Multiplex genotyping using solid phase capturable dideoxynucleotides and mass spectrometry
a technology of solid phase capturable dideoxynucleotides and multi-component genotyping, which is applied in the field of multi-component genotyping using solid phase capturable dideoxynucleotides and mass spectrometry, can solve the problems of limiting the scope of multiplexing, and it is difficult to simultaneously measure dna fragments over a large mass rang
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The following definitions are presented as an aid in understanding this invention.
[0030] The standard abbreviations for nucleotide bases are used as follows: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T), and uracil (U).
[0031] A nucleotide analogue refers to a chemical compound that is structurally and functionally similar to the nucleotide, i.e. the nucleotide analogue can be recognized by polymerase as a substrate. That is, for example, a nucleotide analogue comprising adenine or an analogue of adenine should form hydrogen bonds with thymine, a nucleotide analogue comprising C or an analogue of C should form hydrogen bonds with G, a nucleotide analogue comprising G or an analogue of G should form hydrogen bonds with C, and a nucleotide analogue comprising T or an analogue of T should form hydrogen bonds with A, in a double helix format.
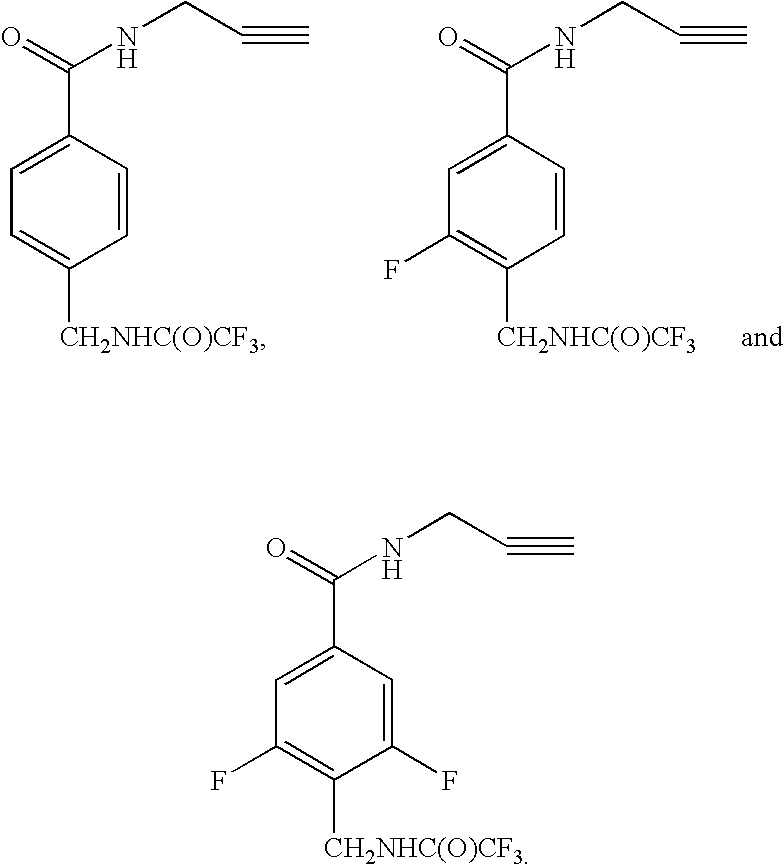
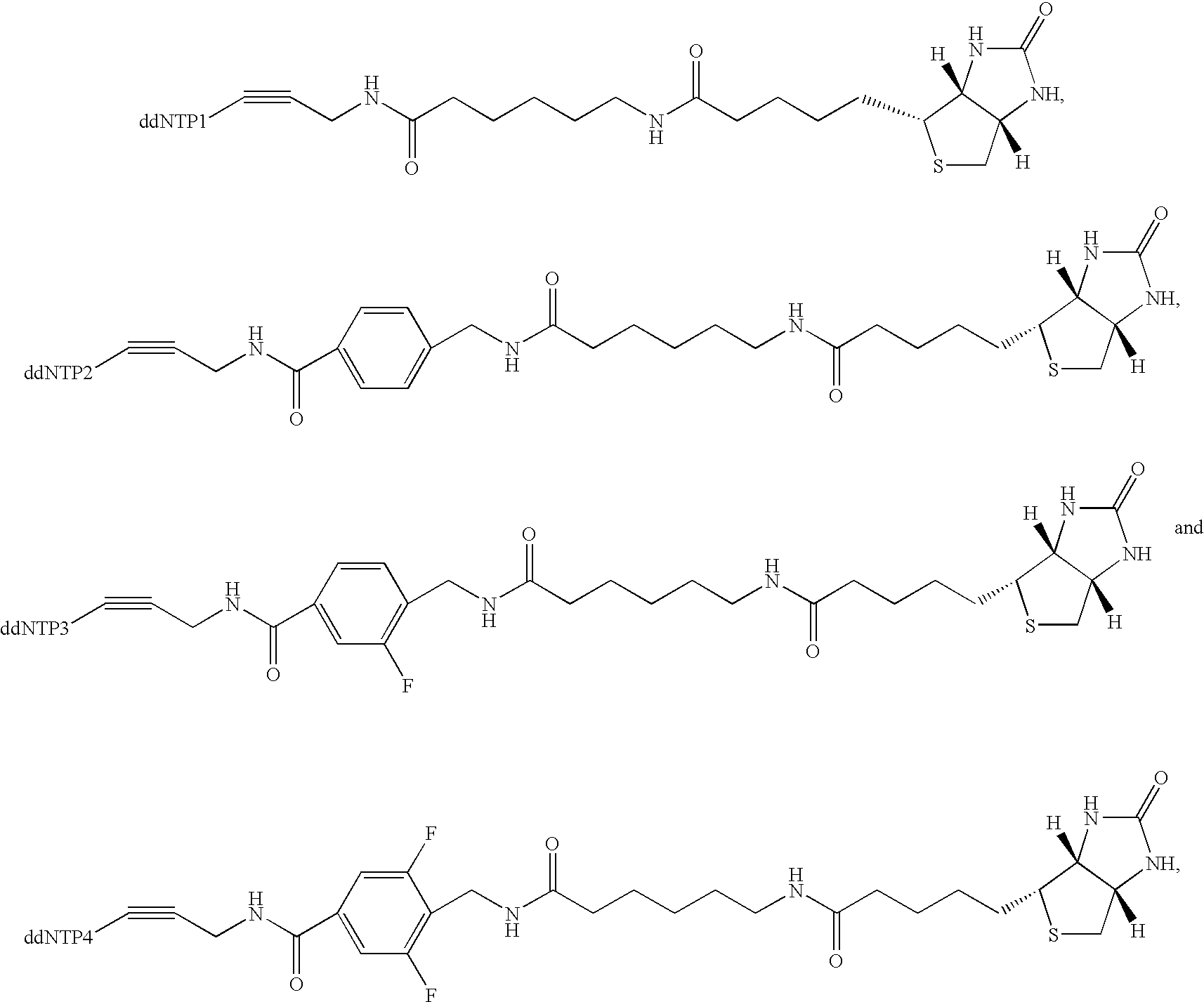
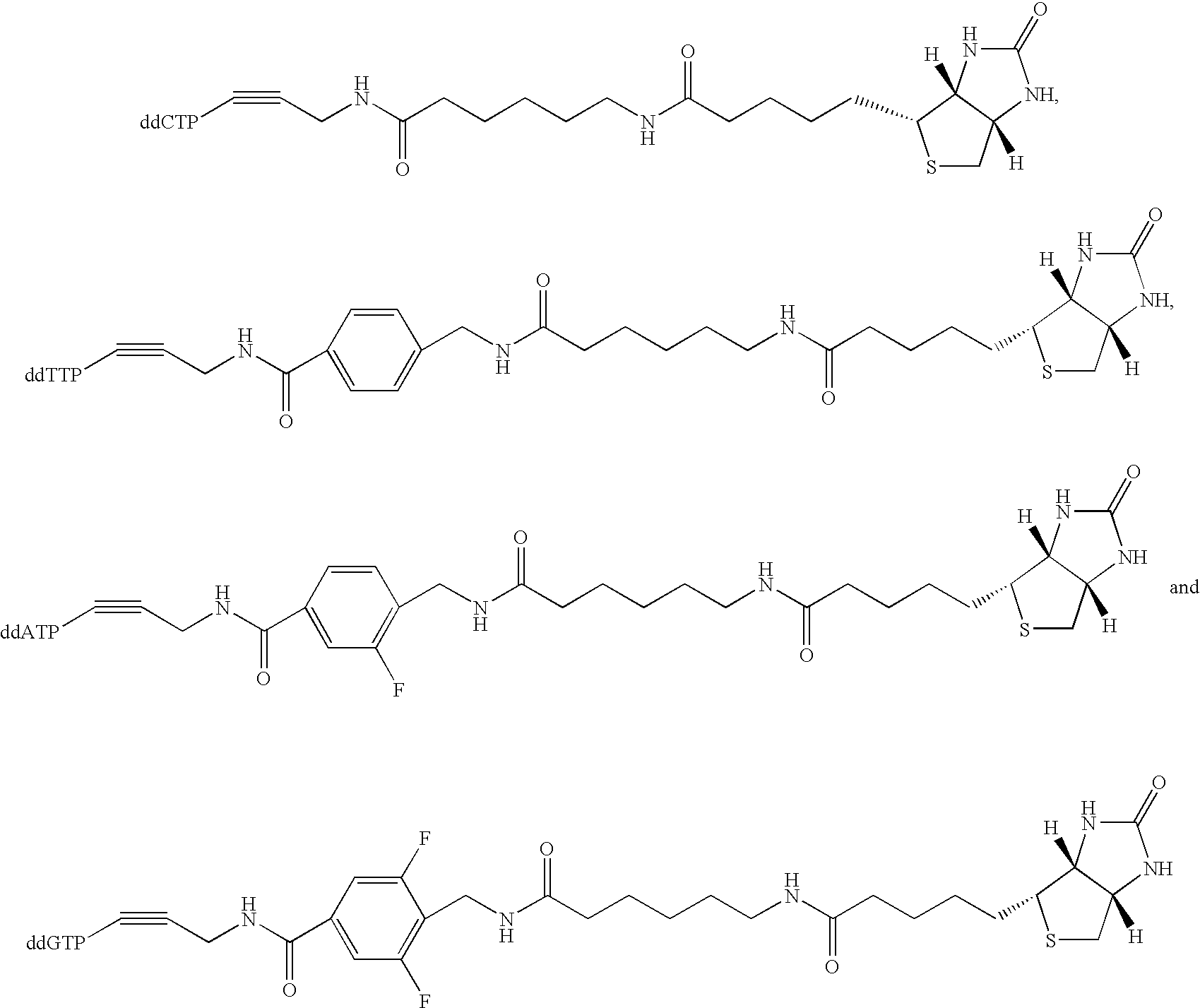
[0032] This invention is directed to a method for determining the identity of a nucleotide present at a predetermined site in a DNA...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com