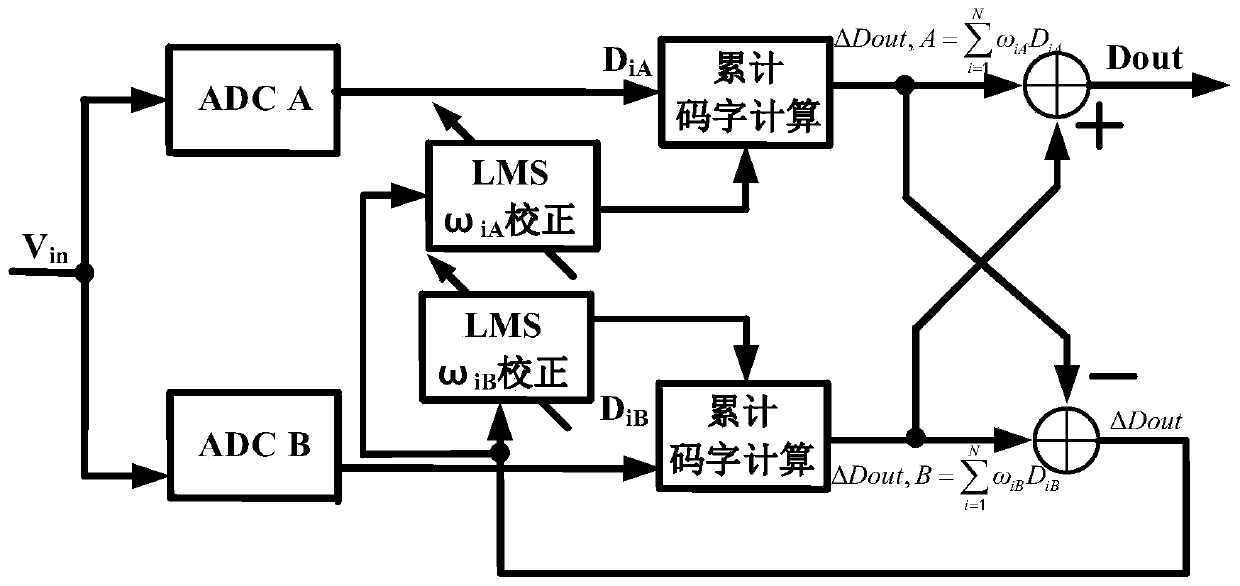
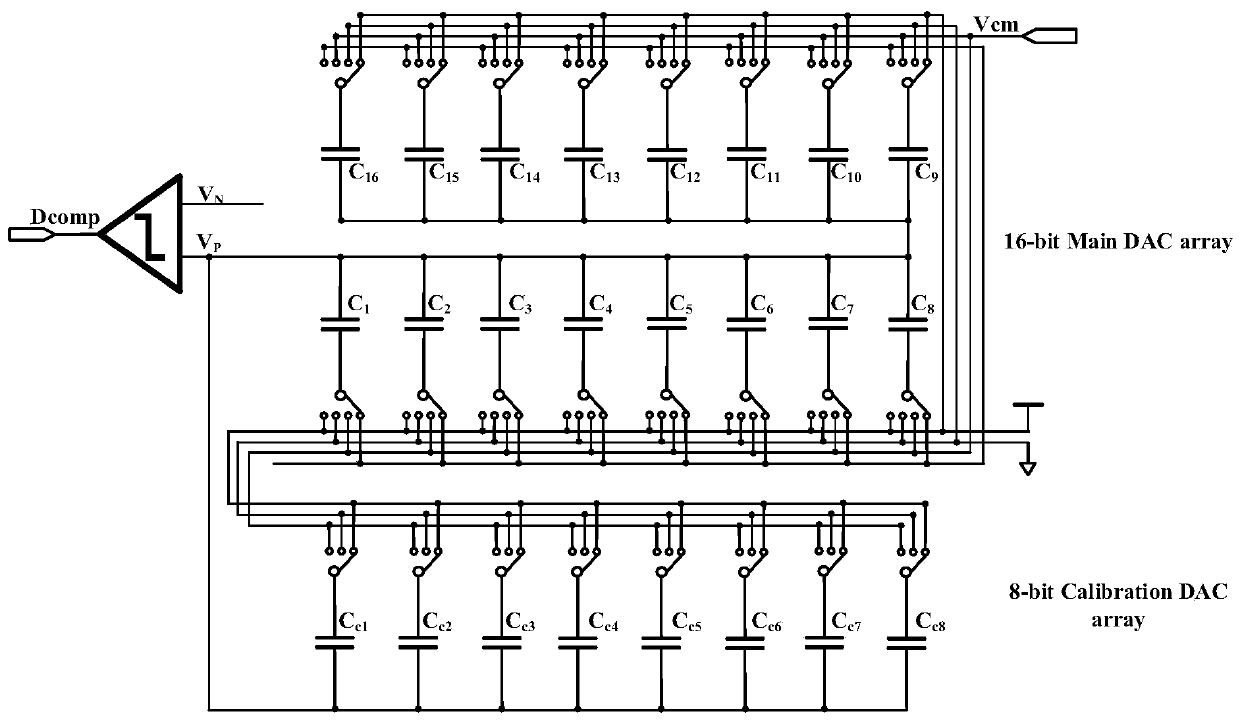
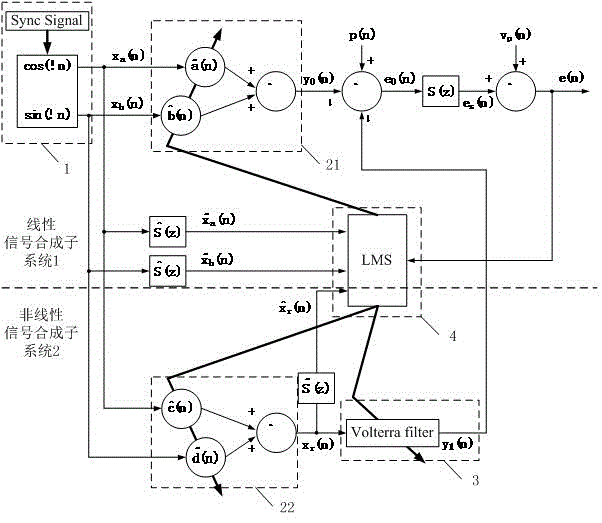
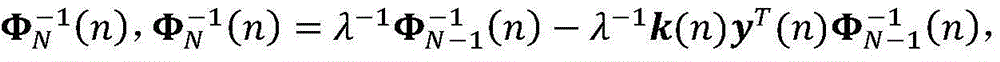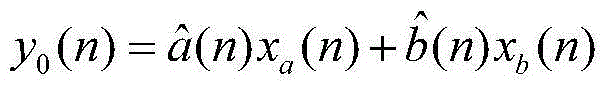Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
127 results about "Least mean square algorithm" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The least mean square (LMS) algorithm is a type of filter used in machine learning that uses stochastic gradient descent in sophisticated ways – professionals describe it as an adaptive filter that helps to deal with signal processing in various ways.
Blind cost criterion timing recovery
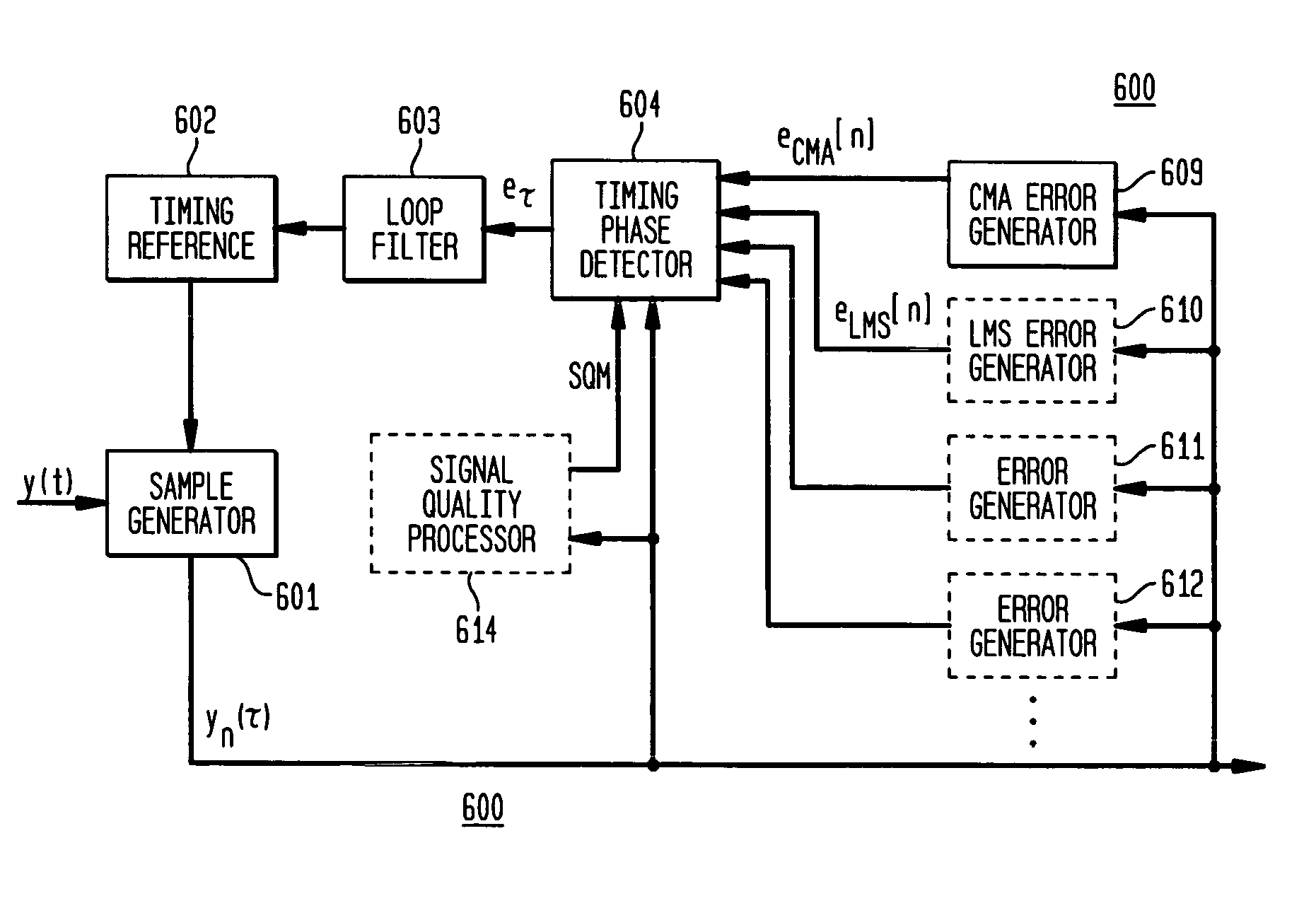
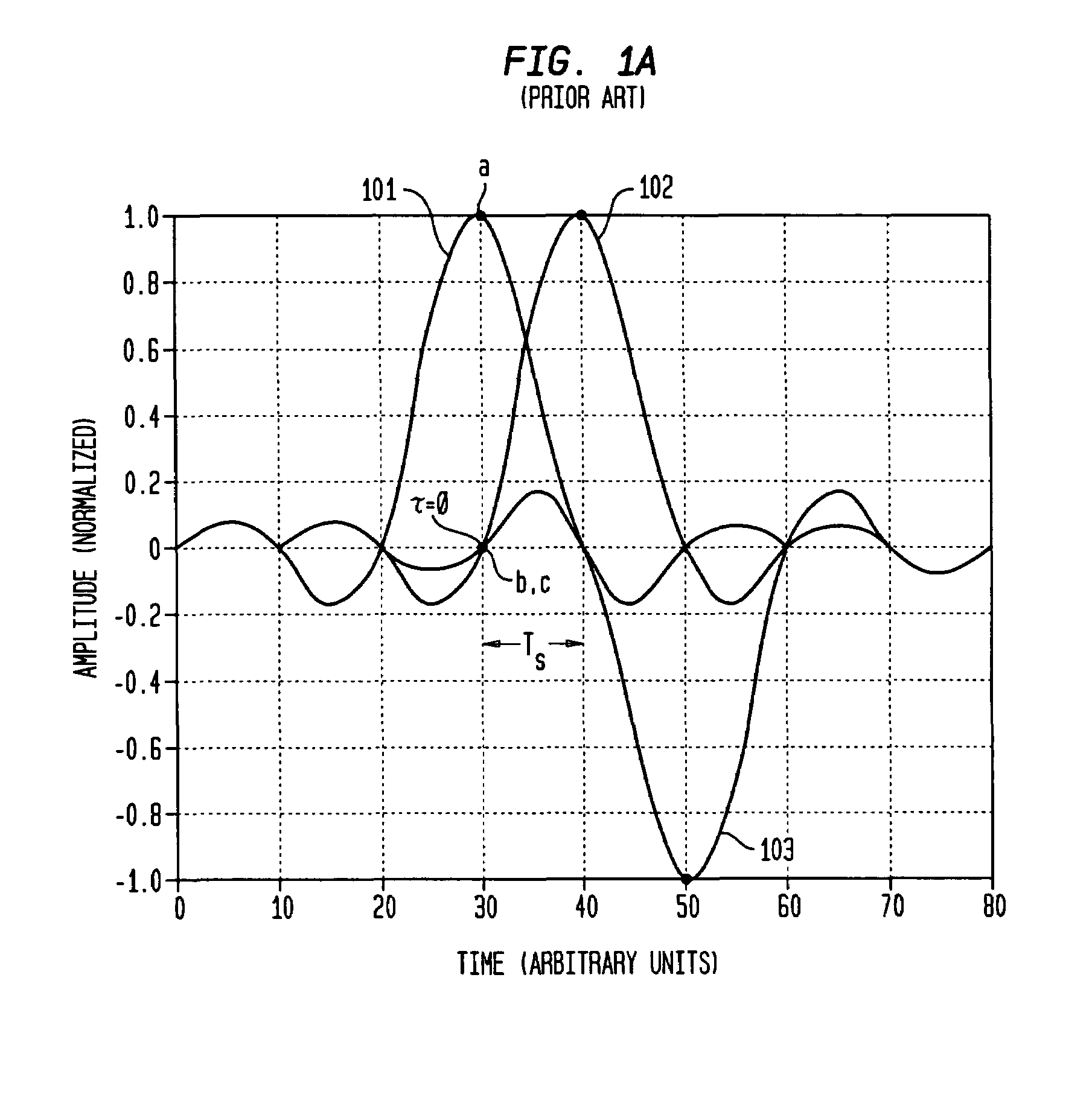
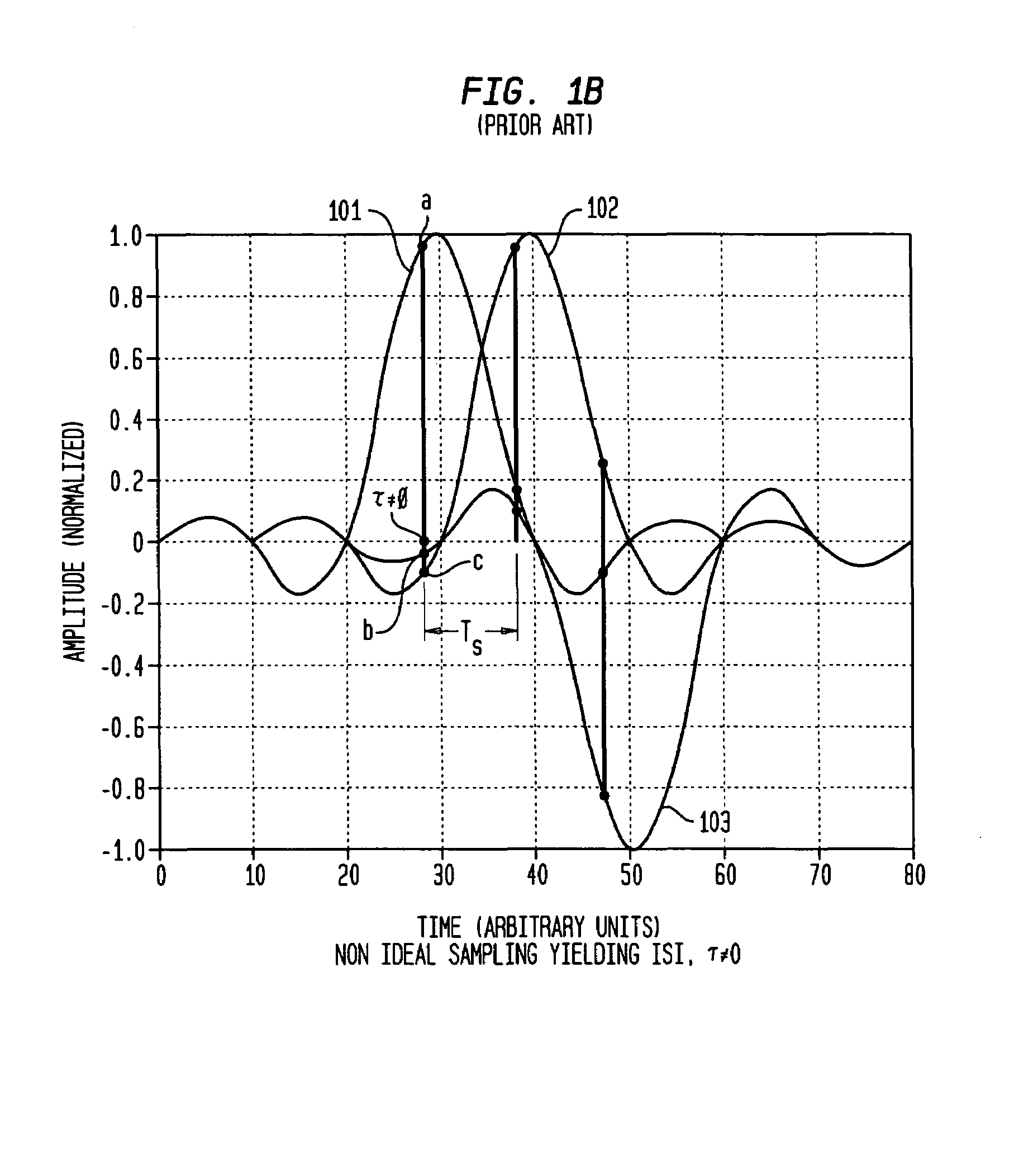
Symbol timing recovery employs a blind cost criterion from the Bussgang class of functions, and its stochastic gradient, to generate a timing phase error used to adjust sampling of received symbols. For one implementation, the estimate is derived in accordance with the Constant Modulus (CM) criterion and its gradient via the CM algorithm (CMA), and the estimate is calculated from a sequence of samples. This estimate is then used to adjust the period and phase of the sample sequence toward the period and phase of the transmitted symbols, driving the timing phase error to zero. The values used may be either i) samples themselves, ii) processed (e.g., interpolated) samples, or iii) equalized and processed samples. In addition, timing phase error estimates for other cost criteria, including the least mean squares algorithm, may be generated. These timing phase error estimates are selected either alone or in combination for deriving the timing phase error used to adjust the period and phase of the sample sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
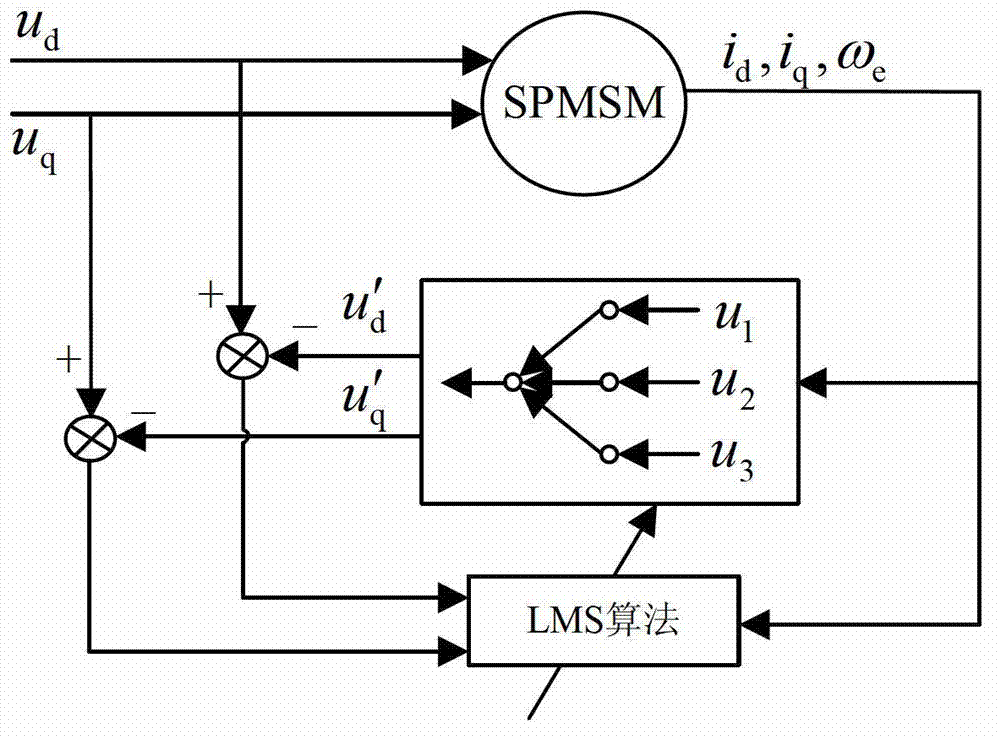
Online decoupling identification method of multiple parameters of PMSM (permanent magnet synchronous motor)
ActiveCN103248306AEliminate false convergenceImprove reliabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
The invention relates to the technical field of PMSMs, solves a coupling problem during online identification of multiple parameters of a surface-mounted type PMSM, and achieves online decoupling identification of PMSM inductance, stator resistance and rotor flux linkage. Accordingly, the technical scheme adopted by the invention is that an online decoupling identification method of multiple parameters of the PMSM comprises the steps as follows: 1) identifying and coupling analysis of parameters of the PMSM; 2) a decoupling identification strategy, wherein voltage deviation before and after D shaft current injection is used for increasing the order of a motor mathematical equation, so that the decoupling identification of multiple parameters of the surface-mounted type PMSM inductance, the stator resistance and the rotor flux linkage are achieved; 3) neural network identifier design, wherein according to a parameter online identification problem of the PMSM, online identification is performed on motor parameters by adopting a self-adaptive neural network structure and a weight convergence algorithm based on a least mean square algorithm. The method is mainly applied to the design and manufacture of the PMSM.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
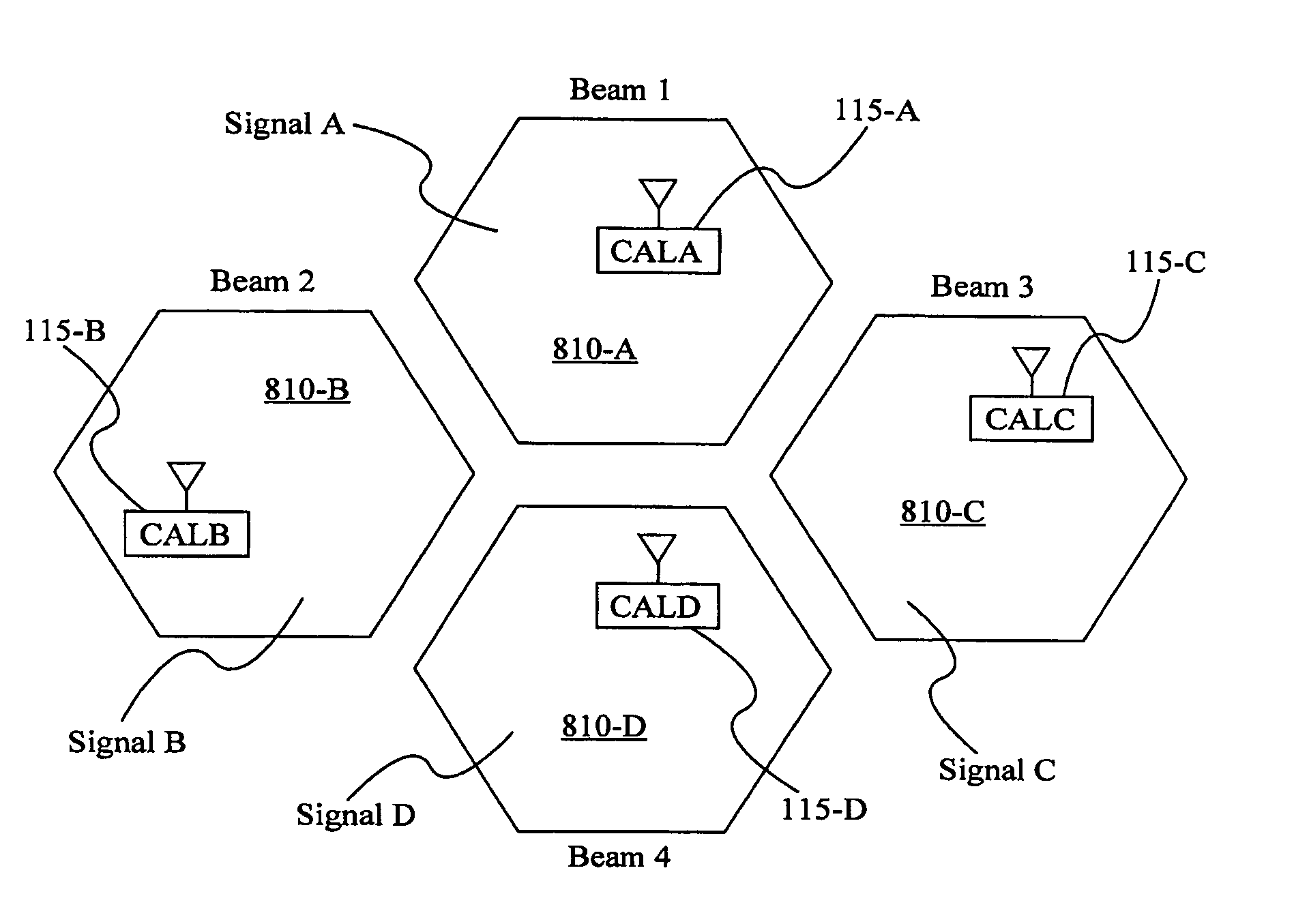
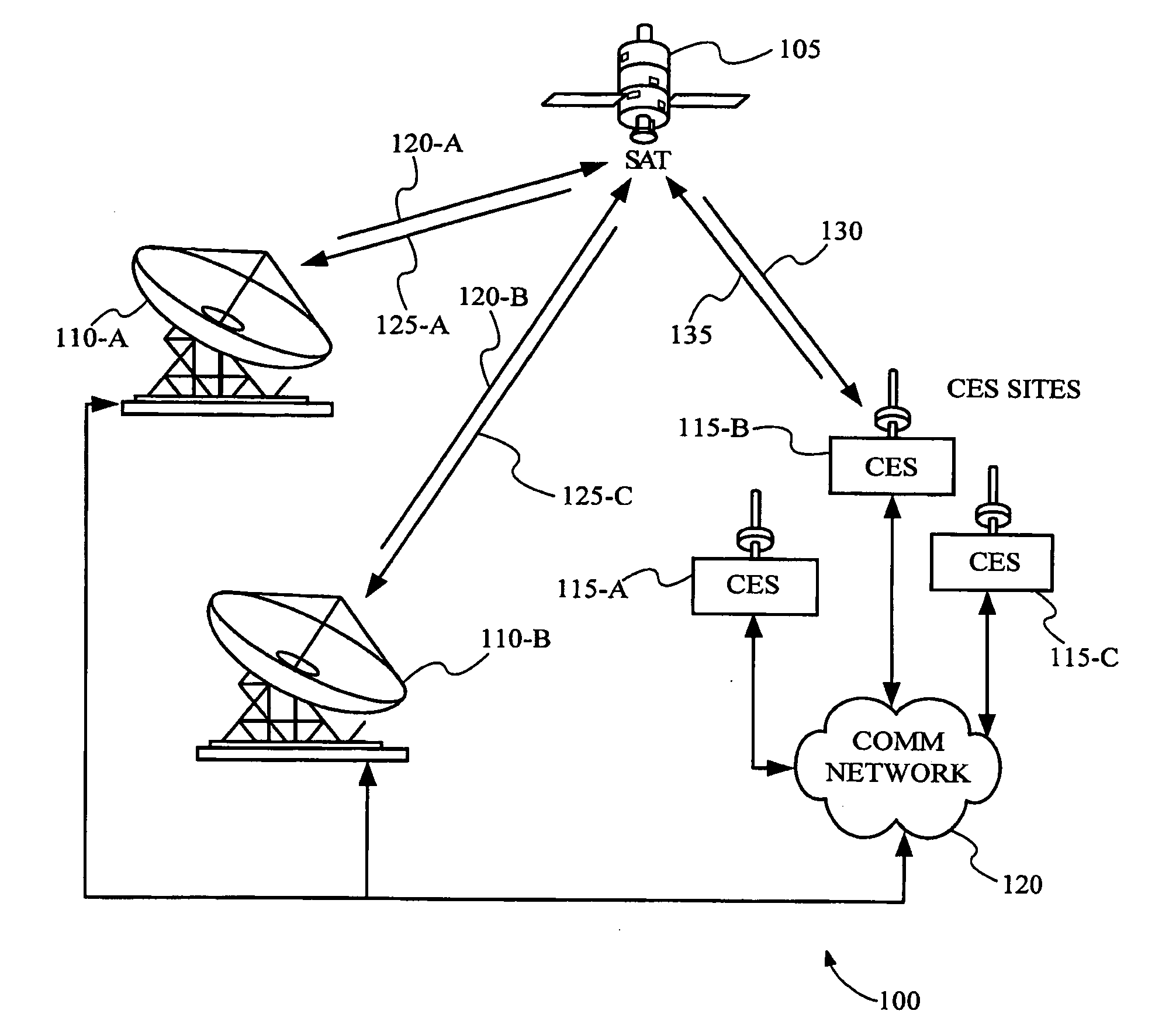
Forward and reverse calibration for ground-based beamforming
ActiveUS8331329B2Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemMean square
Owner:VIASAT INC
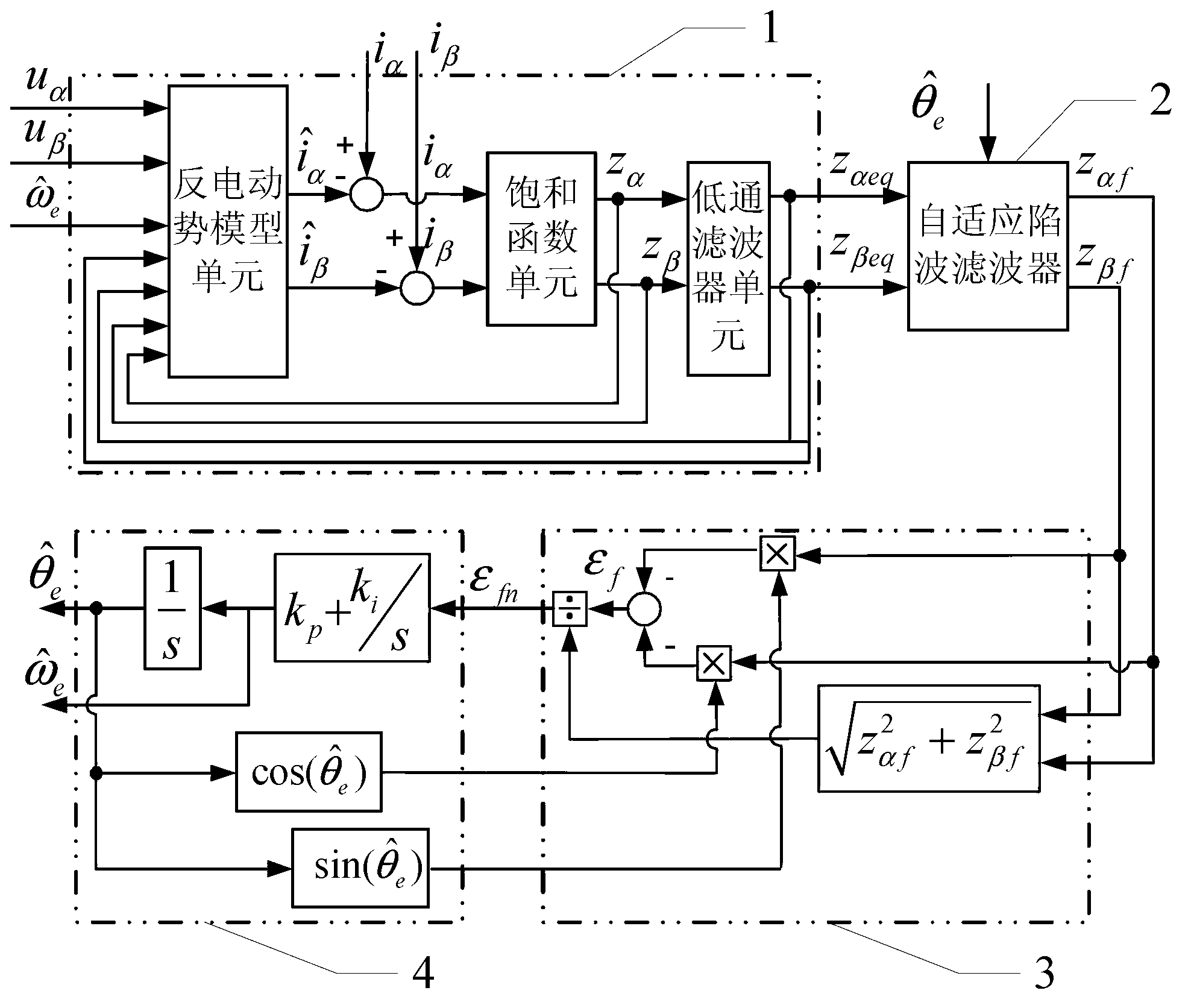
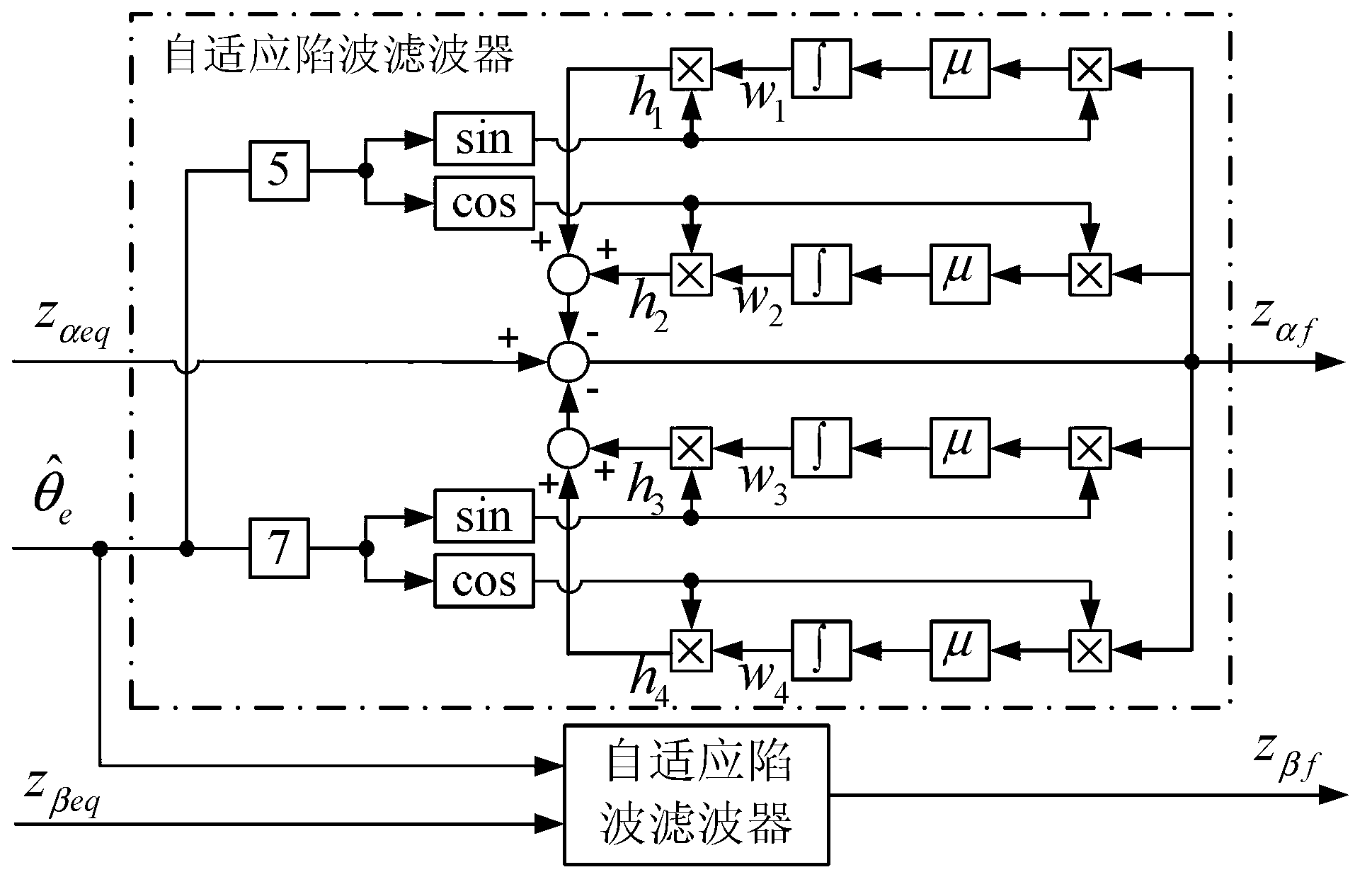
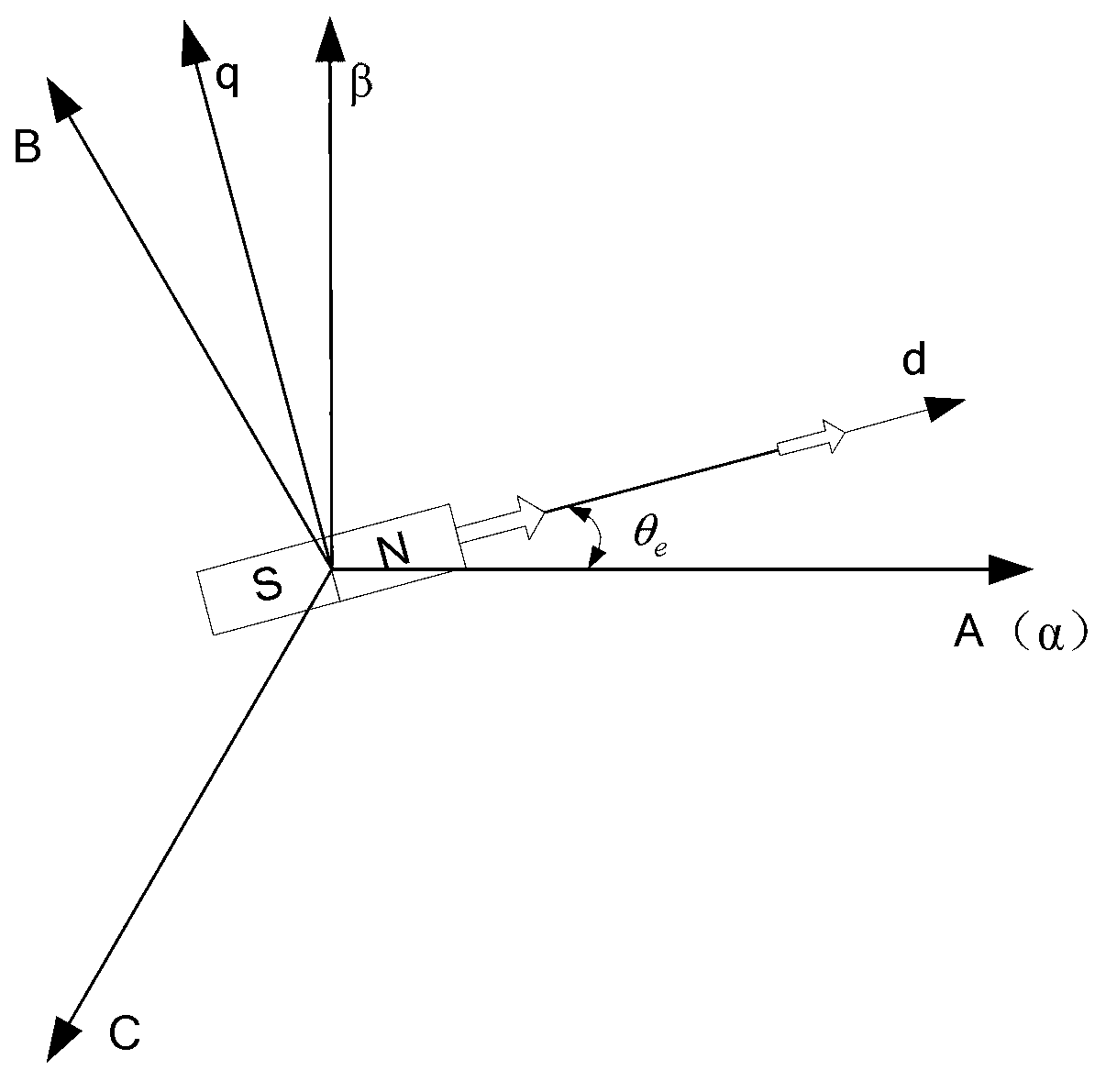
Position observation device and method for rotor of built-in permanent magnetic synchronous motor based on adaptive filtering
ActiveCN103199779AInhibit the influence of pulsation errorImprove controlVector control systemsDynamo-electric converter controlSynchronous motorPosition angle
The invention provides a position observation device and a position observation method for a rotor of a built-in permanent magnetic synchronous motor based on adaptive filtering, and belongs to the field of motor control, solving the problem of the convectional model method that six-time harmonic pulsation observation error is contained in the acquired rotor position angle observation value. The position observation device and the position observation method are respectively an adaptive notch filtering filter signal processing device and an adaptive notch filtering filter signal processing method based on the least mean square algorithm, and the device and the method are used for removing the six-time rotor pulsation error in the control technology model method applicable to a middle and high speed position-free sensor permanent magnetic synchronous motor. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring equivalent back electromotive force information through the model method; regulating through the adaptive notch filtering filter based on the least mean square algorithm; then carrying out normalization processing on the back electromotive force information; and finally acquiring a rotor position observation value through a phase-locked loop. The device and the method provided by the invention are simple and easy to implement, can be used for effectively inhibiting the influence of the six-time pulsation error in the rotor position observation value and improving the performance of the position-free sensor permanent magnetic synchronous motor, and are applicable to a permanent magnetic synchronous motor control system.
Owner:哈工科讯(沈阳)智能工业技术有限公司
Active noise reduction method for automobile
ActiveCN104616667AReduce correlationReduced stabilitySpeech analysisSound producing devicesSound sourcesEngineering
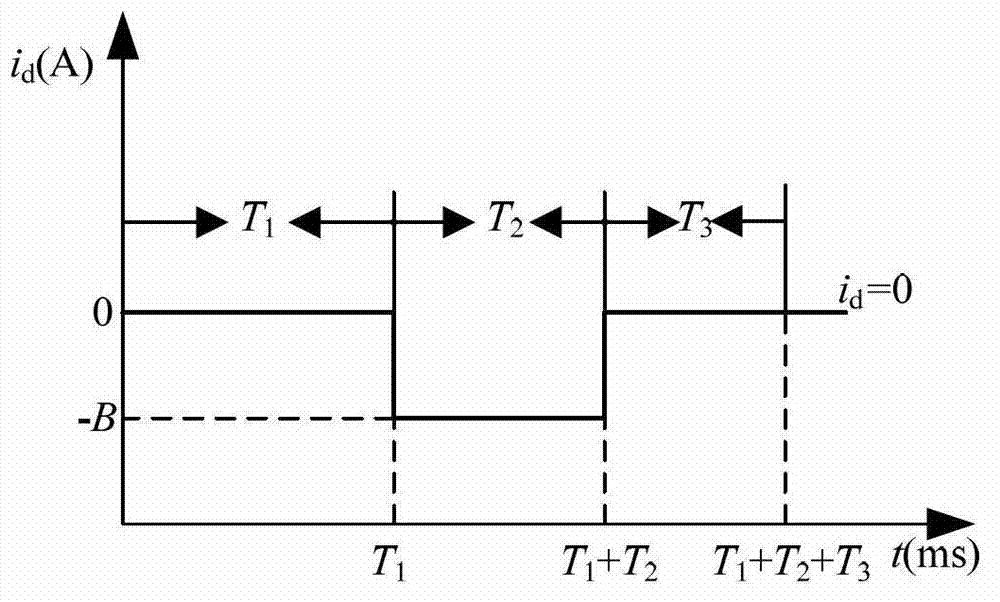
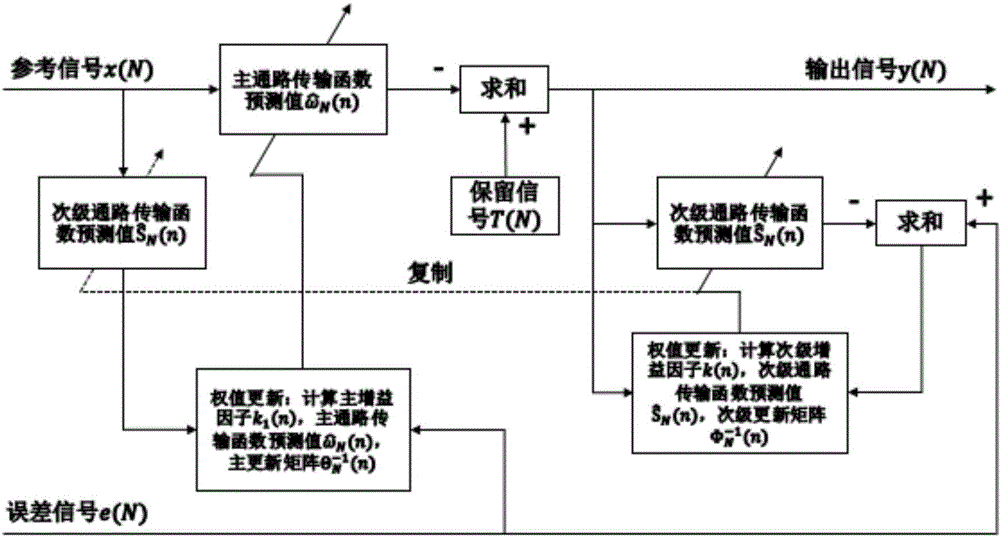
The invention relates to an active noise reduction method for an automobile and belongs to the voice signal processing technical field. The active noise reduction method guides the secondary sound source and adopts the self-adaptive algorithm for controlling the sound signal sent by the secondary sound source, and the outputted secondary sound wave after self-adaptive convergence at the noise reducing point has constant amplitude and reversal phase with the noise at the point for getting the noise reducing target. The algorithm and the method structure are improved based on the original active noise reduction method, the recursive least square method is used for replacing the least mean square algorithm as the core self-adaptive algorithm for the main path transfer function estimation and the secondary path transfer function estimation; the method has strong capability of eliminating the pulse noise and non-stationary noise and has good noise reducing error and noise reducing feed, the stability problem caused by the signal dependency is improved for the retaining signal in the automobile, the useful signal is kept while the noise is reduced and the signal to noise ratio is greatly improved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Forward and reverse calibration for ground-based beamforming
ActiveUS20100177678A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission path divisionMean squareCommunications system
Methods and systems for calibrating the return and forward links of a satellite communication system are provided according to embodiments of the invention. The phase and / or amplitude variations caused by the return and forward links are calculated and / or estimated to aid in beamforming, such as ground-based beamforming. Calibration earth stations, distributed within one or more beam patterns, may be used to transmit calibration codes to the gateway to calibrate the return link. Return links variations may be estimated using a weighted minimum mean square algorithm at the gateway. Forward links may be calibrated with calibration codes transmitted from the gateway through a hybrid matrix to at least one calibration station. Forward calibration links may also calibrate for temperature-dependent signal variations such as diplexer variations at the satellite.
Owner:VIASAT INC
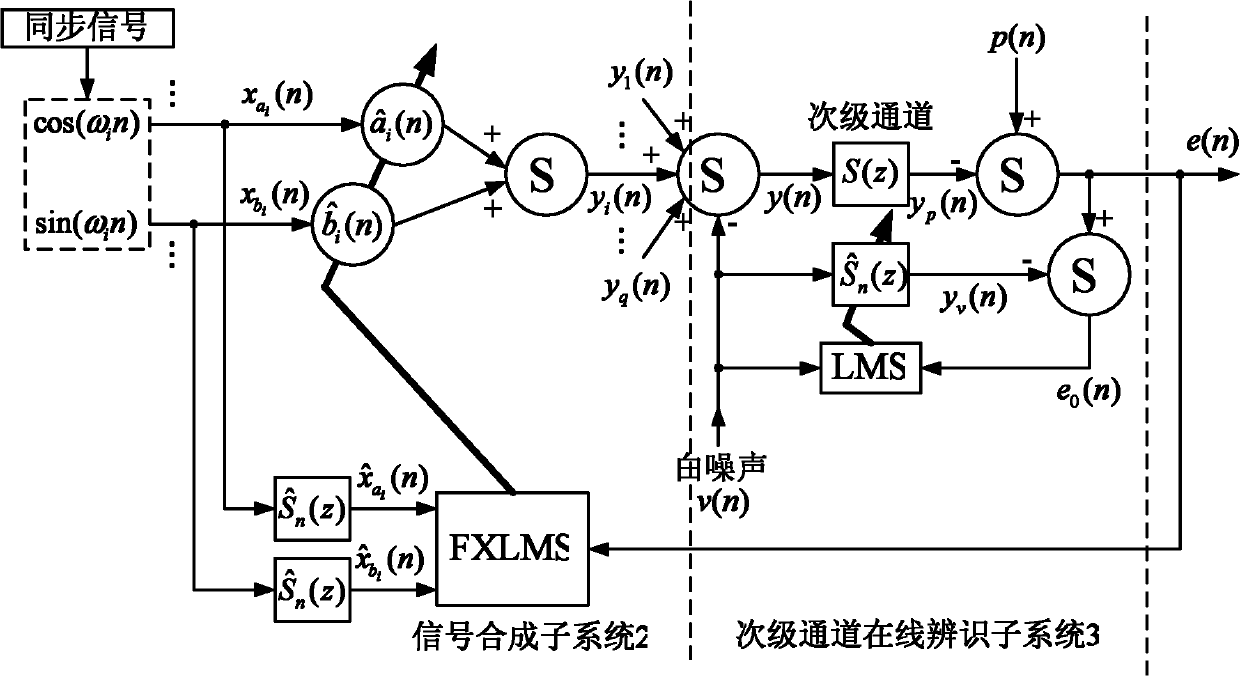
Method for improving performance of feedforward narrow-band active noise control system
InactiveCN101976560AImprove performanceReduce residual noise energy impactSpeech analysisSound producing devicesNoise controlSteady state
The invention discloses a method for improving the performance of a feedforward narrow-band active noise control system, which relates to the field of active noise control, and aims at the situation that the reference signal frequency acquired by a non-acoustic sensor in the feedforward narrow-band active noise control system with a minor access road on-line identification function and the target noise actual frequency are imbalanced and the problem the auxiliary noise brought by the minor access road on-line identification seriously hinders the reduction of the residual noise energy of the system. The control system comprises a frequency compensation subsystem, a signal synthesis subsystem and a minor access road on-line identification subsystem; the frequency compensation subsystem comprises a second-order autoregression module and a least mean square (LMS) algorithm module; the frequency compensation subsystem transmits the cosine component and sinusoidal component of the adjusted reference signal of an ith frequency channel to the signal synthesis; when the frequency imbalance reaches above 50%, the target noise can still be effectively restrained; and when in a steady state, the residual noise energy of the system is reduced to an ideal level, so that the performance of the control system can be further improved and is closer to the practice.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
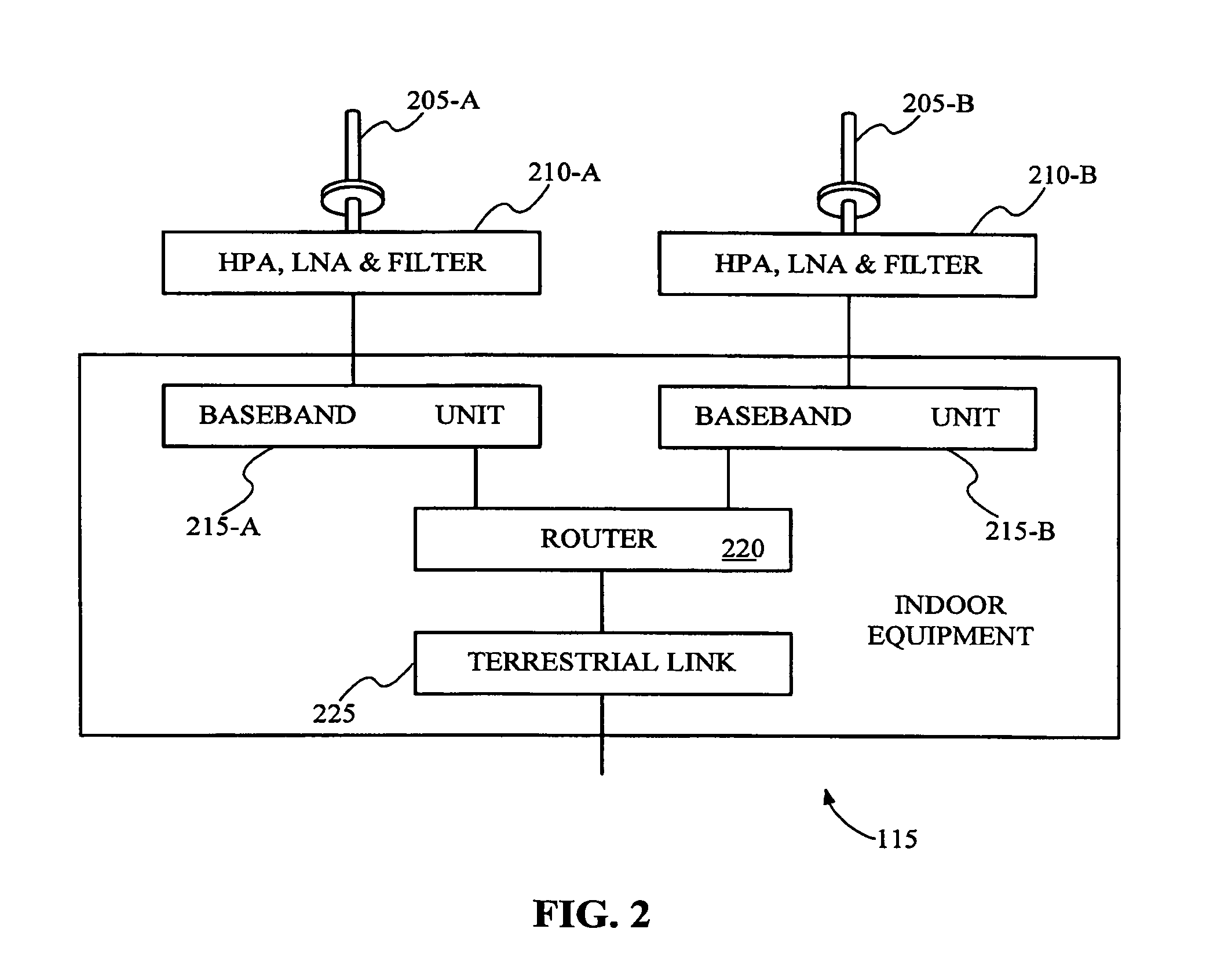
Digital adaptive equalizer for T1/E1 long haul transceiver
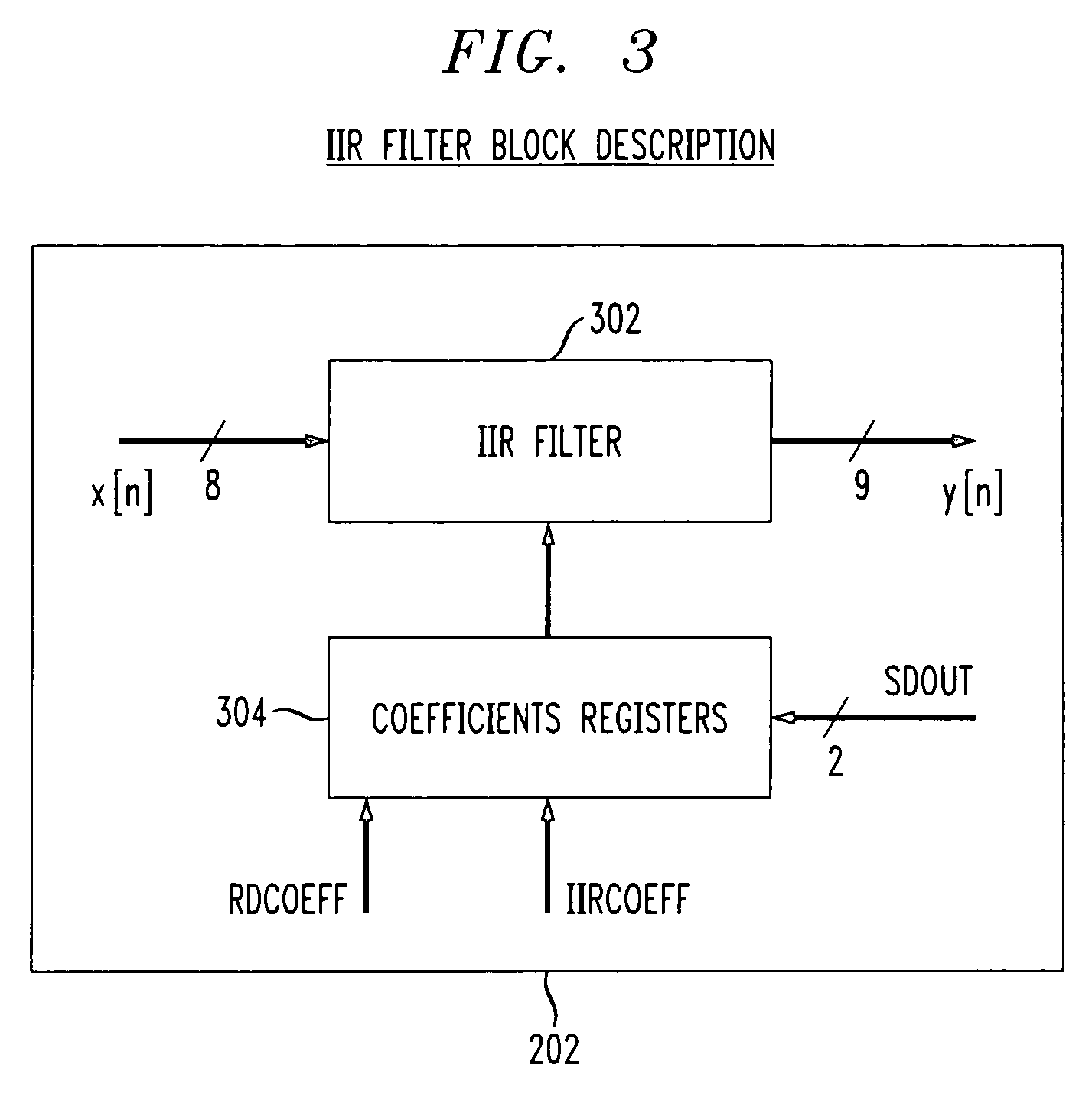
InactiveUS6980592B1Exact matchMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsFinite impulse responseIir filtering
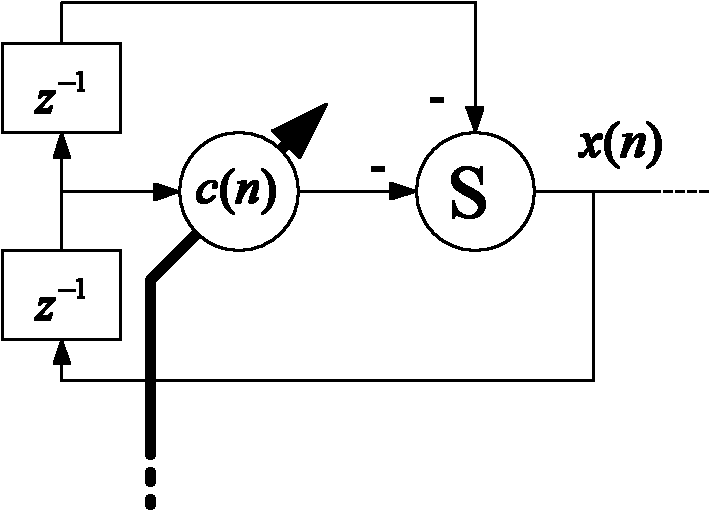
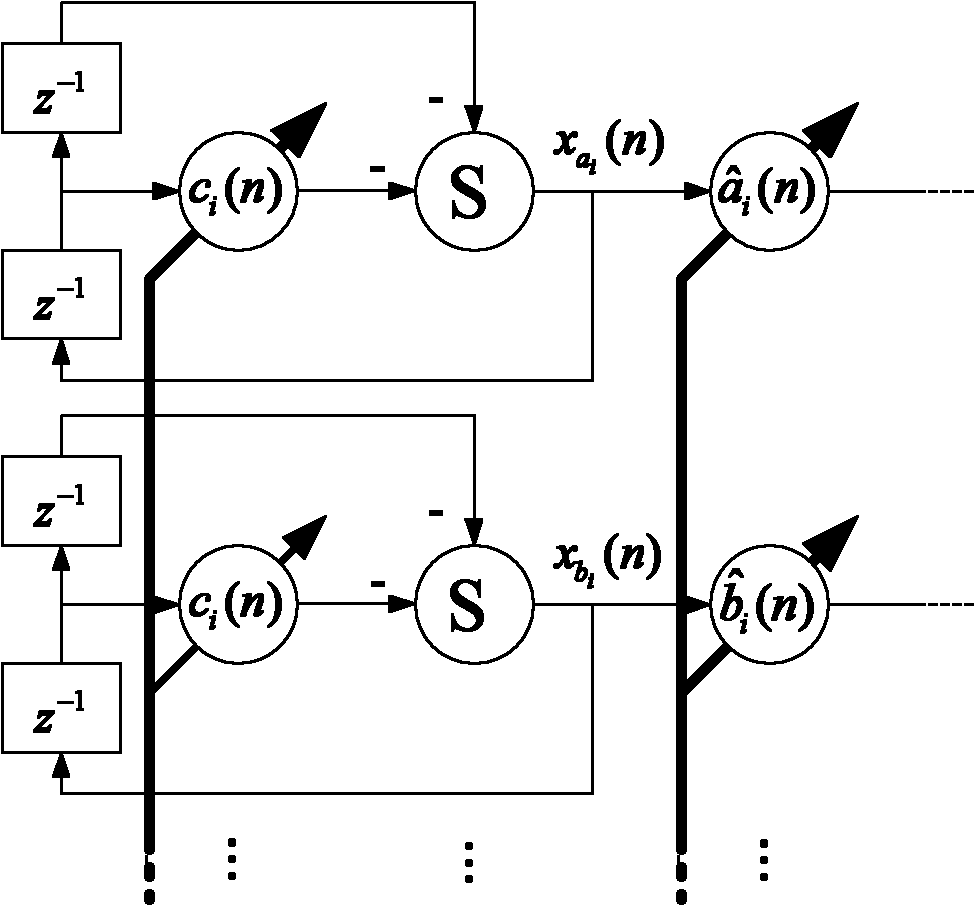
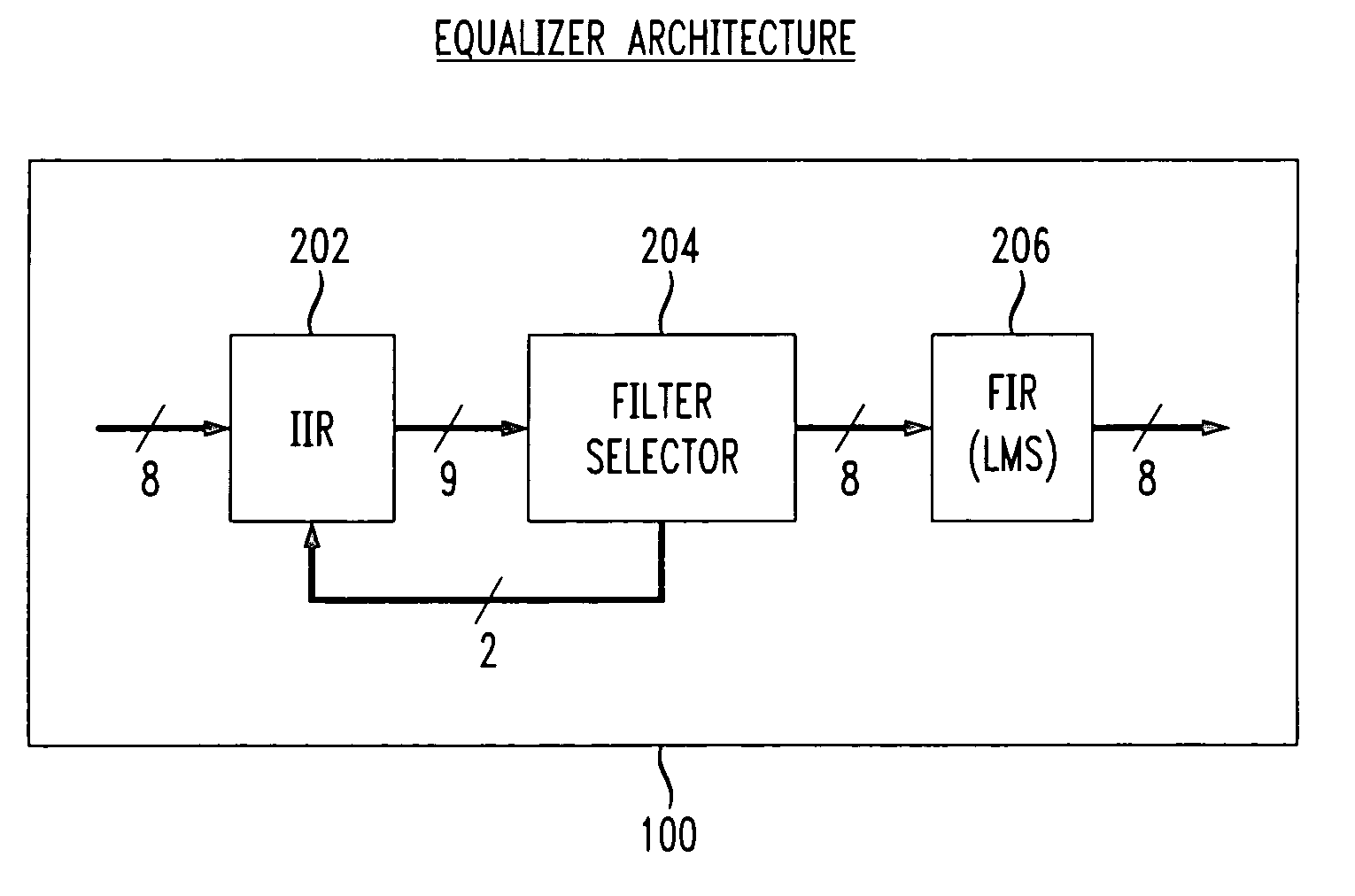
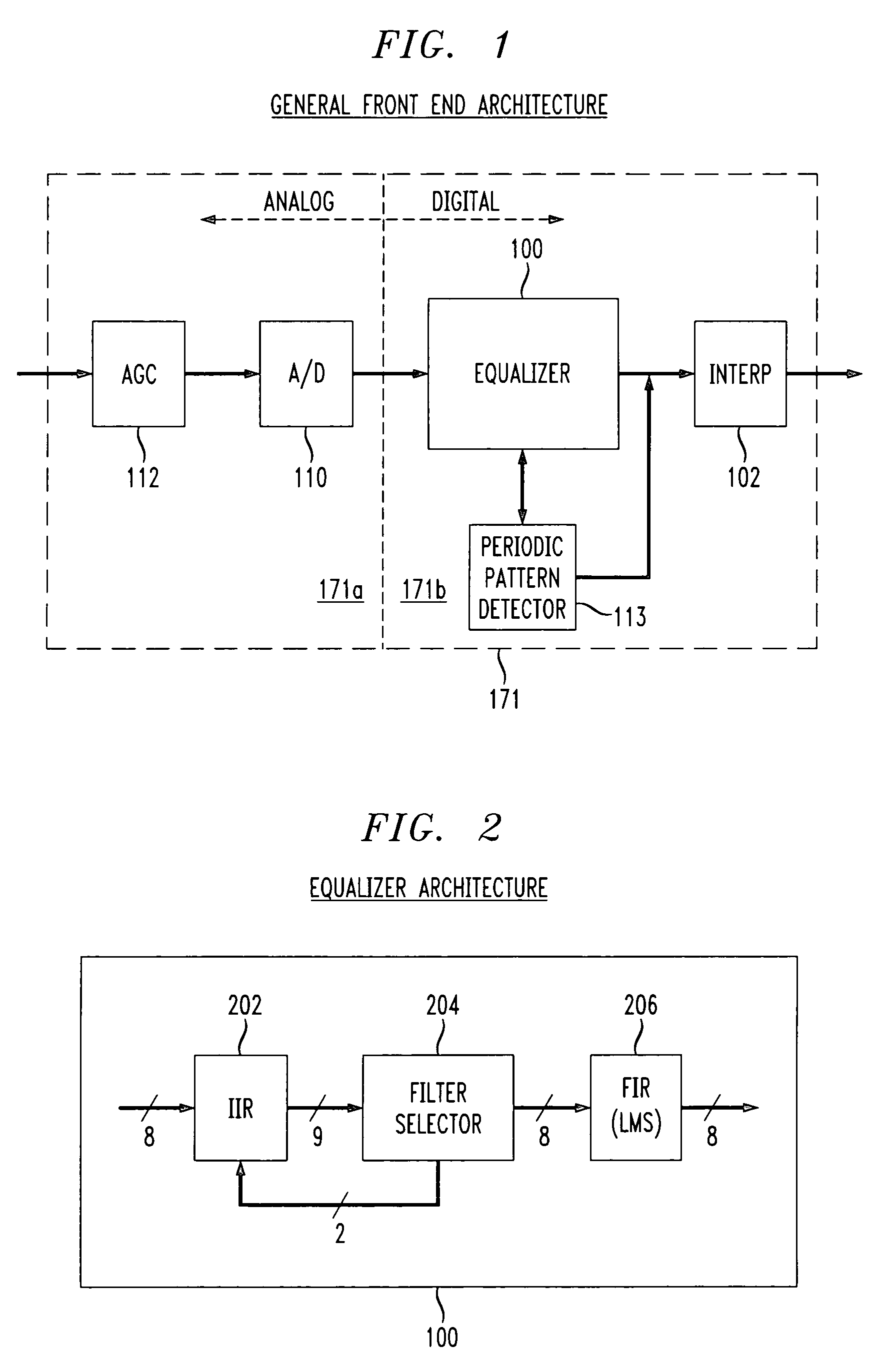
The present invention relates to the implementation of a digital adaptive equalizer for a T1 / E1 long haul transceiver which is capable of adapting to a wide range of cable types, cable lengths, and / or other data transmission impairments, particularly when the transmission path type and / or length are unknown. The digital adaptive equalizer contains two filter blocks, i.e., an IIR filter and a FIR filter, together with a filter selector block to select a best IIR filter based on an error estimation of the received data. Only a few sets of coefficients are found to be necessary to allow proper digital equalization of a large number of cable types and / or lengths. A filter selector block selects a desired set of coefficients corresponding to the optimum IIR filter. The coefficients may be programmed into volatile memory (e.g., RAM) or non-volatile memory (e.g., Flash). Alternatively, the coefficients may be hardwired into the IIR filter. The back end of the digital adaptive equalizer contains an adaptive finite impulse response (FIR) filter. In the disclosed embodiment, the FIR filter uses a least mean square (LMS) algorithm for adaptation to the unknown or changed T1 or E1 transmission channel or medium. The adaptive FIR filter adjusts the output from the IIR filter to accurately match the inverse response of the unknown channel used to transmit the received T1 / E1 signal. Equalization may be temporarily frozen if periodic patterns are detected in the received T1 / E1 signal. A restored T1 or E1 signal is output from the FIR filter, and thus from the digital adaptive equalizer.
Owner:INTEL CORP
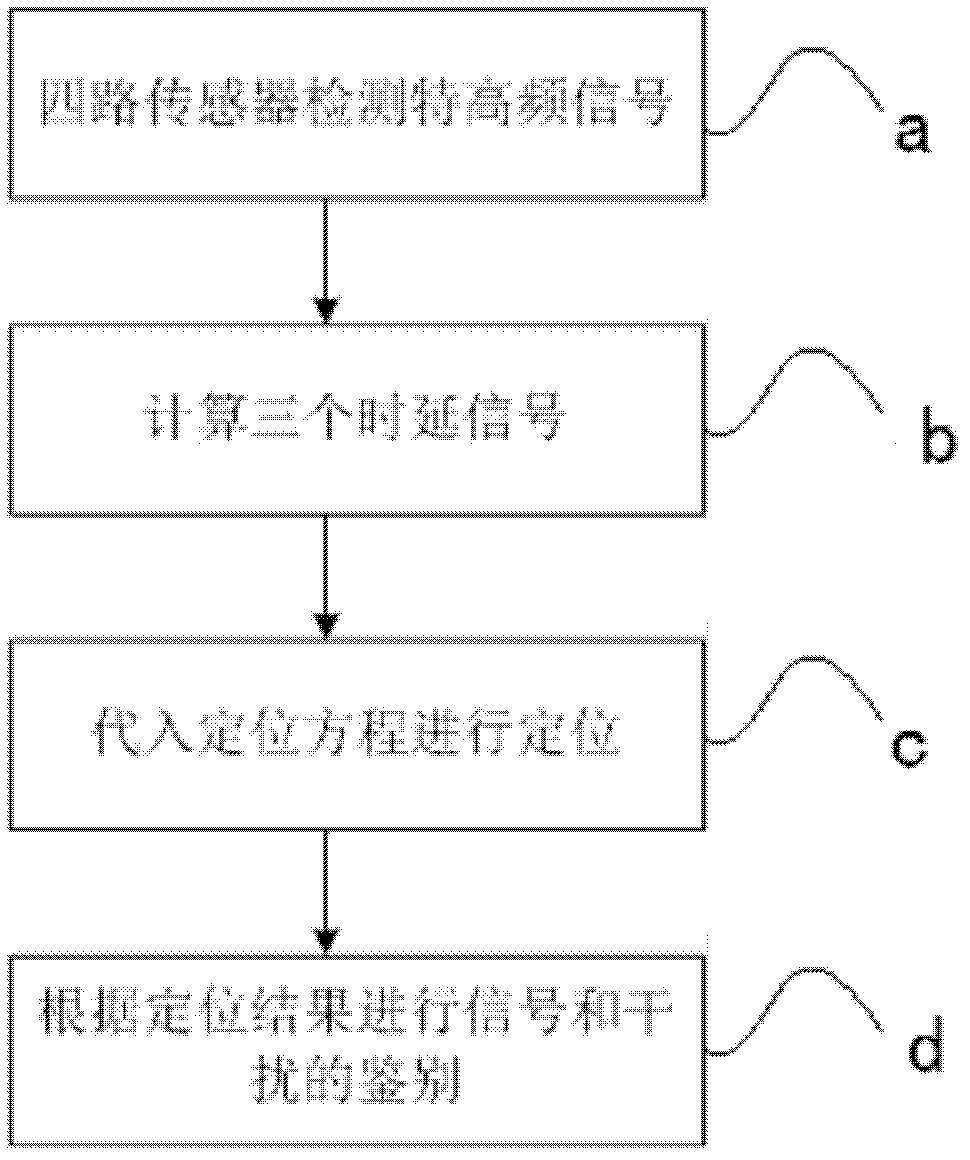
Method for identifying signal and interference signal in ultrahigh frequency partial discharge detection in electrical equipment
ActiveCN102841294AAchieve and improve identificationImprove reliabilityTesting dielectric strengthMean squareTime delays
The invention discloses a method for identifying signals and the interference signals in ultrahigh frequency partial discharge detection in electrical equipment. The method comprises the following steps of: a. acquiring ultrahigh frequency signals near a device to be detected by using four sensors so as to obtain four paths of ultrahigh frequency partial discharge signals; b. carrying out the calculation of time delay by adopting a self-adaptive time delay calculation method based on a minimum mean square algorithm according to the obtained four paths of ultrahigh frequency signals, so as to obtain three time delay values; c. substituting the three time delay values obtained from the calculation into a positioning equation set, and solving the position of a discharge power supply by using a simulated annealing algorithm; and d. judging whether a detected signal comes from the interior or the exterior of the device according to a positioning result of the discharge power supply, so as to identify a partial discharge signal and an interference signal. By adoption of the method, the identification of the discharge signals and the interference signals in the partial discharge detection of the electrical equipment is realized and improved, and particularly the identifications to the discharge signals of periphery equipment and the interference of the equipment to be detected are realized.
Owner:STATE GRID HUBEI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Cable location system using magnetic induction
InactiveUS20030001556A1Current/voltage measurementElectric/magnetic detection for transportElectrical conductorPhase shifted
A method of electronically isolating a conductor by sensing a current signal in the conductor, adjusting the current signal to yield an adjusted signal, and applying the adjusted signal to the conductor to oppose the current signal. Amplifying the signal, as well as phase-shifting the signal may adjust the current signal. The current signal may be sensed using magnetic induction, and the adjusted signal applied to the conductor using magnetic induction as well. The method is carried out using a clamping device that can further evaluate an environment of the conductor, by randomly changing a magnitude and phase of a test signal applied to the conductor, and examining a received signal in response to the changes. A tracking error in the adjusted signal can be handled by predicting a next required phase shift. Prediction coefficients can be calculated utilizing a least means square algorithm. The invention is particularly applicable to the location of obscured (e.g., buried) conductors, and can be incorporated into a cable locator system that applies a trace signal to the target cable to be located. When this trace signal bleeds onto adjacent cables, the clamping devices of the present invention can be used to electronically isolate those cables, i.e., reduce or eliminate unwanted currents arising from coupling with the trace signal. A conventional receiver can then be used to trace the path of the target cable without interference from the nearby cables.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Variable step-size least mean square method for estimation in adaptive networks
The variable step-size least mean square method for estimation in adaptive networks uses a variable step-size to provide estimation for each node in the adaptive network, where the step-size at each node is determined by the error calculated for each node, as opposed to conventional least mean square algorithms used in adaptive filters and the like, where the choice of step-size reflects a tradeoff between misadjustment and the speed of adaptation.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Multi -MIC noise reduction method used for mobile phone
InactiveCN106101351AImprove sound qualityImprove noise reductionSpeech analysisTelephone set constructionsSpectral subtractionFiltration
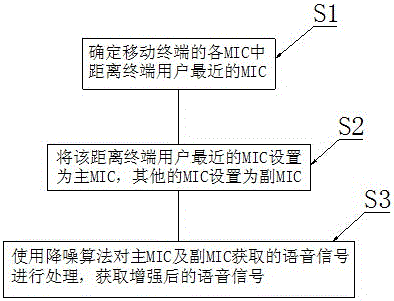
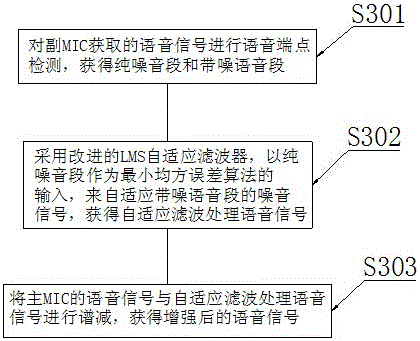
The invention discloses a multi-MIC noise reduction method used for a mobile phone. The multi-MIC noise reduction method comprises the steps of S1, determining an MIC, which is closest to a terminal user, from all the MIC of the mobile terminal; S2, setting the MIC closest to the terminal user as a primary MIC and other MIC as secondary MIC; and S3, processing voice signals obtained by the primary MIC and the secondary MIC by using a noise reduction algorithm so as to obtain enhanced voice signals, wherein the step S3 specifically comprises the sub-steps of S301, performing voice endpoint detection for the voice signals obtained by the secondary MIC so as to obtain a pure noise segment and a noise-carrying voice segment, S302, self-adapting to the noise signals in the noise-carrying voice segment by adopting an improved LMS self-adapting filter and regarding the pure noise segment as the input in a least mean square algorithm of noise so as to obtain the voice signals being subjected to the self-adaptive filtration processing, and S303, performing spectral subtraction for the voice signals of the primary MIC and the voice signals being subjected to the self-adaptive filtration processing so as to obtain enhanced voice signals. The multi-MIC noise reduction method used for the mobile phone is good in noise reduction effect and can improve the tone quality of a mobile terminal.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fast self-optimization self-adaptive signal processing method and device of coherent communication technology
ActiveCN101272188AReduce overheadGood signal processing performanceModulated-carrier systemsSynchronising arrangementSelf adaptiveComputer science
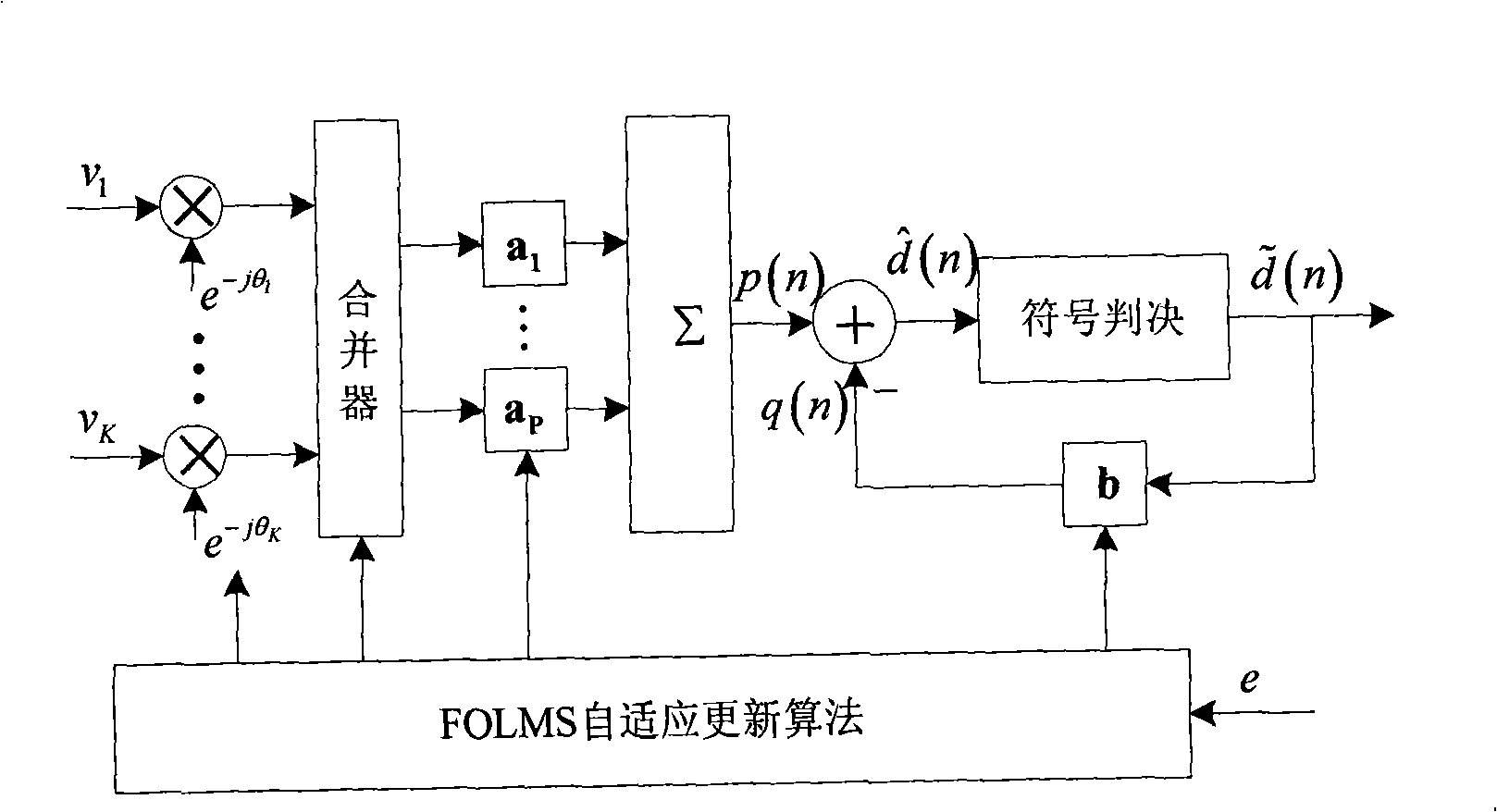
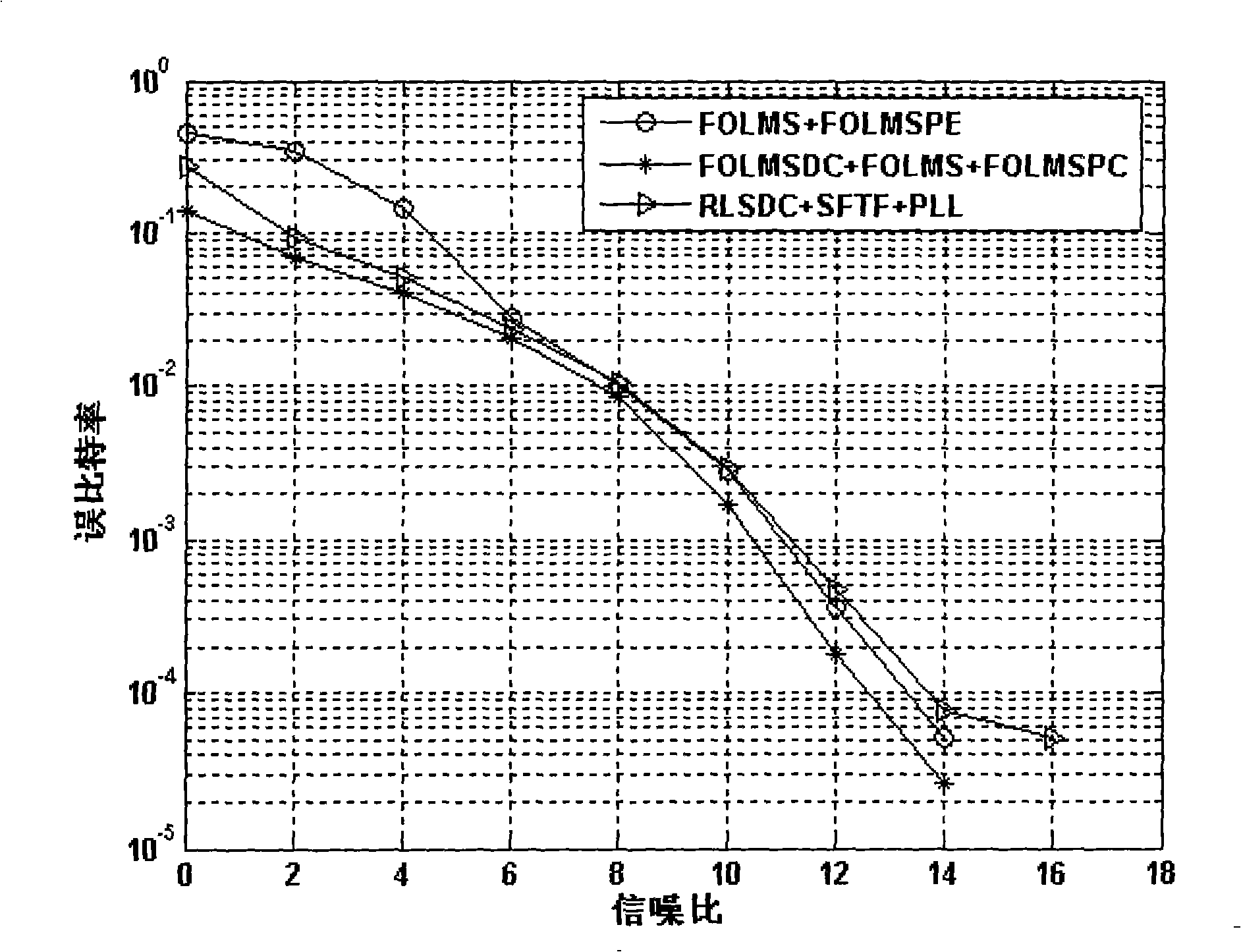
The invention discloses a fast self-optimizing self-adaptive signal processing method and processing device of a coherent communication technology as well as a coherent communication machine which comprises the processing device. The method comprises the steps: a signal is received; phase compensation is carried out on the signal; the signal is simplified and outputted through a diversity combiner; the signal that is simplified and outputted is processed through an equalizer; the signal outputted by the equalizer is carried out symbol judgment, the signal is outputted and simultaneously feeding back to the equalizer to generate an error signal. The device comprises a phase compensation unit, a diversity combiner unit, a self-adaptive judgment feedback equalizer unit, an error signal unit and a self-adaptive updating control unit that are sequentially connected in order. The self-adaptive updating control unit adopts a fast self-optimizing LMS algorithm to update the phase, the diversity combiner parameters and the equalizer parameters. The invention has a better signal processing performance, a lower bit error rate as well as a less calculation amount and saves the hardware cost.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
An aero-engine high-pressure rotor assembly error prediction method
InactiveCN109948207AImprove forecast accuracyCalculation speedNeural learning methodsSpecial data processing applicationsAlgorithmNetwork model
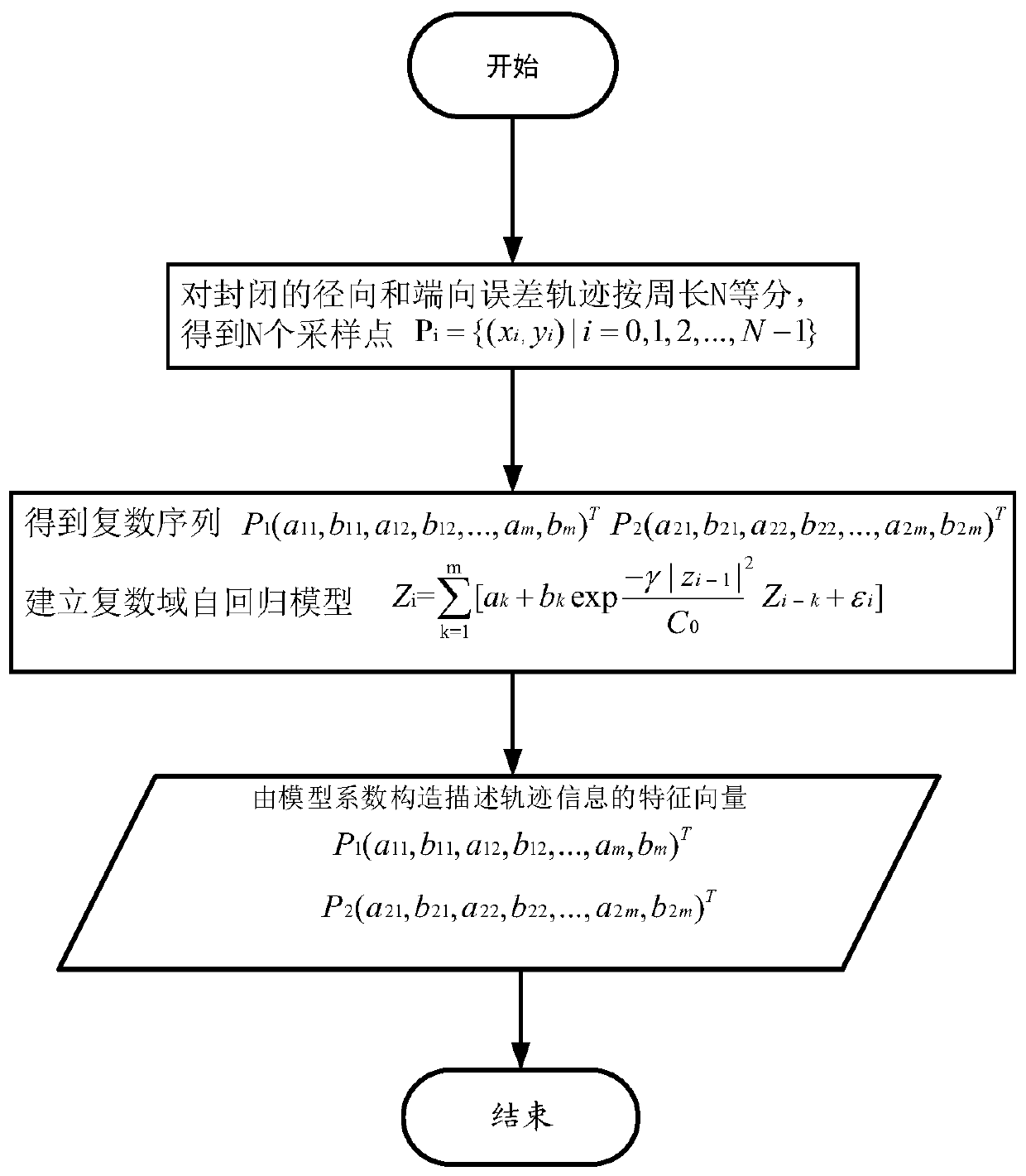
The invention discloses an aero-engine high-pressure rotor assembly eccentricity prediction method. The method comprises the following steps: measuring radial and end jump error contour tracks of a matching surface; carrying out feature extraction on the contour track by using an image recognition method; establishing a complex domain autoregression model to obtain an error track feature vector; taking the seam allowance error feature vector as input, the eccentric position coordinate as output, the Gaussian function as a primary function of the intermediate layer, determining the center position of the hidden layer through K-means dynamic clustering, and estimating the weight of the output layer by using a minimum mean square algorithm to construct an RBF radial primary function neural network model; and substituting the measured data into the model for learning and training, performing error evaluation and model correction by using finite element simulation data, and determining neural network parameters so as to complete aero-engine high-pressure rotor assembly eccentricity prediction. According to the method, the seam allowance morphology error and the assembly deformation areconsidered, and the assembly eccentricity of the high-pressure rotor is predicted more quickly and more accurately.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
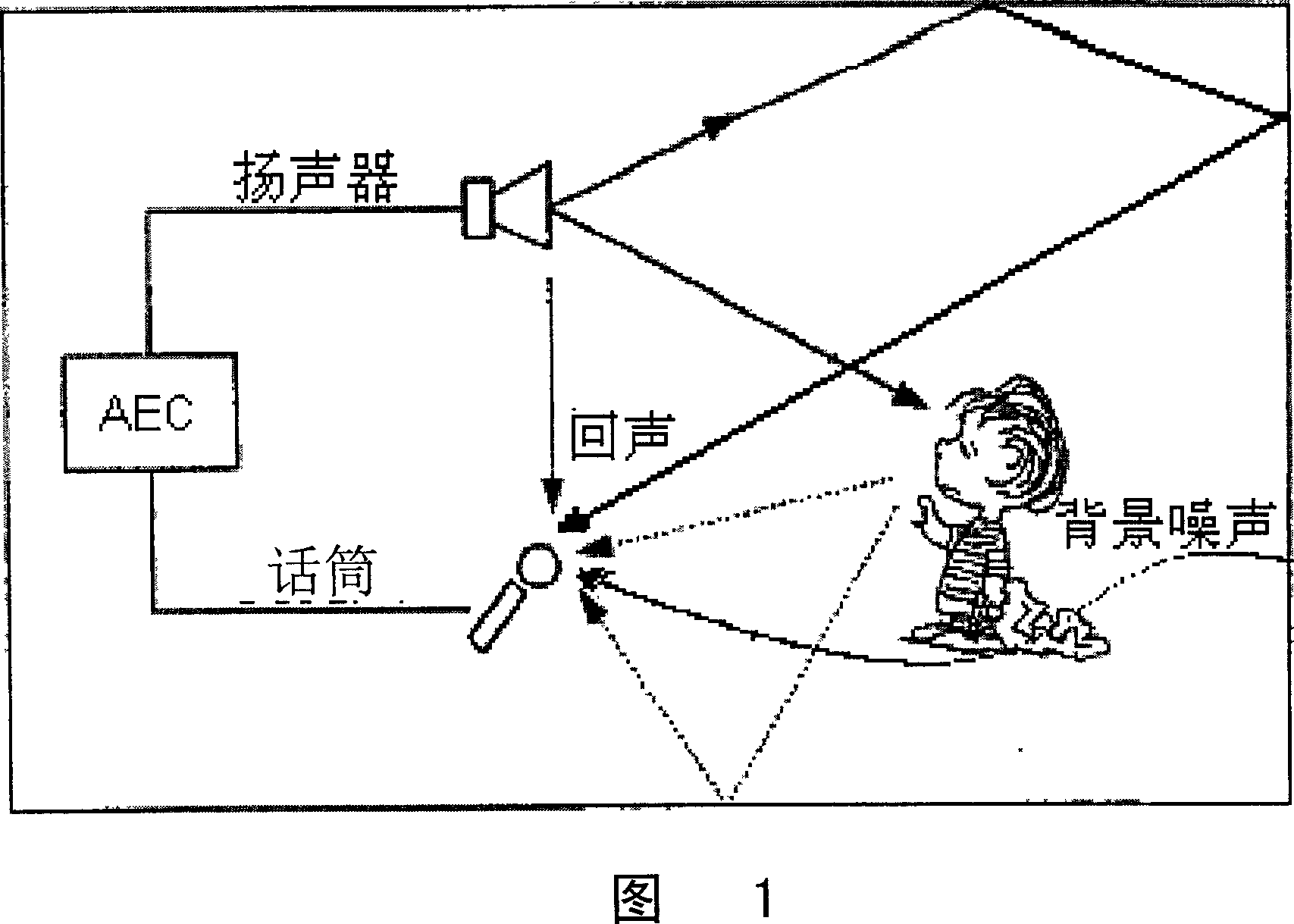
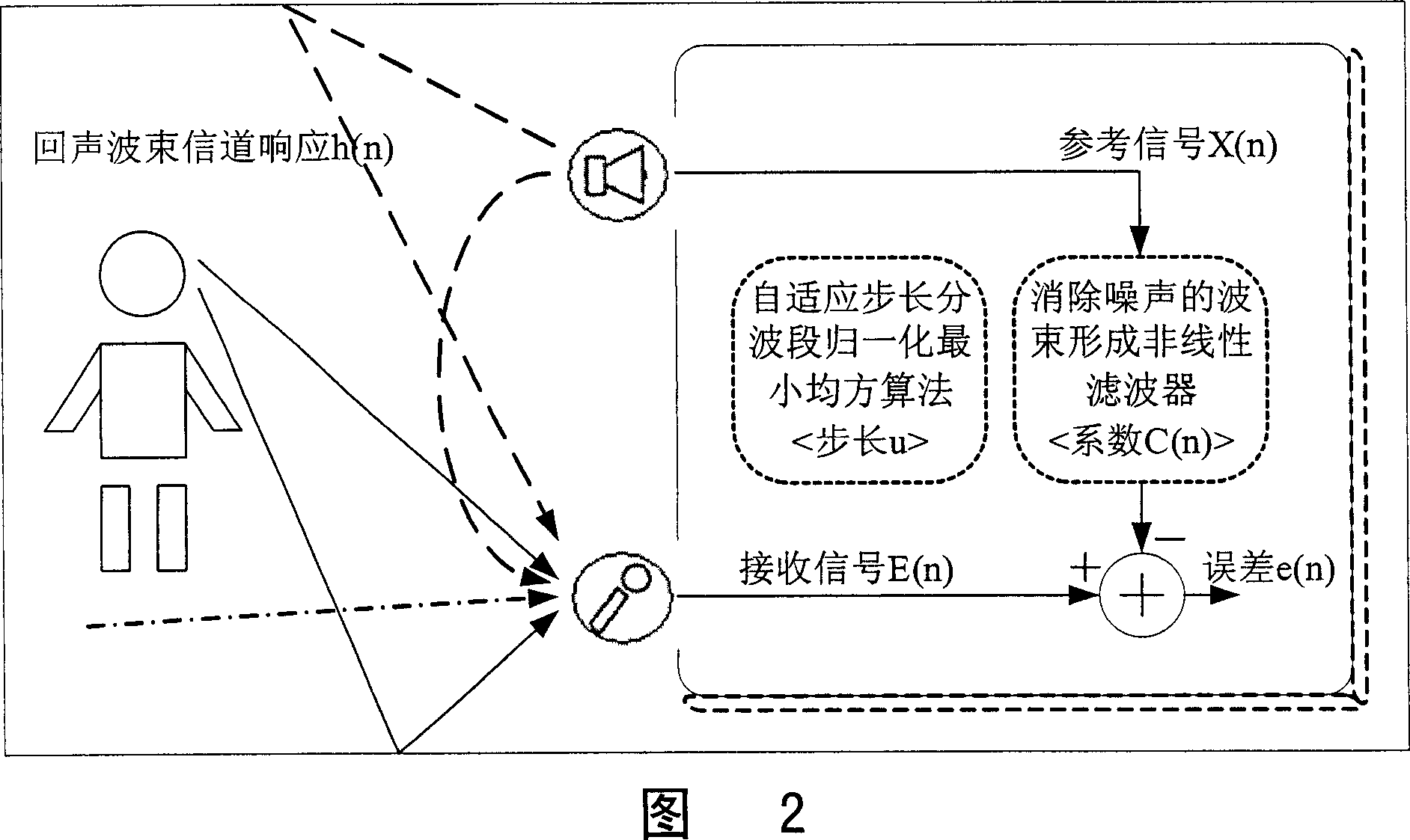
Acoustic echo removing method
InactiveCN1956480AFix the echo problemCancel echoTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsMean squareLinear filter
This invention relates to a method for eliminating acoustic echo including the following steps: the minimum mean square algorithm of adaptive step wave band standardization, eliminating wave beams of noises to form non-linear filter to eliminate acoustic echoes. This invention applies an exclusive adaptive step non-linear filter technology to divide signals into multiple wave bands for process and alter steps adaptively according to the echo environment to eliminate echoes to increase convergence speed and reduce radiation speed to improve the ability for eliminating echo.
Owner:SHANGHAI BEILING
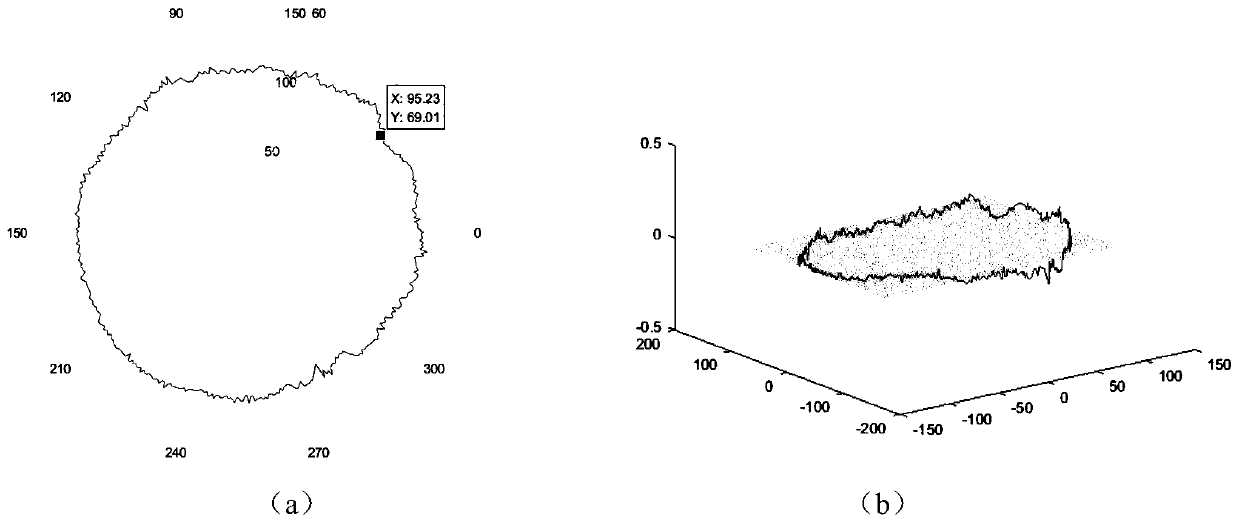
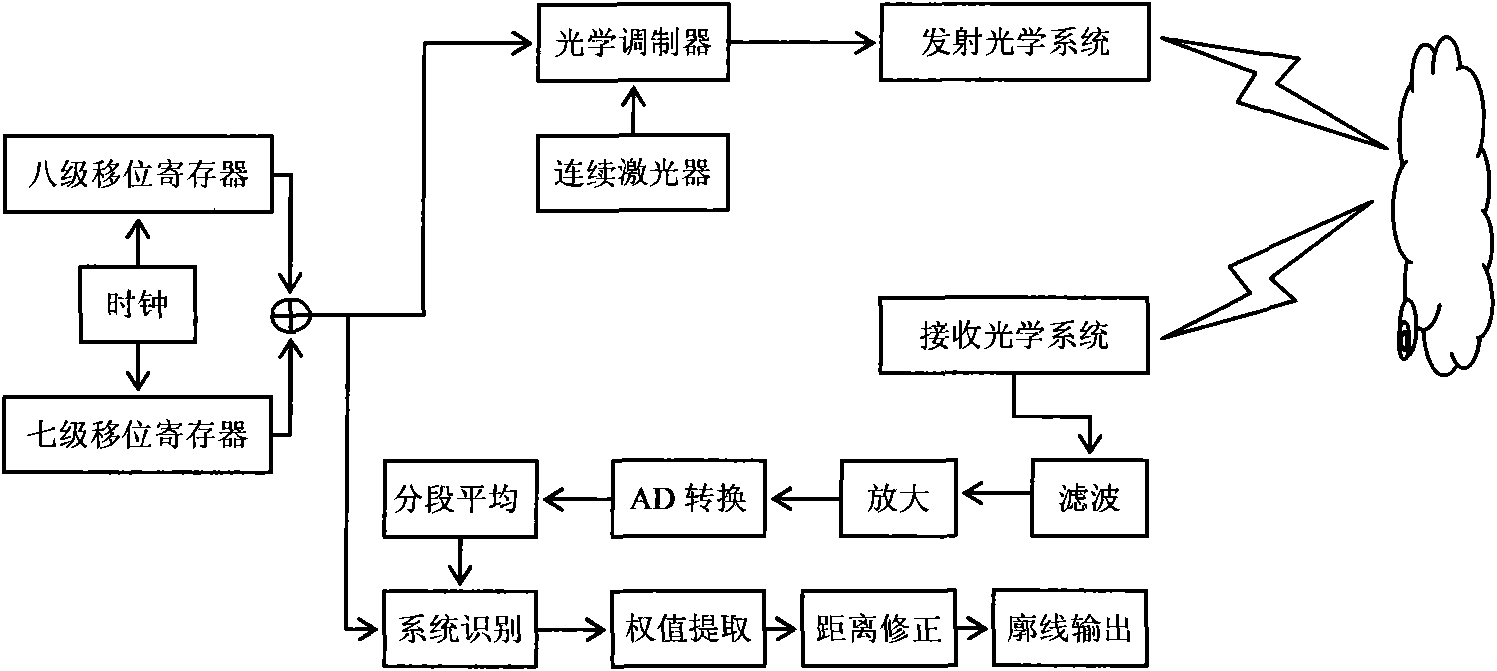
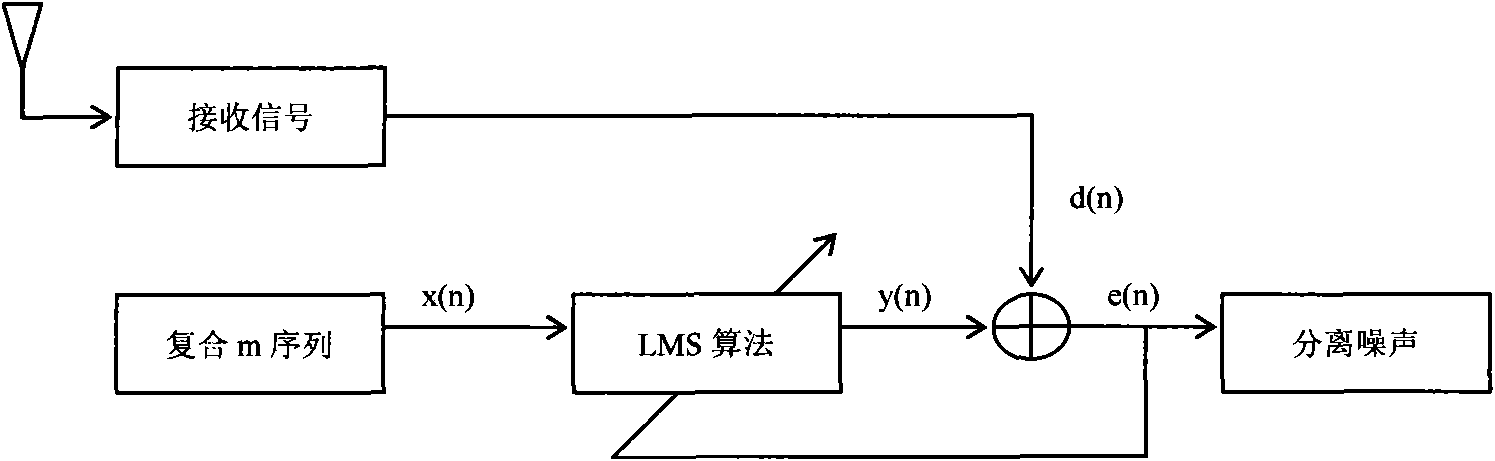
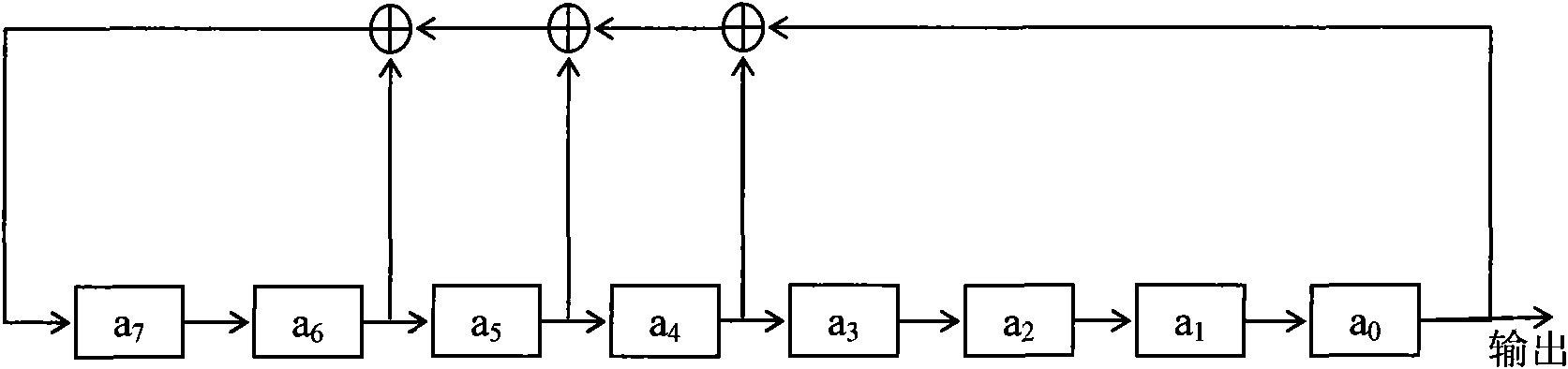
Laser cloud-detection radar signal self-adaptive identification method based on least mean square algorithm
InactiveCN101581787AEfficient extractionSolve design problemsElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationPeak valueCircuit design
The invention relates to a laser cloud-detection radar signal self-adaptive identification method based on a least mean square algorithm, which synchronously compound two m sequences with different cycles so as to generate a compound pseudo-noise sequence and synchronously transmit the sequence to a continuous modulation laser transmitting terminal and a signal receiving terminal respectively; the signal receiving terminal carries out sectional accumulation average calculating operation to a received signal, then adopts an LMS algorithm to substitute the result of the sectional accumulation average calculating operation and the compound pseudo-noise sequence, and finally establishes a laser atmospheric scattering system model by utilizing the convergence result obtained by the LMS algorithm. The method effectively solves the circuit design problem caused by requirement on extremely high pulse peak value power and extremely narrow pulse when a pulse modulating laser radar is applied to the cloud-detection, and also the problems that the receiving terminal needs to collect a large quantity of samples for accumulation and average and the computation workload is large, the resolution is low, the signal-to-noise ratio is low and the like, thus greatly improving the measuring efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
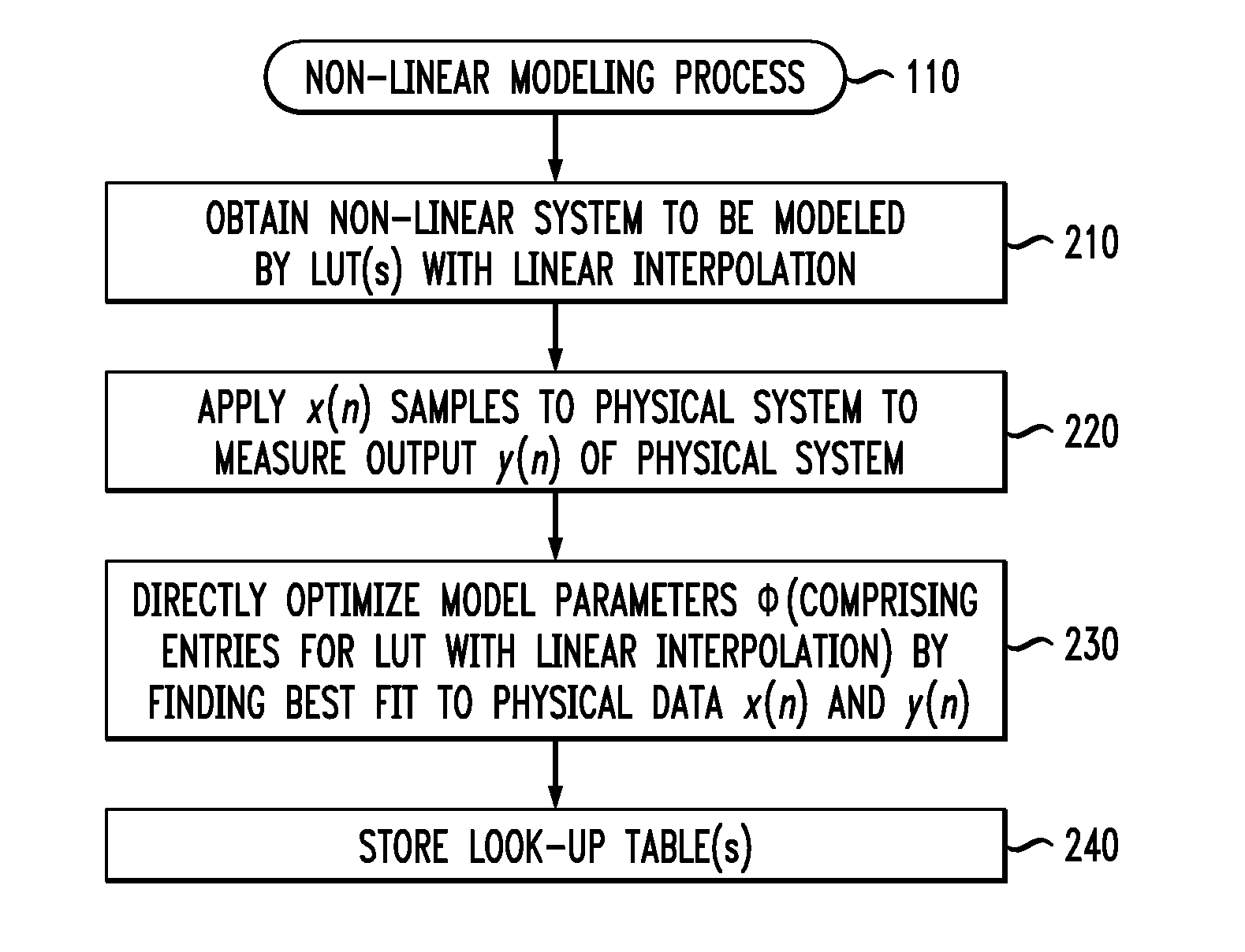
Non-Linear Modeling of a Physical System Using Direct Optimization of Look-Up Table Values
ActiveUS20140316752A1Minimum mean square errorSimple technologyError preventionModulated-carrier systemsDirect computationMean square
Techniques for non-linear modeling of a physical system are provided using direct optimization of look-up table values. A non-linear system with memory is modeled by obtaining physical data for the non-linear system by applying a set of input samples x(n) to the non-linear system and measuring an output y(n) of the non-linear system; directly computing parameters Φ of a memory model for the non-linear system from the physical data, wherein the memory model comprises one or more look-up tables having linear interpolation and wherein the parameters Φ produce a substantially minimum mean square error; and providing the parameters Φ for storage as entries in the one or more look-up tables. The mean square error can be determined, for example, using one or more of a least squares algorithm, a least mean square algorithm and a recursive least squares algorithm. The look-up tables are optionally used in a processor instruction to implement digital pre-distortion.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Smart antenna self-adapting interference suppression method based on least square-lowest mean square
InactiveCN101572574AReduce computationThe amount of calculation increasesSpatial transmit diversityTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFrequency changerFrequency spectrum
The invention relates to a smart antenna self-adapting interference suppression method based on least square-lowest mean square, which is an interference suppression algorithm based on training sequences; and by combining the least square algorithm with the lowest mean square algorithm, the method increases the velocity of convergence of the least mean square algorithm. The method includes the following steps: radio-frequency signals received by array antenna are converted into IF signals by a down converter; the IF signals are processed by the operations of analogue-to-digital conversion and digital down-conversion to obtain zero IF digital signals; the zero IF digital signals obtained in the step 2; and the local training sequence are utilized for carrying out corresponding processing to obtain local reference signals by computation delay; the low snapshot least square algorithm is utilized for calculating the initial weight vector of an aerial array; the weight vector calculated in the step 4 is used as the initial weight vector of the least mean square algorithm, and the least mean square algorithm is utilized for updating the aerial array weight vector; and the array weight vector calculated in the step 5 is adopted for the interference suppression of user data. The method achieves the purposes of increasing the availability of frequency spectrum of the system and reducing the complexity of the system.
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
Method for suppressing acoustic feedback in a hearing device and corresponding hearing device
ActiveUS20110188686A1Adaptation speed decreaseReduce signal amplitudeSignal processingTransducer acoustic reaction preventionAdaptive filterHearing apparatus
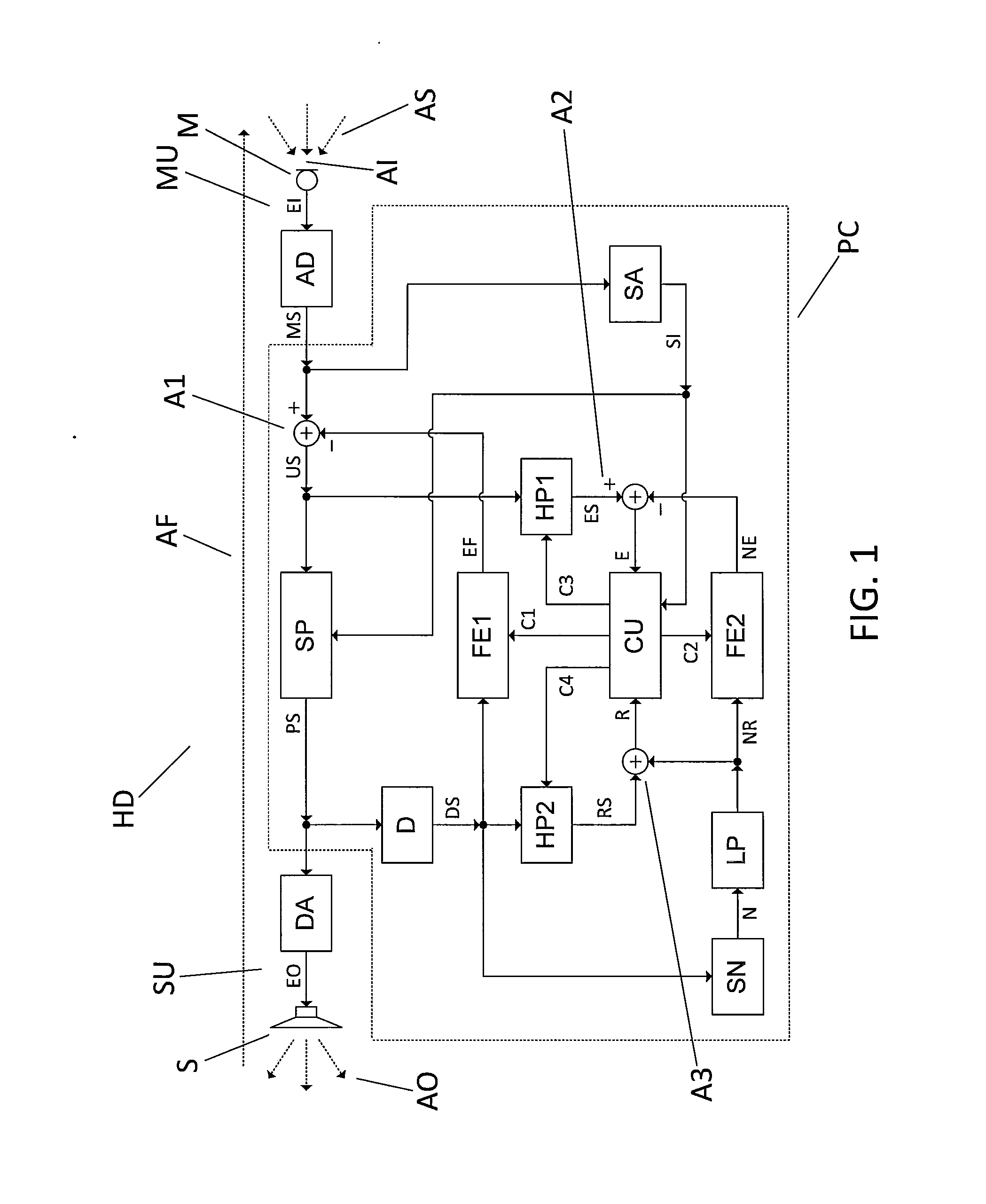
A hearing device (HD) incorporates a method for adaptive cancellation of acoustic feedback (AF). The method comprises generating an estimated feedback signal (EF) and subtracting the estimated feedback signal (EF) from the microphone signal (MS) before feeding it to a signal processor (SP) providing the primary hearing device function. The estimated feedback signal (EF) is generated in an adaptive filter (FE1), which is controlled using a least-mean-square algorithm, which operates on an error signal (E) and a reference signal (R). The algorithm may behave erroneously if the feedback path changes while a signal with low HF content, such as speech, is received. In this case, the hearing device (HD) will not be able to quickly adapt the HF characteristic of the adaptive filter (FE1) to the changed conditions. The adaptive filter (FE1) may thus have an incorrect HF gain when a subsequent signal with high HF content is received. This may lead to whistling or, alternatively, to an unwanted suppression of the subsequent signal. The problem is solved by modifying a filter function (H) applied to the error signal (E) and to the reference signal (R) in dependence on estimated relative amounts of high- and low-frequency signal content in the microphone signal (MS).
Owner:OTICON
Method and apparatus for two-port allpass compensation of polarization mode dispersion
InactiveUS20050175353A1Reduce the valueMinimize cost functionCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionAdaptive filterEngineering
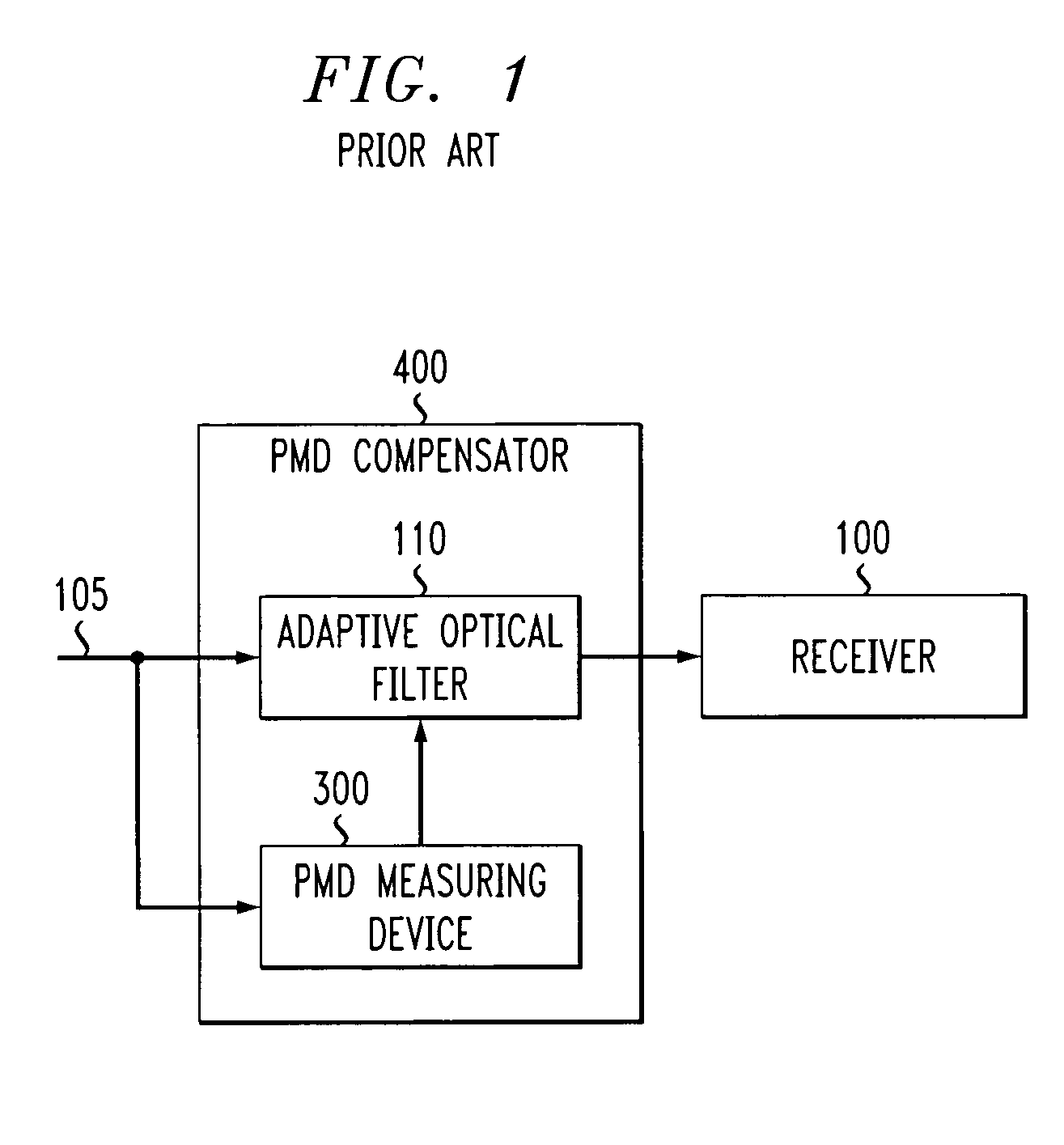
A method and apparatus are disclosed for compensating for polarization mode dispersion using cascaded all-pass filters and directional couplers. The disclosed PMD compensator adjusts the coefficients of an adaptive filter structure involving all-pass filters and directional couplers based on a minimized cost function. In one implementation, a stochastic gradient algorithm, also referred to as the least mean square algorithm, is employed to sequentially reduce the value of the cost function by the method of steepest descent. In one another implementation, convergence is improved by employing a Newton algorithm that uses second derivatives to accelerate convergence.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
System, apparatus, and method for adaptive weighted interference cancellation using parallel residue compensation
InactiveUS20060193374A1Enhanced MAI suppressionImprovement in MAI estimation accuracyError preventionBroadcast transmission systemsMean squareAdaptive weighting
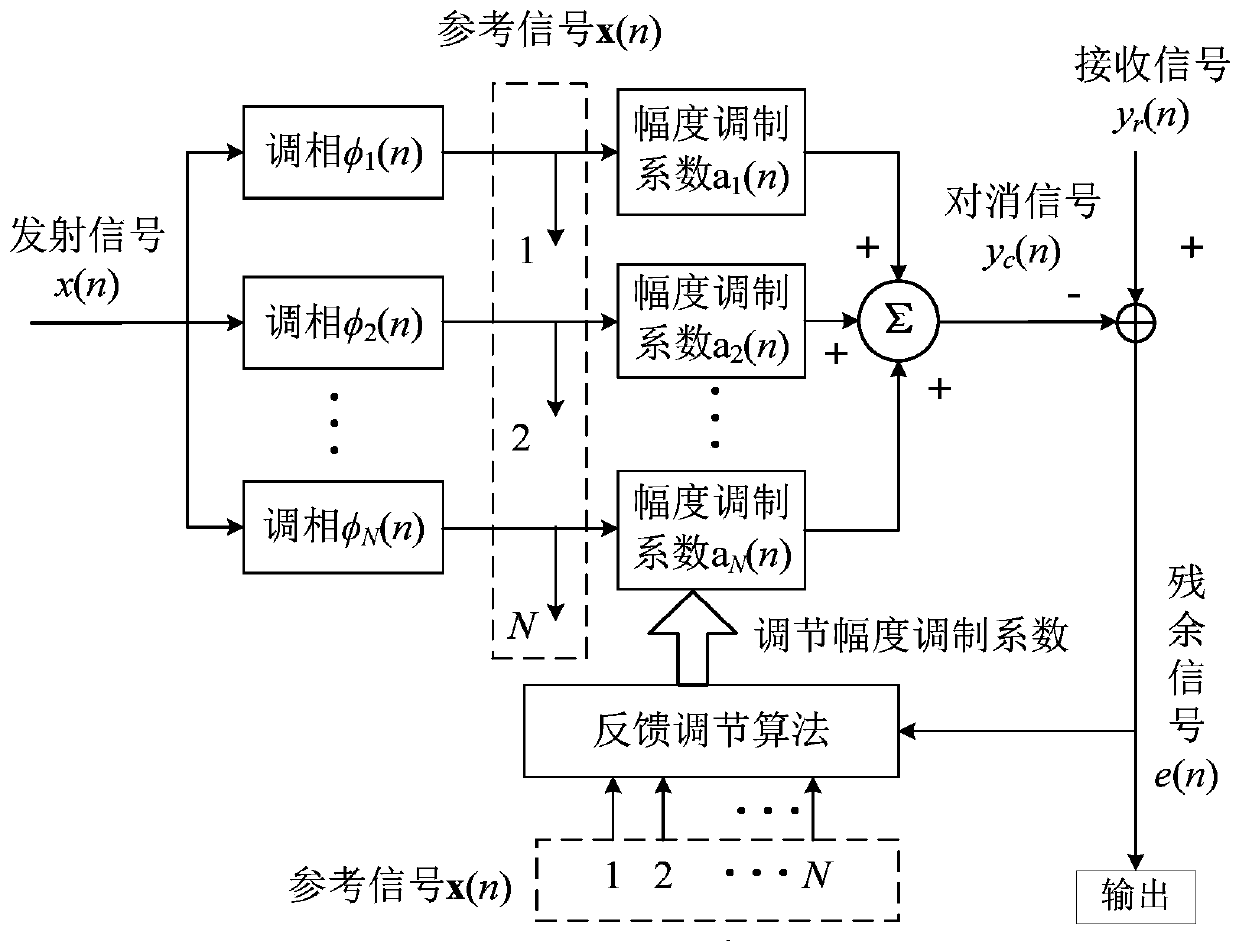
A system, apparatus and method for a multi-stage Parallel Residue Compensation (PRC) receiver for enhanced suppression of the Multiple Access Interference (MAI) in Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) systems. The accuracy of the interference estimation is improved with a set of weights computed from an adaptive Normalized Least Mean Square (NLMS) algorithm. In order to reduce complexity, the commonality of the multi-code processing is extracted and used to derive a structure of PRC to avoid direct interference cancellation. The derived PRC structure reduces the interference cancellation architecture from a complexity that is proportional to the square of the number of users to a complexity that is linear with respect to the number of users. The complexity is further reduced by replacing dedicated multiplier circuits with simple combinational logic.
Owner:CORE WIRELESS LICENSING R L
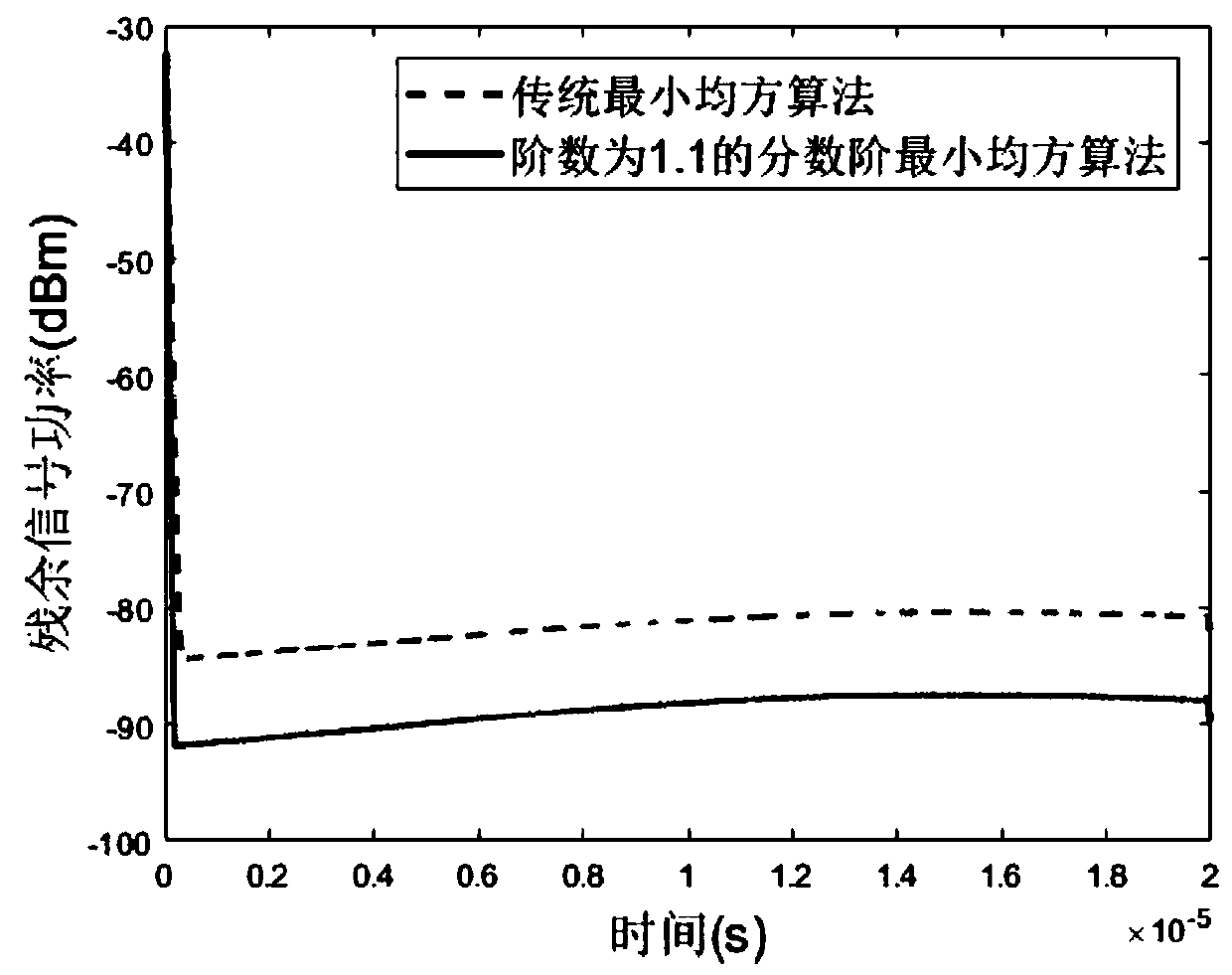
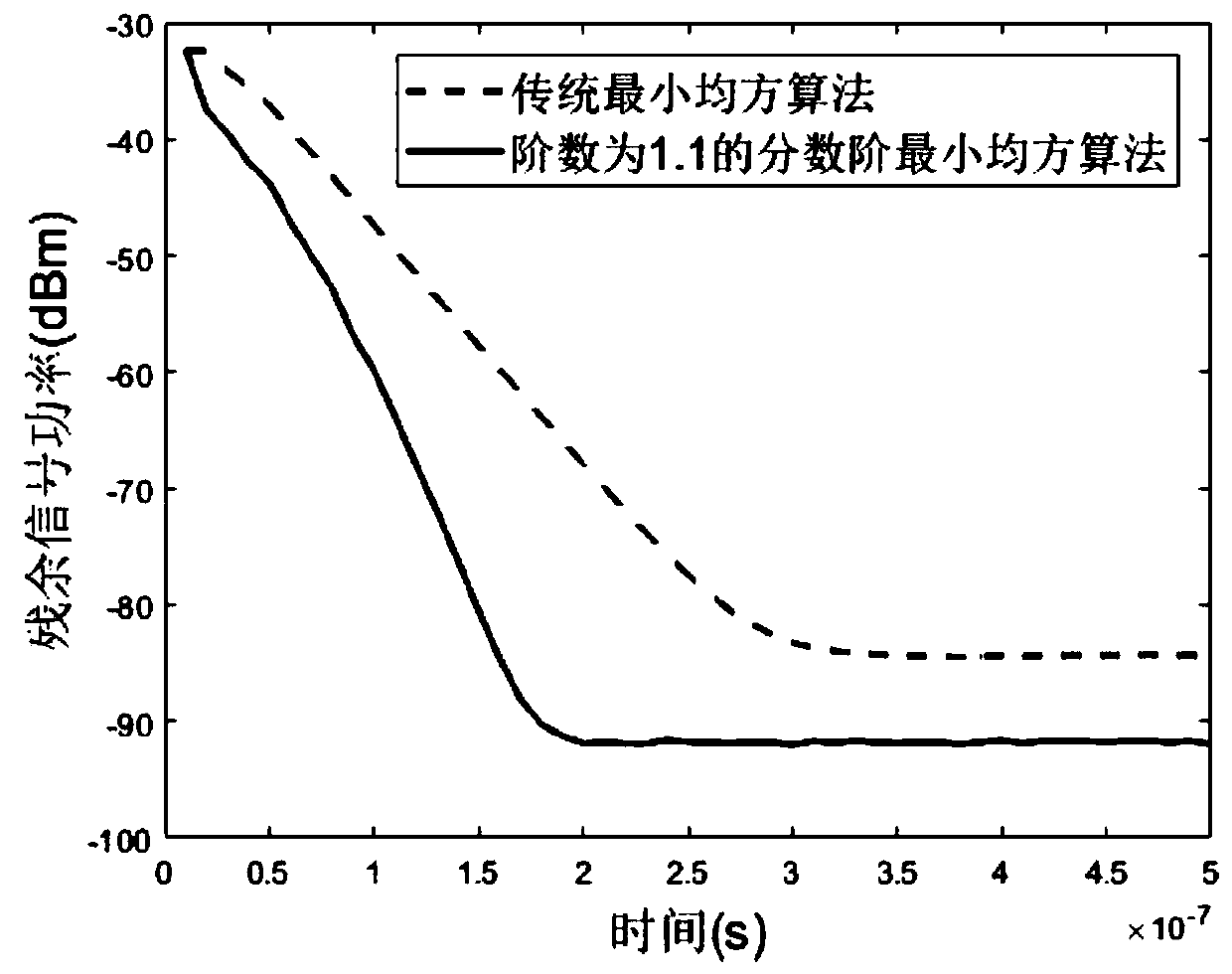
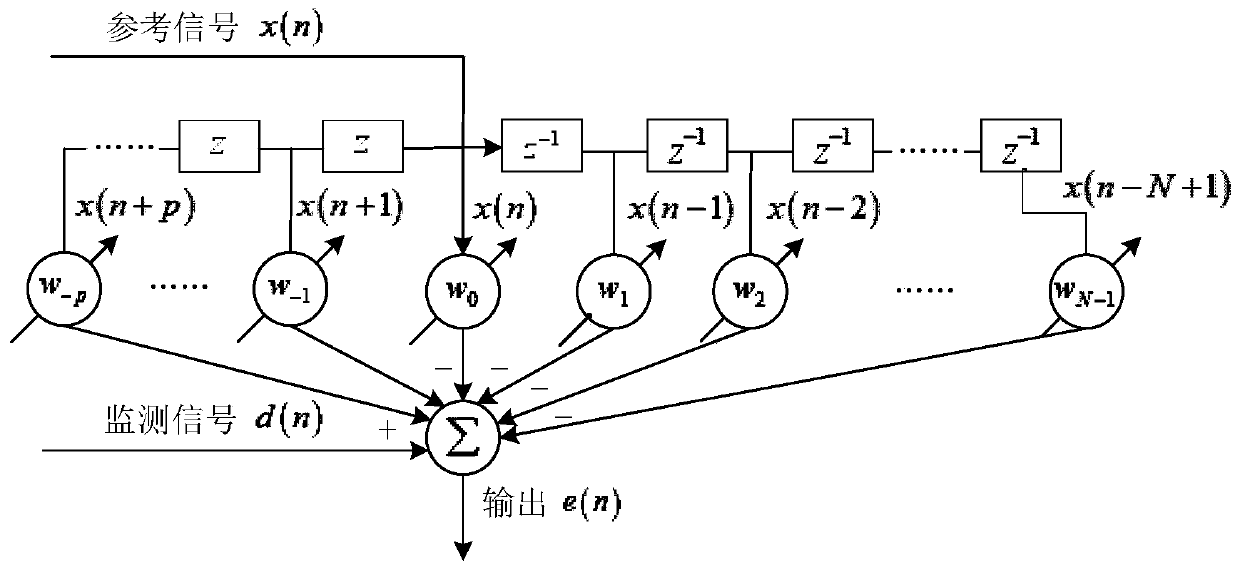
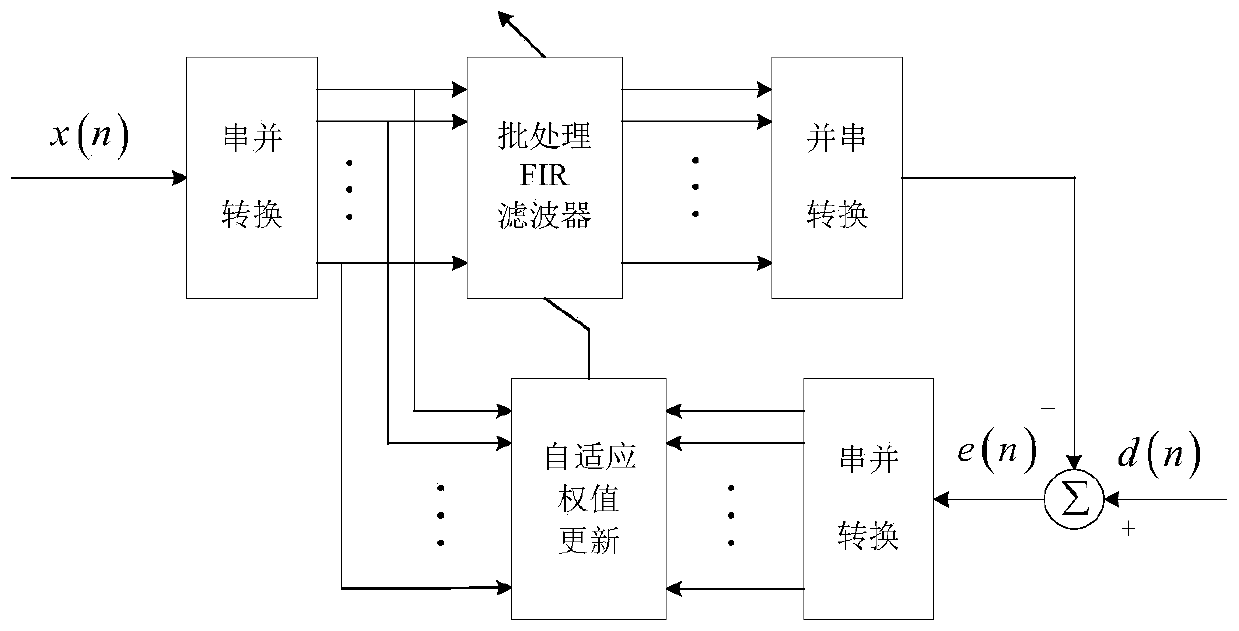
Frequency-modulation continuous-wave radar self-interference elimination method based on fractional order least mean square
ActiveCN110146848AAutomatic adjustment of cancellation structureAdaptable to changeWave based measurement systemsICT adaptationSelf interferenceTarget signal
The invention discloses a frequency-modulation continuous-wave radar self-interference elimination method based on a fractional order least mean square. In the method, a frequency-modulation continuous-wave radar system uses a baseband de-sloping working mode, and operation of radio frequency domain self-interference cancellation is taken as a precondition. The method comprises the following stepsof firstly, carrying out multipath phase modulation on a baseband emission signal of a frequency-modulation continuous-wave radar to generate a reference signal; secondly, carrying out multipath amplitude modulation on the reference signal and generating a cancellation signal through multipath vector synthesis; then, before baseband de-sloping processing, carrying out self-interference cancellation on the cancellation signal and a radar receiving signal; and finally, using a fractional order least mean square algorithm to carry out feedback adjusting on multipath modulation coefficients so that the cancellation signal approaches the self-interference signal and a purpose of self-interference signal elimination is realized. In the invention, the self-interference signal in the radar receiving signal can be restrained and a target signal is not influenced so as to increase a detection probability and precision of the radar to a target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Time domain clutter suppression method suitable for LTE external radiation source radar
ActiveCN110646769AImprove detection abilitySmall amount of calculationWave based measurement systemsFast Fourier transformTime domain
The invention discloses a time domain clutter suppression method suitable for LTE external radiation source radar. According to the method, an original monitoring signal is subjected to sinc functioninterpolation to obtain a monitoring signal linearly combined by limited integer delay reference signals; the interpolated monitoring signal and the reference signal are segmented separately; the segmented monitoring signal, the reference signal and a filter weight are subjected to fast Fourier transform, so that the signal is transformed from the time domain to the frequency domain; clutter suppression is performed according to the minimum mean square algorithm in the frequency domain, and adaptive variable step weight updating is carried out; and finally, the output results of each segment are combined. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that accurate estimation of the fractional delay time is not needed, the interpolated monitoring signal and the reference signalare subjected to batch minimum mean square adaptive filtering; and when the estimated value is close to the real value, the output result is the required target echo signal, the clutter suppression performance of the monitoring channel is improved, and the target detection of a radar system is facilitated.
Owner:SHENZHEN RES INST OF WUHAN UNIVERISTY
Digital background correction method based on least mean square algorithm
ActiveCN110350918ASmallest highest bit capacitanceSolve the problem of invalid calibrationElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingCapacitanceMean square
The invention discloses a digital background correction method based on a least mean square algorithm, which is suitable for a split SAR ADC. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, settinga split SAR ADC, and performing digital background correction based on a minimum mean square algorithm on the set split SAR ADC, wherein the split type SAR ADC comprises two ADC modules, a main DAC capacitor array in each ADC module adopts a non-binary capacitor array; meanwhile, the weight of the highest-order capacitor in the main DAC redundant capacitor array is set to be minimum, so that eachcapacitor including the capacitor with the maximum weight in the main DAC capacitor array can be effectively corrected through random switching of the correction DAC capacitor array, and the linearity and the dynamic range of the ADC are improved; the introduction of the correction DAC random switching mode can effectively solve the problem that the correction is invalid due to the fact that thetwo ADC capacitors are not consistent in direction. In addition, redundancy is introduced into the main DAC capacitor array, so that dynamic errors introduced into the quantization process of the system can be weakened, the correctness of each switching is ensured, and the iteration speed is increased.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA +1
Nonlinear narrowband active noise control method based on Volterra filter
InactiveCN104575512AReduce narrowband noiseEasy to implementSpeech analysisNoise controlNonlinear filter
The invention provides a nonlinear narrowband active noise control method based on a Volterra filter and aimed at a situation that higher harmonic noise is generated after a narrowband noise source is distorted nonlinearly. A linear signal synthesis subsystem (1), a nonlinear signal synthesis subsystem (2), a reference signal generation module and a least mean square algorithm module are used in the method; a reference signal in the method is generated by a synchronous signal generator based on a source noise frequency obtained by a non-acoustic sensor; one part of a secondary source is synthesized through a linear combiner, the other part of the secondary source is synthesized through another linear combiner and the nonlinear Volterra filter, and when primary source noise is distorted nonlinearly, a fundamental component and a higher harmonic component are independently inhibited by a linear filter and the nonlinear Volterra filter respectively. According to the nonlinear narrowband active noise control method, the nonlinearly distorted narrowband noise can be effectively inhibited, and the influence of nonlinearity on system performance can be easily analyzed due to an independent working structure.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Reference signal self-extraction active vibration control method for piezoelectric intelligent structure
InactiveCN102142830ALow application costImprove reliabilityAdaptive networkAdaptive filterControl engineering
The invention aims to provide a reference signal self-extraction active vibration control method for a piezoelectric intelligent structure, particularly an active vibration control method for a piezoelectric intelligent structure based on an adaptive filtering control least mean square algorithm, which directly utilizes a test platform for active vibration control on the piezoelectric intelligent structure to realize reference signal self-extraction active vibration control on adaptive filtering. The method directly extracts a vibration response residual signal from the piezoelectric intelligent vibration structure, constructs a reference signal based on the controller structure and the algorithm process data, meets the correlation with a disturbance signal and enters an algorithm control process. The method solves the problem that an accurate reference signal is difficult to obtain in a practical piezoelectric intelligent structure system, and provides a beneficial technical method for realizing practicability of the adaptive filtering control method on structural vibration.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
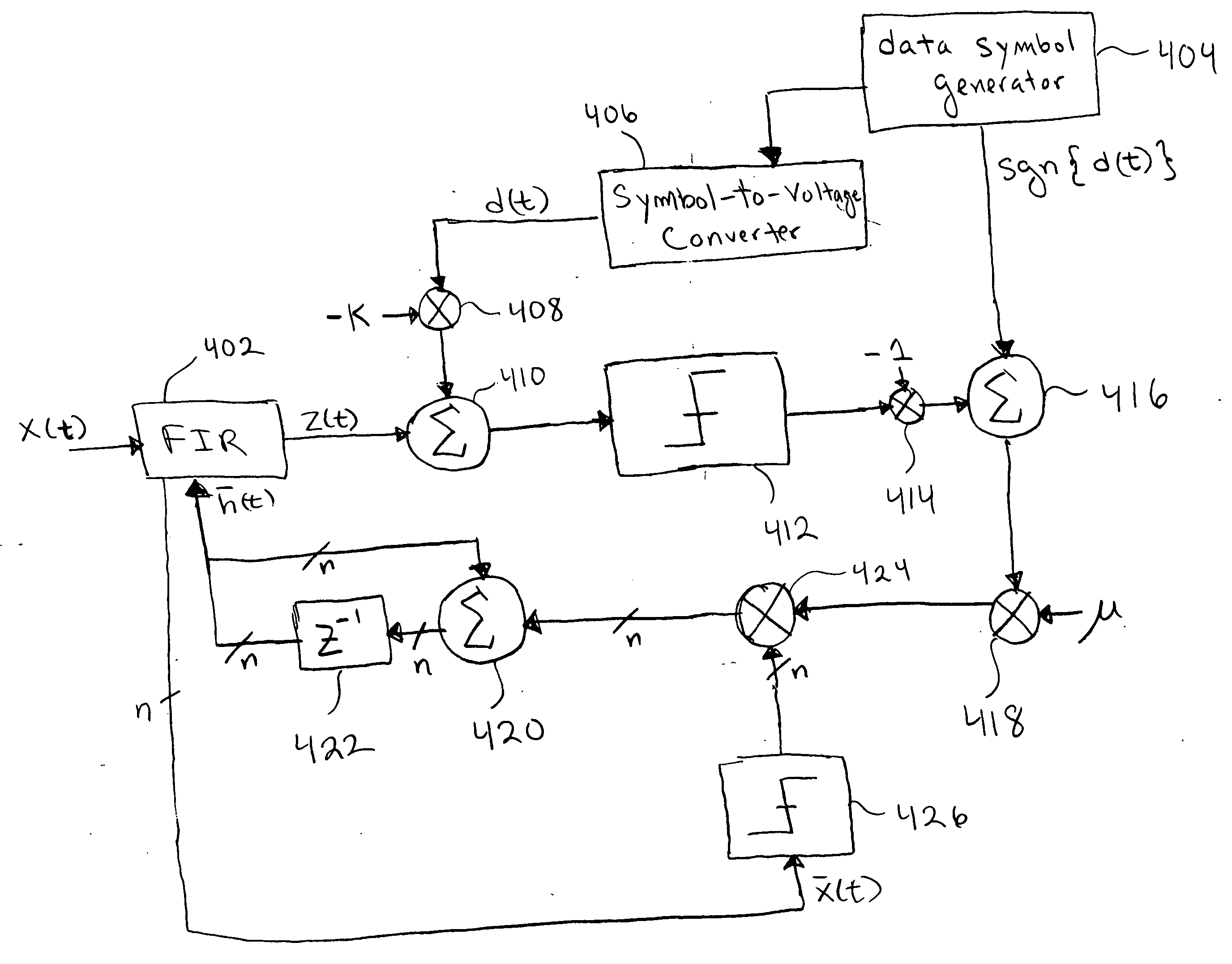
Adaptive equalization using a conditional update sign-sign least mean square algorithm
ActiveUS20050053125A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equlisationFinite impulse responseRound complexity
An adaptive equalizer finite impulse response (FIR) filter for high-speed communication channels with modest complexity, where the filter is iteratively updated during a training sequence by a circuit performing the update: {overscore (h)}(t+1)={overscore (h)}(t)+μ[sgn{d(t)}−sgn{z(t)−Kd(t)}]sgn{{overscore (x)}(t)}, where {overscore (h)}(t) is the filter vector representing the filter taps of the FIR filter, {overscore (x)}(t) is the data vector representing present and past samples of the received data x(t), d(t) is the desired data used for training, z(t) is the output of the FIR filter, μ determines the memory or window size of the adaptation, and K is a scale factor taking into account practical limitations of the communication channel, receiver, and equalizer. Furthermore, a procedure and circuit structure is provided for calibrating the scale factor K.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
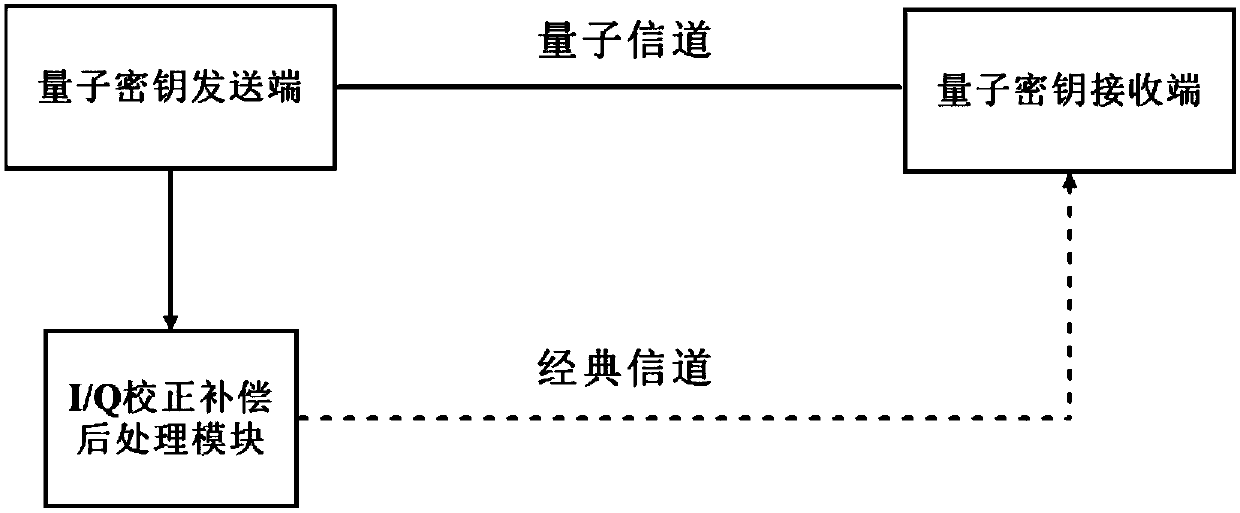
Continuous variable quantum key distribution modulation compensation system and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN107947930AReduce the impactIncrease distanceKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationComputer moduleContinuous variable
The invention discloses a continuous variable quantum key distribution modulation compensation system and a implementation method thereof. A quantum key sending terminal modulates a quantum signal tochange the quantum signal into the form of a plurality of subcarriers, and sends the subcarriers to a quantum key receiving terminal; the quantum key receiving terminal collects and processes the emitted signal, and sends the results to an I / Q correction compensation post processing module; and the I / Q correction compensation post processing module uses the least mean square algorithm to process the received signal. The continuous variable quantum key distribution modulation compensation system can overcome the modulation defects existing in a quantum key distribution system; especially for the imbalance of I / Q, the practical security of the continuous variable quantum key distribution system based on the orthogonal frequency division multiplexing is further improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
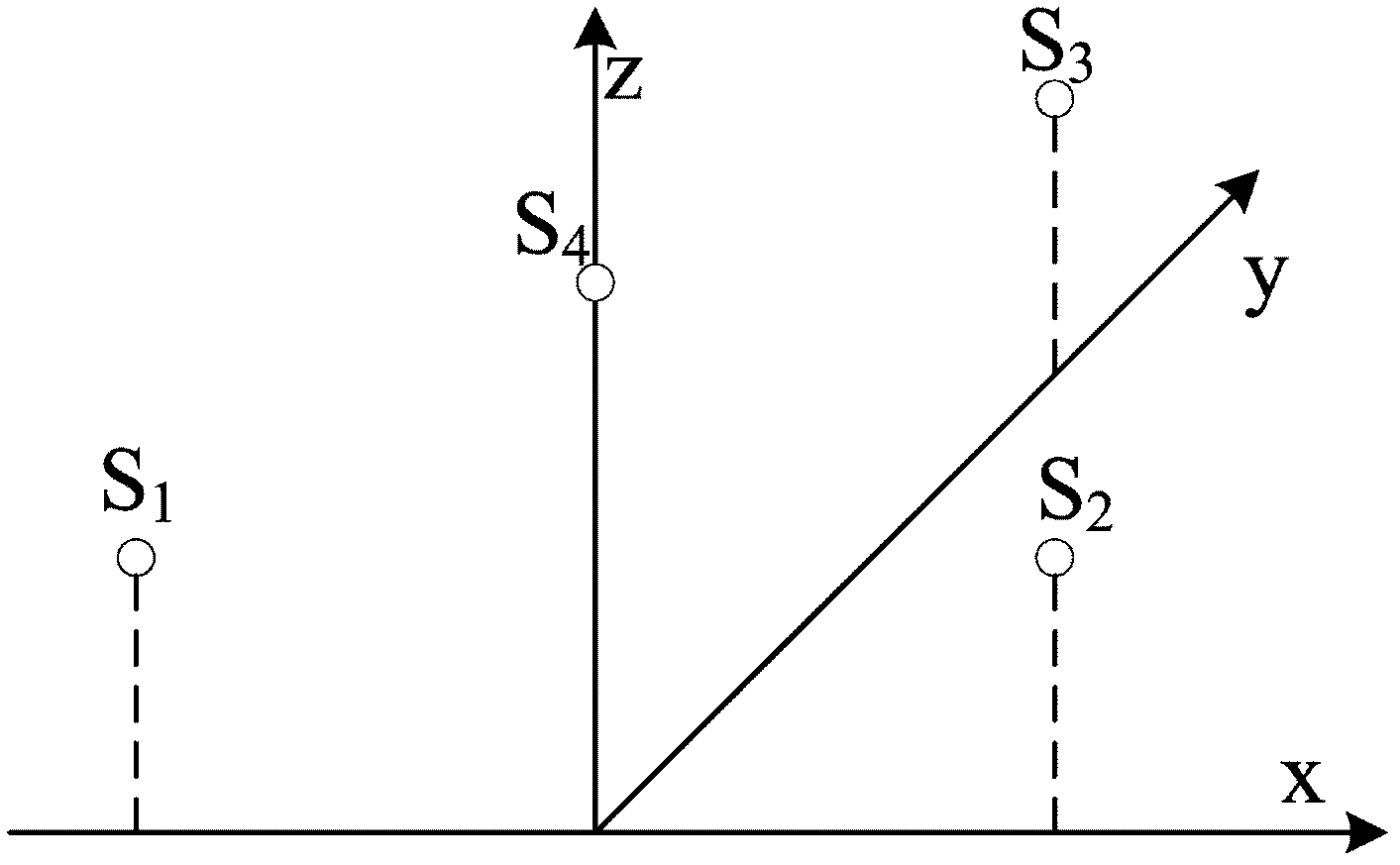
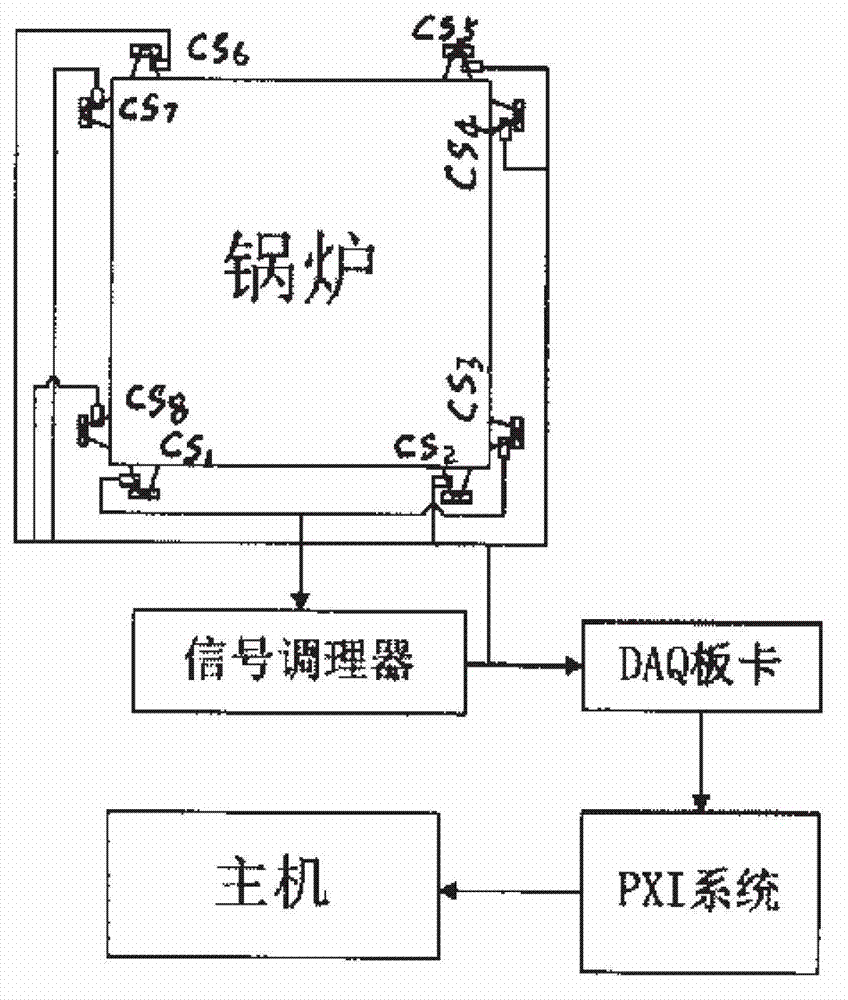
Utility boiler pressure-bearing pipe leakage location method based on plane octave array
The invention discloses a utility boiler pressure-bearing pipe leakage location method based on a plane octave array, belonging to the technical field of thermal power generation utility boiler leakage monitoring. Based on the traditional acoustic thermometry system that a water wall leakage location system with eight measuring points based on the plane octave array is developed, time delay estimation is obtained by an adaptive filter algorithm of the LMS(Least Mean Square) algorithm, and the precise leakage position location of a boiler pressure-bearing pipe is achieved by the adoption of a three dimensional space algorithm improved from the CHAN algorithm in a TDOA (Time Difference of Arrival) location system based on a cellular network. The array arrangement is in reference with the arrangement of the traditional acoustic thermometry, so that temperature measurement and leakage signal location can be performed simultaneously, therefore the utility boiler pressure-bearing pipe leakage location method disclosed by the invention is efficient and precise.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Method and System for Performing Timing Recovery in a Digital Communication System
InactiveUS20080080606A1Multiple-port networksDelay line applicationsCommunications systemSelf adaptive
Processing signals in a digital communication may include equalizing a signal in a timing-recovery system using a frequency domain equalizer. The frequency domain equalizer may be a frequency domain adaptive filter that adapts using a least-mean-square algorithm where at least one tap-weight that corresponds to a pre-cursor may be constrained to zero. The processing may include recovering timing information using a Mueller / Muller timing recovery algorithm that may be aided by using a pre-filter before the equalizer.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com