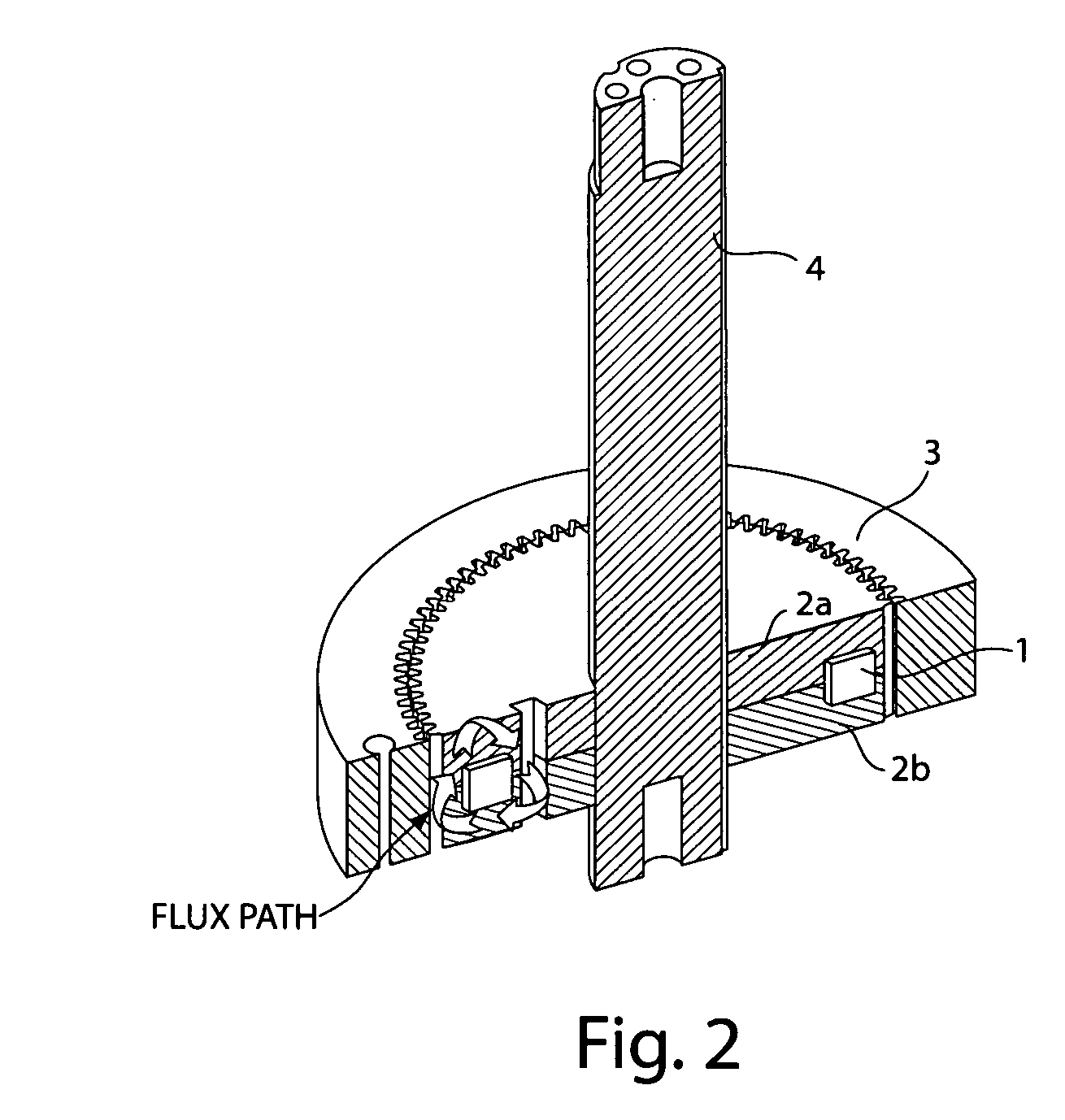
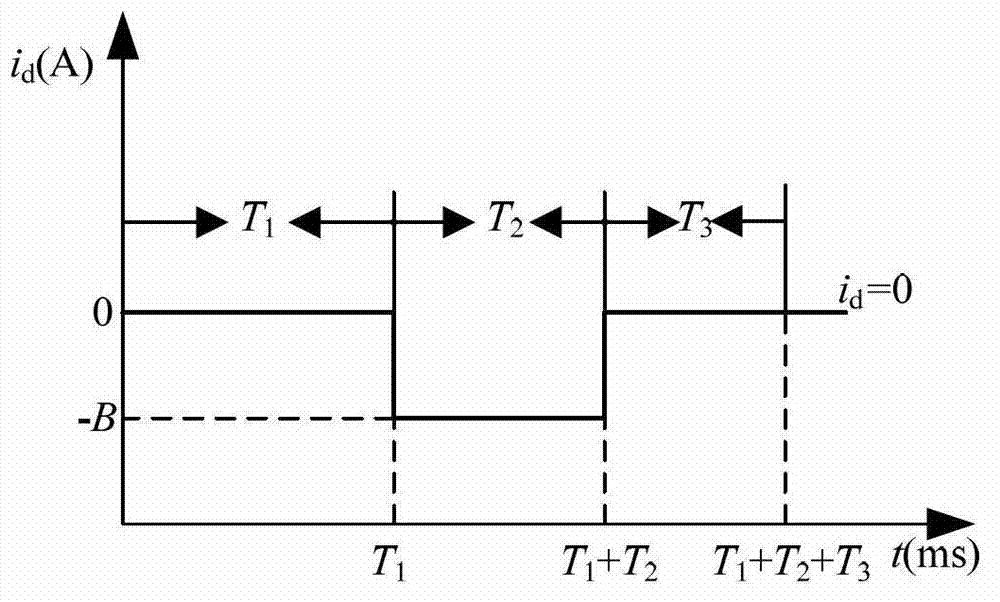
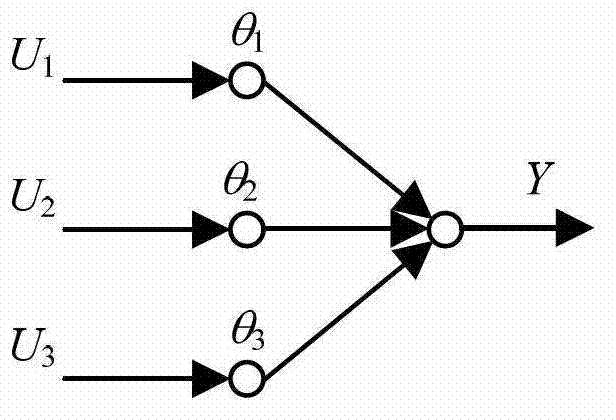
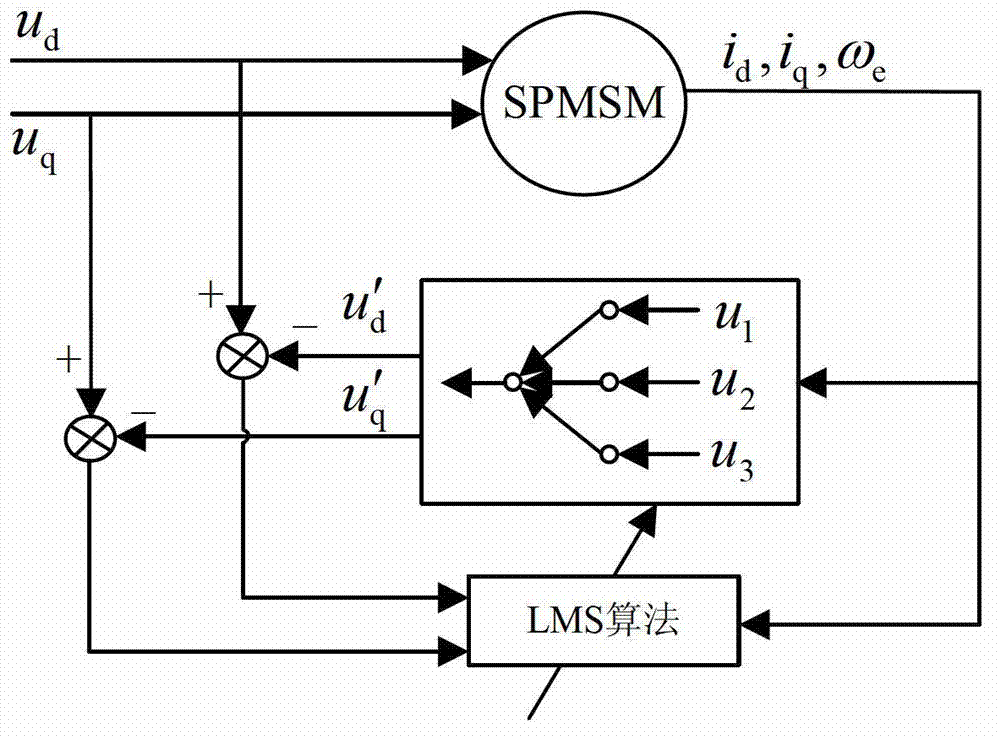
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
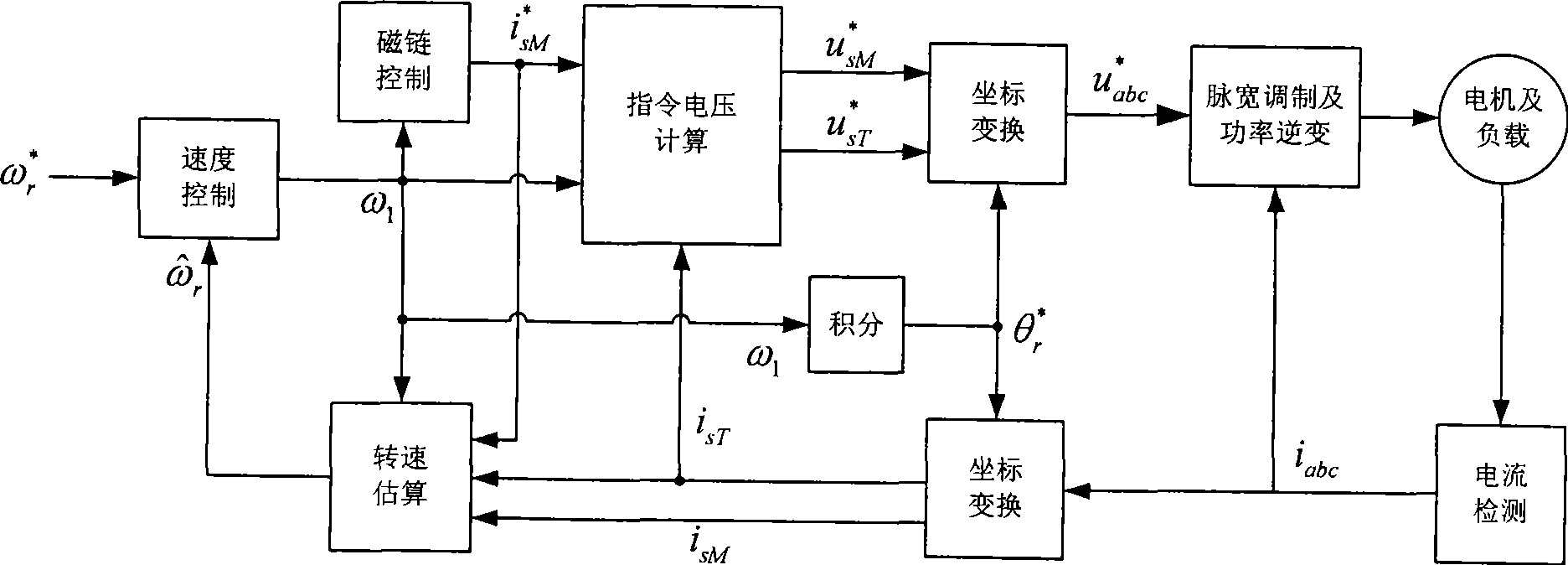
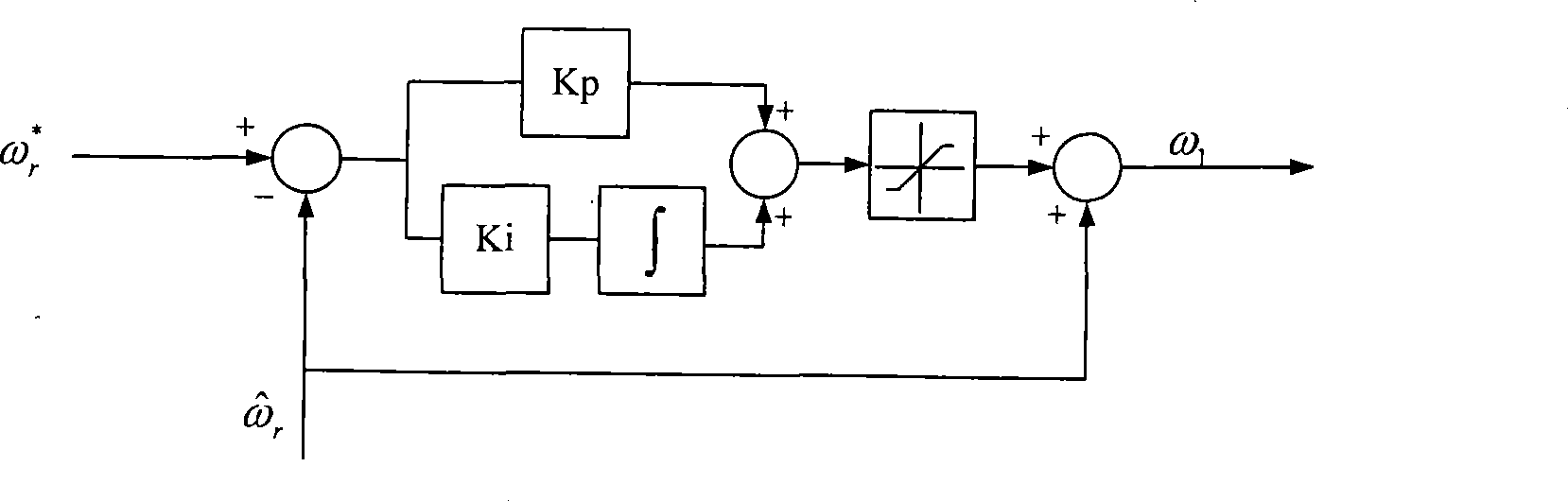
508 results about "Rotor flux" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
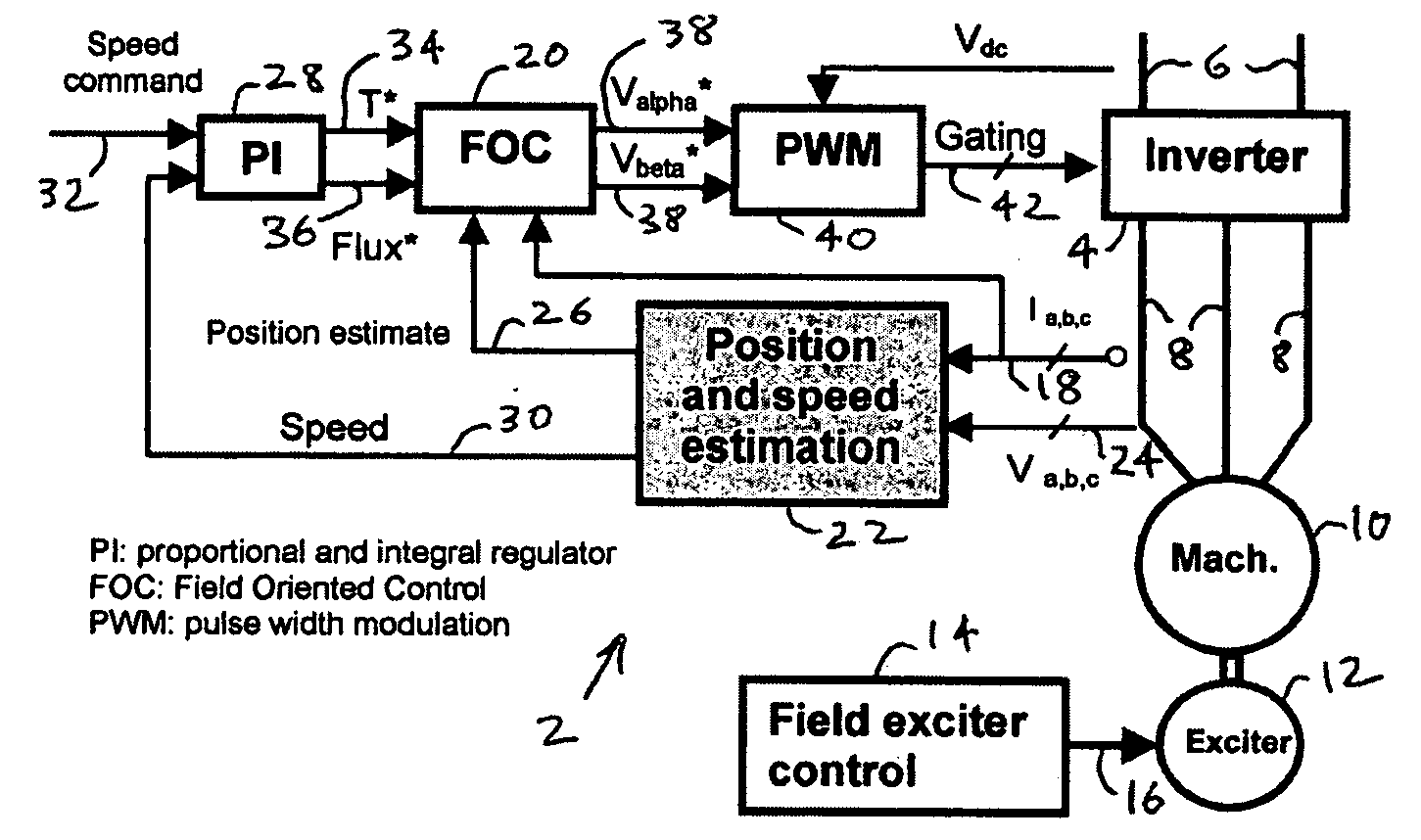
Apparatus and method for permanent magnet electric machine condition monitoring
InactiveUS20130033215A1Improve diagnostic reliabilityImprove reliabilityMotor/generator/converter stoppersElectric motor controlElectric machineRotor flux
An apparatus and method for determining a condition of an electric machine. Search coils are wound around stator teeth and the induced voltage is used to decouple stator and rotor fluxes. The decoupled fluxes allow for machine condition monitoring and fault diagnosis.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Transverse flux switched reluctance motor and control methods
InactiveUS20060091755A1Eliminate end turn lossHigh densitySynchronous generatorsElectronic commutation motor controlTransverse fluxElectric machine
A variable reluctance motor and methods for control. The motor may include N motor phases, where N equals three or more. Each motor phase may include a coil to generate a magnetic flux, a stator and a rotor. A flux-carrying element for the rotor and / or stator may be made entirely of SMC. The stators and rotors of the N motor phases may be arranged relative to each other so that when the stator and rotor teeth of a selected phase are aligned, the stator and rotor teeth in each of the other motor phases are offset from each other, e.g., by an integer multiple of 1 / N of a pitch of the stator or rotor teeth. A fill factor of the coil relative to the space in which it is housed may be at least 60%, and up to 90% or more. The stator and rotor flux-carrying elements together may include at most three separable parts.
Owner:PRECISE AUTOMATION
Online decoupling identification method of multiple parameters of PMSM (permanent magnet synchronous motor)
ActiveCN103248306AEliminate false convergenceImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention relates to the technical field of PMSMs, solves a coupling problem during online identification of multiple parameters of a surface-mounted type PMSM, and achieves online decoupling identification of PMSM inductance, stator resistance and rotor flux linkage. Accordingly, the technical scheme adopted by the invention is that an online decoupling identification method of multiple parameters of the PMSM comprises the steps as follows: 1) identifying and coupling analysis of parameters of the PMSM; 2) a decoupling identification strategy, wherein voltage deviation before and after D shaft current injection is used for increasing the order of a motor mathematical equation, so that the decoupling identification of multiple parameters of the surface-mounted type PMSM inductance, the stator resistance and the rotor flux linkage are achieved; 3) neural network identifier design, wherein according to a parameter online identification problem of the PMSM, online identification is performed on motor parameters by adopting a self-adaptive neural network structure and a weight convergence algorithm based on a least mean square algorithm. The method is mainly applied to the design and manufacture of the PMSM.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Non-position sensor vector control method for double-feed wind power generator
InactiveCN101388639ALow costImprove anti-interference abilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorClosed loop
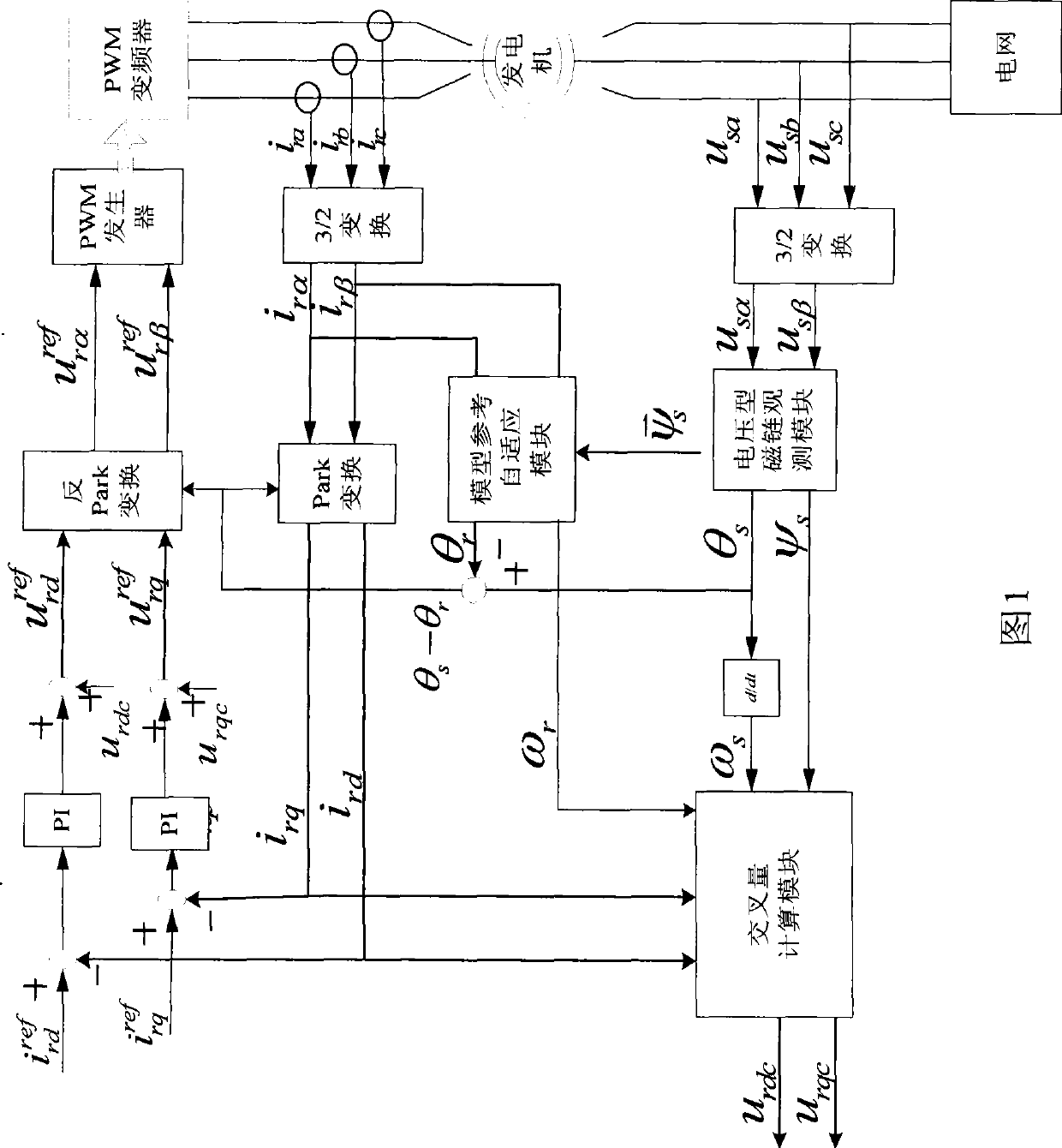
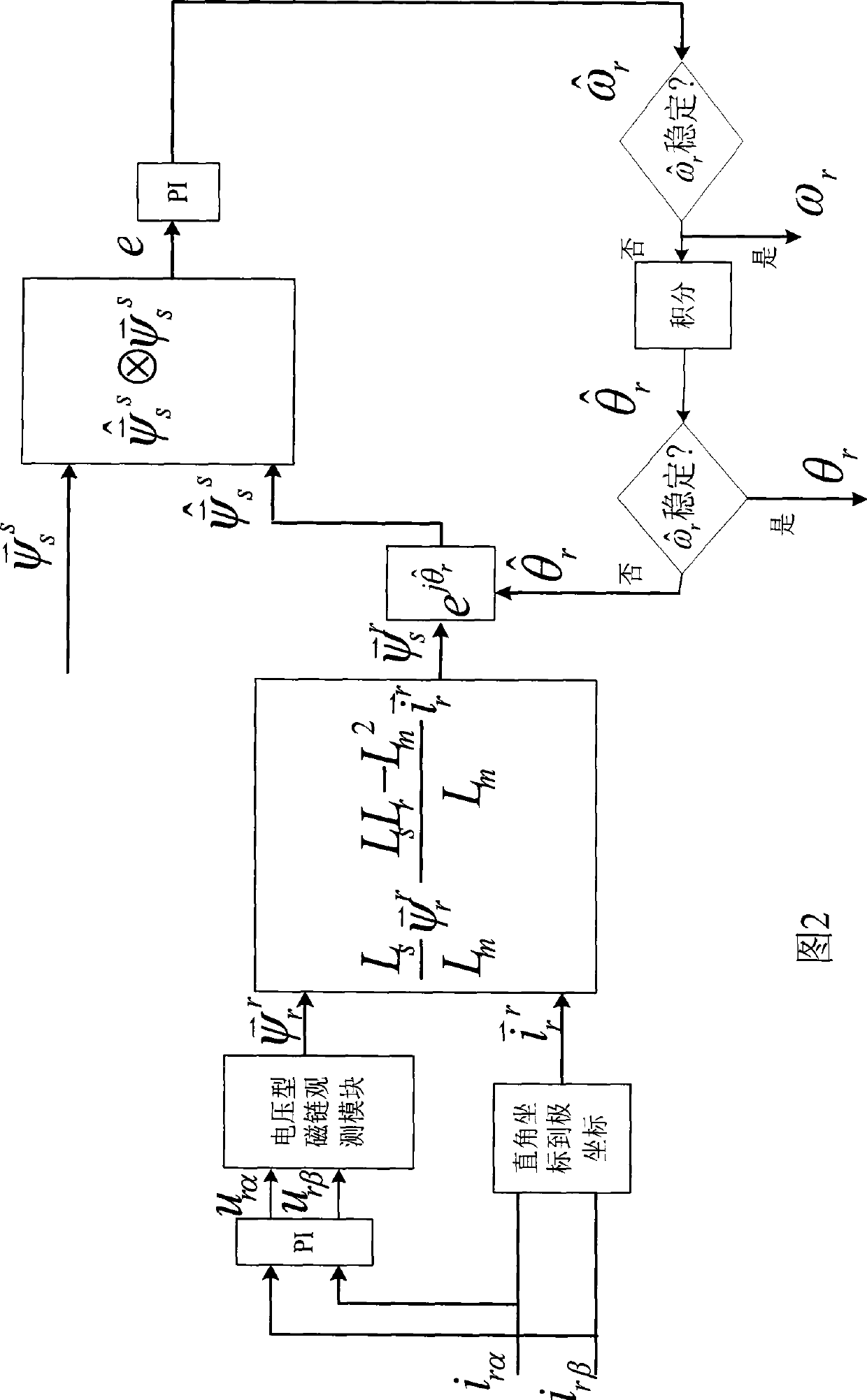
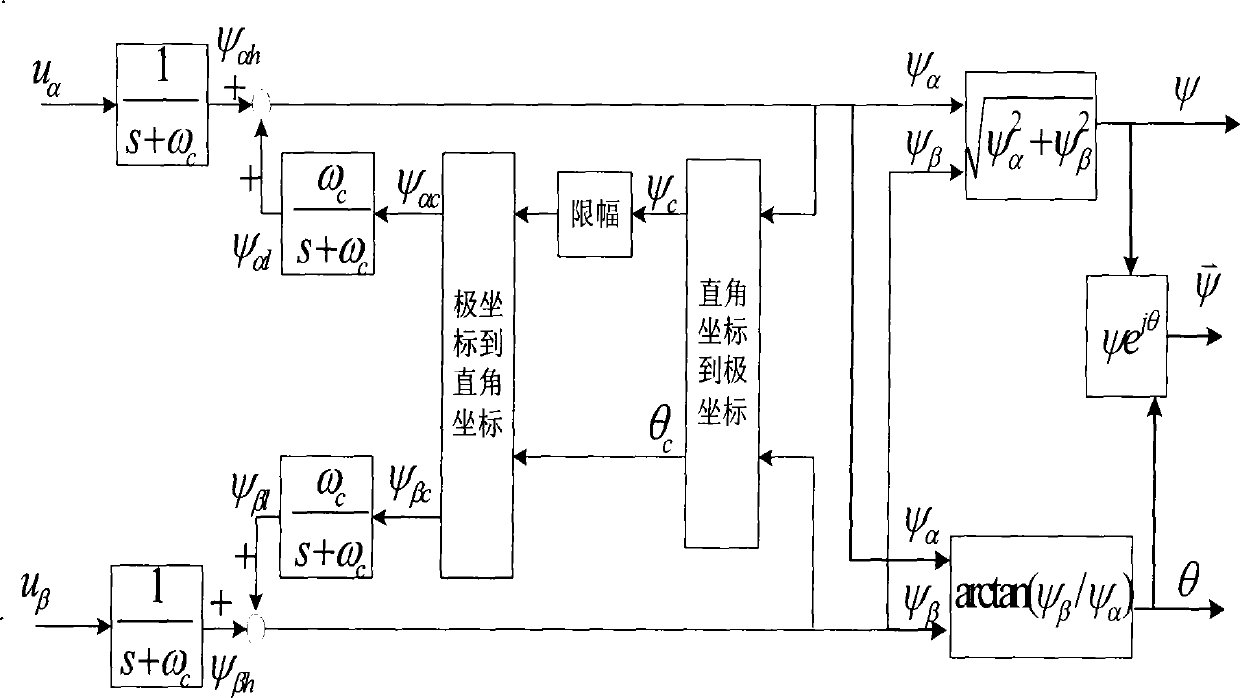
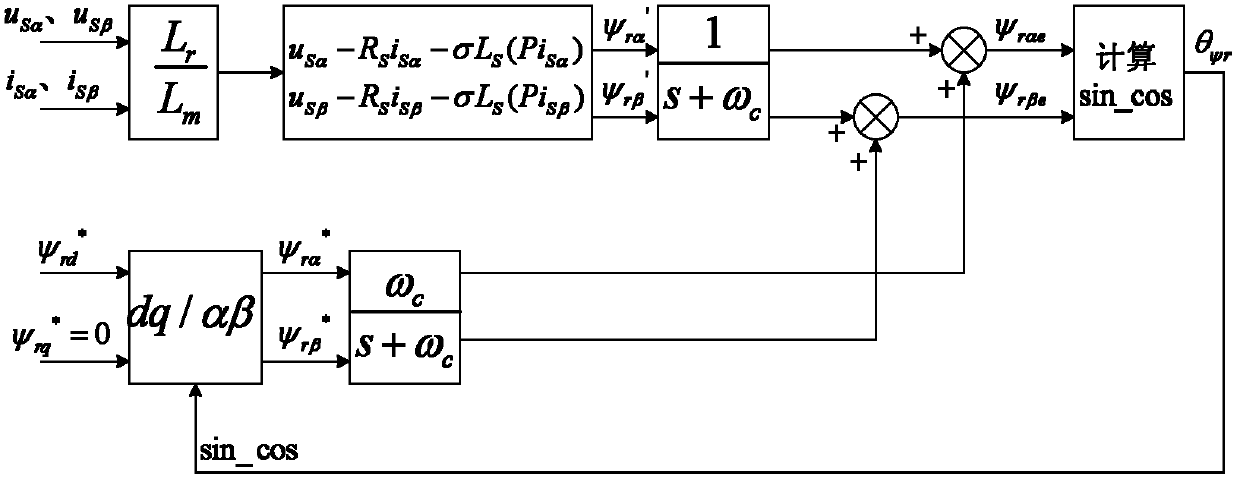
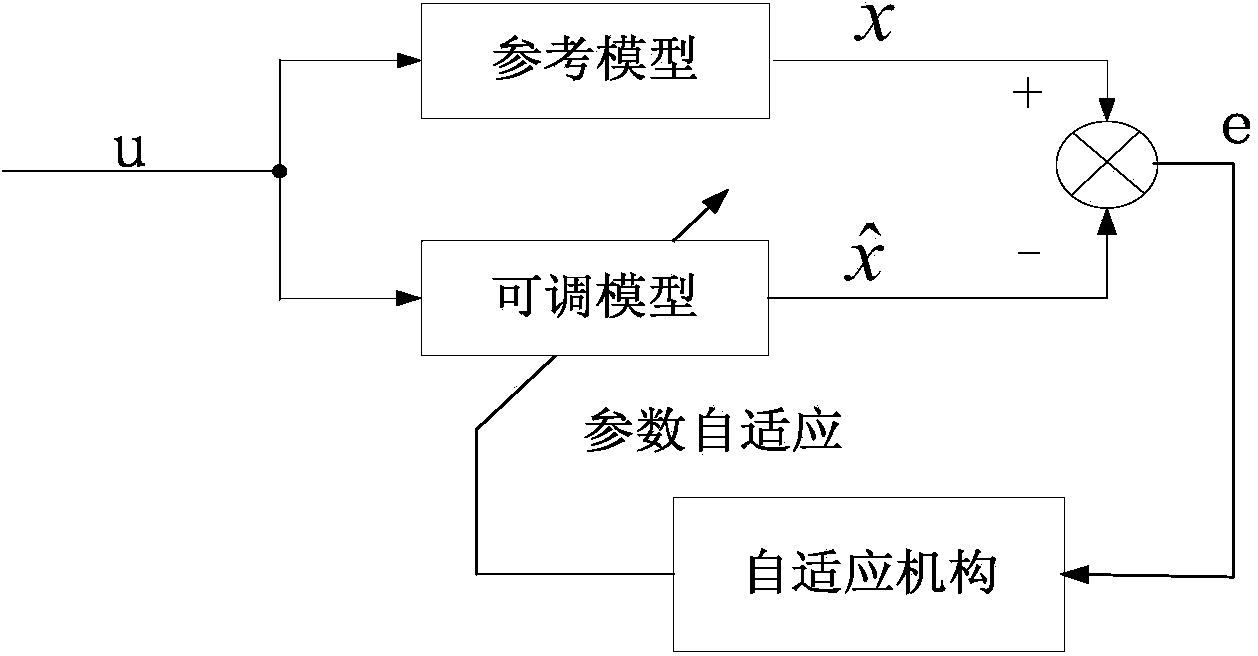
The invention provides a method for controlling without-position sensor vector of a doubly-fed wind generator, wherein the control method adopts closed loop algorithm on the basis of a model reference self-adaptive module to indentify the rotor position and the rotary speed of a double fed wind induction generator. The control of the without-position sensor vector is possible, the cost of a generator system is lowered, and the anti-interference ability is improved. Simultaneously, the control method also adopts a method for improving voltage module observation flux linkages to observe a stator flux linkage under a stator static coordinate and a rotor flux linkage under a rotor static coordinate, the method can solve the problems that flux linkage phases which are obtained through observing the flux linkage through adopting a high pass filtering method are advanced and the amplitude is reduced, and the flux linkage which is corresponding with true value phases and amplitude is obtained.
Owner:北京清能华福风电技术有限公司
Speed sensor-less method for estimating rotor angle and revolving speed of permanent-magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN102437813AImprove dynamic performanceEasy to debugElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageSynchronous motor
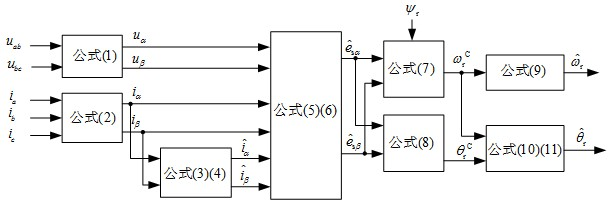
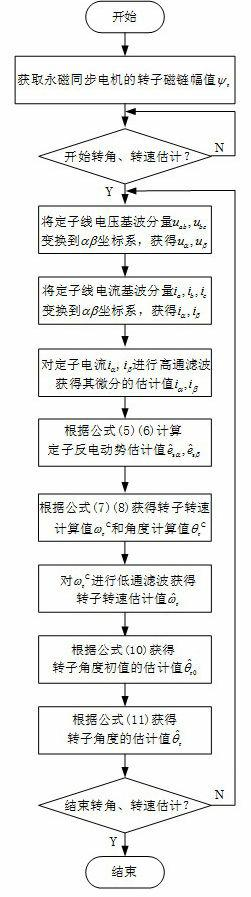
The invention relates to the technical field of electric transmission and control, in particular to a speed sensor-less method for estimating the rotor angle and the revolving speed of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: a. obtaining the rotor flux linkage amplitude Psi<r> of a permanent-magnet synchronous motor; b. transforming a stator voltage fundamental component to be under an alpha beta coordinate system to obtain u<alpha> and u<beta>; c. transforming the stator current fundamental component to be under the alpha beta coordinate system to obtain i<alpha> and i<beta>; d. carrying out highpass filtering on stator current i<alpha> and i<beta> under the alpha beta coordinate system, and obtaining the differential estimation value sum of the stator current; e. obtaining a stator counter electromotive force estimation value; f. obtaining a rotor revolving speed calculation value omega<rC> and a rotor angle calculation value theta<rC>; g. carrying out lowpass filtering on the rotor revolving speed calculation value omega<rC> to obtain a rotor revolving speed estimation value; h. obtaining the estimation value of a rotor angle starting value; and i. obtaining a rotor angle estimation value. The method has the advantages that only forward calculation, instead of a feedback channel, exists in the method for estimating the rotor angle and revolving speed, and except filter delaying, no dynamic regulation process exists.
Owner:DONGFANG ELECTRIC CORP LTD
Speed sensorless vector control method on basis of cascaded high voltage inverter
ActiveCN102420561AIdentification stabilityImprove dynamic and static performanceElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsHyperstability theoryLoop control
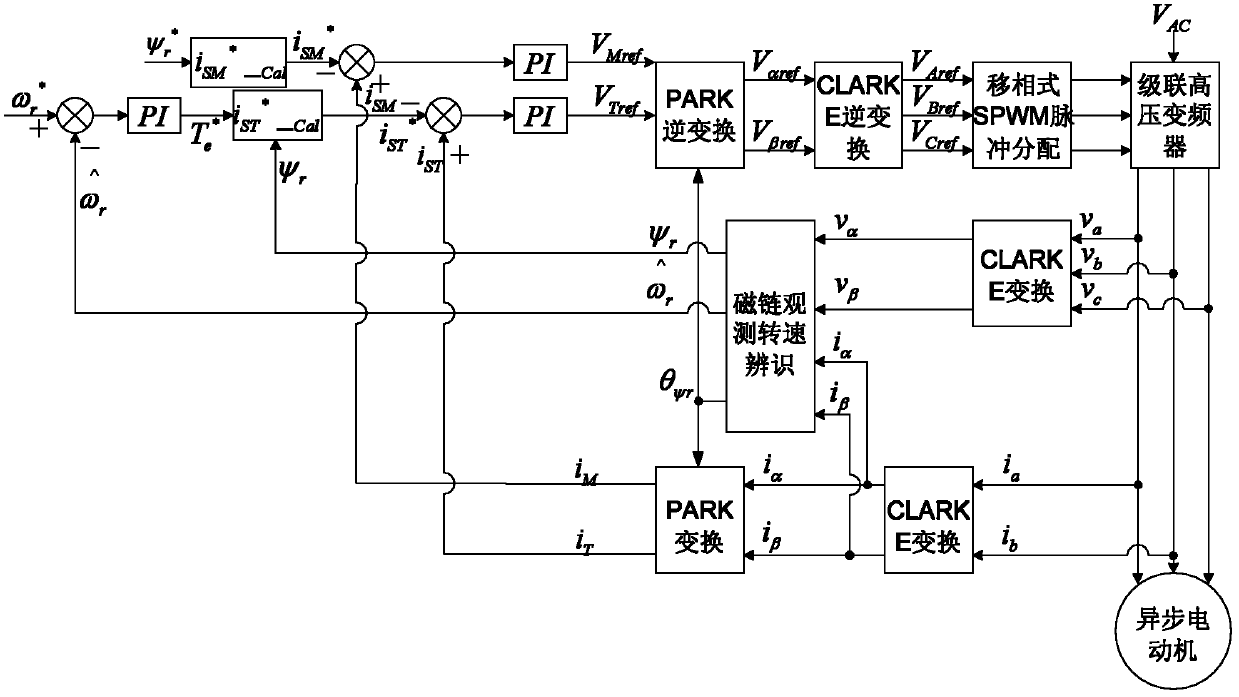
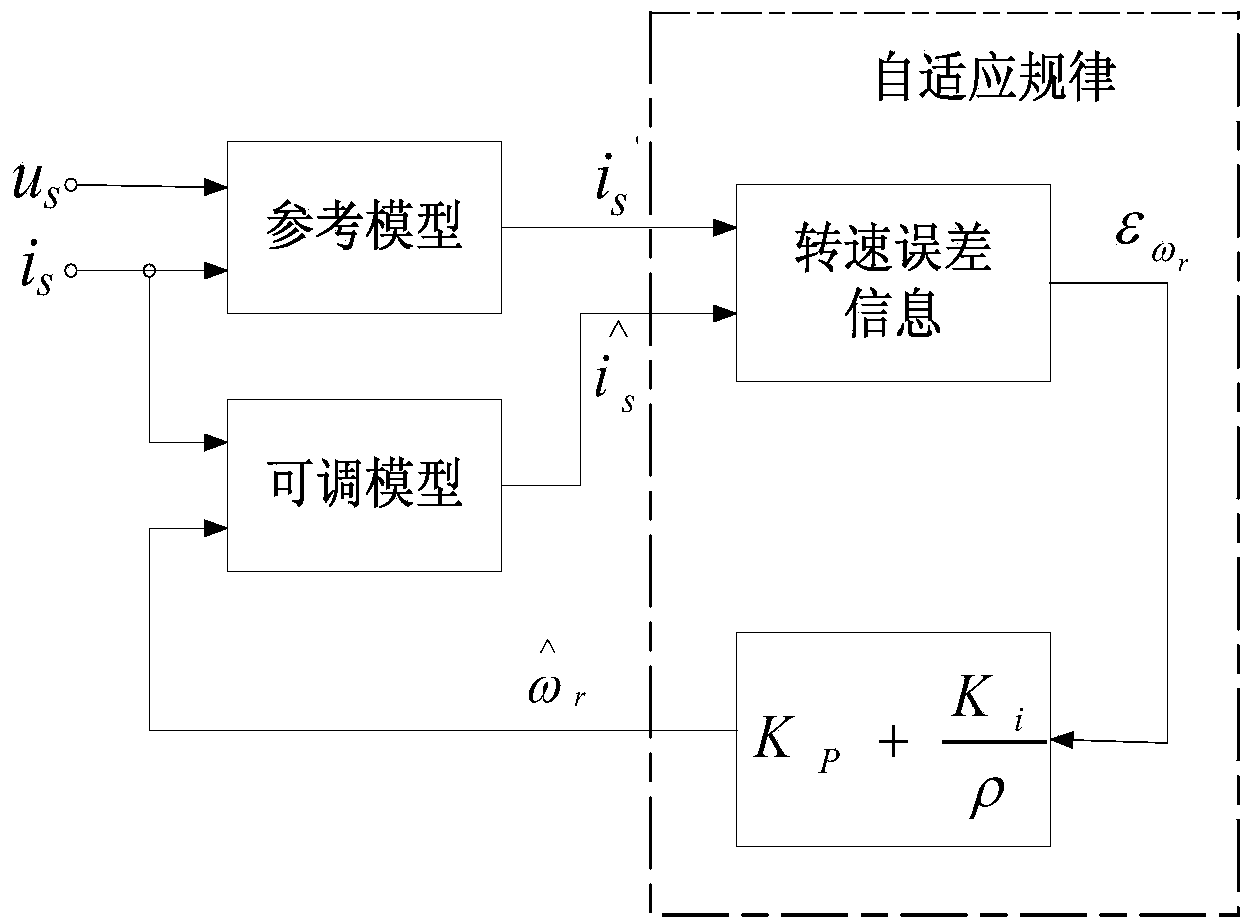
The invention discloses a speed sensorless vector control method on the basis of a cascaded high voltage inverter, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, establishing a rotor flux linkage voltage model; 2, establishing a rotor flux linkage current model; 3, identifying a rotating speed, using the rotor flux linkage current model in a two-phase rotating coordinate system in the step 2 as an adjustable model, using the rotor flux linkage voltage model in the step 1 as a reference model, utilizing a model reference adaptive system, and adopting a Popov hyperstability theory to obtain a rotating speed identifying model; 4, obtaining a three-phase sinusoidal voltage reference signal by speed and current double close loop control; and 5, sending the three-phase sinusoidal voltage reference signal to a phase-shifting SPWM (Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation) distributing plate, controlling a cascaded power unit by utilizing a phase-shifting SPWM control method and controlling the rotating speed of a motor. Due to the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, a speed sensor does not need to be arranged on a motor shaft, the defects caused by the installation of a speed encoder are avoided, and the flux linkage and the rotating speed of the motor can be well estimated.
Owner:GUODIAN NANJING AUTOMATION
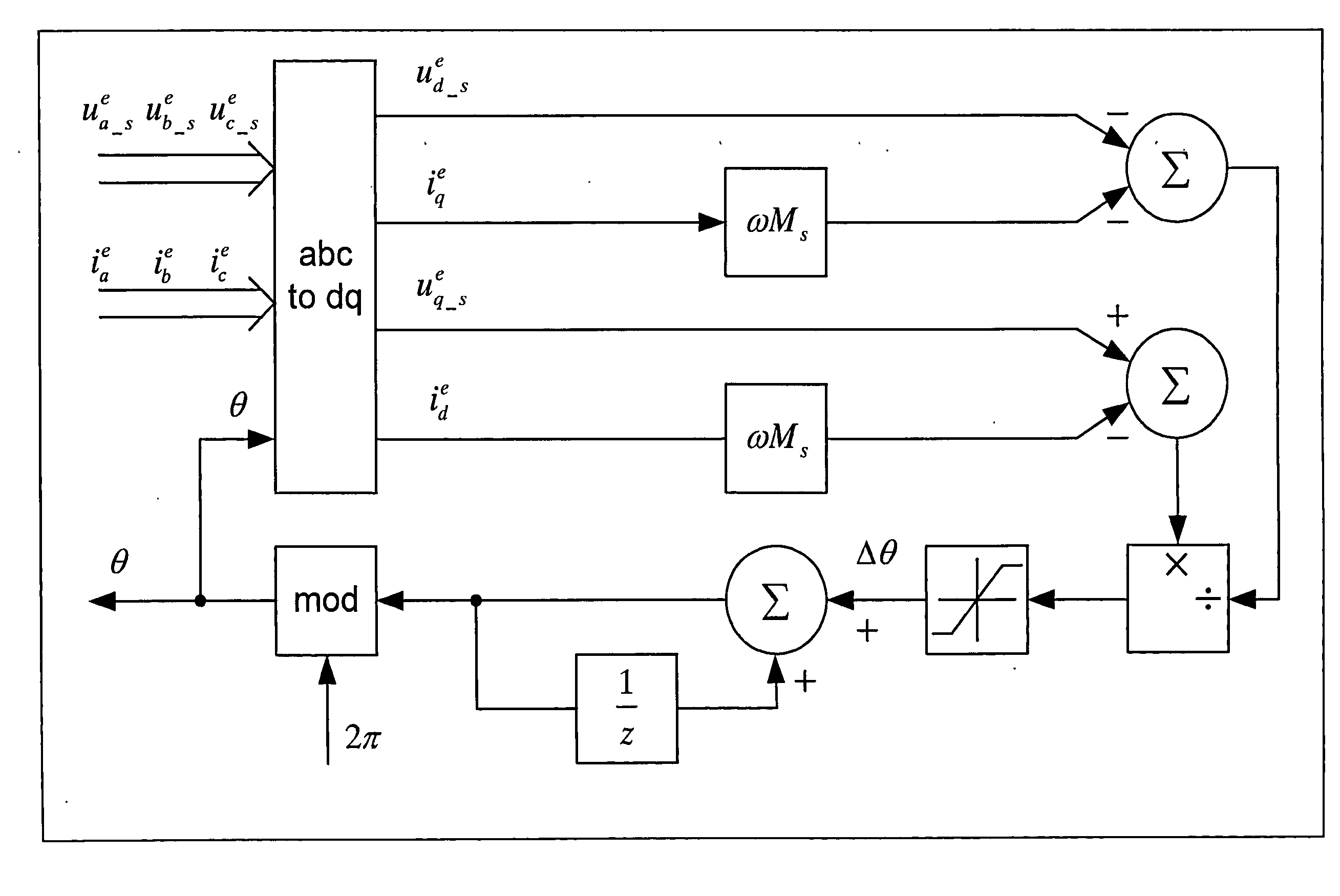
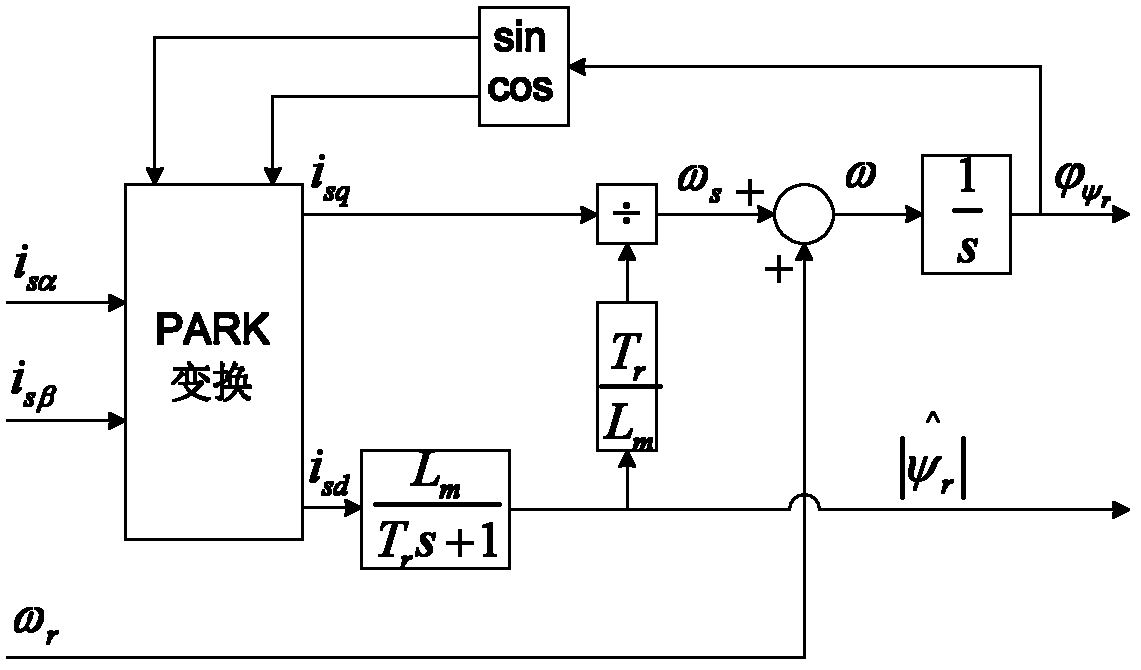
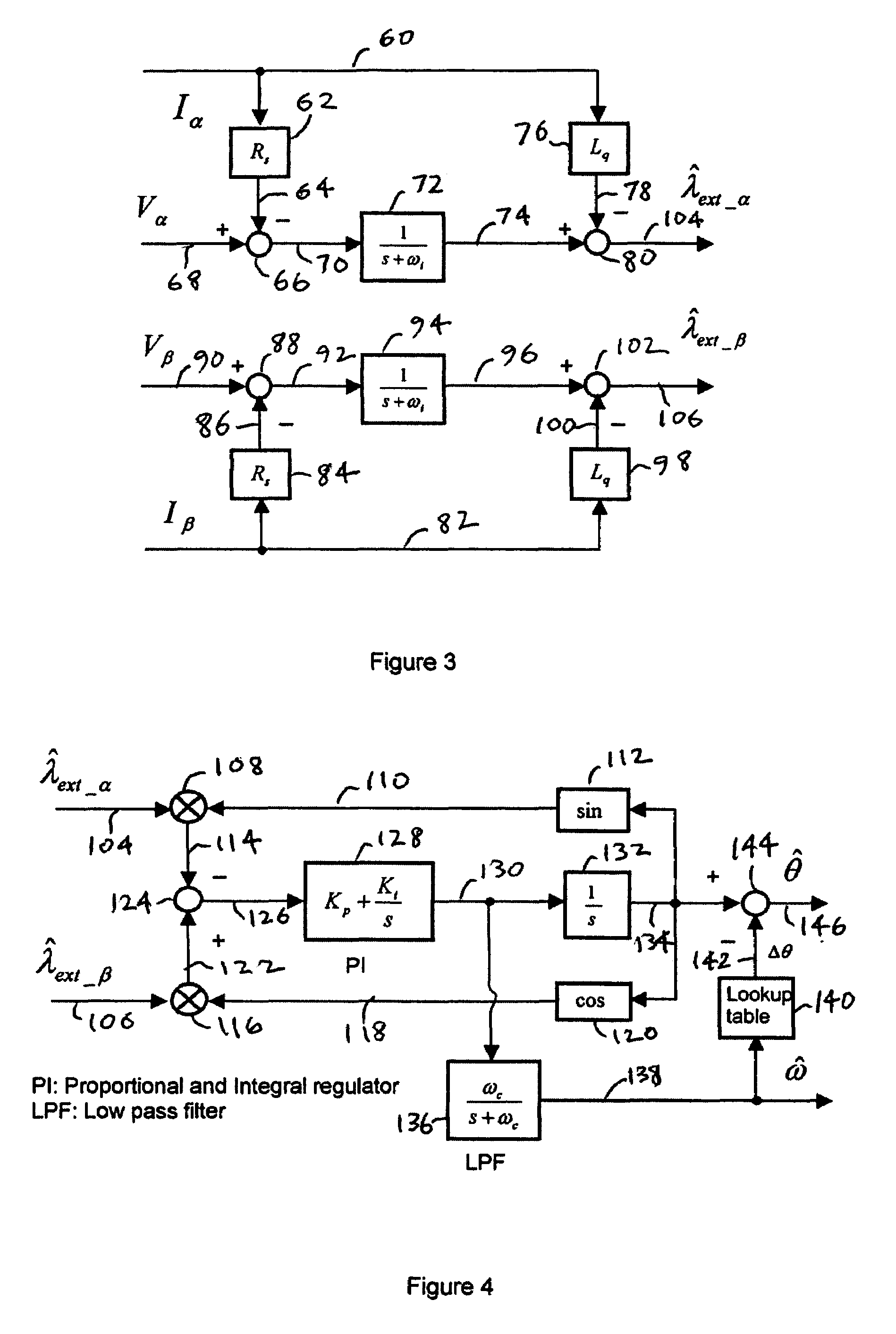
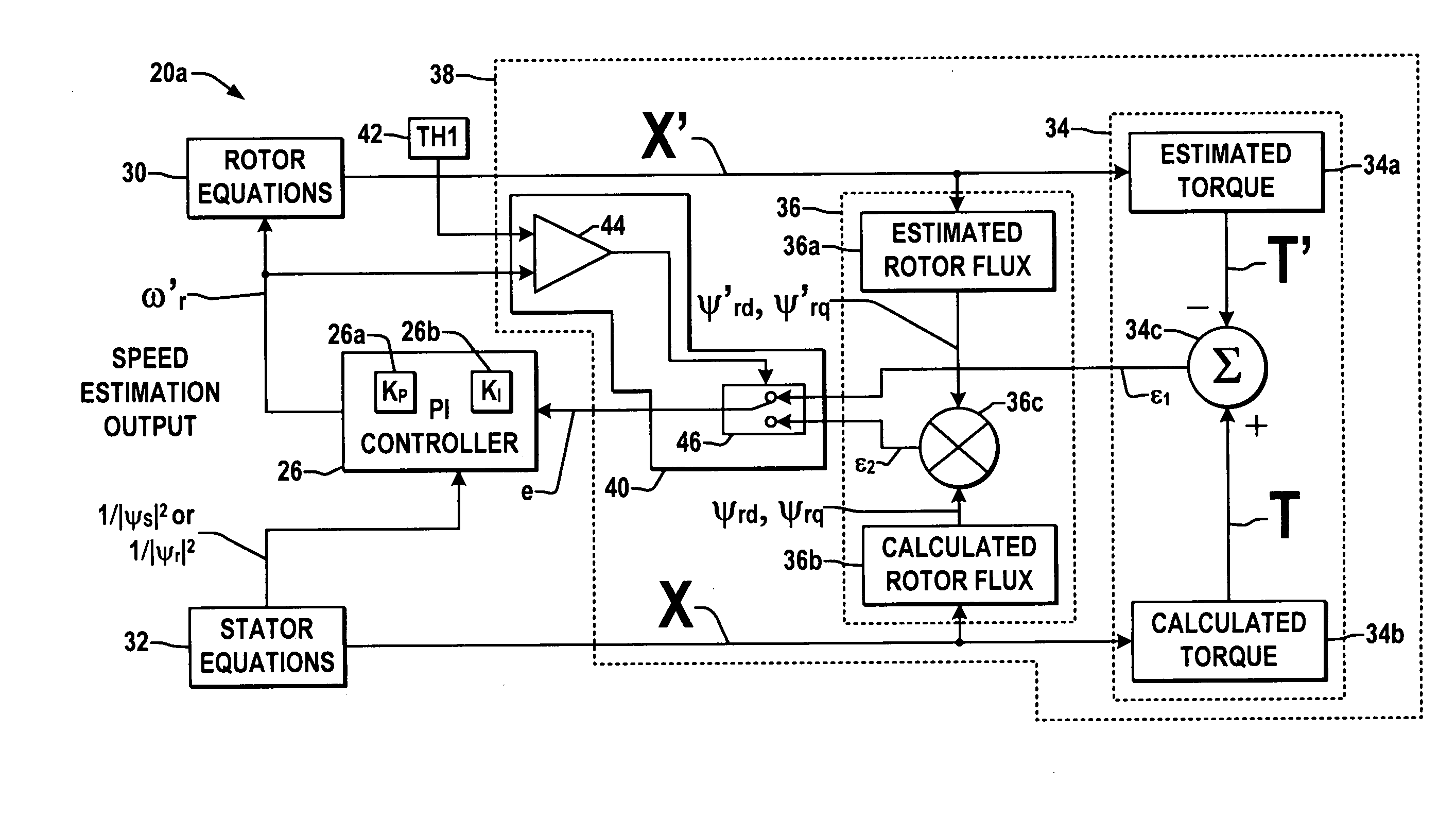
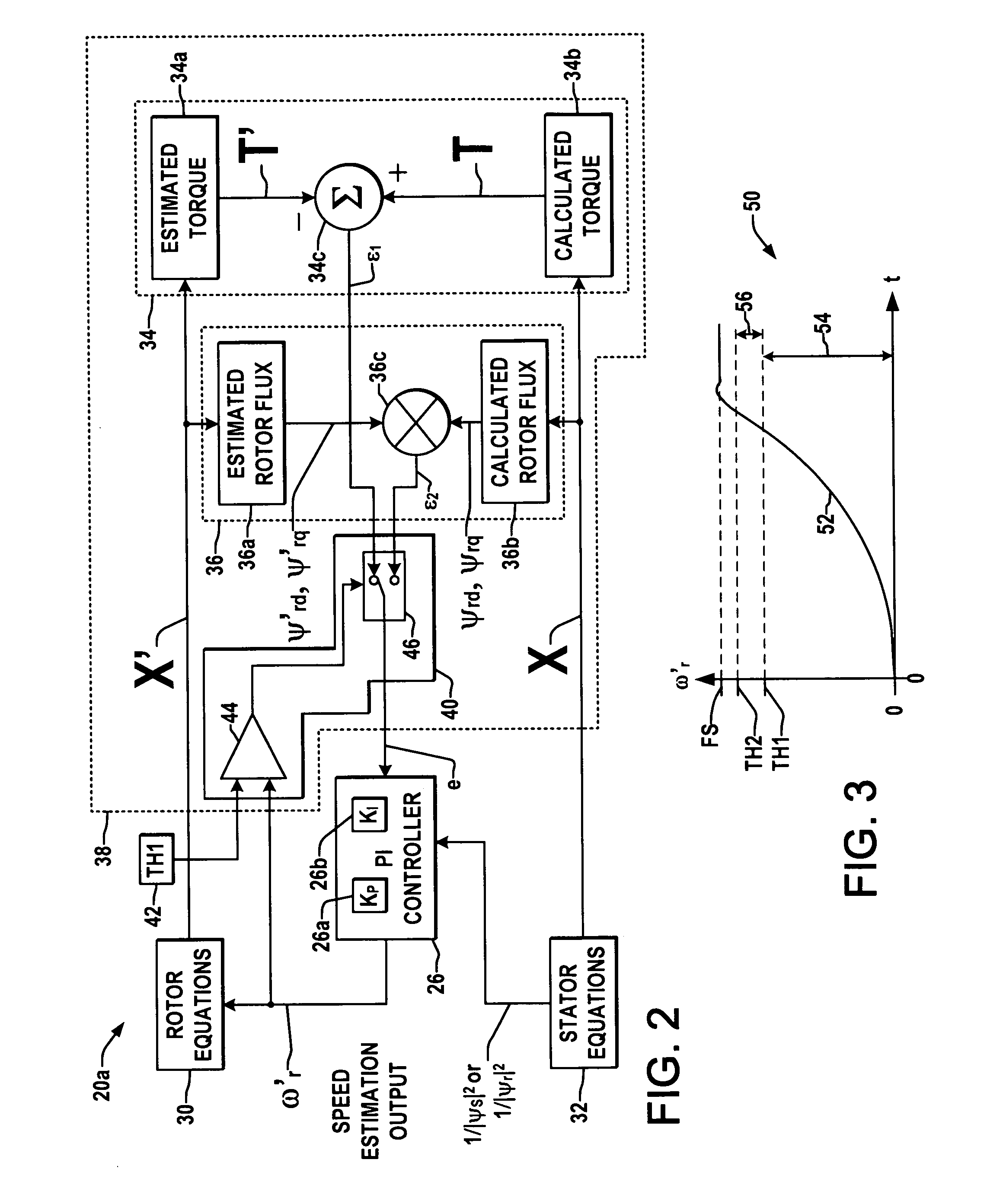
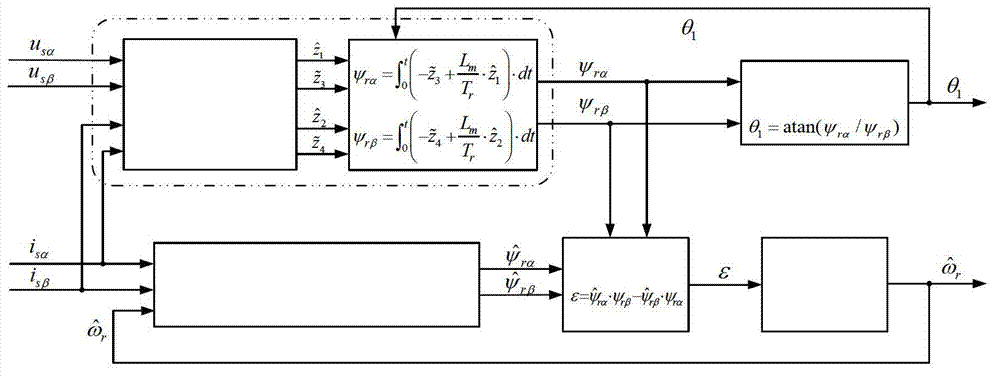
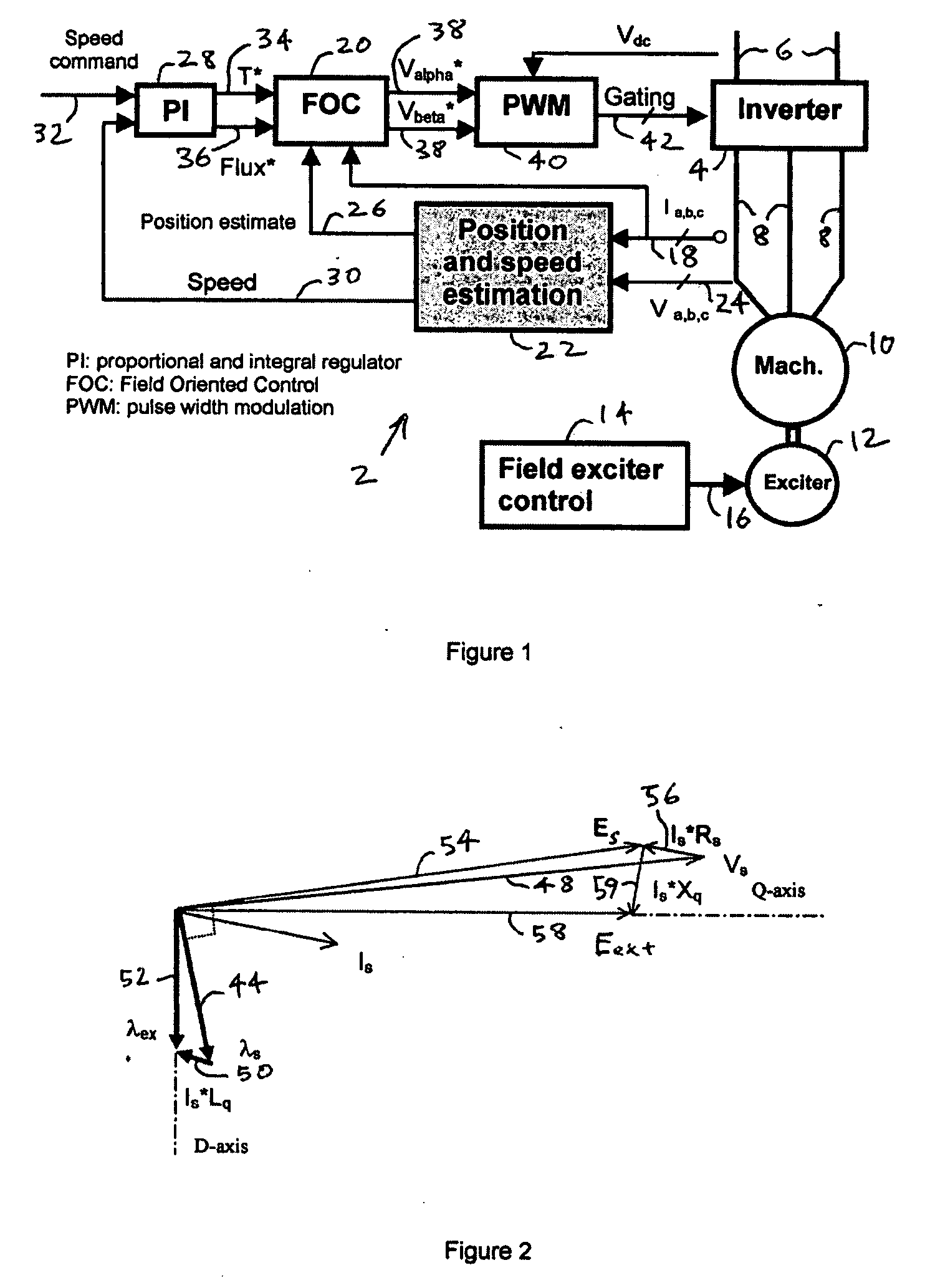
Shaft sensorless angular position and velocity estimation for a dynamoelectric machine based on extended rotor flux
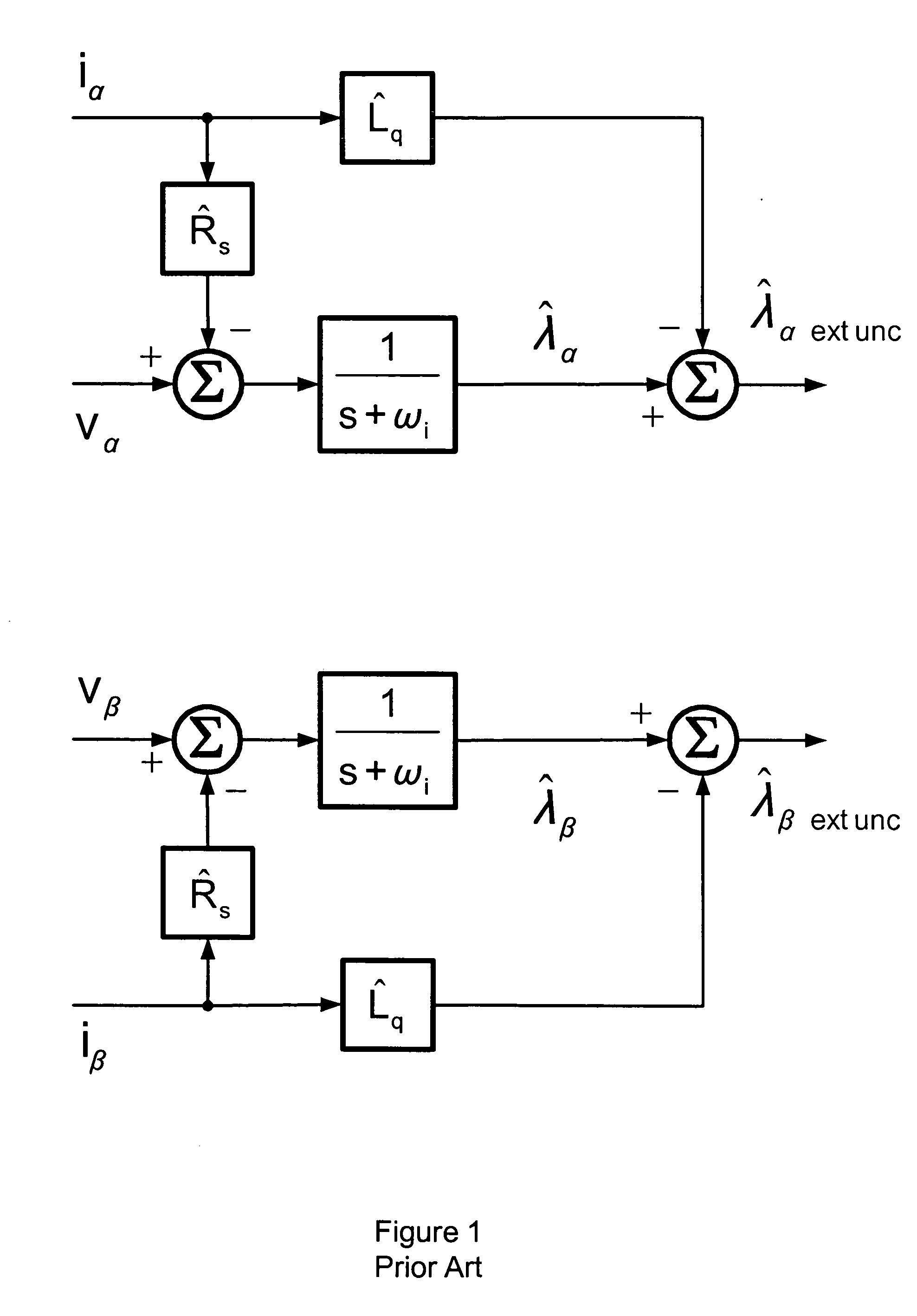
A shaft sensorless rotor angular position and velocity sensing system for a ynamoelectric machine that includes: a reference frame transformation function for transforming measured currents and potentials applied to a stator of the dynamoelectric machine to a two-phase α-β stationary frame to produce transformed currents Iα,Iβ and transformed potentials Vα,Vβ; first and second multipliers to produce signals Iα*RS,Iβ*RS; first and second summers to produce signals Vα,−Iα*RS,Vβ−Iβ*RS; first and second lag functions to produce signals1s+ωi(Vα-Iα*Rs),1s+ωi(Vβ-Iβ*Rs);third and fourth multipliers to produce signals Iα*Lq,Iβ*Lq; third and fourth summers to produce signals1s+ωi(Vα-Iα*Rs)-Iα*Lq,1s+ωi(Vβ-Iβ*Rs)-Iβ*Lqthat correspond to extended rotor flux values λext<sub2>—< / sub2>α,λext<sub2>—< / sub2>β; and a phase lock loop (PLL) to derive estimated rotor angular position and velocity values {circumflex over (θ)}, {circumflex over (ω)} for the dynamoelectric machine from the extended rotor flux values λext<sub2>—< / sub2>α,λext<sub2>—< / sub2>β.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
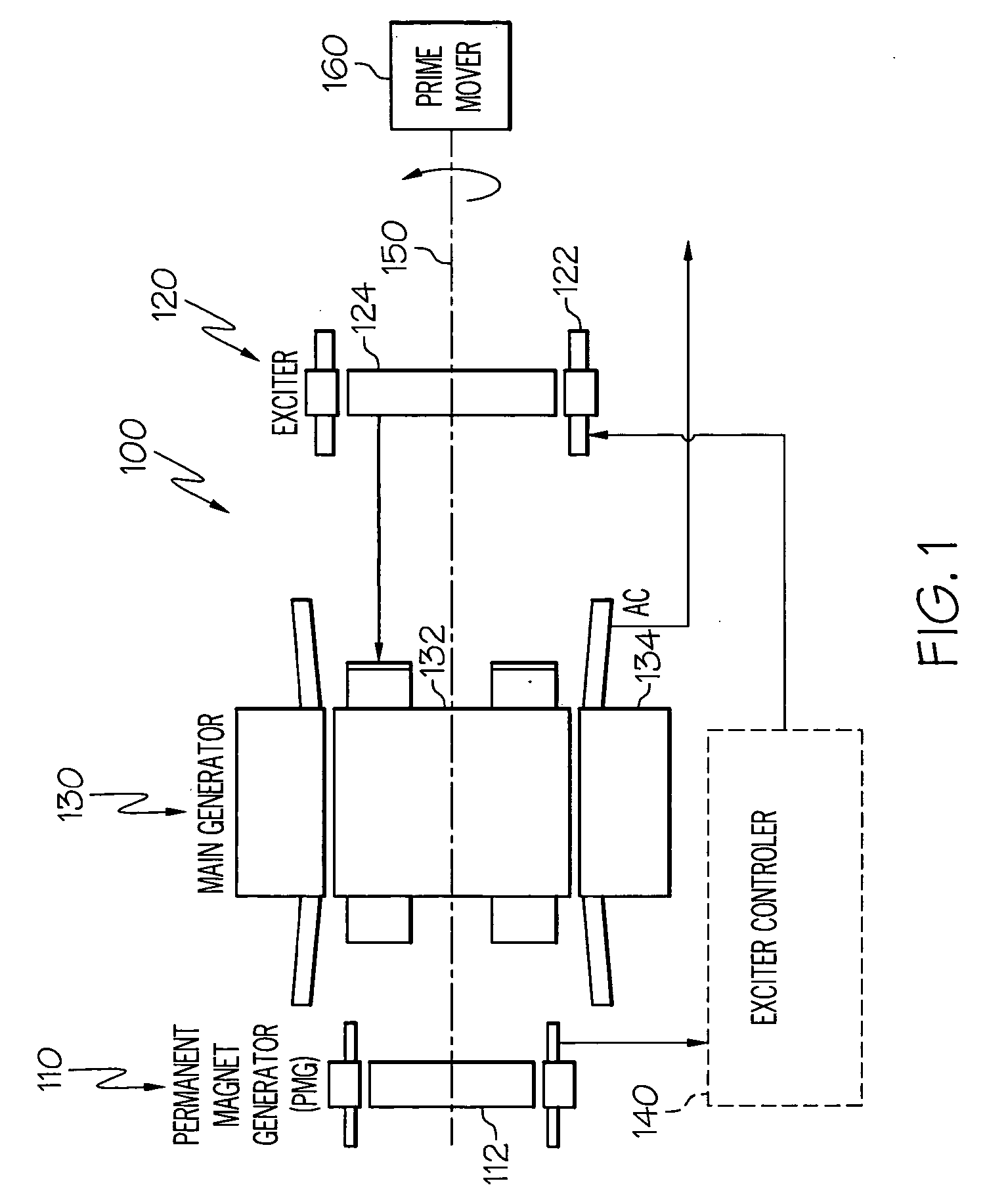
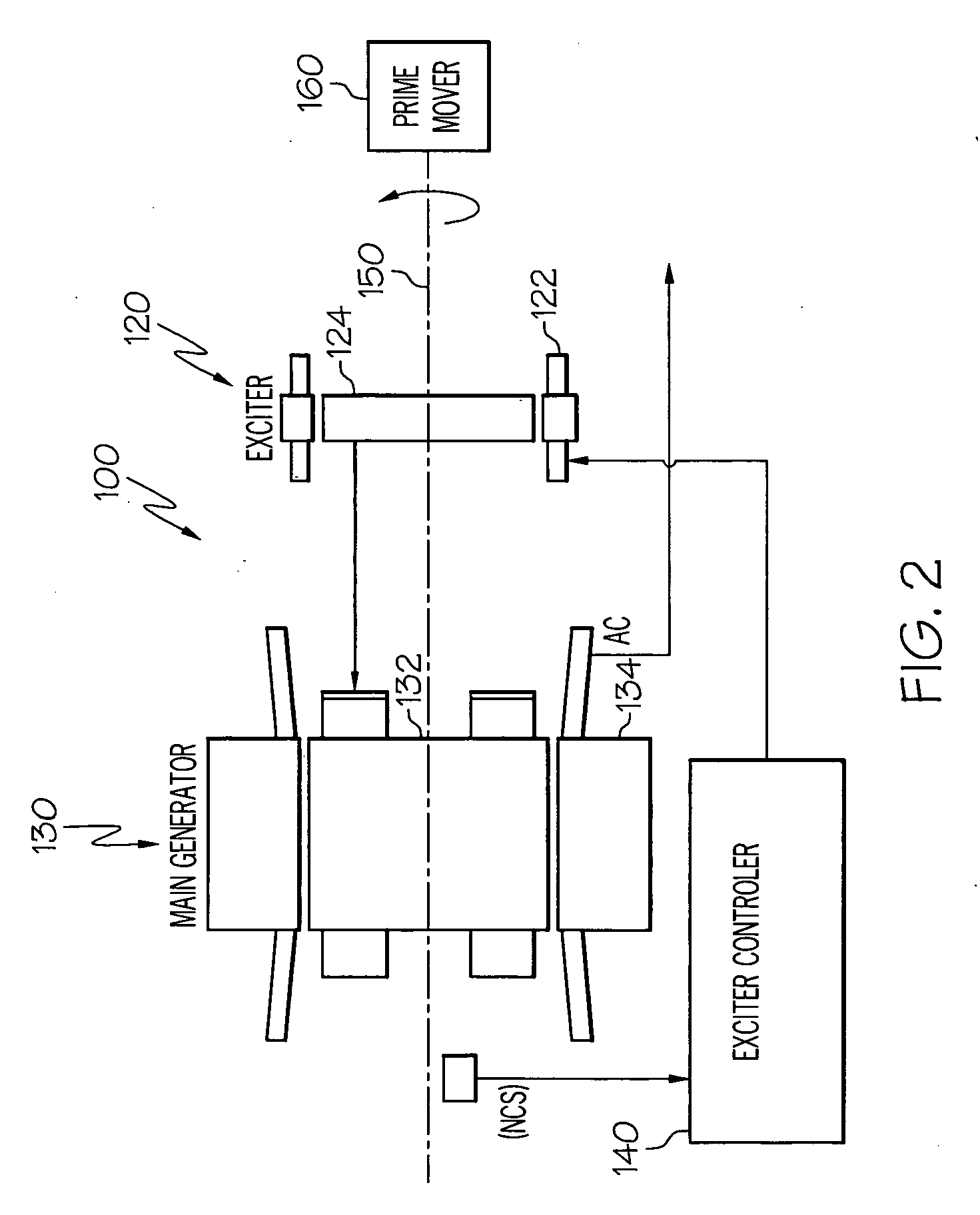
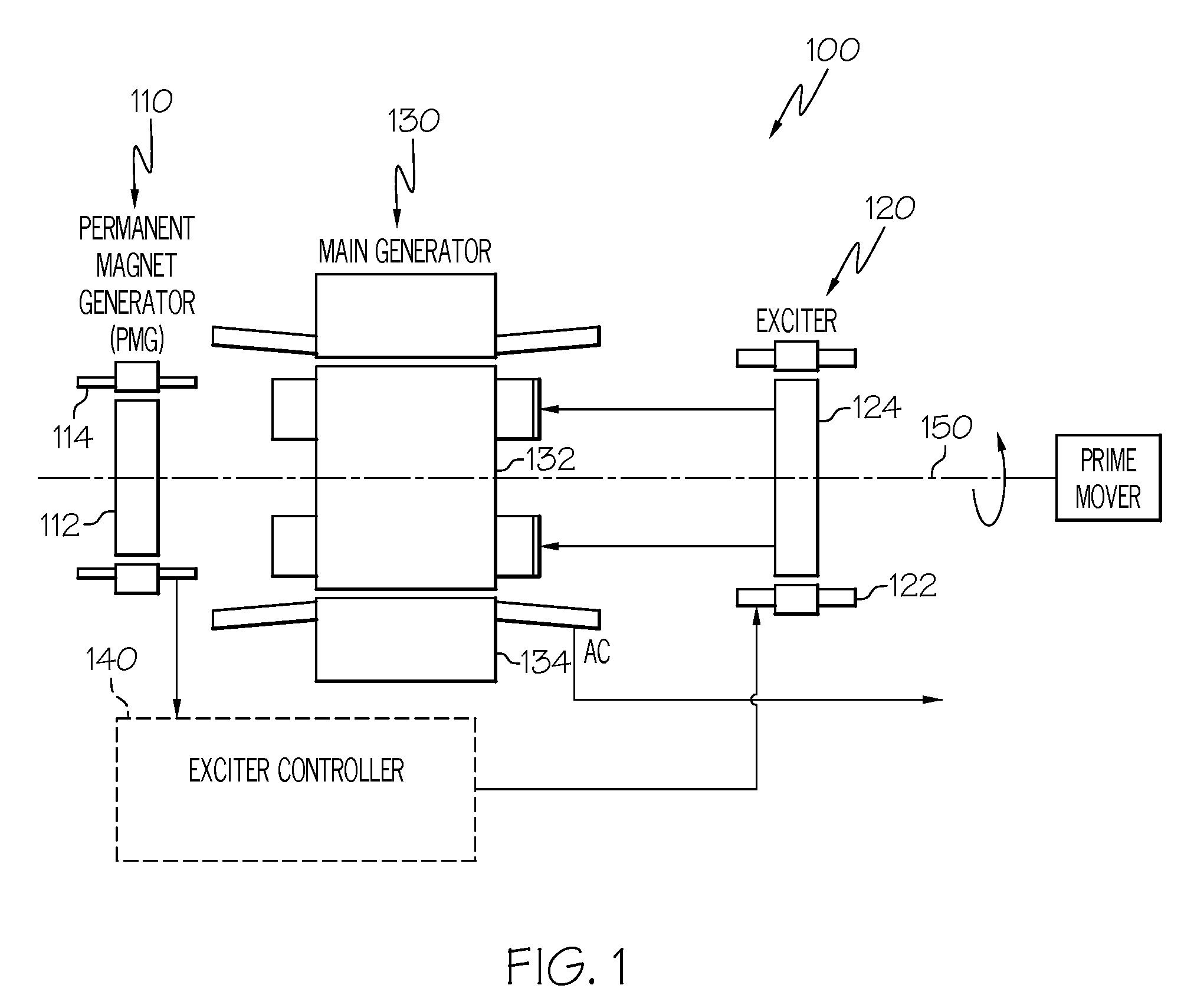
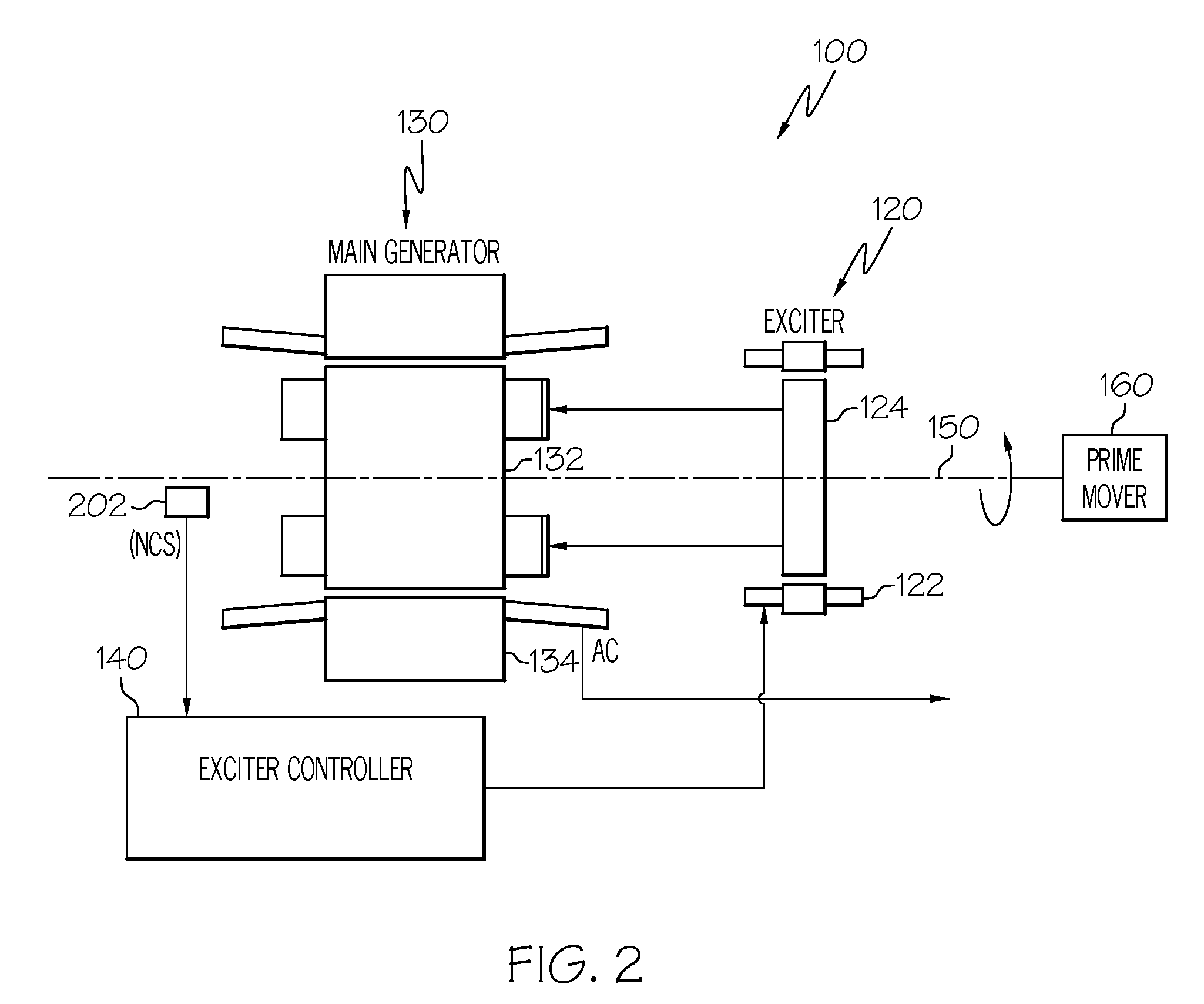
AC generator with independently controlled field rotational speed
InactiveUS20060087293A1Synchronous generatorsGenerator control circuitsElectricityConstant frequency
A generator system is configured to supply relatively constant frequency AC power when driven by a variable speed prime mover, by independently controlling the main rotor flux rotational speed. The generator system includes an exciter stator that induces current in the exciter rotor windings at a desired frequency and phasing. The exciter rotor windings are electrically connected to the main rotor windings, and are thus electrically excited at the same frequency and phasing. Excitation is supplied to the exciter stator from an exciter controller, which controls the frequency and phasing of the exciter excitation, based on the rotational speed of the generator, to maintain a constant output frequency.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
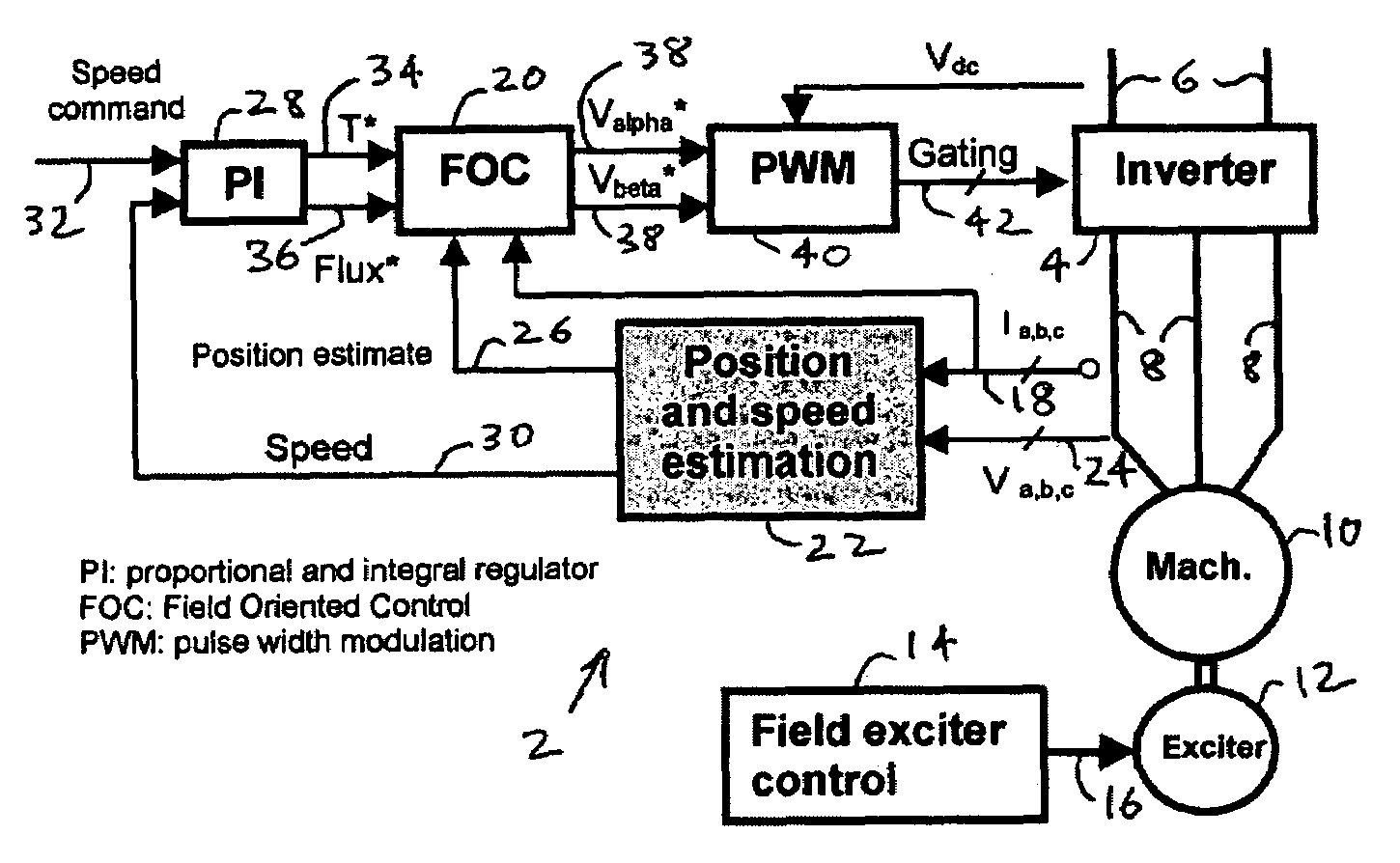
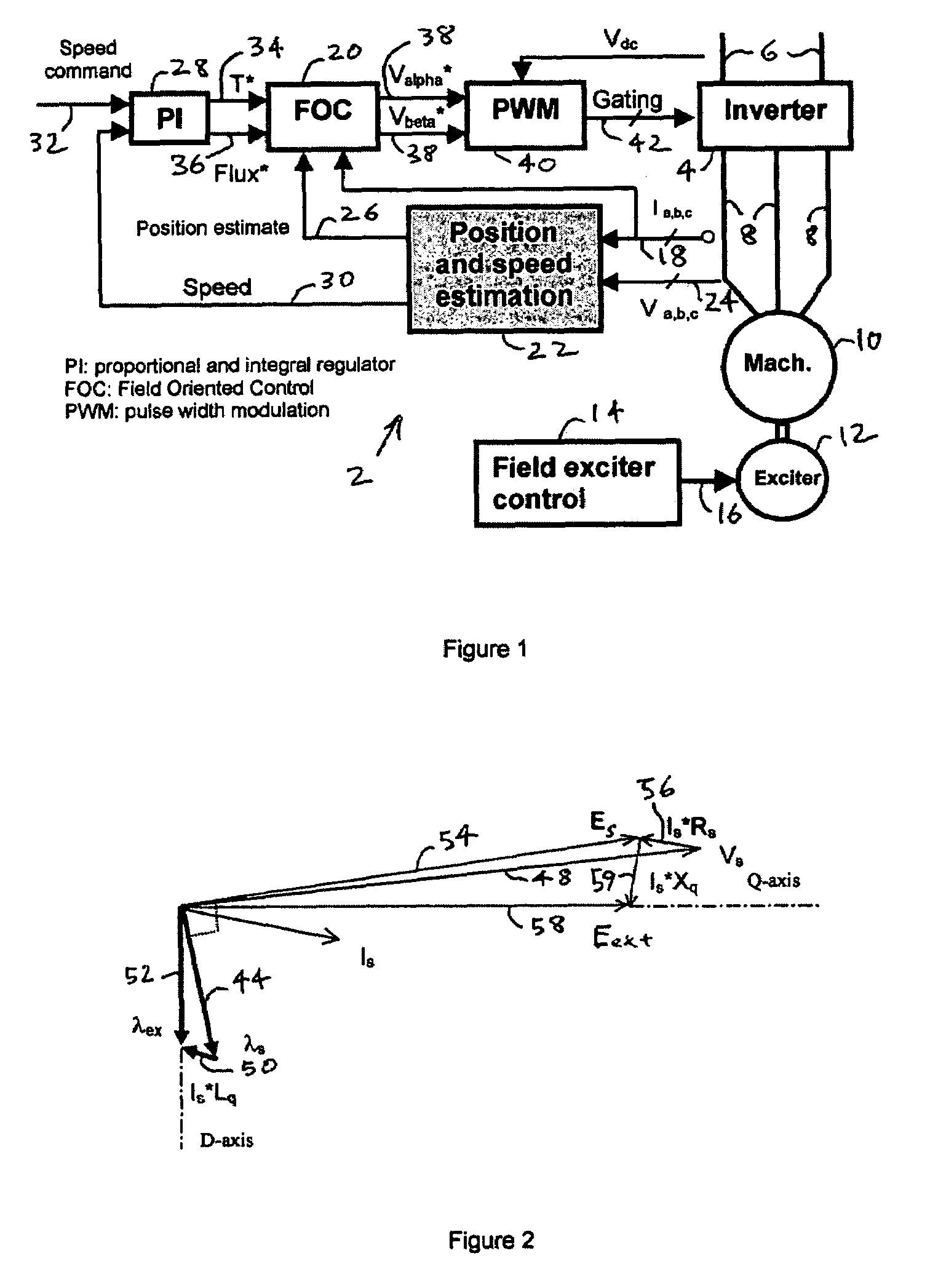
Method and system for sensorless control of an electric motor
Methods and systems for controlling an electric motor are provided. An estimated rotor flux angular position error is generated based on estimated back electromotive force (EMF) values, and based on the estimated rotor flux angular position error, an estimated rotor flux angular position, an estimated electrical synchronous frequency and / or an estimated rotor frequency can be generated.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
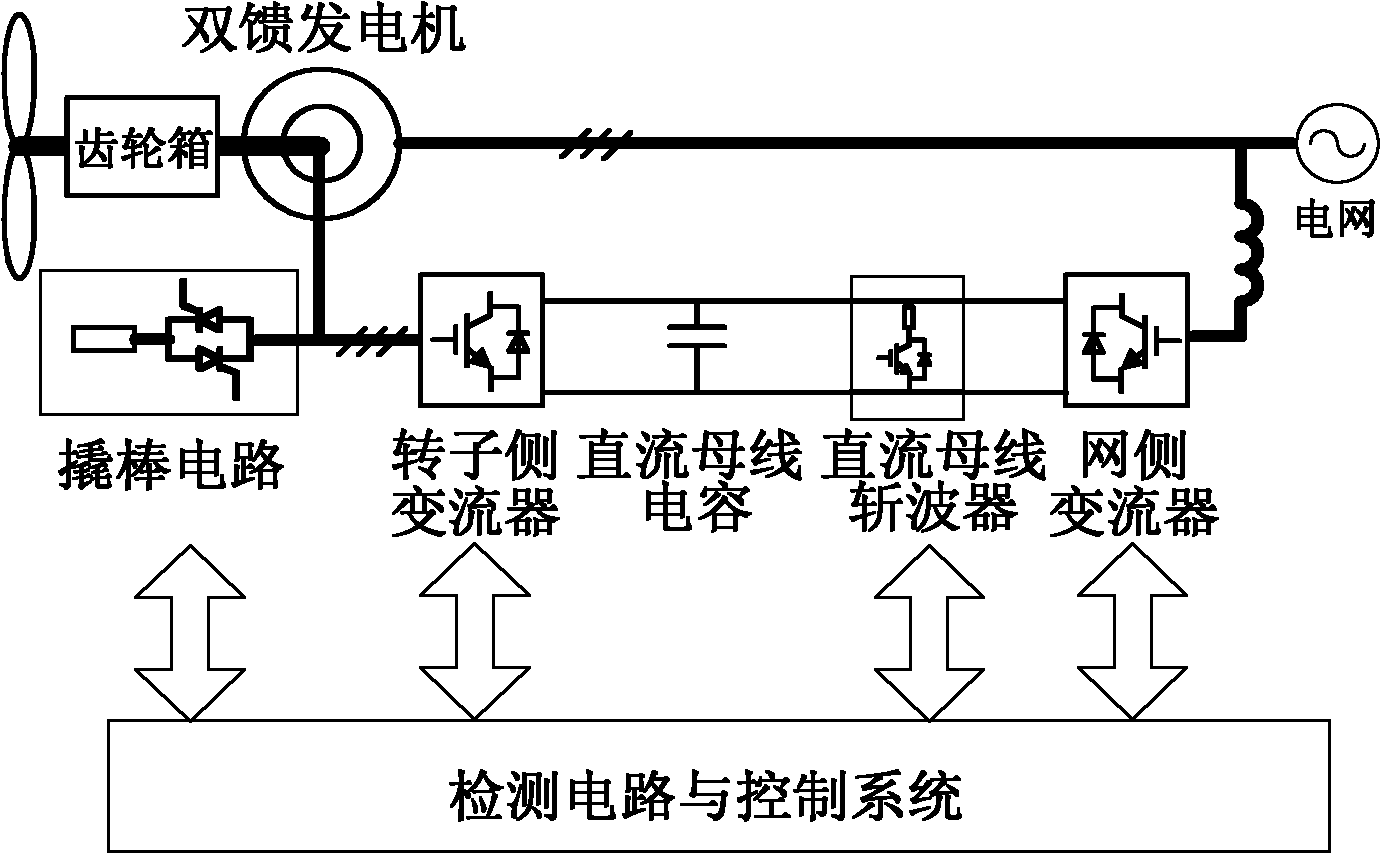
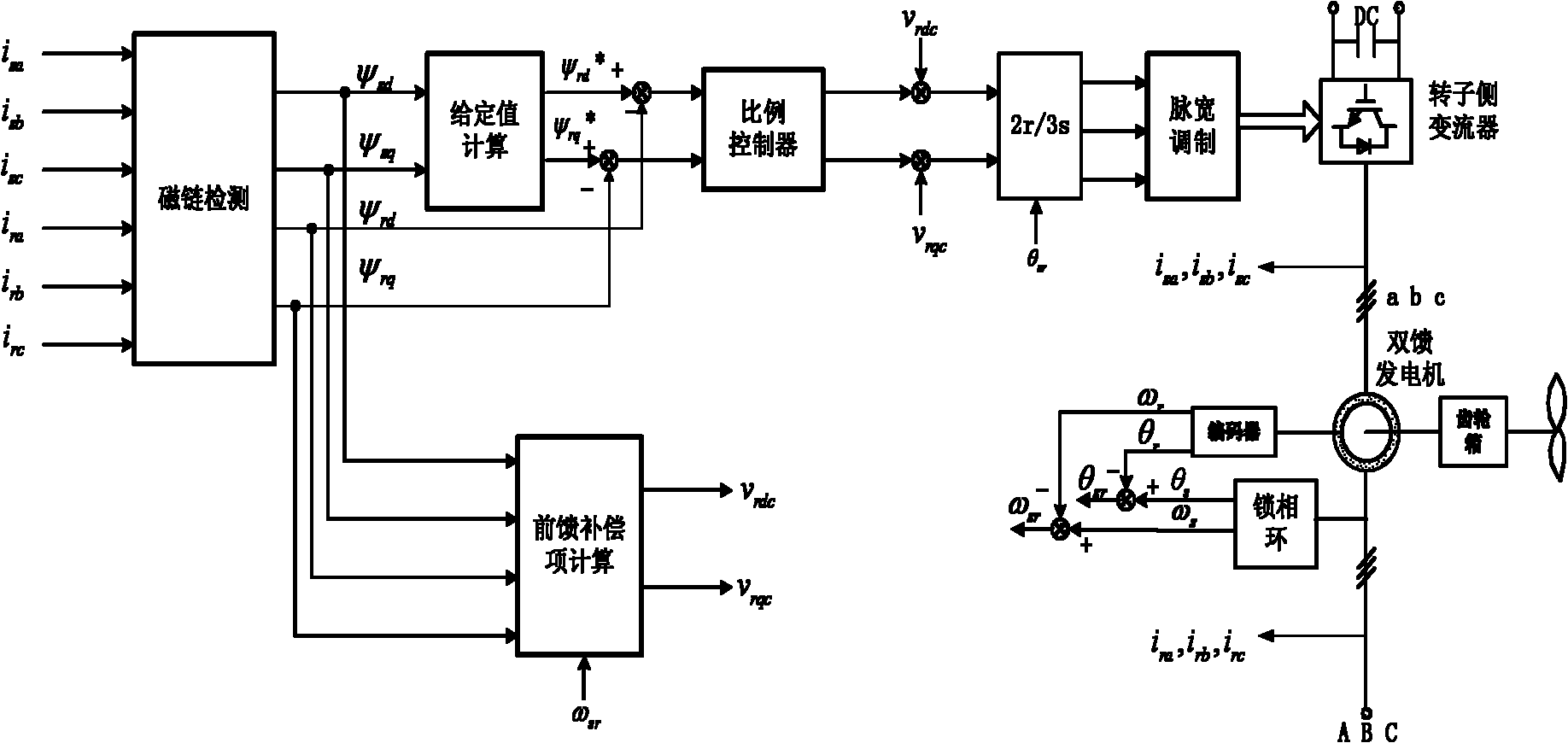
Low-voltage traversing control method for double-fed wind power generation system
ActiveCN102055208ARealize low voltage ride throughImprove economySingle network parallel feeding arrangementsWind energy generationControl mannerCurrent sensor
The invention relates to a low-voltage traversing control method for a double-fed wind power generation system, which belongs to the technical field of wind power generation. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the stator flux and the rotor flux of a double-fed generator are calculated according to the stator current and the rotor current of the double-fed generator which are measured by a current sensor; secondly, the stator flux is multiplied by a corresponding proportionality factor to serve as the set value of the rotor flux of the double-fed generator, so as to control therotor flux; and thirdly, the rotor flux is controlled in the way that as feedforward compensation decoupling is performed, closed-loop control is conducted to the decoupled system, and a rotor-side converter is controlled after pulse-width modulation is conducted to the obtained voltage control quantity of a rotor-side converter, so as to achieve low-voltage traversing control during failures. The low-voltage traversing control method provided by the invention has fast response, and very good traversing effect when symmetrical and asymmetrical drop failures of the network voltage occur, meanwhile, and oscillation of output electromagnetic torque of the double-fed generator can be effectively inhibited. The control method is simple and suitable for engineering application.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System and method for motor speed estimation using hybrid model reference adaptive system
ActiveUS7193387B1Less sensitiveEasy to understandAC motor controlElectric motor controlMotor speedMotor drive
Motor drives, motor speed controllers, motor speed estimation systems, and methods are presented for controlling motor startup speed and for estimating motor speed during startup, in which a speed estimate controller provides a rotor speed estimate based on a first error term from a torque-based MRAS component for a first range of motor speeds and based on a second error term from a rotor flux-based MRAS component for a second range of speeds.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
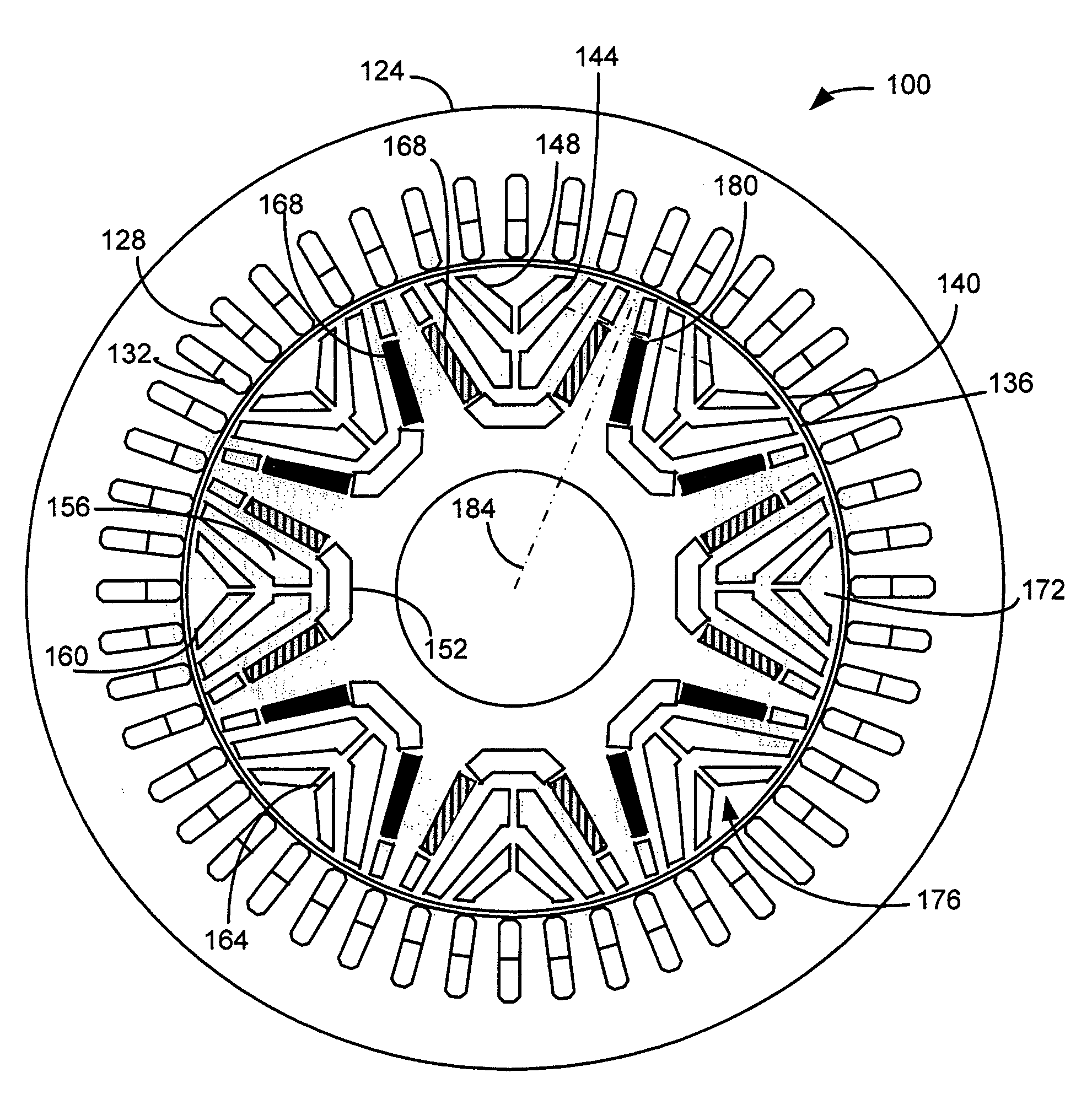
Double-rotor flux-switching machine
ActiveUS20140049124A1Magnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machine detailsCost effectivenessRotor flux
Advantageous machines, such as flux-switching machines (FSMs) are provided. An FSM can be yokeless and can have two rotors, which can be displaced from one another (e.g., by half a pole pitch). An FSM can be a flux-switching permanent magnet machine (FSPMM), and all magnets can be magnetized in the same circumferential direction. FSMs of the subject invention are cost-effective, have high torque density, and can operate well even under fault conditions.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Non-speed sensor vector control method for AC asynchronous motor
InactiveCN101383585AImprove robustnessEasy to chooseElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsControl vectorExcitation current
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
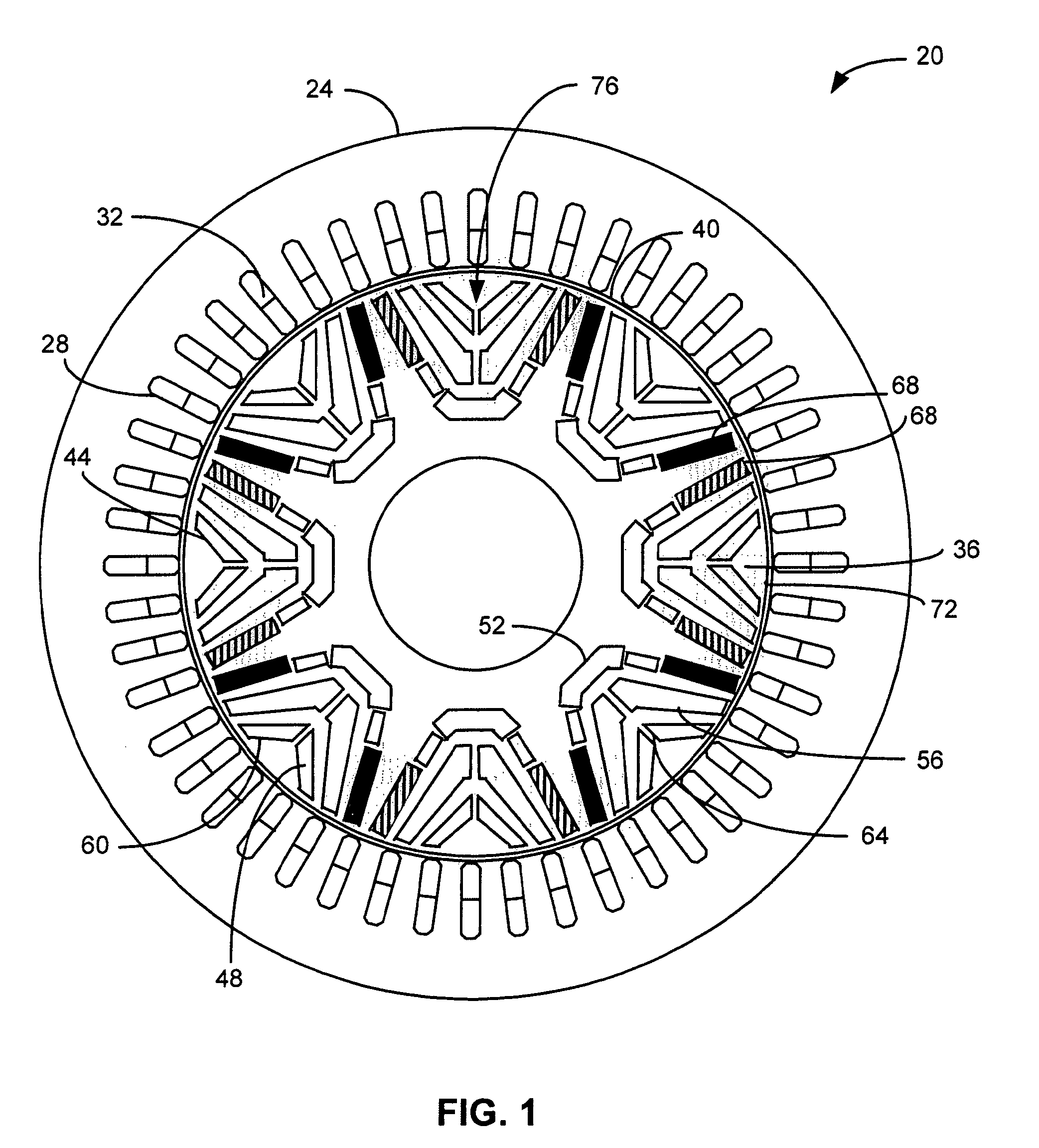
Rotor magnet placement in interior permanent magnet machines
ActiveUS7474029B2Minimize flux variationMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsRotor magnetsRotor flux
A machine includes a stator and a rotor having a plurality of poles. Each pole is formed at least in part by a plurality of permanent magnets recessed within the rotor at a predetermined distance from an outer surface of the rotor. The distance is predetermined to minimize rotor flux variation near the outer surface during rotation of the rotor relative to the stator. Eddy current losses are thereby reduced.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
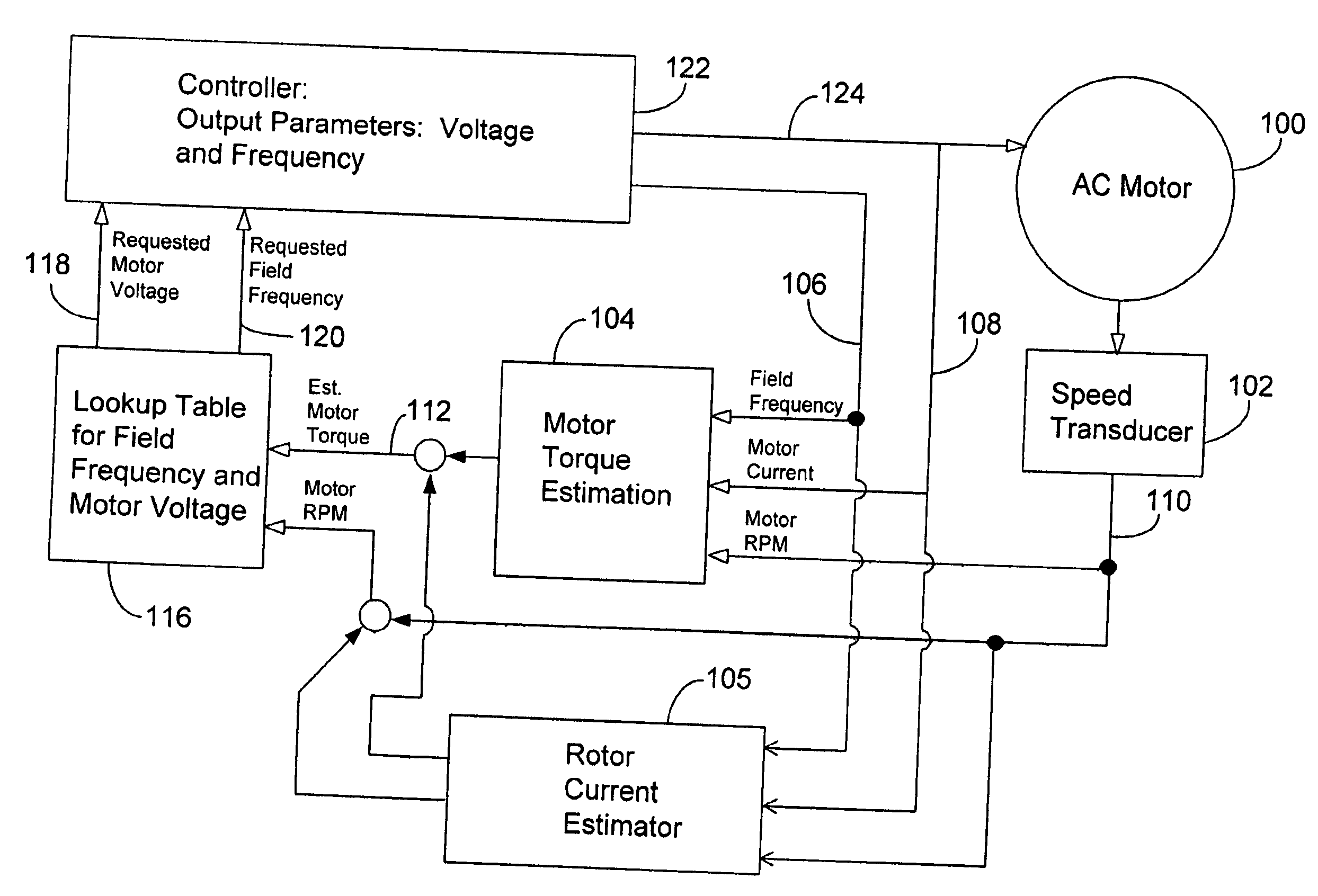
System and method for optimizing motor performance by varying flux
InactiveUS20060038530A1Easy to operateDC motor speed/torque controlGeneral control strategiesControl signalRotor flux
A system for operating an electric motor is described. The system has a torque estimator to determine a load on the motor and a controller configured to generate a motor control signal. The controller continuously adjusts the motor control signal in response to the load on the motor. The motor control signal optimizes the motor's performance by controlling the rotor flux of the motor. The motor control signal can control the voltage or current and frequency applied to the motor.
Owner:PATENT
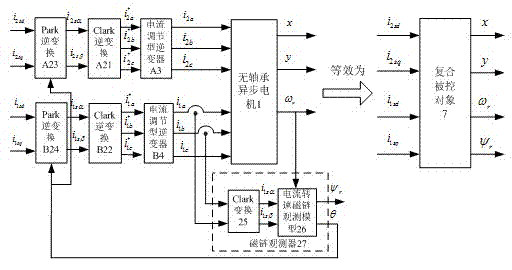
Bearing-free asynchronous motor control method based on neural network inverse system theory
InactiveCN102361429ASelf-learningWith adaptive functionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsLoop controlIntegrator
The invention discloses a bearing-free asynchronous motor control method based on a neural network inverse system theory. A composite controlled object is composed of two sets of Park inverse transformation, two sets of Clark inverse transformation, two sets of current regulating inverters, a flux linkage observer, and a bearing-free asynchronous motor; a fuzzy neural network and integrators form a fuzzy neural network inverse system; and the fuzzy neural network inverse system is in series connection with the composite controlled object; besides, the bearing-free asynchronous motor is decoupled into a pseudo linear system comprising two displacement subsystems, a rotating speed subsystem and a rotor flux linkage subsystem; and the obtained pseudo linear system is introduced into internal model control to form closed-loop control. According to the invention, the control precision is high and there is high robustness on an external disturbance, a parameter change and a modeling error, thereby realizing high-performance control on a bearing-free asynchronous motor.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
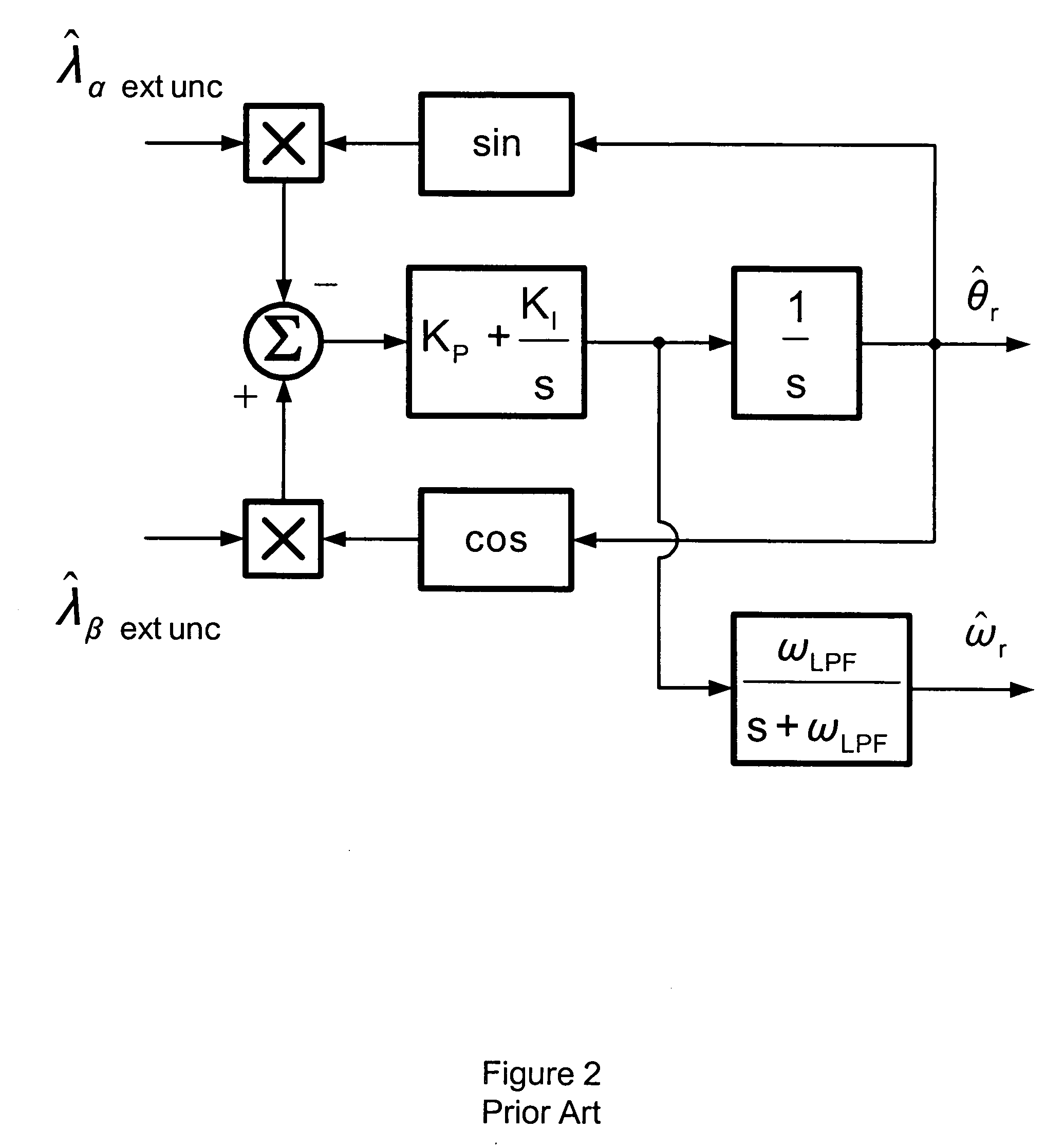
Angular position and velocity estimation for synchronous machines based on extended rotor flux
ActiveUS20070194742A1Electronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersCorrection algorithmIntegrator
A method of correcting the determination of extended rotor flux using a lag function and a correction algorithm that closely approximates a pure integrator function to correct for lag function errors that can extend the EFS control down to dynamoelectric machine speeds corresponding to as low as 10 Hz electrical frequency.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
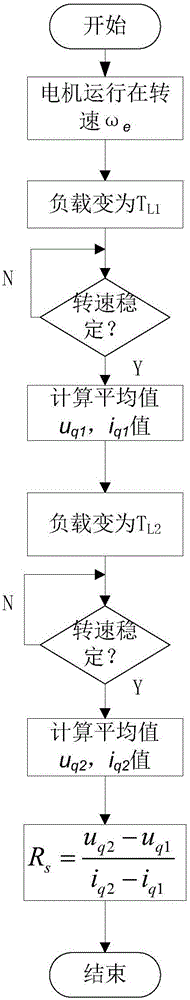
Motor stator resistor recognition method
ActiveCN105119549AElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsStator voltageElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a motor stator resistor recognition method, and the method is used for a surface-mounted PMSM. The method comprises the steps: building a d-q coordinate system based on rotor flux linkage orientation at first; eliminating a non-resistance voltage drop part in a motor stator voltage equation in an operation process of the surface-mounted PMSM; and calculating the resistance of a stator resistor through the voltage and current of a resistor voltage drop part. The method achieves on-line recognition, also can recognize the resistance value of the stator resistor when the motor operates at different speeds, and can recognize the resistance value, which changes because of the impact of motor temperature, of the stator resistor in real time. Compared with a conventional on-line recognition method, the method just needs voltage and current signals during the calculation of the stator resistor, does not need other parameter information of the motor, is simple in algorithm, is easy to achieve through a DSP, and is higher in recognition precision.
Owner:NANJING ESTUN AUTOMATION CO LTD
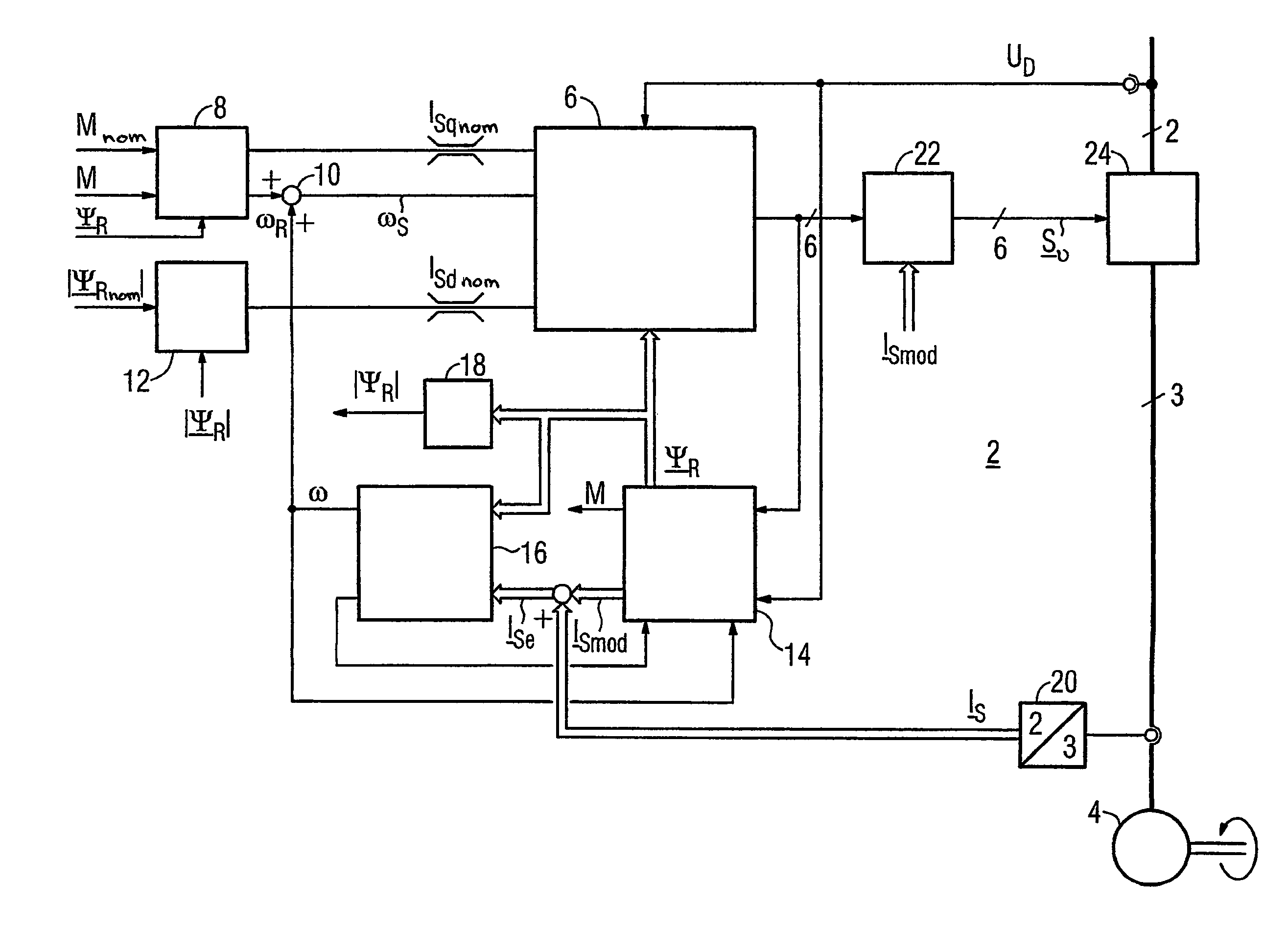
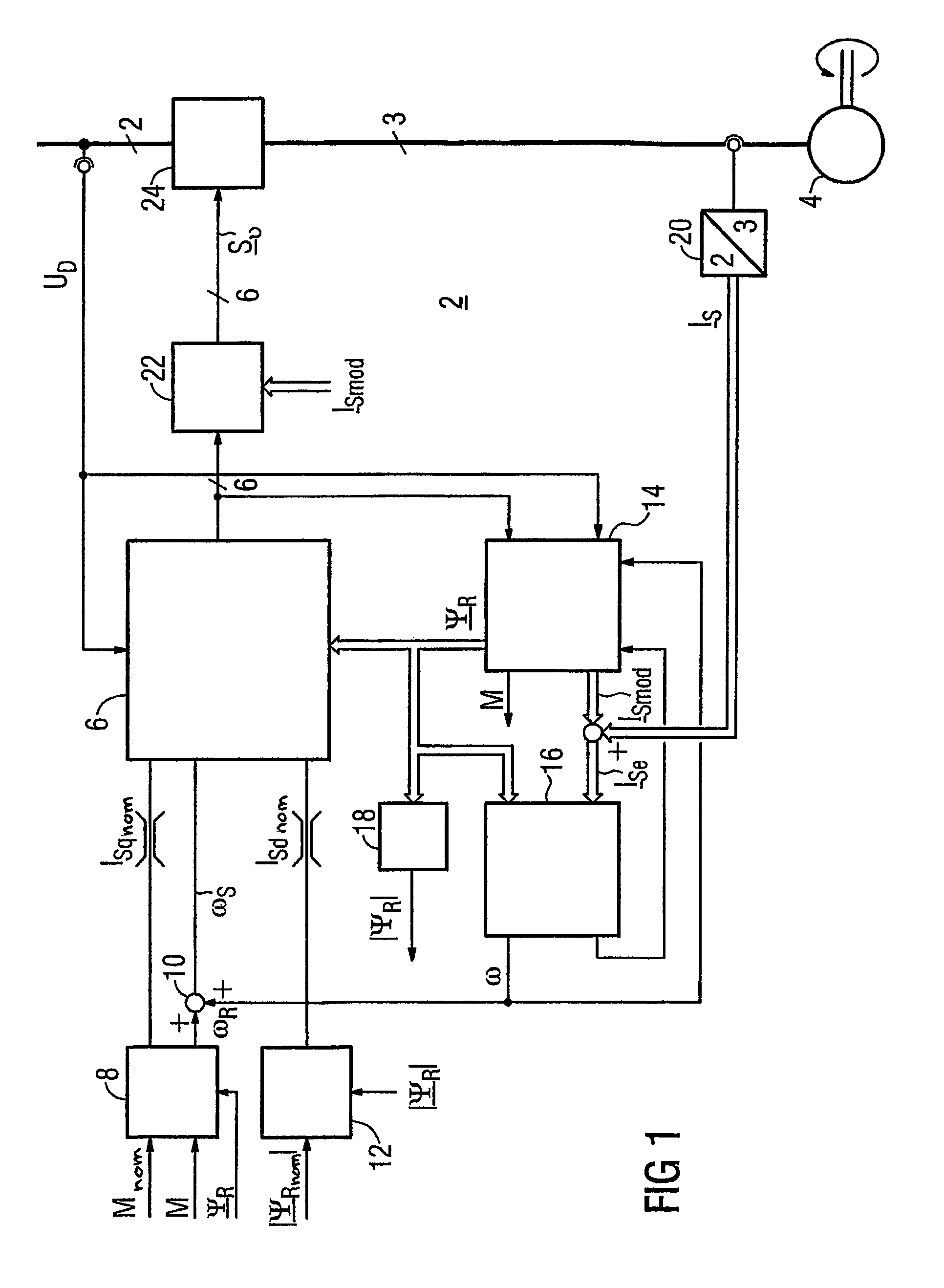
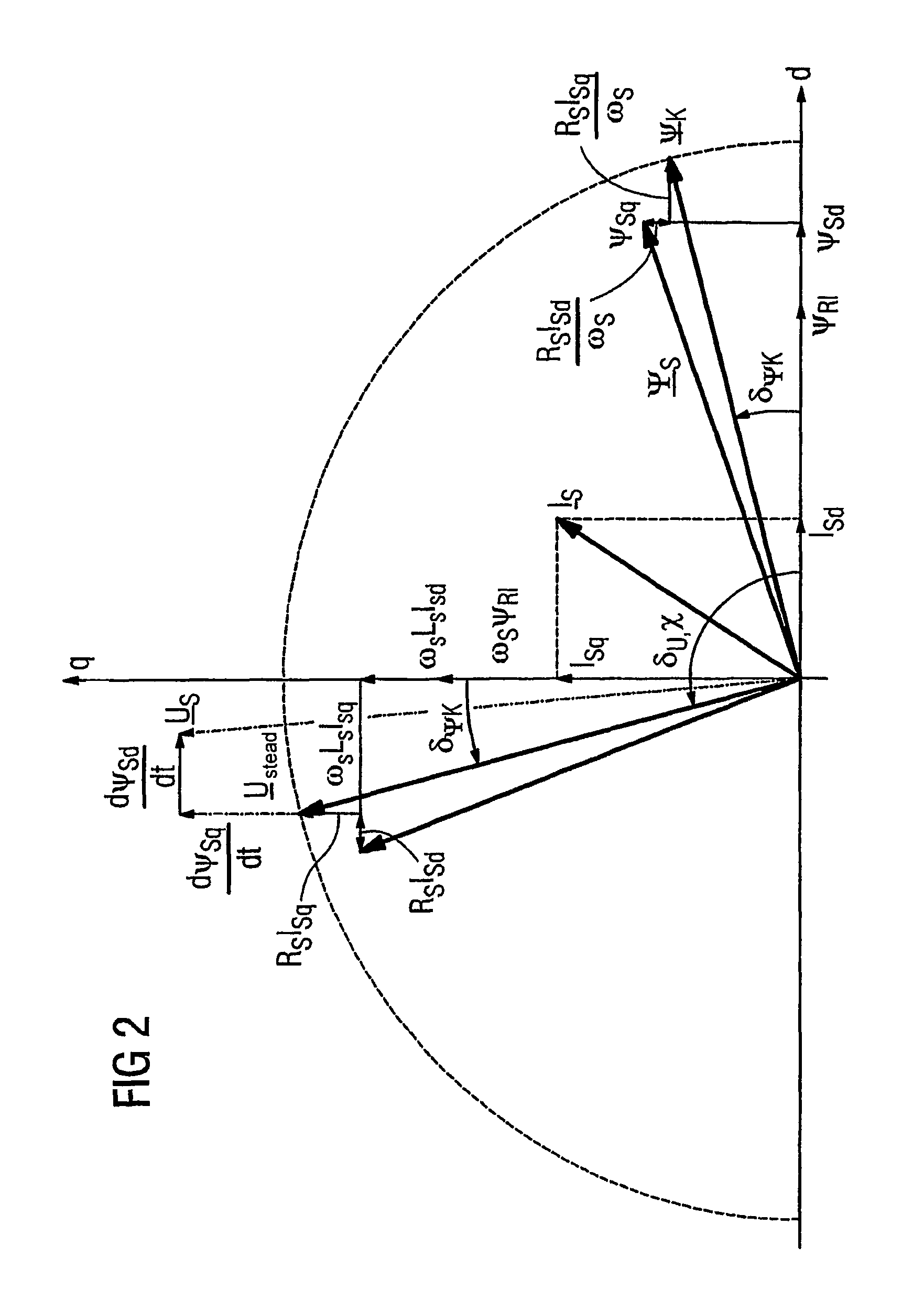
Method for controlled application of a stator current set point value and of a torque set point value for a converter-fed rotating-field machine
InactiveUS7746039B2Avoid disadvantagesBroaden the fieldElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineMagnetic poles
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Observation method and device for electromagnetic torque of salient pole type permanent-magnet brushless direct current motor
InactiveCN102946227AEnables direct torque drive controlElectromagnetic Torque ContinuousElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectromotive forceDirect torque control
The invention relates to an observation method and device for an electromagnetic torque of a salient pole type permanent-magnet brushless direct current motor, and is particularly suitable for the electromagnetic torque and rotation speed control of a motor driving system without position sensors or speed sensors. The observation method and the observation device utilize a rotor counter electromotive force self-adapting stator current observation device, a phase-locked loop based rotor rotation speed and position angle observation device, a rotor counter electromotive force / rotor flux / rotor position angle relation curve, a coordinate conversion device, a stator flux computing device and an electromagnetic torque computing device to observe the electromagnetic torque continuously, instantly and accurately when the position sensors are not available, and observe rotor speed and stator flux in an intermediate variable manner simultaneously, so that the sensorless, high-performance and direct-torque control requirements of the motor are met. The observation method and the device have the advantages of good instantaneity, high observation accuracy, low cost and the like.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method and device for controlling permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN105591582AEasy to controlQuick controlElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsMaximum torquePermanent magnet synchronous motor
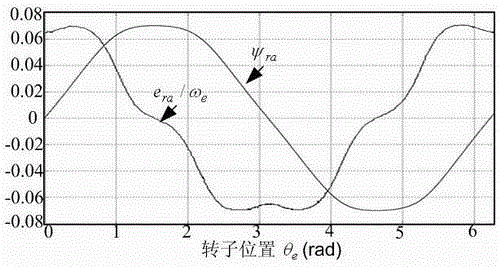
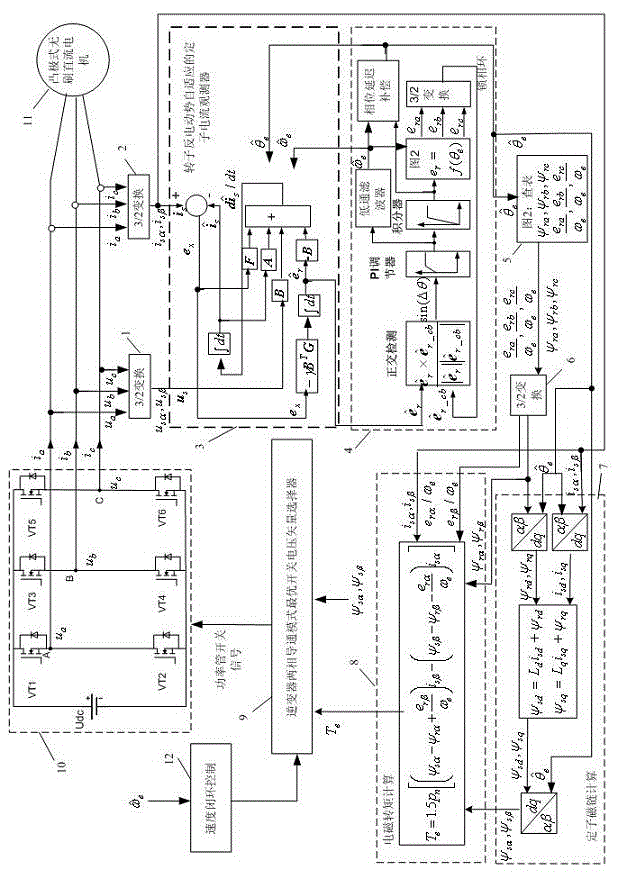
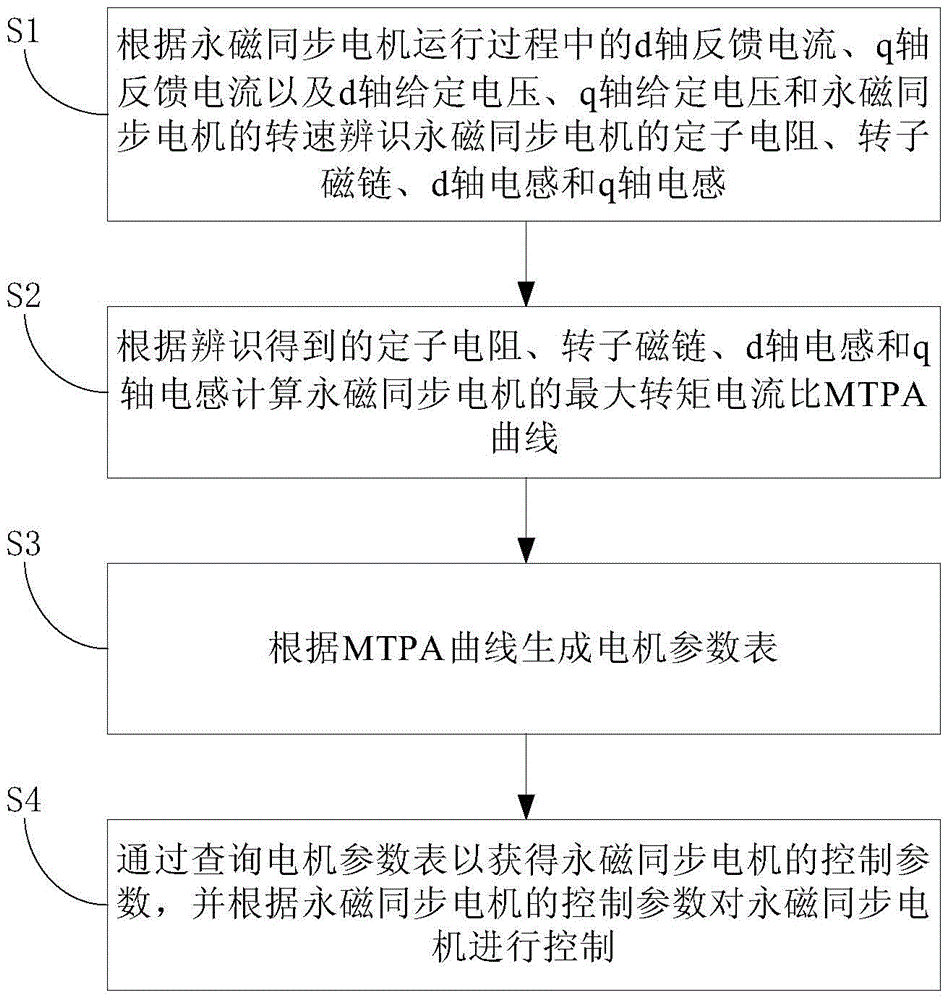
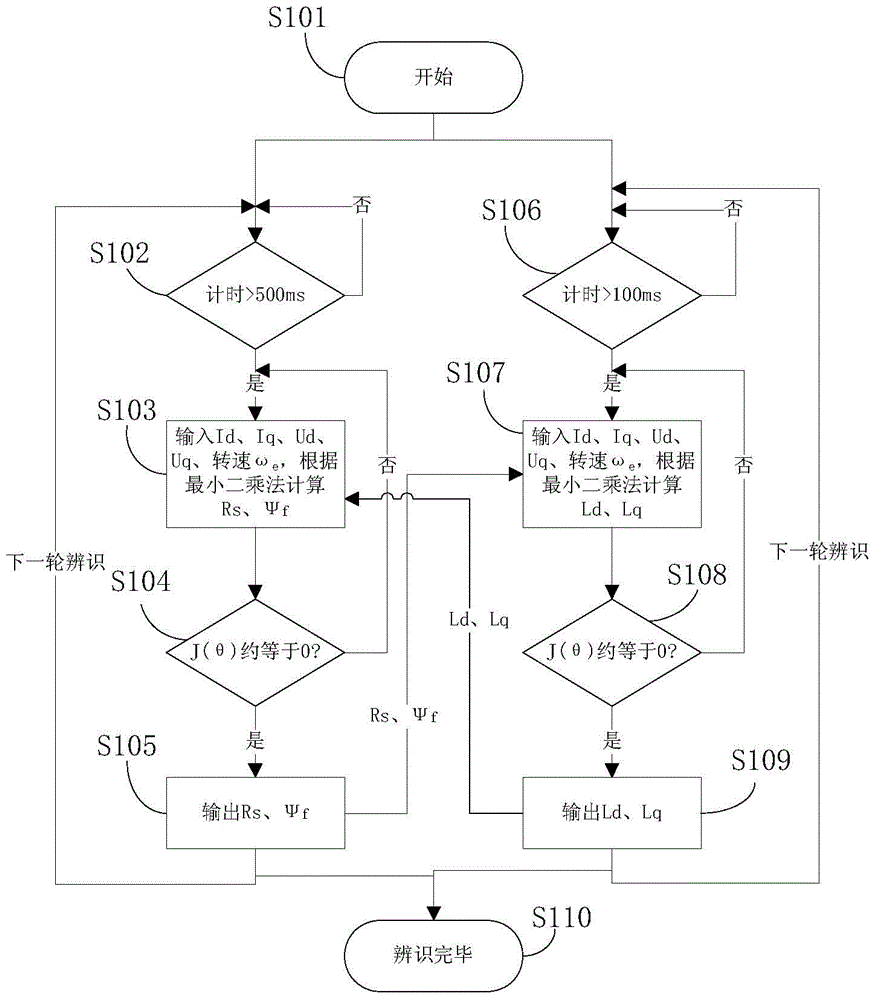
The invention discloses a method of controlling a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps: according to d-axis feedback current, q-axis feedback current, d-axis given voltage and q-axis given voltage during a permanent magnet synchronous motor operation process and the rotation speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, the stator resistance, the rotor flux, the d-axis inductance and the q-axis inductance of the permanent magnet synchronous motor are identified; according to the identified stator resistance, the rotor flux, the d-axis inductance and the q-axis inductance, a maximum torque per ampere (MTPA) curve for the permanent magnet synchronous motor is calculated; according to the MTPA curve, a motor parameter table is generated; and through querying the motor parameter table, control parameters of the permanent magnet synchronous motor are acquired, and according to the control parameters of the permanent magnet synchronous motor, the permanent magnet synchronous motor is controlled. The permanent magnet synchronous motor control method of the invention can improve the control accuracy and the response speed of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. The invention also discloses a device for controlling the permanent magnet synchronous motor.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method for asynchronous motor rotor flux linkage observation and rotation speed identification
InactiveCN102931906AGuaranteed observation accuracyImprove recognition accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsVector control systemFlux linkage
The invention discloses a method for asynchronous motor rotor flux linkage observation and rotation speed identification, which comprises the following steps of: according to stator voltage and current signals measured in real time, observing to obtain a rotor flux linkage through a sliding mode observer based on a super-twisting theory and using the rotor flux linkage as a reference value; using a rotor flux linkage calculated according to a rotor flux linkage current model as an adjustable value; constructing a model reference self-adaptive system (MRAS) based on the rotor flux linkages; and identifying the asynchronous motor rotation speed through the self-adaptive law. The rotation speed identification method provided by the invention has high robustness for the variation of stator resistance, and can provide accurate rotor flux linkages and rotation speed values, thereby being especially suitable for an asynchronous motor vector control system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
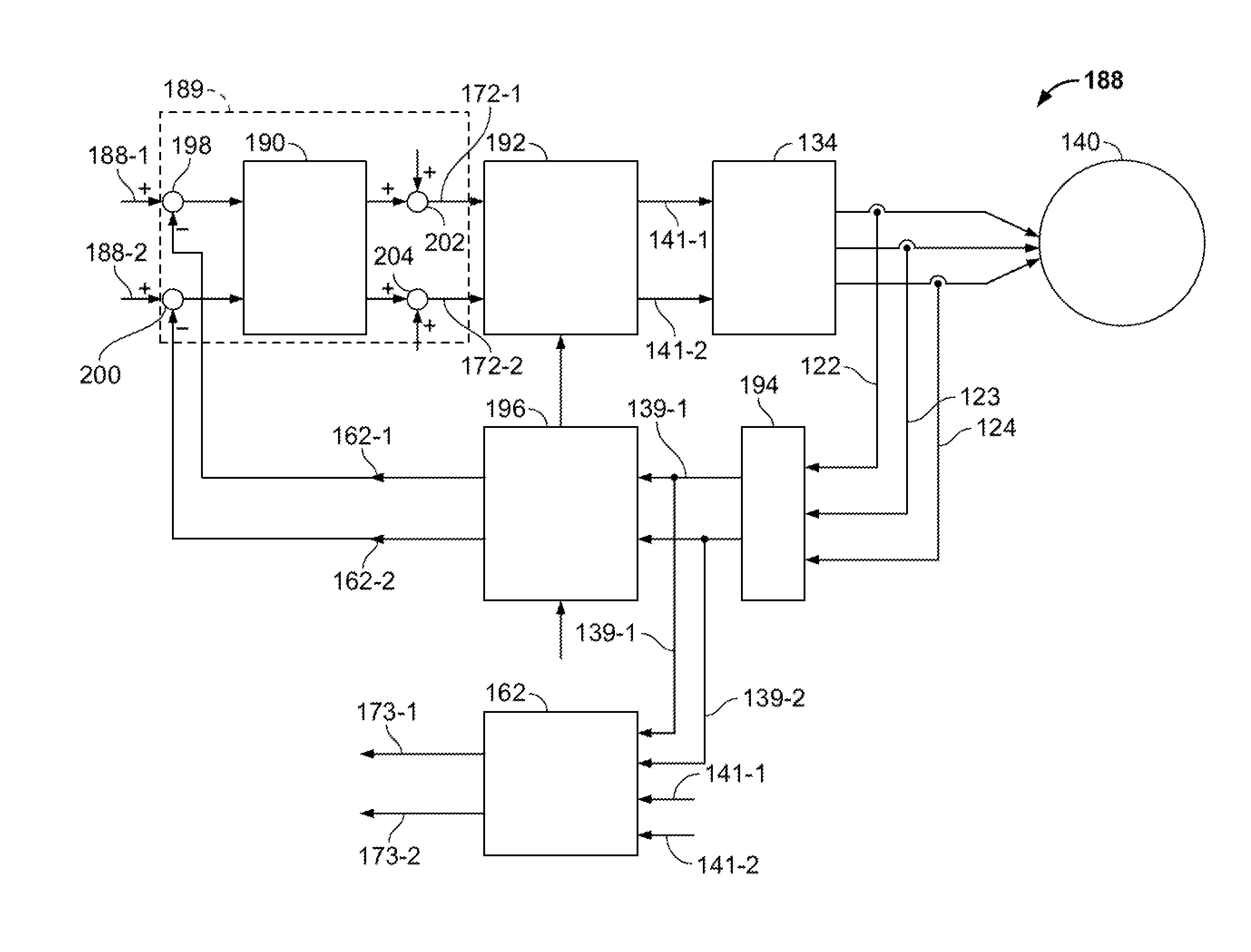
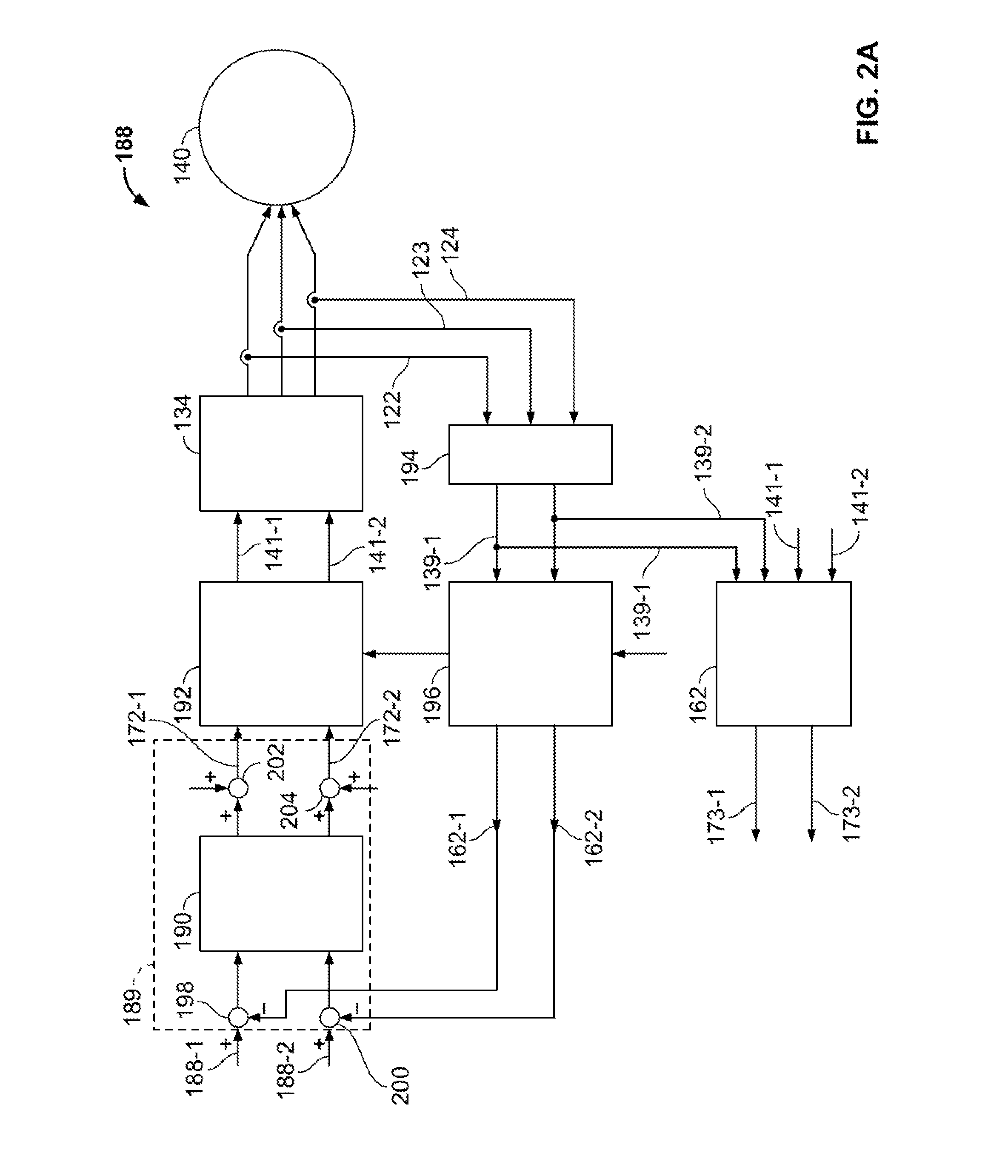
Generator with quadrature ac excitation
InactiveUS20080303490A1Synchronous generatorsEmergency protective circuit arrangementsConstant frequencyExcitation current
A generator system is configured to supply two phase excitation current from an exciter rotor to a main generator rotor. When driven by a variable speed prime mover, the generator system provides relatively constant frequency AC power by independently controlling the main rotor flux rotational speed. The generator system includes an exciter stator that induces current in the exciter rotor windings at a desired frequency and phasing. The exciter rotor windings are electrically connected to the main rotor windings to provide two-phase excitation current to the main rotor windings. Excitation is supplied to the exciter stator from an exciter controller, which controls the frequency and phasing of the exciter excitation, based on the rotational speed of the generator, to maintain a constant output frequency. The exciter frequency control function of the exciter controller may be eliminated when the generator system is driven by a constant speed prime mover or when a narrow band variable frequency output is required.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Method for Controlled Application of a Stator Current Set Point Value and of a Torque Set Point Value for a Converter-Fed Rotating-Field Machine
InactiveUS20080136380A1Avoid disadvantagesBroaden the fieldElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineMagnetic poles
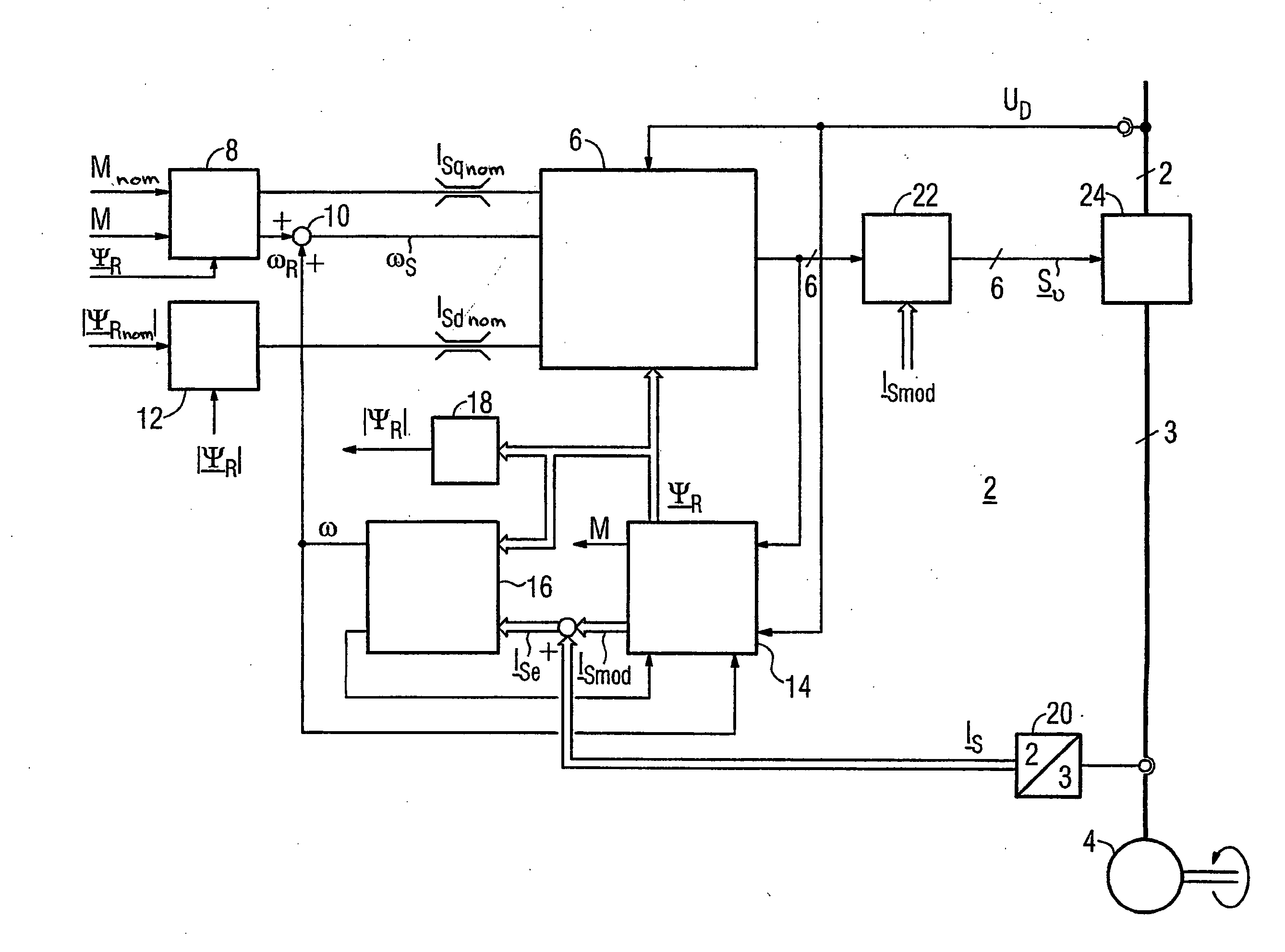
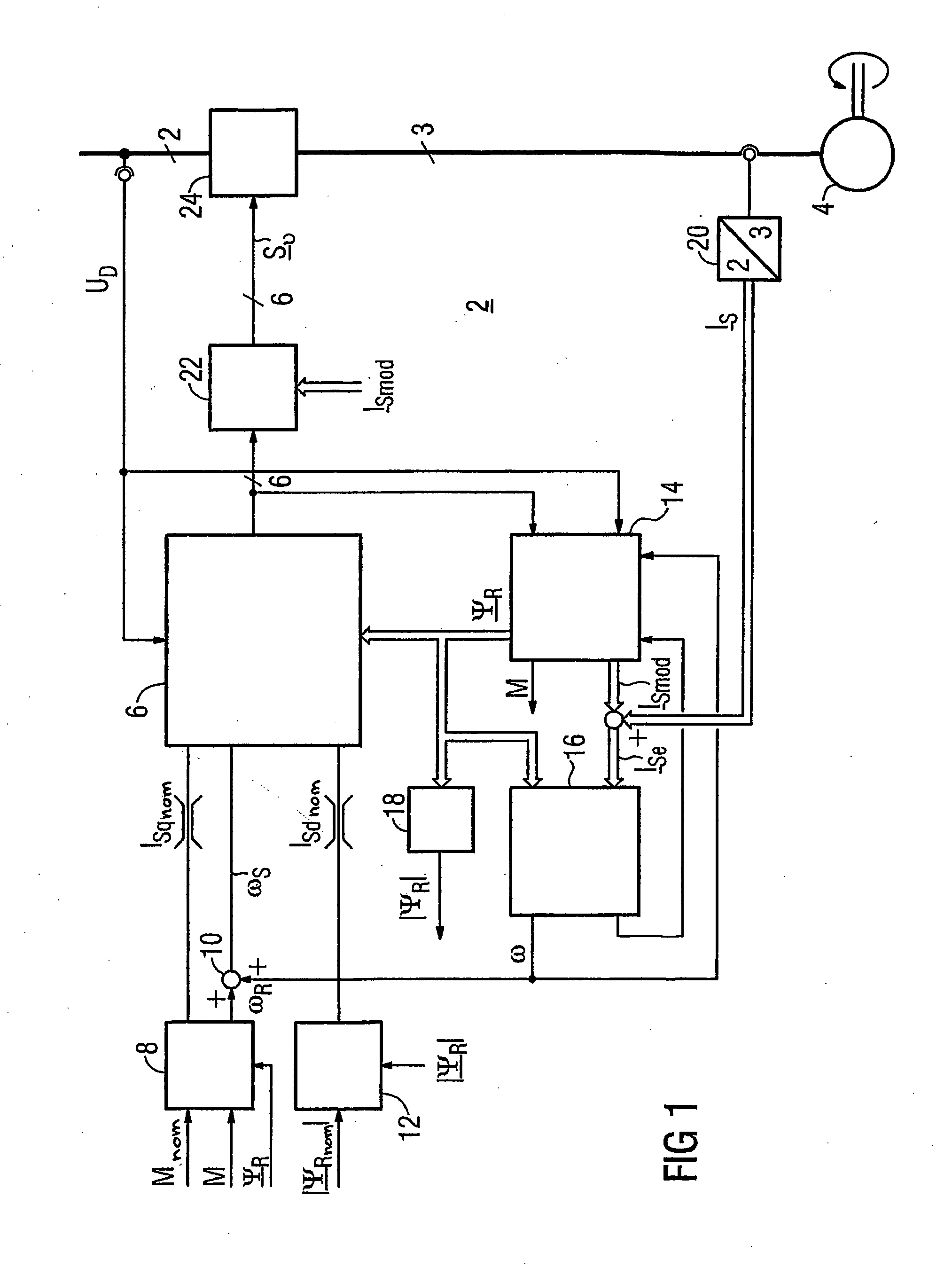
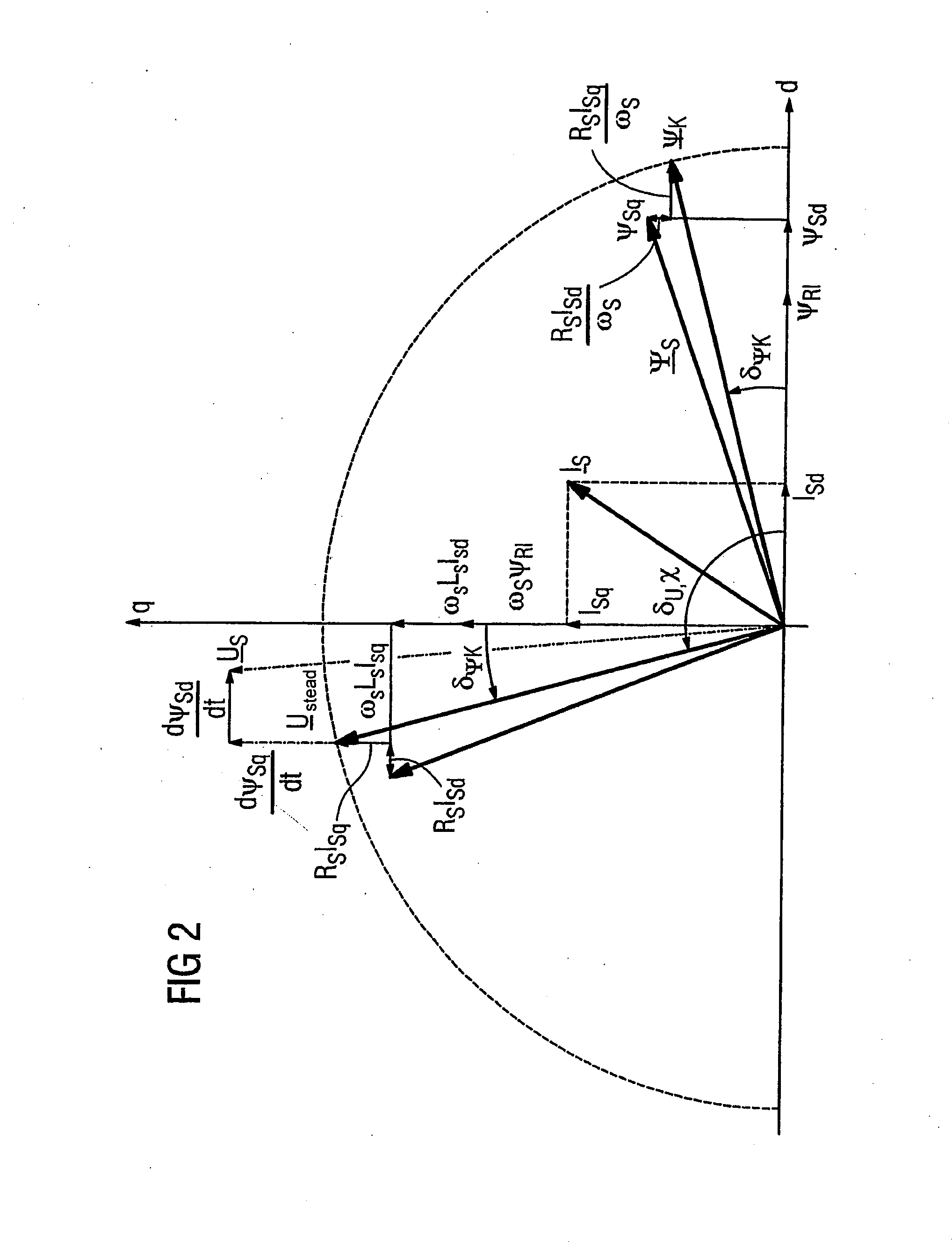
The invention relates to a method for the controlled application of a stator-current target value (ISnom) and a torque target value (Mnom) for a polyphase machine (4) that is supplied by an electronic power converter. According to the invention: current components (ISdnom, ISqnom) in a co-ordinate system (d, q) with a fixed rotor flux or rotating magnetic pole are calculated in accordance with a torque target value and in asynchronous machines in accordance with a rotor-flux target value (ΨRnom), a calculated rotor-flux actual value (Ψ<SB>R< / SB>) or a rotating magnetic-pole flux; a stator-circuit frequency (ω<SB>S< / SB>) is determined; a terminal-flux target value (ΨKnom) is calculated in accordance with the values (ISnom, ISqnom, Ψ<SB>R< / SB>, ω<SB>S< / SB>) by means of the machine parameters (L, R<SB>S< / SB>), said terminal-flux target value being subsequently projected onto a flux-course curve, selected from stored, off-line optimised flux-course curves. This permits the state of the stator current (I<SB>S< / SB>) to be regulated in relation to the rotor flux (Ψ<SB>R< / SB>) or rotating magnetic-pole flux by means of momentary values, facilitating a stationary and dynamic precise control of motor currents (I1,I2,I3) and thus the torques (M) of a polyphase machine (4).
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Digital rotor flux observer
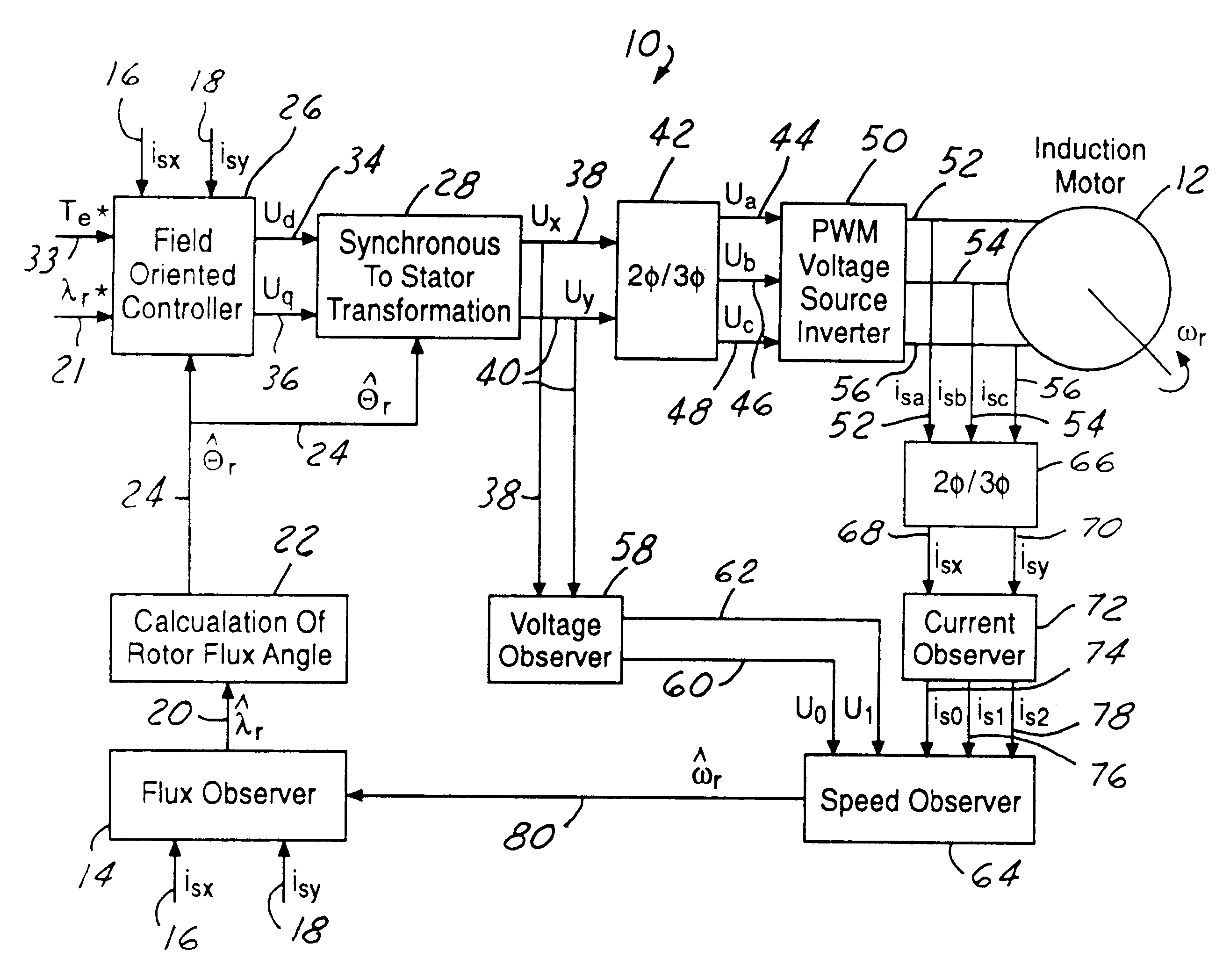
InactiveUS6509711B1Improve performanceIncrease speedElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersInduction motorRotor flux
A system (10) for controlling the torque of an induction motor (12) utilizes a flux observer (14). The flux observer (14) receives stator current inputs (16, 18) and a rotor speed estimate (80) and then outputs a rotor flux estimate (20) that provides increased motor control stability at all speeds.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
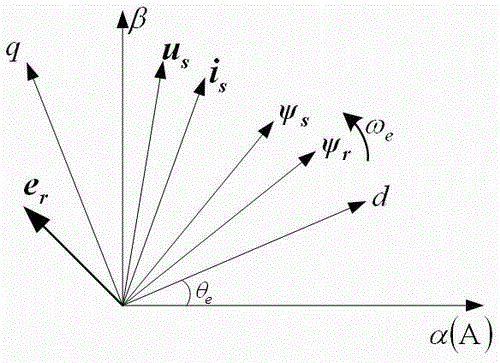
Control method and system of permanent magnet synchronous motor
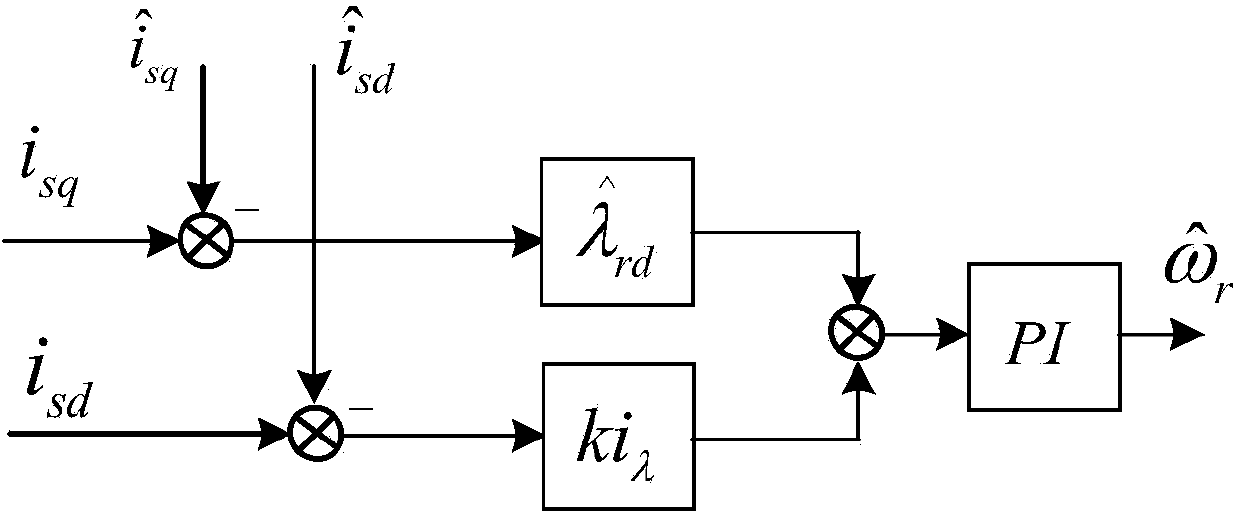
ActiveCN103595328AEffective controlImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsSynchronous motorPosition angle
The invention discloses a control method and system of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. The control method comprises the steps that stator flux linkage of the permanent magnet synchronous motor and stator flux linkage deviation are worked out by the adoption of a voltage model and a current model; stator flux linkage of the synchronous motor and rotor flux linkage of the synchronous motor under a dp coordinate system are worked out by the utilization of a conversion matrix between a two-phase static coordinate system and a two-phase synchronous rotating coordinate system; finally, the rotor position angle and the rotor angular speed of the permanent synchronous motor are worked out through the closed loop phase lock technology of rotor q-axis flux linkage. The control method and system of the permanent magnet synchronous motor have the advantages that on the basis of a non-sensor estimation method of a flux linkage closed loop phase-locked loop of the rotor flux linkage of the permanent magnet synchronous motor and by the adoption of the technology of conducting compensation on the stator flux linkage deviation through the voltage model and the current model, the accuracy of the estimation algorithm is improved and effective control over the permanent magnet synchronous motor in the full-speed range can be realized.
Owner:中广核工程有限公司 +1
Speed sensorless control of an induction machine using a PWM inverter with output LC filter
InactiveUS7084604B2Single-phase induction motor startersVector control systemsVoltage vectorSystem matrix
Owner:ABB OY
Parameter identification method of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN103684182AImproved low-speed control performanceGood low speed control performanceElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlElectrical resistance and conductanceLow speed
A parameter identification method of a permanent magnet synchronous motor. A conventional model is improved with reference to an adaptive structure, i.e., based on an original MRAS1 module, a new MRAS2 module is constructed, so that a cascade model reference adaptive control (CMRAS) module is constructed; the MRAS1 is used for identification of a rotor speed; and the MRAS2 is used for identification of a stator resistance and rotor flux. In the invention, while the rotor speed is fed back in the real time manner, the stator resistance and rotor flux identification value is fed back to a vector control system, so that an influence of motor parameters on the system can be effectively lessened; and since the stator resistance identification value is updated in the real time manner at the low speed, the low speed control performance of the system can be effectively improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Flux linkage error observation-based acquisition method of full-order flux linkage observer of asynchronous motor without speed sensor
ActiveCN103701386AGuaranteed uptimeImprove accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsLow speedLow - observation
The invention discloses a flux linkage error observation-based acquisition method of a full-order flux linkage observer of an asynchronous motor without a speed sensor and belongs to the field of a speed sensorless vector control full-order flux linkage observer. The problem that the existing speed sensorless vector control system causes low observation accuracy of the full-order flux linkage observer due to larger errors of motor parameters when a motor runs at low speed, and finally, the running stability of the system is poor is solved. A full-order flux linkage observer error feedback matrix coefficient is obtained according to the following rules, namely, the pole real part of the observer is smaller than the pole real part of an asynchronous motor, the real parts are both negative numbers, the zero pole real parts of an estimation rotation speed and a transfer function are both negative numbers, the error between an estimation flux linkage and a real flux linkage is utilized, when the motor runs at low speed, the equivalence of the system is a current model, and when the motor runs at high speed, the equivalence of the system is a voltage model. The rotor flux linkage phase position error coefficient ilambda is utilized and the rotor flux linkage amplitude error coefficient k is introduced, so that the estimation rotating speed precision is increased. The flux linkage error observation-based acquisition method of the full-order flux linkage observer of the asynchronous motor without the speed sensor is particularly used in the field of speed sensorless vector control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Shaft sensorless angular position and velocity estimation for a dynamoelectric machine based on extended rotor flux
ActiveUS20060052972A1Improve estimation accuracyVector control systemsDigital computer detailsRotor fluxFlux linkage
A shaft sensorless rotor angular position and velocity sensing system for a dynamoelectric machine that is based on dynamoelectric machine extended flux estimation.
Owner:HAMILTON SUNDSTRAND CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com