Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
243 results about "Vibration compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
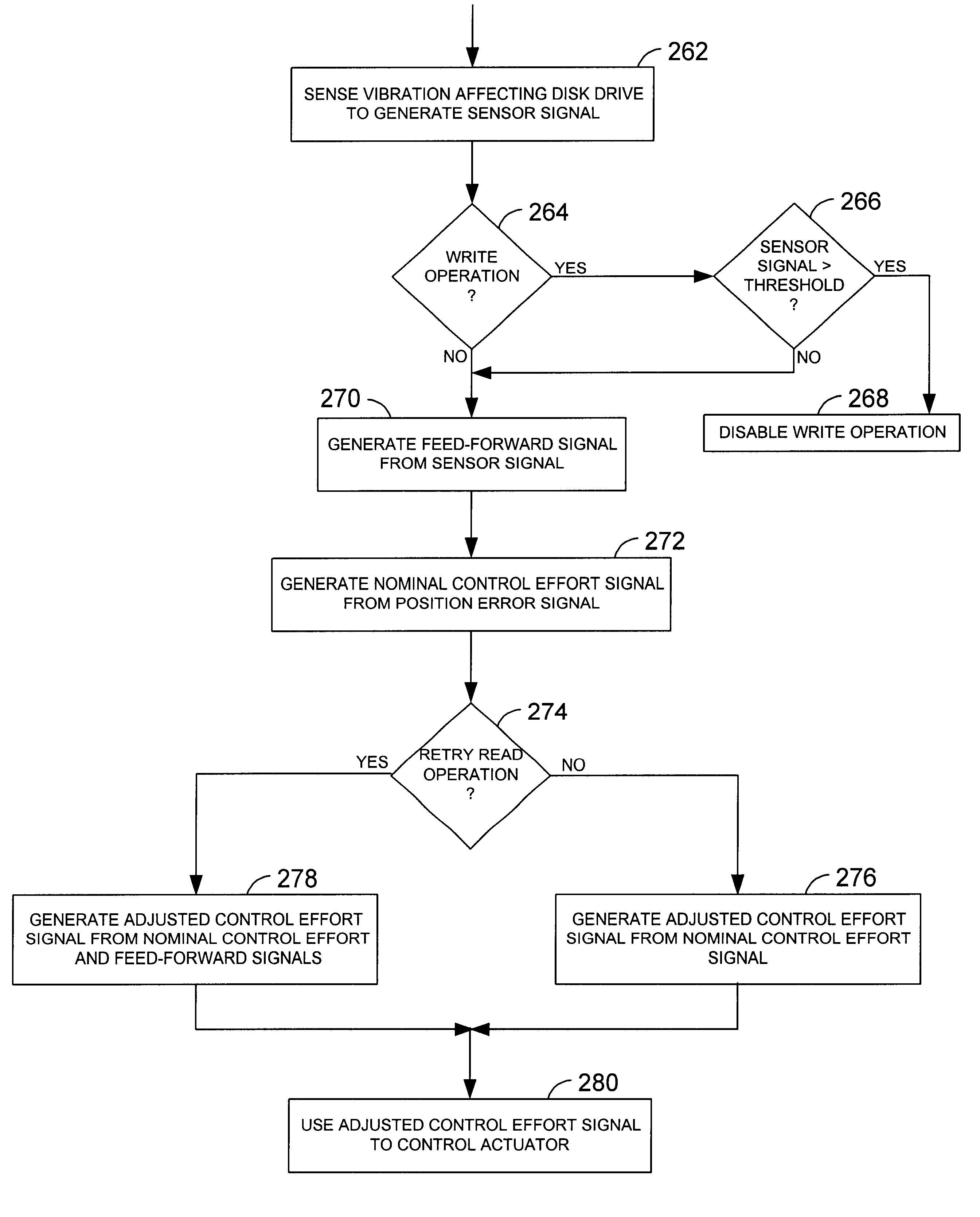
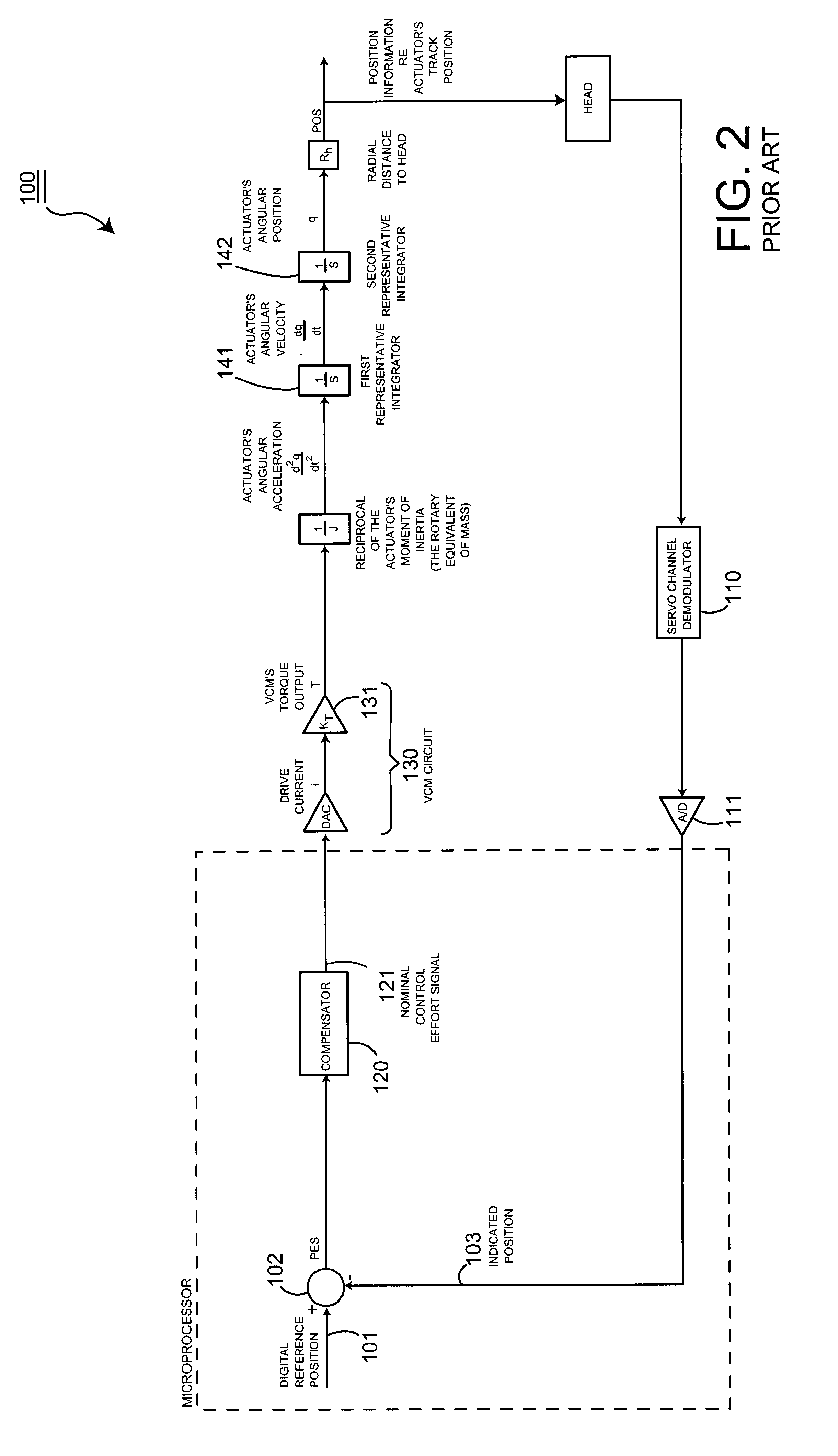
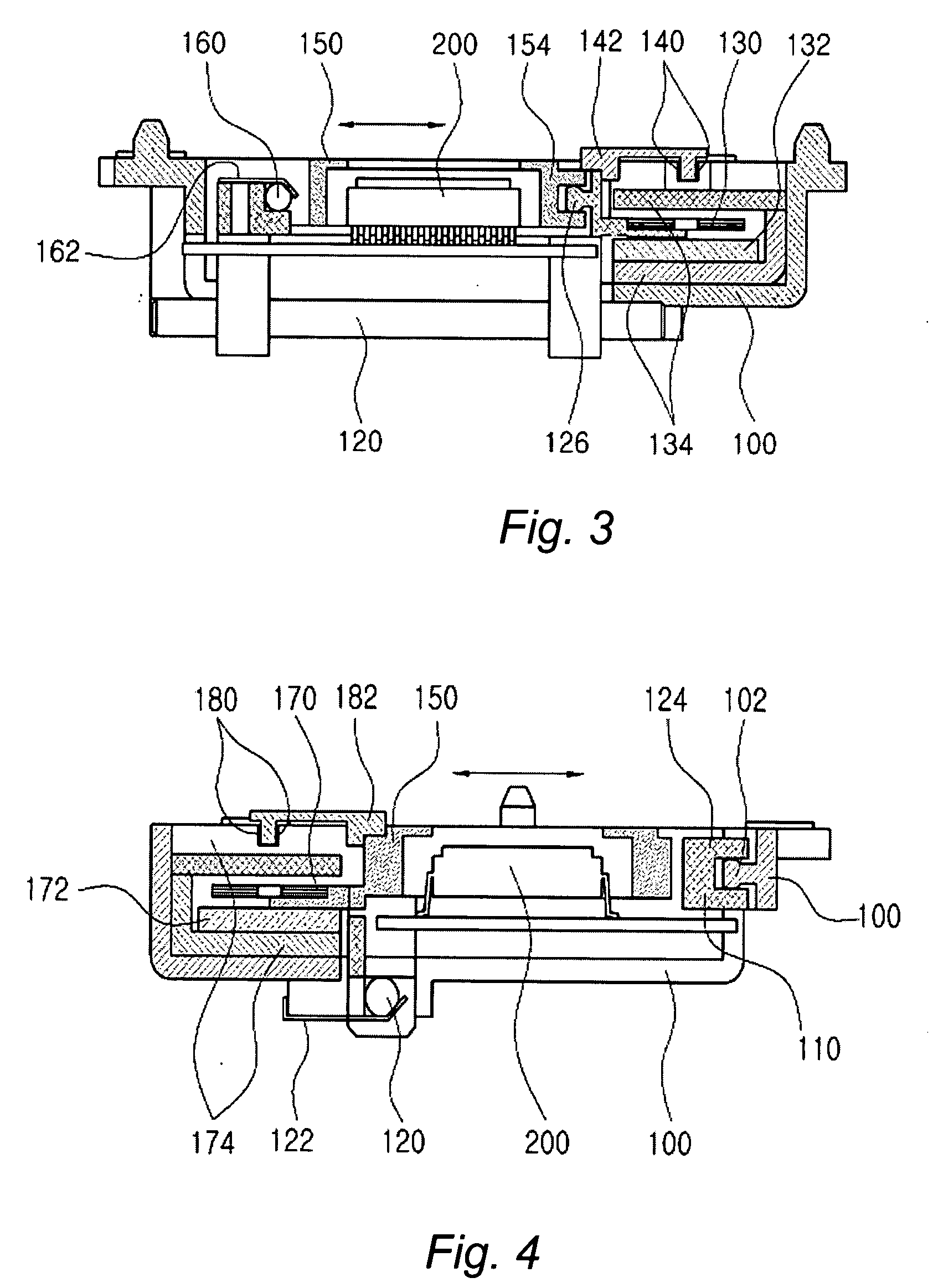
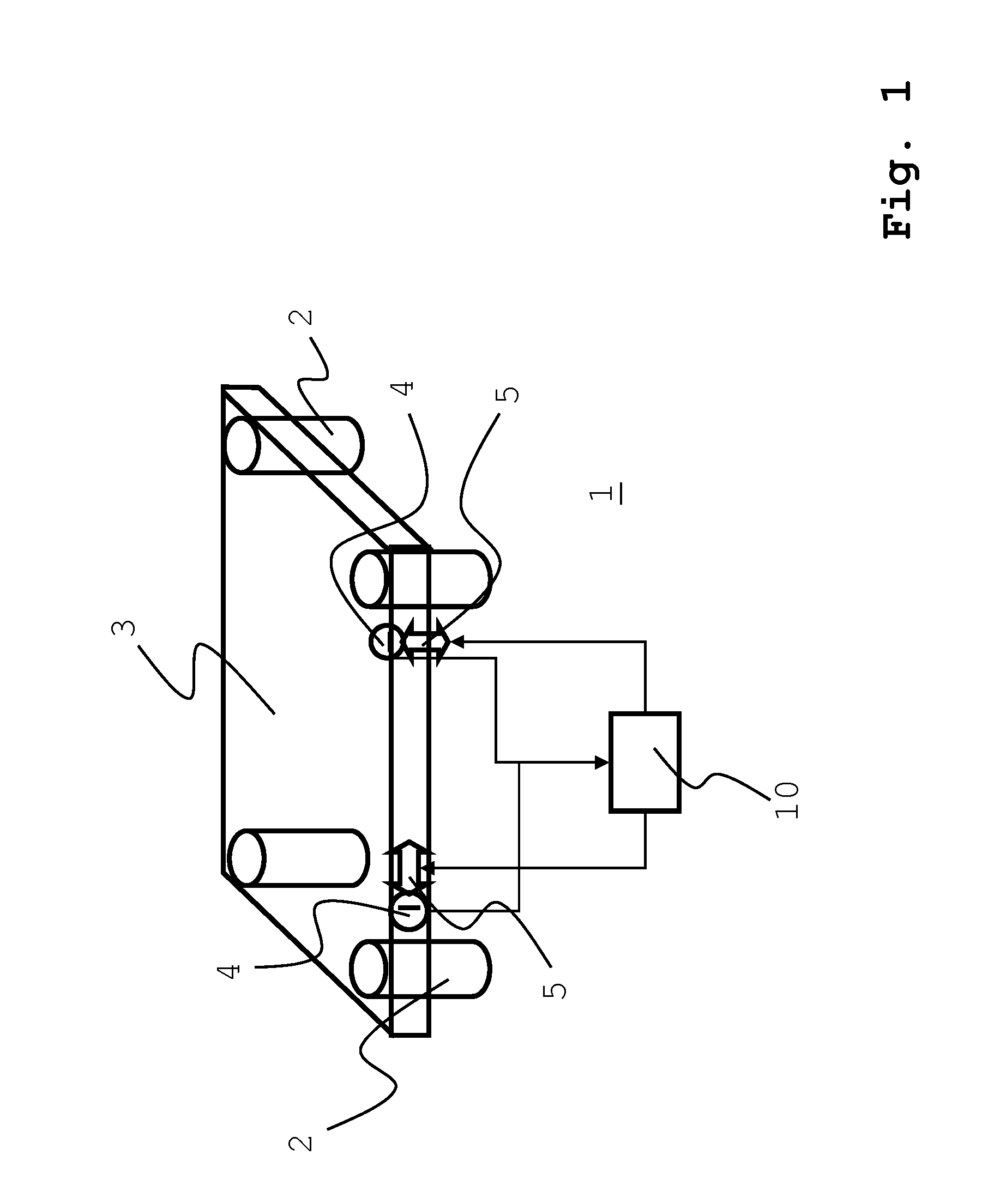
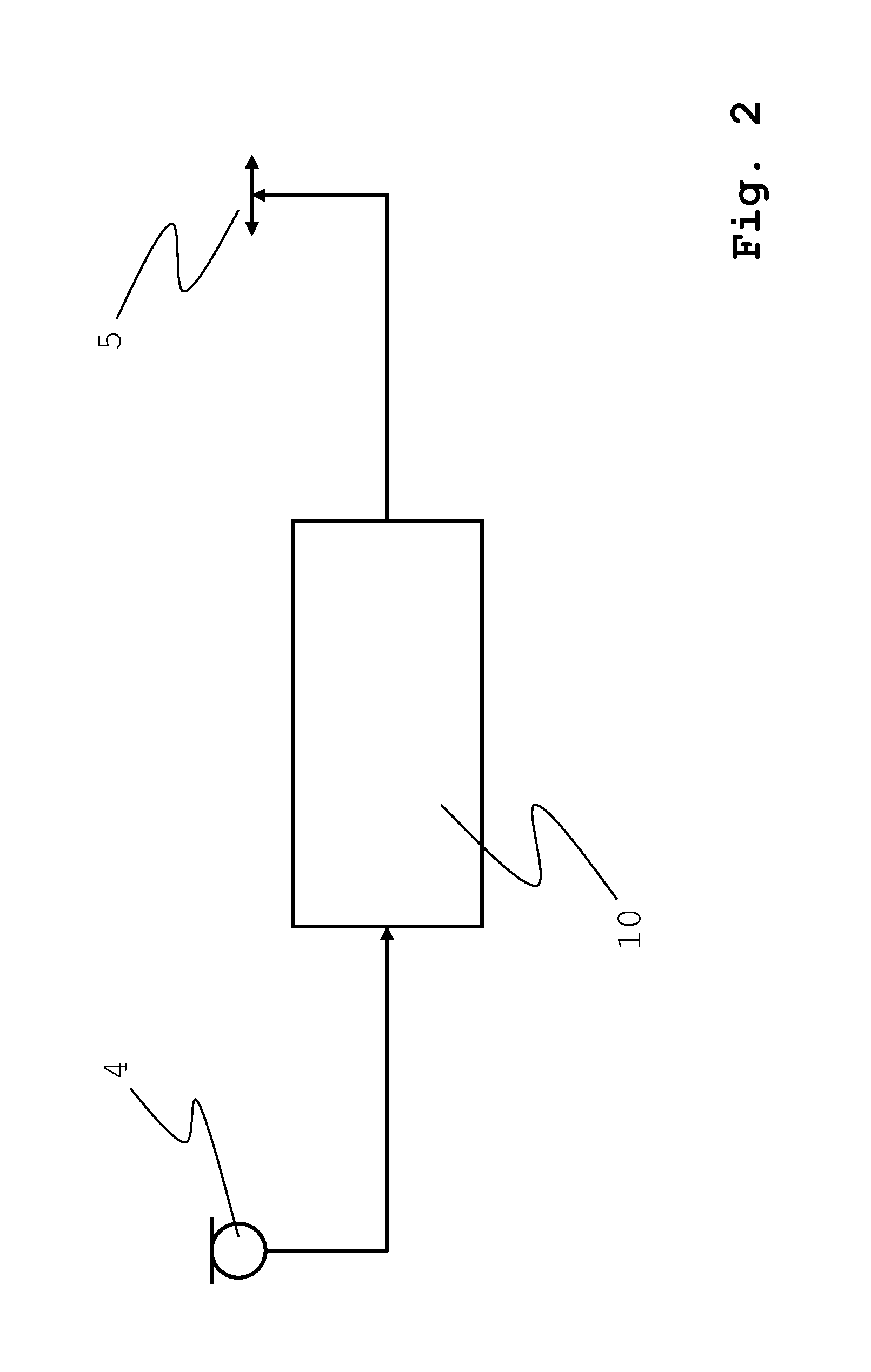
Disk drive employing adaptive feed-forward vibration compensation to enhance a retry operation
A disk drive is disclosed comprising a head, and an actuator, responsive to an adjusted control effort signal, for actuating the head radially over a disk. An adaptive feed-forward signal is generated in response to a vibration affecting the disk drive and combined with a nominal control effort signal to generate the adjusted control effort signal. During a normal read operation the feed-forward signal is substantially removed from the adjusted control effort signal, and during a retry read operation the feed-forward signal is included in the adjusted control effort signal.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
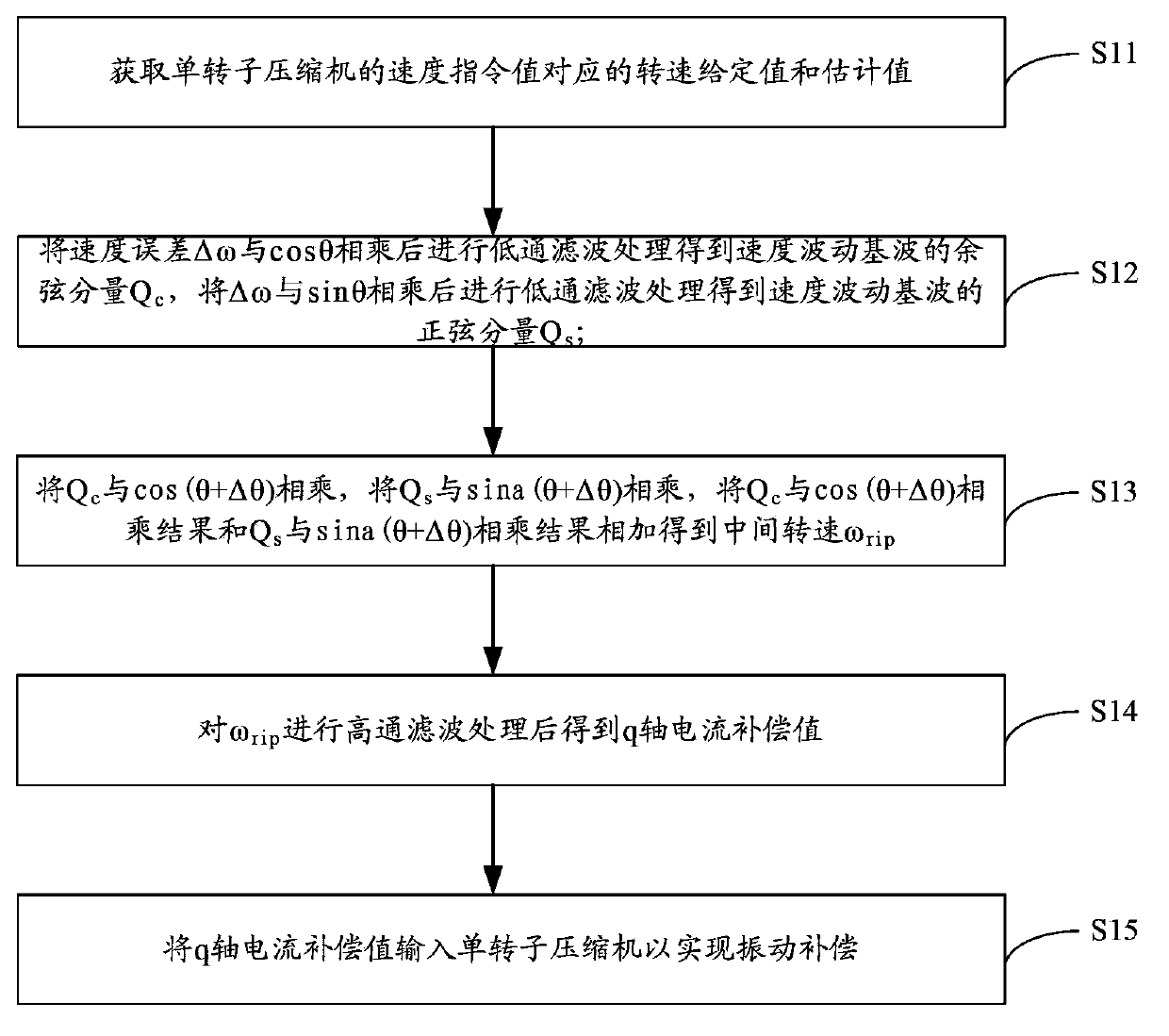
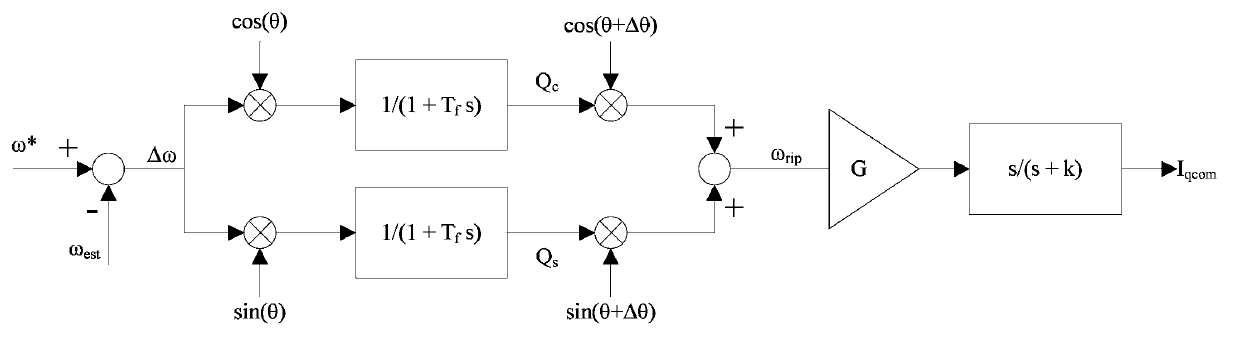
Vibration compensation method for single-rotor compressor and controller
ActiveCN103967794AReduce vibrationImprove noiseRotary/oscillating piston pump componentsLiquid fuel engine componentsVibration compensationHigh-pass filter
The invention is applicable to the technical field of household electrical appliances and provides a vibration compensation method for a single-rotor compressor and a controller. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a rotating speed set value omega* and a rotating speed estimated value omega e corresponding to a speed command value; multiplying a speed error delta omega by cos theta, carrying out low pass filtering so as to obtain the cosine component Qc of a speed fluctuation fundamental wave, multiplying delta omega by sin theta and carrying out low pass filtering so as to obtain the sine component Qs of the speed fluctuation fundamental wave; multiplying Qc by cos (theta+delta theta), multiplying Qs by sin (theta+delta theta) and adding the result of multiplication of Qc by cos (theta+delta theta) and the result of multiplication of Qs by sin (theta+delta theta) together so as to obtain an intermediate rotating speed omega rip; subjecting omega rip to high pass filtering so as to obtain a q-shaft current compensation value; and inputting the q-shaft current compensation value into the single-rotor compressor to realize vibration compensation. With the technical scheme provided by the invention, the advantages of reduction in vibration of the single-rotor compressor and easy realization are obtained.
Owner:GD MIDEA AIR-CONDITIONING EQUIP CO LTD
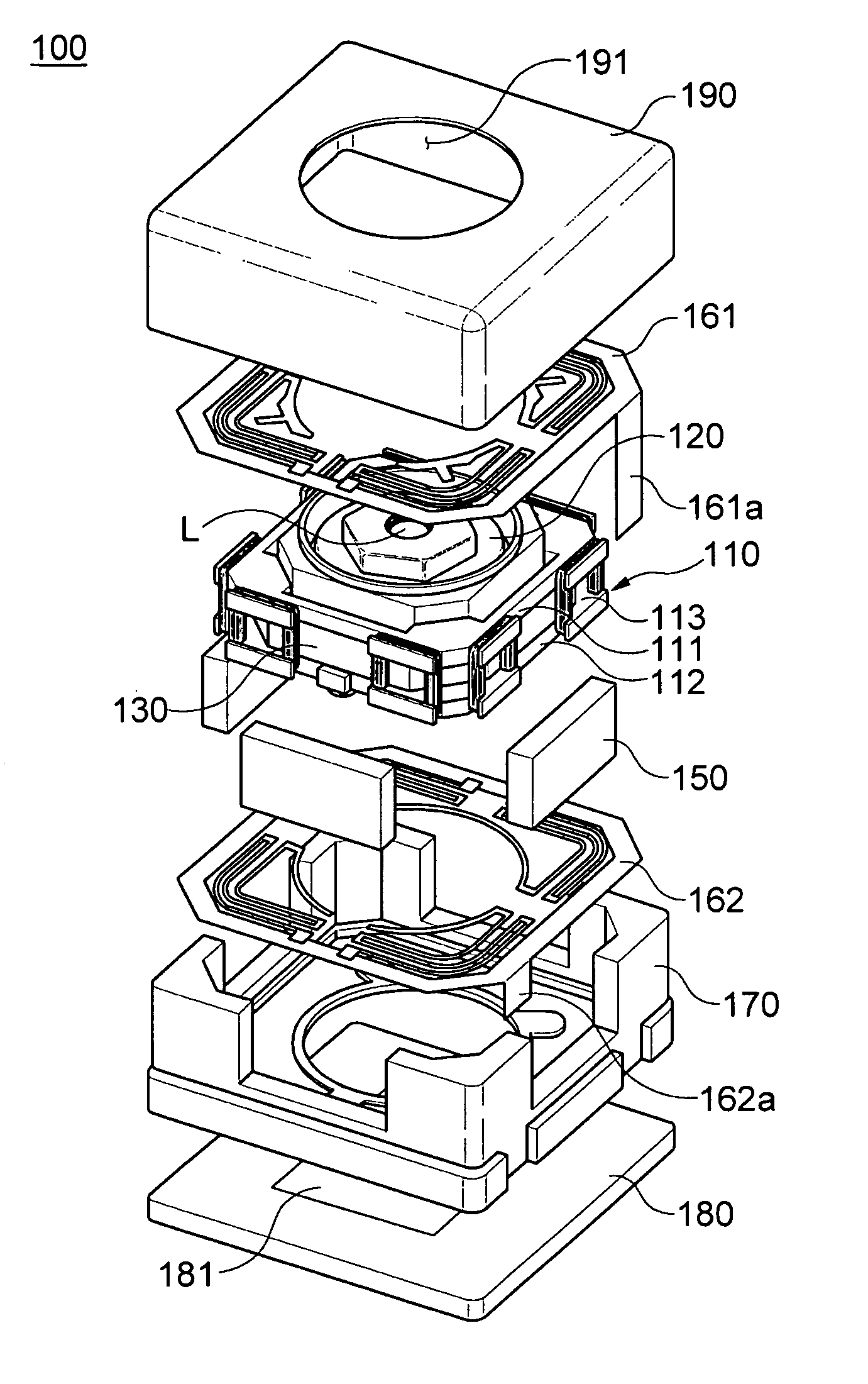
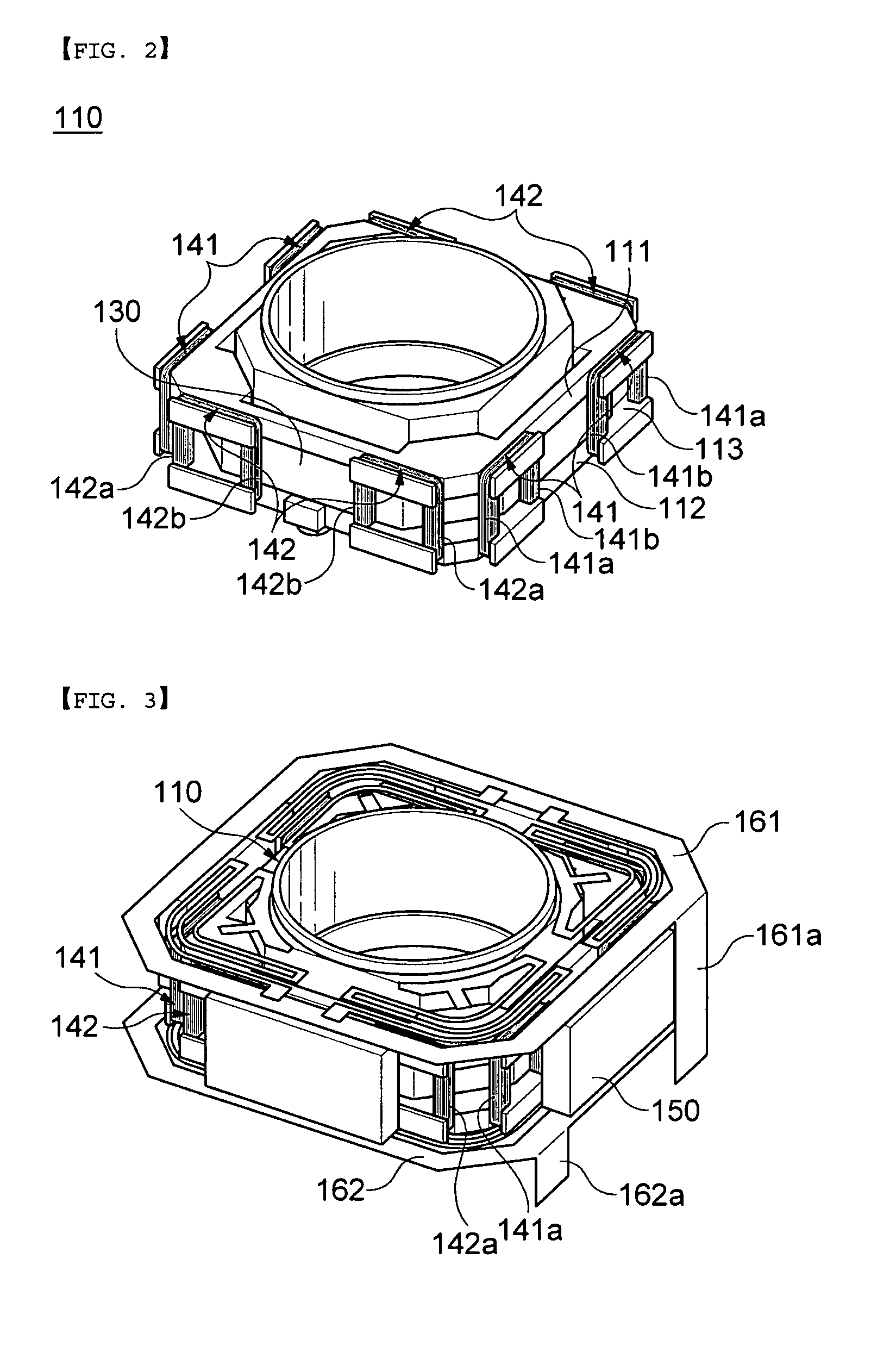
Image photographing device having function for compensating for hand vibration
Disclosed herein is an image photographing device having a function for compensating hand vibration to simultaneously perform auto focusing and hand vibration compensation. The image photographing device having a function for compensating hand vibration includes: a bobbin having a lens unit mounted therein, a driving coil in a Z axis direction wound on an outer peripheral surface thereof, and a driving coil in an X axis direction and a driving coil in a Y axis direction mounted outside the driving coil in a Z direction; a plurality of magnets mounted outside the driving coil in an X axis direction and the driving coil in a Y axis direction; an elastic member elastically combined with an upper portion and a lower portion of the bobbin; a housing into which the bobbin combined with the magnet and the elastic member is inserted; and a shield case combined with an upper portion of the housing.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
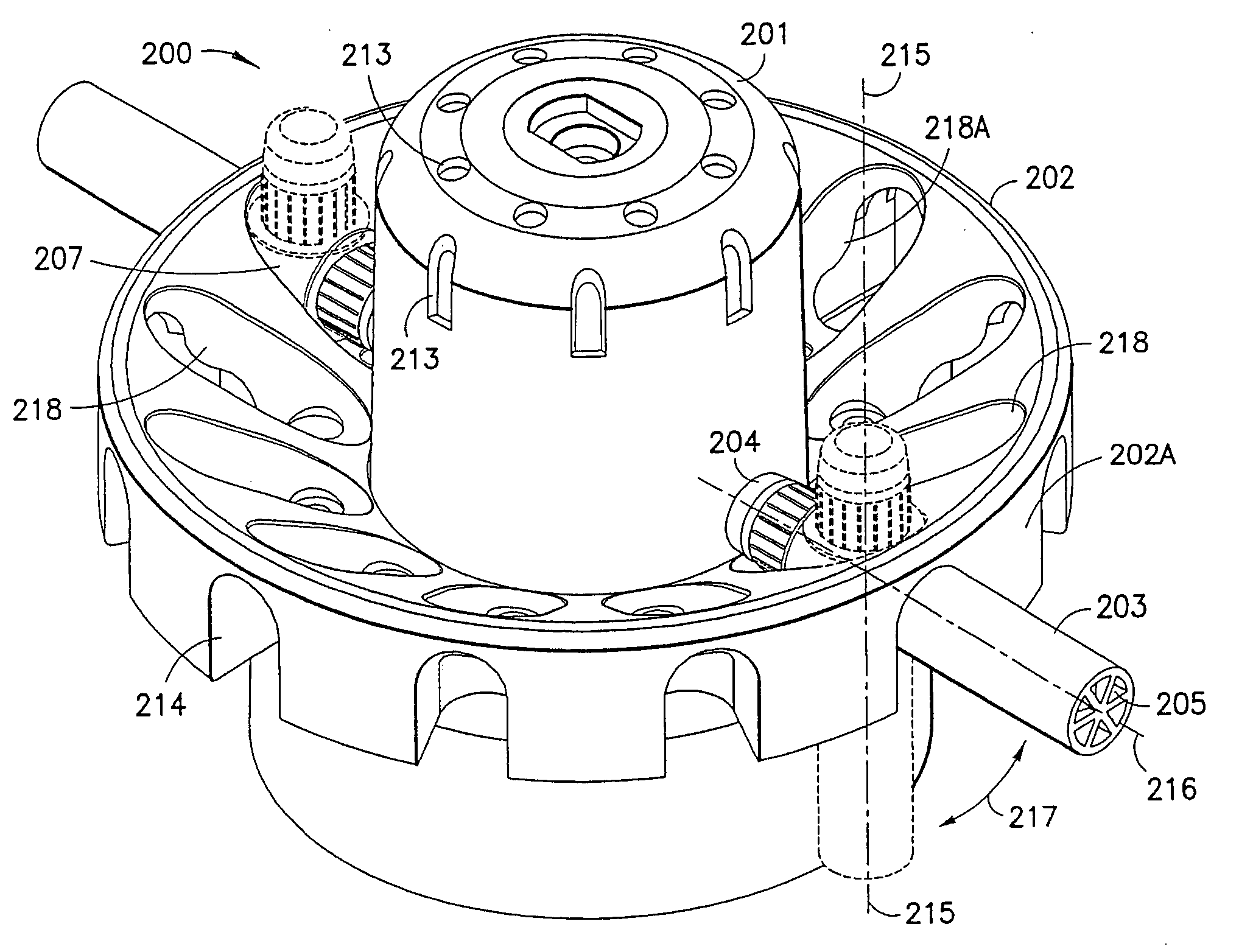
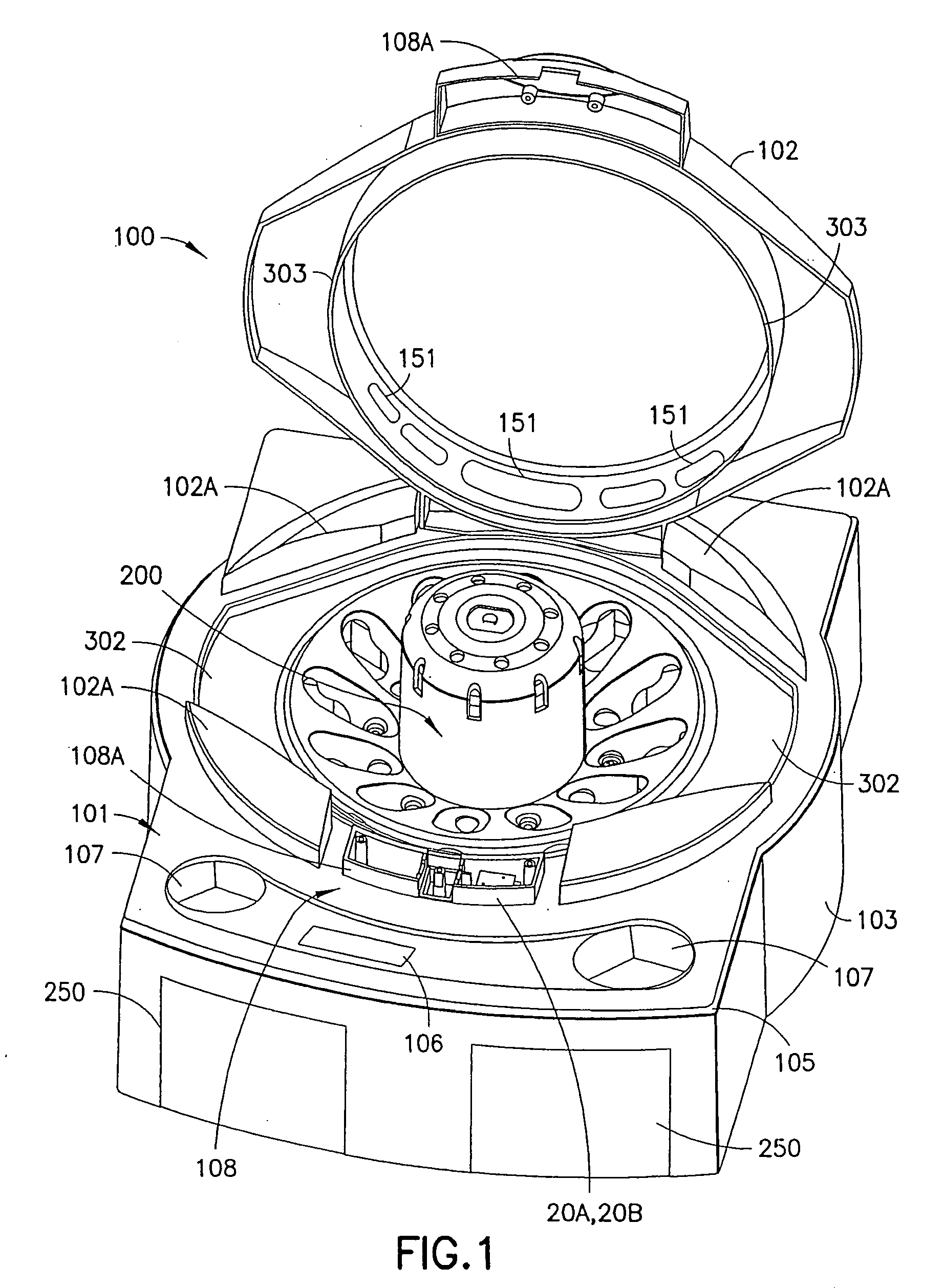
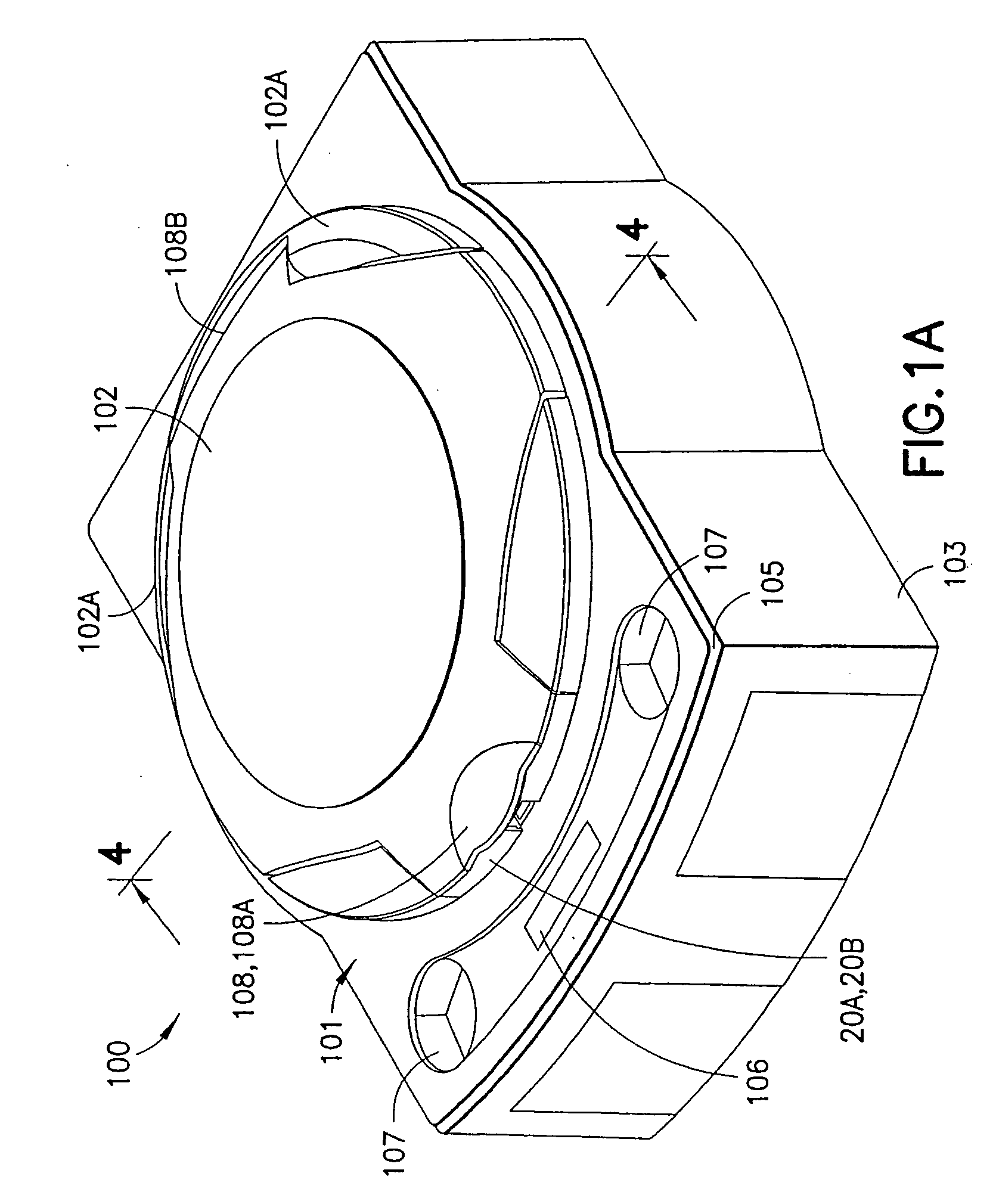
Centrifuge assembly
InactiveUS20070004577A1Minimizes detrimental forceExtend motor lifeCentrifugesAir managementMotor drive
A centrifuge system includes a drive motor mounted independently relative to a sample carrier to eliminate detrimental forces born by a motor drive shaft. The rotatable sample carrier or tray includes a rotating center operably connected to the drive motor. The drive motor cooperates with a resilient mounting system enabling self-centering, force and vibration compensation, and improving motor life. The rotatable sample tray and a sample tube holder have respective operably cooperative contoured surfaces enabling relative smooth pivoting motion in the sample tube holder during rotation, while minimizing sample vibration, and improving the desired sample separation while minimizing sample remixing. An air management system enables effective motor cooling and minimizes sample heating.
Owner:CENTURION LLC
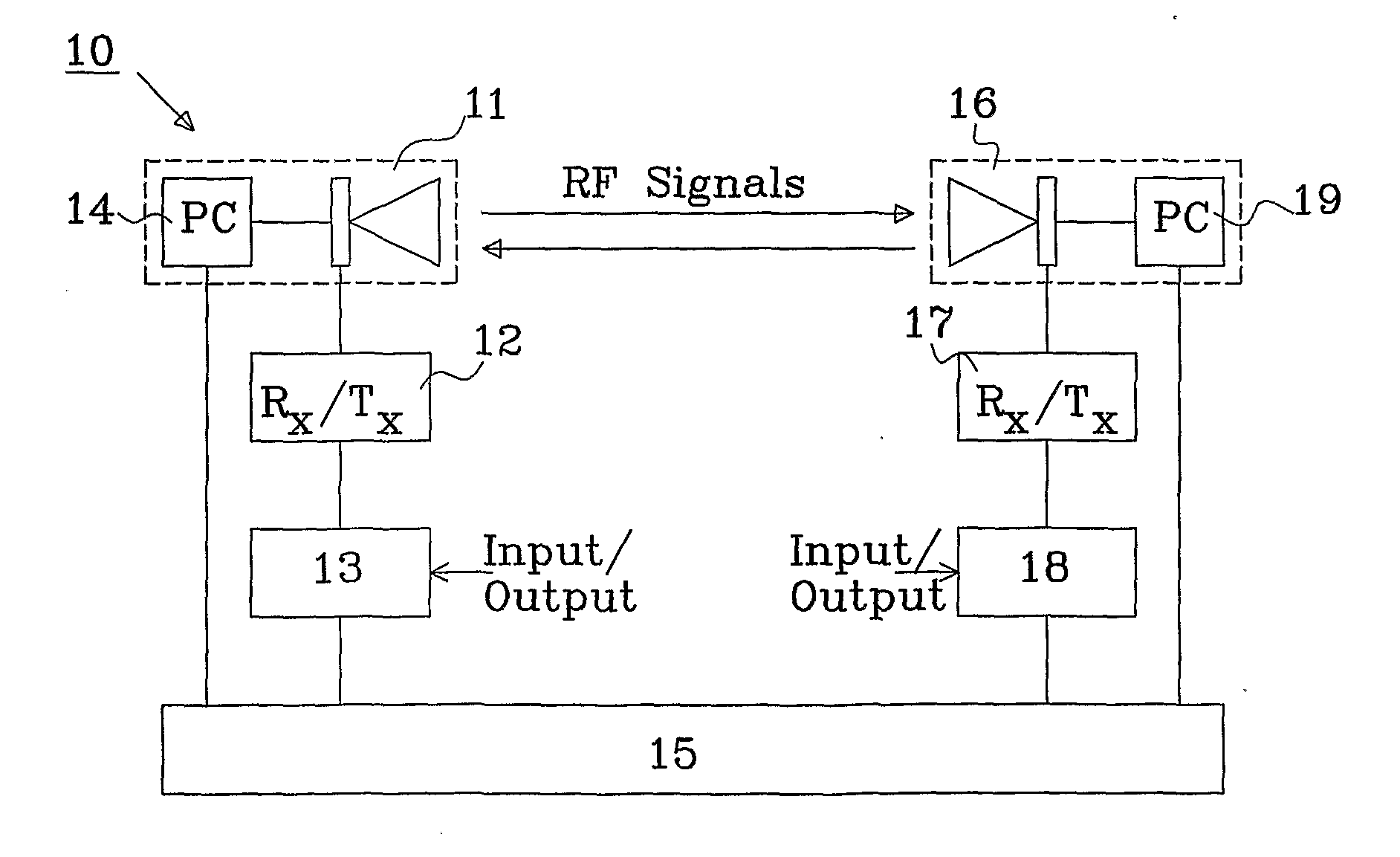
System and method for mast vibration compensation
ActiveUS20110070855A1Reduced stabilityLower requirementTransmitters monitoringReceivers monitoringCommunications systemSelf adaptive
The present invention relates to a system for mast vibration compensation implemented in a communication system including a first node and a second node. The first node comprises a first adaptive antenna mounted in a mast; a receiver connected to said antenna; and a spatial and temporary processing system. The first adaptive antenna is controlled by a first correction signal generated in the spatial and temporary processing system. The correction signal is based on a parameter that indicates that a radio link alignment with a second node is degrading due to mechanical vibrations in the mast. The invention also relates to a method for mast vibration compensation.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
High speed piezoelectric optical system with tunable focal length
ActiveUS7369723B1Curvature can be modifiedAltering focal length of lensCoupling light guidesLensOptical storageLens plate
A varifocal optical system includes a substantially circular membrane deposited on a substrate, and a ring-shaped PZT thin film deposited on the outer portion of the circular membrane. The membrane may be a MEMS-micromachined membrane, made of thermal oxide, polysilicon, ZrO2 and SiO2. The membrane is initially in a buckled state, and may function as a mirror or a lens. Application of an electric voltage between an inner and outer electrode on the piezoelectric thin film induces a lateral strain on the PZT thin film, thereby altering the curvature of the membrane, and thus its focal length. Focal length tuning speeds as high as 1 MHz have been demonstrated. Tuning ranges of several hundred microns have been attained. The varifocal optical system can be used in many applications that require rapid focal length tuning, such as optical switching, scanning confocal microscopy, and vibration compensation in optical storage disks.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Miniature optical anti-vibration camera module
ActiveCN106131435AImplement Jitter CompensationSimple structureTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensFlexible circuits
Owner:SEADEC TECH LTD
Image projection system with vibration compensation
A projection system includes a vibration controlling structure. The projection system includes an imaging unit mounted to a movable platform via a partially compliant mount structure, such that the imaging unit is partially isolated from the platform while projecting an image which is stable with respect to the platform. The imaging unit and partially compliant mounting structures are constructed and arranged to damp vibrational forces on the imaging unit.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High speed piezoelectric optical system with tunable focal length
A varifocal optical system includes a substantially circular membrane deposited on a substrate, and a ring-shaped PZT thin film deposited on the outer portion of the circular membrane. The membrane may be a MEMS-micromachined membrane, made of thermal oxide, polysilicon, ZrO2 and SiO2. The membrane is initially in a buckled state, and may function as a mirror or a lens. Application of an electric voltage between an inner and outer electrode on the piezoelectric thin film induces a lateral strain on the PZT thin film, thereby altering the curvature of the membrane, and thus its focal length. Focal length tuning speeds as high as 1 MHz have been demonstrated. Tuning ranges of several hundred microns have been attained. The varifocal optical system can be used in many applications that require rapid focal length tuning, such as optical switching, scanning confocal microscopy, and vibration compensation in optical storage disks.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Camera system and camera body
InactiveUS20090003813A1Improve vibrationOptical performance is deterioratedTelevision system detailsPrintersRange of movementControl theory
This camera system includes: a vibration compensation unit including a vibration compensation optical system and an image-capturing unit; a drive unit that drives the vibration compensation unit; a detection unit that detects vibration; a position detection unit that detects the position of the vibration compensation unit; a target position determination unit that determines a target position for the vibration compensation unit according to the vibration of the camera; a calculation unit that calculates a drive amount for the drive unit; a range of movement limitation unit that limits the position of the vibration compensation unit within a range; a range setting unit that sets a movement permitted range that is within the range in which the vibration compensation unit can be positioned; and a centering unit that controls the drive unit so that the vibration compensation unit is centered in the center of the movement permitted range.
Owner:NIKON CORP
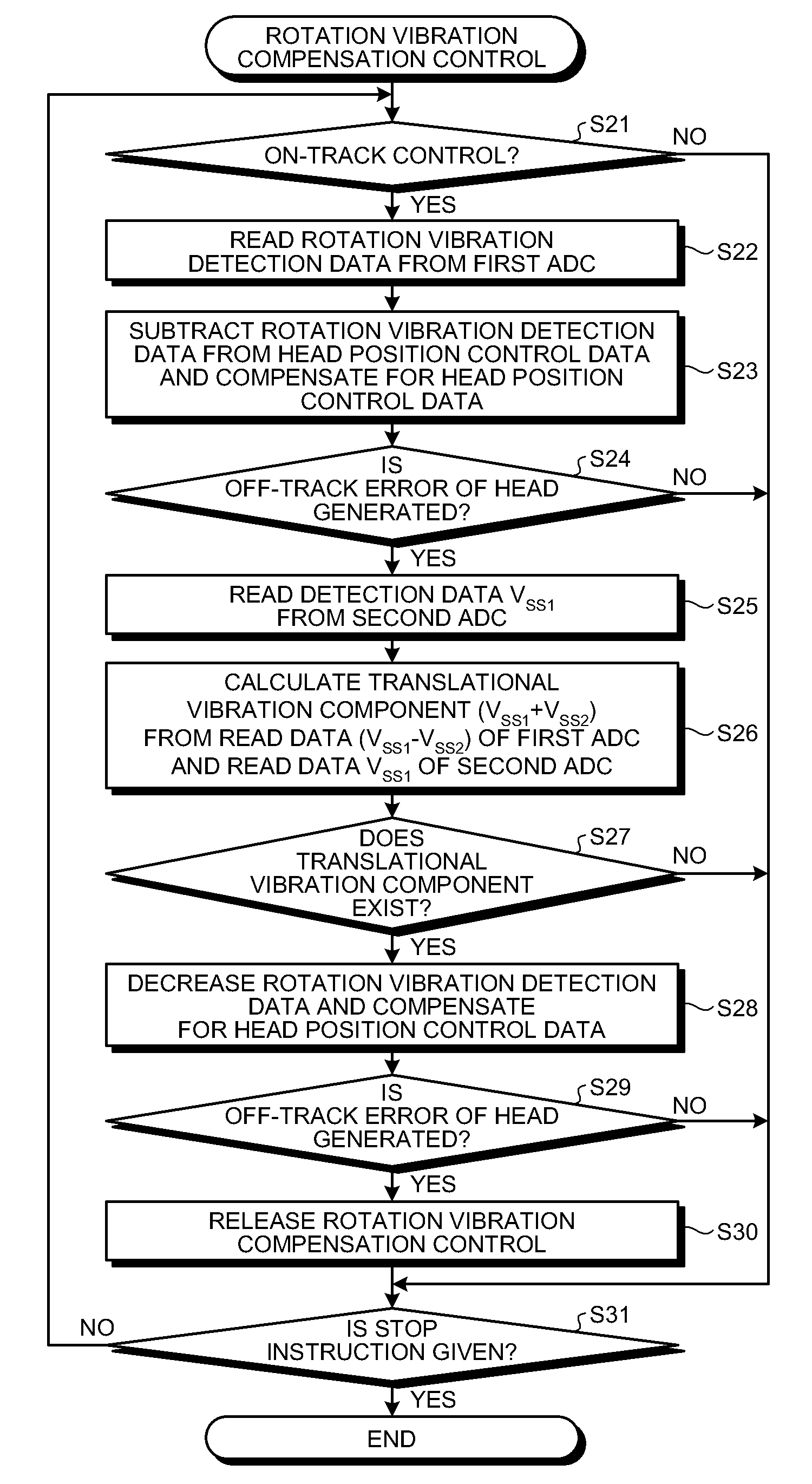
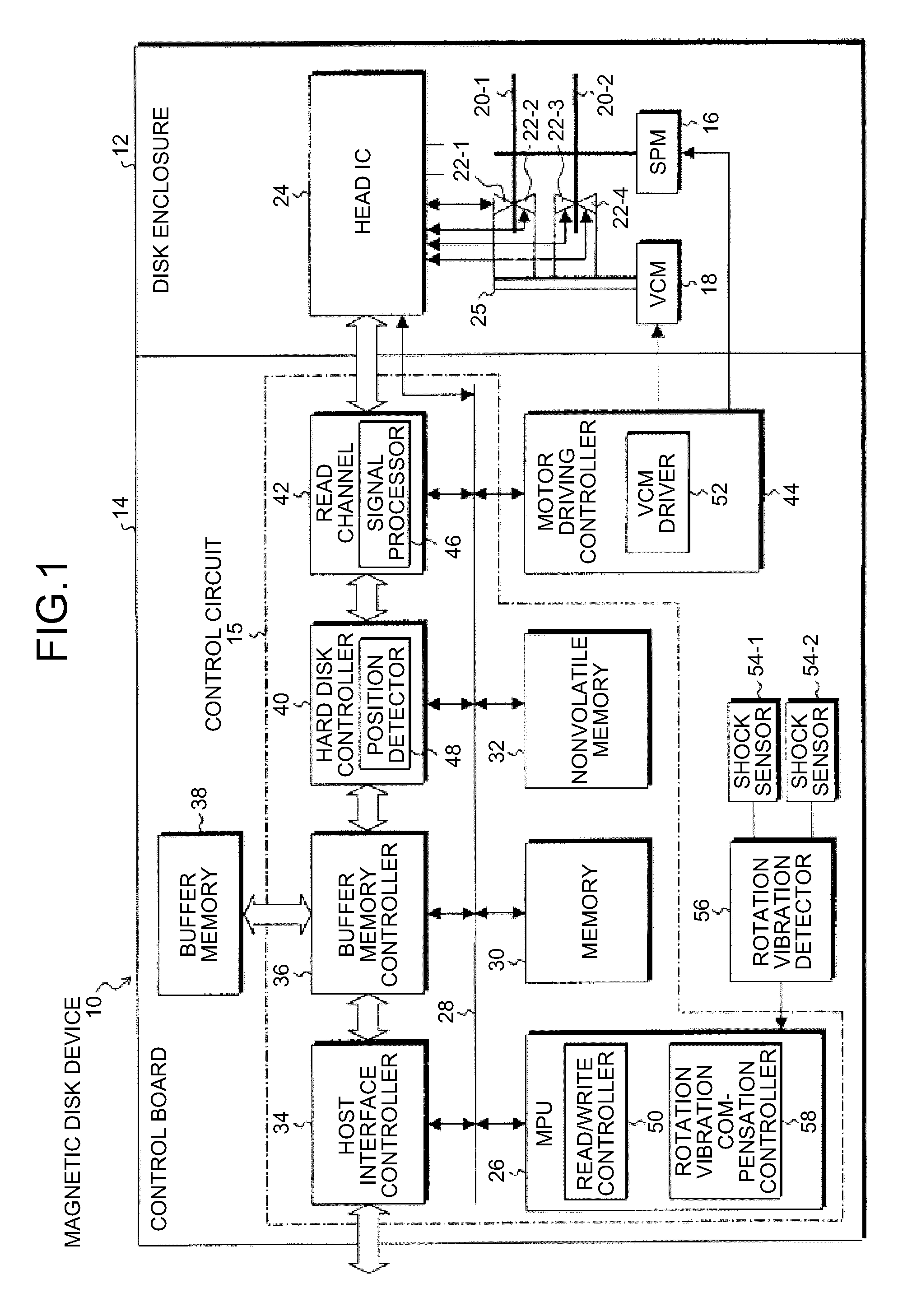
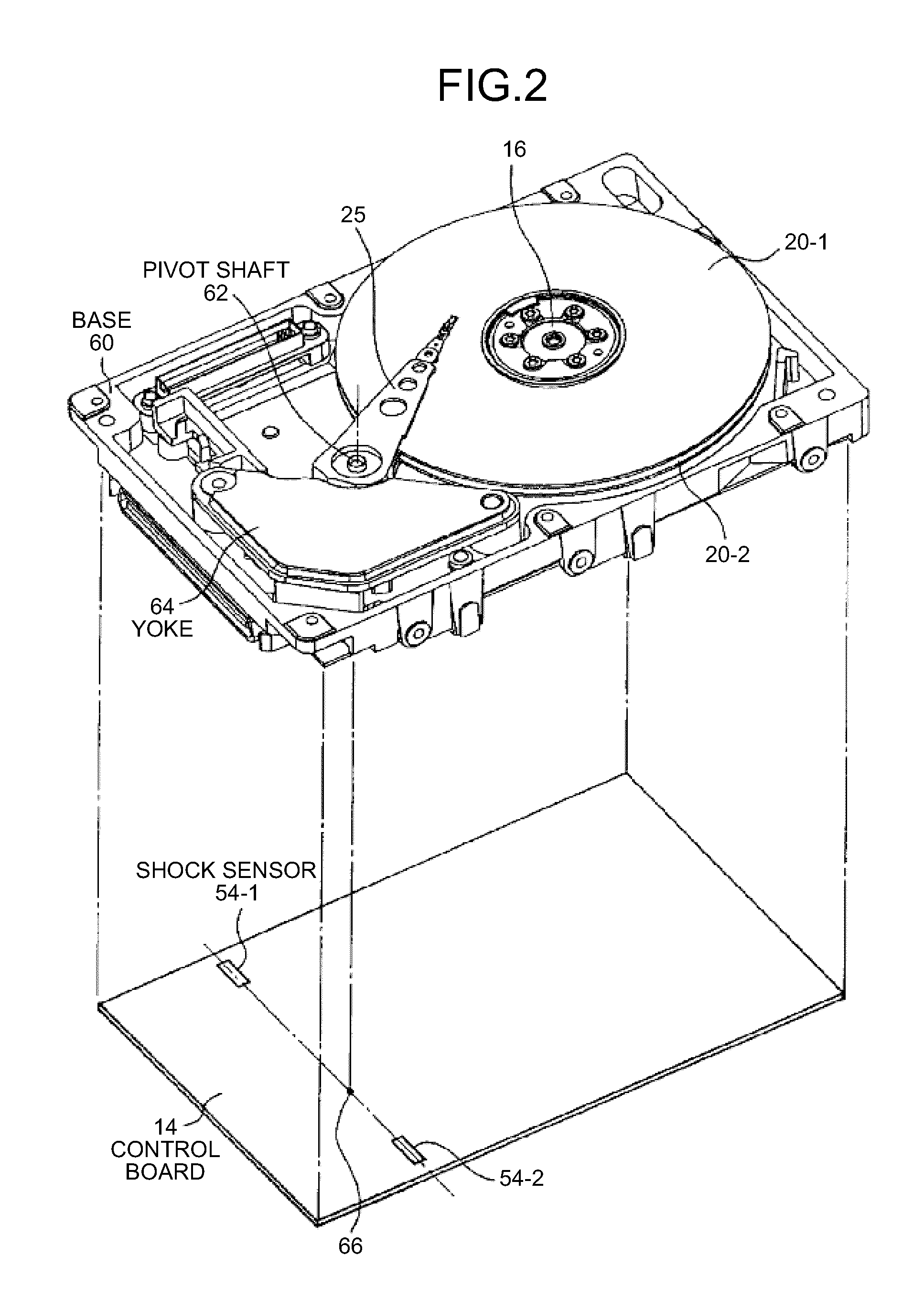
Storage device and control circuit
InactiveUS20100061007A1Record information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsRotational vibrationCentre of rotation
According to one embodiment, a storage device includes a rotary actuator, vibration detectors, an analog operation circuit, an analog-to-digital converter, and a rotation vibration compensation controller. The rotary actuator positions a head with respect to a storage medium to perform reading or writing. The vibration detectors are located substantially on both sides of the rotation center of the rotary actuator, detects rotation vibration component of a one-axis direction, and outputs a vibration detection signal. The analog operation circuit calculates a rotation vibration detection signal proportional to rotation vibration disturbance applied to the rotary actuator by differential amplification of the vibration detection signal. The analog-to-digital converter converts the rotation vibration detection signal into a digital signal and outputs rotation vibration detection data. The rotation vibration compensation controller controls the rotation vibration disturbance applied to the rotary actuator to be eliminated based on the rotation vibration detection data.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Vibration compensation apparatus using a coordinate conversion
ActiveUS7460154B2Reduce restrictionsTelevision system detailsPrintersAngular velocityVibration compensation
A vibration compensation apparatus comprises: an angular velocity detector that detects a plurality of angular velocities in two orthogonal detection axes directions and outputs corresponding angular velocity signals; a compensation unit that compensates vibration in a plurality of compensation axis directions; and a conversion unit that converts the plurality of angular velocity signals obtained by the angular velocity detector or a plurality of vibration compensation signals based on the plurality of angular velocity signals into vibration compensation signals expressed in the coordinates of the compensation axes of the compensation unit. The compensation unit compensates the vibration based on the vibration correction signals converted by the conversion unit.
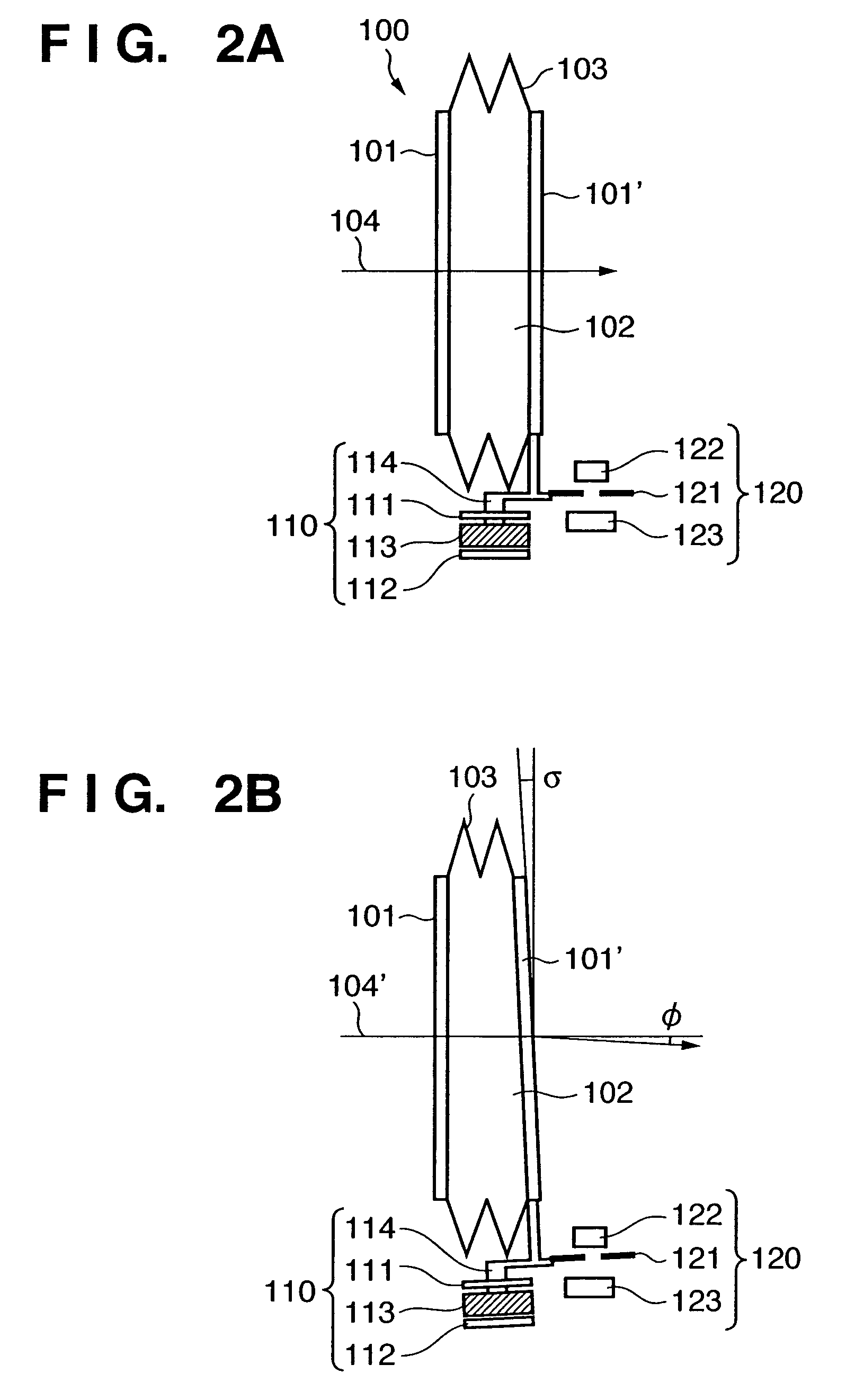
Owner:CANON KK
Active vibration compensation for MRI gradient coil support to reduce acoustic noise in MRI scanners
InactiveUS6894498B2Reduce noiseReduce transmissionElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceEngineeringVibration transmission
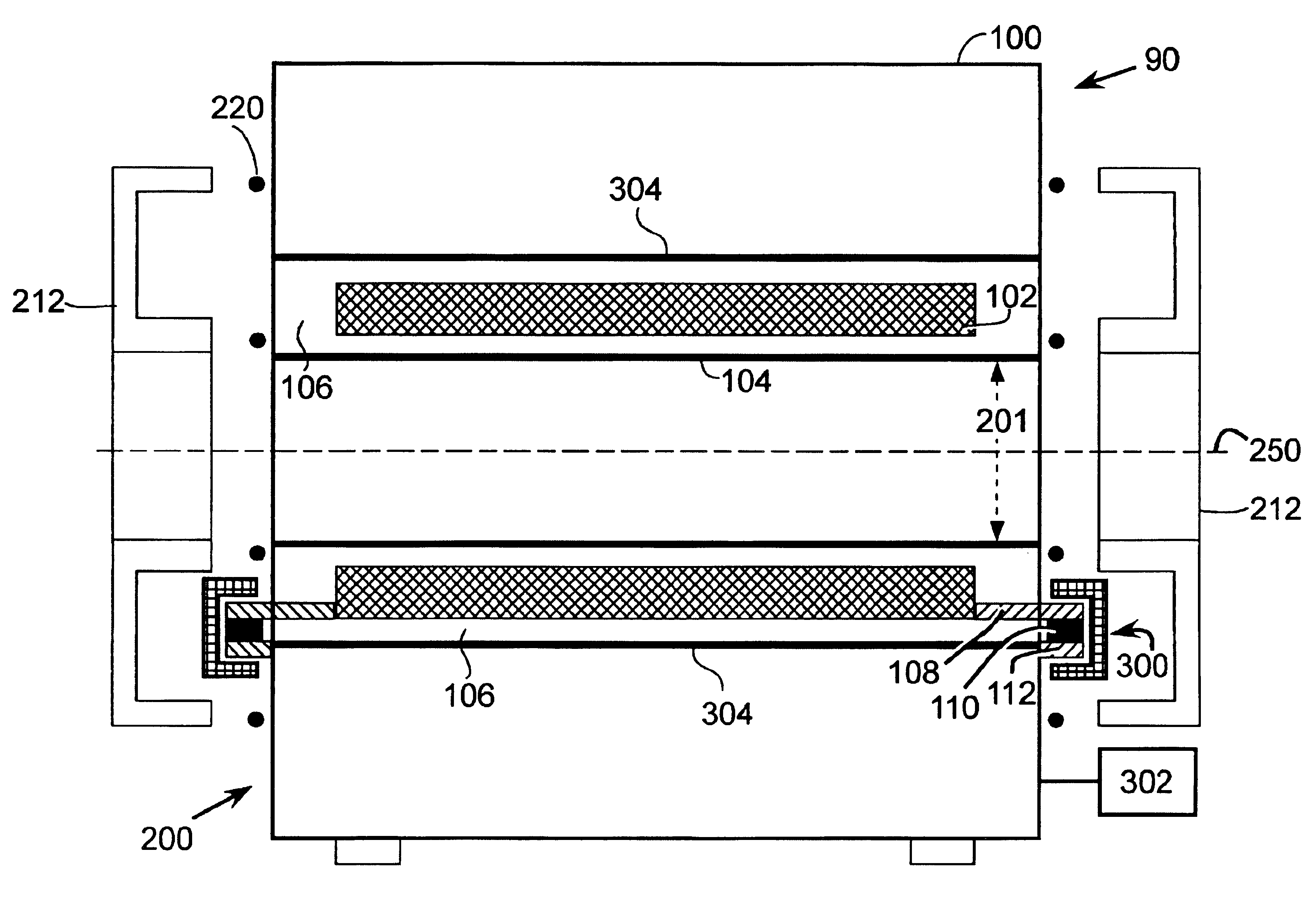
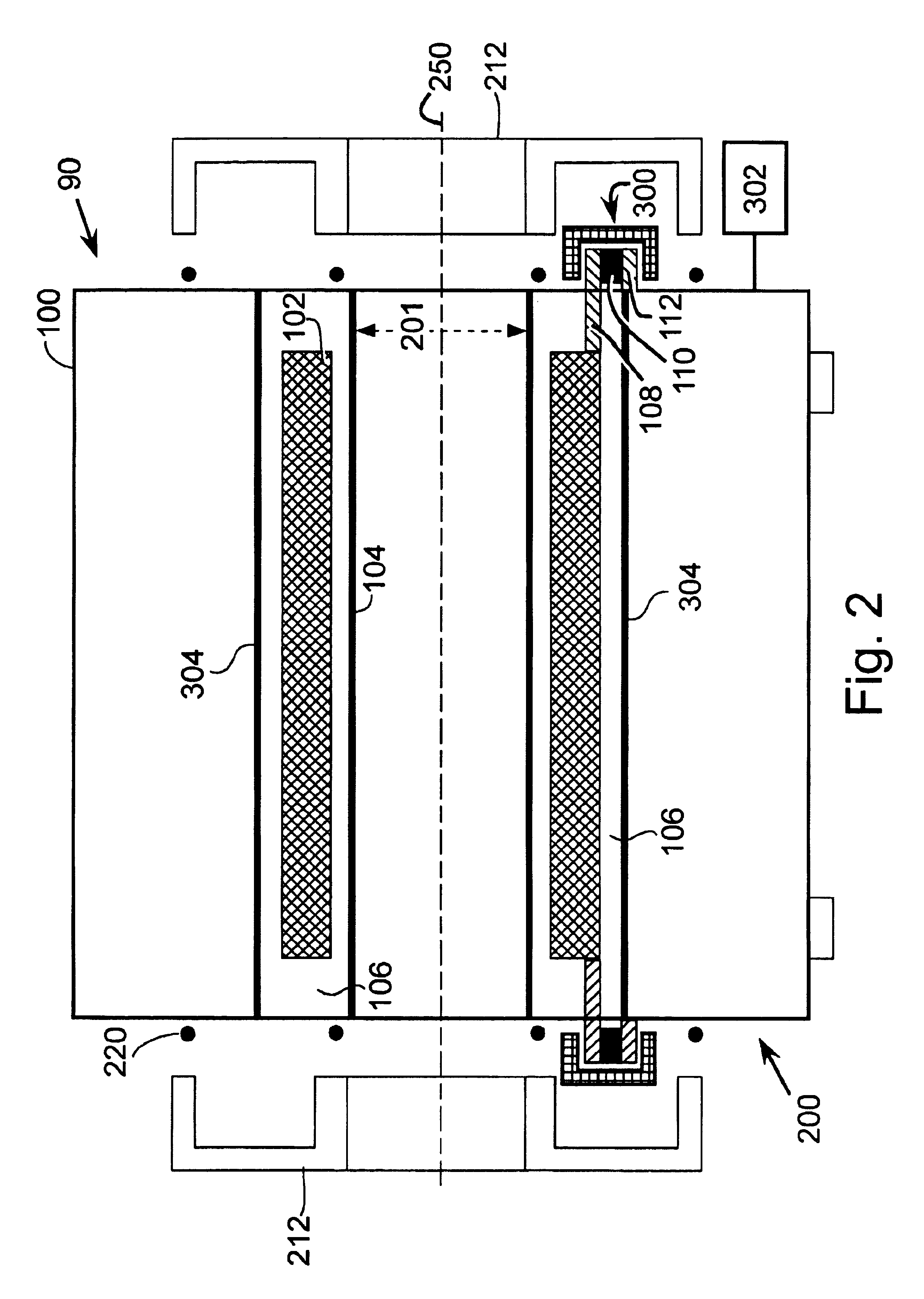
The present invention provides an apparatus for reducing acoustic noise in a magnetic resonance imaging device including a suspension element including at least one resilient element and an active drivable element for applying a compensating force to reduce vibration transmission. The active drivable element is positioned so as to not directly support the weight of the gradient coil assembly, which avoids applying strong forces to relatively fragile active drivable elements, such as piezoelectric force transducers. Force signals for the active drivable element are derived in a feed-forward manner from the applied gradient waveform or from motion of the gradient coil assembly bracket. Alternatively, the active drivable element can be driven by signals derived from measured vibration or other motion of parts of the MRI magnet, gradient coils or rf coils.
Owner:SHARKSTONE
Helicopter-borne laser radar platform three-dimensional attitude angle complex vibration real-time compensation method and device
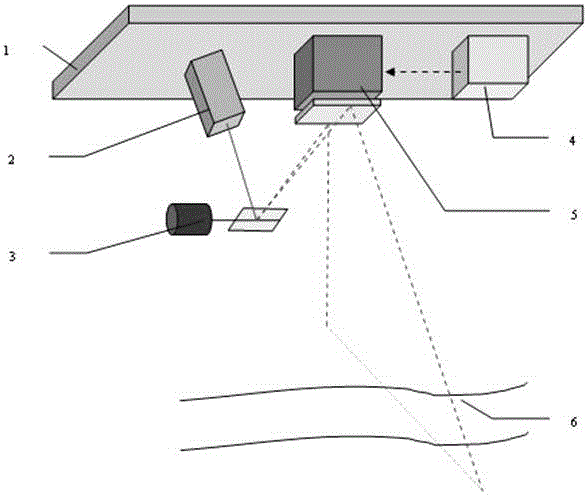
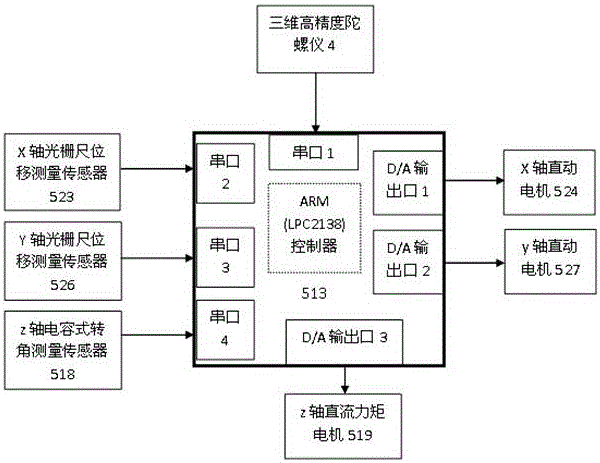
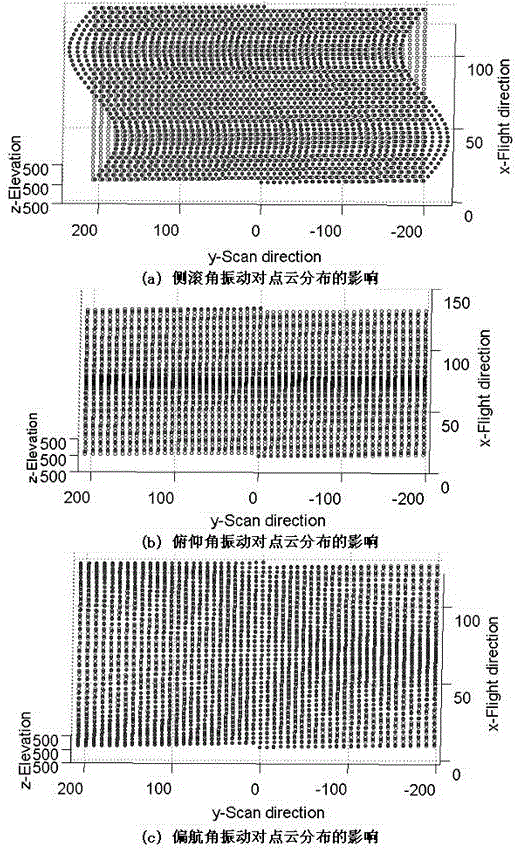
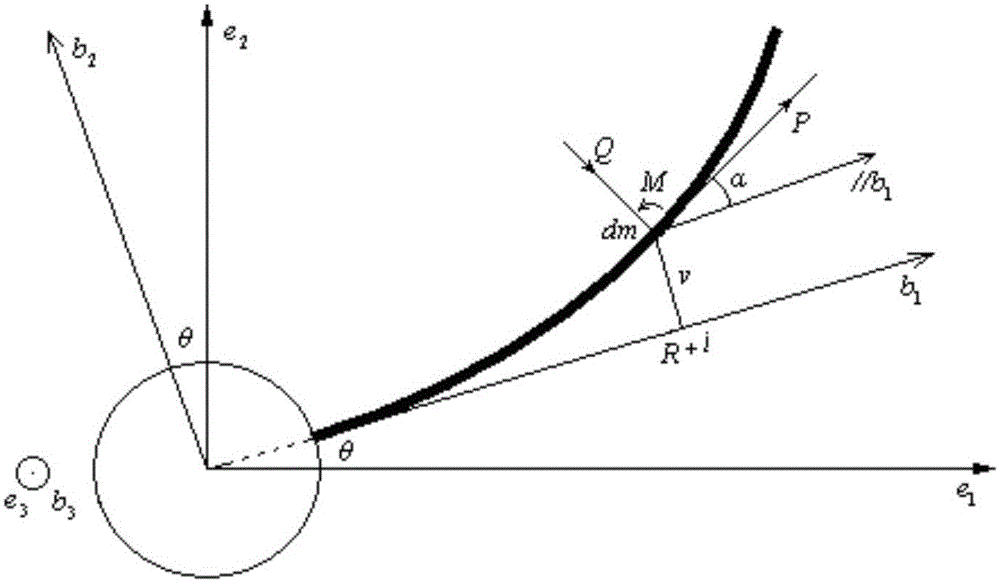
The invention relates to a helicopter-borne laser radar platform three-dimensional attitude angle complex vibration real-time compensation method and device. In a helicopter-borne laser radar system, the three-dimensional attitude angle vibration compensation device is additionally adopted, and the three-dimensional attitude angle vibration compensation is provided with a large-sized reflector. A magnetic universal bearing is adopted to support the large-sized reflector, so that the large-sized reflector can rotate around an x axis and a y axis simultaneously; rotation angle closed-loop control on the rotation of the large-sized reflector around the x axis and the y axis can be realized through adopting a direct-acting motor and a grating ruler displacement sensor, so that the coupling of the rotation of the large-sized reflector around the x axis and the y axis can be realized; and a direct-current torque motor and gear transmission mode is adopted to realize the rotation of the large-sized reflector around a z axis. With the three-dimensional attitude angle vibration compensation device adopted, a laser pulse beam which is deflected because of the influence of airborne platform three-dimensional attitude angle vibration can be corrected to an ideal scanning direction which is realized when airborne platform attitude angle vibration does not exist, and therefore, real-time complete compensation for the airborne platform three-dimensional attitude angle vibration can be realized, and adverse influence of the helicopter-borne platform three-dimensional attitude angle vibration on the measurement point cloud of a laser radar can be eliminated.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Active vibration isolation system
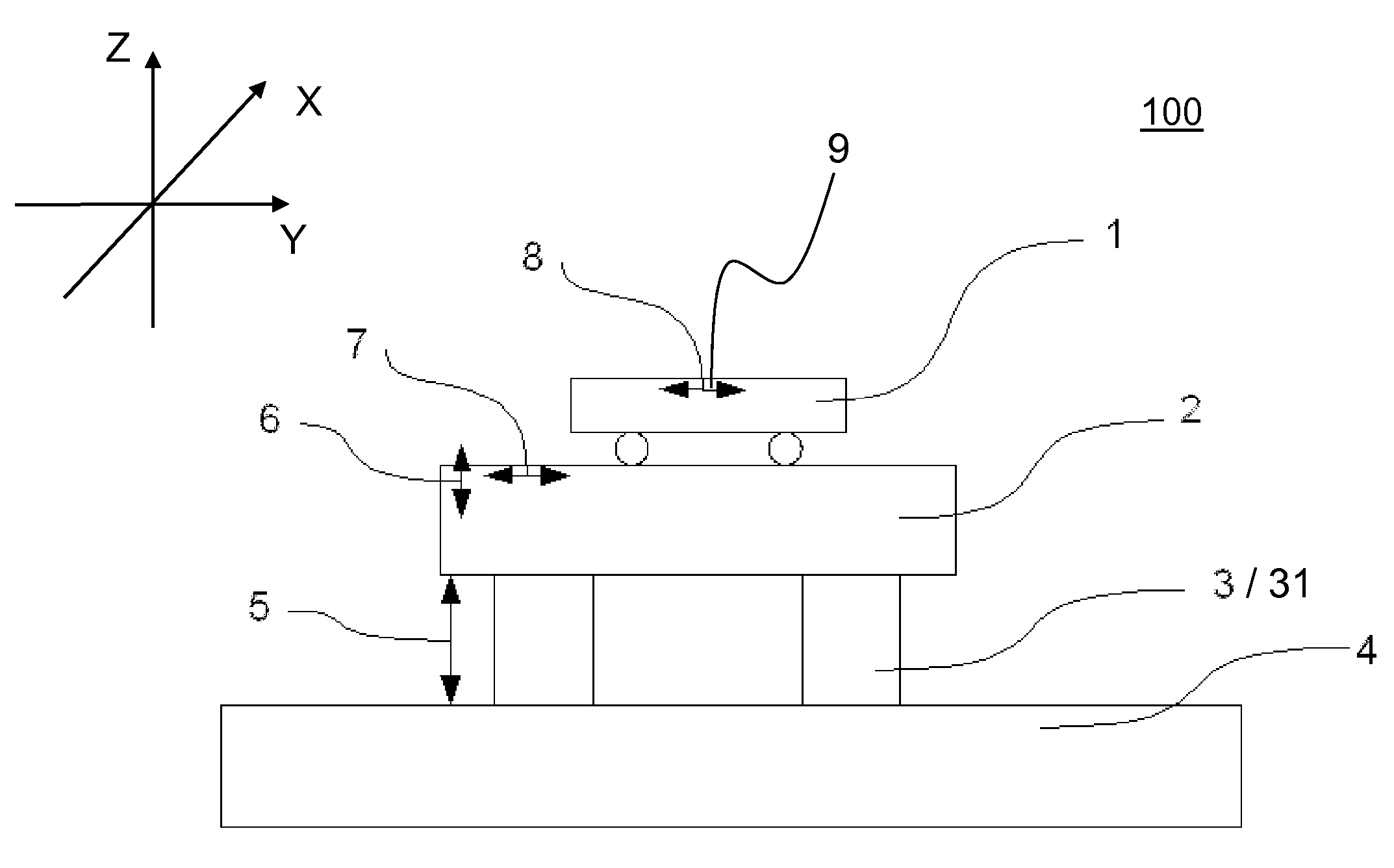
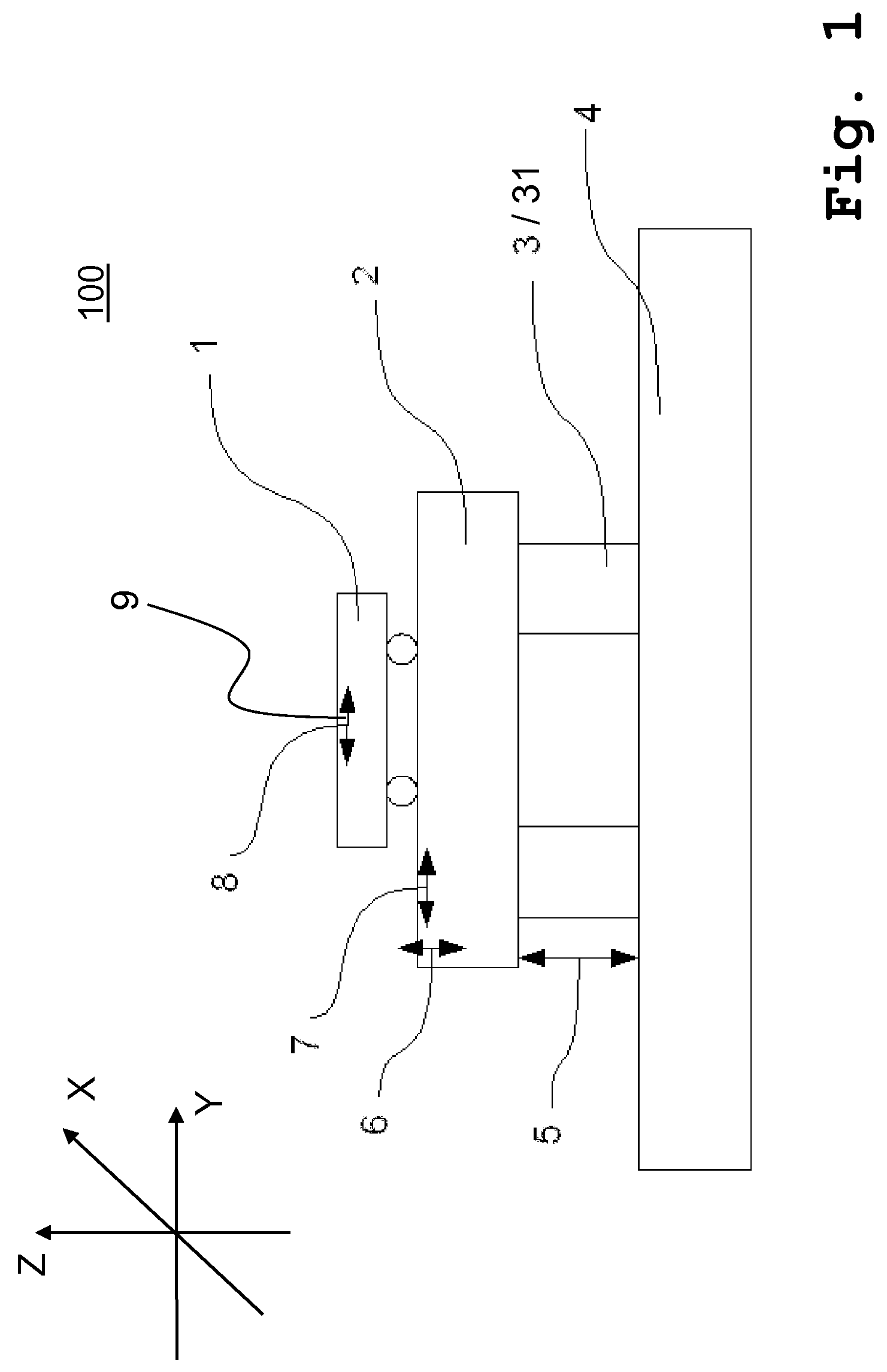
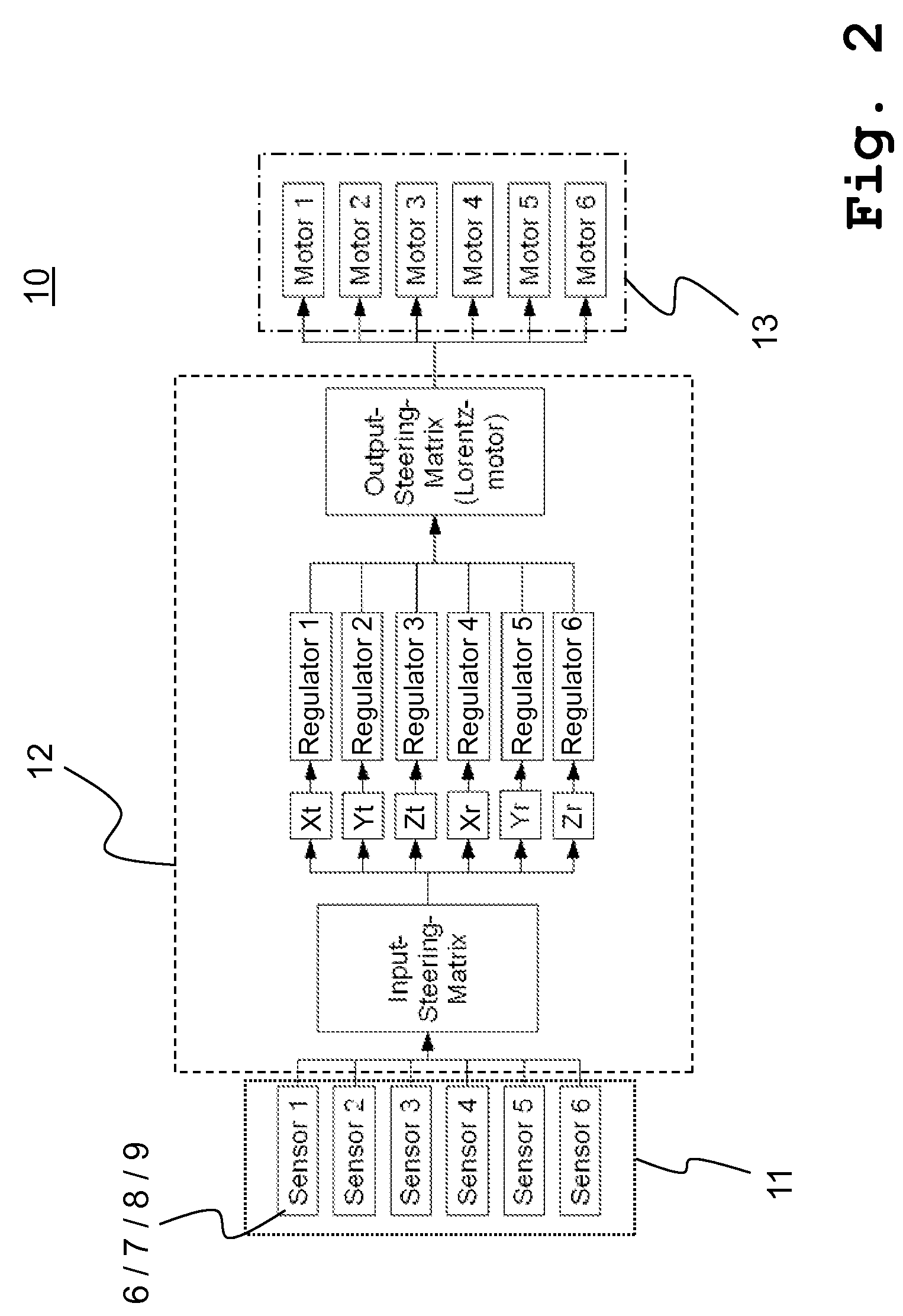
The present invention relates to a method for regulating an active vibration isolation system and to an active vibration isolation system, in particular for a vibration isolated positioning of lithography-devices, wafer-handling-systems and / or microscopes, as for instance scanning microscopes. The active vibration isolation system comprises the following components: a support body for bearing a load which is to be isolated; pneumatic vibration isolators with controllable valves for carrying the support body with respect to the ground; position sensors for providing vertical position signals of the support body; a first regulating system for vibration compensation in at least one degree of freedom in translation (Xt,Yt,Zt) and in at least one degree of freedom in rotation (Xr,Yr,Zr) and a second pneumatic regulating system for vibration compensation in at least one degree of freedom selected from three degrees of freedom (Zt,Xr,Yr) which are effective in vertical direction.
Owner:INTEGRATED DYNAMICS ENG
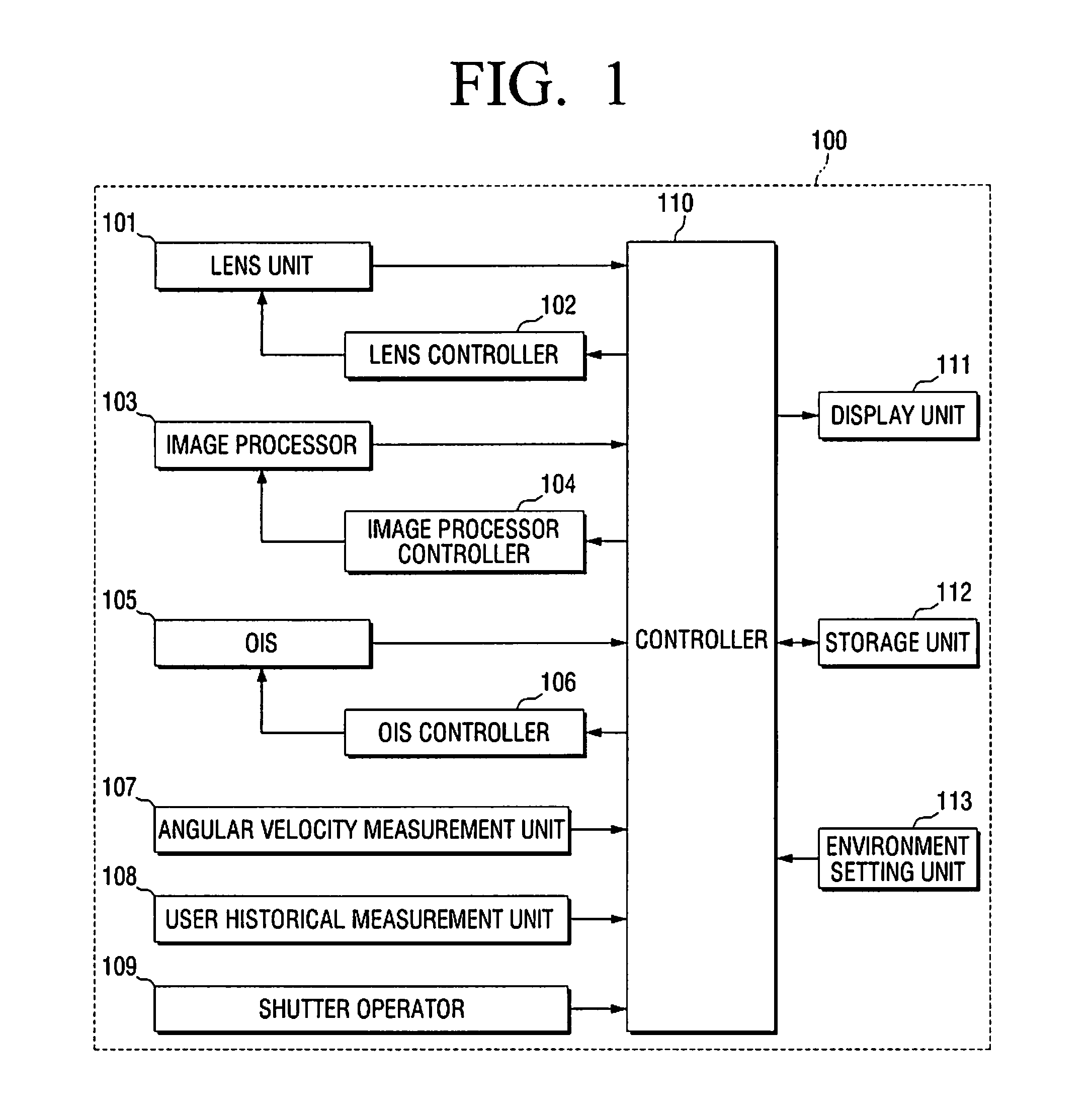
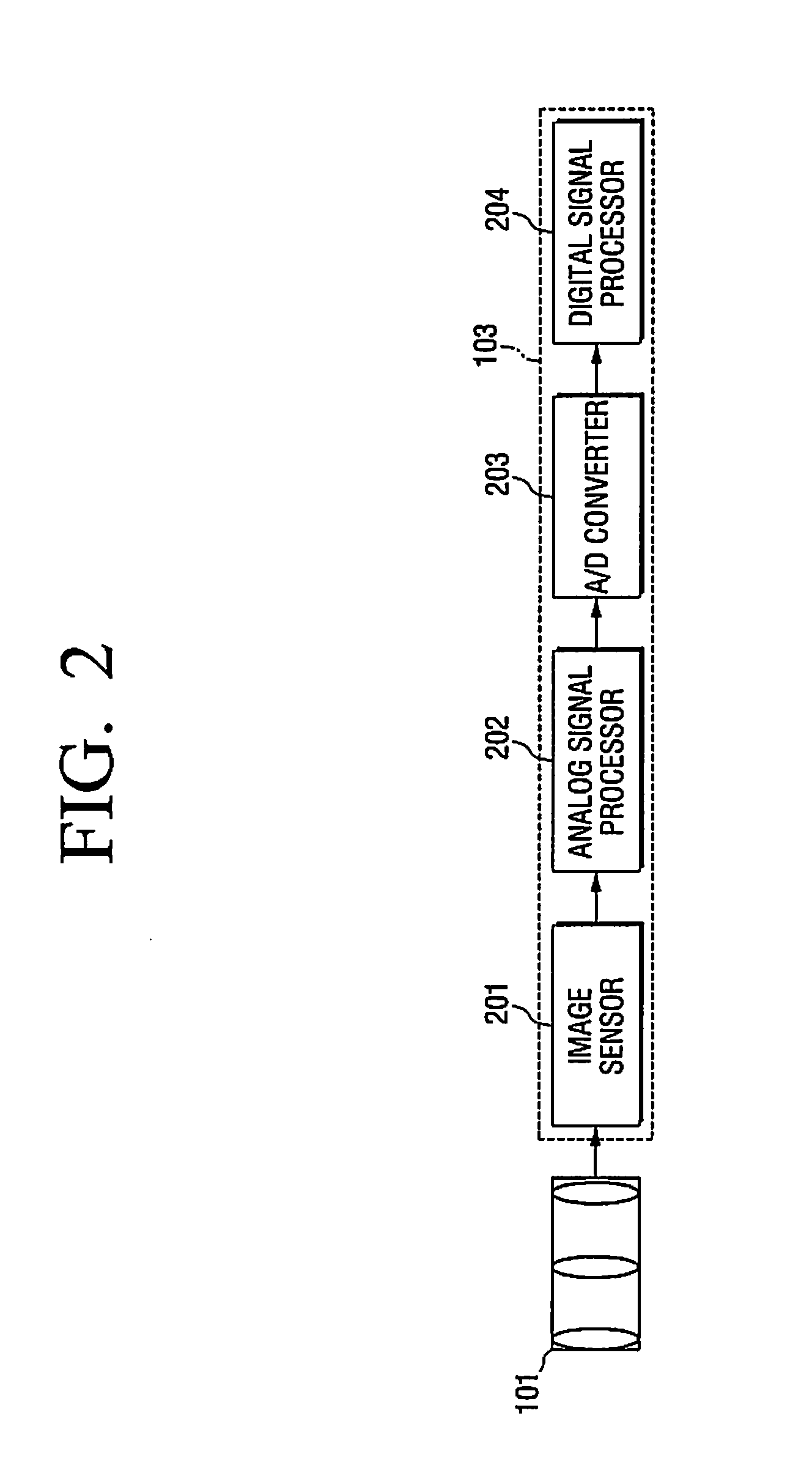
Vibration compensation for image capturing device
InactiveUS20080292296A1Quality imageReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsPrintersEngineeringImage capture
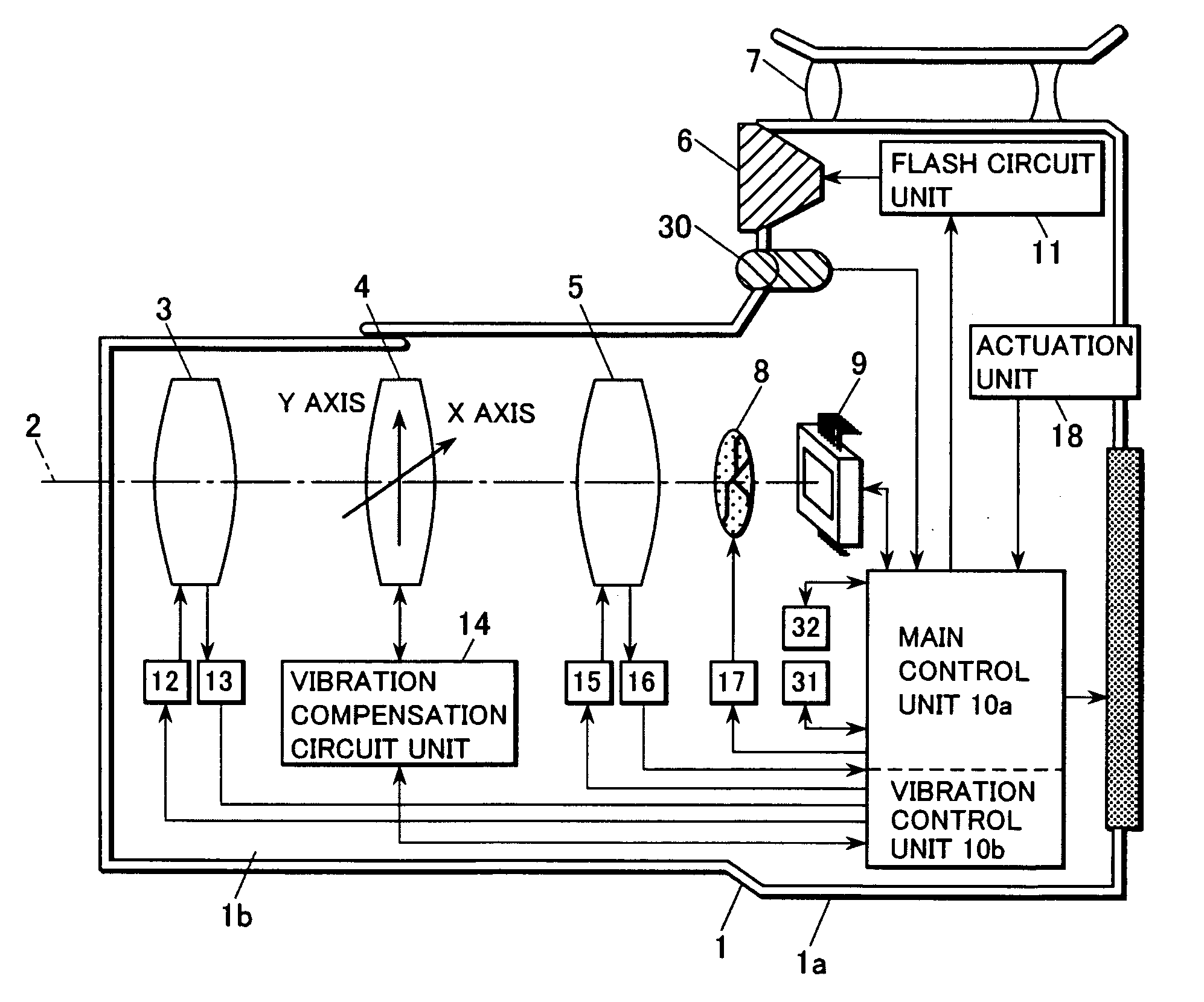
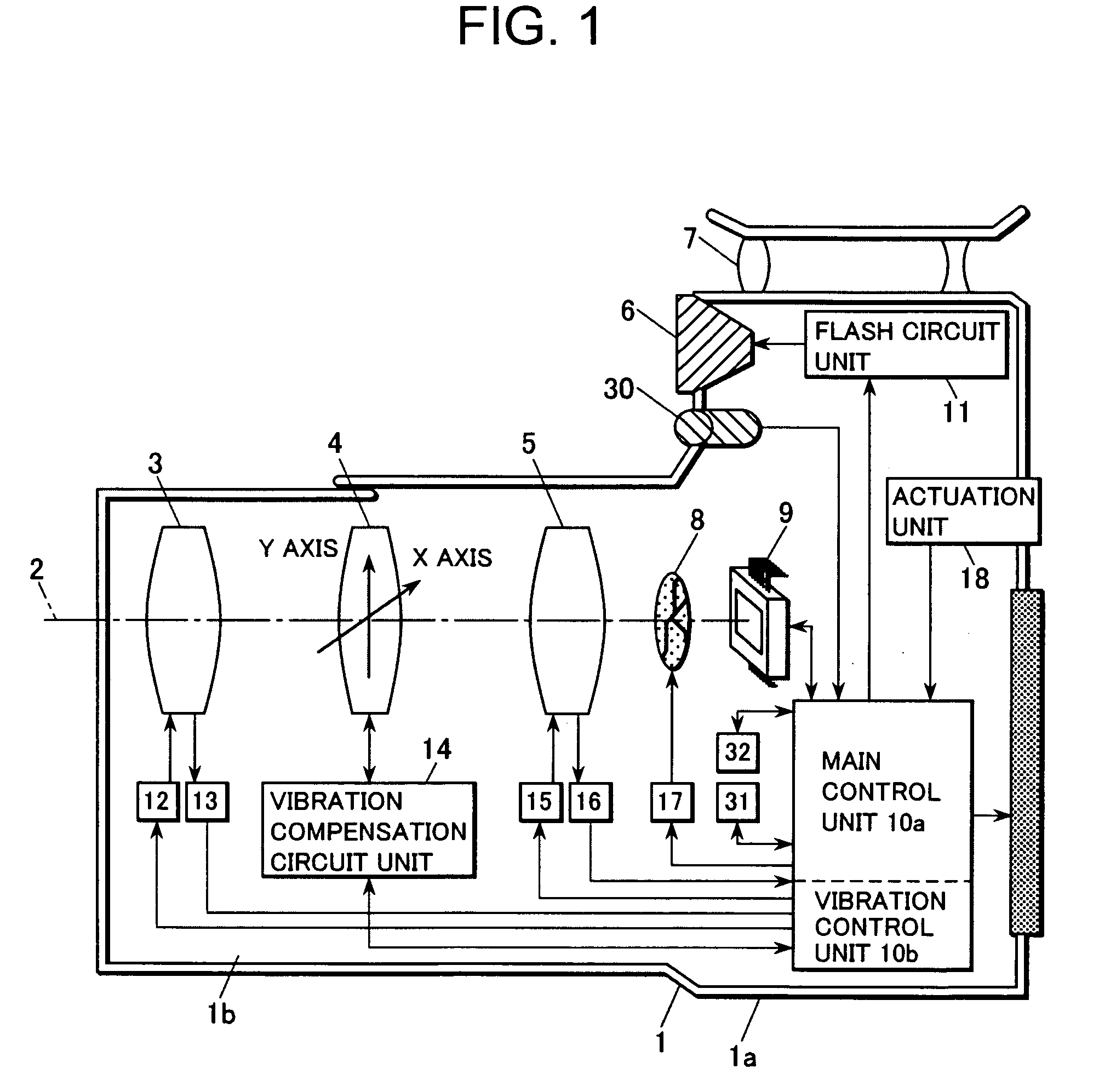
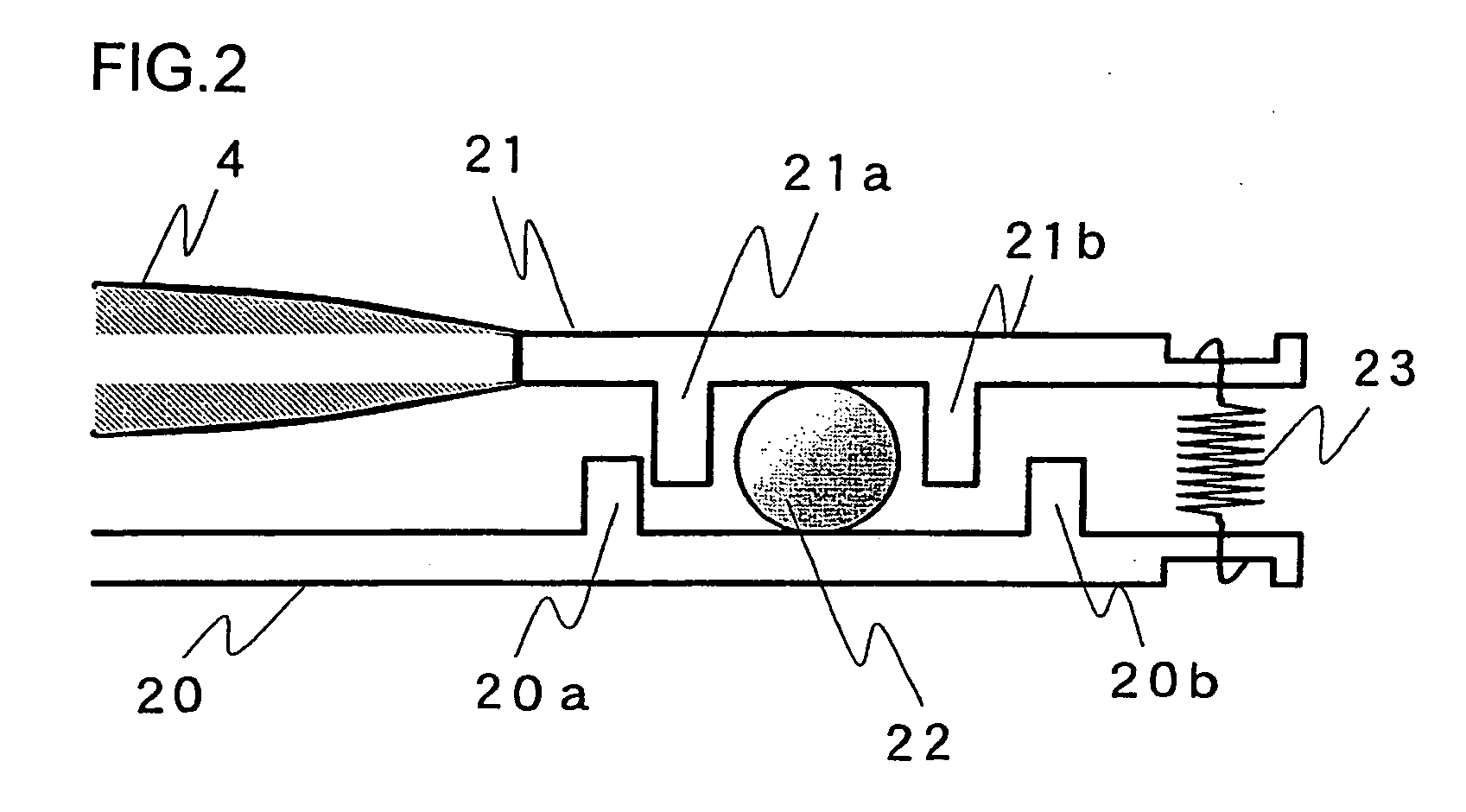
Disclosed herein is an apparatus for compensating for vibration of an image capturing device. The apparatus includes a y-axis stage installed in a support structure so as to be movable in y-axis direction. An x-axis stage is installed on the y-axis stage so as to be movable in x-axis direction on an xy plane. An image sensor is mounted on the x-axis stage. The apparatus is provided with a y-axis driver and an x-axis driver for driving the y-axis stage in the y-axis direction and the x-axis stage in the x-axis direction respectively. A control unit is installed in the image capturing device. The control unit operates to sense vibration of the image capturing device through a separate vibration sensor and to drive the y-axis driver and the x-axis driver to vibrate the image sensor in a way to compensate for the vibration of image capturing device.
Owner:HYSONIC
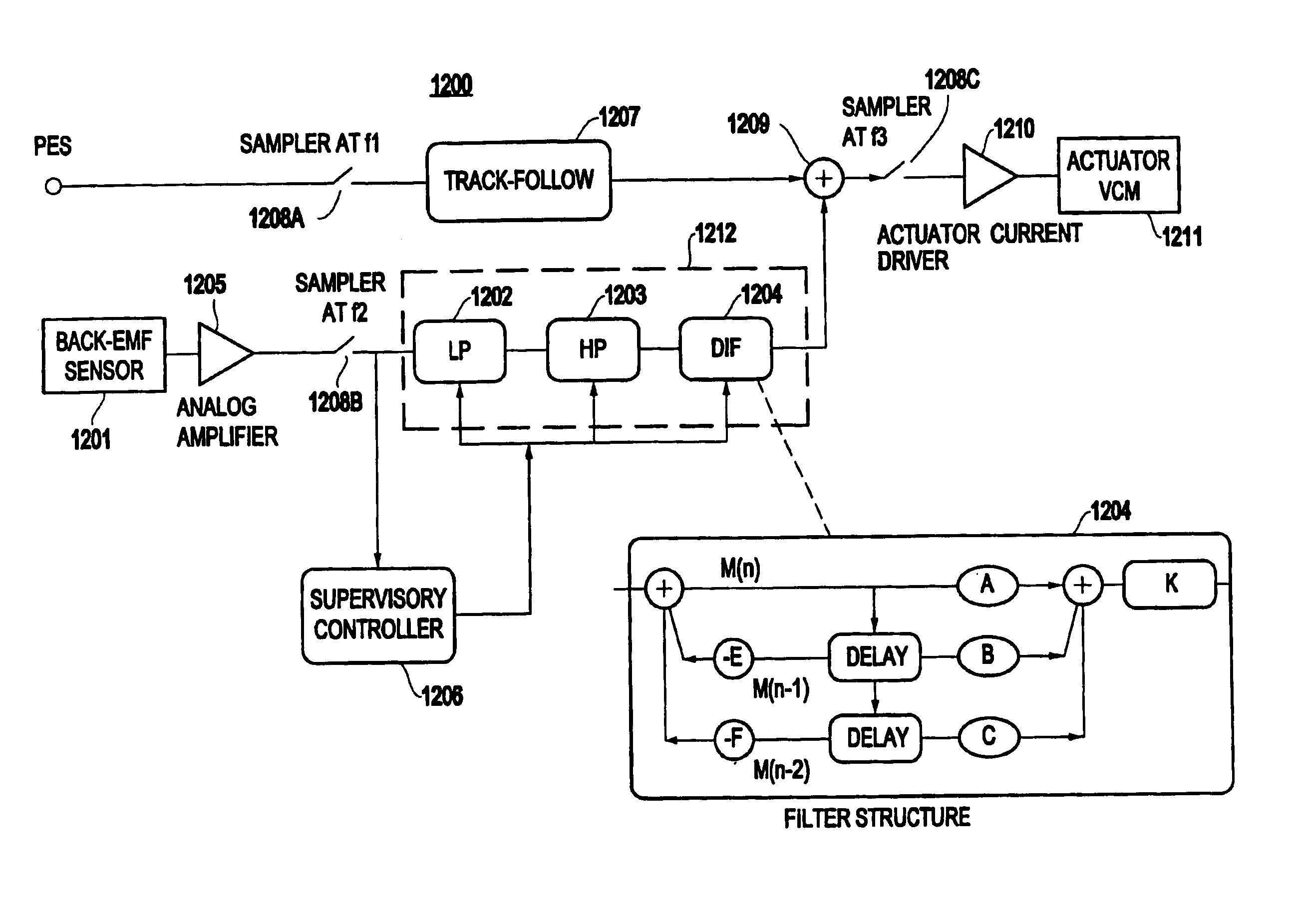
Method and system for rotational velocity-based algorithm for vibration compensation in disk drives
InactiveUS6898046B2Error minimizationReduce positioningTrack finding/aligningApparatus for flat record carriersRotational vibrationRotation velocity
A disk drive (HDD) (and method) subject to linear and rotational vibration, includes an independent sensing unit for sensing a rotational velocity component of the rotational vibration in a predetermined frequency range, and an optimal filter combination for receiving an output from the sensing unit.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
Metro gauge detecting system and detecting method thereof
InactiveCN102914290AHigh sampling frequencyHigh data accuracyProfile tracingMaterial resourcesComputer science
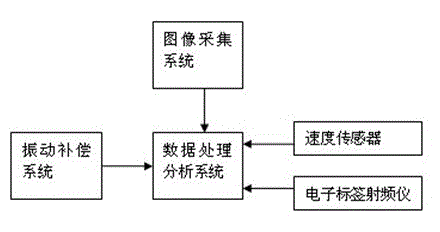
The invention provides a metro gauge detecting system and a detecting method thereof and belongs to the field of urban mass transit gauge detection. The metro gauge detecting system comprises a data processing analyzing system and an image collecting system 10, a vibration compensation system and a positioning system which are respectively connected with the data processing analyzing system. The accuracy and precision can be both increased by the measurement of the metro gauge detecting system in each section of road; the system error is reduced; the control on the system is excellent; the manpower resource and the material resource are simultaneously saved; the efficiency is increased; and the metro gauge detecting system is suitable for high-speed and real-time detection requirement.
Owner:CHENGDU TANGYUAN ELECTRICAL APPLIANCE
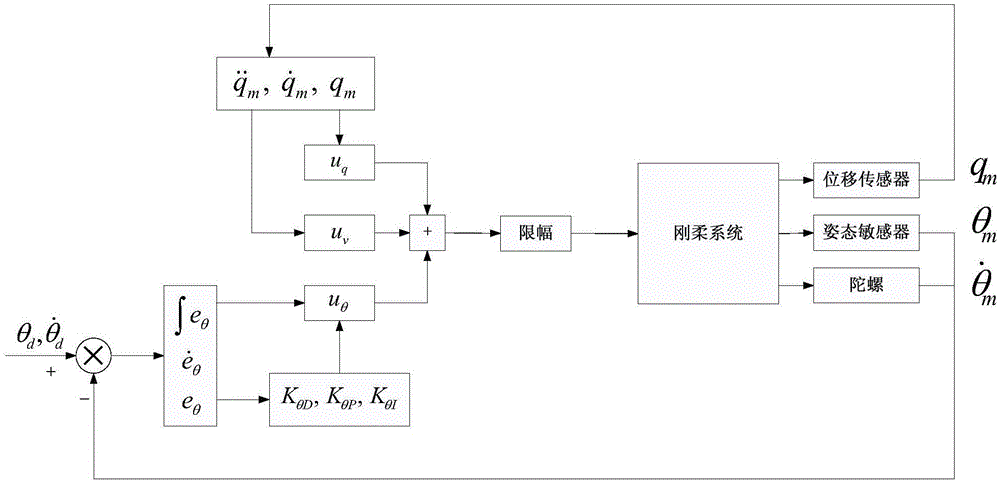
Rigid-flexible system attitude control method based on vibration compensation and state feedback
ActiveCN105045270AFeedforward Compensation ImplementationAchieve flex vibration suppressionAttitude controlAttitude controlPerformance index
Provided is a rigid-flexible system attitude control method based on vibration compensation and state feedback. According to the method, dynamic measuring information of flexible vibration is directly employed, compensation and feedback control of vibration influence is performed in an attitude controller of a central rigid body, and actuators do not need to be arranged on flexible accessories. Conventional PID control is difficult to adapt to the condition of inaccurate parameters or changing parameters of controlled objects, and general adaptive control has internal conflicts between the ensuring of the steady-state performance and the dependence on continuous excitation. According to the method, the state feedback control parameters change with the change of estimation states, good steady-state performance indexes can be maintained by variable system and environment, and the method is especially applicable to attitude control of satellites with large flexible influence and high-stability performance index.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF CONTROL ENG
Current compensation-based unbalance vibration control system for bearingless asynchronous motor
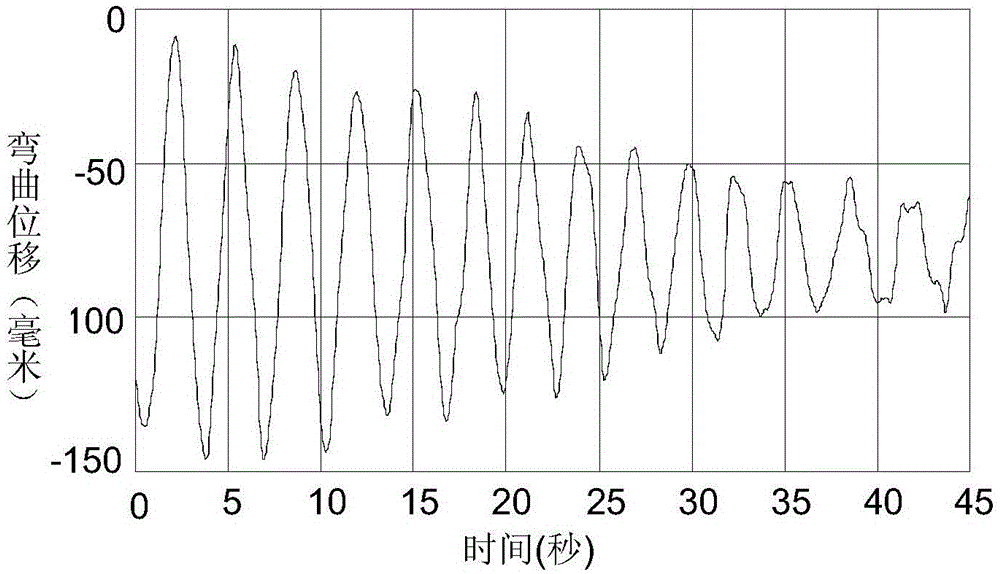
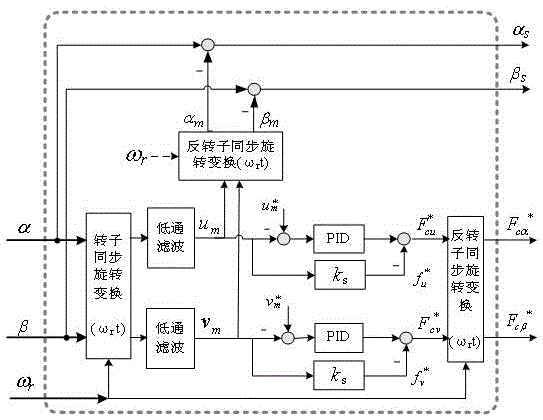
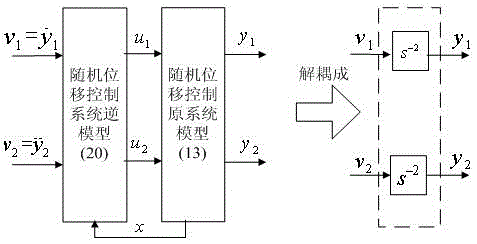
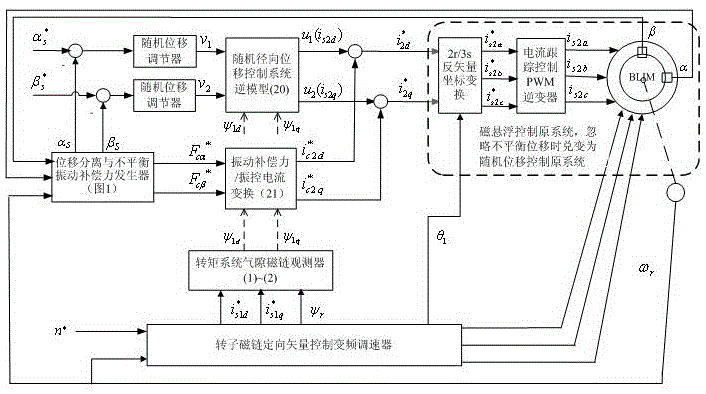
InactiveCN105048913ANovel structureGuaranteed real-timeElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlMotor speedVibration control
The invention discloses a current compensation-based unbalance vibration control system for a bearingless asynchronous motor. A rotor flux linkage-oriented vector control variable-frequency governor provides current to a torque winding to control the rotating speed of the motor and the rotor flux linkage; torque winding stator current components and rotor flux linkage signals are output to an air gap flux linkage observer; two linear integration sub-systems are formed before a random displacement control inverse system is connected to the original system in series; rotor radial displacement is fed into a displacement separation and unbalance vibration compensation force generator to obtain random displacement and unbalance vibration compensation force; the random displacement is fed into the inverse system through a random displacement adjustor to form closed loop control; the inverse system outputs random displacement control current; the unbalance vibration compensation force is subjected to force / flow transformation to obtain unbalance vibration compensation control current; the unbalance vibration compensation control current is correspondingly compared with the random displacement control current to obtain synthetic magnetic levitation control current; and the synthetic magnetic levitation control current is fed into the original system to generate three-phase magnetic levitation control current, so that the unbalance vibration current compensation control on the bearingless asynchronous motor is realized.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
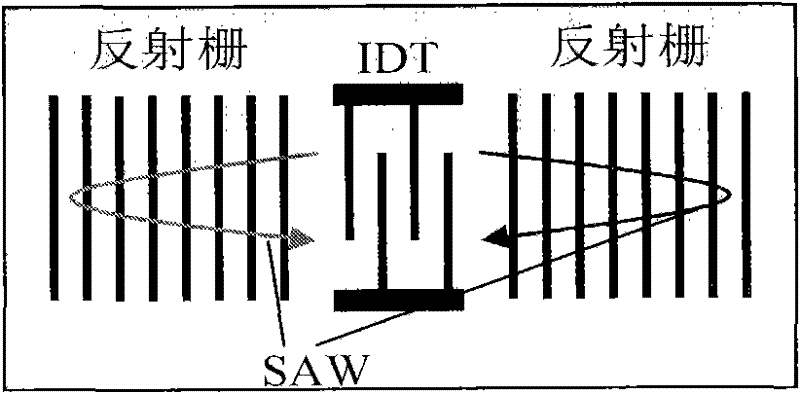
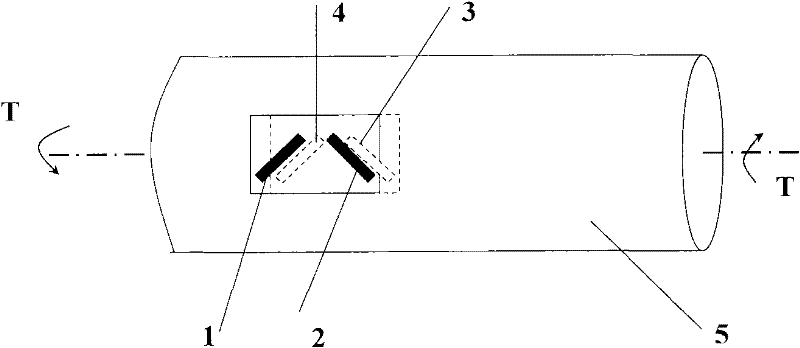
A passive wireless surface acoustic wave torque sensor with temperature and vibration self-compensation
InactiveCN102288339AReduce volumeRealize wireless transmission and receptionWork measurementTorque measurementEngineeringSurface acoustic wave resonators
The invention relates to a sensor suitable for passive wireless measurement of torque. The sensor has temperature and vibration compensation functions. The passive wireless torque sensor of the present invention includes four surface acoustic wave resonators with different center frequencies, a small antenna and an elastic shaft of the sensor. The surface acoustic wave resonator of this sensor uses quartz as the substrate of the resonator. The interdigital transducer and reflection grid are deposited on the substrate, and the piezoelectric effect and inverse piezoelectric effect are used to excite and receive the surface acoustic wave. The four surface acoustic wave resonators of the torque sensor are pasted on the elastic shaft according to the design angle. When torque is applied to the elastic shaft, the four surface acoustic wave resonators can respectively detect the deformation in the pasting direction. The four deformations can be obtained by processing the temperature , Torque information after vibration compensation. The four surface acoustic wave resonators are connected with the antenna, which can realize the wireless transmission of force state information. The invention has the advantages of simple structure, small size, light weight, high precision, passive wireless, and is suitable for passive wireless measurement of torque of important shaft parts such as aerospace, transmission machinery, precision machine tools, and heavy vehicles.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
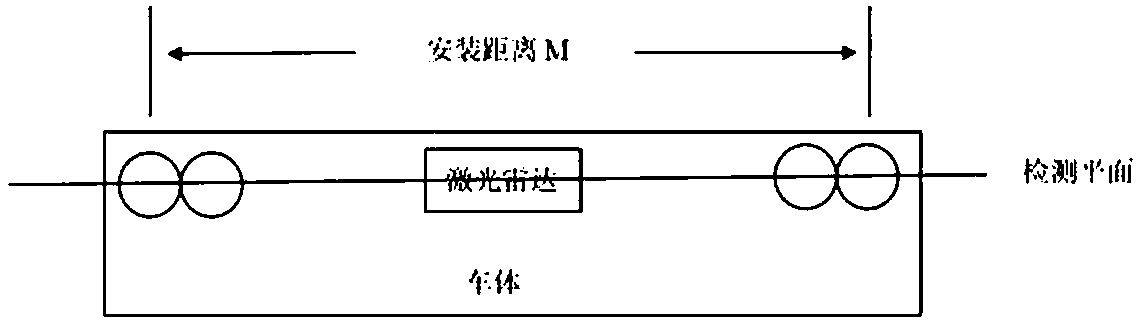
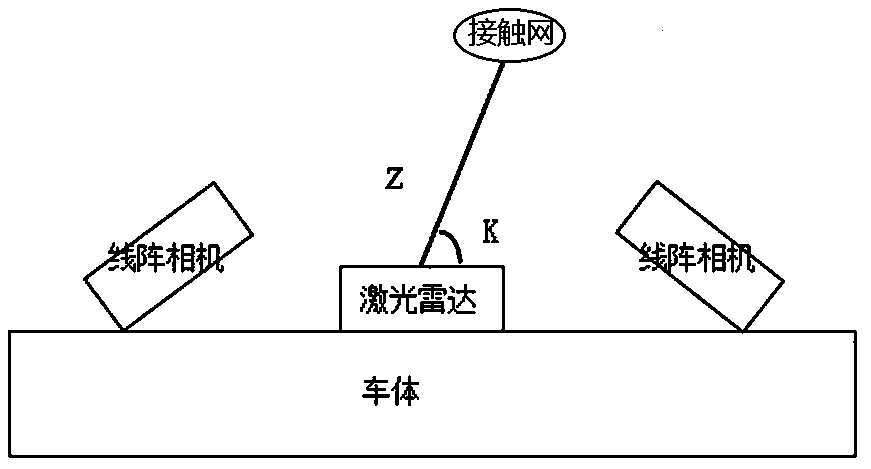
Dynamic detection system and method for geometric parameters of vehicle-mounted non-contact overhead line system
ActiveCN107678036AMeet the requirements of the applicationSimple structureOptical rangefindersElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadarEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of measurement, and discloses a dynamic detection system and method for geometric parameters of a vehicle-mounted non-contact overhead line system. The detection system comprises a geometric detection unit which is arranged at the vehicle roof and used for detecting the overhead line system, a control unit arranged in a vehicle body and a vibration compensation unit which is arranged at the vehicle bottom and used for detecting vibration of the vehicle body, and is characterized in that the geometric detection unit comprises laser radar, linear array cameras and light sources; the laser radar is arranged at the center of the geometric detection unit; two groups of the linear array cameras are set, each group comprises two linear array cameras, the two groups of the linear array cameras are respectively arranged at two sides of the laser radar, and the linear array cameras in the same group are obliquely arranged relative to the vehicle roof;the laser radar and the linear array cameras are distributed at the same straight line, a scanning area of the laser radar and a detection area of the linear array cameras are located at the same detection plane; and the light sources are arranged at two sides of the laser radar. The detection system and method are high in detection precision, simple in structure and easy to install.
Owner:株洲嘉成科技发展股份有限公司
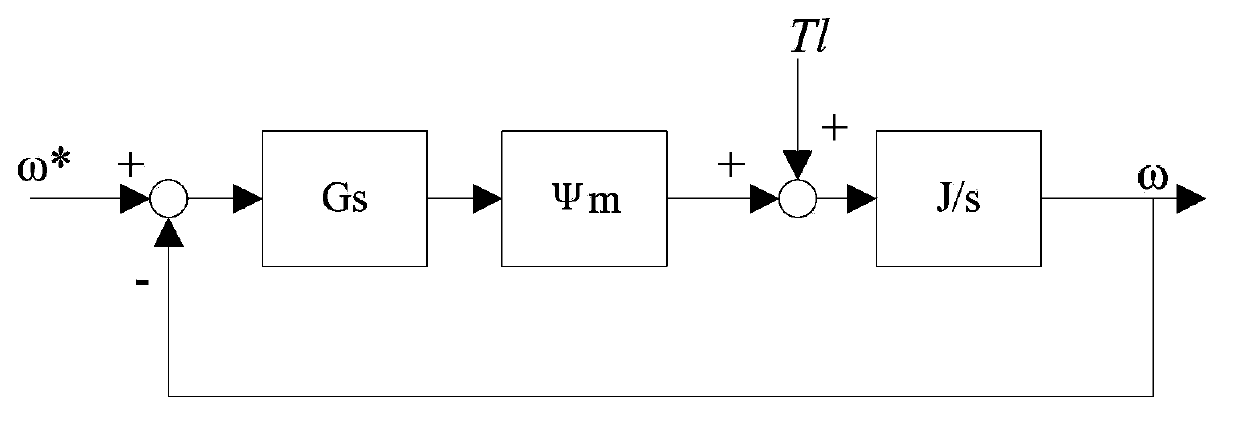
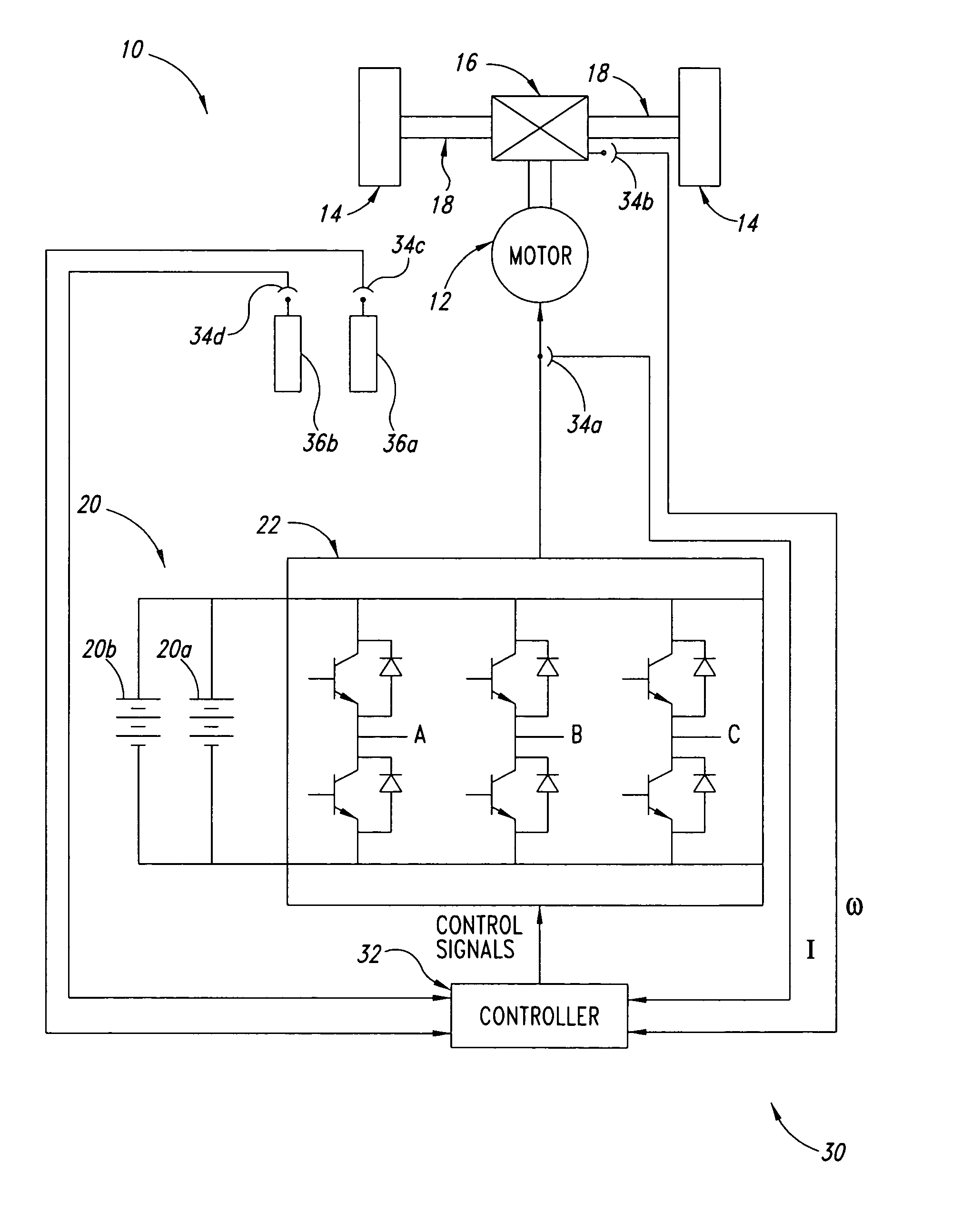
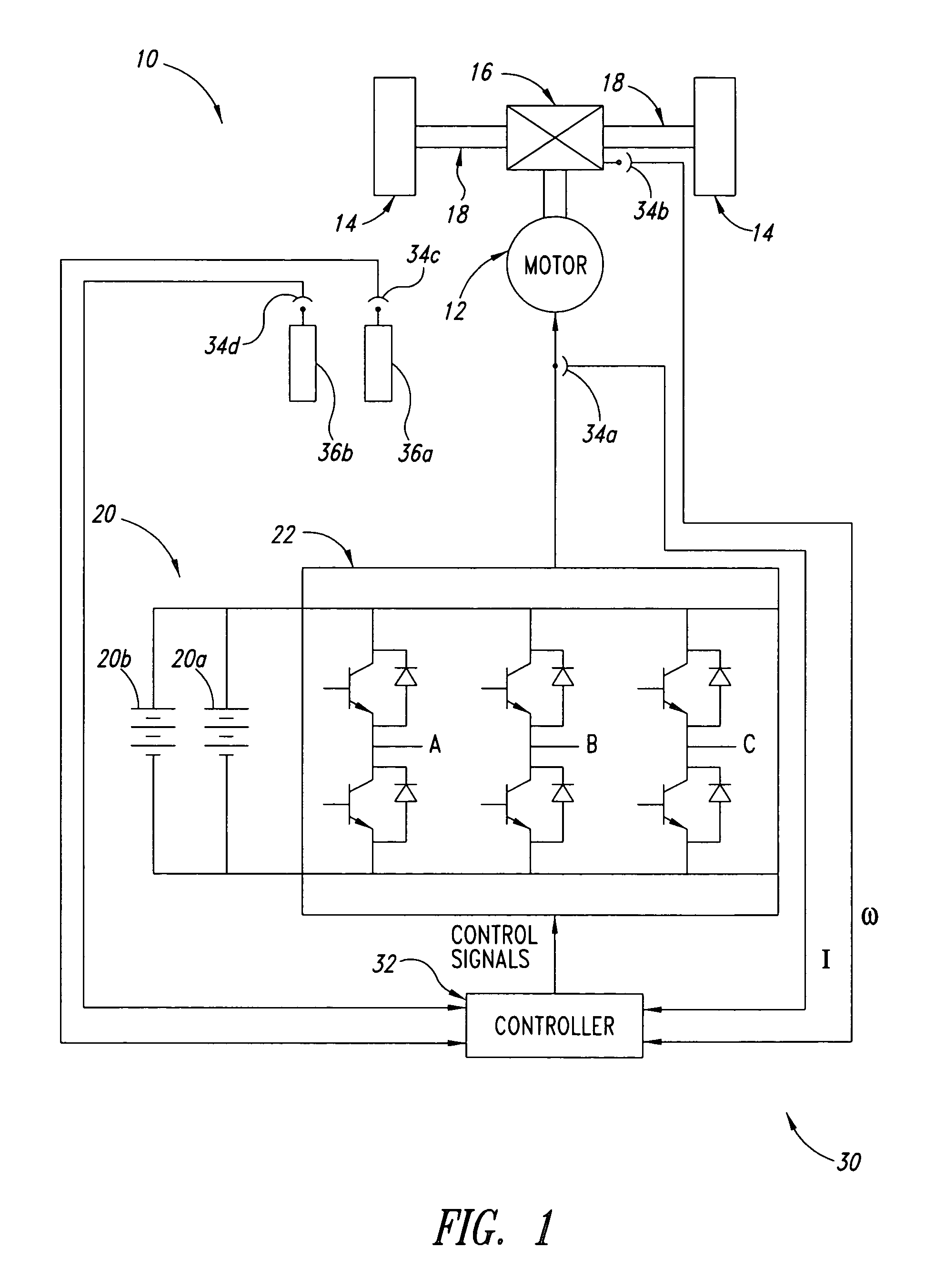
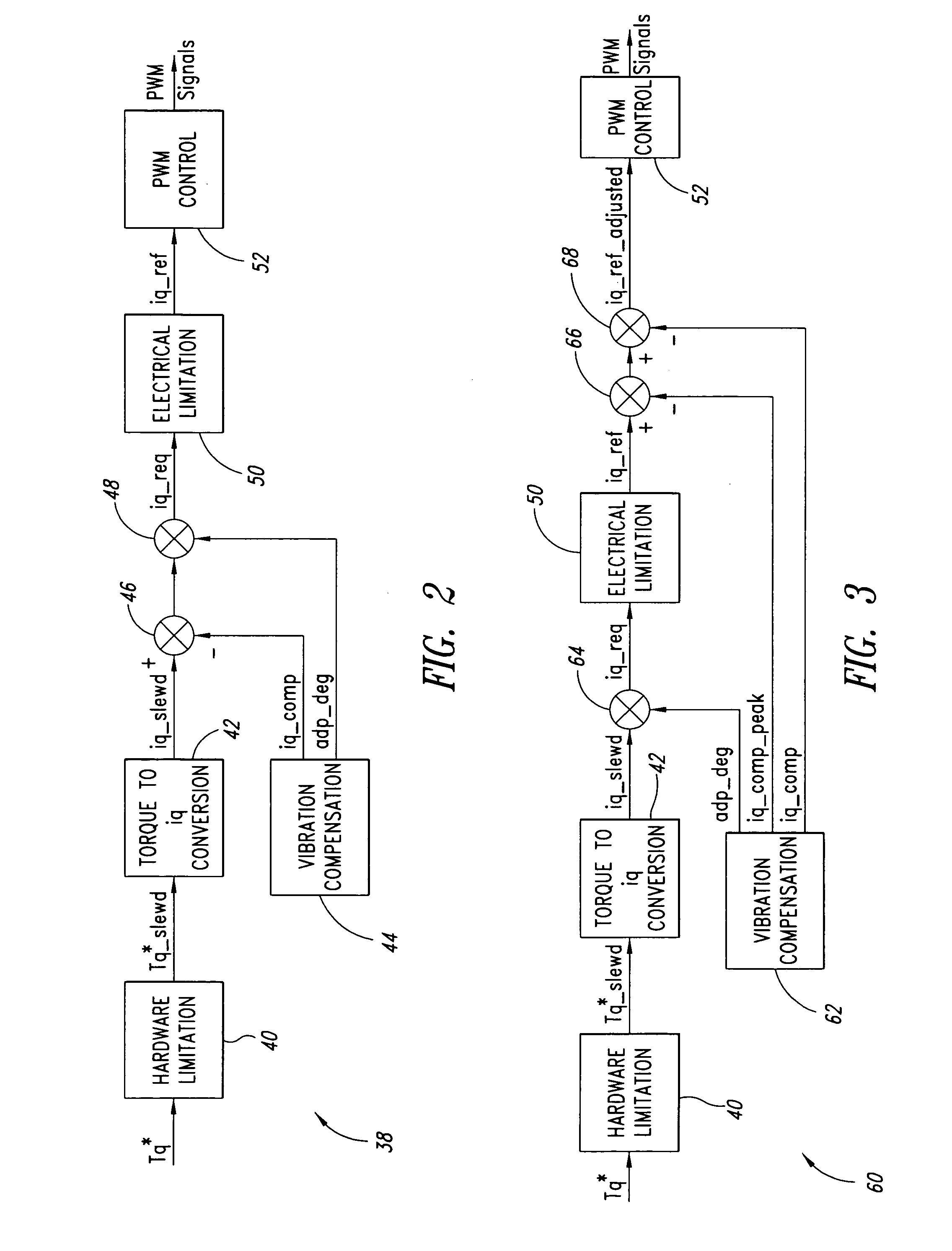
Method, apparatus and article for vibration compensation in electric drivetrains
InactiveUS20050253543A1Reduce and eliminate vibrationElectronic commutation motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlDrivetrainPeak value
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTOMOTIVE SYST INC
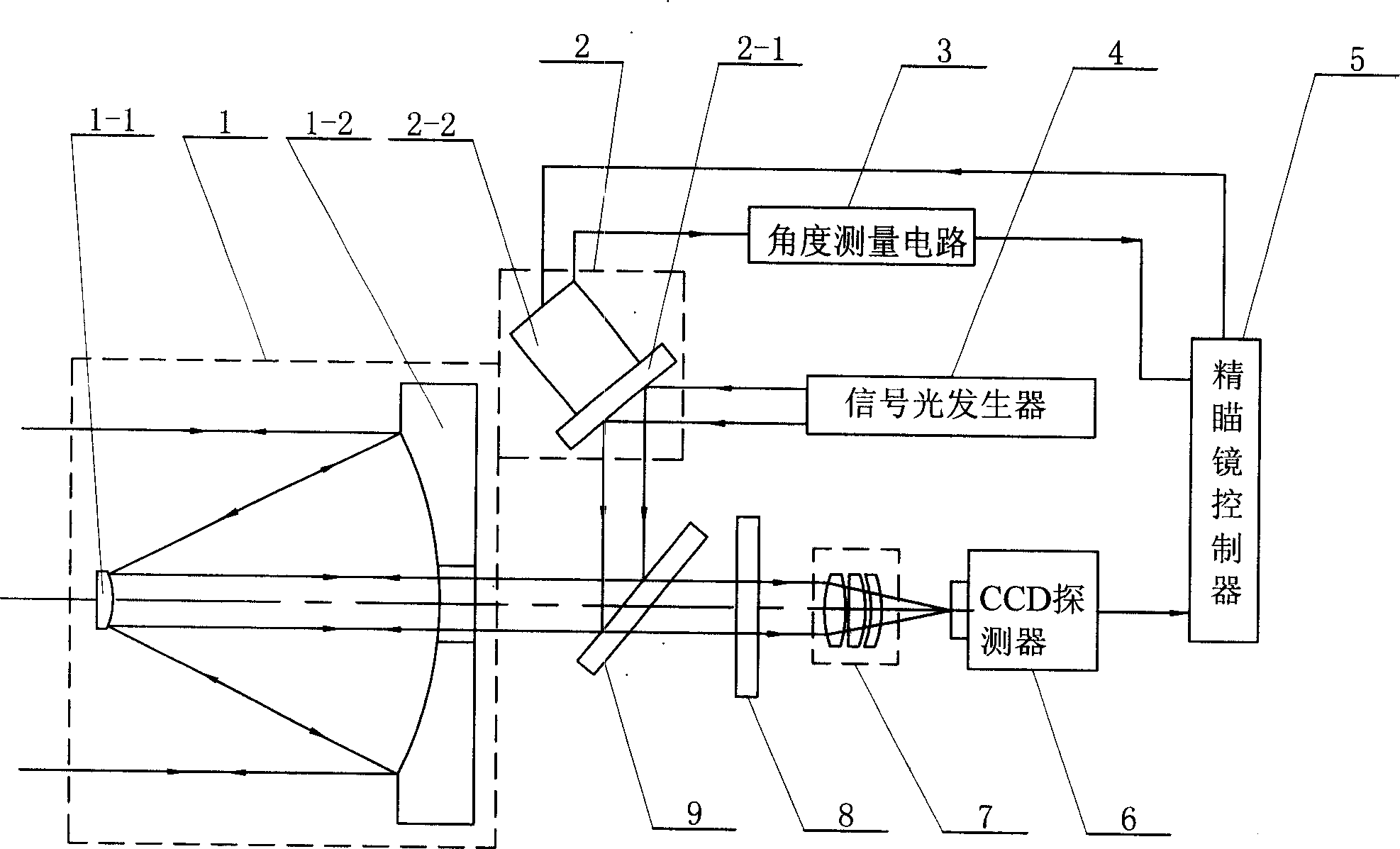
Composite feedback control vibration compensating system based on CCD
InactiveCN1825786APrecise alignmentSignal light pointing deviation reducedSatellite communication transmissionOptical antennaImaging lens
This invention relates to a compound feed back control vibration compensation system based on CCD, in which, the beacon light emitted by a target terminal passes through an optical antenna, a light splitting plate, a filter and an imaging lens set to be imaged on a CCD detector, the signal light output by a signal light generator passes through a total reflection mirror and a light splitting plate to be expanded by the optical antenna and emitted to a target terminal, a precise aiming mirror controller utilizes the CCD detector to get the information of an angle of declination to control the deflection of the total reflection mirror to let signal lights emit to the target terminal along the initial path of the beacon light accurately. The compensation system can detect the vibration of a satellite platform timely.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
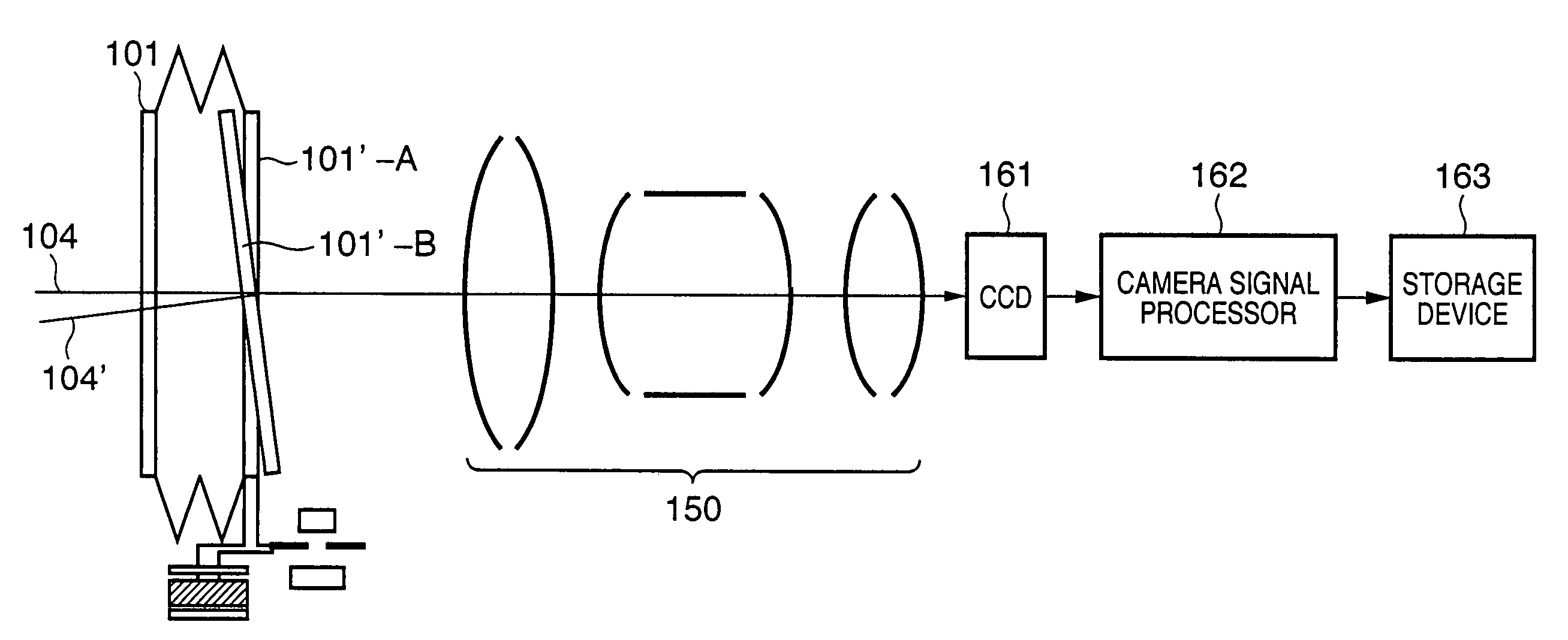
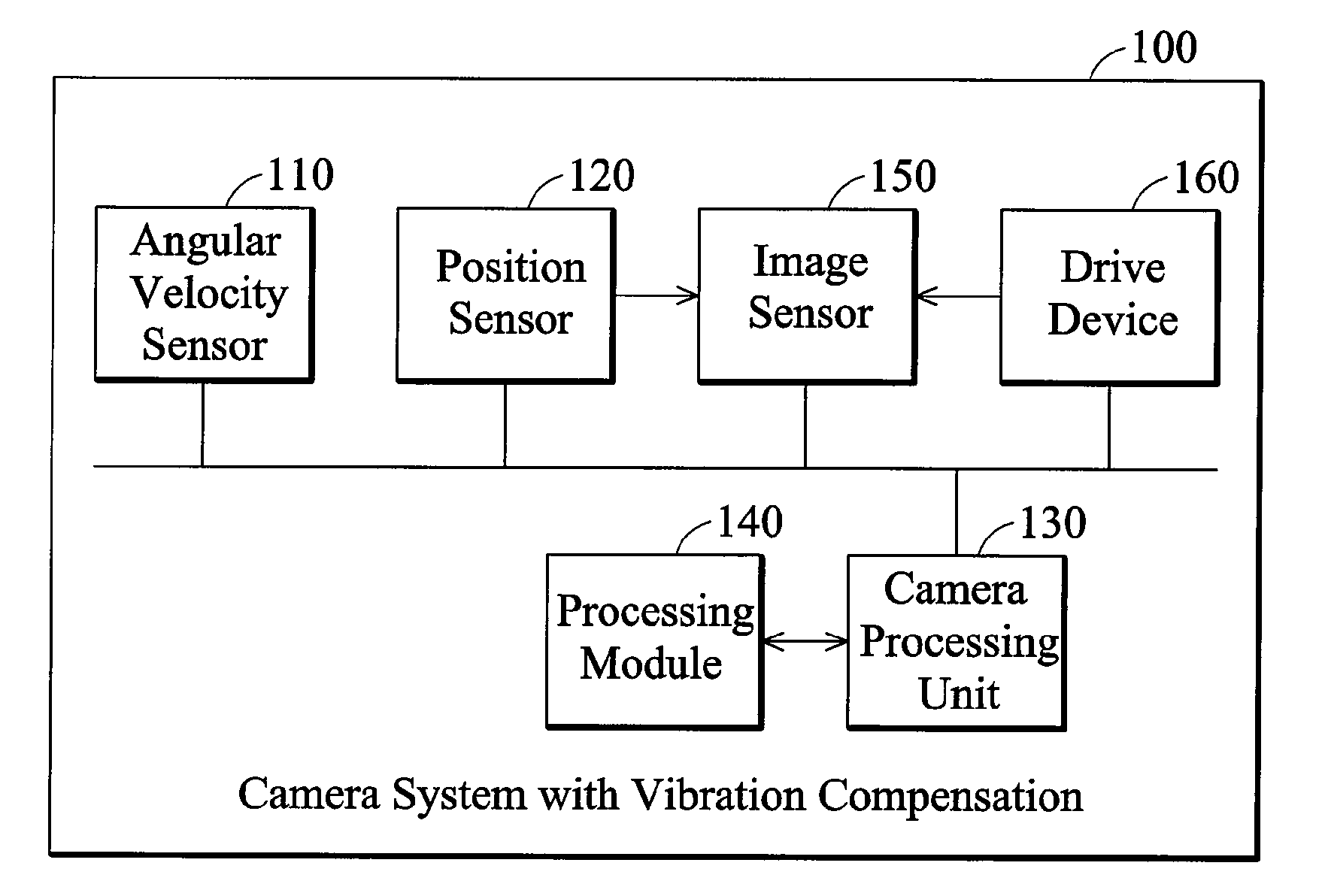
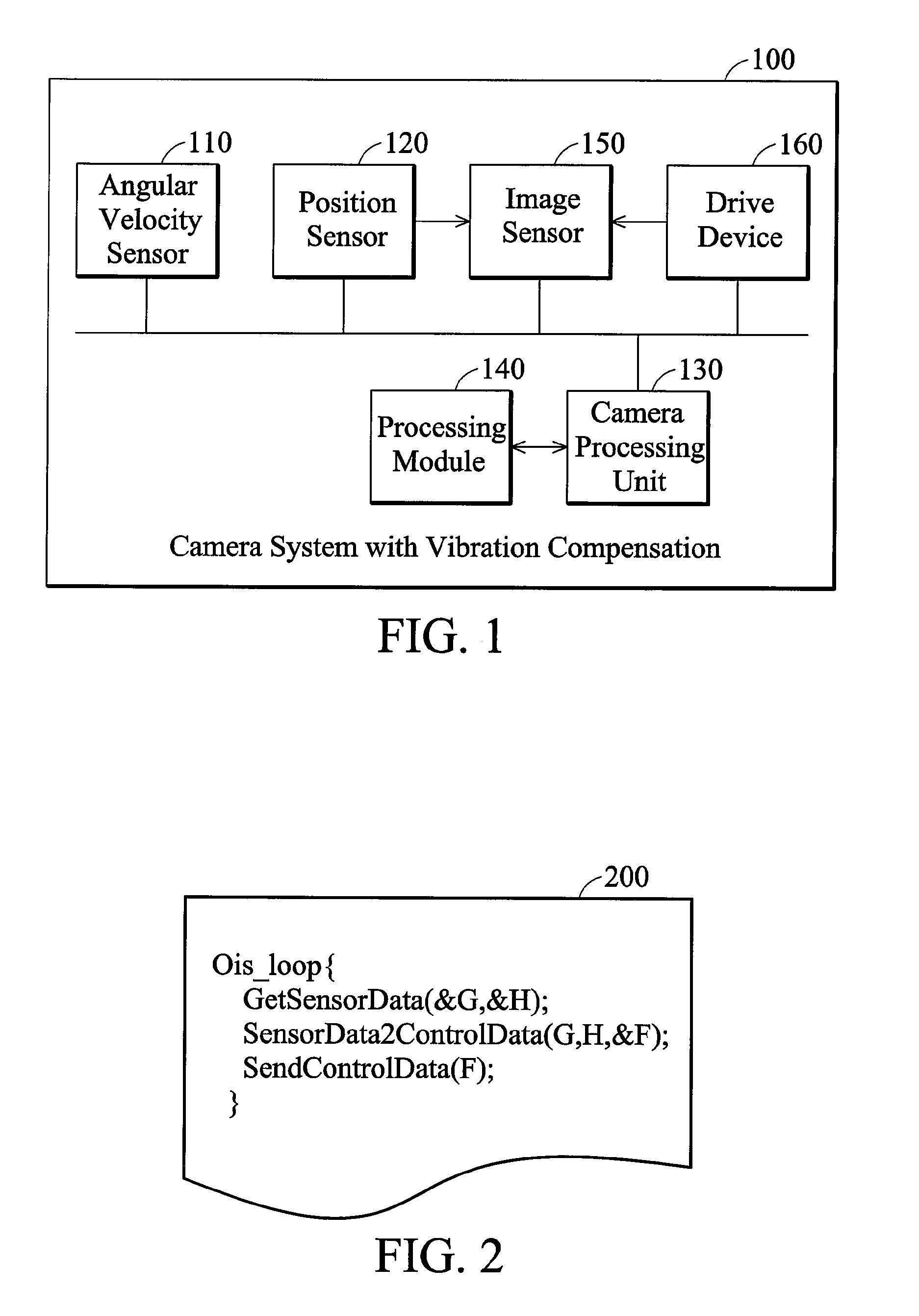
Camera systems with vibration compensation and methods thereof
ActiveUS20080012946A1Television system detailsPicture signal generatorsSensing dataVibration compensation
Camera systems and methods with vibration compensation. The system comprises a first sensor, a second sensor, and a processing module. The first sensor detects an angle variation of a movement of a camera device to generate first sensed data. The second sensor detects a position movement of an image sensor of the camera device to generate second sensed data. The processing module takes the first derivative of the second sensed data, and calculates control information according to the first sensed data and the differential of the second sensed data. The processing module enables a drive device to adjust the position of the image sensor based on the control information.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL INT LTD
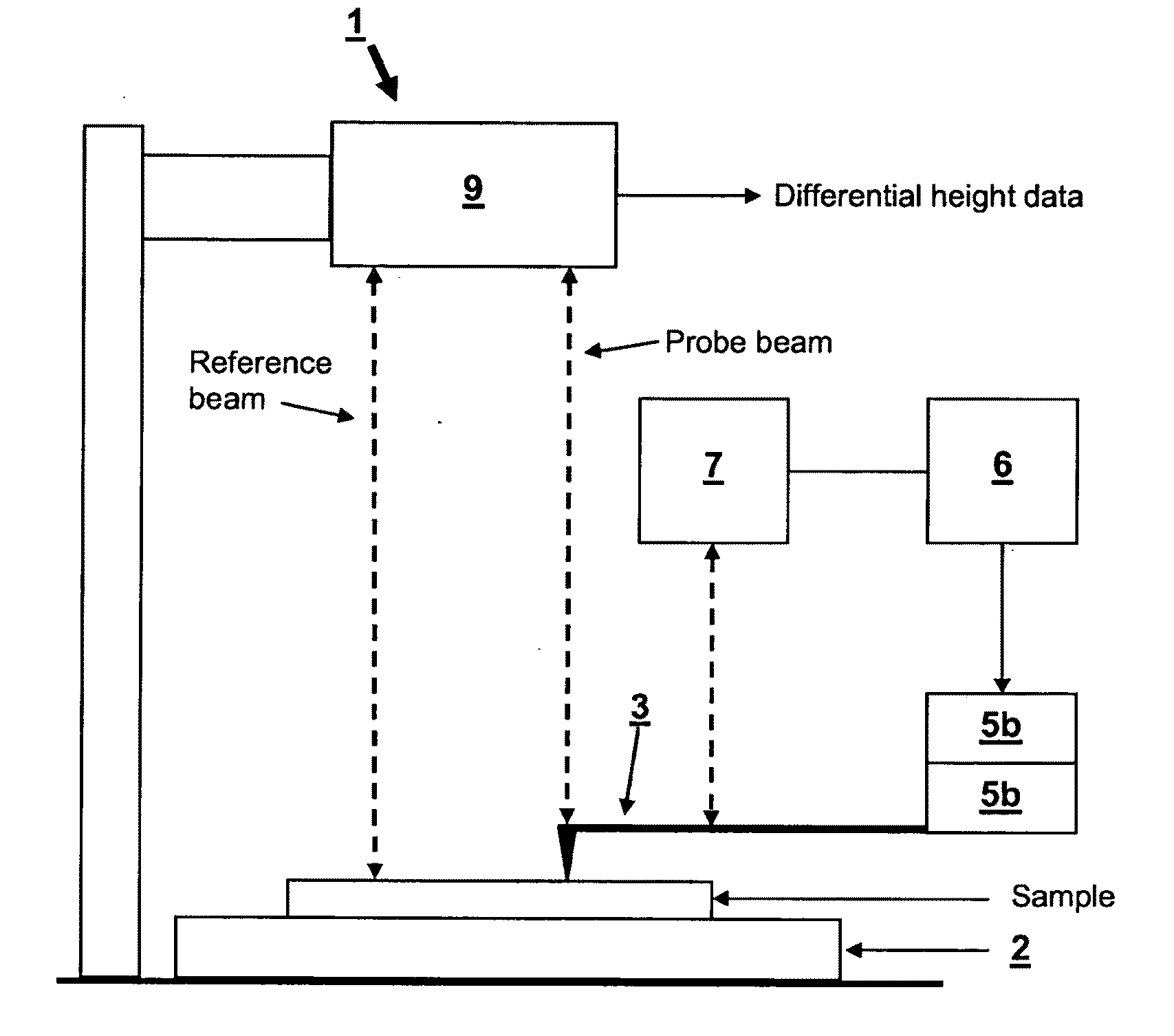
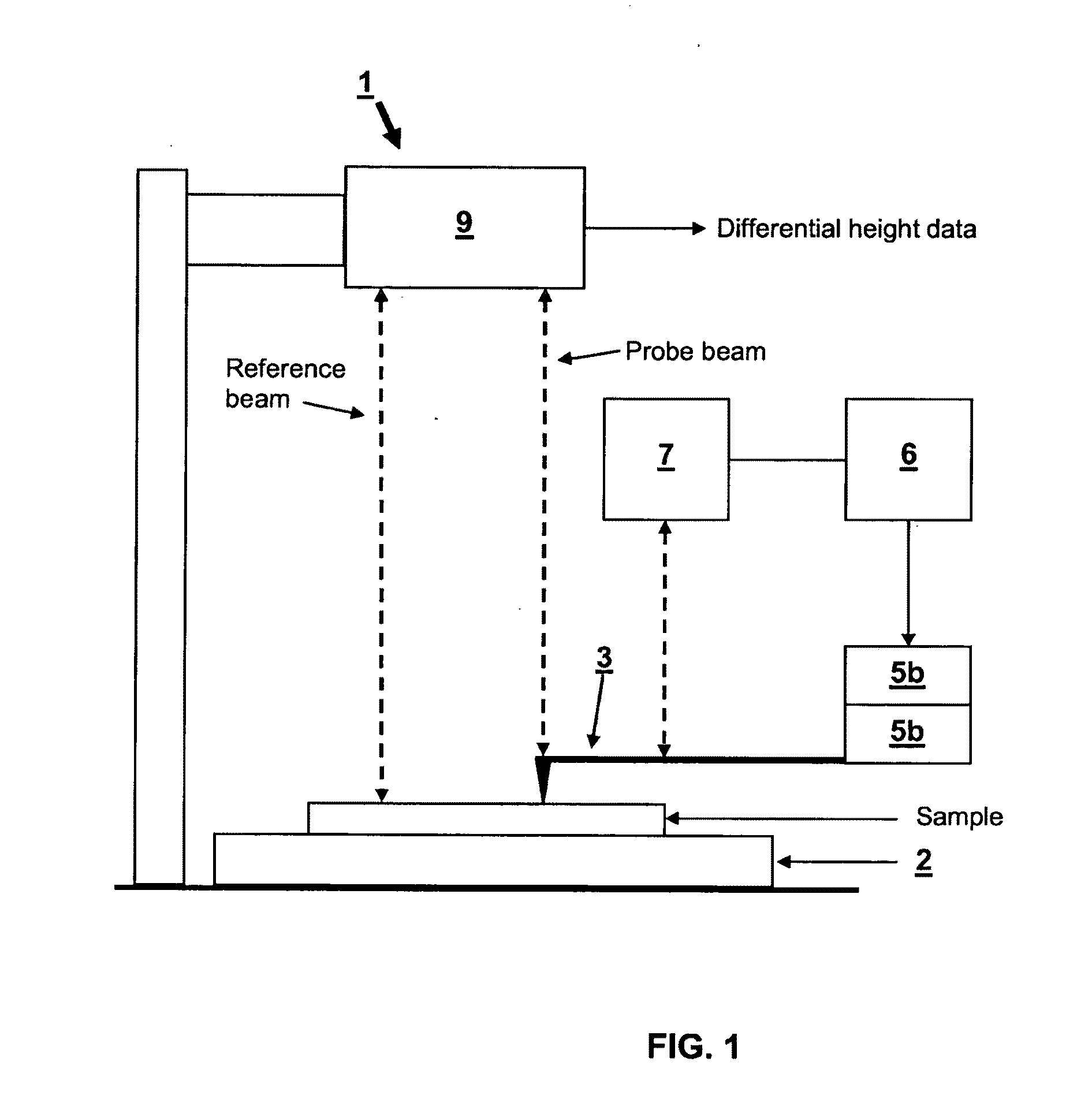
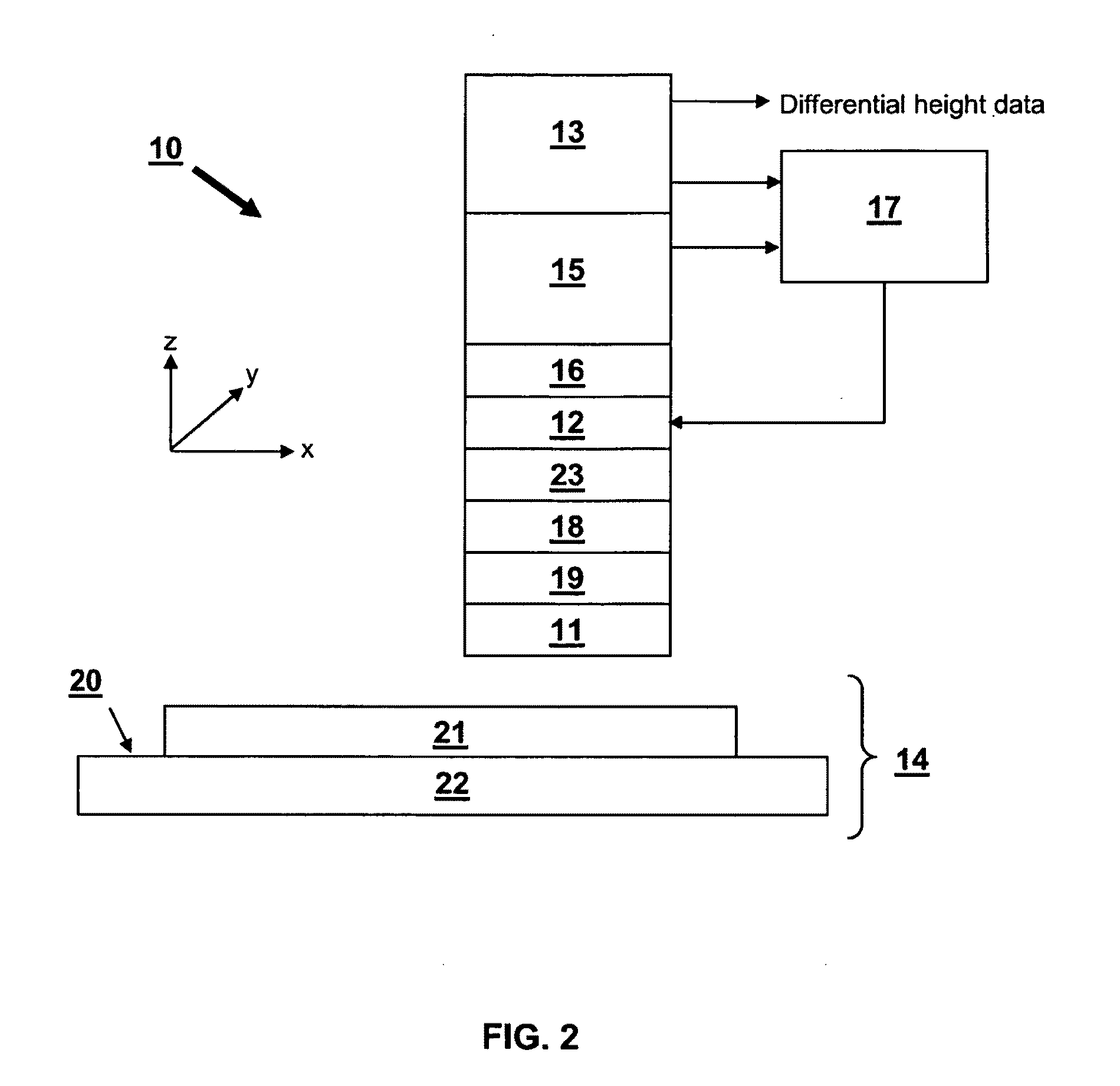
Vibration compensation in probe microscopy
A The local probe microscopy apparatus (1) comprises a probe (3) with translation stages (5a, 5b) for controlling the position of the probe (3) relative to a sample surface. The probe (3) has a feedback mechanism (6, 5 7) for maintaining the deflection of the probe and a height measuring system (9) which includes means for compensating for environmental noise. The local probe microscopy apparatus is particularly suitable for use as a wafer inspection tool in a wafer fabrication plant where the inspection tool is liable to be exposed to significant mechanical vibration.
Owner:INFINITESIMA
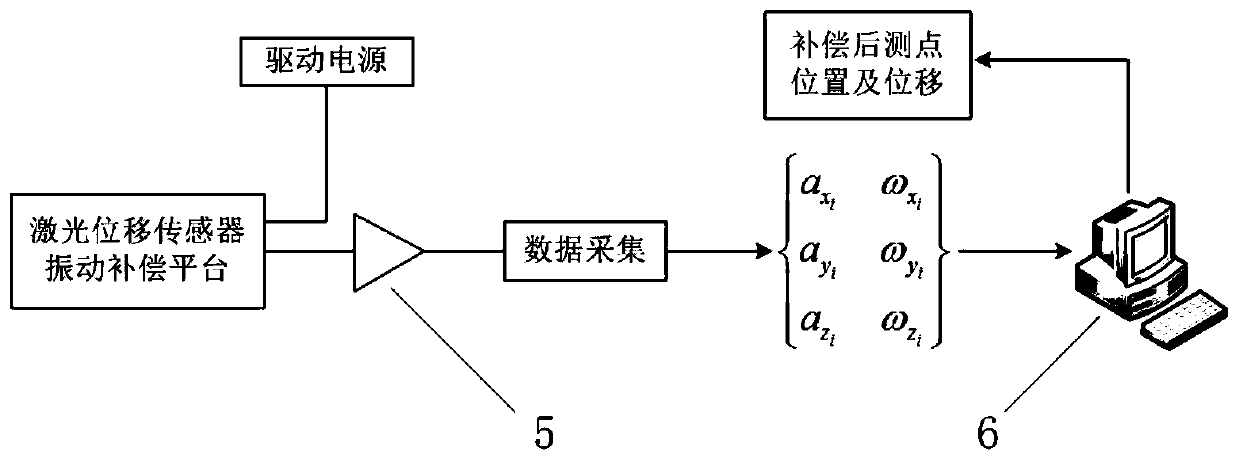
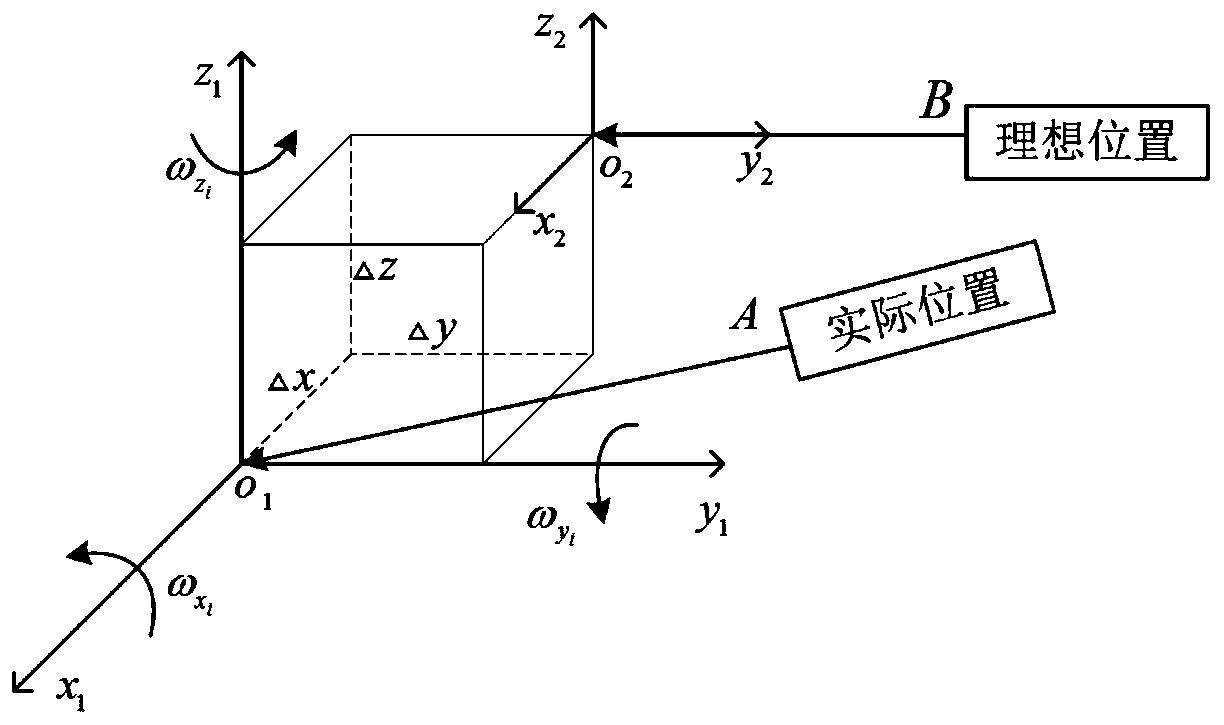
Vibration compensation platform of laser displacement sensor
ActiveCN110672017ACompensation for measurement errorsSimple structureUsing optical meansData acquisitionSignal amplifier
The invention provides a vibration compensation platform of a laser displacement sensor. The vibration compensation platform comprises a laser measurement device, a signal processor and a compensationcalculation device; the laser measurement device comprises a laser displacement sensor, an acceleration sensor, an angular velocity sensor and a fixture; the signal processor comprises a data collection card and a signal amplifier; the data collection card is used for collecting output voltages of the laser displacement sensor, the acceleration sensor and the angular velocity sensor; and the compensation calculation device respectively calculates a displacement, a vibration displacement error and a vibration angle error according to the output voltages of the laser displacement sensor, the acceleration sensor and the angular velocity sensor collected by the data collection card, and substitutes the displacement, the vibration displacement error and the vibration angle error into a shape and position correction matrix to obtain a compensated measurement point position and displacement of the laser displacement sensor. The vibration compensation platform provided by the invention solves the problem that the existing laser displacement sensor is vulnerable to vibration to affect the measurement accuracy of a measured component.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
Method for compensating for vibration and imaging apparatus using the same
InactiveUS20110122269A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImaging equipmentVibration compensation
A method of compensating for vibration and an imaging apparatus are provided. The method of compensating for vibration includes determining whether a vibration compensation starting condition is satisfied, and starting compensating for vibration prior to operating a shutter, if the vibration compensation starting condition is satisfied. Accordingly, a shutter lag is reduced and power consumption is reduced, and accuracy of vibration compensation is improved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical Device With Vibration Compensation
InactiveUS20080278781A1Adjustable spacingCompensation displacementMicroscopesDeformable mirrorMicroscope
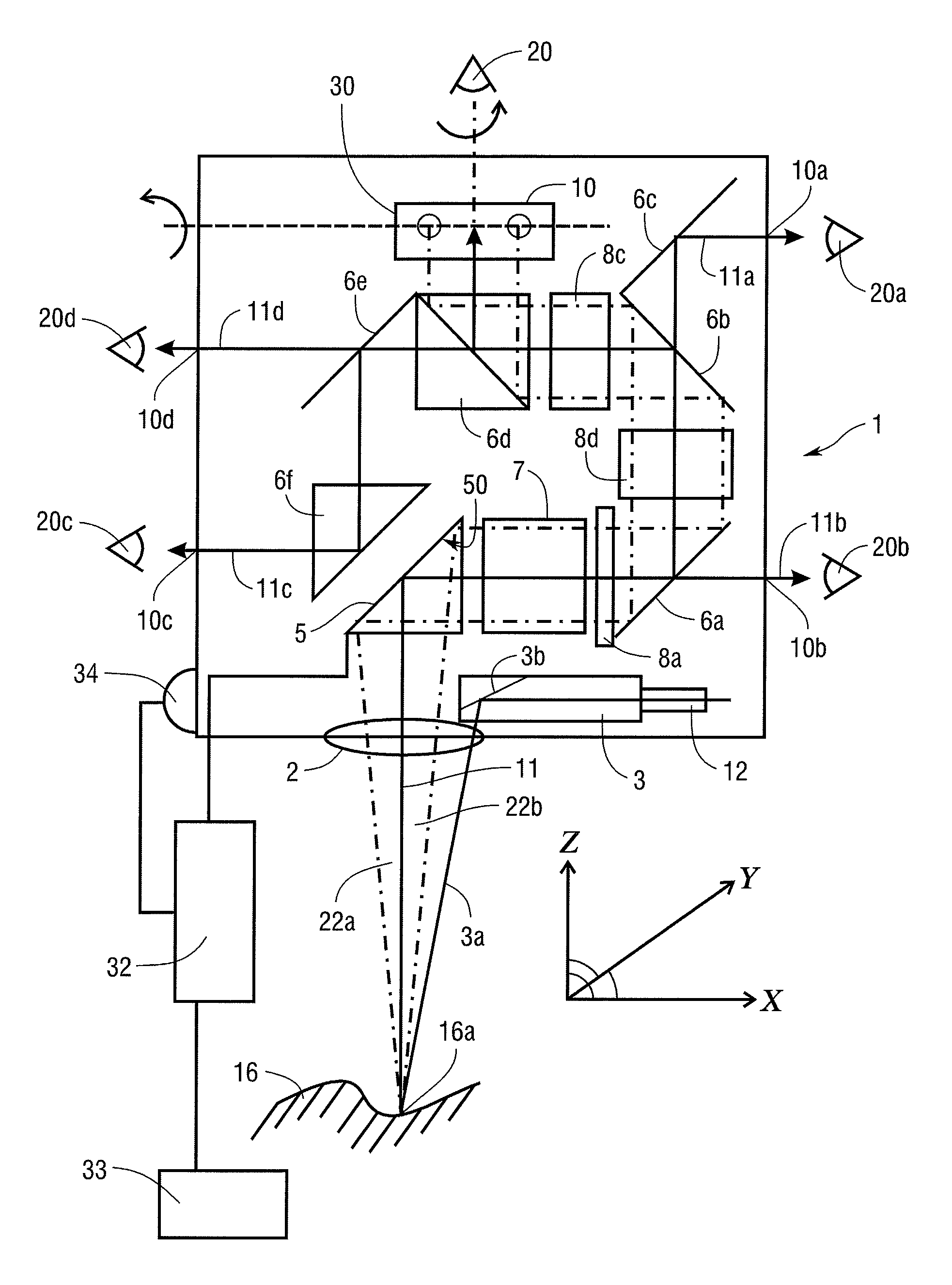
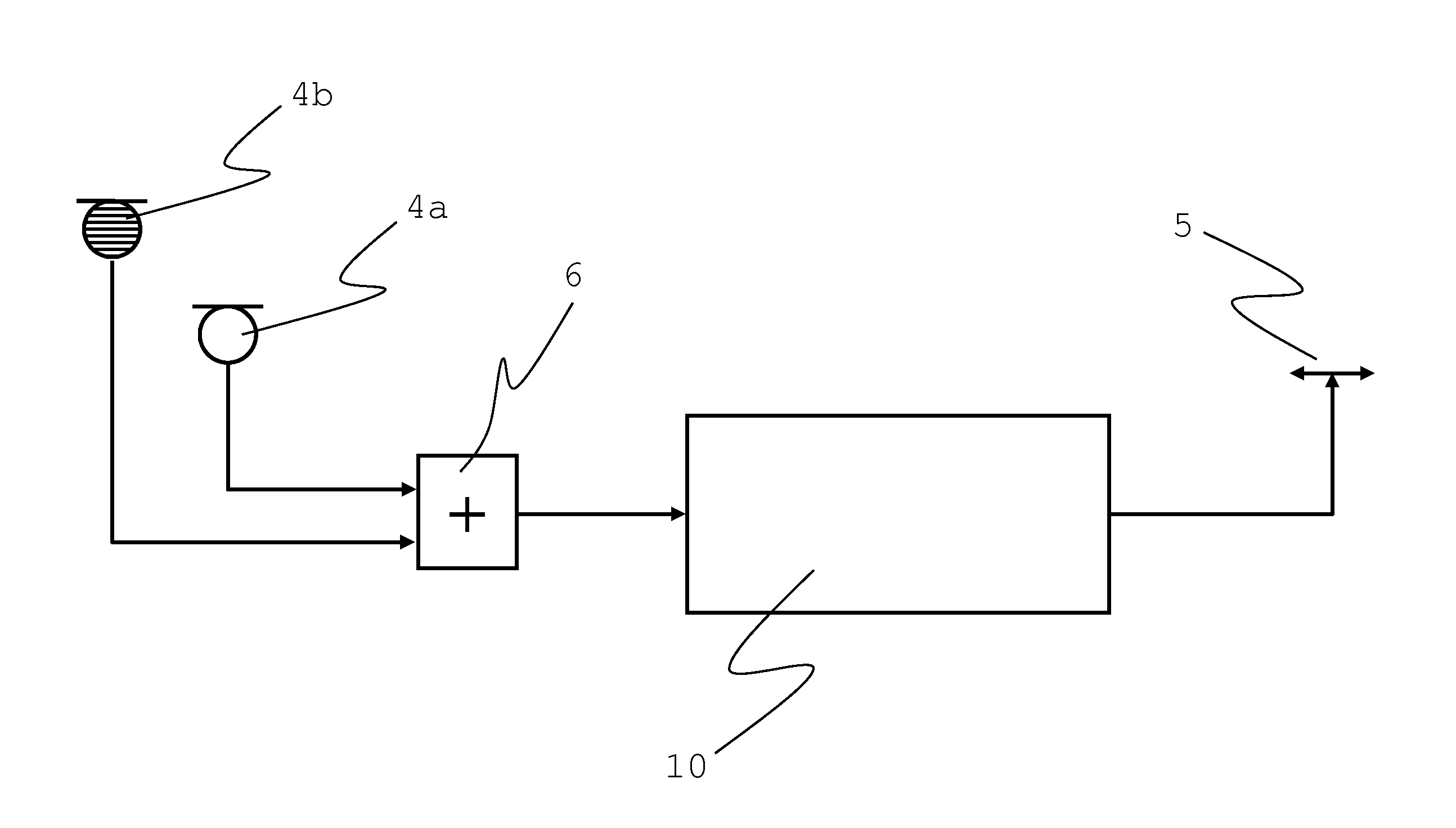
The present invention relates to an optical device, in particular a microscope (1), that comprises a beam path in which is arranged at least one deflection element (5, 6a to 6f) for deflecting the beam path, at least one vibration sensor (34) being arranged in or on the optical device; at least one of the deflection elements (5, 6a to 6f) comprising a mirror having a controllably deformable mirror surface (50); and a control unit (32) being provided that, as a function of the output signal of the vibration sensor (34), applies control to the at least one deflection element (5, 6a to 6f) in order to adjust the mirror surface (50) in such a way that vibrations of the optical device are compensated for by a correspondingly opposite-phase adjustment of the mirror surface (50).
Owner:LEICA INSTR SINGAPORE PTE
Combined motion sensor for use in feedback control systems for vibration isolation
ActiveUS20100211225A1Avoid disadvantagesTemperatue controlStatic/dynamic balance measurementControl signalEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for controlling a vibration isolation system, and an active vibration isolation system for vibration-isolated support of lithographic devices, wafer handling systems, and / or scanning microscopes. For this purpose the following are provided: a number of vibration transducers for supplying sensor signals which are representative of vibrations; a number of actuators for vibration compensation which may be controlled by supplying actuator control signals; a control device which is designed for processing the supplied sensor signals to form the actuator control signals, wherein the vibration transducers have at least one geophone sensor as a first acceleration sensor for detecting vibrations in a first frequency range, and at least one second acceleration sensor, which is different from the first acceleration sensor, for detecting vibrations in a second frequency range which extends the first frequency range.
Owner:INTEGRATED DYNAMICS ENG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com