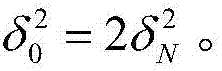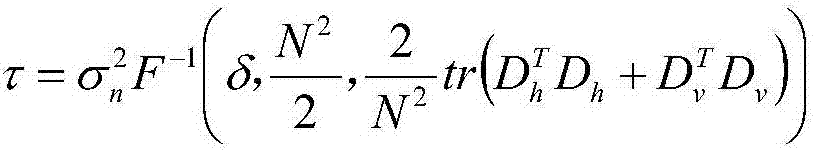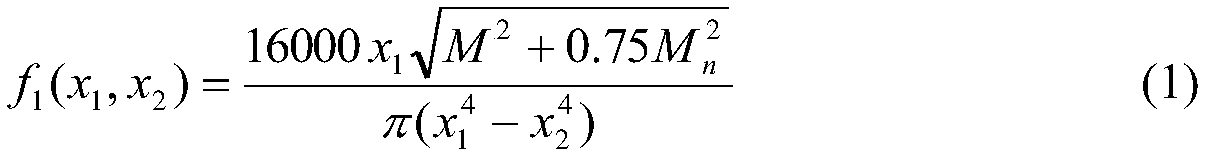Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Cost criterion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
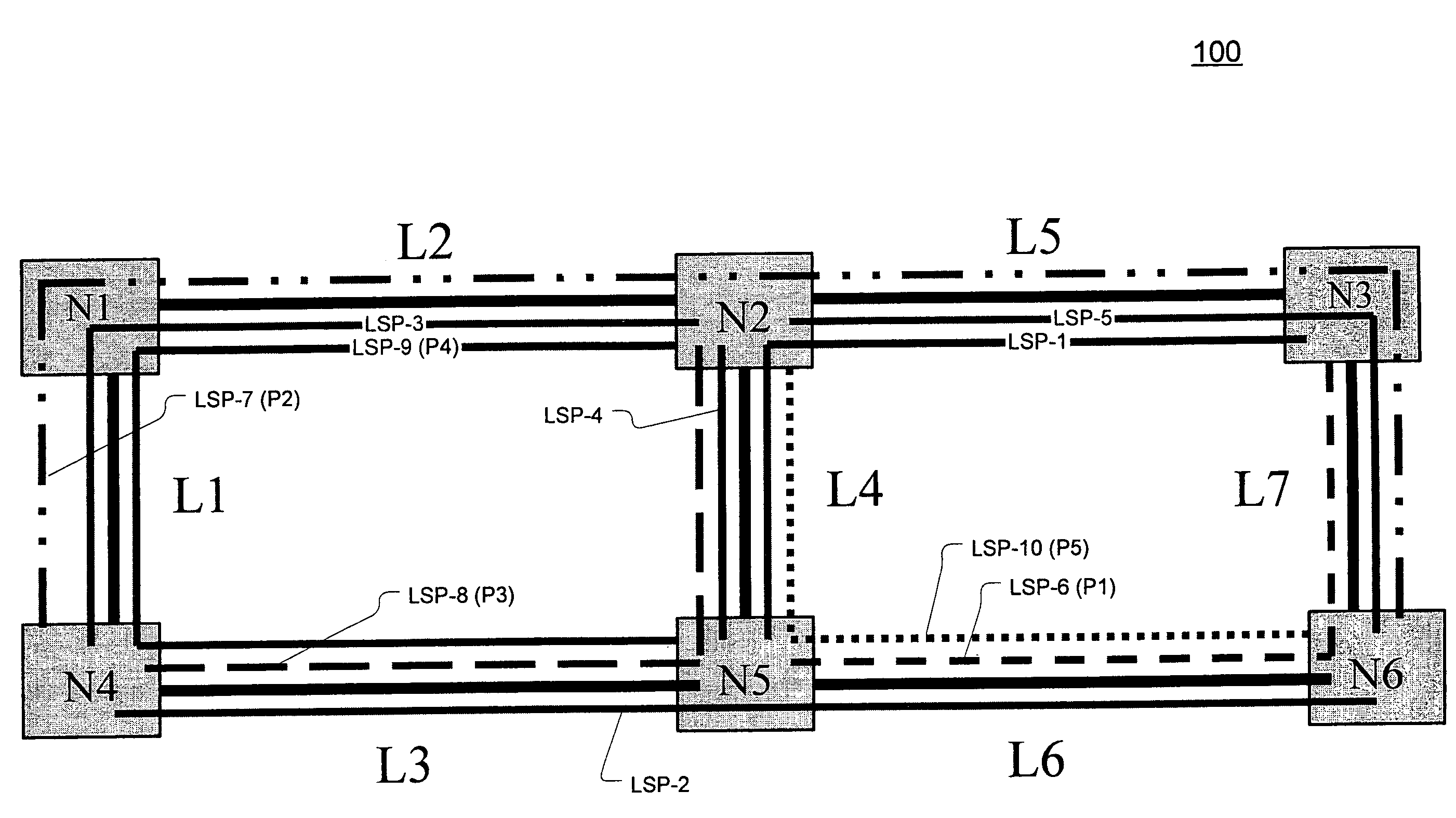
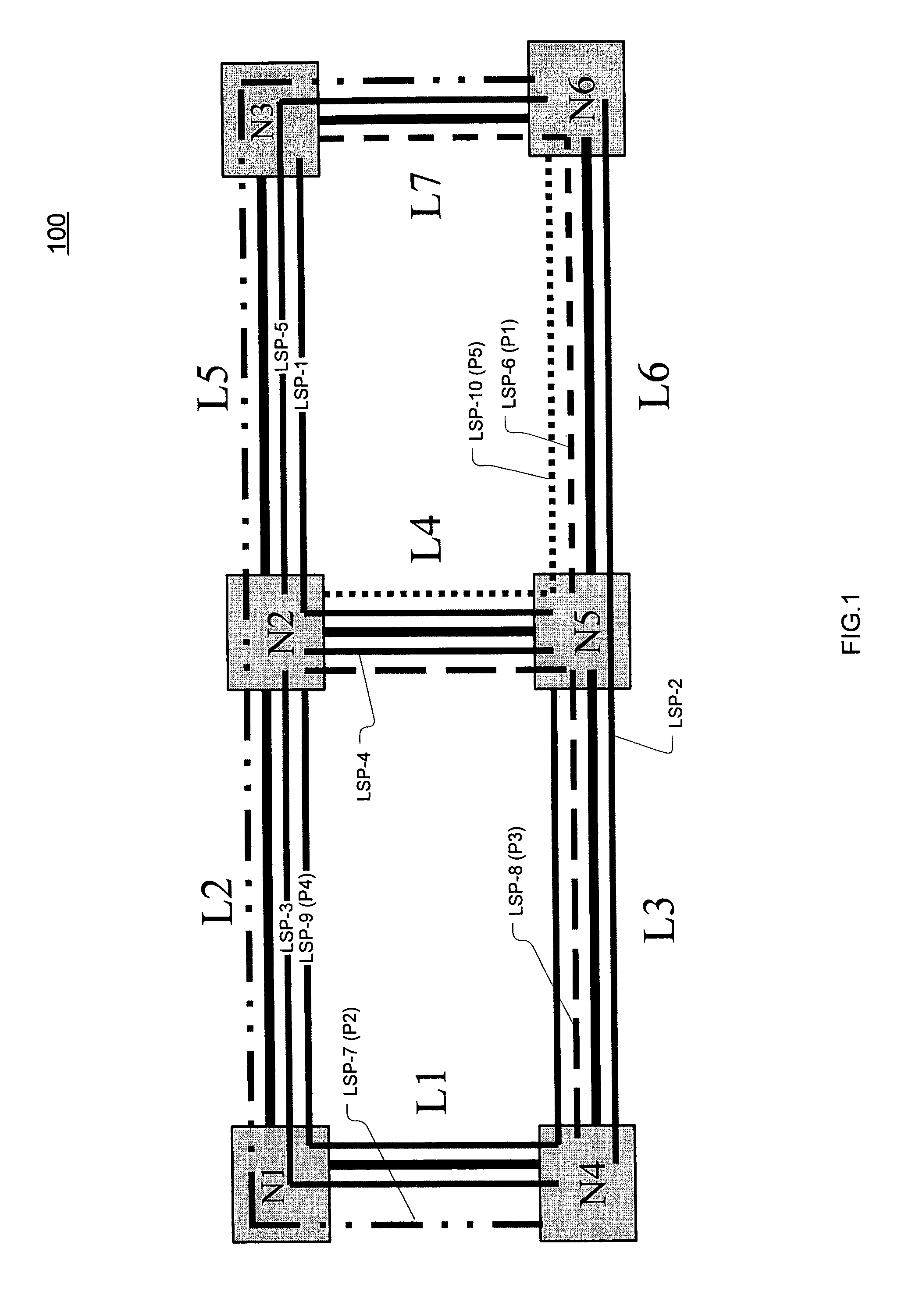
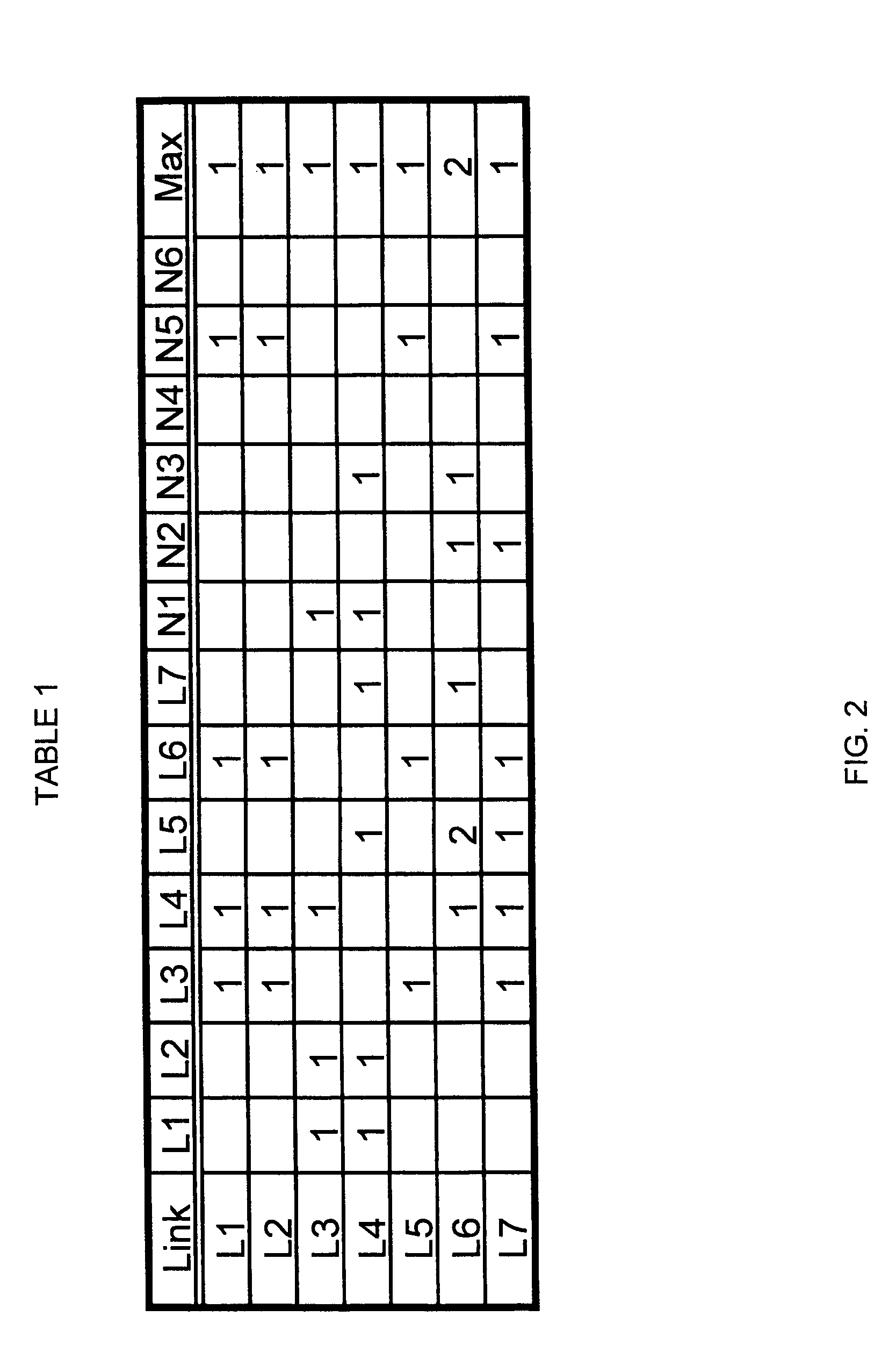
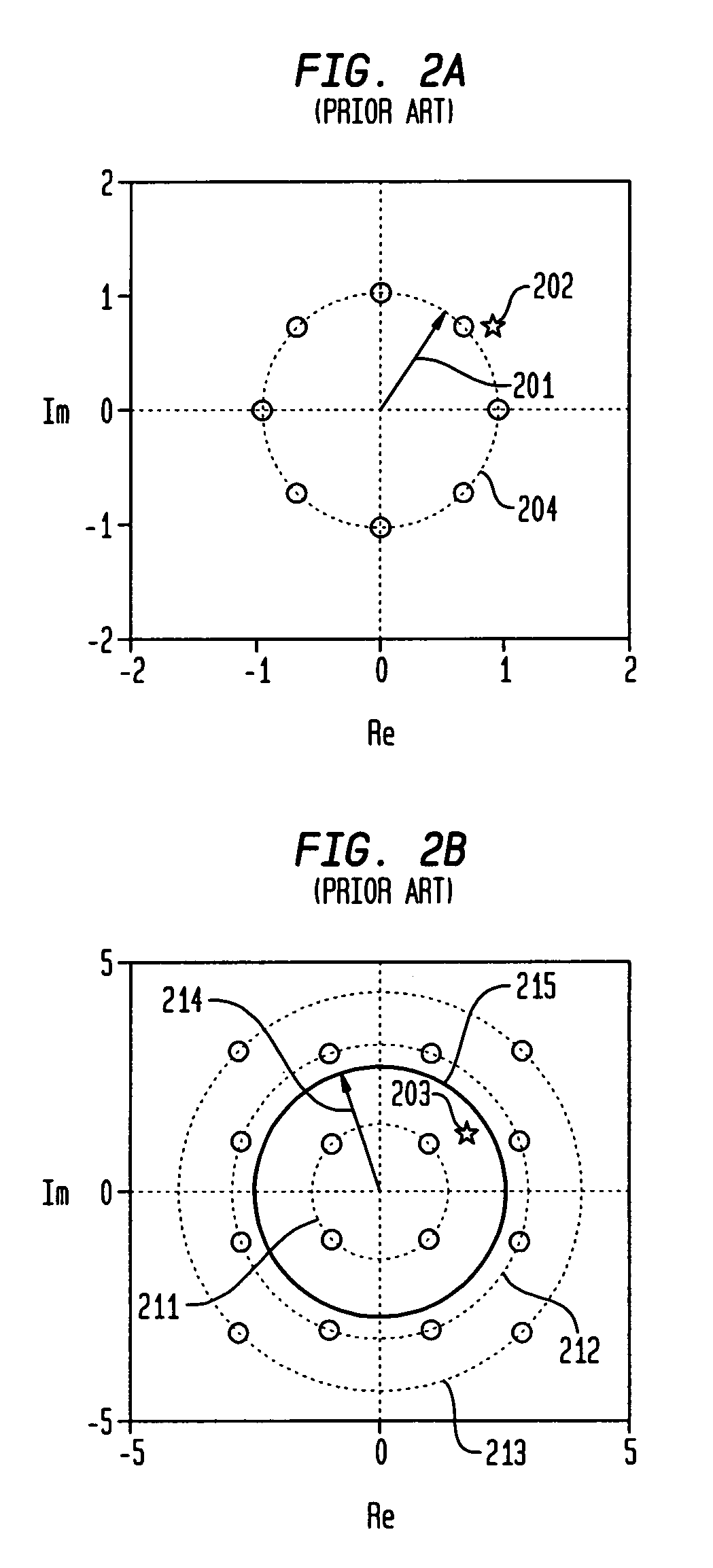
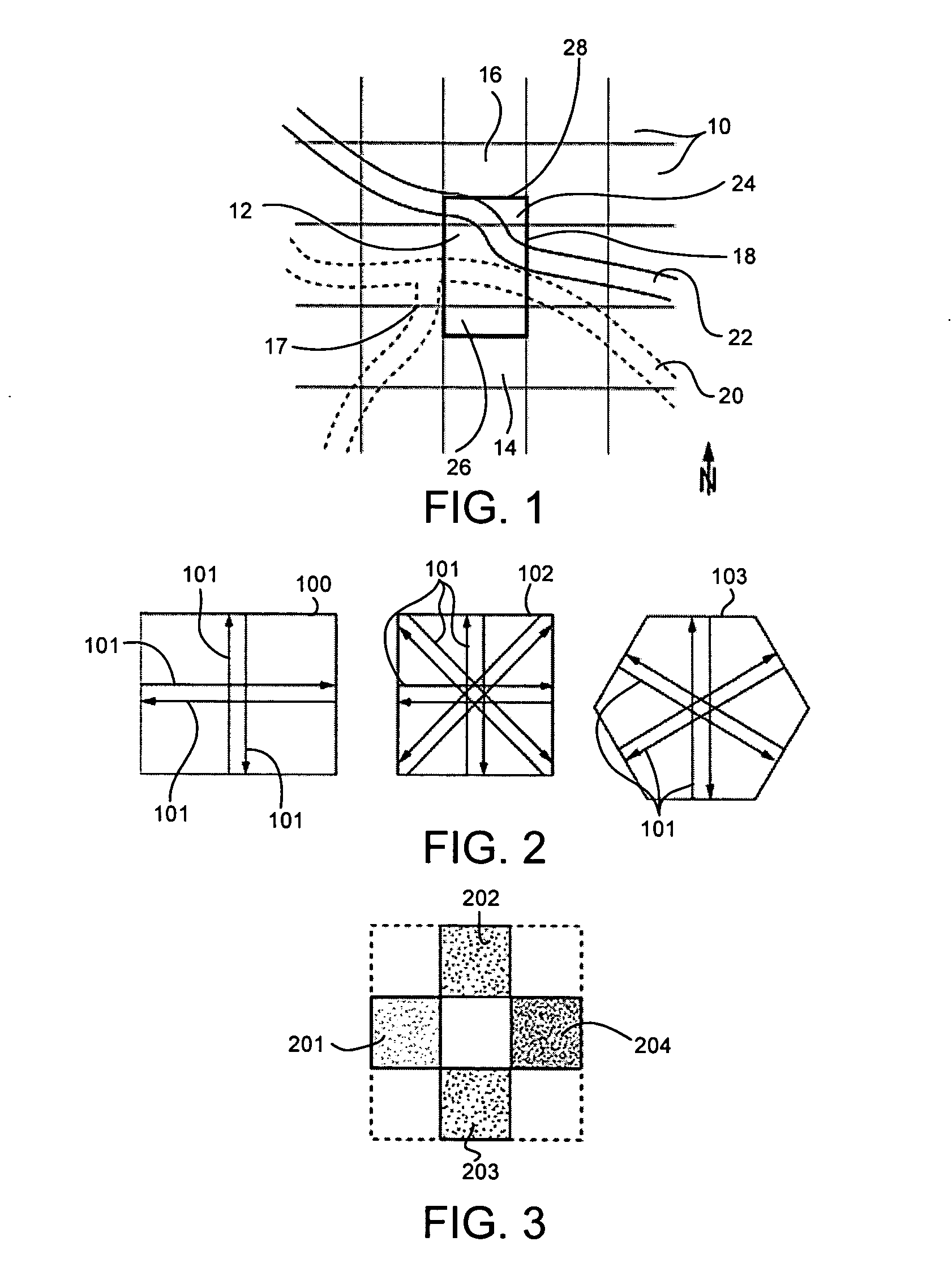
Primary/restoration path calculation in mesh networks based on multiple-cost criteria
A method for determining primary and restoration paths for a new service in a mesh network involves (1) for each of a plurality of candidate primary / restoration path pairs for the new service, generating a path cost for each candidate pair, where the path cost for each restoration path is a function of the sum of the cost of links within the restoration path, and (2) selecting the primary and restoration paths for the new service from the plurality of candidate path pairs based on the path cost. If no sharing is possible, for low utilization links, the cost of links is a function of the administrative weight of the link, whereas for high utilization links, the link cost is a function of the inverse of the available capacity on the link. If sharing is possible, the cost is a function of the inverse of a sharing degree for the link.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
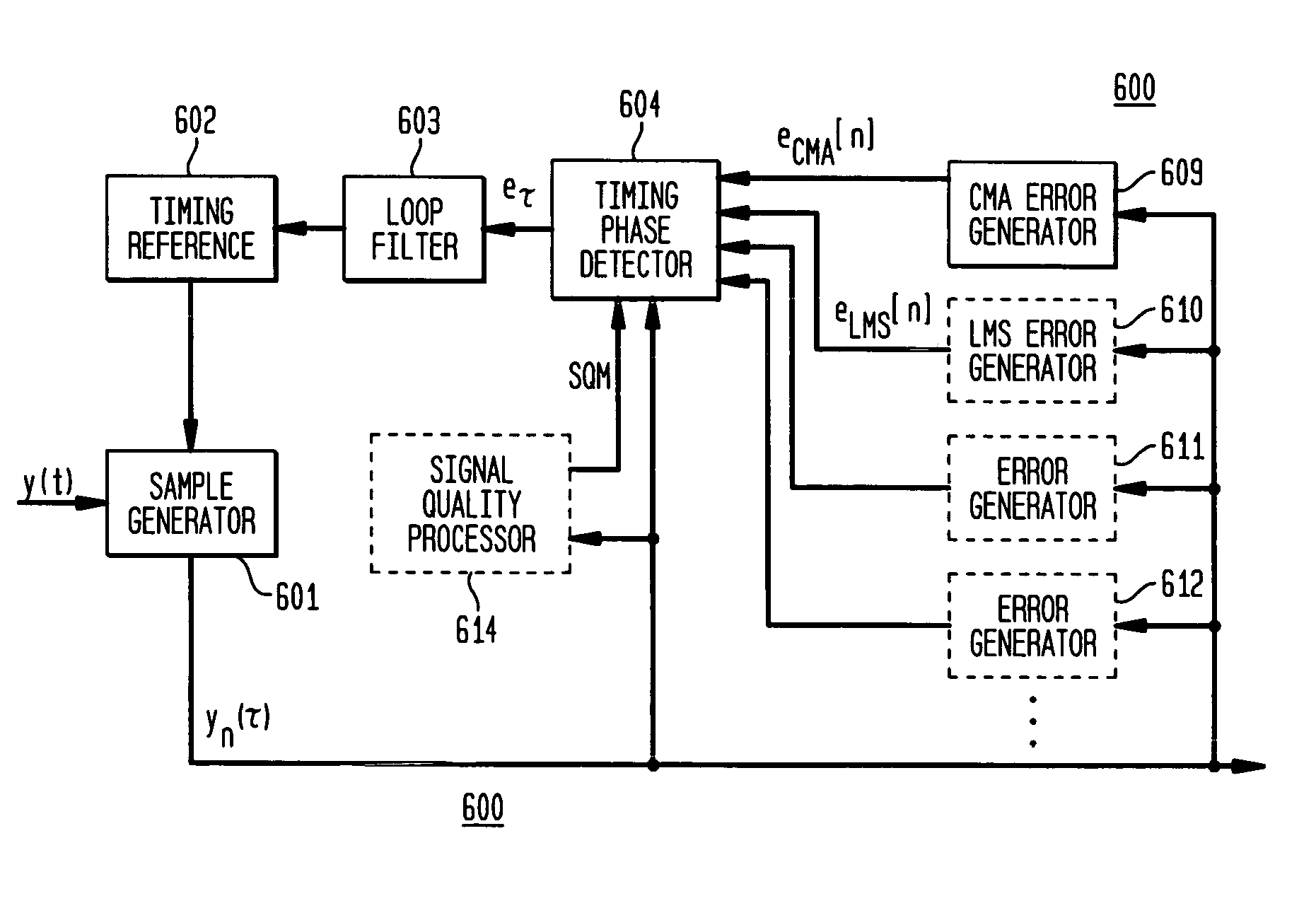
Blind cost criterion timing recovery
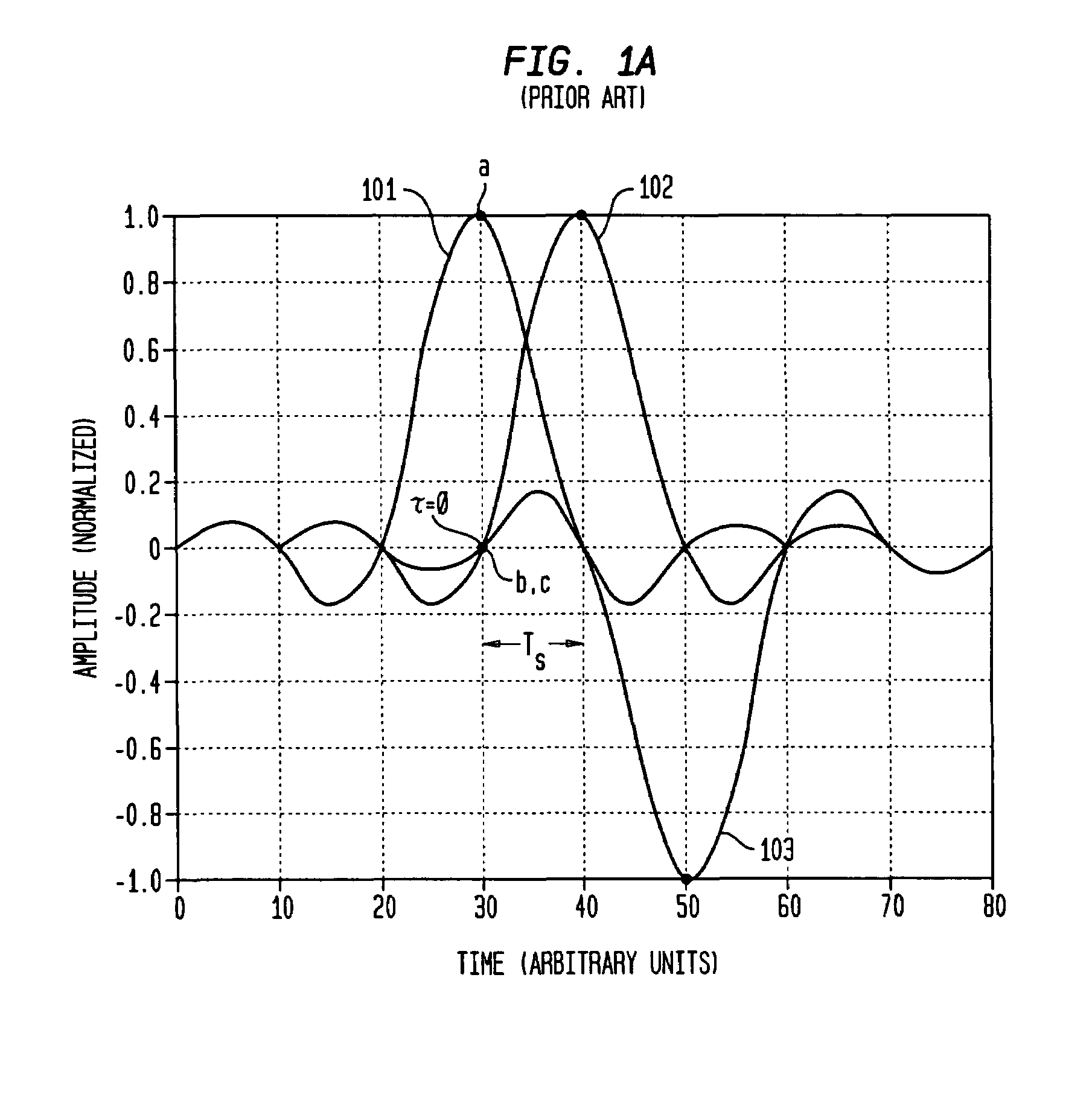
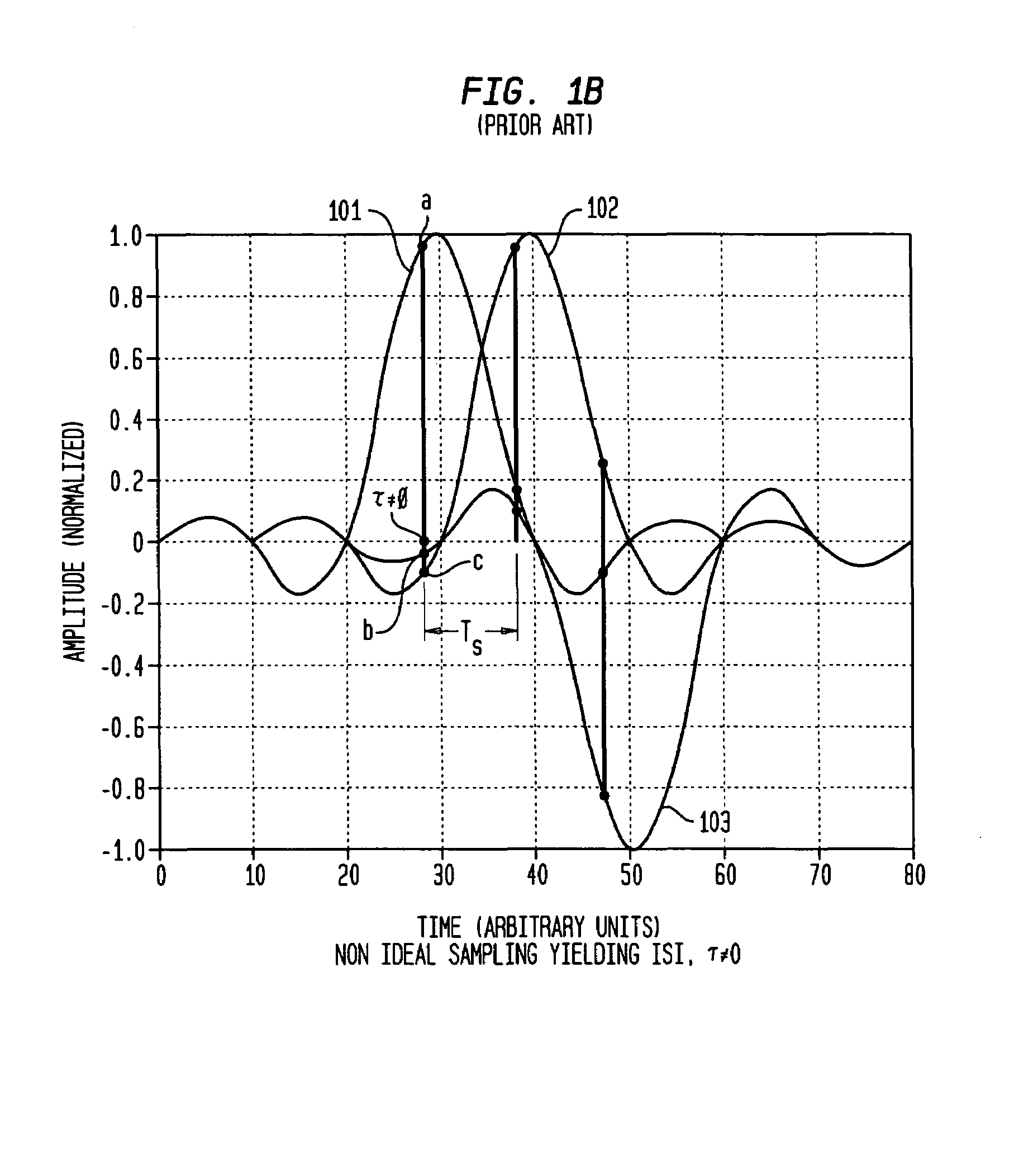
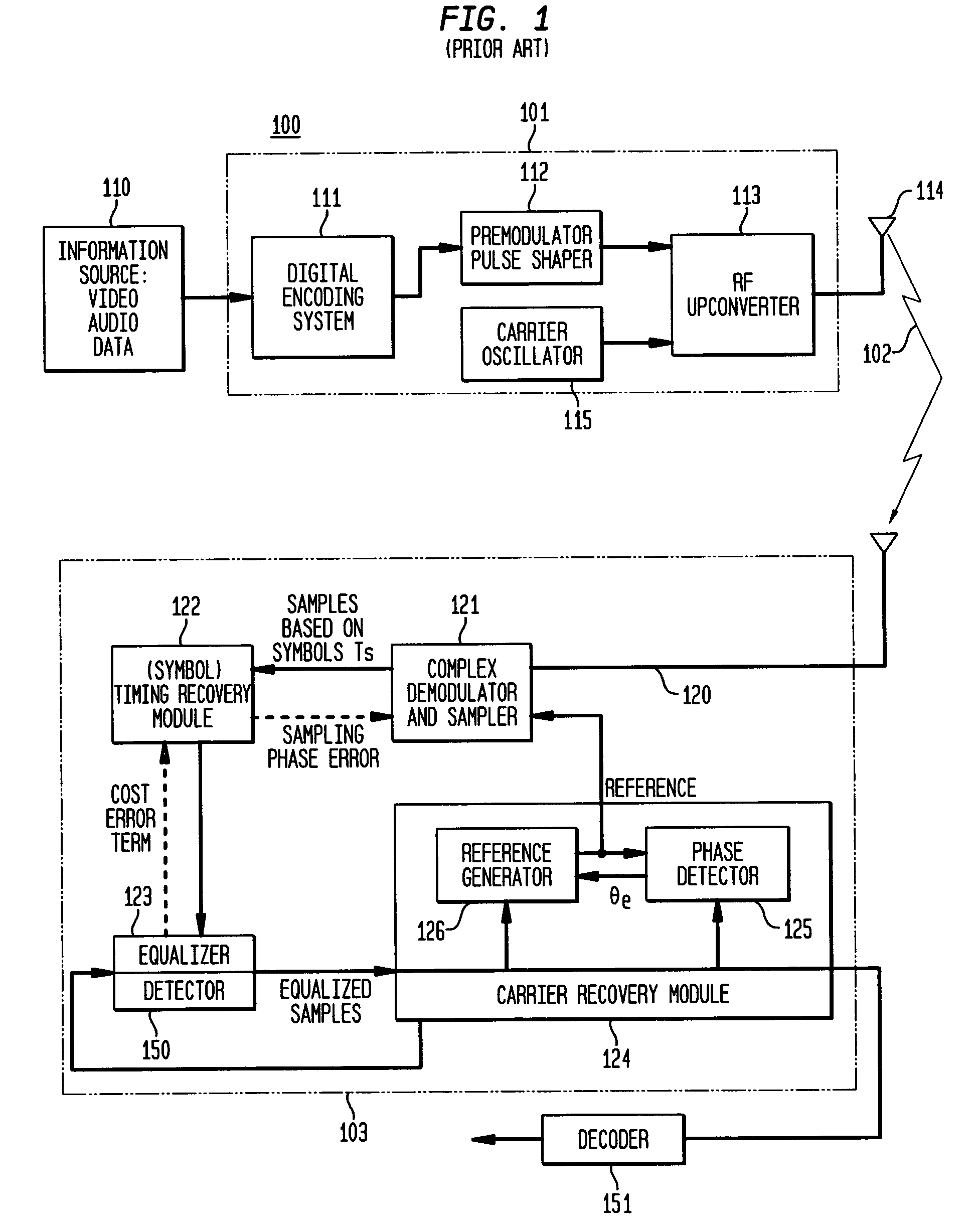
Symbol timing recovery employs a blind cost criterion from the Bussgang class of functions, and its stochastic gradient, to generate a timing phase error used to adjust sampling of received symbols. For one implementation, the estimate is derived in accordance with the Constant Modulus (CM) criterion and its gradient via the CM algorithm (CMA), and the estimate is calculated from a sequence of samples. This estimate is then used to adjust the period and phase of the sample sequence toward the period and phase of the transmitted symbols, driving the timing phase error to zero. The values used may be either i) samples themselves, ii) processed (e.g., interpolated) samples, or iii) equalized and processed samples. In addition, timing phase error estimates for other cost criteria, including the least mean squares algorithm, may be generated. These timing phase error estimates are selected either alone or in combination for deriving the timing phase error used to adjust the period and phase of the sample sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Linear prediction based initialization of a single-axis blind equalizer for VSB signals
ActiveUS7027500B1Minimize output powerMultiple-port networksTelevision system detailsImpulse frequencyEqualization
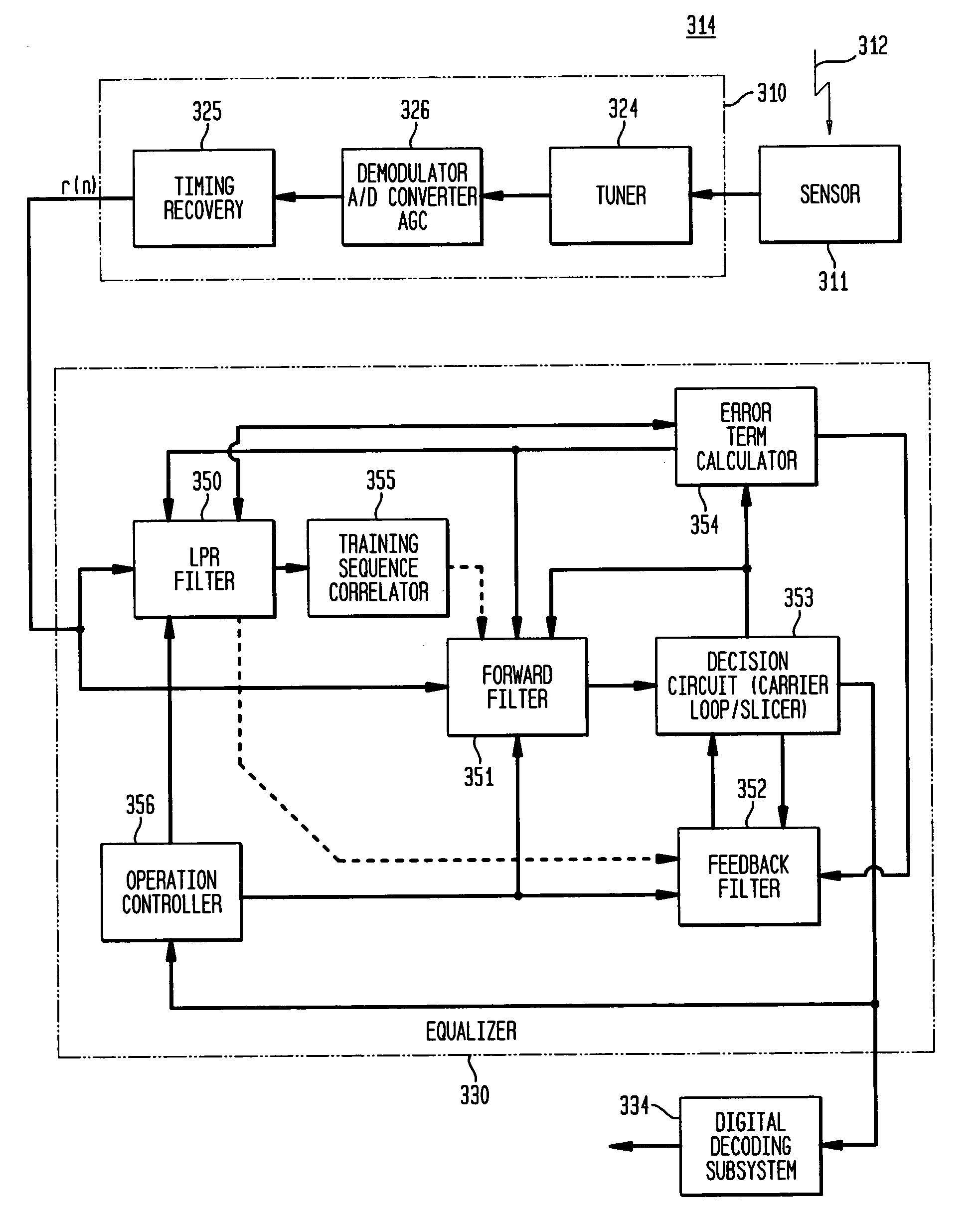
A single-axis receiver processing, for example, complex vestigial sideband modulated signals with an equalizer with forward and feedback filters. Forward and feedback filters have parameters that are initialized and adapted to steady state operation. Adaptive equalization employs linear predictive filtering and error term generation based on various cost criteria. Adaptive equalization includes recursive update of parameters for forward and feedback filtering as operation changes between linear and decision-feedback equalization of either single or multi-channel signals. An adaptive, linear predictive filter generates real-valued parameters that are employed to set the parameters of the feedback filter. In an initialization mode, filter parameters are set via a linear prediction filter to approximate the inverse of the channel's impulse / frequency response and a constant modulus error term for adaptation of the filter parameters. In an acquisition mode, equalization is as linear equalization with a constant modulus error term, and possibly other error terms in combination, for adaptation of the filter parameters. In a tracking mode, equalization is as decision feedback equalization with decision-directed error terms for adaptation of the filter parameters. For some equalizer configurations, feedback filtering is applied to real-valued decisions corresponding to complex-valued received data, and includes real-part extraction of the error term employed for recursive update of filtering parameters. Where a training sequence is available to the receiver, initial parameters for forward filtering are estimated by correlation of the received signal with the training sequence.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
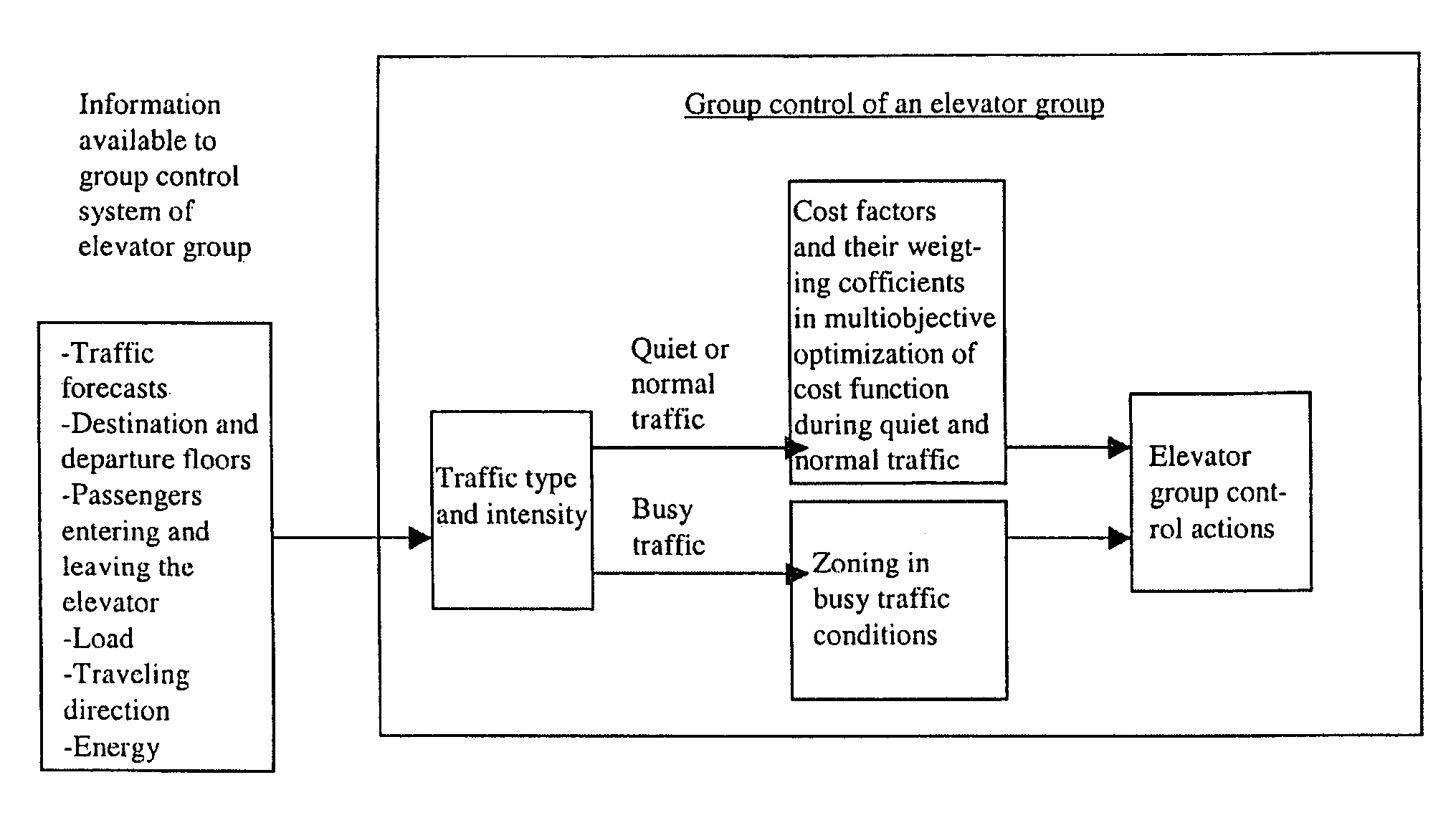
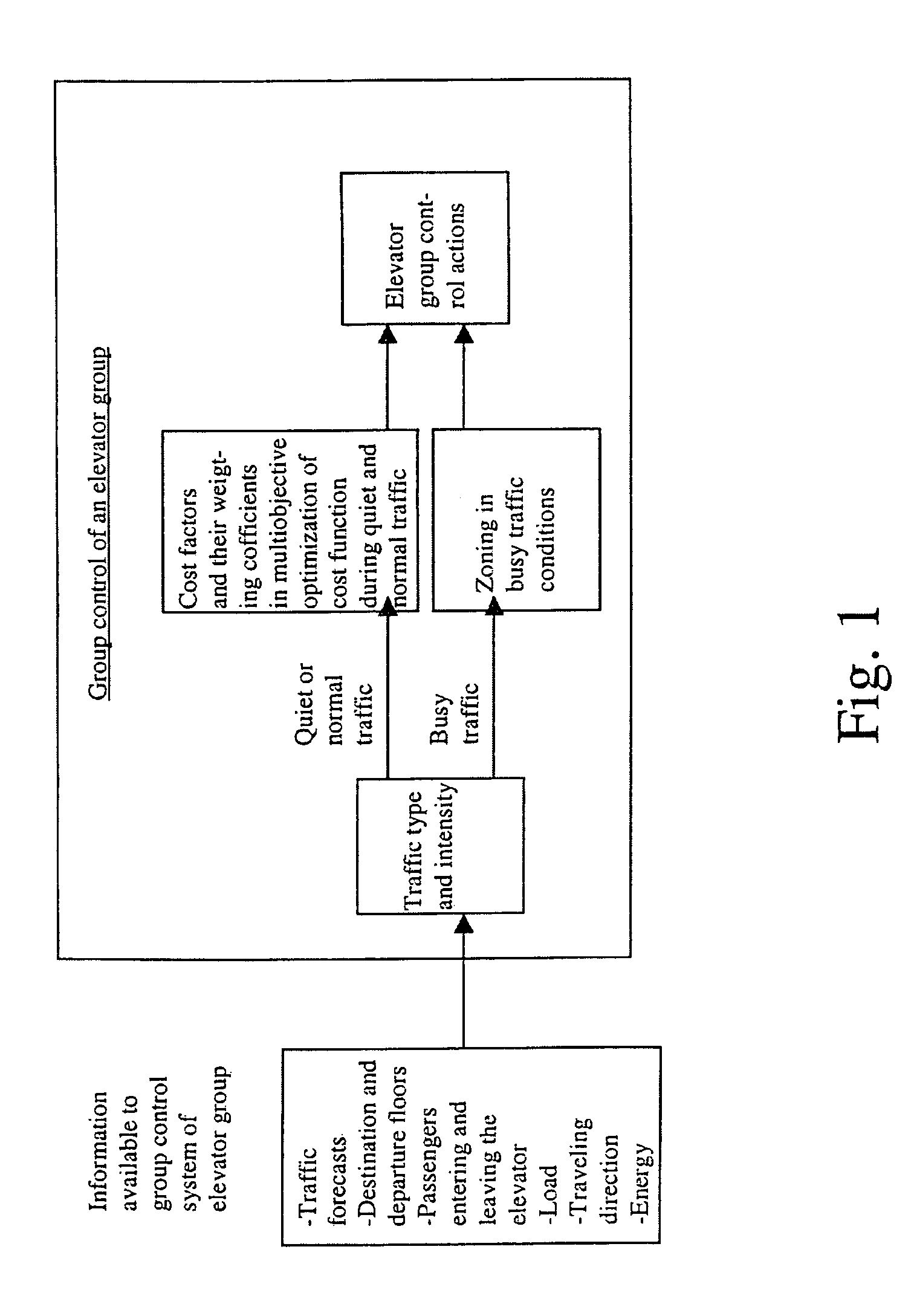
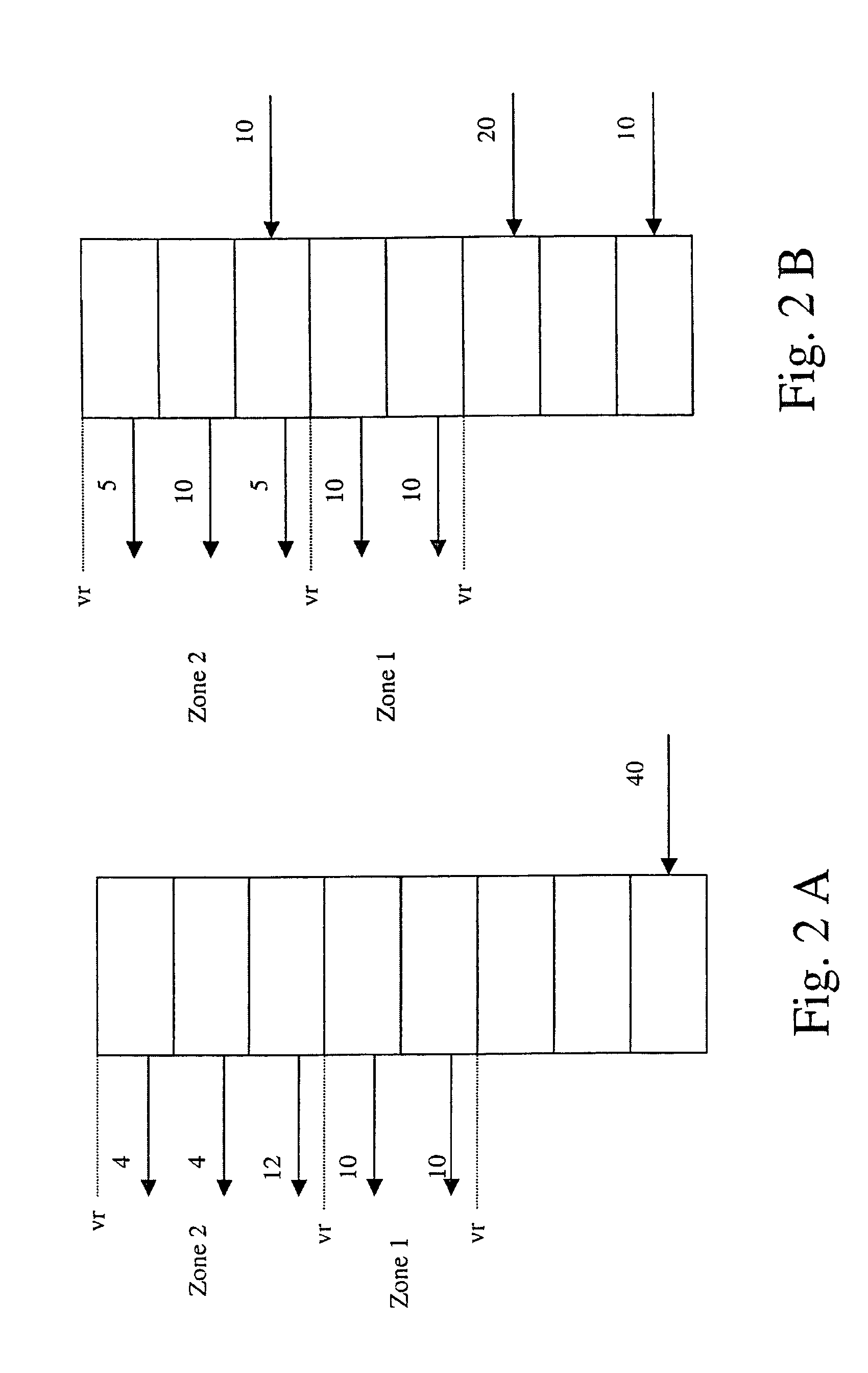
Elevator group control method using destination floor call input
ActiveUS7083027B2Improvement in passenger serviceReduce passenger waiting timeElevatorsTraffic intensitySimulation
A method controls the elevators in an elevator group when destination floor call input is used and the traffic within the elevator group is to be optimized. According to the concept of the method, based on traffic intensity, a cost function is optimized by changing the number of cost criteria from one to several and back and weighting the criteria in different ways in the aforesaid cost function.
Owner:KONE CORP
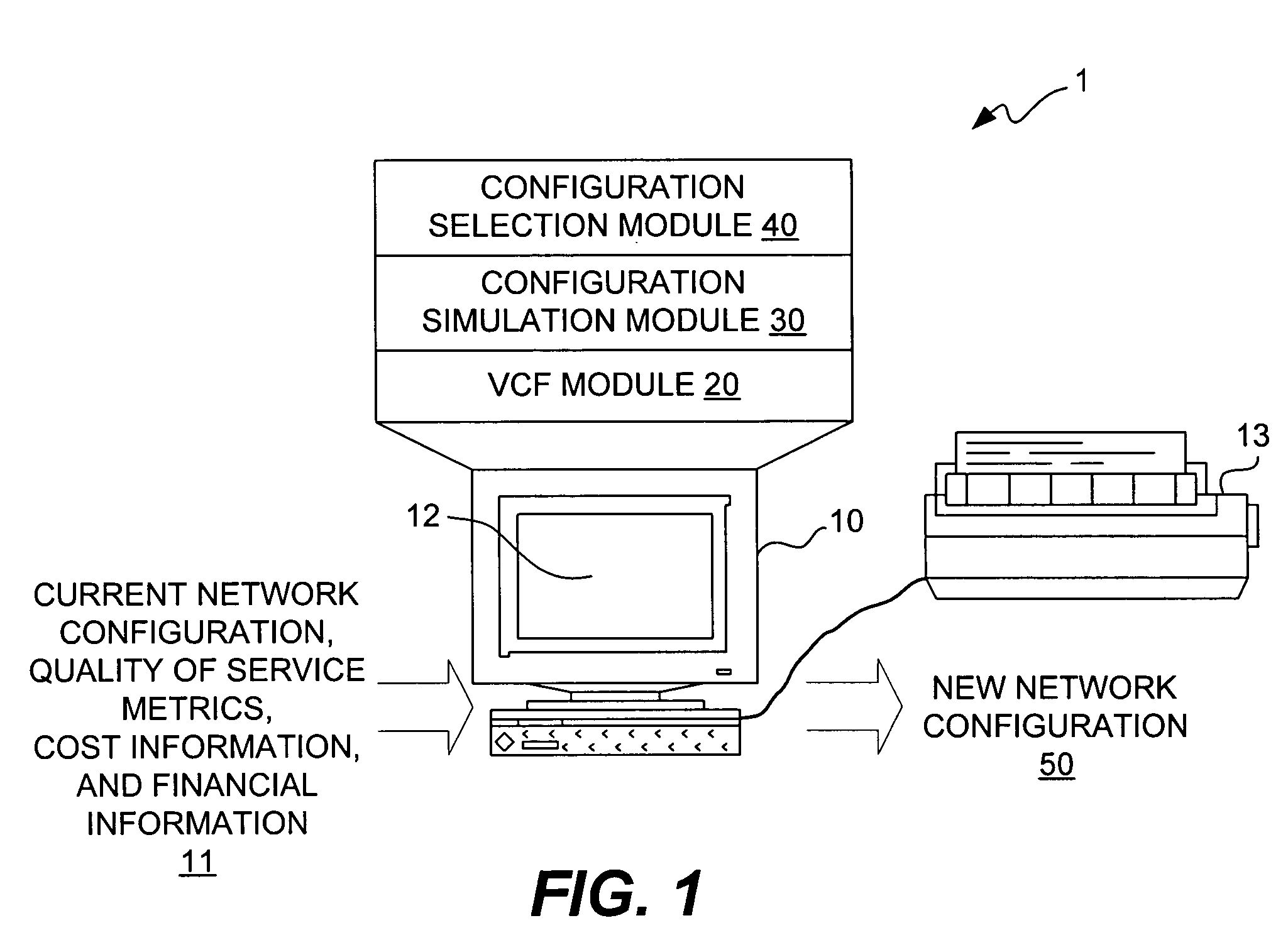
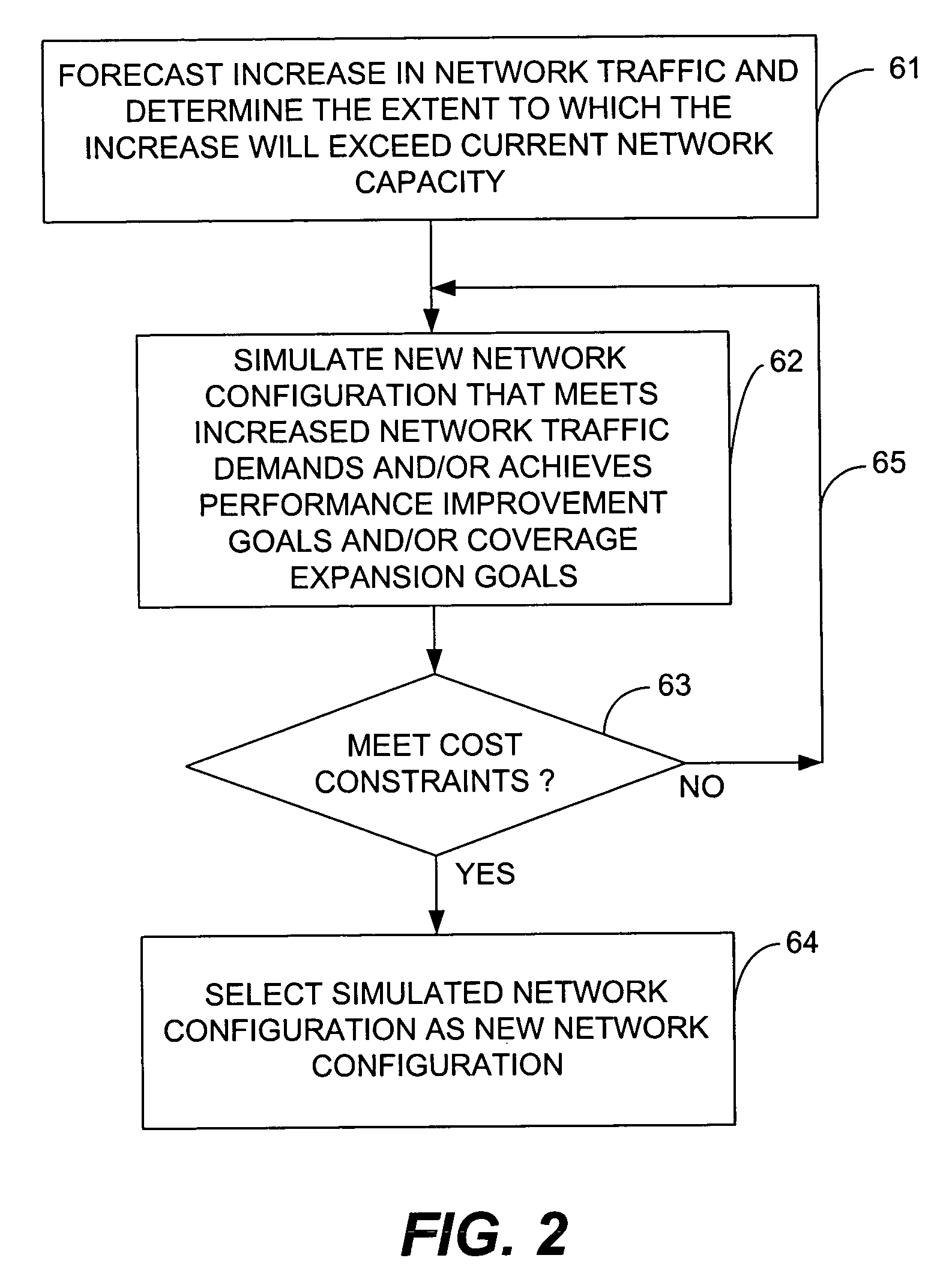
Method and apparatus for automatically determining the manner in which to allocate available capital to achieve a desired level of network quality performance
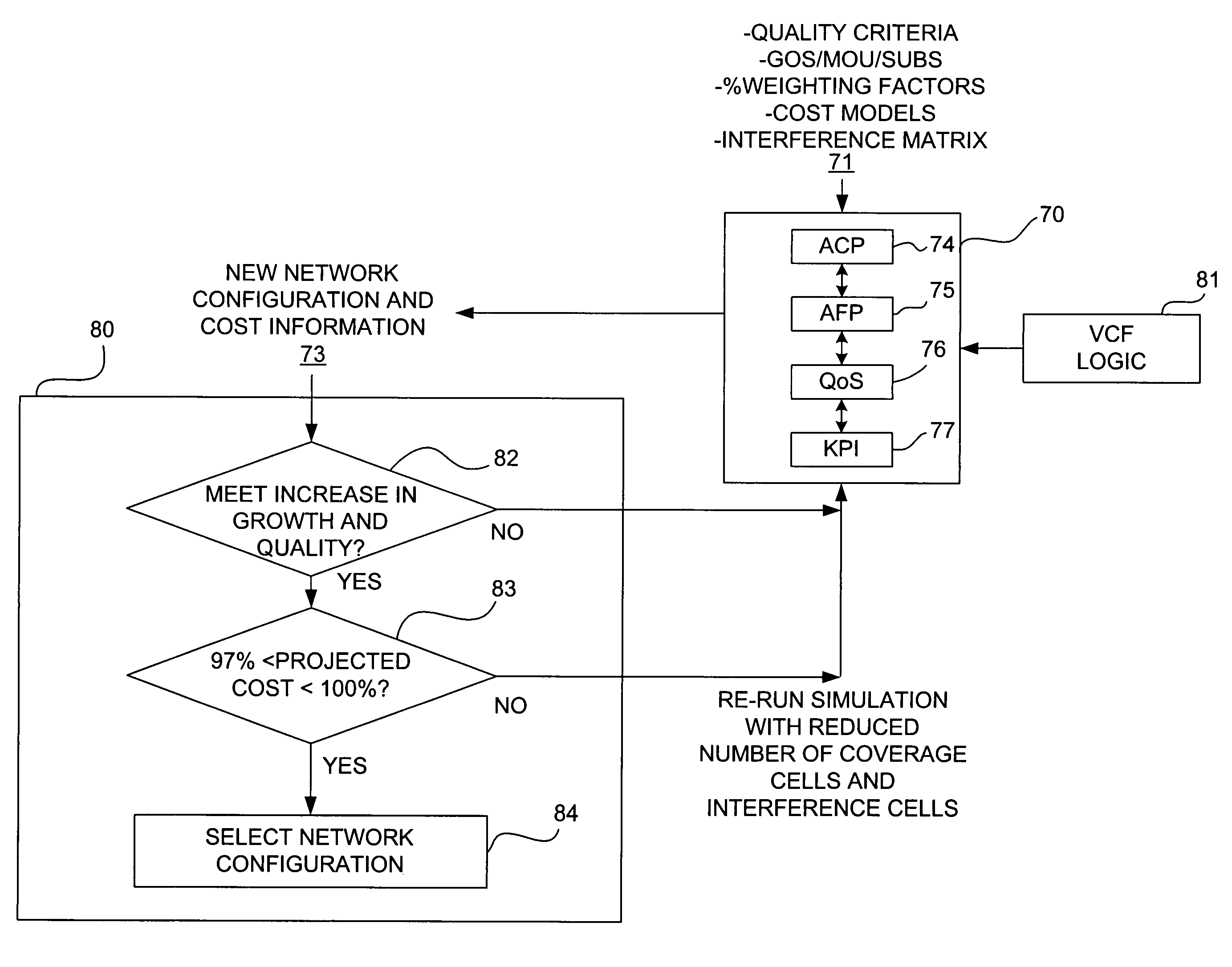
InactiveUS20060083170A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionInternet trafficQuality performance
A method and apparatus for simulating a modification to or expansion of a communications network and for determining whether the simulated modified or expanded network meets cost criteria. First logic forecasts an increase in network traffic. Second logic simulates a modification to or expansion of the network based on the forecasted increase in network traffic and / or based on performance improvement criteria and / or based on coverage expansion criteria. Third logic determines whether the simulated modified or expanded network meets cost criteria.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
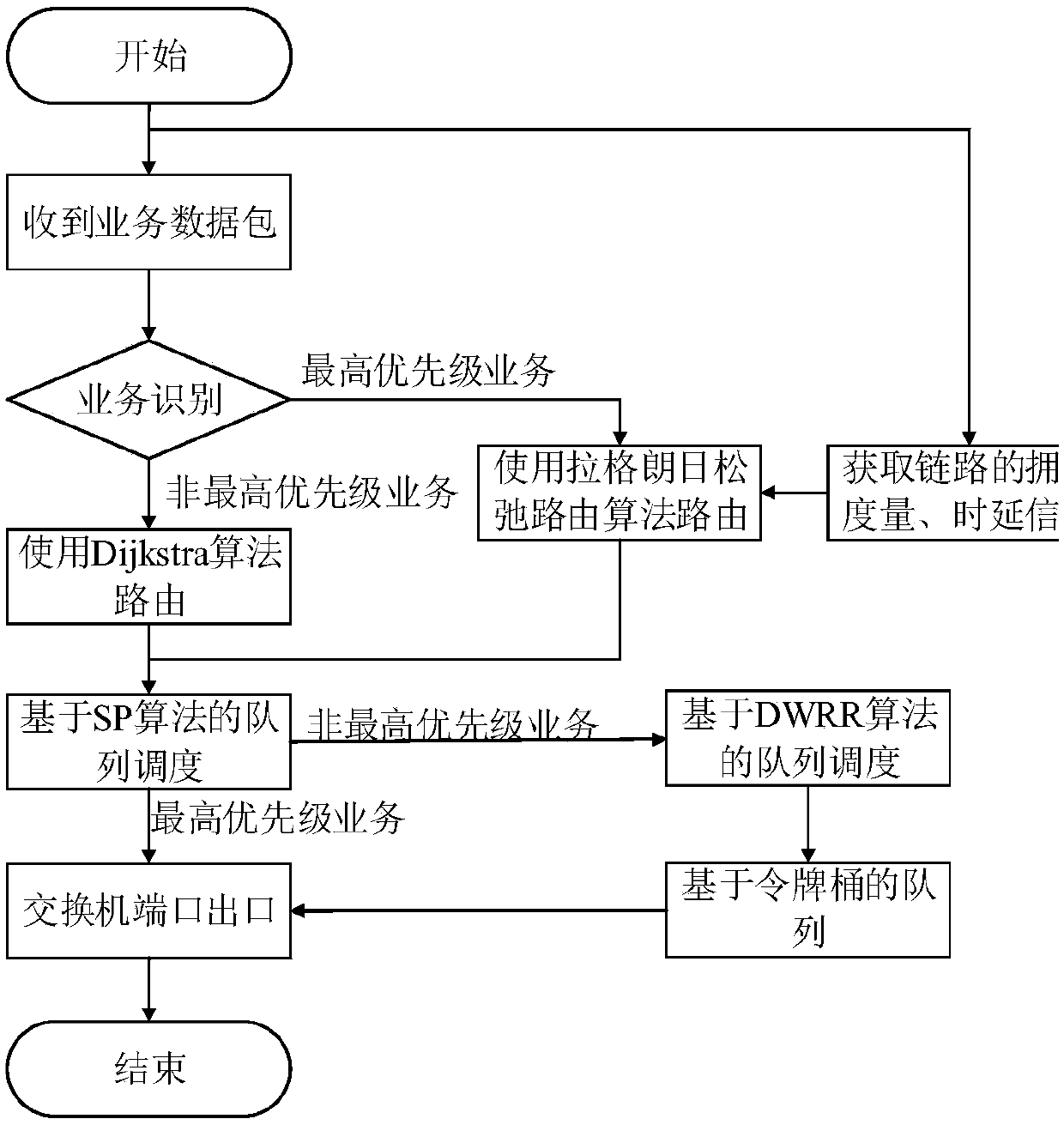
QoS control method of distinguishing service priorities in SDN
ActiveCN107896192AGuaranteed service qualityIncrease profitData switching networksQos quality of serviceData stream
The invention discloses a QoS control method of distinguishing service priorities in a SDN, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing service priority division for data services inthe SDN according to QoS needed for the data services, then, in distinguishing routing, taking link congestion measurement as link cost criteria for a service data stream with the highest priority, and taking time delay needed for the service data stream with the highest priority as a constrain condition, routing through a Lagrange Relaxation aggregation criteria algorithm, and for the other service data streams, routing through a shortest path algorithm using hops as criteria; and in distinguishing queue scheduling, performing differentiated queue scheduling based on service priorities. Themethod provided by the invention guarantees end-to-end time delay of the service with the highest priority as much as possible, also guarantees different QoS of other services with different priorities in a distinguished mode, and meanwhile, the method routes the service with the highest priority to a low-congestion path, thus, utilization rate of network bandwidth and throughput capacity of network data transmission are improved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Automated anomaly detection
ActiveUS7627543B2Avoid overfitting noisy dataError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsData setNoisy data
A method of anomaly detection applicable to telecommunications or retail fraud or software vulnerabilities uses inductive logic programming to develop anomaly characterization rules from relevant background knowledge and a training data set, which includes positive anomaly samples of data covered by rules. Data samples include 1 or 0 indicating association or otherwise with anomalies. An anomaly is detected by a rule having condition set which the anomaly fu,lfils. Rules are developed by addition of conditions and unification of variables, and are filtered to remove duplicates, equivalents, symmetric rules and unnecessary conditions. Overfitting of noisy data is avoided by an encoding cost criterion. Termination of rule construction involves criteria of rule length, absence of negative examples, rule significance and accuracy, and absence of recent refinement. Iteration of rule construction involves selecting rules with unterminated construction, selecting rule refinements associated with high accuracies, and iterating a rule refinement, filtering and evaluation procedure to identify any refined rule usable to test data. Rule development may use first order logic or Higher Order logic.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
System for processing digital map data
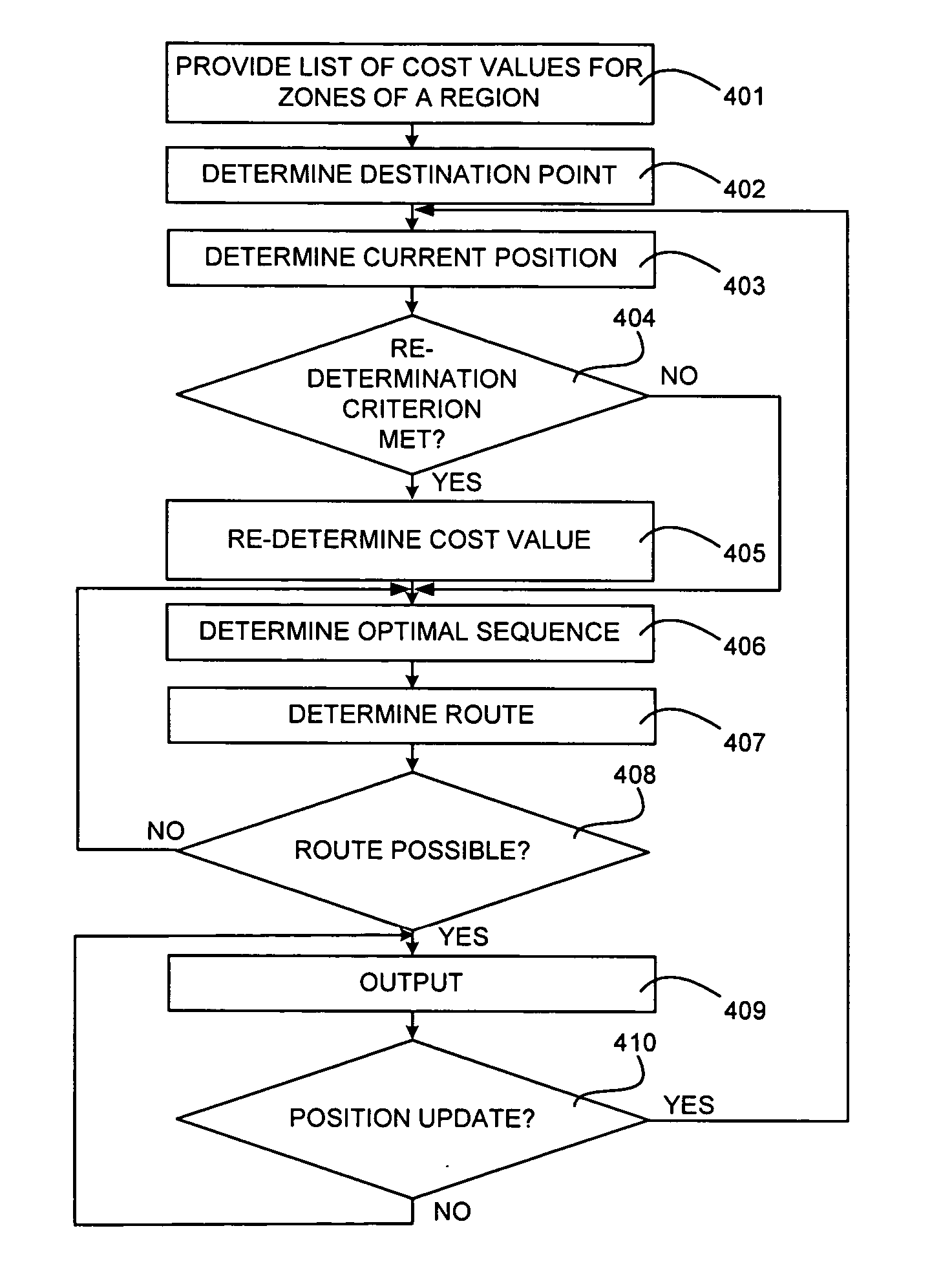
ActiveUS7248184B2Vehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesCost criterionComputer science
A method for processing digital map data for route determination is provided that includes dividing a region into a plurality of zones, and for the zones, automatically determining at least one cost value for at least one direction of travel of the zone based on the digital map data of the zone and a predetermined cost criterion. A method for determining a route between two points is provided that includes dividing a region into a plurality of zones, for the zones, automatically determining at least one cost value for at least one direction of travel of the zone based on the digital map data of the zone and a predetermined cost criterion, and automatically determining at least one sequence of zones connecting the two points, where each zone of the sequence may be adjacent to another zone of the sequence, such that the sum of the cost values of the zones of the sequence may be optimized.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
Method and system for communications routing
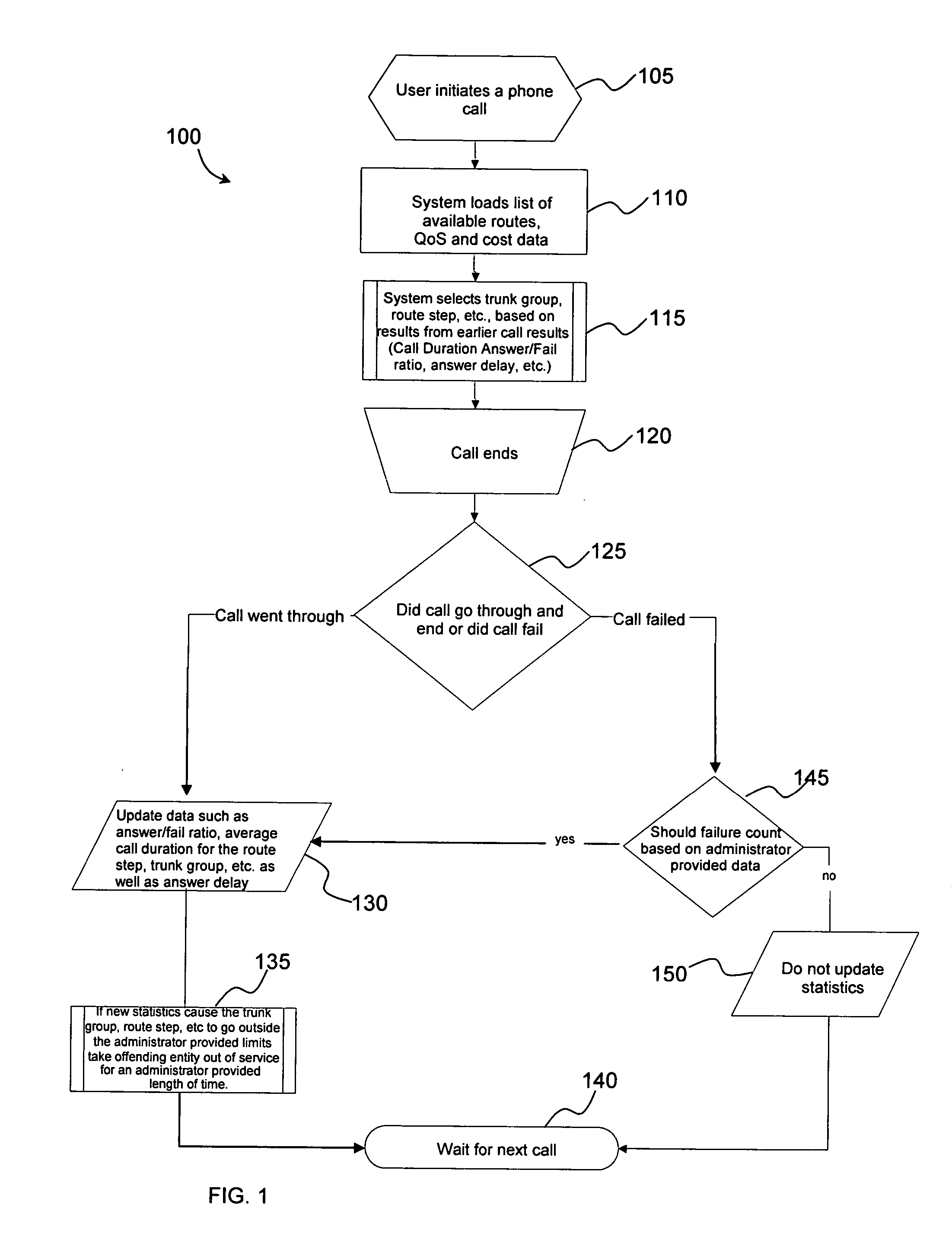
InactiveUS20050281199A1Increase rangeMultiplex system selection arrangementsError preventionQuality of serviceComputerized system
A method and system for communications routing provides an improved range of service quality and cost options. The method includes receiving at a host computer system an indication that a user has placed a telephone call. Next the host computer system receives from a routing database operatively connected to the host computer system both QoS criteria and cost criteria. The QoS criteria and cost criteria are then matched with empirical QoS data and least-cost routing data, respectively. A call route is then determined based on the matched QoS criteria and cost criteria with empirical QoS data and least-cost routing data, respectively. The routing database is then updated based on whether the determined call route provided an acceptable QoS.
Owner:SIMPSON GRANT M F +1
Method and apparatus for automatically determining the manner in which to allocate available capital to achieve a desired level of network quality performance
InactiveUS7929459B2Multiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationInternet trafficQuality performance
A method and apparatus for simulating a modification to or expansion of a communications network and for determining whether the simulated modified or expanded network meets cost criteria. First logic forecasts an increase in network traffic. Second logic simulates a modification to or expansion of the network based on the forecasted increase in network traffic and / or based on performance improvement criteria and / or based on coverage expansion criteria. Third logic determines whether the simulated modified or expanded network meets cost criteria.
Owner:CINGULAR WIRELESS II LLC
System for processing digital map data
ActiveUS20050107950A1Simple further processingVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesComputer scienceCost criterion
A method for processing digital map data for route determination is provided that includes dividing a region into a plurality of zones, and for the zones, automatically determining at least one cost value for at least one direction of travel of the zone based on the digital map data of the zone and a predetermined cost criterion. A method for determining a route between two points is provided that includes dividing a region into a plurality of zones, for the zones, automatically determining at least one cost value for at least one direction of travel of the zone based on the digital map data of the zone and a predetermined cost criterion, and automatically determining at least one sequence of zones connecting the two points, where each zone of the sequence may be adjacent to another zone of the sequence, such that the sum of the cost values of the zones of the sequence may be optimized.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
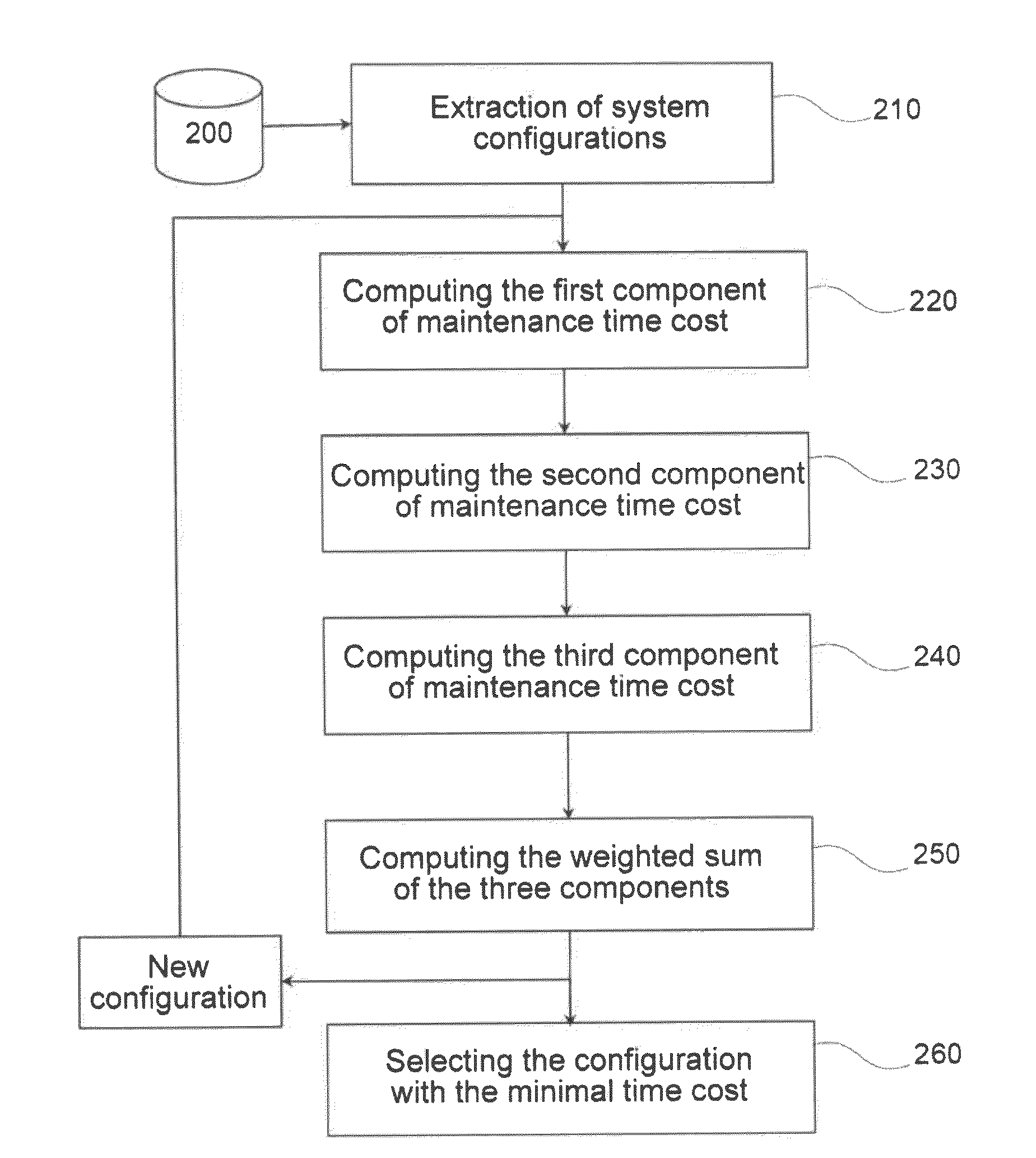
Method and tool for aided aircraft design using a criterion of operational availability
InactiveUS20110218783A1Maintenance operationGeometric CADConfiguration CADAviationComputer Aided Design
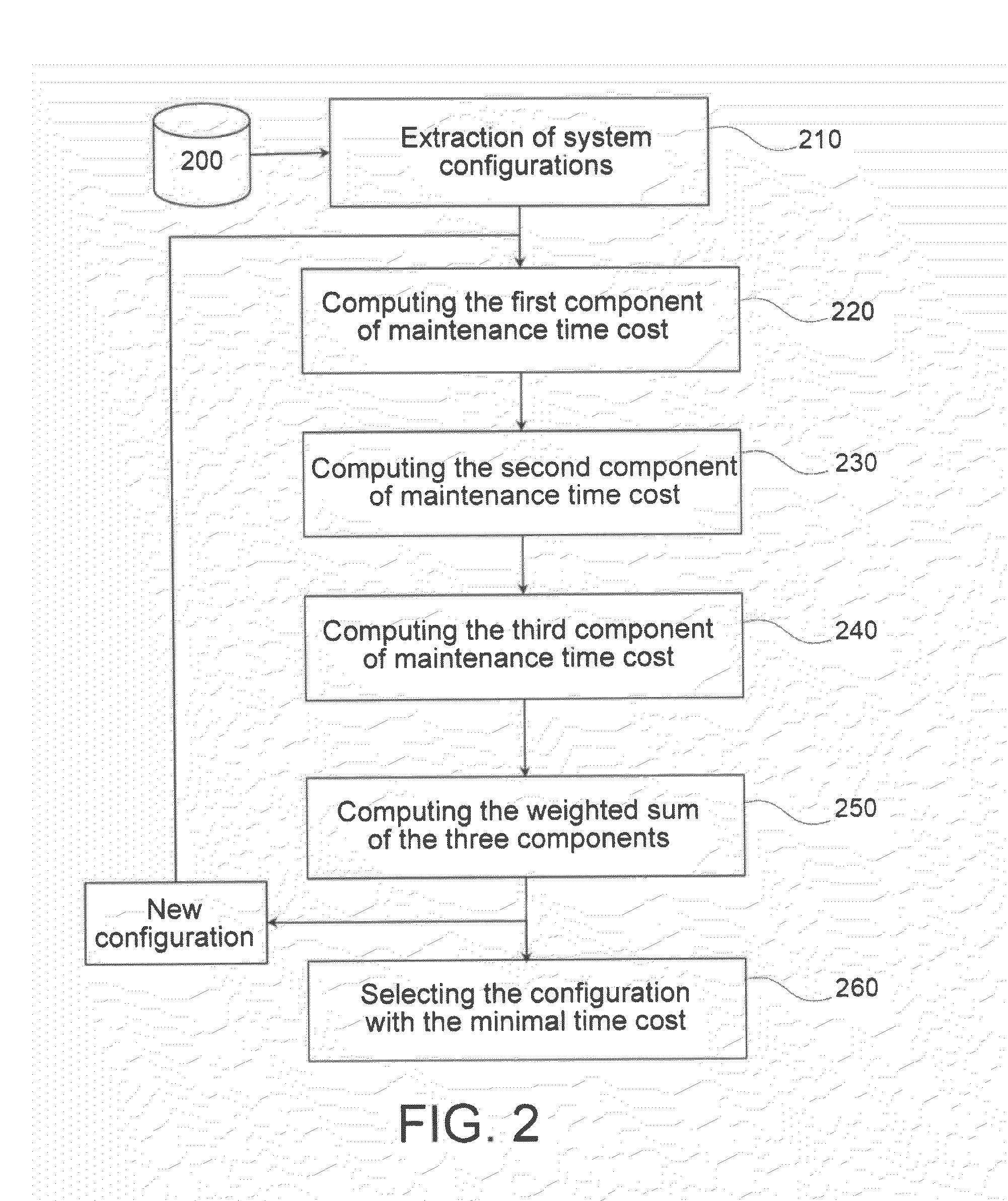
The invention concerns a method for the computer-aided design of an aeronautic system forming all or part of an aircraft, using a criterion of maintenance time cost over a given period of use. The cost is computed as the weighted sum (250) of a first component (220) representing the mean flight time lost during this period, of a second component (230) representing the mean unscheduled maintenance time for this system during said period, and a third component representing the scheduled maintenance time for this system throughout said period. The configuration corresponding to the lowest time cost is then selected (260).
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Timing-driven placement method utilizing novel interconnect delay model
InactiveUS6901571B1Computer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationPin distanceEngineering
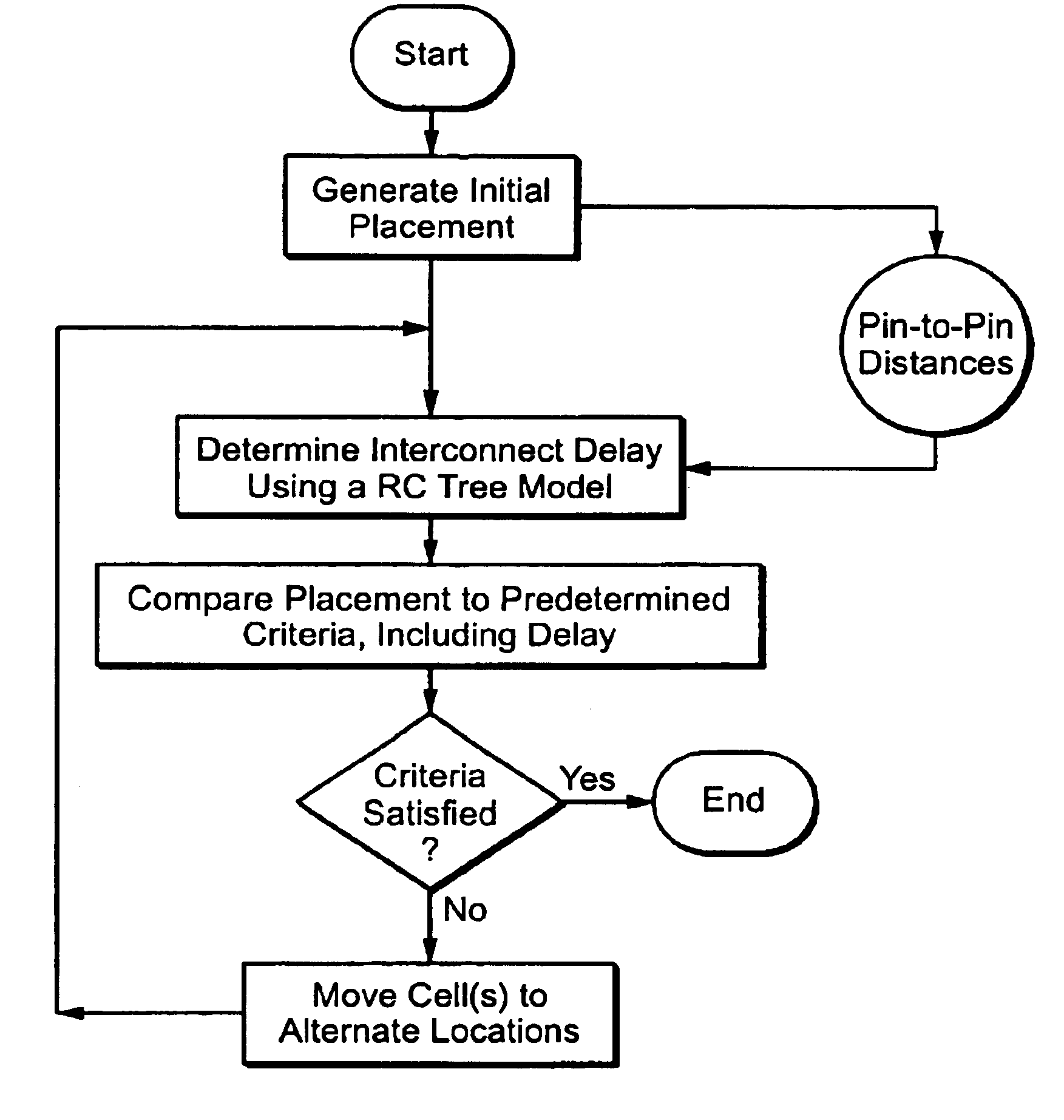
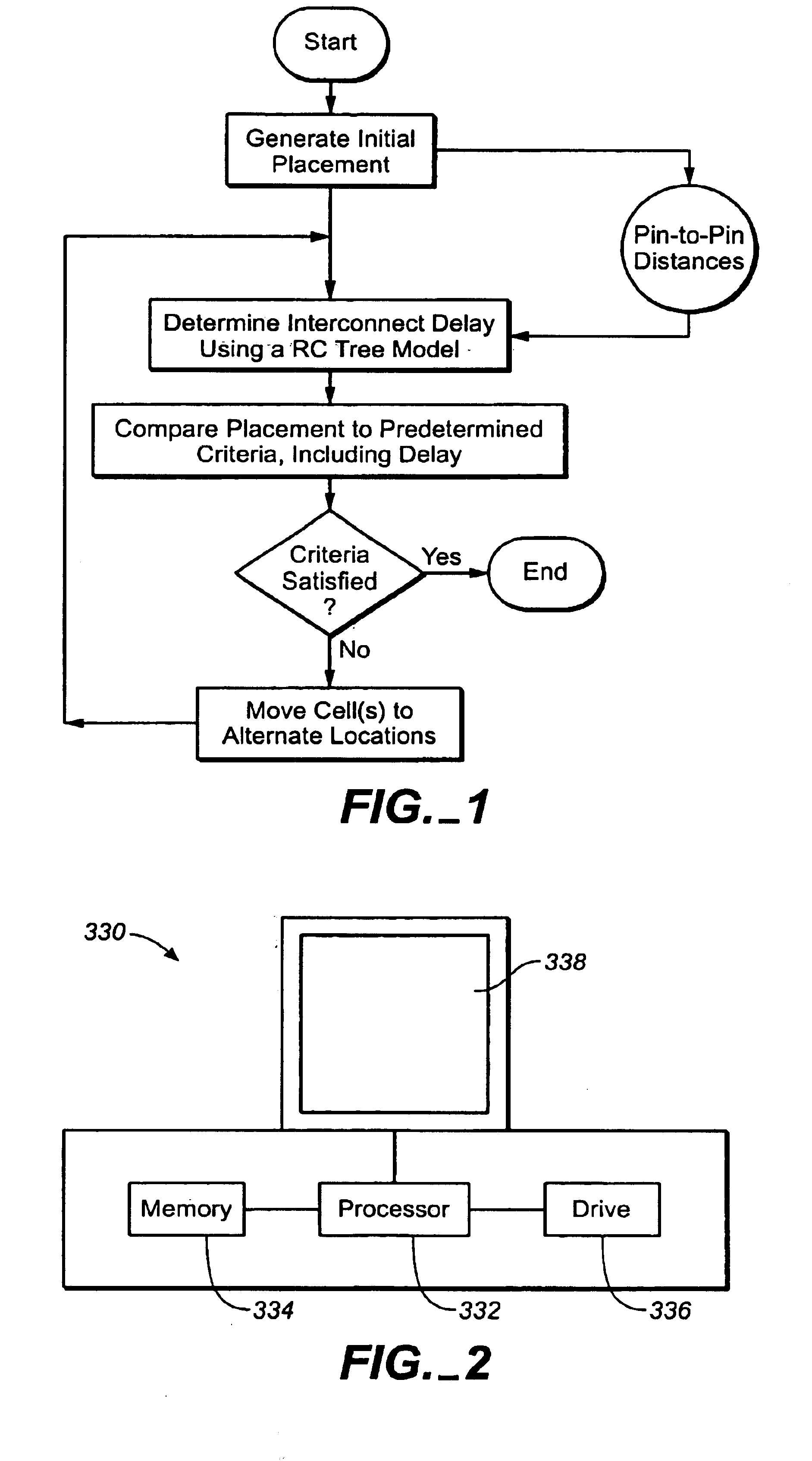
A method for optimal placement of cells on a surface of an integrated circuit, comprising the steps of comparing a placement of cells to predetermined cost criteria and moving cells to alternate locations on the surface if necessary to satisfy the cost criteria. The cost criteria include a timing criterion based upon interconnect delay, where interconnect delay is modeled as a RC tree expressed as a function of pin-to-pin distance. The method accounts for driver to sink interconnect delay at the placement level, a novel aspect resulting from use of the RC tree model, which maximally utilizes available net information to produce an optimal timing estimate. Preferred versions utilize a RC tree interconnect delay model that is consistent with timing models used at design levels above placement, such as synthesis, and below placement, such as routing. Additionally, preferred versions can utilize either a constructive placement or iterative improvement placement method.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
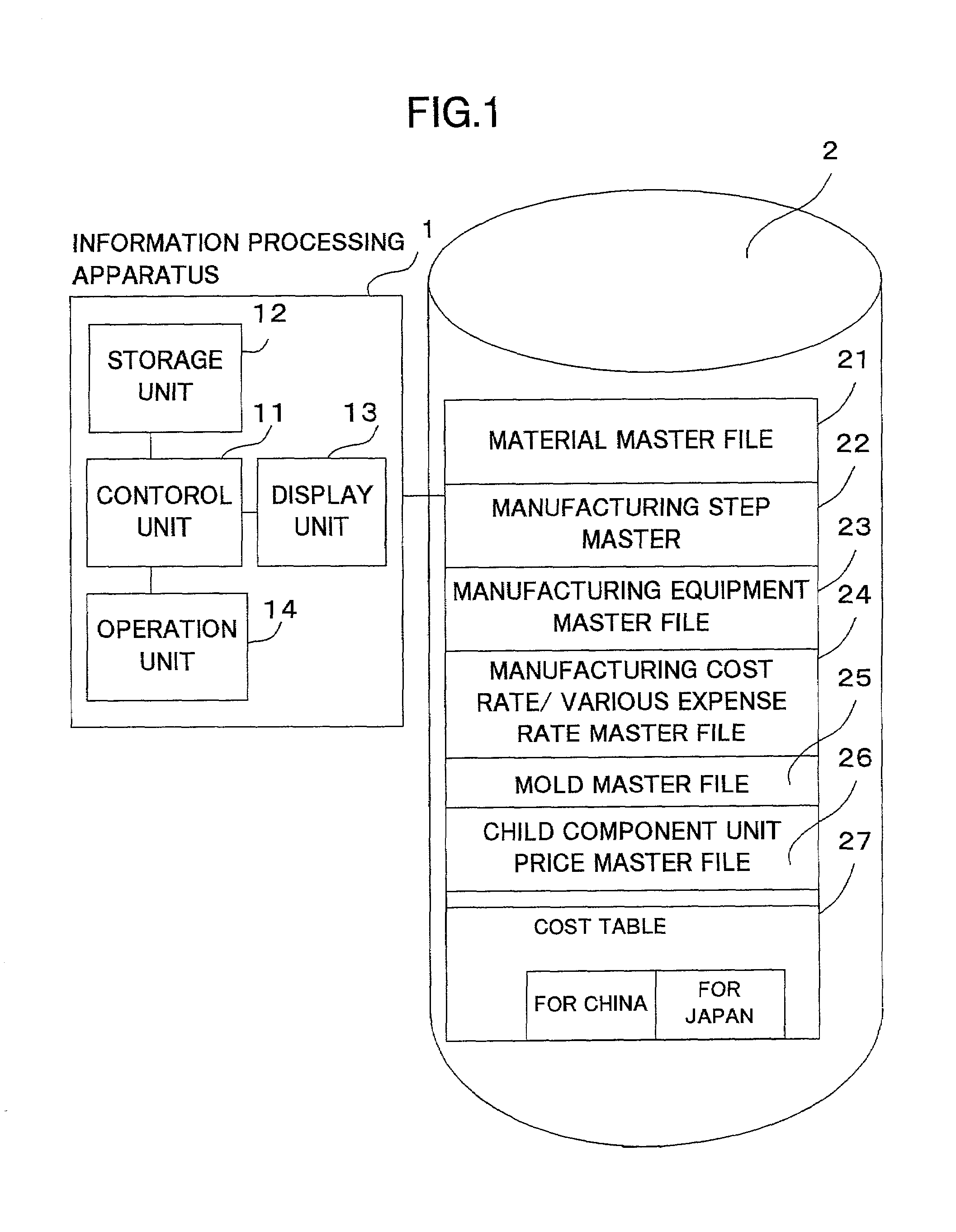
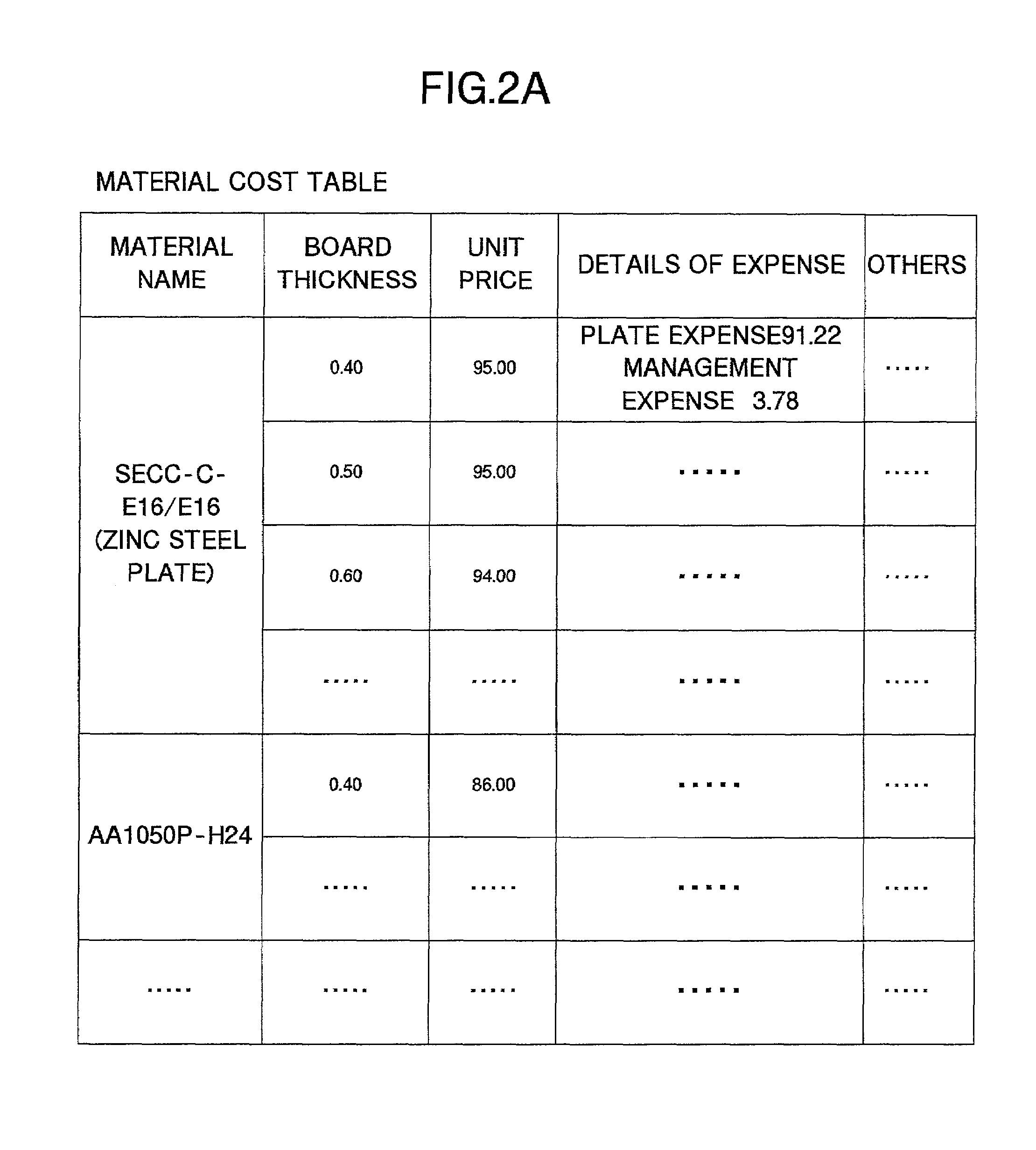
Component cost estimation system, component cost estimation method, cost standard data providing system, cost standard data providing method, recording medium, and computer data signal
InactiveUS7398254B2Good estimateAppropriate costBuying/selling/leasing transactionsResourcesInformation processingExternal storage
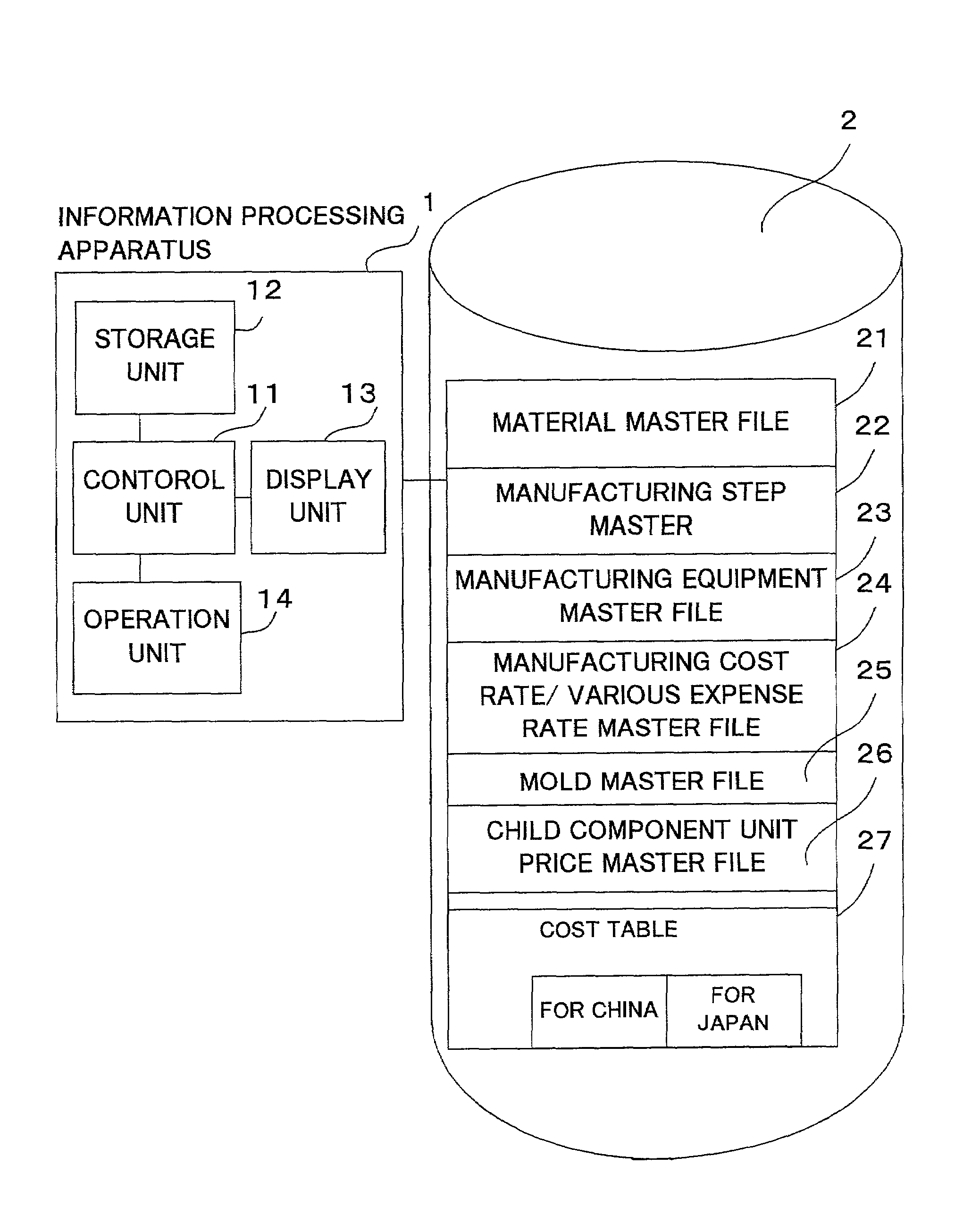
An external storage device of a component cost estimation system stores various cost information representing a component material and its cost in association with each other, and a component manufacturing step and a cost involved in the step in association with each other. An information processing apparatus specifies a material of a component to be manufactured, and a plurality of manufacturing steps. Then, the information processing apparatus retrieves a cost of the specified material, and costs corresponding to the specified manufacturing steps from the cost information, and estimates a cost of the component based on the retrieved costs. The cost of the component is computed by adding up the cost of the material and the costs involved in all the manufacturing steps.
Owner:RICOH KK
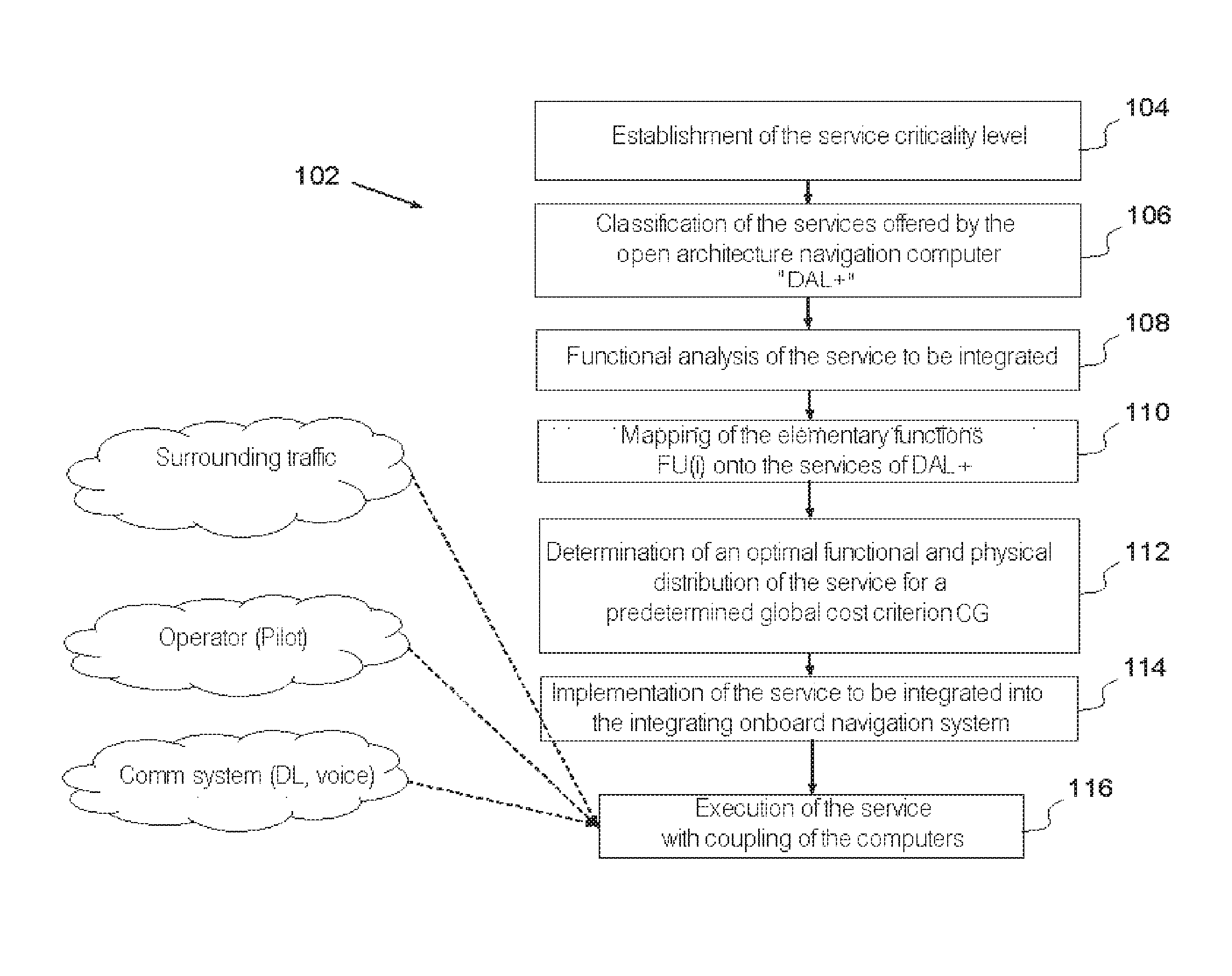
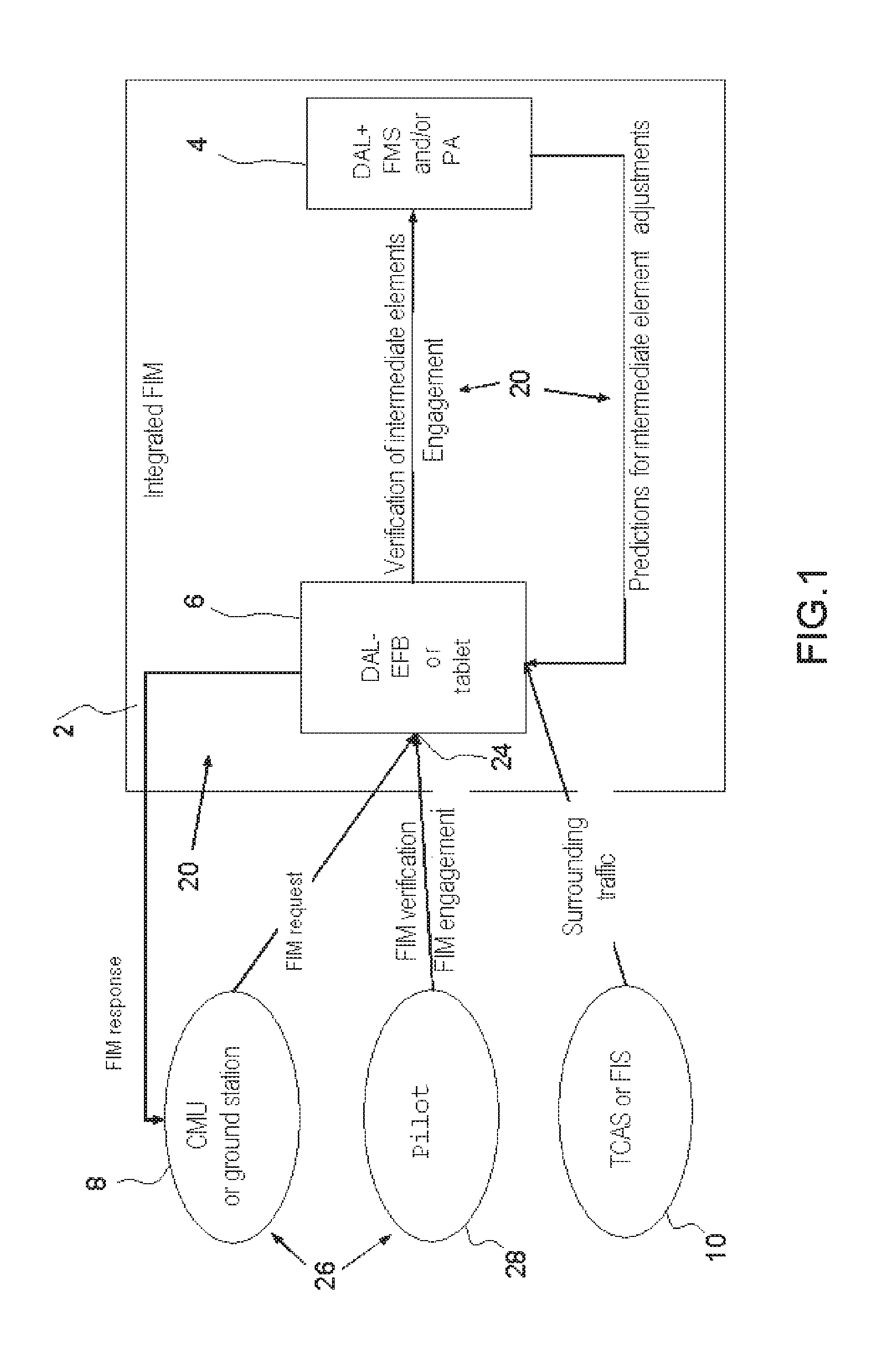
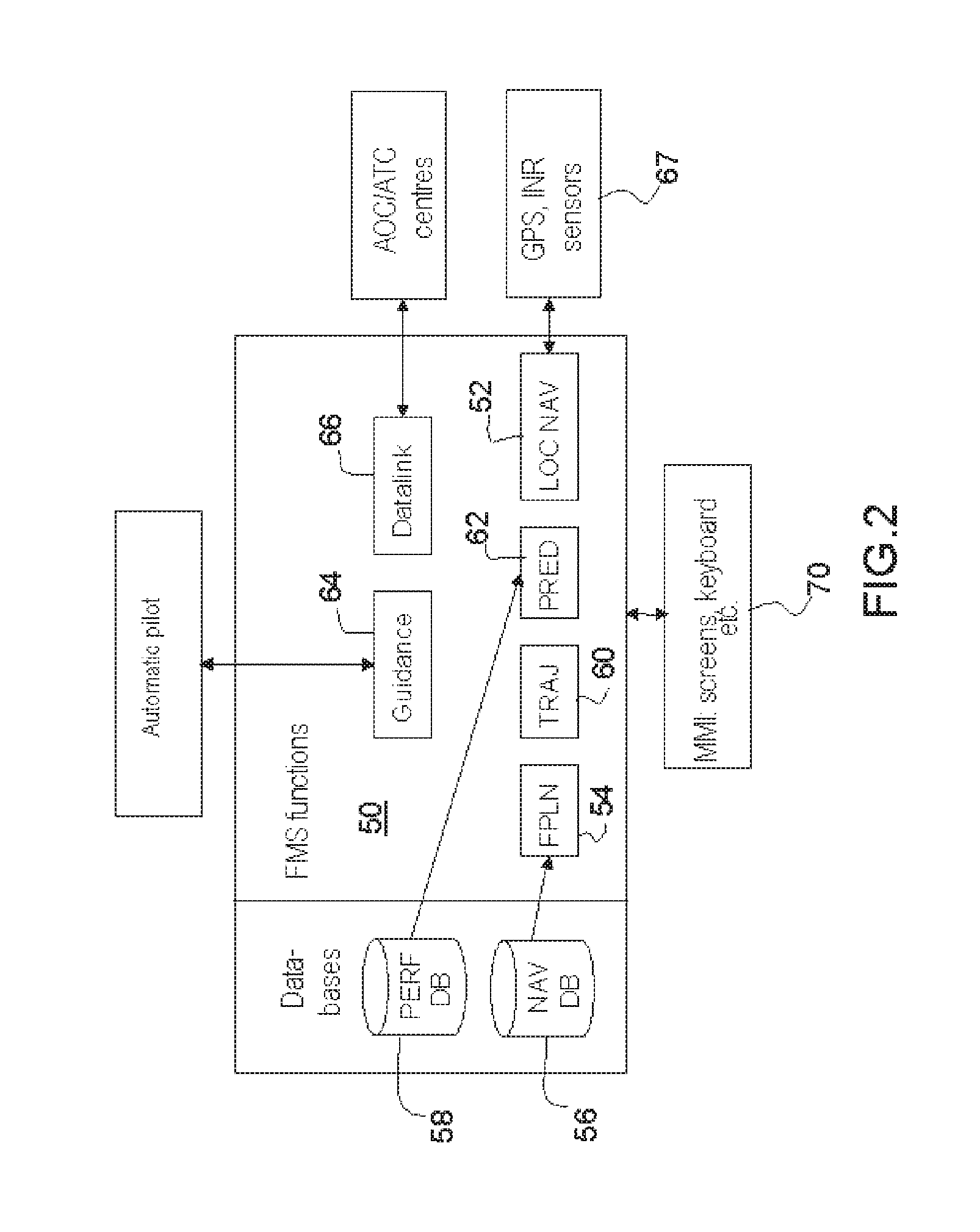
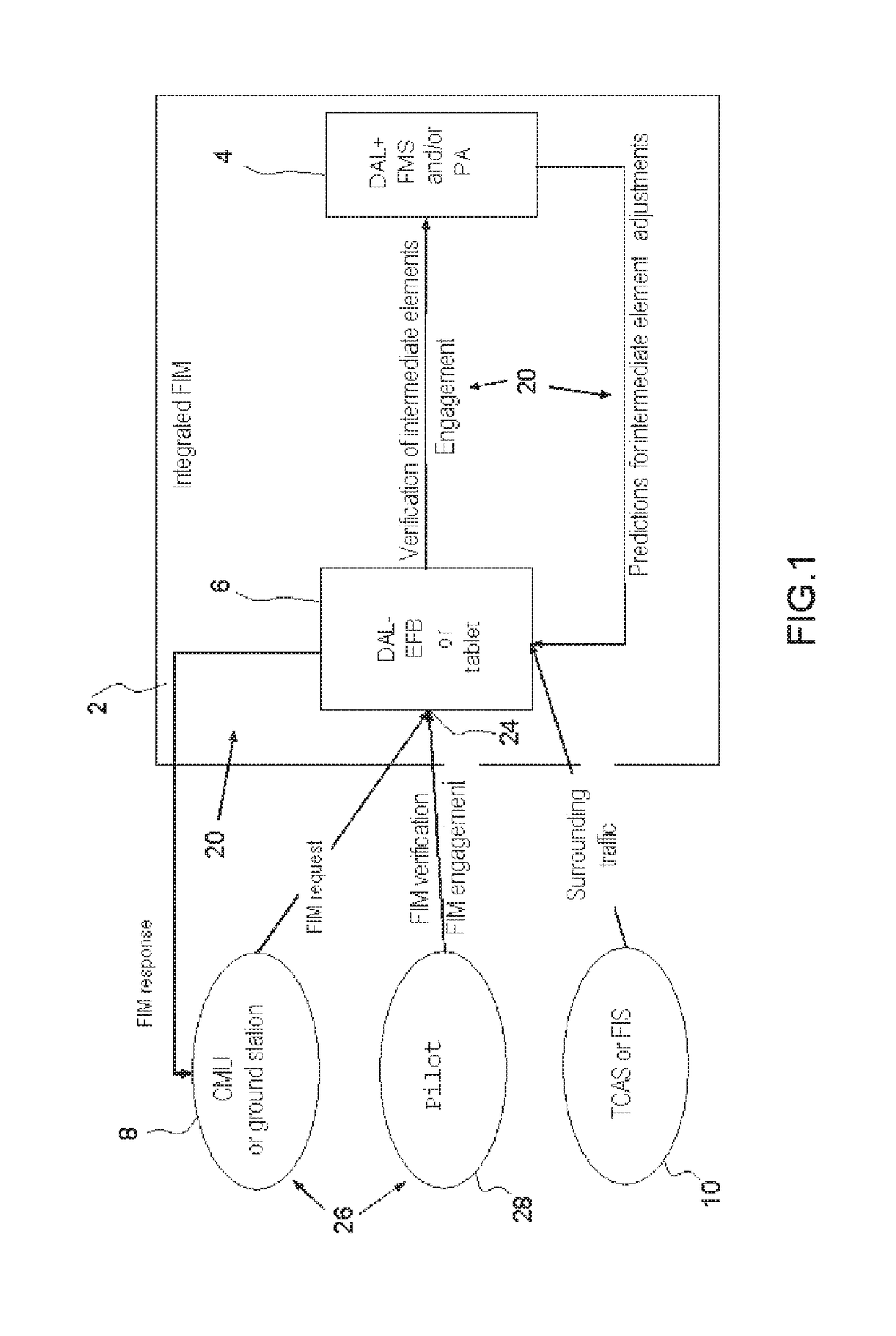
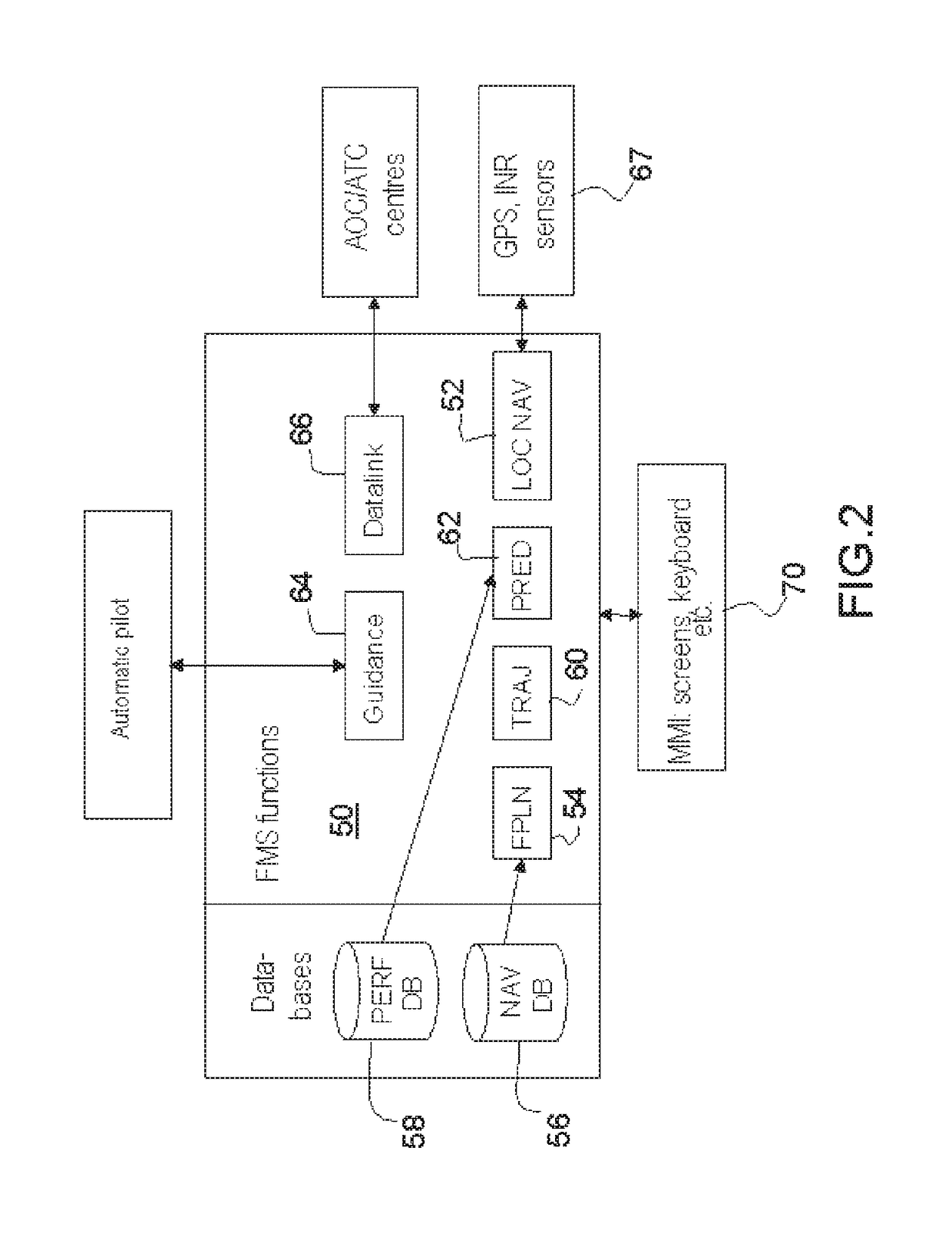
Method for integrating a new service into an avionics onboard system with open architecture of client-server type, in particular for an fim manoeuvre service
ActiveUS20170013061A1Cost in response timeMinimize communication exchangeAircraft componentsMarket predictionsAviationElectronic systems
A method for integrating a new navigation service is implemented in an avionics onboard system comprising a DAL+ core computer and a DAL− peripheral computer for managing the application. The method of integration determines an optimal functional and physical distribution of the elementary functions FU(i) of the new service within the onboard avionics system over the set of possible distributions which minimizes a global cost criterion CG, dependent on several parameters, including at least the additional development cost of the elementary functions integrated within the digital DAL+ core computer, and carries out the integration of the new service.
Owner:THALES SA
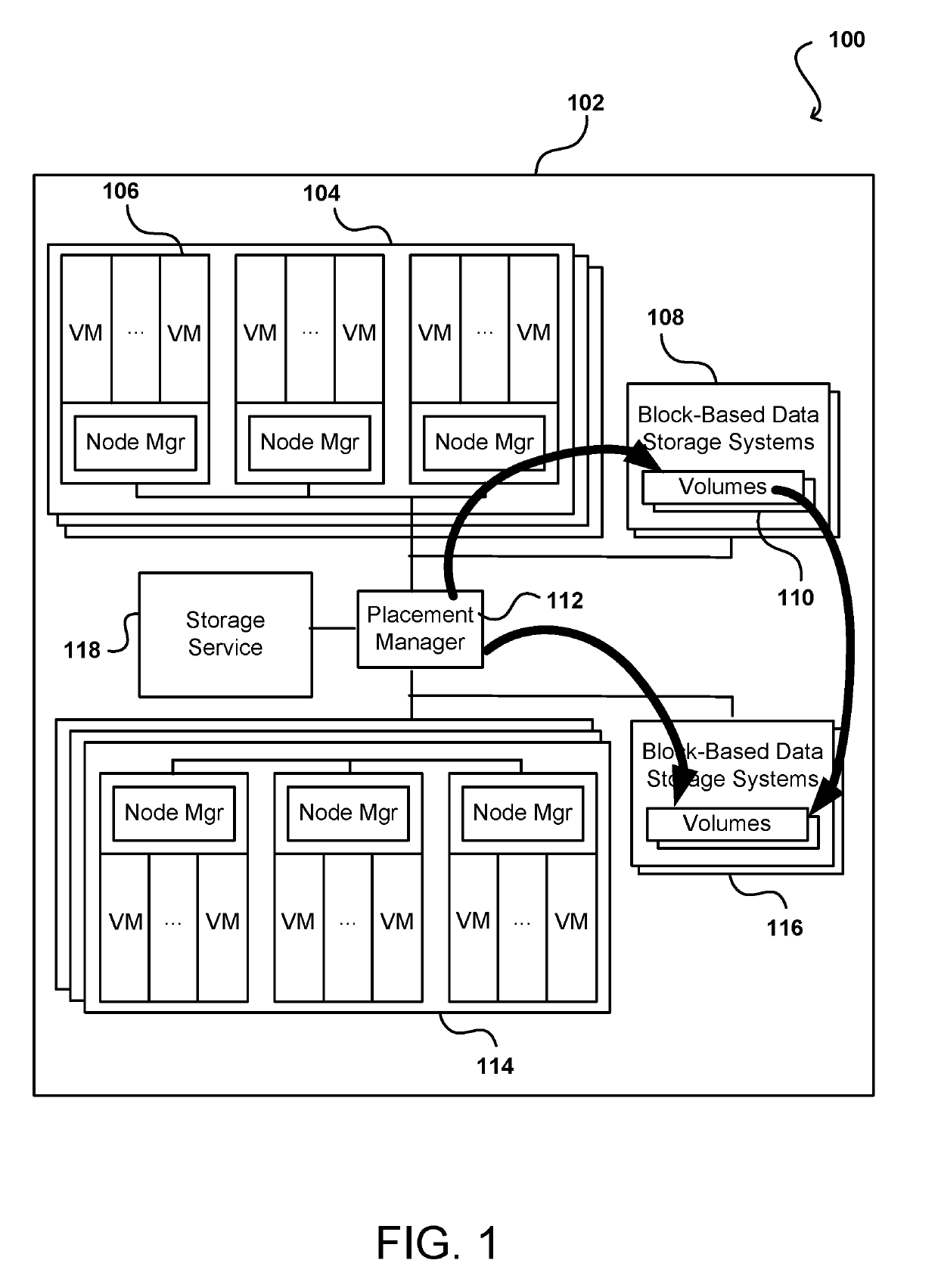
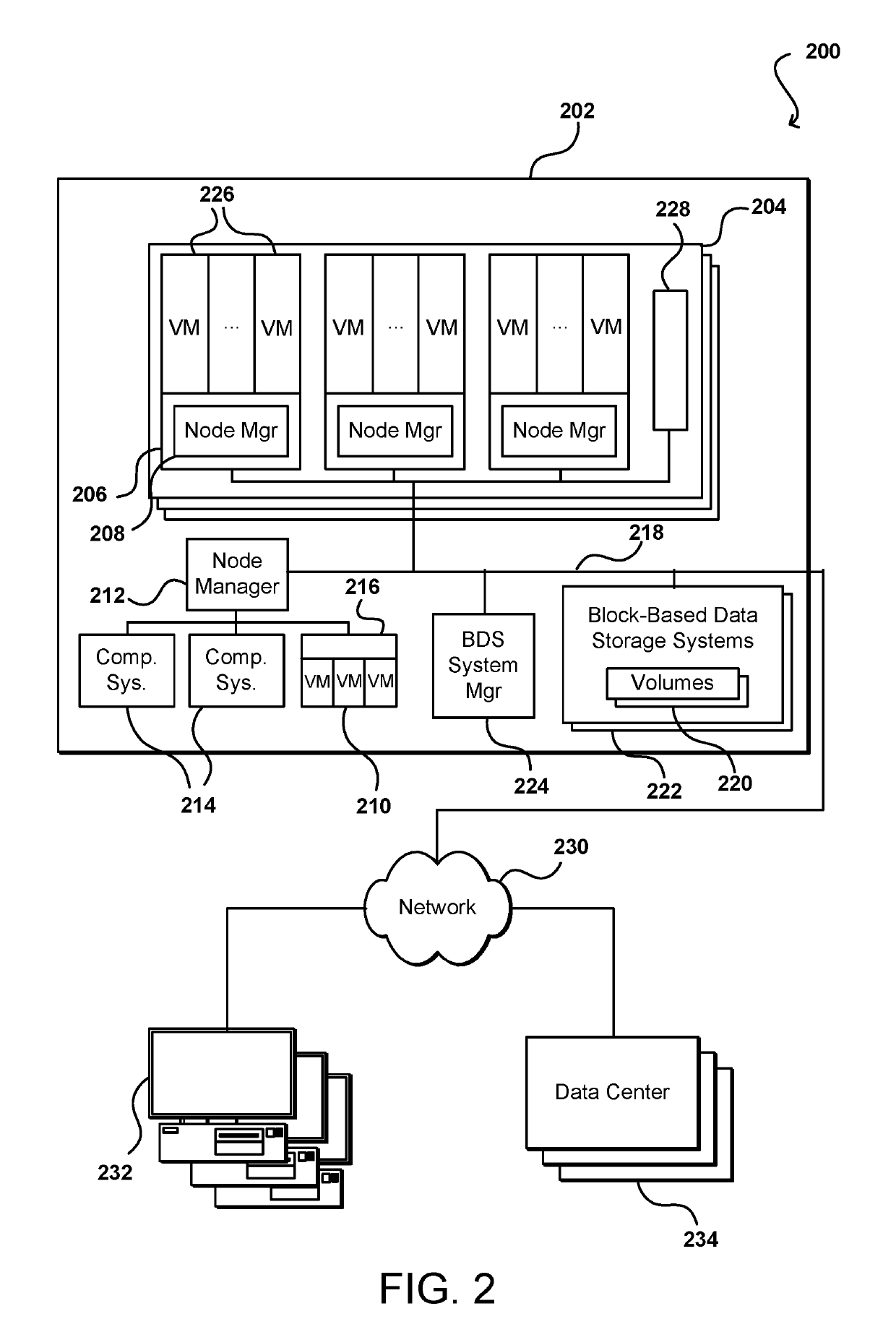
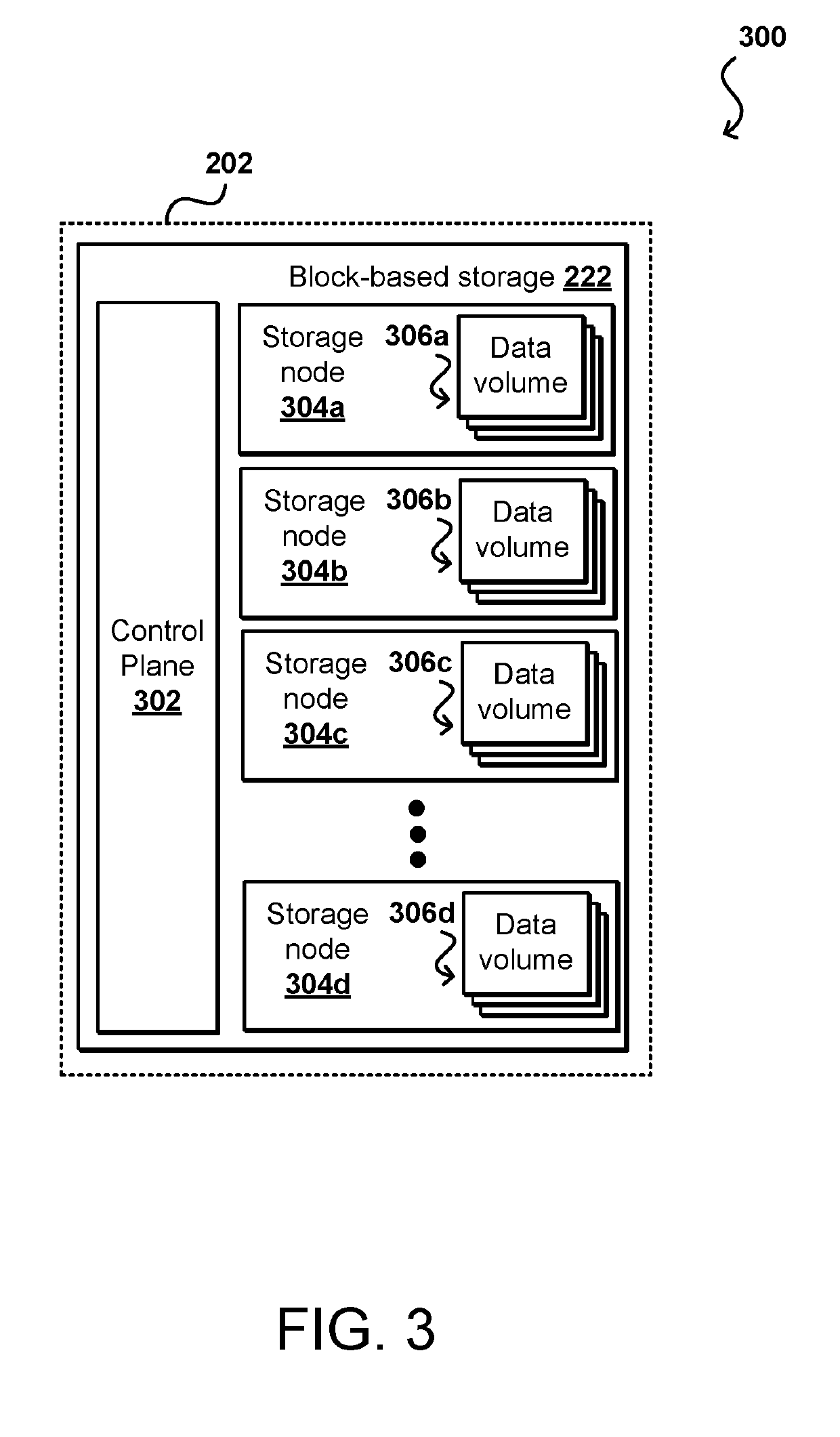
Storage tier-based volume placement
Data volumes for a customer can be placed on various storage tiers, including different hardware types or storage systems, that are determined to be appropriate for the anticipated usage of those data volumes. The actual usage can be monitored to determine one or more types of workload for the data volume, and a determination made as to whether all, or portions, of the data volume could obtain a significant performance improvement by being migrated to a different storage tier. In some instances the chunks or partitions of a volume can be concurrently distributed across multiple different storage tiers in order to satisfy various performance and / or cost criteria. Once workload information is available for a customer, that information can be used to determine the storage tiers for initial placement of subsequent data volumes.
Owner:AMAZON TECH INC
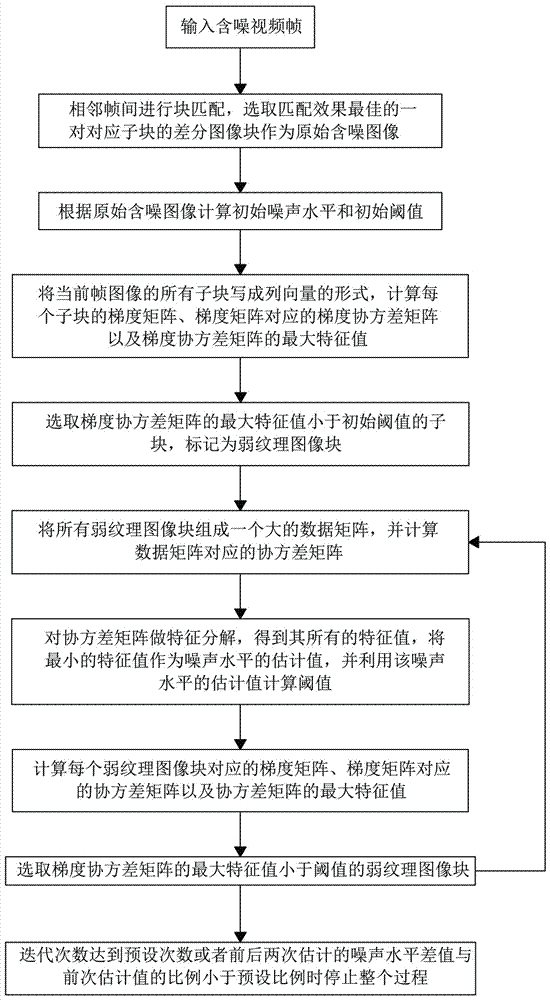
Video noise estimation method based on main component analysis
ActiveCN107295217AHighlight substantive featuresSignificant progressTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputation complexityNoise level
The invention provides a video noise estimation method based on main component analysis. Video sequence correlation is fully used, and similar block searching is carried out between adjacent frames of images, and based on a minimum cost criterion, a differential image between the adjacent frames of images is acquired, and influences of video motion are eliminated, and then a preliminary weak texture difference image is acquired. Noise estimation based on video blocks is introduced, and noise level parameters are acquired in a self-adapting way, and a normal distribution function is adopted as a threshold function of selection of a weak texture block, and then calculation complexity is reduced. The estimated noise level is more accurate by adopting a clear iteration index, and then an underestimation phenomenon under a condition of a high noise level is prevented. The video noise estimation method can be used in a blind video denoising filed, and has advantages of accurate estimation and wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHONGYUAN WISDOM CITY DESIGN RES INST CO LTD
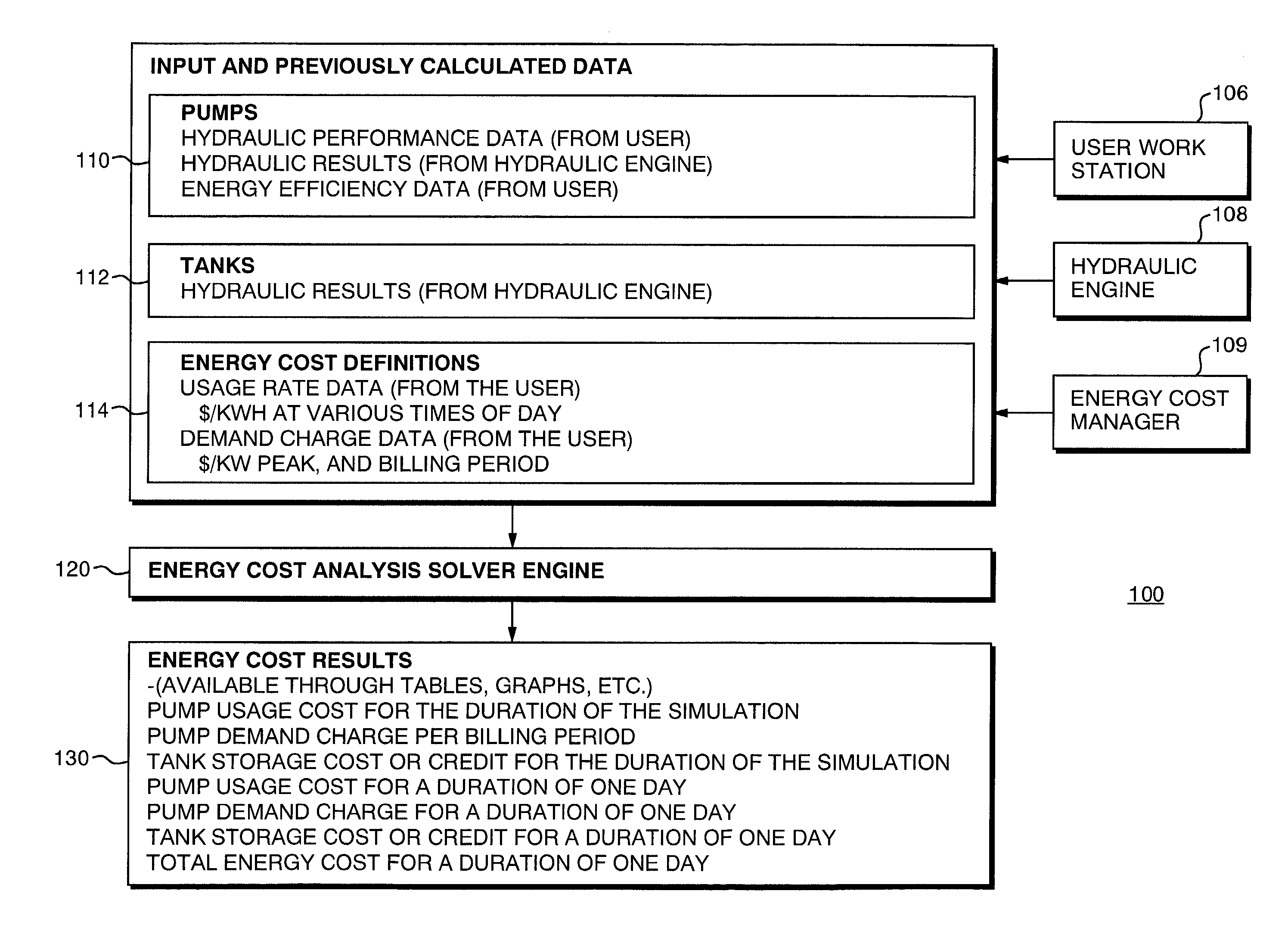
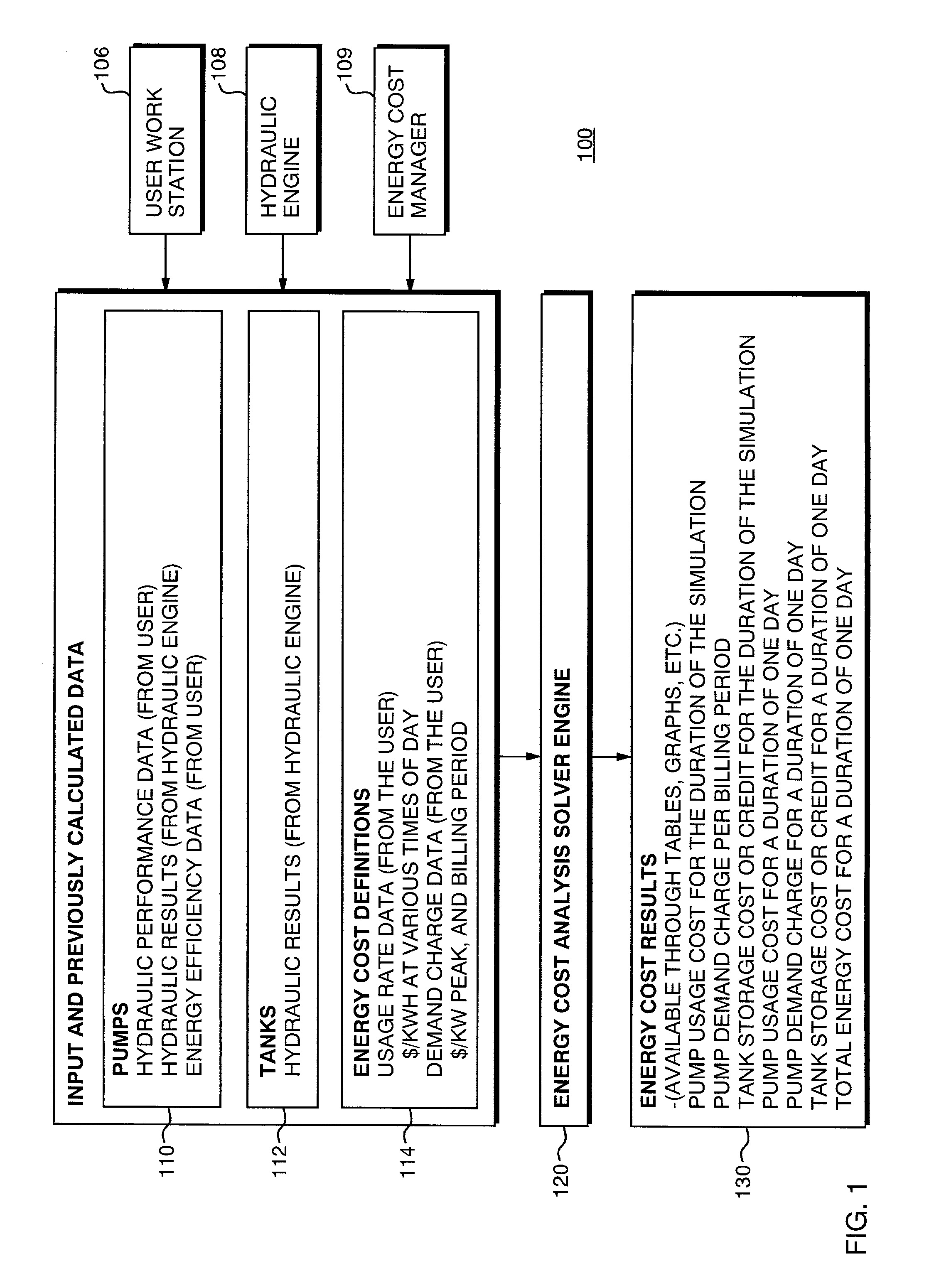
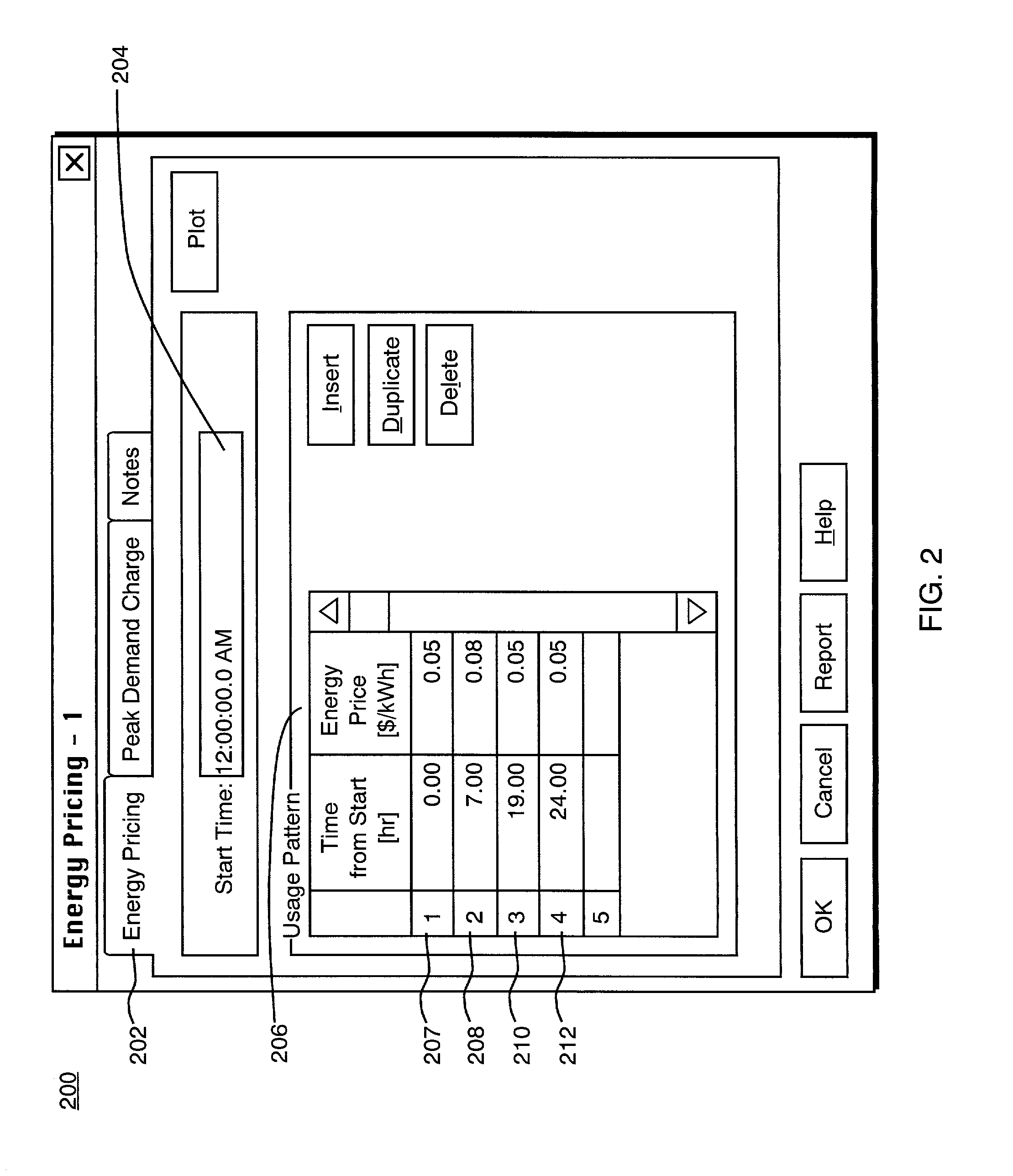
Method and system for providing an energy cost estimation for a water distribution network
A method and system for providing cost estimation in connection with a water distribution network is provided. The method includes estimating the energy cost within a water distribution network associated with pumps pushing water from areas of low hydraulic grade to areas of higher hydraulic grade and using energy in the process, as well as estimating cost equivalents for storage changes that occur as tanks within the system fill or drain. The costs associated with this energy are taking into account. Energy Price Definitions are created that take into account the water utility rate structure for the associated pump and the times are which the pump is operating. The price of energy at the pertinent times is taken into account in an energy cost manager program that interfaces with a database of information about the water distribution network as well as utility rate structures from which can be drawn utility rate information to estimate the electrical energy costs for running the system during a particular simulation. The simulation also takes into account peak periods for the electrical energy usage, and normalizes costs to a common time frame.
Owner:BENTLEY SYST INC
Low-cost solid-state identification device
InactiveUS8099261B2Easy to upgradeShort timeSpecial data processing applicationsIlluminated signsThe InternetEnergy expenditure
The invention describes intelligent configurable apparatus used for identification and status indication for variety of applications: point-of-service locations; buildings / apartment complexes, residential homes; street signs; etc. Apparatus could be stand-alone or expandable plug-in modules interconnected via local area wired and wireless network into identification and status system. Apparatus could be DC powered, including solar. Apparatus has controller and sensors. Based on apparatus configuration and information obtained from sensors, controller performs variety of controls: illumination color / intensity / modulation; power consumption; communication with other controllers over LAN and / or INTERNET. Sensors could detect: presence of object; environmental parameters—temperature, light, sound; power consumption. Configuration parameters include: power consumption, brightness, ambient conditions, and schedule of operation. Power consumption allows apparatus operation based on safety and cost criteria. Apparatus also controls light function and intensity to meet set criteria. This leads to self-contained apparatus automatically driven by set criteria, including cost control.
Owner:BRAUNSTEIN ZACHARY L
Components and parts cost estimating method and system, cost standard information offering method and system
InactiveCN1362683AGood estimateMetal-working apparatusBuying/selling/leasing transactionsInformation processingExternal storage
An external storage device of a component cost estimation system stores various cost information representing a component material and its cost in association with each other, and a component manufacturing step and a cost involved in the step in association with each other. An information processing apparatus specifies a material of a component to be manufactured, and a plurality of manufacturing steps. Then, the information processing apparatus retrieves a cost of the specified material, and costs corresponding to the specified manufacturing steps from the cost information, and estimates a cost of the component based on the retrieved costs. The cost of the component is computed by adding up the cost of the material and the costs involved in all the manufacturing steps.
Owner:RICOH KK
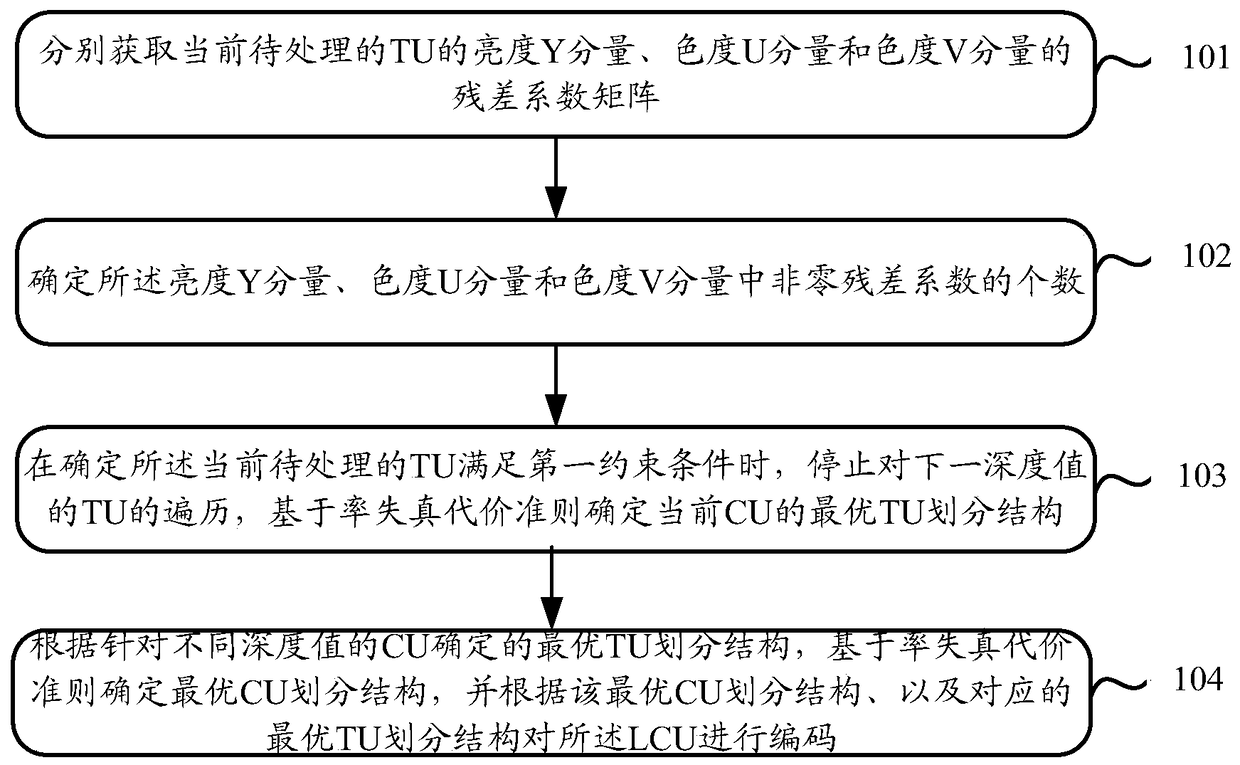
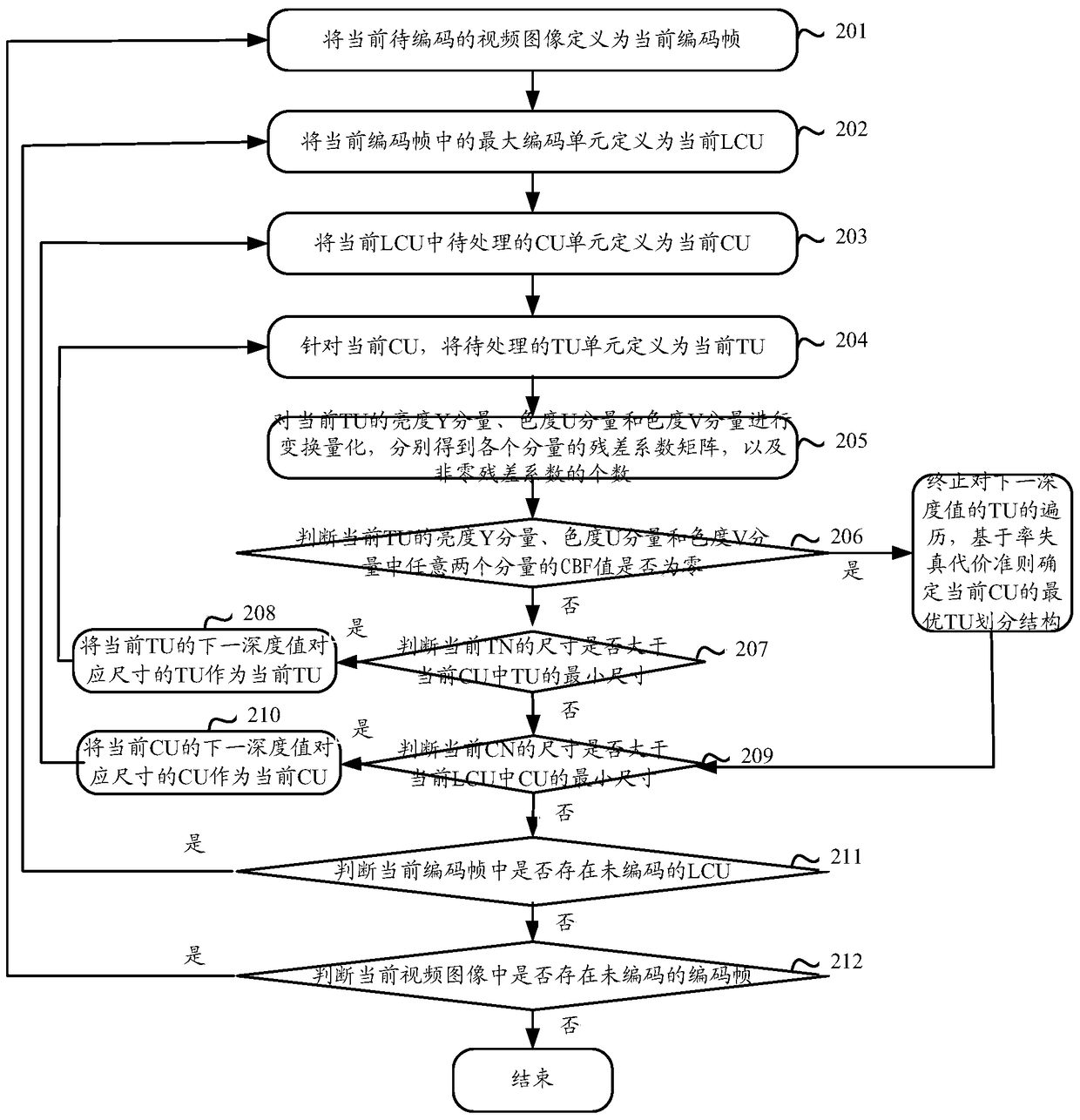
Video coding method and video coding device
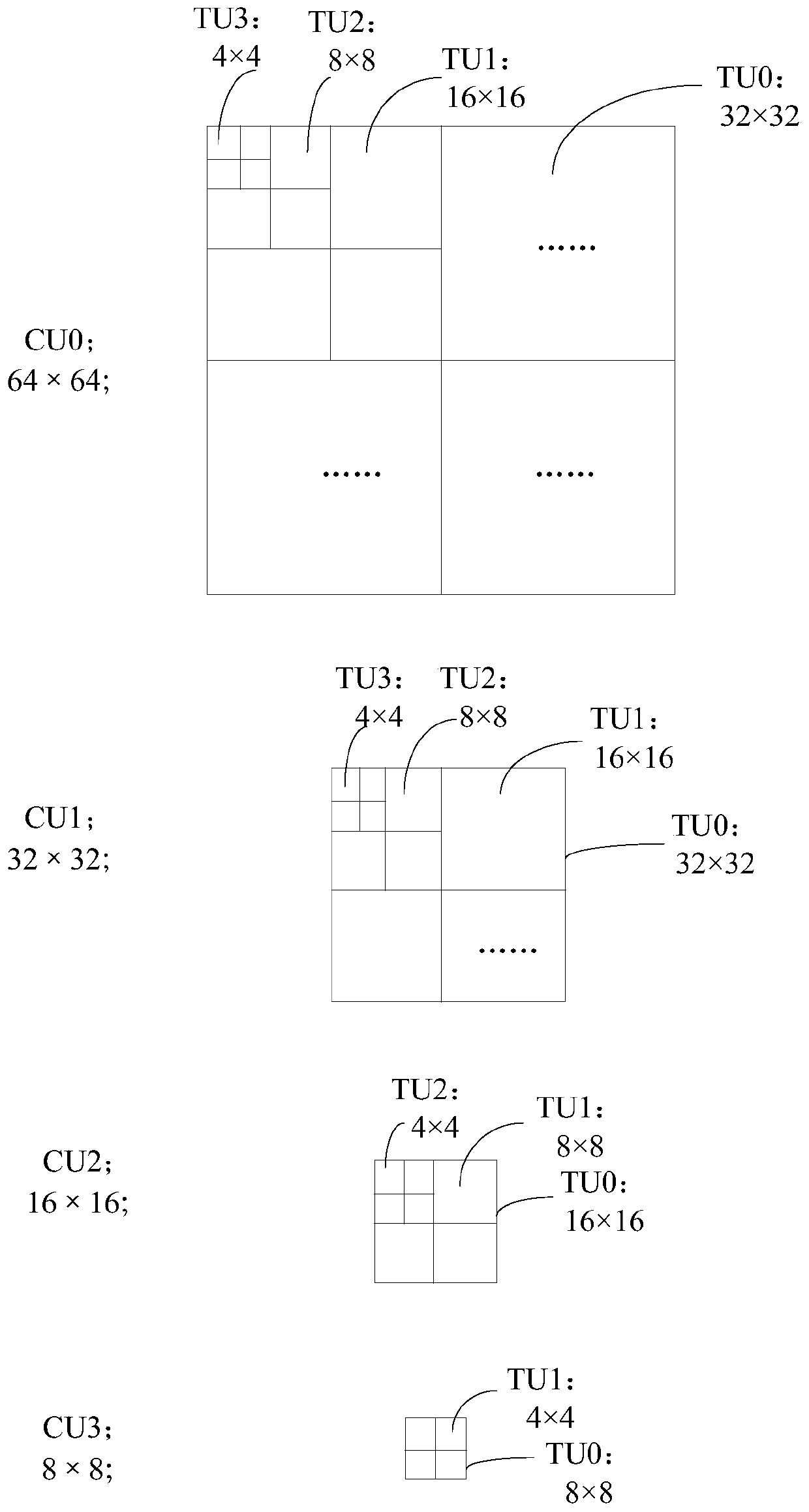
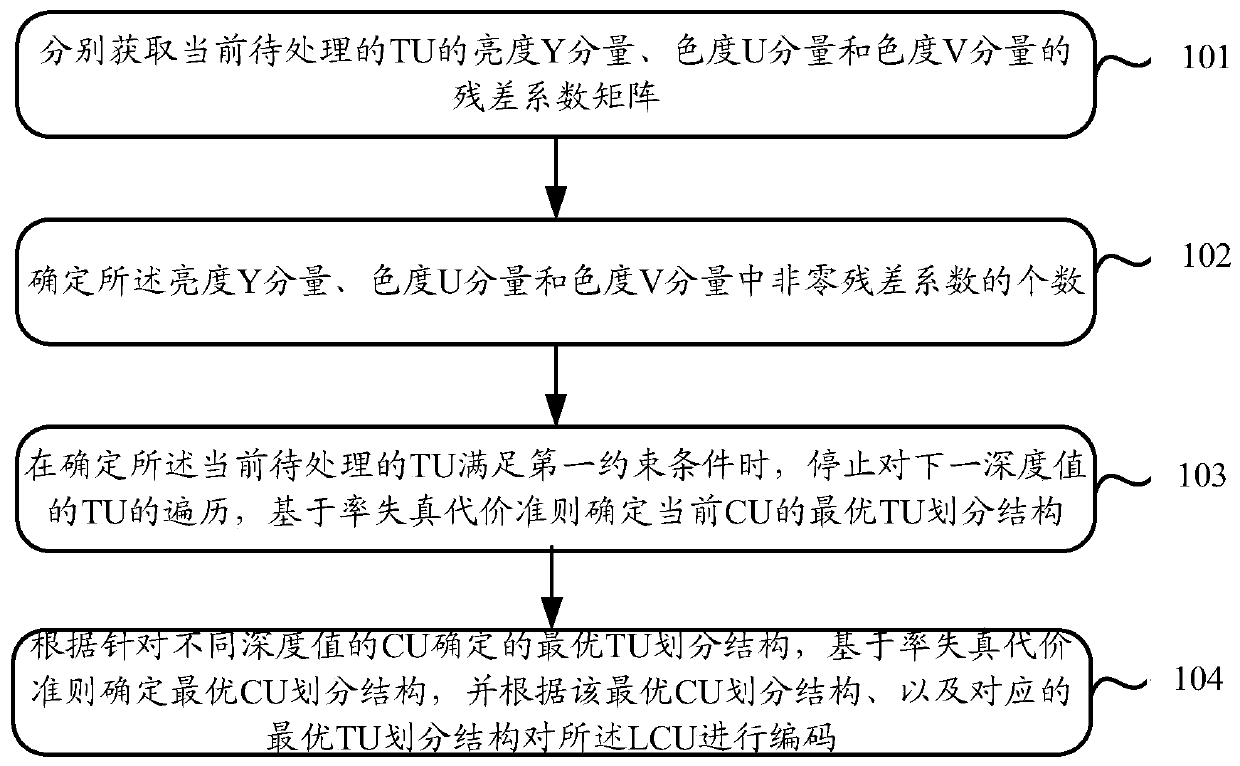
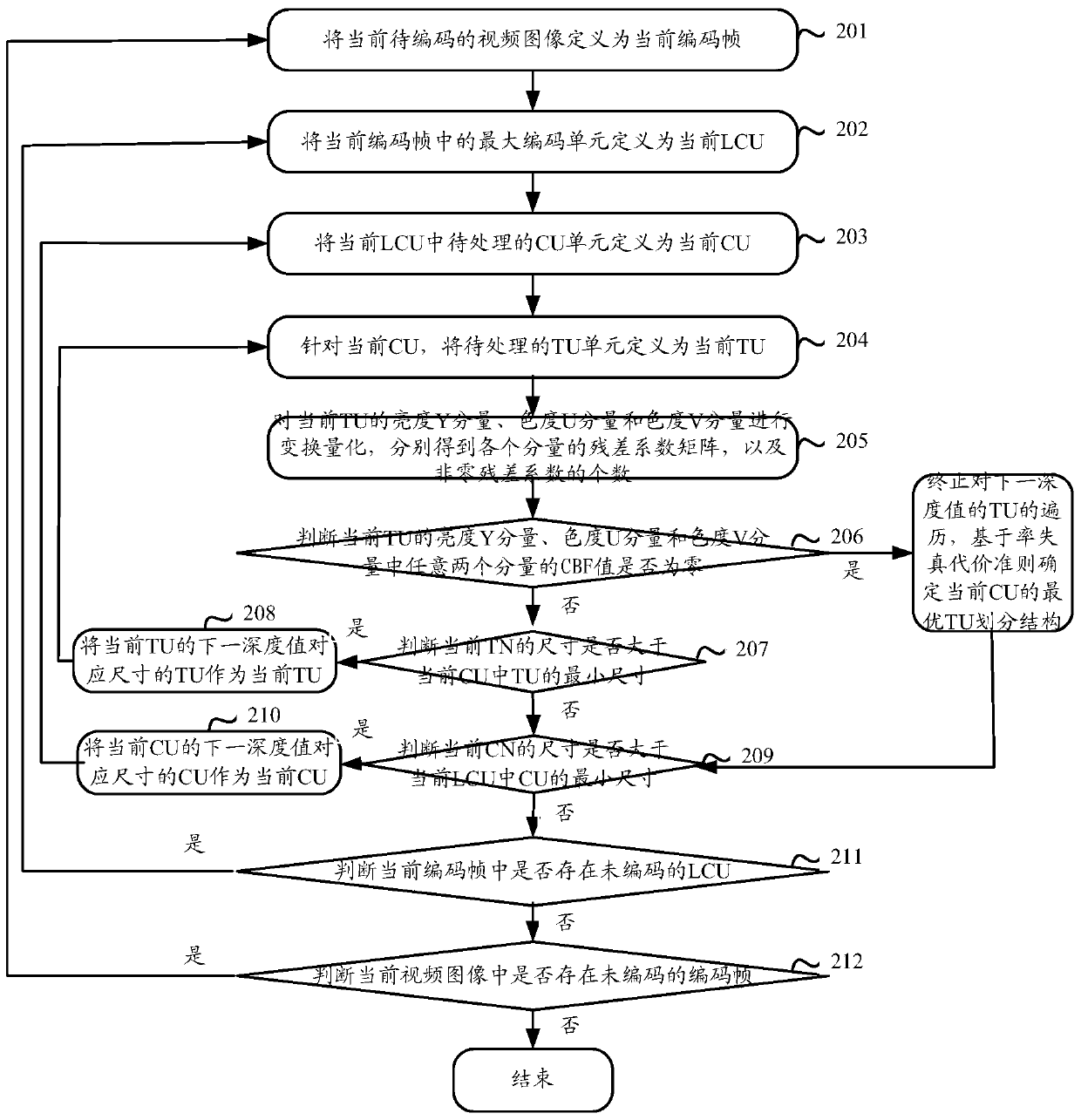
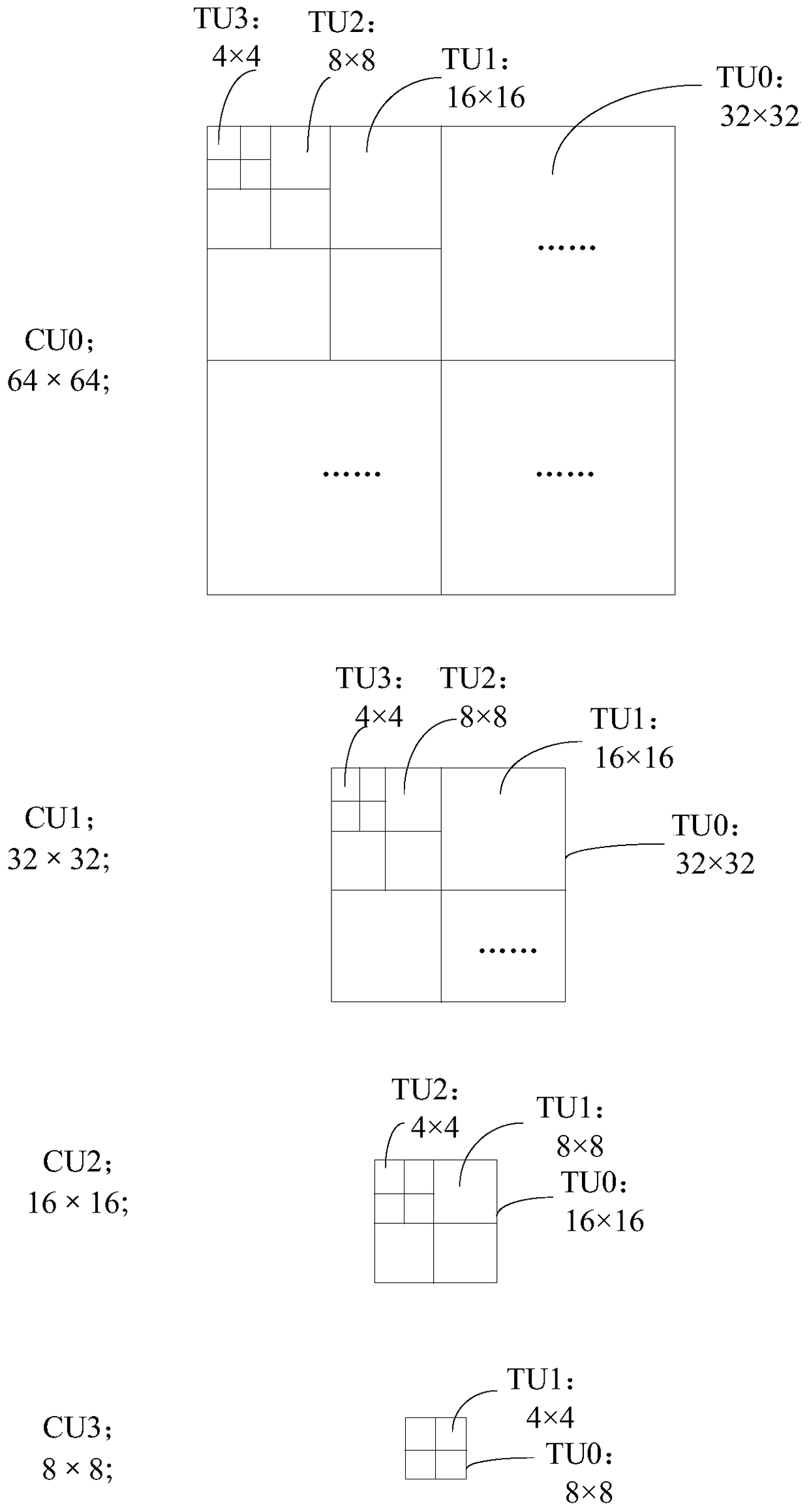
ActiveCN105516719AReduce the number of recursive traversalsShorten the timeDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureVideo encoding
The invention discloses a video coding method and a video coding device. The video coding method is characterized in that the following steps can be carried out sequentially by aiming at coding units CU having different depth values of a determined current largest coding unit LCU in a video frame: residual coefficient matrixes of brightness Y components, chroma U components, and chroma V components of transformation units TU to be processed can be acquired respectively, and the number of the non-zero residual coefficients of the brightness Y components, chroma U components, and chroma V components can be determined; when the TU to be processed is determined to be capable of satisfying the condition that the CBF values of any two components of the brightness Y components, chroma U components, and chroma V components of the TU to be processed are zero, the recursive traversal of the TU can be stopped. The optimal CU division structure can be determined based on the rate-distortion cost criteria, and the coding of the LCU can be carried out according to the optimal CU division structure, and therefore the times of the recursive traversal can be reduced, the time required by the coding can be saved, and the coding complexity can be reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
Method for integrating a new service into an avionics onboard system with open architecture of client-server type, in particular for an FIM manoeuvre service
ActiveUS10154096B2Cost in response timeCost of maintainabilityAircraft componentsMarket predictionsAviationElectronic systems
A method for integrating a new navigation service is implemented in an avionics onboard system comprising a DAL+ core computer and a DAL− peripheral computer for managing the application. The method of integration determines an optimal functional and physical distribution of the elementary functions FU(i) of the new service within the onboard avionics system over the set of possible distributions which minimizes a global cost criterion CG, dependent on several parameters, including at least the additional development cost of the elementary functions integrated within the digital DAL+ core computer, and carries out the integration of the new service.
Owner:THALES SA
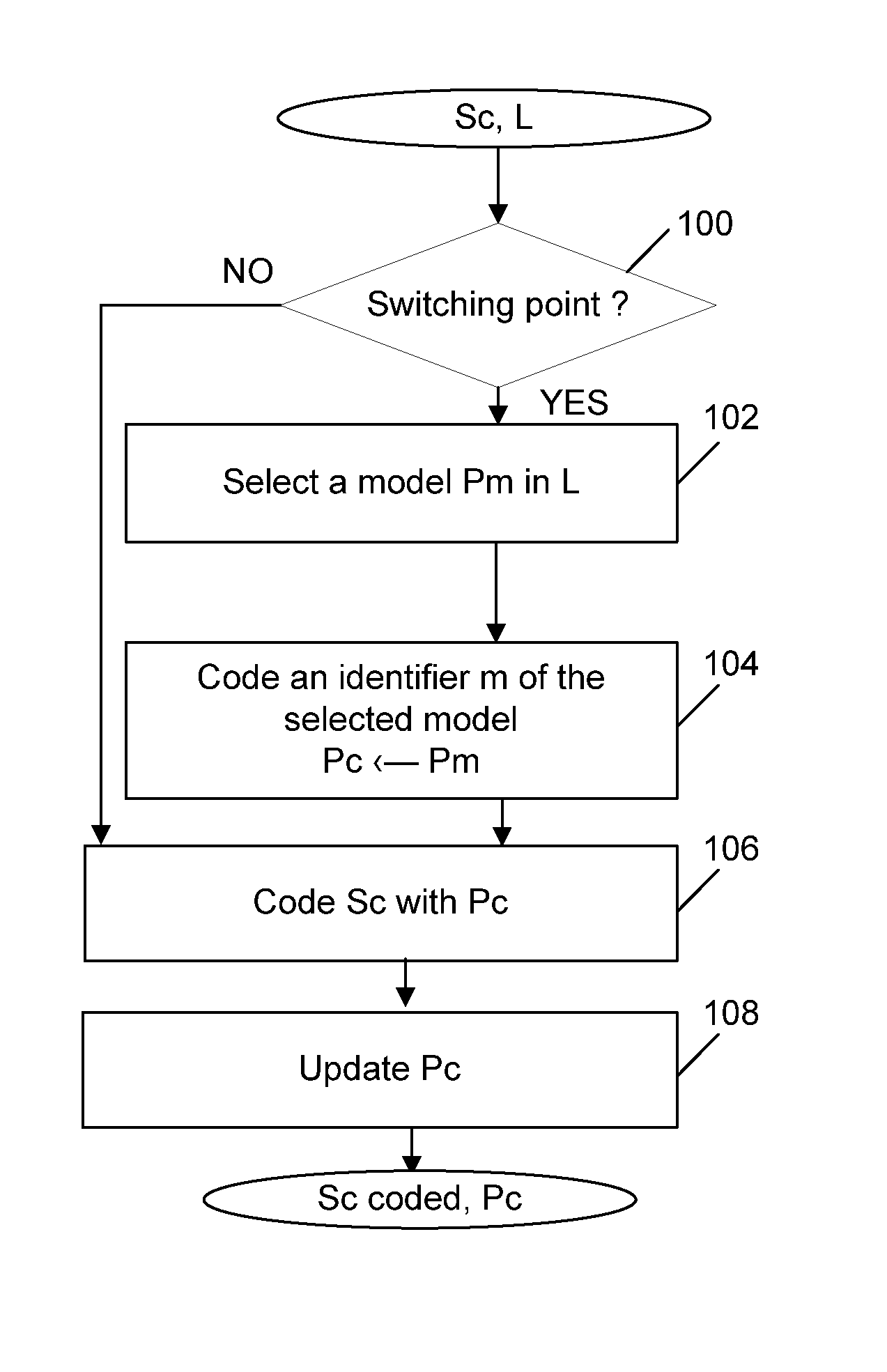
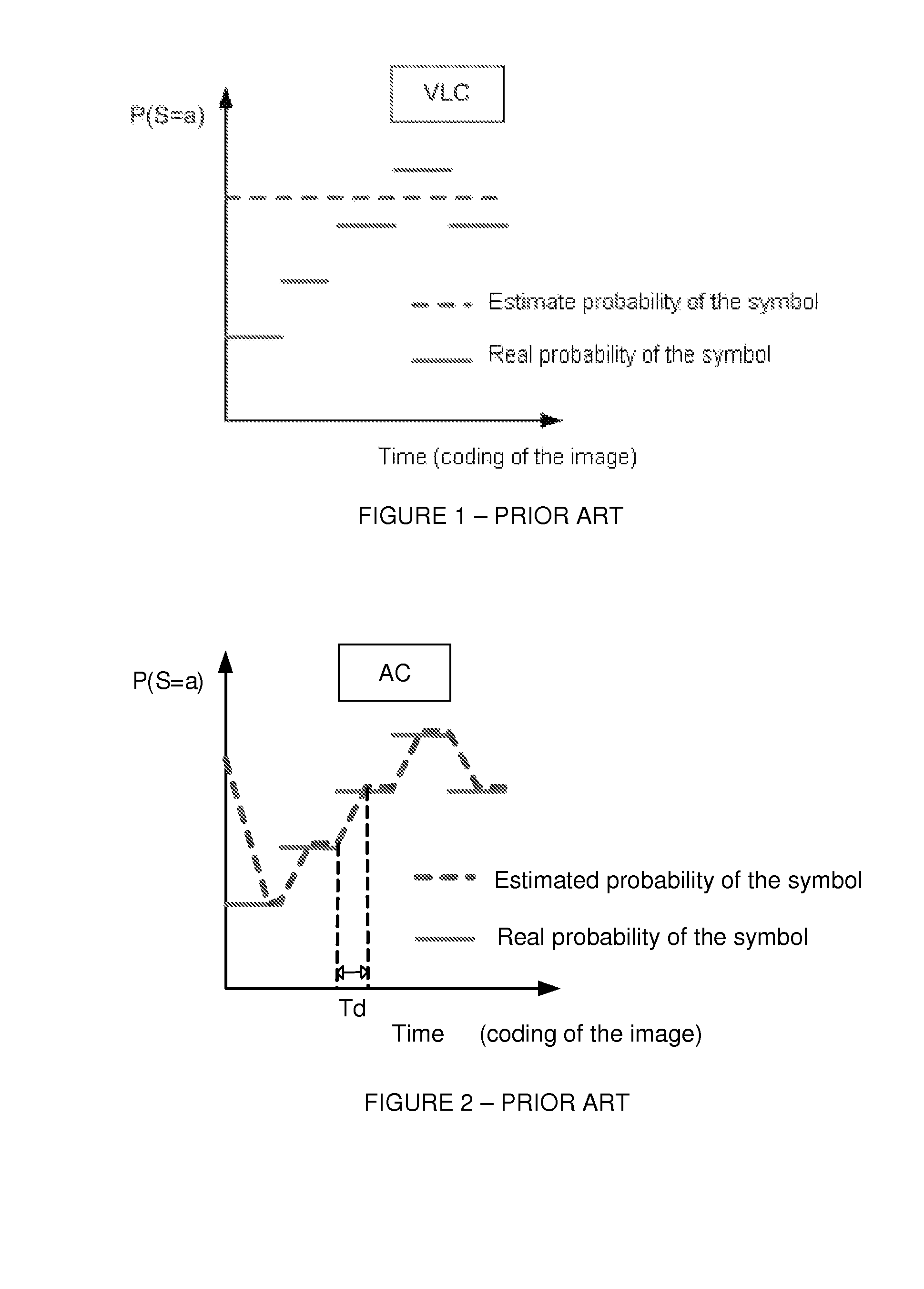
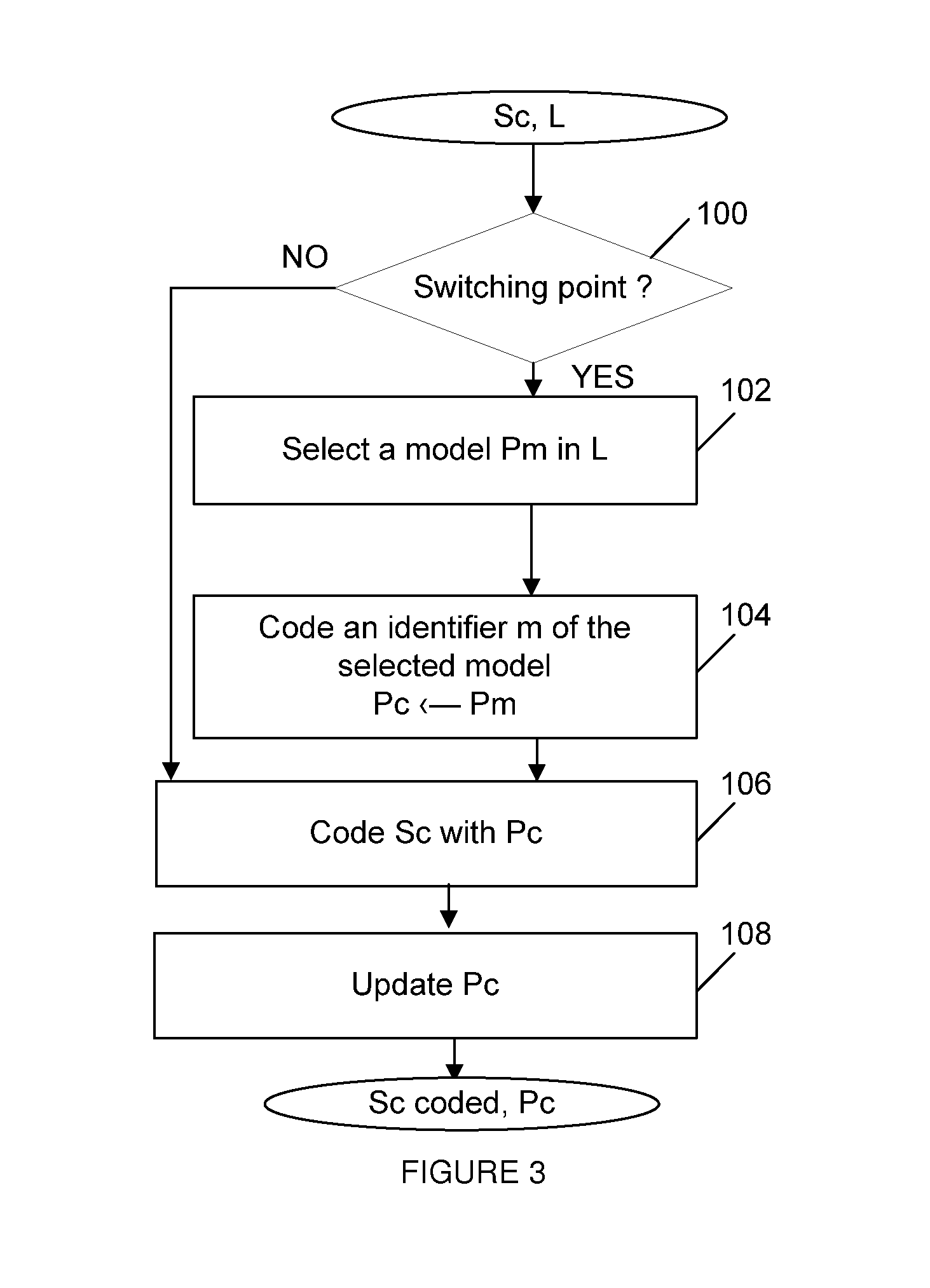
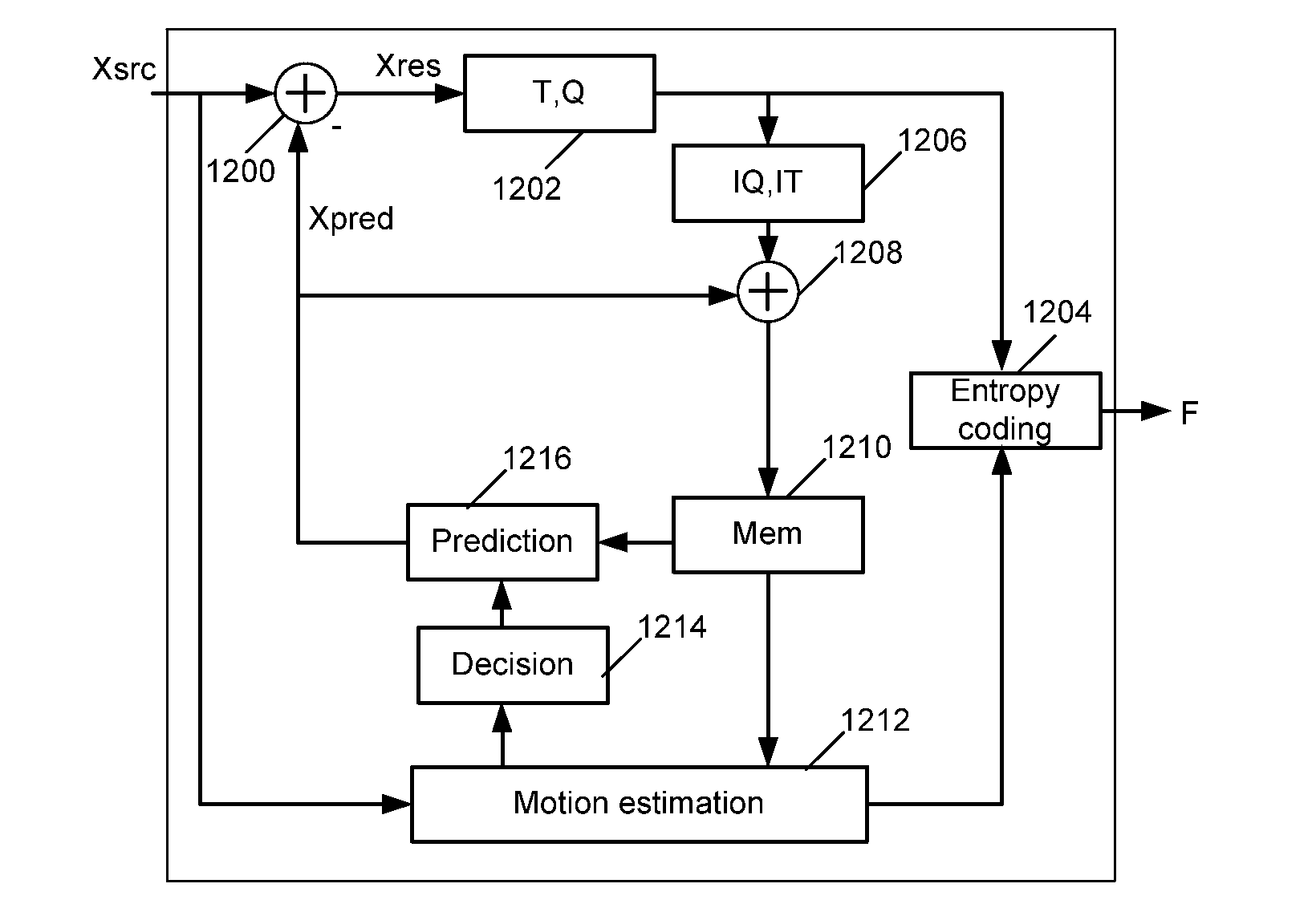
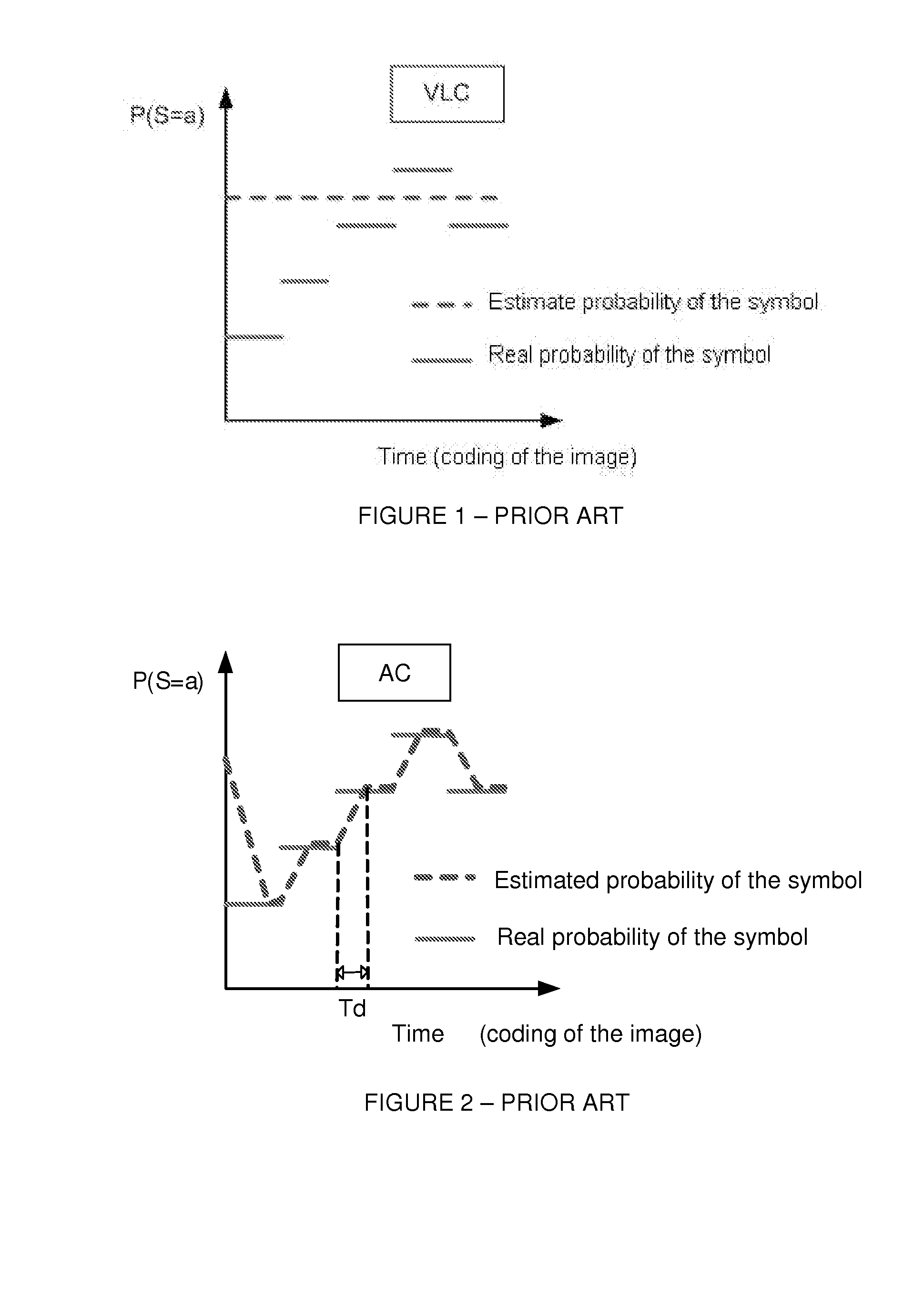
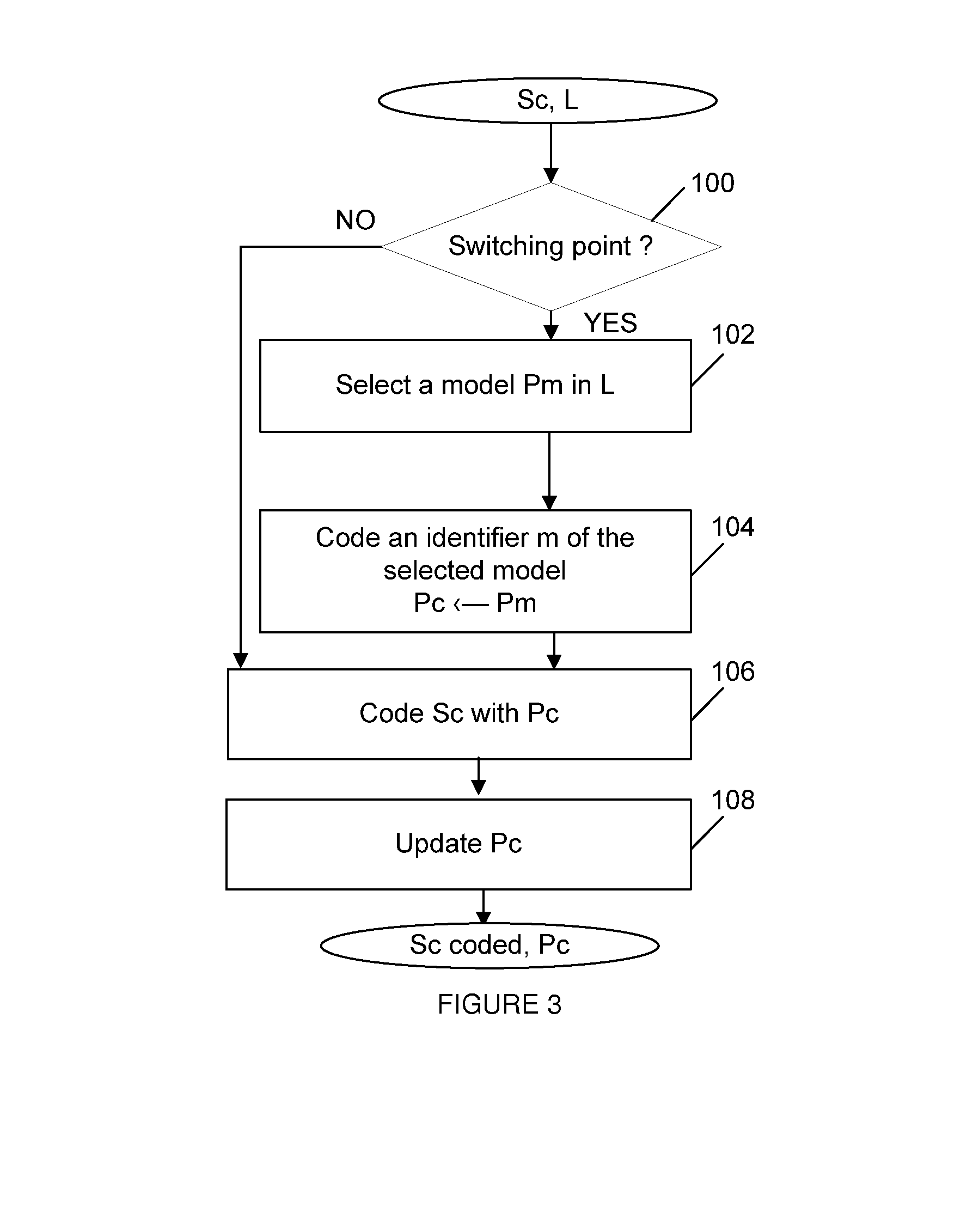
Methods for arithmetic coding and decoding and corresponding devices
ActiveUS8674859B2RealFast approachCode conversionDigital video signal modificationProbit modelAlgorithm
A method for arithmetic coding of symbols in a stream is described. The method comprises the following steps:coding a current symbol with a current probability model, andupdating the current probability model according to the coding of the current symbol.selecting the current probability model in a set of at least two probability models according to a coding cost criterion, andcoding an identifier of the selected probability model.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method and tool for measuring the geometric structure of an optical component
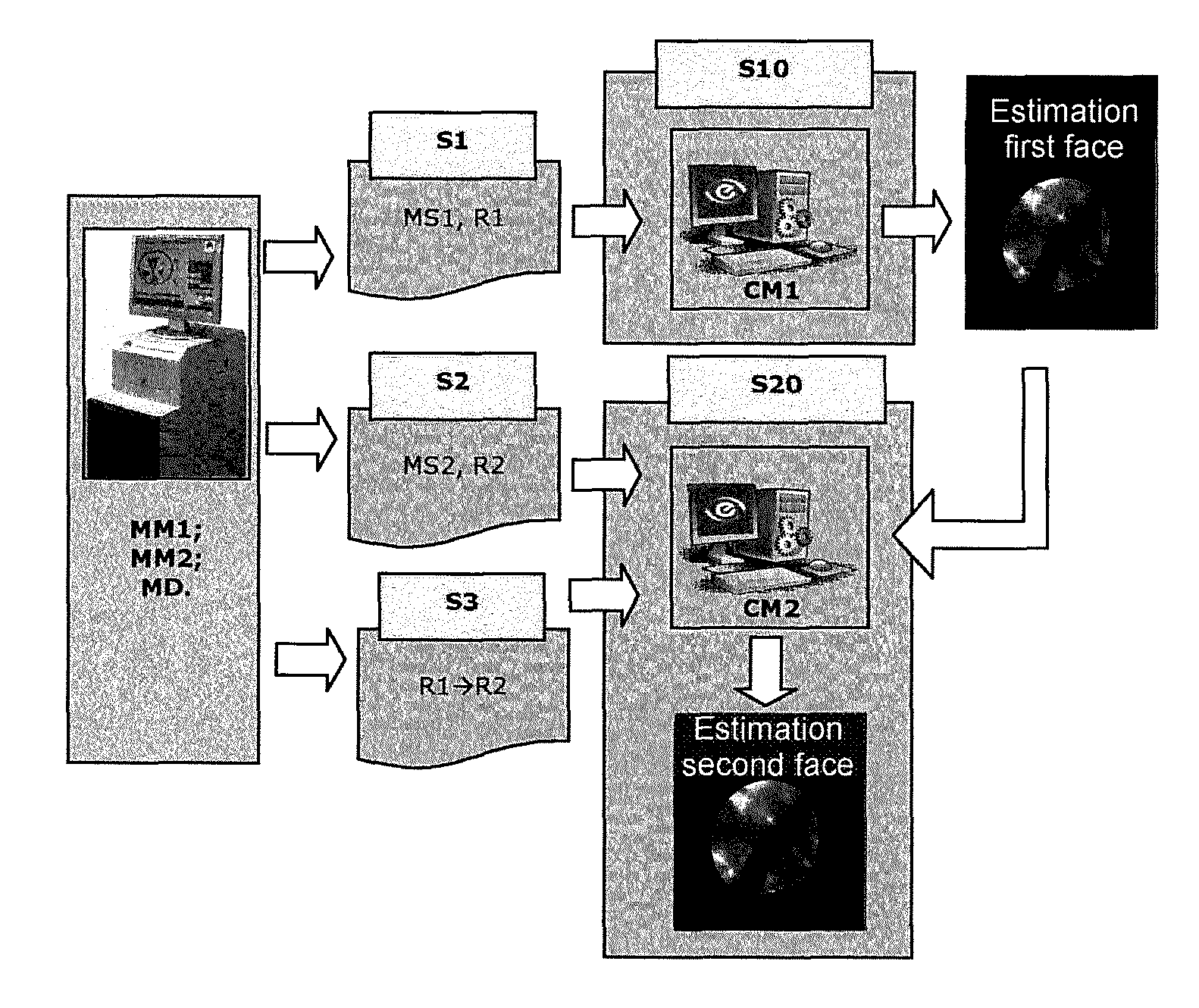
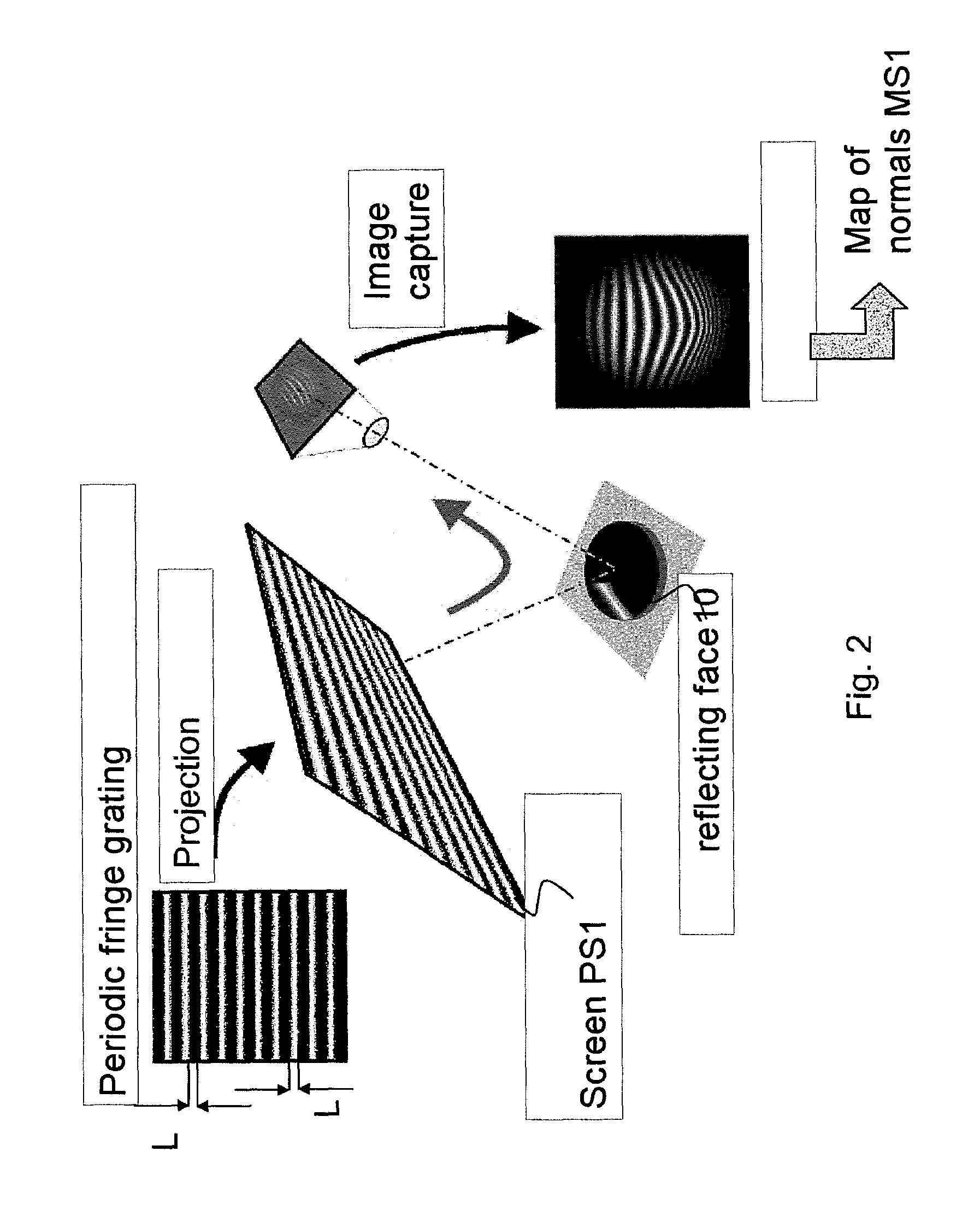
ActiveUS9109976B2Rapid determinationUsing optical meansGeometric properties/aberration measurementComputational physicsCost criterion
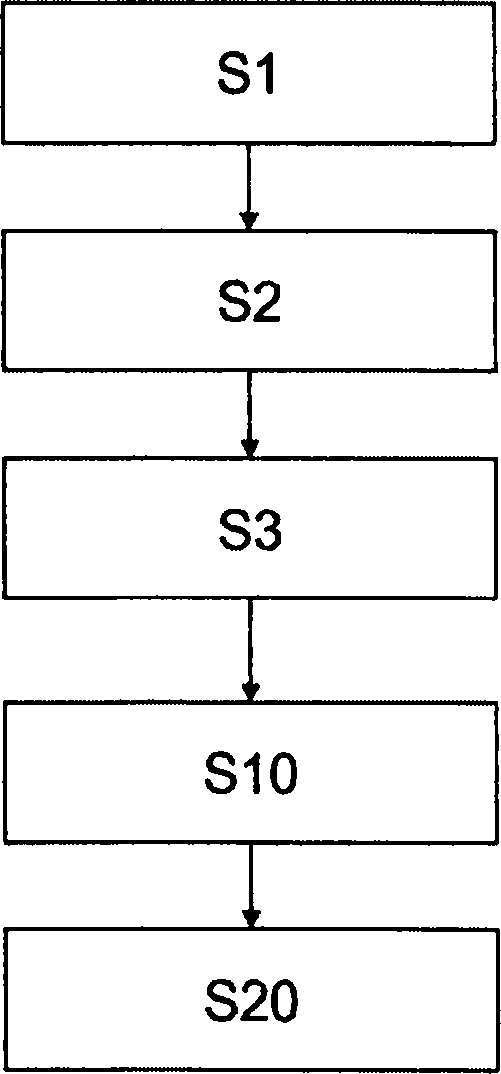
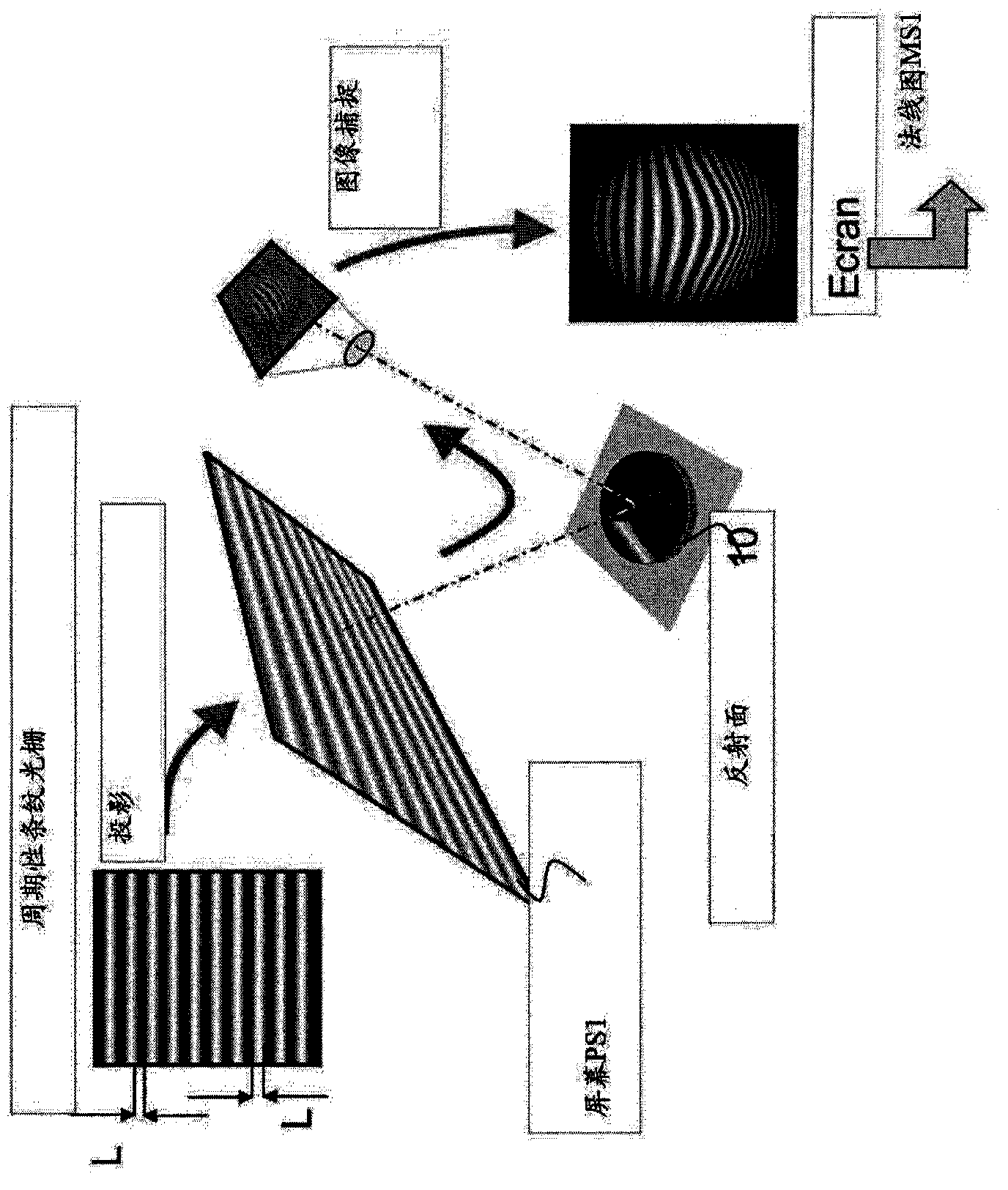
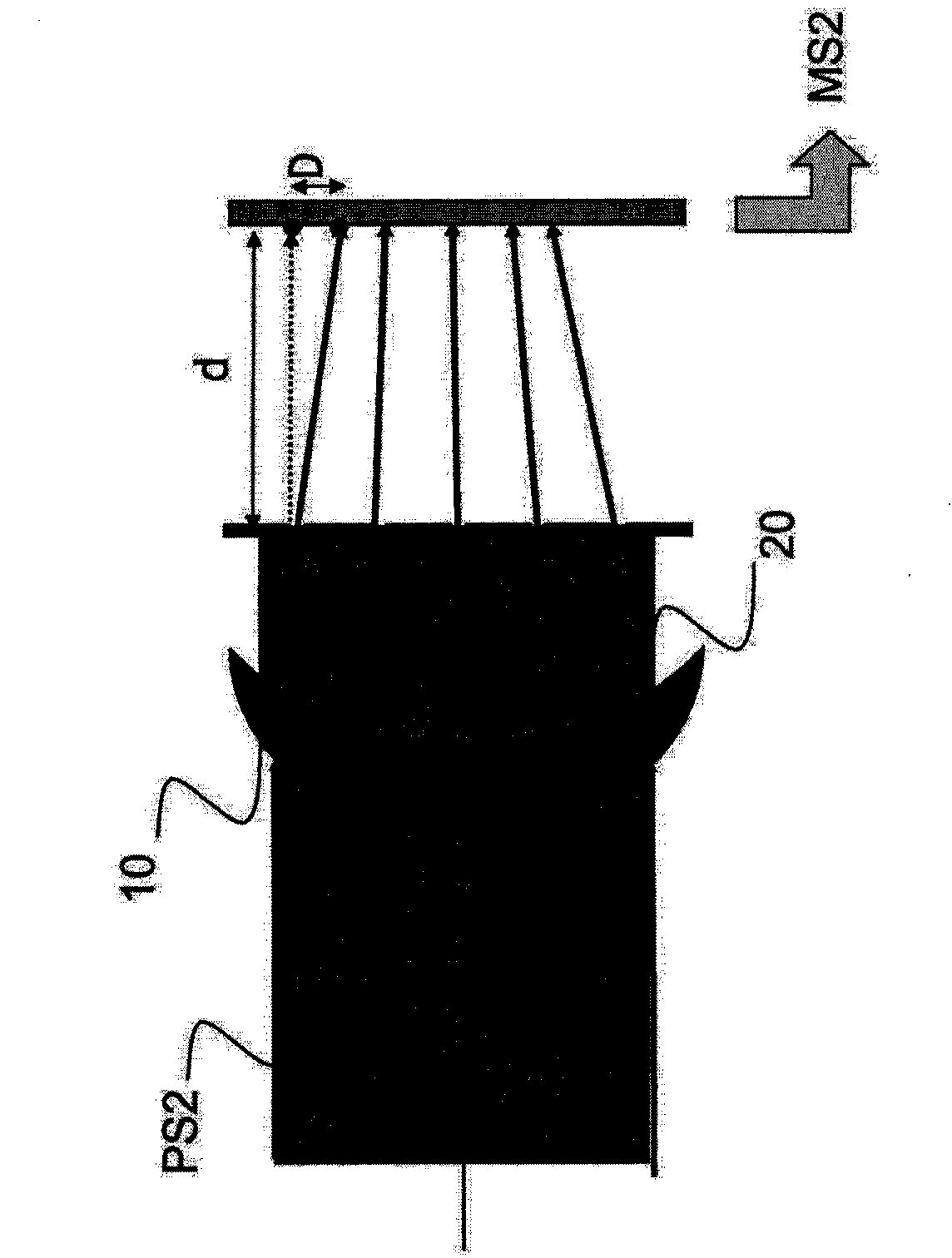
The subject of the present invention is a method and a system for measuring the geometric or optical structure of an optical component. In particular, the invention relates to a method for measuring the geometric structure of a component bounded by a first side (10) and a second side (20), said method comprising steps of: (S1) measuring a first signal (MS1) resulting from a first conversion of a first probe signal (PS1), by at least said first side (10); (S2) measuring a second signal (MS2) resulting from a second conversion of a second probe signal (PS2), by at least said second side (20); (S3) determining a third conversion making it possible to convert a first set of coordinates (R1) associated with the measurement of the first signal (MS1) to a second set of coordinates (R2) associated with the measurement of the second signal (MS2); (S10) estimating said first side (10) using the first signal (MS1), said first simulation and a first cost criterion (V1) quantifying a difference between the estimation (FS1) and the first signal (MS1); and (S20) estimating said second side (20) using the second signal (MS2), said second simulation, said third conversion and a second cost criterion (V2) quantifying a difference between the estimation (ES2) and the second signal (MS2).
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Method and system for measuring the geometric or optical structure of an optical component
ActiveCN104169704AConvenience for subsequent useImplement evaluationUsing optical meansGeometric properties/aberration measurementCost criterionProbe signal
The method involves measuring (S1) a signal (MS1) from conversion of a probe signal by a side of an optical component, and measuring (S2) another signal (MS2) resulting from another conversion of another probe signal by another side. A third conversion is determined (S3) to convert a set of coordinates (R1) to another set of coordinates (R2). The sides are estimated (S10) by using the former signal and the latter signal, simulation of conversions and cost criteria quantifying difference between the former estimation and the former signal and between the latter estimation and the latter signal. An independent claim is also included for a system for measuring a geometric structure of an optical component.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
A multi-criteria design optimization method for the cutter shaft size of a rotary tiller
ActiveCN106372364BSimple designHigh strengthGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsProcess engineeringMulti targeting
The invention relates to a rotary cultivator cutter shaft size multi-criterion design optimization method. According to the rotary cultivator cutter shaft size design, a bearing stress criterion function and a cost criterion function must be taken into consideration simultaneously; when the rotary cultivator cutter shaft size design is established, various restrictive conditions must be met, the minimum value corresponding to each criterion function is solved separately at first, then a multi-target ideal point non-linear planning problem is defined and a rotary cultivator cutter shaft optimal size parameter is finally calculated by a numerical optimization algorithm. The most important characteristic of the method is that the bearing stress criterion and the cost criterion of the rotary cultivator cutter shaft serve as considered targets, the two targets are correlated with a multi-target ideal point method, and the operation is simple and easy to understand; furthermore, the obtained result can meet the requirement of safe operation of the rotary cultivator cutter shaft and also can guarantee the economic property of the rotary cultivator cutter shaft to a great degree.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Rotary cultivator cutter shaft size multi-criterion design optimization method
ActiveCN106372364ASimple designHigh strengthGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsProcess engineeringSafe operation
The invention relates to a rotary cultivator cutter shaft size multi-criterion design optimization method. According to the rotary cultivator cutter shaft size design, a bearing stress criterion function and a cost criterion function must be taken into consideration simultaneously; when the rotary cultivator cutter shaft size design is established, various restrictive conditions must be met, the minimum value corresponding to each criterion function is solved separately at first, then a multi-target ideal point non-linear planning problem is defined and a rotary cultivator cutter shaft optimal size parameter is finally calculated by a numerical optimization algorithm. The most important characteristic of the method is that the bearing stress criterion and the cost criterion of the rotary cultivator cutter shaft serve as considered targets, the two targets are correlated with a multi-target ideal point method, and the operation is simple and easy to understand; furthermore, the obtained result can meet the requirement of safe operation of the rotary cultivator cutter shaft and also can guarantee the economic property of the rotary cultivator cutter shaft to a great degree.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Methods for arithmetic coding and decoding
ActiveUS20120218131A1Reduce coding costsFast approachCode conversionDigital video signal modificationProbit modelAlgorithm
A method for arithmetic coding of symbols in a stream is described. The method comprises the following steps:coding a current symbol with a current probability model, andupdating the current probability model according to the coding of the current symbol.selecting the current probability model in a set of at least two probability models according to a coding cost criterion, andcoding an identifier of the selected probability model.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method for encoding a digital image and associated decoding method, devices, user terminal and computer programs
ActiveCN108781292AImprove forecast qualityImprove compression efficiencyDigital video signal modificationDecoding methodsCurrent element
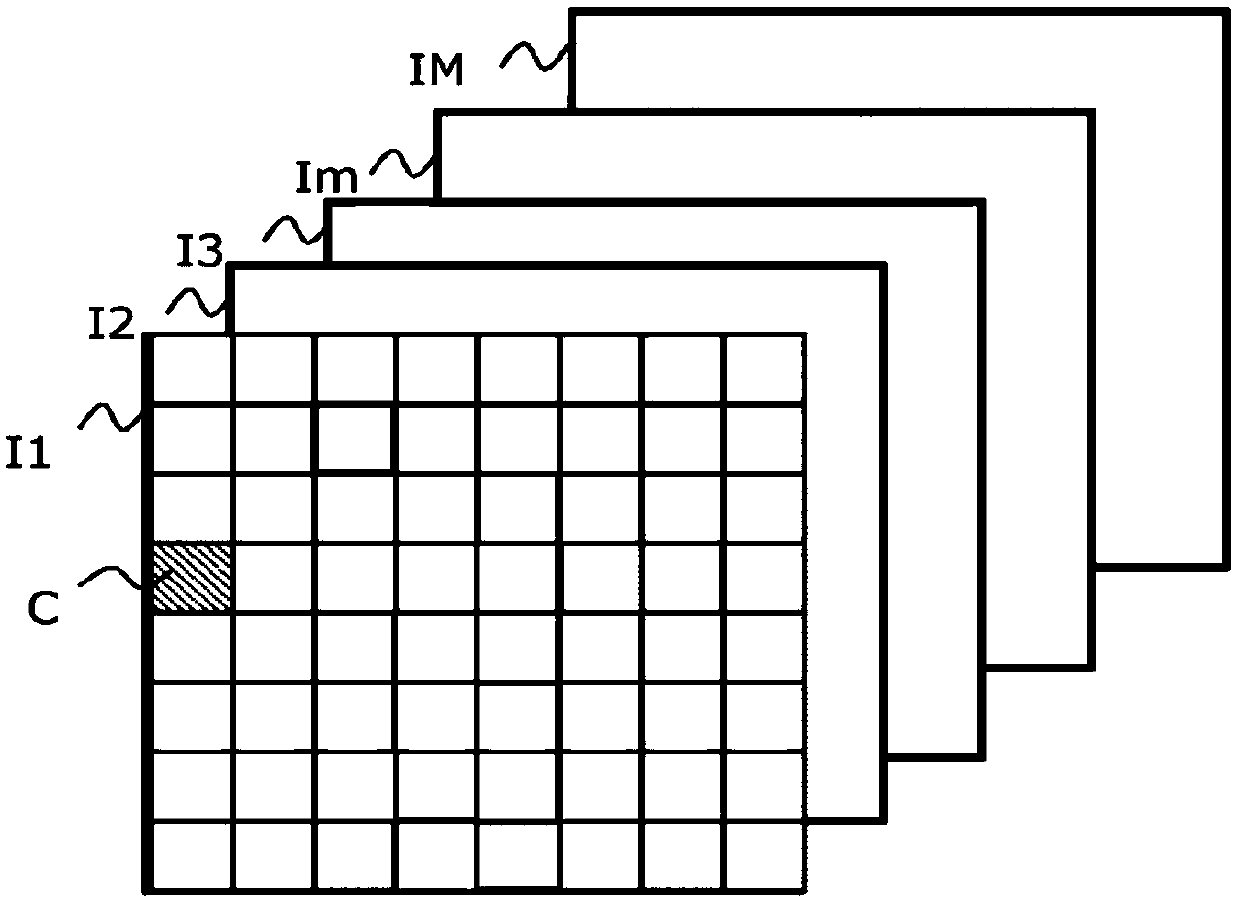
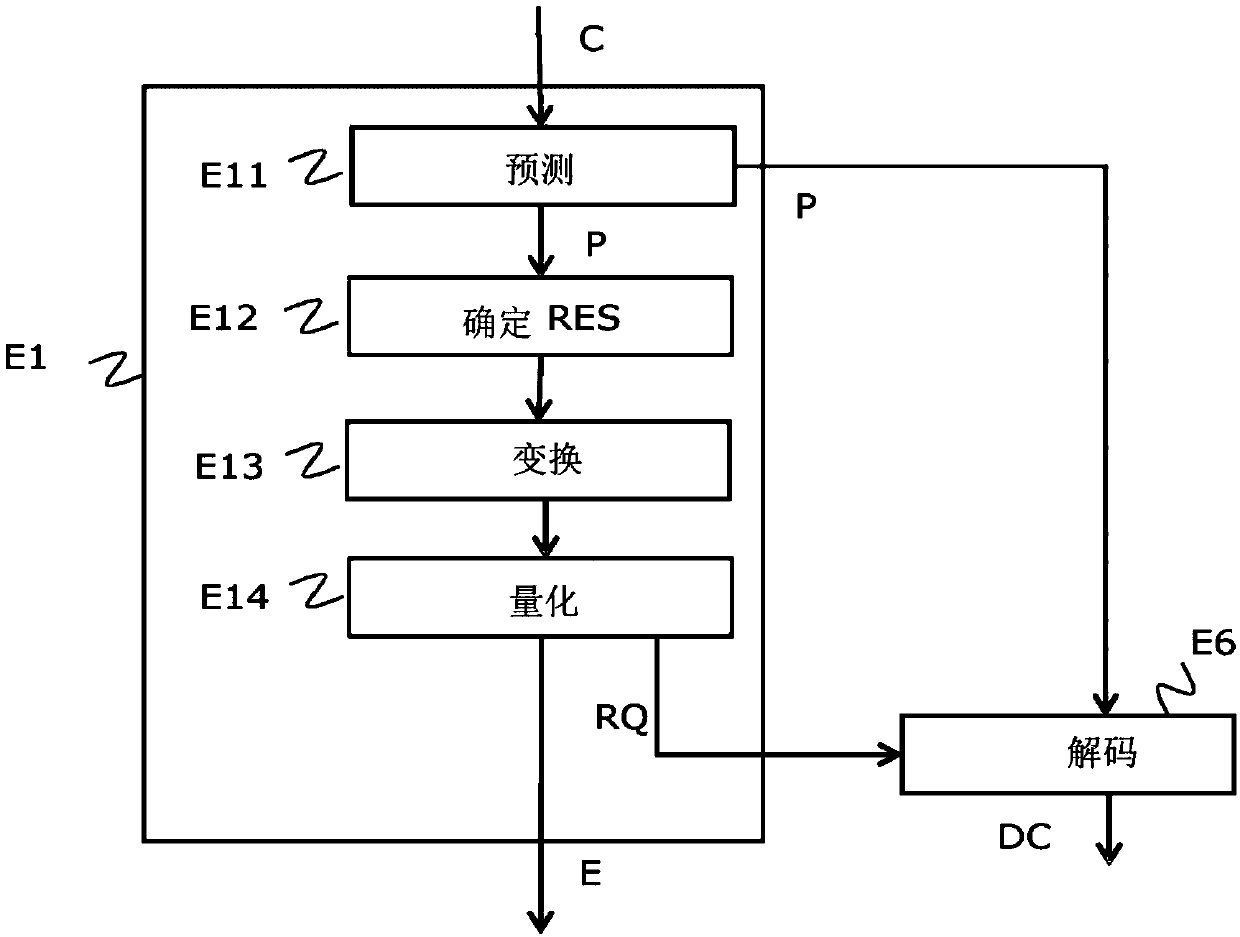
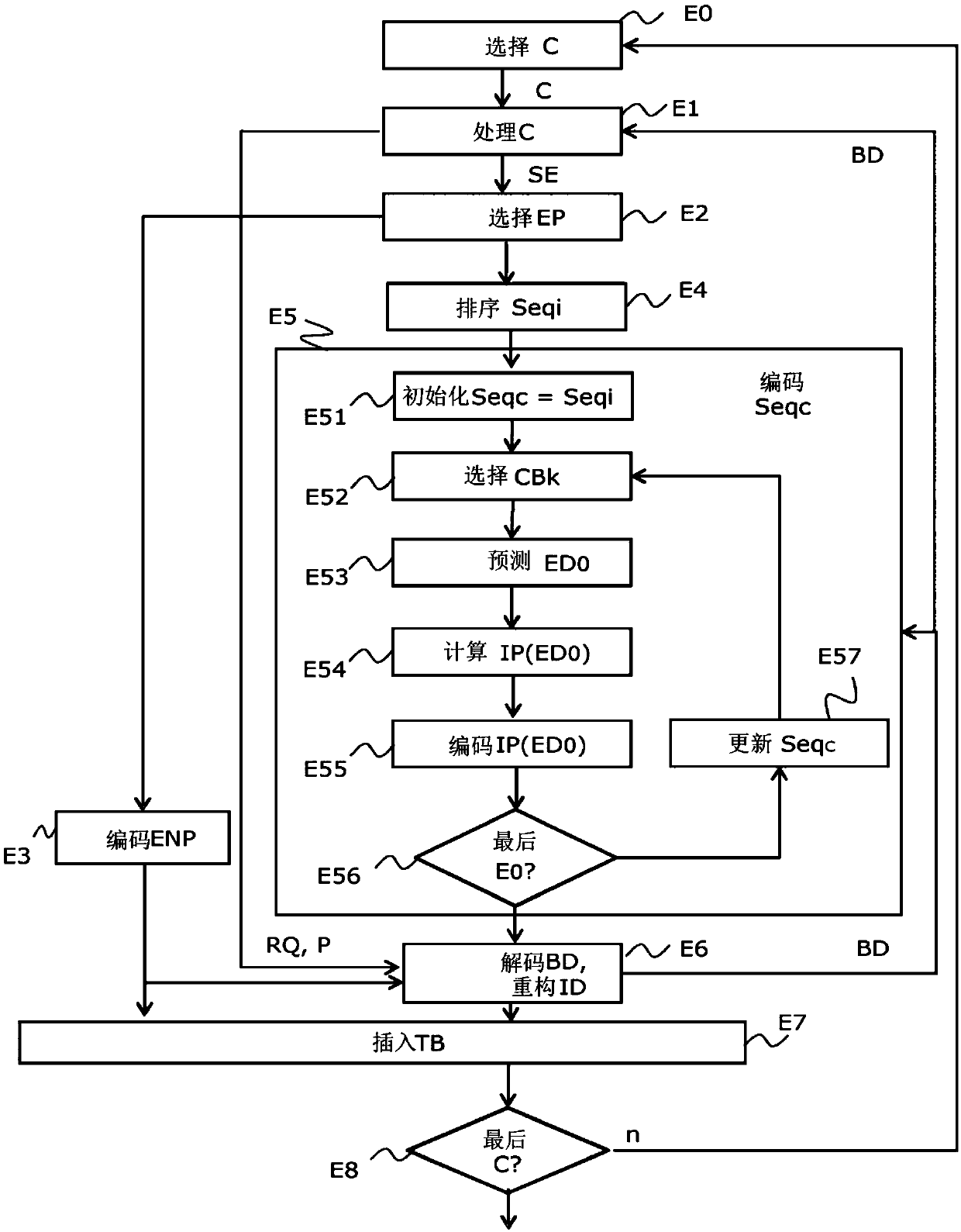
The invention relates to a method for encoding a digital image, said image (Im) being divided into a plurality of blocks of pixels (C) processed in a defined order, said method comprising the following steps, implemented for a current block, of processing (E1) the current block intended to provide a set of description elements of the processed block; selecting (E2) a subset of at least two description elements to predict in the provided set; ordering (E4) the description elements of the subset into an ordered sequence; encoding elements of the sequence. According to the invention, the step ofencoding the elements of the sequence includes browsing the elements of the sequence and includes, for a current element, the following sub-steps: selecting a combination of the values of the description elements of the sequence from a plurality of combinations as a function of a predetermined cost criterion and, from the second element, values of description elements previously processed in the sequence; predicting the current element of the sequence from the value thereof in the selected combination; encoding an indicator representing a difference between the actual value of the current element and its predicted value.
Owner:B COM
A video coding method and device
ActiveCN105516719BReduce the number of recursive traversalsShorten the timeDigital video signal modificationComputer architectureVideo encoding
The invention discloses a video coding method and a video coding device. The video coding method is characterized in that the following steps can be carried out sequentially by aiming at coding units CU having different depth values of a determined current largest coding unit LCU in a video frame: residual coefficient matrixes of brightness Y components, chroma U components, and chroma V components of transformation units TU to be processed can be acquired respectively, and the number of the non-zero residual coefficients of the brightness Y components, chroma U components, and chroma V components can be determined; when the TU to be processed is determined to be capable of satisfying the condition that the CBF values of any two components of the brightness Y components, chroma U components, and chroma V components of the TU to be processed are zero, the recursive traversal of the TU can be stopped. The optimal CU division structure can be determined based on the rate-distortion cost criteria, and the coding of the LCU can be carried out according to the optimal CU division structure, and therefore the times of the recursive traversal can be reduced, the time required by the coding can be saved, and the coding complexity can be reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DAHUA TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com