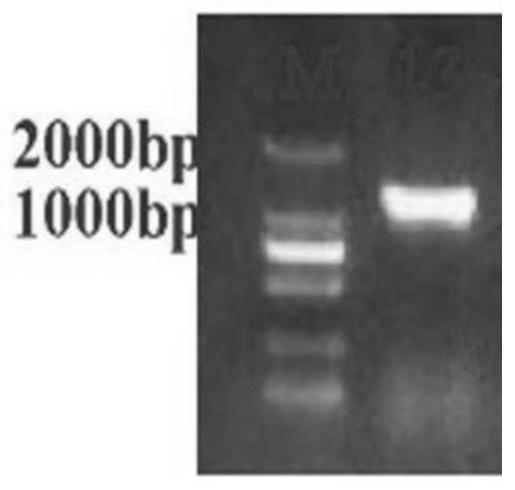
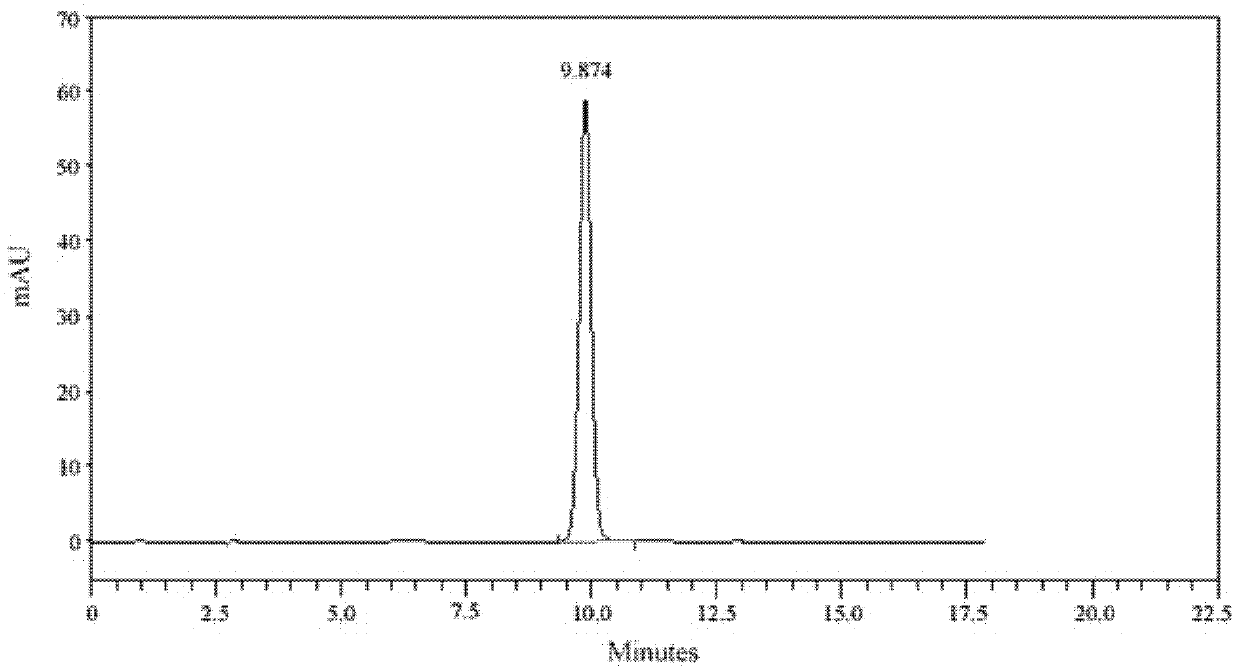
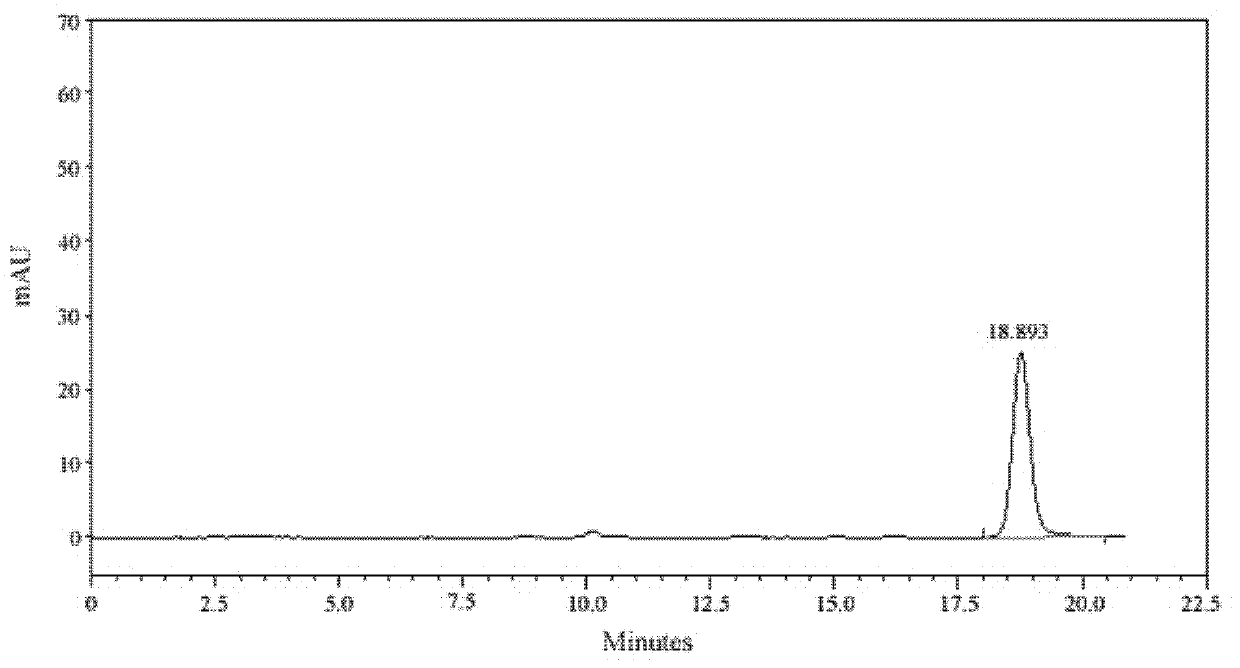
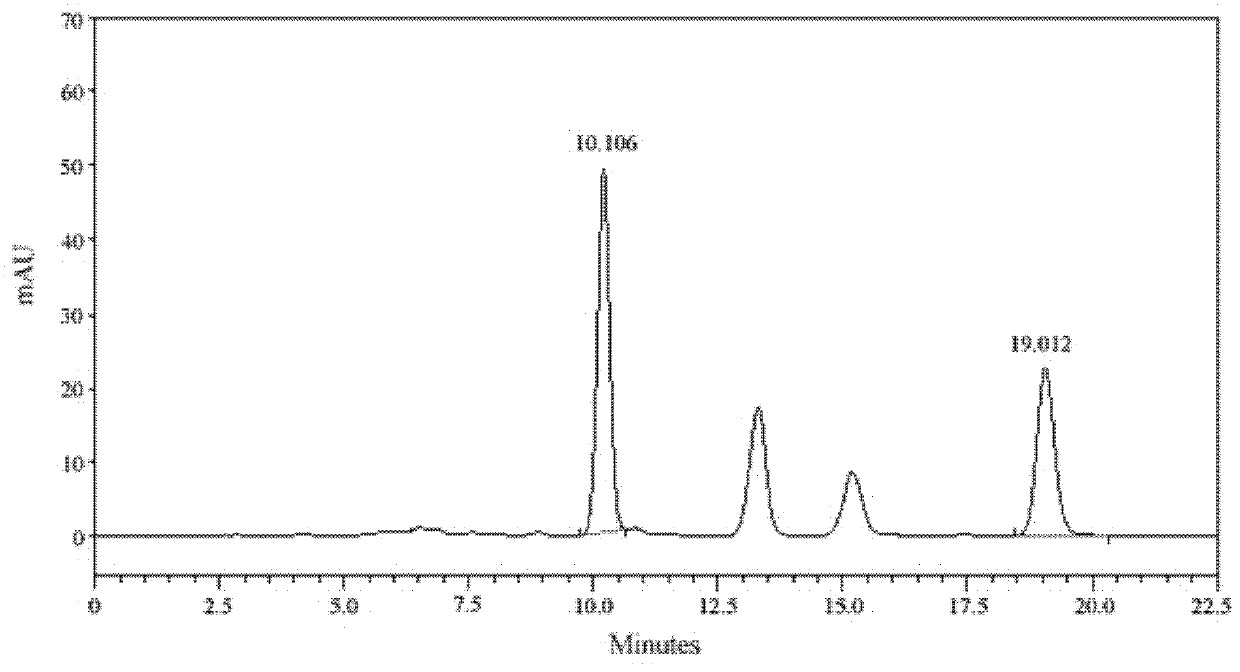
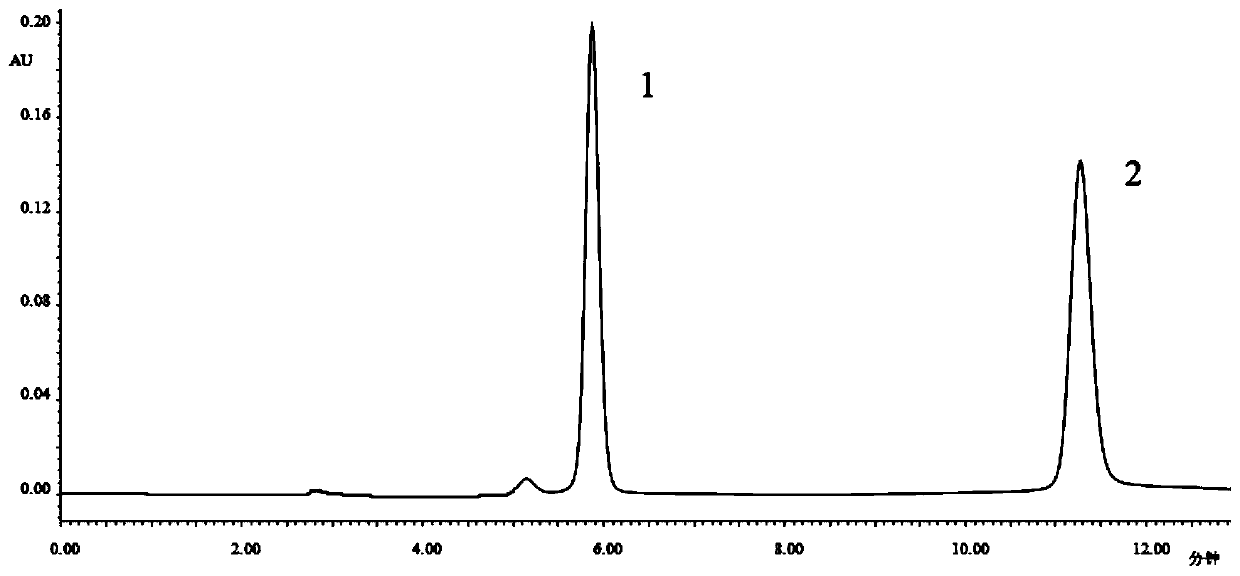
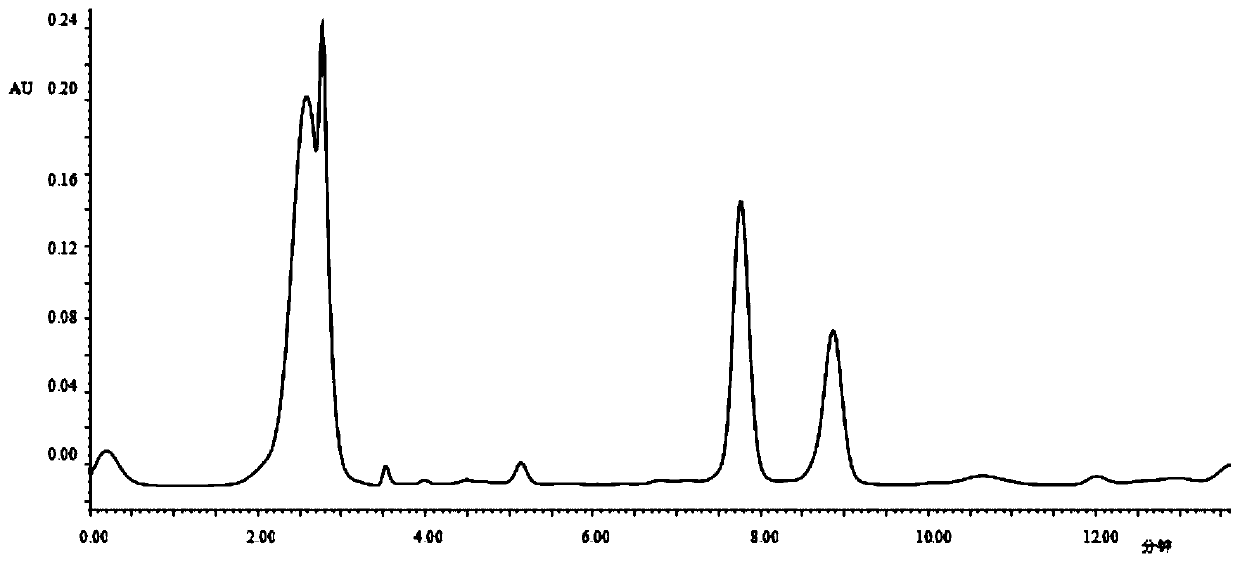
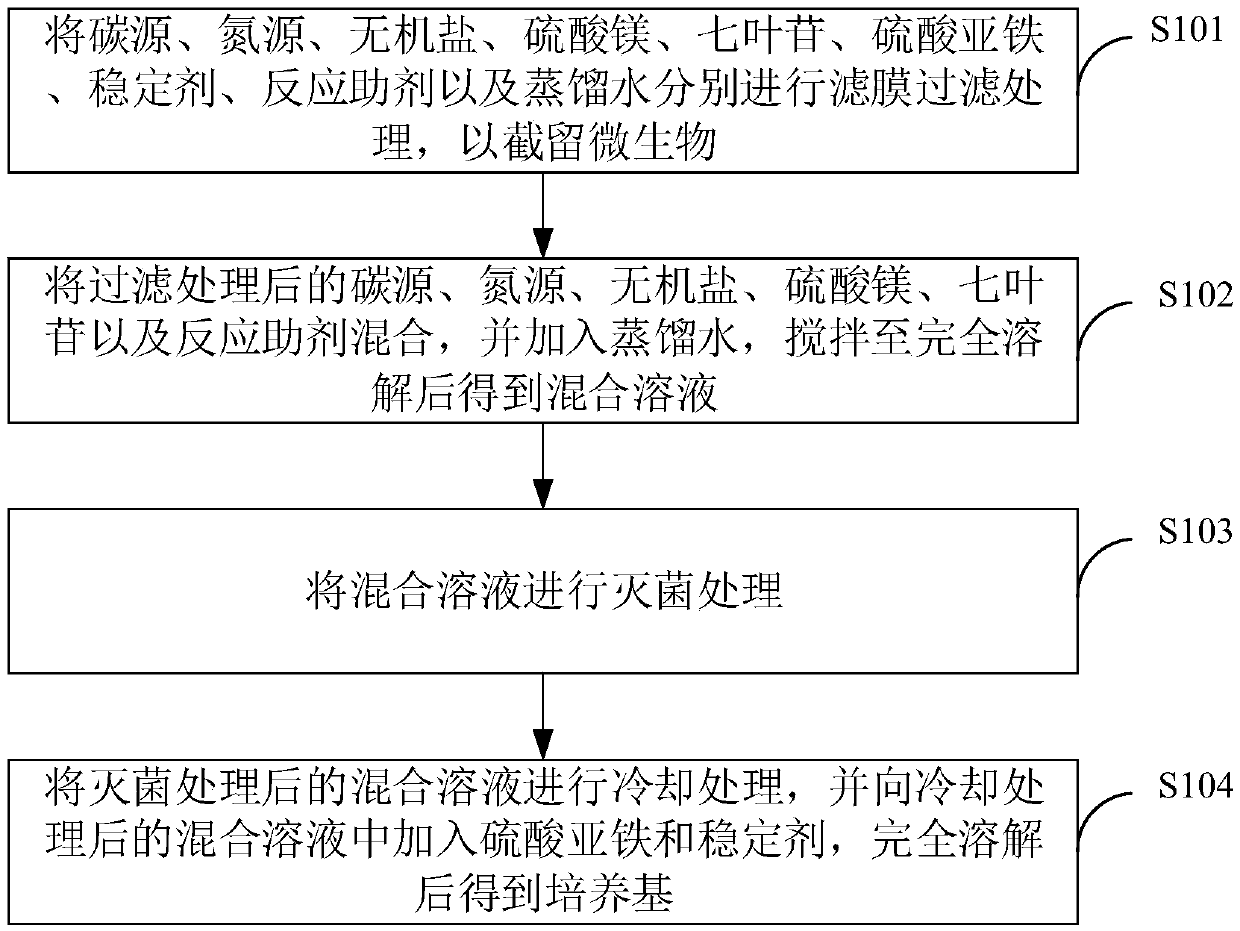
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Aesculin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Aesculin, also called æsculin or esculin, is a coumarin glucoside that naturally occurs in the trees horse chestnut (Aesculus hippocastanum), California buckeye (Aesculus californica), prickly box (Bursaria spinosa), and daphnin (the dark green resin of Daphne mezereum). It is also found in dandelion coffee.
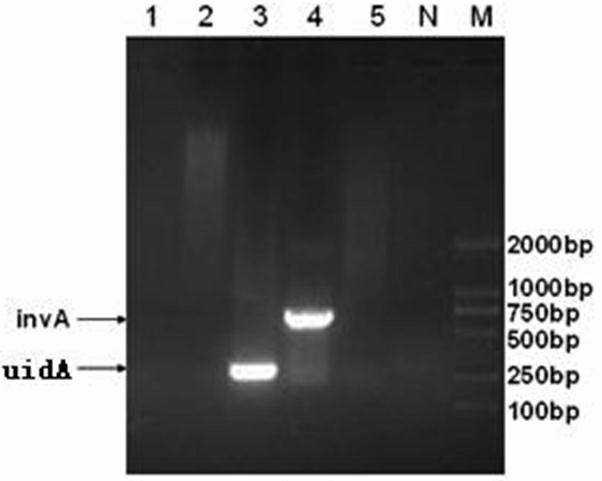
Culture medium for composite enrichment of salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus, and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101412978AShorten enrichment timeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementLithium chlorideStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses a complex enrichment medium used for salmonella, listeria monocytogenes and staphylococcus aureus and a method for preparing the same. The complex enrichment medium comprises the following components in weight portion: 15 to 19 portions of tryptone, 2 to 4 portions of peptone, 2 to 3 portions of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 2 to 3 portions of glucose, 0.5 to 1.5 portions of aesculin, 1, 000 portions of distilled water, 1 to 2.5 portions of sodium pyruvate, 3 to 10.0 portions of mannitol, 1.0 to 25.0 portions of sodium chloride, 1 to 2.5 portions of lithium chloride, 0.0001 to 0.0002 portion of potassium tellurite, and 0.005-0.015 portion of nalidixic acid, wherein the pH value is between 7.1 and 7.5. The complex enrichment medium can inhibit the growth of other pathogenic microorganisms while performing enrichment on three target pathogens, thus the complex enrichment medium can be directly applied to the isolation culture and the biological assay test of target bacteria, and can also be directly applied to a detection technology of a plurality of pathogens based on one detection platform for multiple PCR and the like to make a diagnostic report.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
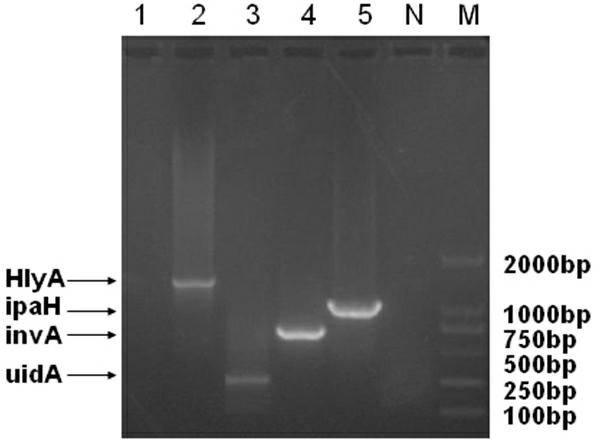
Culture medium capable of simultaneously enriching five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria and preparation method for culture medium
ActiveCN102660474AImprove detection efficiencyLow costBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliFood borne
The invention relates to a culture medium for simultaneous composite enrichment of five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria, namely Salmonella, Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes and Shigella, and a preparation method for the culture medium. Food-borne pathogenic bacteria are a significant reason to cause food positioning, so the rapid and accurate detection of the food-borne pathogenic bacteria has an important practical significance for preventing and controlling food safety incidents. The culture medium is characterized by comprising the following components: 10.0 g of peptone, 10.0 g of sodium chloride, 9.0 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1.5 g of monopotassium phosphate, 0.1 g of cholate, 0.1 mg of potassium tellurite, 1.0 g of lithium chloride, 3.0 g of glucose, 2.0 g of mannitol, 2.5 g of sodium pyruvate, 1.0 g of aesculin and 1,000 mL of distilled water, wherein the pH value is 7.1 to 7.5. The culture medium can simultaneously enrich five kinds of target pathogenic bacteria, can be used for separation and identification of target bacteria, can also be used for the molecular detection of multiple pathogenic bacteria on the same detection platform, provides technical support for a method for rapidly detecting five kinds of pathogenic bacteria in food, and meets the requirement of simultaneous detection of five kinds of food-borne pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES +1
Preparation method and application of cortex fraxini extract
ActiveCN1923194ARemarkable effectSkeletal disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsFraxinCortex Fraxini
The invention relates to a method for preparing ash bark coumarin compound. Wherein, it boils and extracts with water, uses porous resin to separate and purify ash bark coumarin compound; and said compound comprises aesculin, aesculetin, fraxin, and fraxetin, while the total coumarin content is higher than 50%, and the contents of aesculin, aesculetin, fraxin, and fraxetin are higher than 40%, while their ratios are 4-6:1-3:2-4:1. The invention also provides its application in medicine production.
Owner:四川恩威制药有限公司
Composite enrichment medium for five bacteria and preparation method for composite enrichment medium
ActiveCN104195086APromote rapid proliferationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPolymerase L
The invention discloses a composite enrichment medium for salmonella, staphylococcus aureus, escherichia coli, listeria monocytogenes and vibrio parahaemolyticus and a preparation method for the composite enrichment medium. The composite enrichment medium comprises the following components in parts by weight: 5-10 parts of ox brain extract powder, 5-15 parts of ox heart extract powder, 5-15 parts of peptones, 2.5-7.5 parts of sodium chloride, 1-3 parts of glucose, 1.5-3.5 parts of disodium hydrogen phosphate, 1-3 parts of mannitol, 1-3 parts of sodium pyruvate, 1-3 parts of glycine, 1-3 parts of aesculin, and 1000 parts of distilled water, and a pH value of the composite enrichment medium is 7.2-7.5. A preparation method for the composite enrichment medium comprises the following steps: adding the components into distilled water according to the formula, stirring and dissolving the components, regulating the pH value of the mixture, and sterilizing the mixture at high pressure. The five bacteria are main pathogenic bacteria which are needed to be detected according to the national food hygienic standard. The composite enrichment medium can be used for realizing rapid proliferation of the five pathogenic bacteria. After carrying out bacteria enrichment for 16 hours, the concentration of the thallus can be increased to 10<6>CFU / mL-10<9>CFU / mL from 1CFU / mL, so that the thallus can be directly used for carrying out high flux detection on multiple PCRs (polymerase chain reactions), gene chips and micro-fluidic chips, and thus, screening of the five pathogenic bacteria is completed.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +2
Flat-plate sieving method of aesculin for high-yield beta-glucosidase producing strain
The invention discloses a flat plate screening method for high yielding Beta-glucosidase production bacteria by using aesculin. The method comprises the steps of: 1. earth sample collection; 2. enrichment culture; 3. flat plate preparation of the aesculin; 4. flat plate primary screening aesculin; 5. separation and purification; 6. secondary screen by a shaking battle, etc. The invention can fast screen active strain possessing the Beta-glucosidase from samples which contain rich fibrin resources; compared with the method which is reported in published literature which screens Beta-glucosidase production bacteria by using a cellobiose flat plate method, the invention has the remarkable advantages at price; under the condition that obtains 100 strains by screening, the cost of the invention by using the aesculin is only one tenth of the cellobiose flat plate method; in addition, the invention has the advantages of simple operation, reliable result, etc.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
High purity cortex fraxini and its preparation method
This invention provides a preparation of aesculin. The mentioned preparation includes steps such as: extraction, column chromatography, concentration and crystallization. Among them the step of column chromatography is as following: a) centrifugalize or filter extract which is obtained in extracting step, filter liquor or clear supernatant liquid is directly added into macroporous resin column, among them the proportion by weight of cortex medical material and resin is 1:2-1:3;b) After all of the extract pass resin column, use eluting reagent to elute, after elutriant has clarified, begin to collect elutriant, don't stop collecting until collecting 10-15 times of elutriant of column volume.
Owner:SHANGHAI SINE PHARMA LAB
New use of aesculin in preventing and/or treating cardiovascular disease
ActiveCN101129394ALow toxicitySimple extraction processOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderCarotid atherosclerosisSuperoxide
The invention discloses an application of Esculin to prevent and / or treat terminal advanced glycation end-products disease and Cardio-Cerebral-Vascular Disease, especially for the coronary atherosclerosis and arterial atherosclerosis, which is characterized by the following: cracking of terminal advanced glycation end-products, eliminating superoxide anion radical; protecting organism cell from Free-Raducak Injury; antagonizing Experimentative Hyperlipoidemia and decreasing Carotid Atherosclerosis formation. The invention has low toxicity, easy extraction, vast resource, good prospects, which is a perfect Chinese Herb to cure Cardio-Cerebral-Vascular Disease.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Producing microorganism for trans-glycosylation beta-galactosidase
The invention discloses a glycosyl-transferbeta-galactosidase production bacterium, which is characterized by the following: the name of this bacterium is Enterobacter cloacae B5, which is Gram-negative bacterium; the conservation code is CGMCC No.1401; the bacterium shape changes along culture time extension on the LB culture medium from long rod to short rod, ellipsoid shape and ball; the colouring size is 0.5-1.5*0.7-9.0 mm with single, couple or short-chain arrangement; the bacterium can move by peripheral flagellar without gemma and can apply citrate or acetate as only one carbon source, which products acid and gas by fermenting glucose at 37 deg.c and glycerin without gas, hydrolyzing aesculin and indole; V.P. detects positive and methyl red detects negative; the nitrate is reduced and Lys is not decarboxylation with ornithine decarboxylase, arginine dihydrolase and urease; the nucleotide sequence of this bacterium 16S rDNA is described as SEQ ID No.1; the beta-galactosidase can take lactin as substrate, which catalyzes to produce oligomer galactose.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for fluorescent detection of trace uranyl ions
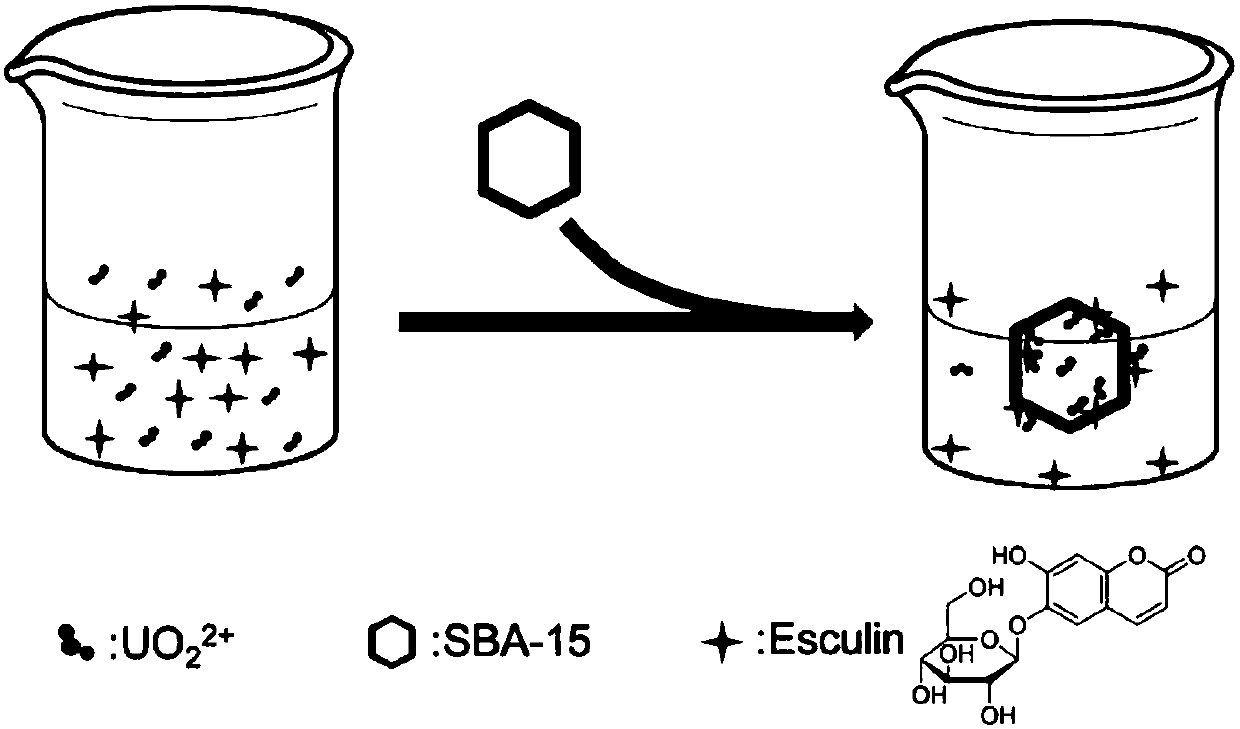
ActiveCN107589098AAccurate determination of concentrationFluorescence/phosphorescenceMolecular sieveUranyl
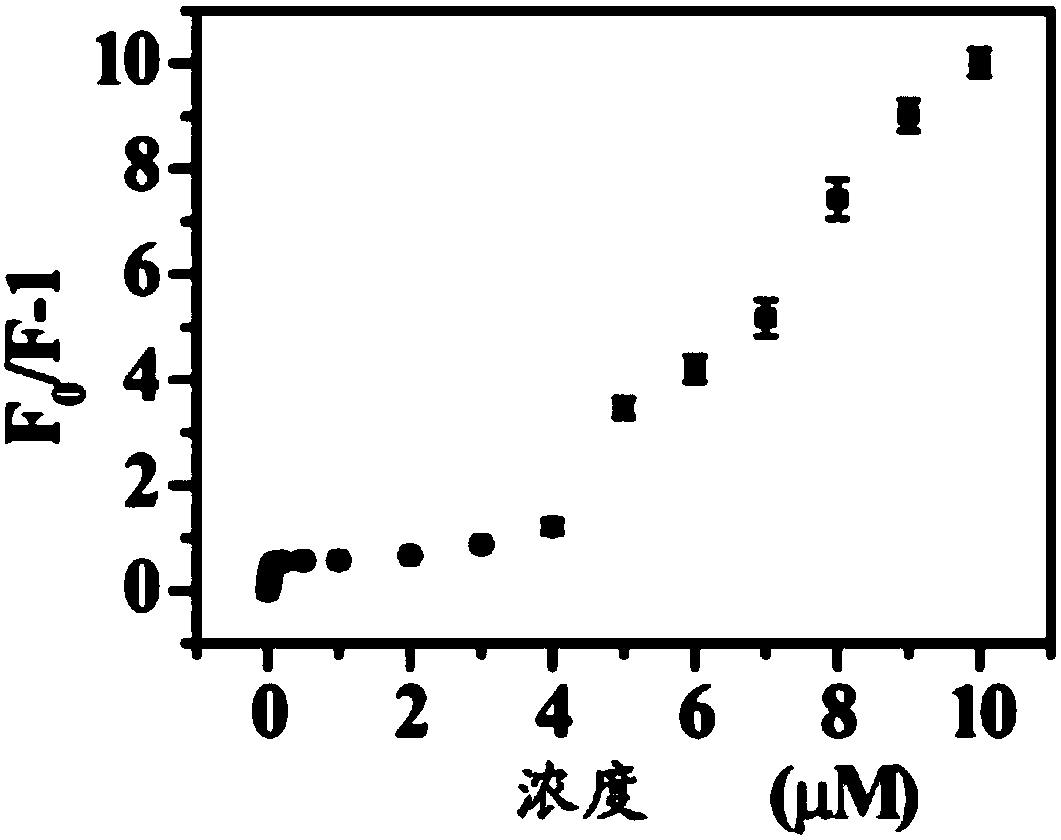
The invention relates to a method for fluorescent detection of trace uranyl ions. The method comprises the following steps: (a) adding aesculin and a mesoporous molecular sieve into an aqueous solution containing uranyl ions and carrying out fluorescent detection to obtain the fluorescence intensity of the aqueous solution; (b) preparing a solution not containing uranyl ions and measuring the fluorescence intensity F<0> of the solution; (c) preparing a solution containing uranyl ions with a different concentration and measuring the fluorescence intensity F<n> of the solution; (d) drafting a curve with F<0> / F<n-1> as a vertical coordinate and the concentration of uranyl ions as a horizontal coordinate; (e) carrying out diluting according to the proportion of the aqueous solution obtained inthe step (a) until the concentration corresponding to the measured fluorescence intensity of the aqueous solution is in a range of 0.001 to 0.05 [mu]mol / L according to the curve drawn in the step (d), and multiplying the concentration by a multiple of the dilution. The method can accurately determine the concentration of uranyl ions in aqueous solutions and has a detection limit of as low as 6 nM.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Aesculin sturgeon skin gelatin film with antioxidant activity and enterococcus faecalis detection ability and a method of preparing the same
ActiveUS20190031840A1Special physicochemical propertyGood film formingFlexible coversWrappersGelatin filmDistilled water
A method of preparing an aesculin sturgeon skin gelatin with antioxidant activity and Enterococcus faecalis detection ability includes: 1) mixing a sturgeon skin gelatin and distilled water in a ratio of 1:15-1:25 (w / v) at 50-70° C. and filtering to obtain a sturgeon skin gelatin solution; 2) adding aesculin and a glycerin solution to the sturgeon skin gelatin solution, stirring the resulted sturgeon skin gelatin solution at 30-50° C. for 30 minutes, and filtering; and 3) removing air bubbles from the sturgeon skin gelatin solution of step 2) under reduced pressure, placing the sturgeon skin gelatin solution on an acrylic glass, and drying the sturgeon skin gelatin solution at in a vented oven 25° C. and 45-55% relative humidity for 24 hours to obtain the aesculin sturgeon skin gelatin film.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for extracting and identifying aesculin, fraxin, fraxetin and resveratrol from ledum palustre l.var.angustum e.busch
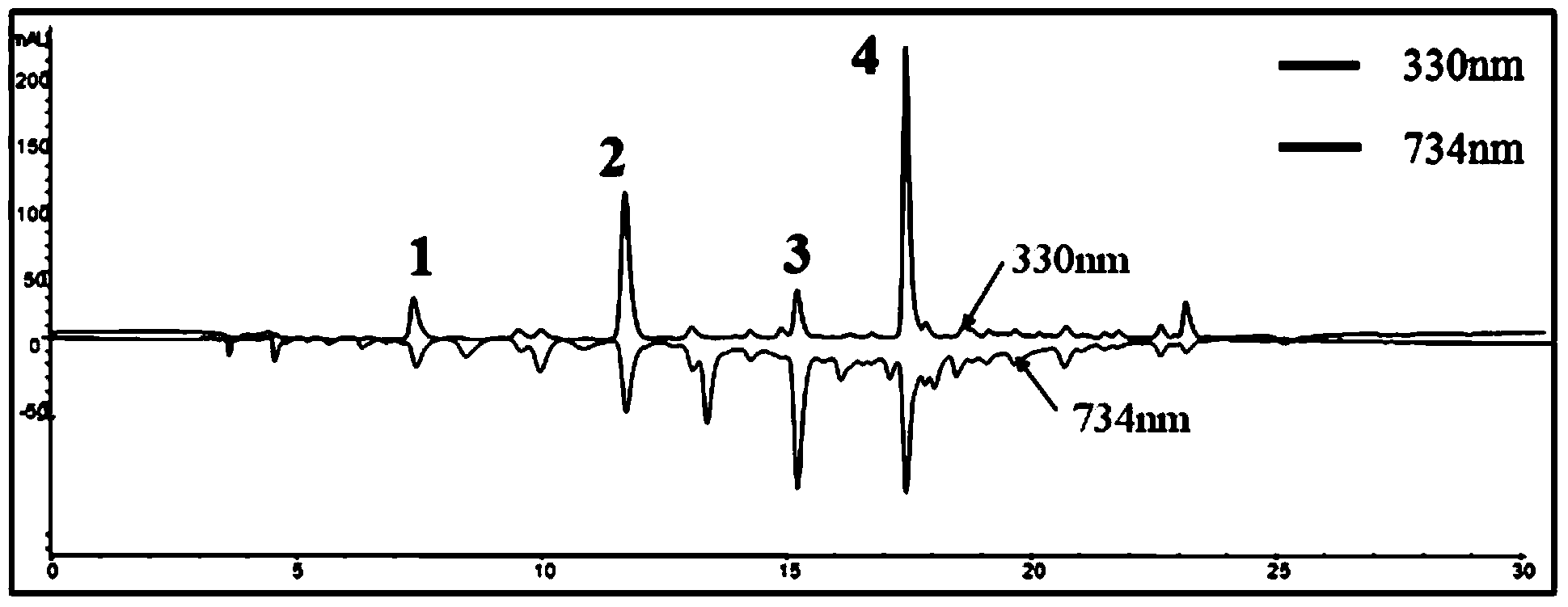
The invention relates to a method for extracting and identifying aesculin, fraxin, fraxetin and resveratrol from ledum palustre l.var.angustum e.busch. The method comprises the following steps: selecting and preprocessing raw materials; adding methanol with the volume percent being 65% and statically extracting a crude extract through using a pressure liquid extract technology at the temperature of 115 DEG C for 20-30 minutes; identifying antioxidant components in an on-line manner through using an on-line HPLC-ABTS<+> process; performing reservation for 7.41 minutes so as to obtain a peak, namely the aesculin, performing the reservation for 11.71 minutes to obtain a peak, namely the fraxin, performing the reservation for 15.22 minutes to obtain a peak, namely the fraxetin and performing the reservation for 17.43 minutes to obtain a peak, namely the resveratrol. According to the method, the steps of extracting and identifying the antioxidant active components are simplified, the four antioxidant active components, namely the aesculin, the fraxin, the fraxetin and the resveratrol can be separated and identified at the same time through a one-time extract process, and the efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINGYIN PHARML
Method for preparing bacterial cell catalyst for catalyzing aesculin transesterification
InactiveCN104726375AOvercome the disadvantages of low purity and easy generation of by-productsMild reaction conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a method for preparing a bacterial cell catalyst for catalyzing the aesculin transesterification. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating a bacterium seed solution into a liquid culture medium according to the inoculation amount of 0.5-25% (v / v), and culturing for 12-96h at the temperature of 25-60 DEG C; and washing the bacterium body by the distilling water and performing vacuum freeze drying to harvest a bacterium dry powder, namely the bacterial cell catalyst. The catalyst is used for high selectively catalyzing the aesculin and an acyl reagent to generate the transesterification. Compared with an enzymic preparation, the bacterial whole cell catalyst obtained from the invention avoids the expensive and miscellaneous enzyme separation and purification processes, has the characteristics of easy preparation and recovery and is beneficial for the scale production; and the catalyst is stable in an organic solvent.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Esculin and fraxin glycosyltransferase protein as well as coding gene and application thereof
The invention discloses aesculin and fraxin glycosyl transferase protein as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The esculetin and fraxin glycosyl transferase protein provided by the invention is a protein as shown in a) or b): a) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in a sequence 2 in a sequence table; b) a protein which is obtained by substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues on the amino acid sequence as shown in the sequence 2 in the sequence table, has the activity of aesculin and / or fraxin glycosyltransferase and is derived from a). Based on related results of high-throughput sequencing of aesculus chinensis, a key enzyme UGTs in the last step of synthesis of fraxin and aesculin is found and identified by using a reverse genetics method, the terminal blank of a coumarin biosynthesis pathway is filled, and glycosyl transferase protein and a coding sequence thereof are provided for further biosynthesis of fraxin and aesculin.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Traditional Chinese medicinal composition Qinpi Jiegu Capsules and quality detection method of preparations of composition
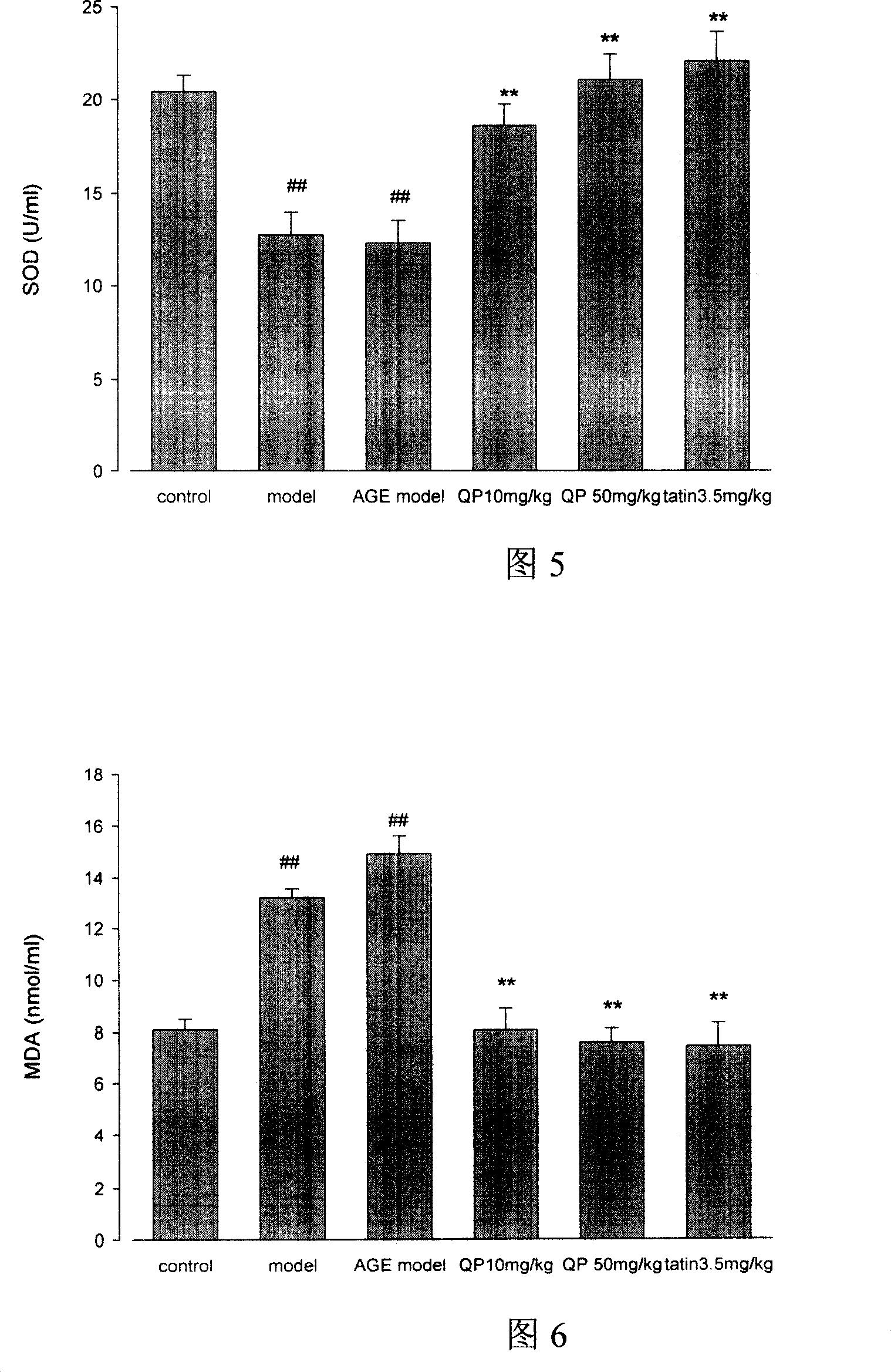
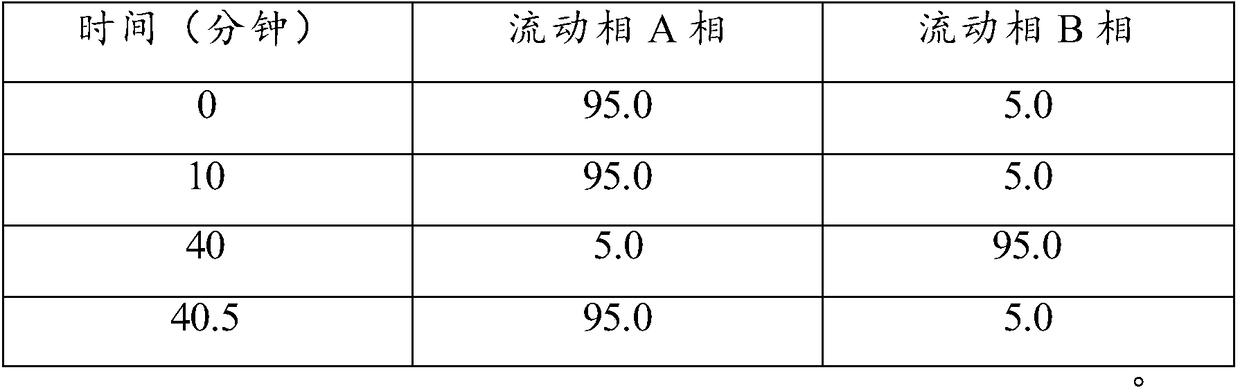
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicinal composition, Qinpi Jiegu Capsules, and a quality detection method of a preparation of the composition, belonging to the technical field of medicine. The existing traditional Chinese medicinal composition, Qinpi Jiegu Capsules, and the quality standards of the preparations of the composition are improved, the identification method of ash bark is improved on the basis of the existing standard, and an identification method of Pyrethrum tatsienense is added. The method is used for measuring the contents of aesculin and aesculetin in the ash bark at the same time under a same mobile phase, and a method for measuring the content of sipeimine in Fritillaria cirrhosa in the preparations is added, so as to further ensure safe, uniform, stable and controllable product quality and ensure the clinic curative effect of the composition and the administration safety of patients.
Owner:JINKE TIBETAN MEDICINE QINGHAI PROV
High purity cortex fraxini and its preparation method
Owner:SHANGHAI SINE PHARMA LAB
Culture medium for composite enrichment of salmonella, Listeria monocytogenes and Staphylococcus aureus, and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101412978BShorten enrichment timeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyLithium chloride
The invention discloses a complex enrichment medium used for salmonella, listeria monocytogenes and staphylococcus aureus and a method for preparing the same. The complex enrichment medium comprises the following components in weight portion: 15 to 19 portions of tryptone, 2 to 4 portions of peptone, 2 to 3 portions of sodium dihydrogen phosphate, 2 to 3 portions of glucose, 0.5 to 1.5 portions of aesculin, 1, 000 portions of distilled water, 1 to 2.5 portions of sodium pyruvate, 3 to 10.0 portions of mannitol, 1.0 to 25.0 portions of sodium chloride, 1 to 2.5 portions of lithium chloride, 0.0001 to 0.0002 portion of potassium tellurite, and 0.005-0.015 portion of nalidixic acid, wherein the pH value is between 7.1 and 7.5. The complex enrichment medium can inhibit the growth of other pathogenic microorganisms while performing enrichment on three target pathogens, thus the complex enrichment medium can be directly applied to the isolation culture and the biological assay test of target bacteria, and can also be directly applied to a detection technology of a plurality of pathogens based on one detection platform for multiple PCR and the like to make a diagnostic report.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of sodium aescinate
ActiveCN108218948AHigh yieldIncrease productivitySugar derivativesSteroidsEthyl acetateTime-Consuming
The invention relates to the technical field of plant extraction and discloses a preparation method of sodium aescinate. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking semen aesculin foralcohol extraction; extracting an obtained extract with chloroform, dichloromethane or ethyl acetate under acidic conditions; sequentially performing salification, decolorization and acetone precipitation on an obtained coarse product of aescine to obtain a coarse product of sodium aescinate; purifying the coarse product of sodium aescinate by a high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC); collecting aescines A, B, C and D; combining to obtain a mixture of the aescines; then, continuing to desalt by the HPLC; collecting a purified product of aescine; and salifying to obtain a purified product of sodium aescinate. The preparation method provided by the invention extracts and preliminarily purifies the semen aesculin by an organic solvent, avoids adopting macroporous adsorption resin andother existing time-consuming processes, and performs HPLC deep purification and desalination processes on this basis, so as to integrally achieve the purposes of significantly shortening a purification cycle and increasing a total yield of sodium aescinate and to improve the production efficiency of sodium aescinate.
Owner:GANSU CHANGEE BIO PHARMA
Application of aesculin XVII or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
PendingCN113876790AReduce accumulationIncrease ALB contentOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiseaseHepatic Diseases
The invention discloses application of aesculin XVII or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in preparation of a medicine for preventing and treating a non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. By constructing a cell model of the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, aesculin XVII can increase the content of ALB, reduce the level of AST, ALT, TG, TNF-alpha and IL-1 beta and reduce formation of lipid droplets in liver cells, and therefore the non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is prevented and treated.
Owner:湖州市食品药品检验研究院
Flat-plate sieving method of aesculin for high-yield beta-glucosidase producing strain
The invention discloses a flat plate screening method for high yielding Beta-glucosidase production bacteria by using aesculin. The method comprises the steps of: 1. earth sample collection; 2. enrichment culture; 3. flat plate preparation of the aesculin; 4. flat plate primary screening aesculin; 5. separation and purification; 6. secondary screen by a shaking battle, etc. The invention can fast screen active strain possessing the Beta-glucosidase from samples which contain rich fibrin resources; compared with the method which is reported in published literature which screens Beta-glucosidase production bacteria by using a cellobiose flat plate method, the invention has the remarkable advantages at price; under the condition that obtains 100 strains by screening, the cost of the invention by using the aesculin is only one tenth of the cellobiose flat plate method; in addition, the invention has the advantages of simple operation, reliable result, etc.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Detection method of traditional Chinese medicinal composition Qinpi Jiegu preparations
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicinal composition, Qinpi Jiegu Capsules, and a quality detection method of a preparation of the composition, belonging to the technical field of medicine. The existing traditional Chinese medicinal composition, Qinpi Jiegu Capsules, and the quality standards of the preparations of the composition are improved, the identification method of ash bark is improved on the basis of the existing standard, and an identification method of Pyrethrum tatsienense is added. The method is used for measuring the contents of aesculin and aesculetin in the ash bark at the same time under a same mobile phase, and a method for measuring the content of sipeimine in Fritillaria cirrhosa in the preparations is added, so as to further ensure safe, uniform, stable and controllable product quality and ensure the clinic curative effect of the composition and the administration safety of patients.
Owner:JINKE TIBETAN MEDICINE QINGHAI PROV
Direct electrochemical method for detecting aesculin and/or aesculetin
PendingCN114235935AExcellent electrochemical responseAccurate detectionMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical responseCyclic voltametry
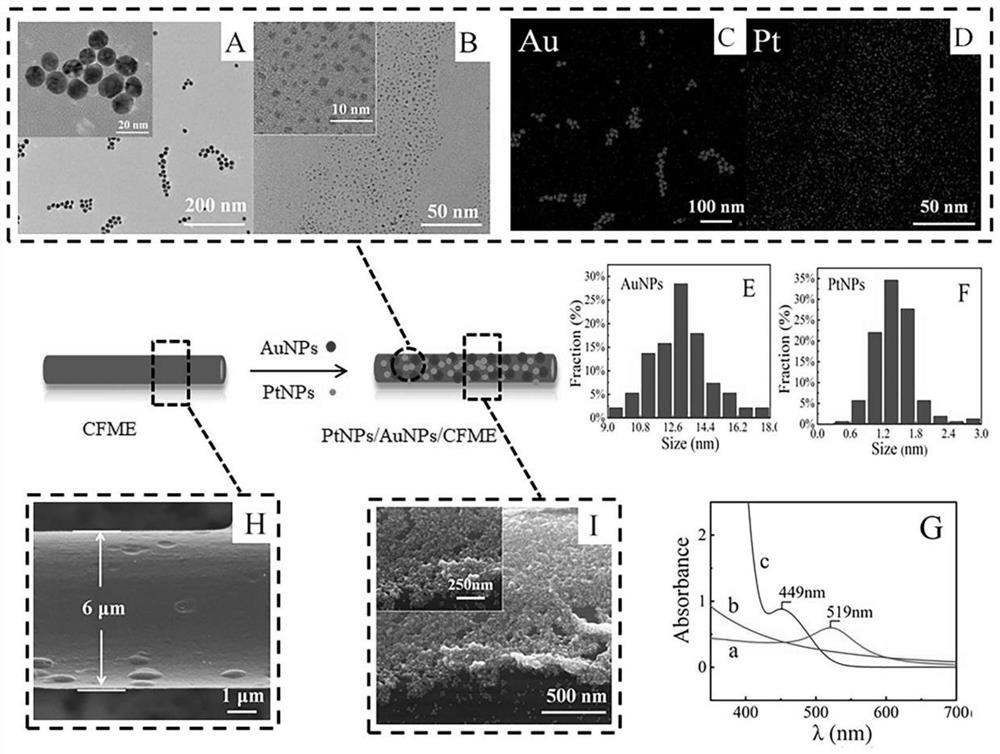
The invention discloses a direct electrochemical method for detecting aesculin and / or aesculetin, which is characterized in that a sample is detected by using a carbon fiber electrode PtNPs / AuNPs / CFME modified by AuNPs and PtNPs through cyclic voltammetry or differential pulse voltammetry. The electrode used in the method has good electrochemical response, one component or both can be accurately detected in a sample with interference of other impurities or in a sample with interference of other impurities or in a sample with interference of other impurities or in a sample with interference of other impurities or in a sample with interference of other impurities or in a sample with interference of other impurities or in a sample with interference of other impurities or in a sample with interference of other impurities or in a sample with two samples, detection results are accurate, detection limit is low, and detection sensitivity and selectivity can be improved in complex biological matrixes.
Owner:SOUTH CENTRAL UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
HPLC quantitative analysis method for aesculin and aesculetin in pulsatilla chinensis powder
InactiveCN110907579ARaise quality standardsAchieve precise quantitationComponent separationMedicinal herbsAnemone chinensis
The invention discloses an HPLC quantitative analysis method for aesculin and aesculetin in pulsatilla chinensis powder. The HPLC quantitative analysis method specifically comprises the following steps: step 1, determining chromatographic conditions; step 2, extraction process: precisely weighing pulsatilla chinensis powder, putting the pulsatilla chinensis powder into a conical flask with a plug,precisely adding methanol and a sealing plug, weighing, carrying out ultrasonic extraction, cooling, weighing again, supplementing the reduced weight with methanol, uniformly shaking, filtering, andtaking the subsequent filtrate; step 3, preparing a solution: preparing a reference substance storage solution, a reference substance solution, a test solution, a negative reference solution and a reference medicinal material solution; step 4, methodological investigation, including specificity test, linear relationship investigation, precision test and accuracy test; and step 5, sample determination: determining the content of a self-made pulsatilla chinensis powder sample and determining the content of commercially available pulsatilla chinensis powder. The method provided by the invention has the technical effect that the effective components aesculin and aesculetin in the pulsatilla chinensis powder can be accurately quantified.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & ECONOMY
Aesculin utilization test medium, preparation method of medium, kit and sample analyzer
PendingCN111118103AReduce misinterpretationRequirement to reduce judgment sensitivityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsInorganic saltsEngineering
The invention discloses an aesculin utilization test medium, a preparation method of the medium, a kit and a sample analyzer. The aesculin utilization test medium at least comprises aesculin, ferroussulfate, a carbon source, a nitrogen source and inorganic salt. By the above mode, misinterpretation on a test result can be reduced, and the detection accuracy can be improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN DYMIND BIOTECH
Producing microorganism for trans-glycosylation beta-galactosidase
The invention discloses a glycosyl-transferbeta-galactosidase production bacterium, which is characterized by the following: the name of this bacterium is Enterobacter cloacae B5, which is Gram-negative bacterium; the conservation code is CGMCC No.1401; the bacterium shape changes along culture time extension on the LB culture medium from long rod to short rod, ellipsoid shape and ball; the colouring size is 0.5-1.5*0.7-9.0 mm with single, couple or short-chain arrangement; the bacterium can move by peripheral flagellar without gemma and can apply citrate or acetate as only one carbon source, which products acid and gas by fermenting glucose at 37 deg.c and glycerin without gas, hydrolyzing aesculin and indole; V.P. detects positive and methyl red detects negative; the nitrate is reduced and Lys is not decarboxylation with ornithine decarboxylase, arginine dihydrolase and urease; the nucleotide sequence of this bacterium 16S rDNA is described as SEQ ID No.1; the beta-galactosidase can take lactin as substrate, which catalyzes to produce oligomer galactose.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Source wastewater biotoxicity detection kit and use method thereof
PendingCN114457140AImprove toleranceFacilitates biotoxicity testingMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment, and discloses a source wastewater biotoxicity detection kit and a use method thereof. The kit comprises a Q1 reagent and an F1 reagent, the Q1 reagent is a culture medium containing aesculin and iron ions; the reagent F1 is prepared from lactobacillus plantarum CR3; the lactobacillus plantarum CR3 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on March 15, 2021, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.22011. The lactobacillus plantarum CR3 has been preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC). According to the method, the lactobacillus plantarum CR3 is applied to source wastewater biotoxicity detection, the culture medium adaptive to the lactobacillus plantarum CR3 is adopted, the wastewater toxicity intensity can be visually reflected through the color development depth of a culture system, the color development is obvious and stable, and whether front-end wastewater can directly enter a rear-end biochemical treatment system or not can be conveniently judged.
Owner:HANGZHOU XIUCHUAN TECH CO LTD
Recovery technology of aesculus chinensis fruit peel extract mother liquid
ActiveCN112321659AHigh yieldReduce waste of resourcesSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationBiotechnologyBotany
The present invention relates to the field of aesculus chinensis fruit peel extract production and particularly discloses a recovery technology of aesculus chinensis fruit peel extract mother liquid.The recovery technology of aesculus chinensis fruit peel extract mother liquid comprises the following steps: material mixing: taking aesculus chinensis fruit peel extract mother liquid and dissolvingthe mother liquid with hot water at 90-95 DEG C to obtain a mixed solution; filtering; adsorption column passing; washing with water; desorption; concentration: performing ultrafiltration and reverseosmosis on a desorption solution, and concentrating the desorption solution until a sugar degree is greater than or equal to 32 to obtain a concentrated solution; and cooling crystallization. The recovery technology can be used for recovering the aesculus chinensis fruit peel extract mother liquid and has an advantage of improving yield of an effective component of aesculin.
Owner:NINGBO GREEN HEALTH PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Aesculin sturgeon skin gelatin film with antioxidant activity and enterococcus faecalis detection ability and a method of preparing the same
ActiveUS10815348B2Special physicochemical propertyGood film formingFlexible coversWrappersBiotechnologyGelatin film
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cortex fraxini coumarin composition
ActiveCN1923194BRemarkable effectSkeletal disorderHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsCortex FraxiniFraxin
The invention relates to a method for preparing ash bark coumarin compound. Wherein, it boils and extracts with water, uses porous resin to separate and purify ash bark coumarin compound; and said compound comprises aesculin, aesculetin, fraxin, and fraxetin, while the total coumarin content is higher than 50%, and the contents of aesculin, aesculetin, fraxin, and fraxetin are higher than 40%, while their ratios are 4-6:1-3:2-4:1. The invention also provides its application in medicine production.
Owner:四川恩威制药有限公司
Method for extracting and identifying aesculin, fraxin, fraxetin and resveratrol from ledum palustre l.var.angustum e.busch
The invention relates to a method for extracting and identifying aesculin, fraxin, fraxetin and resveratrol from ledum palustre l.var.angustum e.busch. The method comprises the following steps: selecting and preprocessing raw materials; adding methanol with the volume percent being 65% and statically extracting a crude extract through using a pressure liquid extract technology at the temperature of 115 DEG C for 20-30 minutes; identifying antioxidant components in an on-line manner through using an on-line HPLC-ABTS<+> process; performing reservation for 7.41 minutes so as to obtain a peak, namely the aesculin, performing the reservation for 11.71 minutes to obtain a peak, namely the fraxin, performing the reservation for 15.22 minutes to obtain a peak, namely the fraxetin and performing the reservation for 17.43 minutes to obtain a peak, namely the resveratrol. According to the method, the steps of extracting and identifying the antioxidant active components are simplified, the four antioxidant active components, namely the aesculin, the fraxin, the fraxetin and the resveratrol can be separated and identified at the same time through a one-time extract process, and the efficiency is remarkably improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN XINGYIN PHARML
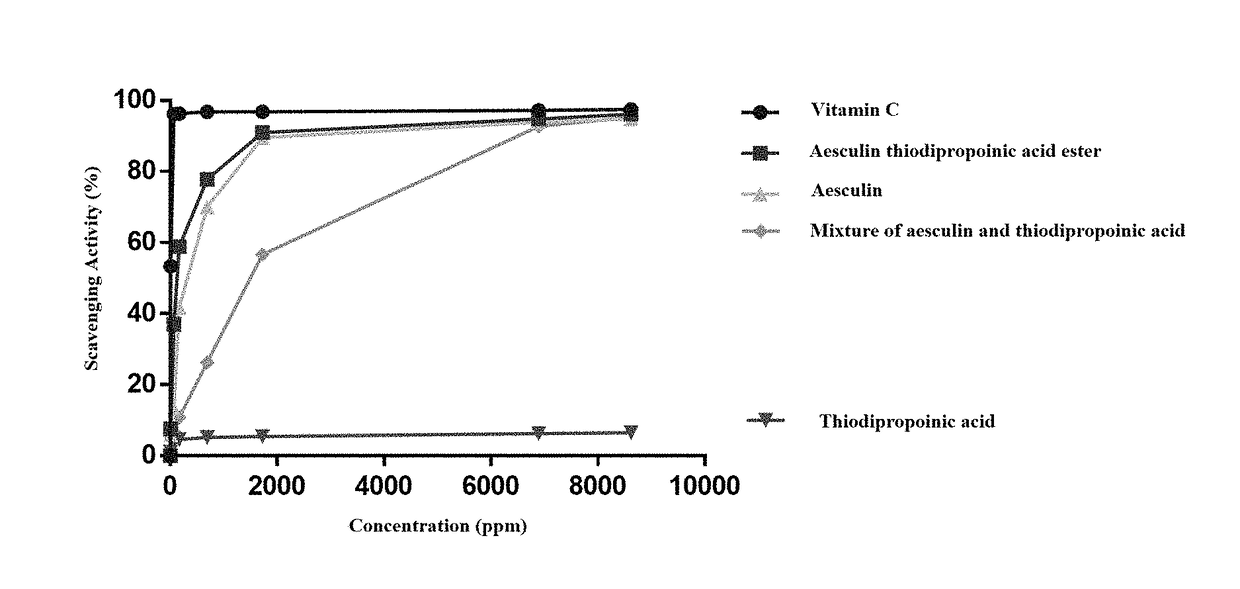
Aesculin thiodipropionic acid ester with antioxidant activity and a method of preparing the same
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com