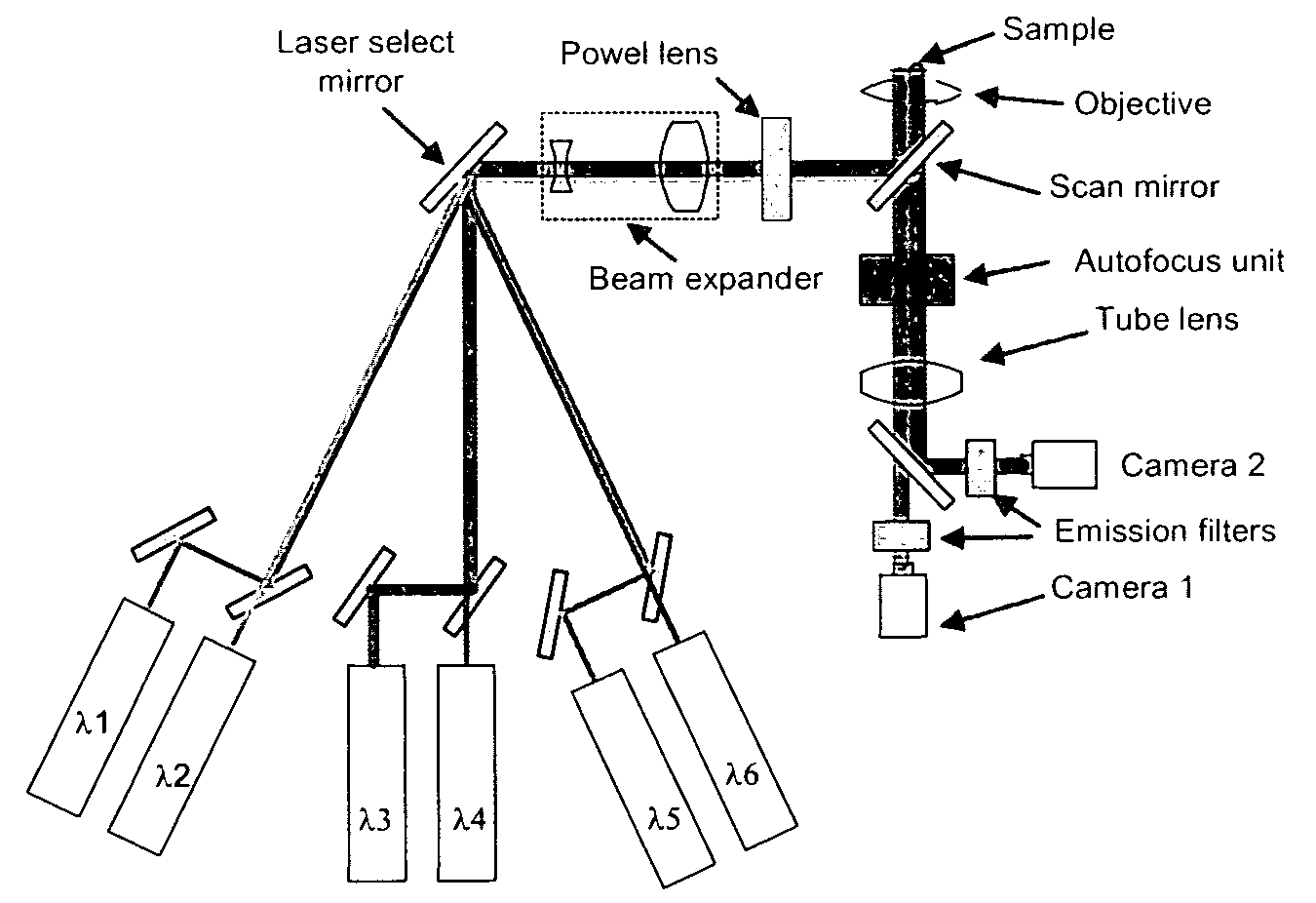
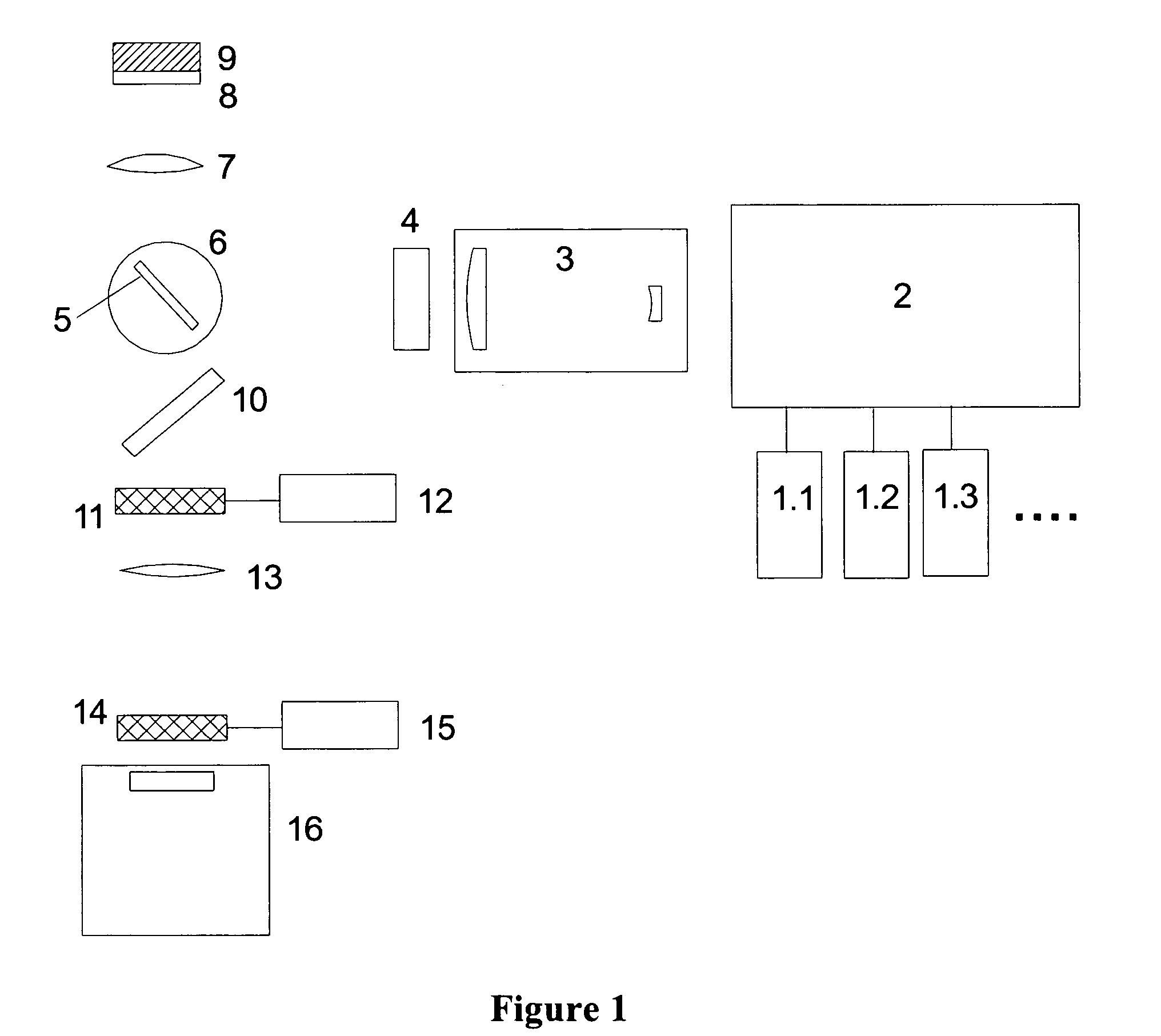
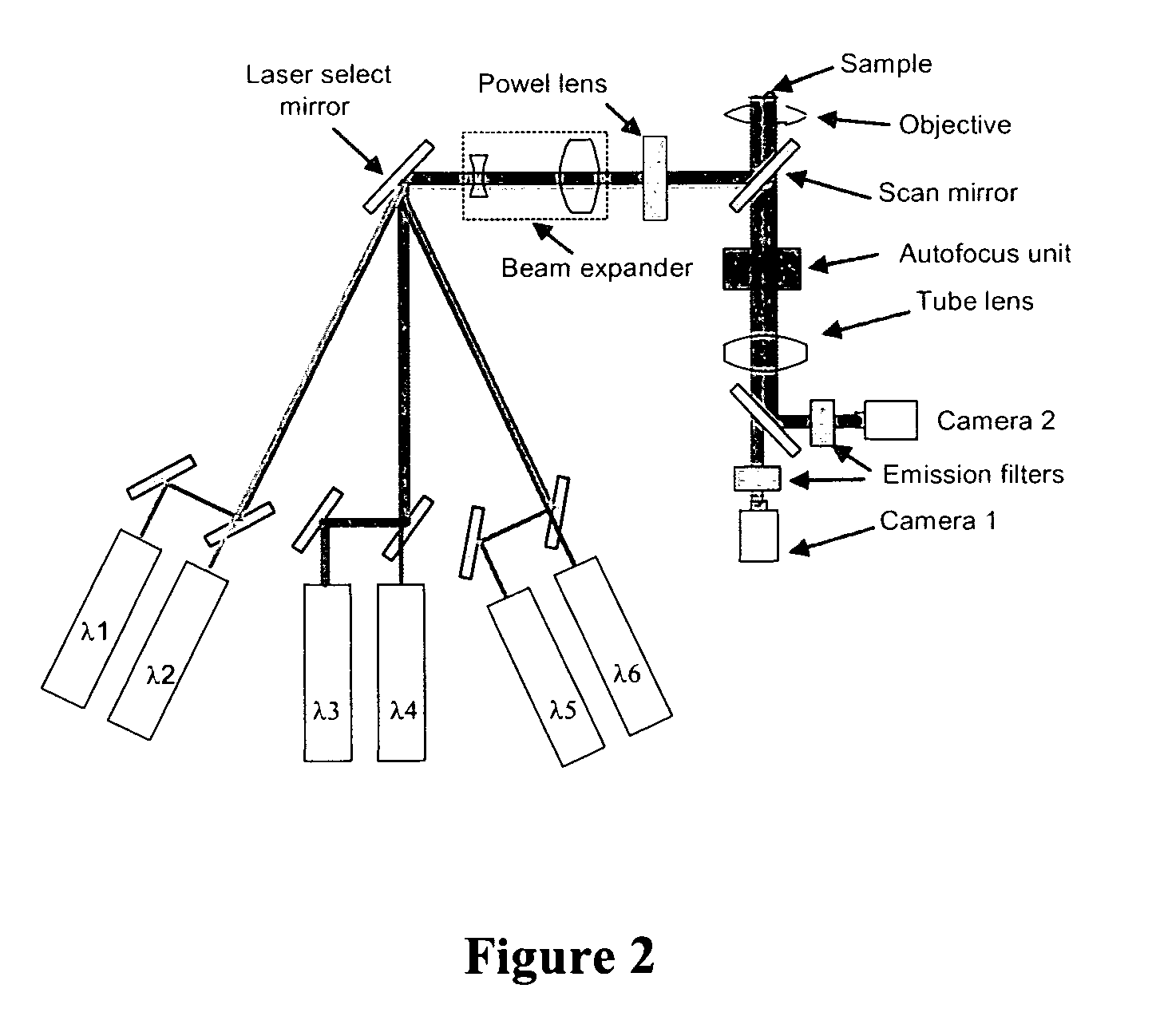
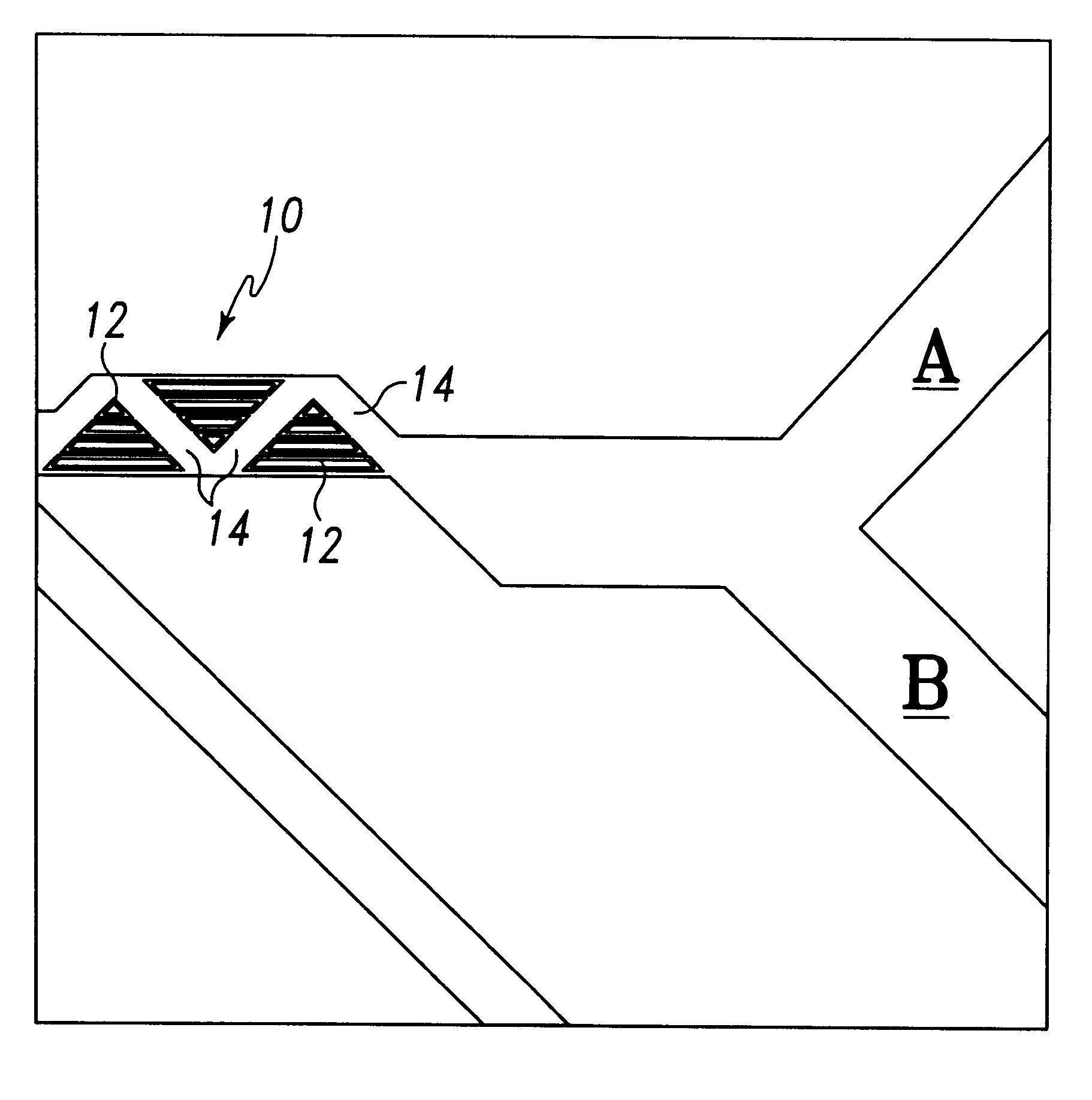
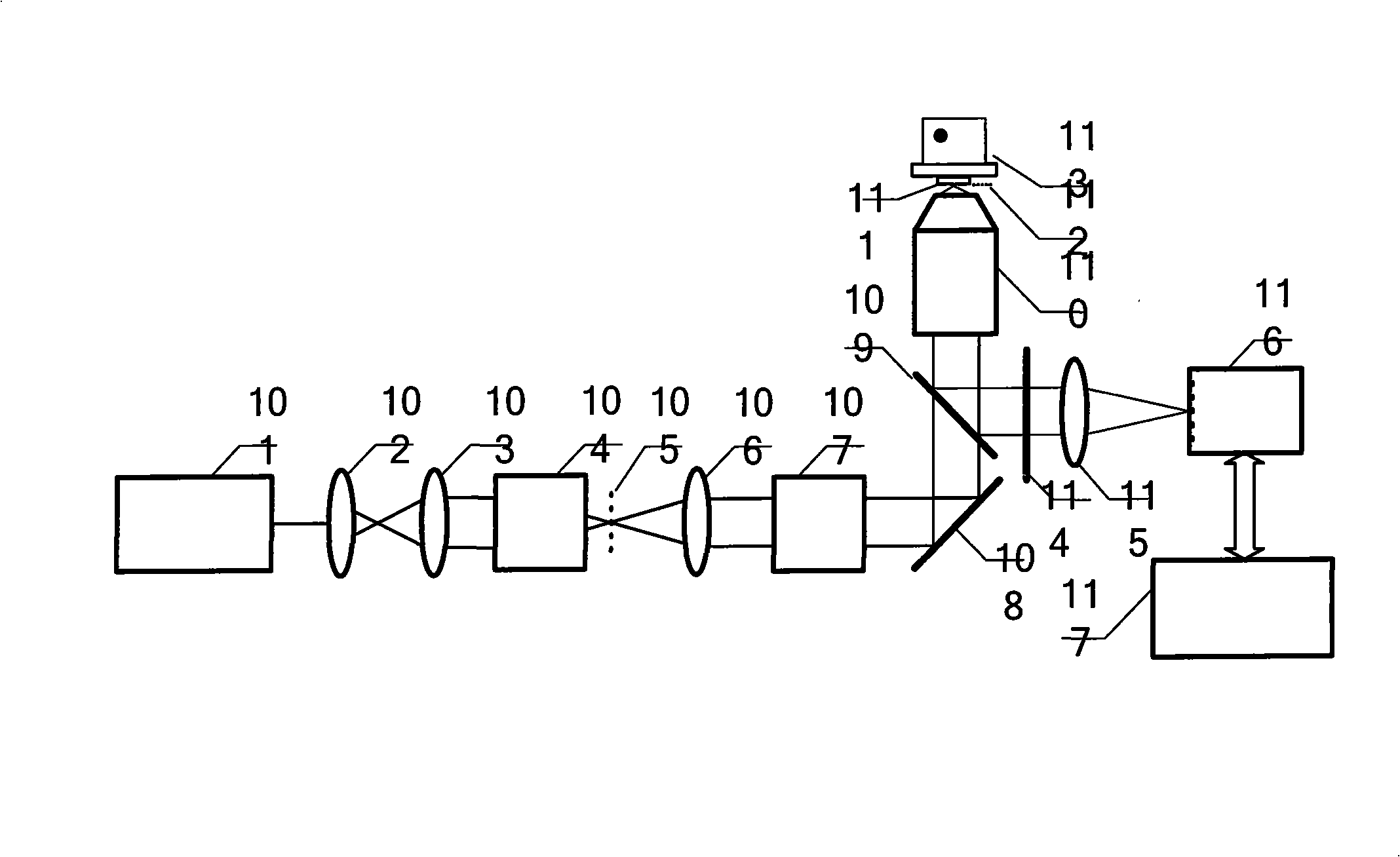
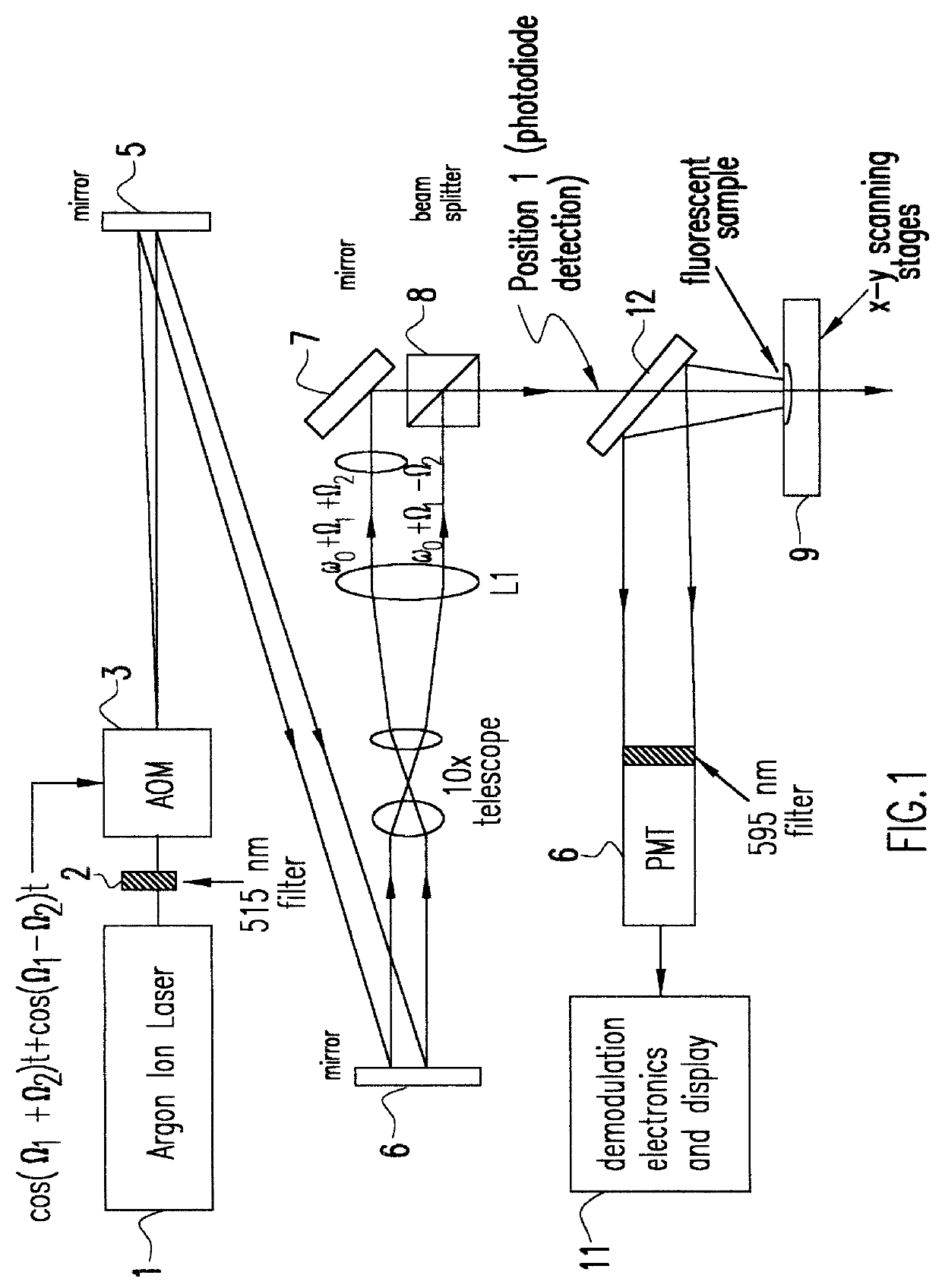
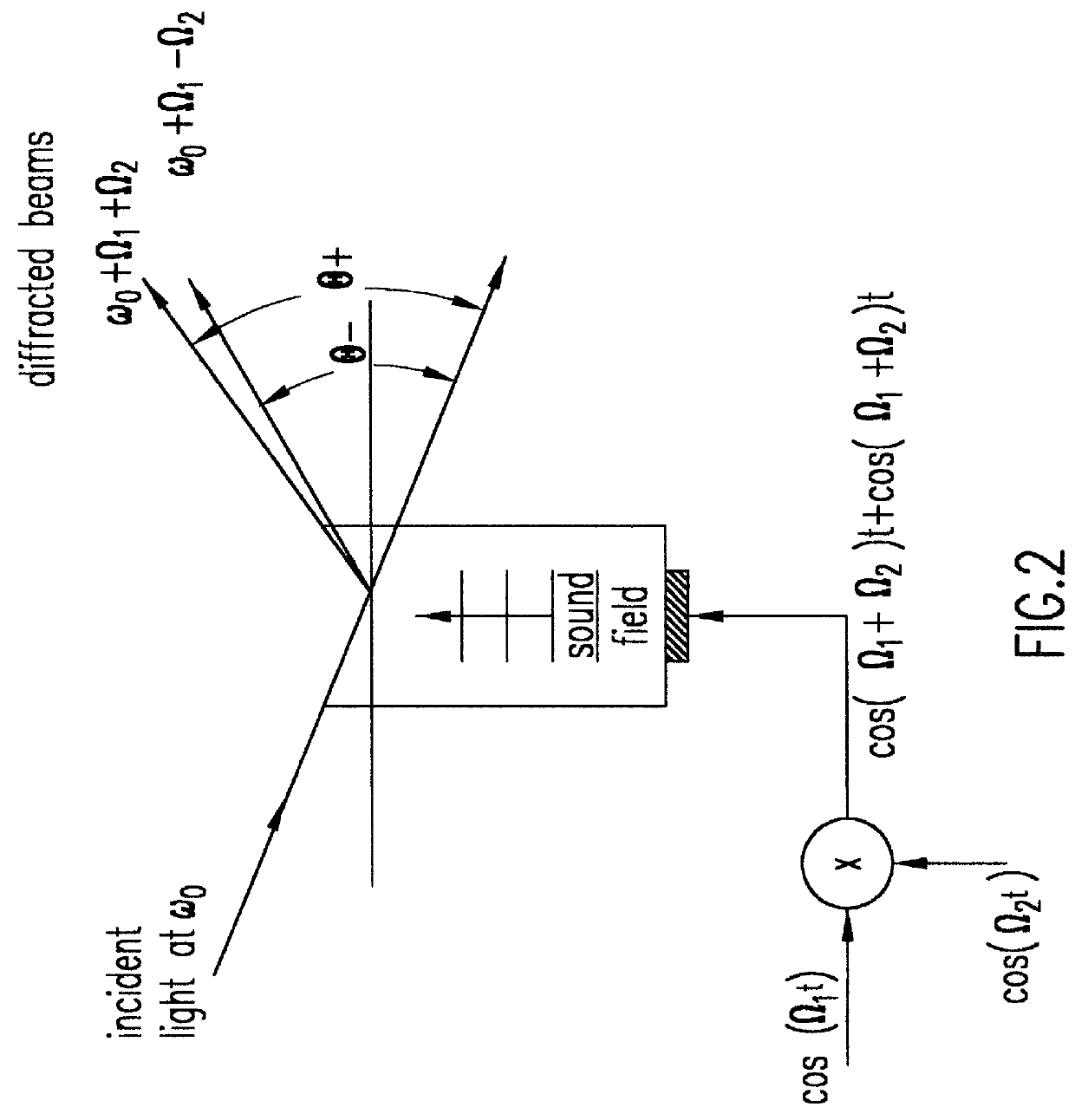
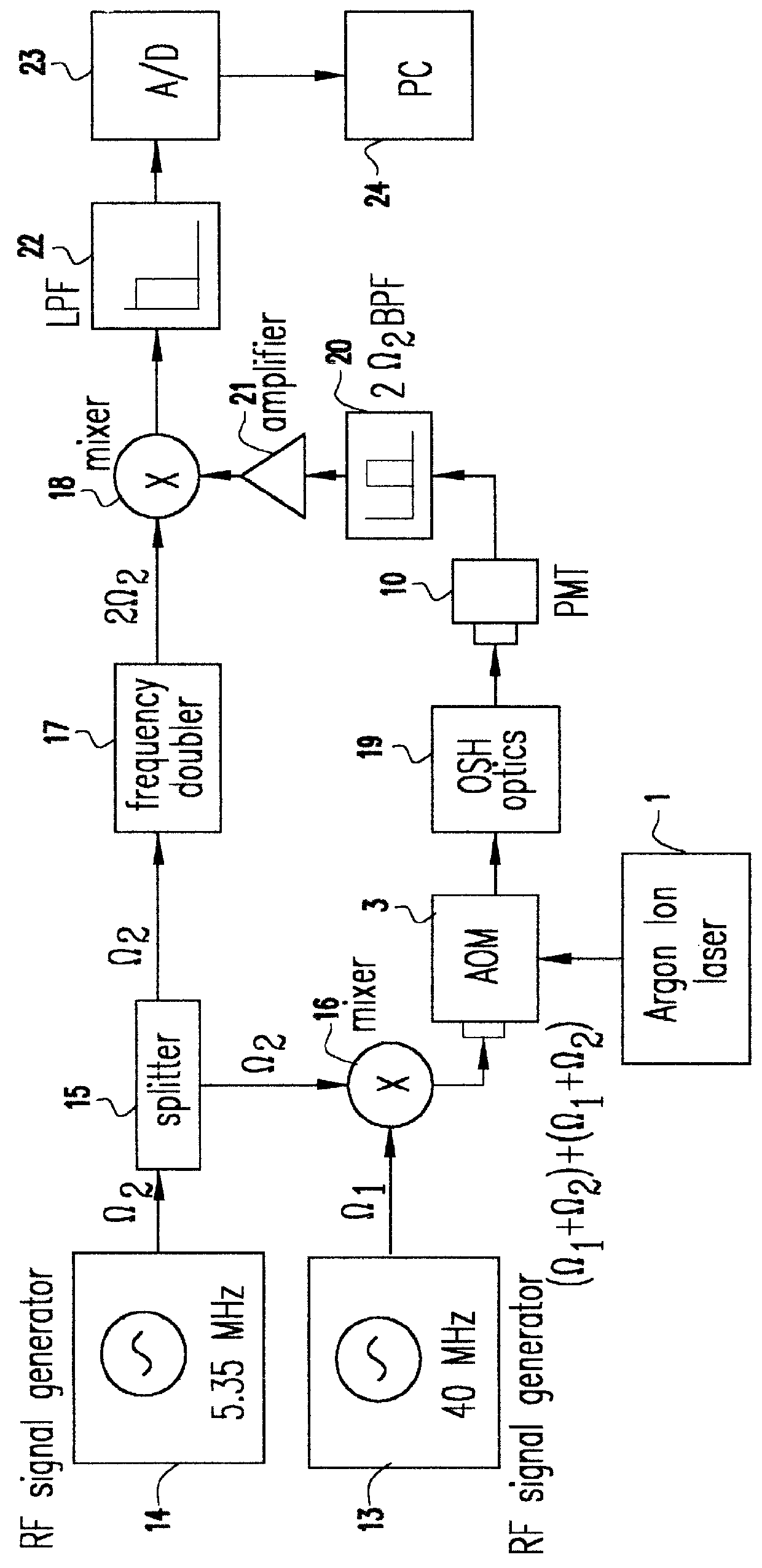
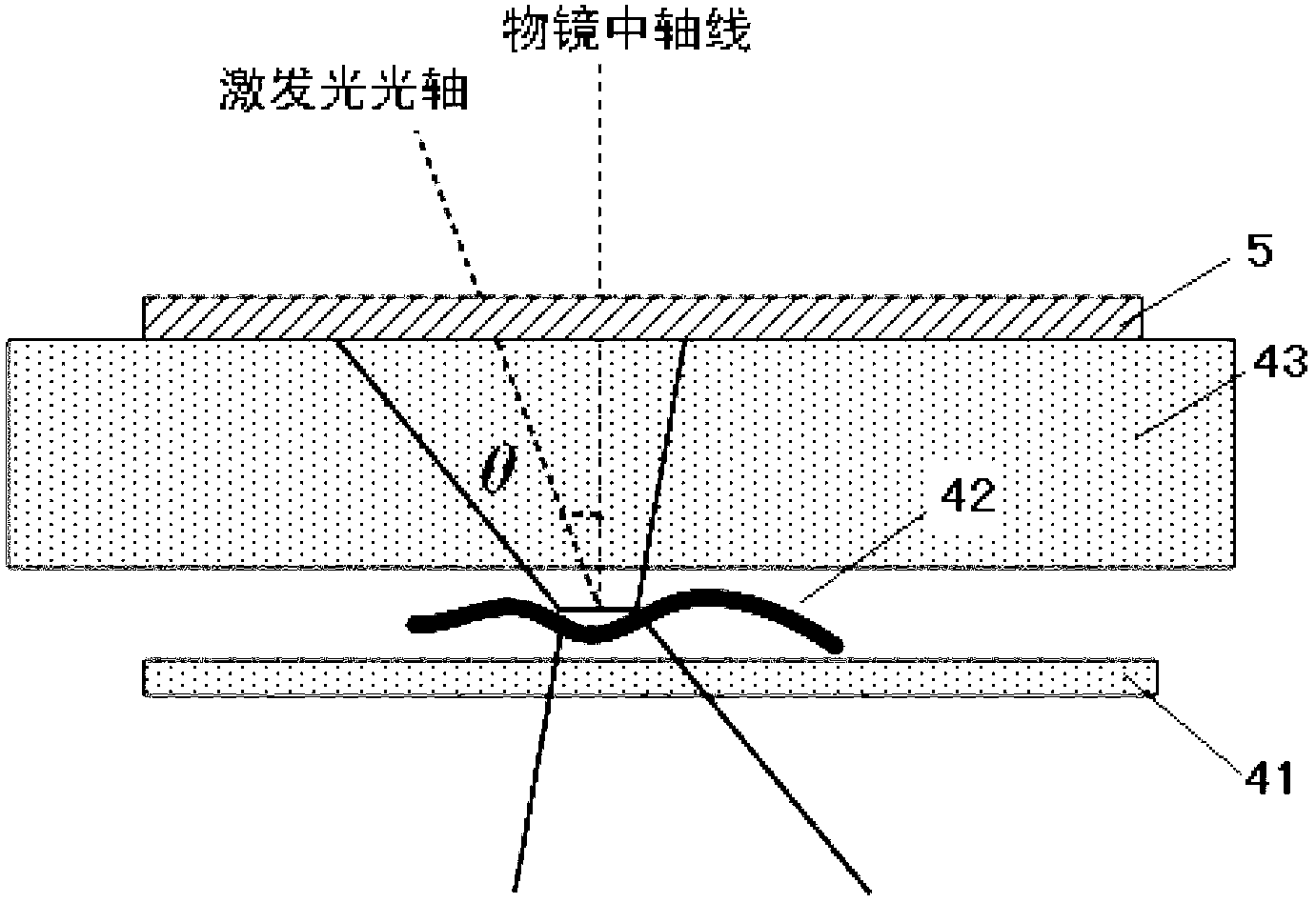
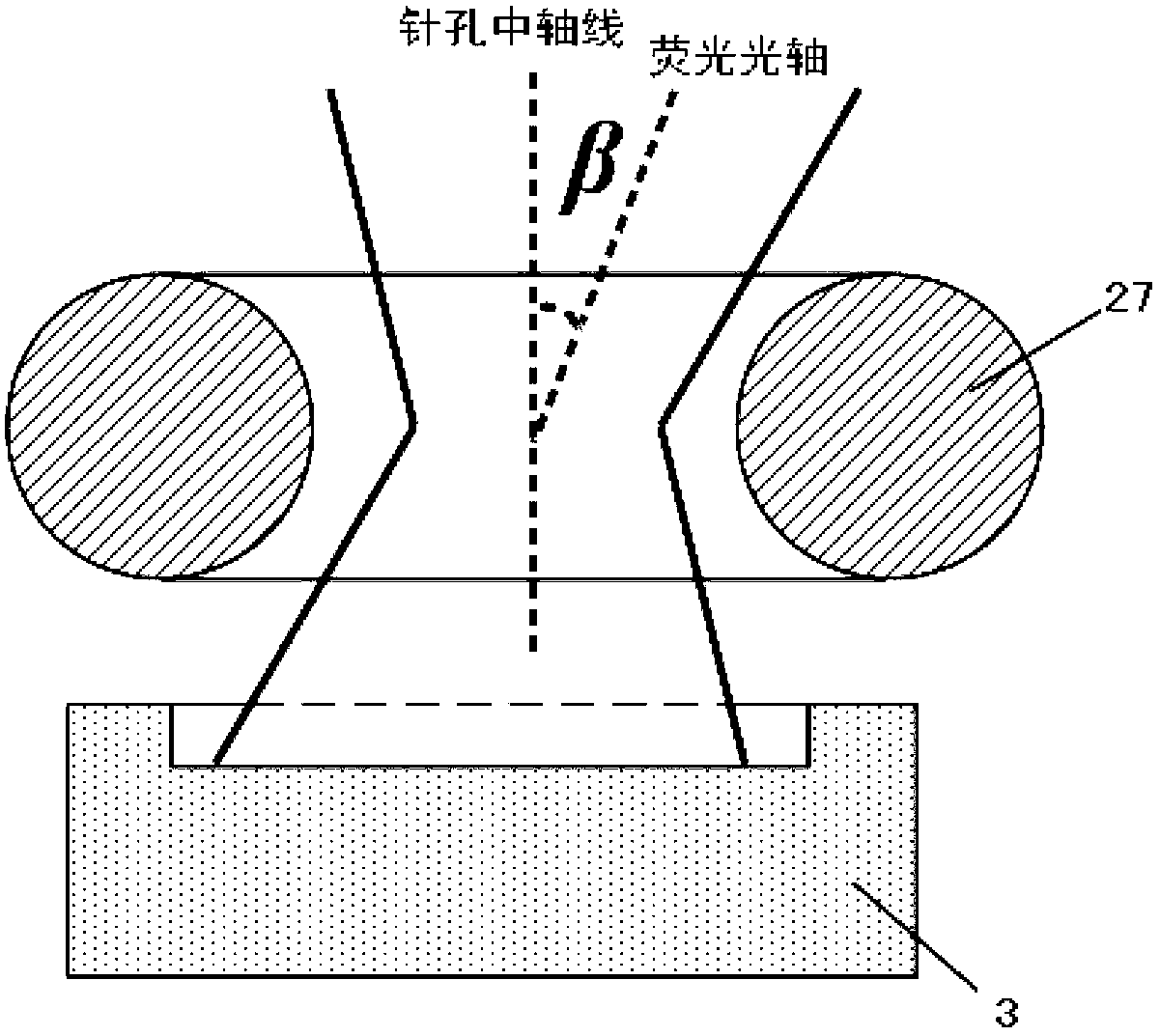
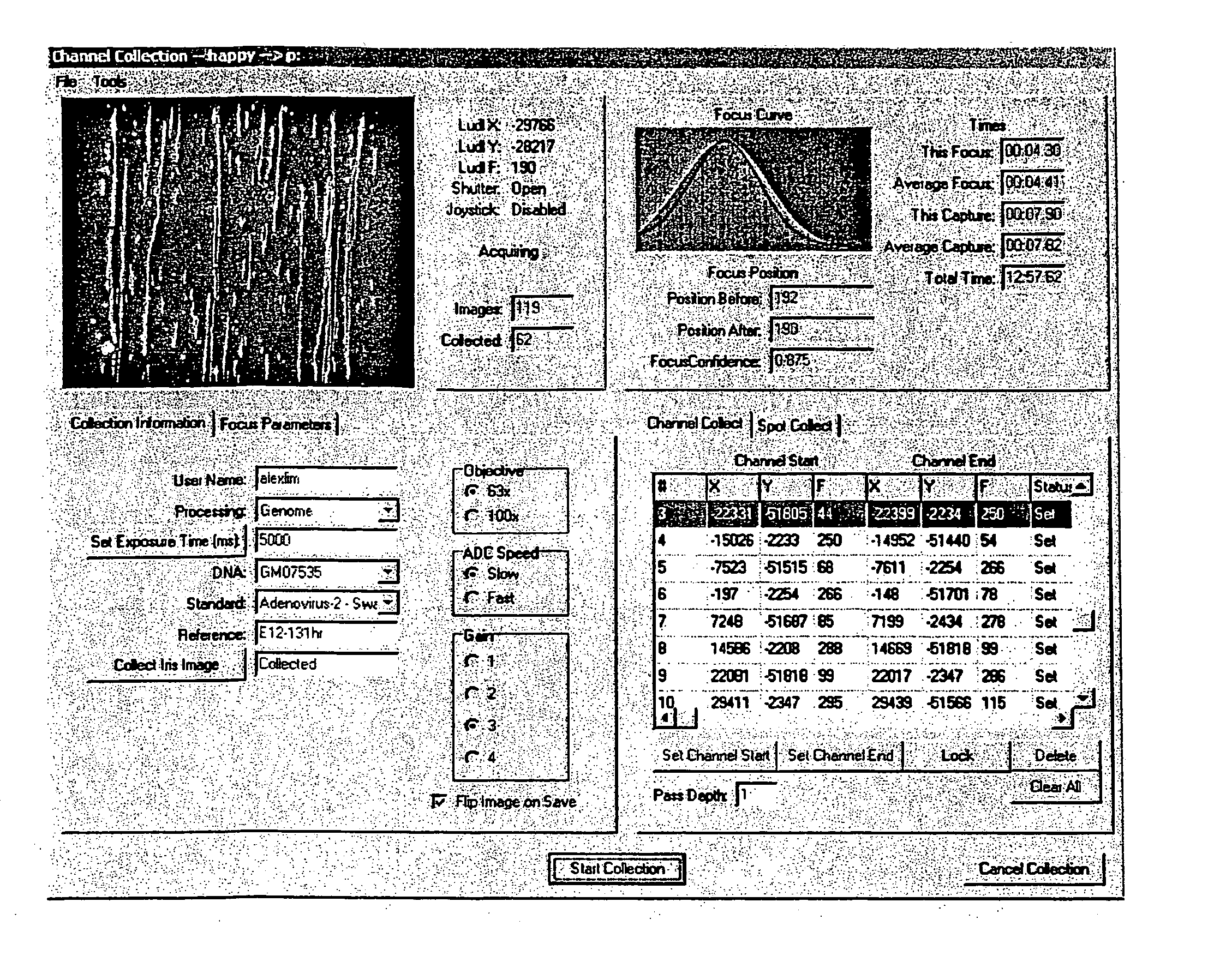
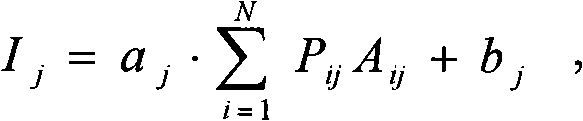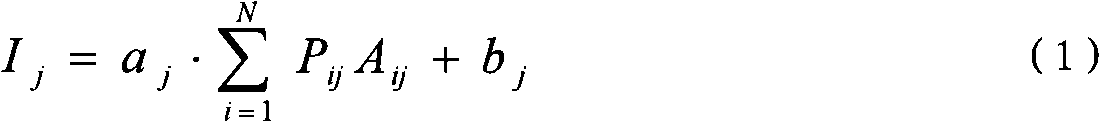Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1068 results about "Fluorescence microscope" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A fluorescence microscope is an optical microscope that uses fluorescence and phosphorescence instead of, or in addition to, scattering, reflection, and attenuation or absorption, to study the properties of organic or inorganic substances. "Fluorescence microscope" refers to any microscope that uses fluorescence to generate an image, whether it is a more simple set up like an epifluorescence microscope or a more complicated design such as a confocal microscope, which uses optical sectioning to get better resolution of the fluorescence image.
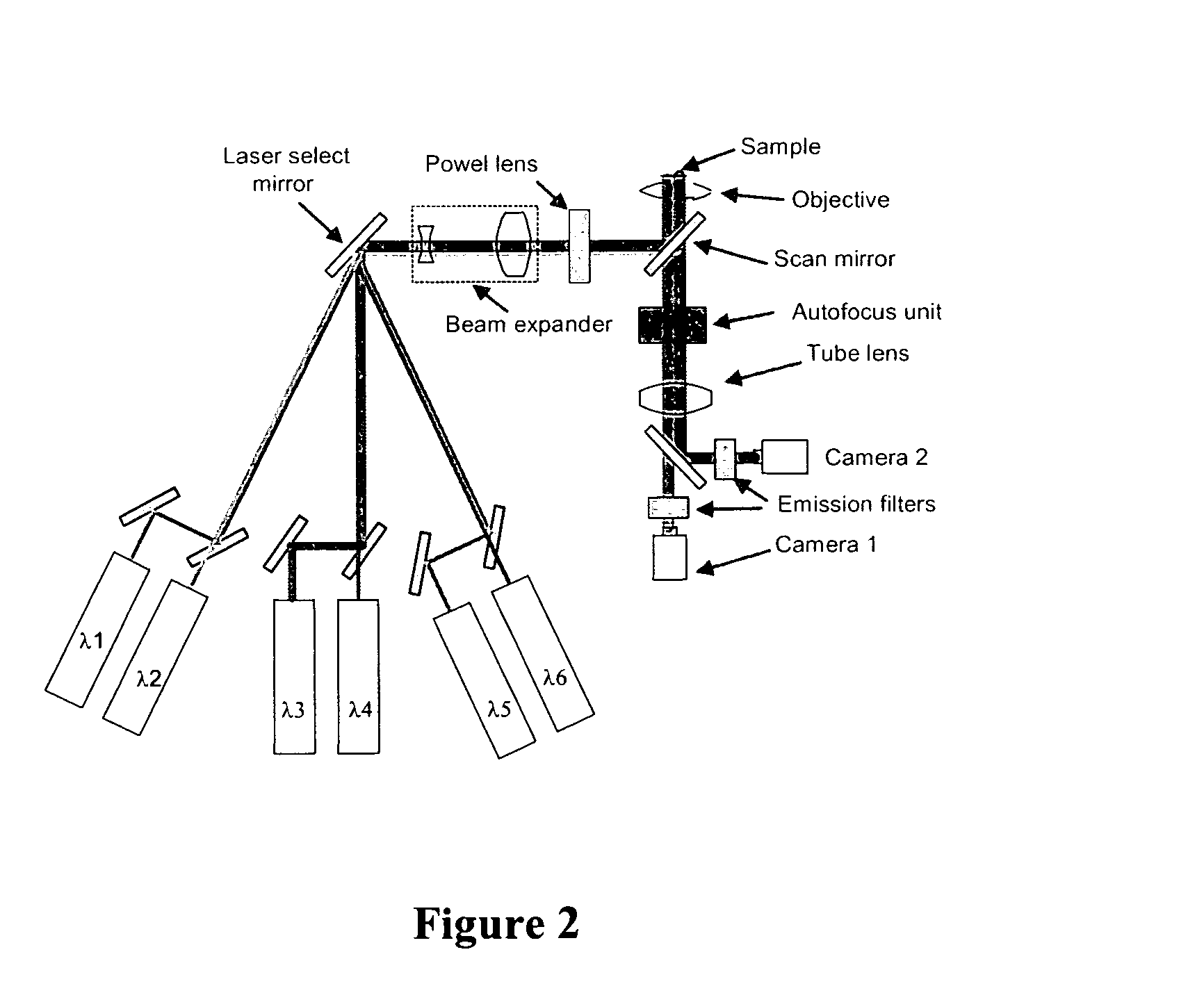
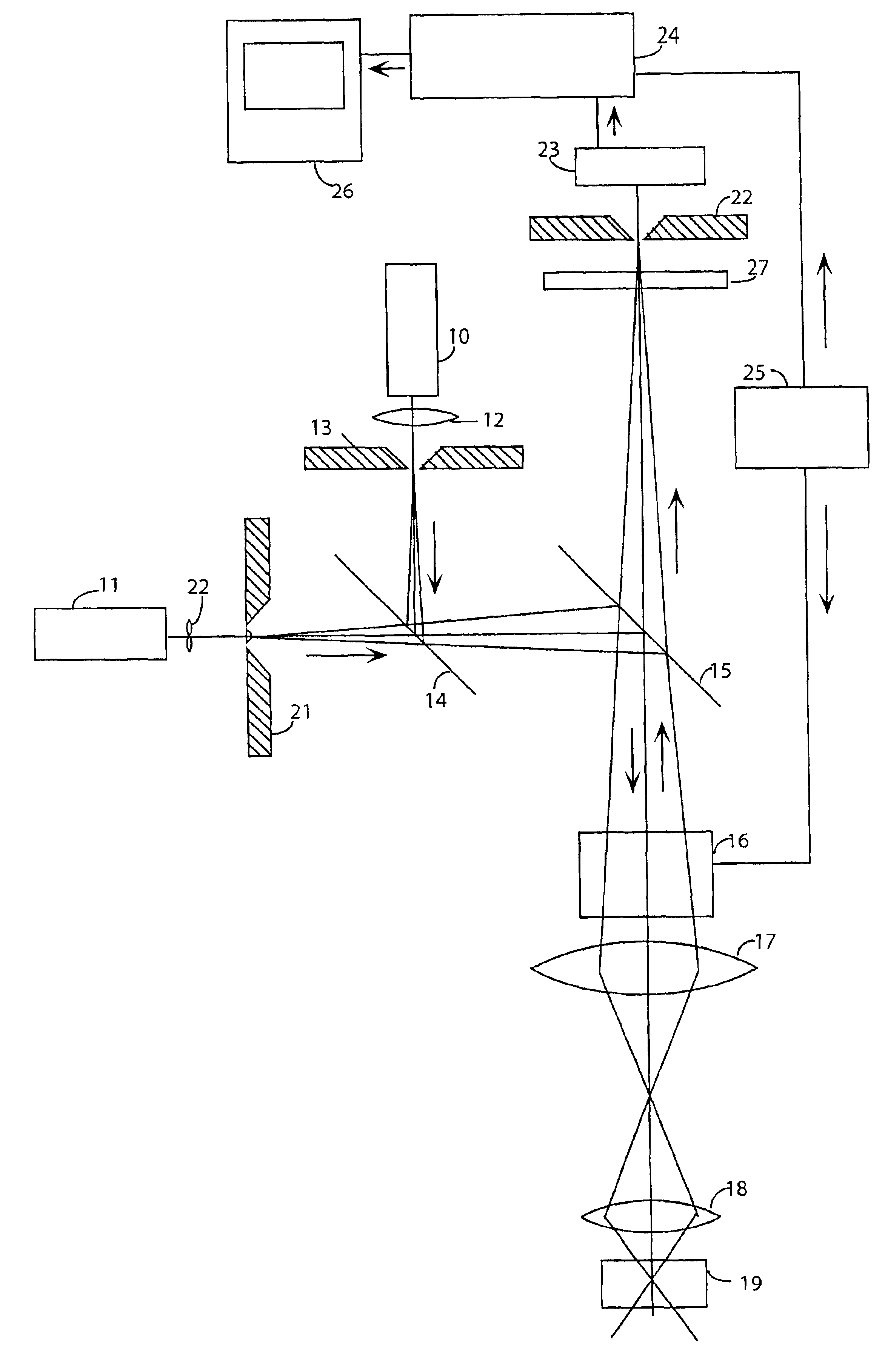
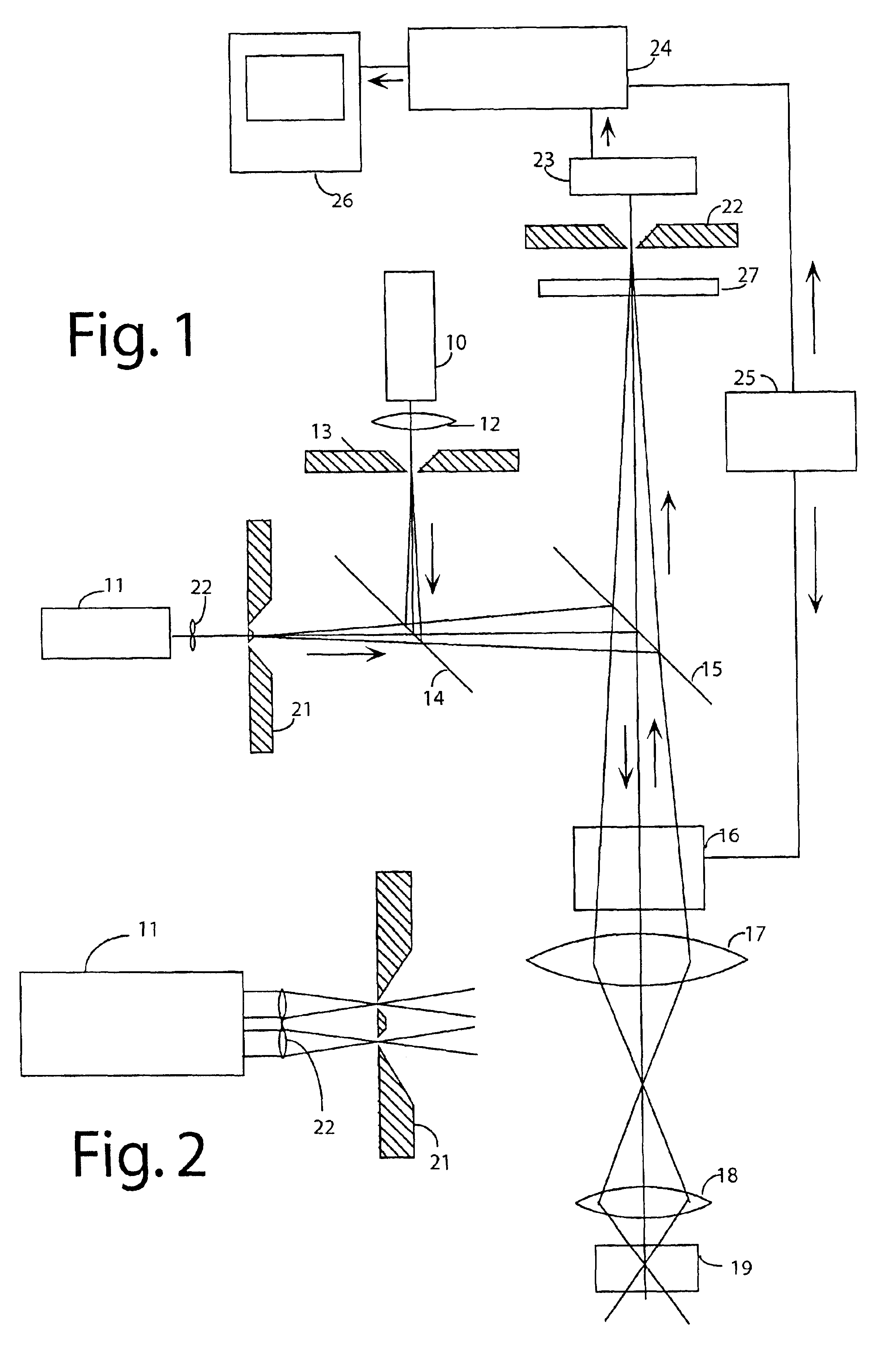
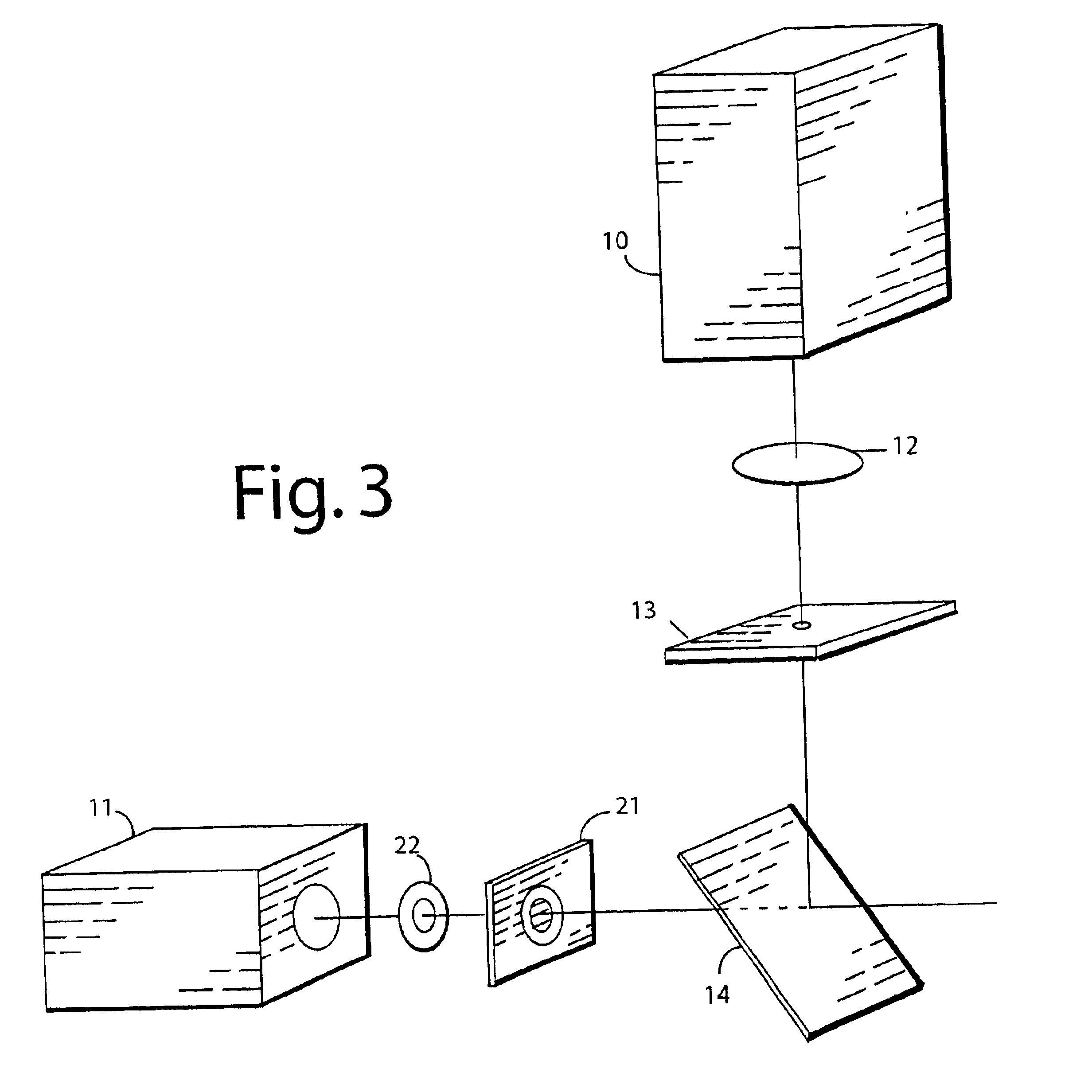
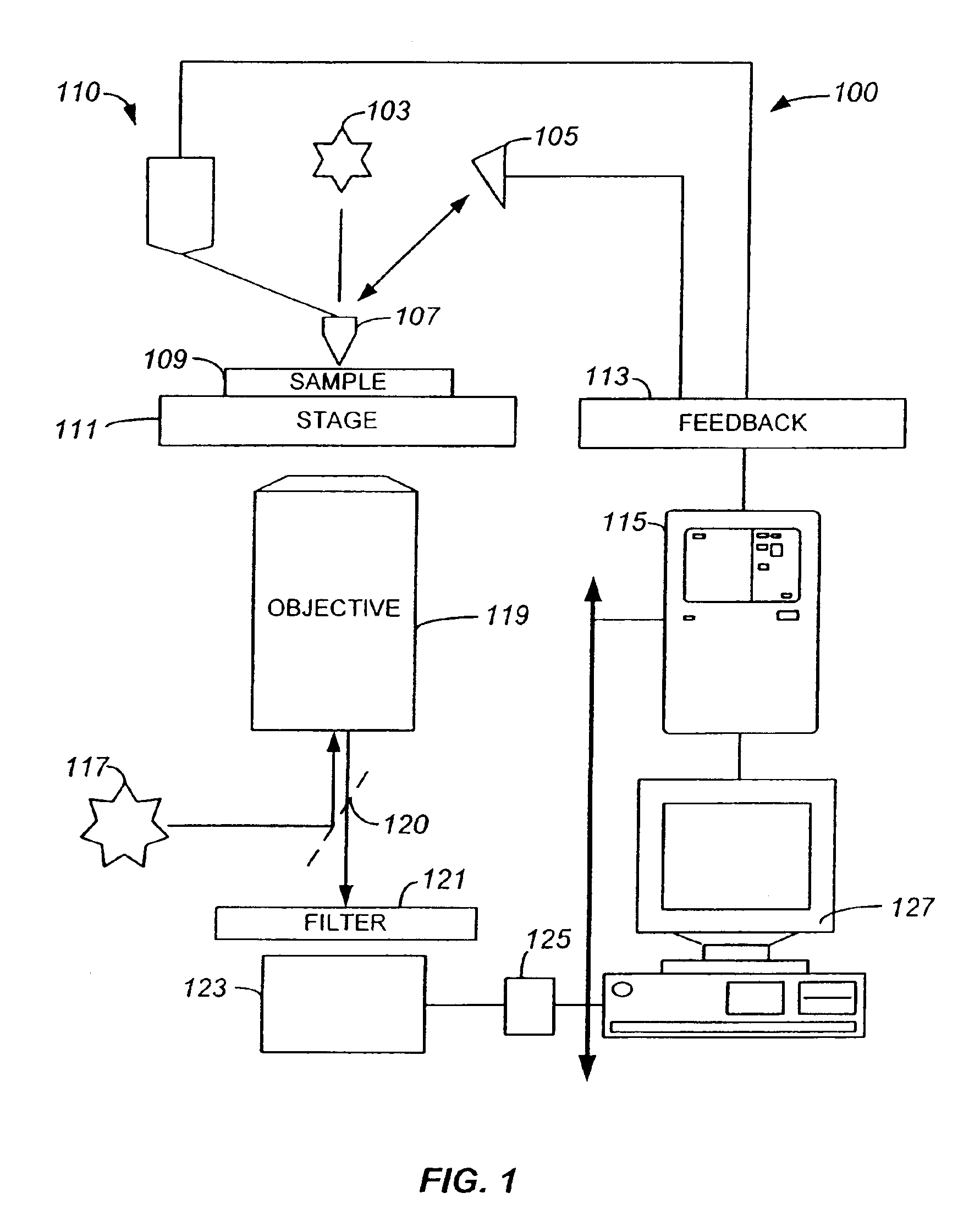
Method and apparatus for fluorescent confocal microscopy
ActiveUS7335898B2Big advantageDrawback can be addressedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide fieldFluorescence microscope
A new and improved confocal fluorescence microscope is presented. The new microscope has significant advantages relative to existing implementations of microscope confocal imagers. In common with previous confocal imagers the instant invention has the advantages relative to conventional wide-field and confocal fluorescence imagers, however it addresses the drawbacks of confocal technology in terms of cost and complexity, and provides significant savings in both due to the simplicity of the components and the elimination of the need of, in particular, spatial filters such as pinholes or slits.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
In situ micromachined mixer for microfluidic analytical systems
The present invention relates to an in situ micromachined mixer for microfluidic analytical systems. In a preferred embodiment, a 100 pL mixer for liquids transported by electroosmotic flow (EOF) is described. Mixing was achieved in multiple intersecting channels with a bimodal width distribution and varying lengths. Five .mu.m width channels ran parallel to the direction of flow whereas larger 27 .mu.m width channels ran back and forth through the network at a 45.degree. angle. All channels were approximately 10 .mu.m deep. It was observed that little mixing of confluent streams occurred in the 100 .mu.m wide mixer inlet channel where mixing would be achieved almost exclusively by diffusion. In contrast, mixing was complete after passage through the channel network in the .apprxeq.200 .mu.m length mixer. Solvent composition was altered by varying the voltage on solvent reservoirs. The high efficiency attained in this mixer was attributed to the presence of a 2 pL vortex in the center of the mixer. Video tracking of fluorescent particles with a fluorescence microscope allowed the position and volume of this vortex to be determined.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
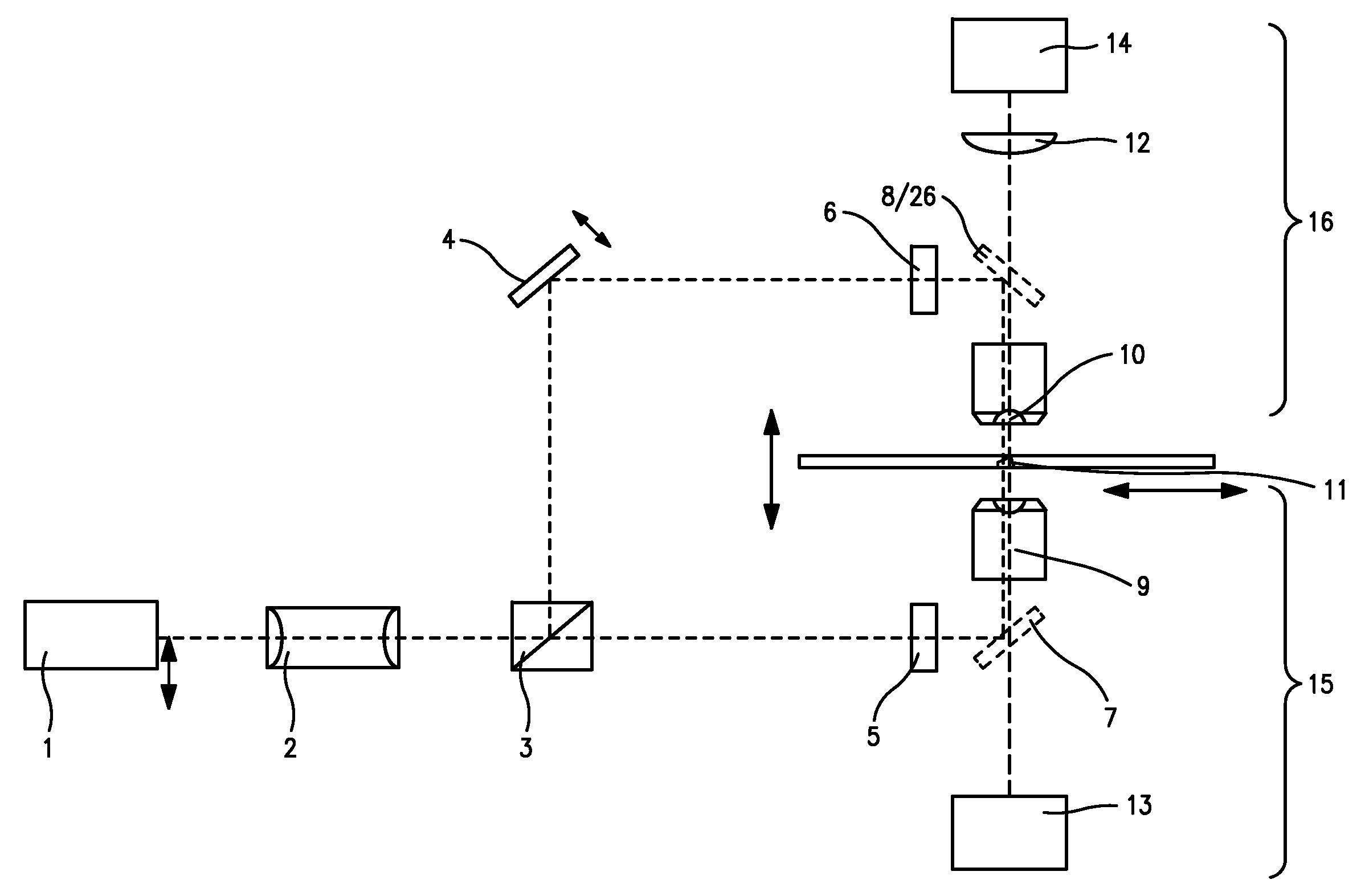
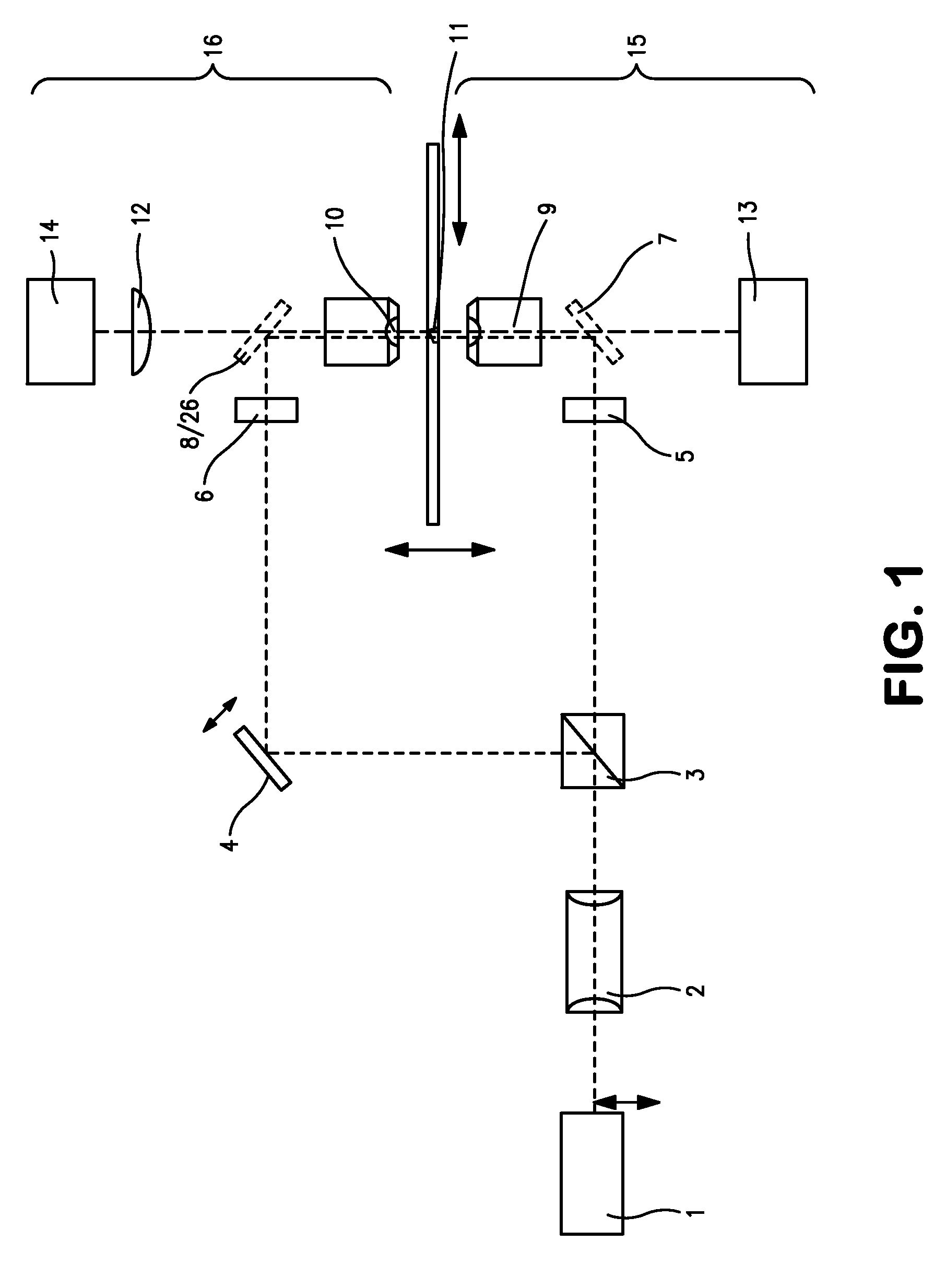
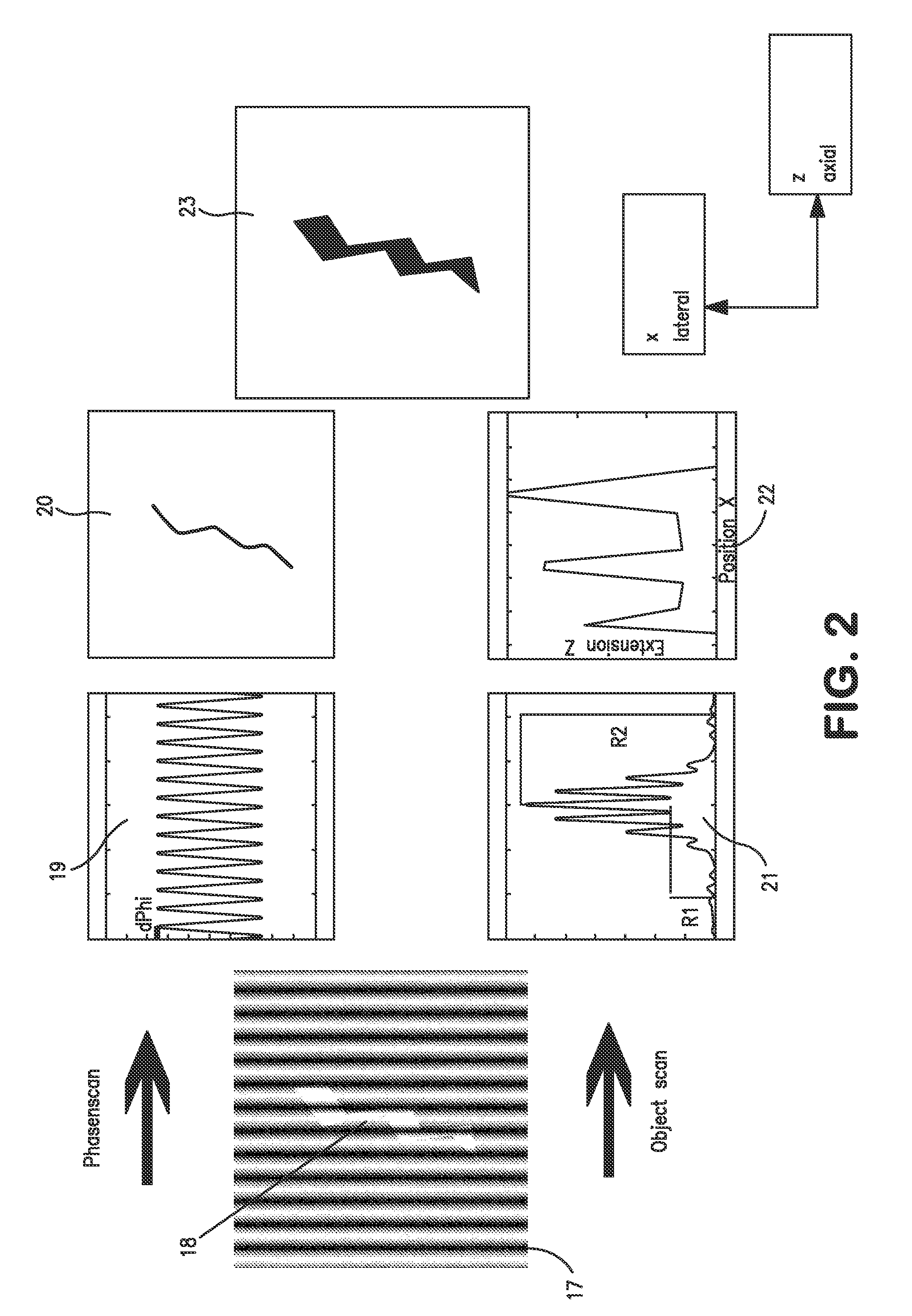
Method and apparatus for fluorescent confocal microscopy
ActiveUS20060017001A1Big advantageDrawback can be addressedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide fieldFluorescence microscope
A new and improved confocal fluorescence microscope is presented. The new microscope has significant advantages relative to existing implementations of microscope confocal imagers. In common with previous confocal imagers the instant invention has the advantages relative to conventional wide-field and confocal fluorescence imagers, however it addresses the drawbacks of confocal technology in terms of cost and complexity, and provides significant savings in both due to the simplicity of the components and the elimination of the need of, in particular, spatial filters such as pinholes or slits.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Method and an apparatus for localization of single dye molecules in the fluorescent microscopy
ActiveUS20090237501A1Simple processOvercome limitationsMaterial analysis by optical meansSignalling system detailsFluorescence microscopeSpatial direction
A method and apparatus are provided for obtaining a sub-resolution spatial information of a sample labeled with at least one type fluorescent label. The sub-resolution spatial information has localization information about the positions of fluorescent molecules of the at least one type fluorescent label in at least one spatial direction. The method acquires localization image data by employing fluorescence localization microscopy. The acquired localization image data is processed to obtain the localization information about the positions of fluorescent molecules of the at least one type fluorescent label in at least one spatial direction. The step of processing includes determining in each of the detected images of the series the positions of the barycenters of the detected fluorescence emission distributions from the single fluorescent molecules of the one or more fluorescent labels in at least one spatial direction.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF HEIDELBERG
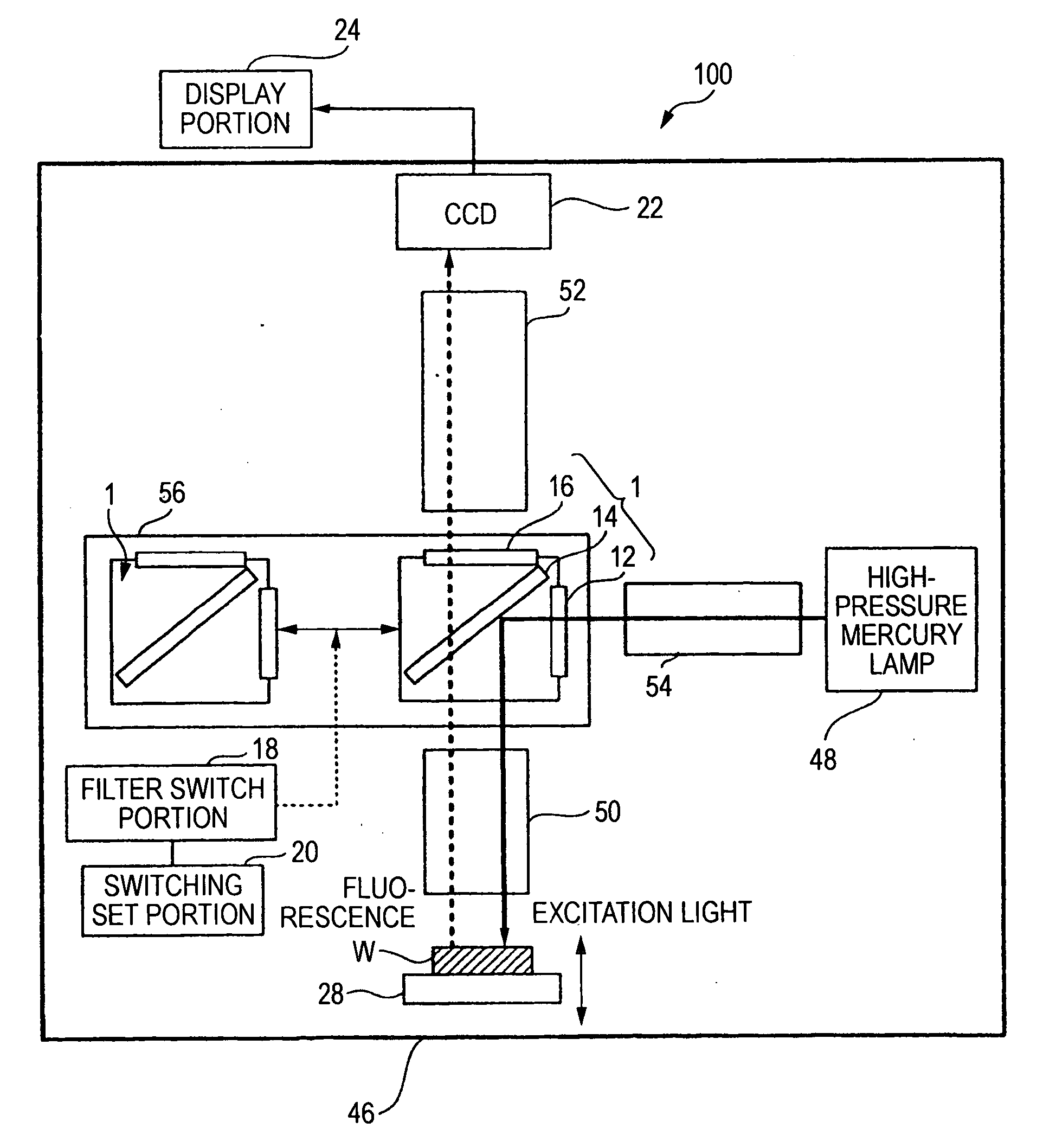
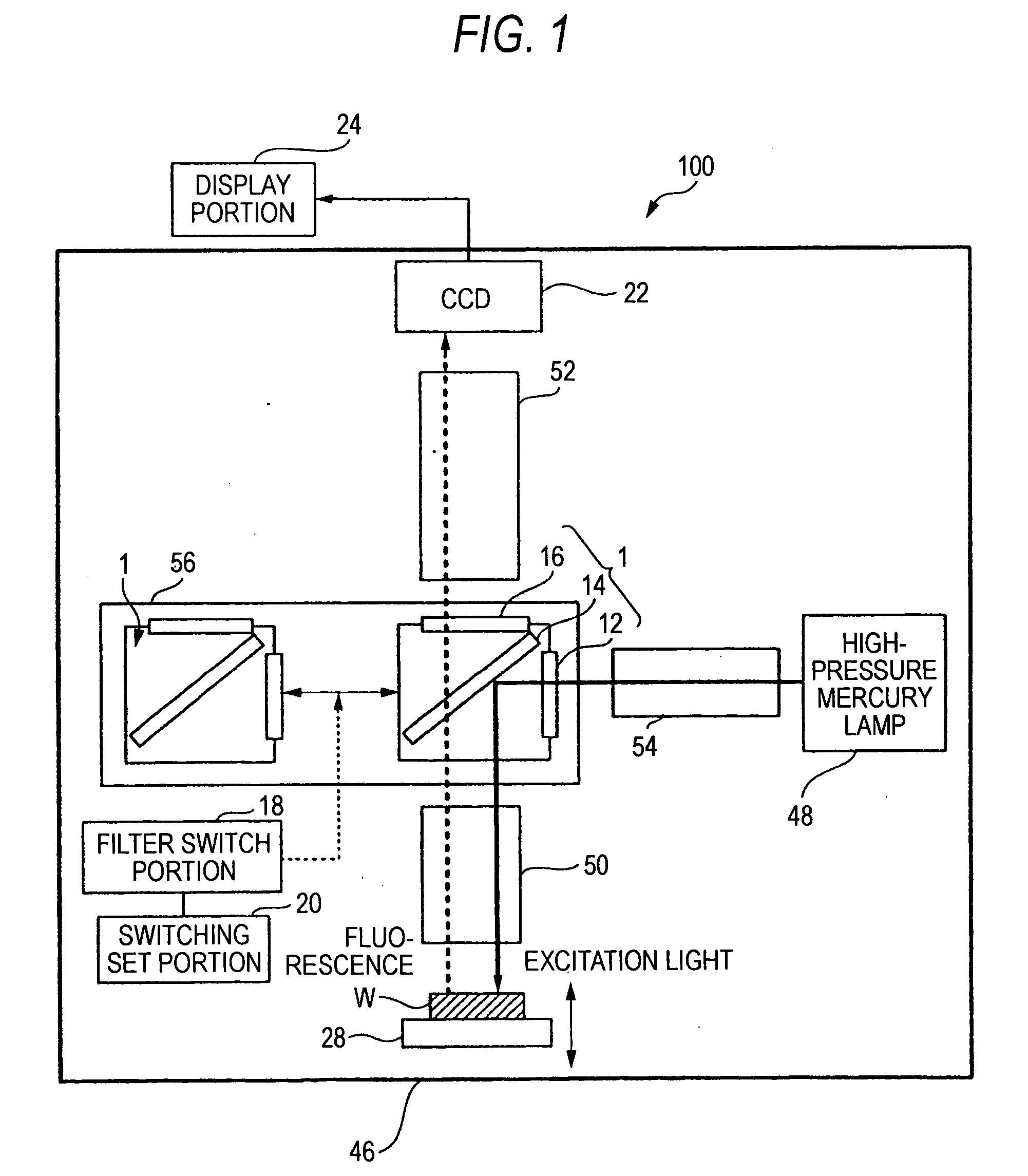
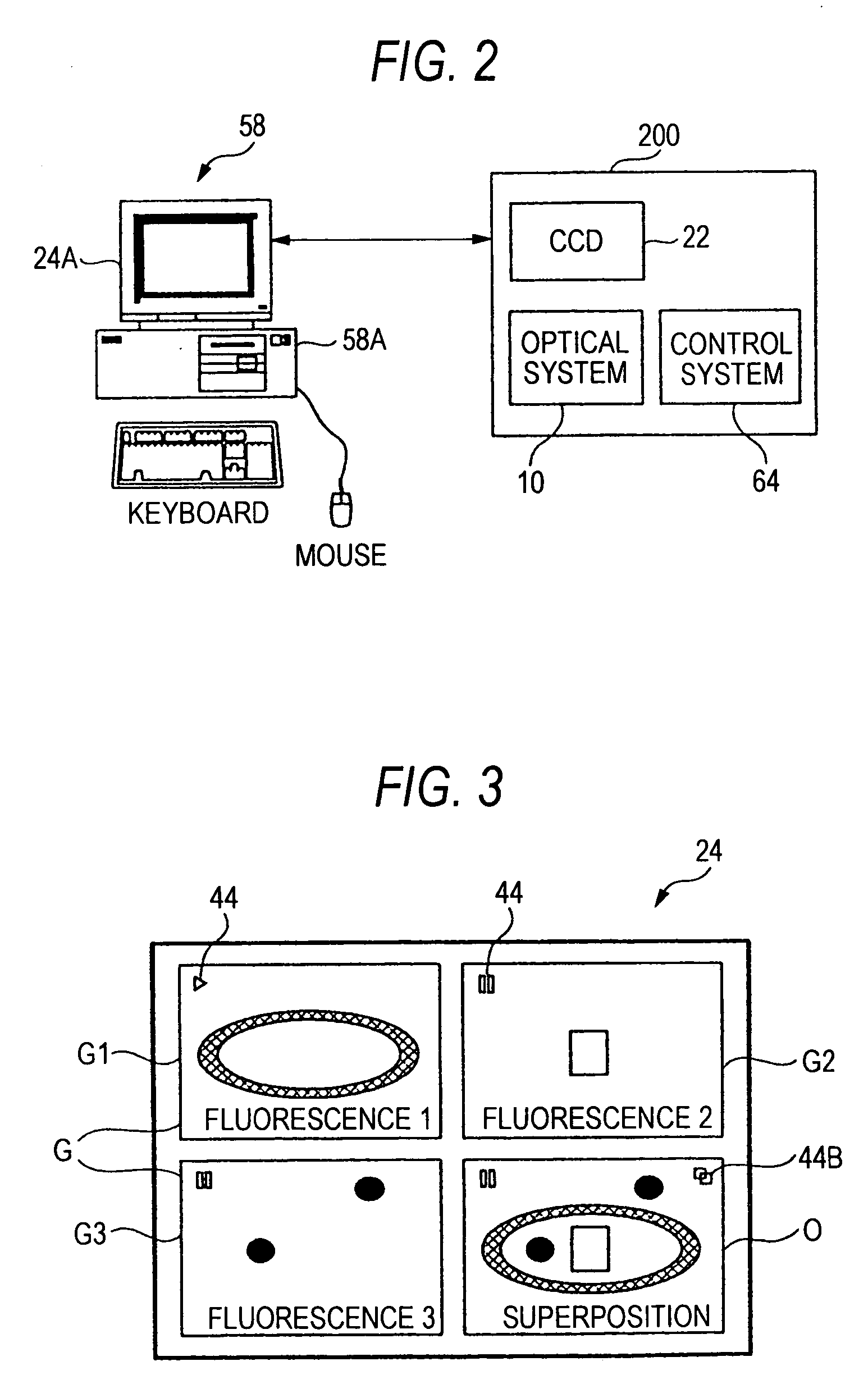
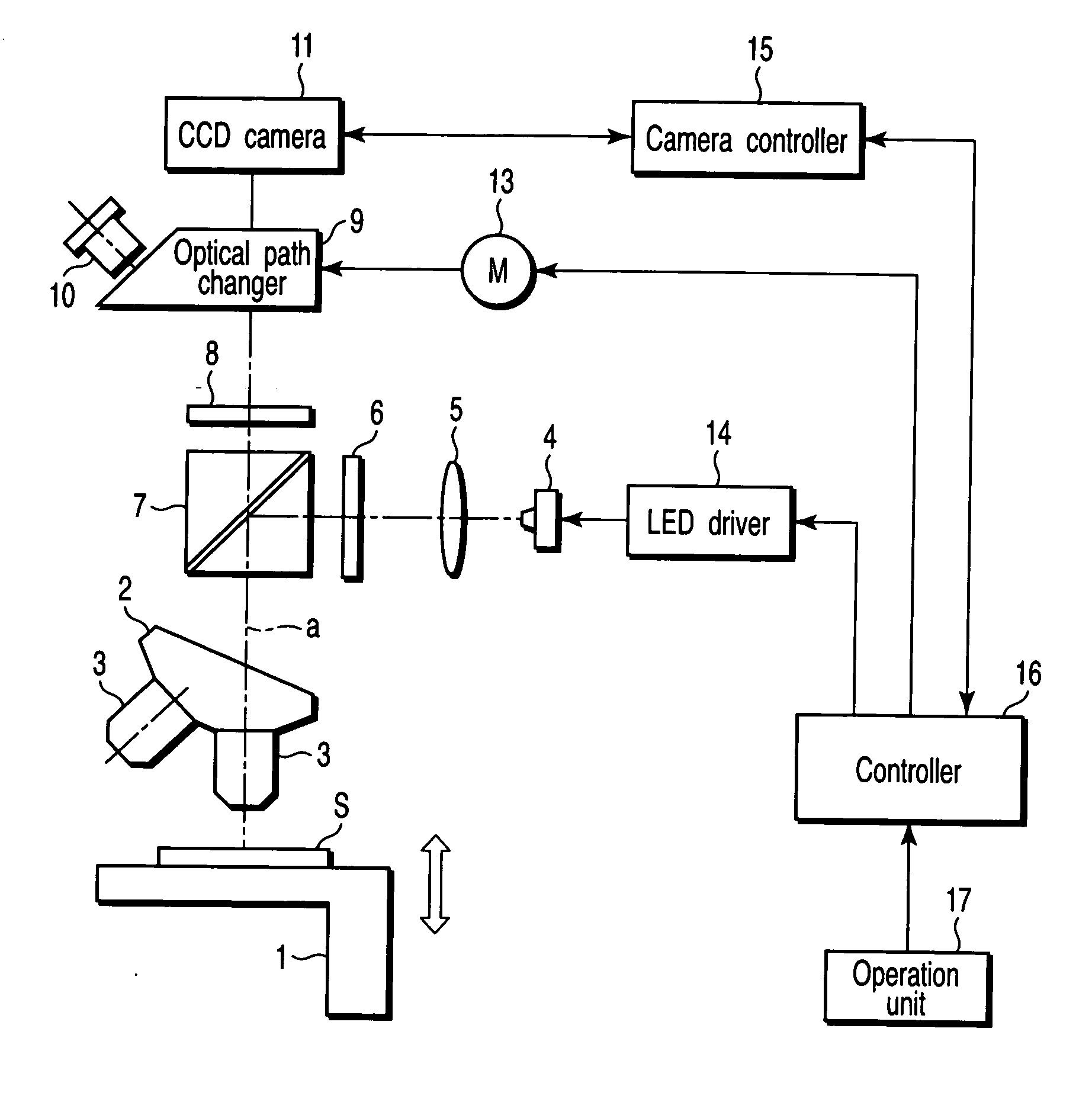
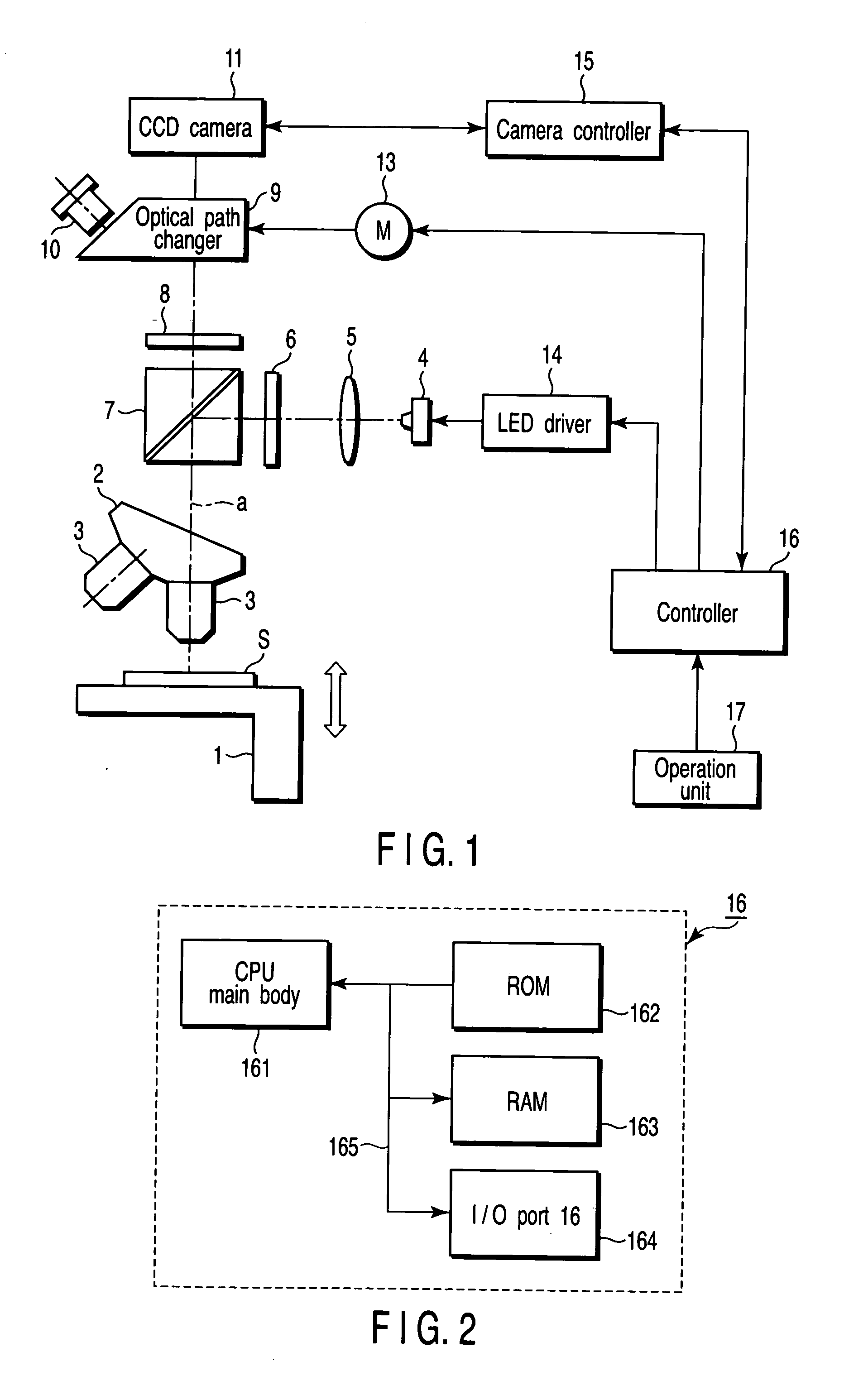
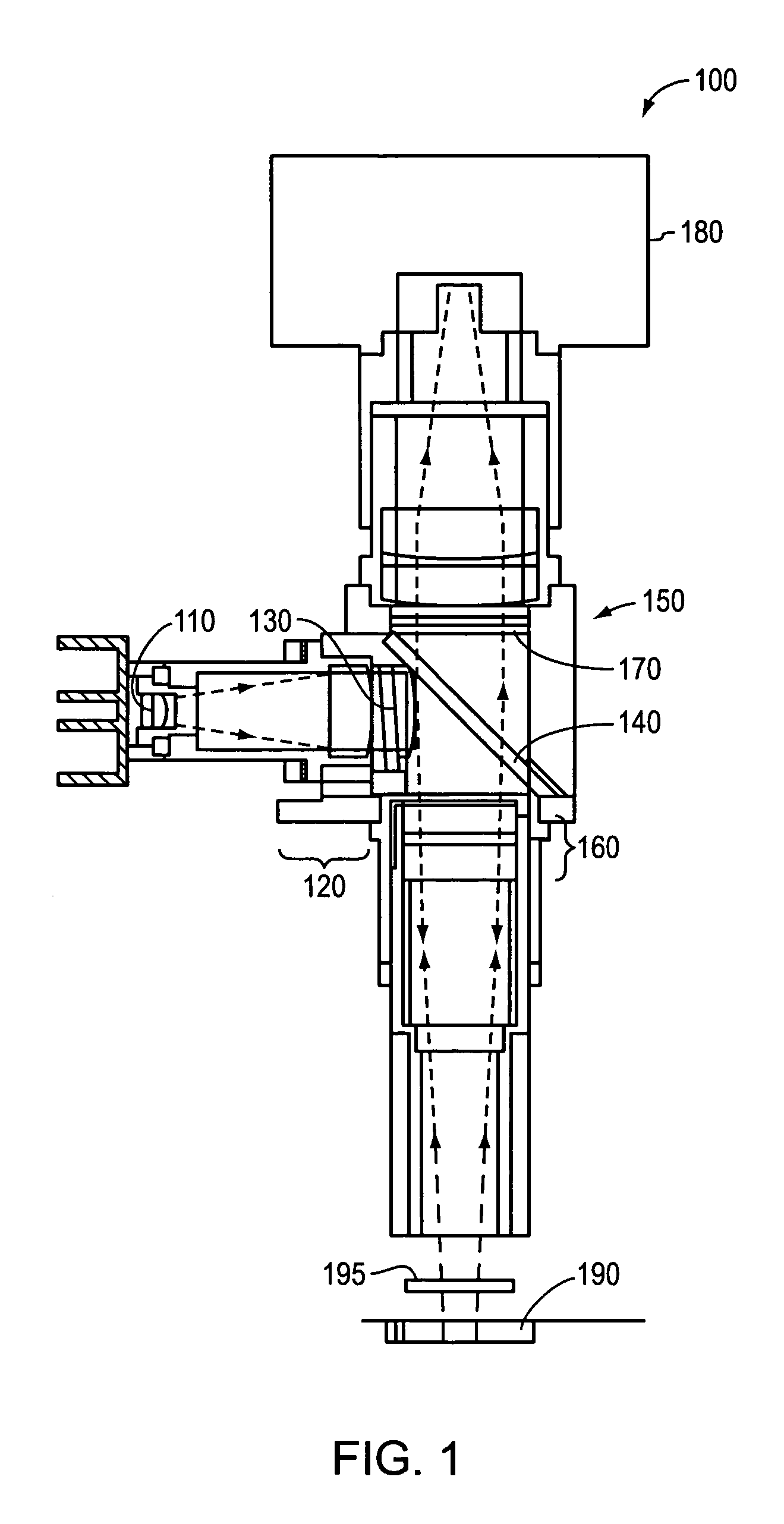
Fluorescence microscope, display method using fluorescence microscope system, and computer-readable medium
InactiveUS20050270639A1Easy to observeAvoid damageMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceAbsorption filterFluorescence microscope
A fluorescence microscope comprises plural types of filter sets including a combination of a excitation filter, a dichroic mirror, and an absorption filter, a filter switch portion for switching the filter sets at a predetermined timing, an imaging portion for picking up an image of a specimen as an observation object by using the filter sets, a display portion having a plurality of image display areas on which the image picked up by the imaging portion are displayed respectively, and a control portion for generating a superposed image on which the images are superposed. In this fluorescence microscope, the imaging portion picks up the image via every filter set in synchronism with a timing which is set by the switching set portion and at which the filter switch portion switches the filter sets, and then the picked-up image is automatically updated and displayed in the image display areas.
Owner:KEYENCE
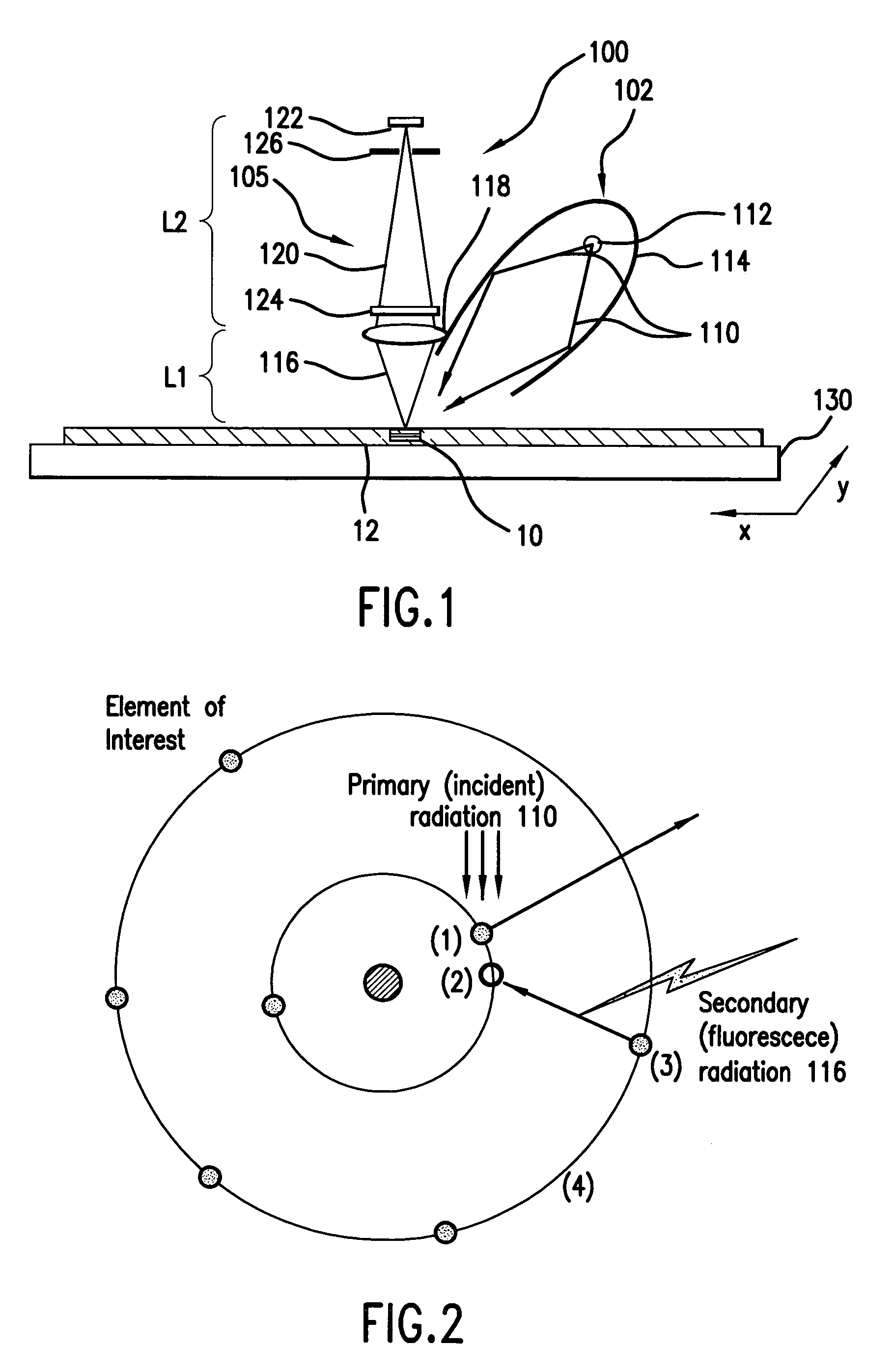
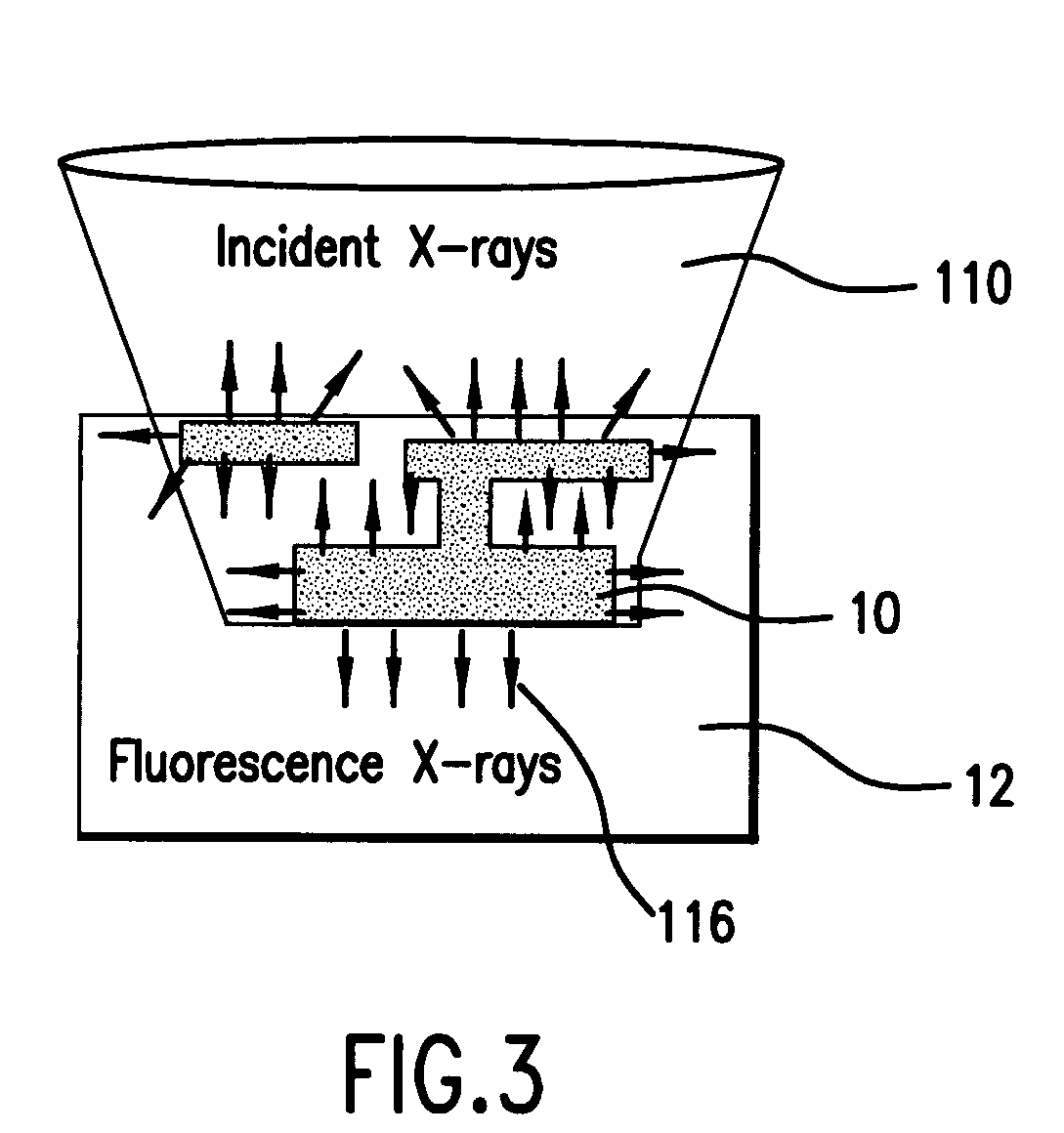
Element-specific X-ray fluorescence microscope and method of operation
InactiveUS7183547B2Enhances preferential imagingEnhance the imageMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesConfocalPeak value
An element-specific imaging technique utilizes the element-specific fluorescence X-rays that are induced by primary ionizing radiation. The fluorescence X-rays from an element of interest are then preferentially imaged onto a detector using an optical train. The preferential imaging of the optical train is achieved using a chromatic lens in a suitably configured imaging system. A zone plate is an example of such a chromatic lens; its focal length is inversely proportional to the X-ray wavelength. Enhancement of preferential imaging of a given element in the test sample can be obtained if the zone plate lens itself is made of a compound containing substantially the same element. For example, when imaging copper using the Cu La spectral line, a copper zone plate lens is used. This enhances the preferential imaging of the zone plate lens because its diffraction efficiency (percent of incident energy diffracted into the focus) changes rapidly near an absorption line and can be made to peak at the X-ray fluorescence line of the element from which it is fabricated. In another embodiment, a spectral filter, such as a multilayer optic or crystal, is used in the optical train to achieve preferential imaging in a fluorescence microscope employing either a chromatic or an achromatic lens.
Owner:CARL ZEISS X RAY MICROSCOPY
Fluorescent microscope
InactiveUS20050152029A1Reduce fadingSave powerRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptoelectronicsFluorescence microscope
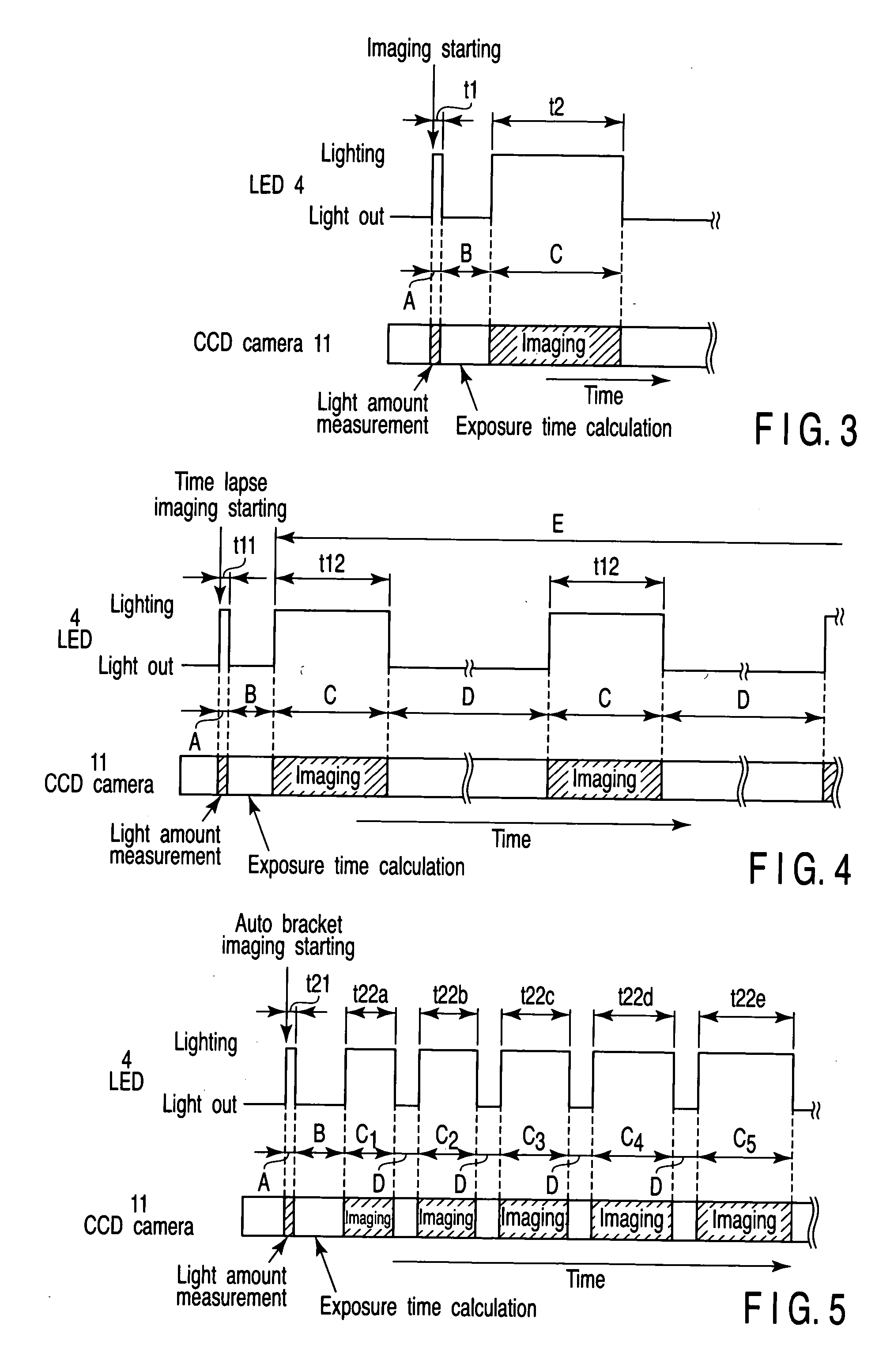
A fluorescent microscope has a light source having a small light emitting element, an illumination optical system which leads light from the light source onto a specimen, an observation optical system to which fluorescence emitted from the specimen is led, an imager which images the fluorescence led to the observation optical system, and a controller which controls lighting / light out of the small light emitting element synchronously with imaging timing of the imager.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method
ActiveCN104614353AFluorescence Imaging RealizationMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescencePicosecond pulsed laserFluorescence microscope
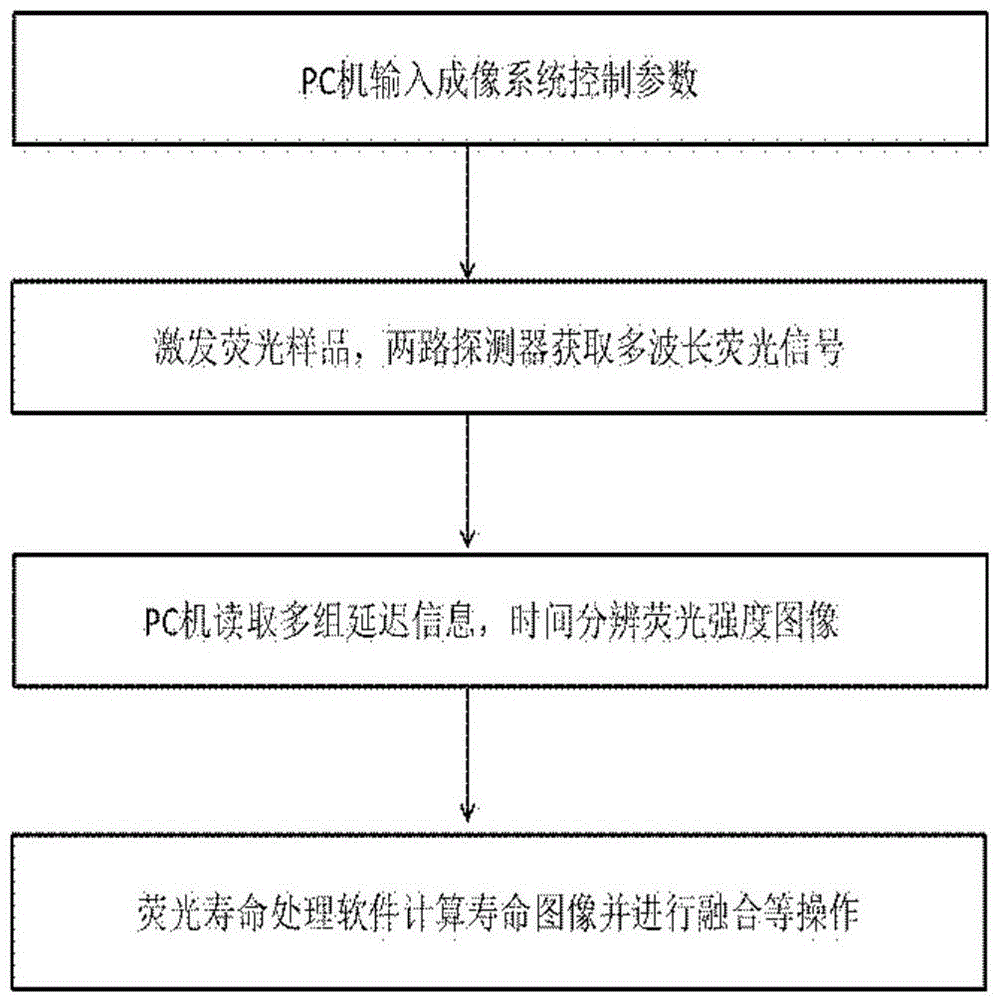
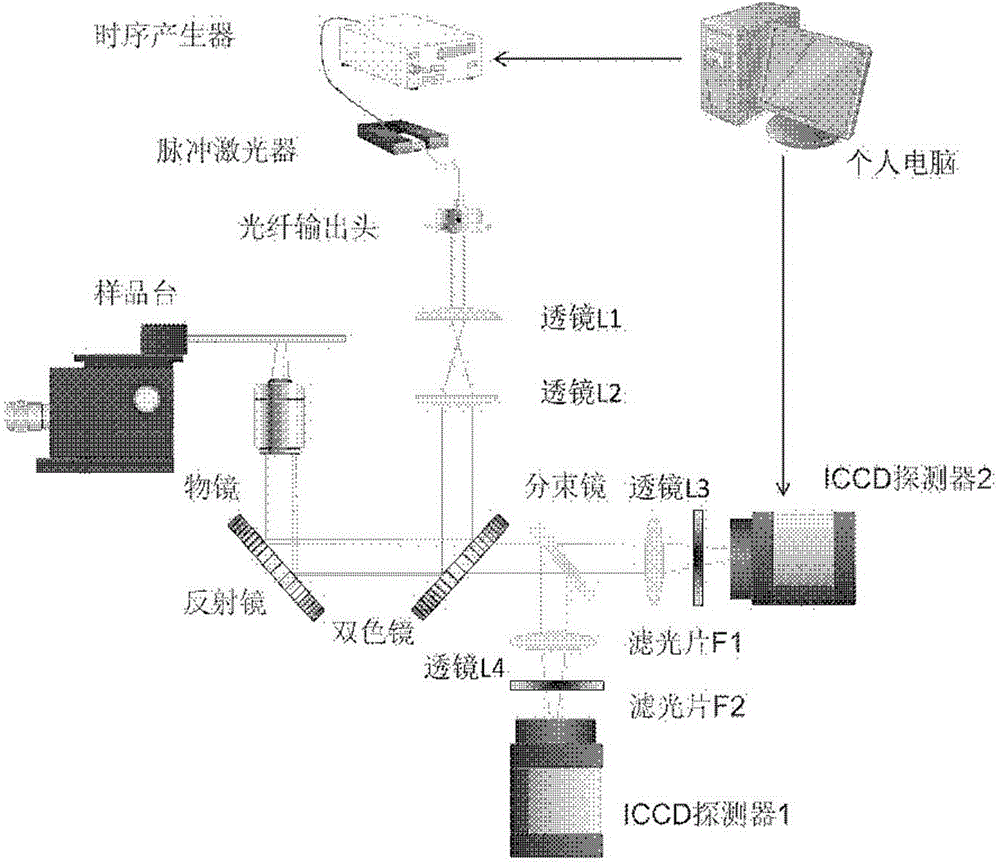
The invention is applicable to the field of optics, biomedicine, life science and the like, and provides a two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, wherein the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system comprises a picosecond pulse laser device, a fluorescent excitation and collection light path, a microscopic objective lens, a light beam lens, a double-ICCD detector, and a control and processing module. The invention further discloses a method for performing multi-spectrum imaging by utilizing the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system. According to the two channel-based multi-spectrum fluorescent imaging microscopic system and method, the limitation of the existing fluorescent microscope and a fluorescent life imaging microscopic system only can acquire single wavelength fluorescent signal with one-time detection can be effectively solved, the simultaneous acquisition of the multi-spectrum fluorescent strength and fluorescent light image aiming at the dynamic process of fluorescent intensity-related detection limited in biomedicine and life science can be performed, so that the research and application ranges of biophotonics can be extended.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and microscope for high spatial resolution examination of samples
InactiveUS20070206278A1Prevent bleachingGood synchronizationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical propertyImage resolution
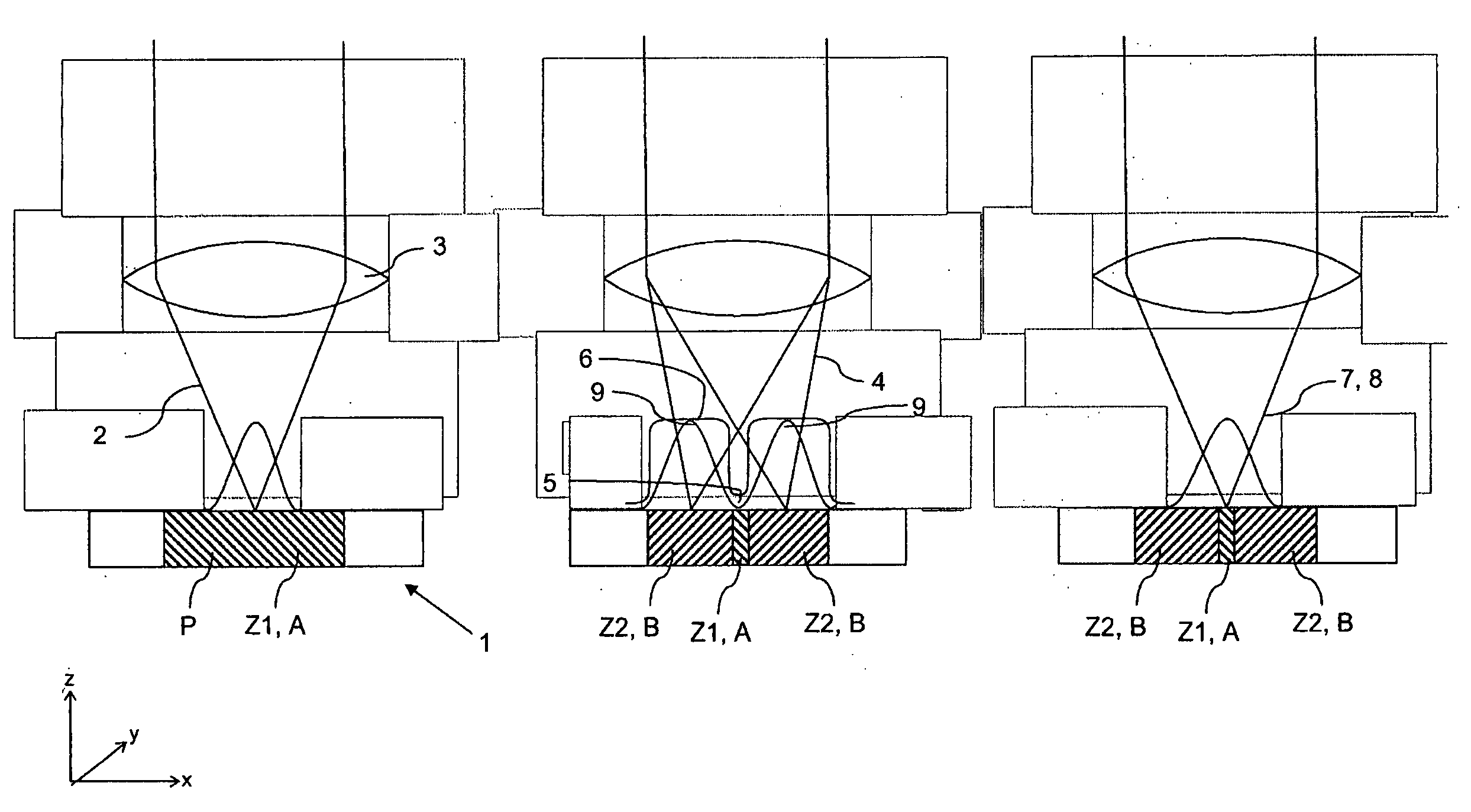
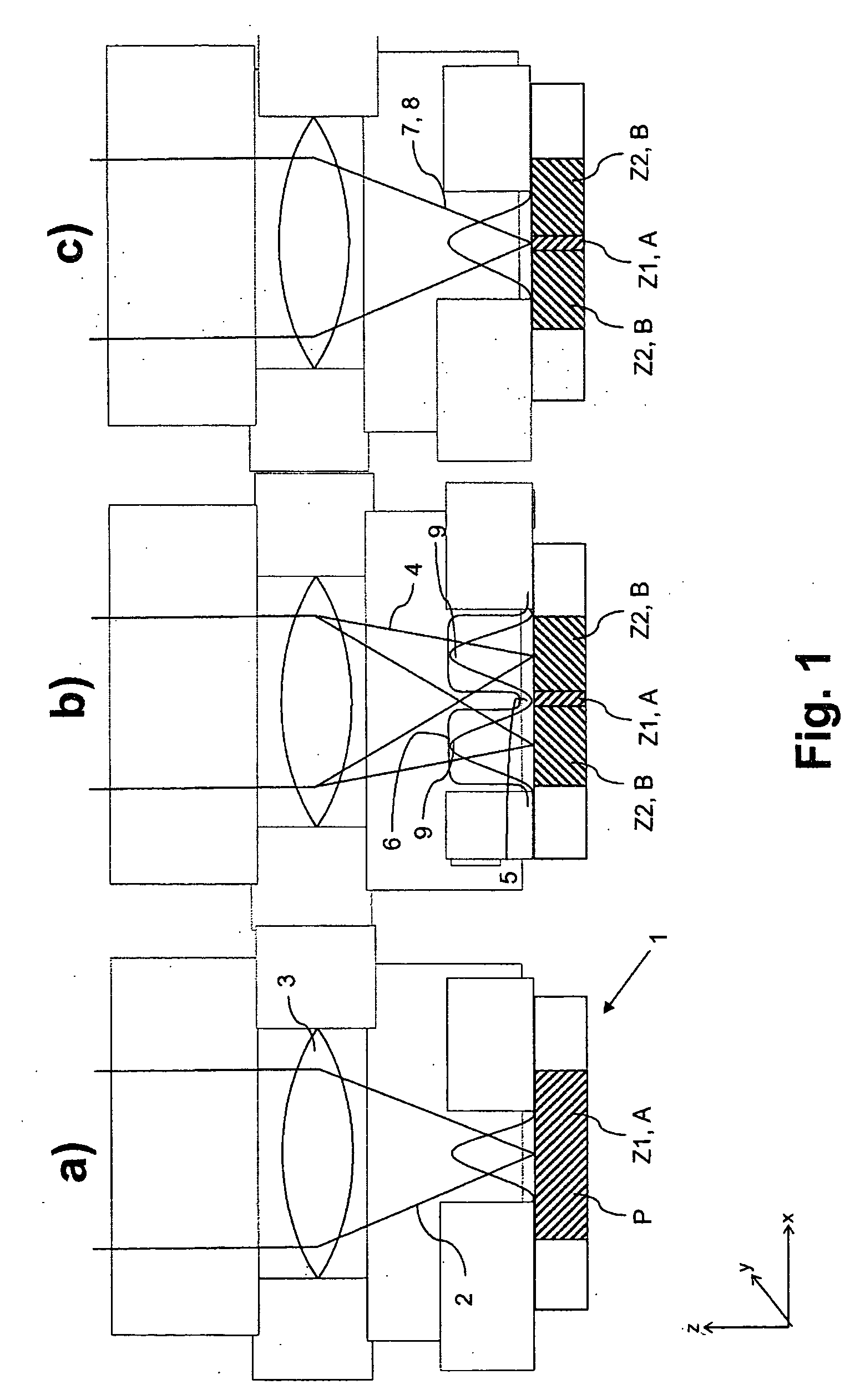
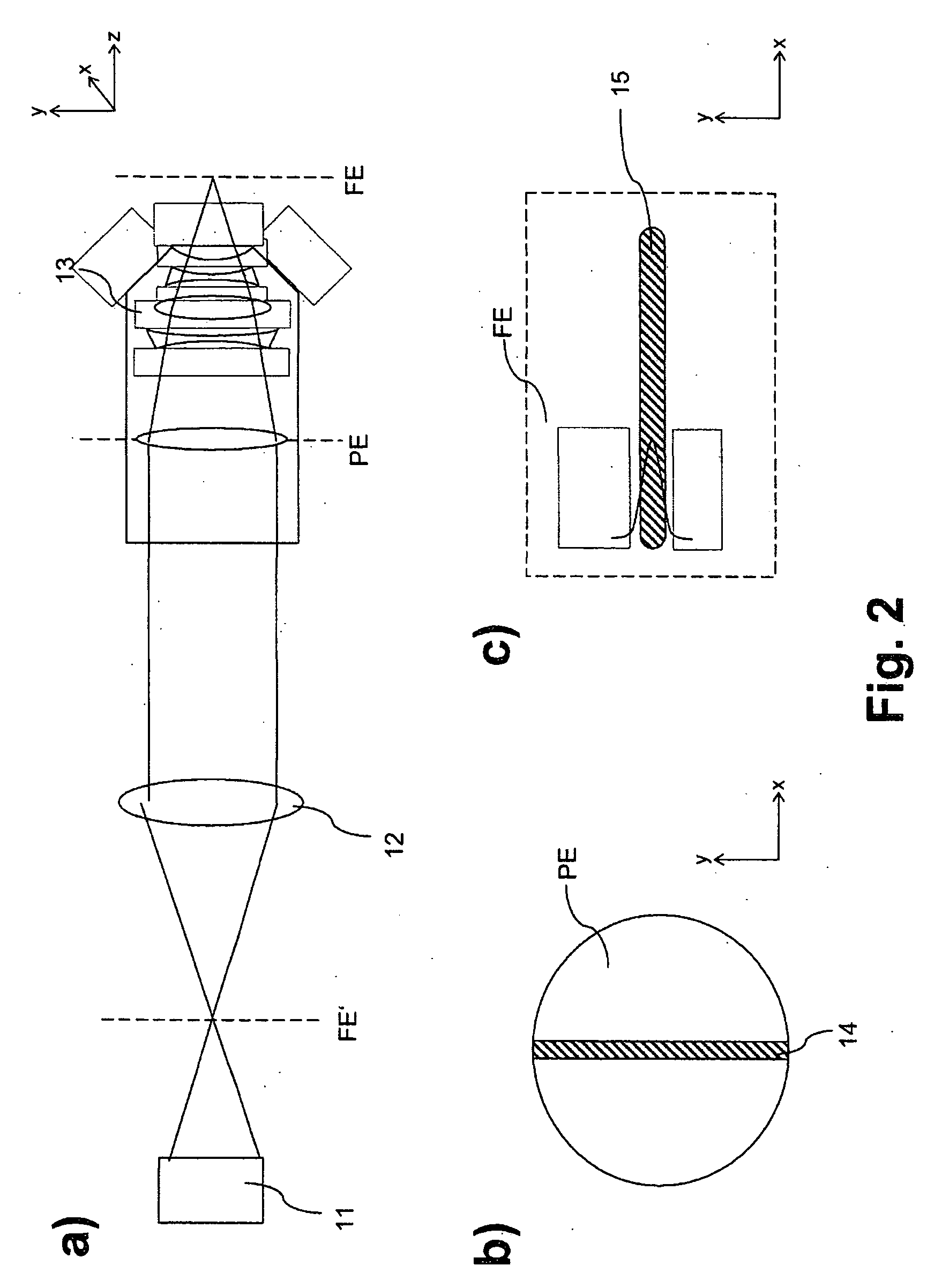
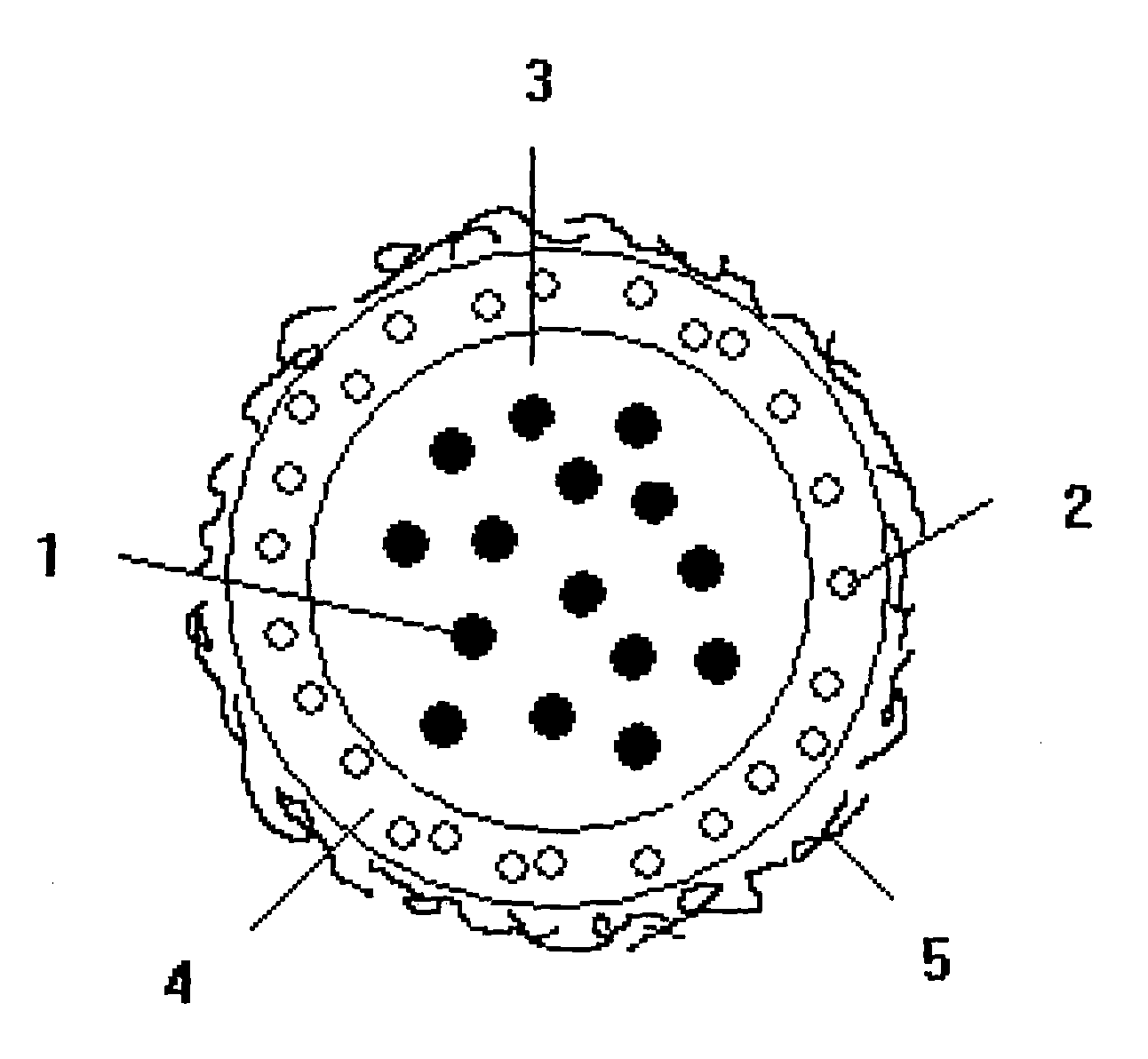
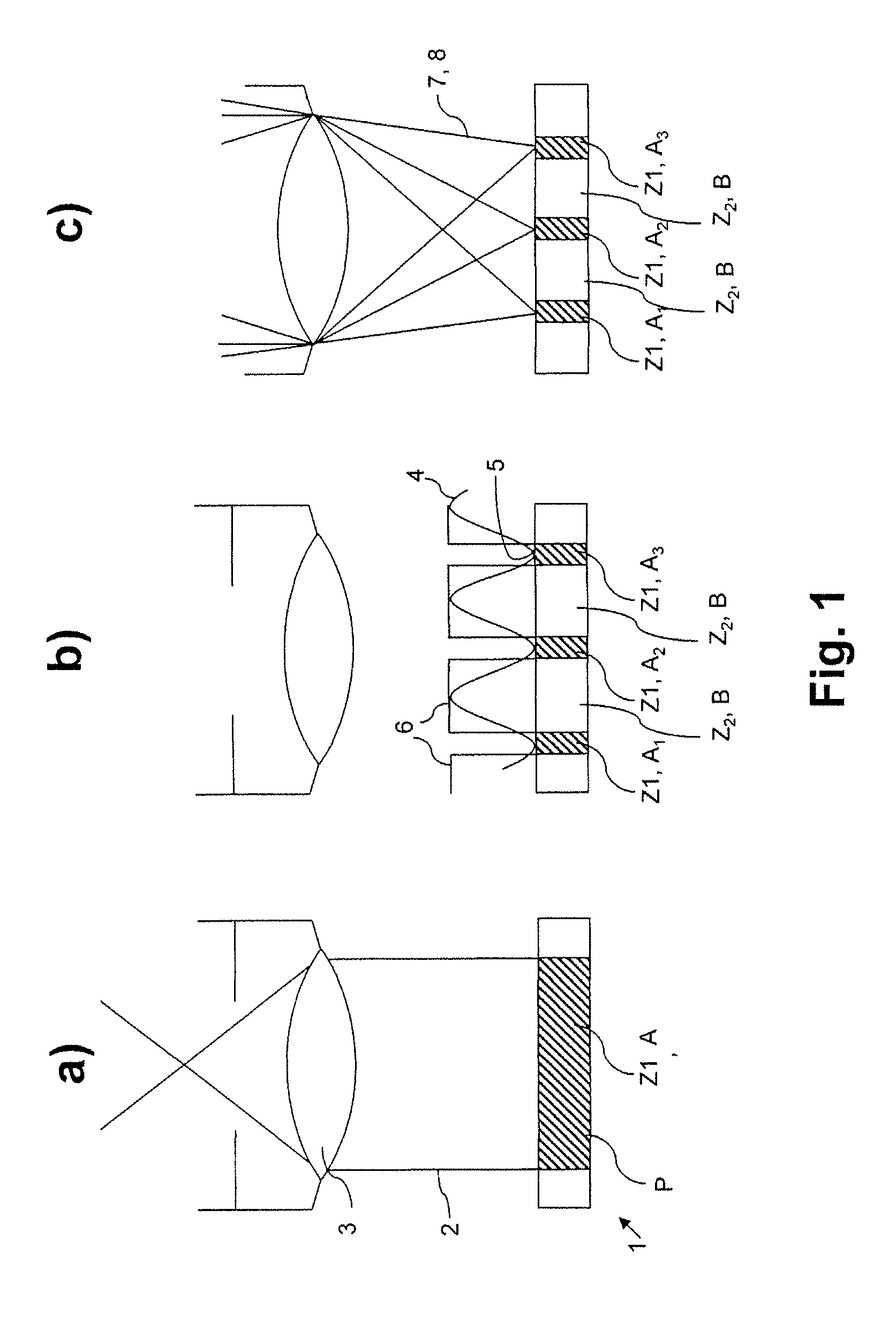
A method and a microscope, in particular a laser scanning fluorescence microscope, for high spatial resolution examination of samples, the sample (1) to be examined comprising a substance that can be repeatedly converted from a first state (Z1, A) into a second state (Z2, A), the first and the second states (Z1, A; Z2, B) differing from one another in at least one optical property, comprising the steps that the substance in a sample region (P) to be recorded is firstly brought into the first state (Z1, A), and that the second state (Z2, B) is induced by means of an optical signal (4), spatially delimited subregions being specifically excluded within the sample region (P) to be recorded, are defined in that the optical signal (4) is provided in the form of a focal line (10) with a cross-sectional profile having at least one intensity zero point (5) with laterally neighboring intensity maxima (9).
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Sensor system with surface-plasmon-polariton (SPP) enhanced selective fluorescence excitation and method
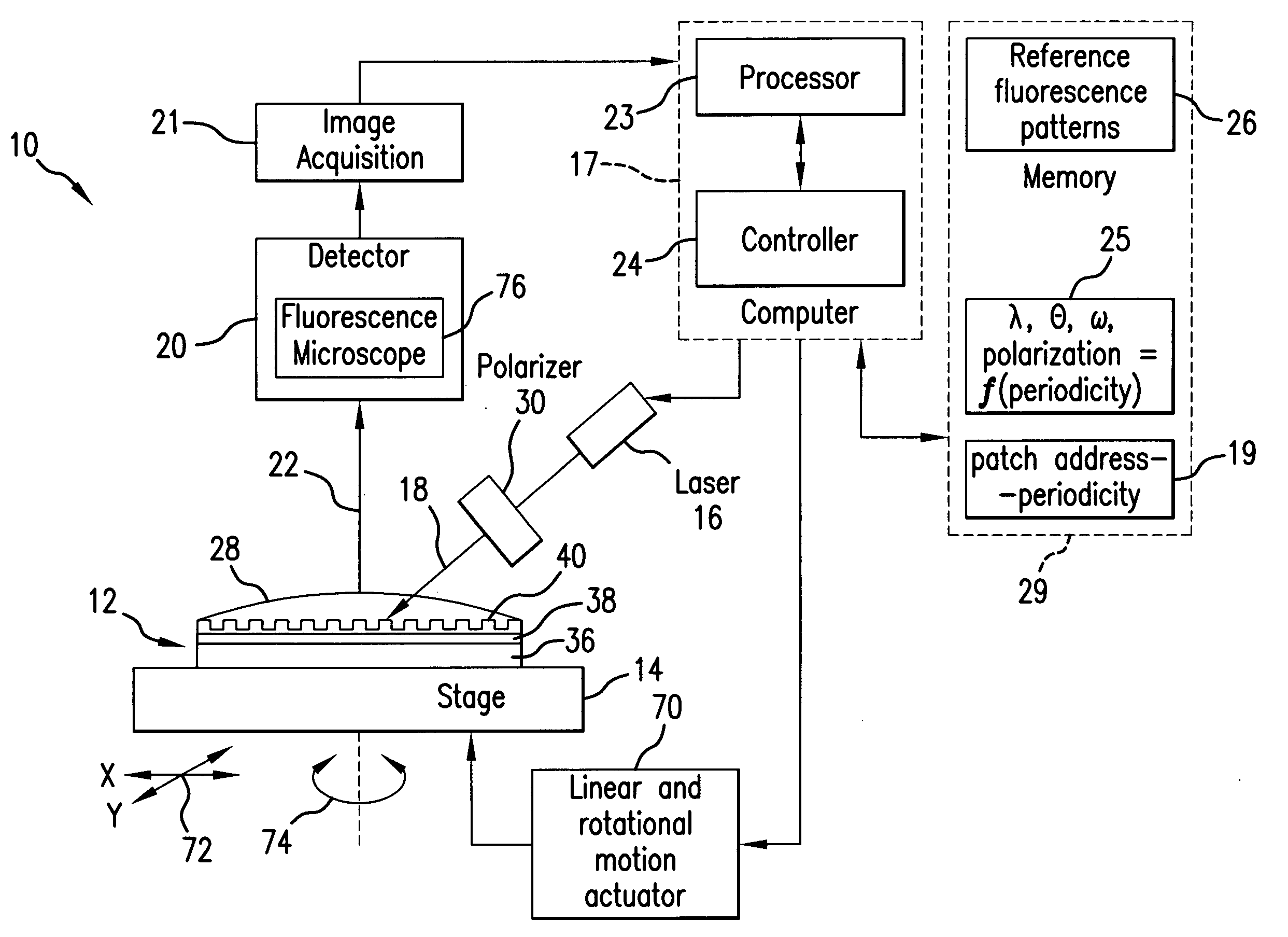
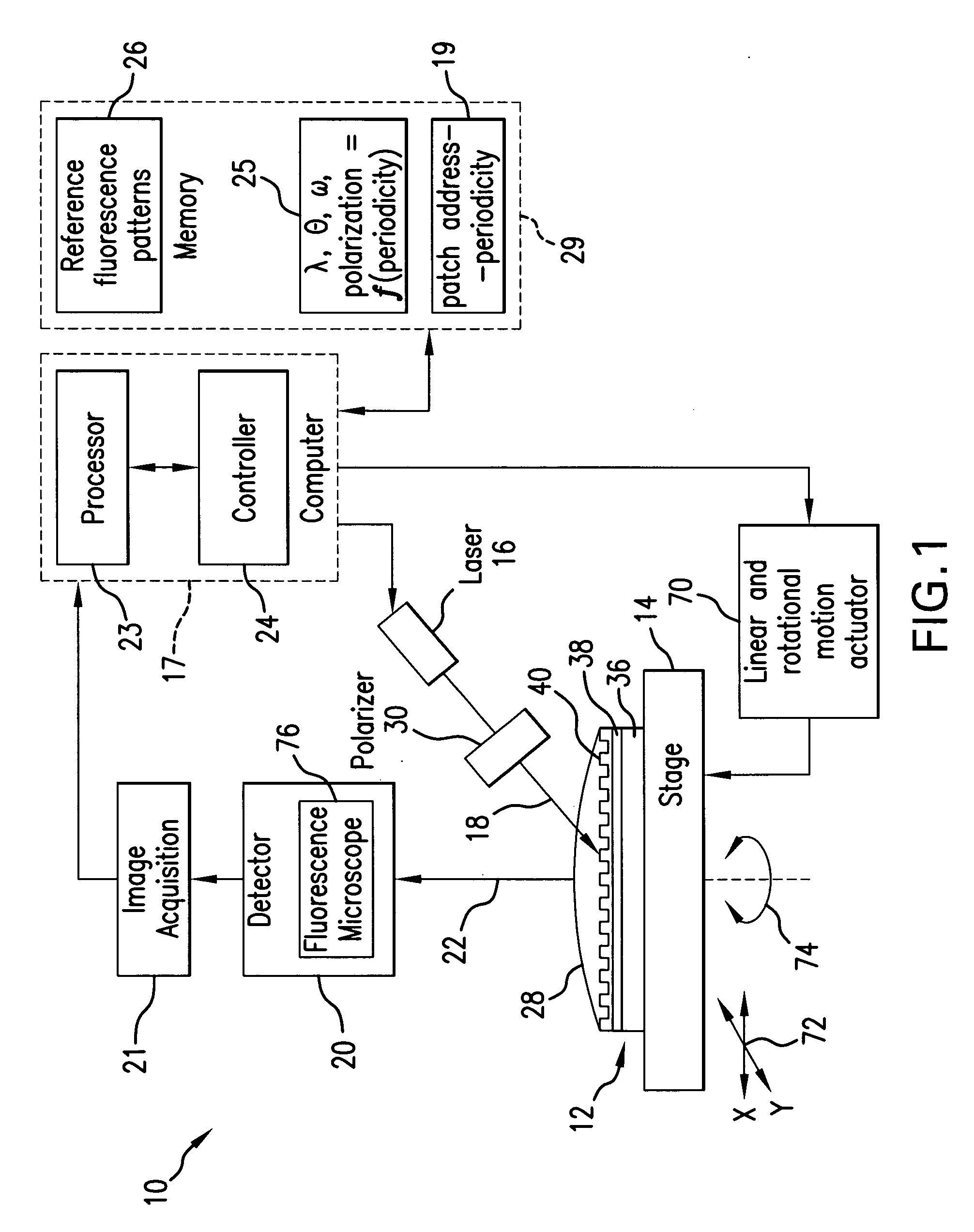
InactiveUS20090045351A1Enhanced selected fluorescence excitationIncrease choicePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansLight beamFluorescence microscope
In a sensor system, an active sensor chip includes an array of periodically-patterned dielectric active sensor patches of different periodicities and geometries formed on a metal film. A specimen under study is positioned on each patch, and the active sensor chip is interrogated by illumination the patches in a predetermined sequence to result in a fluorescence response from each patch enhanced by SPP. The intensity of the fluorescence response is controlled by varying the wavelength, incidence angle, azimuthal orientation and polarization direction of the excitation light beam as the function of the periodicity of the illuminated patch. The system is compatible with commercial fluorescence microscopes and scanned laser interrogation systems.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Method for rapidly detecting and screening staphylococcus aureus
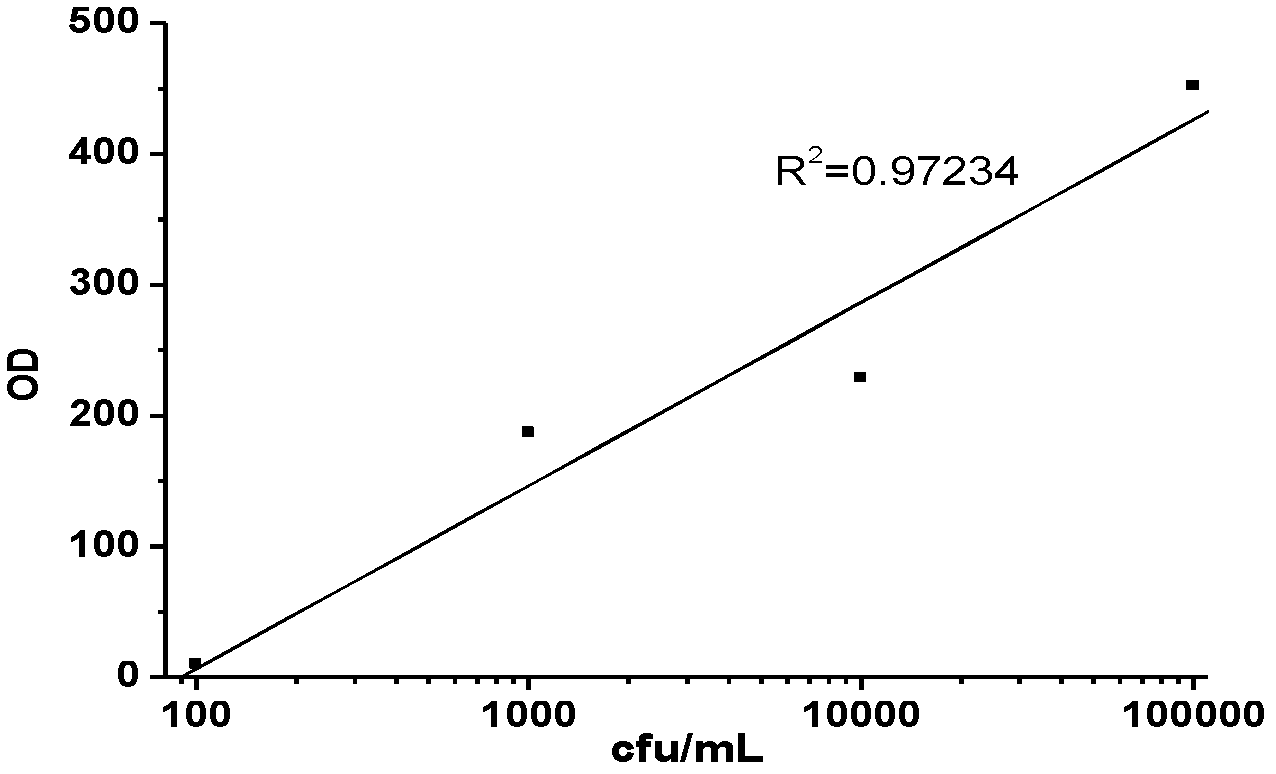
InactiveCN102590506ALower requirementEasy to operateMaterial analysisMicroorganismStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention relates to the detection field of microorganism foodborne pathogens and discloses a method for rapidly detecting and screening staphylococcus aureus, which adopts bio-functionalized superparamagnetic nano particles and immunized quantum dots to immunologically recognize target microorganisms to realize to specificity detection on the foodborne pathogens (staphylococcus aureus). According to the method, target bacteria can be rapidly separated from various samples, and enrichment is also performed efficiently; and besides, bacteria separated by the enrichment can be marked rapidly by fluorescence, so that the bacteria can be qualitatively identified by a fluorescence microscope and can be quantitatively detected by a fluorescence photometer. The method is convenient and simple to operate, and has high reliability and a low requirement on corollary equipment.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for simultaneously carrying out magnetic induction heating, imaging and temperature detecting on tumor cells
InactiveCN101601607ADiagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingMicrosphereMagnetite Nanoparticles
A method for realizing simultaneous magnetic induction heating, imaging and intracellular temperature detecting on tumor cells by virtue of multi-functional nanospheres is provided aiming at the following problems: how magnetic nanoparticles in hyperthermia heat tumor cells as nano heaters after entering the cells and how the local temperature experienced by each cell is measured, so as to further promote the development of tumor magnetic induction hyperthermia technique. The method comprises the following steps: simultaneously combining the magnetic nanoparticles with the function of magnetic induction heating and fluorescent quantum dots with the functions of imaging and temperature detecting in polymeric or inorganic nanospheres, heating the cells by employing the nanospheres combined on the tumor cells under the alternating magnetic field and simultaneously carrying out imaging and temperature detecting on the cells by employing the fluorescent quantum dots under fluorescence microscopes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and microscope for high spatial resolution examination of samples
ActiveUS20070206276A1Improve user friendlinessEasy to operateRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationOptical propertyHigh spatial resolution
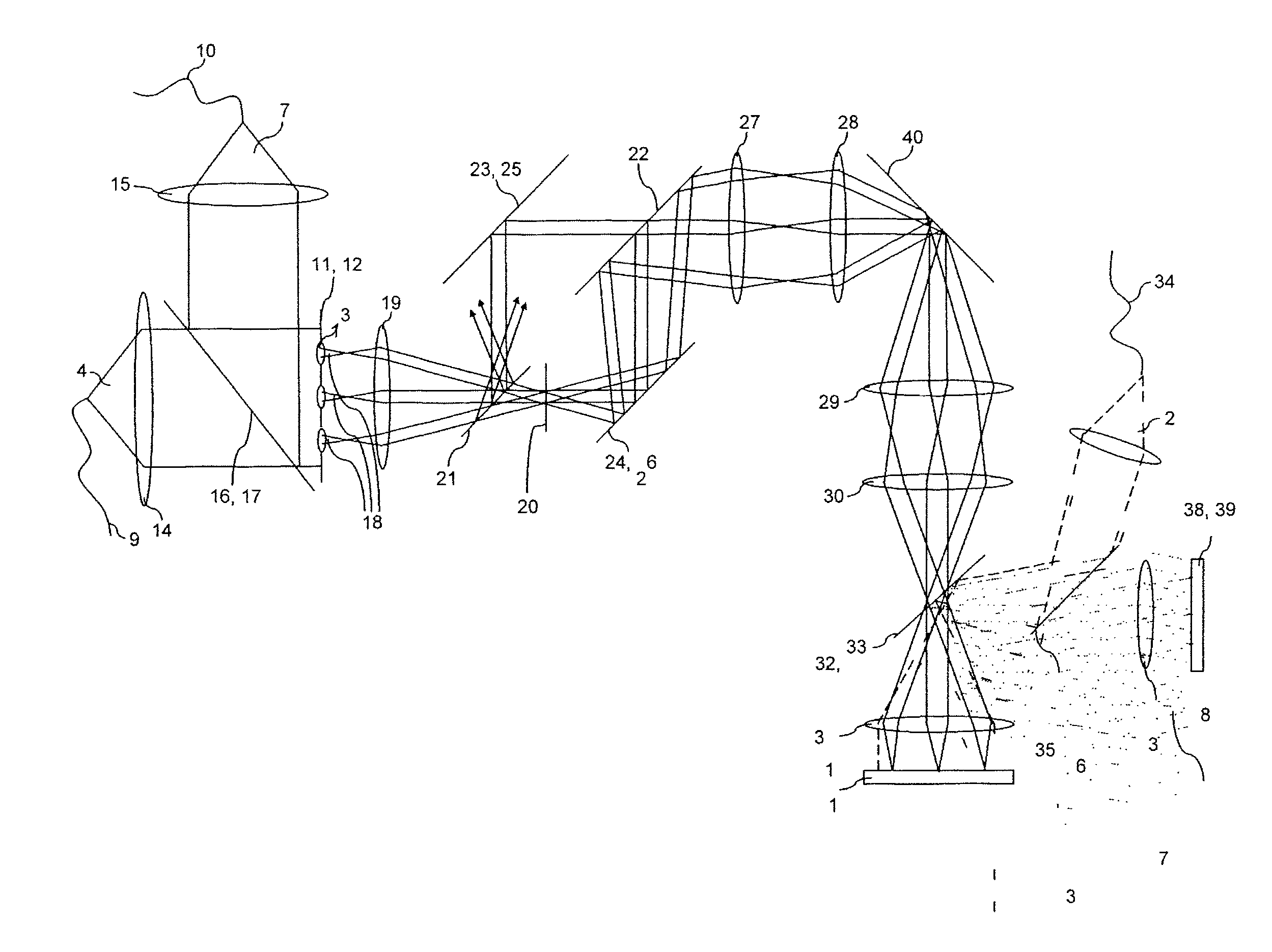
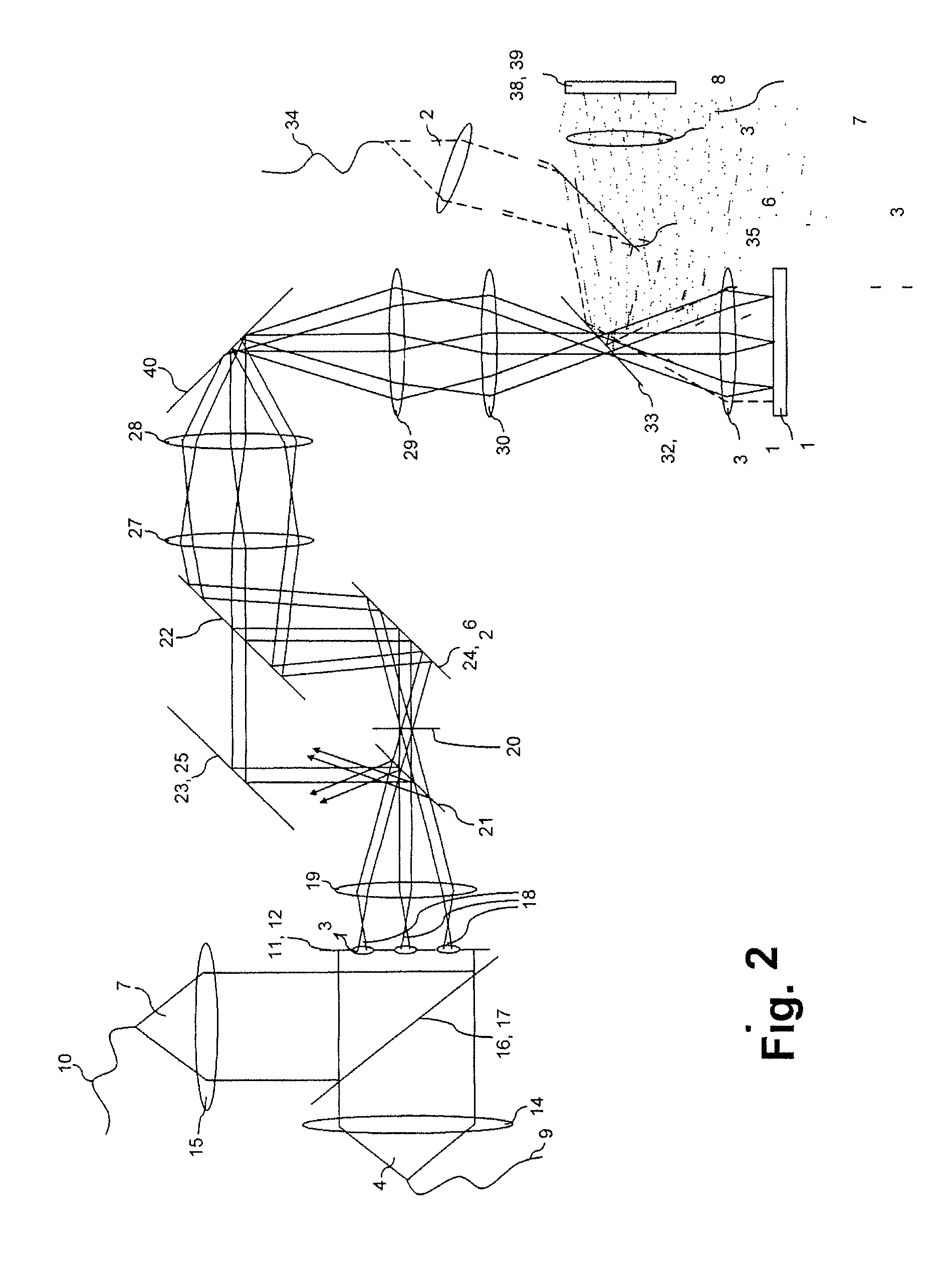
A method and a microscope, in particular a laser scanning fluorescence microscope, for high spatial resolution examination of samples, the sample (1) to be examined comprising a substance that can be repeatedly converted from a first state (Z1, A) into a second state (Z2, B), the first and the second states (Z1, A; Z2, B) differing from one another in at least one optical property, comprising the steps that the substance in a sample region (P) to be recorded is firstly brought into the first state (Z1, A), and that the second state (Z2, B) is induced by means of an optical signal (4), spatially delimited subregions being specifically excluded within the sample region (P) to be recorded, are defined with regard to increasing resolution in any desired direction and with regard to an increased imaging rate by the fact that the optical signal (4) is simultaneously concentrated at a number of focal points, and the focal points are focused into various sites of the sample (1).
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Variable visual field scanning microscope and the method based on fixed light path system
InactiveCN101339129AFlexible conversionMeet different biomedical application requirementsTelescopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescence microscopeDiscretization
The invention discloses a variable-field scanning microscopic method based on a fixed optical path system, and a device thereof. At first, a beam expanding system is used for uniformly expanding laser beams which are transmitted from a laser so as to form uniform laser beams; then a two-dimensional space discrete system is used for the two-dimensional space discretization of the uniform laser beams so as to form a sub-beam of M multiplied by N; the sub-beam of M multiplied by N orderly passes through a collimating lens, a scanning galvanometer, a reflector, a dichroic mirror and a fluorescence microscope, and then focuses on the sample on a sample platform; thus the excited fluorescence can be formed on the sample; the fluorescence microscope is used for collecting the excited fluorescence, which is transmitted into an imaging system after being reflected by the dichroic mirror and focused by a focusing lens. The scanning of the galvanometer and the crossing movement of the sample platform are combined: the scanning step length and the scanning step number of the galvanometer are changed; the area of the unit viewing field is used as the step length to move the sample platform; thus the scanned viewing field can be changed. The scanning microscopic method realizes the flexible switching between the low-resolution large viewing field and the high-resolution small viewing field, and satisfies the requirements in different biomedical applications.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Three-dimensional holographic fluorescence microscope
InactiveUS6038041AInvestigating moving sheetsCharacter and pattern recognitionOptical scanning holographyFluorescence microscope
An optical scanning holography system which requires only a two dimensional scan to record three dimensional information from a fluorescent specimen wherein the optical scanning holography is based on scanning the specimen with a Fresnel zone pattern and detecting and decoding the fluorescent light reflected from the specimen. The flourescent light reflected from the specimen contains three dimensional information about the specimen so that once the fluorescent light is detected and decoded a three dimensional image of the specimen can be obtained and displayed using only the two dimensional scan.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
Superresolution in microlithography and fluorescence microscopy
InactiveUS6903347B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLuminescent dosimetersFluorescenceQuenching
In scanned optical systems such as confocal laser microscopes wherein a beam of light is focused to a spot in a specimen to excite a fluorescent species or other excitable species in the spot, the effective size of the excitation is made smaller than the size of the spot by providing a beam of light of wavelength adapted to quench the excitation of the excitable species, shaping this second beam into a pattern with a central intensity minimum, and overlapping this central minimum with the central intensity maximum of the focused spot, so that within the spot the intensity of quenching light increases with distance from the center of the spot, thereby preferentially quenching excitation in the peripheral parts of the spot, and thereby reducing the effective size of the excitation and thus improving the resolution of the system. In the preferred embodiment of the present invention, the central minimum of quenching light is narrowed further by creating the pattern of quenching radiation in the specimen by imaging onto the focal plane a plurality of pairs of sources of quenching light, arrayed at the vertices of a regular, even-sided polygon, the center of which is imaged in the specimen on the central maximum of exciting radiation, and such that the two members of each pair are on opposite vertices of the polygon and emit light mutually coherent and out-of-phase, and the light emitted by different pairs is incoherent with respect to each other.
Owner:BAER STEPHEN C
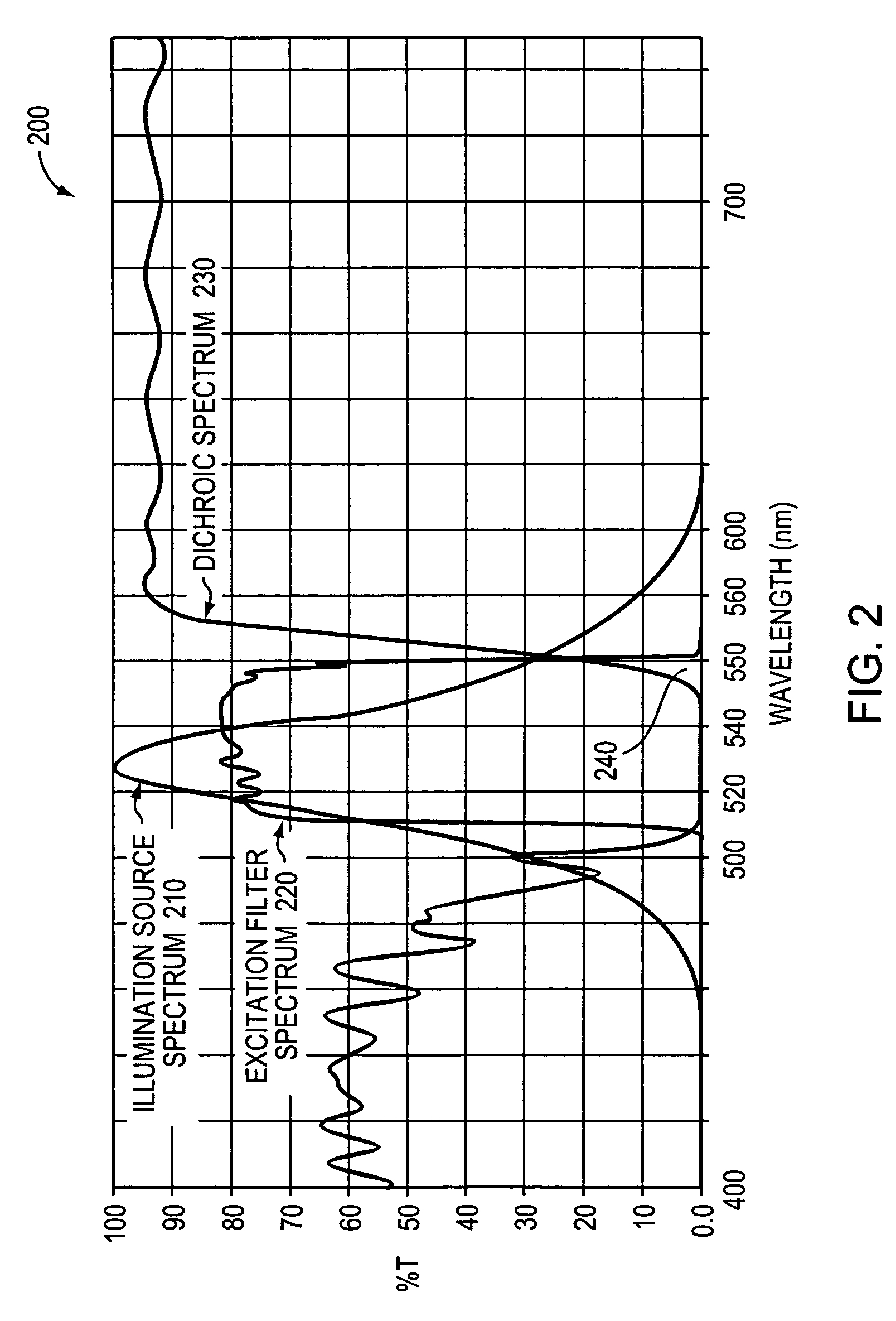
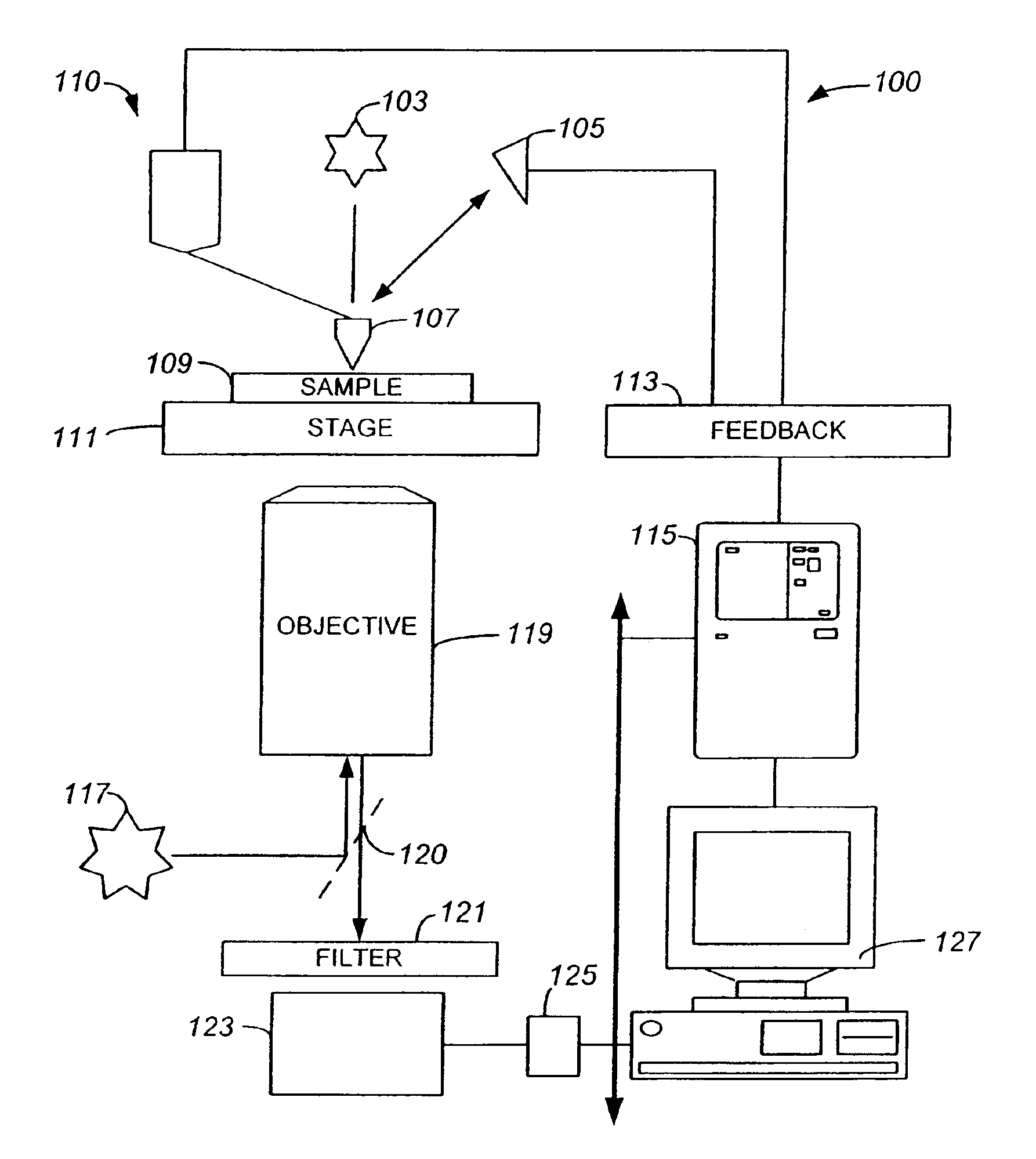
System and method for calibrating a fluorescence microscope
InactiveUS7199360B1Easy to calculateX-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMeasurement deviceFluorescence microscope
A system and method are provided to calibrate fluorescence detection of a fluorescence microscope by using a near-perfectly uniform reflector as a target in combination with temporary removal of the microscope's emission filter. Excitation light is reflected from the near-perfectly uniform reflector back into the microscope's objective optical system and transmitted to a dichroic. A small fraction of the excitation light passes though the dichroic and is measured by a CCD camera or other appropriate measurement device. By measuring the intensity of the residual excitation light at a plurality of points in the field of view, variations in illumination intensity may be determined. Using this, fluorescence detection at different points in the field of view may be readily calibrated.
Owner:AVANTRA BIOSCI CORP
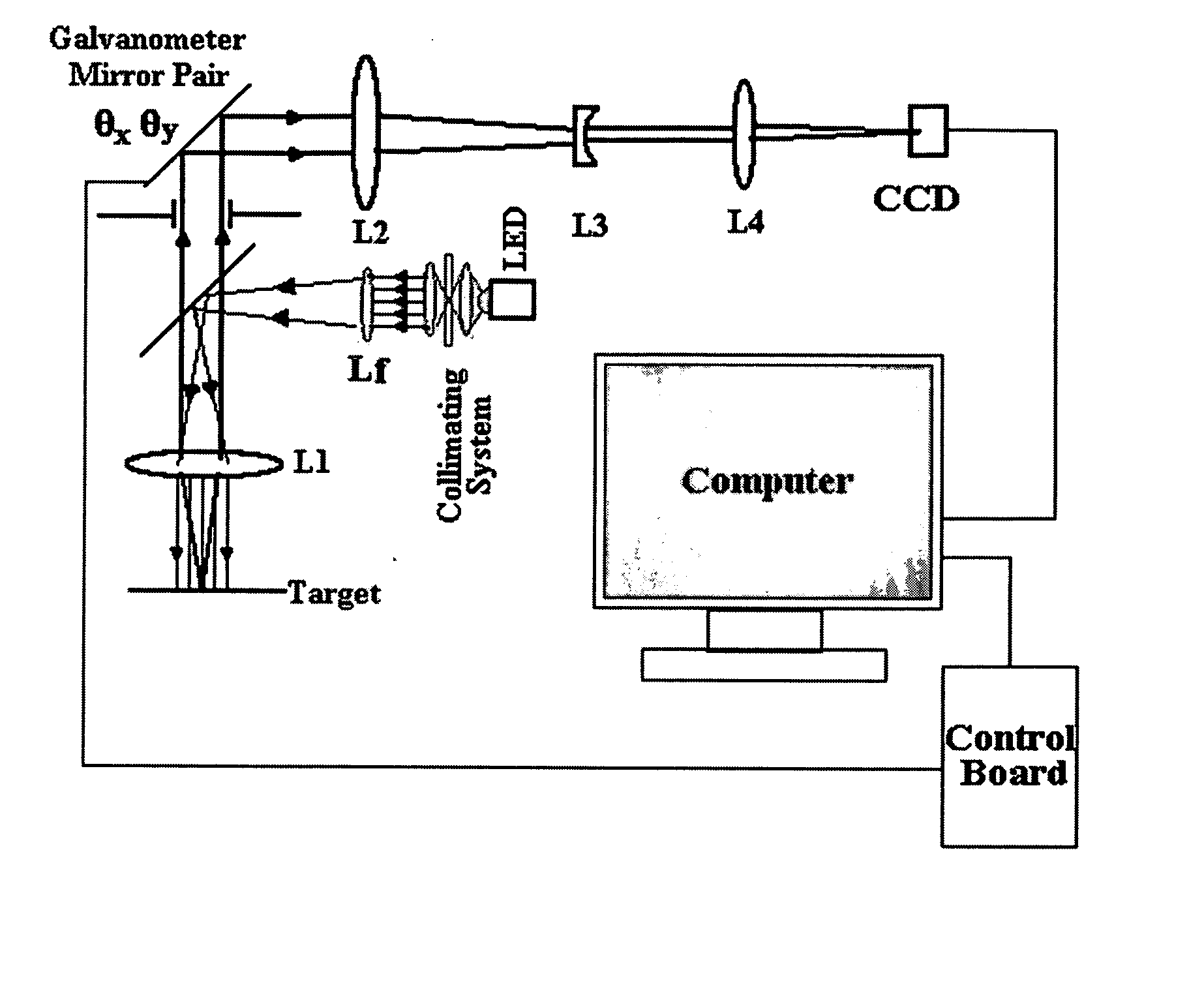
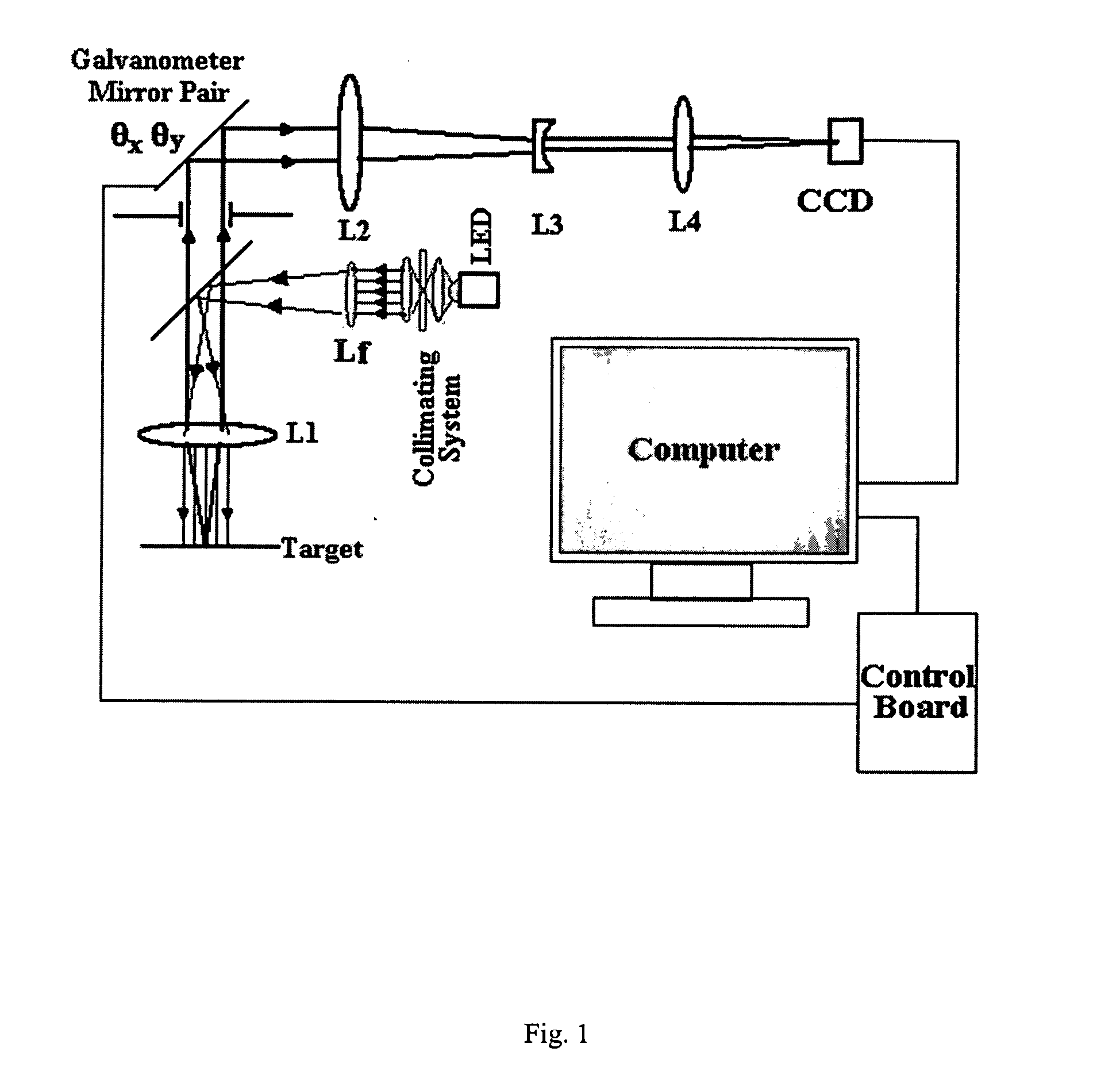
Optical scanning zoom microscope with high magnification and a large field of view
InactiveUS20060291042A1Easy accessEffective enlarged viewing areaMicroscopesFluorescence microscopeHigh resolution image
The computer-controlled optical scanning high magnification microscope imaging system with a large field of view disclosed herein overcomes a previous inability to achieve simultaneous high magnification and large field of view in microscopes. The subject imaging system includes galvanometer scanners, a CCD camera and high brightness LED sources at different wavelengths for rapid acquisition of a large number of high-resolution segmented tile images with a magnification of 800× each. The numerous segmented tiles combine to form a larger viewing field of the target, resulting in a compound image with an effective enlarged viewing area of 1.6×1.2 mm2. The speed and sensitivity of the system make it suitable for high resolution image monitoring of a small segmented area of dimensions 320×240 μm2 with a 4 μm resolution. The microscope can zoom in on each segment of the target without lost of resolution to attain a great degree of spatial detail. With its special capacities, this microscope would be beneficial to medicine, biology, semiconductor inspection, device analysis and quality control, as well as with multiphoton and fluorescence microscopes to image large fields with high resolution.
Owner:ALFANIX TECH
Method and apparatus realizing quasi confocal fluorescent microscopic with dynamic speckle illumination
InactiveCN101303302AGood value for moneySimple structureScattering properties measurementsFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageEffect light
The present invention relates to a novel method and a novel device, incorporating dynamic speckle lighting with a conventional wide field fluorescence microscope organically to implement approximately confocal fluorescence microscopy (i.e., quasi-confocal fluorescence microscopy). The present invention employs an argon ion laser as the light source; the exciting light passes through a scattering object, a relay light path system for expanding and shaping, and then is coupled to the fluorescence microscope and focused to the sample. The stepping and revolution of the scattering object is controlled with a computer to produce a dynamic speckle pattern on the sample. The received fluorescent images are processed to obtain high-resolution spatial chromatographic images under no need to scan condition. The method can be used to obtain high-resolution three-dimensional chromatographic and microscopic image information of biological tissue samples in a non-intrusive manner. The device has simple structure, high cost-performance ratio, and is favorable for post data processing, easy to operate and apply; therefore, the device and method have a wide market application prospect and great significance for clinical diagnosis and life science research.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
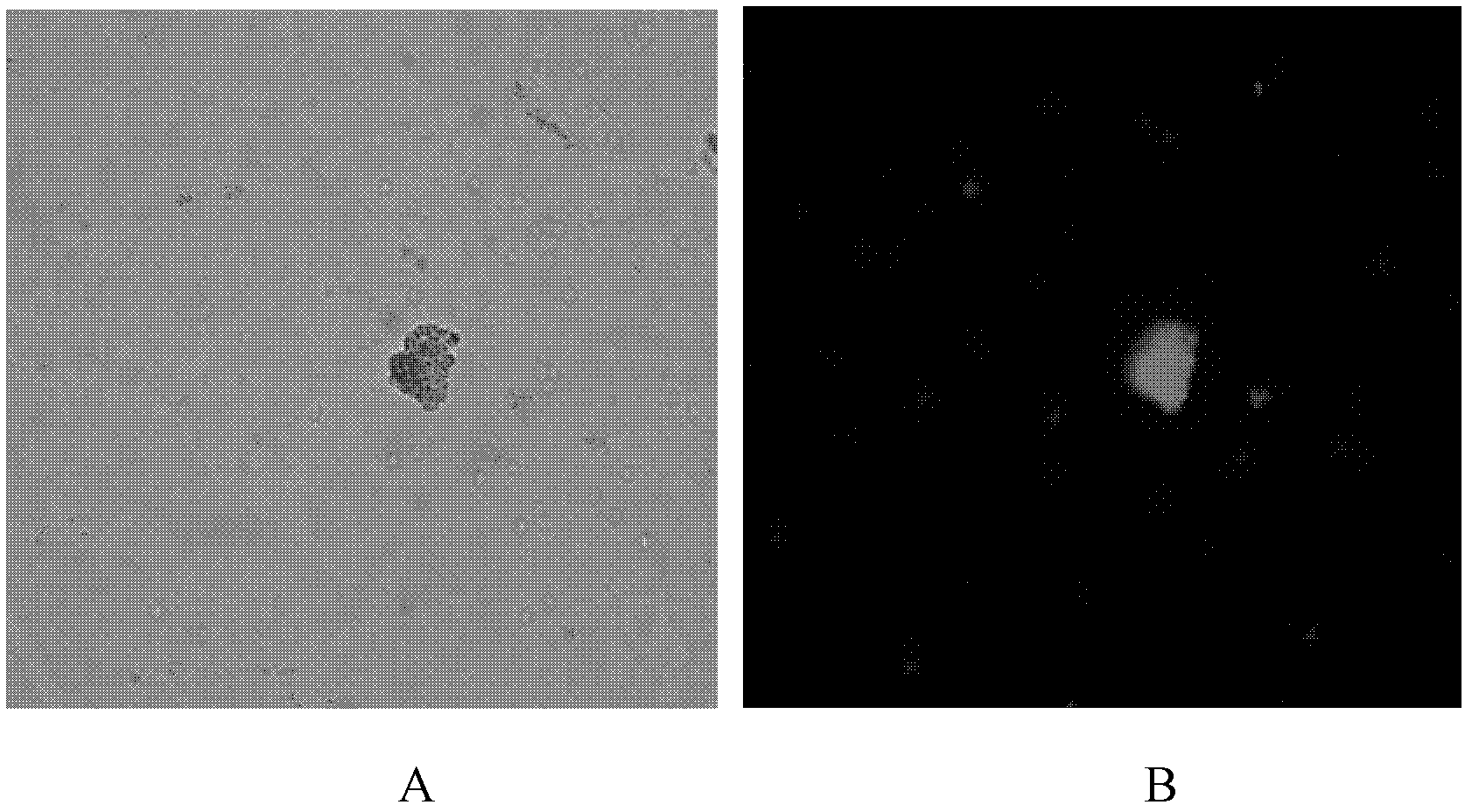
Method for detecting plastic content of marine organism
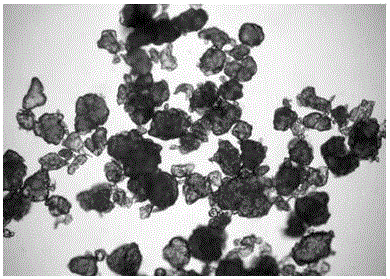
ActiveCN106645049ASimple and fast operationEasy to manufactureFluorescence/phosphorescenceCentrifugationFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a method for detecting the plastic content of a marine organism. The method is characterized by including the steps: drying, crushing and digesting marine organism digestive tracts or muscular tissues; performing density gradient centrifugation for digestion solution; performing microscopic examination for micro-plastics in obtained centrifugal liquid by a fluorescence microscope and a Fourier transform infrared microscope; counting the number of the micro-plastics. The method is simple to operate, high in accuracy and application safety and applicable to marine organism micro-plastic pollution detection.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
Automated imaging system for single molecules
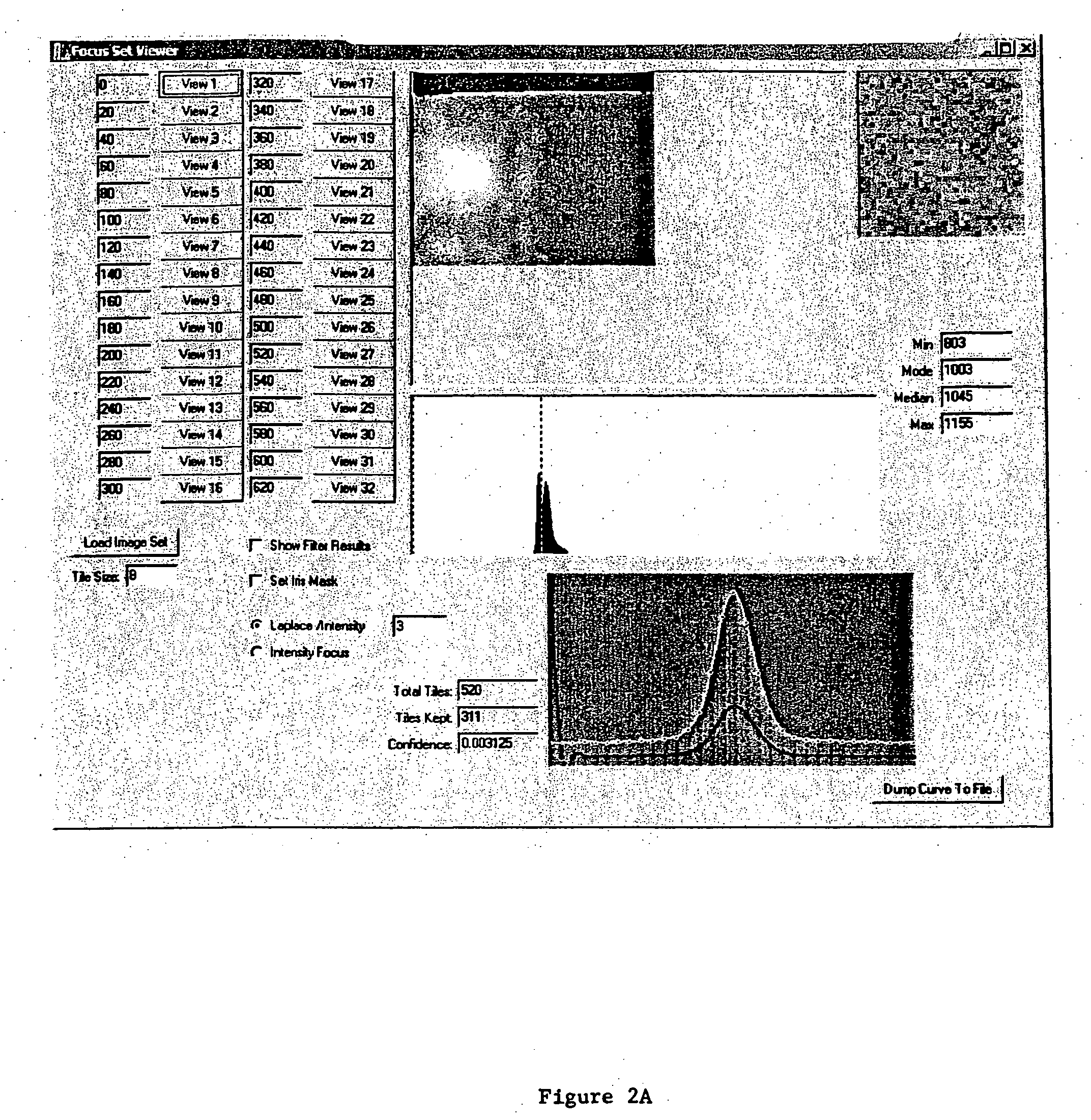
ActiveUS8271251B2Uneven illumination of fluorescence microscopy may be substantially reduced or eliminatedImprove user interactionAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingFluorescence microscopeHandling system
There is provided a high throughput automated single molecule image collection and processing system that requires minimal initial user input. The unique features embodied in the present disclosure allow automated collection and initial processing of optical images of single molecules and their assemblies. Correct focus may be automatically maintained while images are collected. Uneven illumination in fluorescence microscopy is accounted for, and an overall robust imaging operation is provided yielding individual images prepared for further processing in external systems. Embodiments described herein are useful in studies of any macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, peptides and proteins. The automated image collection and processing system and method of same may be implemented and deployed over a computer network, and may be ergonomically optimized to facilitate user interaction.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
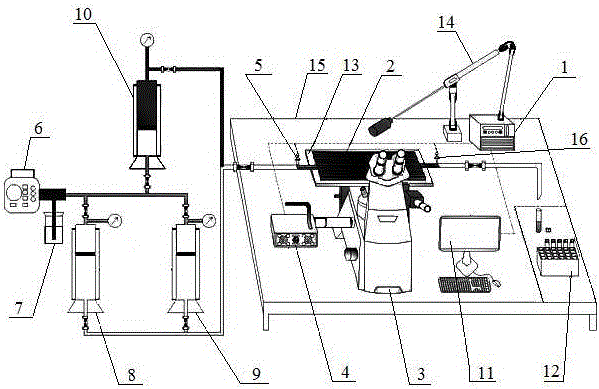
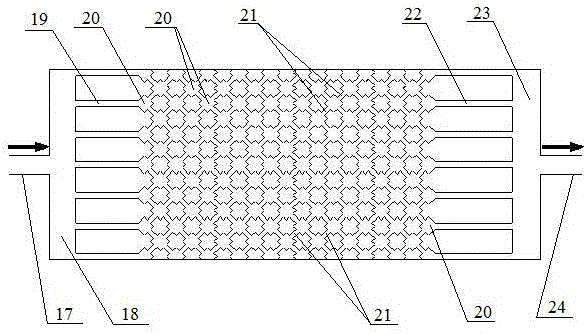
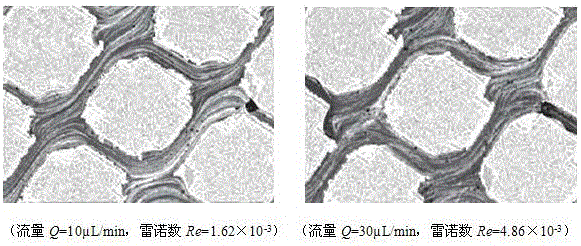
Apparatus and method for measuring elastic turbulence characteristics of viscoelastic polymer in porous medium
The invention relates to an apparatus and method for measuring elastic turbulence characteristics of a viscoelastic polymer in a porous medium, wherein a side connector of a fluorescent microscope of the apparatus is connected to a CCD (couple charged device) camera, a saline container, a polymer solution container and a synthetic oil container that are connected with an oil / water container are parallelly connected between an inlet of a micro metering pump and an inlet of a two-dimensional mesh microscopic simulation model, the two-dimensional mesh microscopic simulation model is provided with an inlet pressure sensor and an outlet pressure sensor, and a light guide arm of a micro field particle image speed-measuring system is positioned right above the two-dimensional mesh microscopic simulation model; all the micro field particle image speed-measuring system, the fluorescent microscope, the inlet pressure sensor and the outlet pressure sensor are connected to a data graphic data station. The apparatus and method are capable of effectively recognizing elastic turbulence of viscoelastic polymer solution in porous medium seepage, and providing qualitative and quantitative description for elastic turbulence characteristics.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
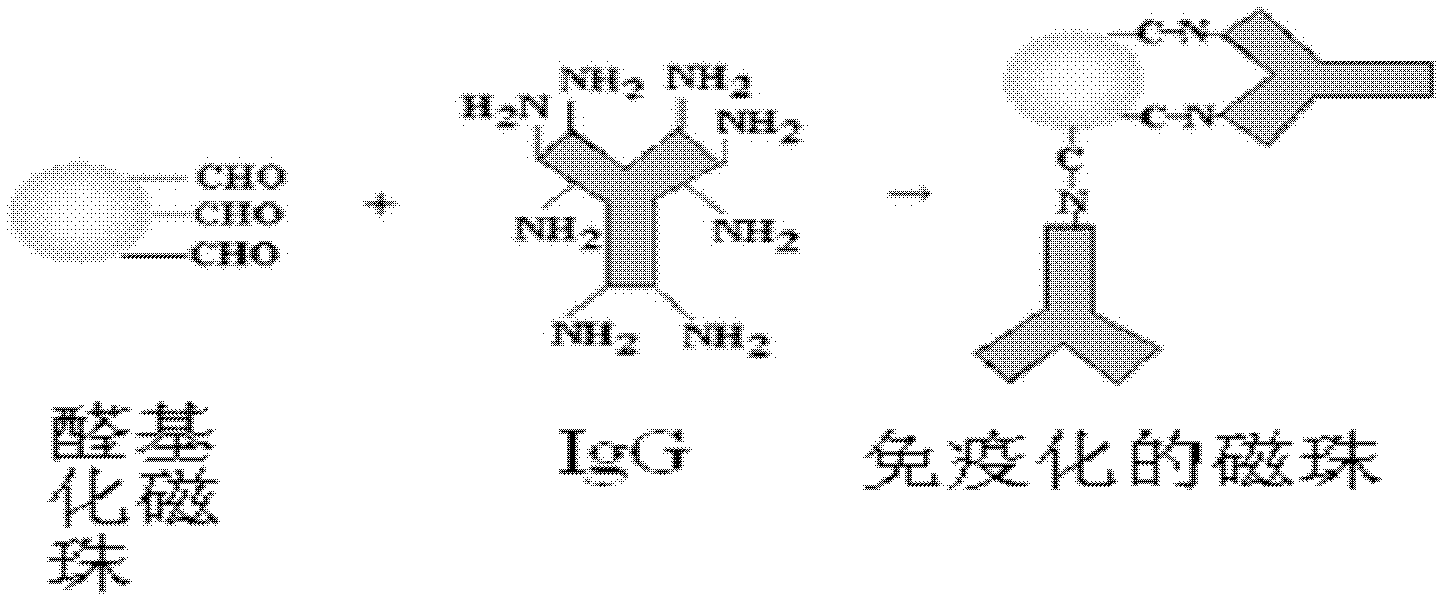
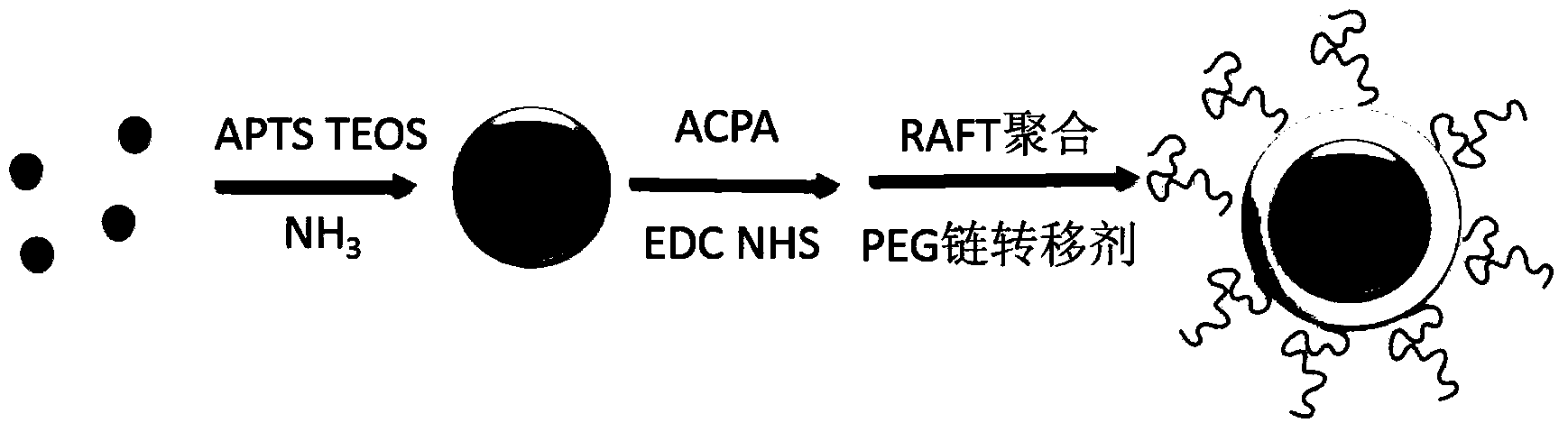
Magnetic molecularly imprinted nano-particle as well as preparation method and application thereof
The invention provides a magnetic molecularly imprinted nano-particle as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The nano-particle can perform specific recognition, trapping, separation and activity inhibition on target protein in a solution in vitro, more importantly, the nano-particle can enter a living cell rapidly under the action of a magnetic field and perform in-situ combination and activity inhibition on the target protein in the living cell, distribution of the nano-particles in the cell can be traced through a fluorescence microscope after fluorescence labeling, and quantitation can be performed through detection of fluorescence intensity.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Integrated micro-fluidic chip and system for capture, culture and administration of single cells
ActiveCN104513787AAvoid pollutionReduce usageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescence microscopeDrug supply
Aiming at the lack of an integrated micro-fluidic chip capable of realizing capture, culture and batch differential administration of single cells simultaneously in the prior, the invention provides an integrated micro-fluidic chip and system for capture, culture and administration of single cells and belongs to application of micro-fluidic chip technologies to the field of cell pharmacology analysis. The integrated micro-fluidic chip comprises a cell capture and culture unit, a drug diffusion unit and a drug supply unit, which are sealed in sequence from top to bottom; the system employing the integrated micro-fluidic chip comprises the integrated micro-fluidic chip, a fluorescence microscope, image processing equipment and a digital injection pump. A preparation method of the integrated micro-fluidic chip comprises the following steps: photo-etching baseplate plane figures on the silicon plates of the three units to etch grooves, pouring a liquid chip material into the grooves, and obtaining the three units after the liquid chip material is solidified; conducting sealing bonding and punching to obtain the integrated micro-fluidic chip. The integrated micro-fluidic chip provided by the invention integrates the three functions of capture, culture and batch differential administration of single cells and effectively avoids sample contamination.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
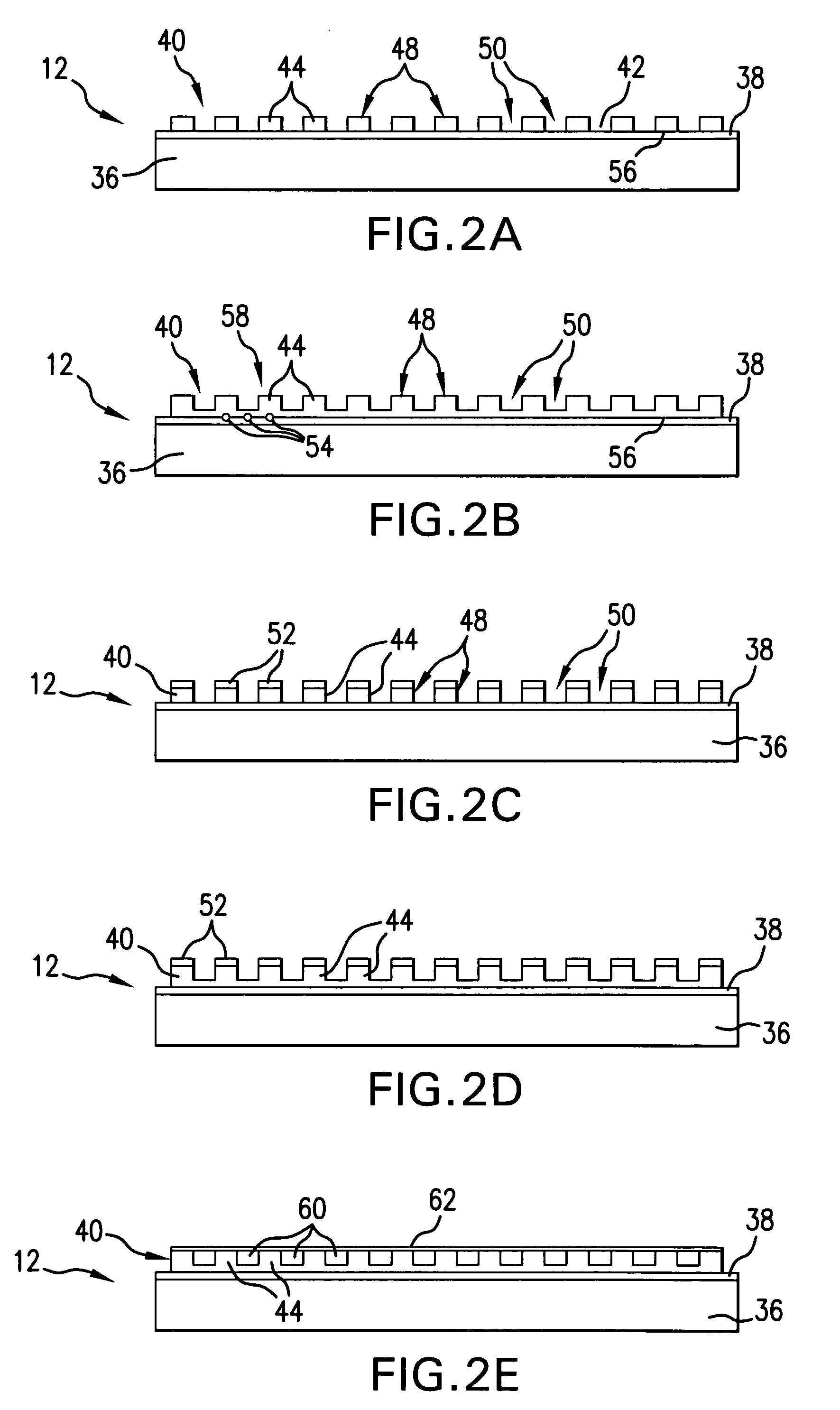
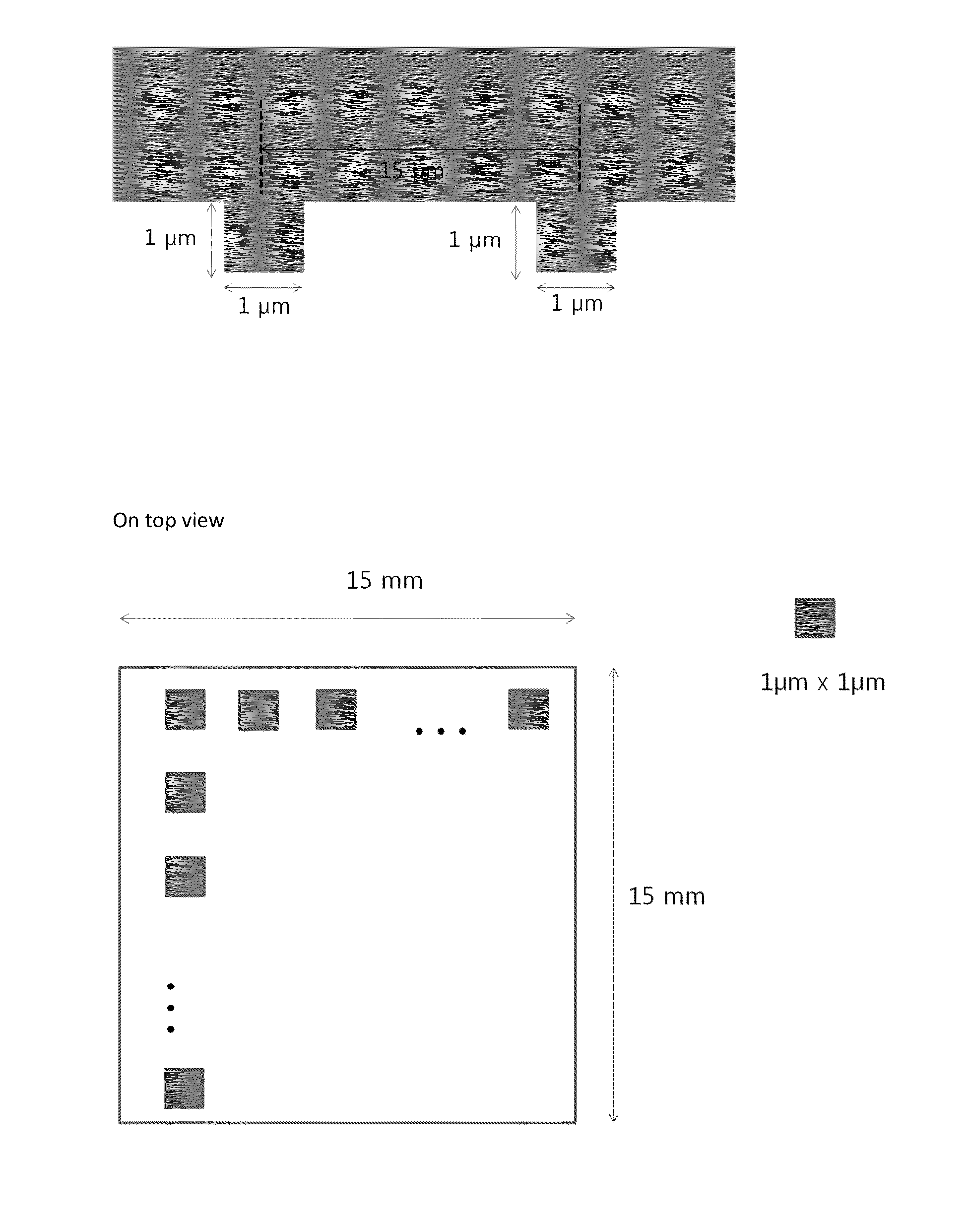
Simple ultra-stable stage with built-in fiduciary markers for fluorescence nanoscopy
ActiveUS8717673B2Efficient and cost-effective and simple provisionEasy to detectCeramic shaping apparatusMicroscopesMicroscopic observationFluorescence microscope
An improved microscope stage mount with built-in fiduciary markers is used for fluorescence microscopy, and comprises: (a) an optically-transparent glass plate adapted for specimen mounting and microscope viewing and comprising a specimen mounting area; and (b) a defined and ordered, two-dimensional microscopic array of fiduciary markers, wherein the markers are polymeric pillars affixed to the plate about the specimen mounting area, wherein the markers provide a three-dimensional spatial reference for the specimen.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method and system of laser scanning phase-microscope imaging
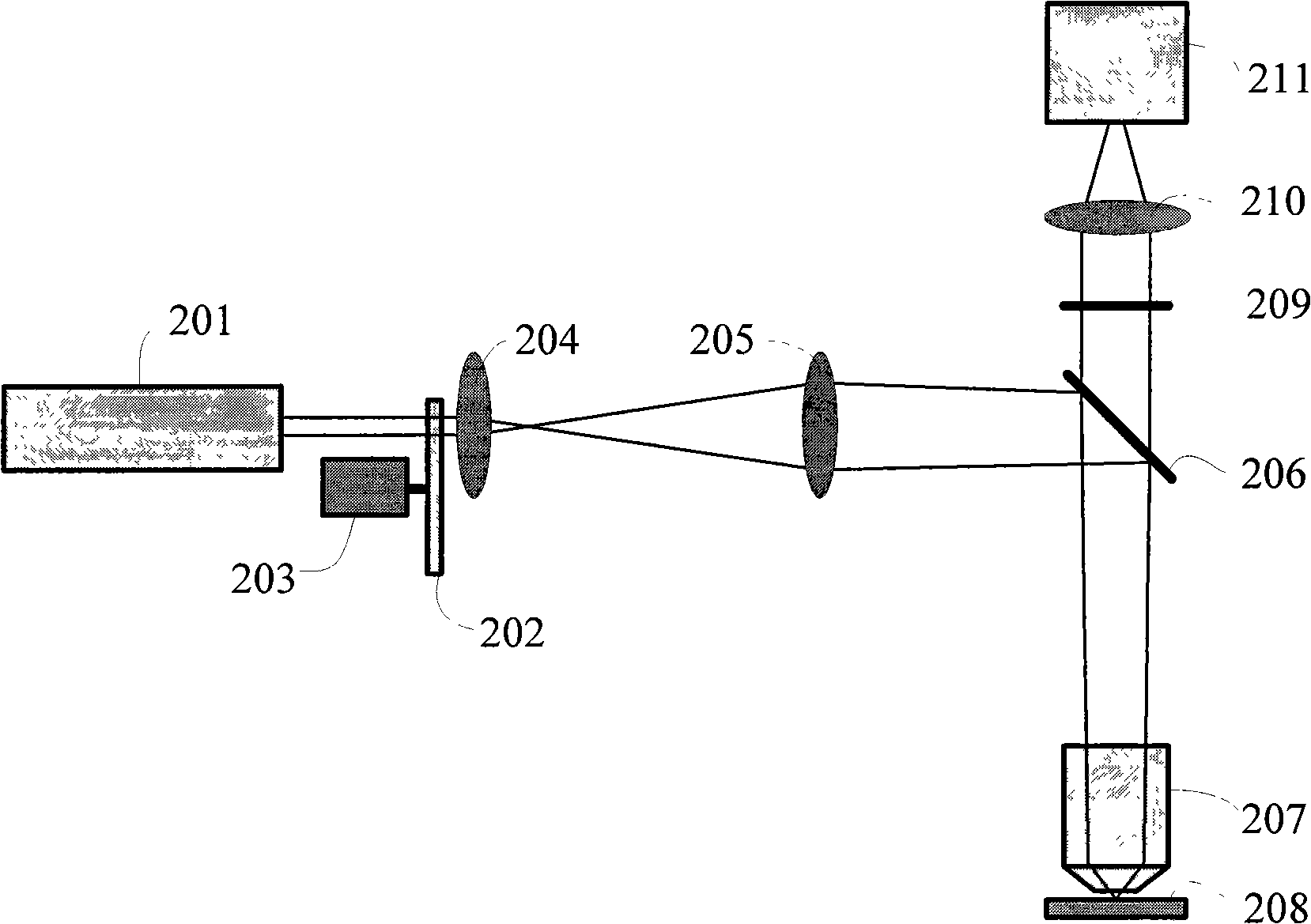
InactiveCN102841083AEnabling label-free imagingReduce complexityMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLaser scanningGalvanometer
The invention relates to a method and a system of laser scanning phase-microscope imaging. The system comprises a fluorescence microscope, a laser confocal laser scanning system and a photoelectric detection system, wherein the laser confocal laser scanning system is arranged in a light inlet hole of the fluorescence microscope; the photoelectric detection system is arranged at a light outlet direction of the laser confocal laser scanning system; an angle between each adjacent optical elements is regulated; a sample slice is arranged on a testing table; a fluorescence medium is added on the top of a glass slide; after being focused and in beam expansion through a dichroscope, an X-directional scanning galvanometer, a Y-directional scanning galvanometer, a scanning mirror and a tube lens, exciting light generated by the laser launches to an object lens and is focused on a biological sample; the exciting light focused on the biological sample launches to the fluorescence medium through the biological sample; the fluorescence medium is excited by the exciting light so as to launch fluorescence; the fluorescence shines and returns along the original light path through the biological sample; the emergent fluorescence launches to a filter and is focused through a convergent lens so as to enter a needle hole; the fluorescence exited by the needle hole is received and processed through the photoelectric detection system so as to obtain a relief structure of the biological sample. The method and system provided by the invention can be widely used in an imaging process of the biological sample.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Automated imaging system for single molecules
ActiveUS20050234656A1Improve user interactionGuaranteed uptimeAnalogue computers for chemical processesBiological testingFluorescence microscopeHandling system
There is provided a high throughput automated single molecule image collection and processing system that requires minimal initial user input. The unique features embodied in the present disclosure allow automated collection and initial processing of optical images of single molecules and their assemblies. Correct focus may be automatically maintained while images are collected. Uneven illumination in fluorescence microscopy is accounted for, and an overall robust imaging operation is provided yielding individual images prepared for further processing in external systems. Embodiments described herein are useful in studies of any macromolecules such as DNA, RNA, peptides and proteins. The automated image collection and processing system and method of same may be implemented and deployed over a computer network, and may be ergonomically optimized to facilitate user interaction.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
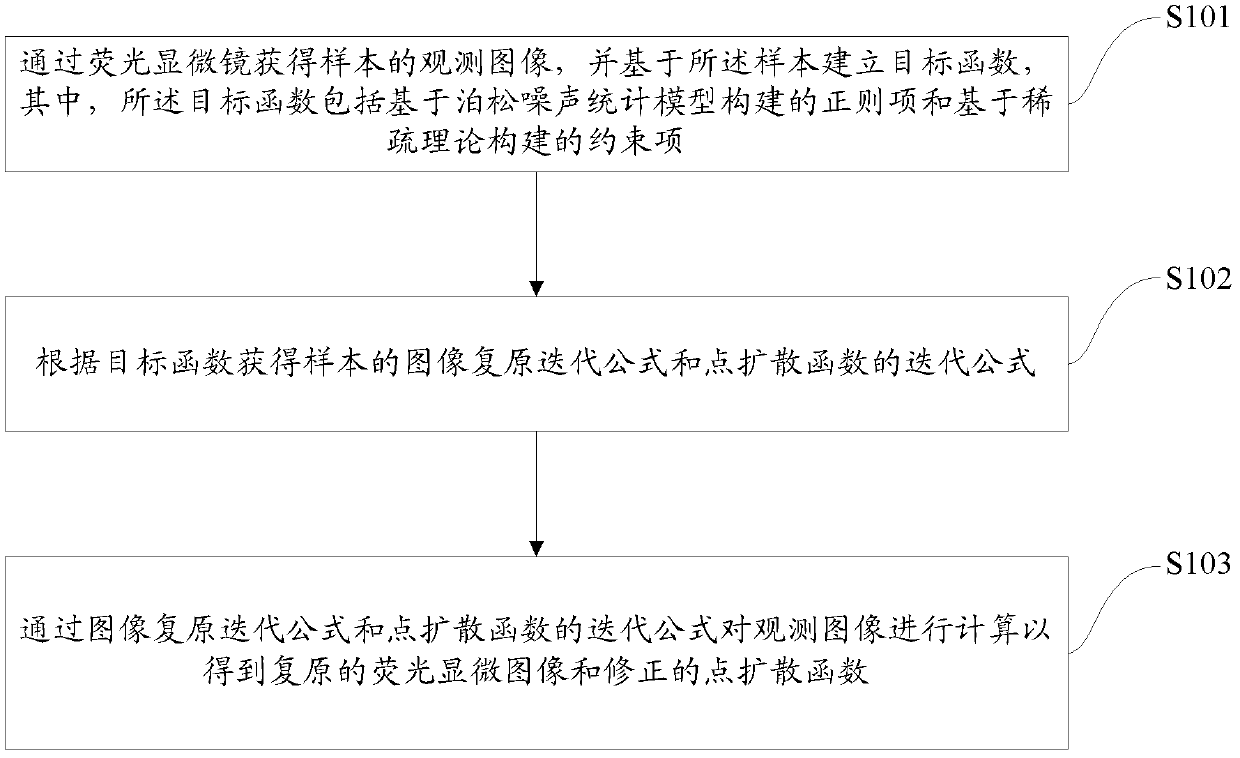
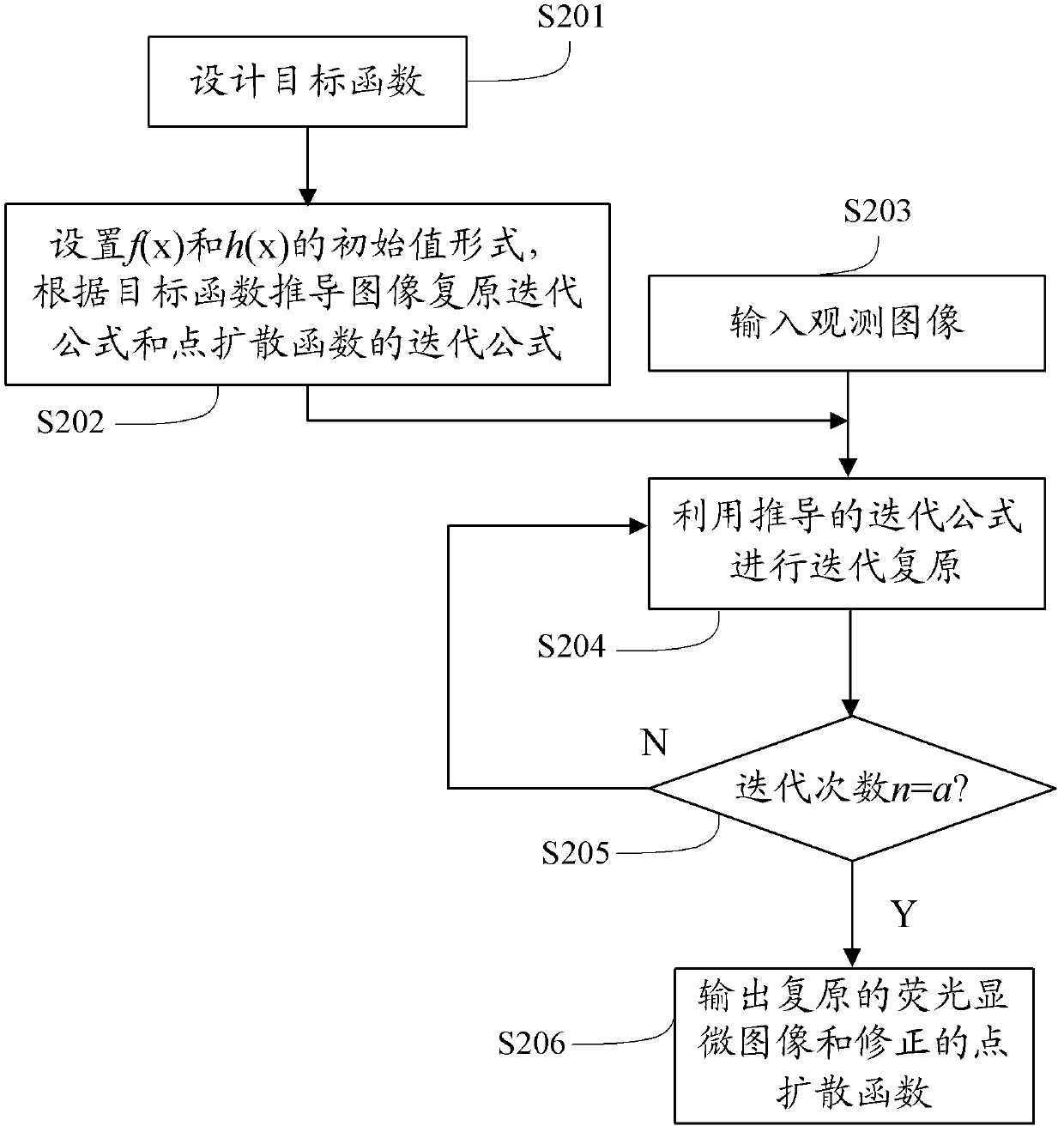
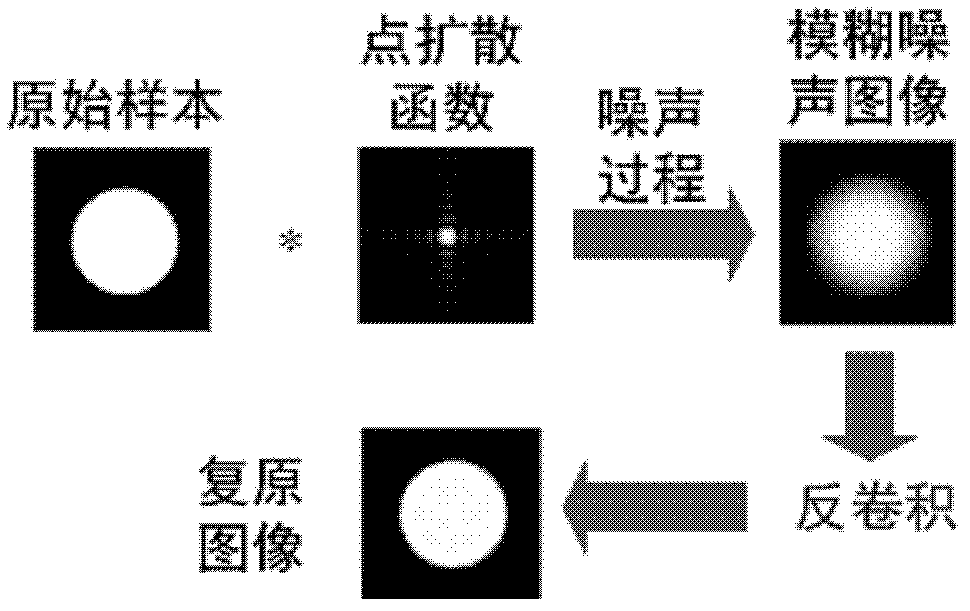
Fluorescent microscopic image restoring method based on blind deconvolution and sparse representation and device thereof
InactiveCN102708543AImprove accuracyKeep detailsImage enhancementPattern recognitionMicroscopic image
The invention provides a fluorescent microscopic image restoring method based on the blind deconvolution and the sparse representation and a device thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: obtaining an observing image of a sample through a fluorescence microscope, and building an objective function based on the sample, wherein the objective function comprises a regular item and a constraint item; obtaining an image restoring iteration formula and a point spreading function iteration formula of the sample according to the objective function; and calculating the observed image through the image restoring iteration formula and the point spreading function iteration formula in order to obtain the restored fluorescent microscopic image and the corrected point spreading function. By using the embodiment of the invention, the contrast ratio and the definition of the restored image are high; the texture details are effectively maintained; the image visual effect is more clear; and naturally, the point spreading function obtained after restoring also has very high degree of accuracy.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
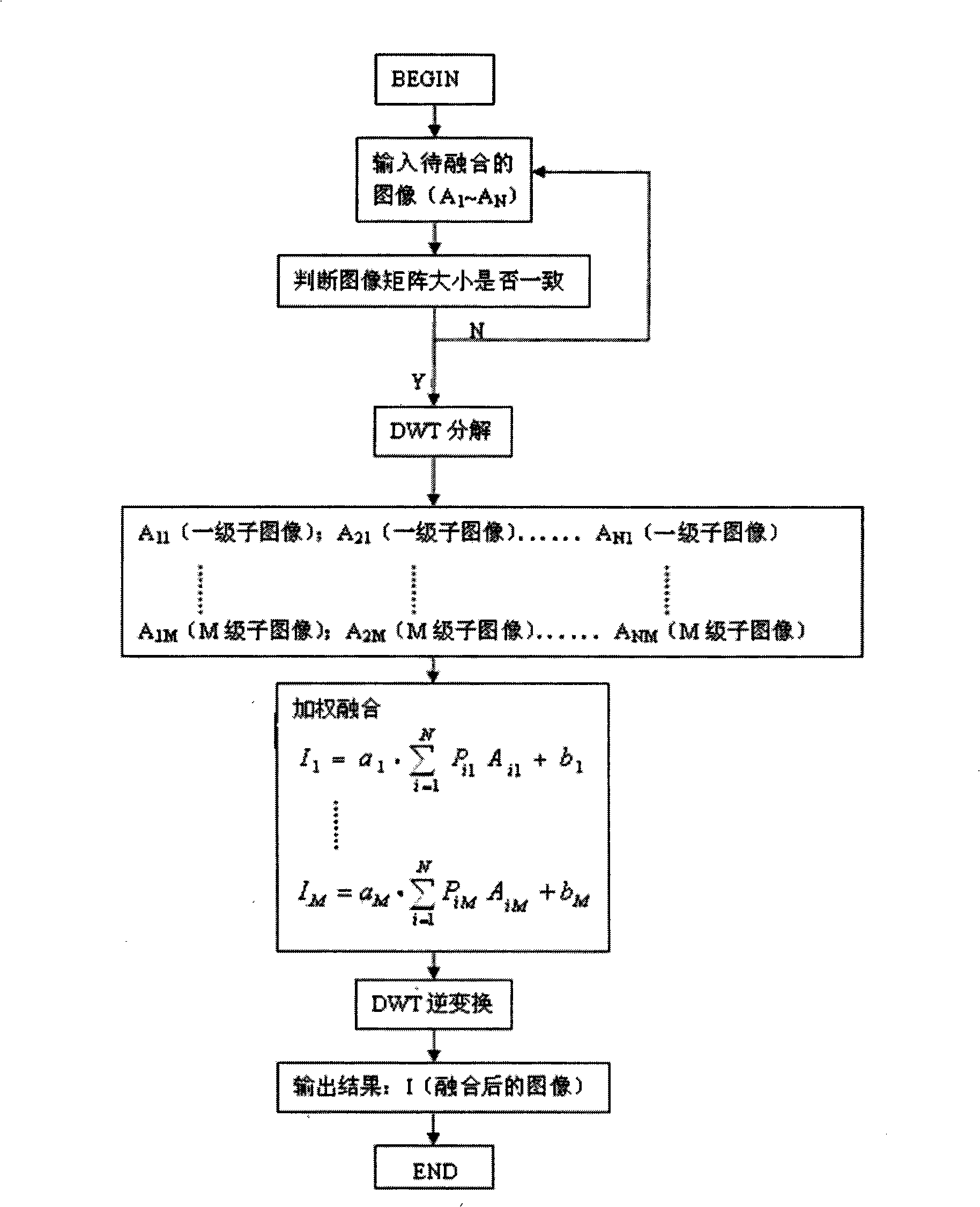
Rock core microscopic various light spectrum image-forming information comprehensive processing method
ActiveCN101339131AHigh utility valueRaman scatteringColor/spectral properties measurementsColor imageFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a comprehensive processing method of multi-spectral imaging information of core microscopy, which is used for comprehensively analyzing and processing the multi-spectral imaging data of the microscopic fluorescence, infrared and Raman of the core with oil in the geological logging of oil. At first, the color image of full color light of the polished section of the core is acquired with the fluorescence microscope; the three-spectral imaging analysis system of the microscopic fluorescence, infrared and Raman is then used for measuring the core sample in the geological logging to acquire the corresponding imaging ''spectral cube'' or spectral ''image cube''; the pixel level blending technology is used for data processing and comprehensive analysis of the three-spectral imaging information; a DWT is used for transforming; noise in the image is eliminated; the sub-images of each level are blended in a weighing way; the DWT is used for inverse transformation to acquire the blended multi-spectral image. The experiment has proven that the data blending technology of the spectral information of the image formed by multi microscopic spectra has higher practical value in the mineralogy, petrology and geochemistry of the core, when compared with each independent spectral imaging method.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Method and system for scanning apertureless fluorescence microscope
InactiveUS6953927B2Narrow transmission widthEnhanced spontaneous emissionNanoinformaticsMaterial analysis by optical meansFluorescence microscopeCantilever
Methods and systems for operating an apertureless microscope for observing one or more features to a molecular sensitivity on objects are described. More particularly, the method includes moving a tip of a probe coupled to a cantilever in a vicinity of a feature of a sample, which emits one or more photons at a detected rate relative to a background rate of the sample based upon the presence of the tip of the probe in the vicinity of the feature. The method modifies the detected rate of the feature of the sample, whereupon the modifying of the detected rate causes the feature of the sample to enhance relative to background rate of the feature.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com