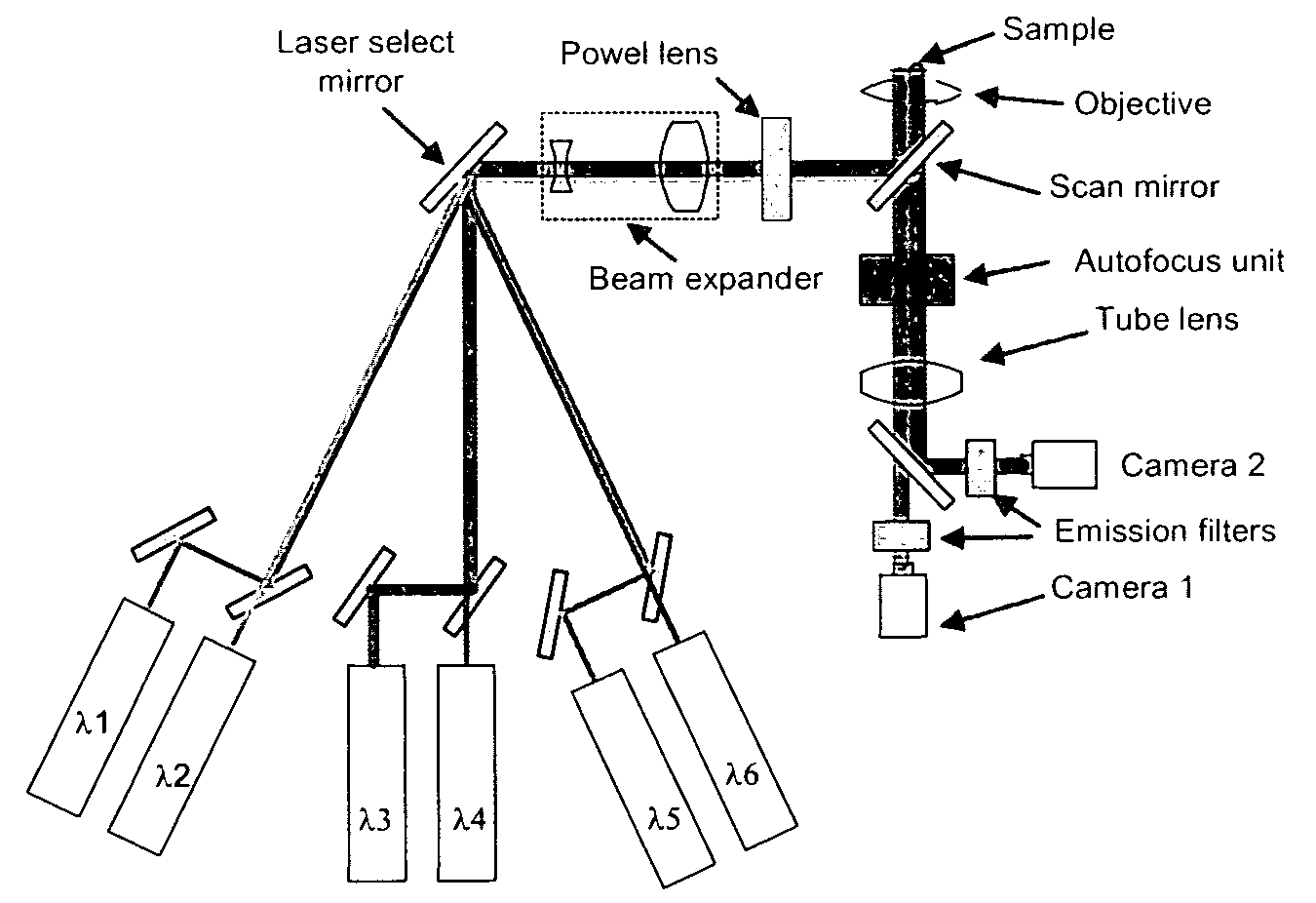
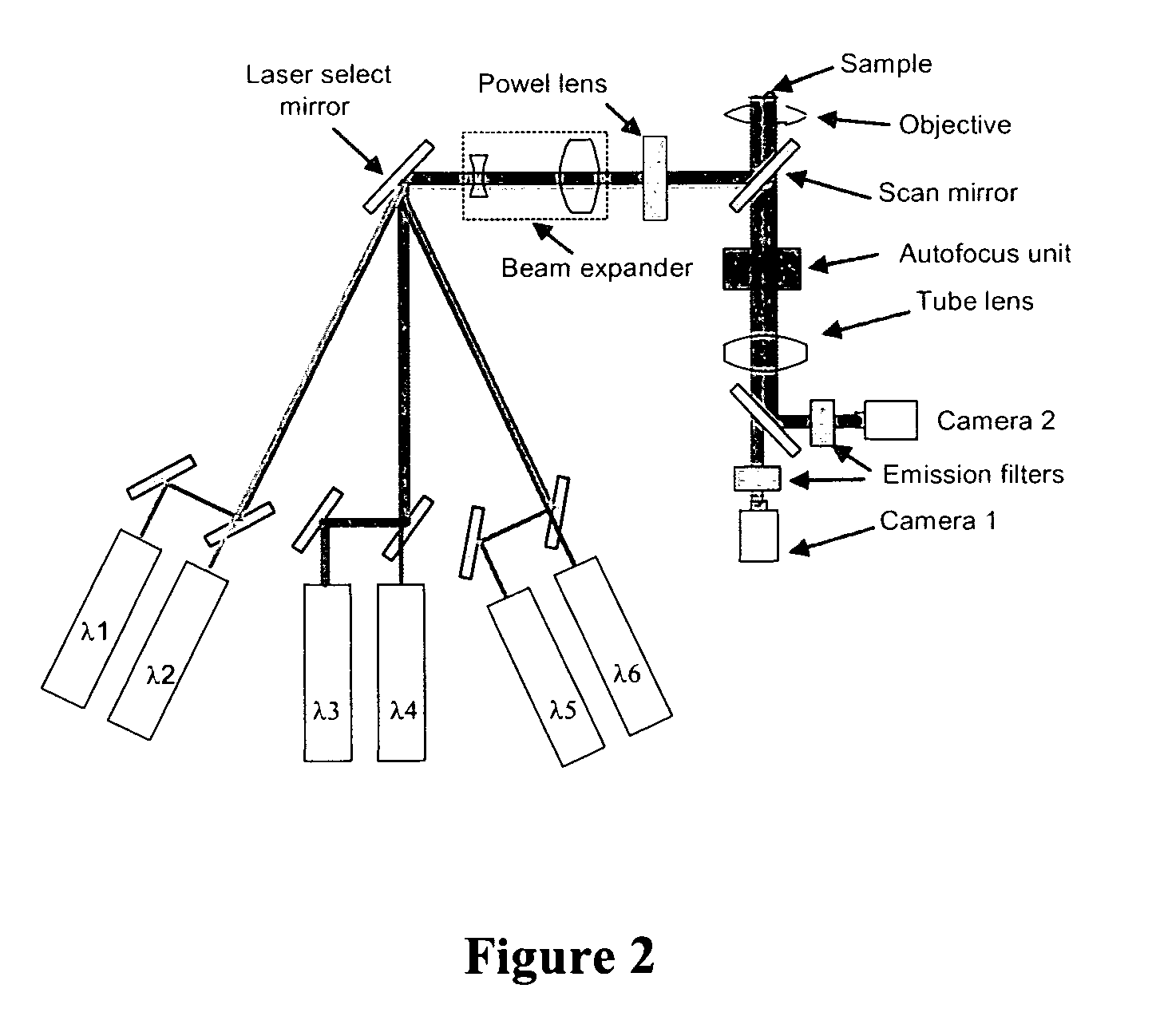
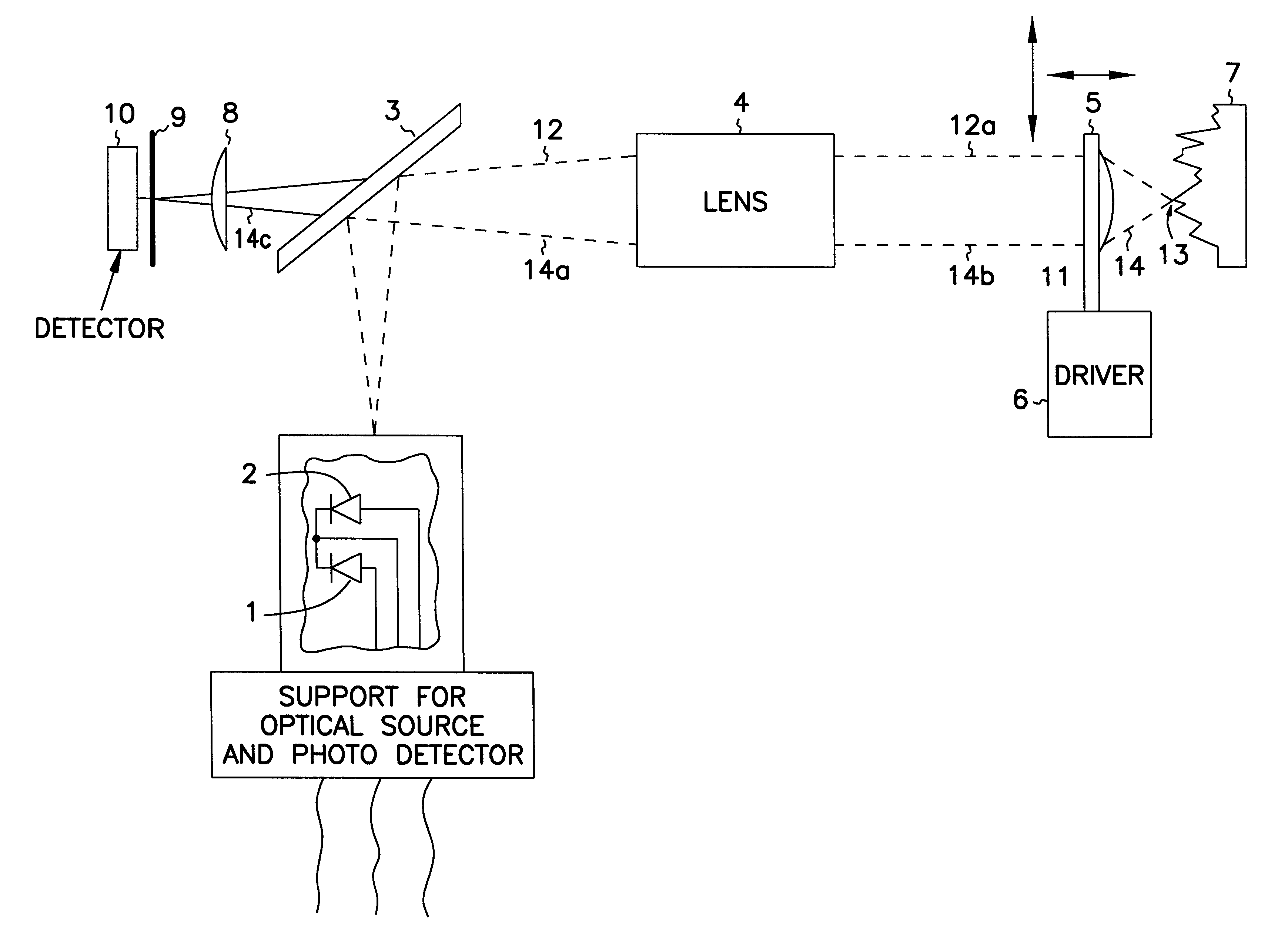
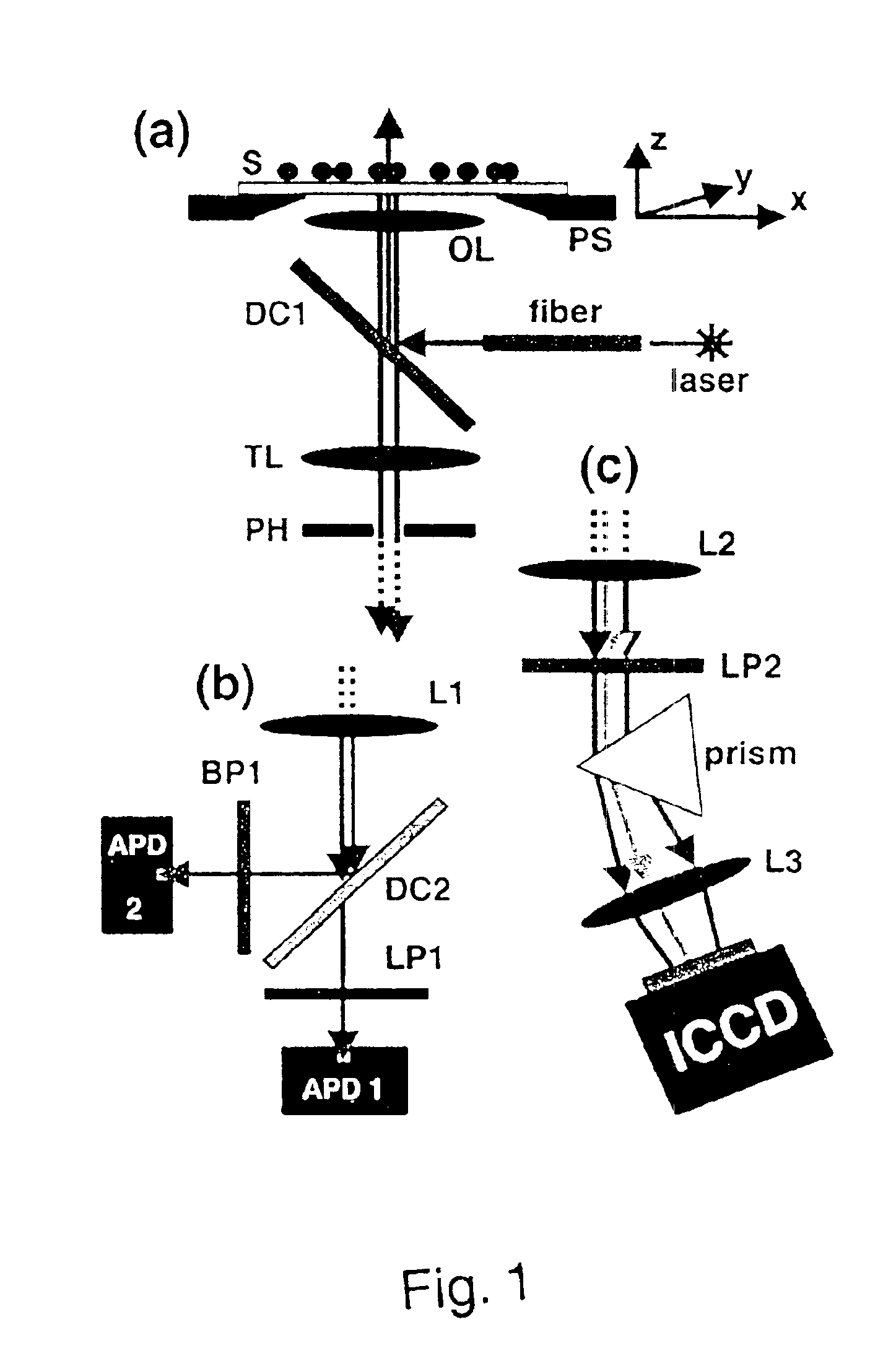
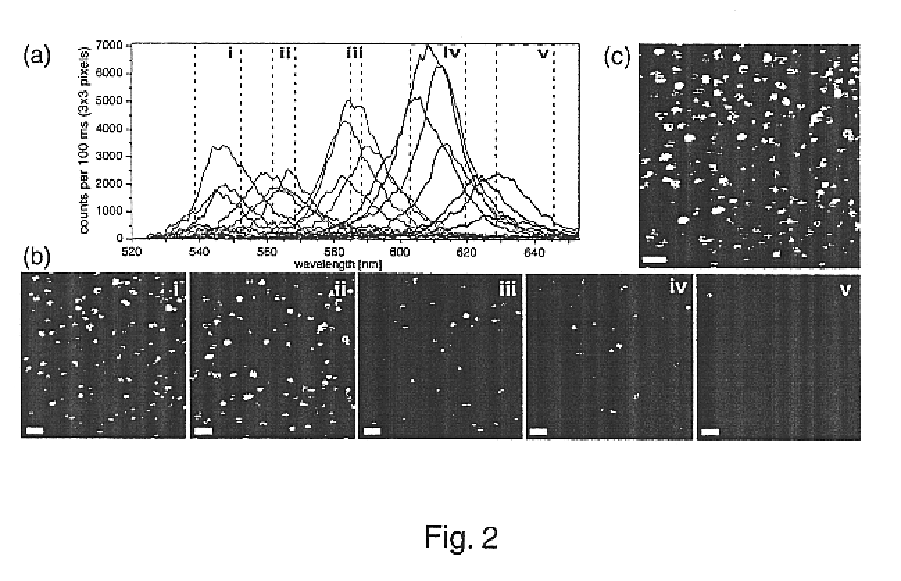
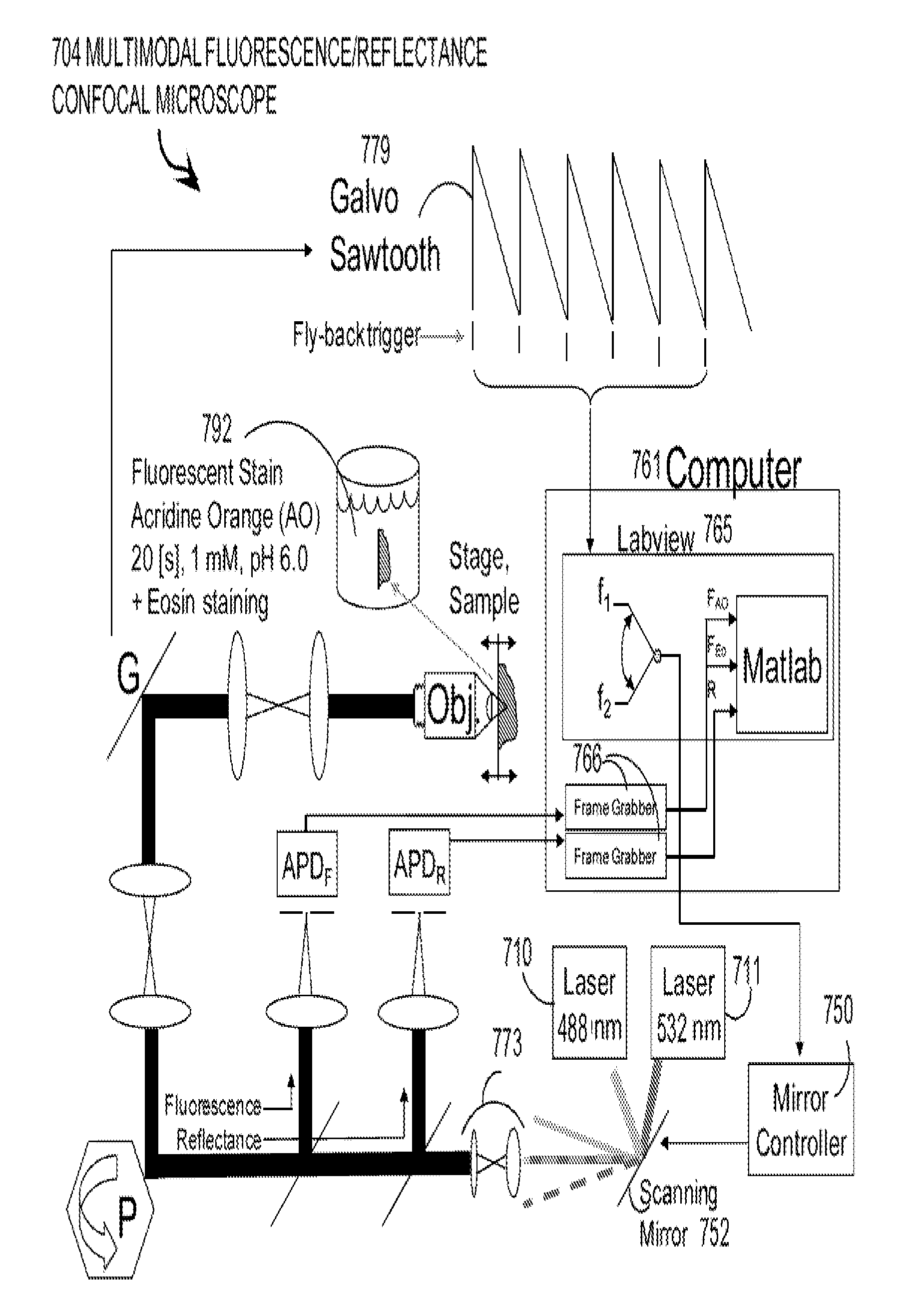
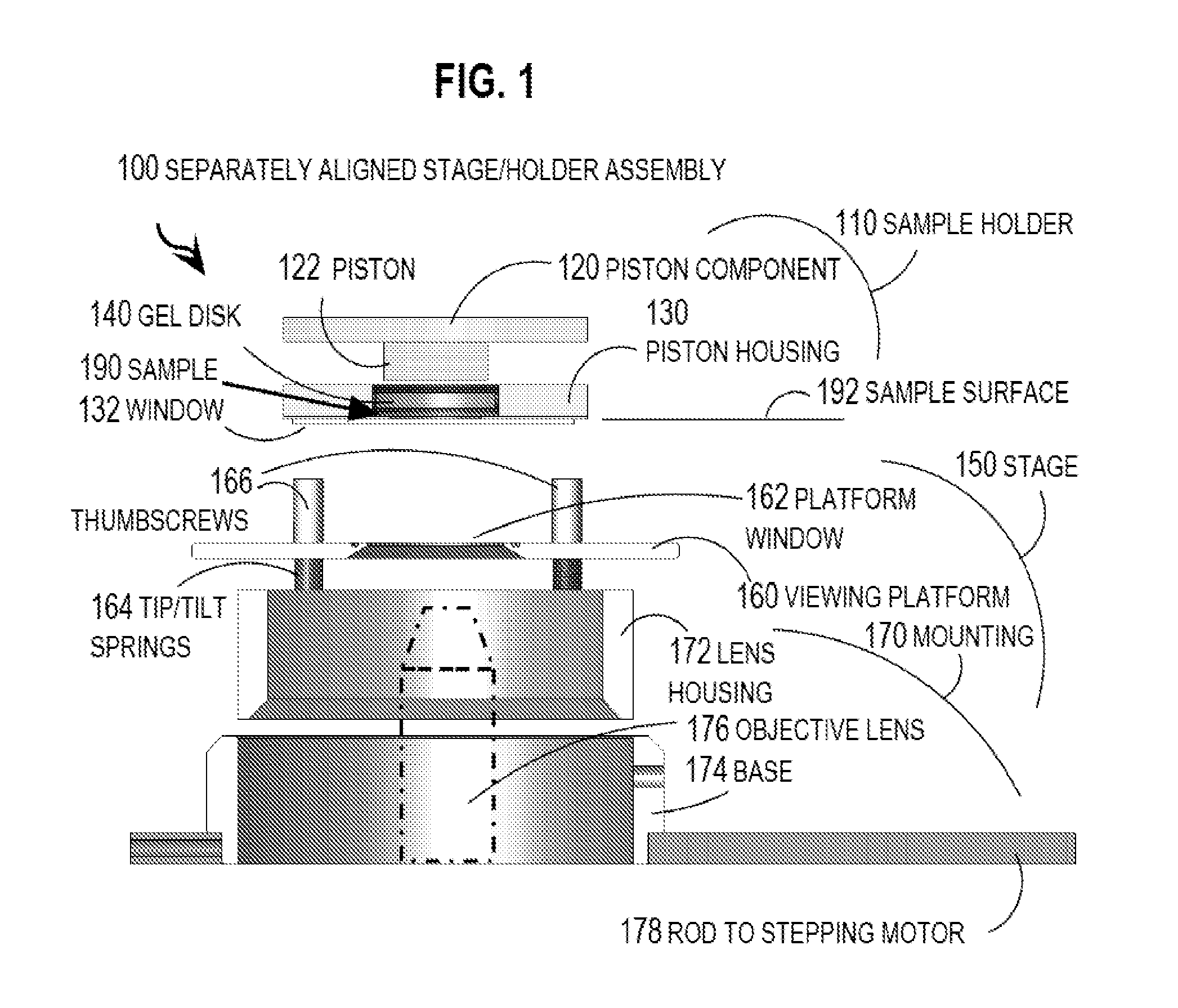
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
705 results about "Confocal microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
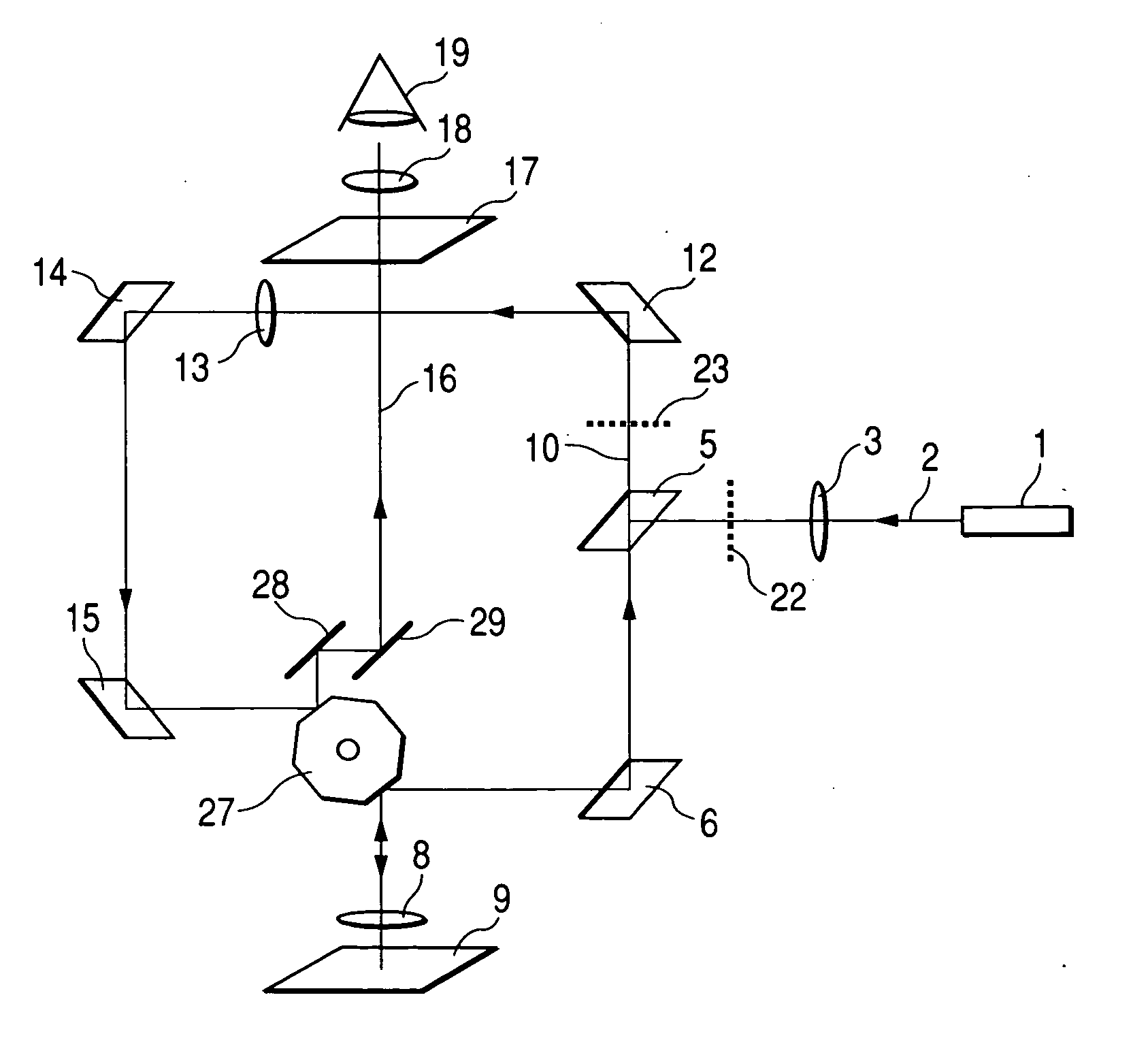
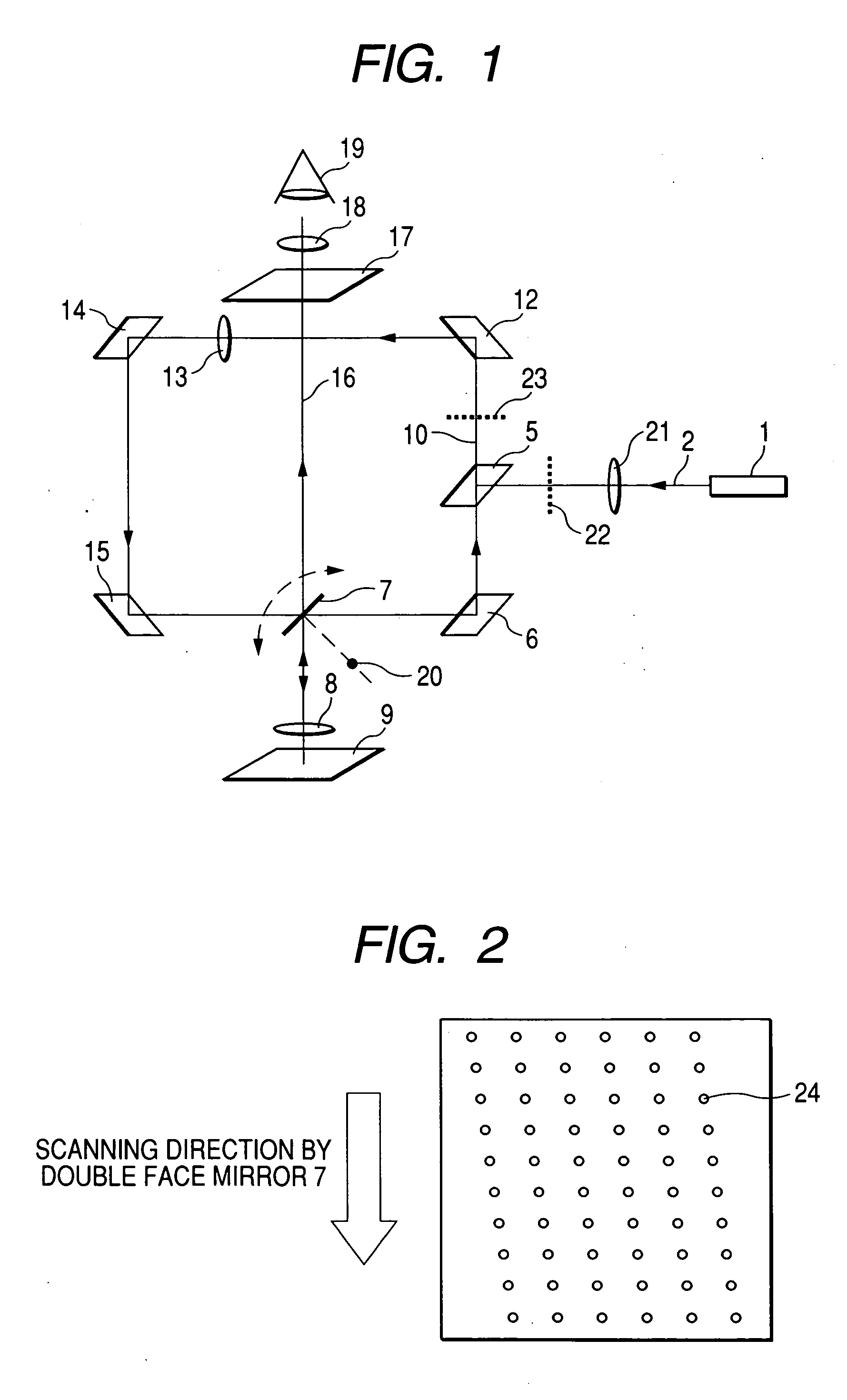
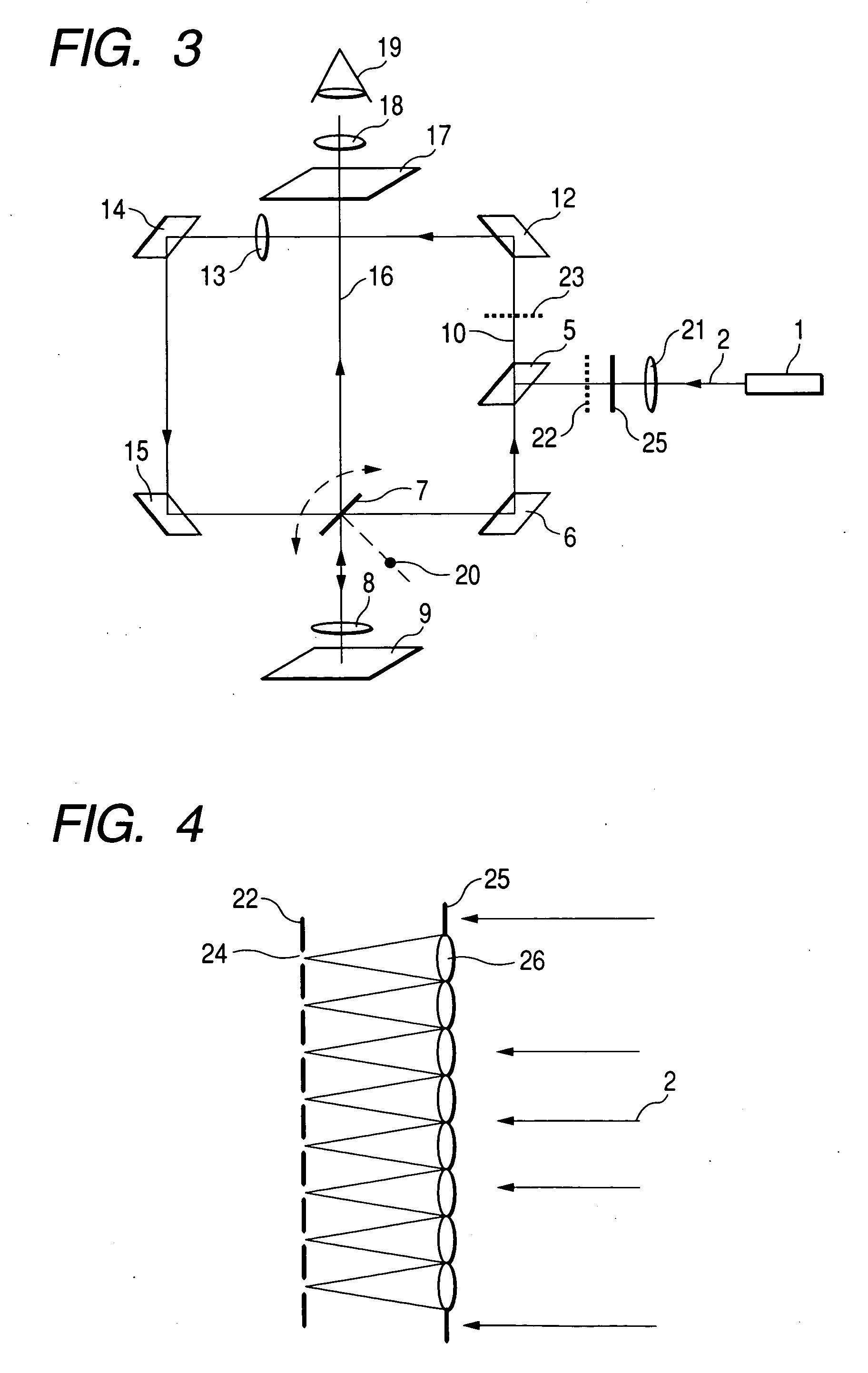
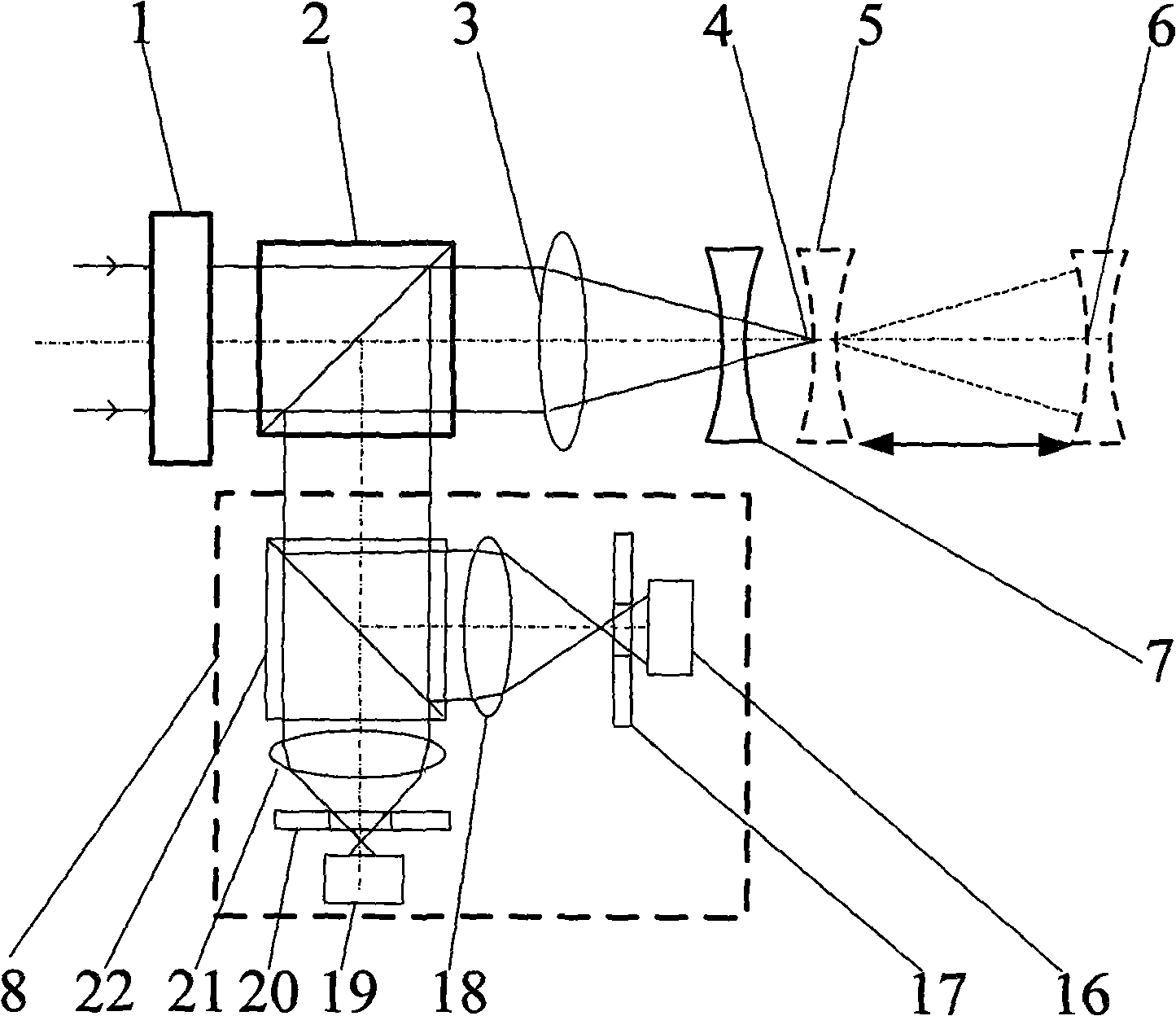
Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser confocal scanning microscopy (LCSM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out-of-focus light in image formation. Capturing multiple two-dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures (a process known as optical sectioning) within an object. This technique is used extensively in the scientific and industrial communities and typical applications are in life sciences, semiconductor inspection and materials science.
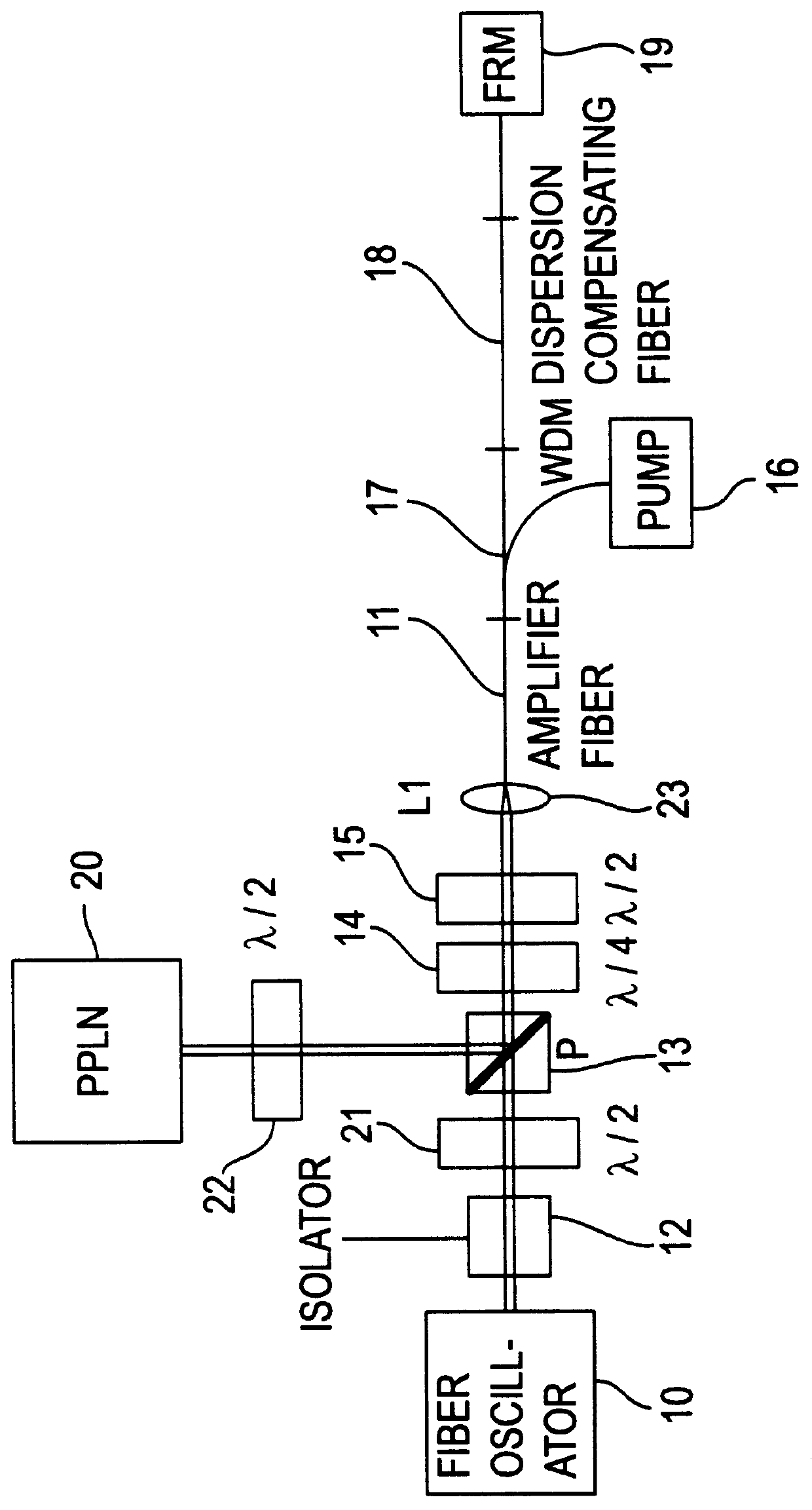
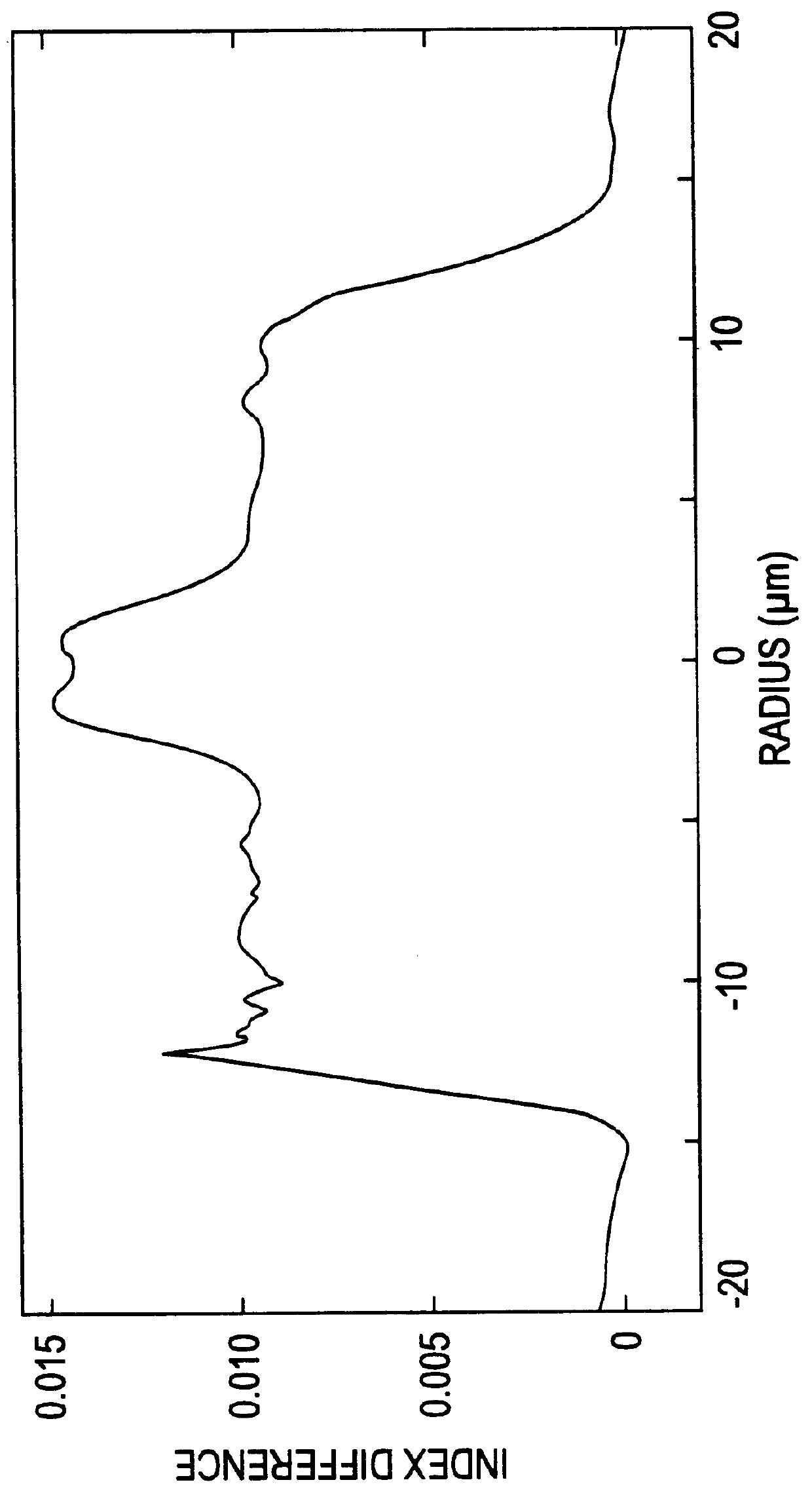
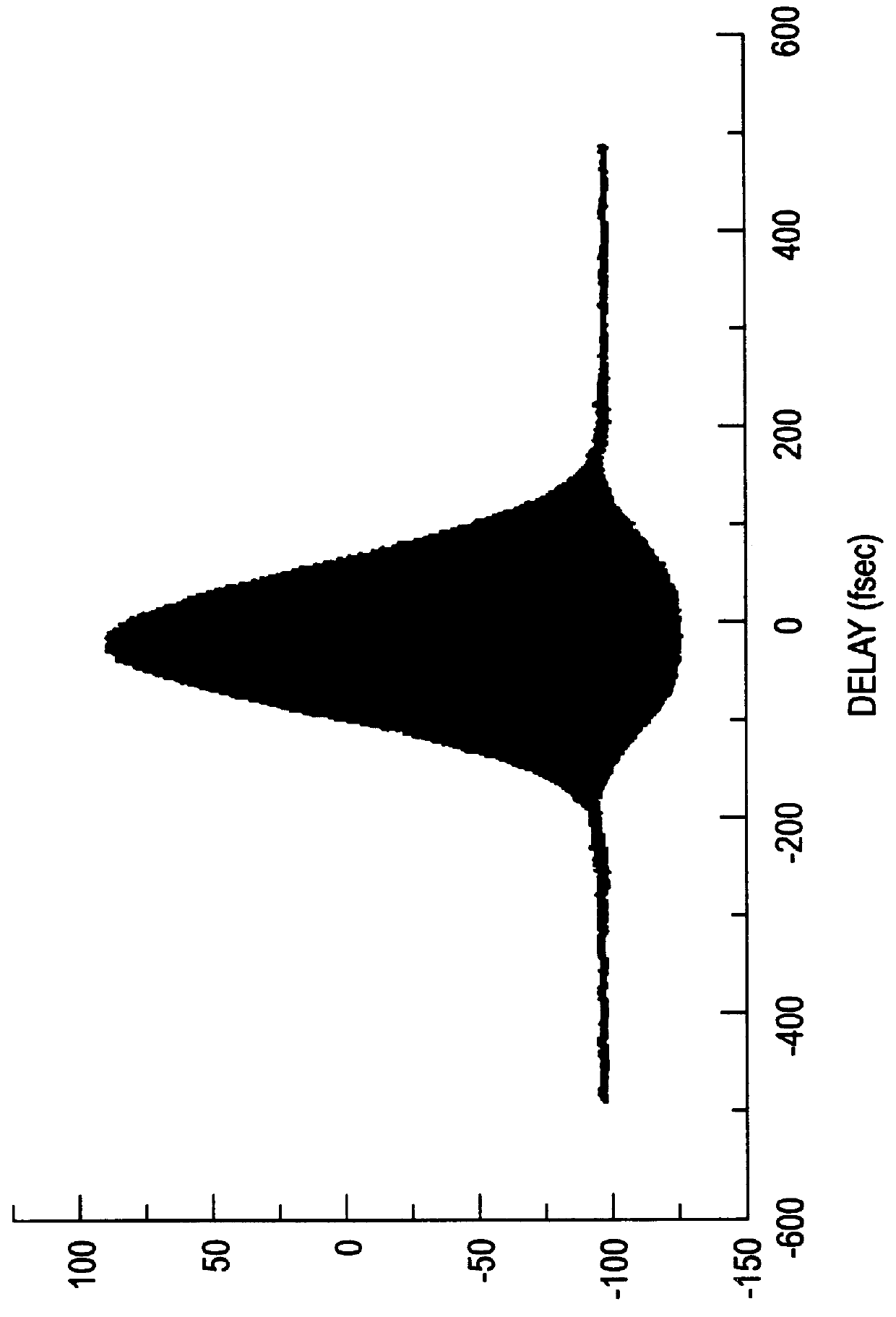
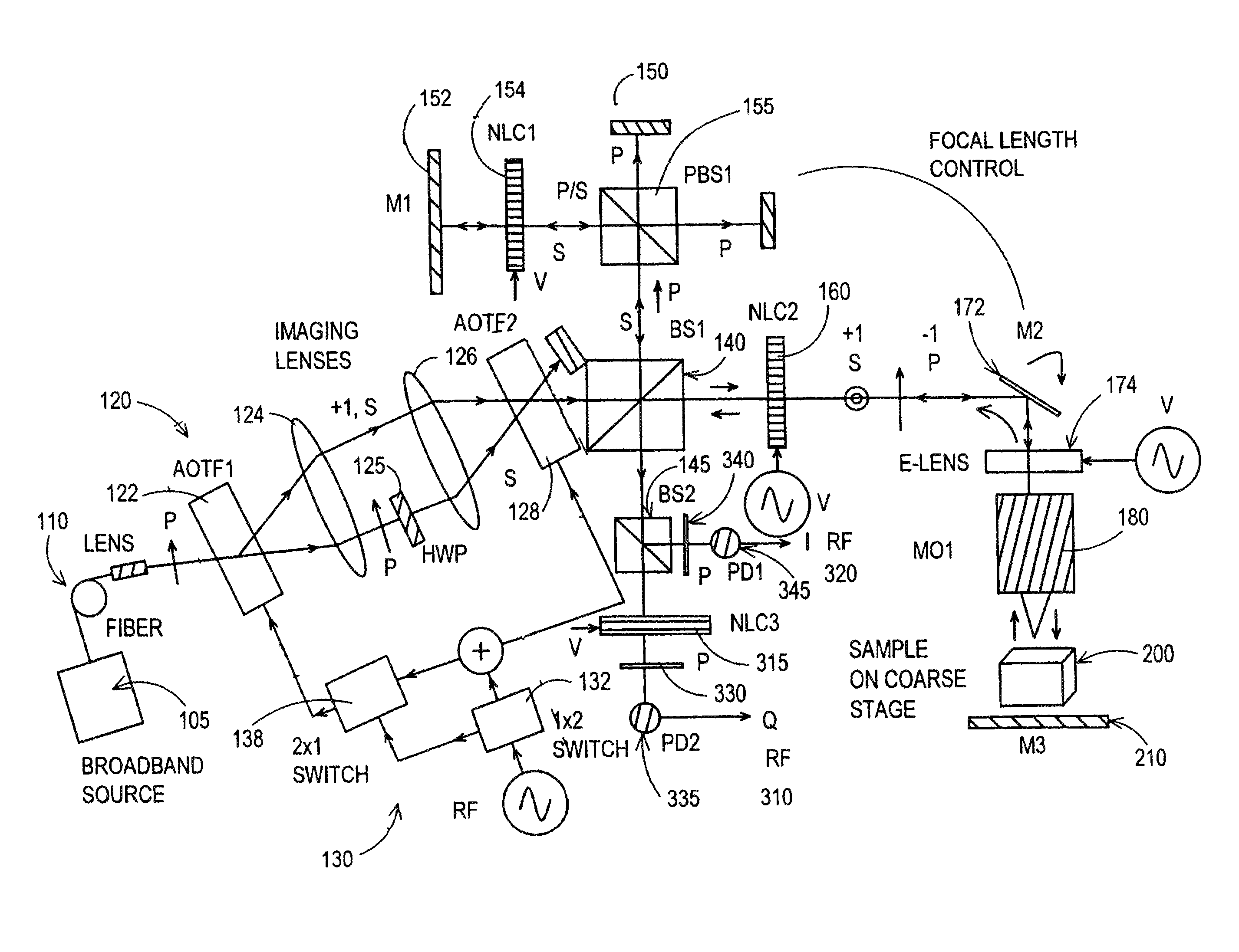
Apparatus and method for the generation of high-power femtosecond pulses from a fiber amplifier
InactiveUS6014249ALong pulse widthLow costLaser using scattering effectsLaser arrangementsFiberDouble-clad fiber
An apparatus generates femtosecond pulses from laser amplifiers by nonlinear frequency conversion. The implementation of nonlinear frequency-conversion allows the design of highly nonlinear amplifiers at a signal wavelength (SW), while still preserving a high-quality pulse at an approximately frequency-doubled wavelength (FDW). Nonlinear frequency-conversion also allows for limited wavelength tuning of the FDW. As an example, the output from a nonlinear fiber amplifier is frequency-converted. By controlling the polarization state in the nonlinear fiber amplifier and by operating in the soliton-supporting dispersion regime of the host glass, an efficient nonlinear pulse compression for the SW is obtained. The generated pulse width is optimized by utilizing soliton compression in the presence of the Raman-self-frequency shift in the nonlinear fiber amplifier at the SW. High-power pulses are obtained by employing fiber amplifiers with large core-diameters. The efficiency of the nonlinear fiber amplifier is optimized by using a double clad fiber (i.e., a fiber with a double-step refractive index profile) and by pumping light directly into the inner core of this fiber. Periodically poled LiNbO3 (PPLN) is used for efficient conversion of the SW to a FDW. The quality of the pulses at the FDW can further be improved by nonlinear frequency conversion of the compressed and Raman-shifted signal pulses at the SW. The use of Raman-shifting further increases the tuning range at the FDW. For applications in confocal microscopy, a special linear fiber amplifier is used.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Confocal self-interference microscopy from which side lobe has been removed
The present invention relates to confocal self-interference microscopy. The confocal self-interference microscopy further includes a first polarizer for polarizing reflected or fluorescent light from a specimen, a first birefringence wave plate for separating the light from the first polarizer into two beams along a polarizing direction, a second polarizer for polarizing the two beams from the first birefringence wave plate, a second birefringence wave plate for separating the two beams from the second polarizer into four beams along the polarizing direction, and a third polarizer for polarizing the four beams from the second birefringence wave plate, in the existing confocal microscopy. Optic-axes of the first and second birefringence wave plates exist on the same plane, optic-axes of the first and second birefringence wave plates are inclined from an optical axis of the entire optical system at a predetermined angle, and self-interference spatial periods of the first and second birefringence wave plates are different from each other.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Endoscopy device with removable tip
The present invention provides an endoscope for in vivo imaging the cells, tissue, organs or body cavities of humans or other animals to observe and locate, diagnosis and / or treat disease. Illumination sources, image detectors, sensors may be provided alone or in combination on the removable tip allowing functional alterations or optimization for a particular procedure. Endoscope features such as an instrument channel supporting tissue sampling, suction, treatment, micro-surgery, optical computed tomography, confocal microscopy, laser or drug treatments, injections, gene-therapy, marking, implanting or other medical techniques are maintained.
Owner:PERCEPTRONIX MEDICAL
Method and apparatus for fluorescent confocal microscopy
ActiveUS7335898B2Big advantageDrawback can be addressedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide fieldFluorescence microscope
A new and improved confocal fluorescence microscope is presented. The new microscope has significant advantages relative to existing implementations of microscope confocal imagers. In common with previous confocal imagers the instant invention has the advantages relative to conventional wide-field and confocal fluorescence imagers, however it addresses the drawbacks of confocal technology in terms of cost and complexity, and provides significant savings in both due to the simplicity of the components and the elimination of the need of, in particular, spatial filters such as pinholes or slits.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Scanning confocal microscope with objective lens position tracking
A calibration device which has at least two targets. Each target has at least one surface exhibiting areas of optical contrast, and each surface has a general plane of orientation. The targets are oriented such that a general plane of orientation of one target is inclined at an angle relative to the general plane of orientation of a surface of the second target which has areas of optical contrast.
Owner:KOVEX CORP
Methods, arrangements and systems for obtaining information associated with a sample using optical microscopy
ActiveUS20090323056A1Raman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryAcoustic waveConfocal microscopy
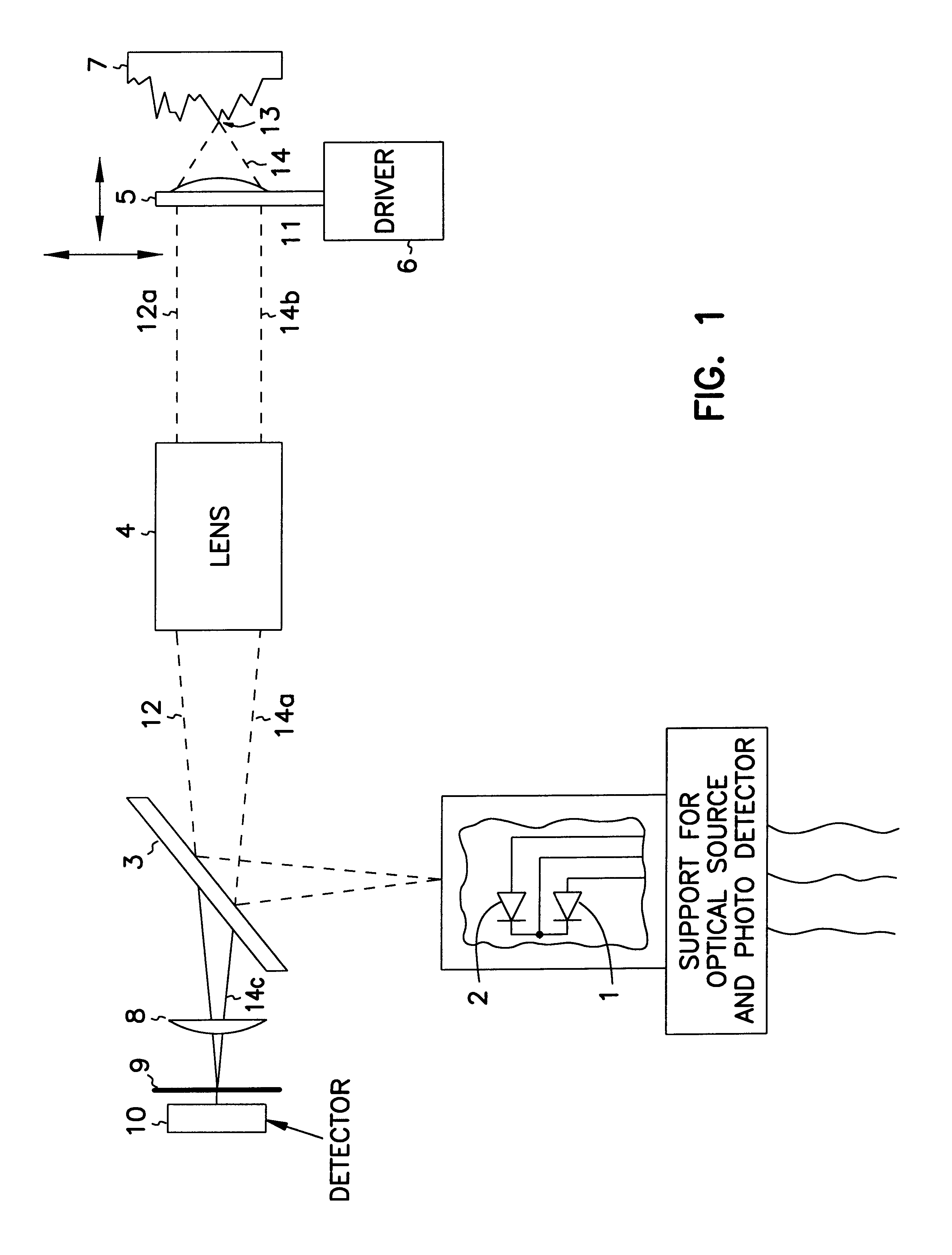
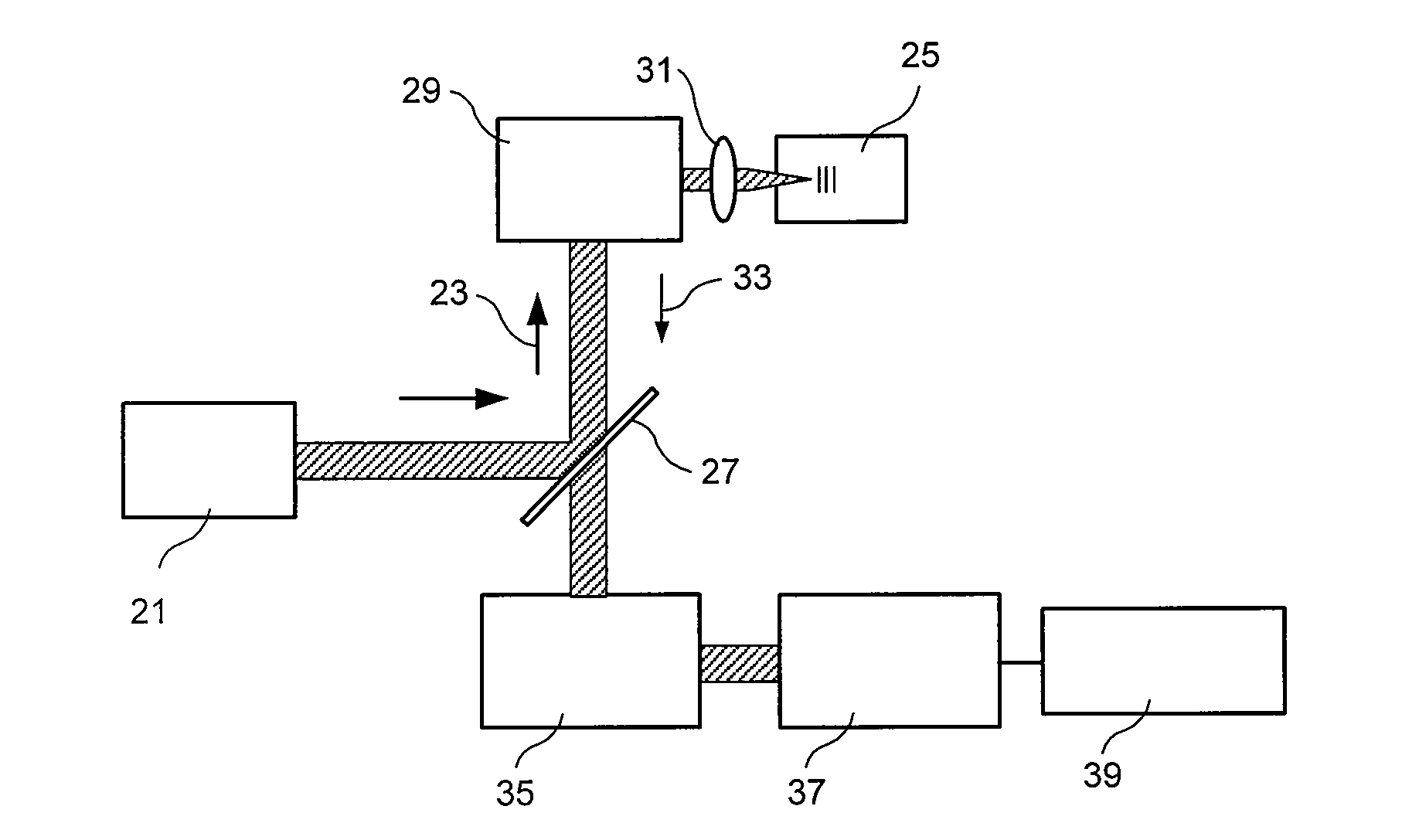
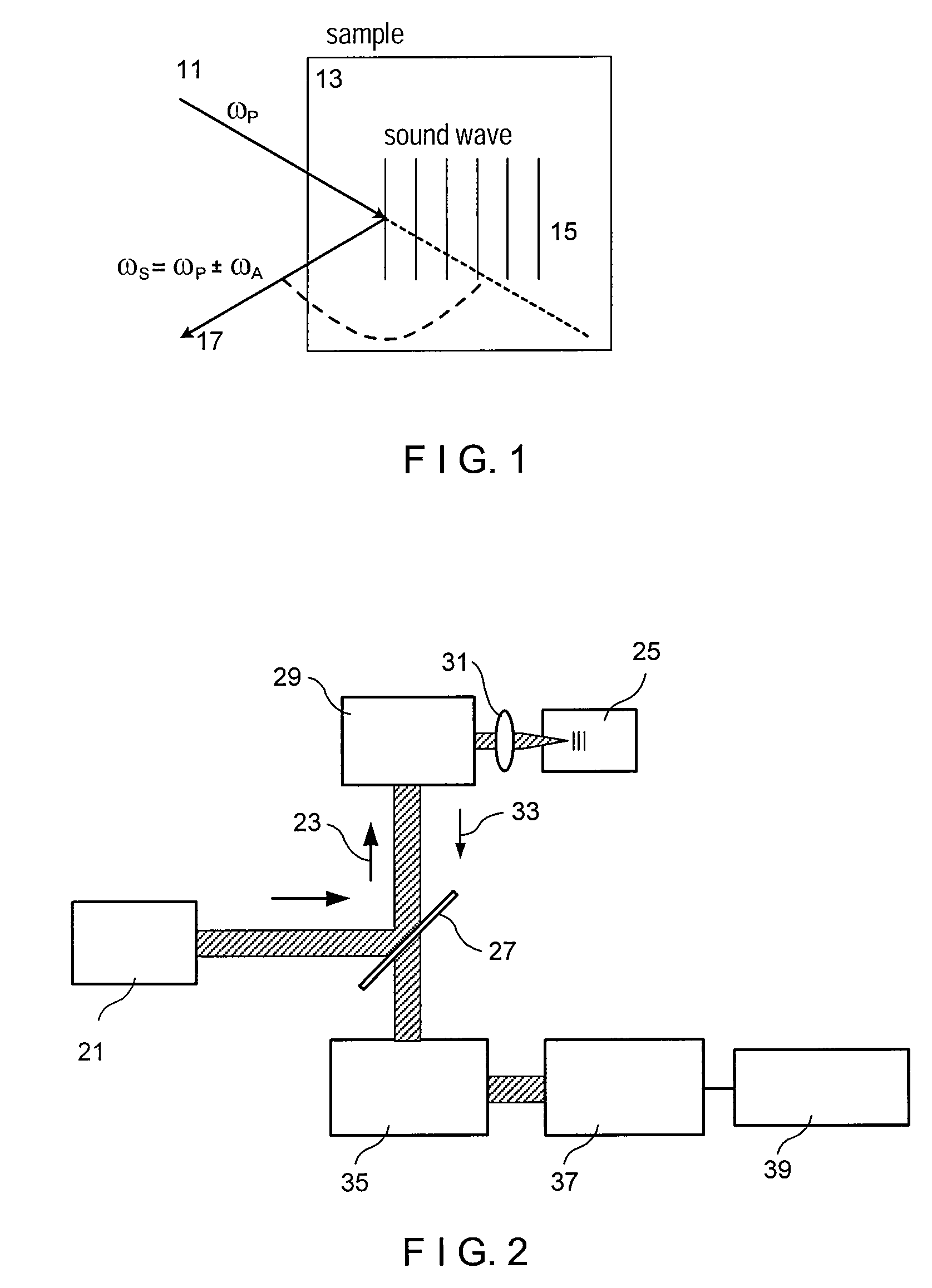
Exemplary embodiments of methods, arrangements and systems for obtaining information about a sample can be provided. For example, in one exemplary embodiment, it is possible to receive a first electro-magnetic radiation from a sample which is based on a second electro-magnetic radiation forwarded to the sample. The first electro-magnetic radiation may have a first frequency and the second electro-magnetic radiation may have a second frequency which is different from the first frequency. The difference between the first and second frequencies can be based on an acoustic wave inside the sample related to at least one characteristic of the sample. Further, it is possible to receive at least a portion of the first electromagnetic radiation and separate it into a particular finite number (N) of frequency component radiations. In addition, it is possible to receive a particular energy of more than 1 / N of energy of the third electro-magnetic radiation, and generate information associated with the sample. Certain exemplary embodiments of the present invention are capable of obtaining information associated with a sample, particularly its mechanical properties, non-contact using electromagnetic radiation.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Confocal microscope
InactiveUS7339148B2Increase speedHigh image resolutionRadiation pyrometryOptical rangefindersCamera lensLight beam
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Method and apparatus for fluorescent confocal microscopy
ActiveUS20060017001A1Big advantageDrawback can be addressedPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersWide fieldFluorescence microscope
A new and improved confocal fluorescence microscope is presented. The new microscope has significant advantages relative to existing implementations of microscope confocal imagers. In common with previous confocal imagers the instant invention has the advantages relative to conventional wide-field and confocal fluorescence imagers, however it addresses the drawbacks of confocal technology in terms of cost and complexity, and provides significant savings in both due to the simplicity of the components and the elimination of the need of, in particular, spatial filters such as pinholes or slits.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Four-dimensional imaging of periodically moving objects via post-acquisition synchronization of nongated slice-sequences
InactiveUS20050259864A1Fast executionMicroscopic object acquisitionLeast squares minimizationOrganism
When the studied motion is periodic, such as for a beating heart, it is possible to acquire successive sets of two dimensional plus time data slice-sequences at increasing depths over at least one time period which are later rearranged to recover a three dimensional time sequence. Since gating signals are either unavailable or cumbersome to acquire in microscopic organisms, the invention is a method for reconstructing volumes based solely on the information contained in the image sequences. The central part of the algorithm is a least-squares minimization of an objective criterion that depends on the similarity between the data from neighboring depths. Owing to a wavelet-based multiresolution approach, the method is robust to common confocal microscopy artifacts. The method is validated on both simulated data and in-vivo measurements
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
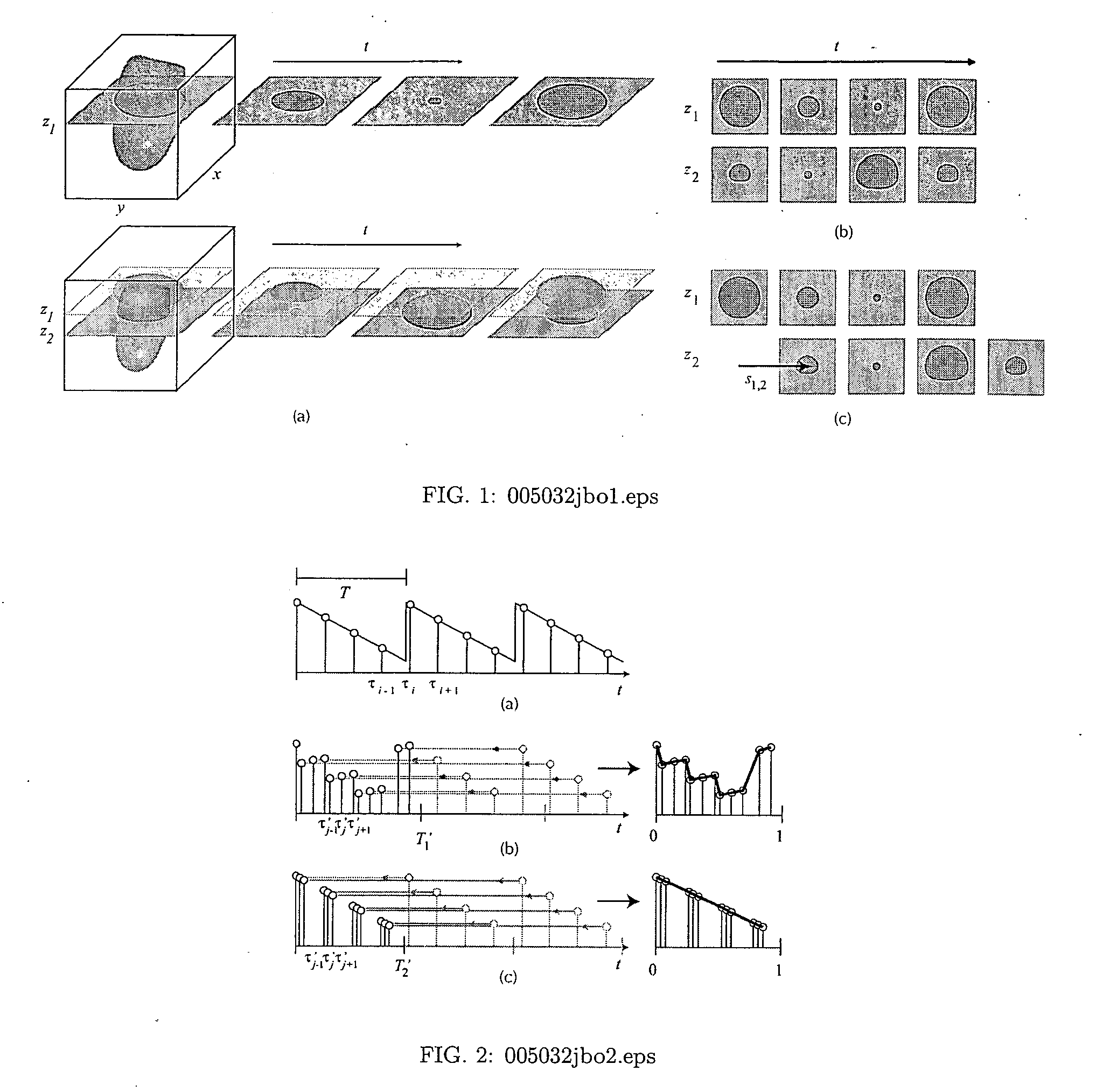
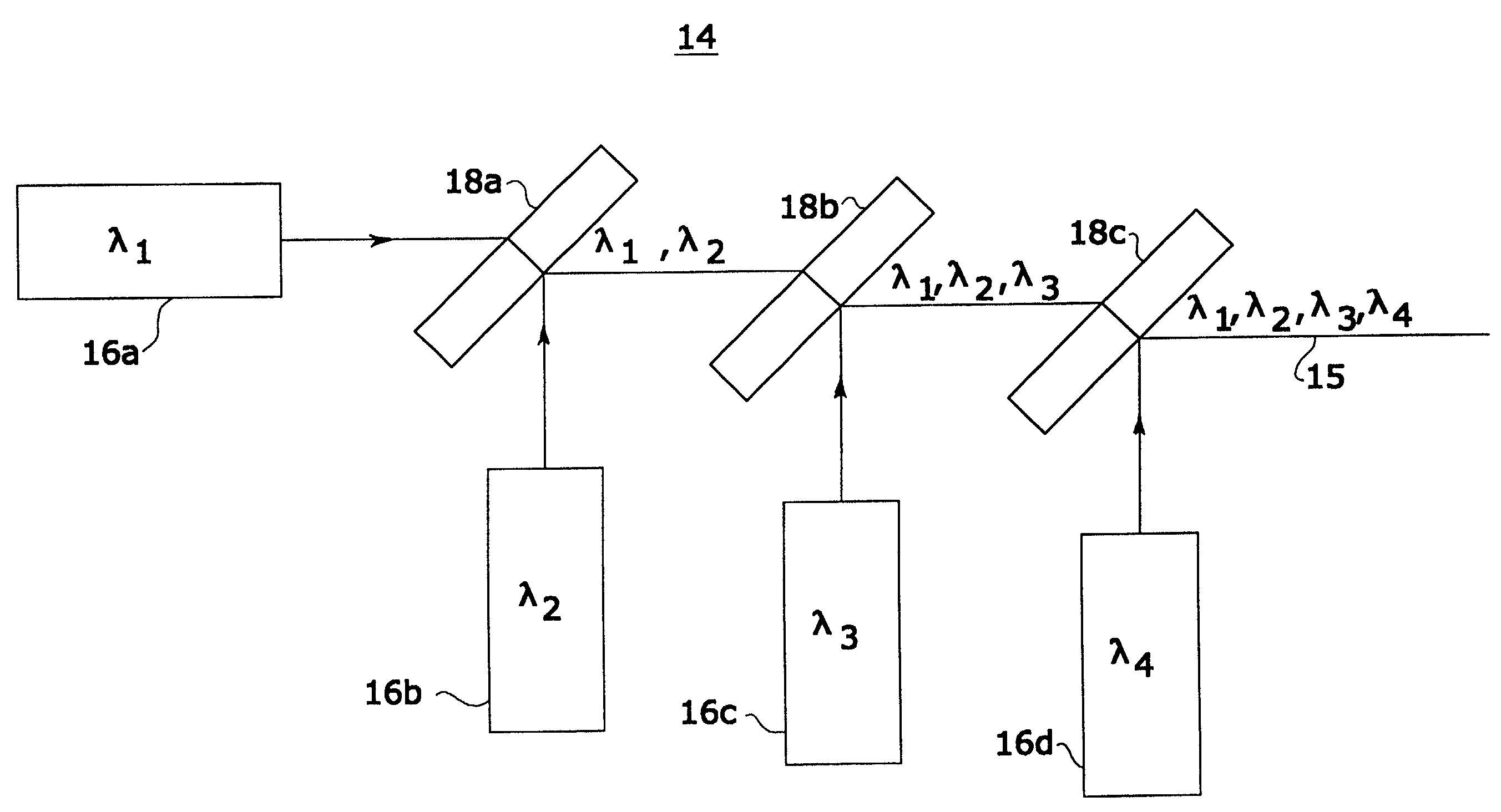
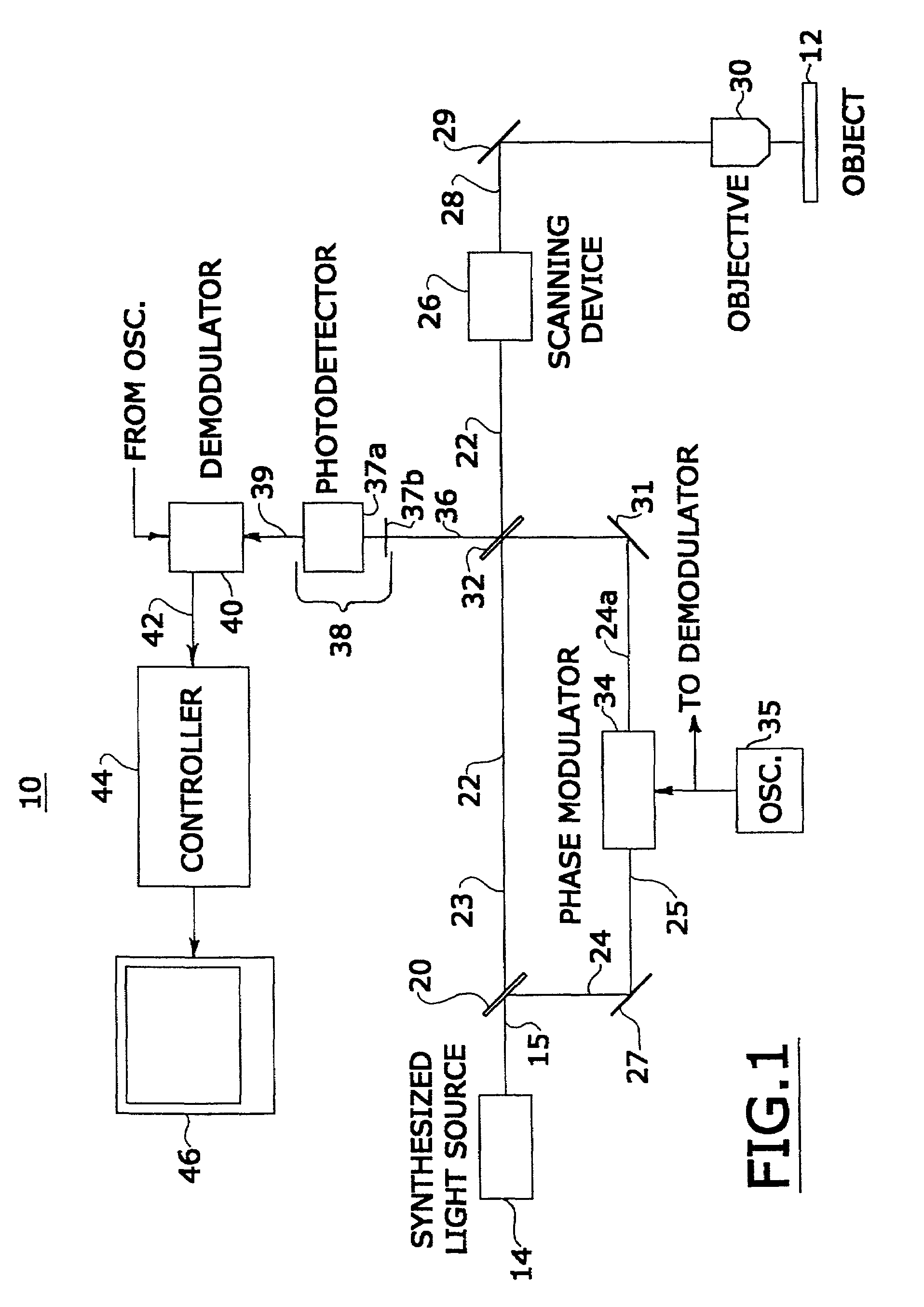
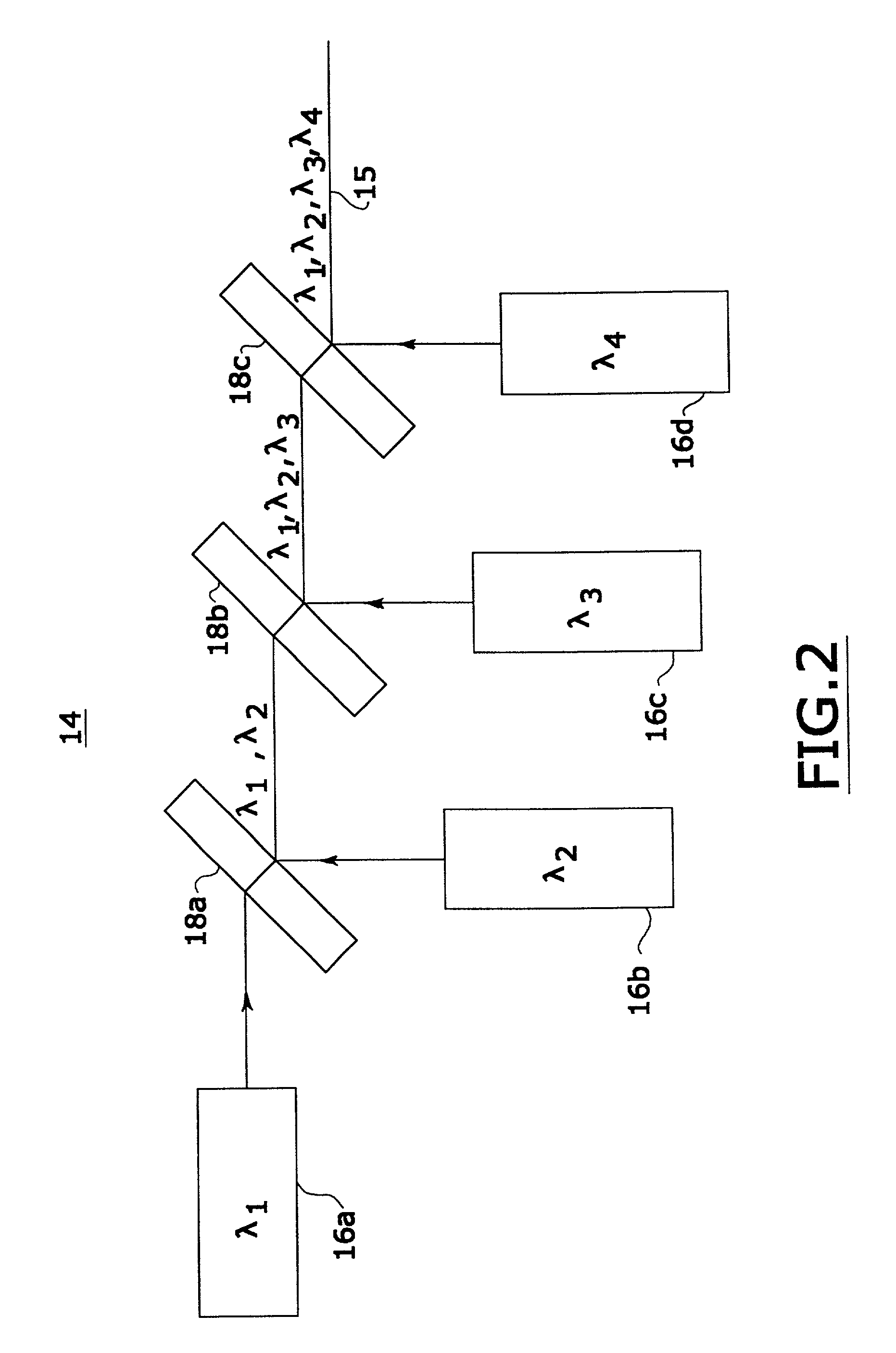
Confocal microscopy
InactiveUS7333213B2Improves confocal microscopyMicroscopesUsing optical meansPhotodetectorDisplay device
An improved confocal microscope system is provided which images sections of tissue utilizing heterodyne detection. The system has a synthesized light source for producing a single beam of light of multiple, different wavelengths using multiple laser sources. The beam from the synthesized light source is split into an imaging beam and a reference beam. The phase of the reference beam is then modulated, while confocal optics scan and focus the imaging beam below the surface of the tissue and collect from the tissue returned light of the imaging beam. The returned light of the imaging beam and the modulated reference beam are combined into a return beam, such that they spatially overlap and interact to produce heterodyne components. The return beam is detected by a photodetector which converts the amplitude of the return beam into electrical signals in accordance with the heterodyne components. The signals are demodulated and processed to produce an image of the tissue section on a display. The system enables the numerical aperture of the confocal optics to be reduced without degrading the performance of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
High speed piezoelectric optical system with tunable focal length
ActiveUS7369723B1Curvature can be modifiedAltering focal length of lensCoupling light guidesLensOptical storageLens plate
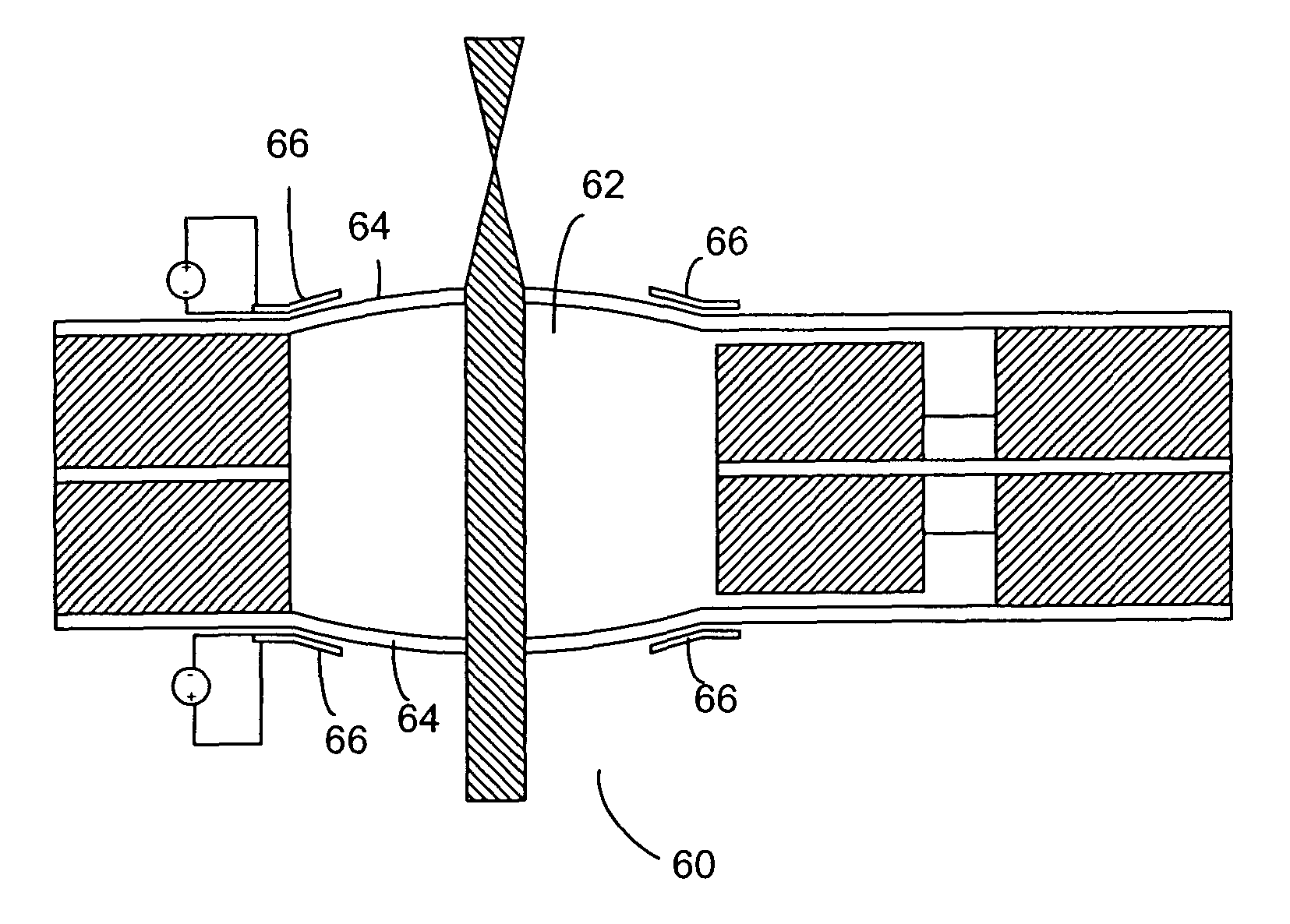
A varifocal optical system includes a substantially circular membrane deposited on a substrate, and a ring-shaped PZT thin film deposited on the outer portion of the circular membrane. The membrane may be a MEMS-micromachined membrane, made of thermal oxide, polysilicon, ZrO2 and SiO2. The membrane is initially in a buckled state, and may function as a mirror or a lens. Application of an electric voltage between an inner and outer electrode on the piezoelectric thin film induces a lateral strain on the PZT thin film, thereby altering the curvature of the membrane, and thus its focal length. Focal length tuning speeds as high as 1 MHz have been demonstrated. Tuning ranges of several hundred microns have been attained. The varifocal optical system can be used in many applications that require rapid focal length tuning, such as optical switching, scanning confocal microscopy, and vibration compensation in optical storage disks.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
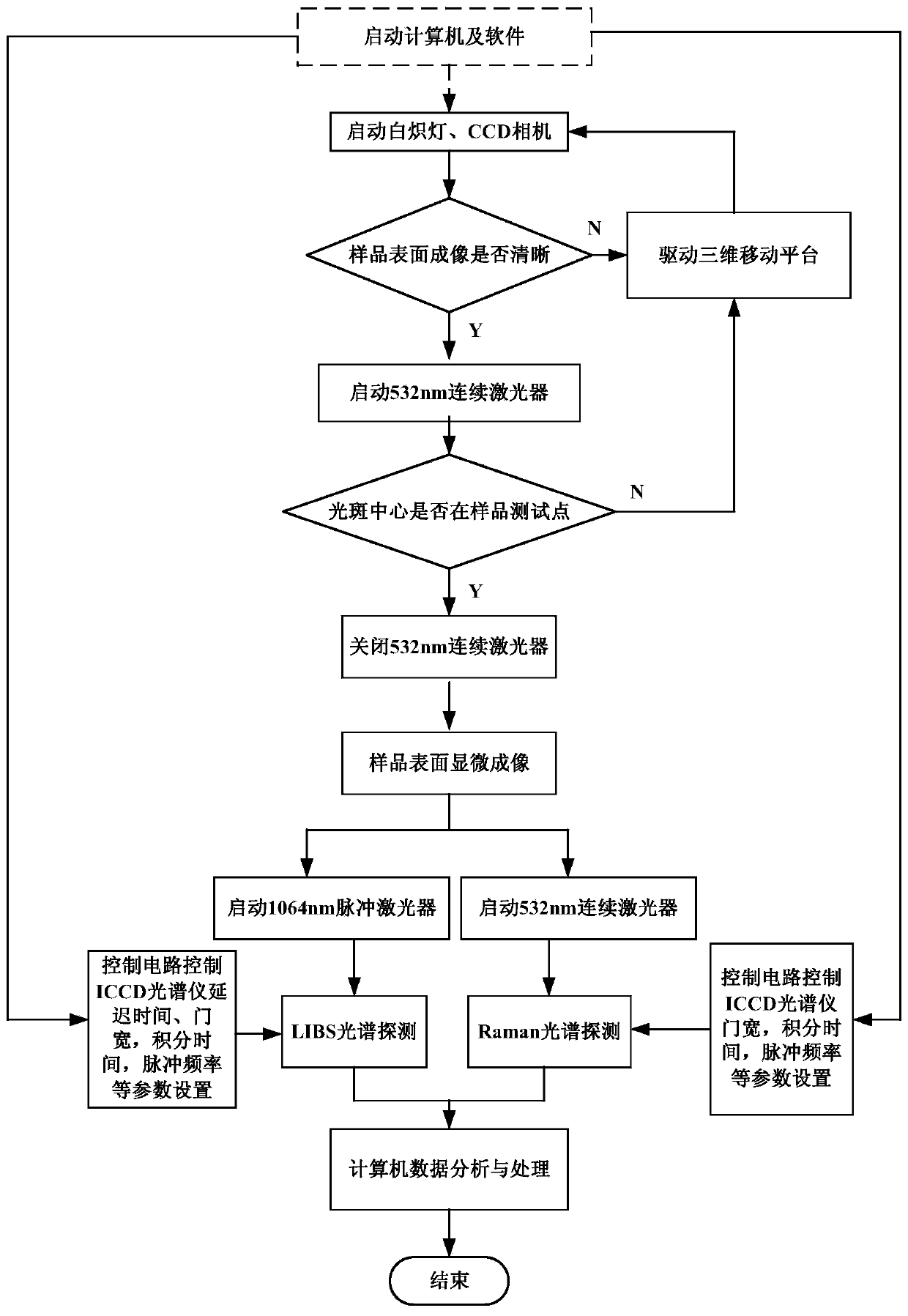
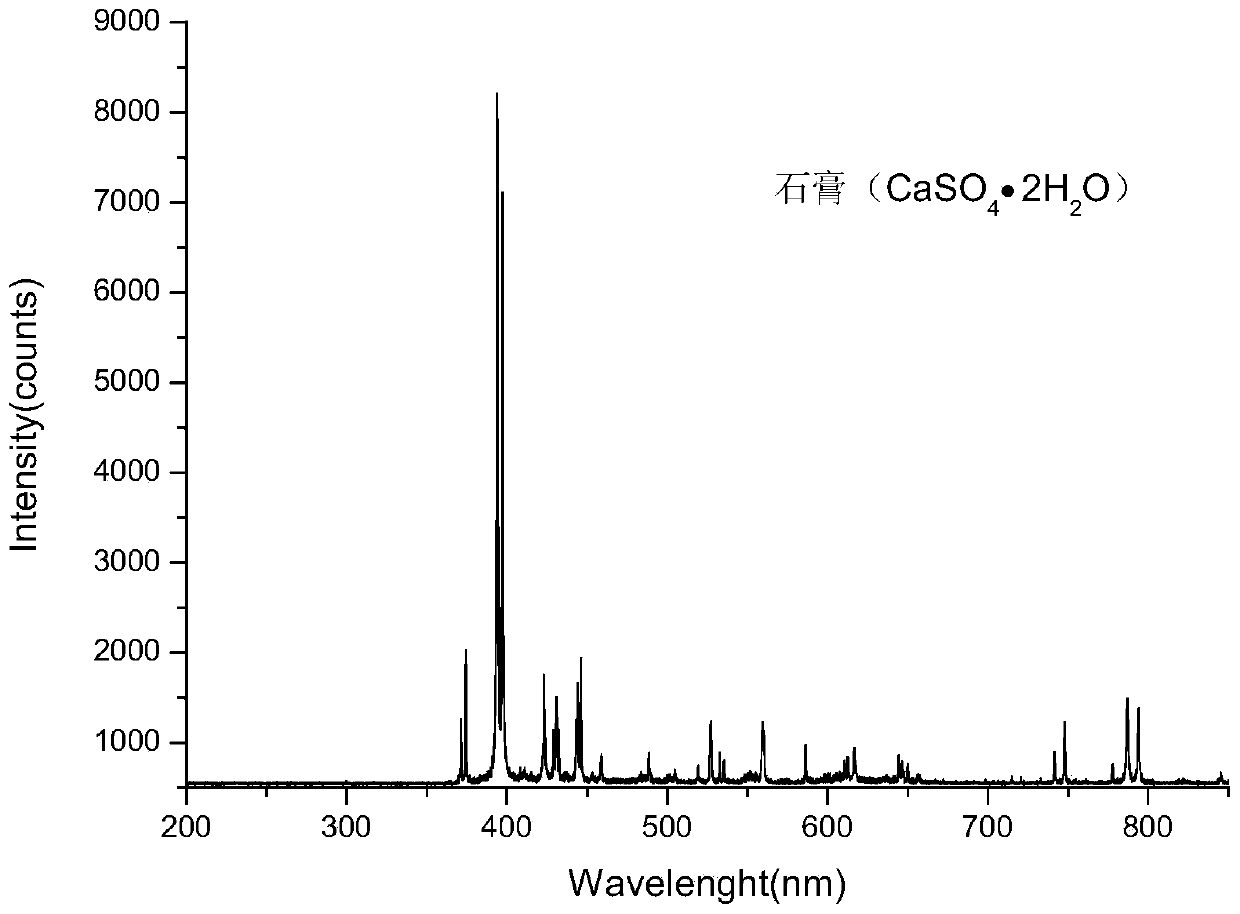
Laser spectrum analyzer combining confocal micro-Raman spectrometer with laser-induced breakdown spectrometer
ActiveCN103743718AAchieve qualitativeRealize quantitative analysisRaman scatteringMicro imagingHigh resolution imaging
The invention provides a laser spectrum analyzer combining a confocal micro-Raman spectrometer with a laser-induced breakdown spectrometer (LIBS). The analyzer comprises a micro-Raman system, a micro LIBS system, a high resolution micro-imaging system, a confocal micro-light path, and a spectrum receiving system with a time resolution function, and automatically switches into a white light micro-imaging observation mode, an automatic focusing mode, a LIBS spectrum working mode, and a Raman spectrum working mode. The significant characteristics of the invention are that compact combination of Raman with LIBS is realized by a micro confocal system; qualitative and quantitative analysis of substance elements at the same minimal position and molecular structure is realized; with the high-resolution imaging function, element spatial discrimination and substance structure chemical analysis can be carried out in micrometers so as to obtain complete information of spatial distribution images of chemical elements, substance structure and physical conditions of a sample.
Owner:东莞市中科原子精密制造科技有限公司
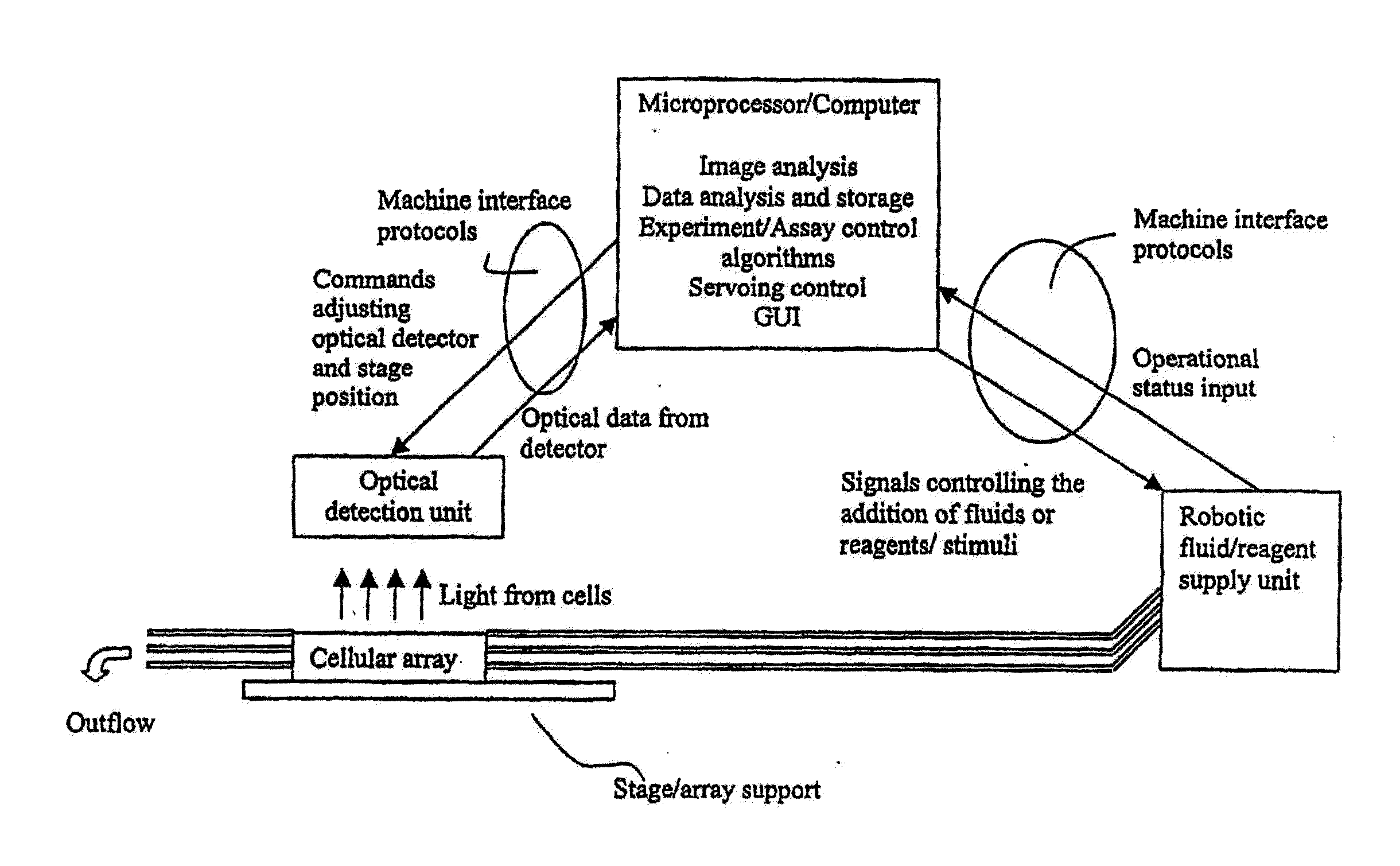
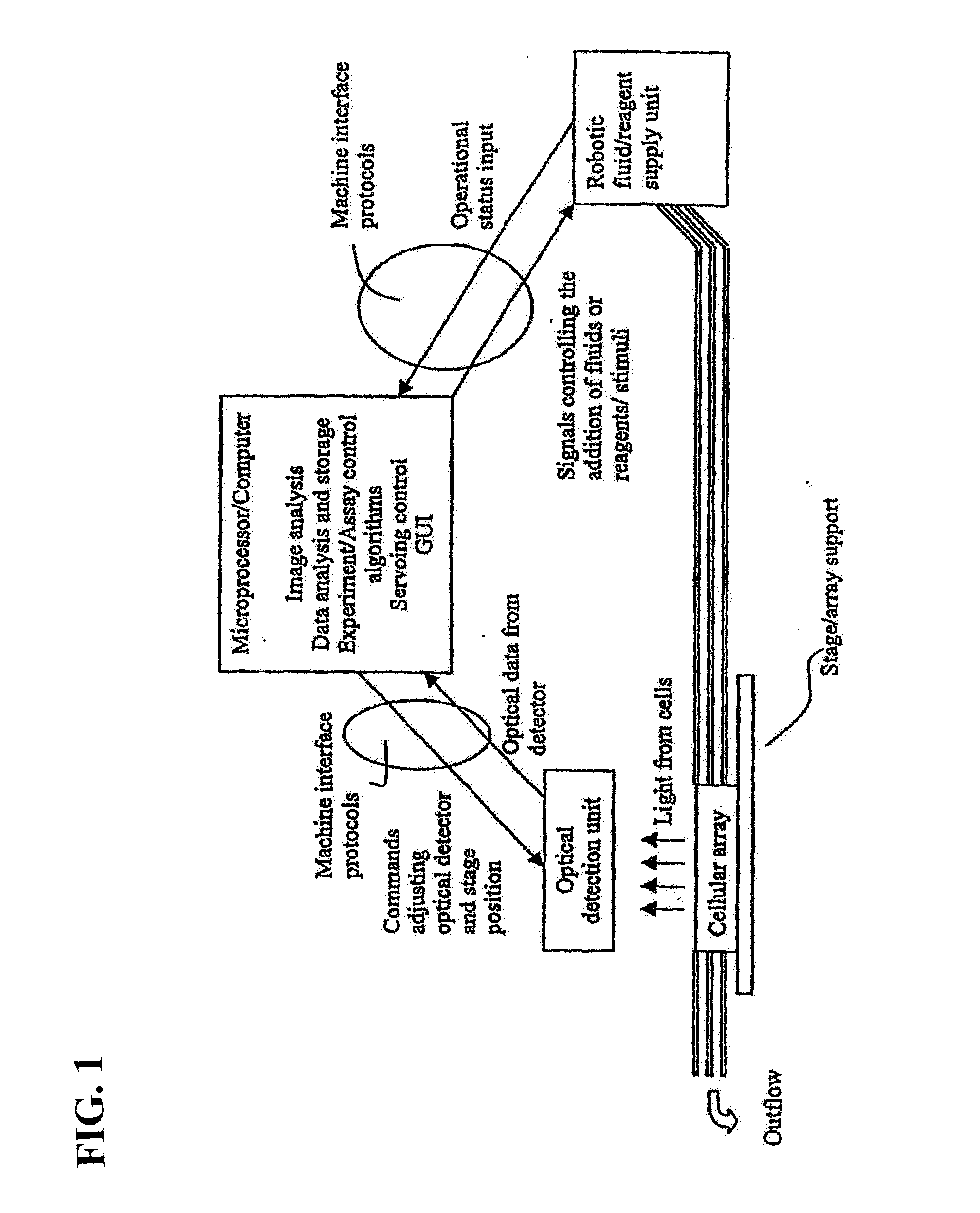
Visual-servoing optical microscopy
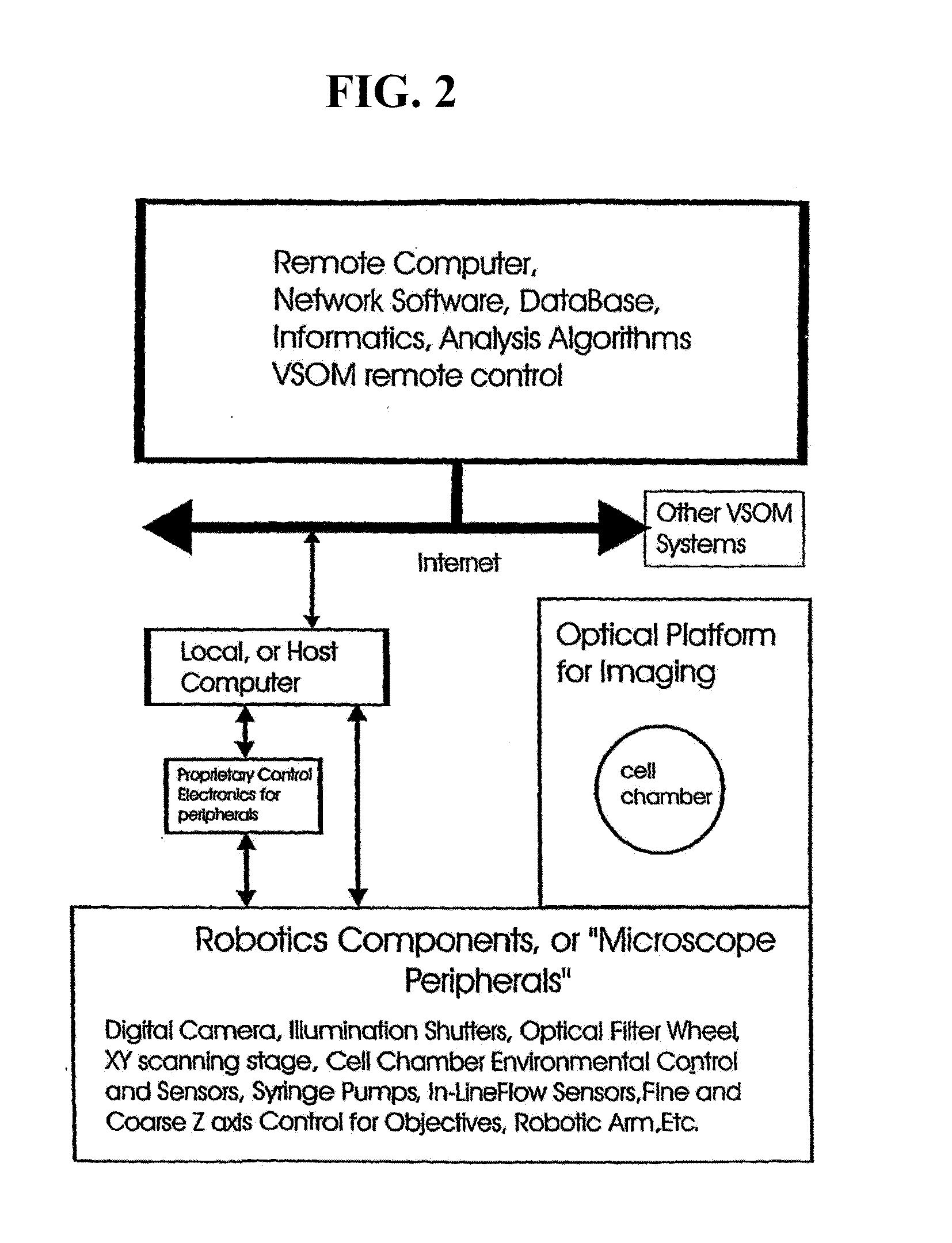
InactiveUS20110216953A1Close monitoringOptimize culture conditionsMicrobiological testing/measurementCharacter and pattern recognitionVisual perceptionCell stress
The present invention provides methods and devices for the knowledge-based discovery and optimization of differences between cell types. In particular, the present invention provides visual servoing optical microscopy, as well as analysis methods. The present invention provides means for the close monitoring of hundreds of individual, living cells over time; quantification of dynamic physiological responses in multiple channels; real-time digital image segmentation and analysis; intelligent, repetitive computer-applied cell stress and cell stimulation; and the ability to return to the same field of cells for long-term studies and observation. The present invention further provides means to optimize culture conditions for specific subpopulations of cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
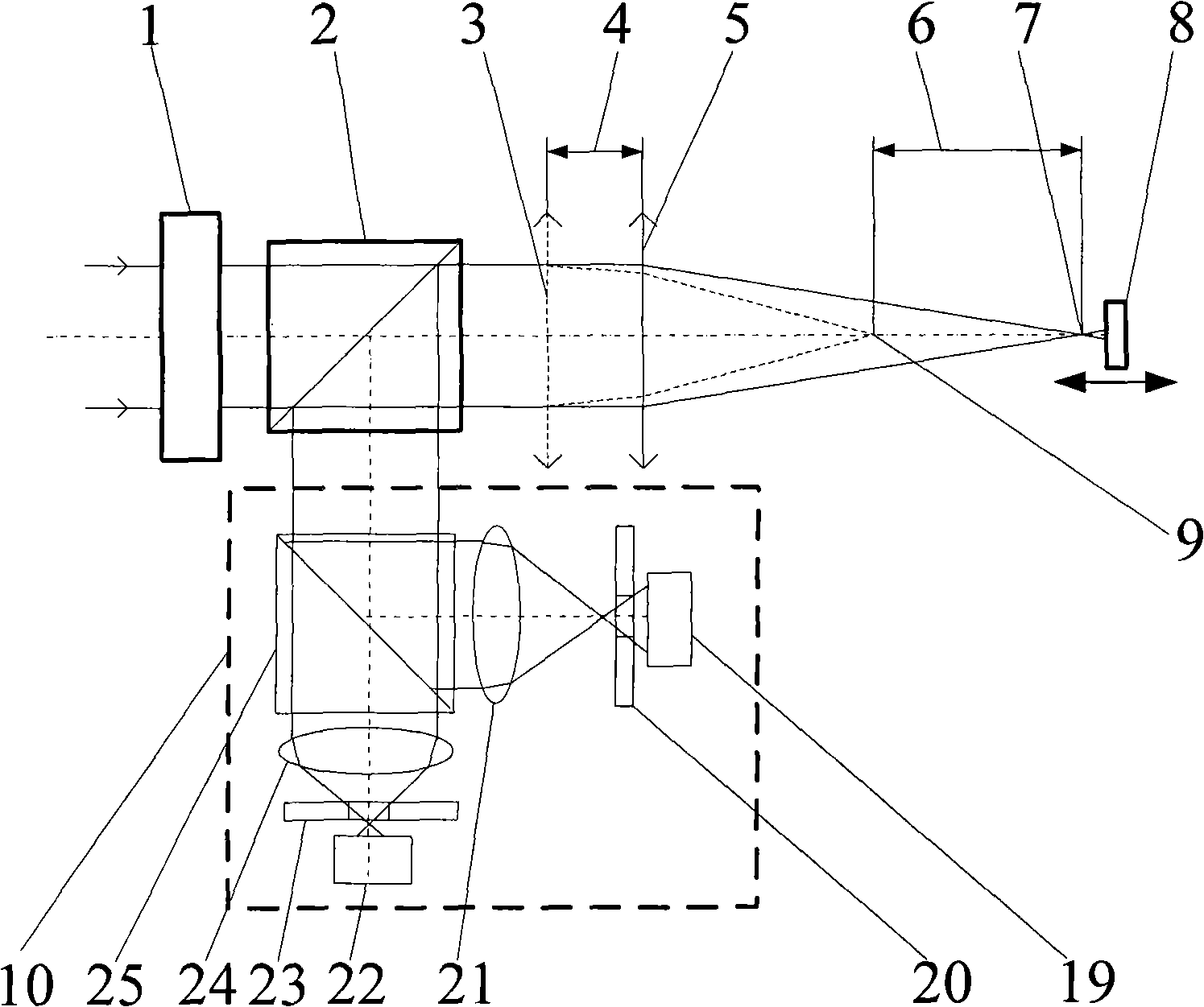
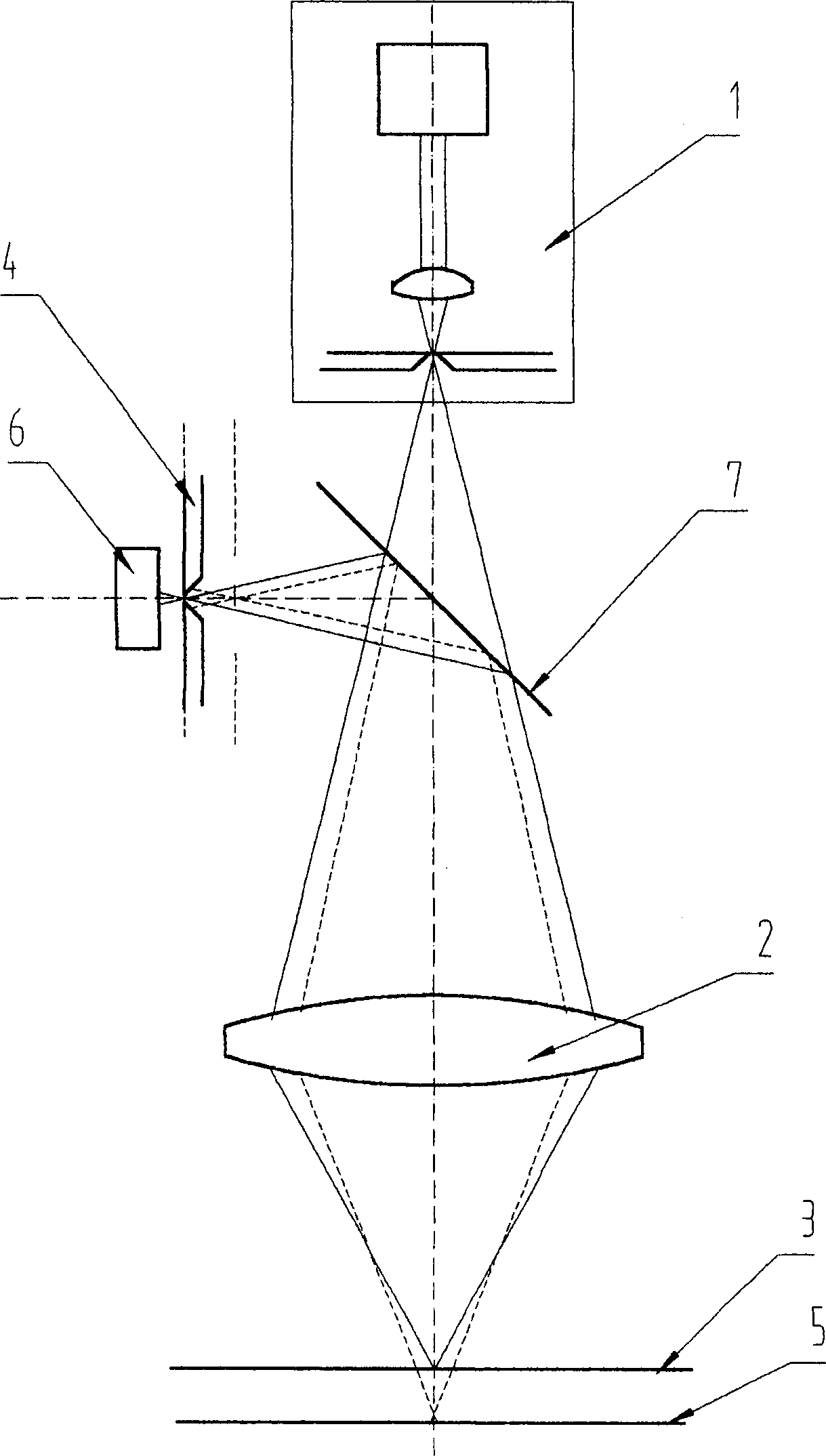
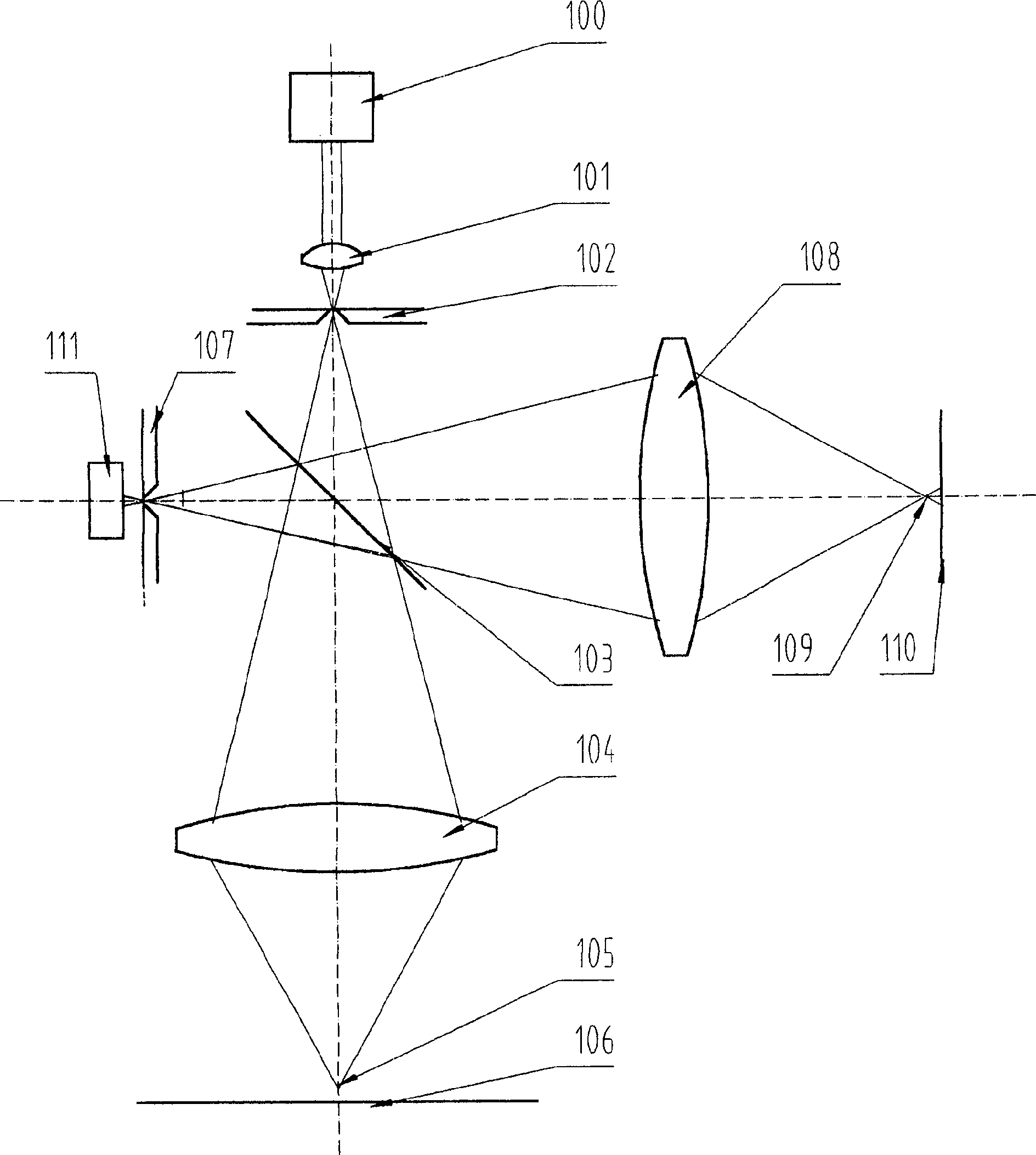
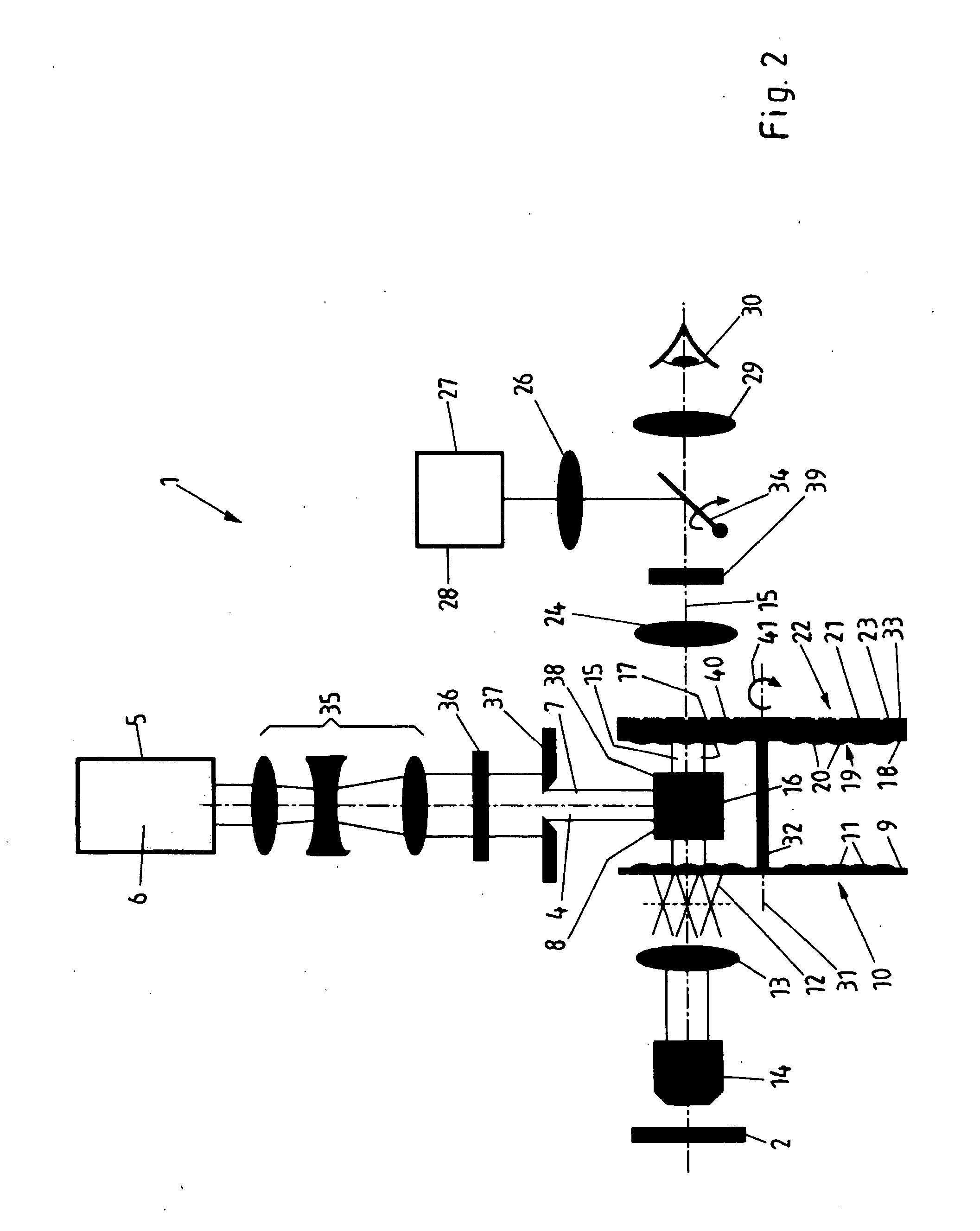
Measuring device and method that operates according to the basic principles of confocal microscopy
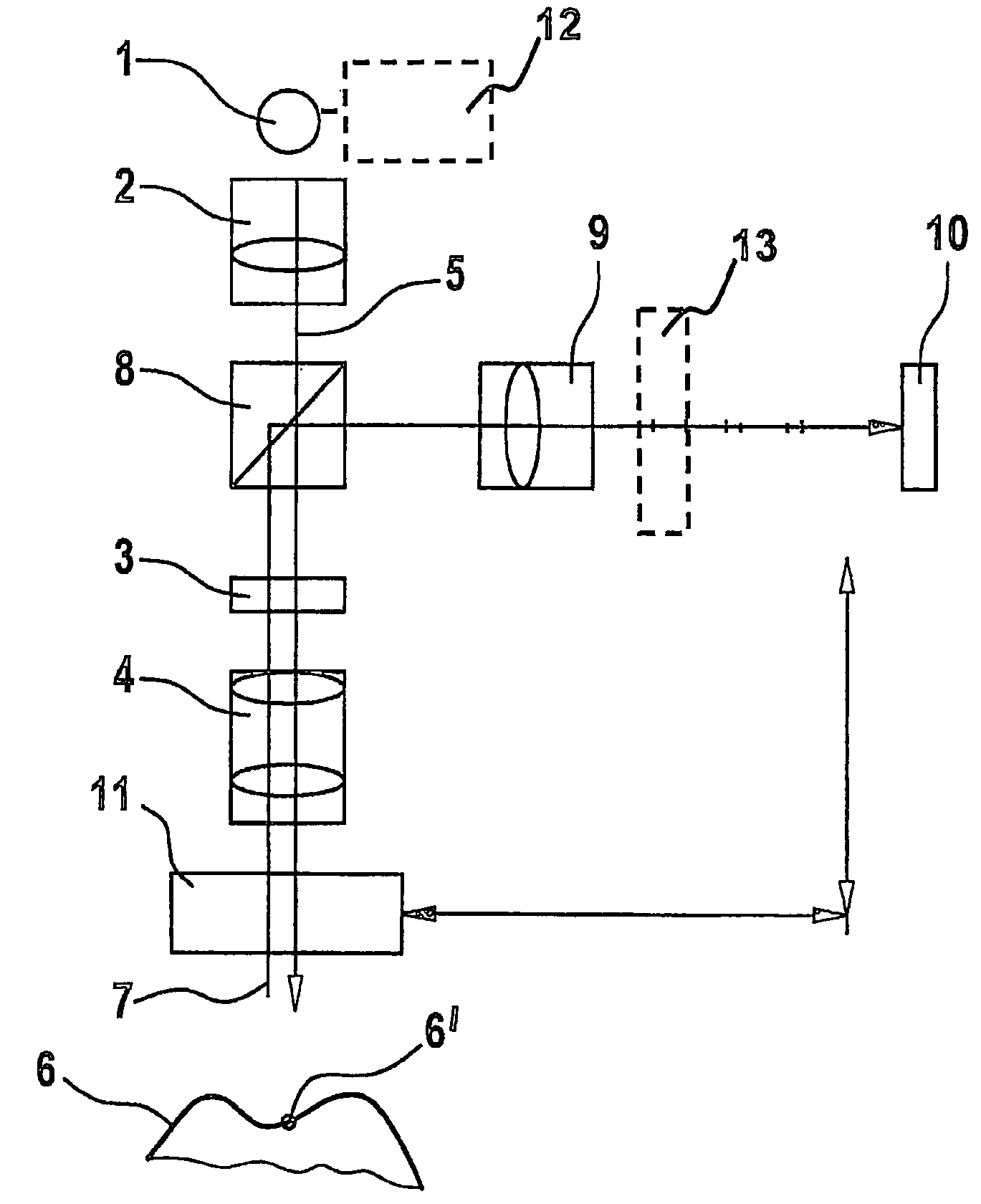
InactiveUS7679723B2Easy to detectAccurate analysisScattering properties measurementsMicroscopesMeasurement deviceObject point
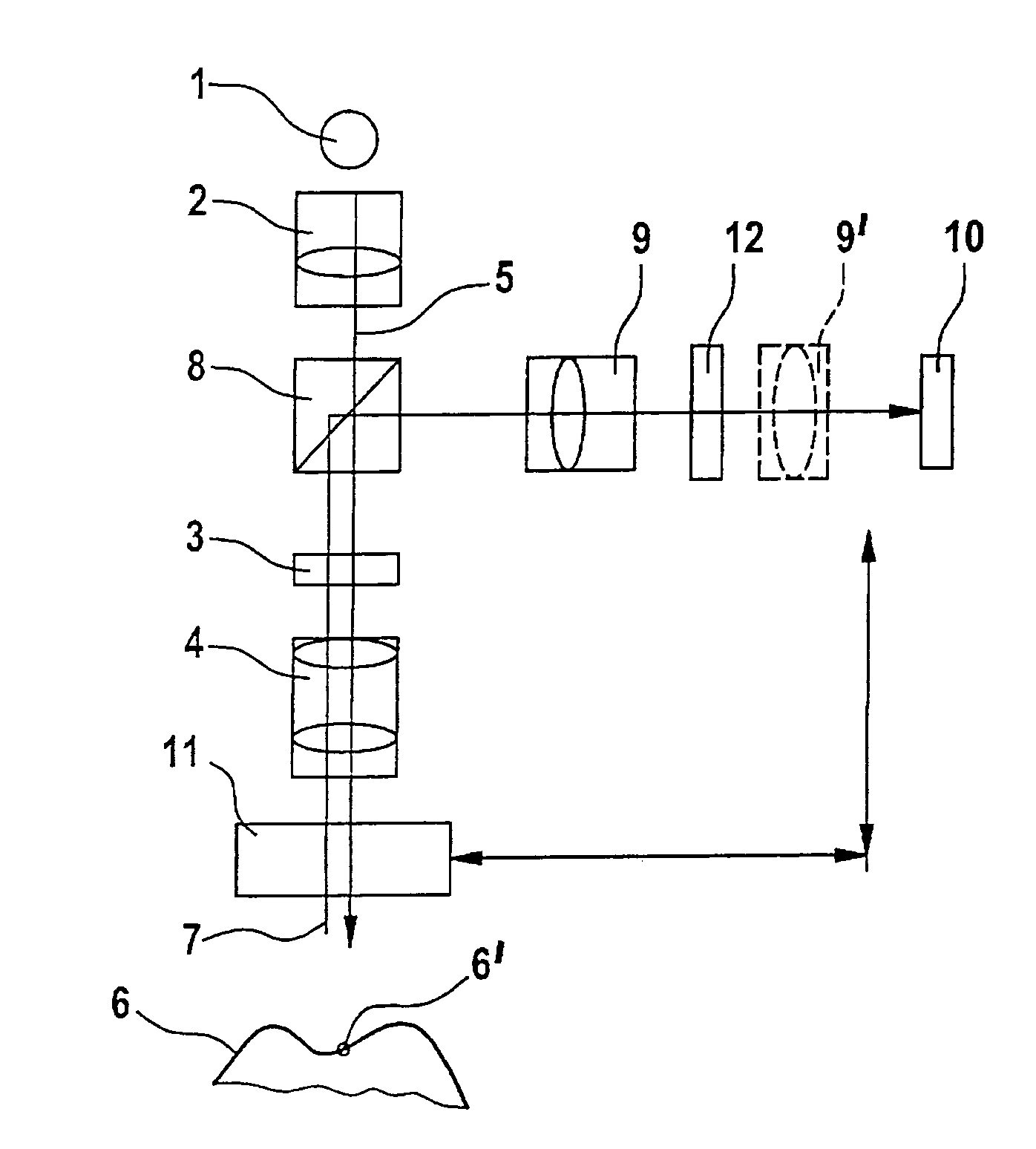
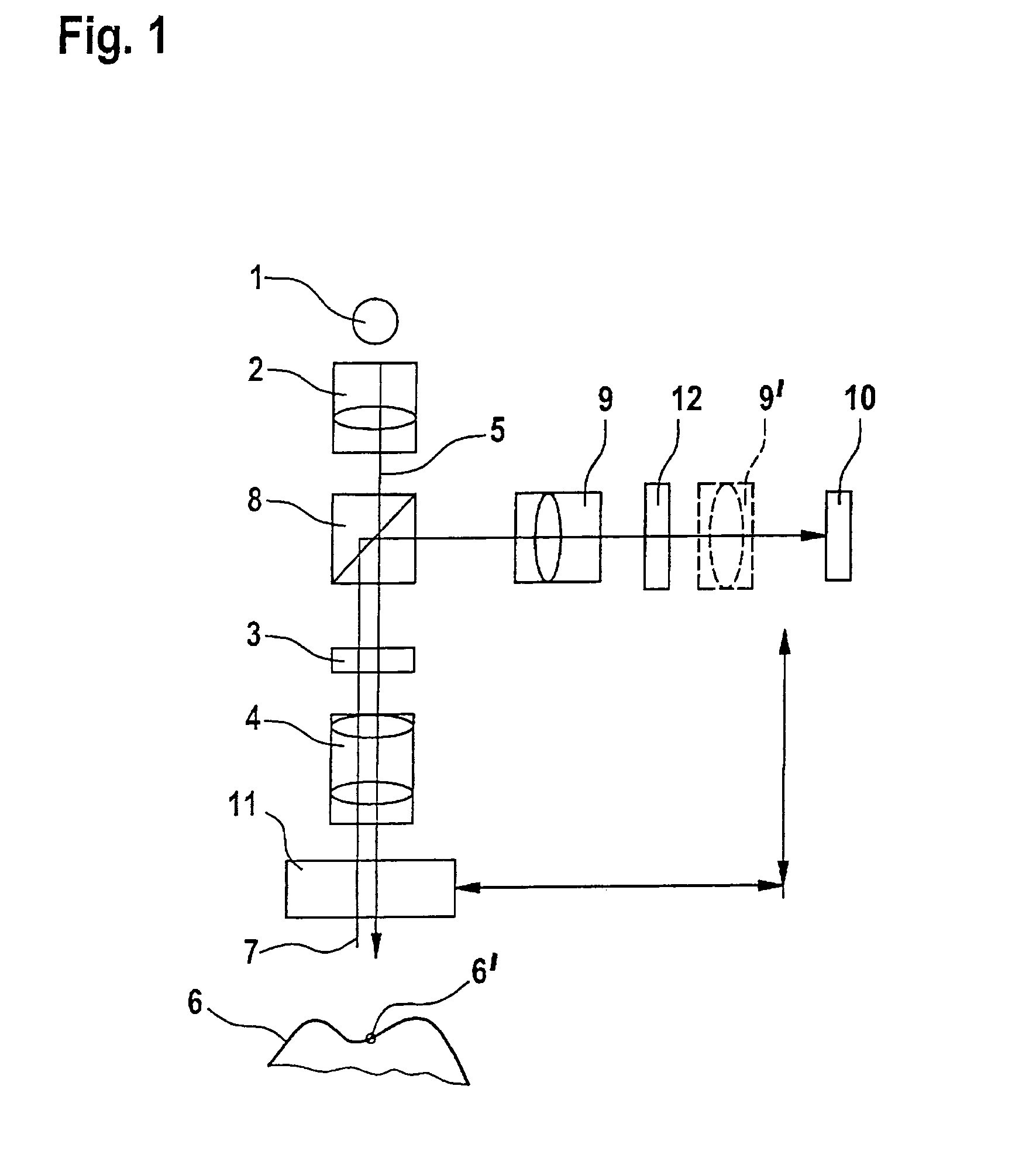
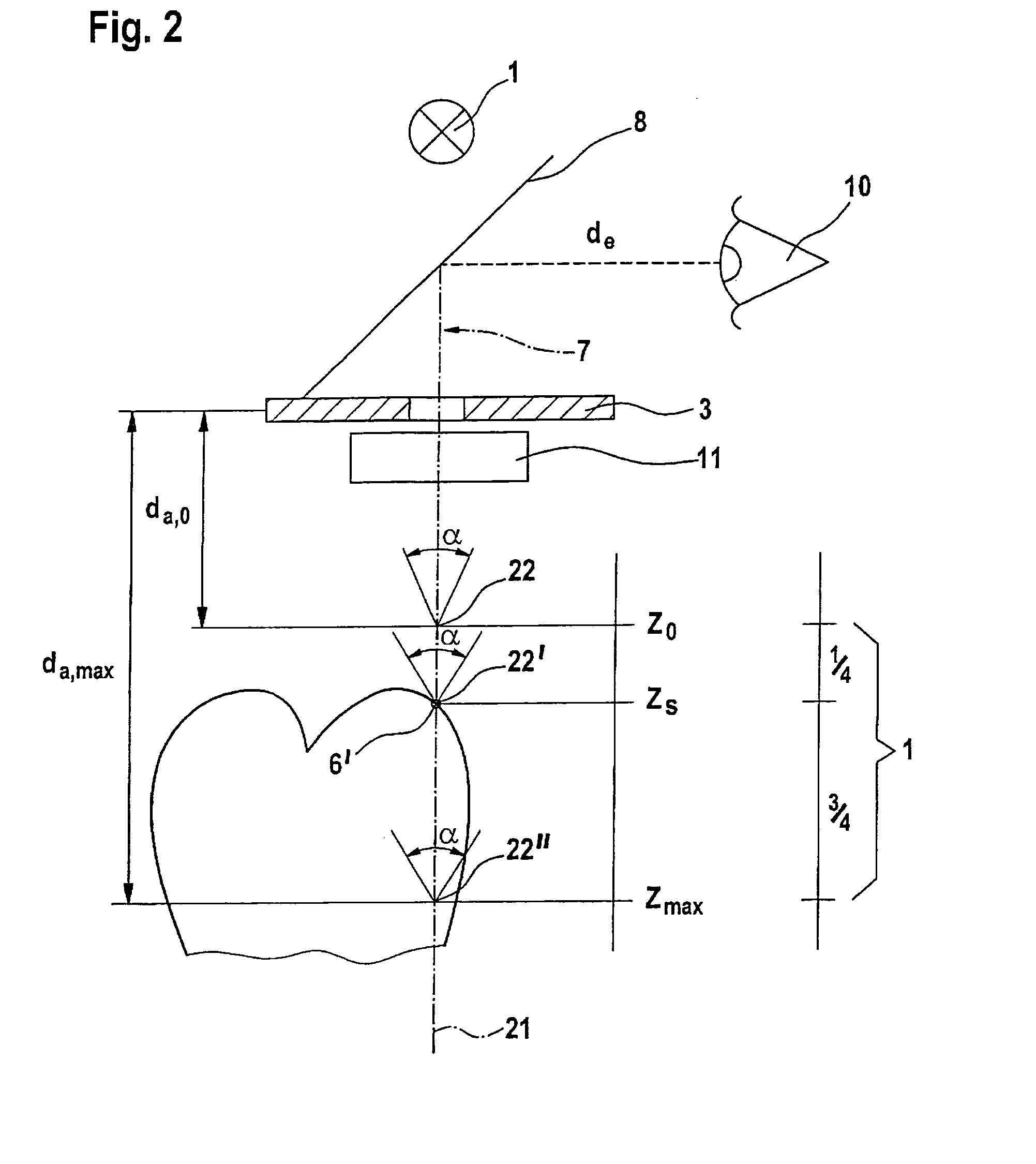
A scanning system for confocal scanning of an object, comprising a light source (1), imaging optics (4) for focusing the light (5) radiated from the light source (1) onto the object (6) to be scanned, and further comprising an image detector (10) for detecting the light (7) from an object point (6′) backscattered from the object (6) and passing through the same imaging optics (4). Means (11) for varying the length of the optical path are disposed in the optical path between the aperture array (3) and the object (6), by which means the optical distance of the image plane can be modified in a specific manner, and means are provided to influence the light (5) radiated by the light source onto the object (6) and / or the light (7) reflected from the object (6) and impinging on the sensor (10), in at least one of its characteristics, during an exposure period (tB1) for acquiring an image, and, during said exposure period (tB1), a profile holds which states a specific relationship between the characteristic of the light (5, 7) and the optical distance of the image plane from the imaging optics (4), and means (10) are provided which provide a measured value dependent on the characteristics of the light of the trajectory of observation (7) over the exposure period (tB1), a height coordinate (Zs) of the object (6) being reconstructable from the measured value achieved during said exposure period (tB1) and a reference value.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
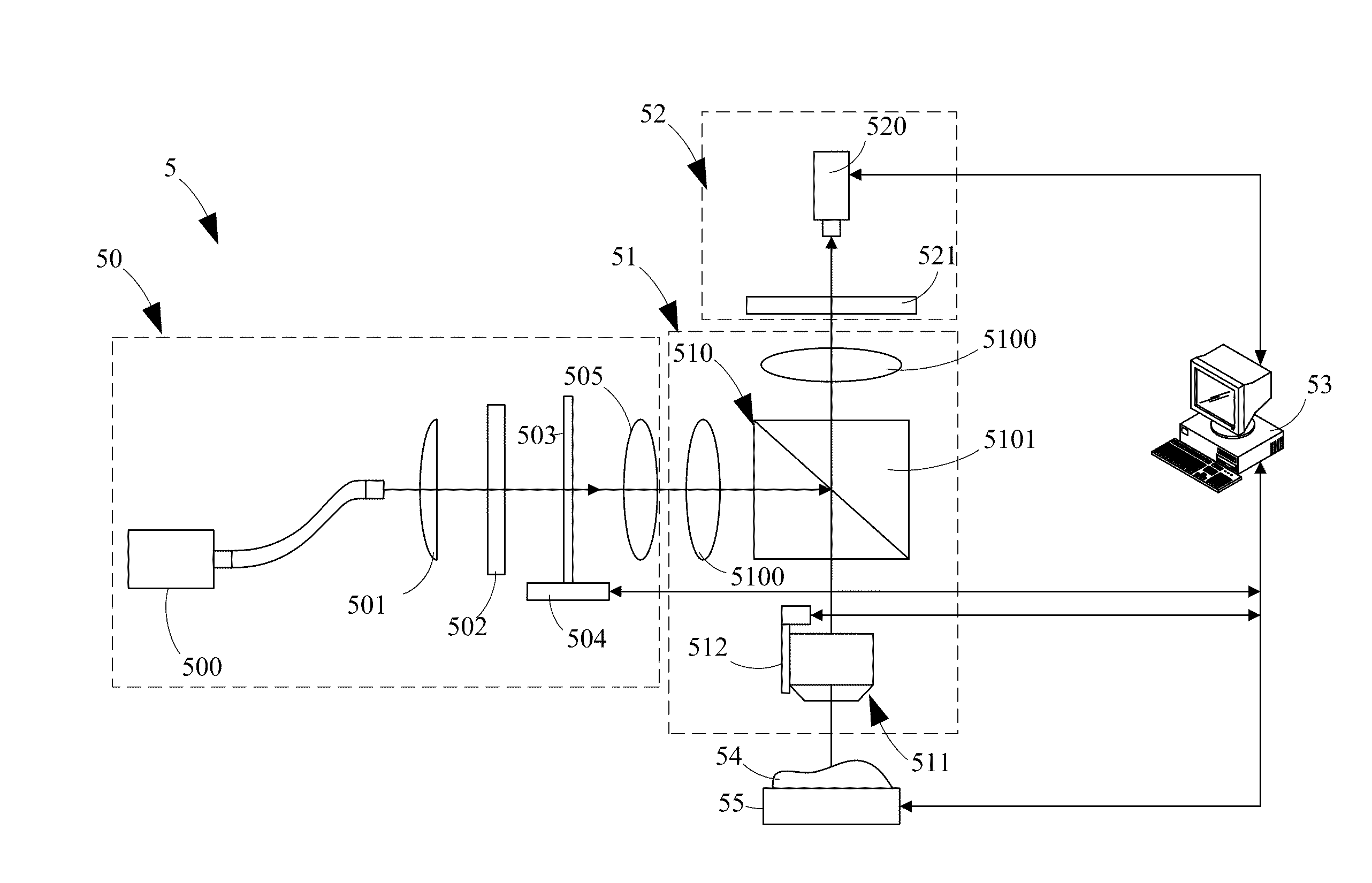
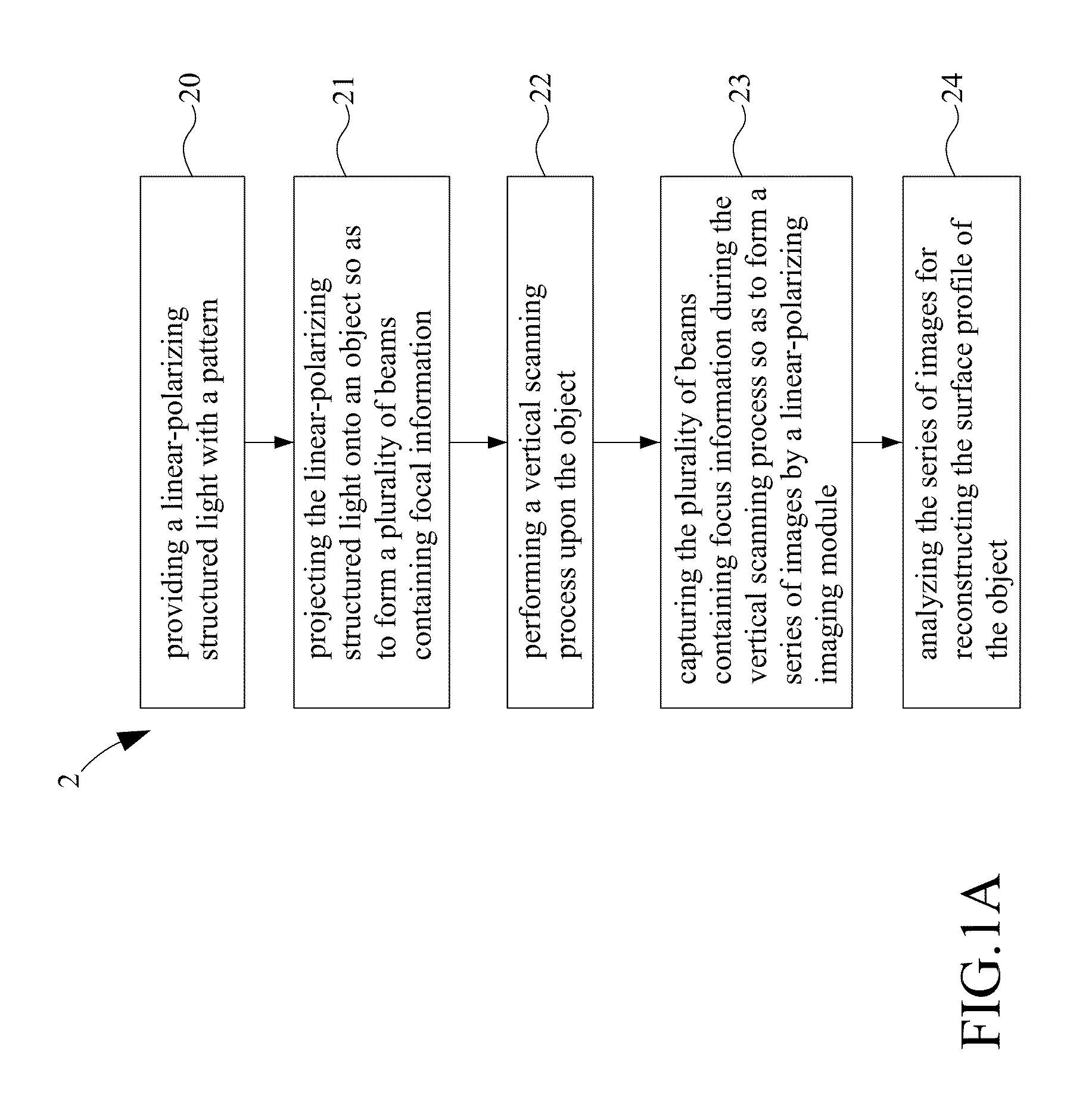
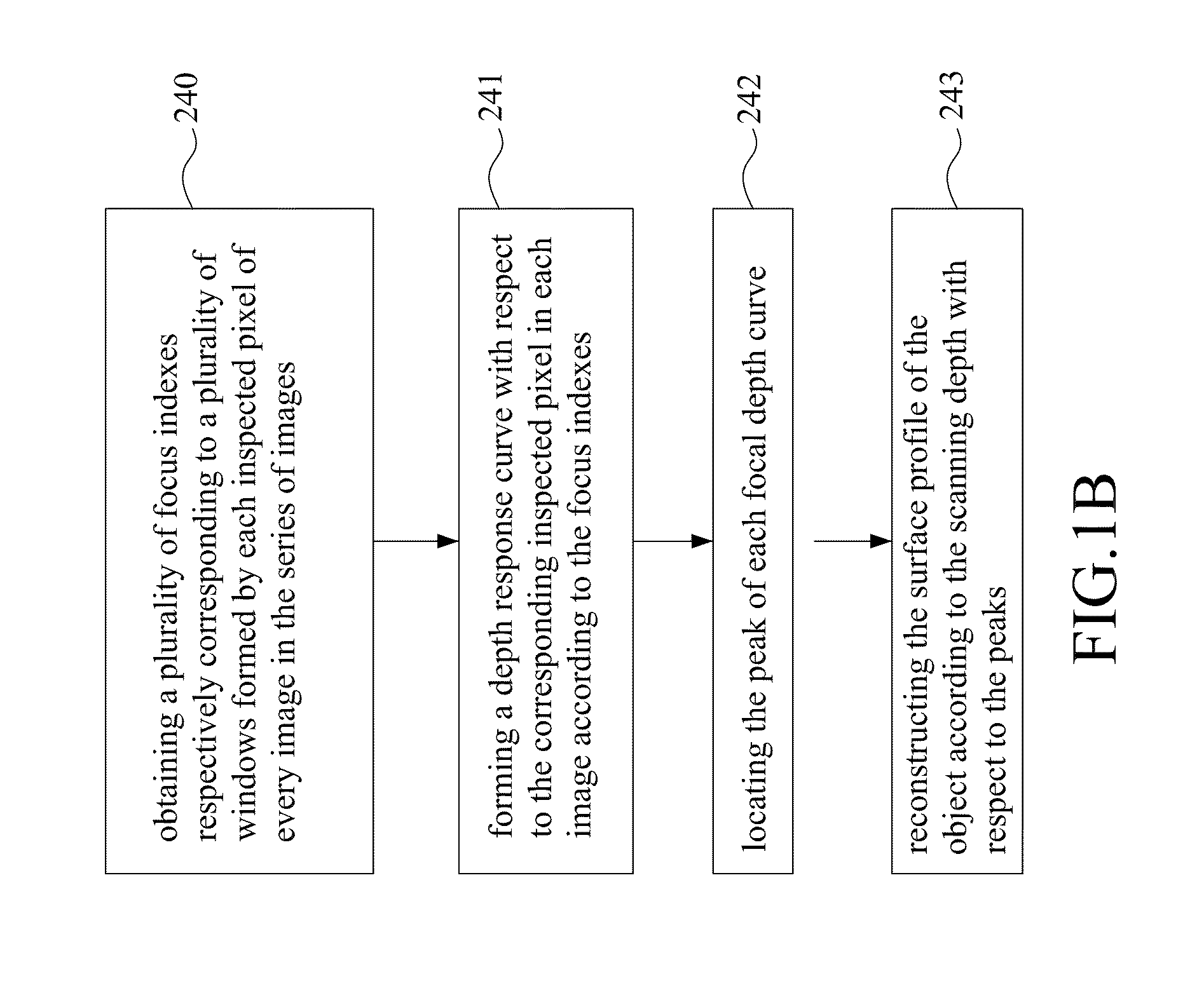
Method and system for three-dimensional polarization-based confocal microscopy
A method and system for three-dimensional polarization-based confocal microscopy are provided in the present disclosure for analyzing the surface profile of an object. In the present disclosure, a linear-polarizing structured light formed by an optical grating is projected on the object underlying profile measurement. By means of a set of polarizers and steps of shifting the structured light, a series of images with respect to the different image-acquired location associated with the object are obtained using confocal principle. Following this, a plurality of focus indexes respectively corresponding to a plurality of inspected pixels of each image are obtained for forming a focus curve with respect to the measuring depth and obtaining a peak value associated with each depth response curve. Finally, a depth location with respect to the peak value for each depth response curve is obtained for reconstructing the surface profile of the object.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST +1
Ultrahigh resolution multicolor colocalization of single fluorescent probes
InactiveUS6844150B2Improve spatial resolutionLimited ability to compensate for aberrationSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementDiffusion functionLasing wavelength
A novel optical ruler based on ultrahigh-resolution colocalization of single fluorescent probes is described. Two unique families of fluorophores are used, namely energy-transfer fluorescent beads and semiconductor nanocrystal (NC) quantum dots, that can be excited by a single laser wavelength but emit at different wavelengths. A novel multicolor sample-scanning confocal microscope was constructed which allows one to image each fluorescent light emitter, free of chromatic aberrations, by scanning the sample with nanometer scale steps using a piezo-scanner. The resulting spots are accurately localized by fitting them to the known shape of the excitation point-spread-function of the microscope.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Rapid confocal microscopy to support surgical procedures
ActiveUS20110116694A1Prevent lateral movementMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationOptical propertyFluorescence
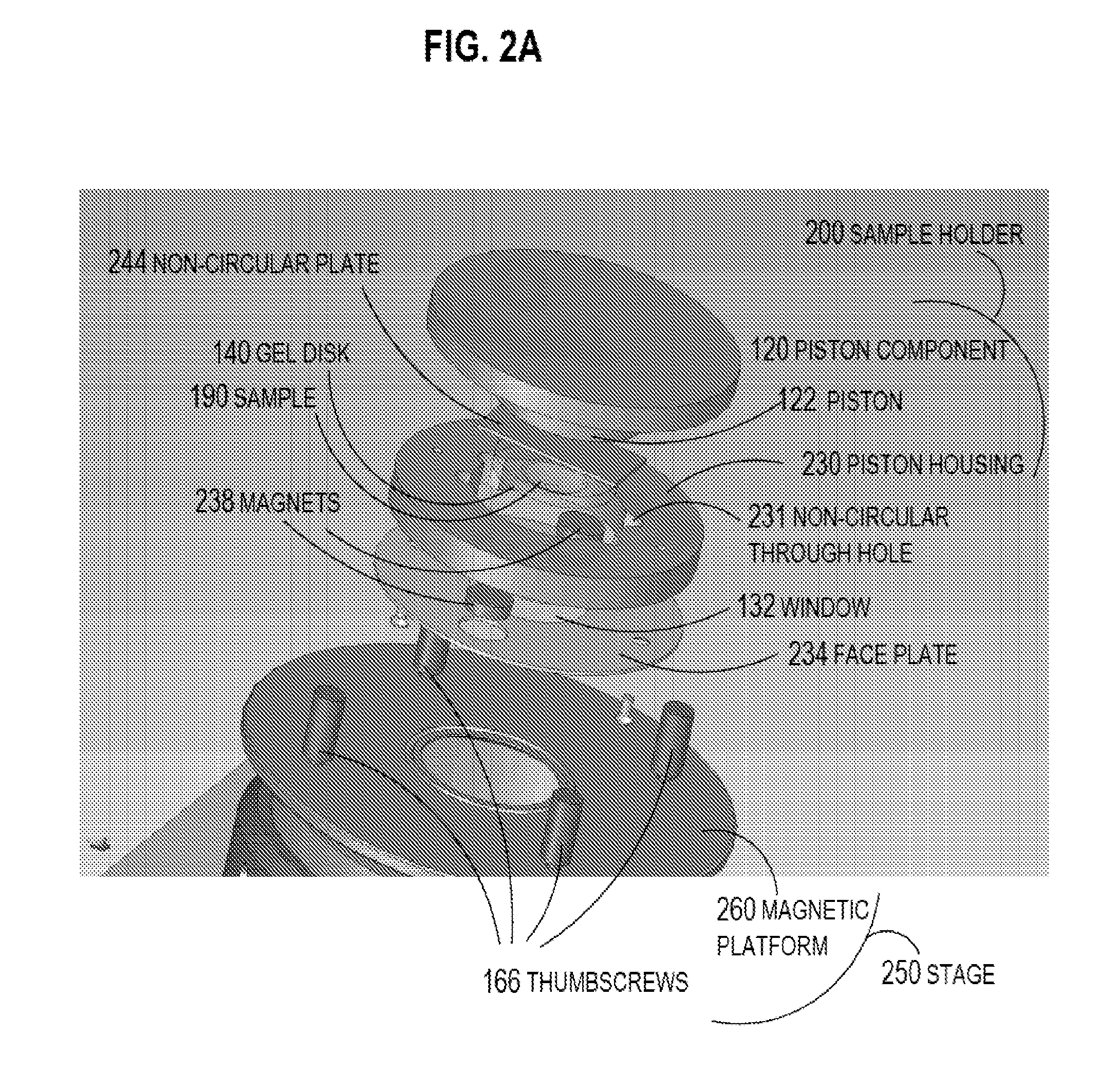
One embodiment of techniques for confocal microscopy includes illuminating a spot on a surface of a biological sample. A first emission intensity from the spot is detected in a first range of optical properties; and a second emission intensity in a second range. A pixel that corresponds to the spot is colored using a linear combination of the first and second emission intensities. Sometimes, the pixel is colored to approximate a color produced by histology. In some embodiments, a surface of a sample is contacted with a solution of acridine orange. Then, a spot is illuminated with a laser beam of wavelength about 488 nanometers (nm). Fluorescence emission intensity is detected above about 500 nm. Sometimes, a certain illumination correction is applied. In some embodiments, a sample holder that compresses a sample is removable from a stage that is fixed with respect to a focal plane of the microscope.
Owner:SLOAN KETTERING INST FOR CANCER RES +1
High-speed measuring device and method based on a confocal microscopy principle
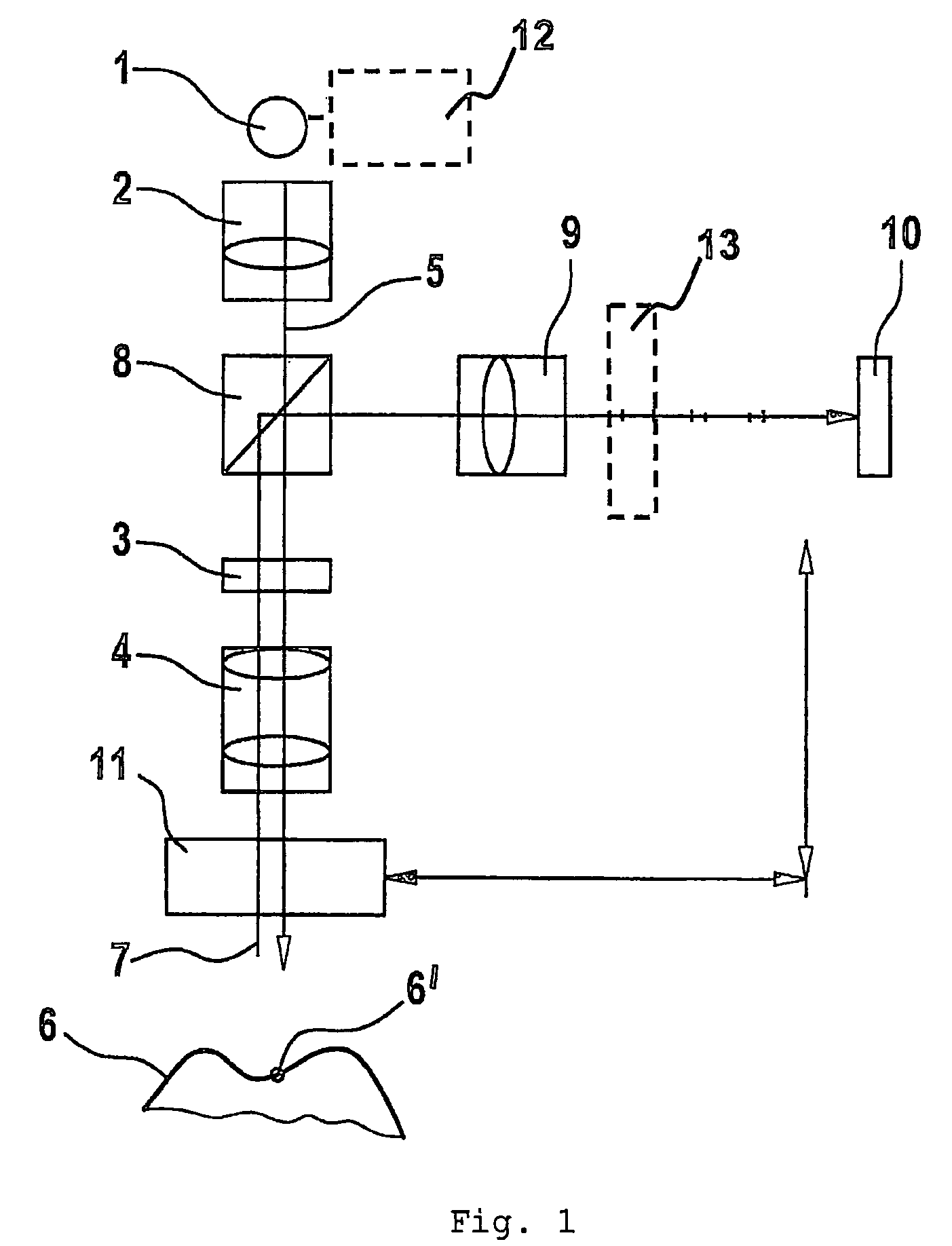
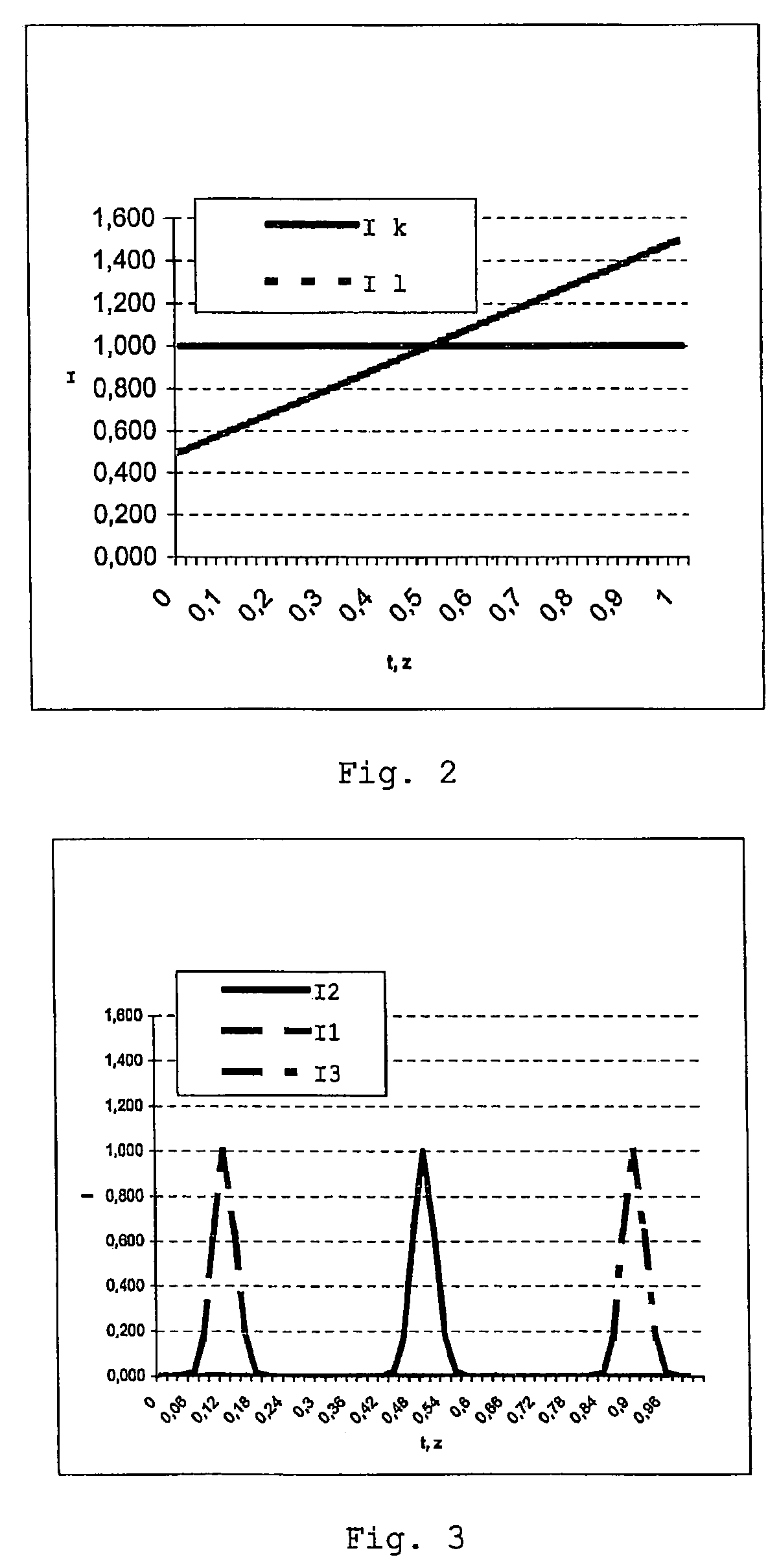
ActiveUS7582855B2No longer be carried outSimple correlationImpression capsMaterial analysis by optical meansMeasurement deviceCo ordinate
The invention relates to a measuring device and a method based on a confocal microscopy principle. The inventive device comprises a light source (1), a diaphragm unit (3) for limiting a beam, an imagine optical system (4) for focusing the light (5) which is irradiated by said source on a measurable object (6) and passes through said diaphragm unit. Said device also comprises an optical system (10) for receiving the light (5) reflected from the object and passing through said optical system or another diaphragm unit disposed in an observation beam (7) and an image receiver (10) which is provided with at least two radiation-sensitive sensor elements (13, 14) (pixel). Said invention is characterized in that, in order to obtain the image of an altitude information-containing measurement, the device is also provided with means (11) for modifying the beam optical path length disposed between the light source (1) and / or the image receiver (10), on one side, and the object (6) on the other and the optical distance (d) of a focal point is modifiable in a predetermined manner. In addition, said intention makes it possible to influence the dependence of an accumulation of charges (Q13, Q14) in at least two sensor elements (13, 14) on the light intensity of the observation beam (7) during the exposure time in such a way that a correlation associated with the optical distance (d) of an image plane can be carried out by the imagine optical system (4), thereby making it possible to reconstitute the altitude co-ordinate (zs) of the object by distributing the intensity values obtained during the exposure time from at least two sensor elements (13, 14).
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
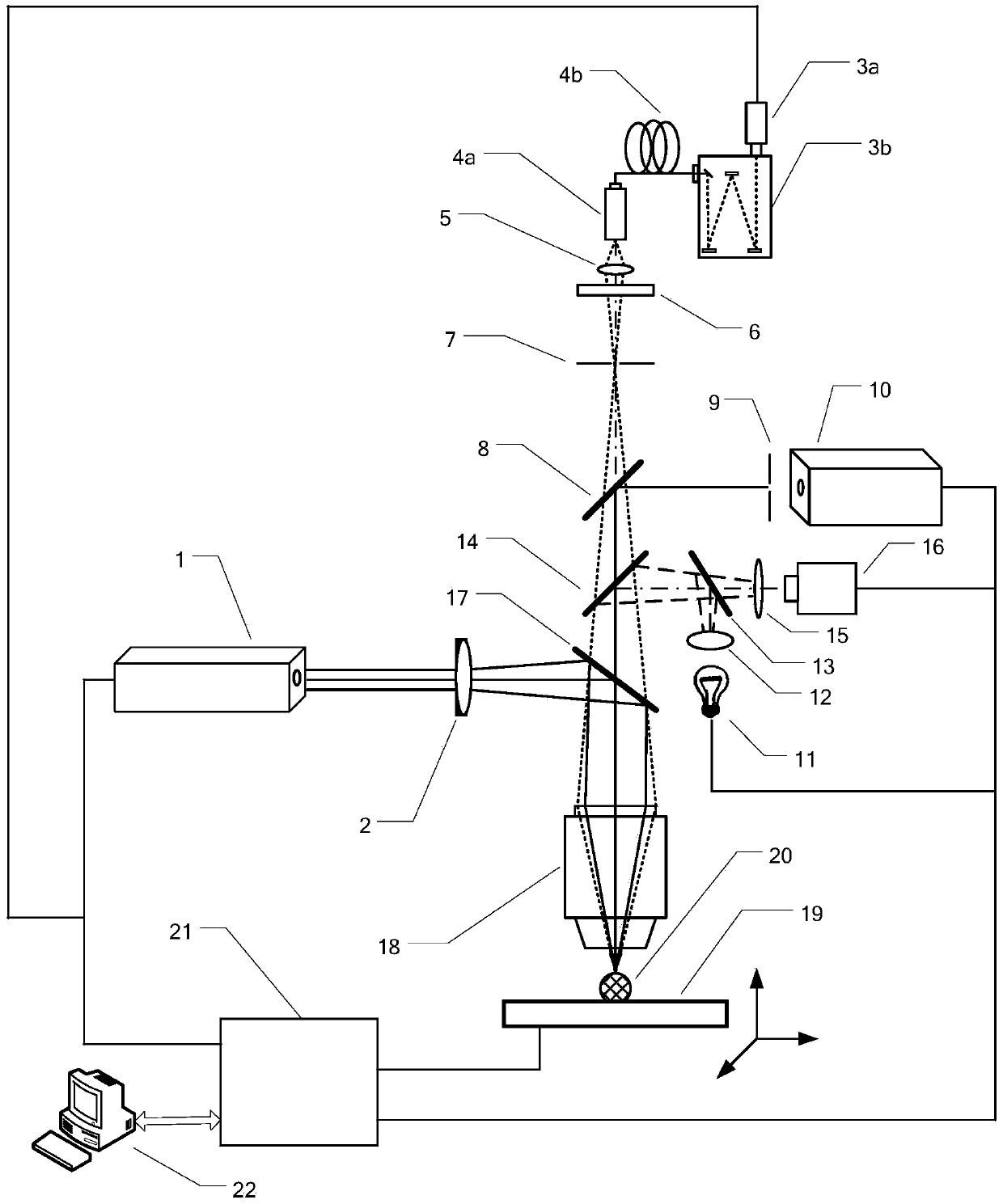
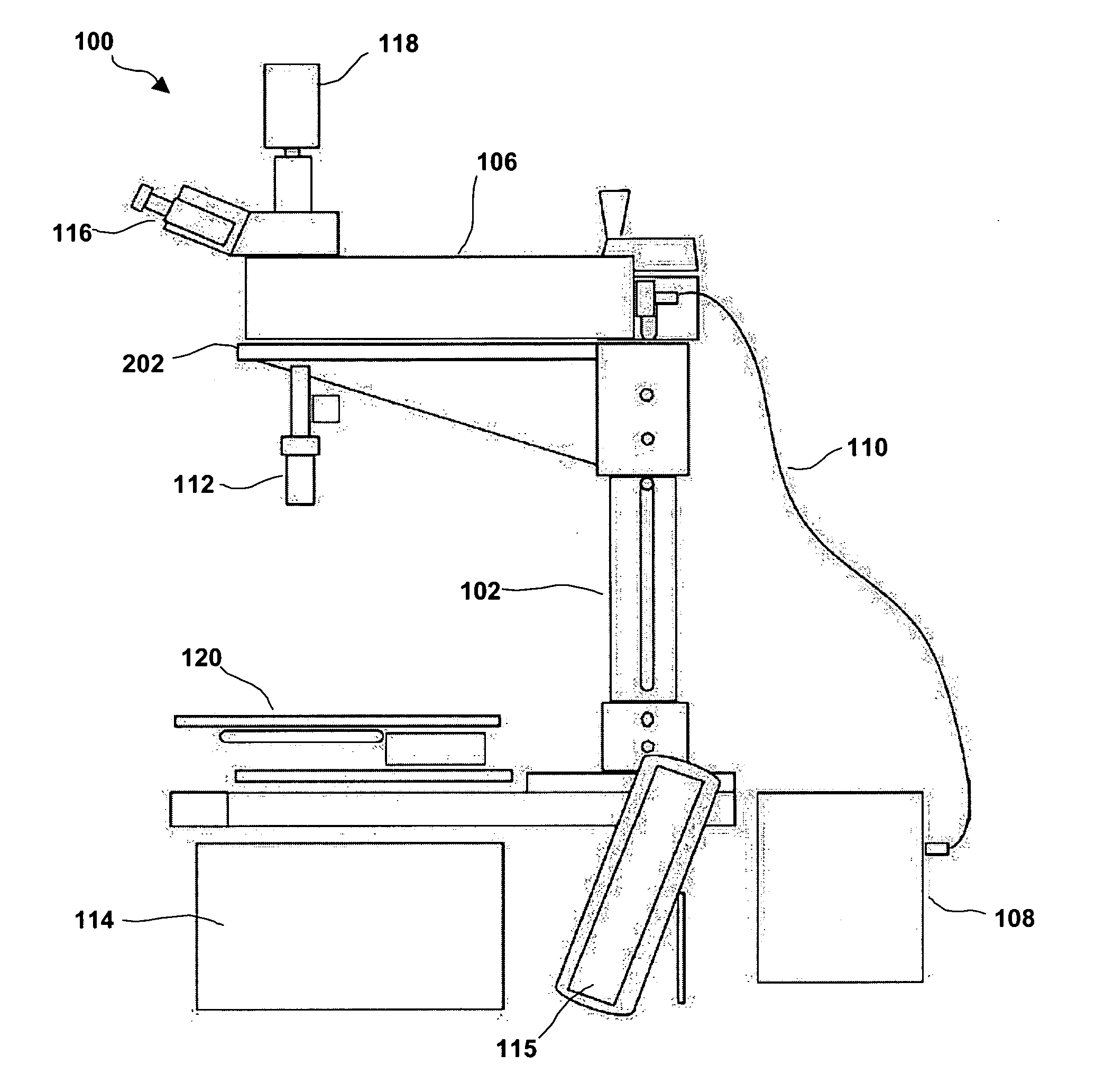
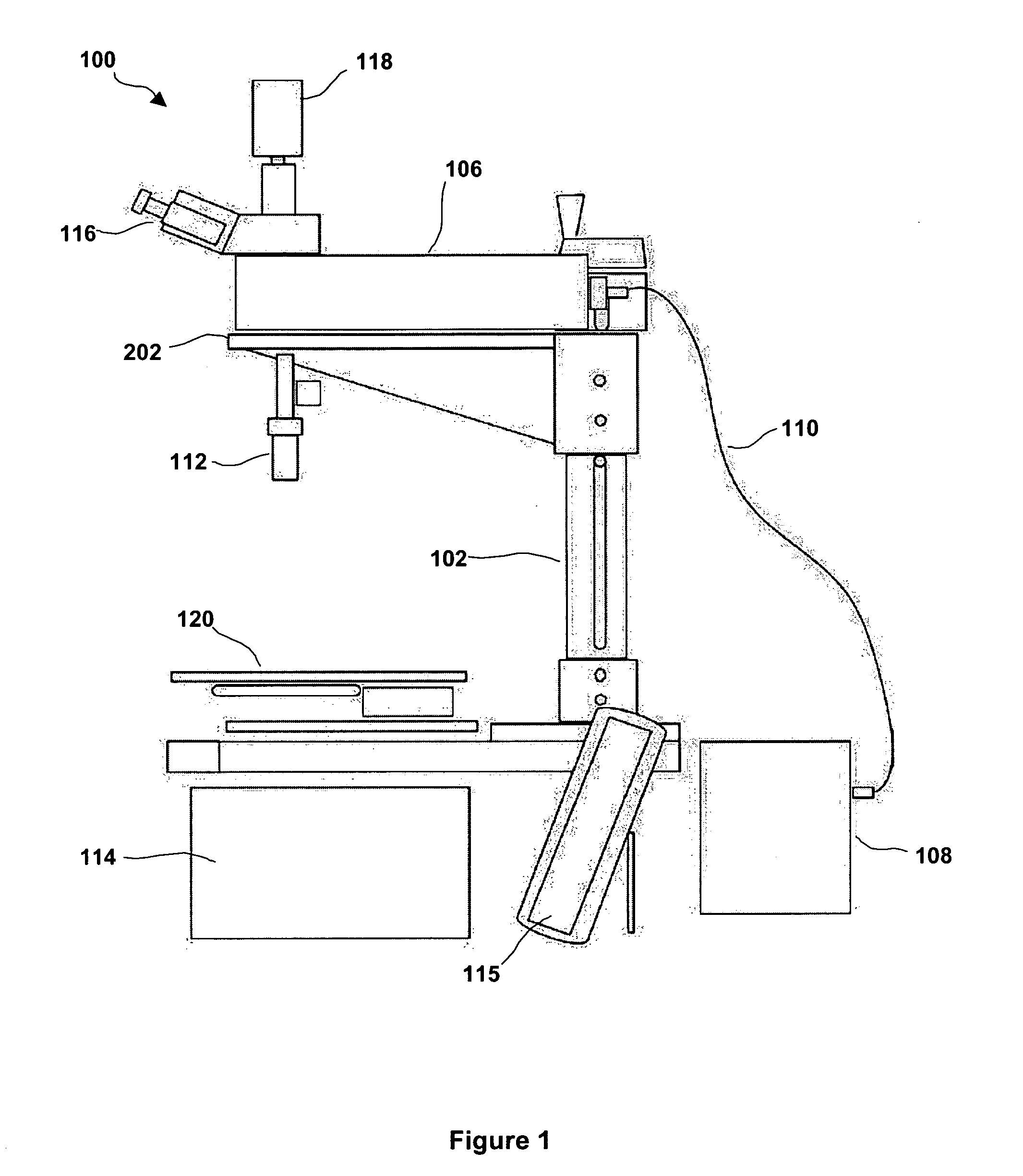
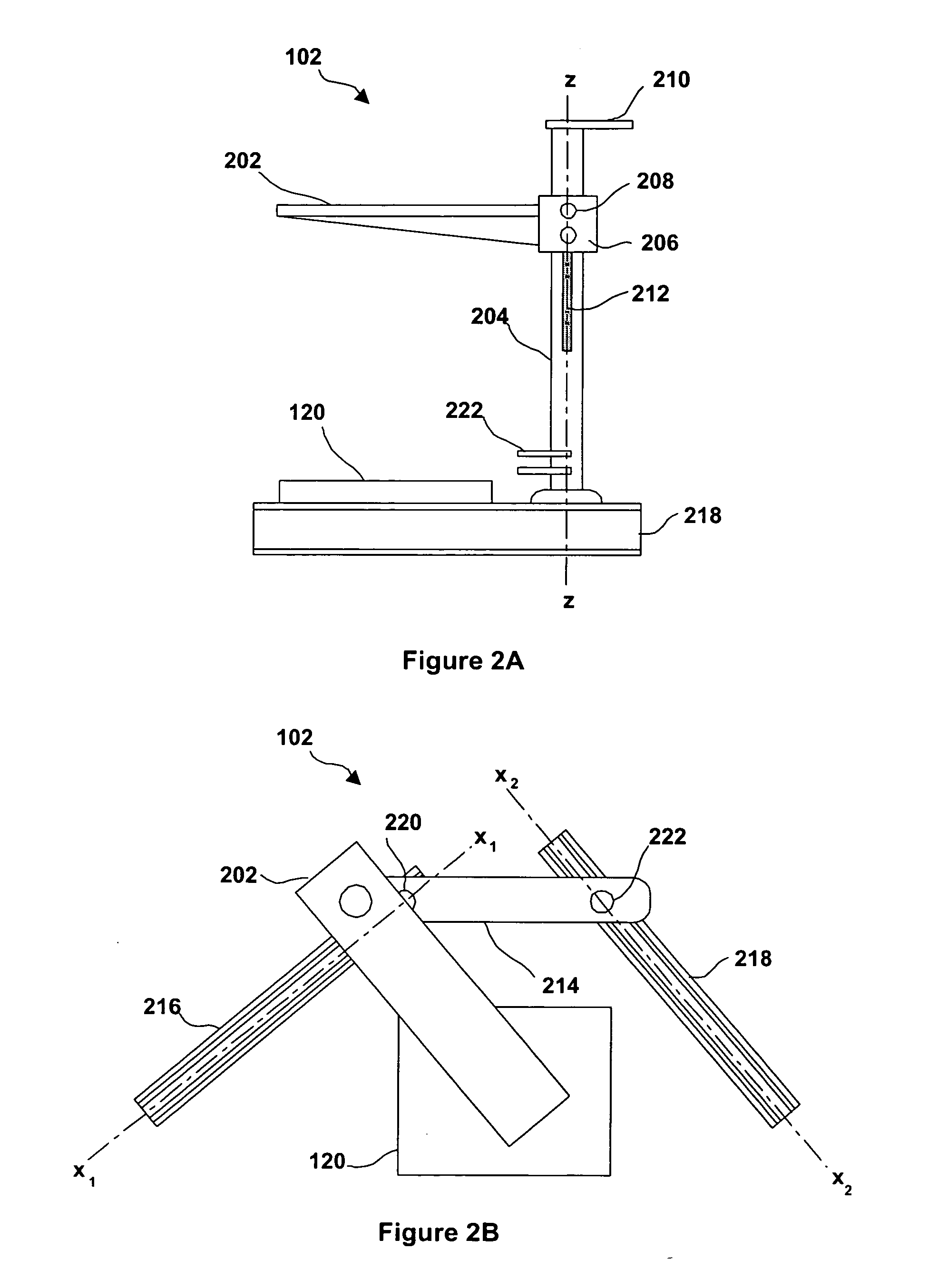
Portable automated confocal microscope
Described is a portable confocal microscope which includes a microscope stand including a shaft having top and bottom ends, a platform connected to the shaft by a height adjustment mechanism, a base member connected to the bottom end of the shaft and first and second elongated channel members slidably and rotatably connected to the base member, an optical assembly including an objective lens including a first position adjustment mechanism for adjusting a position of the objective lens along a first axis, a confocal module transmitting light to and receiving light from a specimen to be imaged via the optical assembly, an image acquisition system recording images through the optical assembly, a specimen stage including a position adjustment mechanism for moving the stage along a second and third axis, and a computer controlling the first and second position adjusting mechanisms to generate an image for recording by the image acquisition system.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Differential confocal combination ultra-long focal length measuring method and apparatus
ActiveCN101403650AReduce measurementReduced impact of focal length measurement accuracyTesting optical propertiesPupilFocal position
The invention belongs to the optical precise measurement technical field and relates to an ultra-long focal distance measuring method and a corresponding apparatus used for a differential confocal combined lens. The method firstly adopts the differential confocal focusing theory to respectively define the focus position of a reference lens and the focus position of the combination of measured lens and reference lens; then the distance delta between two focuses and the distance d<0> between two lenses are measured and then the formula is adopted to figure out the focal distance of the measured lens and the sensitivity for focal distance measurement can be simultaneously enhanced with the pupil filtering technique during the measuring process. The invention firstly puts forward the adoption of the features of the corresponding micro-lens focus while the differential confocal response curve passes the zero point so as to extend the differential confocal microscopy theory to the ultra-long focal distance measurement field and form the differential confocal focusing theory. The invention integrates the differential confocal focusing theory and the lens combination so as to get the advantages that the measurement precision is high and the anti-interference capability is strong. The invention can be applied to the detection for the lens with ultra-long focal distance and the high-precise focal distance measurement in the optical system assembling process.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
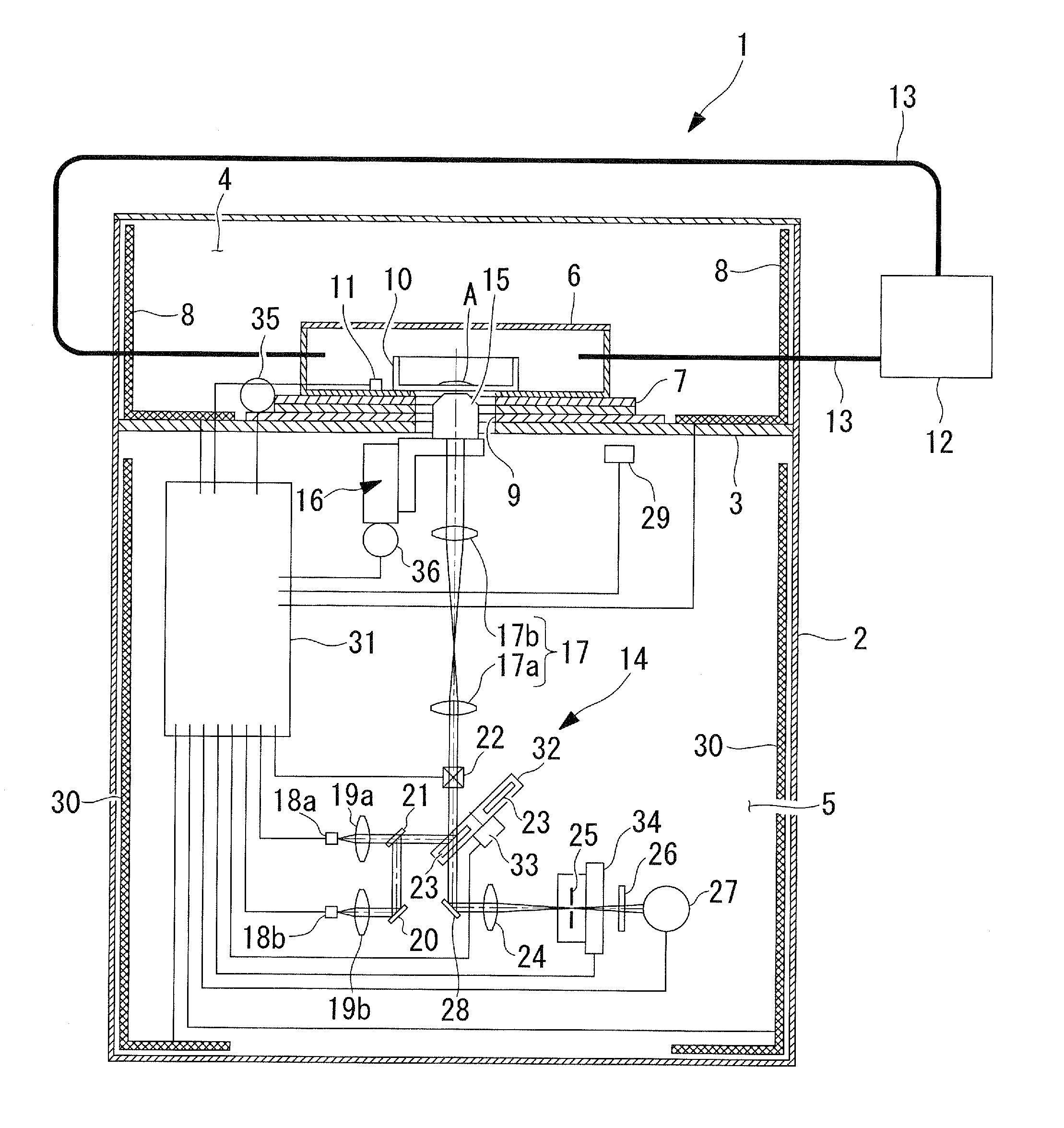
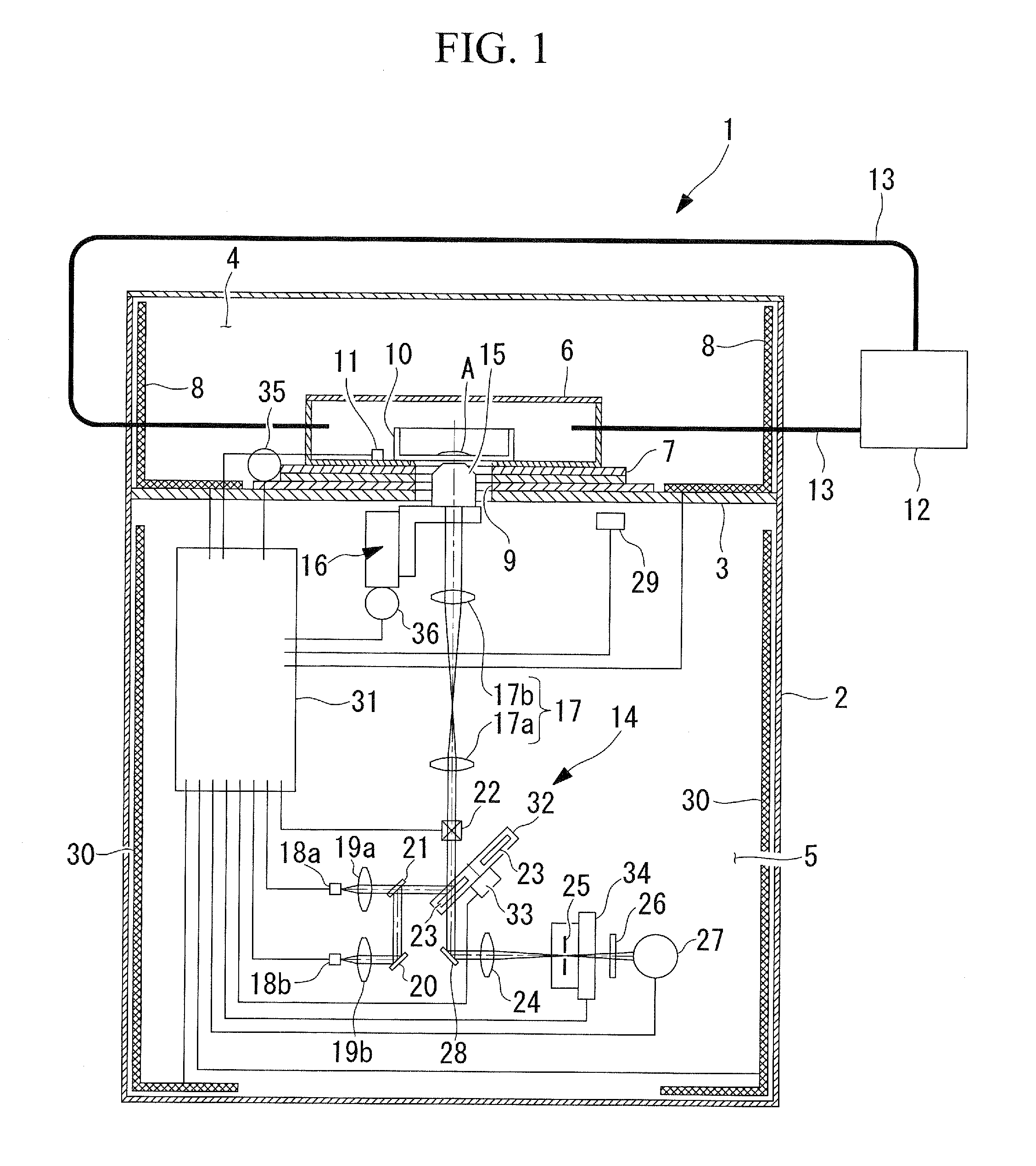
Scanning confocal microscope
A scanning confocal microscope can provide an image while preventing a decrease in brightness and blurring due to strain caused in optical and mechanical systems by thermal effects in a high-temperature, high-humidity incubation container. This scanning confocal microscope includes an incubation container that has a space in which a specimen is disposed and that can maintain an internal environment thereof at a predetermined temperature and high humidity and an optical system space adjacent to the incubation container and separated therefrom based on humidity. The optical system space accommodates a light-scanning unit and a scanner optical system, an objective lens, a confocal pinhole, and a focus adjustment mechanism. The optical system space further accommodates a temperature-maintaining unit for the optical system space to maintain the optical system space at a temperature substantially equal to the temperature in the incubation container.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Relating to scanning confocal microscopy
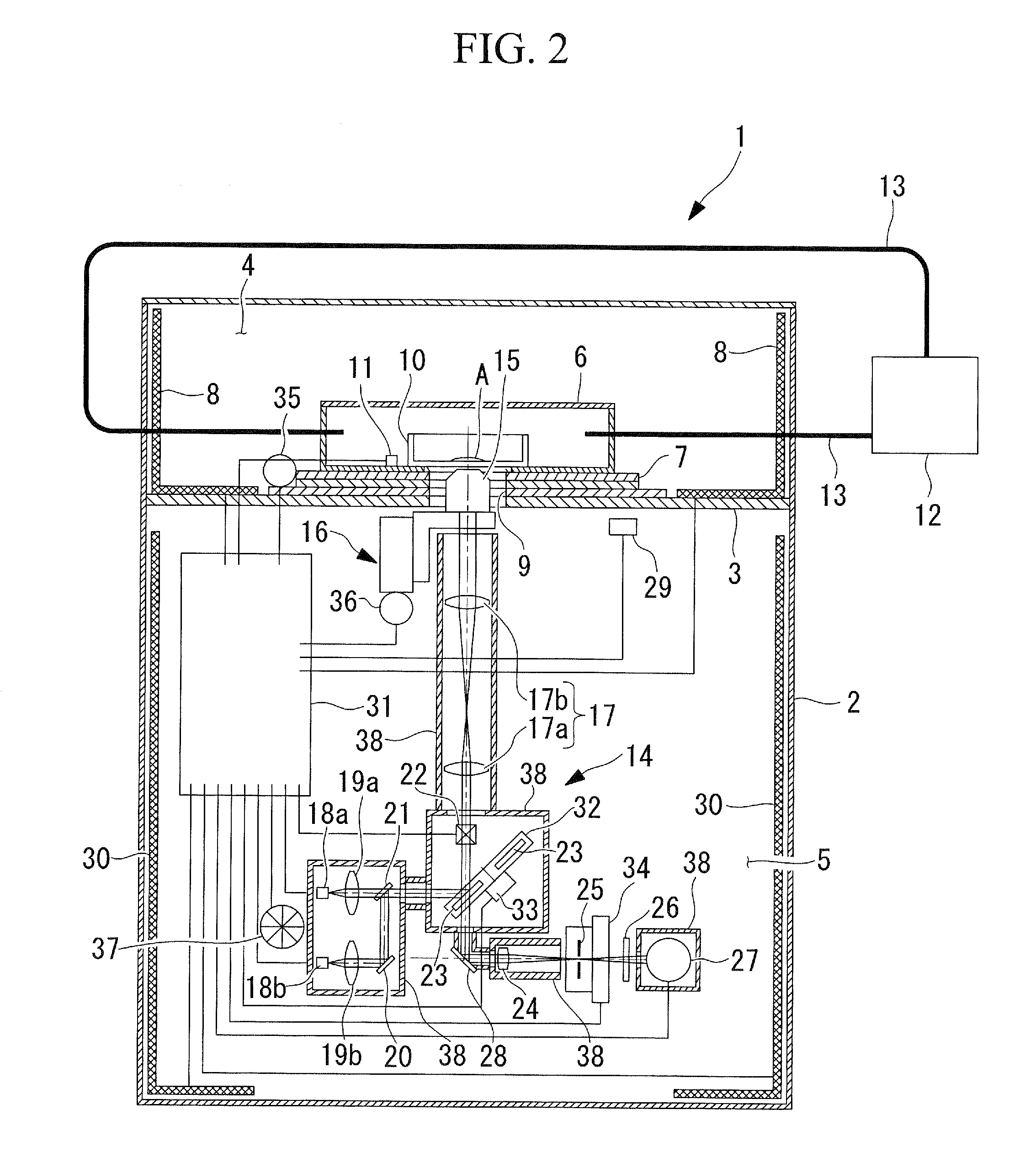
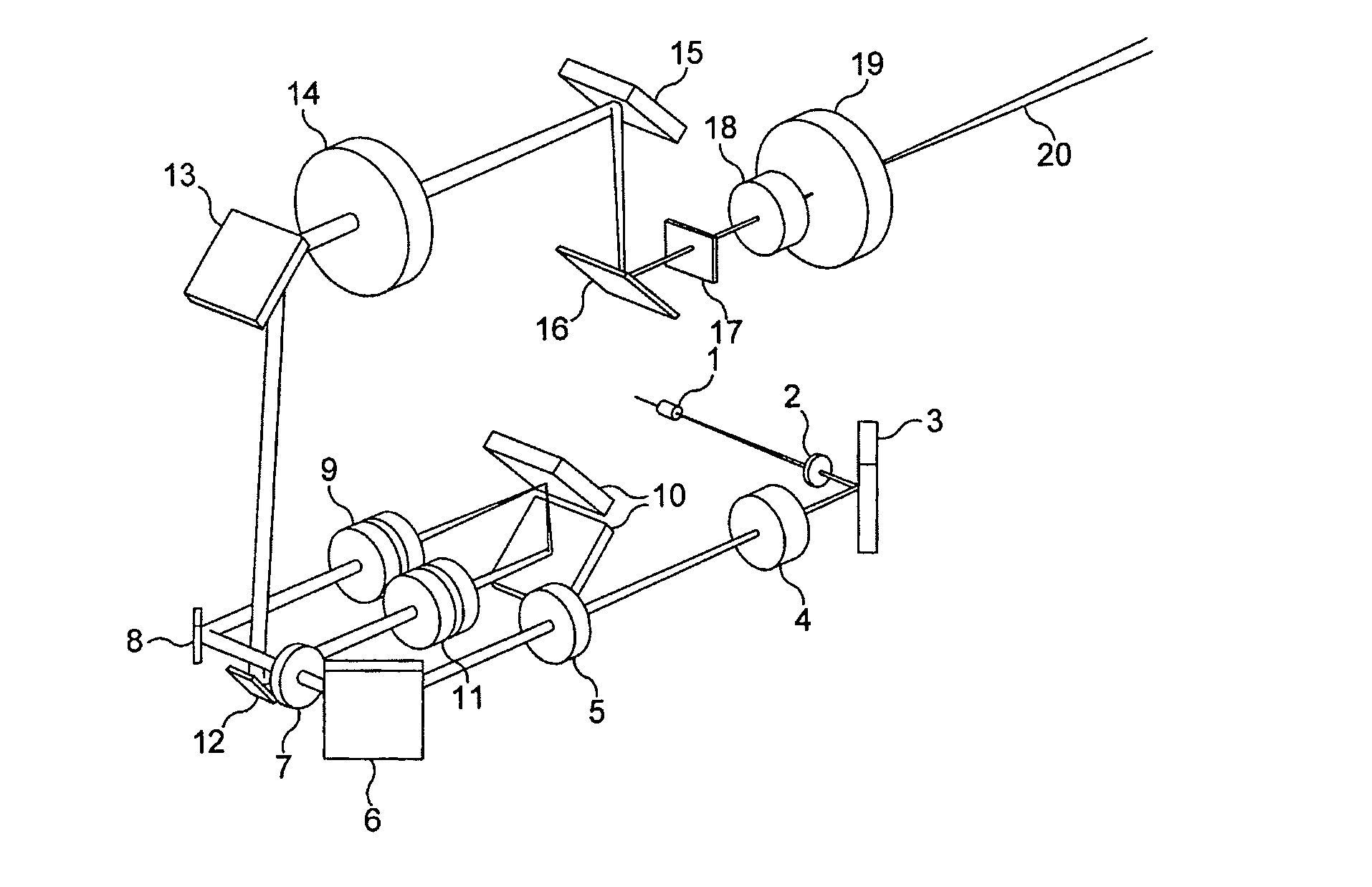
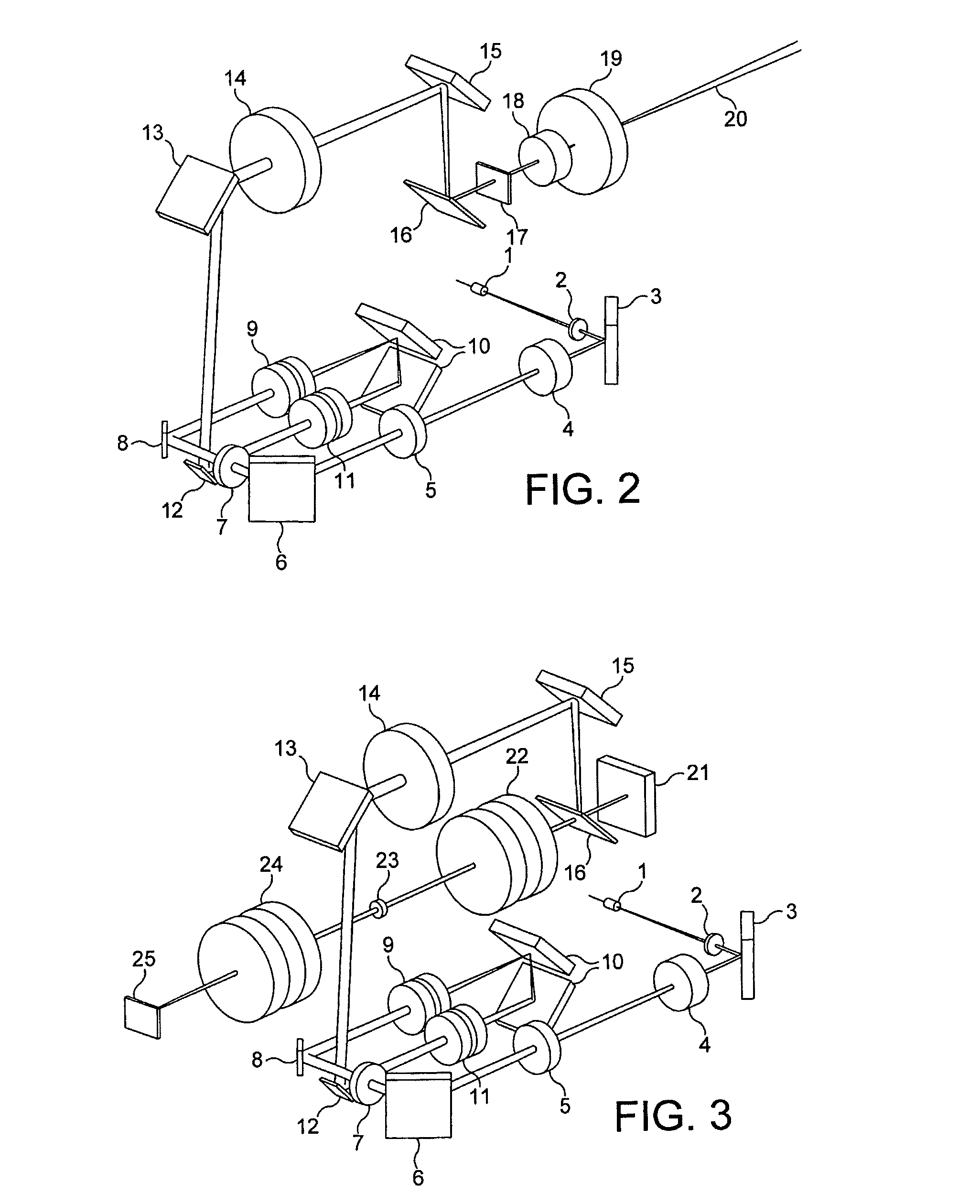
ActiveUS8284484B2Reduce sensitivity to angular misalignmentMicroscopesTelescopesBeam directionLight beam
An assembly (100) and a method are provided for inputting a light beam into a light path extending from the confocal scanning head (102) to the microscope (104) of a scanning confocal microscope system to illuminate a selected region of a sample mounted in the microscope. The assembly comprises a light input for receiving a light beam from a light source; beam directing means (8, 12) for controlling the path of the light beam with reference to the shape of the selected region of the sample; and a beam coupler (16) for selective coupling the light beam into the light path from the confocal scanning head (102) to the microscope (104), with the beam direction being controlled by the beam directing means so as to illuminate the selected region. A scanning confocal microscope system including such an assembly is also described, together with a method of calibrating the system. In addition, an optical switch for selectively switching a light beam between two paths is disclosed.
Owner:PEKINELMER SINGAPORE PTE LTD
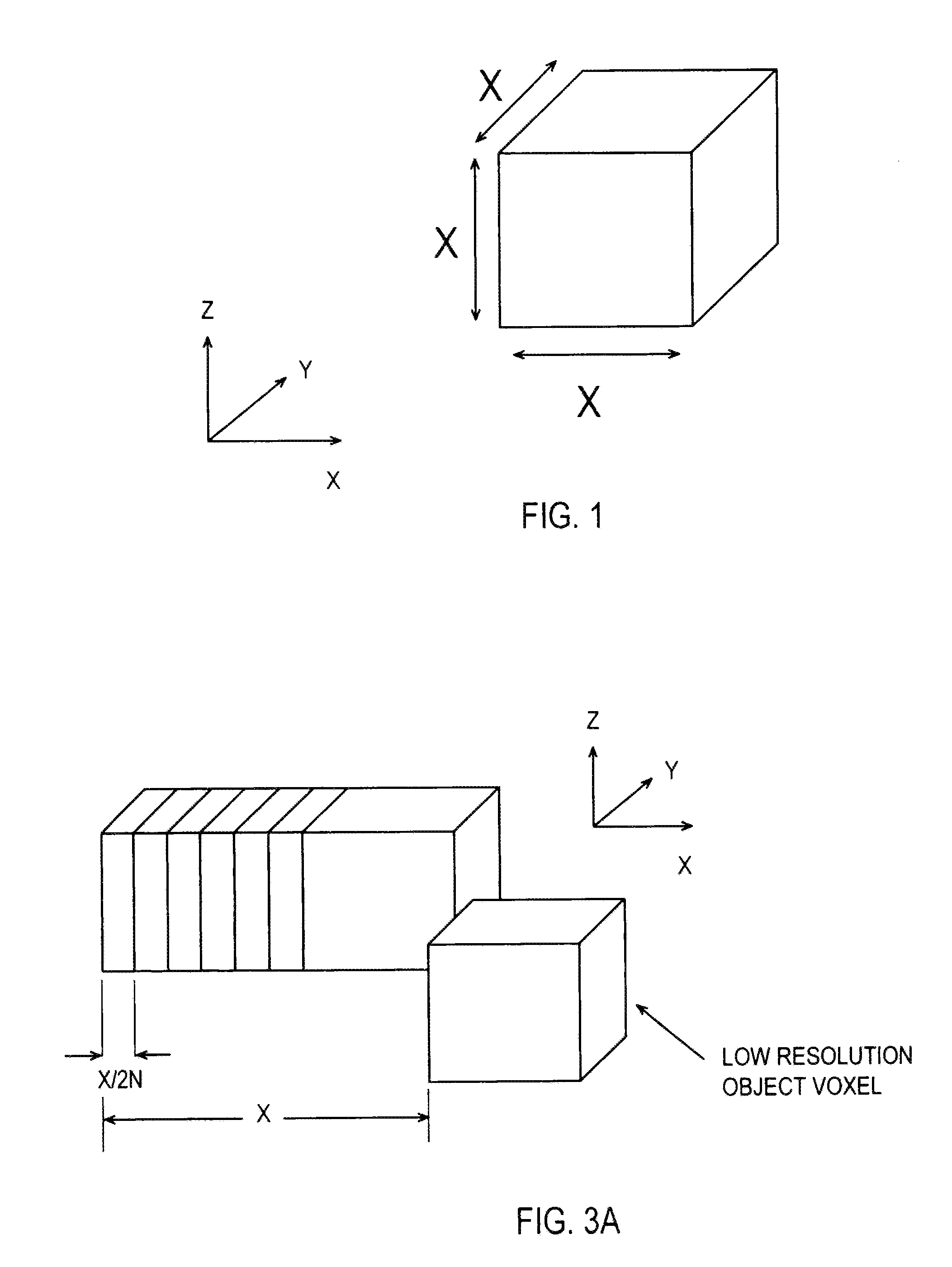
Methods and systems for realizing high resolution three-dimensional optical imaging
InactiveUS7978346B1Reduced dynamic rangeAccurate measurementUsing optical meansMicroscopesData setTest object
Methods and systems for realizing high resolution three-dimensional (3-D) optical imaging using diffraction limited low resolution optical signals. Using axial shift-based signal processing via computer based computation algorithm, three sets of high resolution optical data are determined along the axial (or light beam propagation) direction using low resolution axial data. The three sets of low resolution data are generated by illuminating the 3-D object under observation along its three independent and orthogonal look directions (i.e., x, y, and z) or by physically rotating the object by 90 degrees and also flipping the object by 90 degrees. The three sets of high resolution axial data is combined using a unique mathematical function to interpolate a 3-D image of the test object that is of much higher resolution than the diffraction limited direct measurement 3-D resolution. Confocal microscopy or optical coherence tomography (OCT) are example methods to obtain the axial scan data sets.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
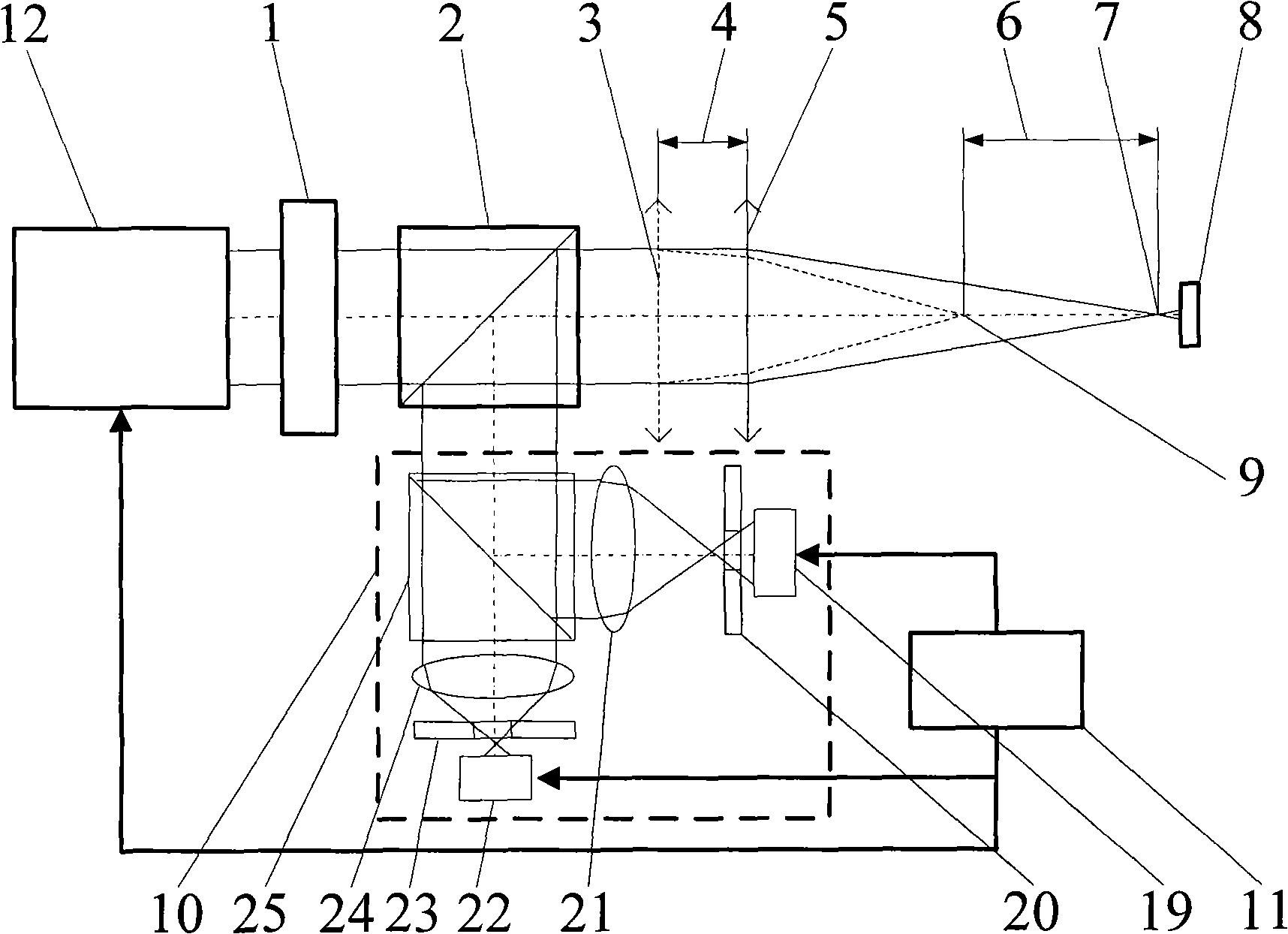
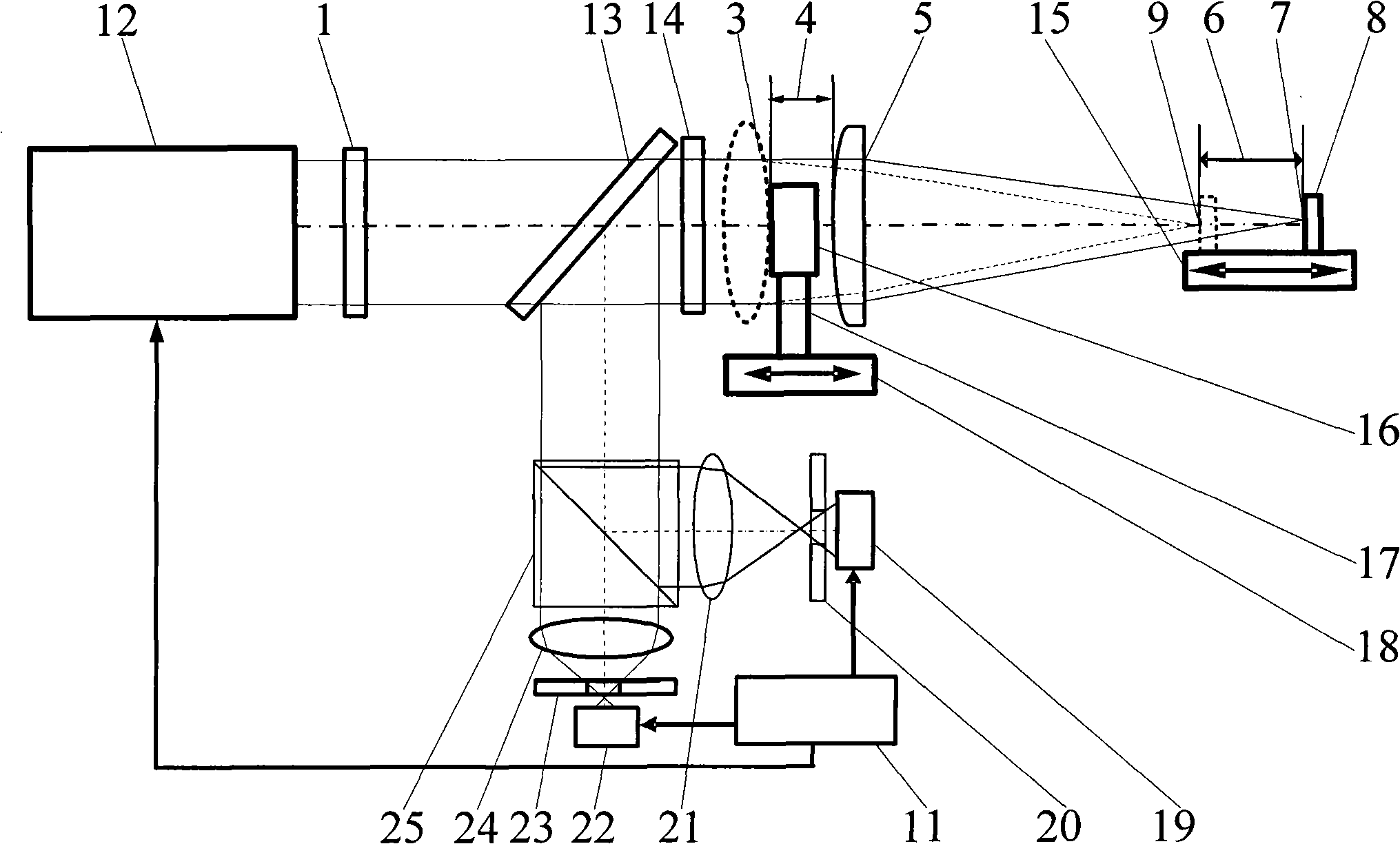
Confocal microscope
InactiveCN1395127AIncrease horizontal resolutionHigh precisionMicroscopesBeam splitterConfocal microscopy
The invented confocal microscope includes the light source part, the beam splitter mirror, the object lens, the worktable used for placing the sample, the conjugate diaphragm and the first detector. The beam splitter mirror splits the incident light into the transmission light and the reflected light. The conjugate diaphragm is conjugated with the focus point of the object lens. The light source part generates the coherent light. The microscope also includes the reflector. One of the transmitted light or reflected light through the object lens irradiates the sample. The other light irradiates the reflector. The light reflected from the sample passes the object lens, going to the beam splitter mirror where it meets the light reflected from the reflector so as to form the interference figure output from the conjugate diaphragm.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
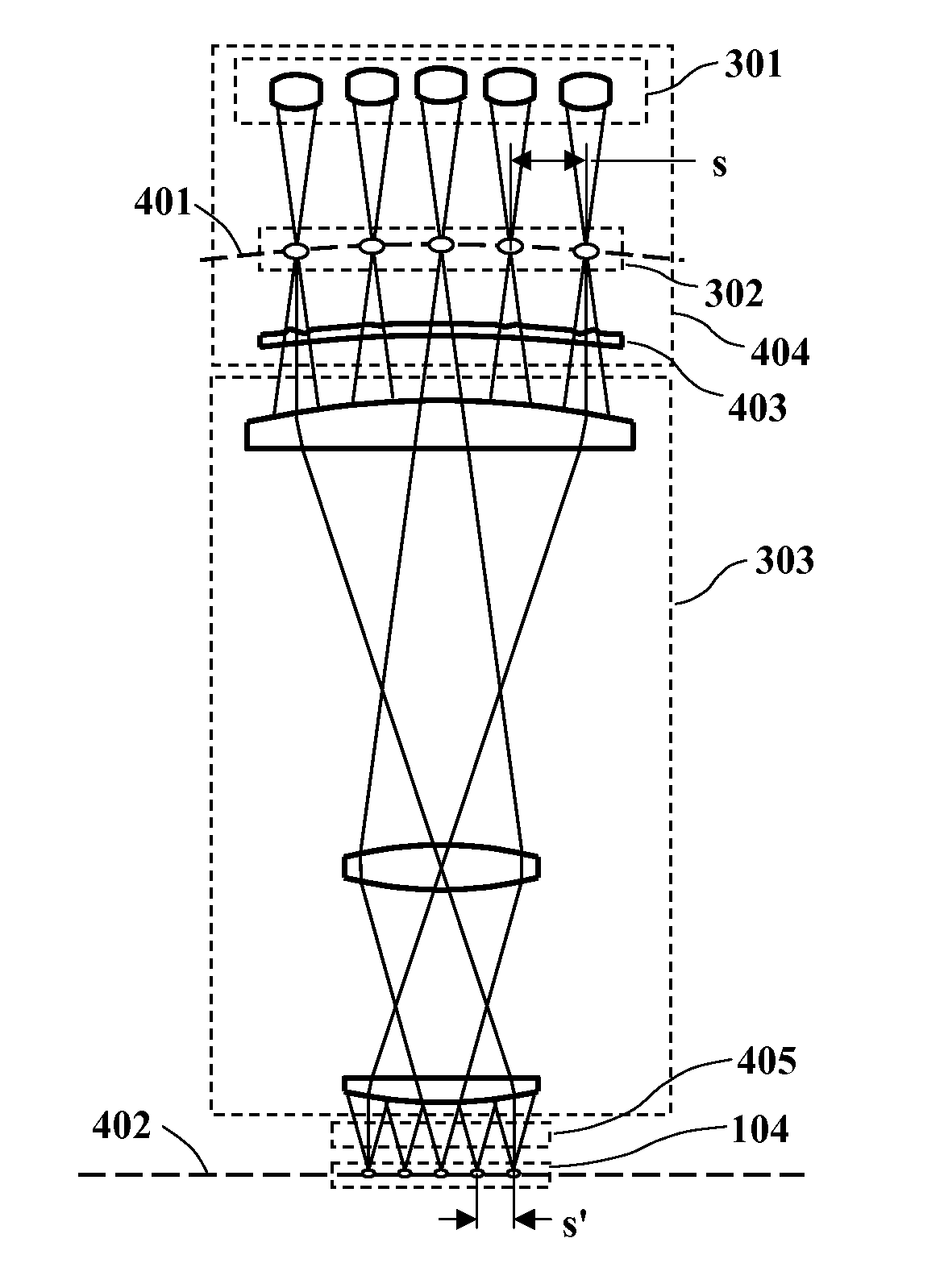
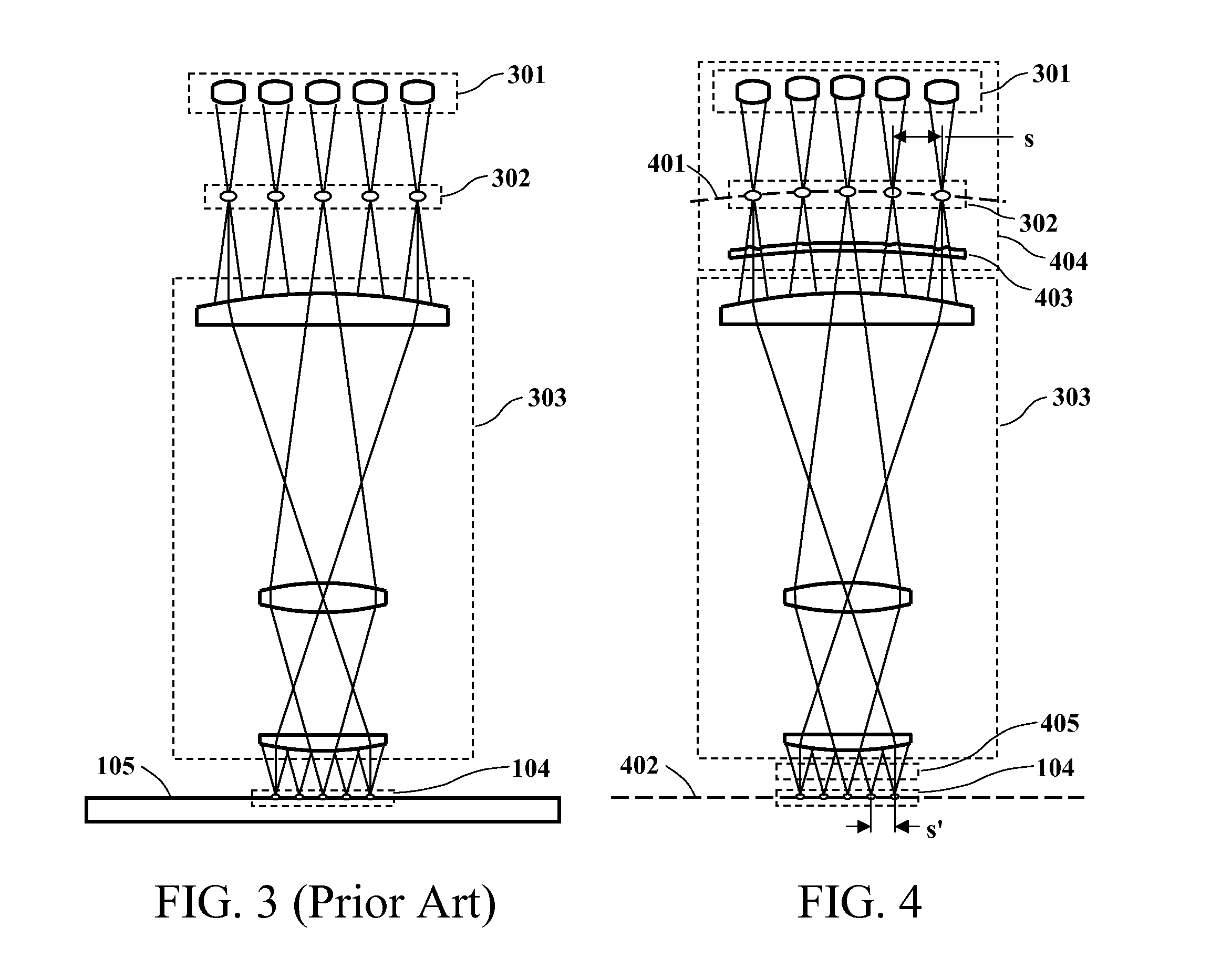
Confocal microscope comprising two microlens arrays and a pinhole diaphragm array
A confocal microscope comprises a microlens array having a plurality of microlenses for splitting a ray bundle of illumination light into a plurality of convergent partial ray bundles which illuminate a sample simultaneously at several measuring points; a beam splitter for separating a beam path of the illuminating light and a beam path of sample light originating from the illumination of the sample and captured in an inverse direction with regard to the illumination light; a pinhole diaphragm array having a plurality of pinhole diaphragms arranged in the beam path of the sample light and corresponding to said microlenses of said microlens array splitting the illumination light; and a further microlens array having a plurality of microlenses corresponding to said microlenses of said microlens array splitting the illumination light. Said microlenses of said microlens array splitting the illumination light and said microlenses of said further microlens array are arranged in the beam path of the sample light. Said beam splitter is arranged in an area between said microlens array splitting the illumination light and said further microlens array; and said pinhole diaphragms of said pinhole diaphragm array are not arranged in the area between said microlens array splitting the illumination light and said further microlens array.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
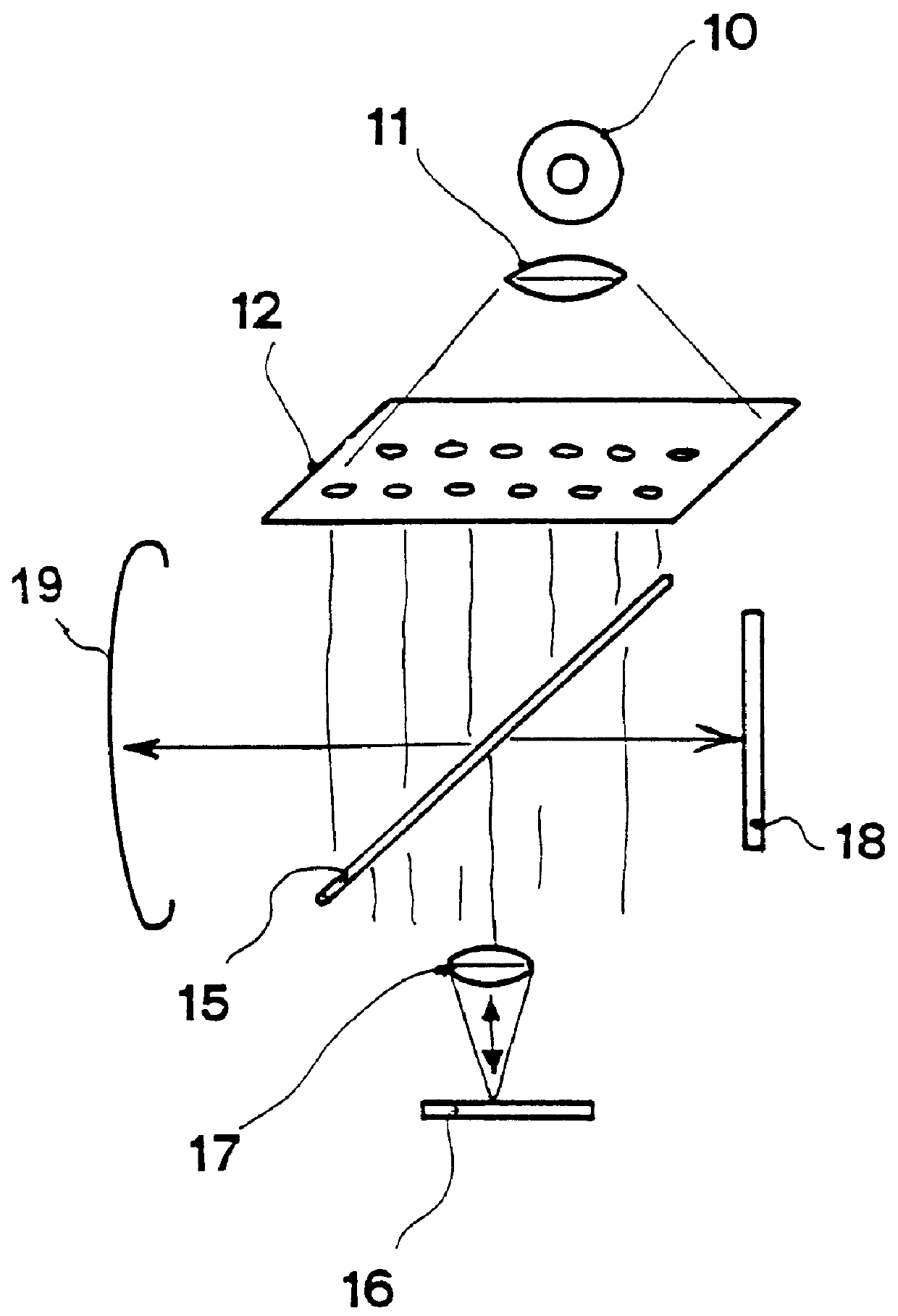
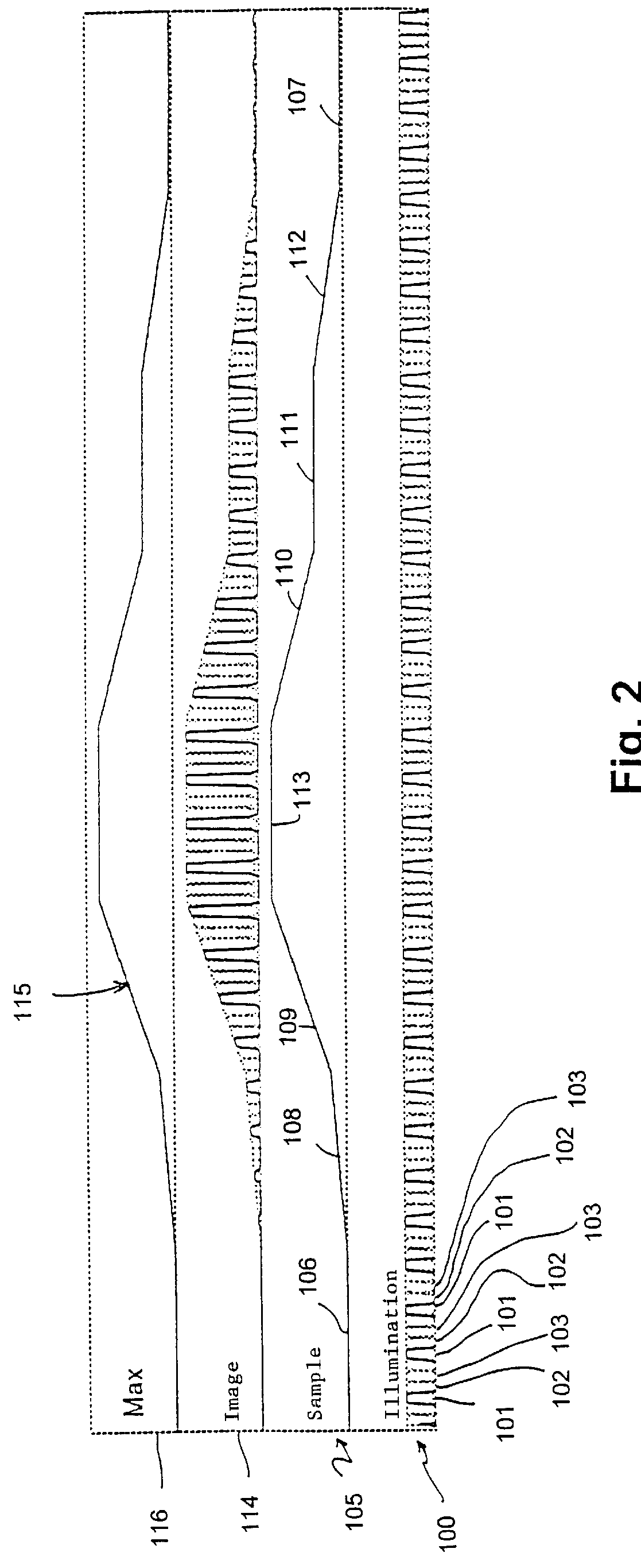
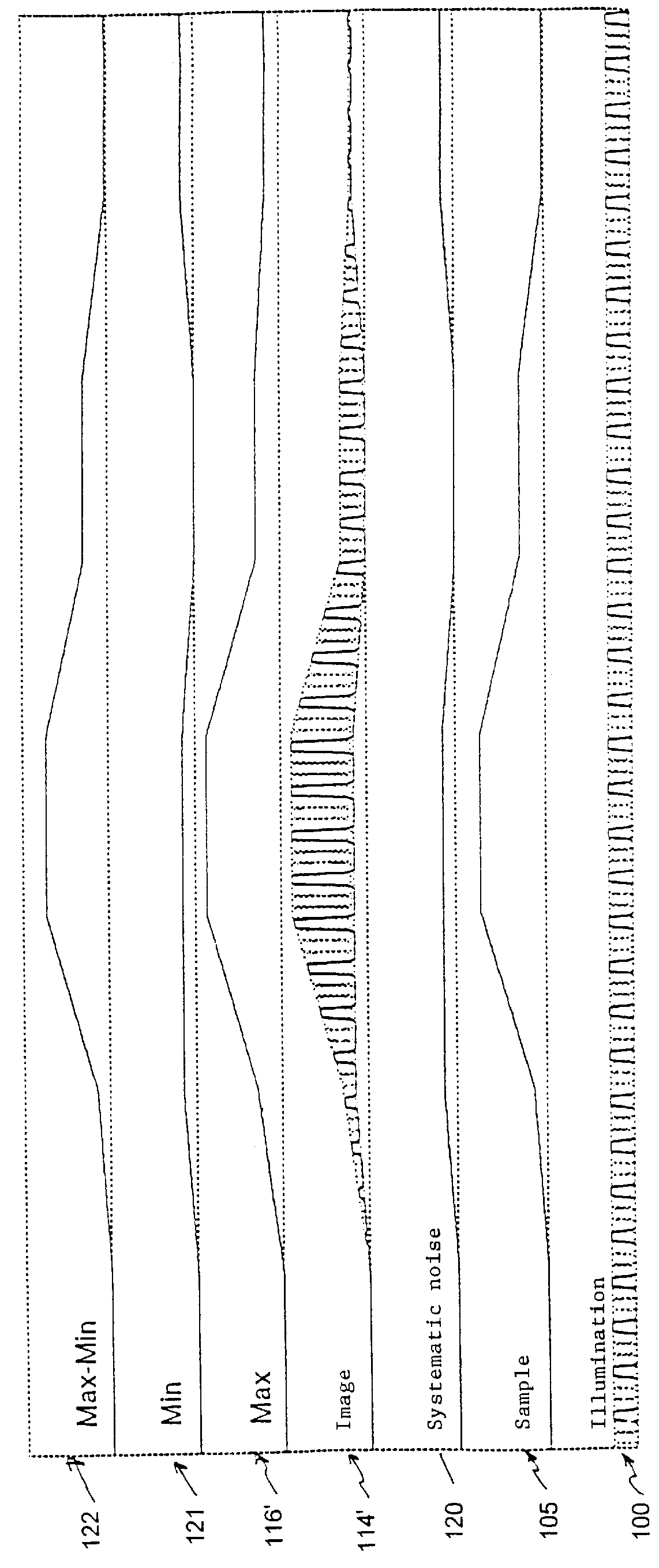
Method for the acquisition of images by confocal microscopy
InactiveUS6016367AEnhanced confocal characteristicReduced scattering effectImage enhancementBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsConfocal scanning microscopyComputer vision
A method for the acquisition of images by means of confocal microscopy in which a new image is calculated which is constituted by the "maxima" among the corresponding elements of each captured image. The new image contains mainly the signal coming from the most luminous and in focus areas and even the signal coming from the less luminous areas, as being out of focus or laterally displaced with respect to the grid positions. A further image is then calculated which is constituted by the "minima" among the corresponding elements of each captured image and the requested confocal image is then obtained by calculating the difference between the "maxima" image and the "minima" image.
Owner:CONSIGLIO NAT DELLE RICERCHE
Confocal microscope
In A confocal microscope, a mirror reflects illumination light to focus on a focal point face of a sample through an object lens. The mirror is rotated to scan a focal point of the illumination light. A confocal image provided based on returned light from the sample. The confocal microscope has a first multipinhole array which has a plurality of pinholes, and to which light emitted from a light source is illuminated, and a second multipinhole array which has a plurality of pinholes, and intercepts light from other than the focal point face out of the returned light from the sample. The first multipinhole array functions as a plurality of point light sources, and the illumination light is light which passes through the pinholes of the first multipinhole array.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Differential confocal curvature radius measurement method and device
InactiveCN101526341AAchieve precise focusReduce the impact of measurement accuracyUsing optical meansPupilConfocal microscopy
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement and relates to a differential confocal lens curvature radius measurement method and a device. The method firstly utilizes the differential confocal focusing principle to respectively determine the positions of a top point and a spherical center of a measured lens and then measures the distance between the two focuses; meanwhile, the curvature radius measurement sensitivity can be improved by the pupil filtering technology during the measurement process. The invention firstly proposes to utilize the characteristic that a differential confocal response curve is corresponding to the top point and the spherical center of the measured lens when passing a zero point to realize the precise focusing, expands the application of differential confocal microscopy principle to the field of curvature radius measurement and forms the differential confocal focusing principle. The invention applies the differential confocal focusing principle and has the advantages of high measurement precision and strong anti-environmental interference ability, thereby being capable of being used in the detection of the lens curvature radius and the high-precision curvature radius measurement during the optical system assembly process.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Three-dimensional confocal microscope
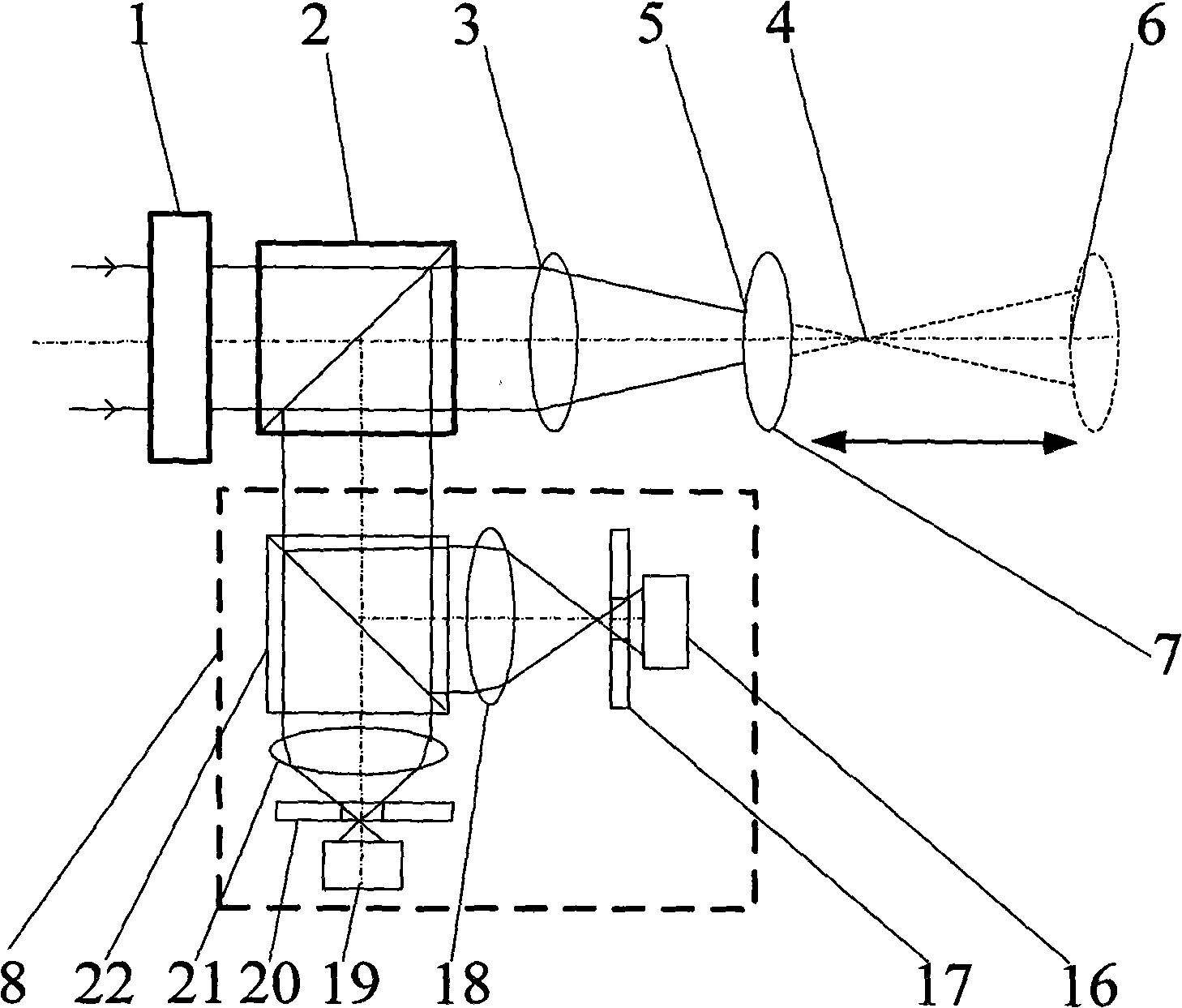
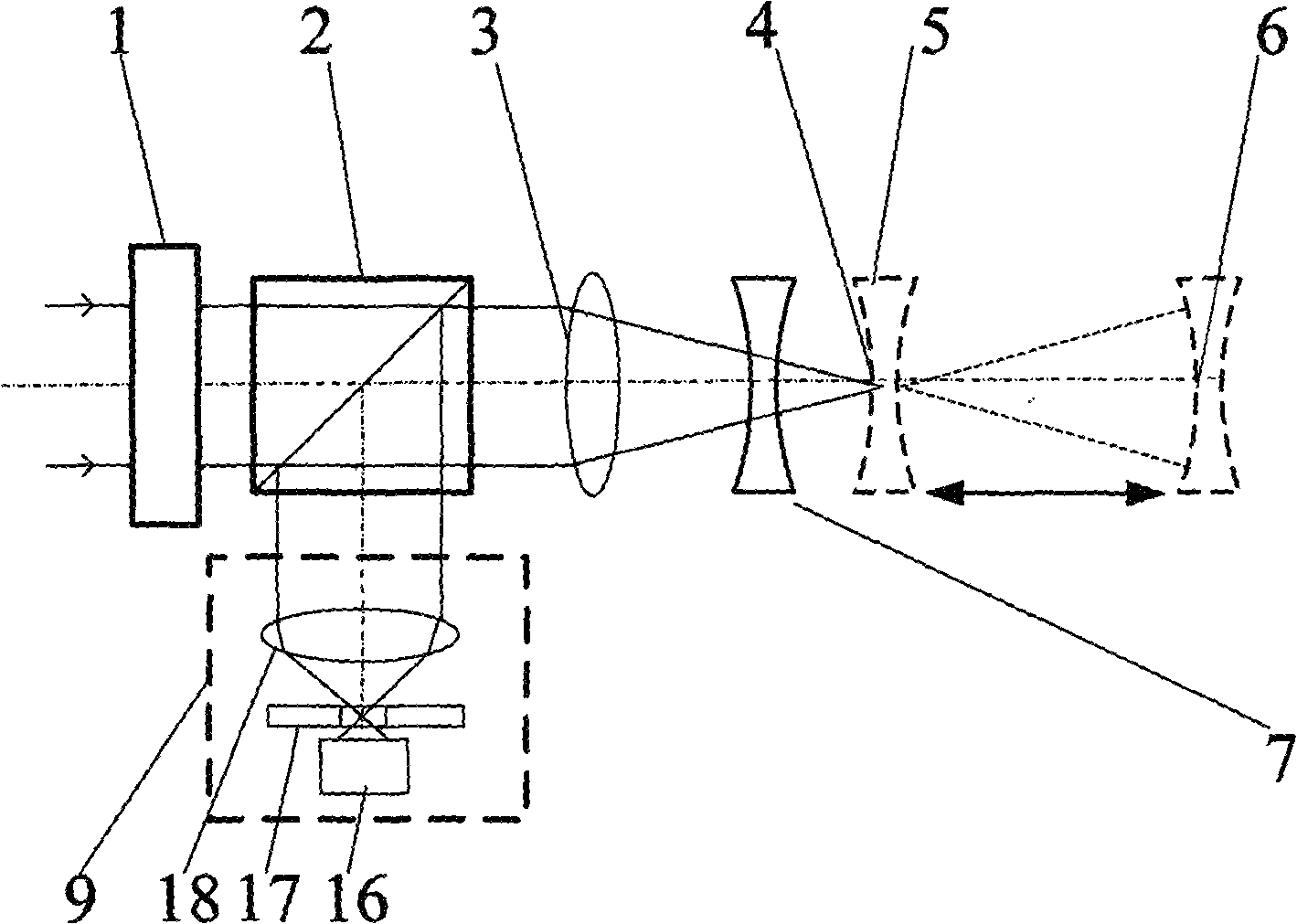
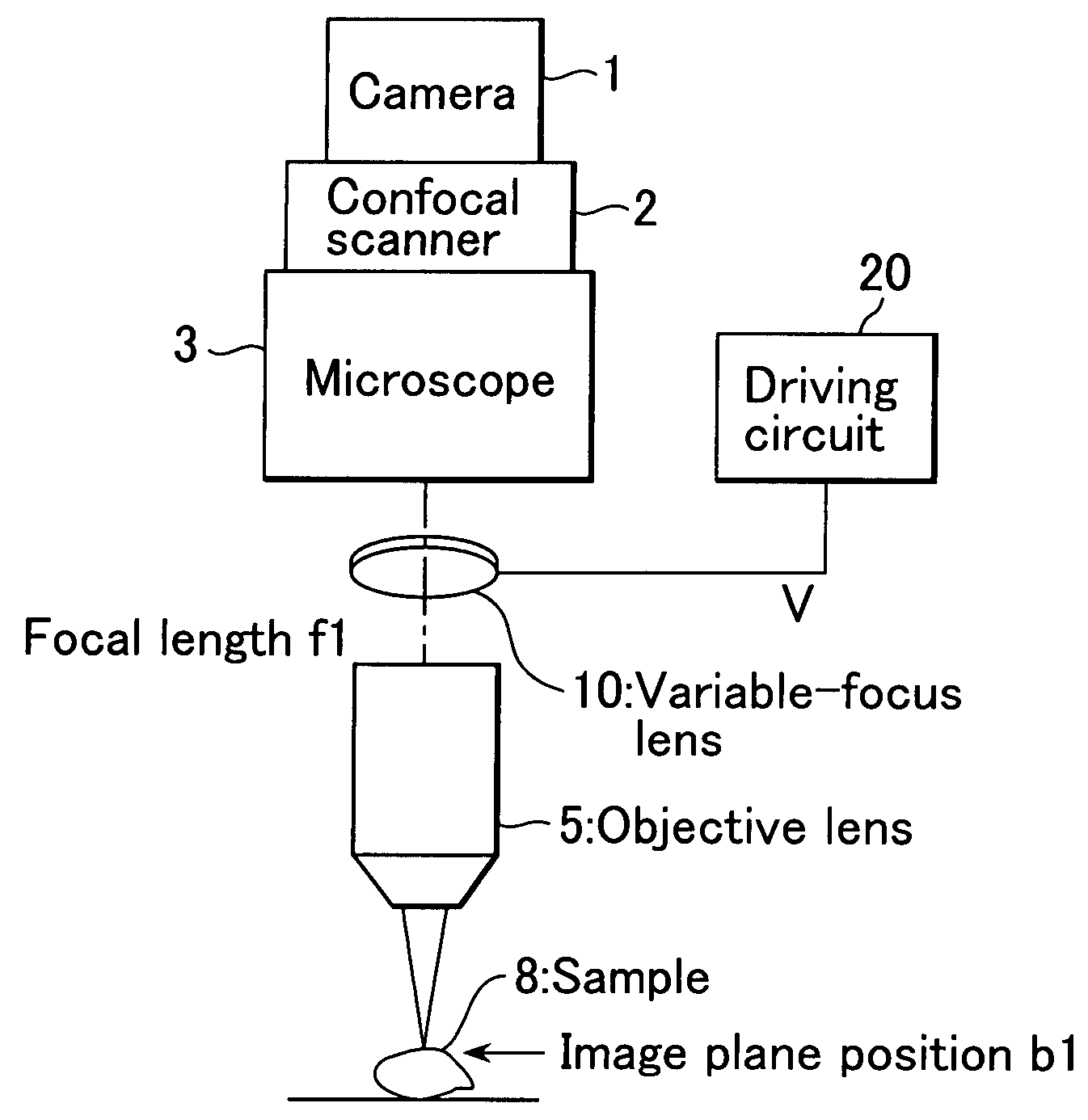
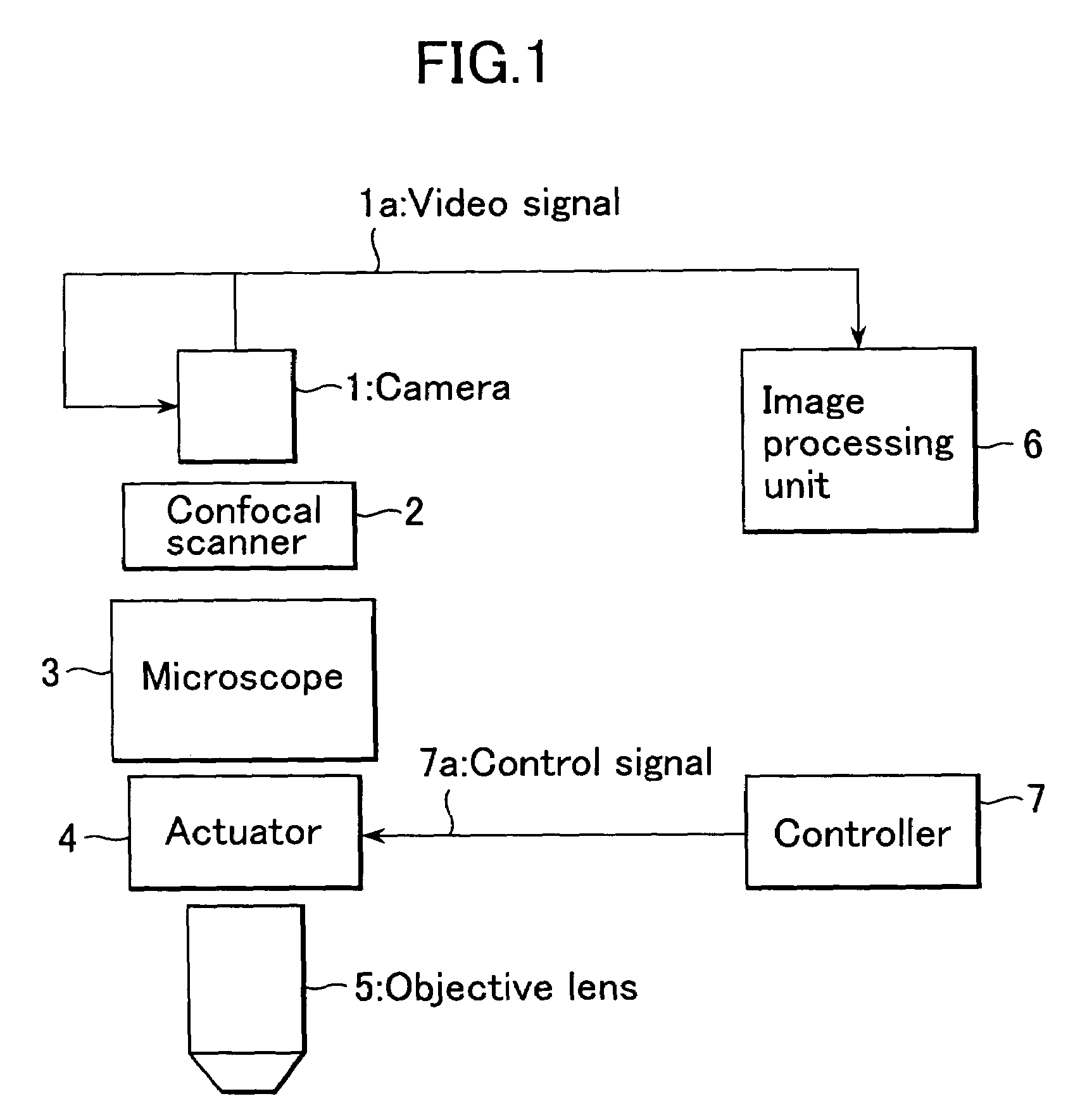
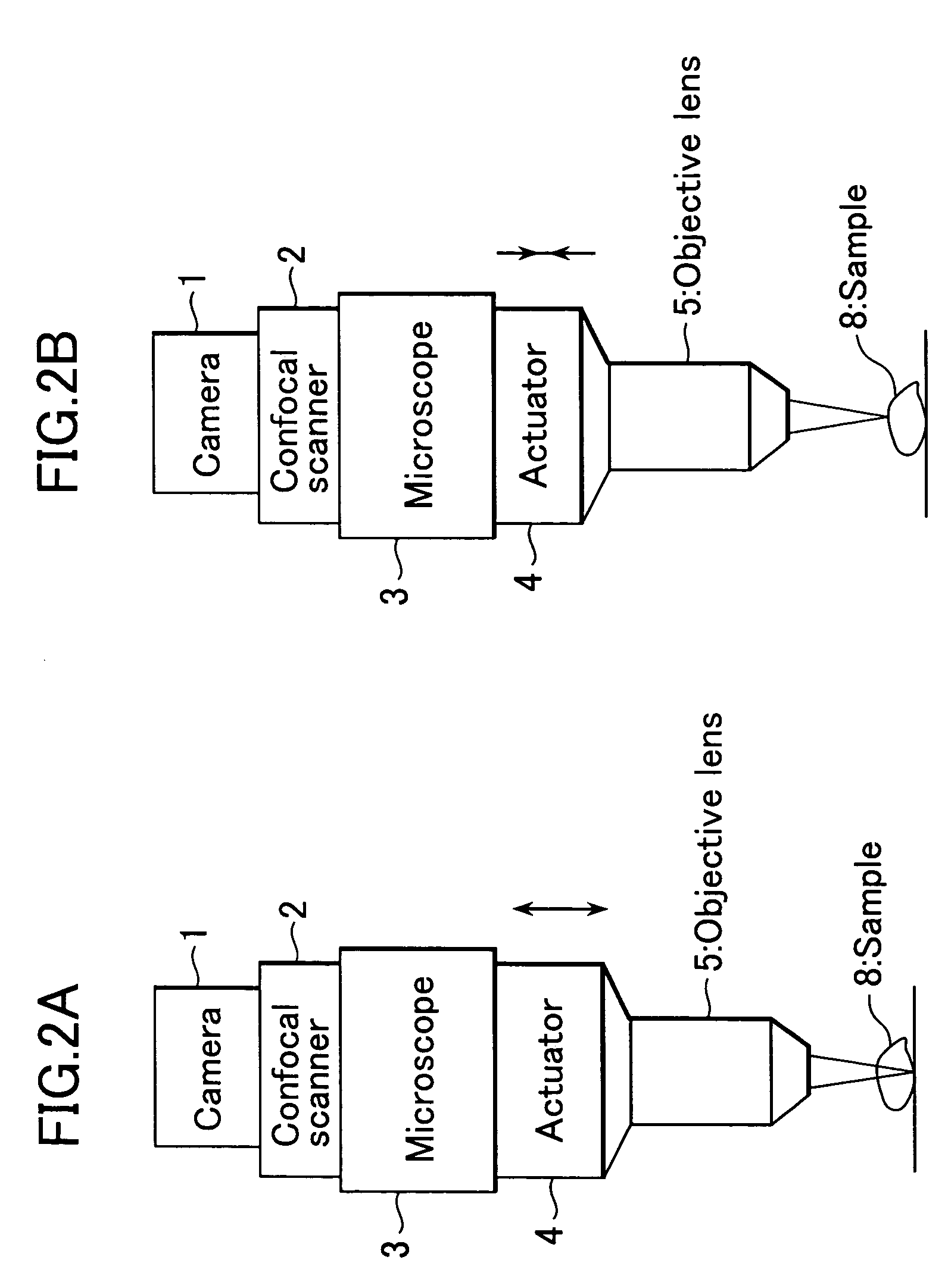
This invention realizes a three-dimensional confocal microscope in which mechanical vibrations do not occur in the scanning unit for scanning in the direction of optical axis, and in which scanning in the direction of optical axis can be carried out at a high speed. This invention has the following features. In the confocal microscope having a confocal scanner attached to an optical microscope and constructed to enable acquisition of an image of a sample as a confocal image by the confocal scanner, a variable-focus lens of surface tension control type having no moving part is uses as the field lens.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Spot-array imaging system for maskless lithography and parallel confocal microscopy
ActiveUS9188874B1Ensure correct executionCorrect chromatic aberrationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMicroscopesCamera lensGrating
In a scanned-spot-array lithography system, a modulated array of radiant-energy source spots is imaged by a projection lens onto a printing surface, which is scanned in synchronization with the spot modulation to print a synthesized, high-resolution raster image. Similarly, in a scanned-spot-array microscopy system, an array of radiant-energy source spots is imaged by a projection lens onto an inspection surface, and radiation reflected from or transmitted through the image spots is collected and detected to acquire a synthesized, high-resolution raster image of the surface. In either case, the spot-generation optics can be configured to counterbalance and neutralize imperfect imaging characteristics of the projection lens, enabling perfectly flat-field, distortion-free, and aberration-free point imaging of the entire spot array. The spot-generation optics can also be further configured to achieve narrow-band achromatization of the optical system, and to optimally control the intensity and polarization characteristics of the image-plane radiation.
Owner:JOHNSON KENNETH C
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com