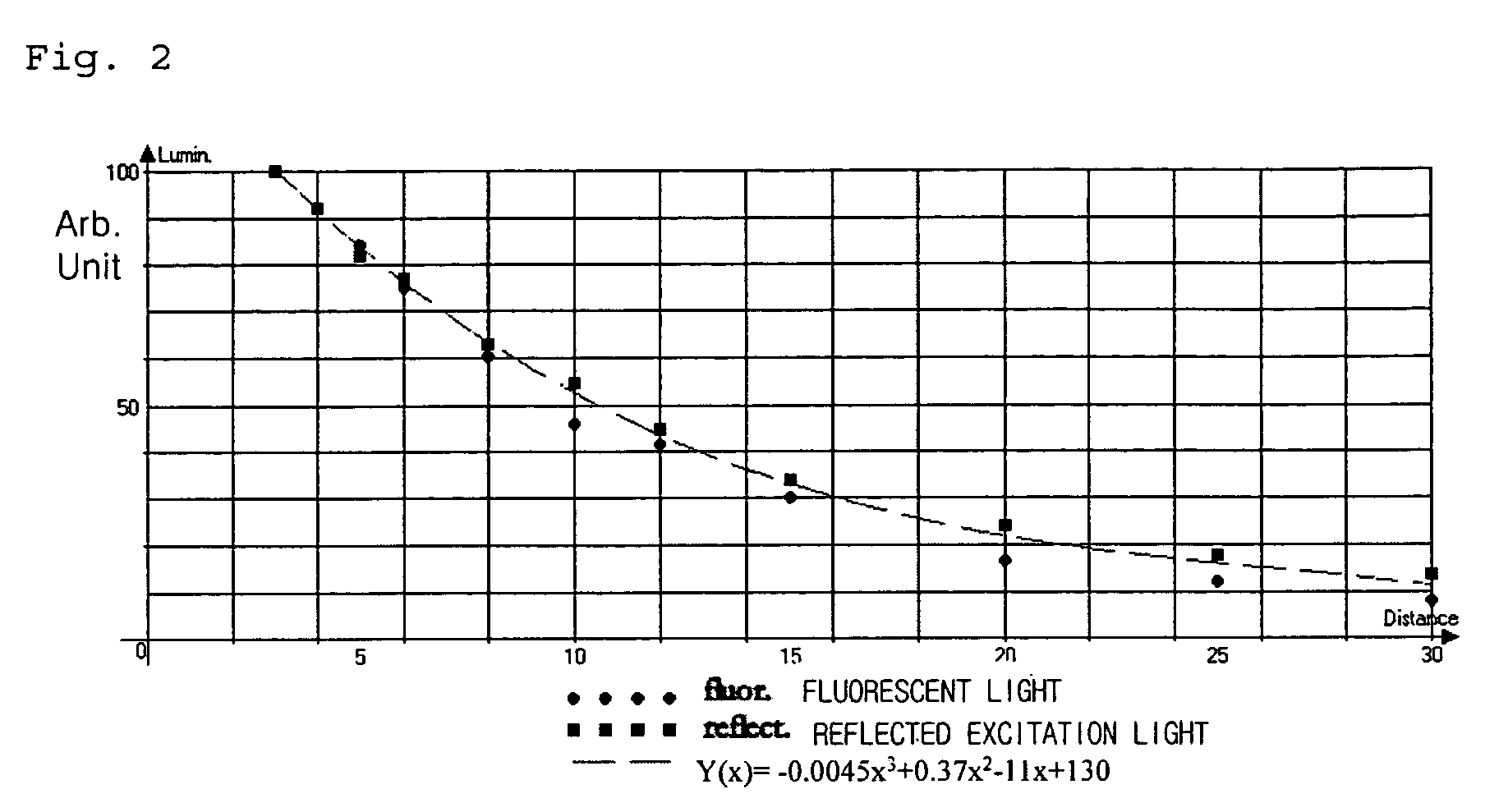
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5635 results about "Fluorescence intensity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
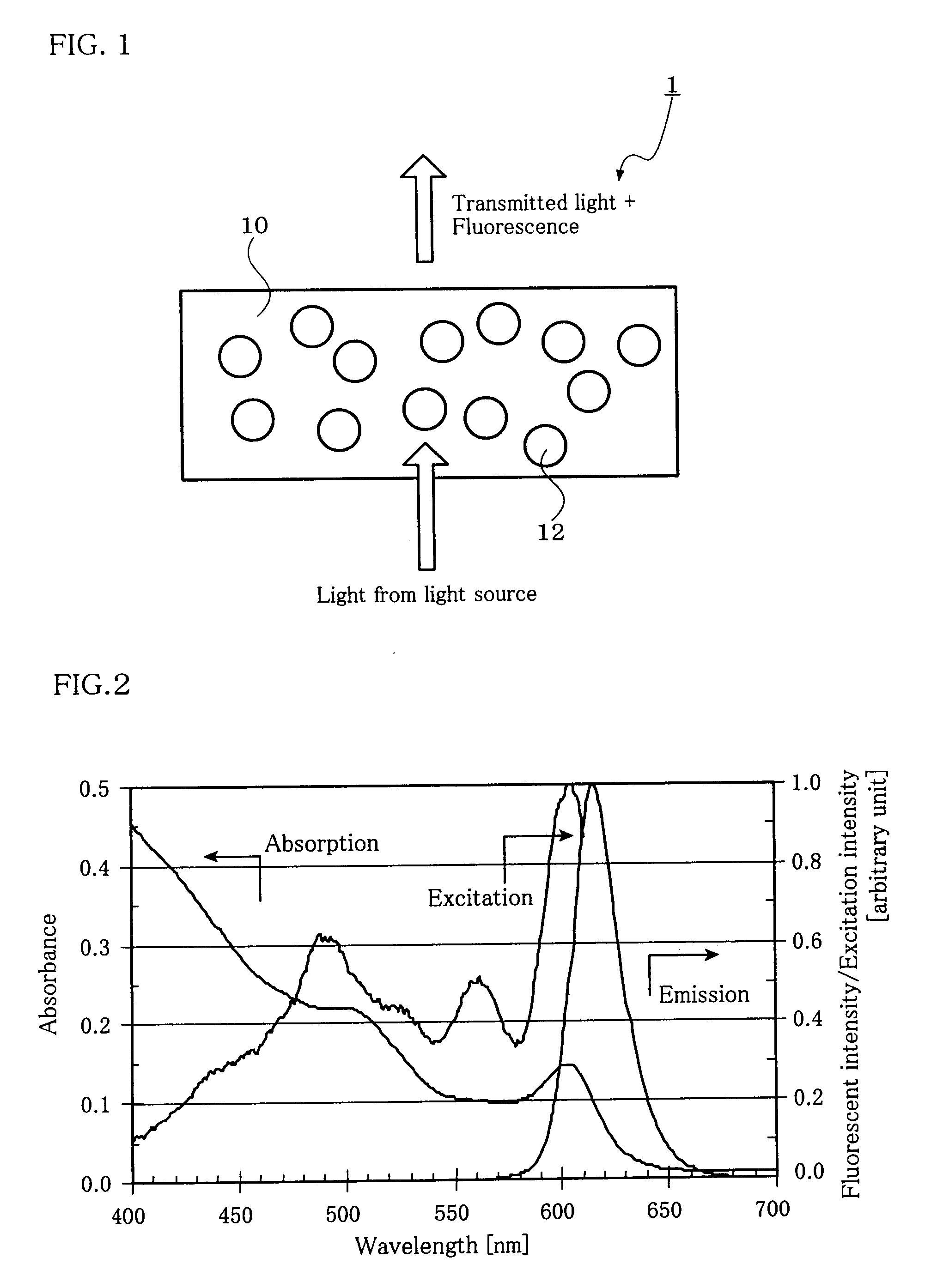
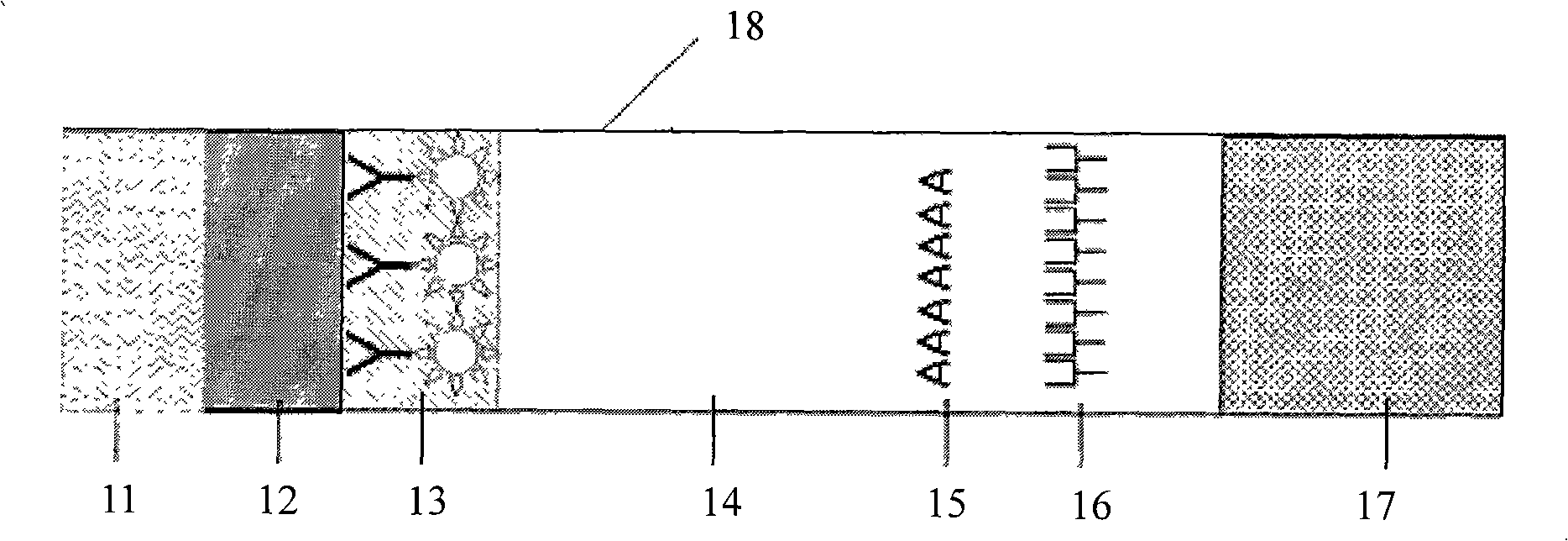
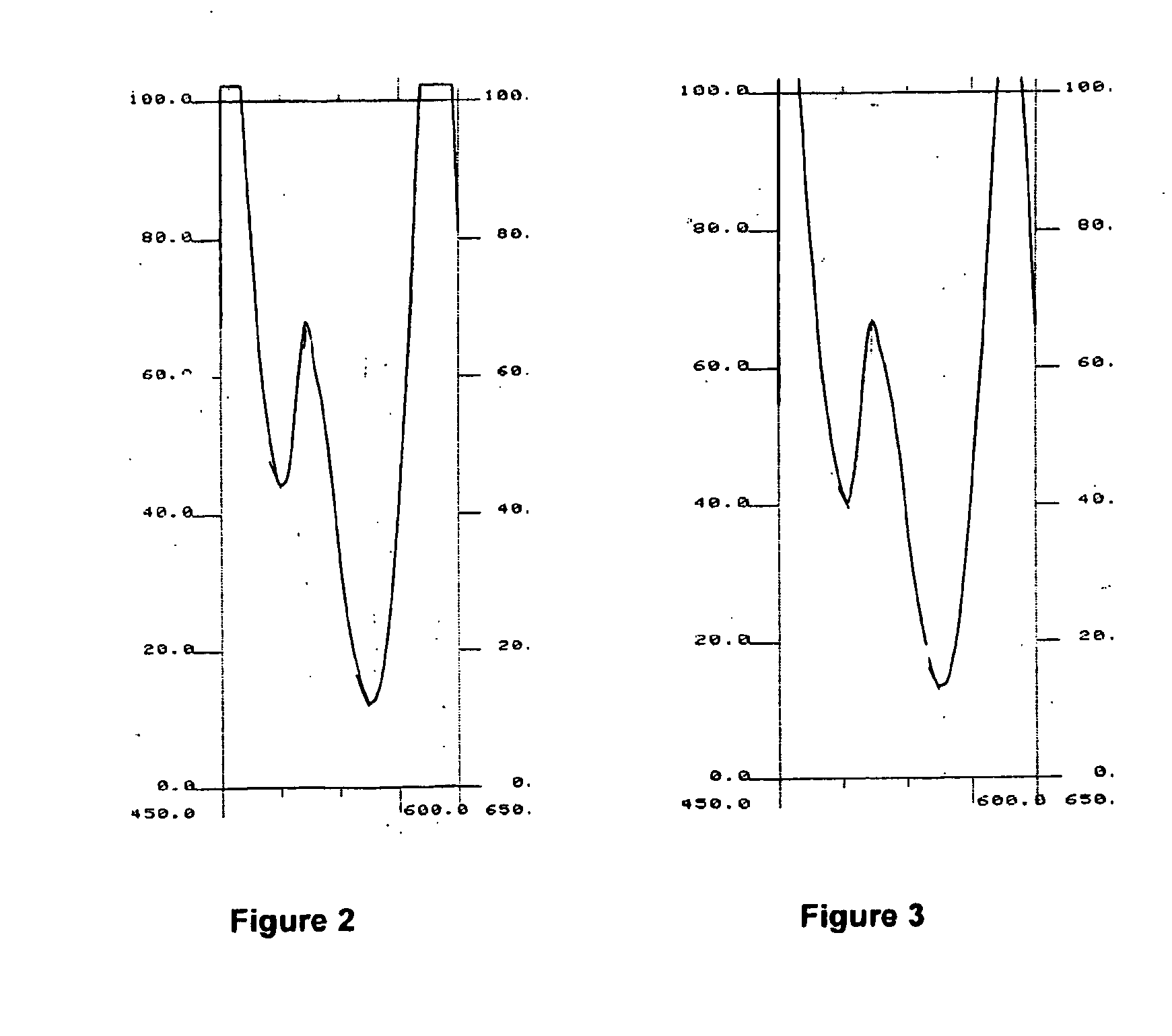
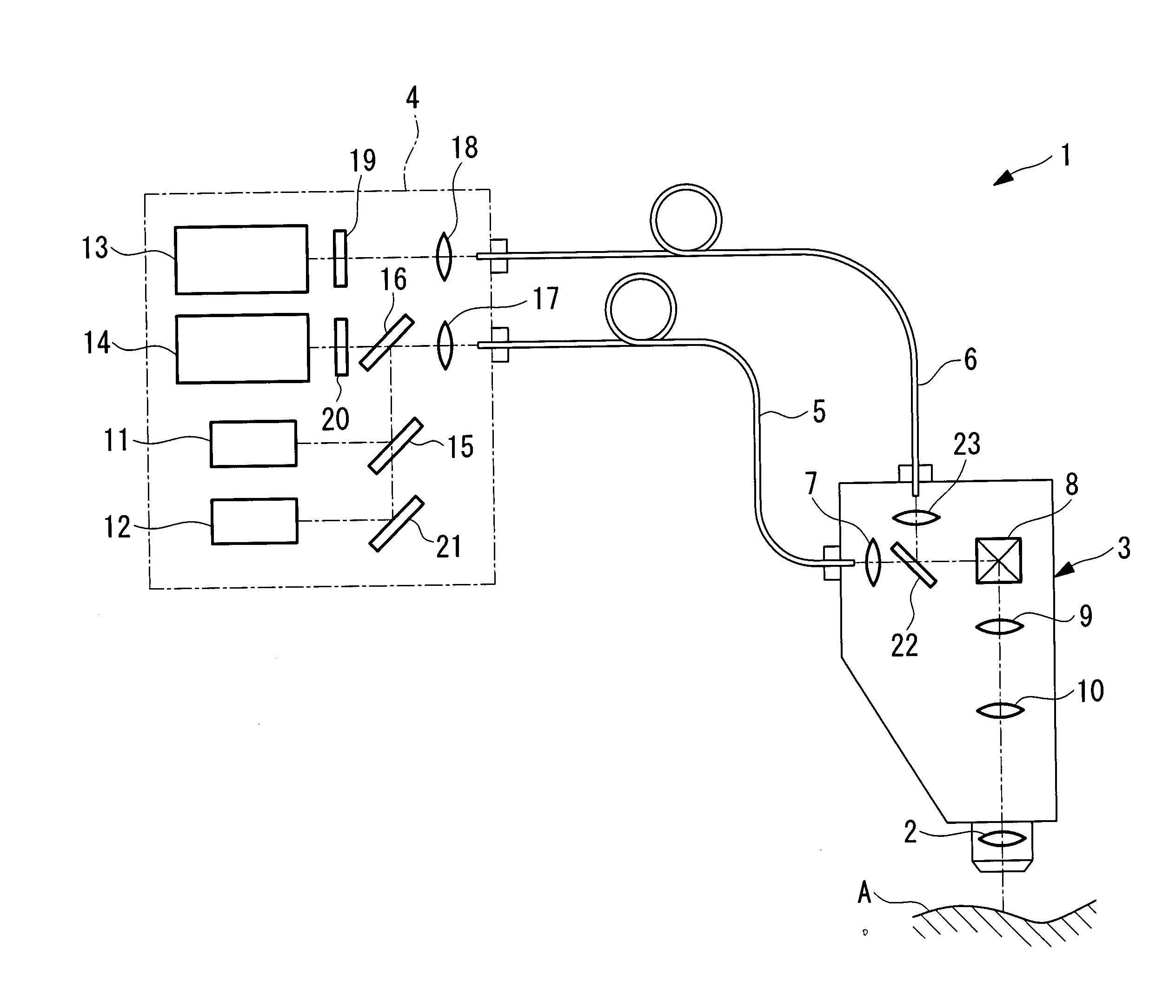
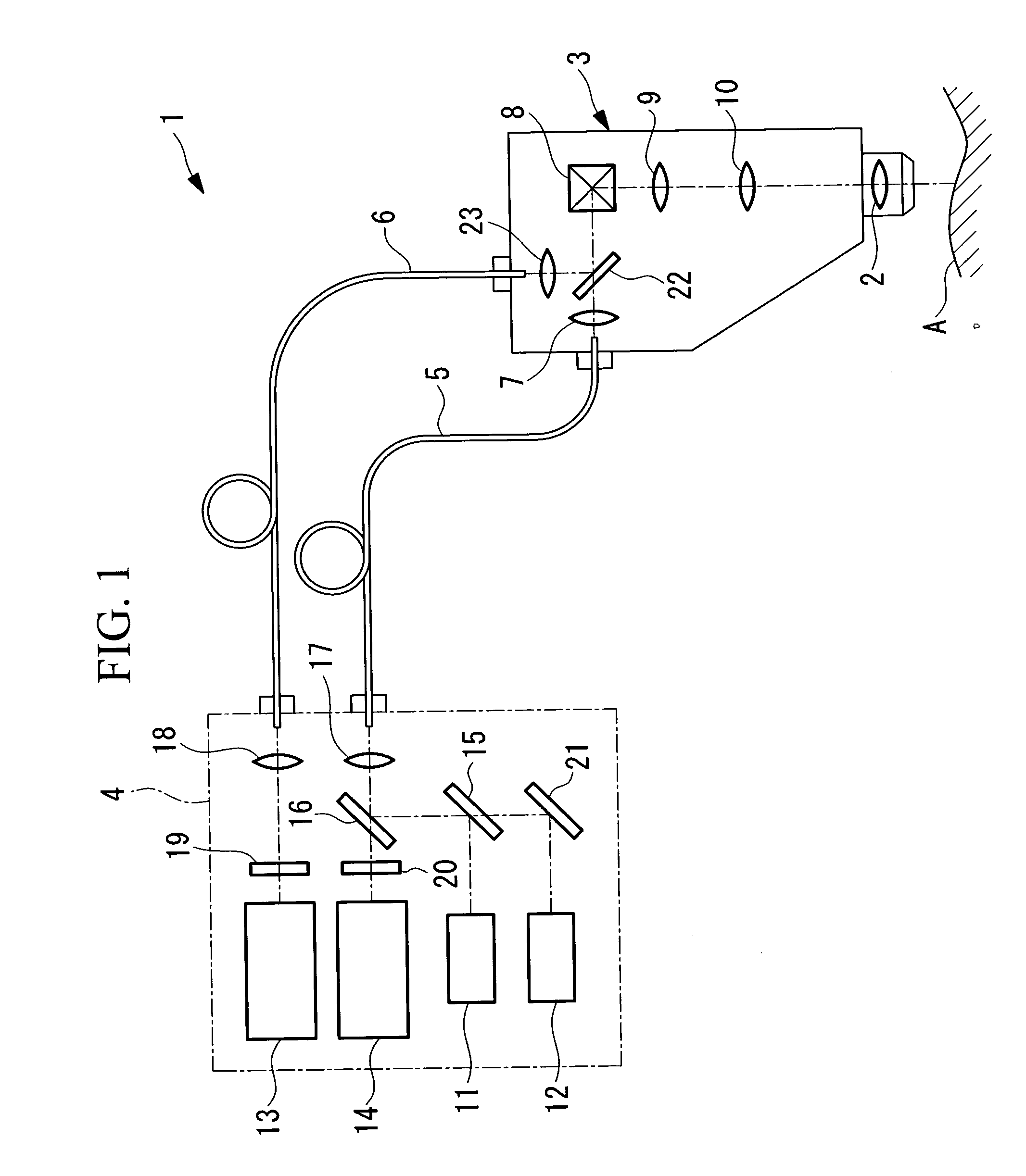
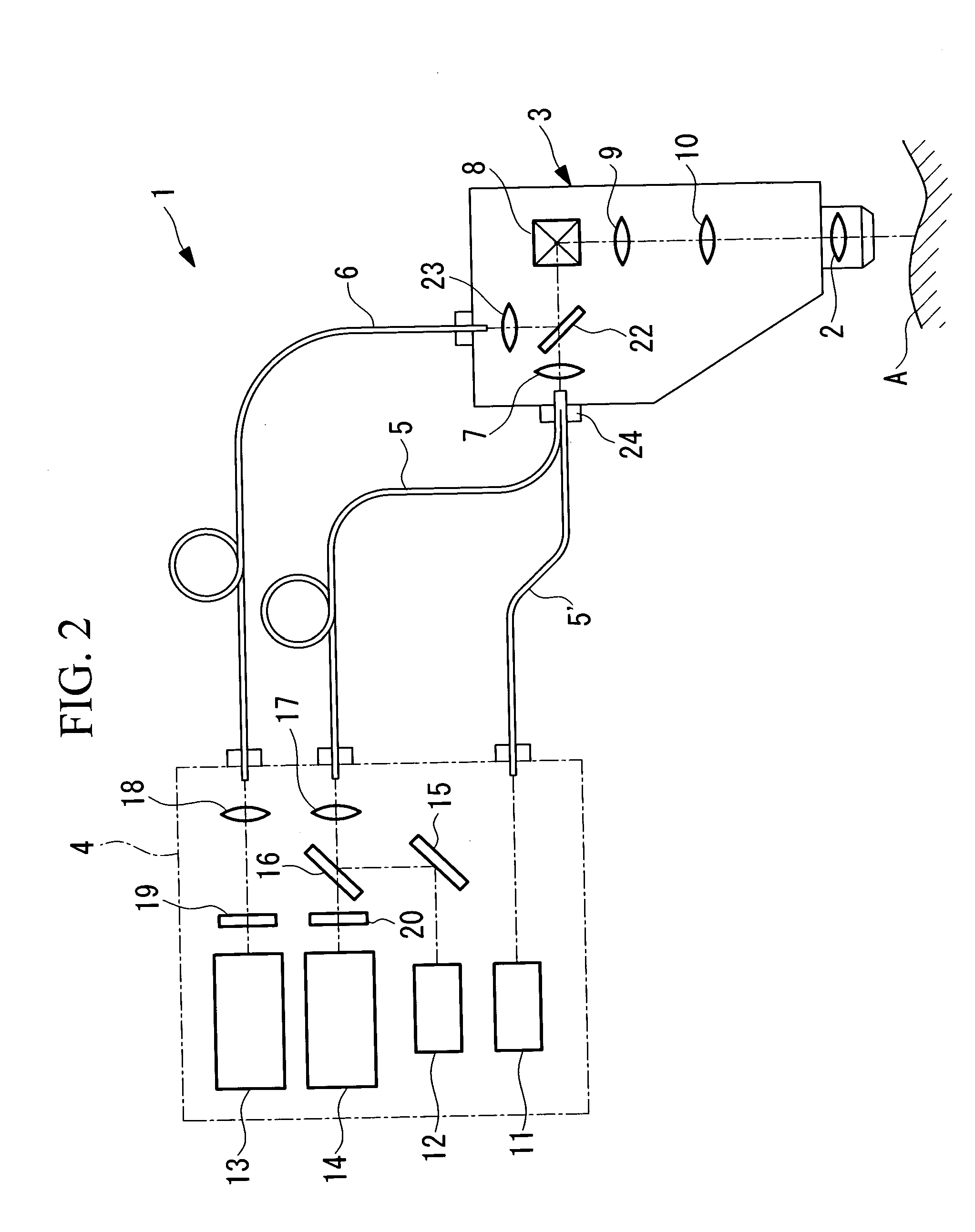
Fluorescence intensity (incl. Fluorescence intensity (incl. FRET) Fluorescence is the emission of light by a molecule (called fluorophore) that has been excited by light with a shorter wavelength than the emitted one. Fluorescence intensity detection is the measurement of this emitted light.
Magnetically-responsive microspheres
InactiveUS6773812B2Easy to doNanomagnetismSynthetic resin layered productsMicrosphereMagnetite Nanoparticles
Microspheres are constructed using magnetic particles. Hybrid microspheres are constructed using fluorescent or luminescent microspheres and magnetic nanoparticles. Reactive moieties on the surface of the resultant particles can be used for attachment of biologically active molecules, thus allowing selective separations and analytical assays to be performed. Distinguishable subsets of microspheres can be constructed based on fluorescent intensities, and separations can be affected based on variable degree of magnetic content.
Owner:LUMINEX
Active CMOS biosensor chip for fluorescent-based detection
ActiveUS7738086B2Detailed characterization of fluorophore labelsRelax requirementsTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryFluorophorePhotodiode
An active CMOS biosensor chip for fluorescent-based detection is provided that enables time-gated, time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy. In one embodiment, analytes are loaded with fluorophores that are bound to probe molecules immobilized on the surface of the chip. Photodiodes and other circuitry in the chip are used to measure the fluorescent intensity of the fluorophore at different times. These measurements are then averaged to generate a representation of the transient fluorescent decay response unique to the fluorophores. In addition to its low-cost, compact form, the biosensor chip provides capabilities beyond those of macroscopic instrumentation by enabling time-gated operation for background rejection, easing requirements on optical filters, and by characterizing fluorescence lifetime, allowing for a more detailed characterization of fluorophore labels and their environment. The biosensor chip can be used for a variety of applications including biological, medical, in-the-field applications, and fluorescent lifetime imaging applications.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Automated sample analysis
ActiveUS7595197B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotomultiplierAnalysis sample
Samples of materials used in industrial processes are analyzed to determine the concentration of certain materials of interest. The quantitative analysis of samples for these materials is provided without the need for manual methods such as titration. Indicators such as fluorescent dyes for which the intensity of fluorescence is indicative of the concentration of a material of interest are used. The dyes are made to fluoresce by means of a light source, and a photomultiplier or other detector capable of measuring light intensity detects the resulting fluorescence. The intensity of fluorescence in the sample is compared to the intensities of fluorescence produced by samples with known concentrations of the material of interest to determine the concentration of the material of interest of the sample.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Magnetic measurement apparatus
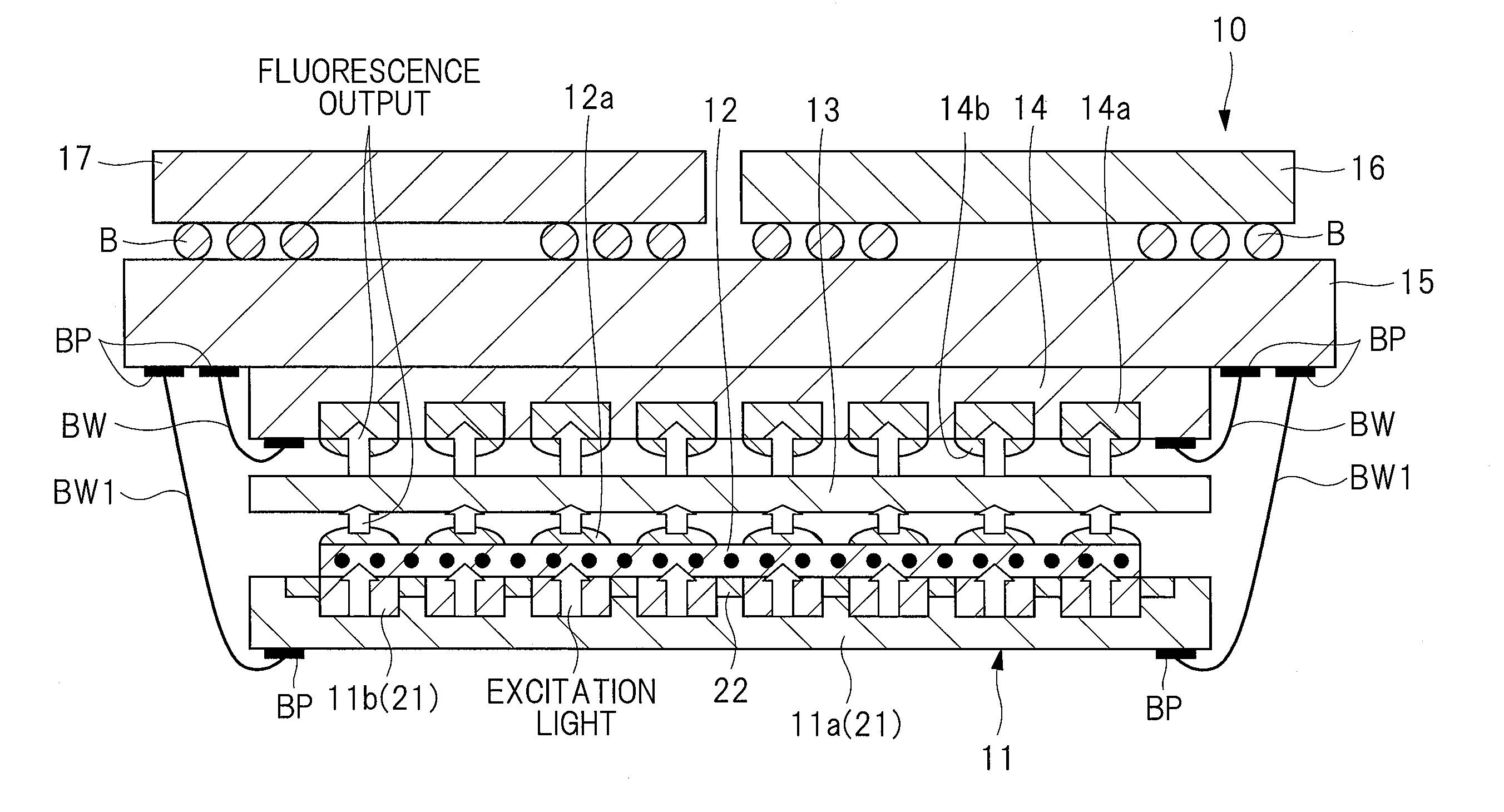
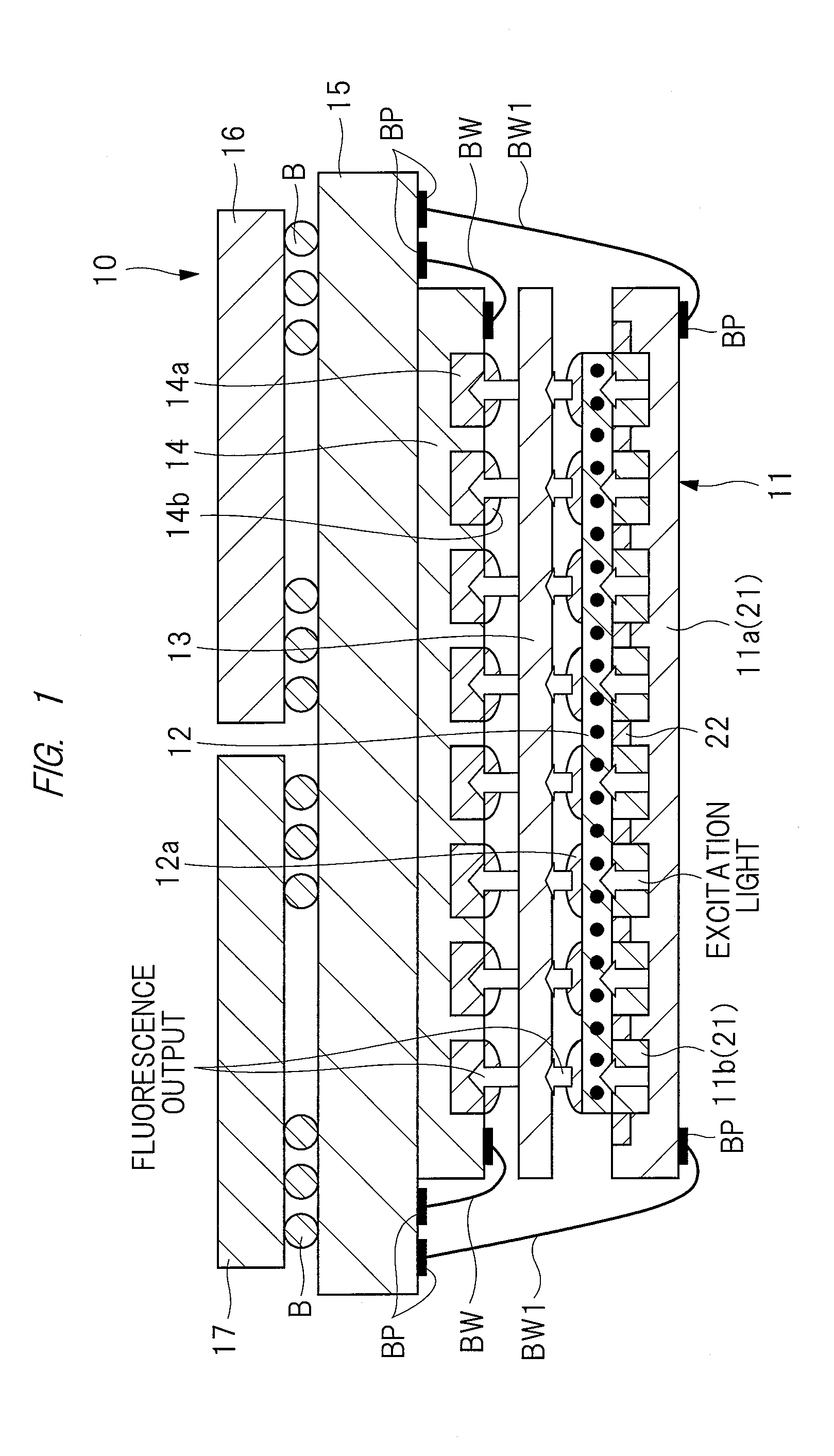
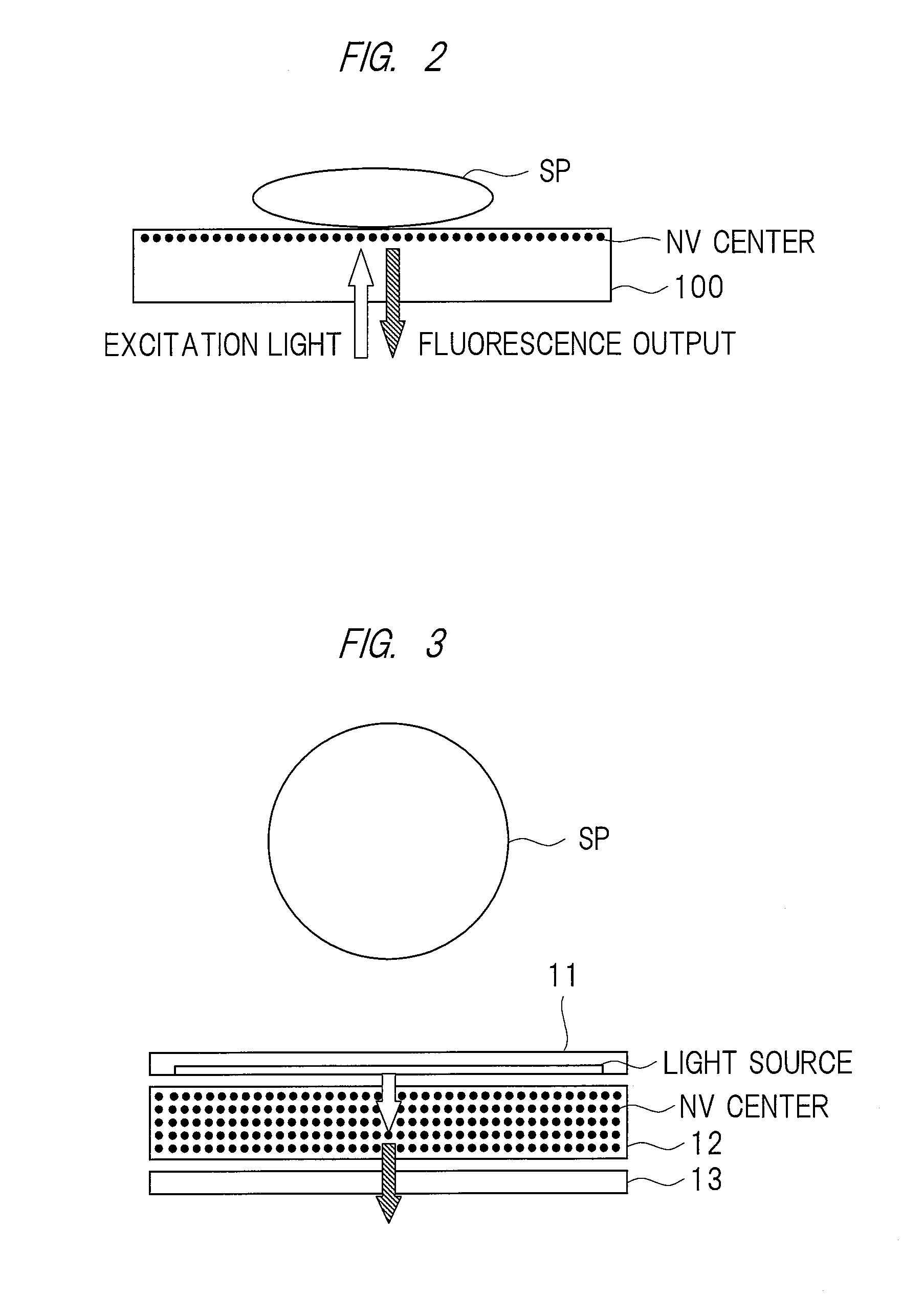
ActiveUS20150374250A1High measurement accuracyImprove detection accuracyPolycrystalline material growthDianostics using fluorescence emissionMagnetic measurementsDiamond crystal
High-accuracy magnetic measurement is performed by efficiently using nitrogen-vacancy pairs in all orientations. A magnetic measurement apparatus includes a diamond crystal and an image sensor. The diamond crystal has nitrogen-vacancy pairs. The image sensor detects the intensities of fluorescence generated by an exciting light applied to the diamond crystal by using a plurality of pixels. The nitrogen-vacancy pairs of the diamond crystal are made to one-to-one correspond to the pixels. The fluorescence generated by one nitrogen-vacancy pair is received by one pixel made to correspond to the nitrogen-vacancy pair.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for probabilistically classifying tissue in vitro and in vivo using fluorescence spectroscopy
InactiveUS7236815B2Faster and effective managementReduce mortalityDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionMultivariate statisticalPrincipal component analysis
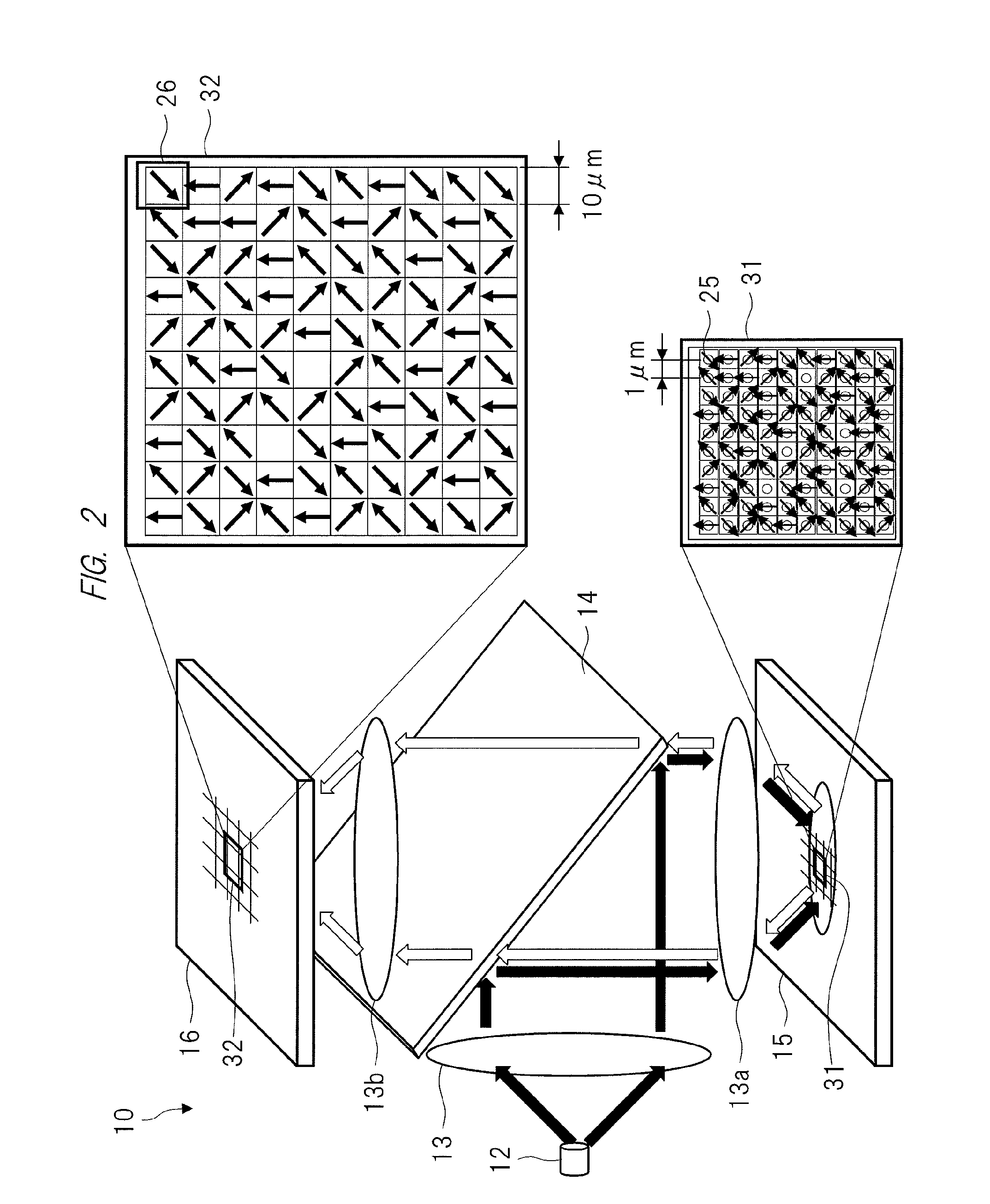
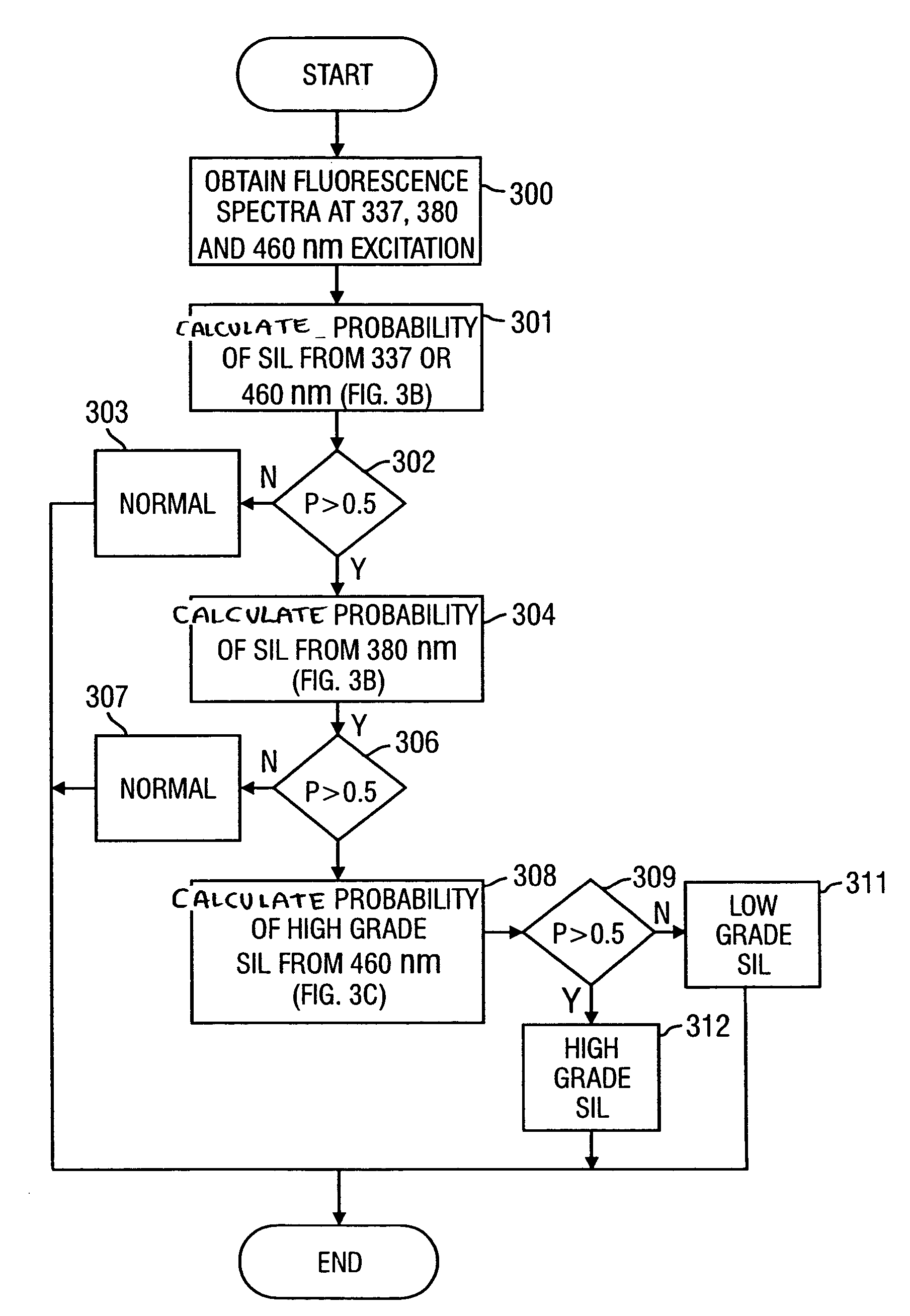
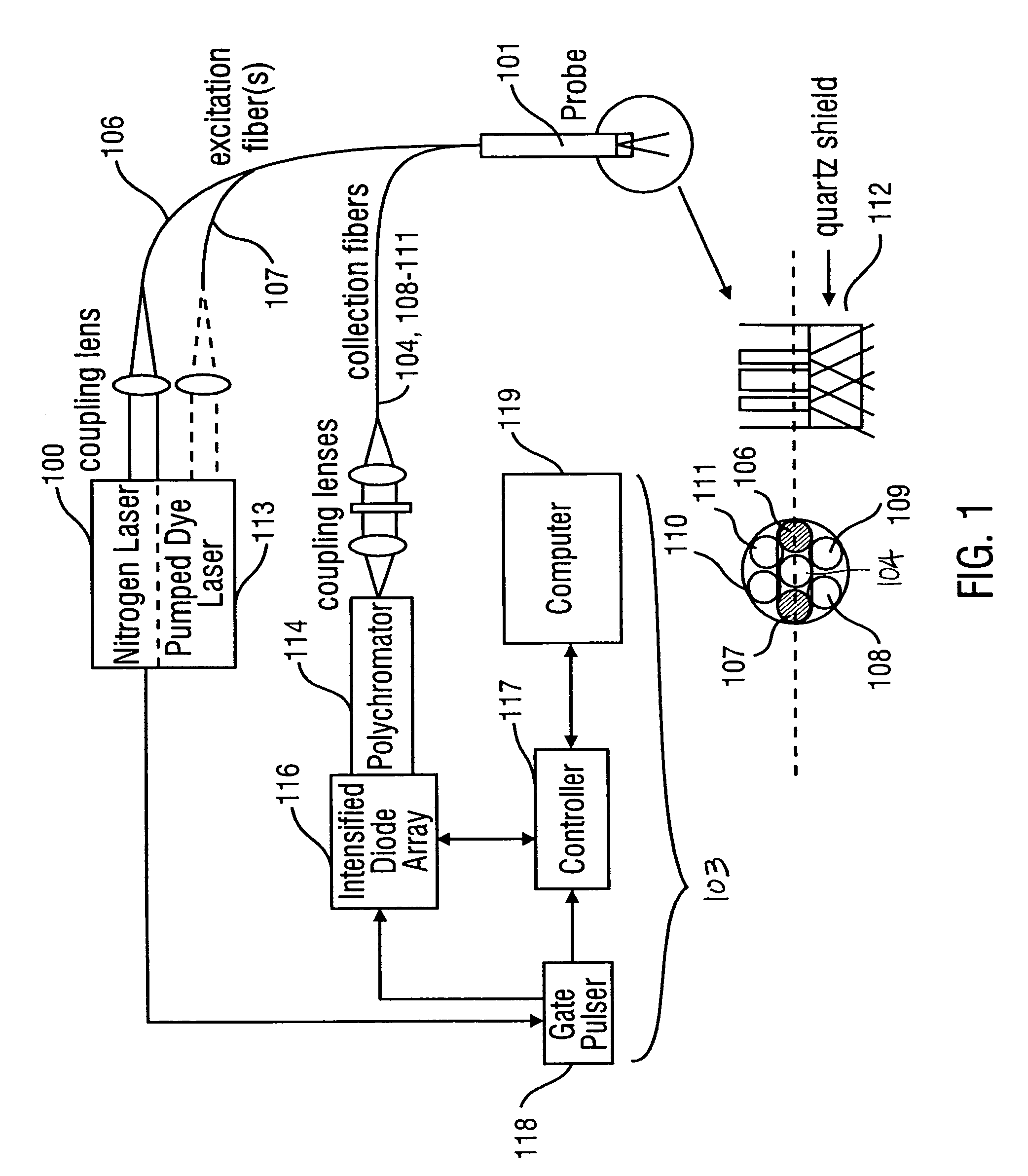
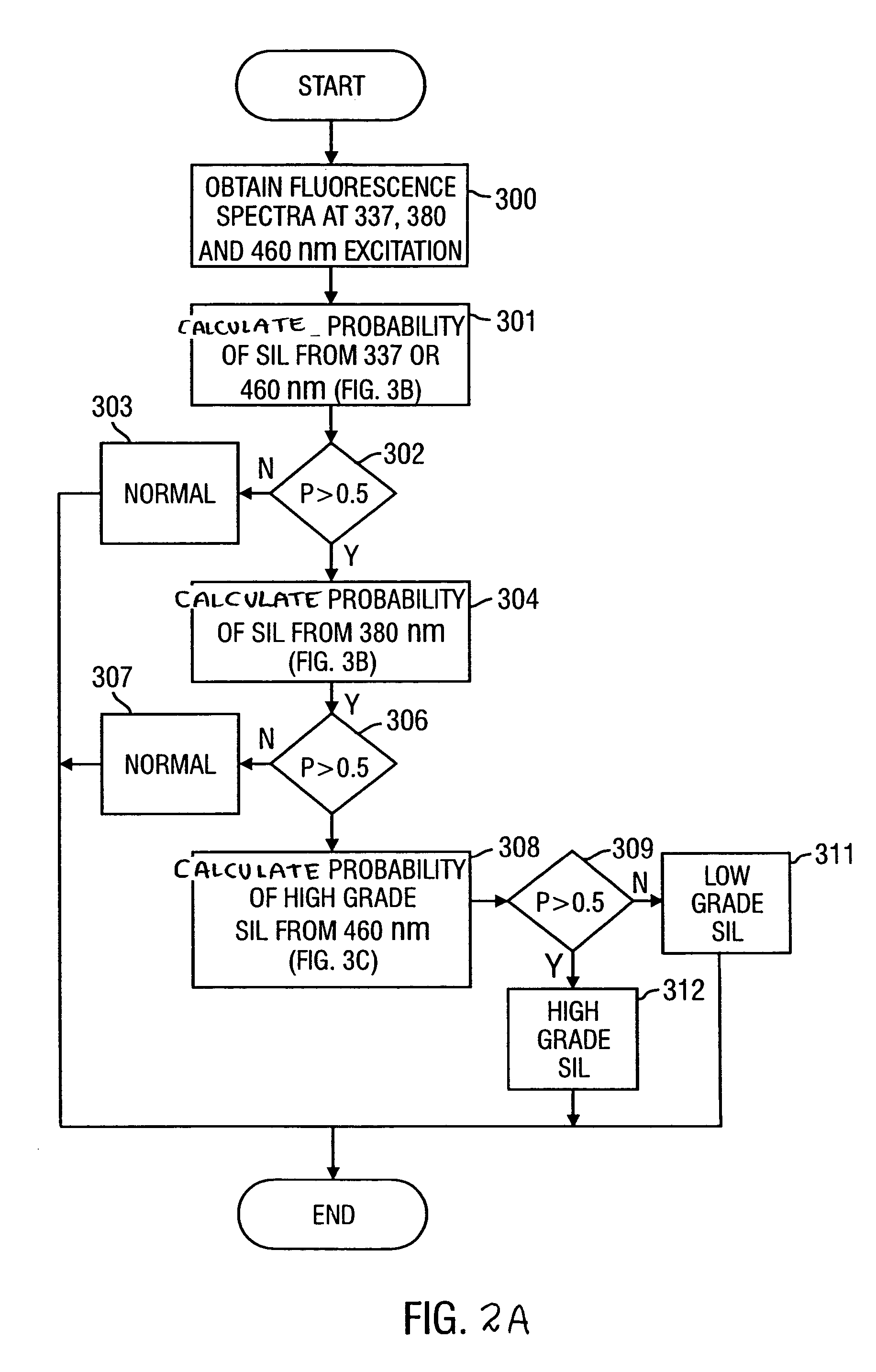
Fluorescence spectral data acquired from tissues in vivo or in vitro is processed in accordance with a multivariate statistical method to achieve the ability to probabilistically classify tissue in a diagnostically useful manner, such as by histopathological classification. The apparatus includes a controllable illumination device for emitting electromagnetic radiation selected to cause tissue to produce a fluorescence intensity spectrum. Also included are an optical system for applying the plurality of radiation wavelengths to a tissue sample, and a fluorescence intensity spectrum detecting device for detecting an intensity of fluorescence spectra emitted by the sample as a result of illumination by the controllable illumination device. The system also include a data processor, connected to the detecting device, for analyzing detected fluorescence spectra to calculate a probability that the sample belongs in a particular classification. The data processor analyzes the detected fluorescence spectra using a multivariate statistical method. The five primary steps involved in the multivariate statistical method are (i) preprocessing of spectral data from each patient to account for inter-patient variation, (ii) partitioning of the preprocessed spectral data from all patients into calibration and prediction sets, (iii) dimension reduction of the preprocessed spectra in the calibration set using principal component analysis, (iv) selection of the diagnostically most useful principal components using a two-sided unpaired student's t-test and (v) development of an optimal classification scheme based on logistic discrimination using the diagnostically useful principal component scores of the calibration set as inputs.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Magnetic measuring device
InactiveUS20160313408A1Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMeasurement deviceOptoelectronics
A magnetic measuring device can be downsized. The magnetic measuring device includes a diamond crystal, a microwave source, a light source array / microwave circuit chip, an image sensor, and a signal controller. The diamond crystal contains a plurality of nitrogen-vacancy pairs. The microwave source generates the microwave that is irradiated to the diamond crystal. The microwave circuit unit in the light source array / microwave circuit chip irradiates the diamond crystal with the microwave. The light source array in the light source array / microwave circuit chip irradiates the diamond crystal with excitation light. The image sensor detects an intensity of fluorescent light generated from the diamond crystal. The signal controller performs image processing of a fluorescent image taken-in by the image sensor, and controls operations of the light source array / microwave circuit chip and the microwave source. The light source array / microwave circuit chip is provided on a first surface side of the diamond crystal, and the image sensor is provided on a second surface side opposed to the first surface of the diamond crystal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
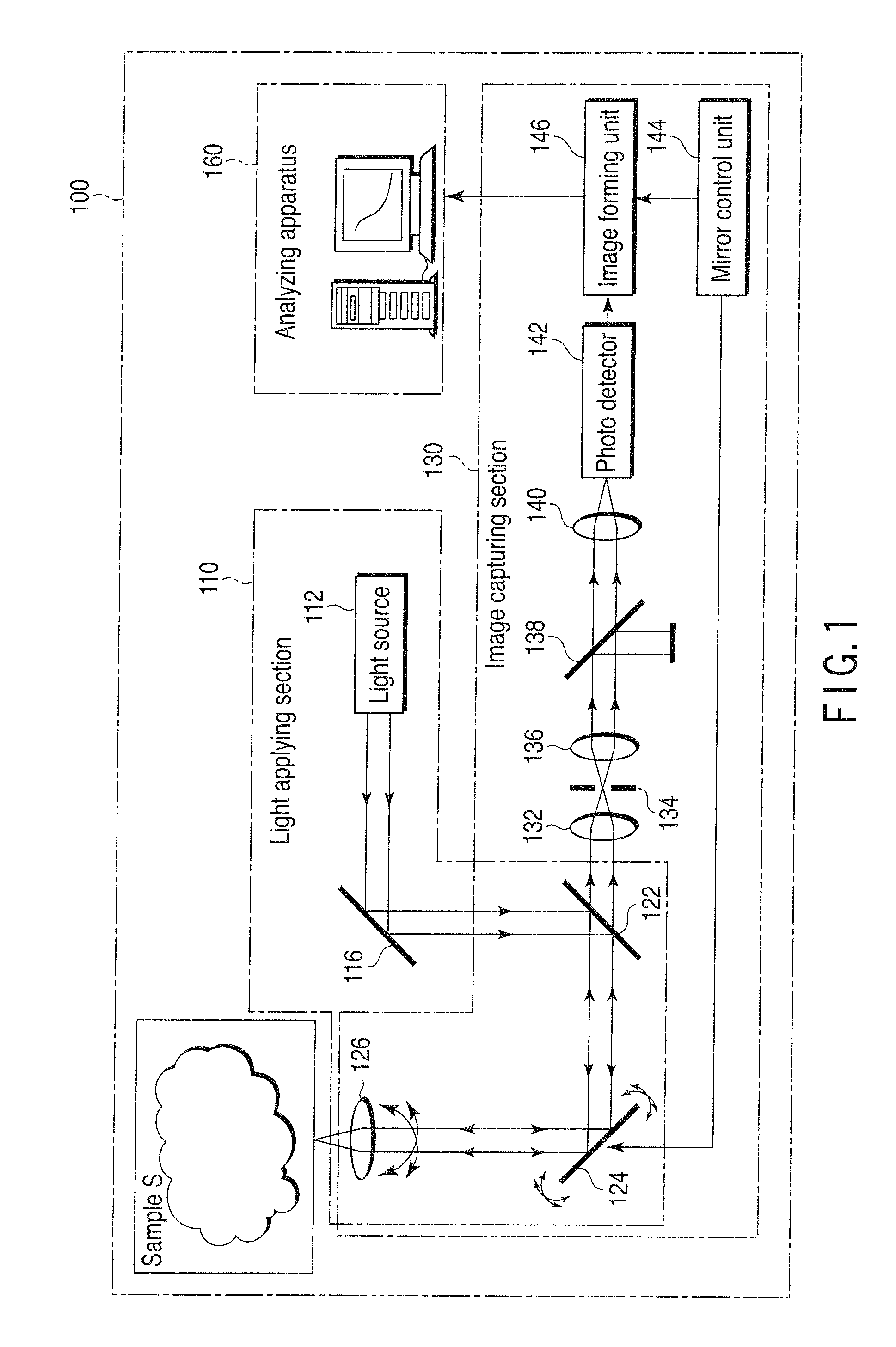
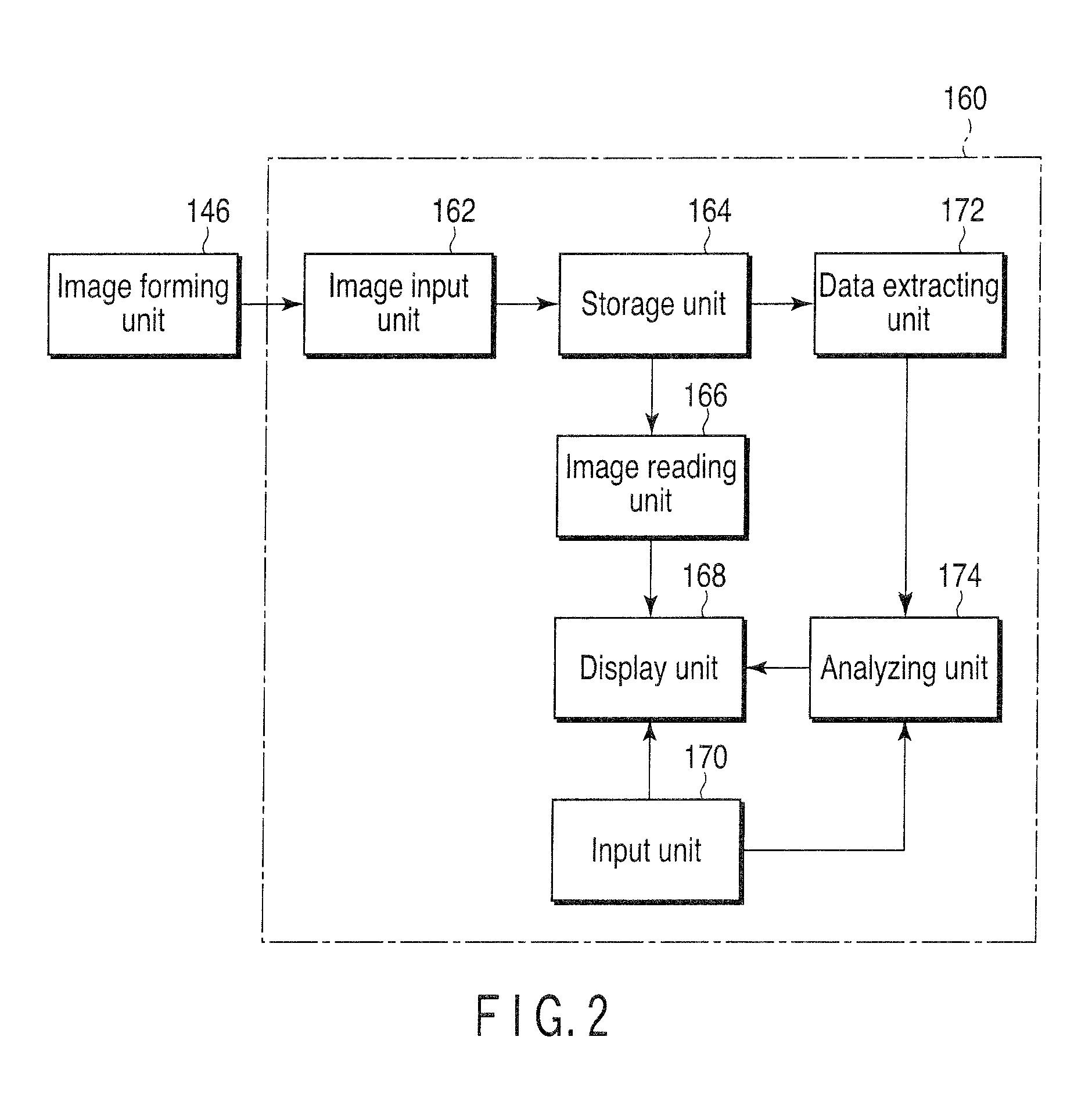
Fluorescent signal analyzing apparatus and fluorescent signal analyzing method
ActiveUS20090252414A1Material analysis by optical meansCharacter and pattern recognitionAnalysis methodComputer science
A fluorescent signal analyzing apparatus includes an image input unit, a storage unit, an extracting unit, and an analyzing unit. At least one fluorescent image of a sample is input to the input unit. The storage unit stores data on the at least one fluorescent image input to the image input unit. The extracting unit extracts, for each of the fluorescent images, data on a fluorescence intensity in a desired region on the at least one fluorescent image from the data on the at least one fluorescent image stored in the storage unit. The analyzing unit calculates at least one of a correlation and a photon counting histogram for the desired region by use of the data on the fluorescence intensity.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Fluorescence conversion medium and color light-emitting device including the same
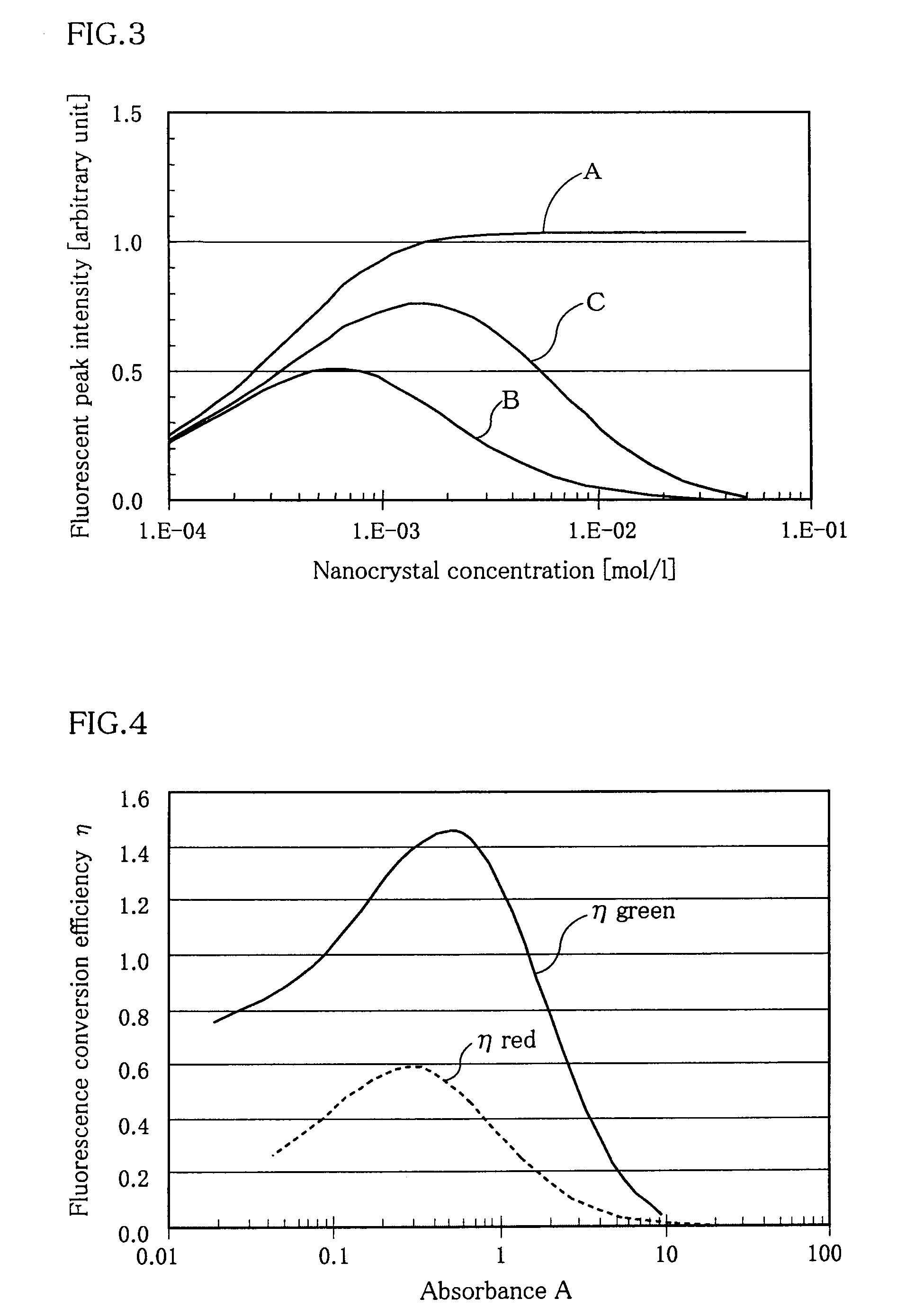
ActiveUS20080029710A1Improve conversion efficiencyDegree of deterioration be relatively smallScattering properties measurementsDiodeLength waveNanocrystal
A fluorescence conversion medium comprising, a fluorescent fine particle formed of an inorganic nanocrystal which absorbs visible and / or near ultraviolet light and emits visible fluorescence, and a transparent medium which disperses the fluorescent fine particle therein, an absorbance at a wavelength where the fluorescent intensity is maximized being in the range of 0.1 to 1.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD +1
Classifying cells based on information contained in cell images
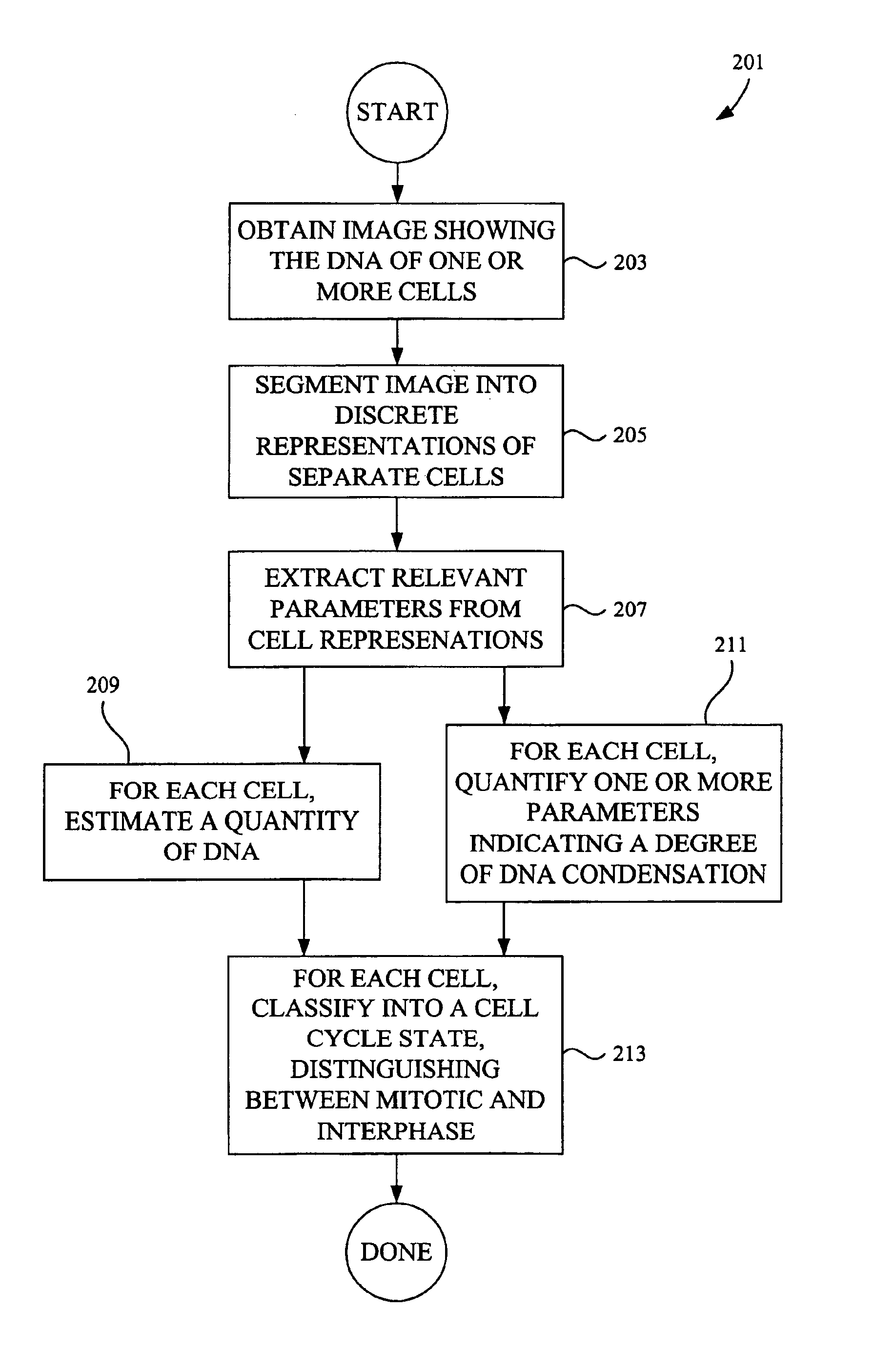
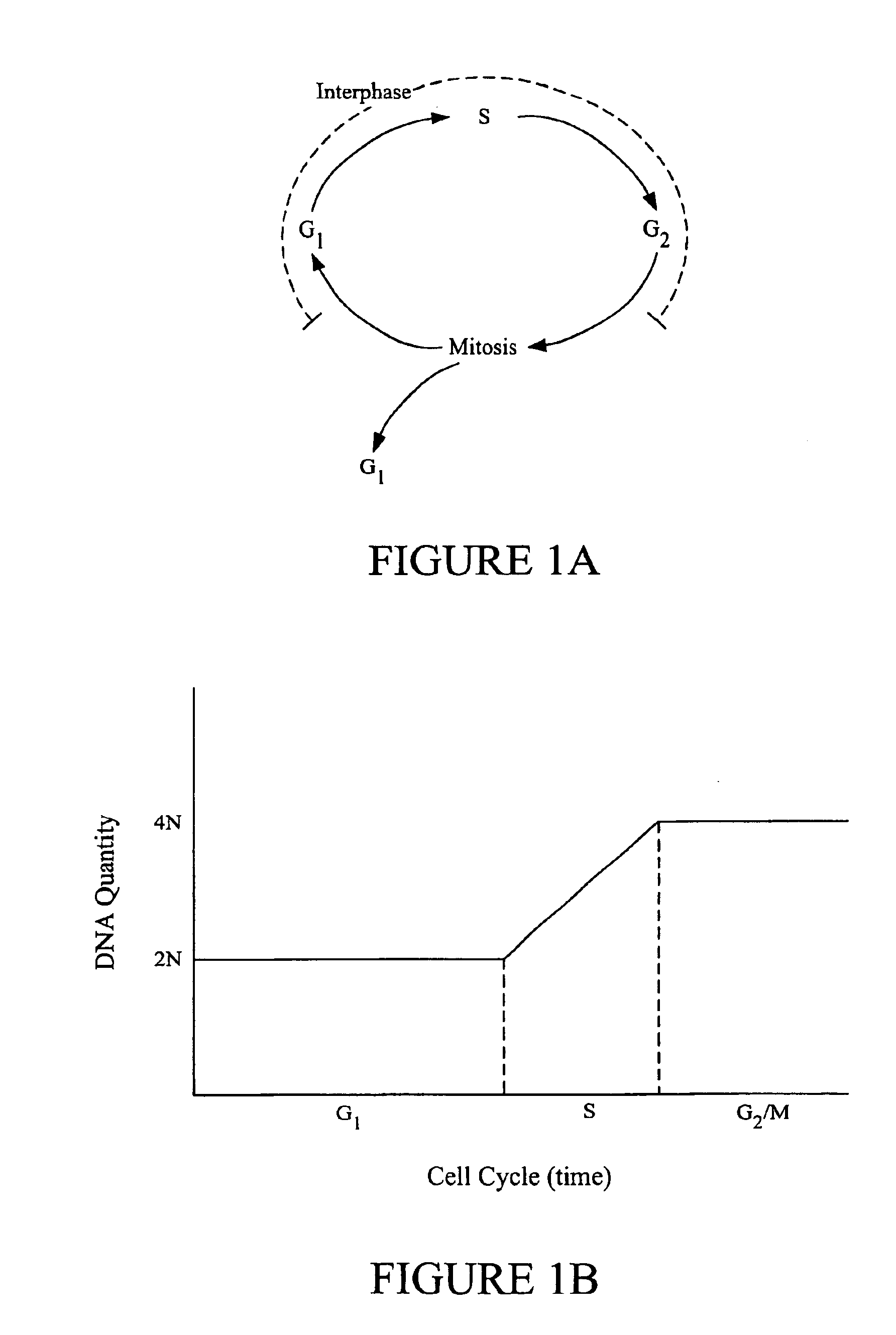
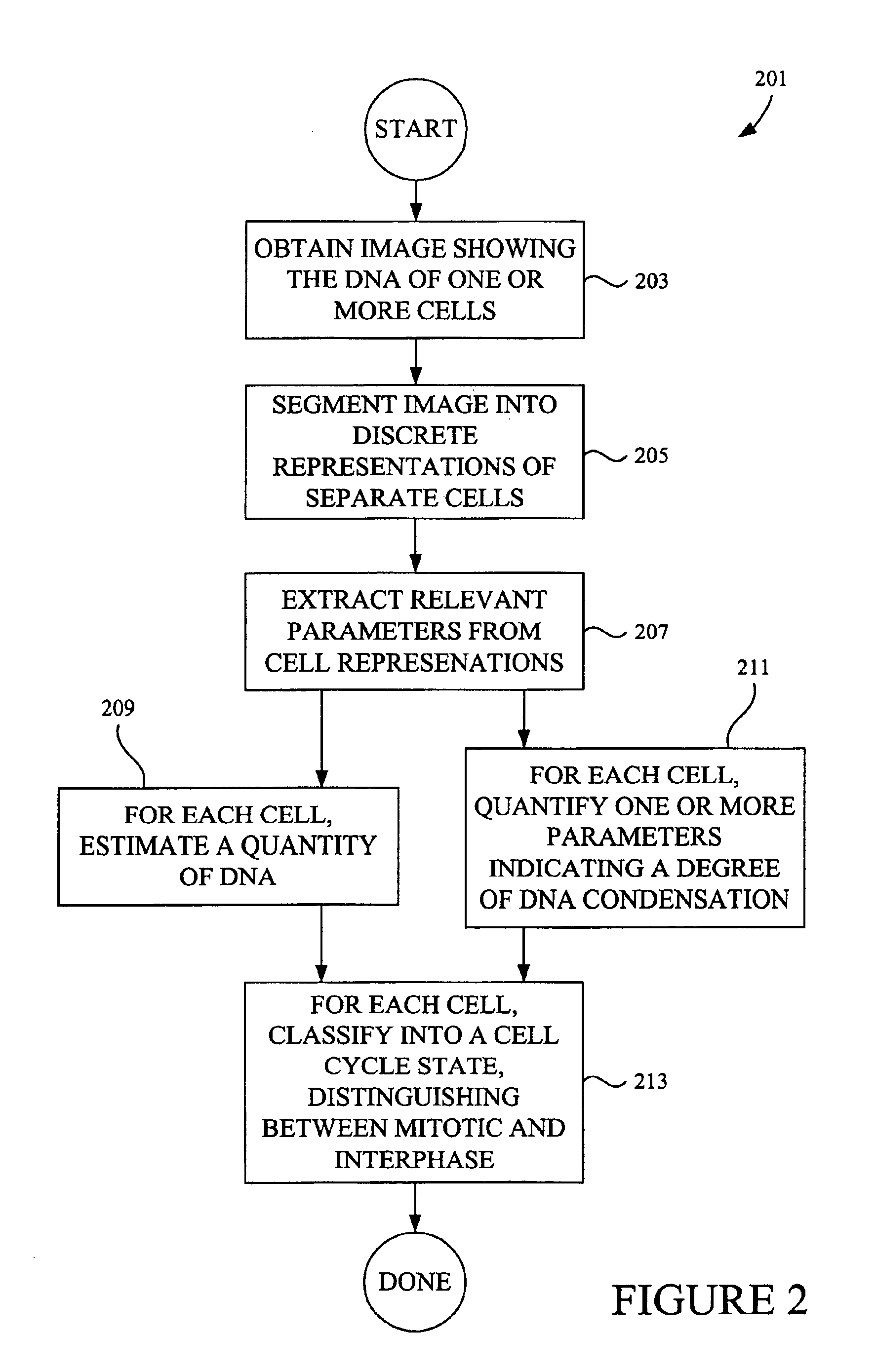
InactiveUS6876760B1Accurate classificationImage enhancementImage analysisImaging analysisPhases of clinical research
Image analysis methods analyze images of cells and place the cells in particular cell cycle phases based upon certain features extracted from the images. The methods can also quantify the total amount of DNA in a cell based on specific features such as fluorescence intensity from fluorescent molecules that bind to DNA. Further, the methods can characterize a cell as mitotic or interphase based on chosen parameters such as the variance in intensity observed in a cell image and / or the size of a region containing DNA. In one example, image analysis methods can classify the cell into one of the following five phases: G1, S, G2, telophase, and an early stage mitotic phase comprised of prophase, metaphase, and anaphase.
Owner:CYTOKINETICS INC
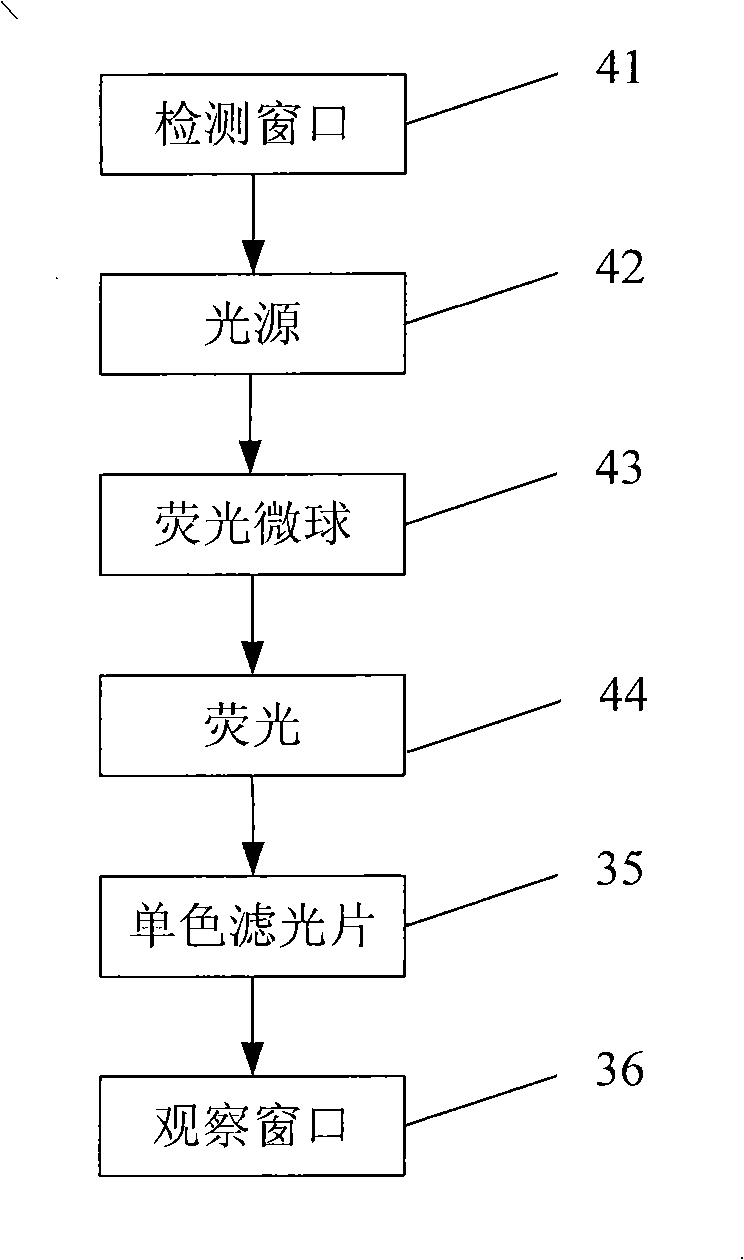
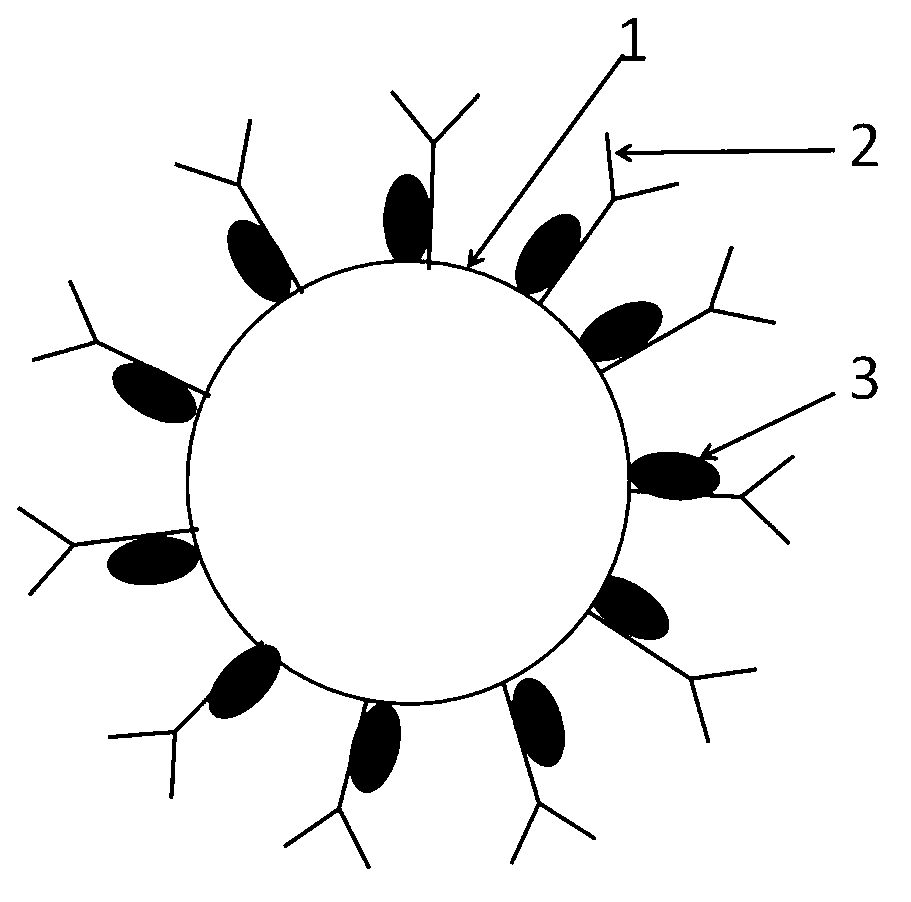
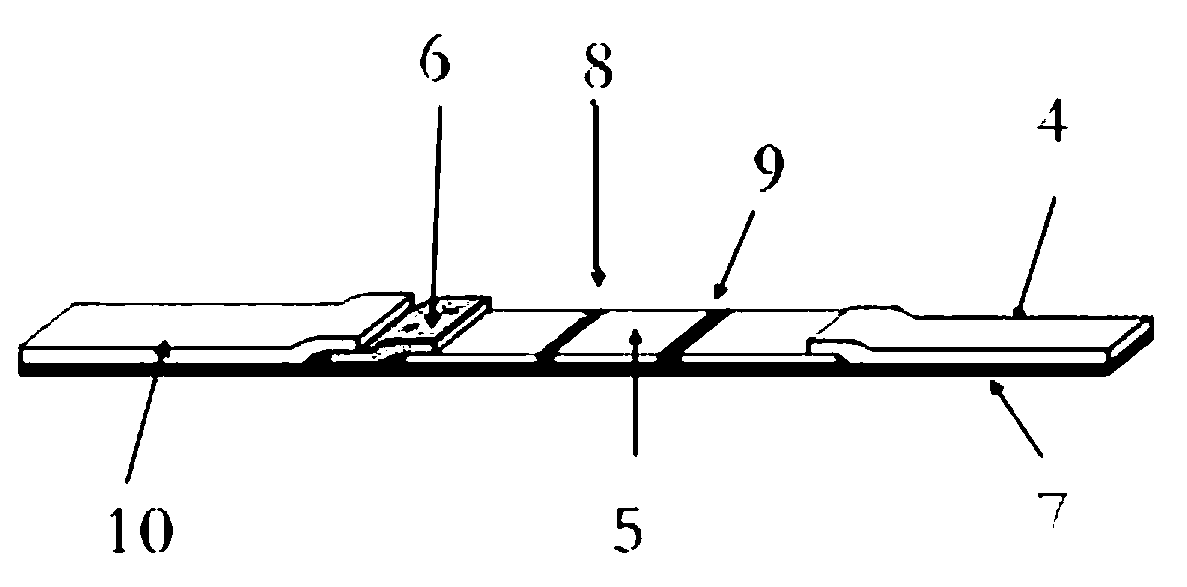
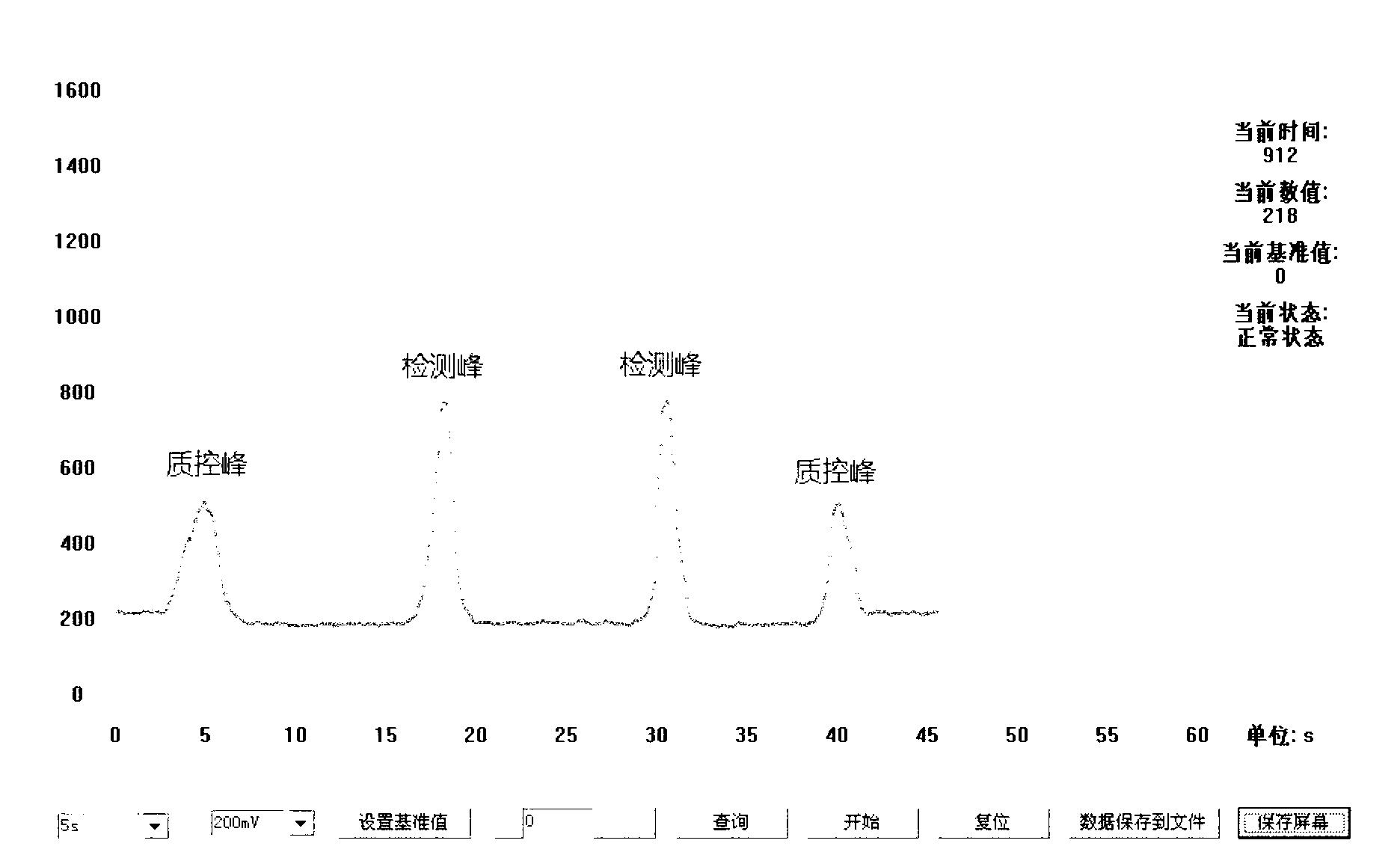
Method for producing fluorescent microballoons immune chromatography test paper stripe and quantitative determination method
ActiveCN101493460ASimple and fast operationHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiberCompound organic
The invention discloses a method for preparing fluorescent microspheres immunochromatographic test paper strip and quantitative detection method. The invention takes the luminous nano-particles of dual-structure silicon dioxide compound organic dye as a marker, uses the immunochromatographic technology for preparing fluorescent microspheres immunochromatographic test paper strip, and then prepares a detection card which consists of a sample pad, a glass fiber membrane, a nitrocellulose membrane and absorbent paper, wherein the nitrocellulose membrane is fixedly provided with a detection line and a quality control line. In the detection process, the best excitation light souce of fluorescent microspheres is used for excitation; after the emitted fluorescence passes through a filter, a CCD scanning technology or fiber-optic technology is used for collecting, accumulating or multiplicating the emitted spectra which is then converted into a numerical signal; then the measured fluorescence intensity of the detection line is multiplied by a correction coefficient, and later the corrected fluorescence intensity is substituted in a standard curve which is preset in a fluorescence analyzer; and finally, the concentration of an object to be measured in the sample can be automatically calculated and obtained by the fluorescence analyzer. The invention has high sensitivity, accurate quantization and easy operation.
Owner:江西中德生物工程股份有限公司
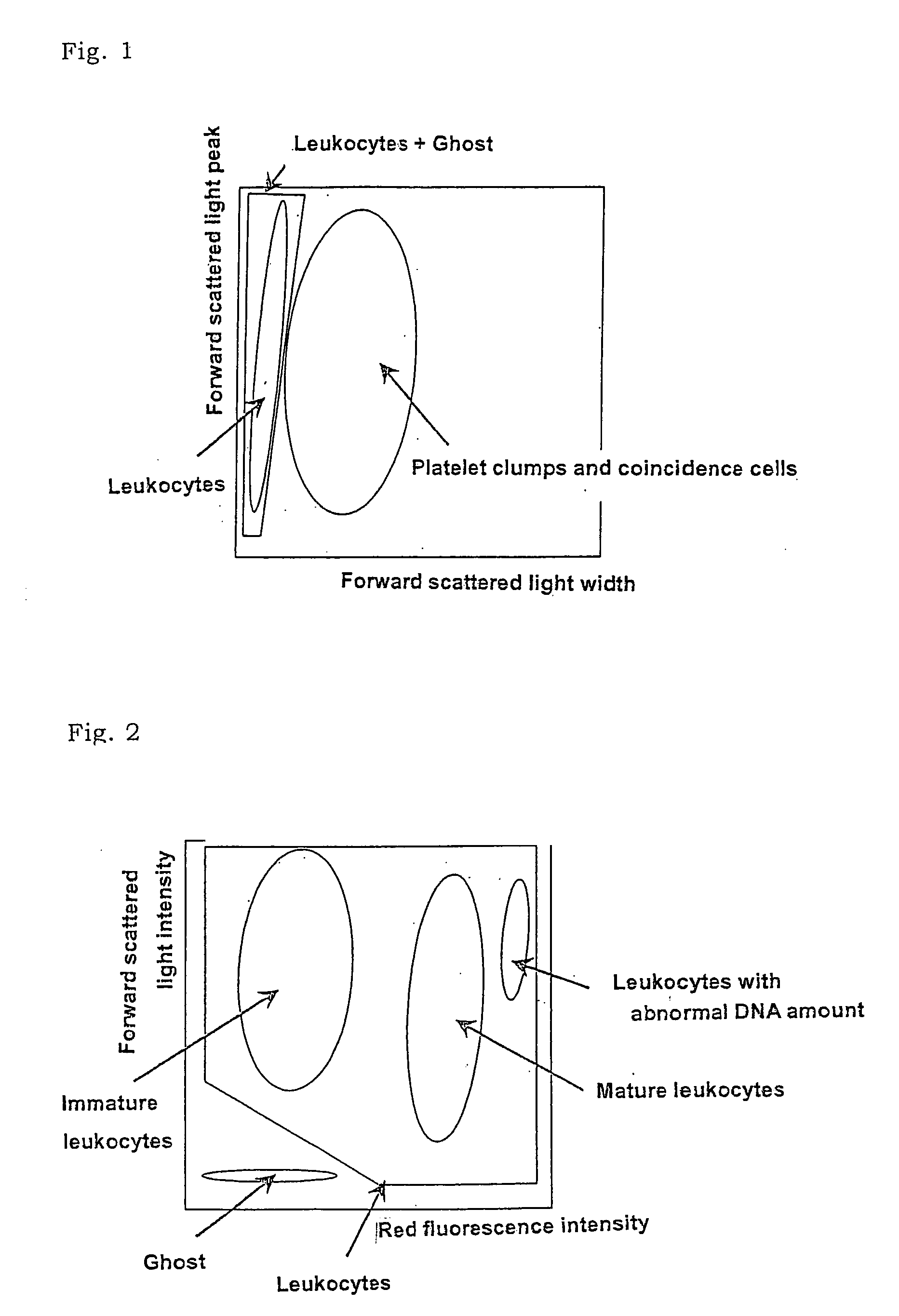
Method of classifying counting leucocytes
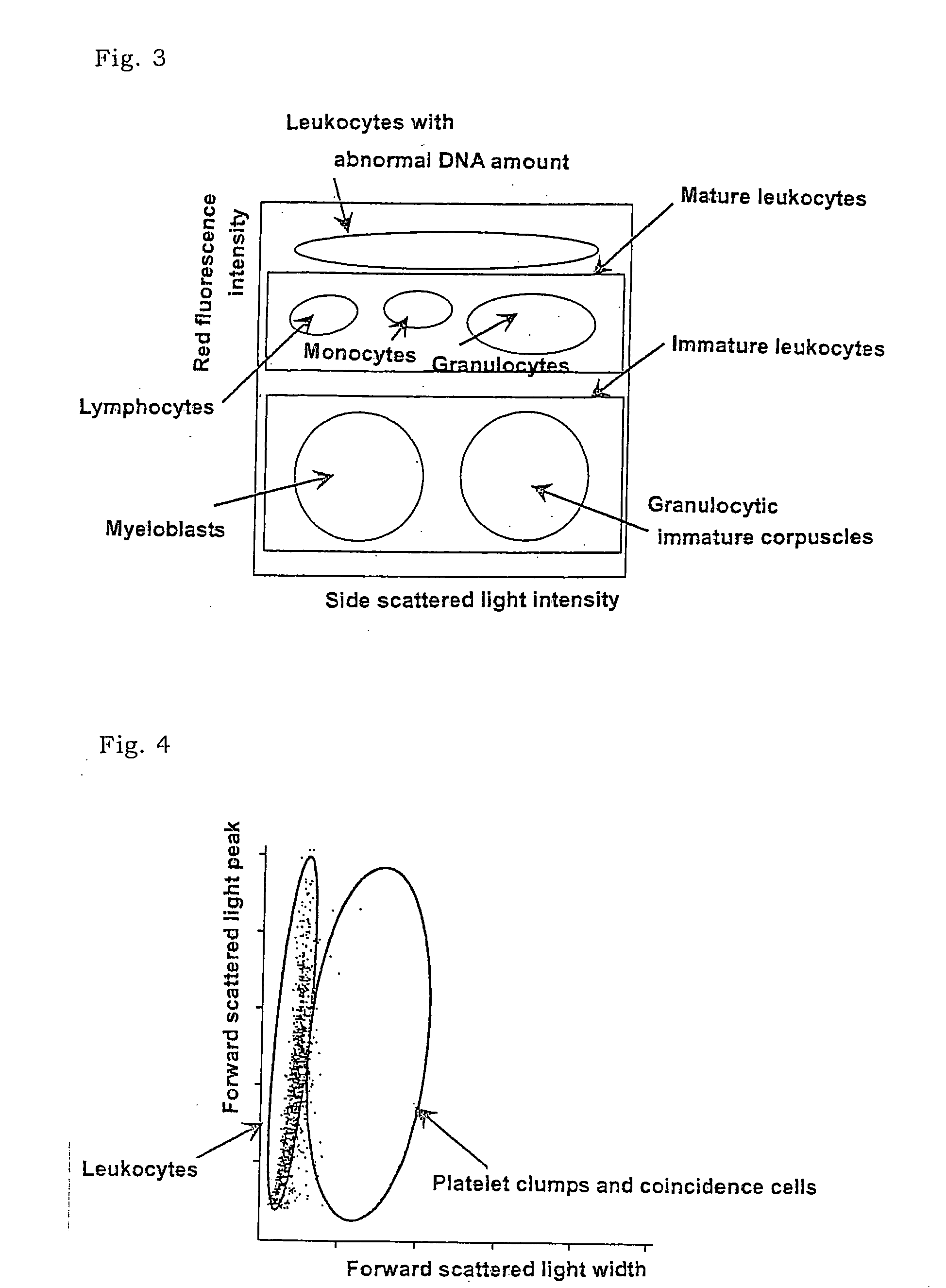
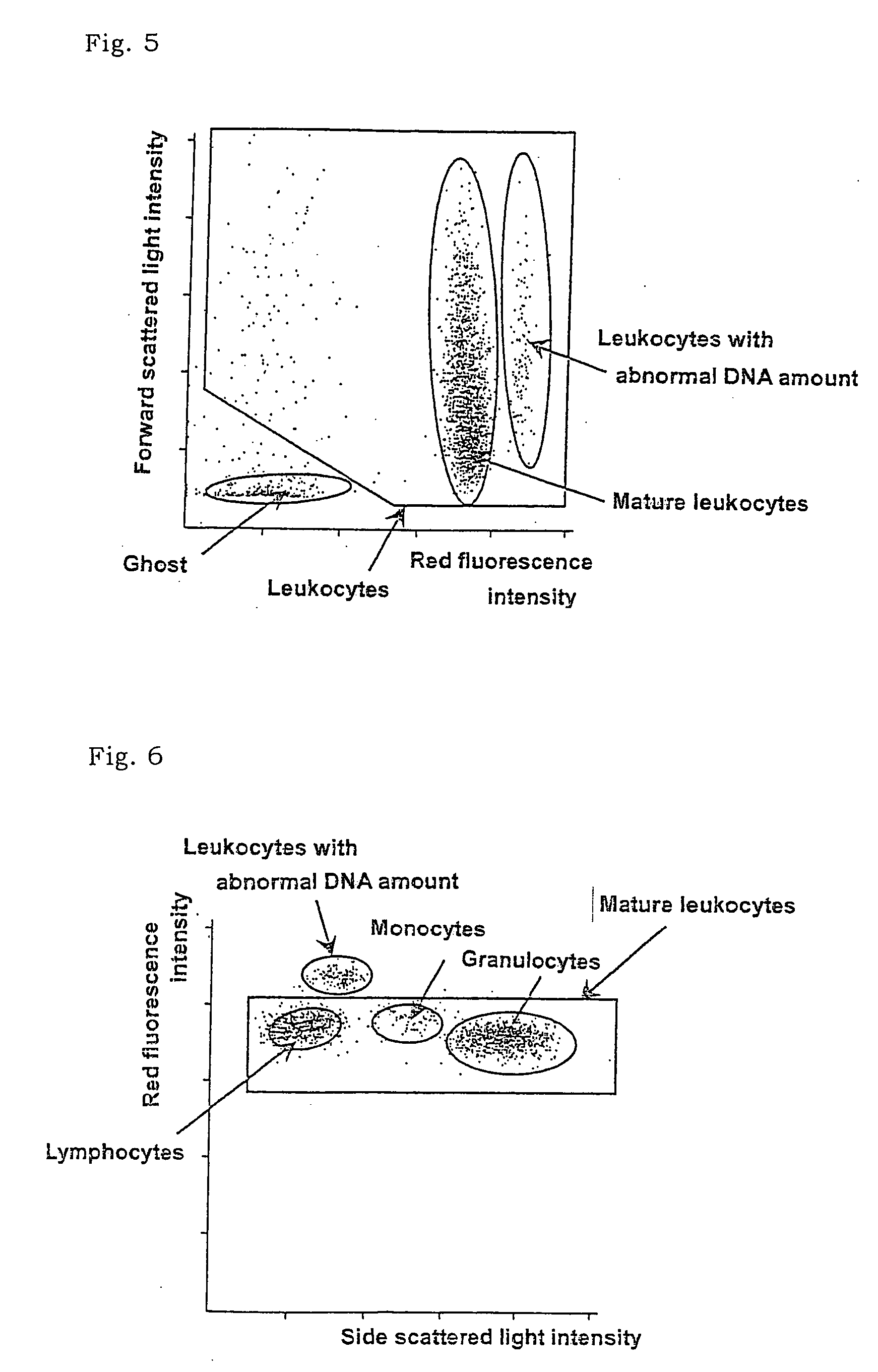
ActiveUS20050202400A1Low costAccurate classificationMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceStainingRed blood cell
There is provided a method for classifying and counting leukocytes with abnormal DNA amount, which comprises: (1) a step of staining cells in a sample obtained from a hematological sample by treatment with a hemolytic agent to lyse erythrocytes, with a fluorescent dye which can make a difference in the fluorescence intensity at least among mature leukocytes, leukocytes with abnormal DNA amount and immature leukocytes; (2) a step of introducing the sample containing the stained cells into a flow cytometer to measure scattered light and fluorescence of the respective cells; (3) a step of classifying leukocytes and coincidence cells / platelet clumps utilizing a difference in the intensity of a scattered light peak and a difference in the scattered light width; (4) a step of classifying and counting mature leukocytes, leukocytes with abnormal DNA amount and immature leukocytes, utilizing a difference in the scattered light intensity and a difference in the fluorescence intensity of leukocytes classified in the step (3).
Owner:SYSMEX CORP
Fluorescent endoscope system having improved image detection module
ActiveUS20050203343A1Efficient compositionEffective displaySurgeryEndoscopesControl signalImage detection
Disclosed is an improved fluorescent endoscope system having reduced factors that cause errors during diagnosis based on quantitative evaluation of fluorescent intensity for improved accuracy of fluorescent endoscopic diagnosis. The fluorescent endoscope system includes an optical source module for providing white light or excitation light; an endoscope assembly having an optical transmission path for transmitting light provided from the optical source module to a diagnostic object and an optical detection module for transmitting reflection light and fluorescent light from the diagnostic object; an optical path split means for splitting the path of the reflection light and fluorescent light transmitted from the endoscope assembly; and a two-chip integration image detection module having a first optical detection chip for detecting the reflection light and outputting a first optical detection signal, a second optical detection chip for detecting the excitation light and outputting a second optical detection signal, a gain control unit for controlling a signal amplification gain value to adjust the brightness of an image detected by the first optical detection chip, a first amplification unit for amplifying the first optical detection signal according to the signal amplification gain value, and a second amplification unit for amplifying the second optical detection signal according to a changing ratio of the signal amplification gain value.
Owner:INTHESMART
Method for highly sensitive quantitative detection of quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatographic assay
ActiveCN102520165ASensitive quantitative detection fastRealize detectionMaterial analysisCritical illnessLinear range
The invention discloses a method for highly sensitive quantitative detection of quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatographic assay. The method includes: building a fluorescence immunochromatographic assay test strip on the basis of optimizing the structure of the test strip and components by the aid of excellent fluorescent characteristics of quantum dots and by means of combining quantum dot fluorescence labeling technology and immunochromatographic assay; detecting fluorescence signal strength of a quantitative belt and a quality control belt by the aid of a fluorescence quantometer and correcting the fluorescence strength of the quantitative belt by the aid of the quality control belt after immunochromatographic assay of the test strip; and further quantitatively detecting analyte according to a standard curve obtained by the fluorescence quantometer. The method is simple, rapid, accurate, low in cost and quite high in sensitivity. Compared with a conventional colloidal gold immunochromatographic assay method, the method has the advantages of fine labeling stability, low non-specificity, high sensitivity, wide linear range and accuracy in quantization. The method is applicable to samples such as blood samples, urine samples, spittle, excrement and the like, and can be applied to detection of critical illness, poison, food safety and the like.
Owner:BEIJING KANGMEI TIANHONG BIOTECH
Two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method
ActiveCN104614353AFluorescence Imaging RealizationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescencePicosecond pulsed laserFluorescence microscope
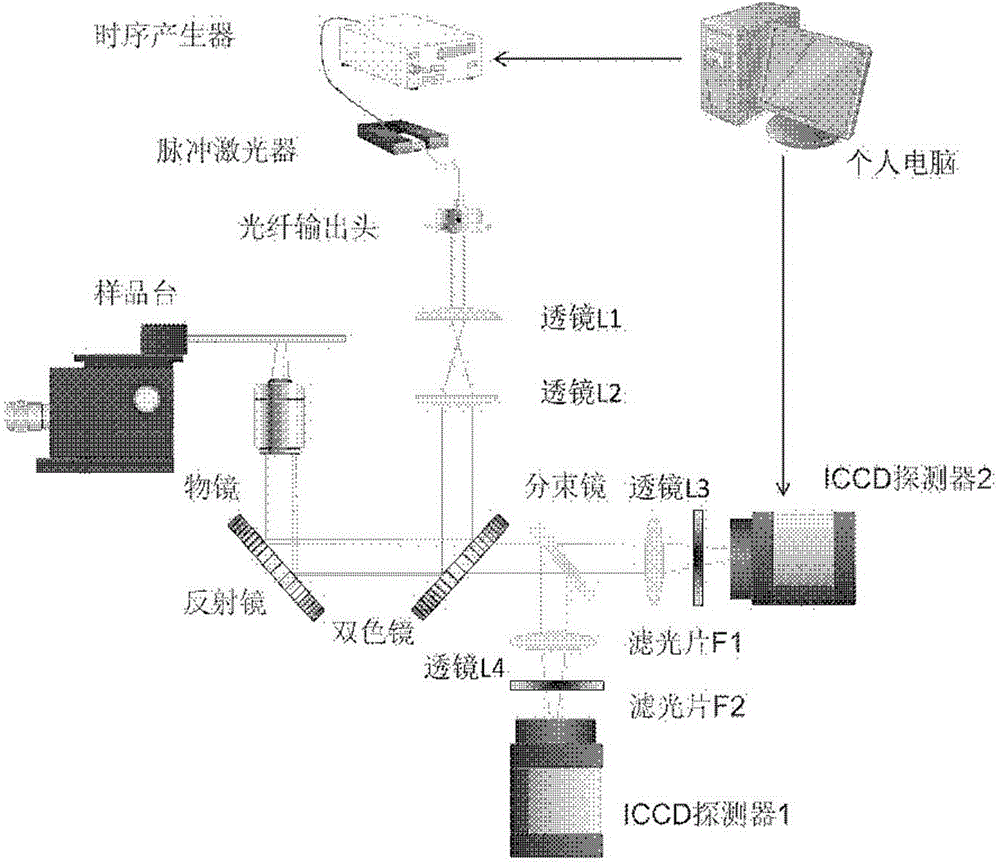
The invention is applicable to the field of optics, biomedicine, life science and the like, and provides a two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, wherein the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system comprises a picosecond pulse laser device, a fluorescent excitation and collection light path, a microscopic objective lens, a light beam lens, a double-ICCD detector, and a control and processing module. The invention further discloses a method for performing multi-spectrum imaging by utilizing the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system. According to the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, the limitation of the existing fluorescent microscope and a fluorescent life imaging microscopic system only can acquire single wavelength fluorescent signal with one-time detection can be effectively solved, the simultaneous acquisition of the multi-spectrum fluorescent strength and fluorescent light image aiming at the dynamic process of fluorescent intensity-related detection limited in biomedicine and life science can be performed, so that the research and application ranges of biophotonics can be extended.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Immunochromatography quantitative determination reagent based on near infrared fluorescence nanoparticle markers
ActiveCN103197074AImprove chromatography propertiesHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysisMicrosphereChemical products
The invention relates to a method based on near infrared fluorescence molecules and nano particle marks as well as an immunochromatography quantitative detection reagent based on near infrared fluorescence nanoparticles. According to the invention, infrared fluorescence is connected with nanoparticles to prepare an immunochromatography test strip based on the near infrared fluorescence nanoparticles. During the detection, an infrared light scanner is utilized, and a quality control line and a sample line are respectively scanned by utilizing near infrared light; and after the fluorescence intensity of a detection line is rectified by utilizing the fluorescence intensity of a quality control line, and a standard curve in a fluorescence analyzer is taken in, the concentration of a to-be-detected matter in a sample can be analyzed and detected. Compared with the direct connection of the near infrared fluorescence molecules and detecting molecules, the near infrared fluorescence nanoparticle immunochromatography improves the detection flexibility obviously, and the lowers the background fluorescence intensity. The marking method and the reagent can be applied to microorganism detection, food safety detection, poison detection as well as rapid dangerous chemical product detection.
Owner:BEIJING RUNBO FUDE BIOLOGICAL TECH DEV
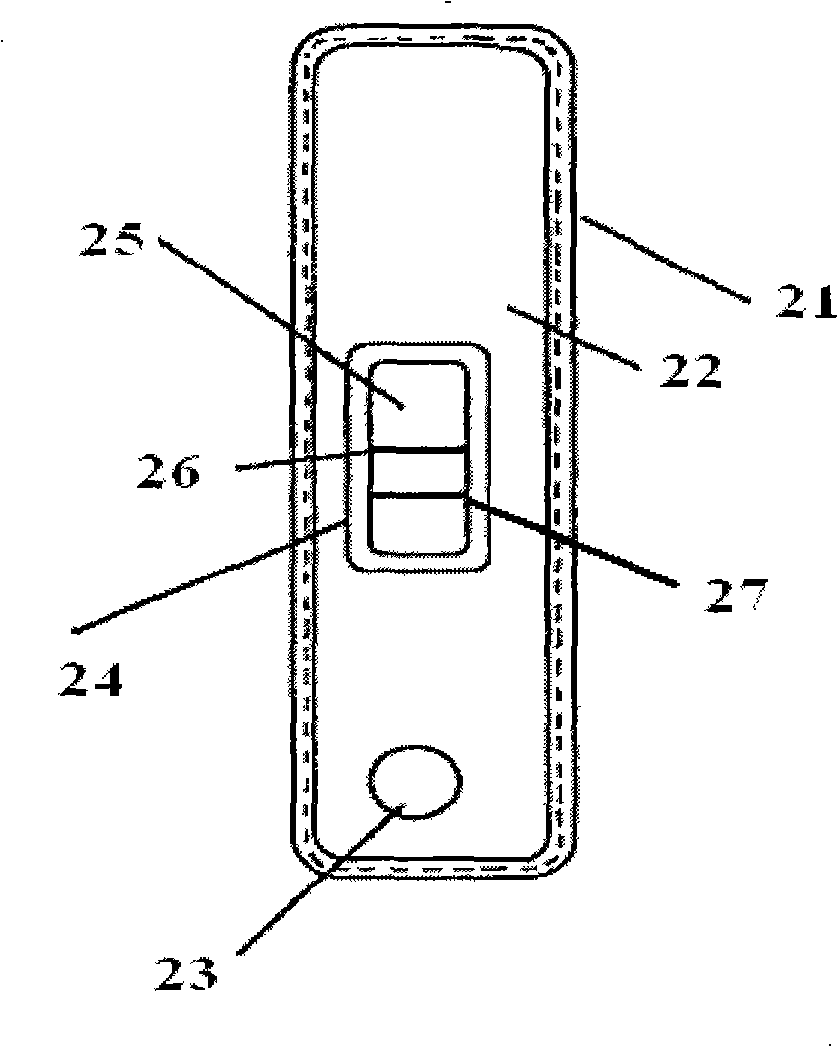
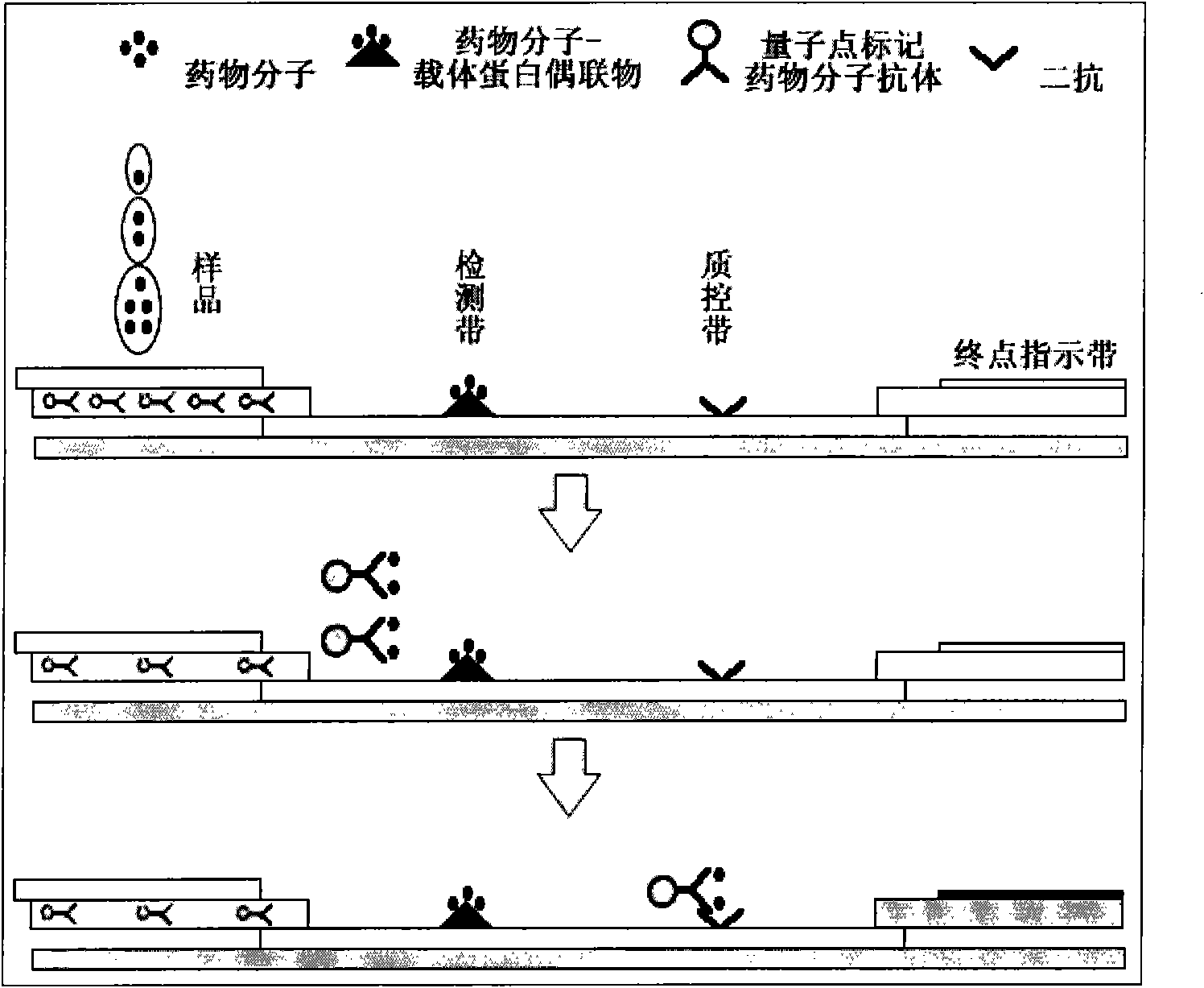
Drug residue competition-type quantum dot-labeled immunochromatography assay test-strip and observation device thereof
The invention provides a drug residue competition-type quantum dot-labeled immunochromatography assay test-strip / detection card and an observation device thereof, comprising the following preparation steps of coating the antibody of quantum dot-labeled drug molecule on a fiberglass film, coating the drug-molecular-carrier protein coupler and second antibody on a pyroxylin film or a cellulose acetate film respectively to form a detection belt and a quality control belt; preparing the immunochromatography assay test-strip from the fiberglass film and the pyroxylin film or the cellulose acetate film on a polyester or plastic plate, and assembling a shell. The quantum dots of the detection belt and the quality control belt on the test-strip is triggered by the ultraviolet LED source of the observation device, and the change of the fluorescent intensity of the observation belt and the quality control belt is observed, thus being capable of quantitatively analyzing the content of the drug molecule in the sample. The invention has simple operation, high sensitiveness and quick quantification, is suitable for detecting the drug residue in the food and can be widely applied to the customhouse, airport, health supervising department, household and the like.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
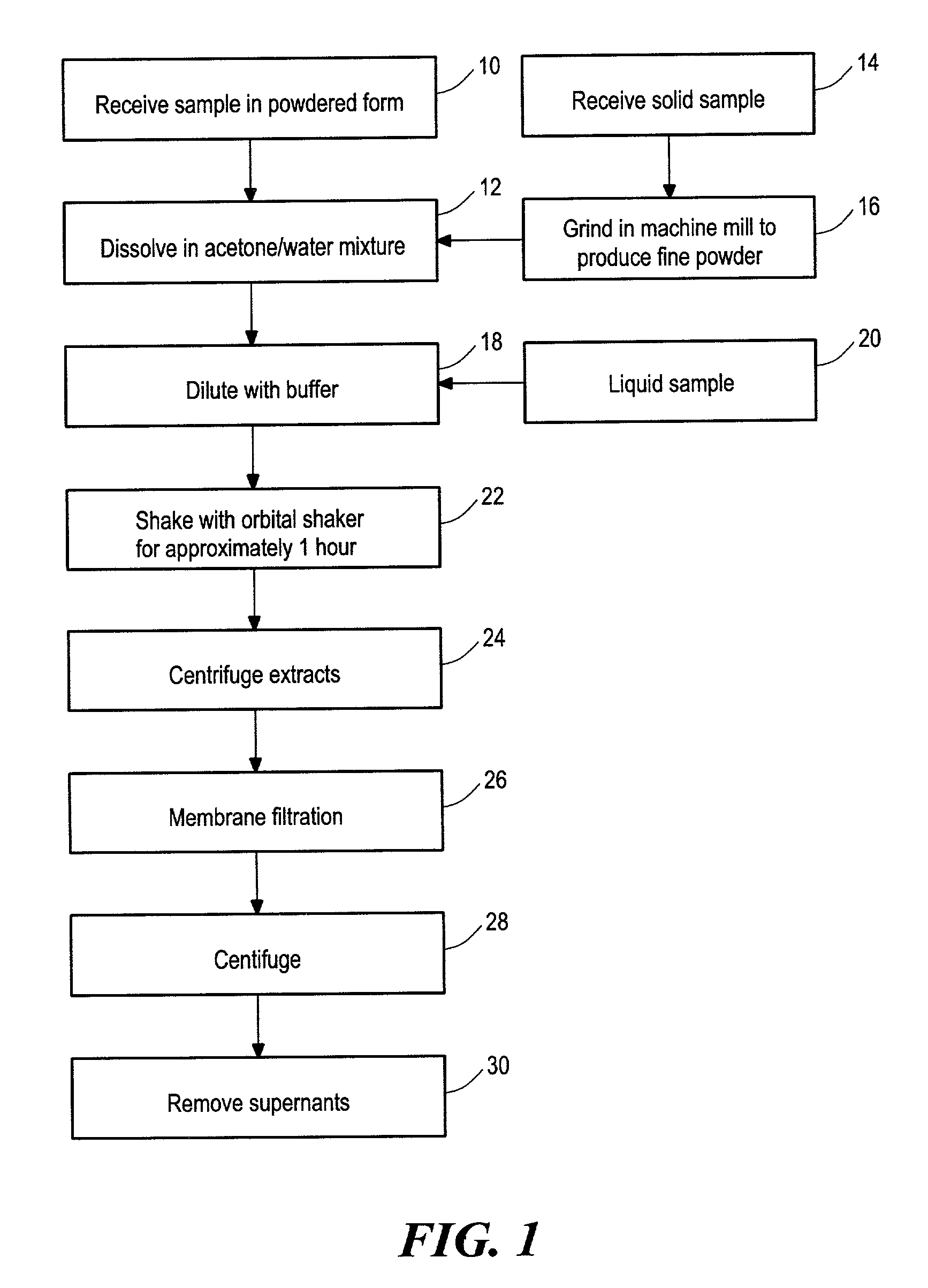
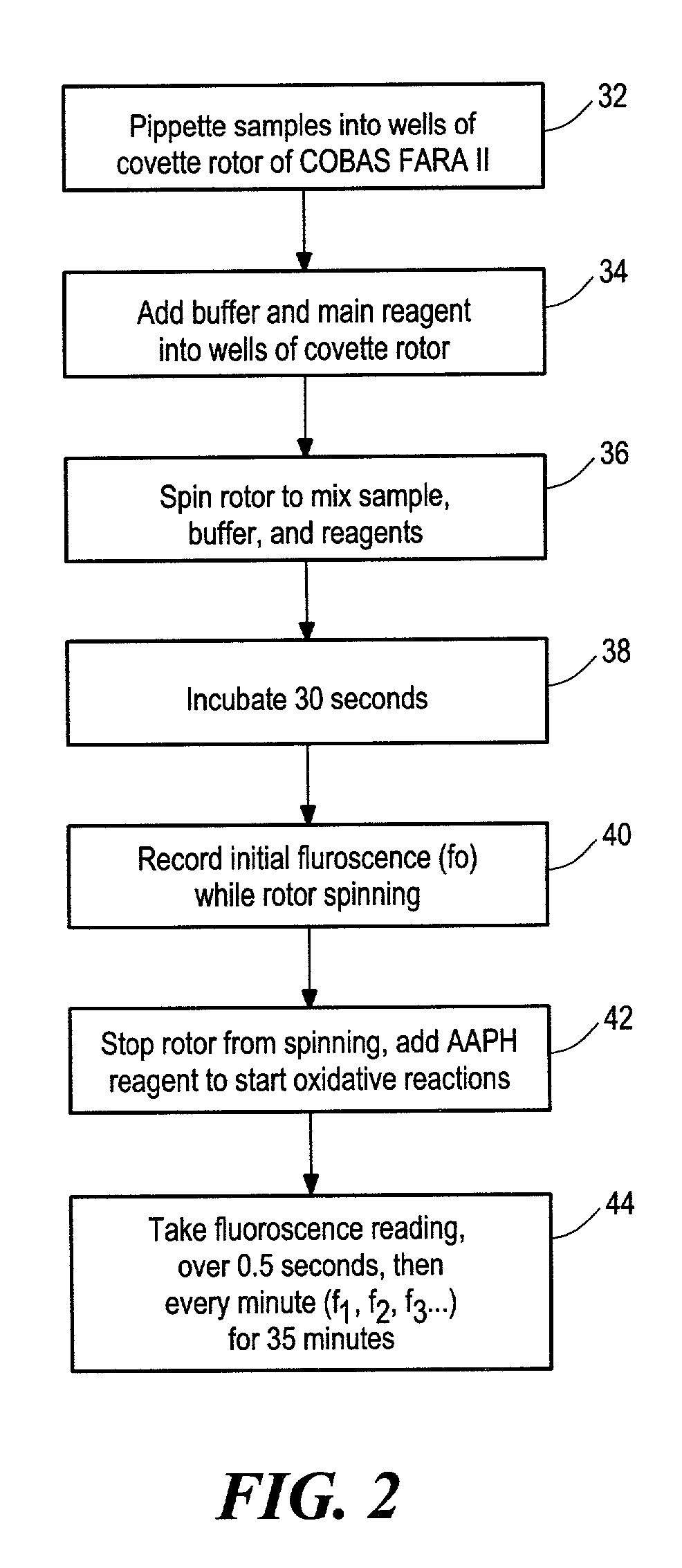
Method for assaying the antioxidant capacity of a sample
InactiveUS7132296B2Simple methodAccurate measurementChemical analysis using combustionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAntioxidant capacitySolubility
A method of assaying the antioxidant capacity of a sample, the method including preparing an extraction solution including a solubility enhancing compound, adding the sample to the extraction solution, extracting the antioxidants present in the sample, adding a fluorescent probe to the extract, adding a free radical generator to the extract, detecting the fluorescence intensity decay of the probe in the presence of the sample over time, and calculating the antioxidant capacity of the sample based on the fluorescence intensity decay of the probe in the presence of the sample.
Owner:BRUNSWICK LAB
Preparation method and application of magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle with shell-core structure
ActiveCN102500291AHigh fluorescence quantum efficiencyExcitation spectral bandwidthMagnetic materialsMicroballoon preparationMicrospherePhysical chemistry
The invention relates to a preparation method and an application of a magnetic fluorescent nanoparticle with a shell-core structure. Firstly, a silica magnetic microsphere with a shell-core structure is prepared by using one or more than one of nanoparticles of Fe3O4, gamma-Fe2O3, MeFe2O4 (Me=Co, Mn, Ni), metal Ni, Co, Fe, and alloy Fe-Co, Ni-Fe as the inner core, and coating a silica shell, and then a fluorescent material (a chelate of Eu3+, Sm3+, Dy3+, Tb3+ and the like) is absorbed on the silica shell. Then, a layer of silica is coated on the surface to improve the stability of the fluorescent magnetic microsphere, and to prevent agglomeration and fluorescent material leakage. A lot of rare earth fluorescent materials are wrapped in the shell layer, so the fluorescence intensity signal of a prepared sample is greatly increased. The nanoparticle has dual functions of enrichment and marking, and has wider application prospects in the biomedical field.
Owner:SHENZHEN BIOEASY BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
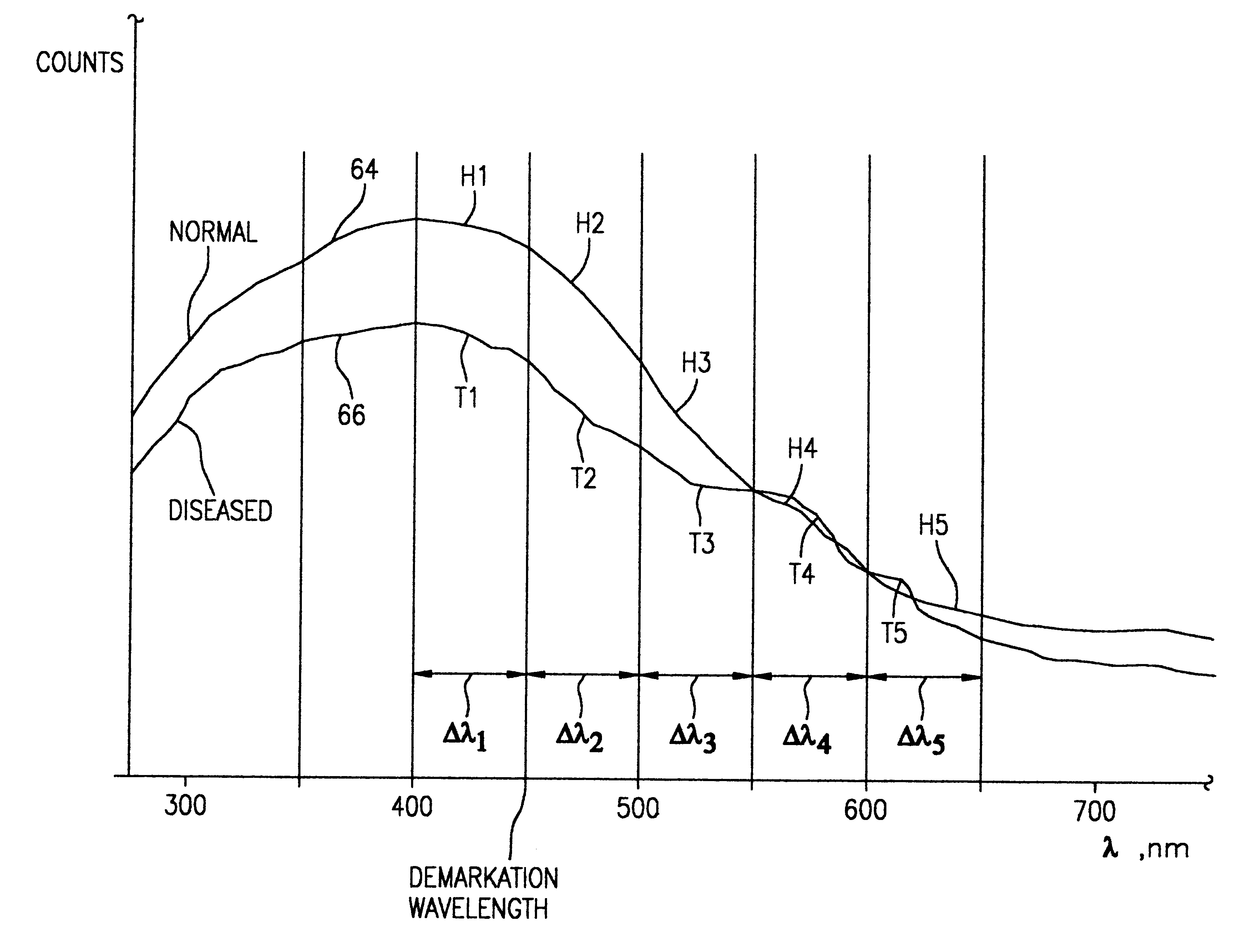
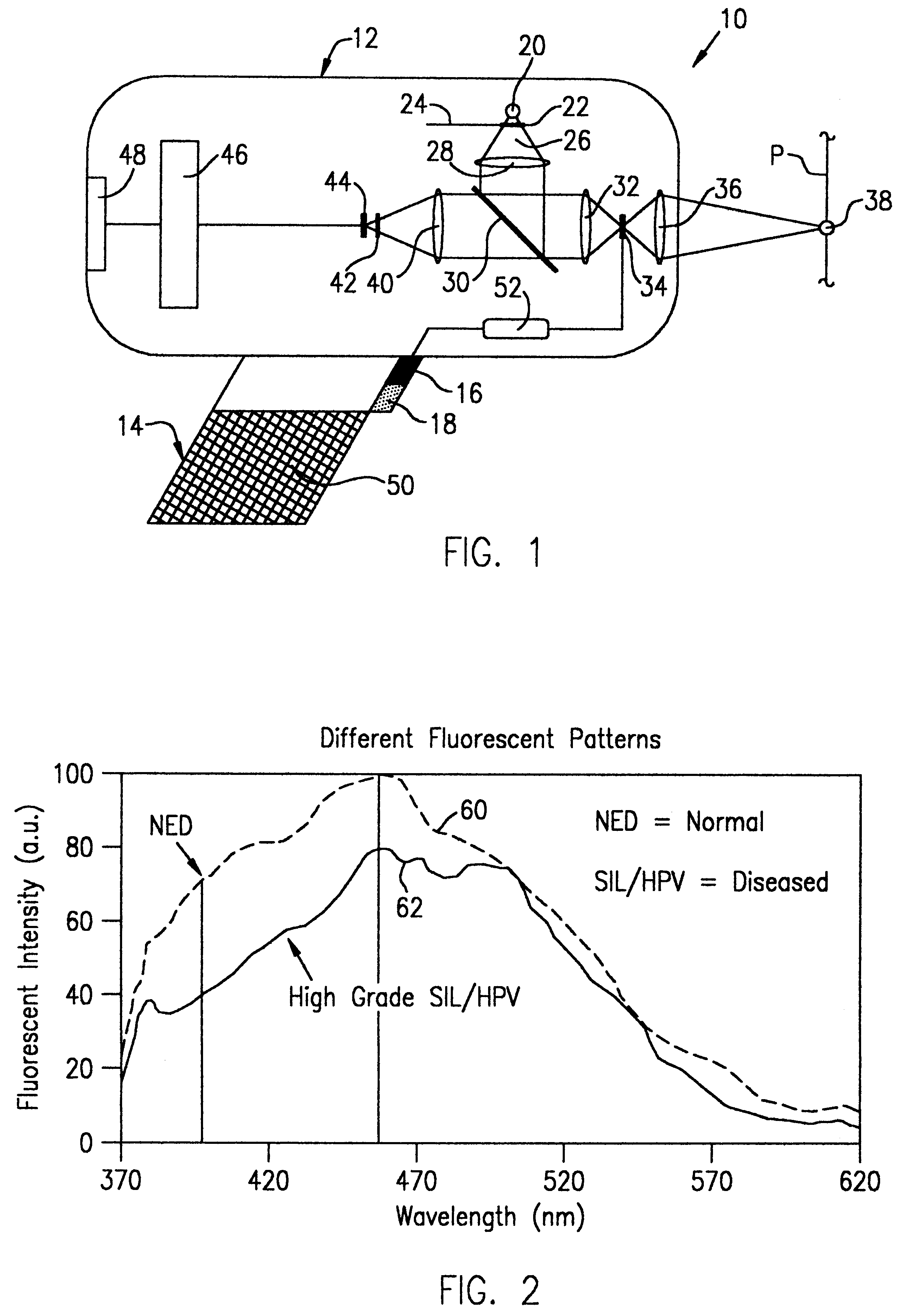
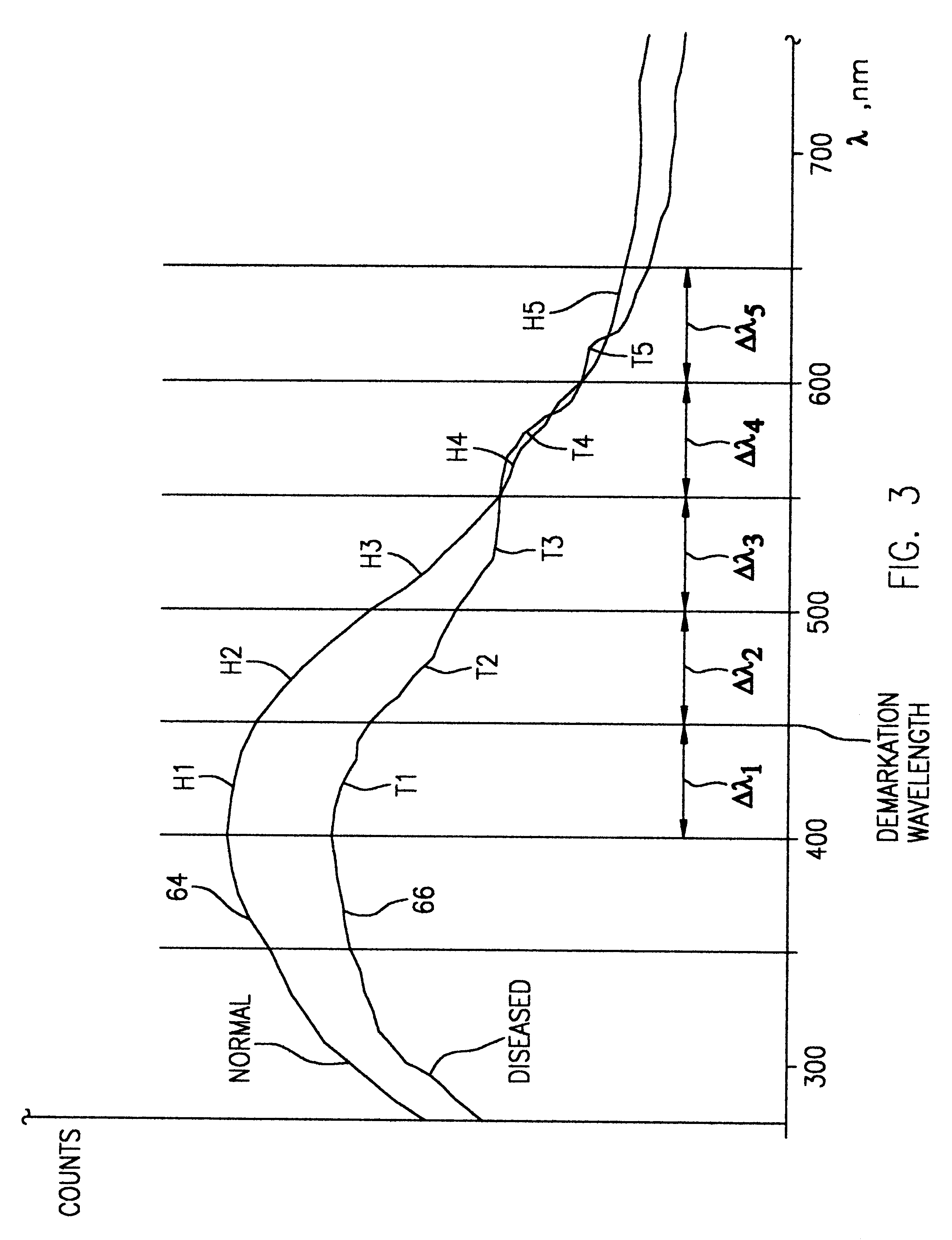
Optical instrument and technique for cancer diagnosis using in-vivo fluorescence emission of test tissue
A hand-held, small, lightweight instrument is disclosed that contains a light source capable of producing radiant energy in the spectral range between approximately 370 and approximately 410 nm, and an optical direction system for irradiating a target tissue by producing an illuminated spot thereon. A collection system is provided for receiving and directing fluorescent emissions in the frequency range between 450 and 700 nm returned from the target area to a detector. A processing system is used to determine the state of the tissue by using at least two and up to five spectral bands, preferably each being larger than 45 nm. Pairs of ratios of fluorescent intensities are compared to identify cancerous cells. An alphanumeric, false-color image and / or audio signal is immediately provided to inform a user of the state of the tissue.
Owner:WOLFE WILLIAM L
Microwave sensor based on NV color center diamond
ActiveCN104360152ASolve the accuracy problemSolution volumeFrequency measurement arrangementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesColour centreNitrogen
The invention discloses a microwave sensor based on an NV color center diamond. A diamond internally containing a Nitrogen-Vacancy color center is adopted as a sensitive element, electronic energy level stimulation is achieved through lasers, an additionally-arranged static magnetic field is scanned, and the microwave frequency and the microwave intensity are measured through fluorescence intensity detection. Dependency of electronic rabi-flopping of the NV color center in the diamond on the external microwave magnetic field is brought into play, high theoretical accuracy and good stability are achieved, the microwave sensor has the advantages of being small in size, low in cost, high in accuracy, large in temperature range, simple in operation condition and the like and rotates on the basis of solid atoms, and the microwave sensor can serve in all the fields with the requirements for the low-cost high-accuracy microwave frequency and intensity detection in the future.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
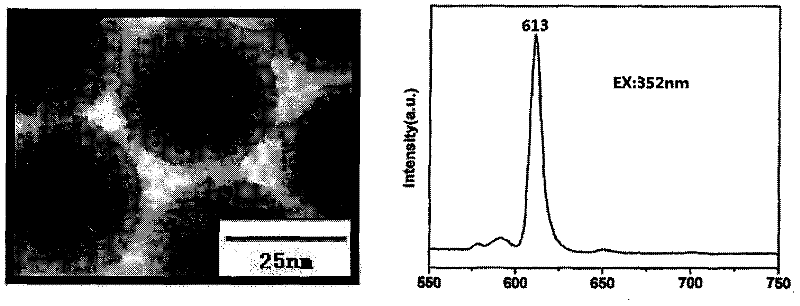
Magnetic fluorescent composite nanoparticle, as well as preparation and use thereof
InactiveCN101503623AGood monodispersityNo reunionLuminescent compositionsOil phaseComposite nanoparticles
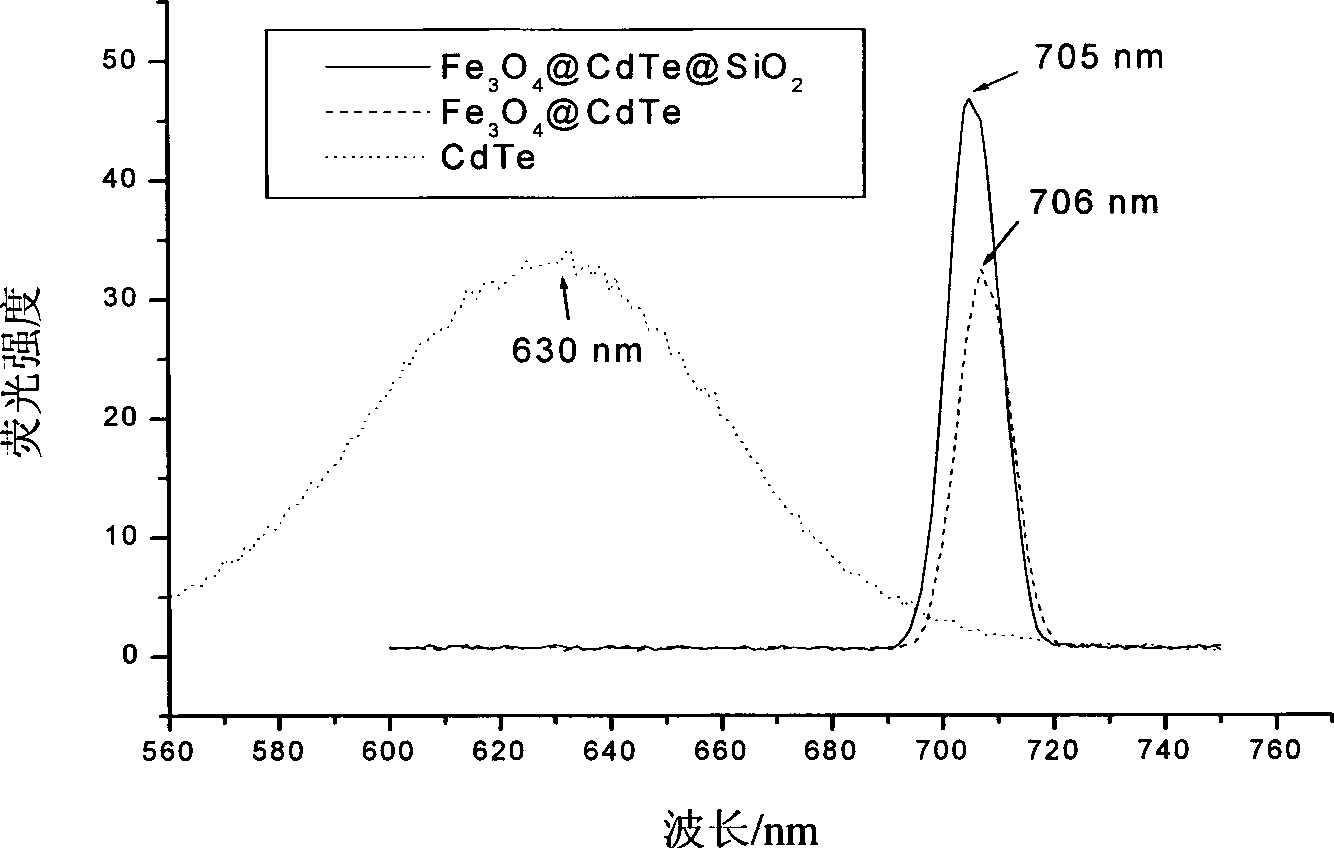
The invention discloses a magnetic luminescent composite nano-particle Fe3O4 / CdTe / SiO2 and a preparation method thereof. The method for preparing the magnetic luminescent composite nano-particle Fe3O4 / CdTe / SiO2 comprises the steps of: firstly preparing hydrophobic monodisperse Fe3O4 nano-particles by adopting a chemical oil-phase high-temperature method, and modifying the surfaces of the hydrophobic Fe3O4 nano-particles to ensure that the hydrophobic Fe3O4 nano-particles are dispersed in a water phase; preparing luminescent CdTe quantum dots of which the surfaces are provided with carboxyl groups, and precipitating the luminescent CdTe quantum dots on the surfaces of the magnetic Fe3O4 nano-particles through the co-precipitation; then utilizing ligand exchange to modify a silane coupling agent on the surfaces of the luminescent CdTe quantum dots; and finally forming an outermost SiO2 coating layer through silane or silicon ester hydrolysis. The diameter of the magnetic luminescent composite nano-particle Fe3O4 / CdTe / SiO2 is between 30 and 50nm; the magnetic luminescent composite nano-particle Fe3O4 / CdTe / SiO2has double functions of magnetism and fluorescence at the same time, has strong and durable fluorescence intensity after labeling rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells, and apparently reduces cellular magnetic resonance signals. The particle has broad application prospect in the fields such as biological labeling, bioseparation and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Flat glass having high transmittance
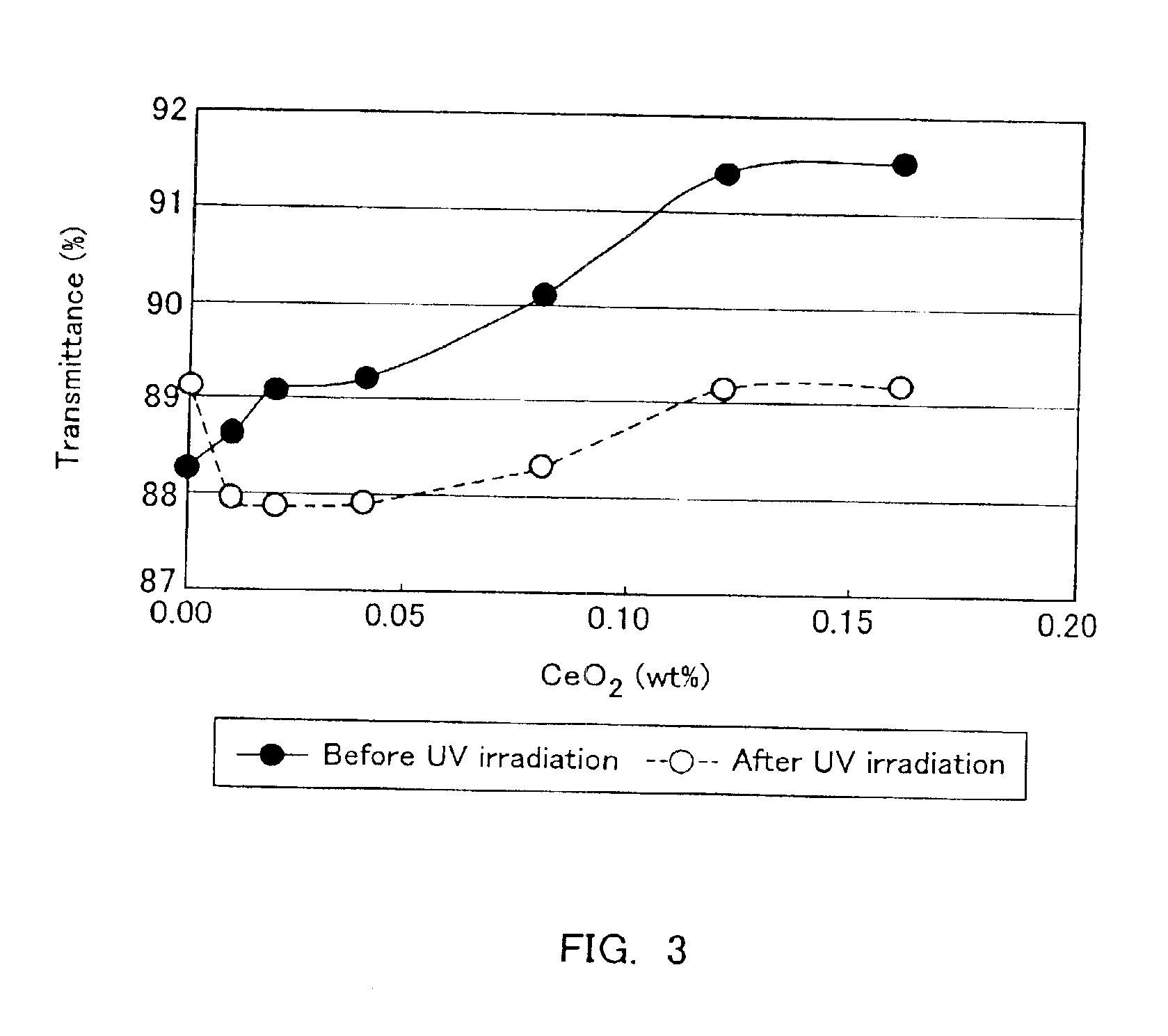
InactiveUS6844280B2High light transmittanceEfficiently emitsSolid-state devicesGlass drawing apparatusFlat glassUltraviolet
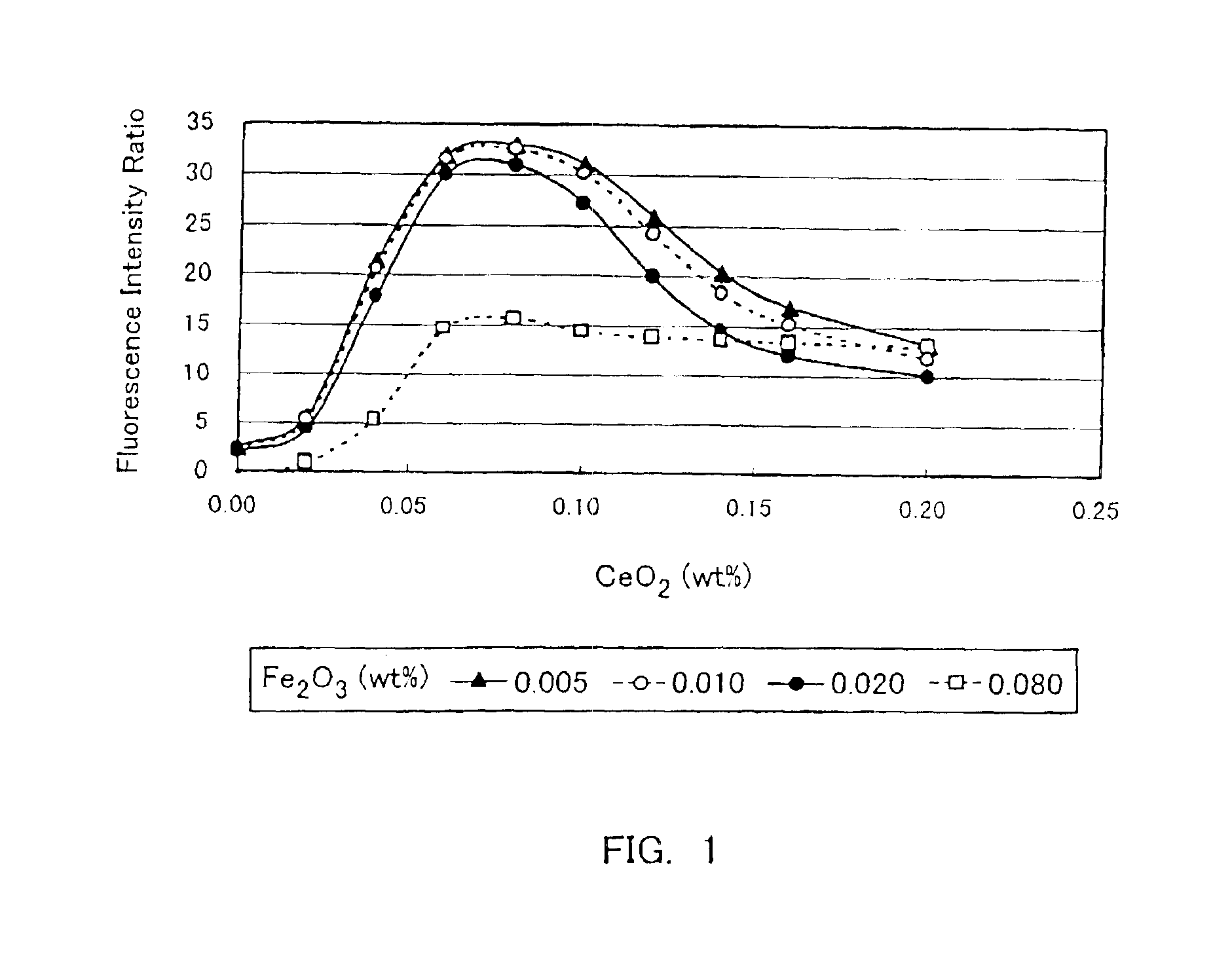
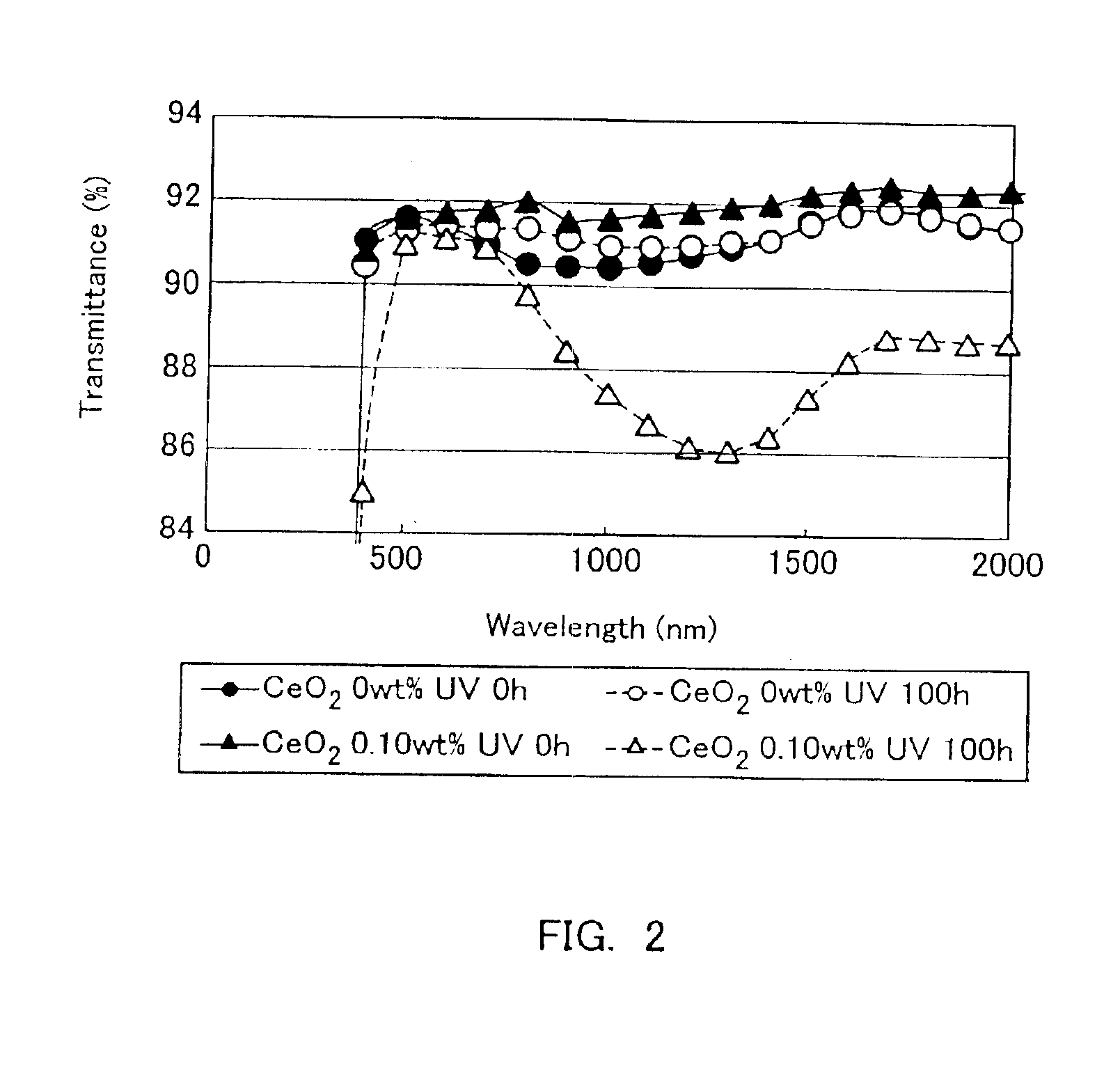
The present invention is to provide a high transmittance glass sheet that has a composition containing as coloring components, expressed in wt. %, 0.005 to less than 0.02% of total iron oxide in terms of Fe2O3, less than 0.008% of FeO, and 0 to 0.25% of cerium oxide and having a ratio of FeO in terms of Fe2O3 to the total iron oxide of lower than 40%, and exhibits high visible light transmittance and solar radiation transmittance. Alternatively, a high transmittance glass sheet is provided that contains not more than 0.06% of total iron oxide and 0.025 to 0.20% of cerium oxide and has a ratio of a fluorescence intensity at 395 nm to a fluorescence intensity at 600 nm of 10% or higher when subjected to ultraviolet irradiation at a wavelength of 335 nm.
Owner:NIPPON SHEET GLASS CO LTD
Fluorescence immune chromatography test paper and preparing method and application thereof
InactiveCN101526534AHigh sensitivityOvercome the easy-to-quench defectBiological testingFiberAntigen
The invention relates to fluorescence immune chromatography test paper which is formed by mutually and sequentially overlapping a sample pad, a combination pad, an antibody carrying film and water absorbing paper on a lining board with adhesive, wherein the combination pad is coated with a fluorescence material antibody 1 composite, a fluorescence-marked material is fluorescein granules or fluorescence material converted by rare earth, the antibody carrying film is a cellulose nitrate film or a nylon film and is respectively connected with an antibody 2 and the T line and the C line of a secondary antibody, the fluorescence material is fluorescein granules or the fluorescence granules converted by the rare earth, and the fluorescein granules are selected from isosulfocyanic acid fluorescein or tetramethyl isosulfocyanic acid rhodamine or tetraethyl rhodamine, and the surface of the fluorescence-marked material is aminated and combined with the antibody by cross-linking reaction. The fluorescence quantitative measuring system is used for detecting the fluorescence strength of the areas of the T line and the C line, and the quantitative detection is completed by the standard curve of the antigen concentration. The invention is suitable for the immune detection of tumor marked objects of urinal fiber-connected protein, and the like.
Owner:沈鹤柏
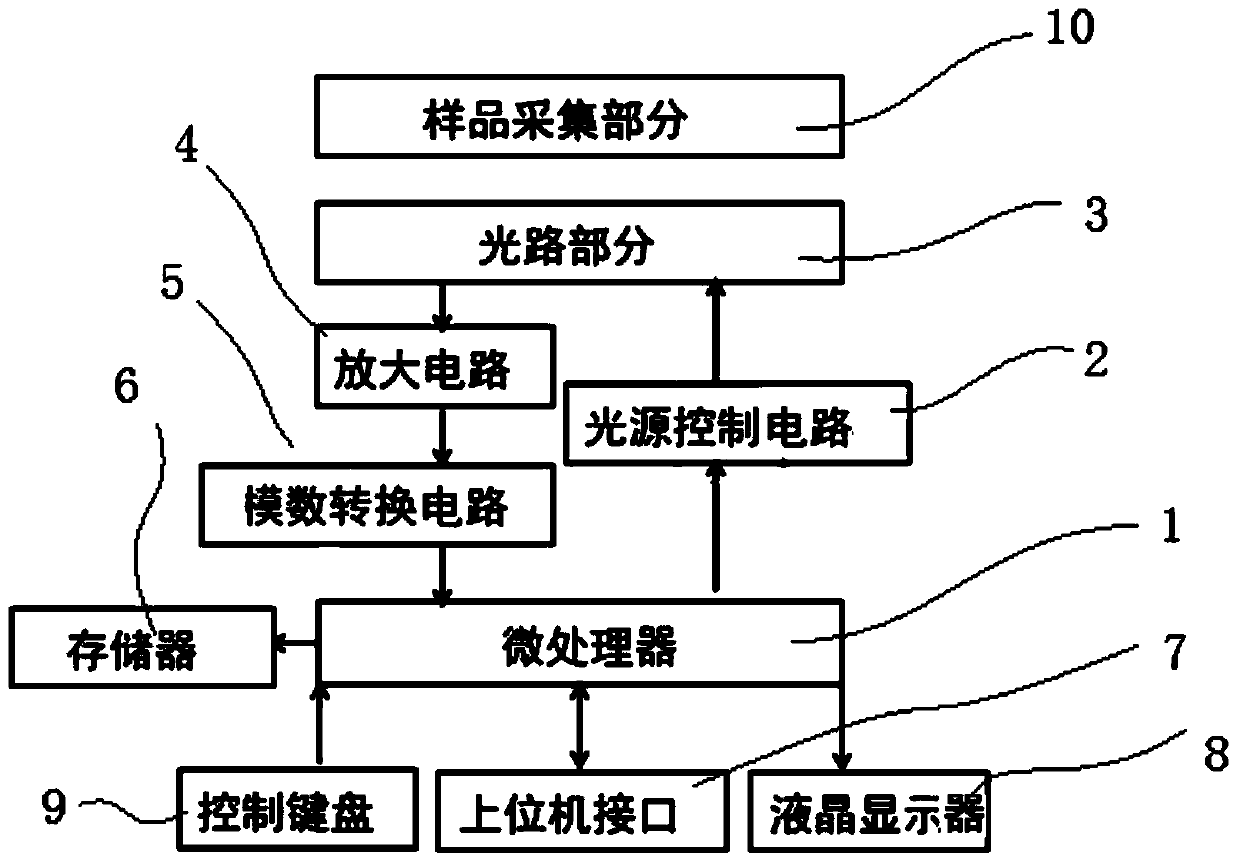
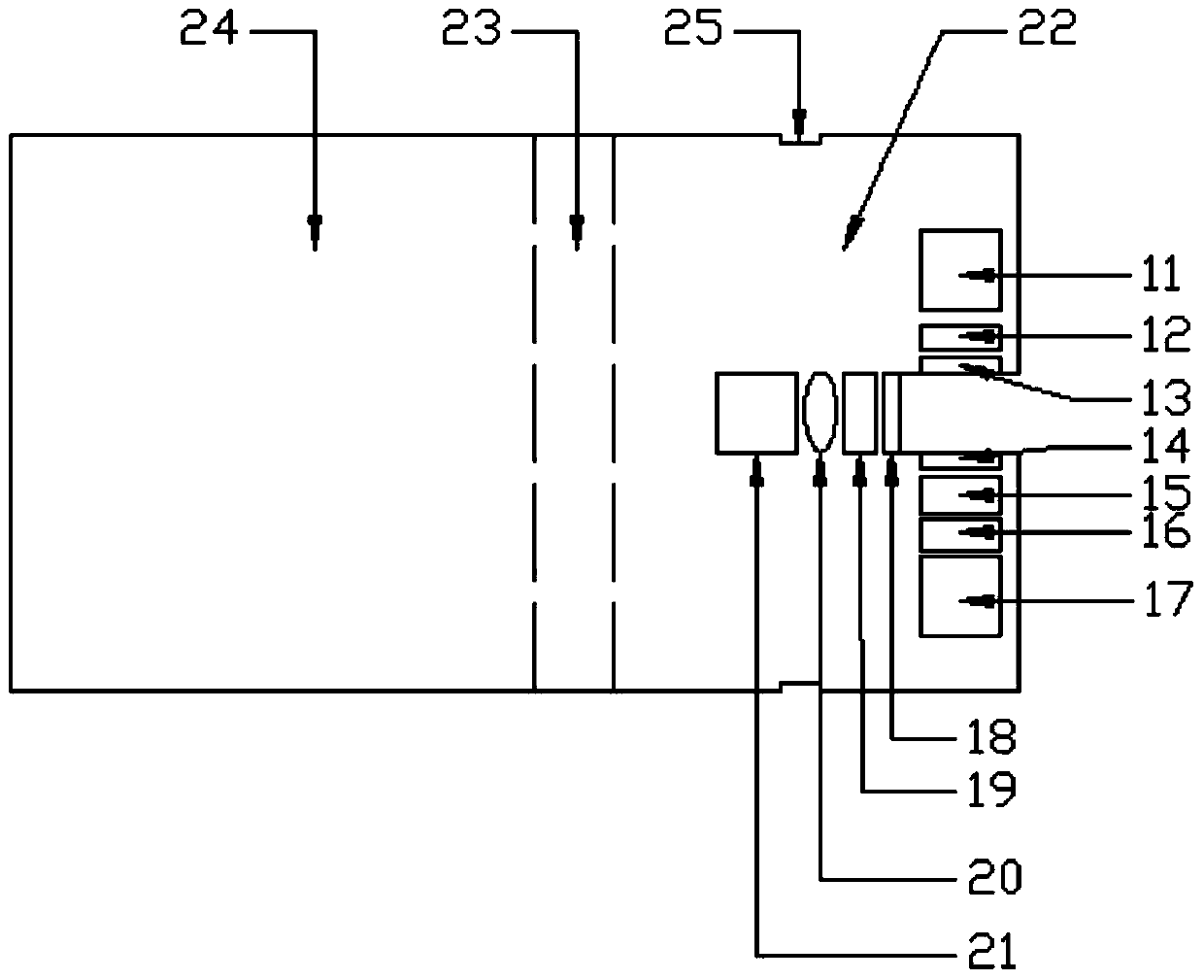
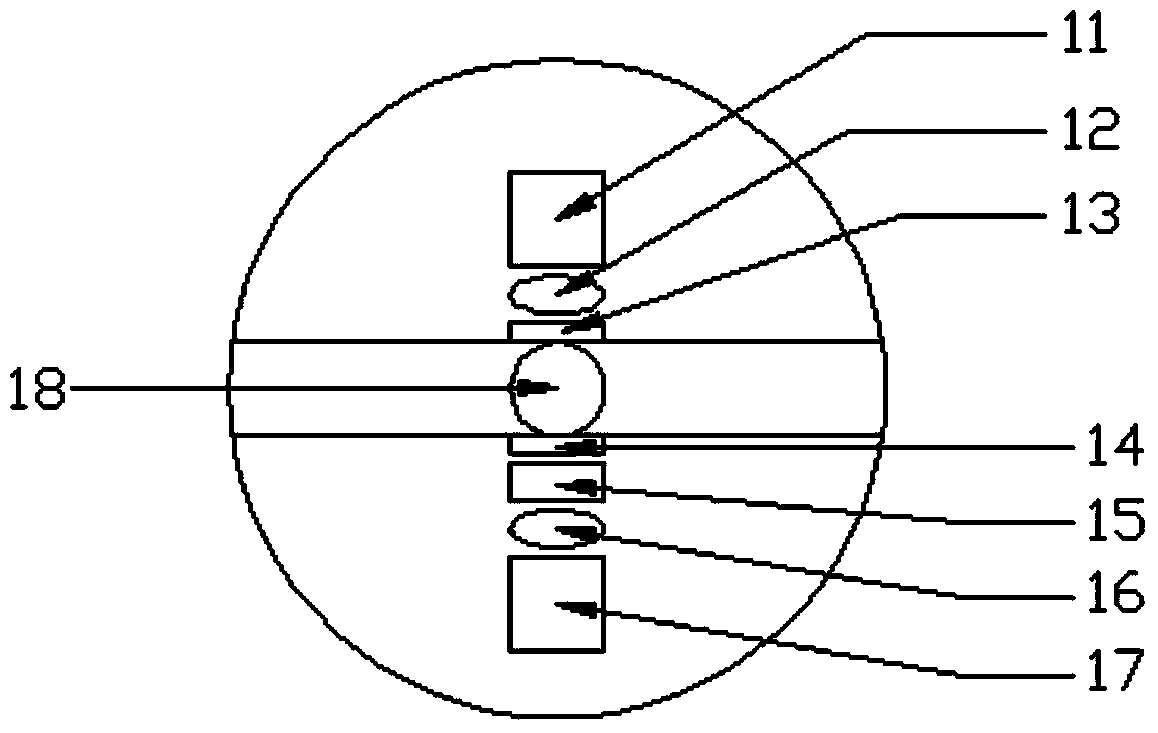
Ultraviolet fluorescence double-signal water quality monitoring device taking LED (light emitting diode) as light source and application method of device
ActiveCN104198391ANo consumptionNo digestion reaction time requiredColor/spectral properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceUltraviolet absorptionUltraviolet fluorescence
The invention discloses an ultraviolet fluorescence double-signal water quality monitoring device taking an LED (light emitting diode) as a light source and an application method of the device, and belongs to the field of environmental monitoring and water treatment. The ultraviolet fluorescence double-signal water quality monitoring device taking the LED as the light source consists of a sample collecting part and a detection part. The application method comprises the steps of selecting a deep ultraviolet LED lamp light source with specific wavelength and a photoelectric detector component according to a three-dimensional fluorescence atlas, detecting fluorescence intensity and ultraviolet absorption at the specific wavelength at the same time and calculating a ratio of the fluorescence intensity to the corresponding ultraviolet absorption. According to the device, no chemical reagent is consumed, monitoring of total concentration change of soluble organic matters in a water body can be realized, change of concentration of fluorescence ingredients such as proteins and humus can be reflected at the same time, and the sensitive, quick, efficient, economical, easy and information-rich on-line monitoring device is provided for the water treatment.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Microscope apparatus and observation method
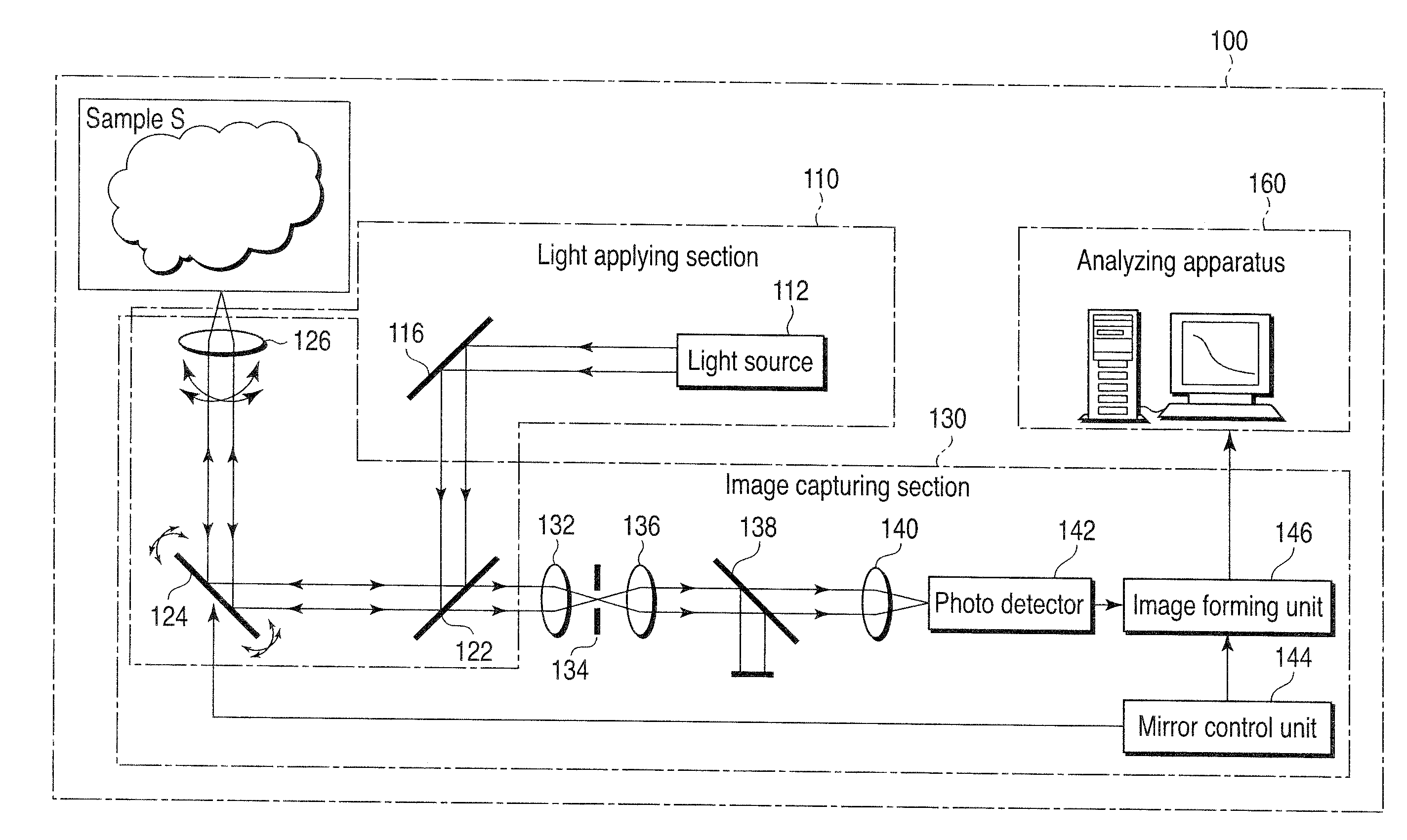
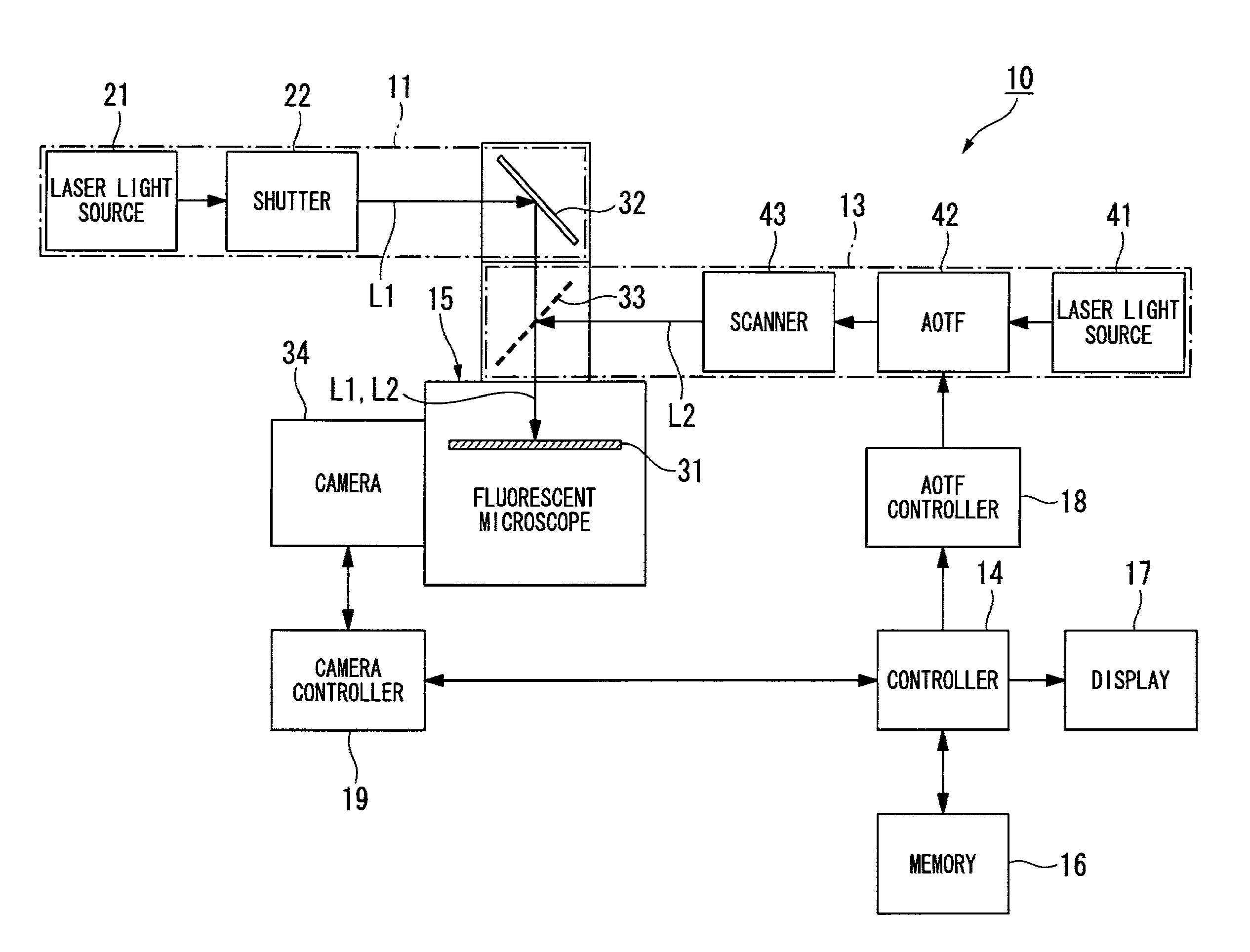
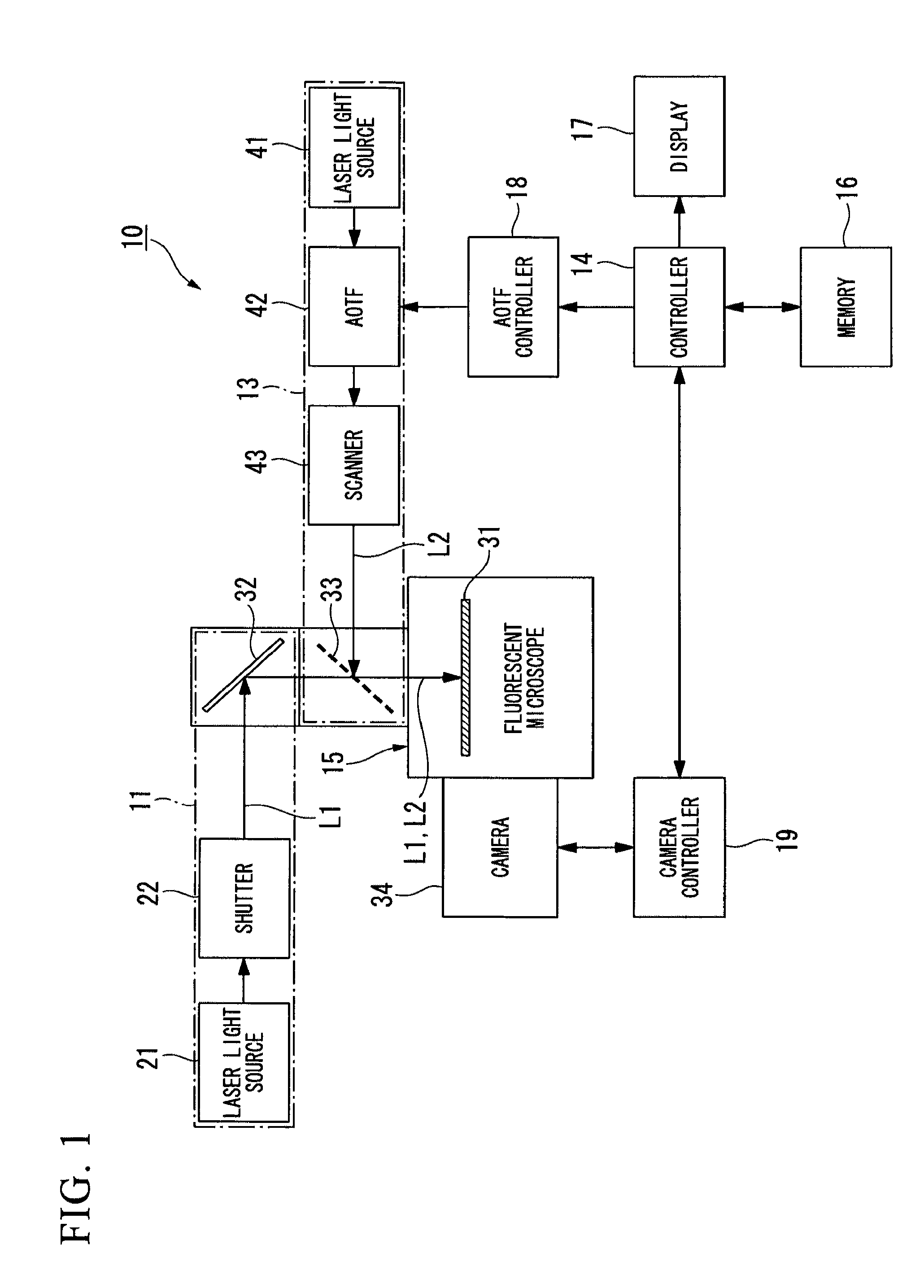
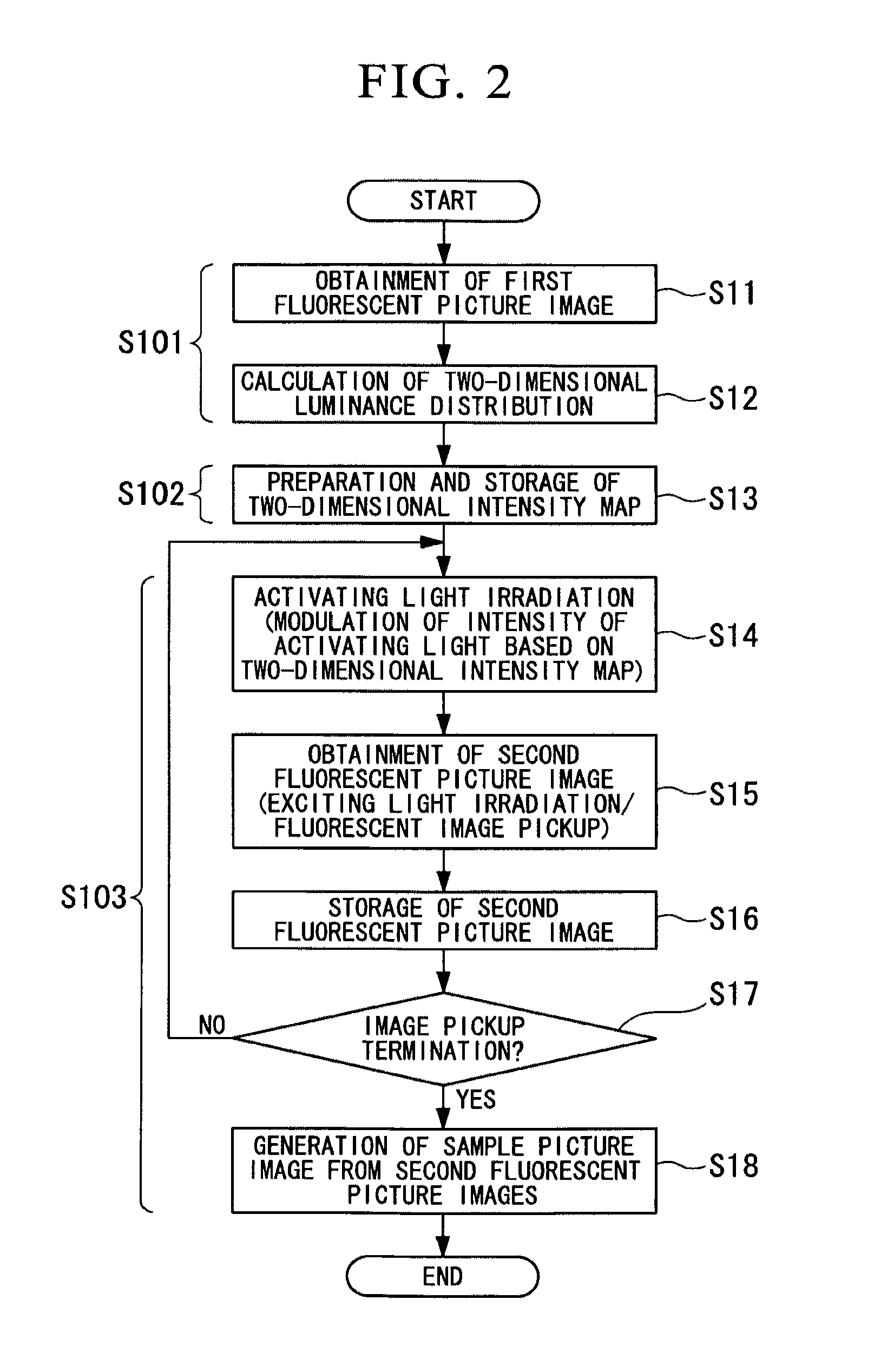
ActiveUS20120062722A1High resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansColor television detailsLight irradiationImage formation
A microscope apparatus comprises: a distribution measurement apparatus with respect to an observation region that comprises a fluorescent material that is activated when irradiated with an activating light, and that emits fluorescence when irradiated with an exciting light of a wavelength different from the activating light, obtains a fluorescent picture image through irradiation with the exciting light, and measures a fluorescent intensity distribution; an irradiation intensity setting apparatus which sets irradiation intensities of the activating light for respective portions of the observation region based on the fluorescent intensity distribution; and a picture image formation apparatus which obtains a plurality of the fluorescent picture images by repeating an operation wherein the observation region is irradiated with the activating light at the set irradiation intensities, and repeating an operation wherein a fluorescent picture image is obtained by irradiating with the exciting light after the activating light irradiation, generating a sample picture image.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Method for assaying nucleic acids by fluorescence
InactiveUS20100264331A1Prevent and limit interferenceEasy to carryRaman/scattering spectroscopyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorophoreLength wave
The invention relates to a method for determining the amount of nucleic acid present in a sample, wherein:—a fluorophore is added to the sample,—fluorescence intensities emitted by the fluorophore at least two emission wavelengths in response to light stimulations at least two excitation wavelengths respectively are measured, and—the amount of nucleic acid present in the sample is deduced from the measured fluorescence intensities.
Owner:BIOCHEMIKON +1
Laser-scanning examination apparatus
InactiveUS20060017920A1Reduce lossesCompact configurationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLaser scanningLaser light
The invention reduces the loss of fluorescence intensity obtained from a specimen to acquire clear fluorescence images when irradiating the specimen with ultrashort-pulse laser light produced by a laser light source. The invention provides a laser-scanning examination apparatus including a laser light source for producing ultrashort-pulse laser light; a laser light source for producing continuous-wave laser light; a measurement head including an optical scanning unit for scanning the laser light on a specimen and an objective optical system; an imaging unit for detecting return light from the specimen in response to the ultrashort-pulse laser light; and an imaging unit for detecting return light from the specimen in response to the continuous-wave laser light. The laser light sources and one imaging unit are connected to the measurement head by an optical fiber, and the other imaging unit is connected to the measurement head by another optical fiber with a larger core diameter.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
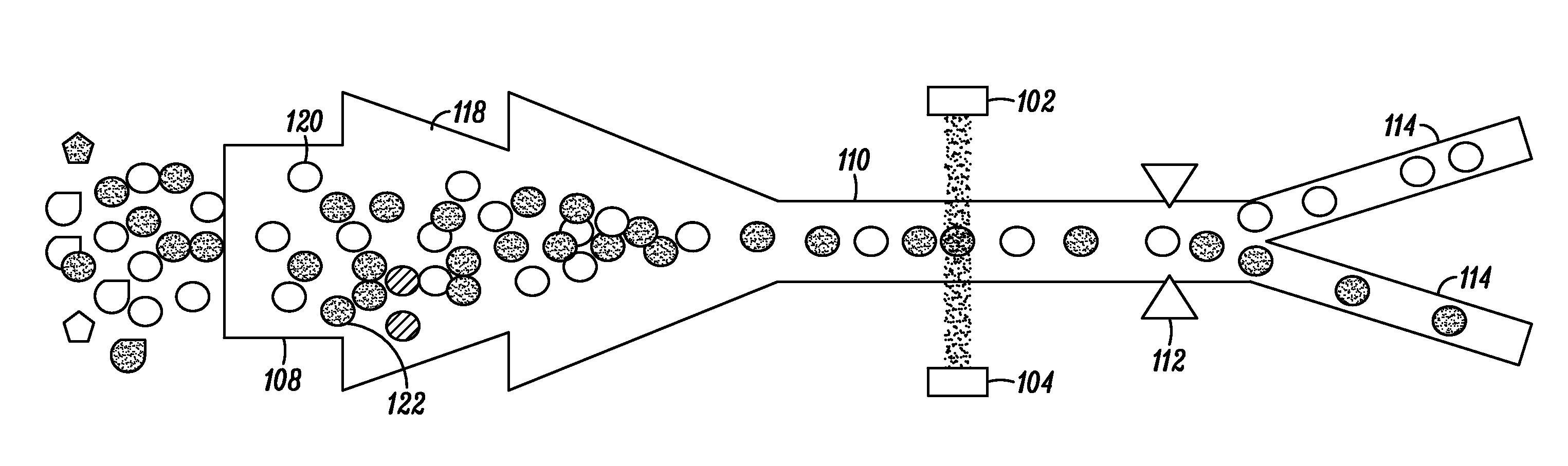
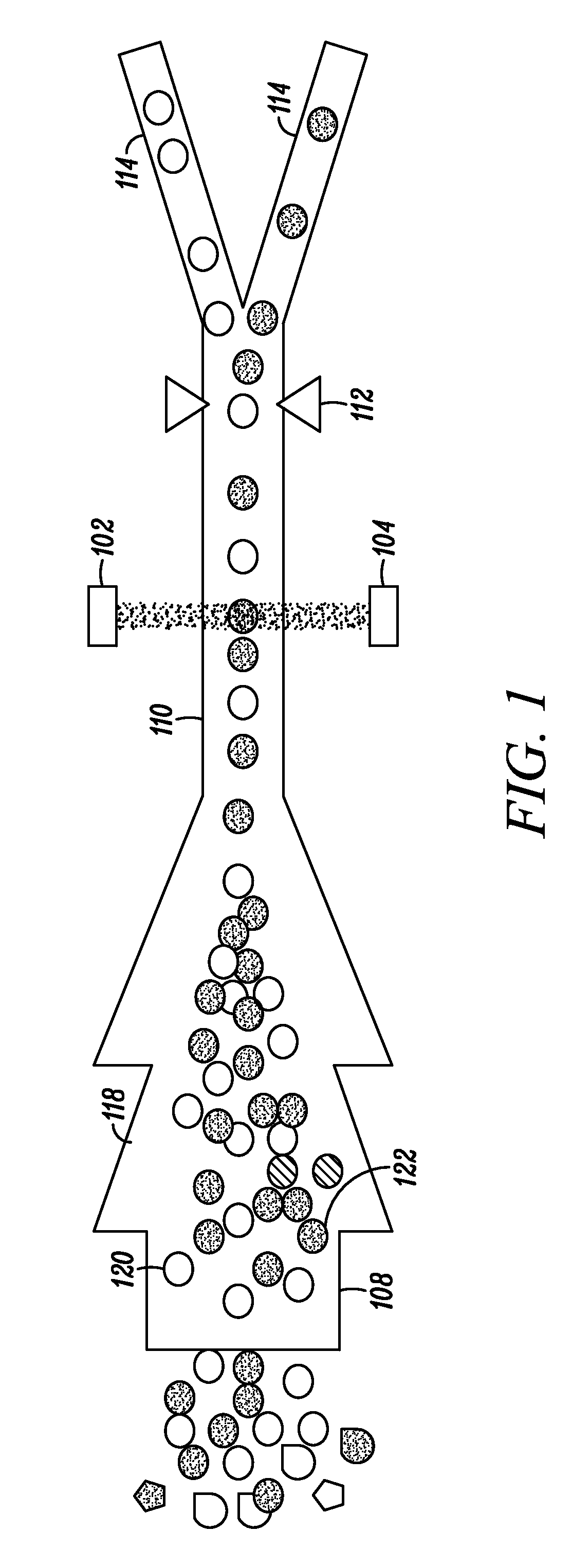
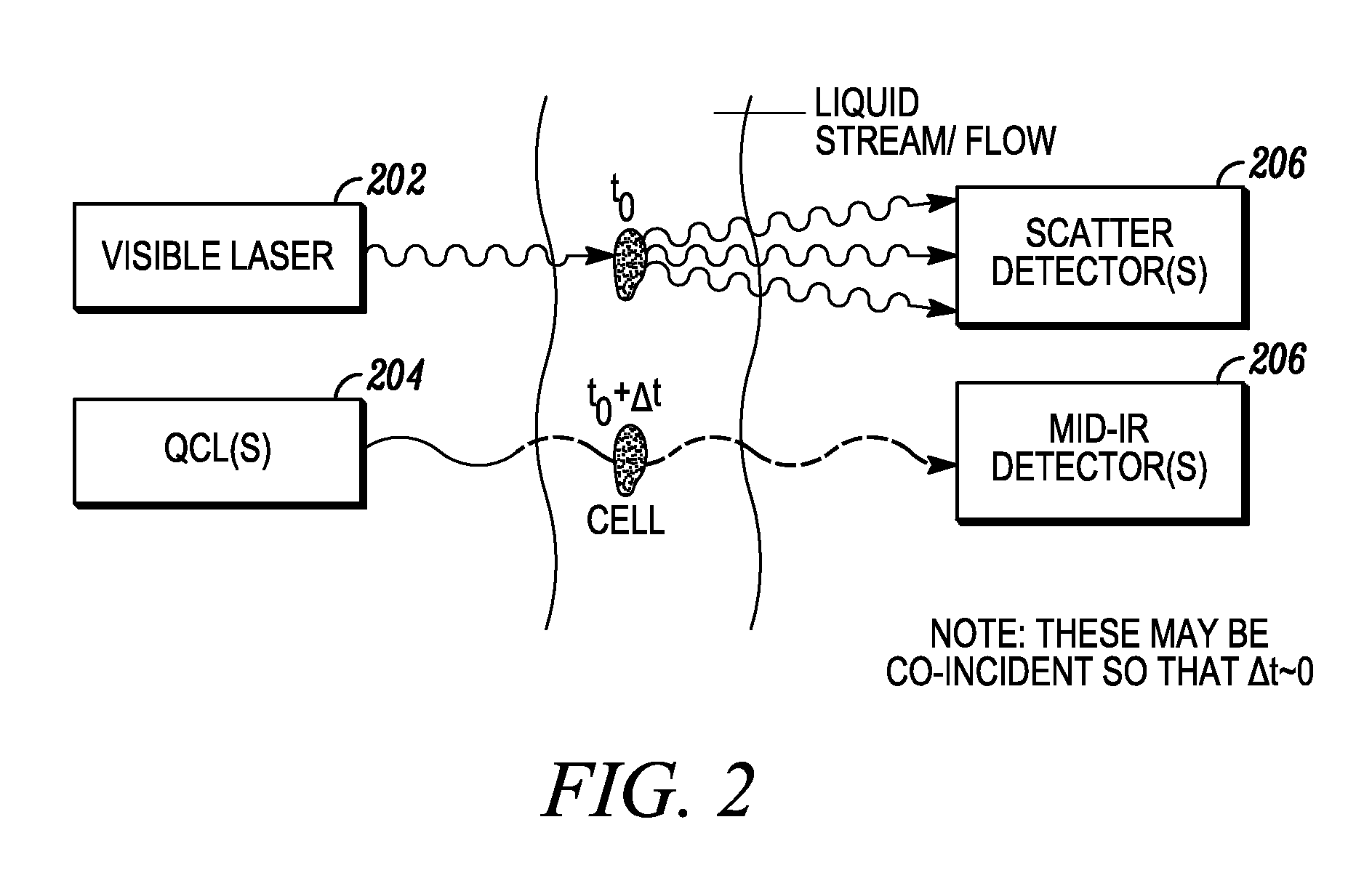
Combined inspection system including mid-ir vibrational spectroscopy and a fluorescent cytometry facility
InactiveUS20120196356A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnalyteSpectroscopy
This disclosure concerns a cytometry system including a handling system that presents single cells to at least one quantum cascade laser (QCL) source. The QCL laser source configured to deliver light to a cell within the cells in order to induce resonant mid-infrared absorption by one or more analytes of the cell. The system includes a laser source that excites at least one fluorophore present in the cell or on the surface of the cell and a fluorescence detector that measures the fluorescence intensity of the fluorophore. A mid-infrared detection facility detects the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light, wherein the transmitted mid-infrared wavelength light and the fluorescence intensity are used to identify at least one cell characteristic.
Owner:1087 SYST
Portable Intelligent Fluorescence and Transmittance Imaging Spectroscopy System
A portable fluorescence and transmittance imaging spectroscopy system for use in diagnosing plant health. The system has a primary LED light source array with spectral wavelengths in the 400-600 nm range, a focus cone that collects the LED light source output and focuses it, a controller that controls the primary LED array to turn it on and off, or certain of the spectral wavelengths on and off such that the primary LED array controllably emits light of a desired wavelength in the range, the light irradiating the plant through the focus cone, a digital imaging device that both spatially and temporally captures a fluorescence image comprising chlorophyll fluorescence emitted by the plant due to the emitted light from the LED array, a leaf holder located proximate to the output of the focus cone to maintain a consistent position and distance between the digital imaging device, the LED light source and the leaf and providing for fixed position and non-destructive leaf imaging and testing, a secondary light source for providing broad-band transmissive light through the leaf, a lens for focusing onto the imaging device the light emitted from the secondary light source, and one or more memory devices that store the fluorescence image and the transmitted light data received by the digital imaging device and store a library of plant fluorescence-intensity data indicative of both healthy plants and stressed or diseased plants, and plant light transmittance data indicative of certain plant conditions.
Owner:LUSSIER ROBERT
High voltage electrospinning method for preparing multi-fluorescence-encoded micro-beads
InactiveCN101338189AEasy to operateWide applicabilityBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsMicrosphere
The invention belongs to the fluorescence-coded technology field and in particular relates to a high voltage electric spinning preparation method of multiplex fluorescence coding microsphere. In the method, fluorescent materials (quantum dots material or fluorescent dyes) with different quantities and different fluorescent characteristics are dispersed in polymer solution (or inorganic matter sol). Then, through the high voltage electric spinning process, the coding microsphere with controllable size and adjustable fluorescent strength and lighting wavelength is obtained. The quantum dots material can be used alone or used in mixing way. The fluorescent material can be used alone or used in mixing way. The flurescent material can also be used together with the quantum dots material. The coding microsphere prepared through the invention can provide fluorescent probes in large quantities for the fields of gene expression, protein-protein interaction, simultaneous detection of various diseases, high throughput screening, combinational chemistry, etc. The method of the invention has the advantages of simple operation, wide application, low cost, stable fluorescence performance, and the like, and is provided with good application and expansion value.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com