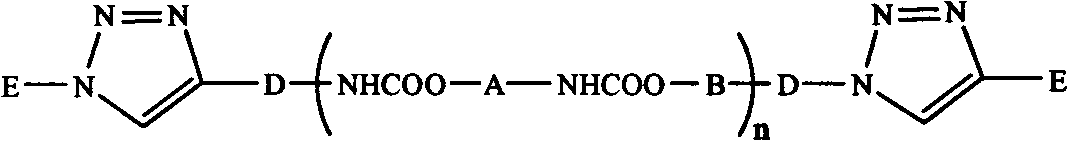Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1052 results about "Click chemistry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
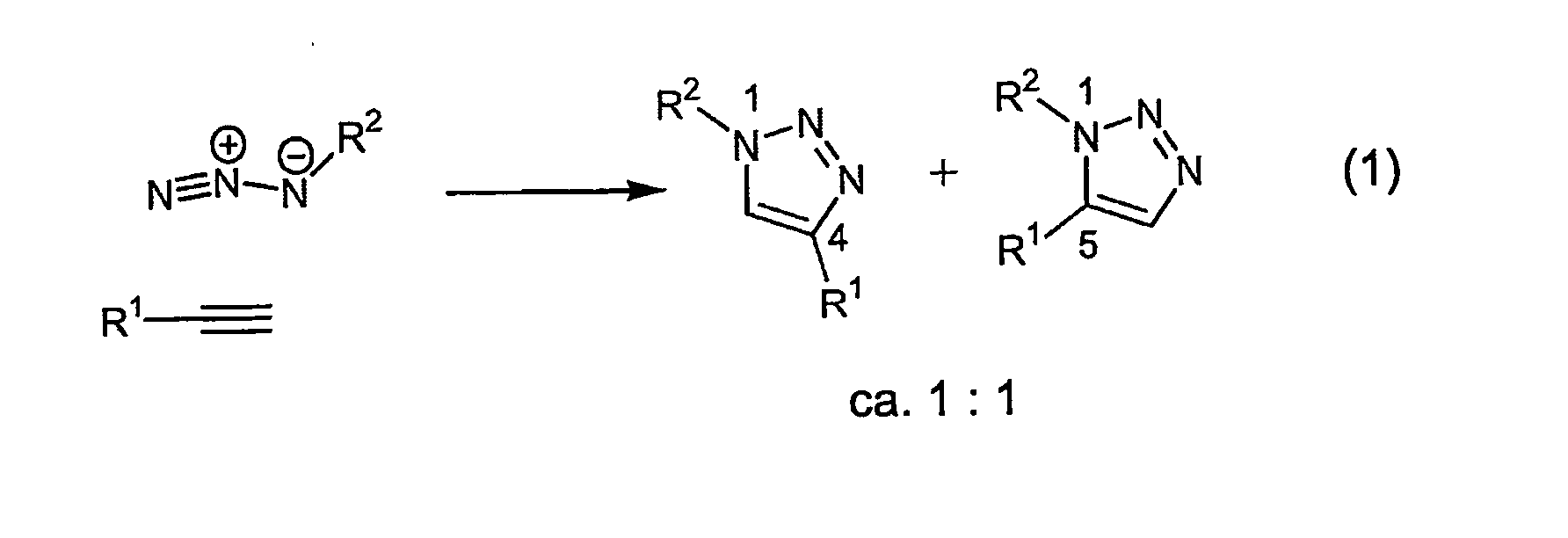
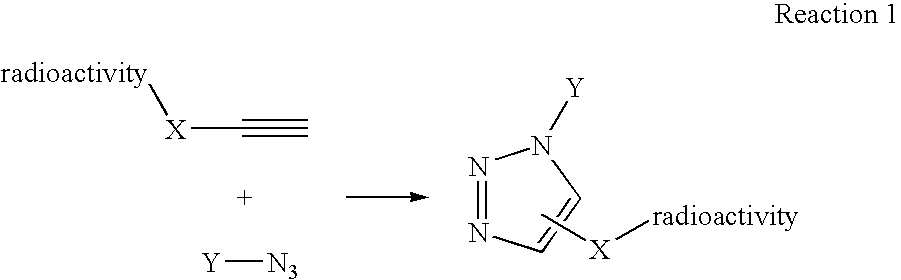
In chemical synthesis, "click" chemistry is a class of biocompatible small molecule reactions commonly used in bioconjugation, allowing the joining of substrates of choice with specific biomolecules. Click chemistry is not a single specific reaction, but describes a way of generating products that follow examples in nature, which also generates substances by joining small modular units. In many applications, click reactions join a biomolecule and a reporter molecule. Click chemistry is not limited to biological conditions: the concept of a "click" reaction has been used in pharmacological and various biomimetic applications. However, they have been made notably useful in the detection, localization and qualification of biomolecules.
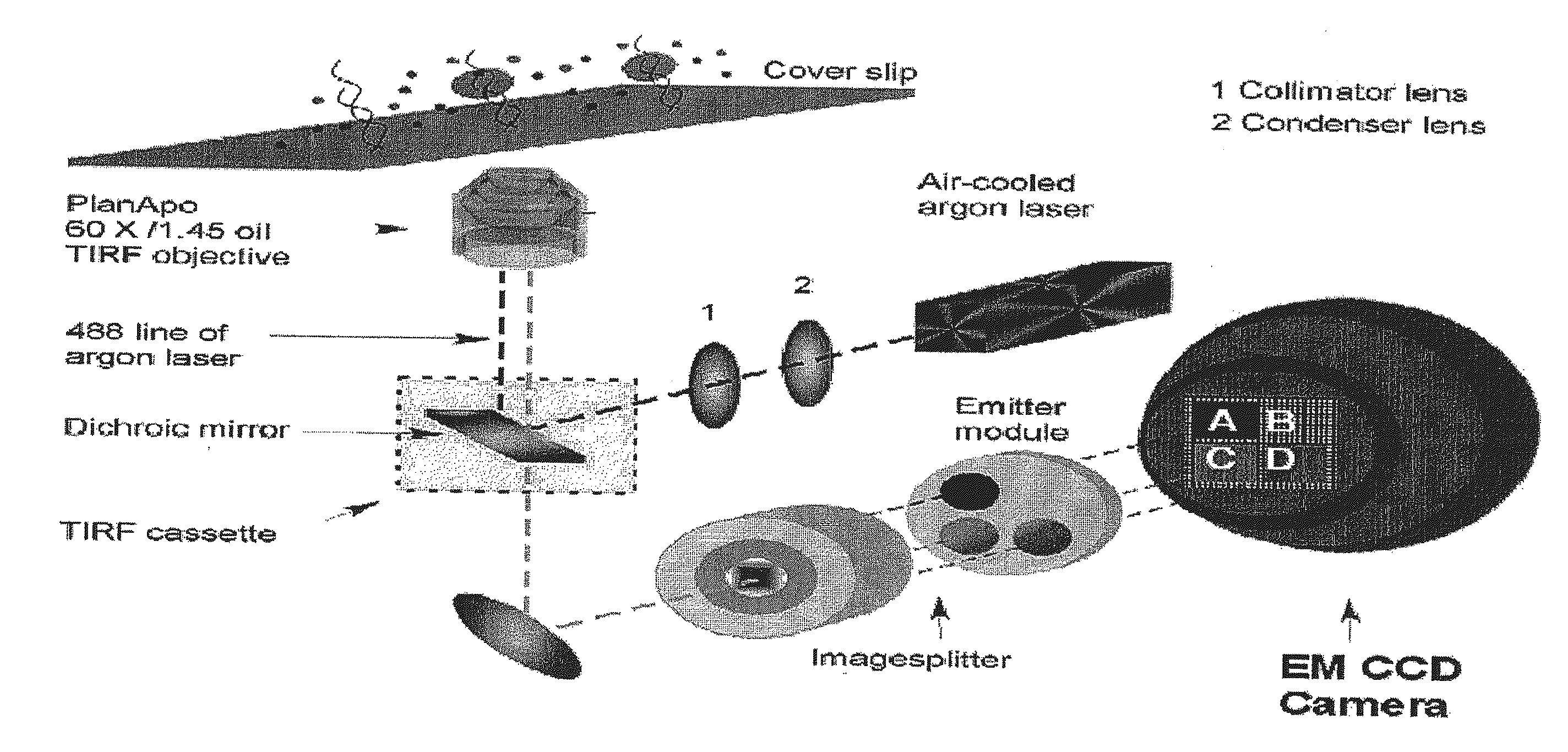
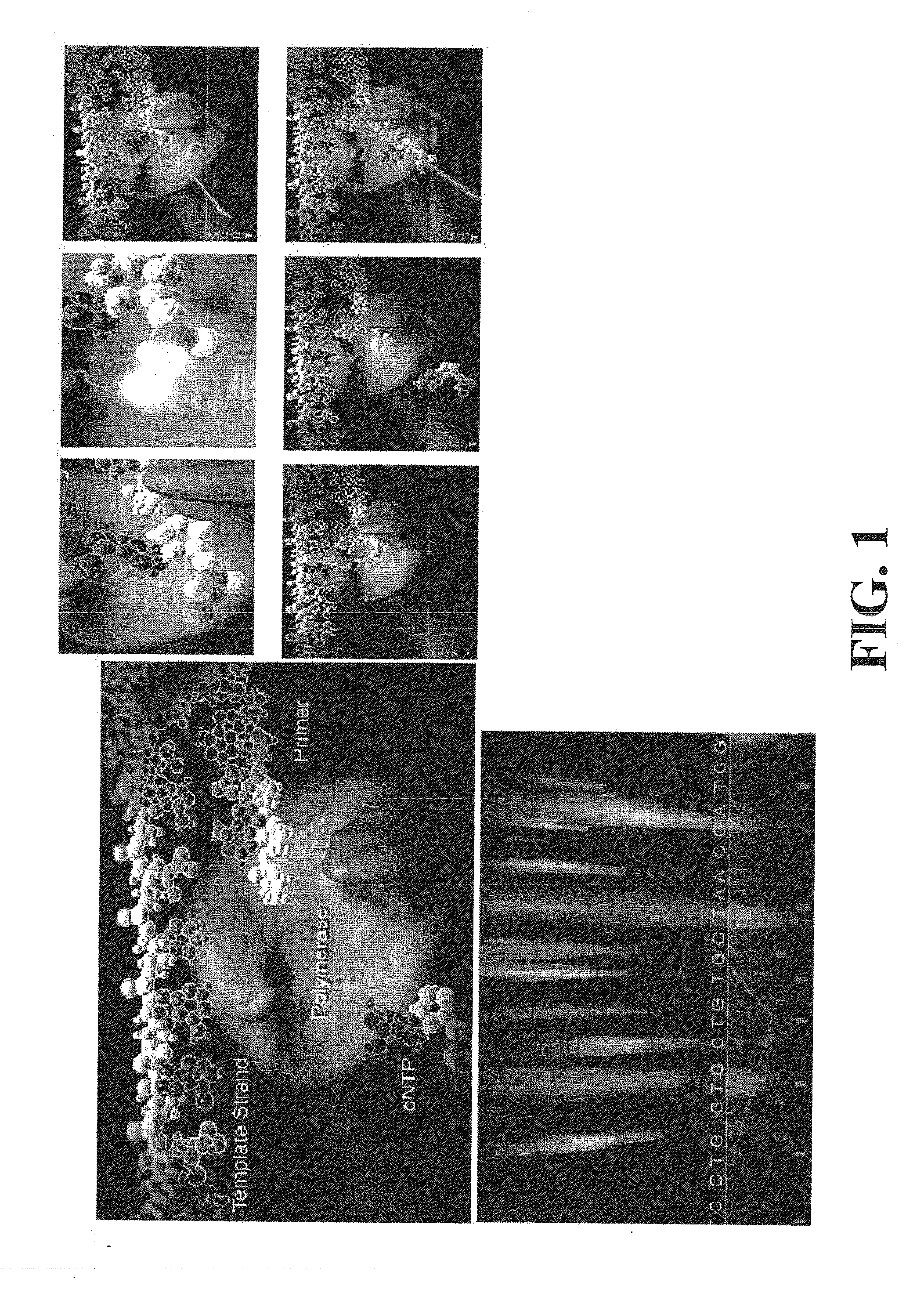
Compositions, methods and systems for single molecule sequencing
InactiveUS20110165652A1Enhanced signalReduce background noiseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSynthesis methods
Compositions, systems and methods of sequencing are disclosed, where the compositions and systems include polymerase enzymes that have been genetically modified to more efficiently incorporate nucleotides including labels having a detectable properties that are released during incorporation, to augment a rate of labeled nucleotide incorporation, to augment a rate of pyrophosphate release, or to augment two or more of these properties and rates. Also disclosed are terminally labeled and dual labeled nucleotides, and click-chemistry based methods of synthesizing the same.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
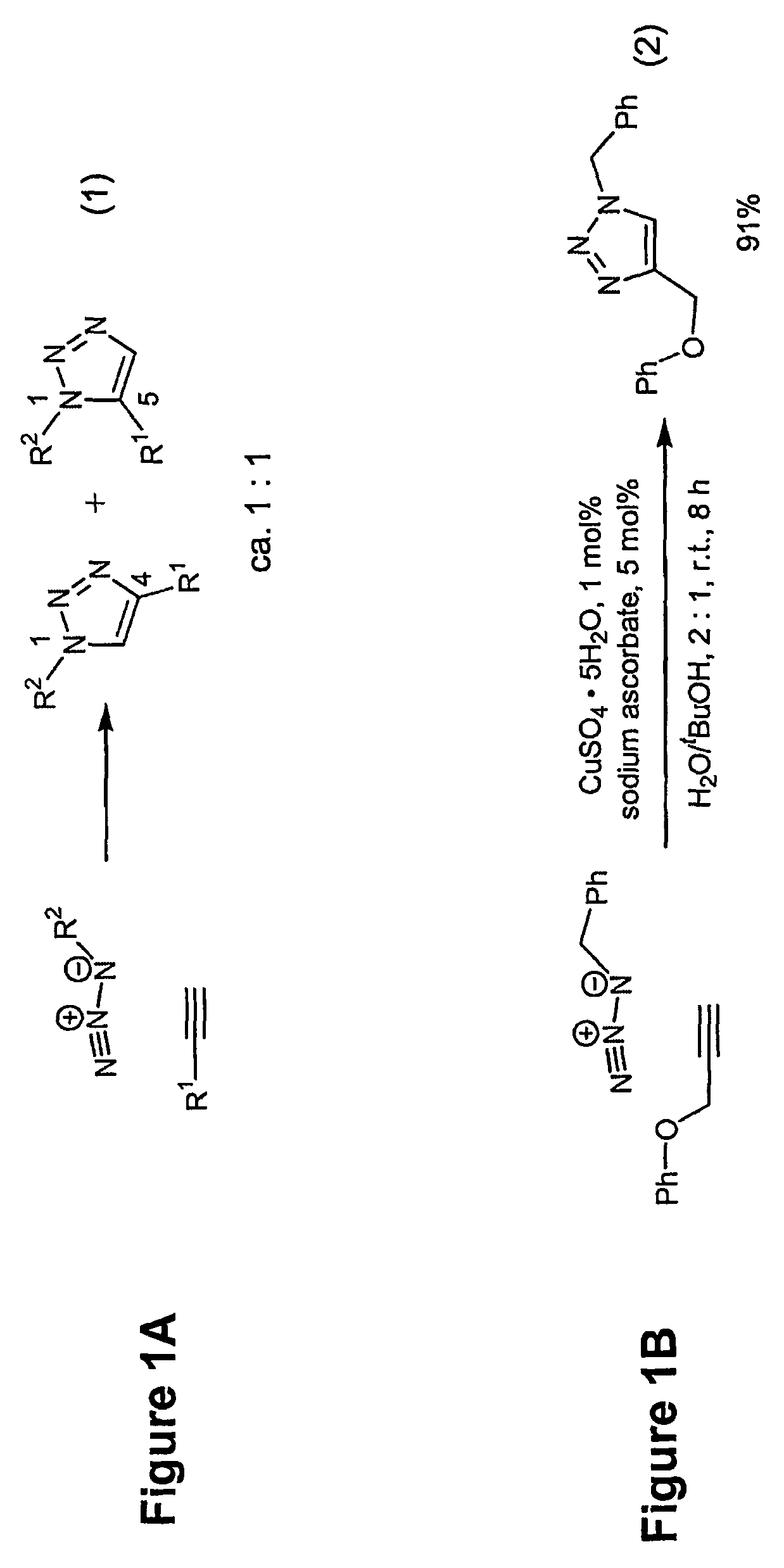
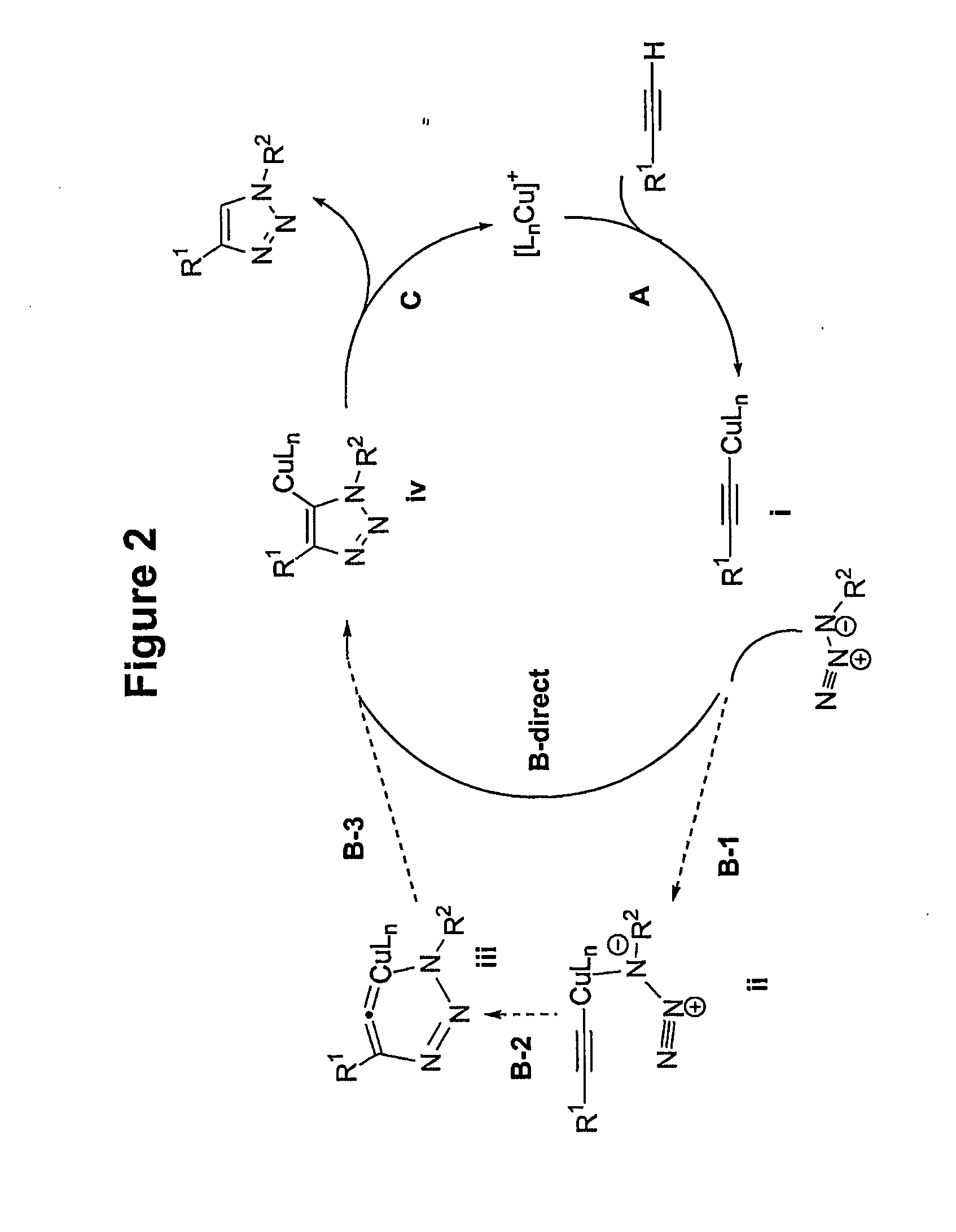
Copper-catalysed ligation of azides and acetylenes
InactiveUS7763736B2Organic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsChemical ligationAqueous alcohol
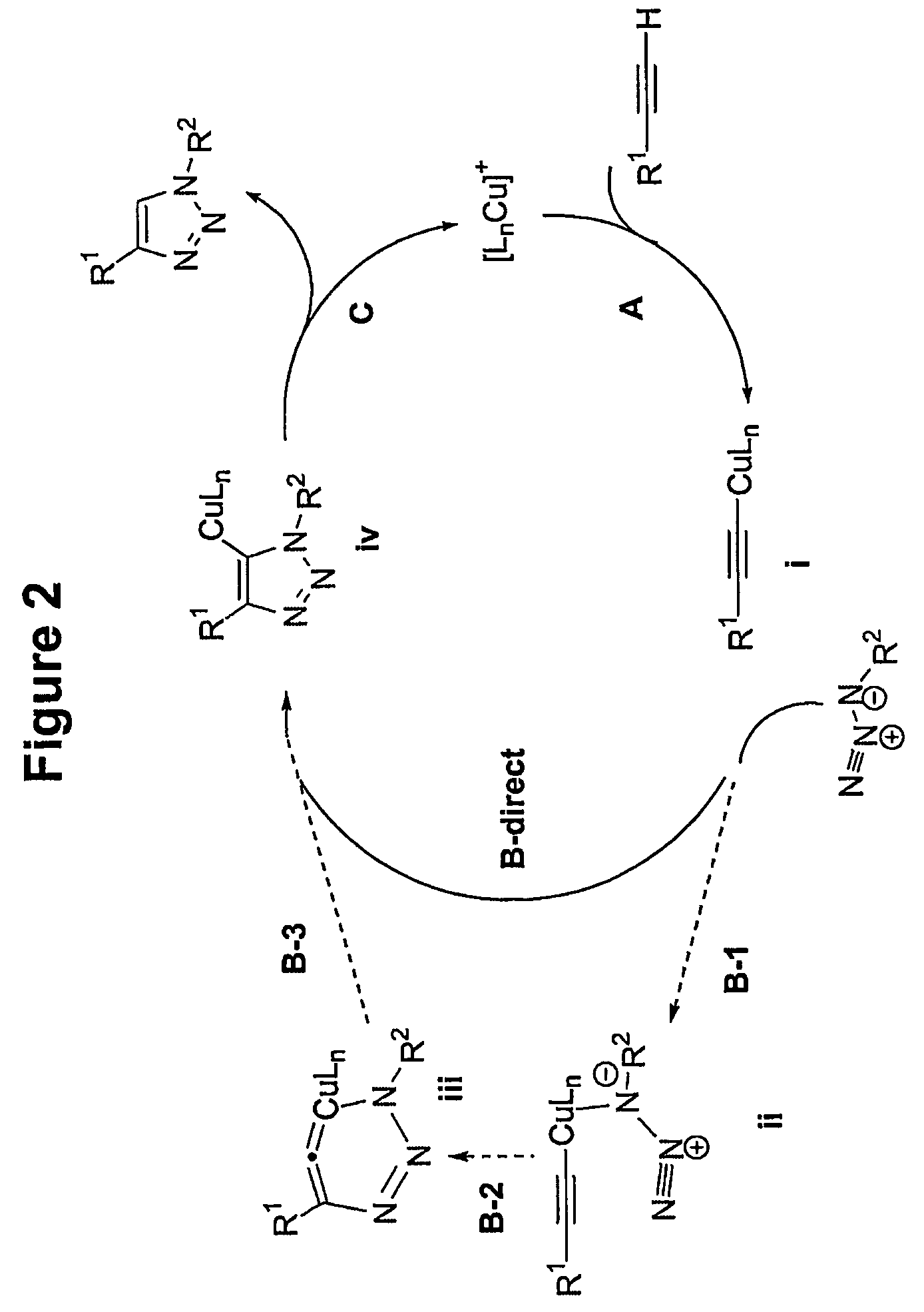
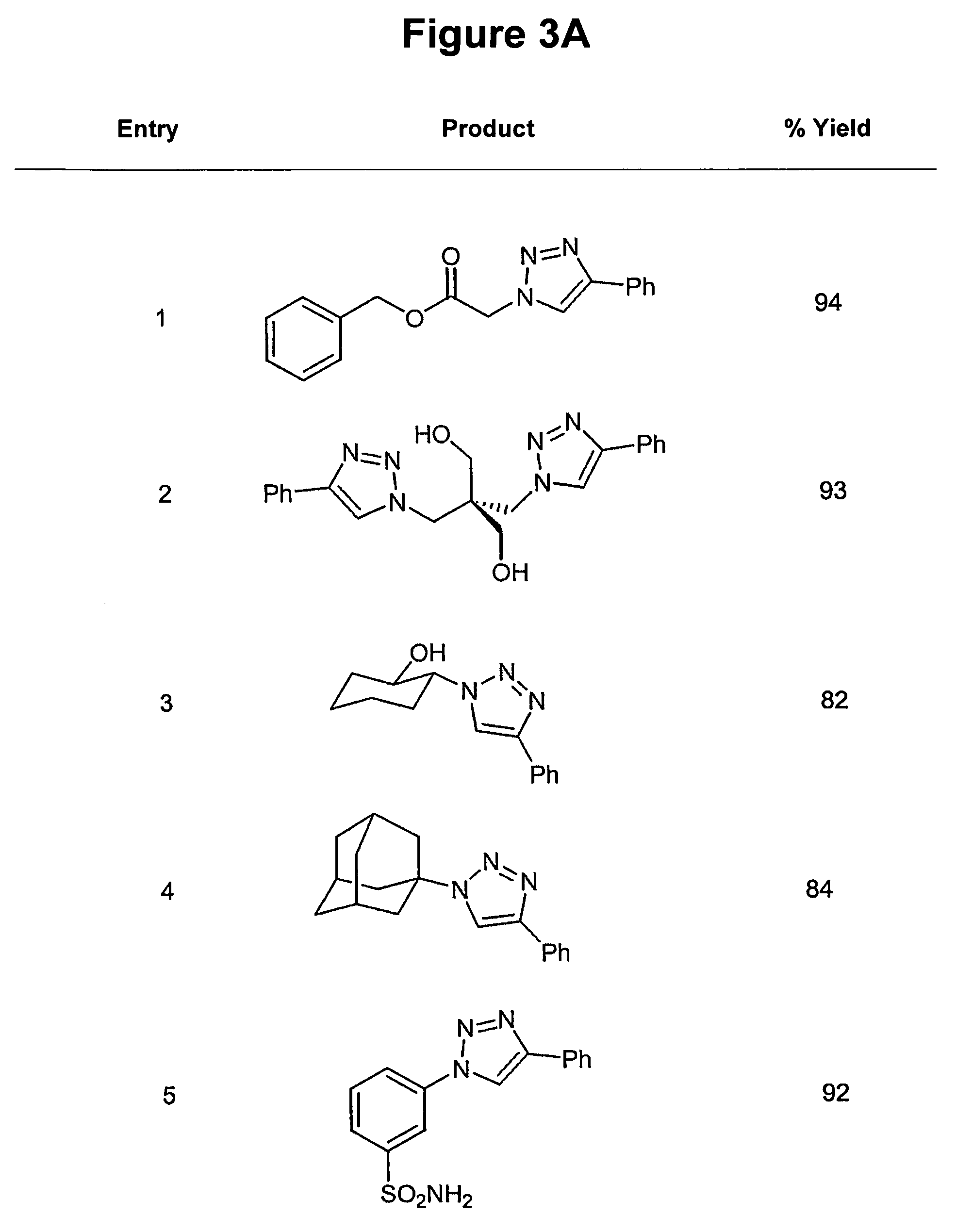
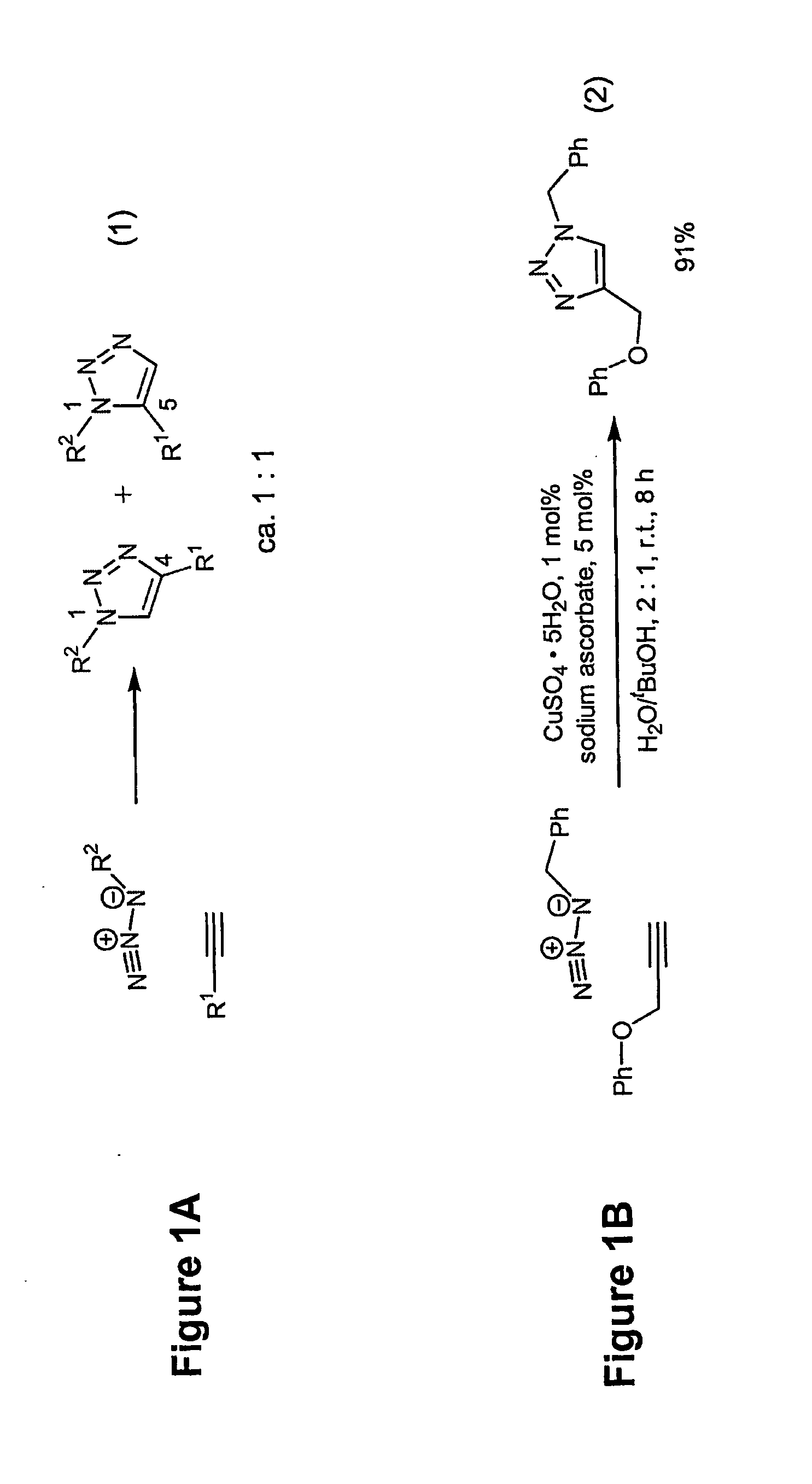
A copper catalyzed click chemistry ligation process is employed to bind azides and terminal acetylenes to provide 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole triazoles. The process comprises contacting an organic azide and a terminal alkyne with a source of reactive Cu(I) ion for a time sufficient to form by cycloaddition a 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole. The source of reactive Cu(I) ion can be, for example, a Cu(I) salt or copper metal. The process is preferably carried out in a solvent, such as an aqueous alcohol. Optionally, the process can be performed in a solvent that comprises a ligand for Cu(I) and an amine.
Owner:TETARD INC
Coating Employing an Anti-Thrombotic Conjugate
InactiveUS20090018646A1Few stepsImprove versatilityStentsOrganic active ingredientsActive agentSide chain
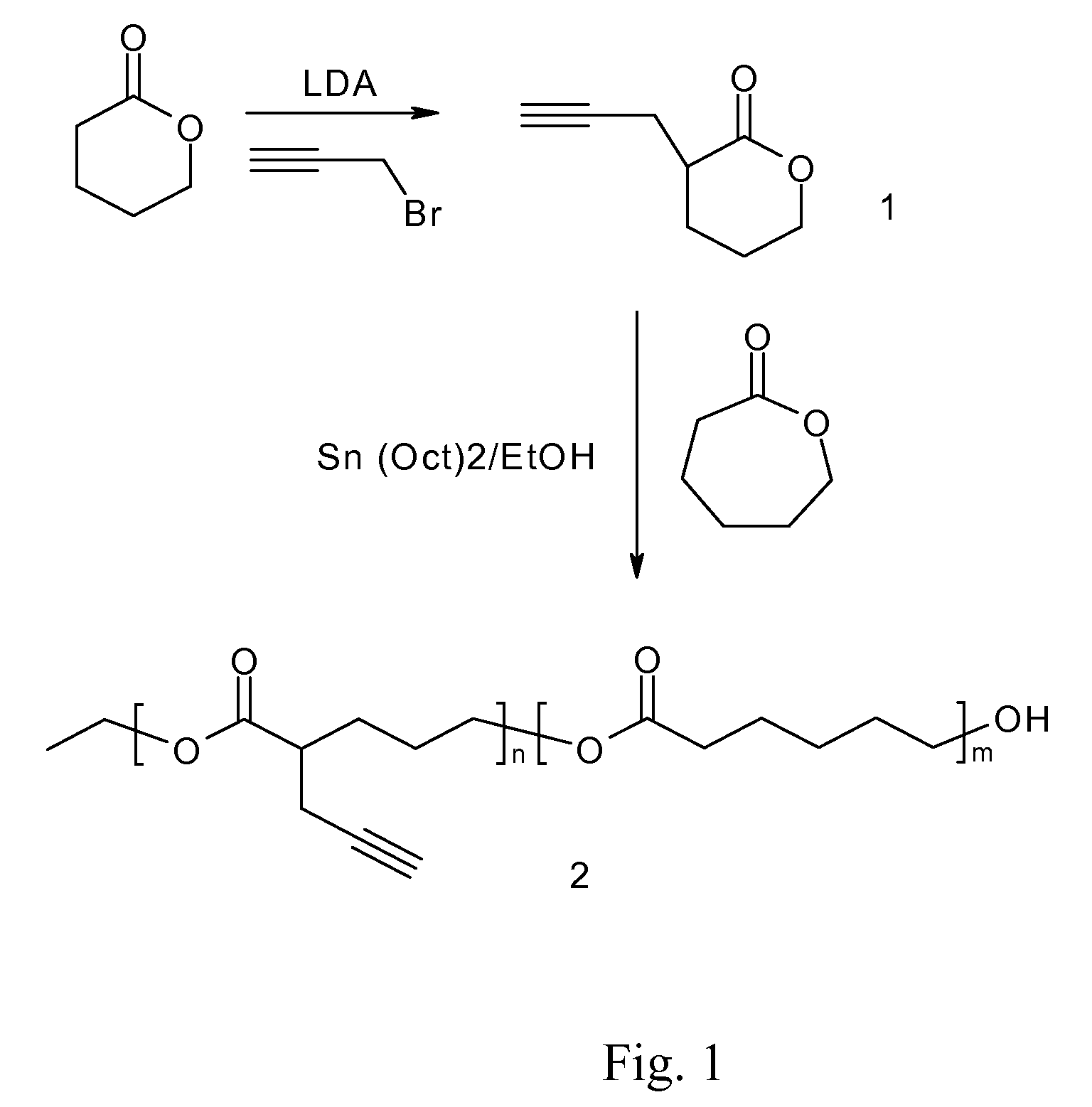
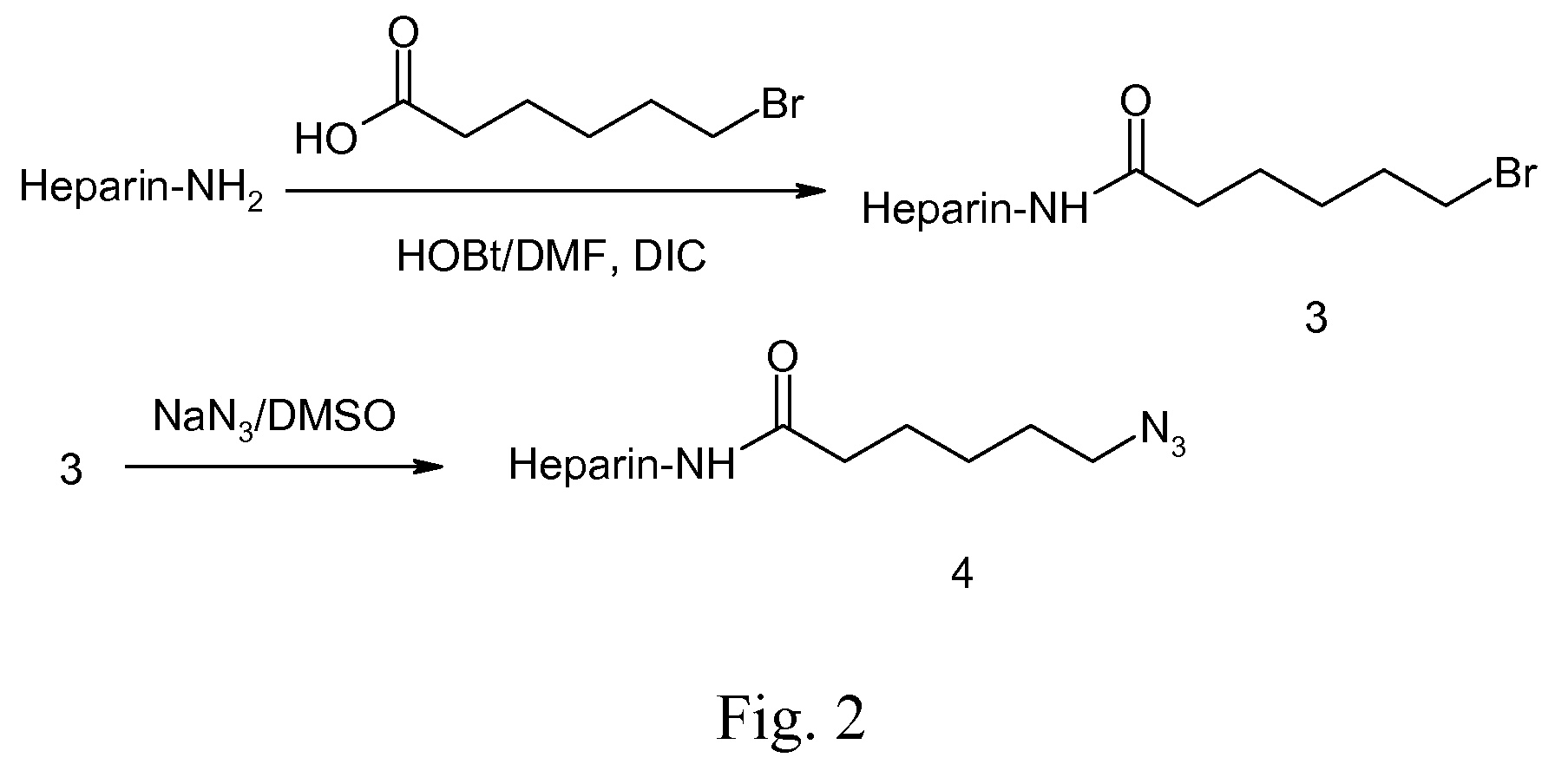
A biodegradable antithrombotic conjugate having heparin and other anti-thrombotic moieties are introduced as side chains to the polymer backbone modified by click chemistry. Various bioabsorbable monomers and dimers such as valerolactone may be used in the monomer derivation, homo- and co-polymerization, and the conjugation with a biologically active molecule by click chemistry. A coating comprising a biocompatible and bioabsorbable polymer anti-thrombotic conjugate is applied to at least a portion of an implantable device to prevent or reduce the formation of thrombosis on the surface of the implantable device. A first or sub-layer of the coating is prepared by mixing a polymeric material and a biologically active agent with a solvent, thereby forming a homogeneous solution. A second or outer layer comprising the present anti-thrombotic conjugate may be applied over the inner drug-containing layers using, for example, a dip coating or spray coating process.
Owner:CORDIS CORP
Preparation of Functional Polymers
The process of the present invention is directed toward conducting highly selective, high yield post polymerization reactions on polymers to prepare functionalized polymers. An embodiment of the present invention comprises conducting click chemistry reactions on polymers. Preferably, the polymers were prepared by controlled polymerization processes. Therefore, embodiments of the present invention comprise processes for the preparation of polymers comprising conducting a click chemistry reaction on a functional group attached to a polymer, wherein the polymer has a molecular weight distribution of less than 2.0. The functional polymers may be prepared by converting an attached functional unit on the polymer thereby providing site specific functional materials, site specific functional materials comprising additional functionality, or chain extended functional materials. Embodiments of the process of the present invention include functionalization reactions, chain extensions reactions, to form mock copolymer linking reactions, and attaching side chains to form graft copolymers, for example.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Preparation of functional polymers
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Bioadhesive Composition Formed Using Click Chemistry
The present disclosure provides compositions which may be utilized as adhesives or sealants in medical and surgical applications. The compositions may, in embodiments, be formed from the cycloaddition reaction of a first component possessing at least one azide group with a second component possessing at least one alkyne group.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method for preparing super-hydrophobic textile from thiol-ene click chemistry-modified fiber
InactiveCN105696306AWashableWear-resistantLiquid repellent fibresAbrasion resistant fibresFiberPolyester
The invention relates to a preparation method of a functional textile, and belongs to the field of textile surface grafting modification. The method for preparing a super-hydrophobic textile from a thiol-ene click chemistry-modified fiber is characterized by comprising the steps that alkali liquor steaming treatment is performed on a polyester fiber, then mercaptosilane is fixed to the surface of the polyester fiber, finally a methacrylate monomer is grafted to the surface of the polyester through a thiol-ene click chemistry reaction to reduce the surface tension of the fiber, and then the super-hydrophobic polyester textile is obtained. The contact angle between the polyester textile prepared through the method and water drops is larger than 150 degrees, and the polyester textile is stable to acid, alkali, salt and solvent and capable of resisting friction and washing and has the very good hydrophobic stability.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Polymers of intrinsic microporosity containing tetrazole groups
InactiveUS8623928B2Extending possible structureIncrease rangeOrganic chemistryOther chemical processesTetrazoleClick chemistry
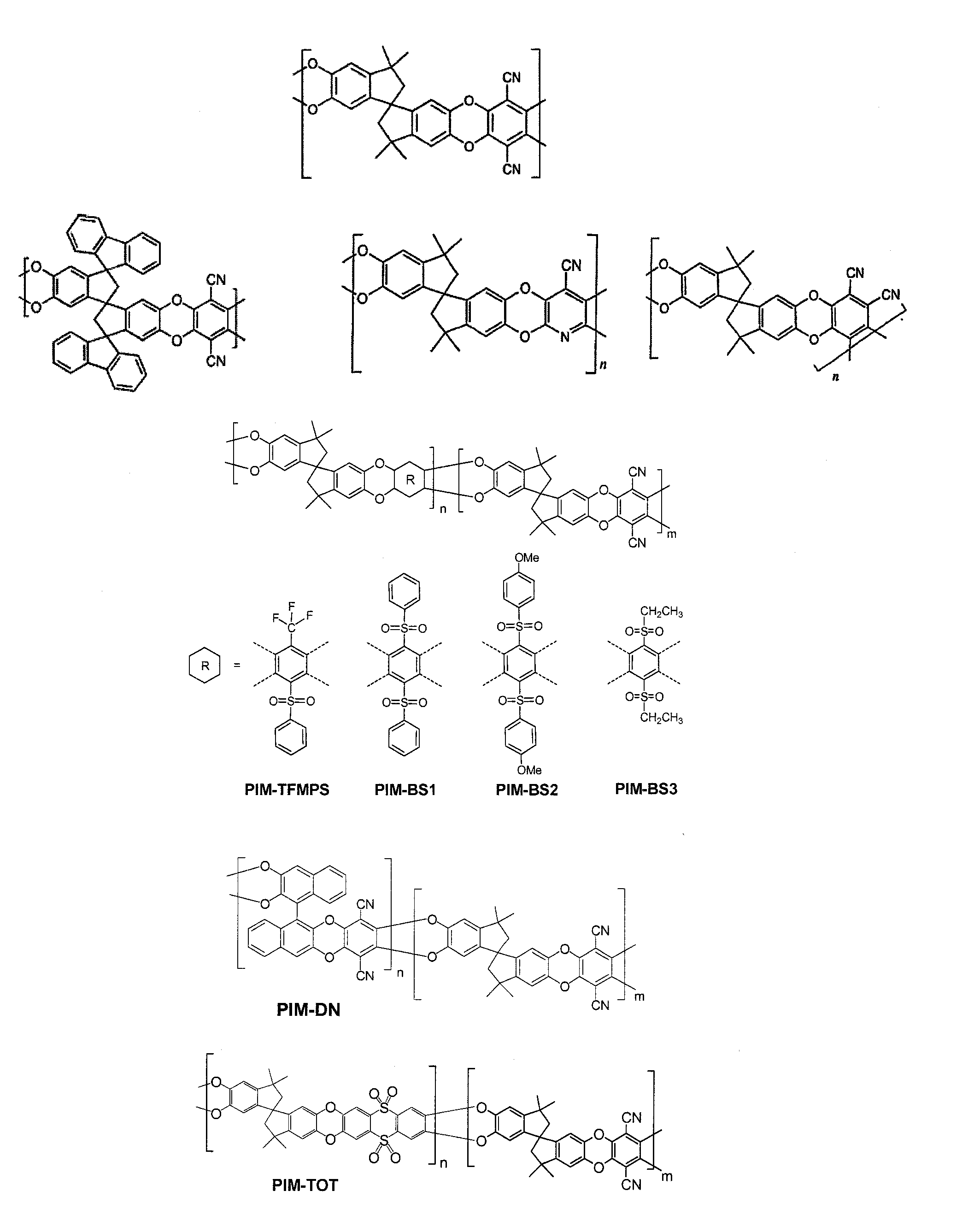
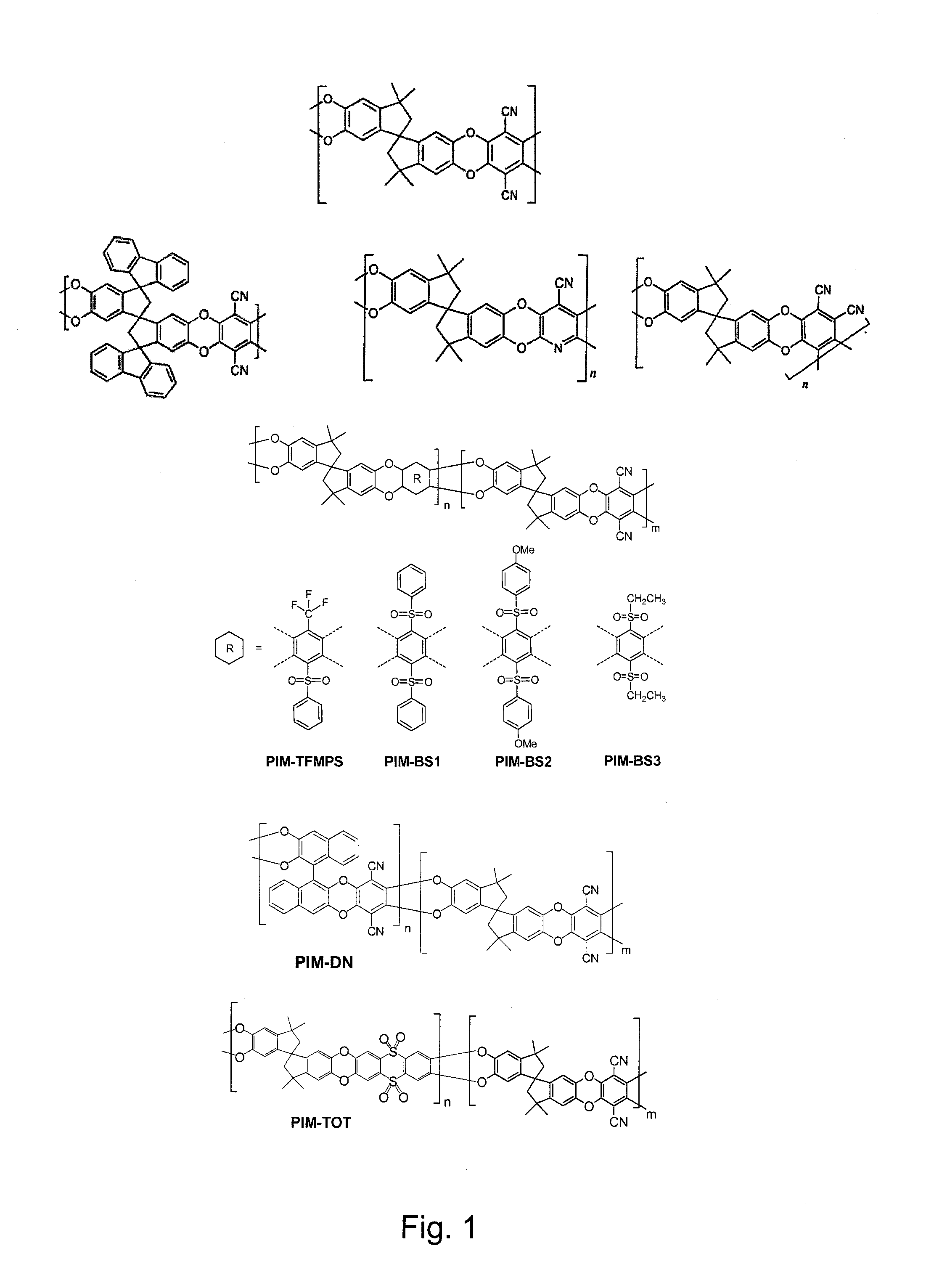
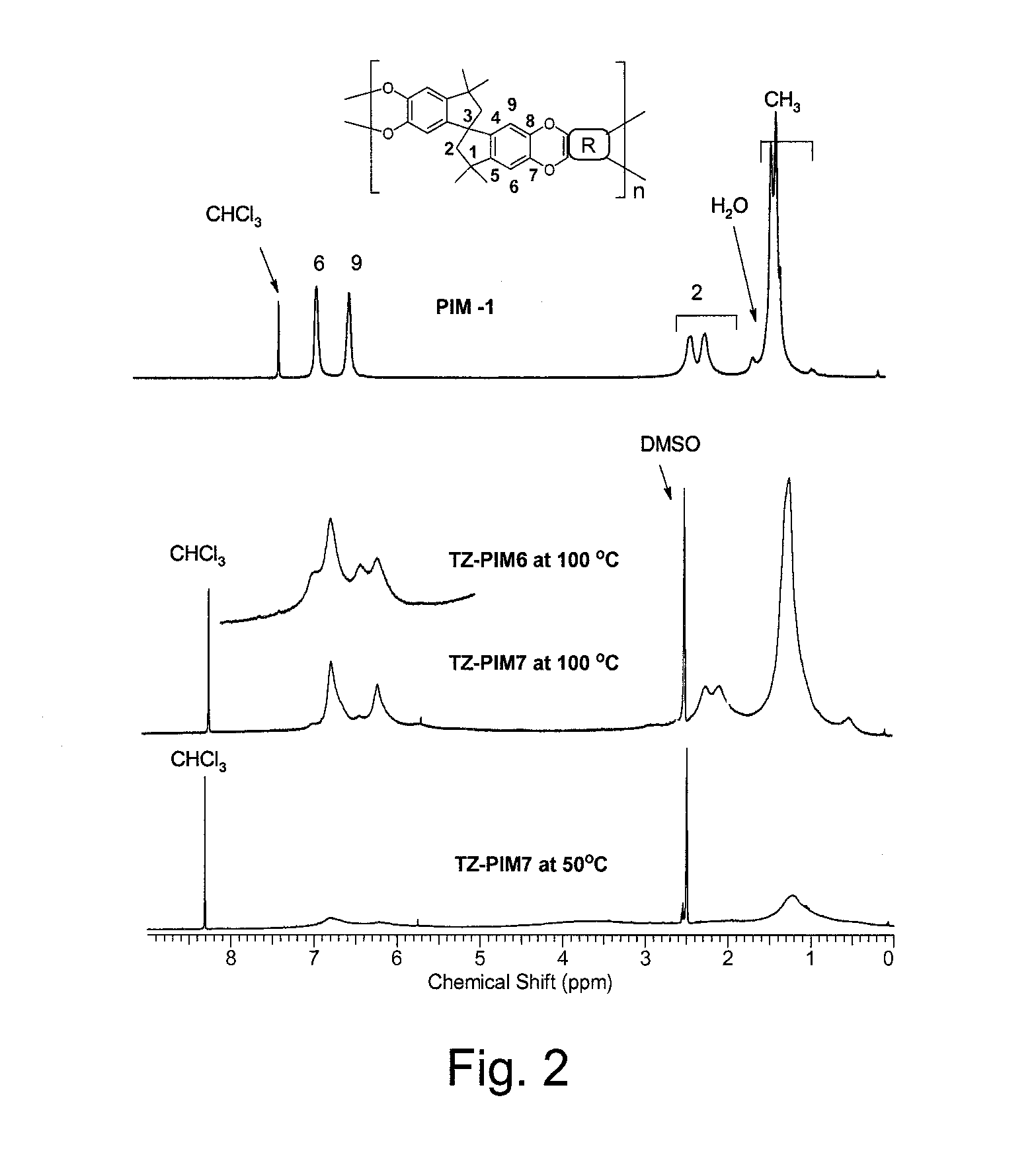
The invention provides a tetrazole-containing polymer of intrinsic microporosity comprising (10) or more subunits, wherein one or more of the subunits comprise one or more tetrazolyl moieties. In one embodiment, a polymer of intrinsic microporosity (PIM-1) was modified using a “click chemistry” [2+3] cycloaddition reaction with sodium azide and zinc chloride to yield new PIMs containing tetrazole units. Polymers of the present invention are useful as high-performance materials for membrane-based gas separation, materials for ion exchange resins, materials for chelating resins, materials for superabsorbents, materials for ion conductive matrixes, materials for catalyst supports or materials for nanoparticle stabilizers.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
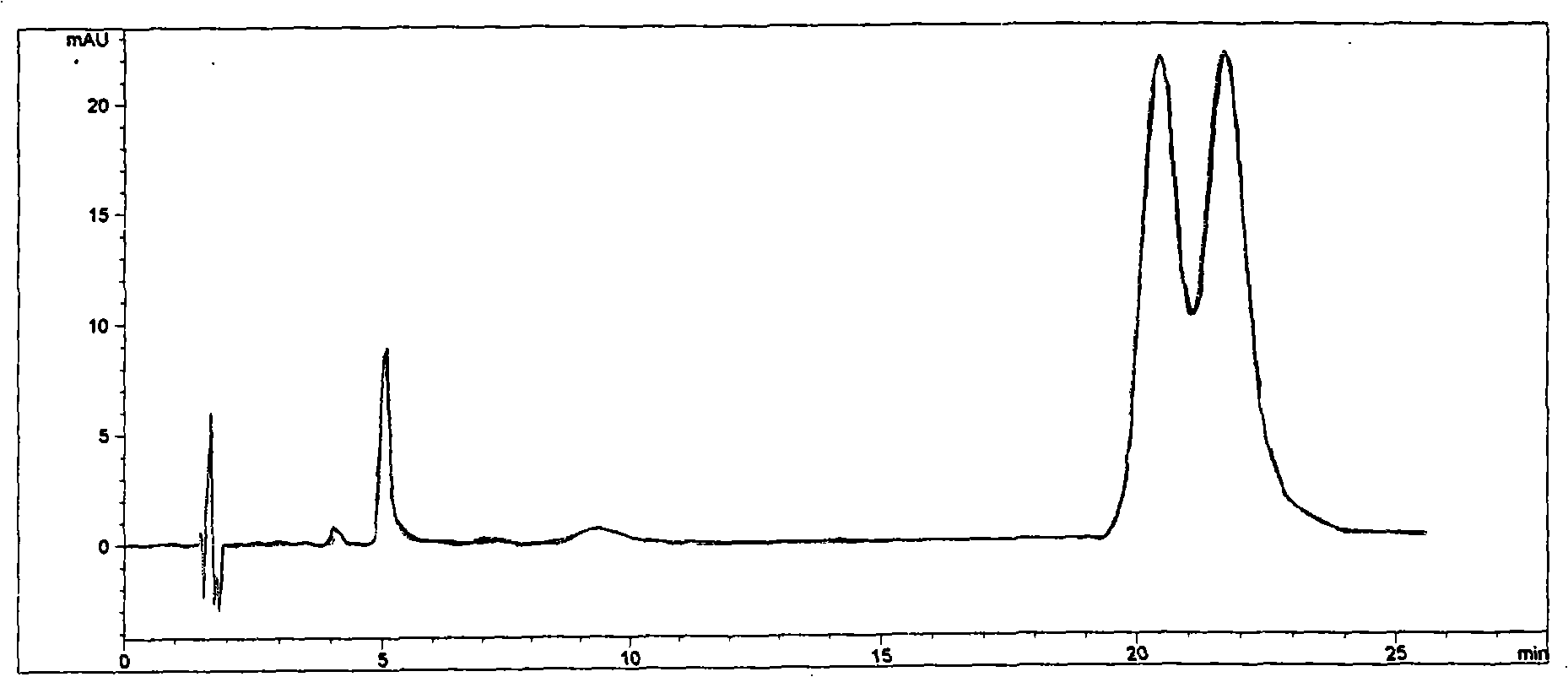
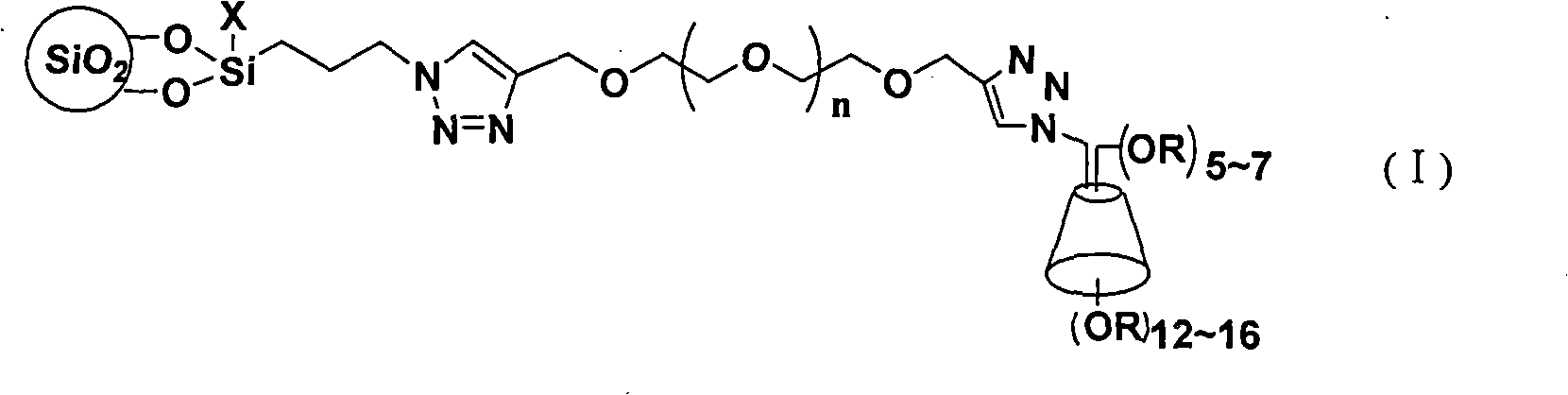
Cyclodextrin chiral chromatogram fixed phase and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101306354AHigh column efficiencyHigh selectivityOther chemical processesAzirineChemical reaction
The invention discloses a cyclodextrin chiral stationary phase, the structure of which is shown in the general formula (I), wherein X is -OCH3 or -OCH2CH3, n is equal to 1-7, and R is -H, -CH3, -COCH3, -COC6H5 and -CONHC6H5. The preparation method of the stationary phase comprises the following steps: a silane coupling agent, sodium azide and a catalyst are added into an organic solvent, then spheroidal silicon is added for preparing azide silica gel derivant; oligomeric ethylene glycol, sodium hydride and propargyl bromide are added into tetrahydrofuran for preparing bialkynyl oligomeric ethylene glycol; monosubstituted nascent and derivative cyclodextrin containing azid groups is prepared; finally, the click chemistry reaction method is used for bonding the cyclodextrin. The cyclodextrin chiral stationary phase has the advantages that the selectivity of the bonding reaction is high, and the surface bonded amount is large; the chiral separation ability is strong, thereby being especially suitable for the chiral separation of a high efficiency liquid chromatography in the reversed-phase mode; the preparation method is simple and has less steps, the bonding reaction is the click chemistry reaction, the reaction condition is mild, and the reaction is carried out in the water solution.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Copper-catalysed ligation of azides and acetylenes
InactiveUS20080214831A1Organic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetalloleSufficient time
A copper catalyzed click chemistry ligation process is employed to bind azides and terminal acetylenes to provide 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole triazoles. The process comprises contacting an organic azide and a terminal alkyne with a source of reactive Cu(I) ion for a time sufficient to form by cycloaddition a 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole. The source of reactive Cu(I) ion can be, for example, a Cu(I) salt or copper metal. The process is preferably carried out in a solvent, such as an aqueous alcohol. Optionally, the process can be performed in a solvent that comprises a ligand for Cu(I) and an amine.
Owner:TETARD INC
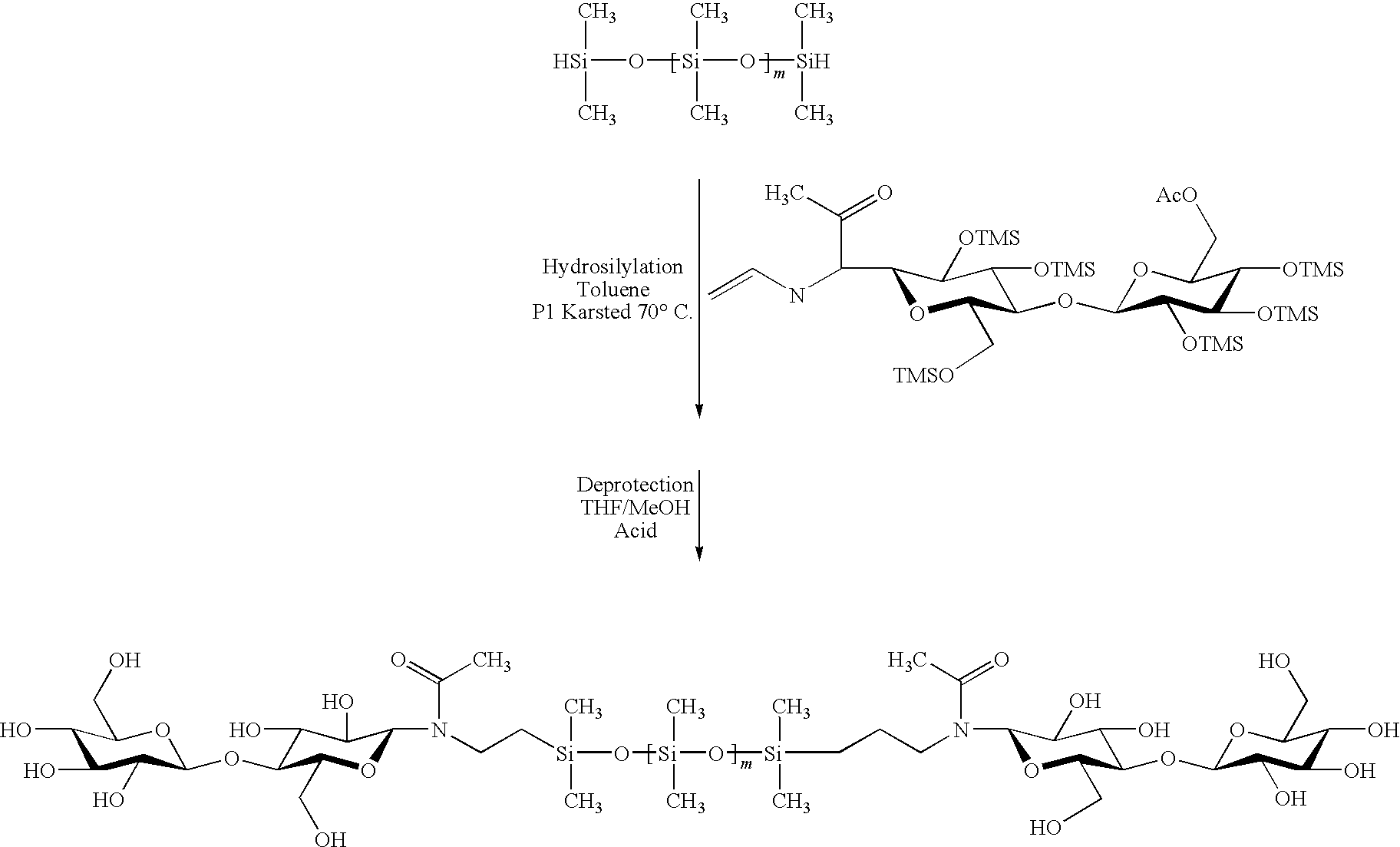
Hybrid compounds based on silicones, and at least one other molecular entity, polymer or otherwise, especially of the polyol type, method for the preparation thereof, and applications of the same
InactiveUS20090253609A1Simple processWithout laborCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPolyesterHybrid compound
The invention relates to novel hybrid compounds comprising at least one silicone entity (Sil) in which at least one of the silicons of Sil is substituted by at least one unit—Ro-B, B being an entity of a variable nature, for example polymer, hydrocarbonated or mineral, selected from a group comprising polyols (e.g. saccharides), silicones, polyalkylene glycols, polyamides, polyesters, polystyrenes, alkyls, alkenyls, alkynyls or aryls, in addition to mineral materials such as silica and the combinations thereof. The bond Ro between the entity Sil and the entity B is obtained by means of “click chemistry” and corresponds to formula (II.1) or (II.2), Z representing a carbon atom or a nitrogen atom. Said hybrid components can be used as emulsifiers, especially for cosmetics.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS +1
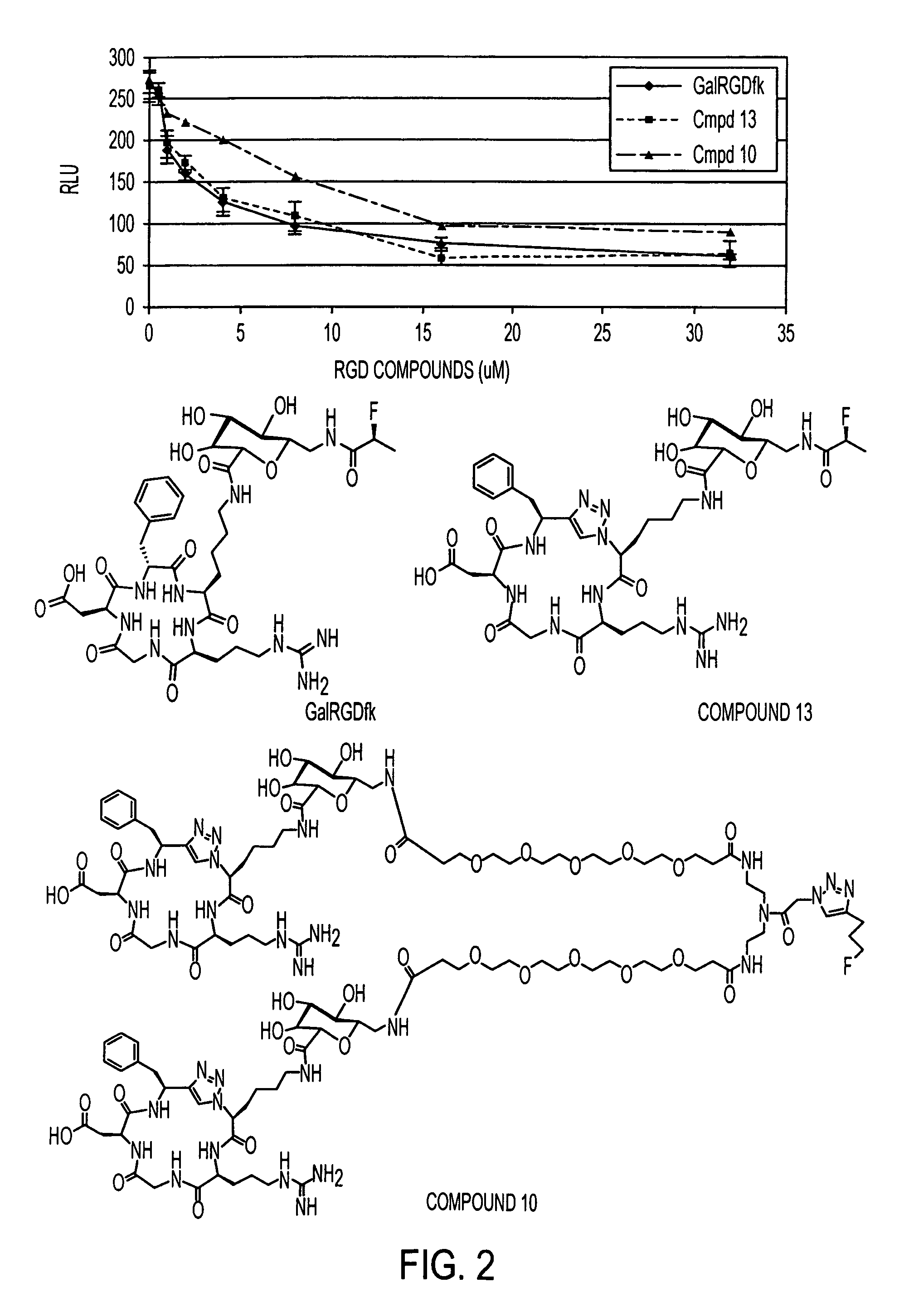
Click chemistry-derived cyclic peptidomimetics as integrin markers
InactiveUS20080213175A1Good metabolic stabilityReduce decreaseAntibacterial agentsBiocideComputed tomographyClick chemistry
The present application is directed to radiolabeled cyclic peptidomimetics, pharmaceutical compositions comprising radiolabeled cyclic peptidomimetics, and methods of using the radiolabeled cyclic peptidomimetics. Such peptidomimetics can be used in imaging studies, such as Positron Emitting Tomography (PET) or Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT).
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
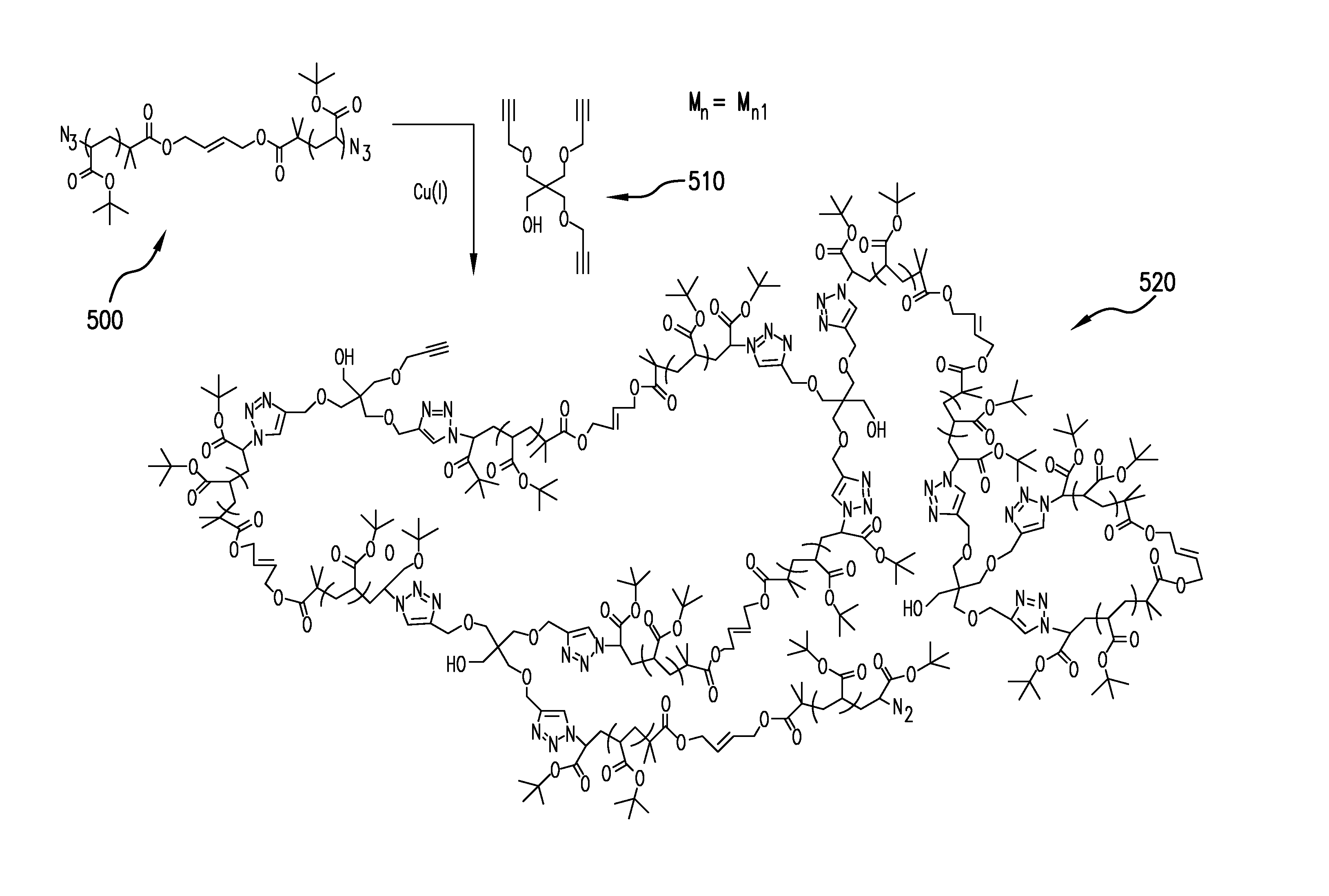
Macromonomers for preparation of degradable polymers and model networks
InactiveUS20090259016A1Suitable for preparationReduce polydispersityOrganic chemistryAtom-transfer radical-polymerizationClick chemistry
The present invention relates to methods for preparing degradable model networks from any monomer functionality with any degradation methodology. It is based on the use of Atom-Transfer Radical Polymerization and CLICK chemistry to form the desired product.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Hybrid compounds based on polyol(s) and at least one other molecular entity, polymeric or non-polymeric, in particular of the polyorganosiloxane type, process for the preparation thereof, and applications thereof
InactiveUS20100048738A1Simple preparation processCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPolyesterPolymer science
The invention relates to novel hybrid compounds comprising at least one polyon entity (Po)—for example oligomer or polymer—in which at least one of the hydroxyl functions of Po is substituted by at least one entity A that can be of a variable nature, for example polymer (e.g. polyorganosiloxane-POS), hydrocarbonated or mineral. The bond Ro between the entity Po and the entity A is obtained by means of “click chemistry” and corresponds to formula (II.1) or (II.2), Z representing —CH— or —N—. A is an entity selected from the group comprising the various polyols of Po, polyorganosiloxanes (POS), polyalkylene glycols, polyamides, polyesters, polystyrenes, alkyls, alkenyls, alkynyls, aryls, and combinations thereof, in addition to mineral materials such as silica and the combinations thereof. Said hybrid components can be used as emulsifiers, especially for cosmetics.
Owner:RHODIA OPERATIONS SAS +1
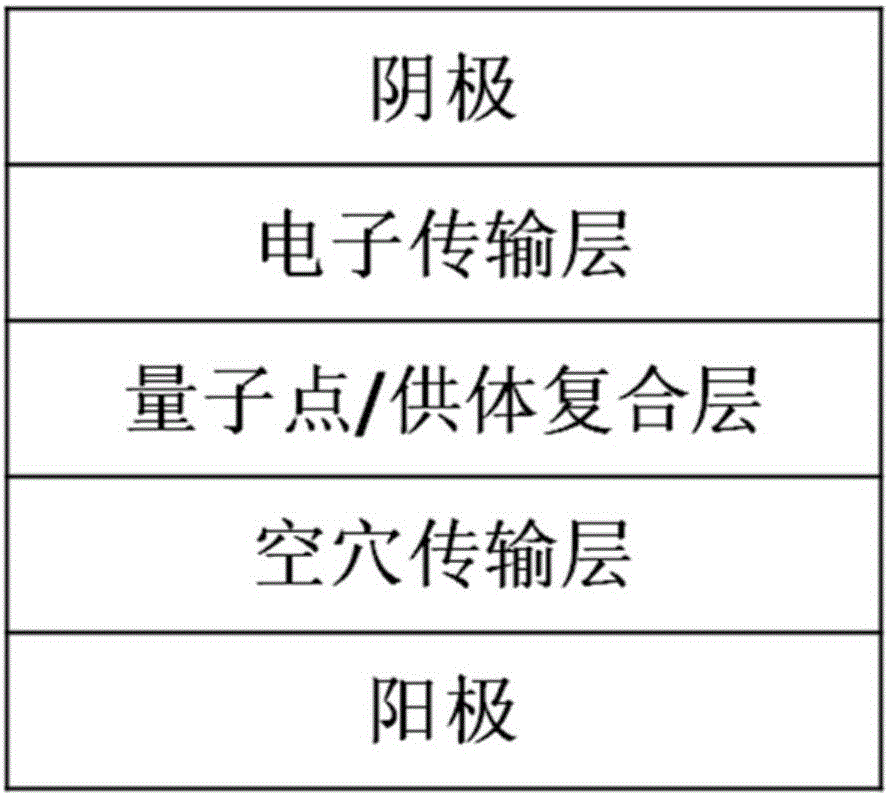
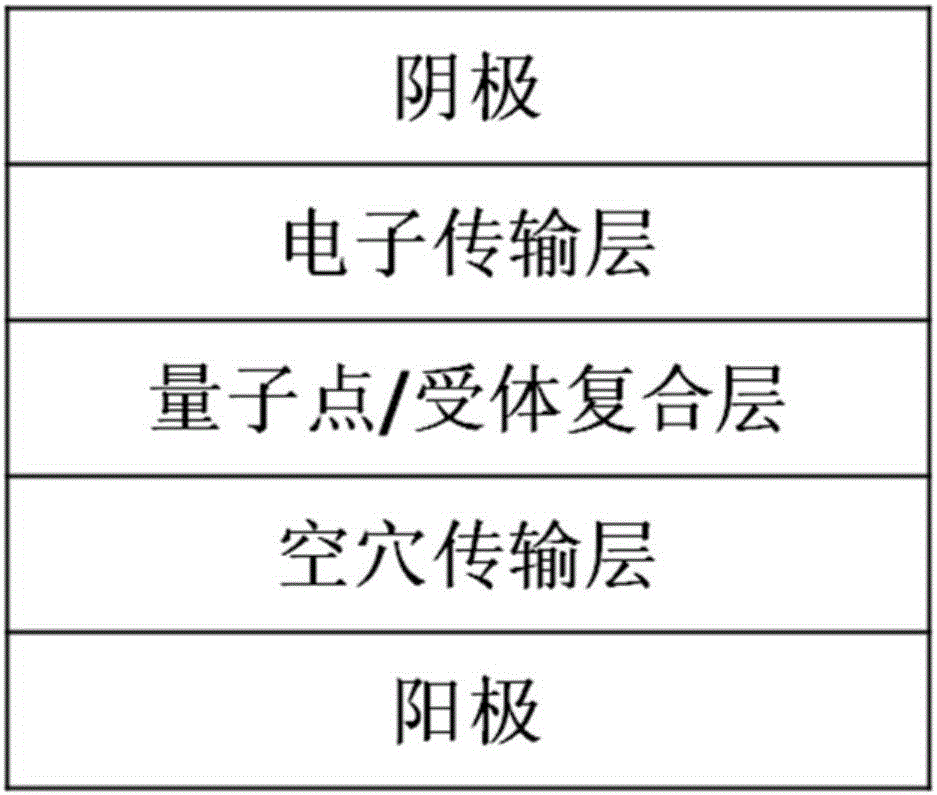
Light emitting diode including quantum dots and energy transfer molecules and fabrication method and display device thereof
InactiveCN106356462AImprove injection abilityImprove energy transferSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFluorescenceClick chemistry
The invention provides a light emitting diode. The light emitting diode comprises a substrate, positive pole, hole transfer layer, emitting layer, electron transport layer and negative pole. The emitting layer comprises quantum dots and energy transfer molecules. The energy transfer molecules crosslink with the quantum dots by click chemistry. The energy transfer molecules, as dispersion medium of the quantum dots, have high electron / hole carrier injection ability, which can promote the production of excitons in energy transfer molecules and realize effective energy transfer from energy transfer molecules to fluorescent quantum dots. At certain voltage, the device can emit within the wavelength range of 380-900nm, with the maximum emitting peak covering ultraviolet to dark red light range. The invention further discloses the fabrication method and electronic display equipment of a light emitting diode.
Owner:SUZHOU XINGSHUO NANOTECH CO LTD
Bioadhesive composition formed using click chemistry
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Surface carboxyl functionalized polystyrene / nano silicon dioxide hybridization material and preparation thereof
The invention discloses a method for preparing surface carboxylic group functional polystyrene / nano-silicon dioxide hybrid material by effectively combining click chemistry and ATRP; in the method, a silane coupling agent is adopted for linking an ATRP evocating agent to a SiO2 particle surface, and polystyrene (PSt) is grafted on the SiO2 particle surface by adopting the ATRP; then, carboxyl is led into a nano-silicon dioxide particle surface modified by the polystyrene by means of the click reaction, thus obtaining the surface carboxylic group functional polystyrene / nano-silicon dioxide hybrid material. After the infrared, nuclear magnetism and thermogravimetry mapping analysis, the surface carboxylic group functional polystyrene / nano-silicon dioxide hybrid material prepared by the invention has good thermal stability and dispersivity; in addition, as the carboxyl has wide reaction range and the characteristic of easy ionization, nano-particles has high reactive behavior so as to be widely applied to the fields such as high polymer material modifying agents, water treatment agents, catalysts, sensing agents and protein carriers.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
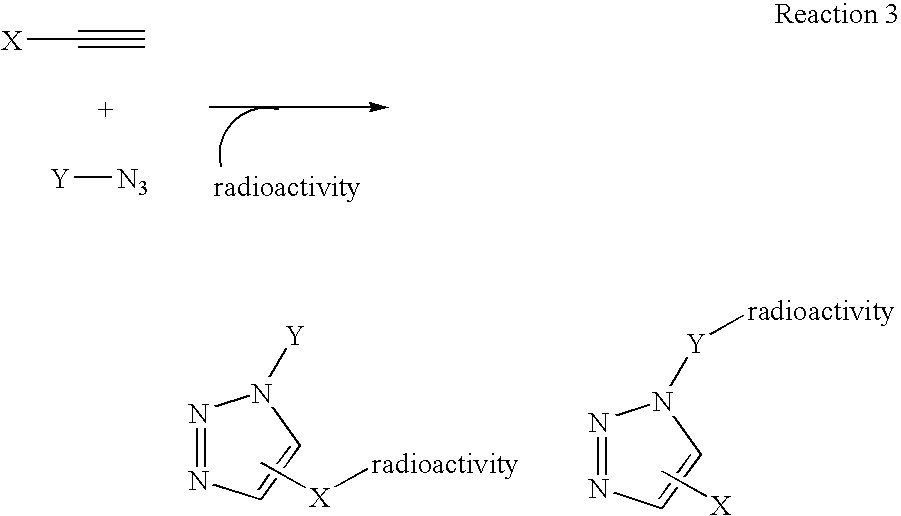
In situ click chemistry method for screening high affinity molecular imaging probes
InactiveUS20060269942A1High expressionPeptide librariesOrganic chemistryChemical synthesisChemical reaction
The invention provides a method for identifying a candidate imaging probe, the method comprising: a) contacting a first library of candidate compounds with a target biomacromolecule, b) identifying a first member from the first library exhibiting affinity for the first binding site; c) contacting the first member identified from the first library affinity for the first binding site with the target biomacromolecule; d) contacting a second library of candidate compounds with the first member and the target biomacromolecule, e) reacting the complementary first functional group with the second functional group via a biomacromolecule induced click chemistry reaction to form the candidate imaging probe; f) isolating and identifying the candidate imaging probe; g) preparing the candidate imaging probe by chemical synthesis; and h) for imaging applications, converting the candidate imaging probe into an imaging probe.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Amphion polymer modified anti-adhesion surface with dopamine as anchor, and making method thereof
The invention discloses an amphion polymer modified anti-adhesion surface with dopamine as an anchor, and a making method thereof. The making method comprises the following steps: modifying the surface of a base material with dopamine methacrylamide under alkaline conditions, wherein the base material is not pretreated before modification; and grafting the surface of the base material with a thio group-containing amphion polymer through a thio-ene click chemical reaction under ultraviolet light initiation conditions to prepare the amphion polymer modified anti-adhesion surface with dopamine as anchor. The base material which can be modified comprises glass flakes, mica sheets, wood blocks, polyethylene glycol terephthalate, nonwoven fabrics, cotton fabrics and metal sheets; and the amphion polymer modified anti-adhesion surface with dopamine as an anchor has a good anti-adhesion effect on bacteria, and the antibacterial adhesion effect of the surface immersed in water for 5d has no obvious decreasing trend.
Owner:广东威凯表面技术有限公司 +1
Click chemistry based metal-organic framework cross-linking membrane and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN105694051AOvercoming dispersionOvercoming the easy agglomeration of particlesOther chemical processesWater contaminantsThiolSolvent free
The invention discloses a click chemistry based metal-organic framework cross-linking membrane and a preparation method and application thereof.Polymerizable double bonds are introduced into MOFs (metal-organic frameworks) through a post-synthetic modification method, and the chemical cross-linking type MOF membrane is prepared in situ by thiol-ene click reaction, so that a novel rapid efficient solvent-free method mild in conditions is provided for MOFs membrane synthesis.By means of applying the strategy, an obtained independent homogeneous MOFs hybrid membrane material is excellent in membrane forming performance and toughness, and the defects of agglomeration of MOFs crystals and poor compatibility between the MOFs and polymers are overcome.The synthesized MOFs membrane material is excellent in selective separation effect on dye molecules in water and has a promising application prospect in the field of membrane separation.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Ultraviolet curing reaction-based fluoride-free and water-repellent finishing method of cotton fabric
InactiveCN106637959AImprove water repellency durabilityHigh activityPhysical treatmentLiquid repellent fibresAcetic acidTriethoxysilane
The invention discloses an ultraviolet curing reaction-based fluoride-free and water-repellent finishing method of cotton fabric. The method comprises the steps of putting the cotton fabric into 3-mercaptopropyl triethoxysilane ethyl acetate solution and carrying out mercapto modification to obtain pretreated cotton fabric; dipping the cotton fabric subjected to mercapto modification into vinyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane solution, and obtaining the fluoride-free and water-repellent cotton fabric, which has a surface with an approximate super-hydrophobic effect, under the ultraviolet curing condition. The reaction is based on the principle of click chemistry, so that a static contact angle is basically remained unchanged after soaping treatment is carried out. Furthermore, according to a test method of AATCC 22-2005 waterproof spray test, the waterproof spray test score of the cotton fabric subjected to water-repellent finishing reaches 95. The ultraviolet curing reaction-based fluoride-free and water-repellent finishing method of the cotton fabric is simple in operation and high in efficiency, obvious in water-repellent effect under the condition that a finishing agent is fluoride-free, and high in finishing washing fastness.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
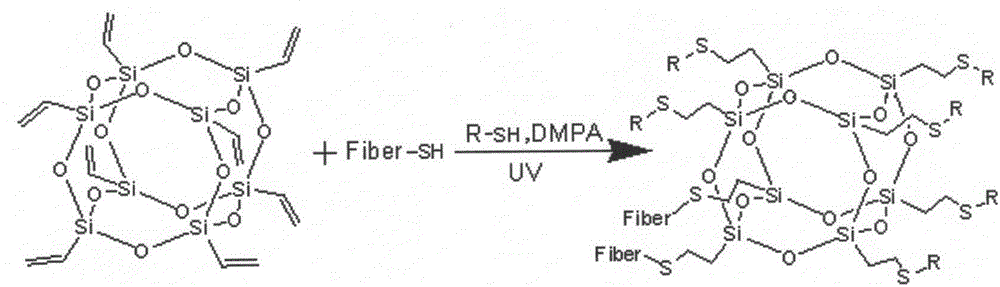
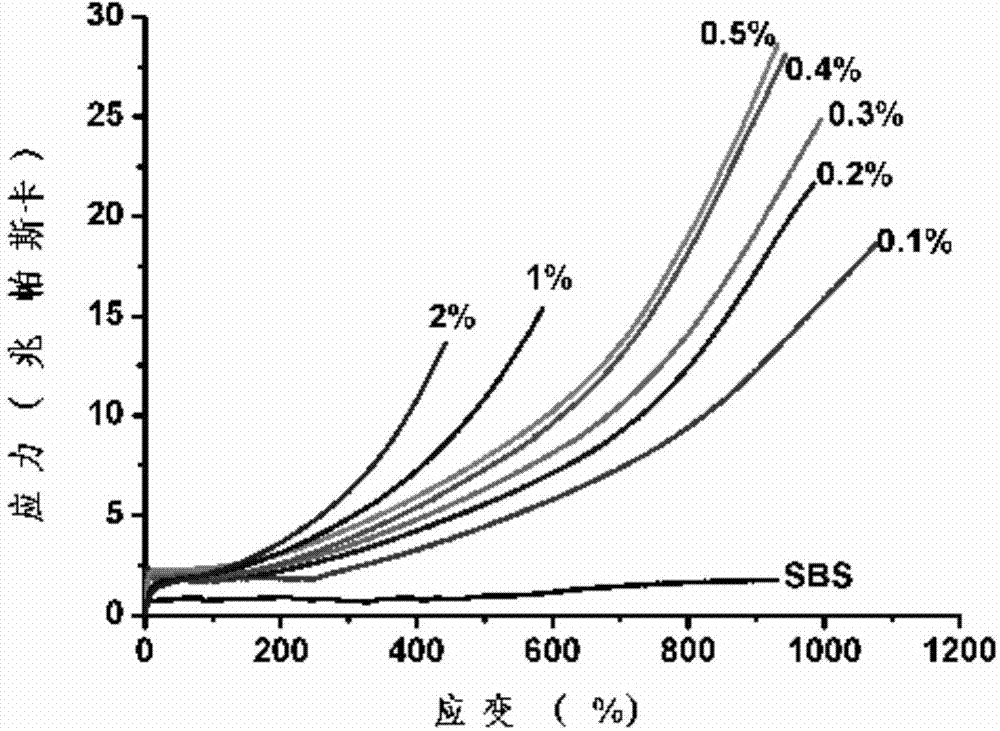
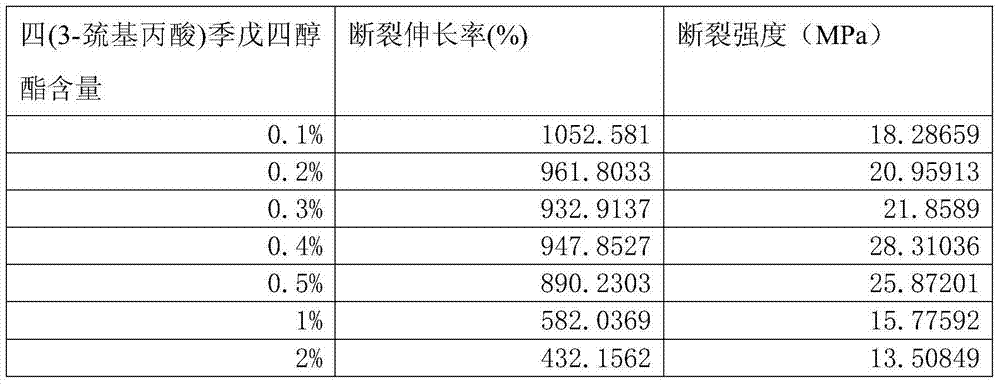
Method for modifying elastomer by using click reaction of thiol-ene
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical material preparation, and particularly relates to a method for modifying an elastomer by using click reaction of thiol-ene. The method is characterized in that isolate double bonds in an elastomer material are crosslinked with an elastomer compound system by using click chemistry of thiol-ene with the participation of polythiol organic molecules under an UV-irradiation condition so as to achieve the purpose of modifying the elastomer material. The method for modifying the elastomer is simple, easy in obtaining of raw materials and relatively low in cost. The obtained composite material has excellent mechanical property and can be widely applied.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Click chemistry method for synthesizing molecular imaging probes
InactiveUS20060263293A1High reaction specificityEfficiently labeledSaccharide with heterocyclic radicalsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLeaving groupChemical reaction
The present disclosure provides a method for preparing a radioactive ligand or radioactive substrate having affinity for a target biomacromolecule, the method comprising: (a) reacting a first compound comprising a first functional group capable of participating in a click chemistry reaction, with a radioactive reagent under conditions sufficient to displace the leaving group with a radioactive component of the radioactive reagent to form a first radioactive compound; (b) providing a second compound comprising a second complementary functional group capable of participating in a click chemistry reaction with the first functional group; (c) reacting the first functional group of the first radioactive compound with the complementary functional group of the second compound via a click chemistry reaction to form the radioactive ligand or substrate; and (d) isolating the radioactive ligand or substrate.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Preparation method for hyperbranched polymer grafted carbon nanotube based on click chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method for a hyperbranched polymer grafted carbon nanotube based on click chemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) subjecting the carbon nanotube to treatment by utilizing concentrated nitric acid so as to obtain an acid-treated carbon nanotube; 2) subjecting the acid-treated carbon nanotube to reaction with a mercapto contained silane coupling agent so as to obtain a mercapto contained silane coupling agent grafted carbon nanotube; 3) subjecting alkyne butanol and mercaptopropionic acid to esterification reaction so as to obtain a hyperbranched monomer; and 4) with a mercapto group on the mercapto contained silane coupling agent grafted carbon nanotube and an alkynyl group contained in the hyperbranched monomer as reactive groups, initiating mercapto-alkynyl click reaction by utilizing ultraviolet light so as to eventually obtain the hyperbranched polymer grafted carbon nanotube. The invention has the following advantages: through light-initiated click reaction, the preparation method reduces the usage amount of a solvent, simplifies post-processing steps, facilitates to large-scale production, and enables active functional groups on the surface layer of the carbon nanotube to be increased through grafting of a hyperbranched polymer coating layer formed on the surface of the carbon nanotube, thereby facilitating to further use of the carbon nanotube.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing high-dispersity nanosilicon dioxide particle
InactiveCN104530769AImprove grafting efficiencyGood dispersionPigment treatment with macromolecular organic compoundsPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsDispersityClick chemistry
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-dispersity nanosilicon dioxide particles. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, modifying nanosilicon dioxide particles to graft an azide group on the surfaces of the nanosilicon dioxide particles, preparing a polymer with a plurality of alkynyl groups on a non-terminal group of the molecular chain in a free radial polymerization mode, and finally the surfaces of the particles with the polymer through click chemistry reaction. The modified nanosilicon dioxide particles prepared by using the method are good in dispersity in organic solvents, overcome the problem of easy conglobation and have great application potential in the fields of coatings, composite materials and the like.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Amphipathic chitosan derivative and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102241790ARich sourcesPreparation reaction conditions are mildOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsChemical reactionClick chemistry
The invention discloses an amphipathic chitosan derivative PAMAM-Cs-DCA (Poly(amido amine)-chitosan-deoxycholic acid). The PAMAM-Cs-DCA is prepared by sequentially grafting a PAMAM unit and a deoxycholic acid unit on a main chain of chitosan by click chemical reaction and amidation reaction. The preparation method has mild reaction conditions, high efficiency and selectivity. The invention also discloses an application of the amphipathic chitosan derivative in preparing an anticancer drug carrier: the amphipathic chitosan derivative forms nanomicelle which takes the PAMAM unit and chitosan asa hydrophilic shell and takes the DCA unit as a hydrophobic core by self assembly in a water solution, wherein hydrophobic anticancer drugs can be coated in the core, and the shell can be compounded with pDNA (plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid) to realize co-transmission of the drugs and genes. Due to the unique molecular structure, the amphipathic chitosan derivative has potential application valuesin the fields of gene therapy, controlled release of drugs, tissue engineering and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for preparing hyperbranched polymer through dual click chemistry
ActiveCN102181054AHigh molecular weightIncrease the degree of branchingUltraviolet lightsEvaporation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a hyperbranched polymer through dual click chemistry. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) adding one mole of bis(thiol) compound, 0.1 to 10 moles of solvent, 0.05 to 2 moles of base catalyst, and 0.9 to 1.1 moles of compound containing alkynyl and alkenyl into a reactor sequentially under the protection of nitrogen, performing sulfydryl-alkene addition reaction at the temperature of between 10 and 40 DEG C for 0.5 to 24 hours, and performing reduced pressure evaporation to remove the solvent; and 2) dissolving the product obtained in the step 1) in 0.25 to 10 moles of solvent under the protection of nitrogen, adding 0.005 to 0.05 mole of photosensitive radical initiator or thermosensitive radical initiator, irradiating by ultraviolet light or heating at the temperature of between 40 and 90 DEG C to produce radical, performing sulfydryl-alkene addition polymerization reaction for 0.5 to 24 hours, and precipitating, separating and drying to obtain the hyperbranched polymer. The method has the advantages of no need of complex AB2 monomer synthesis and purification steps, high speed and efficiency, convenience, wide application range and the like. The obtained hyperbranched polymer containing a large amount of thioether bonds has wide application prospect in the fields of biomedical carriers, high-performance materials, additives and the like.
Owner:杭州德烯科技集团有限公司
Portable copper ion concentration detection method based on click chemistry
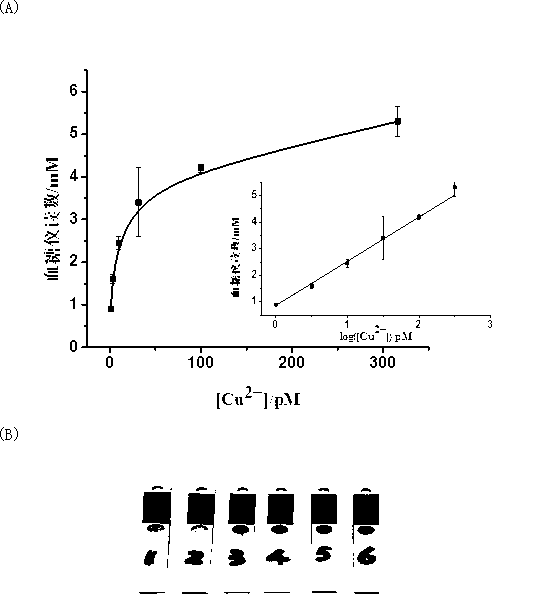
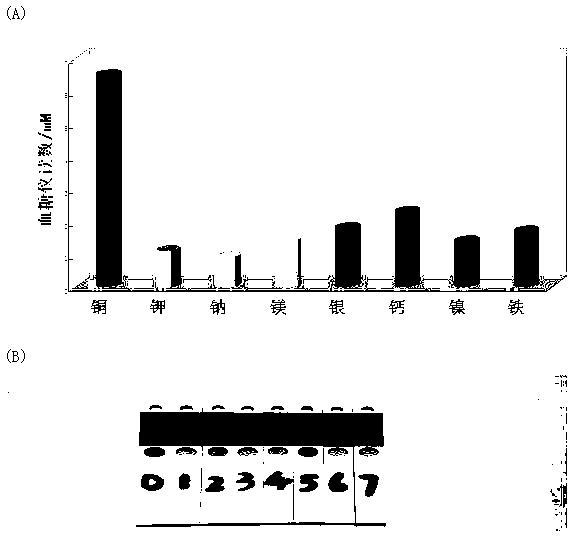
ActiveCN103163130AGood linear responseEasy to operateMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDNA/RNA fragmentationMagnetic beadSodium ascorbate
The invention provides a portable copper ion concentration detection method based on click chemistry and belongs to the field of analytical chemistry. Under the condition that sodium ascorbate reduces cupric into cuprous as a catalyst, a 1,3-dipole cycloaddition reaction is carried out between NDA modified with an azide group and DNA modified with an alkynyl group, so that DNA modified with cane sugar invertase is fixed on magnetic beads; The magnetic beads are separated from a solution, the cleaned magnetic beads are dissolved into a cane sugar solution to carry out enzymatic hydrolysis, and then a reaction solution after enzymatic hydrolysis is measured by adopting a blood glucose meter, so that copper ion concentration can be detected. The portable copper ion concentration detection method provided by the invention takes the blood glucose meter as a platform and can portably and quickly detect the copper ion concentration on site; and the portable copper ion concentration detection method can be applied to copper ion detection in a human body serum sample, and the portable copper ion concentration detection method has the advantages of easy operation, low cost, high sensitivity and good specificity.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Fluorosilicone resin based on click chemistry and preparation method of self-repairing superhydrophobic coating
ActiveCN107556477ARepairableRestore hydrophobicity and oleophobicityLiquid surface applicatorsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsPolyurethane adhesiveSilanes
The invention relates to fluorosilicone resin based on click chemistry and a preparation method of a self-repairing superhydrophobic coating. Through click chemistry, low surface energy and a self-repairing function are led into a multi-level rough structure of nanoparticles fixed by a polyurethane adhesive, and the superhydrophobic / amphiphobic interfacial material with high mechanical strength and the self-repairing function is prepared. As a self-designed low-surface-energy segmental grid structure of polyfunctional fluoroalkyl silane is adopted, by use of the principle that a damaged surface is covered with self-repairing segmental orientation, the defects that low-surface-energy molecules in a conventional self-repairing material are long in migration time and high in probability of loss are overcome, and a new method is provided for realizing quick and long-acting self-repairing of the superhydrophobic coating.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV +1
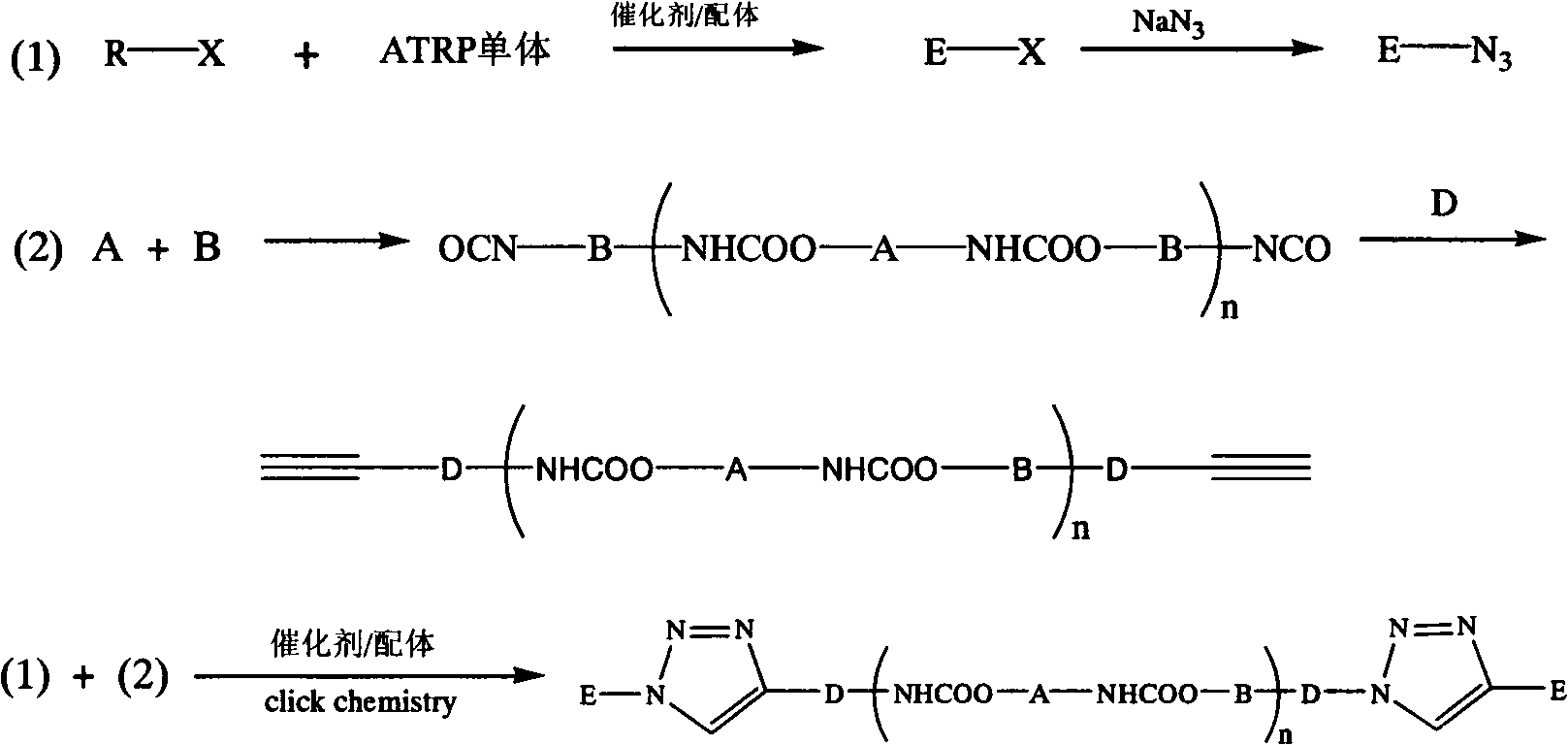
Synthetic method of triblock polymer
InactiveCN102702536ABroaden the way to achievePerfect structural designPolymer scienceSynthesis methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of synthesis and preparation of polymer materials, and discloses a synthetic method of triblock polymer, wherein stepwise polymerization (SGB), atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) and click chemistry method are combined at first; and 1, 3-dipolar cycloaddition reaction is performed to polymer with azido terminal group and polyurethane prepolymer with alkynyl terminal group to successfully synthesize triblock polymer containing triazole ring. The synthesis method provided by the invention overcomes the defects in traditional block polymer synthesis that reaction conditions are strict, molecular weight distribution is controlled difficultly, and selectable classes of monomers are less, and has the advantages of high conversion rate, mild reaction conditions, narrow molecular weight distribution and strong controllability. The triblock polymer provided by the invention has potential application in ways of medicine slow release, solubilizers and surfactants.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com