Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Fair queuing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Fair queuing is a family of scheduling algorithms used in some process and network schedulers. The algorithm is designed to achieve fairness when a limited resource is shared, for example to prevent flows with large packets or processes that generate small jobs from consuming more throughput or CPU time than other flows or processes.
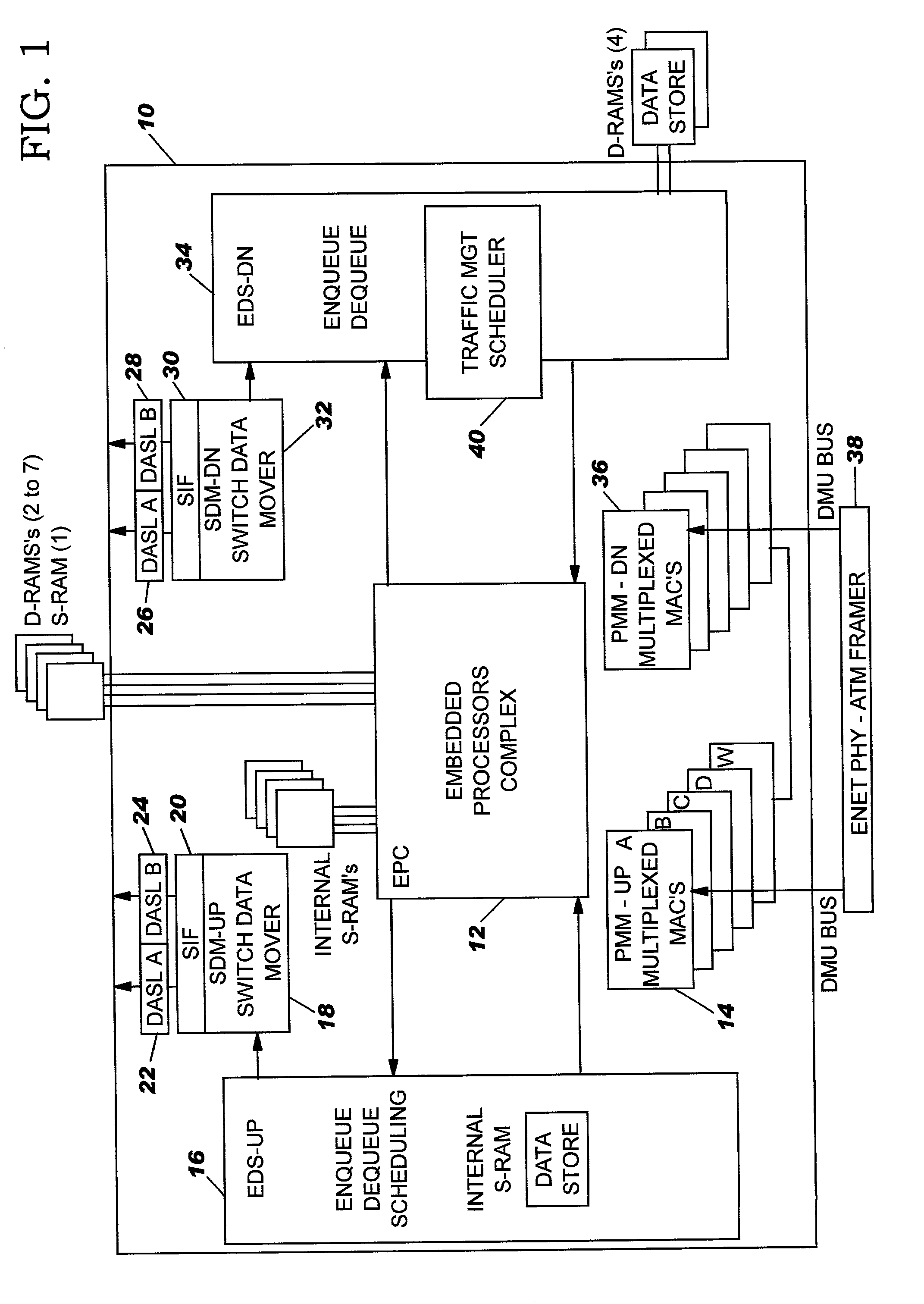
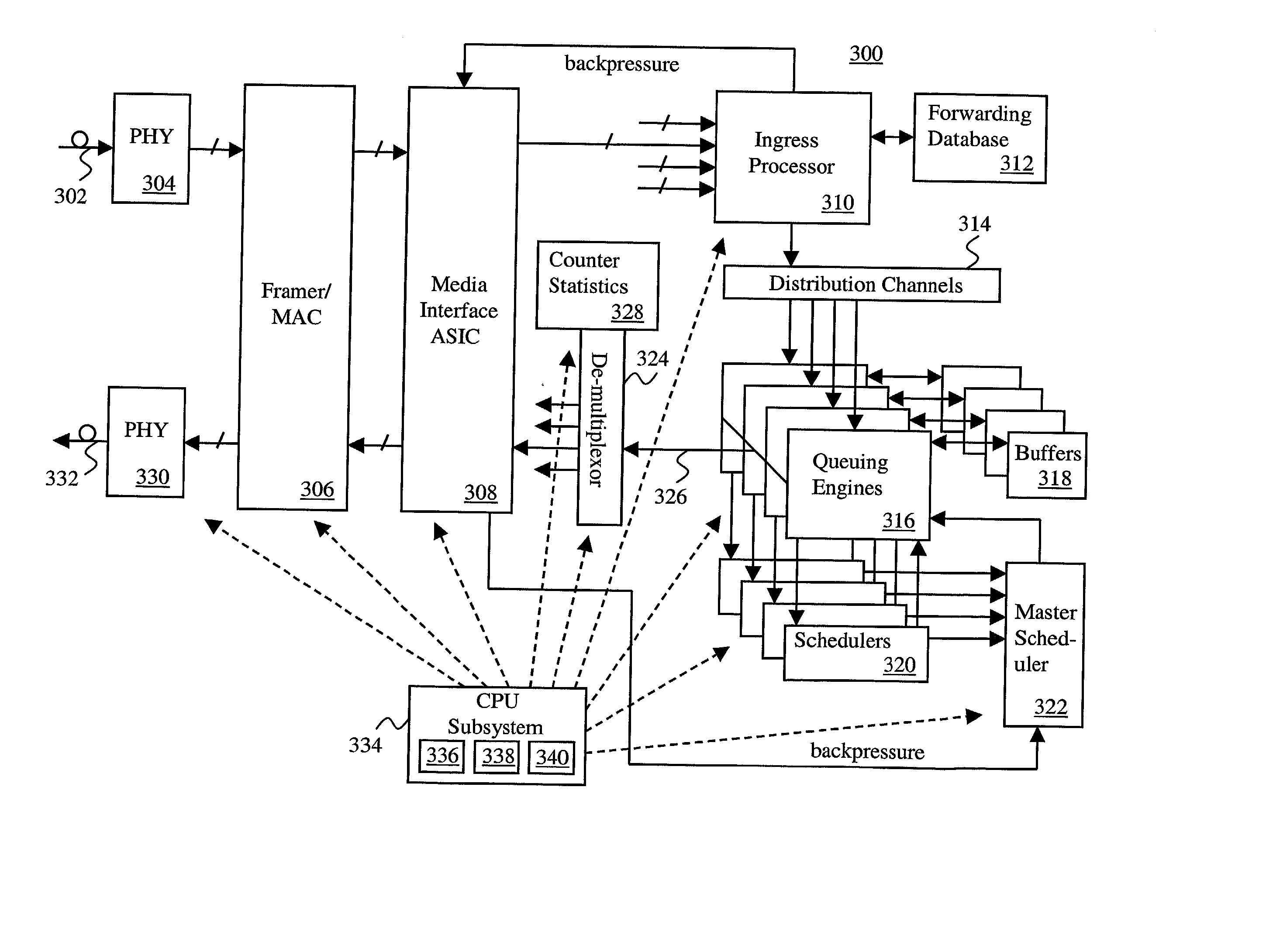
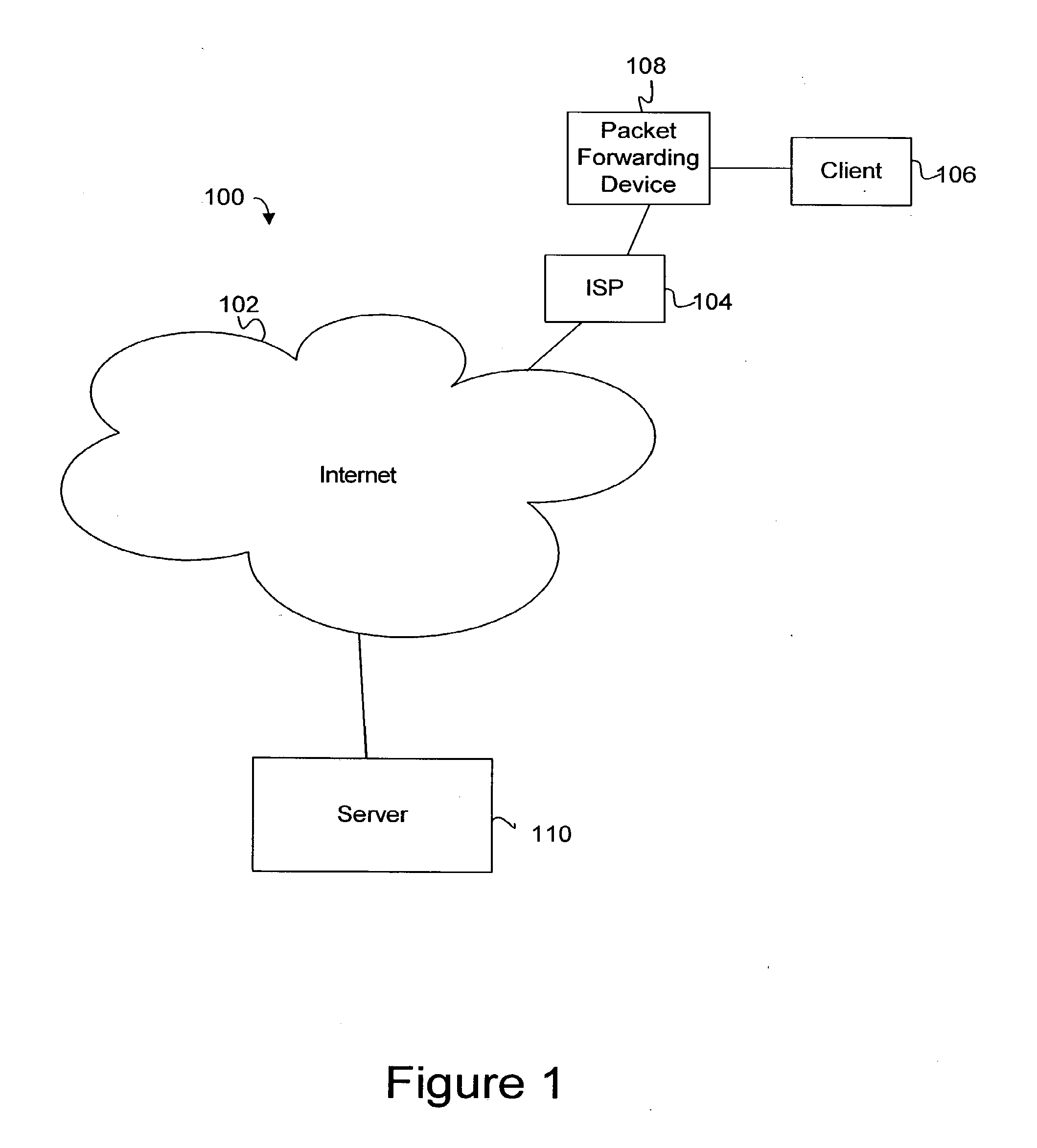
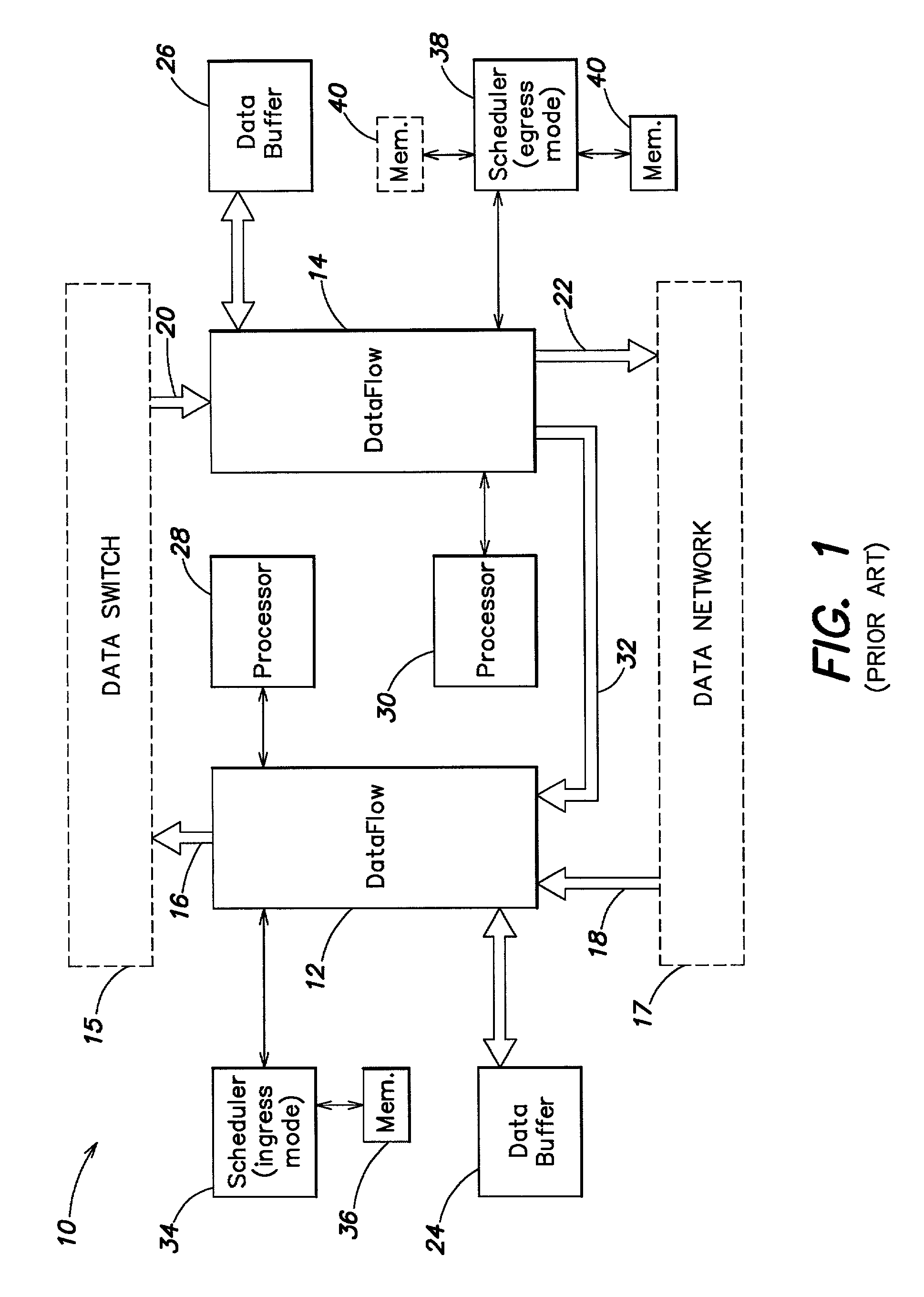
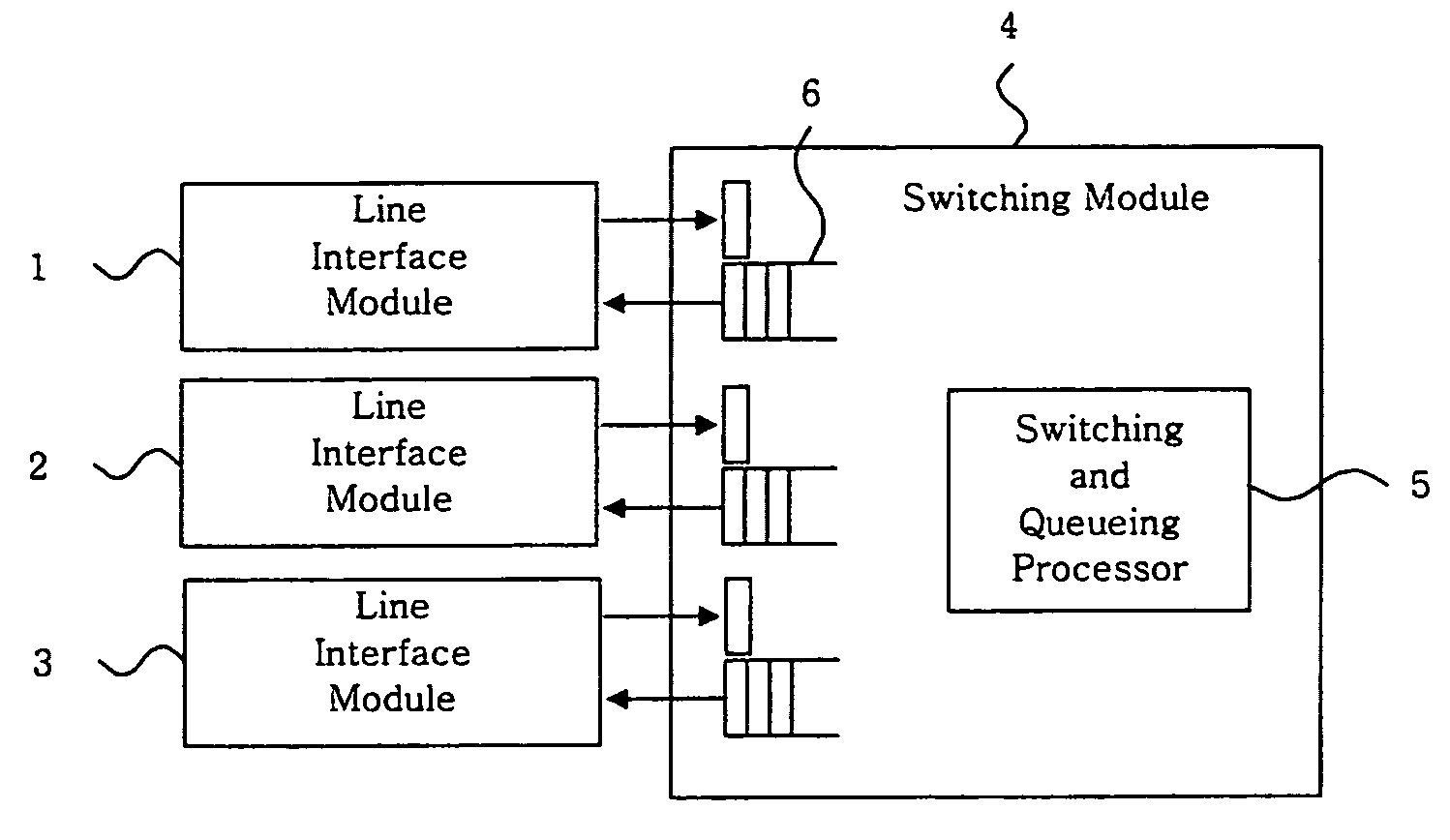
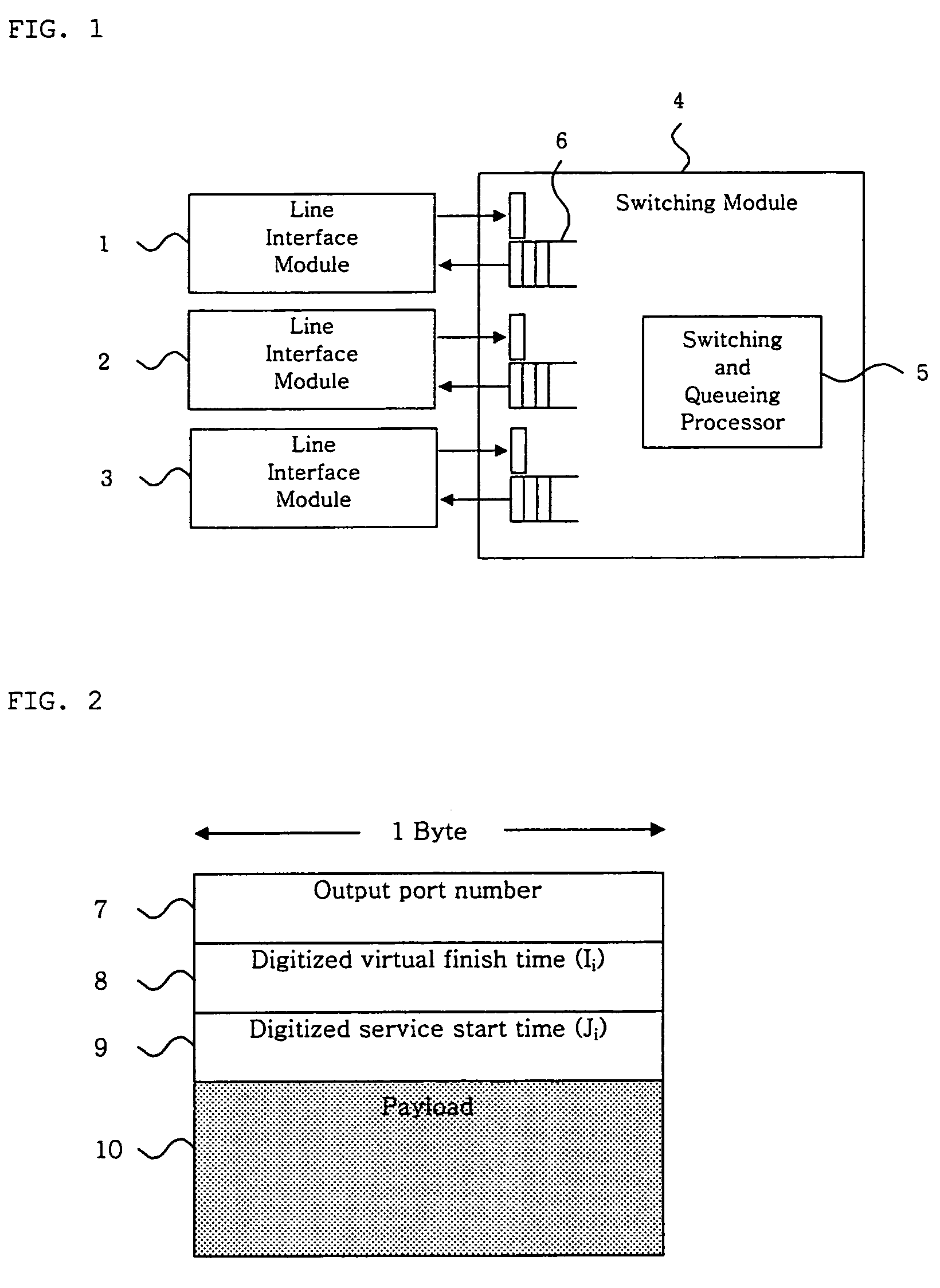
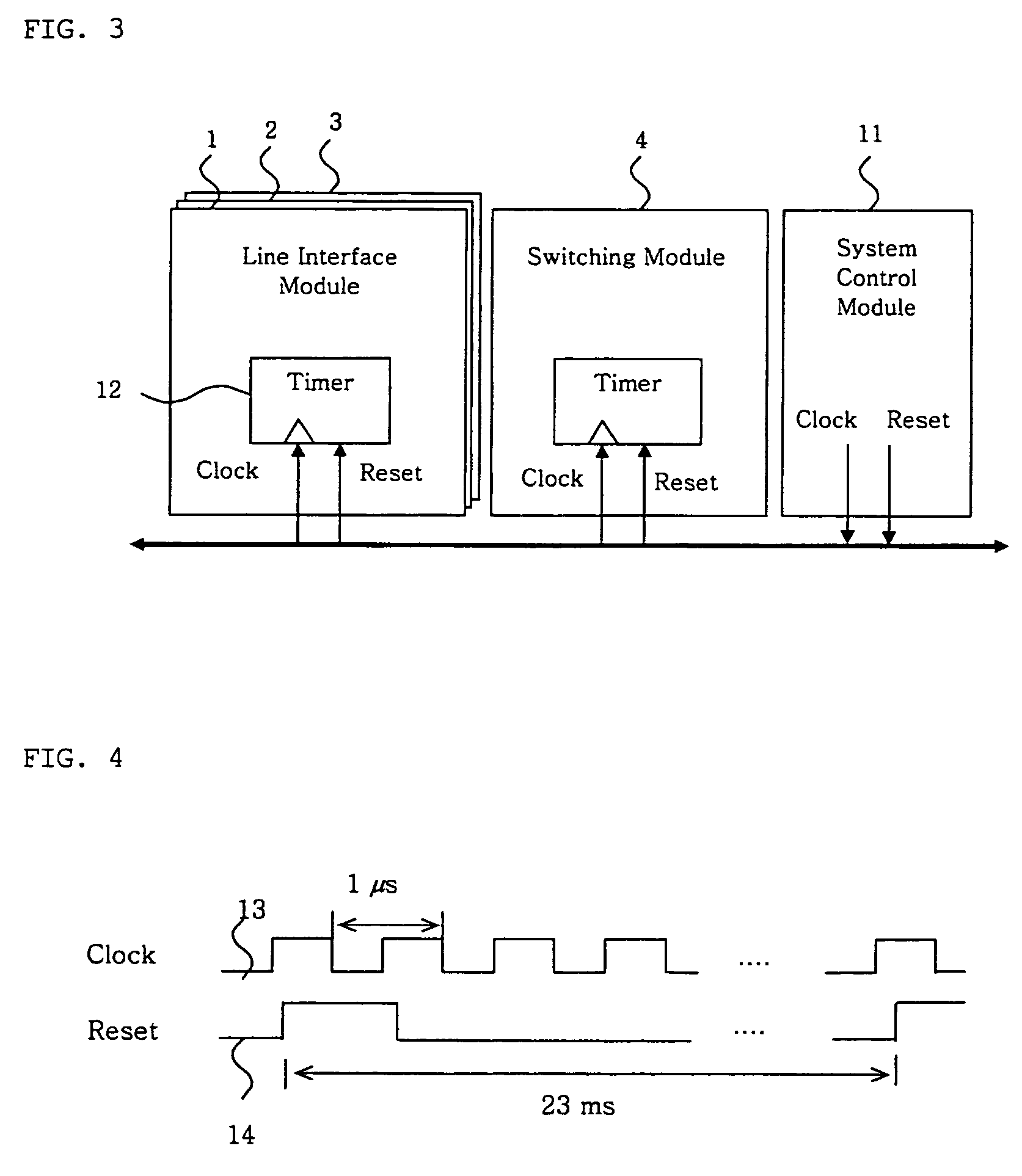
Method for providing integrated packet services over a shared-media network
InactiveUS6563829B1Good serviceError preventionTransmission systemsQos quality of serviceExchange network
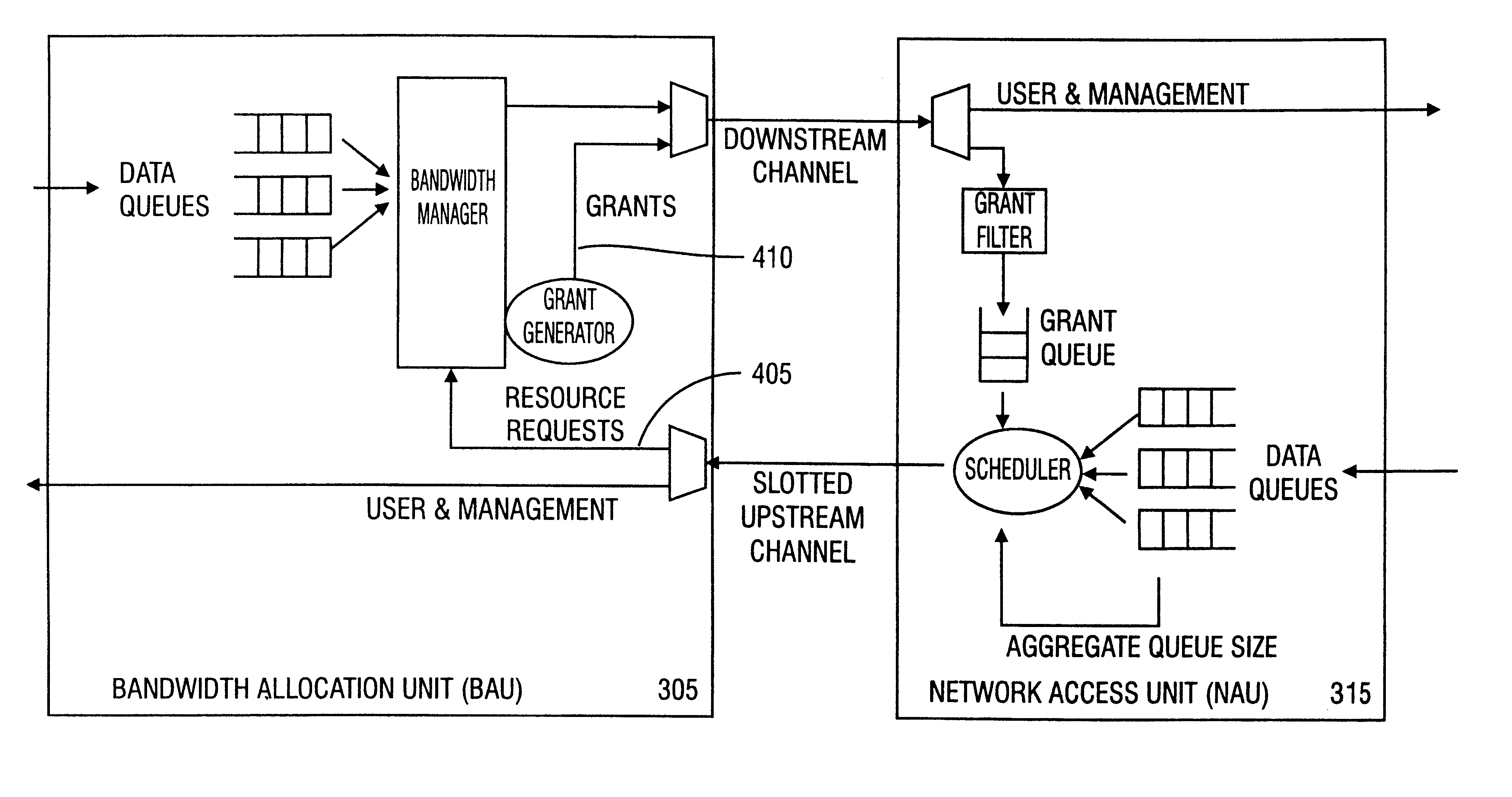
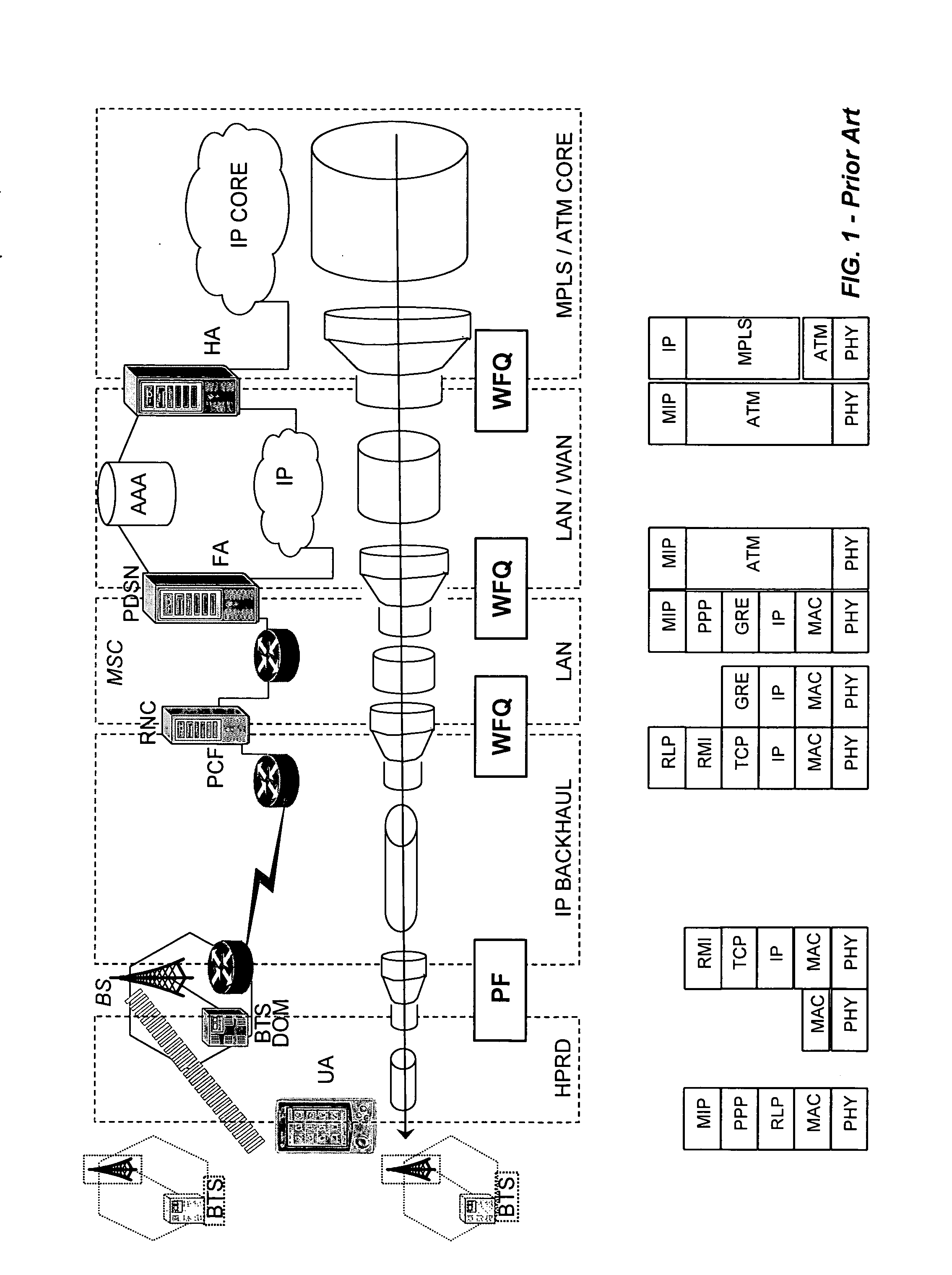
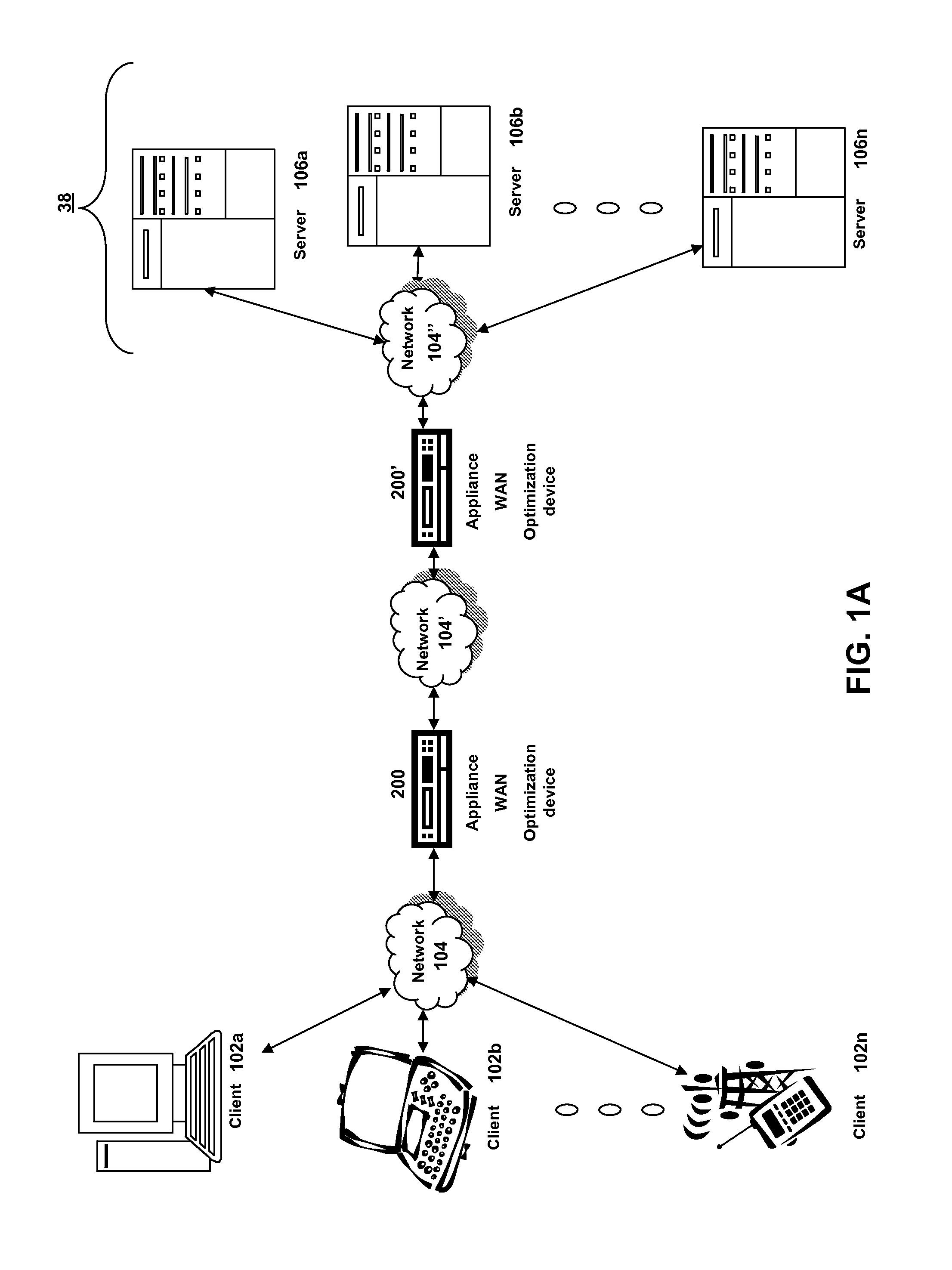
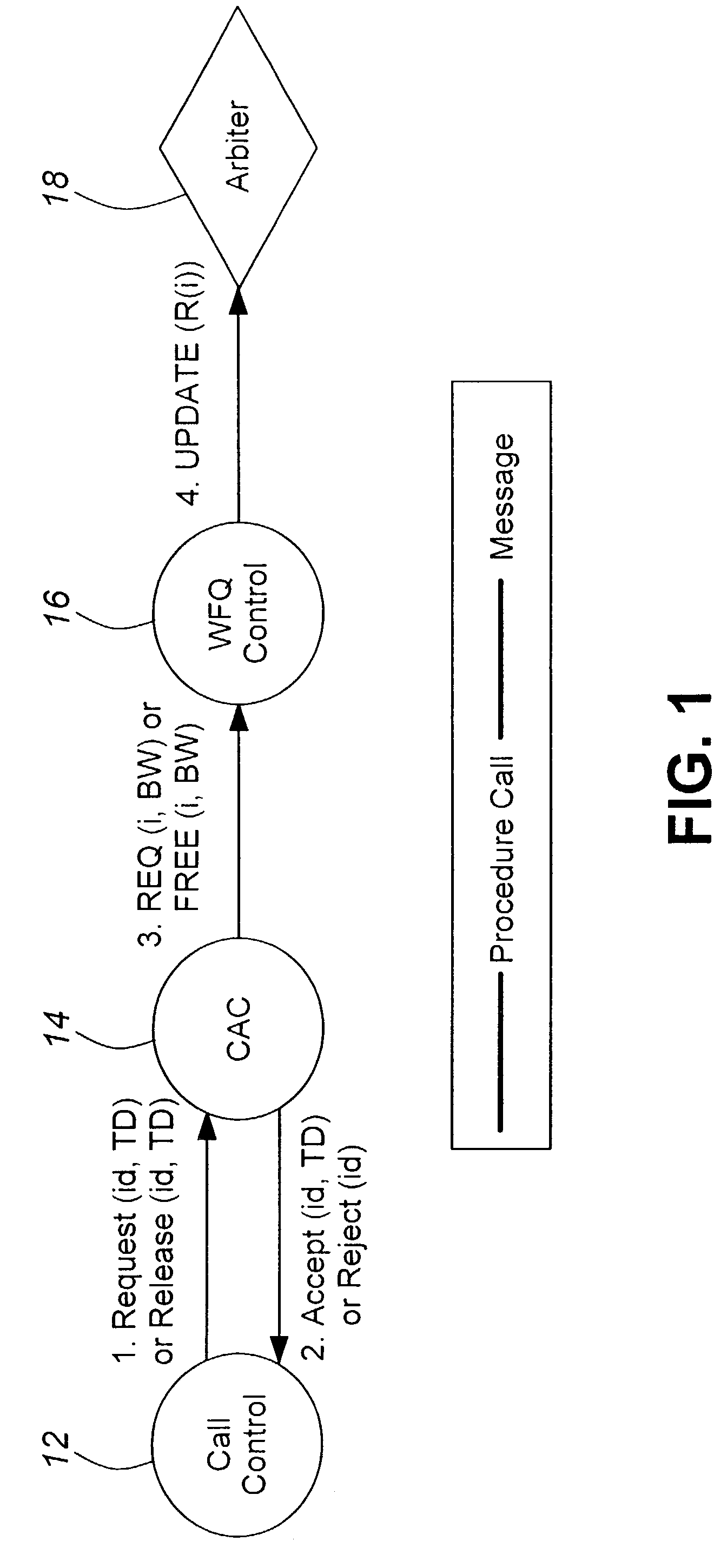
A method in accordance with the invention allocates bandwidth, fairly and dynamically, in a shared-media packet switched network to accommodate both elastic and inelastic applications. The method, executed by or in a head-end controller, allocates bandwidth transmission slots, converting requests for bandwidth into virtual scheduling times for granting access to the shared media. The method can use a weighted fair queuing algorithm or a virtual clock algorithm to generate a sequence of upstream slot / transmission assignment grants. The method supports multiple quality of service (QoS) classes via mechanisms which give highest priority to the service class with the most stringent QoS requirements.
Owner:AMERICAN CAPITAL FINANCIAL SERVICES
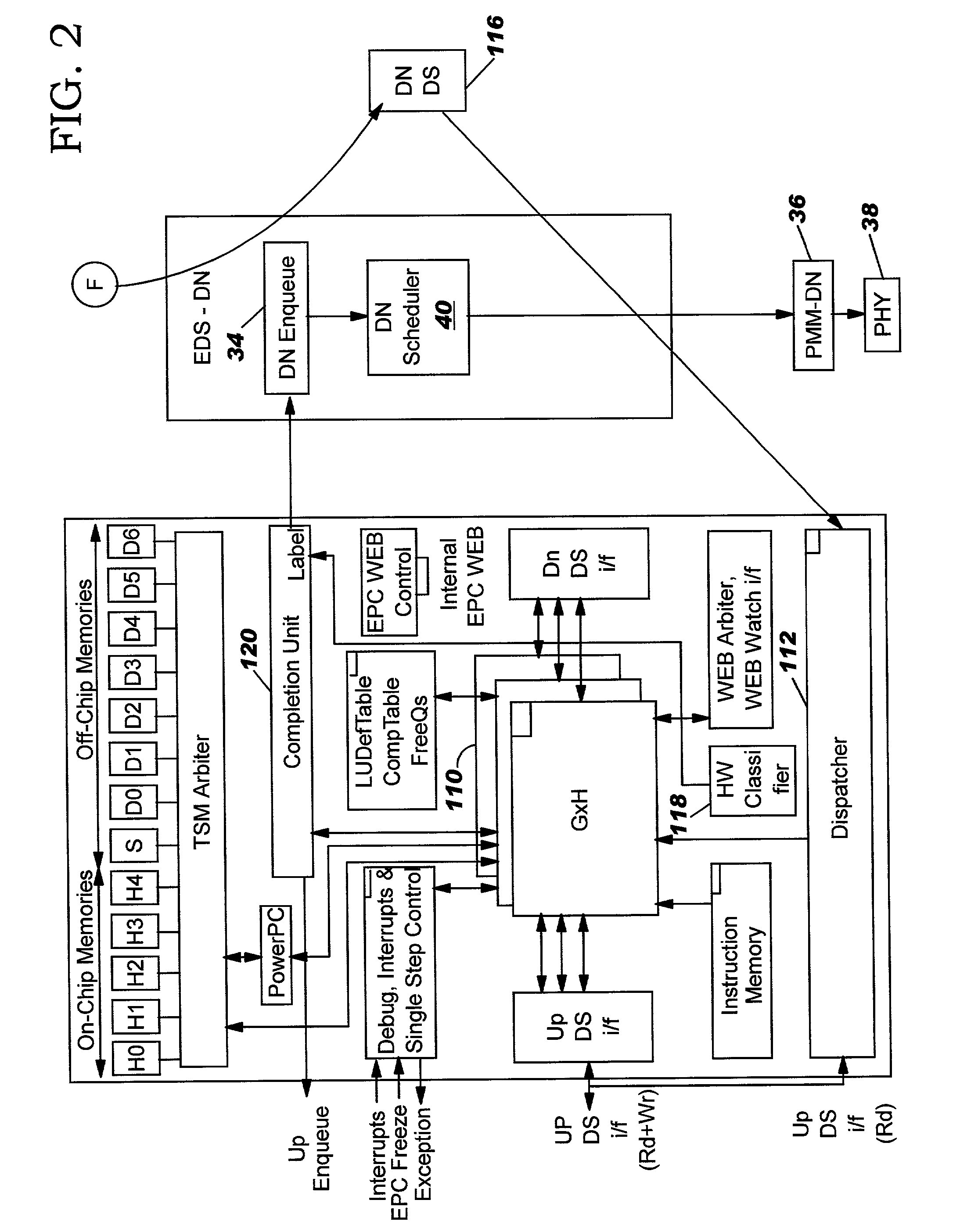
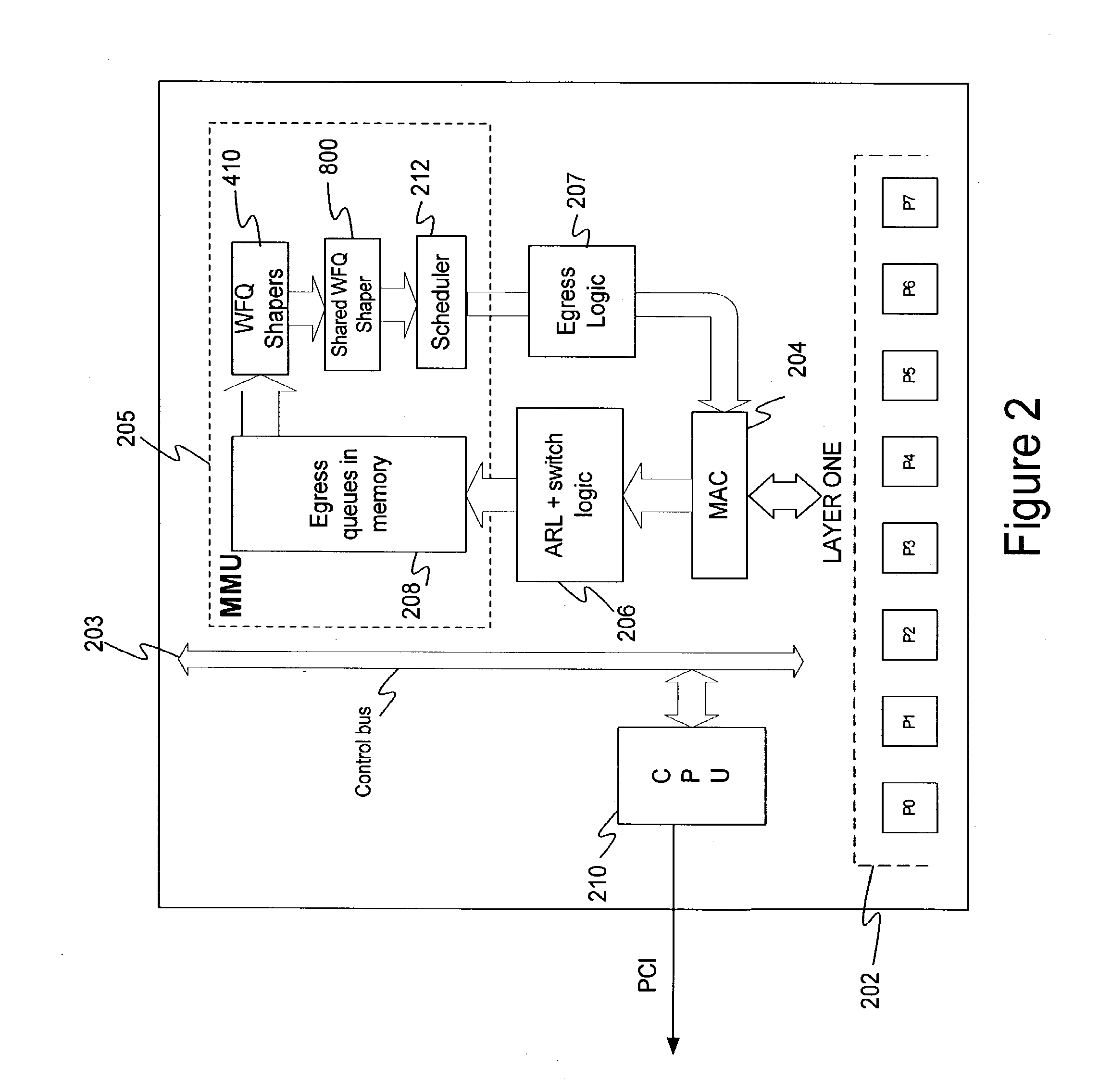
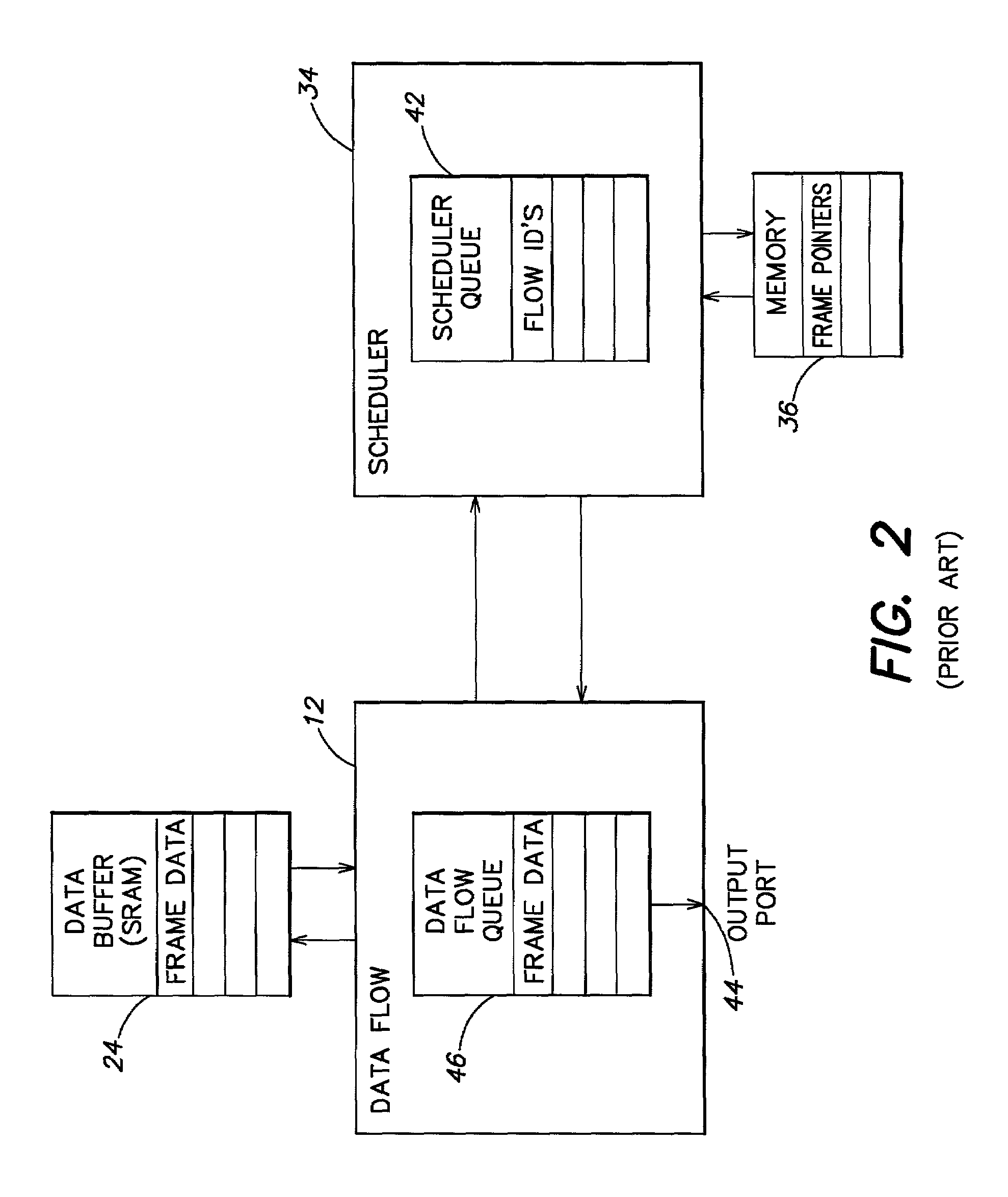
Method and system for network processor scheduling based on service levels
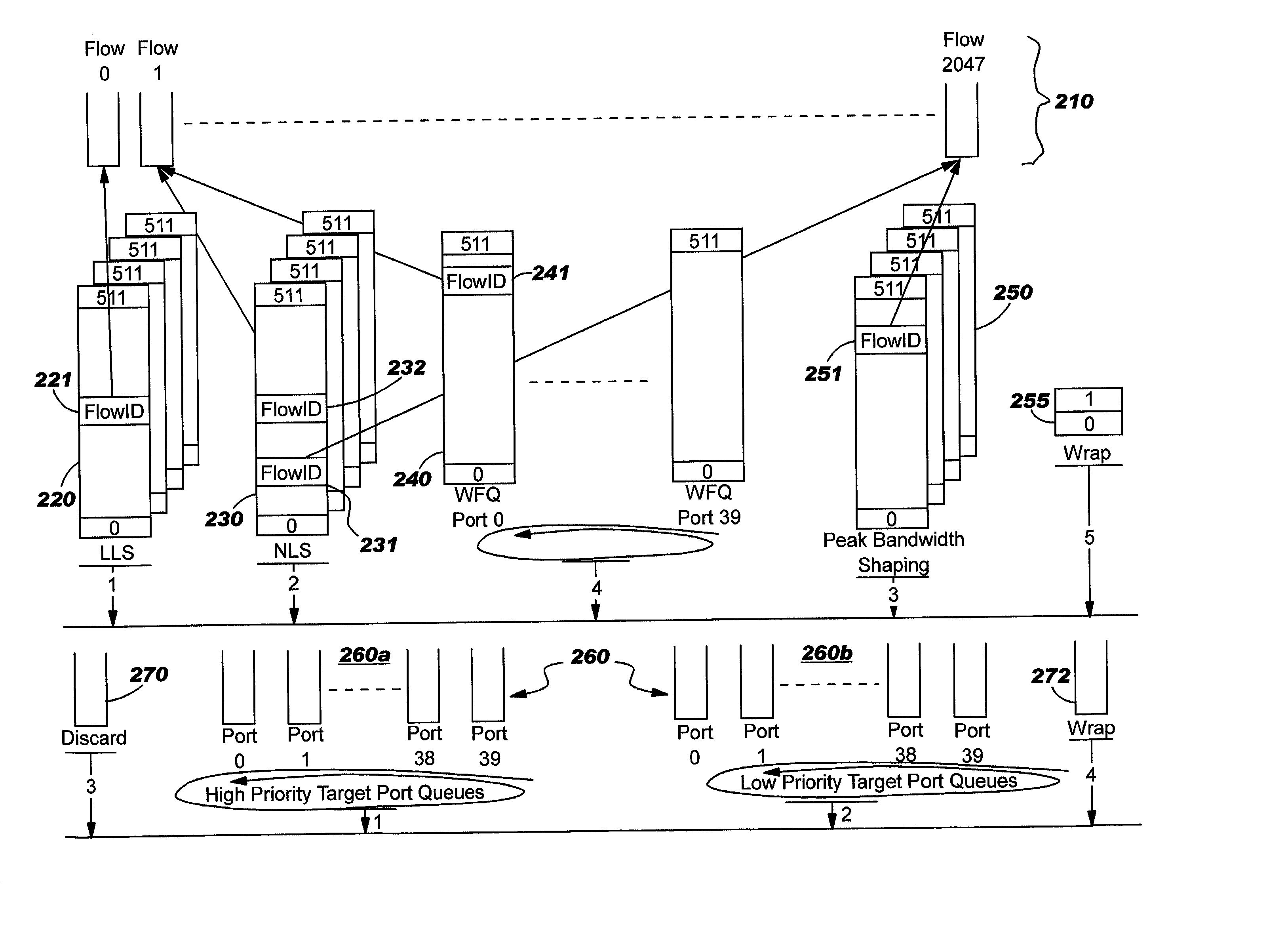
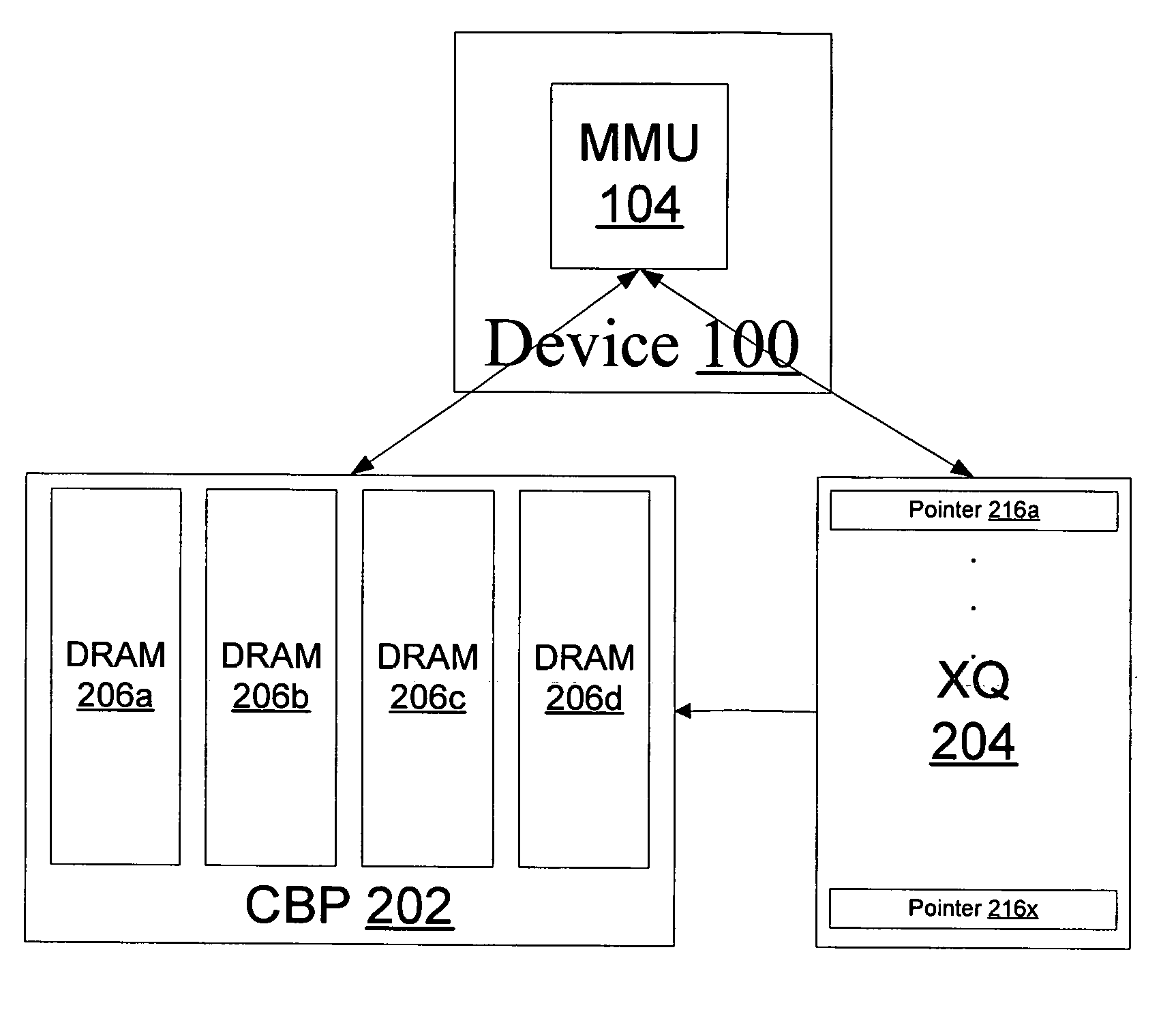
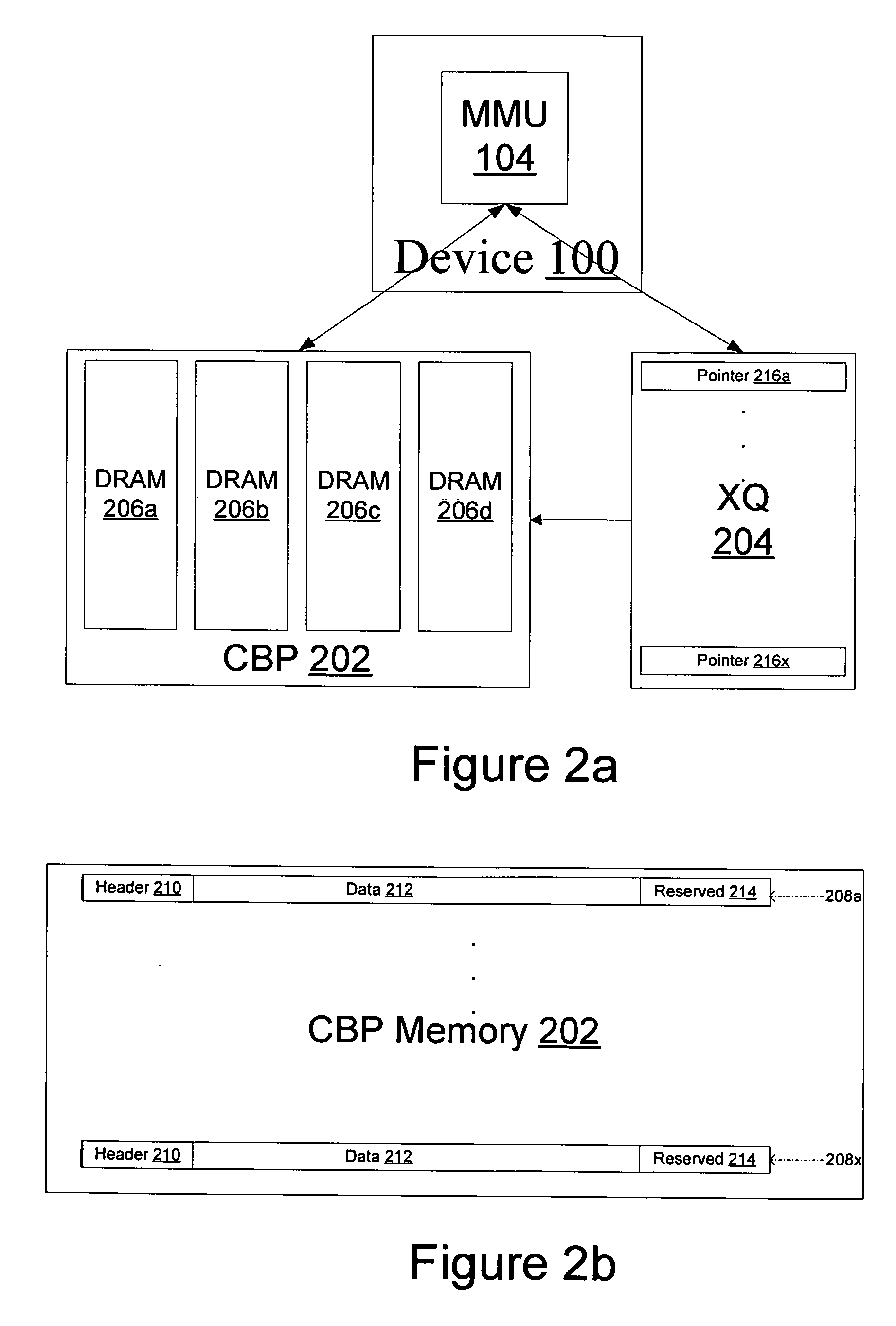
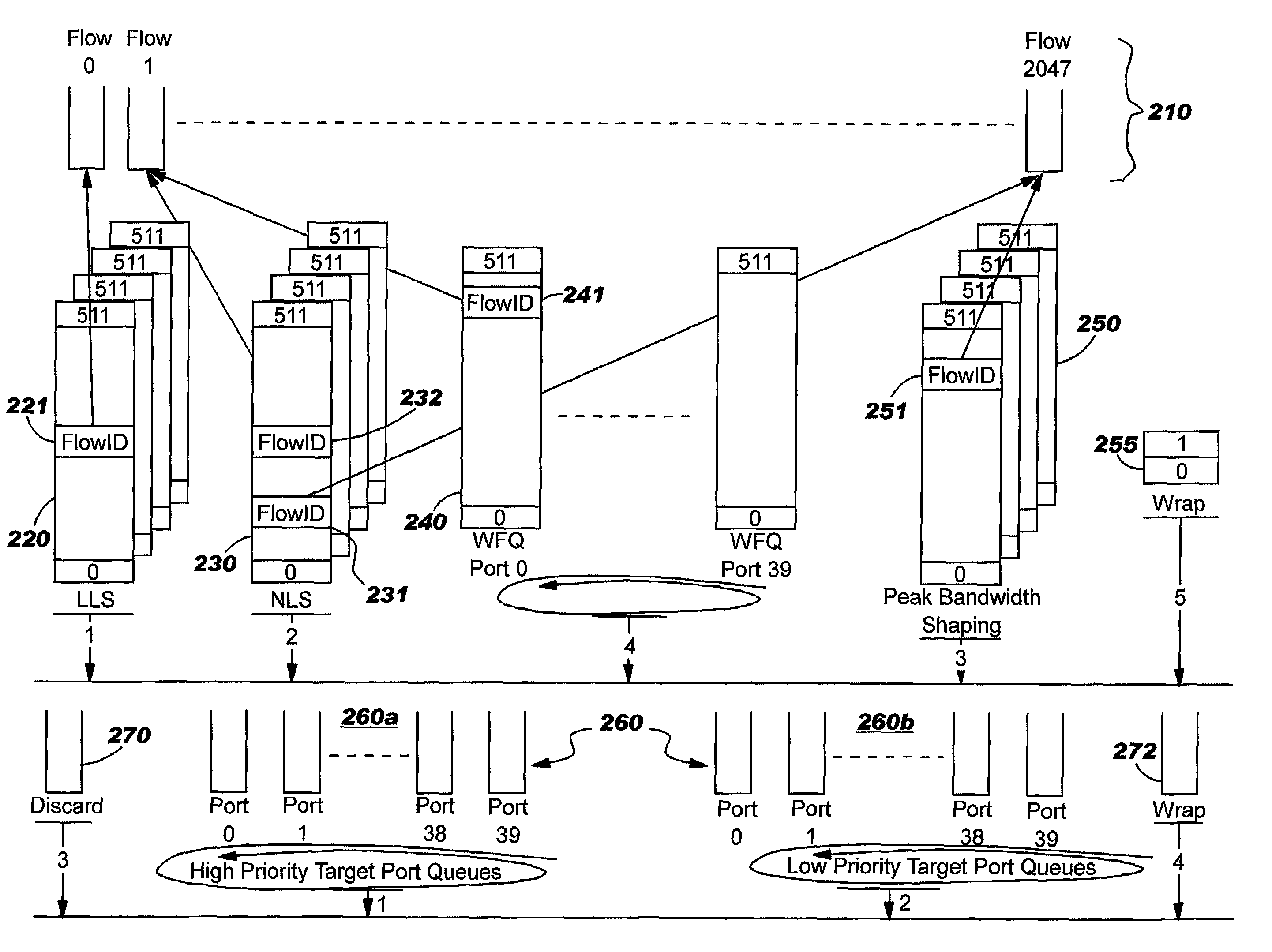
A system and method of moving information units from an output flow control toward a data transmission network in a prioritized sequence which accommodates several different levels of service. The present invention includes a method and system for scheduling the egress of processed information units (or frames) from a network processing unit according to service based on a weighted fair queue where position in the queue is adjusted after each service based on a weight factor and the length of frame, a process which provides a method for and system of interaction between different calendar types is used to provide minimum bandwidth, best effort bandwidth, weighted fair queuing service, best effort peak bandwidth, and maximum burst size specifications. The present invention permits different combinations of service that can be used to create different QoS specifications. The "base" services which are offered to a customer in the example described in this patent application are minimum bandwidth, best effort, peak and maximum burst size (or MBS), which may be combined as desired. For example, a user could specify minimum bandwidth plus best effort additional bandwidth and the system would provide this capability by putting the flow queue in both the NLS and WFQ calendar. The system includes tests when a flow queue is in multiple calendars to determine when it must come out.
Owner:IBM CORP
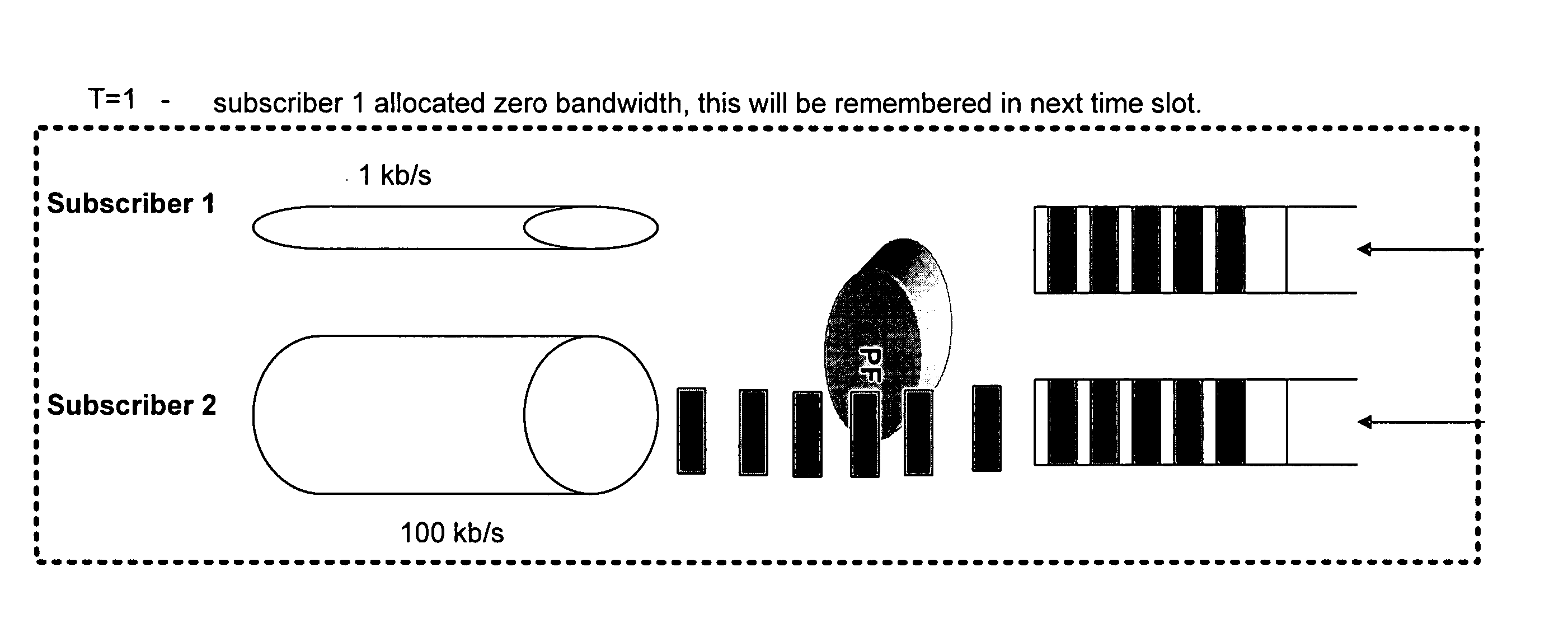
Integrated packet latency aware QoS scheduling using proportional fairness and weighted fair queuing for wireless integrated multimedia packet services
ActiveUS20070041364A1Network traffic/resource managementIn VoIP networksPacket communicationPacket scheduling
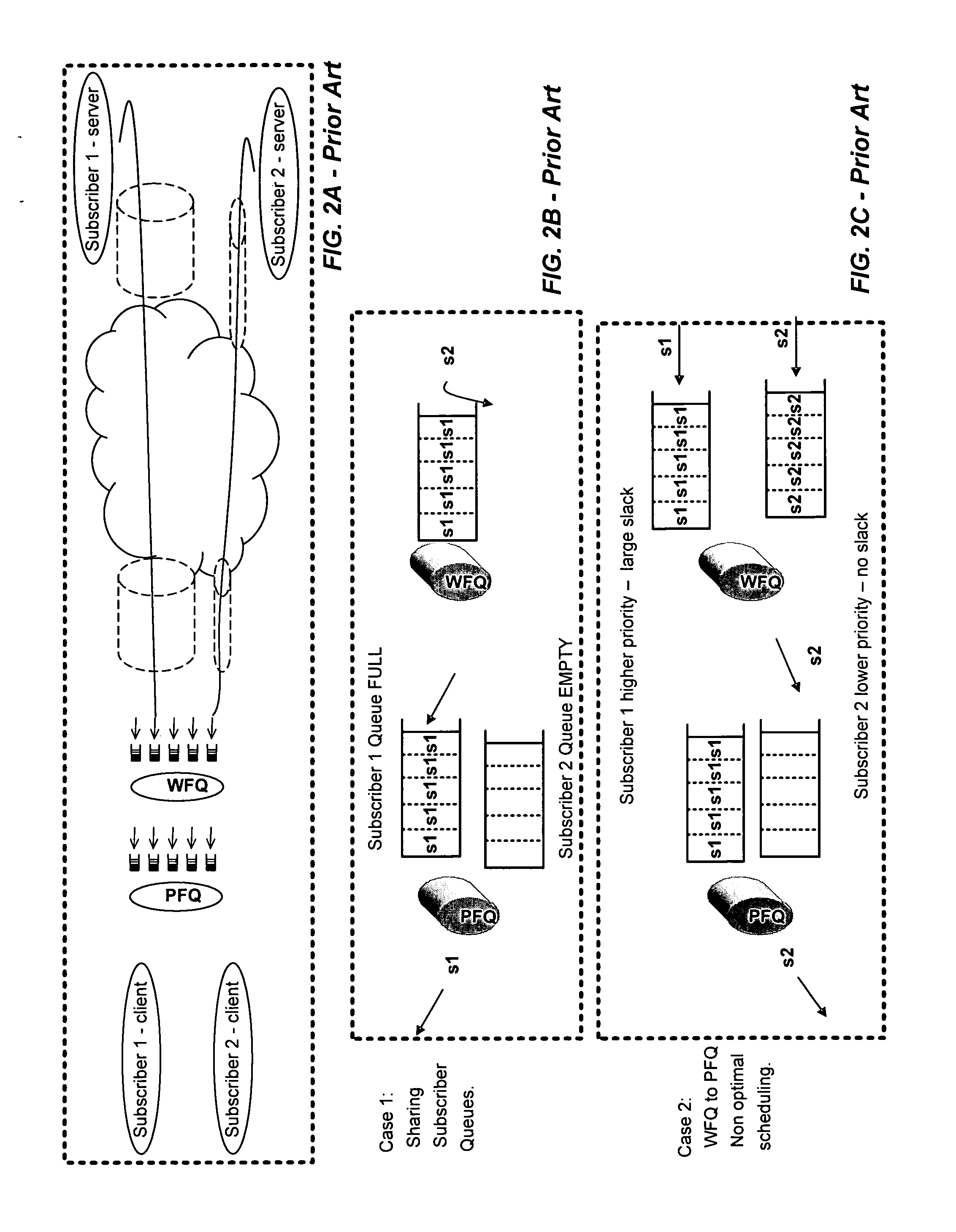
Packet communication networks for transmission to wireless subscriber devices utilize both wireline and wireless packet routing components. The routing elements of these two different types often implement different packet scheduling algorithms, typically a form of Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) in the wireline portion of the network and Proportional Fairness (PF) queuing in the wireless domain. To improve resource allocation and thus end to end quality of service for time sensitive communications, such as integrated multimedia services, the present disclosure suggests adding the notion of slack time into either one or both of the packet scheduling algorithms. By modifying one or more of these algorithms, e.g. to reorder or shuffle packets based on slack times, global optimal resource allocations are possible, at least in certain cases.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
Weighted fair queuing-based methods and apparatus for protecting against overload conditions on nodes of a distributed network
InactiveUS7342929B2Data switching by path configurationSecuring communicationComputer networkNetwork on
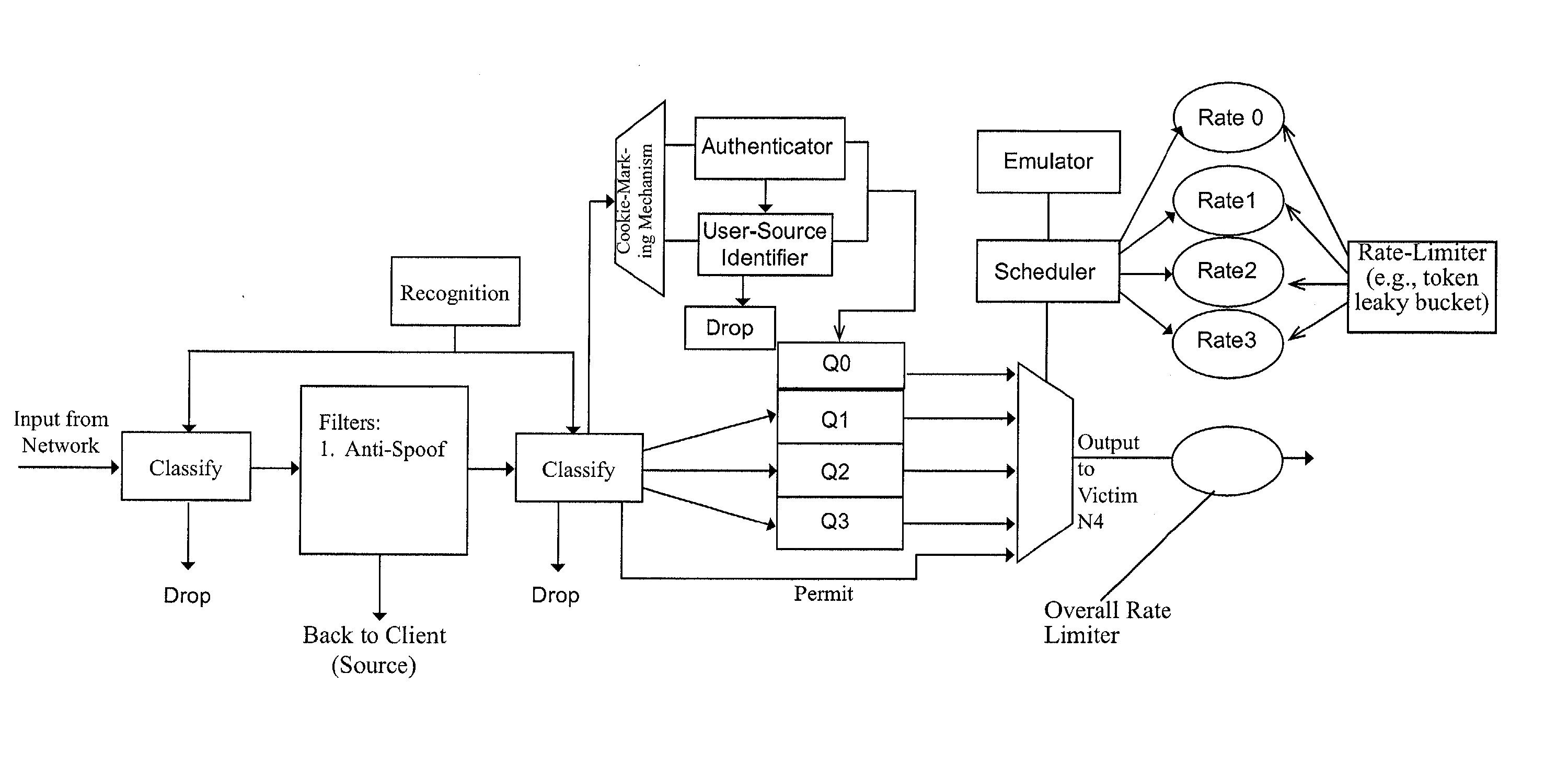
An improved network device that controls throughput of packets received thereby, e.g., to downstream devices or to downstream logic contained within the same network device. The network device comprises a scheduler that schedules one or more packets of a selected class for throughput as a function of a weight of that class and weights of one or more other classes. The weight of at least the selected class is dynamic and is a function of a history of volume of packets received by the network device in the selected class. An apparatus for protecting against overload conditions on a network, e.g., of the type caused by DDoS attacks, has a scheduler and a token bucket mechanism, e.g., as described above. Such apparatus can also include a plurality of queues into which packets of the respective classes are placed on receipt by the apparatus. Those packets are dequeued by the scheduler, e.g., in the manner described above, for transmittal to downstream devices (e.g., potential victim nodes) on the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
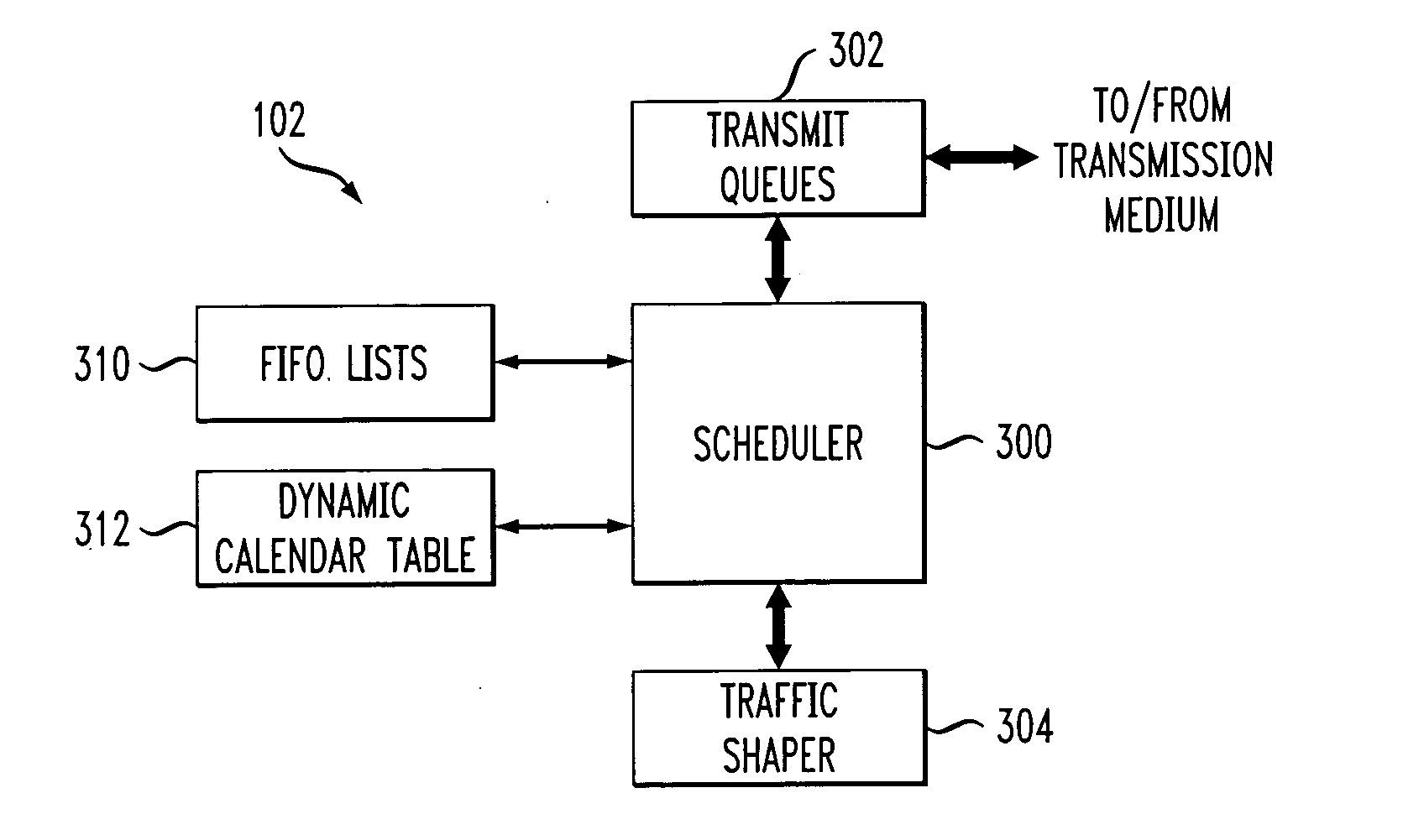
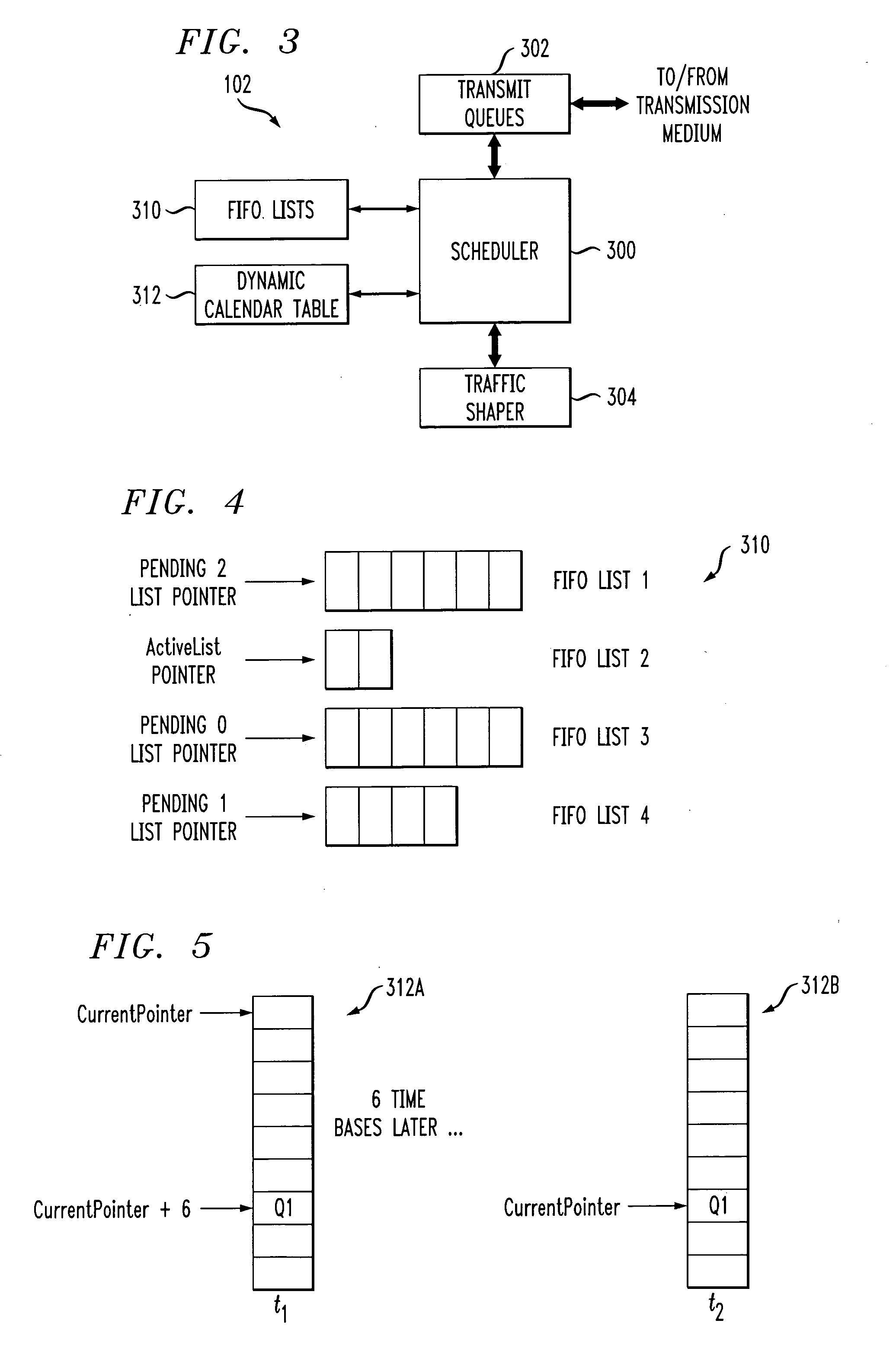
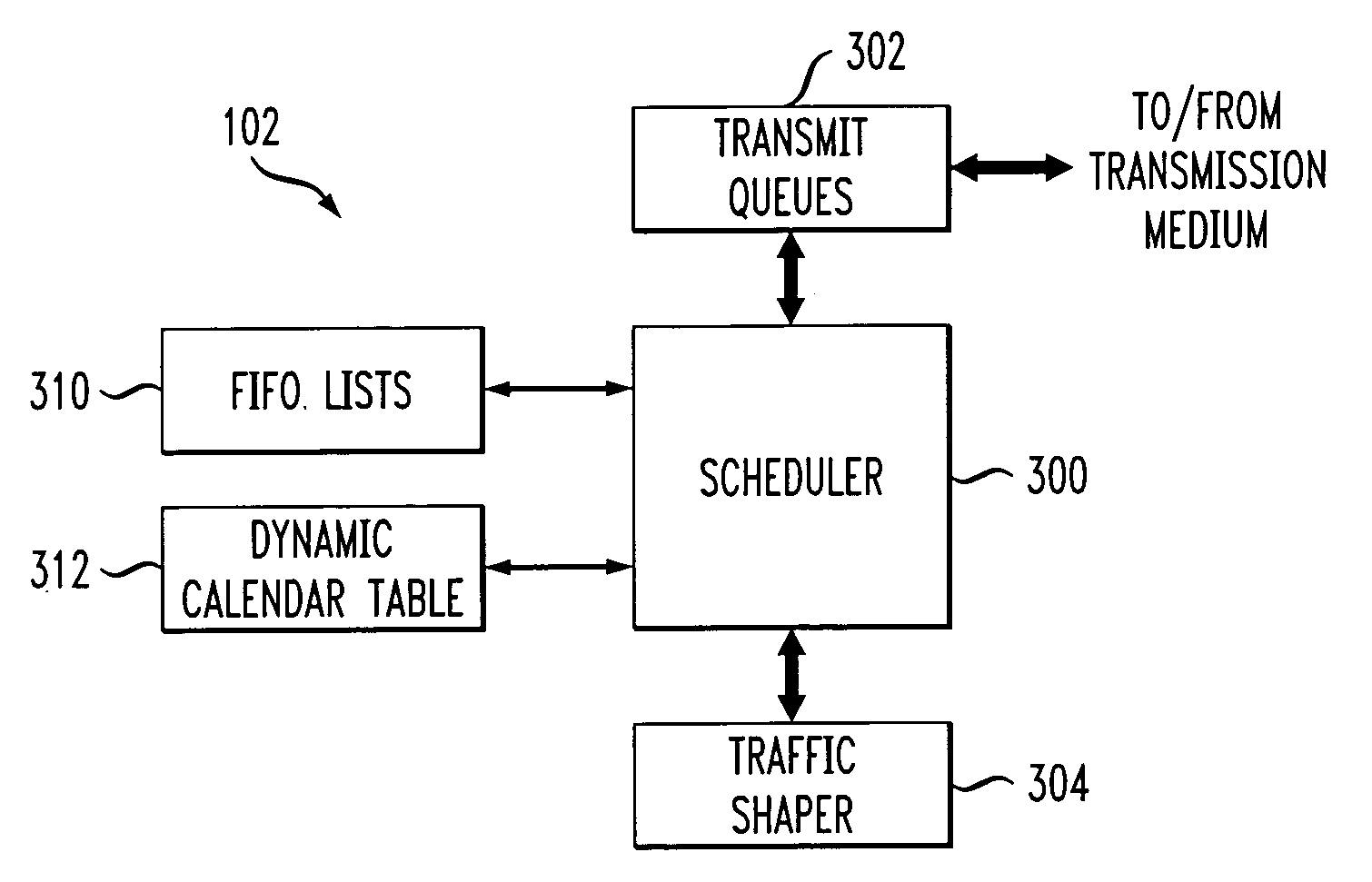
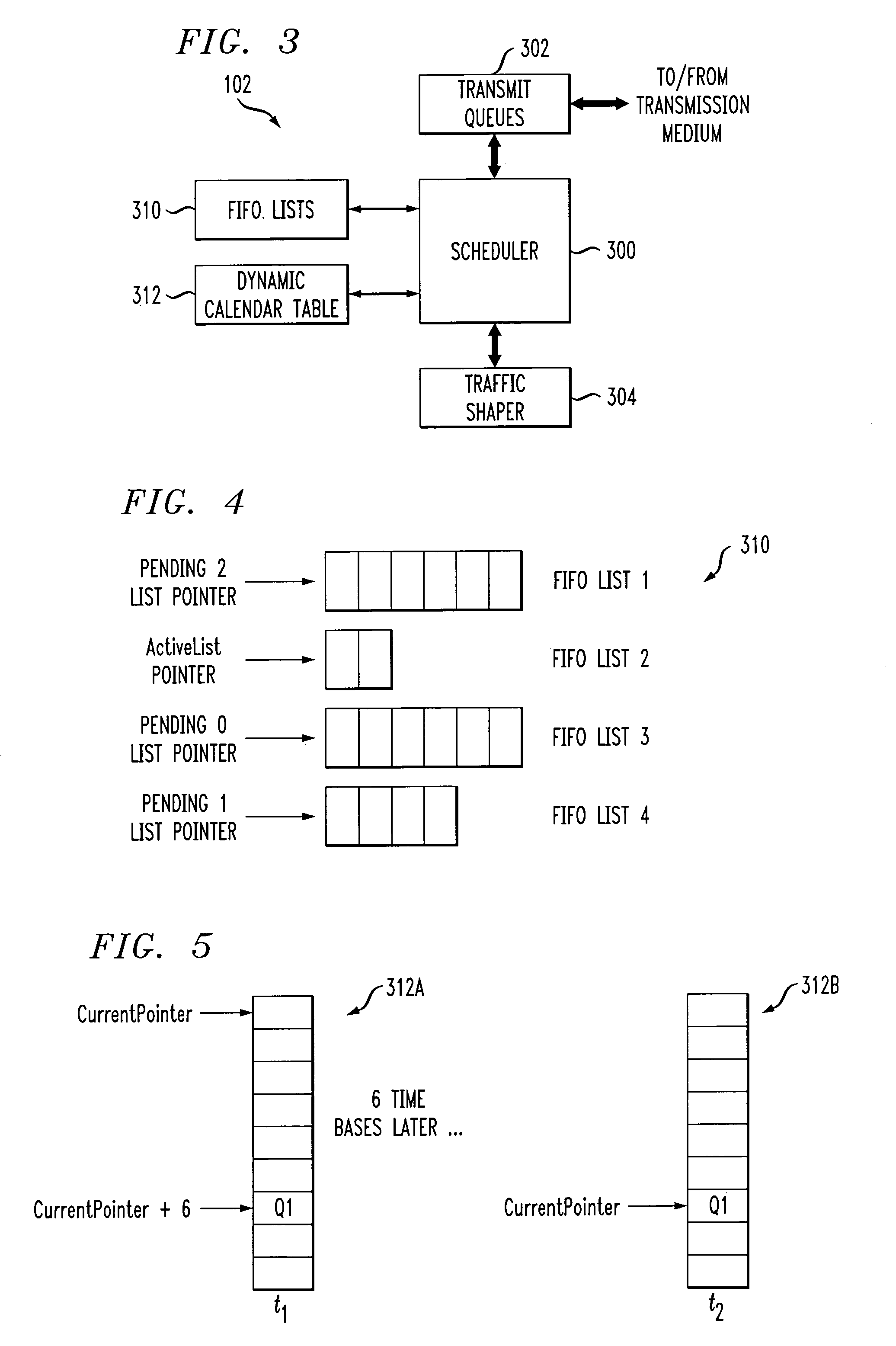
Processor with scheduler architecture supporting multiple distinct scheduling algorithms
InactiveUS20050111461A1Sufficient flexibilityApplication of processData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionFair queuingWeighted fair queueing
A processor includes a scheduler operative to schedule data blocks for transmission from a plurality of queues or other transmission elements, utilizing at least a first table and a second table. The first table may comprise at least first and second first-in first-out (FIFO) lists of entries corresponding to transmission elements for which data blocks are to be scheduled in accordance with a first scheduling algorithm, such as a weighted fair queuing scheduling algorithm. The scheduler maintains a first table pointer identifying at least one of the first and second lists of the first table as having priority over the other of the first and second lists of the first table. The second table includes a plurality of entries corresponding to transmission elements for which data blocks are to be scheduled in accordance with a second scheduling algorithm, such as a constant bit rate or variable bit rate scheduling algorithm. Association of a given one of the transmission elements with a particular one of the second table entries establishes a scheduling rate for that transmission element. The scheduler maintains a second table pointer identifying a current one of the second table entries that is eligible for transmission.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Active queue management toward fair bandwidth allocation
InactiveUS7324442B1Low priorityMinimal implementation overheadError preventionTransmission systemsQueue management systemManagement process
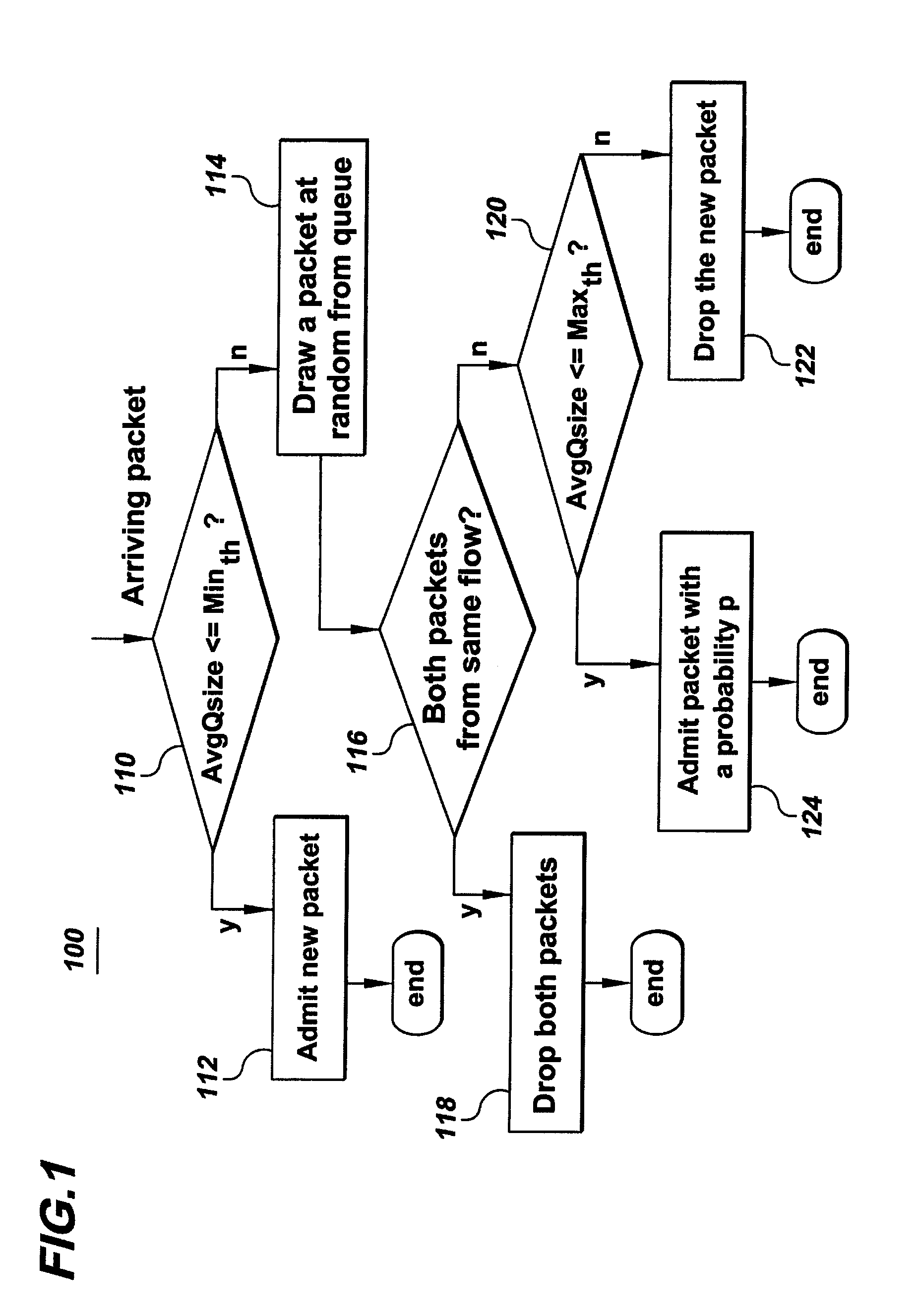
In a packet-queue management system, a bandwidth allocation approach fairly addresses each of n flows that share the outgoing link of an otherwise congested router. According to an example embodiment of the invention, a buffer at the outgoing link is a simple FIFO, shared by packets belonging to the n flows. A packet priority-reduction (e.g., packet dropping) process is used to discriminate against the flows that submit more packets / sec than is allowed by their fair share. This packet management process therefore attempts to approximate a fair queuing policy. The embodiment is advantageously easy to implement and can control unresponsive or misbehaving flows with a minimum overhead.
Owner:SANDFORD UNIV
Apparatus for switching data in high-speed networks and method of operation
ActiveUS7154885B2Fast outputReduce Algorithmic ComplexityMultiplex system selection arrangementsData switching by path configurationStructure of Management InformationFair queuing
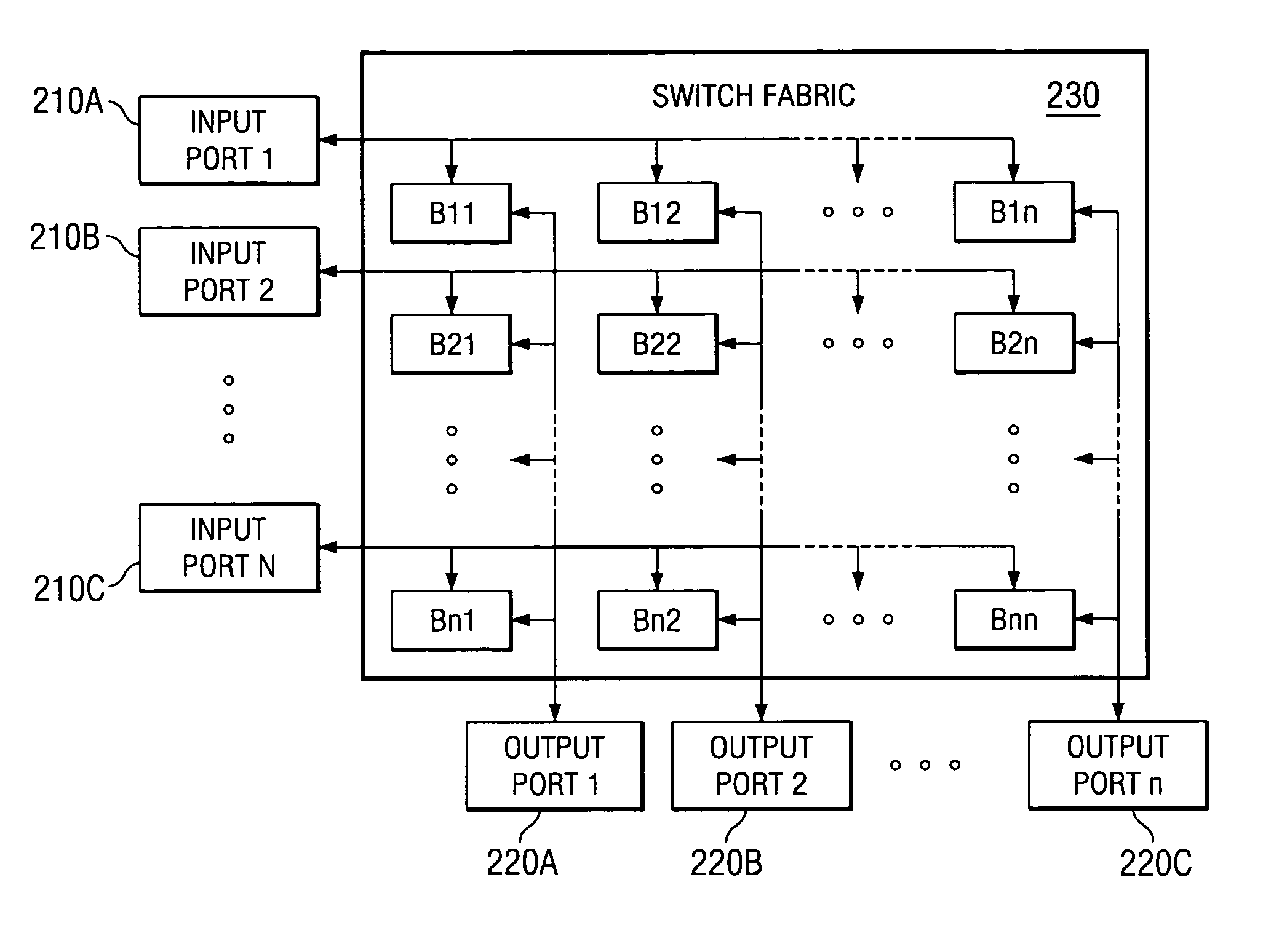
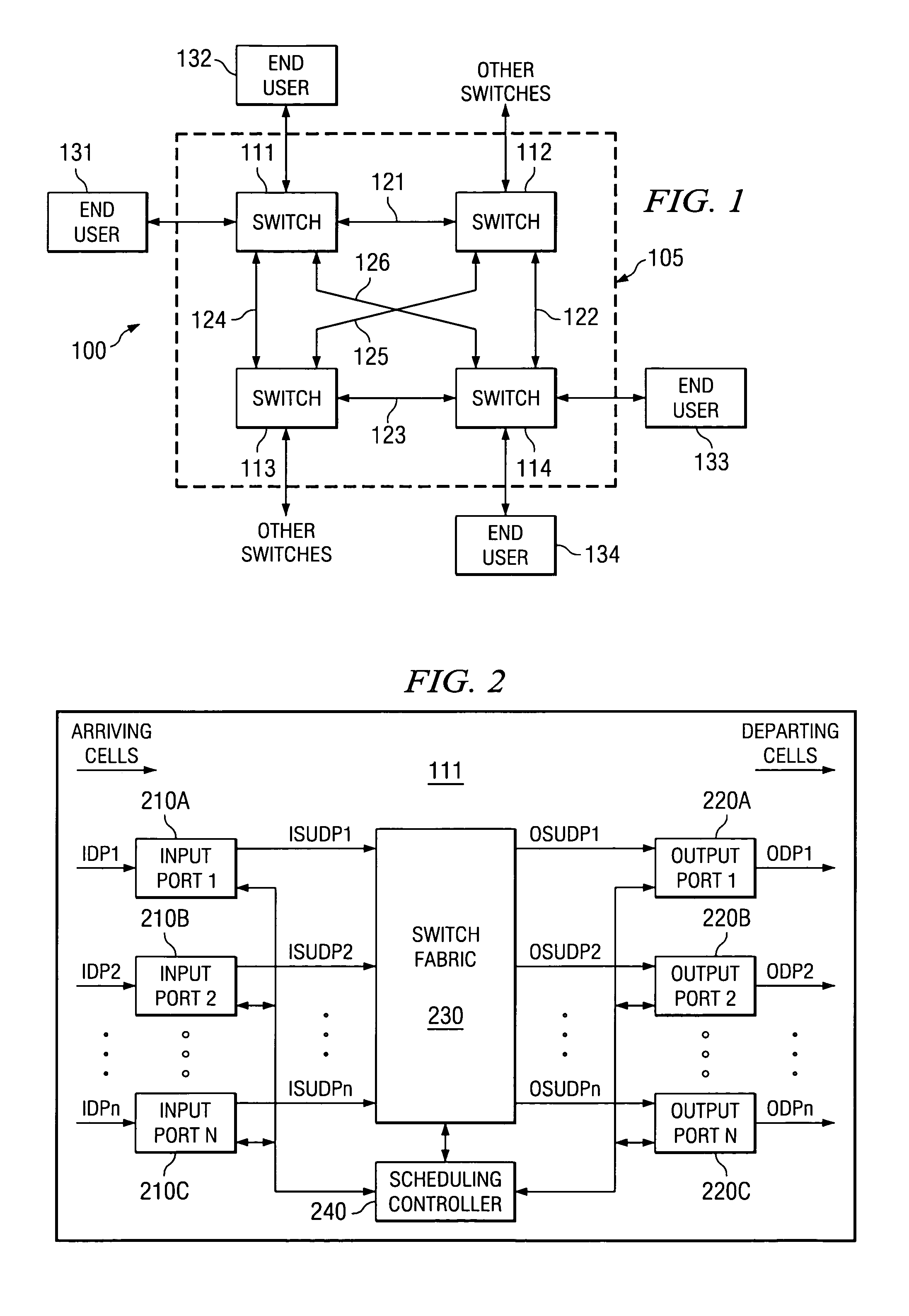
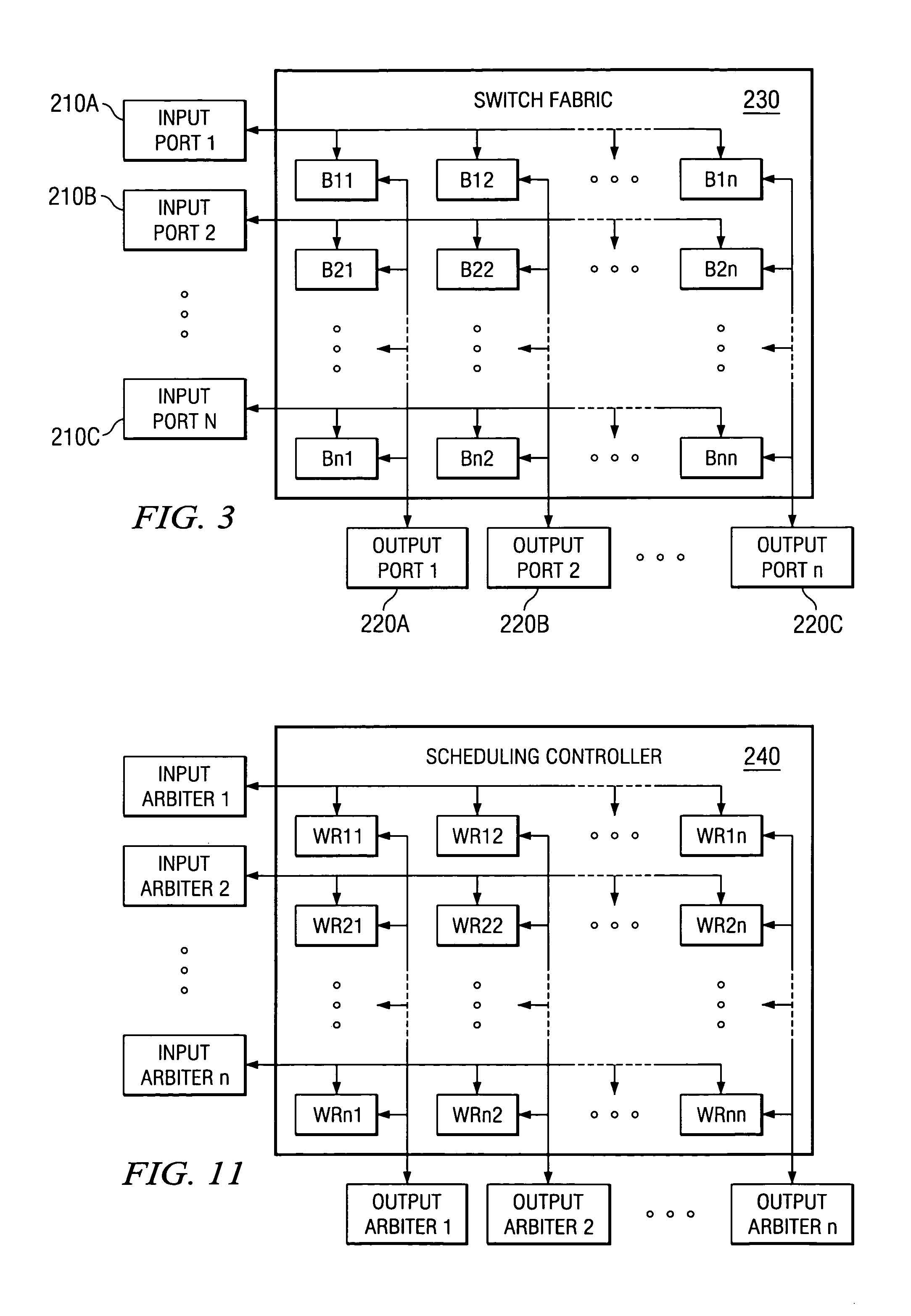
A packet switch for switching cells comprising fixed-size data packets. The packet switch comprises: 1) N input ports for receiving and storing cells in input queues; 2) N output ports for receiving and storing cells from the N input ports in output queues; 3) a switch fabric for transferring the cells from the N input ports to the N output ports, the switch fabric comprising an internally buffered crossbar having N×N internal buffers, wherein each internal buffer is associated with a crosspoint of one of the N input ports and one of the N output ports; and 4) a scheduling controller for selecting a first one of a plurality of queued head-of-line (HOL) cells from the input queues to be transmitted to a first one of the N×N internal buffers according to a fair queuing algorithm in which each of the queued HOL cells is allocated a weight of Rij and wherein the scheduling controller selects a first one of a plurality of HOL cells buffered in a second one of the N×N internal buffers to be transmitted to a first one of the output queues according to a fair queuing algorithm in which each of the internally buffered HOL cells is allocated a weight of Rij.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS LTD
Weighted-fair-queuing relative bandwidth sharing
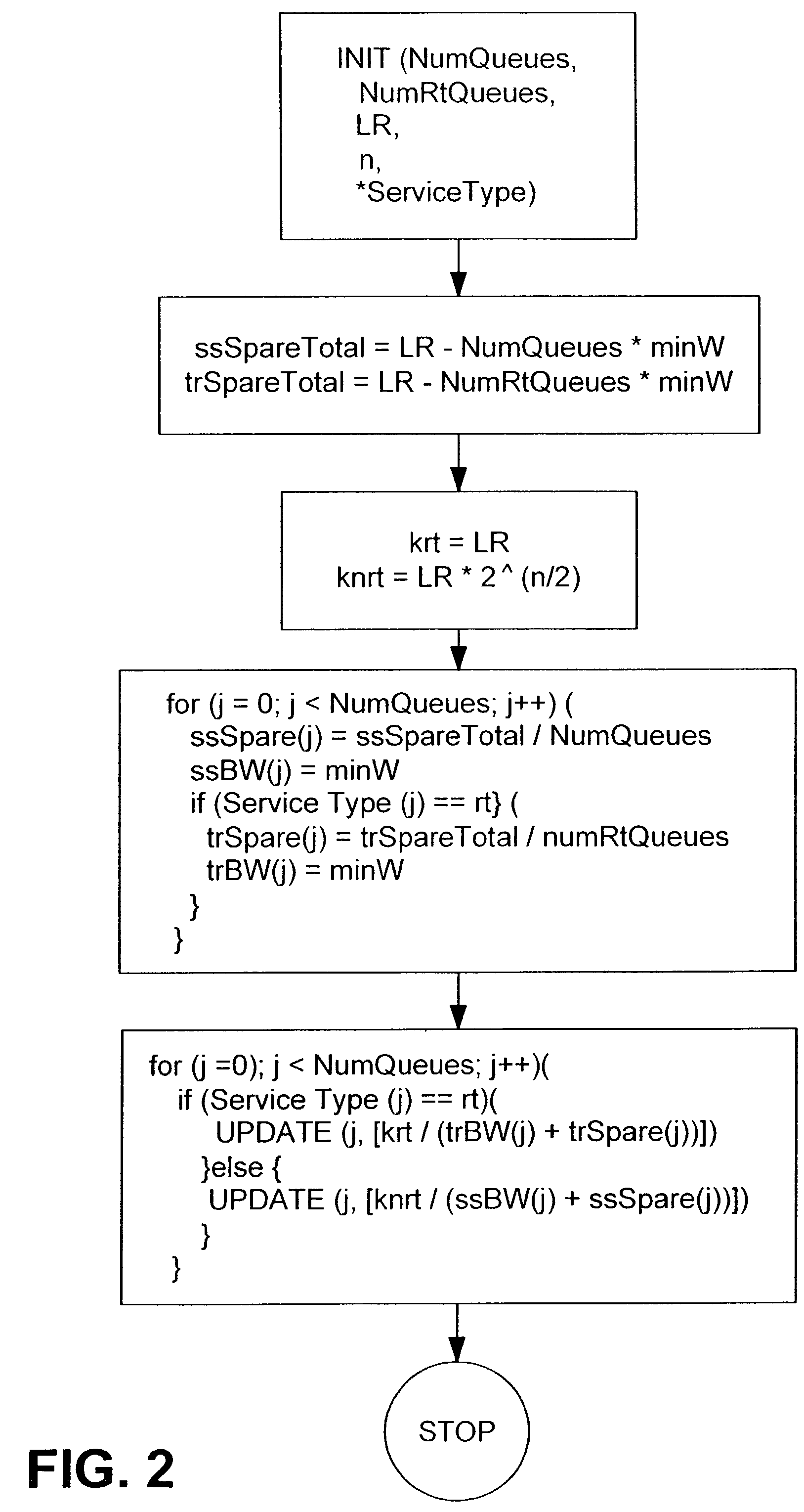
A network device for scheduling packets in a plurality of queues. The network device includes a plurality of configurable mechanisms, each of which is configured to process information in one of a plurality of queues based on a predefined bandwidth. A scheduler services an associated one of the plurality of queues based on the predefined bandwidth. The network device also includes means for tracking whether or not the plurality of queues has exceeded a predefined threshold. If the plurality of queues has exceeded the predefined threshold, a new bandwidth allocation is calculated for each of the plurality of queues. The new bandwidth allocation replaces the predefined bandwidth and is proportional to the predefined bandwidth for each of the plurality of queues.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Packet transmission scheduling in a data communication network
InactiveUS20020126690A1Easy to handleRadio transmissionNetworks interconnectionHeap (data structure)Fair queuing
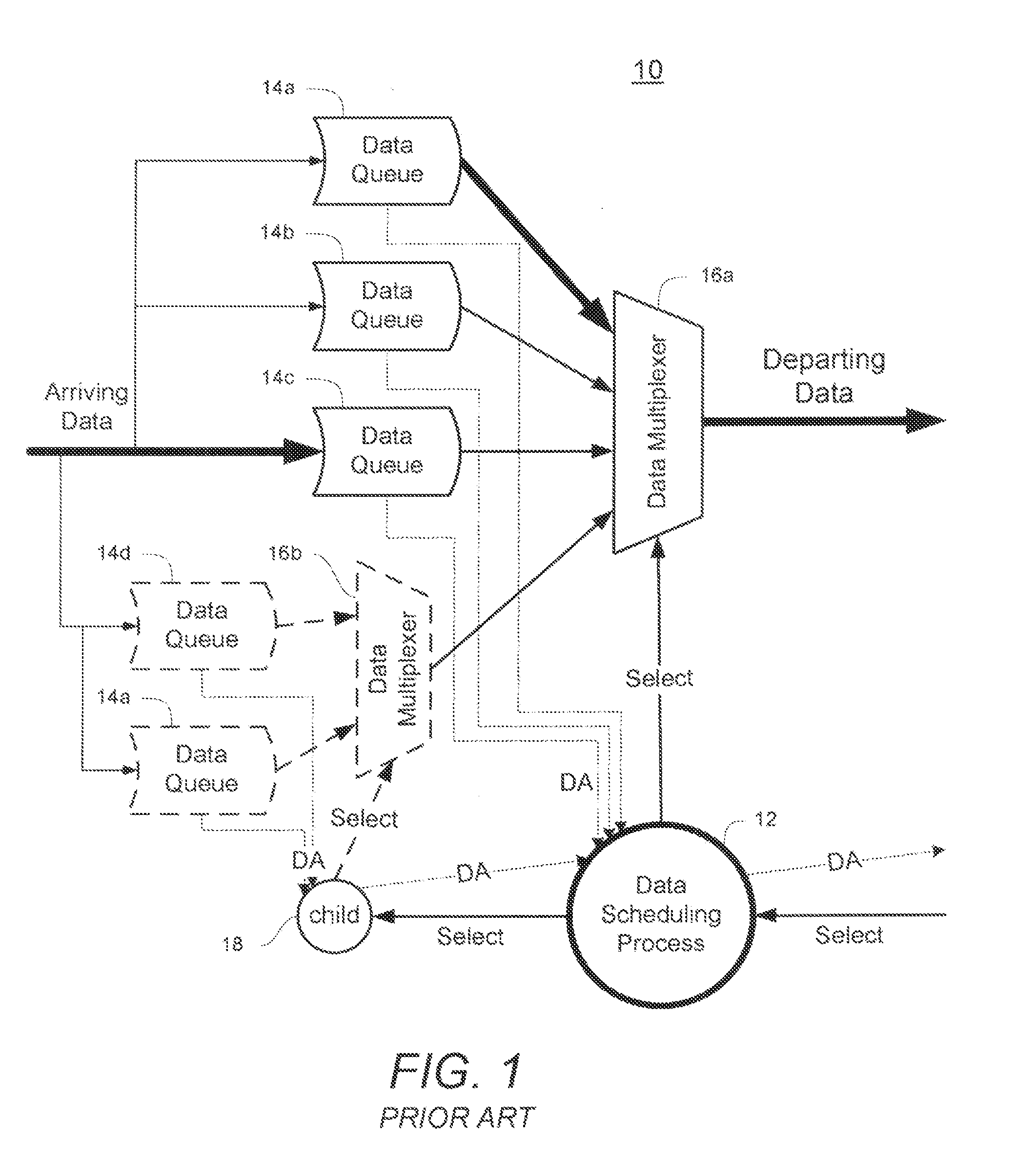
The present invention is directed toward methods and apparatus for packet transmission scheduling in a data communication network. In one aspect, received data packets are assigned to an appropriate one of a plurality of scheduling heap data structures. Each scheduling heap data structure is percolated to identify a most eligible data packet in each heap data structure. A highest-priority one of the most-eligible data packets is identifying by prioritizing among the most-eligible data packets. This is useful because the scheduling tasks may be distributed among the hierarchy of schedulers to efficiently handle data packet scheduling. Another aspect provides a technique for combining priority schemes, such as strict priority and weighted fair queuing. This is useful because packets may have equal priorities or no priorities, such as in the case of certain legacy equipment.
Owner:MAPLE OPTICAL SYST
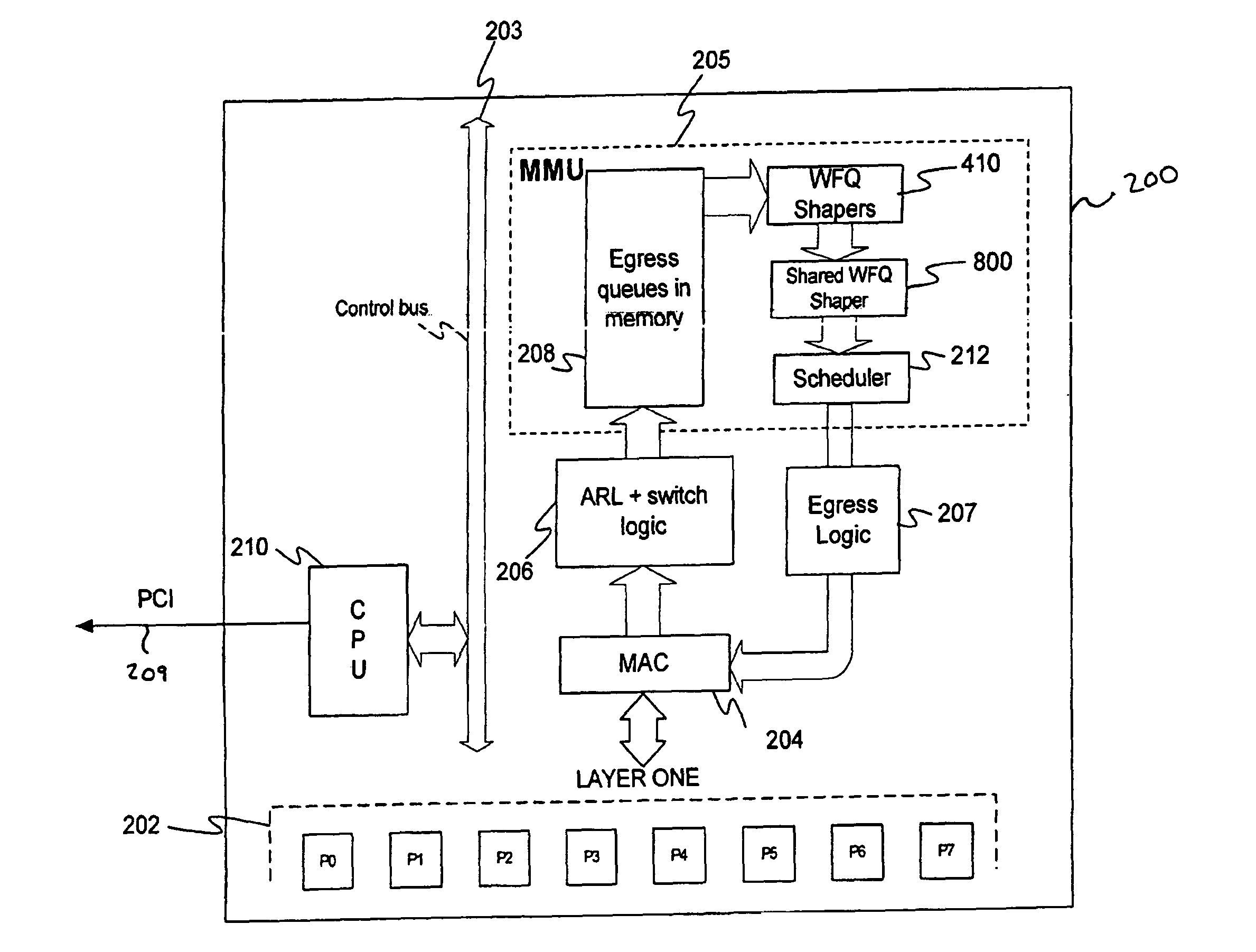
Shared weighted fair queuing (WFQ) shaper
InactiveUS20100302942A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFair queuingWeighted fair queueing
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
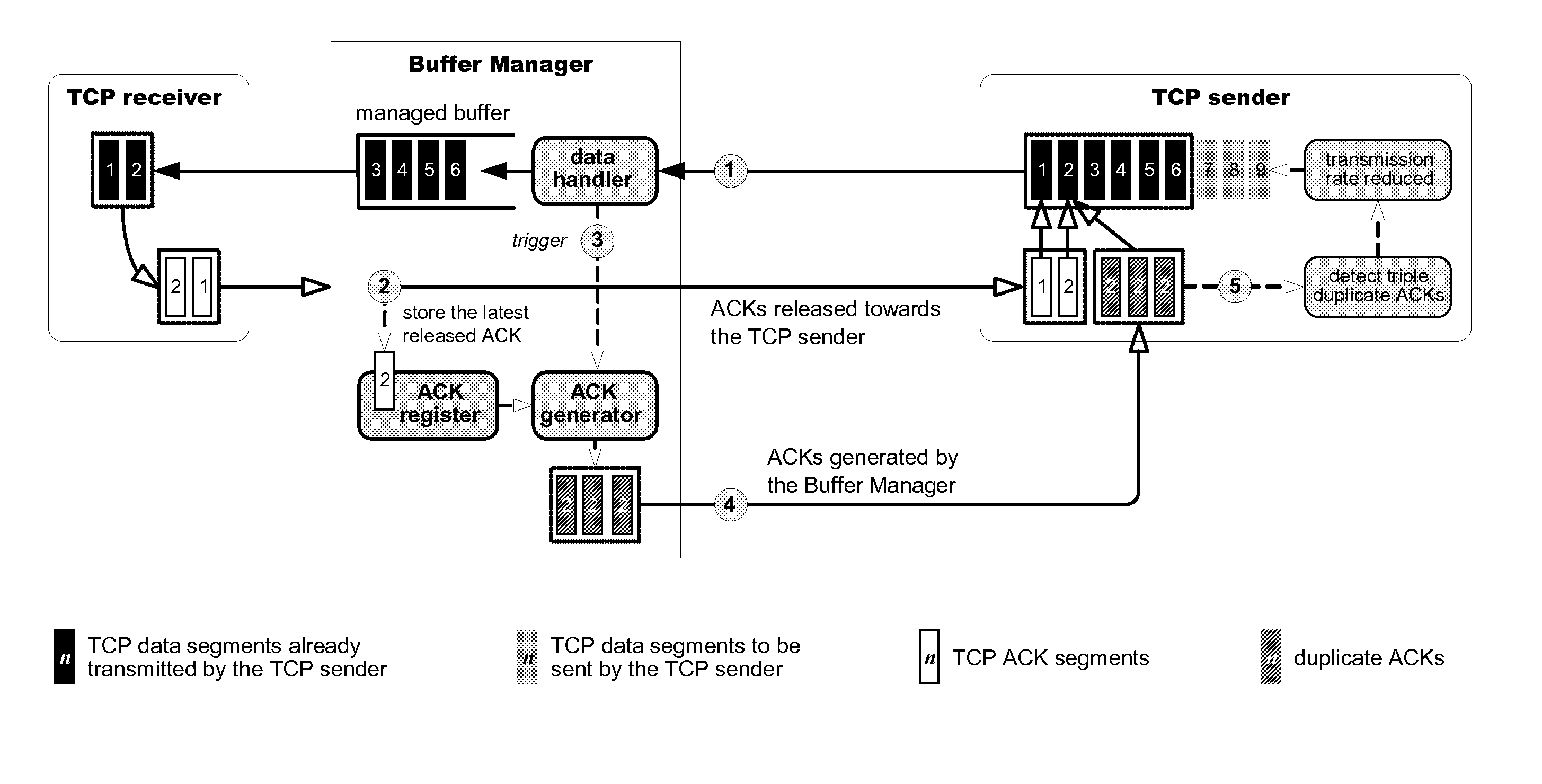
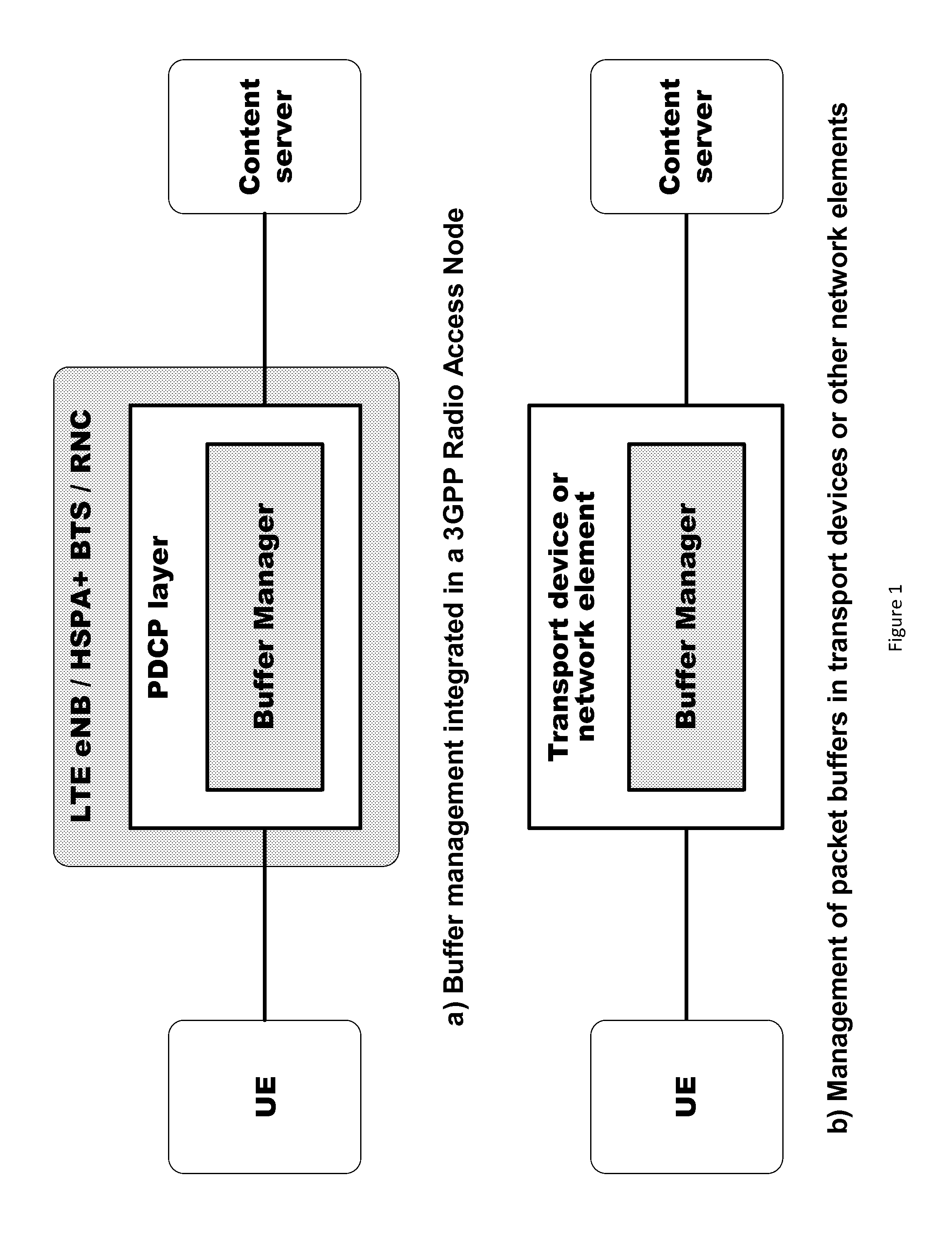
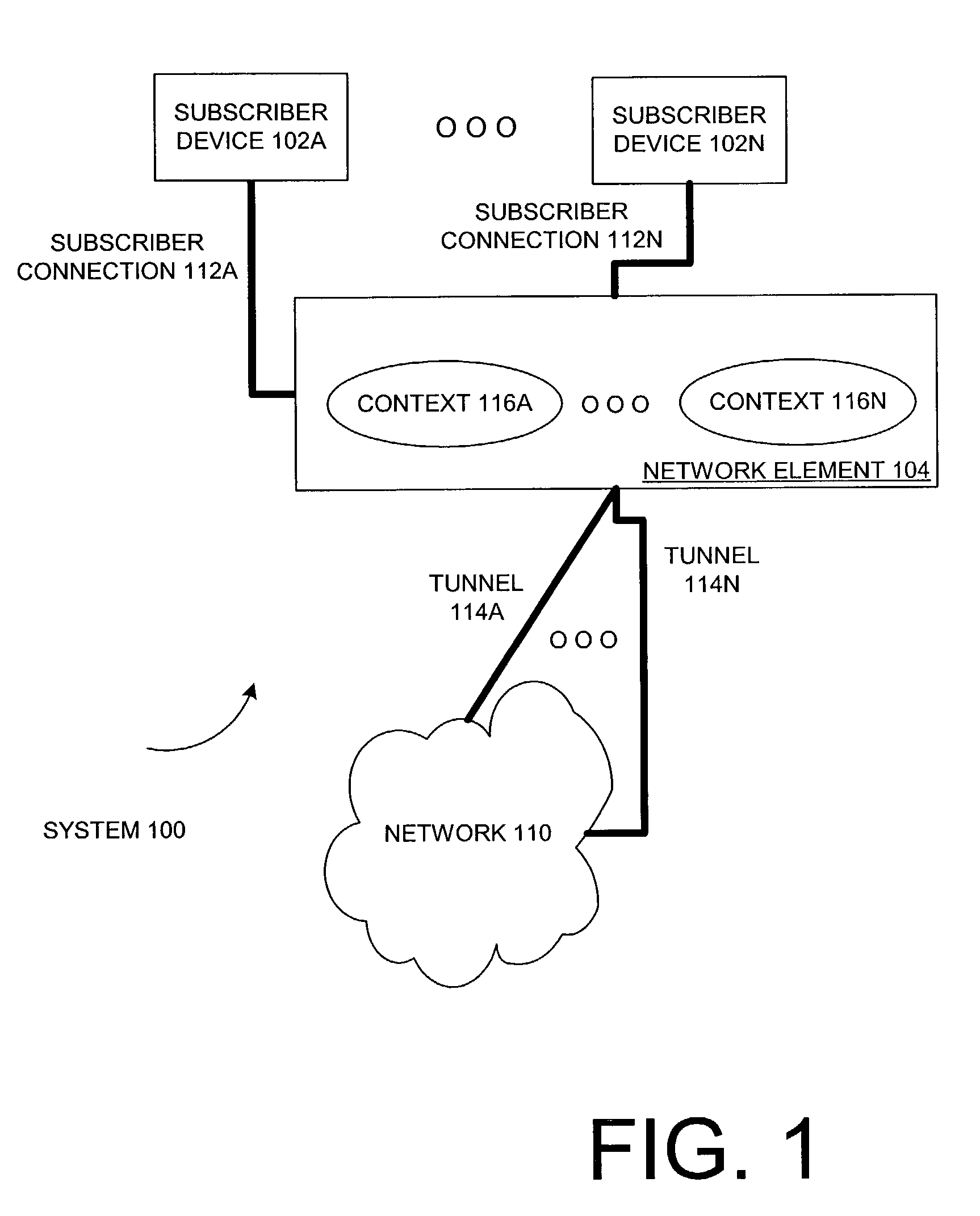
Network-side buffer management
Various communication systems may benefit from buffer management. For example, systems employing a packet data convergence protocol may be enhanced with network-side buffer management that is configured to manipulate transmission control protocol packet senders. A method can include receiving a plurality of packets at a buffer of a buffer manager. The method can also include manipulating, by the buffer manager, pacing of transmission control protocol senders of the packets. The method can further optionally include fair queuing the packets and / or performing flow incubation on the packets.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Method, device and system for realizing addition of traffic shaping token
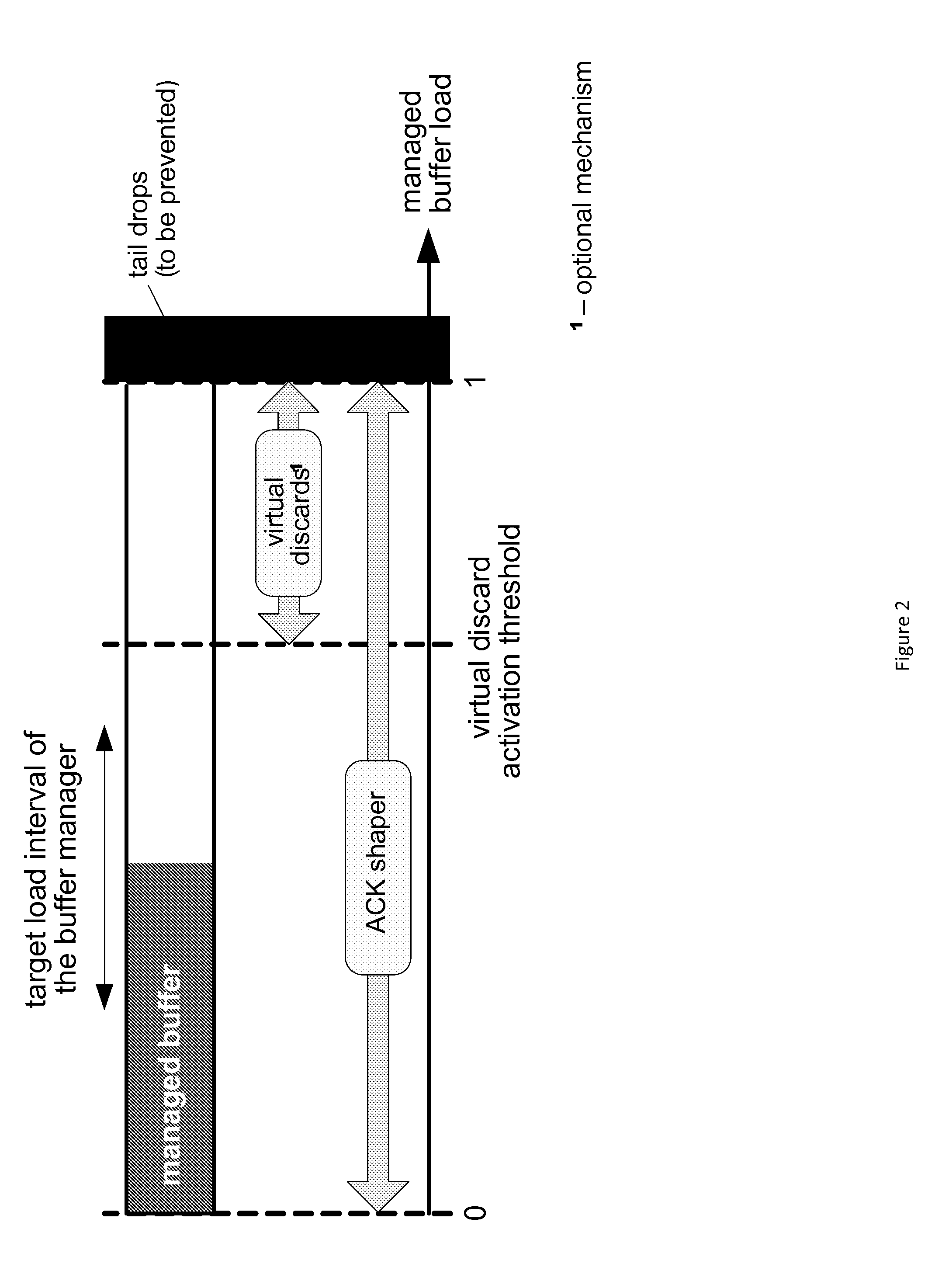
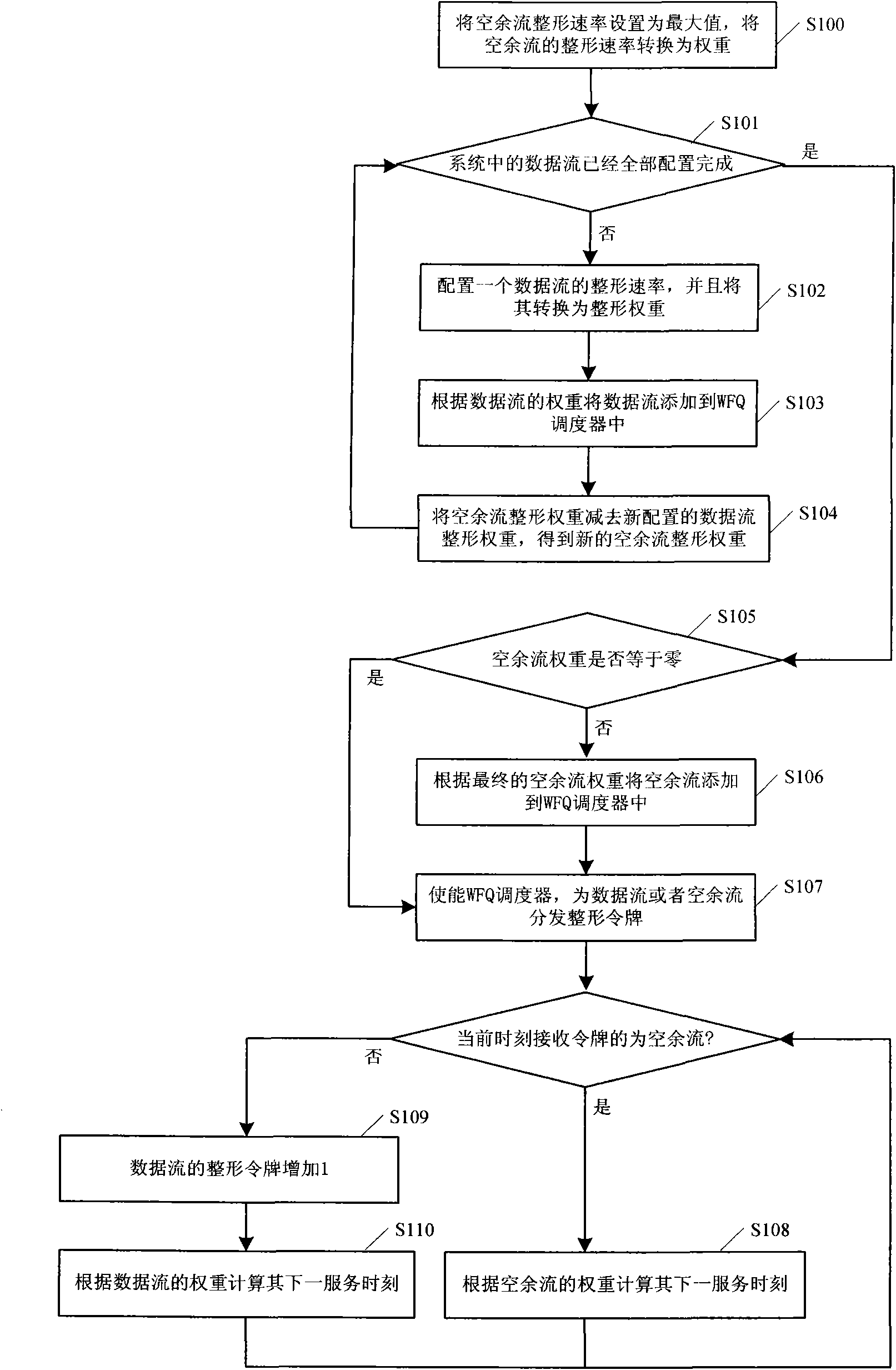
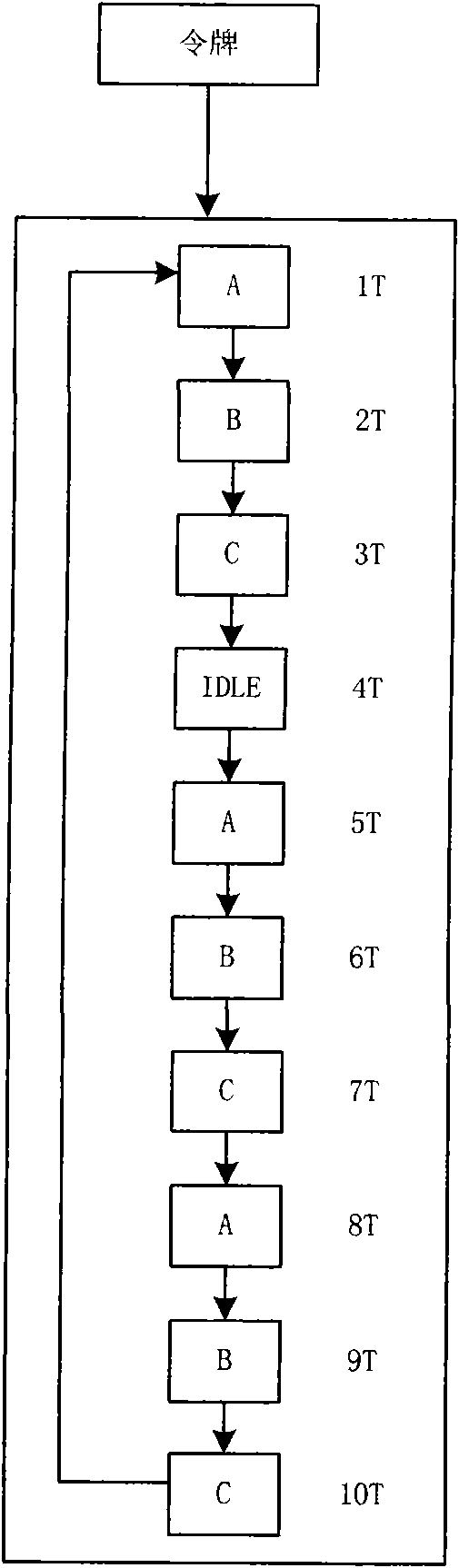
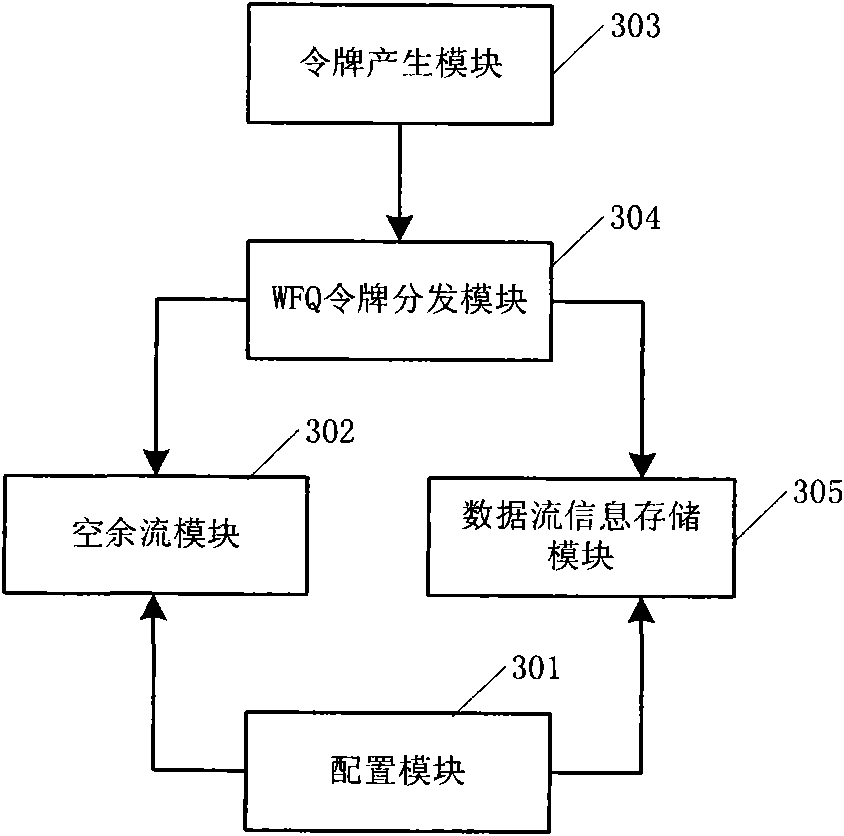
The invention discloses a method for realizing addition of a traffic shaping token, which comprises the following steps: A. allocating a shaping rate to each data stream, converting the shaping rate to a shaping weight, and adding each data stream to a weighted fair queuing (WFQ) token distribution module according to the shaping weight of each data stream; and at the same time of performing step A, calculating the latest idle stream weight; B, according to the idle stream weight, adding the idle stream to the WFQ token distribution module; and C, adding a token to each data stream or idle stream by the WFQ token distribution module according to set intervals. The invention also discloses a corresponding device and a corresponding system. The method, the device and the system add tokens to each data stream and idle stream in a mode of allocating corresponding shaping rates and shaping weights to different data streams so as to realize the shaping of various data streams and achieve good effect.
Owner:ZTE CORP
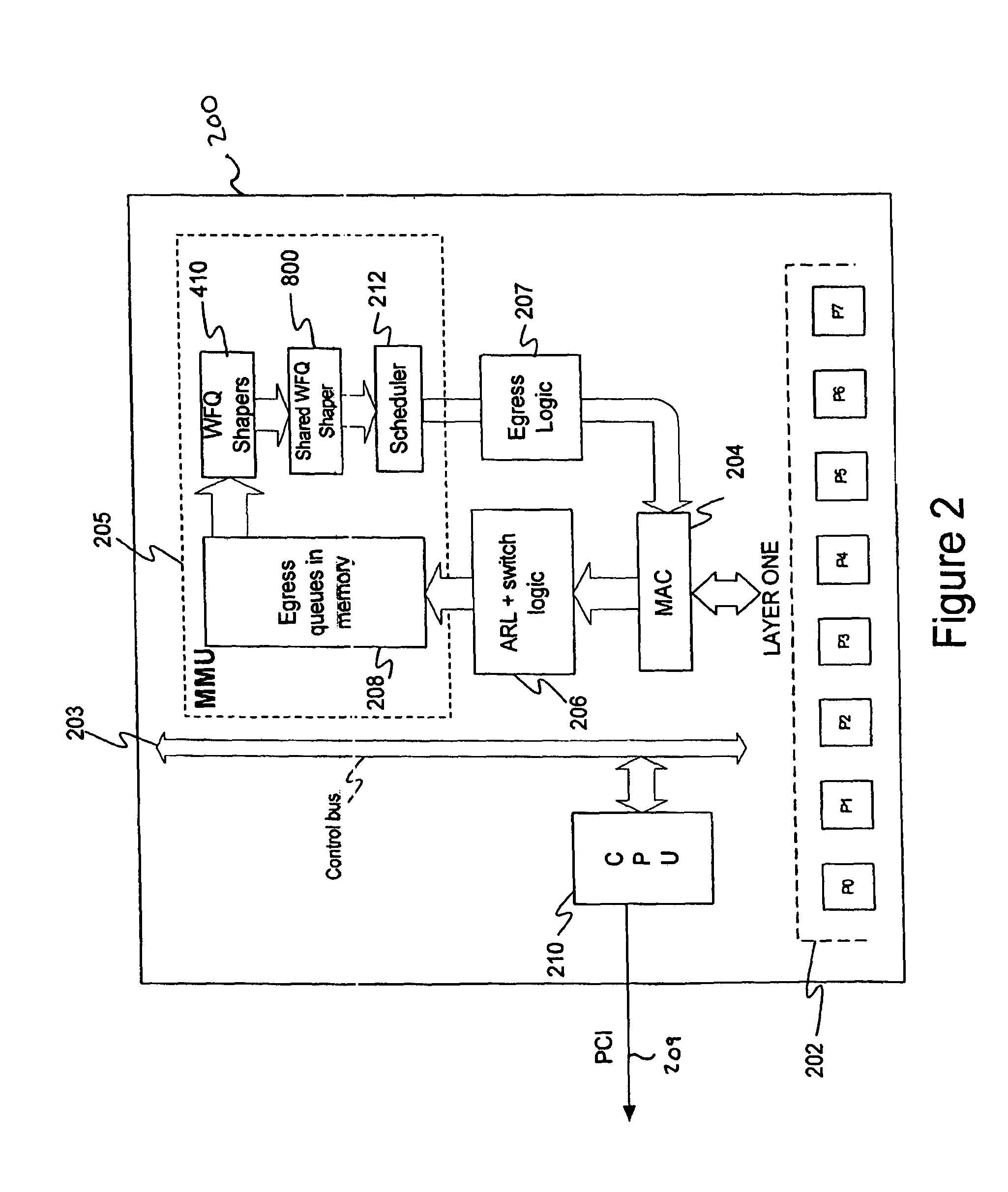
Shared weighted fair queuing (WFQ) shaper
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
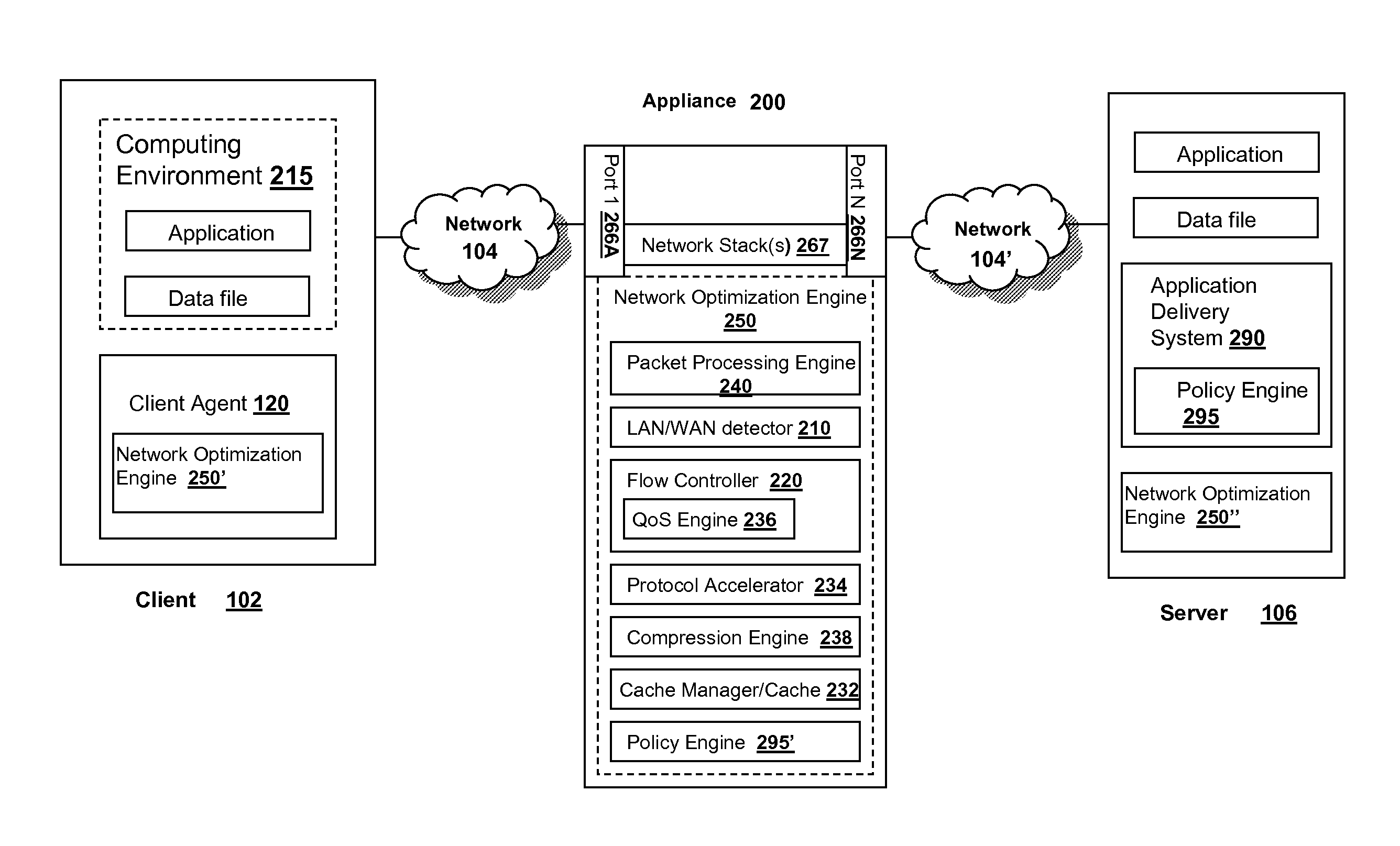
Systems and methods for providing virtual fair queuing of network traffic
ActiveUS20100226247A1Low transfer rateError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityQuality of service
Systems and methods for dynamically controlling bandwidth of connections are described. In some embodiments, a proxy for one or more connections may allocate, distribute, or generate indications of network congestion via one or more connections in order to induce the senders of the connections to reduce their rates of transmission. The proxy may allocate, distribute, or generate these indications in such a way as to provide quality of service to one or more connections, or to ensure that a number of connections transmit within an accepted bandwidth limit. In other embodiments, a sender of a transport layer connection may have a method for determining a response to congestion indications which accounts for a priority of the connection. In these embodiments, a sender may reduce or increase parameters related to transmission rate at different rates according to a priority of the connection.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method and system for network processor scheduling based on service levels
InactiveUS7123622B2Easy to useMinimal overheadError preventionTransmission systemsMaximum burst sizeComing out
A system and method of moving information units from an output flow control toward a data transmission network in a prioritized sequence which accommodates several different levels of service. The present invention includes a method and system for scheduling the egress of processed information units (or frames) from a network processing unit according to service based on a weighted fair queue where position in the queue is adjusted after each service based on a weight factor and the length of frame, a process which provides a method for and system of interaction between different calendar types is used to provide minimum bandwidth, best effort bandwidth, weighted fair queuing service, best effort peak bandwidth, and maximum burst size specifications. The present invention permits different combinations of service that can be used to create different QoS specifications. The “base” services which are offered to a customer in the example described in this patent application are minimum bandwidth, best effort, peak and maximum burst size (or MBS), which may be combined as desired. For example, a user could specify minimum bandwidth plus best effort additional bandwidth and the system would provide this capability by putting the flow queue in both the NLS and WFQ calendar. The system includes tests when a flow queue is in multiple calendars to determine when it must come out.
Owner:IBM CORP
Quality of service packet scheduler design
ActiveUS20130343194A1Error preventionTransmission systemsCommitted information rateLatency (engineering)
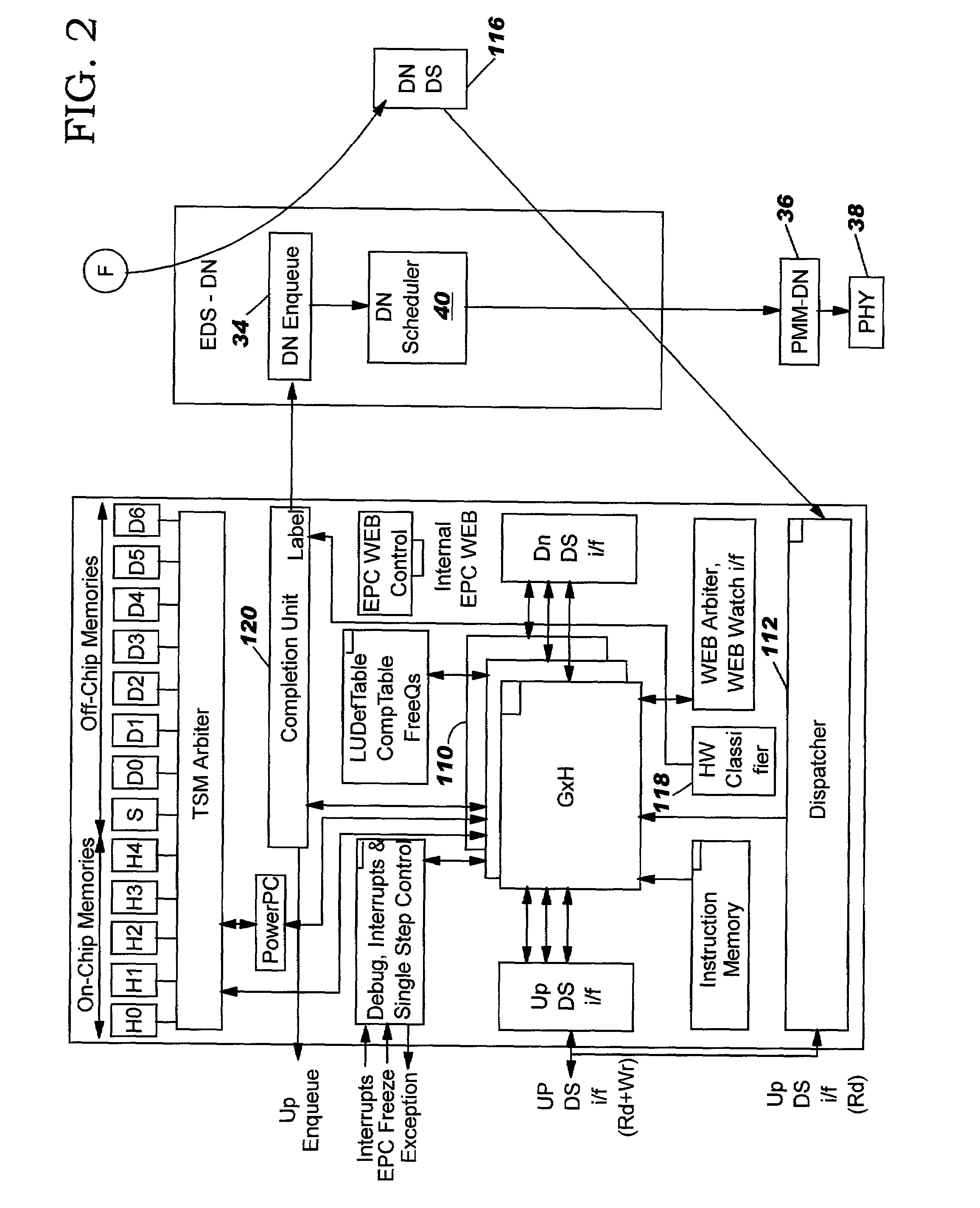
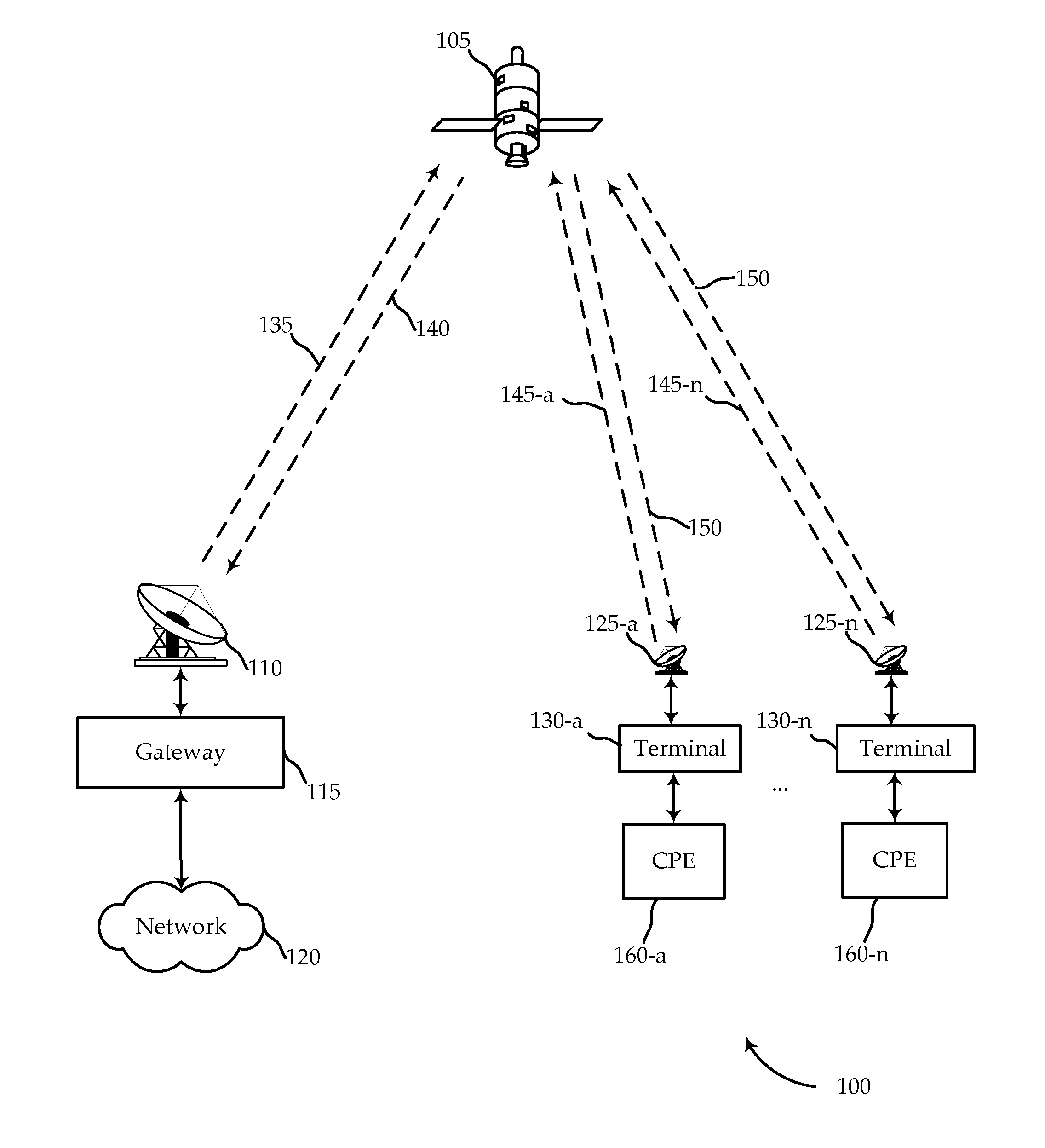
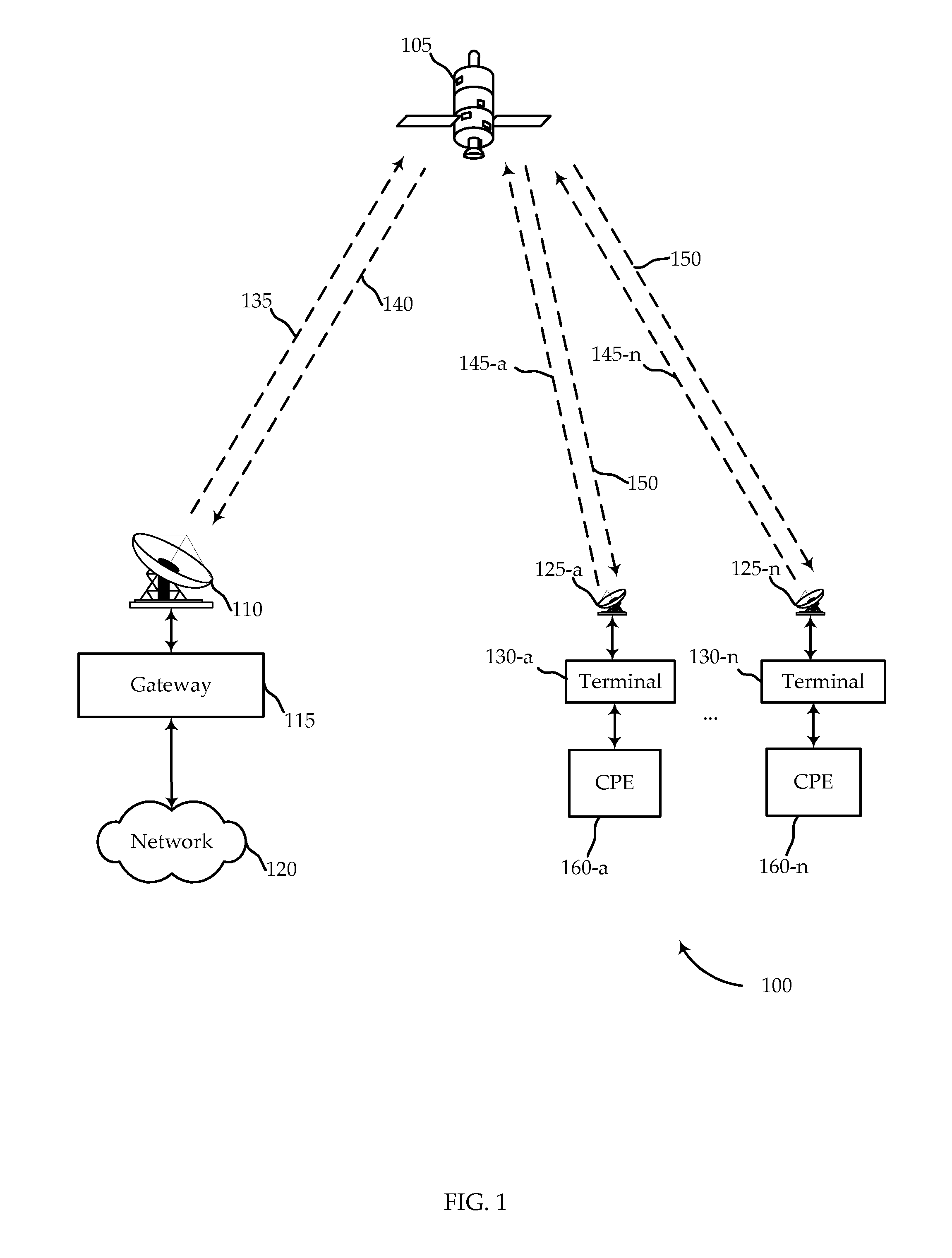
Systems, methods, devices, and processors are described for quality of service (QoS) packet scheduling in satellite communications systems. A packet received at the QoS packet scheduler may be assigned a virtual departure time utilizing novel self-clocked fair queuing techniques. The virtual departure time for a packet assigned to a queue may depend on a different weight assigned to the queues. Queues may be treated as low latency queues in some cases and may be provided with committed information rates in other cases. Low latency queues may be assigned weights equal to infinity, or the reciprocal of the weight equal to zero. Queues with committed information rates may assign different weights to packets depending on whether the rate that packets are received exceeds the committed information rate. Packets may then be scheduled based on their virtual departure time order.
Owner:VIASAT INC
Bandwidth sharing using emulated weighted fair queuing
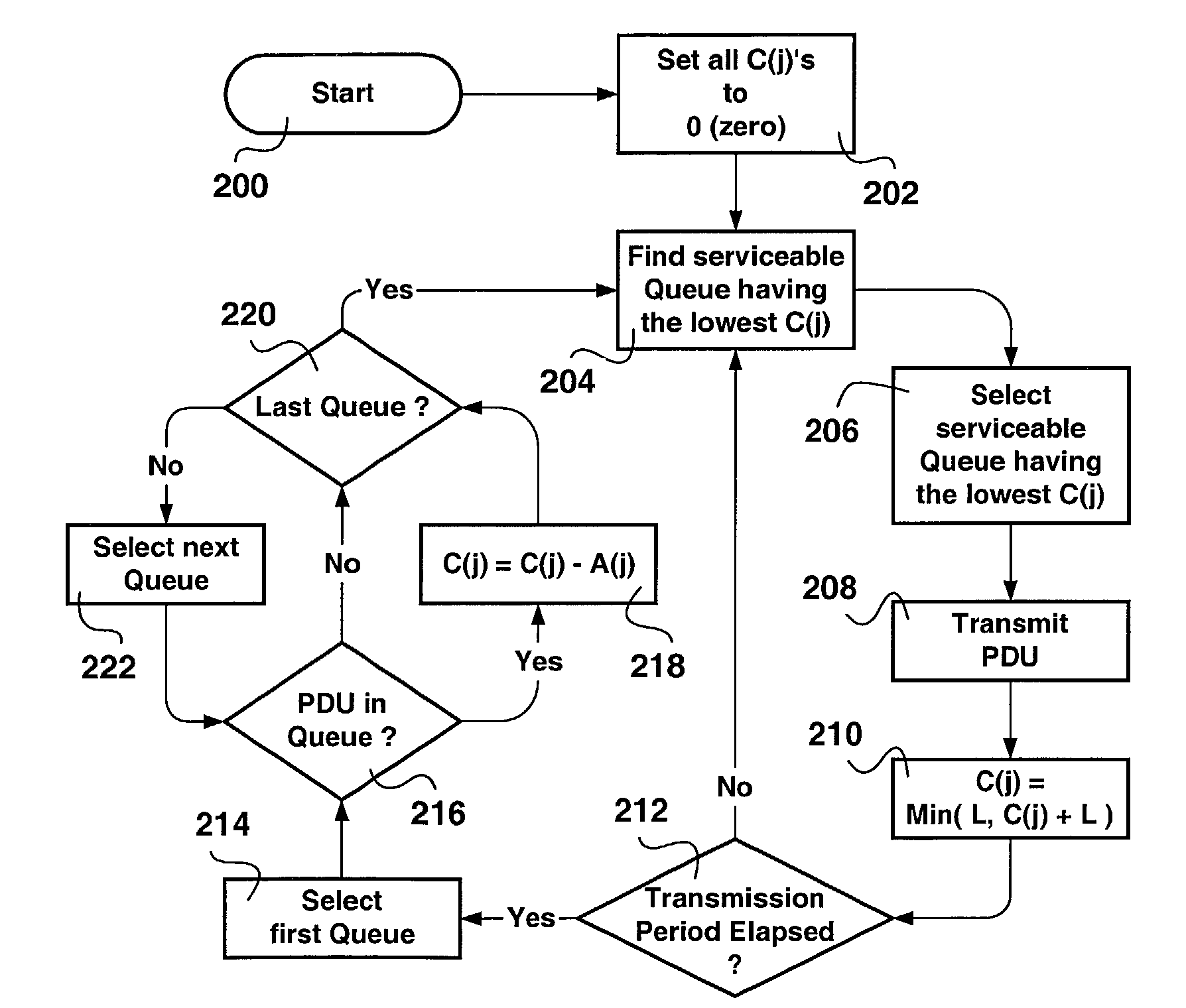
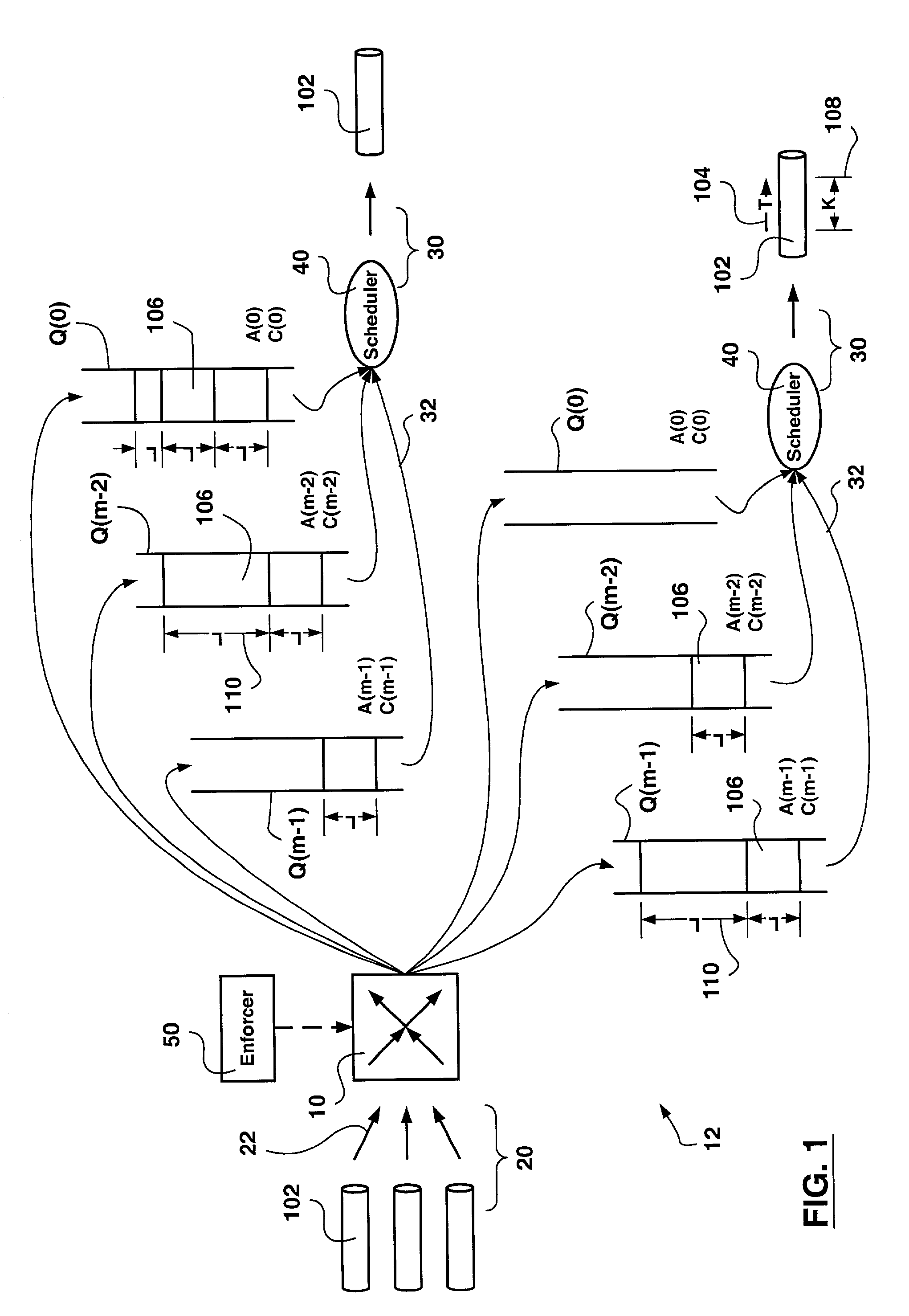
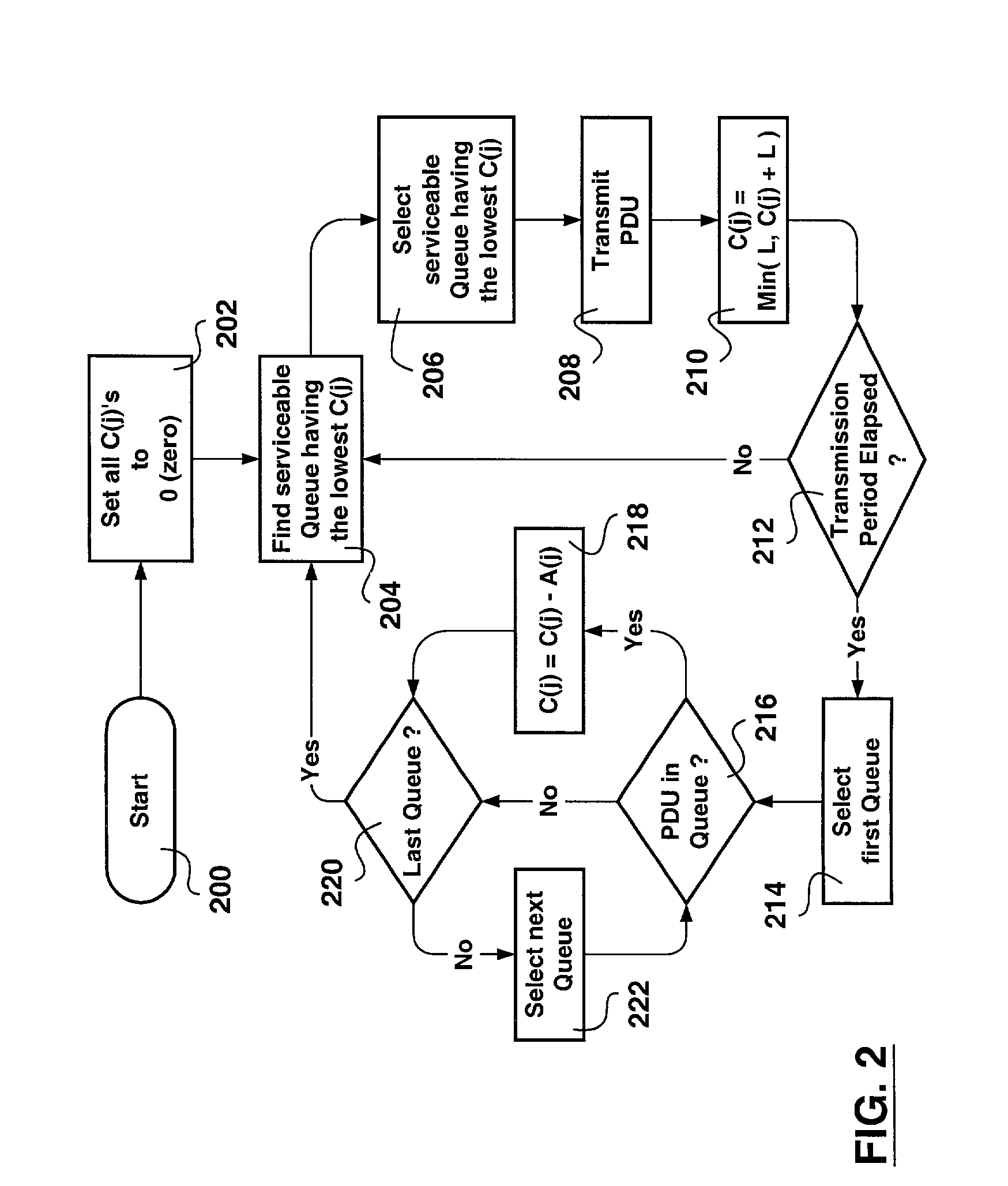
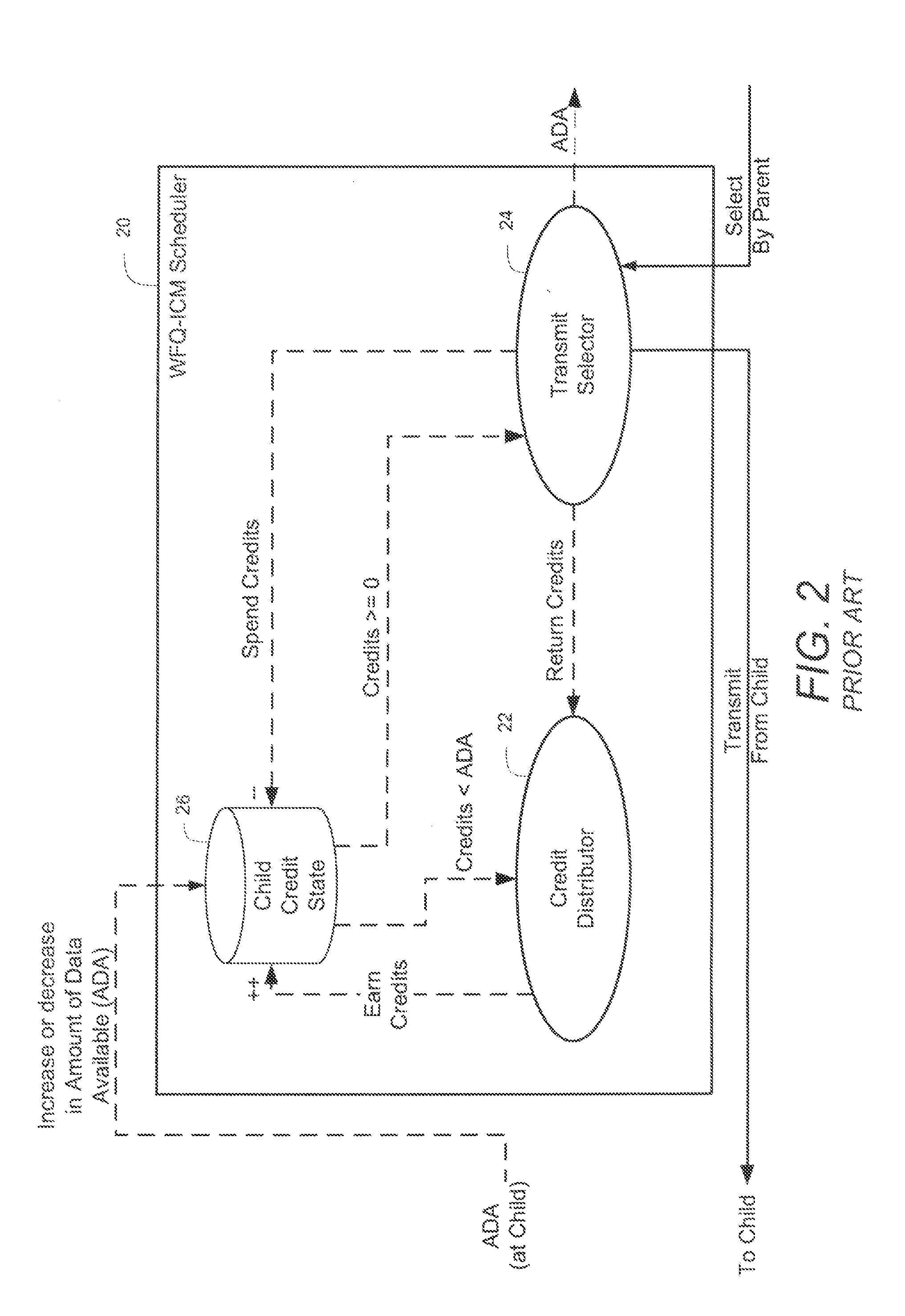
A method of scheduling queue servicing in a data packet switching environment is provided. The method includes a sequence of cyclical steps. The output queues are scheduled for servicing on a least credit value basis. An output queue is selected from a group of output queues associated with a communications port. The selected output port has at least one Payload Data Unit (PDU) pending transmission and a lowest credit value associated therewith. At least one PDU having a length is transmitted from the selected output queue and the credit value is incremented taking the length of the transmitted PDU into consideration. The transmission of PDUs is divided into transmission periods. Once per transmission period credit values associated with output queues holding PDUs pending transmission are decremented in accordance with transmission apportionments assigned for each output queue. The method emulates weighted fair queue servicing with minimal computation enabling hardware implementation thereof.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Weighted fair queue having extended effective range
InactiveUS7187684B2High resolutionIncrease rangeError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsExtended coverageImage resolution
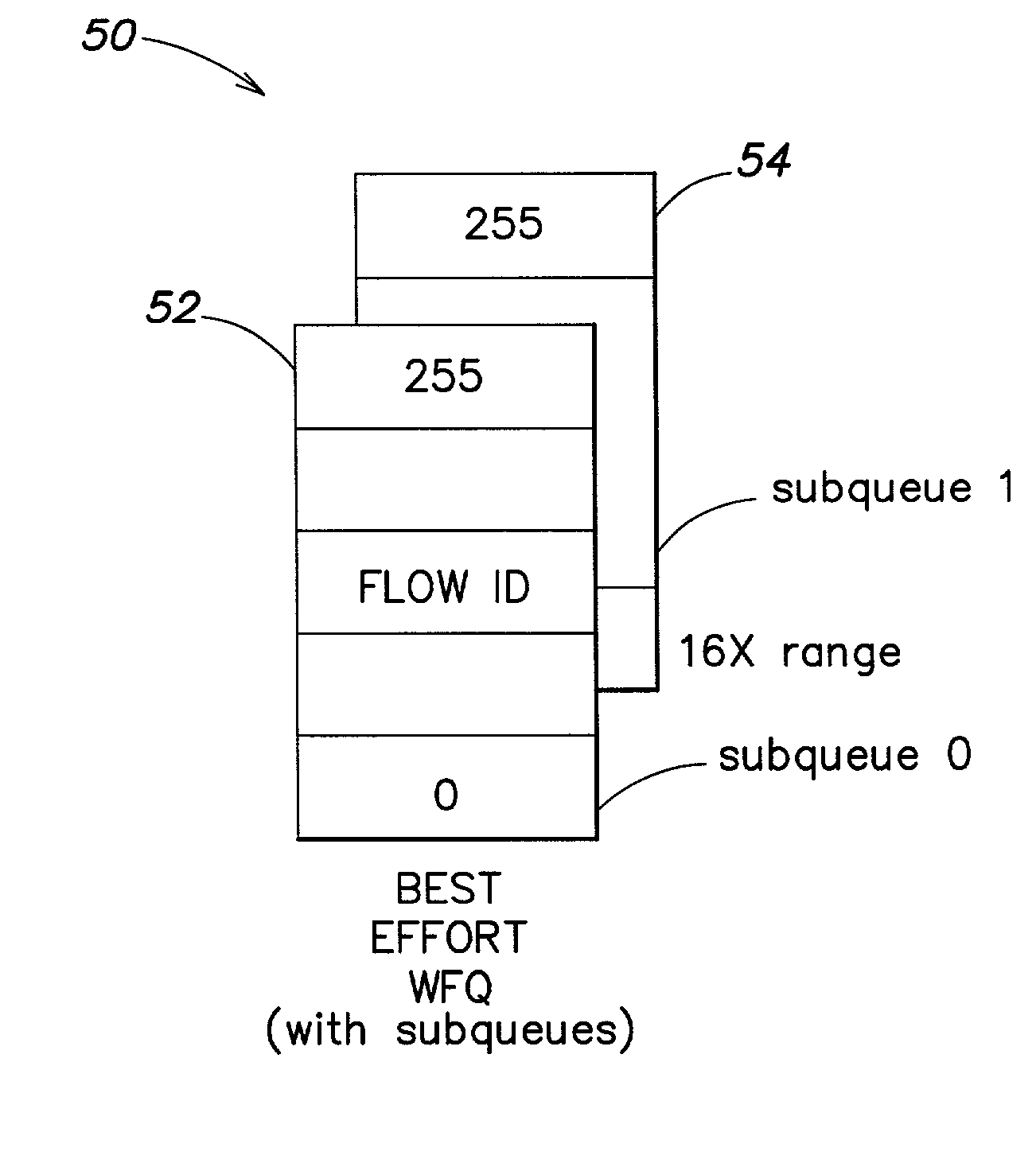
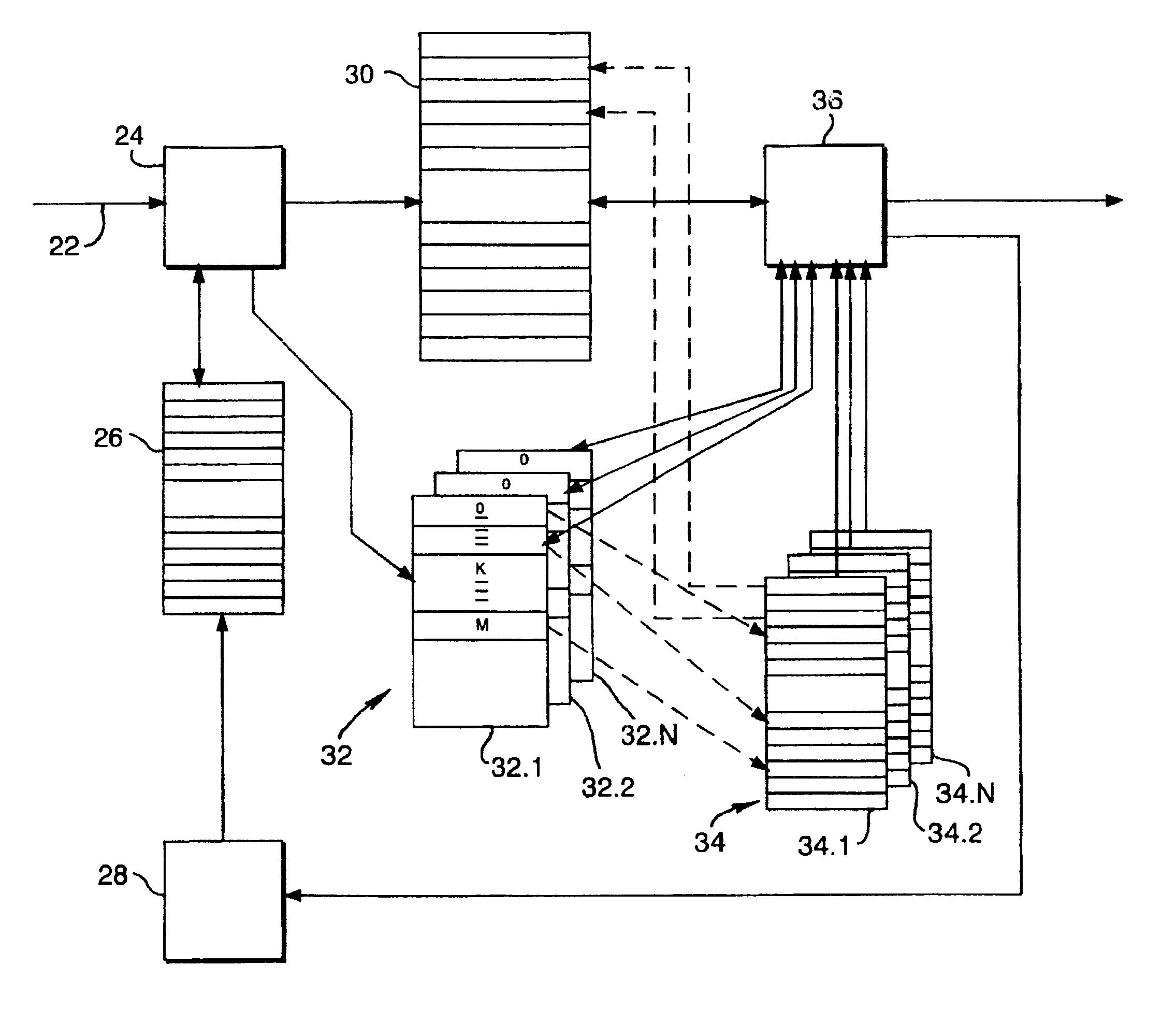
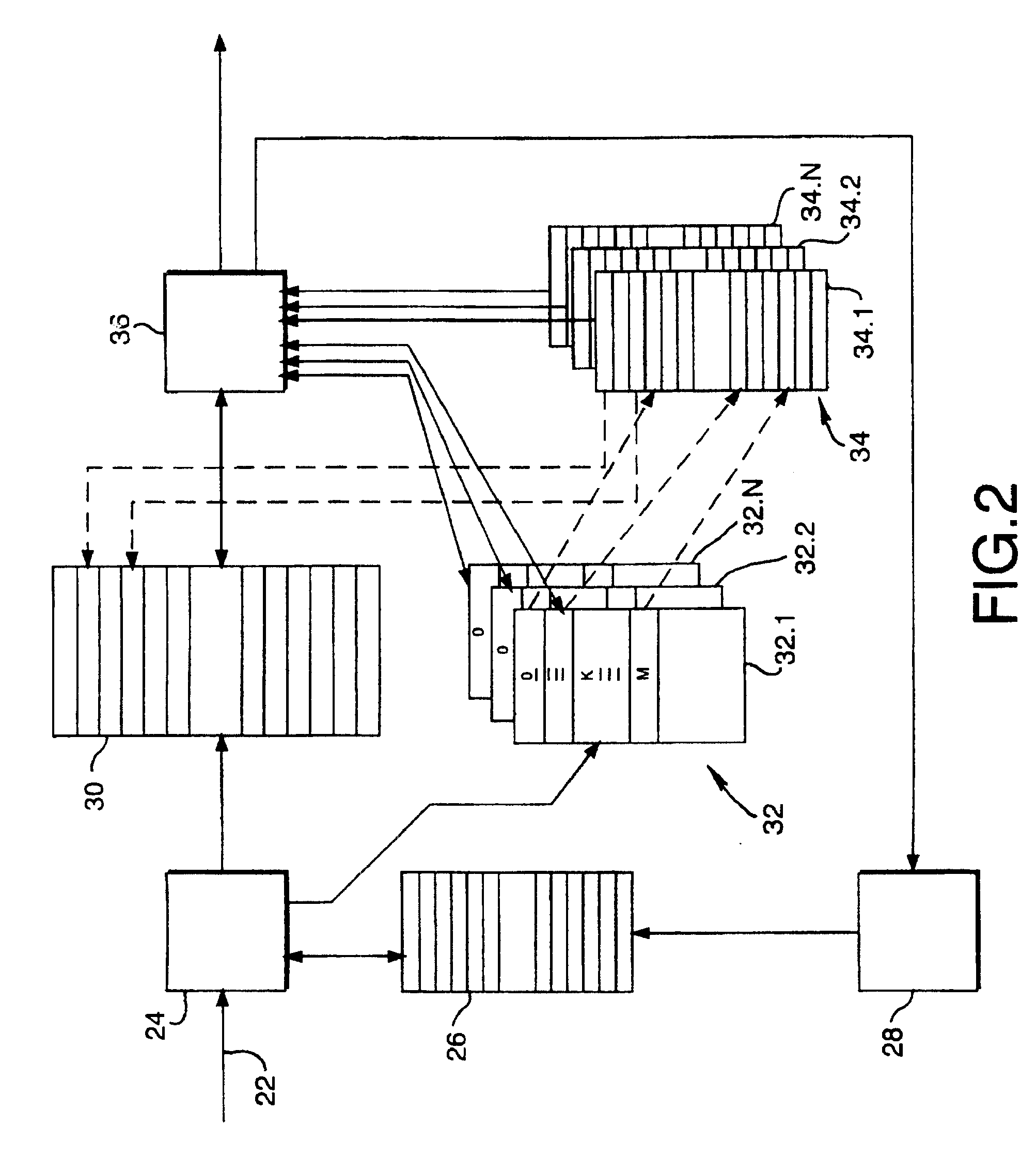
A scheduler for a network processor includes a scheduling queue in which weighted fair queuing is applied to define a sequence in which flows are to be serviced. The scheduling queue includes at least a first subqueue and a second subqueue. The first subqueue has a first range and a first resolution, and the second subqueue has an extended range that is greater than the first range and a lower resolution that is less than the first resolution. Flows that are to be enqueued within the range of highest precision to the current pointer of the scheduling queue are attached to the first subqueue. Flows that are to be enqueued outside the range of highest precision from the current pointer of the scheduling queue are attached to the second subqueue. Numerous other aspects are provided.
Owner:IBM CORP
Priority-based efficient fair queuing for quality of service classification for packet processing
InactiveUS7283472B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of serviceFair queuing
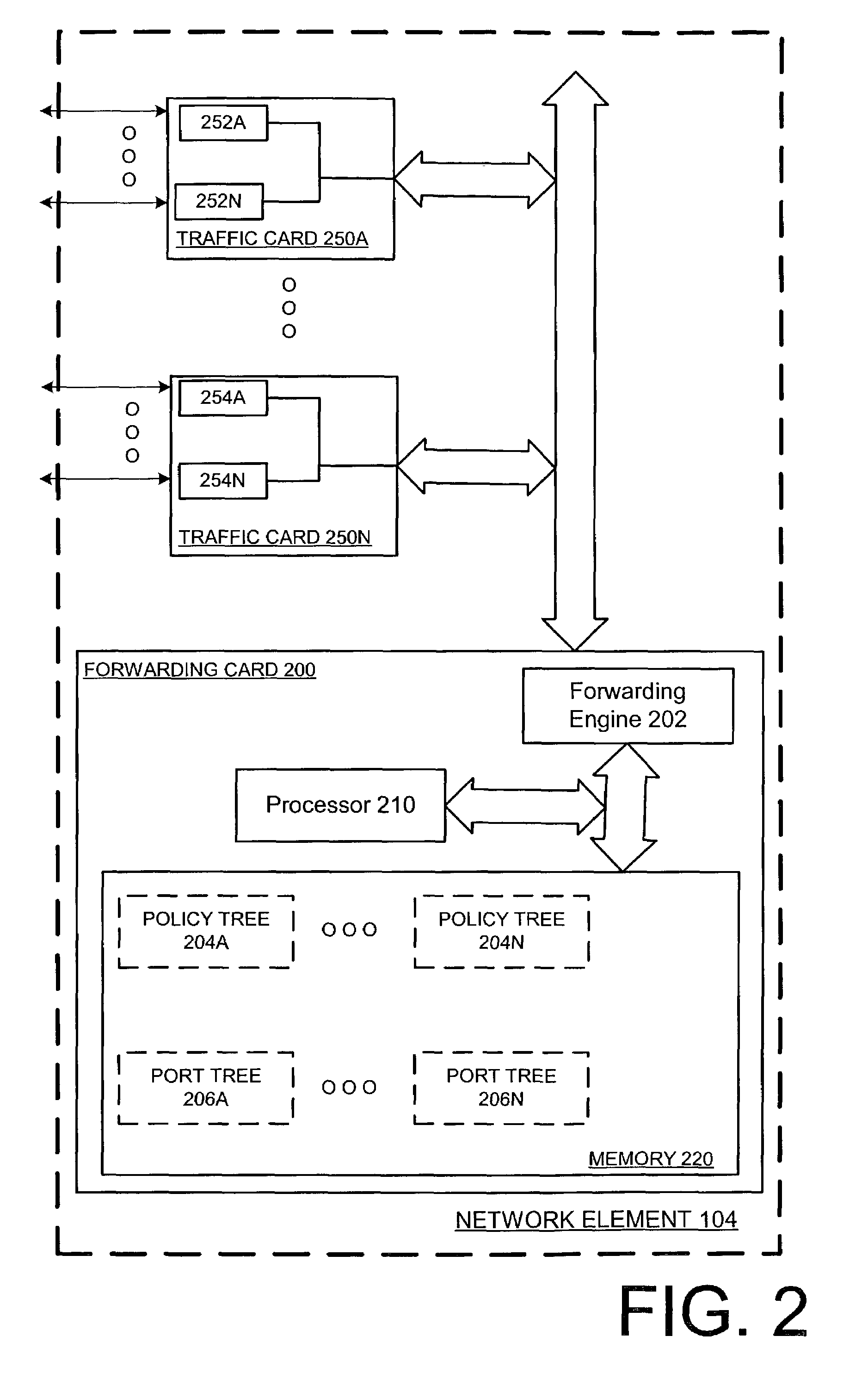
In one embodiment, a method comprises recursively selecting a child node of a previously selected node of a port tree and having a highest priority among nodes of a same level within the port tree, until the selected node has associated egress queues of an egress port. The method also includes outputting a number of packets from the associated egress queues of the selected node in a current processing cycle. The number of packets outputted is based on an allocated bandwidth for the associated egress queues, in which the allocated bandwidth accounts for a deficit from a previous processing cycle.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for weighted fair queuing
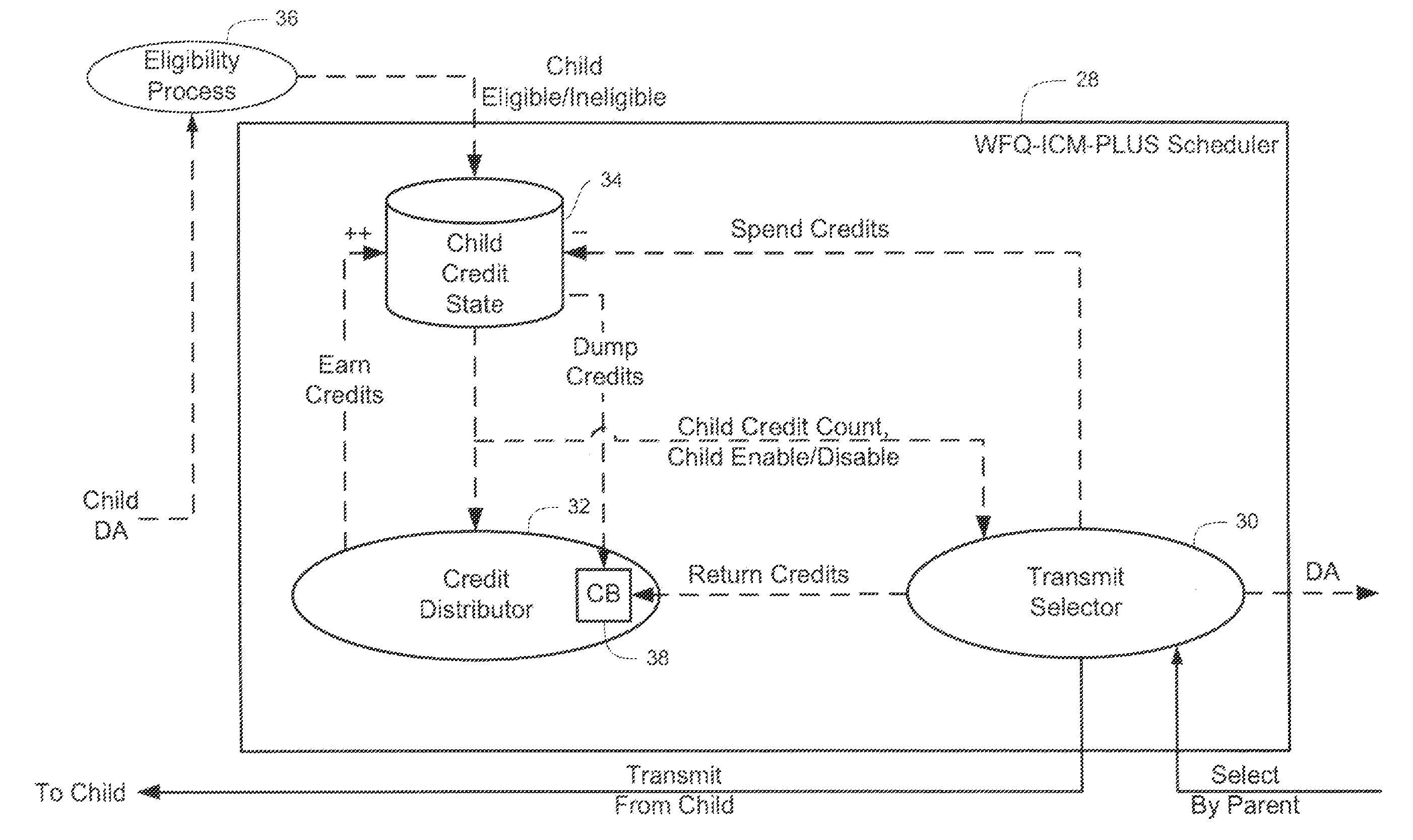
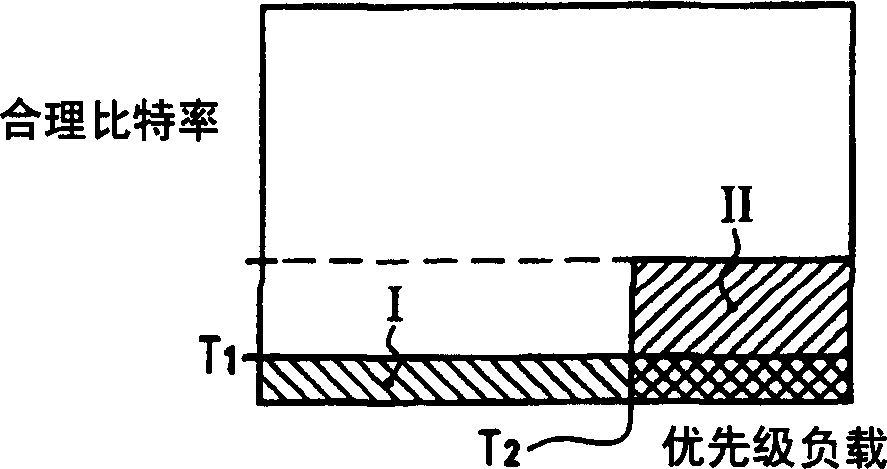
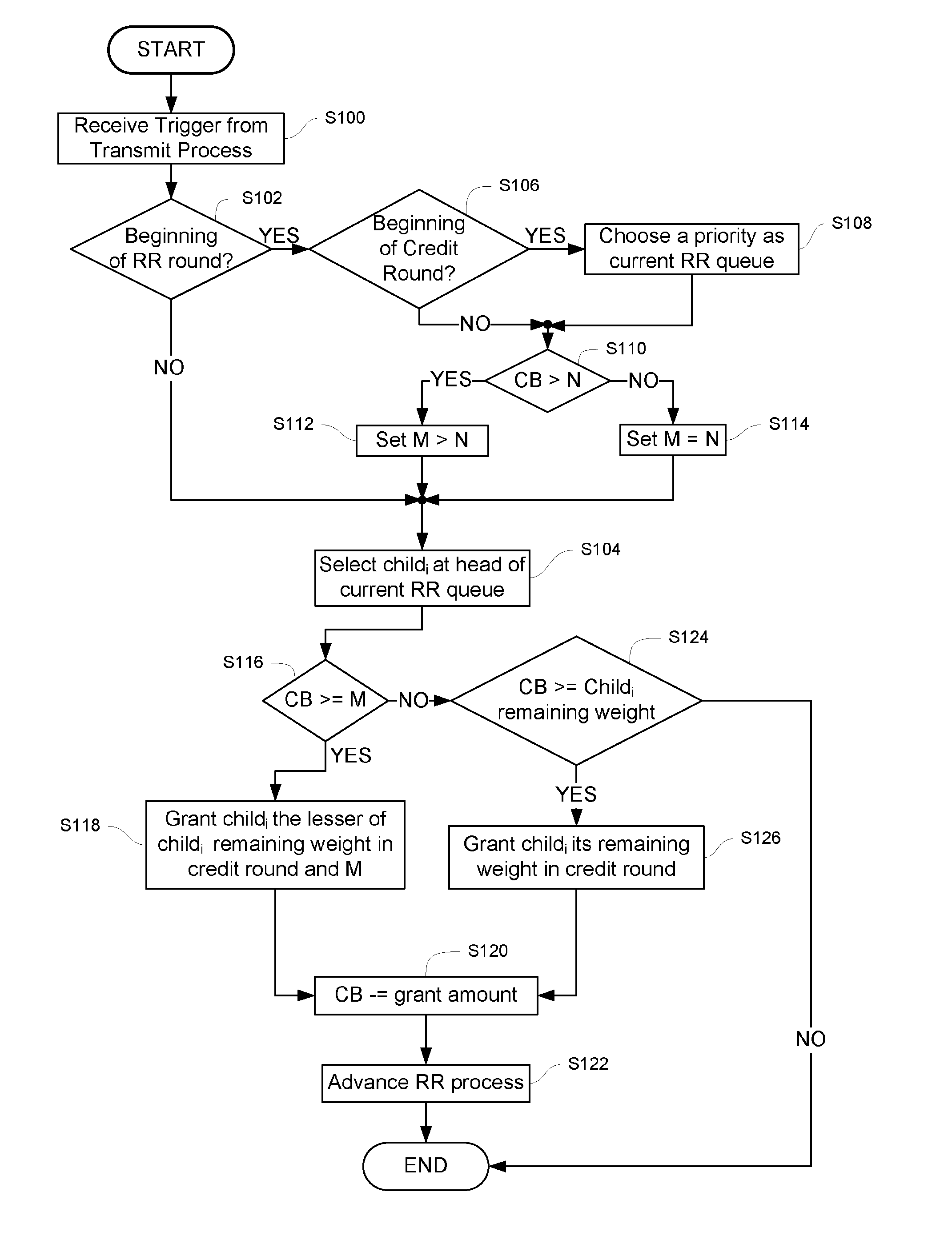
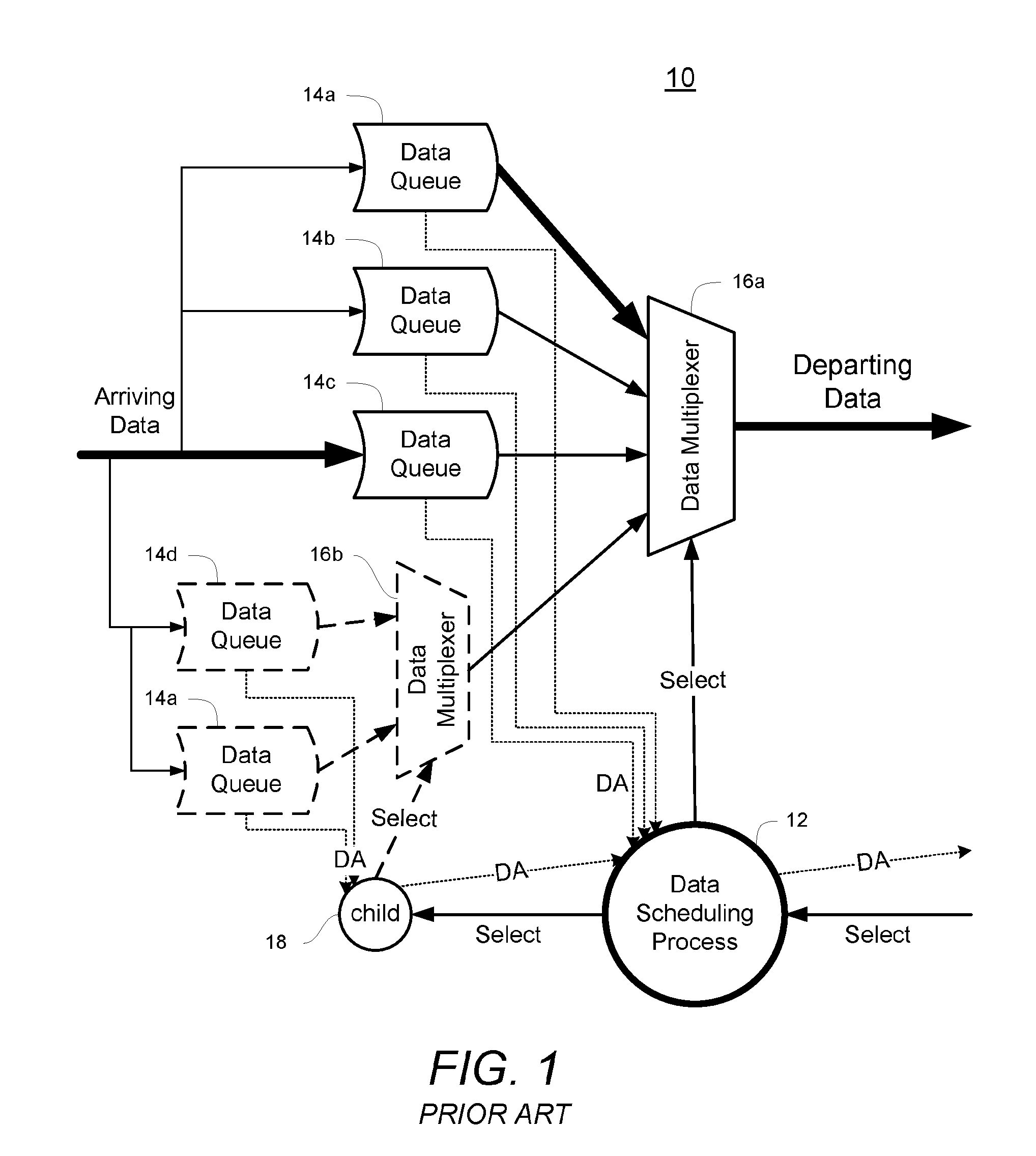
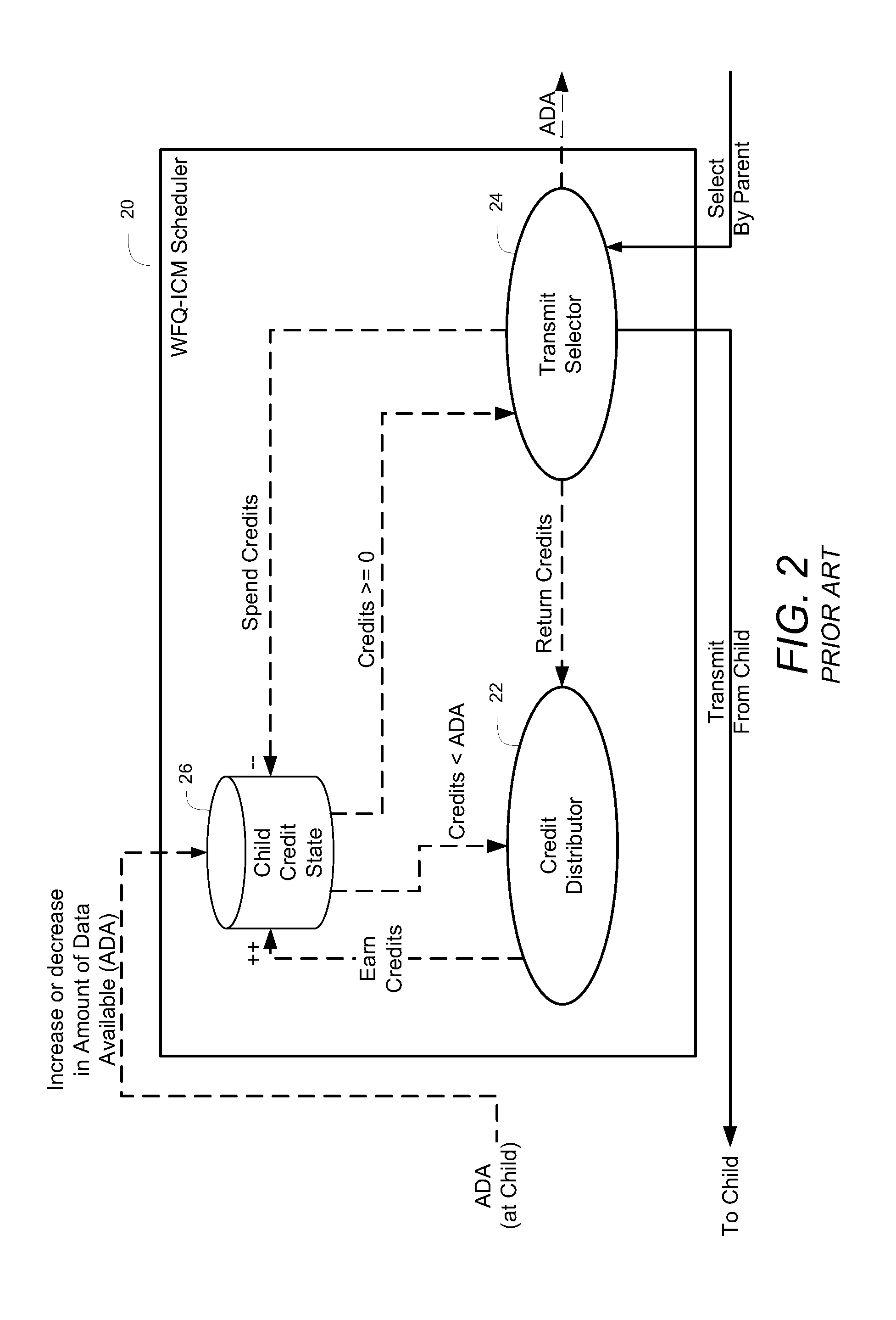
A system for scheduling data for transmission in a communication network includes a credit distributor and a transmit selector. The communication network includes a plurality of children. The transmit selector is communicatively coupled to the credit distributor. The credit distributor operates to grant credits to at least one of eligible children and children having a negative credit count. Each credit is redeemable for data transmission. The credit distributor further operates to affect fairness between children with ratios of granted credits, maintain a credit balance representing a total amount of undistributed credits available, and deduct the granted credits from the credit balance. The transmit selector operates to select at least one eligible and enabled child for dequeuing, bias selection of the eligible and enabled child to an eligible and enabled child with positive credits, and add credits to the credit balance corresponding to an amount of data selected for dequeuing.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
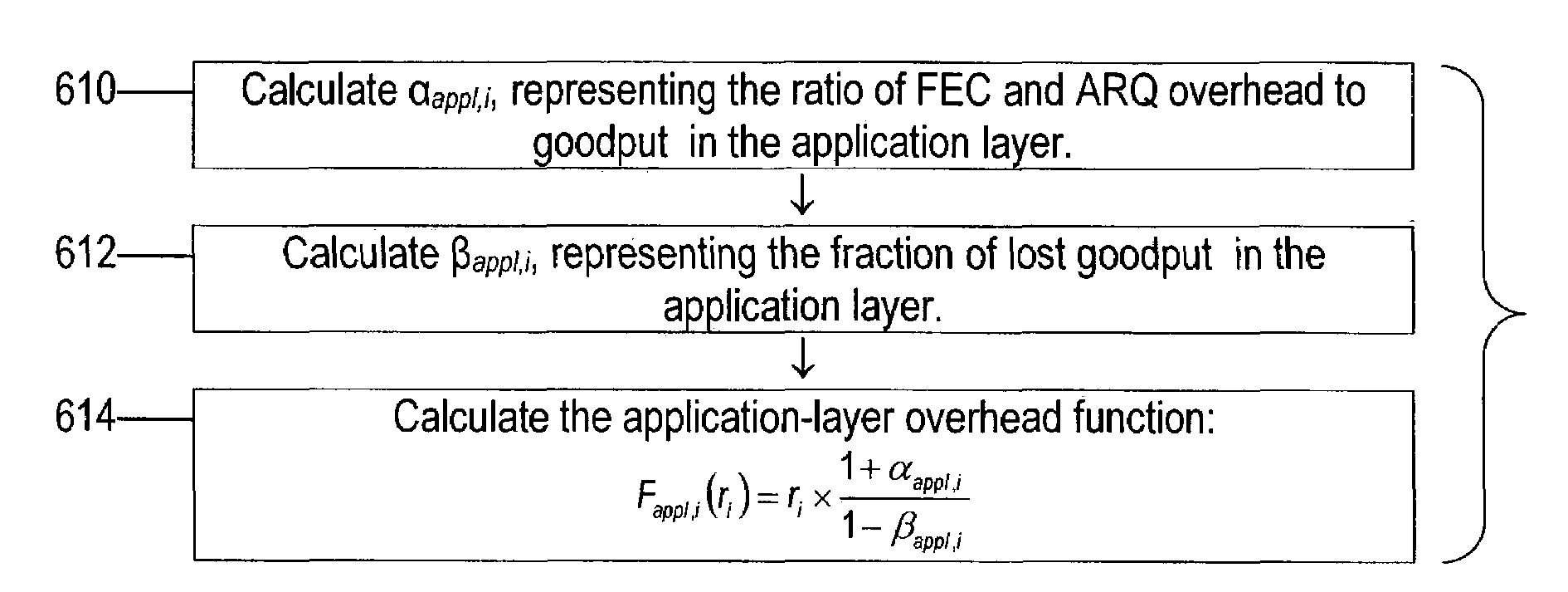
Systems and methods for goodput guarantee through adaptive fair queuing
InactiveUS7397805B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementData streamTransport layer
Disclosed herein are systems and methods for communicating a number of data flows on a single communications channel. In one embodiment, a method of communicating a number of data flows on a shared communications channel includes the acts of (1) calculating a set of optimum goodput rates for the data flows, in order to maximize a total utility of the data flows, (2) calculating a set of optimum throughput rates for the data flows based on the optimum goodput rates, and (3) transmitting the data flows on the shared communications channel with the optimized throughput rates. Optimization is preferably done using utility functions that indicate the utility of the data flows as a function of their goodput rates. The method can additionally block temporarily a transport layer of at least one of the data flows if the transport layer of that data flow is bottlenecked.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
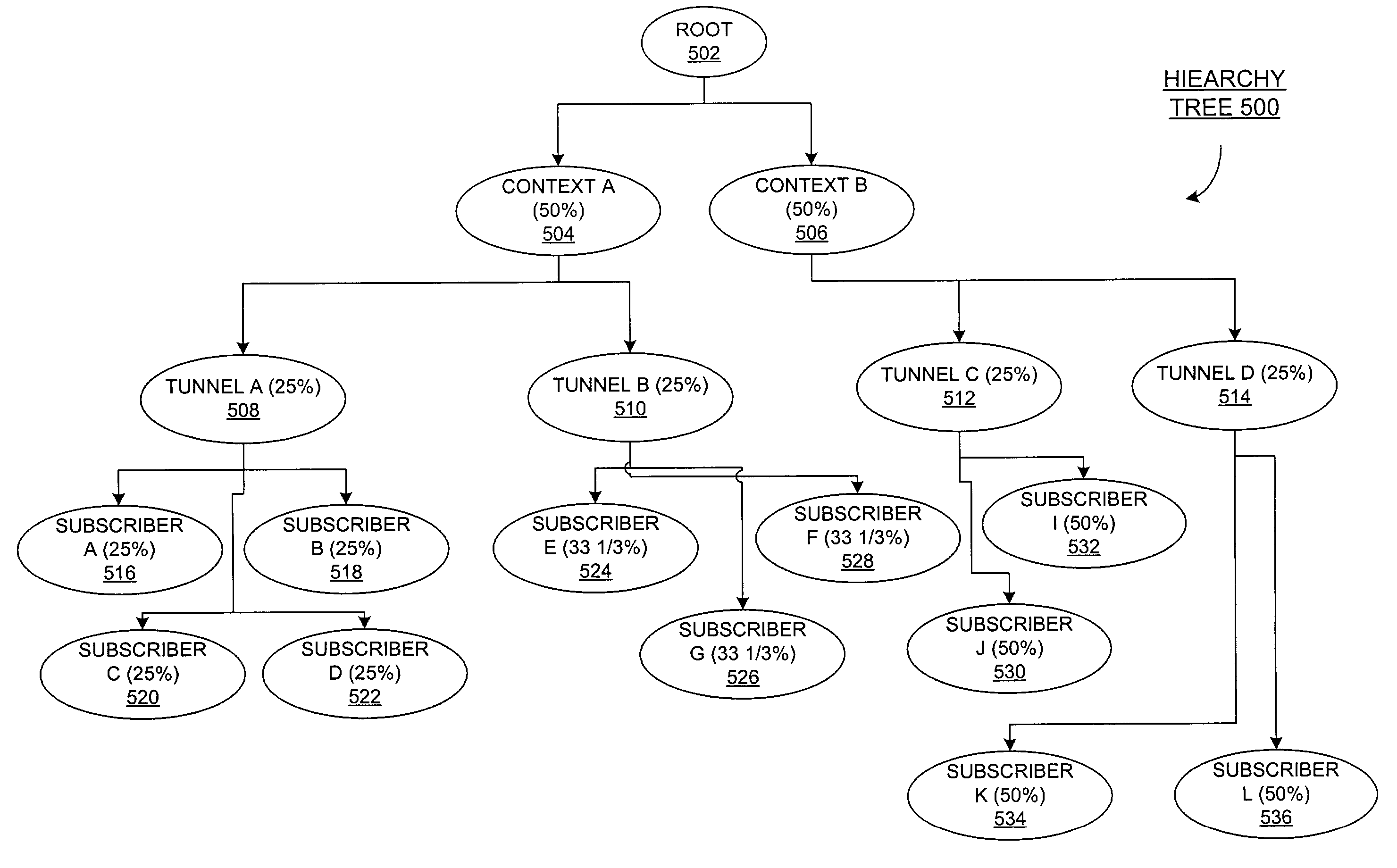
Method and system for bandwidth distribution
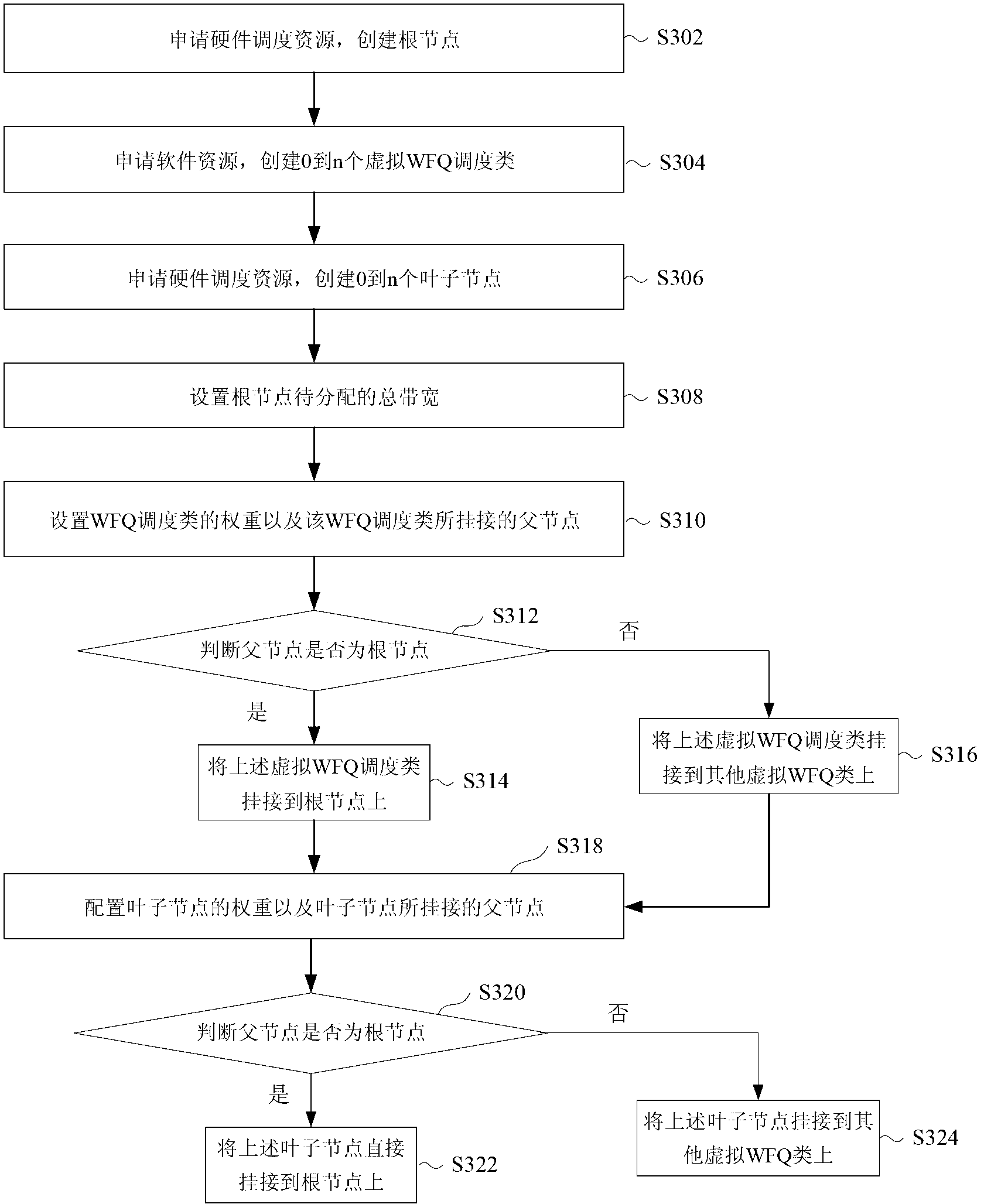
InactiveCN103067308ASolve the problem that cannot be applied to HQOS businessFlexible Bandwidth Allocation MethodHybrid transportRelationship - FatherDistribution method
The invention discloses a method and a system for bandwidth distribution. According to the method, child nodes accept first bandwidths which are distributed for the child nodes by a father child, wherein the first bandwidths are distributed by the father node according to the weighted values of the child nodes, and the child nodes distribute the first bandwidths according to the weighted value of each node of one or a plurality of nodes of the child nodes. The technical scheme is applicable to weighted fair queuing (WFQ) scheduling on multilevel and multi-service scenes and provides the flexible method for the bandwidth distribution for the multilevel and multi-service scenes.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Packet data switching apparatus
InactiveUS6490640B1Input/output for user-computer interactionData switching networksArray data structureFair queuing
There is disclosed a packet data switch which allows fair queuing, by assigning a priority value to received data, without requiring time-consuming searches, by storing pointers to the buffer memory in a first memory, and accessing the pointers through a second memory which is in the form of an array, addressable by the priority value. There is further disclosed a system which combines fair queuing and FIFO queuing, to avoid the need for excessive array size.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Router using clock synchronizer for distributed traffic control
InactiveUS7583683B2Increase speedGuaranteed service qualityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityTime limit
A router using distributed processing for FIB look-up and fair queuing algorithm is invented. The real-time traffic includes voice and video and should be transmitted in a certain time limit. Otherwise, the quality of the traffic is affected and the information is no longer useful. Packet scheduler in the router transmits packets within the time limit. However, the packet scheduler is not fast enough compared to the link speed and the size of the router. This invention uses a plurality of processors and almost identical time for each processor. FIB look-up and switching are performed by different processors to reduce the processing time. The traffic control algorithm can be performed independently by each processor. Thus, the processing speed of the entire router can be raised.
Owner:CHA YANG SOON
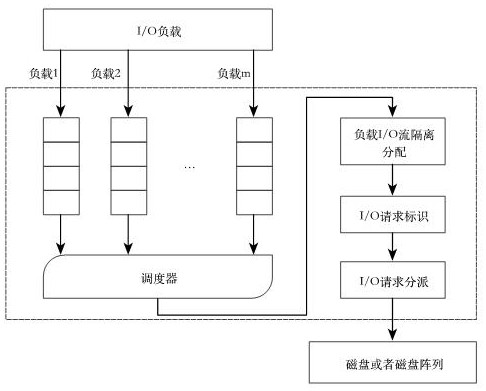
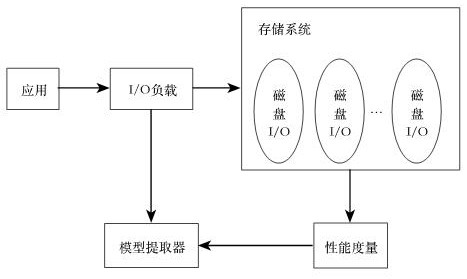
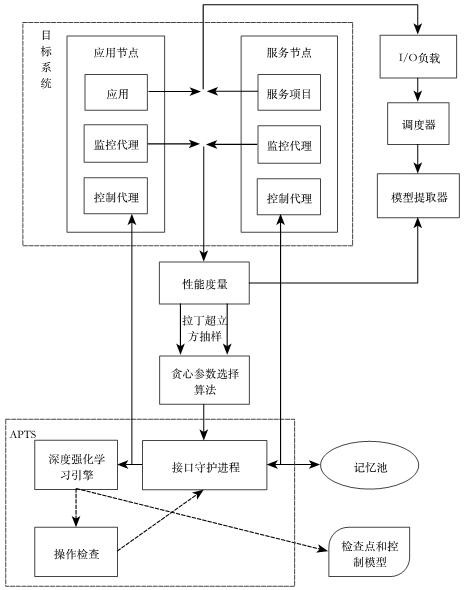
Storage system self-adaptive parameter tuning method based on deep learning
PendingCN111752708AImprove performance qualityImprove service qualityProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationEngineeringLinear regression
The invention discloses a storage system self-adaptive parameter tuning method based on deep learning. The method comprises the steps of I / O bandwidth management of the storage system, I / O load feature recognition and system parameter self-adaptive adjustment and optimization, wherein the I / O bandwidth management is that the bandwidth is allocated through a reinforced fair queuing scheduling algorithm, and an application program can obtain reasonable bandwidth resources. The I / O load feature identification is to perform performance modeling on the storage system by means of a multiple linear regression theory, and dynamically extract a performance model of the storage system by detecting load features. According to the system parameter self-adaptive adjustment and optimization, parametershaving large influence on the performance of the storage system are selected through a Latin hypercube sampling method and a greedy parameter selection algorithm, then an optimization model is trainedthrough a deep neural network, and parameter configuration with the optimal system performance is obtained. The I / O bandwidth can be reasonably managed, load characteristics are detected and identified, important parameters are automatically selected, and the performance of the storage system is optimized.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Method and apparatus for implied specification of service quality in network
ActiveCN1551580AGuaranteed service qualitySufficient qualityStore-and-forward switching systemsQuality of serviceNetwork link
The device has a scheduling module for scheduling packets in a queue as a function of a priority. The scheduling is performed based on analyzing an incoming bit rate of flows relative to a fair bit rate and a fair queuing with priority algorithm. A fair bit rate value represents the bit rate achieved by a data flow. A priority load value is transmitted in a certain time period divided by duration of that time period. An Independent claim is also included for a method of treating packets of flows on a network link.
Owner:宇东集团有限公司
Method and system for weighted fair queuing
A system for scheduling data for transmission in a communication network includes a credit distributor and a transmit selector. The communication network includes a plurality of children. The transmit selector is communicatively coupled to the credit distributor. The credit distributor operates to grant credits to at least one of eligible children and children having a negative credit count. Each credit is redeemable for data transmission. The credit distributor further operates to affect fairness between children with ratios of granted credits, maintain a credit balance representing a total amount of undistributed credits available, and deduct the granted credits from the credit balance. The transmit selector operates to select at least one eligible and enabled child for dequeuing, bias selection of the eligible and enabled child to an eligible and enabled child with positive credits, and add credits to the credit balance corresponding to an amount of data selected for dequeuing.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Processor with scheduler architecture supporting multiple distinct scheduling algorithms
InactiveUS7477636B2Sufficient flexibilityApplication of processData switching by path configurationRadio transmissionFair queuingWeighted fair queueing
Owner:INTEL CORP
Adaptive service weight assignments for ATM scheduling
InactiveUS6993040B2Data switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsAdaptive servicesFair queuing
A system and method for adaptively assigning queue service weights to an ATM traffic management controller in order to reduce service weight update calculations. The implementation of a fair weighted queuing scheme on a network is divided into two functions: queue arbitration; and queue weight configuration. Queue arbitration is performed via a virtual time-stamped fair queuing algorithm. The queue weight configuration is performed via a reconfigurable weighted fair queuing controller wherein bandwidth requirements are calculated in response to connection setup and release values.
Owner:ALCATEL CANADA
Weighted-fair-queuing relative bandwidth sharing
ActiveUS7948896B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsFair queuingWeighted fair queueing
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com