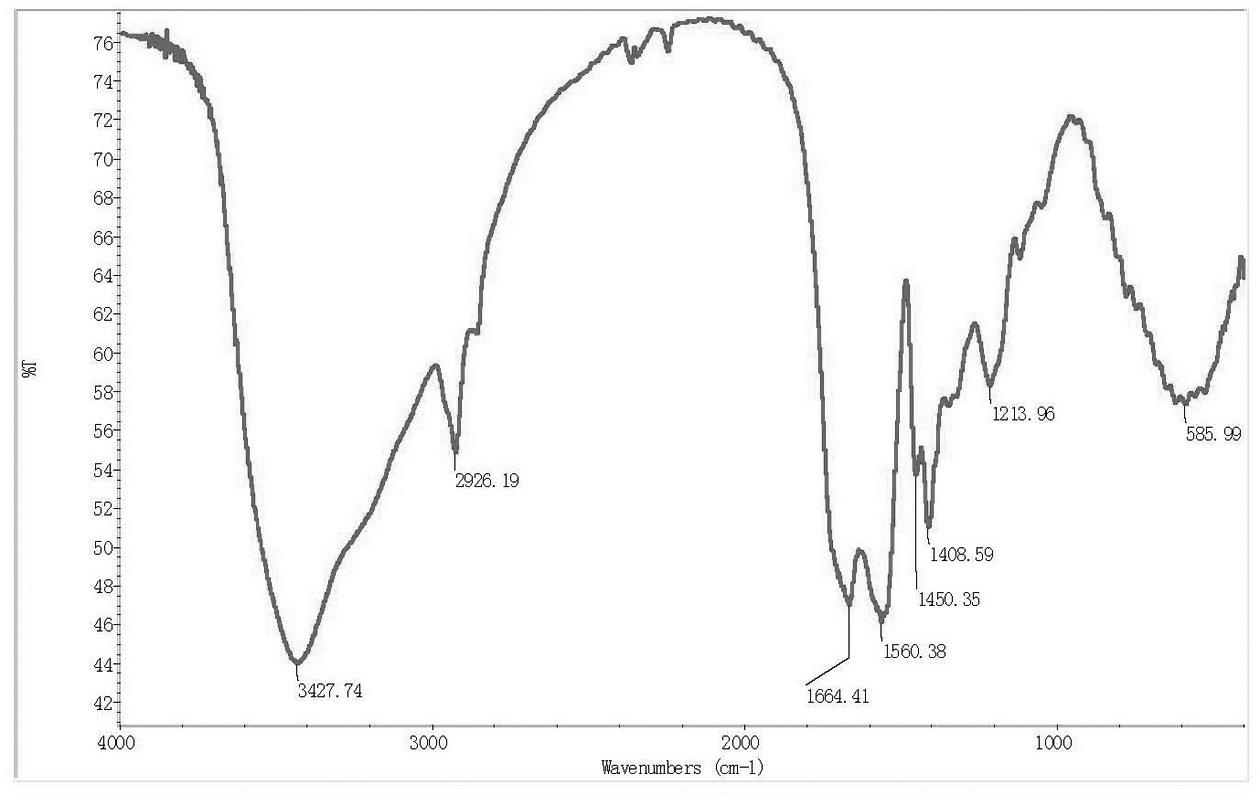
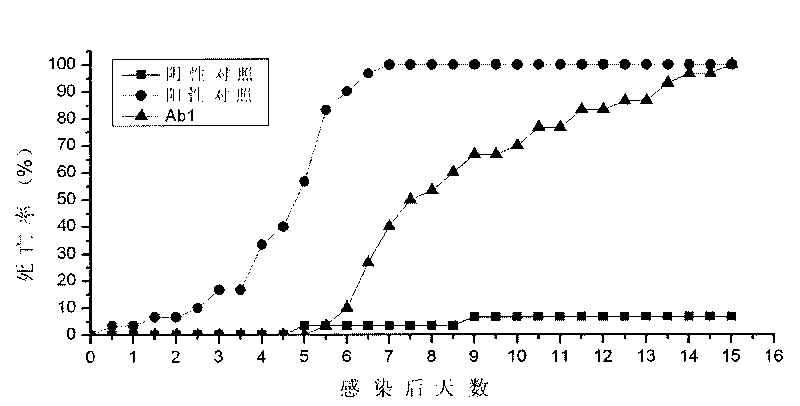
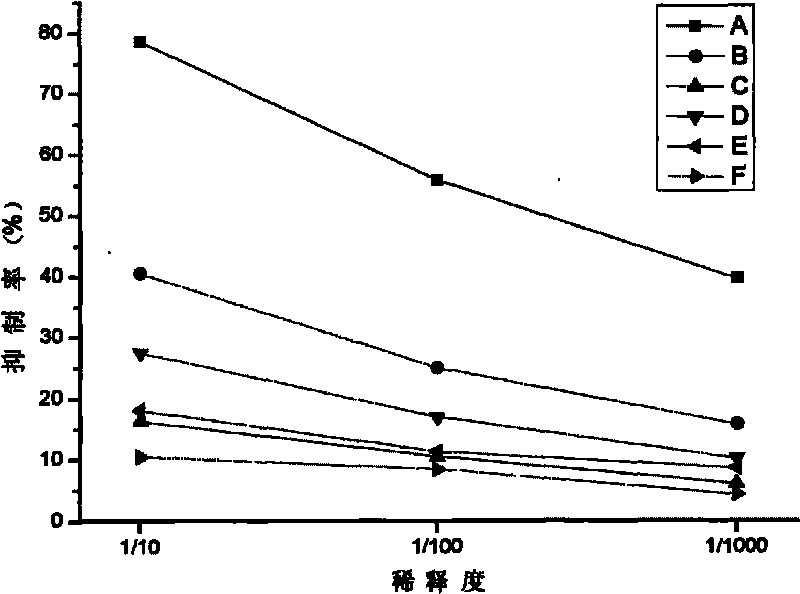
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
109 results about "Microscopic method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
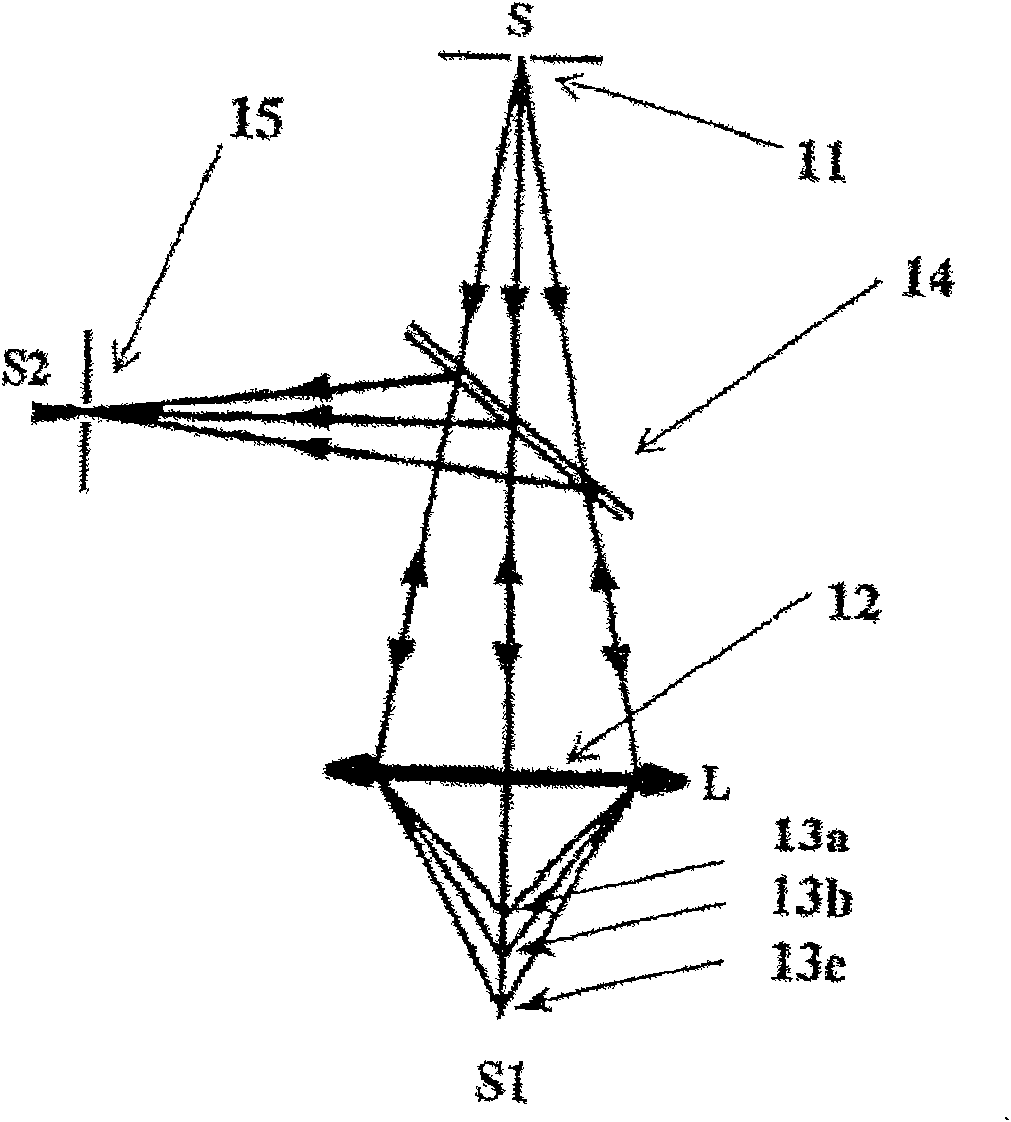
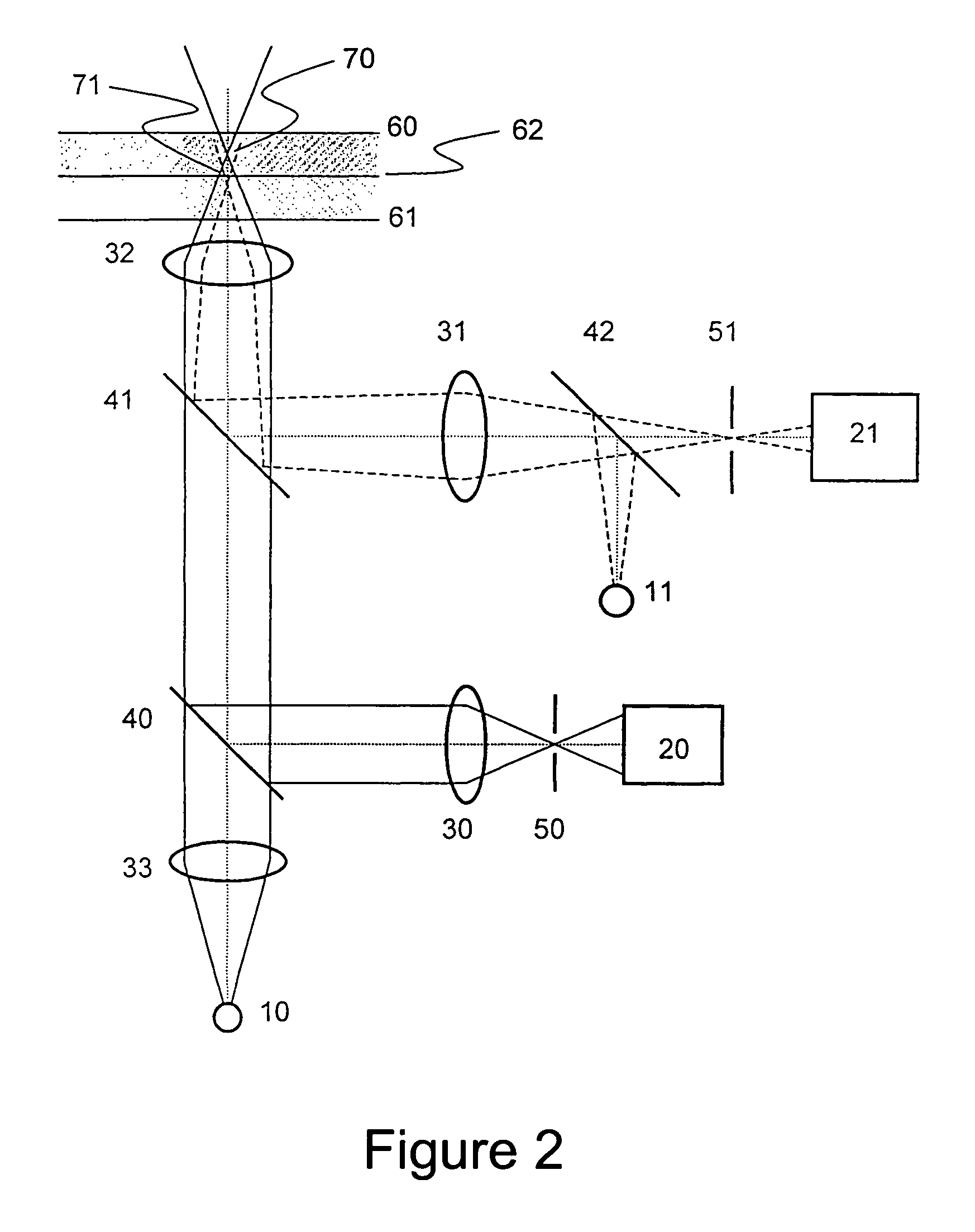
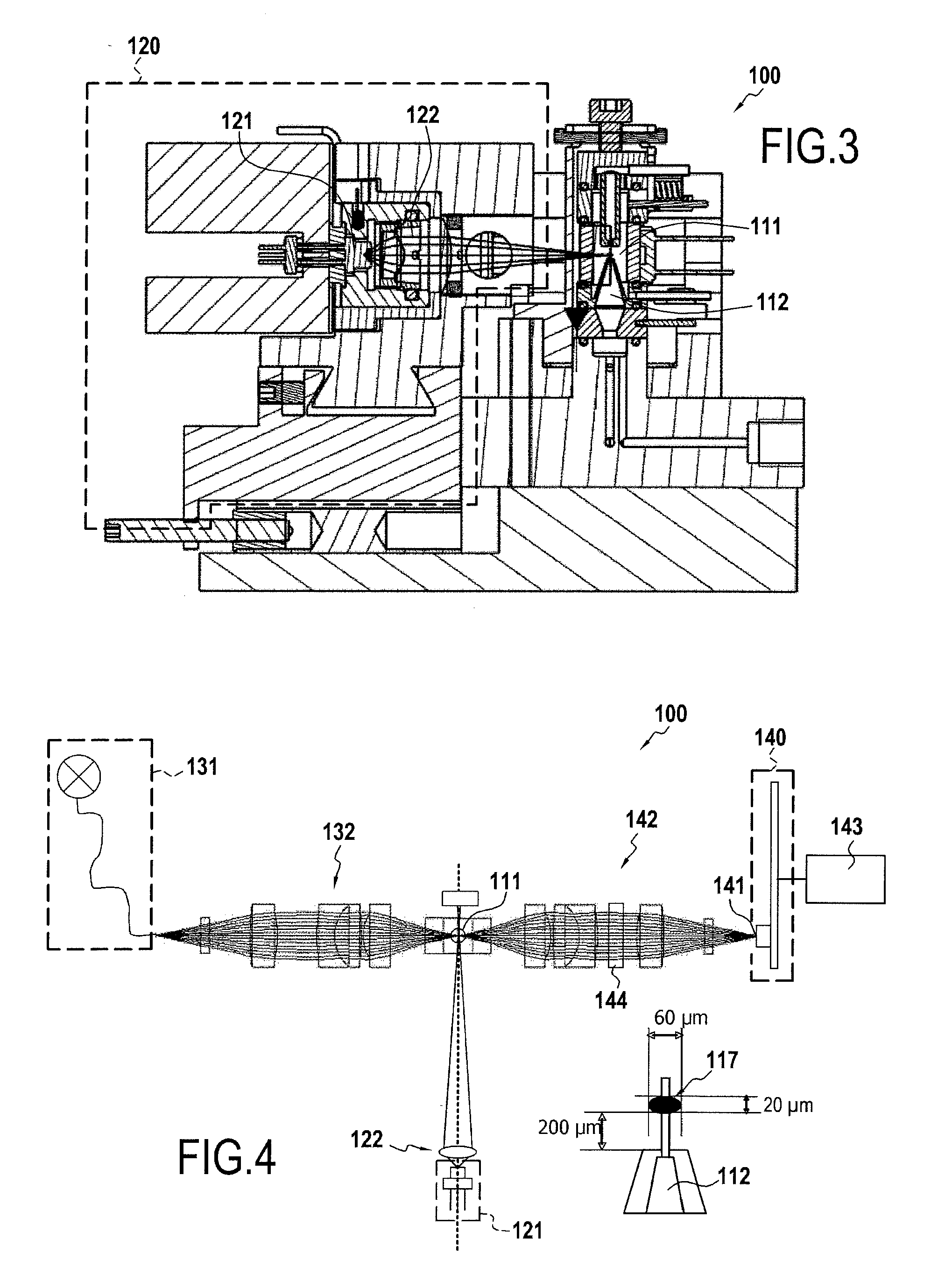
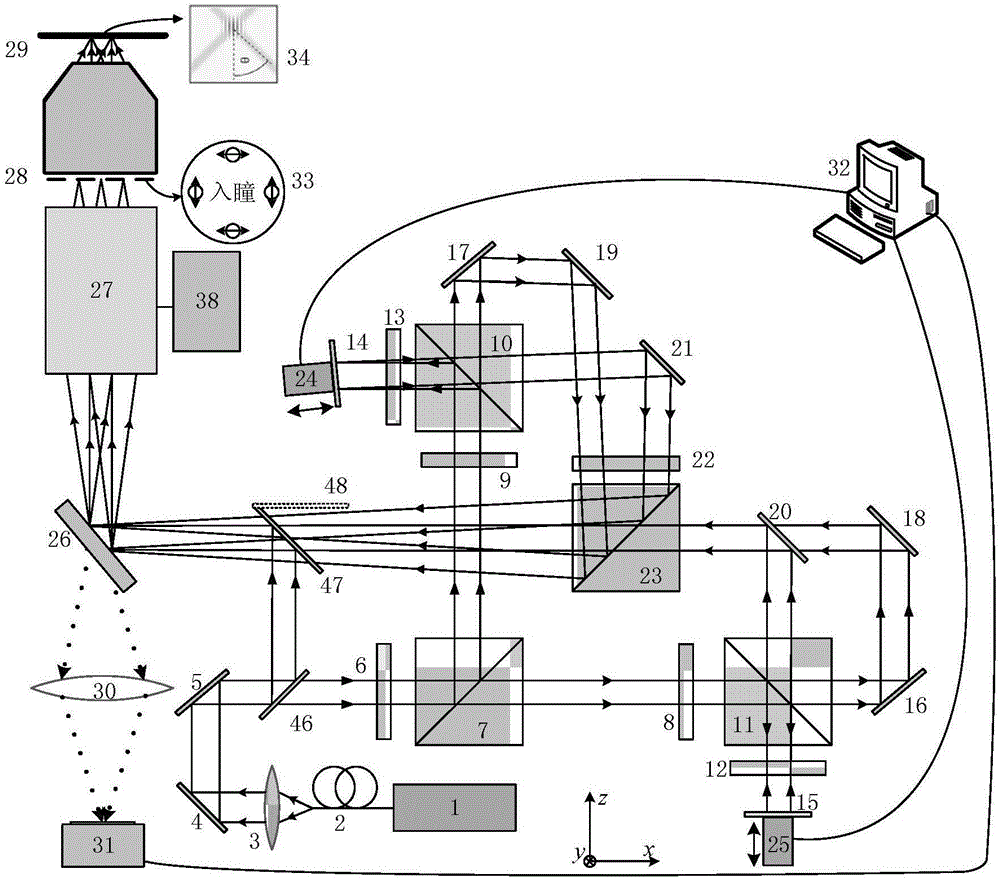
Linear multi-wavelength confocal microscope module and confocal microscopic method and system thereof
ActiveCN101872064AAccurate and fast profile measurementMeasurement rate increaseOptically investigating flaws/contaminationUsing optical meansSpectral dispersionMulti wavelength
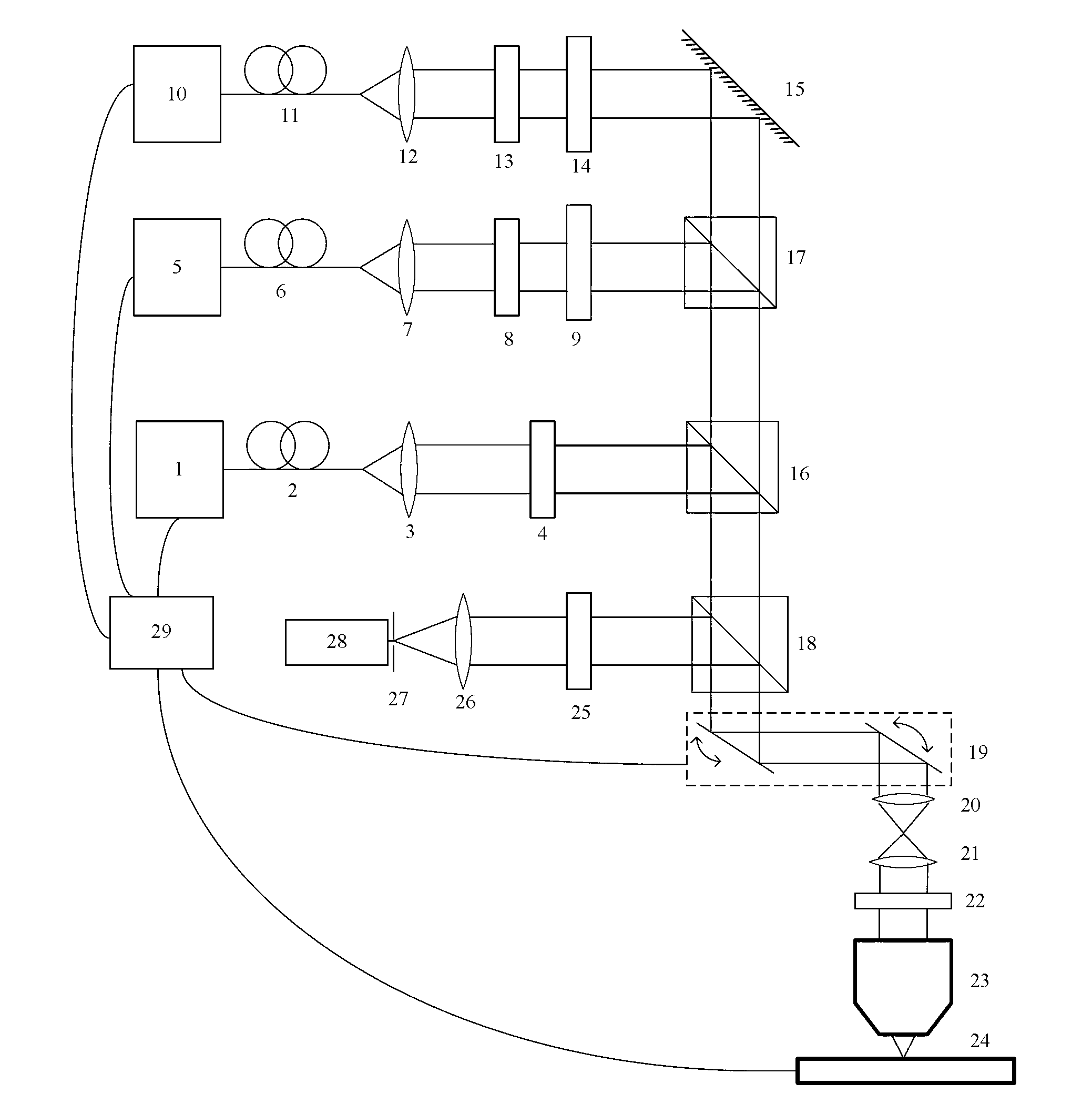
The invention provides a linear multi-wavelength confocal microscopic system, which uses more than two chromatic lenses to enable a linear incident light field to generate dispersed rays and to enable rays with different wavelengths to be focused at different positions. Moreover, the invention utilizes a linear multi-wavelength confocal microscope module with a linear scanning confocal principle and a light source dispersion technique to develop a long-field-depth high-definition optical micro-morphological profile microscopic method and a system by using a confocal microscopic technique with optical sectioning capacity and in combination with the high definition of spectral dispersion. The method and the system of the invention use a broadband light source. By adopting a dispersion objective module, the broadband light source is enabled to generate axially dispersed rays which are focused at different depths, the focused surface reflectance spectrum is obtained simultaneously, spatial filtering is conducted through a slit, the peak position of a spectral focusing response curve is accurately sensed by a linear spectral image sensing unit and thereby sectional profile measurement can be finished accurately and rapidly.
Owner:陈亮嘉
Variable visual field scanning microscope and the method based on fixed light path system
InactiveCN101339129AFlexible conversionMeet different biomedical application requirementsTelescopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescence microscopeDiscretization
The invention discloses a variable-field scanning microscopic method based on a fixed optical path system, and a device thereof. At first, a beam expanding system is used for uniformly expanding laser beams which are transmitted from a laser so as to form uniform laser beams; then a two-dimensional space discrete system is used for the two-dimensional space discretization of the uniform laser beams so as to form a sub-beam of M multiplied by N; the sub-beam of M multiplied by N orderly passes through a collimating lens, a scanning galvanometer, a reflector, a dichroic mirror and a fluorescence microscope, and then focuses on the sample on a sample platform; thus the excited fluorescence can be formed on the sample; the fluorescence microscope is used for collecting the excited fluorescence, which is transmitted into an imaging system after being reflected by the dichroic mirror and focused by a focusing lens. The scanning of the galvanometer and the crossing movement of the sample platform are combined: the scanning step length and the scanning step number of the galvanometer are changed; the area of the unit viewing field is used as the step length to move the sample platform; thus the scanned viewing field can be changed. The scanning microscopic method realizes the flexible switching between the low-resolution large viewing field and the high-resolution small viewing field, and satisfies the requirements in different biomedical applications.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Scanning microscopic method having high axial resolution
InactiveUS7202953B1Reliable detectionHigh resolutionSpectrum investigationScattering properties measurementsImage resolutionMicroscope
The invention relates to a method for optically detecting at least one entity which is arranged on a substrate. The at least one entity is scanned with a measuring volume using at least one radiation source and a confocal optic. During a scanning process an auxiliary focus is generated by means of at least one second radiation source and a second optic. Radiation generated by the first radiation source is collimated by a first optic and radiation generated by the second radiation source is collimated by a second optic. A retroreflection from the auxiliary focus is detected by at least one detector and is used to measuring the position of an interface and, thus, for indirectly positioning the measuring volume. The position of the auxiliary focus relative to the measuring volume is adjustable in a defined manner.
Owner:EVOTEC BIOSYST
Rapid three-dimensional (3D) super-resolution microscopic method and device
InactiveCN105487214ANo splittingReduce photobleaching effectMicroscopesUsing optical meansSpatial light modulatorOptical power
The invention discloses a rapid three-dimensional super-resolution microscopic method. The method comprises that a laser beam is converted into linearly polarized light after being collimated, phase modulation is carried out on the linearly polarized light, the linearly polarized light is converted into circularly polarized light, the circularly polarized light is projected to a sample to be measured, and pilot light emitted by scanning points of the sample to be measured is collected; and 3D scanning is carried out on the sample. Phase modulation comprises primary phase modulation and secondary phase modulation, a spatial light modulator which modulates the phase of an s light component of the linearly polarized light is used in the primary phase modulation, a spatial light modulator which modulates the phase of a p light component of the linearly polarized light is used in the secondary phase modulation, and a 3D super-resolution image is obtained according to the effective pilot light intensity. The invention also discloses a rapid 3D super-resolution microscopic device. According to the invention, optical power is lower, the photobleaching effect is weakened, 3D imaging is rapid, the device is simple, and light splitting is not needed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Phase microscopic device for transmission type samples and phase microscopic method
ActiveCN102645739AOvercome the disadvantage of being difficult to accurately measure phase informationPhase-affecting property measurementsMicroscopesMicroscopic imageTarget surface
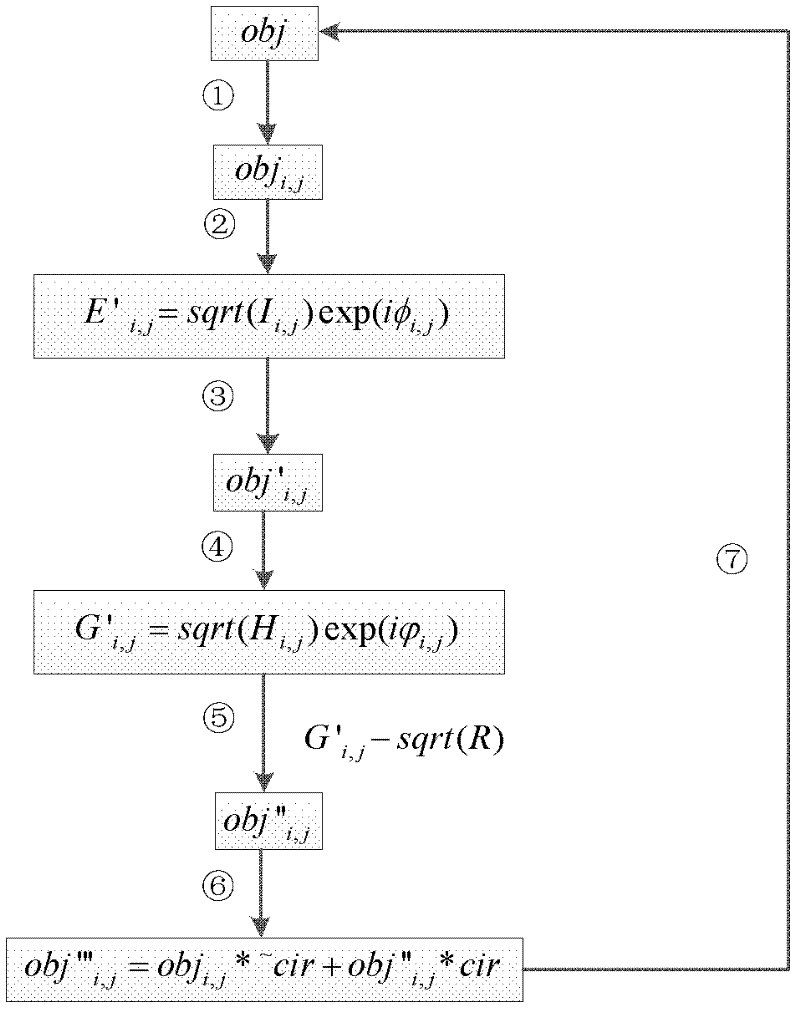
The invention discloses a phase microscopic device for transmission type samples and a phase microscopic method. Based on a coaxial holographic light path, an amplified real image of a transmission type object, after being scanned by using a small hole, is taken as object light, scattering spots are formed on a target surface of a detector at a distance and interfered with plane waves in the same direction, the light intensity distributions formed when the scattering spots exist separately and the scattering spots are interfered with reference light are respectively recorded when the small hole is located at different positions, meanwhile, a situation that the reference light is not changed is ensured, and the light intensity distribution of the reference light is recorded once. A reproductive image (including amplitude and phase) with a size far larger than the size of the target surface of the detector is obtained in a mode of carrying out an iterative operation by using a computer. A reproductive image produced in the invention not only has the interference of zero-order images and conjugate images, but also can carry out phase microscopic imaging on a transmission type sample with a size far larger than the size of the target surface of the detector because a mode of small-hole scanning and prevention is adopted; and because of the introduction of the reference light, compared with a common iterative algorithm, the convergence speed is faster.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Intensity difference based three-dimensional super-resolution microscopic method and device
ActiveCN102798622AFast imagingEasy to operatePolarisation-affecting propertiesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLight beamSignal light
The invention discloses a intensity difference based three-dimensional super-resolution microscopic method, which includes the following steps of: 1) starting a confocal imaging mode, converting the light beam sent out from a first light source into first linearly polarized light; 2) projecting the first linearly polarized light onto a sample to be tested; 3) collecting the signal light sent by the sample to be tested, thus obtaining first signal light intensity I1; 4) switching to a negative confocal imaging mode, converting the light beams sent out from a second light source and a third light source into second linearly polarized light and third linearly polarized light respectively; 5) carrying out phase modulation on the second linearly polarized light and the third linearly polarized light, and then converting them into a first modulated light beam and a second modulated light beam respectively; 6) projecting the first modulated light beam and the second modulated light beam onto the sample to be tested; 7) collecting the signal light sent by the sample to be tested, thus obtaining second signal light intensity I2; and 8) calculating effective signal light intensity I so as to obtain a super-resolution image. The invention also discloses an intensity difference based three-dimensional super-resolution microscopic device.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Devices, methods, and systems relating to super resolution imaging
ActiveUS20170307440A1Improve imaging resolutionImprove accuracyRaman scatteringMicroscopesWide fieldSuperresolution
Certain examples disclose systems and methods for imaging a target. An example method includes: a) activating a subset of light-emitting molecules in a wide field area of a target using an excitation light; b) capturing one or more images of the light emitted from the subset of the molecules illuminated with the excitation light; c) localizing one or more activated light emitting molecules using one or more single molecule microscopic methods to obtain localization information; d) simultaneously capturing spectral information for the same localized activated light emitting molecules using one or more spectroscopic methods; e) resolving one or more non-diffraction limited images of the area of the target using a combination of the localization and spectral information for the localized activated light emitting molecules; and 0 displaying the one or more non-diffraction limited images.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Three-dimensional fluorescent differential super-resolution microscopic method and device
The invention discloses a three-dimensional fluorescent differential super-resolution microscopic device which comprises a laser, an electric sample stage carrying a sample to be detected, and a microobjective for projecting light rays to the electric sample stage, wherein a polarizer for converting a beam emitted by the laser into linear polarized light, a first half wave plate for modulating a polarization direction of the linear polarized light, a space light modulation module for sequentially modulating a horizontal component and a vertical component of the beam and a scanning galvanometer system for light path deflection of circularly polarized light are sequentially arranged between the laser and the microobjective; the circularly polarized light emitted by the scanning galvanometer system is projected by the microobjective onto the sample to be detected; the device further comprises a detection system acquiring signal light emitted by the sample to be detected, and a computer controlling the space light modulation module and the scanning galvanometer system. The invention further discloses a microscopic method achieved on a basis of the three-dimensional fluorescent differential super-resolution microscopic device.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Handheld confocal skin microscopic method and handheld confocal skin microscopic device
ActiveCN105424601AAchieve constant conjugationEnabling Real-Time In Vivo Confocal MicroscopyFluorescence/phosphorescenceLight beamSignal light
The invention discloses a handheld confocal skin microscopic method and a handheld confocal skin microscopic device. The device includes: a light source and detection module being connected to an optical signal through a single-mode fiber, and a handheld movable confocal scanning module. A control device is connected to the light source and detection module and the handheld movable confocal scanning module. In the device, a confocal light path is modularized and includes the light source and detection module, which is used for providing an excited light beam for the system and detecting feedback signal light, and the handheld movable confocal scanning module, which is used for focusing the excited light beam to form a two-dimensional scanning light spot on a focused plane and collecting the feedback signal light of a sample. The two modules are connected to each other through the single-mode fiber. With the handheld movable confocal scanning module, real-time in-vivo confocal microscopic imaging can be flexibly achieved. The single-mode fiber, as a point light source and a detection wave filtering pinhole of the handheld movable confocal scanning module, achieves constant conjugation of the point light source and the detection wave filtering pinhole, thereby eliminating influence on conjugation due to vibration during a use process.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPTO MEDIC TECH CO LTD
Super-resolution microscopic method and device of time-gated wide-field stimulated emission
InactiveCN103487421AFast imagingImprove energy utilizationFluorescence/phosphorescenceTime gatingWide field
The invention discloses a super-resolution microscopic method of time-gated wide-field stimulated emission. The method comprises the steps as follows: 1), exciting light is projected to a to-be-tested sample by a microscope objective, and the to-be-tested sample is subjected to wide-field excitation to generate fluorescence; 2), depletion light is similarly projected to the to-be-tested sample after modulated by a beam modulation module, so that illumination light spots in a dark-spot array are formed, and stimulated emission depletion is performed in a wide-field excitation area; 3), fluorescence emitted by the to-be-tested sample after subjected to the stimulated emission depletion is collected by the microscope objective and focused and projected to a photoelectric sensor, so that a fluorescence image of the to-be-tested sample is obtained; 4), the to-be-tested sample is moved horizontally, step 1) to step3) are repeated, and horizontal two-dimensional scanning is performed on the to-be-tested sample to obtain fluorescence images corresponding to scanning positions; and 5), all fluorescence images are moved horizontally and superimposed to recover a two-dimensional super-resolution image finally. The invention further discloses a super-resolution microscopic device of the time-gated wide-field stimulated emission.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Automatic counting instrument for body cell of milk / bacteria through direct microscopic method
InactiveCN101050416ASimple structureImprove counting accuracyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMilk sampleEngineering
This invention provides a direct microscopic examination method milk somatic cells / bacteria automatic counter. The automatic counter comprises: a sampling / smearing apparatus, a dyeing apparatus, a washing / drying apparatus, a microscopic detecting apparatus, a convey apparatus for conveying the milk sample as well as glass slide to and out of the sampling / smearing zone, and another convey apparatus for conveying the smeared glass slide to the dyeing zone, washing / drying zone and microscopic detecting zone, which comprises multi-stage glass slide convey mechanisms and glass slide running mechanisms. The automatic analyzer comprises a smearing apparatus, a dyeing apparatus, a washing / drying apparatus a microscopic detecting apparatus and a control apparatus for convey apparatuses. This invention divides direct microscopic examination method milk somatic cells / bacteria analysis and assay into multiple mechanical actions performed by different apparatuses, and sets corresponding working positions and working zones. The working positions and working zones are connected via the convey apparatuses, and can reasonably and effectively perform automatic detection under the control of the control apparatus. The automatic counter has high counting precision and repeat precision, and the working efficiency is largely increased.
Owner:HANGZHOU ULTRASUN TECH
Method and apparatus for the combined analysis of a sample with objects to be analyzed
ActiveUS20100263098A1Analysed more efficiently and more accuratelyMaterial analysis by optical meansNanotechnologyComputer scienceBiological objects
The invention relates to a method for the combined analysis of a sample with objects to be analysed, in particular a sample with biological objects, in which measurement results for one or more of the objects to be analysed in the sample are obtained by analysing the one or more objects to be analysed by an imaging method of measurement, probe-microscopic measurement results are obtained for the one or more objects to be analysed by analysing the one or more objects to be analysed by a probe-microscopic method of measurement, and the measurement results and the probe-microscopic measurement results are assigned to one another, after optional prior intermediate processing. Furthermore, the invention relates to an apparatus for carrying out combined analysis of a sample with objects to be investigated, in particular a sample with biological objects.
Owner:JPK INSTR +1
Optical sheet illumination microscopic method and device based on differential
ActiveCN103837513AGuaranteed imaging depthAchieving super-resolution imagingMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLight spotFluorescence
The invention discloses an optical sheet illumination microscopic method based on differential; the method comprises the following steps: 1, a lighting beam after beam expanding is converted into parallel polarized light and vertical polarized light; 2, the parallel polarized light is individually used, the parallel polarized light with a light spot as a solid center is regarded as a first illumination light converted to a first circular polarized illumination light, the first circular polarized illumination light is focused to a surface of a fluorescence sample through a focusing module, and the fluorescence emitted by the fluorescence sample is collected to obtain a first photo; 3, the vertical polarized light is individually used and modulated into a second illumination light having a hollow light spot, the second illumination light is converted into a second circular polarized illumination light and focused to a surface of the fluorescence sample through the focusing module, and the fluorescence emitted by the fluorescence sample is collected to obtain a second photo; 4, a computer carries out difference treatment for the two photos in the step 2and the step 3, thereby completing scanning of the sample. The invention also discloses an optical sheet illumination microscopic device based on differential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Microscopic system and microscopic method based on in-situ three-dimensional enhanced display
InactiveCN104280886AImprove operational flexibilityPortable and miniaturizedMicroscopesStereoscopic photographyMiniaturizationComputer vision
The invention discloses a microscopic system and microscopic method based on in-situ three-dimensional enhanced display. By means of the microscopic system and microscopic method, a user can clearly and unceasingly observe an entity within a large view field range. The microscopic system comprises an entity observation device, a naked-eye three-dimensional display device and the in-situ three-dimensional display device. The entity observation device is aligned with an entity area and used for making the user directly obtain an entity visual image in real time. The naked-eye three-dimensional display device is used for providing a naked-eye true three-dimensional image related to the content of the entity visual image. The in-situ three-dimensional display device is connected with the entity observation device and the naked-eye three-dimensional display device and used for displaying the entity visual image and the naked-eye true three-dimensional image to the user after conducting in-situ three-dimensional perspective and fusion on the entity visual image and the naked-eye true three-dimensional image. The microscopic system has the advantages of being simple in structure, high in operation flexibility, capable of meeting different requirements, capable of achieving high-resolution three-dimensional fusion display or system portability and miniaturization, and the like.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Electrooptic measurement device and method intended for classifying and counting microscopic elements
ActiveUS20110089340A1Easy to implementLow costPhotometryInvestigating moving fluids/granular solidsMeasurement deviceFluorescence
The invention relaters to a device (100) for biological analysis by measurement of photoluminescence in a fluid in a measurement tank (111). This device (100) comprises at least two light sources (121, 131) adapted to emit in different spectral areas respectively appropriate for measurement of absorption and fluorescence, and a sensor device (140) comprising a sensor (141), an optical system (142), and filter means (144), which three elements are mutualized in accordance with the invention to enable absorption and / or fluorescence to be measured. In accordance with the invention the internal gain of the sensor (141) is configurable to enable the fluorescence and absorption measurements to be executed sequentially.
Owner:HORIBA ABX SAS
Non-linear super-resolution microscopic method and device adopting photon recombination
InactiveCN105510290ASimple structureFast imagingFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh power lasersDetector array
The invention discloses a non-linear super-resolution microscopic method adopting photon recombination. The method comprises steps as follows: 1), an illuminating beam after collimation and beam expanding is converted into linear polarization light, the linear polarization light is modulated into circular polarization light and is focused on a fluorescence sample, and hollow light spots are formed for illumination; 2), the fluorescence sample is stimulated to emit saturated fluorescence, and fluorescence imaging is realized by a detector array consisting of multiple photoelectric detectors; 3), the hollow light spots detected by the detectors are subjected to corresponding translation and then are overlaid, an image of a first solid light spot is obtained, and imaging of a corresponding scanning point is realized. The invention further discloses a non-linear super-resolution microscopic device adopting the photon recombination. According to the method and the device, the non-linear effect of fluorescence is realized through high-power laser illumination, a single pinhole detector arranged on an image surface in traditional confocal microscopic imaging is replaced with the pinhole detector array, the photon recombination technology is adopted, the device is simplified, and the imaging speed is increased.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Laser scanning saturate structured light illumination microscopic method and device based on phase modulation
InactiveCN107092086ALower requirementIncrease horizontal resolutionMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLaser scanningOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a laser scanning saturate structured light illumination microscopic method based on phase modulation, and the method comprises the steps: enabling an illumination light beam after collimation to be converted into linear polarized light; loading a phase (0-phi) in a first direction to the linear polarized light, and adjusting the polarization direction of the linear polarized light; scanning a sample through the linear polarized light after the adjustment of the polarization direction, forming a first laser scanning saturate structured light illumination pattern where the sample is excited to generate fluorescent light, and collecting a first fluorescent light signal; loading a phase (0-phi) in a second direction to the linear polarized light, and adjusting the polarization direction of the linear polarized light; scanning a sample through the linear polarized light after the adjustment of the polarization direction, forming a second laser scanning saturate structured light illumination pattern where the sample is excited to generate fluorescent light, and collecting a second fluorescent light signal; carrying out the processing of the first and second fluorescent light signals, and obtaining a super-resolution image with the improved lateral resolution. The invention also discloses a laser scanning saturate structured light illumination microscopic device based on phase modulation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for detecting intracellular interaction between biomolecules
The present invention relates to a quantitative non-microscopic method of detecting intracellular interactions between biomolecules, on living cells, in response to a biological or pharmacological stimulation, by a time-resolved proximate energy transfer effect between two members of a fluorescence donor / acceptor pair.
Owner:CIS BIO INT
Super-resolution fluorescence microscopic method and apparatus based on photoactivation and structured light illumination
ActiveCN106124468AGood serviceCompatible with wide field of viewFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescencePhase difference
The invention discloses a super-resolution fluorescence microscopic apparatus based on photoactivation and structured light illumination. The apparatus comprises a light source module having a first laser for fluorescence activation, a second laser for fluorescence excitation, and a frequency selection switching module for switching between the two lasers; a regulation unit for regulating a light beam output from the light source module to two beams of p polarized light and two beams of s polarized light capable of interference and for changing the interference phase difference of the two groups of light beams; a dichroic mirror, on the surface of which interference fringes are formed via the two beams of p polarized light and two beams of s polarized light, and which reflects a mesh structured light illumination comprising bright spots and dark spots in array distribution and taken as an irradiation sample; and an imaging unit comprising a converging module for changing the spacing between interference fringes, a microobjective projecting a light beam emerging from the converging module to the microobjective of a sample, and a camera for conducting stimulated radiation fluorescence imaging of the sample. The invention further discloses a super-resolution fluorescence microscopic method based on photoactivation and structured light illumination.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method of exciting molecules out of a first state into a second states using an optical signal
ActiveUS7224452B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsExcitation beamHigh spatial resolution
In a fluorescence-microscopic method of examining a sample with high spatial resolution, the sample is first cooled to a temperature of below 5° C.; next the cooled sample is transferred out of a ground state into a fluorescent state within an area captured by a detector using an excitation beam of light; next the cooled sample is subject to de-excitation of excited molecules by stimulated emission in the area captured by the detector, except at desired measuring points, using an de-exciting beam of light, the de-exciting beam of light having a spatial intensity distribution comprising a zero point located at the desired measuring points, and the excited sample being transferred back into its ground state by the de-exciting beam of light; and then fluorescence light spontaneously emitted by the cooled sample is measured with the detector, the detector detecting fluorescence light that is emitted only from the measuring points.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Multichannel fluorescent microscopy composite microscopic system
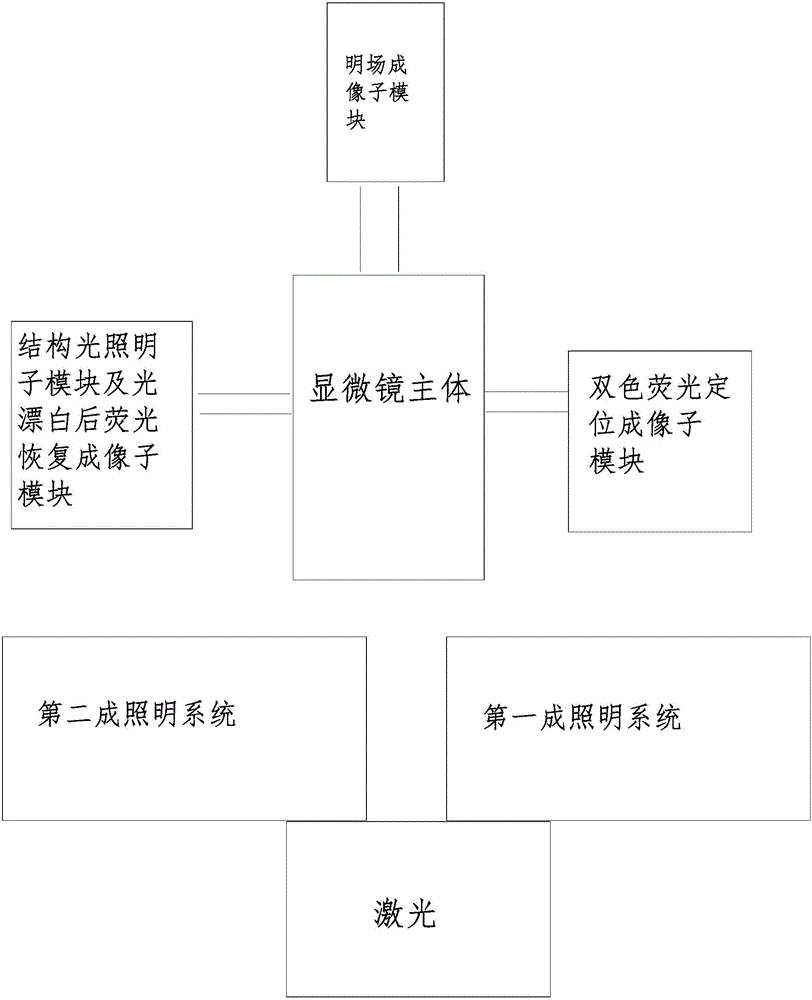
The invention provides a multichannel fluorescent microscopy composite microscopic system, and belongs to the technical field of microscopes. The multichannel fluorescent microscopy composite microscopic system comprises a microscope body, an imaging module and a composite lighting module. A mechanical rotating mirror is controlled to change the light path of the composite lighting module through a control system, and light matched with the imaging module and modulated through different modes is selected to enter the microscope body by the mechanical rotating mirror to perform lighting on a sample. The device has four functions including a two-color fluorescent localization microscopic function, a structured light lighting microscopic function, a function of fluorescent recovery after photobleaching and a bright field imaging function respectively. The appropriate method can be selected to perform high spatial resolution or high time resolution imaging on the sample in a bioexperiment according to the characteristics of the sample and the imaging requirements, and different modes of imaging can be performed on the same position of the same sample so that the problem of one-sidedness of the imaging result of the single microscopic method can be solved.
Owner:宁波力显智能科技有限公司
Super-resolution microscopic method and device based on fluorescence lifetime difference
InactiveCN103048299AIncrease limit resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageTime gating
The invention discloses a super-resolution microscopic method based on fluorescence lifetime difference. The super-resolution microscopic method comprises the following steps: (1) focusing an excitation beam and a suppressed beam by a large numerical aperture microscope objective and scanning a fluorescence sample is scanned simultaneously by taking circularly polarized light as the excitation beam and taking the circularly polarized light coded by vortex phase as the suppressed beam; (2) collecting fluorescence emitted by the fluorescence sample by utilizing the large numerical aperture microscope objective and obtaining a view picture of fluorescence intensity image by a photoelectric sensing device; (3) obtaining corresponding fluorescence lifetime information by analyzing the fluorescence intensity information of the fluorescence intensity image; (4) setting a time gate for separating a long-life fluorescence image and a short-life fluorescence image from the fluorescence intensity information; and (5) setting a weight and subtracting the weighted long-life fluorescence image from the short-life fluorescence image to obtain a final super-resolution microscopic image. The invention also discloses a super-resolution microscopic device based on the fluorescence lifetime difference.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Microscopic method based on wide field stimulated emission difference and microscopic device based on wide field stimulated emission difference
InactiveCN103852458ASimple structureEasy to operateMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic imageFluorescence
The invention discloses a microscopic method based on wide field stimulated emission difference. The method comprises the steps of firstly, carrying out wide field illumination and image formation on a sample, and then forming two beams of vertically polarized light (s light) and two parallel polarized light (p light) by utilizing laser and through two Wollaston prisms; carrying out illumination and image formation on the fluorescent sample by the interference light spot formed by line polarization focus of the four beams of light; carrying out differential treatment on the image obtained under the wide field and the image obtained under the interference light spot like a field emission display (FED), wherein the size of the dark spot is smaller than the diffraction limit, so that the image can be obtained in the dark spot by super-resolution; finally, controlling the interference light spot to move on the sample by a scanning galvanometer to obtain the whole microscopic image of the sample. The invention also discloses a microscopic device based on wide field stimulated emission difference; the device is simple in structure and convenient to operate, and rapid super-resolution microscopic imaging based on wide field stimulated emission difference can be realized, so that the device can be used for the field of optical microscopic imaging.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
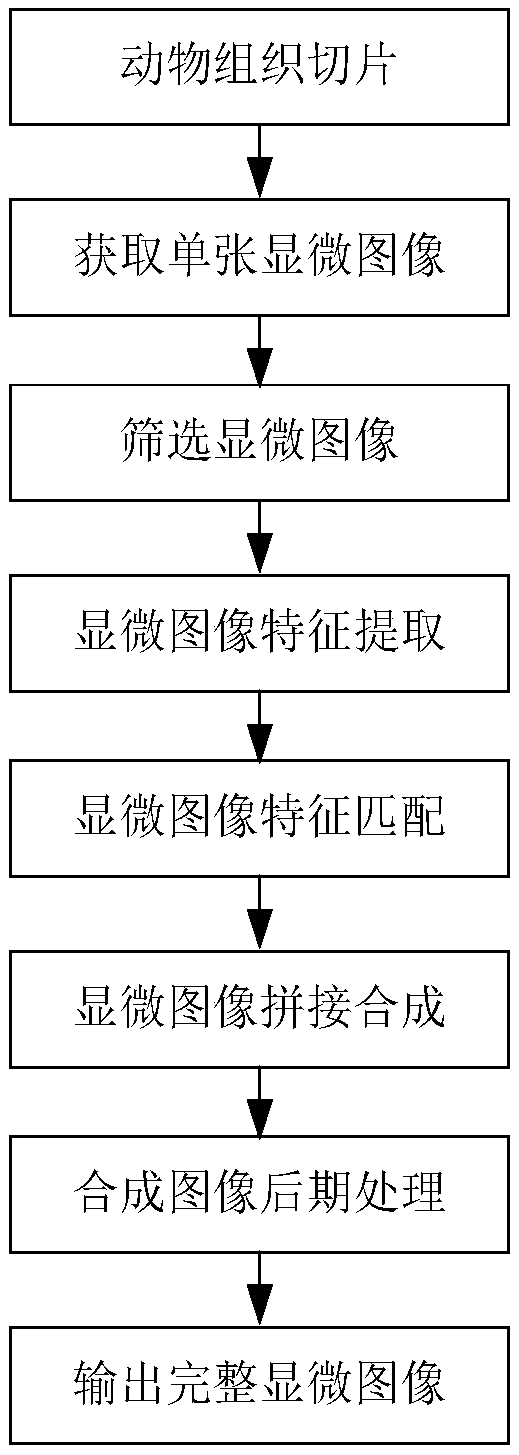
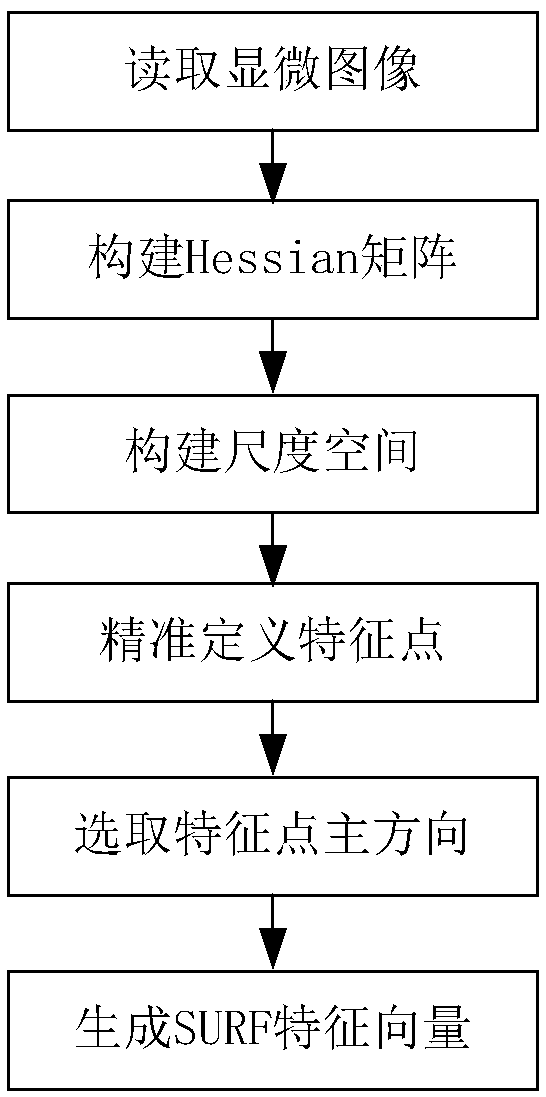
Plane splicing synthesis method of tissue slice microscopic images
InactiveCN108830788AEasy to observeMeet the requirements of 3D reconstructionImage enhancementImage analysisMicroscopic imageSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a plane splicing synthesis method of tissue slice microscopic images. The method comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining to-be-spliced microscopic images; (2) extracting features of the microscopic images; (3) matching the features of the microscopic images; (4) performing splicing synthesis on the microscopic images. The invention has the advantages of making up defects of a prior slice microscopic image synthesis method and achieving efficient and accurate plane splicing synthesis of animal tissue slice microscopic images.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Method of acquiring microscopic image with super field depth
InactiveCN103499879ALarge depth of fieldKeep it lightweightMicroscopesMicroscopic imageDepth of field
The invention provides a method of acquiring a microscopic image with super field depth. The method comprises the steps: adding a liquid lens with focal length controlled by voltage in a digital microscope light path, performing a series of focusing on the continuous depth range of an observed object by utilizing the liquid lens as a variable focal length element, shooting a series of continuous local focusing pictures, and fusing a super-field-depth clear image including focus information of all heights by utilizing an image fusion processing means. The position where the liquid lens is optimized so as to maintain the amplification factor unchanged in the focus variation process. According to the method, the problems that the traditional optical microscope is excessively small in field depth and objects in a certain depth range cannot be clearly imaged can be effectively solved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Contour microscopic method and device
InactiveCN102589466AIncrease horizontal resolutionSimple structureUsing optical meansImage resolutionPolarizer
The invention discloses a contour microscopic method and device. The device comprises a laser, a single-mode optical fiber, a first collimating lens, a first polarizer, a first polarization beam splitter, a 1 / 4 wave plate, a second lens, a third lens, a 1 / 2 wave plate, a second polarization beam splitter, a first detection optical fiber, a second detection optical fiber, a differential detector, a master computer, a nano translation table and a sample platform used for placing a sample to be detected. According to the invention, a contour image of an object is obtained by virtue of a transverse difference, and transverse resolution of a system is effectively improved. The contour microscopic device disclosed by the invention has a simple structure, the transverse resolution is obviously improved and can reach up to 200nm or below, and the contour microscopic device disclosed by the invention can be applied to the optical microscopy field and nano-scale high-accuracy detection, measurement and manufacturing fields.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Direct microscopic method body cell/ microbe automatic counting instrument sampling device for milk
InactiveCN101007998AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed uniformityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDirect microscopyRepeatability
The invention provides a sampling device of direct microscopy milk somatic cell / bacteria automatic counting apparatus. It comprisese upper lifting gearing, driving device for upper lifting gearing, one or more lower lifting gearing controlled by upper lifting gearing; said lower lifting gearing is connected with a sampling smearing head and is fixed on rotary supporting device, the position of said lower lifting gearing is relative to the position of upper lifting gearing, said sampling device is provided with driving device of rotary supporting device and driving device for upper lifting gearing and control gear of rotary supporting driving device. The invention employs simple construction to realize automatic sample and smear, fits cleaning device to realize automatic clean for sampling smear head, the work of all sampling smar head can be carried out at the same time with high efficiency; the sampling smear operation is automatically finished, the running parameter is convenient for moderation, control is accurate, repeatability is good, and the smear milk samling can be ensured accuracy, homogeneity and forming.
Owner:HANGZHOU ULTRASUN TECH
Multiple-scattering super-resolution microscopic method and apparatus under micro-nano illumination
ActiveCN105301753AFreedom of manipulationSave the trouble of coupling and connectingMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesMicro nanoMicroscopic image
The present invention discloses a multiple-scattering super-resolution microscopic method under micro-nano illumination including the steps as follows: 1) employing a micro-nano light source as a micro-nano structure sample having single spatial frequency so that the multiple scattering appears in the interior of the micro-nano structure sample; 2) performing light field imaging for the sample having single spatial frequency through a microscope, and performing spectral analysis for the imaging so as to obtain the frequency shift amount of the micro-nano light source; 3) replacing the structural sample having single spatial frequency with a structural sample having various single spatial frequencies, and establishing a frequency shift database of the micro-nano light source corresponding to various spatial frequencies; 4) observing the sample to be detected by utilizing the micro-nano light source, irradiating the sample to be detected within a 360-degree range, and performing imaging through the microscope during the irradiation process so as to obtain the corresponding frequency shift image. 5) performing frequency spectrum reduction and reconstruction for the frequency shift image according to the frequency shift database so as to obtain the super-resolution microscopic image of the sample to be detected. The present invention also discloses a multiple-scattering super-resolution microscopic apparatus under micro-nano illumination.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Qualitative detection method for EKS fibers
The invention relates to a qualitative detection method for EKS fibers, comprising the following steps orderly: (1) combustion detection, (2) microscope detection, (3) dissolution detection, (4) nitrogen-containing color reaction test, (5) chlorine-containing test, and (6) infrared spectroscopy detection. The method is an integrated method for detecting fibers. According to the invention, the microscope observation method, combustion method, infrared spectroscopy method, dissolution method and the like are used for integrated detection of fibers; the combustion method or microscopic method can be used for finding out a big class of the fibers at first, then other methods can be used for eliminating other fibers one by one, and finally the variety of the fibers can be determined. The detection method has the advantages of accuracy and rapidness, and can save test samples.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHONGTIAN TEXTILE TESTING
Envelope protein VP28 idiotype monoclonal antibody against shrimp white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101691403APrevention and Control of Shrimp WSSV DiseaseImmunoglobulins against virusesAntiviralsAntigenBinding site
The invention discloses an envelope protein VP28 idiotype monoclonal antibody against shrimp white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) and a preparation method thereof. The antibody is secreted by a hybridoma cells with the collection number of CCTCC-CT200938, is prepared by taking anti-WSSV-VP28 monoclonal antibody (Ab1) as antigen, can bind with anti-WSSV-VP28 antibody of hare, and has the capability of competing with WSSV to bind with the anti-WSSV-VP28 antibody of the hare. The anti-WSSV-VP28 idiotype monoclonal antibody (Ab3) prepared by taking the antibody as antigen can bind with the WSSV, the binding site of the anti-WSSV-VP28 idiotype monoclonal antibody (Ab3) and the WSSV is located on an envelope, and the Ab3 can neutralize WSSV infection and has Ab1 properties. In the invention, the idiotype antibody is applied in the research of WSSV for the first time; a screening system is established, which uses an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method and a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method for detection; the fact that Ab3 has properties of Ab1 is proved by adopting an indirect immnnofluotesent method (IIF), a gold labeling immunoelectron microscopic method and crayfish in vivo neutralization tests, thus proving that the monoclonal antibody in the invention has the property to simulate original antigen WSSV-VP28.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com