Super-resolution microscopic method and device based on fluorescence lifetime difference
A fluorescence lifetime and super-resolution technology, used in fluorescence/phosphorescence, material excitation analysis, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the system signal-to-noise ratio, adverse effects of the resolution ability, and reducing the fluorescence signal intensity, and achieve high system signal-to-noise ratio, structure, etc. Simple, small system changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0058] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments, but the present invention is not limited thereto.
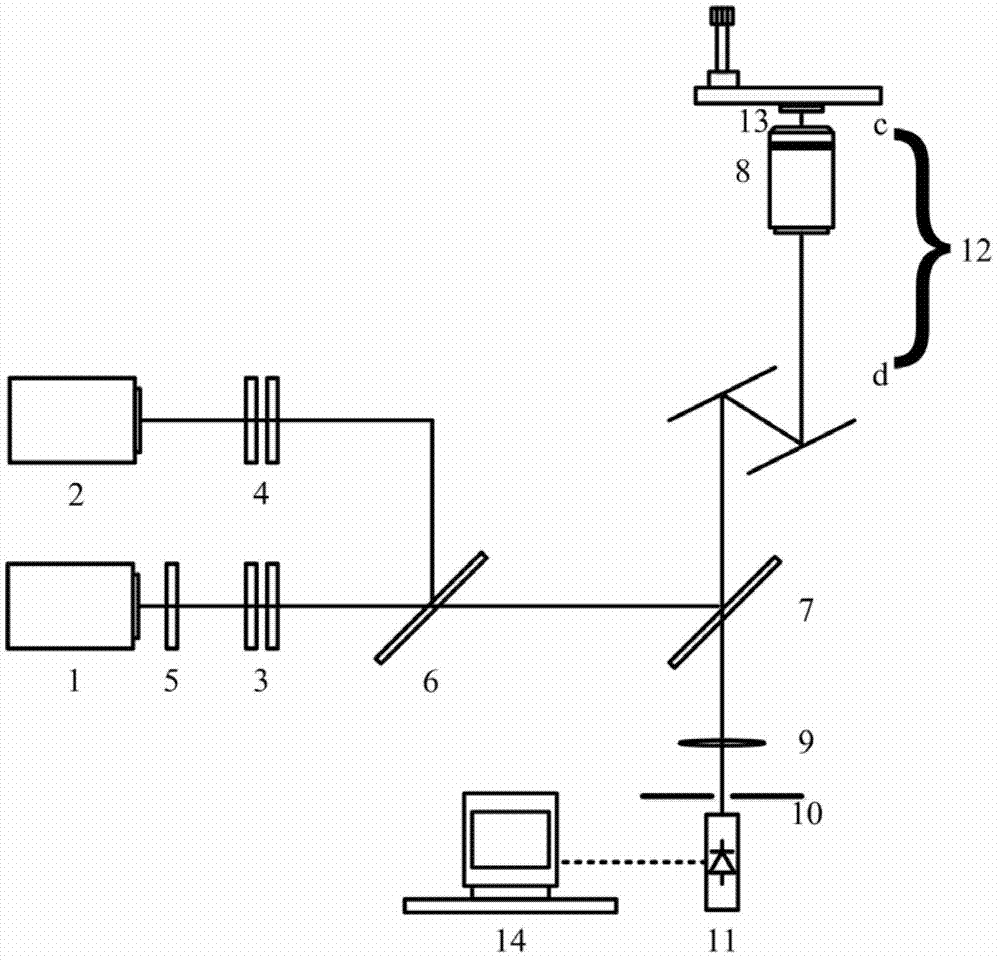
[0059] like figure 1 As shown, a super-resolution microscopy device based on fluorescence lifetime difference, including:
[0060] First laser 1, second laser 2, first polarization state converter 3, second polarization state converter 4, phase encoder 5, first dichroic mirror 6, second dichroic mirror 7, large numerical aperture microscope Objective lens 8, convex lens 9, pinhole 10, photoelectric sensor 11, scanner 12, fluorescent sample 13, computer 14. The pinhole 10 and the photoelectric sensing device 11 are in conjugate positions with the fluorescent sample 13 .
[0061] All the optical elements and fluorescent samples mentioned above include the first laser 1, the second laser 2, the first polarization state converter 3, the second polarization state converter 4, the phase encoder 2, the firs...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com