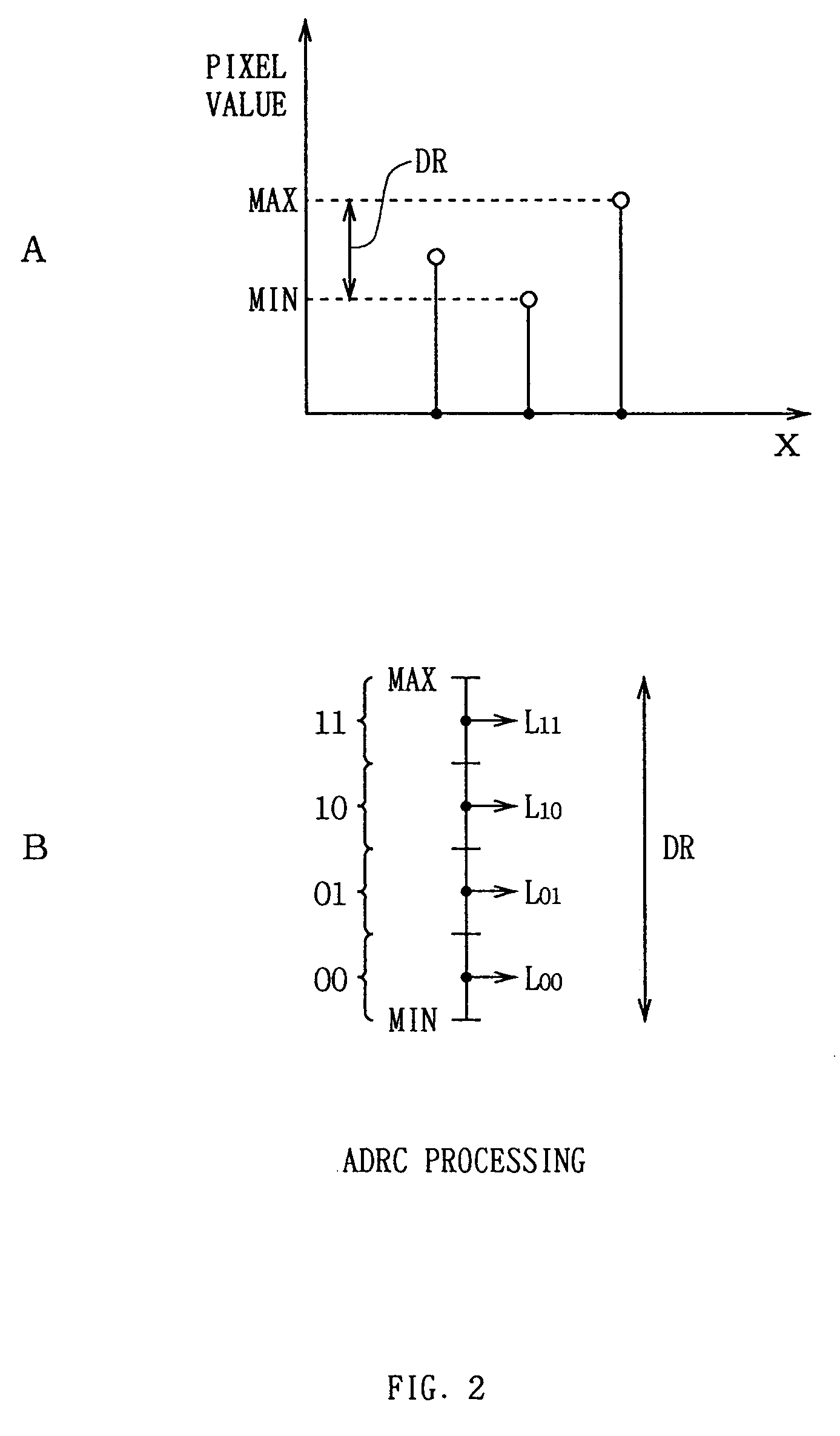Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "ISDB" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting (ISDB; Japanese: 統合デジタル放送サービス, Tōgō dejitaru hōsō sābisu) is a Japanese standard for digital television (DTV) and digital radio used by the country's radio and television networks. ISDB replaced NTSC-J analog television system and the previously used MUSE Hi-vision analogue HDTV system in Japan, and will be replacing NTSC, PAL-M and PAL-N in South America and the Philippines. Digital Terrestrial Television Broadcasting (DTTB) services using ISDB-T started in Japan in December 2003 and in Brazil in December 2007 as a trial. Since then, many countries have adopted ISDB over other digital broadcasting standards.
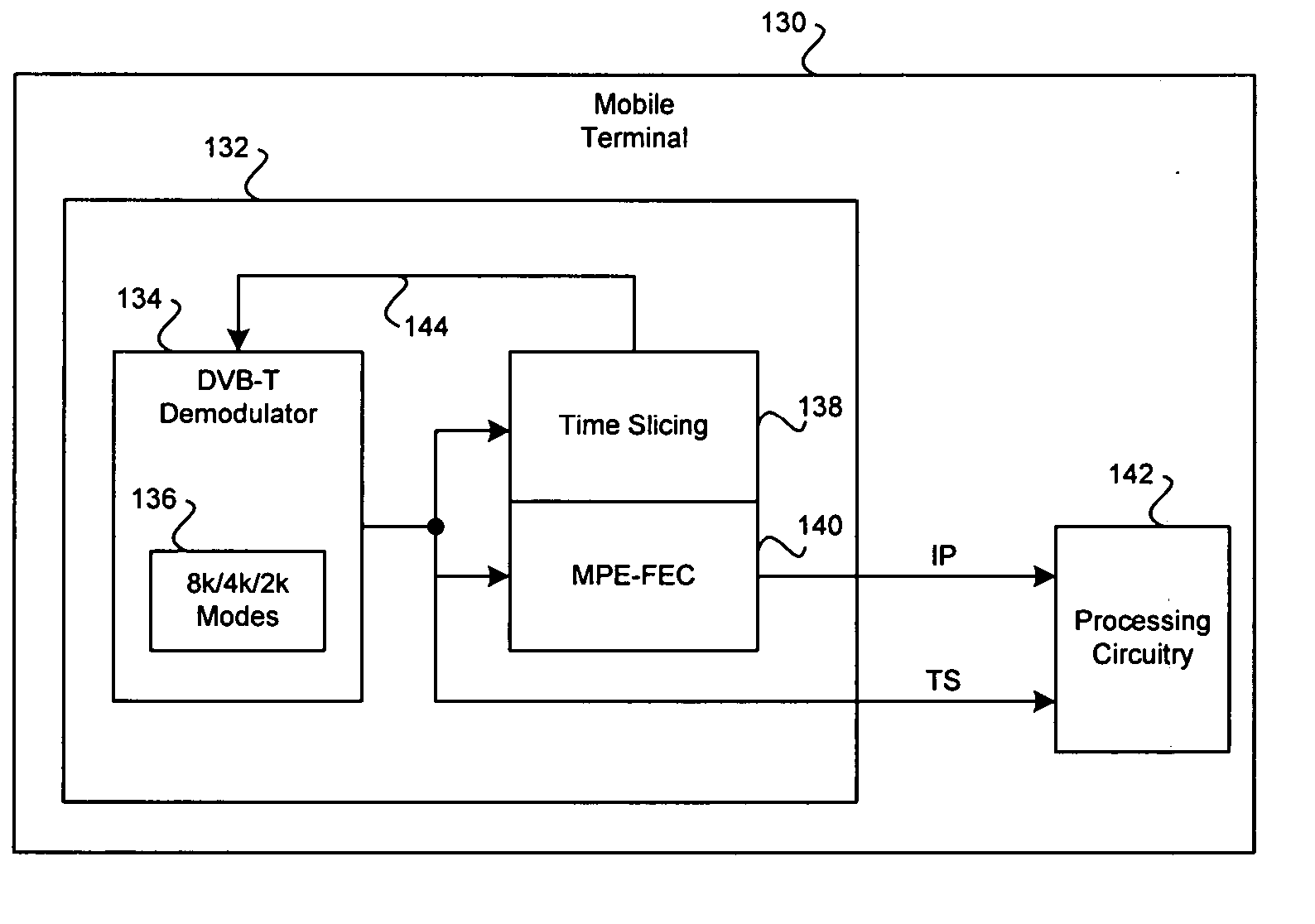
Method and system for mobile receiver antenna architecture for handling various digital video broadcast channels
ActiveUS20060130101A1Television system detailsGHz frequency transmissionDigital videoBroadcast channels
A method for an antenna architecture may comprise receiving at a first radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) integrated within a mobile terminal, first signals via at least a first antenna, where the first signals may comprise signals within a 2100 MHz band. Second signals may be received at a second RFIC integrated within the mobile terminal via at least one of the first antenna and at least one other antenna, where the second signals may comprise signals within at least one of an 1800 MHz band and a 900 MHz band. Third signals may be received at at least a third RFIC integrated within the mobile terminal via at least one of the first antenna and at least one other antenna, where the third signals may comprise VHF / UHF broadcast signals within at least one of a DVB broadcast band, an ATSC broadcast band and an ISDB broadcast band.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and system for mobile receiver antenna architecture for handling various digital video broadcast channels
A method for an antenna architecture may comprise receiving at a first radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC) integrated within a mobile terminal, first signals via at least a first antenna, where the first signals may comprise signals within a 2100 MHz band. Second signals may be received at a second RFIC integrated within the mobile terminal via at least one of the first antenna and at least one other antenna, where the second signals may comprise signals within at least one of an 1800 MHz band and a 900 MHz band. Third signals may be received at at least a third RFIC integrated within the mobile terminal via at least one of the first antenna and at least one other antenna, where the third signals may comprise VHF / UHF broadcast signals within at least one of a DVB broadcast band, an ATSC broadcast band and an ISDB broadcast band.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
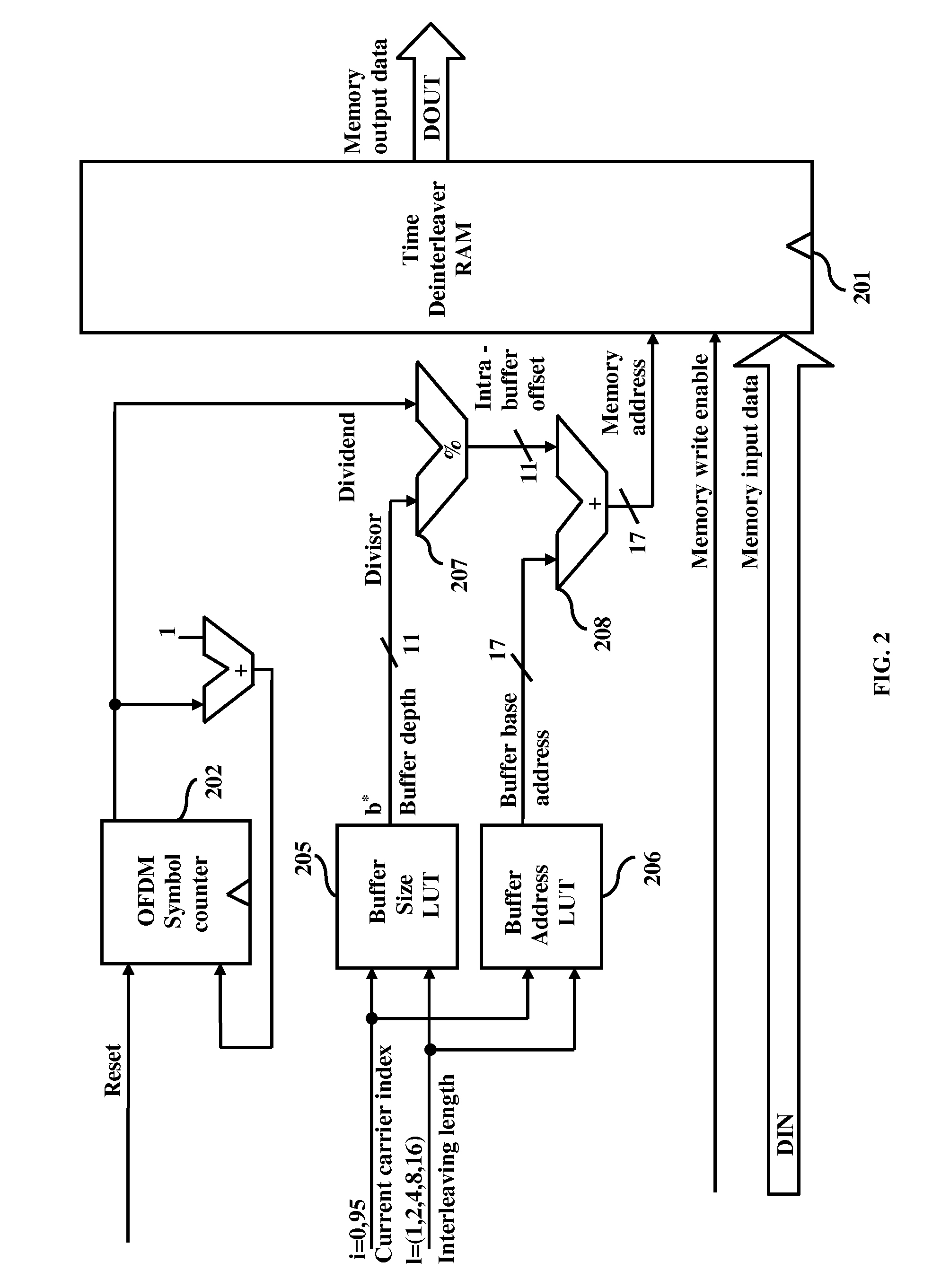
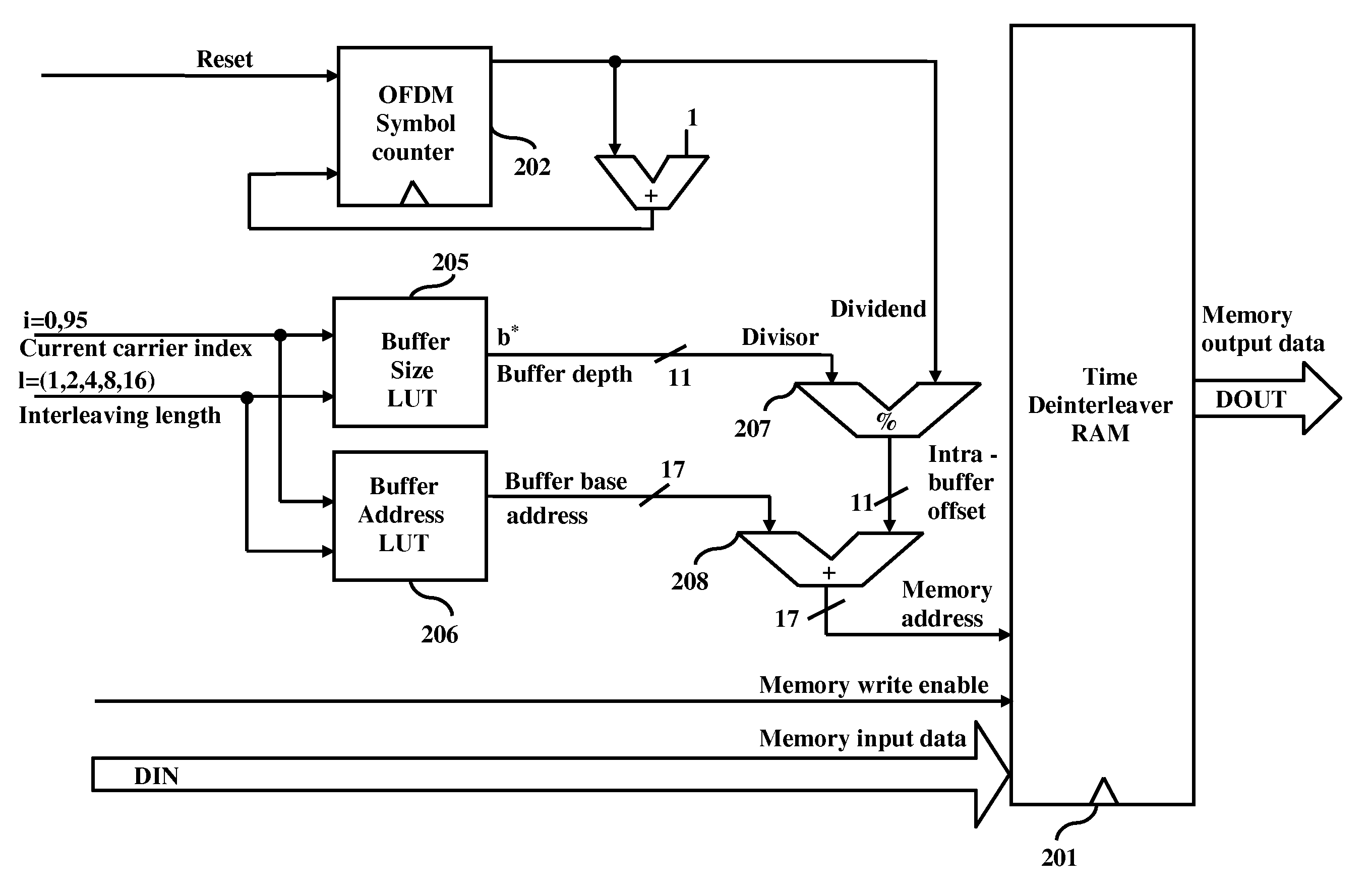
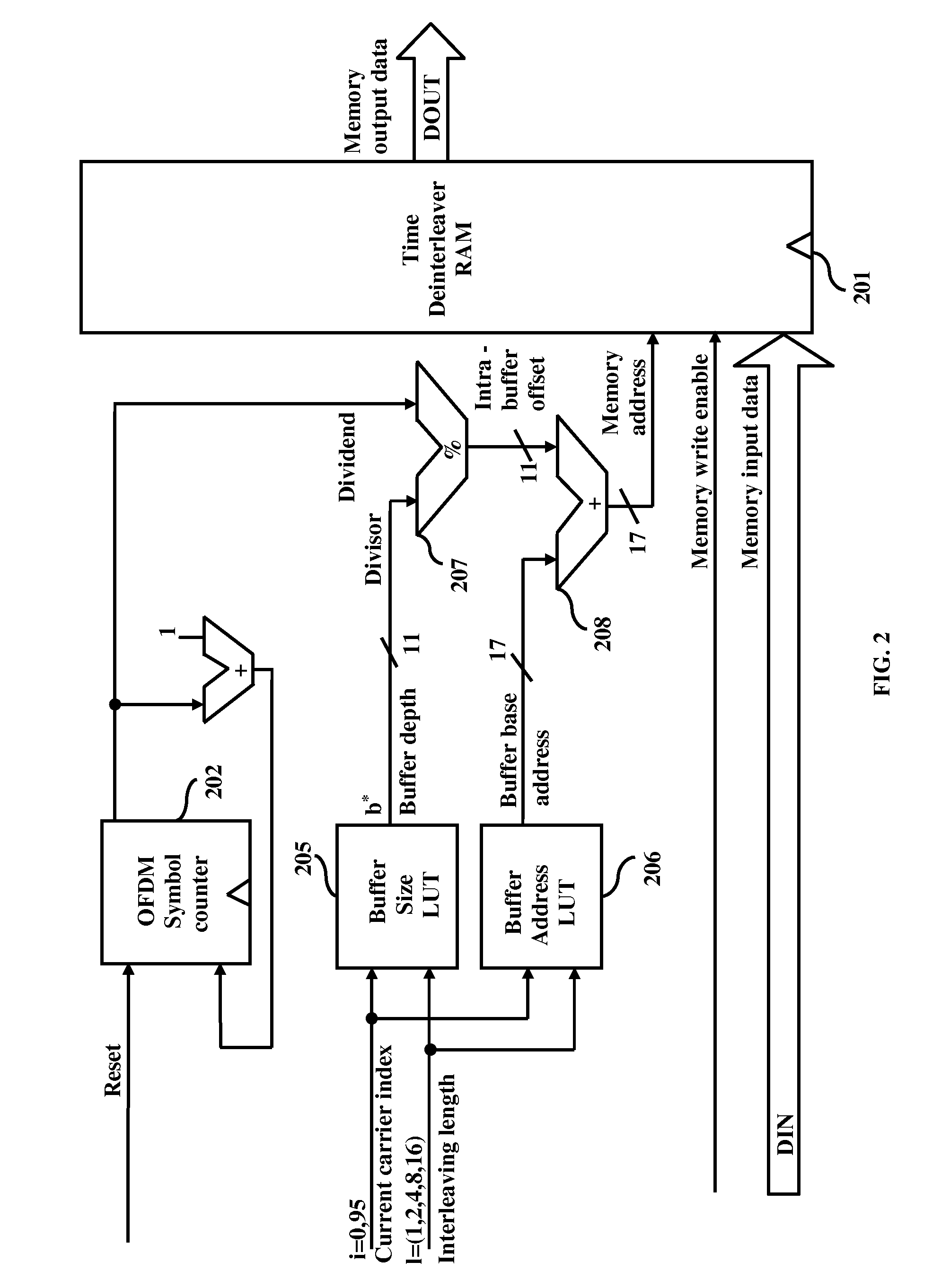
Area and power efficient architectures of time deinterleaver for isdb-t receivers
A method and apparatus for de-interleaving interleaved data in a deinterleaver memory in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) based Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting Terrestrial (ISDB-T) receiver. In different embodiments, the apparatus comprises of a OFDM symbol counter along with a divider or a buffer pointer RAM with circular pointer logic, a first lookup table to obtain delay buffer size and interleaving lengths for a given OFDM transmission layer, and a second lookup table to obtain buffer base address and interleaving lengths for a given OFDM transmission layer.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
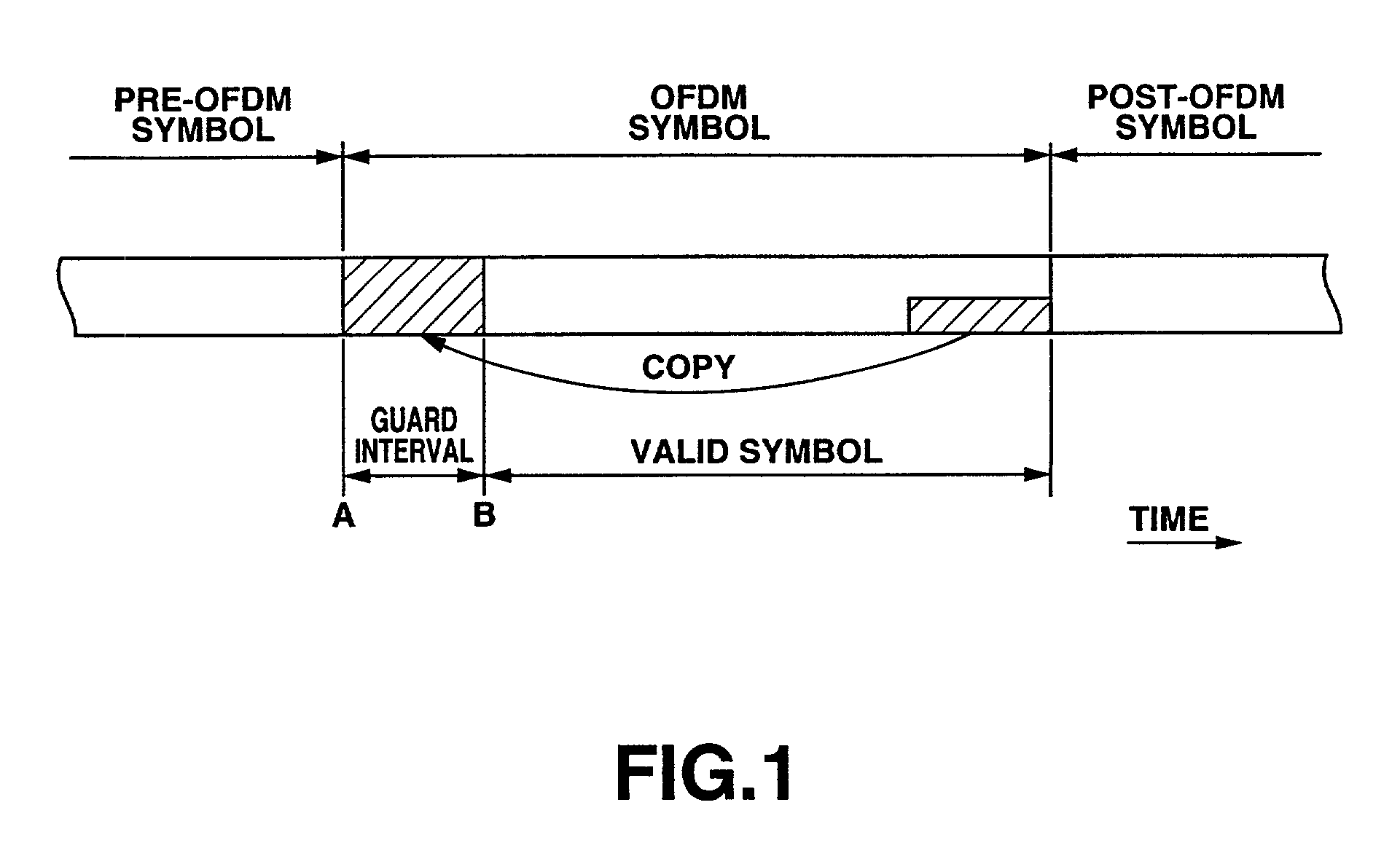
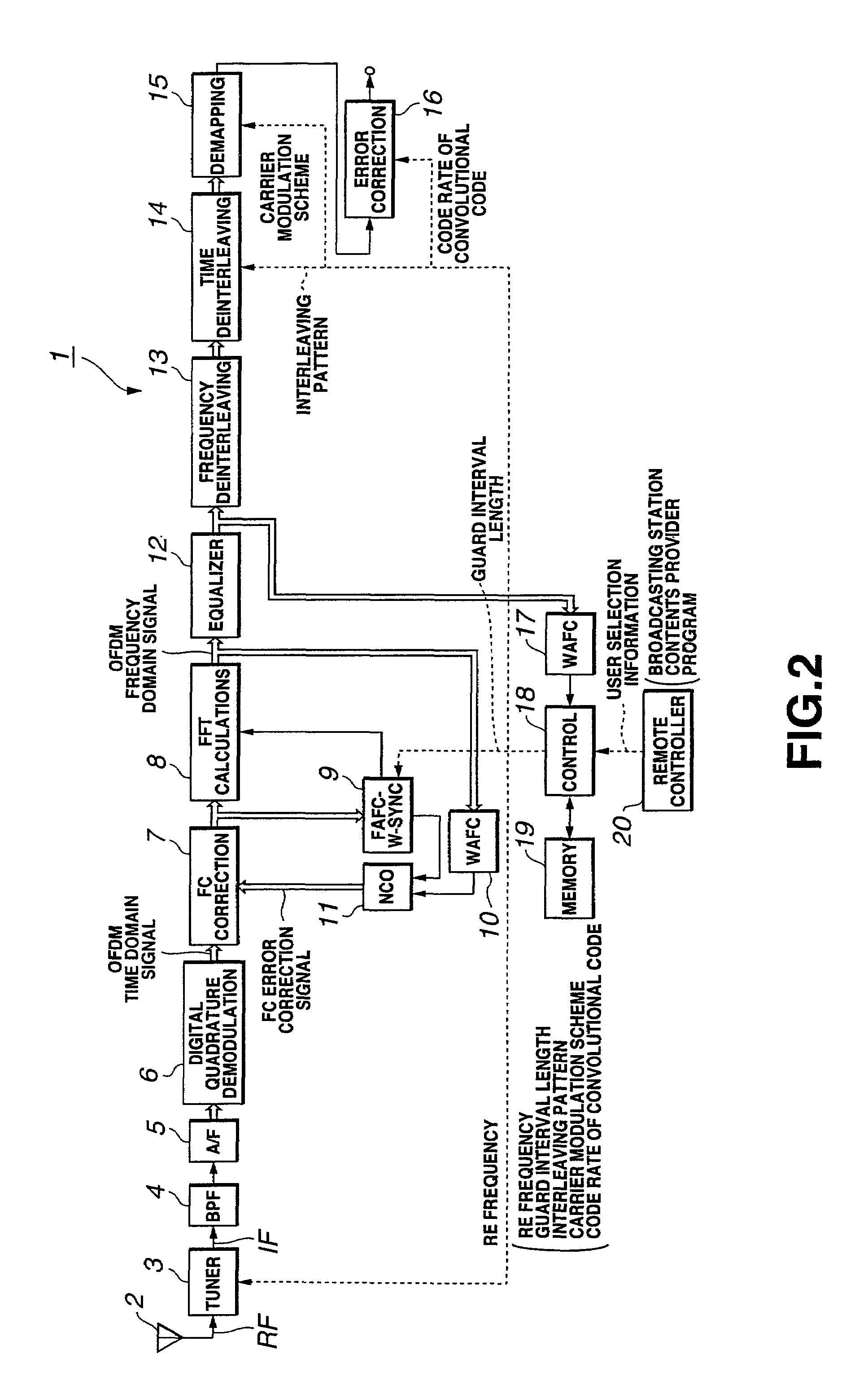
Reception apparatus
InactiveUS6956812B2Short rise timeTelevision system detailsFrequency-division multiplexCarrier signalGuard interval
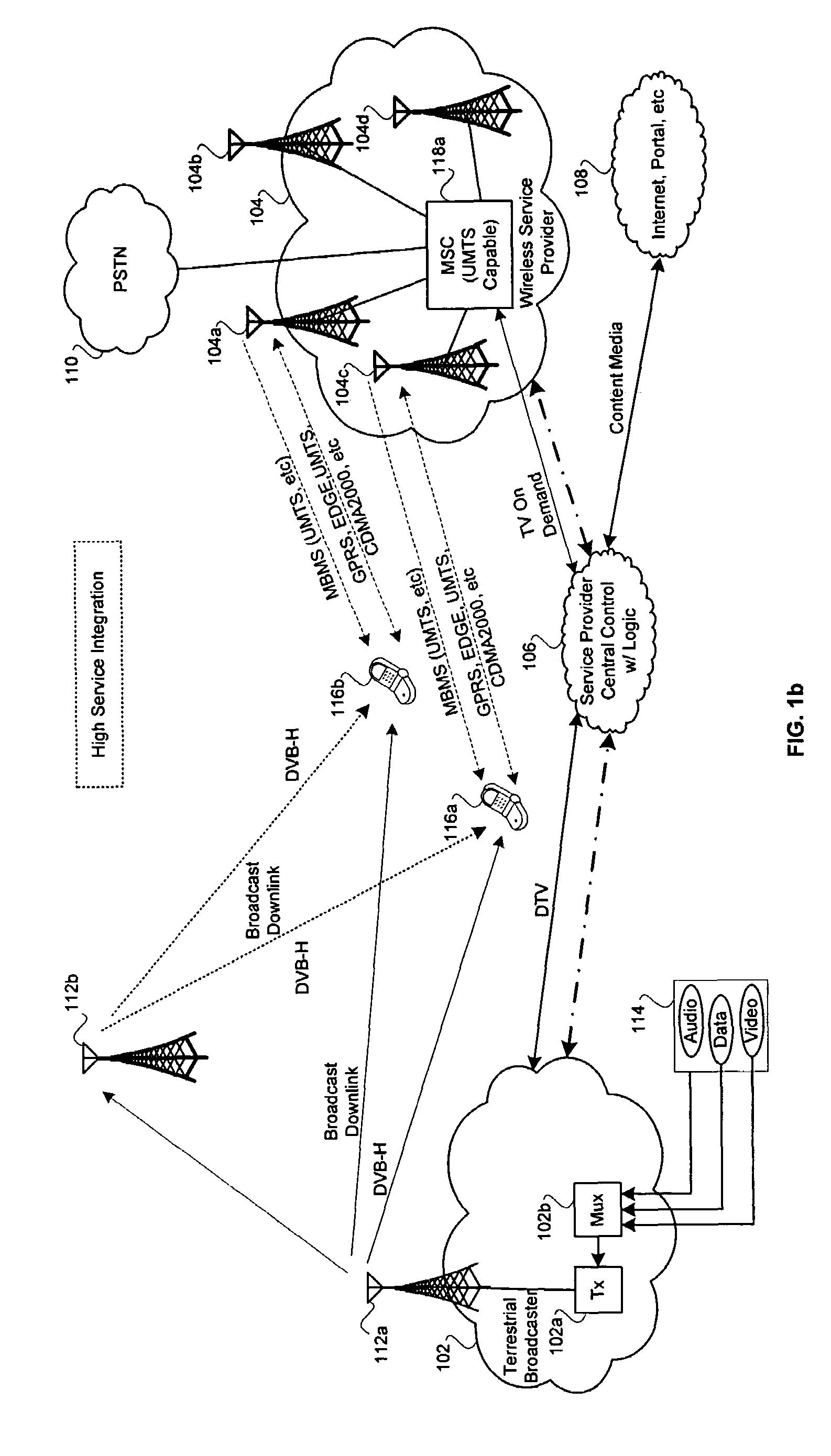
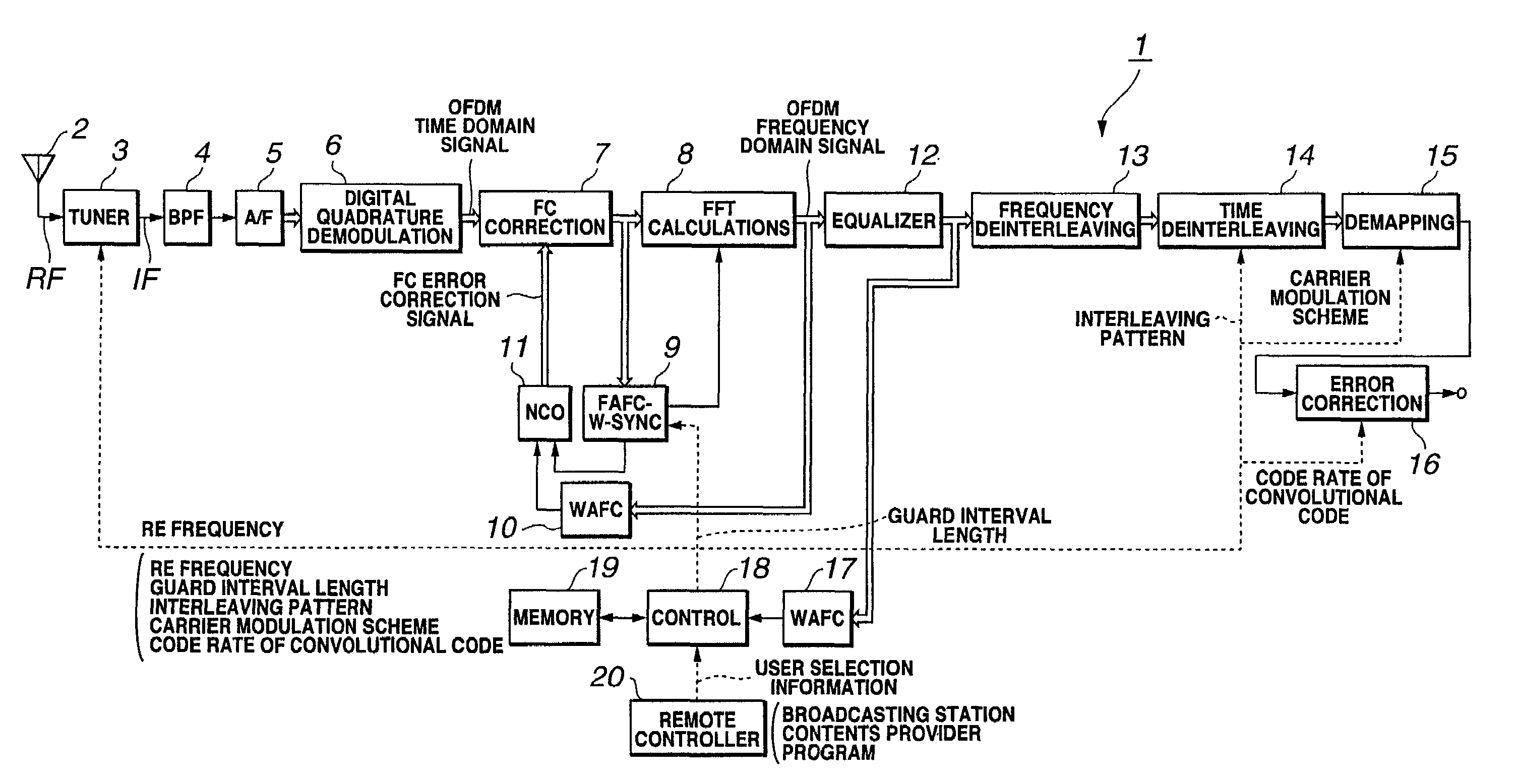
A reception apparatus for OFDM signals having a short initial rise time since start of reception until outputting the sound and / or a picture. An OFDM reception apparatus 1 of the ISDB-T standard presets the TMCC information at the outset in a memory 19 in association with each broadcasting station. This TMCC information contains the information on the RF frequency and the guard interval length, time interleaving pattern information, the information on the carrier modulation scheme and the information on the code rate of the convolutional code. When a user selects a broadcasting station, a control circuit 18 reads out the TMCC information associated with the broadcasting station from the memory 19. The control circuit 18 affords the read-out TMCC information to each circuit to set e.g., the guard interval or the carrier modulation scheme.
Owner:SONY CORP
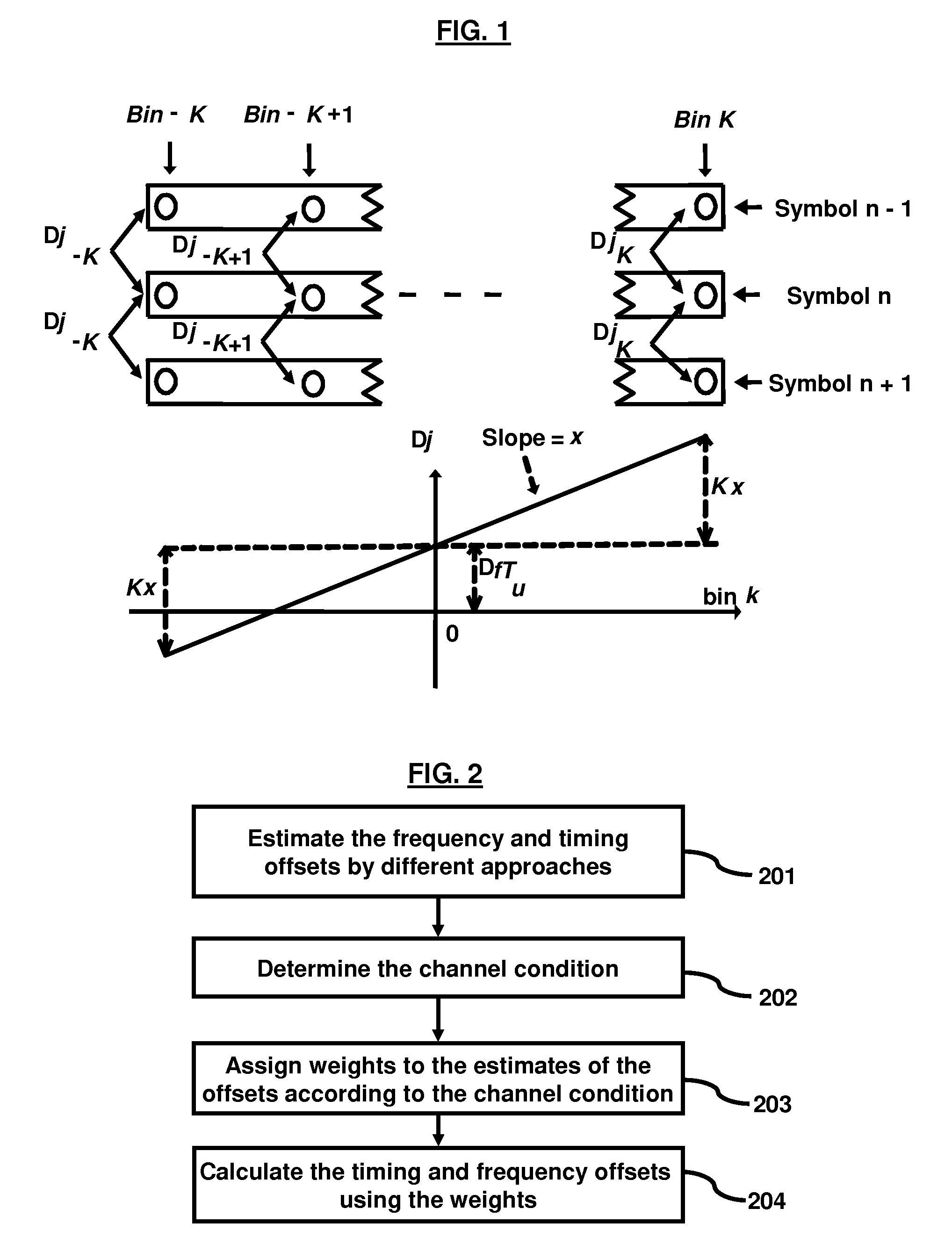
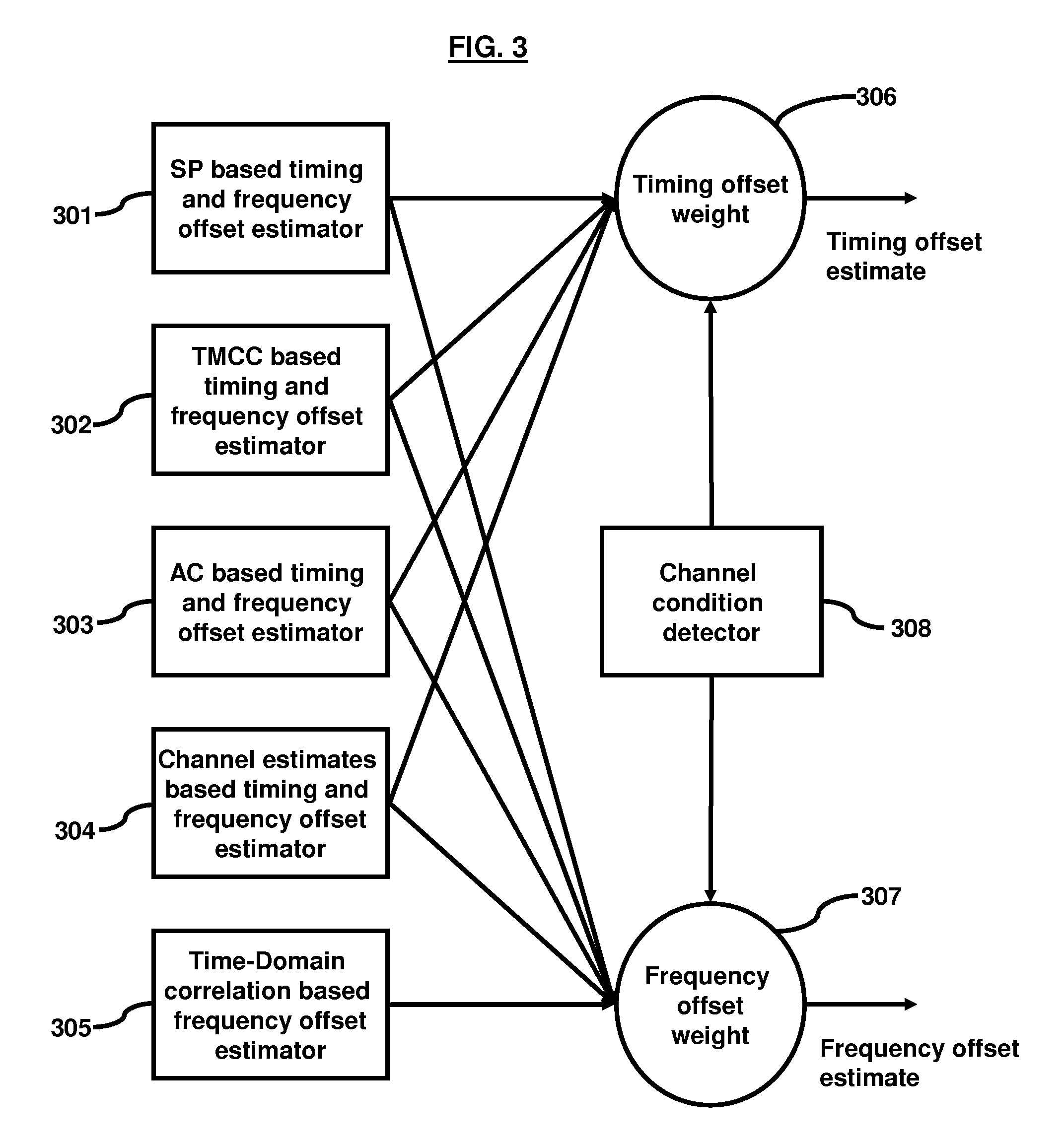
Time and frequency domain based approaches for fine timing and frequency estimations in isdb-t and isdb-tsb receiver design
A method and apparatus for estimating timing and frequency offsets in an ISDB-T and ISDB-TSB receiver. In different embodiments, the method comprises estimating timing and frequency offsets by different estimation processes; assigning weights to the timing and frequency offsets according to the channel condition; and calculating timing and frequency offsets using the estimates of timing and frequency offsets and the weights.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Area and power efficient architectures of time deinterleaver for ISDB-T receivers
A method and apparatus for de-interleaving interleaved data in a deinterleaver memory in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) based Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting Terrestrial (ISDB-T) receiver. In different embodiments, the apparatus comprises of a OFDM symbol counter along with a divider or a buffer pointer RAM with circular pointer logic, a first lookup table to obtain delay buffer size and interleaving lengths for a given OFDM transmission layer, and a second lookup table to obtain buffer base address and interleaving lengths for a given OFDM transmission layer.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
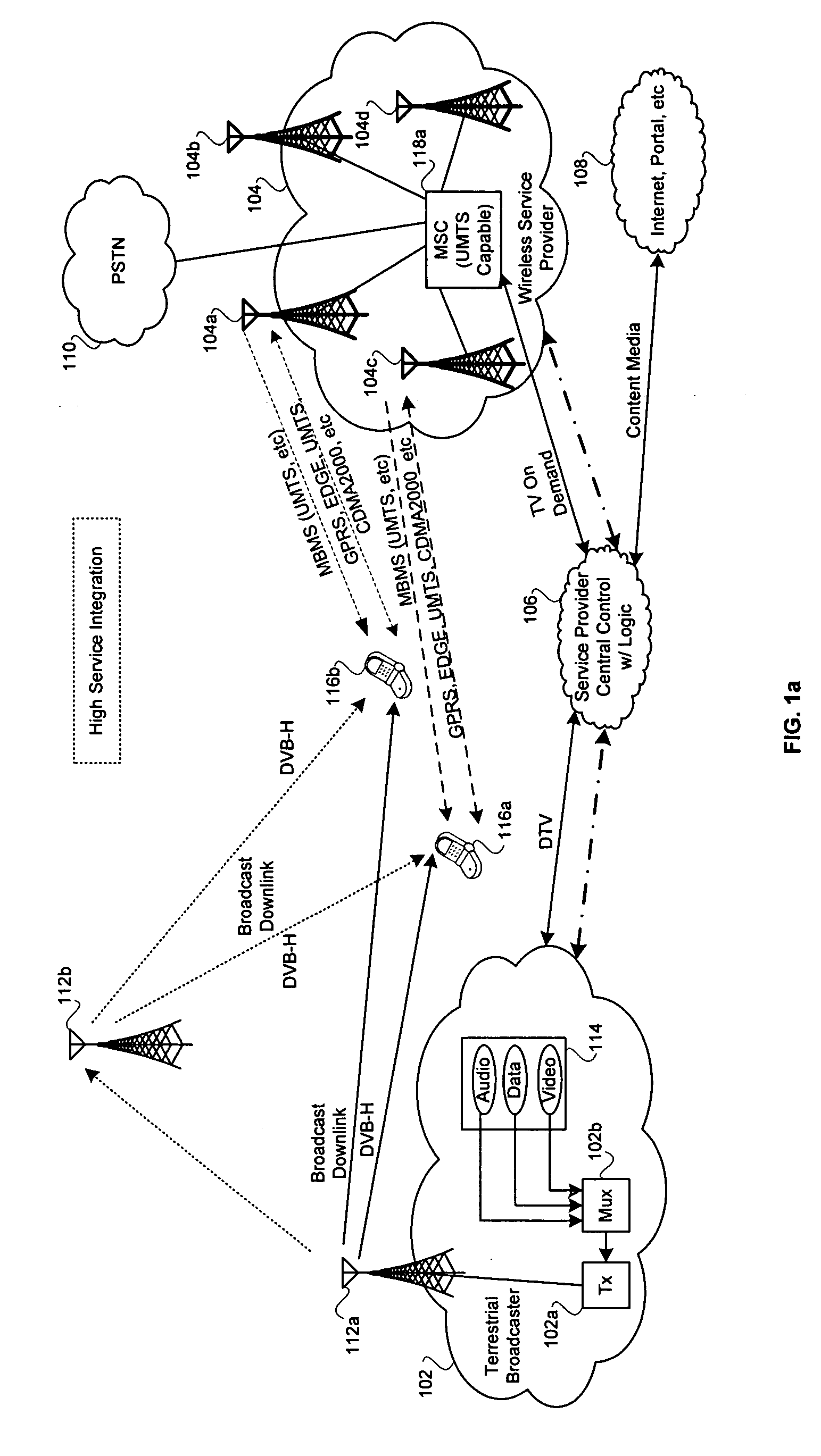
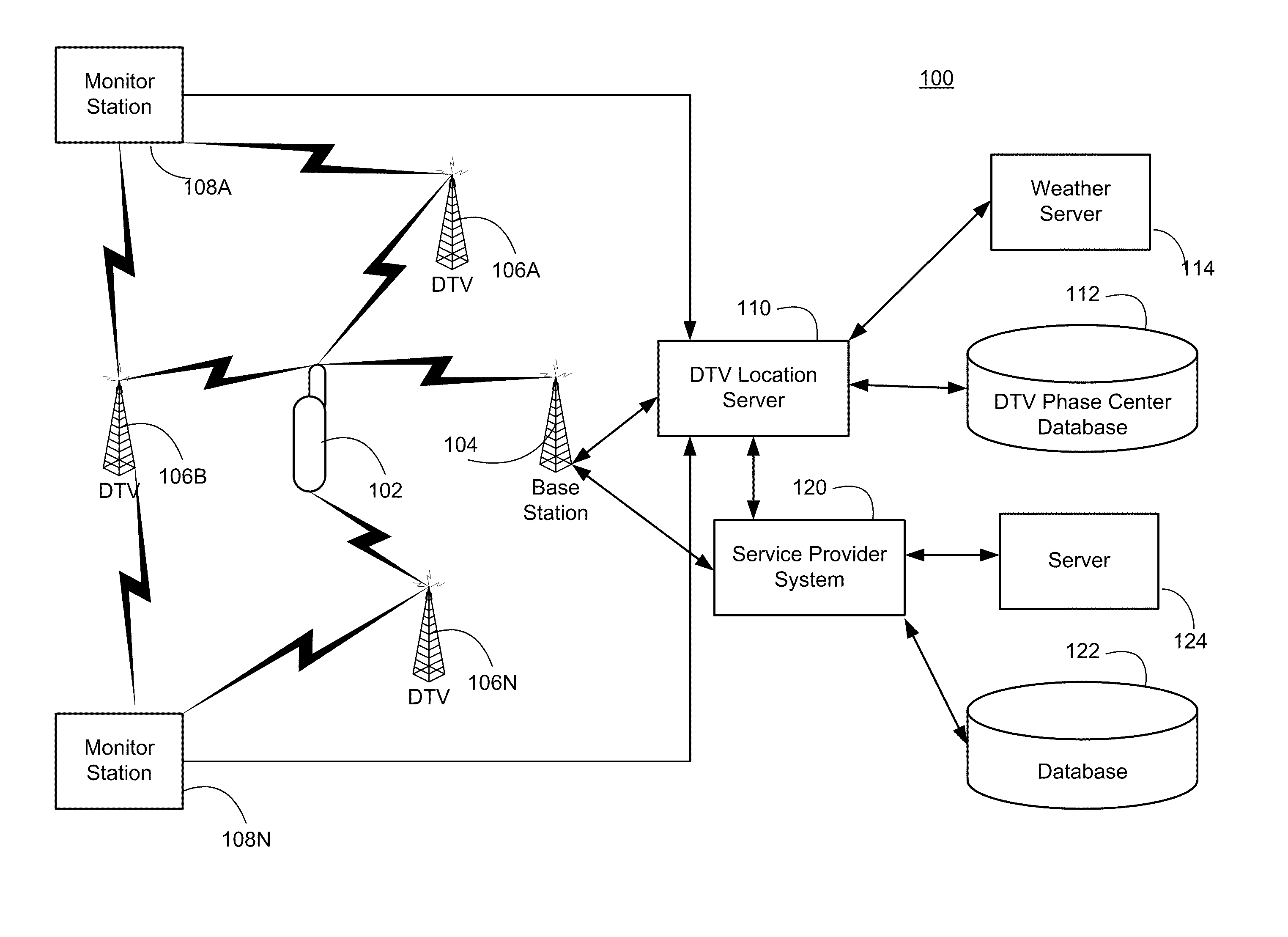
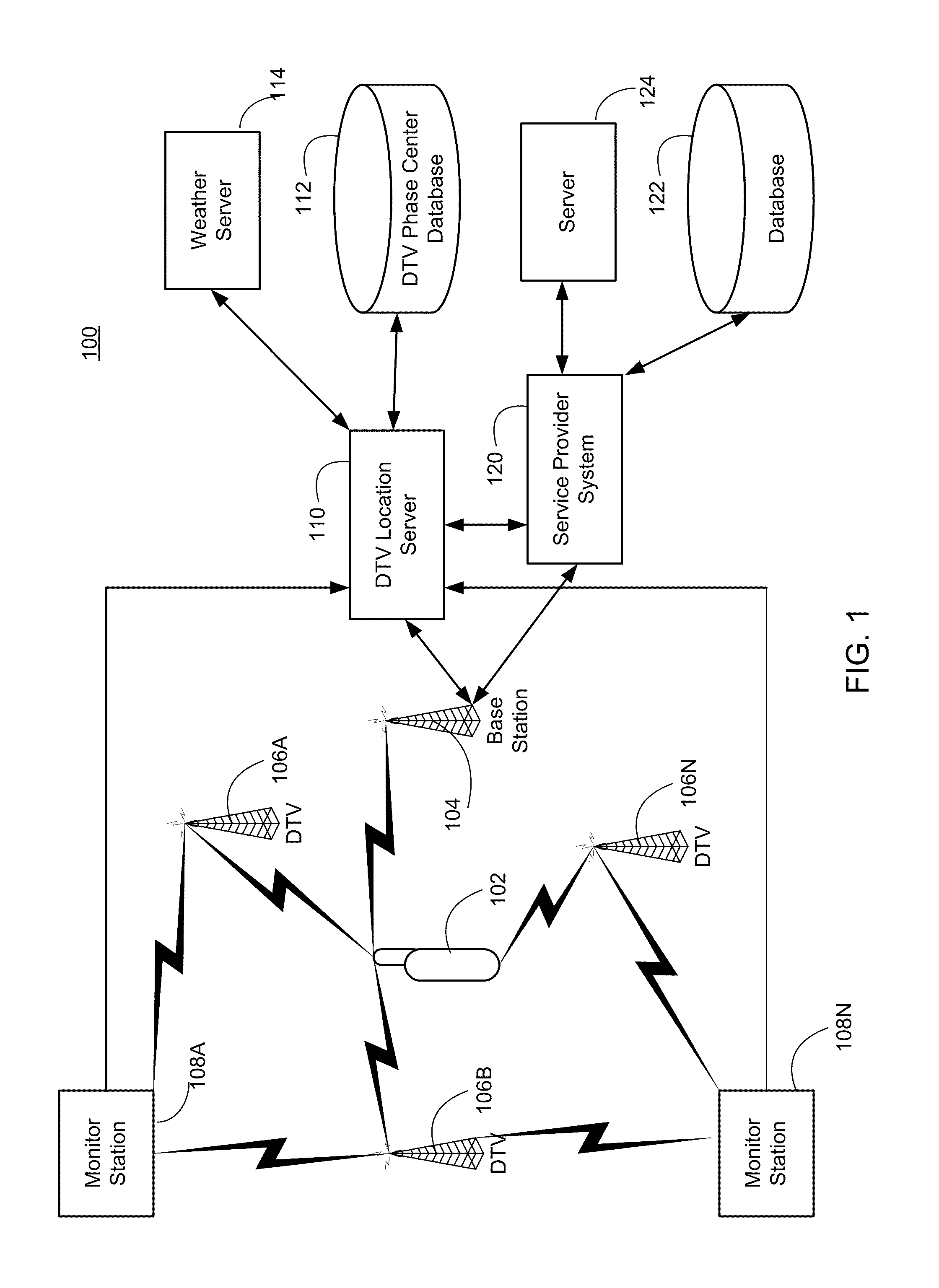
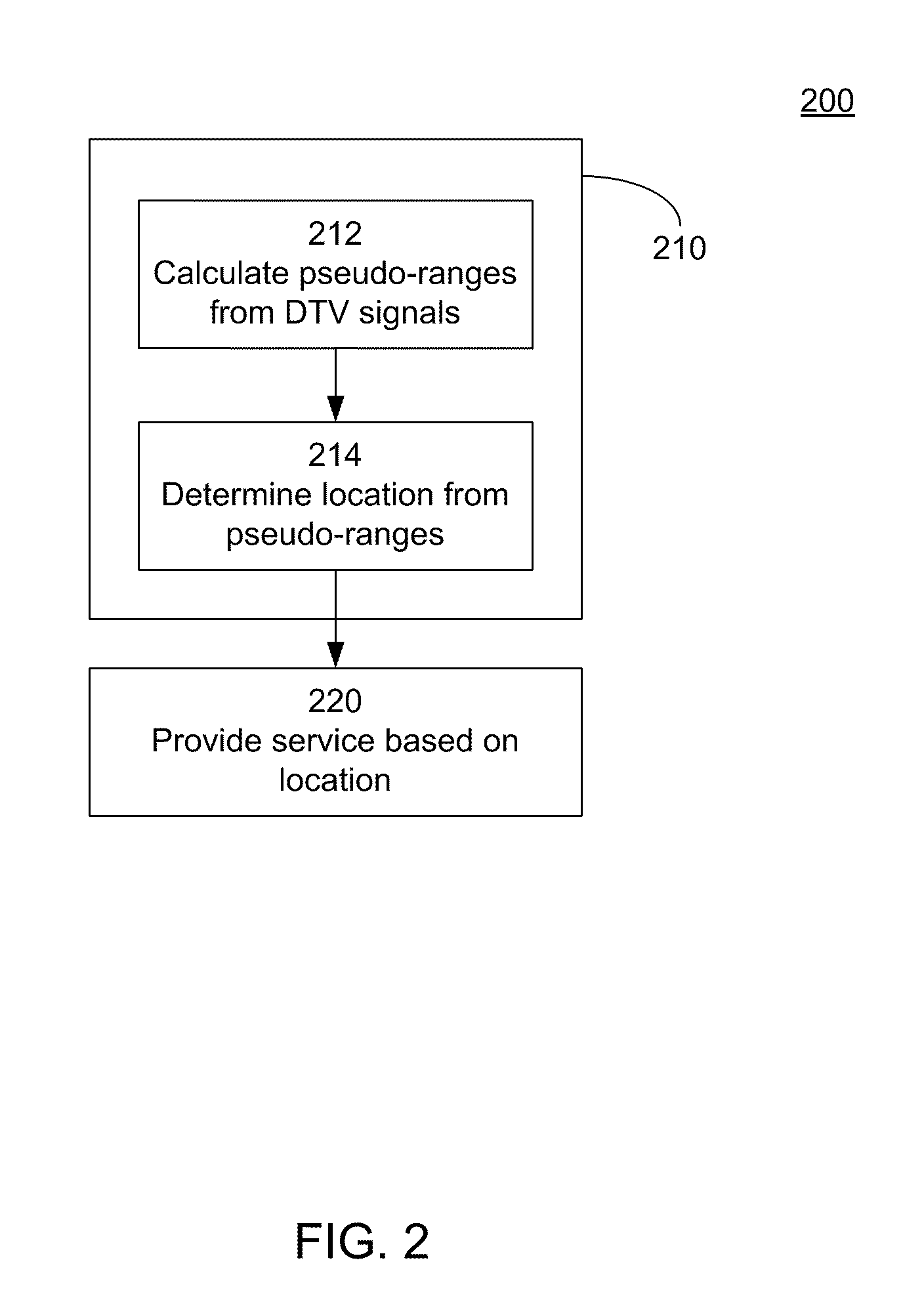
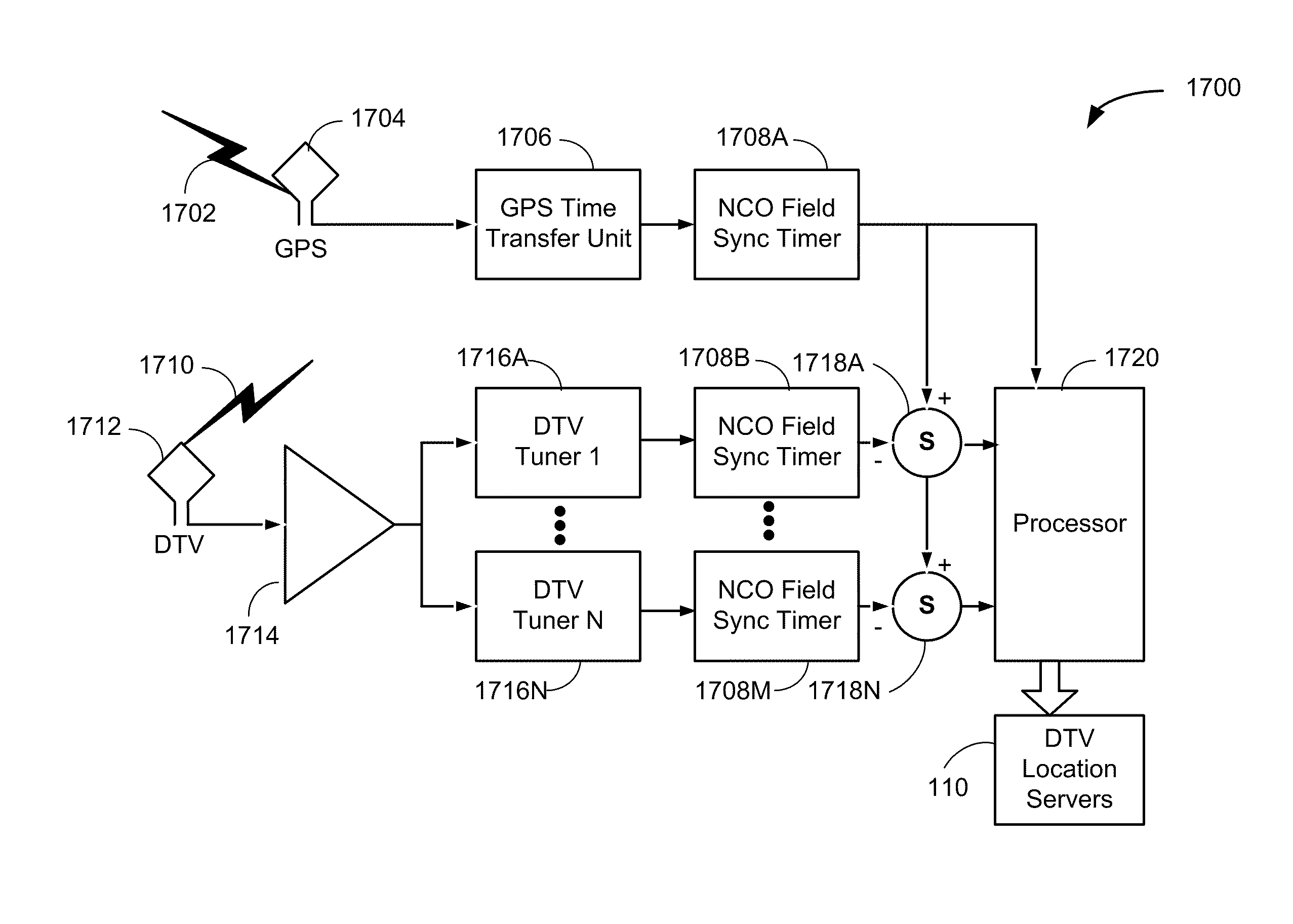
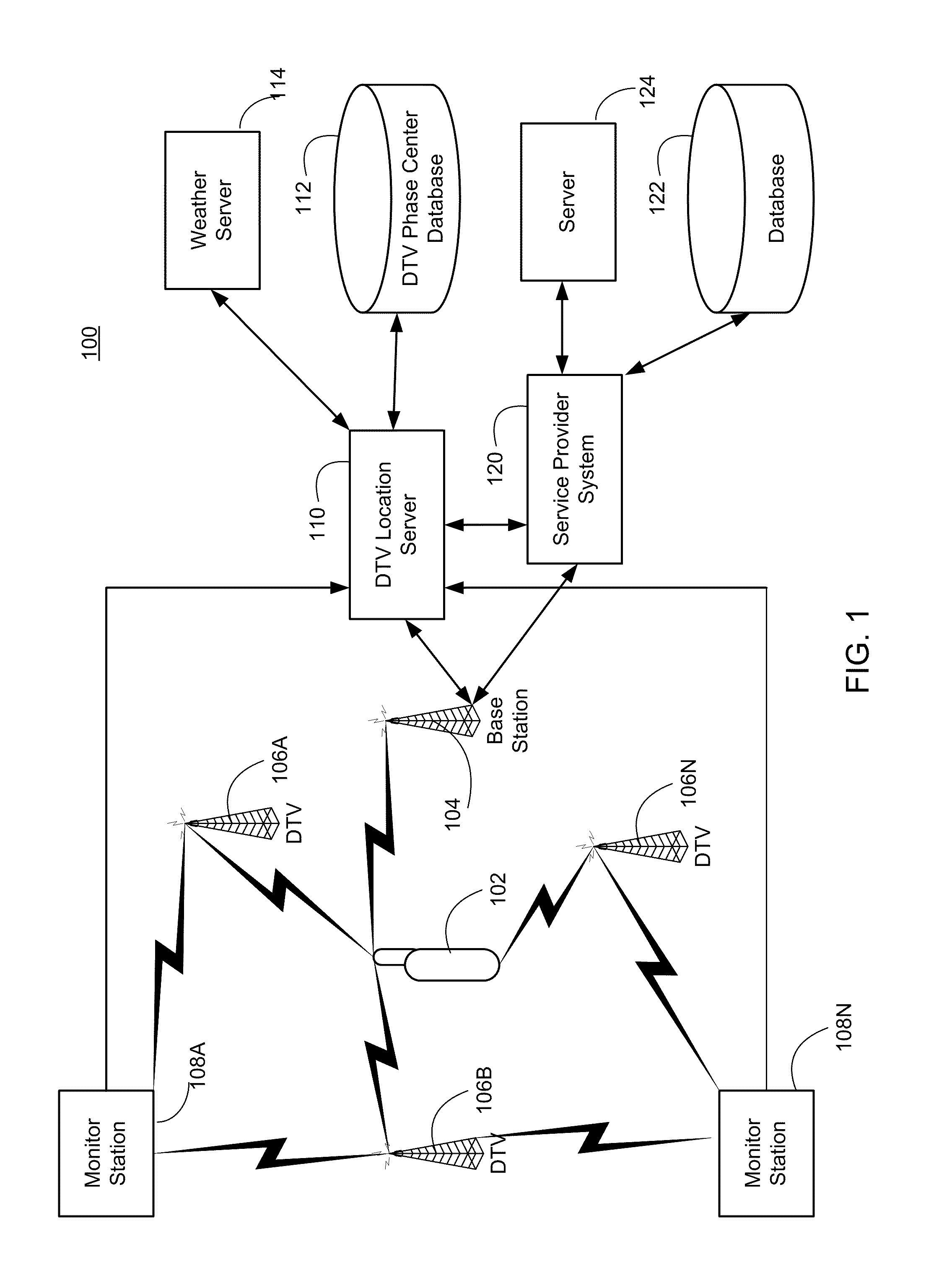
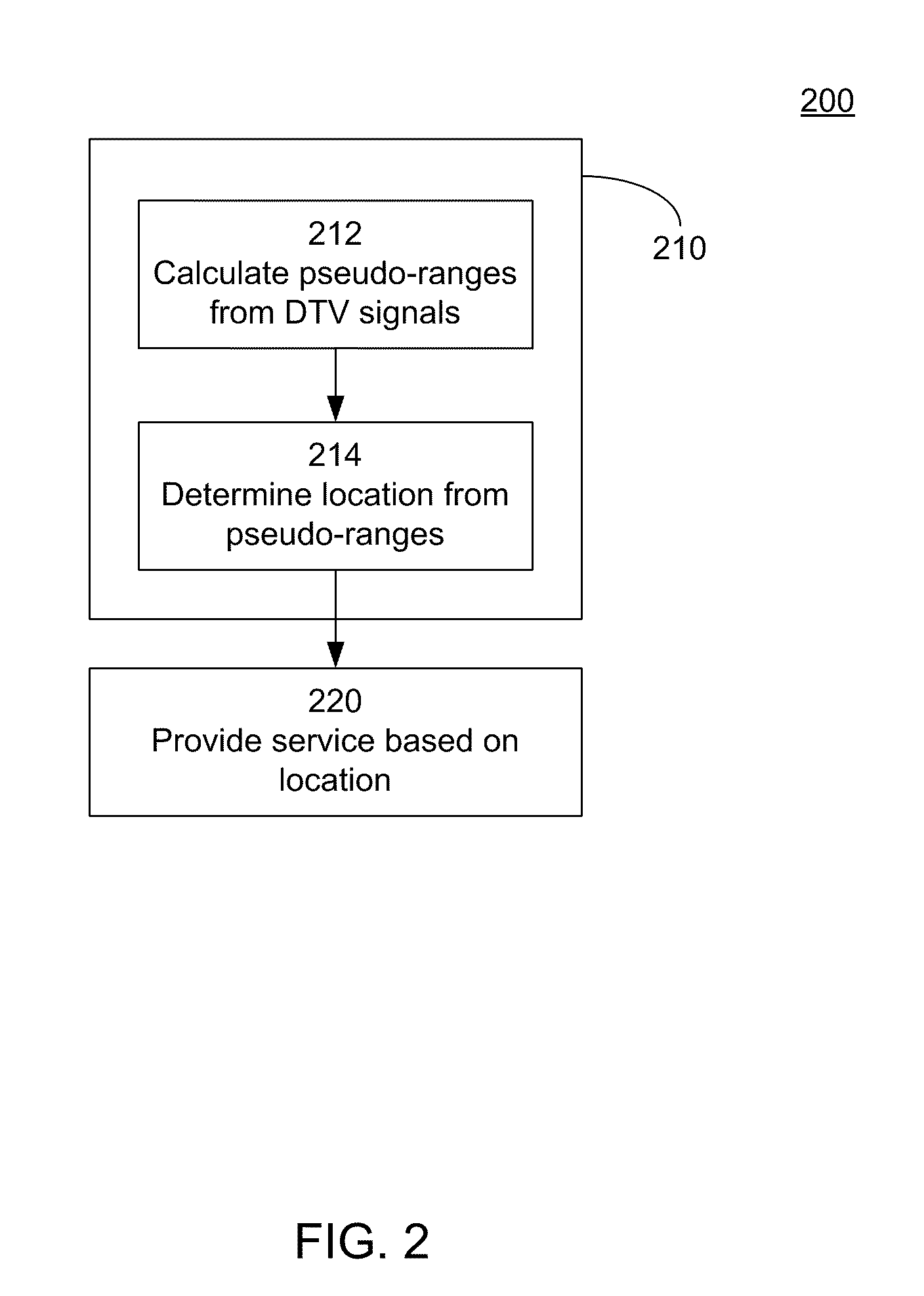
Navigation services based on position location using broadcast digital television signals
InactiveUS8041505B2Simple and inexpensive implementationStrong and large bandwidth signalPulse modulation television signal transmissionIndoor gamesDigital television transitionEngineering
A service depends on the location of a device. The device location is determined using DTV signals. More specifically, the device location is determined based on pseudo-ranges between the device and a plurality of digital television (DTV) transmitters and the pseudo-ranges are determined based on broadcast DTV signals received by the device from the DTV transmitters. Examples of DTV signals include the American Television Standards Committee (ATSC) signals, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial (DVB-T) signals and the Japanese Integrated Service Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial (ISDB-T) signals.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
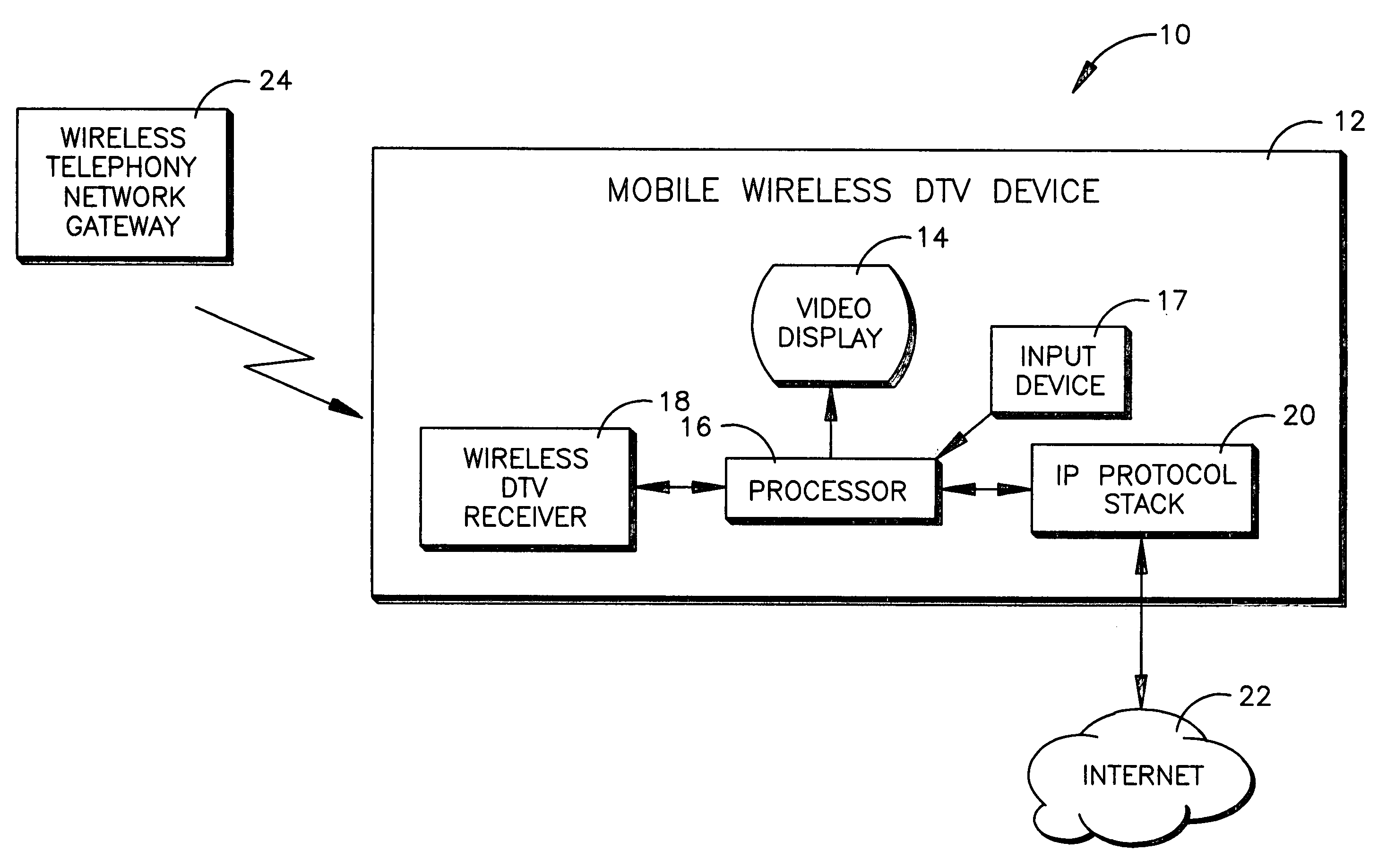
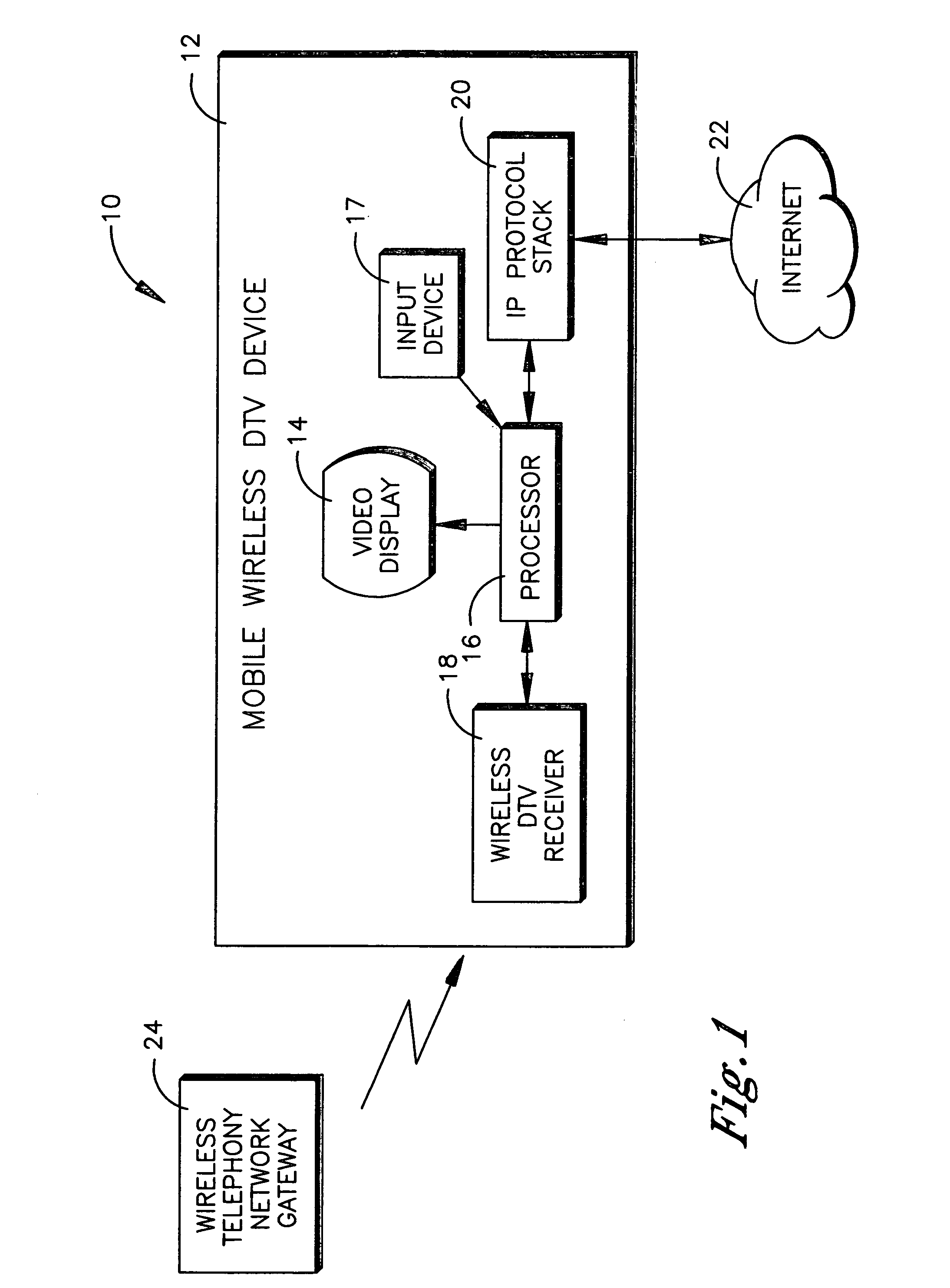
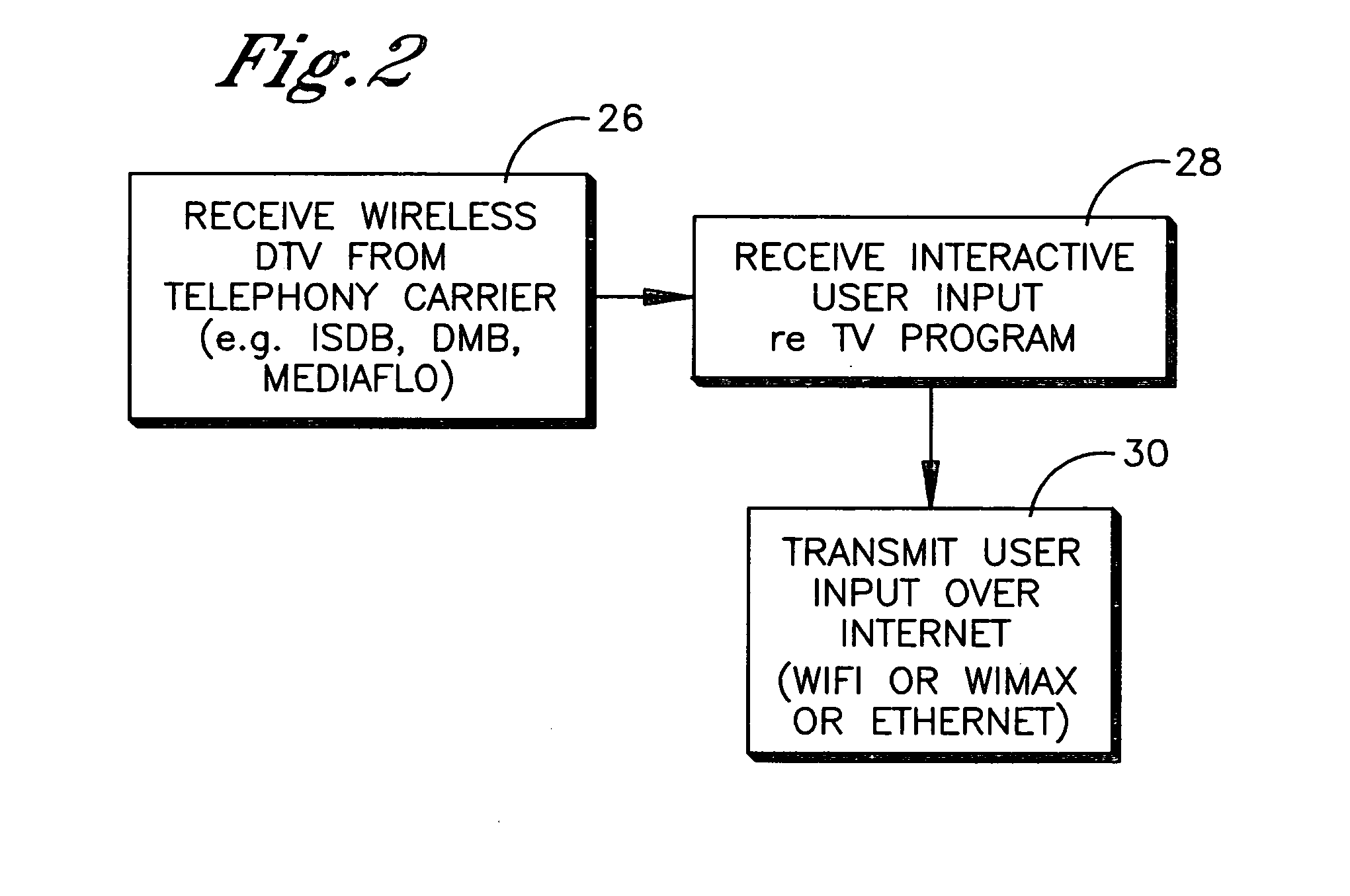
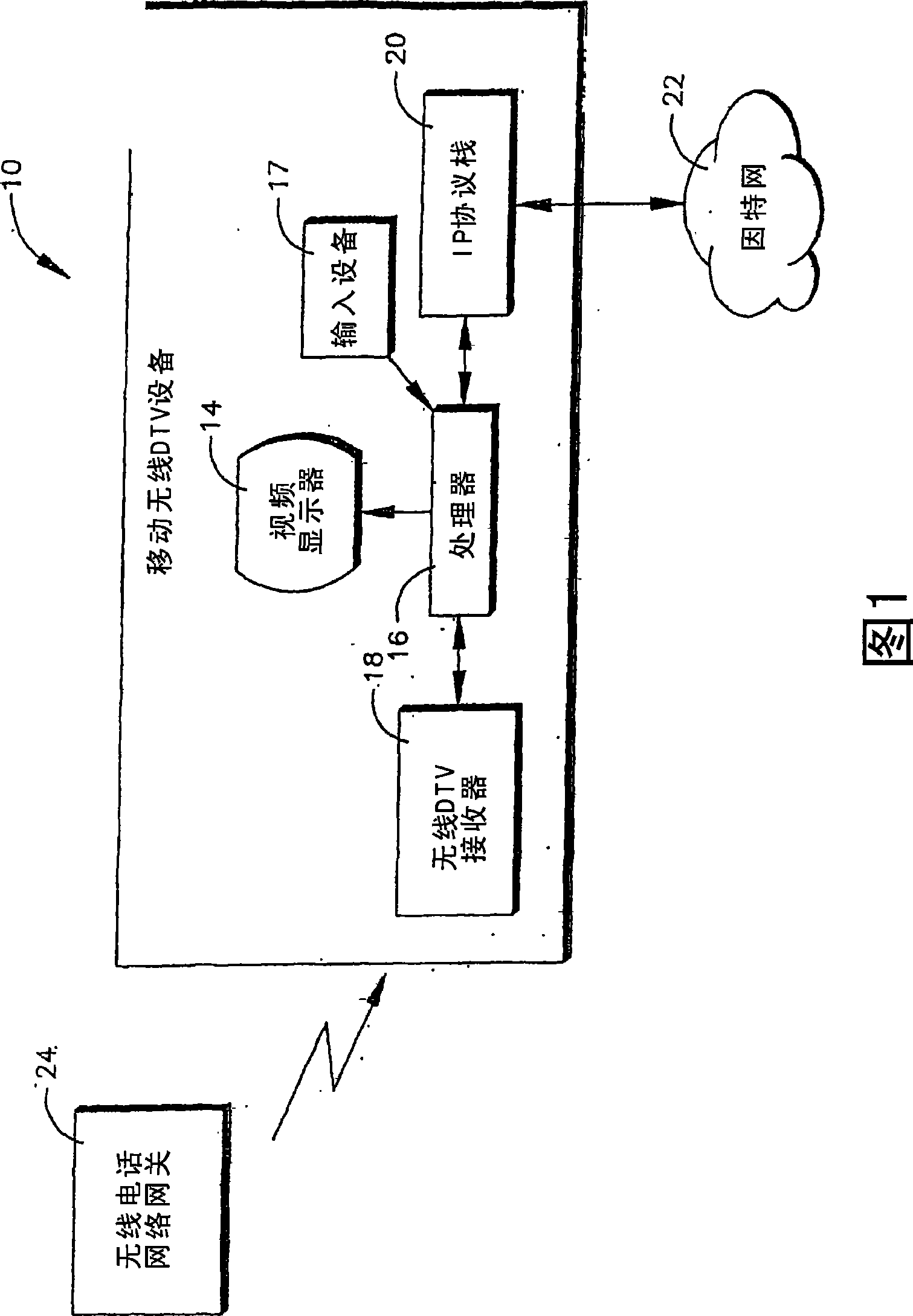
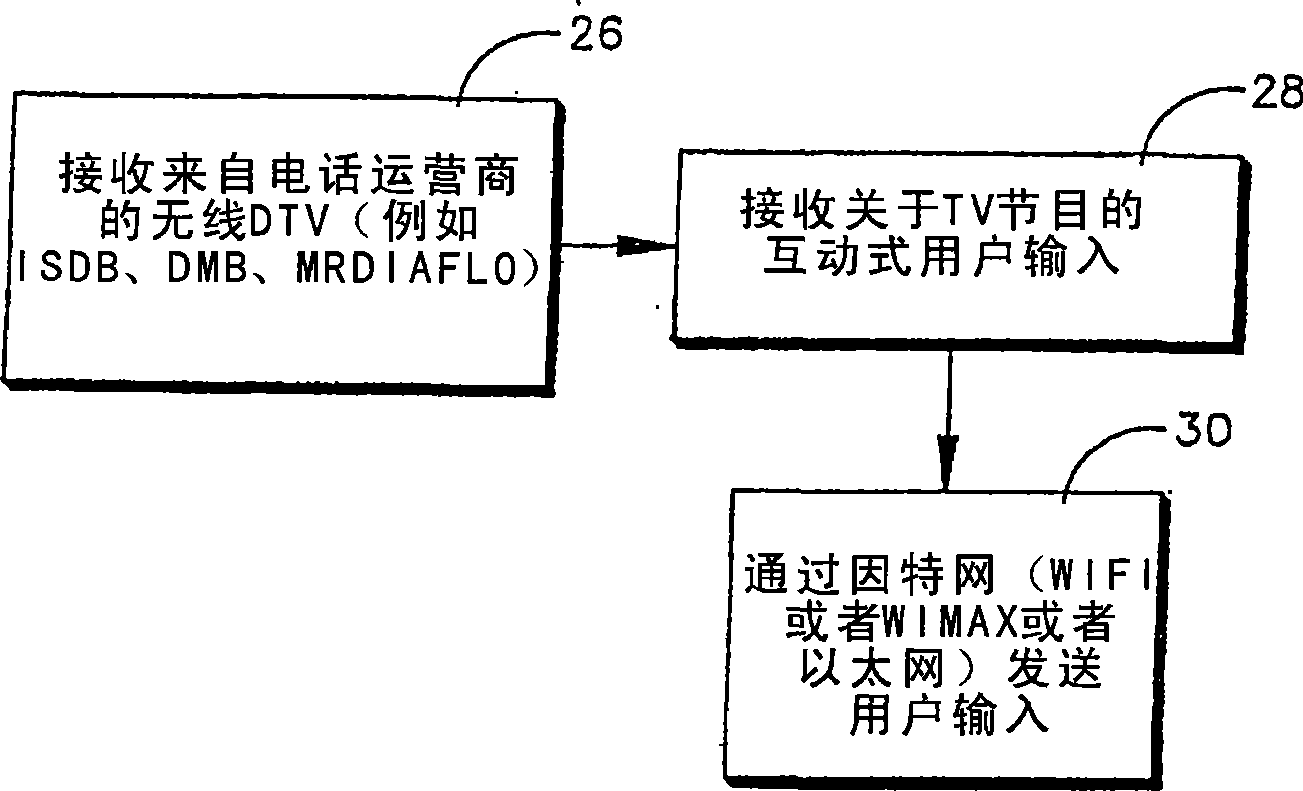
Interactive mobile wireless digital TV
InactiveUS20070174887A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsDisplay deviceMediaFLO
A wireless telephone receives DTV signals over a wireless telephony carrier network in ISDB, DMB, DVB-H, MediaFlo™, and the like for presentation of TV programming on the display of the telephone. The user can input signals to interact with the TV programming, and the user signals are wirelessly transmitted using a non-telephony network such as WiFi, WiMax, or wireless Ethernet.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
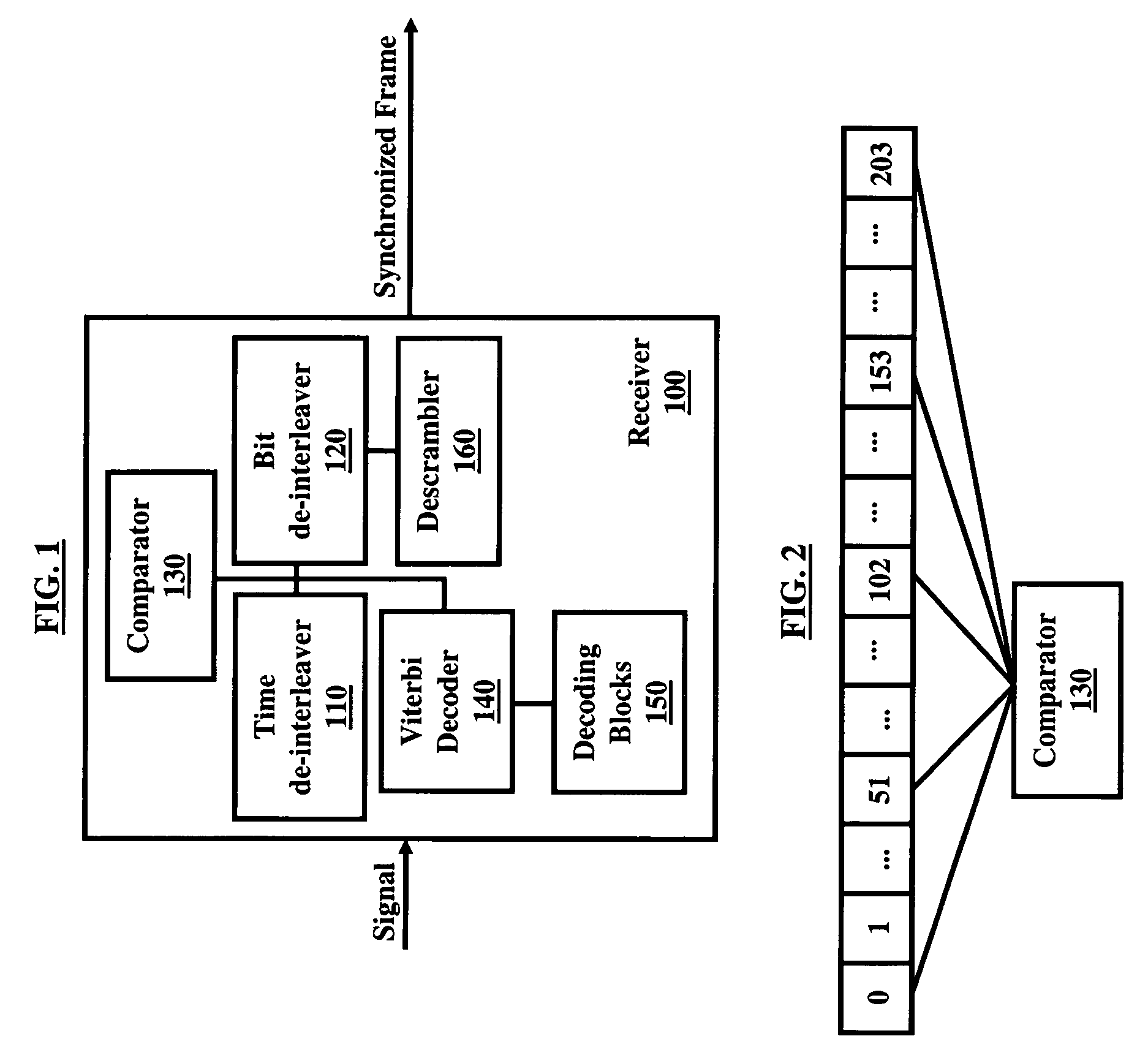
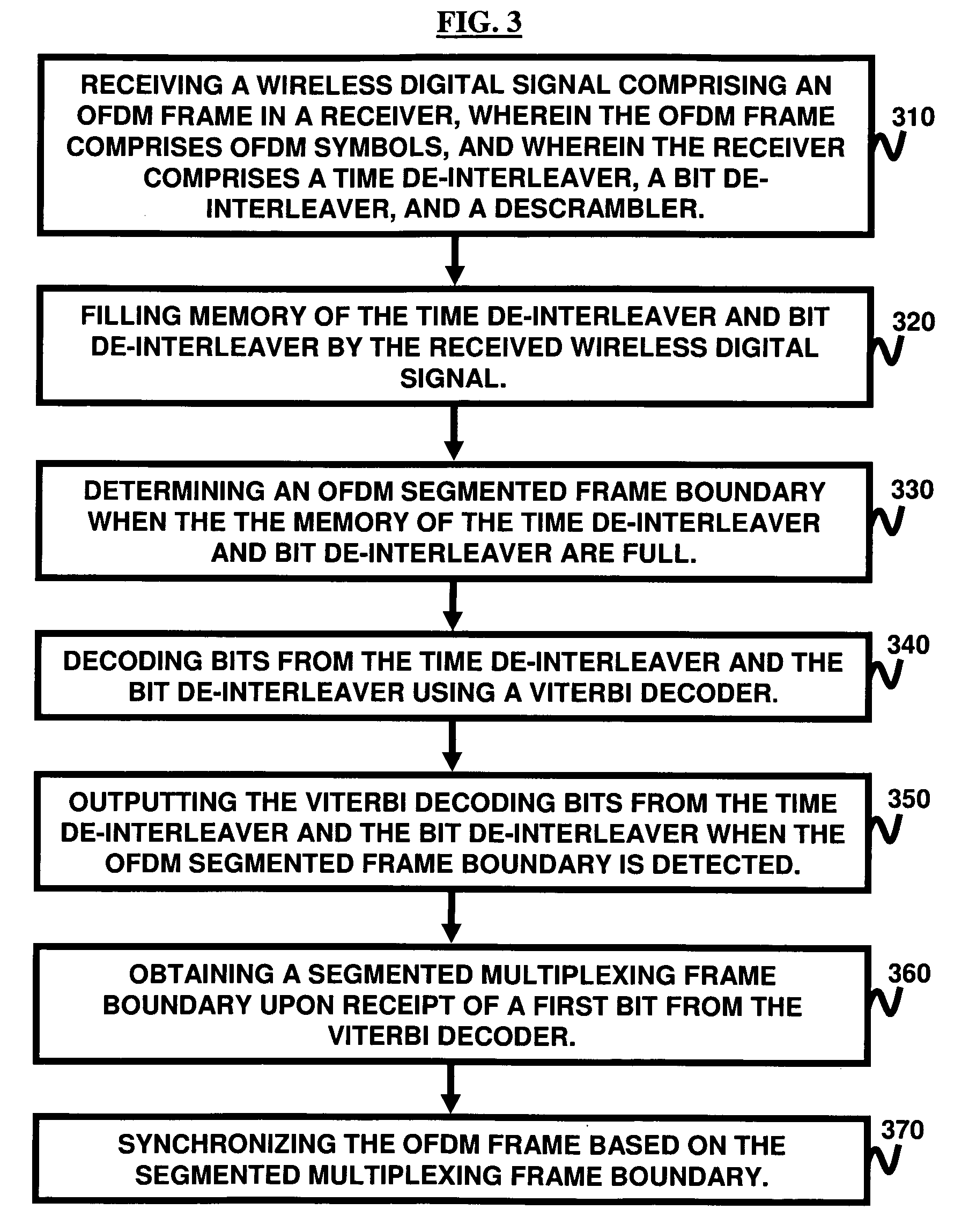
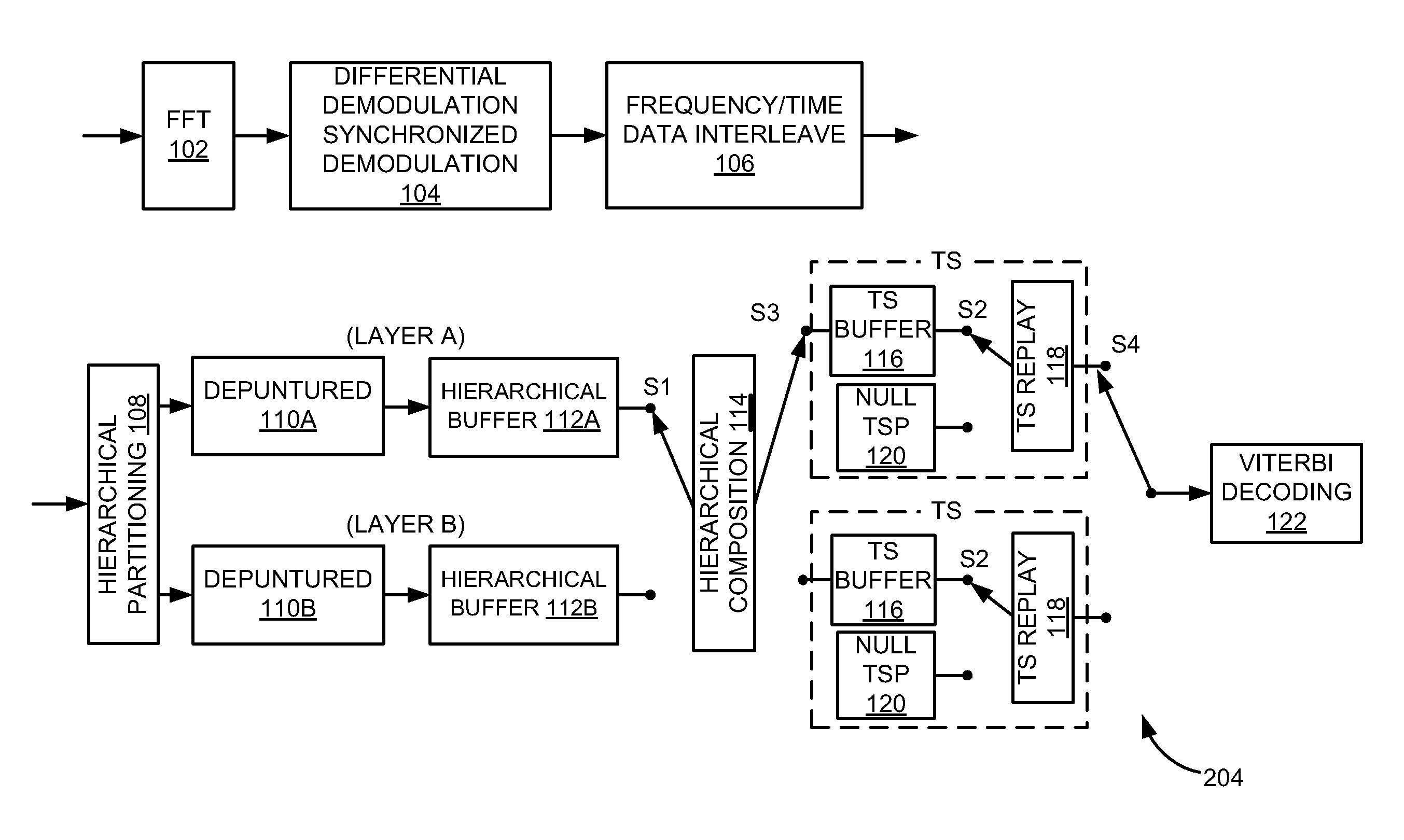
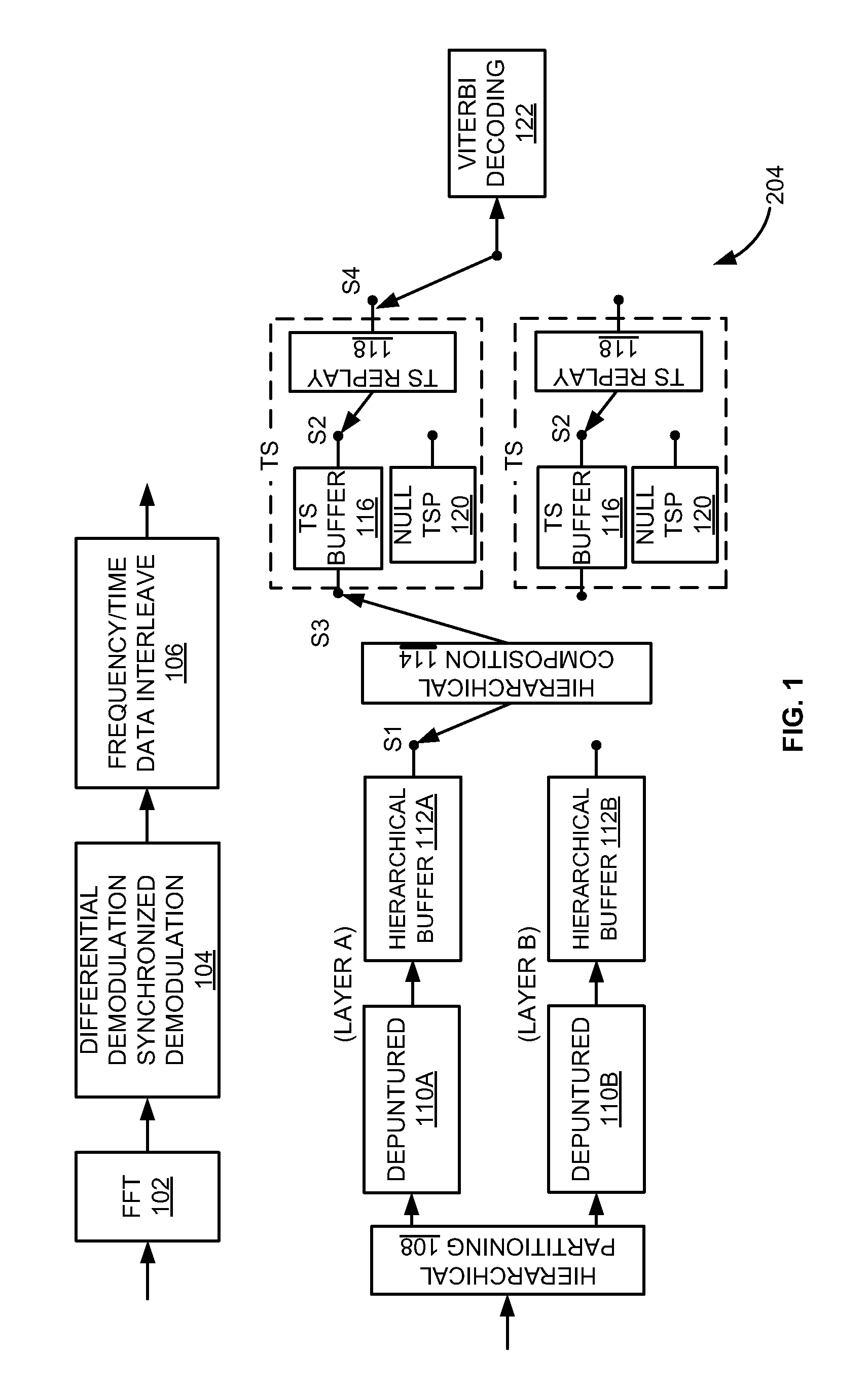
Segmented-frame synchronization for isdb-t and isdb-tsb receiver
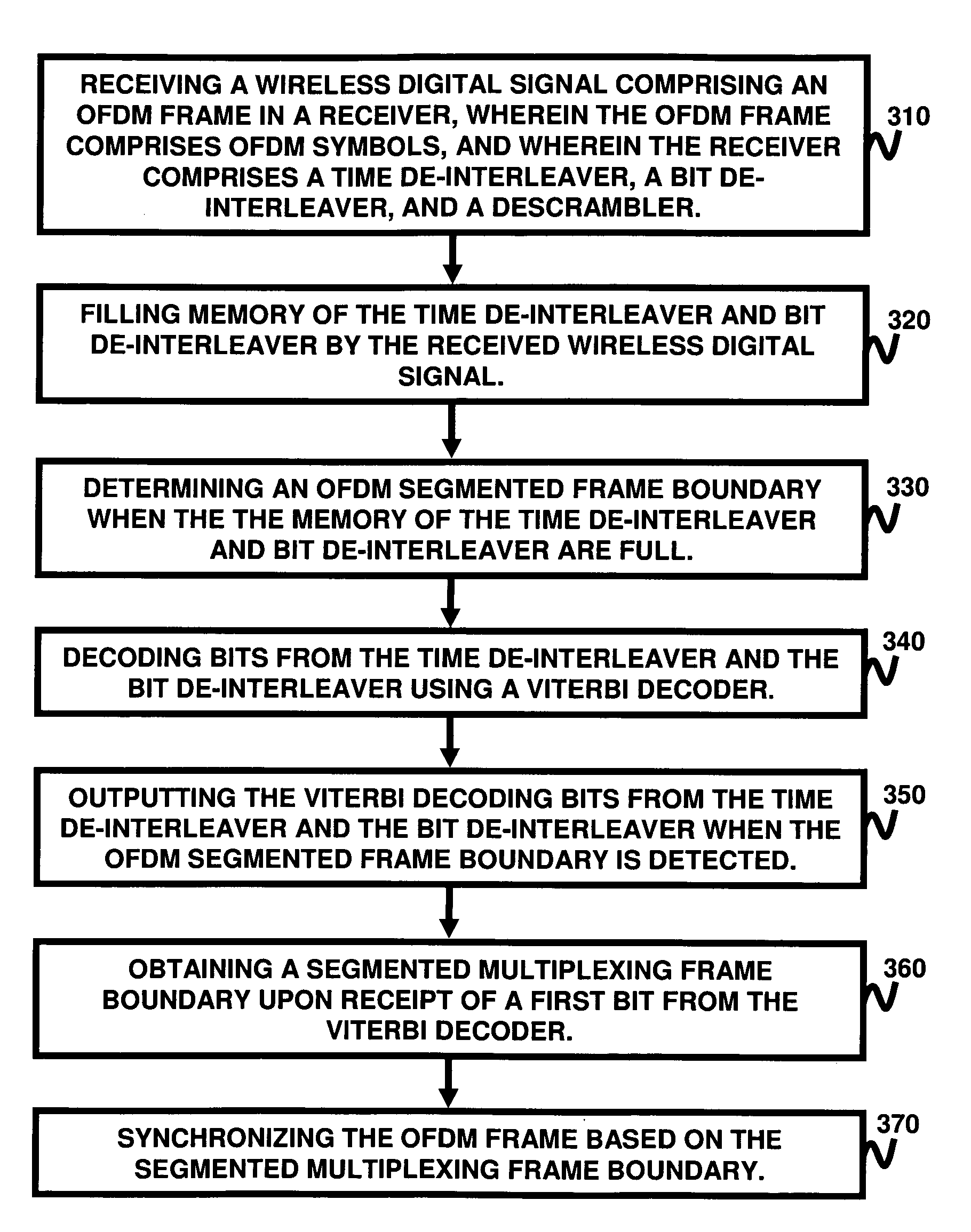
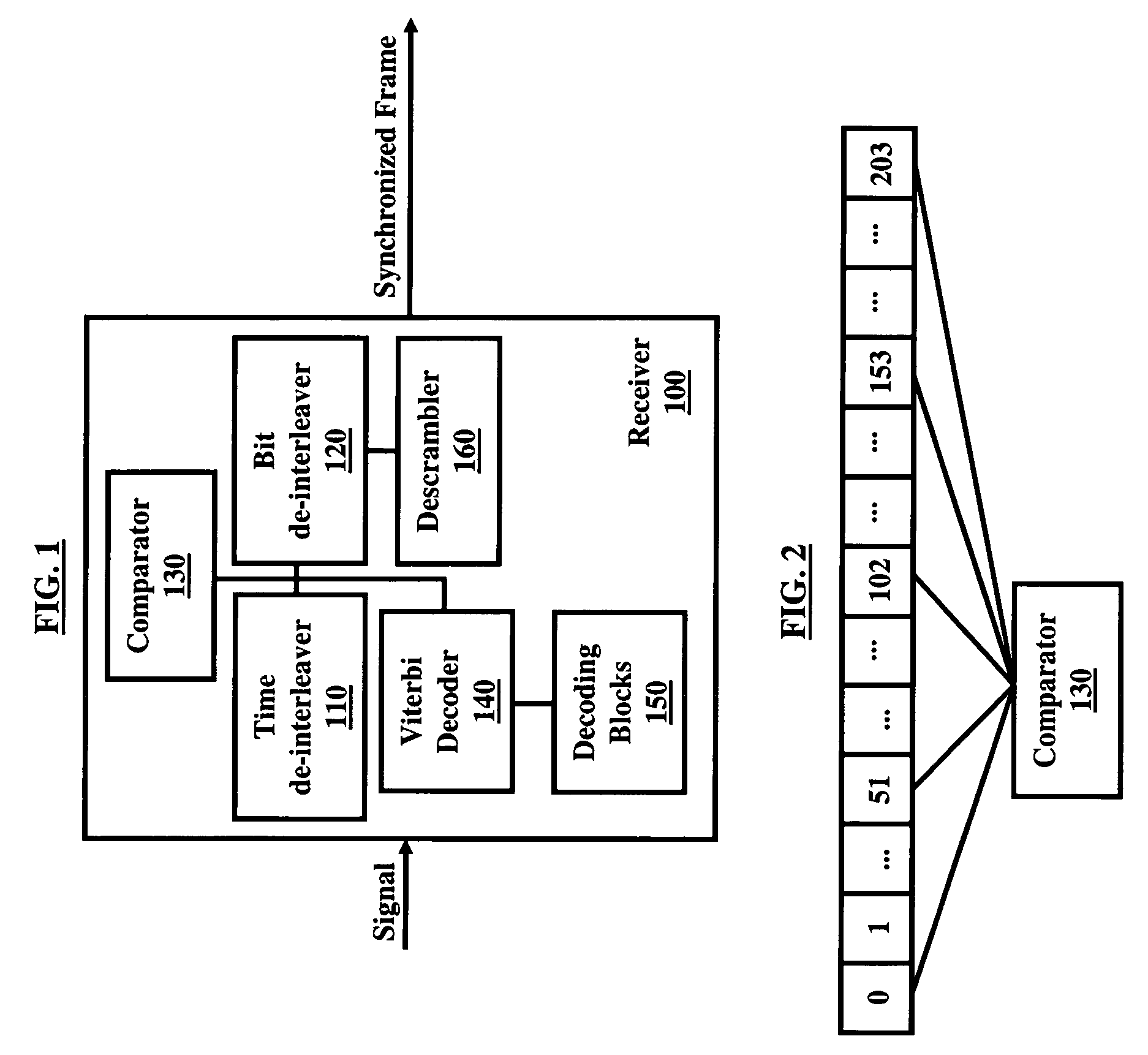
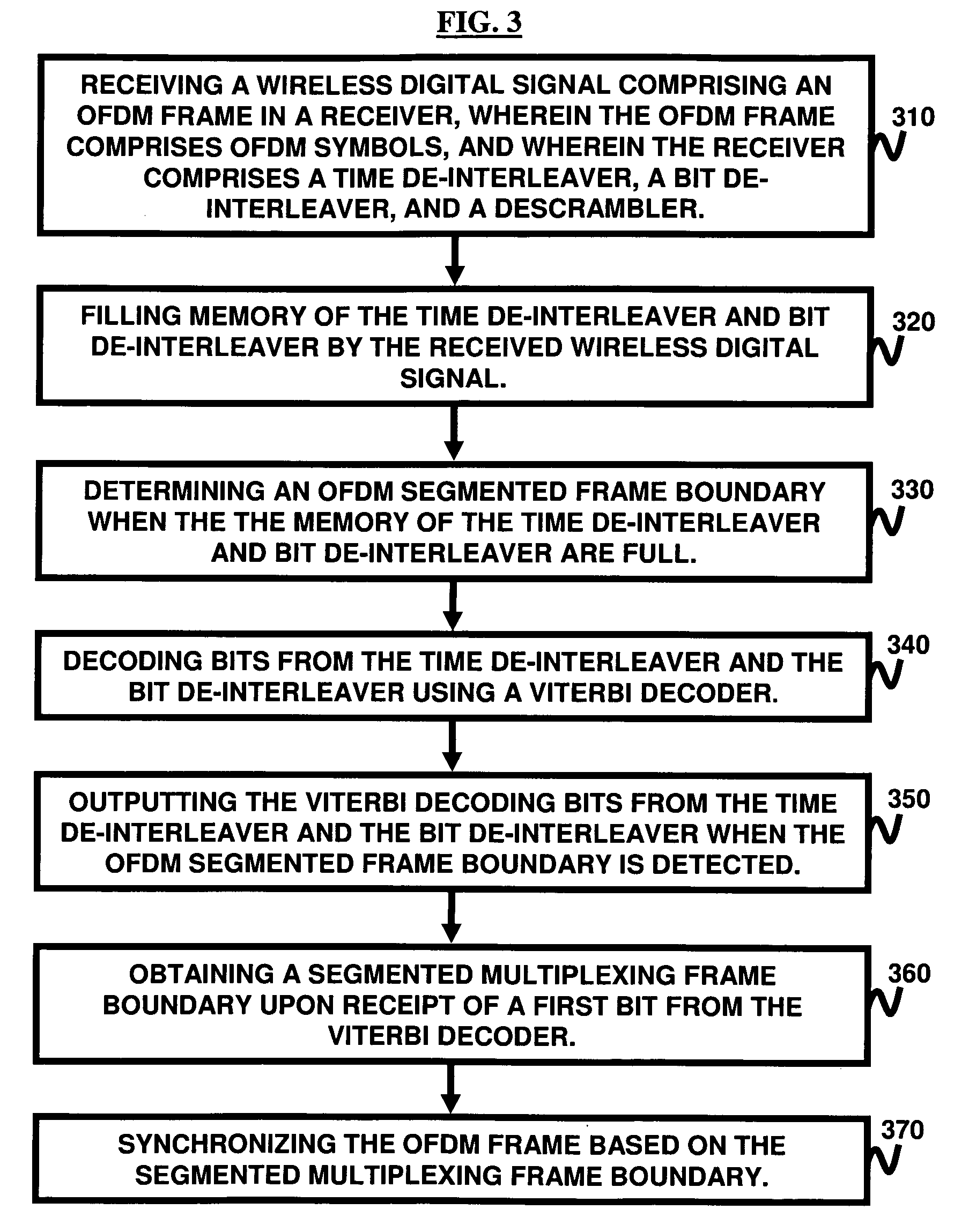
A technique for segmented frame synchronization for Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial (ISDB-T) and Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial Sound Broadcasting (ISDB-TSB) systems, wherein the method comprises receiving a wireless digital signal comprising an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) frame, further comprising ODFM symbols, in a receiver and wherein the receiver comprises a time de-interleaver, a bit de-interleaver, and a descrambler; filling memory of time de-interleaver and bit de-interleaver by the received wireless digital signal; determining an OFDM segmented frame boundary when memory of the time de-interleaver and bit de-interleaver are full; decoding bits from time de-interleaver and bit de-interleaver using a Viterbi decoder; outputting the Viterbi decoding bits from time de-interleaver and bit de-interleaver when the OFDM segmented frame boundary is detected; obtaining a segmented multiplexing frame boundary upon receipt of the first bit from the Viterbi decoder; and synchronizing the OFDM frame based on the segmented multiplexing frame boundary.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
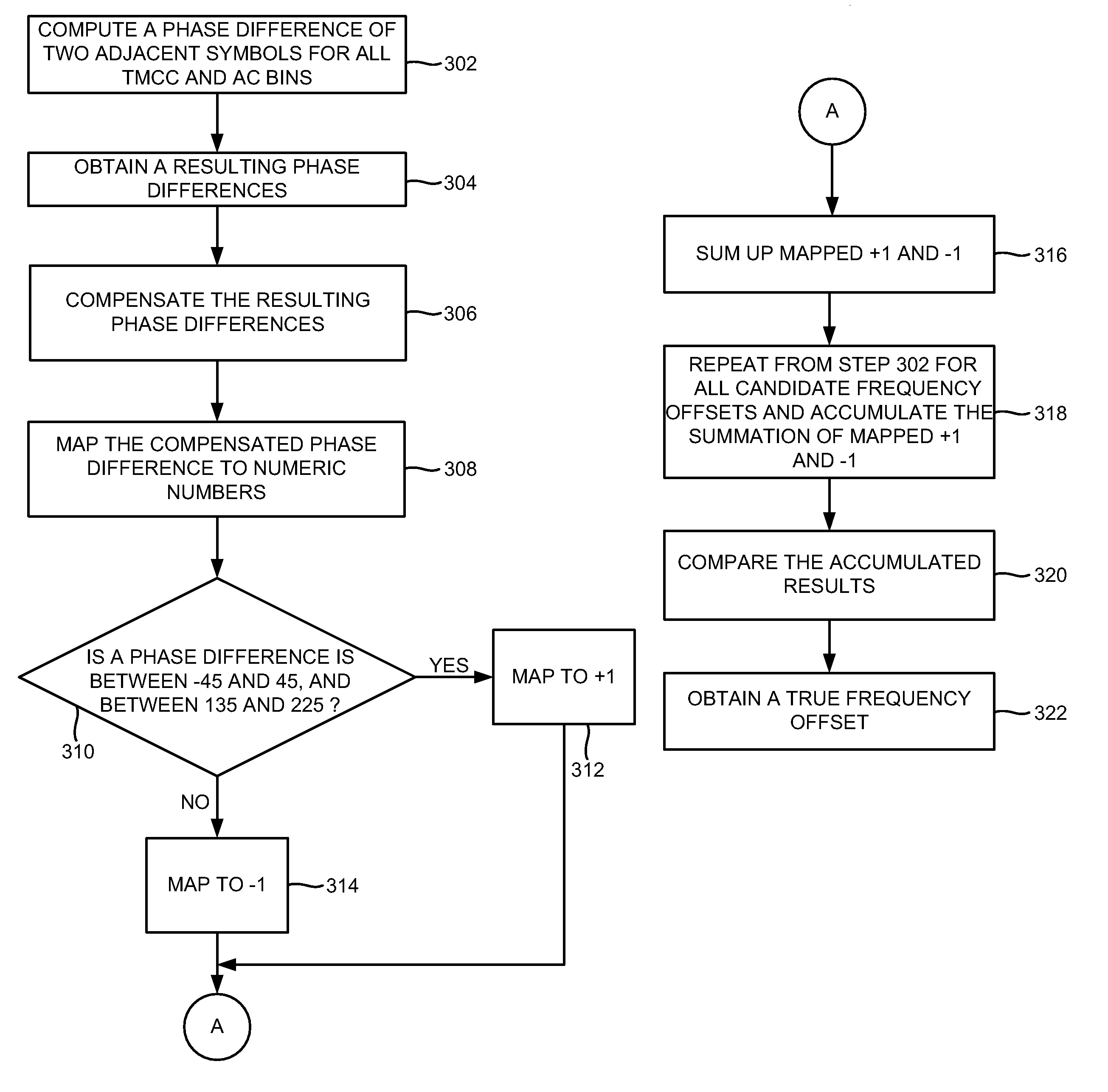
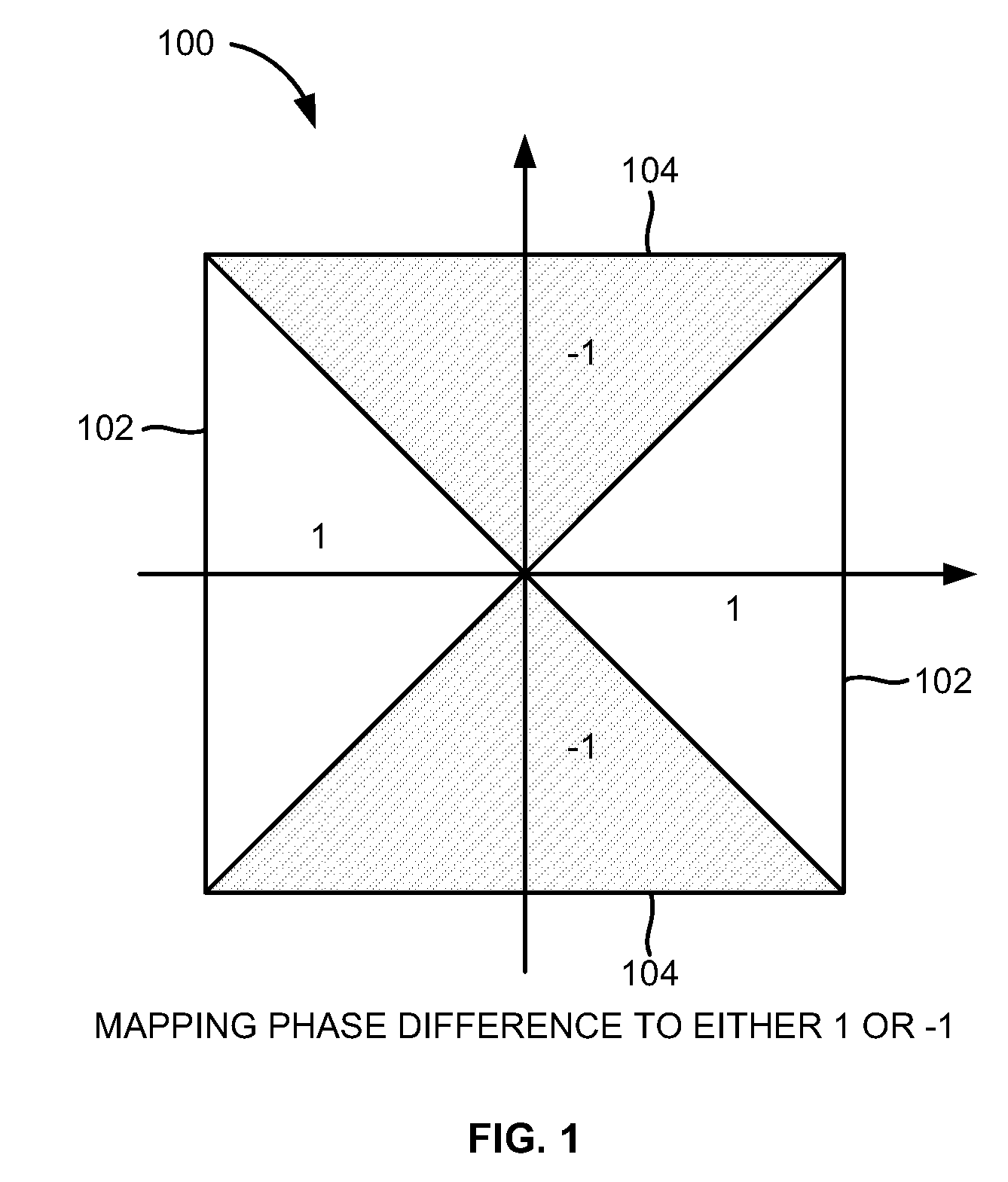
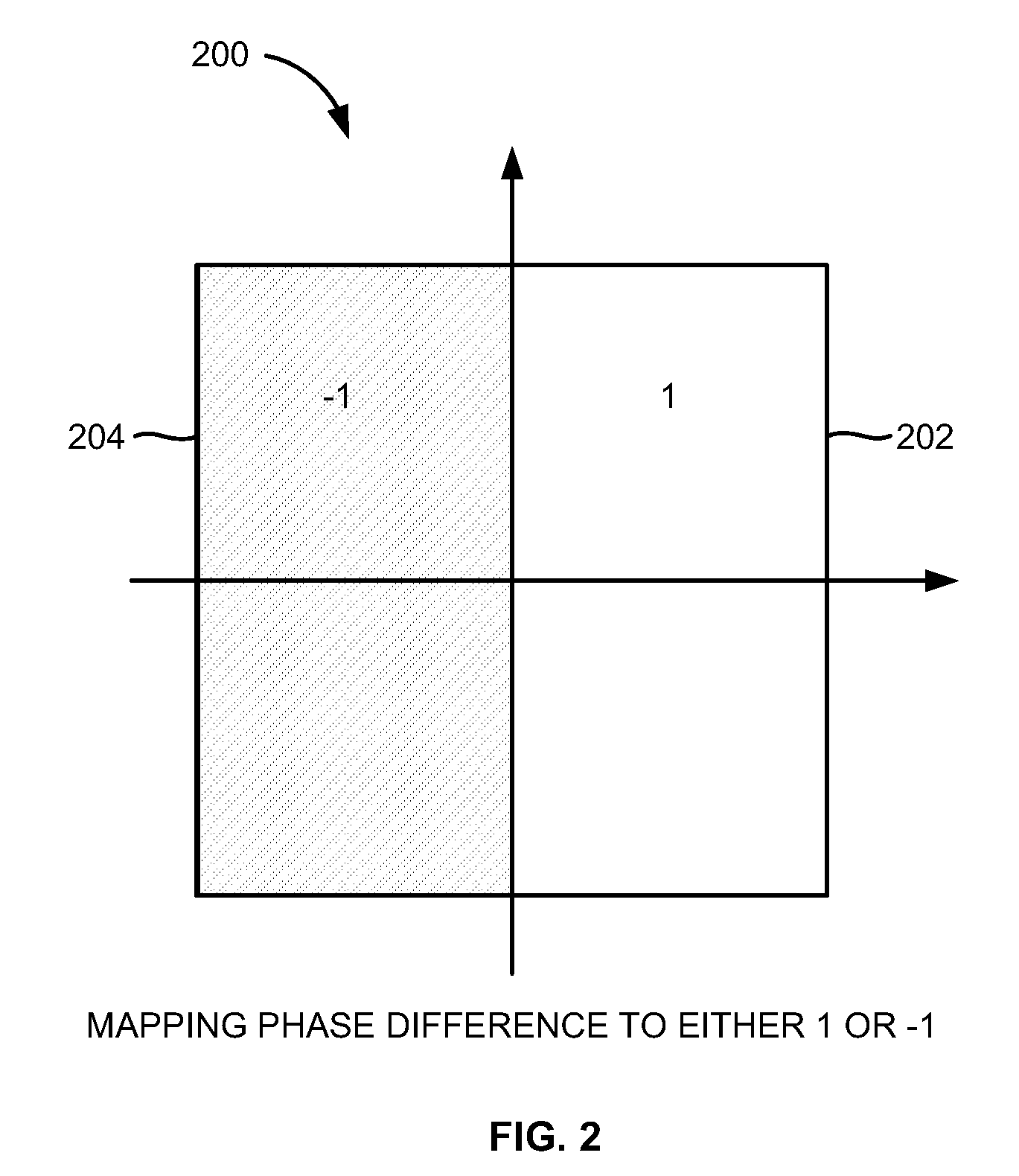
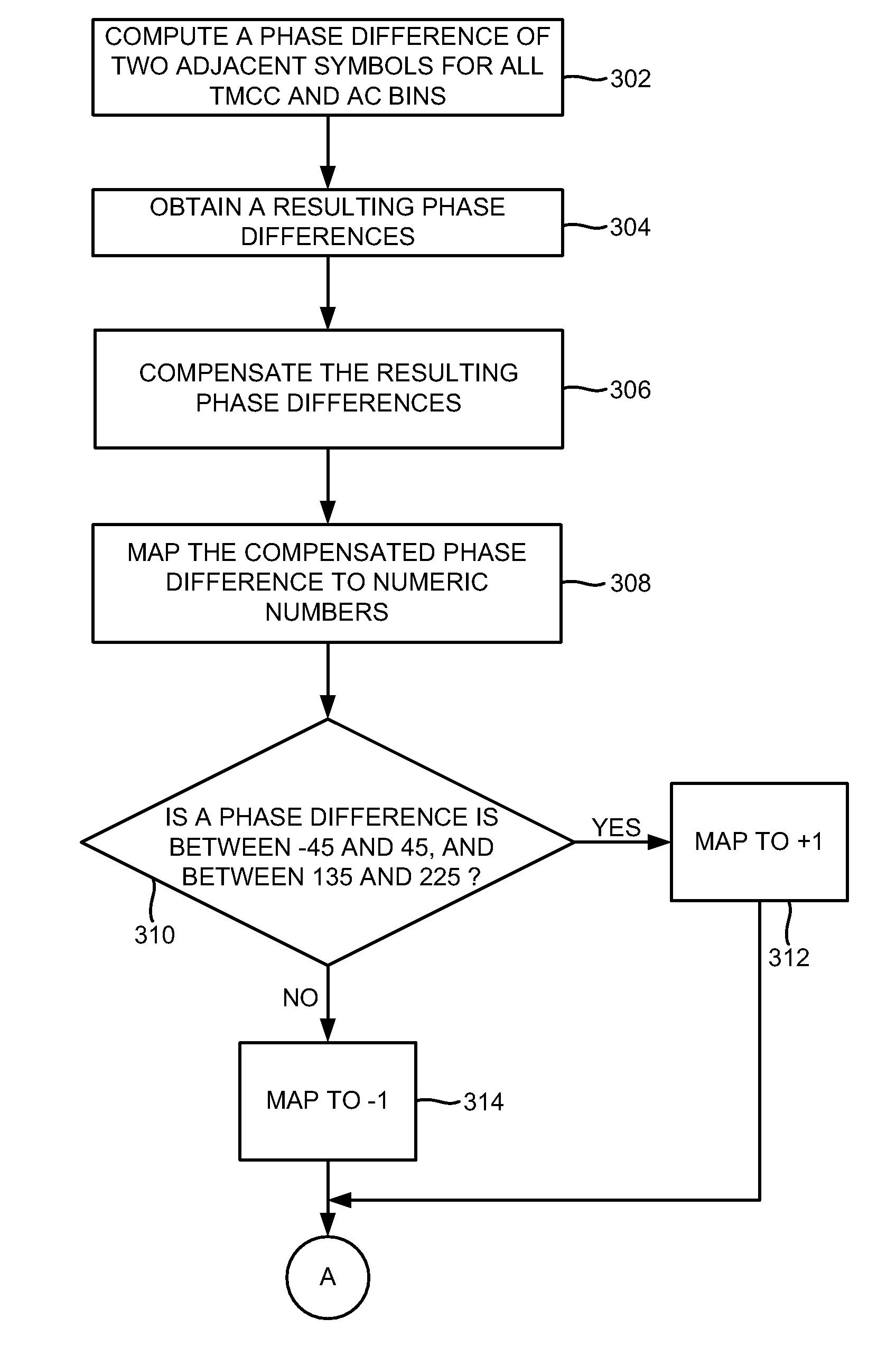
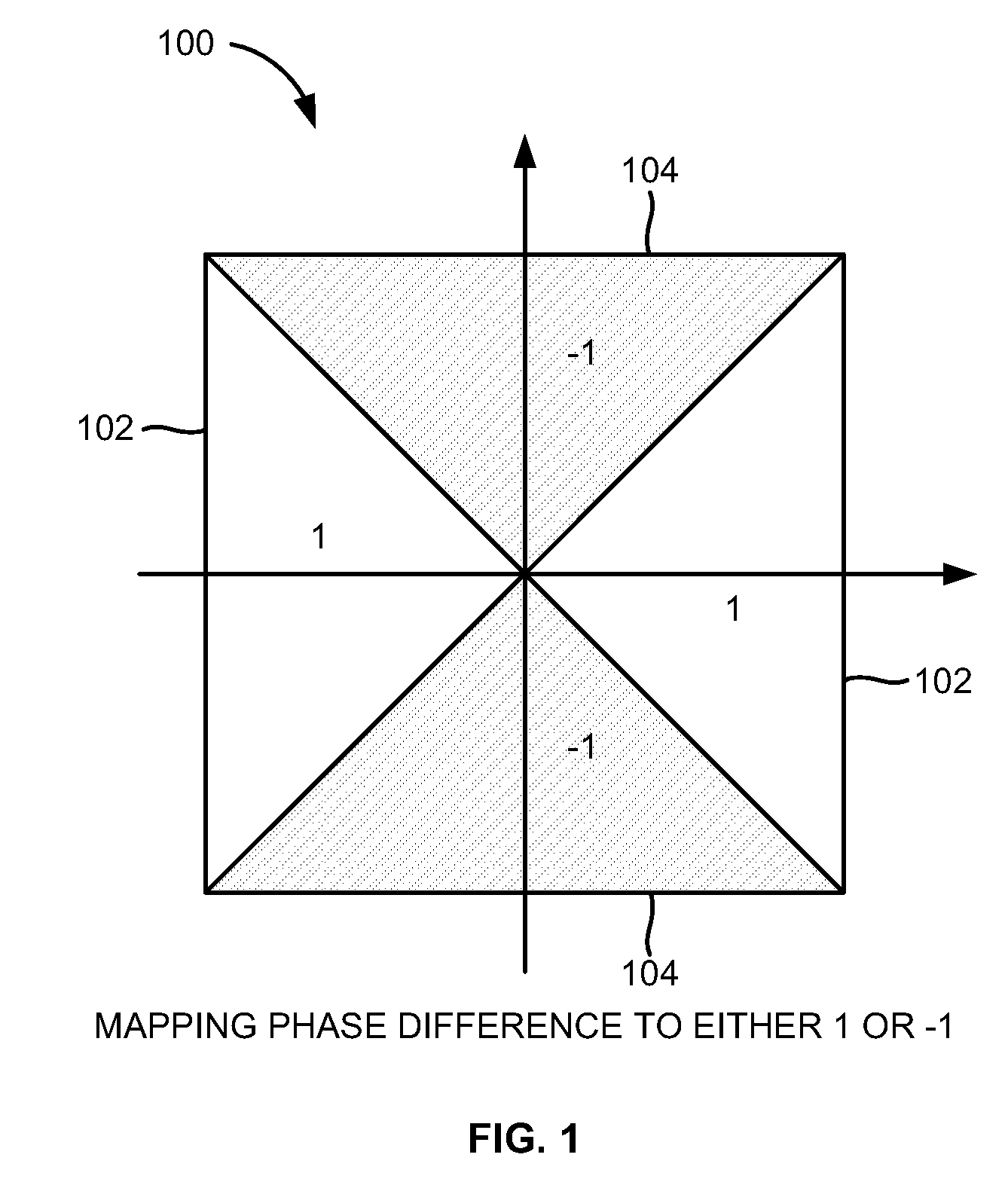
Coarse frequency offset estimation in ISDB receivers
InactiveUS8064553B2Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationMultiplexingFast Fourier transform
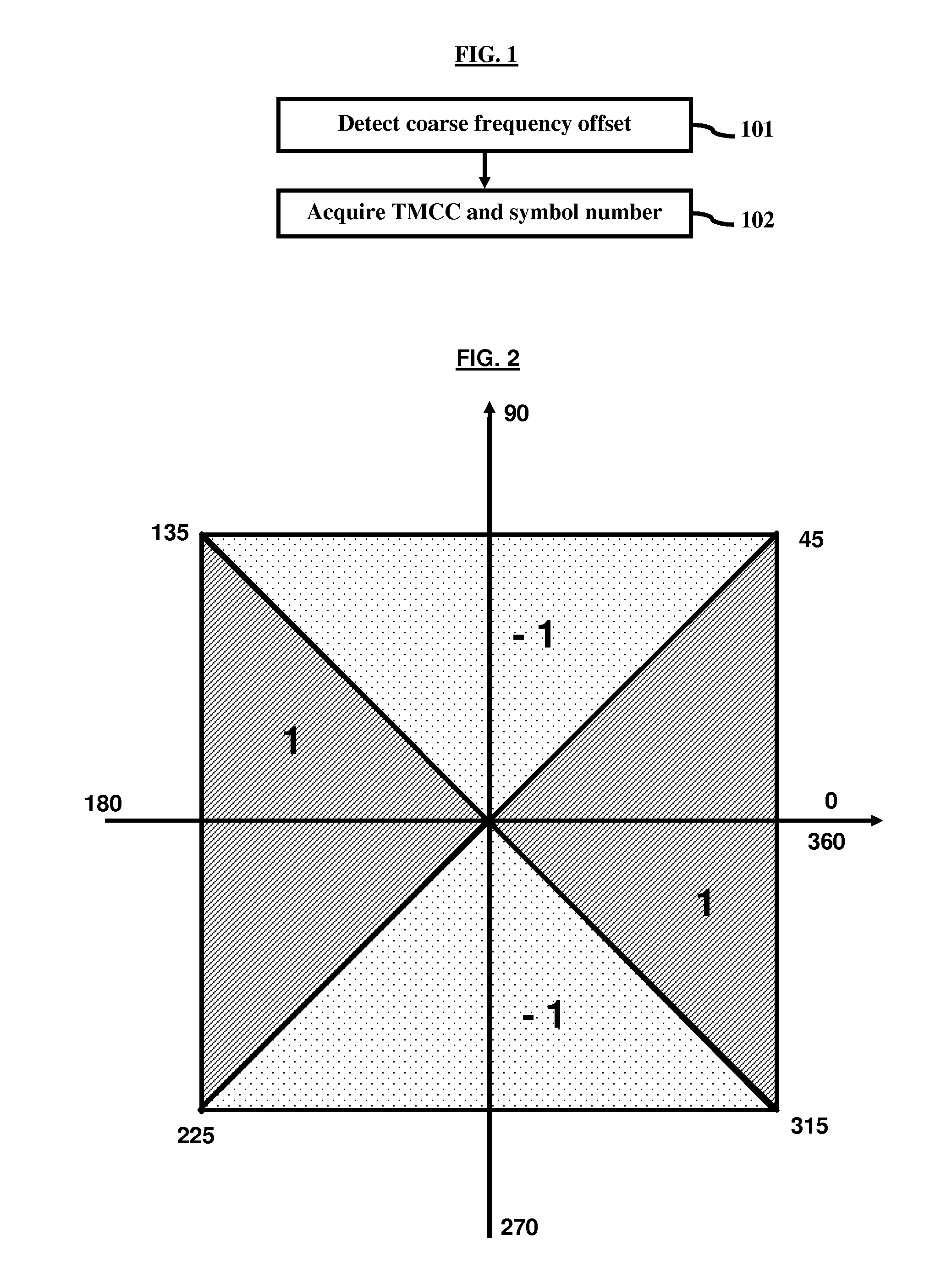
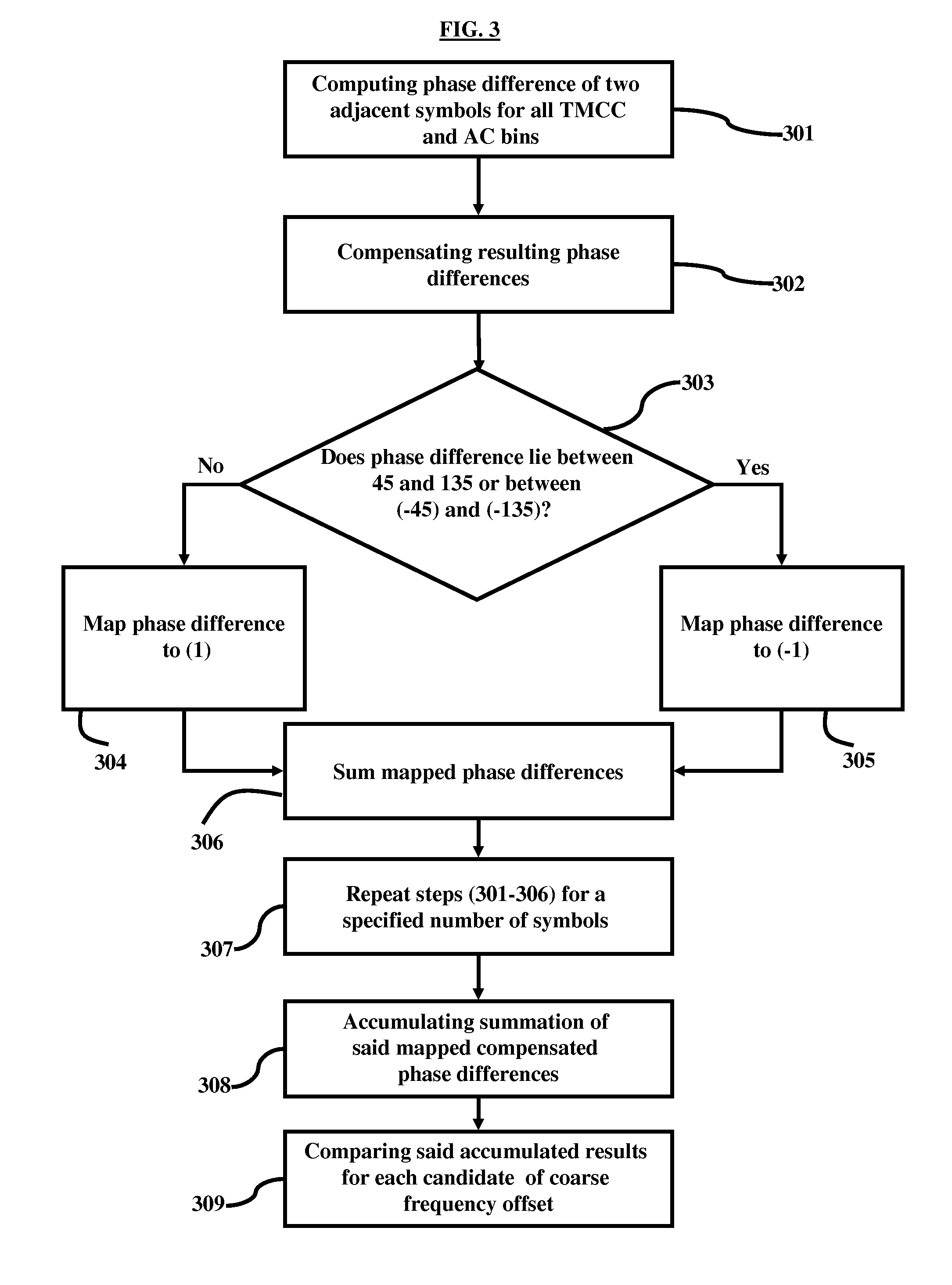
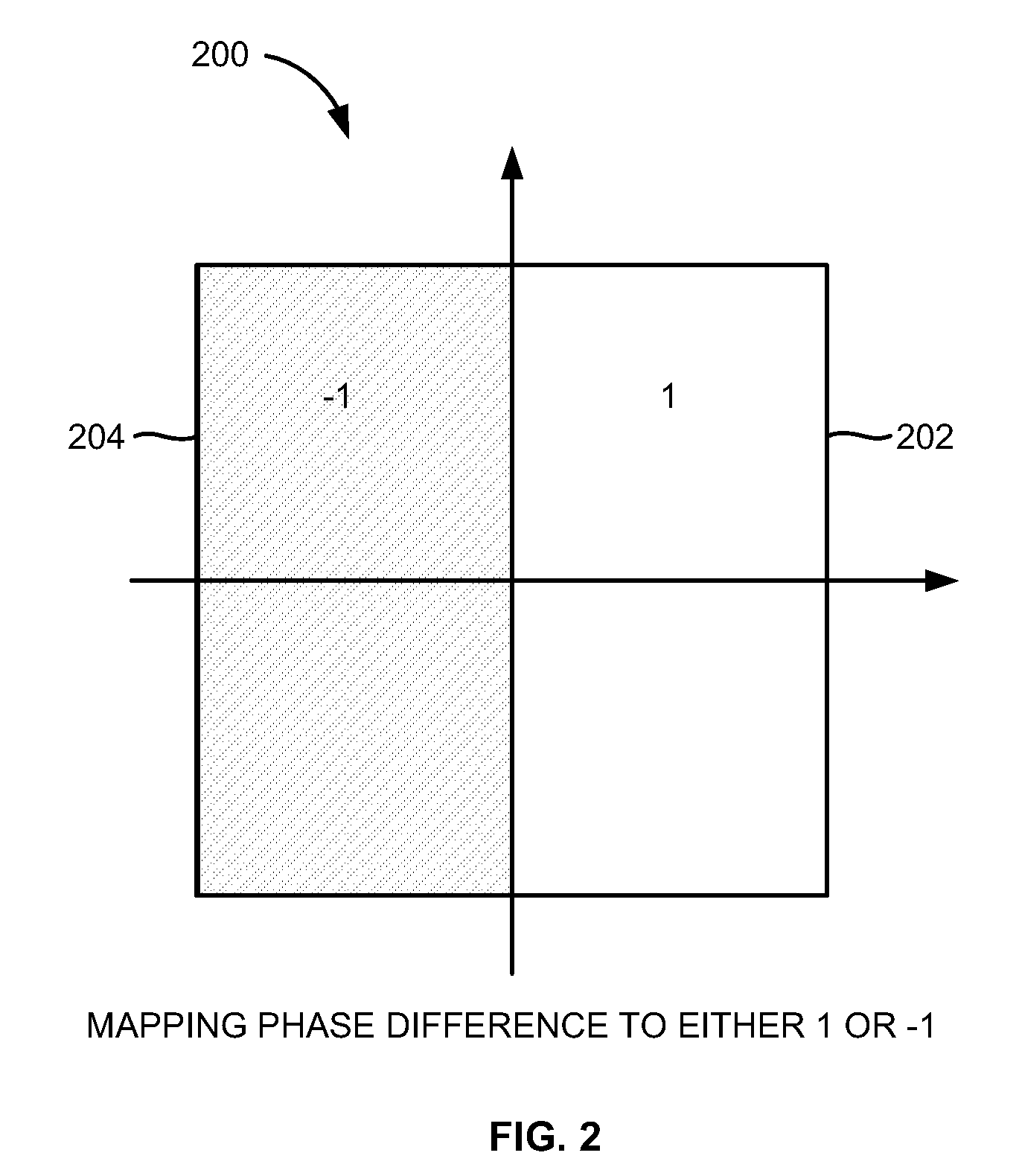
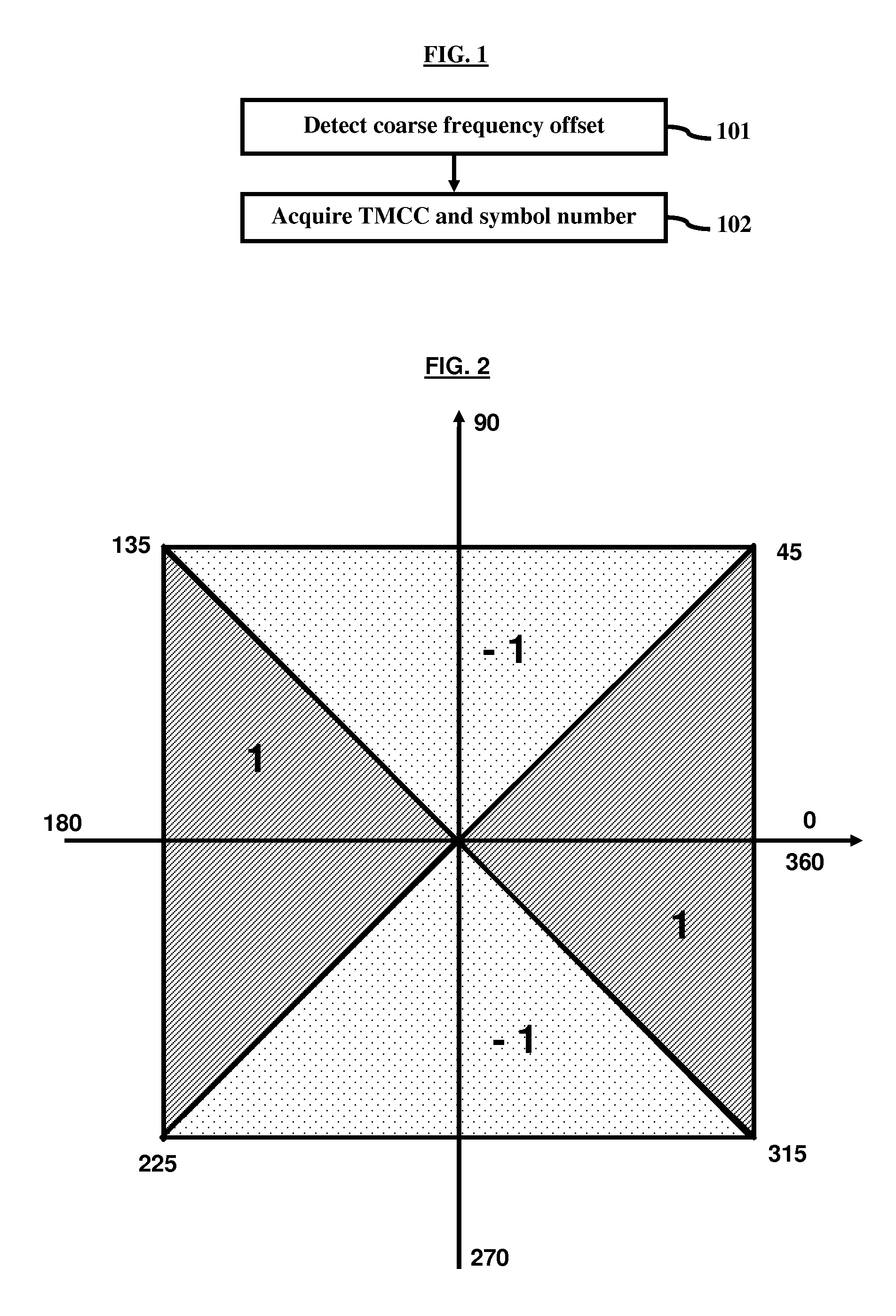
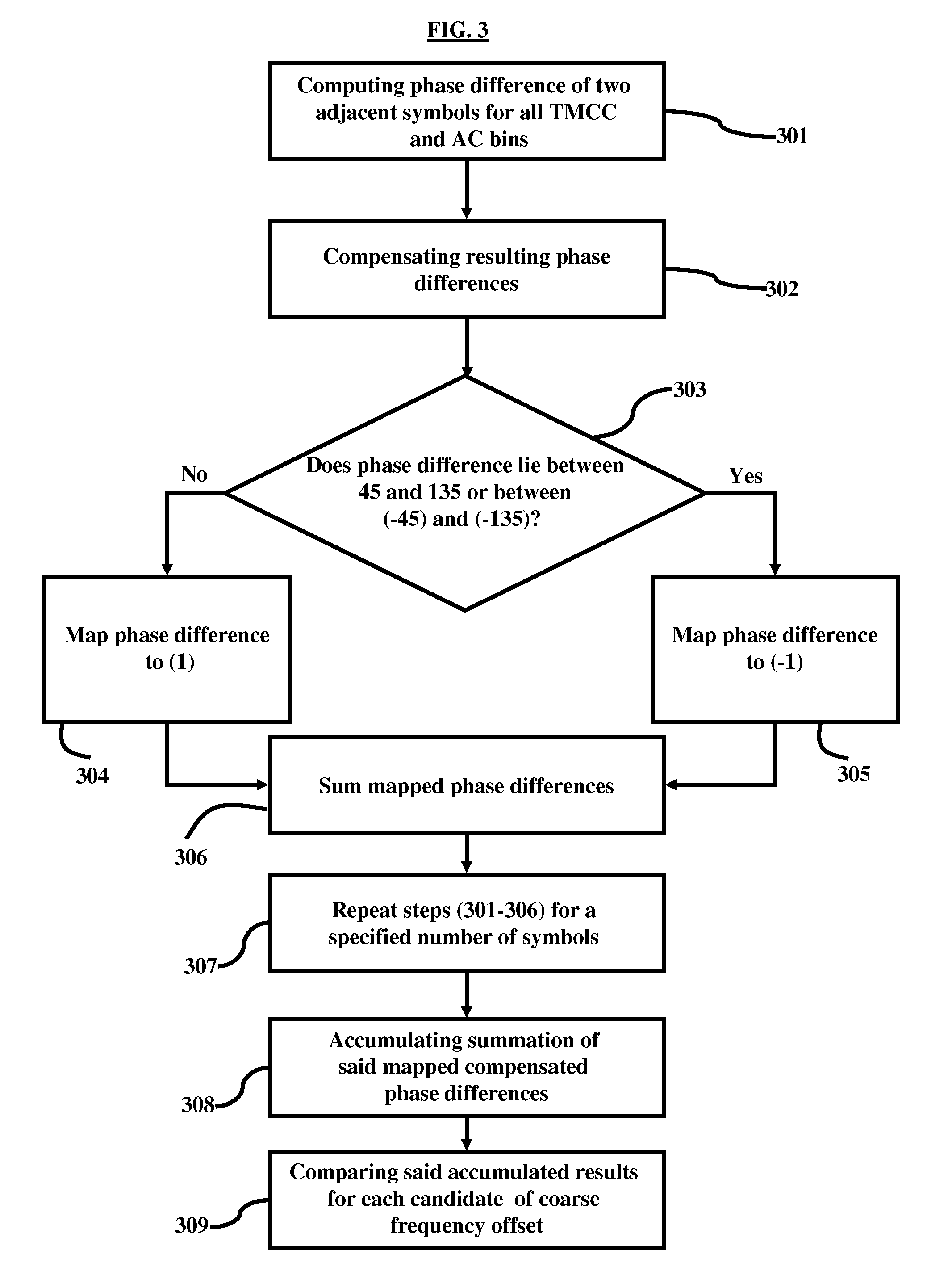
A method of estimating a coarse frequency offset in a receiver includes providing at least one candidate frequency offset in Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbols having transmission and multiplexing configuration control (TMCC) bins and auxiliary channel (AC) bins, modulating the TMCC bins and AC bins using differential binary phase shift keying (DBPSK) modulation, estimating a phase difference between a first symbol and a second symbol for the candidate frequency offset of the TMCC and AC bins to obtain a resulting phase difference, correcting the resulting phase difference based on a difference between the candidate frequency offset and a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) center bin to obtain a corrected phase difference, mapping the corrected phase difference to numeric numbers, and adding the numeric numbers for the candidate frequency offset to obtain a summation result. The numeric numbers correspond to at least one of +1 or −1.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
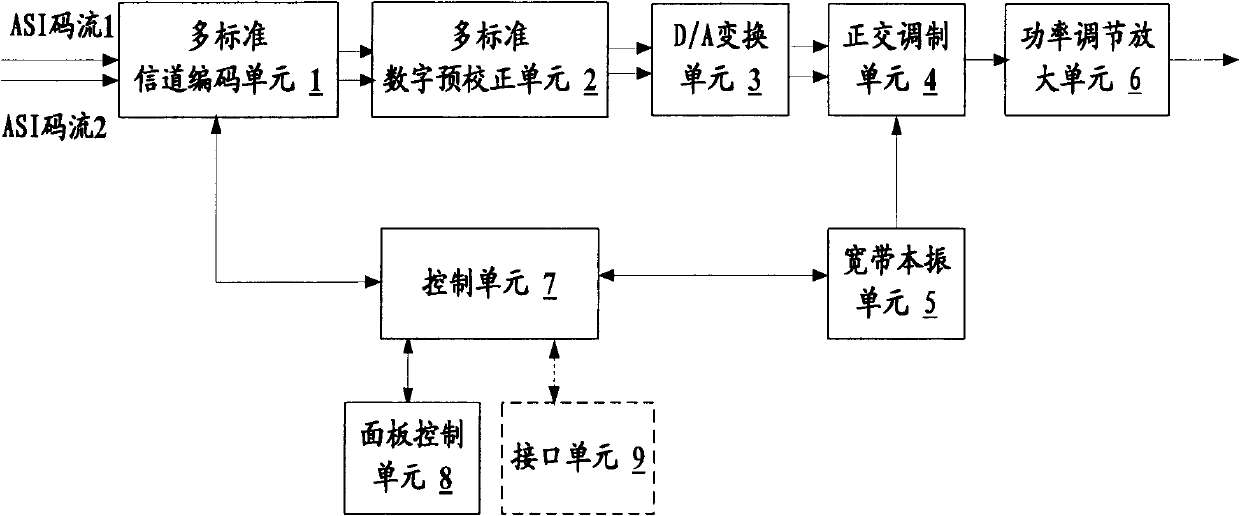
Multimode digital television exciter
ActiveCN102572328AImplementation of digital television standardsEnable mobilityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDigital Video BroadcastingControl unit
Owner:BEIJING BBEF SCI & TECH
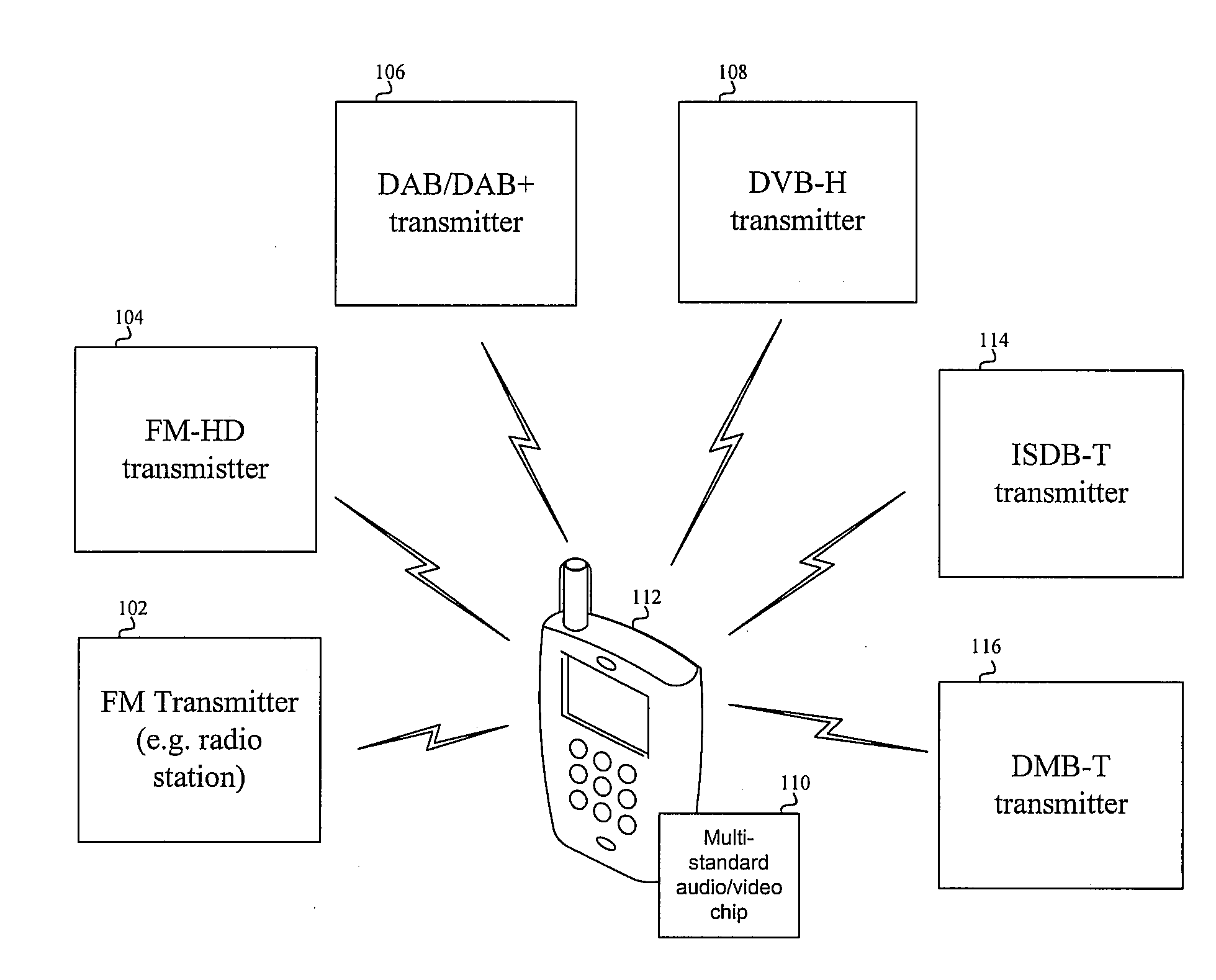
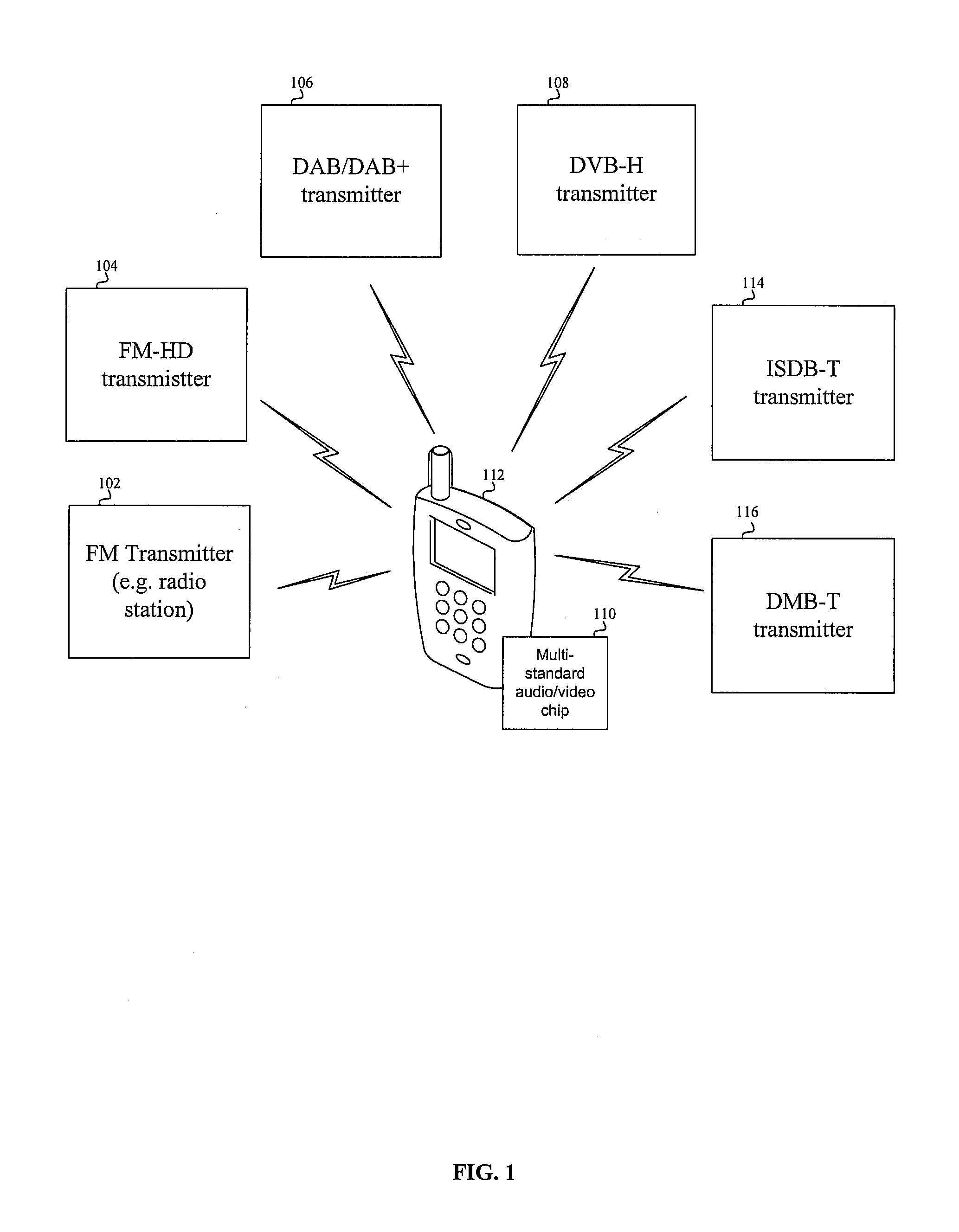
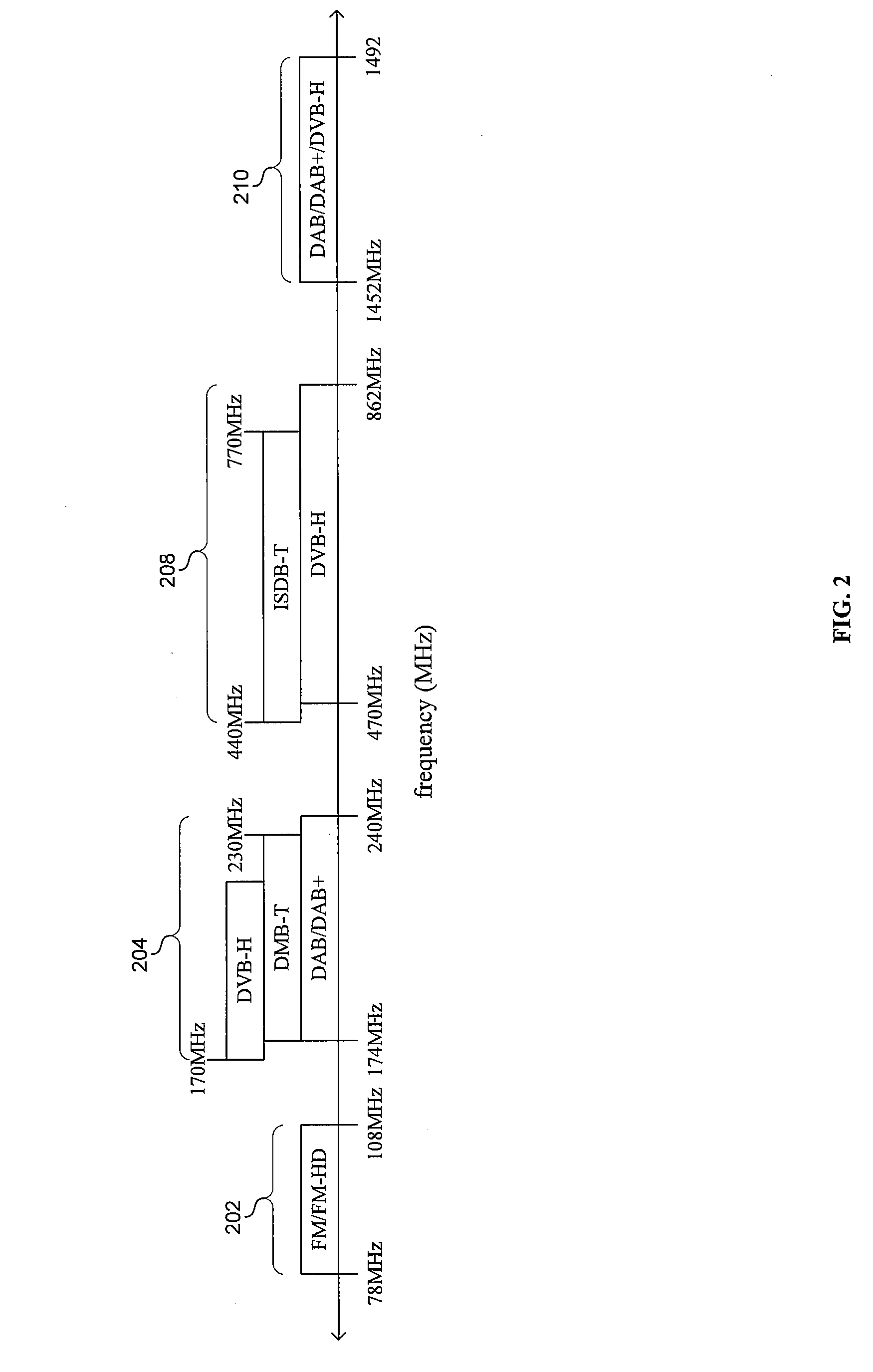
Method and system for an integrated multi-standard audio/video receiver
InactiveUS20090278994A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsInformation typeGeolocation
Aspects of a method and system for an integrated multi-standard audio and / or video receiver are provided. In this regard, a single audio / video receiver chip may be enabled to receive and process signals adhering to plurality of terrestrial digital audio and / or video standards, and the chip may be configurable based on a format of a desired signal. Exemplary standards may comprise FM broadcast, FM HD, DAB, DAB+, DVB-H, ISDB-T, and DMB-T. One or more RF processing paths and / or one or more baseband processing paths may be configured based on, for example, a frequency of a received signal, a geographical location in which the chip is operated, a modulation scheme of a received signal, and / or the type of information being received. The chip may be configured via software, firmware, and / or manually.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
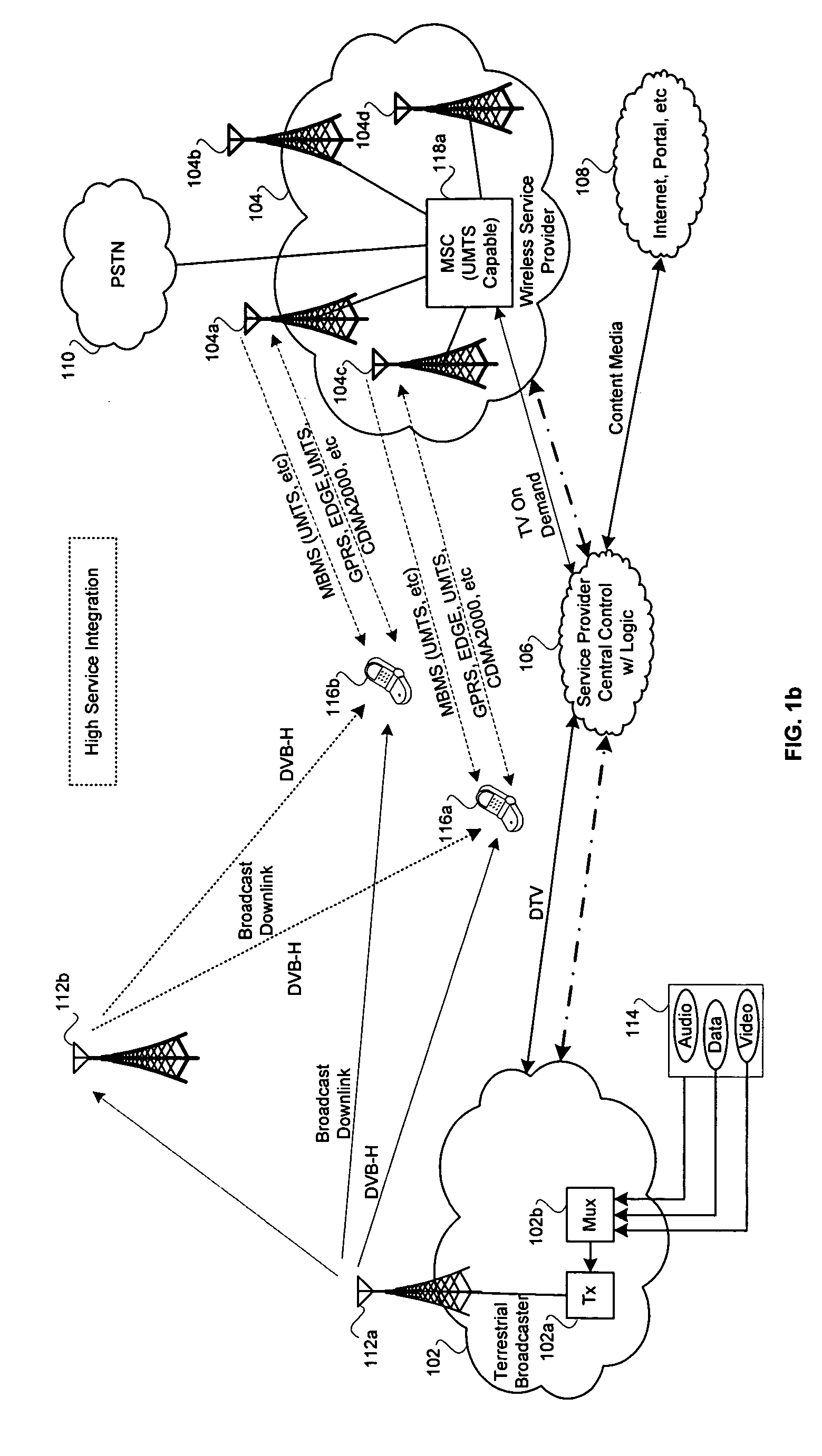
Navigation Services Based on Position Location Using Broadcast Digital Television Signals
InactiveUS20100292920A1Increase coverageSimple and inexpensive implementationPulse modulation television signal transmissionIndoor gamesDVB-TDigital broadcasting
A service depends on the location of a device. The device location is determined using DTV signals. More specifically, the device location is determined based on pseudo-ranges between the device and a plurality of digital television (DTV) transmitters and the pseudo-ranges are determined based on broadcast DTV signals received by the device from the DTV transmitters. Examples of DTV signals include the American Television Standards Committee (ATSC) signals, the European Telecommunications Standards Institute Digital Video Broadcasting-Terrestrial (DVB-T) signals and the Japanese Integrated Service Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial (ISDB-T) signals.
Owner:TRUE POSITION INC
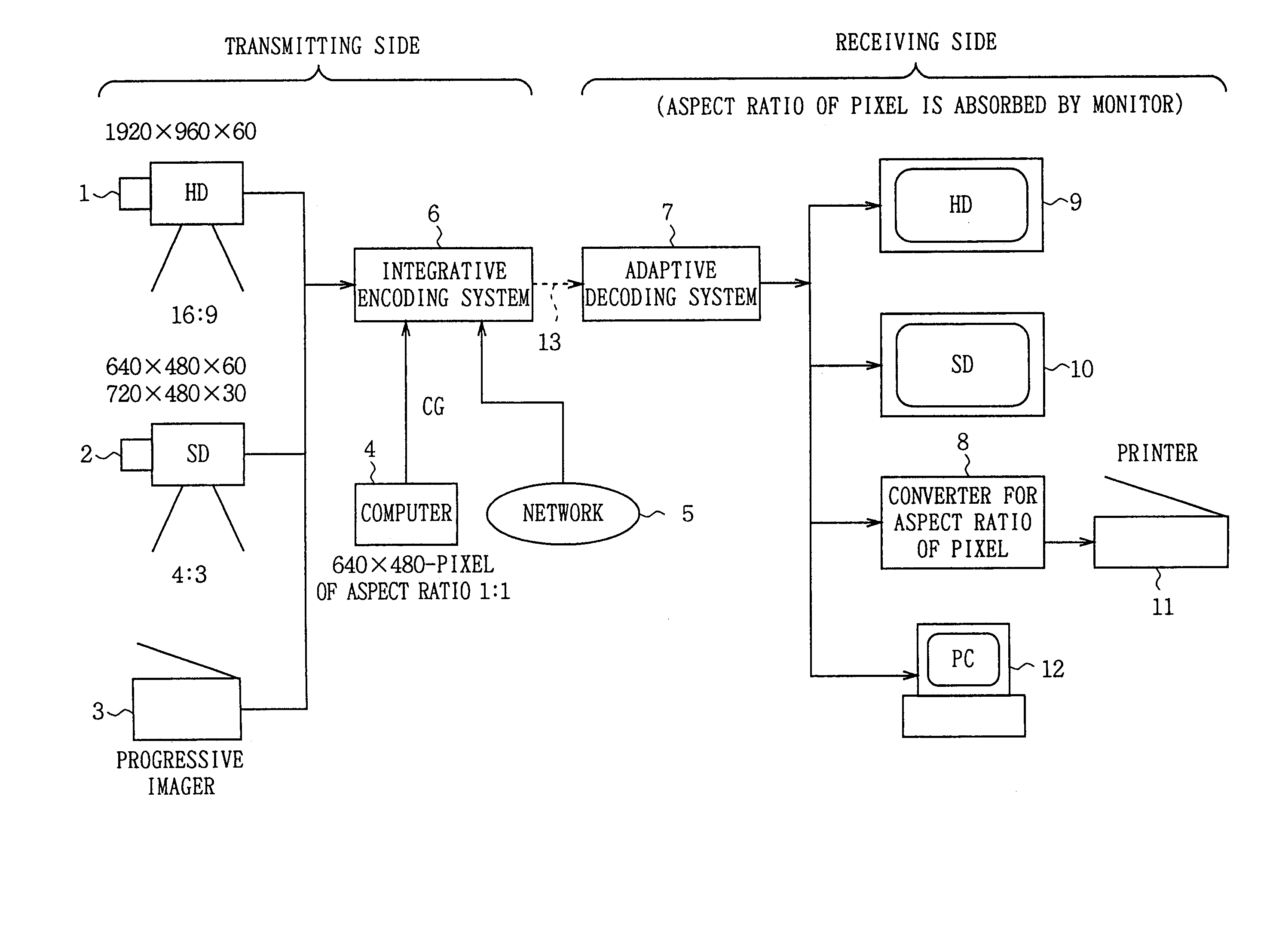
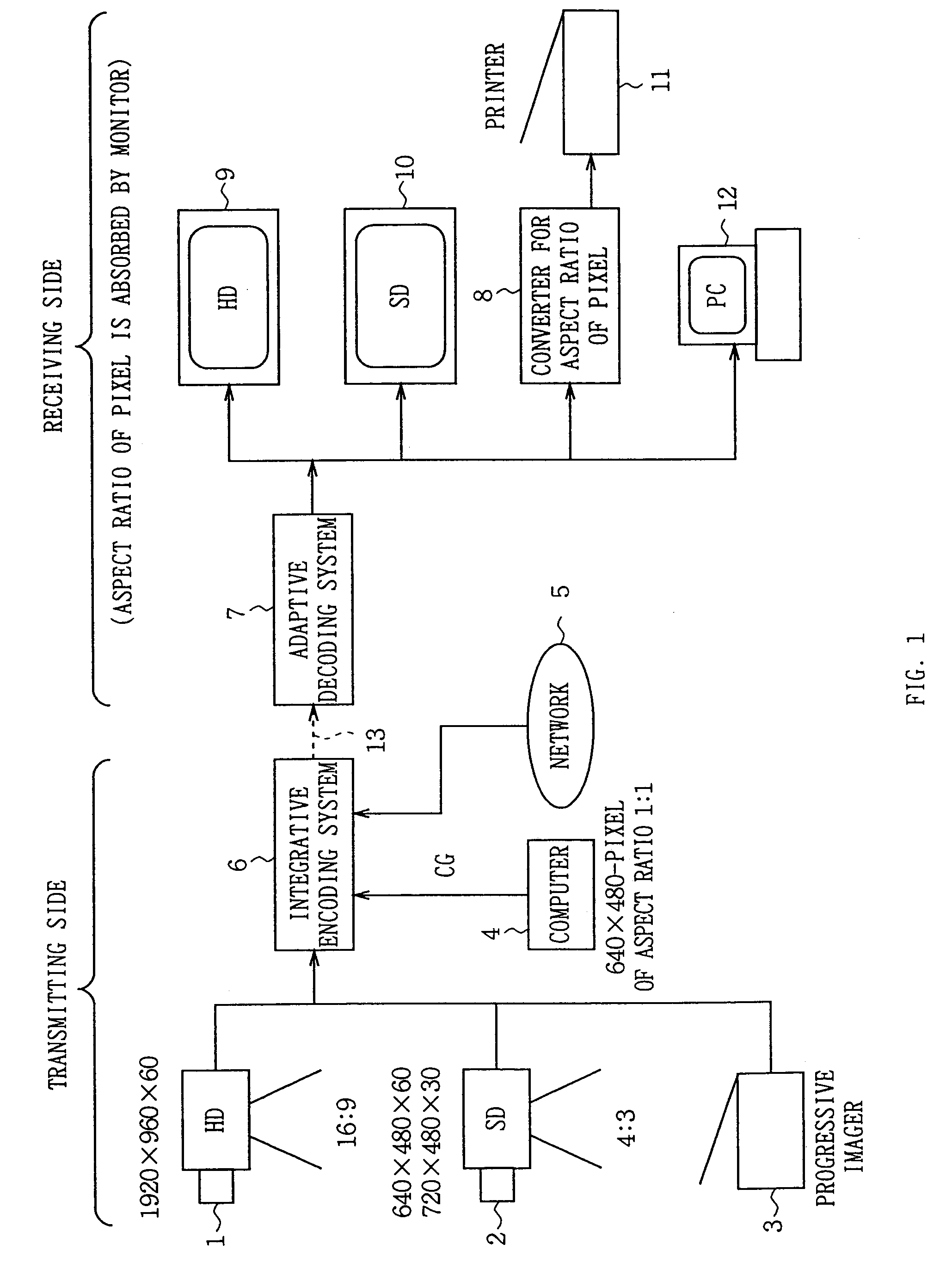
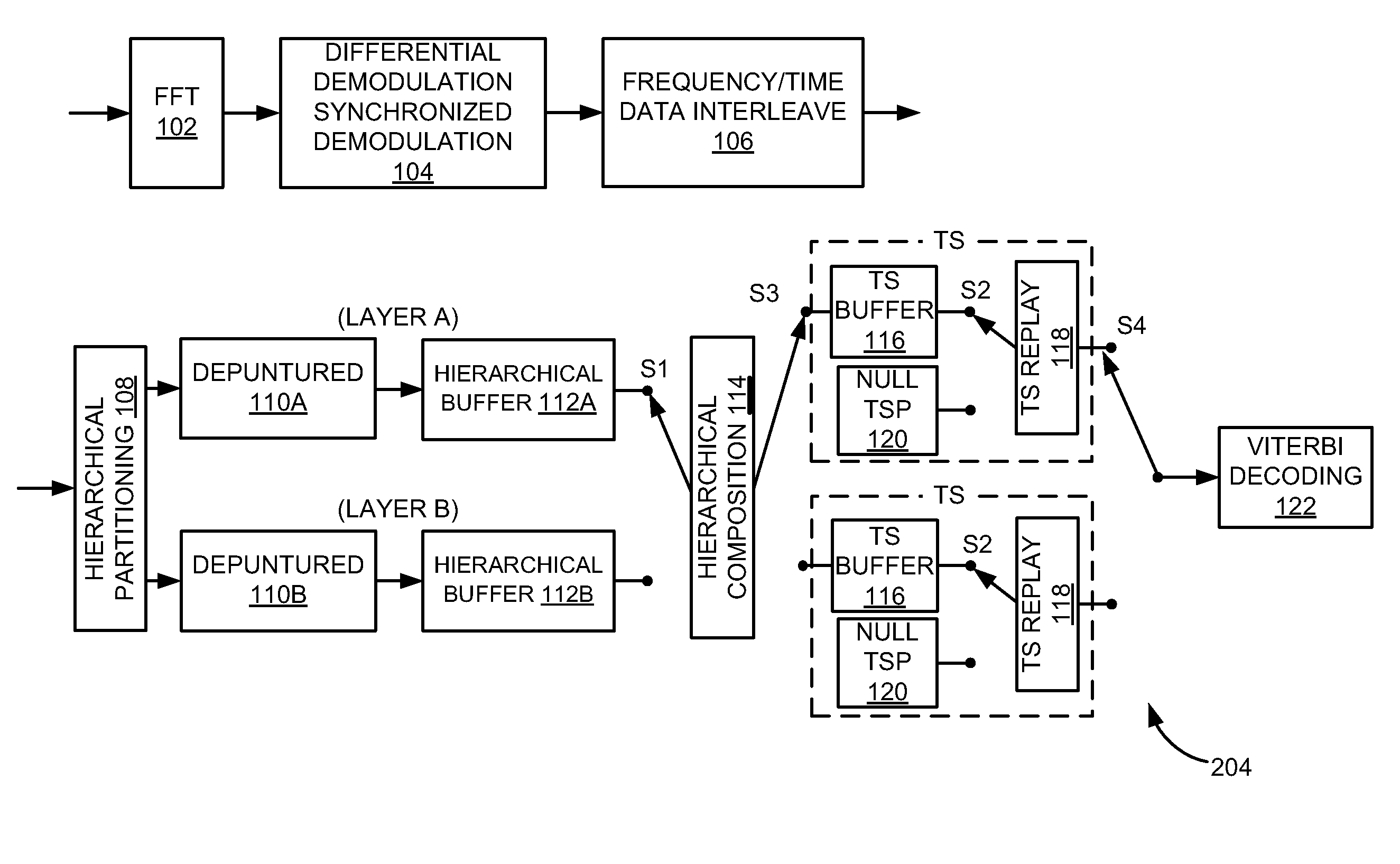
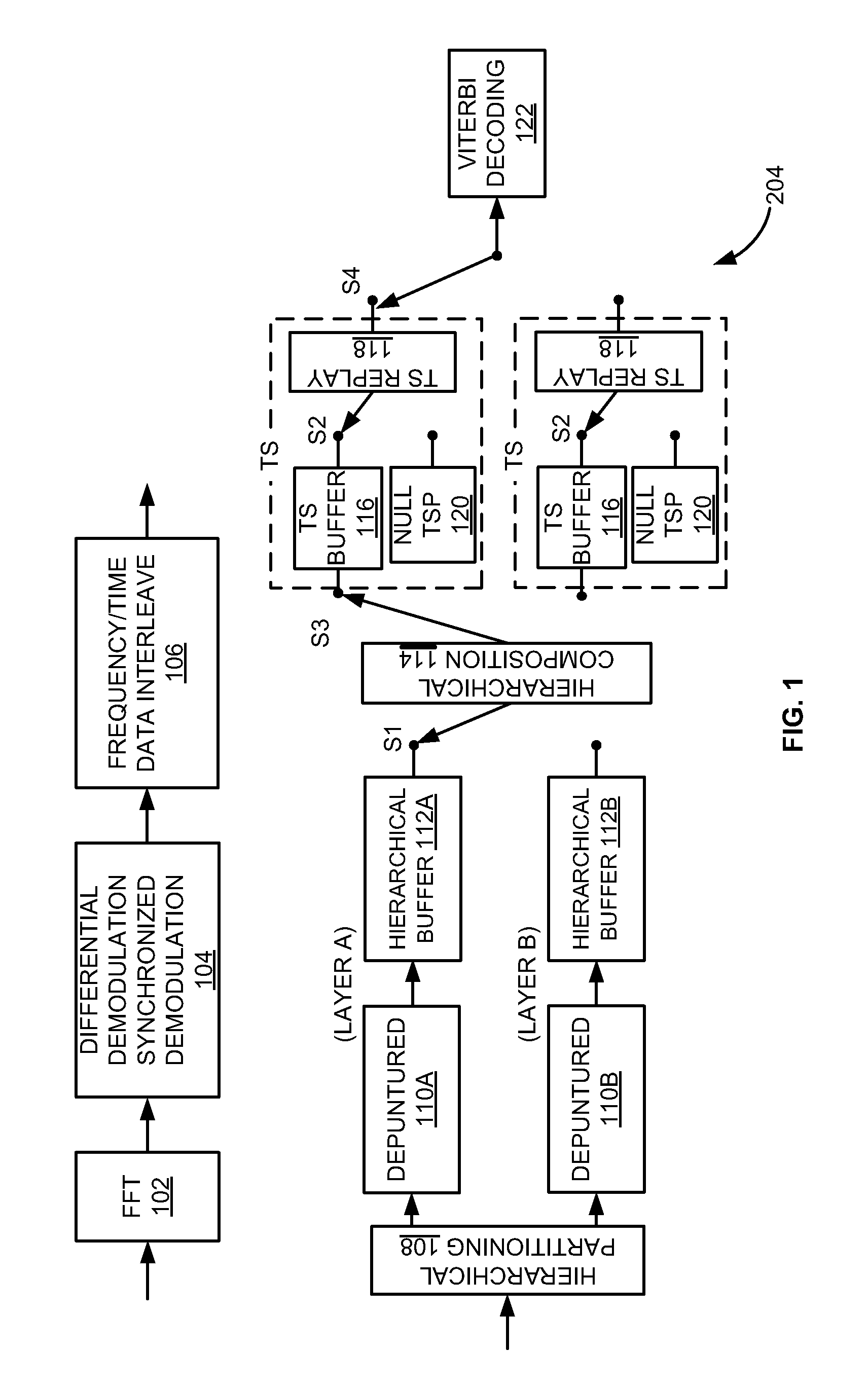
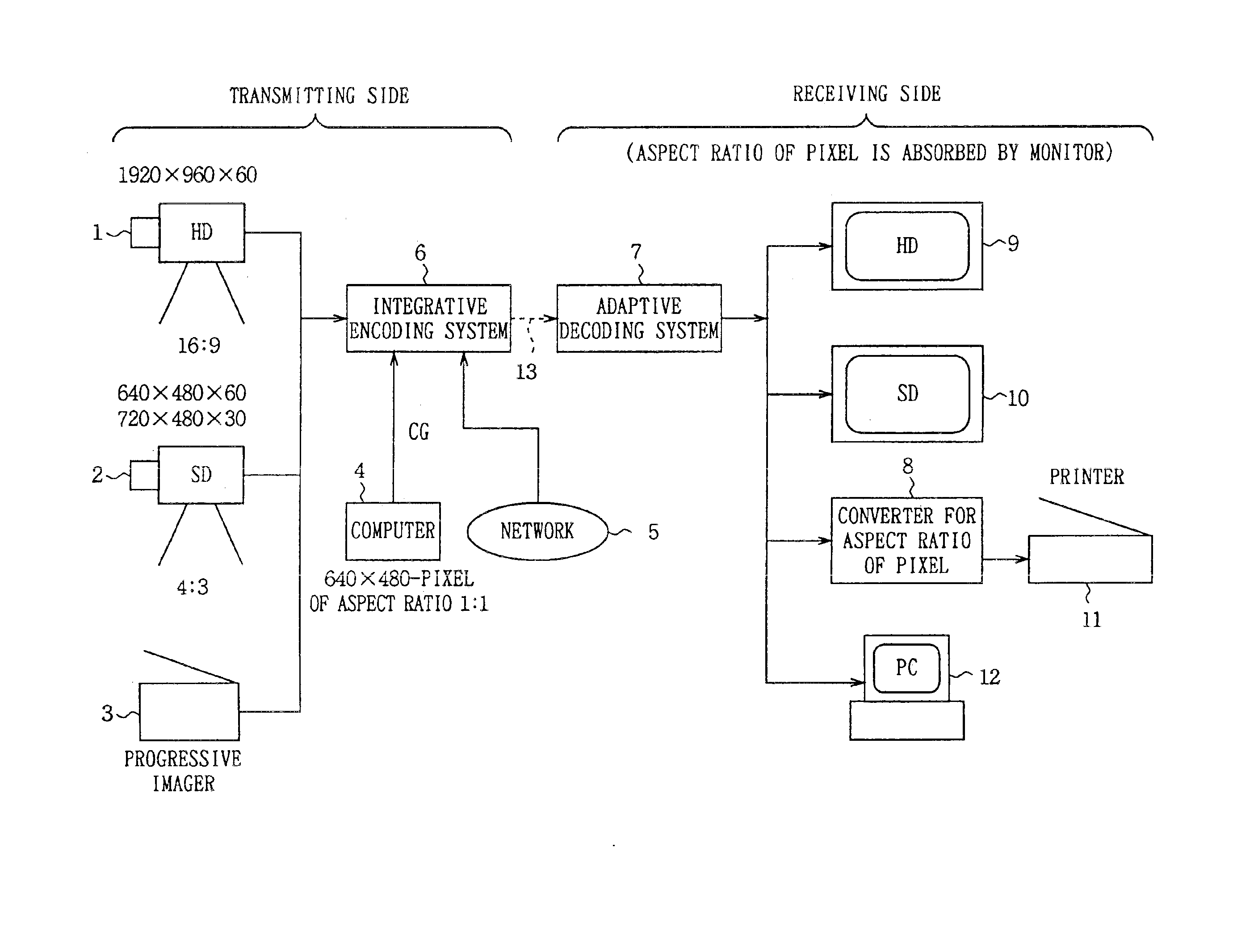
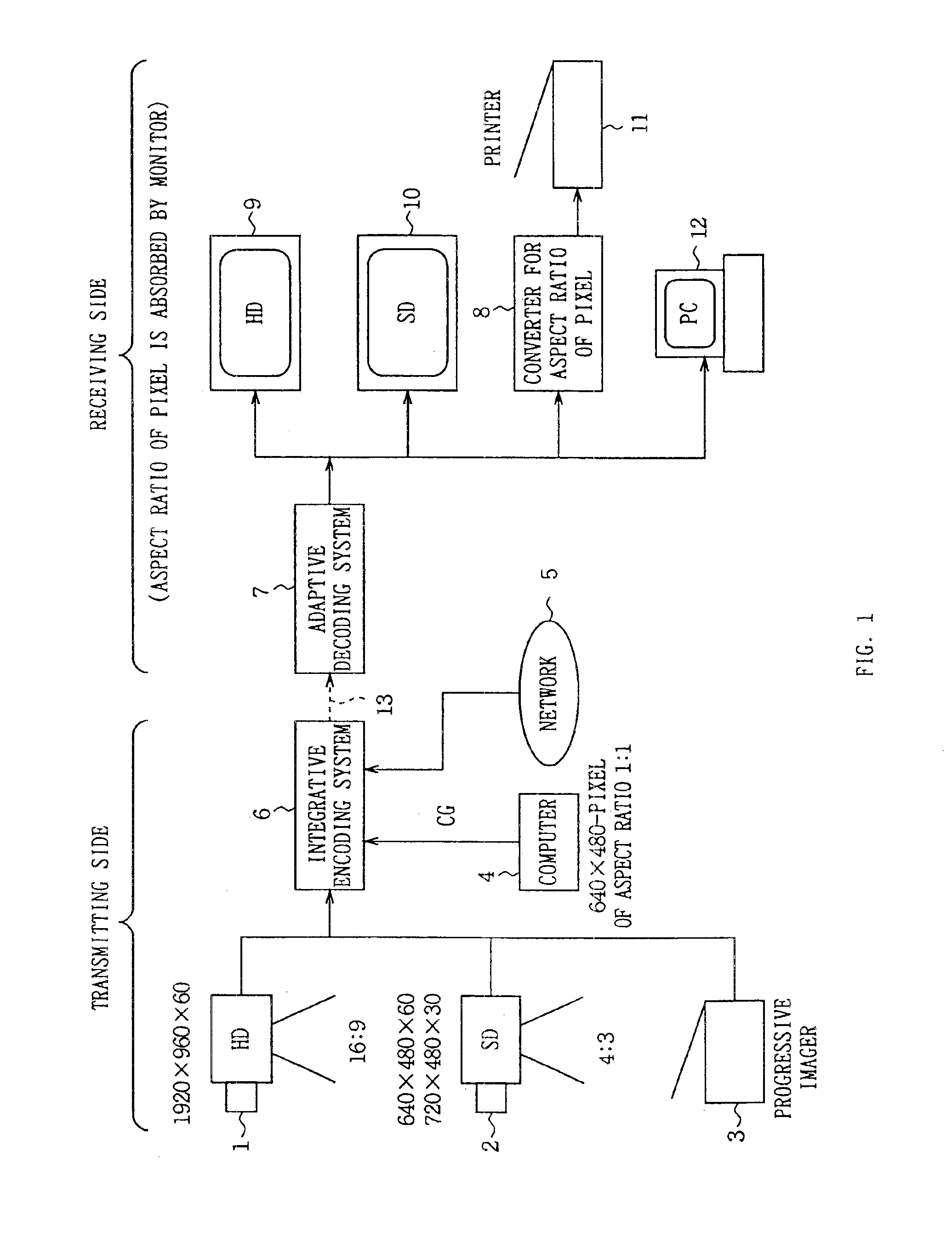
Integrative encoding system and adaptive decoding system
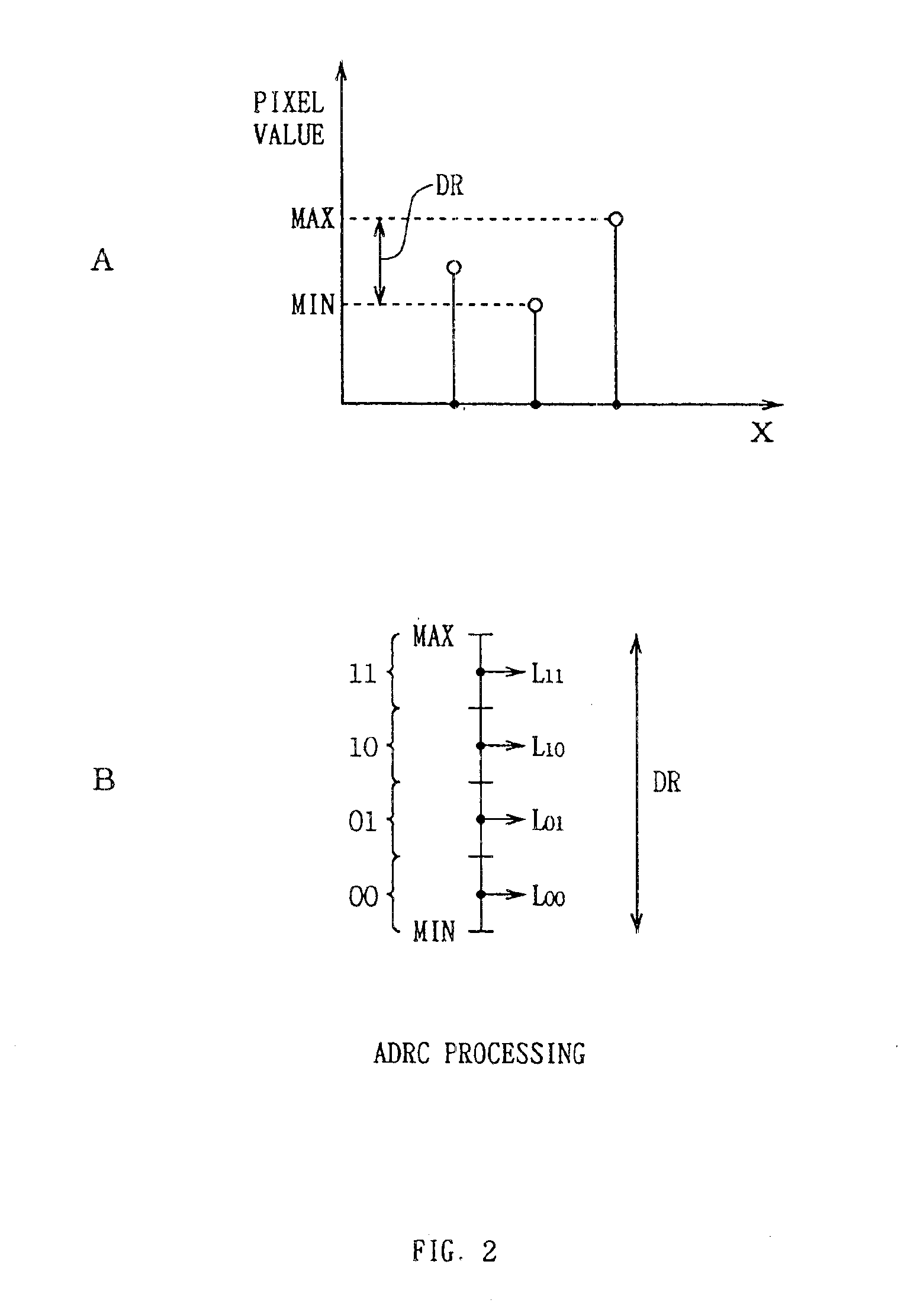
An integrative encoding system for encoding and transmitting a plurality of video signals having different resolutions that correspond to a plurality of display units. The integrative encoding system has a compression processor, an editing processor, and an integrated services digital broadcasting (ISDB) transmitter. In a first embodiment, the compression processor performs adaptive dynamic range coding (ADRC) to compress each of said plurality of video signals on a block basis by reducing the dynamic range. In another embodiment,the compression processor performs hierarchical encoding on the plurality of video signals by selectively replacing pixels of a higher resolution level with pixels from a lower resolution level calculated by combining pixels from said higher resolution level; thereby encoding a hierarchy of resolution levels within the plurality of video signals without increasing the amount of data. An adaptive decoding system receives and decodes the transmitted plurality of video signals for display by the plurality of display units.
Owner:SONY CORP
Low complexity high performance tmcc acquisition in isdb-t and isdb-tsb receivers
ActiveUS20090232264A1Broadcast information characterisationSpecific information broadcast systemsTelecommunicationsFrequency offset
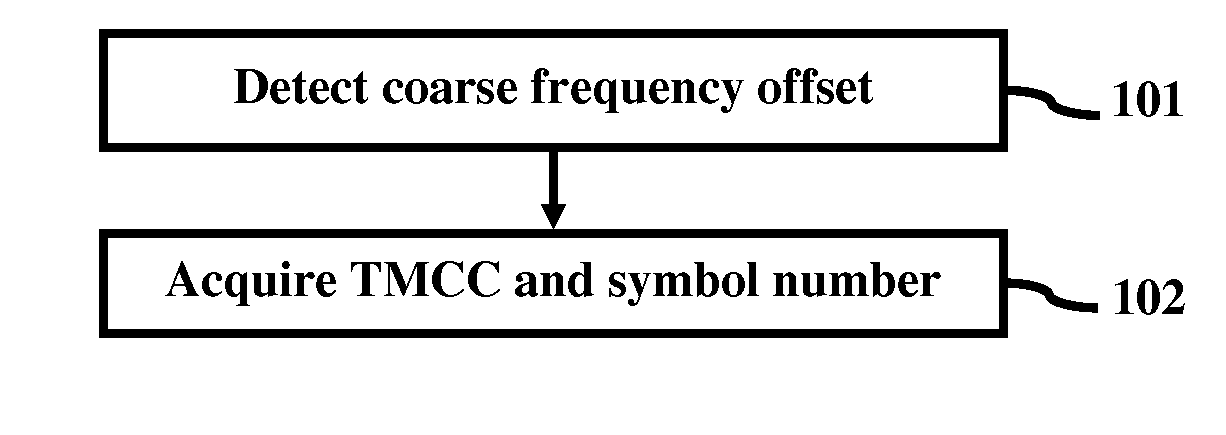
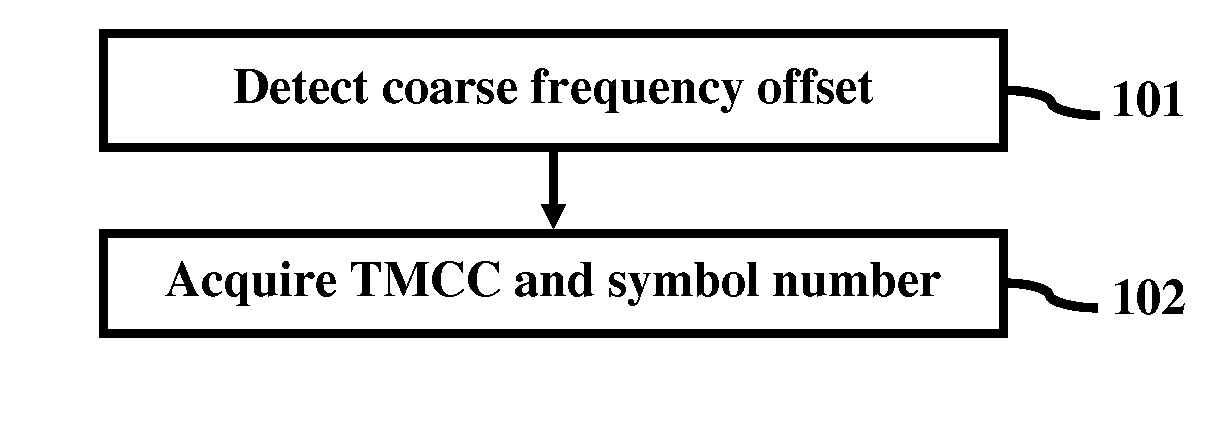
A method of TMCC information acquisition in an ISDB-T / TSB receiver comprises detecting coarse frequency offset in the receiver to identify bins that have TMCC information; and acquiring TMCC and symbol number information from the identified bins. The detecting process may be conducted using different methods and the acquiring process may be conducted using different methods. The TMCC information acquisition method saves memory space and provides enhanced performance by using coarse frequency offset to identify the bins that have TMCC information and obtaining the TMCC and symbol number information from the identified bins.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
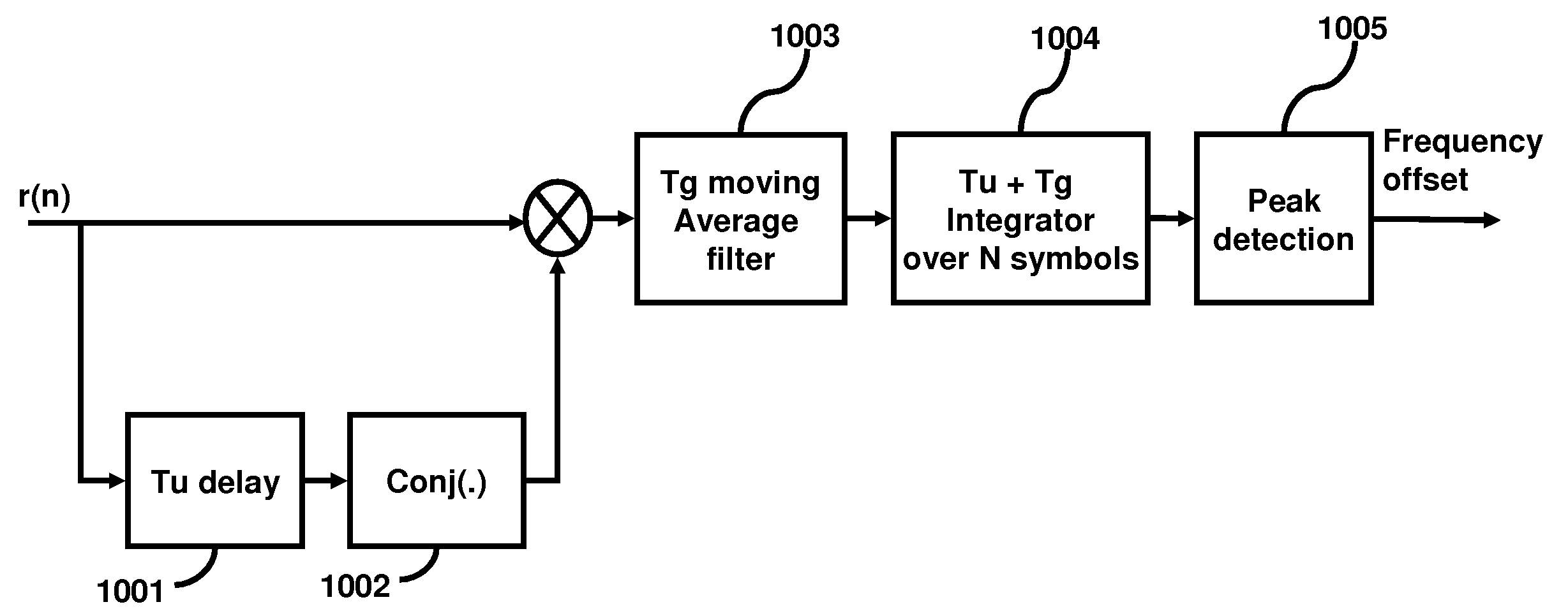
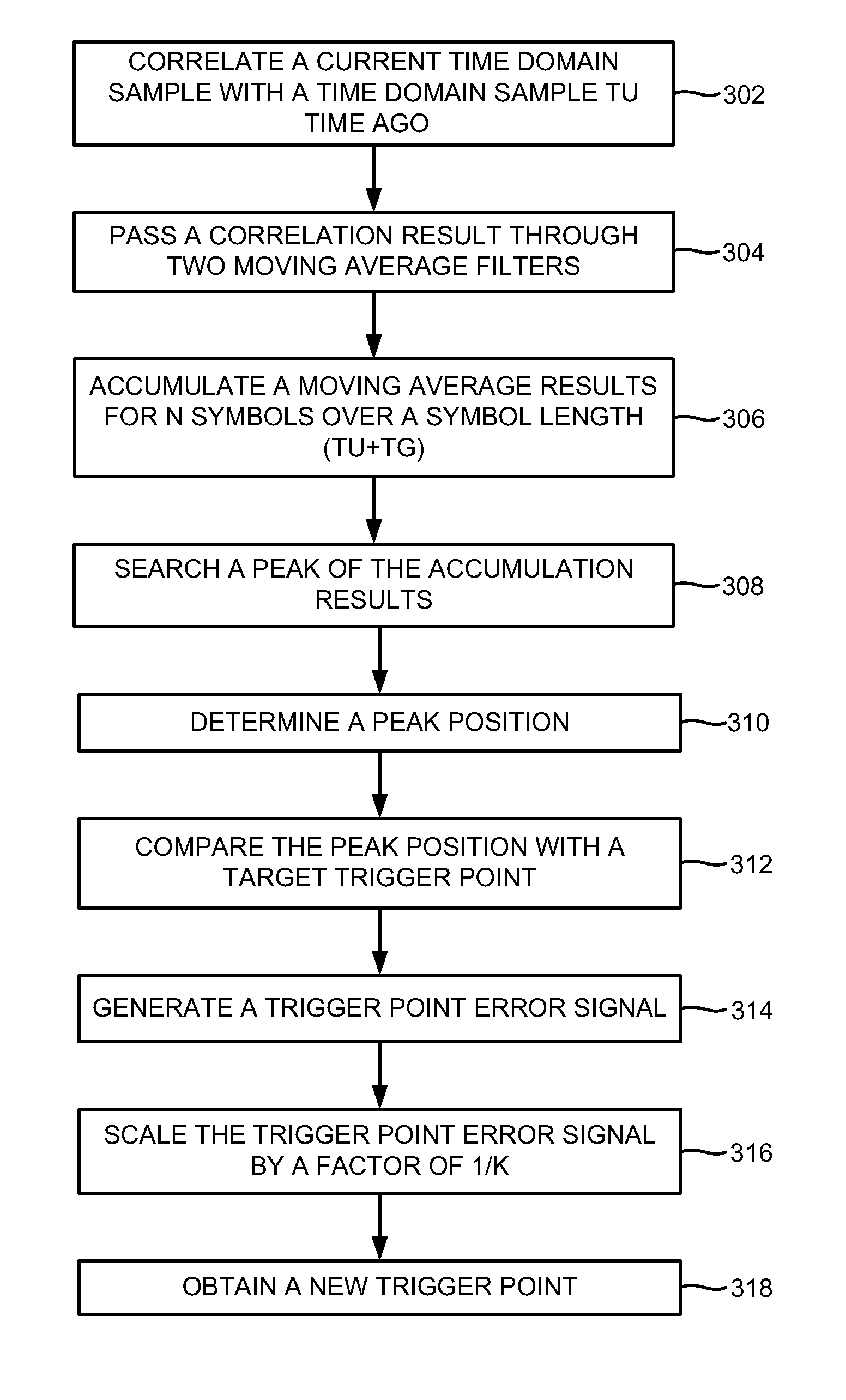
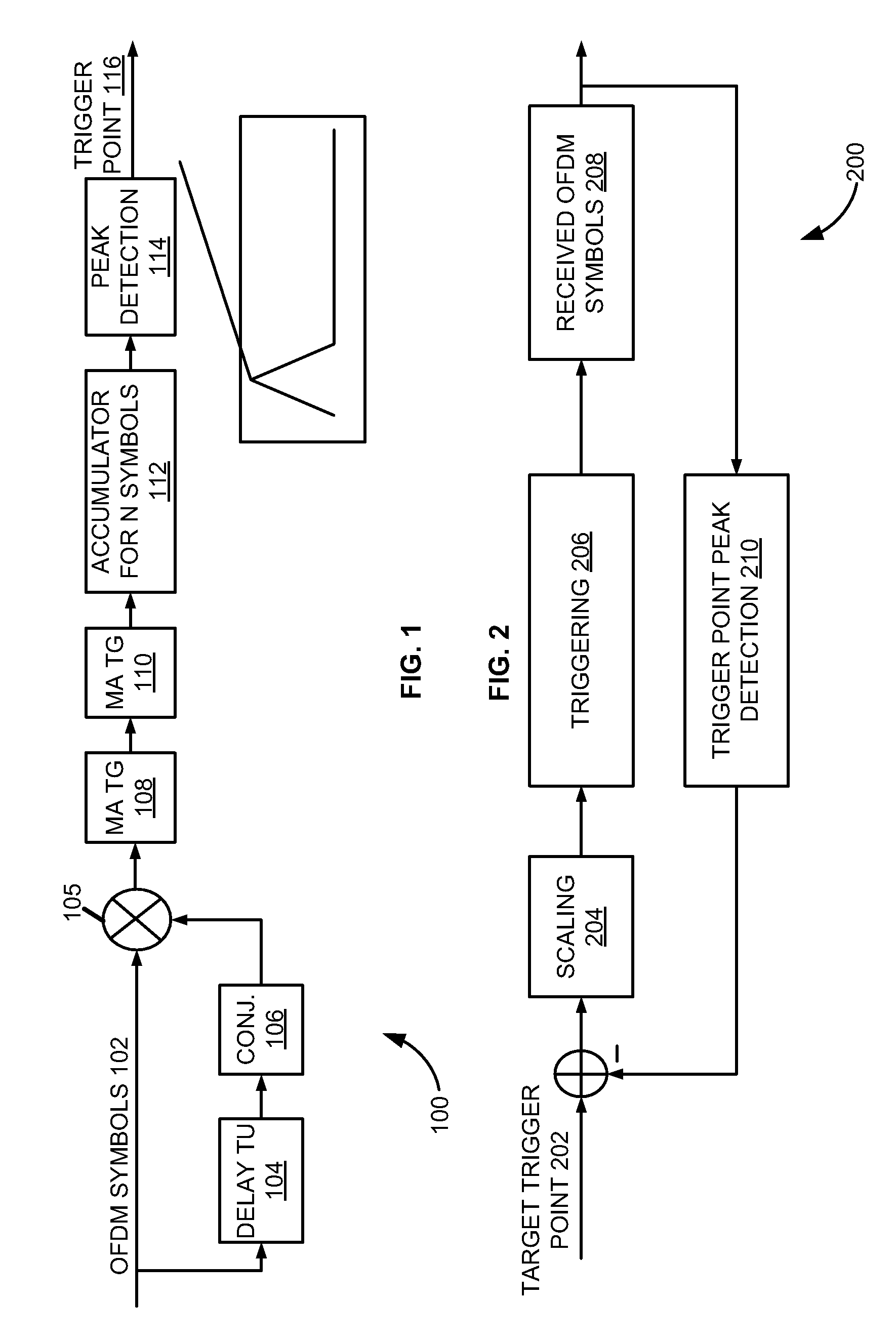
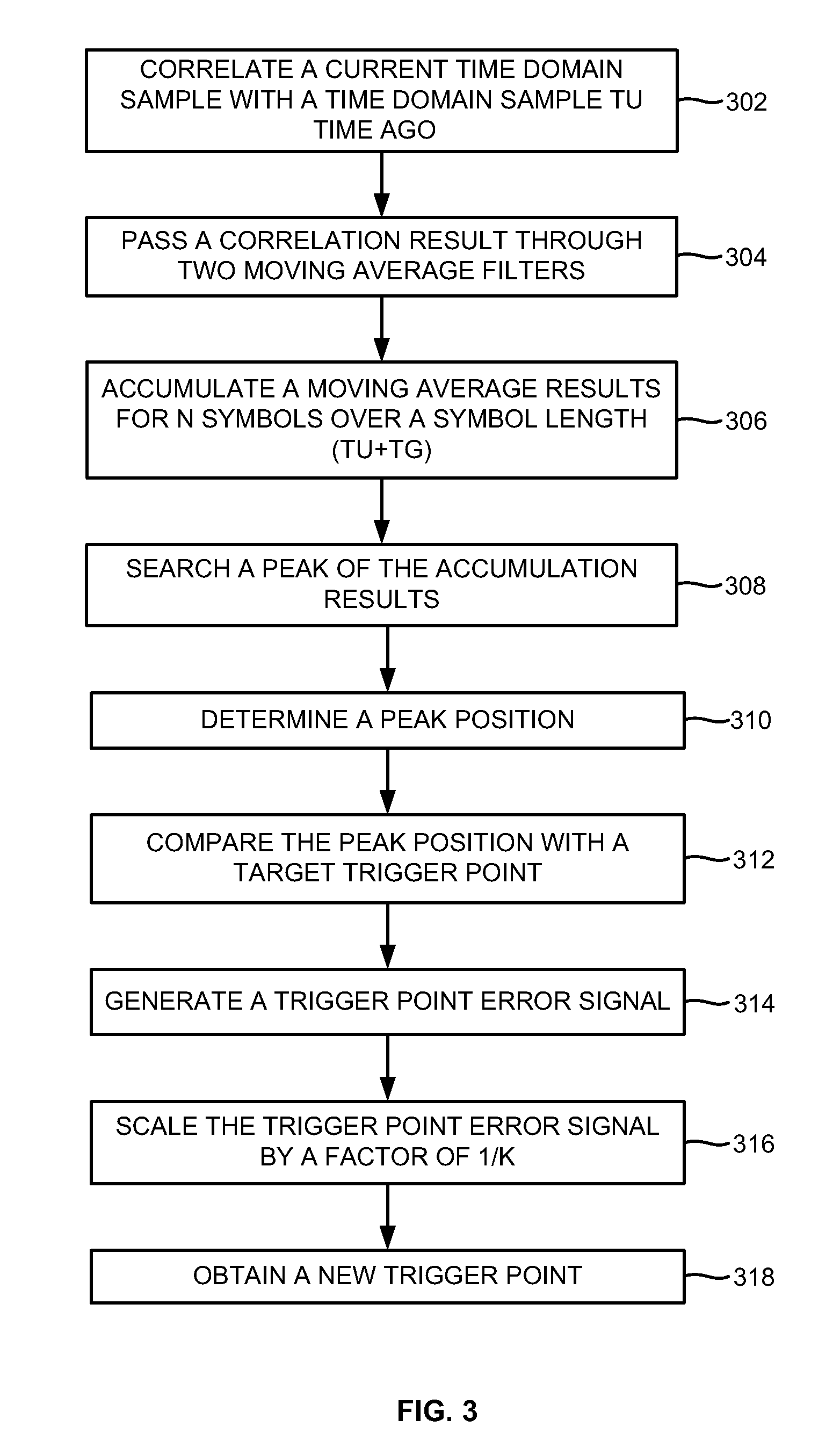
Time domain based approach for fast fading channel FFT trigger point tracking in ISDB receivers
A method of fast fading channel Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) trigger point tracking in an integrated services digital broadcasting (ISDB) receiver includes inputting a signal in a fading channel including N Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbols, determining an average correlation result of a current time-domain sample of the signal and a previous time-domain sample taken previously of the signal, accumulating the average correlation result for at least one of the OFDM symbols, determining a peak of the average correlation result to obtain a peak position, and identifying the peak position as a trigger point of the input signal. The peak position may be compared with a first trigger point to generate a trigger point error signal. The first trigger point may be set at the middle of a guard of an OFDM symbol to generate the trigger point error signal.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
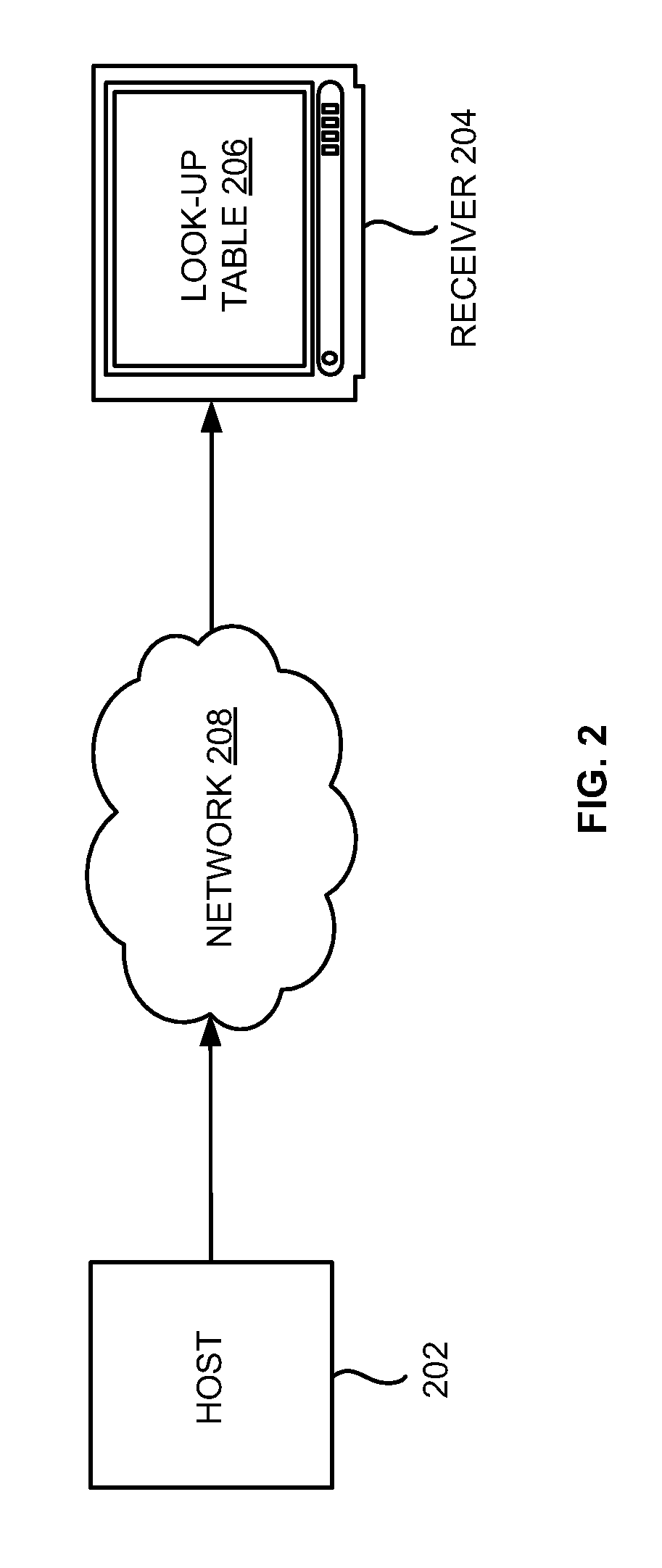
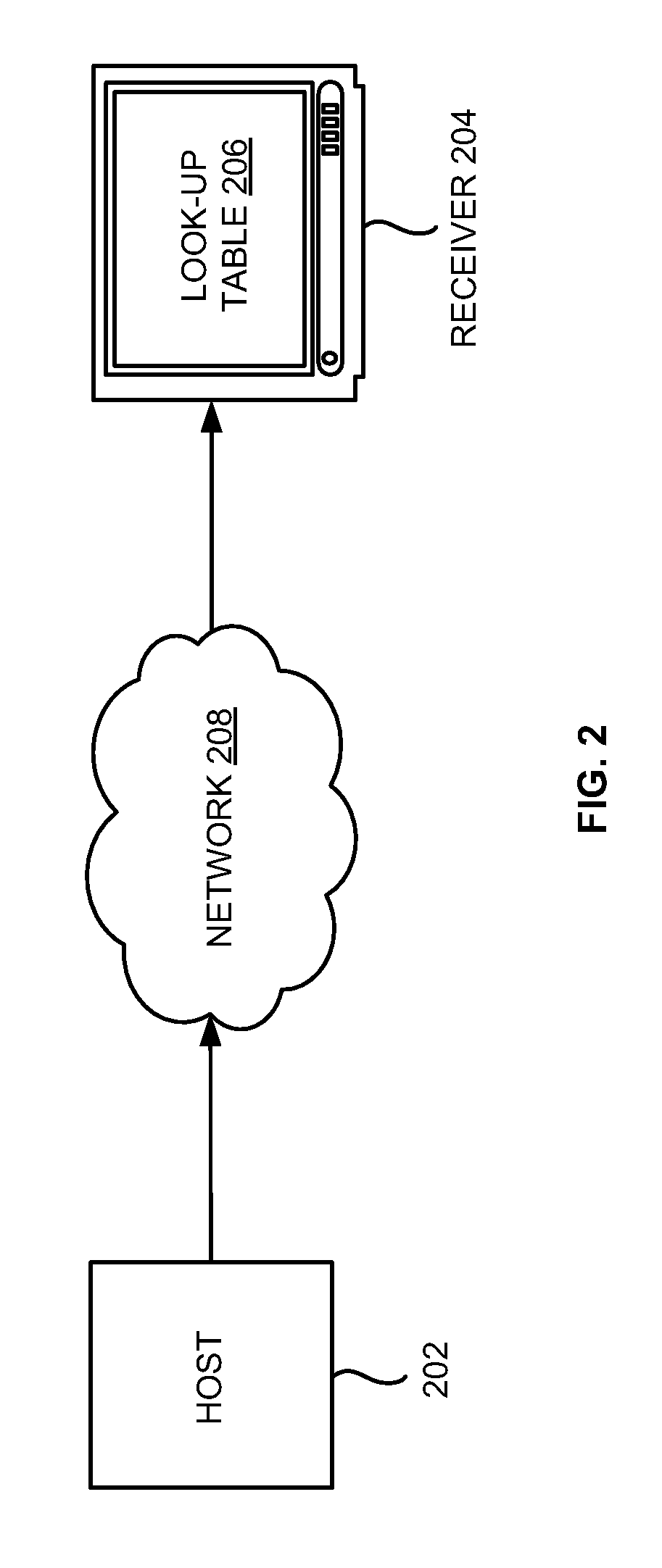
Look-Up Table Based Approach for Layer Combining in ISDB-T and ISDB-TSB Receivers
InactiveUS20090268735A1Modulated-carrier systemsData switching by path configurationMultiplexingCombined method
A method of layer combining based on generating a look-up table in an Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting (ISDB) receiver includes obtaining a transmission parameter configuration, generating the look-up table based on the transmission parameter configuration, assembling a null transport stream packets and a valid transport stream packets from a plurality of layers of a multiplexing frame, and generating a completed transport packet stream using the look-up table. The receiver may generate the look-up table by at least one of generating the look-up table in real time or selecting from a look-up table set based on the transmission parameter configuration. The transmission parameter configuration may include at least one of a transmission mode, a guard interval, a modulation, and a coding rate. The look-up table may define an order of the null transport stream packets and the valid transport stream packets from the plurality of layers in the multiplexing frame.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Integrative encoding system and adaptive decoding system
An integrative encoding system for encoding and transmitting a plurality of video signals having different resolutions that correspond to a plurality of display units. The integrative encoding system has a compression processor, an editing processor, and an integrated services digital broadcasting (ISDB) transmitter. In a first embodiment, the compression processor performs adaptive dynamic range coding (ADRC) to compress each of said plurality of video signals on a block basis by reducing the dynamic range. In another embodiment, the compression processor performs hierarchical encoding on the plurality of video signals by selectively replacing pixels of a higher resolution level with pixels from a lower resolution level calculated by combining pixels from said higher resolution level; thereby encoding a hierarchy of resolution levels within the plurality of video signals without increasing the amount of data. An adaptive decoding system receives and decodes the transmitted plurality of video signals for display by the plurality of display units.
Owner:SONY CORP
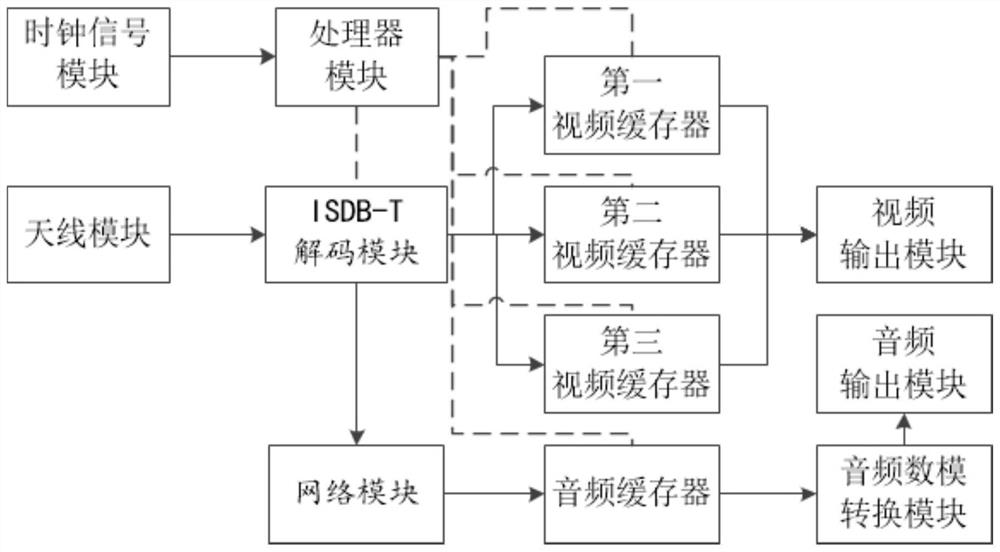
COAX interface television ISDB-T signal processing method and system thereof
ActiveCN109167943AIncrease refresh rateQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPattern recognitionAudio frequency
The invention provides a COAX interface television ISDB-T signal processing method and a system thereof, through the method and the system, processing is performed on the ISDB-T signal to achieve a higher refresh rate of video data and higher quality audio data playback, with good practicability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHANGJIA ELECTRONICS
Symmetric pilot processing for robust timing offset and frequency offset estimation in ISDB-T and ISDB-TSB receivers
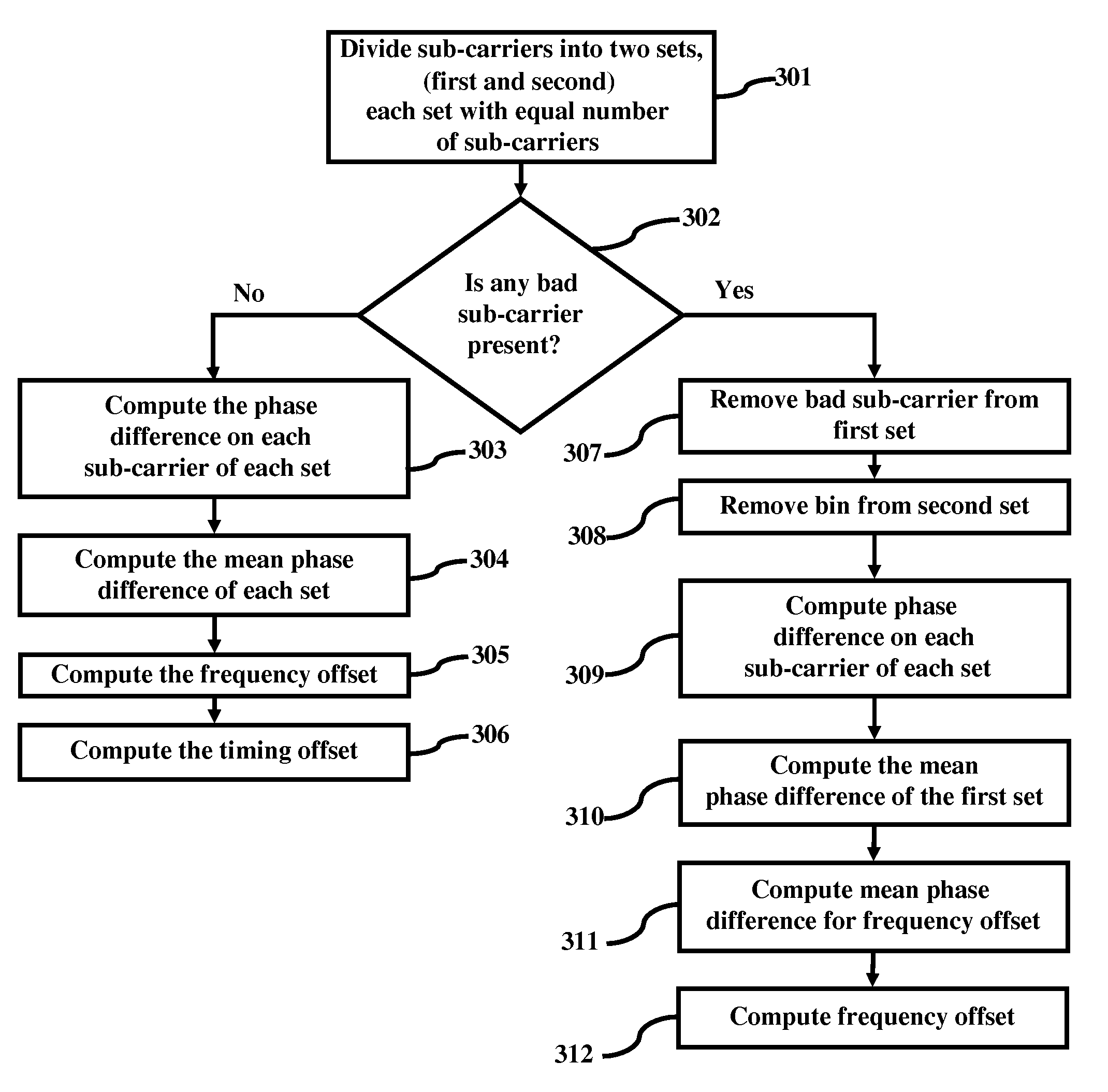
ActiveUS7912157B2Carrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceCarrier signal
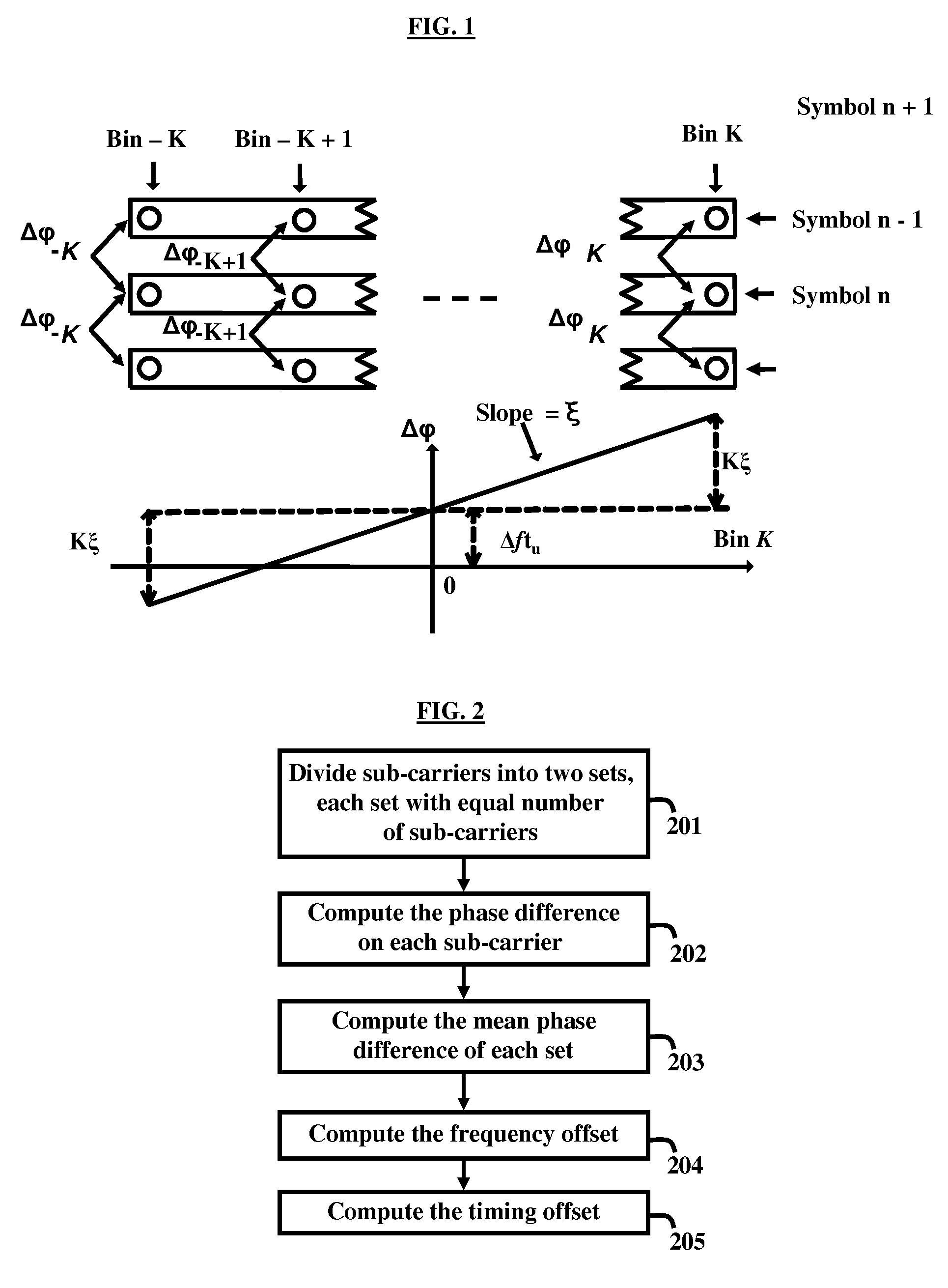
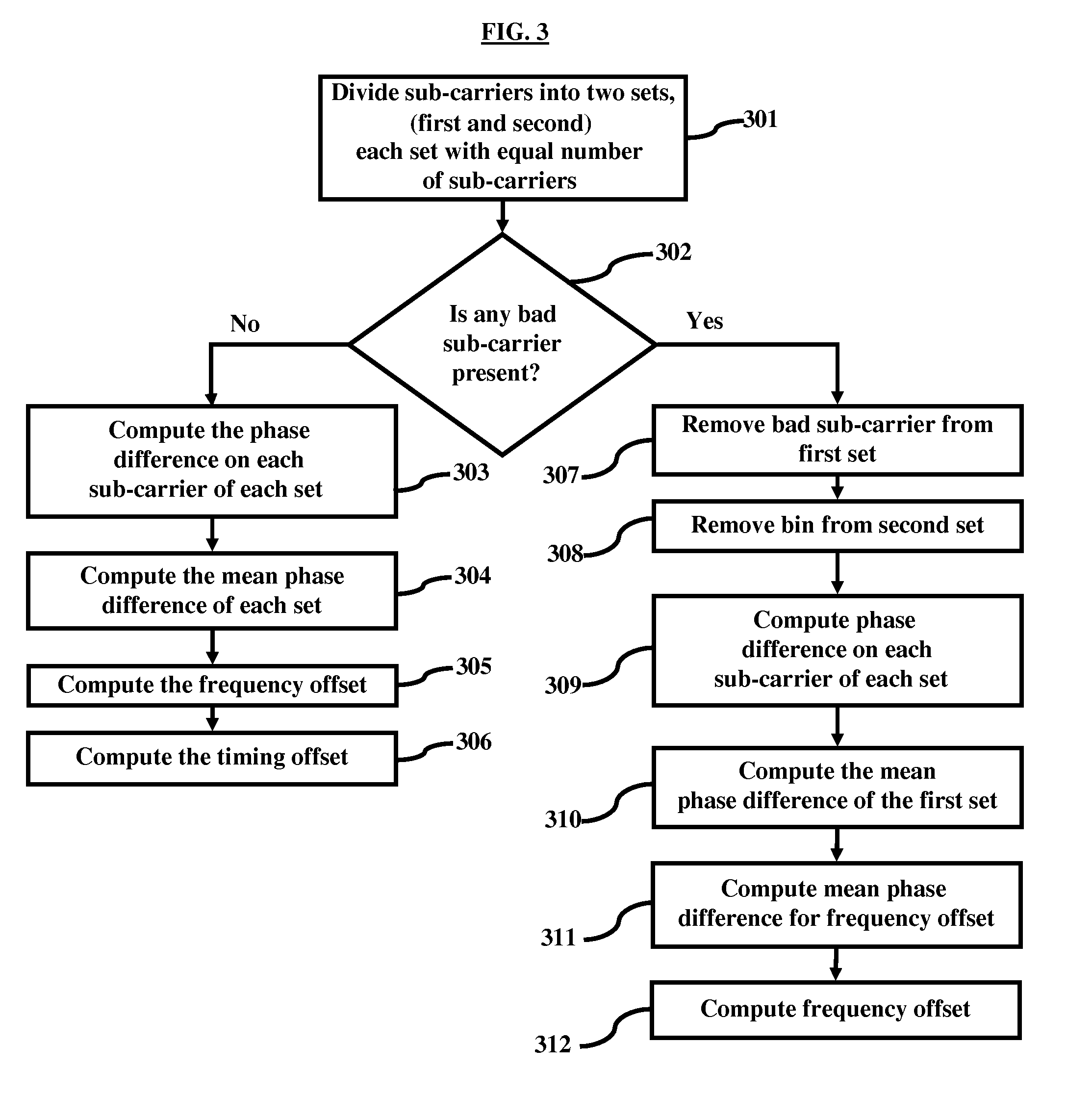
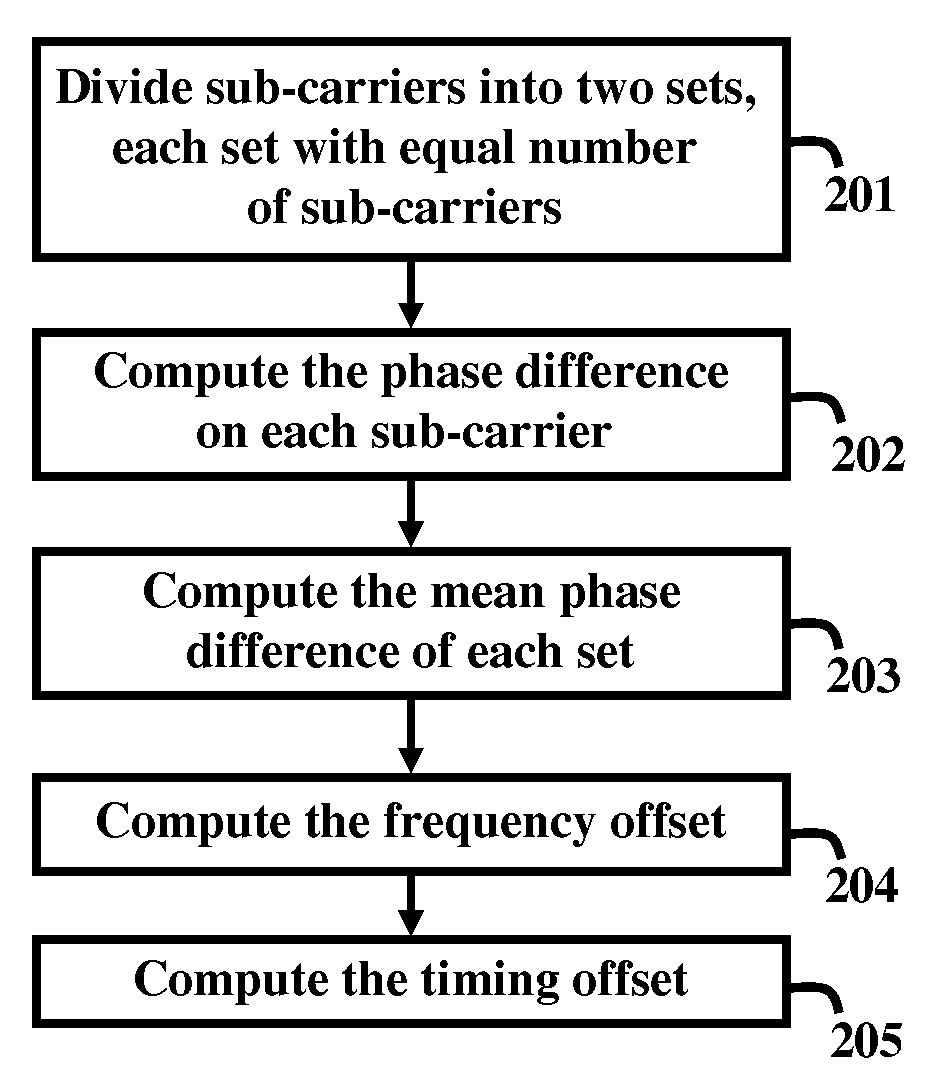
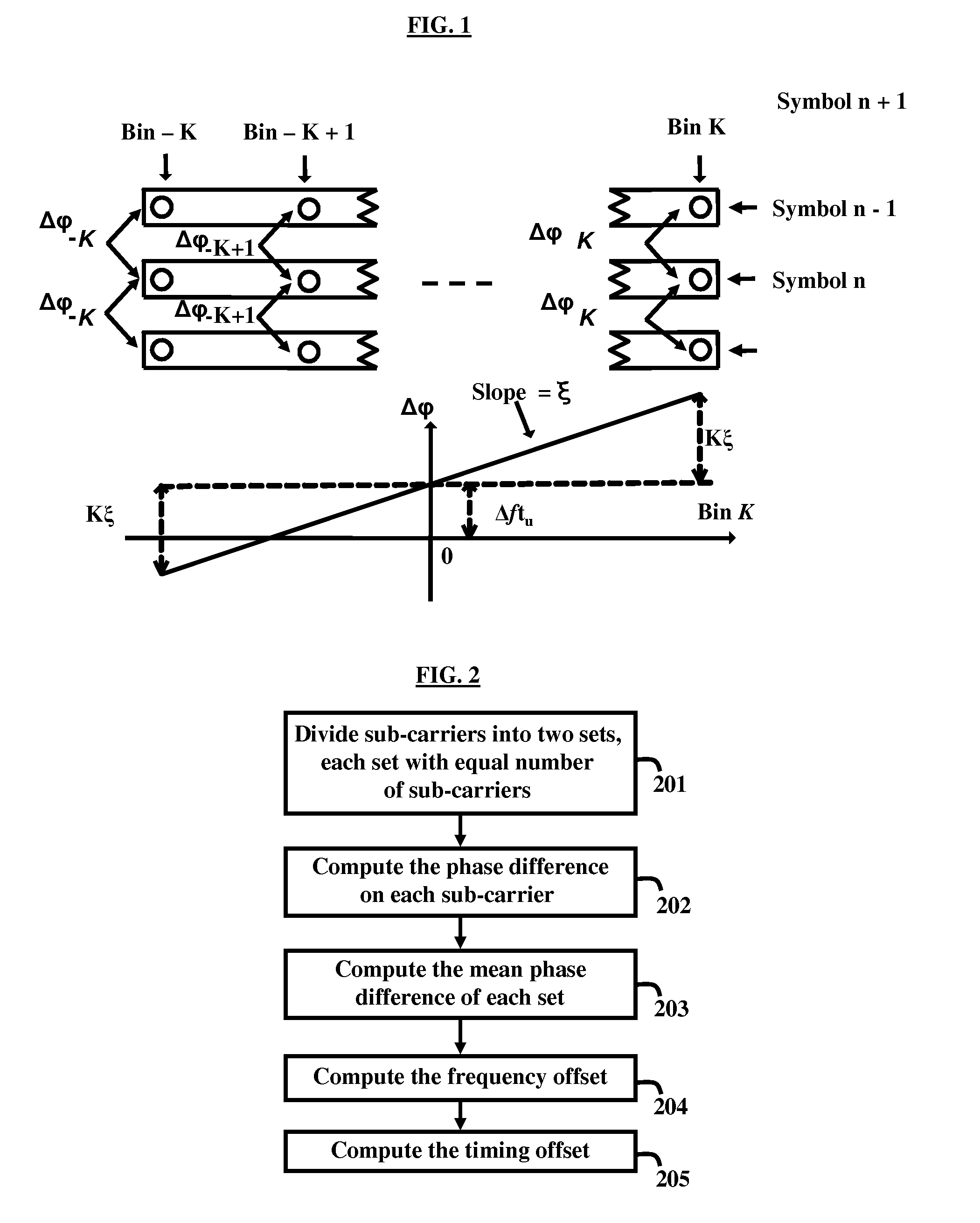
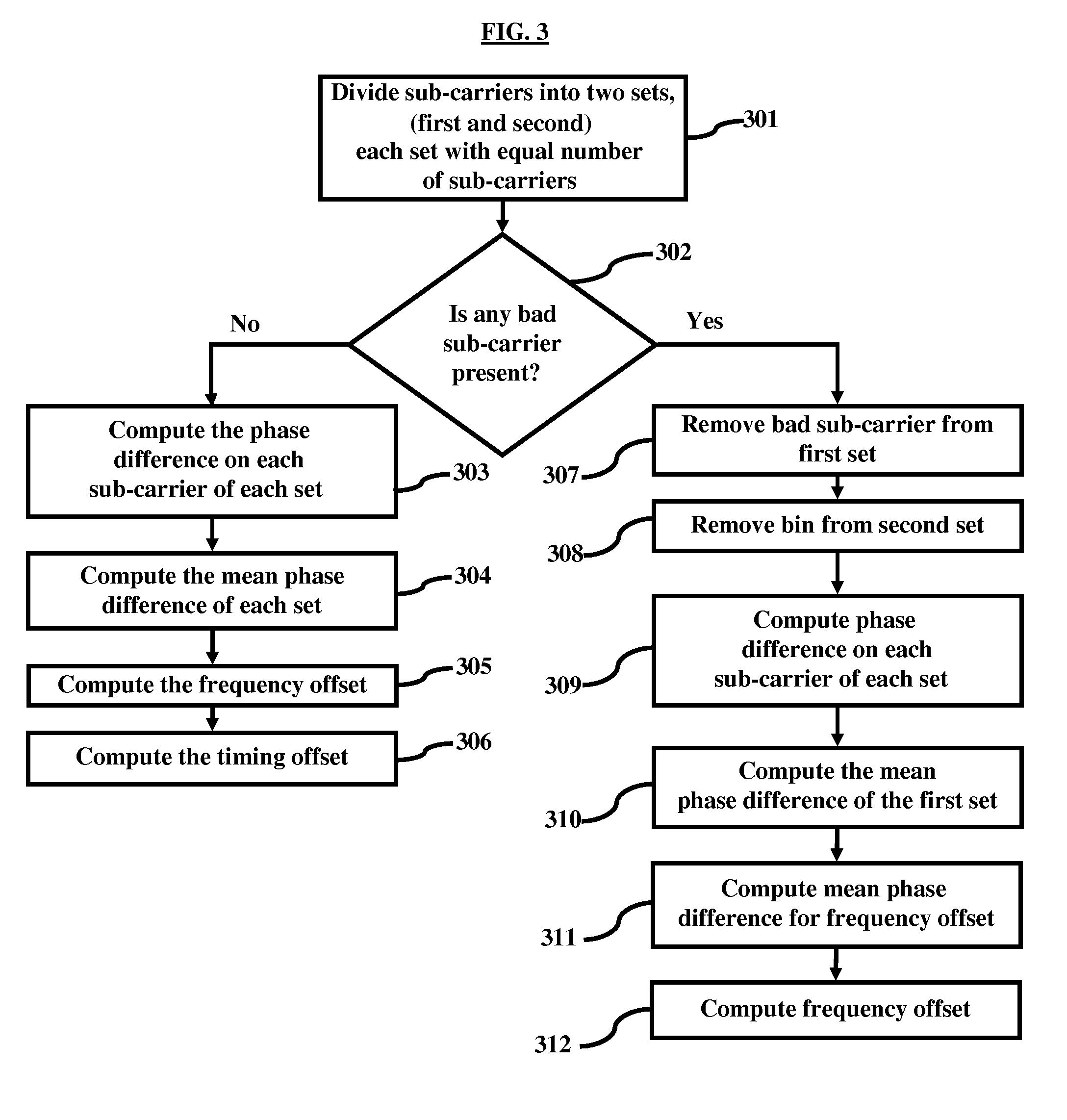
Timing and frequency offset processing in sub-carriers is performed in an Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial (ISDB-T) receiver system. Sub-carriers are divided into two sub-sets, where the sub-sets contain an equal number of sub-carriers. Subsequently bad sub-carriers are removed, if present, from first sub-set of the sub-sets, and corresponding sub-carriers from a second sub-set of the sub-sets are also removed. Further, a phase difference on each sub-carrier from each sub-set is computed, and mean phase differences of each of the sub-sets are computed. Furthermore, frequency offset is computed by averaging the mean phase differences of the sets.
Owner:NEWPORT MEDIA
Symmetric pilot processing for robust timing offset and frequency offset estimation in isdb-t and isdb-tsb receivers
ActiveUS20090252262A1Carrier regulationAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsPhase differenceCarrier signal
Timing and frequency offset processing in sub-carriers is performed in an Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting-Terrestrial (ISDB-T) receiver system. Sub-carriers are divided into two sub-sets, where the sub-sets contain an equal number of sub-carriers. Subsequently bad sub-carriers are removed, if present, from first sub-set of the sub-sets, and corresponding sub-carriers from a second sub-set of the sub-sets are also removed. Further, a phase difference on each sub-carrier from each sub-set is computed, and mean phase differences of each of the sub-sets are computed. Furthermore, frequency offset is computed by averaging the mean phase differences of the sets.
Owner:NEWPORT MEDIA
Segmented-frame synchronization for ISDB-T and ISDB-TSB receiver
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Interactive mobile wireless digital tv
InactiveCN101371579AAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsTwo-way working systemsDisplay deviceMediaFLO
A wireless telephone 10 receives DTV signals over a wireless telephony carrier network 24 in ISDB, DMB, DVB-H, MediaFlo(TM), and the like for presentation of TV programming on the display of the telephone. The user can input signals to interact with the TV programming, and the user signals are wirelessly transmitted using a non-telephony network 22 such as WiFi, WiMax, or wireless Ethernet.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
Coarse Frequency Offset Estimation in ISDB Receivers
InactiveUS20090268850A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsSecret communicationMultiplexingPhase difference
A method of estimating a coarse frequency offset in a receiver includes providing at least one candidate frequency offset in Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) symbols having transmission and multiplexing configuration control (TMCC) bins and auxiliary channel (AC) bins, modulating the TMCC bins and AC bins using differential binary phase shift keying (DBPSK) modulation, estimating a phase difference between a first symbol and a second symbol for the candidate frequency offset of the TMCC and AC bins to obtain a resulting phase difference, correcting the resulting phase difference based on a difference between the candidate frequency offset and a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) center bin to obtain a corrected phase difference, mapping the corrected phase difference to numeric numbers, and adding the numeric numbers for the candidate frequency offset to obtain a summation result. The numeric numbers correspond to at least one of +1 or −1.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Memory sharing of time and frequency de-interleaver for ISDB-T receivers
InactiveUS7945746B2Modulated-carrier systemsForward error control useRandom access memoryMemory sharing
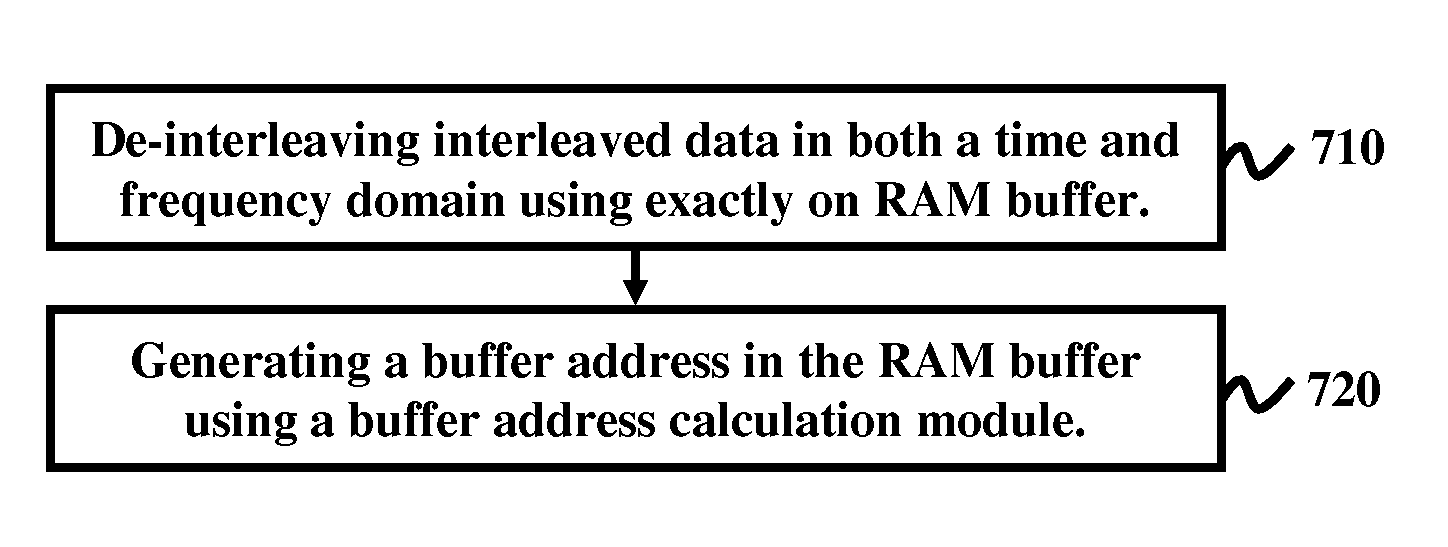
Time and frequency de-interleaving of interleaved data in an Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting Terrestrial (ISDB-T) receiver includes exactly one random access memory (RAM) buffer in the ISDB-T receiver that performs both time and frequency de-interleaving of the interleaved data and a buffer address calculation module for generating buffer address in the buffer. The system performs memory sharing of the time and frequency de-interleaver for ISDB-T receivers and reduces the memory size required for performing de-interleaving in an ISDB-T receiver and combines the frequency and time de-interleaver buffers into one RAM thereby reducing the memory size.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Time delay and time domain interleaving method for integrated services digital broadcasting-terrestrial (ISDB-T) system
ActiveCN102075717BImplementation delayAchieve burstTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTime domainCarrier signal
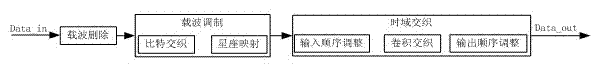
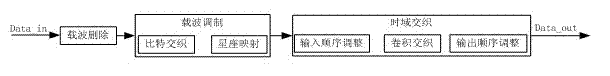
The invention relates to a time delay and time domain interleaving method for an integrated services digital broadcasting-terrestrial (ISDB-T) system, which comprises the following steps of: (1) carrier wave deletion: deleting corresponding carrier wave length according to the time relay regulation length; (2) carrier wave modulation: realizing bit interleaving and bit-to-symbol mapping; and (3) time domain interleaving: realizing convolutional interleaving according to different modes and interleaving lengths. The time delay and time domain interleaving method disclosed by the invention doesnot need additional memory devices to realize the data delay, and the same functions can be realized only through a small quantity of logical resources. Meanwhile, input carrier wave symbols respectively and simultaneously carry out input sequence regulation before and after domain interleaving, a plurality of carrier wave symbols are continuously read in rows, and the outburst of a plurality of data is realized.
Owner:成都德芯数字科技股份有限公司
Time delay and time domain interleaving method for integrated services digital broadcasting-terrestrial (ISDB-T) system
ActiveCN102075717AAchieve burstReduce clock frequencyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsTime domainTime delays
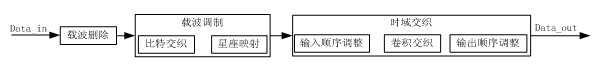
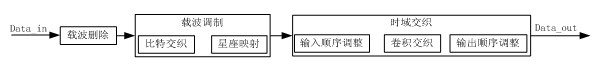
The invention relates to a time delay and time domain interleaving method for an integrated services digital broadcasting-terrestrial (ISDB-T) system, which comprises the following steps of: (1) carrier wave deletion: deleting corresponding carrier wave length according to the time relay regulation length; (2) carrier wave modulation: realizing bit interleaving and bit-to-symbol mapping; and (3) time domain interleaving: realizing convolutional interleaving according to different modes and interleaving lengths. The time delay and time domain interleaving method disclosed by the invention does not need additional memory devices to realize the data delay, and the same functions can be realized only through a small quantity of logical resources. Meanwhile, input carrier wave symbols respectively and simultaneously carry out input sequence regulation before and after domain interleaving, a plurality of carrier wave symbols are continuously read in rows, and the outburst of a plurality of data is realized.
Owner:成都德芯数字科技股份有限公司
Low complexity high performance TMCC acquisition in ISDB-T and ISDB-TSB receivers
ActiveUS8159929B2Broadcast information characterisationSpecific information broadcast systemsTelecommunicationsFrequency offset
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Coax interface TV isdb-t signal processing method and system
ActiveCN109167943BIncrease refresh rateQuality improvementTelevision system detailsColor television detailsEngineeringHuman–computer interaction
The invention provides a COAX interface television ISDB-T signal processing method and a system thereof, through the method and the system, processing is performed on the ISDB-T signal to achieve a higher refresh rate of video data and higher quality audio data playback, with good practicability.
Owner:GUANGZHOU CHANGJIA ELECTRONICS
Look-up table based approach for layer combining in ISDB-T and ISDB-TSB receivers
InactiveUS7822039B2Modulated-carrier systemsData switching by path configurationMultiplexingCombined method
A method of layer combining based on generating a look-up table in an Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting (ISDB) receiver includes obtaining a transmission parameter configuration, generating the look-up table based on the transmission parameter configuration, assembling a null transport stream packets and a valid transport stream packets from a plurality of layers of a multiplexing frame, and generating a completed transport packet stream using the look-up table. The receiver may generate the look-up table by at least one of generating the look-up table in real time or selecting from a look-up table set based on the transmission parameter configuration. The transmission parameter configuration may include at least one of a transmission mode, a guard interval, a modulation, and a coding rate. The look-up table may define an order of the null transport stream packets and the valid transport stream packets from the plurality of layers in the multiplexing frame.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com