Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1374 results about "Qos quality of service" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
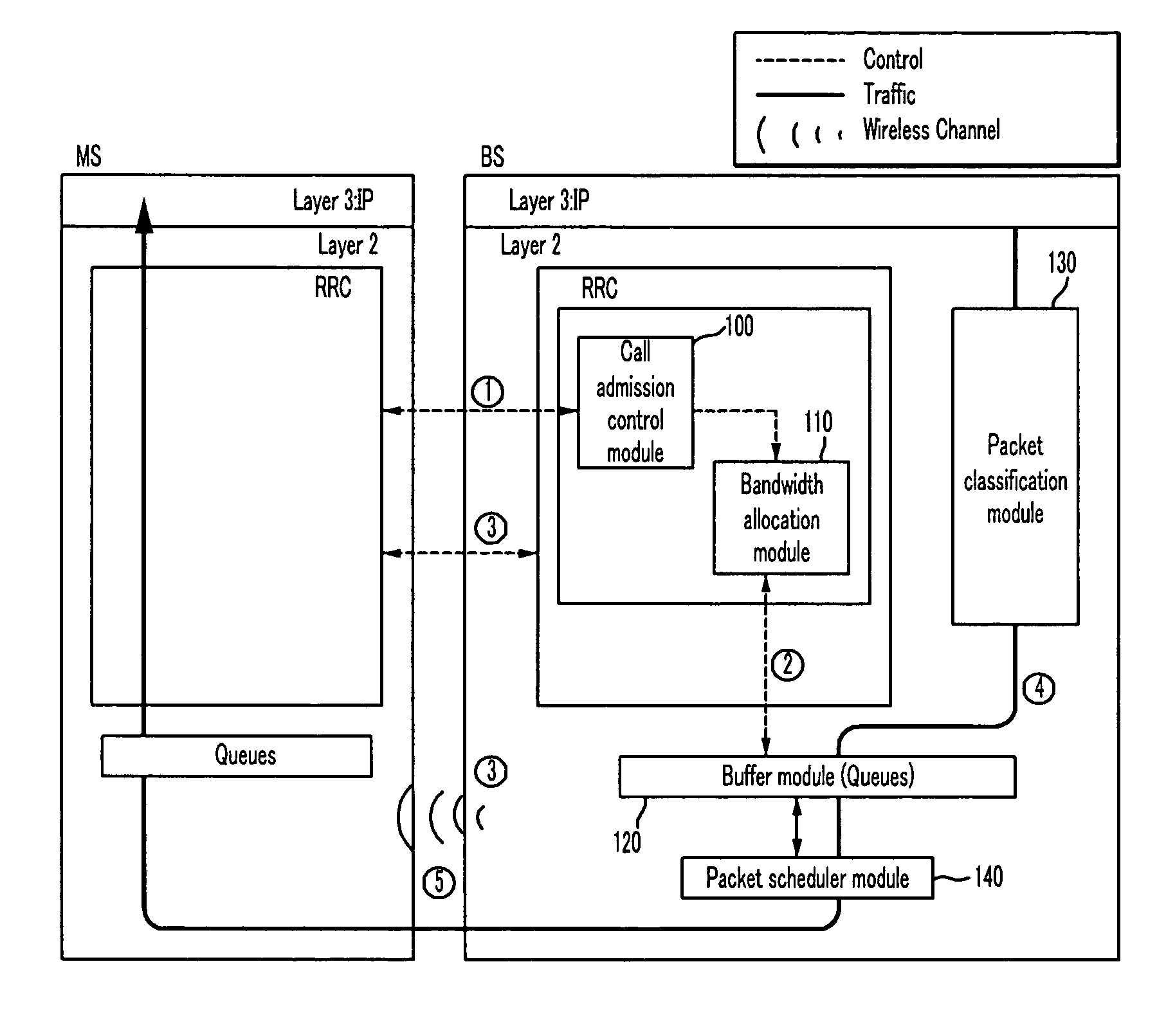
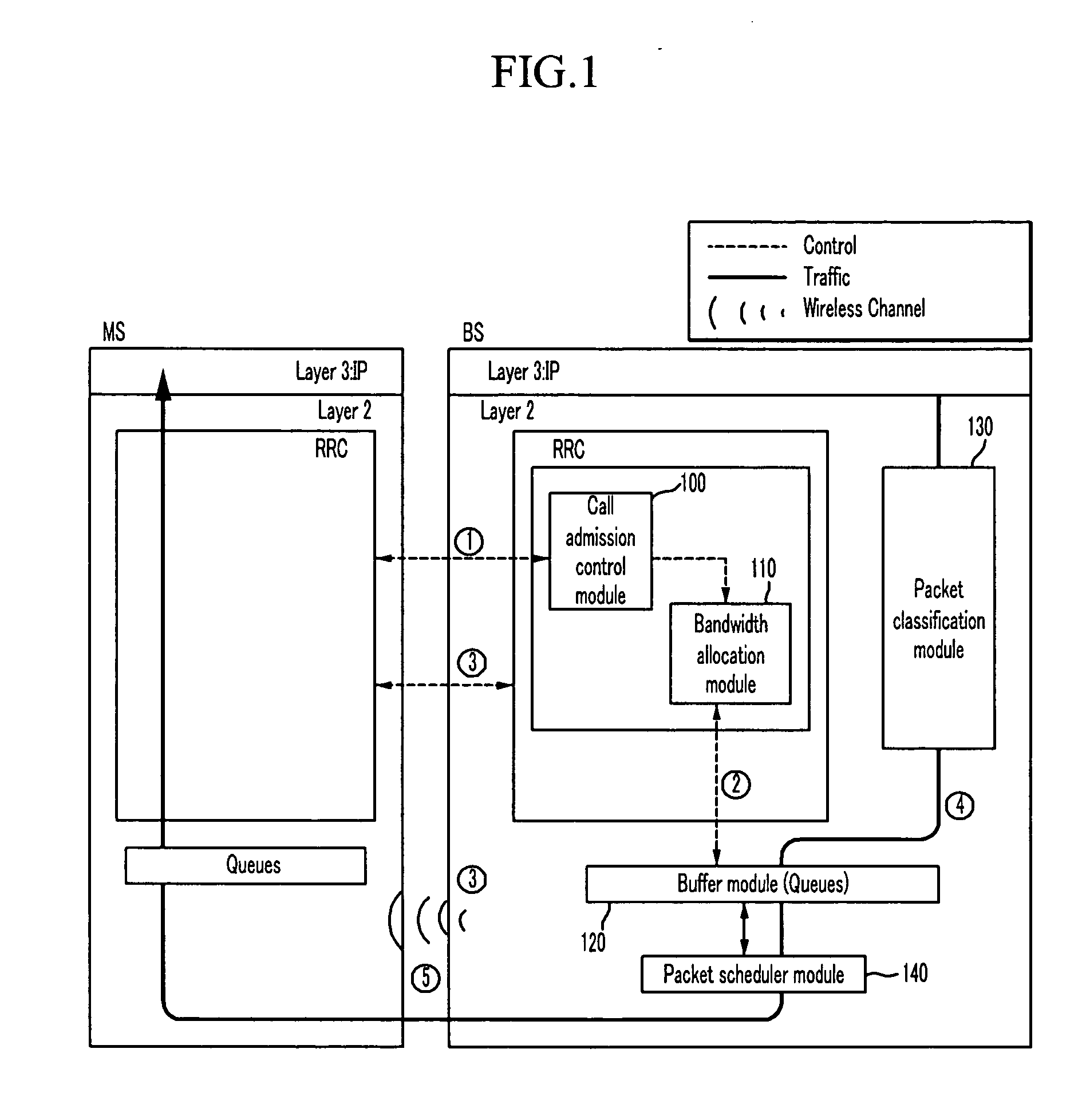
Quality of service (QoS) refers to a network’s ability to achieve maximum bandwidth and deal with other network performance elements like latency, error rate and uptime. Quality of service also involves controlling and managing network resources by setting priorities for specific types of data (video, audio, files) on the network.
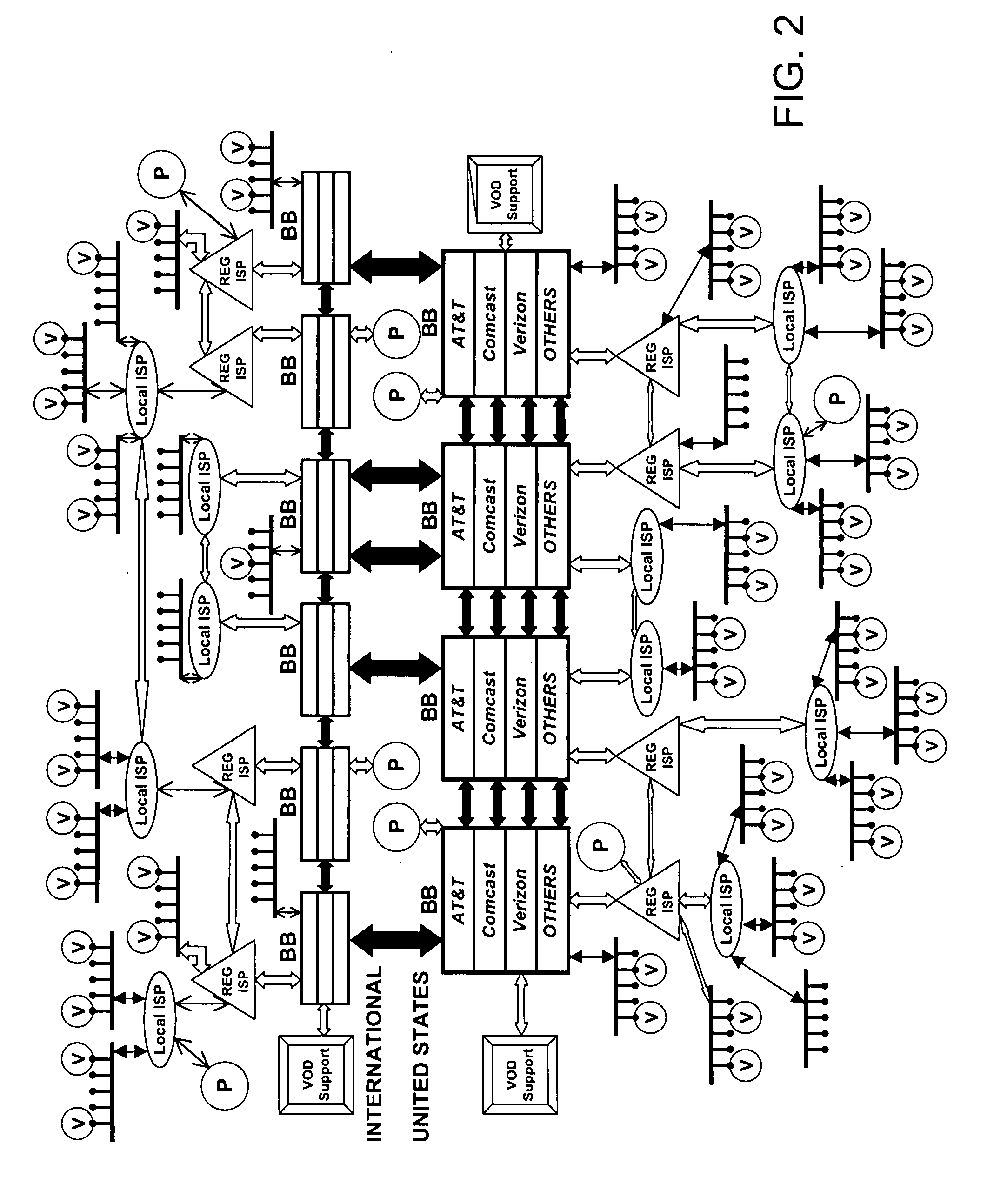
Media delivery using quality of service differentiation within a media stream
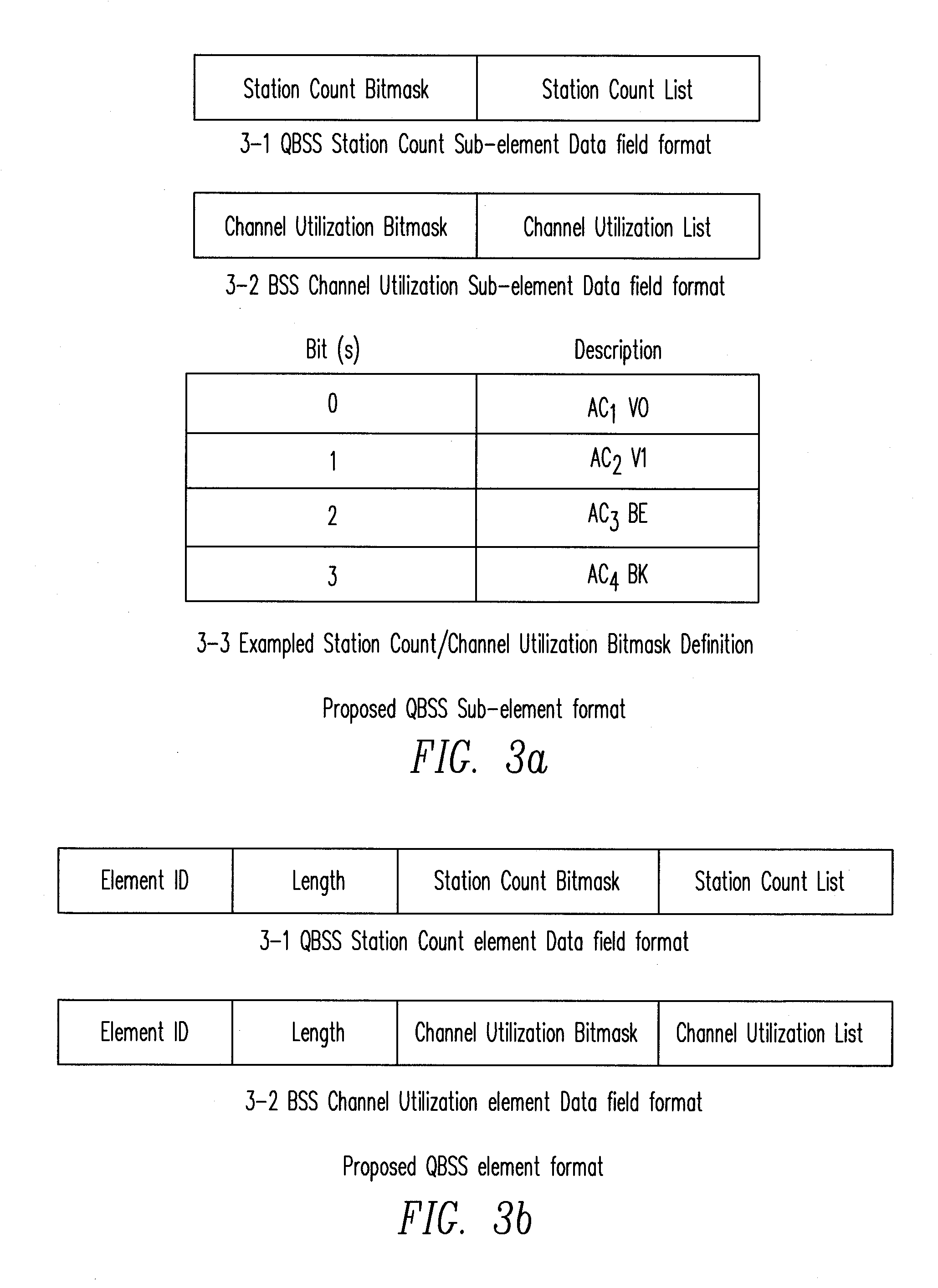
ActiveUS20050100022A1Equal qualityError preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementQos quality of serviceStation
A WLAN system adapted to apply QoS differentiation to a media stream to be transmitted from a transmitting station (STA) to a receiving STA of that system. The transmitting STA processes the media stream to generate a base sub-stream and one or more enhancement sub-streams for subsequent transmission over a wireless communication channel and assigns different priorities to different sub-streams. Depending on the channel conditions, the transmitting STA may select to discard, without transmission, portions of data from enhancement sub-streams. The selection process is based on the assigned priority and operates to preserve as much of relatively high-priority data as possible. The receiving STA then processes the received data to generate a reconstructed media stream, which provides signal quality equal to or better than the signal quality supported by the base sub-stream. Advantageously, a WLAN system of the invention is adapted to change signal quality dynamically and incrementally in a manner commensurate with current channel conditions without the need for communication between the higher and lower network layers. In addition, it provides gradual and graceful degradation of signal quality when channel conditions deteriorate as opposed to abrupt degradation inherent in analogous prior art systems.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
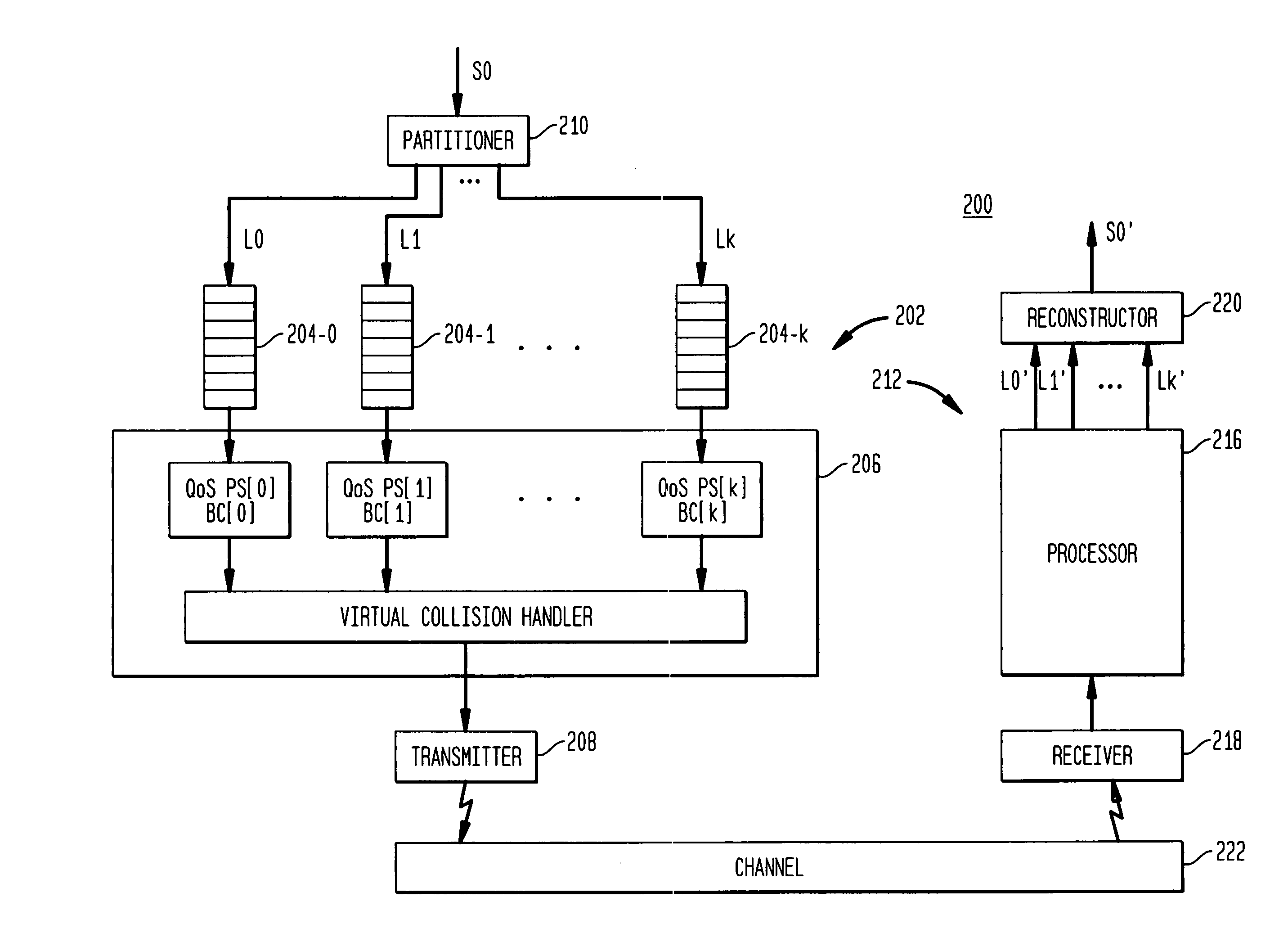
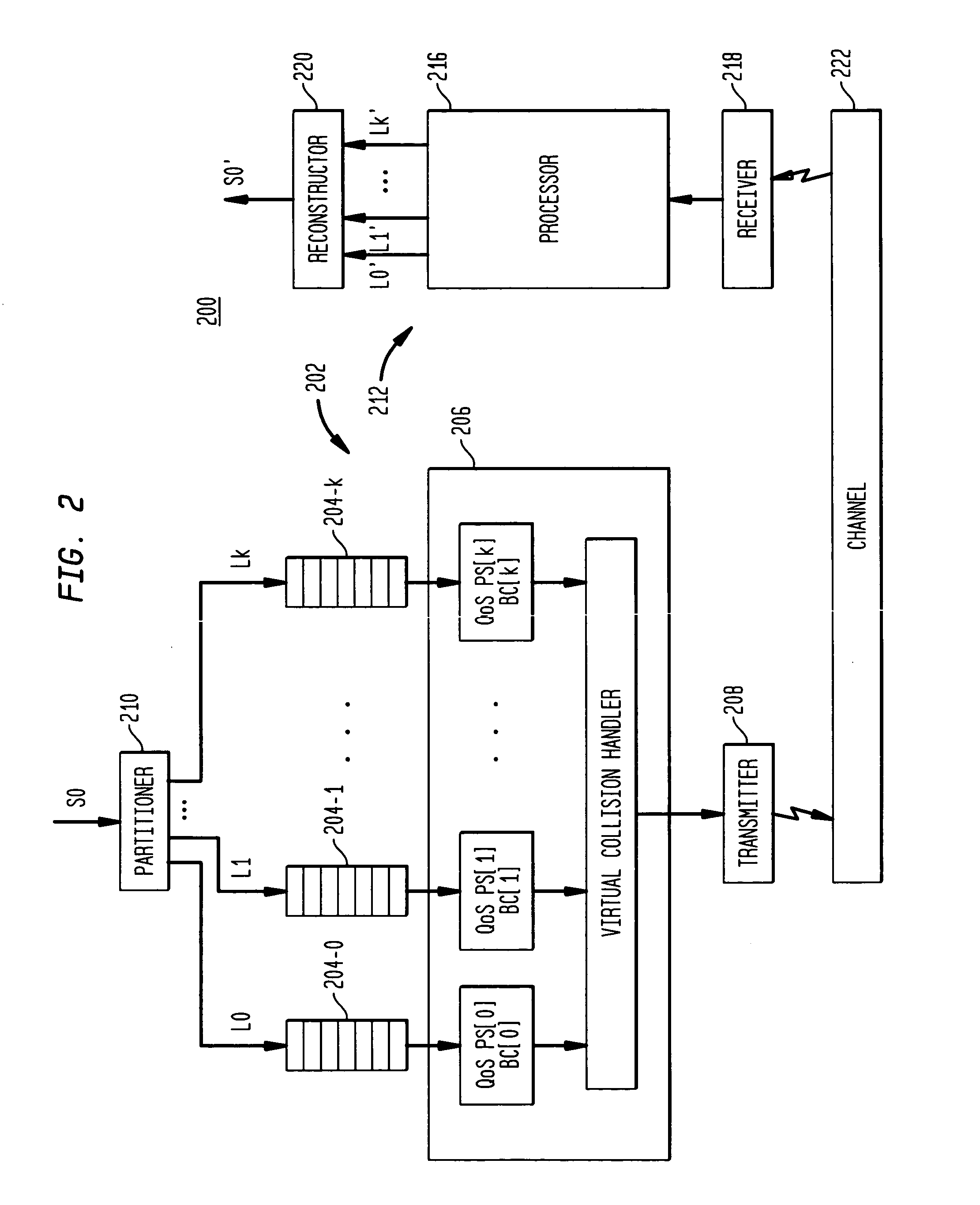
Method and computer program product for internet protocol (IP)-flow classification in a wireless point to multi-point (PtMP) transmission system
InactiveUS7251218B2Special service provision for substationError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorQuality of serviceWireless access point
A system and method for Internet Protocol (IP) flow classification group IP flows in a packet-centric wireless point to multi-point telecommunications system is disclosed. The method comprises analyzing an IP flow in a packet-centric manner, classifying the IP flow, scheduling the IP flow for transmission over a shared wireless bandwidth between a wireless base station and at least one subscriber customer premises equipment (CPE) station, allocating the shared wireless bandwidth to a communication of the IP flow between the wireless base station and a subscriber CPE station so as to optimize end-user quality of service (QoS) associated with the IP flow.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Push-Pull Based Content Delivery System
InactiveUS20080059631A1Maximize QoSImprove scalabilityDigital computer detailsTelevision systemsClosed loop feedbackPush pull
QoS is built into a peer network within existing Internet infrastructure itself lacking QoS, by enabling a network peer to continuously discern the network's ability to deliver to that peer a particular Content Object (distributed in groups of component Packages among neighboring VOD peers) within predetermined times. Content Objects are divided into groups of component Packages and distributed to Clusters of neighboring network peers, enhancing QoS upon subsequent retrieval. Tracking Files (lists of network peers storing Package groups) and Tracking Indexes (lists of network peers storing Tracking Files) are generated to facilitate “on demand” Content Objects retrieval. Dynamically monitoring network traffic (including VOD functionality, bandwidth and reliability) creates “distributed closed-loop feedback,” and in response, attributes of individual network peers (e.g., Trust Level and membership within a particular Cluster) are modified, and “content balancing” functions performed (e.g., redistribution of Package groups among network peers) enables maintaining high QoS.
Owner:VODDLER GRP
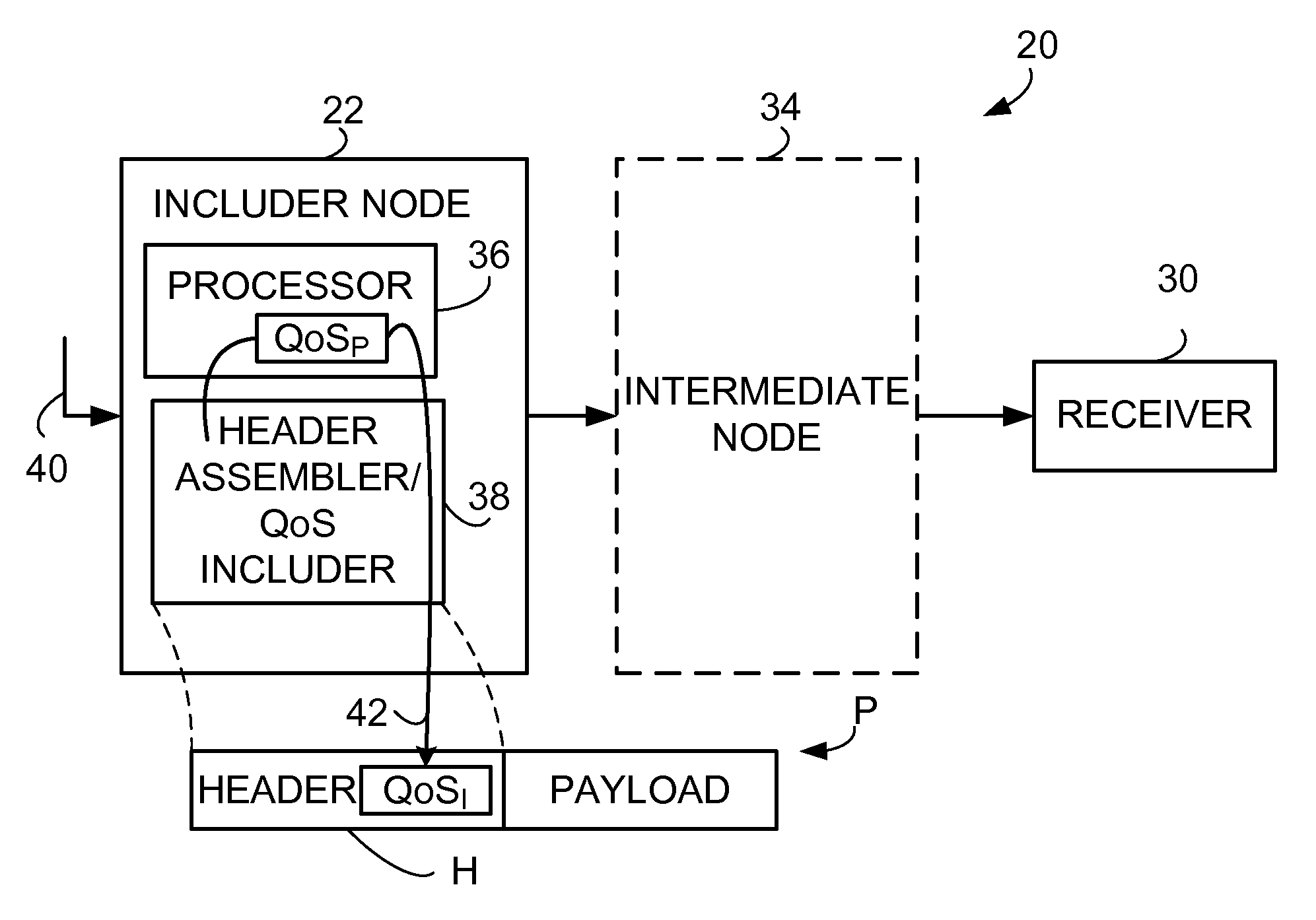
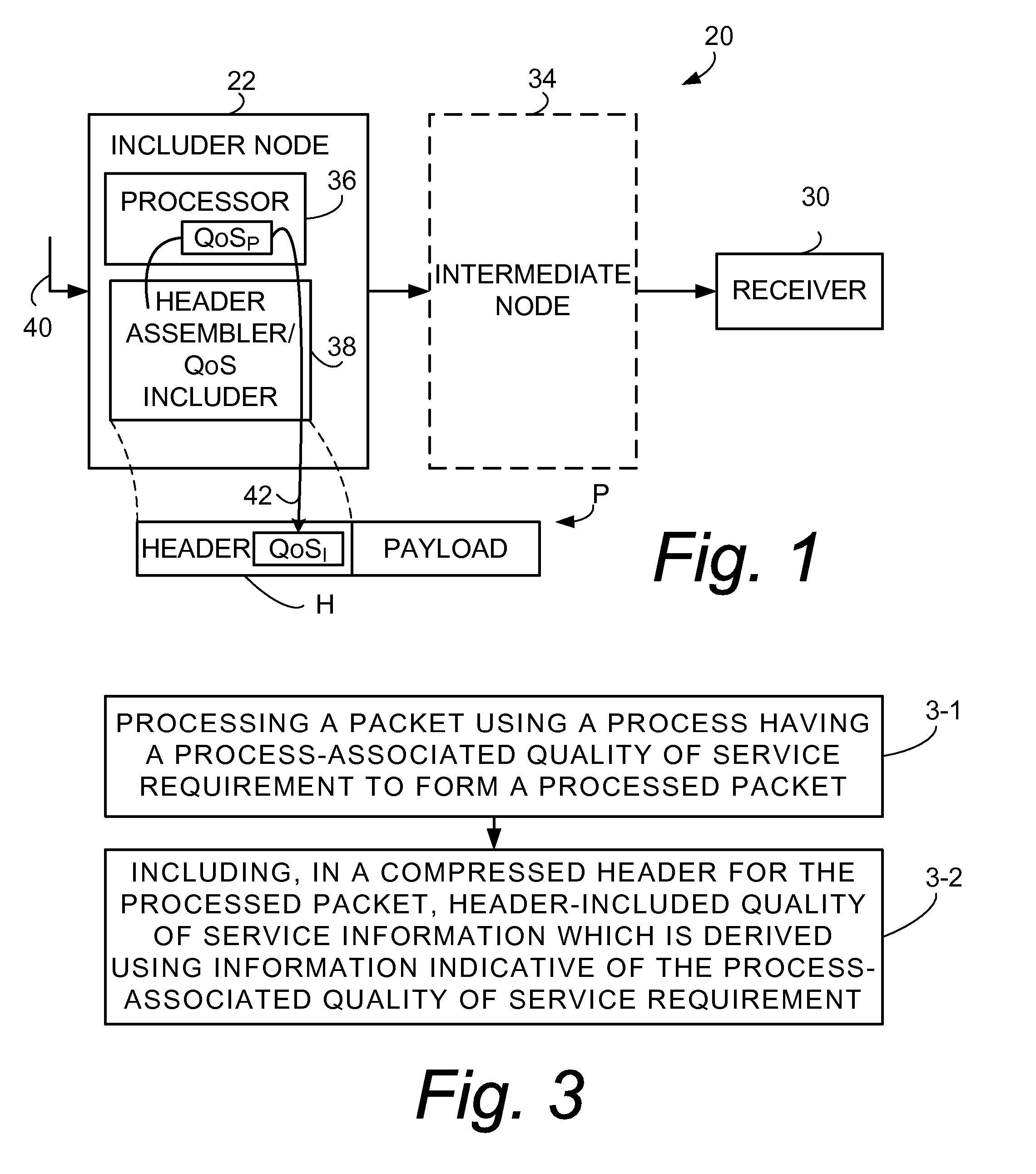
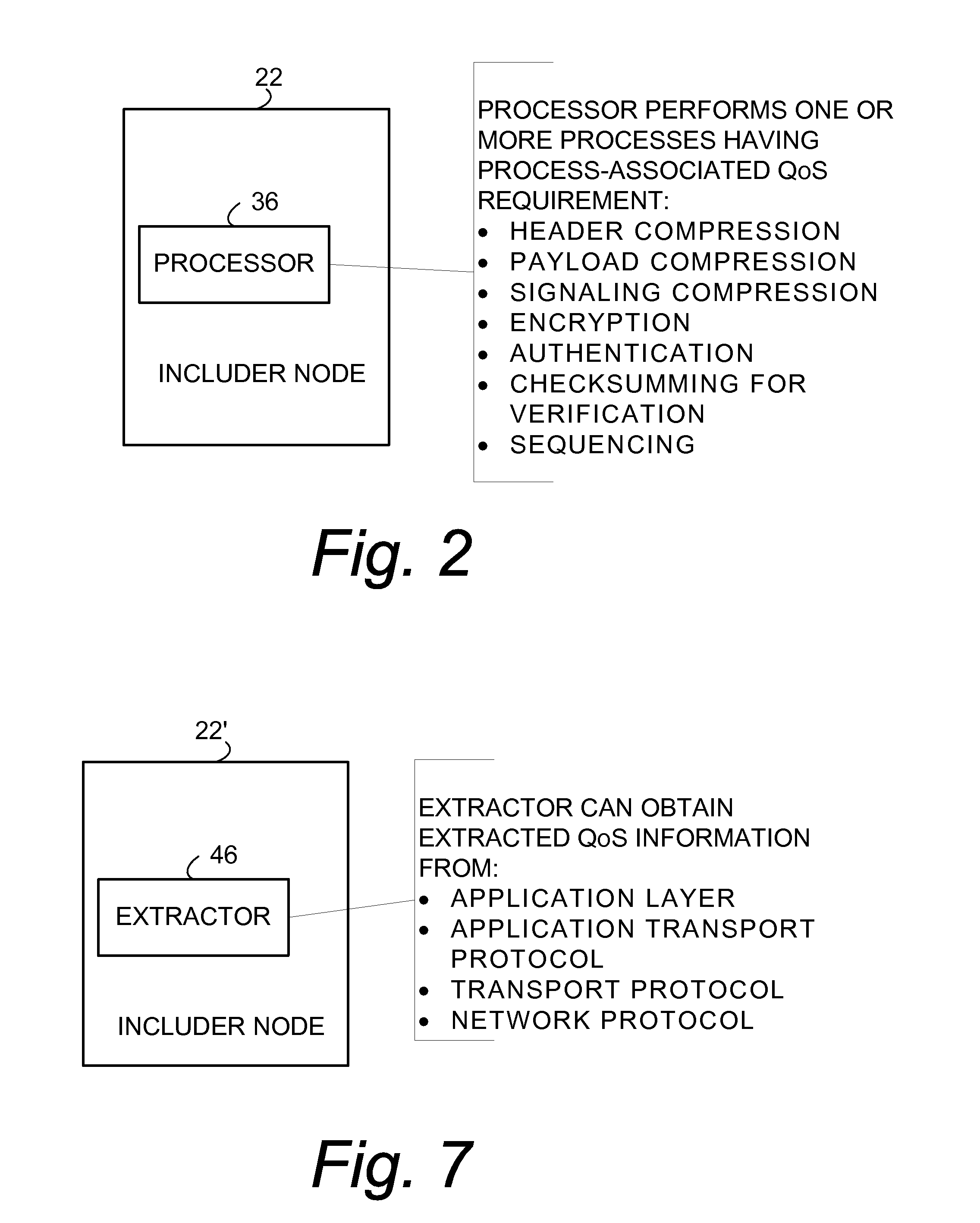
Inclusion of Quality of Service Indication in Header Compression Channel
Quality of service information (QoSI) is included with a compressed header of a data packet and can be utilized by nodes supporting the header compression channel to perform QoS enforcements at a sub-flow granularity level. A basic mode of a method comprises (1) processing a packet using a process having a process-associated quality of service requirement to form a processed packet, and (2) including, with a compressed header for the processed packet, the header-included quality of service information which is derived using information indicative of the process-associated quality of service requirement. In another mode the header-included quality of service information is derived both from the process-associated quality of service requirement and quality of service information extracted from the received packet.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for providing a cdn with granular quality of service
InactiveUS20110078230A1Increase contentMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionClient-sideBroadband
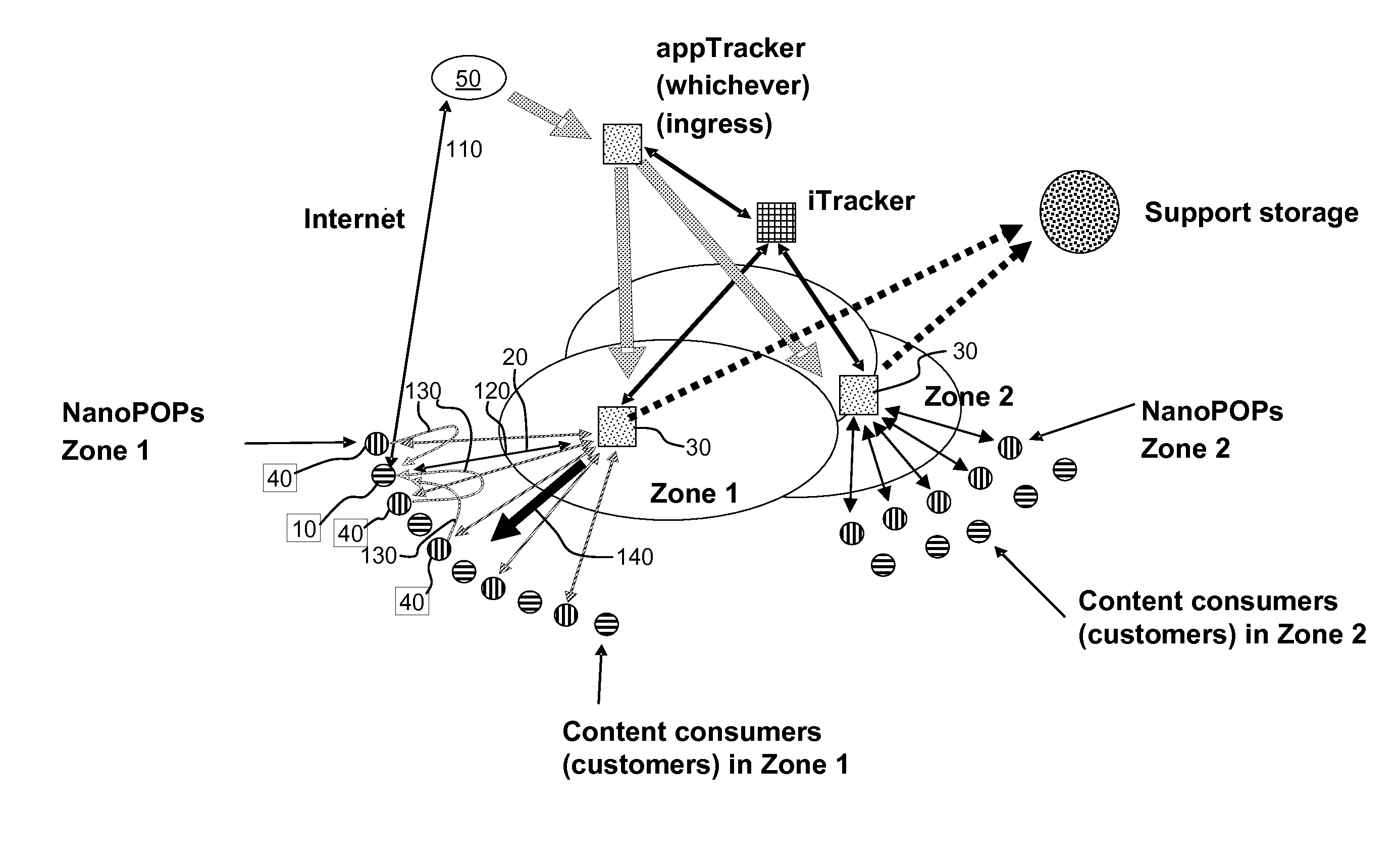
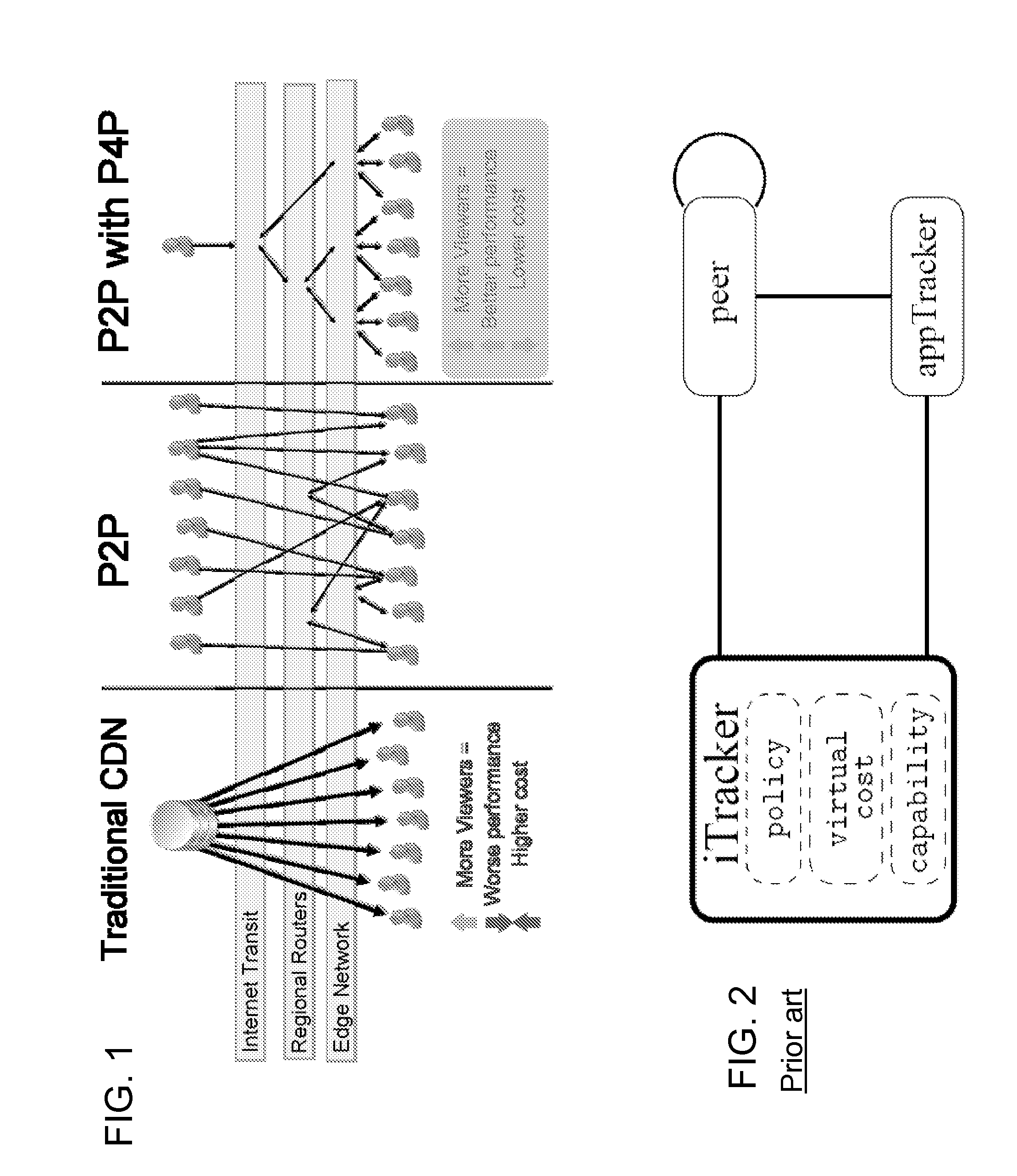
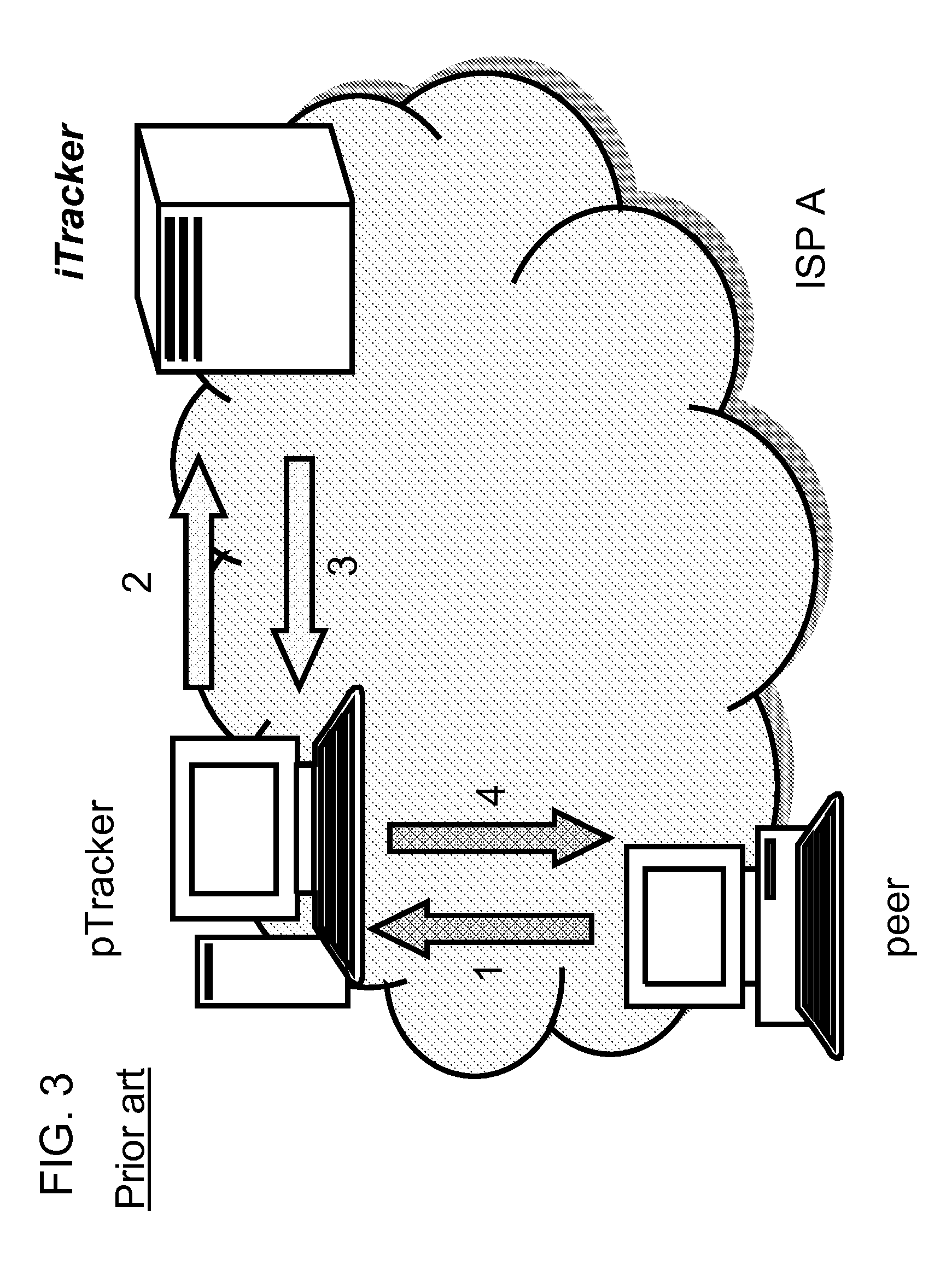
In a method of providing granular quality of service in a hybrid content distribution network of classical distribution in a network via client-server plus very distributed mechanisms operating peer to peer inside the network, content is replicated in a large number of endpoint nodes, some of which are CPEs of broadband subscribers, and backed by a few storage servers to ensure content availability. Traffic is delivered by a mixture of P4P for choice of seeds and selection of good neighborhoods for quick content download. The ISP uses the unsold physical capacity of the link for CDN service and other underutilized resources, and enforces seeding at many nodes including broadband subscriber CPEs. By having a large farm of nano-datacenters distributed across the network, including the premises of broadband customers, the ISP can maintain and run a CDN. A tracker determines where to seed the content, depending on the number of broadband subscribers requesting the content, the geographical distribution of requested content, and the Service Level Agreement between content providers and the ISP. The tracker can seed a sufficient number of nodes to ensure redundancy.
Owner:TELEFONICA SA
Data link control proctocol for 3G wireless system
InactiveUS6542490B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelElectronic circuit testingTelecommunications linkDual mode
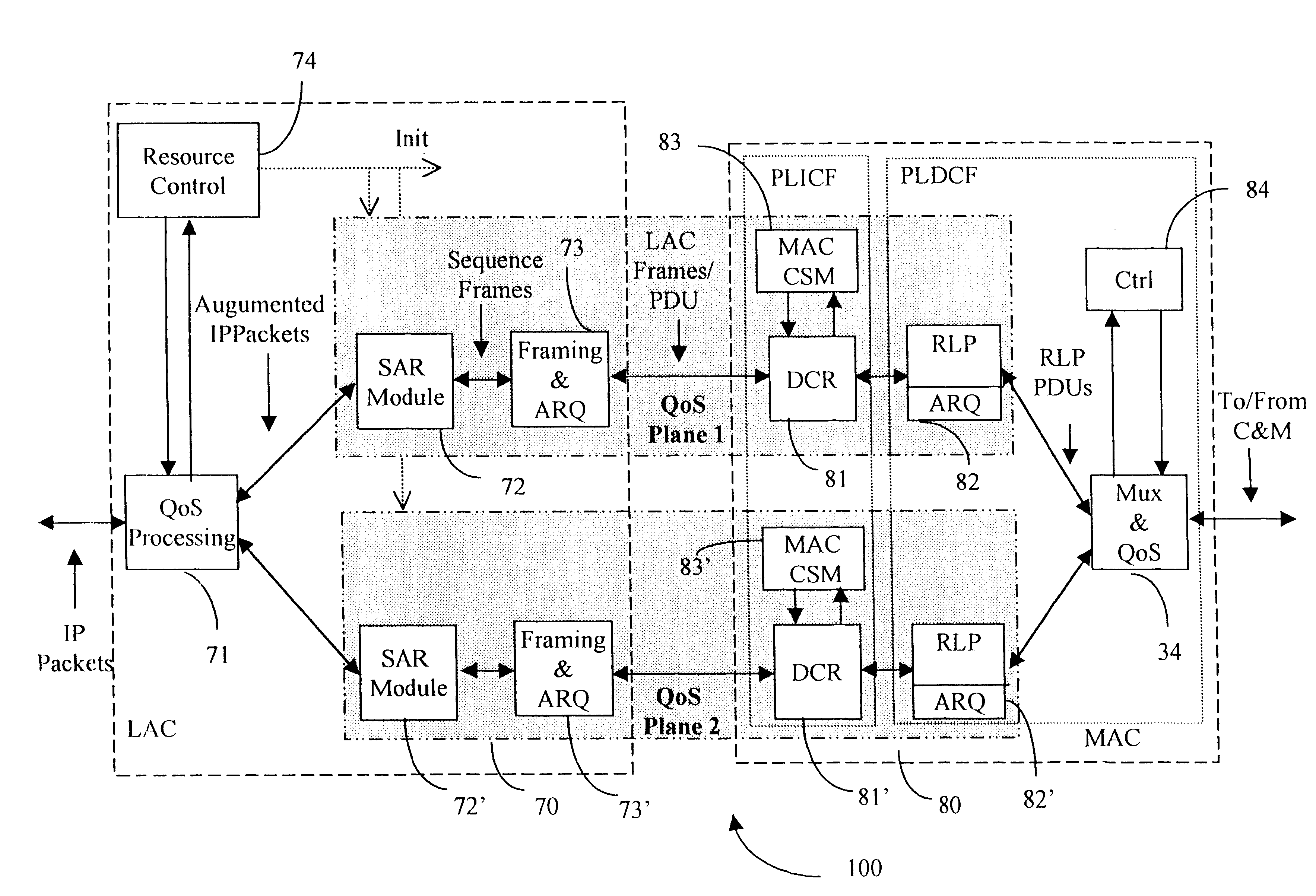
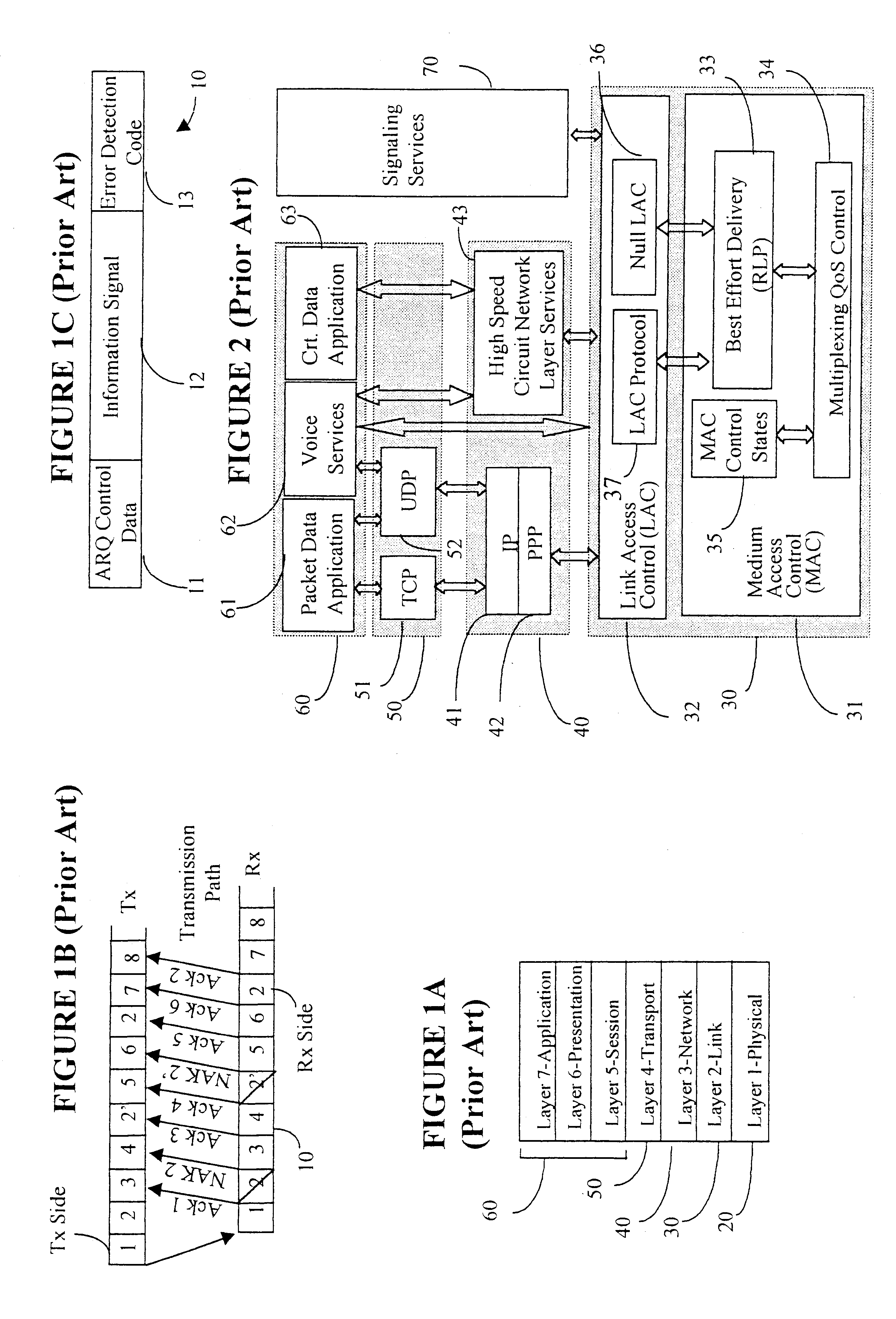
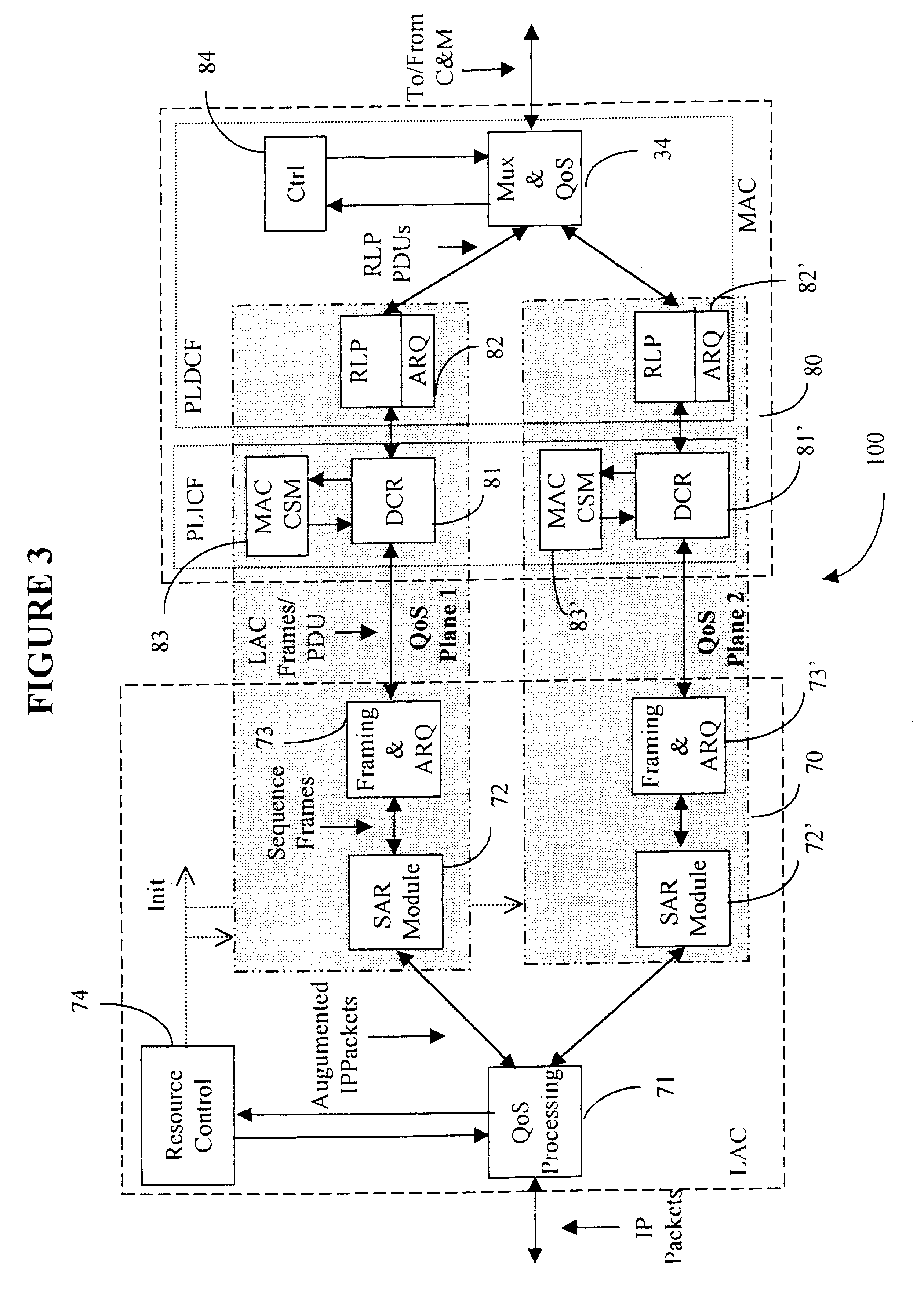
A Data Link Control protocol for 3G wireless communication system for direct support for network layer protocols, e.g. the Internet Protocol (IP), is provided. The Link Layer disclosed comprises a Link Access Control (LAC) sublayer and a Medium Access Control (MAC) sublayer. At a transmit end of the wireless system, a plurality of Quality of Service (QoS) data planes are created to directly support the IP QoS. Each QoS data plane is optimized to handle QoS requirements for a corresponding Class of Service (CoS). Data packets received at the LAC sublayer are directed to a QoS data plane according to the particular QoS information they contain and processed according to the particular QoS requirement to generate variable size LAC frames. The variable size LAC frames are transmitted to the MAC sublayer for generating radio link protocol data units (RLP PDUs) to be transmitted to a receiving end. A new level of error correction is provided at the LAC sublayer as the size of the LAC PDUs can be dynamically adjusted in response to the conditions of the communication link. A dual mode ARQ is provided at the MAC sublayer to improve the quality of the air transmission for bursty as well as non-bursty traffic conditions.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method for billing IP broadband subscribers
InactiveUS7760711B1Metering/charging/biilling arrangementsTelephonic communicationQuality of serviceLeast cost
A method of billing a variable bit rate communication between a first terminal and a distant terminal to a broadband subscriber permits changing billing parameters during a call in real time in response to user inputs including user requested changes in quality of service, changes in data rate and changes in preferred service provider. A variable bit rate communication to be billed has a variable quality of service related to the degree of utilization of a plurality of different networks. The billing method comprises the steps of i.) receiving user identification data at a first terminal and data representing a required bit rate and a default quality of service selected by the user, ii.) verifying the user identification data to be associated with the broadband service subscriber, iii.) determining least cost alternative network resources available for achieving the communication at the user selected default quality of service and the required bit rate, iv.) determining cost data associated with the network resources, v.) outputting to the user a least cost for the communication according to their selected default quality of service and alternative least cost network resources, vi.) coupling the first terminal and the distant terminal via the least cost determined network resources at the default quality of service and the required bit rate responsive to user authorization and vii.) billing for the communication at the default quality of service and according to the required bit rate after the termination of the communication.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
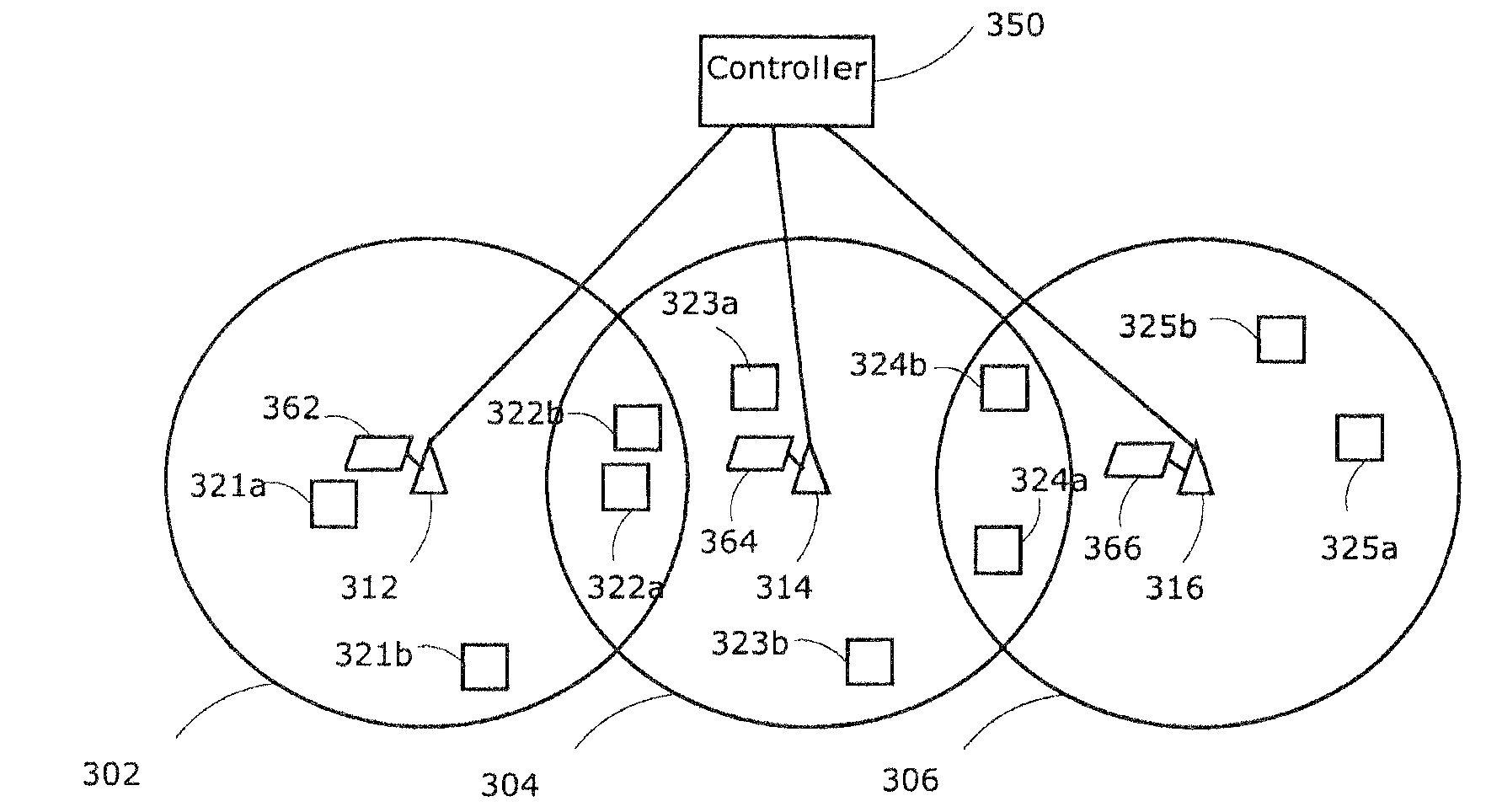
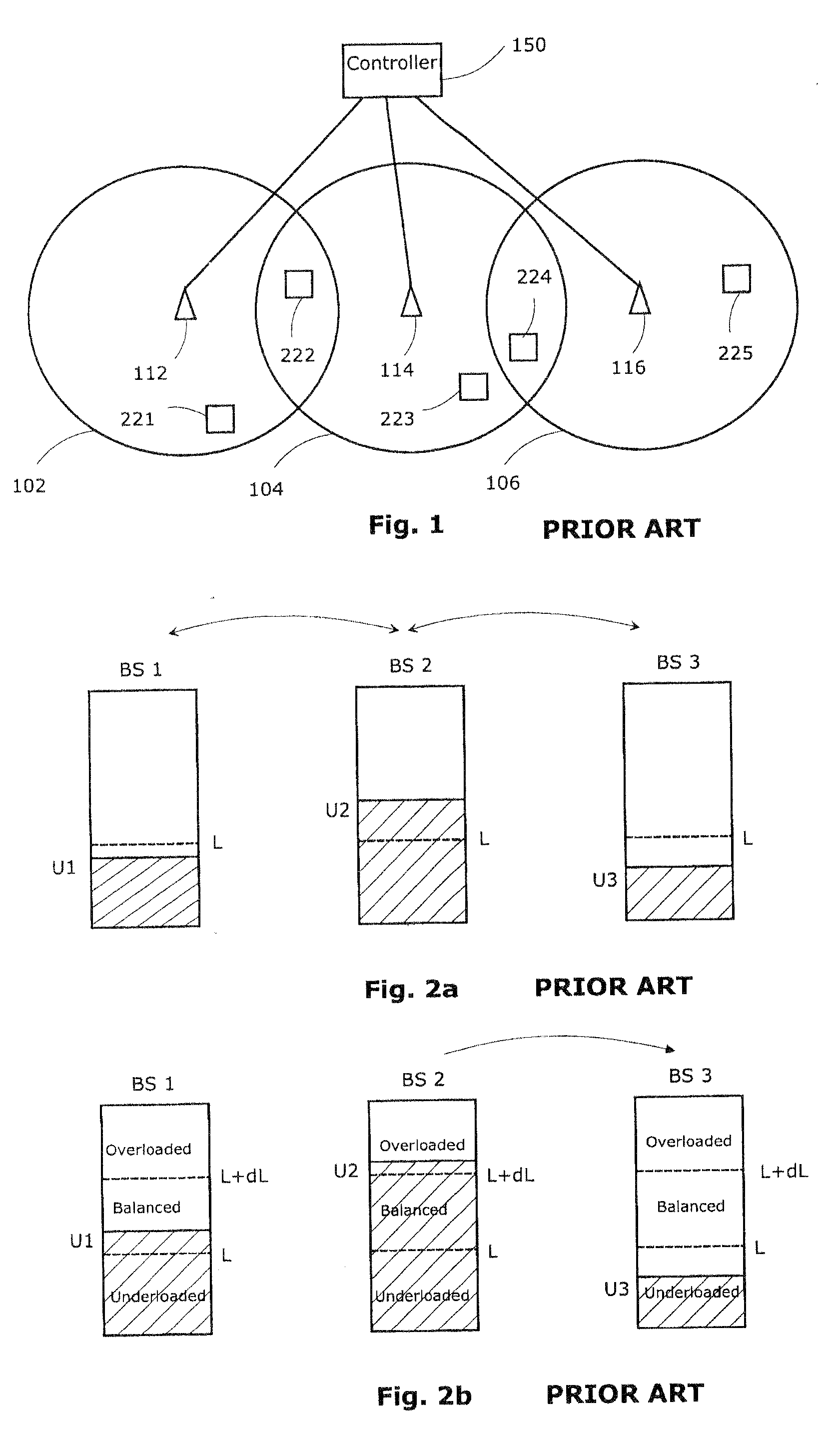
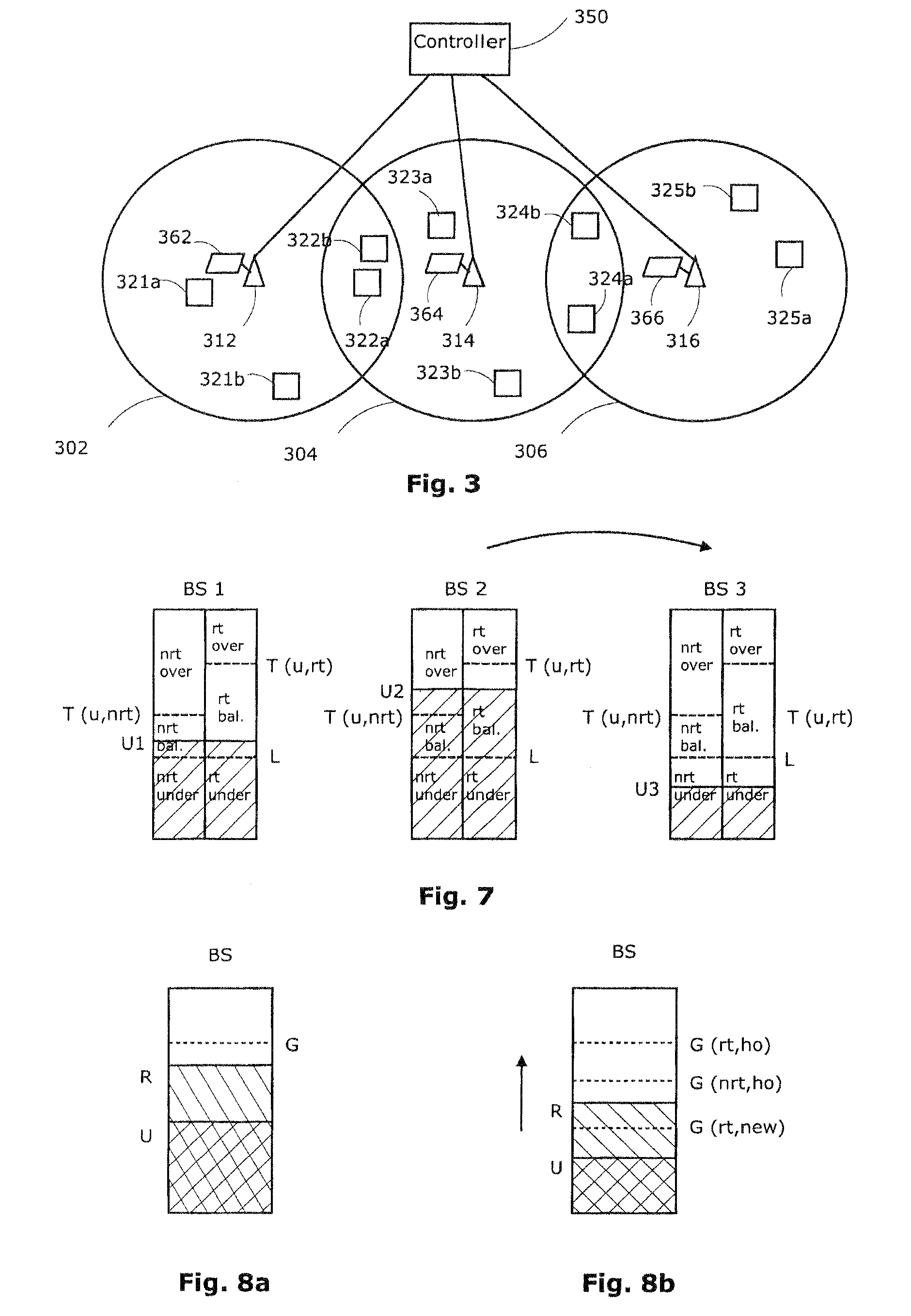
Load balancing in mobile environment
InactiveUS20090163223A1Unbalanced loadImprove QoSRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless communicationResource utilizationHandover
In next generation wireless networks such as a Mobile WiMAX traffic prioritization is used to provide differentiated quality of service (QoS). Unnecessary ping-pong handovers that result from premature reaction to fluctuating radio resources pose a great threat to the QoS of delay sensitive connections such as VoIP which are sensitive to scanning and require heavy handover mechanisms. Traffic-class-specific variables are defined to tolerate unbalance in the radio system in order to avoid making the system slow to react to traffic variations and decreasing system wide resource utilization. By setting thresholds to trigger load balancing gradually in fluctuating environment the delay sensitive connections avoid unnecessary handovers and the delay tolerant connections have a chance to react to the load increase and get higher bandwidth from a less congested BS. A framework for the resolution of static user terminals in the overlapping area within adjacent cells will be described.
Owner:ELEKTROBIT WIRELESS COMM LTD
Method for providing integrated packet services over a shared-media network
InactiveUS6563829B1Good serviceError preventionTransmission systemsQos quality of serviceExchange network
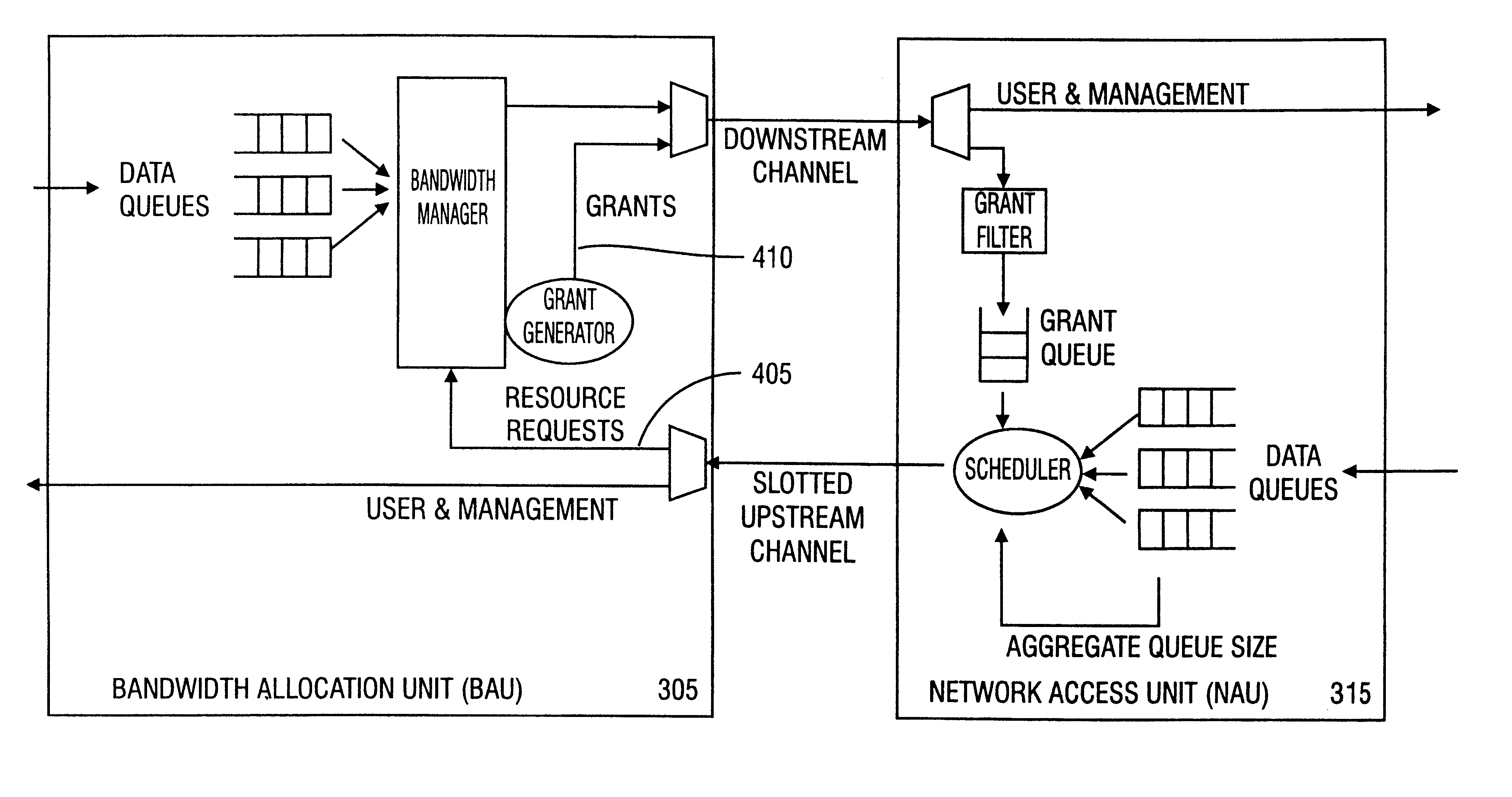
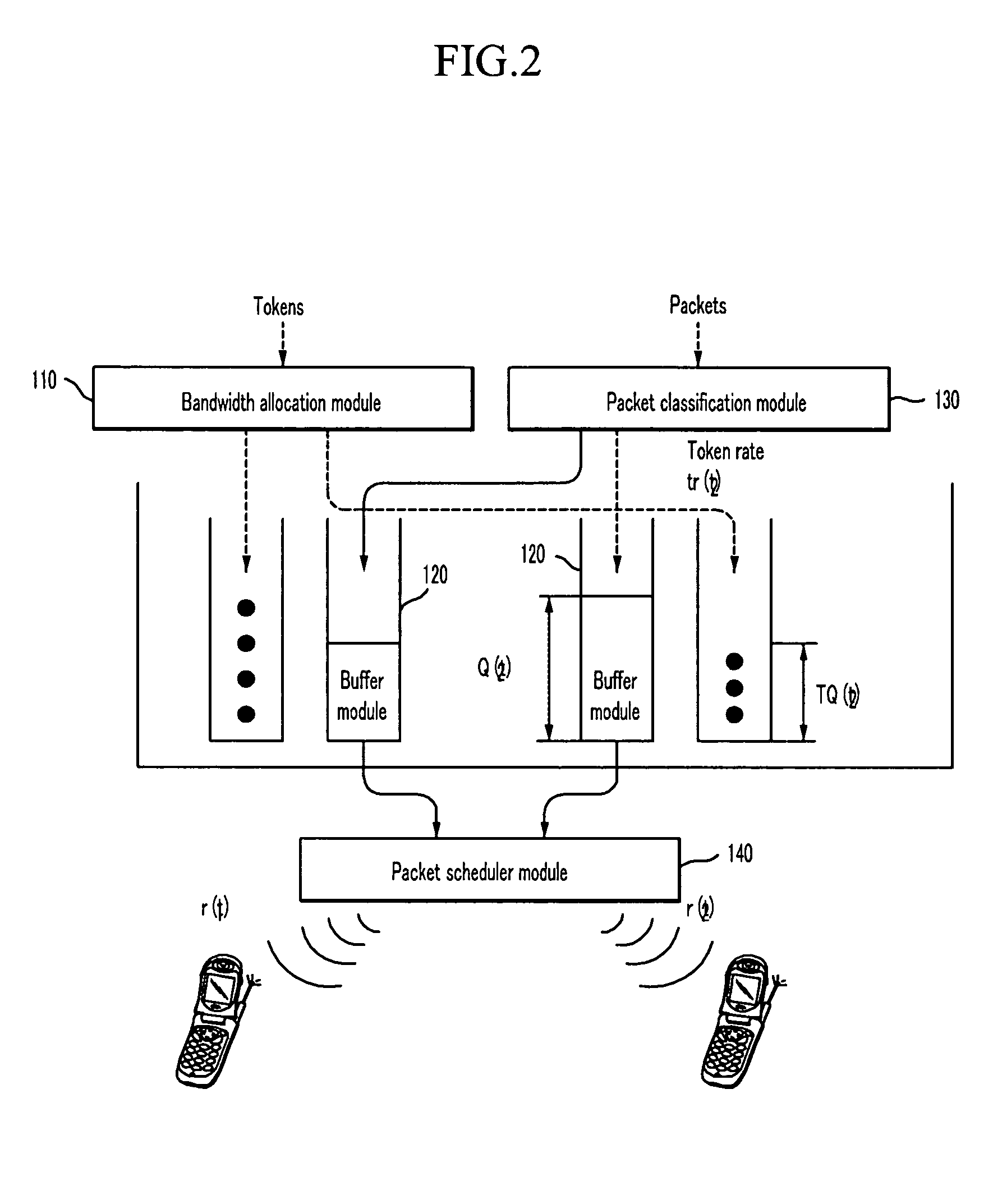
A method in accordance with the invention allocates bandwidth, fairly and dynamically, in a shared-media packet switched network to accommodate both elastic and inelastic applications. The method, executed by or in a head-end controller, allocates bandwidth transmission slots, converting requests for bandwidth into virtual scheduling times for granting access to the shared media. The method can use a weighted fair queuing algorithm or a virtual clock algorithm to generate a sequence of upstream slot / transmission assignment grants. The method supports multiple quality of service (QoS) classes via mechanisms which give highest priority to the service class with the most stringent QoS requirements.
Owner:AMERICAN CAPITAL FINANCIAL SERVICES
Sequence numbers for multiple quality of service levels
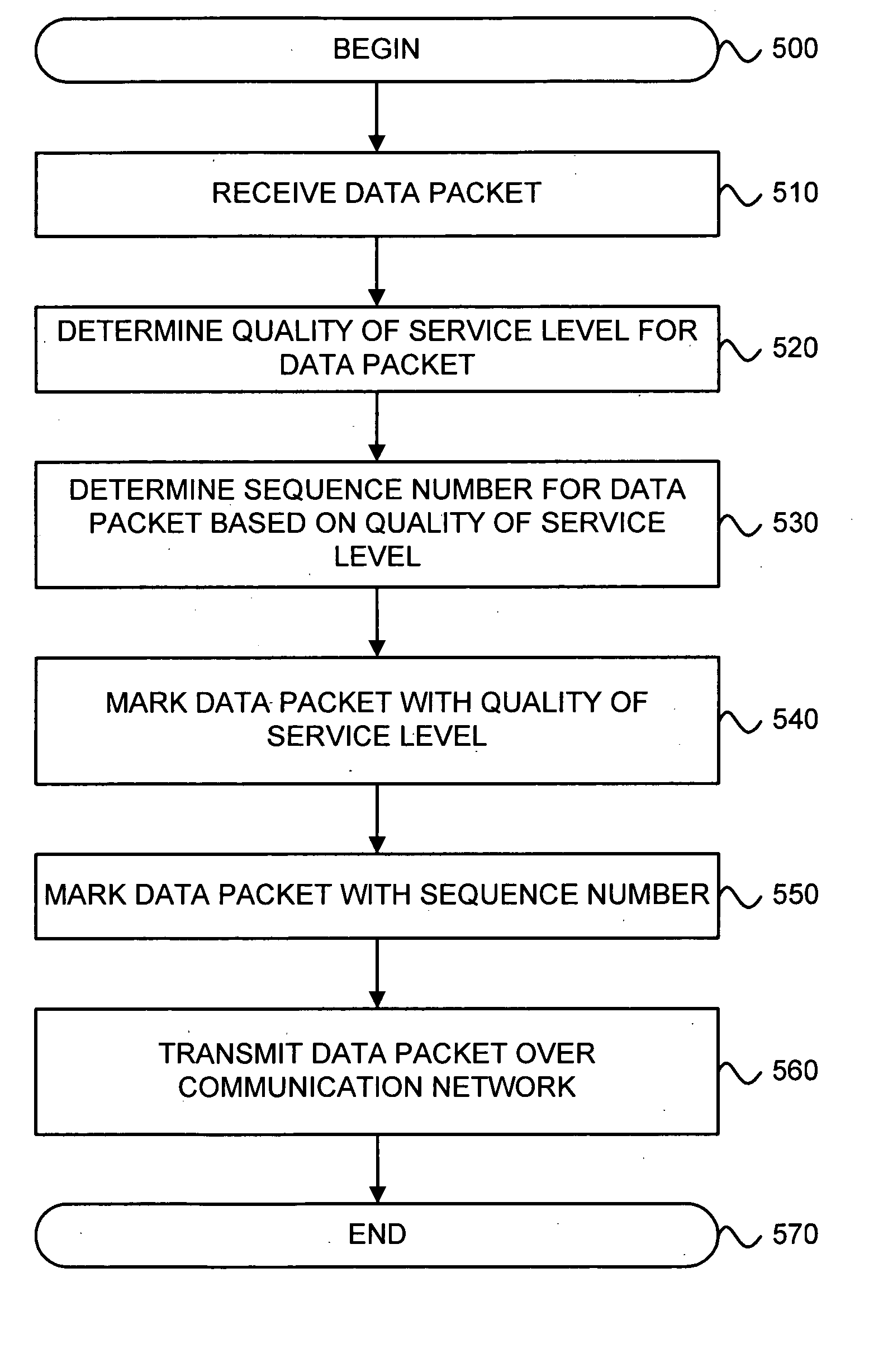
InactiveUS20070115812A1Good communication controlReduce dropError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceData pack
A system for providing communications using sequence numbers for multiple quality of service (QoS) levels includes a first network device. The first network device receives a data packet and determines a QoS level for the data packet. The first network device also determines a sequence number for the data packet based on the QoS level. The first network device then marks the data packet with the sequence number. The system also may include a second network device. The second network device receives from the first network device the data packet marked with the sequence number based on the QoS level of the data packet. The second network device determines an expected sequence number window based on the QoS level of the data packet. The second network device then determines whether the sequence number of the data packet is within the expected sequence number window for the QoS level.
Owner:SILVER PEAK SYSTEMS
Methods, systems and computer program products for workload distribution based on end-to-end quality of service
InactiveUS6965930B1Resource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsData processing systemQos quality of service
Methods, systems and computer program products provide for distributing workload between data processing systems executing an application which communicates over a network, by receiving a request for a connection to the application over the network, obtaining workload information for the data processing systems, obtaining network quality of service (QoS) information associated with communications over the network for the data processing systems and utilizing the workload information and the corresponding network quality of service information for the data processing systems so as to provide workload metrics. The requested connection to the application is distributed based on the generated workload metrics.
Owner:IBM CORP
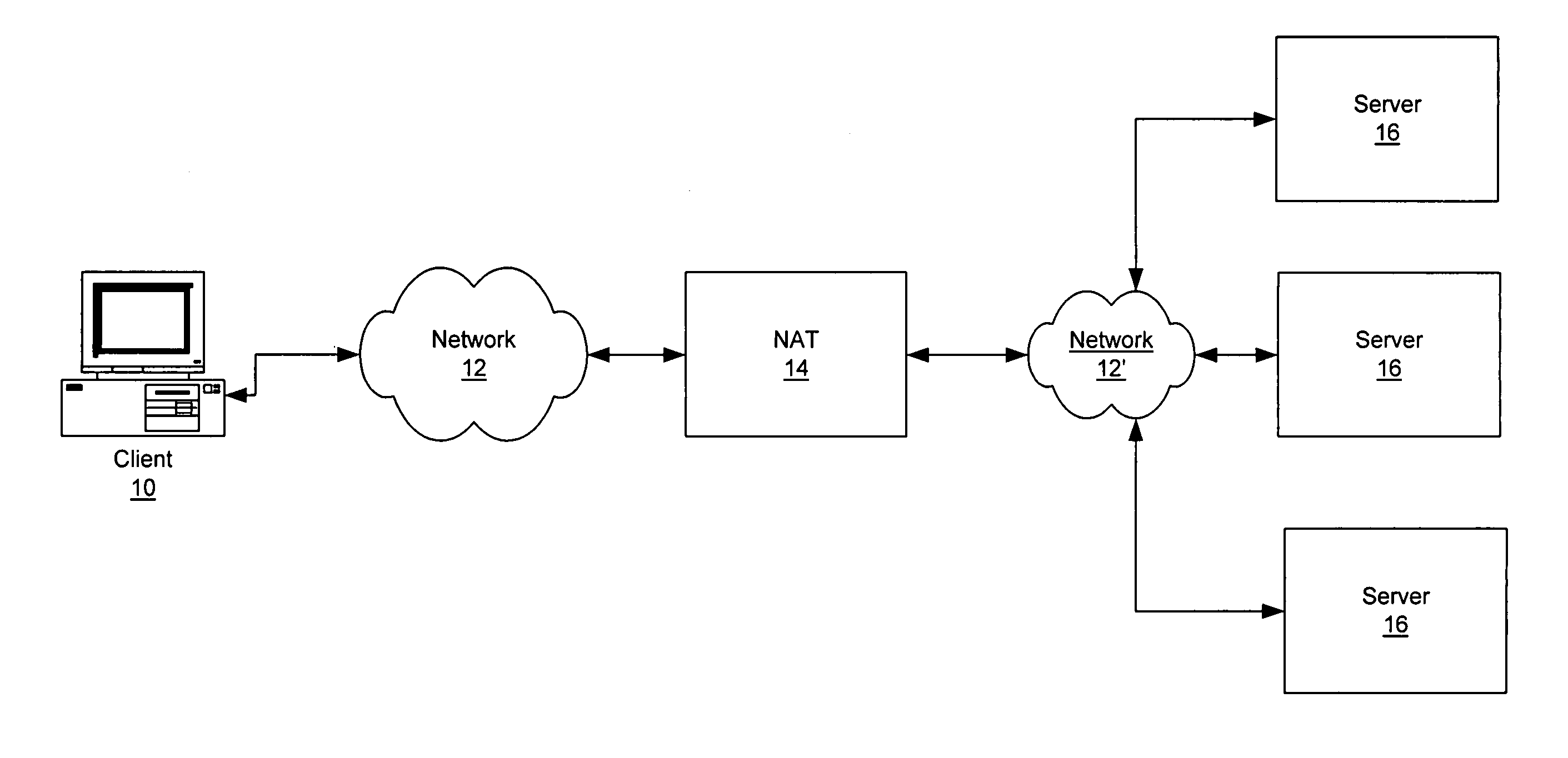
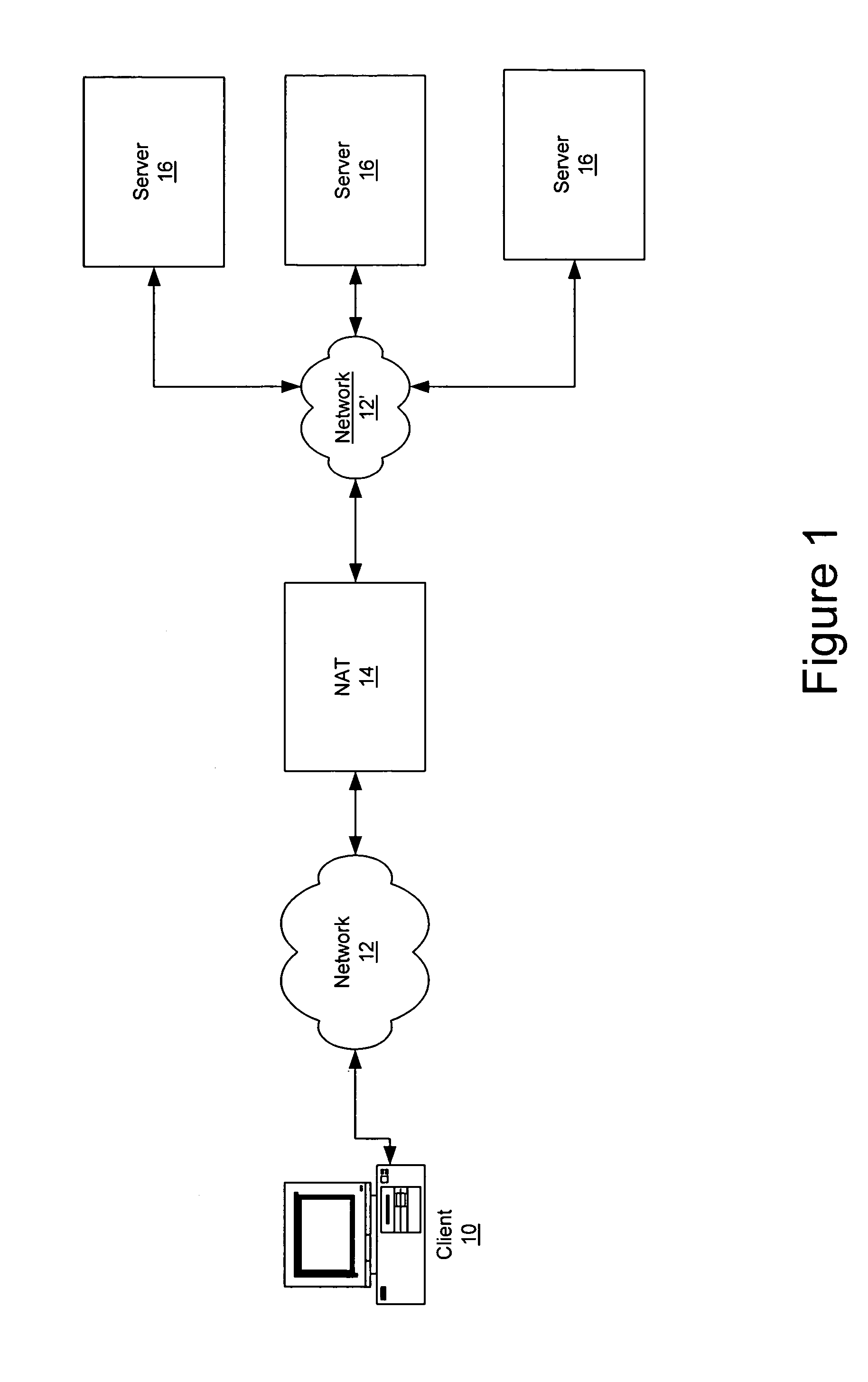
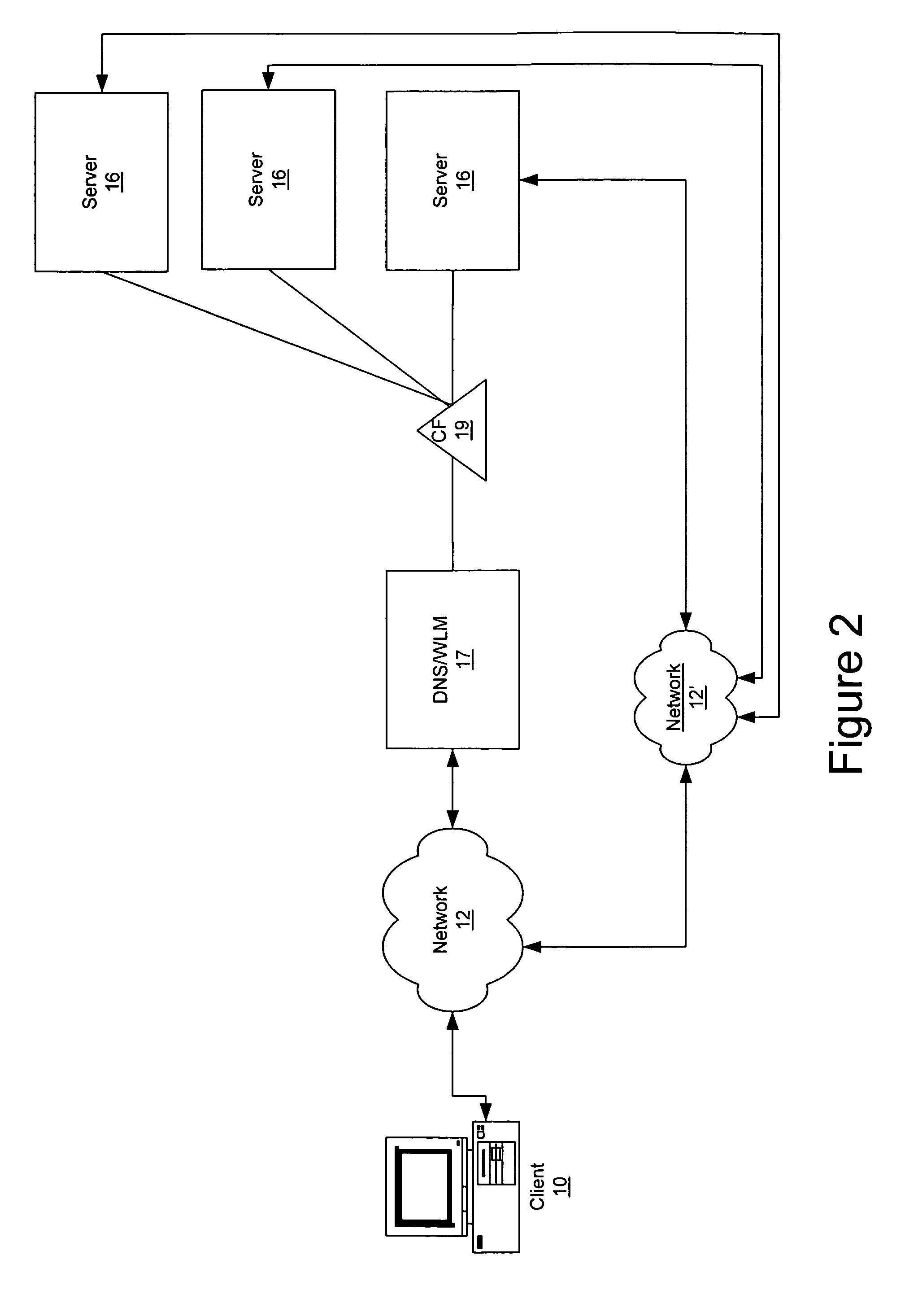
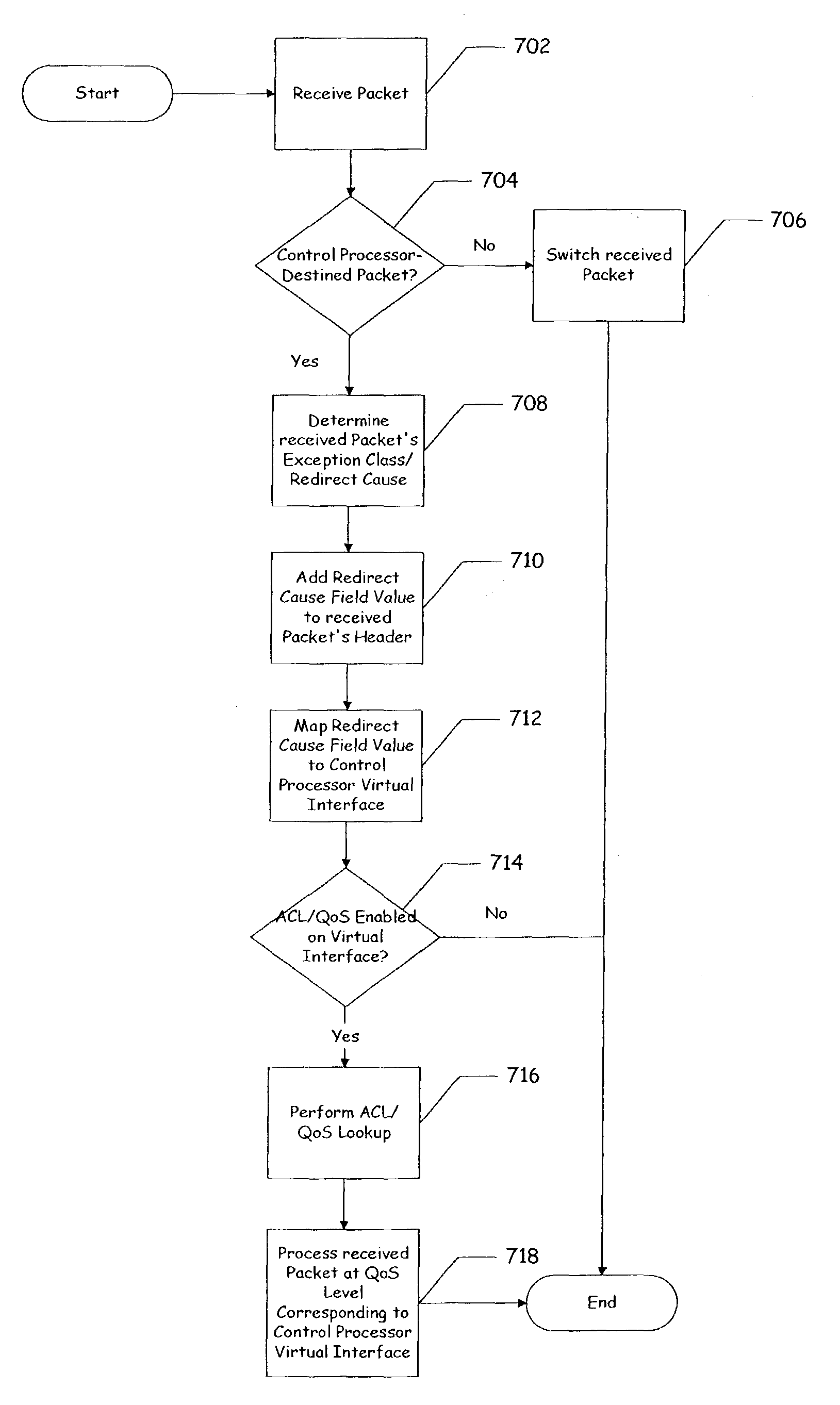
Method and apparatus to apply aggregate access control list/quality of service features using a redirect cause
ActiveUS7953885B1Fine granularityDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceDistributed computing
A method and apparatus to apply aggregate ACL / QoS features using a redirect cause is disclosed. According to one embodiment of the present invention, a control processor configured to support a plurality of virtual interfaces is provided, wherein each of the plurality of virtual interfaces is associated with a quality of service level. According to another embodiment, each quality of service level is associated with a processing bandwidth of the control processor. According to yet another embodiment, a control processor interface is provided coupled to the control processor which is configured to select a virtual interface of the plurality of virtual interfaces using data of a received data unit, and to transfer the received data unit to the selected virtual interface.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
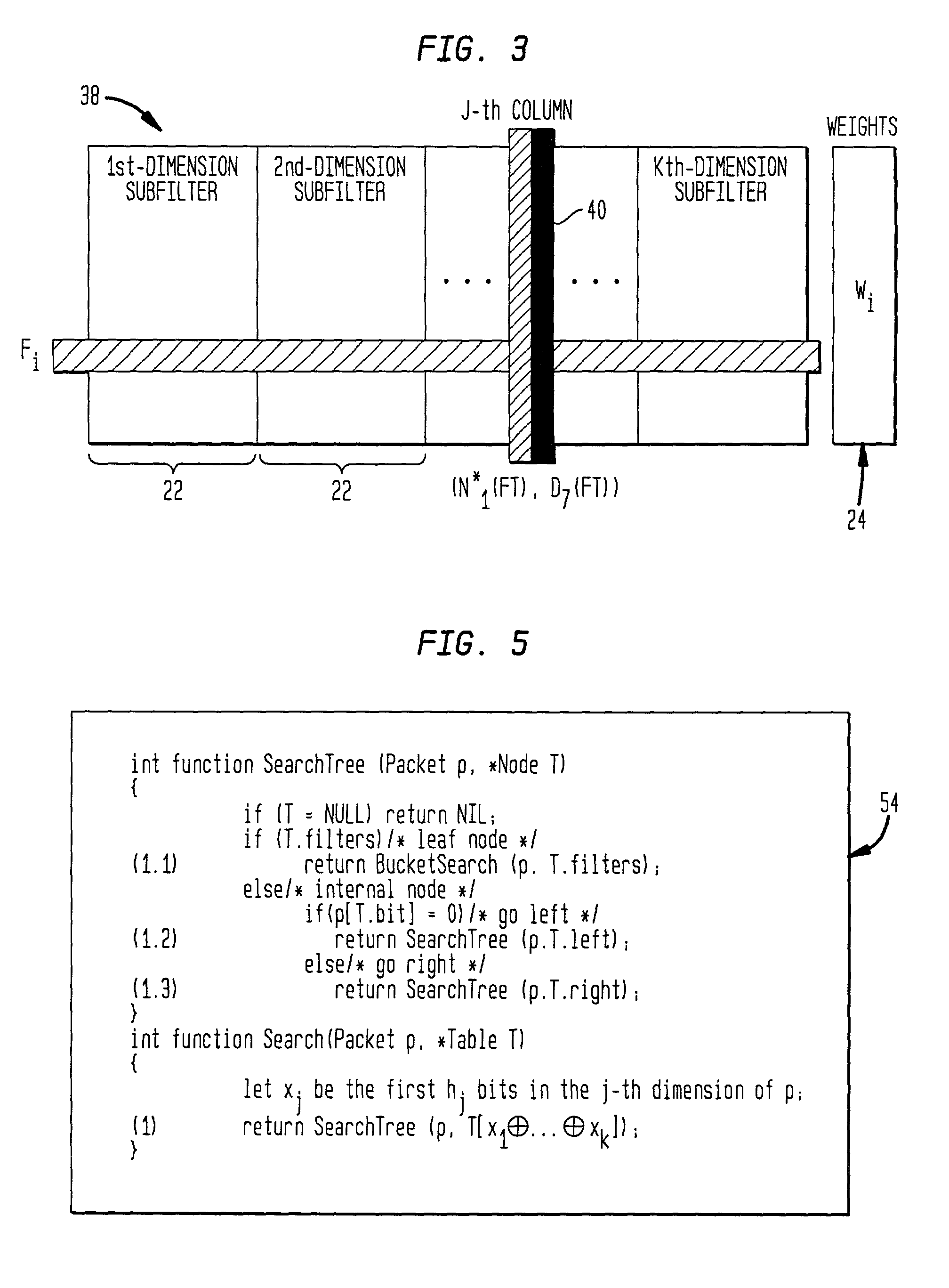
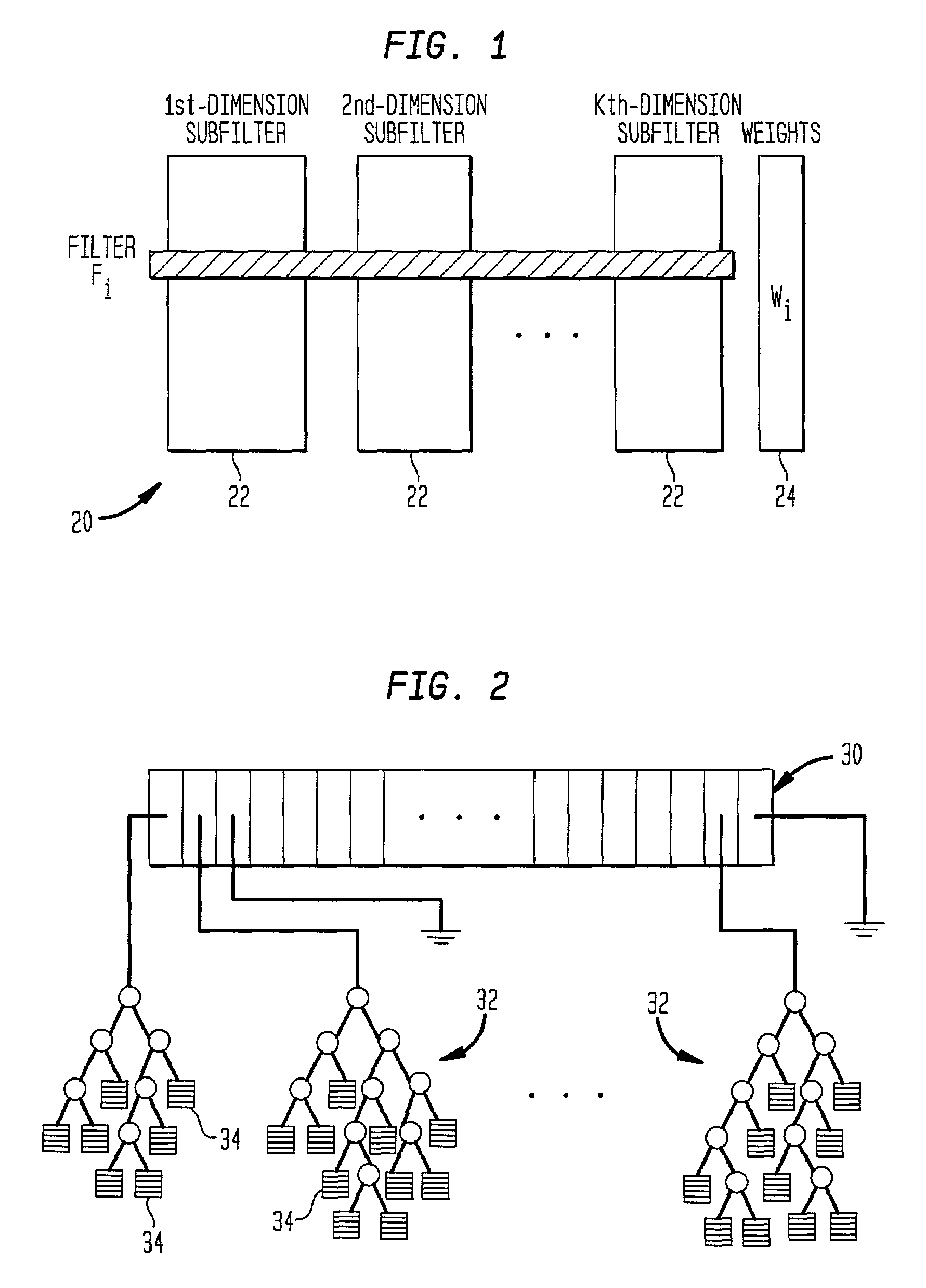
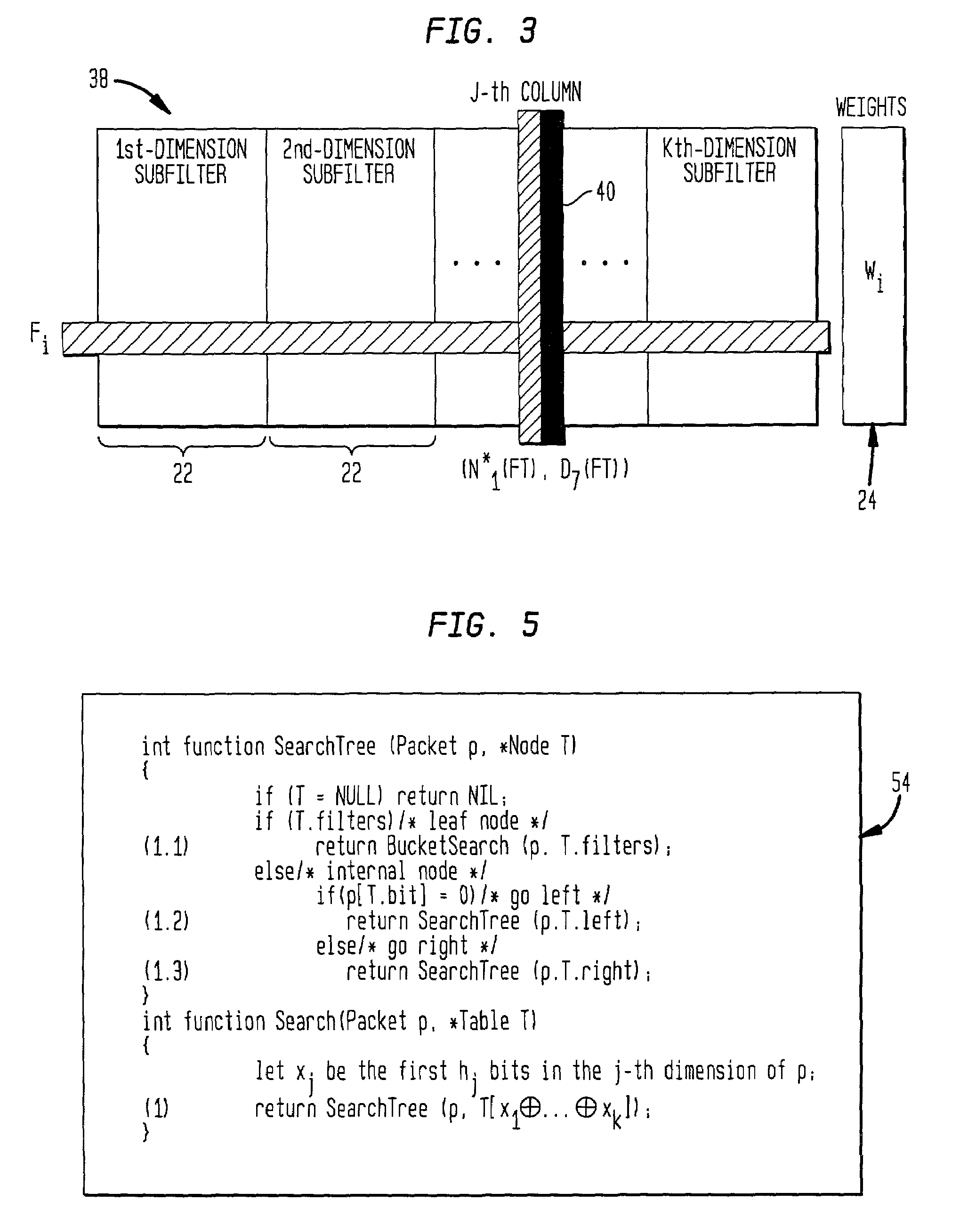
Modular packet classification
InactiveUS20020023089A1Avoid explosionDepth is minimizedDigital data processing detailsData switching by path configurationQos quality of serviceData pack
The novel method and system for classifying packets through the use of filters combines heuristic tree search with the use of filter buckets. This provides high performance and reasonable storage requirement, even when applied to large number of filters (from 4K to 1 million). In addition, the novel method can adapt to the input packet distribution by taking into account the relative filter usage. The capability of employing a large number of filters in a packet classifciation system is useful in providing value-added services, such as security, quality of service (QoS), load balancing, and traffic accounting.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
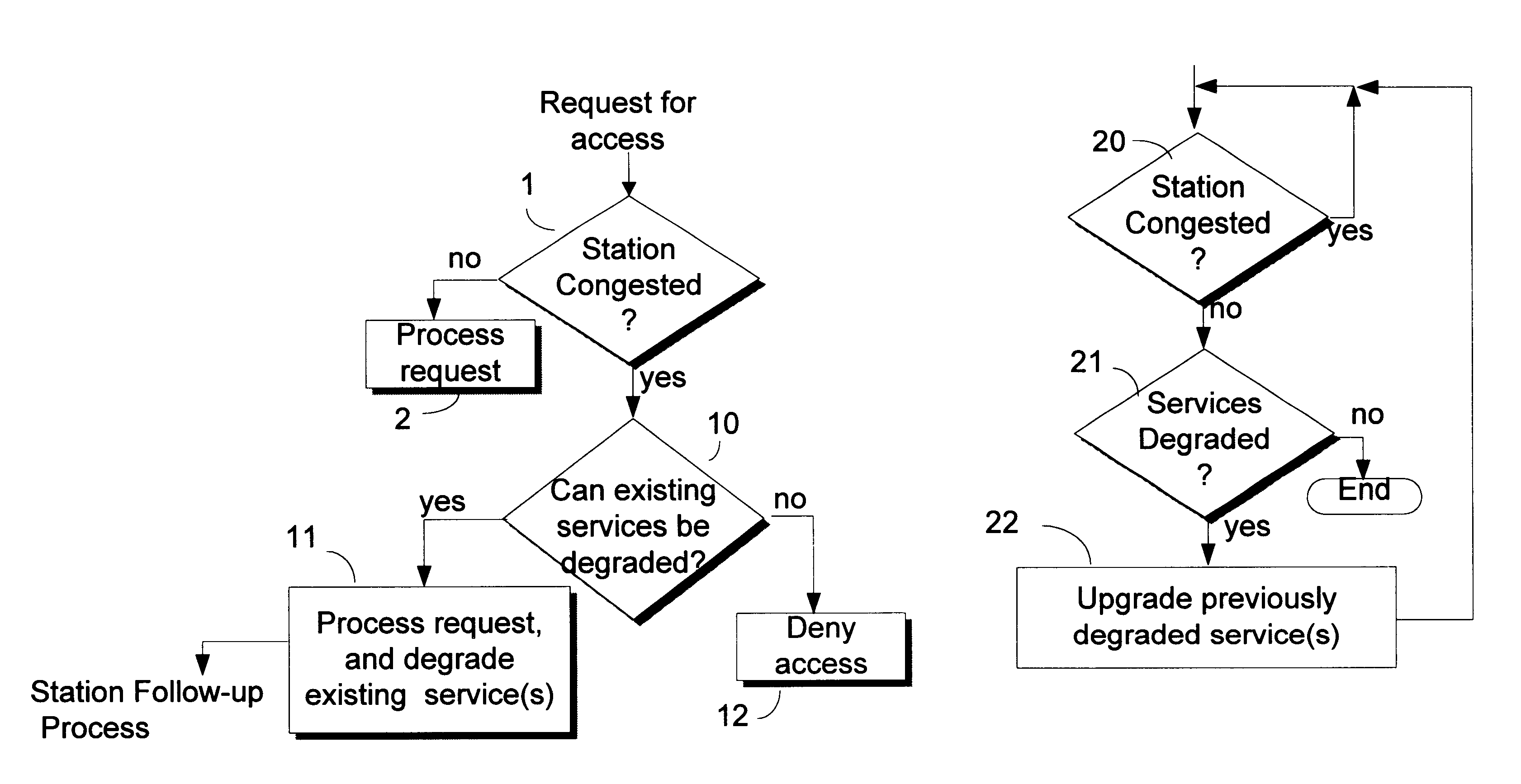
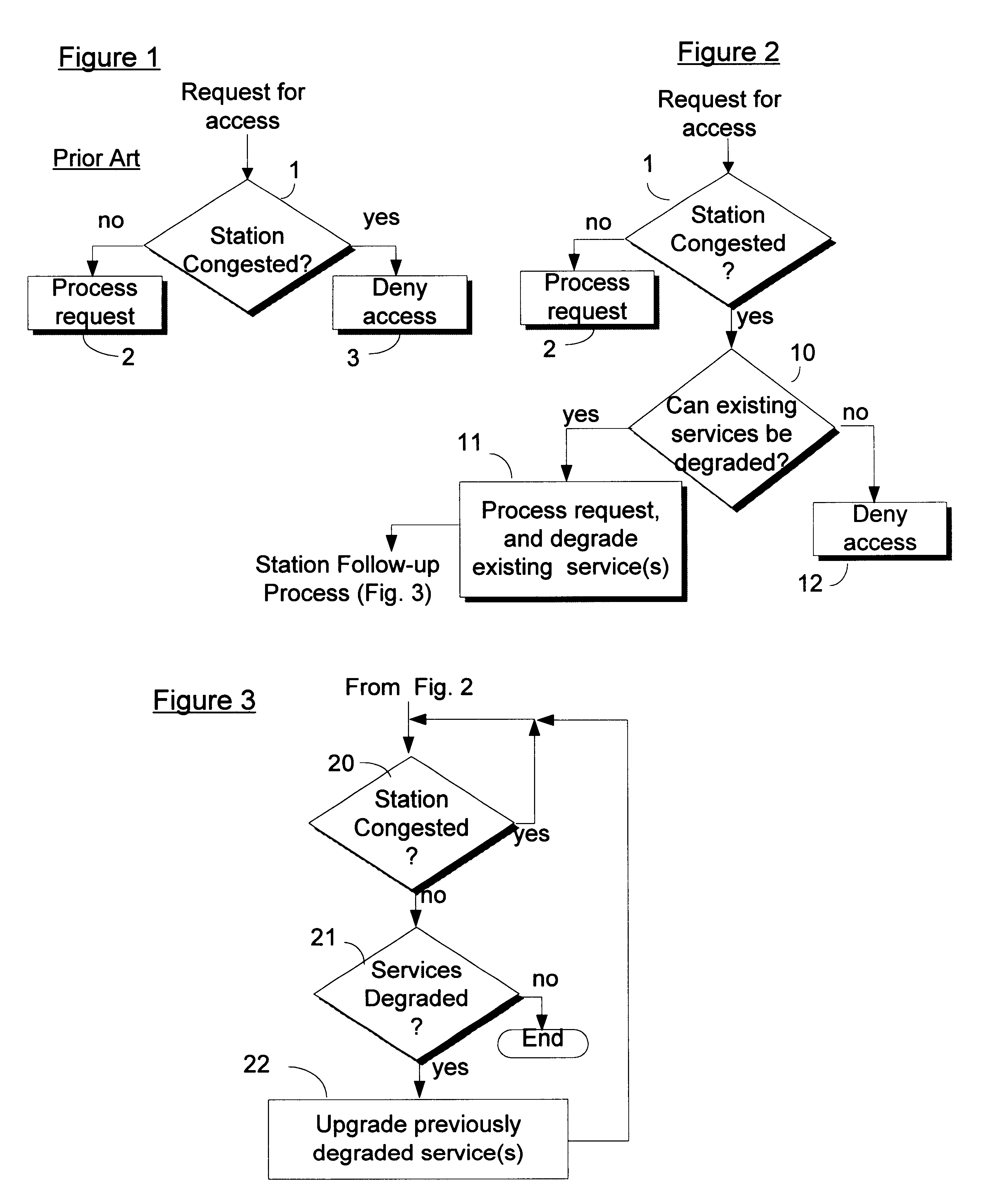
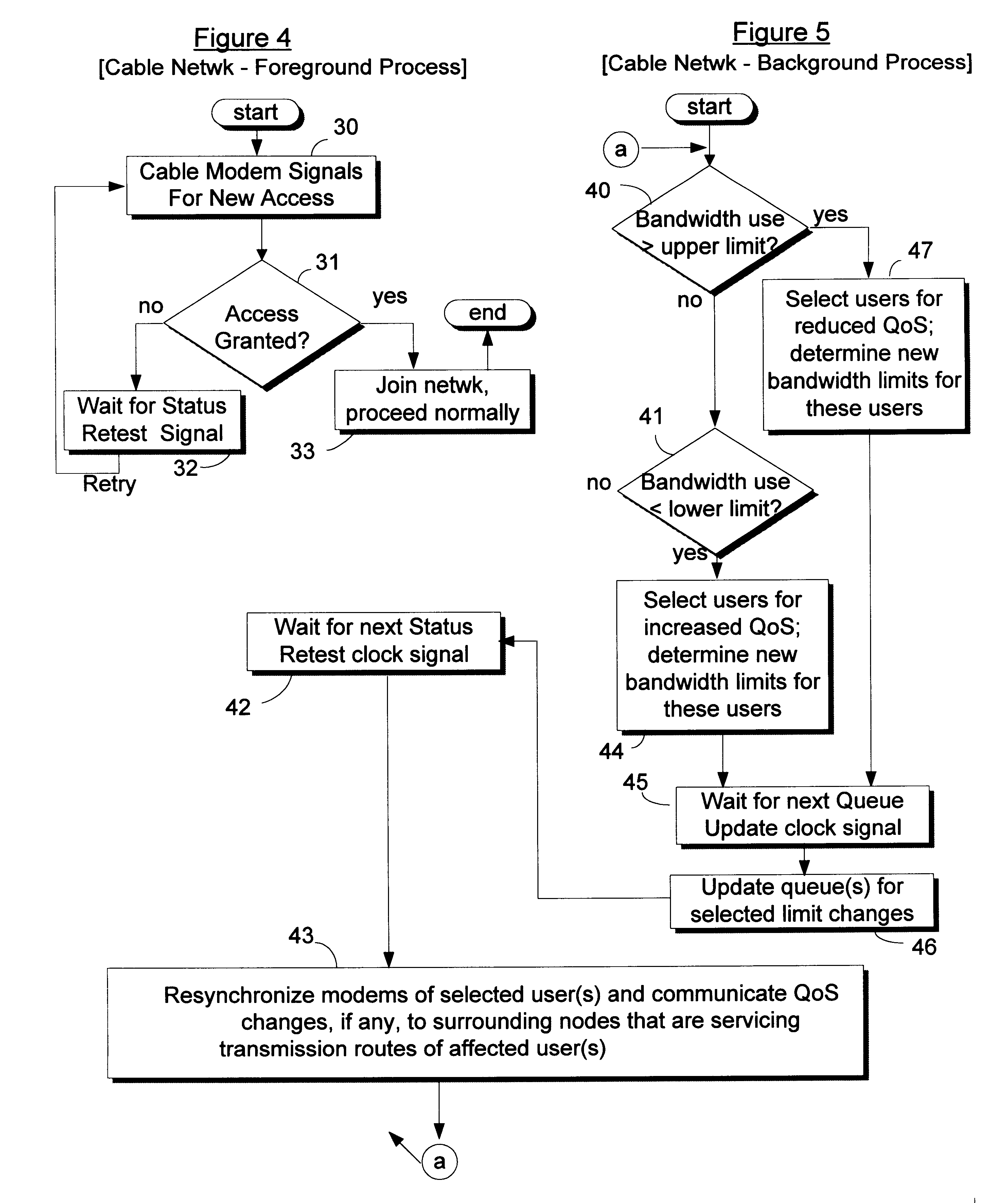
Improving access to congested networks
InactiveUS6345038B1Reduce usageError preventionTransmission systemsData transmissionQuality of service
For a station in a data communication network having a predefined limit of congestion for handling data immediately undergoing transmission through the station, a system for improving service given to network users requesting new access services to support new transmissions through the same station while the predefined congestion limit is exceeded. This system contains: a first element for determining when the predefined limit is exceeded by existing data transmissions through the station; and a second element, responsive to requests for new access services that are received while the predefined limit is being exceeded for: concurrently processing the request for new service and reducing the quality of service (QoS) to selected users. The reductions in QoS generally have the effects of reducing the speed / priority of handling of data being transmitted to or from the selected users, and of freeing up of sufficient bandwidth to accommodate the requested new access services. The system includes a third element for restoring / upgrading QoS, to users whose QoS has been reduced, when bandwidth usage subsides to a level allowing for such restoration. This latter level is sufficiently less than the congestion limit to provide a hysteresis effect that delays actions by the third element sufficiently to prevent successive actions of said second and third elements from producing unstable fluctuations in the operation of the station. Arrangements are disclosed for applying the invention in a cable television network environment and in private network environments serving a single business enterprise such as a banking institution.
Owner:IBM CORP
Dynamic bandwidth allocation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070133407A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDynamic bandwidth allocationDistribution method
The present invention relates to a bandwidth allocation apparatus and a method thereof. The present invention provides a method for adaptively allocating and controlling radio channels to multimedia traffic having various characteristics. Particularly, the present invention proposes a method for maximizing a system resource use rate while satisfying a communication QoS requirement for individual video traffic. Therefore, the adaptive bandwidth allocation method according to the present invention guarantees system performance and user-required communication QoS.
Owner:KT CORP +2
Technique for ethernet access to packet-based services
ActiveUS7092389B2Convenient and efficientThe process is convenient and fastNetworks interconnectionMetropolitian area networksTraffic volumeReceipt
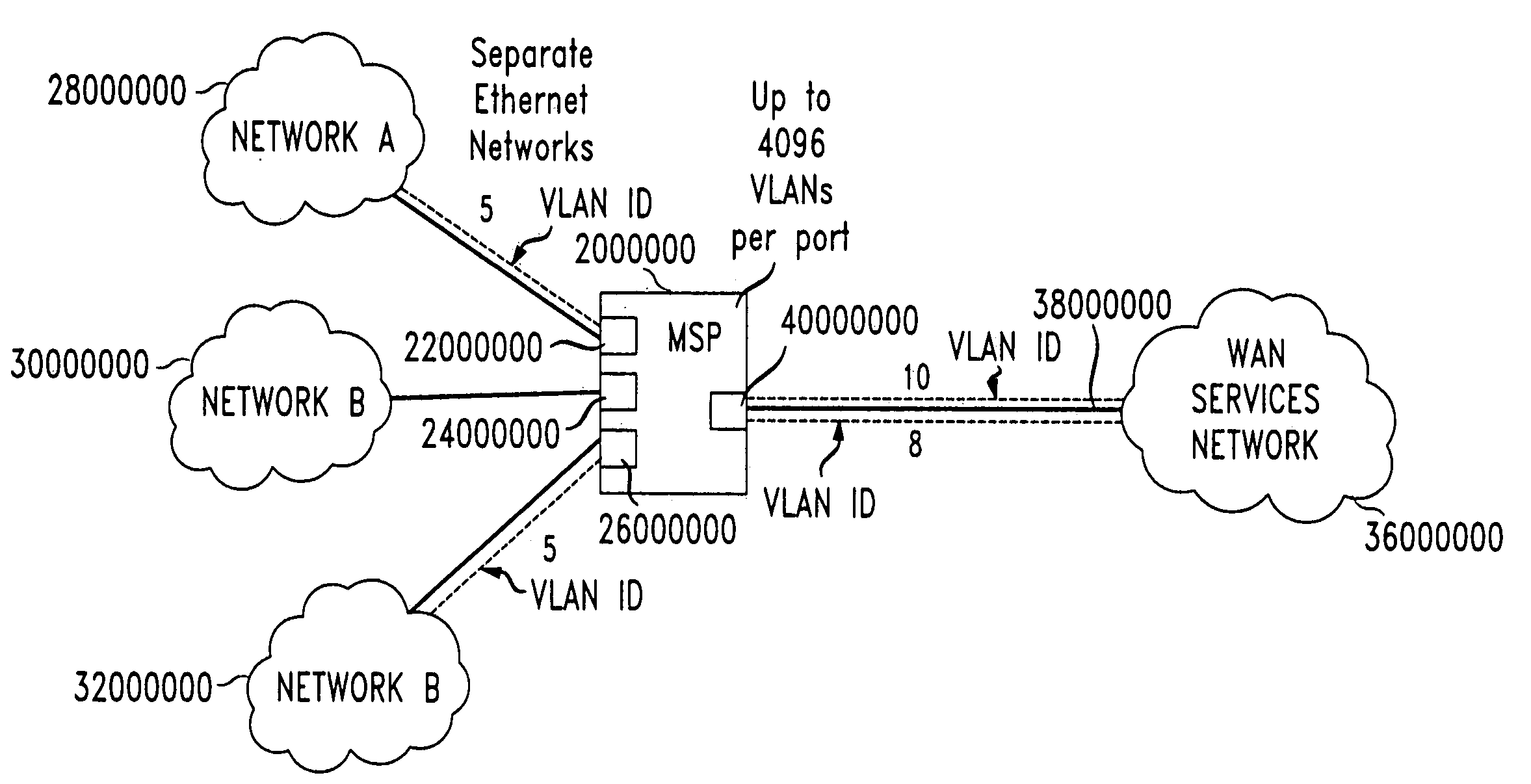
An Ethernet Metropolitan Area Network (10) provides connectivity to one or more customer premises (161,162,163) to packet-based services, such as ATM, Frame Relay, or IP, while advantageously providing a mechanism for assuring security and regulation of customer traffic. Upon receipt of each customer-generated information frame (20), an ingress Multi-Service Platform (MSP) (122) “tags” the frame with a customer descriptor (22′) that specifically identifies the recipient customer. In practice, the MSP tags each frame by overwriting the Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) identifier (22) with the customer descriptor. Using the customer descriptor in each frame, a recipient Provider Edge Router (PER) (18) or ATM switch can map the information as appropriate to direct the information to the specific customer at its receiving site. In addition, the customer descriptor (22′) may also include Quality of Service (QoS) information, allowing the recipient Provider Edge Router (PER) (18) or ATM switch to afford the appropriate QoS level accordingly. Each Ethernet switch may advantageously overwrite the VLAN identifier at an incoming port with a second tag associated with an egress port to increase the scale associated with single switch.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
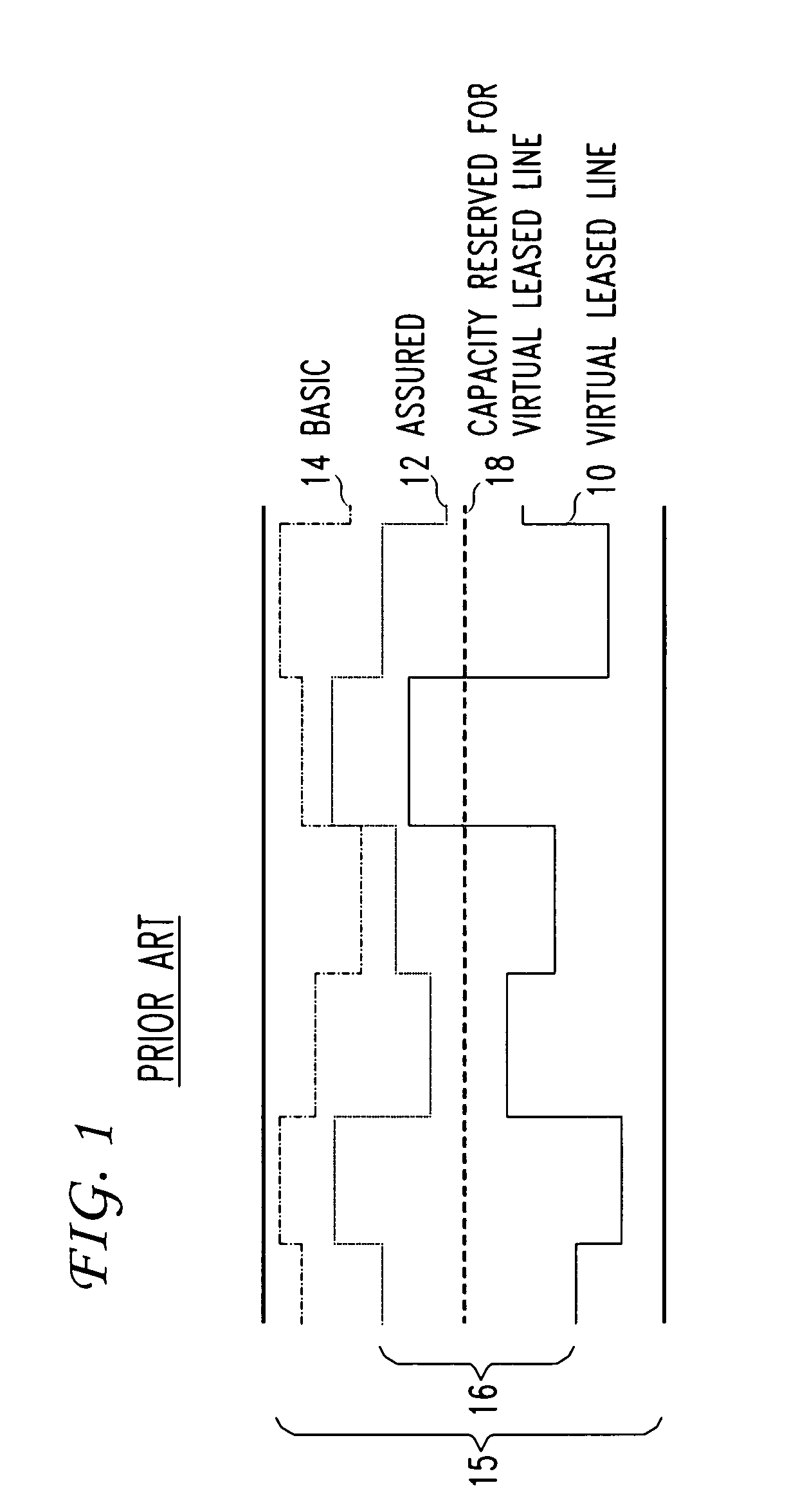
Methods And Systems For Dynamic Bandwidth Management For Quality Of Service In IP Core And Access Networks
InactiveUS20080130495A1Easy to useStringent qualityError preventionTransmission systemsPresent methodKey issues
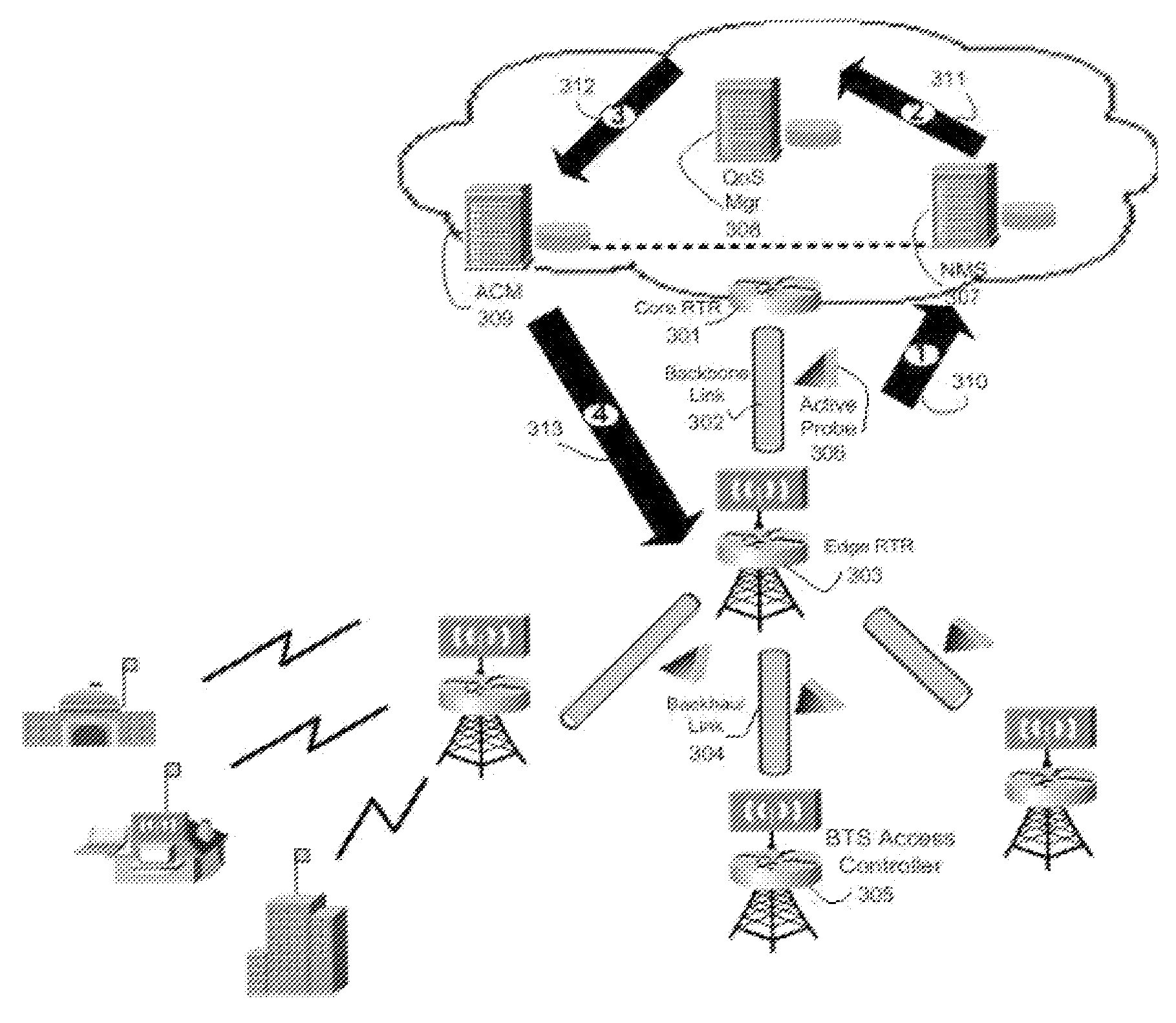
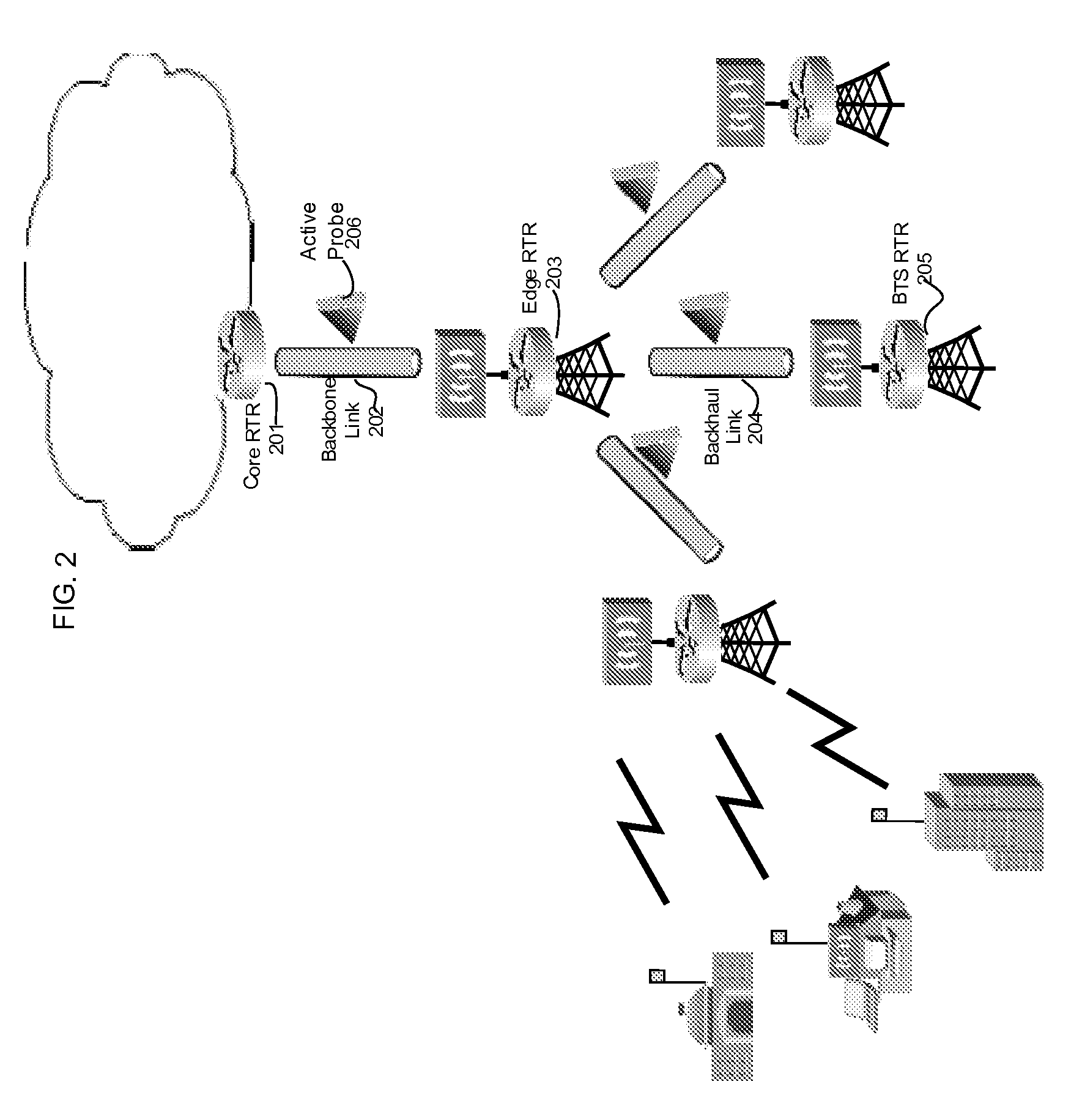
Proper allocation of network bandwidth is a crucial issue in rendering certain performance guarantees to meet the growing customer demands. Hence, allocation methodologies must explicitly be carried out for these guarantees to be given as efficiently as possible since the shared resources are limited. This invention presents methods and systems for Dynamic Bandwidth Management (DBM) and Quality of Service (QoS) in packet-based networks. DBM is an algorithm that dynamically adjusts the resource allocation in the IP Access Networks based upon measured QoS at the IP Core Network through an implementation of a Feedback Control Mechanism to manage available core transport bandwidth. Such a Feedback Control Mechanism is capable of maintaining a condition of non-congestion, a sufficient and necessary condition to meet end-to-end QoS requirements in a Next Generation Network (NGN). The emphasis is given on the system implementation of QoS policies for the fair distribution of network resources through a scalable architecture comprising key Resource and Admission Control Functional (RACF) entities, namely: a Network Management System (NMS), a QoS Manager, an Access Controller Manager (ACM), the Access Controllers, and the active probes.
Owner:LATITUDE BROADBAND
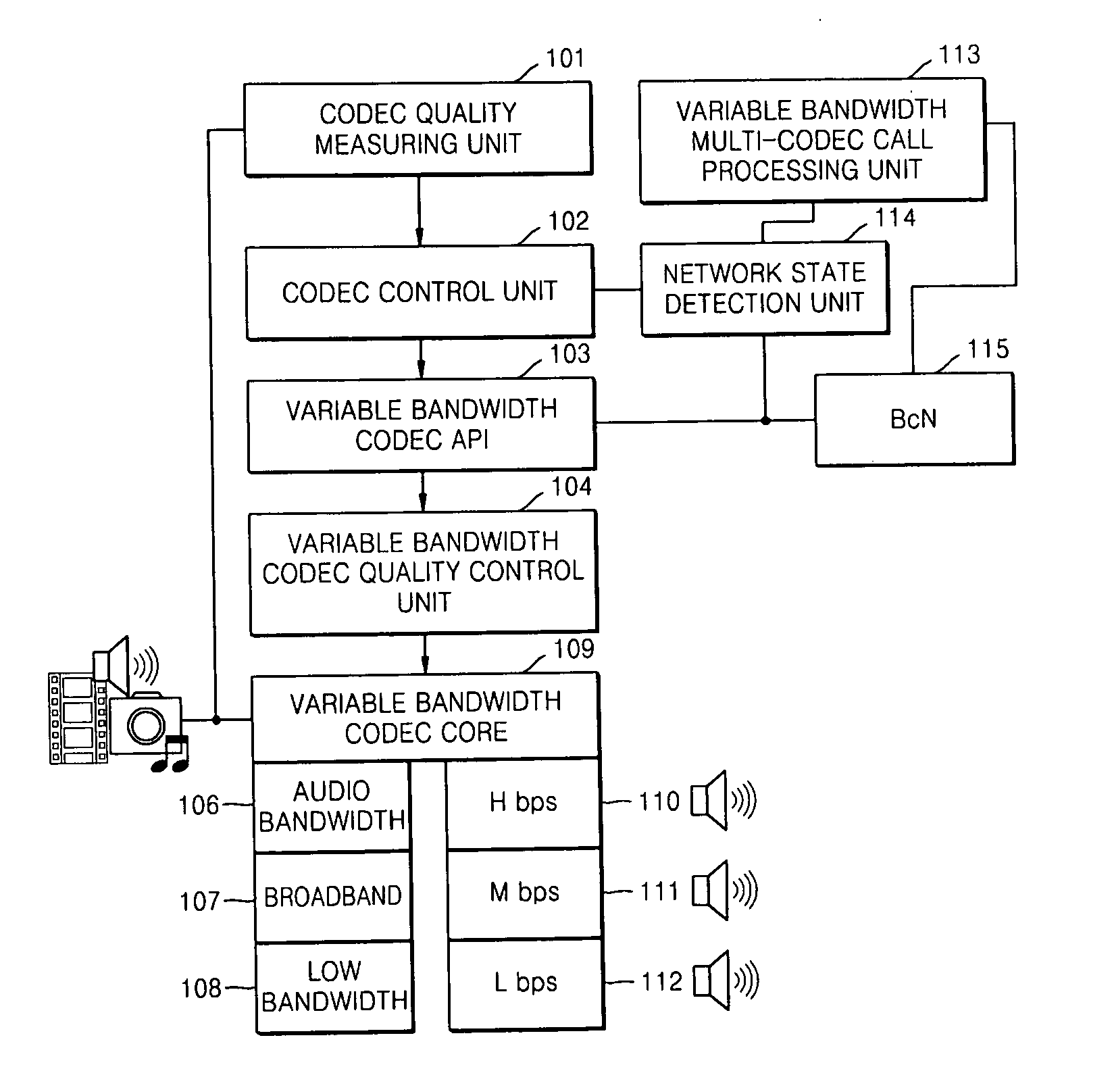
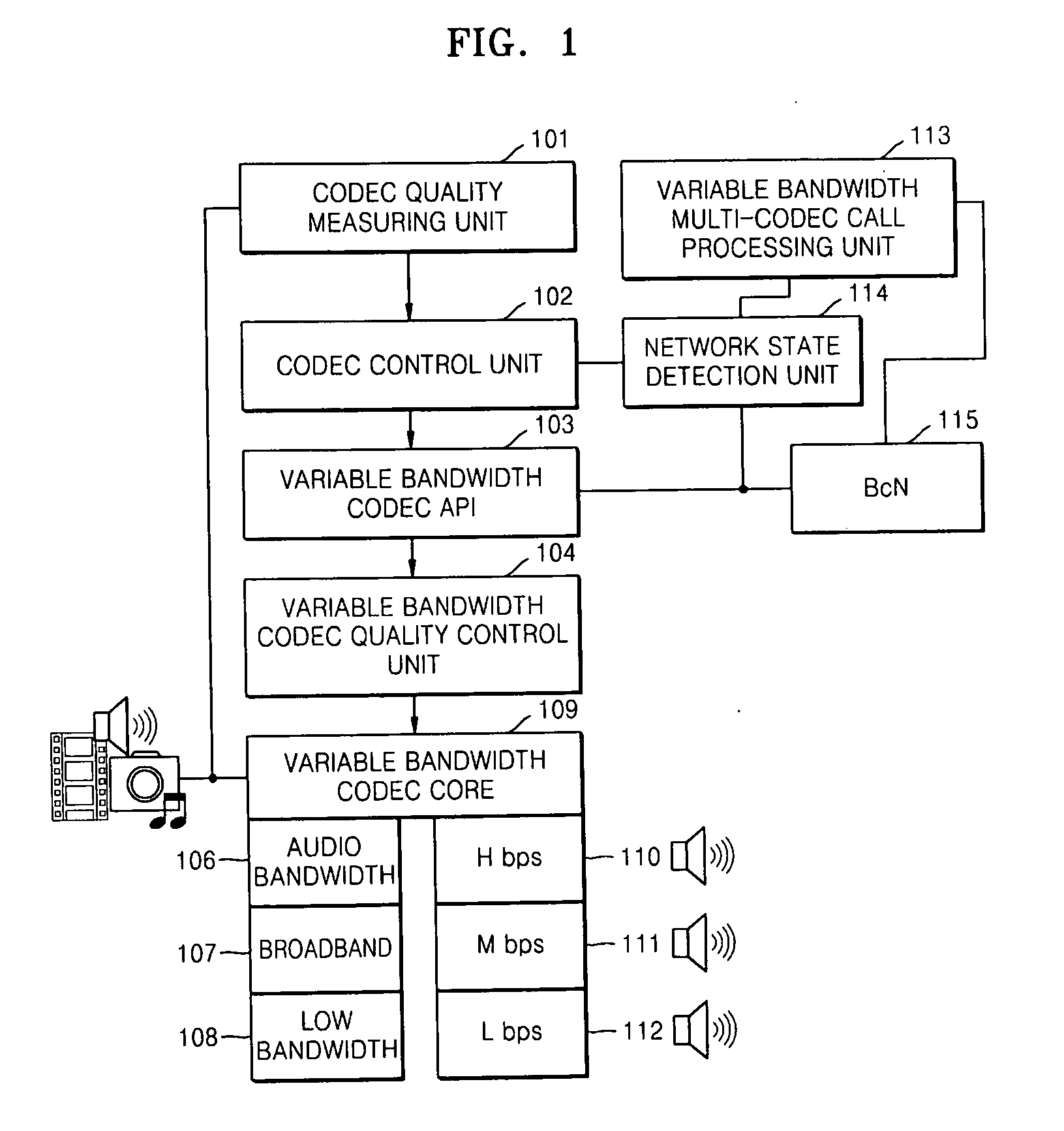
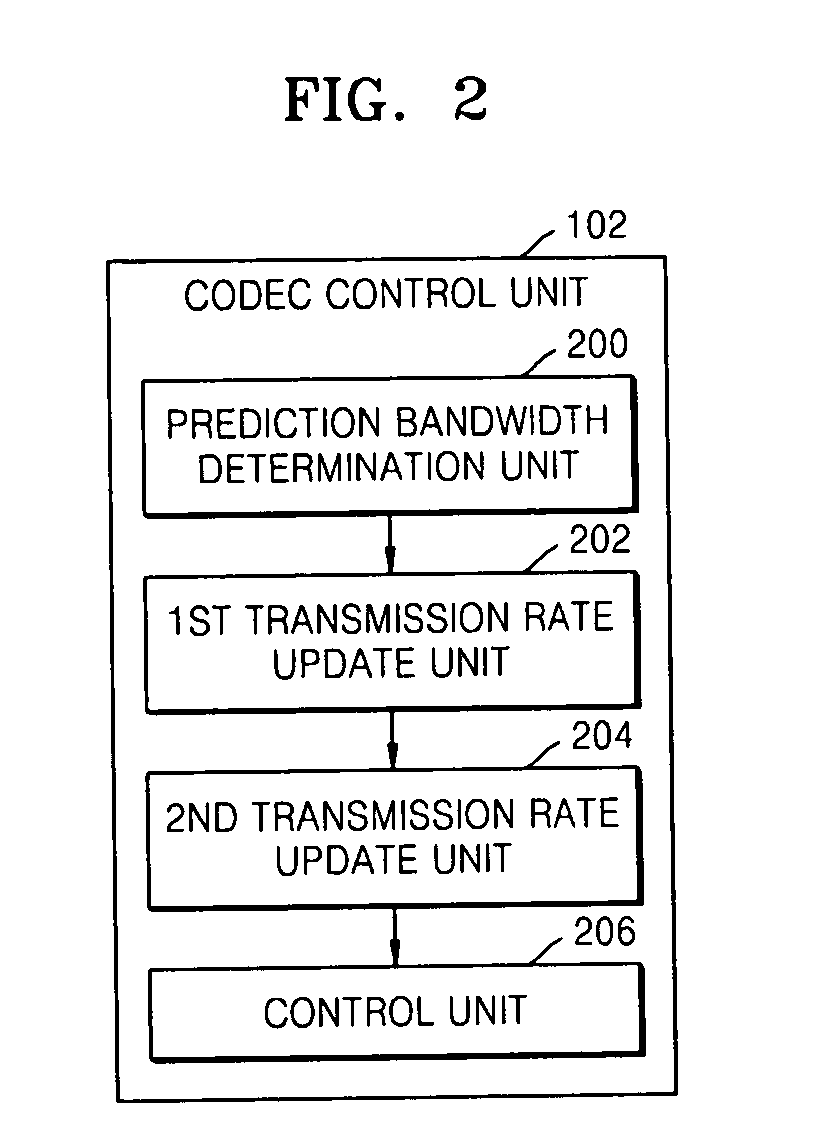
Apparatus and method of variable bandwidth multi-codec QoS control
InactiveUS20070133441A1Quality improvementLower quality of serviceError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
An apparatus and method of variable bandwidth multi-codec quality of service (QoS) control are provided. The apparatus for controlling the QoS of a variable bandwidth multi-codec includes: a network state detection unit detecting a network state including at least one of a packet loss ratio, a packet loss interval, and a packet delay time based on an RTP packet transmitted to and received from a destination for which a call connection is established; and a codec control unit updating a transmission rate by comparing the detected resultant value with an already set reference value and increasing or decreasing the transmission rate, and controlling the variable bandwidth multi-codec to code data with the updated transmission rate. According to the apparatus and method, data can be coded with a codec transmission rate suitable for a network state identified during a voice call after the call is set up.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
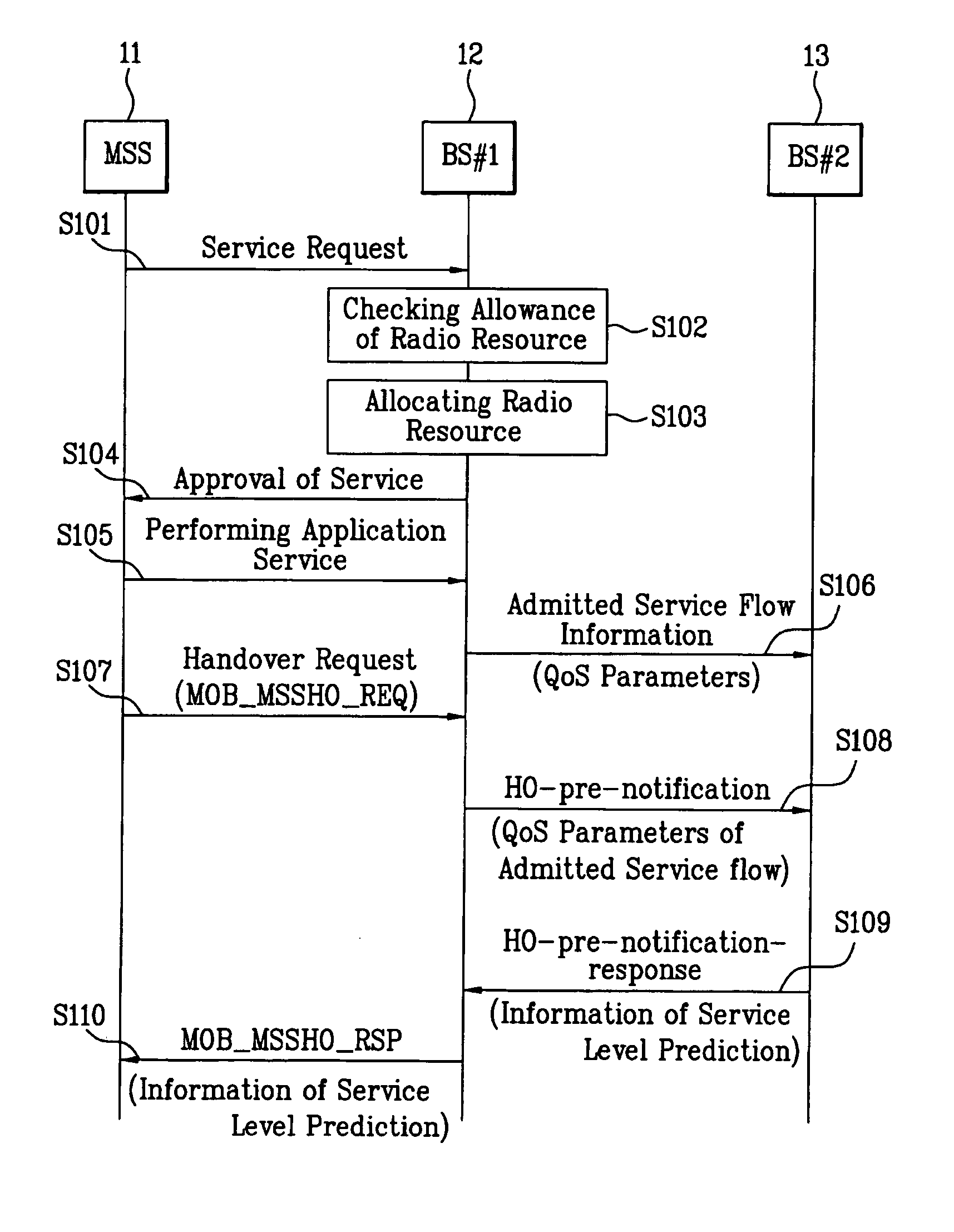
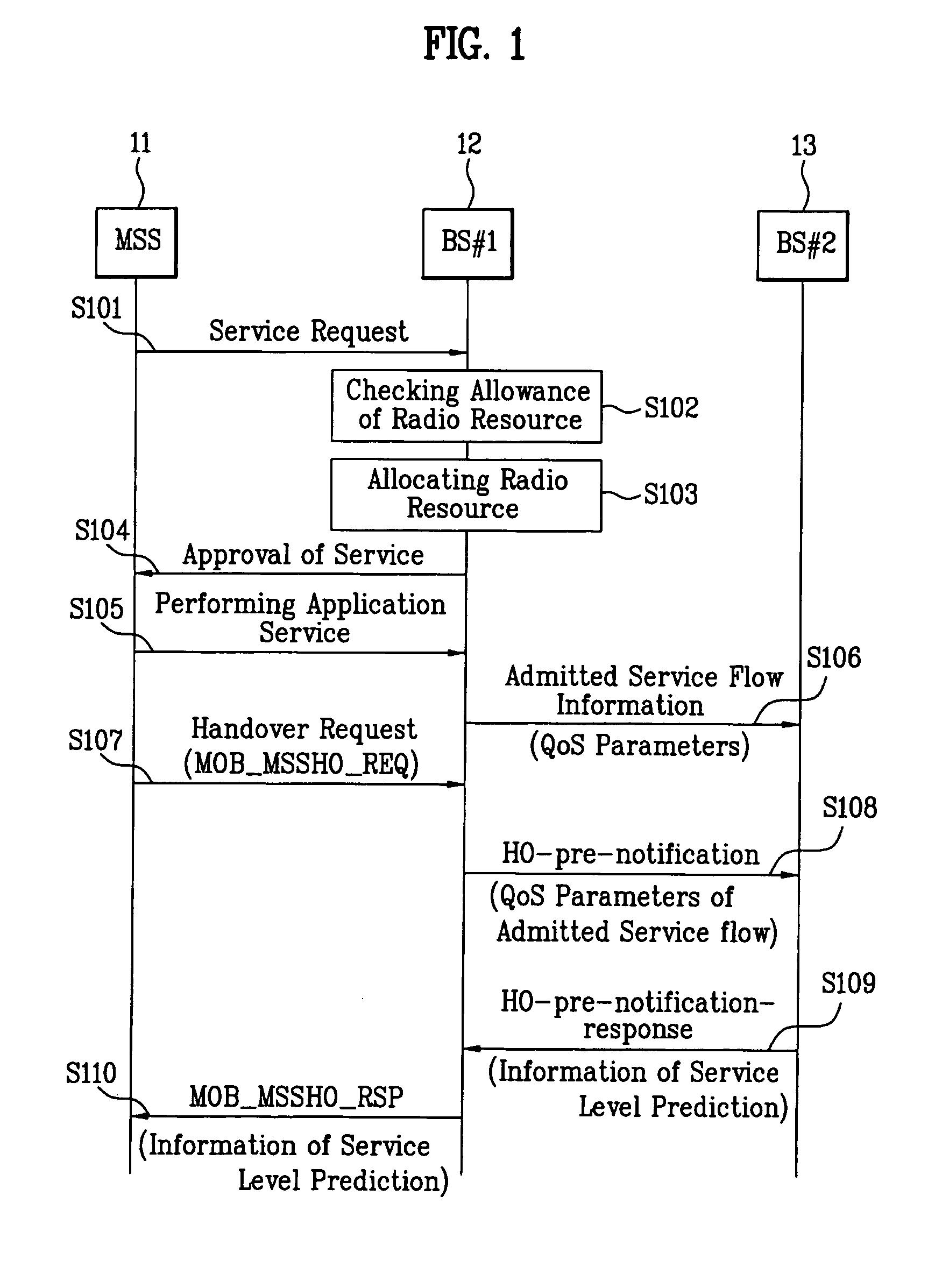
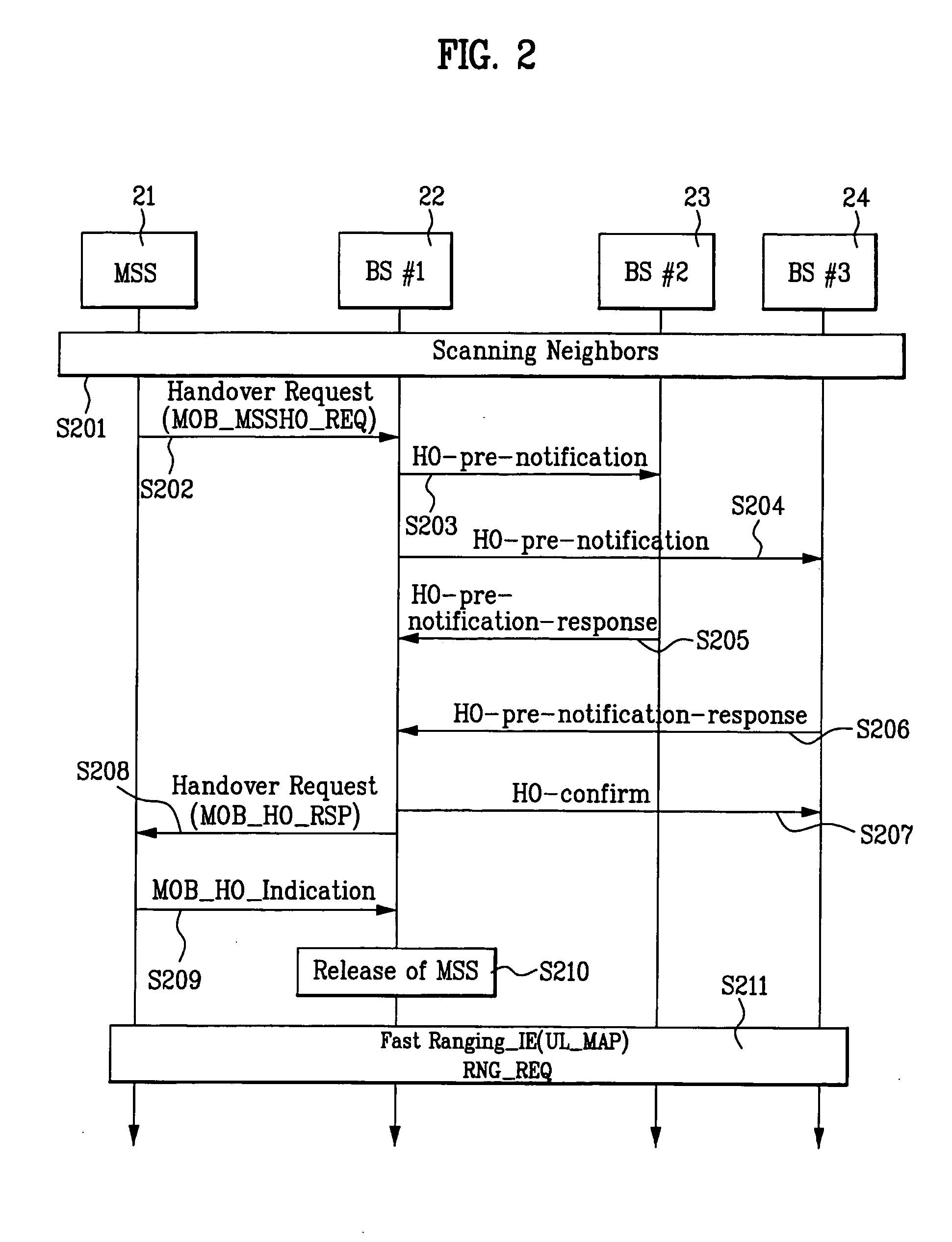
Mobile broadband wireless access system for transferring service information during handover
InactiveUS20050239465A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceService flow
The present invention is related to transmitting quality of service (QoS) information of a target base station for admitted service flows during a handover operation. The invention comprises providing a service to a mobile station from a serving base station and receiving at the serving base station a handover request from the mobile station. The serving base station the provides a handover notification to a target base station, wherein the handover notification comprises a QoS parameter associated with the service. The serving base station then receives from the target base station a handover notification response, wherein the handover notification response comprises service level prediction information that is determined in response to the QoS parameter associated with the service. Finally, the serving base station provides a handover response to the mobile station, the handover response comprising the service level prediction information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
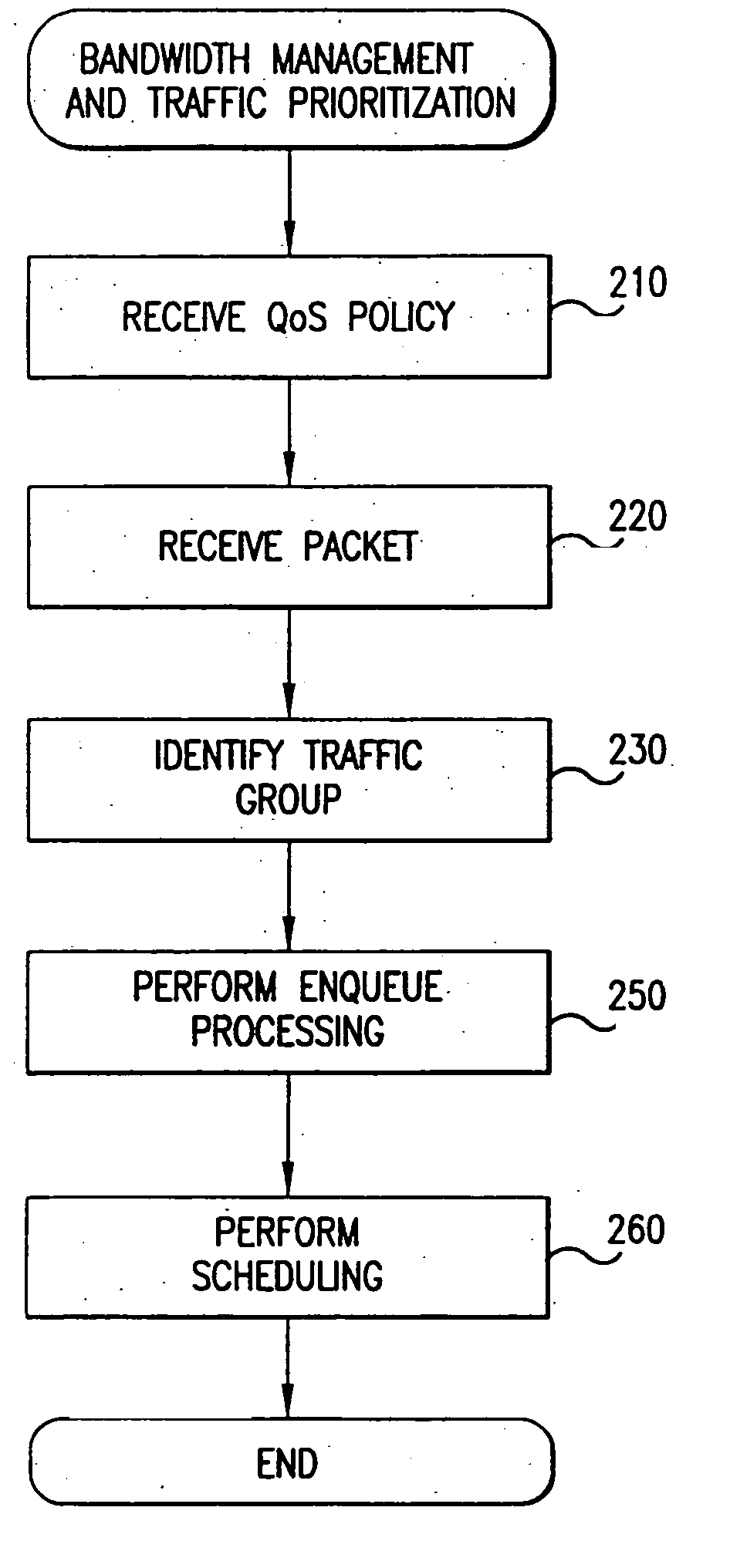
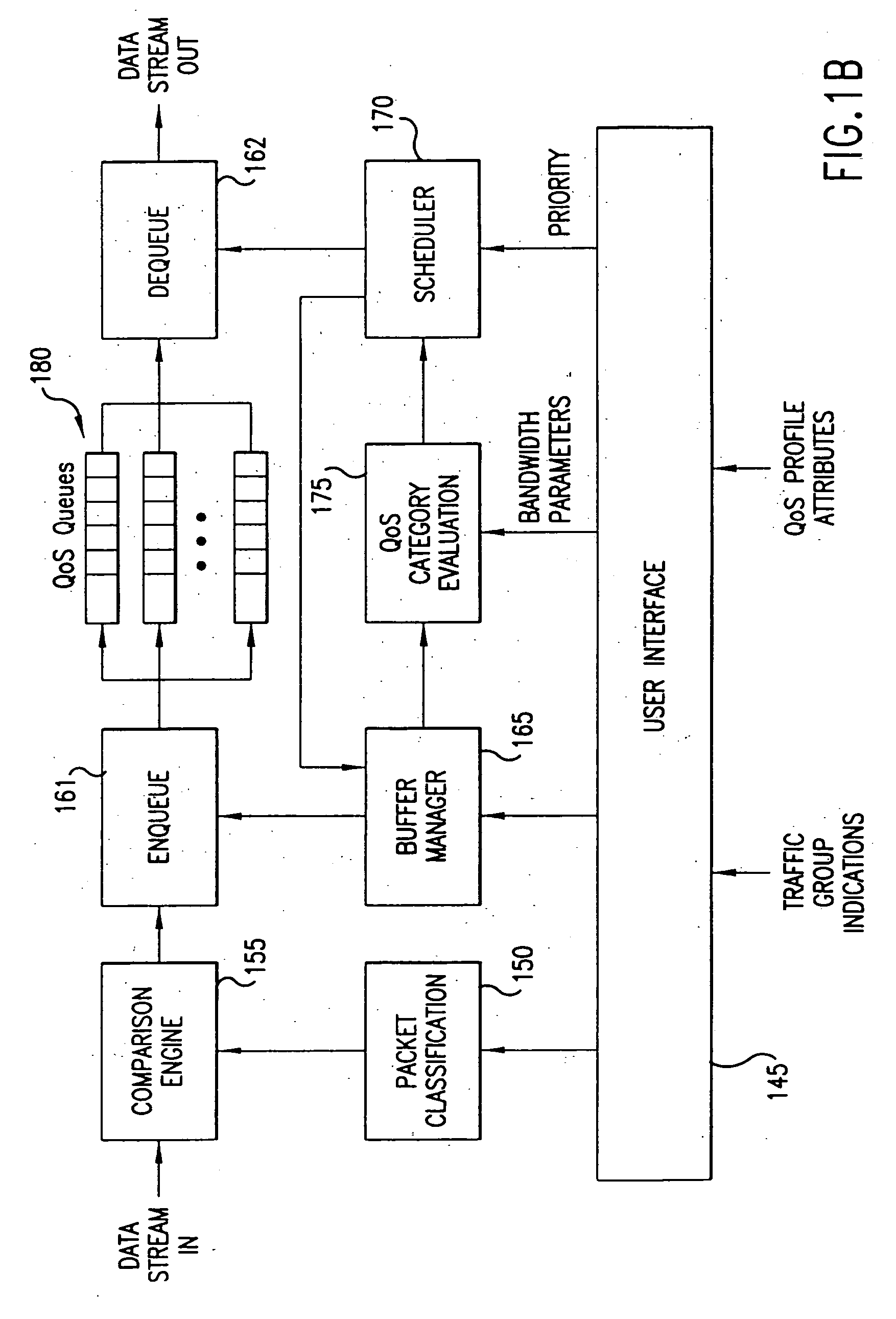
Policy based quality of service
A flexible, policy-based, mechanism for managing, monitoring, and prioritizing traffic within a network and allocating bandwidth to achieve true quality of service (QoS) is provided. According to one aspect of the present invention, a method is provided for managing bandwidth allocation in a network that employs a non-deterministic access protocol, such as an Ethernet network. A packet forwarding device receives information indicative of a set of traffic groups, such as: a MAC address, or IEEE 802.1p priority indicator or 802.1Q frame tag, if the QoS policy is based upon individual station applications; or a physical port if the QoS policy is based purely upon topology. The packet forwarding device additionally receives bandwidth parameters corresponding to the traffic groups. After receiving a packet associated with one of the traffic groups on a first port, the packet forwarding device schedules the packet for transmission from a second port based upon bandwidth parameters corresponding to the traffic group with which the packet is associated. According to another aspect of the present invention, a method is provided for managing bandwidth allocation in a packet forwarding device. The packet forwarding device receives information indicative of a set of traffic groups. The packet forwarding device additionally receives information defining a QoS policy for the traffic groups. After a packet is received by the packet forwarding device, a traffic group with which the packet is associated is identified. Subsequently, rather than relying on an end-to-end signaling protocol for scheduling, the packet is scheduled for transmission based upon the QoS policy for the identified traffic group.
Owner:ARISTA NETWORKS
Network control apparatus and method with quality of service controls
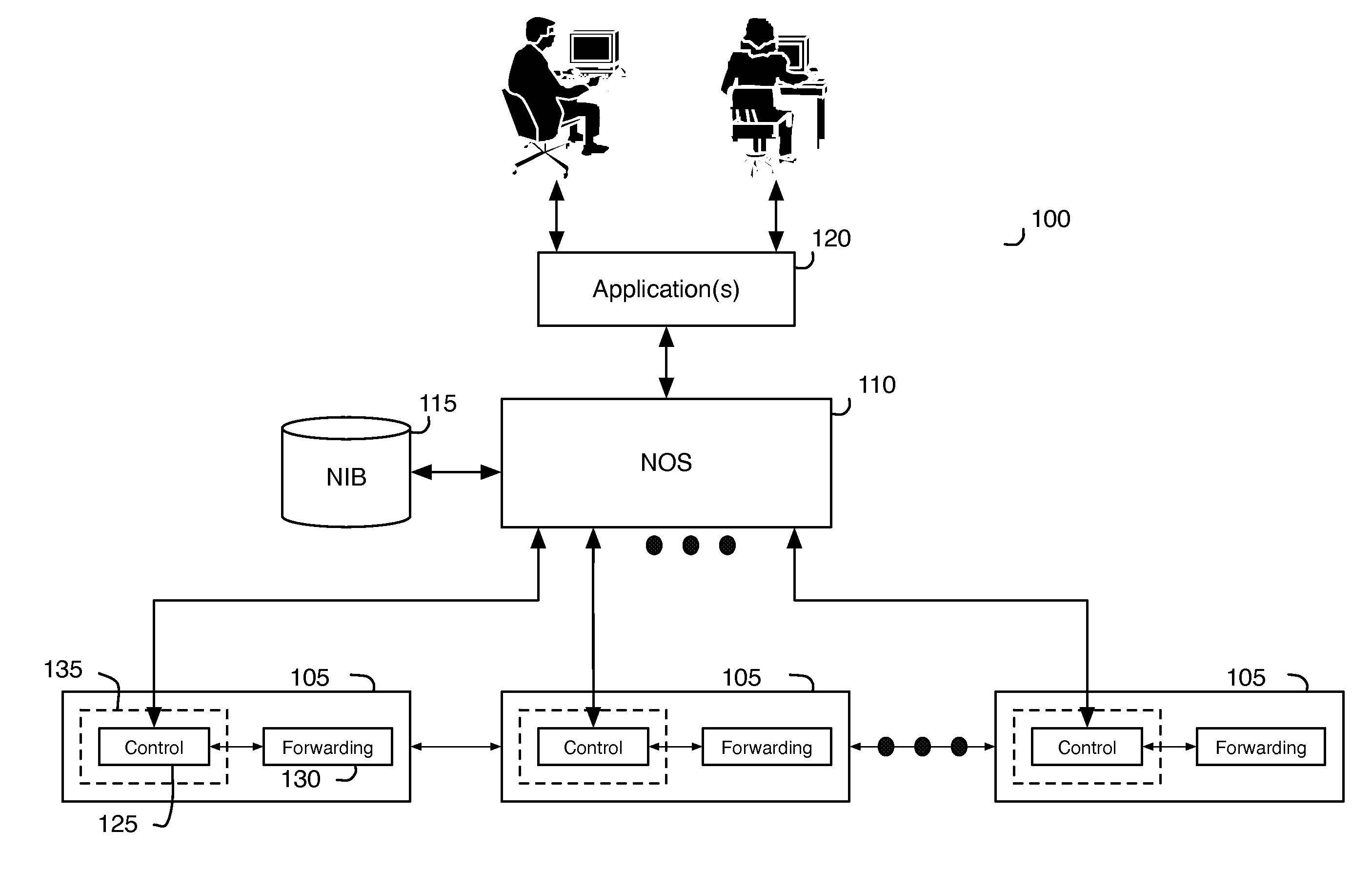
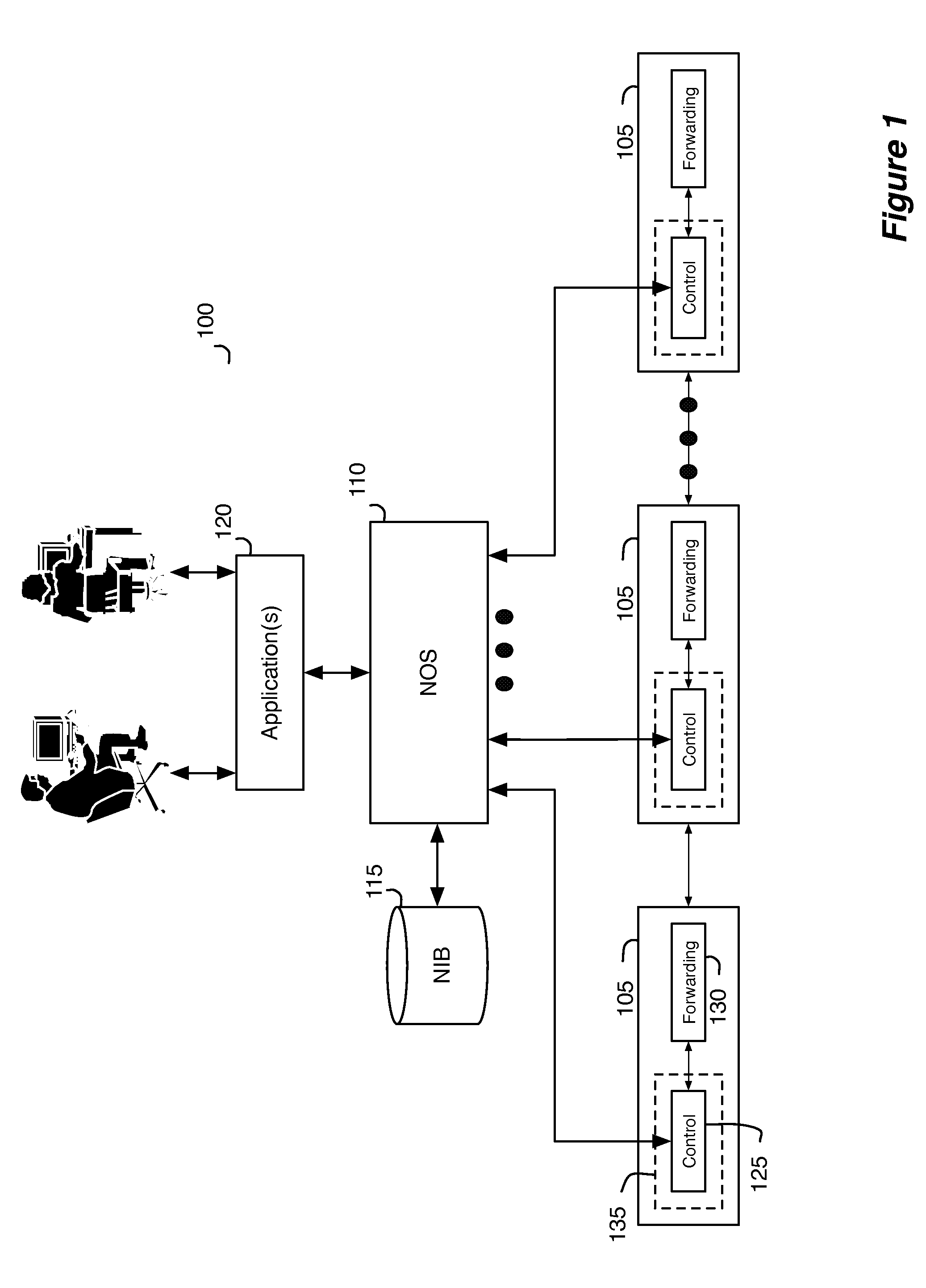
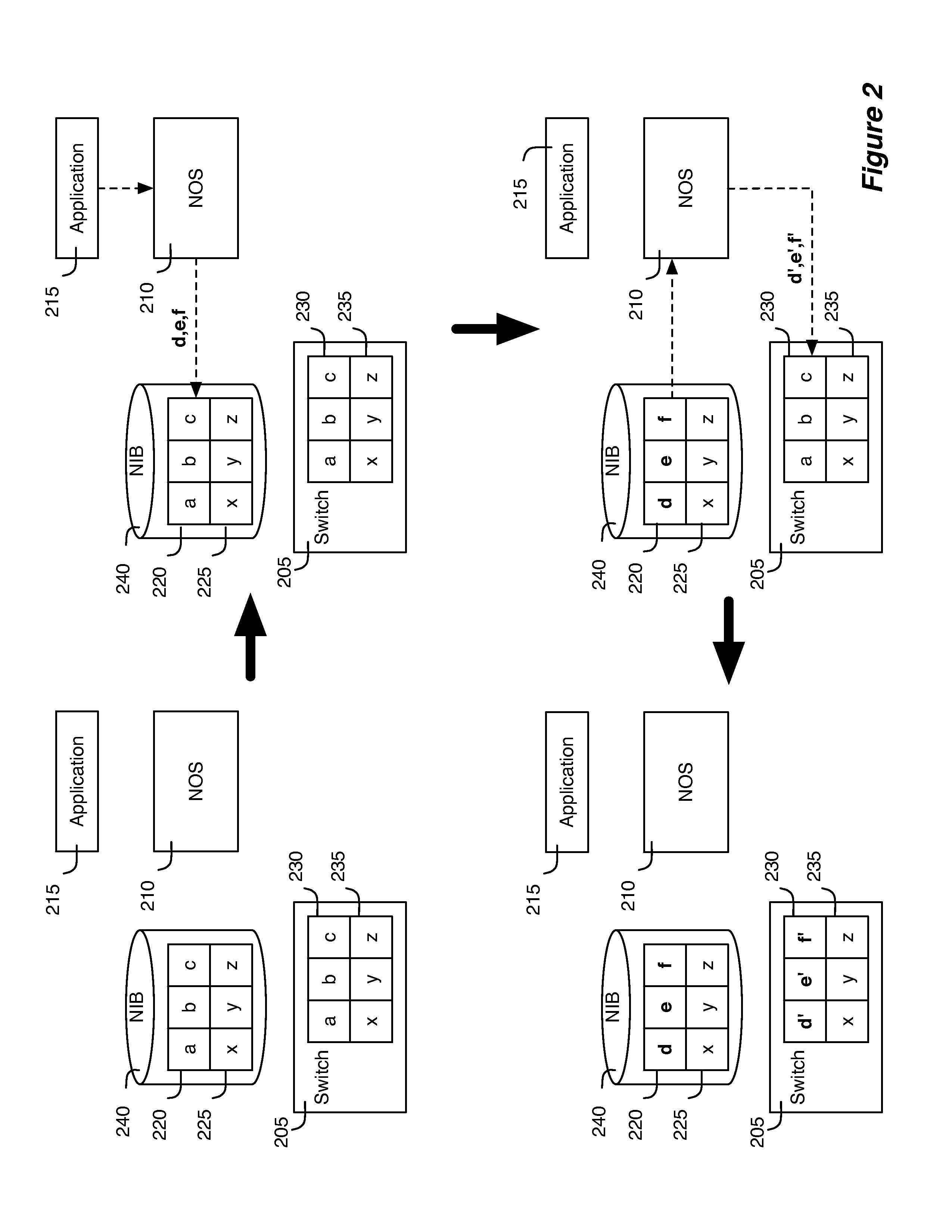
ActiveUS20130058358A1Fault responseDigital computer detailsQos quality of serviceData transformation
A control application of some embodiments allows a user to enable a logical switching element for Quality of Service (QoS). QoS in some embodiments is a technique to apply to a particular logical port of a logical switching element such that the switching element can guarantee a certain level of performance to network data that a machine sends through the particular logical port. The control application of some embodiments receives user inputs that specify a particular logical switch to enable for QoS. The control application may additionally receive performance constraints data. The control application in some embodiments formats the user inputs into logical control plane data. The control application in some embodiments then converts the logical control plane data into logical forwarding data that specify QoS functions.
Owner:NICIRA
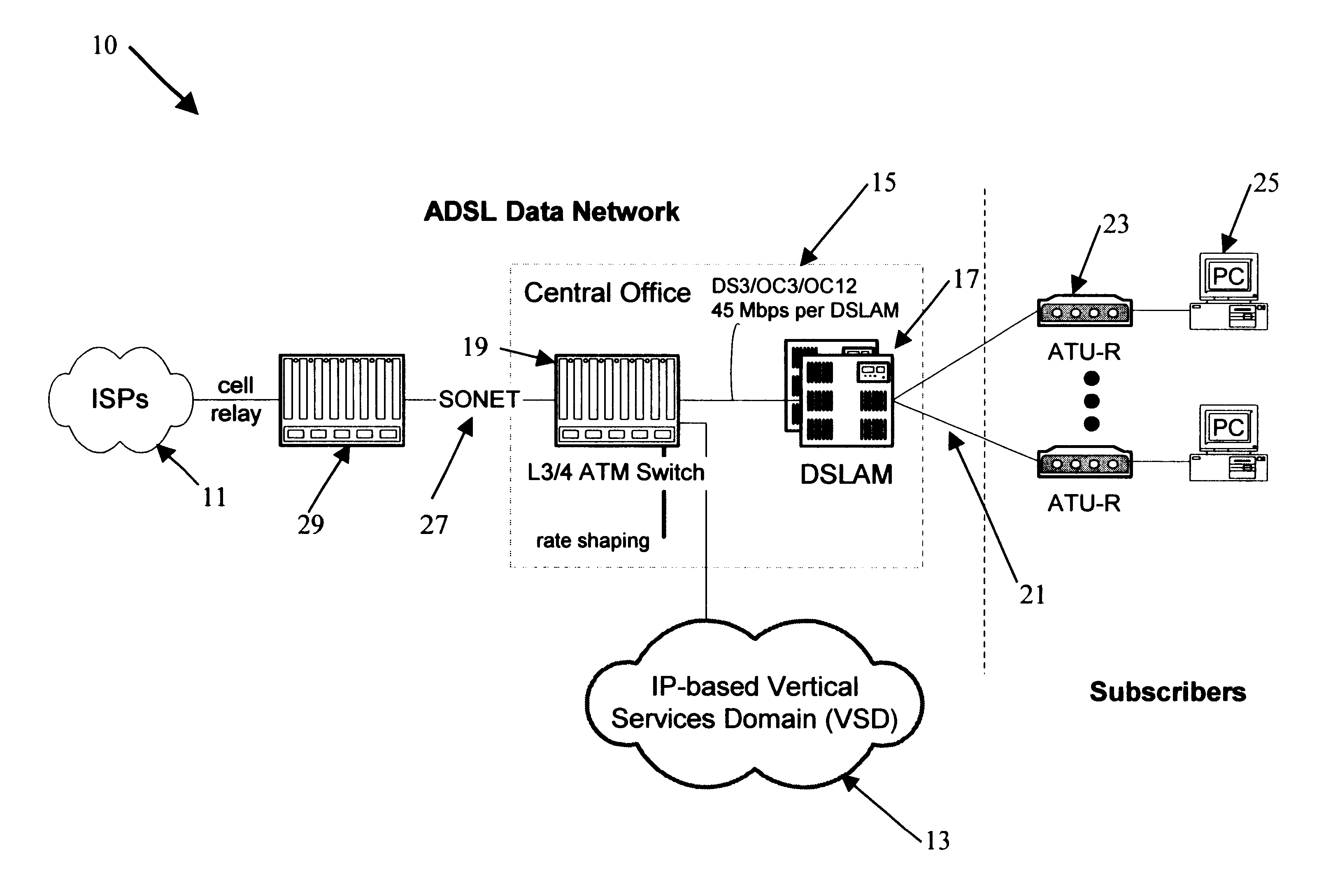
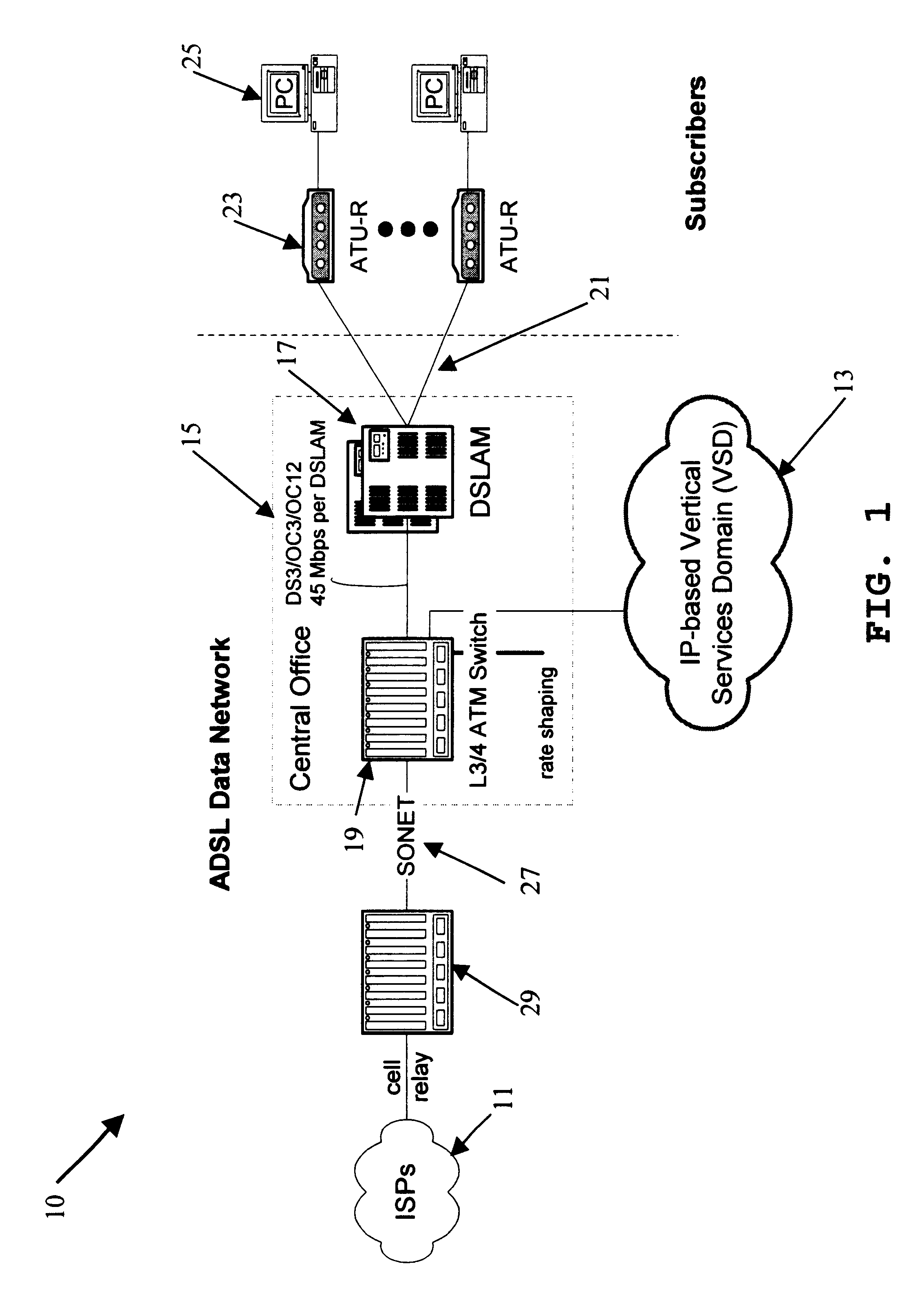
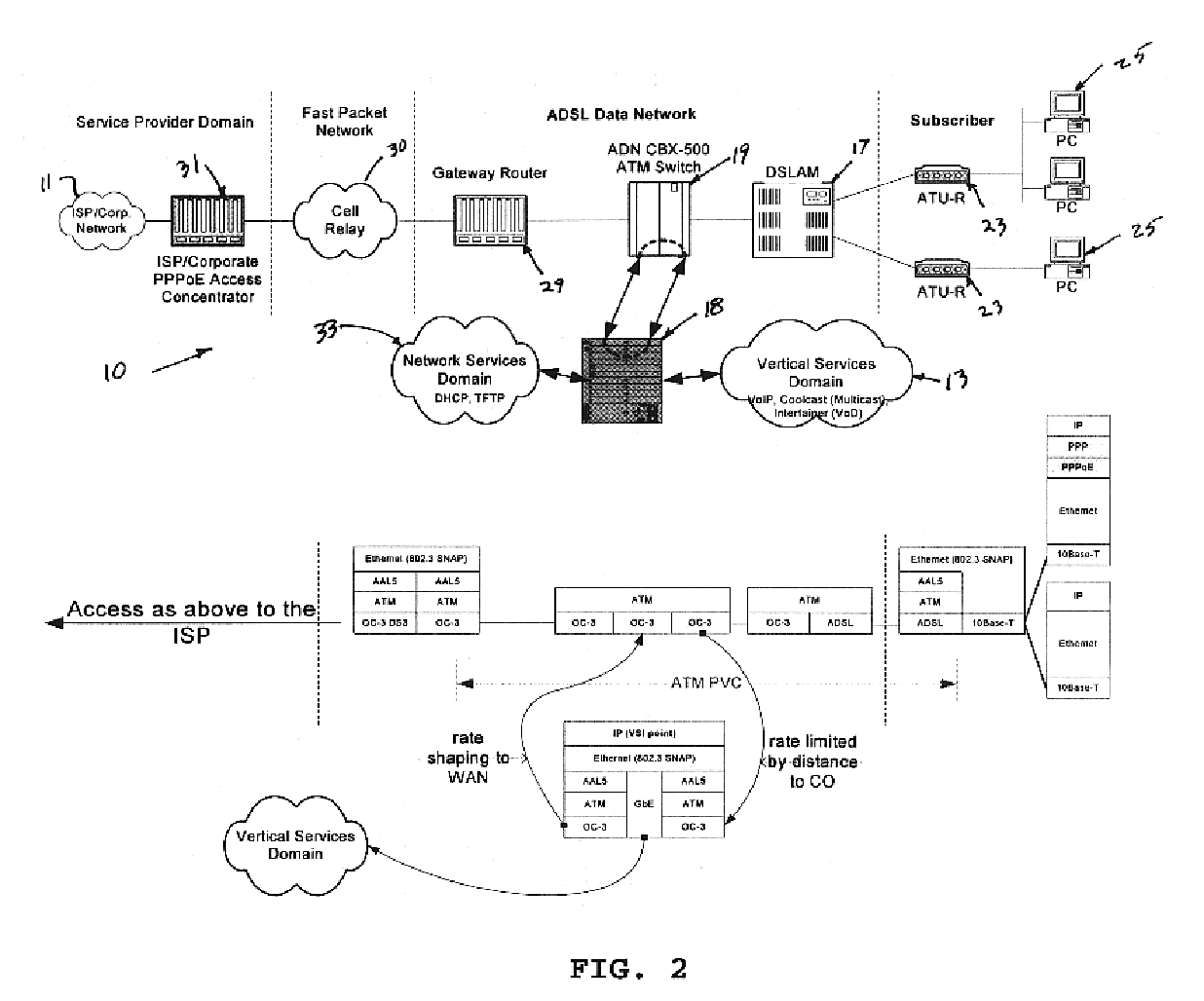
Support for quality of service and vertical services in digital subscriber line domain
InactiveUS6904054B1Increased cost-effectivenessReduce demandTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceFrame based
Offering vertical services to subscribers and service providers is an avenue to immediately improve the competitiveness of digital subscriber line access service, for example of the type offered by a local exchange carrier. To deliver high-quality vertical services, however, the underlying ADSL Data Network (ADN) or the like needs to establish Quality of Service (QoS) as a core characteristic and offer an efficient mechanism for insertion of the vertical services. The inventive network architecture introduces QoS into the ADN, in a manner that enables the delivery of sophisticated and demanding IP-based services to subscribers, does not affect existing Internet tiers of service, and is cost-effective in terms of initial costs, build-out, and ongoing operations. The architecture utilizes a switch capable of examining and selectively forwarding packets or frames based on higher layer information in the protocol stack, that is to say on information that is encapsulated in the layer-2 information utilized to define normal connectivity through the network. The switch enables segregation of upstream traffic by type and downstream aggregation of Internet traffic together with traffic from a local vertical services domain.
Owner:RAKUTEN INC
Systems and Methods of QoS for Single Stream ICA
ActiveUS20120230345A1Service quality is excessiveImprove latencyData switching by path configurationHigh level techniquesQuality of serviceTransport layer
The present solution provides quality of service (QoS) for a stream of protocol data units via a single transport layer connection. A device receives via a single transport layer connection a plurality of packets carrying a plurality of protocol data units. Each protocol data unit identifies a priority. The device may include a filter for determining an average priority for a predetermined window of protocol data units and an engine for assigning the average priority as a connection priority of the single transport layer connection. The device transmits via the single transport layer connection the packets carrying those protocol data units within the predetermined window of protocol data units while the connection priority of the single transport layer connection is assigned the average priority for the predetermined window of protocol data units.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
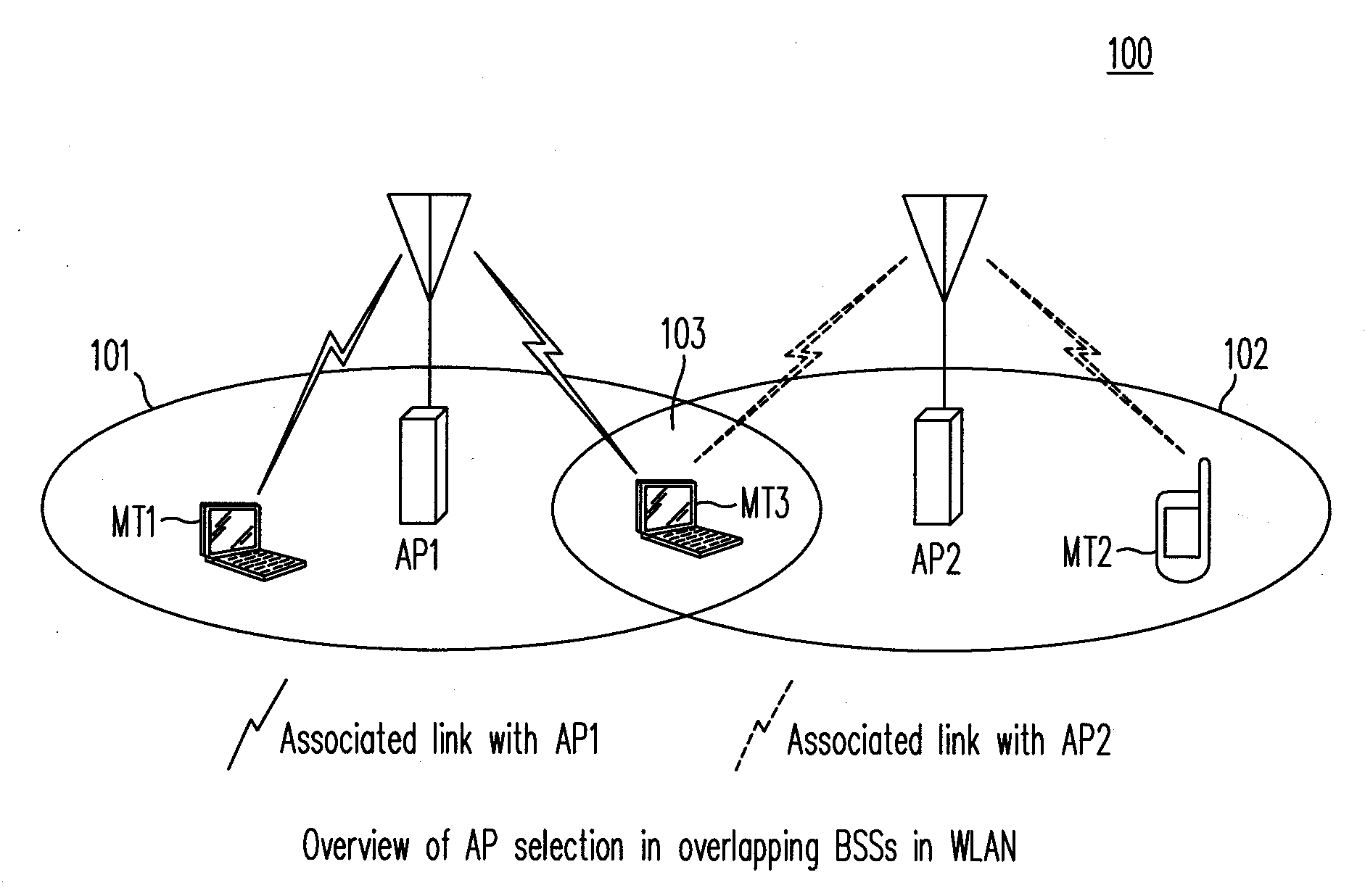
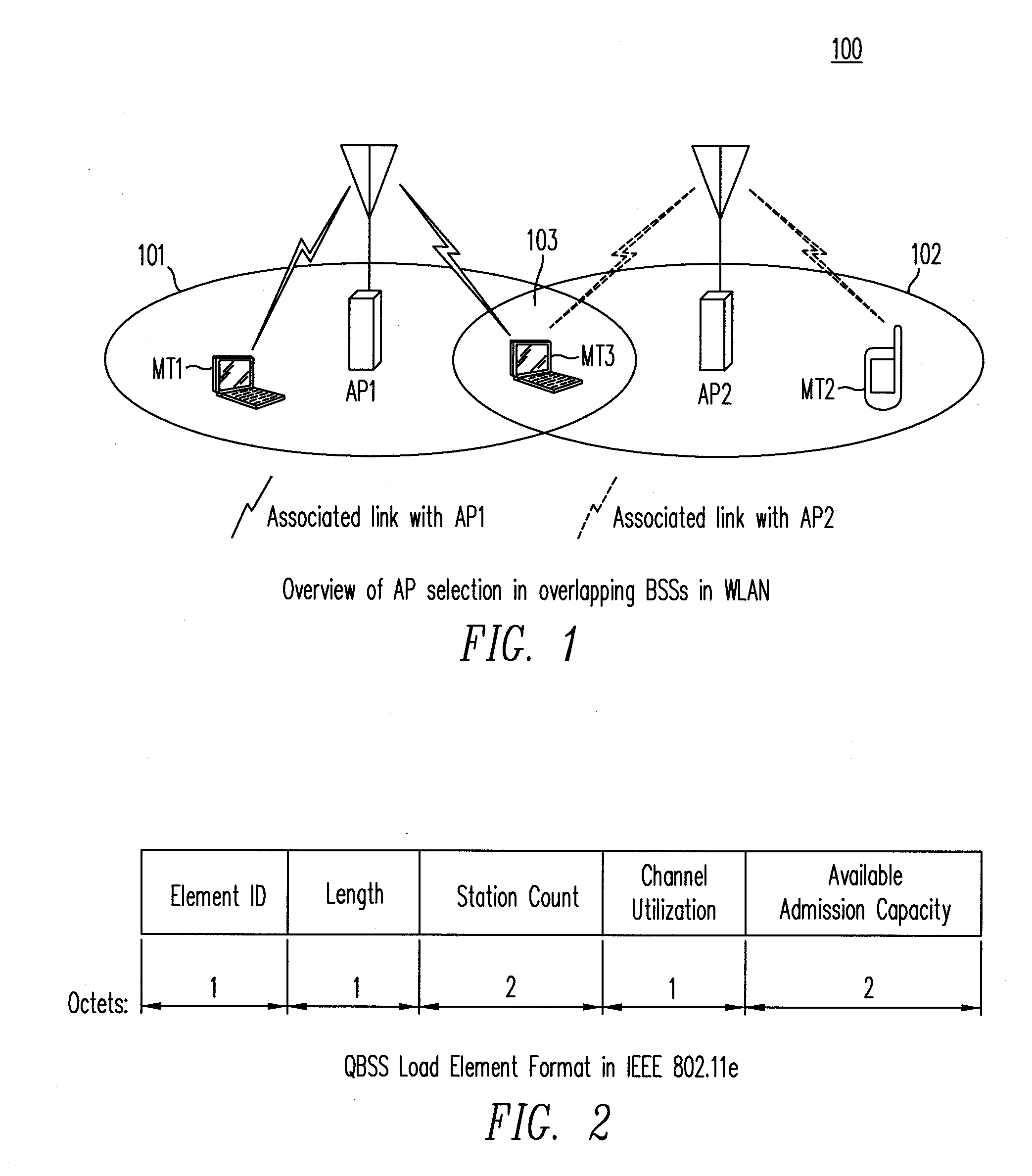
Method and Apparatus for Access Point Selection in Wireless LAN
ActiveUS20080102852A1Improve performanceSensitive to delay characteristicError preventionTransmission systemsTransmission throughputQos quality of service
A method and an apparatus select an access point (AP) in a wireless LAN to associate or reassociate, based on considerations that take into account the quality-of-service (QoS) status of the stations (STAs) and the potential hidden terminal effect. The method utilizes advertised or requested information obtained from an AP which includes the QoS status in each basic service set (BSS) and estimates the potential hidden terminal (HT) effect based on local channel sensing by the STA. The method selects the AP in a manner that reduces the possibility of collision from equal and higher priority HTs, thus providing greater transmission throughput and improving performance.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Method and device for quality measuring of streaming media services
InactiveUS20140201330A1Easy to mergeLow costMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionMass parameterQuality measurement
Method and probe device for quality measuring in IP streaming of audio, video, or a synchronized mix of both, performing:receiving a streaming media flow at a user's end,measuring at least one network parameter which indicates QoS and / or QoE,extracting frames from the streaming at the user's end,analyzing the frames at the user's end by searching for determined errors and delivering at least a quality parameter defined by certain results of said searching;correlating each measured network parameter and each delivered quality parameter at the user's end and returning the results to the IP network operator though a control and configuration interface.The operator uses the control and configuration interface to configure at the user's end how to perform the correlation between the parameters, taking into account in said correlation the user's preferences described by an ontology.
Owner:TELEFONICA SA
Modular packet classification
InactiveUS7039641B2Avoid explosionDepth is minimizedDigital data processing detailsData switching by path configurationQuality of serviceTraffic capacity
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for provisioning and monitoring internet protocol quality of service
InactiveUS6973033B1Minimum utilization of linkSimple processError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesDifferentiated service
An architecture, design, and realization for providing Quality of Service (QoS) to Internet Protocol (IP) networks based on a three-class differentiated service scheme where the service provider uses a resource management system and a schedule optimizer to enable the optimal use of bandwidth and buffer resources at each node or router along the various links between the ingress and egress points in a network. The resource reservation system checks to determine if sufficient bandwidth resources are available along the path requested by the customer for a particular class. The schedule optimizer ensures that sufficient buffer resource allocations and parameter settings are made to optimally reach the predetermined QoS criteria for each of the three classes. The system also contains a mechanism supporting resource reservations providing additional resources along alternative paths if the selected path links fail in the network.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
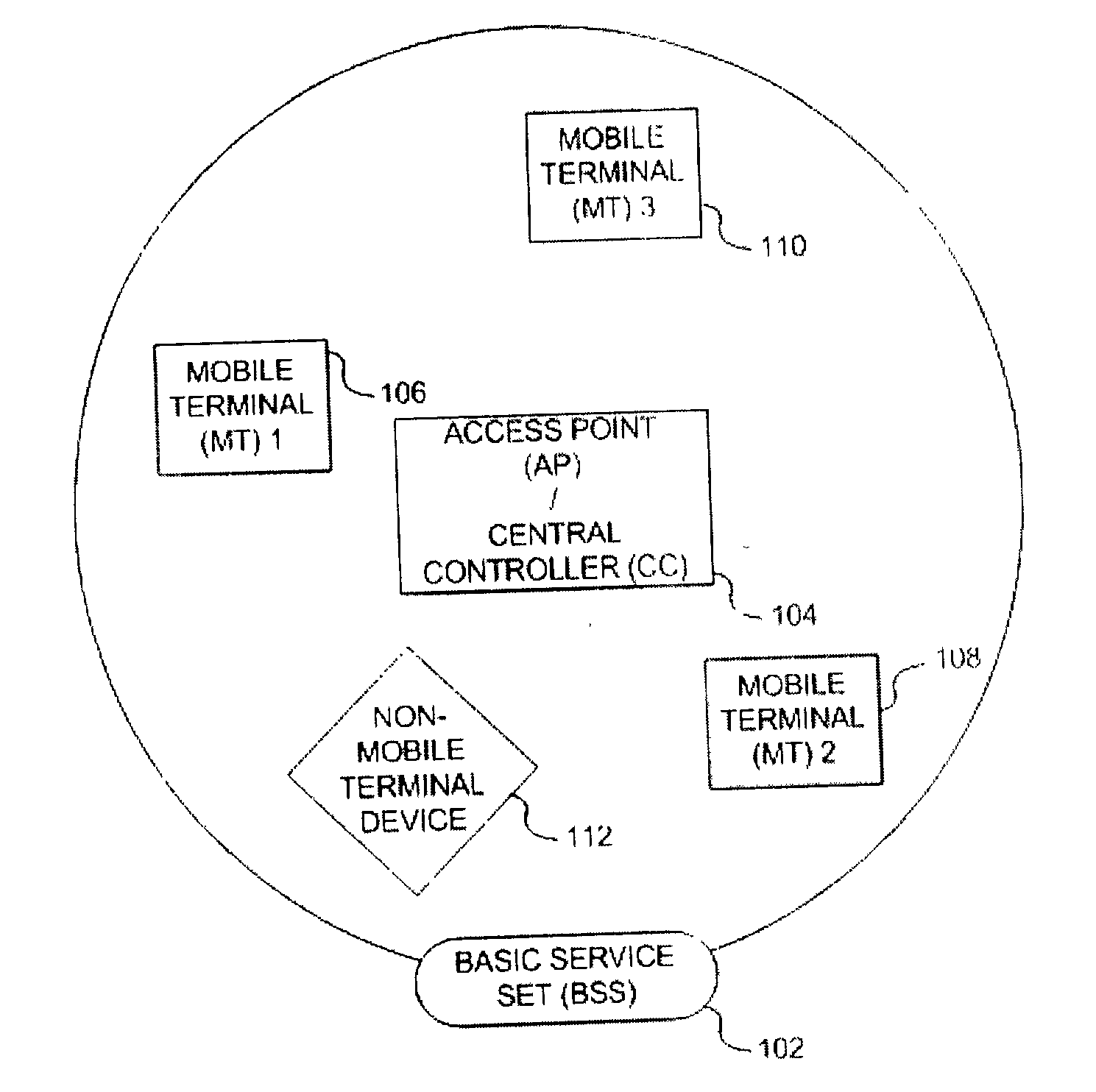
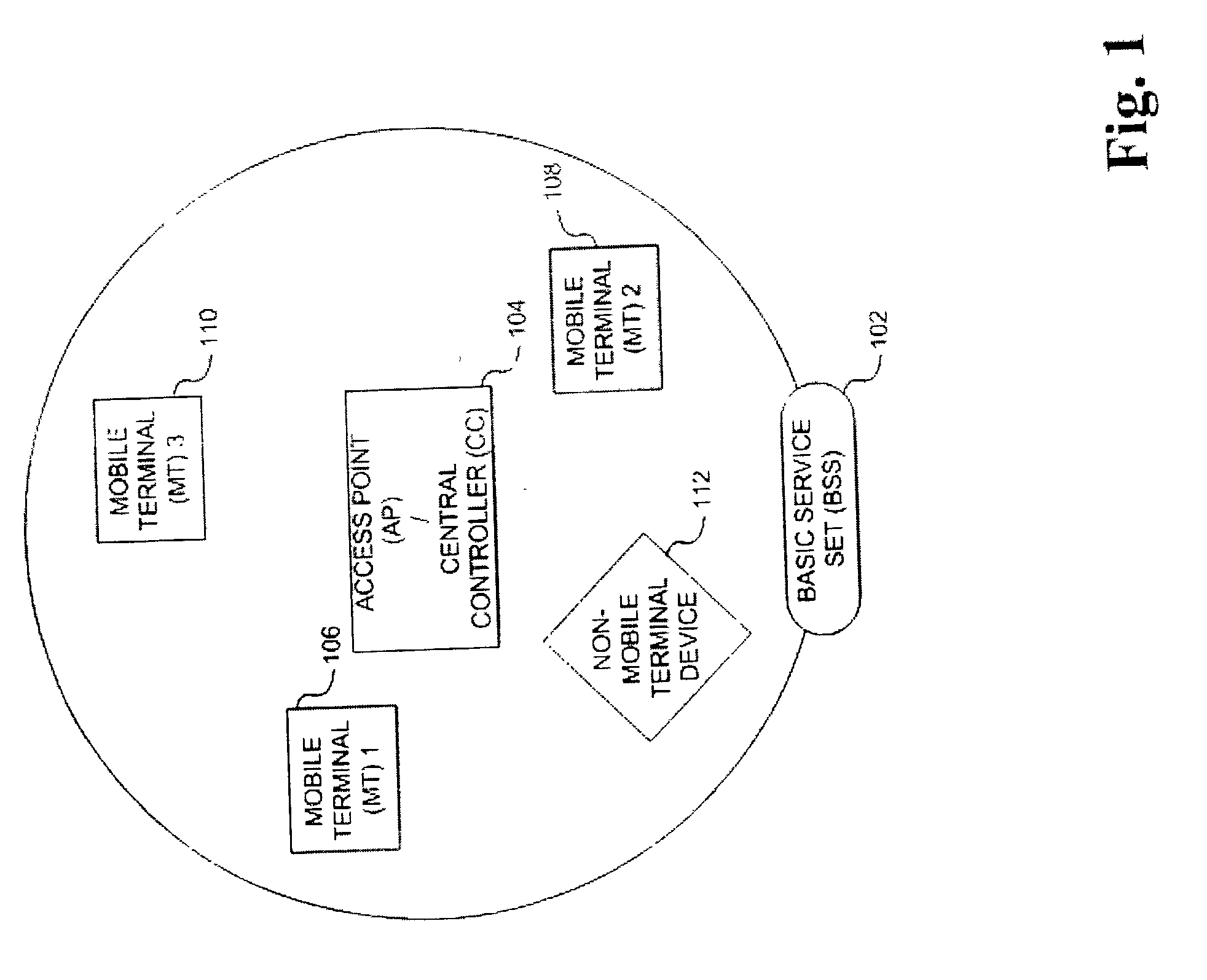
Method and apparatus for assuring quality of service in wireless local area networks
InactiveUS20040037257A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesQuality of serviceReliable transmission
A method and apparatus is described for maintaining quality of service (QoS) between a central controller and a set of mobile terminals (MTs) located within the coverage area of a basic service set (BSS) in a wireless local area network (WLAN). Upon a detection of a connection request by an MT and determining if adequate resources are available, establishing a connection with the MT using the most robust physical layer (PHY) mode with a sufficiently large set of packets to fulfill throughput requirements, if adequate resources are available and additional resources can be allocated. If adequate resources are not available, then attempting to allocate additional resources. In addition, a method is described for providing reliable transmission for a critical packet in a connection, including the steps of transmitting the critical packet at a first PHY mode; determining if adequate resources in the connection are available; and, transmitting a duplicate packet on a second PHY mode if adequate resources are available.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Routing cost based network congestion control for quality of service
ActiveUS20060067213A1Reduce loadError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCost metricQuality of service
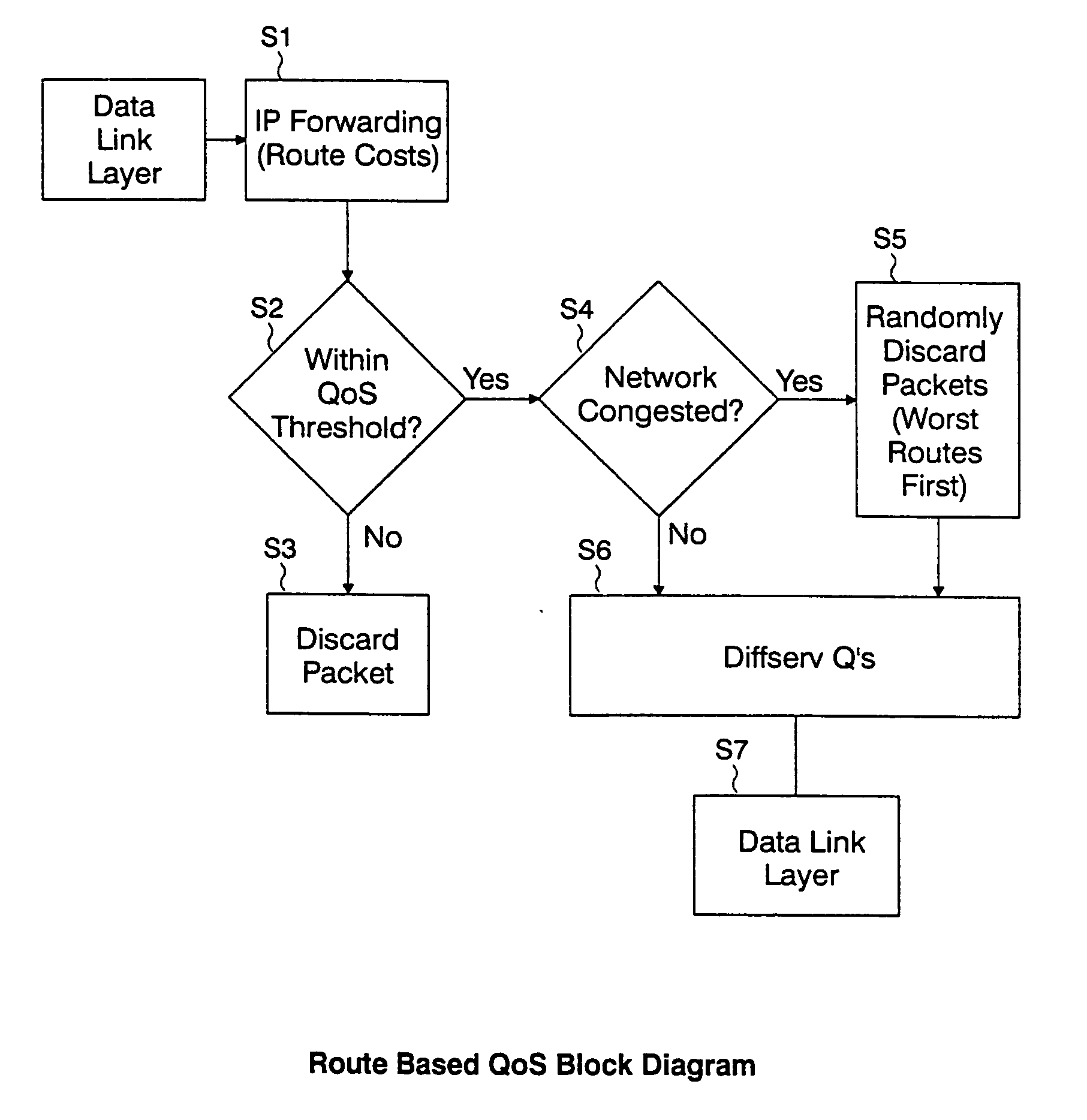
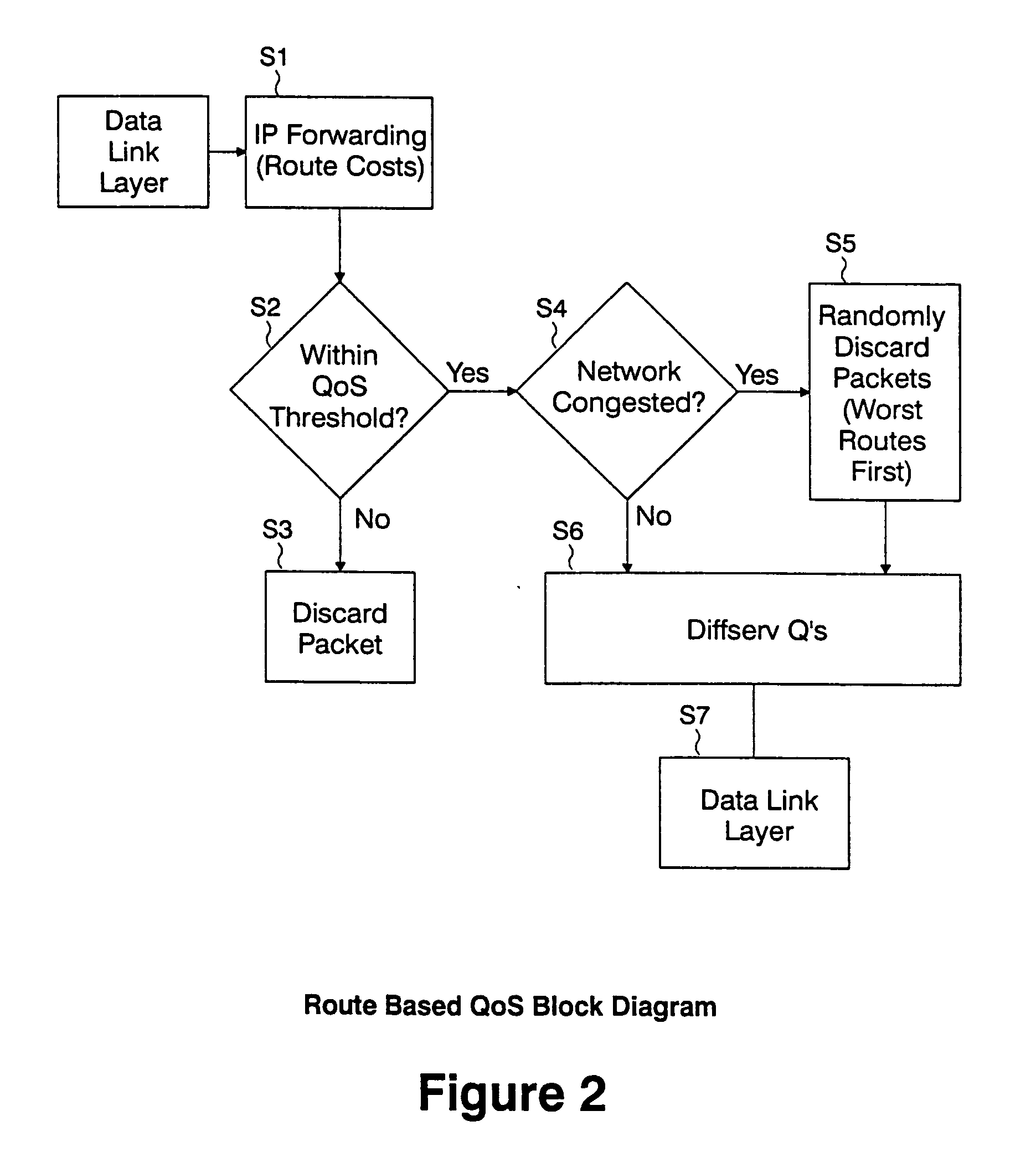
A method and system of congestion control in a network are provided. A required quality of service (QoS) parameter, such as a maximum allowable latency, for a packet received at a queue in the network, and a route cost metric, such as accumulated and estimated latency, are determined, and the packet is either discarded if the route cost metric exceeds the required QoS parameter, or a discard bias value is set for the packet. Also, if the required QoS parameter exceeds the route cost metric, the method includes determining whether a congestion condition exists in the network, and if the congestion condition exists, biasing the packet for discard based on its latency if the route cost metric for the packet exceeds a threshold. The network may be an IP network, and a network such as a mobile ad hoc network (MANET).
Owner:GE LIGHTING SOLUTIONS LLC
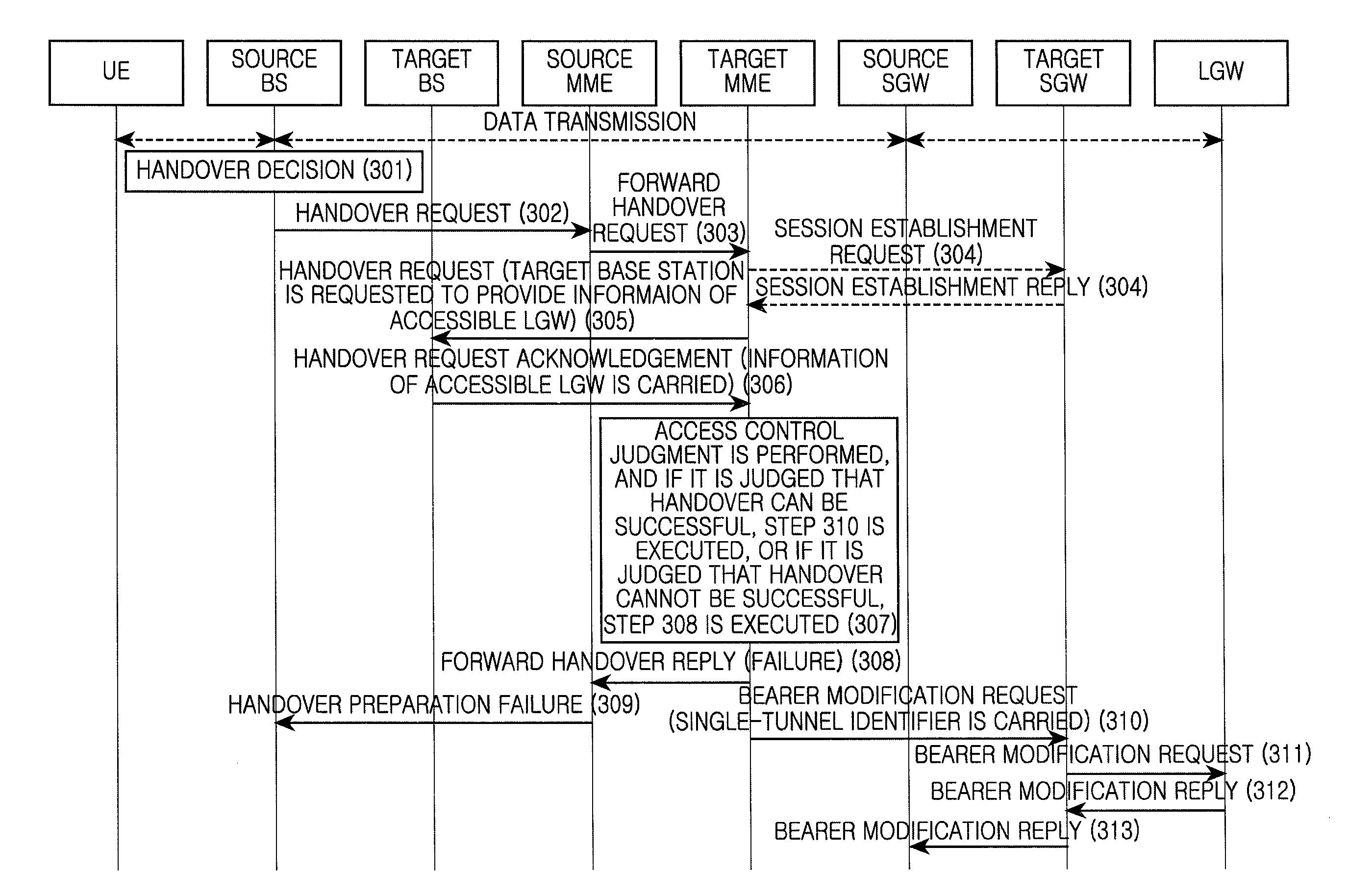
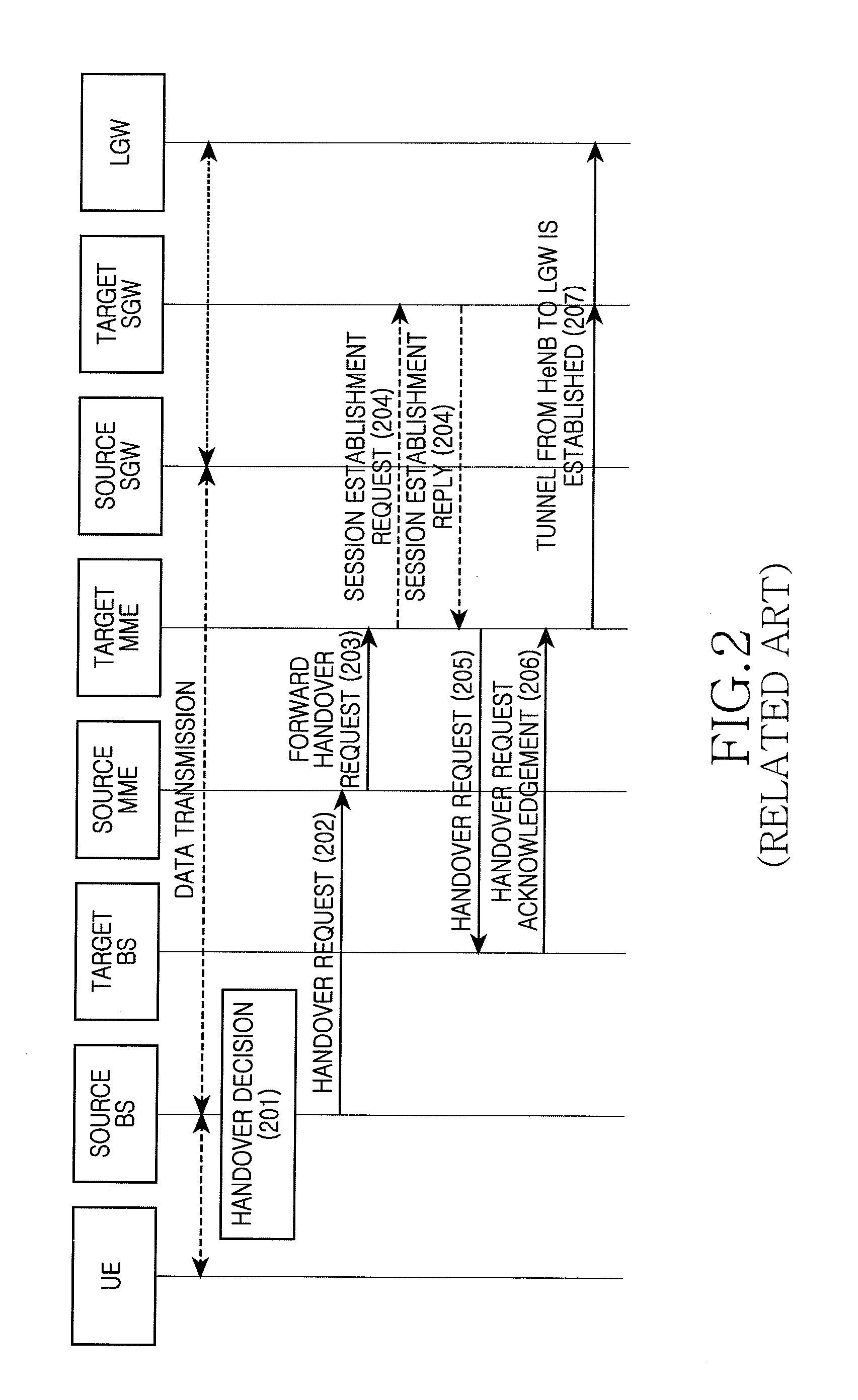
Handover method supporting terminal mobility
ActiveUS20110274087A1Reduce wasted signaling resource resourceReduce resource wireless resourceNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionQuality of serviceUser equipment
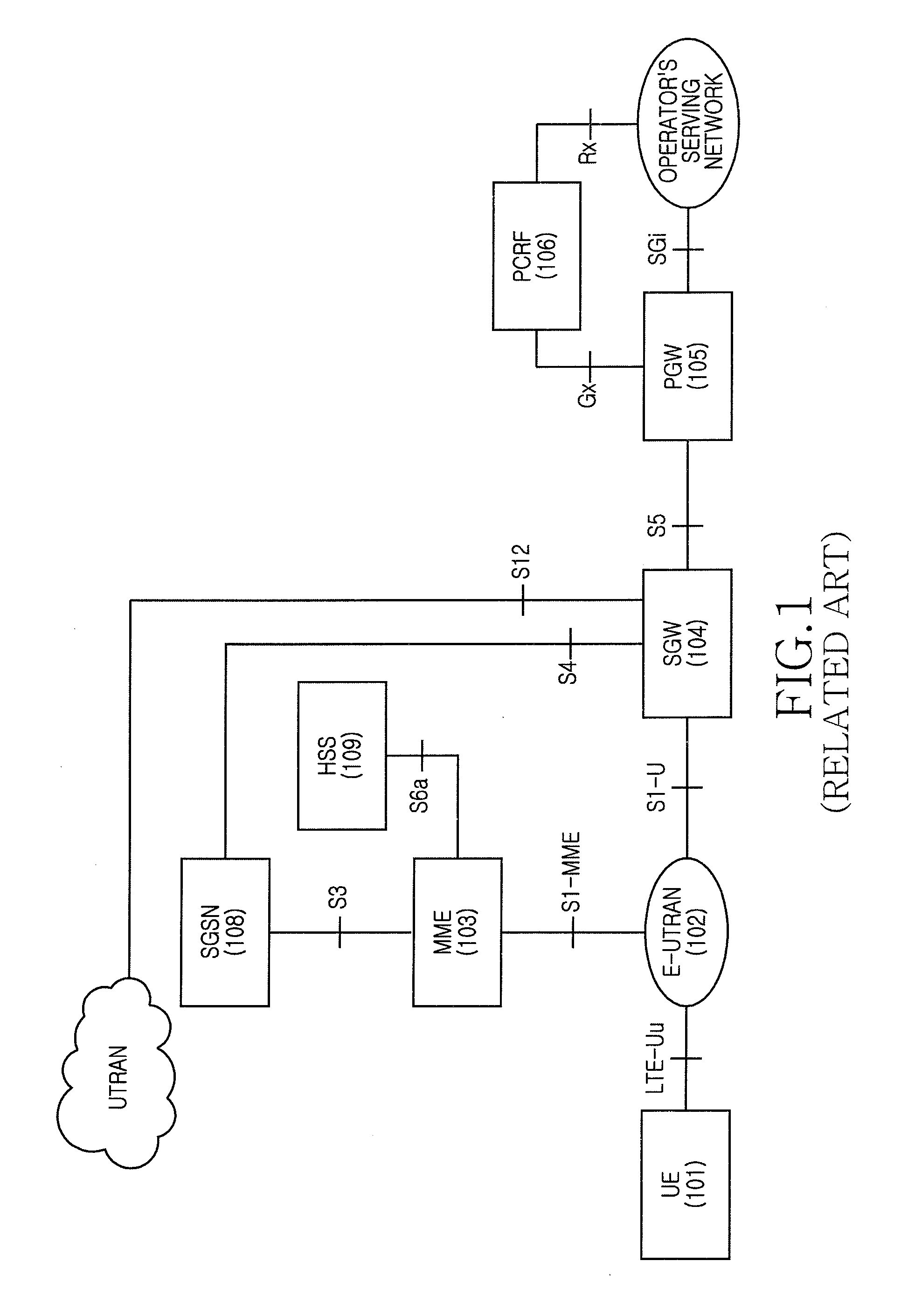
A handover method for supporting terminal mobility is provided. Before a target core network node updates bearer information according to a target base station to which a User Equipment (UE) performs the handover, an access control determination procedure is added. According to the access control determination information provided by the target base station, if it is determined that the bearer supporting a Selected Internet Protocol (IP) Traffic Offload (SIPTO) or Local IP Access (LIPA) service is permitted to perform the handover, the target core network node updates the bearer information. If it is determined that the bearer supporting the SIPTO or LIPA service is not allowed to perform the handover, the handover failure is notified with respect to the bearer not allowed to perform the handover, and the bearer information is not updated, thus the wasted signaling resource and wireless resource are reduced. Alternatively, during the handover to the target network by the UE or after the handover to the target network, the bearer release or deactivation is performed for the bearer not allowed to perform the handover, so that the UE can re-initiate the bearer establishment process with respect to the bearer not allowed to perform the handover, thus an optimized bearer is established and the Quality of Service (QoS) is ensured.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com